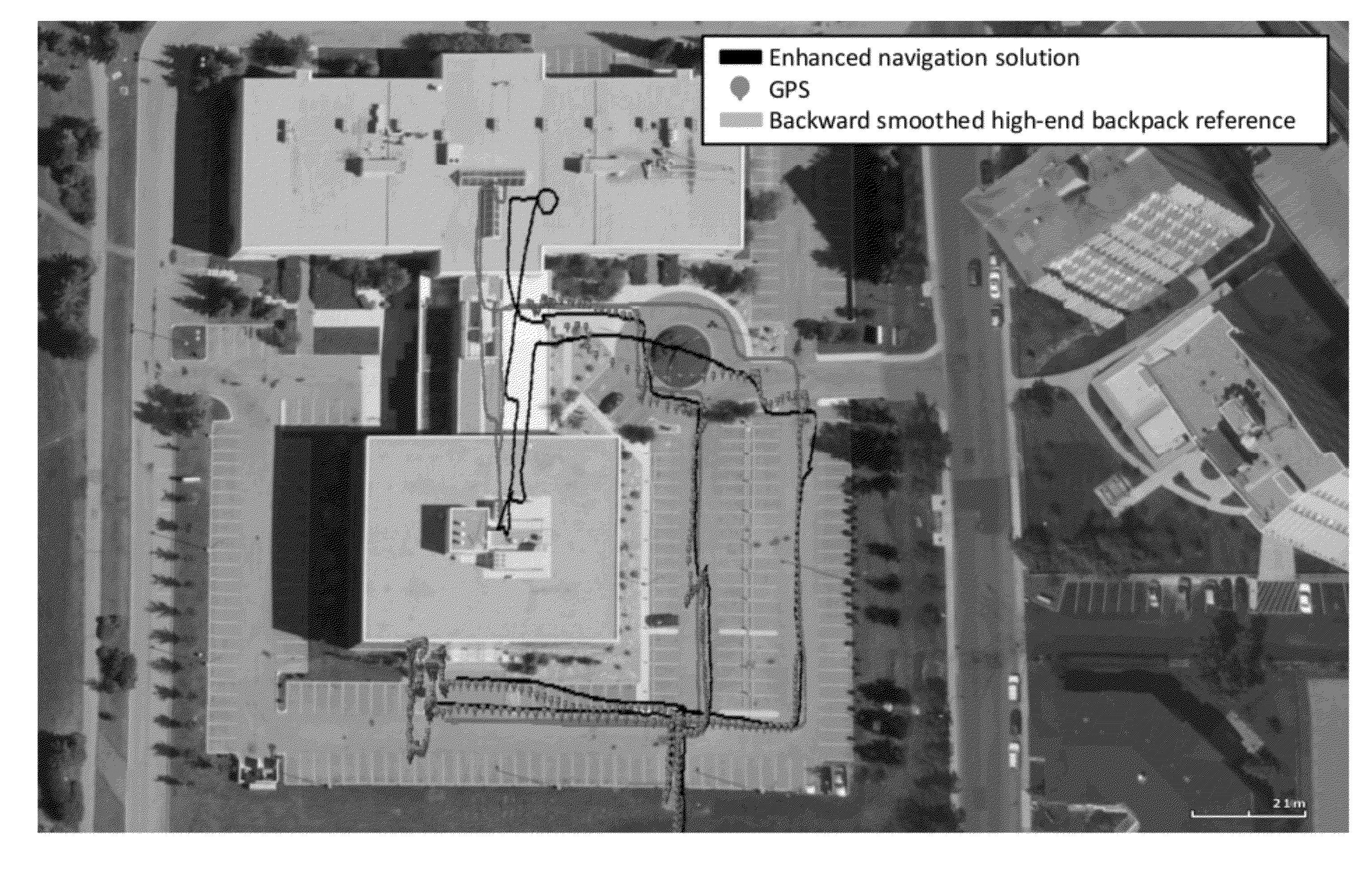Patents
Literature
2593 results about "Magnetometer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
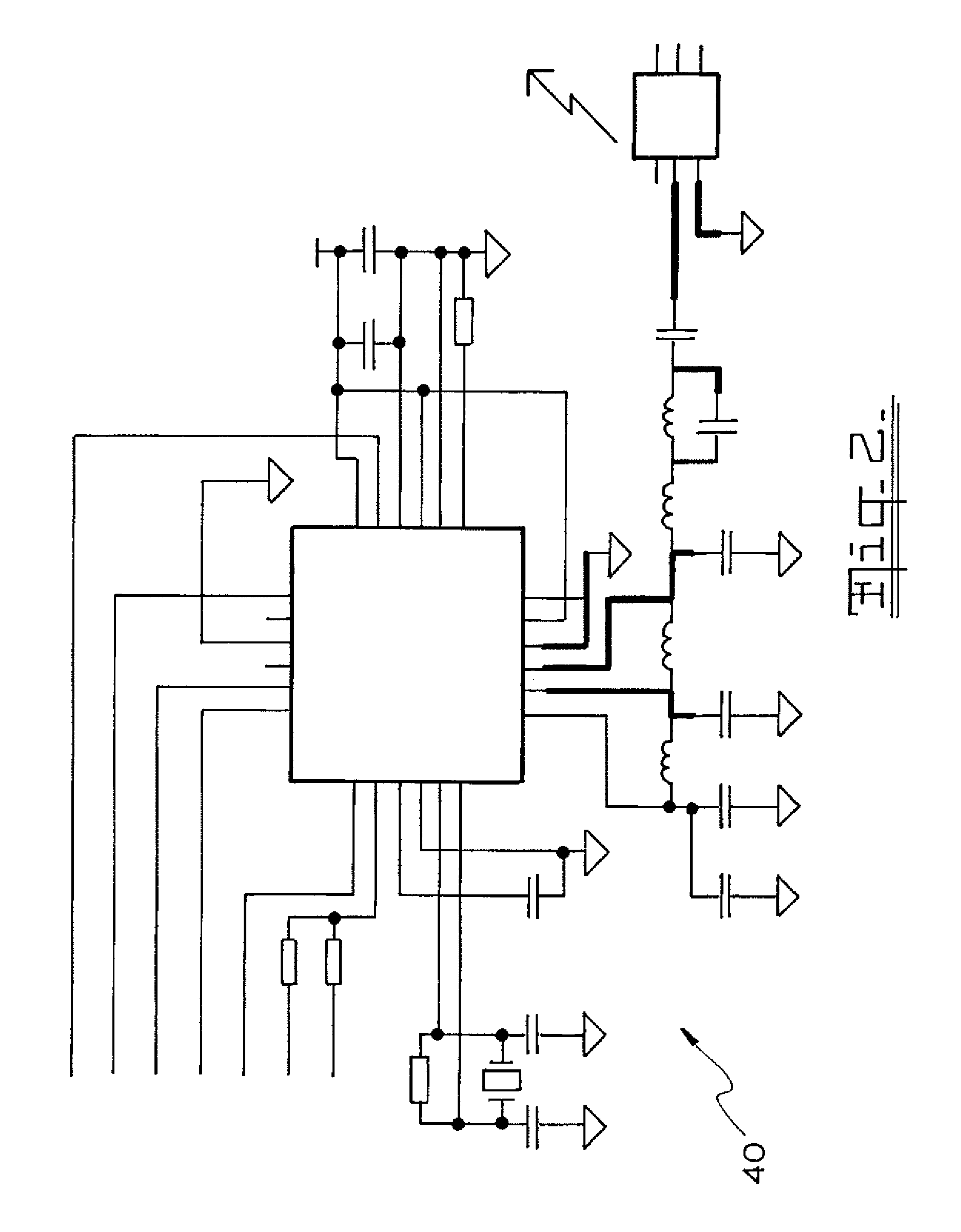
A magnetometer is a device that measures magnetism—the direction, strength, or relative change of a magnetic field at a particular location. The measurement of the magnetization of a magnetic material (like a ferromagnet) is an example. A compass is one such device, one that measures the direction of an ambient magnetic field, in this case, the Earth's magnetic field.
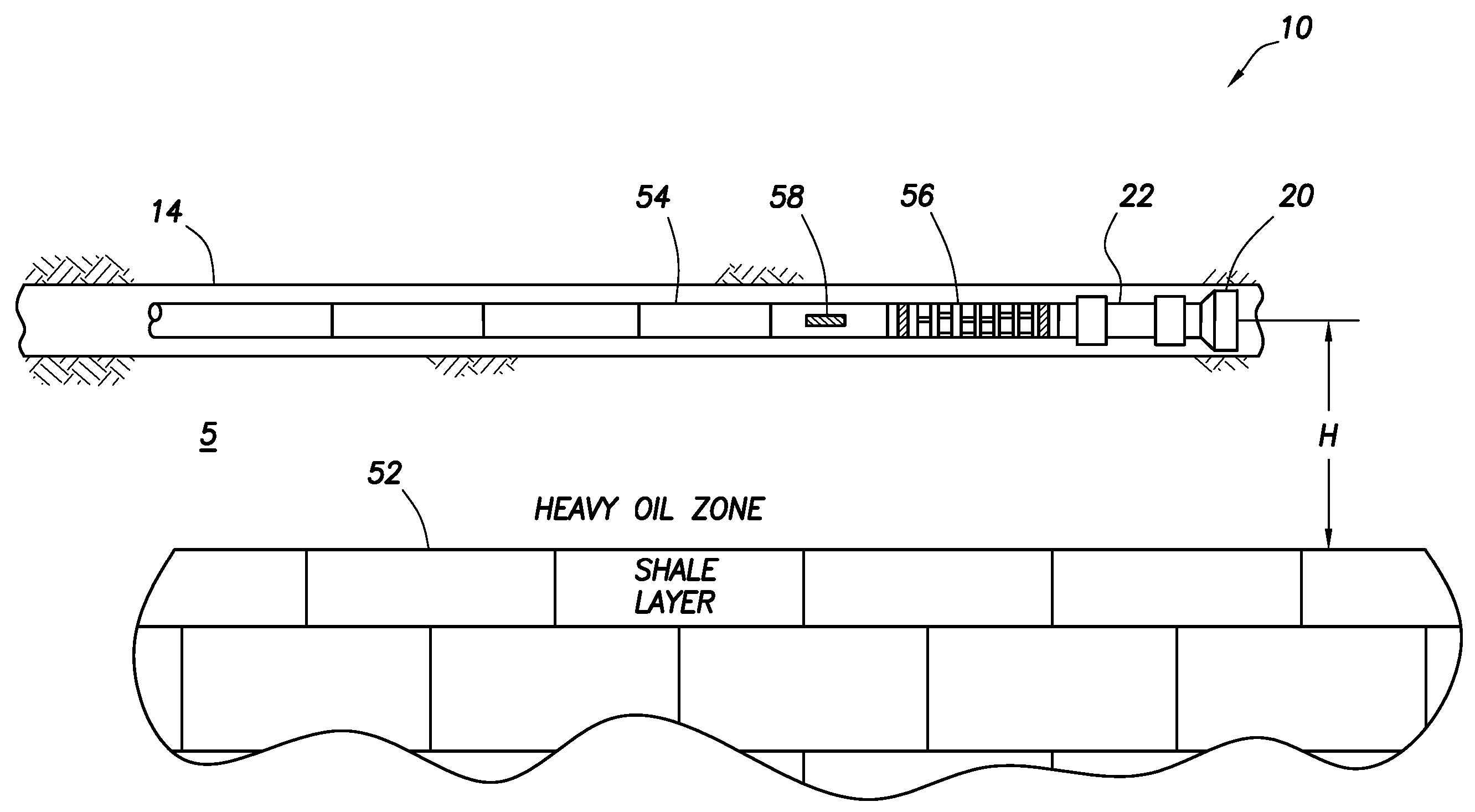
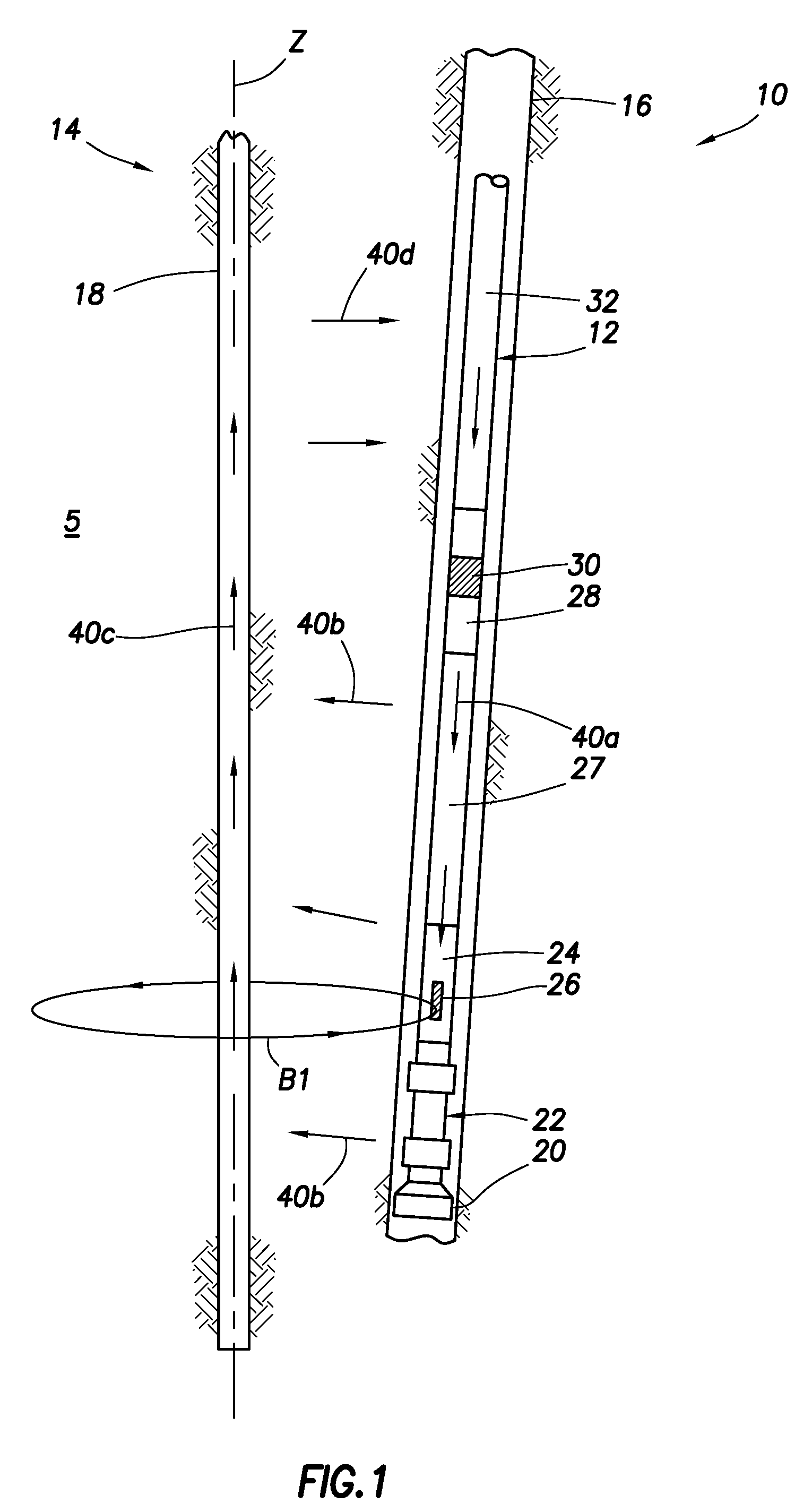
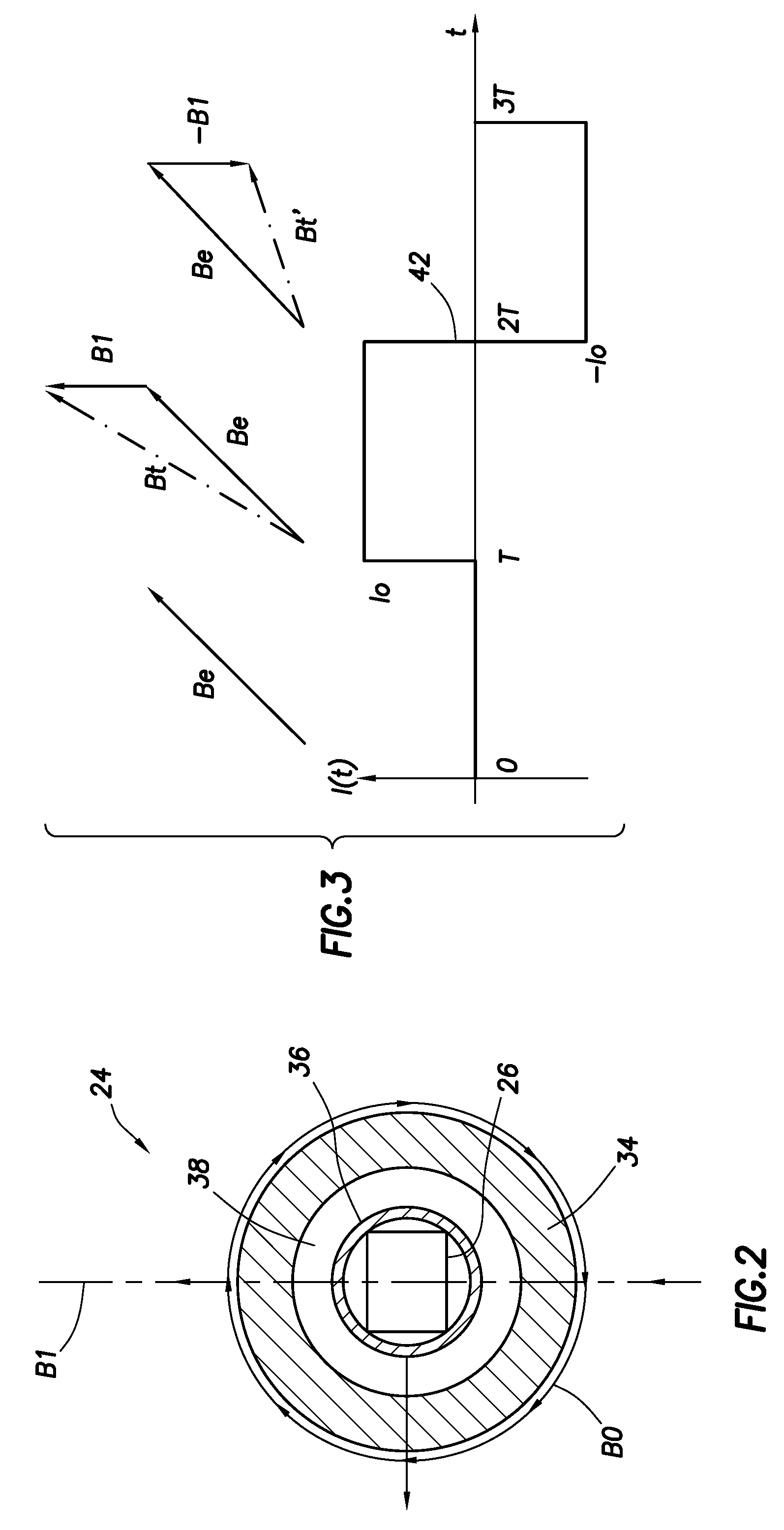
Actively controlled rotary steerable system and method for drilling wells
InactiveUS6092610AEfficient rotary speedPromote productionDrilling rodsConstructionsAccelerometerDirectional drilling
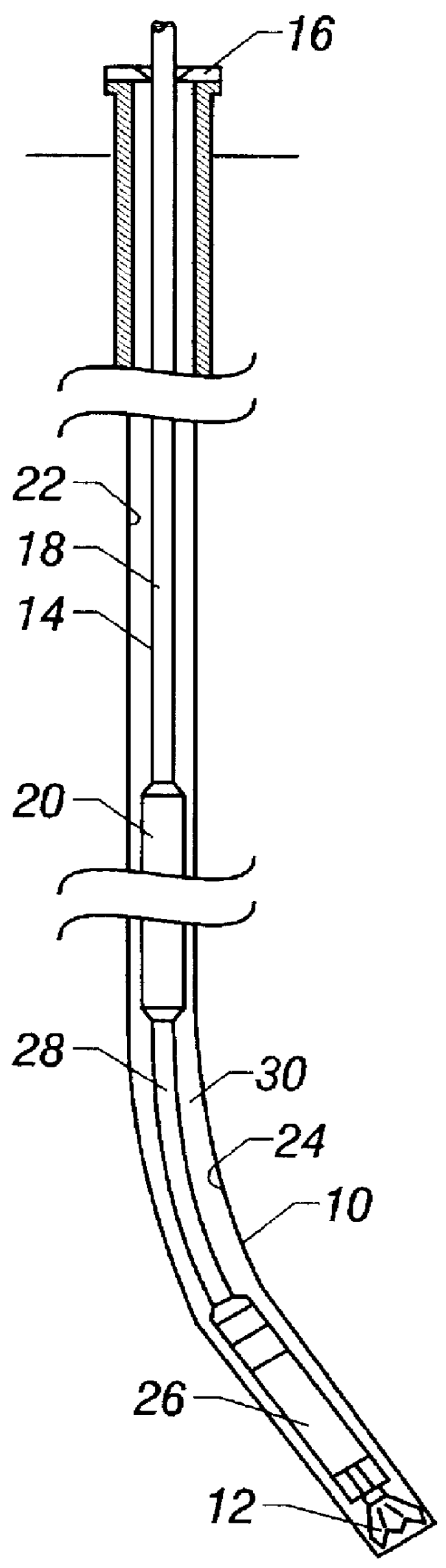
An actively controlled rotary steerable drilling system for directional drilling of wells having a tool collar rotated by a drill string during well drilling. A bit shaft has an upper portion within the tool collar and a lower end extending from the collar and supporting a drill bit. The bit shaft is omni-directionally pivotally supported intermediate its upper and lower ends by a universal joint within the collar and is rotatably driven by the collar. To achieve controlled steering of the rotating drill bit, orientation of the bit shaft relative to the tool collar is sensed and the bit shaft is maintained geostationary and selectively axially inclined relative to the tool collar during drill string rotation by rotating it about the universal joint by an offsetting mandrel that is rotated counter to collar rotation and at the same frequency of rotation. An electric motor provides rotation to the offsetting mandrel with respect to the tool collar and is servo-controlled by signal input from position sensing elements such as magnetometers, gyroscopic sensors, and accelerometers which provide real time position signals to the motor control. In addition, when necessary, a brake is used to maintain the offsetting mandrel and the bit shaft axis geostationary. Alternatively, a turbine is connected to the offsetting mandrel to provide rotation to the offsetting mandrel with respect to the tool collar and a brake is used to servo-control the turbine by signal input from position sensors.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Method and apparatus for determining location of characteristics of a pipeline
InactiveUS6243657B1High degreeHigh precisionTime indicationSynchronous motors for clocksKaiman filterComputerized system
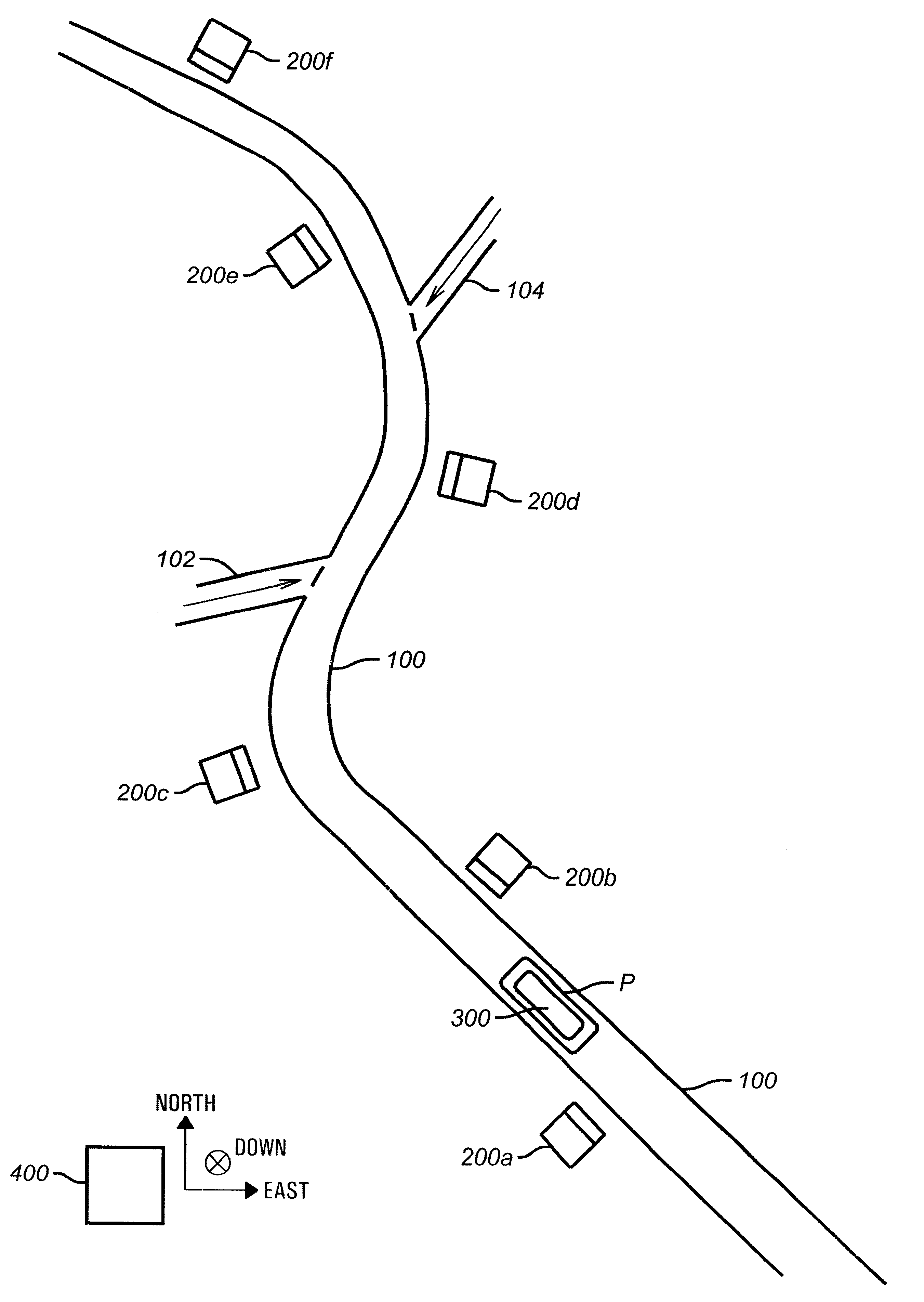
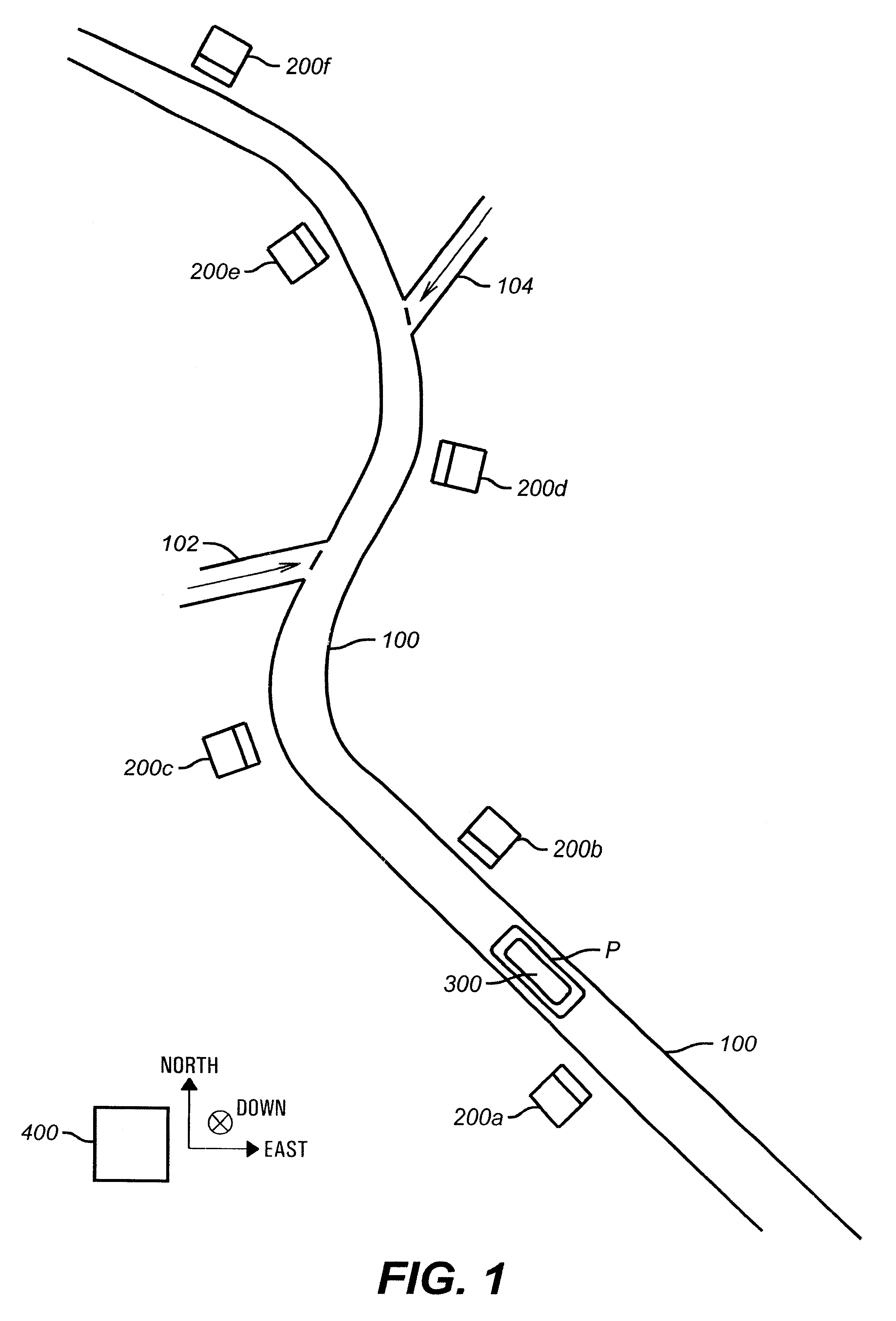
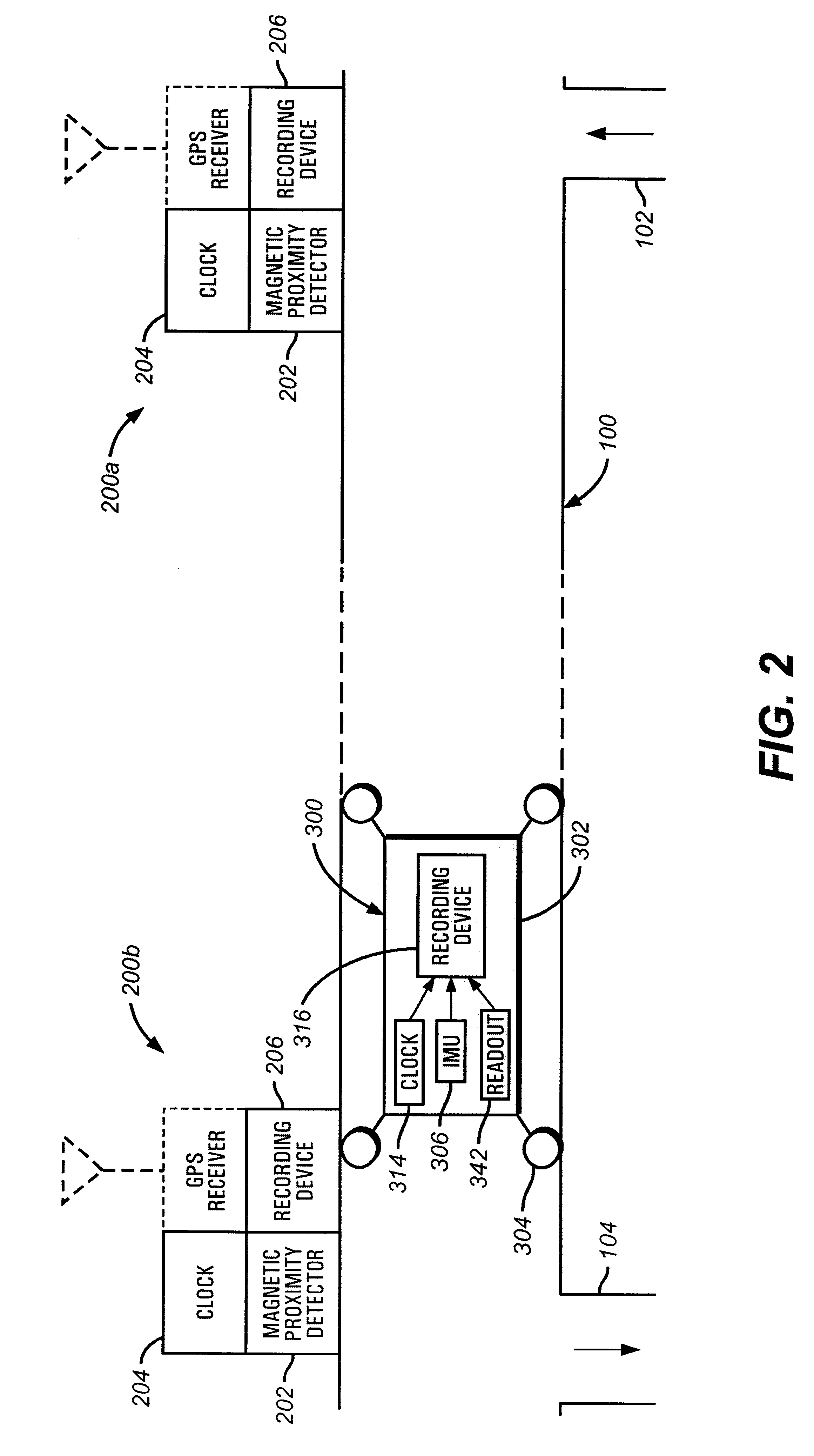
A pipeline inspection and defect mapping system includes a pig having an inertial measurement unit and a pipeline inspection unit for recording pig location and defect detection events, each record time-stamped by a highly precise onboard clock. The system also includes several magloggers at precisely known locations along the pipeline, each containing a fluxgate magnetometer for detecting the passage of the pig along the pipeline and further containing a highly precise clock synchronized with the clock in the pig. The locations of the various magloggers are known in a north / east / down coordinate system through a differential global positioning satellite process. Finally, a postprocessing off-line computer system receives downloaded maglogger, inertial measurement, and odometer data and through the use of several Kalman filters, derives the location of the detected defects in the north / east / down coordinate frame. Consequently, a task of identifying sites for repair activity is much simplified.
Owner:PIPELINE INTEGRITY INT INC FORMERLY BRITISH GAS INSPECTION SERVICES INC +1
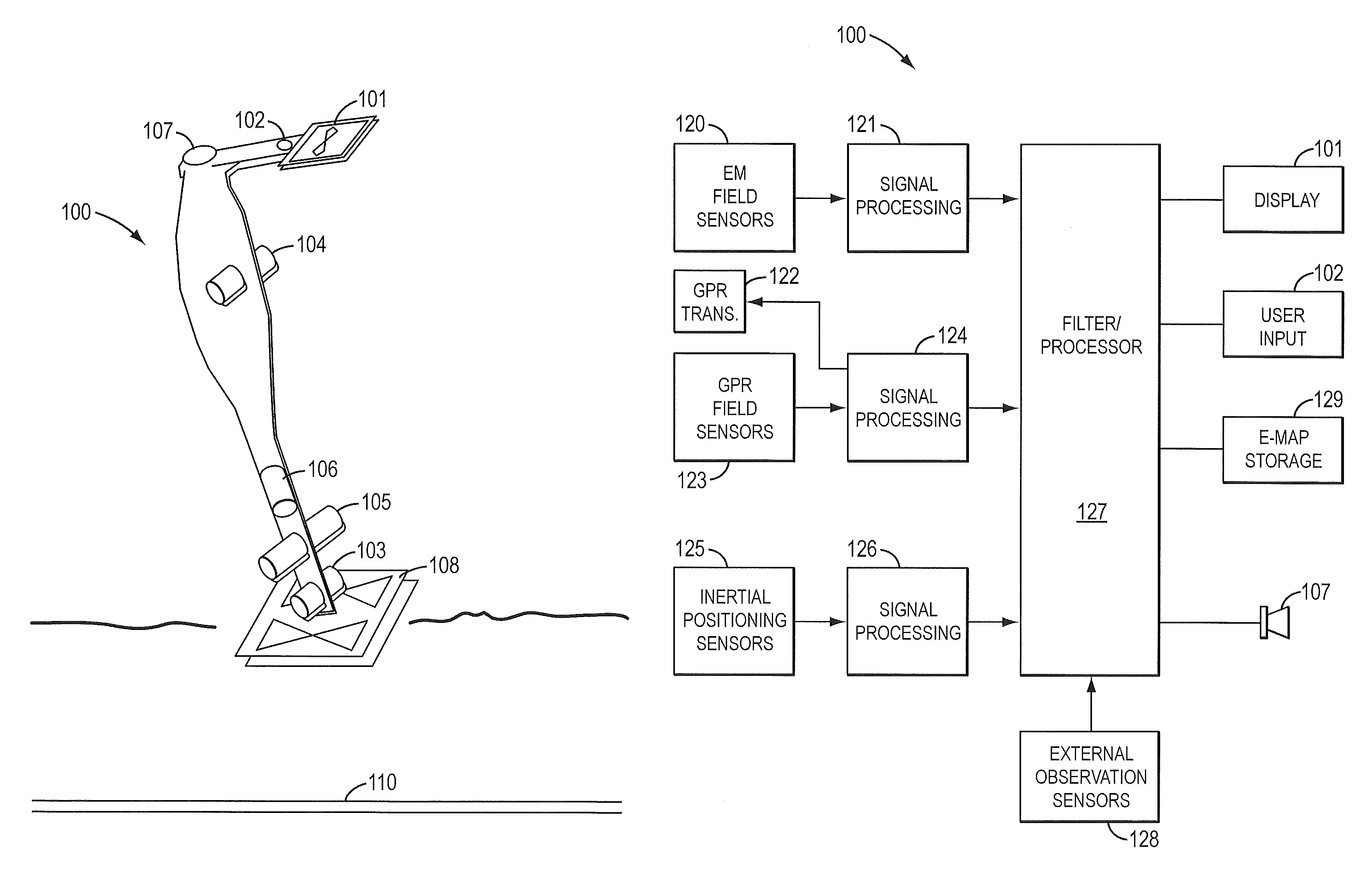
Sensor fusion for model-based detection in pipe and cable locator systems
ActiveUS20060055584A1Improve positionSatellite radio beaconingDetection using electromagnetic wavesAccelerometerGyroscope
Line locator systems that fuse traditional sensors used in a combined pipe and cable locator (electromagnetic coils, magnetometers, and ground penetrating radar antennas) with low cost inertial sensors (accelerometers, gyroscopes) in a model-based approach are presented. Such systems can utilize inexpensive MEMS sensors for inertial navigation. A pseudo-inertial frame is defined that uses the centerline of the tracked utility, or an aboveground fixed object as the navigational reference. An inertial sensor correction mechanism that limits the tracking errors over time when the model is implemented in state-space form using, for example, the Extended Kalman Filter (EKF) is disclosed.
Owner:BUSAN TRANSPORTATION CORPORATION
Method Of Manufacture And The Use Of A Functional Proppant For Determination Of Subterranean Fracture Geometries
ActiveUS20090288820A1Accurate imagingPromote recoveryMaterial nanotechnologyElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingElectricityGeophone
Proppants having added functional properties are provided, as are methods that use the proppants to track and trace the characteristics of a fracture in a geologic formation. Information obtained by the methods can be used to design a fracturing job, to increase conductivity in the fracture, and to enhance oil and gas recovery from the geologic formation. The functionalized proppants can be detected by a variety of methods utilizing, for example, an airborne magnetometer survey, ground penetrating radar, a high resolution accelerometer, a geophone, nuclear magnetic resonance, ultra-sound, impedance measurements, piezoelectric activity, radioactivity, and the like. Methods of mapping a subterranean formation are also provided and use the functionalized proppants to detect characteristics of the formation.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
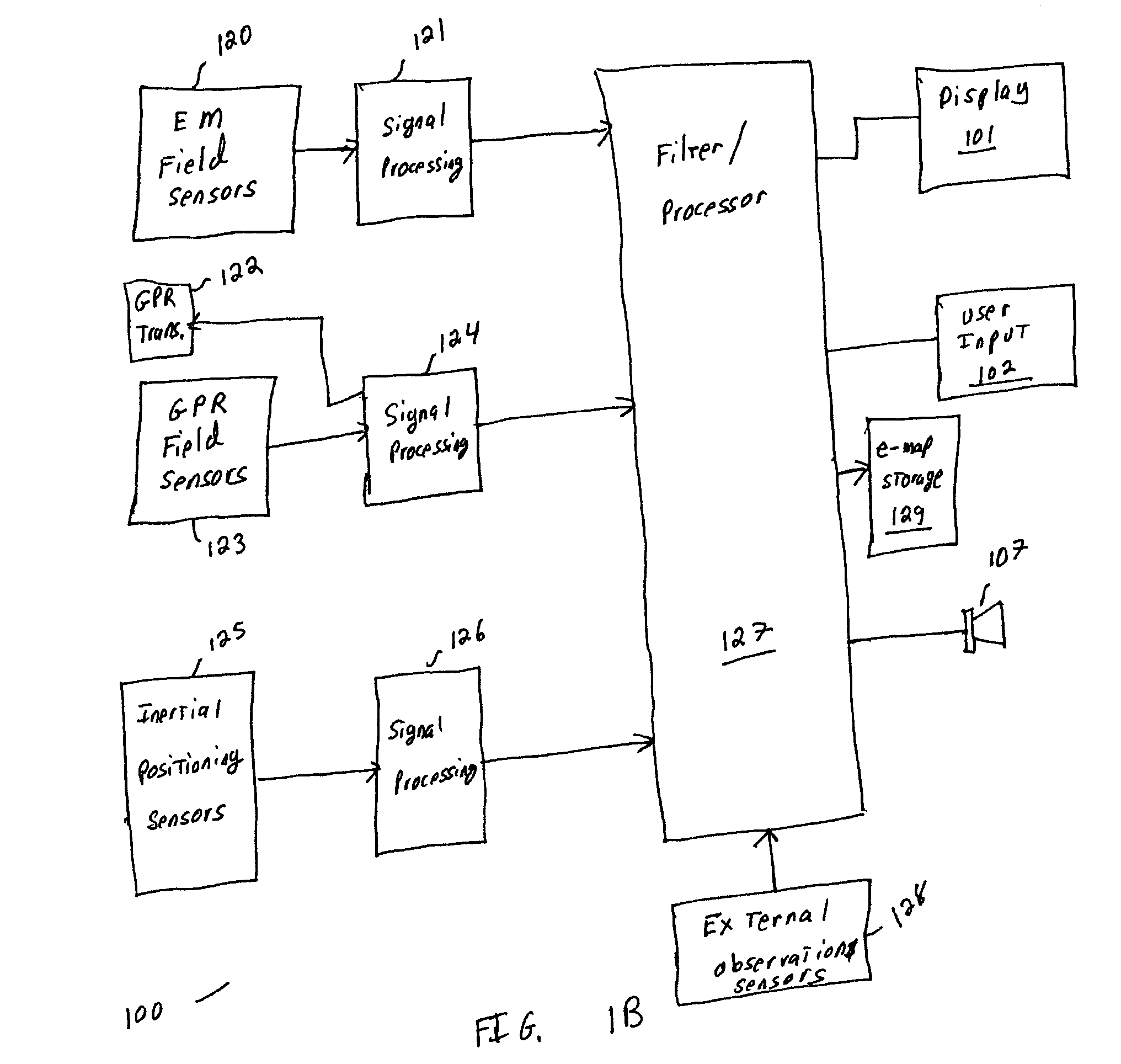
Motion-activated control with haptic feedback
InactiveUS20060061545A1High fidelity haptic outputCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingHand held devicesMagnetometer
A mechanism for sensing the changing positional and orientation of a hand held device as it is moved by the device user to control the state or operation of the hand held device and one or more vibrotactile transducers positioned on the body of the hand held device to provide haptic feedback stimuli to the user indicative of the state of the device. The mechanism employs the combination of accelerometers for obtaining inertial data in three degrees of freedom, gyro sensor for obtaining roll, pitch and yaw angular motion data, a GPS system for providing position data, and magnetometers for providing directional data. This sensor data may be used to control the functioning of the hand held device; for example to control display scrolling, and the vibratory stimuli fed back to the user provides an indication of the effects of the gestural movements the user imparts to the device.
Owner:MEDIA LAB EURO IN VOLUNTARY LIQUIDATION +1
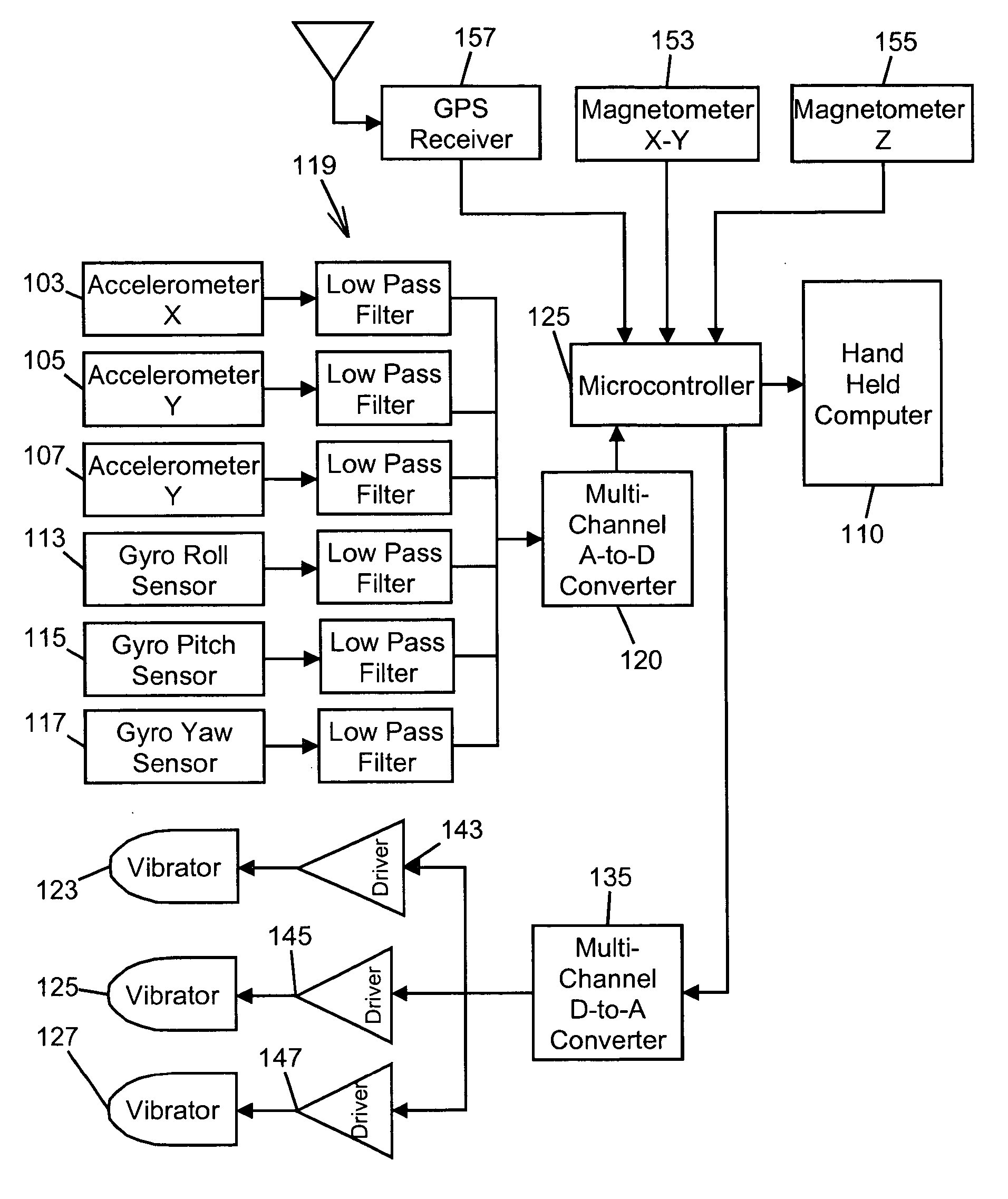
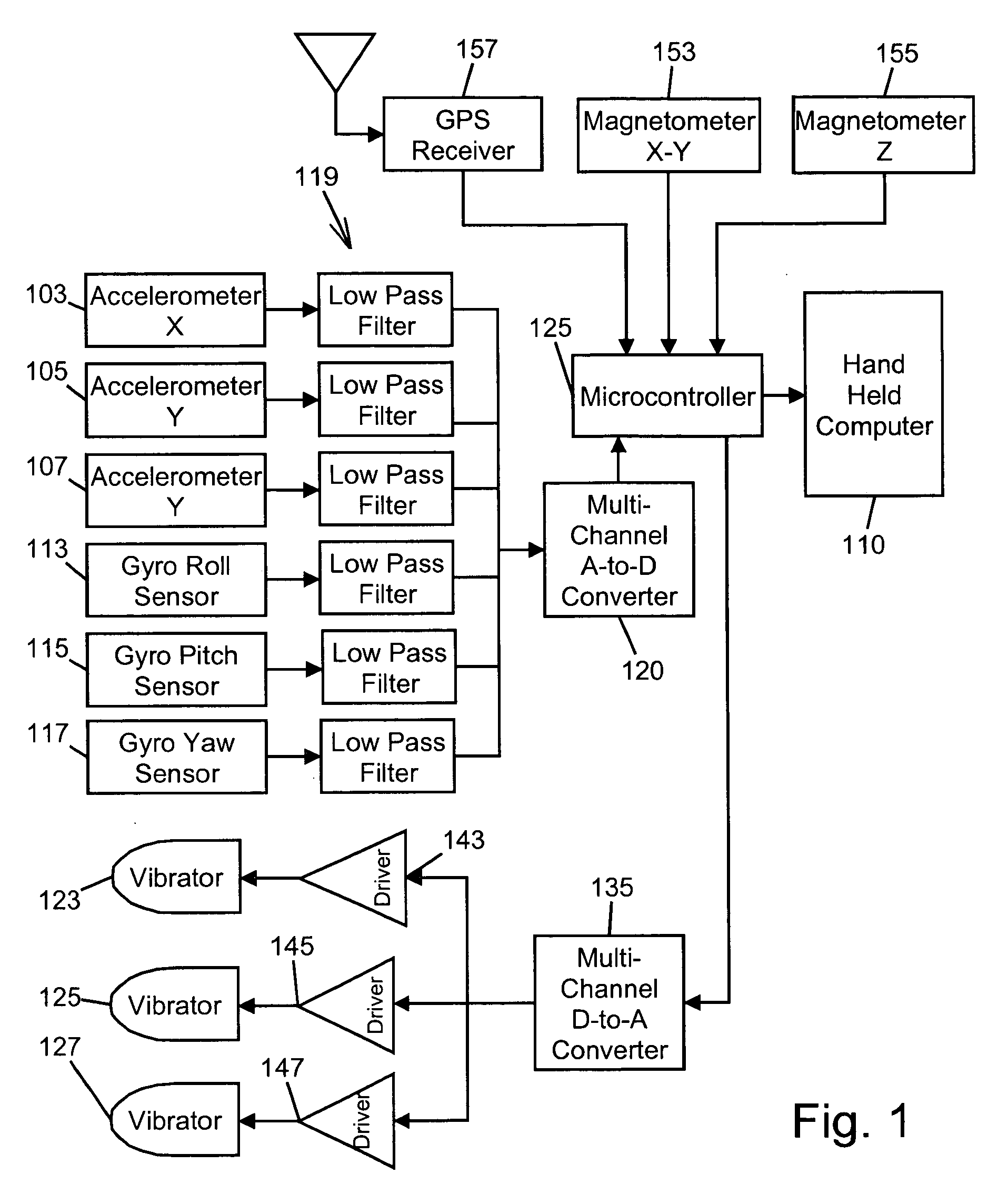
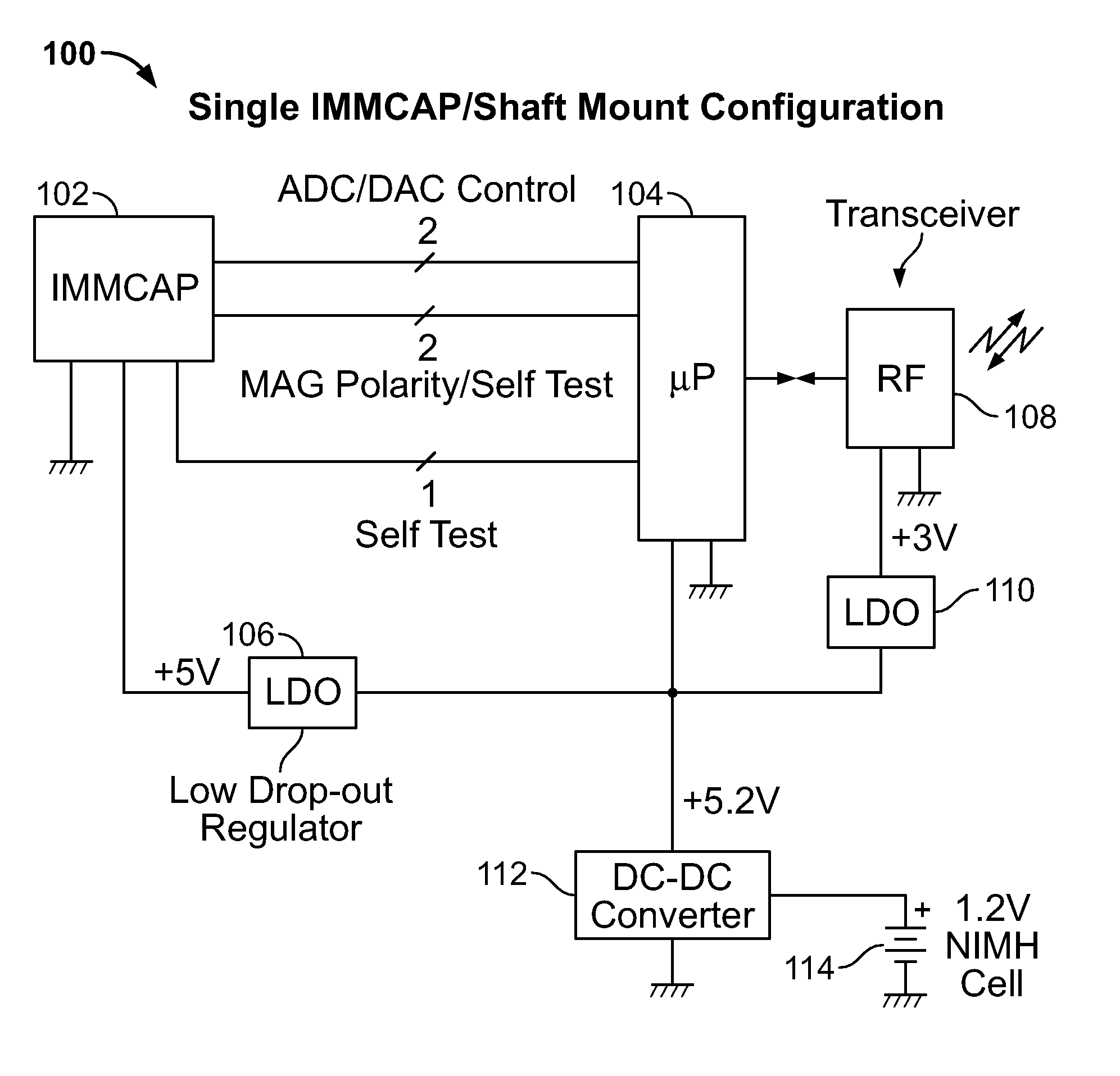
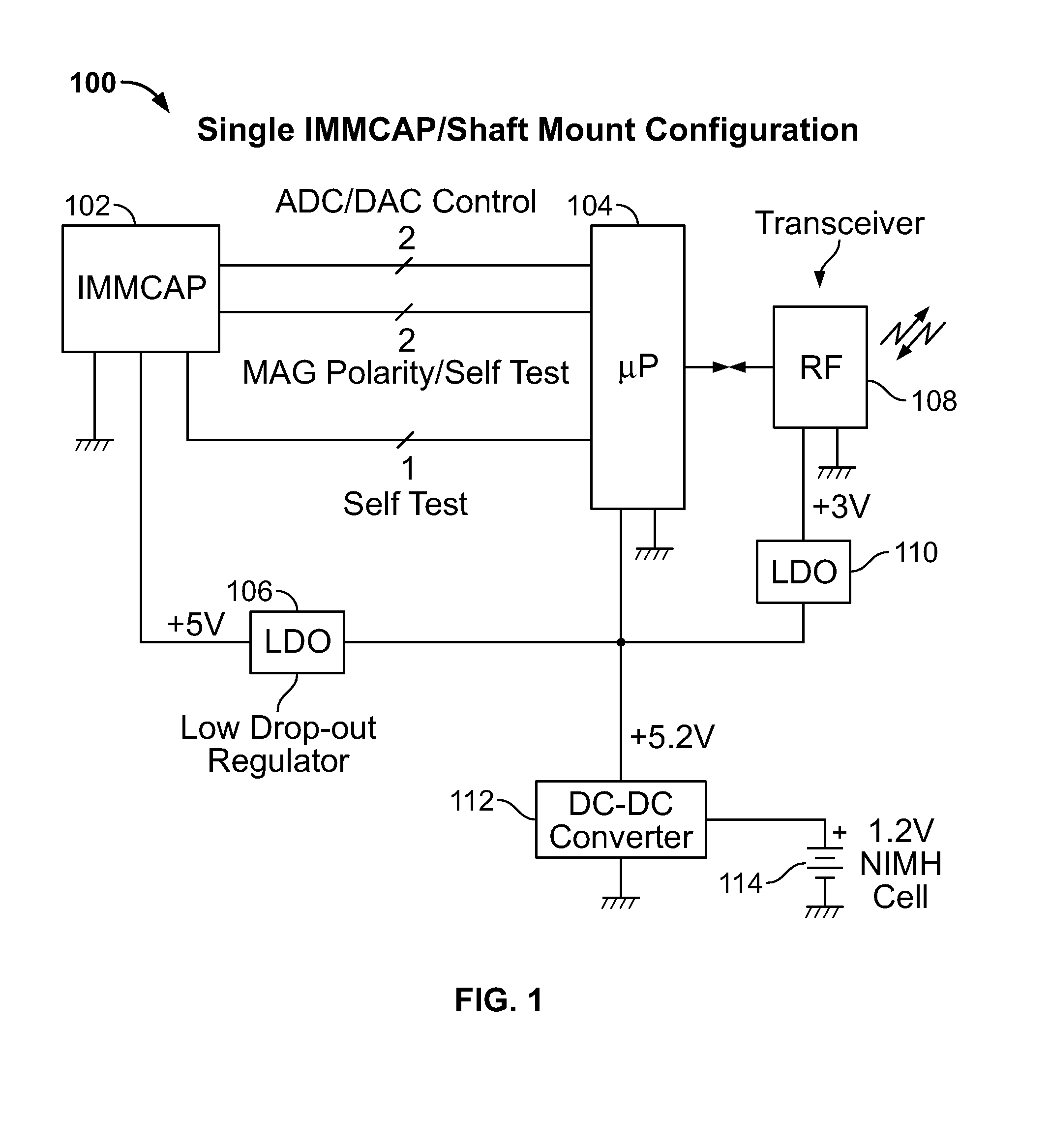
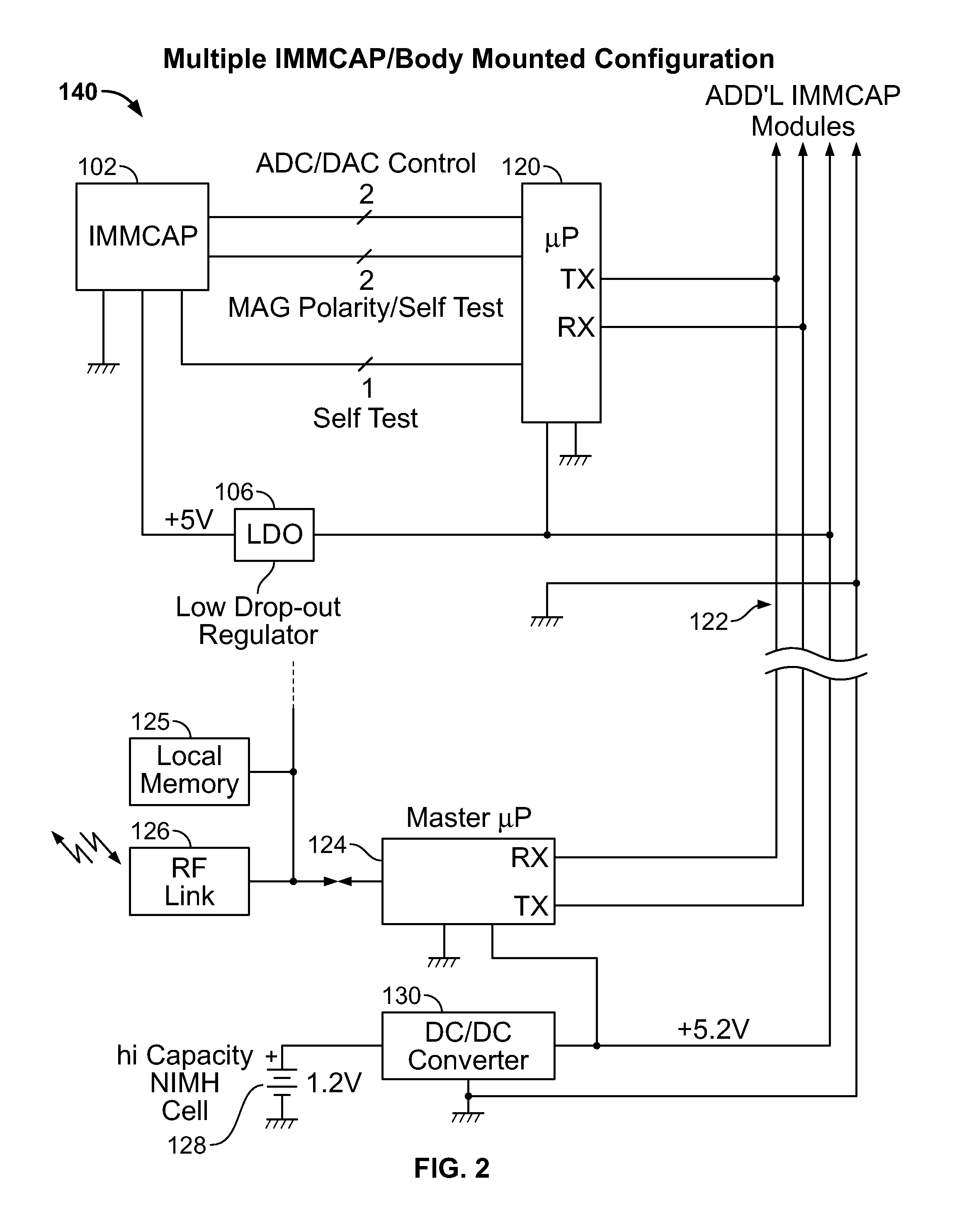
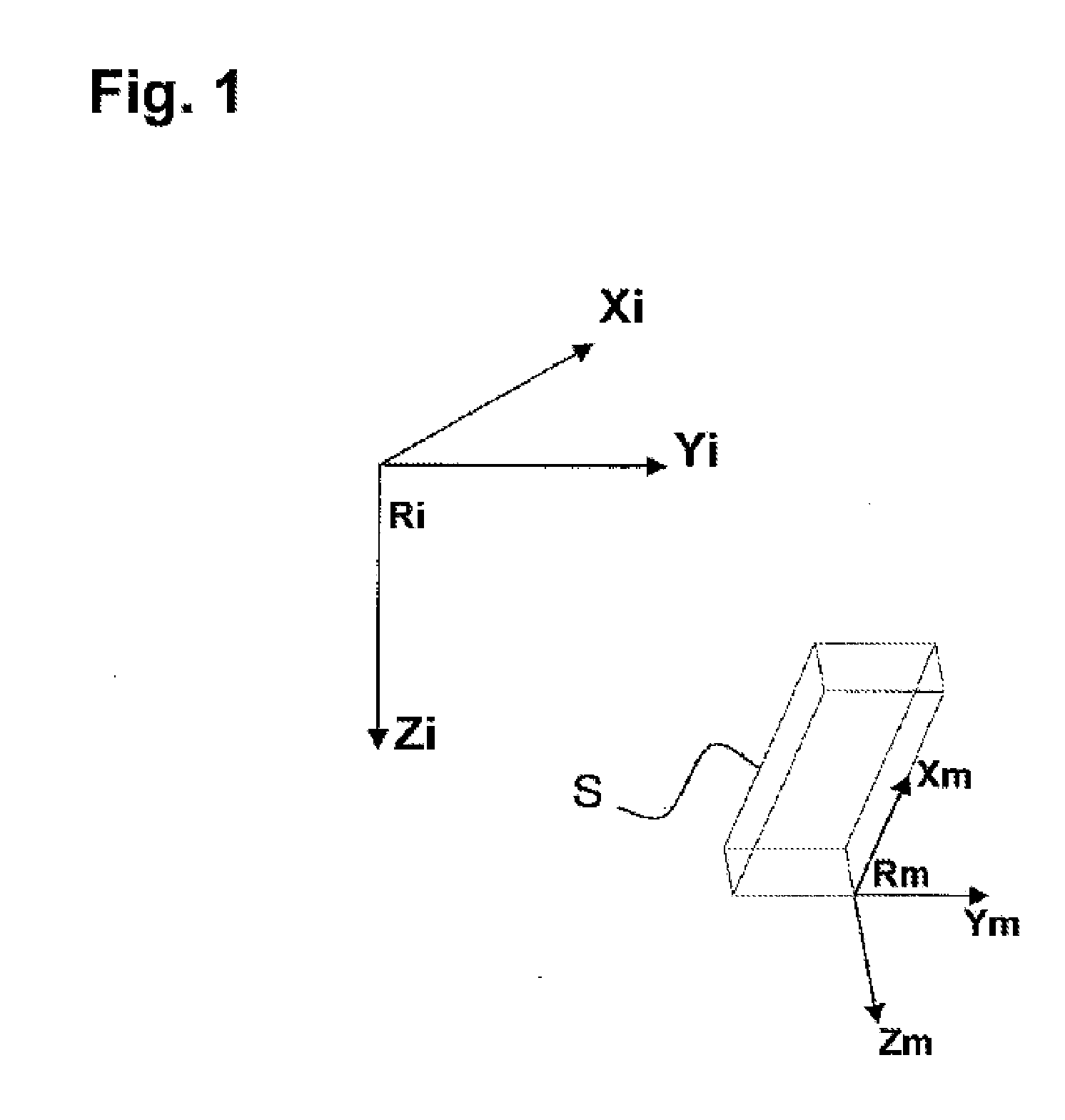
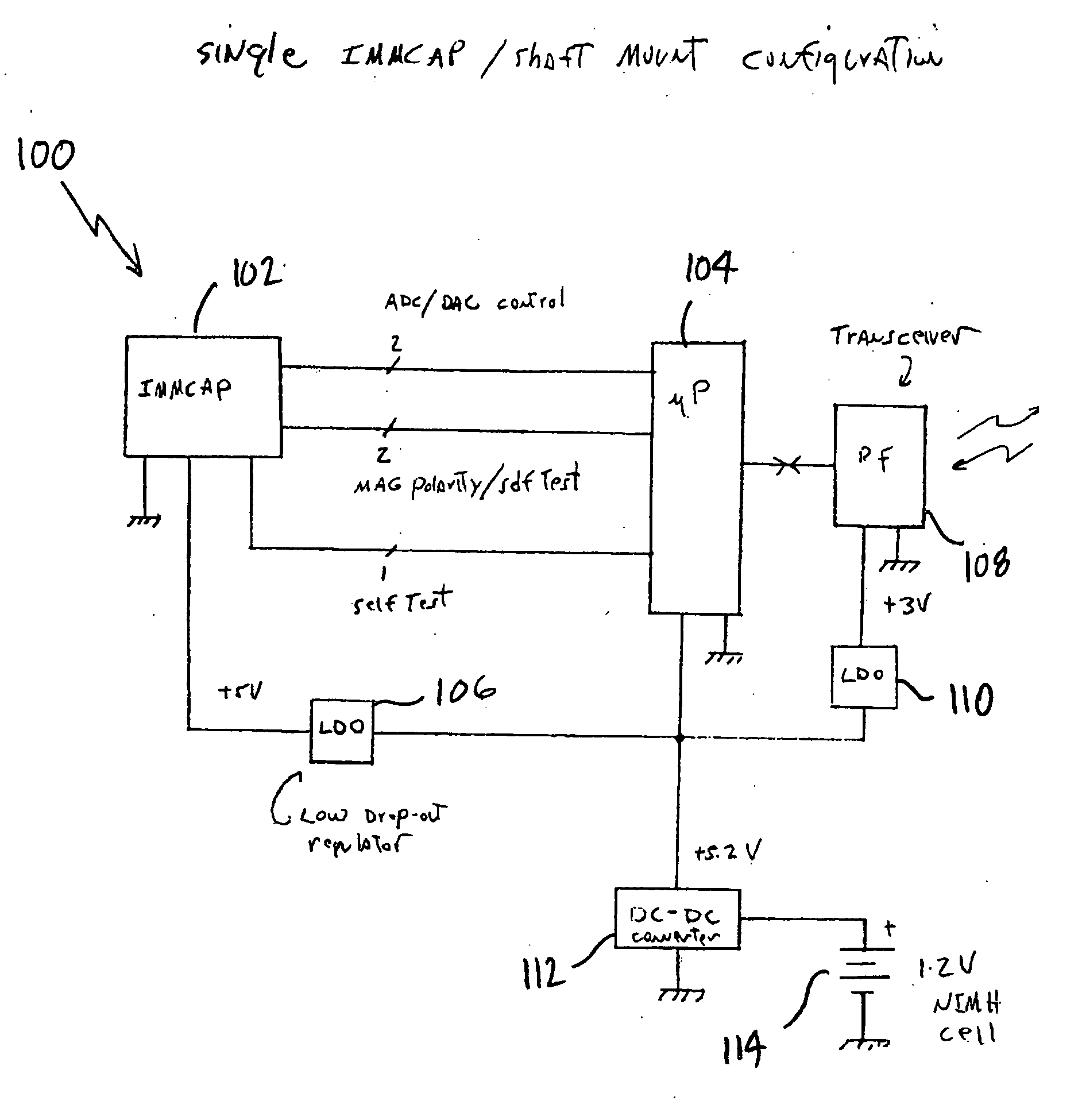
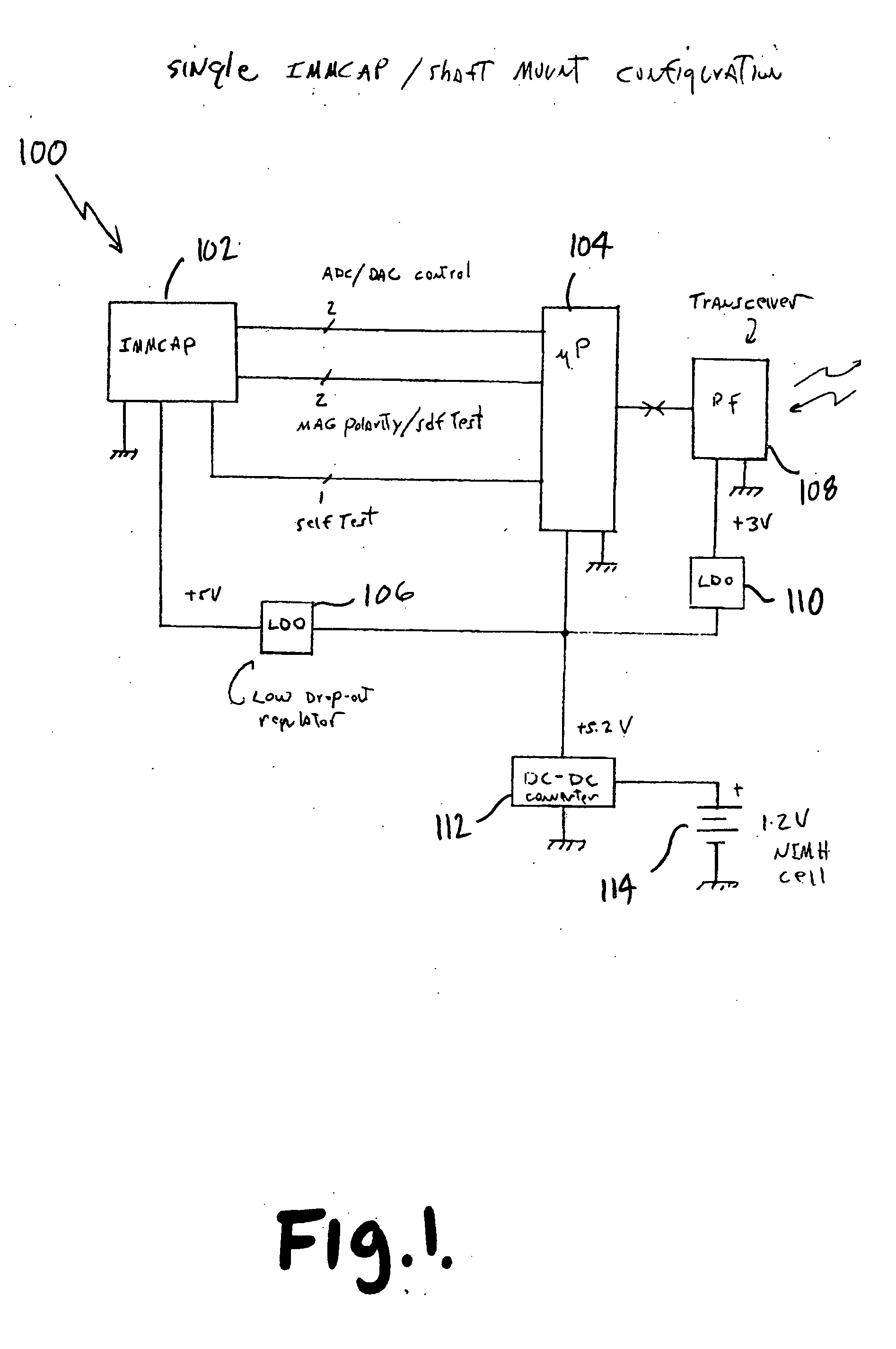
Single/multiple axes six degrees of freedom (6 DOF) inertial motion capture system with initial orientation determination capability
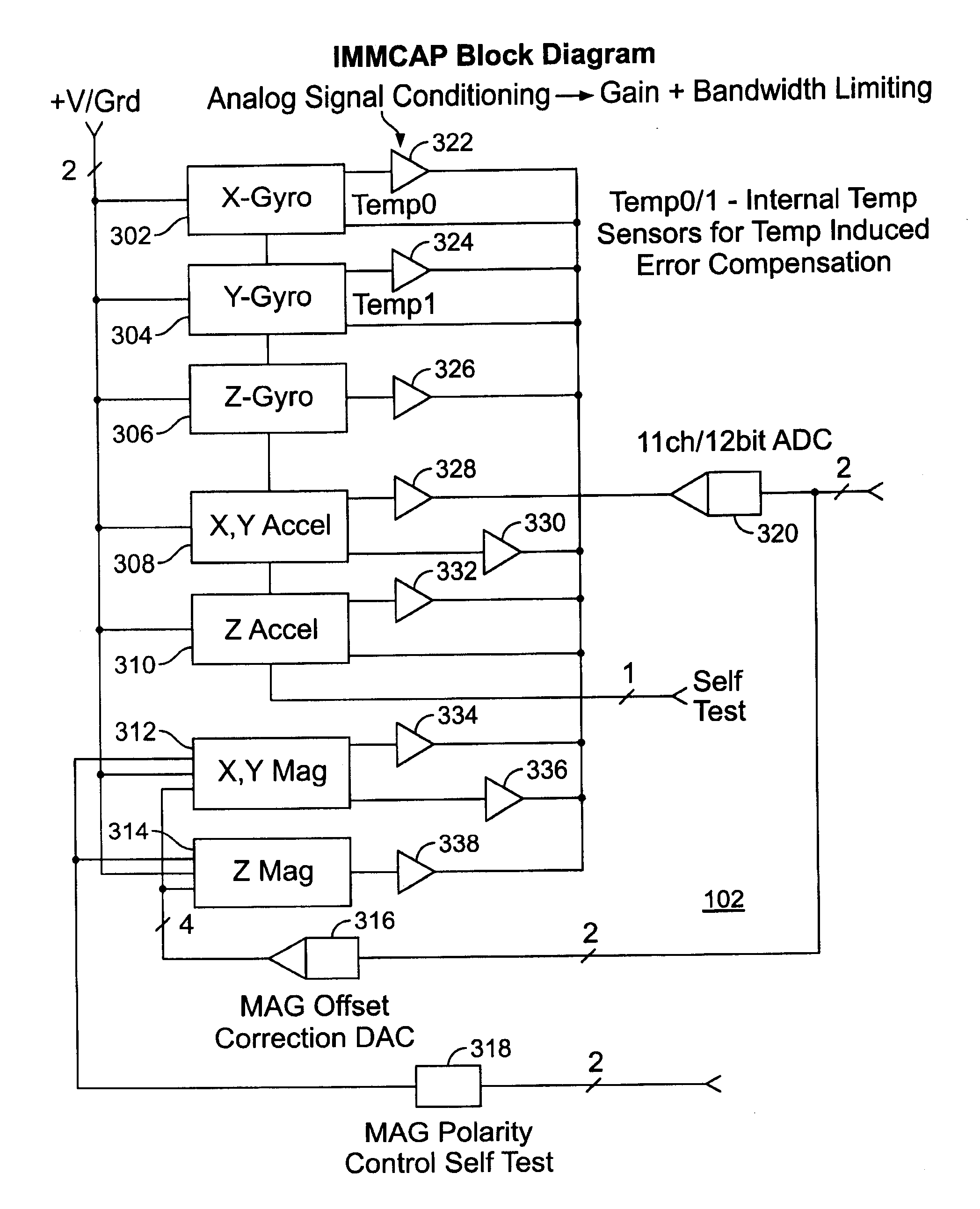
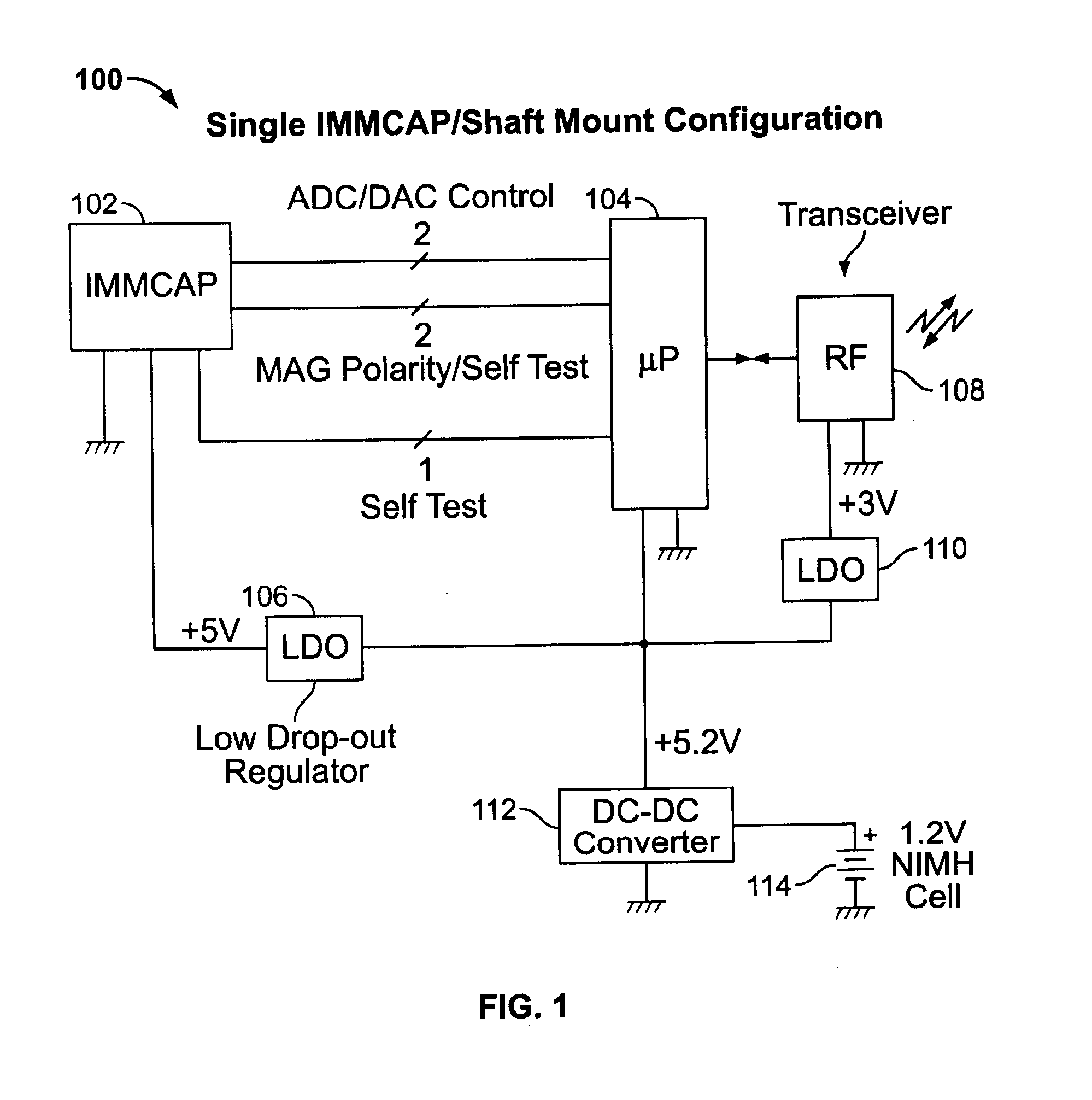
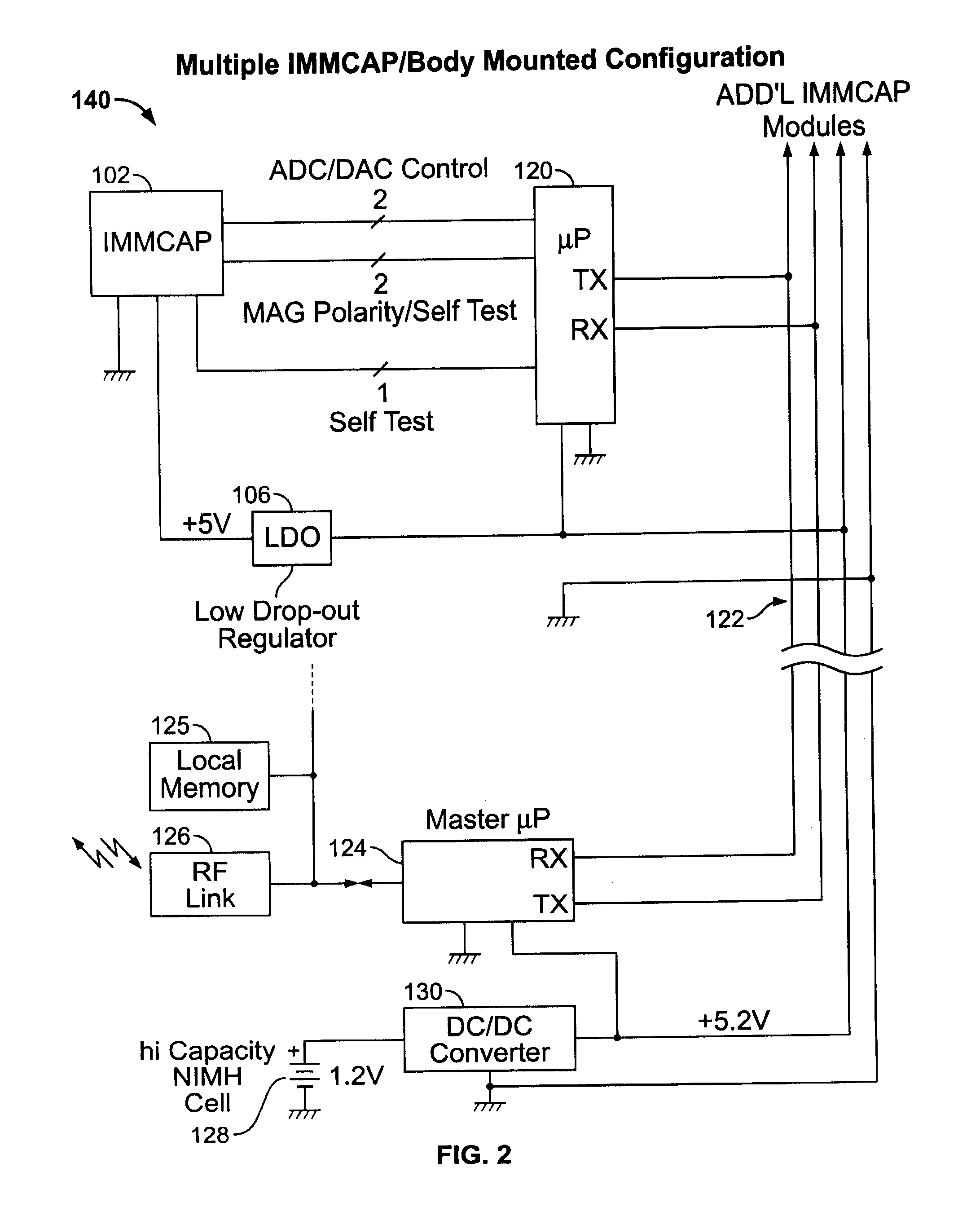
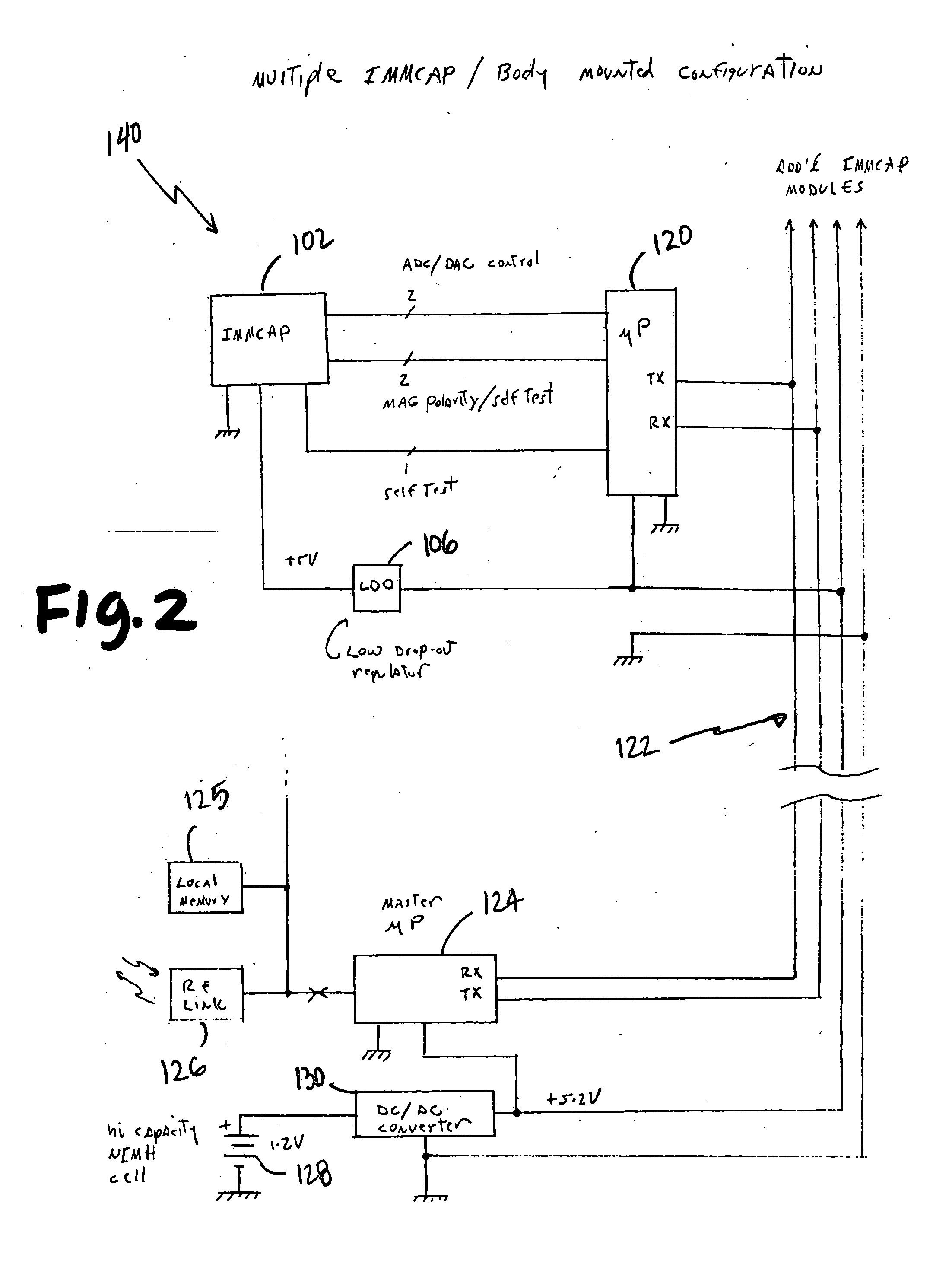
A highly miniaturized electronic data acquisition system includes MEMS sensors that can be embedded onto moving device without affecting the static / dynamic motion characteristics of the device. The basic inertial magnetic motion capture (IMMCAP) module consists of a 3D printed circuit board having MEMS sensors configured to provide a tri-axial accelerometer; a tri-axial gyroscope, and a tri-axial magnetometer all in communication with analog to digital converters to convert the analog motion data to digital data for determining classic inertial measurement and change in spatial orientation (rho, theta, phi) and linear translation (x, y, z) relative to a fixed external coordinate system as well as the initial spatial orientation relative to the know relationship of the earth magnetic and gravitational fields. The data stream from the IMMCAP modules will allow the reconstruction of the time series of the 6 degrees of freedom for each rigid axis associated with each independent IMMCAP module.
Owner:MAGNETO INERTIAL SENSING TECH
Means and method for assessing the geometry of a subterranean fracture during or after a hydraulic fracturing treatment
A method is given of fracturing a subterranean formation including the step of a) pumping at least one device actively transmitting data that provide information on the device position, and further comprising the step of assessing the fracture geometry based on the positions of said at least one device, or b) pumping metallic elements, preferably as proppant agents, and further locating the position of said metallic elements with a tool selected from the group consisting of magnetometers, resistivity tools, electromagnetic devices and ultra-long arrays of electrodes, and further comprising the step of assessing the fracture geometry based on the positions of said metallic elements. The method allows monitoring of the fracture geometry and proppant placement.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Motion sensing apparatus, systems and techniques
InactiveUS20070219744A1Gymnastic exercisingNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsDigital data3d print
A highly miniaturized electronic data acquisition system includes MEMS sensors that can be embedded onto moving device without affecting the static / dynamic motion characteristics of the device. The basic inertial magnetic motion capture (IMMCAP) module consists of a 3D printed circuit board having MEMS sensors configured to provide a tri-axial accelerometer; a tri-axial gyroscope, and a tri-axial magnetometer all in communication with analog to digital converters to convert the analog motion data to digital data for determining classic inertial measurement and change in spatial orientation (rho, theta, phi) and linear translation (x, y, z) relative to a fixed external coordinate system as well as the initial spatial orientation relative to the know relationship of the earth magnetic and gravitational fields. The data stream from the IMMCAP modules will allow the reconstruction of the time series of the 6 degrees of freedom for each rigid axis associated with each independent IMMCAP module.
Owner:C LAN WIRELESS
Method for estimating the direction of a moving solid
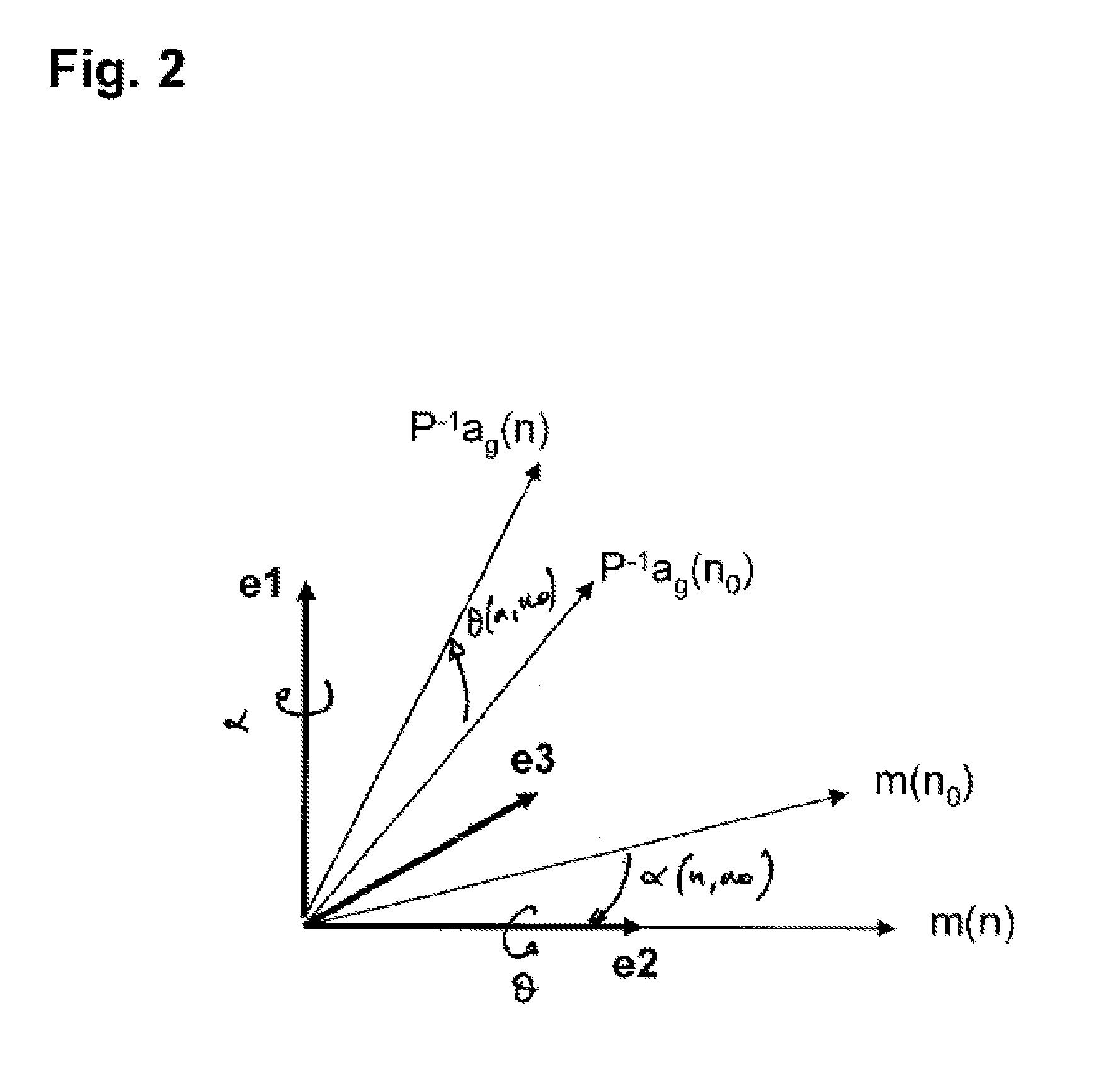
InactiveUS20120185204A1Digital computer detailsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsMagnetometerInertia
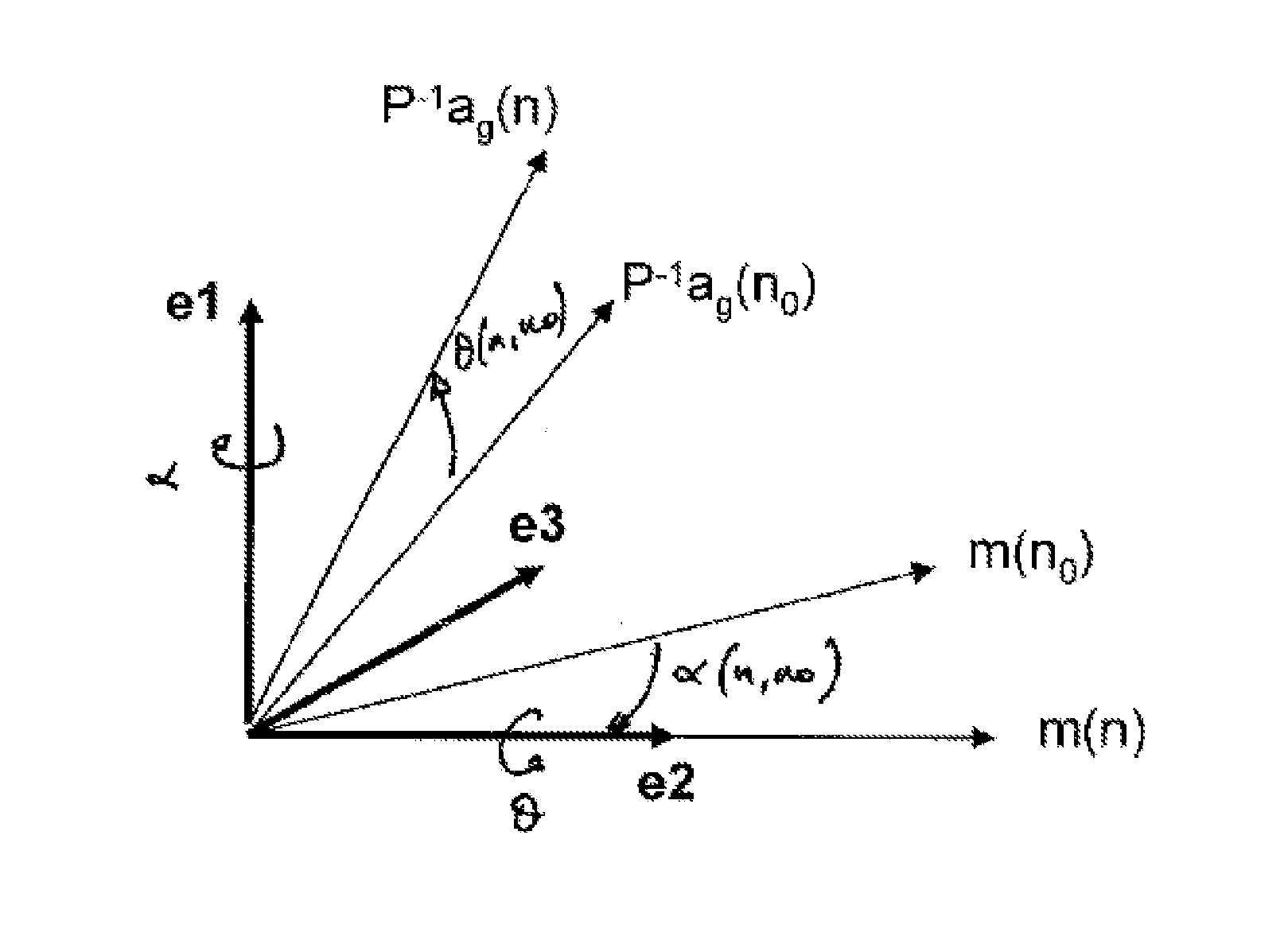
The invention relates to a method for estimating the orientation in an inertial reference frame of a solid in motion equipped with an accelerometer and a magnetometer which are mounted on said solid.According to this method, an orientation of the solid is measured at a reference instant, said orientation being defined by a rotation matrix for rotating from the mobile reference frame of the solid at the reference instant to the inertial reference frame. A rotation matrix for rotating between the orientation of the solid at a subsequent instant n and said orientation of the solid at the reference instant is thereafter estimated. The orientation of the solid at the instant n is thereafter determined with the aid of the previously estimated rotation matrix and of the known orientation of the solid at the reference instant.
Owner:MOVEA +1
Single/multiple axes six degrees of freedom (6 DOF) inertial motion capture system with initial orientation determination capability
A highly miniaturized electronic data acquisition system includes MEMS sensors that can be embedded onto moving device without affecting the static / dynamic motion characteristics of the device. The basic inertial magnetic motion capture (IMMCAP) module consists of a 3D printed circuit board having MEMS sensors configured to provide a tri-axial accelerometer; a tri-axial gyroscope, and a tri-axial magnetometer all in communication with analog to digital converters to convert the analog motion data to digital data for determining classic inertial measurement and change in spatial orientation (rho, theta, phi) and linear translation (x, y, z) relative to a fixed external coordinate system as well as the initial spatial orientation relative to the know relationship of the earth magnetic and gravitational fields. The data stream from the IMMCAP modules will allow the reconstruction of the time series of the 6 degrees of freedom for each rigid axis associated with each independent IMMCAP module.
Owner:MAGNETO INERTIAL SENSING TECH
Marine electromagnetic measurement system
InactiveUS6842006B2Electric/magnetic detection for transportAcoustic wave reradiationOcean bottomMeasurement device
A sea-floor electromagnetic measurement device for obtaining underwater measurements of earth formations including a central structure and arms attached to the central structure so that they can pivot relative to the central structure. An electrode is attached to the end of each of the arms or to the central structure, and / or magnetometers are attached to the arms. A method for undertaking sea-floor electromagnetic measurements of earth formations including measuring electric fields at a selected distance from a central structure of an electromagnetic measurement system. Magnetic fields are then measured at the same location.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Automatic calibration of a three-axis magnetic compass
InactiveUS7451549B1Sure easyLess computing powerNavigation instrumentsTesting/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesData setAccelerometer
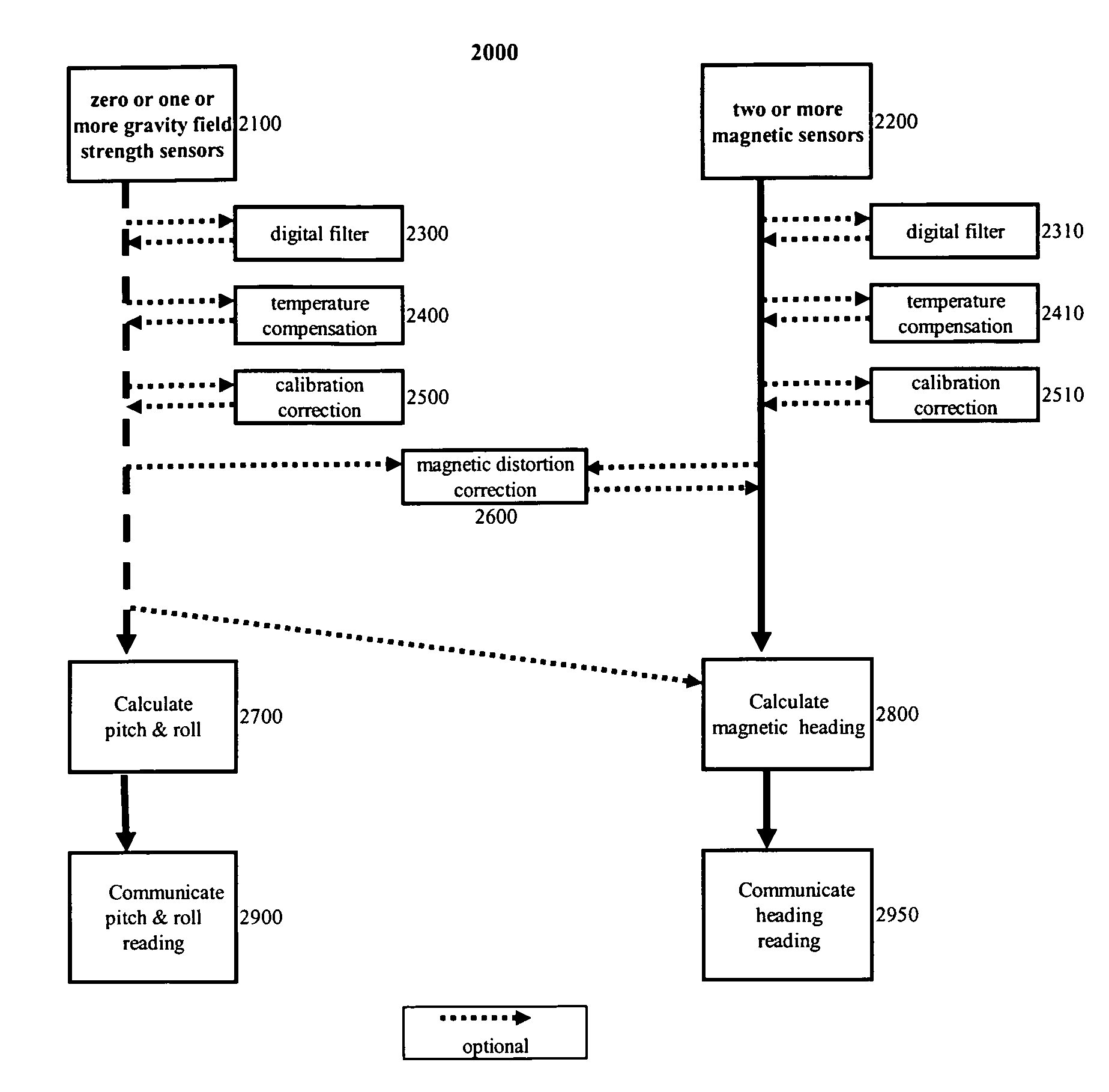
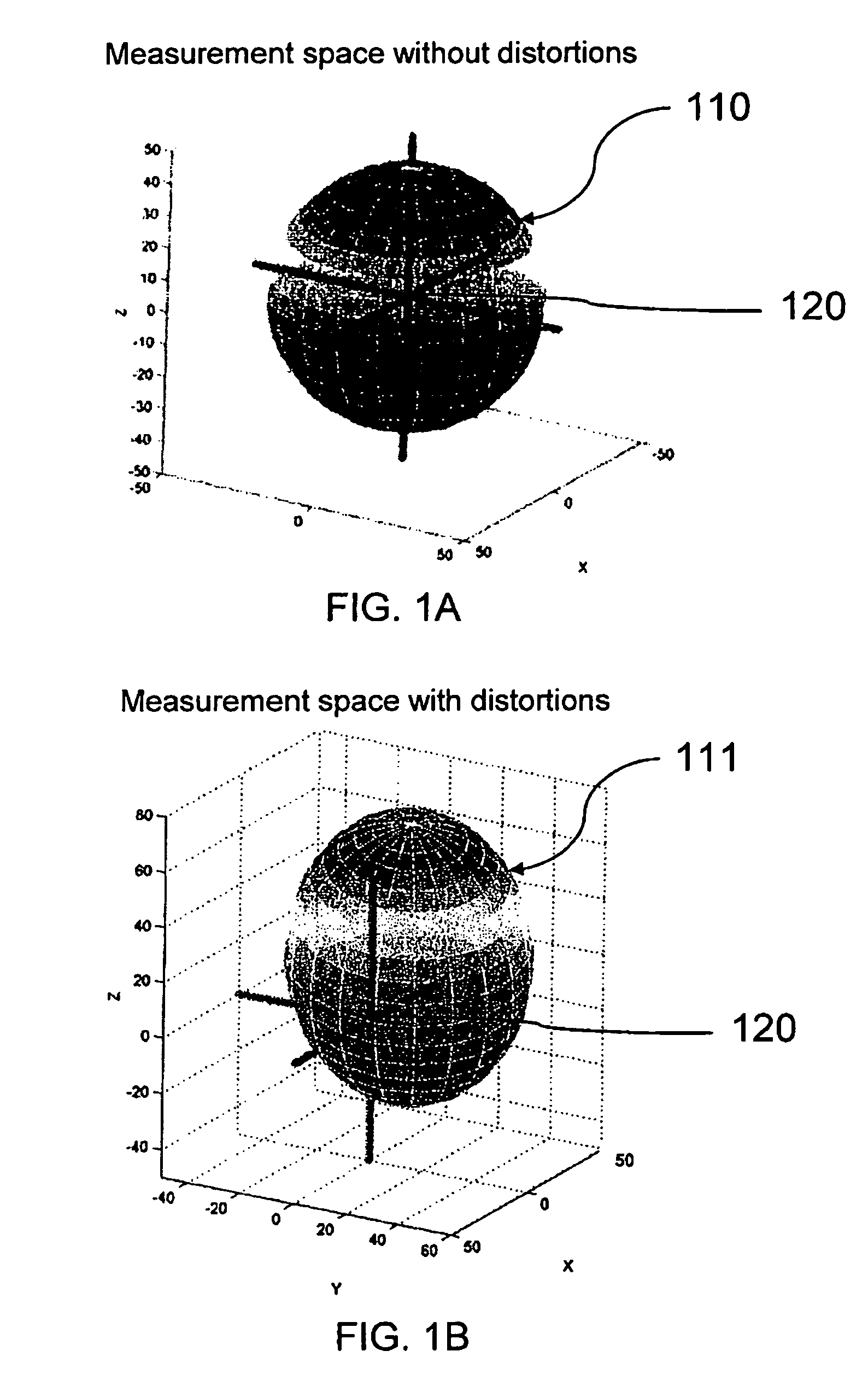
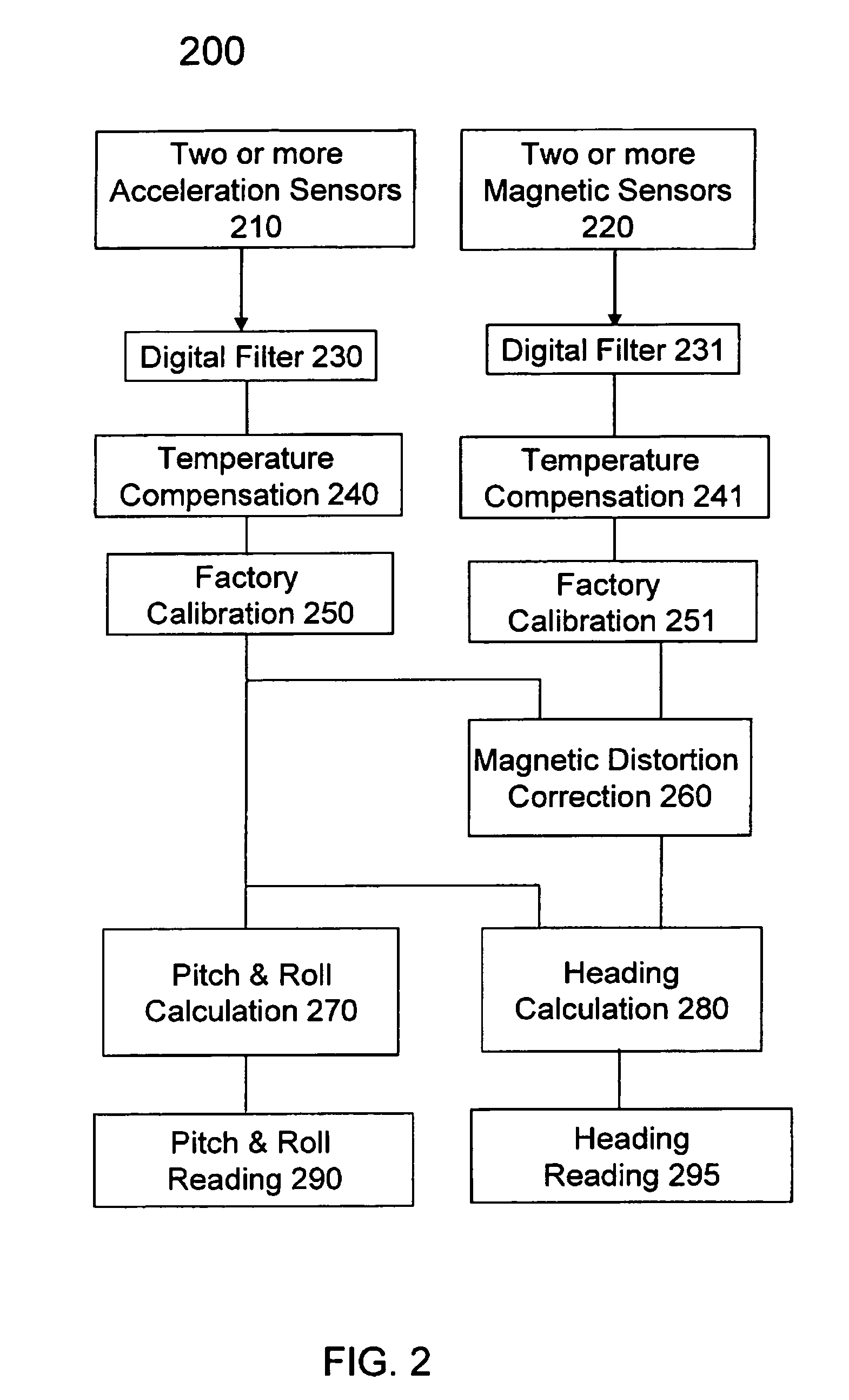
A magnetic compass apparatus and method to account for magnetic distortion while determining a magnetic heading is disclosed. The method enables a compass module, comprising at least two magnetometers, to characterize its magnetic environment dynamically, while collecting data of a geomagnetic field; a user moves an apparatus through various orientations; the environment may or may not contain magnetic distortion influences. Data gathered by magnetometers and, optionally, accelerometers are processed through at least two filters before being transferred as a processed data set for repetitive measurement calculations. A series of calculations is executed recursively in time by solving one or more linear vector equations using processed data.
Owner:P&I
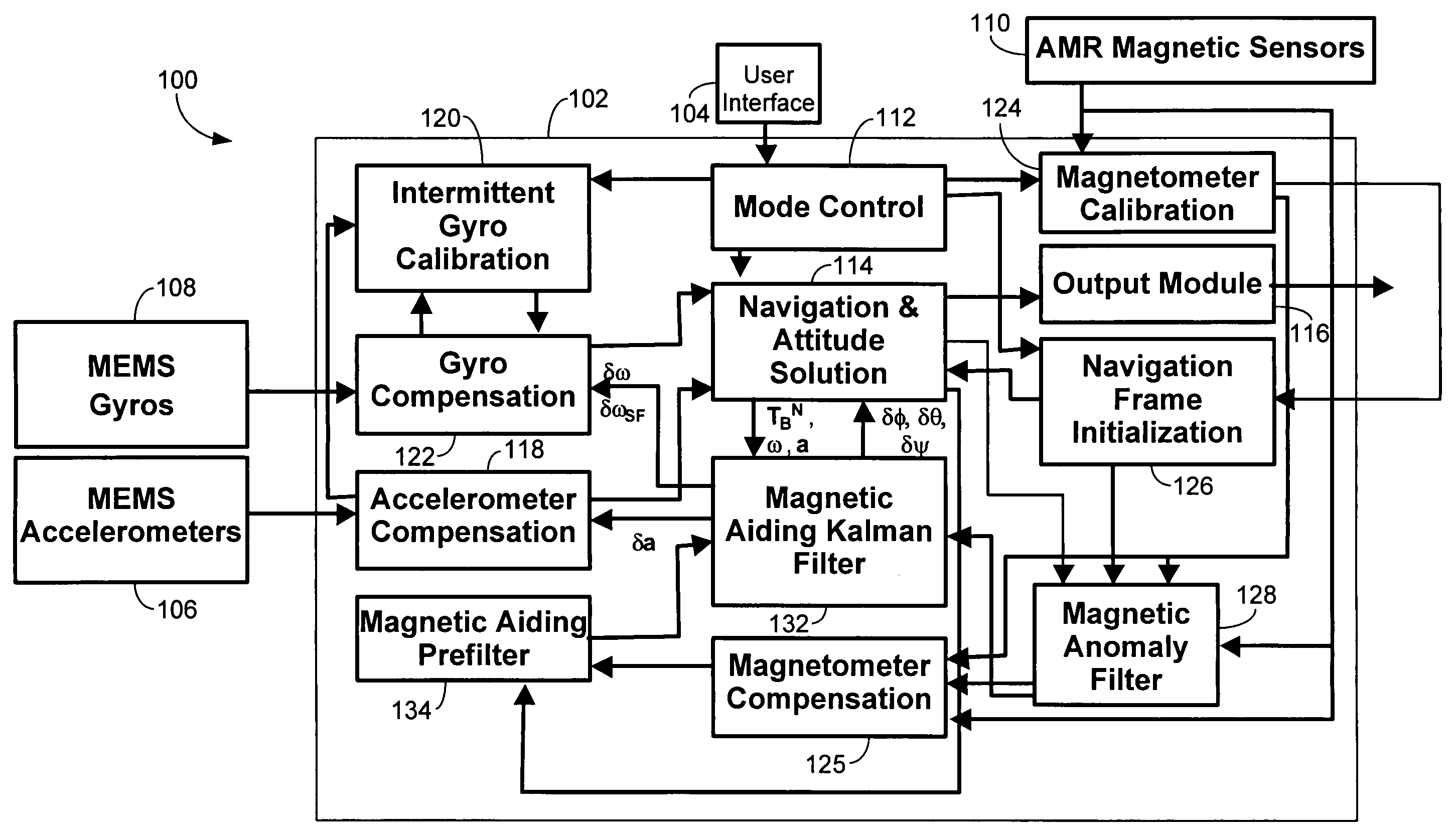
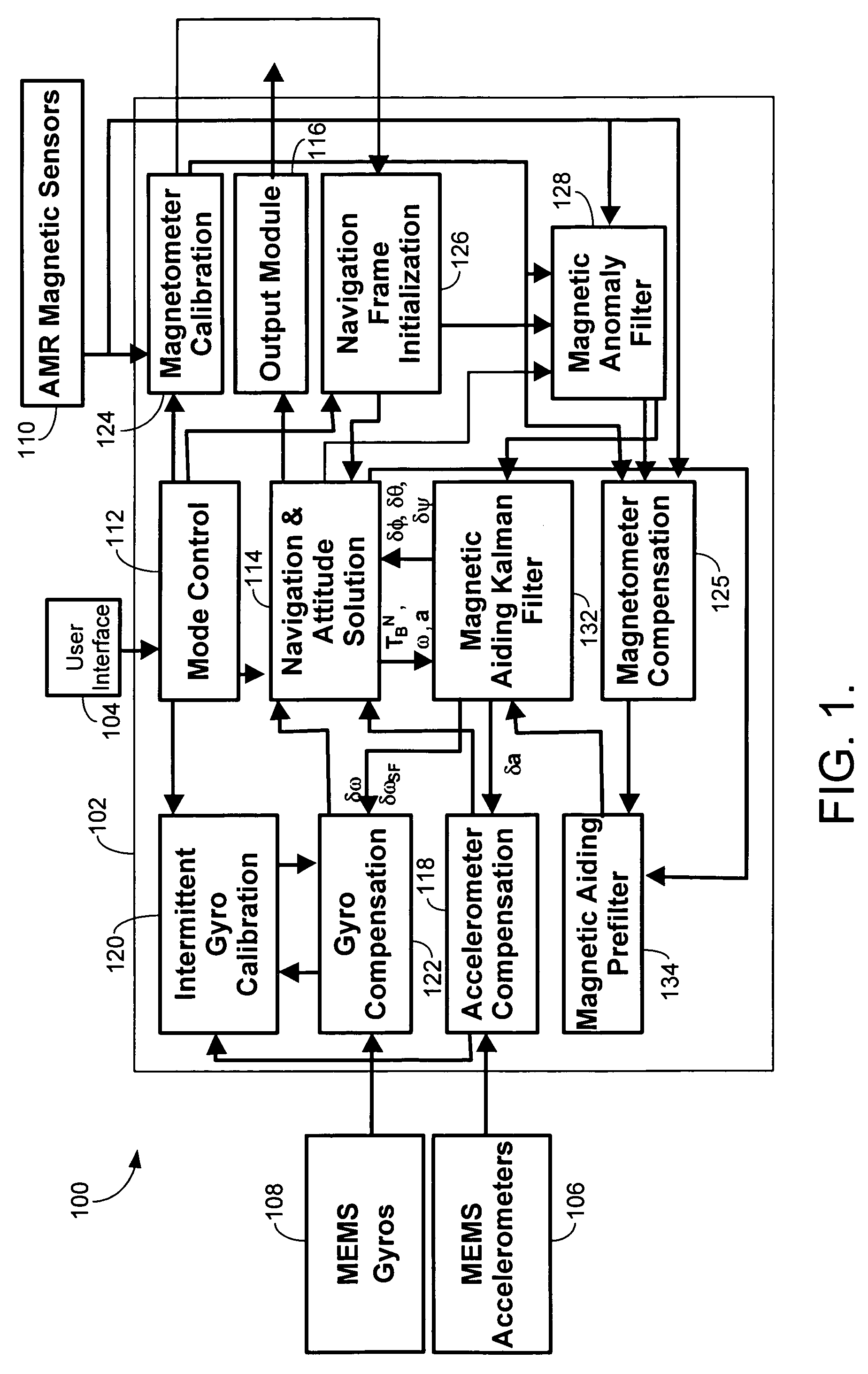
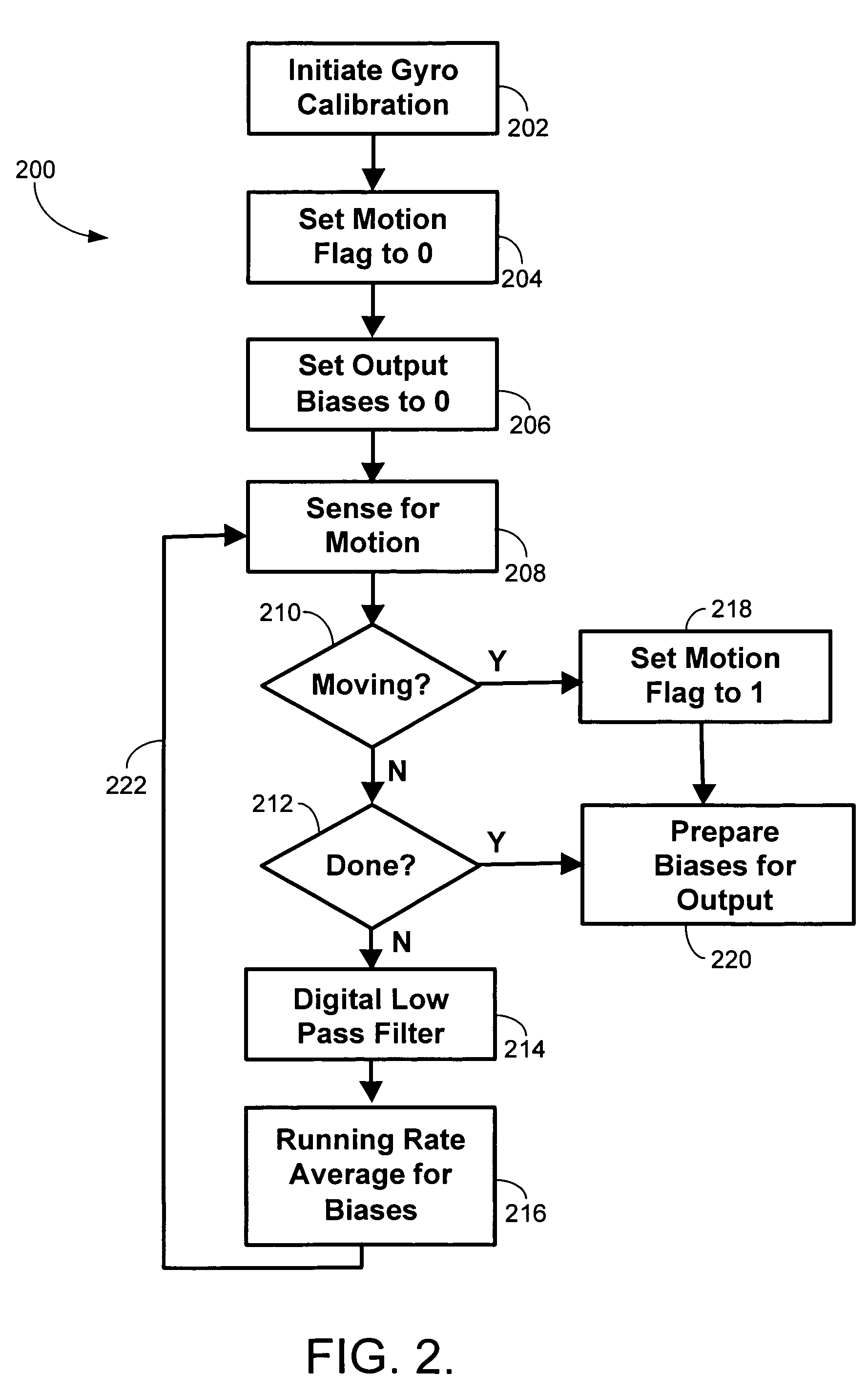
Self-calibrated azimuth and attitude accuracy enhancing method and system (SAAAEMS)
ActiveUS20090089001A1Digital computer detailsSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsAccelerometerGyroscope
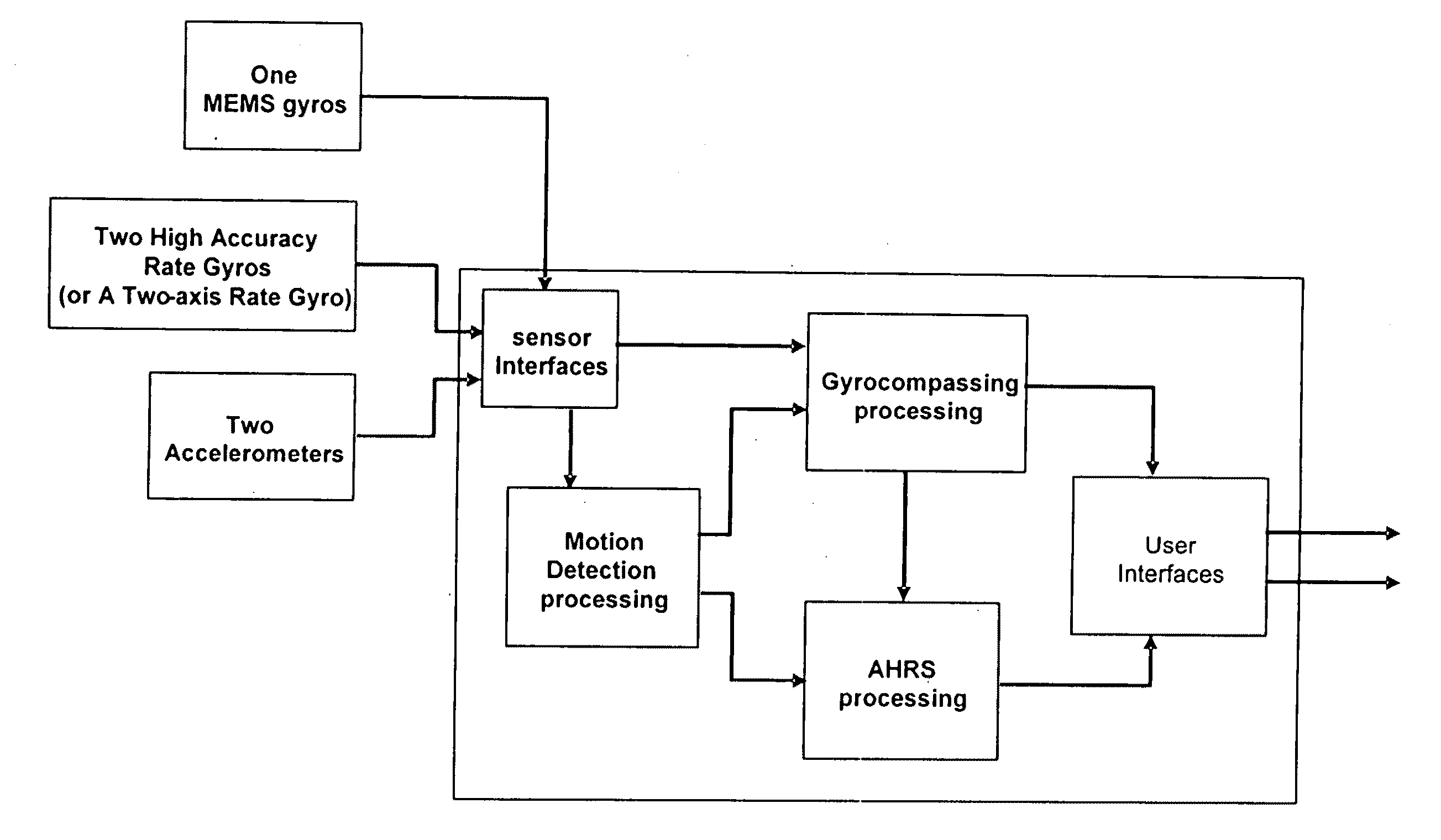
A method and system for Self-calibrated Azimuth and Attitude Accuracy Enhancing are disclosed, wherein SAAAEMS approach is based on fully auto-calibration self-contained INS principles, not depending on magnetometers for azimuth / heading determination, and thus the system outputs and performance are not affected by the environmental magnetic fields. In order to reduce the system size and cost, this new innovative methods and algorithms are used for SAAAEMS system configuration and integration. Compared to a conventional INS for gyrocompassing, AGNC's approach uses a smaller number of high accuracy sensors: SAAAEMS uses only one 2-axis high accuracy gyro (for example, one DTG) instead of 3-axis; the third axis gyro is a MEMS gyro. It uses only 2 high accuracy accelerometers instead of 3, since the two accelerometers are used only for gyrocompassing not for navigation. These two changes to the conventional INS system configuration remarkably reduce the whole system size and cost. SAAAEMS, uses dynamic gyrocompassing processing for isolation of Base motion disturbance / interference and vibration. SAAAEMS provides a method and system for using automatic methods for system calibration.
Owner:AMERICAN GNC
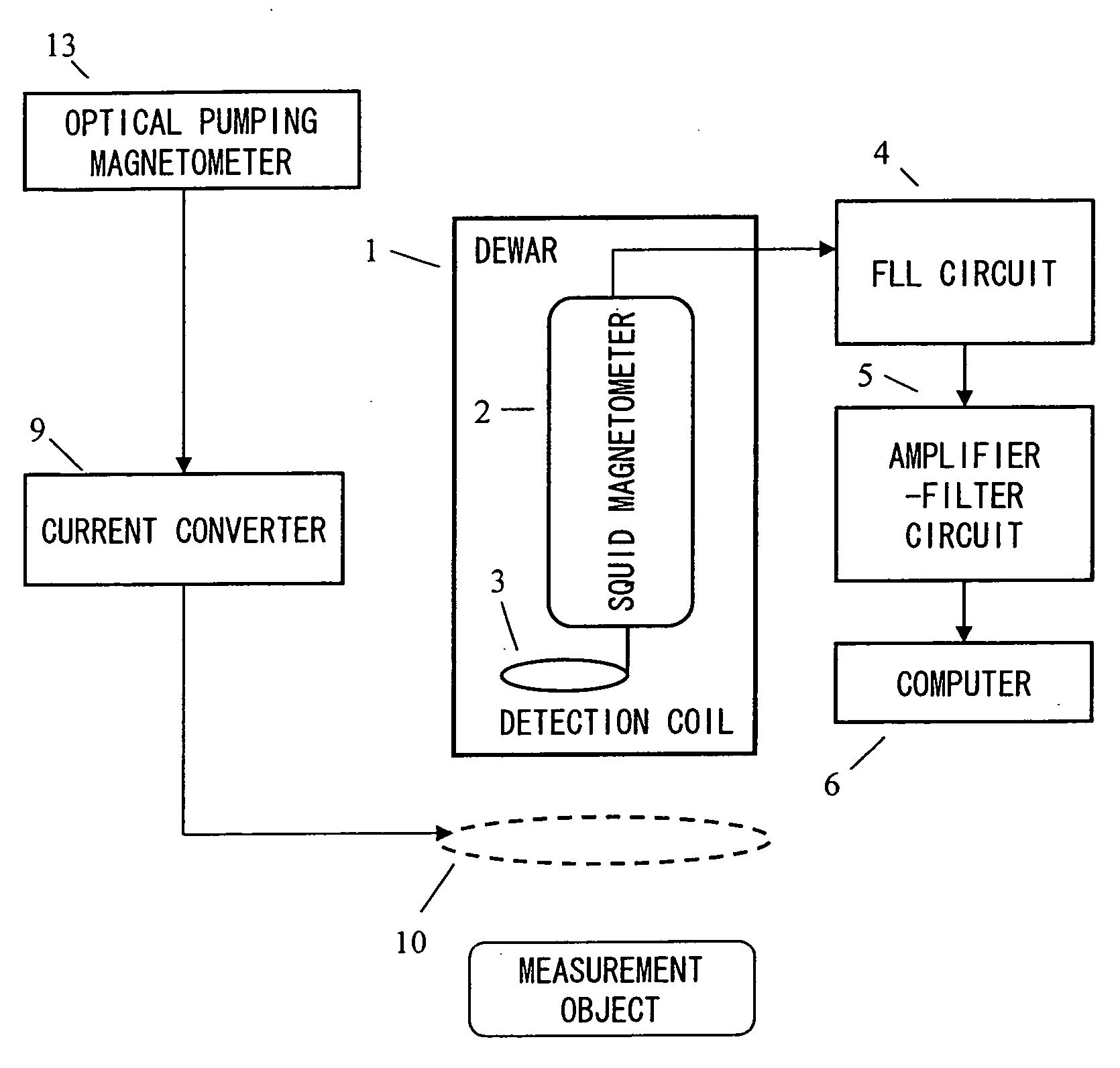
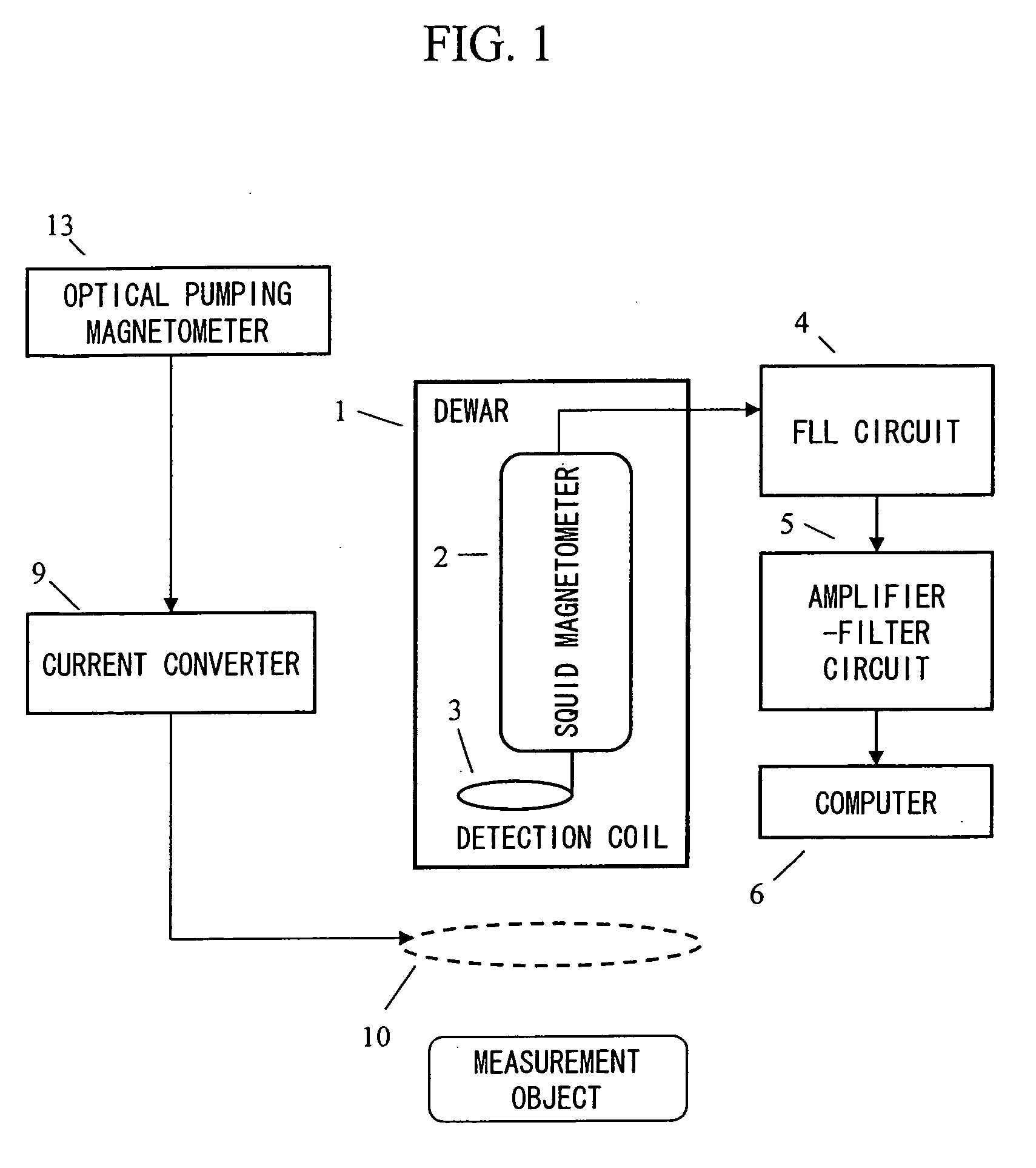
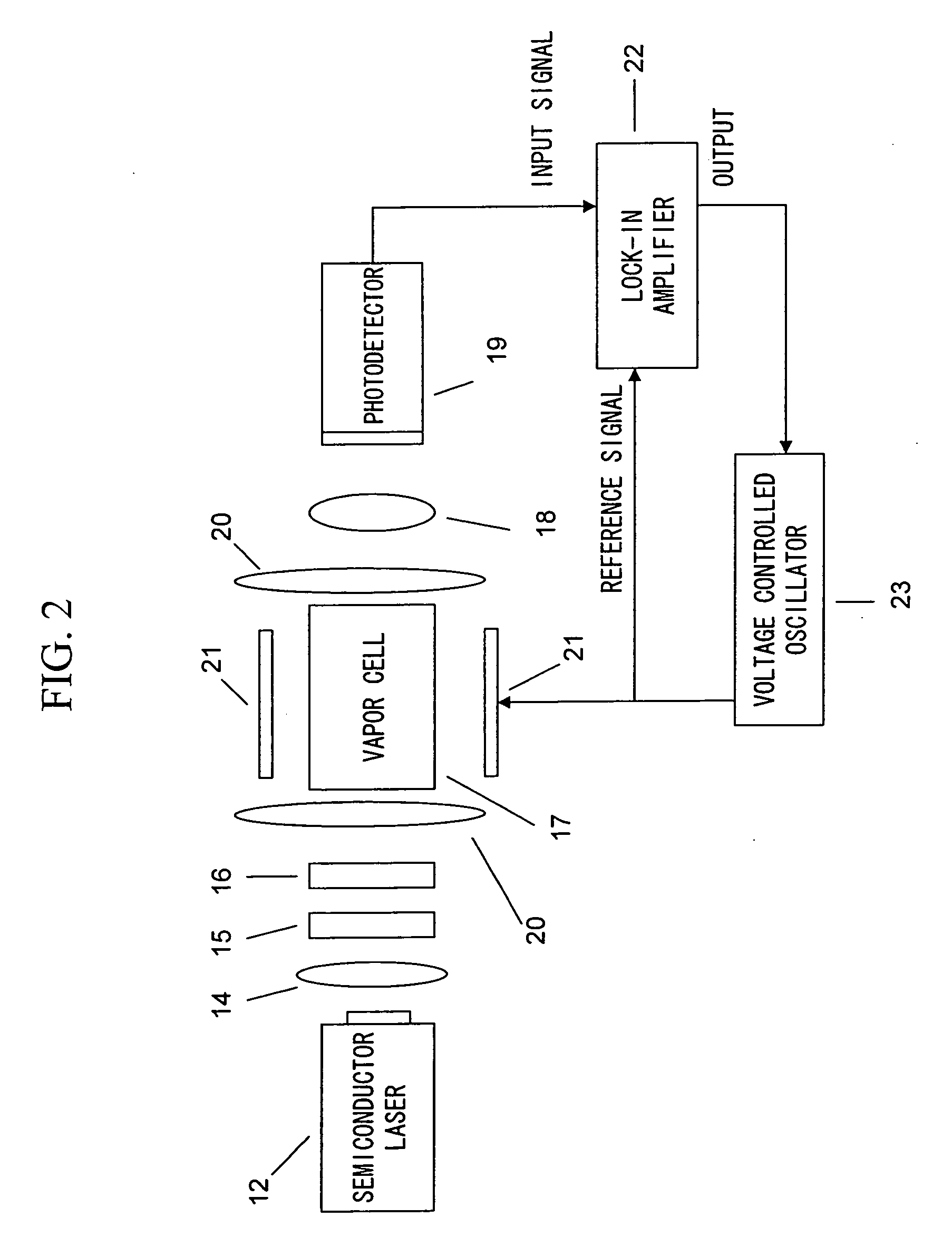
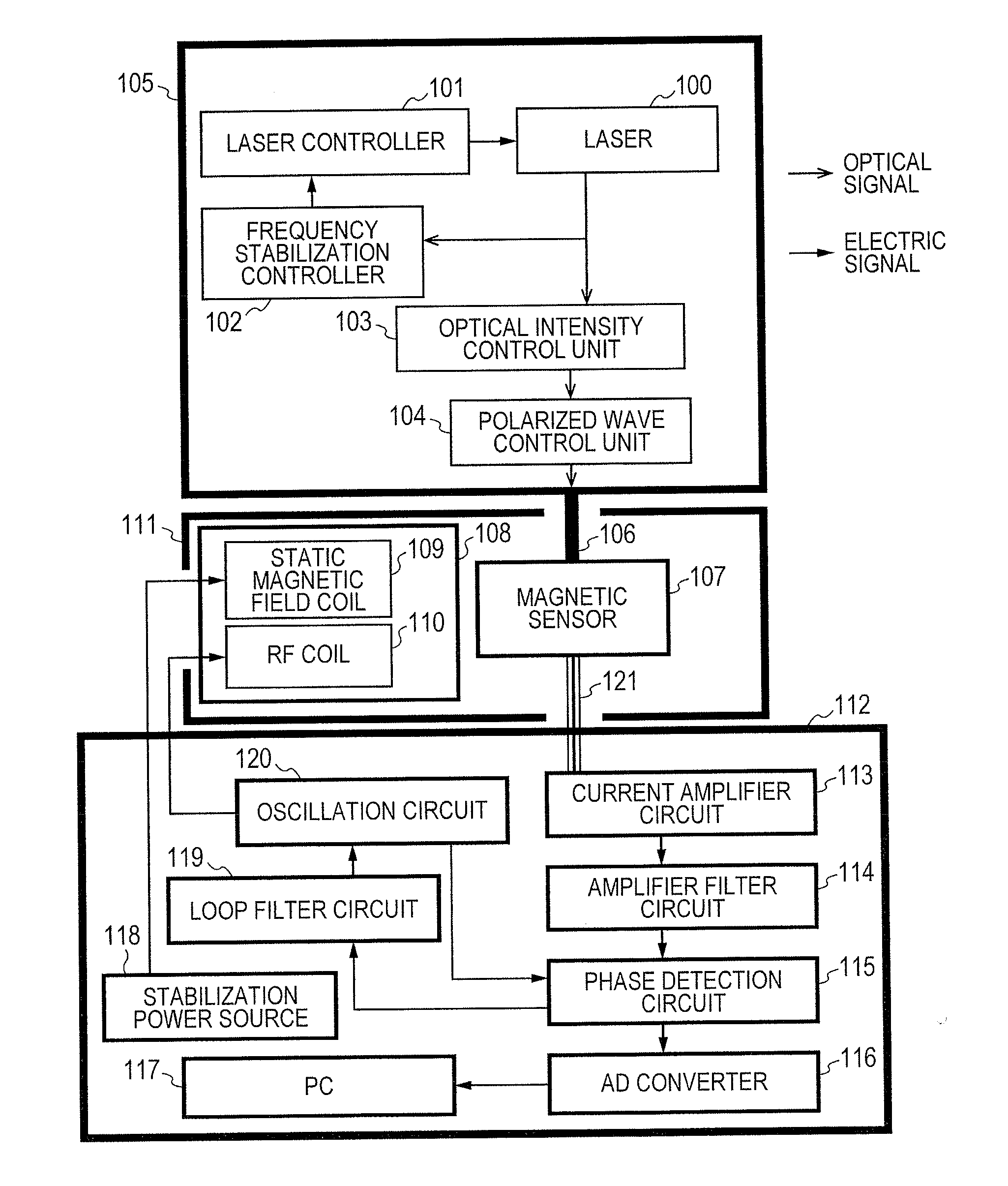
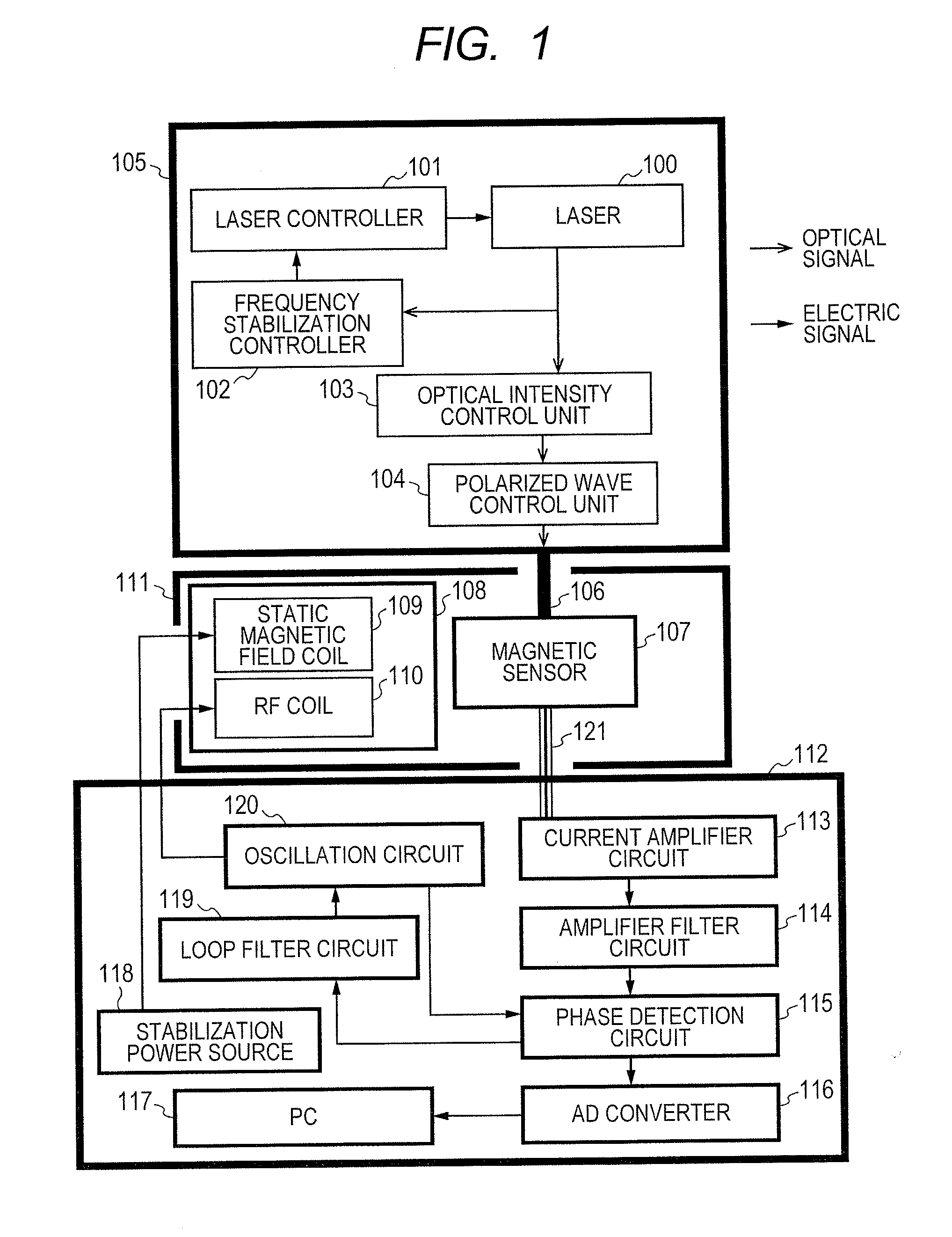
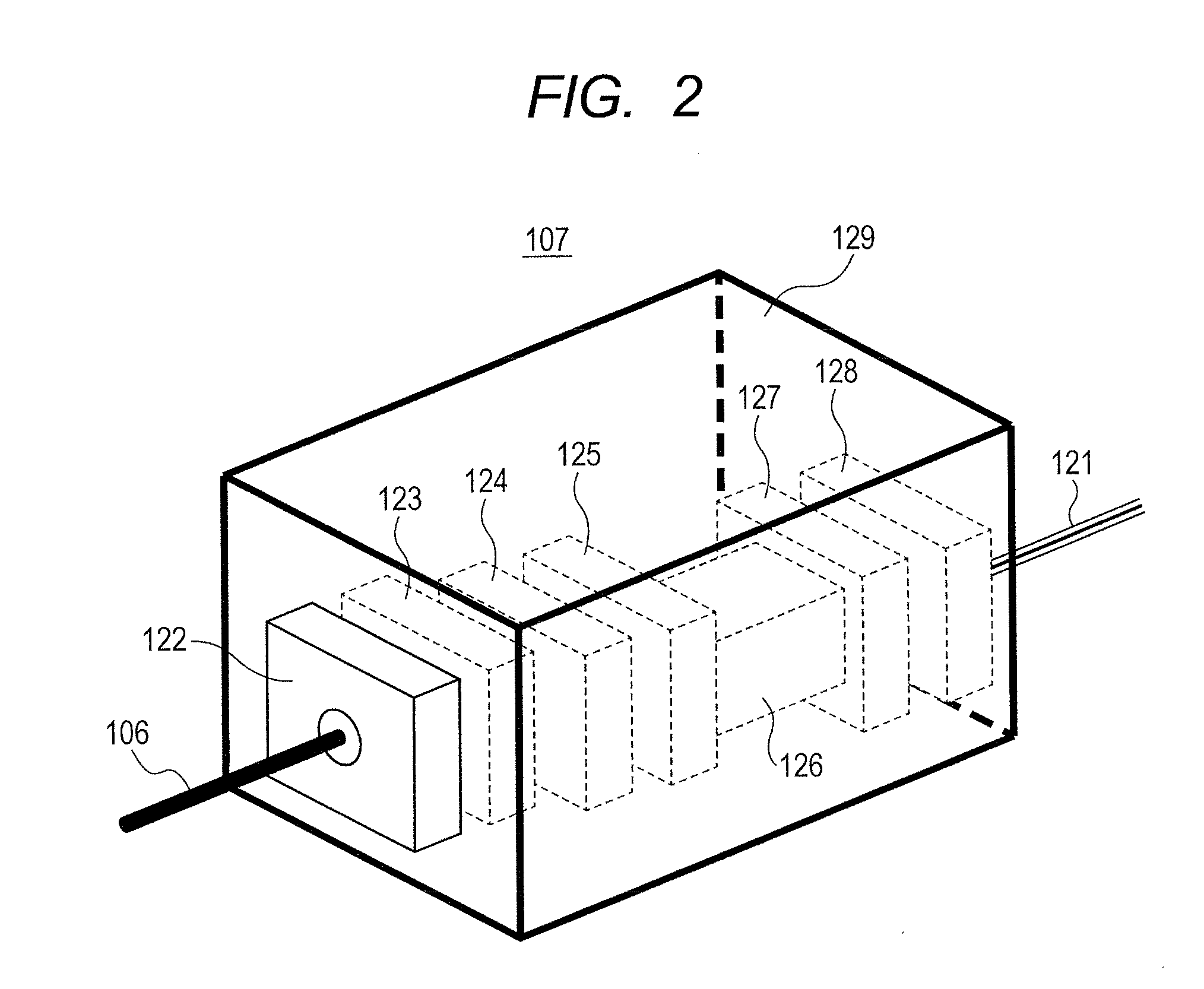
Magnetic field measurement system and optical pumping magnetometer
ActiveUS20070120563A1Reduce magnetic noiseAffect operationSuperconductors/hyperconductorsMagnetic field measurement using superconductive devicesElectricityComing out
Provided is a highly accurate optical pumping magnetometer, in which a static magnetic field and an oscillating field to be applied to a vapor cell are stabilized. To this end, the optical pumping magnetometer includes: Helmholtz coils for applying a constant static magnetic field to a vapor cell serving as a magnetic field detector; fluxgate magnetometers for detecting environmental magnetic noise in two directions of X-axis direction and Y-axis direction other than Z-axis direction which is a direction for detecting a magnetic field coming out of a measurement object while locating the vapor cell in the center thereof; magnetometer drive circuits for driving the fluxgate magneotometers; current converters for converting outputs of the magnetometer drive circuits into amount of currents; and magnetic field generating coils for generating a magnetic field in a phase opposite to the environmental magnetic noise in the two directions.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Inertial/magnetic measurement device
Disclosed is a system and method for onboard optimal estimation of heading, pitch, and roll through real-time measurement of magnetic field, acceleration and angular motion in three dimensions. Magnetometer information is used to create an initial reference from which movement is measured. Thus, the process does not have to start when the body is in a known position. Further, the device does not have to continually rely on accelerometer data to get roll and pitch. To do this magnetic field data is used to complement gyro information. The magnetic data is used to estimate pitch, roll, and heading.
Owner:GENERAL ATOMICS
Method and apparatus for locating well casings from an adjacent wellbore
ActiveUS20070126426A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingConstructionsEngineeringConductive materials
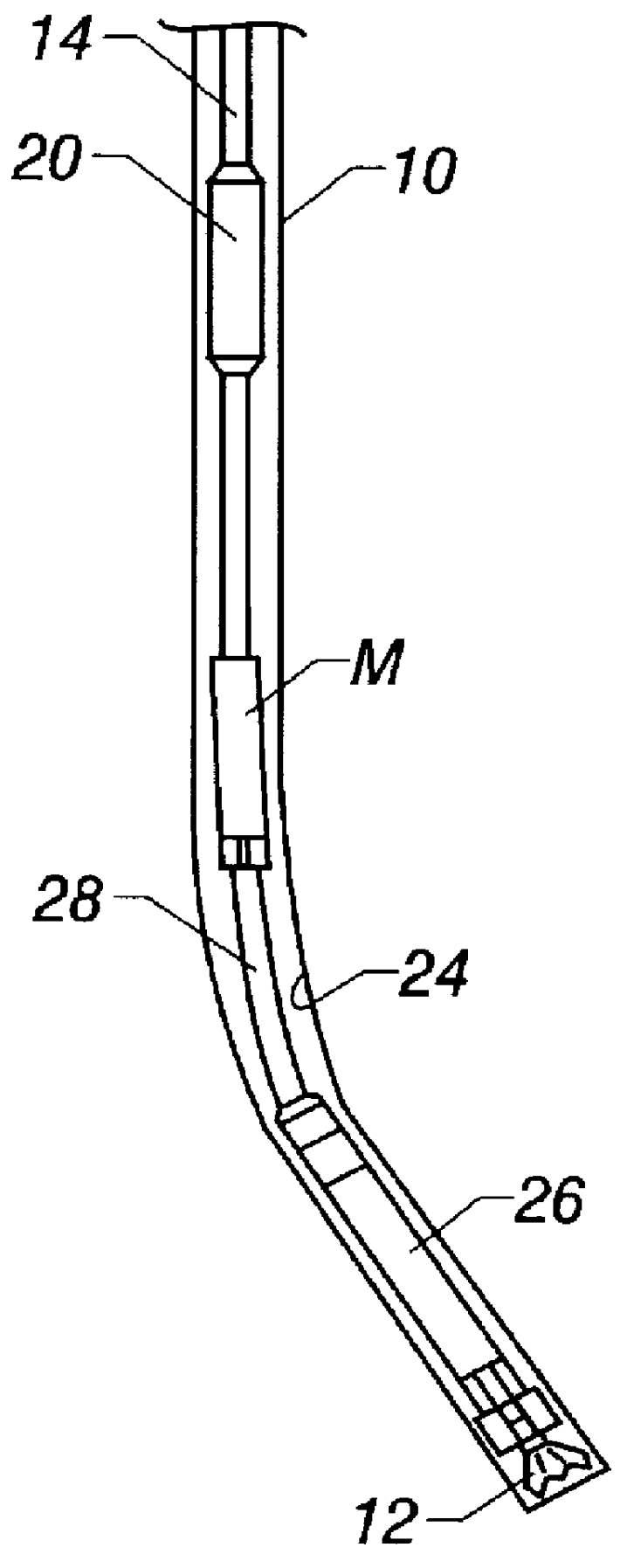
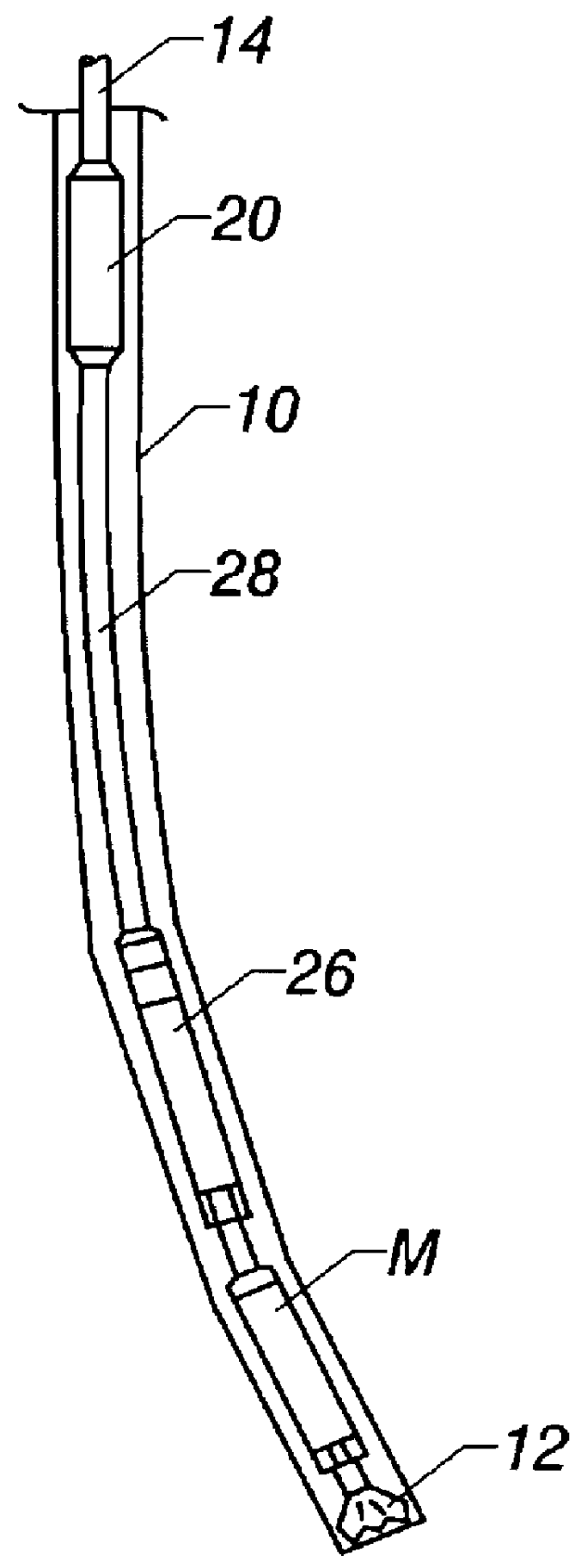
A wellbore tool for locating a target wellbore containing a conductive member from a second wellbore and directing the trajectory of the second wellbore relative to the target wellbore includes an electric current driver having an insulated gap; a three-axis magnetometer positioned within a non-magnetic housing that is disposed within a non-magnetic tubular, the three-axis magnetometer positioned below the electric current driver; a drill bit positioned below the three-axis magnetometer; a hollow tubular connected between the electric current driver and the three-axis magnetometer; and a measurement-while-drilling tool. The current driver generates an electric current across the gap to the portion of the tool below the insulated gap. In a method a current is generated across the insulated gap to the portion of the tool below the insulated gap to the conductive material in the target wellbore returning to a portion of the bottom hole assembly above the insulated gap thereby producing a target magnetic field. Measuring the target magnetic field at the bottom hole assembly and the earth's magnetic field; and determining the position of the second wellbore relative to the target wellbore. Then steering the bottom hole assembly to drill the second wellbore along a trajectory relative to the target wellbore.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Sports Sensor
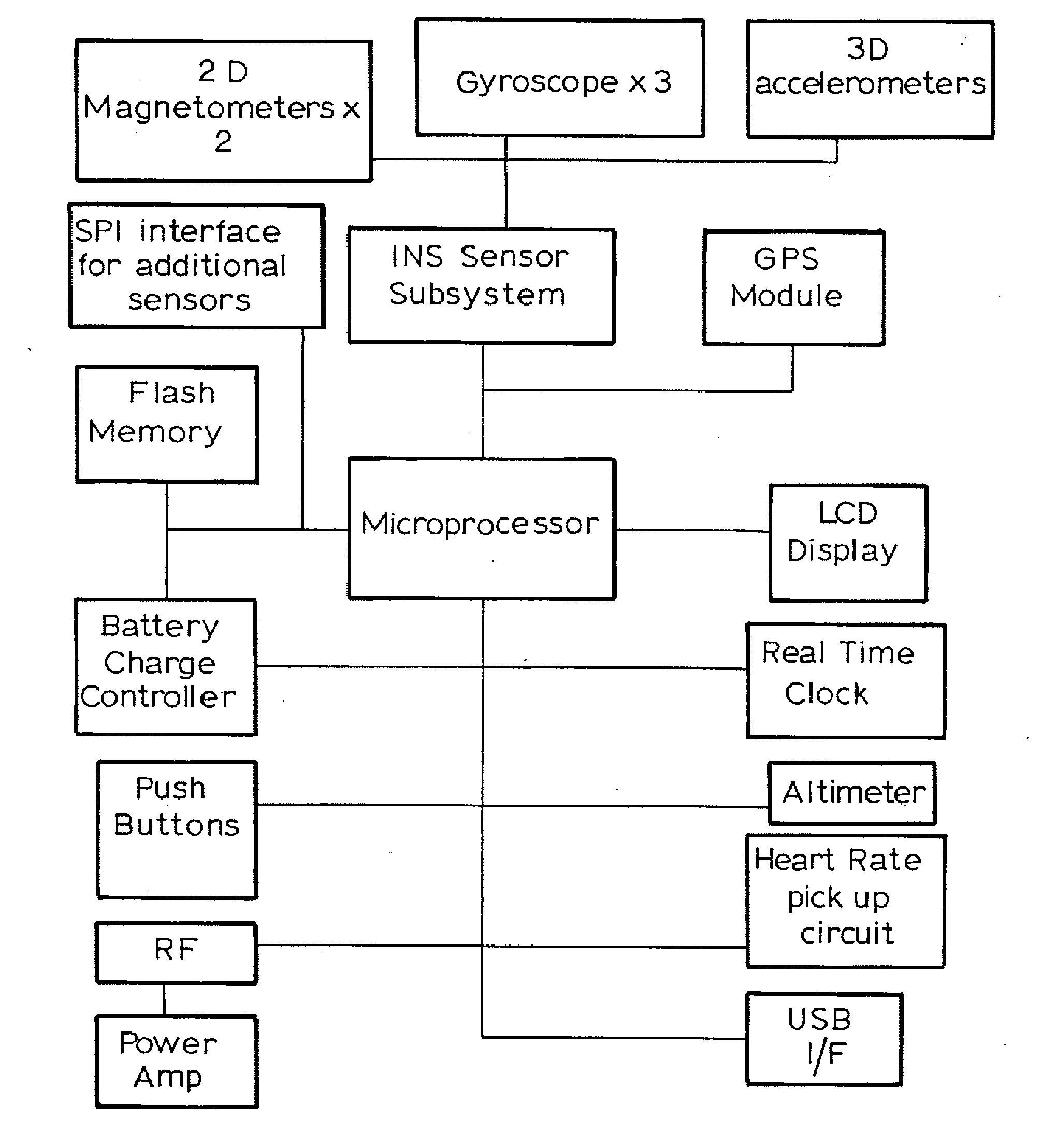
ActiveUS20080284650A1Show efficiencyShow powerGymnastic exercisingPosition fixationGyroscopeAccelerometer
A data logger for a monitoring sports which includes an accelerometer, a gyro sensor to sense angular displacement, a GPS unit to sense position and velocity, a magnetometer to sense direction of movement, a heart rate monitor, and a controller programmed to manipulate the data and provide a display of the heart rate, speed, and other sport parameters. The data can be stored or transmitted to a remote computer for use by the coach. The device is useful in football codes, athletics, swimming, snow sports and cycling.
Owner:CATAPULT GRP INT
Sports sensor
ActiveUS8036826B2Accurate outputSimple mathematicsGymnastic exercisingPosition fixationGyroscopeAccelerometer
A data logger for a monitoring sports which includes an accelerometer, a gyro sensor to sense angular displacement, a GPS unit to sense position and velocity, a magnetometer to sense direction of movement, a heart rate monitor, and a controller programmed to manipulate the data and provide a display of the heart rate, speed, and other sport parameters. The data can be stored or transmitted to a remote computer for use by the coach. The device is useful in football codes, athletics, swimming, snow sports and cycling.
Owner:CATAPULT GRP INT
Robot navigation method and device based on multi-sensor data fusion
InactiveCN106681330ARealize autonomous navigationTaking into account the costPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesUltrasonic sensorGyroscope
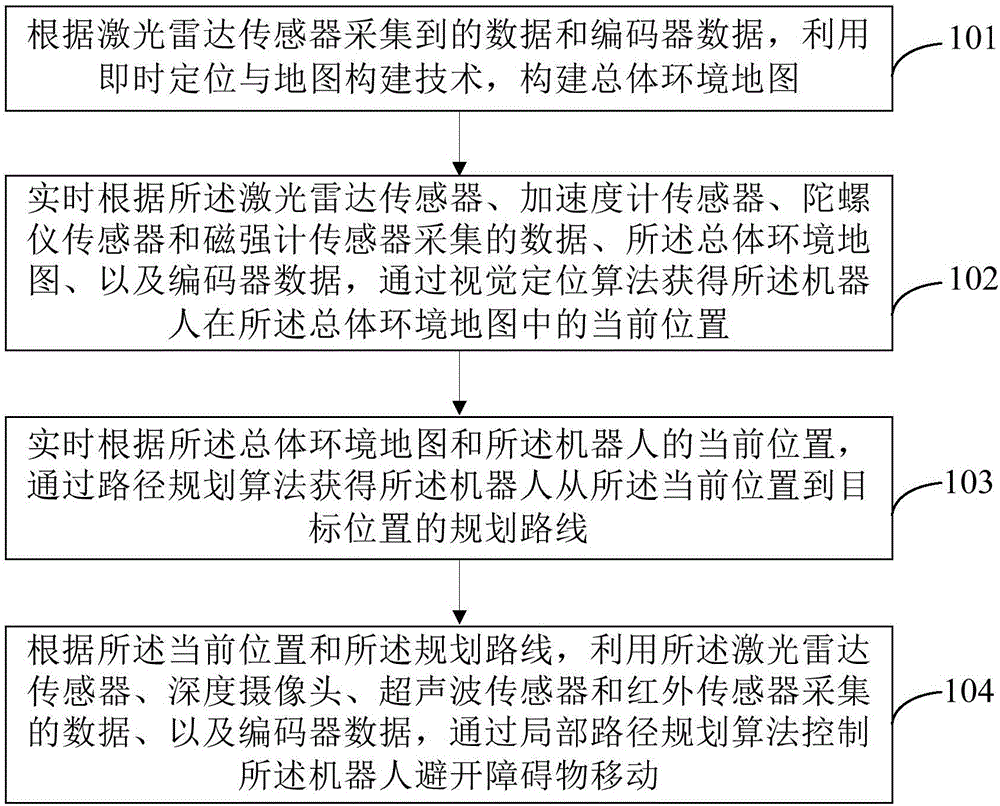
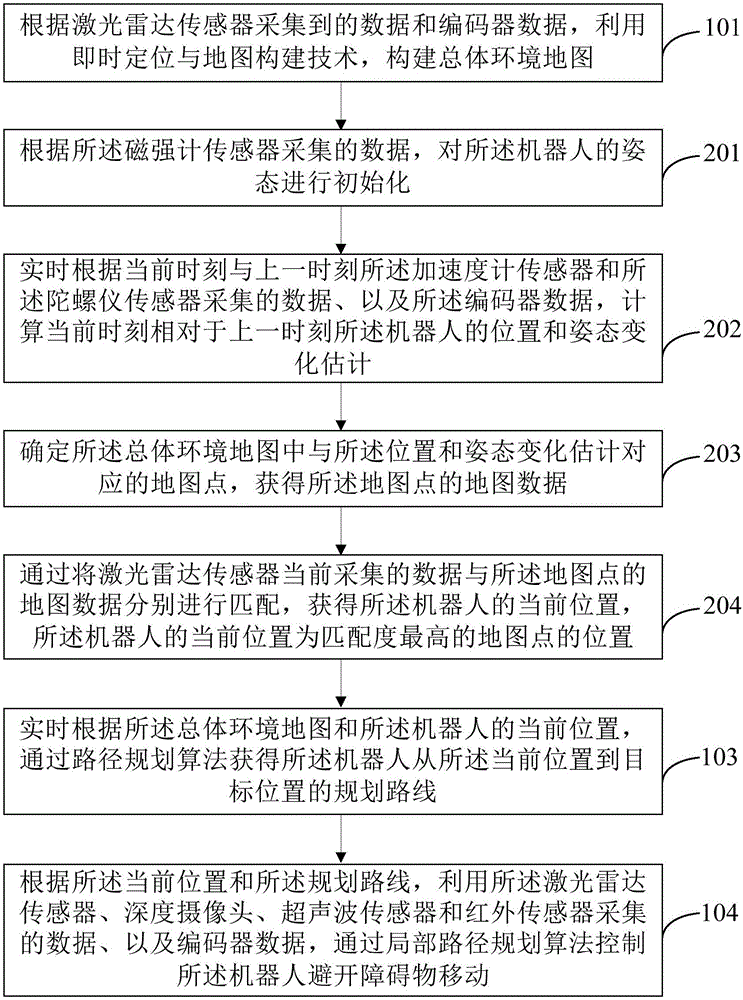
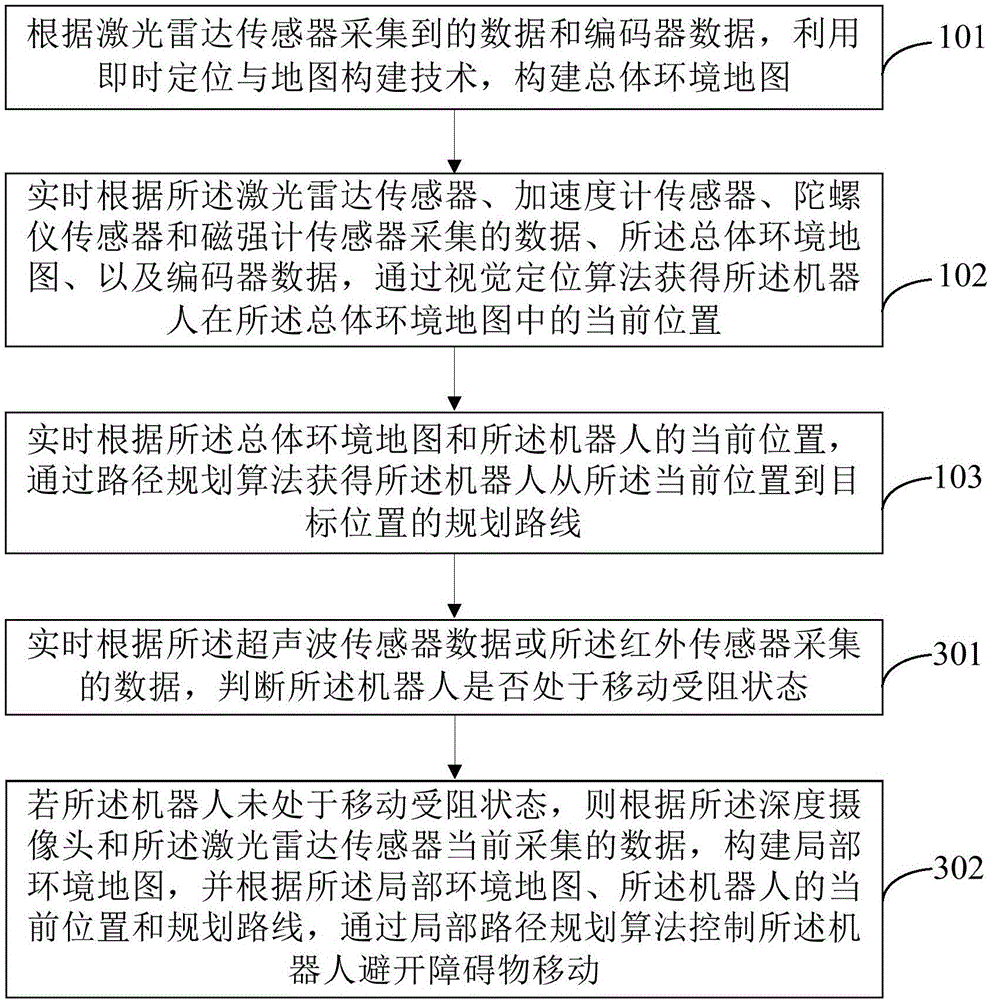
The invention provides a robot navigation method and device based on multi-sensor data fusion. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a map of a total environment according to data acquired by a laser radar sensor and data of an encoder; acquiring the current position of a robot in the map of the total environment in real time according to data acquired by a laser radar sensor, an accelerometer sensor, a gyroscope sensor and a magnetometer sensor, the map of the total environment and the data of the encoder; acquiring a planned route of the robot from the current position to a targeted position in real time according to the map of the total environment and the current position of the robot; and controlling the robot to keep away from barriers during movement by the data which are acquired by the laser radar sensor, a deep camera, an ultrasonic sensor and an infrared sensor and the data of the encoder. On the basis of reasonable utilization of the sensors to realize navigation of the robot, the method is flexibly applied to various scenes, costs are considered, and the autonomous navigation effect can be achieved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
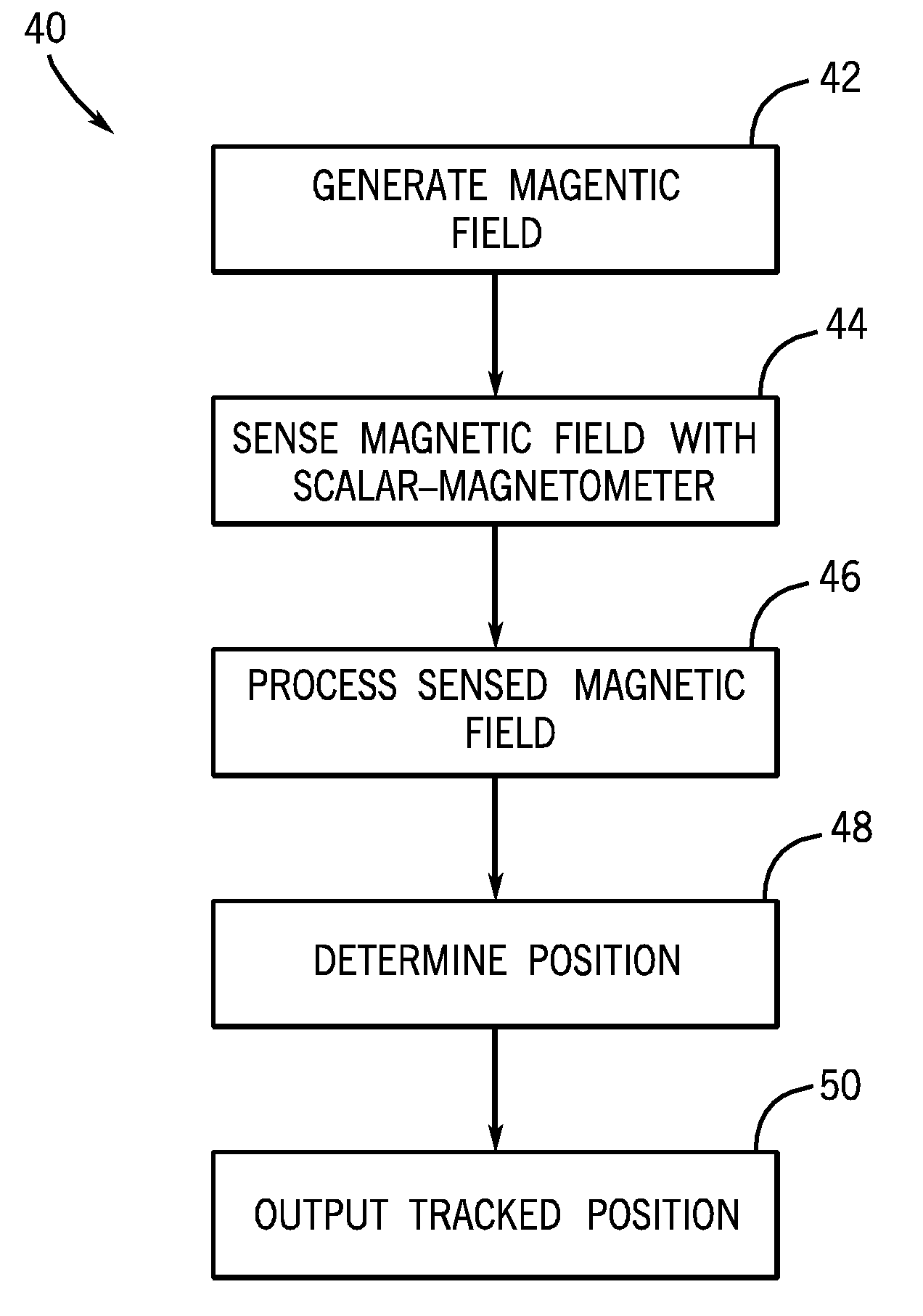
Electromagnetic tracking employing scalar-magnetometer
ActiveUS20090079426A1Electrical testingMagnetic property measurementsMagnetic tension forceElectromagnetic field
Provided is an electromagnetic tracking system, including at least one electromagnetic field receiver having at least one scalar-magnetometer, at least one electromagnetic field transmitter, and tracker electronics. Also provided is a method for electromagnetic tracking, including generating at least one magnetic field, sensing the at least one magnetic field with at least one scalar-magnetometer, and determining a relative position of the at least one scalar-magnetometer based on the sensed at least one magnetic field.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC
Intuitive multiple degrees of freedom portable control device
A control device for a vehicle or mechanism includes a portable displacement controller which permits a non-technical user to achieve effective control of the vehicle or mechanism, by moving the portable displacement controller intuitively with little learning effort. A first sensing device, attached to the displacement controller, detects the user's controlling motion. A second sensing device, attached to the object being controlled, detects motion thereof. An interface device receives signals from the sensing devices, processes those signals to determine relative motion of the controlling motion and the object's motion and outputs a control signal in accordance with the processed signals. The sensing devices each detect motion in six degrees of freedom; the sensing devices each include a three-axis accelerometer, a three-axis gyroscope, and a three-axis magnetometer. In specific embodiments, the accelerometers, gyroscopes, and magnetometers include micro-electromechanical system (MEMS) devices.
Owner:MEASUREMENT SYST
Unmanned Airborne Vehicle For Geophysical Surveying
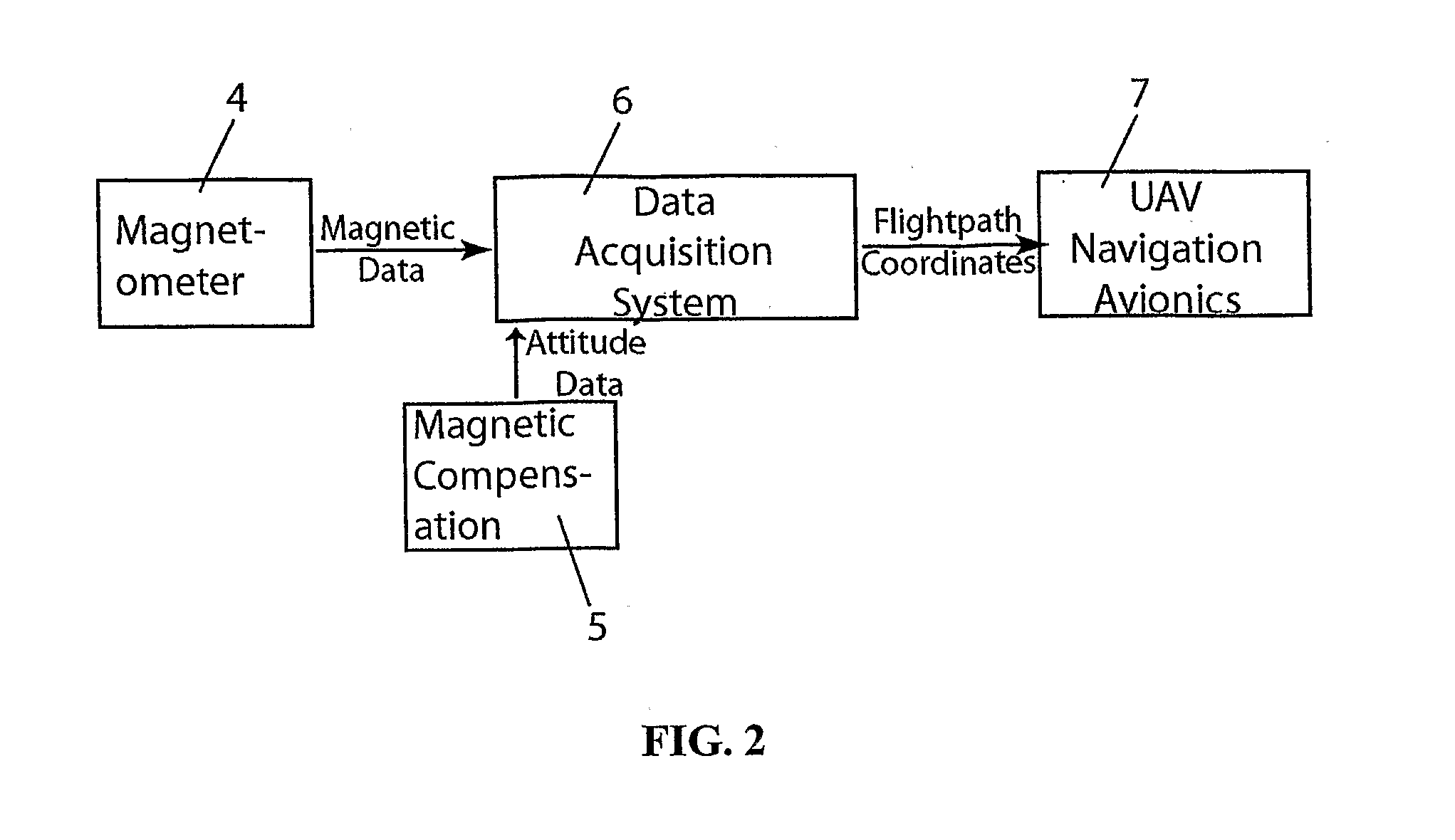
InactiveUS20080125920A1Low costEasy mappingAircraft componentsAnalogue computers for vehiclesAviationData acquisition
An un-manned airborne vehicle (UAV), for acquiring aeromagnetic data for geophysical surveying at low altitude on land or over water, comprising an extended fuselage that is adapted to hold and maintain magnetometer and a magnetic compensation magnetometer at a minimum distance from the avionics and propulsion systems of the UAV. The magnetometer measures magnetic anomalies and the magnetic compensation magnetometer measures magnetic responses corresponding to the pitch, yaw and roll of the UAV. A data acquisition system stores and removes the magnetic response measurements from the magnetic anomaly measurements. The data acquisition system also stores a survey flight plan and transmits the same to the avionics system. The generator of the UAV is shielded and the propulsion system is stabilized to reduce magnetic and vibrational noises that can interfere with the operation of the magnetometer.
Owner:FUGRO AIRBORNE SURVEYS
Noninvasive Method And System For Monitoring Physiological Characteristics And Athletic Performance
InactiveUS20110130643A1Easy to monitorPhysical therapies and activitiesElectroencephalographyExercise performanceChest region
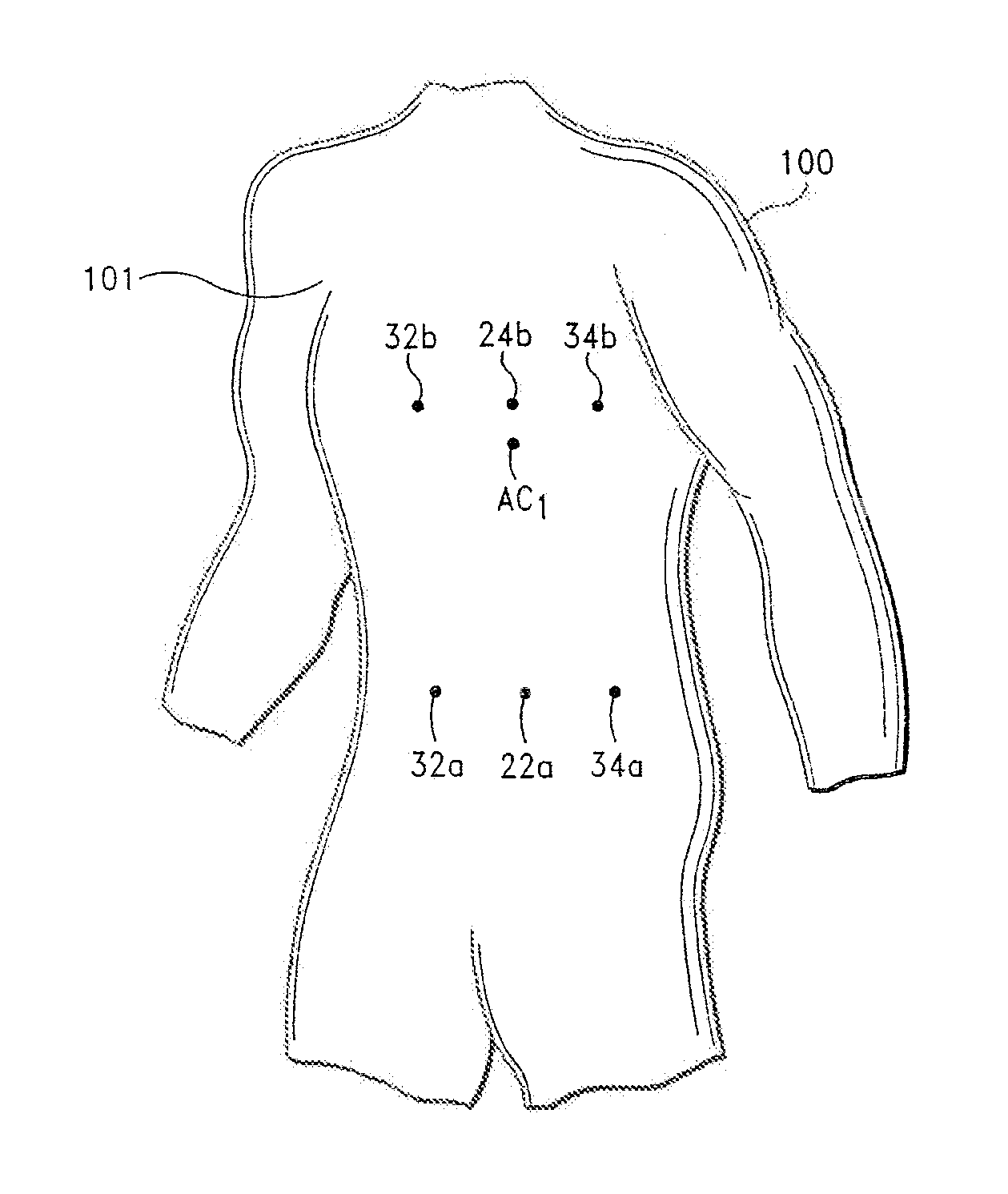
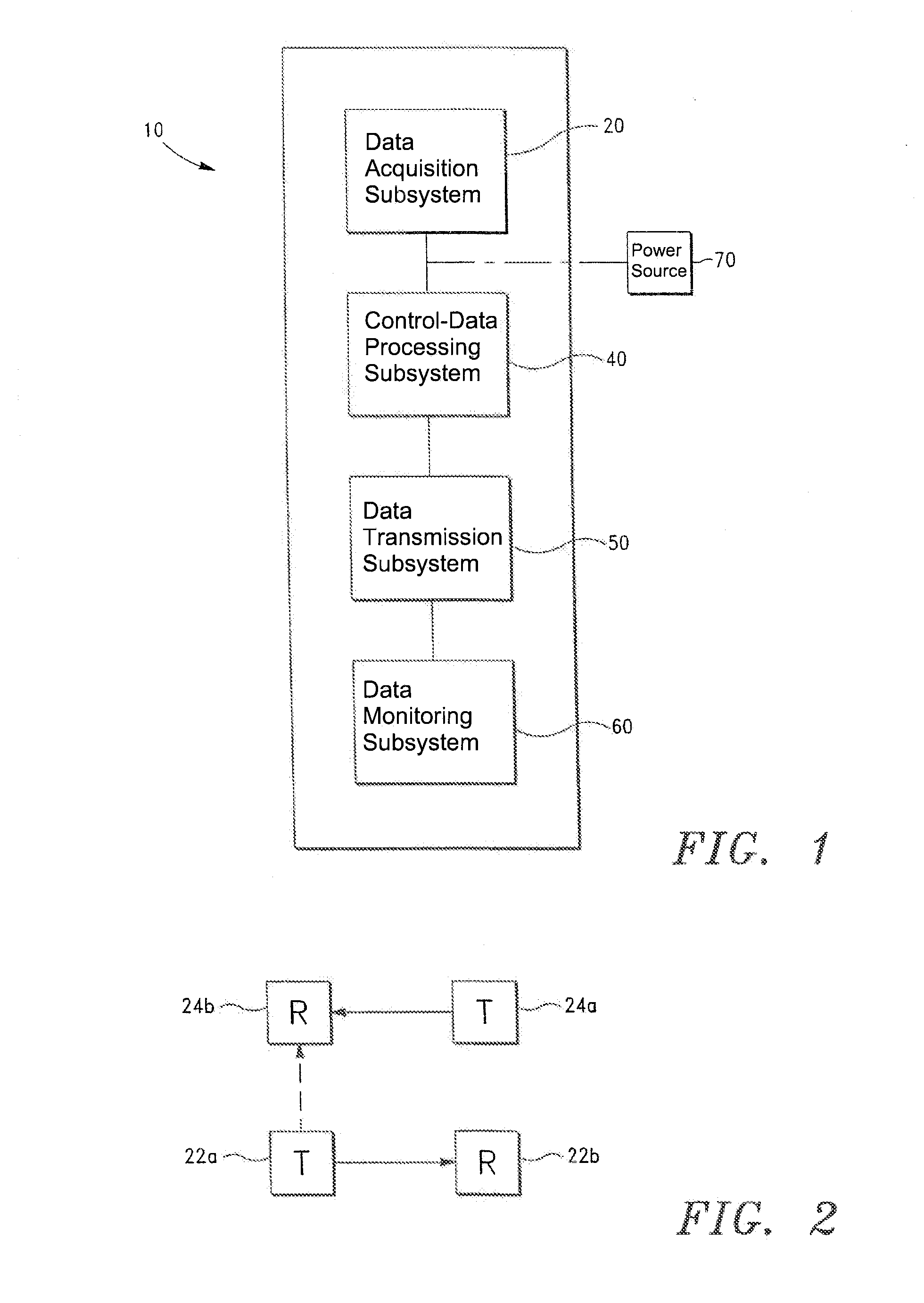
A physiological monitoring system for noninvasively monitoring physiological parameters of a subject, comprising a fitness monitoring system for monitoring physiological parameters of a subject engaged in a physical activity, in accordance with one embodiment of the invention, includes (i) a monitoring garment adapted to cover at least a portion of a subject's torso, (ii) a magnetometer subsystem including a first magnetometer and a second magnetometer, wherein the first and second magnetometers are responsive to changes in distance therebetween, wherein the magnetometer subsystem is configured to generate and transmit a signal representative of a change in the distance between the first and second magnetometers, wherein the first and second magnetometers are incorporated into the monitoring garment, and wherein the first and second magnetometers are proximate to the subject's chest region when the monitoring garment is worn by the subject.
Owner:ADIDAS
Three dimensional golf swing analyzer
ActiveUS8696482B1Increase swingNegligible weightPhysical therapies and activitiesGymnastic exercisingGyroscopeRadio receiver
An apparatus and method for golf swing analysis is described using a first microprocessor, a three-axis accelerometer capable of transmitting linear acceleration data to the first microprocessor, a three-axis gyroscope capable of transmitting angular velocity data to the first microprocessor, data processing, a radio transmitter for transmitting processed data, and a housing for holding the components, which attaches to a golf club. A three-axis magnetometer capable of transmitting directional orientation data to the first microprocessor is used to allow a user to choose a target line. Communication occurs between the apparatus and a portable device with a radio receiver, memory and a computer program that processes the data into graphical data and statistical data and displays the swing graphically after a user swings the golf club. The user will be able to analyze and try to improve his or her golf swing.
Owner:SWINGBYTE
Method of manufacture and the use of a functional proppant for determination of subterranean fracture geometries
ActiveUS8168570B2Accurate imagingPromote recoveryElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMaterial nanotechnologyGeophoneElectricity
Proppants having added functional properties are provided, as are methods that use the proppants to track and trace the characteristics of a fracture in a geologic formation. Information obtained by the methods can be used to design a fracturing job, to increase conductivity in the fracture, and to enhance oil and gas recovery from the geologic formation. The functionalized proppants can be detected by a variety of methods utilizing, for example, an airborne magnetometer survey, ground penetrating radar, a high resolution accelerometer, a geophone, nuclear magnetic resonance, ultra-sound, impedance measurements, piezoelectric activity, radioactivity, and the like. Methods of mapping a subterranean formation are also provided and use the functionalized proppants to detect characteristics of the formation.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Optical Pumping Magnetometer
ActiveUS20130265042A1Easy to controlGuaranteed uptimeElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceFrequency stabilizationPhotodetector
Stable magnetic field measurement is enabled without collapse of polarization or fluctuation of intensity of a laser beam incident on a glass cell of an optical pumping magnetic sensor. Excitation light generated with a light source, having optimized light intensity and polarized wave, through frequency stabilization, intensity control and polarized-wave control, is introduced via a polarized wave holding optical fiber to a magnetic sensor provided in a magnetic shield, and magnetic field measurement is performed by optical pumping using magneto-optical properties of spin-polarized alkali metal. The magnetic sensor has a structure where a lens, a polarization optical device, the glass cell and a photodetector, are integrally accommodated in a non-magnetic case.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Sensor fusion for model-based detection in pipe and cable locator systems
ActiveUS7834801B2Improve positionSatellite radio beaconingElectric/magnetic detectionGyroscopeAccelerometer
Line locator systems that fuse traditional sensors used in a combined pipe and cable locator (electromagnetic coils, magnetometers, and ground penetrating radar antennas) with low cost inertial sensors (accelerometers, gyroscopes) in a model-based approach are presented. Such systems can utilize inexpensive MEMS sensors for inertial navigation. A pseudo-inertial frame is defined that uses the centerline of the tracked utility, or an aboveground fixed object as the navigational reference. An inertial sensor correction mechanism that limits the tracking errors over time when the model is implemented in state-space form using, for example, the Extended Kalman Filter (EKF) is disclosed.
Owner:BUSAN TRANSPORTATION CORPORATION
Device position estimates from motion and ambient light classifiers
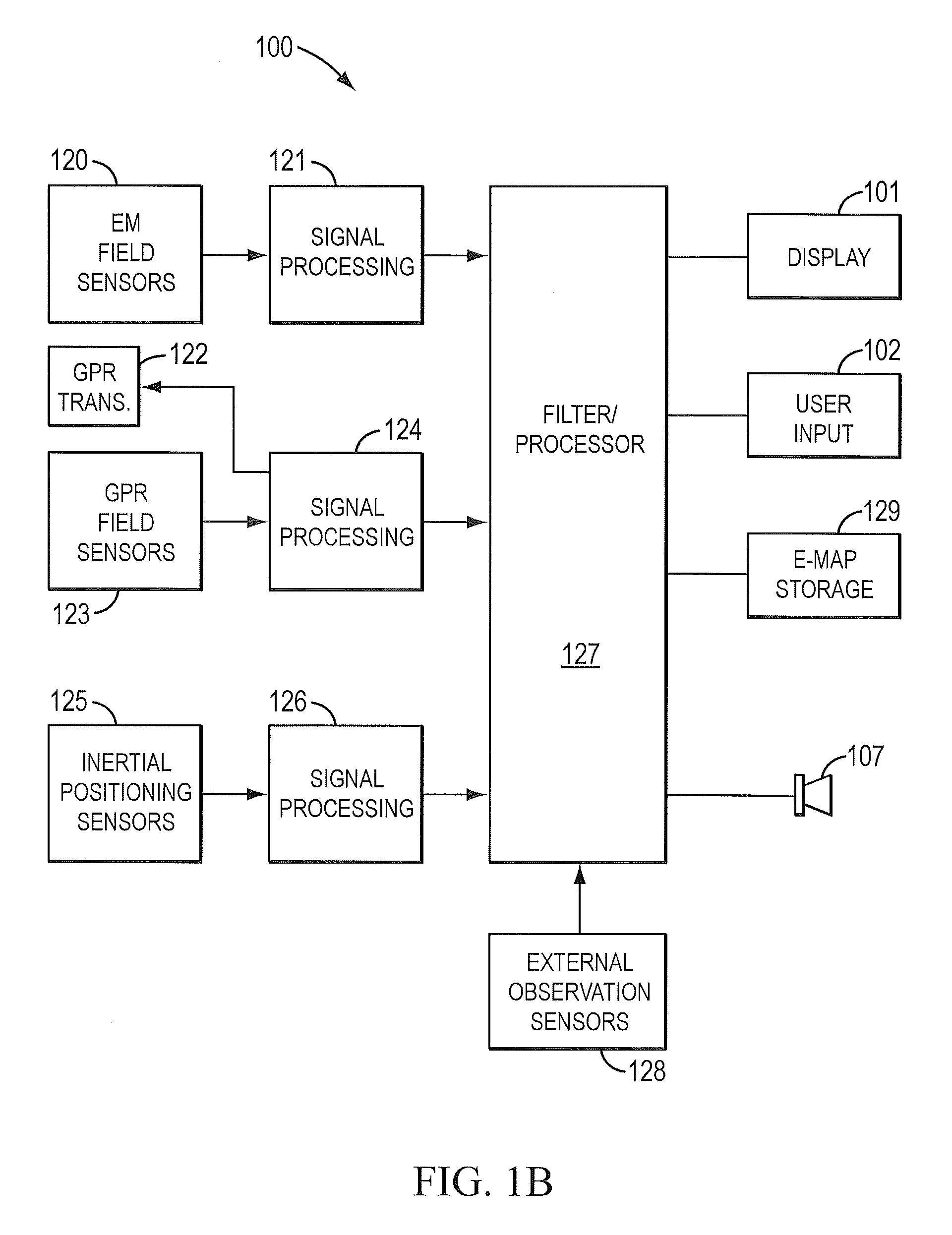
ActiveUS20120265482A1Digital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsProximity sensorAccelerometer
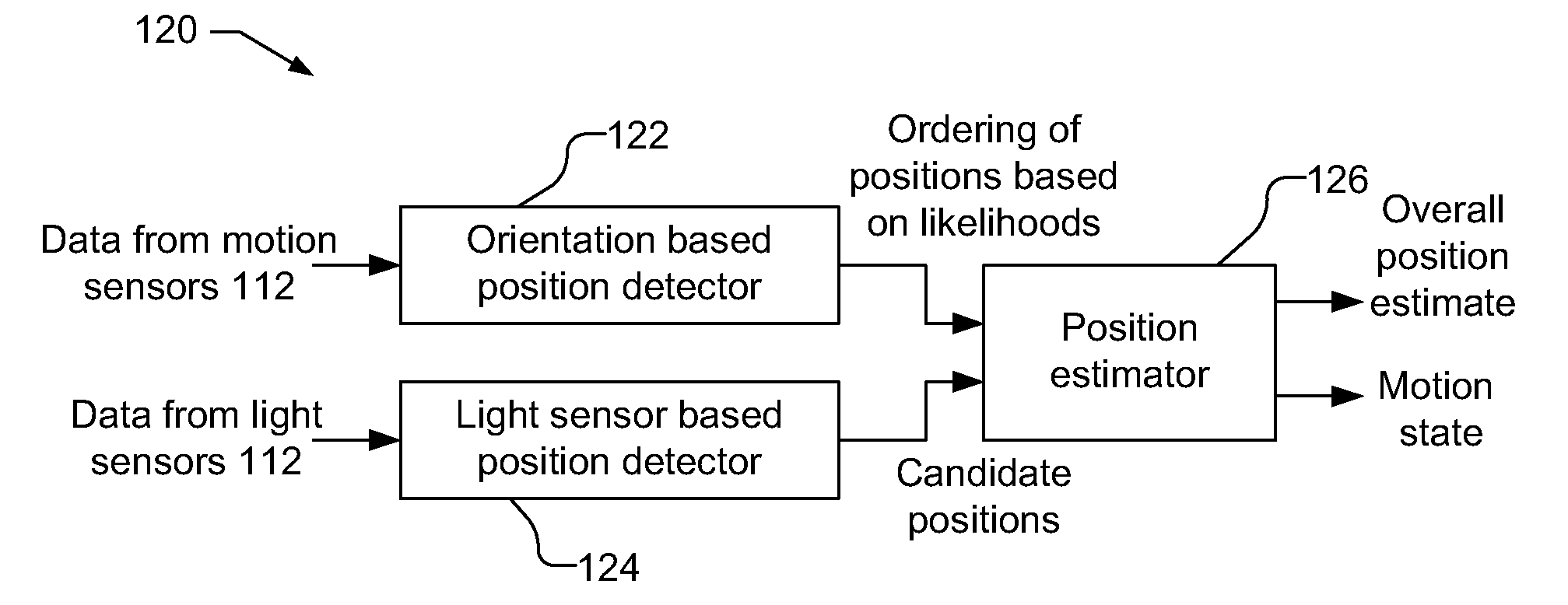
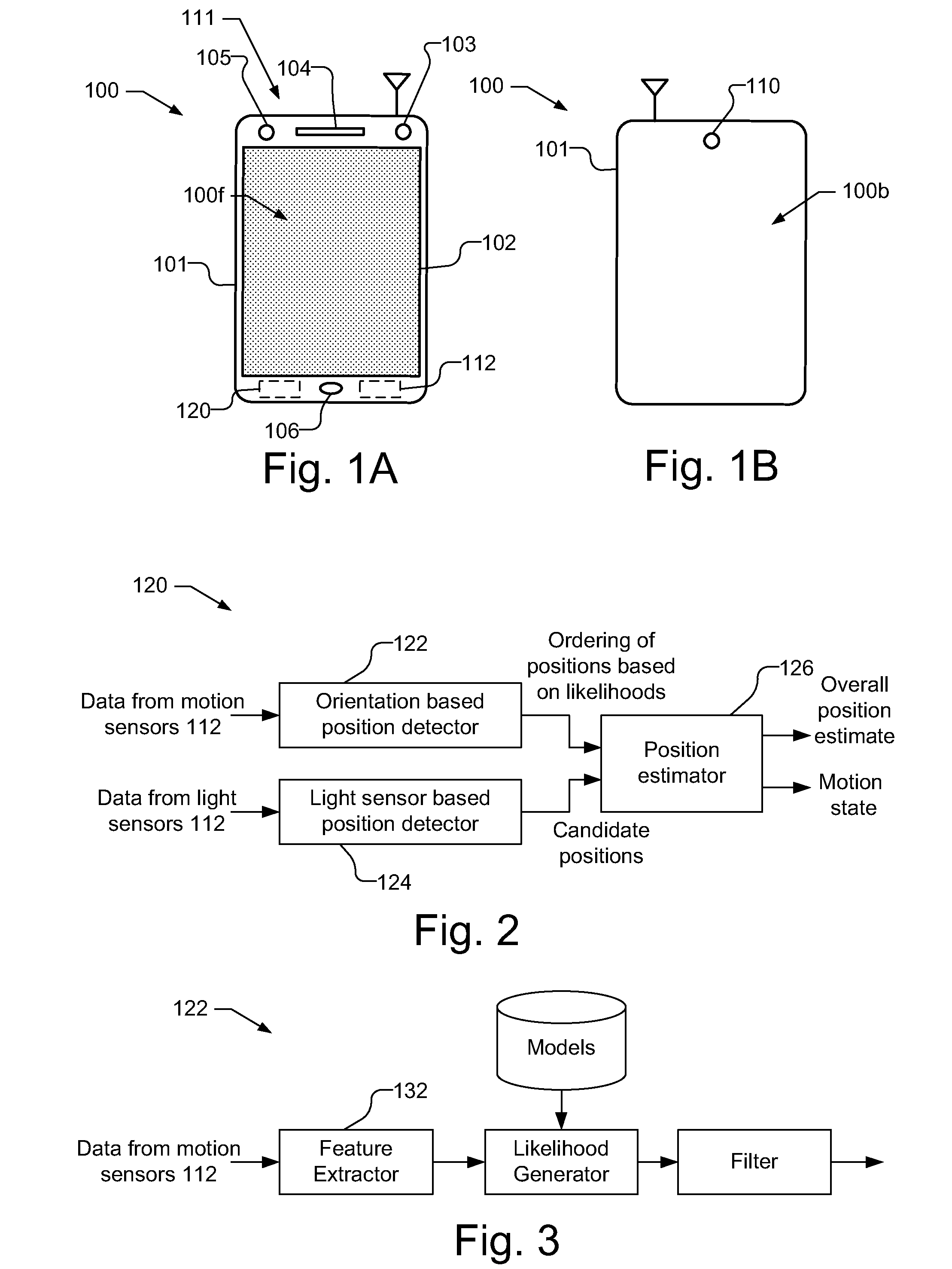
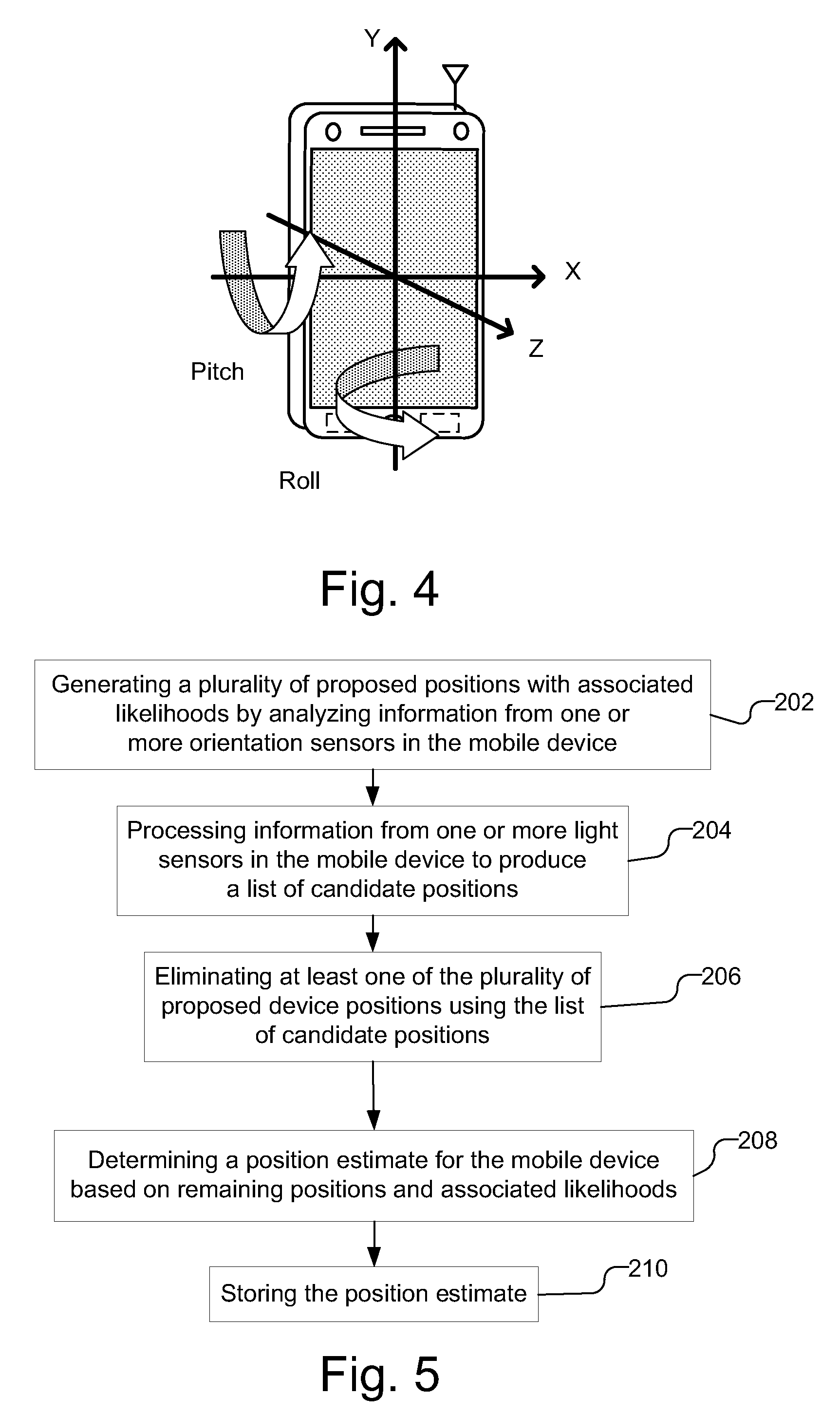
A position estimate for a mobile device is generated using data from motion sensors, such as accelerometers, magnetometers, and / or gyroscopes, and data from light sensors, such as an ambient light sensor, proximity sensor and / or camera intensity sensor. A plurality of proposed positions with associated likelihoods is generated by analyzing information from the motion sensors and a list of candidate positions is produced based on information from the light sensors. At least one of the plurality of proposed positions is eliminated using the list of candidate positions and a position estimate for the mobile device is determined based on the remaining proposed positions and associated likelihoods. The proposed positions may be generated by extracting features from the information from the motion sensors and using models to generate likelihoods for the proposed positions. The likelihoods may be filtered over time. Additionally, a confidence metric may be generated for the estimated position.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Human body attitude calculation method based on quaternion and Kalman filtering
InactiveCN107478223AEffective Data FusionHigh precisionNavigation by terrestrial meansNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsAccelerometerGyroscope
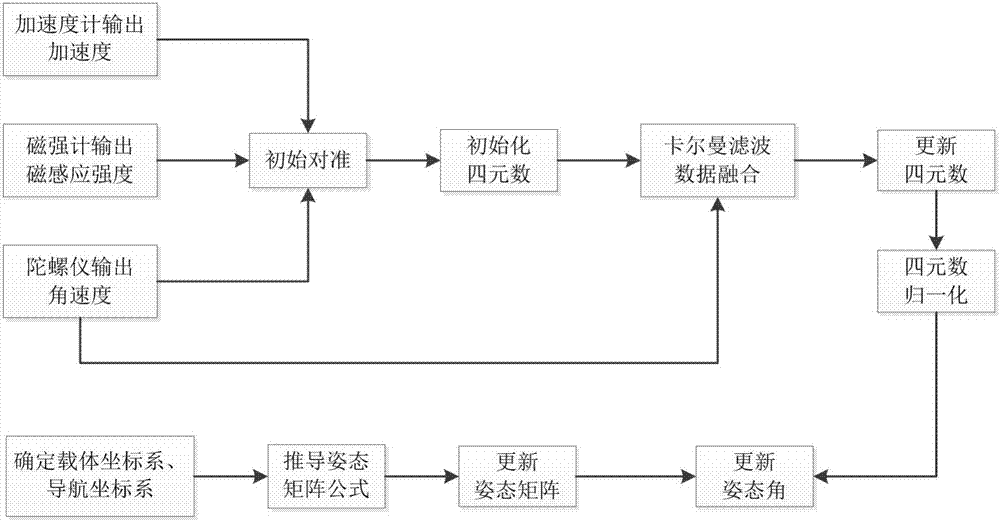
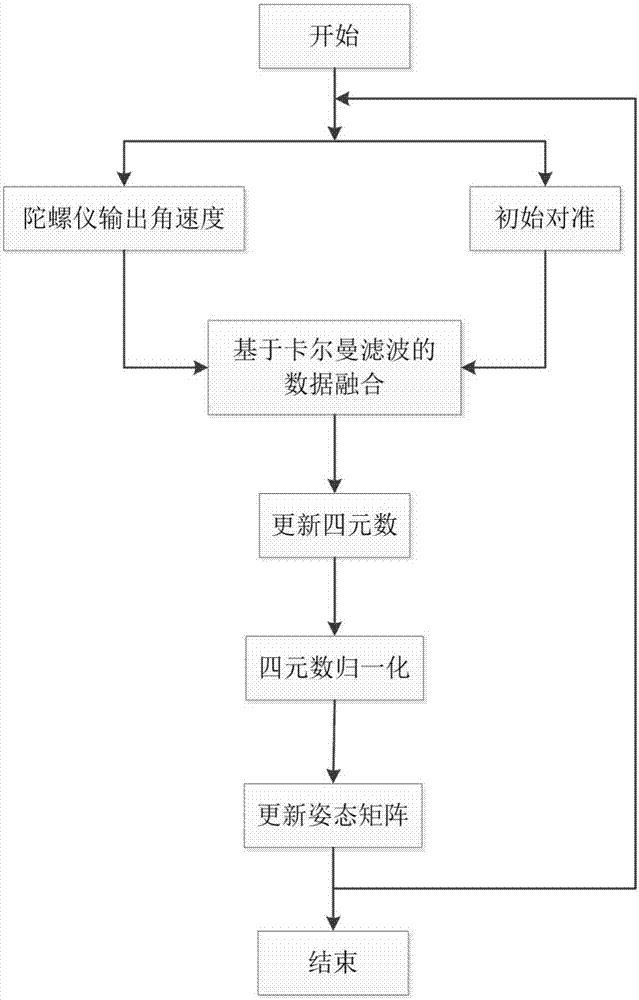
The invention discloses a human body attitude calculation method based on quaternion and Kalman filtering. The method comprises determining a vector coordinate system and a navigation coordinate system, determining an attitude matrix, respectively acquiring accelerated speed, angular velocity and magnetic induction intensity signals through an accelerometer, a gyroscope and a magnetometer, carrying out initial alignment on a human body attitude detection system, calculating initial attitude angles such as a pitching angle, a rolling angle and a heading angle, transforming the initial attitude angles into initial quaternion, carrying out system modeling according to a quaternion differential equation, inputting the initial quaternion as a measured value, carrying out data fusion on the attitude data through a Kalman filtering algorithm, outputting an estimated value which is updated quaternion, carrying out normalization processing on the updated quaternion to obtain final posture information, updating the attitude matrix and acquiring updated attitude angles. The human body attitude estimation method effectively improves the accuracy of human posture detection, has a fast response speed, has good stability and instantaneity and has a broad application prospect.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
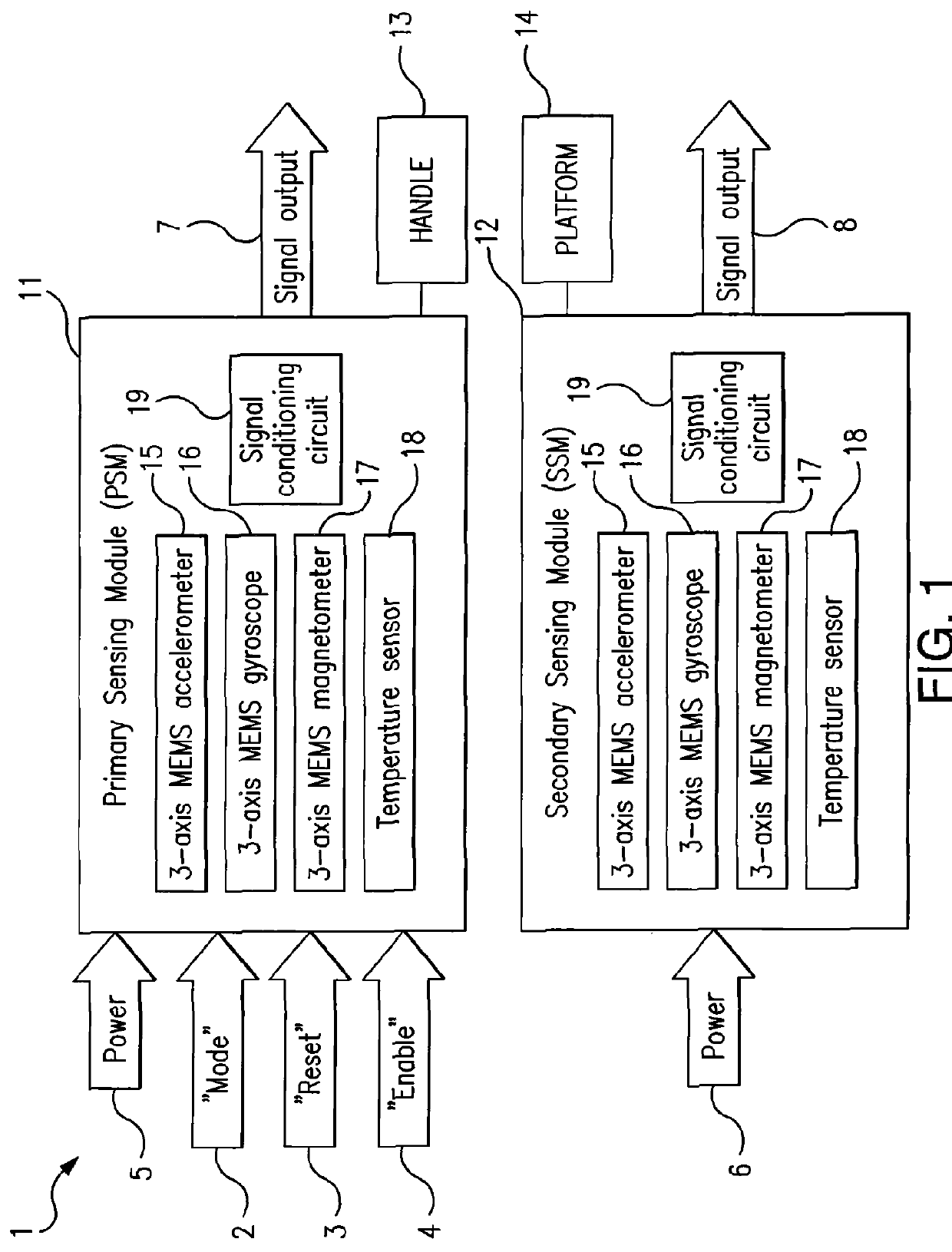
Methods of attitude and misalignment estimation for constraint free portable navigation
ActiveUS20120245839A1Reducing and removing effect of orientation changeImprove usabilityDigital computer detailsSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsAccelerometerGyroscope
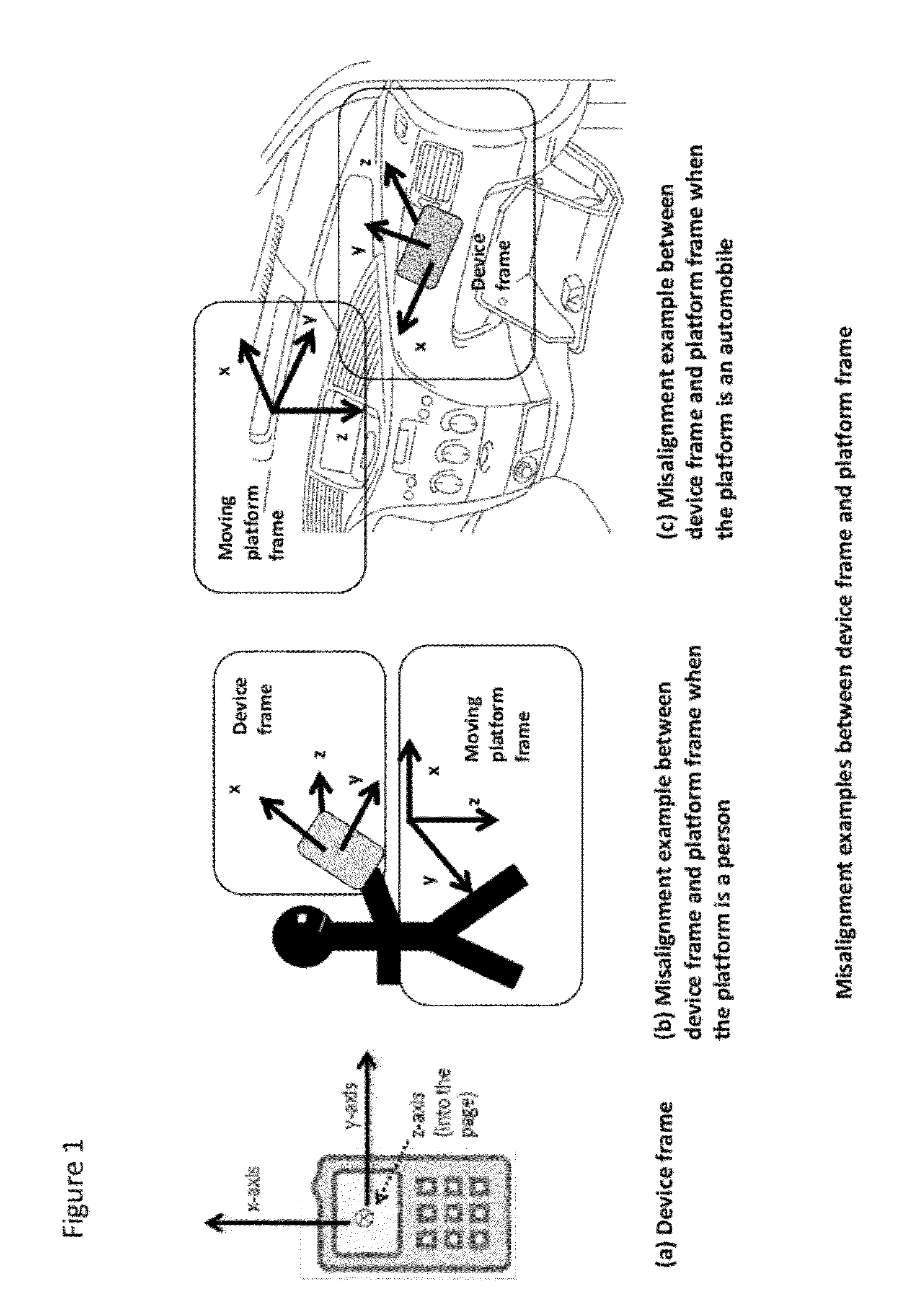
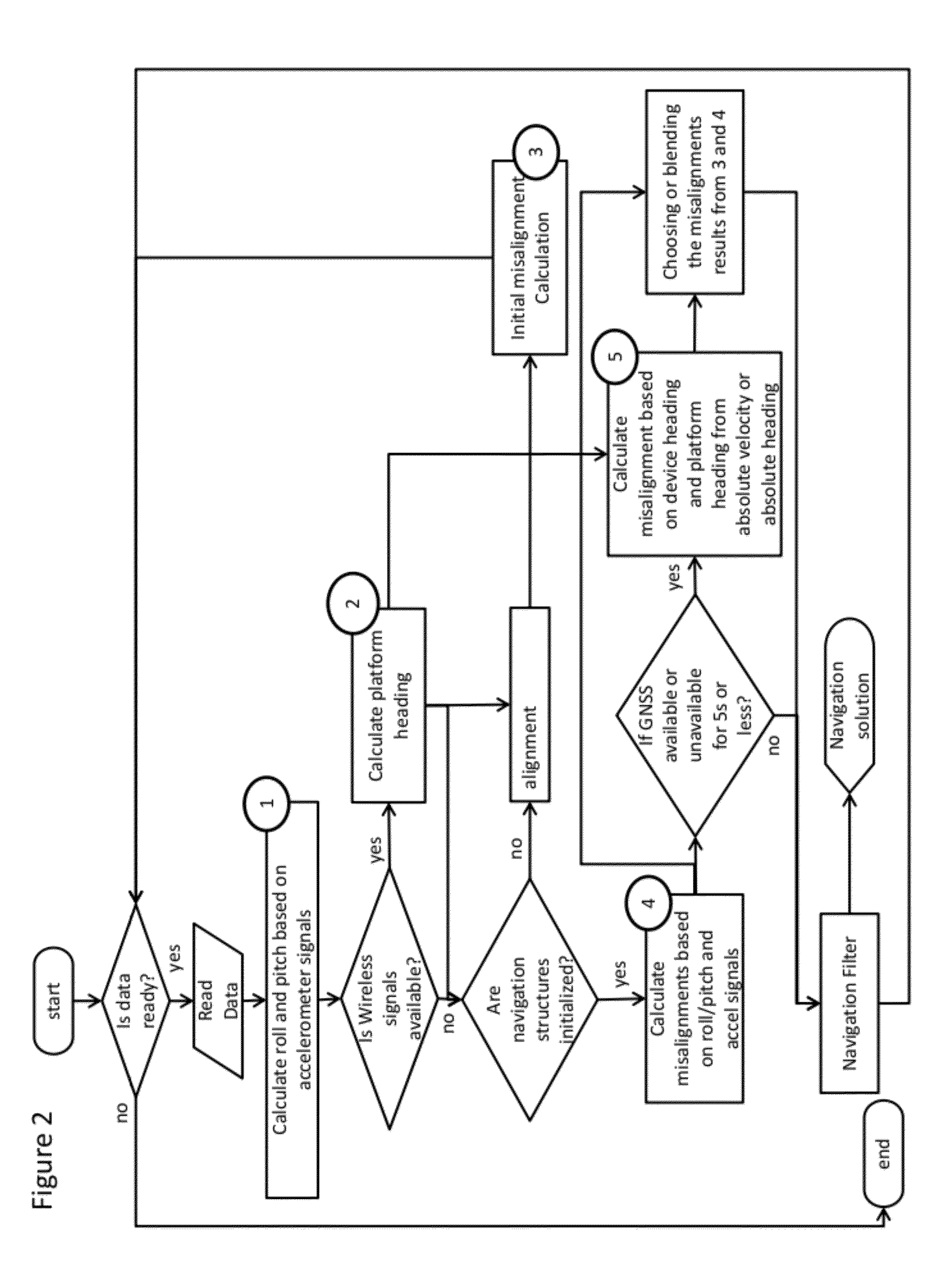
The present disclosure relates to methods of enhancing a navigation solution about a device and a platform, wherein the mobility of the device may be constrained or unconstrained within the platform, and wherein the navigation solution is provided even in the absence of normal navigational information updates (such as, for example, GNSS). More specifically, the present method comprises utilizing measurements from sensors (e.g. accelerometers, gyroscopes, magnetometers etc.) within the device to calculate and resolve the attitude of the device and the platform, and the attitude misalignment between the device and the platform.
Owner:TRUSTED POSITIONING
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com