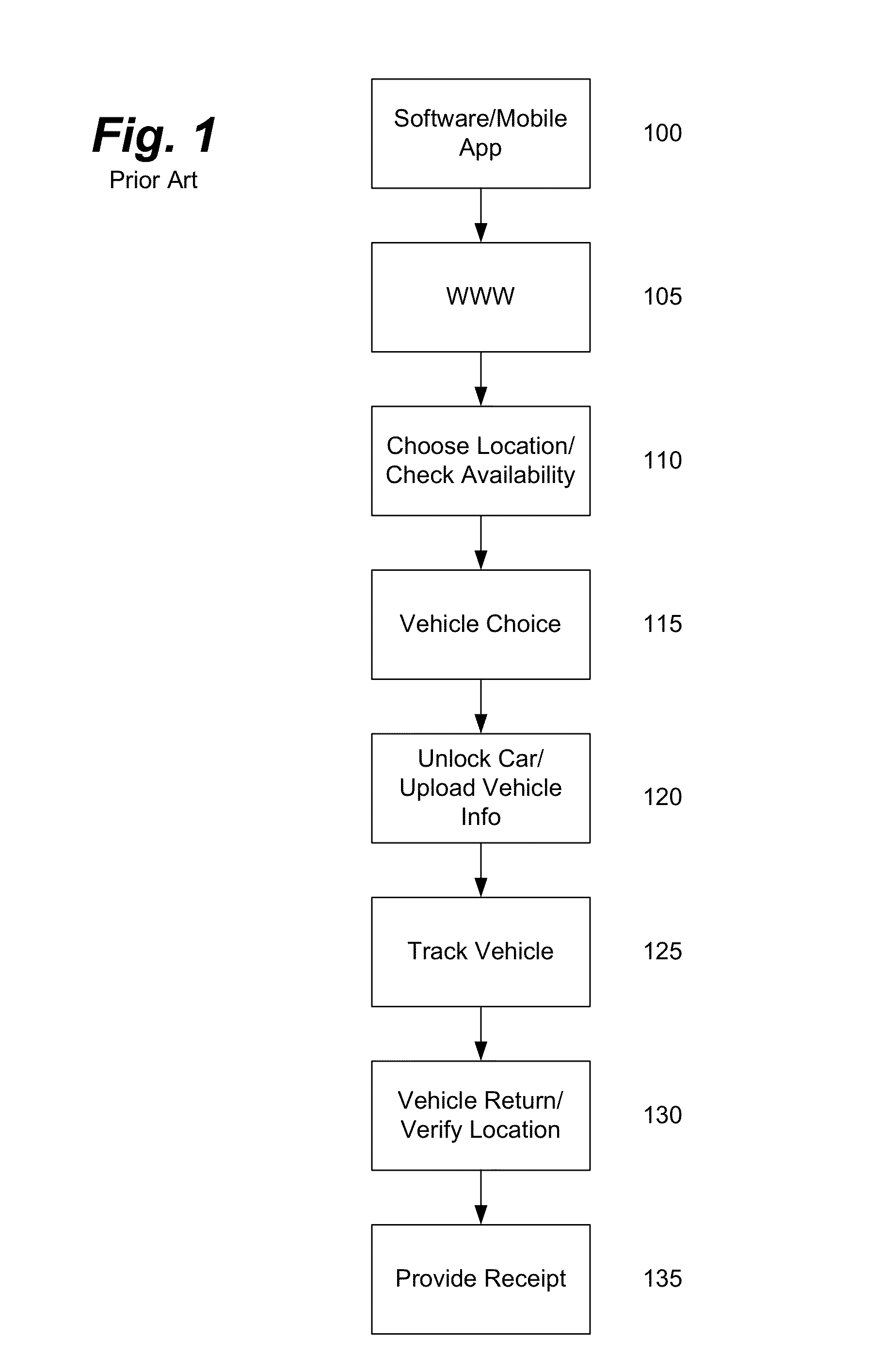
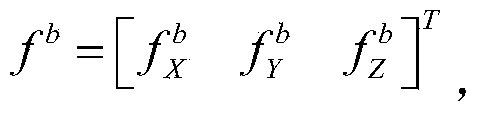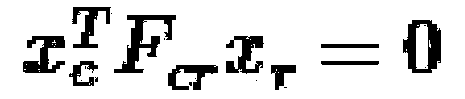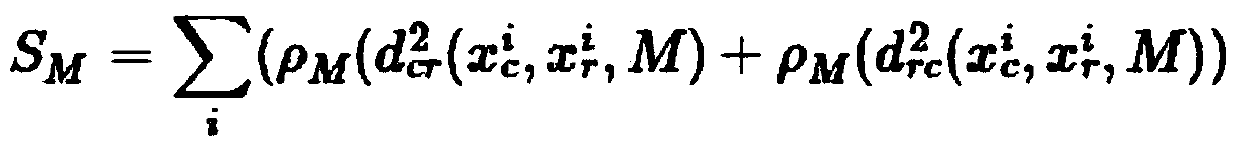Patents
Literature
1088 results about "Odometer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An odometer or odograph is an instrument used for measuring the distance traveled by a vehicle, such as a bicycle or car. The device may be electronic, mechanical, or a combination of the two. The noun derives from the Ancient Greek word ὁδόμετρον, hodómetron, from ὁδός, hodós ("path" or "gateway") and μέτρον, métron ("measure"). Early forms of the odometer existed in the ancient Greco-Roman world as well as in ancient China. In countries using Imperial units or US customary units it is sometimes called a mileometer or milometer, the former name especially being prevalent in the United Kingdom and among members of the Commonwealth.
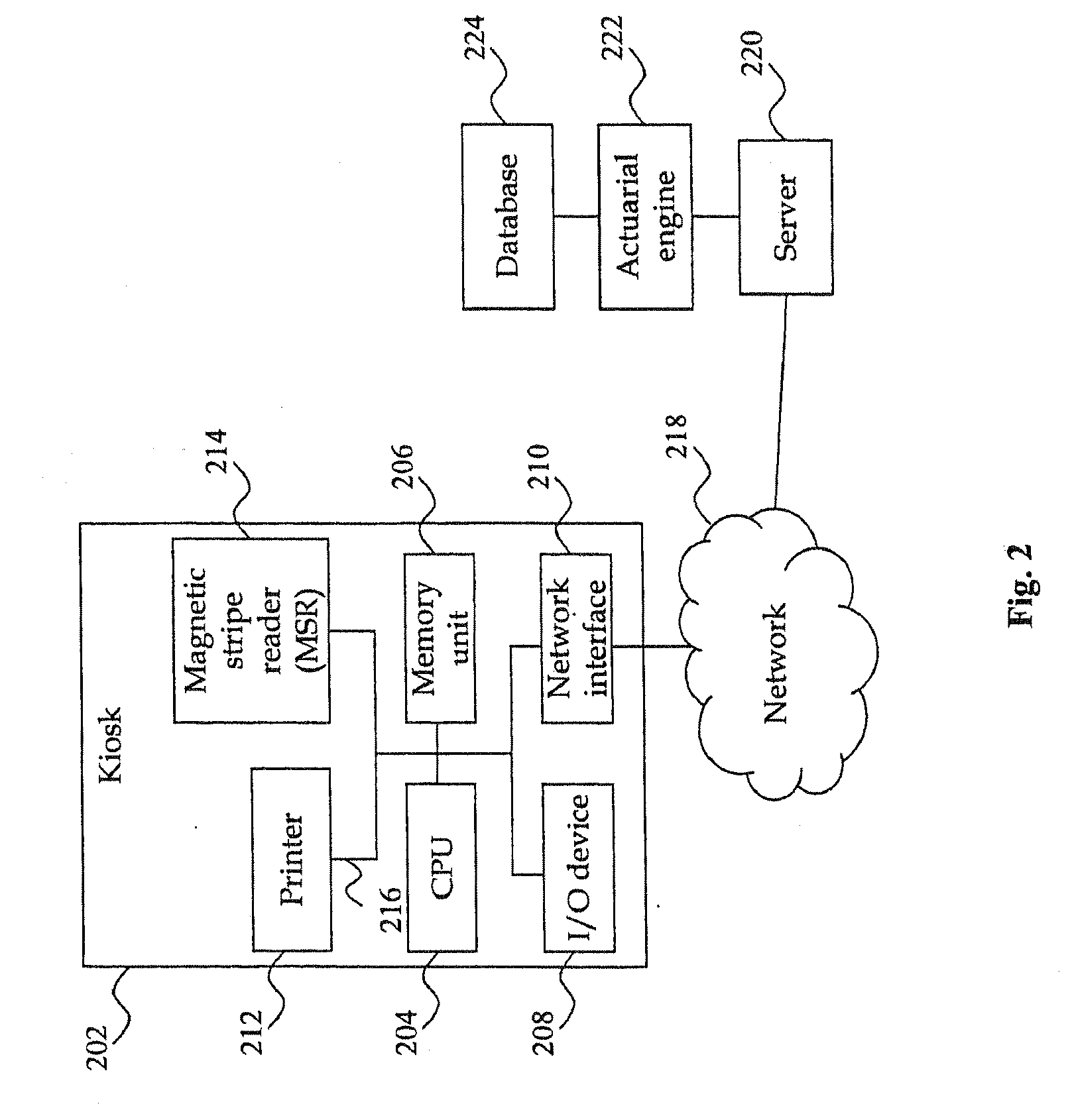
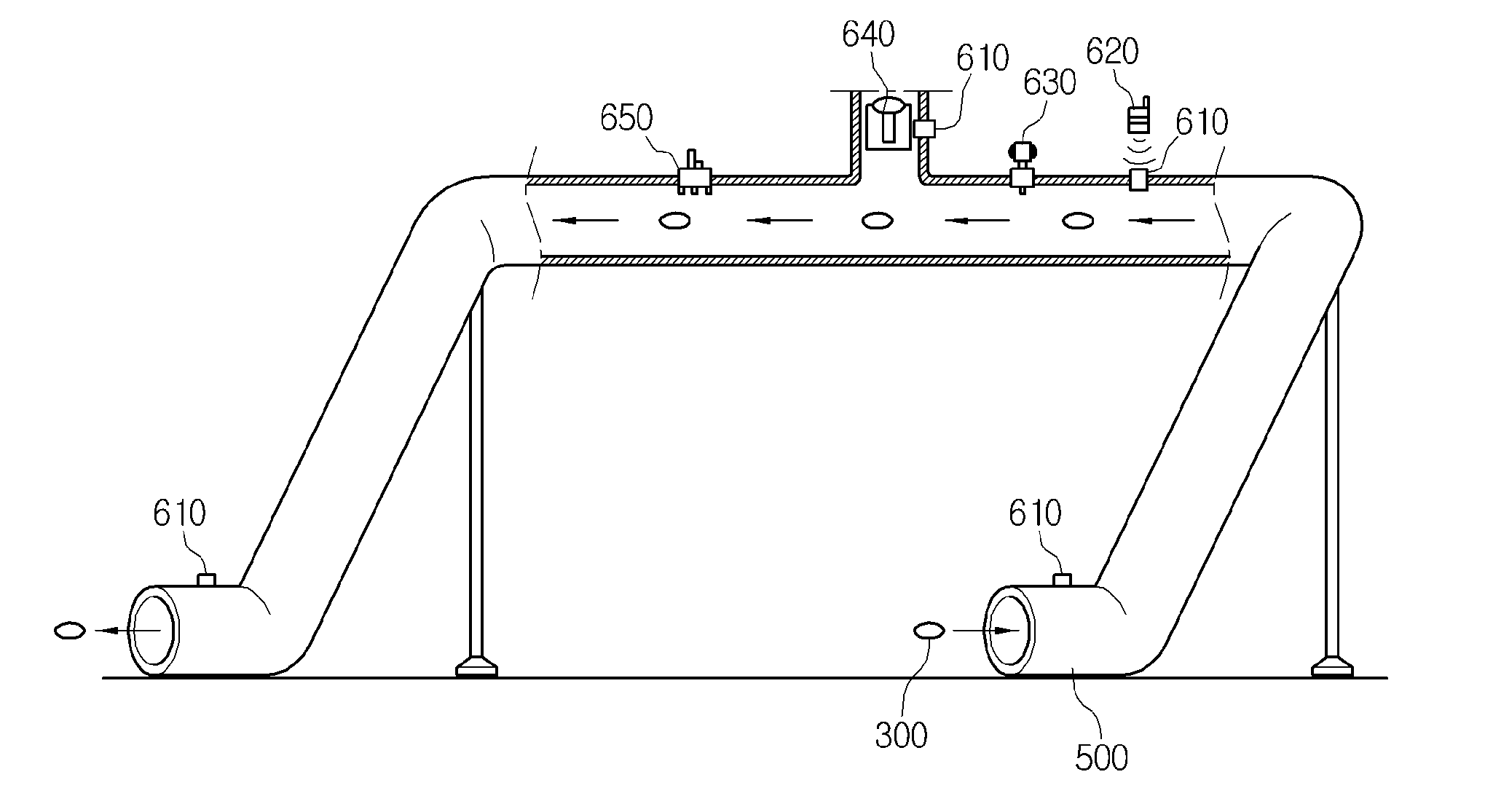
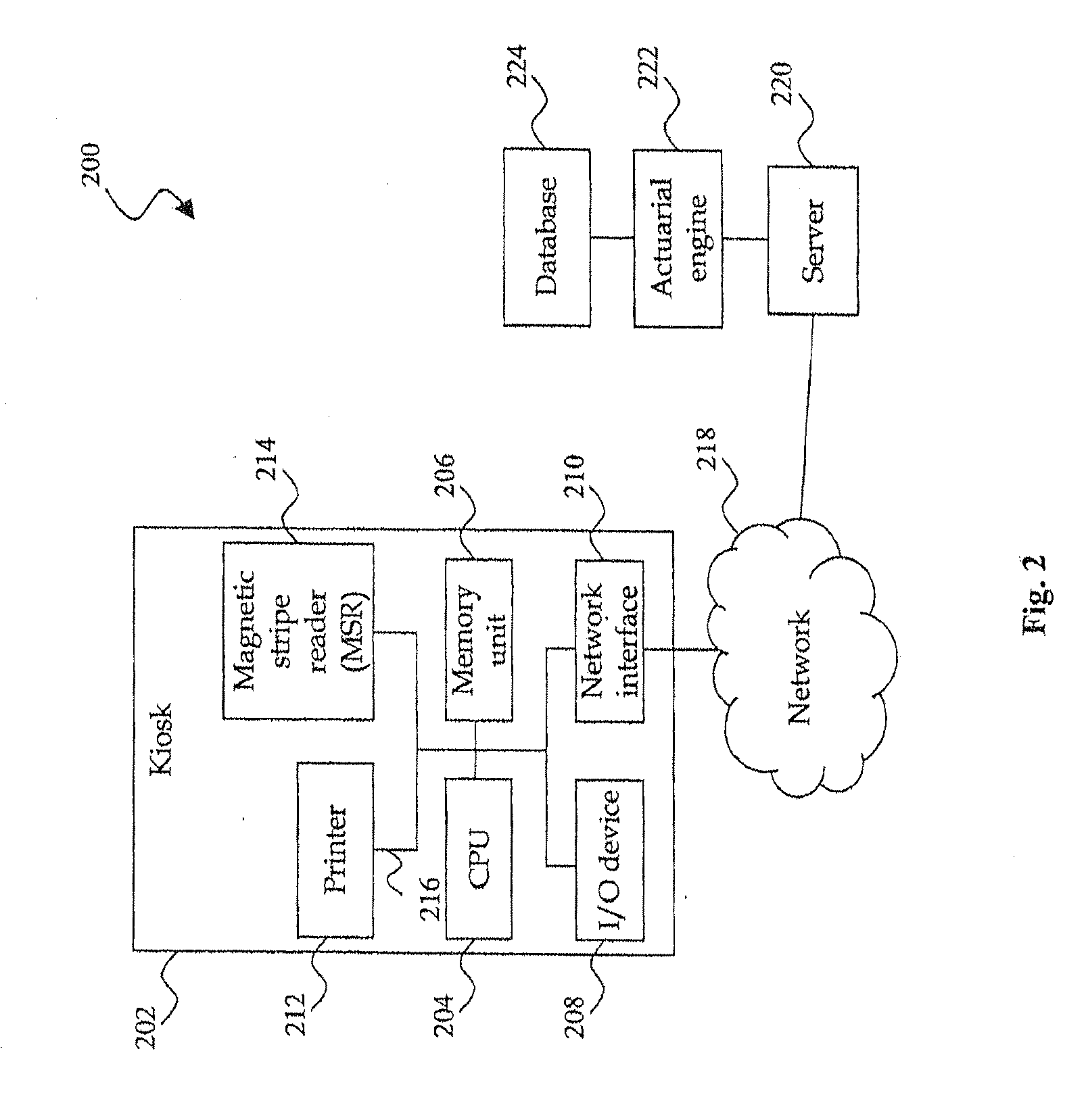
Method and apparatus for determining location of characteristics of a pipeline
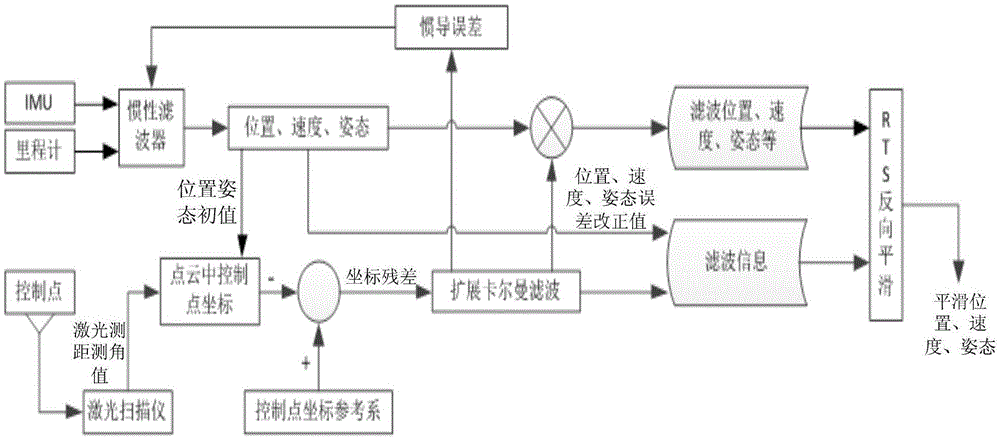
InactiveUS6243657B1High degreeHigh precisionTime indicationSynchronous motors for clocksKaiman filterComputerized system
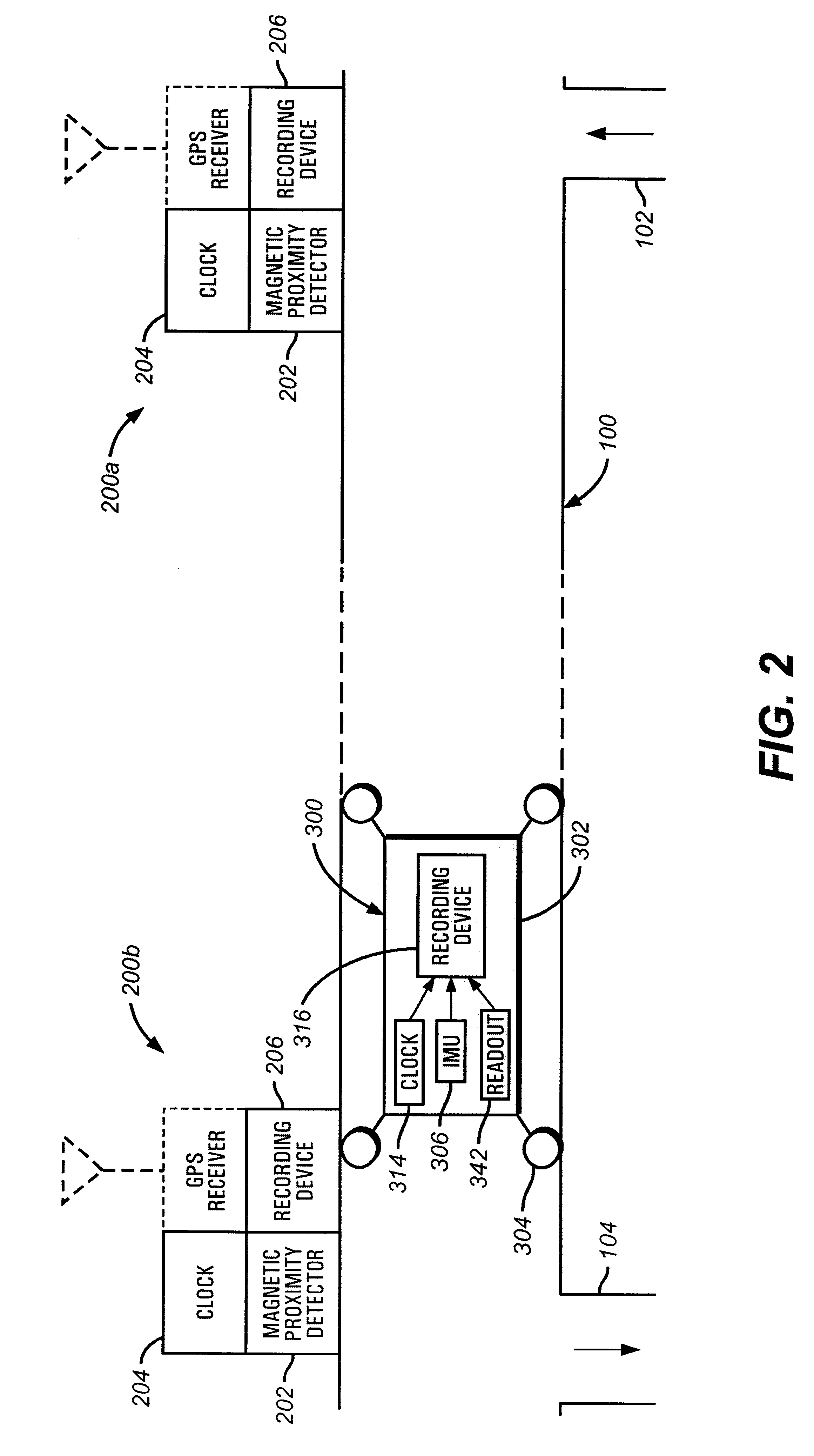
A pipeline inspection and defect mapping system includes a pig having an inertial measurement unit and a pipeline inspection unit for recording pig location and defect detection events, each record time-stamped by a highly precise onboard clock. The system also includes several magloggers at precisely known locations along the pipeline, each containing a fluxgate magnetometer for detecting the passage of the pig along the pipeline and further containing a highly precise clock synchronized with the clock in the pig. The locations of the various magloggers are known in a north / east / down coordinate system through a differential global positioning satellite process. Finally, a postprocessing off-line computer system receives downloaded maglogger, inertial measurement, and odometer data and through the use of several Kalman filters, derives the location of the detected defects in the north / east / down coordinate frame. Consequently, a task of identifying sites for repair activity is much simplified.
Owner:PIPELINE INTEGRITY INT INC FORMERLY BRITISH GAS INSPECTION SERVICES INC +1
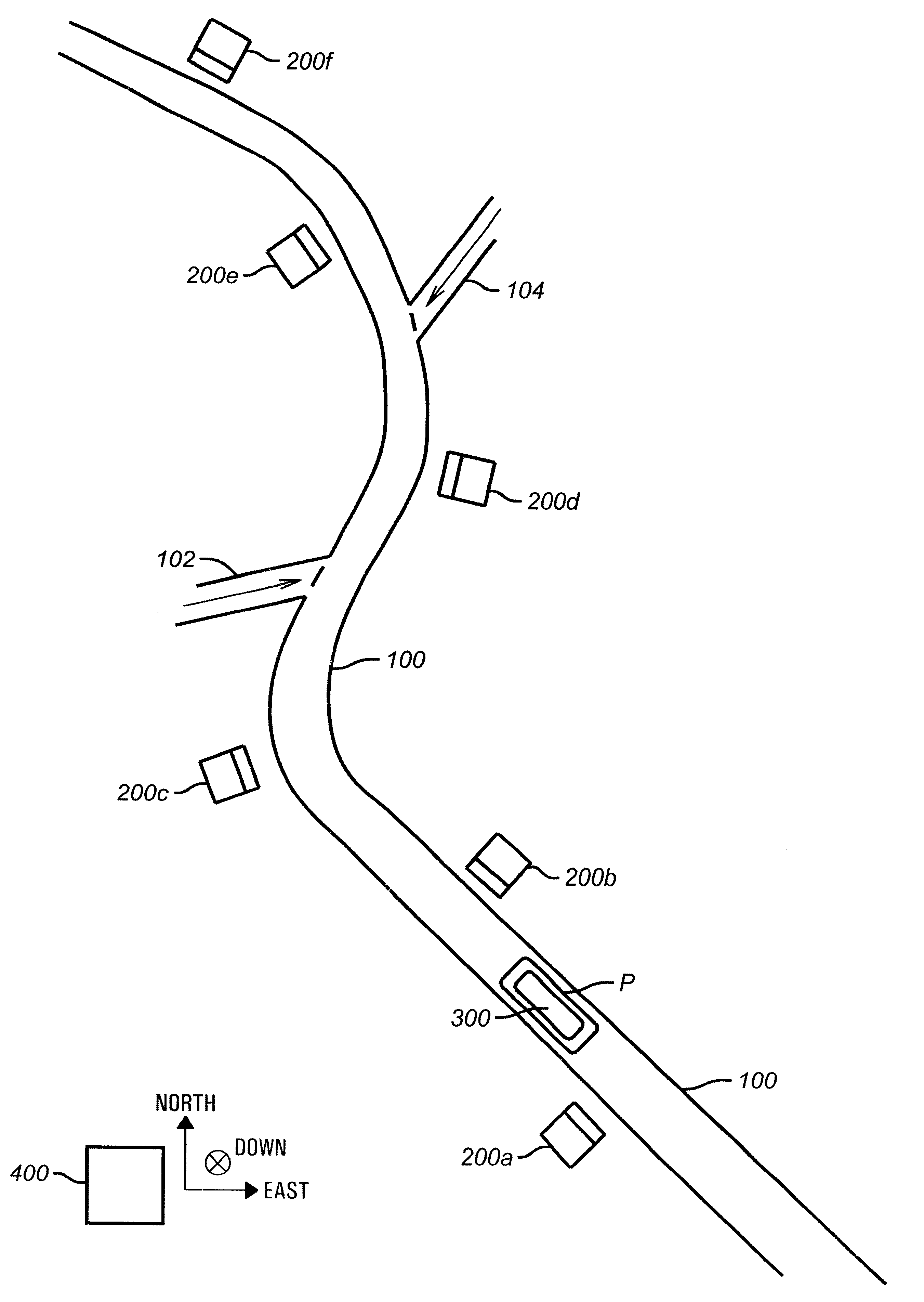
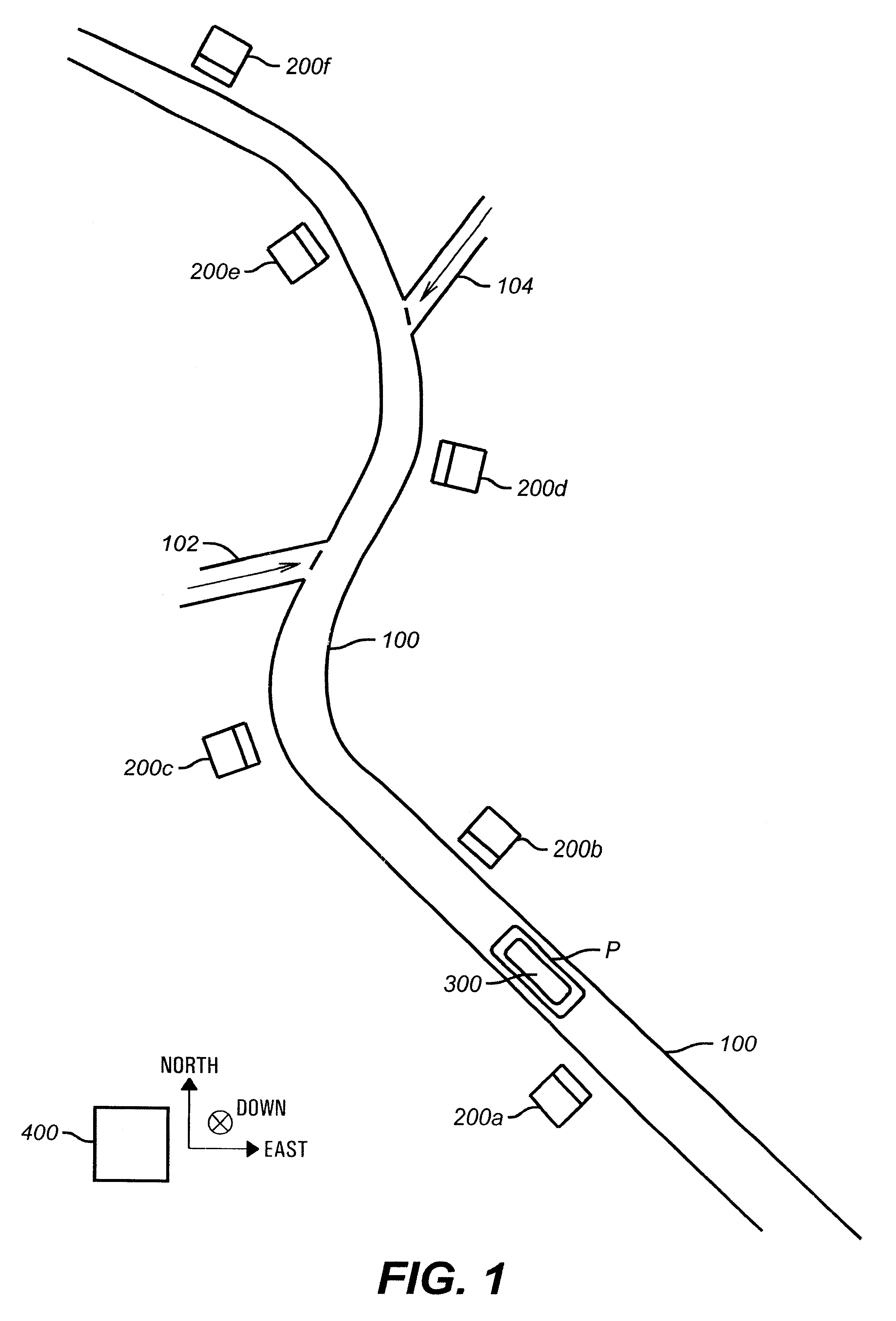
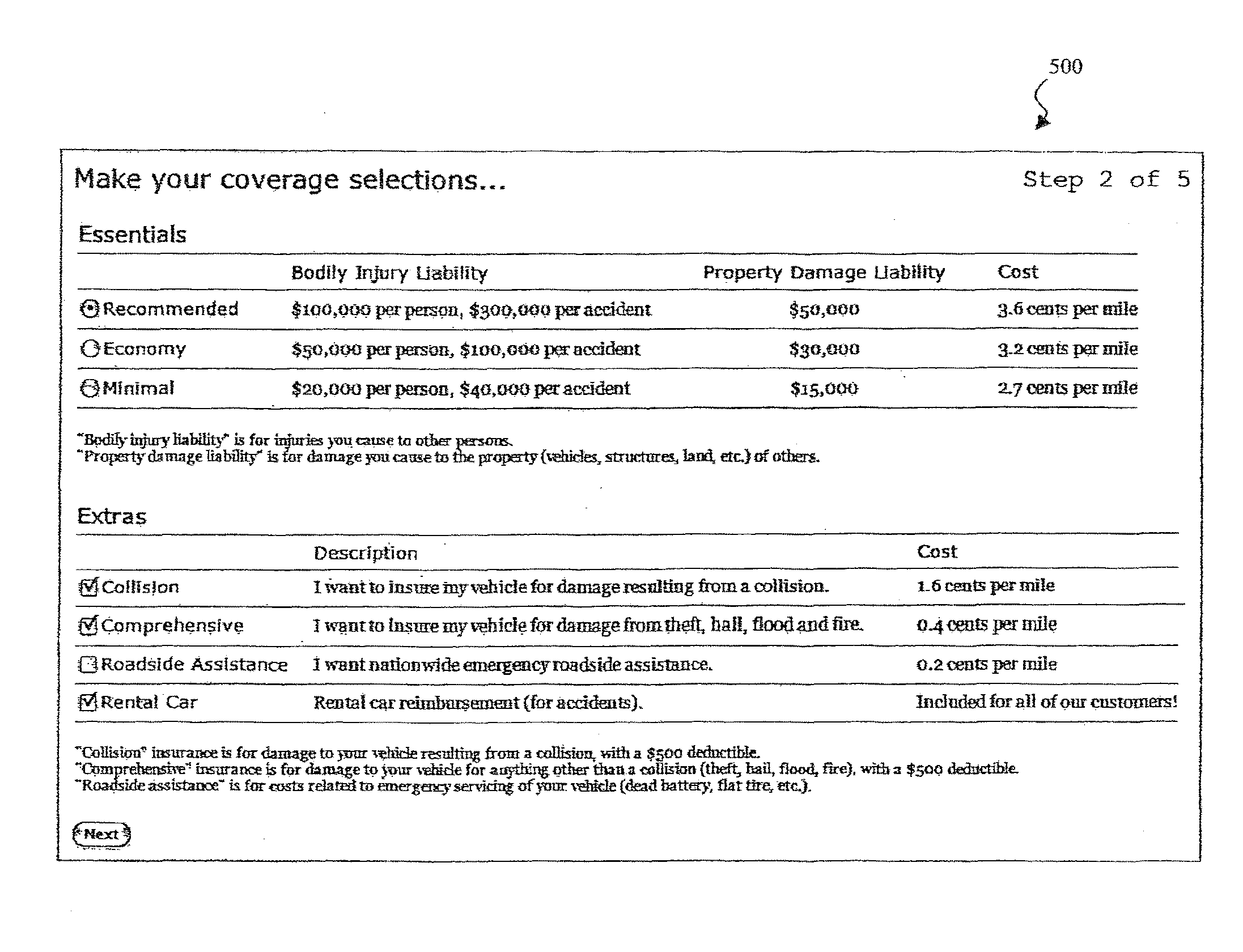
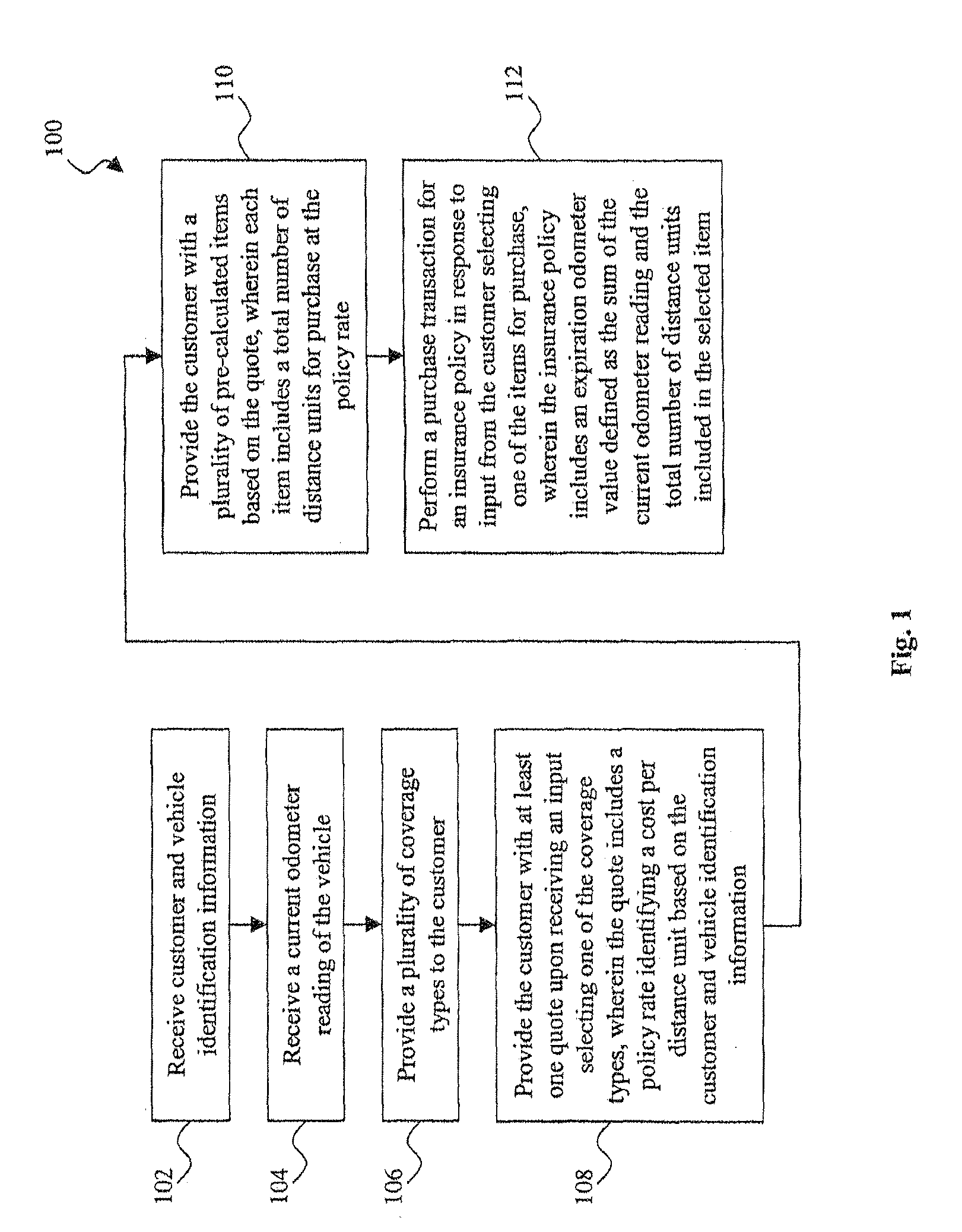
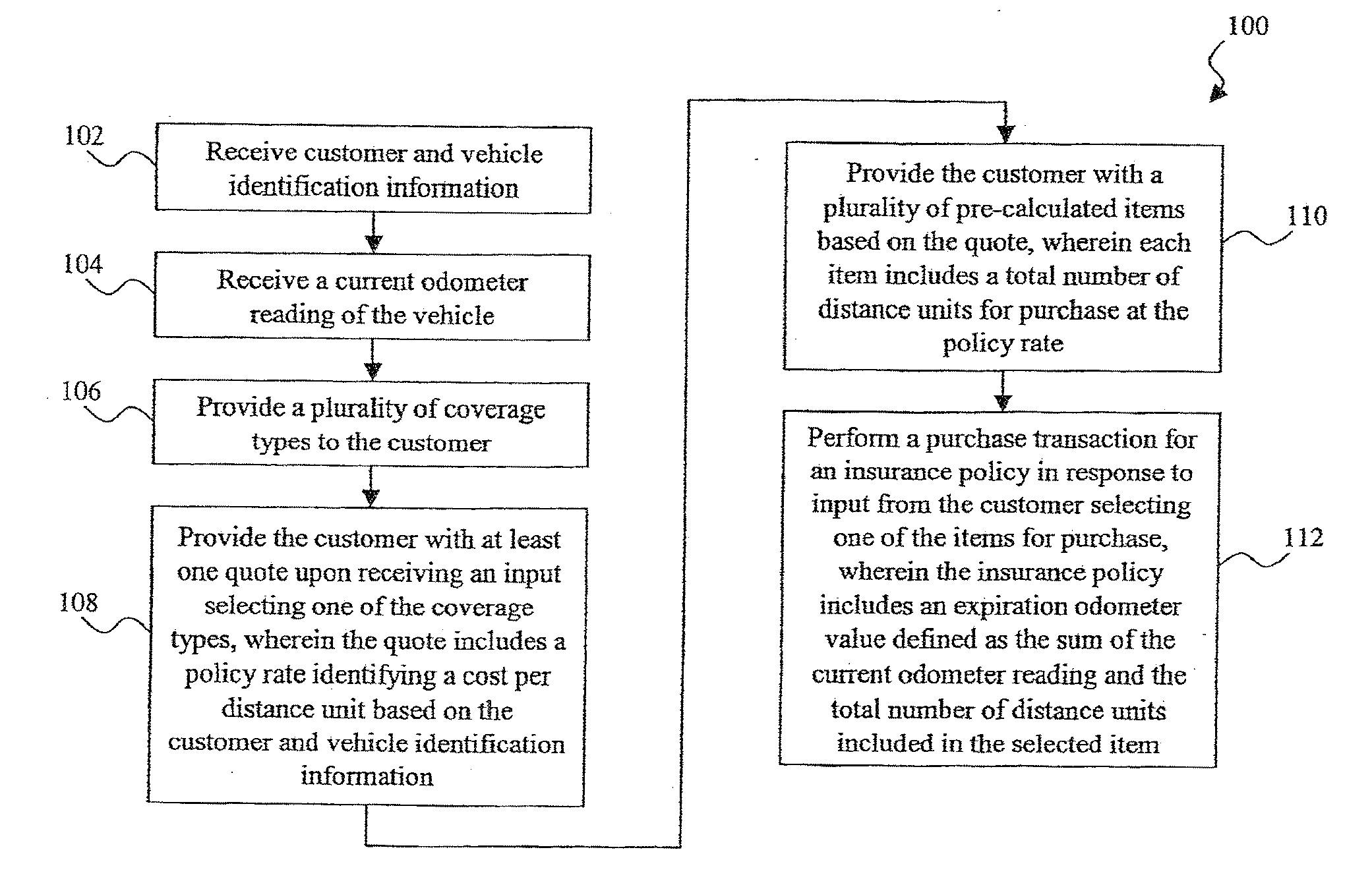
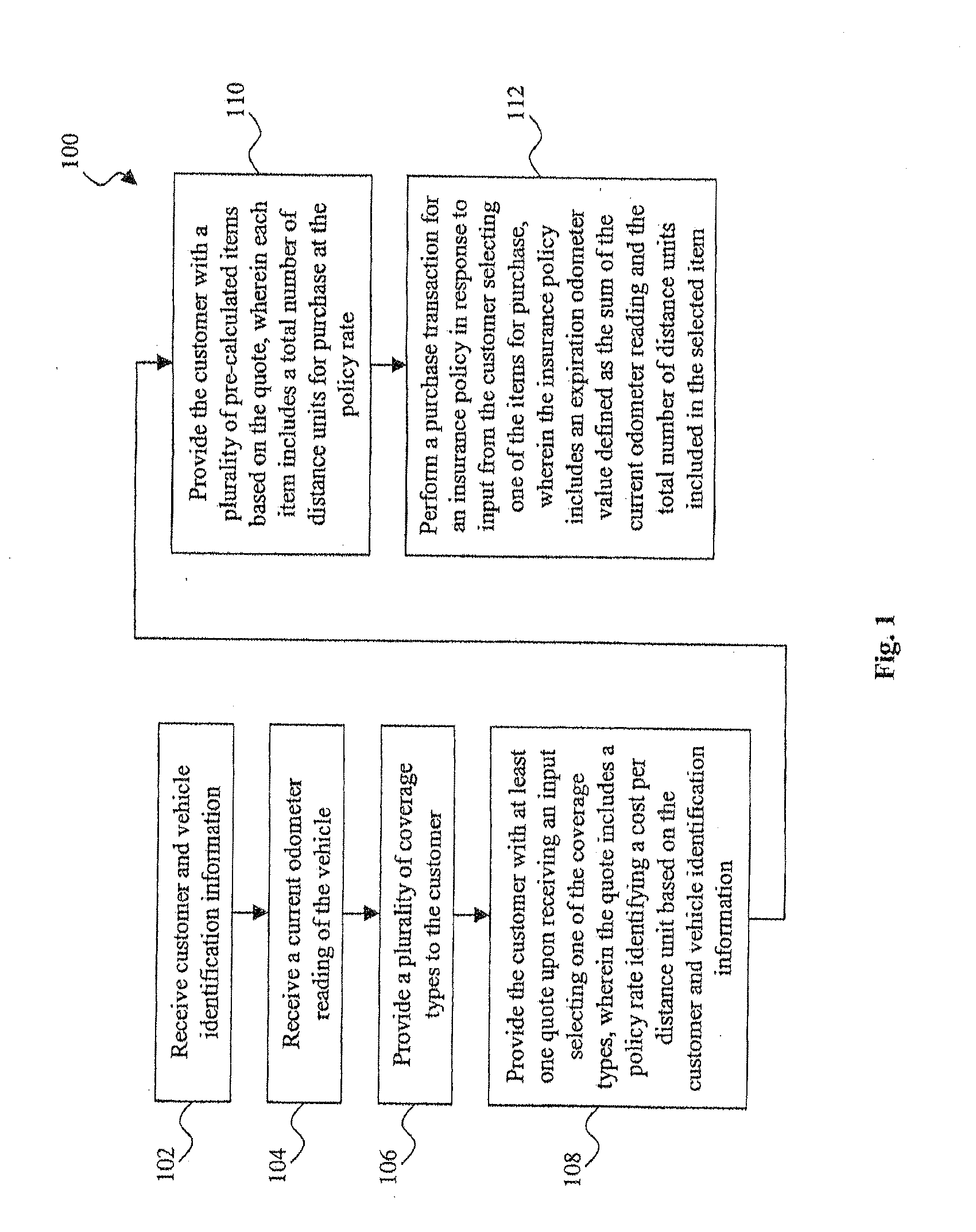
System and method for the assessment, pricing, and provisioning of distance-based vehicle insurance
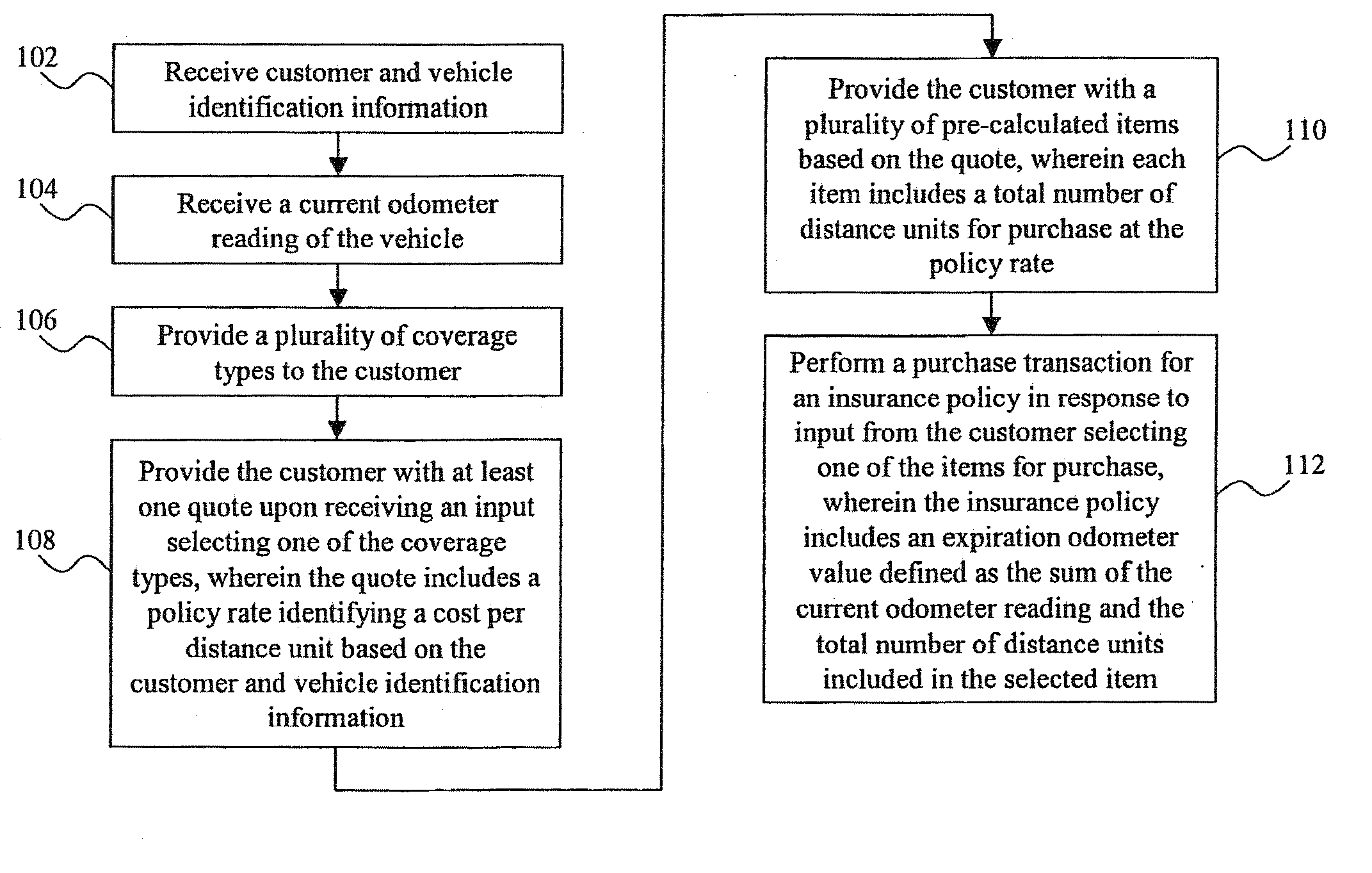
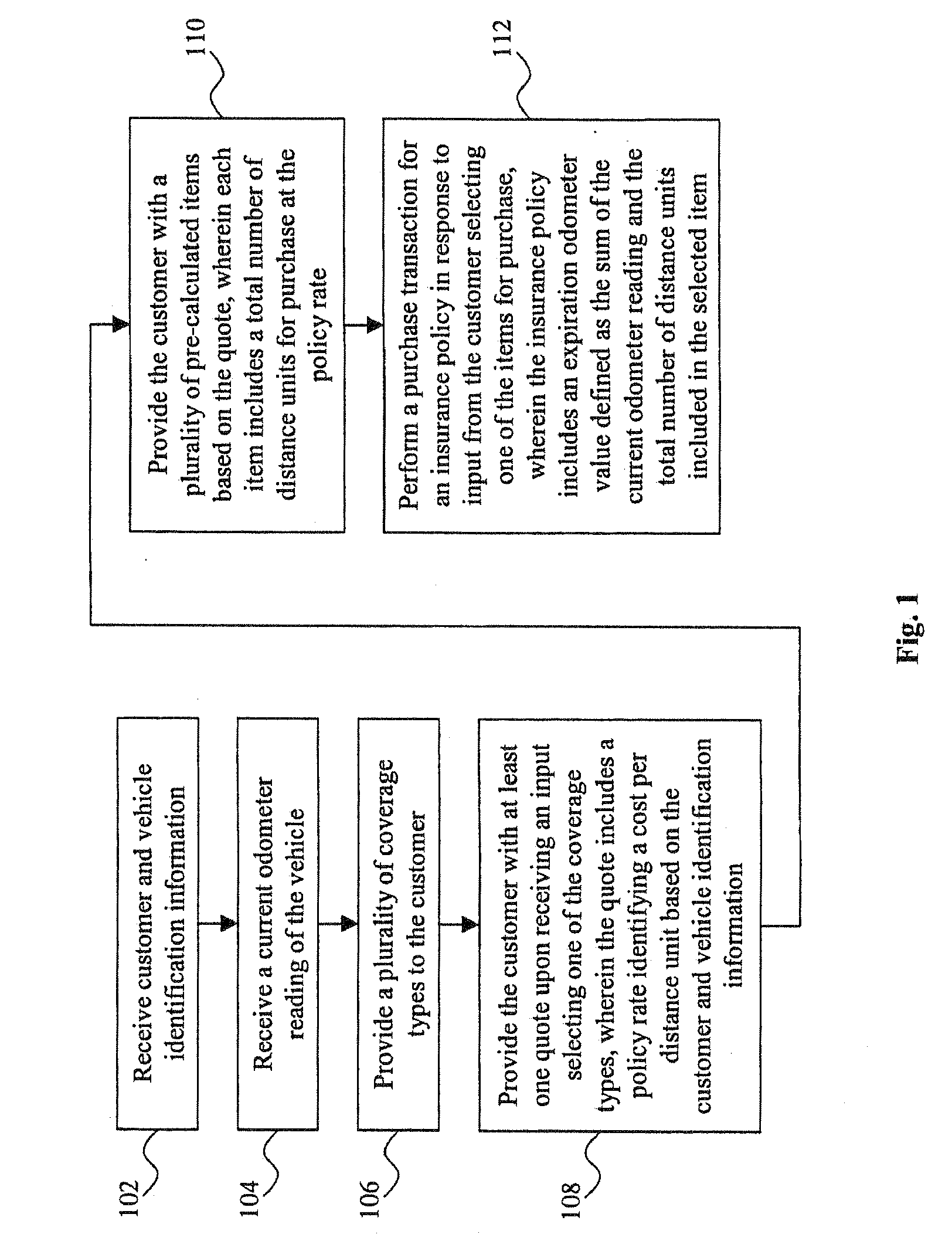
A method of assessing, pricing, and provisioning distance-based vehicle insurance is disclosed. The method includes receiving a vehicle identification number of a vehicle to be insured from a customer, receiving an preliminary odometer reading of the vehicle to be insured from the customer, and obtaining from the customer a legally binding declaration that the preliminary odometer reading is true and accurate. The method includes insuring the vehicle during a policy period defined by coverage for a preselected number of units distance from the preliminary odometer reading.
Owner:STATE FARM MUTAL AUTOMOBILE INSURANCE COMPANY
Internet-based method for determining a vehicle's fuel efficiency
InactiveUS6988033B1Determine vehicle 's fuel efficiencyData augmentationVehicle testingAnalogue computers for vehiclesTraffic capacityElectricity
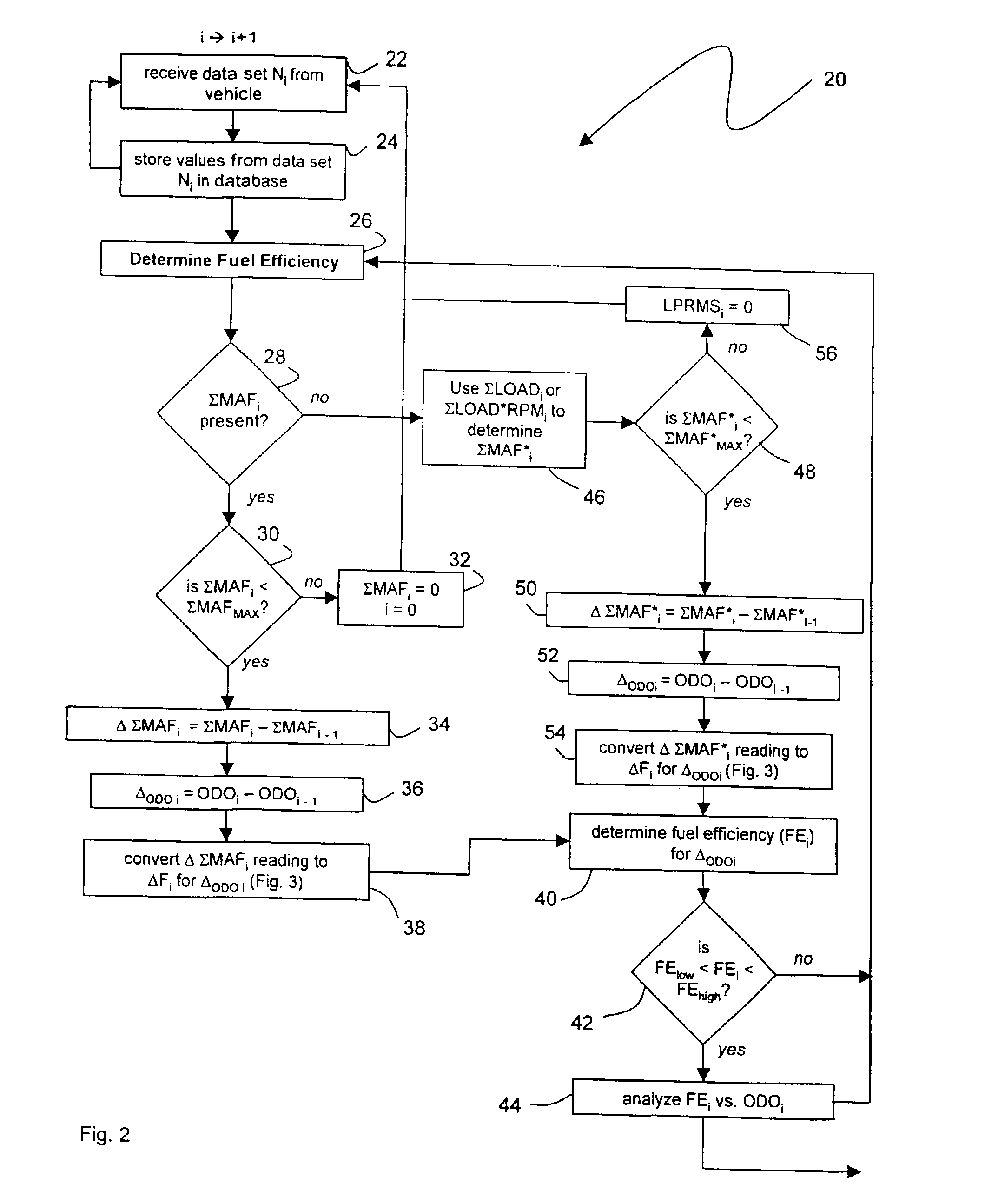
The invention provides a method and device for characterizing a vehicle's fuel efficiency and amount of fuel consumed. The method features the steps of: 1) generating a data set from the vehicle that includes vehicle speed, odometer calculation, engine speed, load, mass air flow; 2) transferring the data set to a wireless appliance that includes i) a microprocessor, and ii) a wireless transmitter in electrical contact with the microprocessor; 3) transmitting a data packet comprising the data set or a version thereof with the wireless transmitter over an airlink to a host computer system; and 4) analyzing the data set with the host computer system to determine a status of the vehicle's fuel efficiency.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
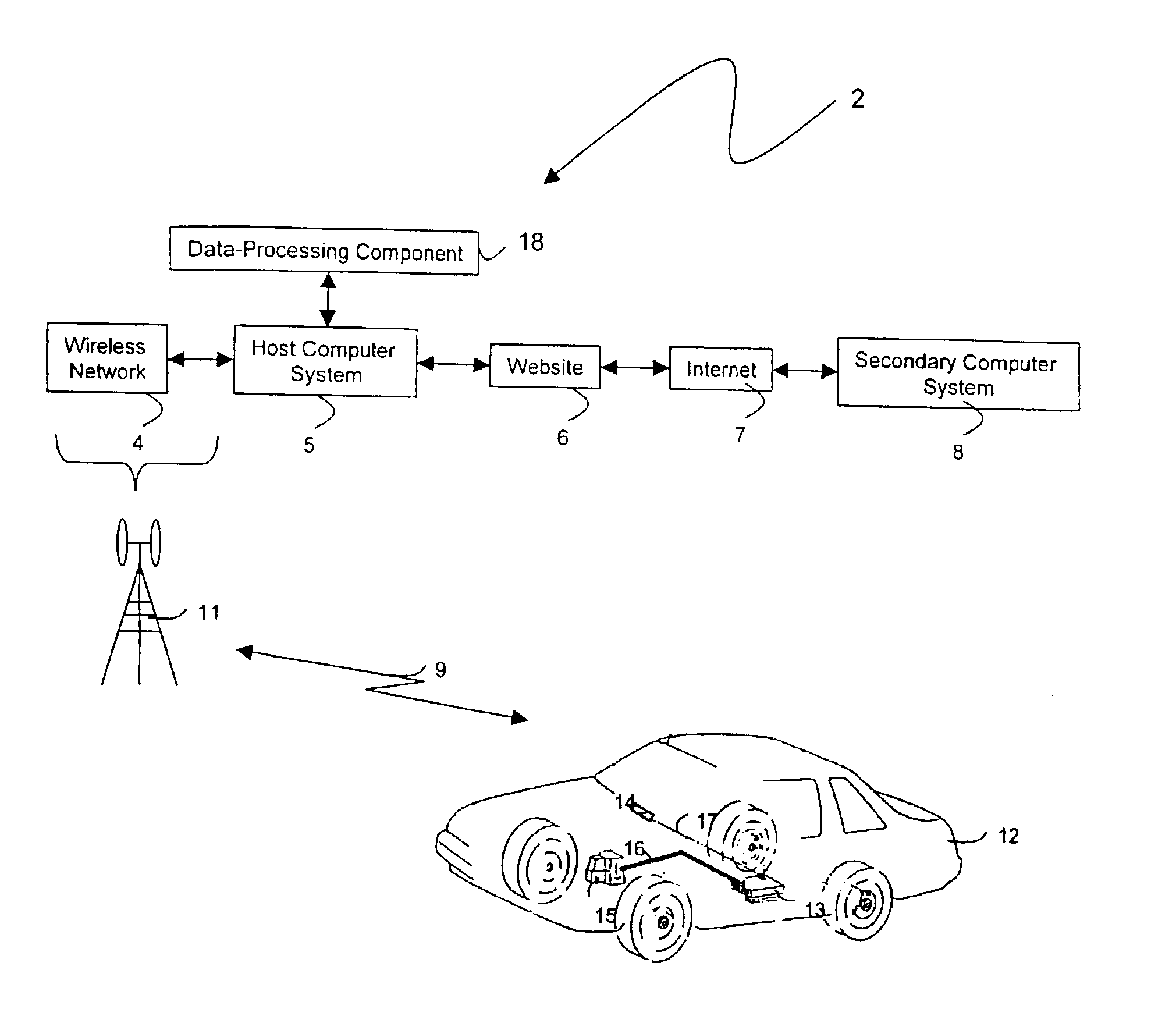
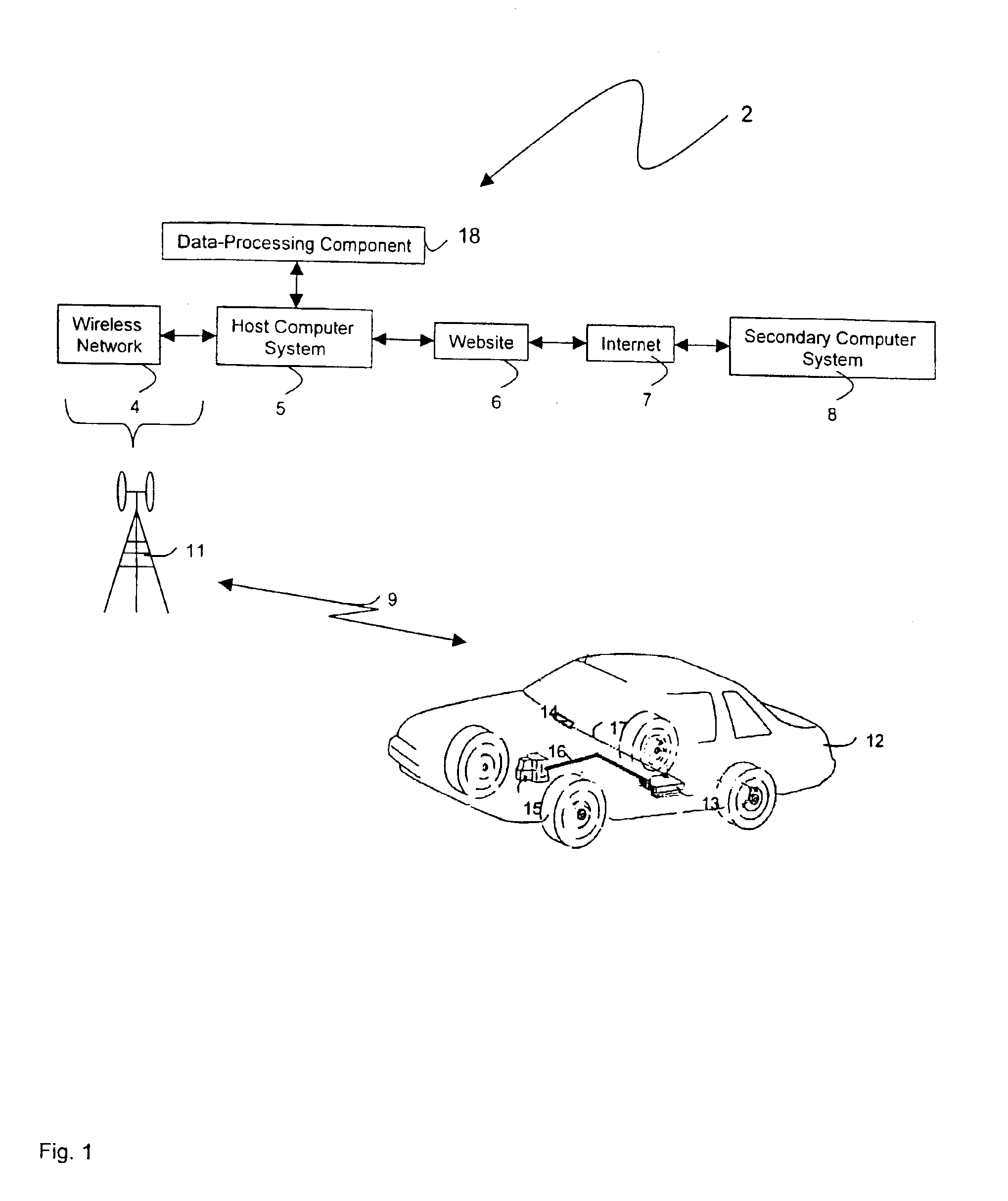
Technique for effectively providing to a vehicle information concerning a condition of the vehicle
InactiveUS6987964B2Frequency-division multiplex detailsRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesThe InternetOdometer
In an automobile, communications to and from the automobile are in the form of messages. Such messages are referred to as “electronic car-mail” or “C-mail” messages as each message has a destination or origination address which includes an identifier, e.g., a vehicle identification number (VIN), identifying the automobile. The messages may be delivered to the automobile from a remote server through a communications network, e.g., the Internet. One such message may contain a recall notice to the automobile. Another message may contain just-in-time map information for navigation, depending on the current location of the automobile. Yet another message may contain advertising information concerning selected entities, e.g., restaurants, gas stations, department stores, etc., also depending on the current location of the automobile. The messages transmitted from the automobile to the remote server may contain, e.g., GPS information identifying the location of the automobile, dynamic data furnished by sensors in the automobile for analysis, an odometer reading and a speedometer reading for records, etc.
Owner:SILVER STATE INTELLECTUAL TECH
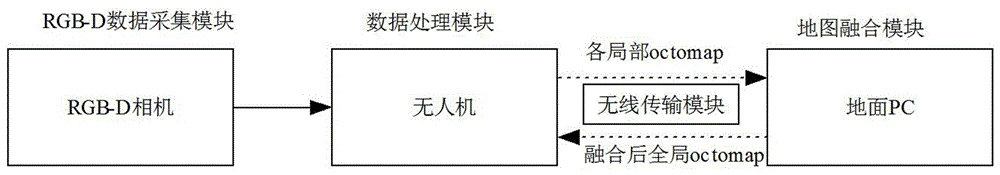
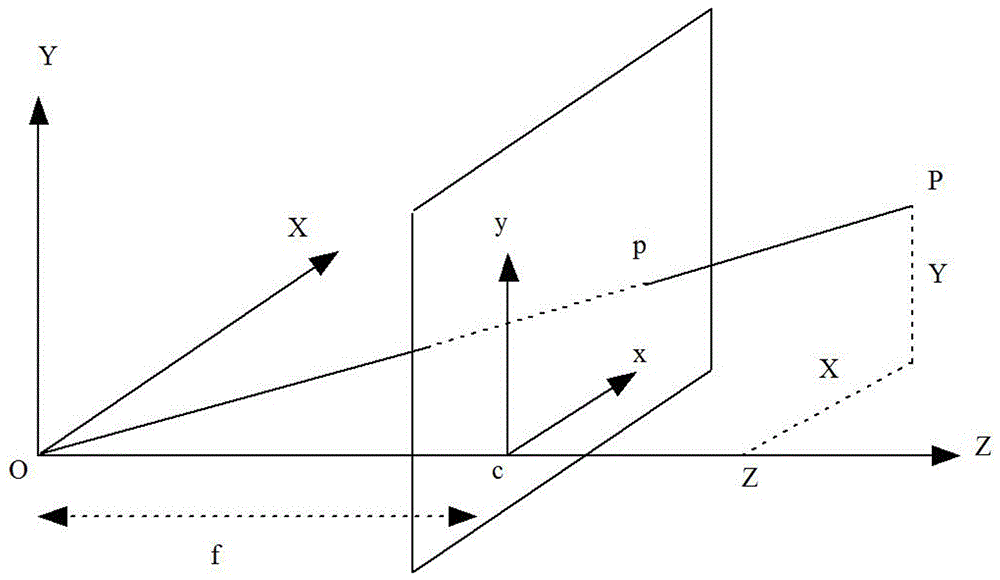
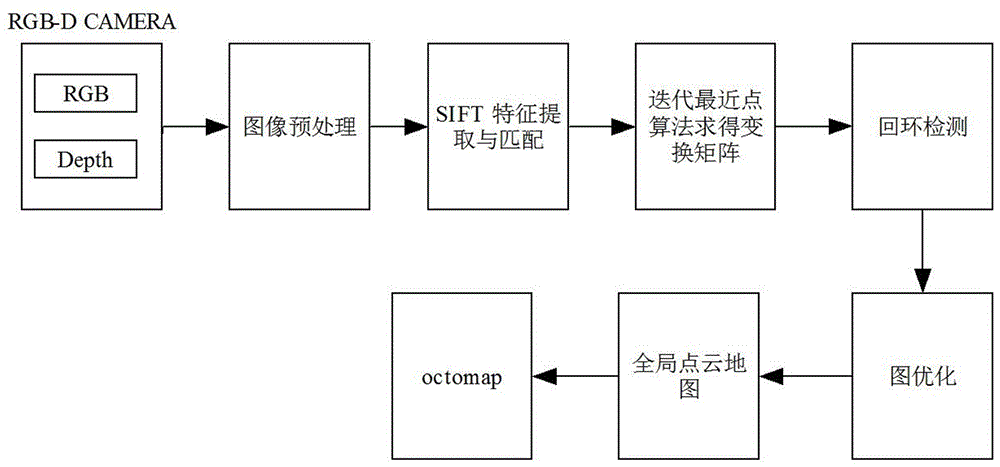
Map merging method of unmanned aerial vehicle visual SLAM under city complex environment
InactiveCN106595659ASmall amount of calculationReduce the hidden danger of lossNavigational calculation instrumentsVehicle position/course/altitude controlWireless transmissionUncrewed vehicle
The invention discloses a map merging method of unmanned aerial vehicle visual SLAM under city complex environment. The method comprises the steps of 1, collecting an image through an RGB-D camera installed on each unmanned aerial vehicle, utilizing the unmanned aerial vehicle to conduct pretreatment on the image, and then conducting image registration; 2, constructing a visual odometer, and achieving loop detection; 3, optimizing the posture of the unmanned aerial vehicle; 4, constructing an octomap map, and achieving real-time on-line SLAM; 5, transmitting the octomap into a ground computer, merging a local octomap into a global octomap, and then transmitting the merged all-region octomap to the unmanned aerial vehicle. According to the map merging method of the unmanned aerial vehicle visual SLAM under the city complex environment, calculated quantity is reduced, real-time on-line SLAM can be achieved, and hidden danger of information losses brought by unstable wireless transmission is reduced; meanwhile, the task execution time is shortened, the task execution efficiency is improved, hidden danger brought by insufficient unmanned aerial vehicle cruising ability, finally more precise positioning can be obtained, and a more precise map can be established.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
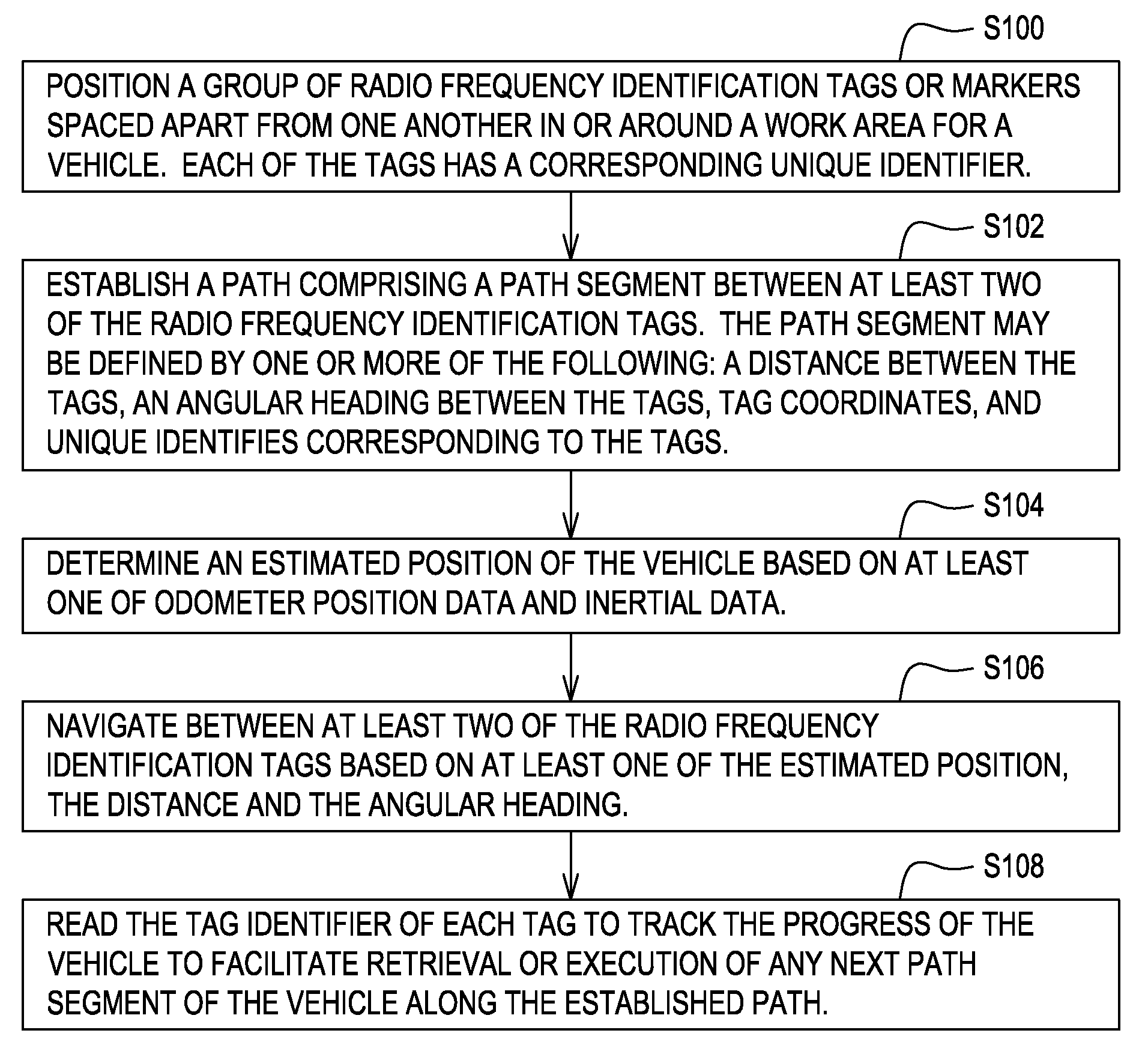
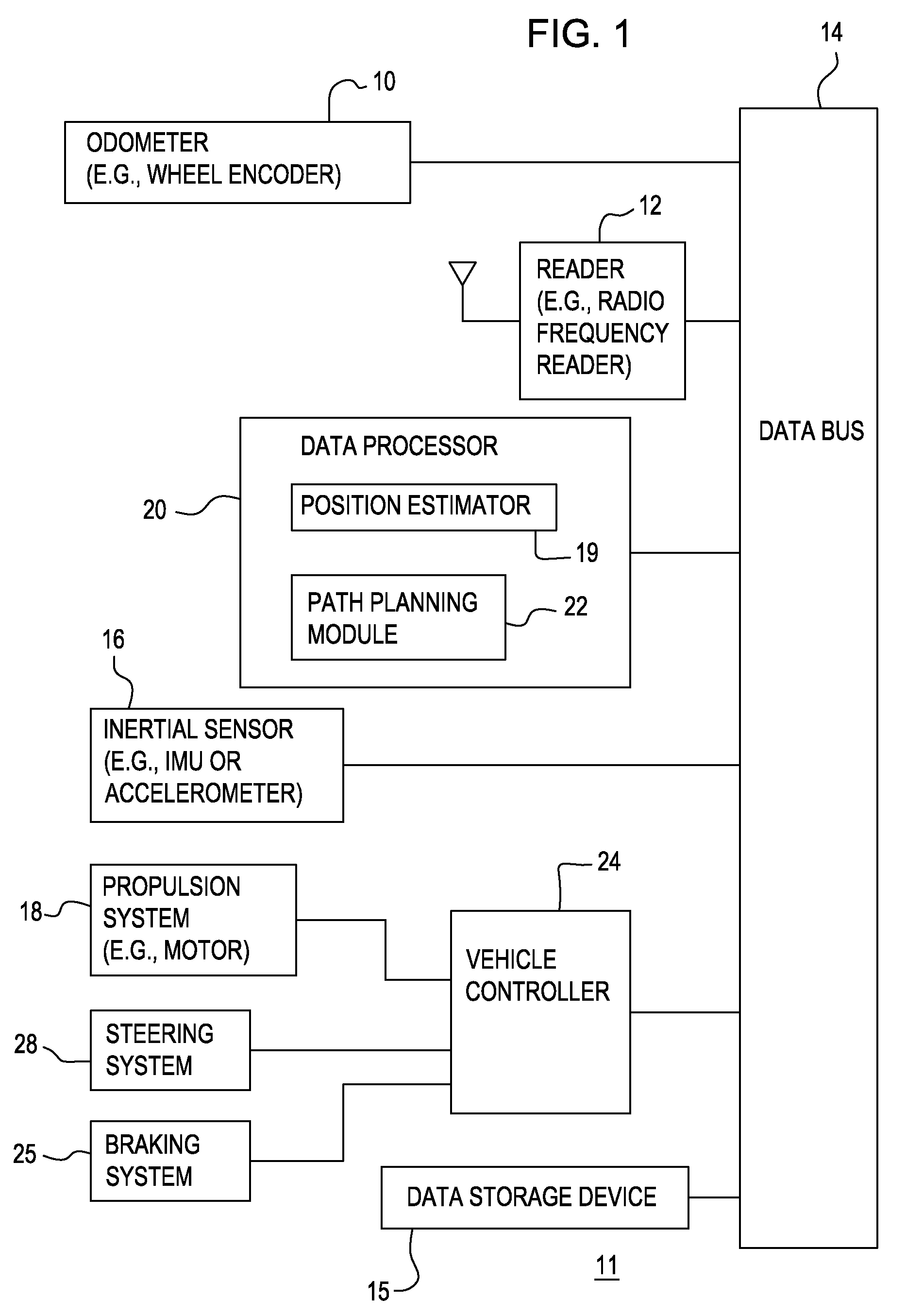
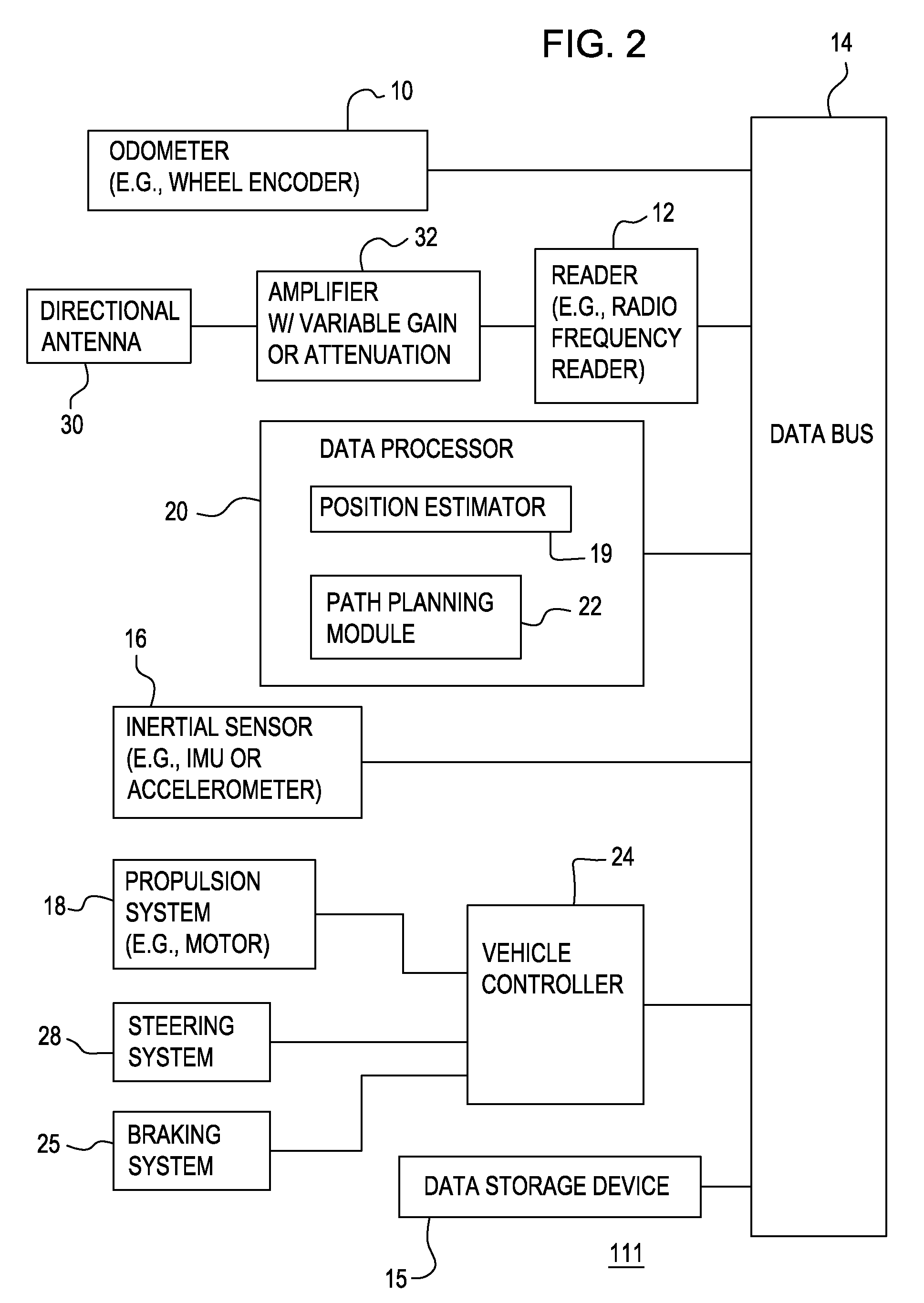
Method and system for determining a position of a vehicle
ActiveUS20100141483A1Road vehicles traffic controlSubscribers indirect connectionAccelerometer dataUnique identifier
Radio frequency identification tags are spaced apart from one another in or around a work area for the vehicle. Each of the tags has a corresponding unique identifier. A path planning module establishes a path comprising a path segment between at least two of the radio frequency identification tags. The path segment comprises at least one of a distance between the tags, an angular heading between the tags, and unique identifiers corresponding to the tags. A data processor determines an estimated position of the vehicle based on at least one of odometer data and accelerometer data. A vehicle controller navigates between at least two of the radio frequency identification tags based on the estimated position, the distance and the angular heading. A reader reads the tag identifiers of each tag to track the progress of the vehicle to facilitate execution of or retrieval of any next path segment of the vehicle along the established path.
Owner:DEERE & CO
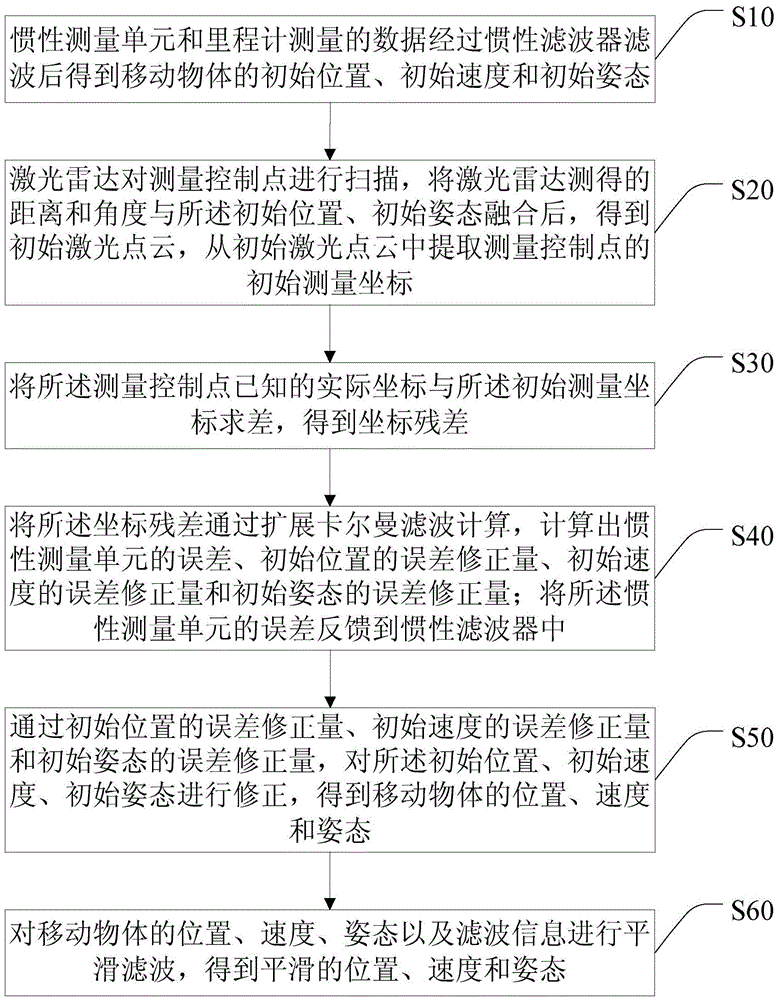
Positioning and posture determining method and system of mobile object
ActiveCN105628026AHigh-precision positioning and attitude determinationLimit error divergenceNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsInertial measurement unitMobile object
The invention discloses a positioning and posture determining method and system of a mobile object. A unified extended kalman filtering model integrating laser radar control target data, inertial measurement unit data and odometer data is constructed through an inertial measurement unit, an odometer and laser radar. The model is built on the basis of a dynamical model and an error model of the inertial measurement unit, the laser radar control target data are introduced into a kalman filtering equation, the error state vector of IMU / odometer combination is calculated, error divergence is limited, and thus high-precision position and posture are obtained; therefore, high-precision positioning and posture determining of the mobile object are achieved without satellite navigation signals.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
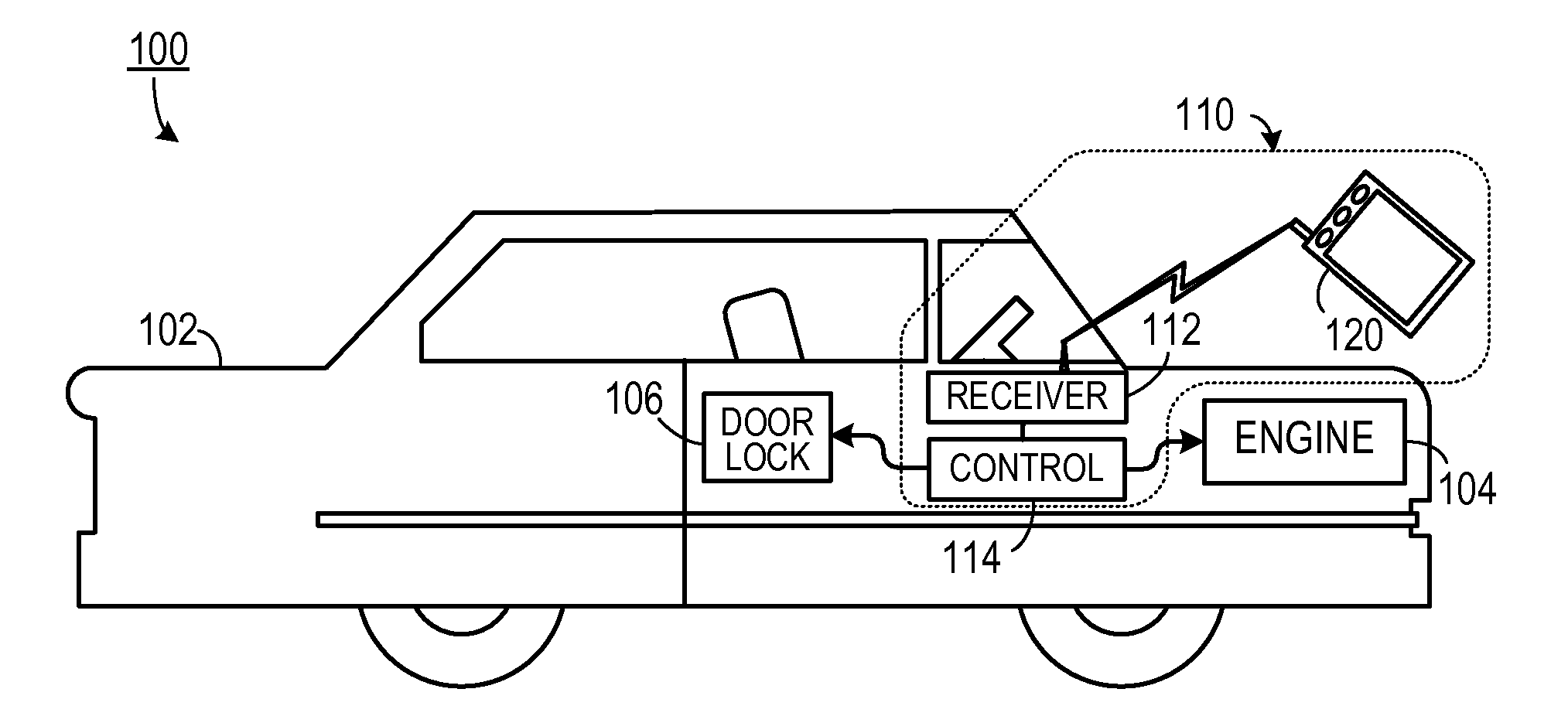
Wearable computing system, method and device
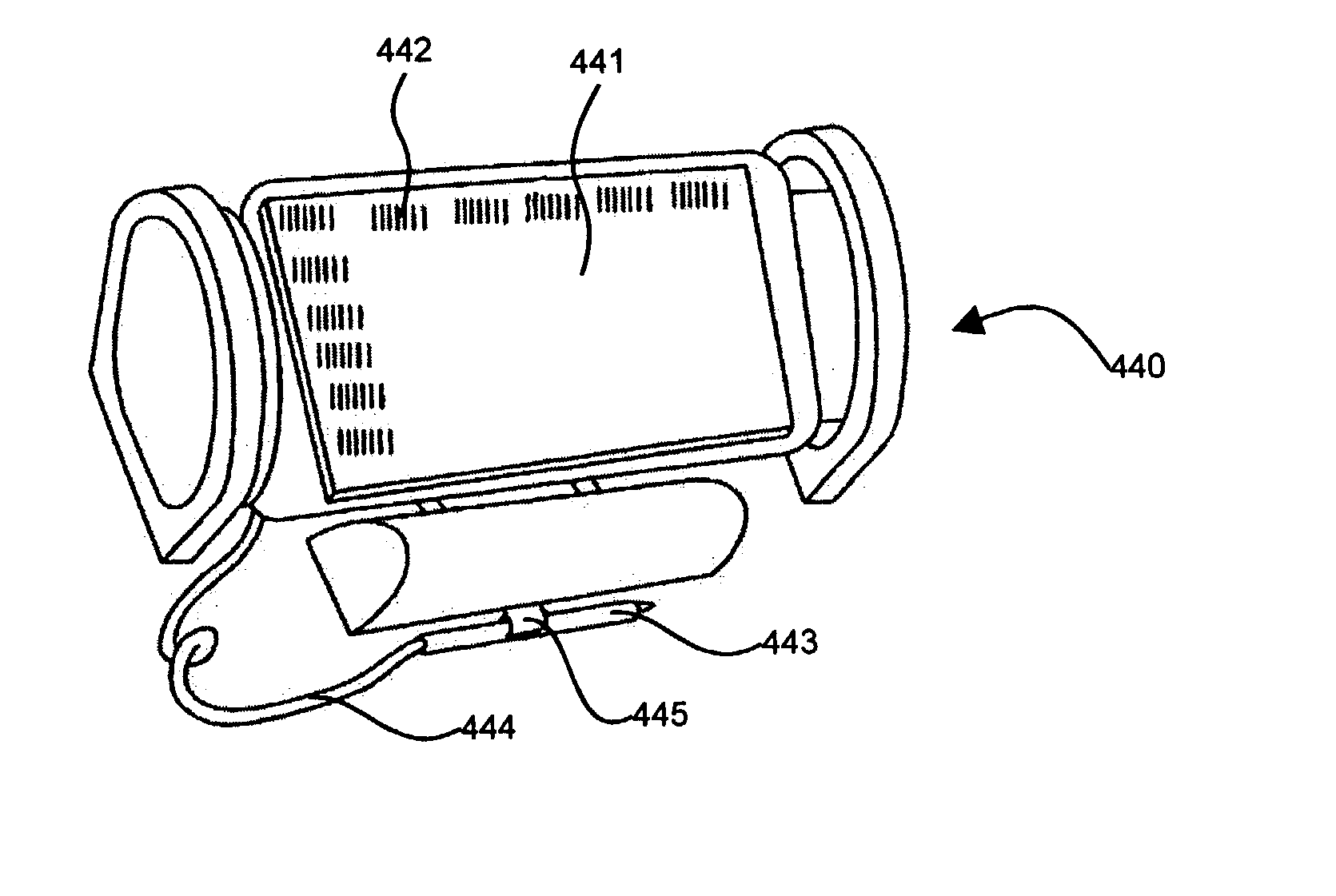
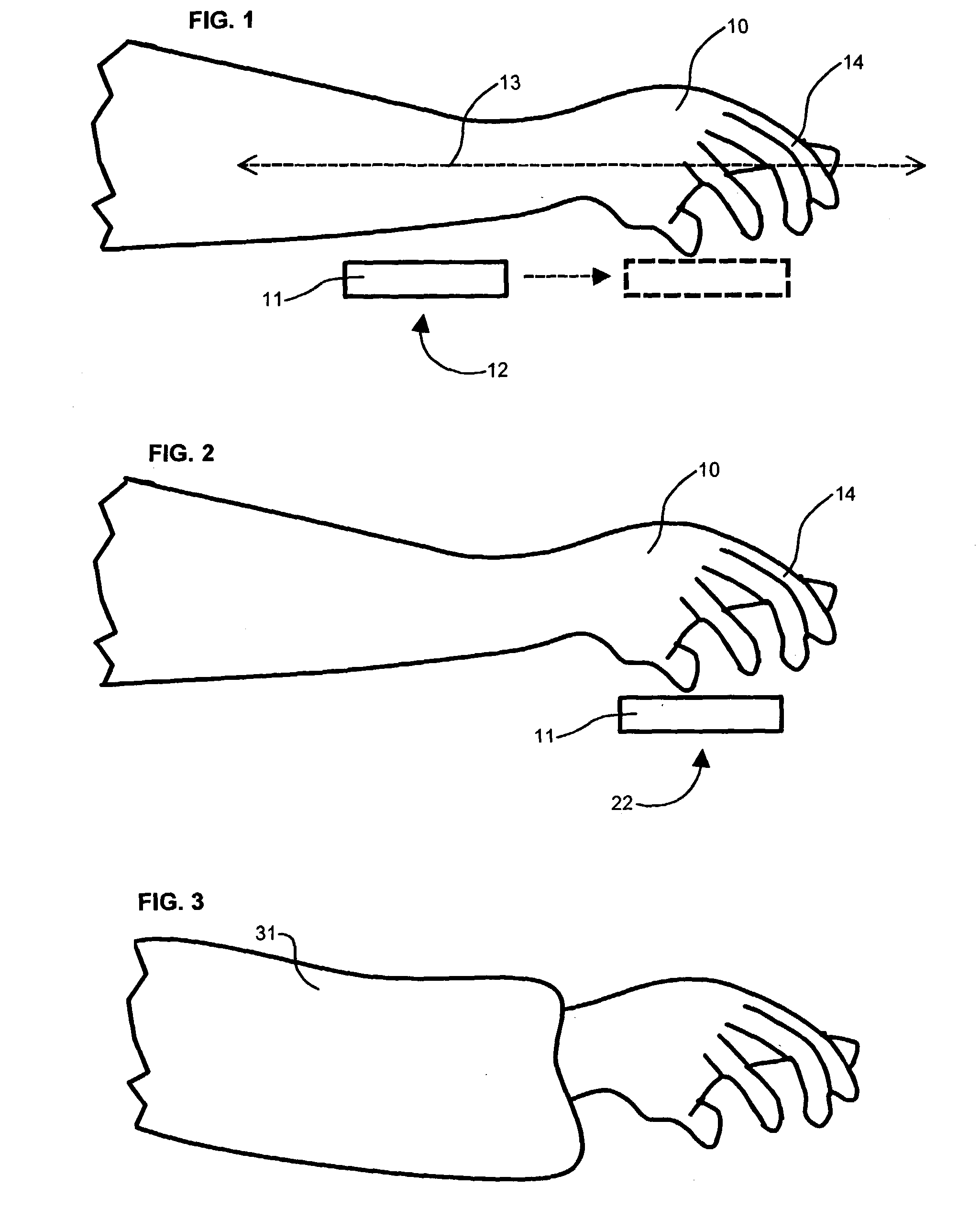
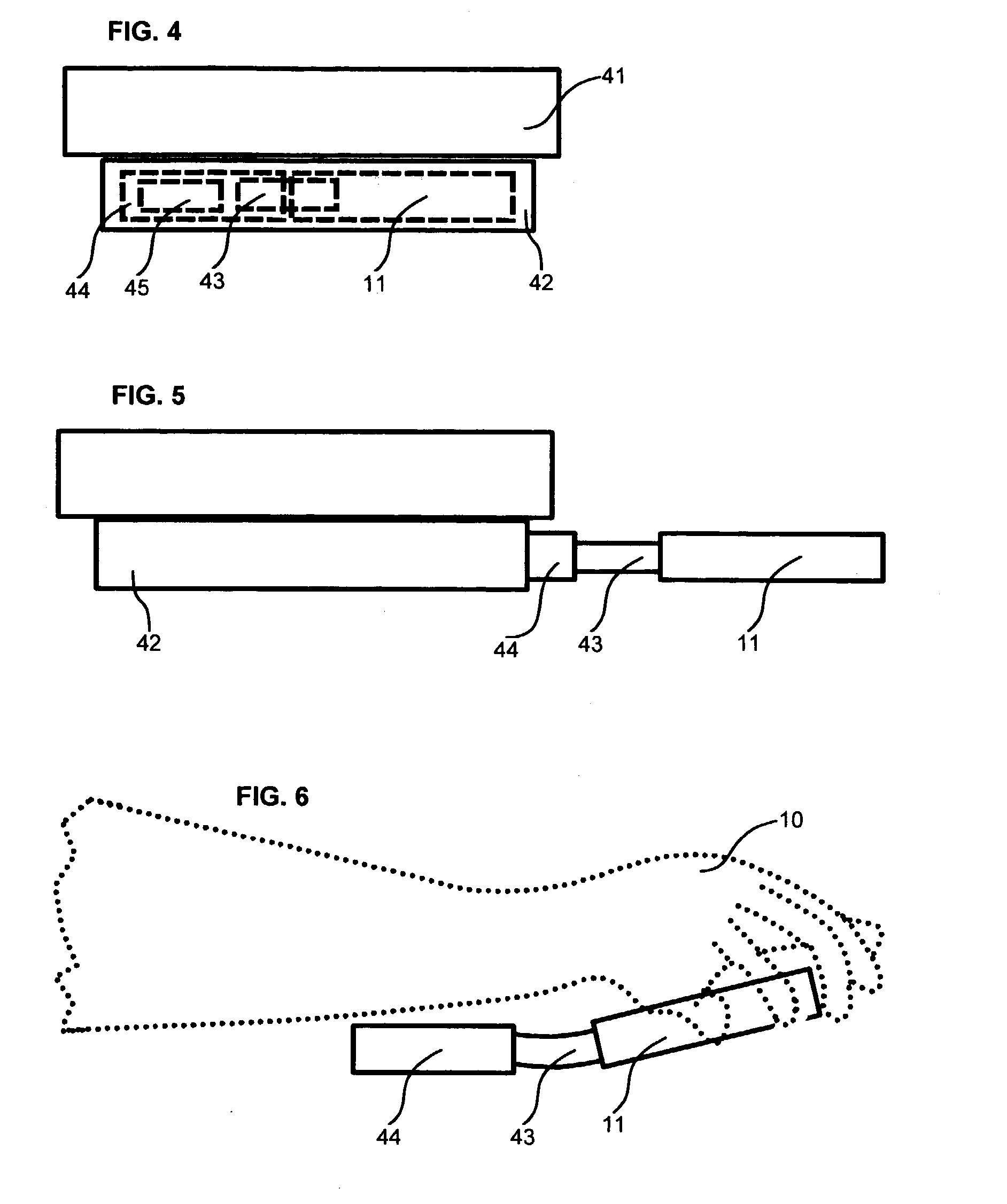
InactiveUS20030209604A1Input/output for user-computer interactionVisual indicationsAir filtrationDocking station
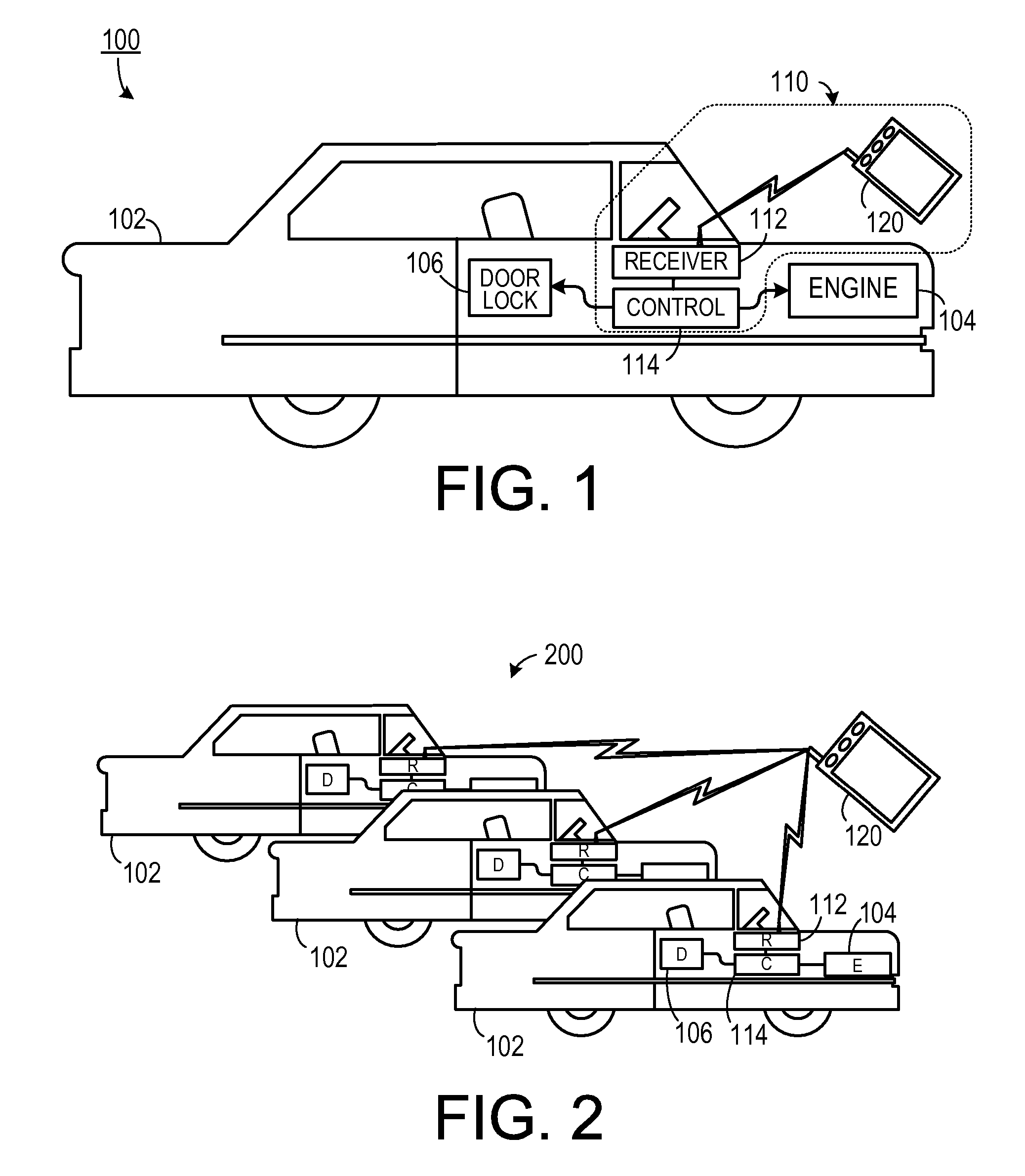
Disclosed is a wrist-wearable electronic interface movably mounted on an arm-attachment mechanism. Interface moves from under-sleeve wrist-adjacent position to palm-adjacent position where it can be manipulated by the hand of the arm wearing the device. Alternately adaptable to telephones, audio recorders, remote controls, auto ID equipment, telephone call-blocking, and more. Alternative embodiment provides a wrist-mounted docking station. Another alternative embodiment includes a superior carpal tunnel syndrome therapy device. The system also includes novel battery chargers: (1) window-mounted, solar-powered; (2) mounted in an automobile that also includes an improved odometer, license plate, and cabin air filtration system.
Owner:SEARCH & SOCIAL MEDIA PARTNERS
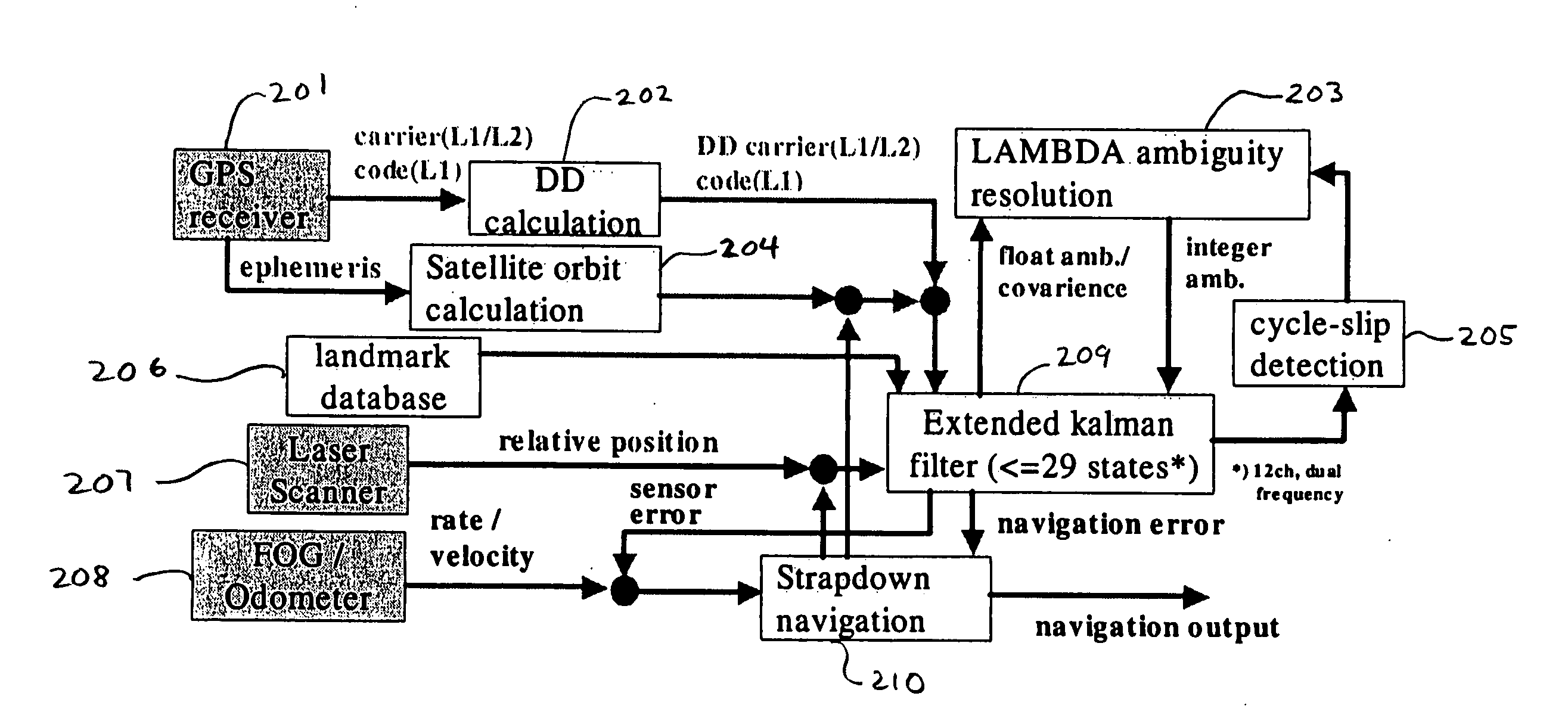
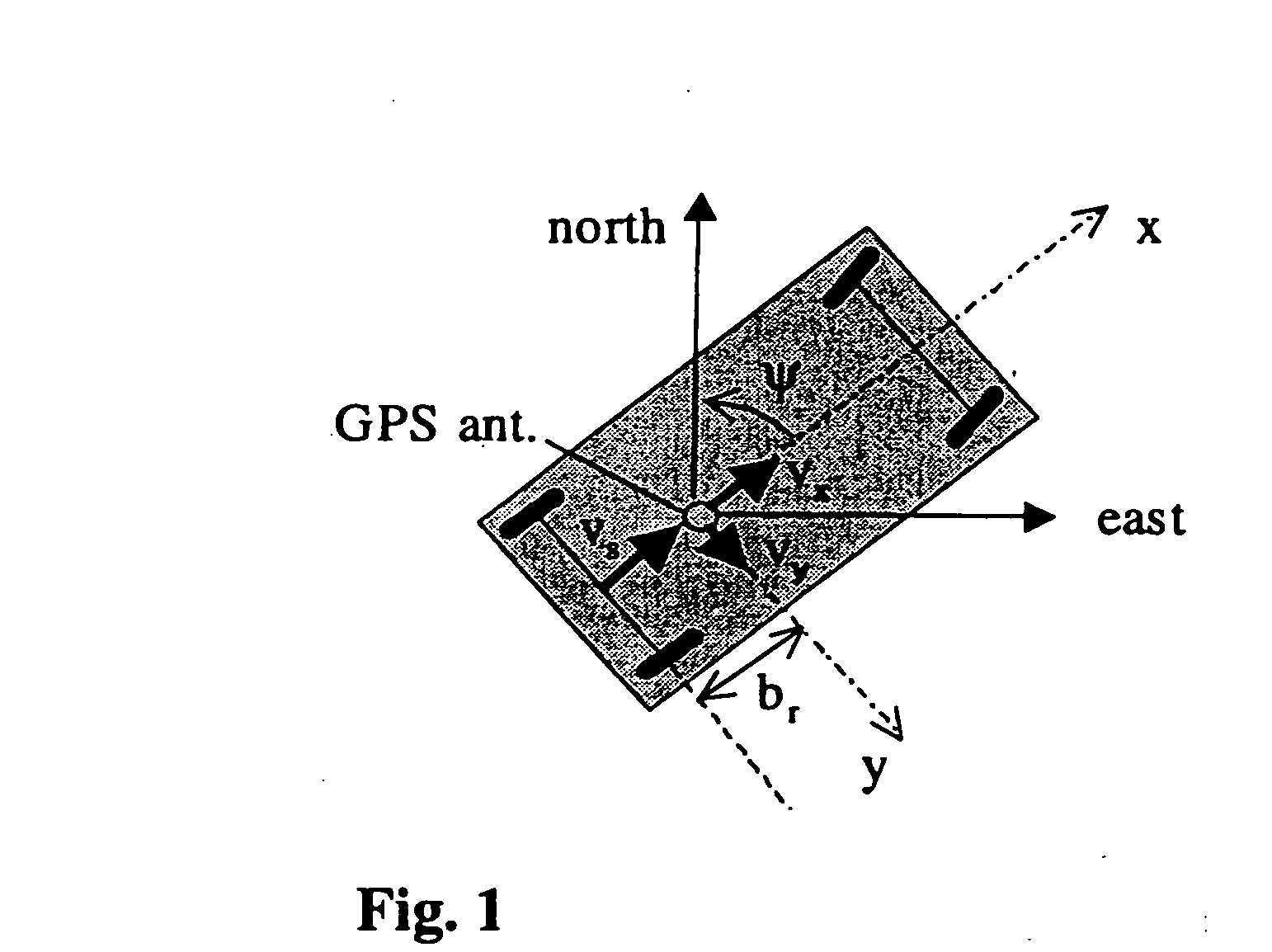
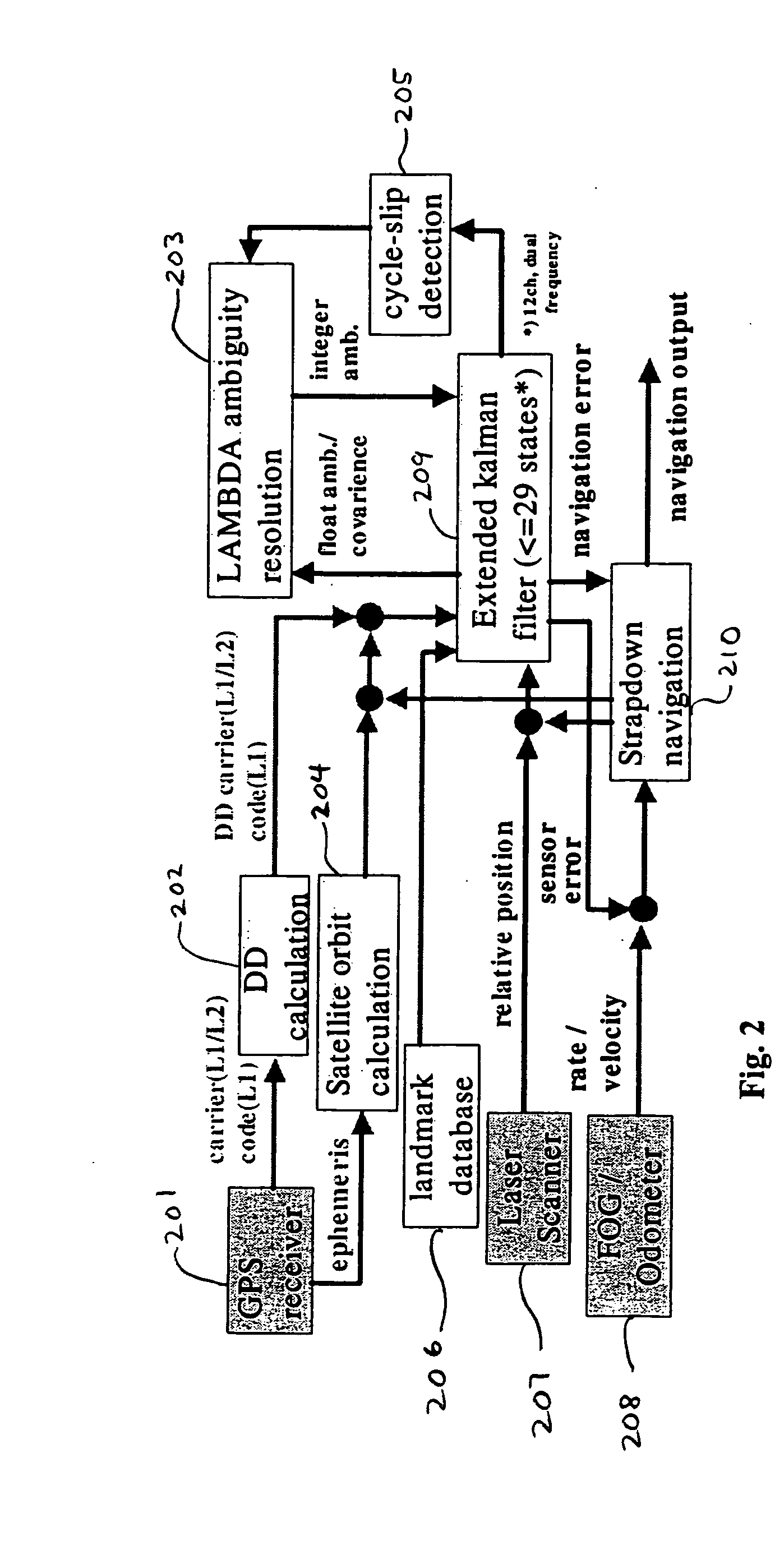
System for autonomous vehicle navigation with carrier phase DGPS and laser-scanner augmentation
A horizontal navigation system aided by a carrier phase differential Global Positioning System (GPS) receiver and a Laser-Scanner (LS) for an Autonomous Ground Vehicle (AGV). The high accuracy vehicle navigation system is highly demanded for advanced AGVs. Although high positioning accuracy is achievable by a high performance RTK-GPS receiver, the performance should be considerably degraded in a high-blockage environment due to tall buildings and other obstacles. The present navigation system is to provide decimetre-level positioning accuracy in such a severe environment for precise GPS positioning. The horizontal navigation system is composed of a low cost Fiber Optic Gyro (FOG) and a precise odometer. The navigation errors are estimated using a tightly coupled Extended Kalman Filter (EKF). The measurements of the EKF are double differenced code and carrier phase from a dual frequency GPS receiver and relative positions derived from laser scanner measurements.
Owner:AUTO TECH GRP LLC
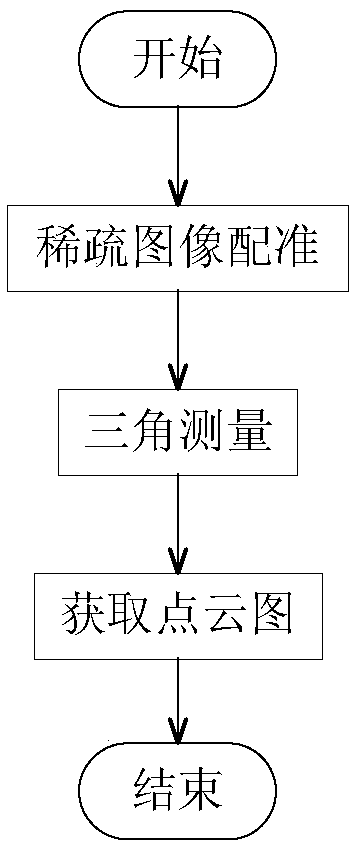
Apparatus and method for generating three-dimensional map using structured light
ActiveUS20090125175A1Distance measurementPosition/course control in two dimensionsCamera moduleOdometer
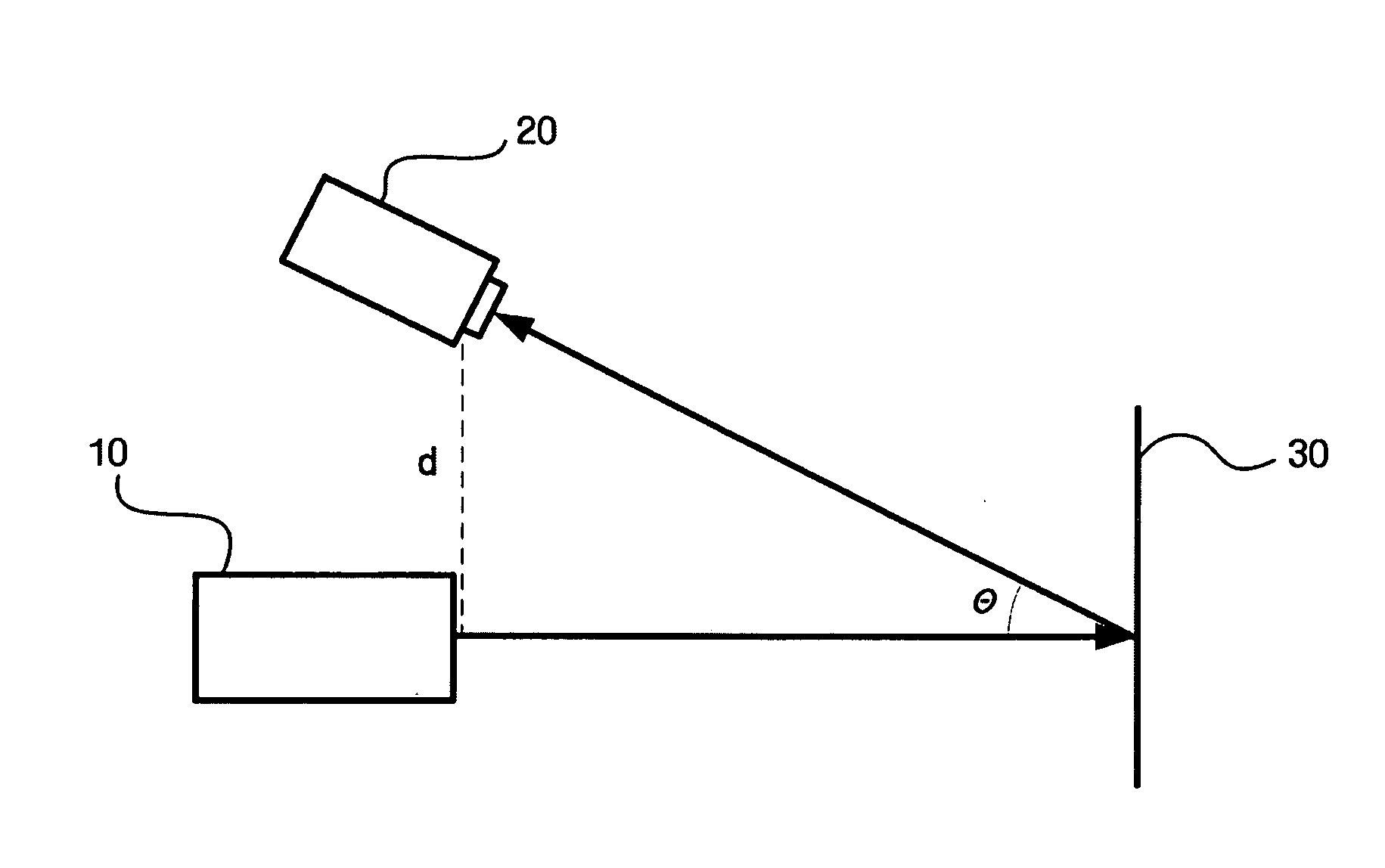
A three-dimensional map-generating apparatus and method using structured light. The apparatus for generating a three-dimensional map using structured light includes an odometer detecting the pose of a mobile robot, and a distance-measuring sensor including a light source module that emits light upward and a camera module that captures an image formed by light reflected from an obstacle, and measuring a distance to the obstacle using the captured image. The apparatus measures a distance to the obstacle using the distance-measuring sensor while changing the relative pose of the mobile robot, thereby generating a three-dimensional map.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
System and method for the assessment, pricing, and provisioning of distance-based vehicle insurance
A method for assessing, pricing, and provisioning distance-based vehicle insurance is disclosed. Receiving identification information of a customer and an associated vehicle, a current odometer reading of the vehicle, and a garaging location of the vehicle is disclosed. The customer is provided with a quote including a policy rate identifying a cost per distance unit based on the customer and vehicle identification information and the garaging location. Performing a purchase transaction for an insurance policy in response to the customer selecting one of the items for purchase, wherein coverage provided by the insurance policy expires based on the earlier of an odometer expiration value occurring and a predetermined time limit is disclosed. The expiration odometer value is the sum of the current odometer reading and the total number of distance units included in the selected item. The current odometer reading is not audited prior to or during the purchase transaction.
Owner:STATE FARM MUTUAL AUTOMOBILE INSURANCE
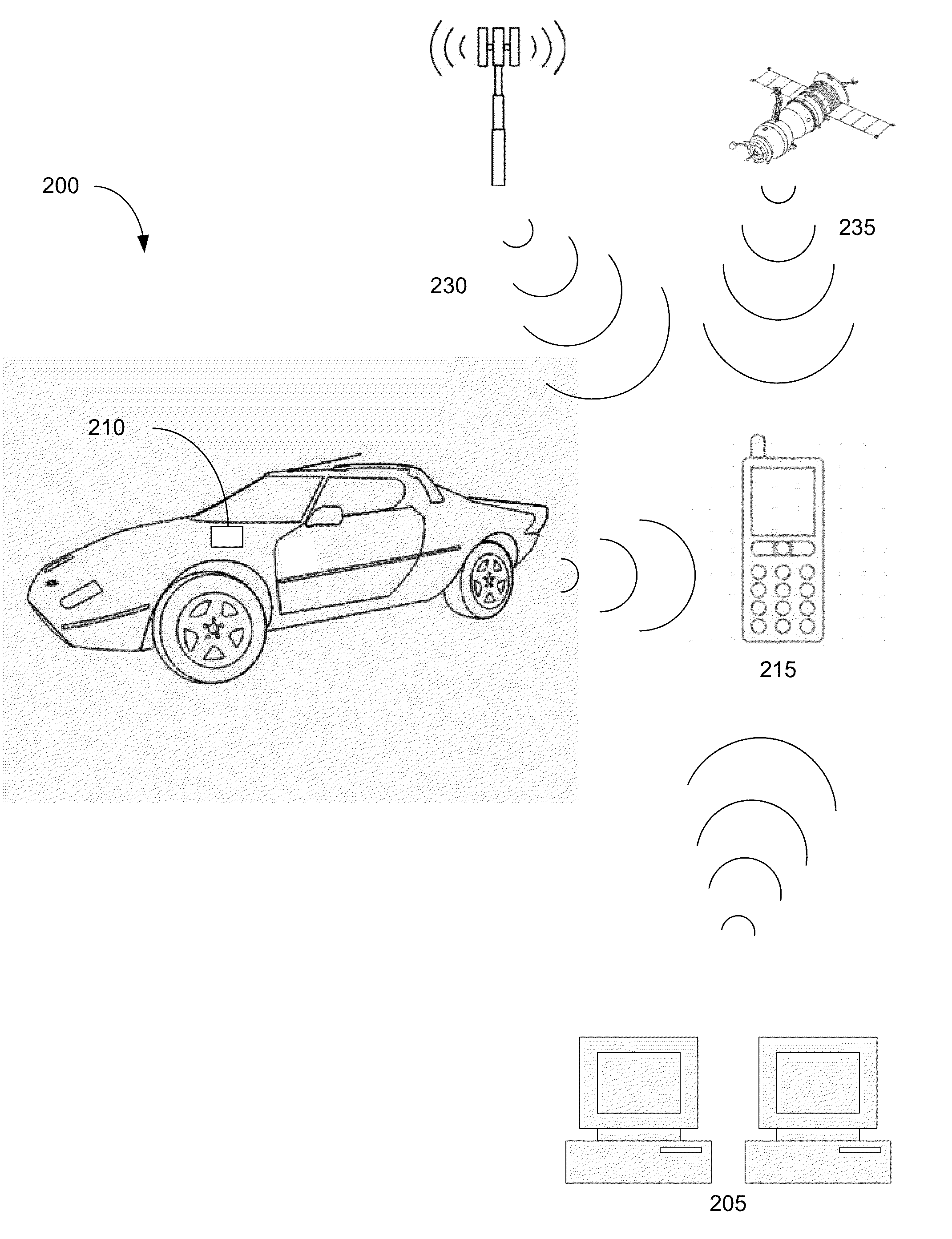
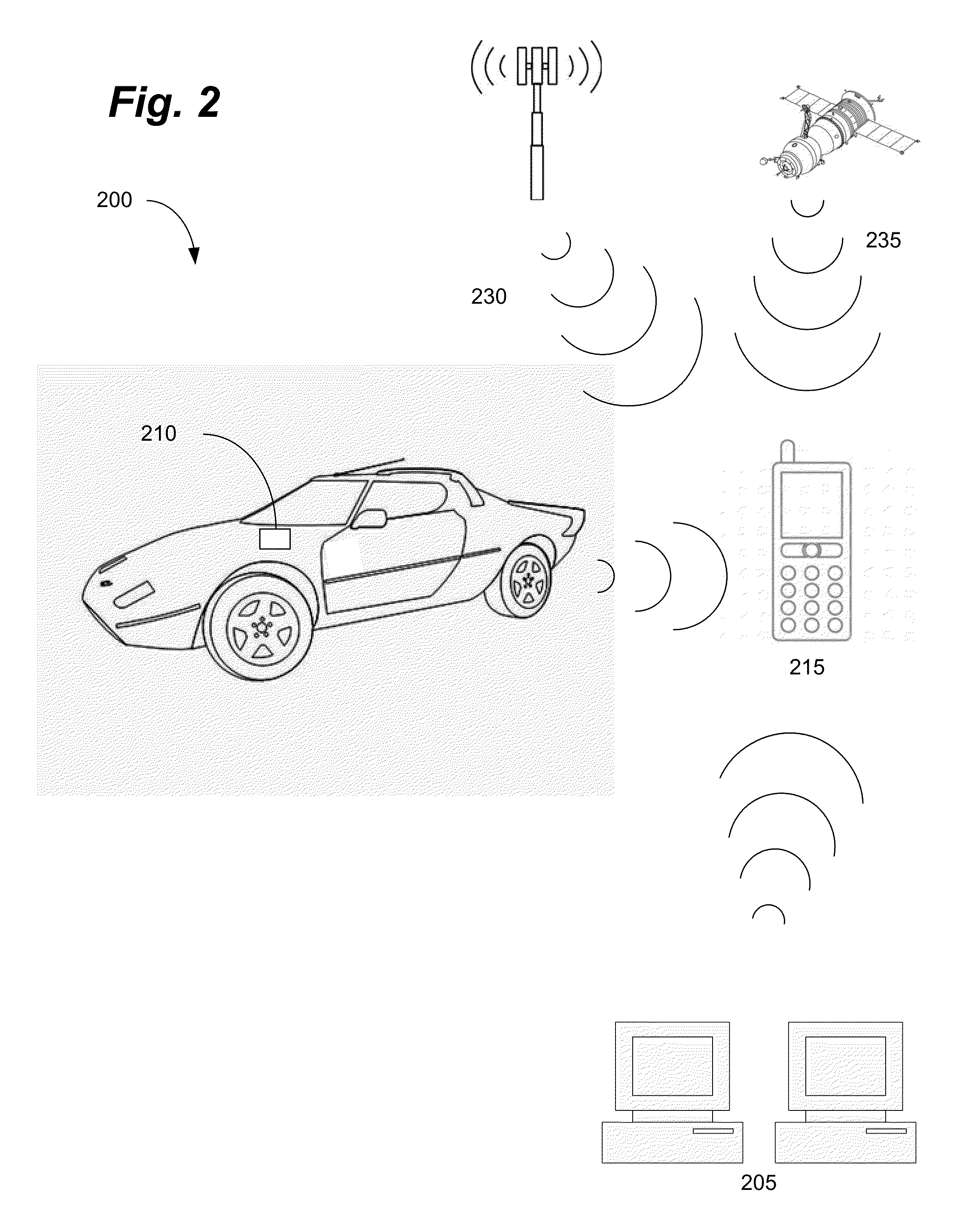
Remote vehicle rental systems and methods
ActiveUS20140156111A1Reduce infrastructure complexityLow costTicket-issuing apparatusDigital data processing detailsOperational costsOdometer
A system for renting vehicles is disclosed. The system can comprise a vehicle access communicator (“VAC”) capable of interfacing with one or more functions of a rental vehicle and a user provided portable electronic device. The VAC can control various functions of the vehicle including, but not limited to, the door locks and / or enabling / disabling the vehicle. The VAC can also monitor various functions of the vehicle including, but not limited to, the fuel level and / or the odometer readings. The VAC can connect to the portable electronic device using a suitable connection method to access additional functionality such as, for example and not limitation, locations services, cellular, and / or internet access. The VAC and the portable electronic device can be used to provide a rental system with reduced infrastructure and operating costs. The system can enable the use of “Green Zones” to provide permanent or temporary vehicle rental areas.
Owner:I D SYST
Apparatus for acquiring 3-dimensional geomatical information of underground pipes and noncontact odometer using optical flow sensor and using the same
InactiveUS20100211354A1Effective maintenanceEffective preservationOptical rangefindersMeasuring wheelsOptical flowOdometer
An apparatus to acquire 3-dimensional geographical information of an underground pipe includes an in-pipe transfer unit which moves along the inside of the underground pipe, a sensing unit which senses 3-dimensional location information of the in-pipe transfer unit, and an information storage unit which stores a value measured by the sensing unit. Accordingly, the depth at which the underground pipe is located as well as 2-dimensional location information of the underground pipe is stored in the information storage unit so that maintenance and repair of the underground pipe can be carried out with greater efficiency.
Owner:WATER RESOURCES ENG +1
Fleet tracking system with reporting feature
In a method of tracking usage habits of a vehicle having a standard vehicle data port, in which a user identification, a start date, a start time, and a start odometer reading are recorded a local vehicle data storage medium upon receipt of an authorized user identification. A shutoff date, a shutoff time and a shutoff odometer reading are recorded in the local vehicle data storage medium upon sensing engine shutoff. A request for vehicle usage information is received from an off-board data storage device. In response thereto the user identification, the start date, the start, the start odometer reading, the shutoff date, the shutoff time and the shutoff odometer reading are transmitted from the local vehicle data storage medium to the off-board data storage device. A report that includes the user identification, the start date, the start, the start odometer reading, the shutoff date, the shutoff time and the shutoff odometer reading, is transmitted from the off-board data storage device to a remote computer, via a global computer network.
Owner:UNDERDAHL CRAIG T +1
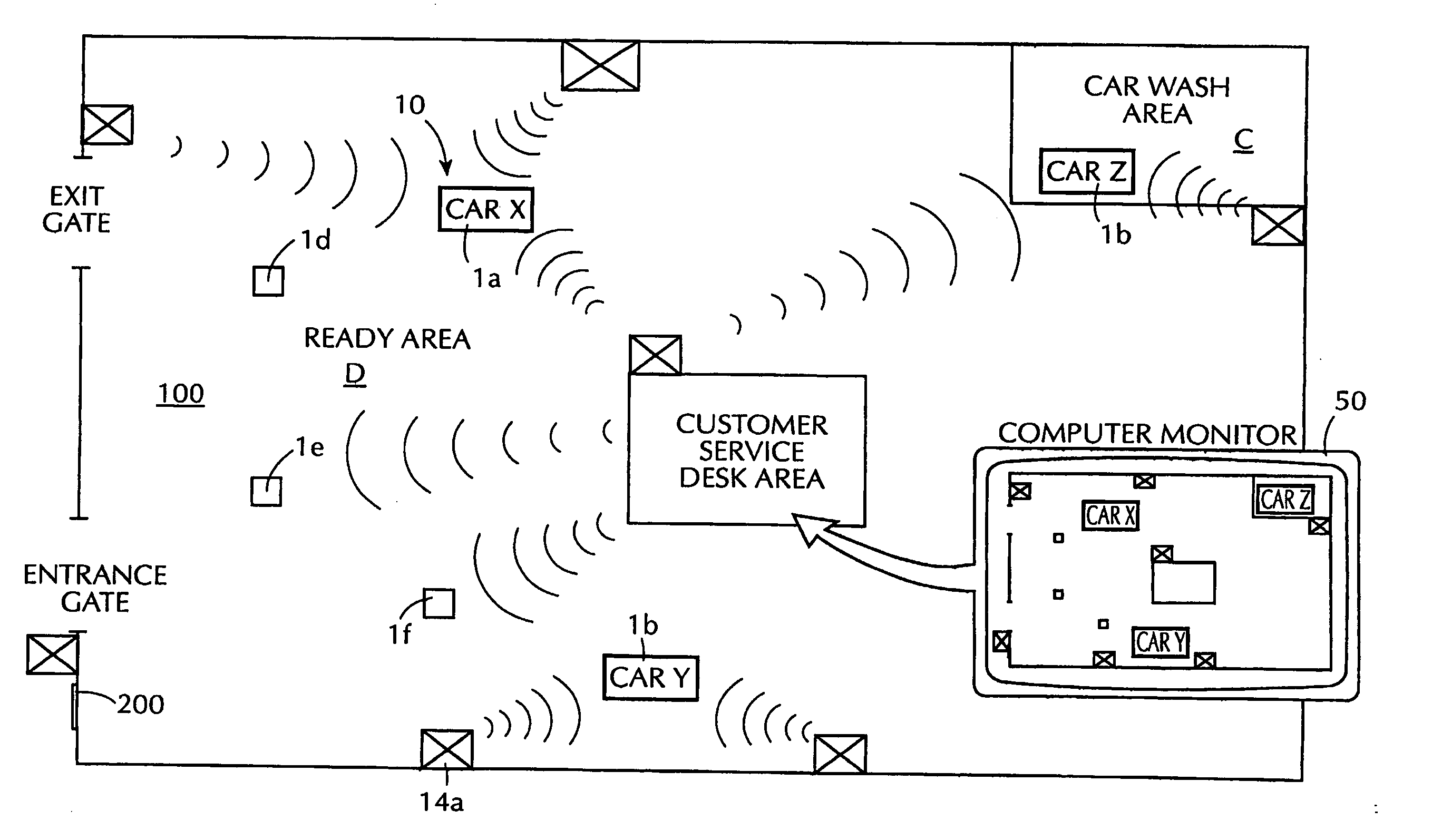
Fully automated vehicle rental system
InactiveUS20050108089A1Accurate calculationTicket-issuing apparatusDetection of traffic movementIn vehicleFuel tank
An automated vehicle rental system with individual vehicle transmitting sensors for keeping track of vehicle mileage, fill state of vehicle fuel tank, and localized position status in a rental lot. Sensors are linked to the vehicle odometer reading and to the vehicle fuel tank float sensor with compensation for types of driving and fuel fill-ups which affect float level readings. The sensors are integrated with or are linked with communicating tags operable in a defined site for ultimate communication of stored vehicle related sensor data, vehicle location and type to a central data base for automatically completely effecting check out, charges and state of vehicle readiness for renewed rental. The transmitting sensors are adapted to avoid interference between sensors of other vehicles during multiple transmissions. Also included is an in-vehicle check out and payment device operatively linkable to the transmitting sensor of the vehicle.
Owner:I D SYST
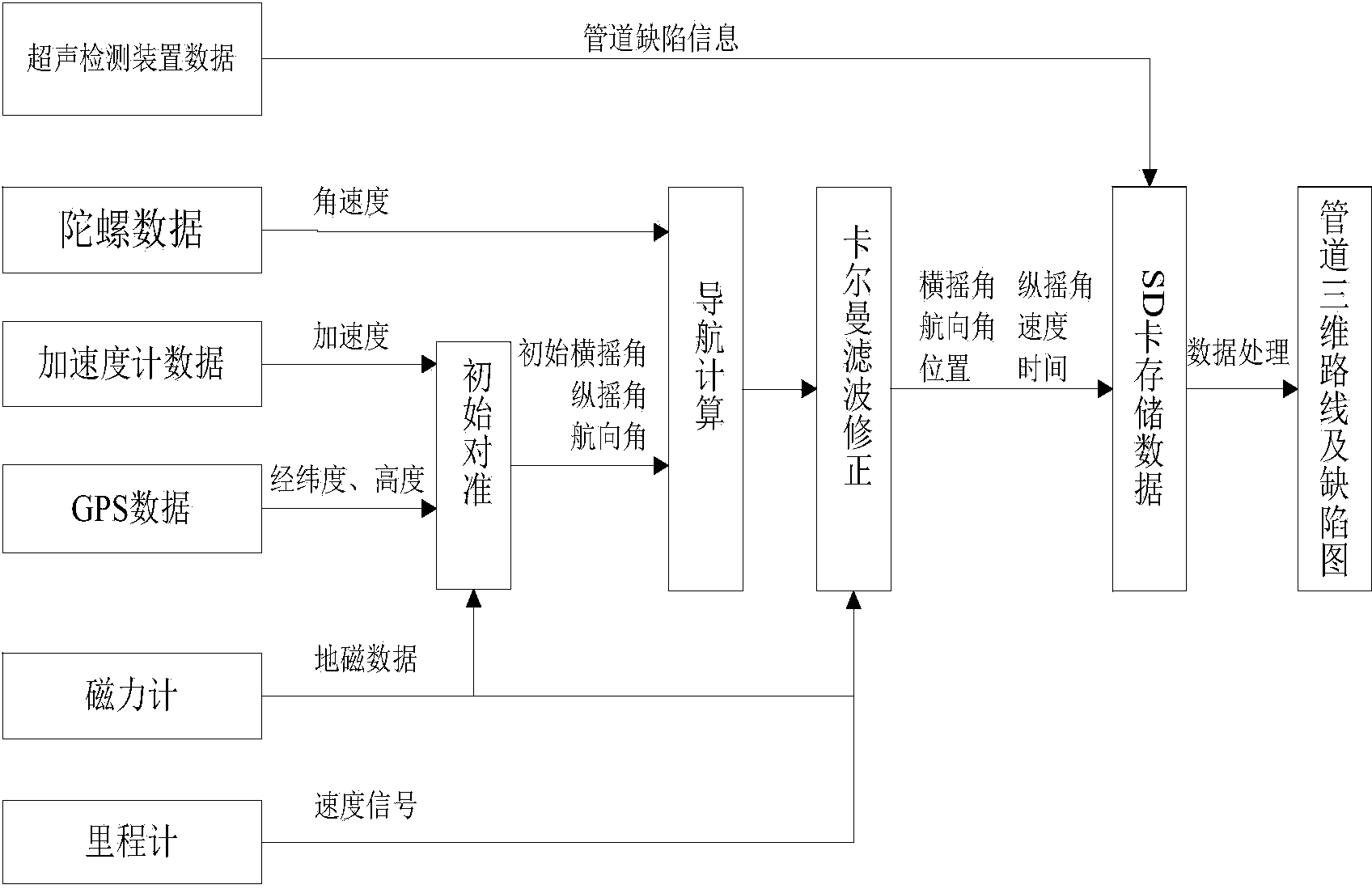
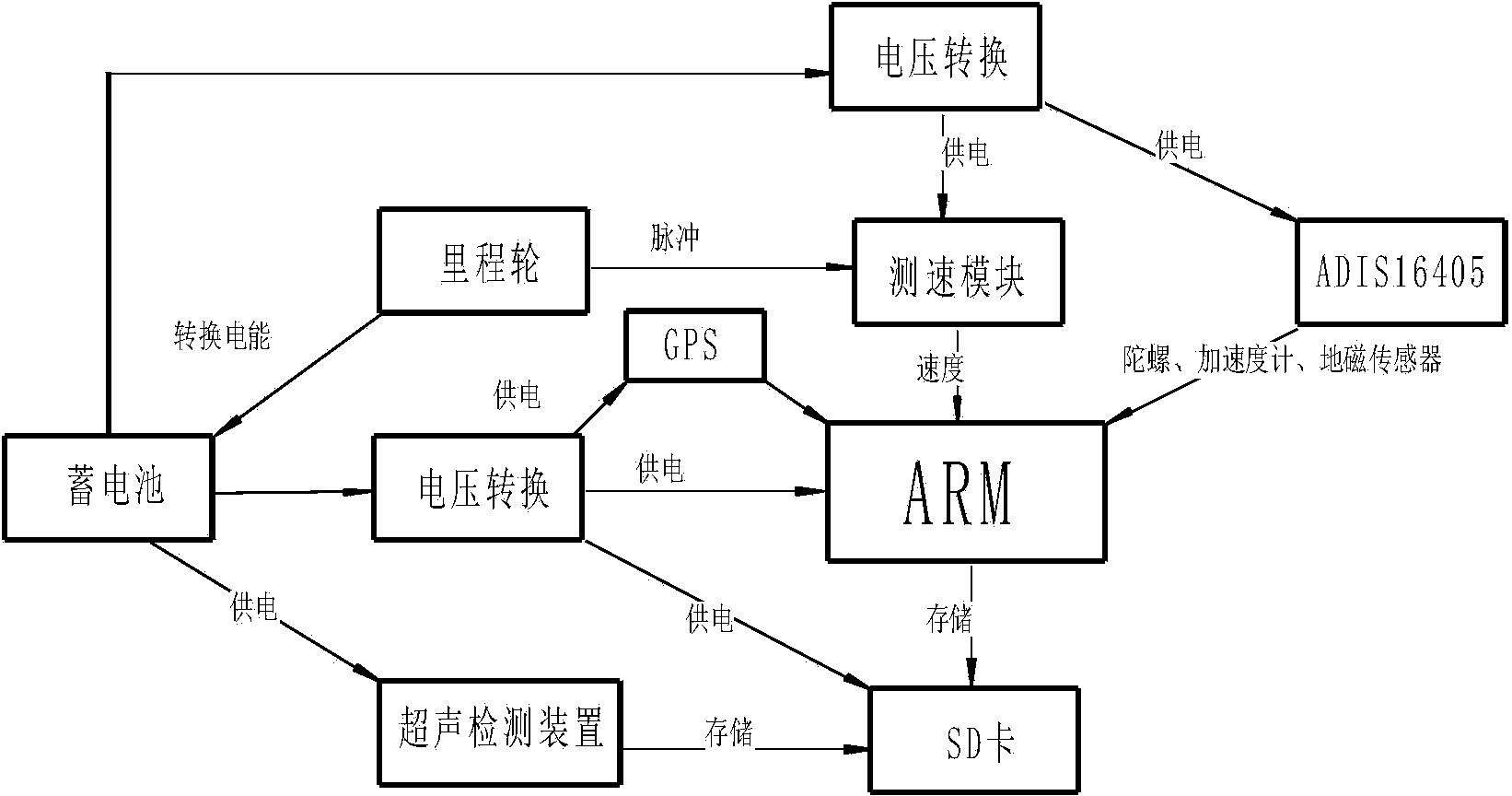
MEMS (Micro Electro Mechanical System) inertial measurement unit-based pipeline surveying and mapping and defect positioning device and pipeline surveying and mapping and defect positioning method thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of pipeline surveying and mapping, and in particular relates to an MEMS (Micro Electro Mechanical System) inertial measurement unit-based pipeline surveying and mapping and defect positioning device and a pipeline surveying and mapping and defect positioning method thereof. The MEMS inertial measurement unit-based pipeline surveying and mapping and defect positioning device comprises a measurement unit, a correction unit, a defect detection unit, a power supply unit and a data processing and memory unit. Compared with the conventional inventions and papers and the like, the MEMS inertial measurement unit is lower in cost, and has a wider pipe diameter application range of being 60 mm at minimum besides the autonomy. The MEMS inertial measurement unit is combined with an odometer, a flux-gate magnetometer and an ultrasonic detection device. The pipeline surveying and mapping problem without laying a fixed-point magnetic scale is solved, meanwhile, the information on a defect position is detected and marked, and convenience is provided for the maintenance and strengthening of pipeline defects. An odometer wheel is also connected with a power generation device, so that the problems caused by external power supply are solved.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
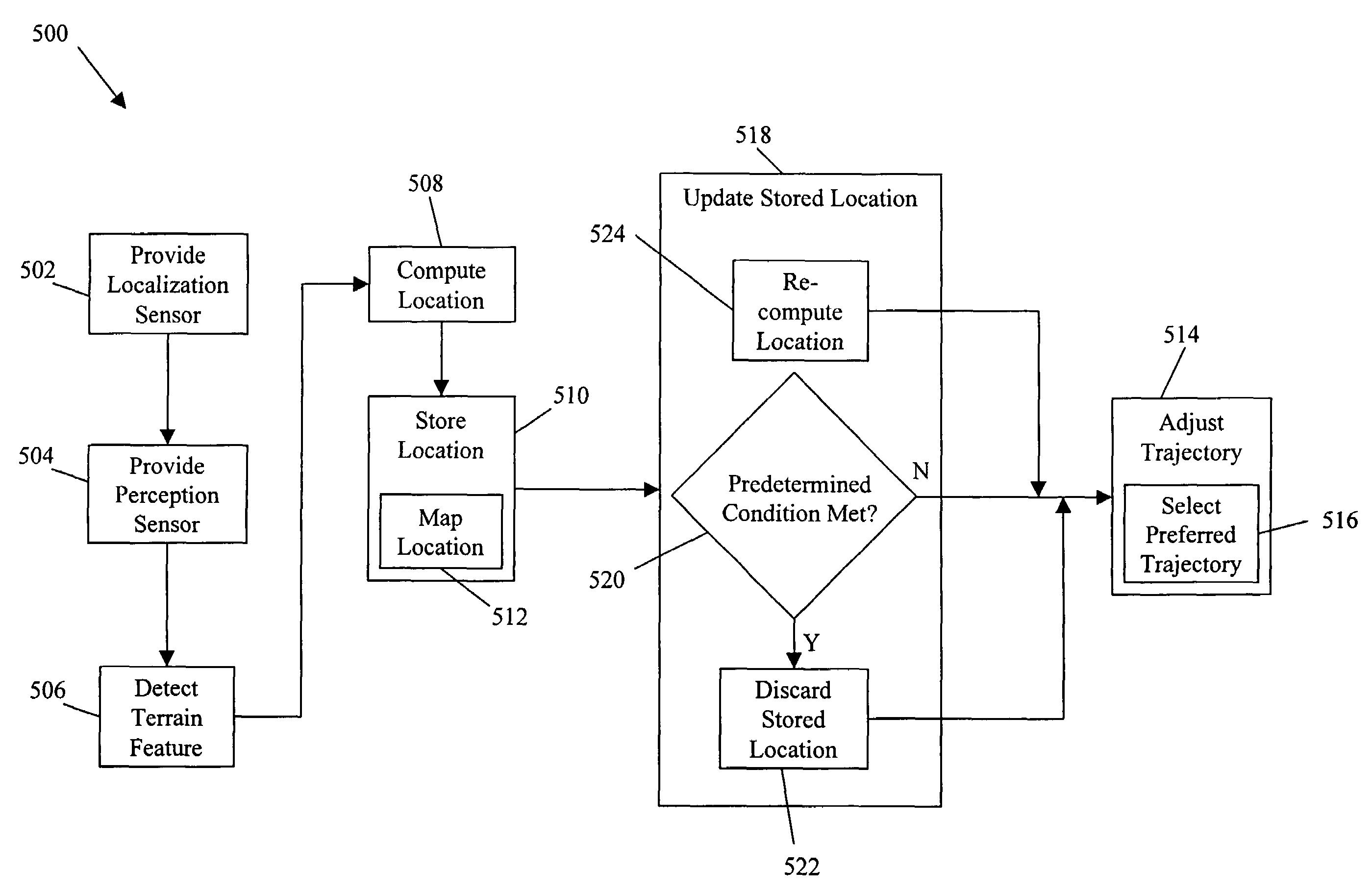
System and method for terrain feature tracking
System and method for tracking obstacles by an autonomous vehicle. Localization sensors (i.e., sensors to measure pitch, roll, and yaw, and systems including an inertial navigation system, a compass, a global positioning system, or an odometer) detect the position of the vehicle. Perception sensors (e.g., LIDAR, stereo vision, infrared vision, radar, or sonar) assess the environment about the vehicle. Using these sensors, locations of terrain features relative to the vehicle are computed and kept up-to-date. The vehicle trajectory is adjusted to avoid terrain features that are obstacles in the path of the vehicle.
Owner:IROBOT CORP
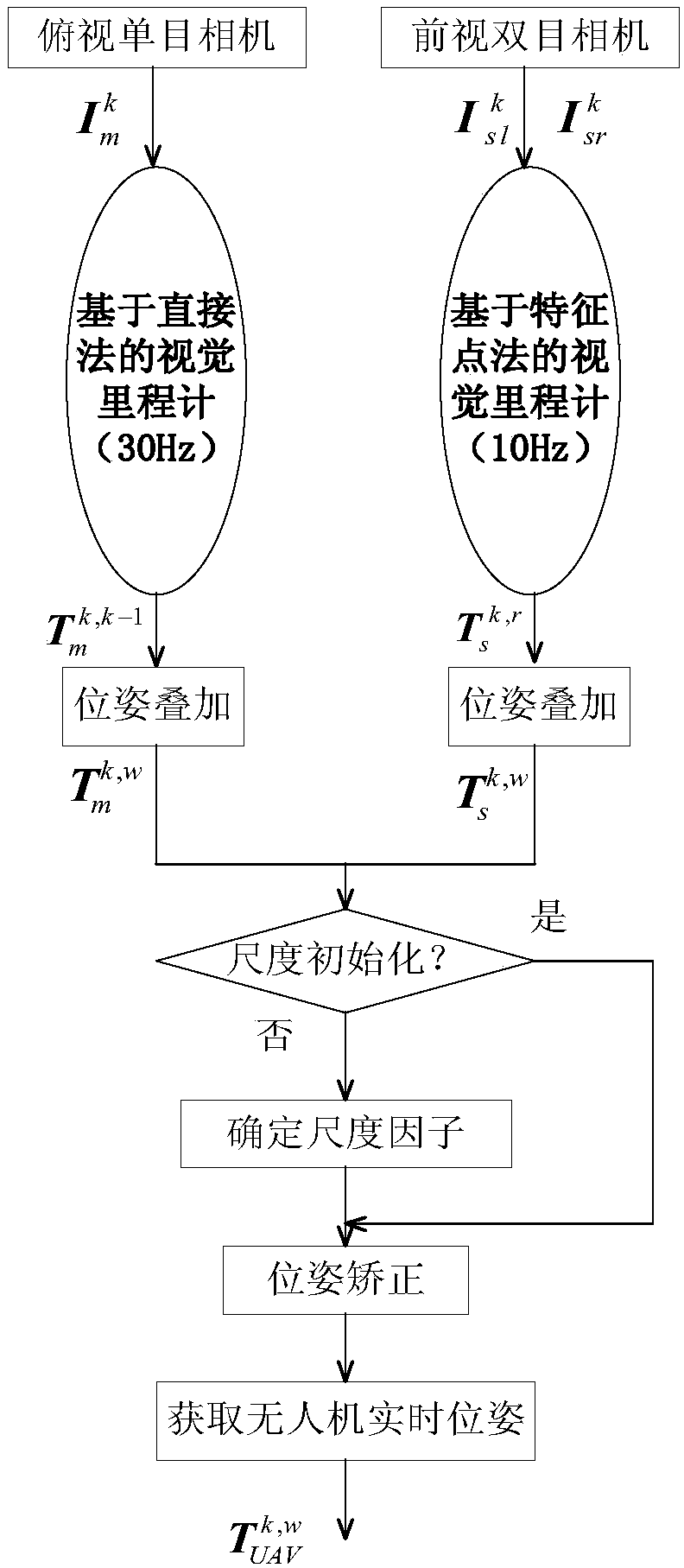
Simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) method for unmanned aerial vehicle based on mixed vision odometers and multi-scale map
ActiveCN109029417AReal-time accurate and reliable positioningShorten operation timeNavigational calculation instrumentsSimultaneous localization and mappingEnvironmental perception
The invention discloses a simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) method for an unmanned aerial vehicle based on mixed vision odometers and a multi-scale map, and belongs to the technical field of autonomous navigation of unmanned aerial vehicles. According to the SLAM method, an overlooking monocular camera, a foresight binocular camera and an airborne computer are carried on an unmanned aerial vehicle platform; the monocular camera is used for the visual odometer based on a direct method, and binocular camera is used for the visual odometer based on feature point method; the mixed visual odometers conduct information fusion on output of the two visual odometers to construct the local map for positioning, and the real-time posture of the unmanned aerial vehicle is obtained; then theposture is fed back to a flight control system to control the position of the unmanned aerial vehicle; and the airborne computer transmits the real-time posture and collected images to a ground station, the ground station plans the flight path in real time according to the constructed global map and sends waypoint information to the unmanned aerial vehicle, and thus autonomous flight of the unmanned aerial vehicle is achieved. Real-time posture estimation and environmental perception of the unmanned aerial vehicle under the non-GPS environment are achieved, and the intelligent level of the unmanned aerial vehicle is greatly increased.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
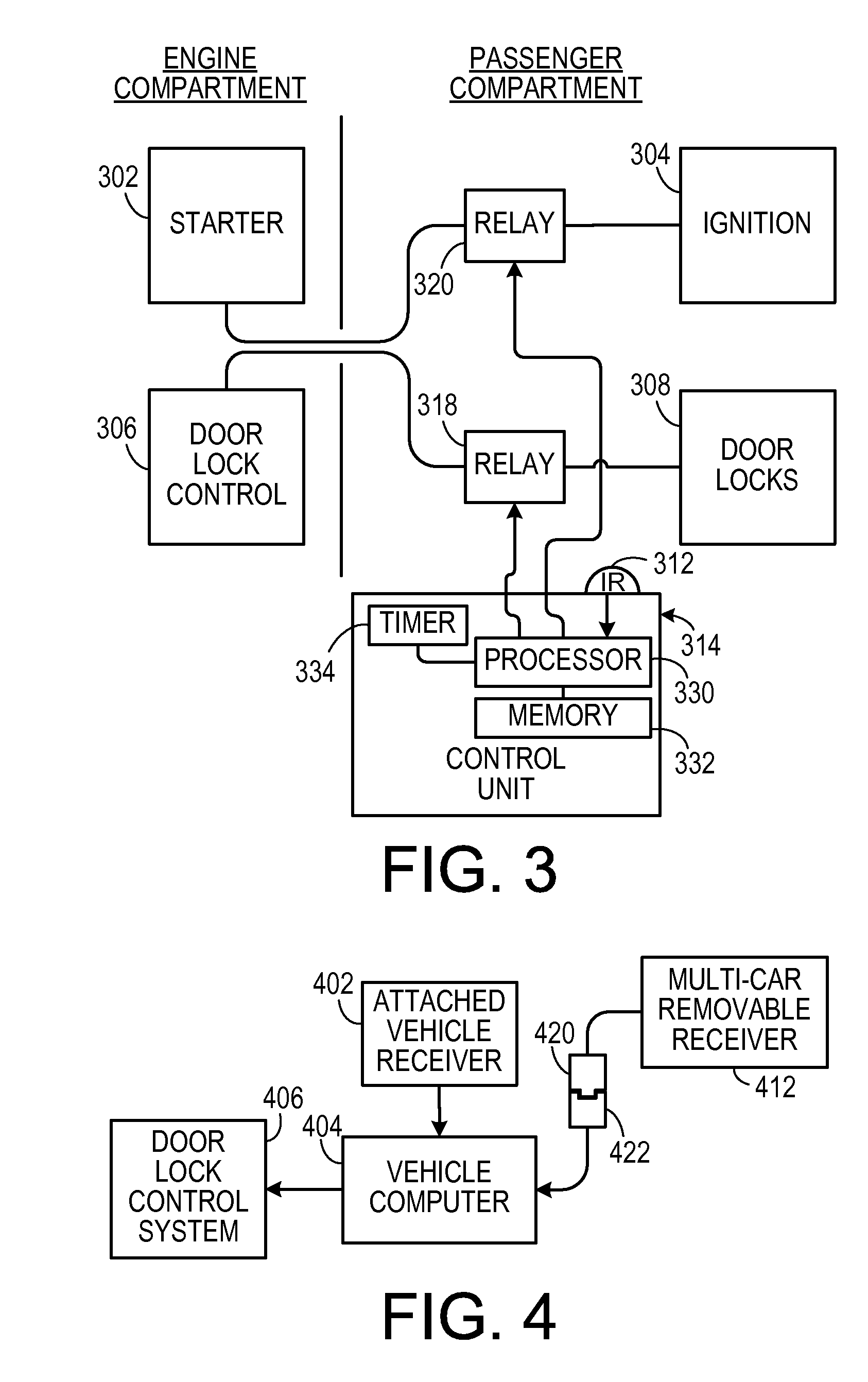
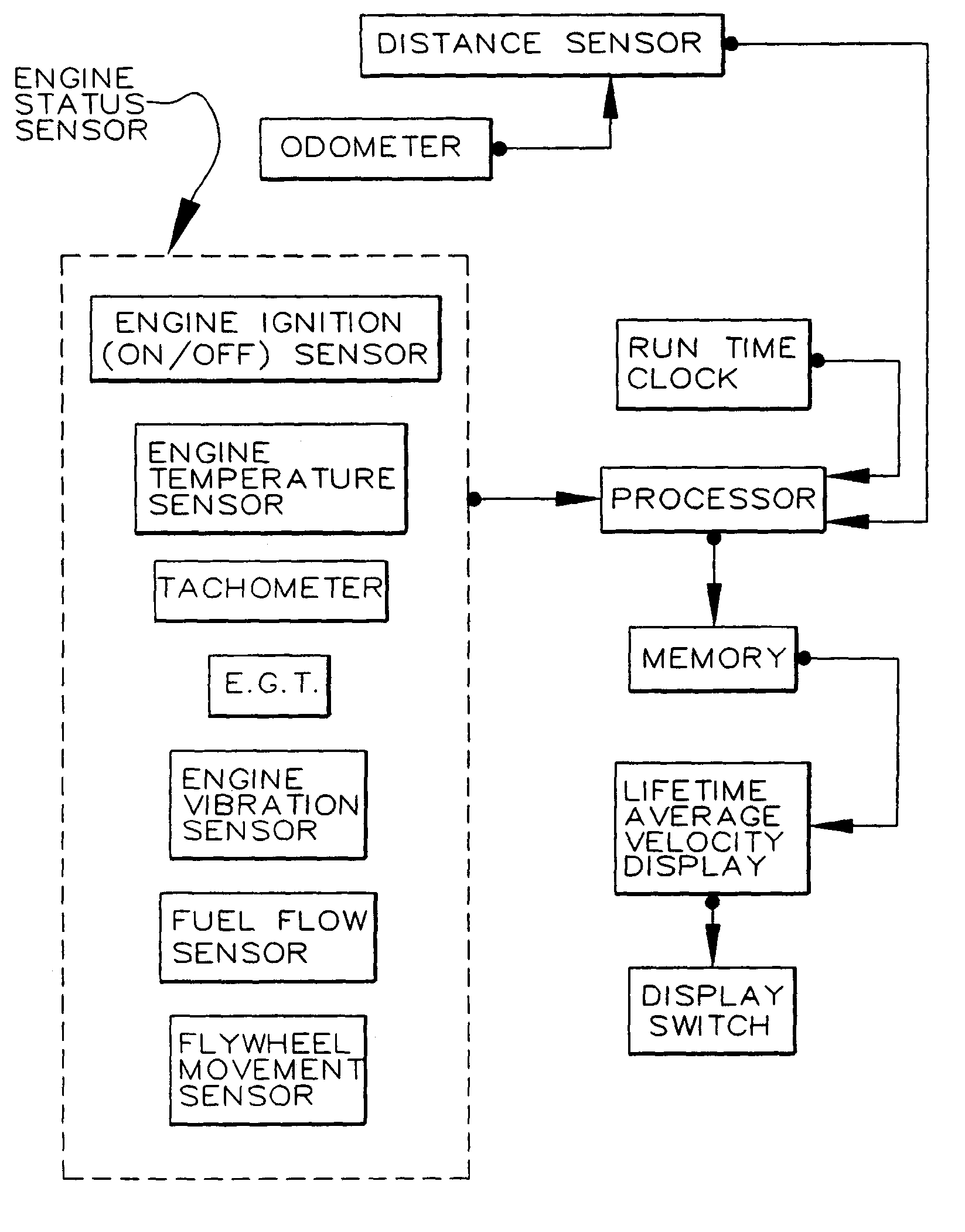
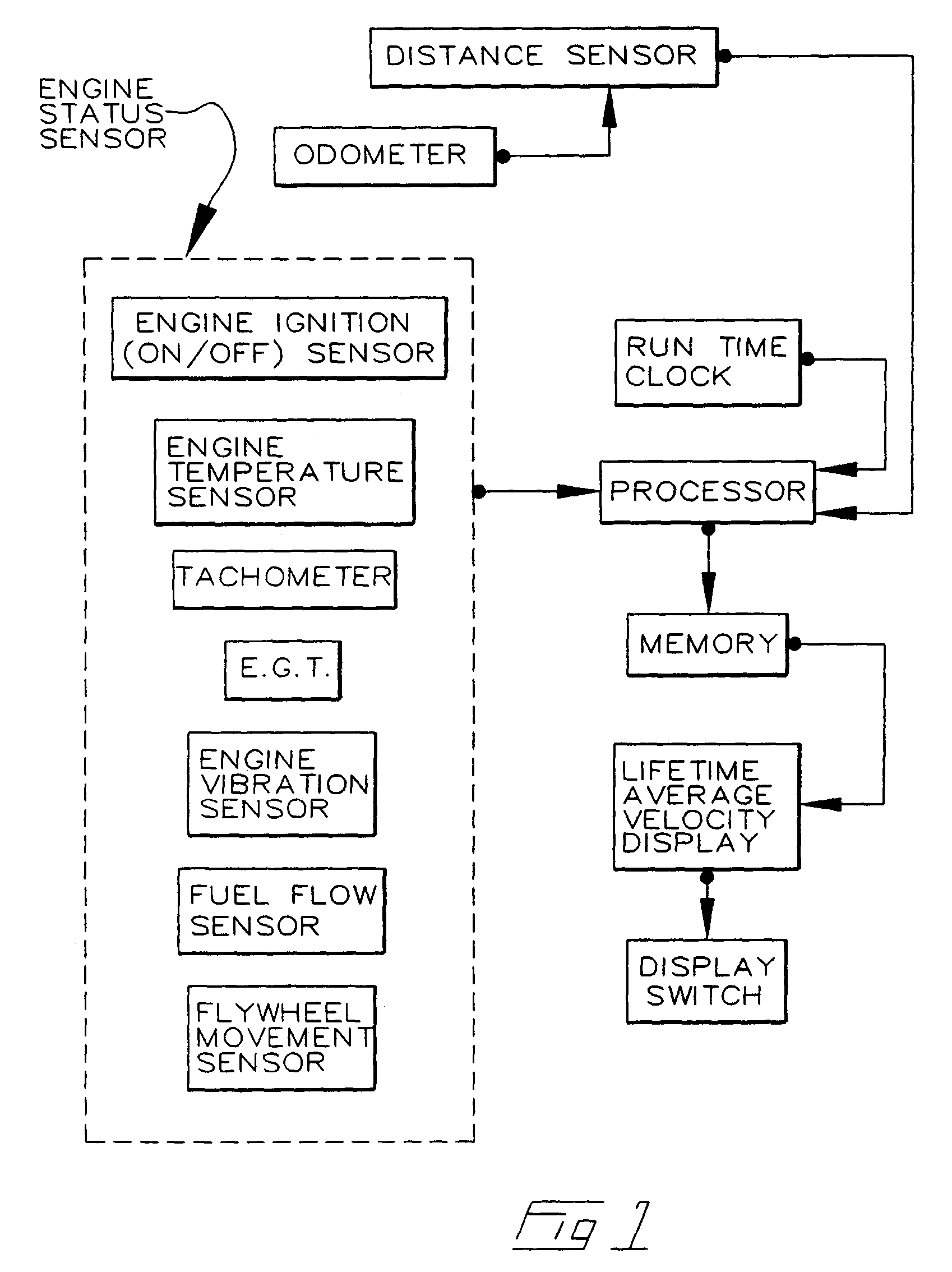
Tamper-evident use-indicating odometer and engine-timer
The present invention relates generally to the provision in an automobile of a tamper-evident combined Odometer and Engine Run-time recorder, optionally with display of average speed or indication of type of vehicle use.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Wearable positioning and path guidance method based on binocular camera under outdoor operating environment
ActiveCN106840148APreserve the characteristics of compact informationBoot supportNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsSatellite radio beaconingSimulationClosed loop
The invention discloses a wearable positioning and path guidance method based on a binocular camera under an outdoor operating environment. The wearable positioning and path guidance method comprises the following steps: 1) letting an operator perform environmental exploration, traversing the whole operation site environment along an operation path and positioning by utilizing a binocular vision odometer and a GPS as well as IMU data, and meanwhile creating an operating environment overview map; 2) in the processes of real-time positioning and path guidance, performing global metric positioning by utilizing the binocular vision odometer and topological positioning by utilizing closed-loop detection at the same time; 3) when a loop is judged to be closed, calculating position deviation by utilizing scene features, performing deviation correction on a current global position and completing sample base updating; 4) performing operation task path planning and operation path guidance prompt by utilizing a topological overview map and real-time positioning results, and pushing information to a user. A reliable and real-time operation path guidance and positioning function is provided aiming at a wearable operation auxiliary system for equipment routing inspection, operation and maintenance and other class-A tasks under the outdoor environment.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Robot navigation positioning system and method
InactiveCN109959377AEliminate cumulative errorsAchieve optimizationNavigational calculation instrumentsPosition/course control in two dimensionsPath lengthMultiple sensor
The invention discloses a robot navigation positioning system and method, which are used for map construction, positioning and path planning of a robot. The method comprises the following steps: S100,positioning is carried out, in the positioning step, the robot detects surrounding environment information through multiple sensors, and later, based on an adaptive particle filtering SLAM algorithmand in match with different odometers, real-time map construction and positioning are completed; and S200, path planning is carried out, in the path planning step, a two-phase hybrid state A*-based path planning algorithm is adopted, after a path length and the number of extended nodes are obtained when path planning is carried out on a rasterized map, a higher rasterized map is obtained through parsing and extension, and the acquired path length and the acquired number of extended nodes are used as input of fuzzy reasoning, a heuristic weight is obtained through fuzzy reasoning and is used asinput of search of a second stage, and path planning is performed on a higher rasterized map. The system and the method disclosed in the invention can not only adapt to different environments but also can perform dynamic path planning.
Owner:BEIJING ORIENT XINGHUA TECH DEV CO LTD
Modular unmanned vehicle positioning method and system based on visual inertia laser data fusion
ActiveCN111595333ACorrect the bias defectImprove environmental adaptabilityImage enhancementImage analysisMultiple sensorEngineering
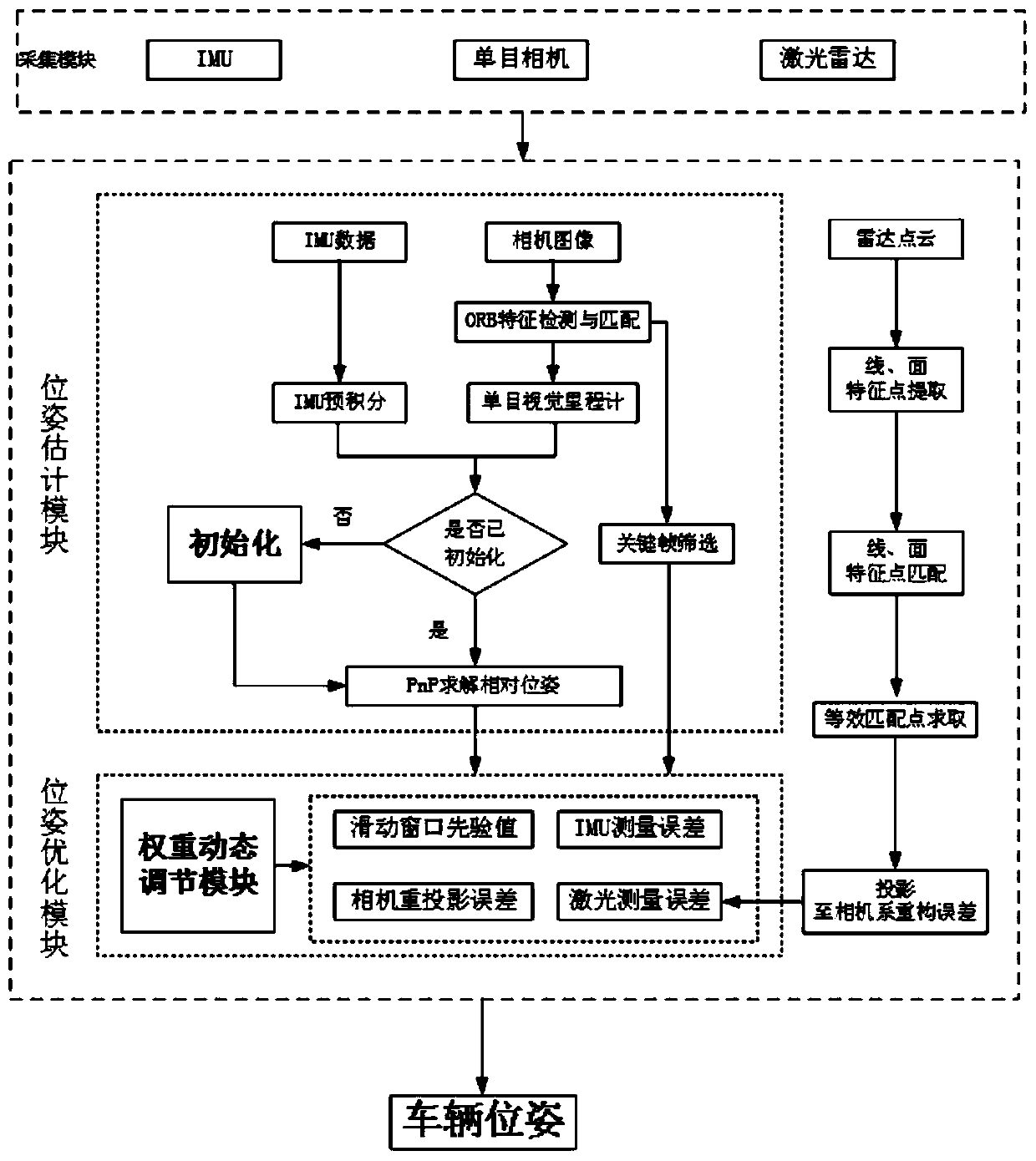
The invention discloses a modular unmanned vehicle positioning method and system based on visual inertia laser data fusion. The method comprises the following steps that (1), an acquisition module acquires current information of an unmanned vehicle through a monocular camera, a laser radar and an IMU; (2), according to the current information of the driverless vehicle collected in the step (1), apose estimation module performs pose estimation of the vehicle through a monocular odometer and an IMU pre-integration model to obtain pose information of the unmanned vehicle; and (3), a pose optimization module establishes a multi-sensor fusion optimization model according to the pose estimation information in the step (2), a weight coefficient dynamic adjustment module adjusts the optimizationproportion of each sensor to enhance the environmental adaptability, the optimal pose of the vehicle is obtained after optimization, and the optical pose is converted into a world coordinate system to obtain the real-time pose of the vehicle. The method can meet the requirements for accuracy and robustness of positioning of the unmanned vehicle in a complex environment, and is suitable for positioning of the unmanned vehicle in the complex environment.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
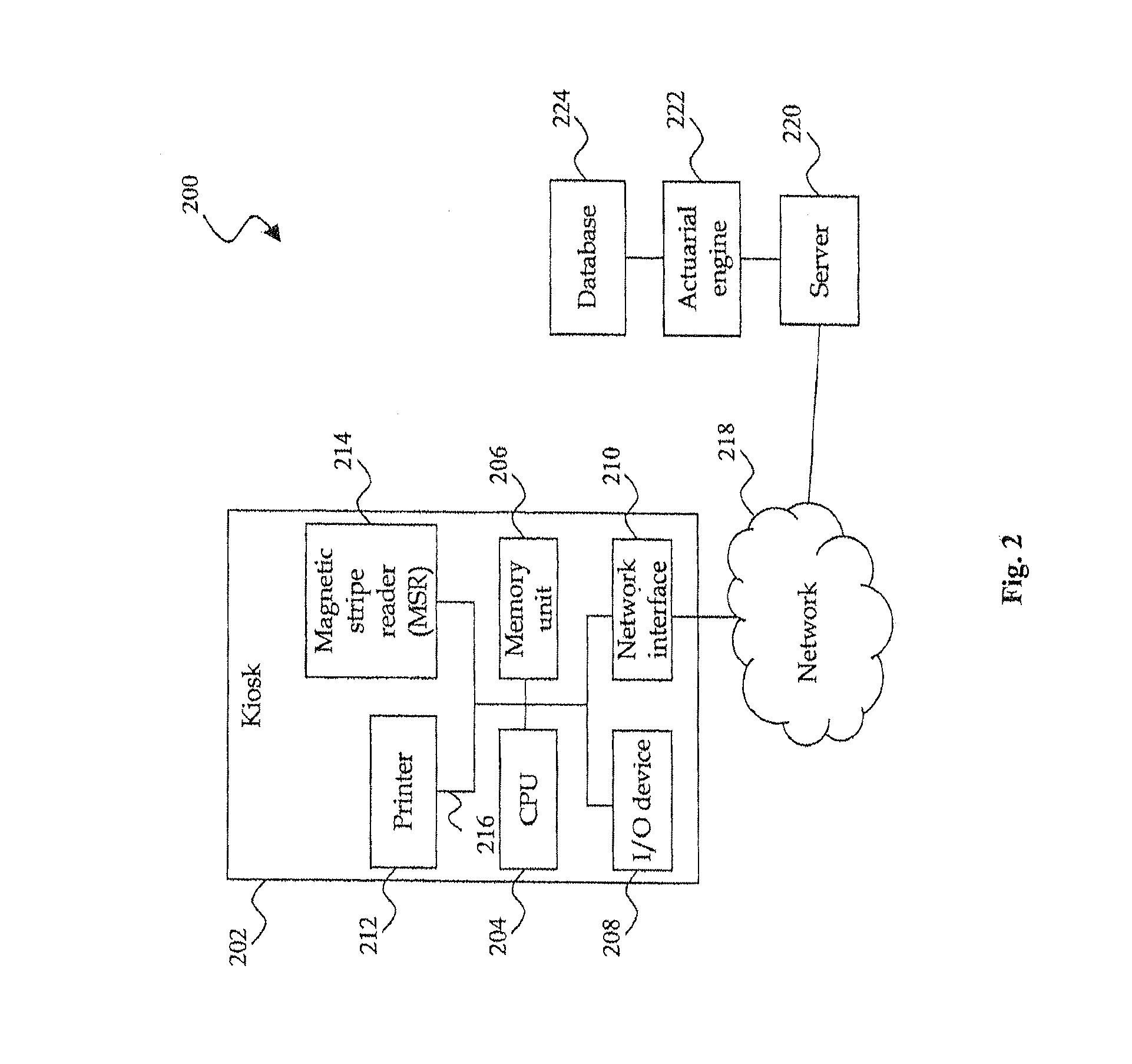
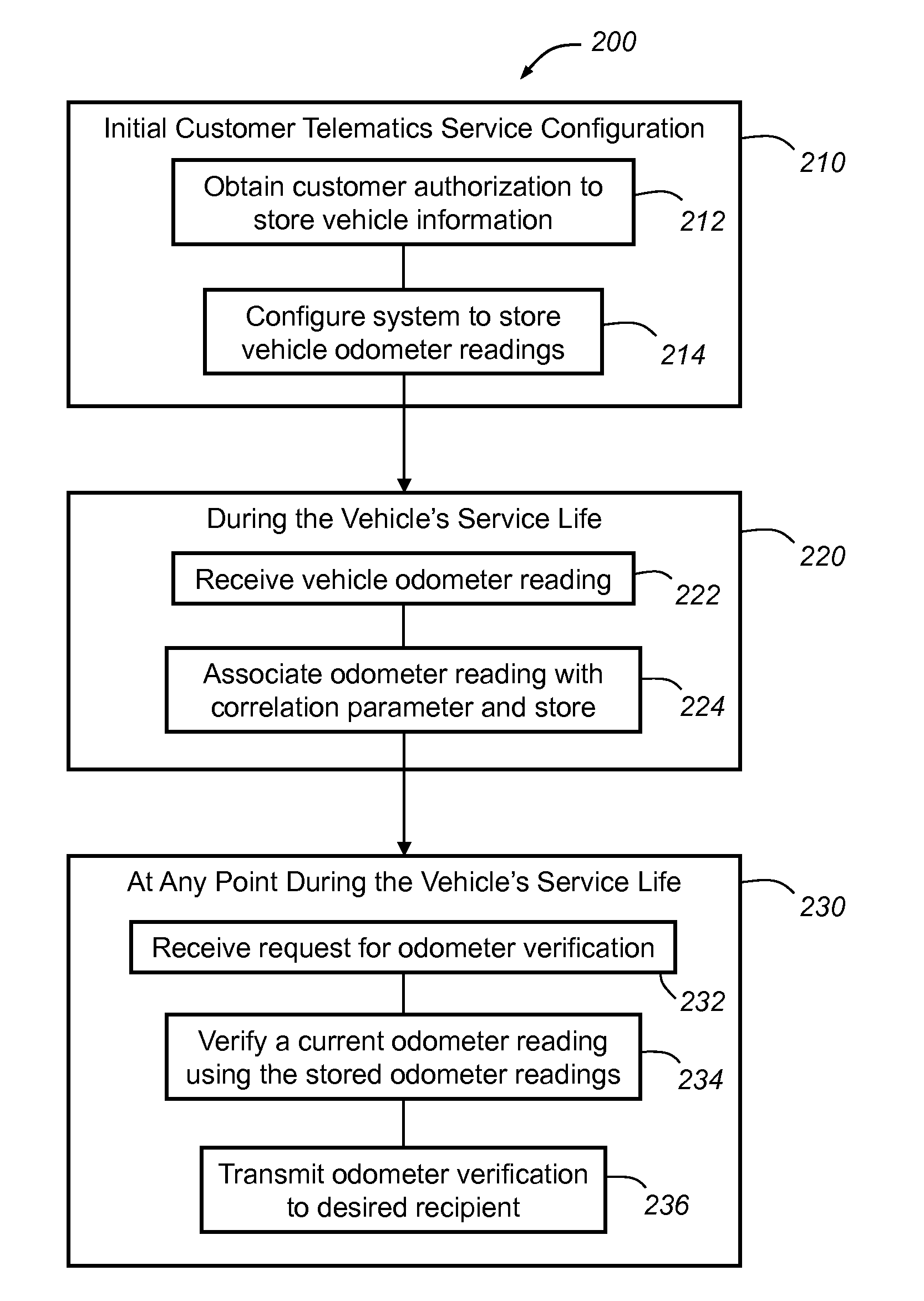
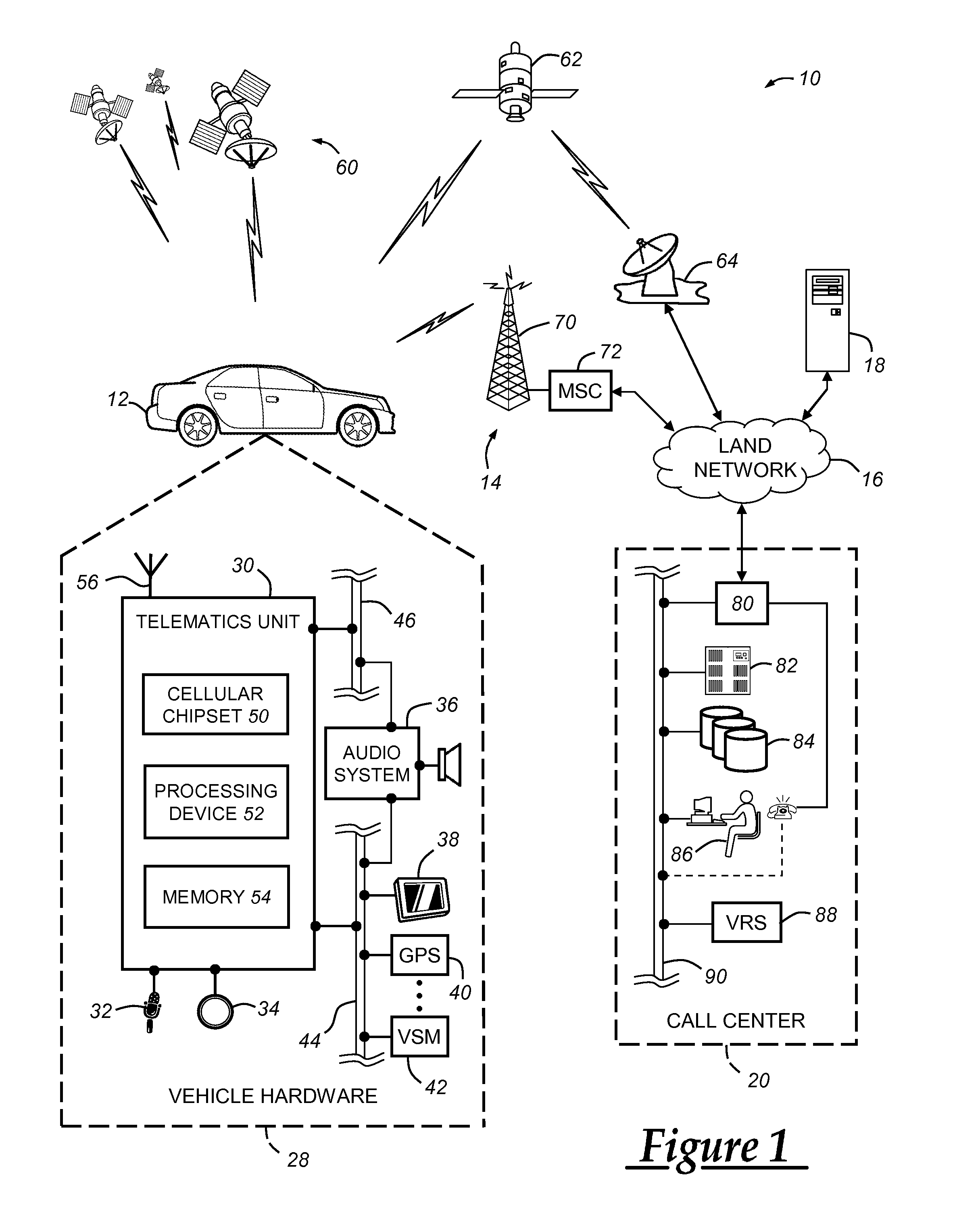
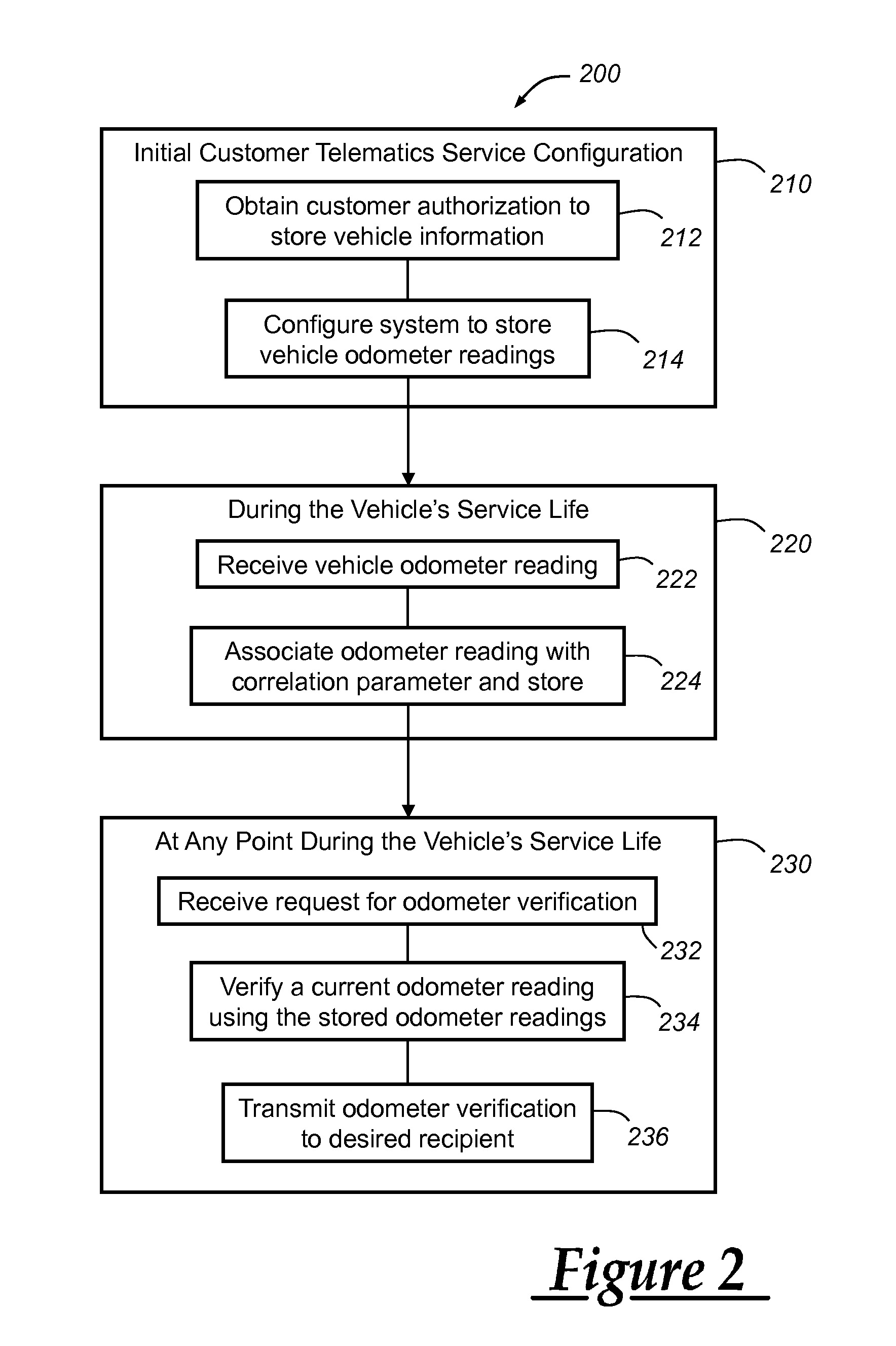
Odometer verification and reporting using a telematics-equipped vehicle
ActiveUS20120262283A1Registering/indicating working of vehiclesOptical signallingOdometerAuthorization
A system and method for providing an odometer verification for a vehicle. The method carried out by the system includes the steps of: (a) receiving authorization from a customer to periodically store odometer information obtained from the customer's vehicle; (b) configuring at least one processing device such that it automatically stores odometer readings and associated correlation parameter values for the vehicle; (c) receiving a request for an odometer verification; (d) analyzing the odometer readings and associated correlation parameter values in response to the request; (e) determining a verification result based on the analysis; and (f) sending the verification result to a recipient in response to the determination.
Owner:GENERA MOTORS LLC +1
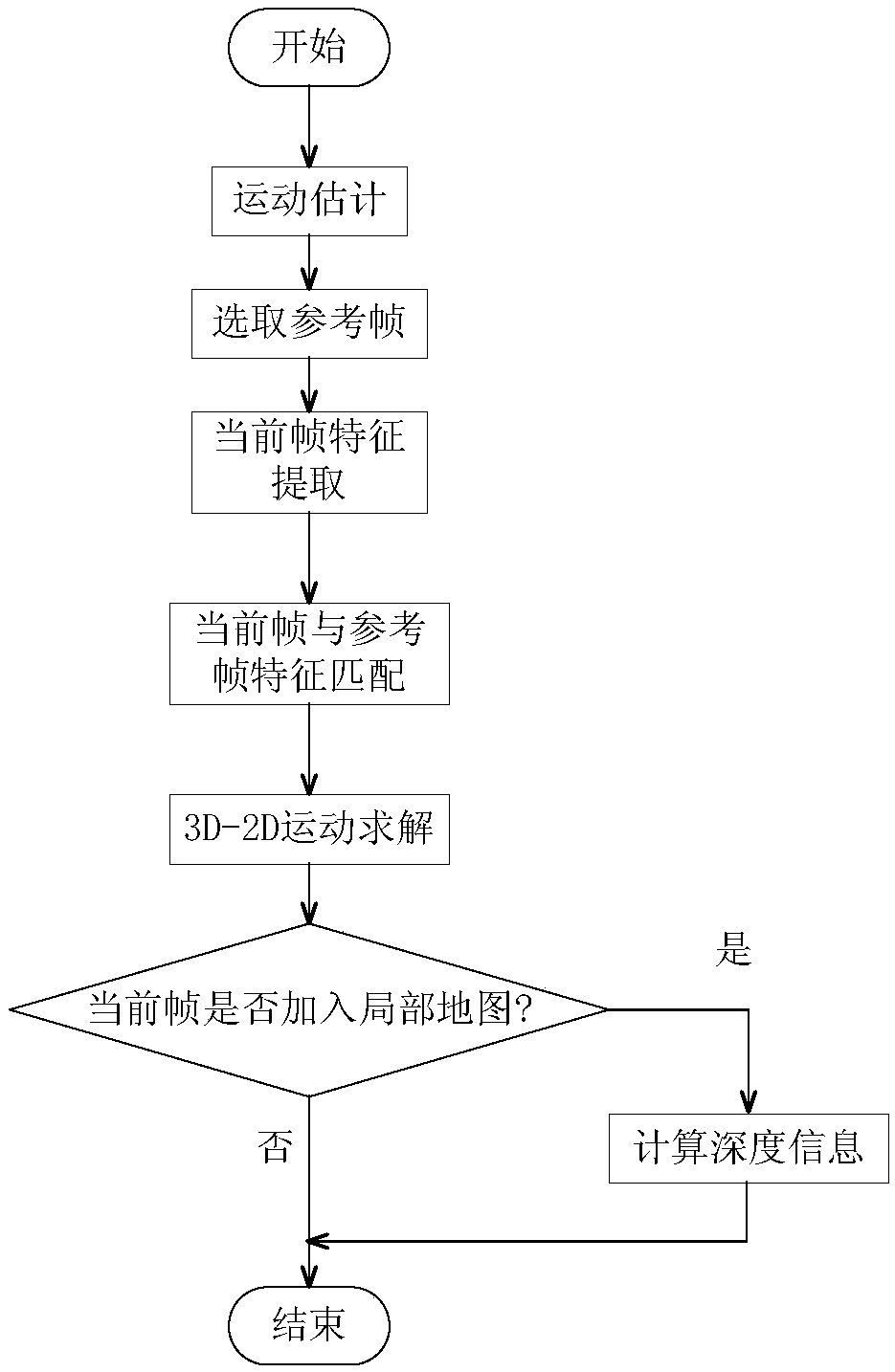
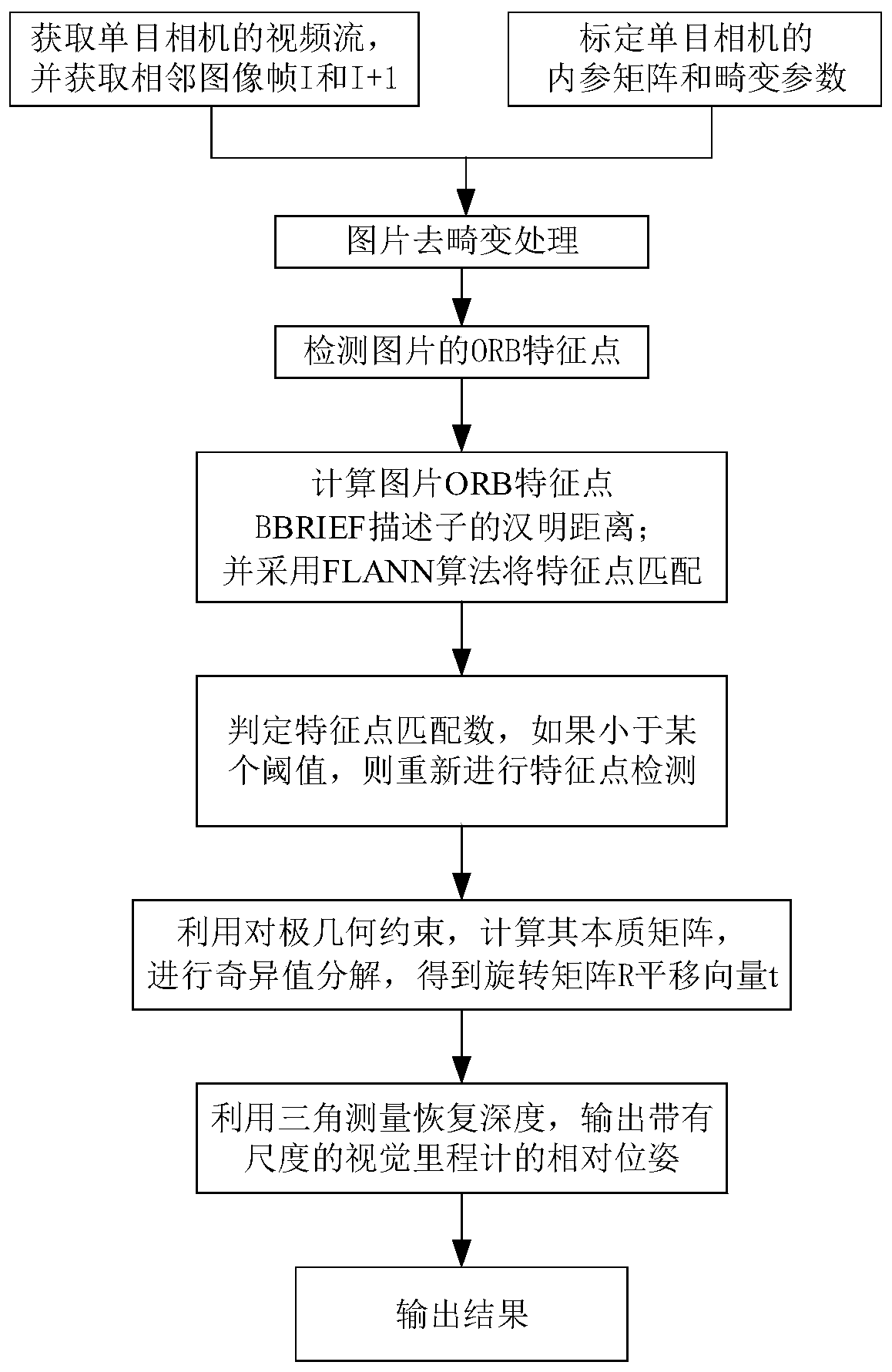
A fast monocular vision odometer navigation and positioning method combining a feature point method and a direct method
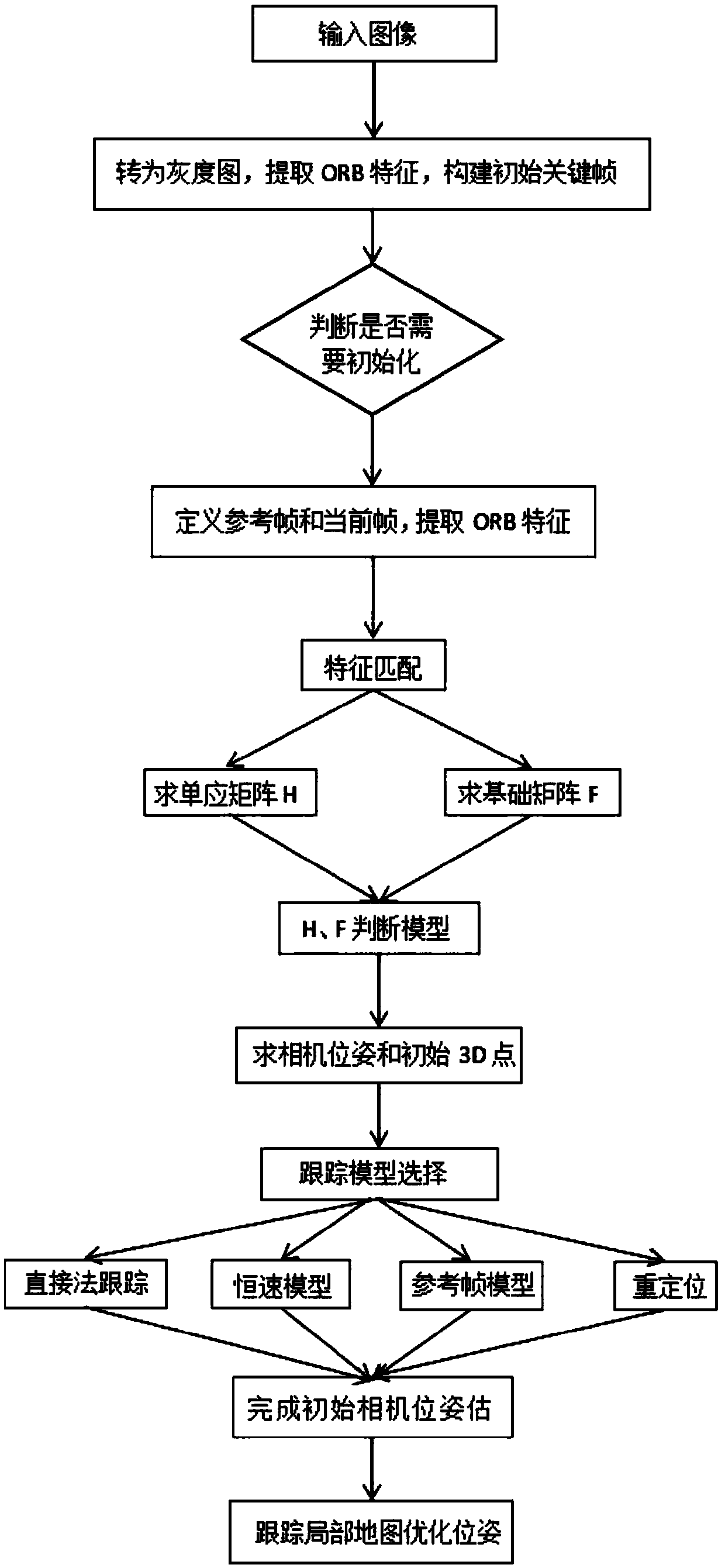
ActiveCN109544636AAccurate Camera PoseFeature Prediction Location OptimizationImage enhancementImage analysisOdometerKey frame
The invention discloses a fast monocular vision odometer navigation and positioning method fusing a feature point method and a direct method, which comprises the following steps: S1, starting the vision odometer and obtaining a first frame image I1, converting the image I1 into a gray scale image, extracting ORB feature points, and constructing an initialization key frame; 2, judging whether thatinitialization has been carry out; If it has been initialized, it goes to step S6, otherwise, it goes to step S3; 3, defining a reference frame and a current frame, extracting ORB feature and matchingfeatures; 4, simultaneously calculating a homography matrix H and a base matrix F by a parallel thread, calculating a judgment model score RH, if RH is great than a threshold value, selecting a homography matrix H, otherwise selecting a base matrix F, and estimating a camera motion according to that selected model; 5, obtaining that pose of the camera and the initial 3D point; 6, judging whetherthat feature point have been extracted, if the feature points have not been extracted, the direct method is used for tracking, otherwise, the feature point method is used for tracking; S7, completingthe initial camera pose estimation. The invention can more precisely carry out navigation and positioning.
Owner:GUANGZHOU UNIVERSITY
Method and System for Accurate Reconstruction of Mileage Reports
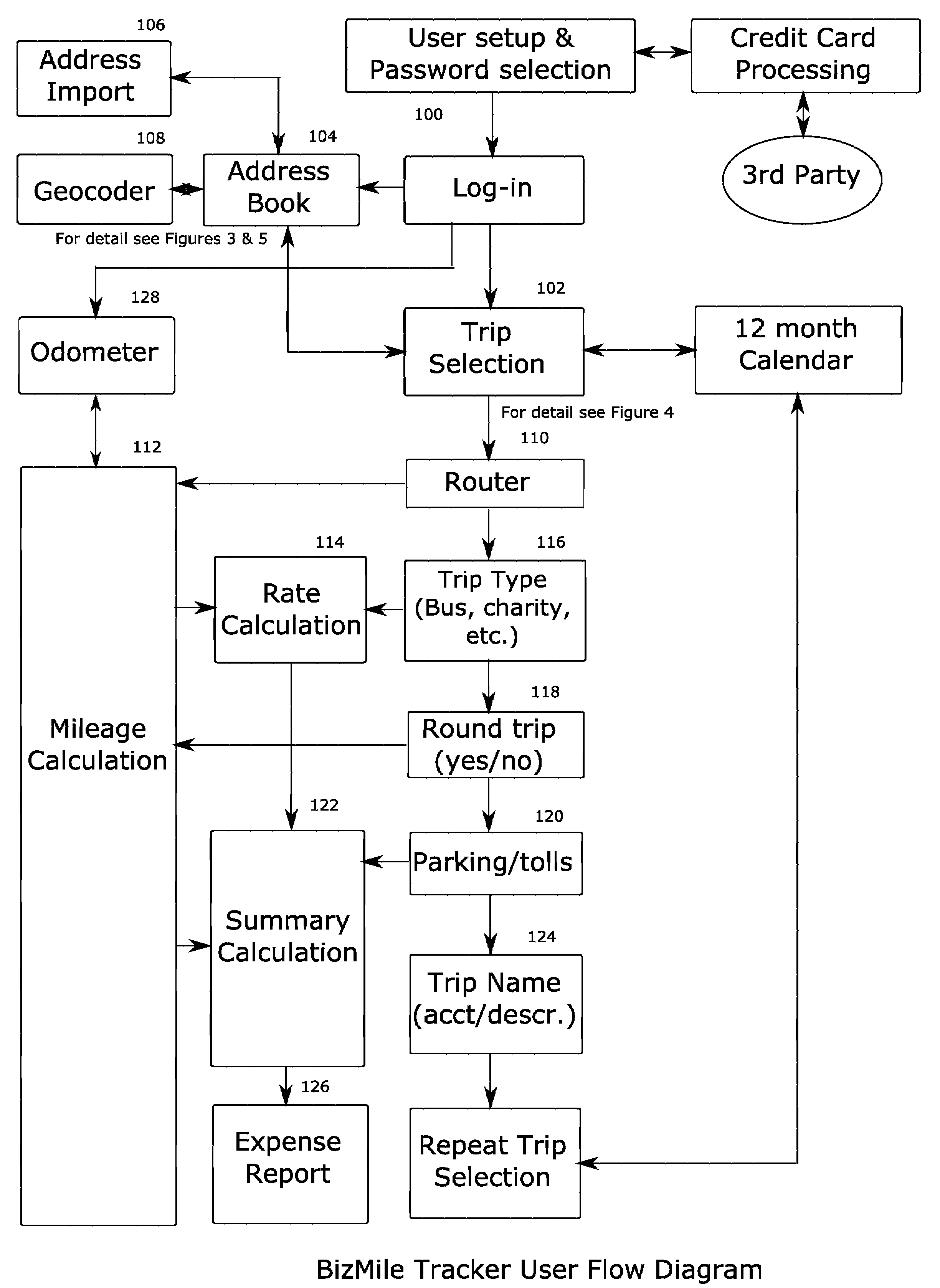
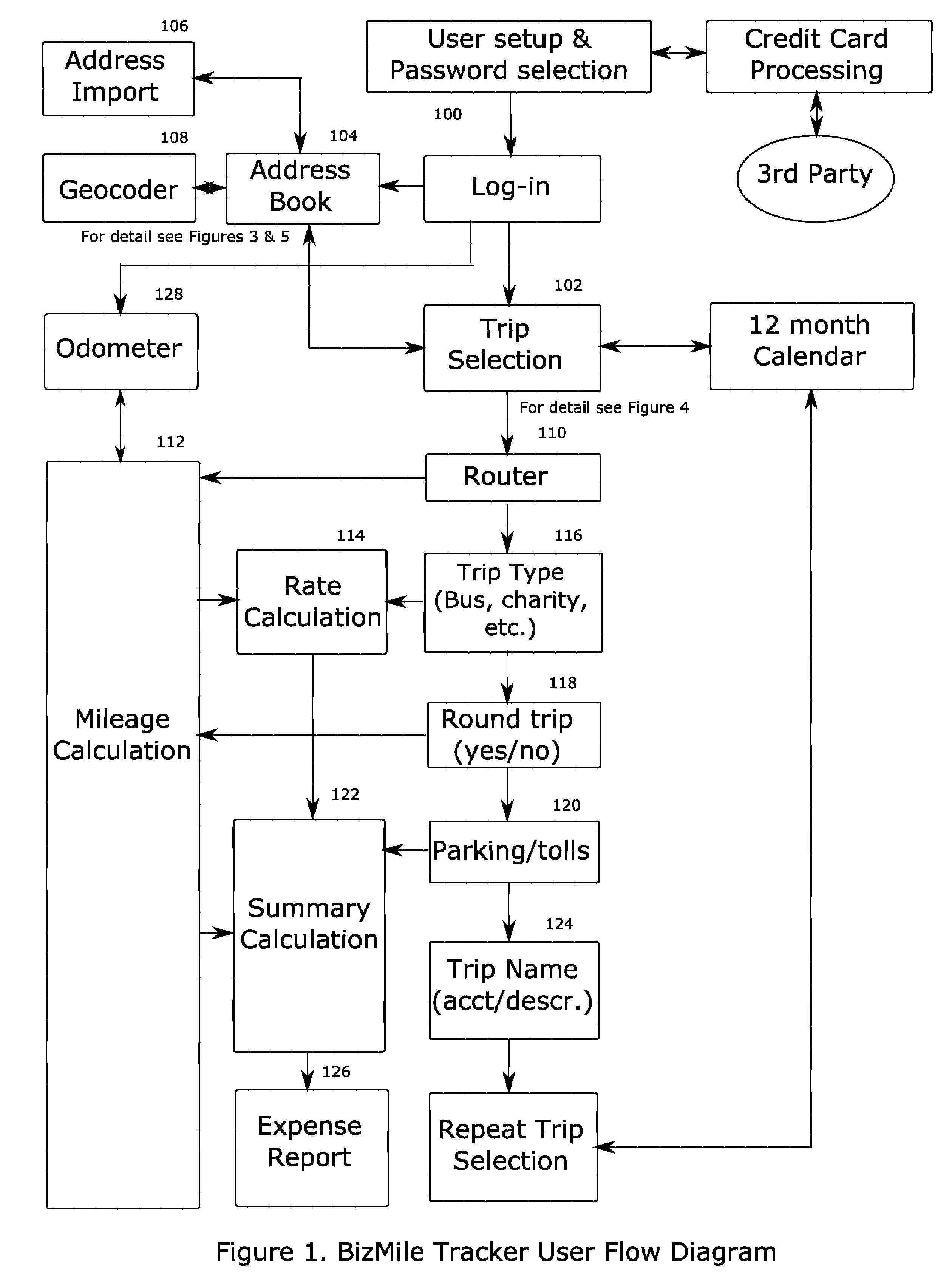
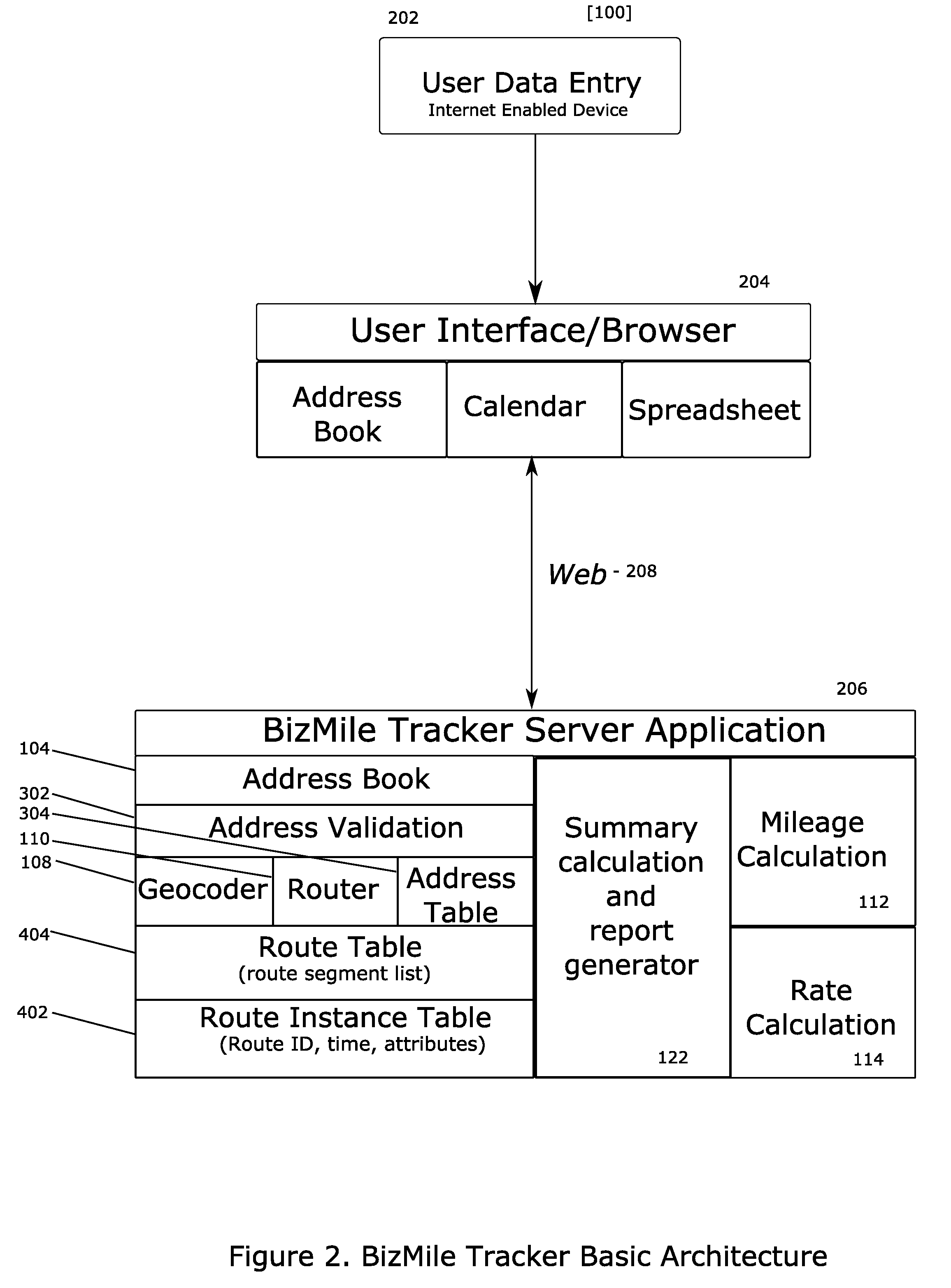
InactiveUS20070250258A1Instruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlUser inputData mining
A method or system for accurately reconstructing mileage and travel expense, wherein a user inputs travel information including addresses for a starting location, intermediate destination points, an end location, and the purpose of the trip. A routing system determines a route from the starting point through all of the intermediate destination points to the end point. This route is made up of segments which are the portions of the route between any two addresses. A mileage calculation system then obtain the length of each of the segments, and a rate calculation system calculates the expense rate to apply to each of the segments based on the character of the segment. A summary calculation system then calculates the expense of a trip along each of the segments and outputs a report for the user to submit as an expense report, support a tax deduction, or keep for their records.
Owner:BIZMILE
System and method for the assessment, pricing, and provisioning of distance-based vehicle insurance
A method of assessing, pricing, and provisioning distance-based vehicle insurance is disclosed. The method includes receiving a vehicle identification number of a vehicle to be insured from a customer, receiving an preliminary odometer reading of the vehicle to be insured from the customer, and obtaining from the customer a legally binding declaration that the preliminary odometer reading is true and accurate. The method includes insuring the vehicle during a policy period defined by coverage for a preselected number of units distance from the preliminary odometer reading.
Owner:STATE FARM MUTUAL AUTOMOBILE INSURANCE
Inertia/visual odometer combined navigation and positioning method based on measurement model optimization
ActiveCN108731670AEfficient use ofHigh precisionNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsAccelerometerGyroscope
The invention discloses an inertia / visual odometer combined navigation and positioning method based on measurement model optimization. A state equation of a combined navigation system is established,errors of an inertial sensor are expanded into system state variables including random constant drifting of a gyroscope, one-order markoff process drifting of the gyroscope and one-order markoff process drifting of an accelerometer; then, a visual odometer is taken as an angular velocity, linear velocity and position sensor to acquire measurement data, and a measurement equation is established; finally, in the carrier motion process, the navigation errors are fed back and corrected in real time, and a navigation result of an inertial navigation system after errors are corrected is obtained. According to the method, angular velocity, linear velocity and position information of the visual odometer can be effectively utilized in the carrier motion process, effective fusion with inertial navigation is realized, the accuracy and the reliability of the combined navigation system are improved, and the method is applicable to engineering applications.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Device and method for detecting defects of inner and outer walls of pipeline based on three-axis magnetic flux leakage and eddy current
ActiveCN102798660ASave electricityImprove detection qualityMaterial magnetic variablesNon destructiveElectricity
The invention relates to a device and a method for detecting defects of inner and outer walls of a pipeline based on three-axis magnetic flux leakage and eddy current, and belongs to the technical field of non-destructive testing. The device comprises a magnetic flux leakage detector, a data processing and storing device, a power supply, at least three odometer wheels and an eddy current detector, wherein the eddy current detector consists of an eddy current sensor and is a device used for detecting the defects on inner and outer surfaces of the pipeline. According to the device provided by the invention, a magnetic flux leakage detection method and an eddy current detection method are combined by using different characteristics of the magnetic flux leakage detection method and the eddy current detection method, so that the function of distinguishing the defect of the inner wall from the defects of the outer wall is realized; and in addition, the method provided by the invention is favorable in detection quality and simple in operation and can be widely applied to non-destructive detection of oil transmission pipelines in the industrial fields of petroleum, petrifaction and the like.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
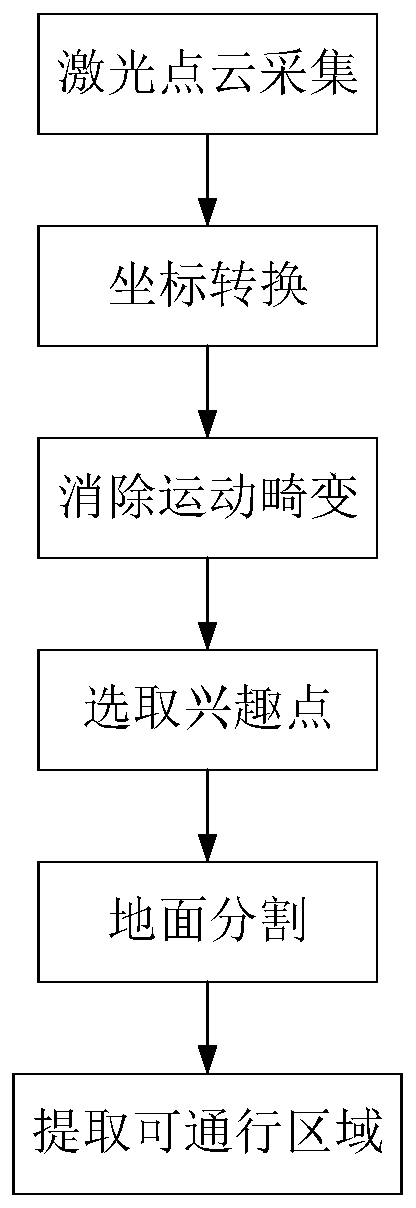
Road passable area detection method based on three-dimensional laser radar
PendingCN110244321AMotion distortion removalEliminate Motion Distortion IssuesElectromagnetic wave reradiationPoint cloudRadar
The invention provides a road passable area detection method based on three-dimensional laser radar. The road passable area detection method comprises the steps of: obtaining surrounding information of a vehicle by adopting three-dimensional laser radar, and collecting point cloud data; eliminating the motion distortion of the point cloud by combining the odometer information of the vehicle; extracting laser point cloud interest points according to the point cloud data after motion distortion is eliminated, wherein extracting laser point cloud interest points mainly comprises rejecting data points located out of an area at a certain height above the laser radar; performing ground segmentation by adopting the height information of the extracted laser point cloud interest points and combining the RANSAC algorithm, and distinguishing the ground point cloud and the obstacle point cloud; and rasterizing the distinguished obstacle point cloud, extracting data points closest to the vehicle in each grid, and combining the data points to obtain boundary points of the passable area. According to the invention, the problem of motion distortion generated during the motion of the point cloud is eliminated, so that the surrounding information expressed by the point cloud is more accurate.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Simultaneous localization and mapping method based on vision and laser radar
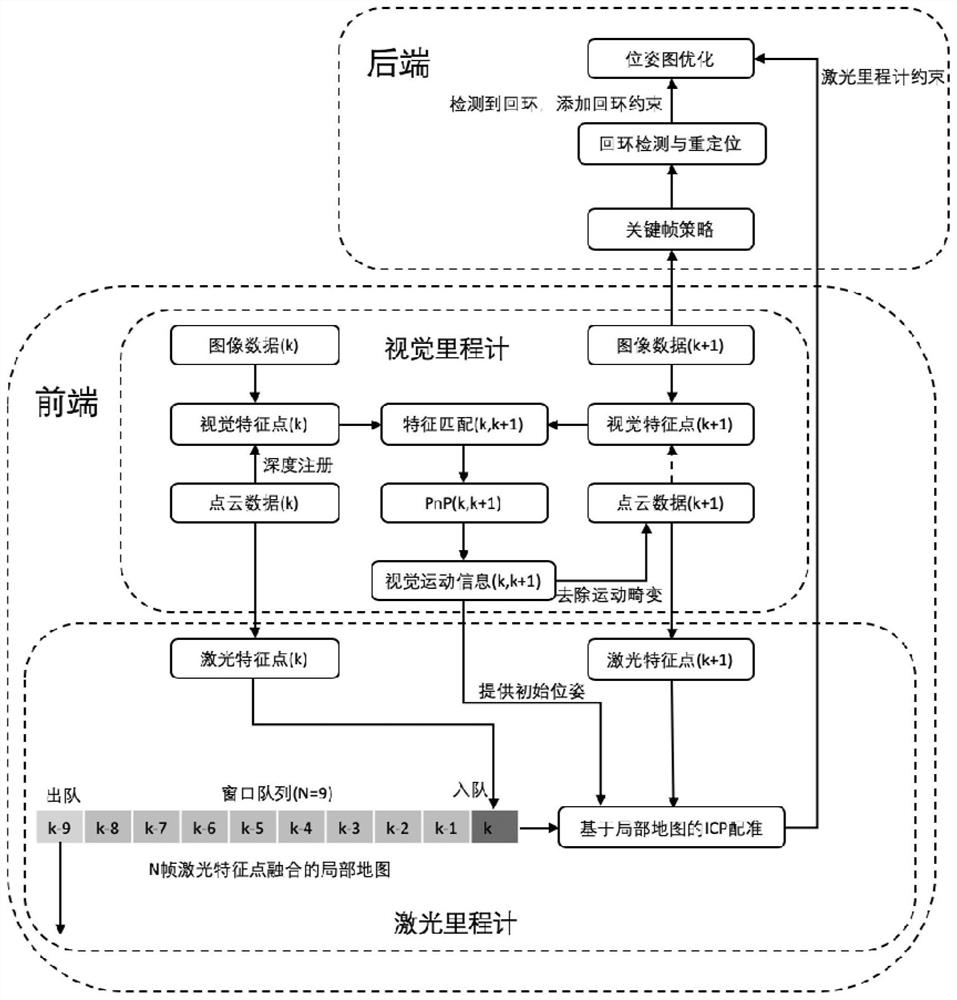
InactiveCN112258600AAccurate initial poseIterative convergence is fastImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionSimultaneous localization and mappingPoint cloud
The invention discloses a simultaneous localization and mapping method based on vision and laser radar, and belongs to the field of SLAM. According to the method, the laser odometer and the visual odometer are operated at the same time, the visual odometer can assist the laser point cloud in better removing motion distortion, and meanwhile the point cloud with motion distortion removed can be projected to the image to serve as depth information for motion calculation of the next frame. After the laser odometer obtains a good initial value, the laser odometer is prevented from falling into a degradation scene due to the defects of a single sensor, and the odometer achieves higher positioning precision due to the addition of visual information. A loop detection and repositioning module is achieved through a visual word bag, and a complete visual laser SLAM system is formed; after loop is detected, the system performs pose graph optimization according to loop constraints, accumulated errors after long-time movement are eliminated to a certain extent, and high-precision positioning and point cloud map construction can be completed in a complex environment.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com