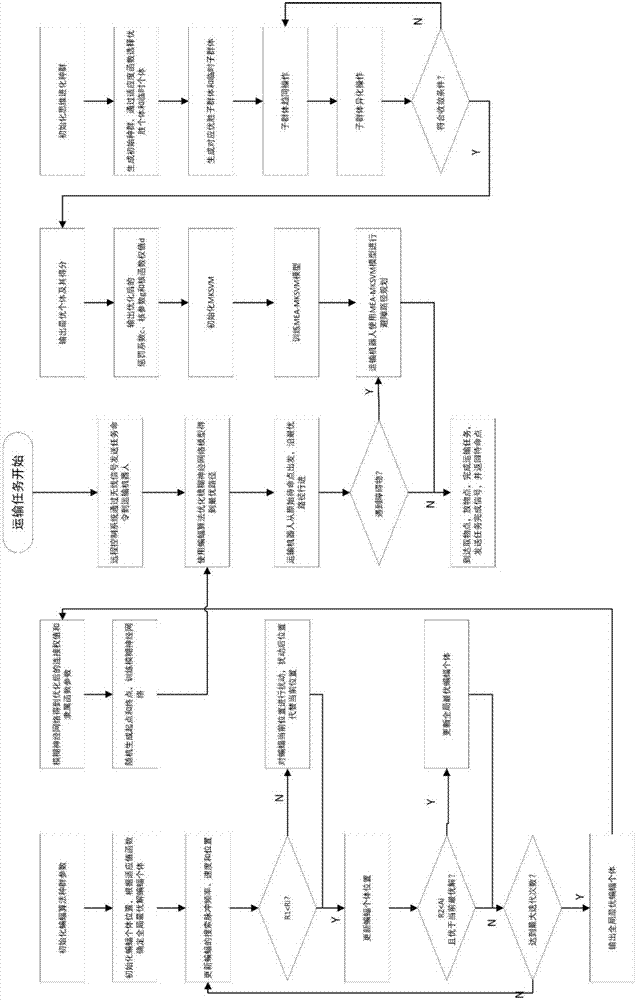
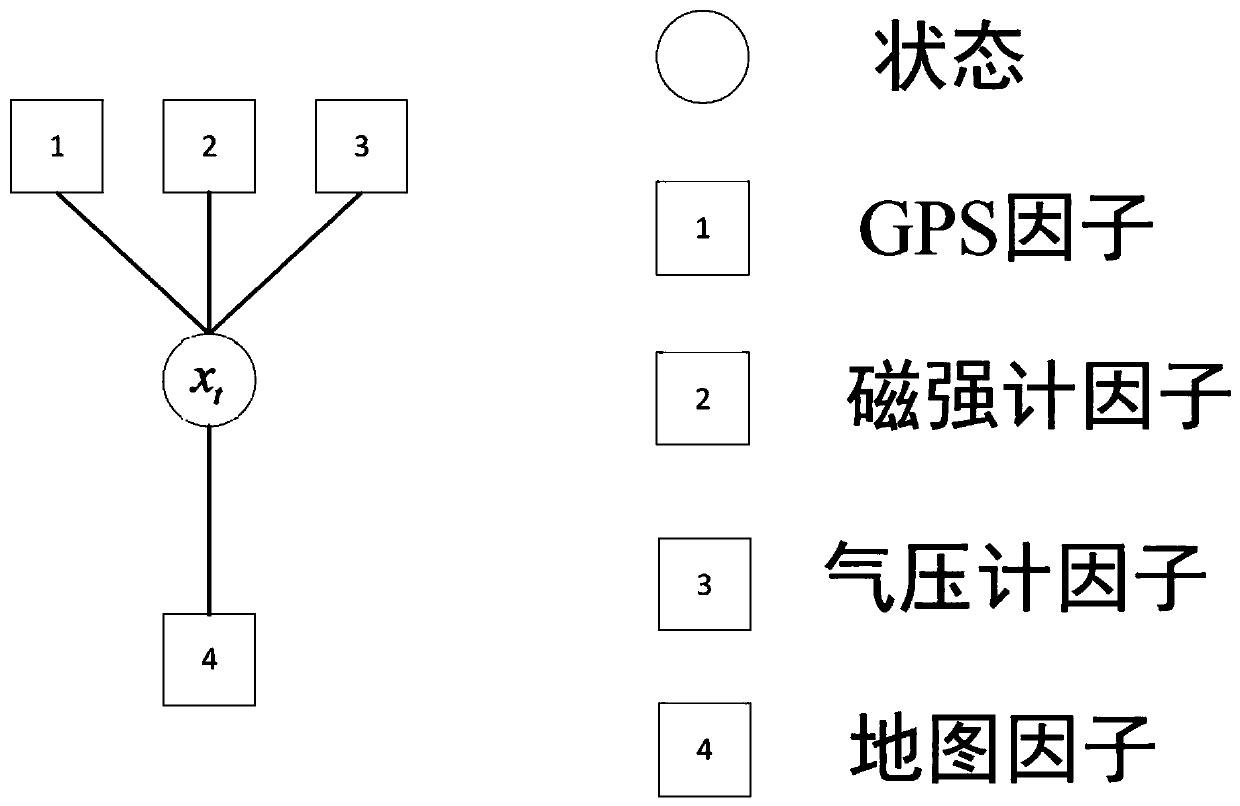
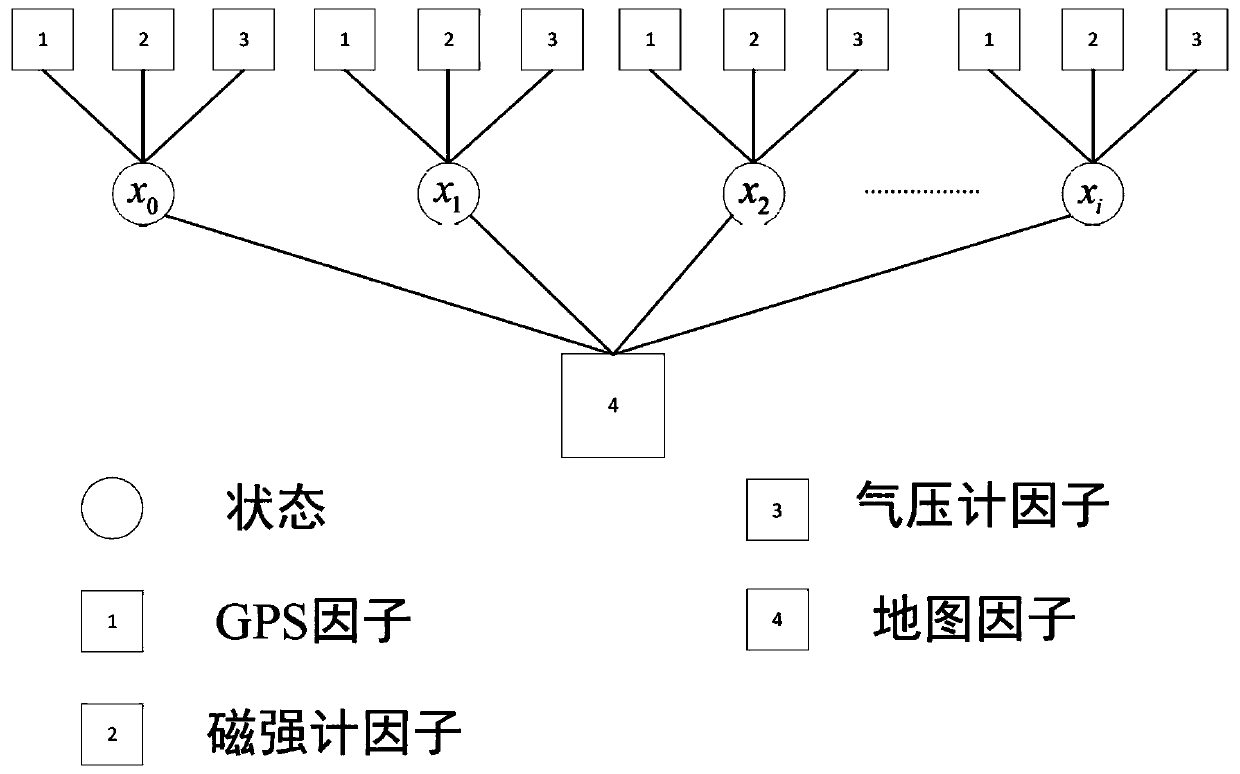
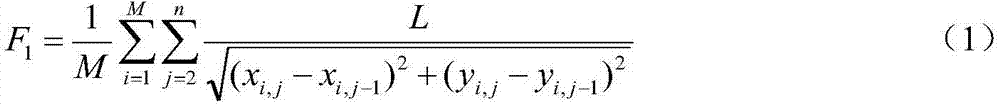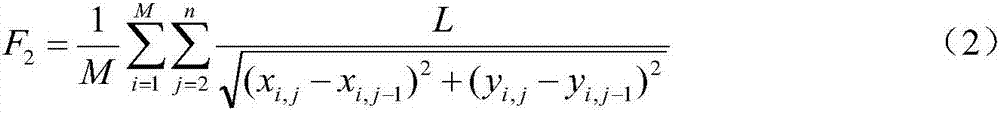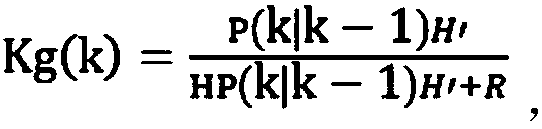Patents
Literature
517 results about "Global Map" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Global Map is a set of digital maps that accurately cover the whole globe to express the status of global environment. It is developed through the cooperation of National Geospatial Information Authorities (NGIAs) in the world. An initiative to develop Global Map under international cooperation, the Global Mapping Project, was advocated in 1992 by Ministry of Construction, Japan (MOC) at the time (the current Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism, Japan-MLIT).
System and method for generating lane-level navigation map of unmanned vehicle
ActiveCN106441319AWide applicabilityDetailed and rich map dataInstruments for road network navigationGlobal Positioning SystemPositioning system
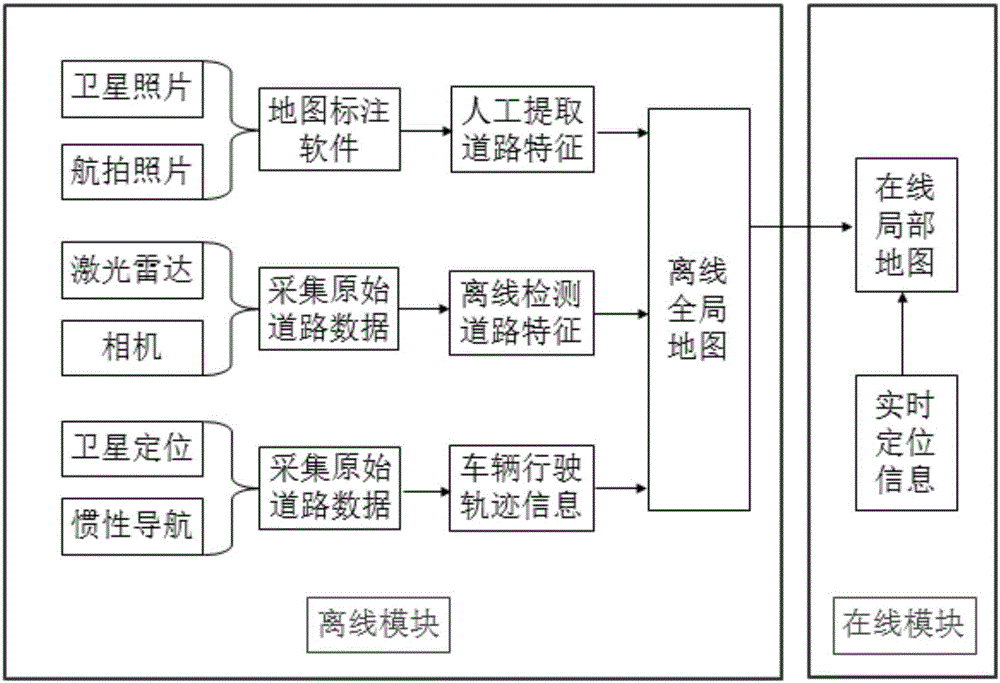
The invention relates to a system and method for generating a lane-level navigation map of an unmanned vehicle based on multi-source data. The lane-level navigation map comprises an offline global map part and an online local map part. According to an offline module, within a target region where the unmanned vehicle runs, original road data is acquired through satellite photos (or aerial photos), a vehicle sensor (laser radar and a camera) and a high-precision integrated positioning system (a global positioning system and an inertial navigation system), then the original road data is subjected to offline processing, multiple kinds of road information are extracted, and finally the road information extracting results are fused to generate the offline global map. The offline global map is stored through a layered structure. According to an online module, when the unmanned vehicle automatically drives in the target region, the road data in the offline global map is extracted according to real-time positioning information, and the online local map with the vehicle as the center within the fixed distance range is drawn. The system and method can be applied to fusion sensing, high-precision positioning and intelligent decisions of the unmanned vehicle.
Owner:安徽中科星驰自动驾驶技术有限公司
Mobile robot cascading map building method based on remarkable scenic spot detection
InactiveCN103278170ARealize online creationSolve the key problems of automatic segmentationInstruments for road network navigationImage analysisComputer scienceMobile robot navigation
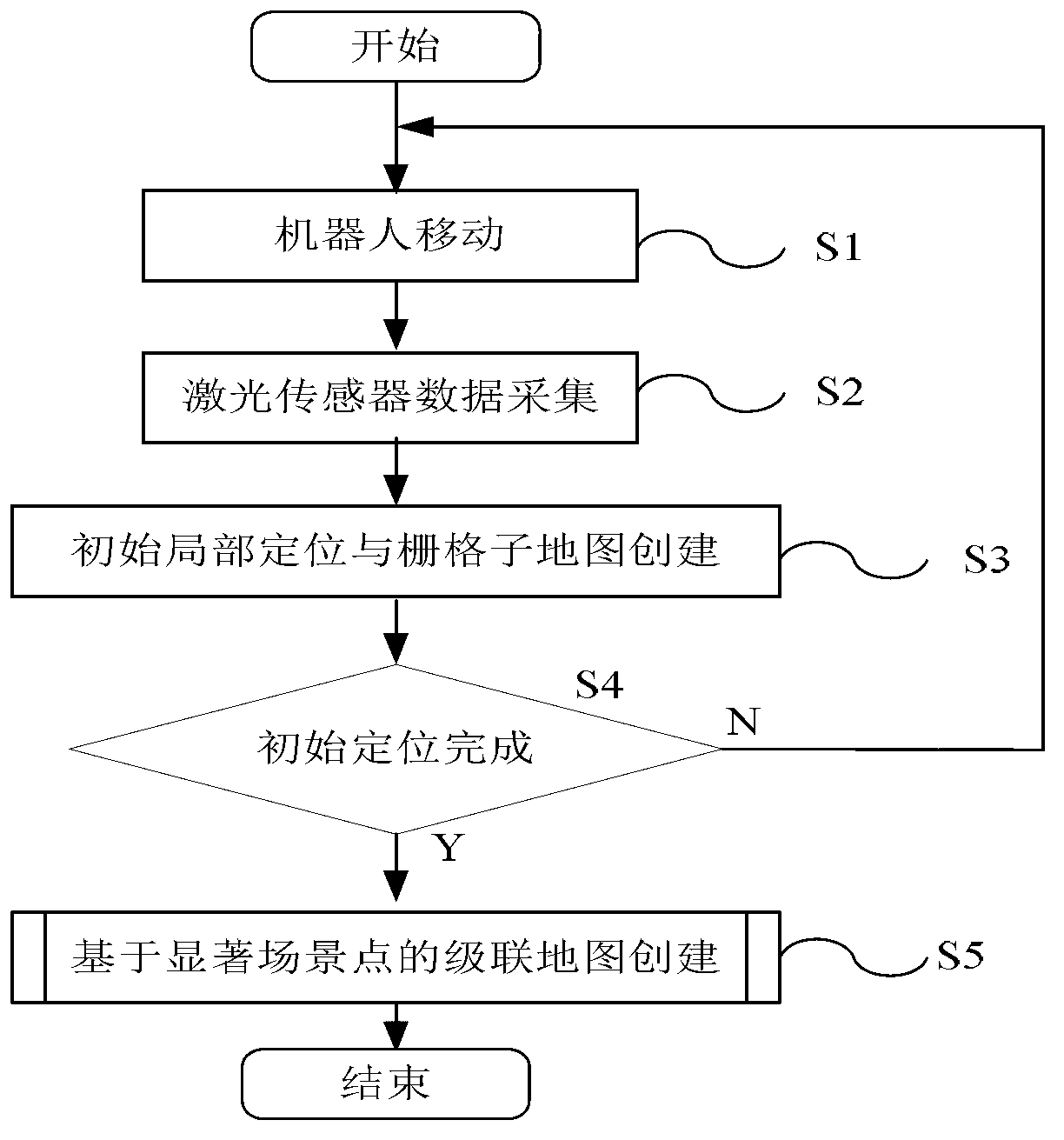
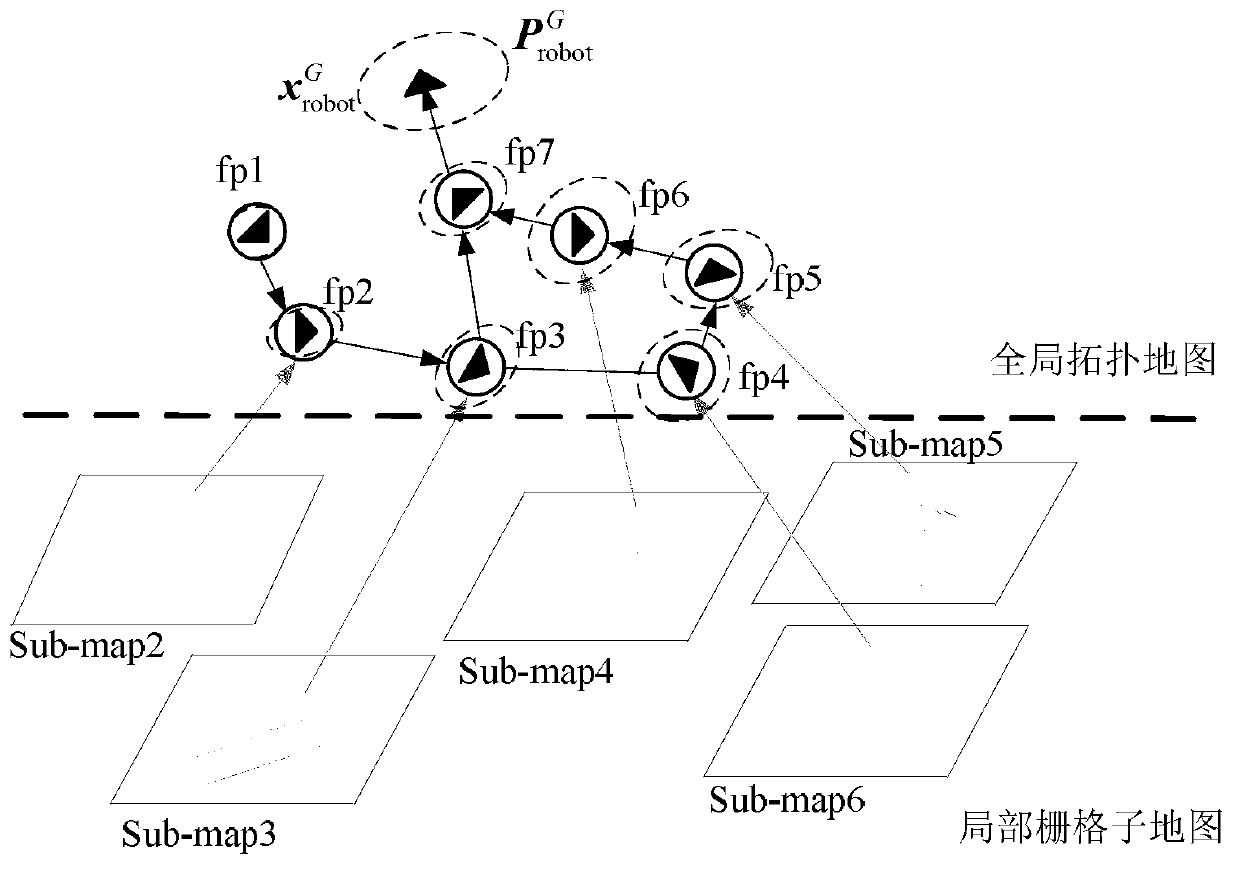
The invention relates to the technical field of mobile robot navigation and discloses a mobile robot cascading map building method based on remarkable scenic spot detection. The mobile robot cascading map building method comprises the steps of: 1) according to image data collected by a mobile robot sensor, carrying out on-line detection on a road sign of a natural scene corresponding to a remarkable scene so as to generate a topological node in a global map; 2) updating the pose of a mobile robot and a local grid map; and 3) building a global topological map structure by taking a remarkable scenic spot as the topological node, and optimizing the topological structure by introducing a weighted scanning and matching method and a relaxation method on the basis of the closed detection of trajectory of the robot to ensure the global consistency of the topological map. The mobile robot cascading map building method is applicable to the autonomous path planning and navigation application for various mobile robots in large indoor environment ranges such as a plurality of rooms and corridors.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Determination method and apparatus for position and orientation of mobile robot
ActiveCN105928505AImplement initializationTimely detection of pose errorsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsPicture interpretationSimultaneous localization and mappingElectricity
Embodiments of the invention relate to a determination method and apparatus for the position and orientation of a mobile robot. The method comprises the following steps: in virtue of simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) technology, establishing a global map of an environment where the mobile robot plays a navigation role by using a laser scanner; when the mobile robot is energized, establishing a local map of an environment in the energization moment of the mobile robot by using a laser scanner in virtue of SLAM technology; and subjecting the local map to image matching in the global map so as to obtain the initial position and orientation of the mobile robot in the global map. According to the embodiments of the invention, the absolute position and orientation of the mobile robot in the global map in the moment the mobile robot is energized and started can be obtained, thereby realizing initialization of the position and orientation of the mobile robot; moreover, determined position and orientation of the mobile robot can be further corrected.
Owner:SMART DYNAMICS CO LTD
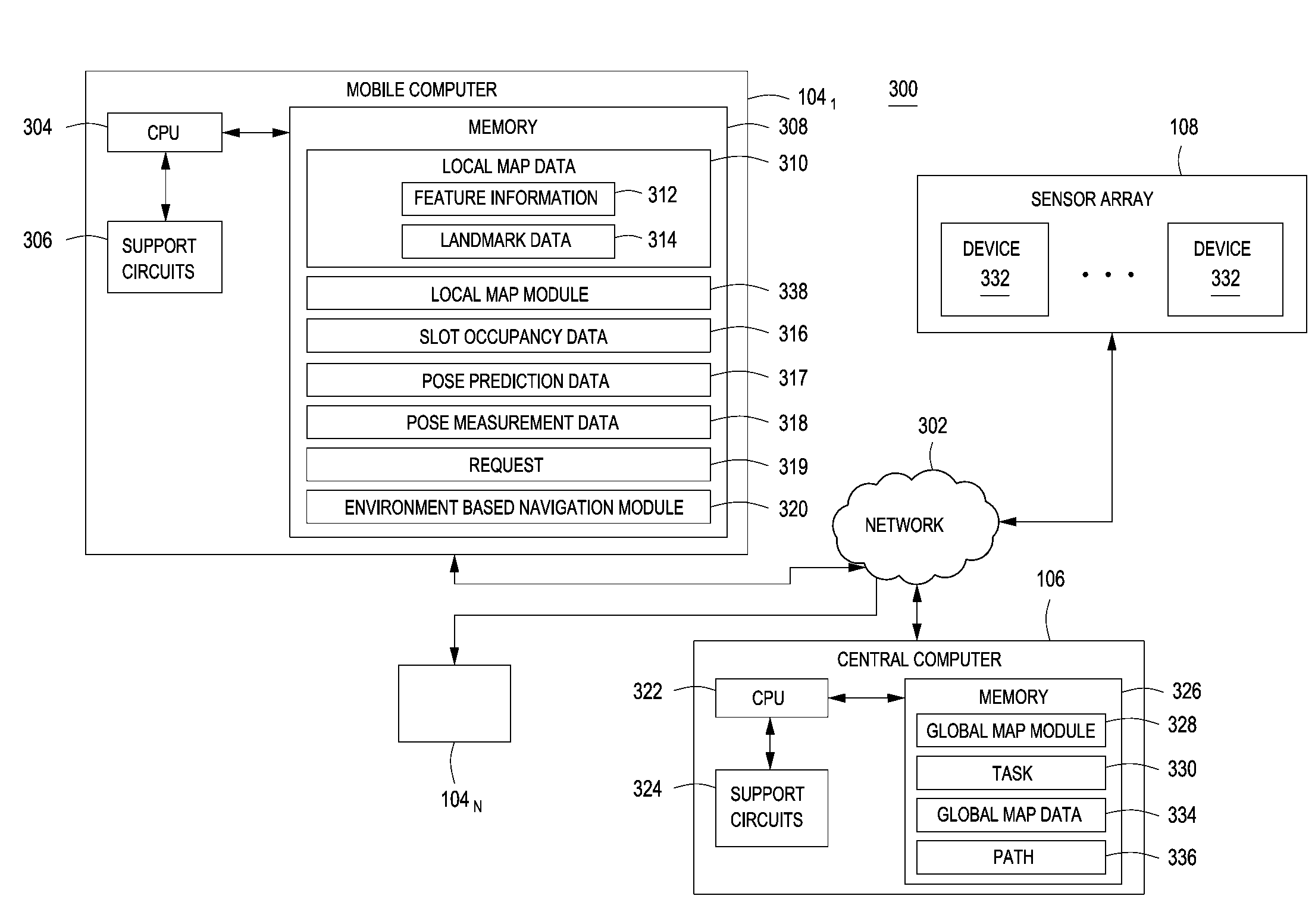
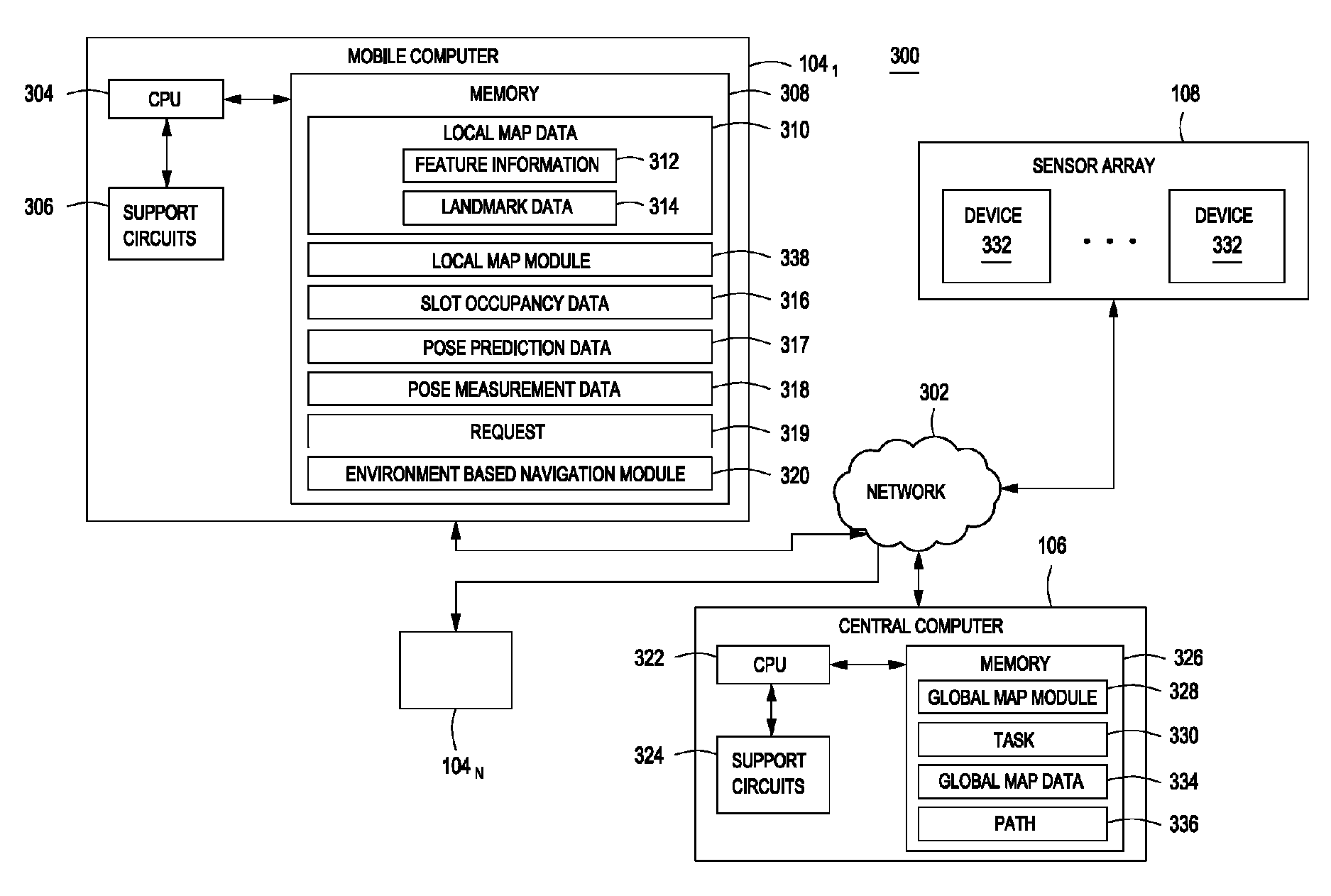
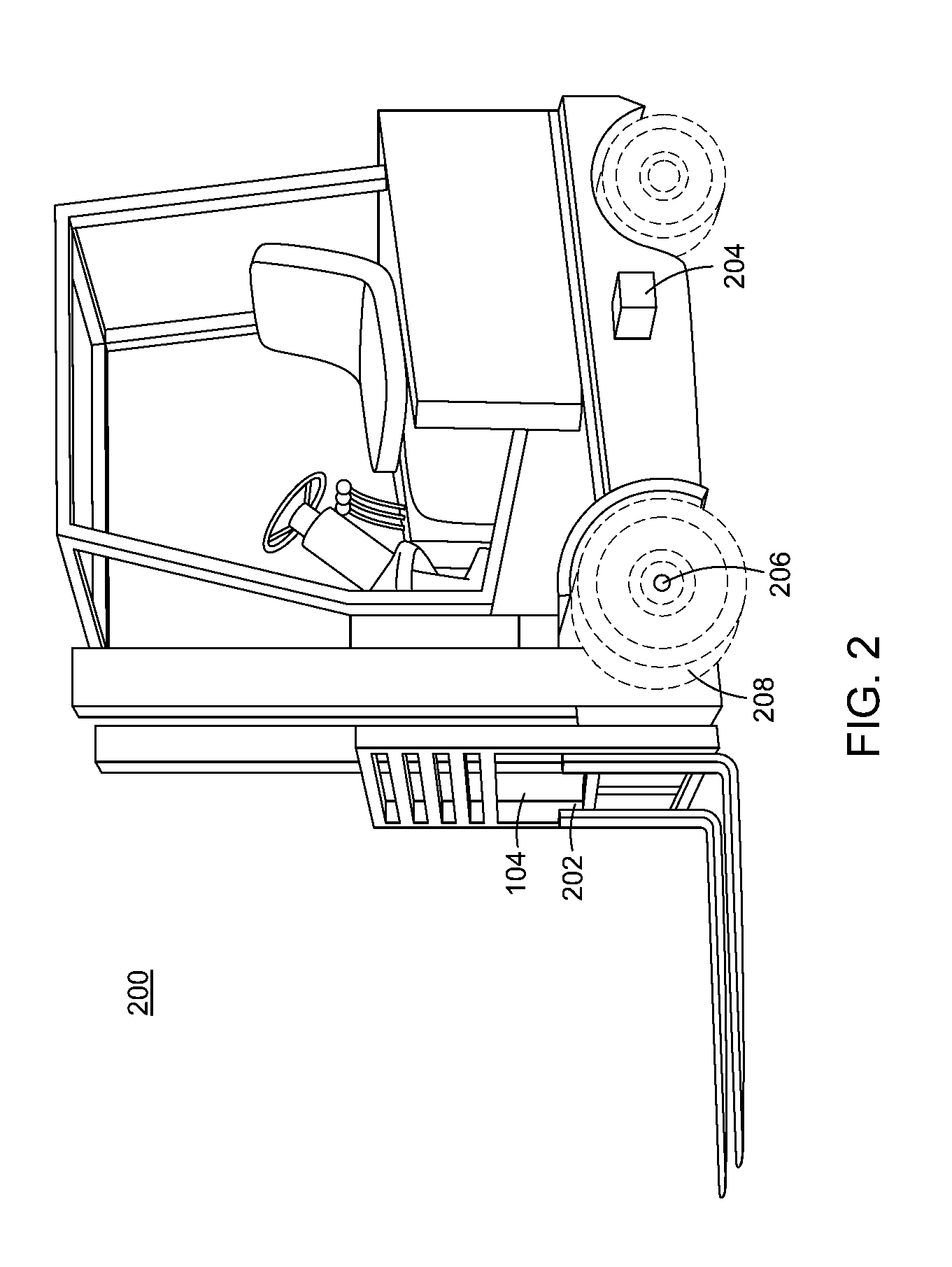
Method and apparatus for sharing map data associated with automated industrial vehicles
ActiveUS20120323431A1Instruments for road network navigationLifting devicesComputer sciencePhysical context
A method and apparatus for sharing map data between industrial vehicles in a physical environment is described. In one embodiments, the method includes processing local map data associated with a plurality of industrial vehicles, wherein the local map data comprises feature information generated by the plurality of industrial vehicles regarding features observed by industrial vehicles in the plurality of vehicles; combining the feature information associated with local map data to generate global map data for the physical environment; and navigating an industrial vehicle of the plurality of industrial vehicles using at least a portion of the global map data.
Owner:CROWN EQUIP CORP
High-precision map generation system and method based on high-definition ortho-photo map
ActiveCN104573733AHigh resolutionAccurate calculationCharacter and pattern recognitionMaps/plans/chartsInformation processingRadar
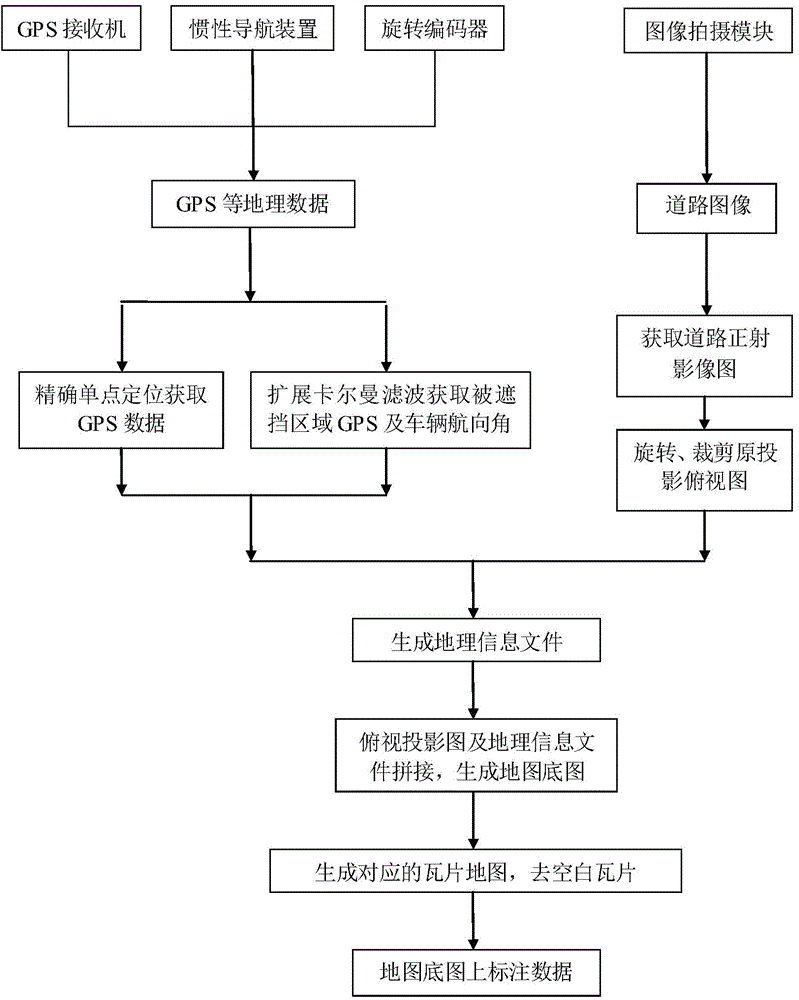
The invention provides a high-precision map generation system and a high-precision map generation method based on a high-definition ortho-photo map. The system comprises an image shooting module, a horizontal laser radar, a GPS (global positioning system) processing module, an inertial navigation module, a rotary encoder, an image and data preprocessing module and a geographical information processing module, wherein the vehicle-mounted image shooting module is used for acquiring a road image; the laser radar is used for scanning a barrier and acquiring geographical information data; the precision of GPS information is optimized; the ortho-photo map of the road image is acquired and then is rotated and sheared to generate corresponding geographical information file operation; a full ortho-photo map sequence and a corresponding geographical information file are combined and spliced to generate a base map of a global map; various types of geographical information data are marked on the base map of the map. According to the method and the system, a high-precision navigation map can be generated, and the data precision can reach centimeter level; the method and the system are extremely high in practical value on an advanced auxiliary driving system and an unmanned vehicle.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Mobile robot obstacle avoidance navigation method and system
InactiveCN105116902AGuaranteed accuracyGuaranteed validityPosition/course control in two dimensionsHome environmentSimulation
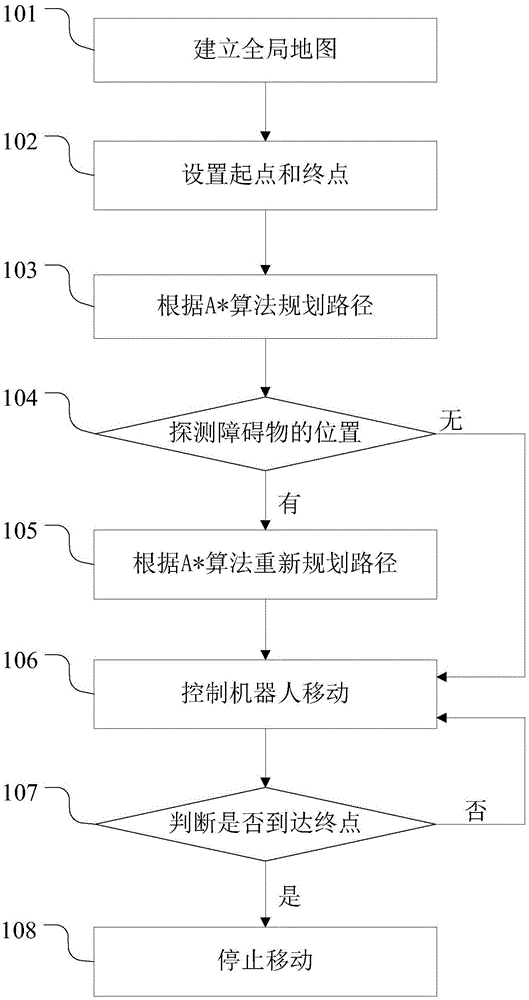
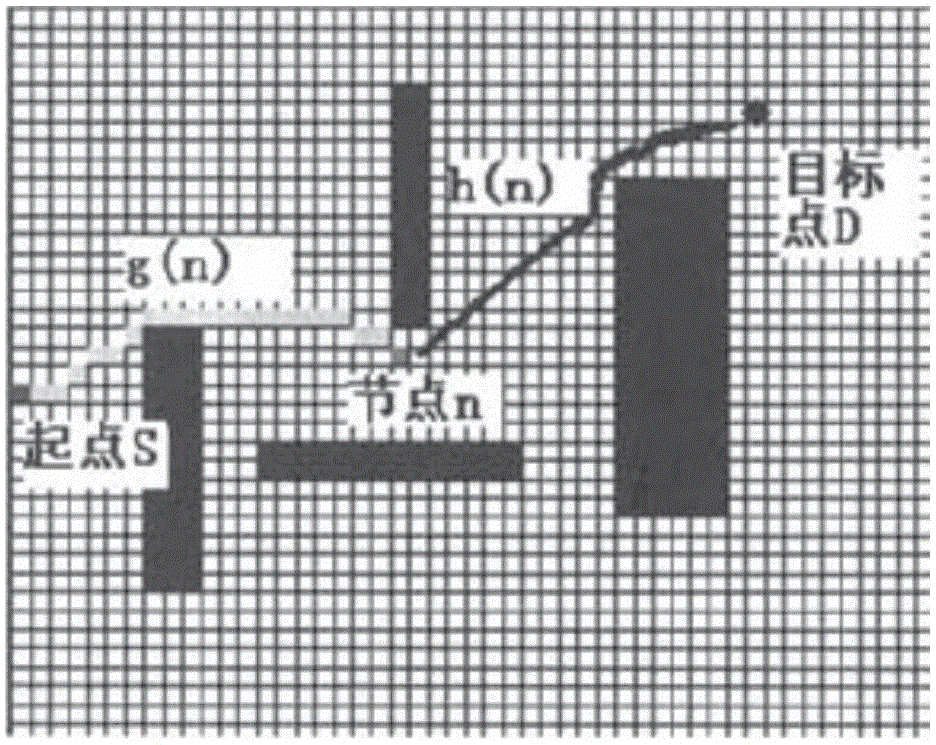
The invention discloses a mobile robot obstacle avoidance navigation method and system. The method includes the following steps that: a global map of a home environment is established; the starting point and destination of the movement of a robot are set; the movement path of the robot is planned according to the A* algorithm; the position of a obstacle is marked in the global map; the movement path of the robot is re-planned according to the A* algorithm; the robot is controlled to move according to the planned path; and the robot arrives at the destination and stops moving. With the mobile robot obstacle avoidance navigation method and system of the invention adopted, unknown environment can be detected, so that the information of unknown obstacles can be obtained, and the estimation function is adopted to plan the shortest and most economical path, and therefore, the equipment cost of the obstacle avoidance navigation of the robot can be decreased; the position and movement attitude of the robot can be monitored in real time, and the walking attitude of the robot can be adjusted and controlled in real time, and the accuracy and effectiveness of the obstacle avoidance navigation of the robot can be ensured.
Owner:BEIJING EVOLVER ROBOTICS CO LTD
Mobile robot indoor environment exploration system and control method based on ROS
InactiveCN105487535AImprove reusabilityFast traversePosition/course control in two dimensionsData matchingSimulation
The invention discloses a mobile robot indoor environment exploration system and control method based on a ROS (Robot Operating System). The system is based on the ROS, and can realize independent exploration and positioning on indoor environment by a robot. The system mainly uses an iRobot differential drive chassis and UTM 30LX laser radar. An upper computer can obtain position positioning information of the robot and an indoor environment exploration path track in real time, and through data matching of the laser radar, a global map formed by connecting local maps is obtained. The invention provides a more intelligent unknown environment exploration system, provides great convenience and safety guarantee for disaster environment rescue, realizes information interaction of indoor environment perception, and has very good convenience and practicality.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
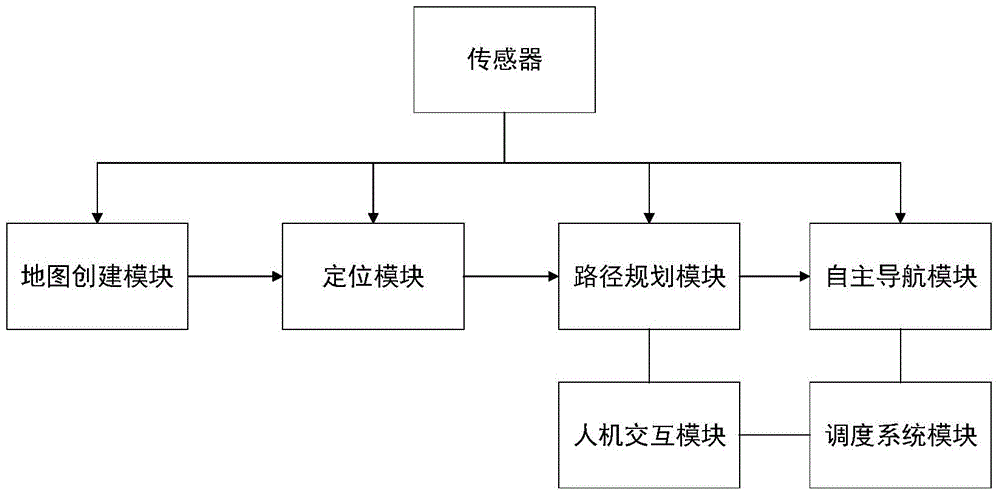
Automatic guided vehicle based on map matching and guide method of automatic guided vehicle
ActiveCN104596533AImprove environmental adaptabilityEasy to changeInstruments for road network navigationOptimum routeAutomated guided vehicle
The invention provides an automatic guided vehicle based on map matching and a guide method of the automatic guided vehicle. The automatic guided vehicle comprises a map creation module, a location module, a human-machine interaction module, a route planning module, an autonomous navigation module and a dispatching system module, wherein the map creation module is used for creating an environmental map; the automatic guided vehicle utilizes the carried location module to match the observed local environmental information with a preliminarily created global map to obtain pose information under the global situation; the human-machine interaction module is used for displaying the information and working state of the automatic guided vehicle in the map in real time; the route planning module is used for planning a feasible optimum route in the global map; the automatic guided vehicle is autonomously navigated by virtue of the autonomous navigation module according to the planned route; the dispatching system module is used for dispatching the automatic guided vehicle closest to a calling site to go to work. By adopting the automatic guided vehicle, no other auxiliary location facility is needed, no alteration is made for the environment, the capability of the automatic guided vehicle is completely depended, the automatic guided vehicle is utterly ignorant to the environment, and no priori information is provided.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
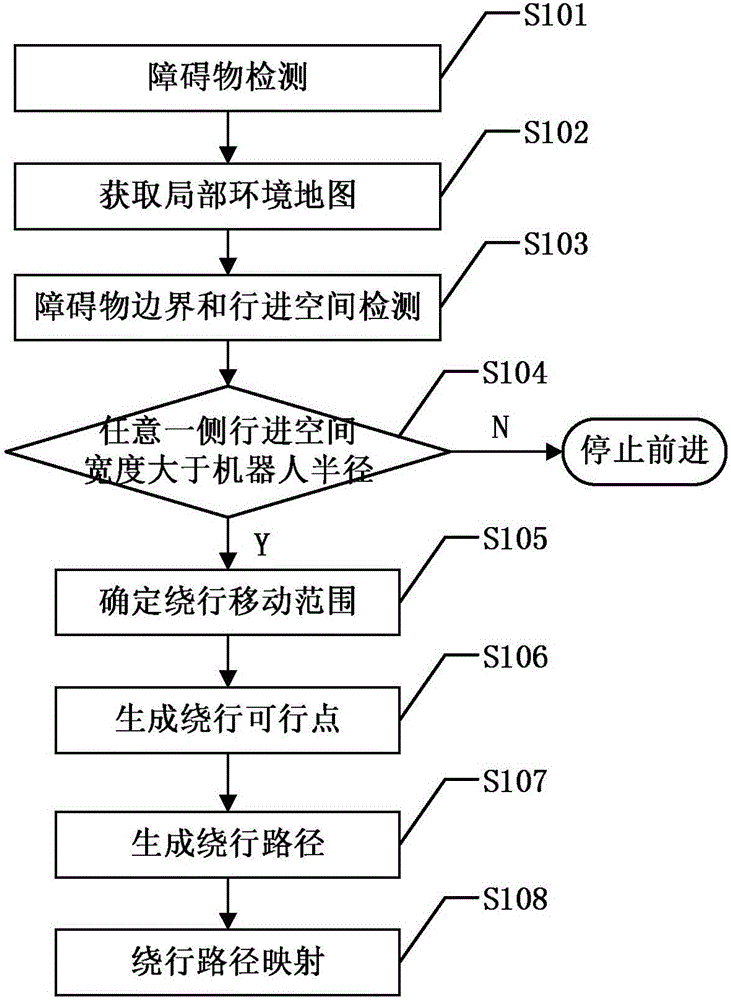
Temporary robot obstacle avoidance method based on depth camera
ActiveCN106054900AImprove intelligenceWill not affect understandingPosition/course control in two dimensionsObstacle avoidanceLocal environment
The invention discloses a temporary robot obstacle avoidance method based on a depth camera. If a robot detects an obstacle when moving along a set global navigation path, the depth camera installed on the robot is used to shoot through deflecting left and right angles and acquire a depth map; the map is processed so as to acquire a local environment map; in the local environment map, traveling spaces of left and right sides of the obstacle are detected; and the side with a large width is selected and used as a circumambulating traveling space. A circumambulating moving scope rectangular is drawn. Circumambulating feasible points are generated in the circumambulating moving scope rectangular. The feasible points are selected from the circumambulating feasible points so as to generate a circumambulating path. The circumambulating path is mapped into a global map. An end point of the mapped circumambulating path is connected to a next travelling node on an original global navigation path so as to complete temporary obstacle avoidance. By using the method of the invention, temporary robot obstacle avoidance can be high-efficiently and accurately completed; and after circumambulating and the obstacle avoidance, the robot is returned to the original global navigation path so that intelligence of the robot is increased.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
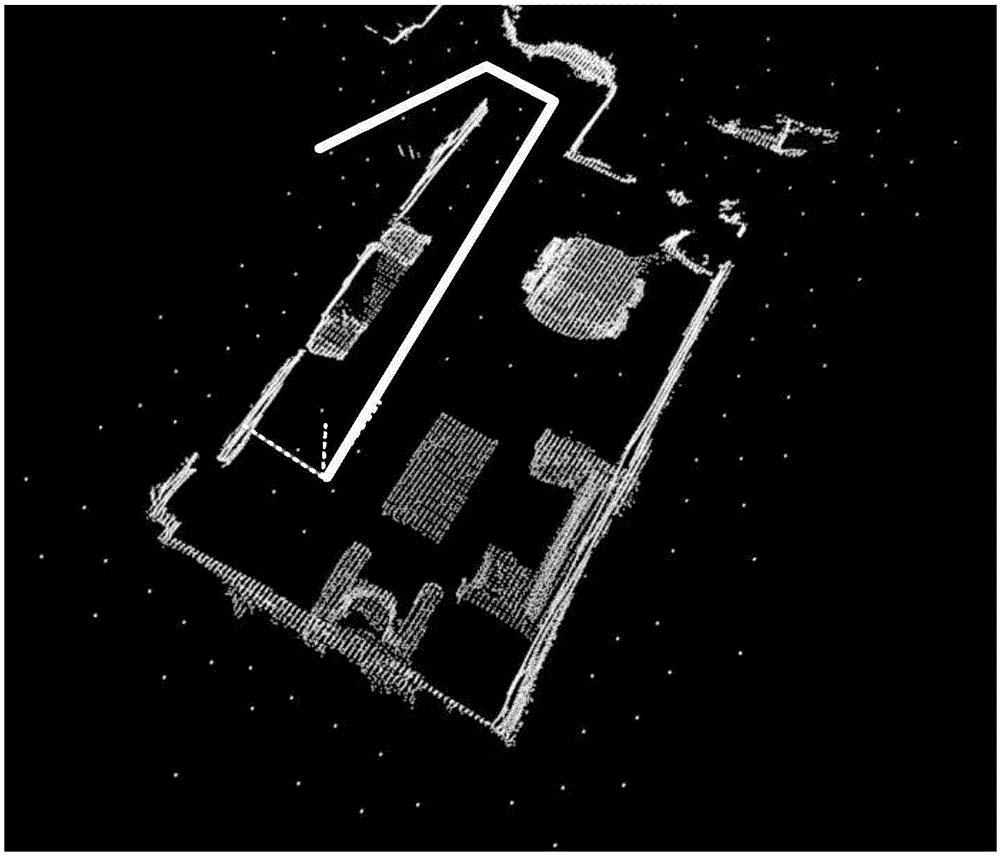
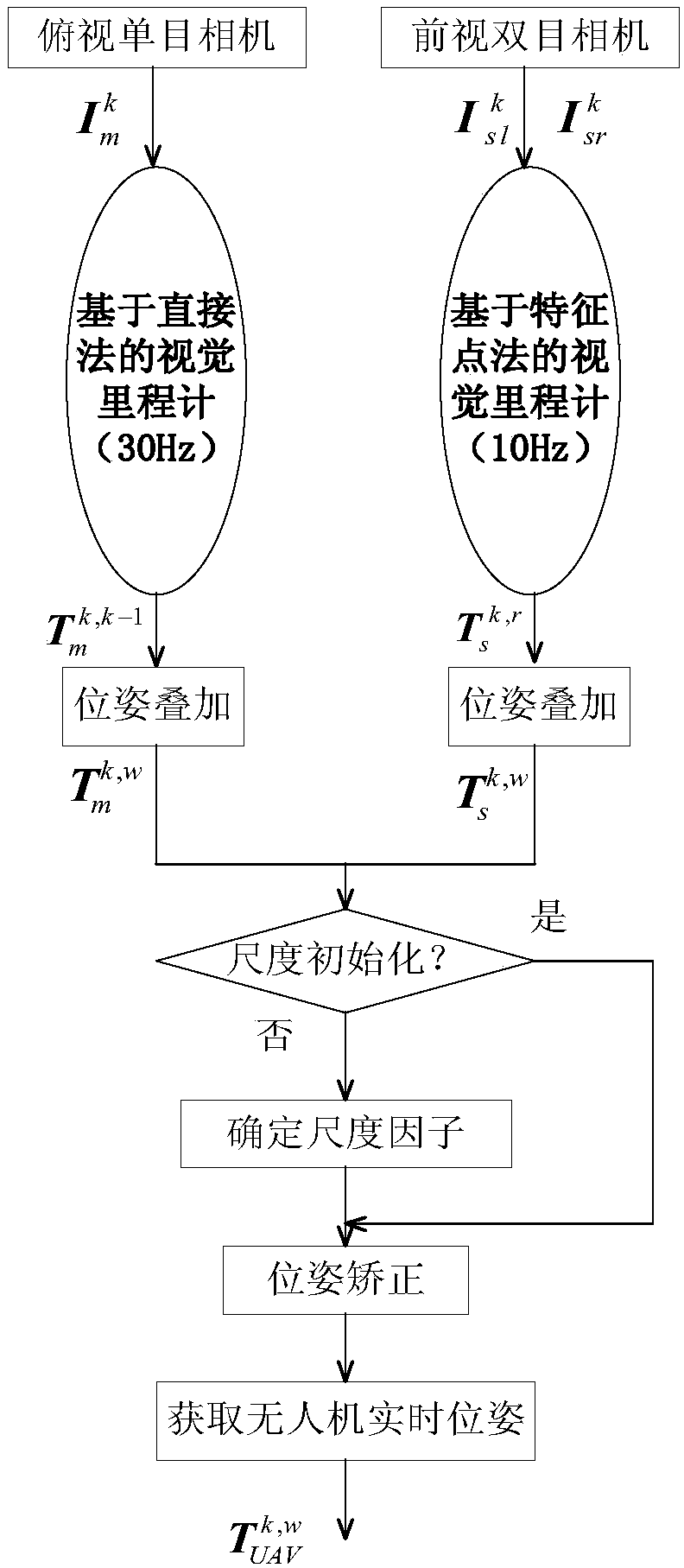
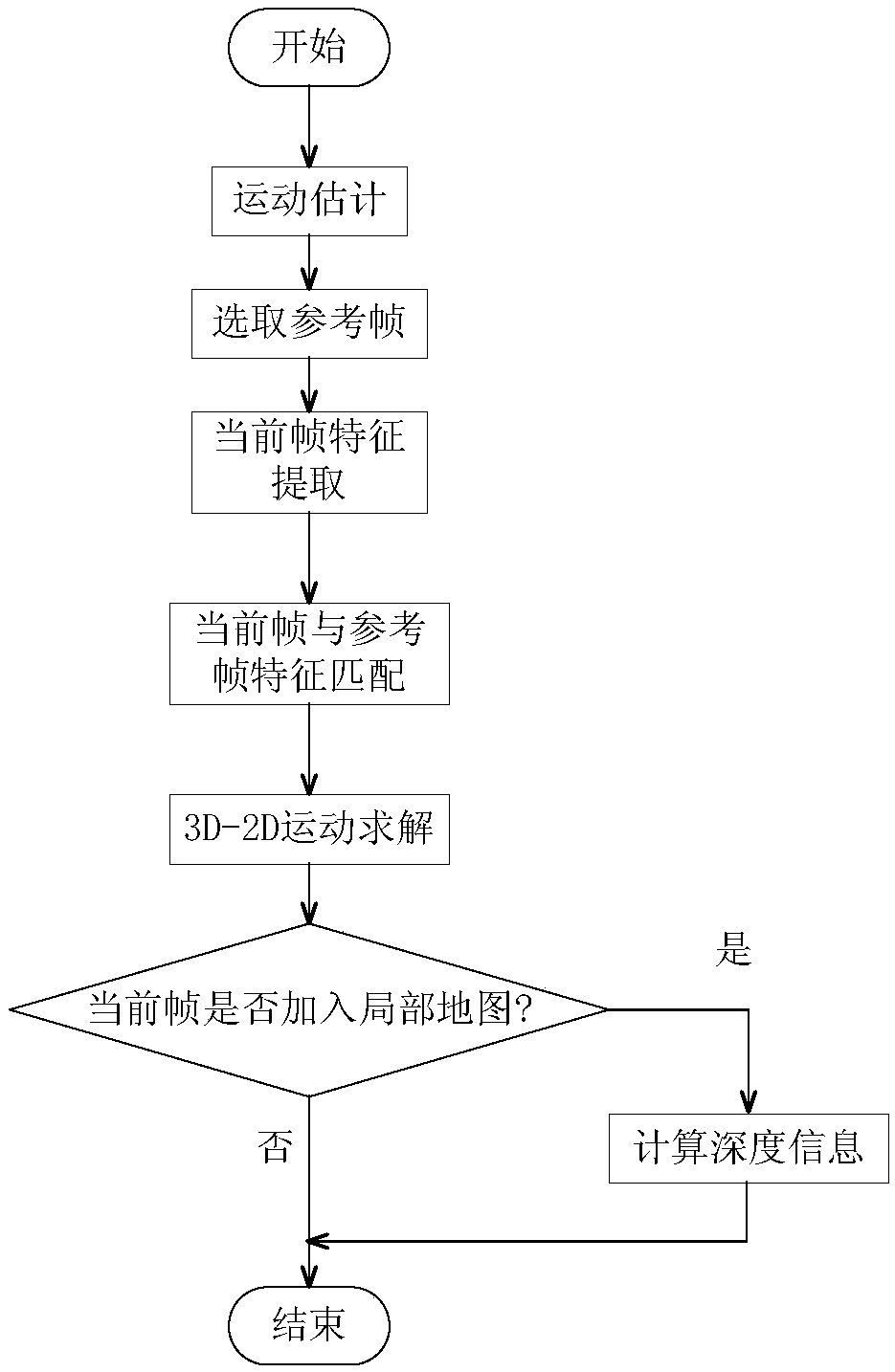
Simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) method for unmanned aerial vehicle based on mixed vision odometers and multi-scale map
ActiveCN109029417AReal-time accurate and reliable positioningShorten operation timeNavigational calculation instrumentsSimultaneous localization and mappingEnvironmental perception
The invention discloses a simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) method for an unmanned aerial vehicle based on mixed vision odometers and a multi-scale map, and belongs to the technical field of autonomous navigation of unmanned aerial vehicles. According to the SLAM method, an overlooking monocular camera, a foresight binocular camera and an airborne computer are carried on an unmanned aerial vehicle platform; the monocular camera is used for the visual odometer based on a direct method, and binocular camera is used for the visual odometer based on feature point method; the mixed visual odometers conduct information fusion on output of the two visual odometers to construct the local map for positioning, and the real-time posture of the unmanned aerial vehicle is obtained; then theposture is fed back to a flight control system to control the position of the unmanned aerial vehicle; and the airborne computer transmits the real-time posture and collected images to a ground station, the ground station plans the flight path in real time according to the constructed global map and sends waypoint information to the unmanned aerial vehicle, and thus autonomous flight of the unmanned aerial vehicle is achieved. Real-time posture estimation and environmental perception of the unmanned aerial vehicle under the non-GPS environment are achieved, and the intelligent level of the unmanned aerial vehicle is greatly increased.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Indoor unknown structure identification method based on laser scanning
ActiveCN103148804AAdaptableImprove scalabilityCharacter and pattern recognitionUsing optical meansLaser rangingMobile laser scanning
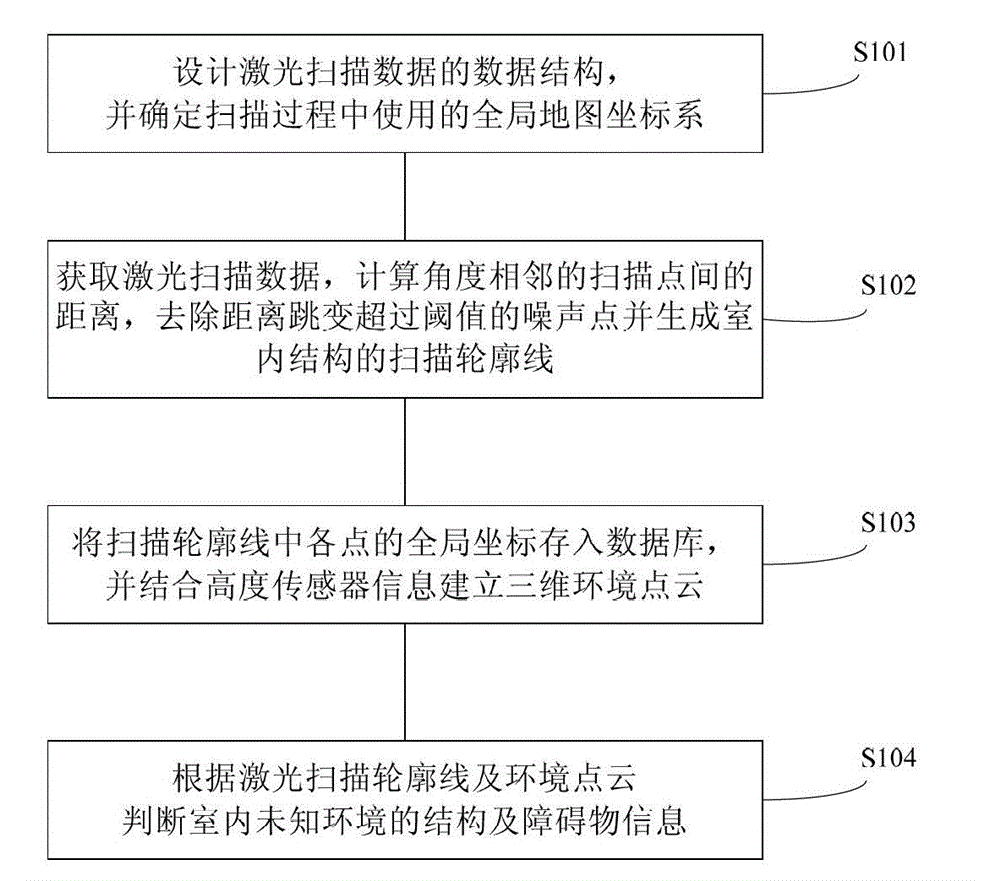
The invention discloses an indoor unknown structure identification method based on laser scanning. The method comprises the following steps of designing a data structure of laser scanning data, and determining a global map coordinate system used in the scanning process; adopting a laser rangefinder to obtain laser scanning data, calculating the distance between scanning points with adjacent angles, and performing denoising pretreatment, generating a scanning contour of the indoor structure; saving the global coordinates of various points in the scanning contour into a database, and establishing a three-dimensional environmental point cloud by combining height sensor information; and according to the scanning contour and the environmental point cloud, identifying an indoor unknown environmental structure and barrier information. The method provided by the invention is complete in structure and real-time in data processing, and has strong adaptability and expandability.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Geographical environmental characteristic map construction and navigation method based on data mining
InactiveCN103389103AAccurate associationImprove accuracyInstruments for road network navigationMaps/plans/chartsFeature vectorPoint cloud
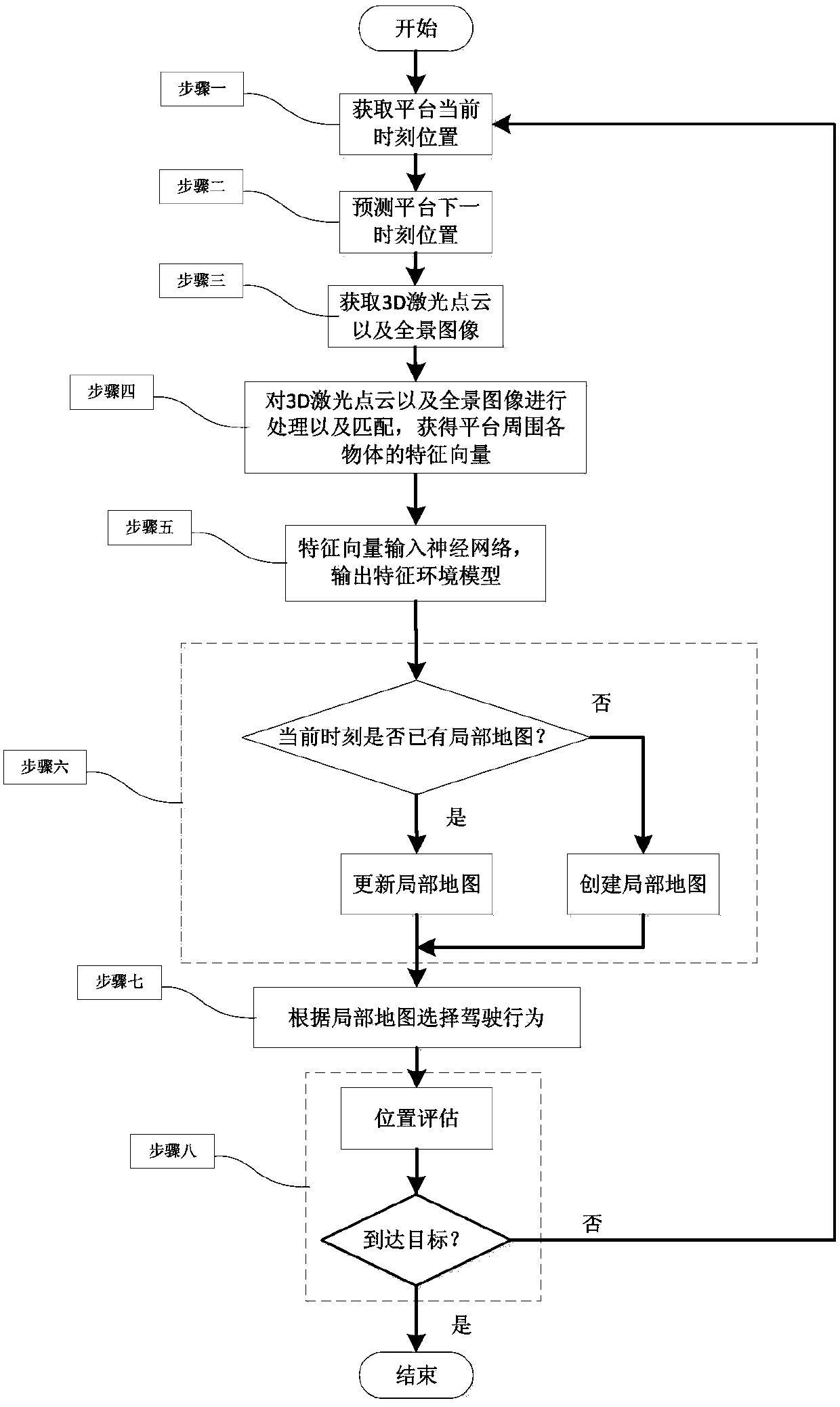
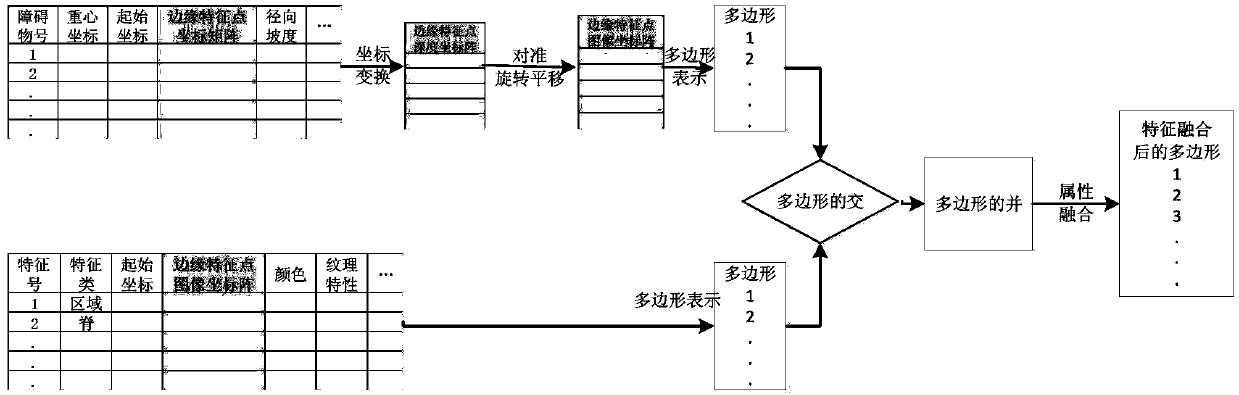
The invention discloses a geographical environmental characteristic map construction and navigation method based on data mining, and belongs to the field of automatic control. The method comprises the following flow: firstly performing processing and matching on a current 3D laser-point cloud of the surrounding environment of a platform and a panoramic picture, to acquire characteristic vectors of each object in the platform surrounding environment; secondly inputting the characteristic vectors of each object into a neural network which classifies the characteristic vectors and outputs a characteristic environmental model; thirdly according to the characteristic environmental model, establishing a current local map or updating an original local map; and finally based on a current position of the platform and a predicted next-moment position, selecting a routine for driving according to the local map. If the platform does not reach a final goal, the flow is repeated; and if the platform reaches the final goal, the flow is finished and the final local map is a global map. The method is applicable to geographical environment map construction and navigation of a ground unmanned mobile platform.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
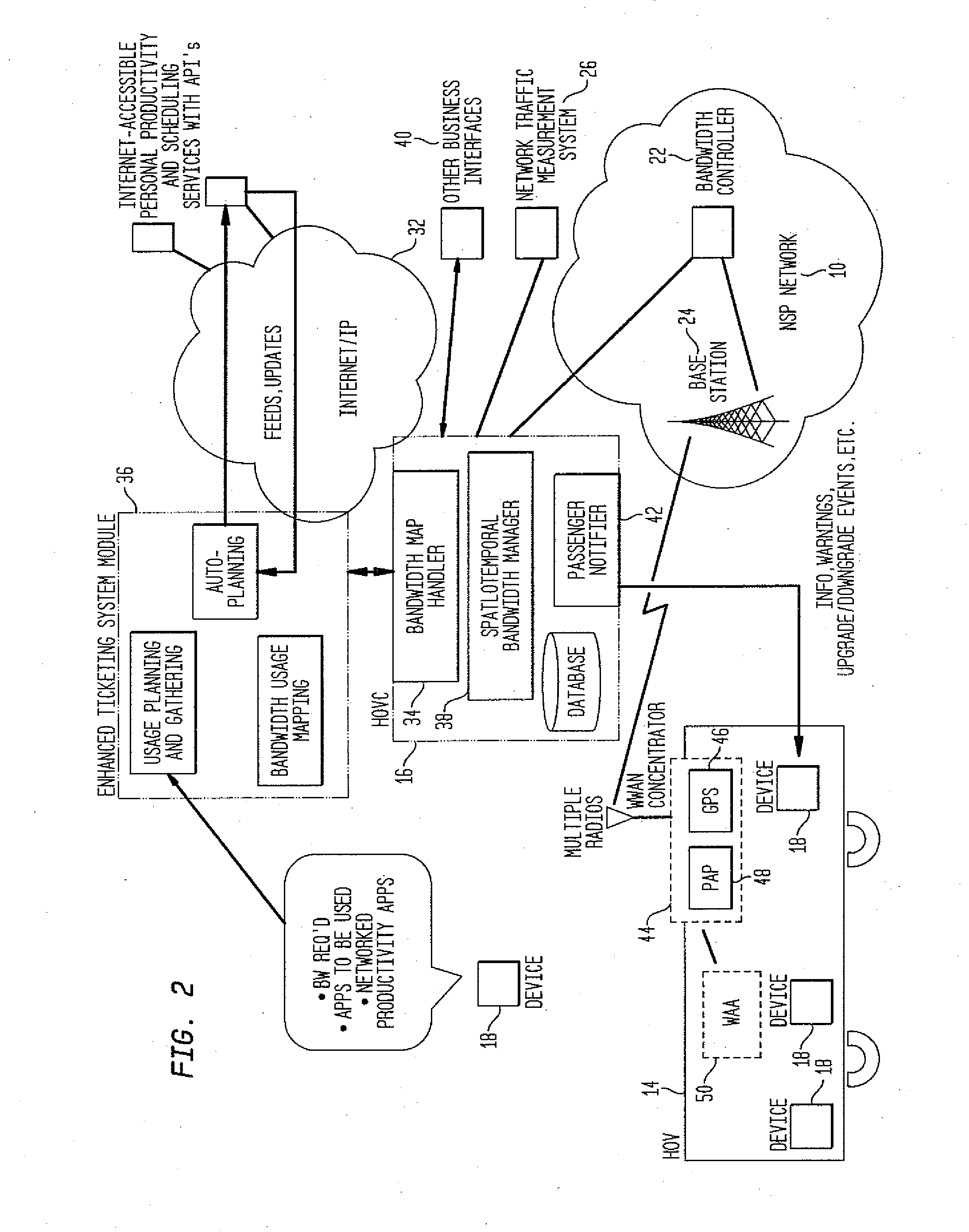
Method and system to manage wireless communications of high-occupancy vehicles
ActiveUS20090279483A1Convenient wireless communicationSolve insufficient capacityNetwork topologiesWireless commuication servicesProduction rateConcentrator
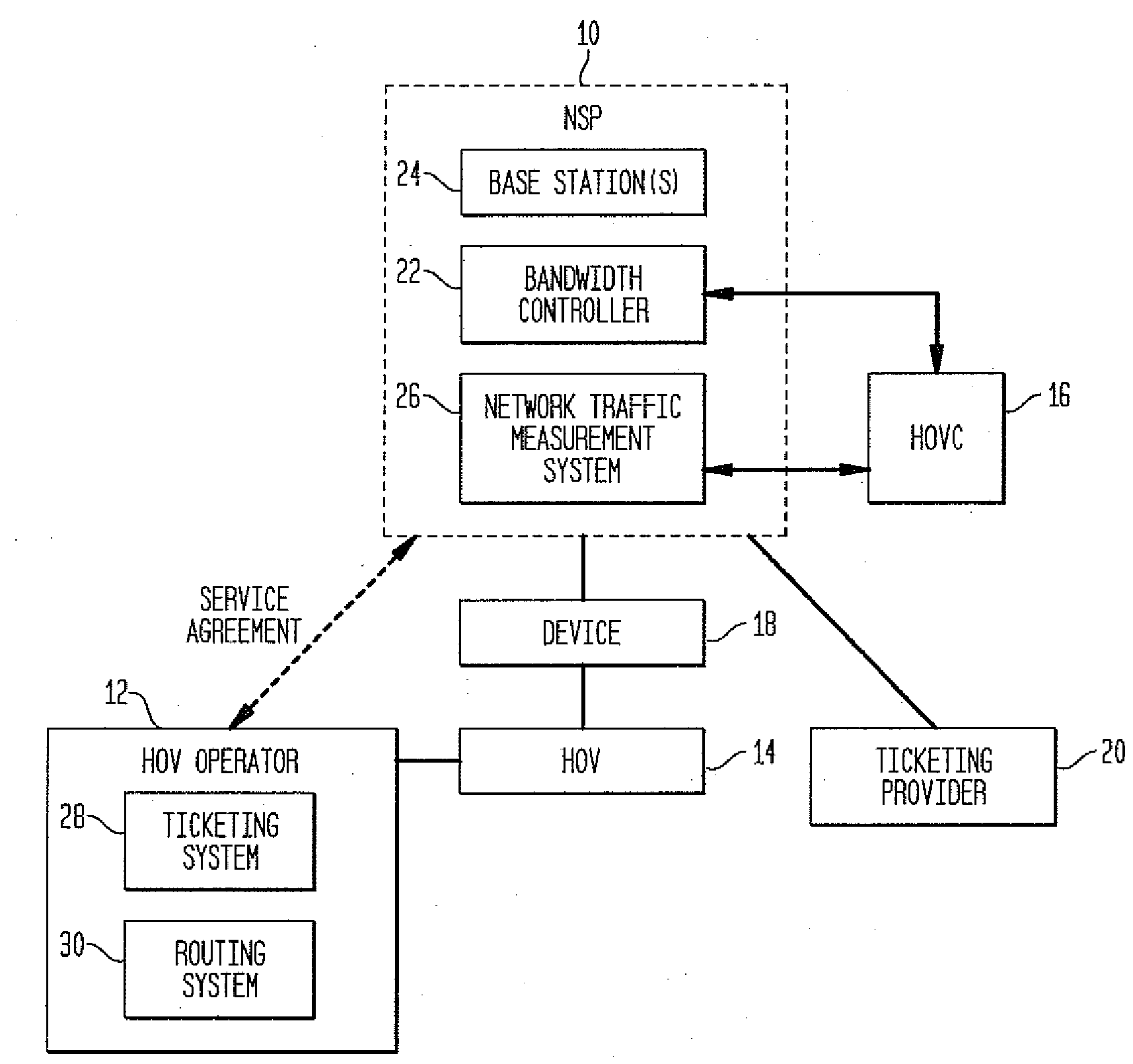
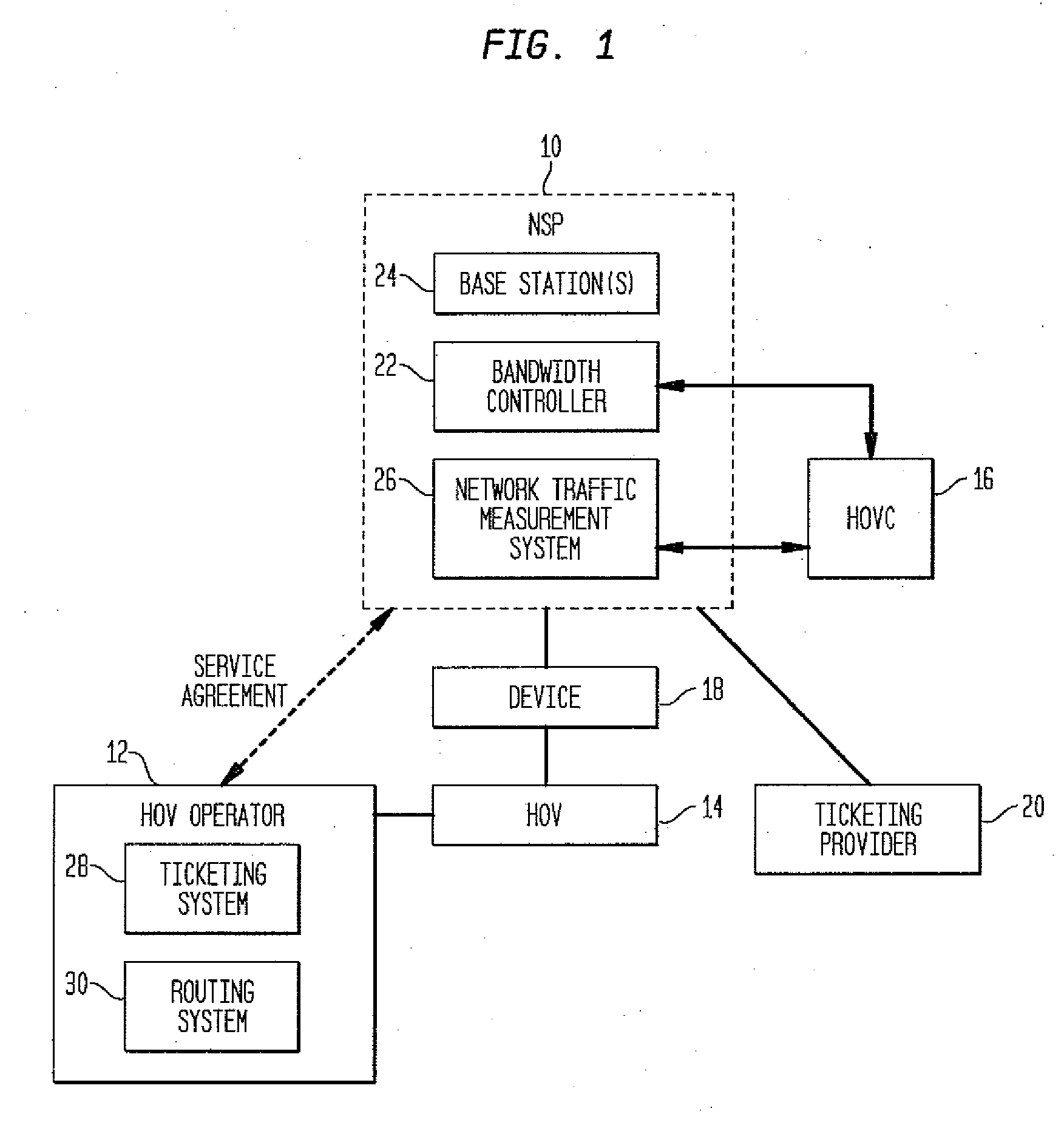
A system and method for managing wireless communications for a plurality of devices in a high occupancy vehicle is presented. The method comprises steps of creating a global bandwidth usage map across all vehicles, routes, and passengers, transmitting the global bandwidth usage map to a vehicle controller, interpreting the global bandwidth usage map and creating a local usage map, and commanding a wireless concentrator to manage the wireless communications for the devices in accordance with the local usage map. Further, the global map can be created by gathering ticket and route information, obtaining customer productivity data from a network, and parsing obtained data into canonical form. A step of inputting the ticketing information by one of the user, and a ticketing agent can be included. A step of displaying messages using a wireless access application residing on the device can be included.
Owner:TELCORDIA TECHNOLOGIES INC
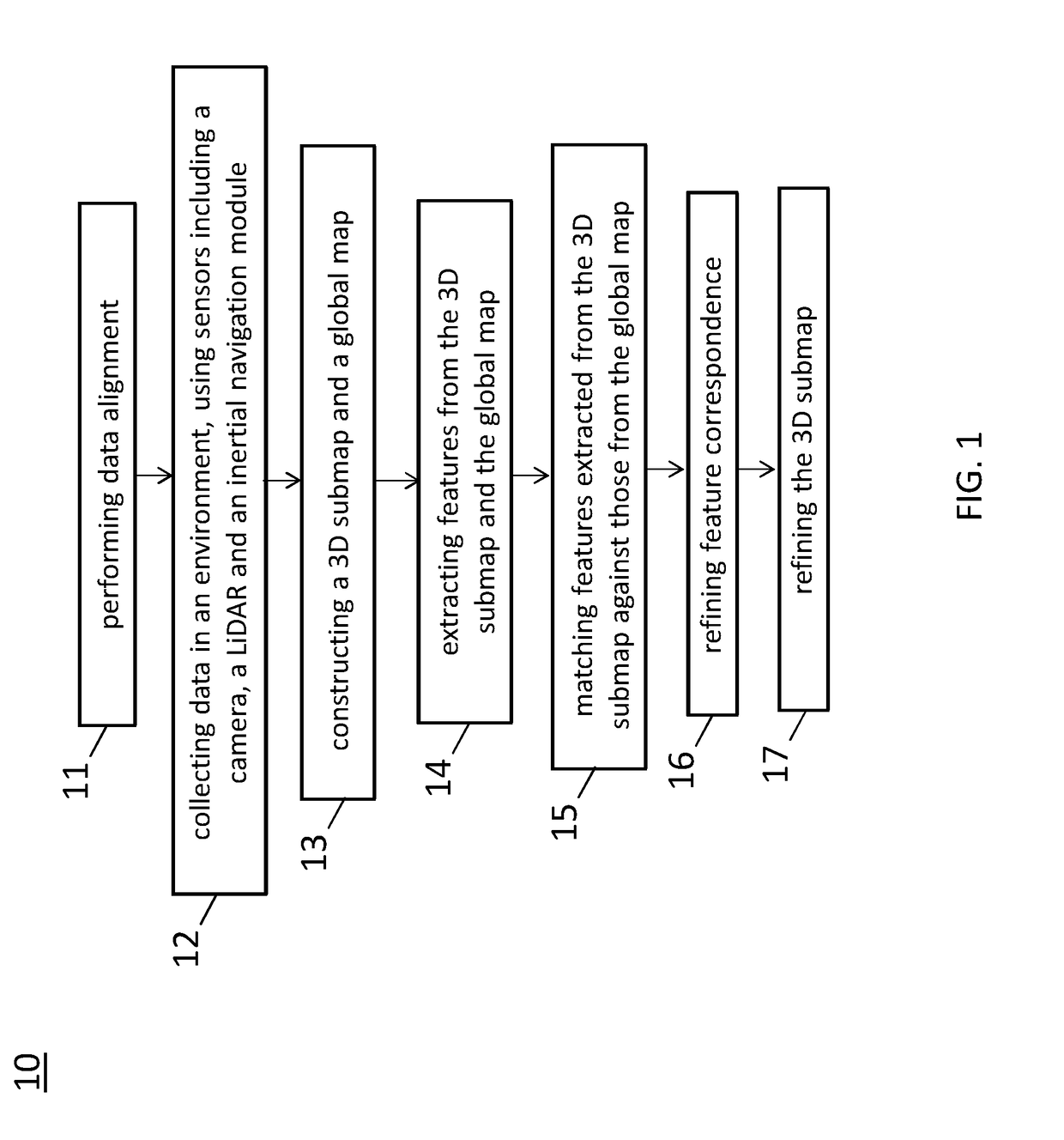
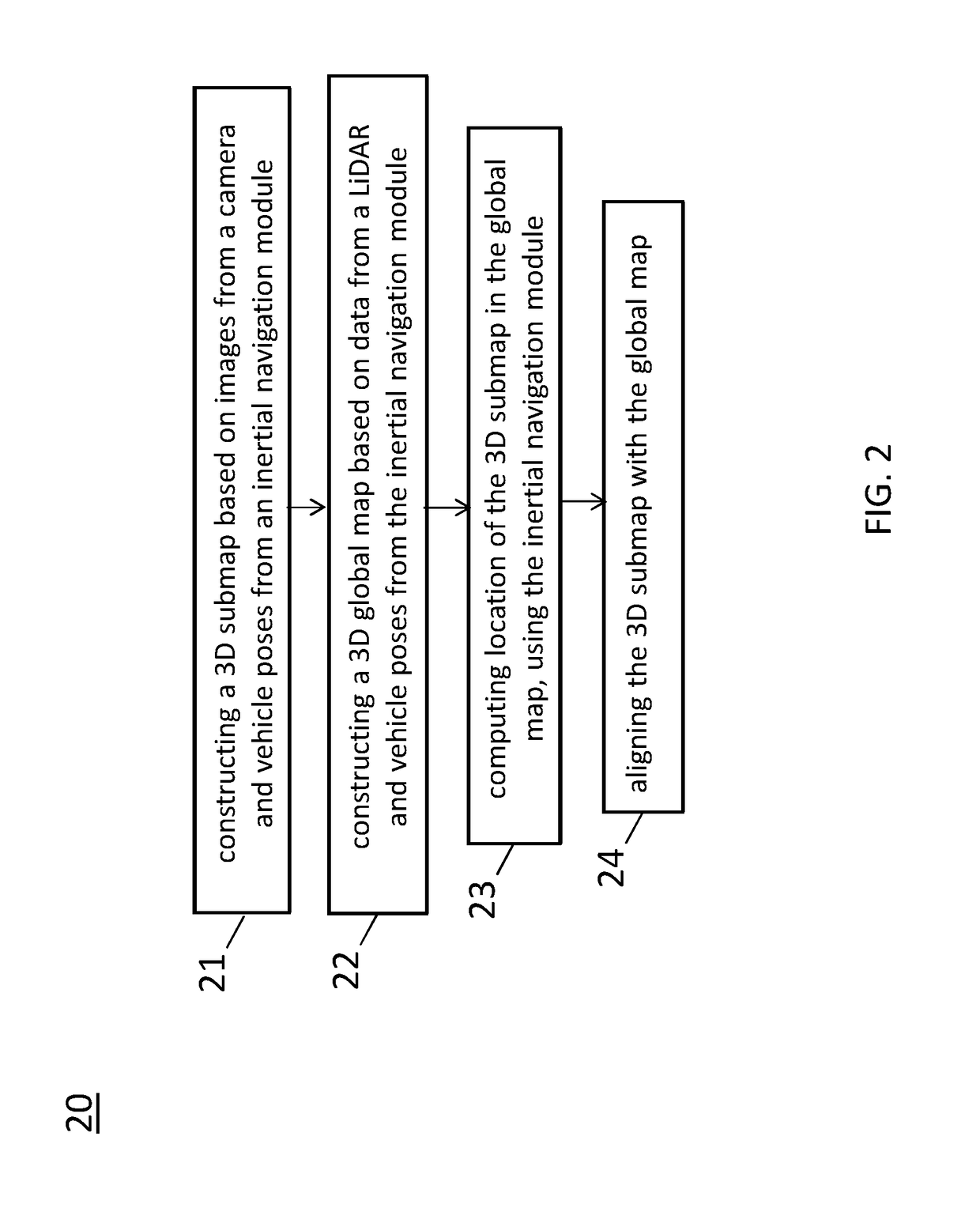
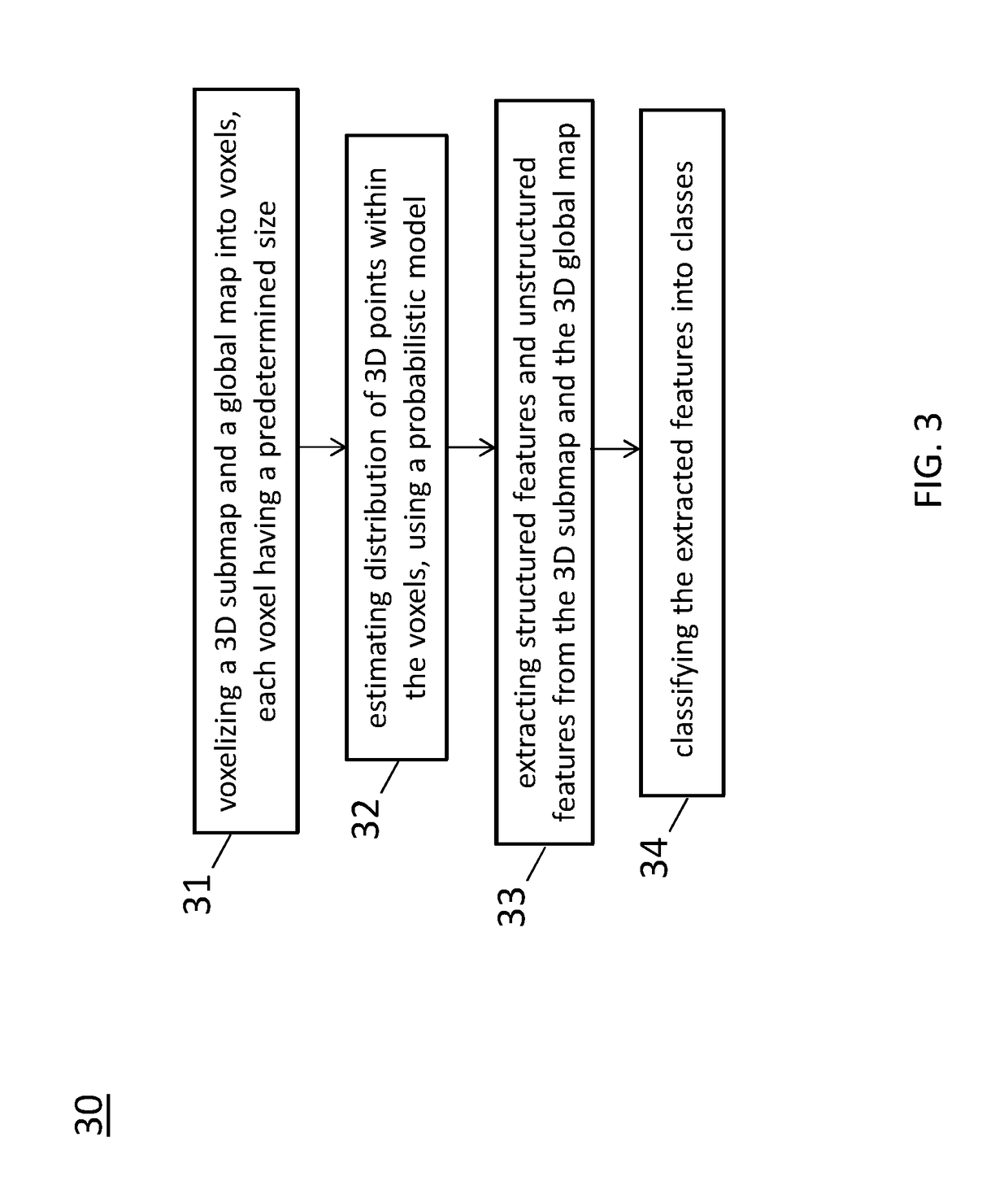
Feature matching and correspondence refinement and 3D submap position refinement system and method for centimeter precision localization using camera-based submap and lidar-based global map
ActiveUS20190065863A1Instruments for road network navigationNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsRadarVehicle driving
A method of localization for a non-transitory computer readable storage medium storing one or more programs is disclosed. The one or more programs comprise instructions, which when executed by a computing device, cause the computing device to perform by one or more autonomous vehicle driving modules execution of processing of images from a camera and data from a LiDAR using the following steps comprising: computing, in response to features from a 3D submap and features from a global map, matching score between corresponding features of a same class between the 3D submap and the global map; selecting, for each feature in the 3D submap, a corresponding feature with the highest matching score from the global map; determining a feature correspondence to be invalid if a distance between corresponding features is larger than a threshold; and removing the invalid feature correspondence.
Owner:TUSIMPLE INC
Multi-neural network control planning method for robot path in intelligent environment
ActiveCN107272705AEasy to implementImprove delivery efficiencyPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesIntelligent environmentSimulation
The invention provides a multi-neural network control planning method for a robot path in an intelligent environment. The method comprises the steps that 1 a global map three-dimensional coordinate system is constructed for the carrying area of a carrier robot to acquire a walkable area coordinate in the global map three-dimensional coordinate system; 2 a training sample set is acquired; 3 the global static path planning model of the carrier robot is constructed; and 4 starting and ending coordinates in a transportation task are input into the global static path planning model based on a fuzzy neural network to acquire the corresponding optimal planning path for the carrier robot. According to the invention, the global static path planning model and a local dynamic obstacle avoidance planning model are separately established; the nonlinear fitting property of the neural network is used to find the global optimal solution quickly; and the problem of falling into a local optimum in common path planning is avoided.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
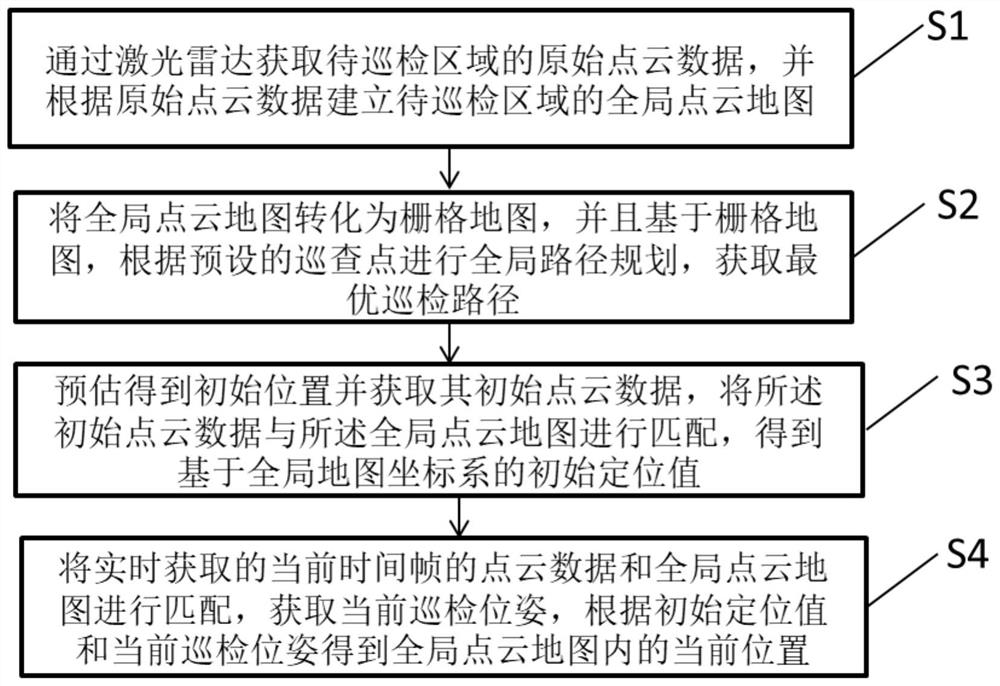
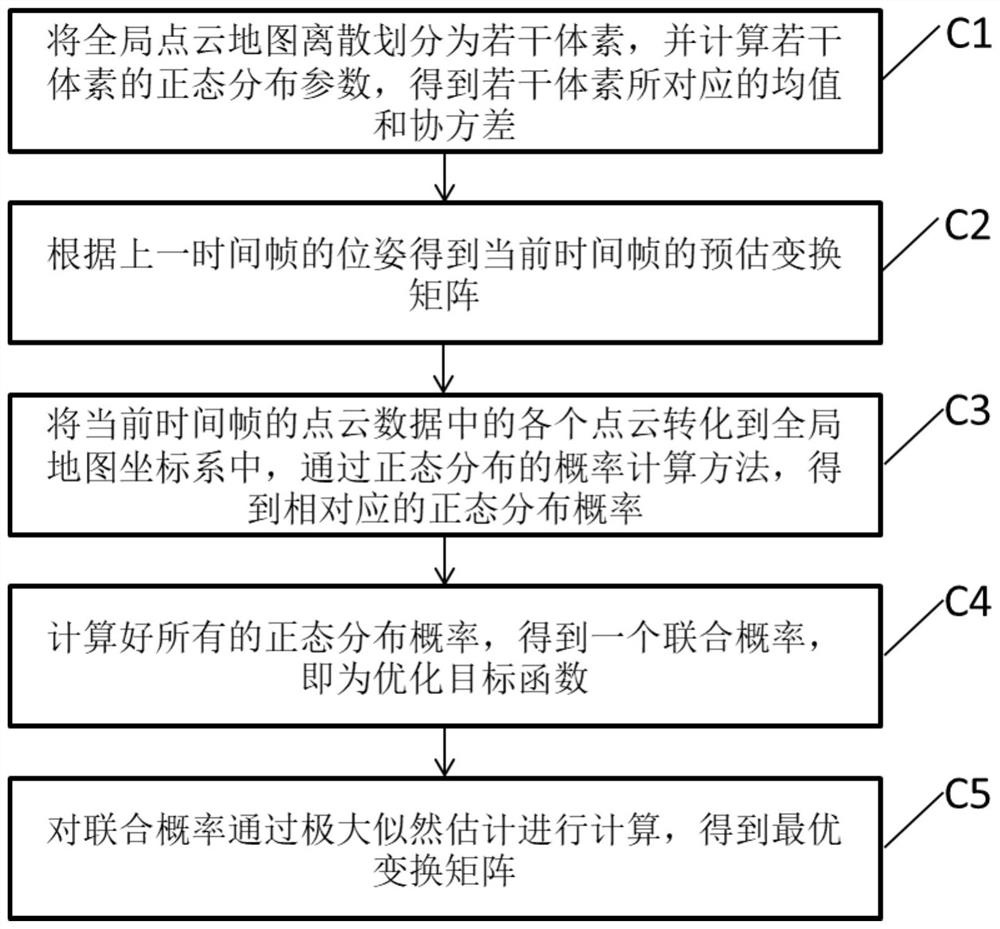
Three-dimensional laser radar positioning and navigation method for intelligent inspection and inspection robot
ActiveCN112014857ARealize three-dimensional perceptionRealize functionInternal combustion piston enginesElectromagnetic wave reradiationPoint cloudElectromagnetic interference
The invention discloses a three-dimensional laser radar positioning and navigation method for intelligent inspection. The method comprises the steps of S1 acquiring original point cloud data of a to-be-inspected area through a laser radar, and establishing a global point cloud map; S2 converting the global point cloud map into a grid map, and performing global path planning according to preset patrol points to obtain an optimal patrol path; S3 estimating to obtain an initial position, obtaining initial point cloud data of the initial position, and matching the initial point cloud data with theglobal point cloud map to obtain an initial positioning value based on a global map coordinate system; and S4 through matching of the current frame point cloud data obtained in real time and the global point cloud map, obtaining a current inspection pose. As the method is realized by utilizing the three-dimensional laser radar, the functions of three-dimensional perception, autonomous path planning and positioning navigation of the environment can be well realized, and the inspection precision of the inspection robot is improved; GPS positioning navigation does not need to be adopted, and theanti-electromagnetic interference capacity is high.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE SYST ENG INST
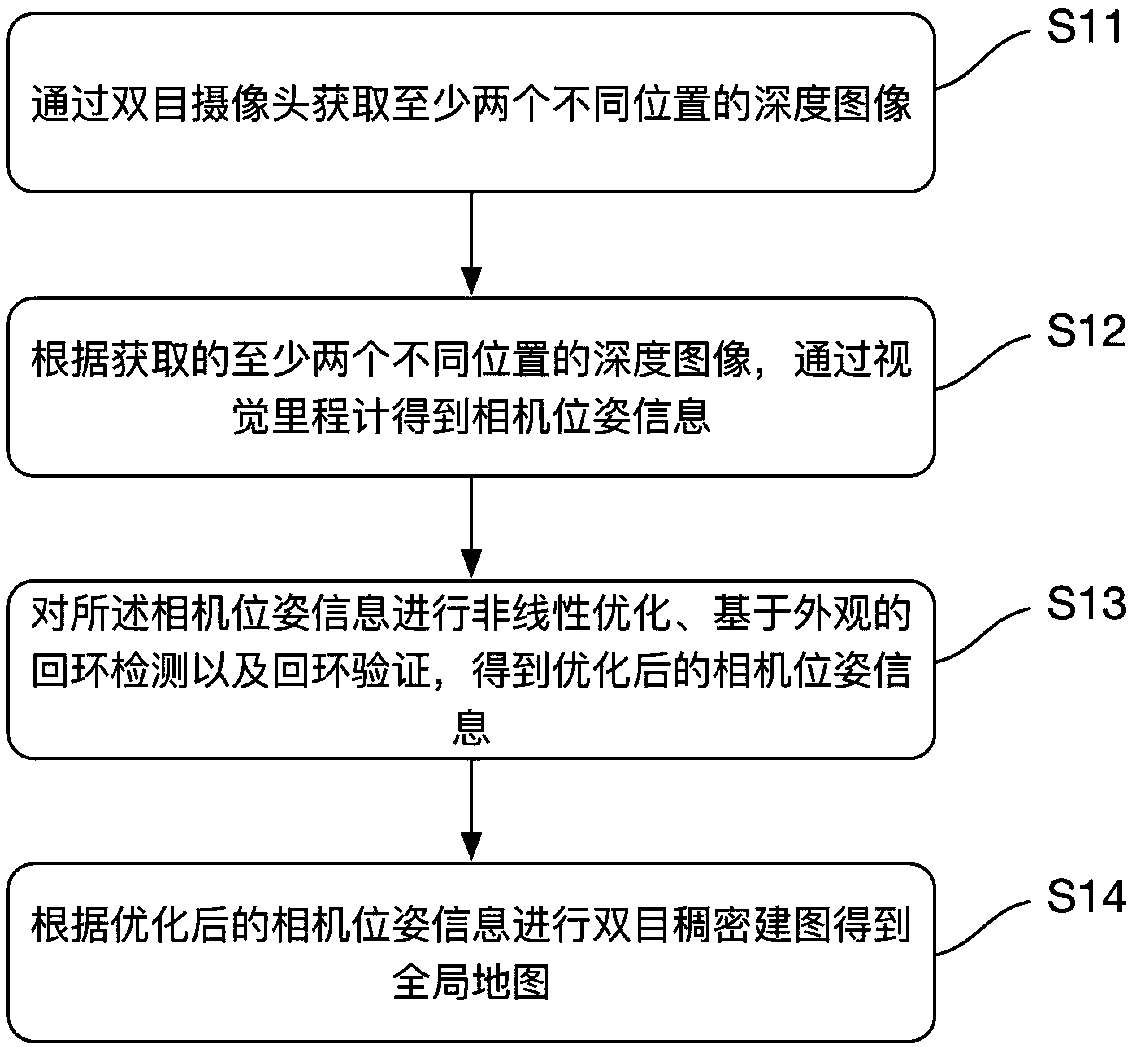
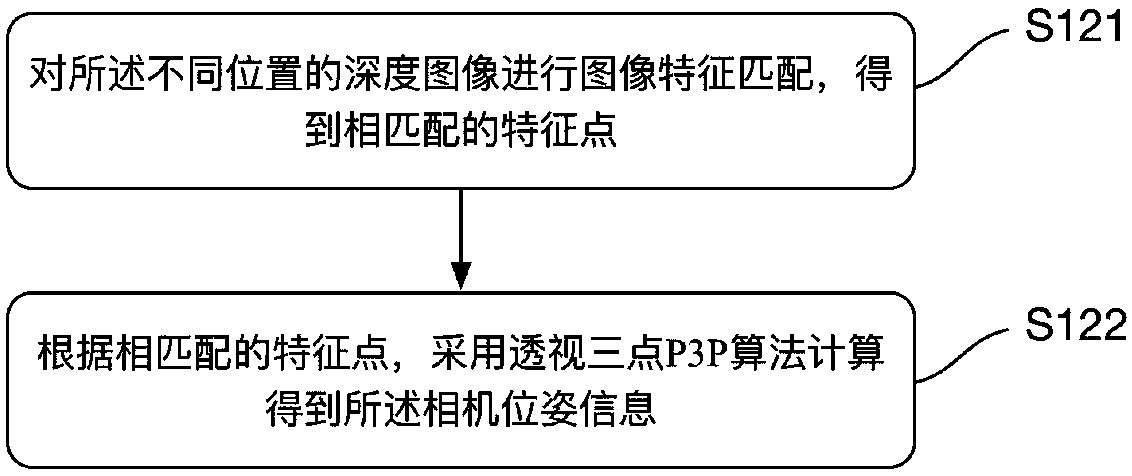
Unmanned-aerial-vehicle visual-SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping) method based on binocular camera, unmanned aerial vehicle and storage medium
ActiveCN107808407AResolve interferencePrecise positioningImage enhancementImage analysisSimultaneous localization and mappingUncrewed vehicle
The invention discloses an unmanned-aerial-vehicle visual-SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping) method based on a binocular camera, an unmanned aerial vehicle and a computer-readable storage medium. The method includes the steps of: acquiring depth images of at least two different locations through the binocular camera; obtaining camera pose information through a visual odometer according to the acquired depth images of the at least two different locations; carrying out nonlinear optimization, appearance-based circle loop detection and circle loop verification on the camera pose information to obtain optimized camera pose information; and carrying out binocular dense mapping according to the optimized camera pose information to obtain a global map. According to the method, the depthimages of the different locations are acquired through the binocular camera, and binocular dense mapping is carried out after use of the visual odometer, nonlinear optimization, circle loop detectionand circle loop verification to obtain the global map; and on the one hand, the interference problem existing with adopting of RGB-D cameras can be solved, and on the other hand, more precise localization can be realized, and the more precise map is established.
Owner:EHANG INTELLIGENT EQUIP GUANGZHOU CO LTD
Method and Apparatus for Generating a Map from Landmarks
InactiveUS20120230550A1Reduce in quantityComparable accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionVehicle position/course/altitude controlPattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)
A method and apparatus for generating a map from landmarks. The method and apparatus may involve the use of a processor circuit. An embodiment may consist of a platform with a processor circuit, and various different sensors for landmark generation that are known to the art such as a plurality of cameras and / or laser rangefinders. Landmarks are stored in a data structure with their past untransformed landmarks. New landmark data is matched using previous stored untransformed landmarks. Generally current position is only used for matching when backtracking or closing the loop. Landmarks are grouped with other landmarks that are visible in the same time interval. In these groups, dynamic landmarks are identified computationally efficiently using binning. Using basis landmarks in a group, a map relative to these basis landmarks is generated that is translation and rotation invariant. These relative maps are linked together to form a global map. Current position is non cumulative and generated by comparing currently observed landmarks to their global positions. The advantages of this method and apparatus is that it is computationally real time, has dynamic landmark detection and has comparable accuracy to other methods known in the art.
Owner:KRAUT JACOB
Route planning method, route planning device and autonomous mobile device
InactiveUS20110166737A1Smooth travelNavigation instrumentsDistance measurementProgram planningEngineering
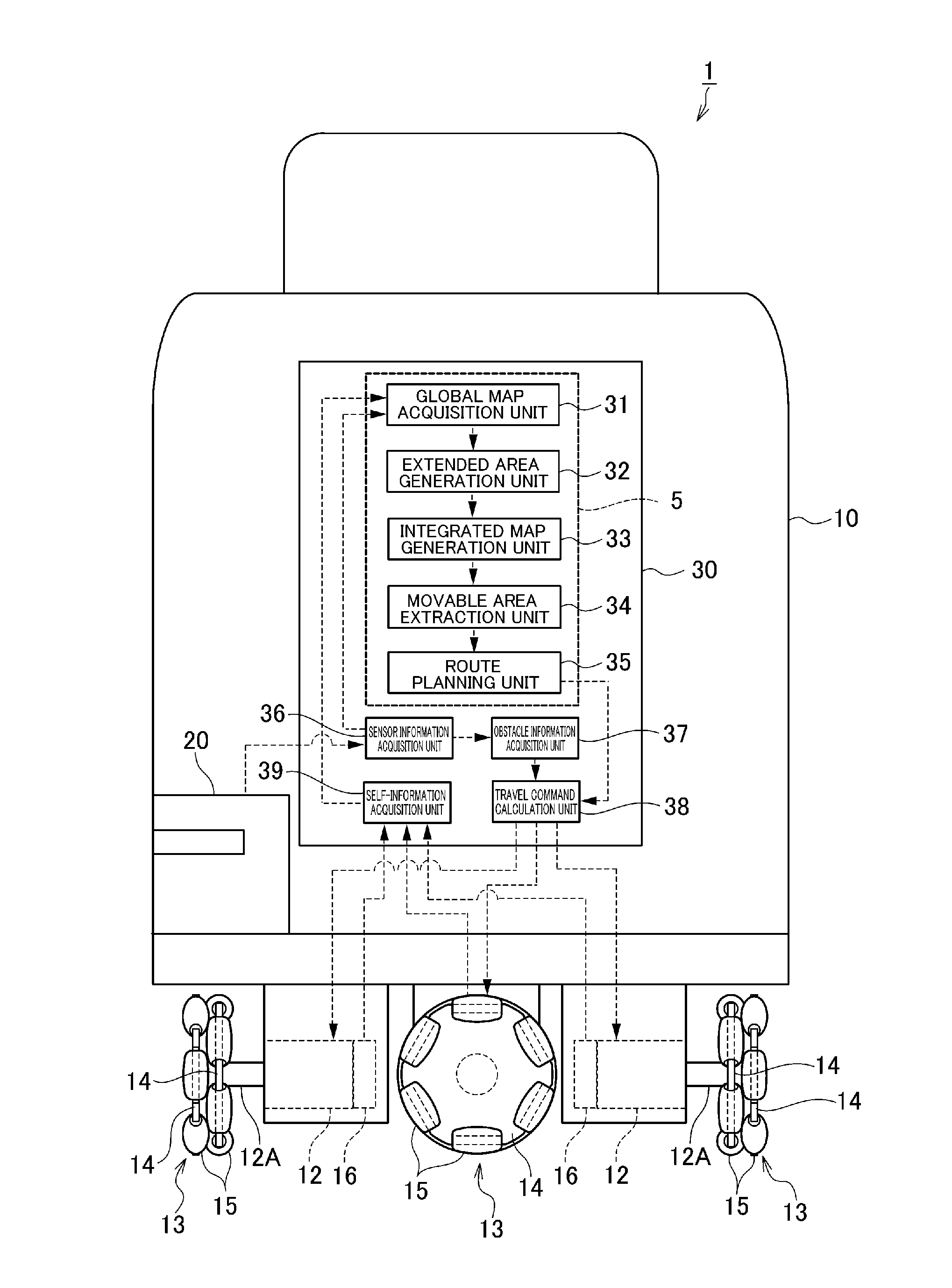
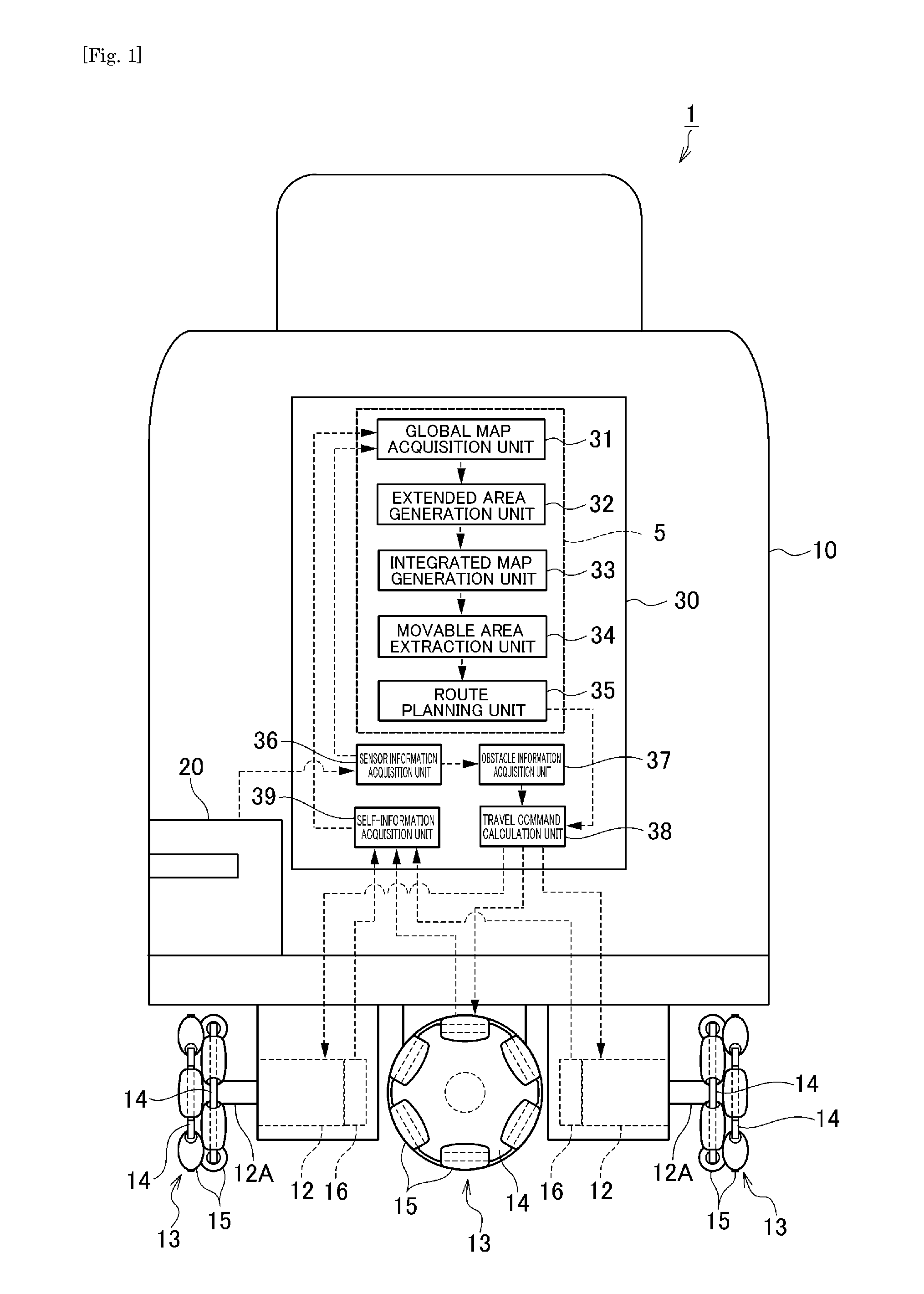
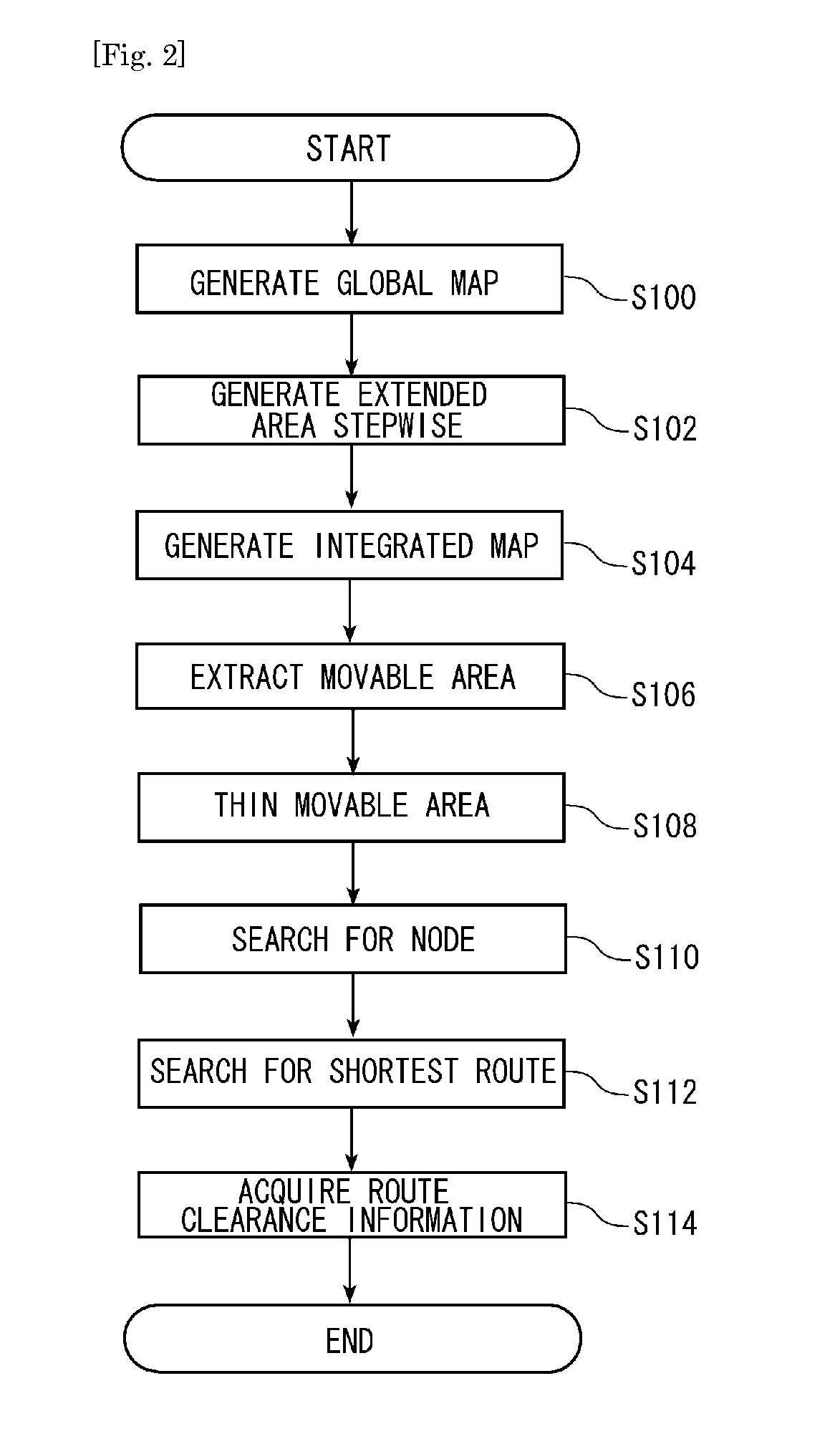
A route planning device that is capable of comprehending, in advance, a route clearance at a pass-through point on a planned travel route, includes a global map acquisition unit arranged to generate a global map showing an obstacle area in which an obstacle exists, an extended area generation unit arranged to generate an extended obstacle area and three extended area by extending stepwise an outline of the obstacle area contained in the global map, an integrated map generation unit arranged to generate an integrated map by superposing for integration of the extended obstacle area with the three extended areas; a movable area extraction unit arranged to extract a movable area from the integrated map and thinning the same, and a route planning unit arranged to acquire a route clearance at a sub goal according to the extended areas on the integrated map to which the sub goal on the travel route belongs, upon planning the travel route from the thinned movable area.
Owner:MURATA MASCH LTD
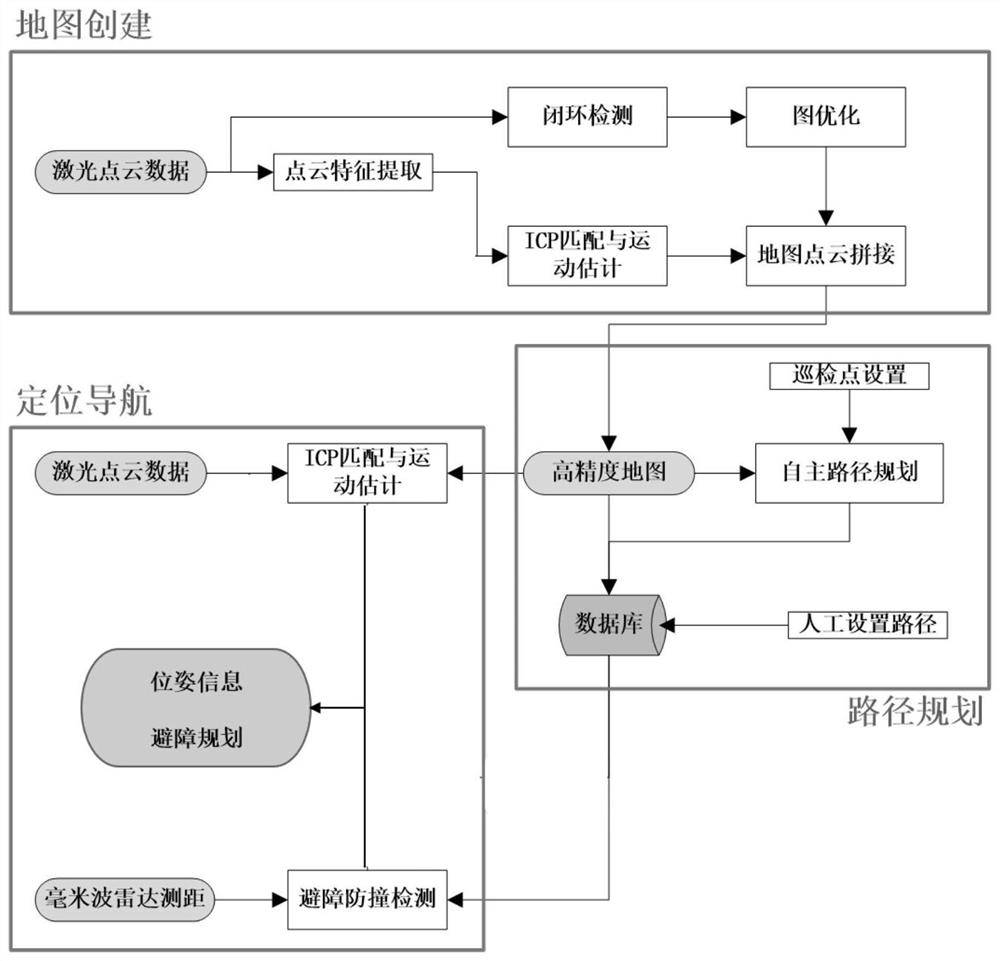
Inspection robot navigation system and method based on RTK Beidou and laser radar
InactiveCN107817509AAddress market constraintsFix security issuesSatellite radio beaconingElectromagnetic wave reradiationCurve fittingRoad surface
The invention relates to an inspection robot navigation system and method based on RTK Beidou and a laser radar. The inspection robot navigation system based on RTK Beidou and laser radar includes a robot movement station and a background management server, wherein the robot movement station includes a robot body, a control module, a positioning navigation module, a wireless communication module and a power supply management module; the control module, the positioning navigation module, the wireless communication module and the power supply management module are arranged on the robot body; thepositioning navigation module includes a laser radar and an RTK / SINS unit; a navigation map employs the design scheme combined with a global map and a local map; the global map construction draws ina mode that the robot records the track, and the navigation mode uses a preview PID algorithm; and the local map construction employs the laser radar to record the obstacle discrete data points and restore the obstacle edge information through the clustering step, the curve fitting step and other steps, and uses the artificial potential field path planning obstacle avoidance mode. Compared with the prior art, the inspection robot navigation system and method based on RTK Beidou and a laser radar have the advantages of being high in navigation positioning precision, having no demand for pavement reconstruction, being high in environment adaptability, and being high in work stability.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIVERSITY OF ELECTRIC POWER
Method and apparatus for sharing map data associated with automated industrial vehicles
ActiveUS8594923B2Instruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlComputer sciencePhysical context
A method and apparatus for sharing map data between industrial vehicles in a physical environment is described. In one embodiments, the method includes processing local map data associated with a plurality of industrial vehicles, wherein the local map data comprises feature information generated by the plurality of industrial vehicles regarding features observed by industrial vehicles in the plurality of vehicles; combining the feature information associated with local map data to generate global map data for the physical environment; and navigating an industrial vehicle of the plurality of industrial vehicles using at least a portion of the global map data.
Owner:CROWN EQUIP CORP
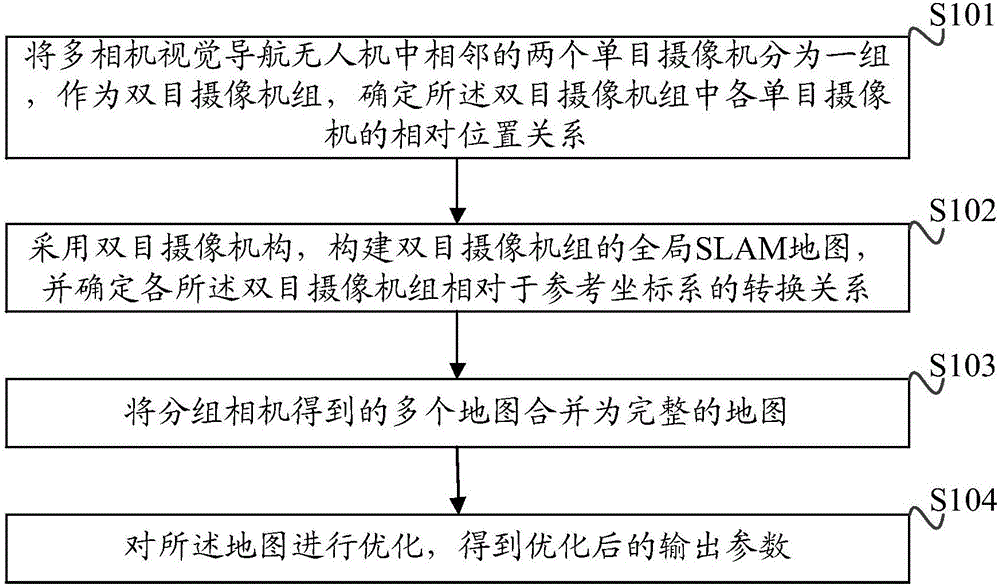
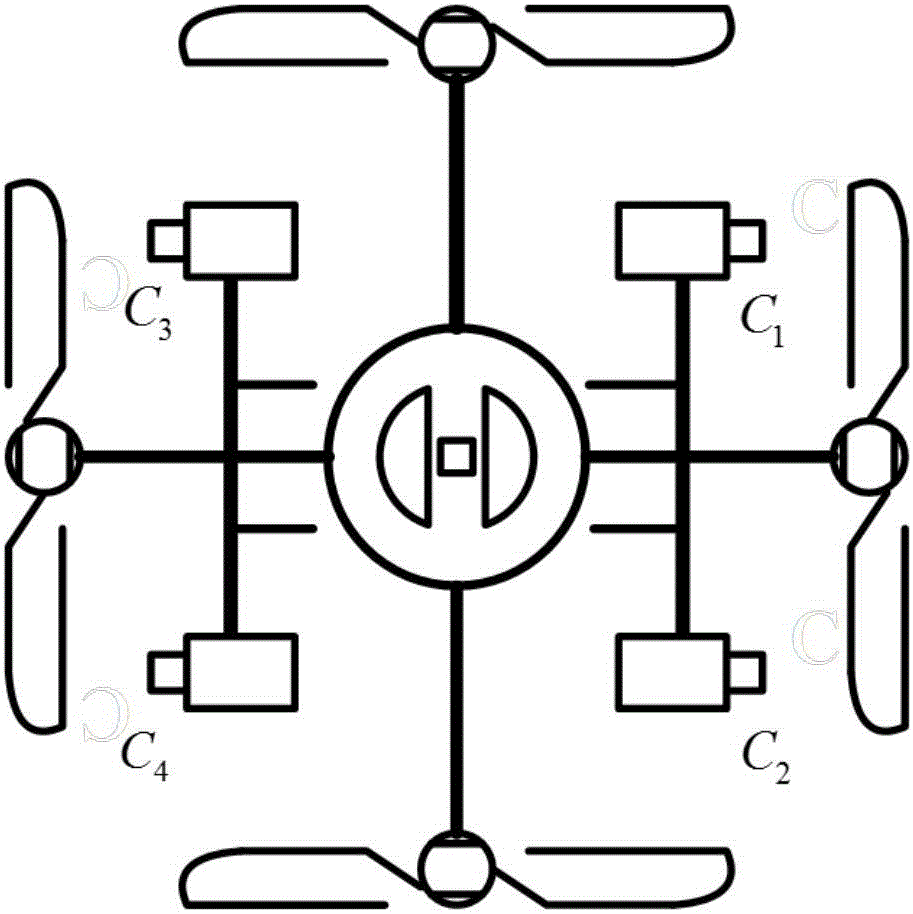
Camera calibration method and device for visual navigation unmanned aerial vehicle
The invention discloses a camera calibration method and device for a visual navigation unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV). The method comprises steps of: grouping two adjacent monocular cameras in a multi-camera visual navigation UAV as a binocular camera group, and determining the relative position relation of respective monocular cameras in the binocular camera group; constructing a global SLAM map of the binocular camera group by using a binocular camera mechanism and determining the conversion relation of each binocular camera group relative to a reference coordinate system; merging maps obtained by the grouped cameras into a complete map; and optimizing the map to obtain an optimized output parameter. The method and the device are simple and easy to implement, and avoid a complex calibration block selection process. A continuous global map established in the calibration process can be used for the visual positioning and navigation of the UAV, reduces algorithm complexity of system real-time computing, and simplifies the operation procedure of a traditional calibration method.
Owner:CHENGDU TOPPLUSVISION TECH CO LTD
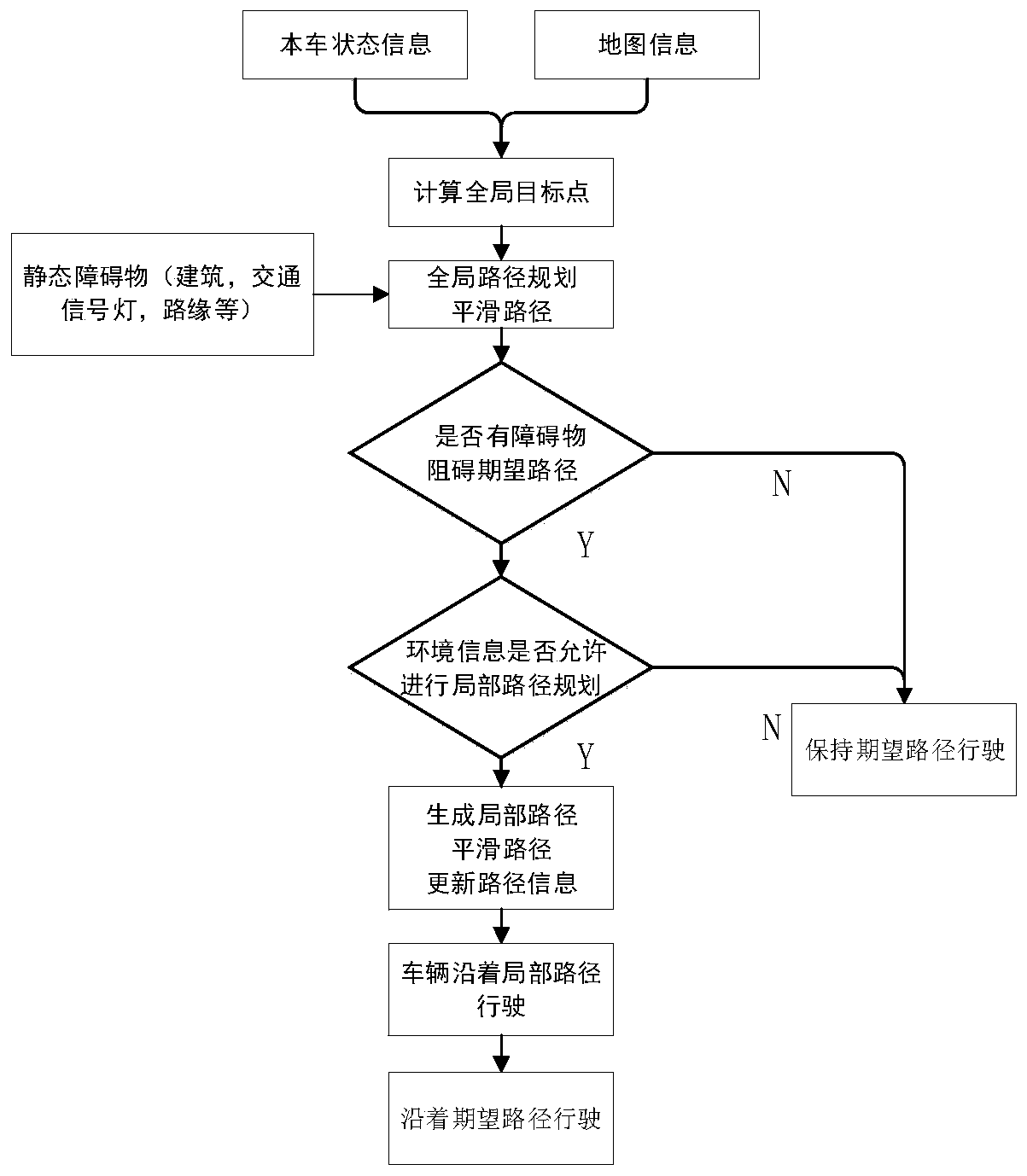
Driverless vehicle path planning method and device
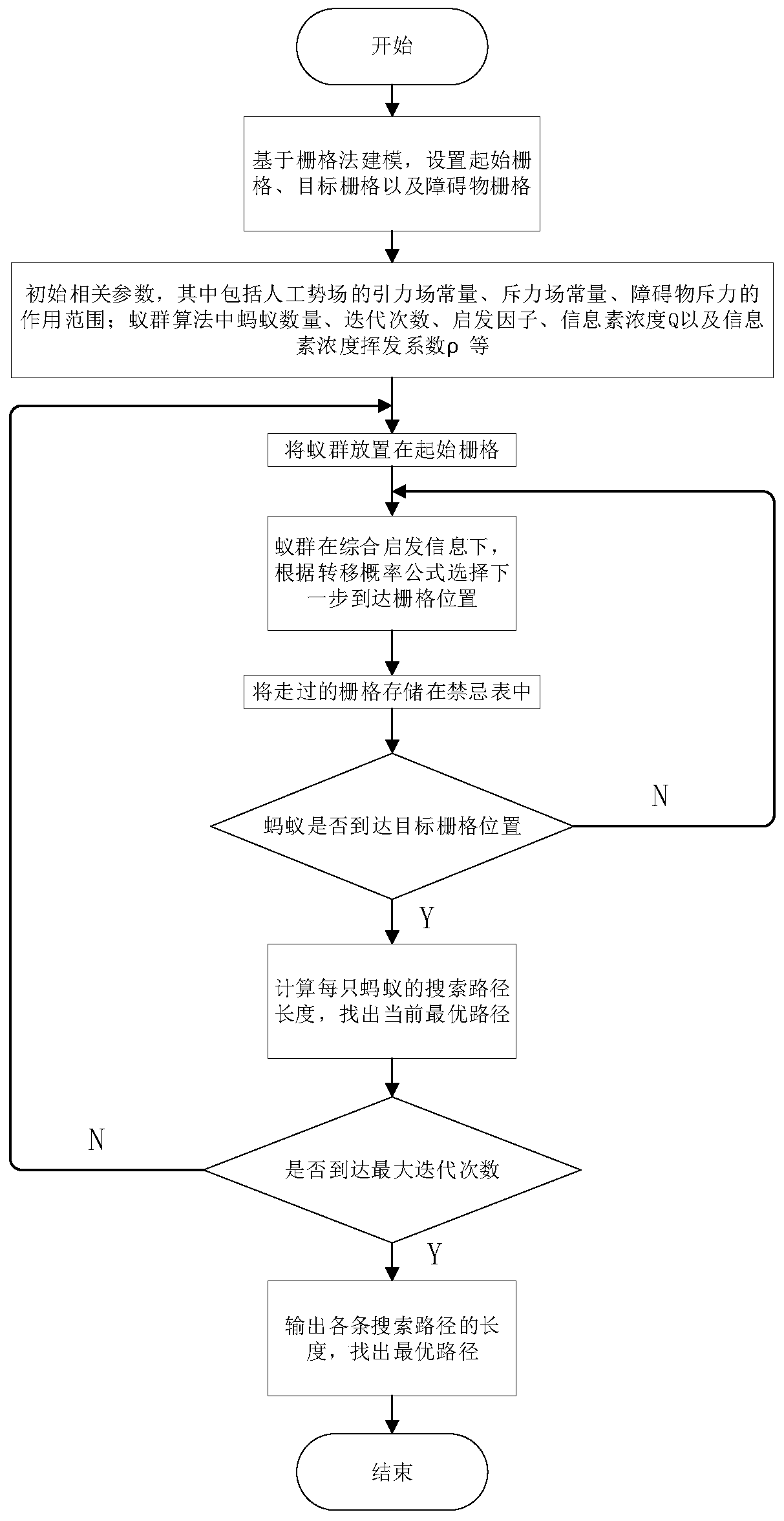
ActiveCN110333714AEfficient and reasonable planningImprove operational efficiencyPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesPotential fieldPlanning approach
The invention discloses a driverless vehicle path planning method and device. The driverless vehicle path planning method comprises the following steps: S1, locating a current vehicle: obtaining the location of the current driverless vehicle as a starting point according to a differential GPS / INS system, then selecting a target point, loading the data of a global map, and reading the vehicle status information; S2, planning a global path: establishing a global raster map according to the coordinate information of the starting point and the target point, using a modified artificial potential field-ant colony algorithm to plan the global path, and generating a desired path; S3, driving and analyzing the current road condition by the vehicle, and analyzing and judging whether local path planning is needed or not according to the obtained sensor information; S4, selecting a local path planning strategy; and S5, sending the generated path information to a vehicle control layer. The invention improves the running efficiency of the program; and the vehicle can efficiently and reasonably plan a safe path in a complex and varied environment; therefore, the global optimality and local real-time performance of the path planning are ensured.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
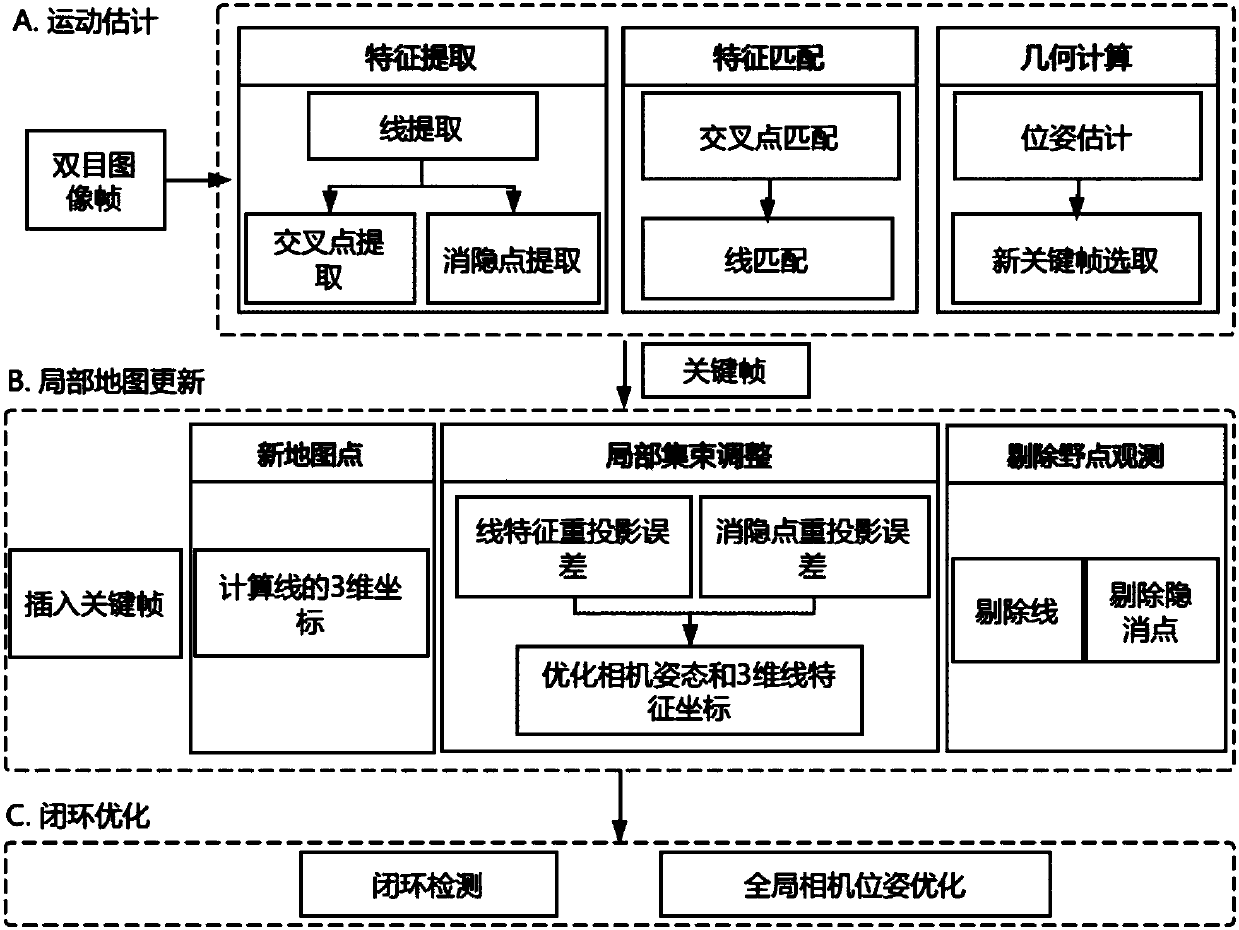
Robot synchronous positioning and map construction method and system
The invention discloses a robot synchronous positioning and map construction method based on line segment features and line segment vanishing points, and the robot synchronous positioning and map construction method is applied to the positioning and map construction of a robot in an unknown environment. The robot synchronous positioning and map construction method comprises the steps of: extracting line segment features, intersection points and vanishing points from images, establishing line segment matching between the images according to the intersection points, estimating camera poses according to line segment matching results, and selecting a new keyframe; and inserting the keyframe into a map, calculating three-dimensional coordinates of the newly-added line segment features, performing cluster adjustment on local map, and removing outlier observation; and performing closed-loop detection and global map optimization based on the intersection points. The invention further discloses a synchronous positioning and map construction system. The robot synchronous positioning and map construction method and the robot synchronous positioning and map construction system can be appliedto the positioning and map construction of the robot in the unknown environment, and is particularly suitable for structured or semi-structured scenes, such as indoor environments, outdoor environments with buildings, and the like.
Owner:上海阅面网络科技有限公司
Deep network-based multi-strategy global crowd analysis method
InactiveCN108717528AImprove robustnessRealize linkage monitoringCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesImaging FeaturePerspective transformation
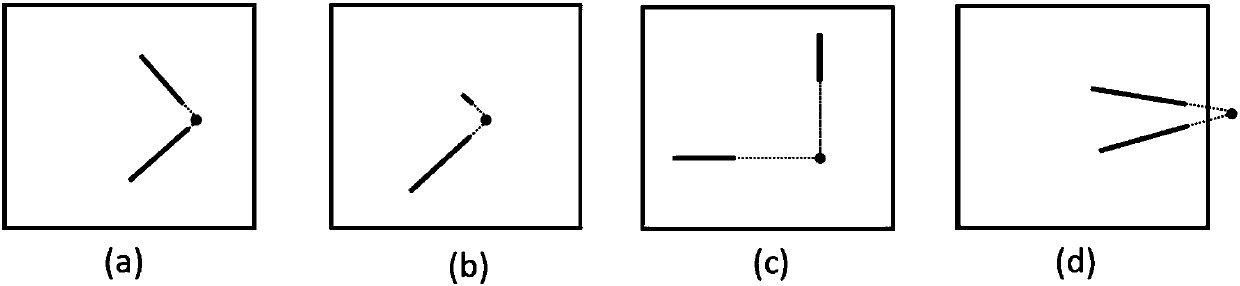
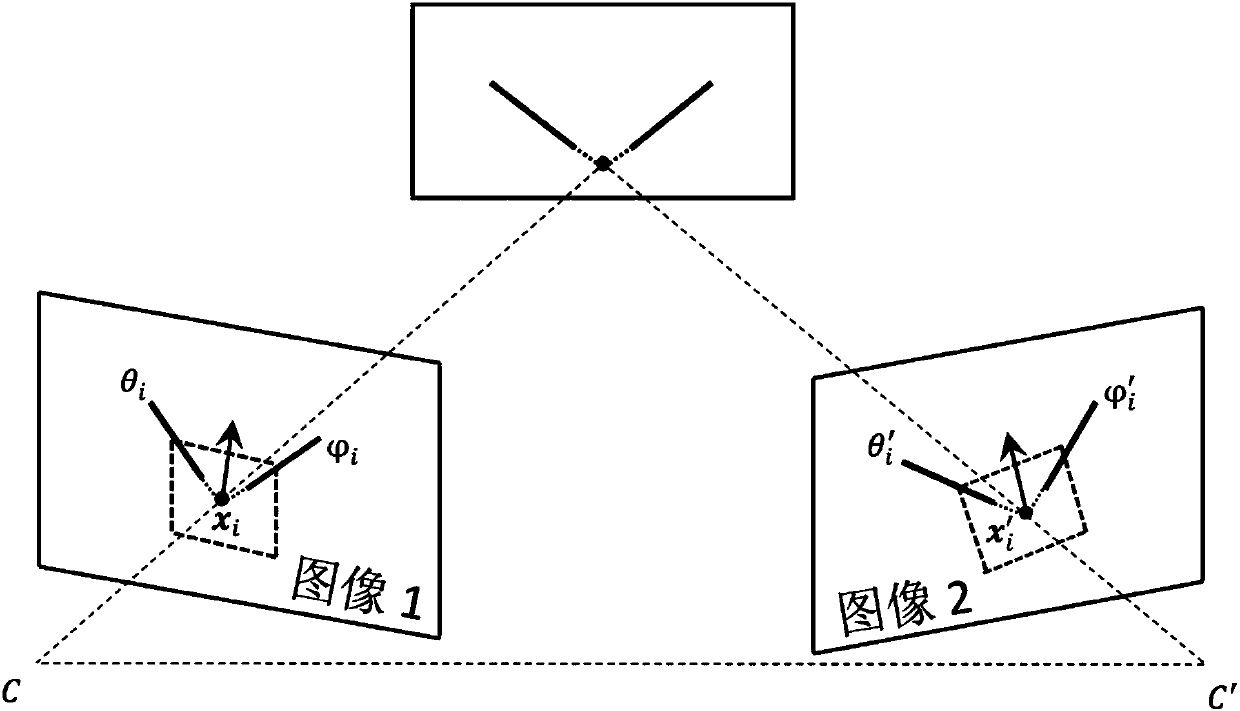
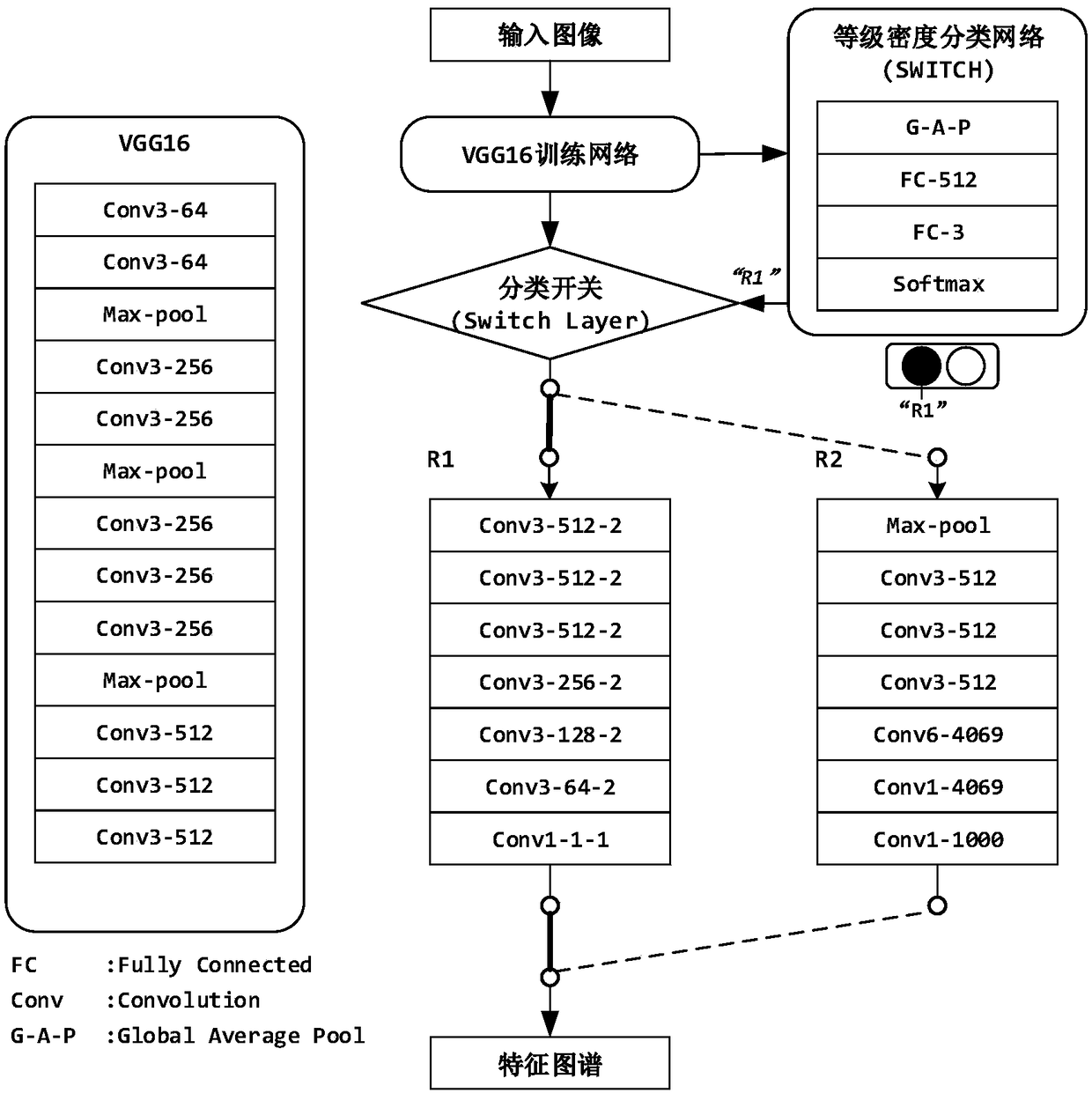
The invention provides a deep network-based multi-strategy global crowd analysis method. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, monitor area modeling: drawing a global map schematic diagram, establishing a layer for a direction and a range corresponding to a global map in a camera monitor area, and waiting for import of crowd density data; secondly, for a monitor scene of each camera, obtaining a space visual angle mapping graph of a displayed monitor image through perspective transformation, namely, overlook visual angle mapping from side-looking visual angle of the camera to the ground; obtaining image features through a VGG16 transfer learning method, mapping pre-blocks input into the images to a feature layer through strides, carrying out SWITCH judgement on the image features of each block, and selecting to carry out density estimation or pedestrian detection operation on the image through an R1 density estimation network of an R2 pedestrian detection network; and integrating the pedestrian detection or density estimation result of each block to form a density map, and mapping the estimated density map onto the layer through perspective transformation so as to conveniently carry out accurate supervision on the global crowd condition.
Owner:苏州平江历史街区保护整治有限责任公司
Landslide emergency treatment engineering exploration design method based on remote sensing assistance of small unmanned aerial vehicle
InactiveCN105444740AIncrease performanceReduce on-site work timePhotogrammetry/videogrammetryGeological investigationEngineering
The invention relates to a landslide emergency treatment engineering exploration design method based on remote sensing assistance of a small unmanned aerial vehicle. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: rapidly acquiring a high-definition picture of a landslide engineering region in field by using a small unmanned aerial vehicle remote sensing system; generating an orthophoto remote sensing result of the landslide engineering region through digital photogrammetry software processing; making a large-scale line global map by using the orthophoto remote sensing result; carrying out indoor visual auxiliary engineering geological investigation based on an orthophoto and a three-dimensional model; programming a visual conventional engineering geological map according to an on-site engineering geological investigation result; carrying out an auxiliary treatment engineering design based on the visual engineering geological map; programming a visual and conventional landslide emergency treatment engineering design plane map.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
Visual SLAM method based on multi-feature fusion
InactiveCN110060277AHigh precisionReal-time useImage enhancementImage analysisSimultaneous localization and mappingError function
The invention discloses a visual SLAM method based on multi-feature fusion, and relates to the field of robot visual positioning and mapping. The invention discloses a multi-feature fusion vision SLAM(simultaneous localization and mapping) method based on a depth camera, which solves the vision positioning problem under the condition that pure point features fail by fully using point-line features extracted from an image and constructing plane features according to the point-line features. A self-adaptive threshold method is adopted to extract point features, so that more uniform point features can be obtained; line features are extracted, short and small line segments are deleted, and the segmented line segments are combined to improve the accuracy of line feature matching; wherein the point-line features are used for estimating the inter-frame pose and constructing a local map; a surface feature is calculated by adopting a minimum parameter method to reduce the calculated amount; the point, line and plane features are tightly coupled by constructing a back projection error function of the fusion features, and a global map is constructed to carry out global pose optimization. Thevisual SLAM method is high in precision, good in real-time performance and high in robustness, and the problem that the visual SLAM precision is reduced or even a system fails in a low-texture environment based on a feature point method is solved.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
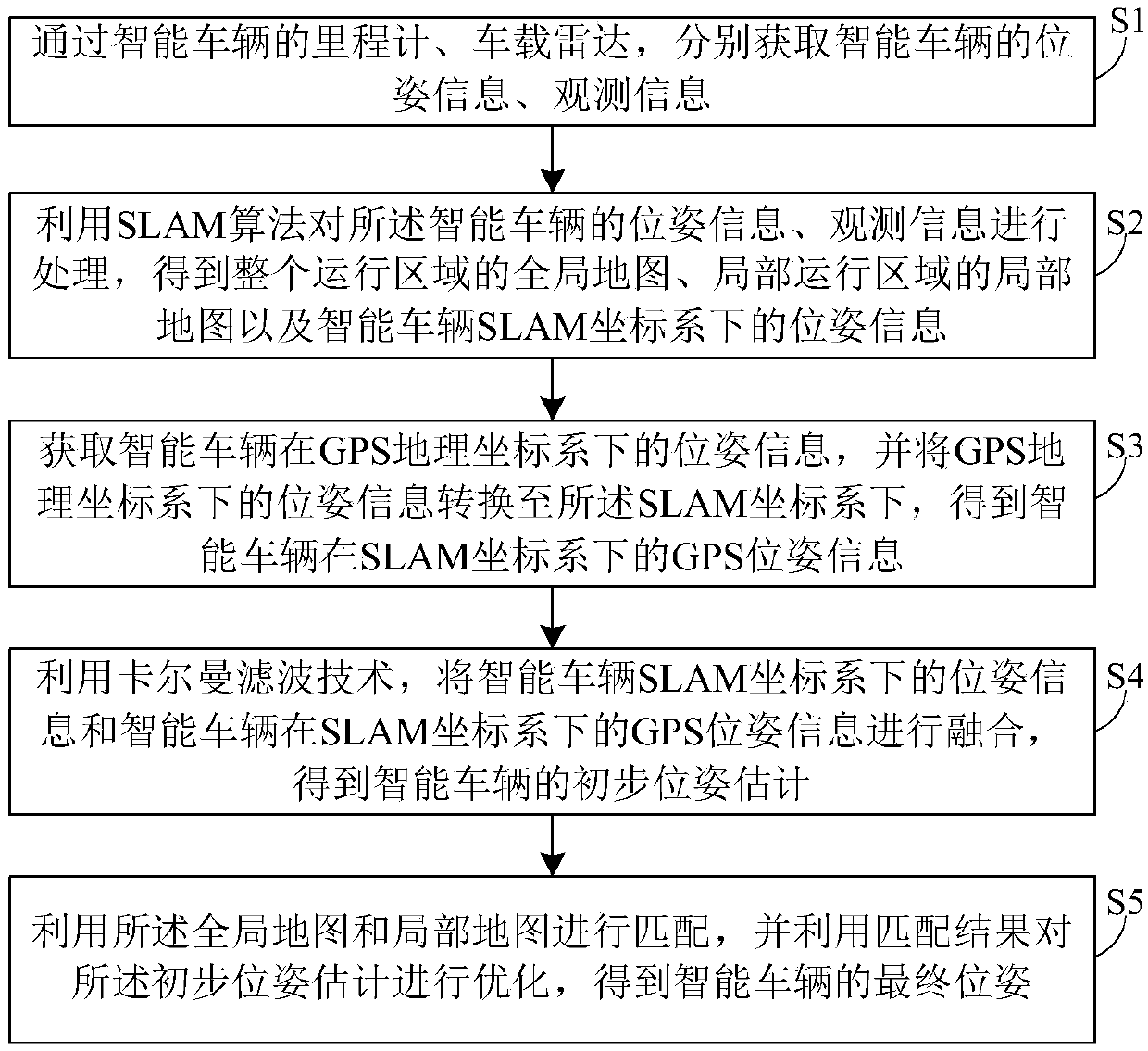
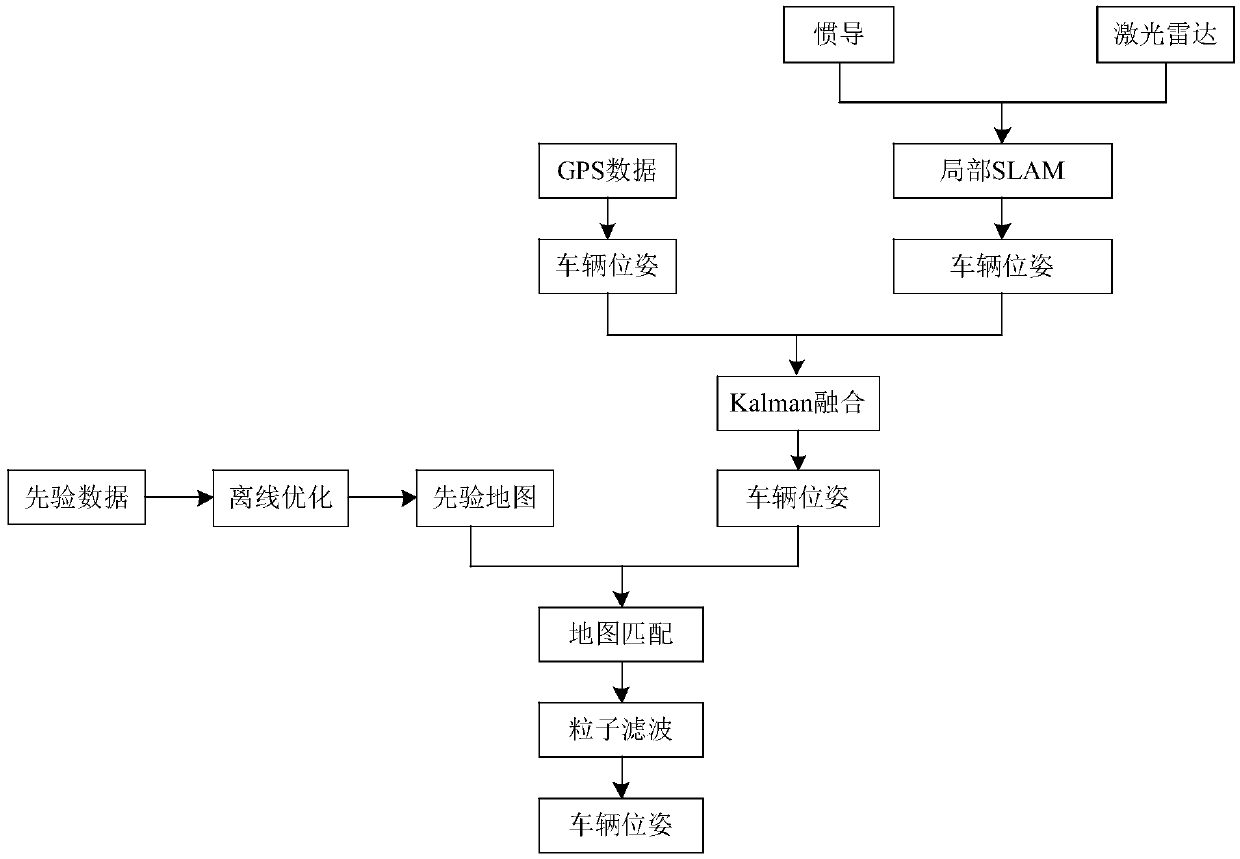
Intelligent vehicle location method based on prior map
ActiveCN108759833AThe solution accuracy is not highAccurate global map informationNavigational calculation instrumentsSatellite radio beaconingRadarLocal map
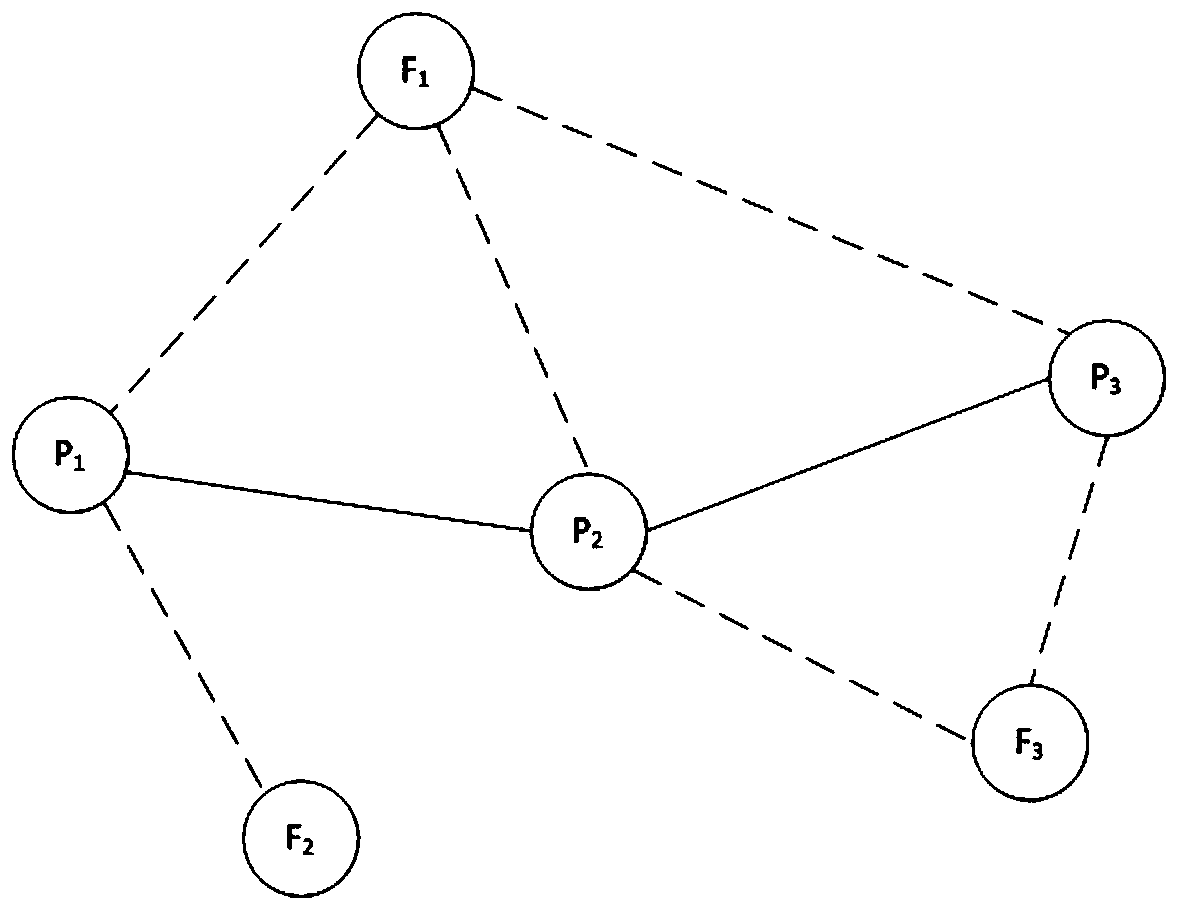
The invention discloses an intelligent vehicle location method based on prior map, including the following steps: 1) by means of an odometer and a vehicle-mounted radar on the intelligent vehicle, respectively acquiring pose information and observation information of the intelligent vehicle; 2) by means of SLAM algorithm, processing the pose information and observation information of the intelligent vehicle to obtain a global map of the whole driving area, a local map of a local driving area, and pose information of the intelligent vehicle under a SLAM coordinate system; 3) acquiring GPS poseinformation of the intelligent vehicle and converting the GPS pose information into the SLAM coordinate system to obtain the GPS pose information of the intelligent vehicle in the SLAM coordinate system; 4) fusing the pose information and the GPS pose information in the SLAM coordinate system through Kalman filtering to obtain initial pose estimation of the intelligent vehicle; 5) matching the global map and the local map, and optimizing the initial pose estimation on the basis of the matched result, thus obtaining final pose of the intelligent vehicle. The method greatly improves precise andaccuracy of a location result of the intelligent vehicle.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Intelligent luggage car
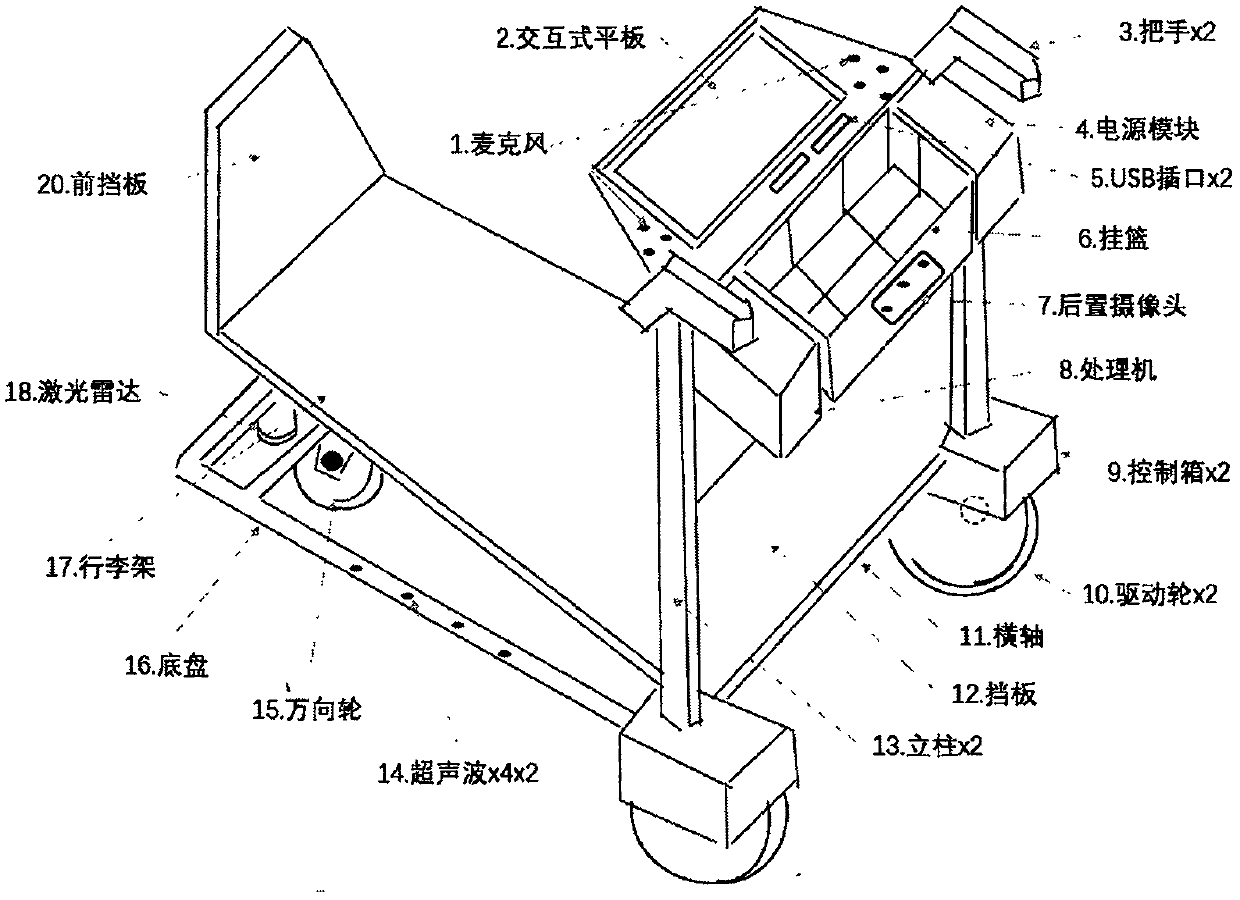
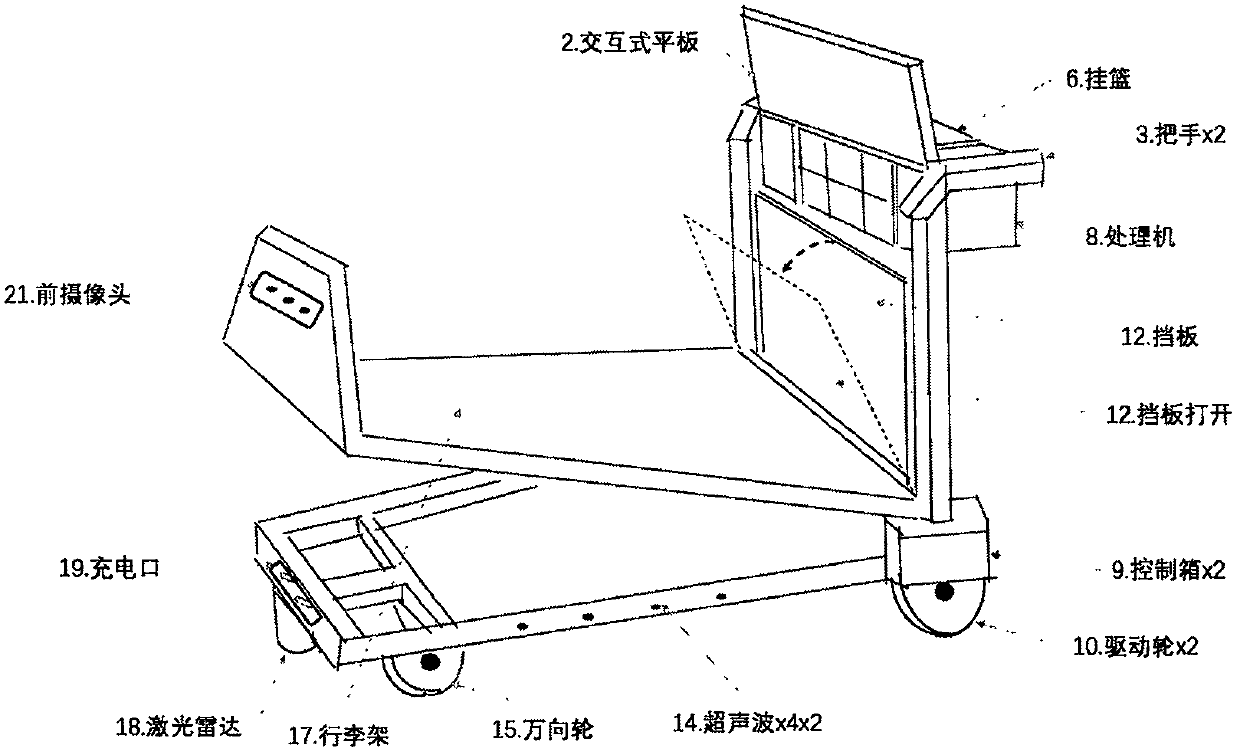
ActiveCN109703607AEasy to useAvoid hittingBatteries circuit arrangementsApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingParking areaRadar
The invention relates to an airport intelligent luggage car or a high-speed railway station luggage car, which belongs to the field of airport, high-speed railway station, shopping mall conveying, orfiled of unmanned conveying of materials in hospitals or factories. The conventional system cannot deal with the situation that flow density is quite large in dynamic environment. Compared with the conventional system, the invention has the following innovations in aspects that multisensor fusion identification of pedestrians and moving targets and location and localization and mapping: 1) a global map is formed through the collaboration of each car, and updating and refining are conducted based on the local environment information uploaded by each car in real time; 2) multiple sensors, a laser radar, vision, a mile meter, an inertial measuring unit (IMU)) are fused, greatly improving positioning precision; 3) the vision and the laser radar are fused, rapidly and effectively identifying pedestrians and moving targets; 4) automatic charging and self-returning are conducted, saving a large amount of labor; 5) the car can be parked in a parking area in an inserting manner, saving parkingspace and achieving good order. The whole system is strong in practicality and easy to be implemented.
Owner:北京眸视科技有限公司
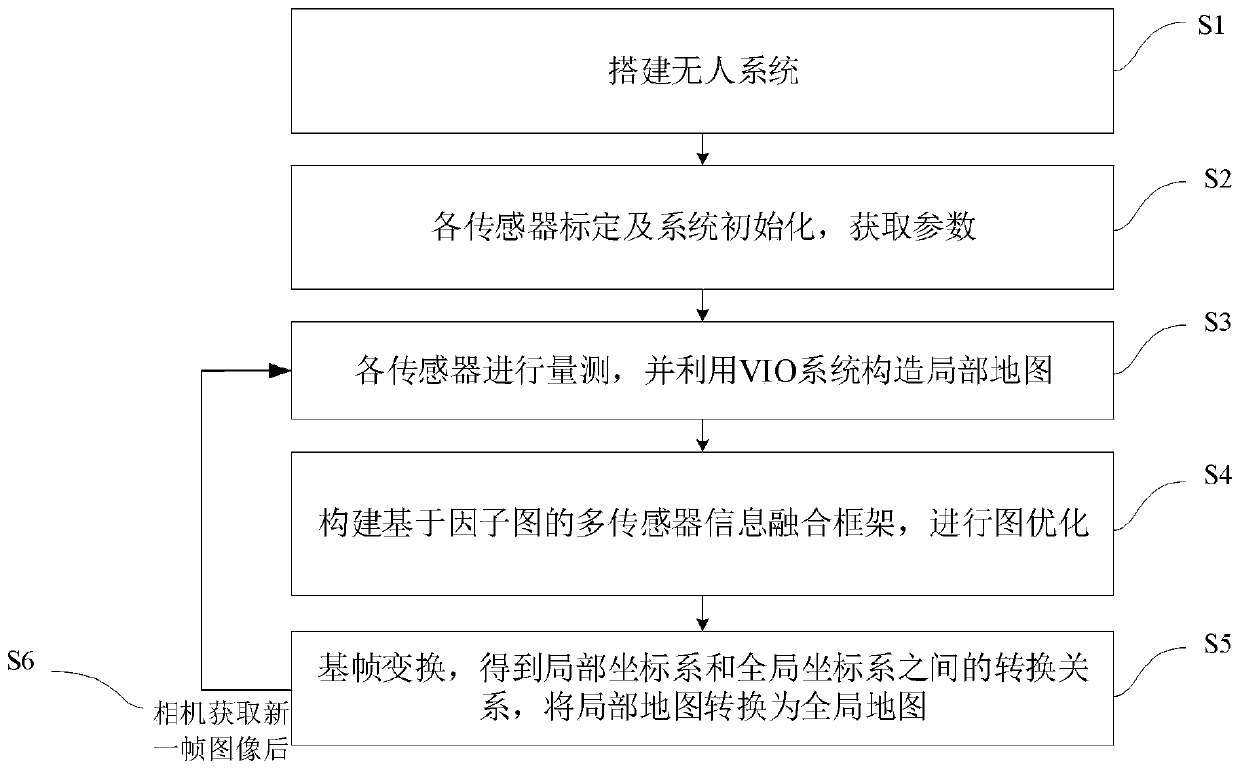
Whole-course pose estimation method based on global map and multi-sensor information fusion
ActiveCN110706279AAccurate pose estimation throughout the processHigh precisionImage analysisUncrewed vehicleOdometer
The invention provides a whole-course pose estimation method based on global map and multi-sensor information fusion, and relates to the field of navigation. The method comprises: firstly, building anunmanned aerial vehicle system comprising sensors; calibrating the sensors to obtain corresponding parameters of each sensor, and initializing an unmanned aerial vehicle system; acquiring measurementinformation of the current pose of the carrier unmanned aerial vehicle by utilizing each sensor, and constructing and maintaining a local map by utilizing image information of a visual inertia odometer VIO system; and constructing a factor graph-based multi-sensor information fusion framework, optimizing by utilizing the factor graph to obtain an optimal state variable of each current frame of the VIO system corresponding to the unmanned aerial vehicle system, updating a conversion relationship between a local coordinate system and a global coordinate system under the current frame, and converting a local map into a global map. Measurement of all sensors carried by the unmanned aerial vehicle and global map information can be fused by using a global optimization mode so that accuracy andreliability of pose estimation of the unmanned aerial vehicle system can be enhanced.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
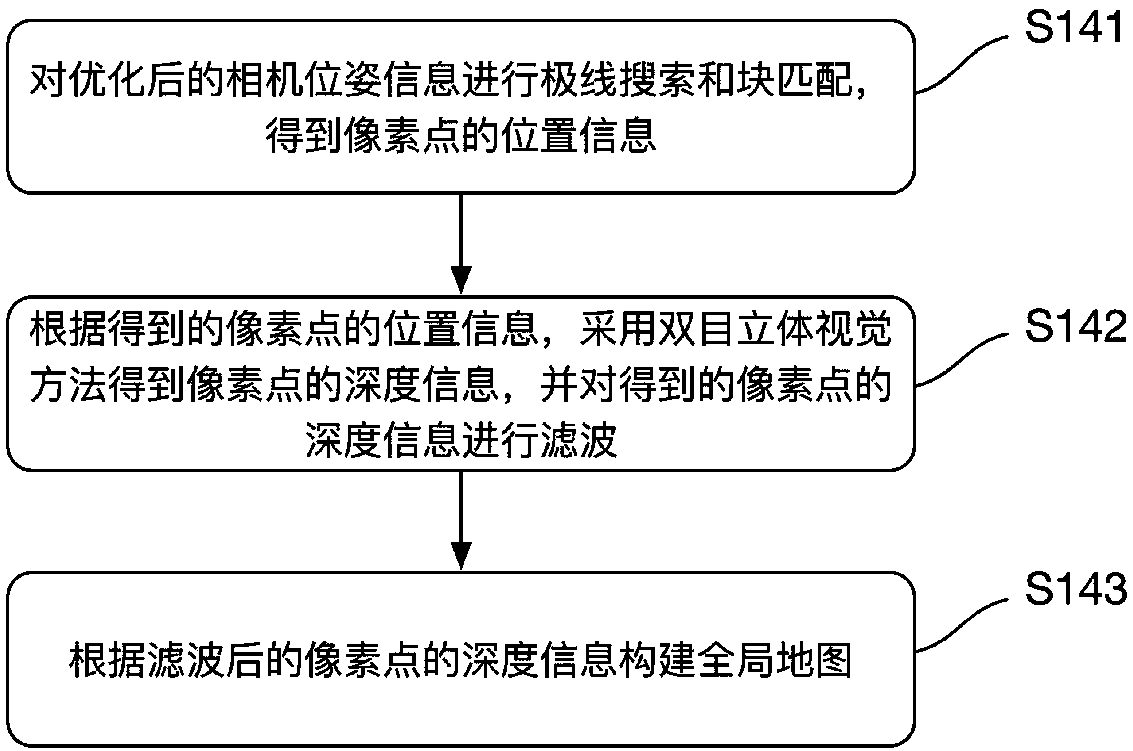
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com