Patents
Literature
8619 results about "Laser scanning" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In modern surveying, the general meaning of laser scanning is the controlled deflection of laser beams, visible or invisible. Within the field of 3D object scanning, laser scanning (also known as lidar) combines controlled steering of laser beams with a laser rangefinder. By taking a distance measurement at every direction the scanner rapidly captures the surface shape of objects, buildings and landscapes. Construction of a full 3D model involves combining multiple surface models obtained from different viewing angles, or the admixing of other known constraints. Small objects can be placed on a revolving pedestal, in a technique akin to photogrammetry.
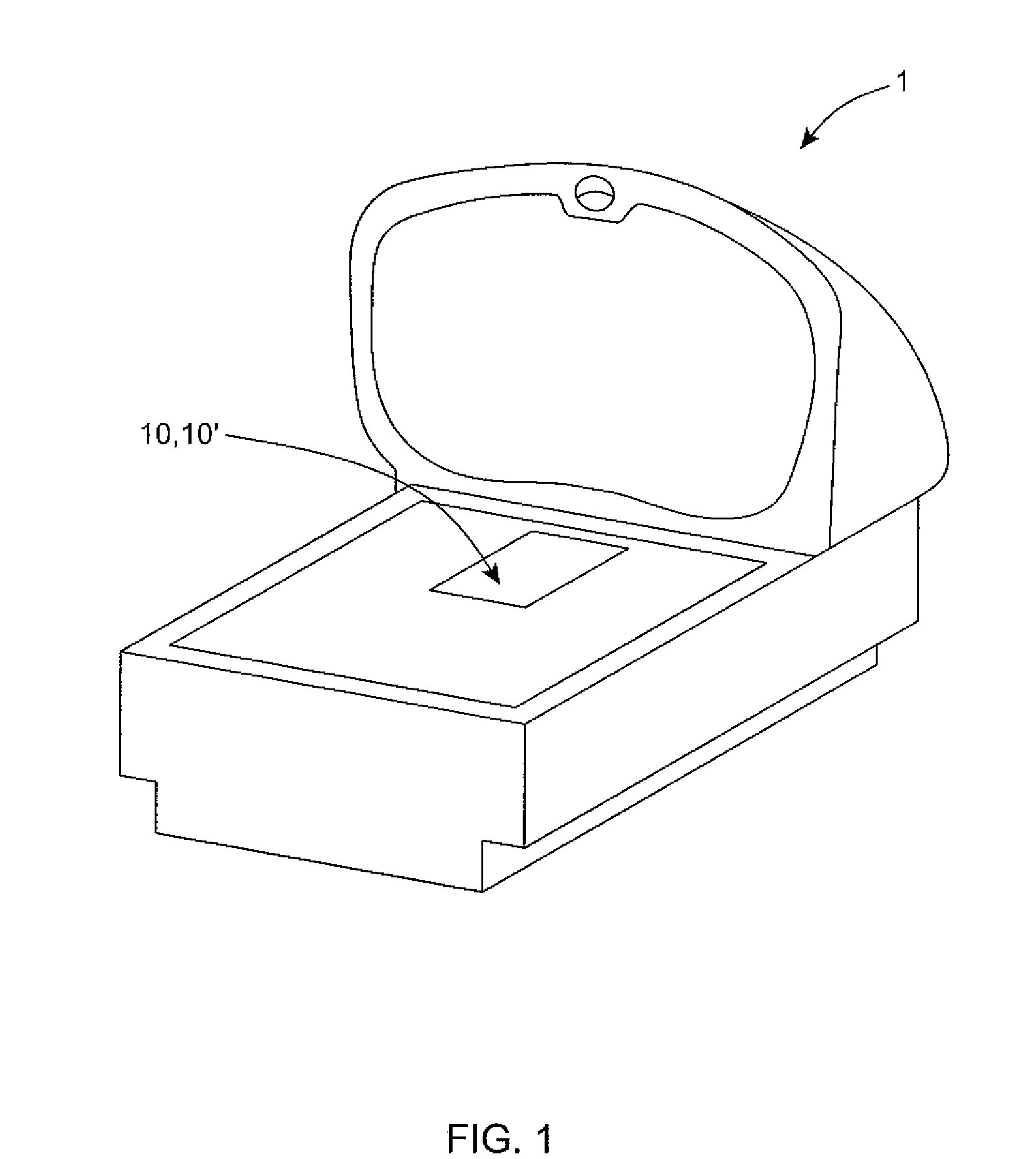
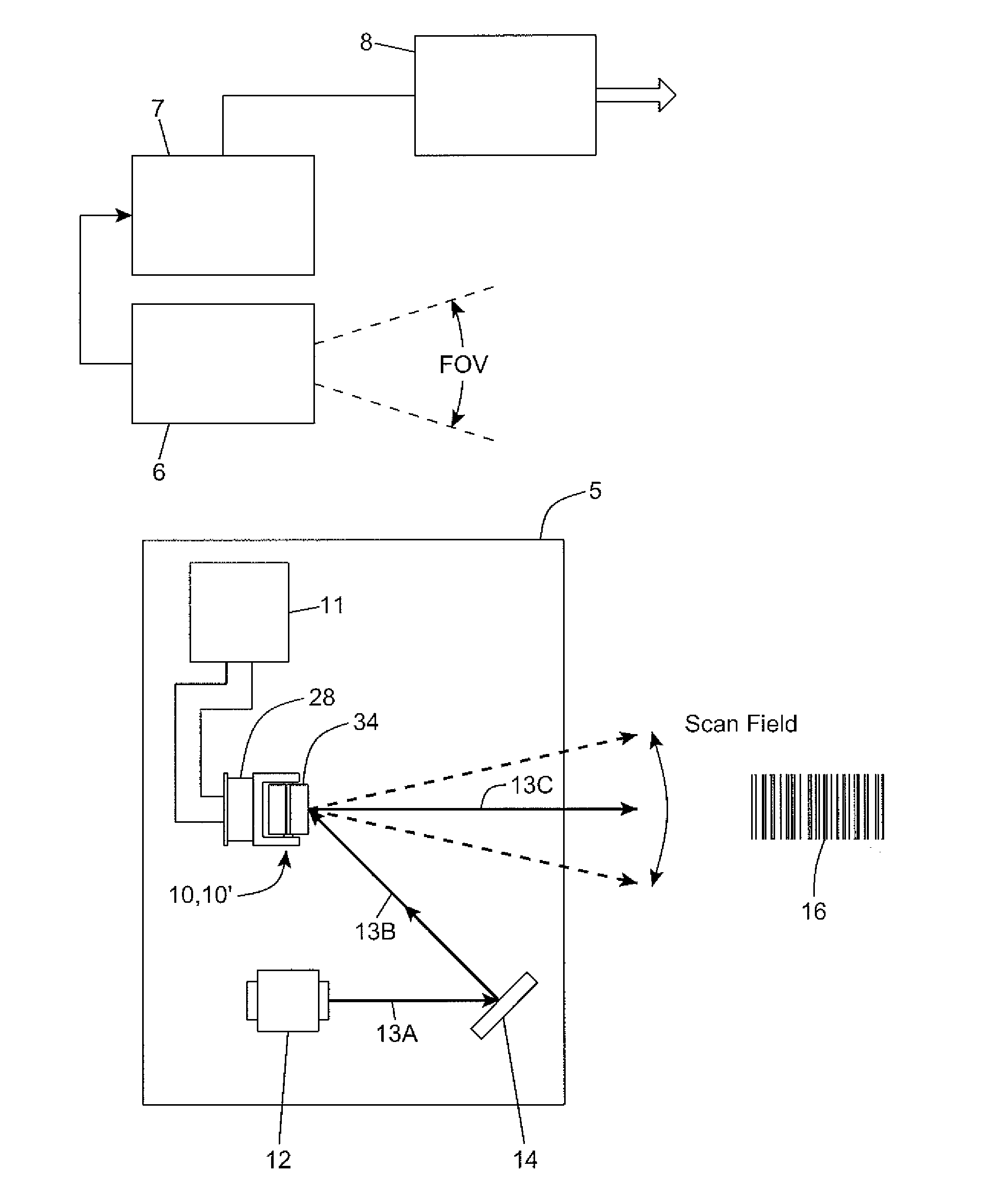
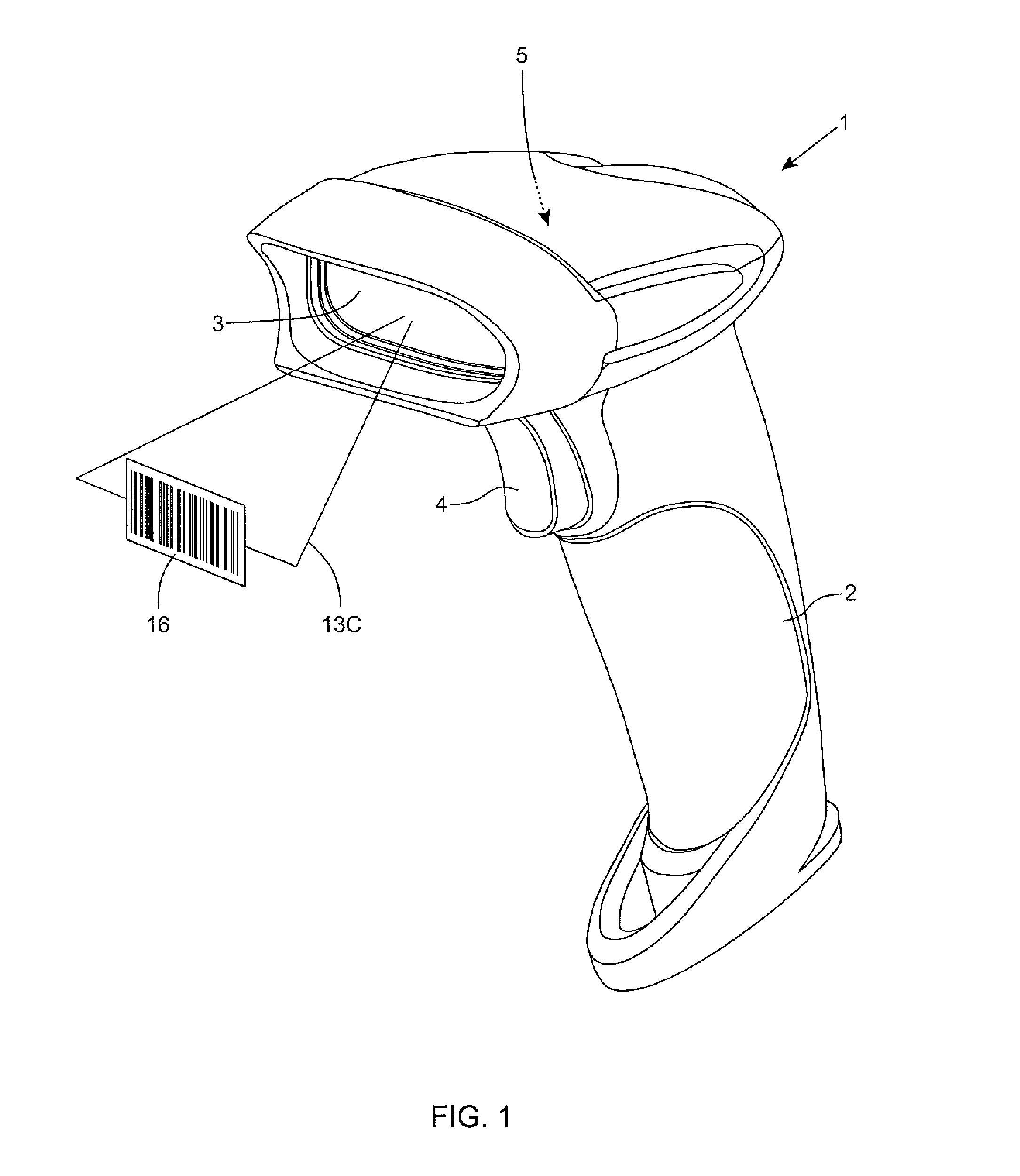
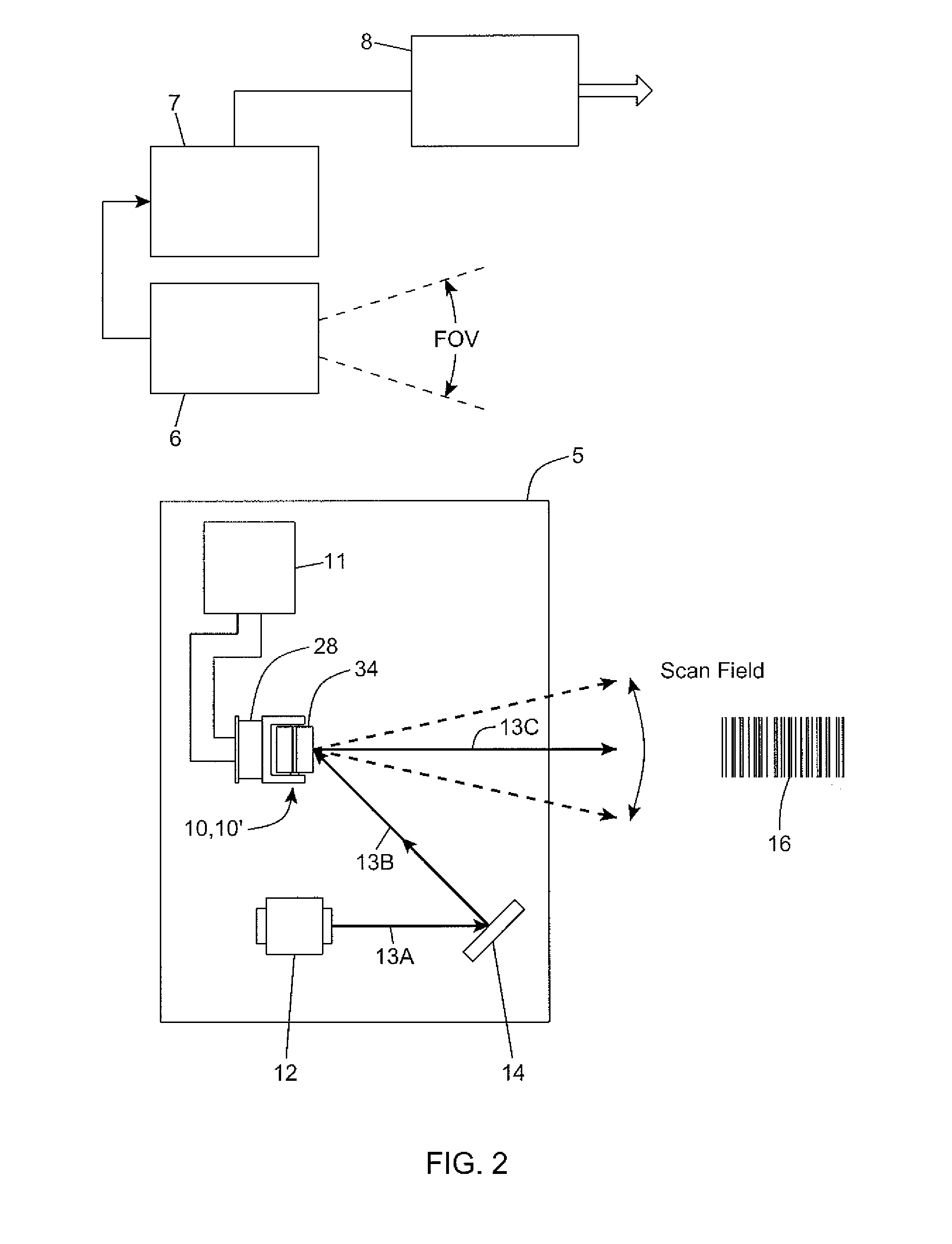
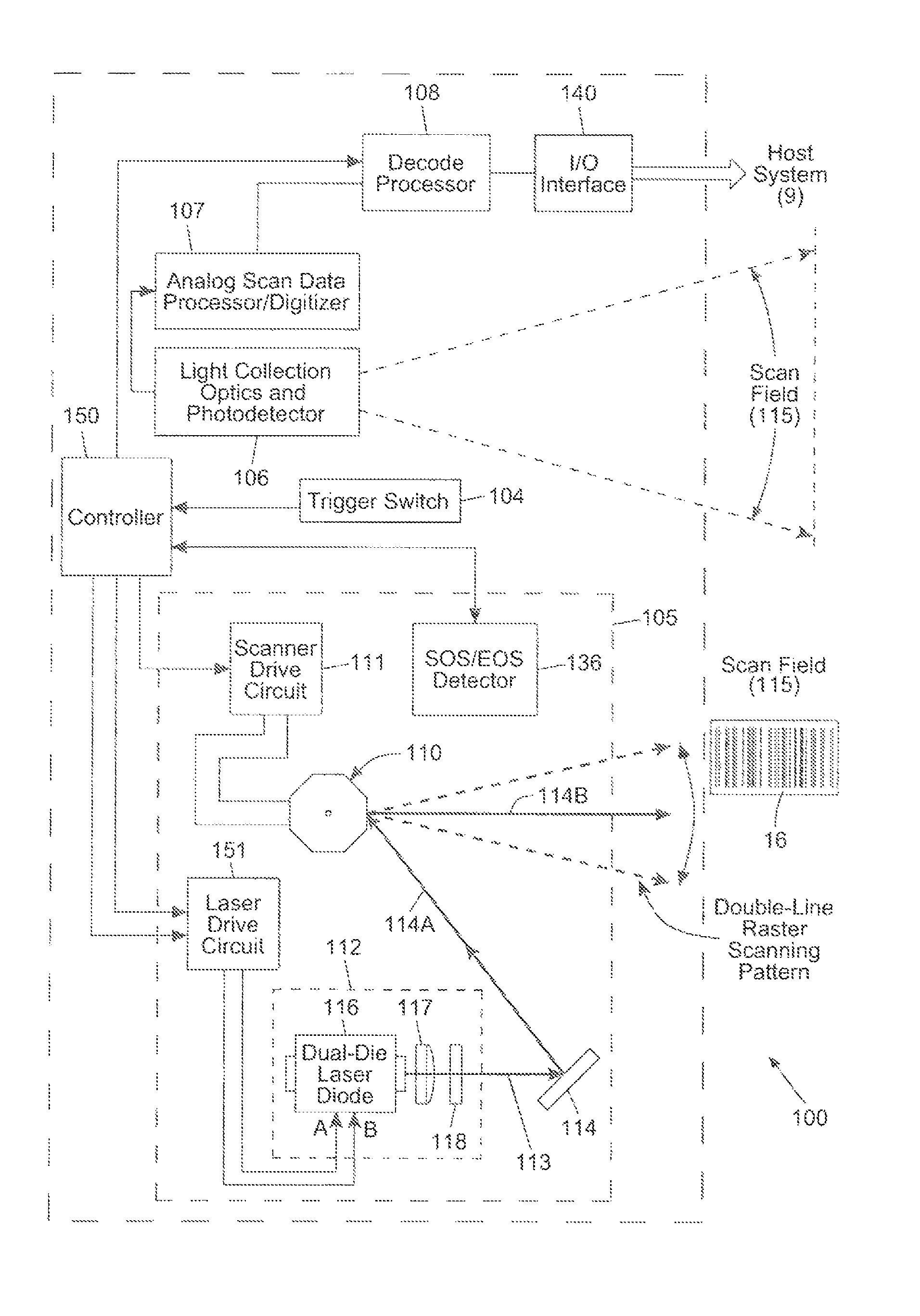
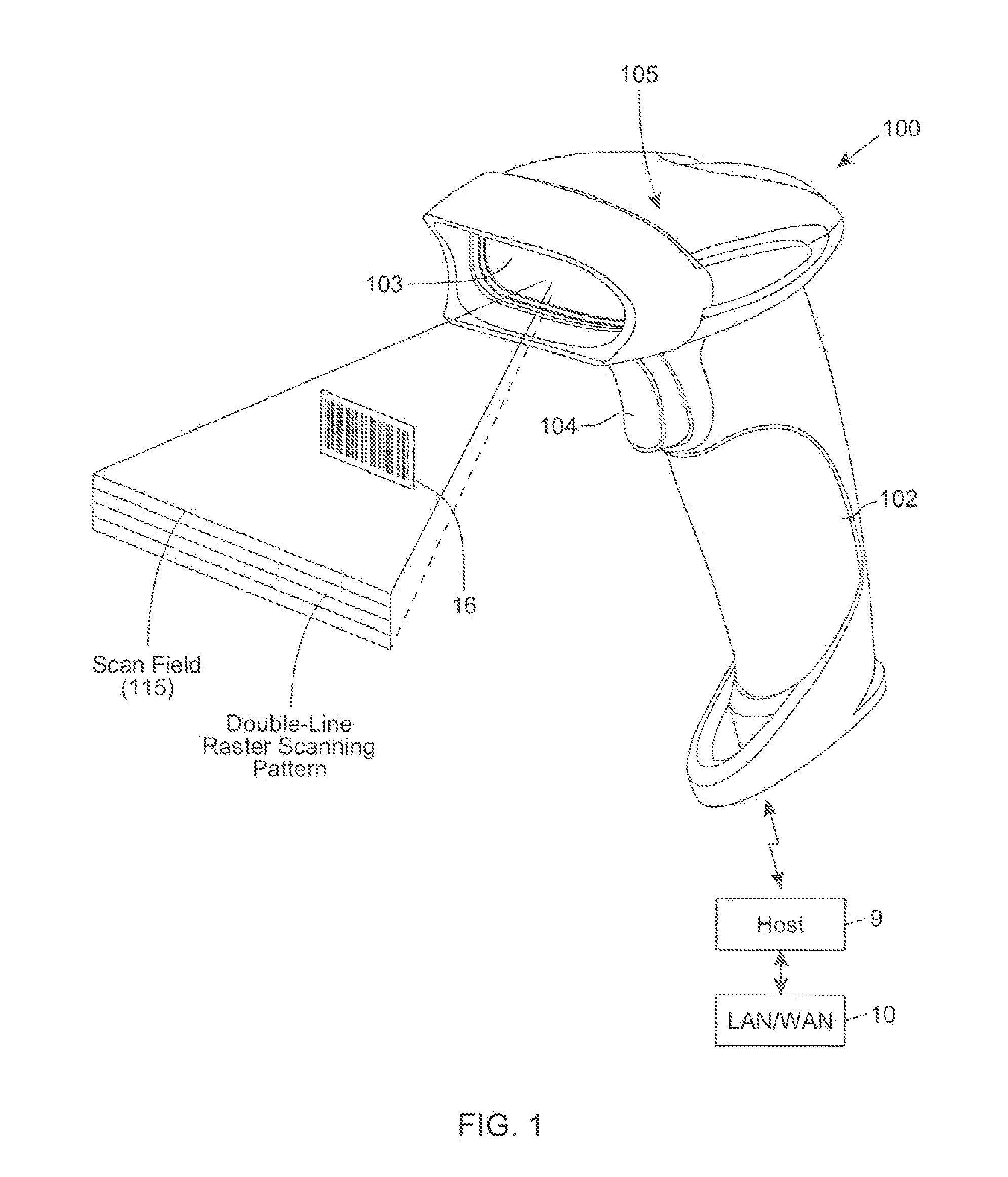
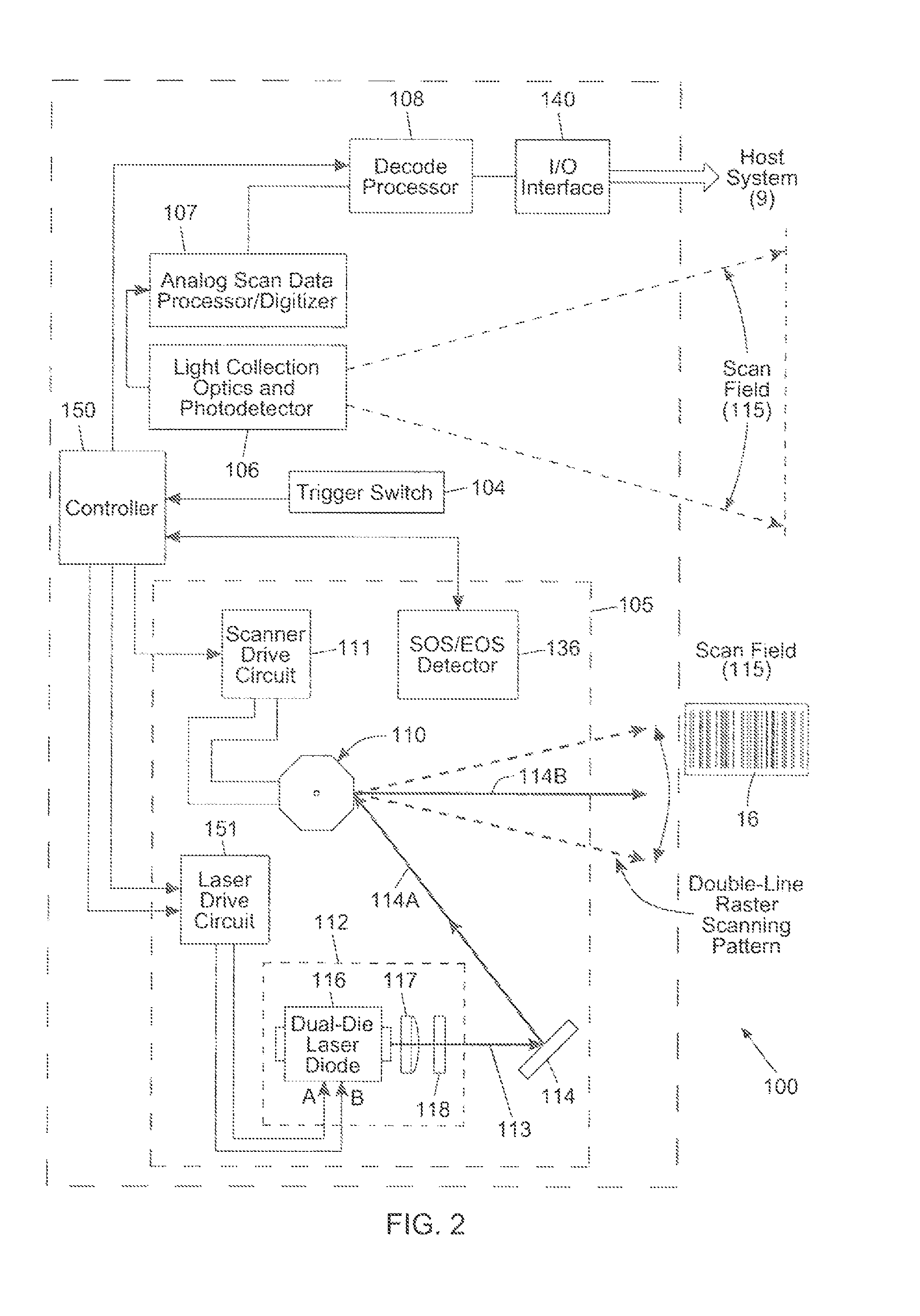
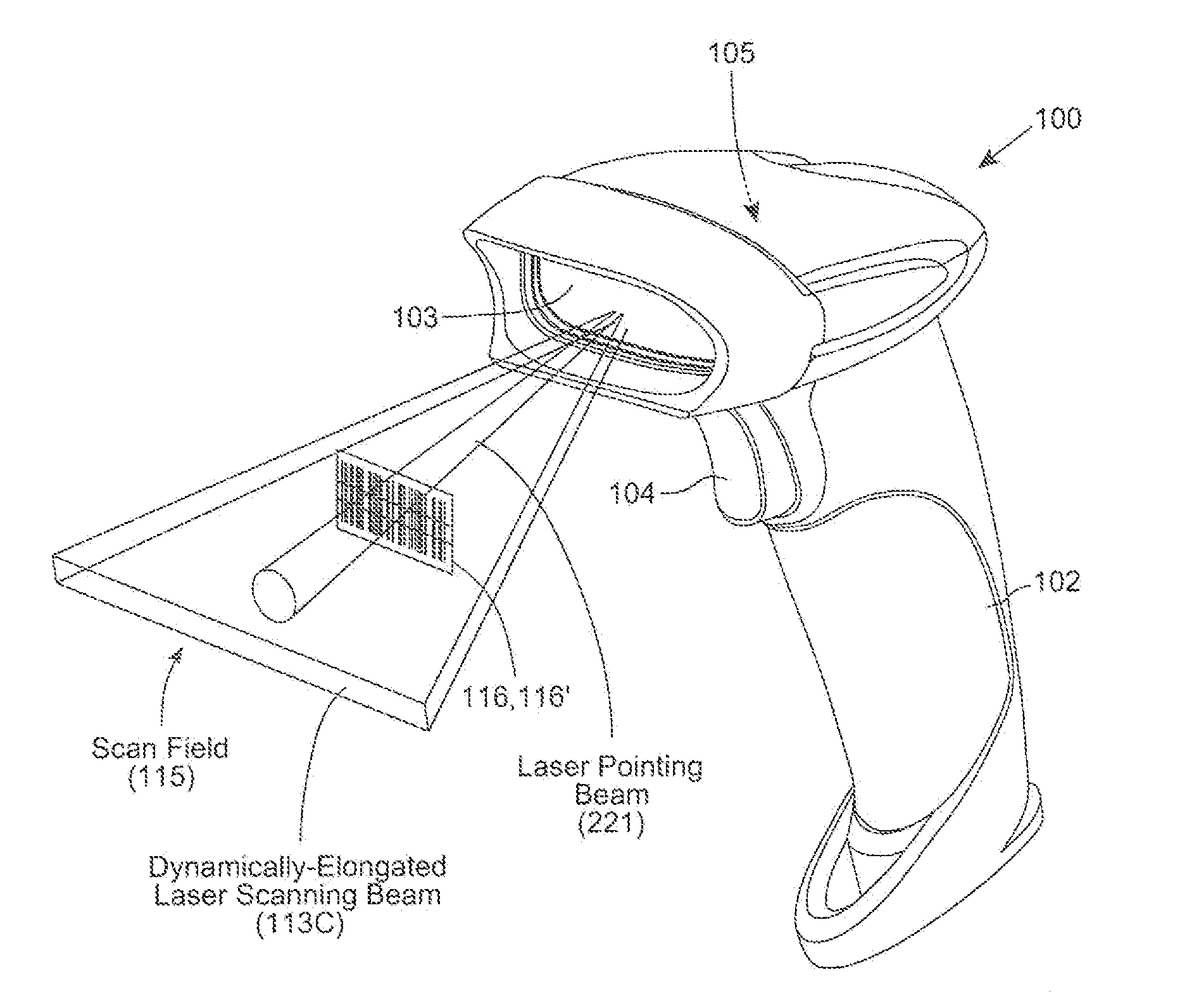
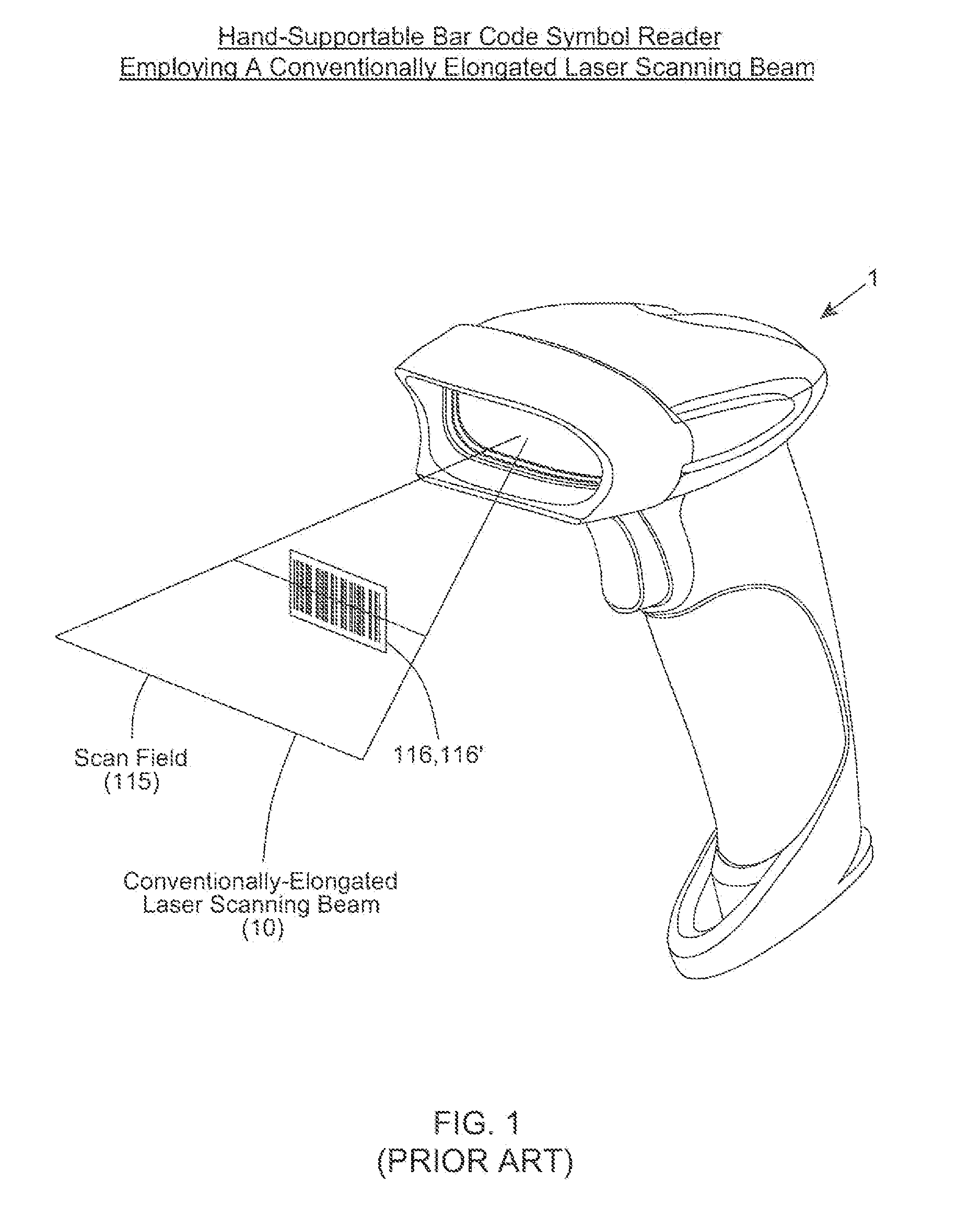
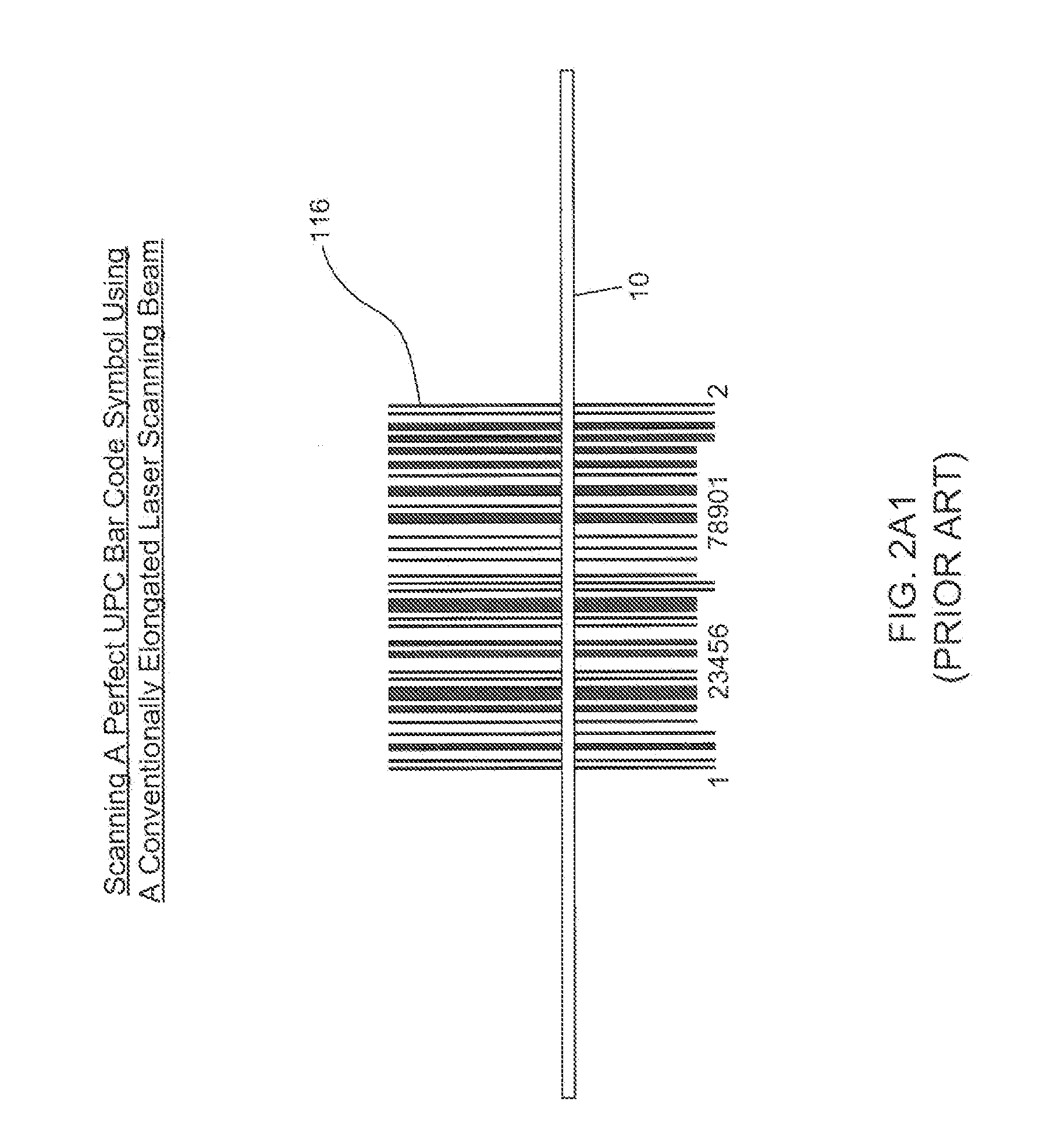
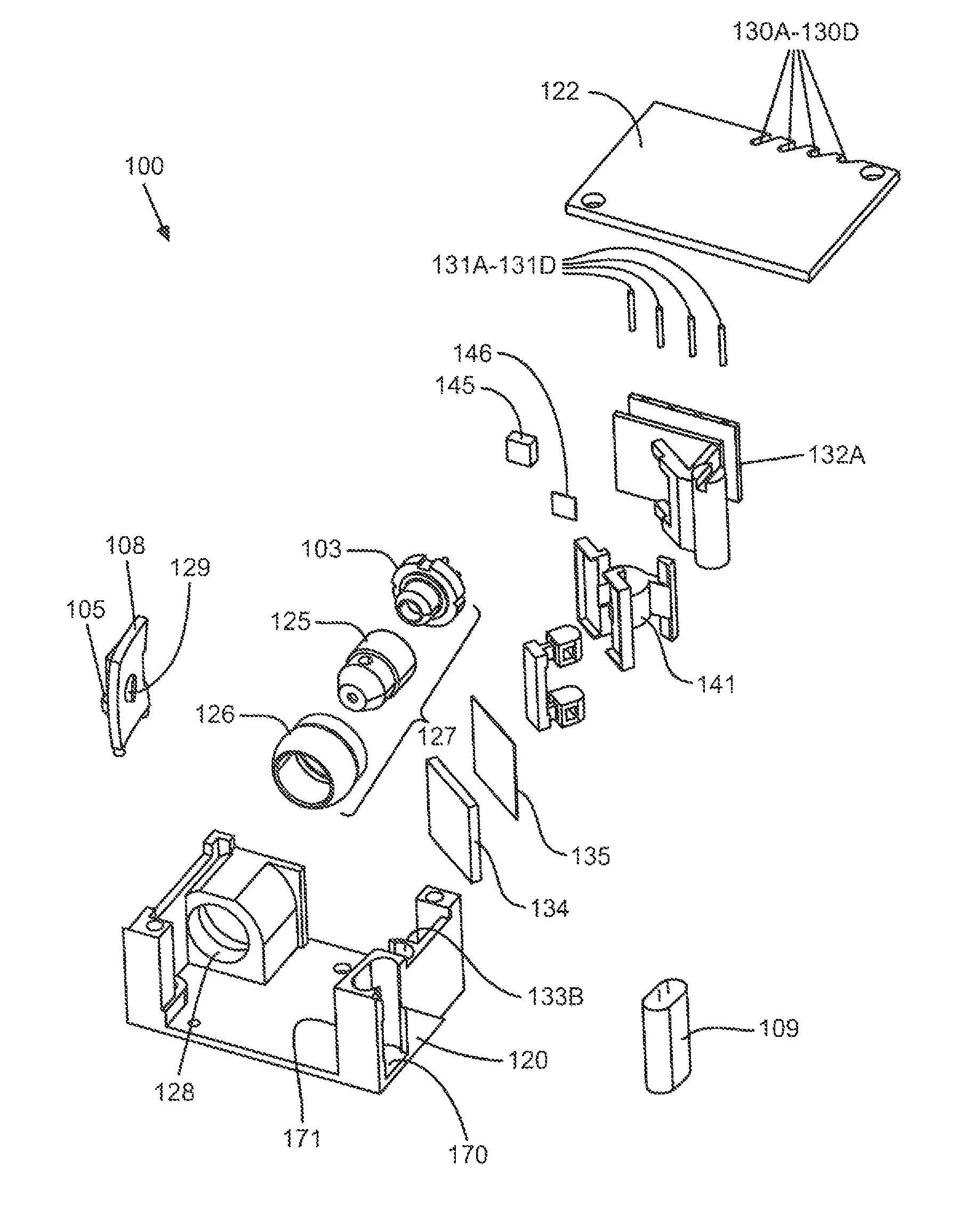
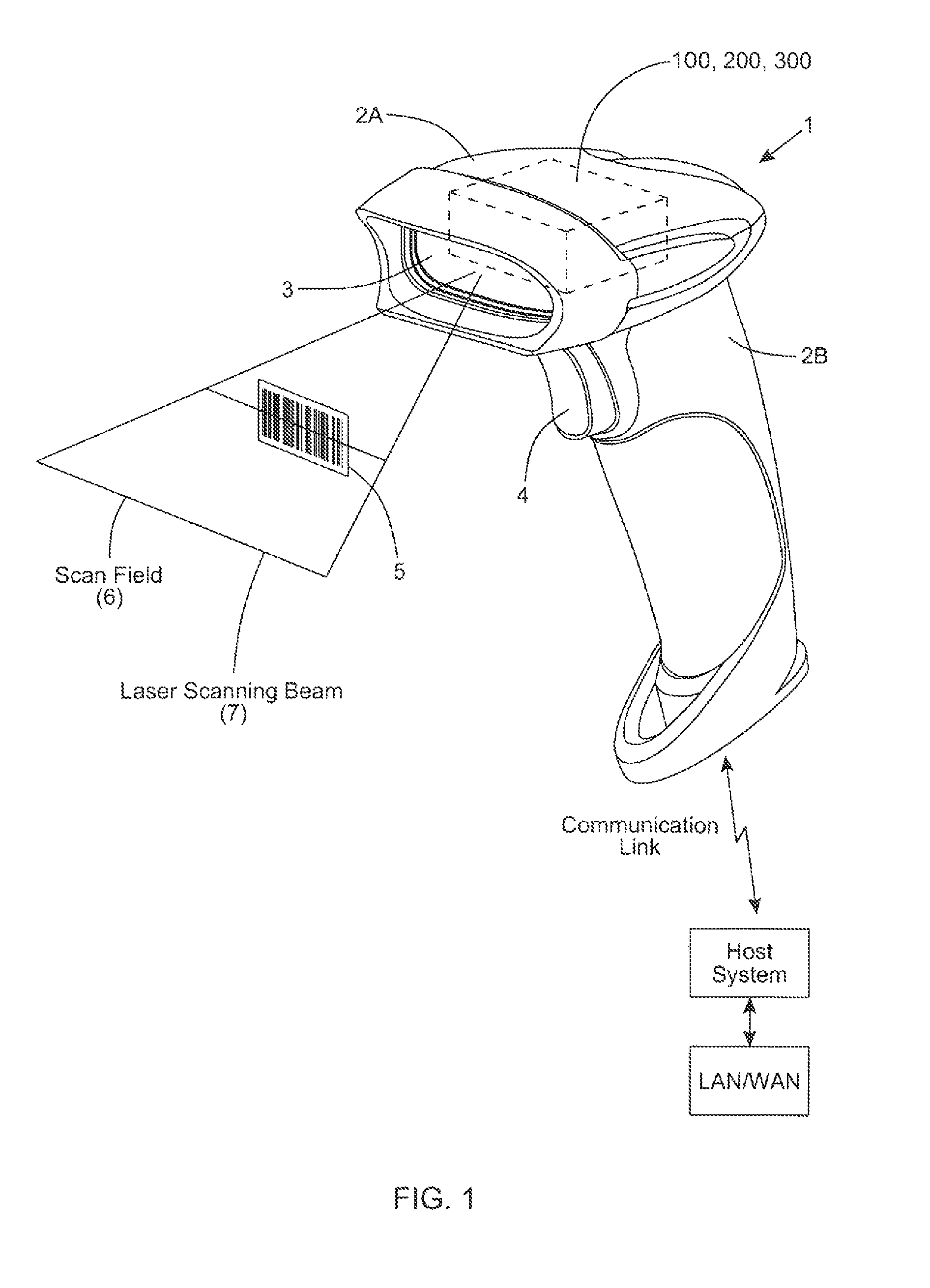
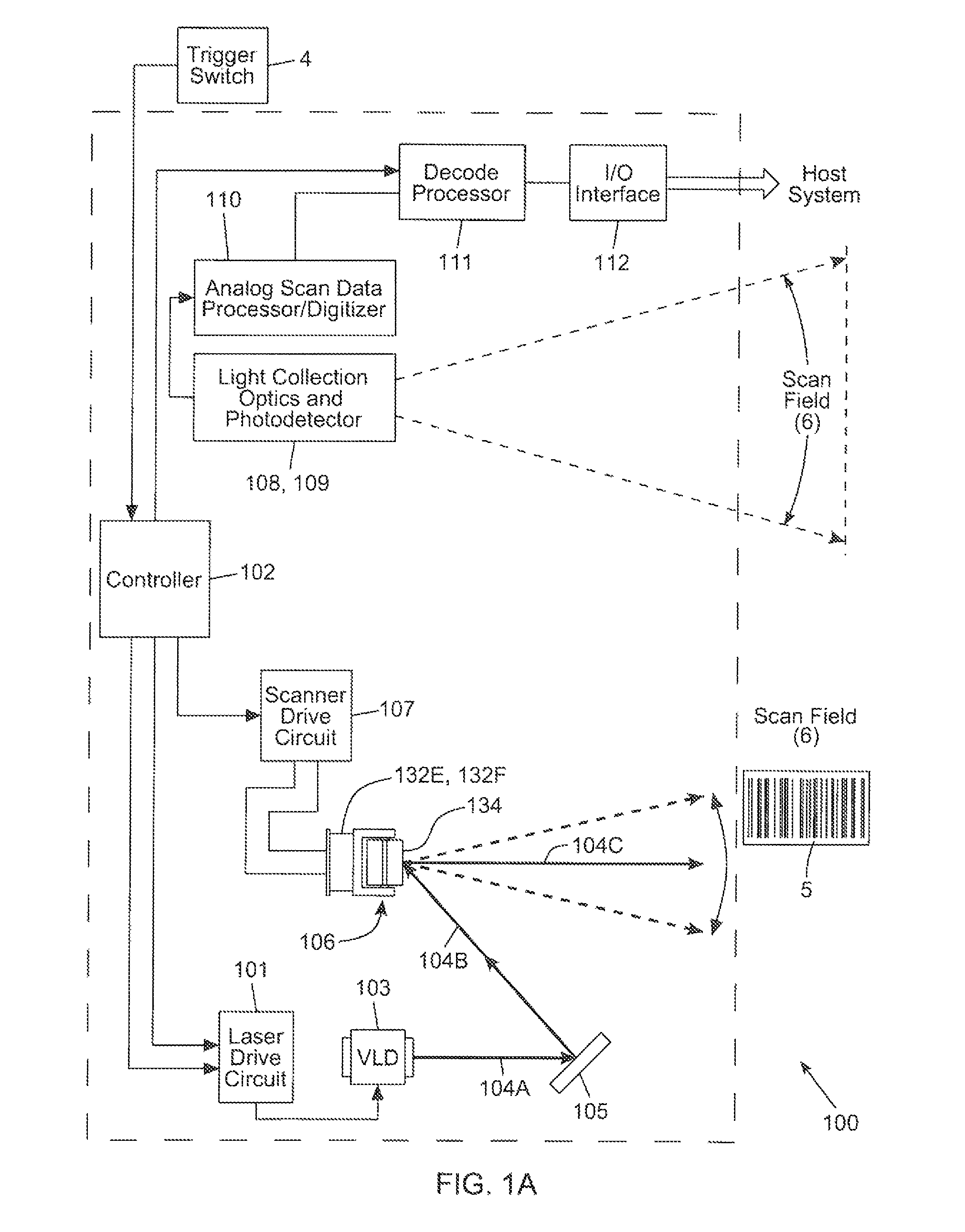
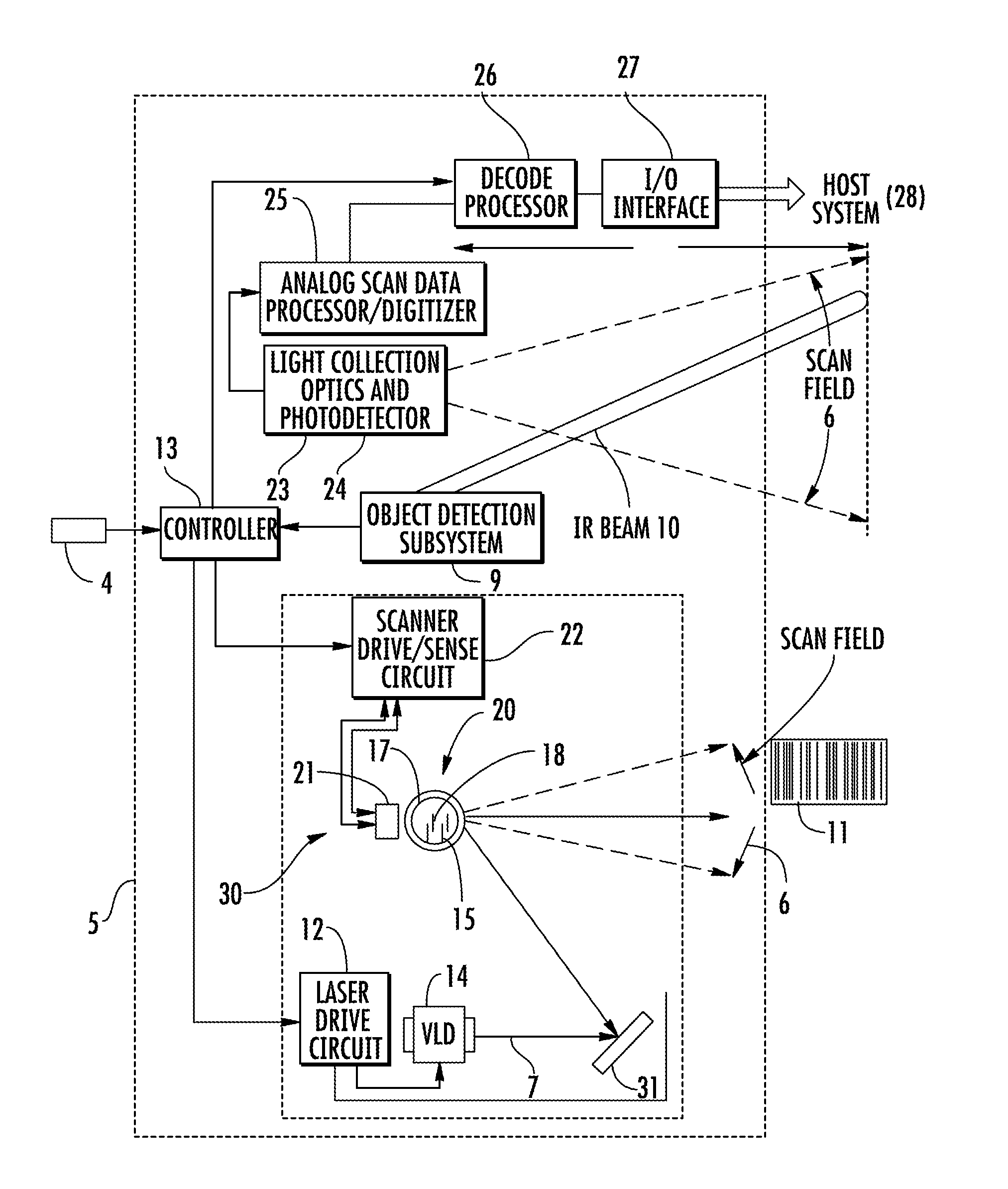
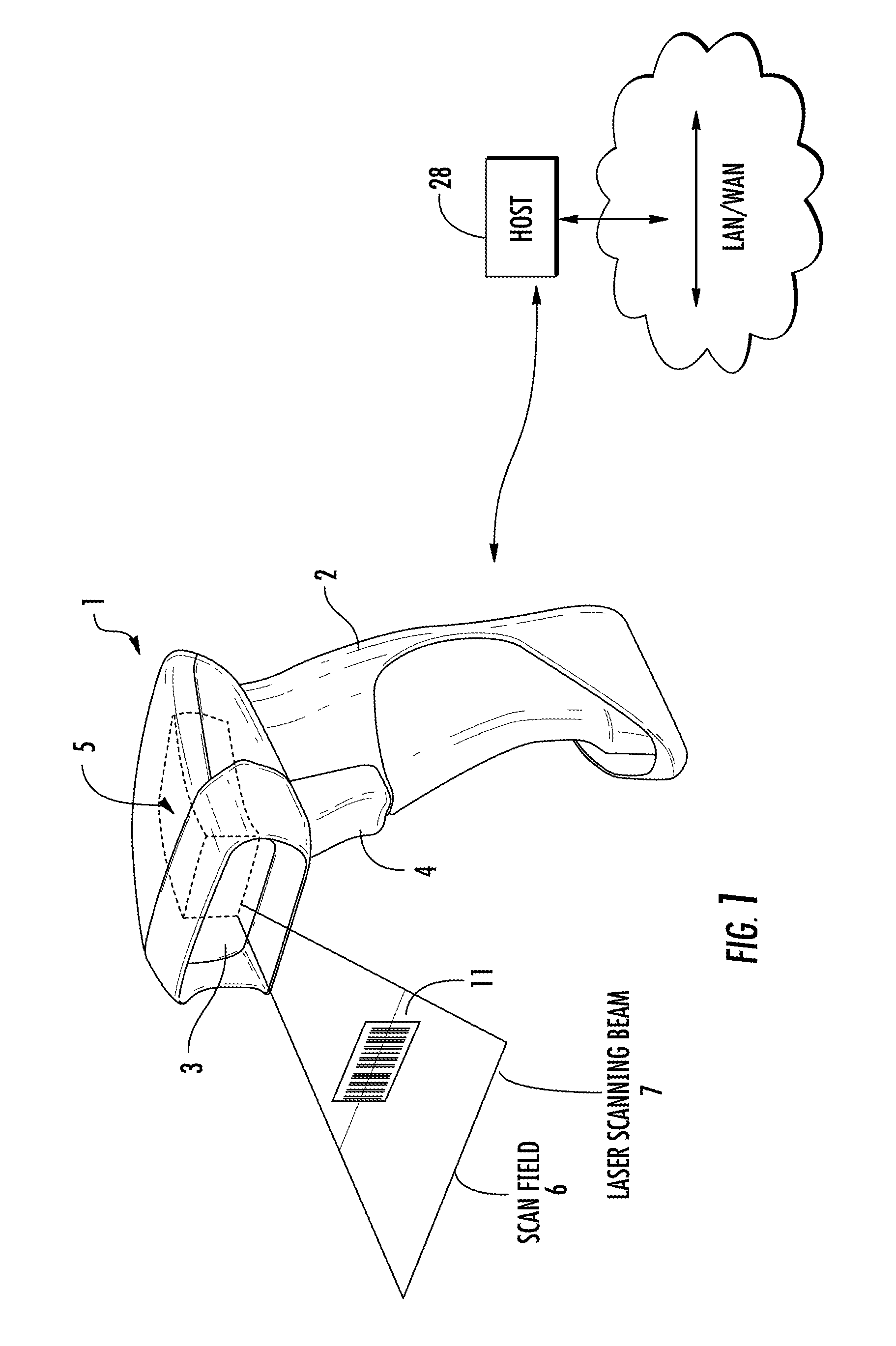
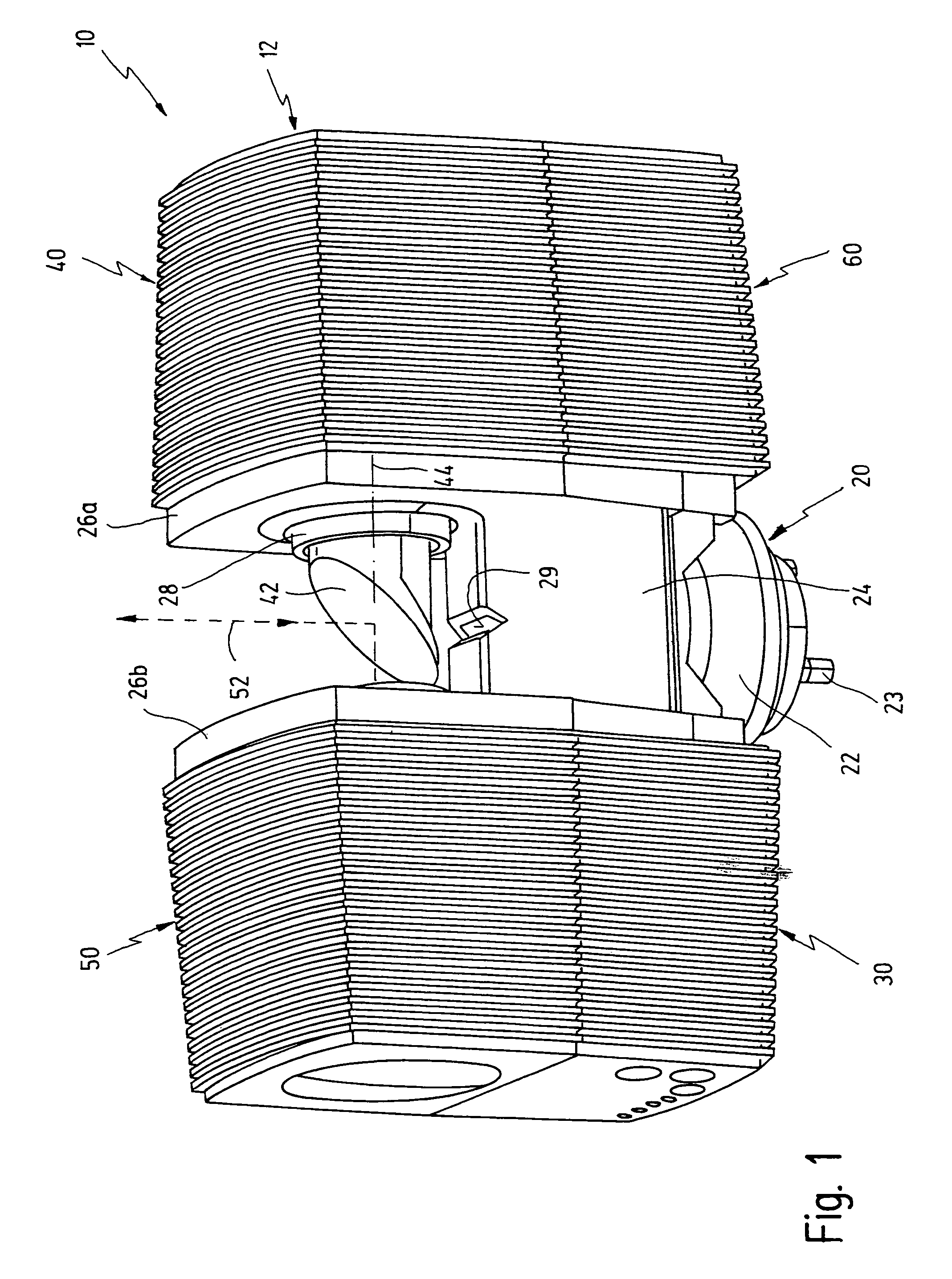
Bar code symbol reading system employing an extremely elongated laser scanning beam capable of reading poor and damaged quality bar code symbols with improved levels of performance
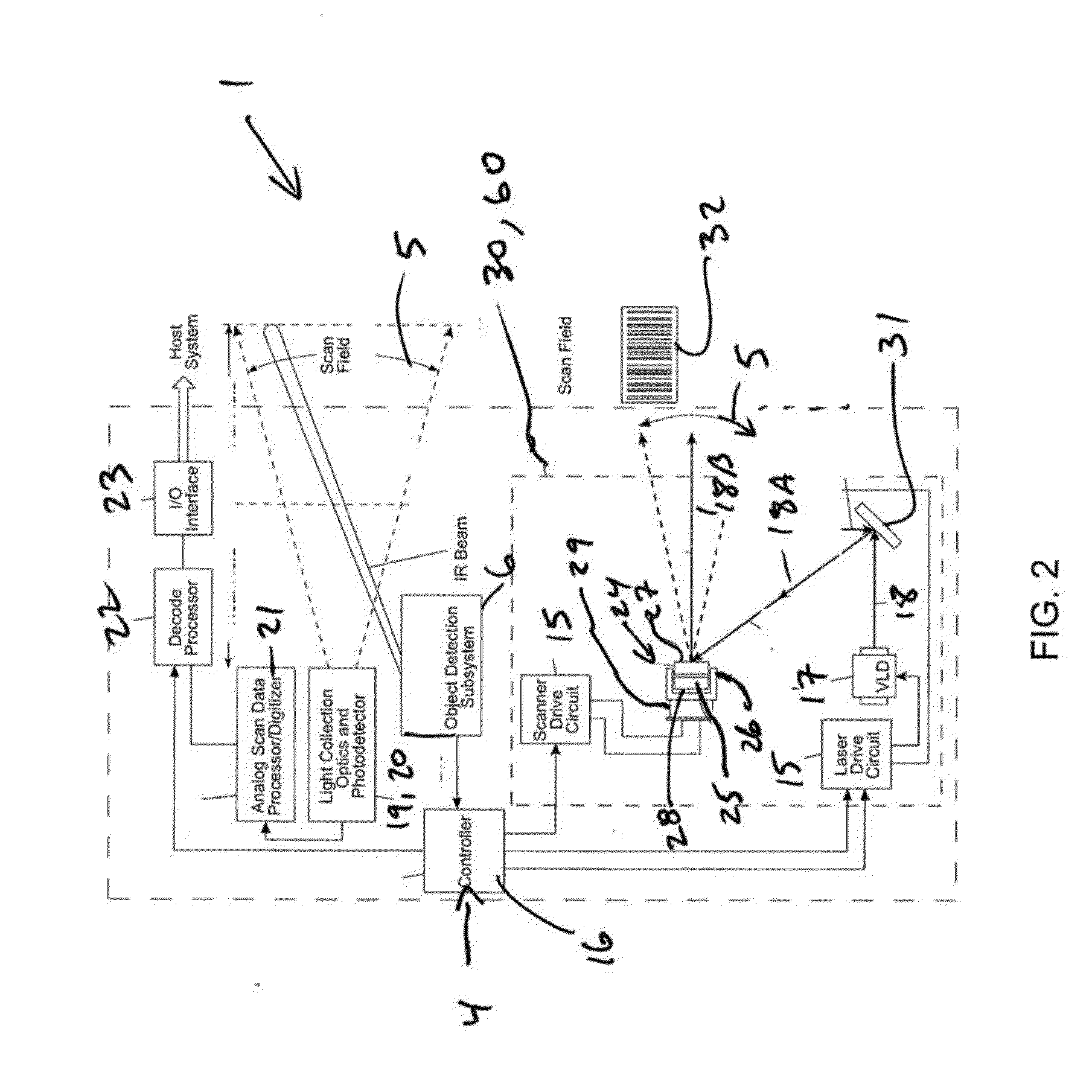
ActiveUS8376233B2Increase reflectionOptimized laser beam characteristicsTelevision system scanning detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionLaser scanningLight beam
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR
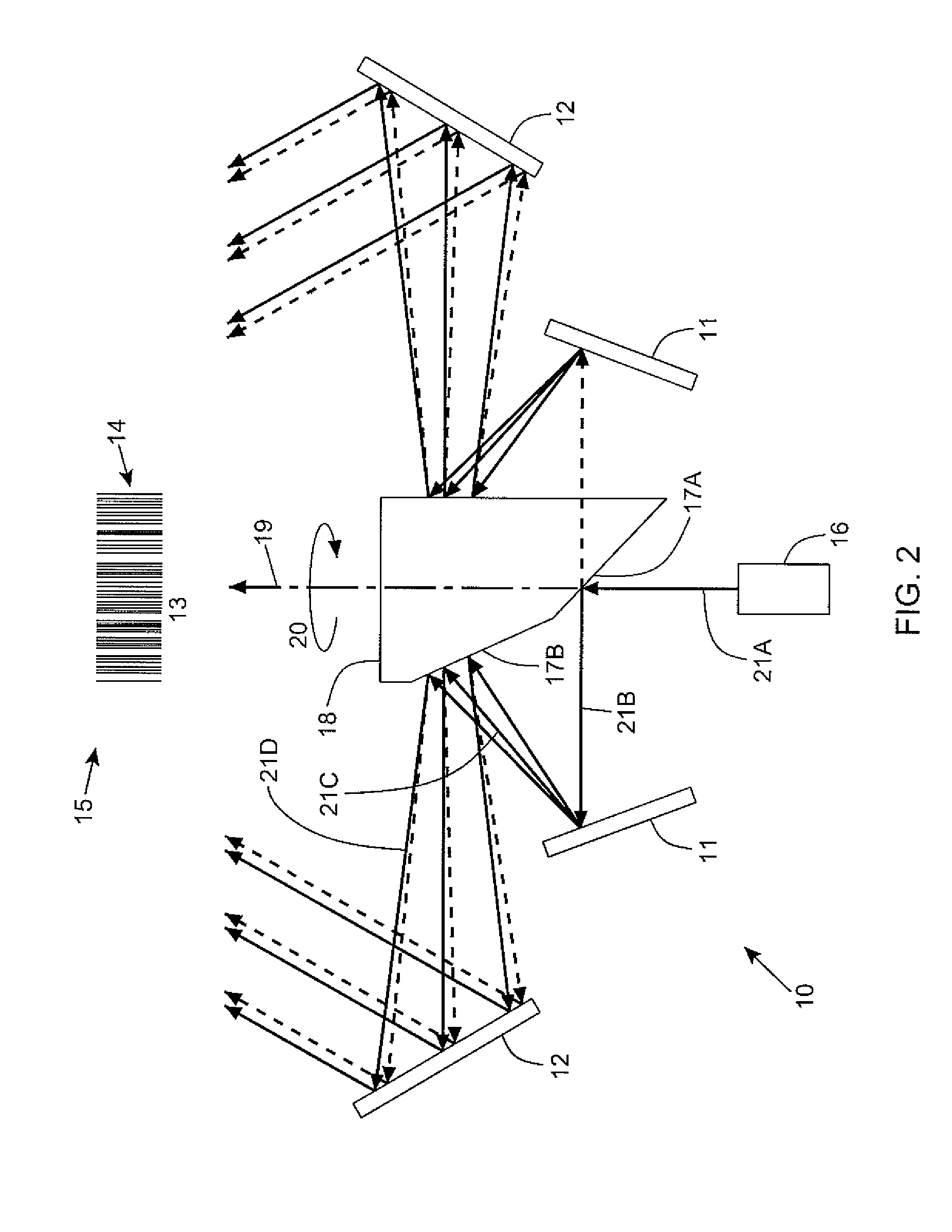
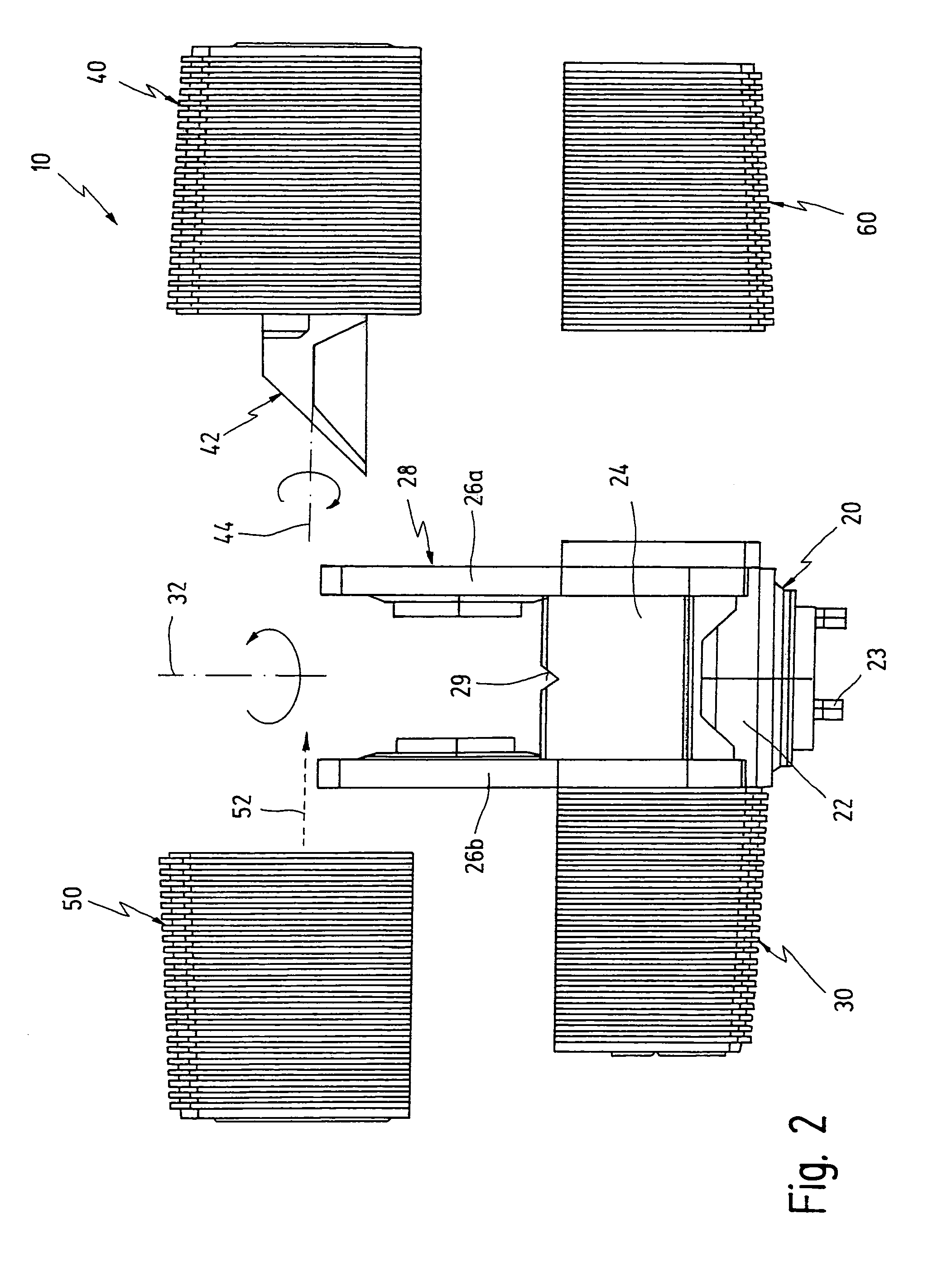
Laser scanning assembly having an improved scan angle-multiplication factor
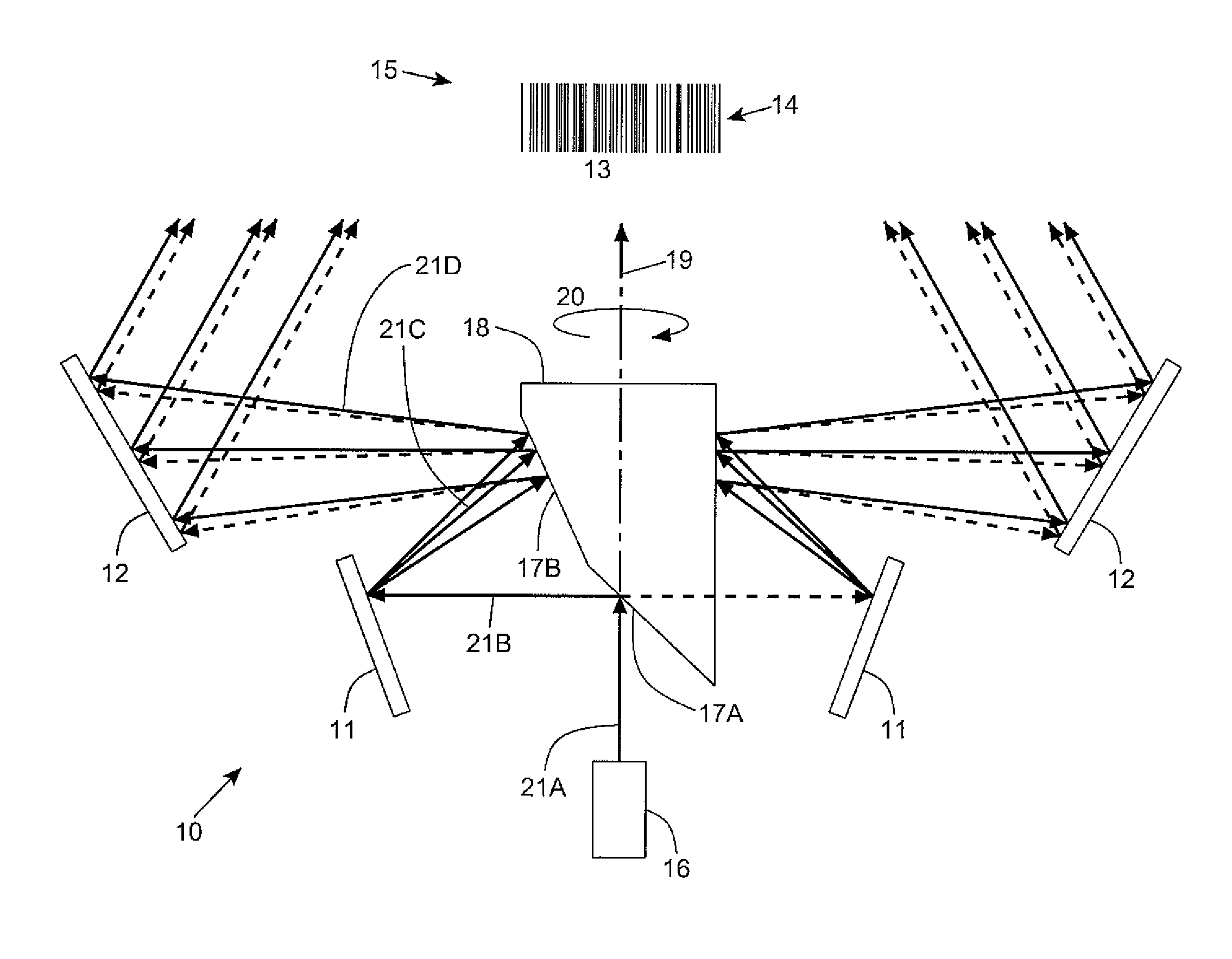
InactiveUS8408469B2Increase multipleUniform collectionMirrorsBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsRotational axisAcute angle
A laser scanning system for generating a laser scanning pattern in a scanning field, while amplifying the scan-angle multiplication factor of rotating mirrors employed therein. The laser scanning system employs rotatable laser scanning assembly having an axis of rotation and first and second rotating mirrors with normal vectors that are coplanar with each other and said rotational axis, and which form an acute angle substantially less than 90 degrees so as to provide a laser scanning assembly with a scan angle multiplication factor that is greater than 2.0. A cluster of stationary mirrors mounted about the first and second rotating mirrors, for sweeping a laser beam off the cluster of stationary mirrors after a laser beam has been reflected off the first rotating mirror, then reflected off the second rotating mirror, and then directed outwardly towards an array of pattern mirrors, so as to generate a resultant laser scanning pattern within the scanning field.
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR INC
Scanning assembly for laser based bar code scanners
InactiveUS20120111946A1Easy to manufactureLow costSensing by electromagnetic radiationOptical elementsBarcodeLaser scanning
A laser scanning assembly for use in a host system, including a mirror support element and a permanent magnetic element supported on a flexural element made from flexible material being supported by a pair of shaft half sections forming a stationary shaft, about which an axis of rotation is formed. The mirror support element and the permanent magnetic element have first and second recesses which accommodate the width of the stationary shaft so that a mirror and permanent magnet subassembly, formed by the mirror support element and the magnetic element, is free to oscillate about the stationary shaft when an electromagnetic coil is driven by a drive circuit and generates magnetic forces that act on the permanent magnetic element.
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR
Method of and apparatus for multiplying raster scanning lines by modulating a multi-cavity laser diode
ActiveUS8678285B2Improve featuresHigh densityCharacter and pattern recognitionSensing by electromagnetic radiationGratingLaser scanning
A method of and apparatus for generating a multiple raster-type scanning pattern by modulating a multi-cavity laser diode in such a way that it sequentially generates different laser beams synchronously during different laser scanning cycles, while the output laser beams are directed incident upon a rotating polygonal laser scanning element. The system does not require additional moving parts beyond the rotating polygon scanning element so as to reduce complexity and simplify construction of the laser scanning mechanism.
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR INC
Code symbol reading system employing dynamically-elongated laser scanning beams for improved levels of performance
InactiveUS20130043312A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioAverage out defectsCharacter and pattern recognitionSensing by electromagnetic radiationLight beamLaser scanning
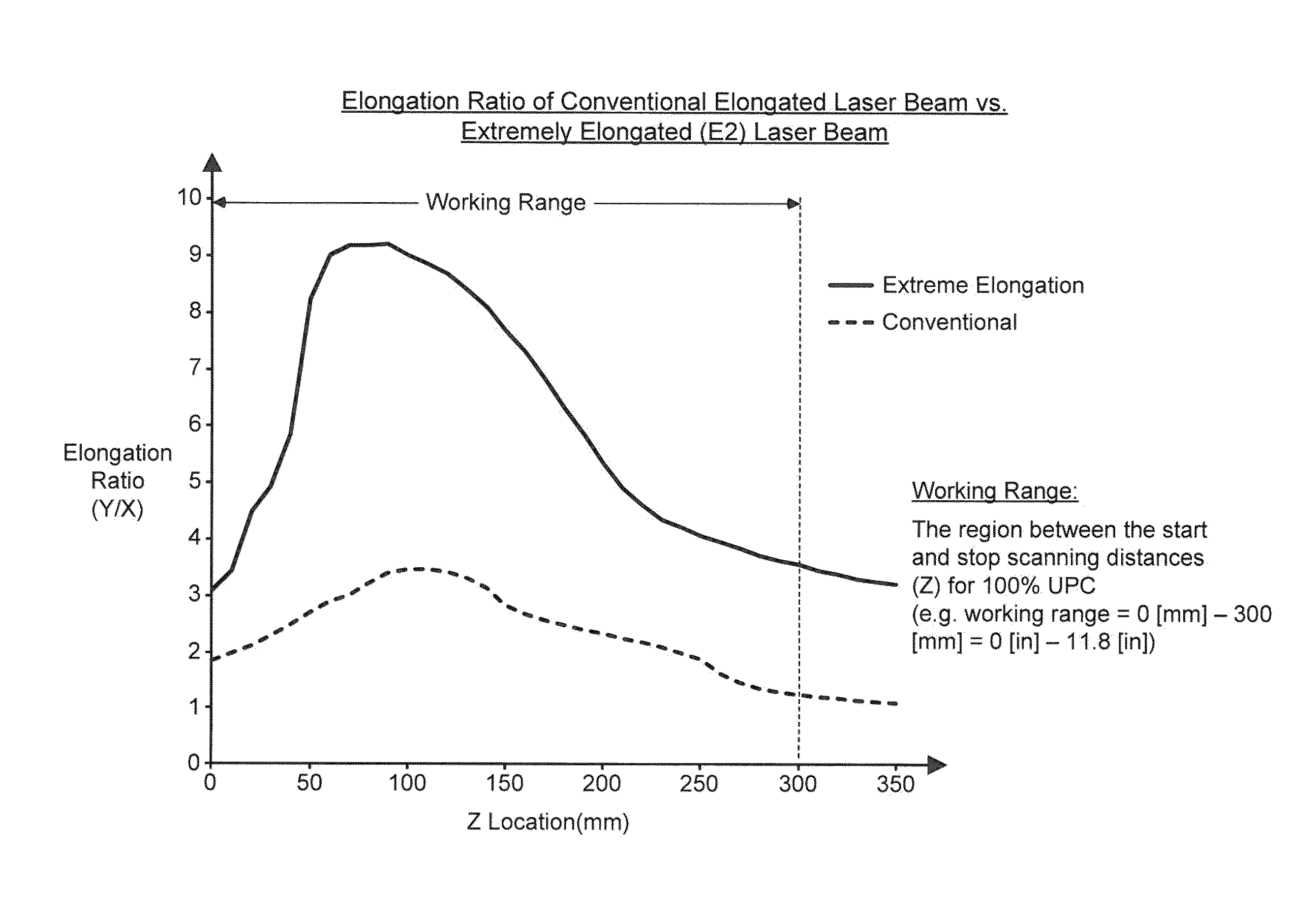
A laser scanning bar code symbol reading system for scanning and reading poor quality and damaged bar code symbols in flexible operating conditions. The system includes a housing having a light transmission window; a dynamically-elongated laser beam production module, including a multi-cavity visible laser diode (VLD), for producing a dynamically-elongated laser beam having (i) a direction of propagation extending along a z reference direction, (ii) a height dimension being indicated by the y reference direction, and (iii) a width dimension being indicated by the x reference direction, where x, y and z directions are orthogonal to each other. Each dynamically-elongated laser beam is characterized by an elongation ratio (ER) that is defined as Y / X where, for any point within the working range of the laser scanning bar code symbol reading system, extending along the z direction, (i) Y indicates the beam height of the dynamically-elongated laser beam measured in the Y reference direction, (ii) X indicates the beam width of the dynamically-elongated laser beam measured in the X reference direction, and (iii) the beam height (Y) and the laser beam width (X) are measured at 1 / e2 intensity clip level. A laser scanning mechanism is provided for scanning the dynamically-elongated laser beam out the light transmission window and across a scanning field defined external to the housing, in which a bar code symbol is present for scanning by the dynamically-elongated laser scanning beam.
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR
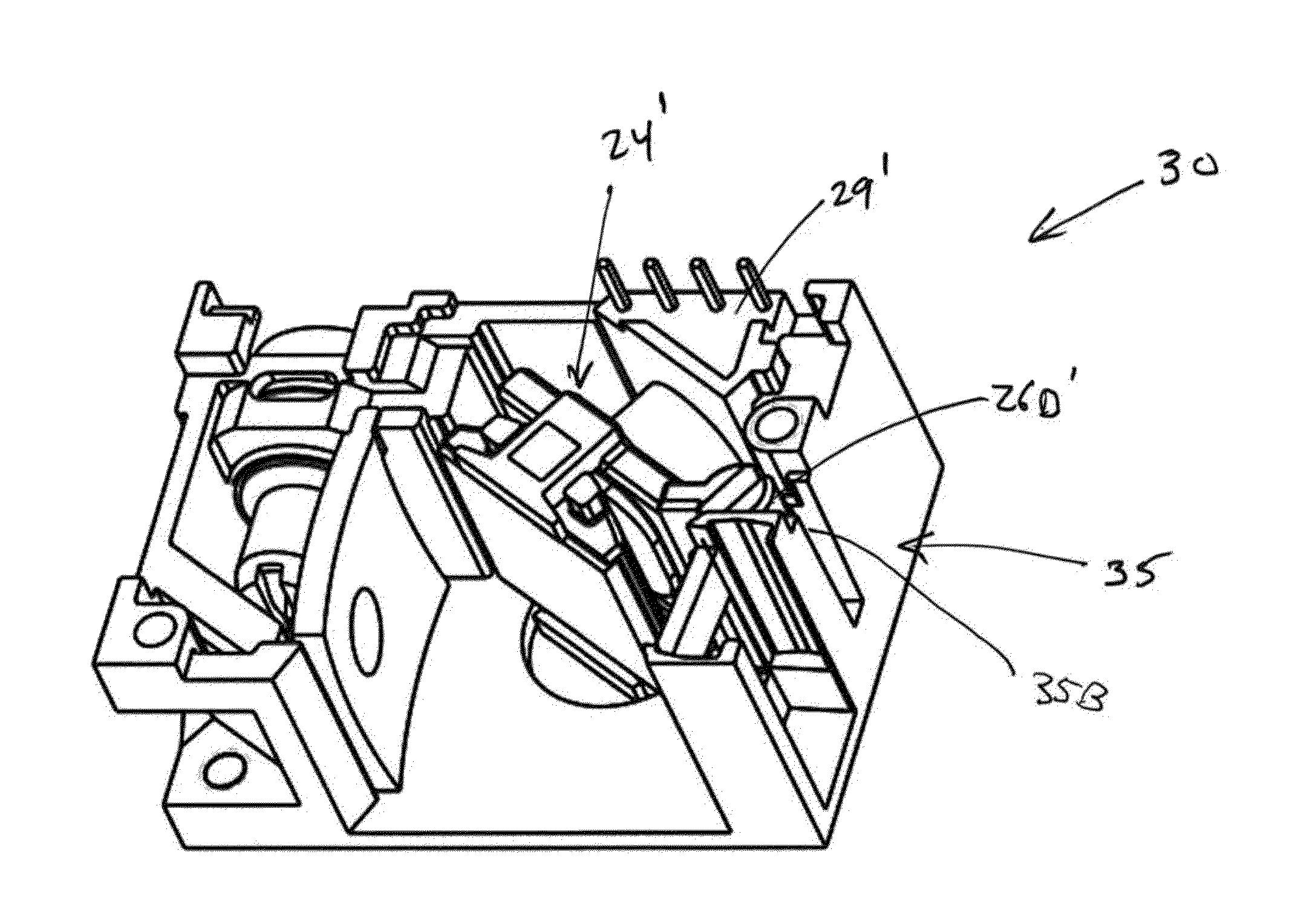
Laser scanning module with rotatably adjustable laser scanning assembly
A laser scanning module employing a laser scanning assembly mounted within a module housing using a mechanism that allows the laser scanning assembly to be rotated to an angular position within the engine housing so that light collection, beam folding and light collection mirrors in the module housing are optically aligned. A PC board is mounted on a side of the housing and has a configuration of elongated apertures of open-ended and / or closed geometry, arranged in a non-parallel manner. An electromagnetic coil structure, associated with the laser scanning assembly, has a linear array of electrically-conductive pins that project through the configuration of elongated holes, at locations along the elongated holes that are determined by the angular rotation of the laser scanning assembly attained during optical alignment conditions during manufacture.
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR
Laser scanning module employing a laser scanning assembly having elastomeric wheel hinges
ActiveUS20140197239A1Less electric powerSpace minimizationSensing by electromagnetic radiationOptical elementsLaser scanningMirror mount
A laser scanning module employs a scan mirror and magnet rotor subassembly supported by a stator structure using a pair of elastomeric wheel hinges. The scan mirror and magnet rotor subassembly includes: a scan mirror and magnet rotor subassembly having a rotor frame having a pair of rotor support posts aligned along a scan axis passing through the rotor frame; a scan mirror mounted on the rotor frame; and a permanent magnet mounted on the rotor frame. The elastomeric wheel hinge includes a central portion having an aperture for passage and fixed attachment of one rotor support post, a plurality of elastomeric spoke portions extending from the central portion and radially extending from the central aperture to a circumferential rim portion connected to the outer end portion of each spoke portion so as to form the elastomeric wheel hinge.
Owner:HAND HELD PRODS
Laser scanning modules embodying silicone scan element with torsional hinges
ActiveUS8915439B2Easy to integrateSpace minimizationMirrorsRecord carriers used with machinesLaser scanningRestoring force
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR
Method of using camera sensor interface to transfer multiple channels of scan data using an image format
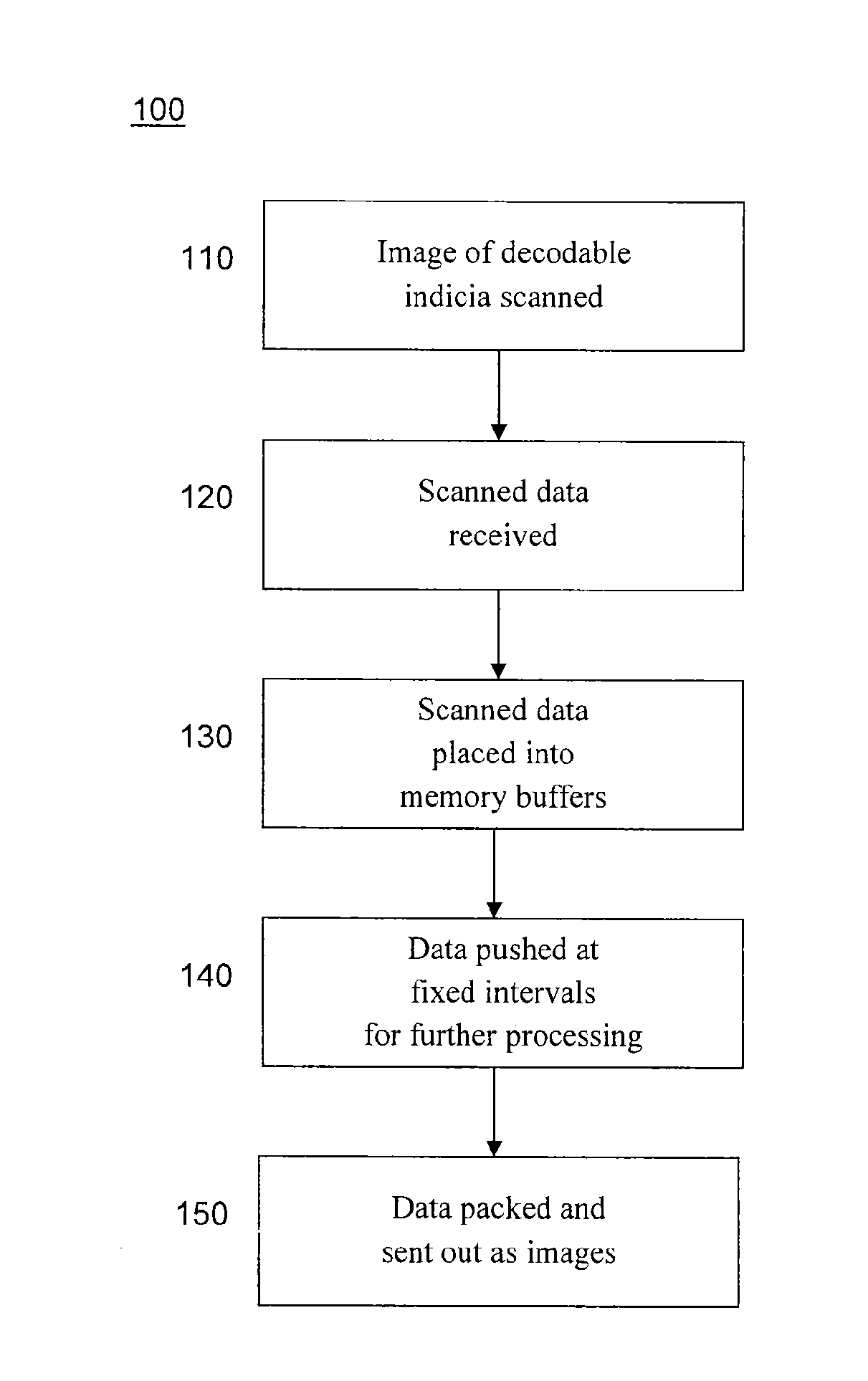
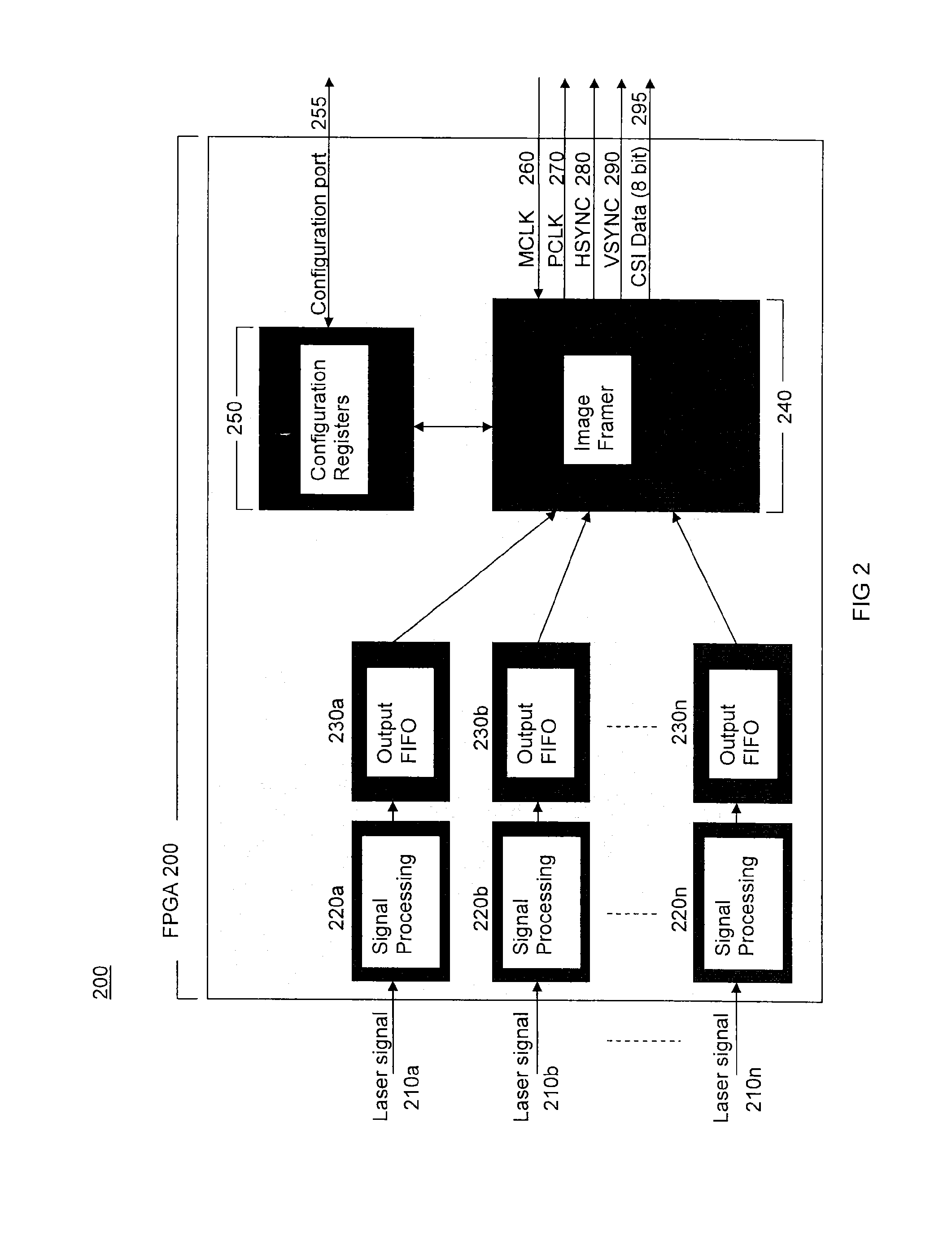
ActiveUS20150053768A1Solve the slow scanning speedSolve excessive overheadCharacter and pattern recognitionRecord carriers used with machinesLaser scanningEngineering
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
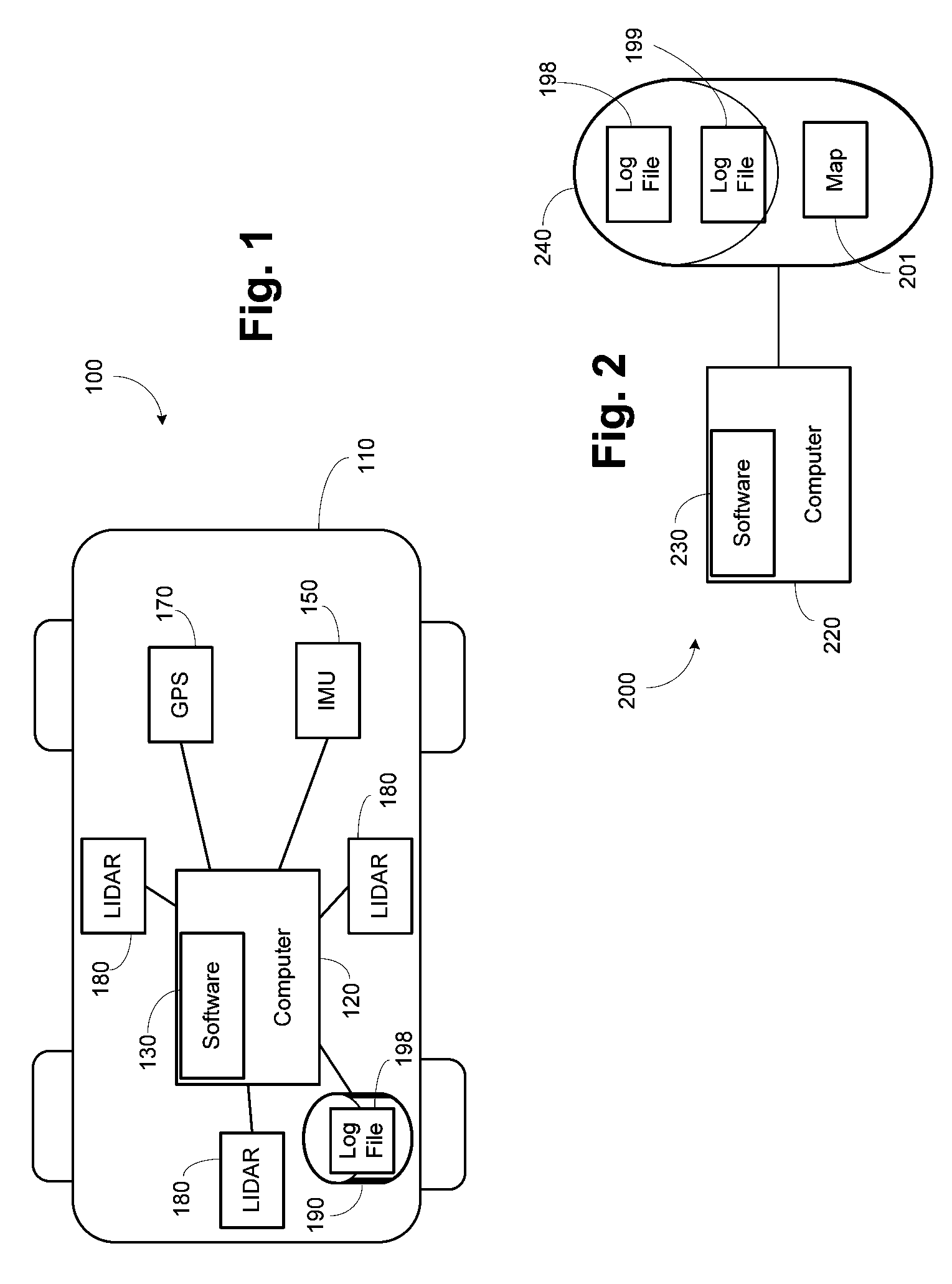
Pobabilistic methods for mapping and localization in arbitrary outdoor environments
InactiveUS20080033645A1Maximize likelihoodNavigational calculation instrumentsPosition fixationTerrainLand based
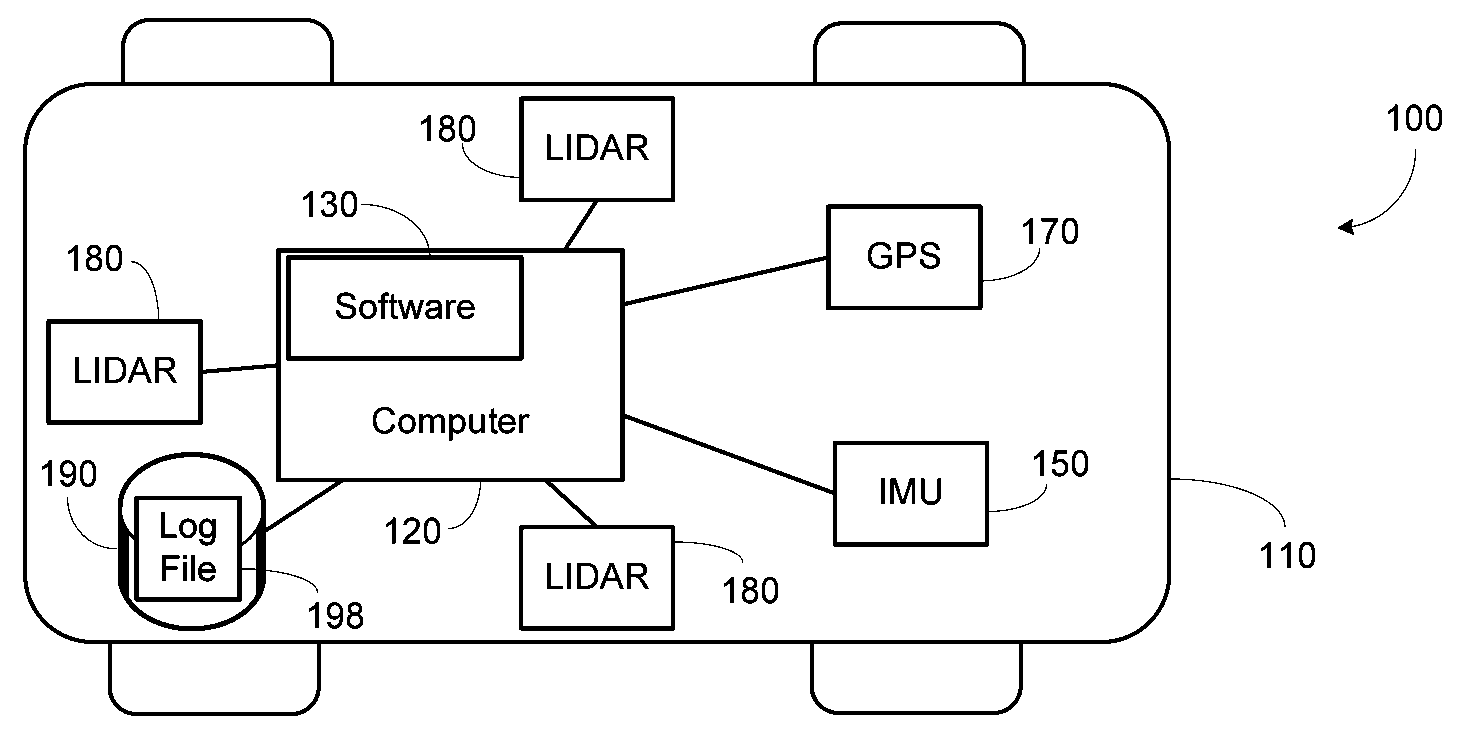
Systems and methods which provide mapping an arbitrary outdoor environment and positioning a ground-based vehicle relative to this map. In one embodiment, a land-based vehicle travels across a section of terrain, recording both location data from sensors such as GPS as well as scene data from sensors such as laser scanners or cameras. These data are then used to create a high-resolution map of the terrain, which may have well-defined structure (such as a road) or which may be unstructured (such as a section of desert), and which does not rely on the presence of any “landmark” features. In another embodiment, the vehicle localizes itself relative to this map in a subsequent drive over the same section of terrain, using a computer algorithm that incorporates incoming sensor data from the vehicle by attempting to maximize the likelihood of the observed data given the map.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Controlled architecture ceramic composites by stereolithography
InactiveUS6283997B1Quality improvementFast preparationProgramme controlAdditive manufacturing apparatusCeramic compositeMetallurgy
A process for producing a ceramic composite having a porous network. The process includes providing a photocurable ceramic dispersion. The dispersion consists of a photocurable polymer and a ceramic composition. The surface of the dispersion is scanned with a laser to cure the photocurable polymer to produce a photocured polymer / ceramic composition. The photocured composition useful as a polymer / ceramic composite, or the polymer phase can be removed by heating to a first temperature that is sufficient to burn out the photocured polymer. It is then heated to a second temperature that is higher than the first temperature and is sufficient to sinter the ceramic composition to produce a purely ceramic composition having a porous network.Preferably and more specifically, the process uses a stereolithographic technique for laser scanning. The process can form a high quality orthopedic implant that dimensionally matches the bone structure of a patient. The technique relies upon laser photocuring a dense colloidal dispersion into a desired complex three-dimensional shape. The shape is obtained from a CAT scan file of a bone and is rendered into a CAD file that is readable by the stereolithography instrument. Or the shape is obtained directly from a CAD file that is readable by the stereolithography instrument.
Owner:UNITED STATES SURGICAL CORP +2
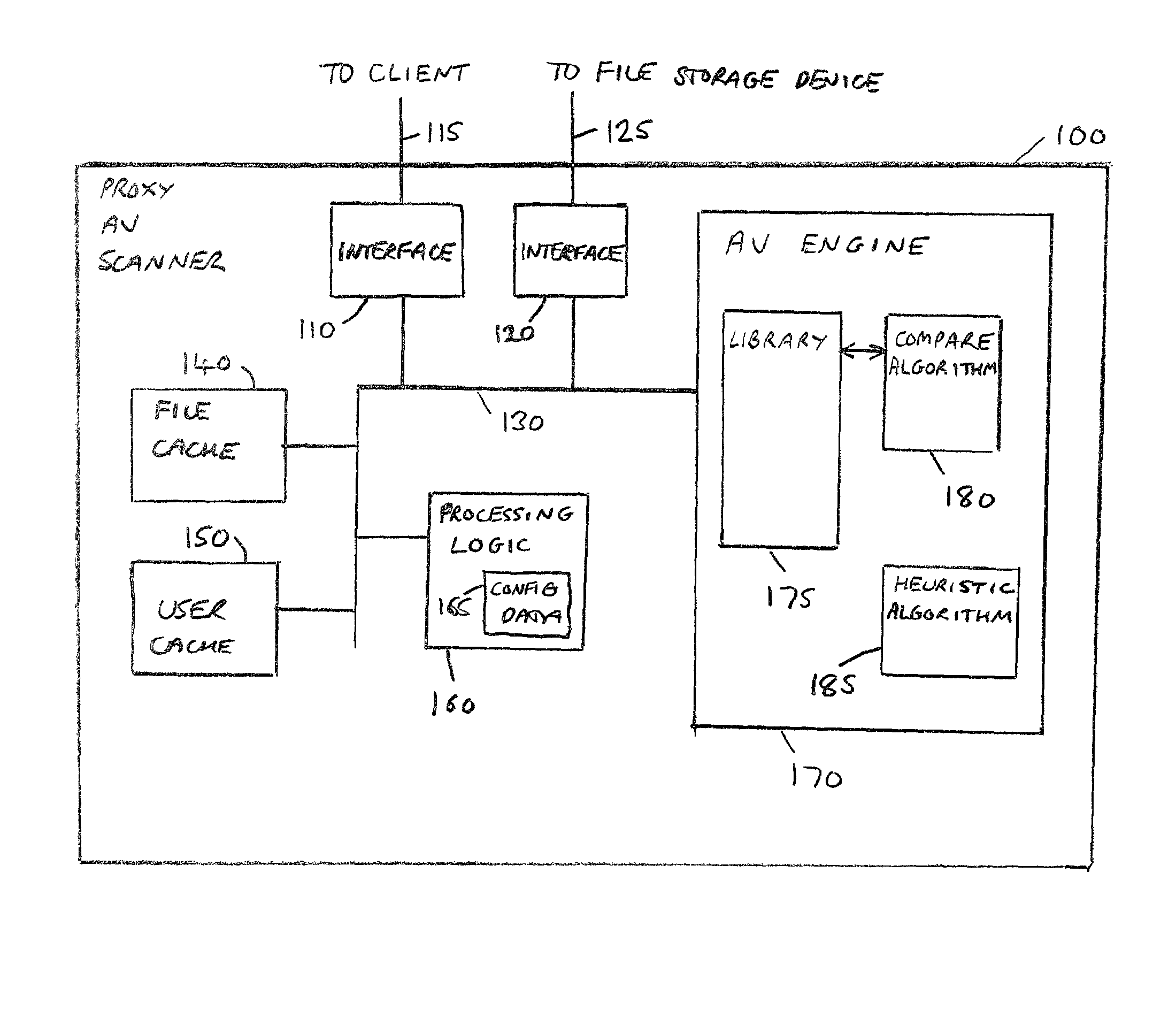
Handling of malware scanning of files stored within a file storage device of a computer network
InactiveUS7093002B2Reduce the possibilityCost effectiveMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionOperational systemLaser scanning
The present invention provides a load balancing device, computer program product, and method for balancing the load across a plurality of proxy devices arranged to perform malware scanning of files stored within a file storage device of a computer network. The computer network has a plurality of client devices arranged to issue access requests using a dedicated file access protocol to the file storage device in order to access files stored on the file storage device. The load balancing device is arranged so as to intercept access requests issued to the file storage device, and comprises a client interface for receiving an access request issued to the file storage device using the dedicated file access protocol. Further, the load balancing device comprises load balancing logic for applying a predetermined load balancing routine to determine to which proxy device to direct the received access request, and a proxy device interface for sending the access request to the proxy device determined by the load balancing logic, each proxy device being coupled to the file storage device. This enables a very efficient system to be developed for performing malware scanning of files stored within the file storage device, whilst enabling that system to be developed independently of the particular file storage device being used in the computer network, or the operating system being run on that file storage device.
Owner:MCAFEE LLC
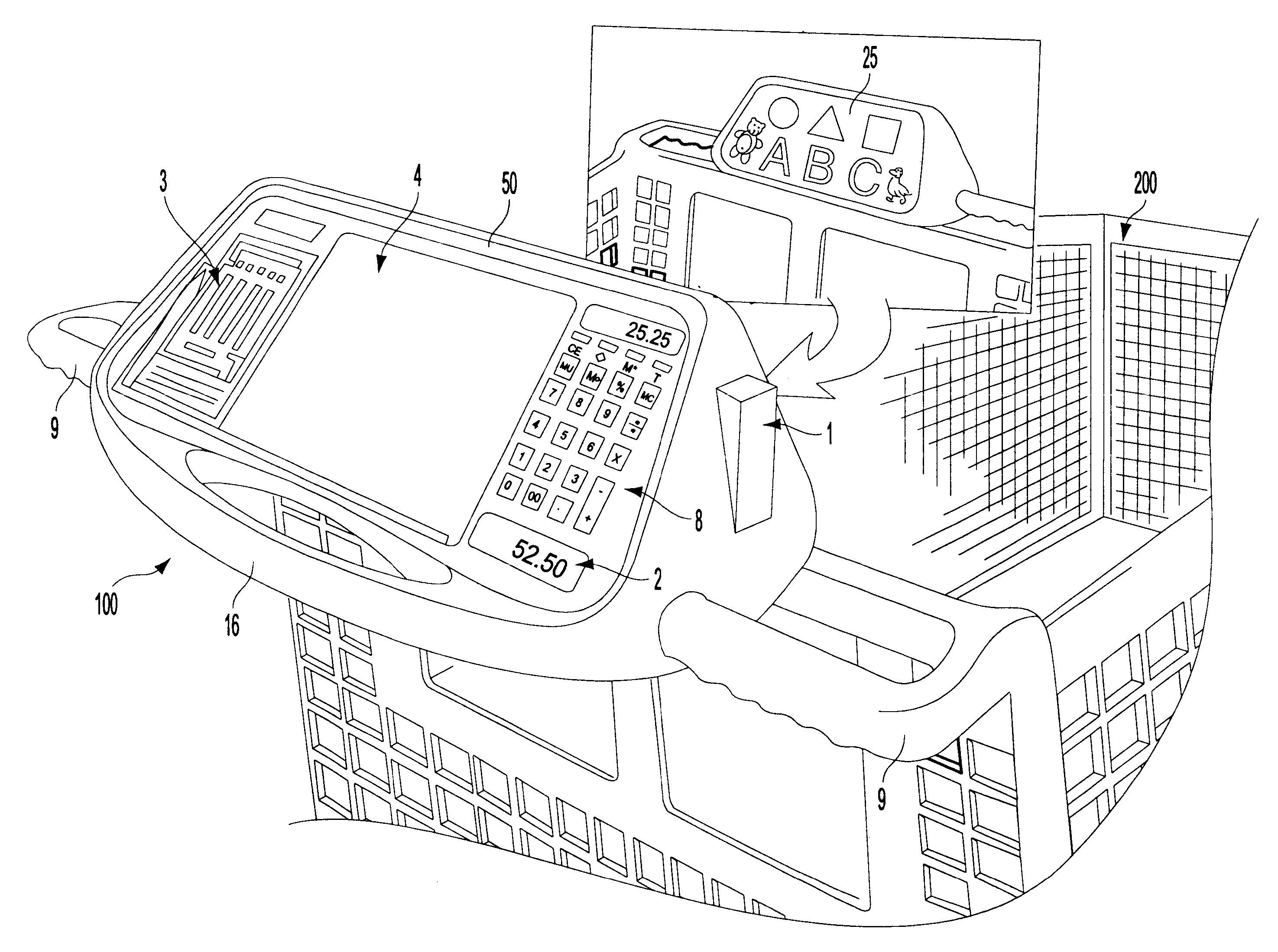
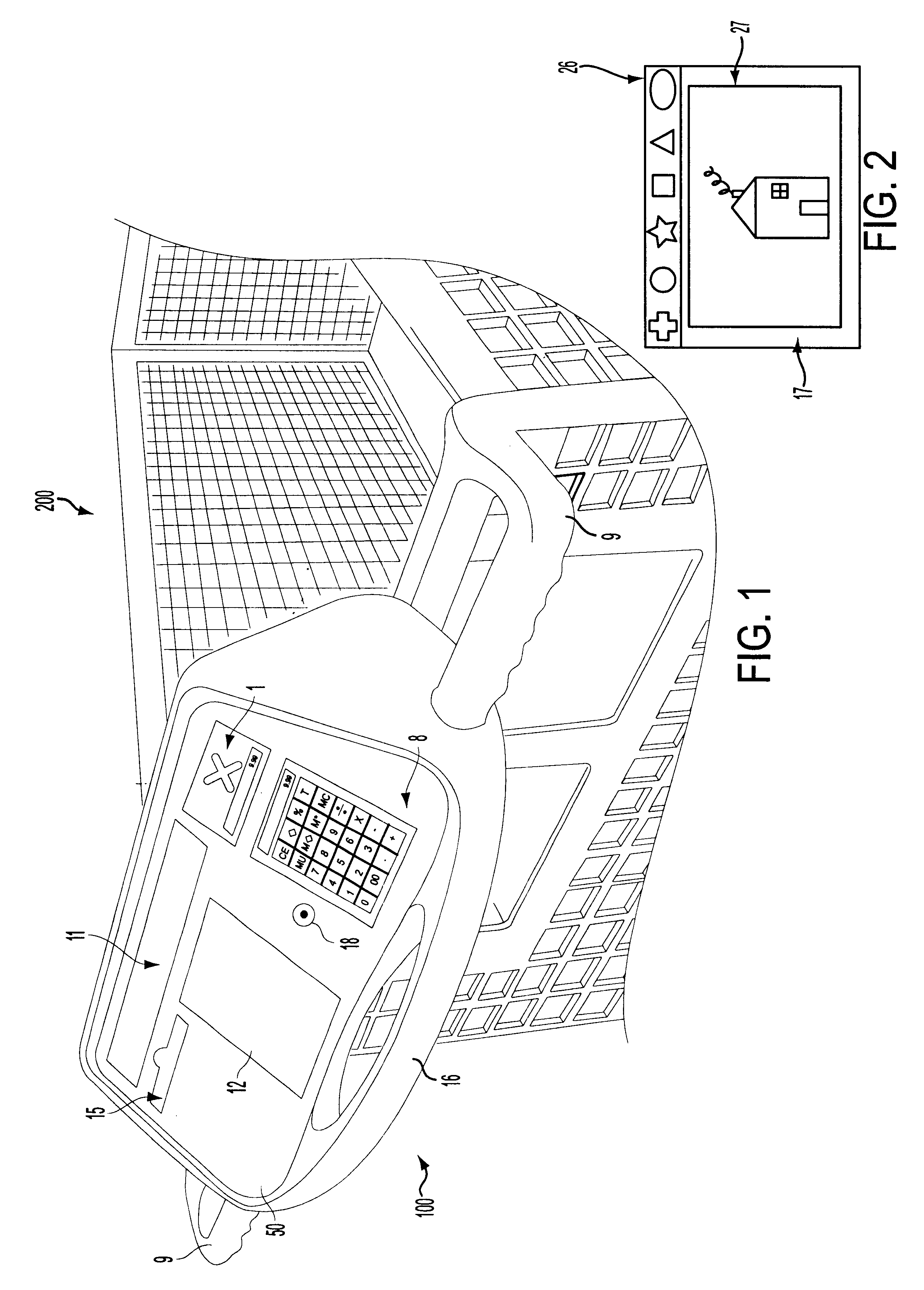
Self scanning and check out shopping cart-based electronic advertising system
InactiveUS6484939B1Credit registering devices actuationCash registersComputer graphics (images)Barcode
A console for the input and display of consumer product information such as pricing, etc. The console may be built into the handle of the shopping cart or as a retrofit application on existing handles. The console has a product information input device for numerical values such as product pricing, cost per unit, etc. The apparatus has a calculator and output display for such data. Some space on the console will likely be dedicated to a display panel for advertising. The console may be equipped with a bar code scanner as an alternate means of inputting such consumer data. The console should have an output display, such as a monitor, and / or a readout in order to display the product information such as: cost per unit. A video monitor may be used in connection with the console in order to provide advertising information related to products.
Owner:SMART MEDIA OF DELAWARE
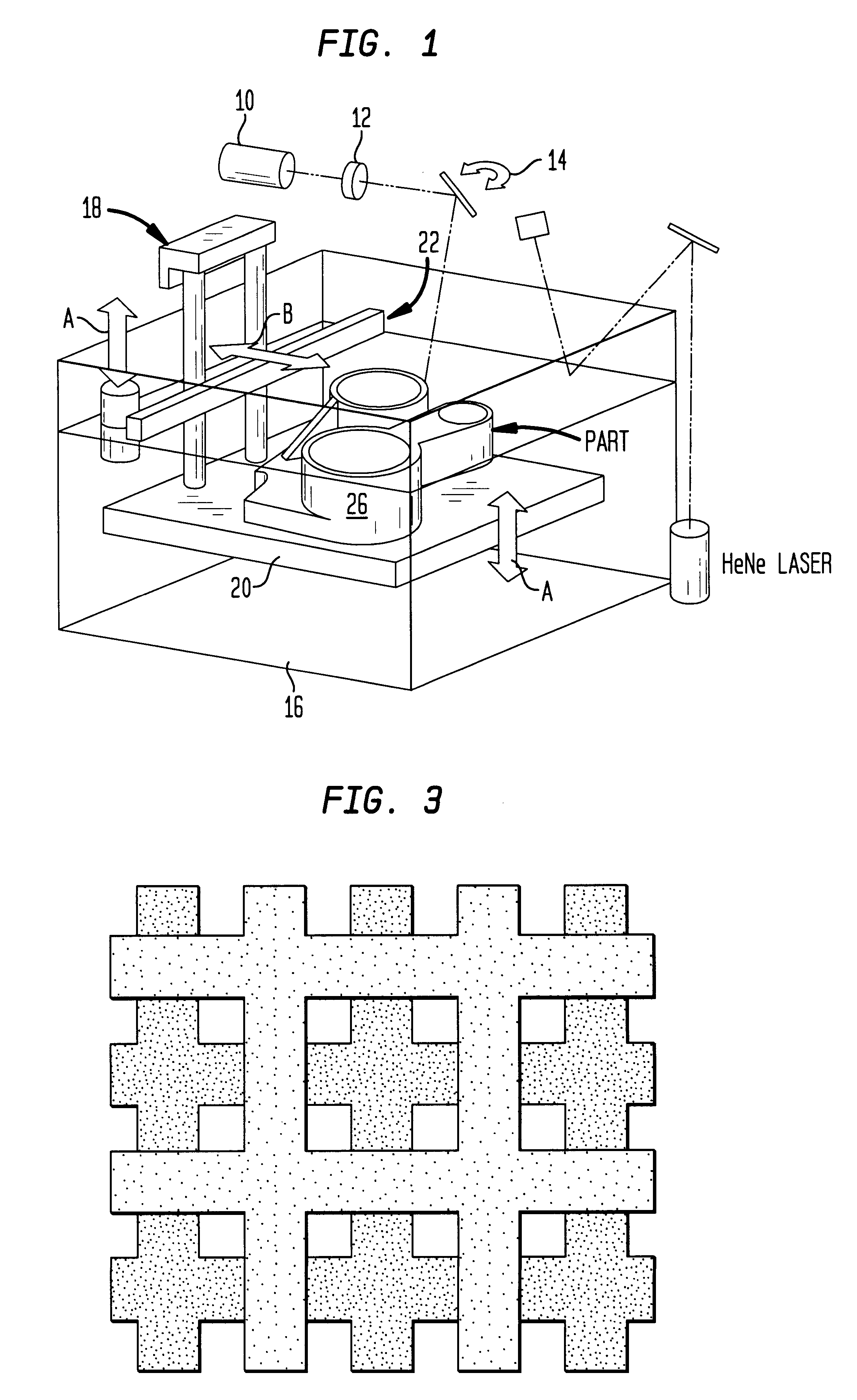
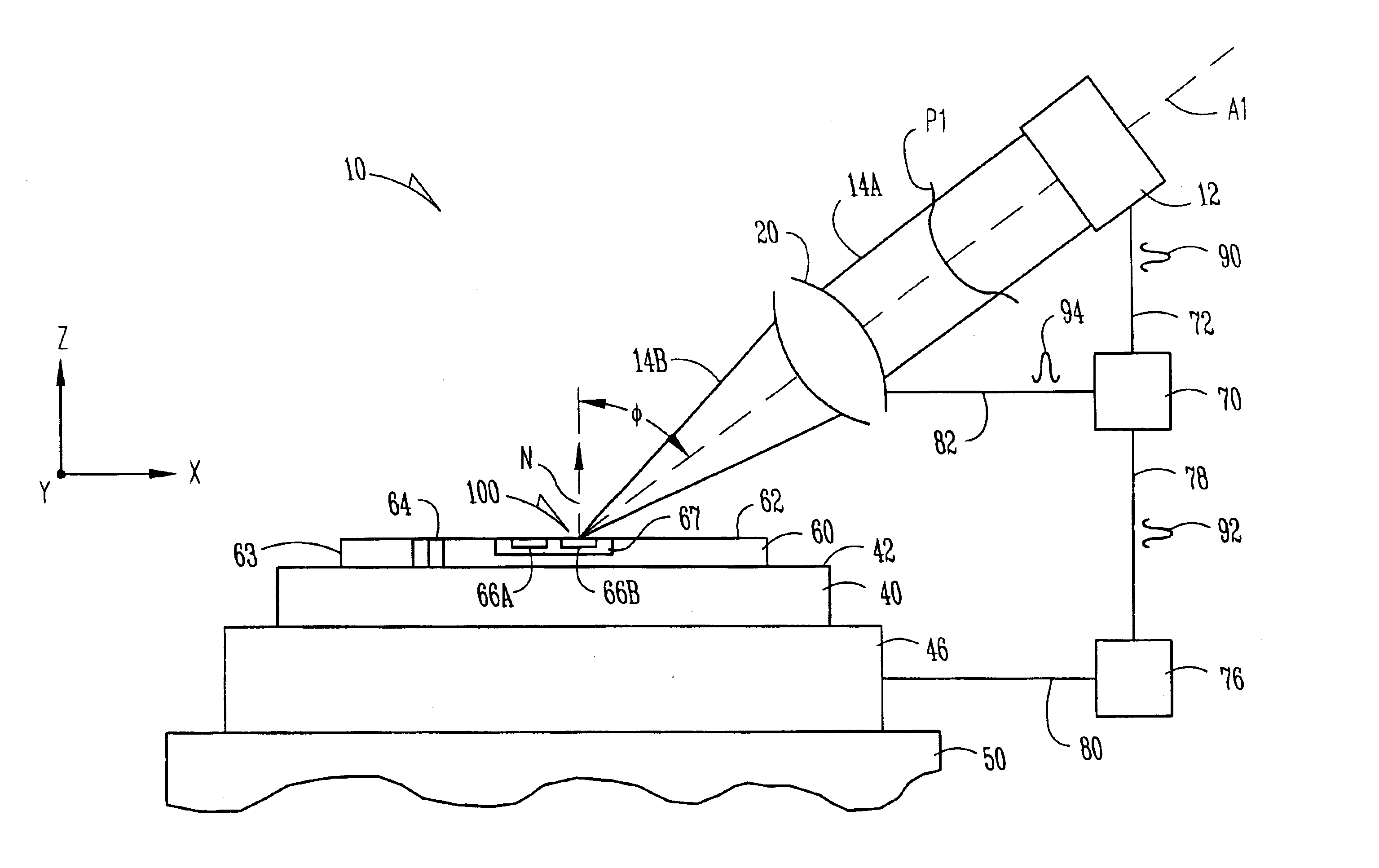
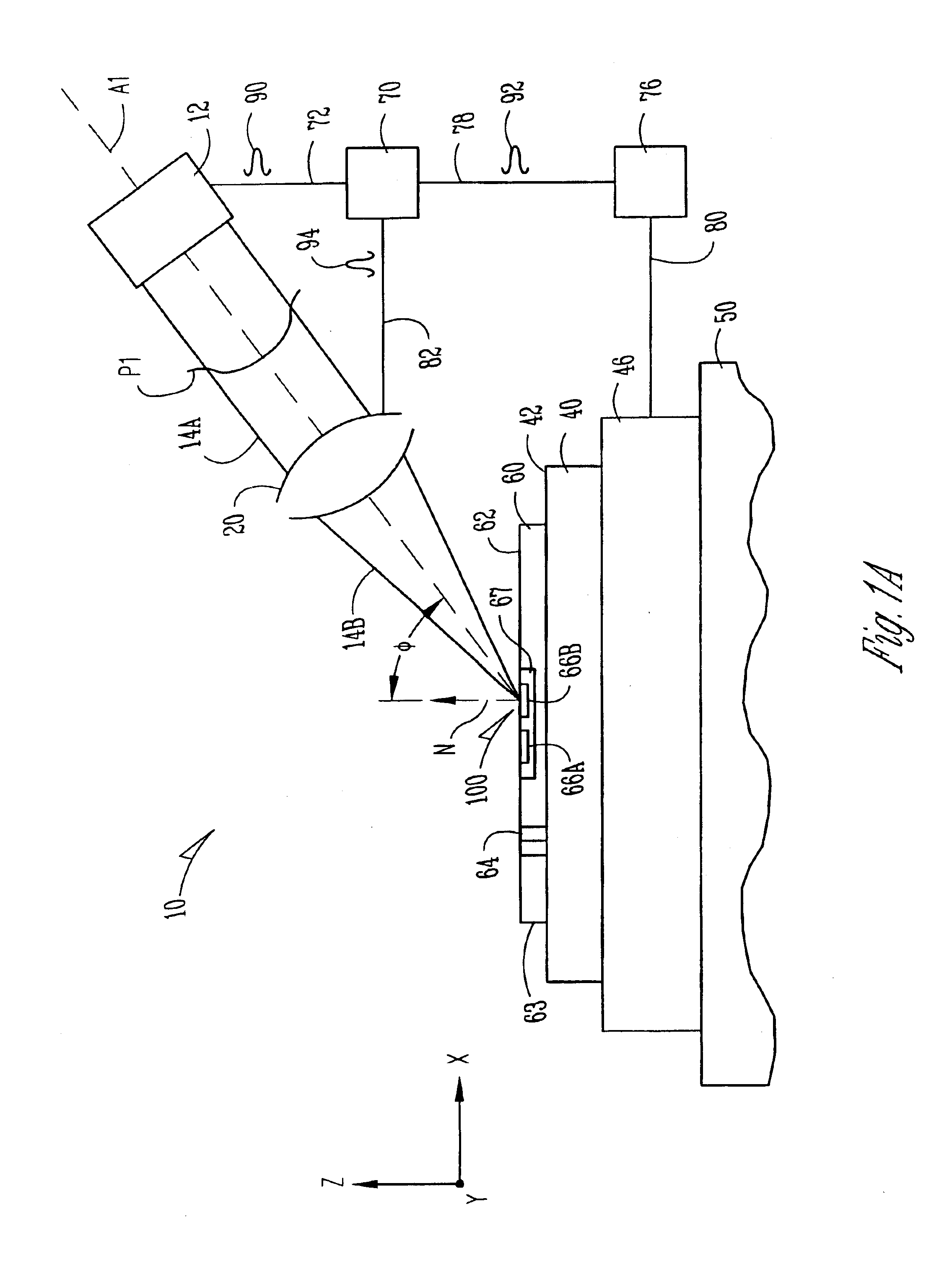
Laser scanning apparatus and methods for thermal processing
InactiveUS6747245B2Laser detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLaser scanningProcess region
Apparatus and methods for thermally processing a substrate with scanned laser radiation are disclosed. The apparatus includes a continuous radiation source and an optical system that forms an image on a substrate. The image is scanned relative to the substrate surface so that each point in the process region receives a pulse of radiation sufficient to thermally process the region.
Owner:VEECO INSTR
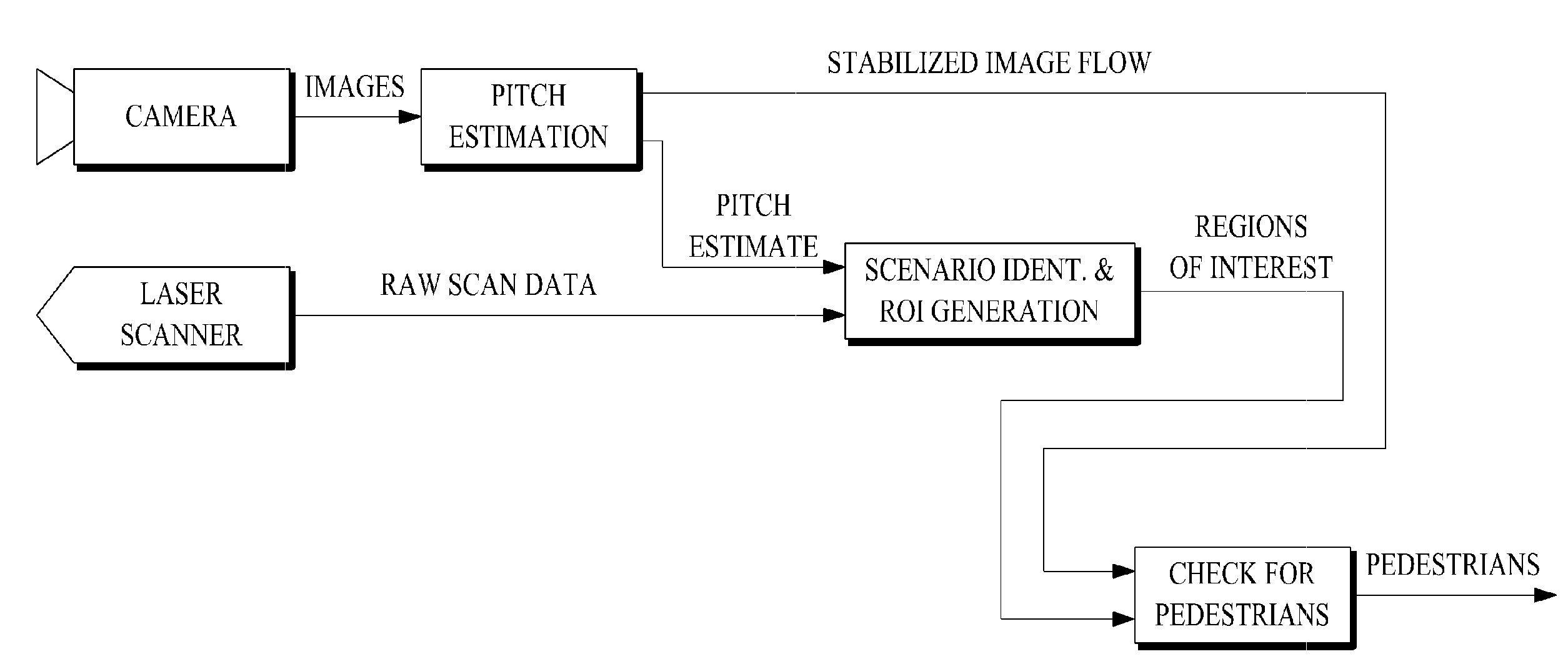
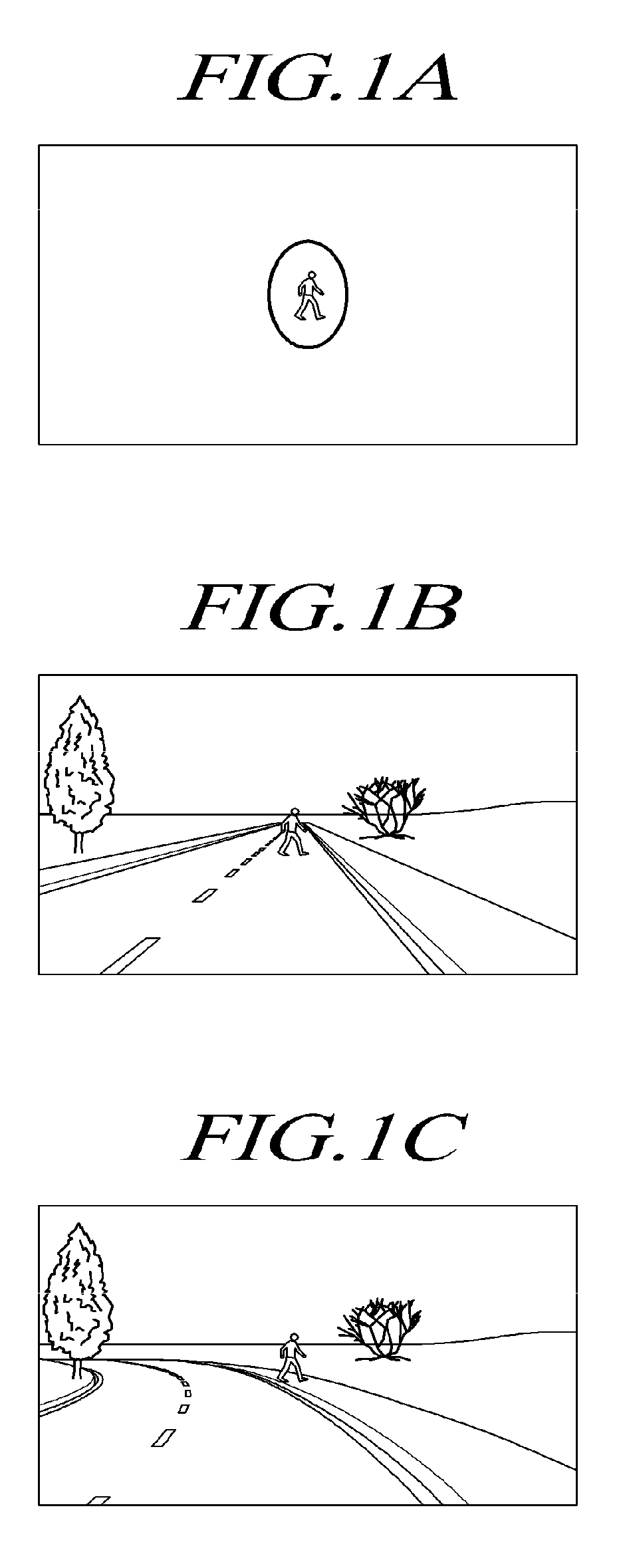
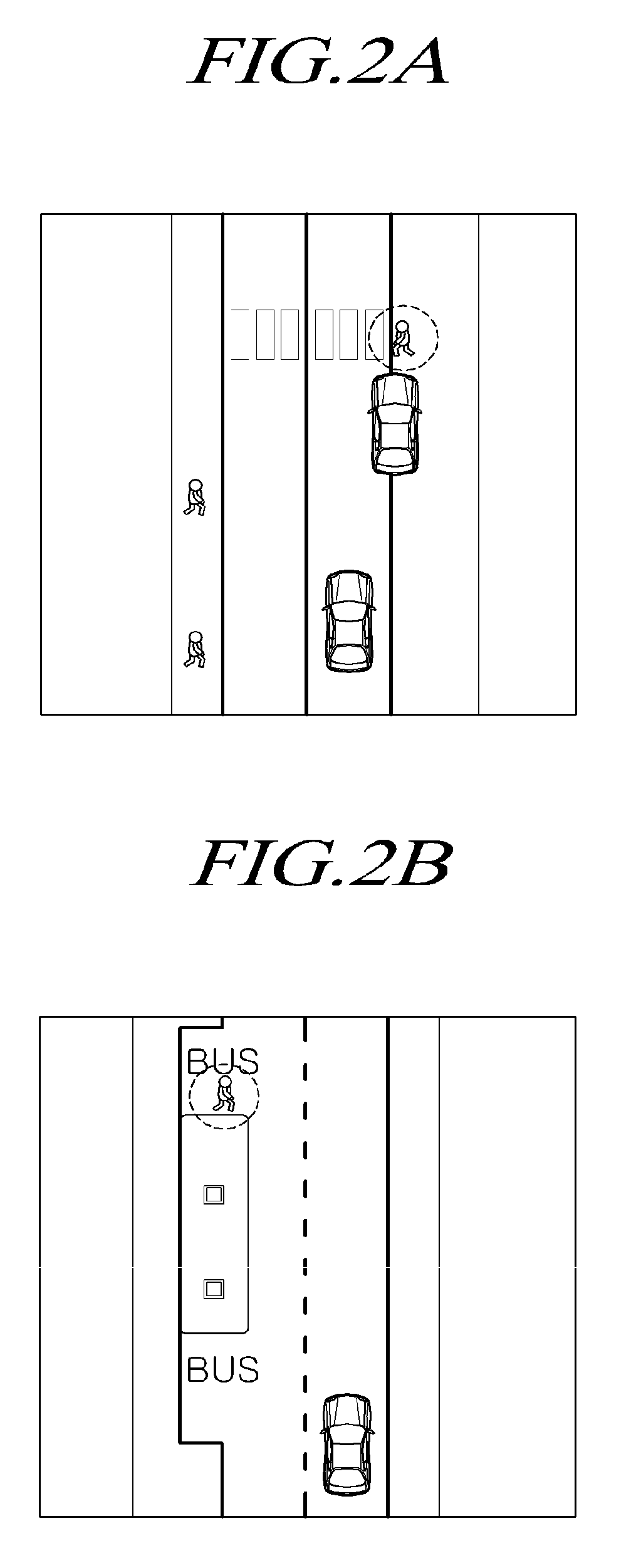
Apparatus, method for detecting critical areas and pedestrian detection apparatus using the same
ActiveUS20090303026A1Optimize timingAvoid collisionPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementAnti-collision systemsOnboard computerVisual perception
An apparatus, method for detecting critical areas and a pedestrian detection apparatus using the same are provided. An application of the pedestrian detection system is provided to help limit critical urban environment to particular areas. Contrary to traditional pedestrian detection systems that localize every pedestrians appearing in front of the subject vehicle, the apparatus first finds critical areas from urban environment and performs a focused search of pedestrians. The environment is reconstructed using a standard laser scanner but the subsequent checking for the presence of pedestrians is performed by incorporating a vision system. The apparatus identifies pedestrians within substantially limited image areas and results in boosts of timing performance, since no evaluation of critical degrees is necessary until an actual pedestrian is informed to the driver or onboard computer.
Owner:HL KLEMOVE CORP
Scannable barcode display and methods for using the same
InactiveUS6877661B2Facilitates redemptionClear wellCharacter and pattern recognitionRecord carriers used with machinesData centerData acquisition
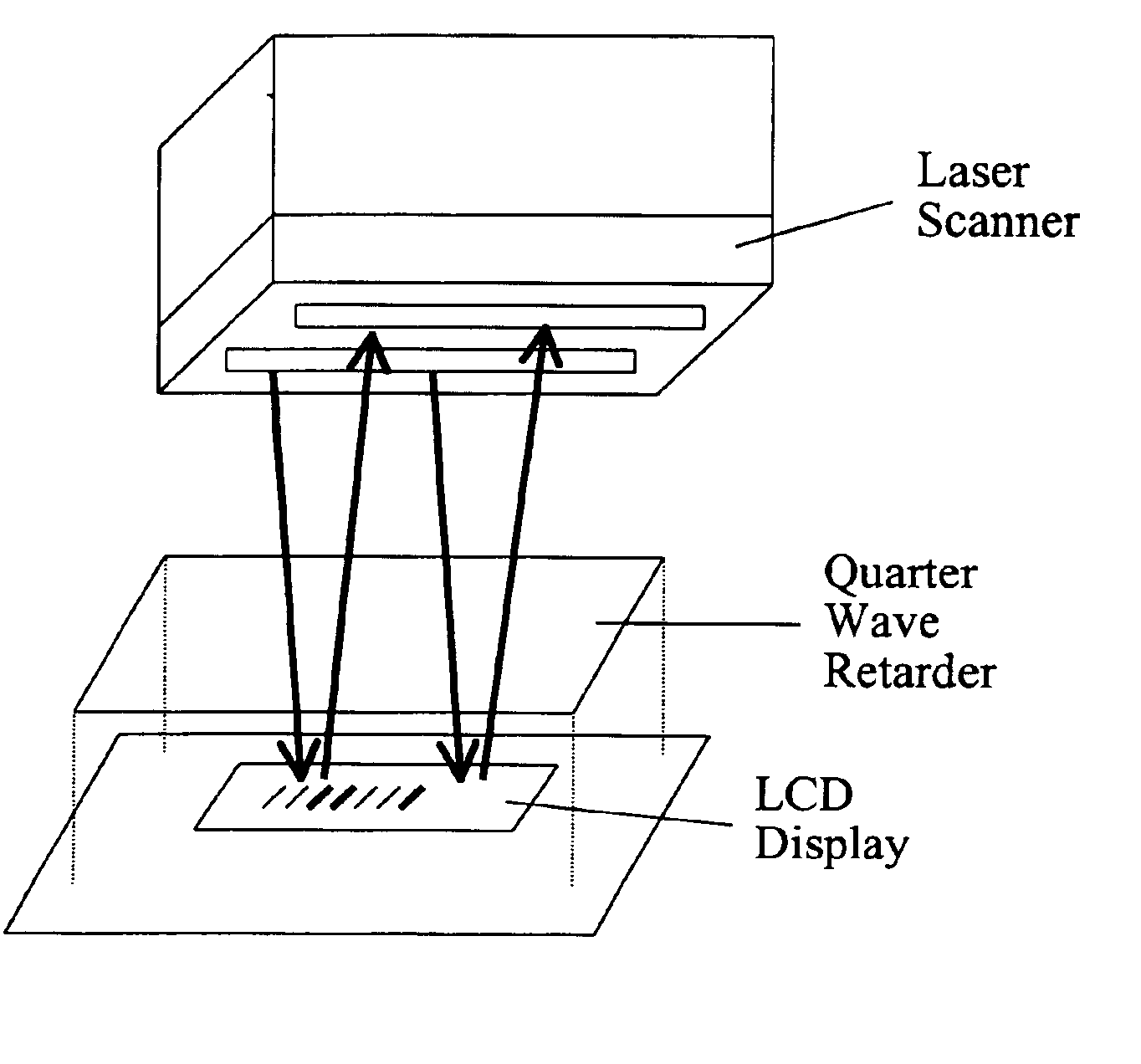
A system and method for implementing a wireless data transmission scheme through the use of a display capable of displaying symbolic information, a data acquisition device capable of identifying and capturing said displayed information and a mitigation device adapted to allow the data acquisition device to capture the symbolic information. The symbolic information may be a barcode displayed on an LCD outputting linearly polarized light. The data acquisition device may be a laser scanner, and the mitigation device may be a quarter wave retarder located between the display and the scanner. A larger system may utilize this wireless system or a different front end in a more generalized backend information transfer system. The backend system may include a centralized data center adapted to be used with retail couponing, ticketing, digital receipts, or a plurality of other information systems in which data is used separately from its storage location.
Owner:WEBB RICHARD M +4
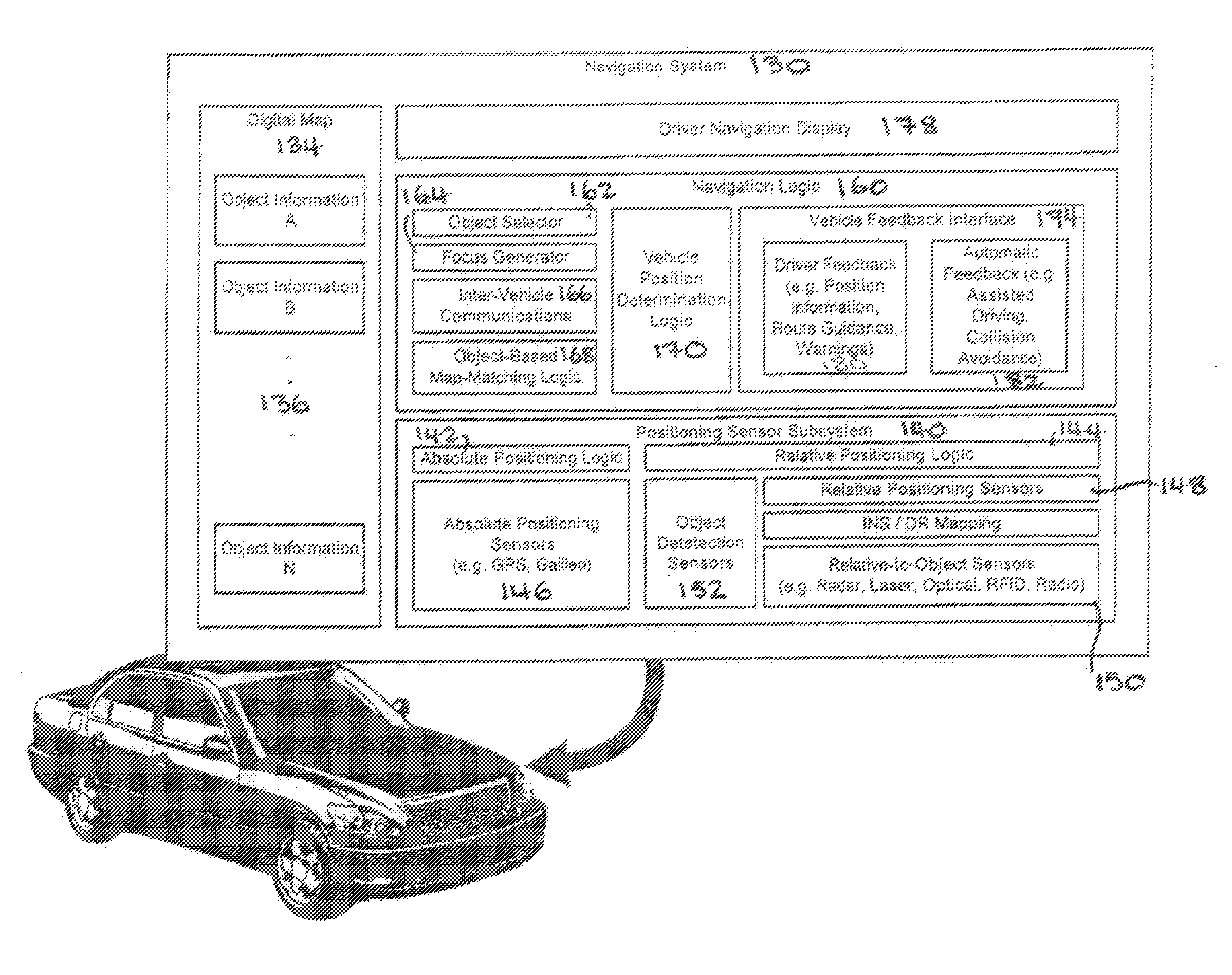
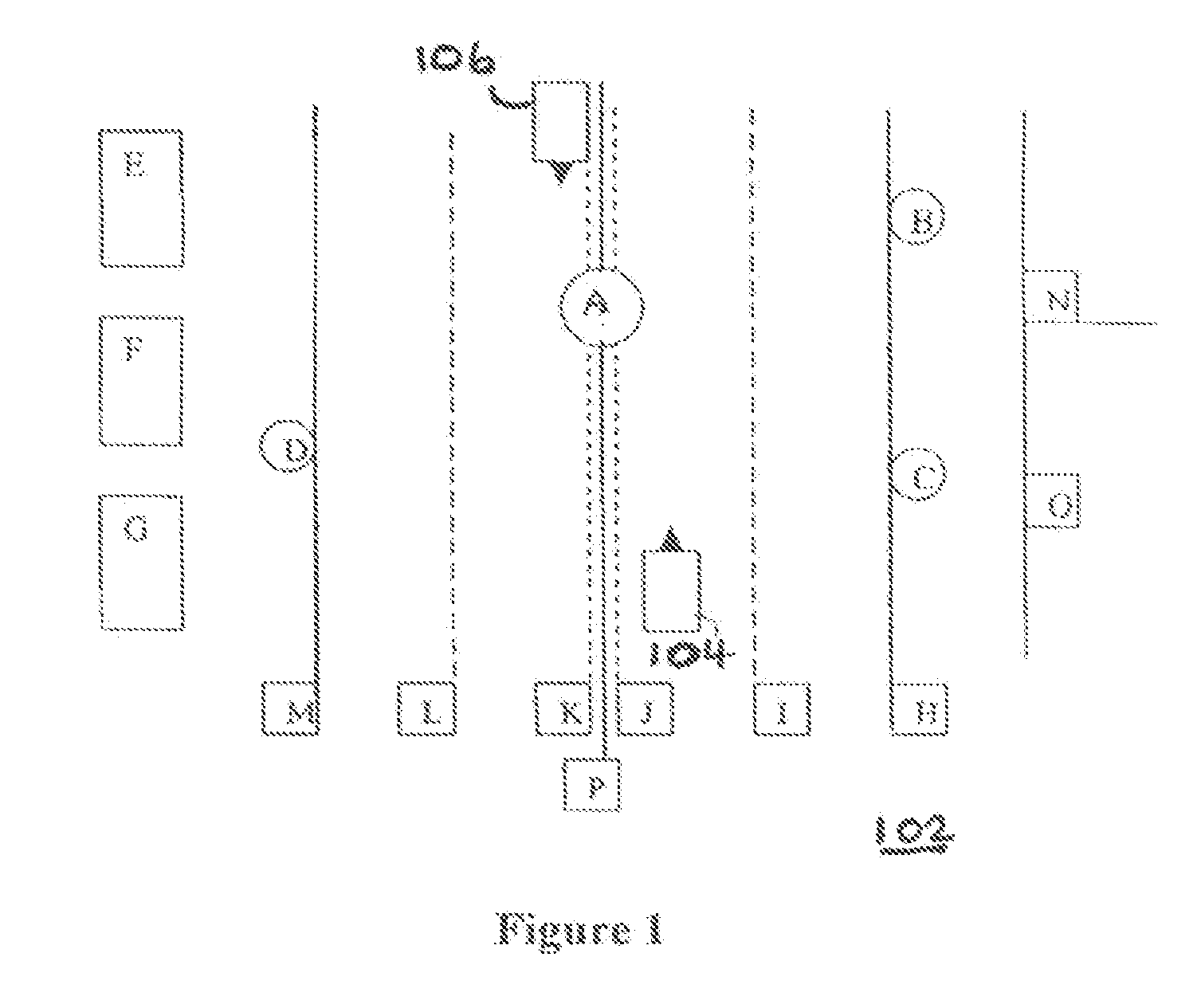
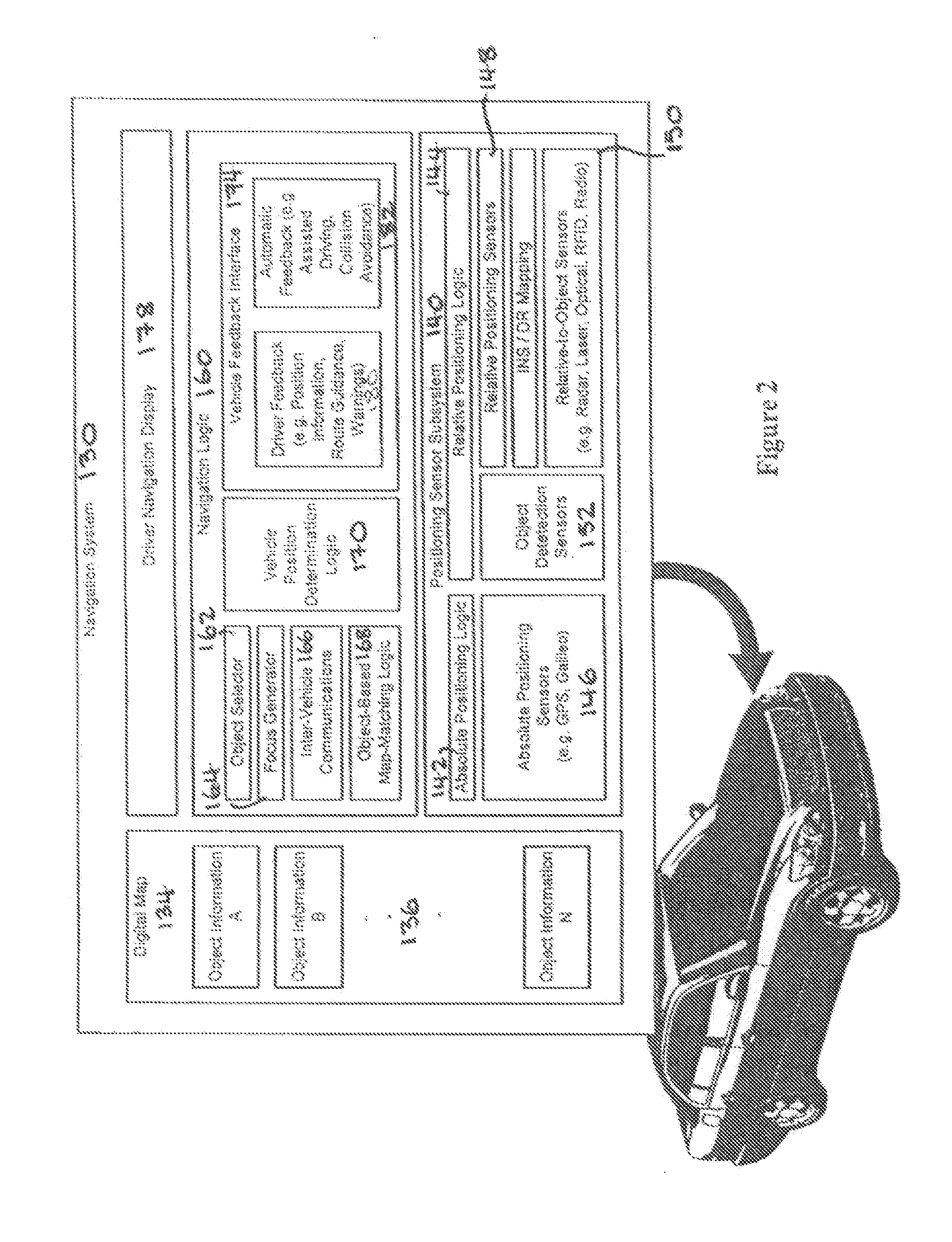
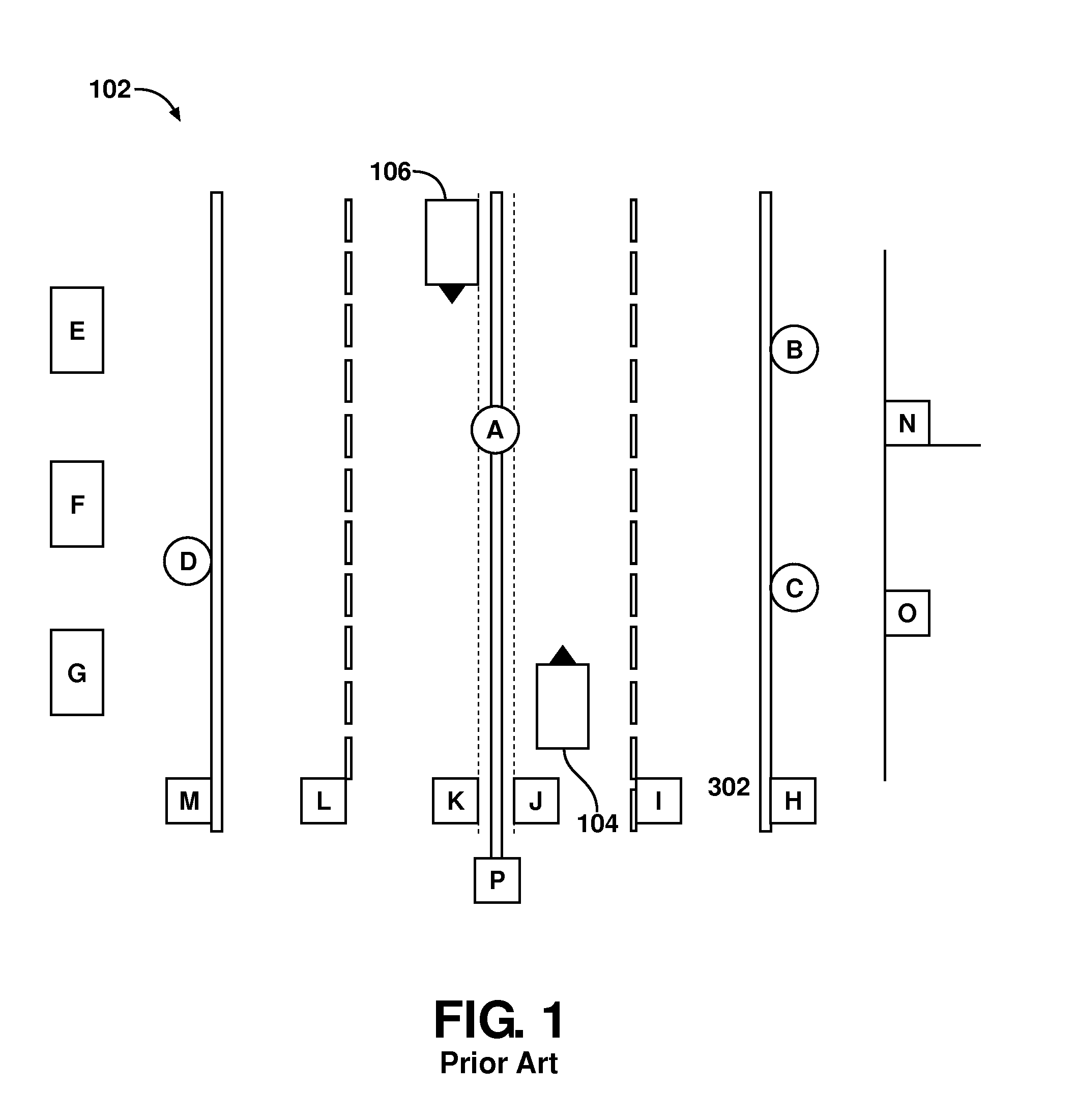
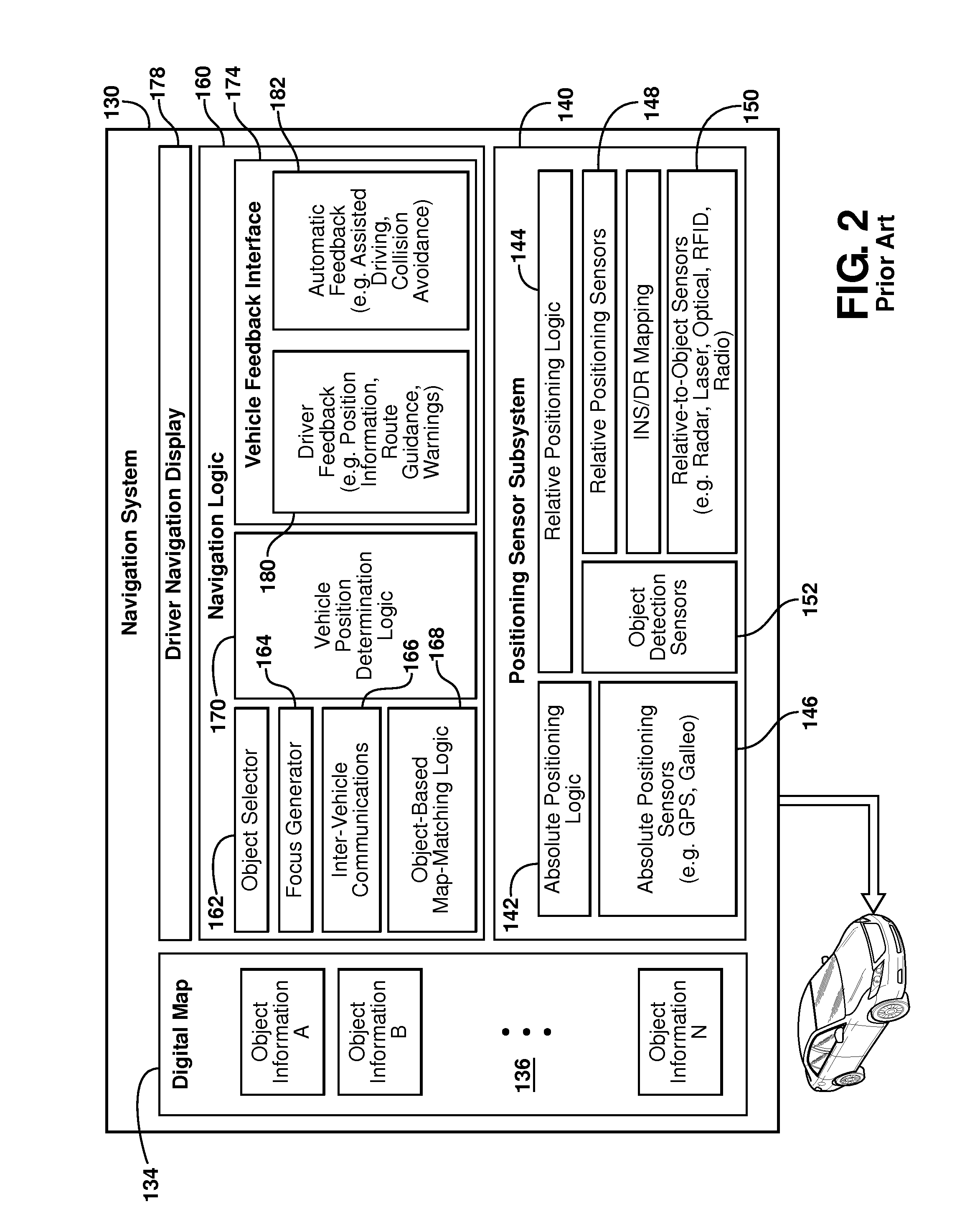
System and method for vehicle navigation and piloting including absolute and relative coordinates
InactiveUS20080243378A1Enhanced driving directionAccurate locationInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlRadarLaser scanning
A navigation system for use in a vehicle. The system includes an absolute position sensor, such as GPS, in addition to one or more additional sensors, such as a camera, laser scanner, or radar. The system further comprises a digital map or database that includes records for at least some of the vehicle's surrounding objects. These records can include relative positional attributes and traditional absolute positions. As the vehicle moves, sensors sense the presence of at least some of these objects, and measure the vehicle's relative position to those objects. This information, together with the absolute positional information and the added map information, is used to determine the vehicle's location, and support features such as enhanced driving directions, collision avoidance, or automatic assisted driving. In accordance with an embodiment, the system also allows some objects to be attributed using relative positioning, without recourse to storing absolute position information.
Owner:TELE ATLAS NORTH AMERICA
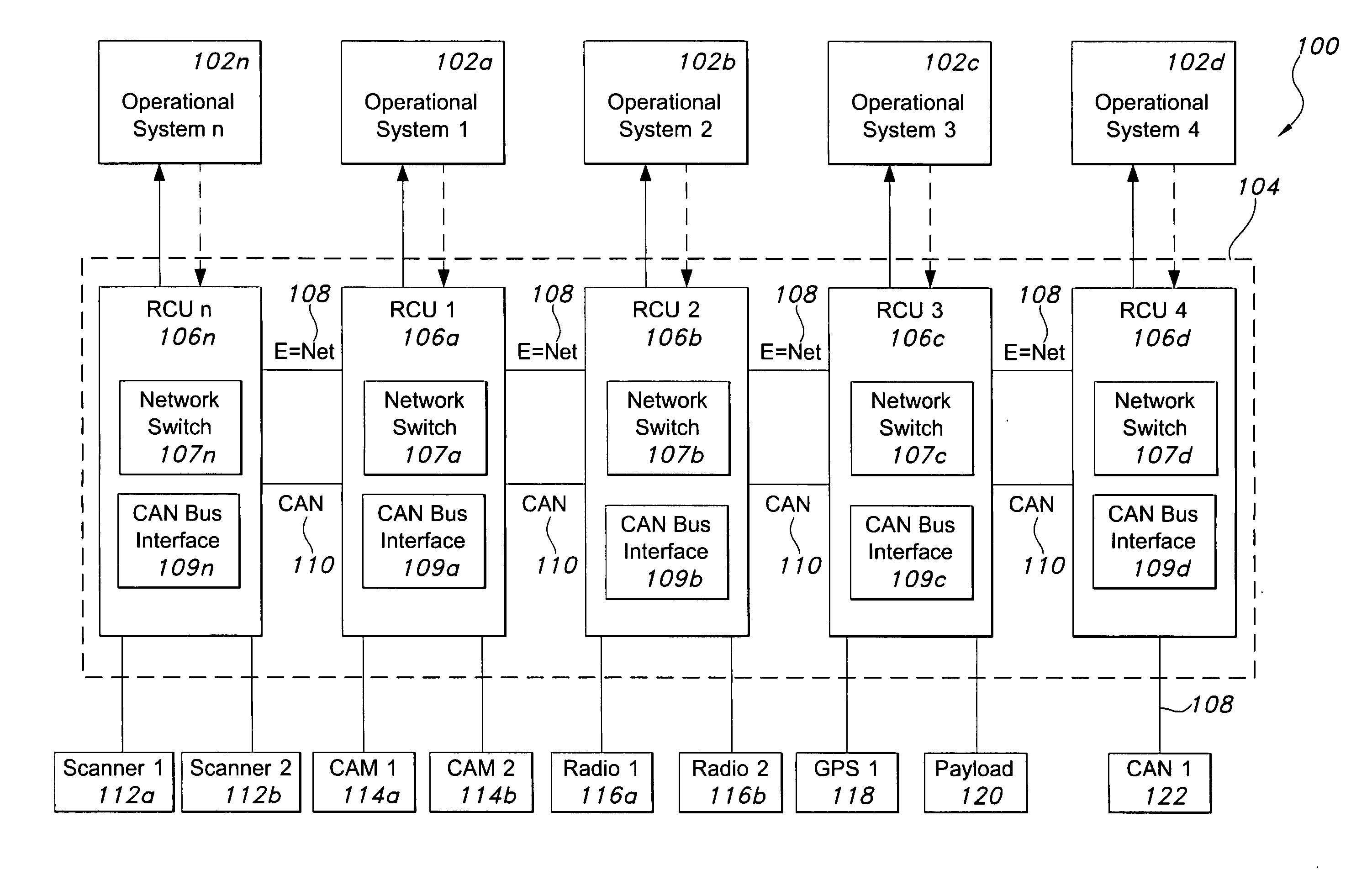
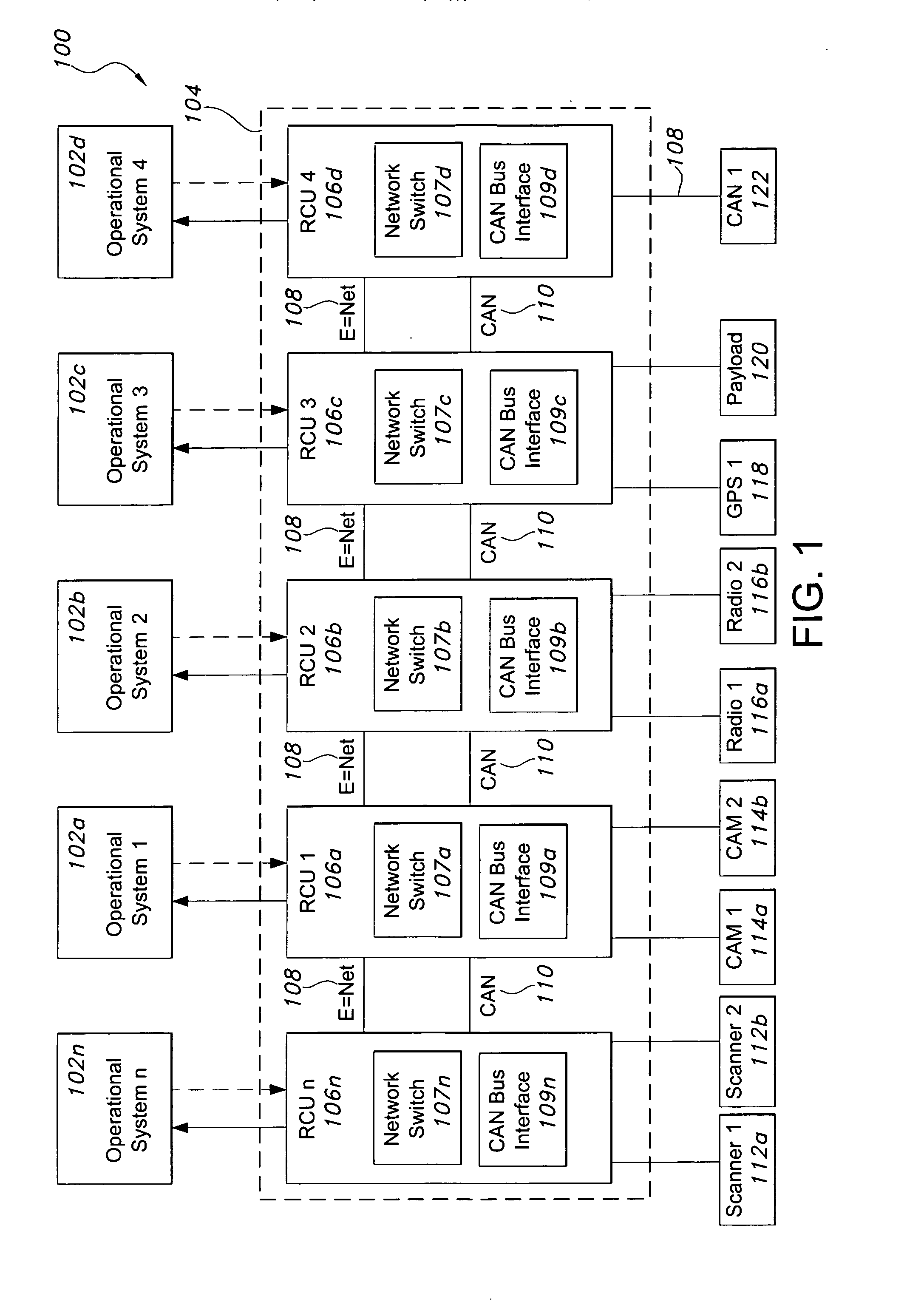
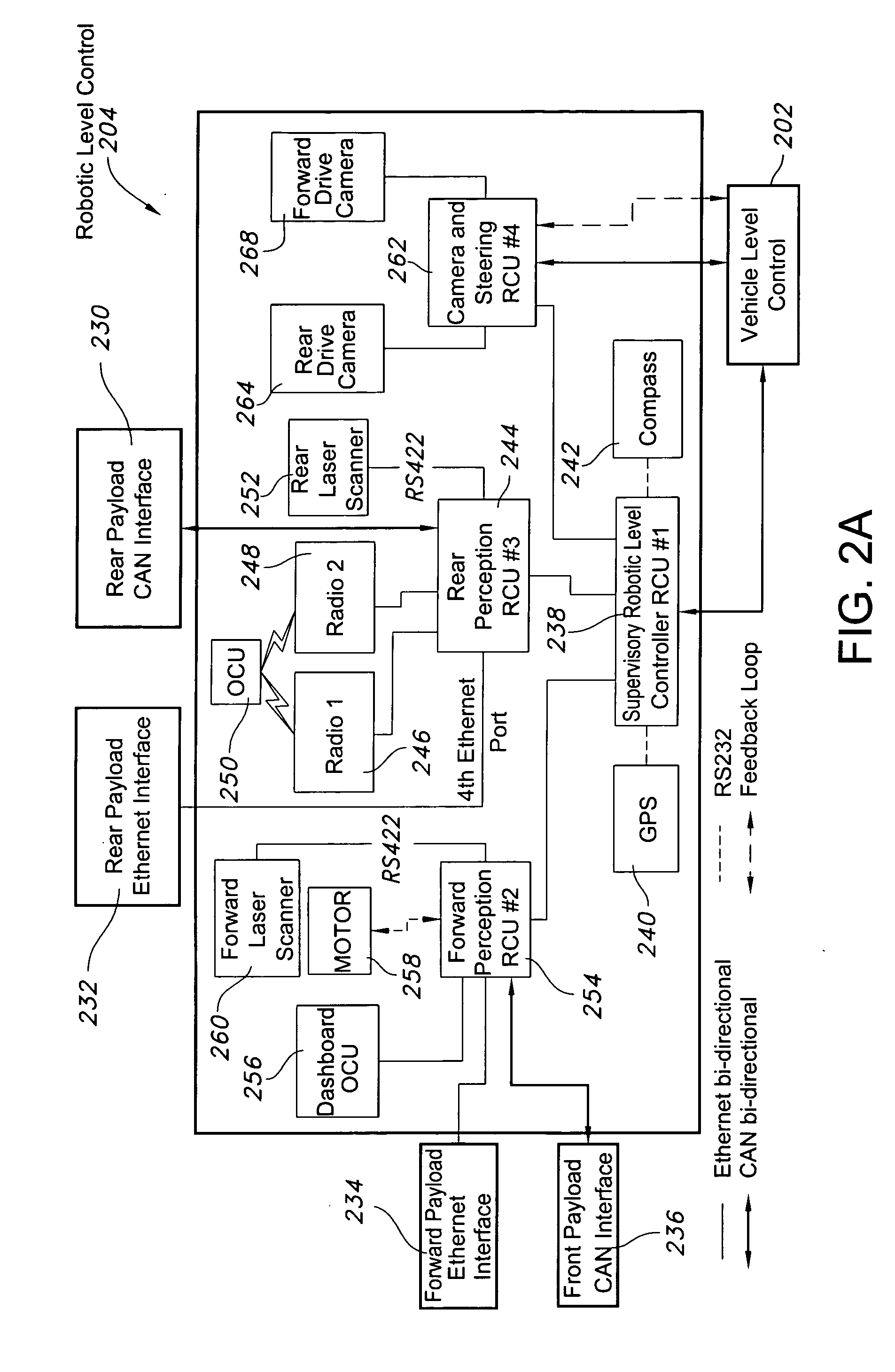
Networked multi-role robotic vehicle
ActiveUS20070198144A1Autonomous decision making processAutomatic initiationsControl signalControl system
An autonomous vehicle and systems having an interface for payloads that allows integration of various payloads with relative ease. There is a vehicle control system for controlling an autonomous vehicle, receiving data, and transmitting a control signal on at least one network. A payload is adapted to detachably connect to the autonomous vehicle, the payload comprising a network interface configured to receive the control signal from the vehicle control system over the at least one network. The vehicle control system may encapsulate payload data and transmit the payload data over the at least one network, including Ethernet or CAN networks. The payload may be a laser scanner, a radio, a chemical detection system, or a Global Positioning System unit. In certain embodiments, the payload is a camera mast unit, where the camera communicates with the autonomous vehicle control system to detect and avoid obstacles. The camera mast unit may be interchangeable, and may include structures for receiving additional payload components.
Owner:DEERE & CO +1
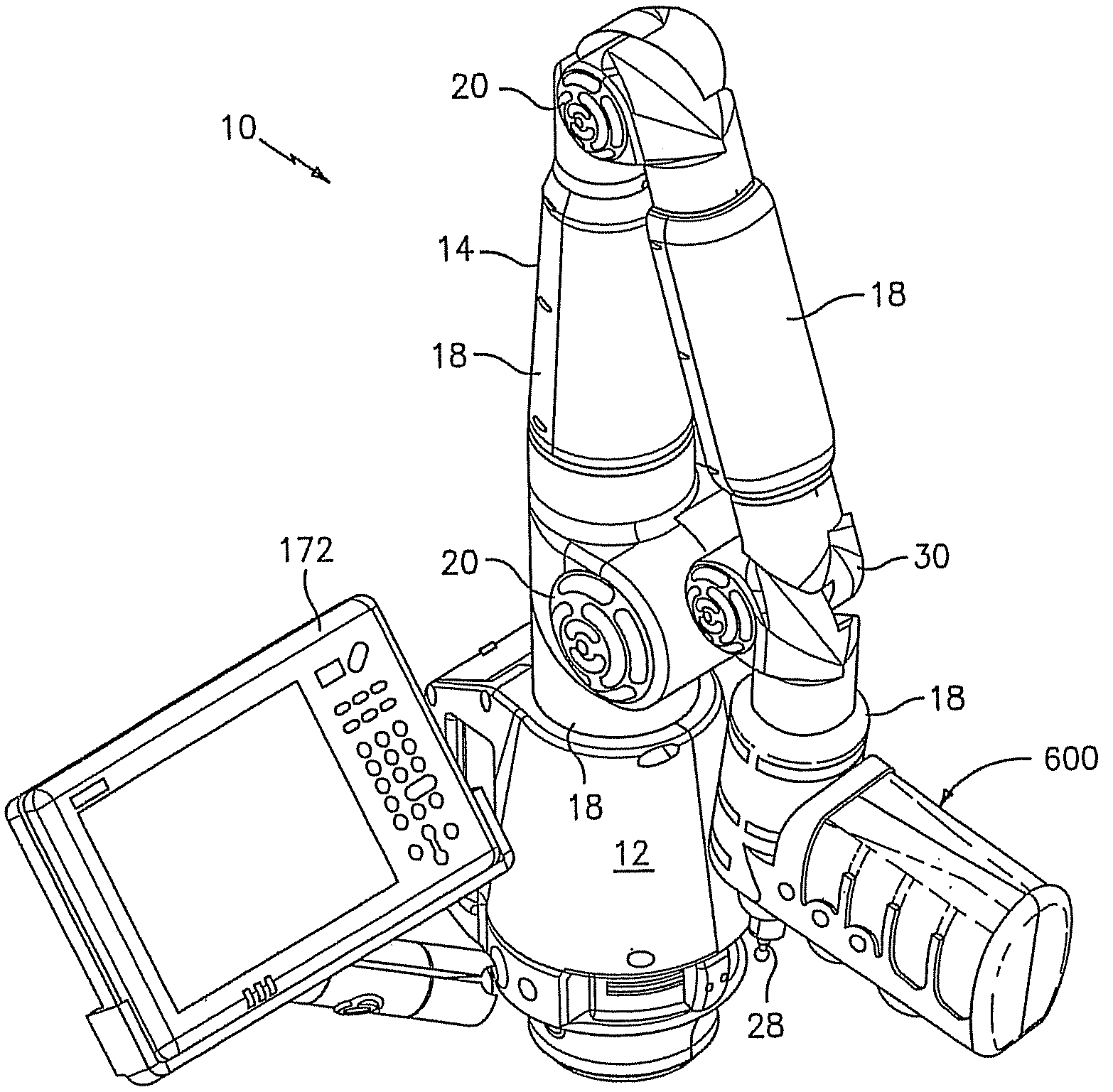
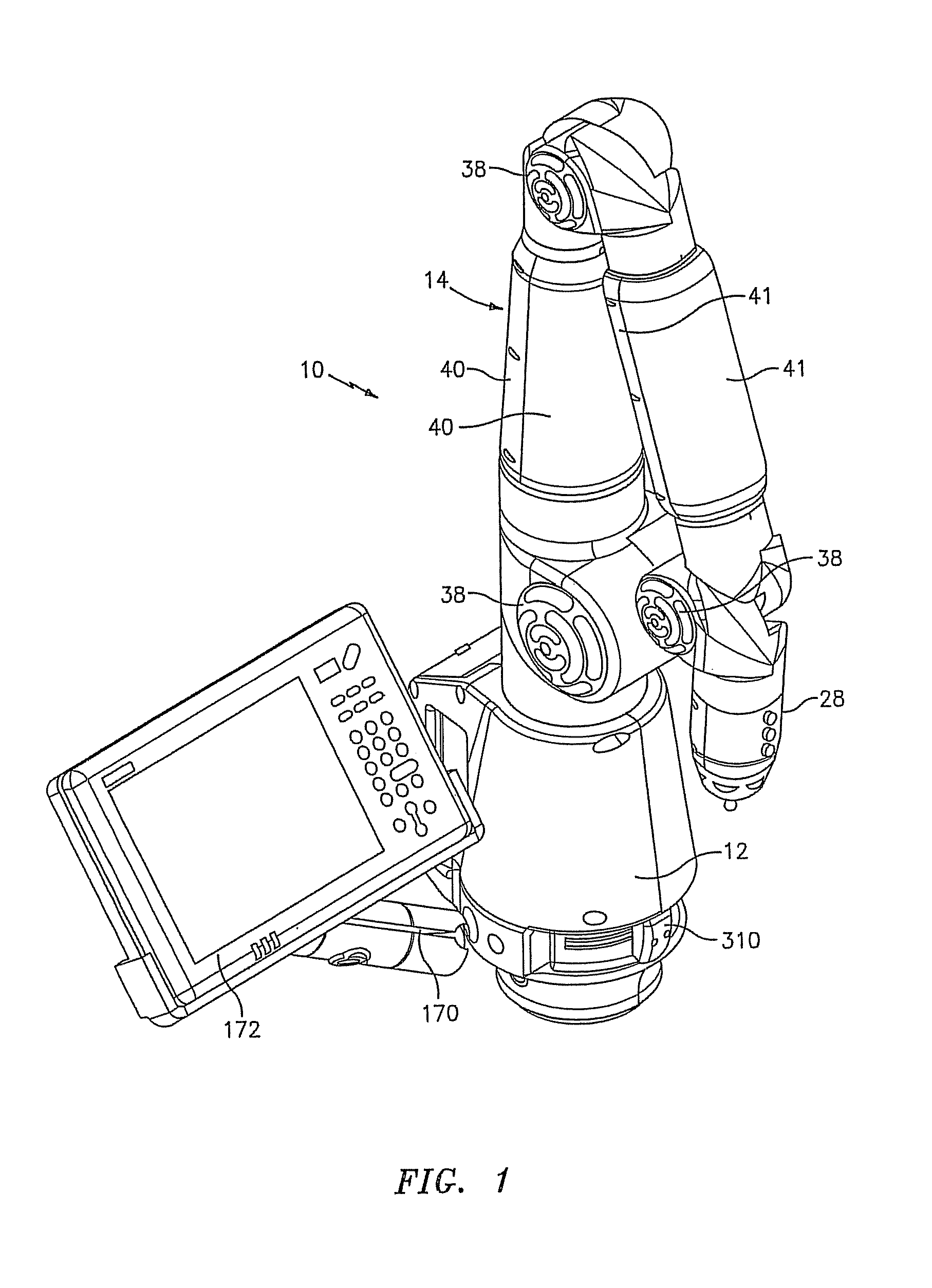
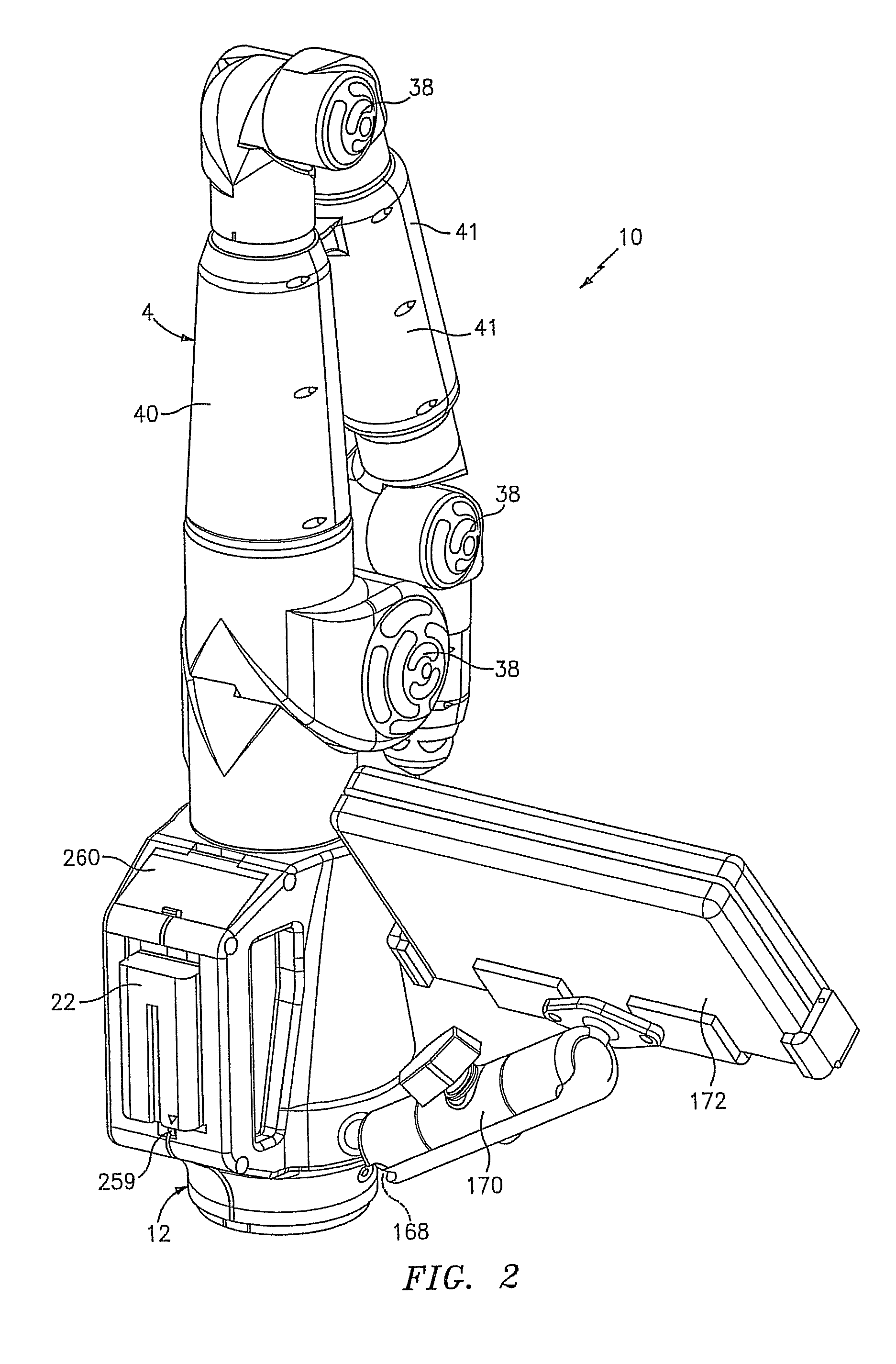
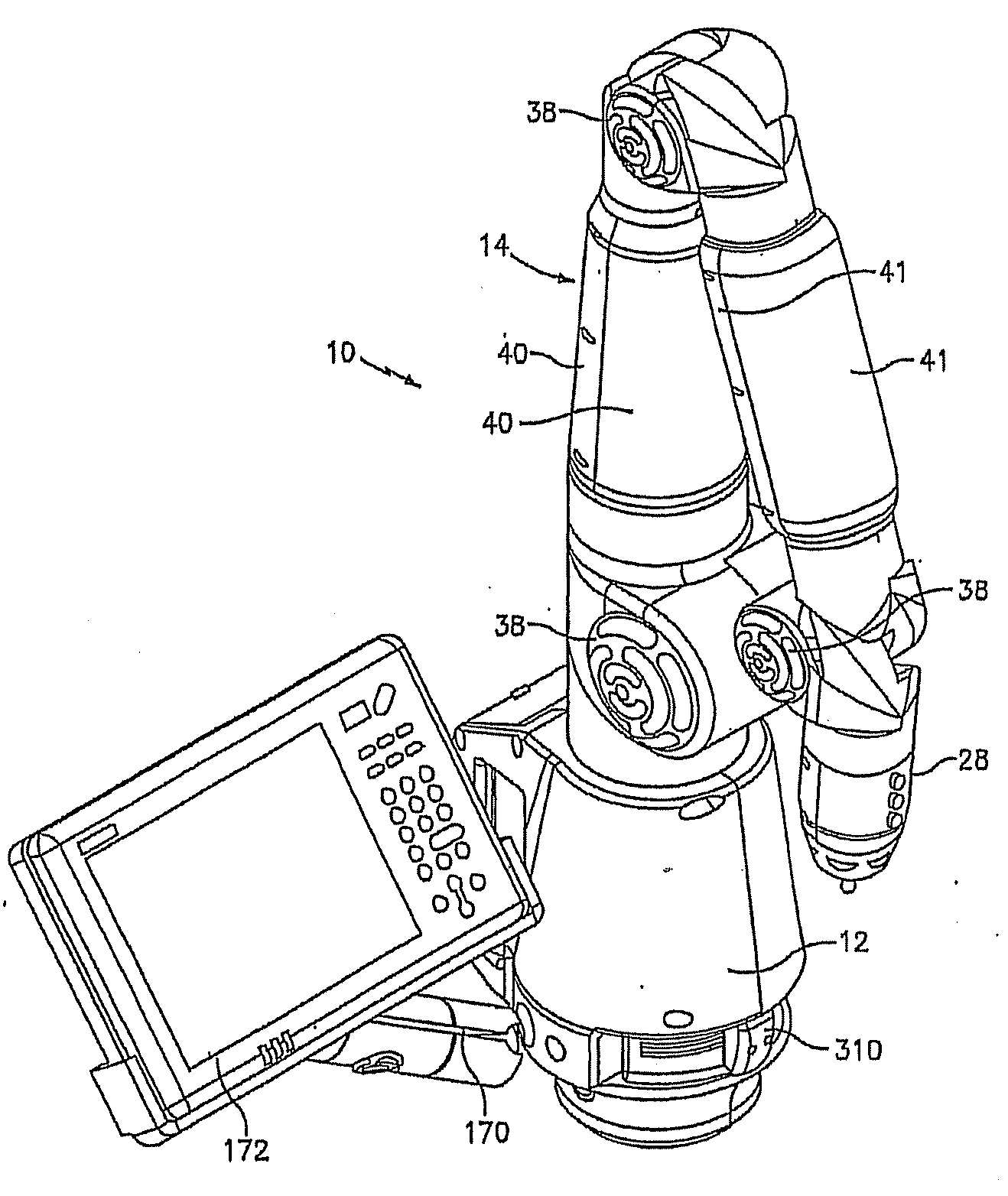
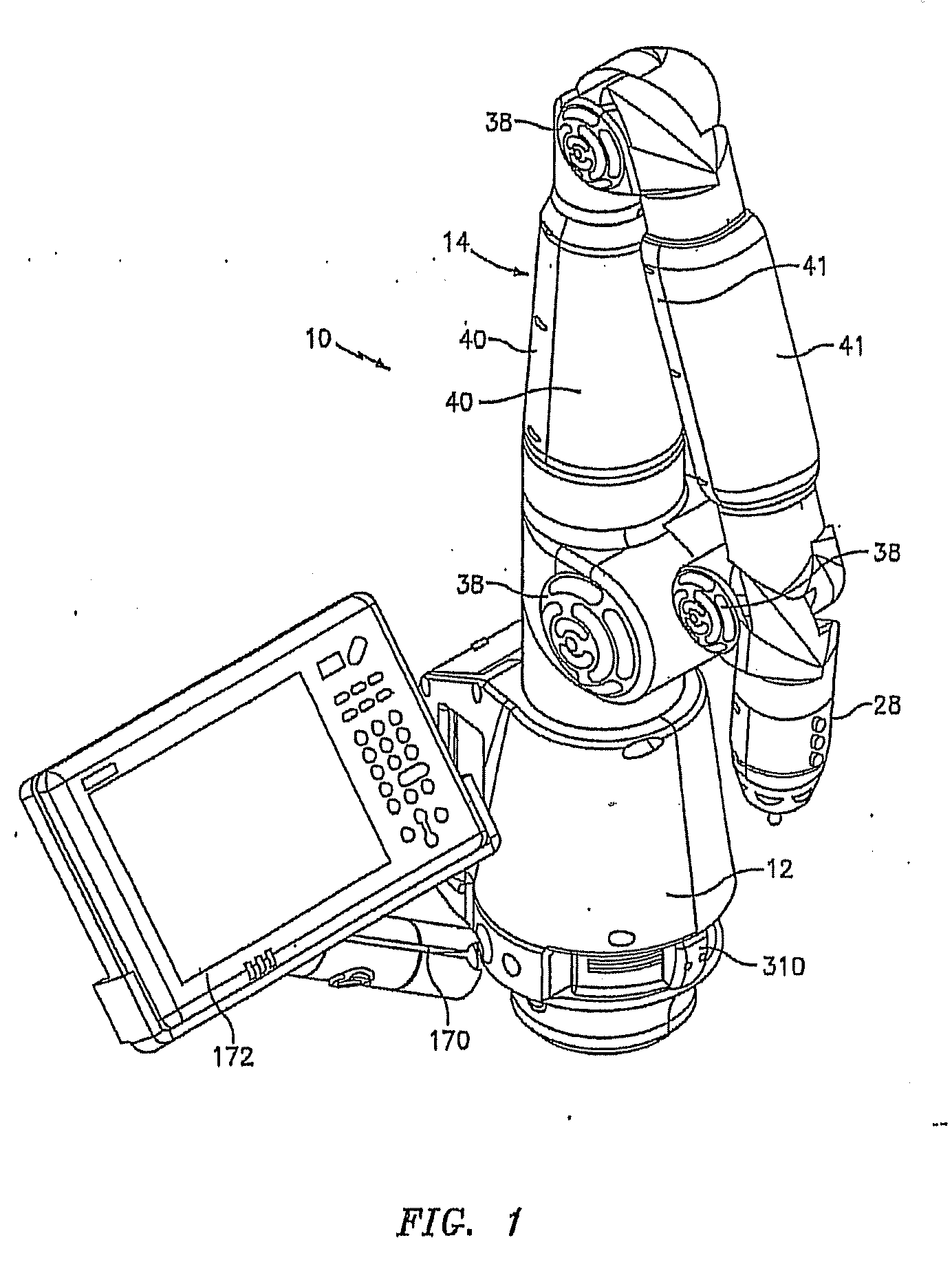
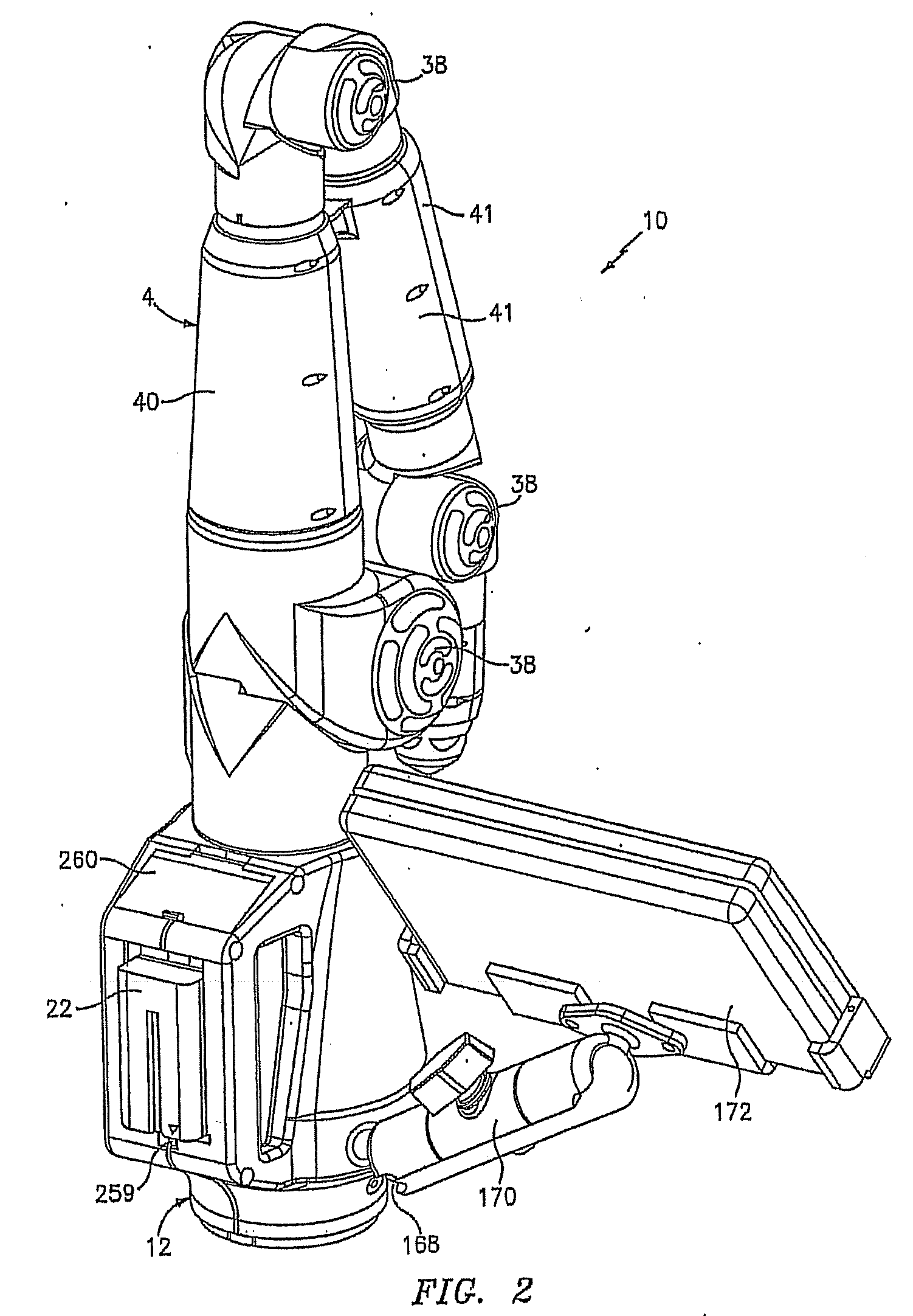
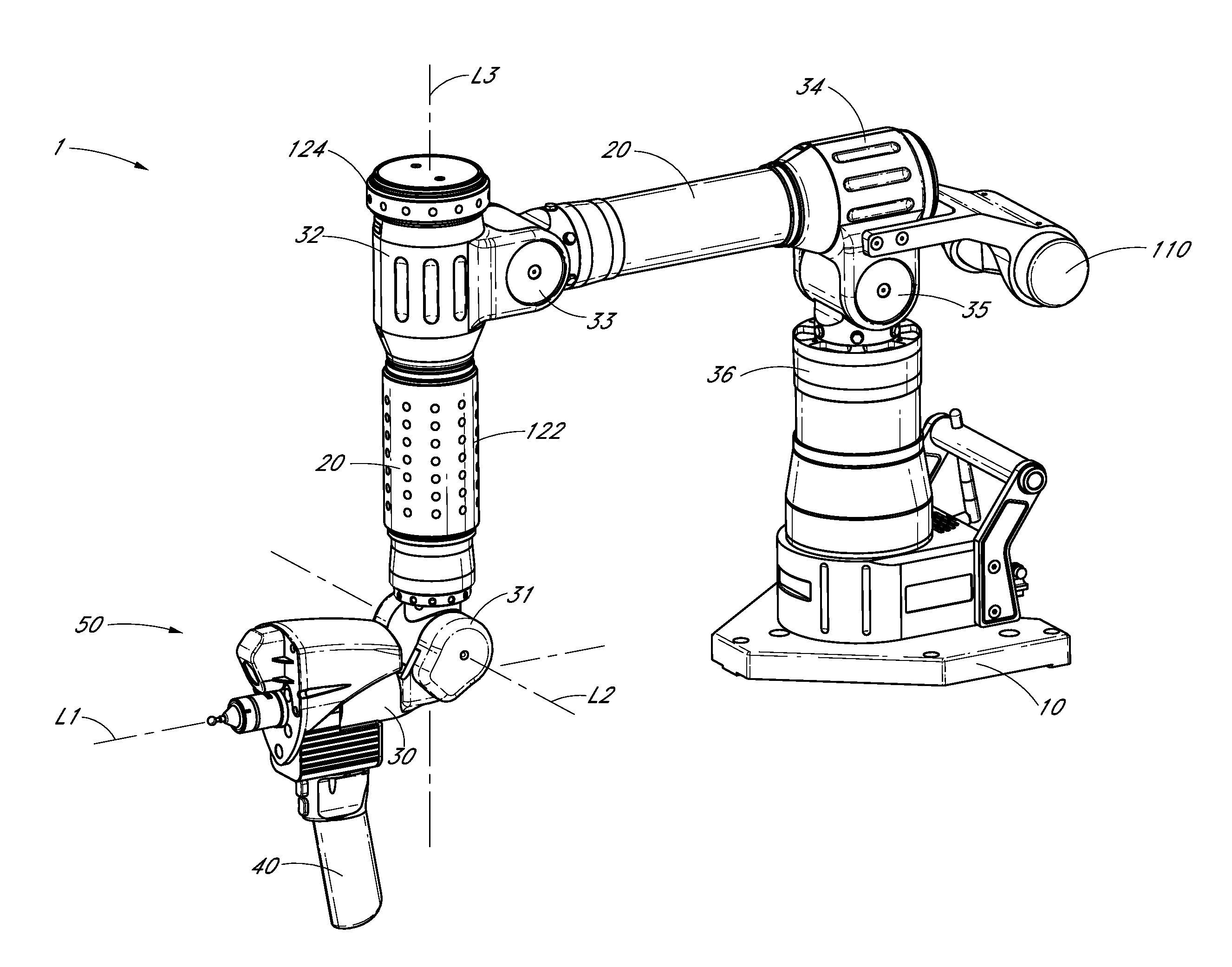
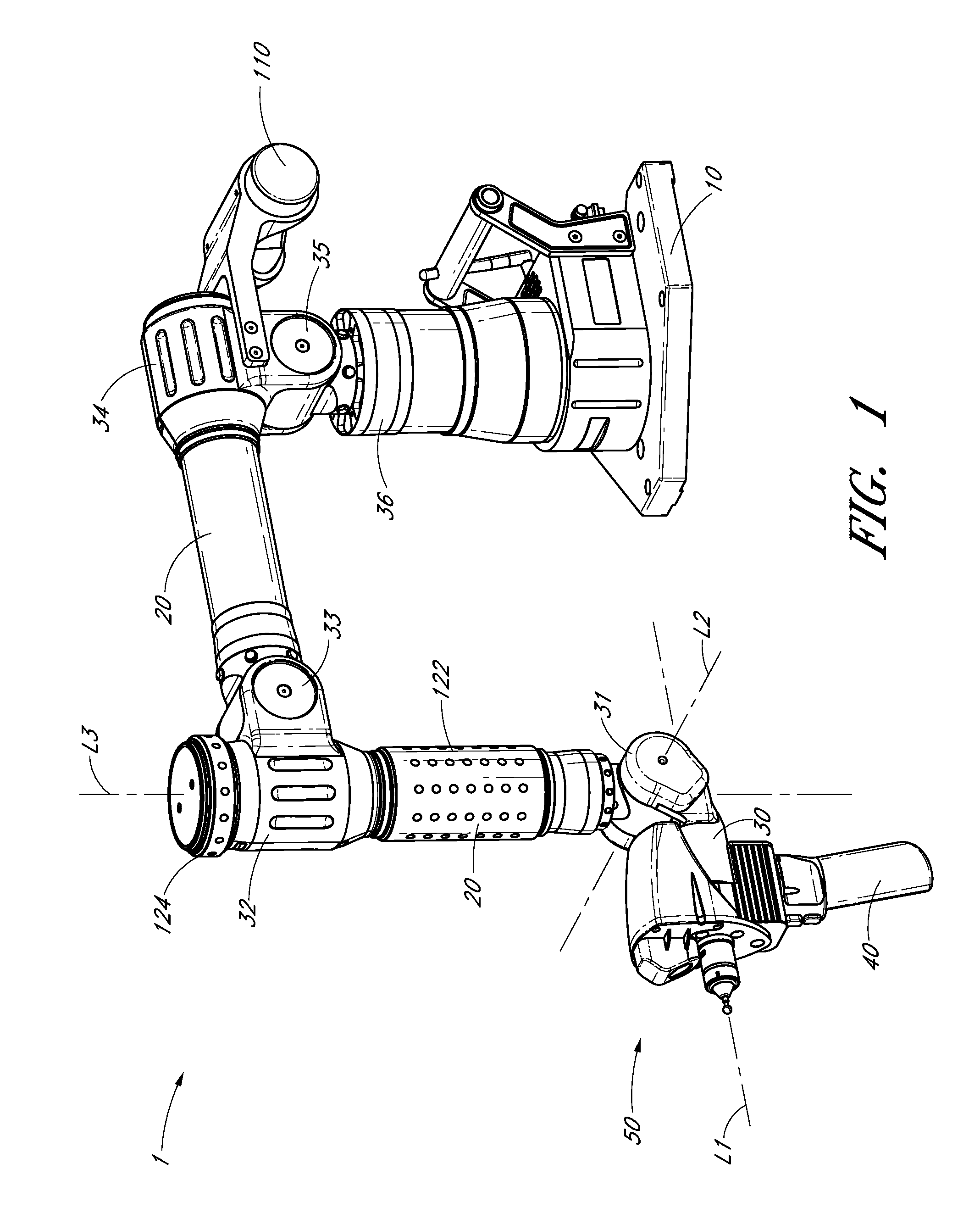
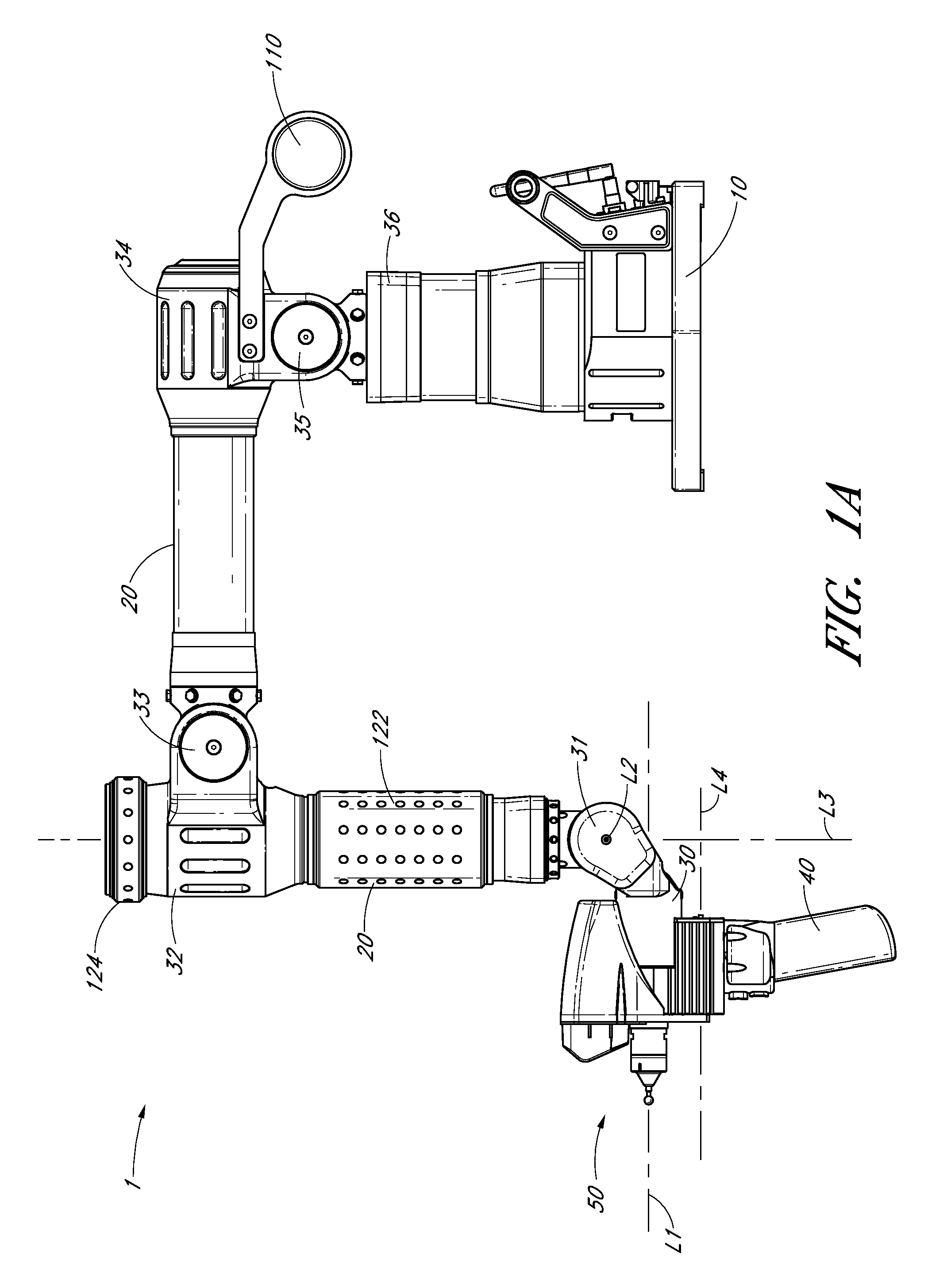
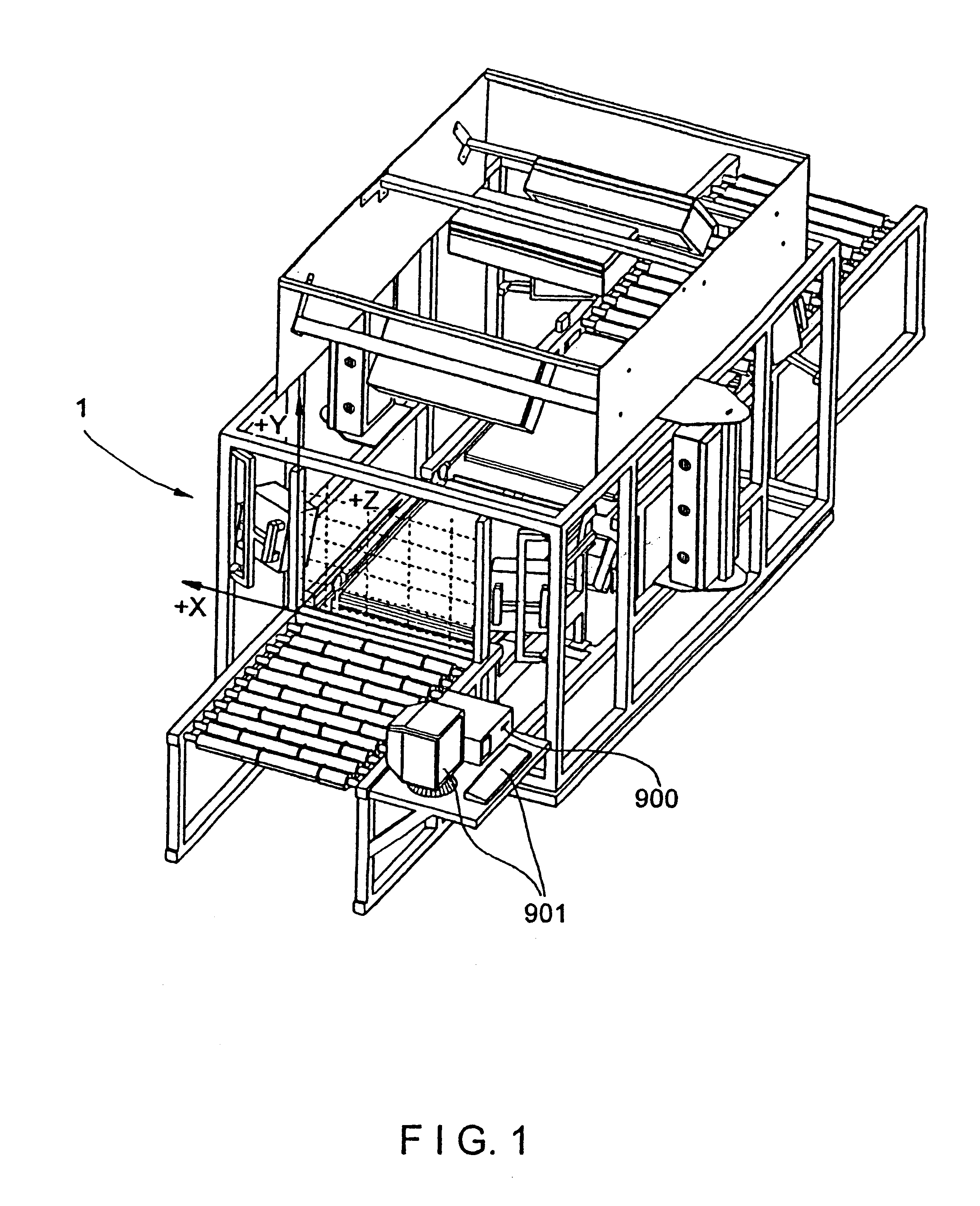
Portable coordinate measurement machine with integrated line laser scanner
InactiveUS7246030B2Easy to convertEasy to distinguishDigital computer detailsMechanical clearance measurementsLaser scanningBiomedical engineering
A portable coordinate measurement machine for measuring the position of an object in a selected volume includes a positionable articulated arm having a plurality of jointed arm segments. The arm includes a measurement probe having an integrated line laser scanner mounted thereon. The laser may be a thermally stabilized laser.
Owner:FARO TECH INC
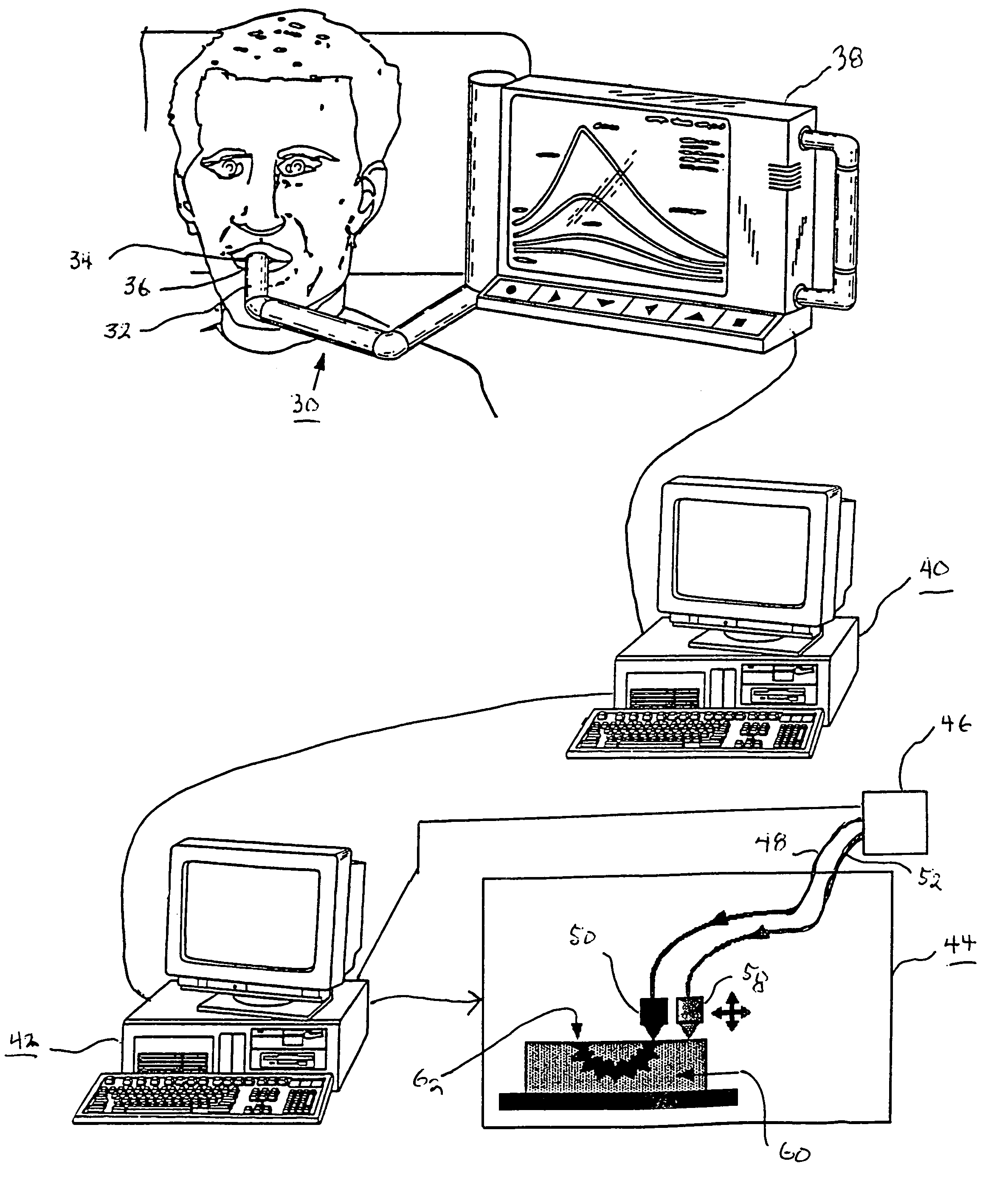
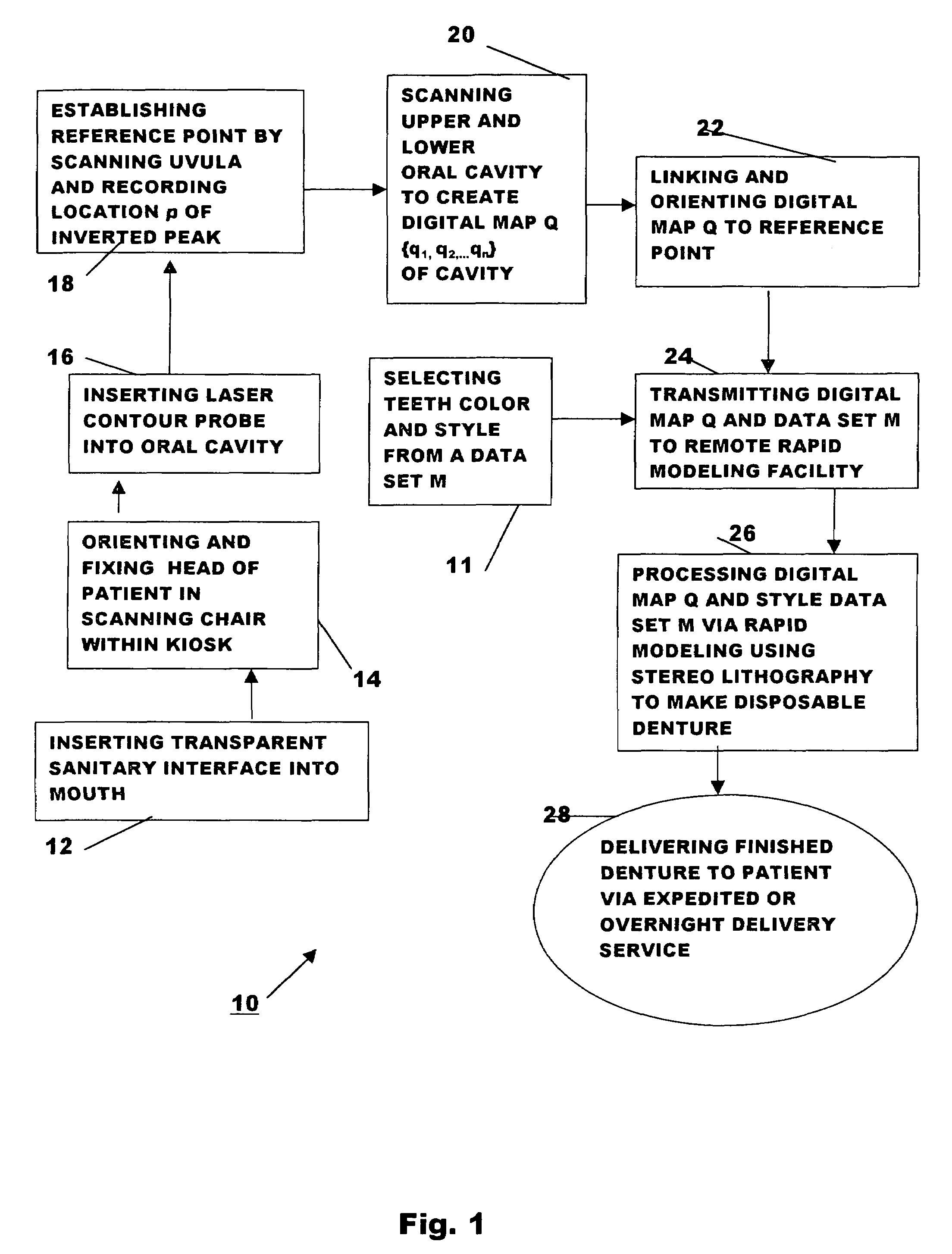
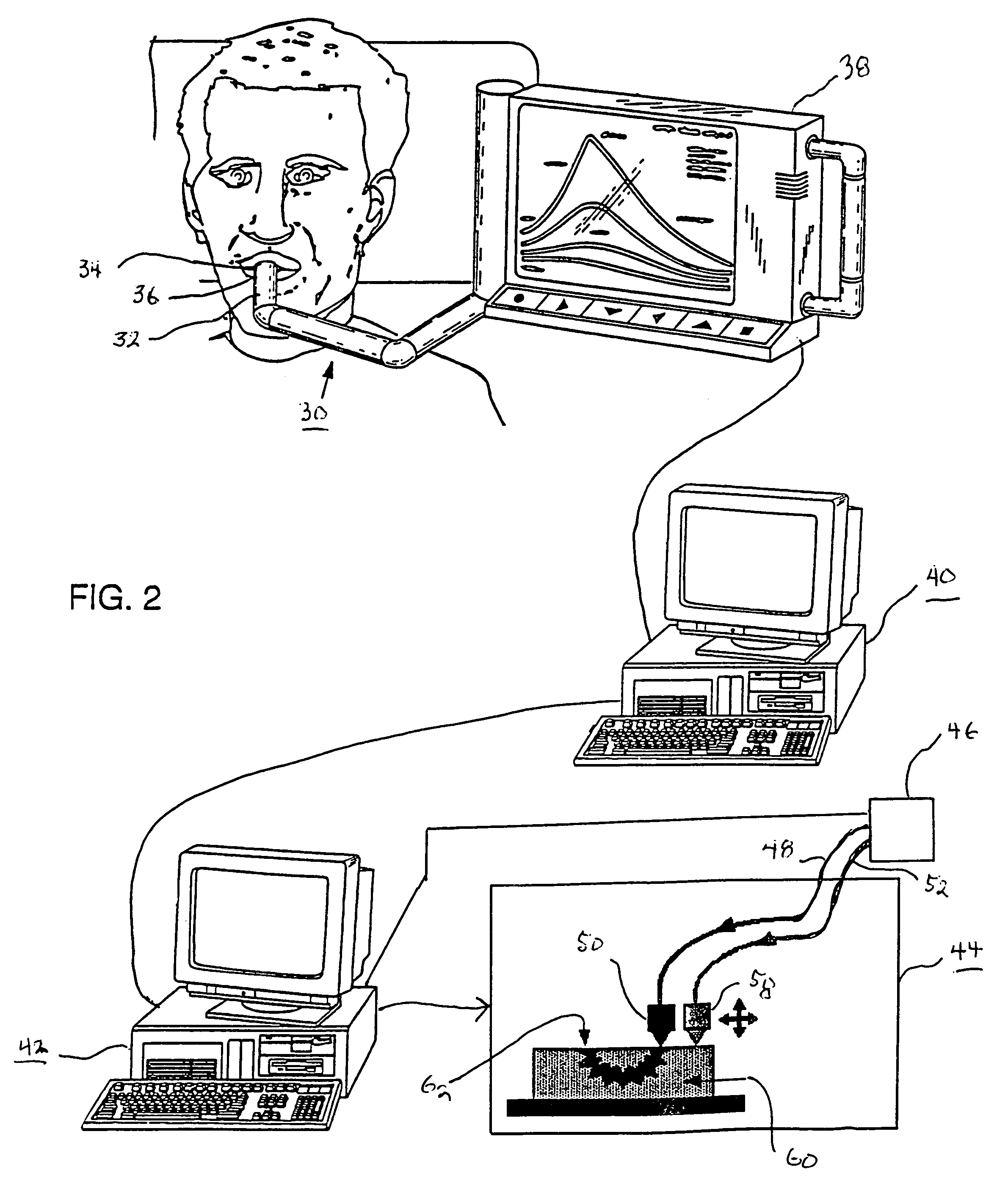
Method for automatically creating a denture using laser altimetry to create a digital 3-D oral cavity model and using a digital internet connection to a rapid stereolithographic modeling machine
InactiveUS7153135B1Low costFit closelyAdditive manufacturing apparatusImpression capsDenturesLaser scanning
A method is presented for rapidly making and delivering directly to a consumer a full upper and / or lower denture on the basis of contemporaneous digital image information laser scanned from the person's oral cavity after all respective upper and / or lower teeth have been removed, the delivery of the denture occurring substantially contemporaneously with the creation of the contemporaneous digital image information and optionally including and based on archived digital image information laser scanned from the person's oral cavity before all respective upper and / or lower teeth have been removed and digitally stored. According to which this contemporaneous digital image information and archival digital image information of the oral cavity is converted, by means of what is called the rapid prototyping technique and thus with a processing step (20) and a combination of an optional laser scanning step (18) solely for archiving the oral cavity when upper and / or lower teeth are present and a repetition of the laser scanning step (18) at a subsequent time when upper and / or lower teeth have been removed, a pre-selected block of plastic is used in a processing step (26) at a remote rapid modeling facility for receiving and processing digital information to form the block of plastic or like material into a denture of which at least a part is formed to substantially perfectly fit in juxtaposed relationship to the corresponding gums of the consumer. At least, pre-selected outer or non-juxtaposing is selected for manufacture of the denture using an arbitrary archived digital image not derived from the consumer's oral cavity image but selected by the consumer for its style, cosmetic characteristics, for example, color of teeth, size and variety of teeth, and / or perceived suitability.
Owner:THOMAS RICHARD J
Portable coordinate measurement machine with integrated line laser scanner
InactiveUS20090187373A1Programme-controlled manipulatorTesting/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesLaser scanningEngineering
A portable coordinate measurement machine for measuring the position of an object in a selected volume comprises includes an a positionable articulated arm having a plurality of jointed arm segments. The arm includes a measurement probe having an integrated line laser scanner mounted thereon. The laser may be a fiber coupled laser. Wireless data transfer and communication capability for the CMM is also possible.
Owner:FARO TECH INC
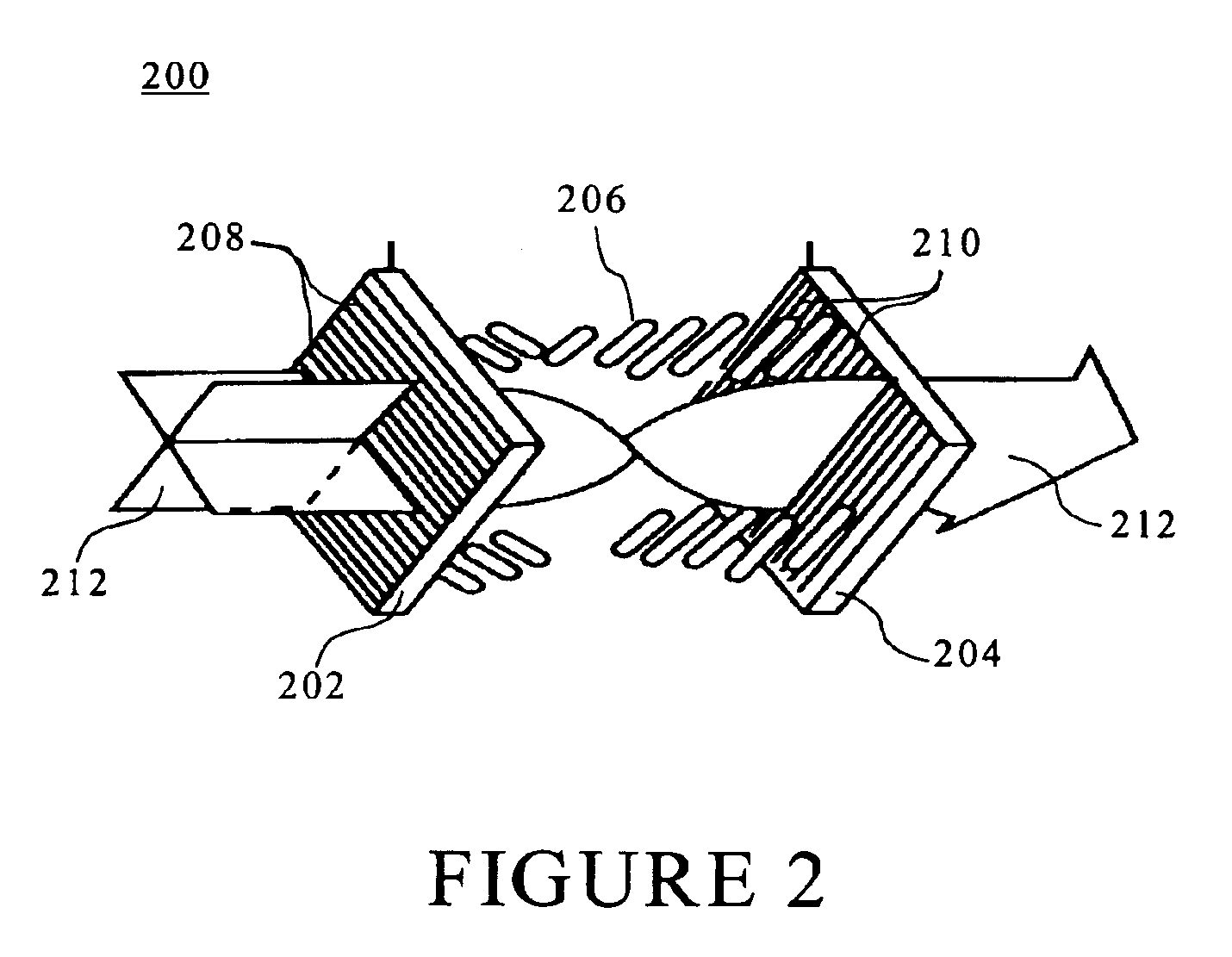
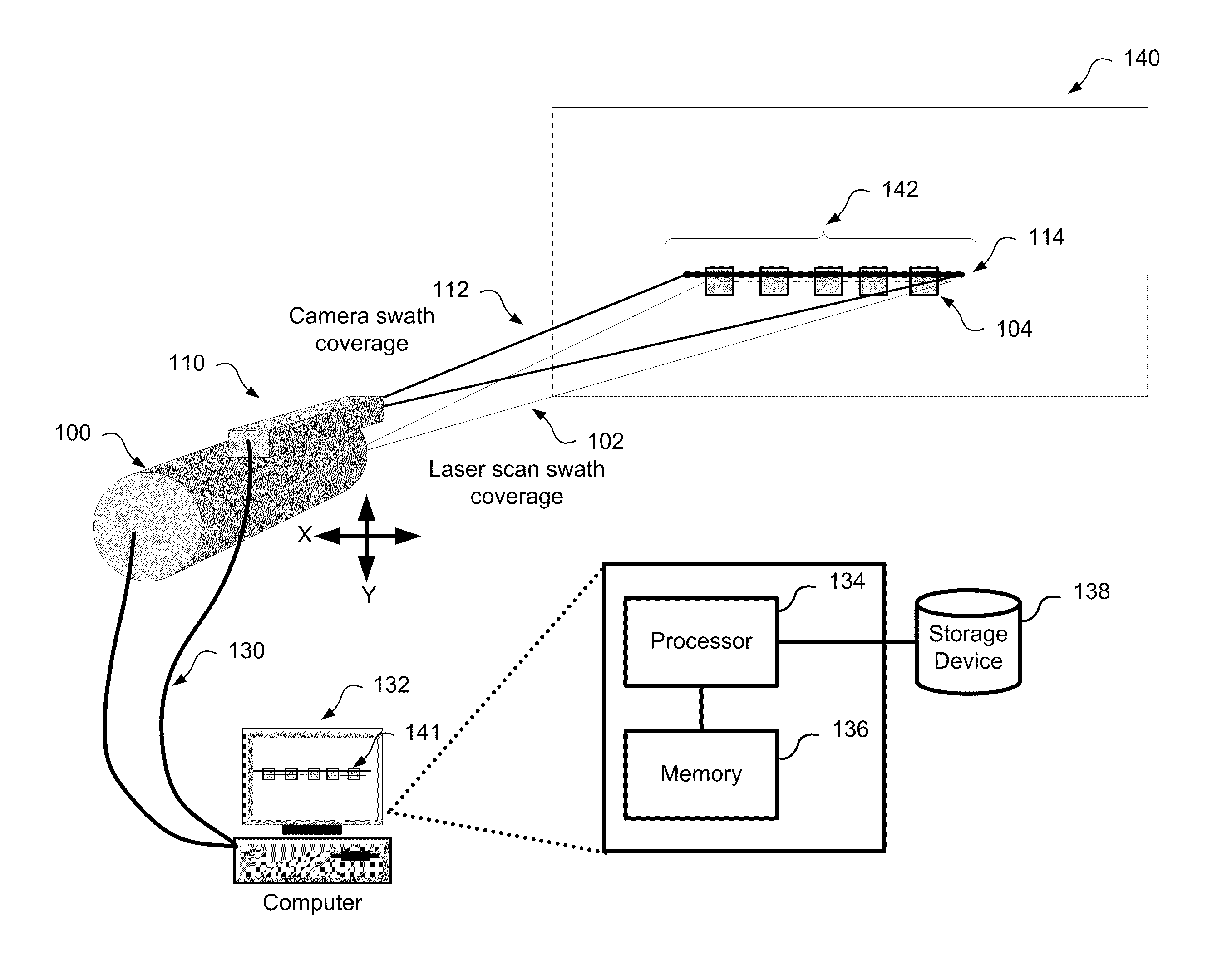
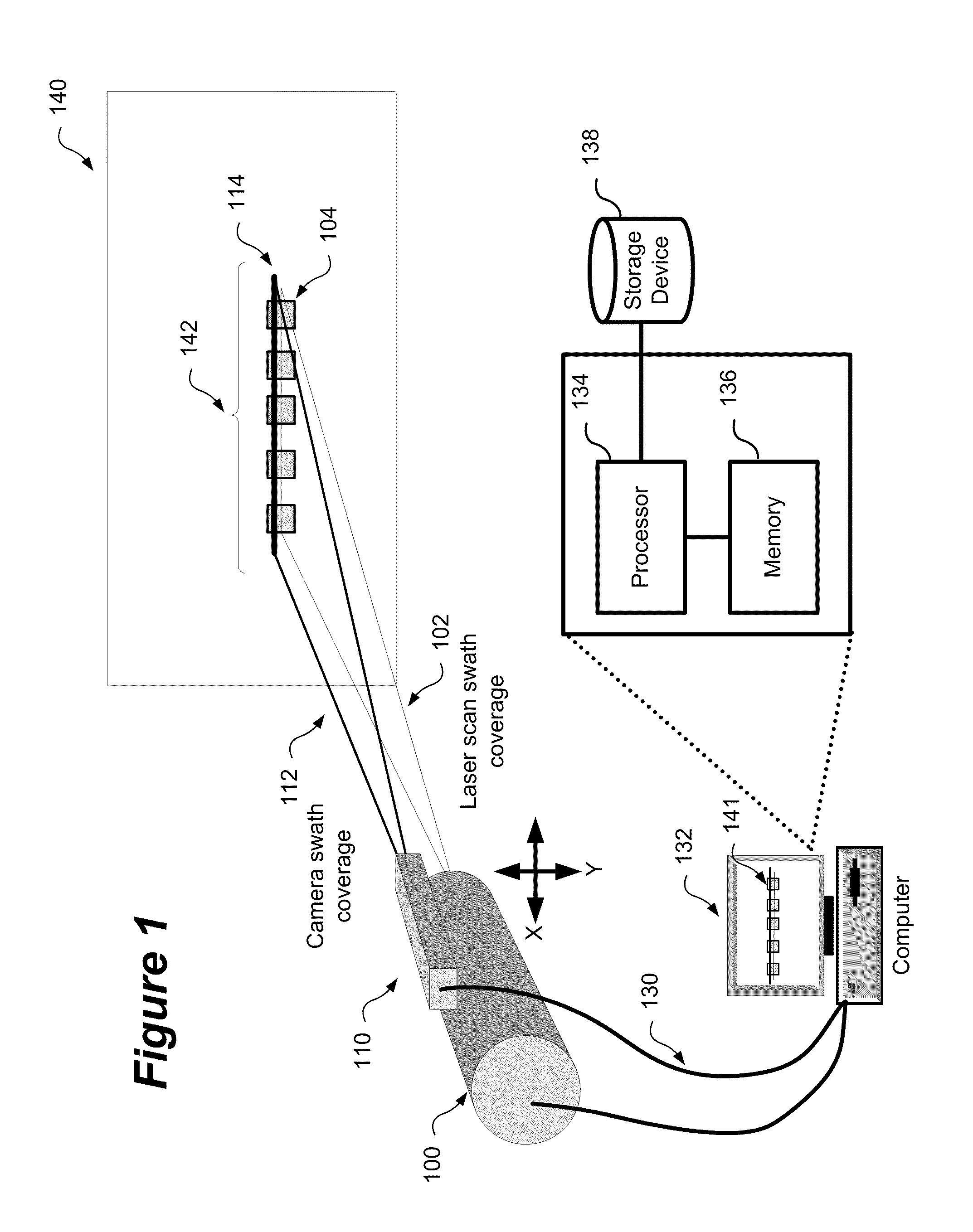
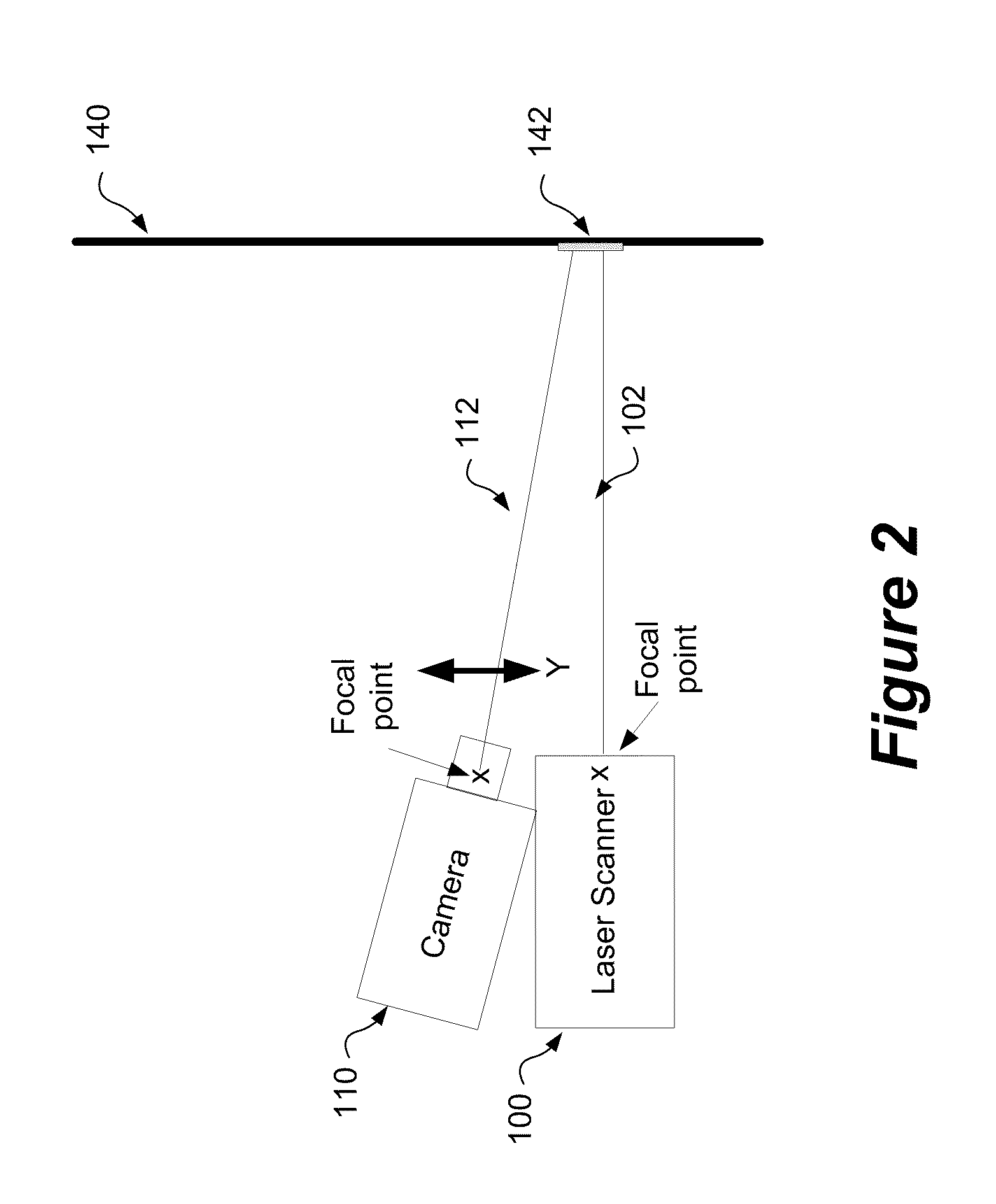
Method and system for aligning a line scan camera with a lidar scanner for real time data fusion in three dimensions
An apparatus and method for aligning a line scan camera with a Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) scanner for real-time data fusion in three dimensions is provided. Imaging data is captured at a computer processor simultaneously from the line scan camera and the laser scanner from target object providing scanning targets defined in an imaging plane perpendicular to focal axes of the line scan camera and the LiDAR scanner. X-axis and Y-axis pixel locations of a centroid of each of the targets from captured imaging data is extracted. LiDAR return intensity versus scan angle is determined and scan angle locations of intensity peaks which correspond to individual targets is determined. Two axis parallax correction parameters are determined by applying a least squares. The correction parameters are provided to post processing software to correct for alignment differences between the imaging camera and LiDAR scanner for real-time colorization for acquired LiDAR data.
Owner:AMBERCORE SOFTWARE
Laser scanning modules embodying silicone scan element with torsional hinges
ActiveUS20130200158A1Easy to integrateSpace minimizationMirrorsSensing by electromagnetic radiationLaser scanningRestoring force
Laser scanning module employing a scan mirror and magnet rotor subassembly supported by a stationary stator structure. The scan mirror and magnet rotor subassembly includes: a silicone frame having a pair of silicone torsional hinges (i.e. posts) aligned along a scan axis and a supported by a pair of support elements associated with the stator structure, to support the scan mirror and magnet rotor subassembly. When the scan mirror and magnet rotor subassembly is rotated about its scan axis, by forces generated by an electromagnetic coil structure acting on the permanent magnet mounted on silicone frame, the silicone torsional hinges are elastically distorted and generate linear restoring forces which return the rotor subassembly back to its home position about the scan axis.
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR
Articulating measuring arm with laser scanner
ActiveUS20100095542A1Easy to removeEasy to replaceUsing optical meansMechanical measuring arrangementsMeasurement deviceClassical mechanics
A coordinate measurement device comprises an articulated arm having a first end, a second end, and a plurality of jointed arm segments therebetween. Each arm segment defines at least one axis of rotation. A laser scanner assembly is coupled to the second end of the arm and is rotatable about a last axis of rotation of the articulated arm. The laser scanner assembly comprises a laser and an image sensor. The laser is positioned on an opposite side of the last axis of rotation from the image sensor.
Owner:HEXAGON METROLOGY INC
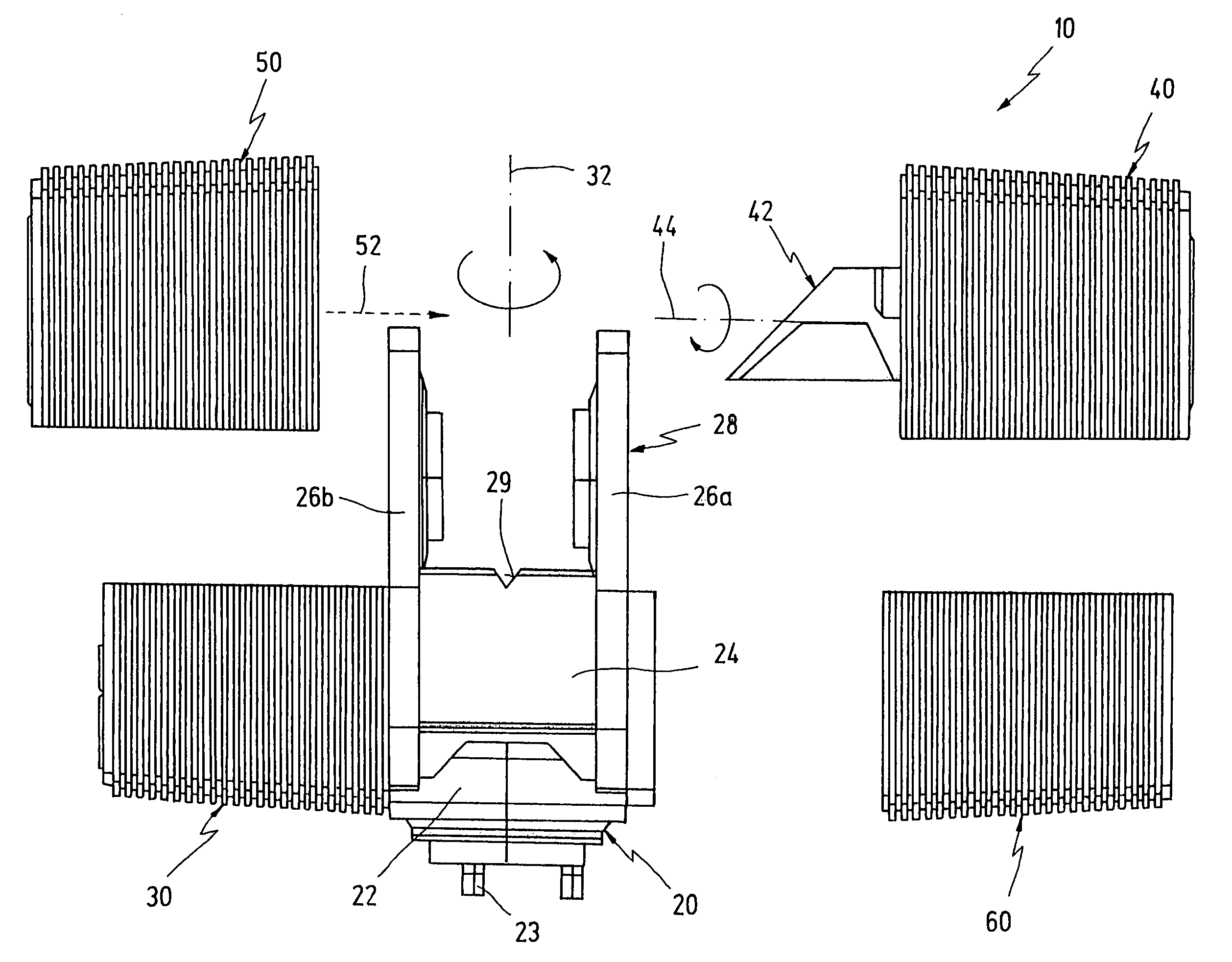
Laser scanner
ActiveUS7430068B2Lower purchase priceExpand the measurement rangeWave based measurement systemsPictoral communicationComputer moduleLight beam
A laser scanner has a first axis and a second axis extending essentially transversely to the first axis. A measuring head is adapted to be rotated about the first axis. The measuring head has at least a first, a second, and a third module, wherein at least the first module and the third module are releasably connected to each other. A first rotary drive for rotating said measuring head is comprised within the first and the second modules. A rotary mirror is adapted to be rotated about the second axis. The rotary mirror is comprised within the third module. A second rotary drive is provided for rotating the rotary mirror. The second drive is likewise comprised within the third module. A transmitter is provided in the measuring head for transmitting a light beam. A receiver is provided in the measuring head for receiving the light beam after a reflection thereof by an object located at a distance from the laser scanner. A computer is provided in the measuring head for processing signals embedded within the received light beam.
Owner:FARO TECH INC
Selective laser solidification apparatus and method
ActiveUS20160114432A1Good quality spotSmall radiusAdditive manufacturing apparatusArc welding apparatusLaser scanningLaser beams
A selective laser solidification apparatus including; a powder bed onto which powder layers can be deposited, at least one laser module for generating a plurality of laser beams for solidifying the powder material deposited onto the powder bed, a laser scanner for individually steering each laser beam to solidify separate areas in each powder layer, and a processing unit. A scanning zone for each laser beam is defined by the locations on the powder bed to which the laser beam can be steered by the laser scanner. The laser scanner is arranged such that each scanning zone is less than the total area of powder bed and at least two of the scanning zones overlap. The processing unit is arranged for selecting, for at least one powder layers, which laser beam to use to scan an area of the powder layer located within a region wherein the scanning zones overlap.
Owner:RENISHAW PLC
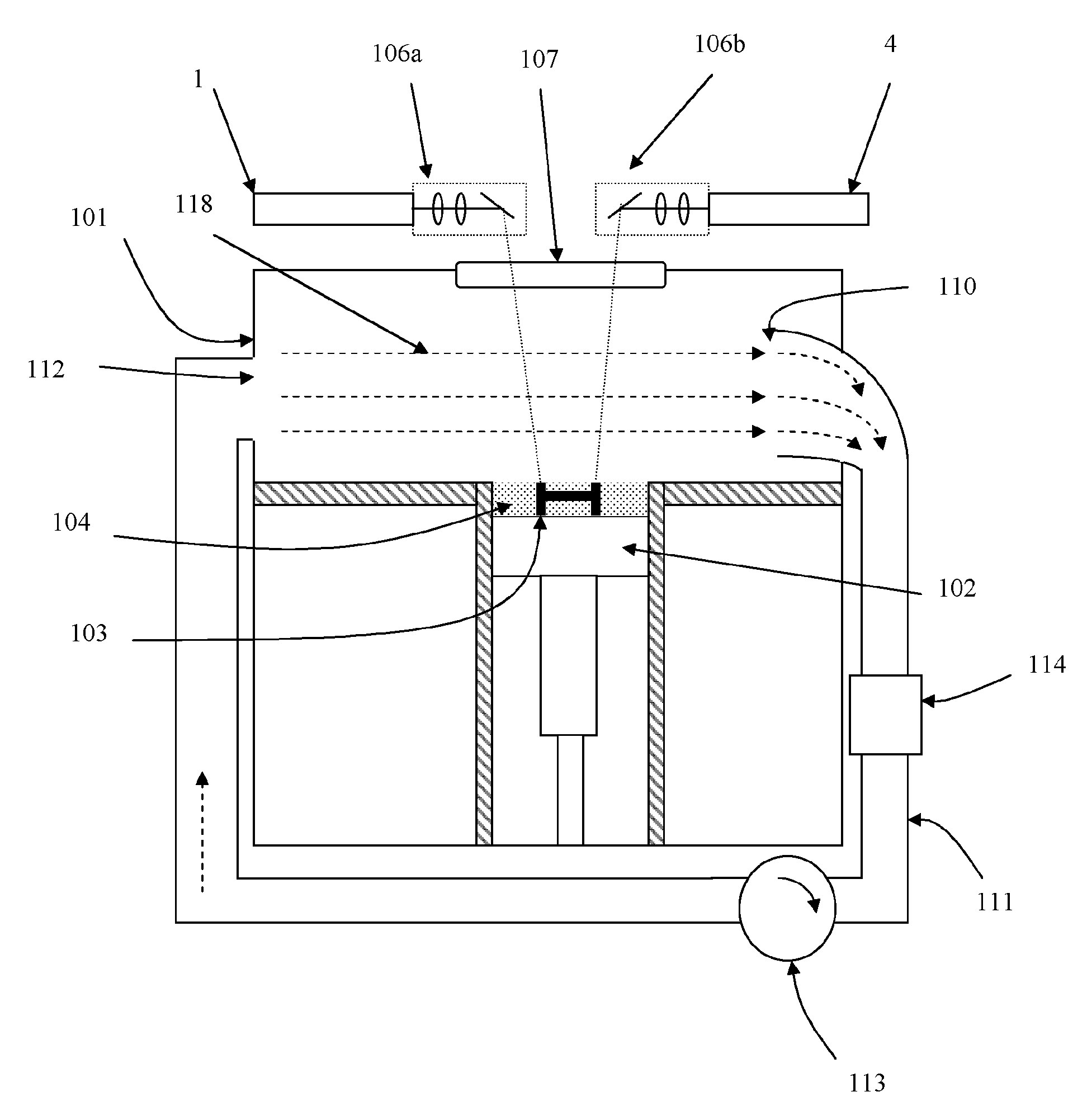
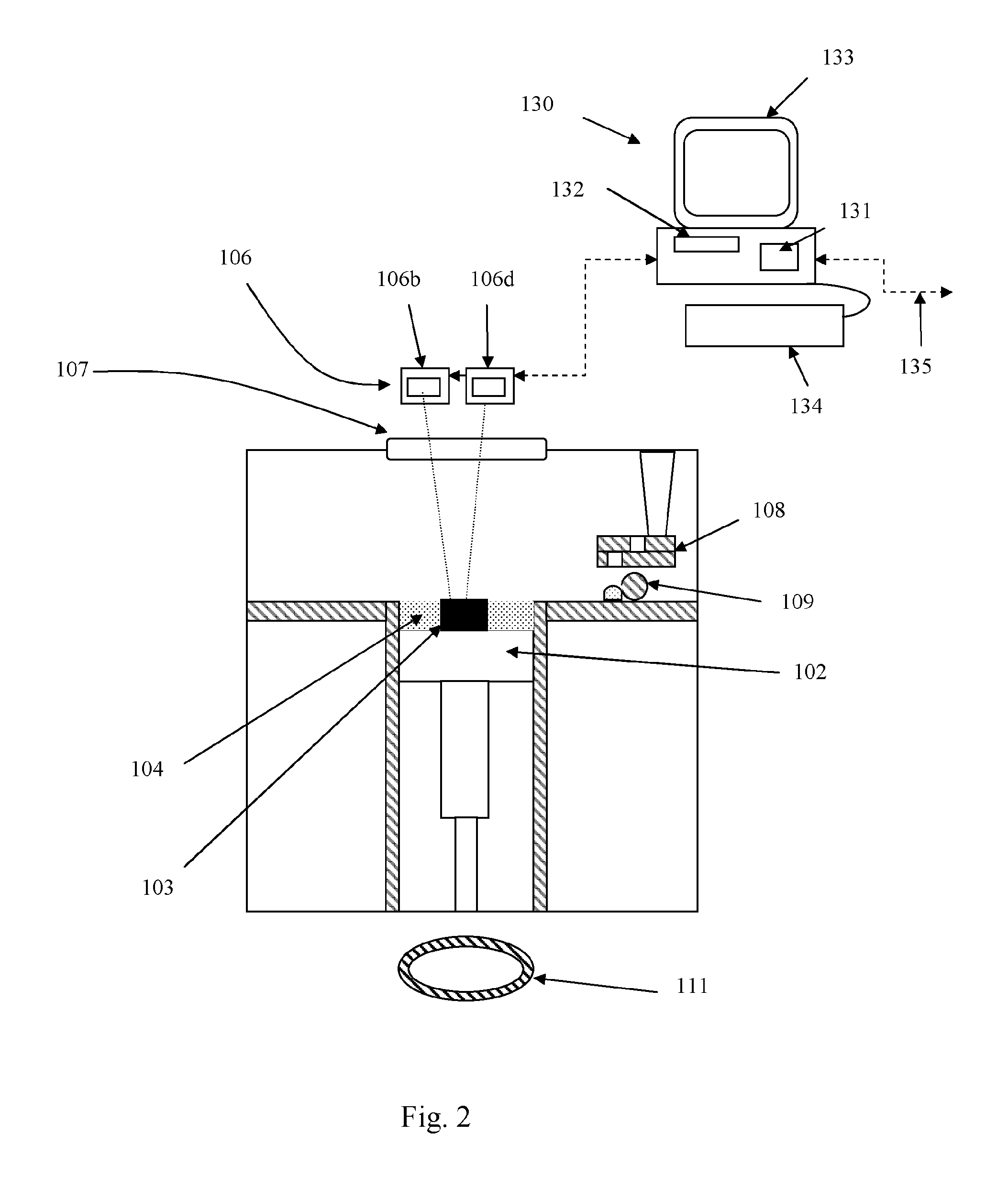
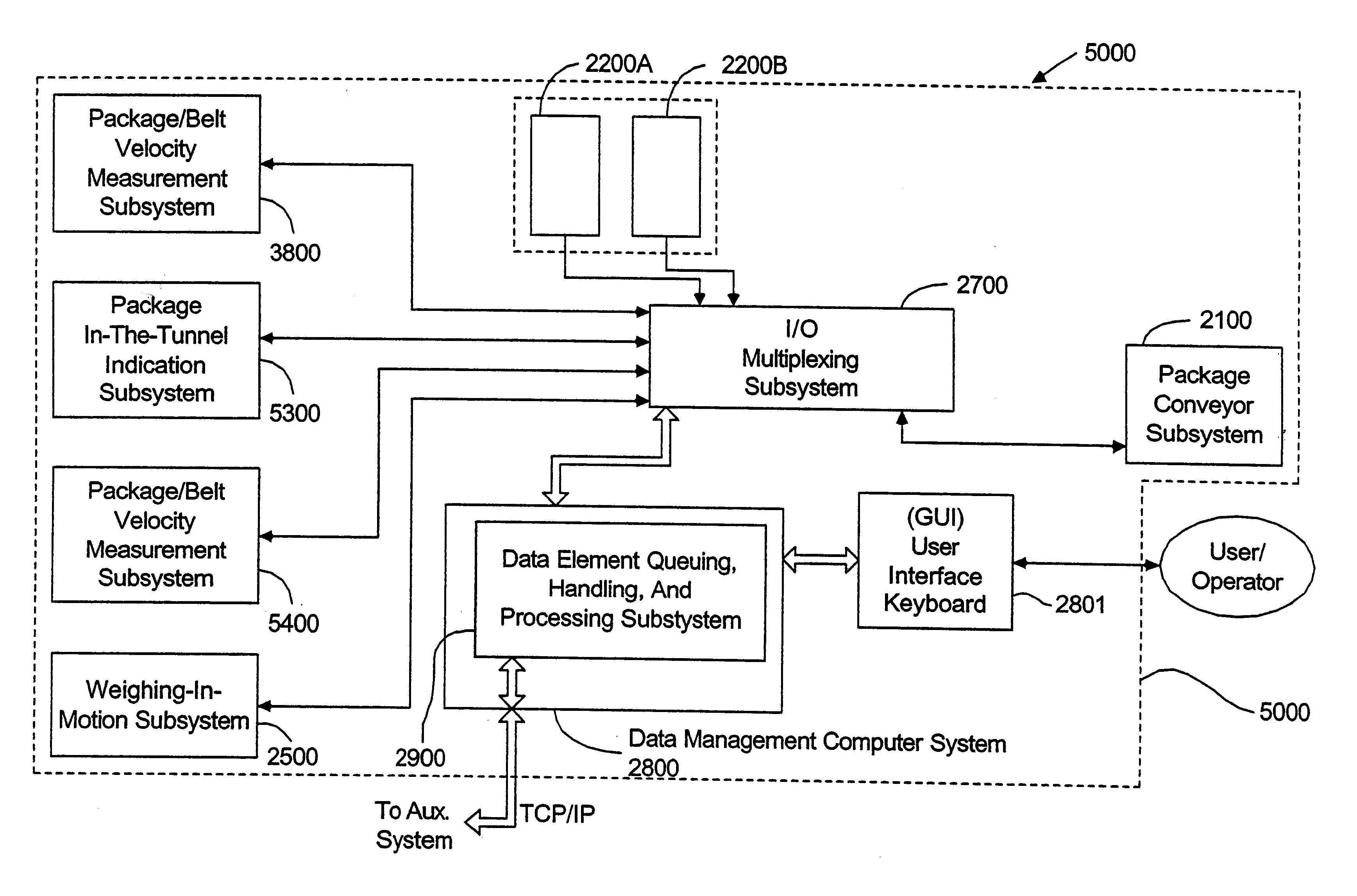
Automated method of and system for dimensioning objects transported through a work environment using contour tracing, vertice detection, corner point detection, and corner point reduction methods on two-dimensional range data maps captured by an amplitude modulated laser scanning beam
InactiveUS6705526B1Guaranteed uptimeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCo-operative working arrangementsMathematical modelLaser scanning
A fully automated package identification and measuring system, in which an omni-directional holographic scanning tunnel is used to read bar codes on packages entering the tunnel, while a package dimensioning subsystem is used to capture information about the package prior to entry into the tunnel. Mathematical models are created on a real-time basis for the geometry of the package and the position of the laser scanning beam used to read the bar code symbol thereon. The mathematical models are analyzed to determine if collected and queued package identification data is spatially and / or temporally correlated with package measurement data using vector-based ray-tracing methods, homogeneous transformations, and object-oriented decision logic so as to enable simultaneous tracking of multiple packages being transported through the scanning tunnel.
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR
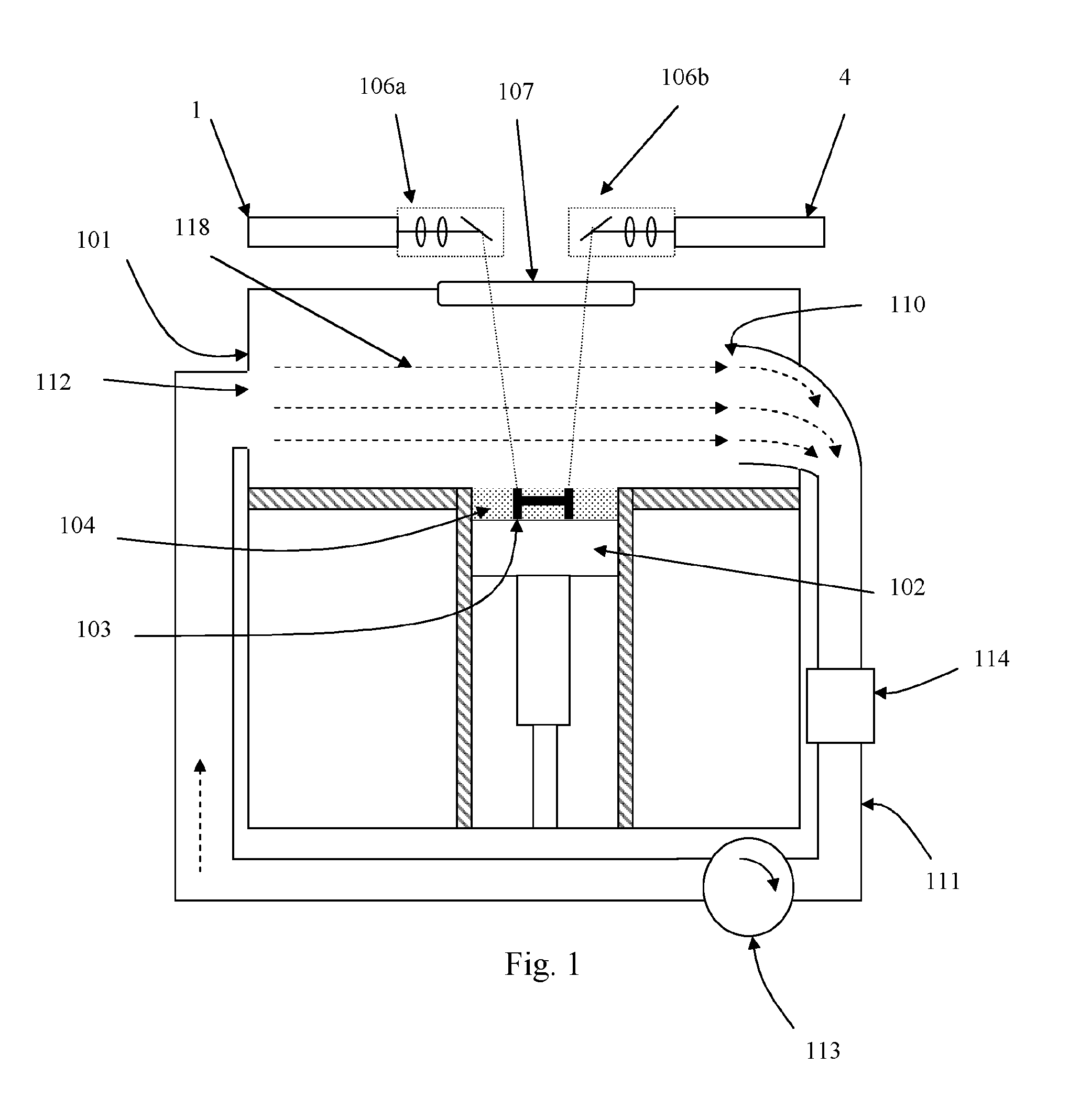
Automated system and method for identifying and measuring packages transported through a laser scanning tunnel
A fully automated package identification and measuring system, in which an omni-directional holographic scanning tunnel is used to read bar codes on packages entering the tunnel, while a package dimensioning subsystem is used to capture information about the package prior to entry into the tunnel. Mathematical models are created on a real-time basis for the geometry of the package and the position of the laser scanning beam used to read the bar code symbol thereon. The mathematical models are analyzed to determine if collected and queued package identification data is spatially and / or temporally correlated with package measurement data using vector-based ray-tracing methods, homogeneous transformations, and object-oriented decision logic so as to enable simultaneous tracking of multiple packages being transported through the scanning tunnel.
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR
System and method for vehicle navigation using lateral offsets
ActiveUS20120271540A1Enhanced driver assistance featureSimple calculationInstruments for road network navigationAnti-collision systemsRadarLaser scanning
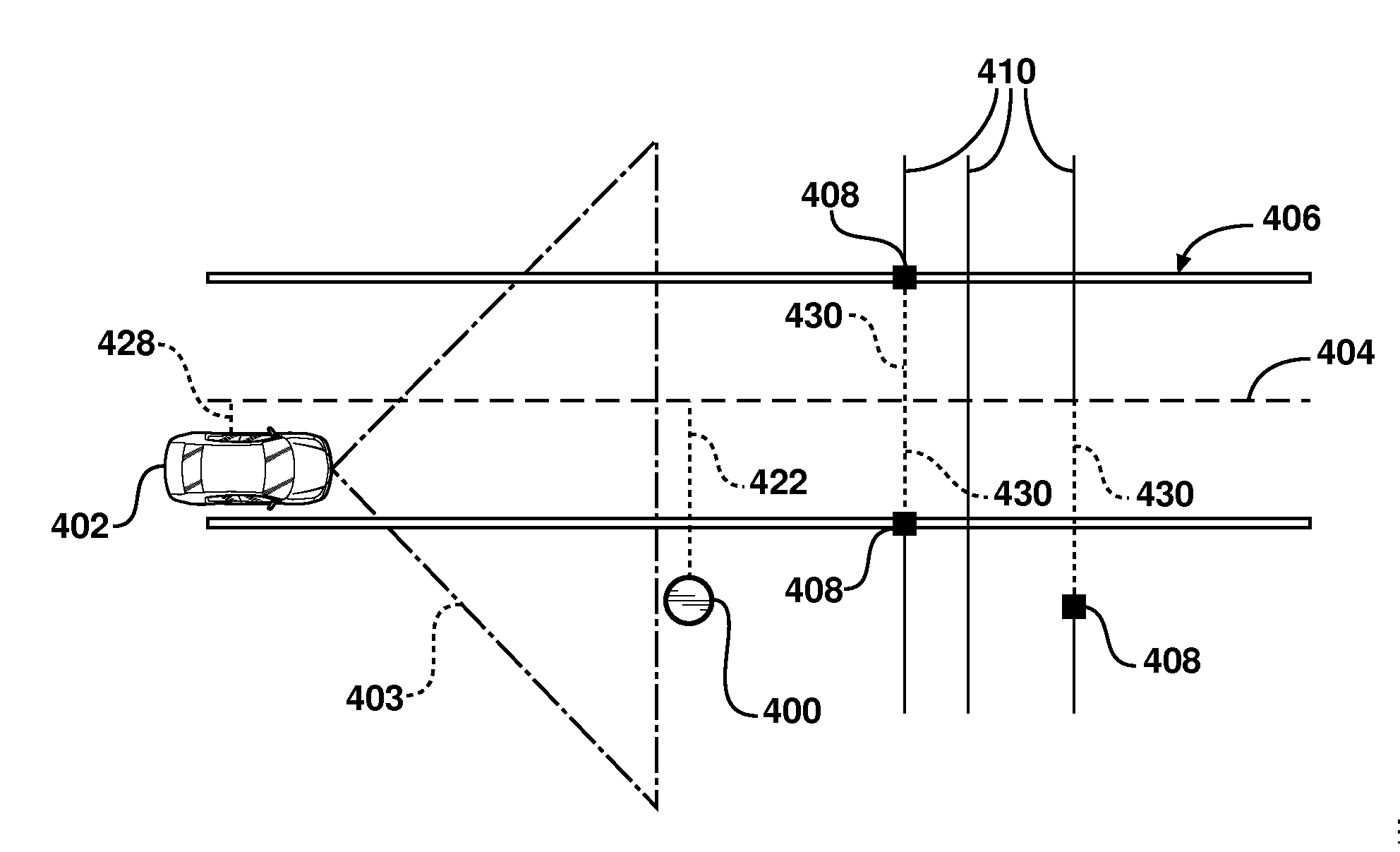
A navigation system for use in a vehicle (402). The system includes an absolute position sensor, such as GPS, in addition to one or more additional sensors, such as a camera, laser scanner, or radar. The system further comprises a digital map or database that includes records for at least some of the vehicle's surrounding objects (400). These records can include relative positional attributes with respect to a reference axis (404). As the vehicle (402) moves, sensors sense the presence of at least some of these objects (400), and measure the vehicle's relative position to those objects. This information is used to determine the vehicle's instantaneous lateral offset (428) relative to the reference axis (404), and support features such as enhanced driving directions, collision avoidance, or automatic assisted driving. The system also allows new objects (408, 414) to be attributed using relative positioning, and thereby factored into the enhanced navigation features.
Owner:TOMTOM POLSKA
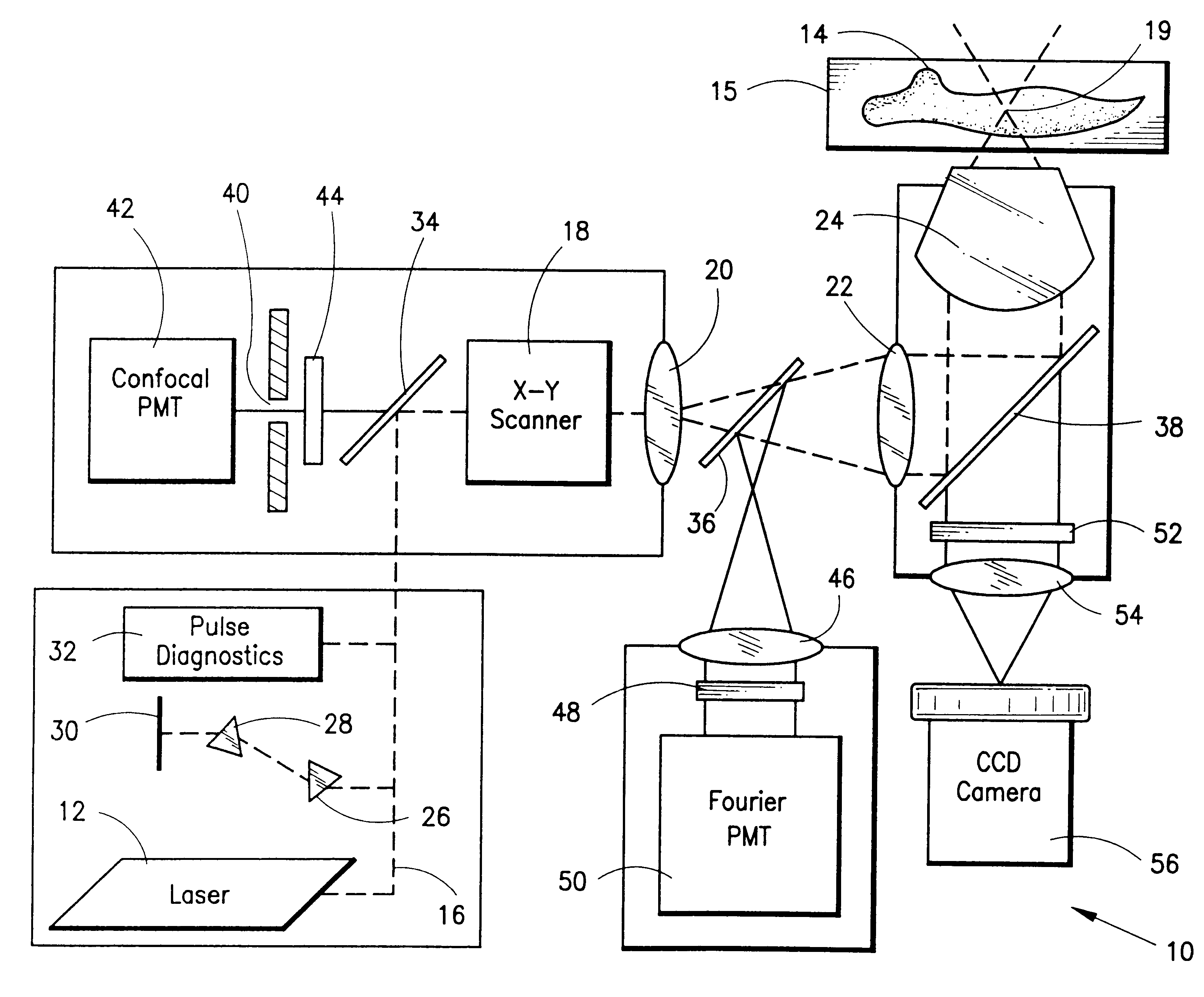
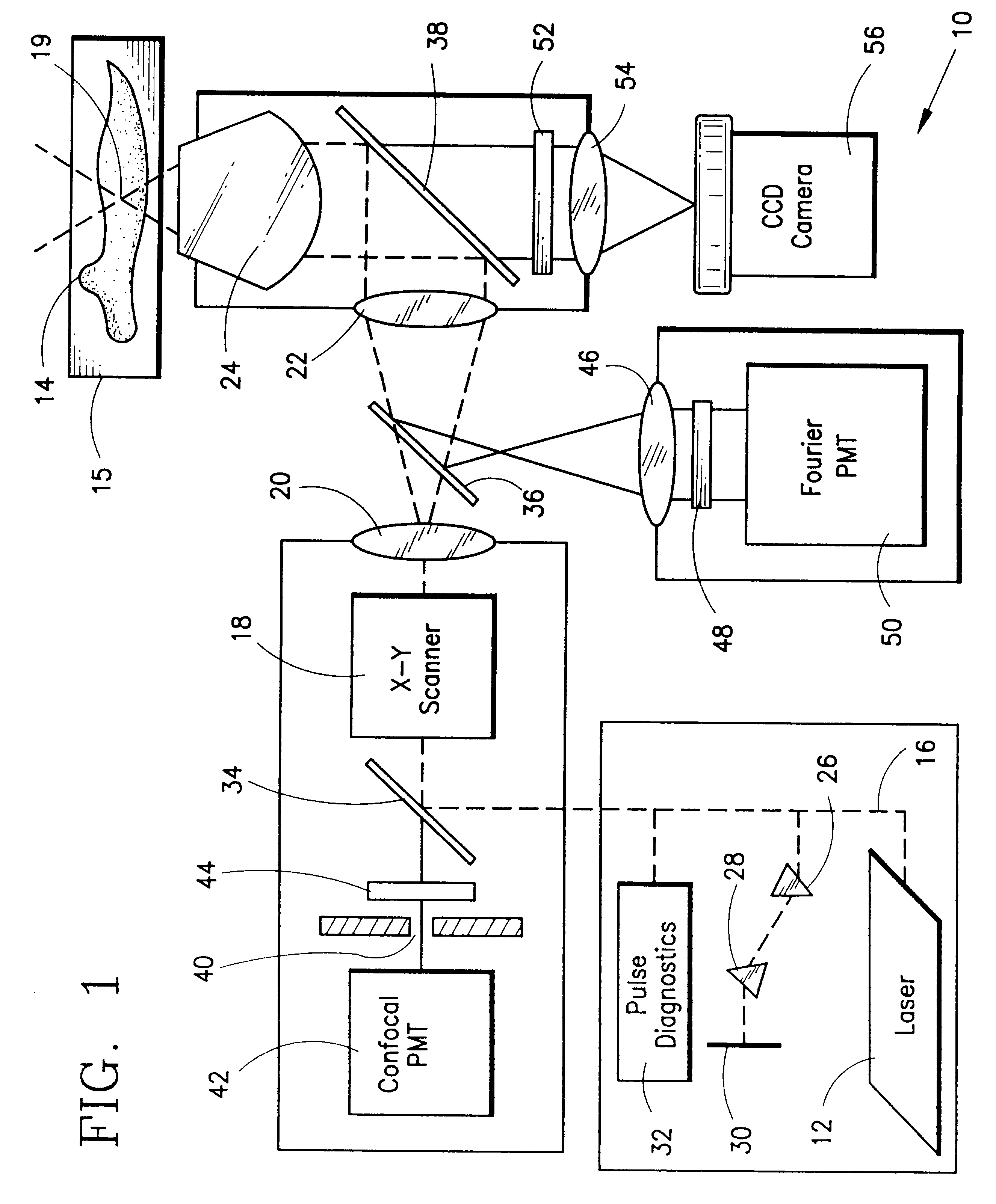
Multi-photon laser microscopy
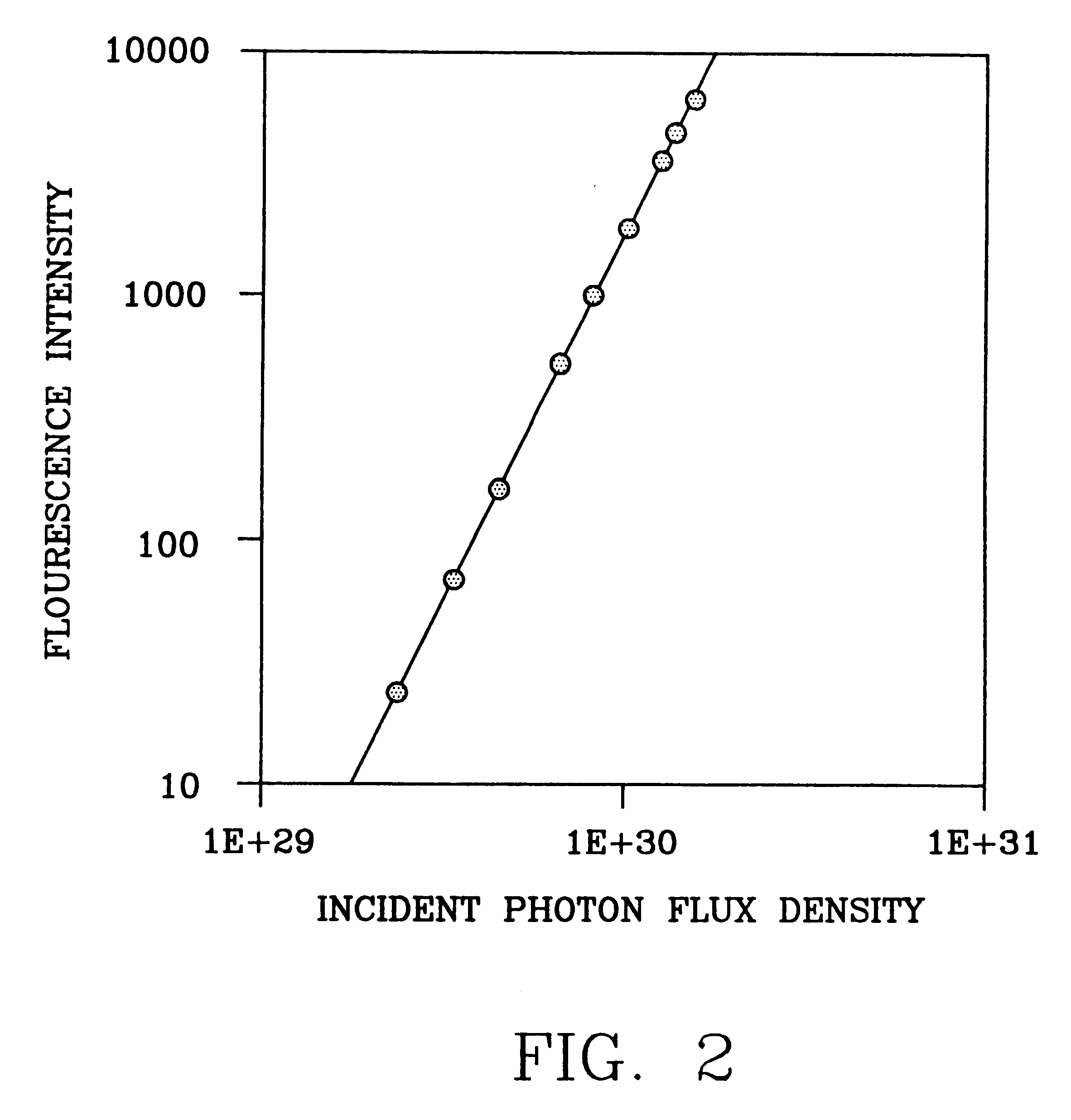
InactiveUS6344653B1Less photodamageExpand the scope of useLaser detailsPhotometryConfocal laser scanning microscopeLaser scanning microscope
A laser scanning microscope produces molecular excitation in a target material by simultaneous absorption of three or more photons to thereby provide intrinsic three-dimensional resolution. Fluorophores having single photon absorption in the short (ultraviolet or visible) wavelength range are excited by a beam of strongly focused subpicosecond pulses of laser light of relatively long (red or infrared) wavelength range. The fluorophores absorb at about one third, one fourth or even smaller fraction of the laser wavelength to produce fluorescent images of living cells and other microscopic objects. The fluorescent emission from the fluorophores increases cubicly, quarticly or even higher power law with the excitation intensity so that by focusing the laser light, fluorescence as well as photobleaching are confined to the vicinity of the focal plane. This feature provides depth of field resolution comparable to that produced by confocal laser scanning microscopes, and in addition reduces photobleaching and phototoxicity. Scanning of the laser beam by a laser scanning microscope, allows construction of images by collecting multi-photon excited fluorescence from each point in the scanned object while still satisfying the requirement for very high excitation intensity obtained by focusing the laser beam and by pulse time compressing the beam. The focused pulses also provide three-dimensional spatially resolved photochemistry which is particularly useful in photolytic release of caged effector molecules, marking a recording medium or in laser ablation or microsurgery. This invention refers explicitly to extensions of two-photon excitation where more than two photons are absorbed per excitation in this nonlinear microscopy.
Owner:WEBB WATT W +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com