Patents
Literature
165 results about "Phototoxicity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Phototoxicity, also called photoirritation, is a chemically induced skin irritation, requiring light, that does not involve the immune system. It is a type of photosensitivity. The skin response resembles an exaggerated sunburn. The involved chemical may enter into the skin by topical administration or it may reach the skin via systemic circulation following ingestion or parenteral administration. The chemical needs to be "photoactive," which means that when it absorbs light, the absorbed energy produces molecular changes that cause toxicity. Many synthetic compounds, including drug substances like tetracyclines or fluoroquinolones, are known to cause these effects. Surface contact with some such chemicals causes photodermatitis; many plants cause phytophotodermatitis. Light-induced toxicity is a common phenomenon in humans; however, it also occurs in other animals.
Multi-photon laser microscopy
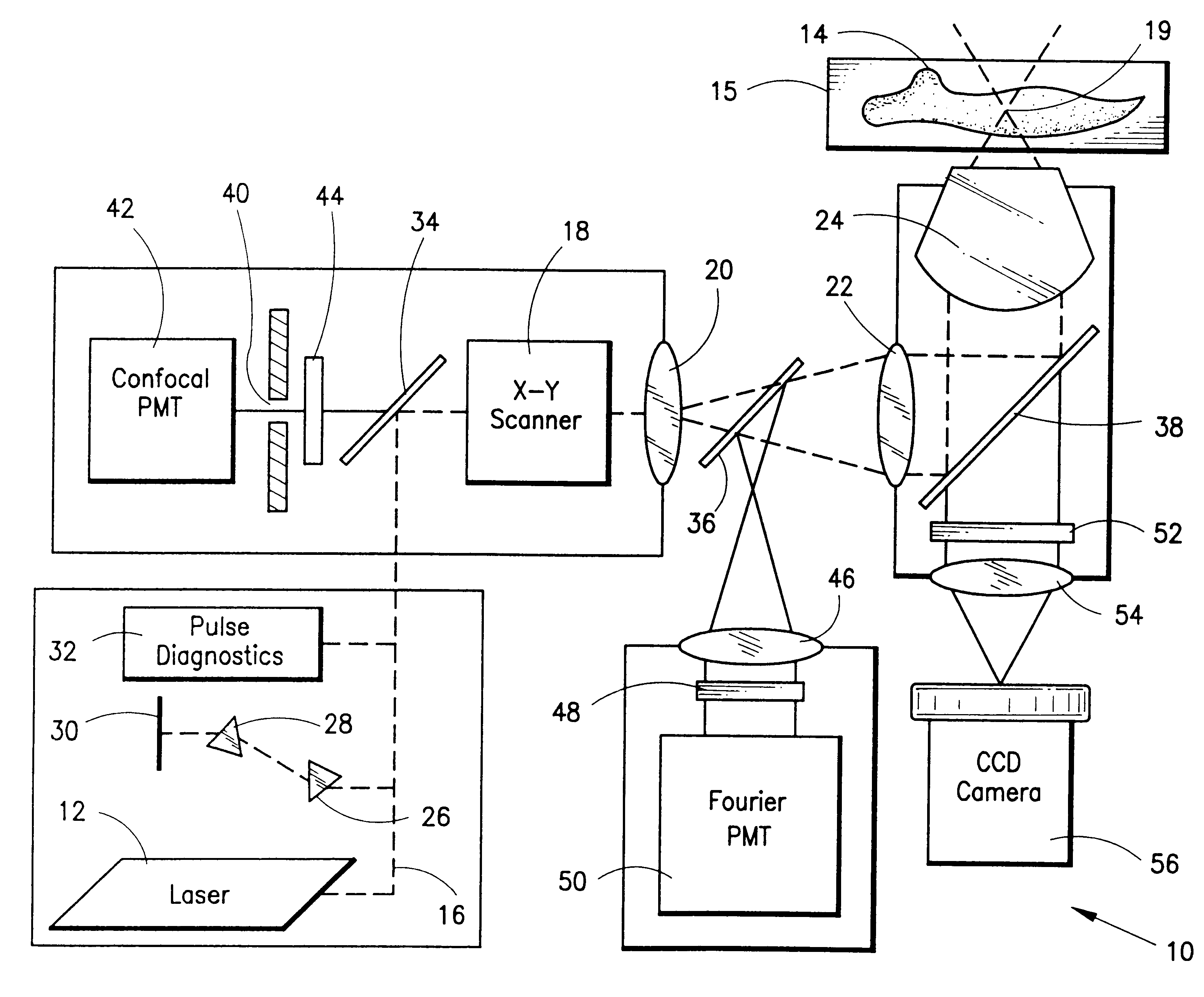
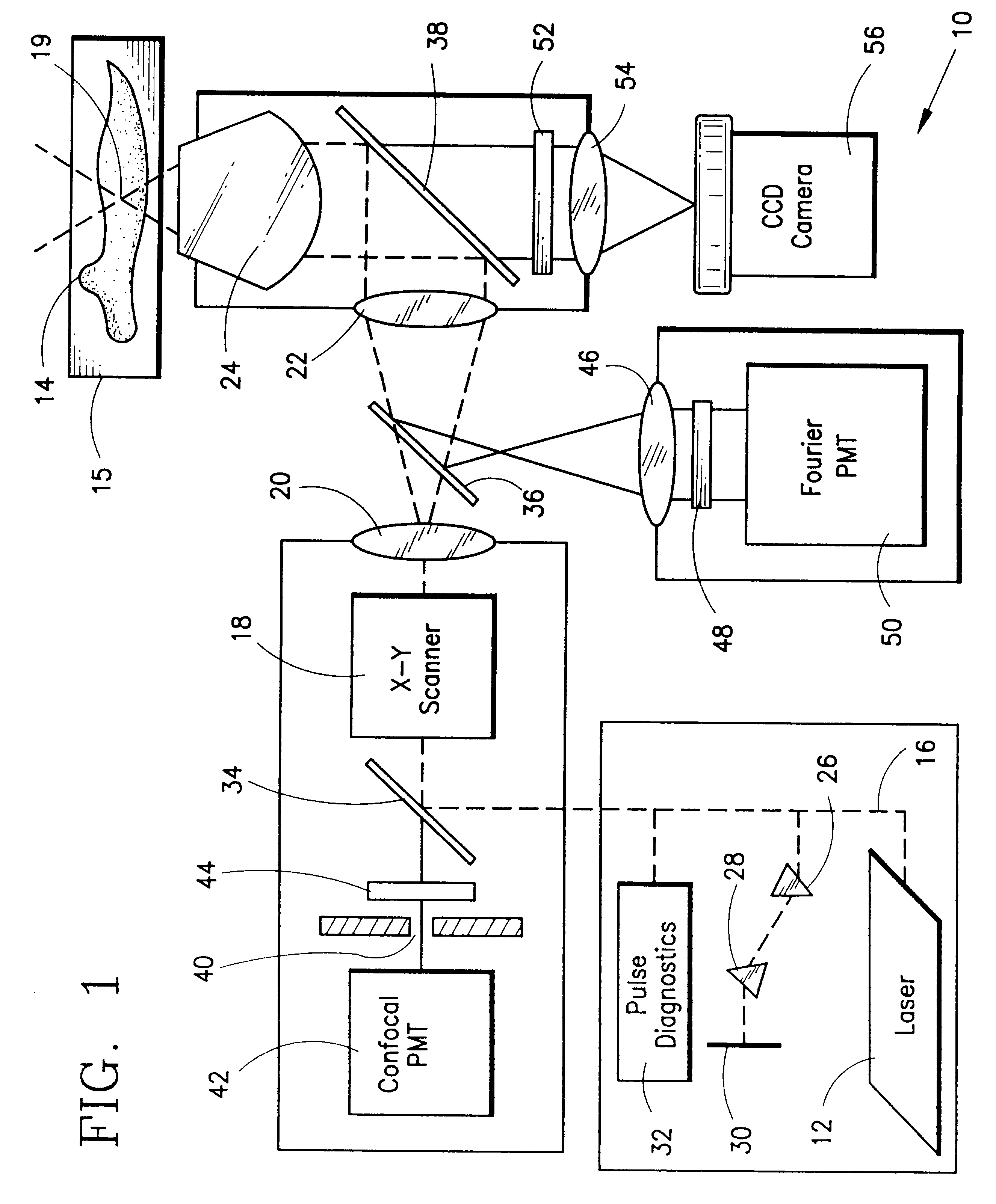
InactiveUS6344653B1Less photodamageExpand the scope of useLaser detailsPhotometryConfocal laser scanning microscopeLaser scanning microscope
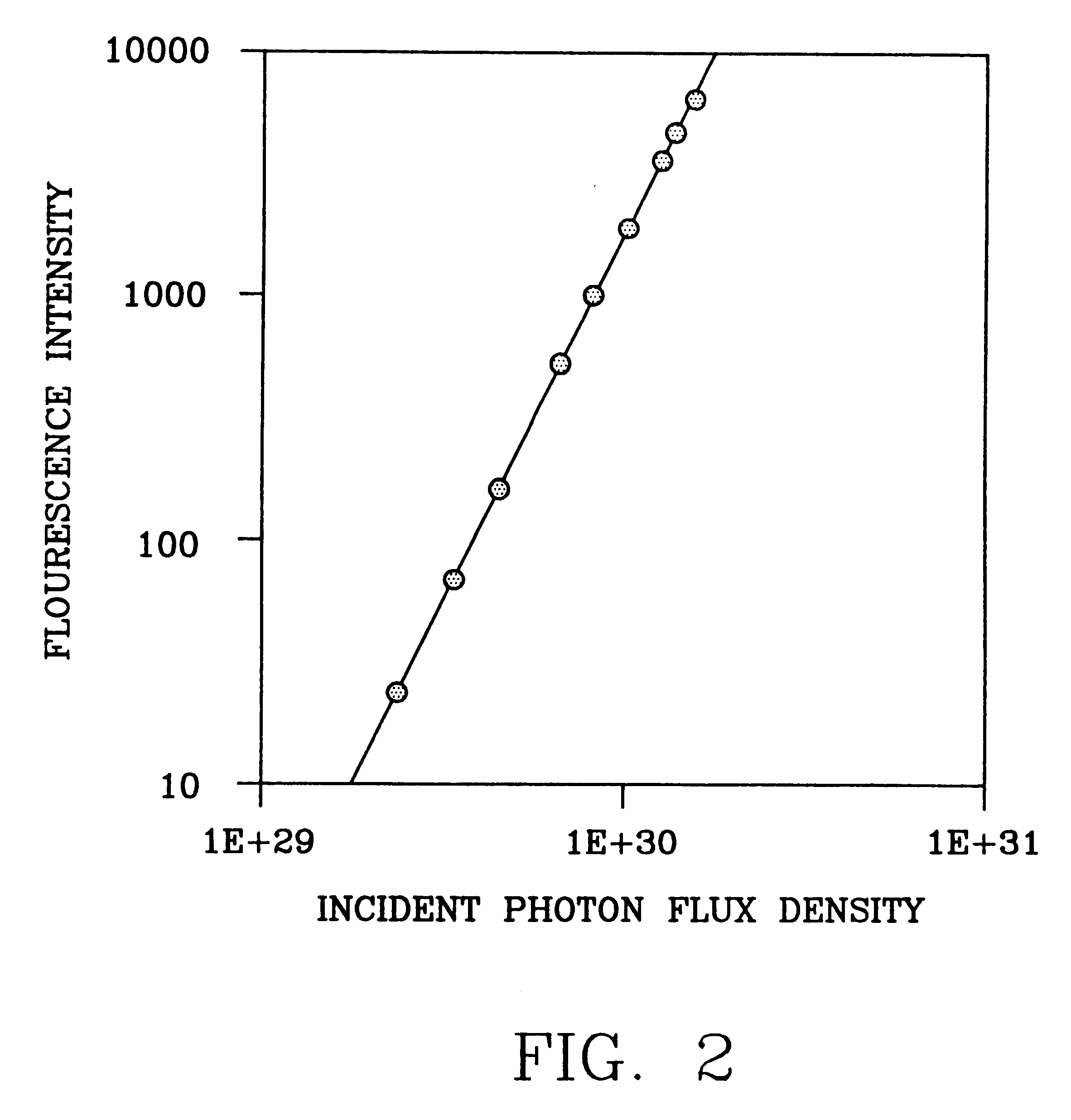
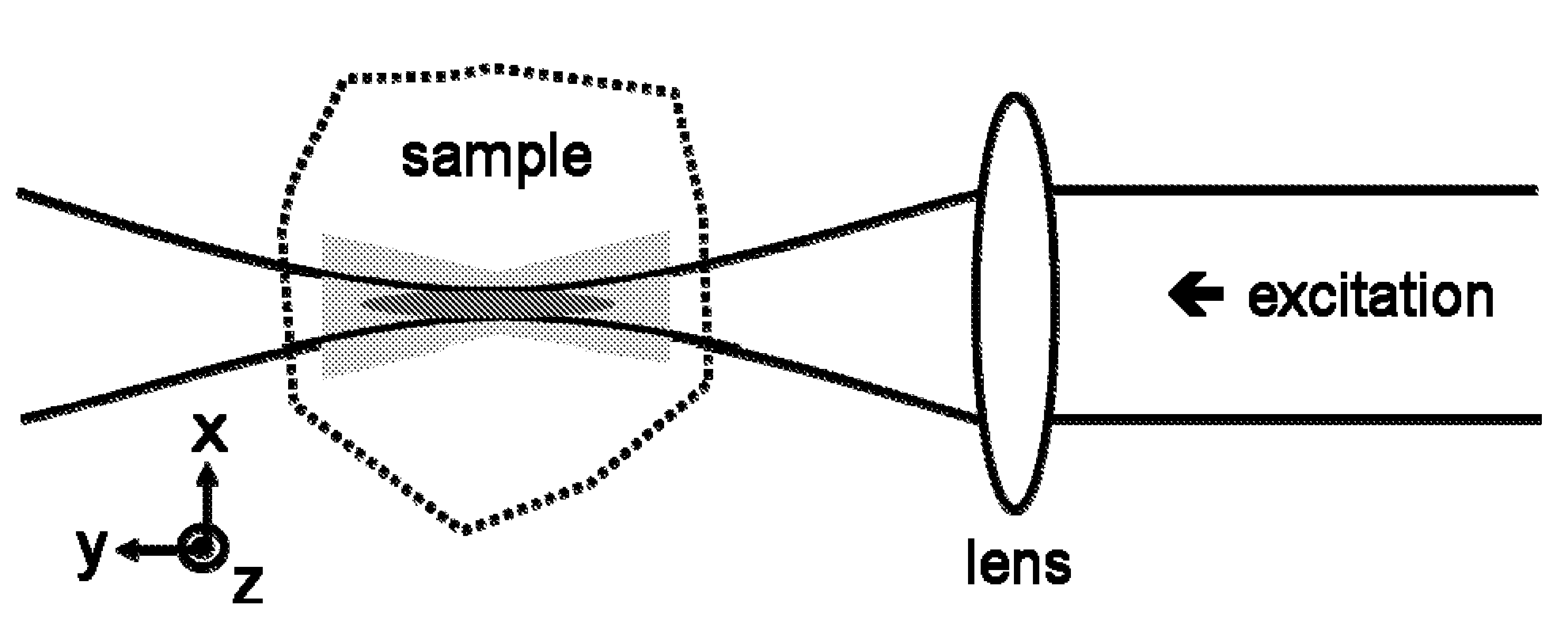
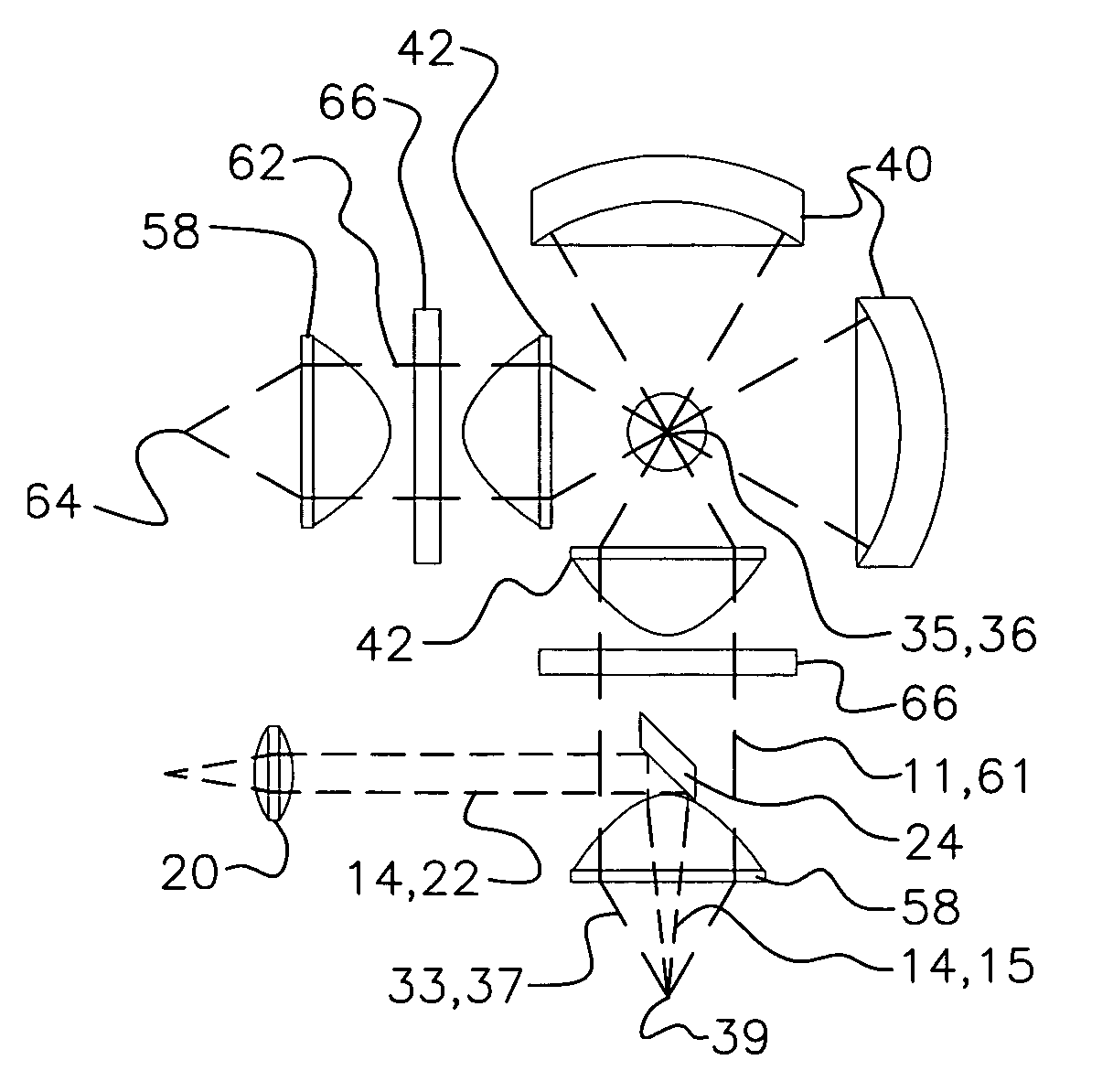
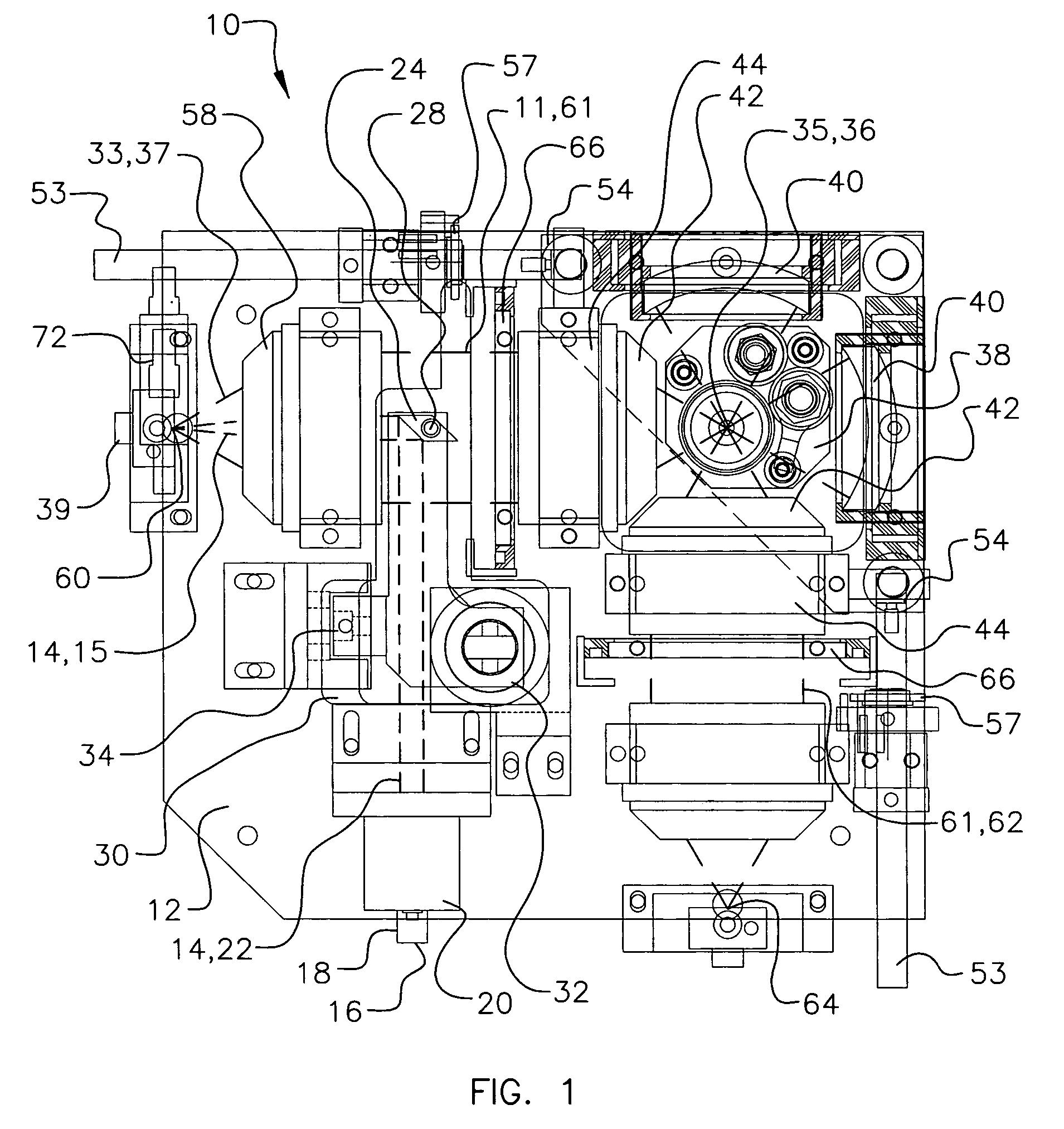
A laser scanning microscope produces molecular excitation in a target material by simultaneous absorption of three or more photons to thereby provide intrinsic three-dimensional resolution. Fluorophores having single photon absorption in the short (ultraviolet or visible) wavelength range are excited by a beam of strongly focused subpicosecond pulses of laser light of relatively long (red or infrared) wavelength range. The fluorophores absorb at about one third, one fourth or even smaller fraction of the laser wavelength to produce fluorescent images of living cells and other microscopic objects. The fluorescent emission from the fluorophores increases cubicly, quarticly or even higher power law with the excitation intensity so that by focusing the laser light, fluorescence as well as photobleaching are confined to the vicinity of the focal plane. This feature provides depth of field resolution comparable to that produced by confocal laser scanning microscopes, and in addition reduces photobleaching and phototoxicity. Scanning of the laser beam by a laser scanning microscope, allows construction of images by collecting multi-photon excited fluorescence from each point in the scanned object while still satisfying the requirement for very high excitation intensity obtained by focusing the laser beam and by pulse time compressing the beam. The focused pulses also provide three-dimensional spatially resolved photochemistry which is particularly useful in photolytic release of caged effector molecules, marking a recording medium or in laser ablation or microsurgery. This invention refers explicitly to extensions of two-photon excitation where more than two photons are absorbed per excitation in this nonlinear microscopy.
Owner:WEBB WATT W +1
Multiple-photon excitation light sheet illumination microscope
ActiveUS20110122488A1Radiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationDiagnostic Radiology ModalityFluorescence
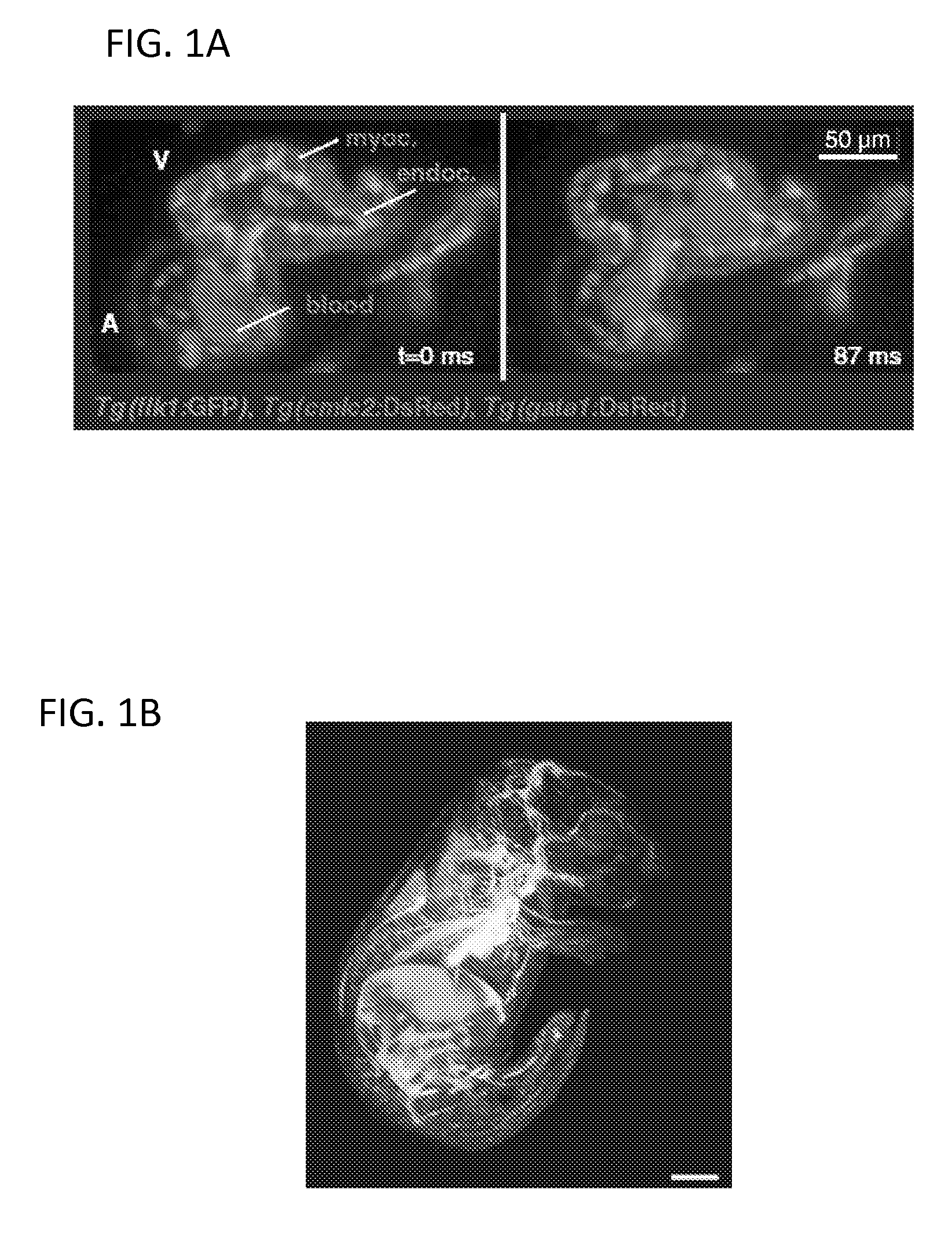
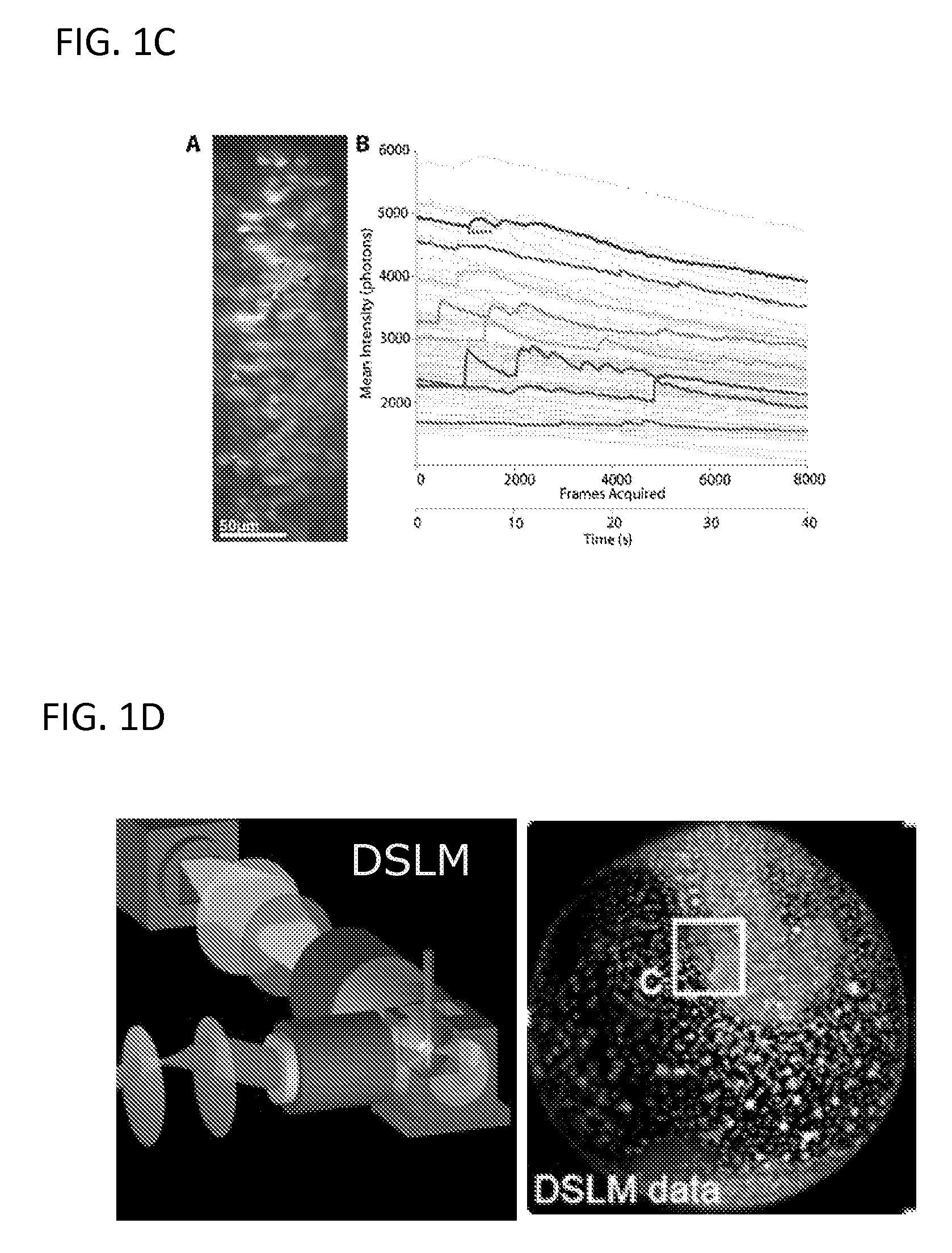
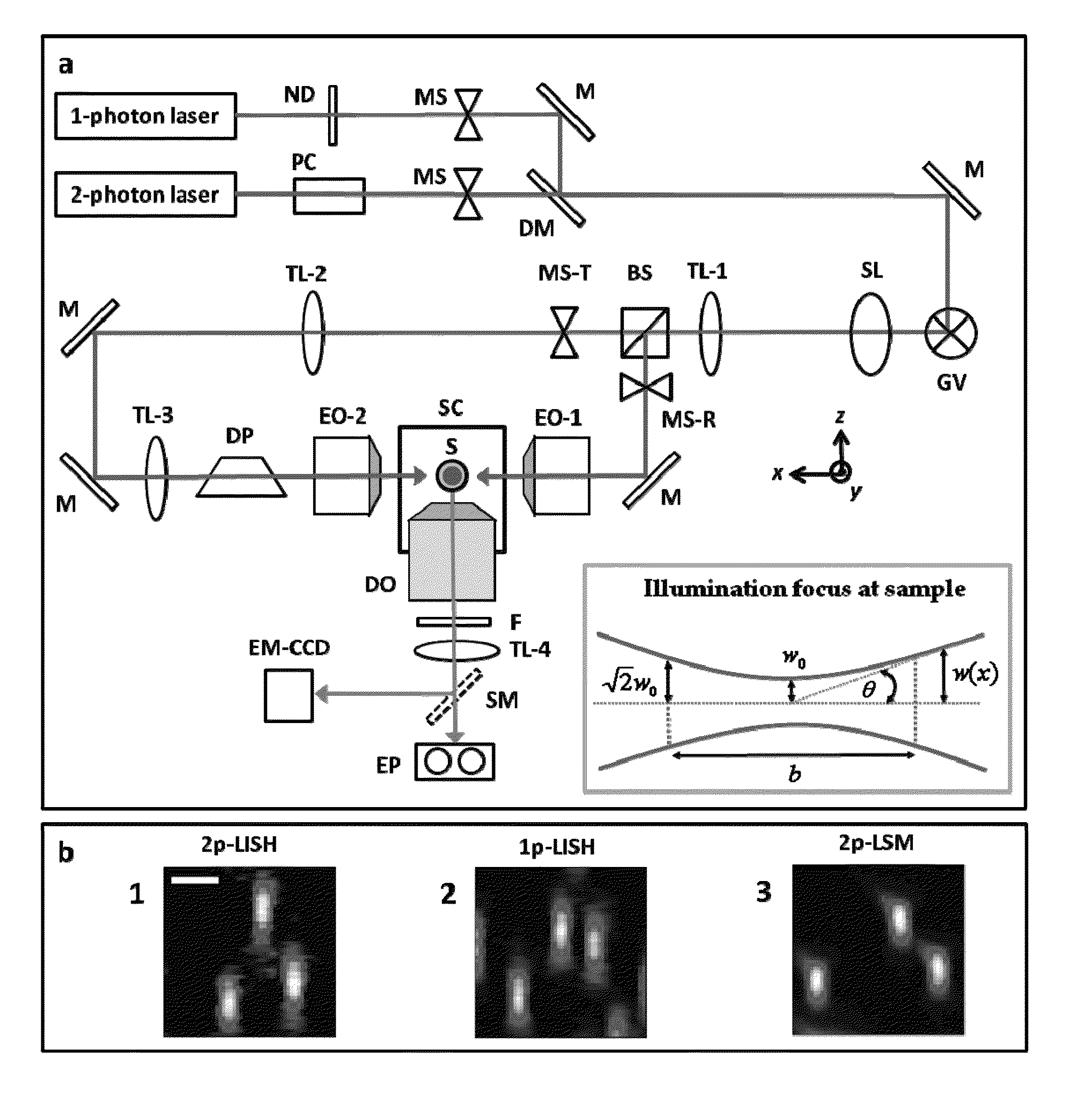
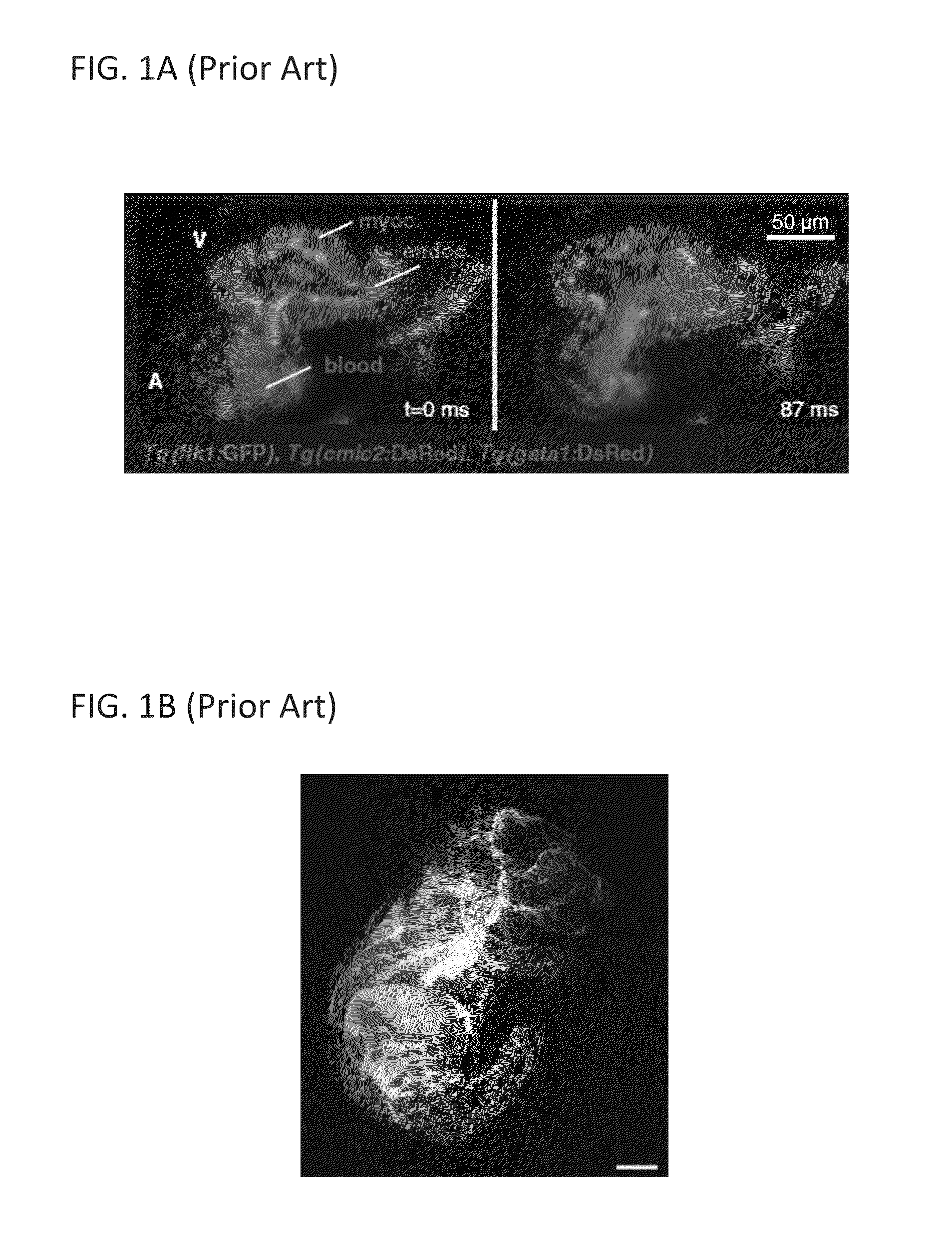
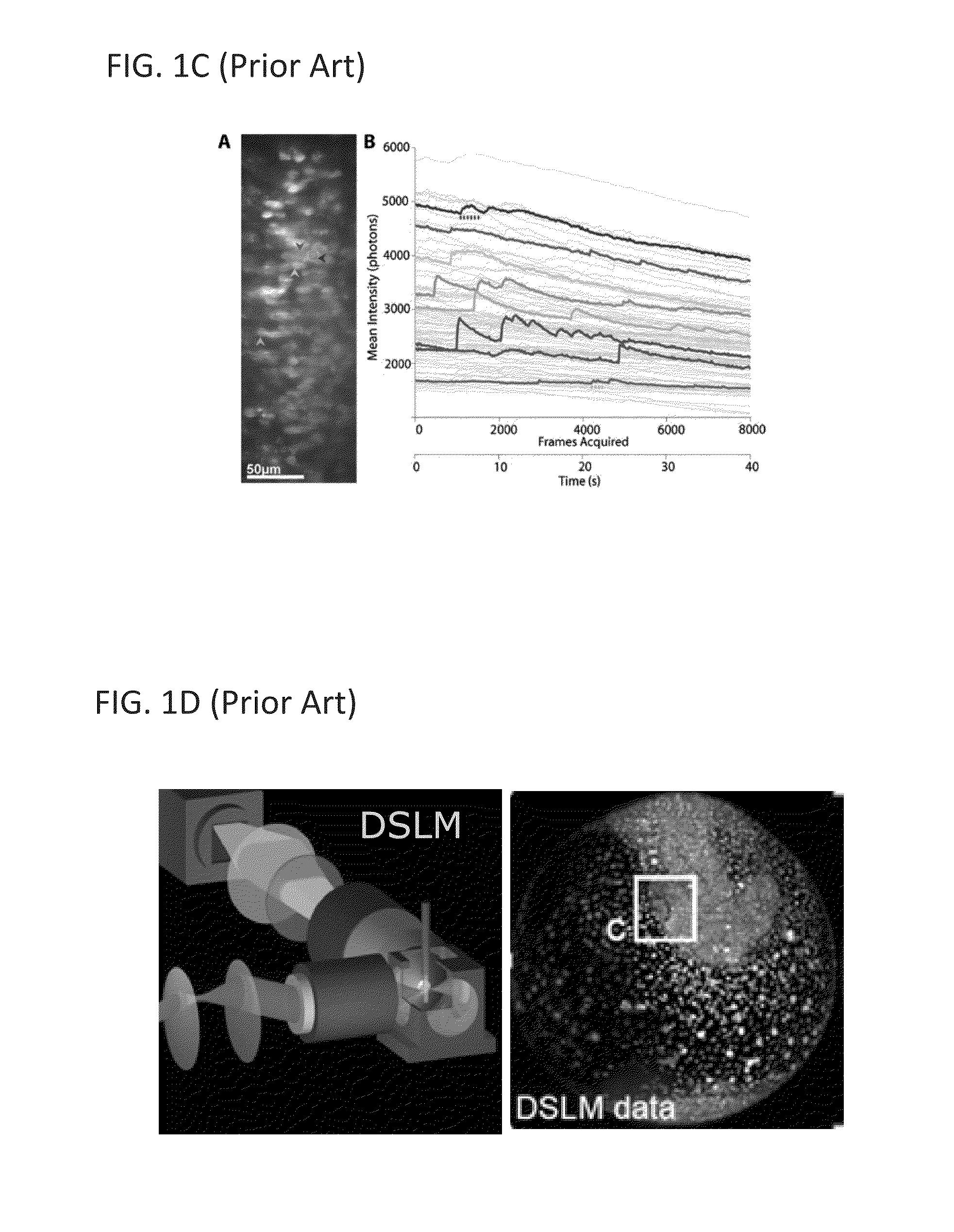
An apparatus for and method of performing multi-photon light sheet microscopy (MP-LISH), combining multi-photon excited fluorescence with the orthogonal. illumination of light sheet microscopy are provided. With live imaging of whole Drosophila and zebrafish embryos, the high performance of MP-LISH compared to current state-of-the-art imaging techniques in maintaining good signal and high spatial resolution deep inside biological tissues (two times deeper than one-photon light sheet microscopy), in acquisition speed (more than one order of magnitude faster than conventional two-photon laser scanning microscopy), and in low phototoxicity are demonstrated. The inherent multi-modality of this new imaging technique is also demonstrated second harmonic generation light sheet microscopy to detect collagen in mouse tail tissue. Together, these properties create the potential for a wide range of applications for MP-LISH in 4D imaging of live biological systems.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Coaxial illuminated laser endoscopic probe and active numerical aperture control
A coaxial illuminated laser endoscopic probe and active numerical aperture control apparatus and method of use, succinctly known as an illumination and laser source, capable of selectively providing illumination light and laser treatment light through a single optical fiber. The apparatus and method is especially useful during ophthalmic surgery. The present art is capable of providing the aforesaid through an optical fiber of such small size that heretofore said fiber was only useable for laser treatment light only. The present art also, with its unique optical system, allows for two illumination light outputs from a single illumination source. The apparatus utilizes a phototoxicity risk card to calibrate the system to prior art or safe illumination levels since the unique optical system provides illumination light of greater intensity than the prior art.
Owner:SYNERGETICS
System and method for selective light inhibition
A film suitable for use in an ophthalmic system is provided. The film may selectively inhibit blue light within the wavelength range of 400 nm to 460 nm to reduce phototoxic light to the eye while maintaining photopic vision, and may be color balanced to allow for the system into which the film is incorporated to be perceived as colorless to a viewer observing and / or using the system. The system may have a photopic and scotopic luminous transmission of 85% or more and a phototoxicity ratio of less than 80%. When used in an ophthalmic system or other system disposed between an observer's eye and a light source, the film may reduce the flux of blue light to the internal structures of the eye while reducing or minimizing dilation of the pupil.
Owner:HIGH PERFORMANCE OPTICS
Optical Filter for Selectively Blocking Light
The present invention is directed to an optical filter that attenuates specific areas of the visible spectrum corresponding to the peaks of absorption of both the S-cone and rod cells within the human retina. The optical filter can be configured to also selectively block at least a portion of light centered at either one or both of the peak absorptive wavelengths of the human M and L-cone cells. The optical filter can be included within or on any optical system that is able to transmit all or part of the visible spectrum. As such, the present invention also provides an optical system that acts as a phototoxicity filter for the eye and can be used in conjunction with any material where visible light has at least partial transmittance.
Owner:CHIAVETTA III STEPHEN V
System and method for selective light inhibition
A film suitable for use in an ophthalmic system is provided. The film may selectively inhibit blue light within the wavelength range of 400 nm to 460 nm to reduce phototoxic light to the eye while maintaining photopic vision, and may be color balanced to allow for the system into which the film is incorporated to be perceived as colorless to a viewer observing and / or using the system. The system may have a photopic and scotopic luminous transmission of 85% or more and a phototoxicity ratio of less than 80%. When used in an ophthalmic system or other system disposed between an observer's eye and a light source, the film may reduce the flux of blue light to the internal structures of the eye while reducing or minimizing dilation of the pupil.
Owner:HIGH PERFORMANCE OPTICS
Non-linear structure light illumination microscopic imaging method and system
ActiveCN104515759AImprove imaging resolutionReduce bleaching effectFluorescence/phosphorescenceRapid imagingFluorescence
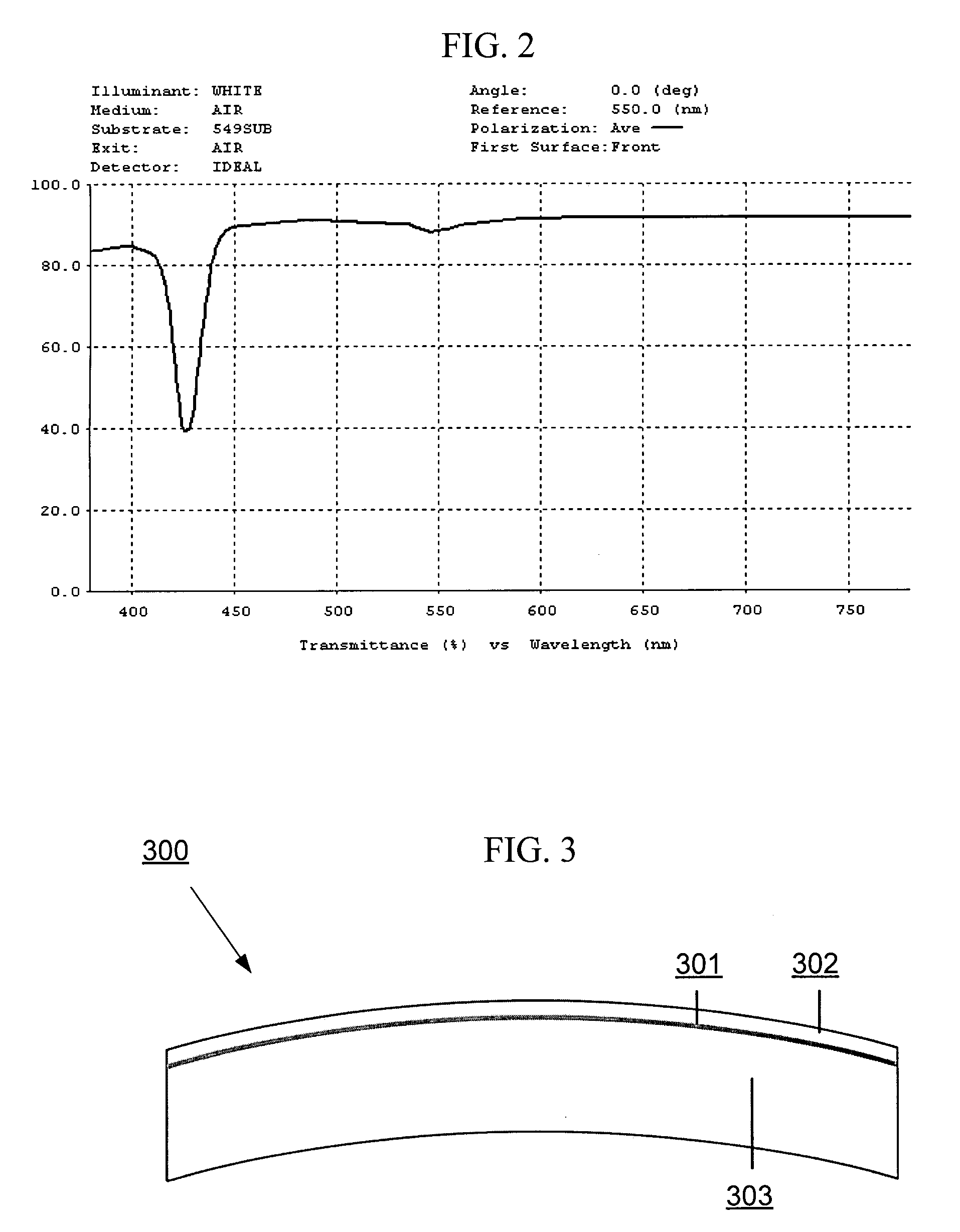
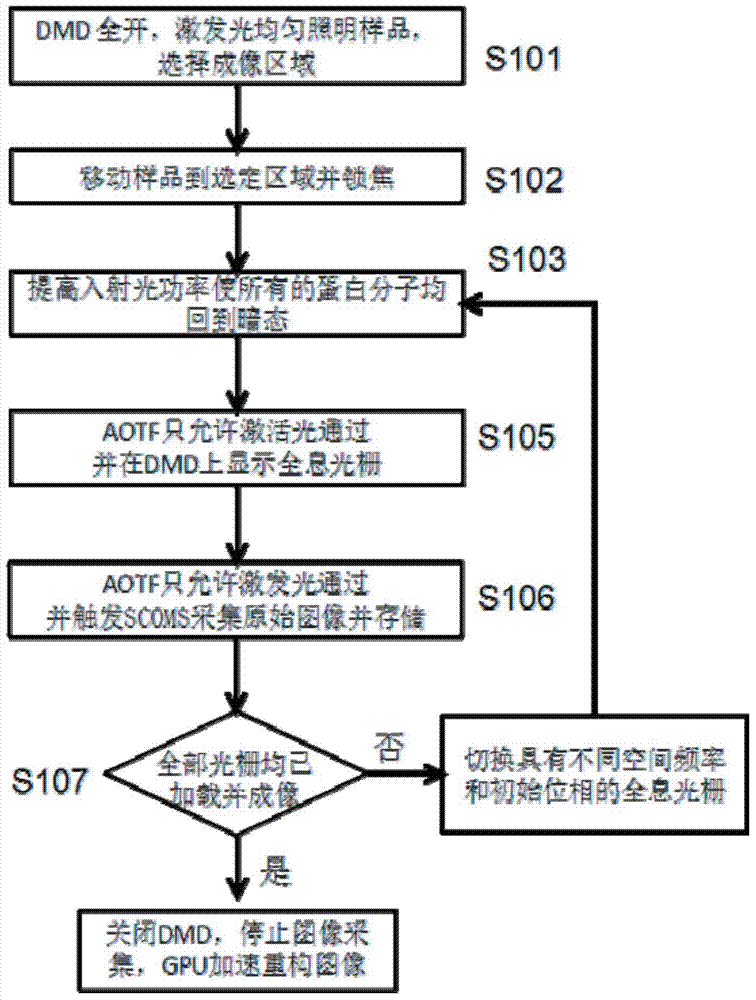
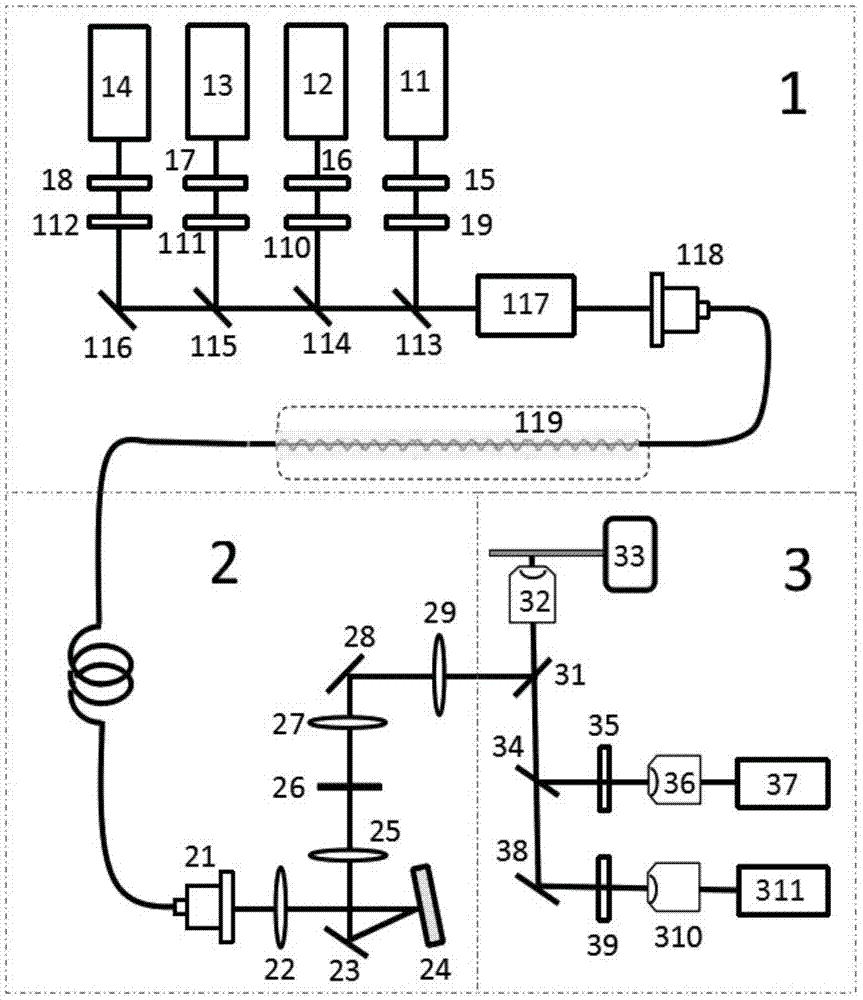
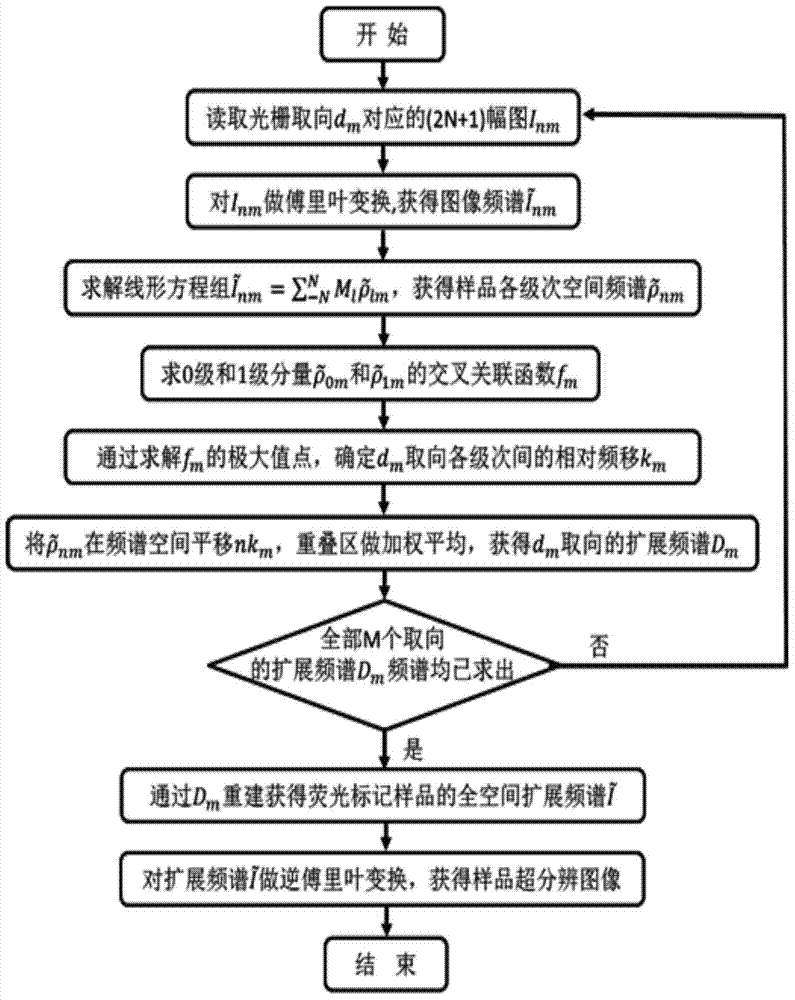
The invention discloses a non-linear structure light illumination microscopic imaging method which comprises the following steps: 1) loading a computed hologram on a digital microscopic array; 2) generating a first spatial structure light field which meets sine distribution and is used for activating fluorescent protein, and radiating the first spatial structure light field to the surface of a sample, so as to convert a part of protein to be in an illuminated state from a dark state; 3) radiating the sample in a second spatial structure light field so as to enable fluorescent protein in the bright state to emit fluorescent light, collecting the fluorescent light, and imaging in a photoelectric detector; 4) repeating the step 2) and the step 3), acquiring a plurality of spatial frequencies, acquiring a plurality of initial phases in each direction to obtain a plurality of original images, and reestablishing a super-resolution image according to a GPU acceleration algorithm. The invention further discloses a non-linear structure light illumination microscopic imaging system. The non-linear structure light illumination microscopic imaging method has the advantages of relatively high system imaging resolution, high fluorescent drifting resistance, low phototoxicity and rapid imaging.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Use of human amniotic mesenchymal stem cell exosome
InactiveCN104382827AReduce attackAvoid damageCosmetic preparationsPowder deliveryMortality rateMesenchymal stem cell
The invention relates to the field of stem cells, and discloses novel use of a stem cell exosome, and particularly discloses novel use of a human amniotic mesenchymal stem cell exosome. The experiment result shows that a human amniotic mesenchymal stem cell is capable of promoting growth of HDF cells, improving the activity of SOD (Superoxide Dismutase) enzyme in the cells, reducing attacks and damages to the cells caused by oxygen radicals generated by ultraviolet radiation induction, and reducing the death rate of the cells. The use shows that the human amniotic mesenchymal stem cell exosome has an anti-photoaging effect, and meanwhile, the human amniotic mesenchymal stem cell exosome is free of phototoxicity, so that application of the human amniotic mesenchymal stem cell exosome in preparation of an anti-ageing preparation is provided. The invention also provides an anti-ageing preparation of the human amniotic mesenchymal stem cell exosome.
Owner:GUANGZHOU SALIAI STEMCELL SCI & TECH CO LTD
Apparatus and method for three dimensional image reconstruction
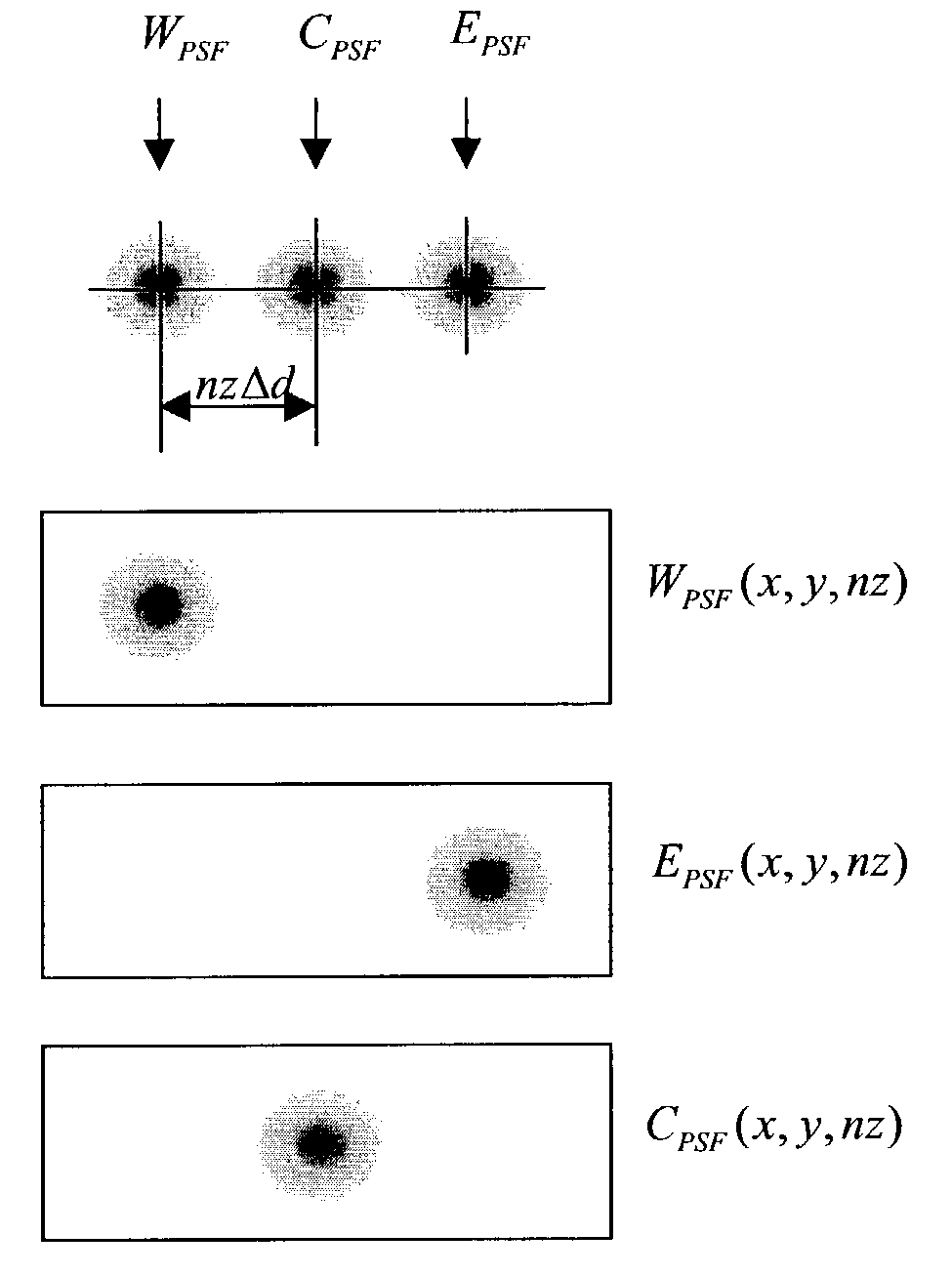
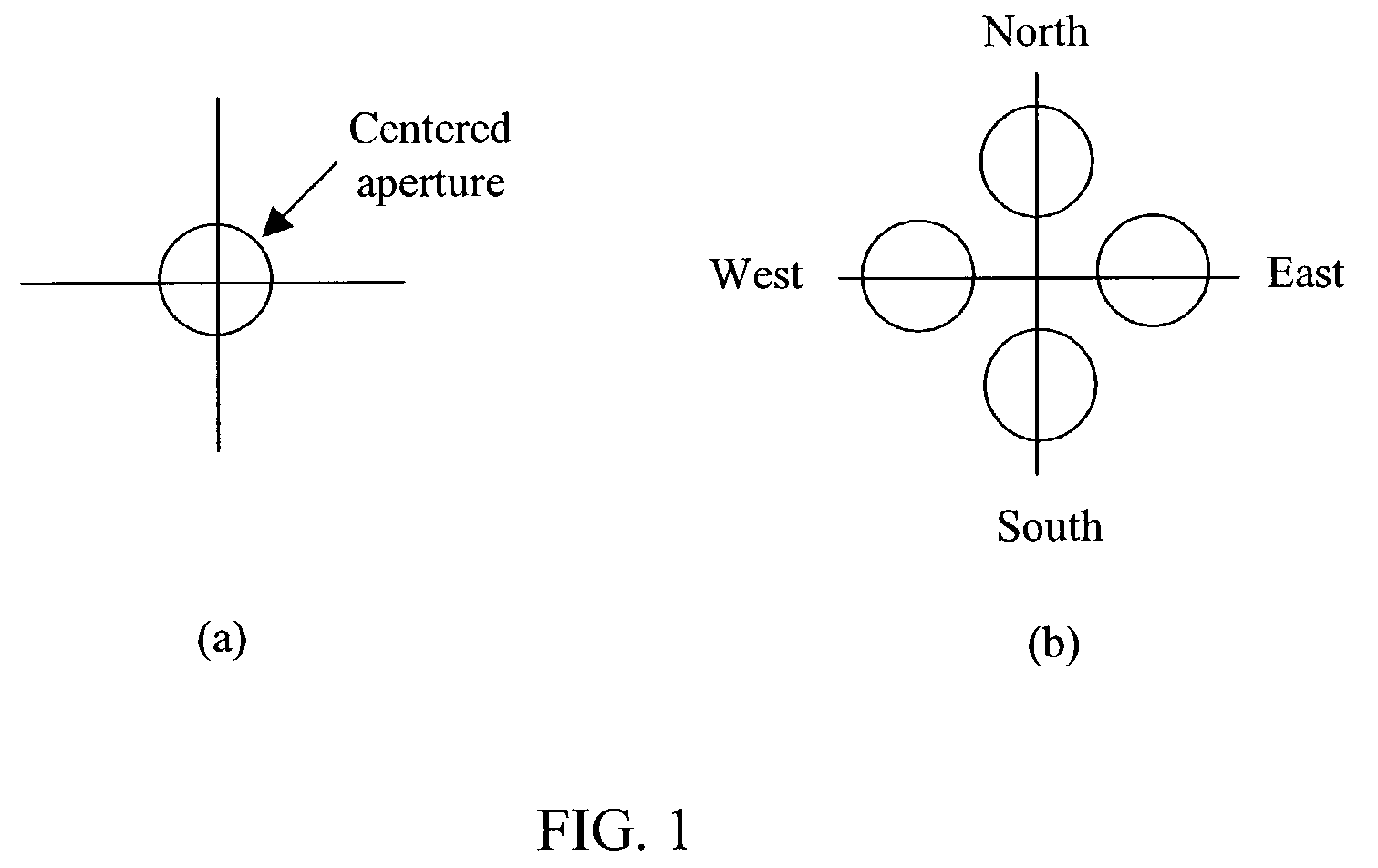
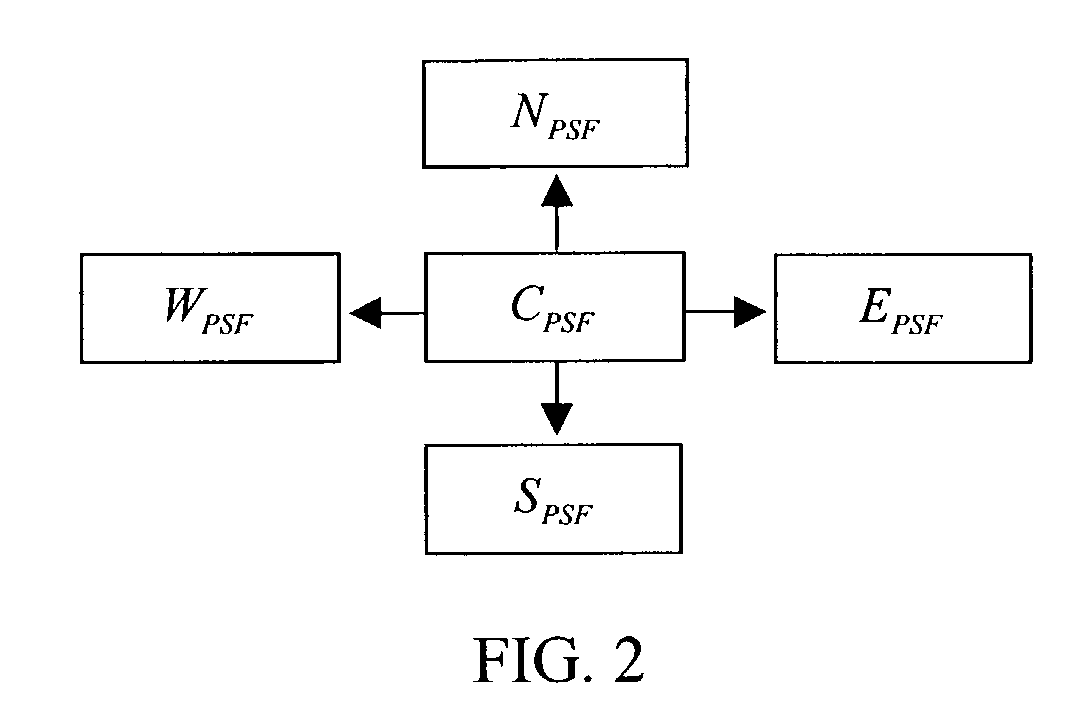
InactiveUS7197193B2Improve image acquisition efficiencyEliminate effect caused by motionImage enhancementImage analysisPoint spread functionDiffusion function
An instrument to acquire and methods to obtain three-dimensional (3D) images from a series of two-dimensional (2D) images which are obtained without moving the relative positions of the target, the detector, or the focusing lens is disclosed. The 2D images consist of one centered image obtained with the aperture at the center of optical system, and at least two directional images obtained with apertures at off-axis locations. The images can be obtained simultaneously or sequentially. The blurred 2D images are sectioned by computational method using point spread function of the optical system resulting in a set of decoupled 2D layers of the 3D object. The layered images are then sharpened by deconvolution using point spread function. The 3D reconstructed image is displayed. This technique provides fast data acquisition and fast image reconstruction and eliminates problems associated with motion, phototoxicity and photobleaching.
Owner:CREATV MICROTECH
Super-resolution differential interference phase contrast microscopic imaging system and microscopic imaging method
The invention discloses a super-resolution differential interference phase contrast microscopic imaging system. The system comprises a microscope, a light source, a first lens, a first reflecting mirror, a spatial light modulator, a third lens, a light barrier, a fourth lens and a charge coupled device (CCD), and the microscope is provided with a differential interference phase contrast imaging module. Simultaneously, the invention further discloses a microscopic imaging method based on the imaging system. According to the imaging system and the imaging method, extra sample preparation processes are not required, photobleaching effects and phototoxicity effects are absent, and the imaging contrast ratio is high.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Multiple-photon excitation light sheet illumination microscope
An apparatus for and method of performing multi-photon light sheet microscopy (MP-LISH), combining multi-photon excited fluorescence with the orthogonal illumination of light sheet microscopy are provided. With live imaging of whole Drosophila and zebrafish embryos, the high performance of MP-LISH compared to current state-of-the-art imaging techniques in maintaining good signal and high spatial resolution deep inside biological tissues (two times deeper than one-photon light sheet microscopy), in acquisition speed (more than one order of magnitude faster than conventional two-photon laser scanning microscopy), and in low phototoxicity are demonstrated. The inherent multi-modality of this new imaging technique is also demonstrated second harmonic generation light sheet microscopy to detect collagen in mouse tail tissue. Together, these properties create the potential for a wide range of applications for MP-LISH in 4D imaging of live biological systems.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Fluorescent probe and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106833623AStrong forceEasy to pile upOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceSolubilityDouble bond
The invention provides a fluorescent probe represented by the formula (I), wherein R1 and R2 are independently selected from H or an aromatic vinyl group, and at least one of R1 and R2 is the aromatic vinyl group; R3 is selected from H, F, Cl, Br, OH, OCH3, N(CH3)2 or C1-C6 alkyl; and R4 is selected from C1-C6 alkyl. Compared with the prior art, because the fluorescent probe provided by the invention has a relatively large electronic conjugated system and plane, the intensity of the intramolecular charge transfer effect can affect the molecular fluorescence emission intensity; when the fluorescent probe and the G-quadruplex generate a specific action, the flexibility of intramolecular rotatable double bonds is restricted, the intramolecular charge transfer effect is enhanced, and the fluorescence is also enhanced significantly; moreover, the fluorescent probe provided by the invention has the advantages of low biotoxicity, phototoxicity and photobleaching property, good light stability, good water solubility and good cell membrane permeability.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Living cell laser scanning co-focusing microscope imaging system
InactiveCN102621117ACompact structureHigh precisionMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceLaser scanning
The invention relates to a living cell laser scanning co-focusing microscope imaging system, which is characterized by comprising a laser scanning co-focusing microscope and a fluorescent signal collecting device, wherein the fluorescent signal collecting device comprises a culture dish, a converging lens and a reflecting type narrow-band light filter, the converging lens and the reflecting type narrow-band light filter are arranged in the culture dish, the bottom of the culture dish is provided with a culture dish bottom plate used for placing cells to be tested, the converging lens is fixedly arranged on the culture dish through a lens clamping frame, the cells to be tested on the culture dish bottom plate are positioned on the focal plane of the converging lens, the reflecting type narrow-band light filter is positioned right above the converging lens, and an objective lens of the laser scanning co-focusing microscope is positioned right under the culture dish bottom plate. The living cell laser scanning co-focusing microscope imaging system has the advantages that the structure is compact, the precision is high, the fluorescent signal collection efficiency of the laser scanning co-focusing microscope can be effectively improved, the phototoxicity and the light bleaching degree are reduced, and a technical means is provided for obtaining reliable experiment results.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
Methods and compositions for dose-dependent photodynamic therapy of disorders
InactiveUS20090259167A1Potent vascular PDT reactionBiocideOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseAmino-Levulinic Acid
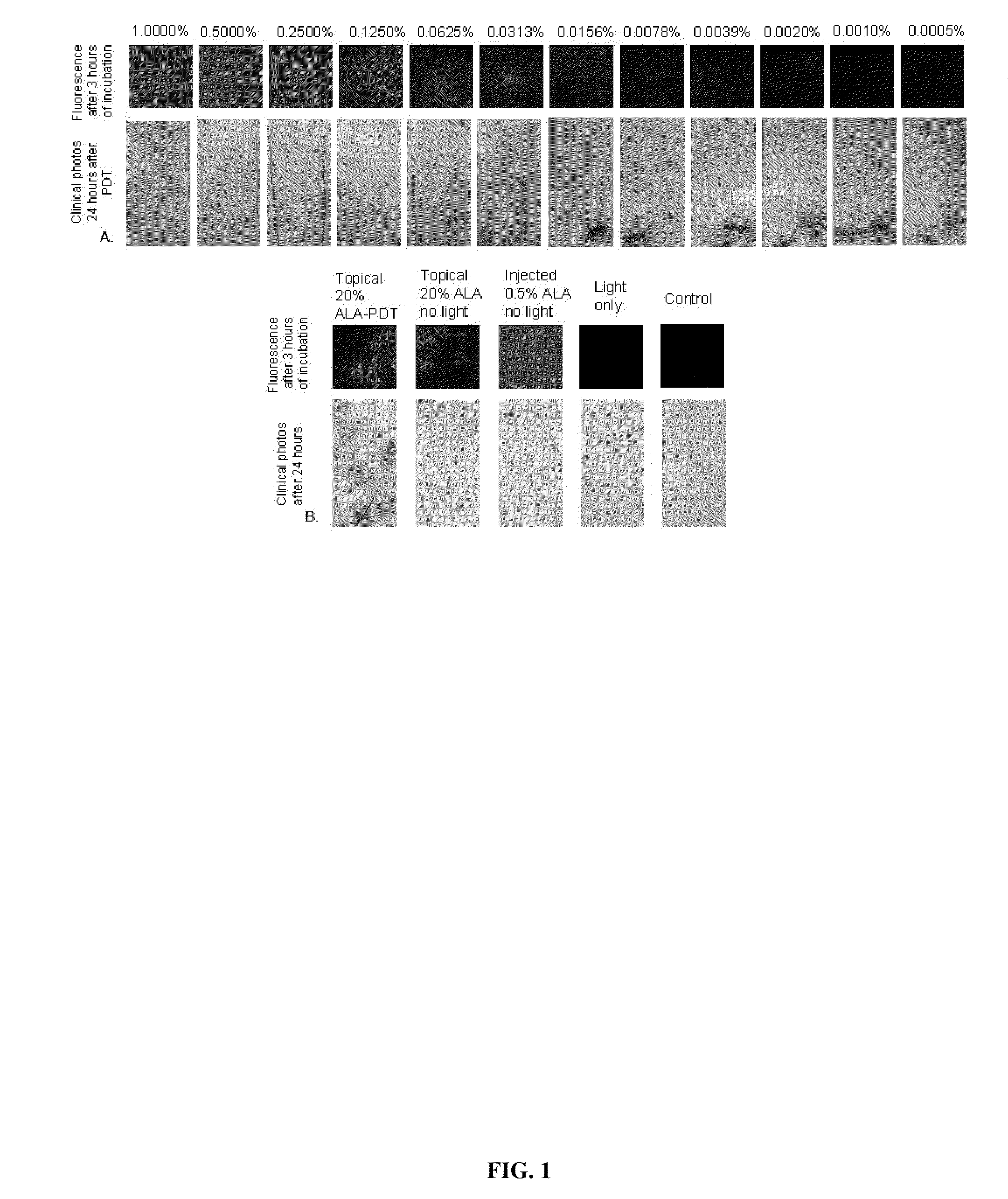
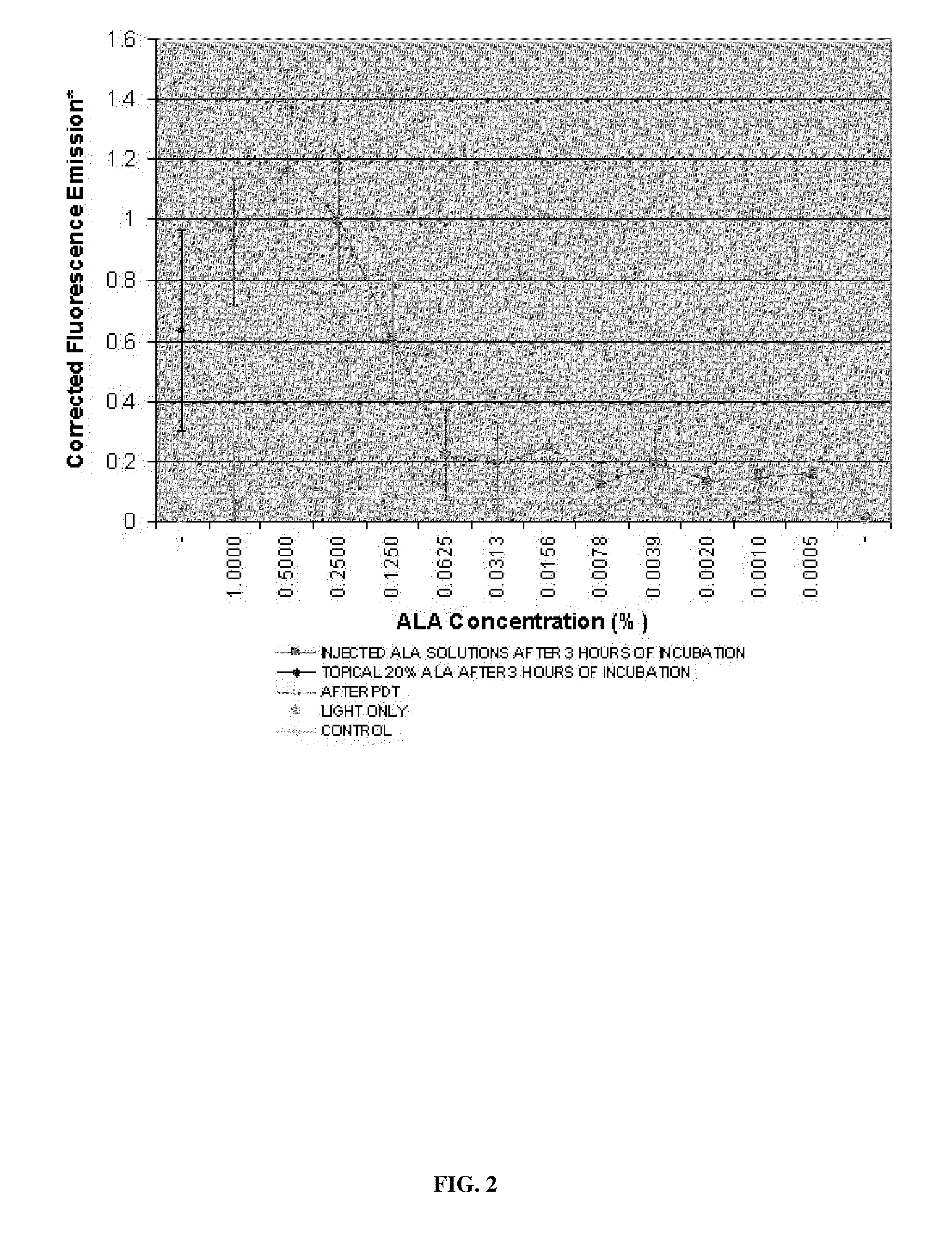
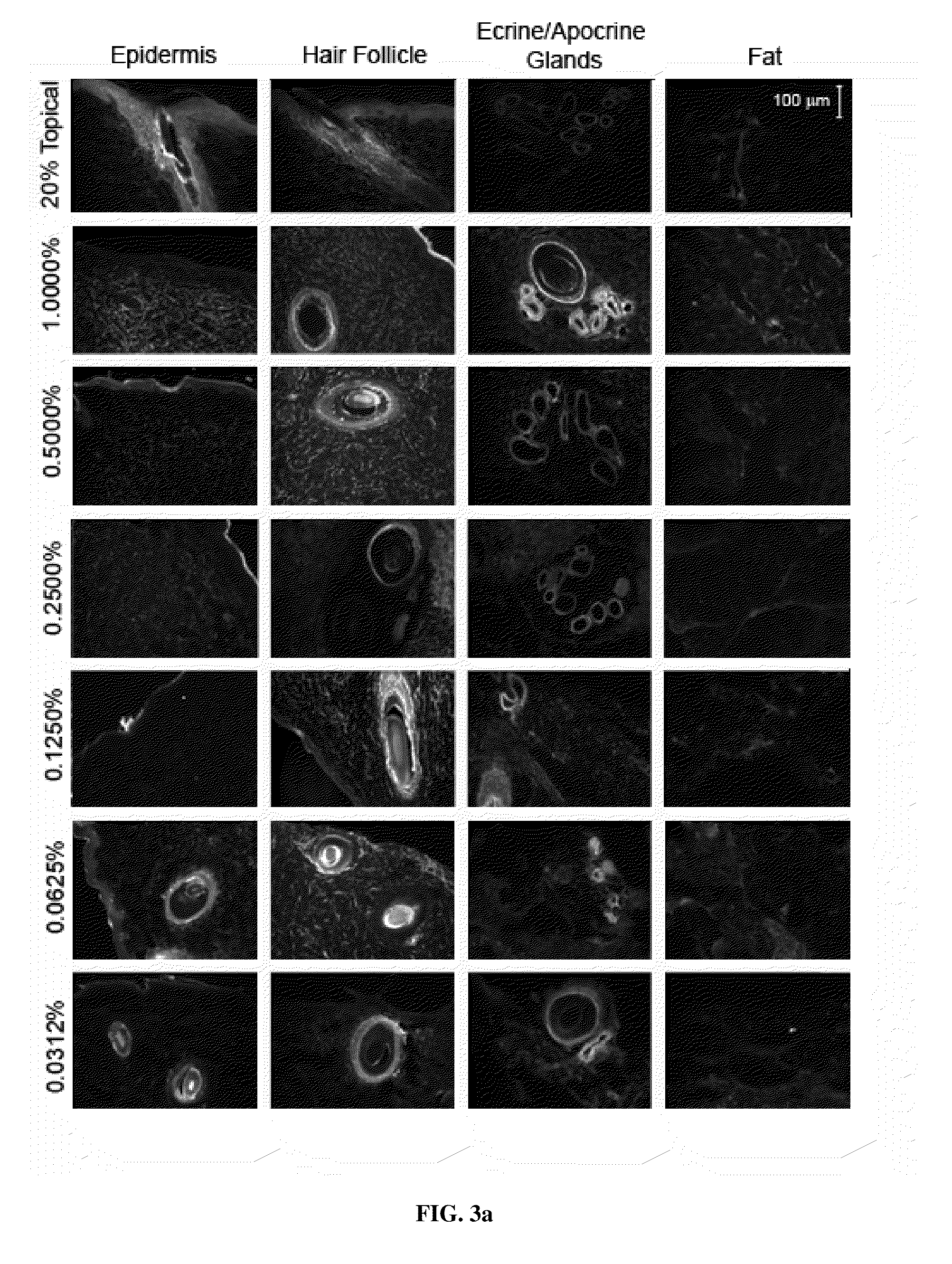
The invention provides methods and compositions for treating a tissue disorder in a subject by parenterally administering a solution of aminolevulinic acid (ALA) or a derivative thereof that is not greater than 1.0 percent by weight into a local subcutaneous or dermal region of the subject; and administering high fluence light to said bodily area to produce a phototoxic species in said local region, thereby treating a tissue disorder in the subject.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Coaxial illuminated laser endoscopic probe and active numerical aperture control
InactiveUS20070139924A1Improve efficiencyLittle or no light outputLaser surgeryLighting elementsFiberPhototoxicity
A coaxial illuminated laser endoscopic probe and active numerical aperture control apparatus and method of use, succinctly known as an illumination and laser source, capable of selectively providing illumination light and laser treatment light through a single optical fiber. The apparatus and method is especially useful during ophthalmic surgery. The present art is capable of providing the aforesaid through an optical fiber of such small size that heretofore said fiber was only useable for laser treatment light only. The present art also, with its unique optical system, allows for two illumination light outputs from a single illumination source. The apparatus utilizes a phototoxicity risk card to calibrate the system to prior art or safe illumination levels since the unique optical system provides illumination light of greater intensity than the prior art.
Owner:EASLEY JAMES C +2
Coaxial illuminated laser endoscopic probe and active numerical aperture control
ActiveUS20050033389A1Improve efficiencyLittle or no light outputLaser surgeryElectrotherapyFiberPhototoxicity
A coaxial illuminated laser endoscopic probe and active numerical aperture control apparatus and method of use, succinctly known as an illumination and laser source, capable of selectively providing illumination light and laser treatment light through a single optical fiber. The apparatus and method is especially useful during ophthalmic surgery. The present art is capable of providing the aforesaid through an optical fiber of such small size that heretofore said fiber was only useable for laser treatment light only. The present art also, with its unique optical system, allows for two illumination light outputs from a single illumination source. The apparatus utilizes a phototoxicity risk card to calibrate the system to prior art or safe illumination levels since the unique optical system provides illumination light of greater intensity than the prior art.
Owner:SYNERGETICS
Surgical microscope for ophthalmology
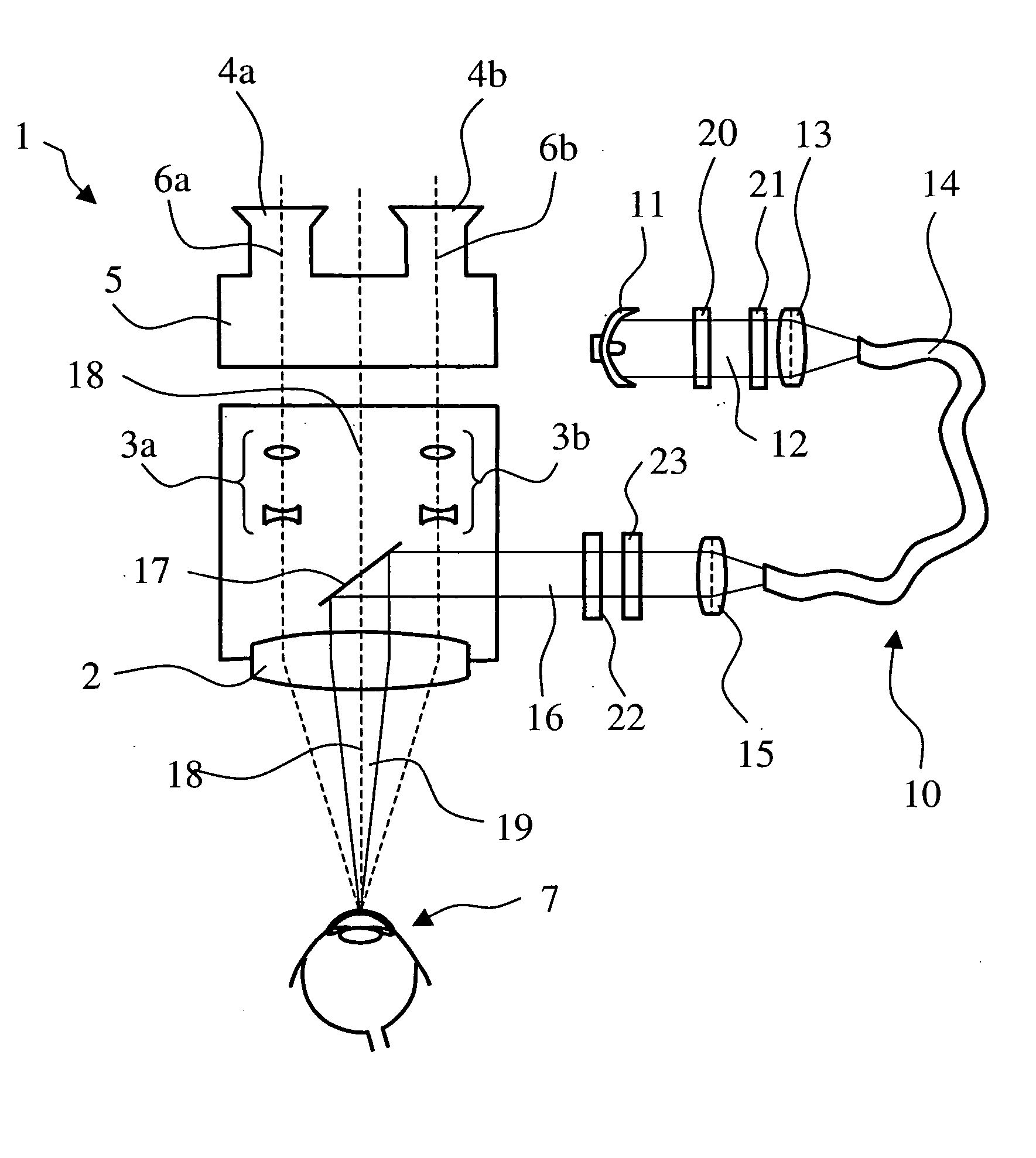
ActiveUS20050117209A1Contrast-rich and detail-accurate viewing imageReduce phototoxicityDiagnosticsSurgical instrument detailsOphthalmologyUltraviolet
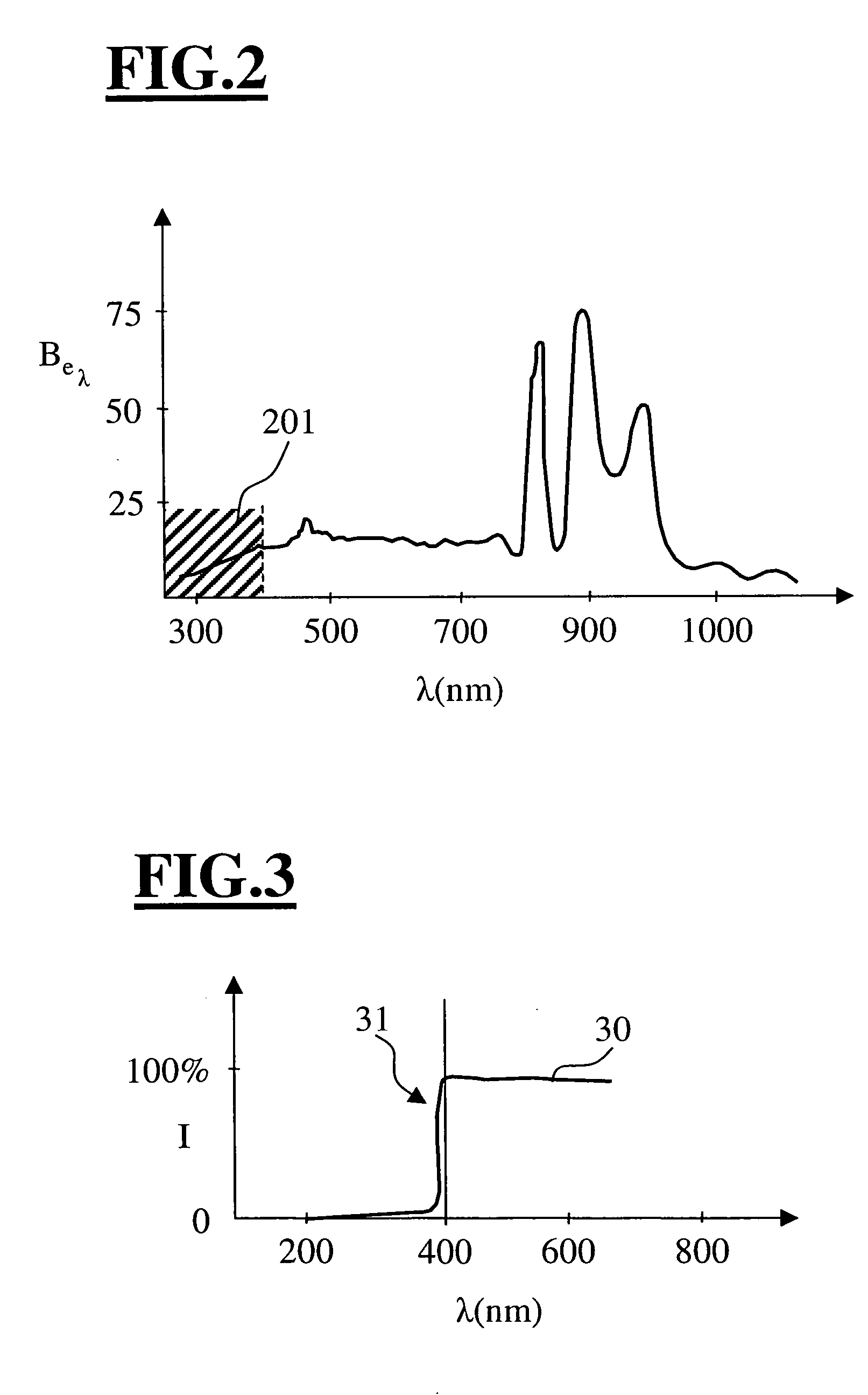
A surgical microscope (1) for ophthalmology includes a tube unit (4) which permits viewing an area (5) of surgery, especially a forward section of the eye, through a microscope main objective (2). The surgical microscope (1) includes an illuminating system (10) which makes available the illuminating light to illuminate the surgical area (5), especially the forward section of the eye. To provide daylight-like illuminating light, the illuminating system includes a xenon illuminating light source (11) or a metal halogen illuminating light source. At least one interference filter (22, 23) is provided in the illuminating beam path (15a). The cutoff frequency of the interference filter lies such that illuminating light in the ultraviolet range is filtered out and illuminating light in the visible wavelength range is attenuated, if at all, to an insignificant extent in order to reduce the phototoxicity of the illuminating light for the human eye.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Fullereneporphyrin derivate photosensitizer as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103724356AIncrease profitTo overcome the shortcoming of needing sufficient oxygen concentrationAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsCancer cellPhotosensitizer
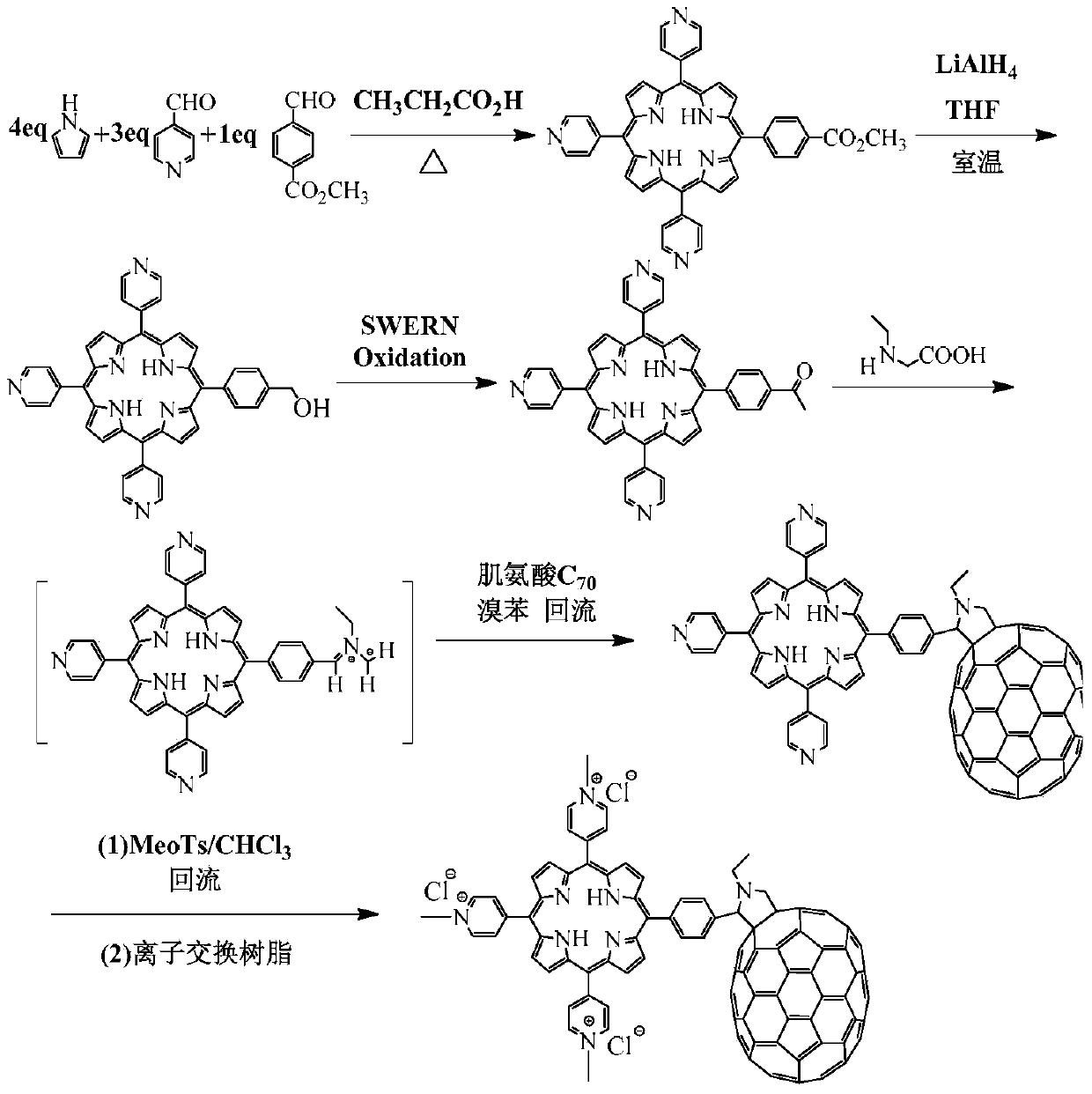
The invention discloses a fullereneporphyrin derivate photosensitizer as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The structural formula of the fullereneporphyrin derivate photosensitizer is shown as the formula I. The fullereneporphyrin derivate photosensitizer can overcome the defect that a traditional photosensitizer needs enough oxygen concentration, and effective reactive oxygen can still be generated under the low oxygen concentration, so that a good treatment effect can be achieved. The fullereneporphyrin derivate photosensitizer has the advantages of high phototoxicity, low dark toxicity, high selectivity in pickup of cancer cells and the like, and has a broad spectrum, a killing effect on cancer cells and a remarkable bacteria killing effect. Most of all, the fullereneporphyrin derivate can be metabolized in a mouse body, and is a novel photosensitizer with a good prospect.
Owner:赤峰福纳康生物技术有限公司 +1
Near infrared fluorescence probe adopting nile blue as parent, preparation method thereof and applications thereof
ActiveCN103820104AAccurate responseGood cell membrane permeabilityOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceCell membraneNile blue stain
The invention relates to a near infrared fluorescence probe adopting nile blue as a parent, a preparation method thereof and applications thereof. The fluorescence probe has a structure shown as the general formula I as the attached drawing 1. The fluorescence probe can effectively improve deficiencies of tumor labeling fluorescence probes at present, can sensitively and accurately response to target cells COX-2 expression amount of which is abnormal, and is suitable for effective specific near infrared fluorescence probes labeling living tumor cells. The fluorescence probe provided by the invention is simple in synthesis and products are easy to obtain. The fluorescence probe provided by the invention has a very low fluorescence background in non-tumor cells and high fluorescence signals in tumor cells, and has strong specific labeling function for tumor cells. In addition, compounds of the type have good cell membrane permeability, low biotoxicity, low phototoxicity and low photobleaching capability and can locate a special organelle of a certain kind tumor cell.
Owner:SICHUAN ANKERUI NEW MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
Hybrid material of silica-curcumin and derivatives thereof as well as preparation method of hybrid material
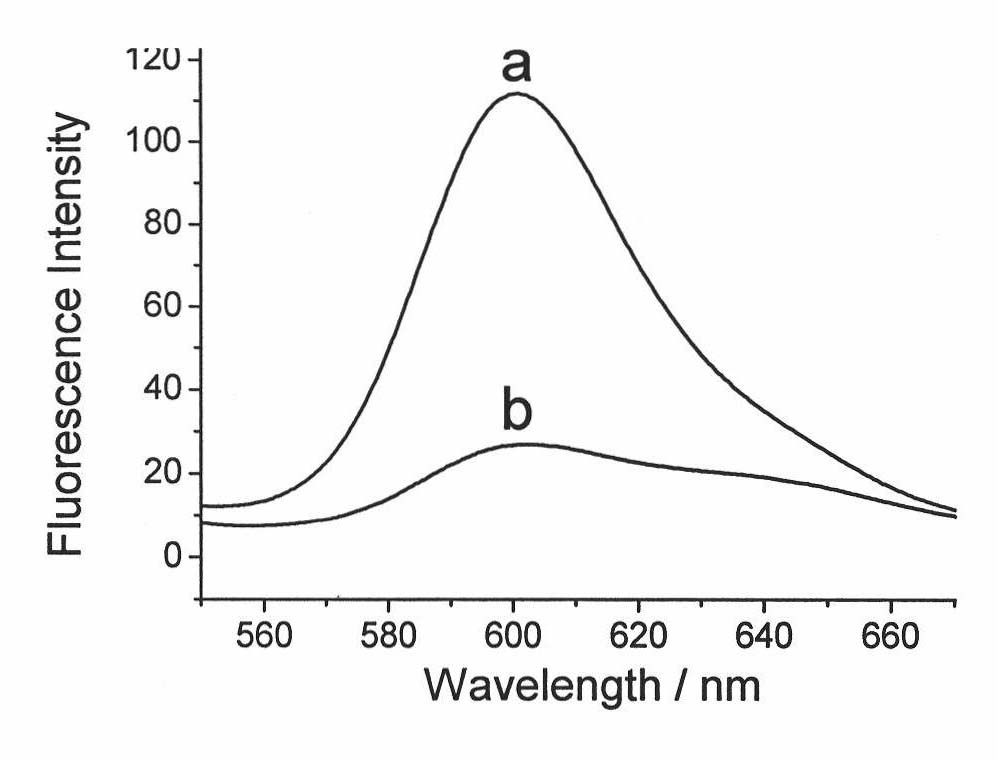
InactiveCN101796961AStrong phototoxic reactionImprove antibacterial propertiesBiocideFungicidesRare earth ionsHybrid material
The invention relates to the field of novel functional material researches, in particular to a hybrid material of silica-curcumin and derivatives thereof as well as a preparation method of the hybrid material. The hybrid material is prepared in such a way that the curcumin or the derivatives thereof with bioactivities are grafted with silica through an amino-silane coupling agent; and the prepared hybrid material can be also further in coordinated bonding with Cu2+, Zn2+, Fe2+, Fe3+ or rare earth ions so as to form the hybrid materials containing metal ions. Compared with the curcumin per se, the prepared hybrid material has stronger antibacterial properties, thermodynamic stability and dispersibility as well as stronger fungal and bacterial phototoxicity reaction and can be used as additives of photosensitive materials, multifunctional anti-bacterial pigment, paints, and the like.
Owner:LESHAN NORMAL UNIV
Phthalocyanine compound, preparation method and application as single/two-photon fluorescent probe in cancer targeting and mitochondria labeling
ActiveCN104861039AHigh affinityOvercome phototoxicityMicrobiological testing/measurementLuminescent compositionsCancer targetingFluorescence
The invention relates to a phthalocyanine compound, a preparation method and an application as a single / two-photon fluorescent probe in cancer targeting and mitochondria labeling. The phthalocyanine compound has a structure of formula (I) and is an asymmetric phthalocyanine metal complex; R represents a polypeptide containing an RGD sequence, n is 0-6; the phthalocyanine compound not only has unique selectivity for cancer cells, but also can realize specific localization in live cell mitochondria, and is a multifunctional fluorescent probe. The invention also provides the preparation method of the phthalocyanine compound, wherein the preparation method is simple in process and wide in application range. The phthalocyanine compound overcomes the common phototoxicity of phthalocyanine; under 12 J / cm<2> of red light irradiation energy, the survival rate of cells is above 95%; and the phthalocyanine compound has good application value in two-photon tumor imaging and mitochondria imaging.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Preparation method and application in preparation of photodynamic therapy medicines of fat-soluble photosensitizer loaded on inorganic salt carrier
InactiveCN101850118AEasy to prepareEasy to operateOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderDispersitySolubility
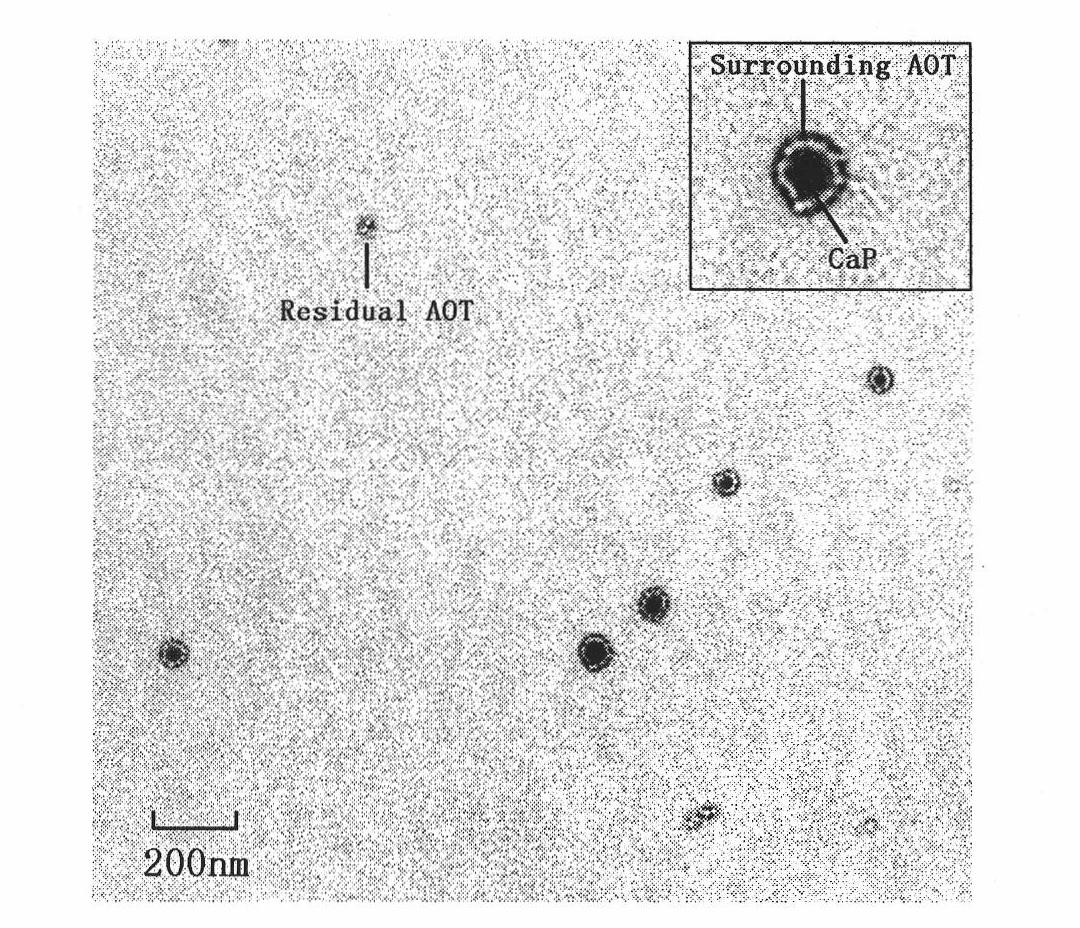
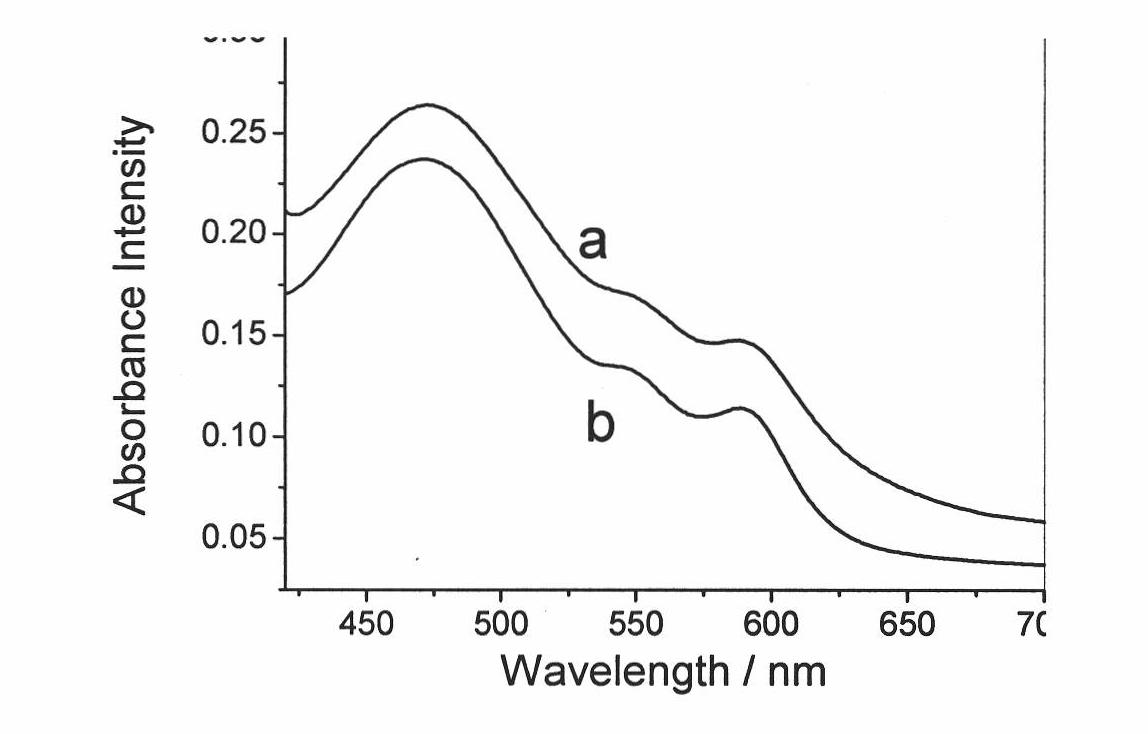
The invention relates to a preparation method and application in the preparation of photodynamic therapy medicines of a fat-soluble photosensitizer loaded on inorganic salt carrier or modified surface inorganic salt carrier. The preparation method comprises the following steps: in or without the presence of surfactant, firstly adding distilled water, DMSO solution of fat-soluble photosensitizer, chloride solution and phosphate solution, performing magnetic stirring, and obtaining calcium phosphate nanoparticles with the grain size less than 100nm of fat-soluble photosensitizer after the reaction, wherein the molar ratio of chloride solution to phosphate solution is 1:10-10:1. The preparation method of the invention is simple, is easy to operate and has high stability and low cost; the diameter of the prepared nanoparticles is about 70nm, thus facilitating the preparation and storage of the product; the nanoparticles have high water-solubility and good dispersity, and can be used to promote the effective transmission of the fat-soluble photosensitizer in blood and eliminate the toxic or side effects of the fat-soluble photosensitizer which is used alone; and the nanoparticles have low toxicity in the dark and high phototoxicity.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
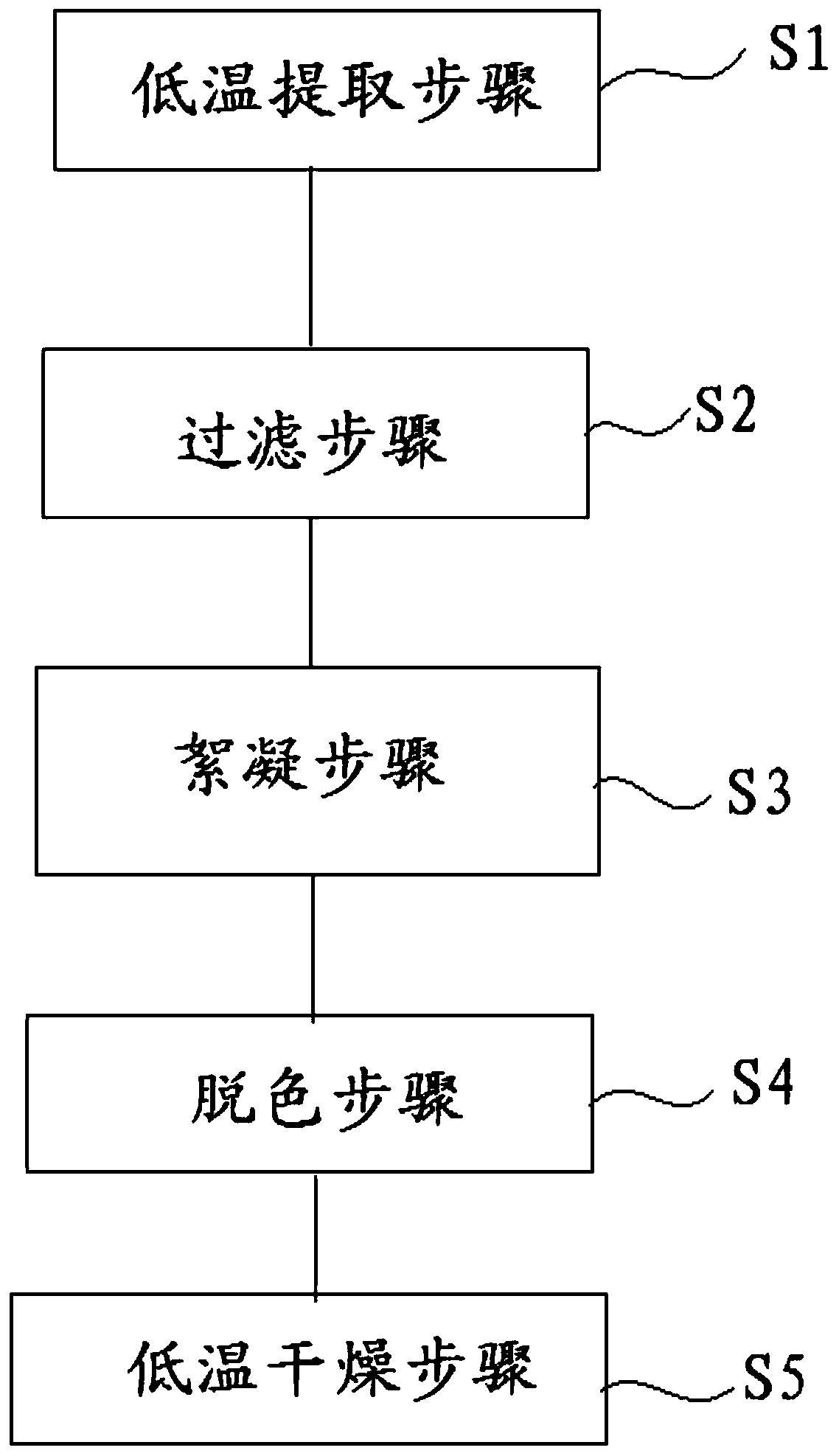
Preparation method and application of purslane extract
ActiveCN110201012AReduce consumptionAvoid damageCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsFiltrationPurslane extract
The invention discloses a preparation method of a purslane extract. The preparation method includes the steps of low-temperature extraction, filtration, flocculation, decoloration and low-temperaturedrying. The preparation method is simple and feasible, the energy consumption is significantly lower than that of a conventional extraction method, and the method is suitable for industrial production; the purslane extract obtained by the method ensures that chemical components of purslane are not destroyed to the greatest extent, main components polysaccharides and organic acids have high stability in different batches, do not contain prohibited substances norepinephrine and dopamine, and have not skin phototoxicity, and the purslane extract can be used as the active component of skin care products and pharmaceutical auxiliaries and plays anti-inflammatory, anti-irritating, allergy-relieving and other functions.
Owner:YUNNAN BOTANEE BIO TECH GRP CO LTD +1
Certain plant growth regulators (PGRs) as safener to Glyphosate for application to Glyphosate-tolerant crops
InactiveUS20050187108A1Improve scalabilityReduce capacityBiocideDead animal preservationGrowth plantGlyphosate
When the Glyphosate-tolerant crops, known as Round-Up Ready crops, are sprayed with Glyphosate in the field, the crops may exhibit some extent of phototoxicity, although the weeds are killed, as intended. Use of safener additive in present invention as plant growth regulator (PGR), along with Glyphosate, will result in reduced phototoxicity to the crops and thus better crops growth, while the herbicidal activities of Glyphosate are not affected.
Owner:LT BIOSYN
Coaxial illuminated laser endoscopic probe and active numerical aperture control
InactiveUS20070139950A1Improve efficiencyLittle or no light outputLaser surgeryEndoscopesFiberPhototoxicity
A coaxial illuminated laser endoscopic probe and active numerical aperture control apparatus and method of use, succinctly known as an illumination and laser source, capable of selectively providing illumination light and laser treatment light through a single optical fiber. The apparatus and method is especially useful during ophthalmic surgery. The present art is capable of providing the aforesaid through an optical fiber of such small size that heretofore said fiber was only useable for laser treatment light only. The present art also, with its unique optical system, allows for two illumination light outputs from a single illumination source. The apparatus utilizes a phototoxicity risk card to calibrate the system to prior art or safe illumination levels since the unique optical system provides illumination light of greater intensity than the prior art.
Owner:EASLEY JAMES C +3
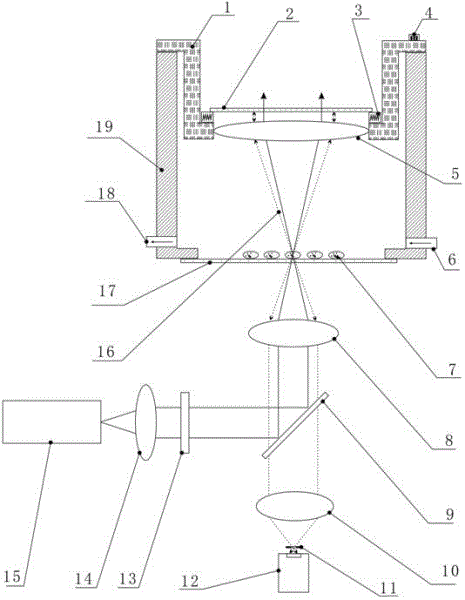
Phototoxicity experiment detection device
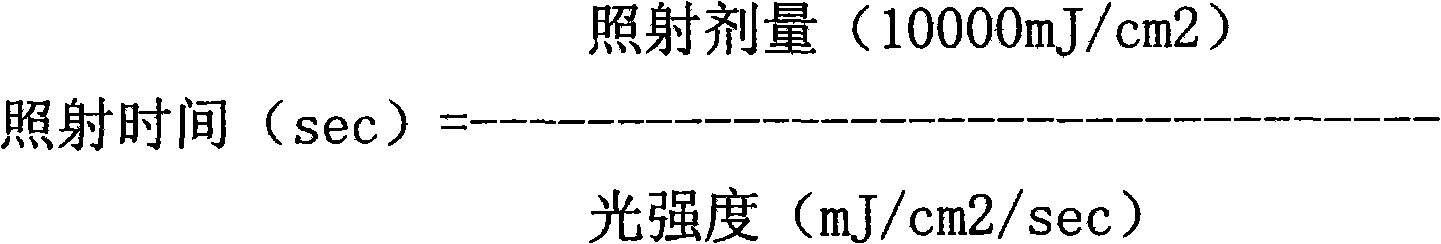
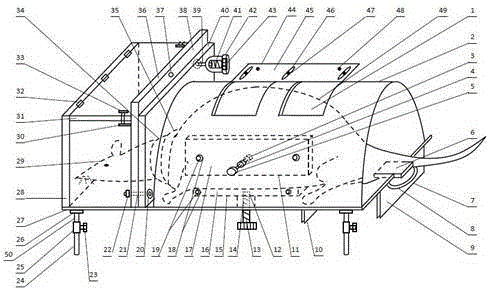
InactiveCN101554340AControllable light intensityControllable exposure timeDiagnosticsSurgeryHuman exposureUltraviolet
The invention provides a phototoxicity experiment detection device which comprises a lightproof experimental bin body. The lightproof experimental bin body is internally provided with a plurality of uviol lamps with UVA of single wavelength of 365nm as an experimental light source and a plurality of small animals fixing brackets. The front face of the experimental bin body is provided with movable observation windows on which glass capable of filtering ultraviolet waves is arranged. A sterilizer, a ventilation installation and a temperature and humidity controller are arranged in the experimental bin body to enable the environment in the bin body to meet experiment requirement. The experimental bin body is internally provided with an ultraviolet irradiation detector for detecting the intensity of the experiment light source. With the computer control of the experimental process, experimental data can be stored in a computer or experiment reports are printed through a printer. The invention has the advantages that the injury reaction of chemical substances to a human body exposed in ultraviolet irradiation is detected; the light intensity and irradiation time can be controlled, the interference of stray light is less, the experimental efficiency is high, the experimental environment is safe, and the experimental data is accurate.
Owner:范维林
Novel chlorin e6 derivatives, pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, as well as preparation methods and applications of novel chlorin e6 derivatives and pharmaceutically acceptable salts
ActiveCN107987081AGood treatment effectLow toxicityOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderVinyl etherSenile macular degeneration
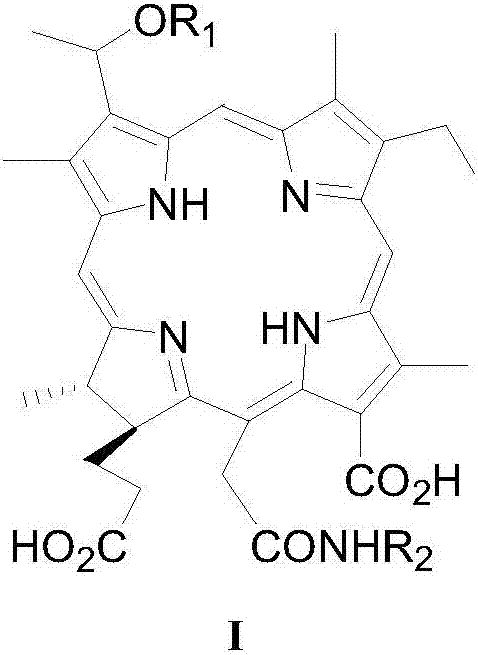
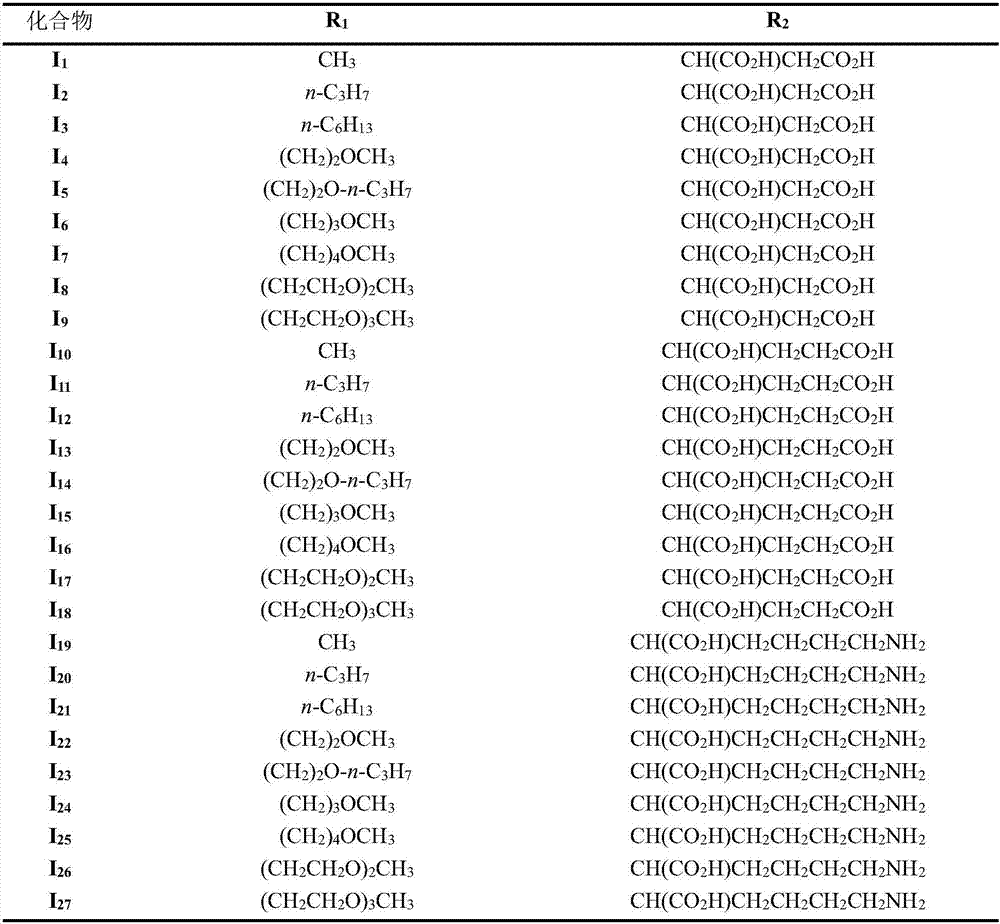
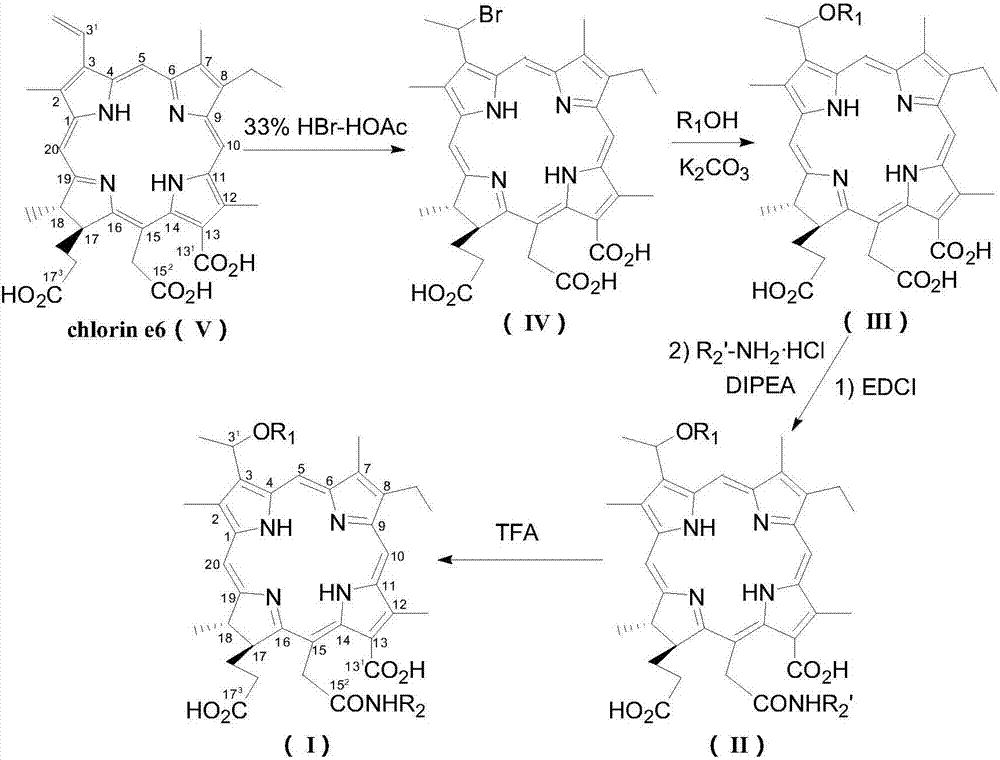
The invention relates to novel chlorin e6 derivatives, pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, as well as preparation methods and applications of the novel chlorin e6 derivatives and the pharmaceutically acceptable salts and belongs to the technical field of medicines. The chlorin e6 ether amino acid derivatives comprise compounds shown as the general structural formula I and optical isomers ofthe general structural formula I. The preparation method of the novel chlorin e6 derivatives comprises steps as follows: 3-vinyl in chlorin e6 is etherified, and 15-ethylcarboxyl and amino acid are subjected to peptides formation. The chlorin e6 ether amino acid derivatives and the pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof can be taken as photodynamic antitumor drugs for application. Compared with an existing clinically applied similar photosensitizer talaporfin, the chlorin e6 ether amino acid derivatives have the advantages of being high in photodynamic antitumor activity, high in ratio ofdark toxicity to phototoxicity and the like and can be applied to preparation of new photodynamic antitumor drugs including photodynamic cancer treating drugs, photodynamic treatment drugs for benignvascular diseases such as senile macular degeneration and nevus flammeus as well as photodynamic treatment drugs for condyloma acuminate.
Owner:SHANGHAI BIOPHY BIOLOGICAL PHARM CO LTD
Phototoxicity exposure experimental animal fixing and protecting device
InactiveCN105342721AConvenient, quick and safe fixationConvenient, fast, safe and protectiveAnimal fetteringAnimal scienceMedicine
The invention provides a phototoxicity exposure experimental animal fixing and protecting device. The phototoxicity exposure experimental animal fixing and protecting device comprises a circular fixing frame which is arranged on a plane-shaped bottom plate and can fix experimental animals. An adjustable covering device and a side ejecting device are arranged on the circular fixing frame. A fixing shackle is arranged on the front side of the circular fixing frame and can clamp experimental animals. A top covering plate connected with the upper end of a front vertical plate at the front end of the bottom plate protects heads of experimental animals against phototoxic damage when conducting downward covering. A belly ejecting device is arranged at the bottom of the circular fixing frame and ejects back exposed epidermis of experimental animals so that the back exposed epidermis can not move when receiving phototoxicity exposure experiments. An excrement leakage opening located at excretory pores of experimental animals is located in the rear portion of the bottom plate. An excrement collector special for collecting excrement excreted by experimental animals is arranged below the excrement leakage opening. Four supporting leg frames are arranged at the four corners of the bottom plate and can adjust the height and the flatness. The phototoxicity exposure experimental animal fixing and protecting device has the advantages that the device which can conveniently, rapidly and safely complete experimental animal fixation and protection when phototoxicity exposure experiments are conducted is developed, and problems on this aspect are solved.
Owner:TIANJIN HOPE IND & TRADE
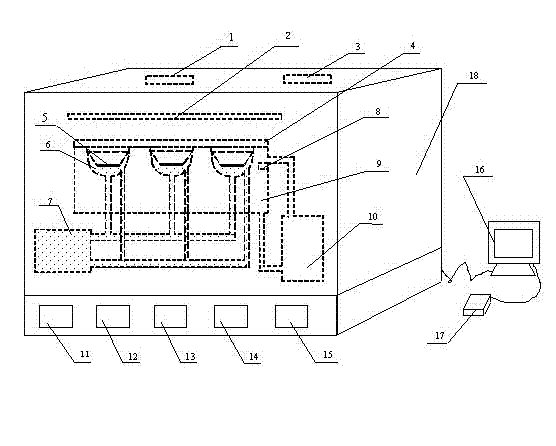
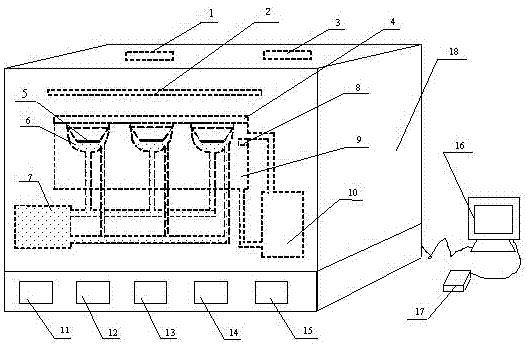
Cell phototoxicity experimental detection device
InactiveCN102199532AAccurate control of experimental precisionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsChemical industryUltraviolet
The invention provides a cell phototoxicity experimental detection device. The cell phototoxicity experimental detection device comprises a lightproof experimental chamber, wherein the top of the lightproof experimental chamber is provided with a plurality of ultraviolet radiation light sources which can emit 365nm of ultraviolet A; the inside of the experimental chamber is provided with a plurality of cell culture solution cavities which can be fixed by cell diaphragm plates, an upper ultraviolet quartz window protects the cell diaphragm plates to be isolated from the outside and ensures that the cell diaphragm plates are radiated by the ultraviolet radiation light sources; an incubation cavity is connected with an incubation controller and a cell culture solution supply device which are required for the survival of cells; the inside of the experimental chamber is provided with an ultraviolet and ozone disinfector, a ventilation device and a humidity and temperature controller to ensure that the experimental environment meets requirements; an radiation light probe detects the intensity of the UVA ultraviolet radiation light sources and is controlled by a computer; and the experimental parameters can be stored to the connected computer or printed by a printer. The invention has the following beneficial effects: the invention provides the cell phototoxicity experimental detection device and the device can be widely used in the cell phototoxicity scientific researches of the fields such as chemical industry, hygienic toxicology, environmental friendliness, labor occuplational disease prevention and medical science.
Owner:TIANJIN HOPE IND & TRADE
Preparation method of targeting porphyrin fluorescent molecule and gold nanorod dyad
InactiveCN102940892ANot easy to cause non-specific release in vivoImproving the effect of early diagnosis and treatmentEnergy modified materialsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsN dimethylformamideAnticarcinogen
The invention relates to a preparation method of dyad, particularly relates to a preparation method of targeting porphyrin fluorescent molecule and gold nanorod dyad and solves technical problems that porphyrin fluorescent molecules are prone to gather on the skin and eyes to generate phototoxicity due to poor targeting when the porphyrin fluorescent molecules are transported in bodies and gold nanorods can not stably exist in polar solvents. The method includes preparing a golden seed solution, preparing a gold nanorod growing solution, preparing a polyethylene glycol stabilized gold nanorod solution, preparing the dyad, mixing biomolecules or anticarcinogen and the dyad with N, N-dimethylformamide for reaction, performing centrifugation, dispersing precipitates in methyl alcohol, and then performing separation again to obtain the targeting porphyrin fluorescent molecule and gold nanorod dyad. According to the prepared targeting porphyrin fluorescent molecule and gold nanorod dyad, effects of early-stage tumor diagnosis and treatment can be improved, side effects on normal organizations can be reduced, and the dyad can be connected with biomacromolecules and the anticarcinogen which have targeting actions so that targeting capacity and tumor treatment effects are further improved.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com