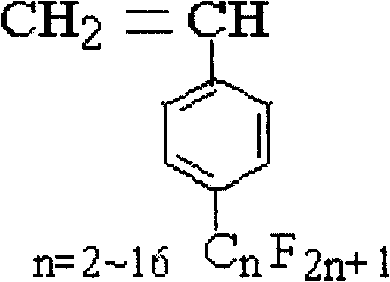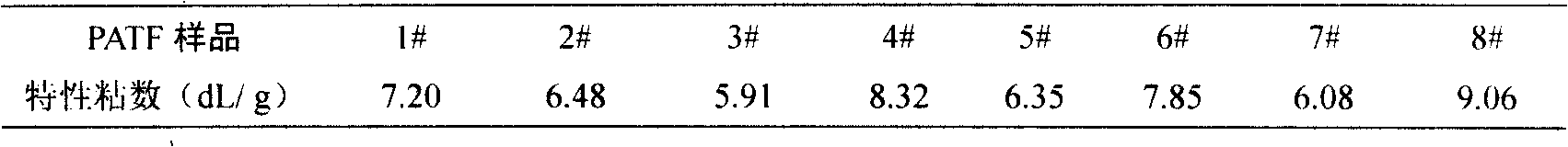Patents
Literature
756results about How to "Strong force" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
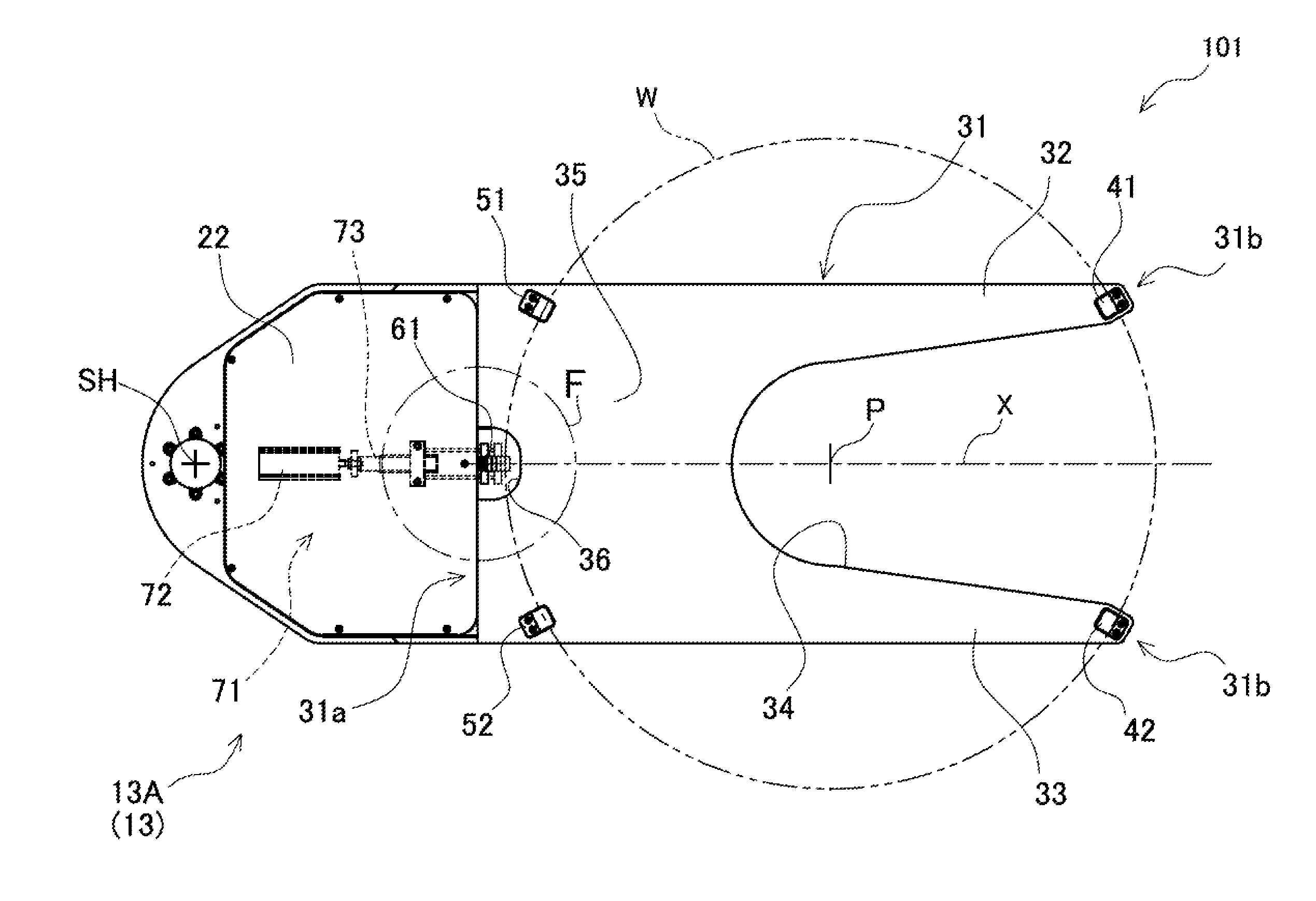
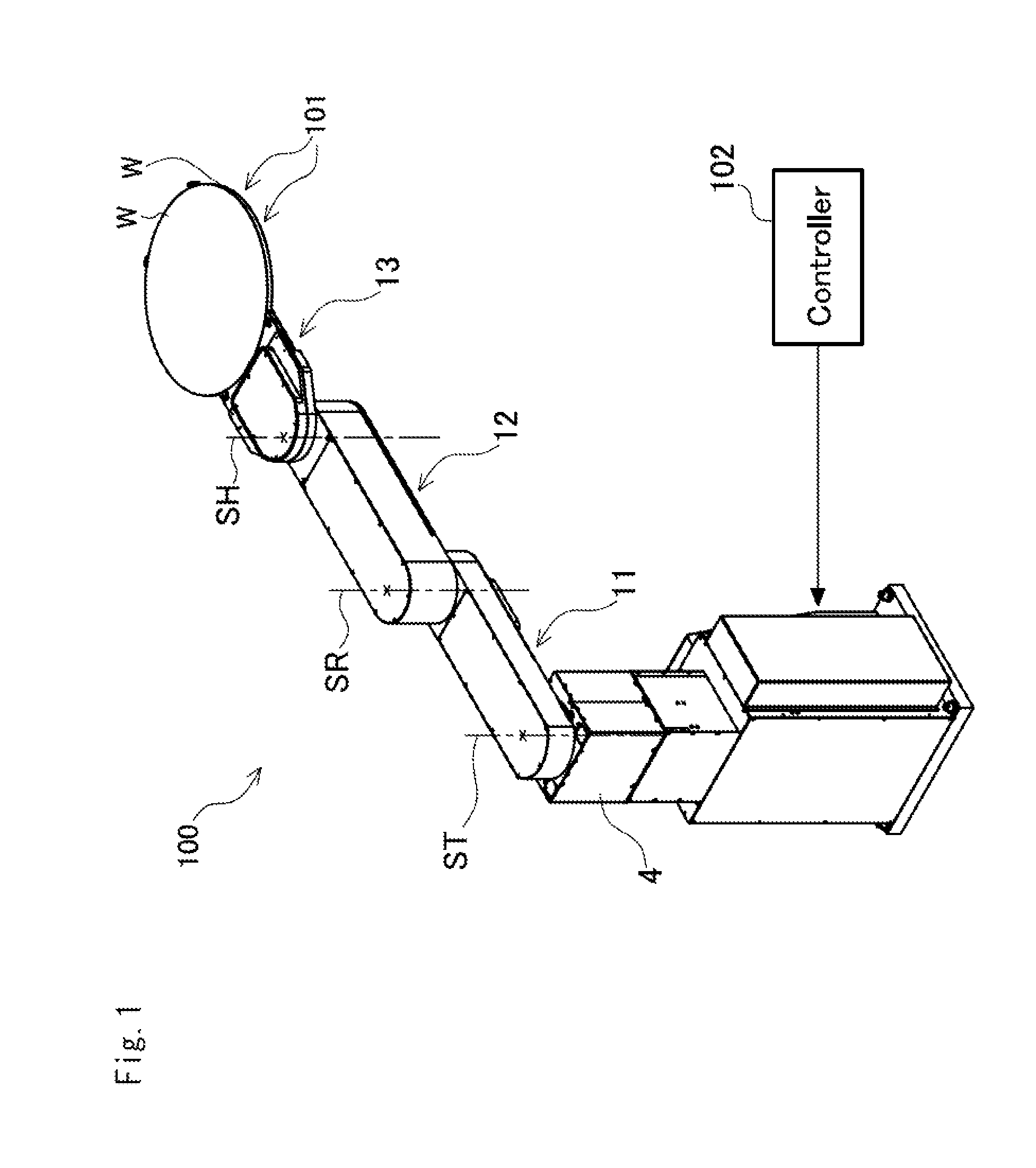
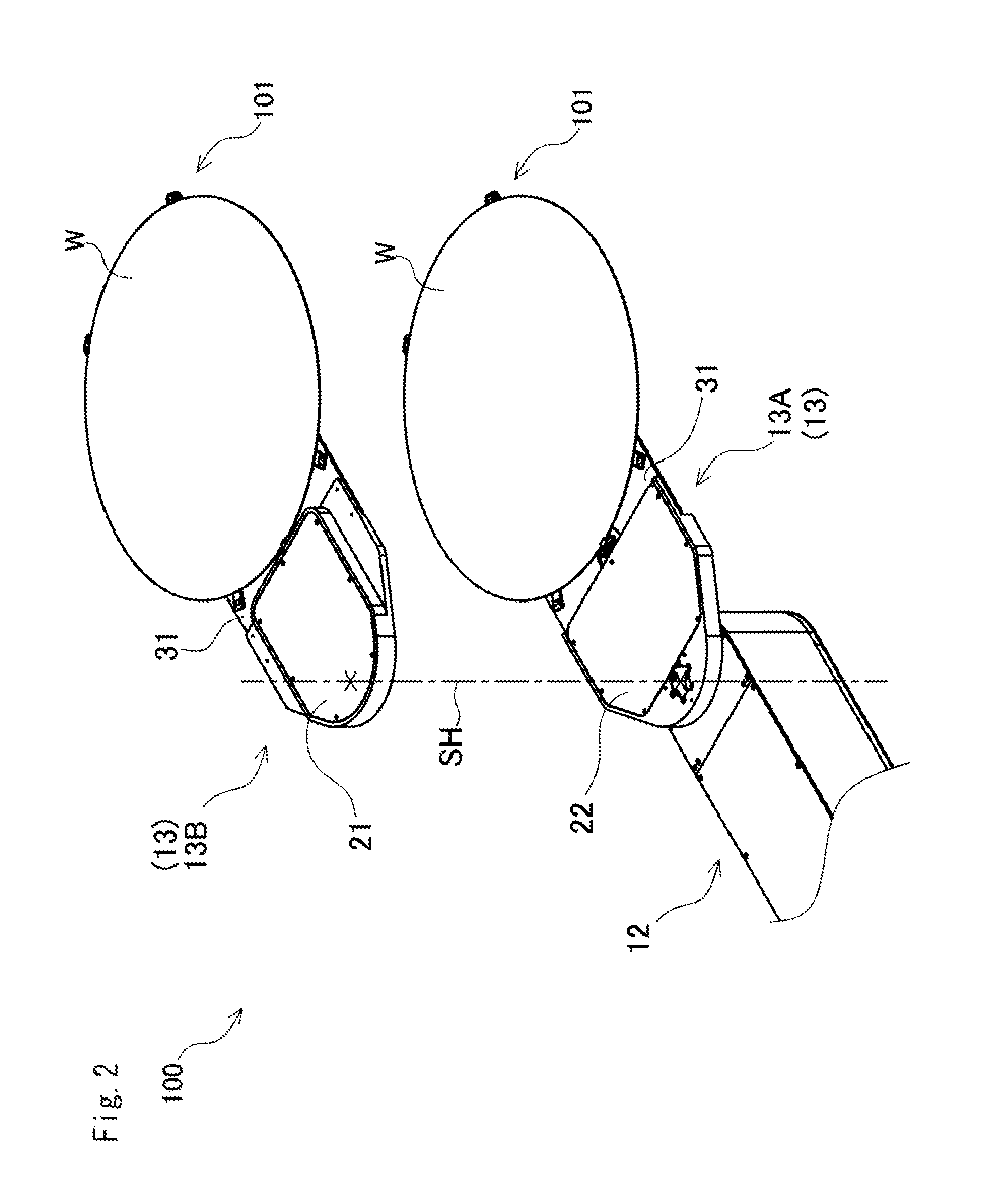
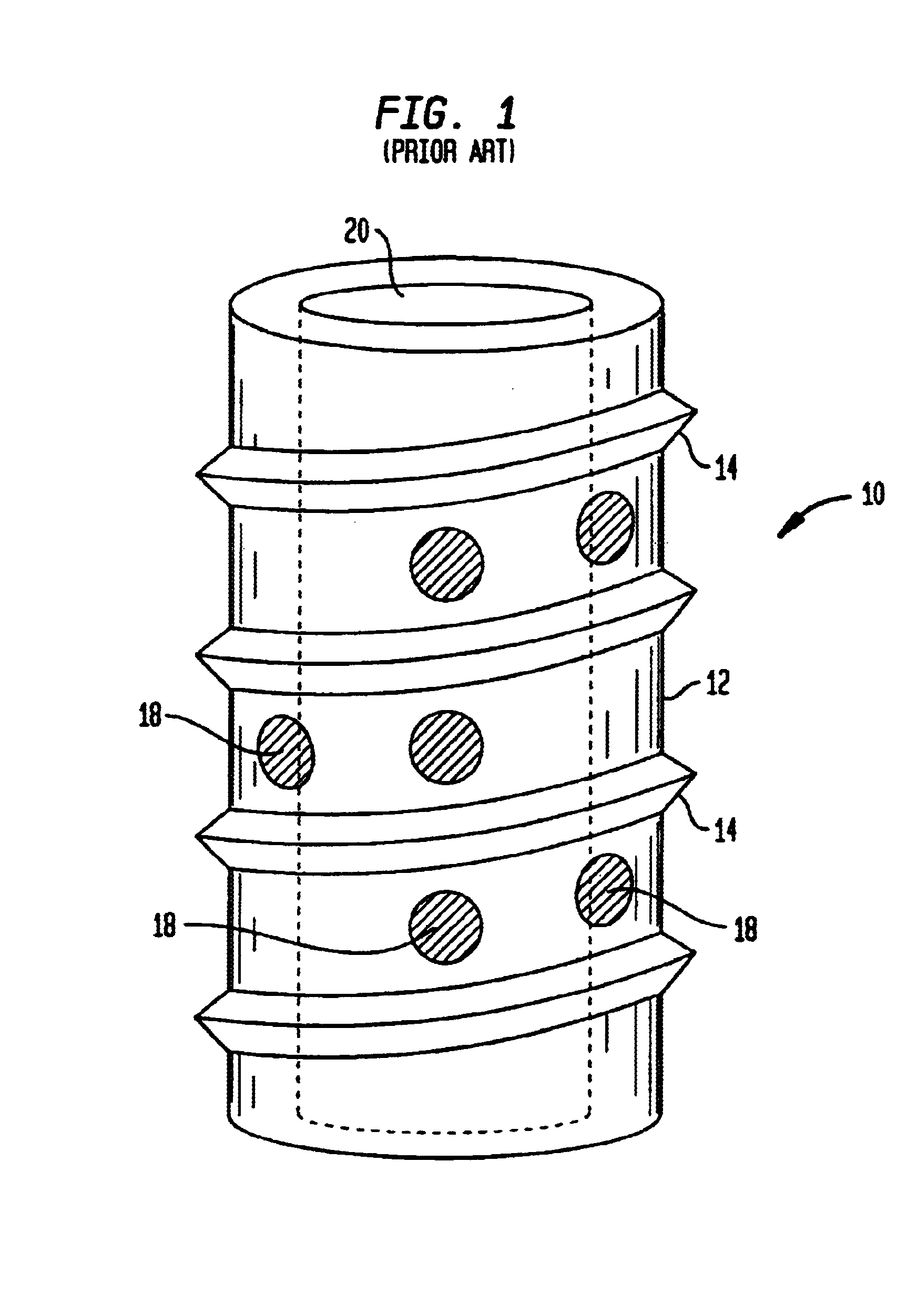
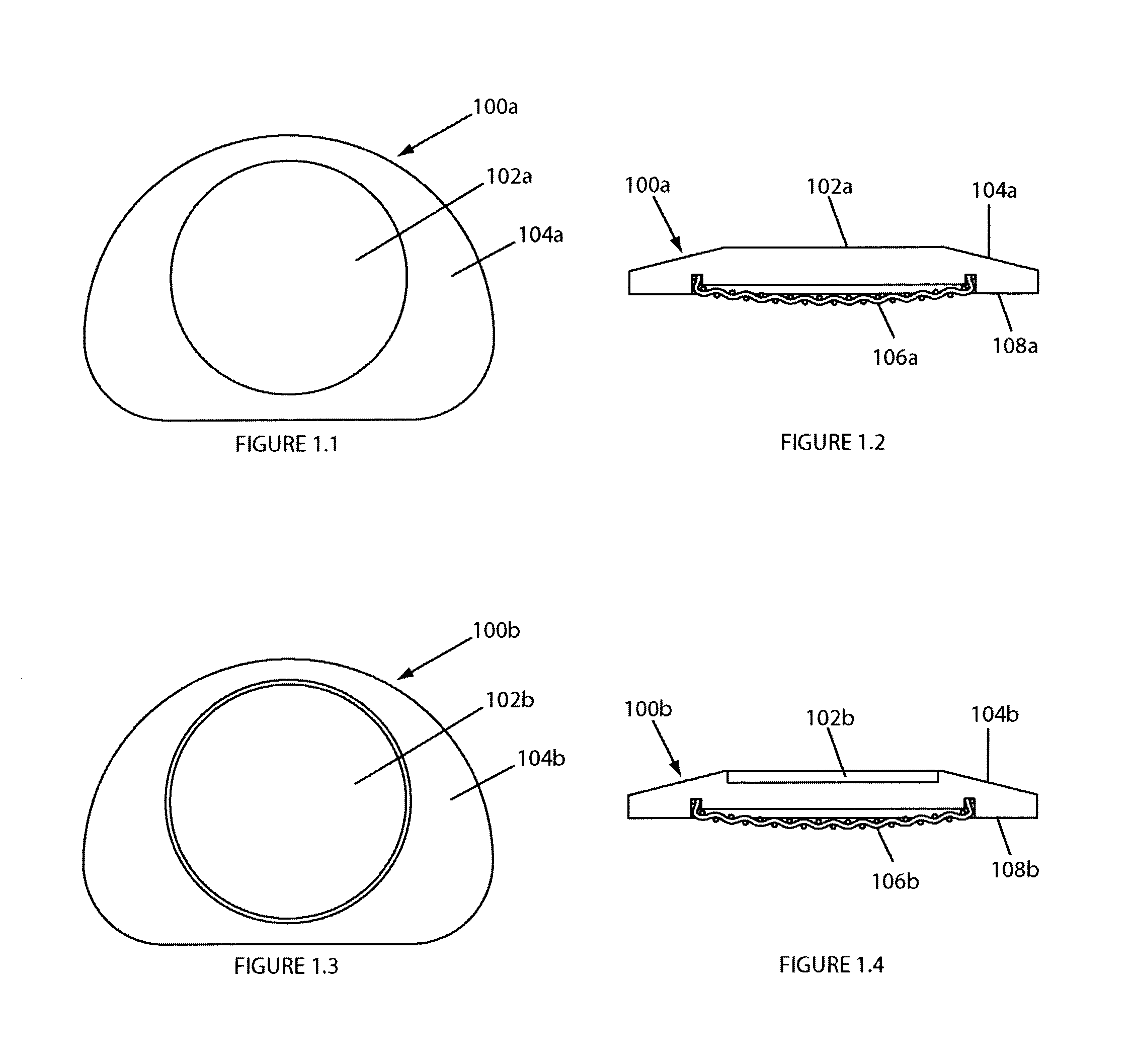
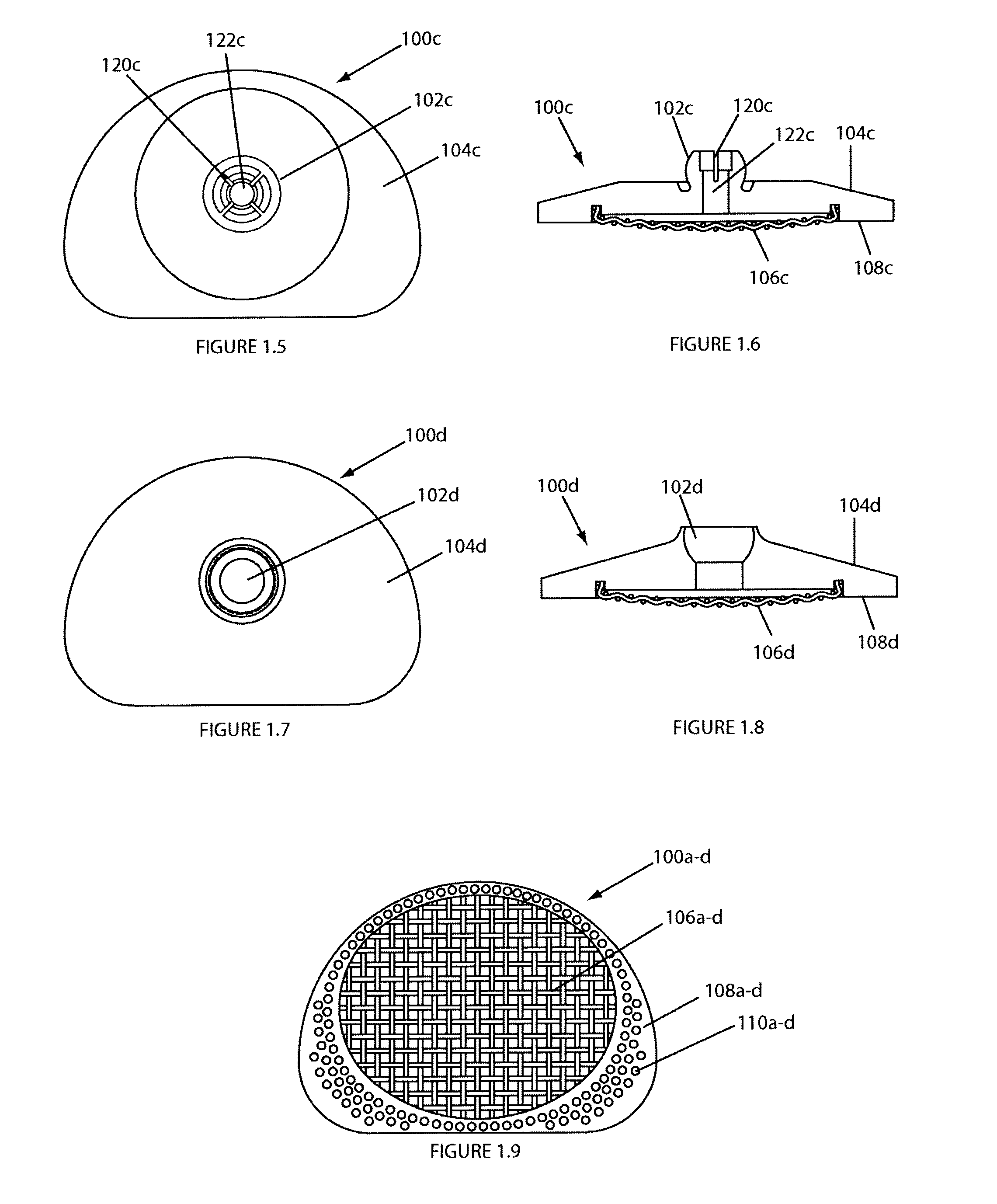
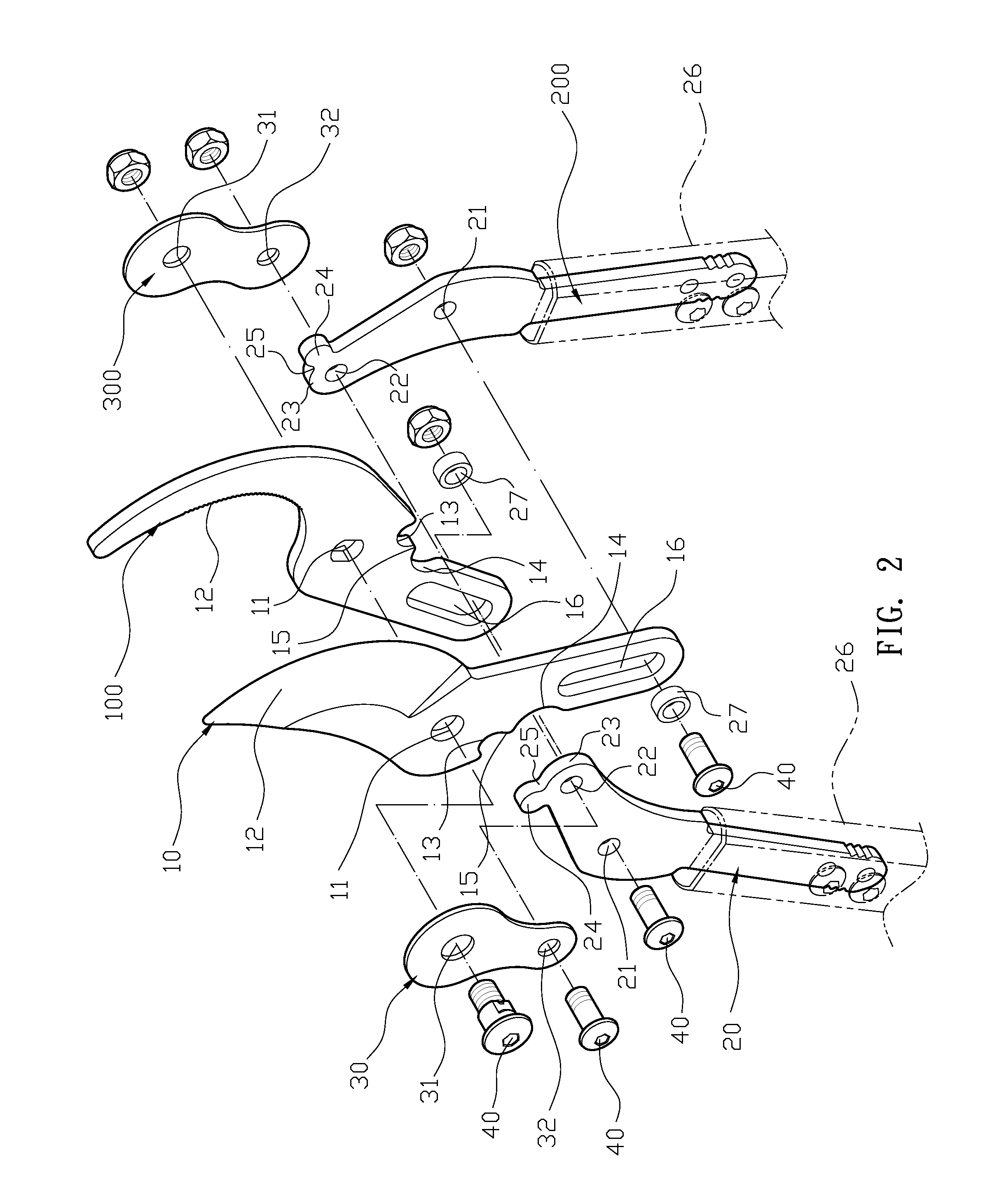
Clamping device and workpiece conveying robot
InactiveUS8764085B2High positionalImprove retentionGripping headsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:SINFONIA TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
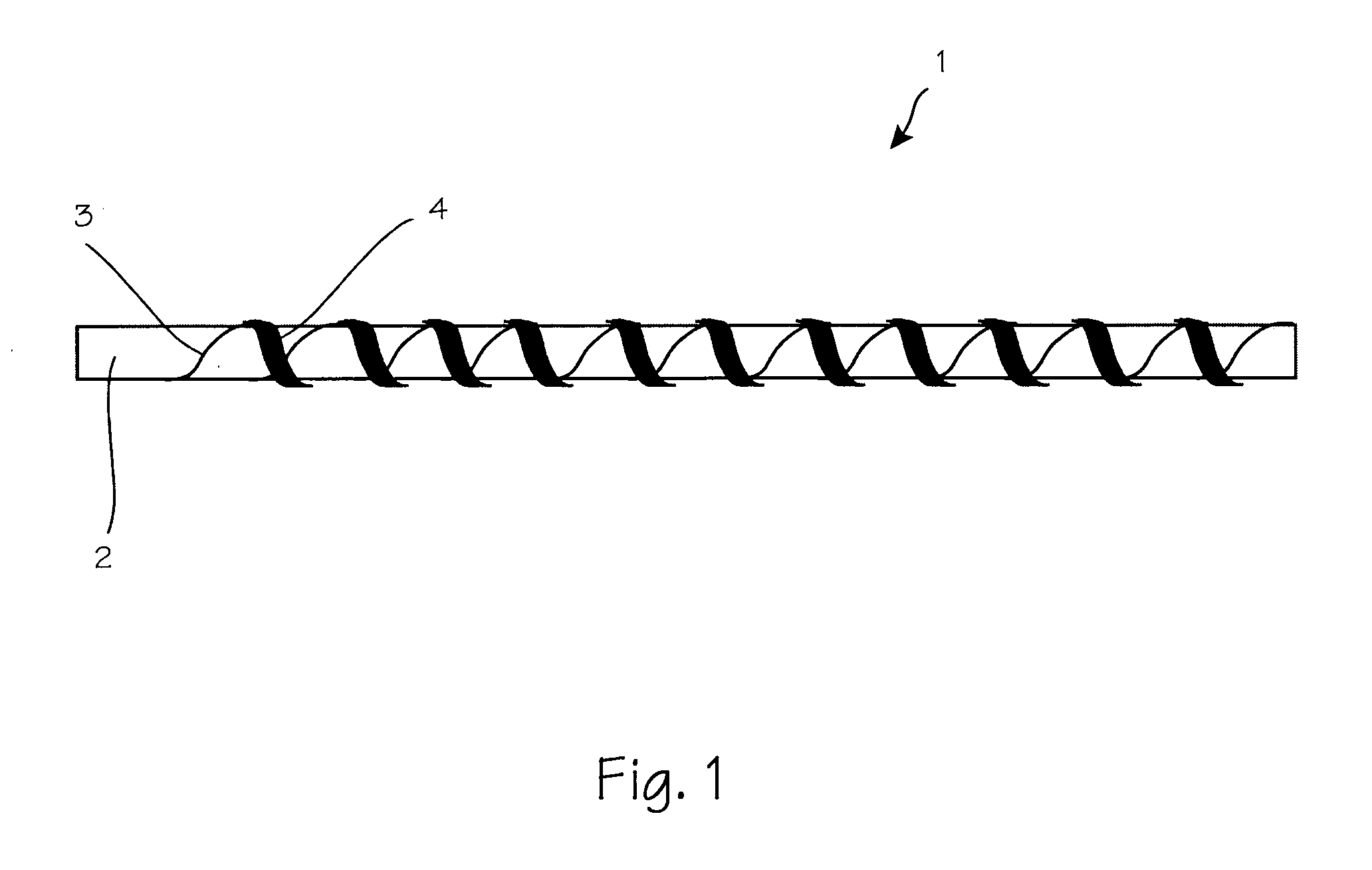
Electrically conductive yarn
InactiveUS20050282009A1Strong forcePrevent elongationNon-insulated conductorsHeating element shapesYarnEngineering
A yarn that is electrically conductive, that can be elongated considerably, at least briefly, without loss of conductivity, and that exhibits improved elongation properties.
Owner:W ZIMMERMANN
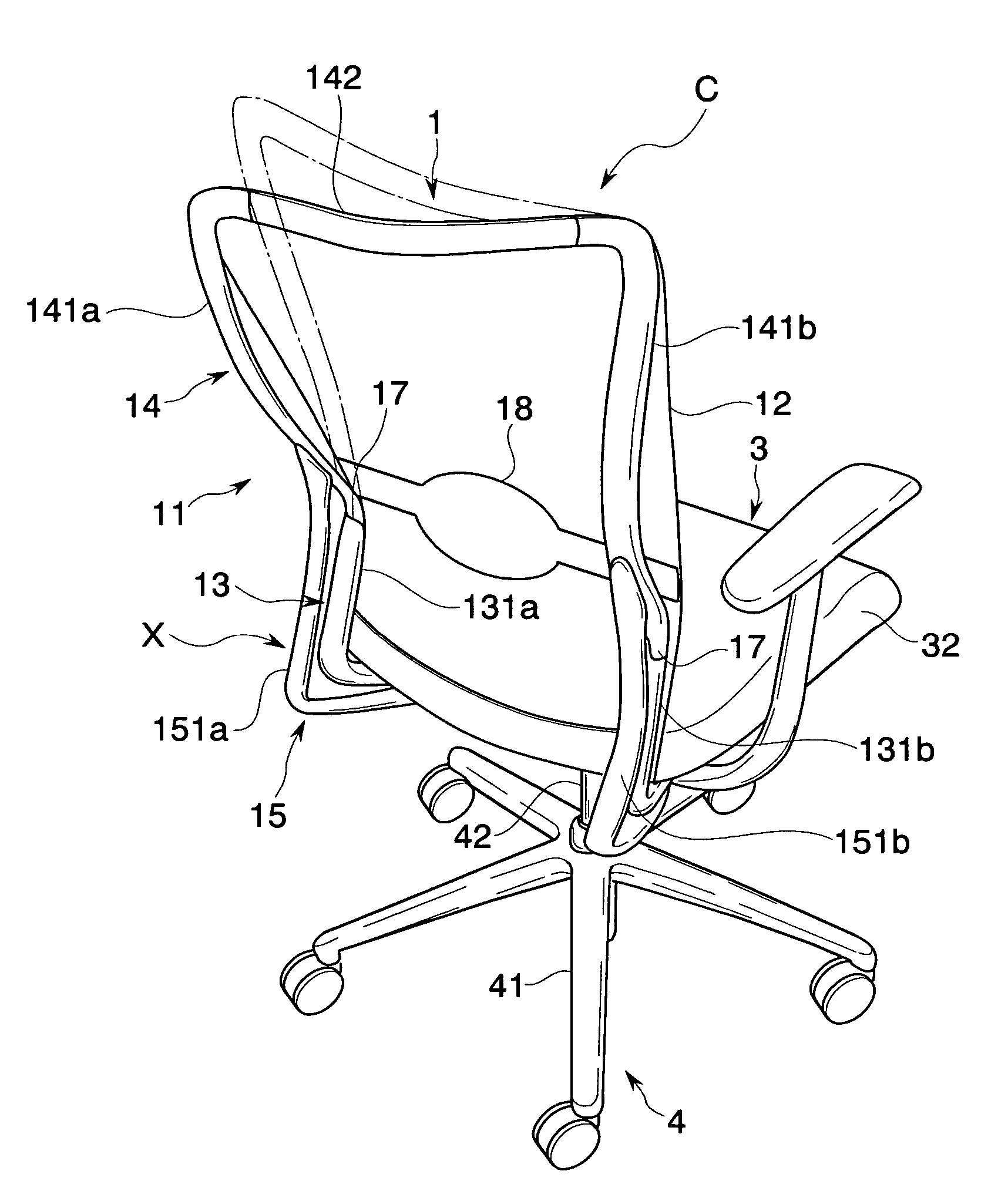
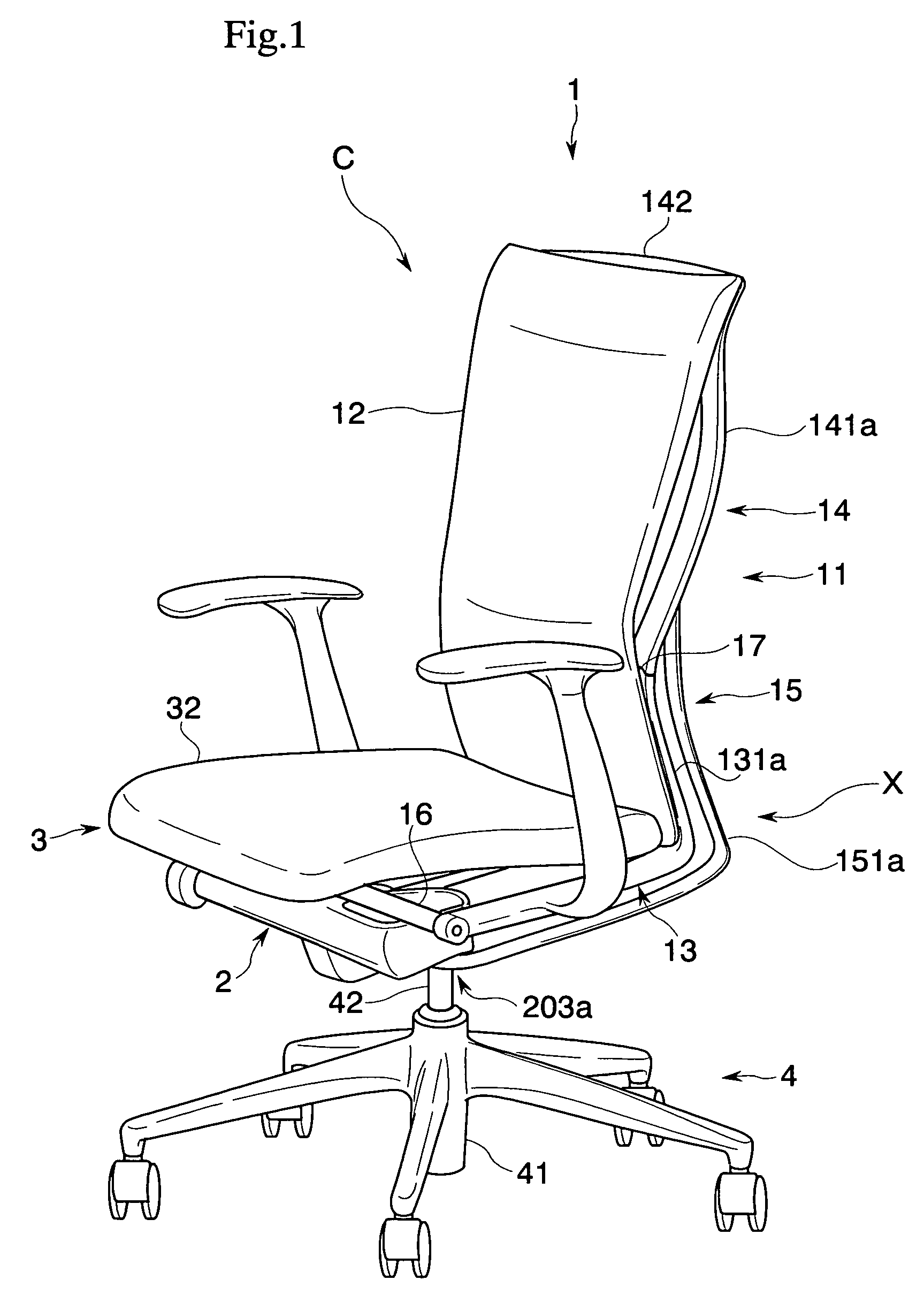
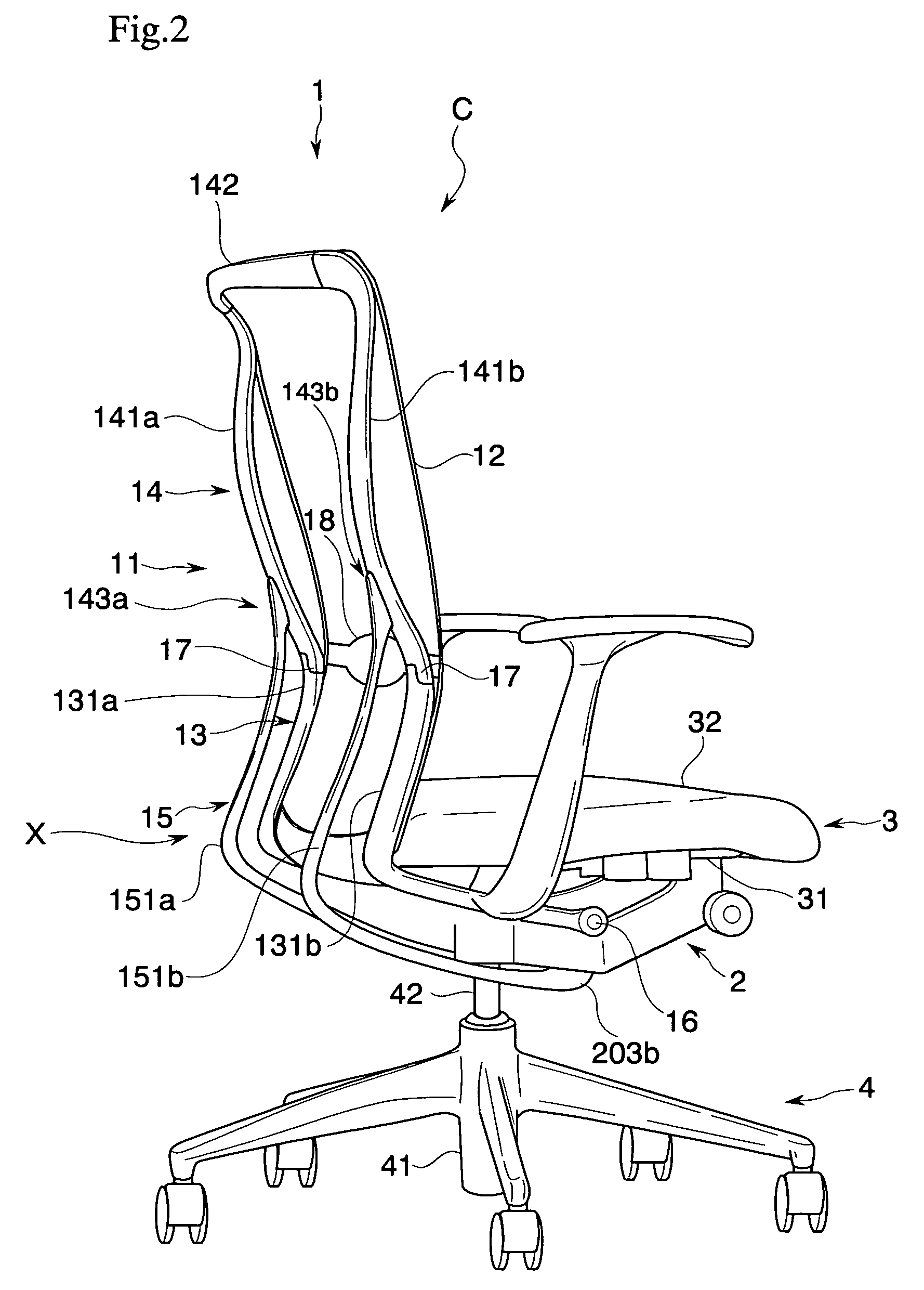
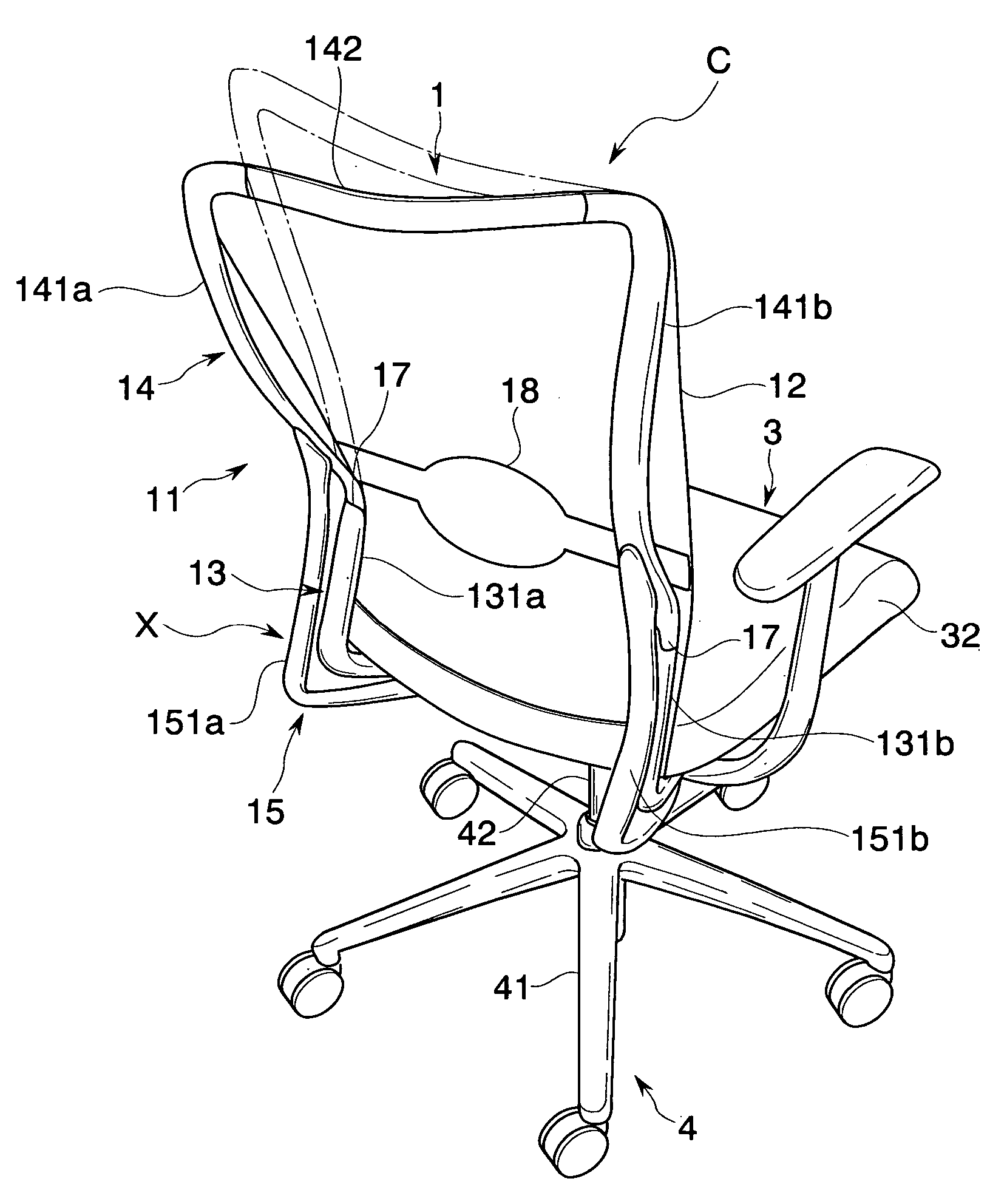
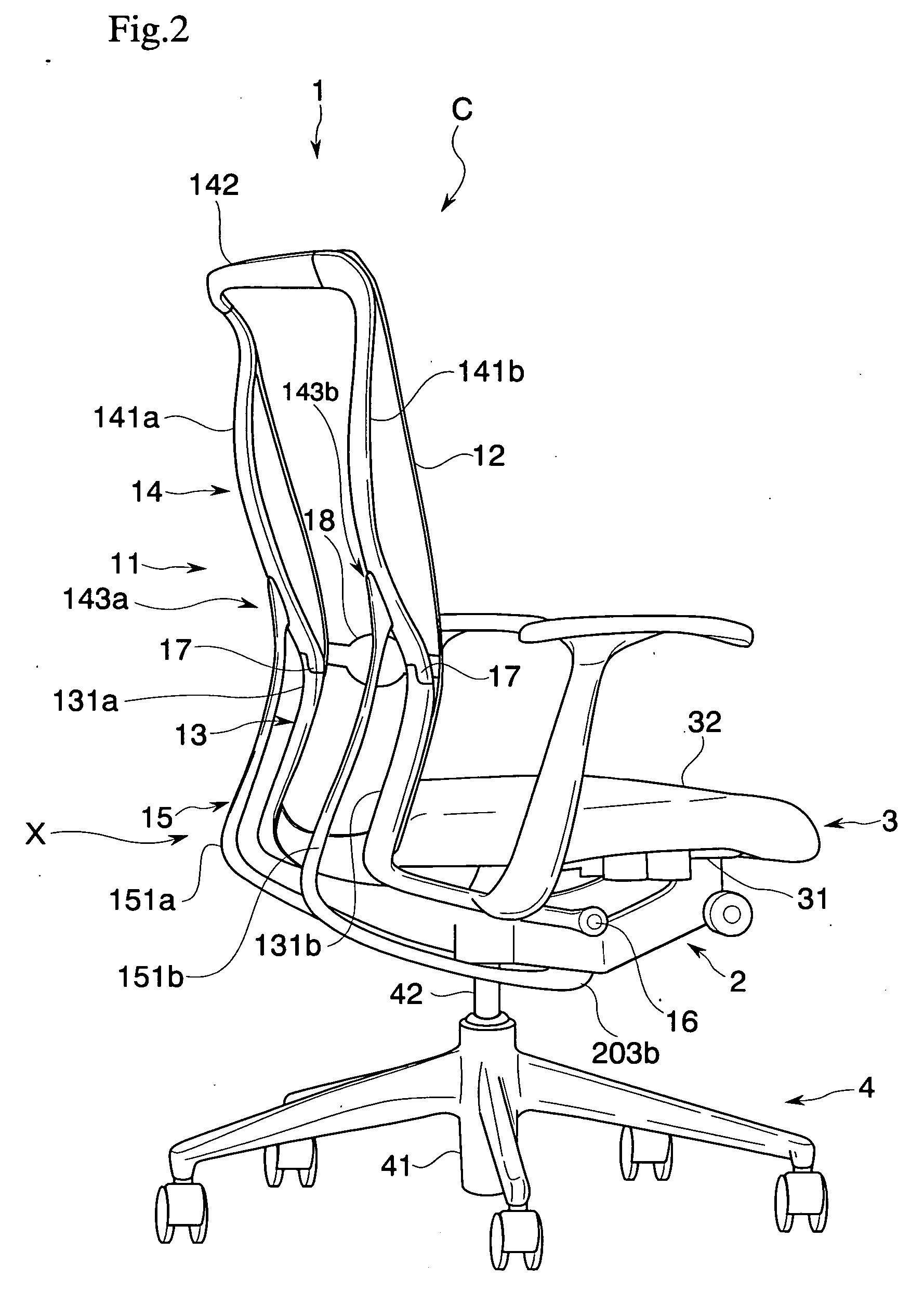
Chair
There is provided a chair that realizes a state preferably following a motion of a sitter in accordance with a posture of the relevant sitter, and a state preferably supporting the sitter. The chair includes a lower frame portion supported so as to be capable of rocking between a standing position and a rearward tilting position with respect to a base, and an upper frame portion supported so as to be capable of rocking between a normal position and a rear end position with respect to the relevant lower frame portion. Furthermore, upper frame portion biasing that elastically biases the upper frame portion from the rear end position to the normal position is provided. This upper frame portion biasing is adapted to change an elastically biasing force to the upper frame portion corresponding to a position in the rocking movement of the lower frame portion.
Owner:KOKUYO CO LTD
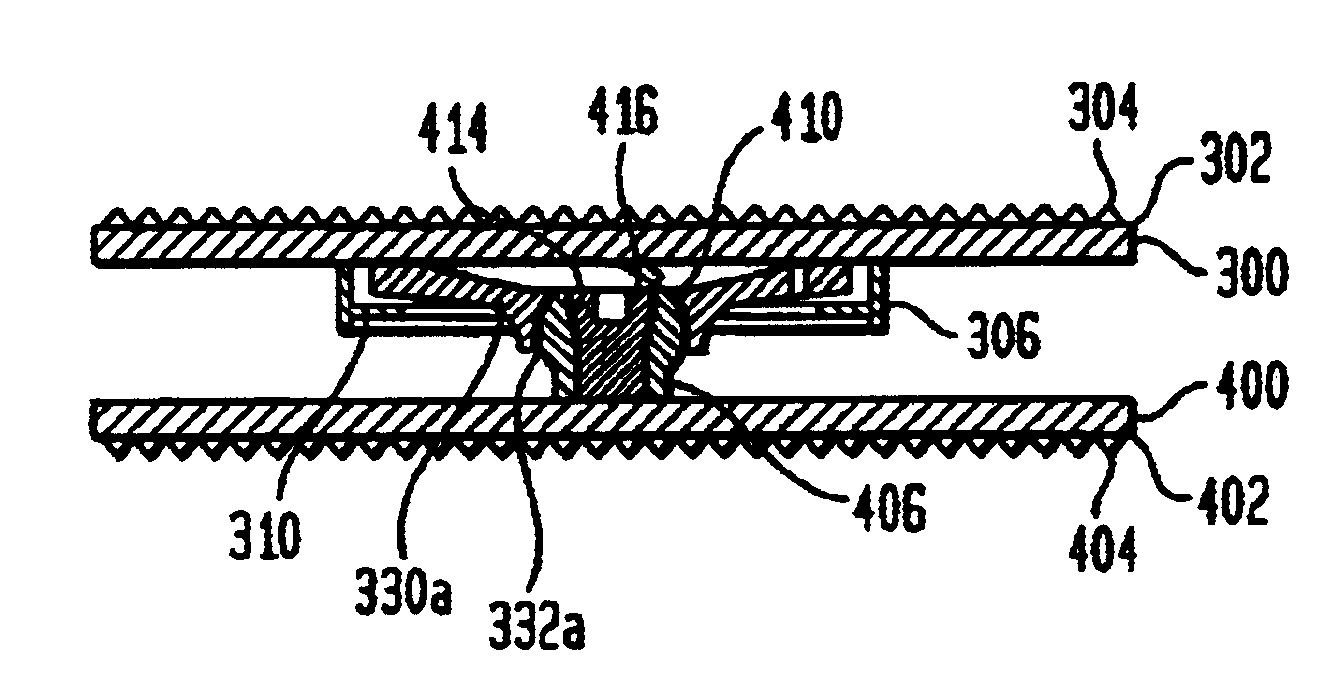
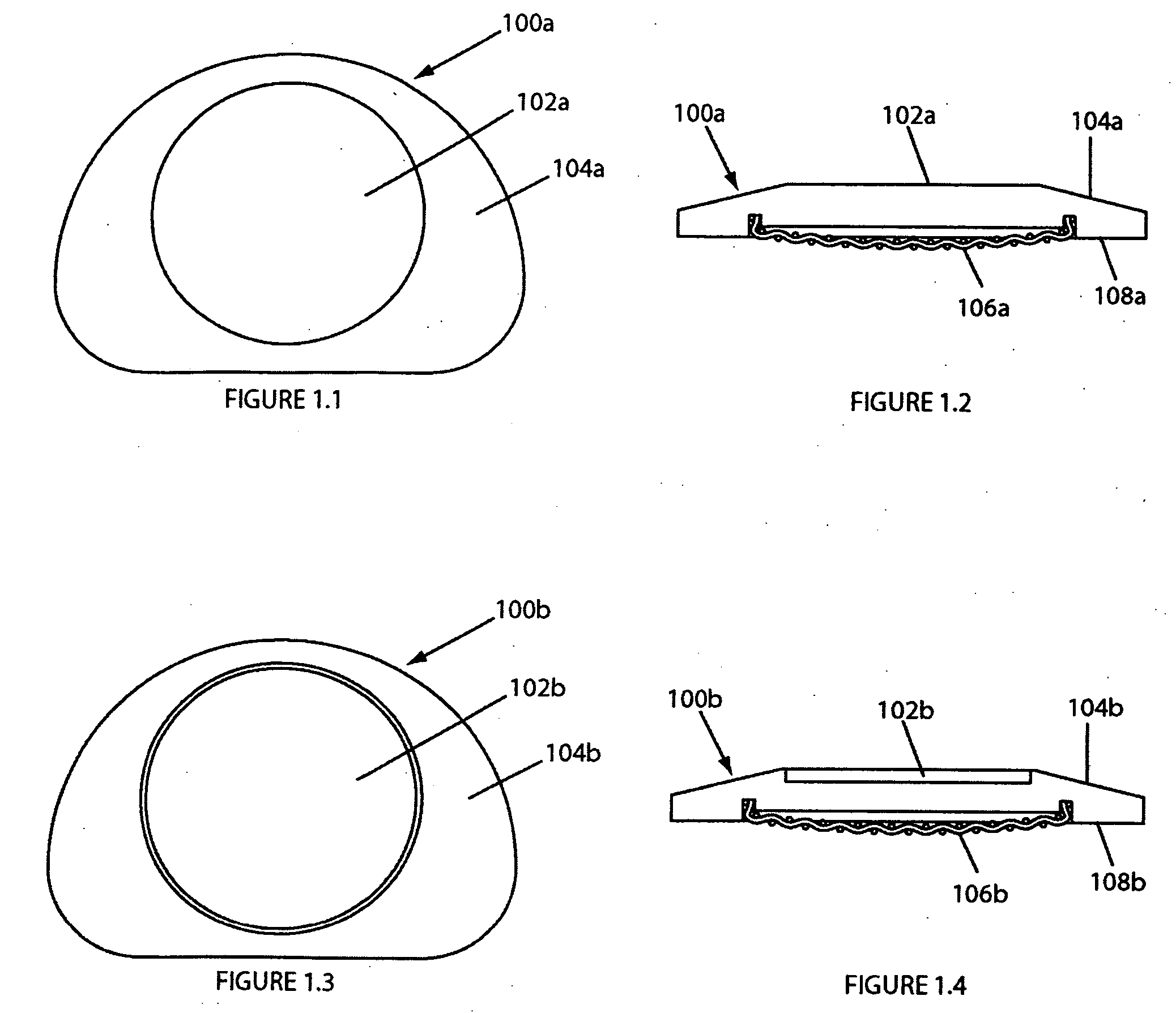
Artificial intervertebral disc having a slotted belleville washer force restoring element
InactiveUS6918934B2Avoid skewImprove securityJoint implantsSpinal implantsIntervertebral discVertebral bone
An artificial disc having a pair of opposing plates for seating against opposing vertebral bone surfaces, separated by at least one spring mechanism. The preferred spring mechanism is at least one spirally slotted belleville washer, and in some embodiments the belleville washer is also radially thinning or thickening. Various illustrated embodiments use two washers or one washer. For double washer embodiments, the wide ends of the washers seat against respective opposing plates, in some embodiments each being maintained thereagainst by a retaining wall and ring or a circular recess and retaining shield. For single washer embodiments, the narrow end of the washer can be modified to have a curvate socket for rotatably mounting onto a semispherical protuberance extending from one of the plates.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
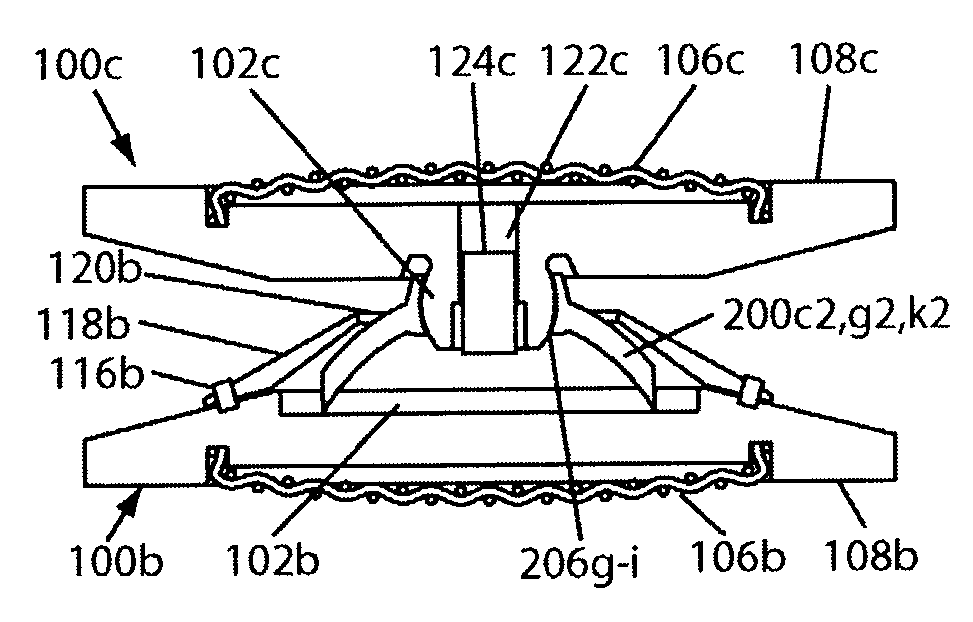
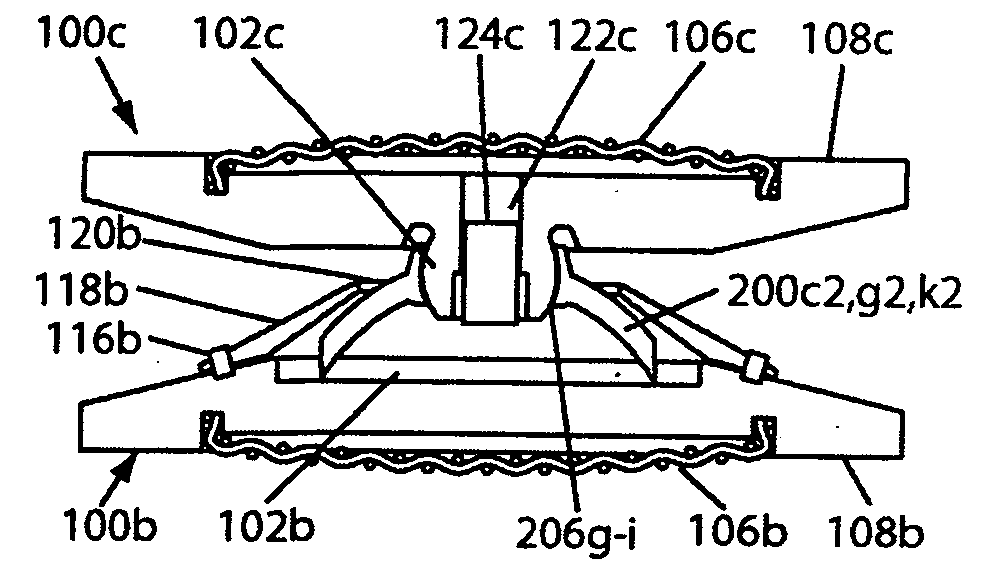
Artificial intervertebral disc having a spider spring force restoring element
InactiveUS7122055B2Improve cycle lifeImprove securityJoint implantsSpinal implantsCouplingIntervertebral disc
An artificial disc having a pair of opposing plates for seating against opposing vertebral bone surfaces, separated by a spider spring having a plurality of spring arms extending radially from a central hub. Various spring arm embodiments disclosed include spring arms that are straight, bowed, grooved, wavy, thinning, or thickening; and spring arms with parallel sides, radially outwardly diverging sides, or radially outwardly diverging and curving sides. Various spider spring embodiments disclosed include spider springs with central hubs that are solid, bored, have curvate sockets, or have semispherical protuberances. Various plate embodiments disclosed include plates having, on inwardly facing surfaces, a curvate socket, a semispherical protuberance, a circular recess, or a flat surface. The spider springs are disposable between the plates, through various disclosed couplings, so that the plates compress, rotate and angulate freely relative to one another, enabling the artificial disc to mimic a healthy natural intervertebral disc.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Method for synthesizing composite material of organic - inorganic bentonite
InactiveCN101003374AOvercome the disadvantage of easy falling offStrong forceSilicon compoundsPorositySodium Bentonite
This invention discloses a method for synthesizing organic-inorganic bentonite composite. The method comprises: utilizing bentonite as the main material, performing inorganic modification through cation-exchange reaction by using hydroxyl aluminum aqueous solution, torrefying to obtain hydroxyl-containing aluminum-pillared bentonite with high porosity and high specific surface area, and reacting between the hydroxyls and silylation agent to graft silane groups onto aluminum-pillared bentonite and obtain organic-inorganic bentonite composite. The organic-inorganic bentonite composite has both the advantages of inorganic pillared bentonite such as high porosity and high specific surface area, and those of organic bentonite such as high organic carbon content and high hydrophobicity thus can be used to treat organic waste gases and wastewater with a good effect by surface adsorption as well as distribution.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
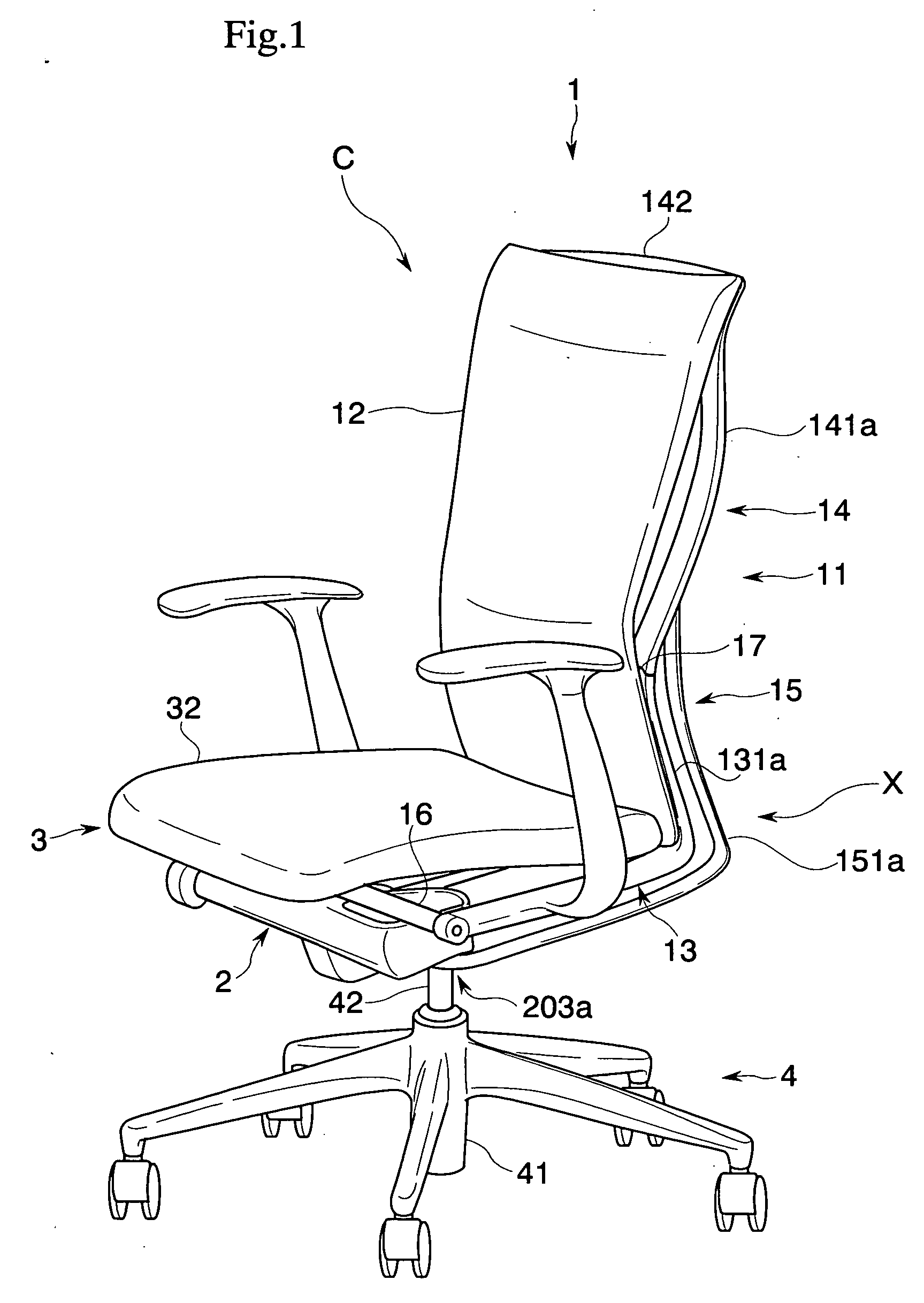
Chair
There is provided a chair that realizes a state preferably following a motion of a sitter in accordance with a posture of the relevant sitter, and a state preferably supporting the sitter. The chair includes a lower frame portion supported so as to be capable of rocking between a standing position and a rearward tilting position with respect to a base, and an upper frame portion supported so as to be capable of rocking between a normal position and a rear end position with respect to the relevant lower frame portion. Furthermore, upper frame portion biasing means that elastically biases the upper frame portion from the rear end position to the normal position is provided. This upper frame portion biasing means is adapted to change an elastically biasing force to the upper frame portion corresponding to a position in the rocking movement of the lower frame portion.
Owner:KOKUYO CO LTD
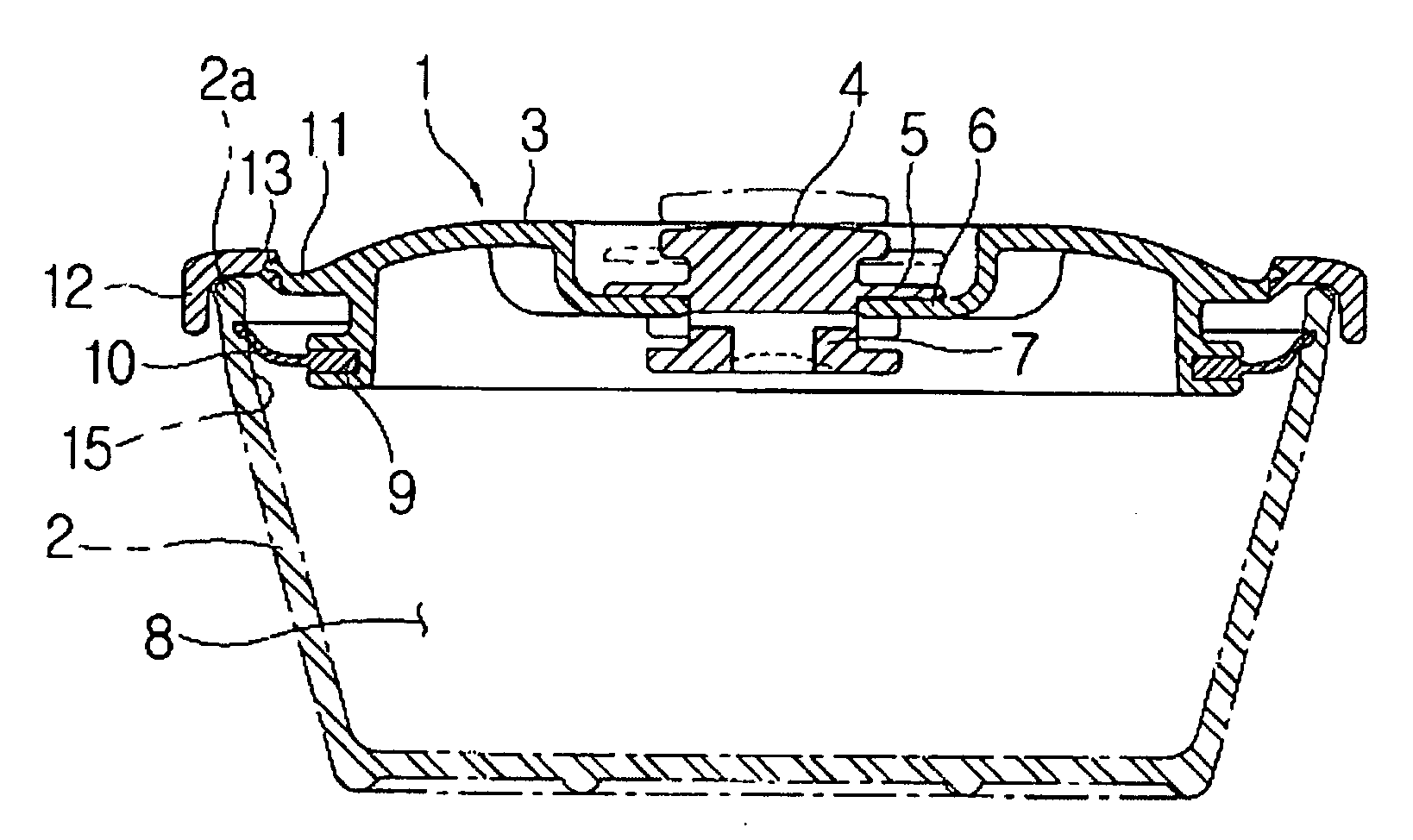
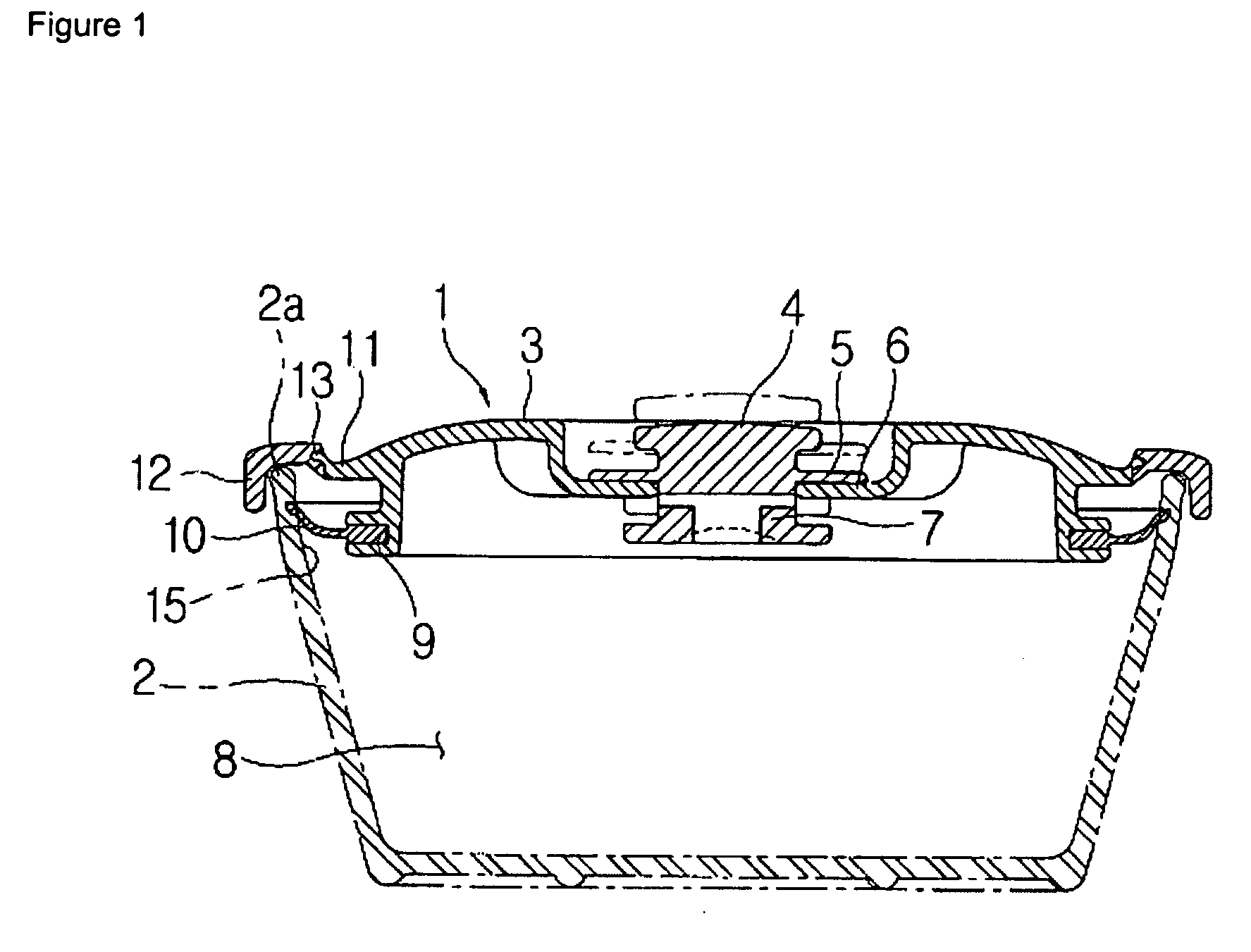
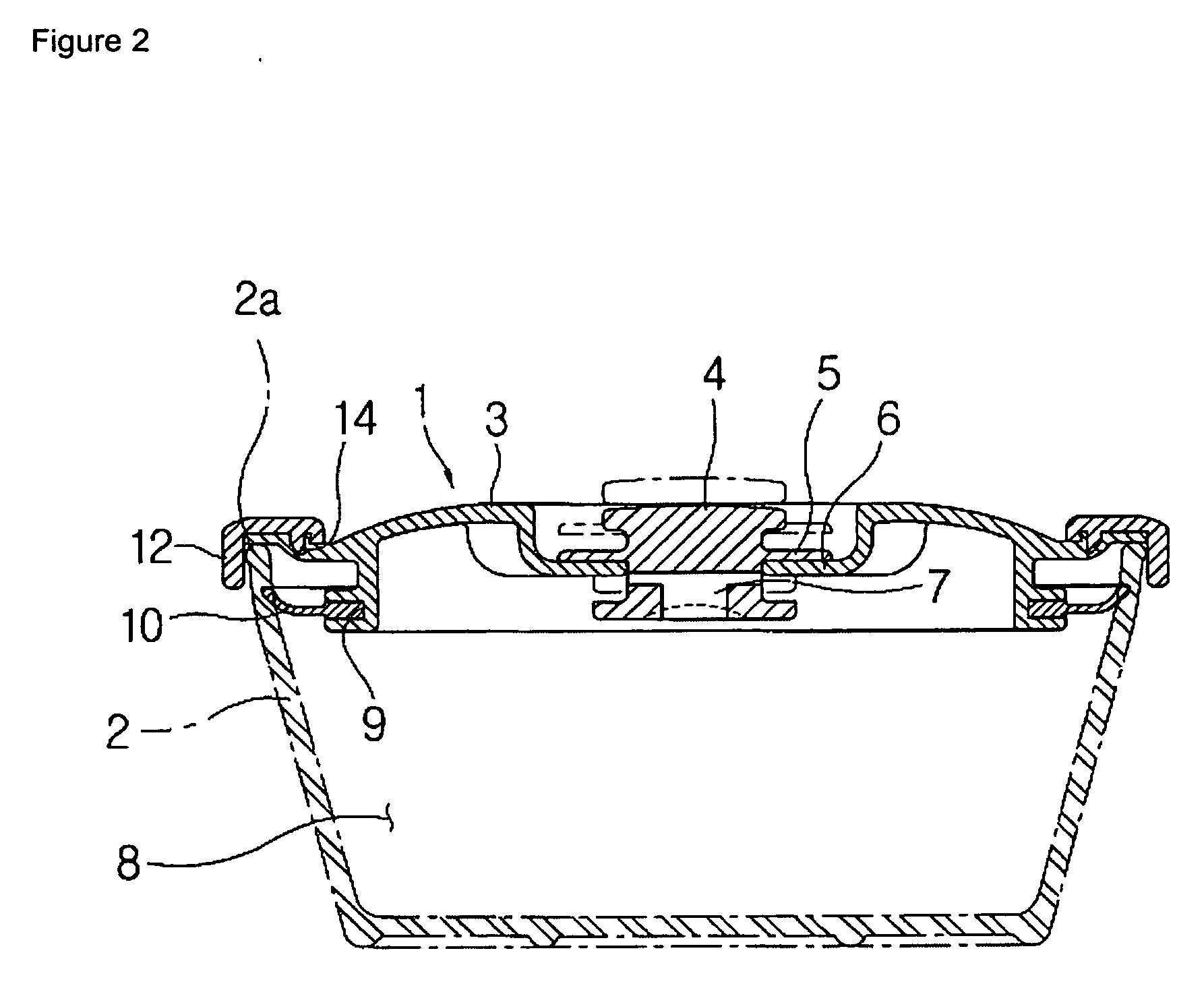
Sealed container lid of vacuum valve operation type
InactiveUS20070095849A1Strong sealing forceSimplifying engagement structureBagsRemovable lids/coversEngineeringInjection moulding
A sealed container lid of a vacuum valve operation type is provided, in which an engagement structure of a silicon packing is simple, and a relatively strong sealing force is obtained. A process for engaging or disengaging a lid to a container body may be performed based one-touch method. The sealed contained lid of a vacuum valve operation type comprises a body which is injection-molded and has a circular groove formed in a horizontally and outwardly opened shape for an engagement of the silicon packing, and a downwardly bent peripheral part which is formed at an outer peripheral part of the body based on a double injection method while surrounding the same.
Owner:HANA COBI PLASTIC
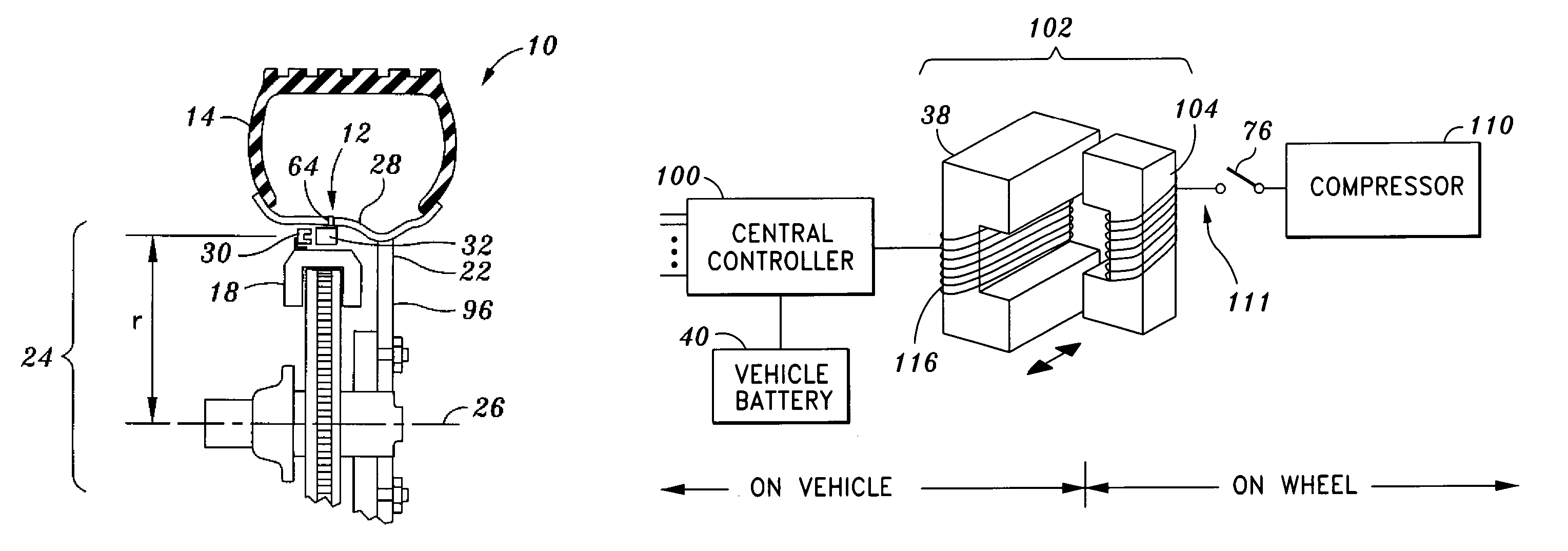
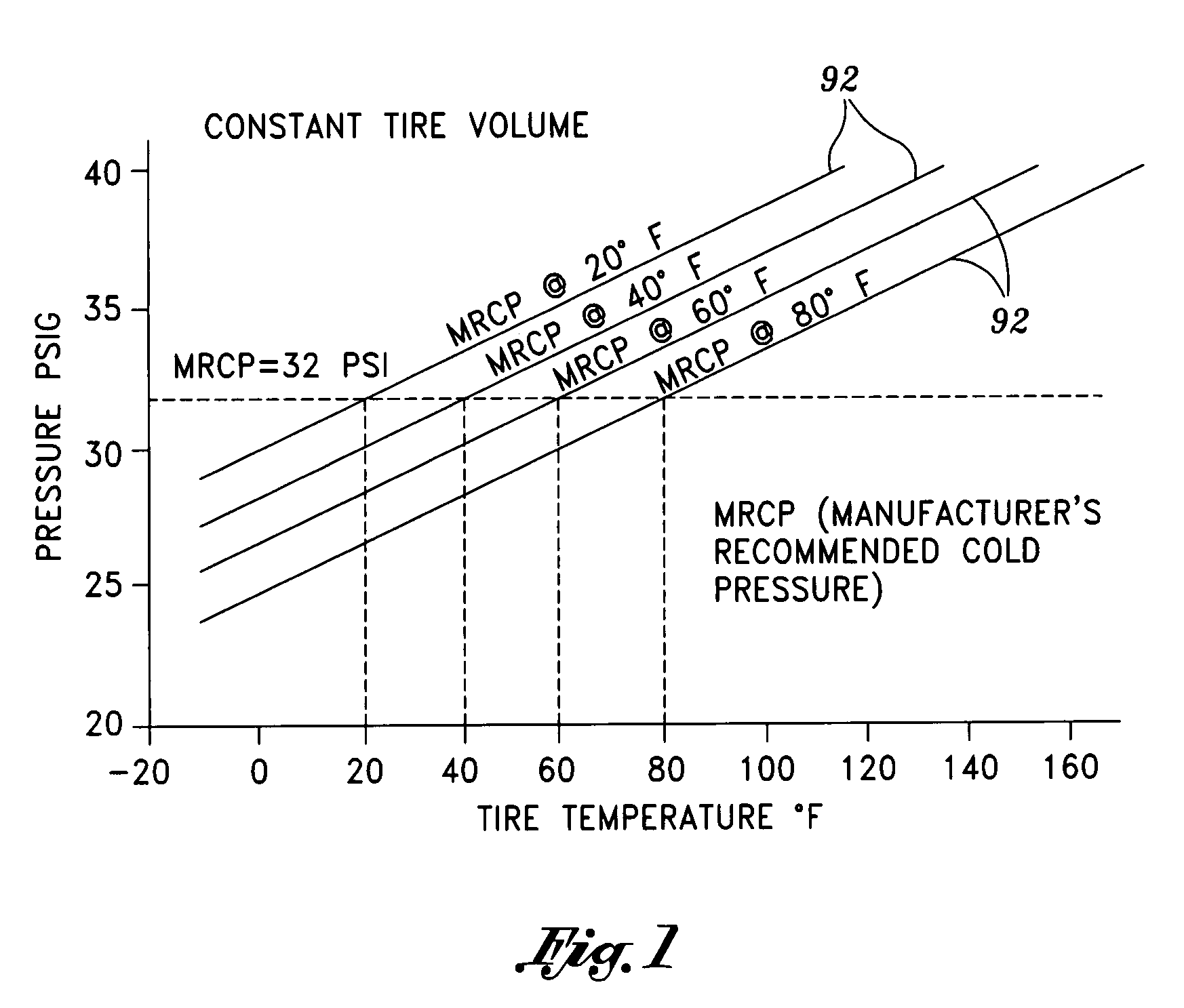
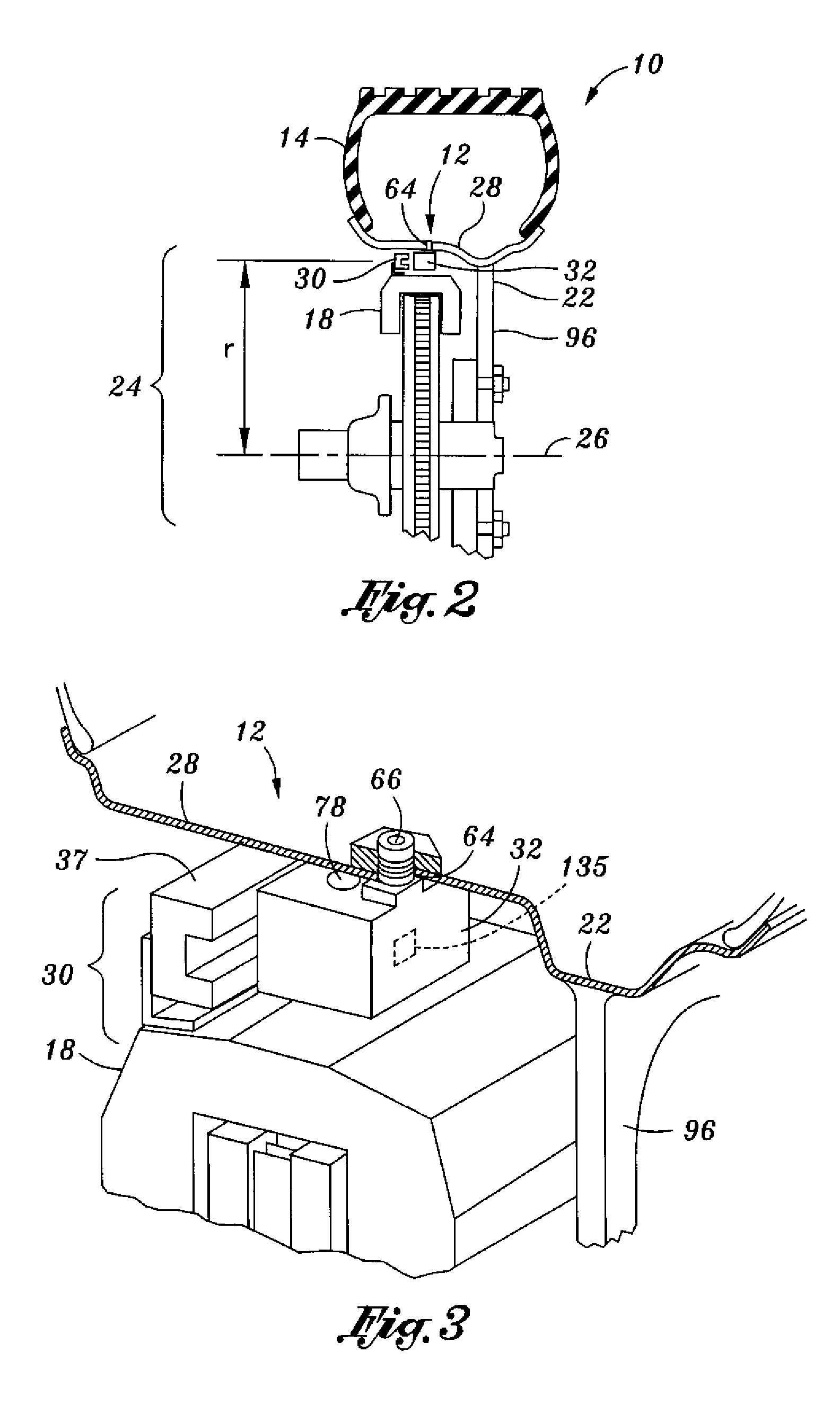
Tire pressure maintenance device
InactiveUS7784513B2Small valueStrong forceTyre measurementsTyre-inflating valvesElectricityTransformer
A device for maintaining a desired inflation pressure within a tire mounted on a wheel of a vehicle which includes a microcompressor having a flexible compression chamber and a magnetic element not on the wheel. As the compressor passes the magnet each wheel revolution, a small amount of atmospheric air is pumped into the tire, if needed. The magnet and the compressor need no other contact with the vehicle or the wheel and require no energy source on the wheel. An alternative embodiment uses an electrical coil on the wheel to pass the magnet inducing a voltage that drives a compressor on the wheel. As the coil passes the electromagnet it provides a split transformer that transfers electrical power to the wheel and permits two-way pulse data communication between the wheel and the vehicle.
Owner:LOEWE RICHARD THOMAS
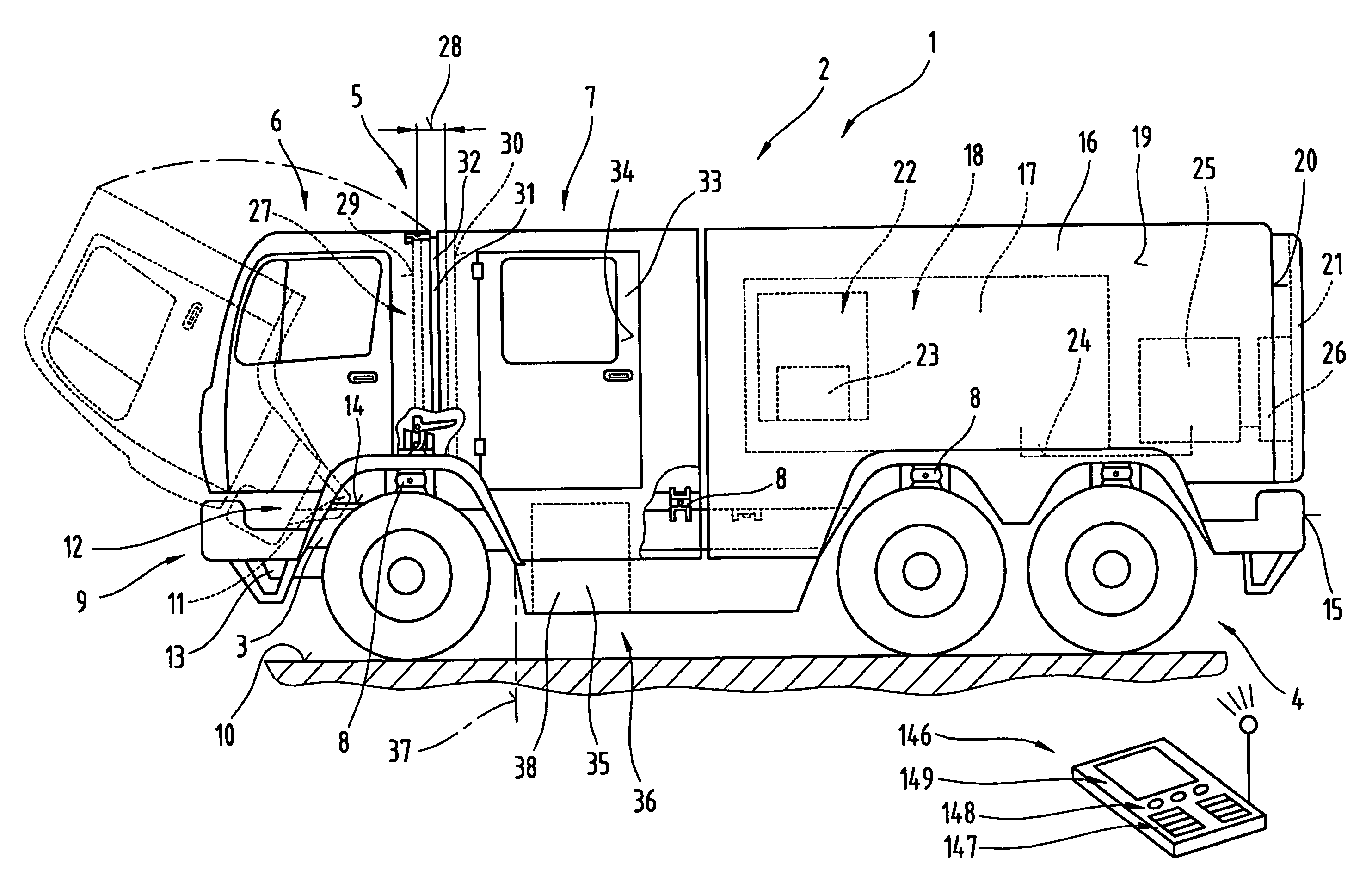
Fire engine
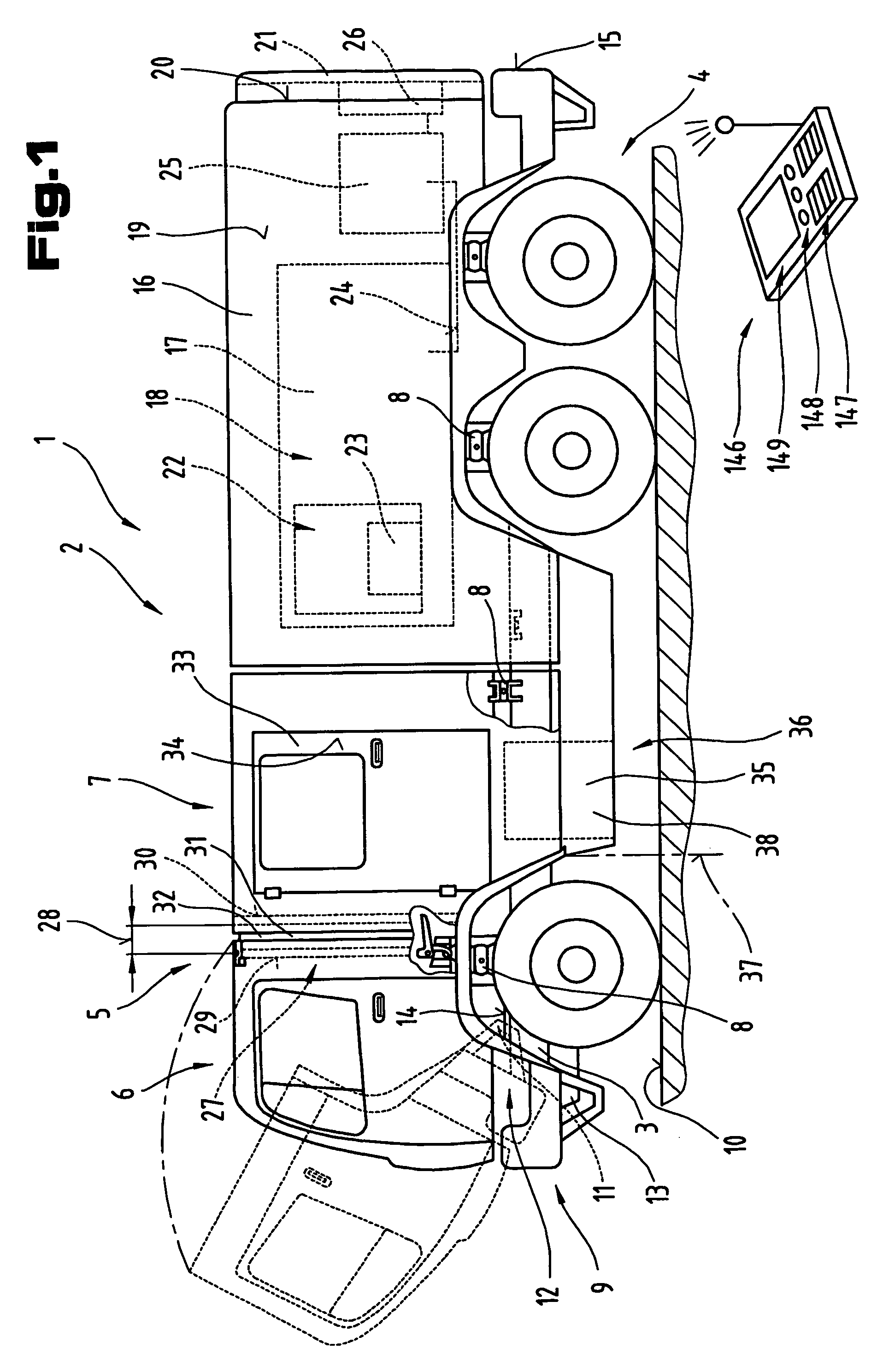
InactiveUS7213872B2Rapid and safe entryStrong forceVehicle seatsFire rescueDriver/operatorVehicle frame
A truck, in particular a fire-fighting utility vehicle. The vehicle has a structure mounted on a chassis frame with a driver's cab pivotable about a horizontal axis extending transversely to the travel direction. A crew and / or equipment cab is also mounted on the chassis frame communicating with the driver's cab via a releasable connecting mechanism forming a passageway. Independently of the driver's cab and the crew and / or equipment cab, a utility structure is mounted on the chassis frame having built-in fixtures for storing tools and equipment and optionally having extinguisher units consisting of at least a tank, extinguisher pump, etc. and mounting devices are provided at entry and / or operating openings in transverse and / or longitudinal side walls of the structure.
Owner:ROSENBAUER INT
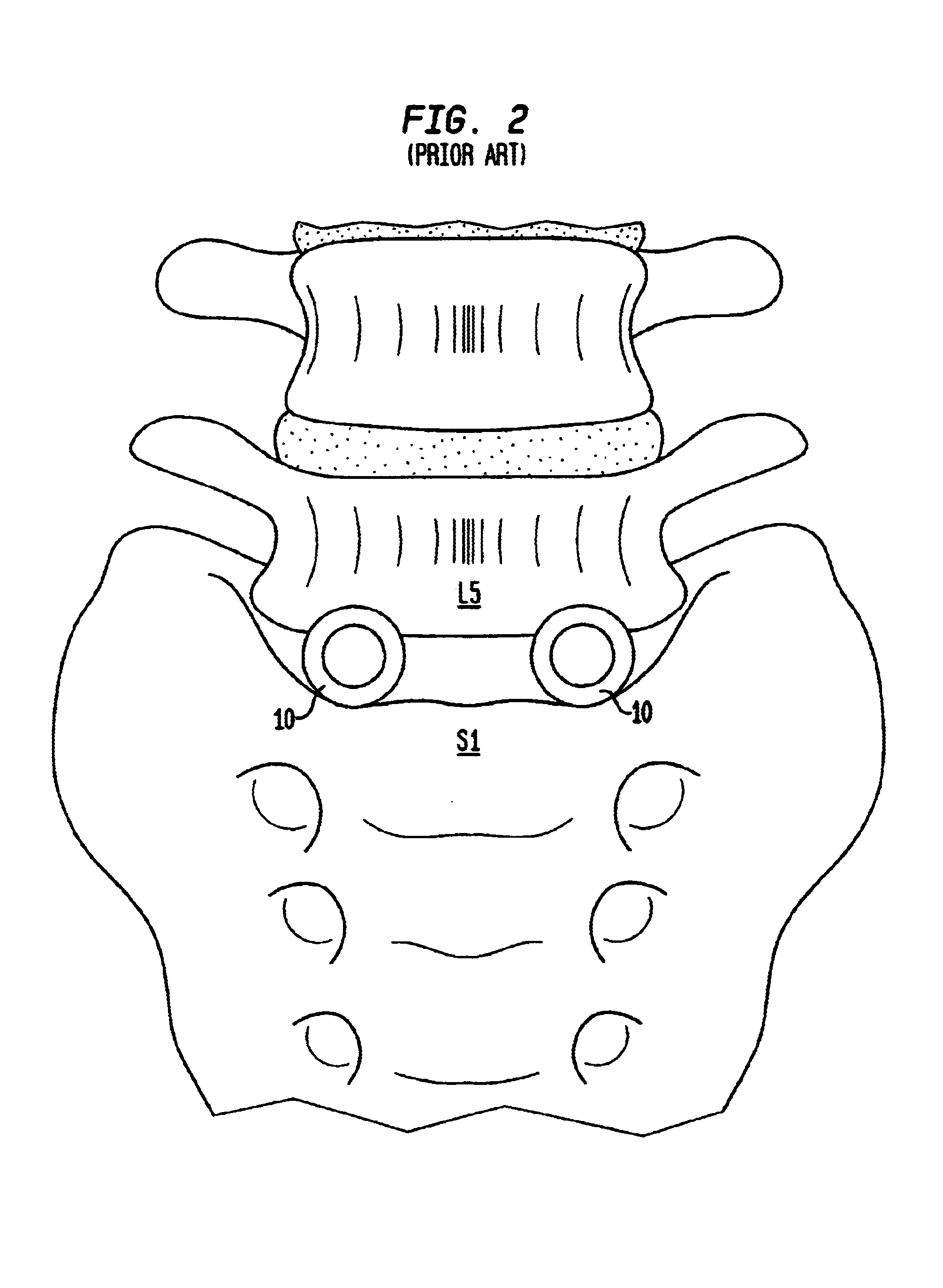
Intervertebral implant having features for controlling angulation thereof
InactiveUS20060235529A1Improve securityStrong forceJoint implantsSpinal implantsSpherical formBiomedical engineering
An intervertebral implant includes a first plate having an inner surface, an outer surface, a ball shaped protuberance projecting from the inner surface and an annular groove surrounding the ball shaped protuberance. The implant includes a second plate having an inner surface, an outer surface, a curvate socket formed in the inner surface of the second plate and a raised rim surrounding the curvate socket. The first and second plates are assembled together so that the inner surfaces of the plates oppose one another and the ball shaped protuberance is disposed in the curvate socket and the annular groove aligned with the raised rim. The assembled first and second plates angulate and rotate relative to one another.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
Solvent for making liquid crystal alignment film, materials for the alignment film, and method for manufacturing liquid crystal display
InactiveUS20120135661A1Quality improvementImprove imidization rateOrganic chemistryOther chemical processesChemical structureCrystallography
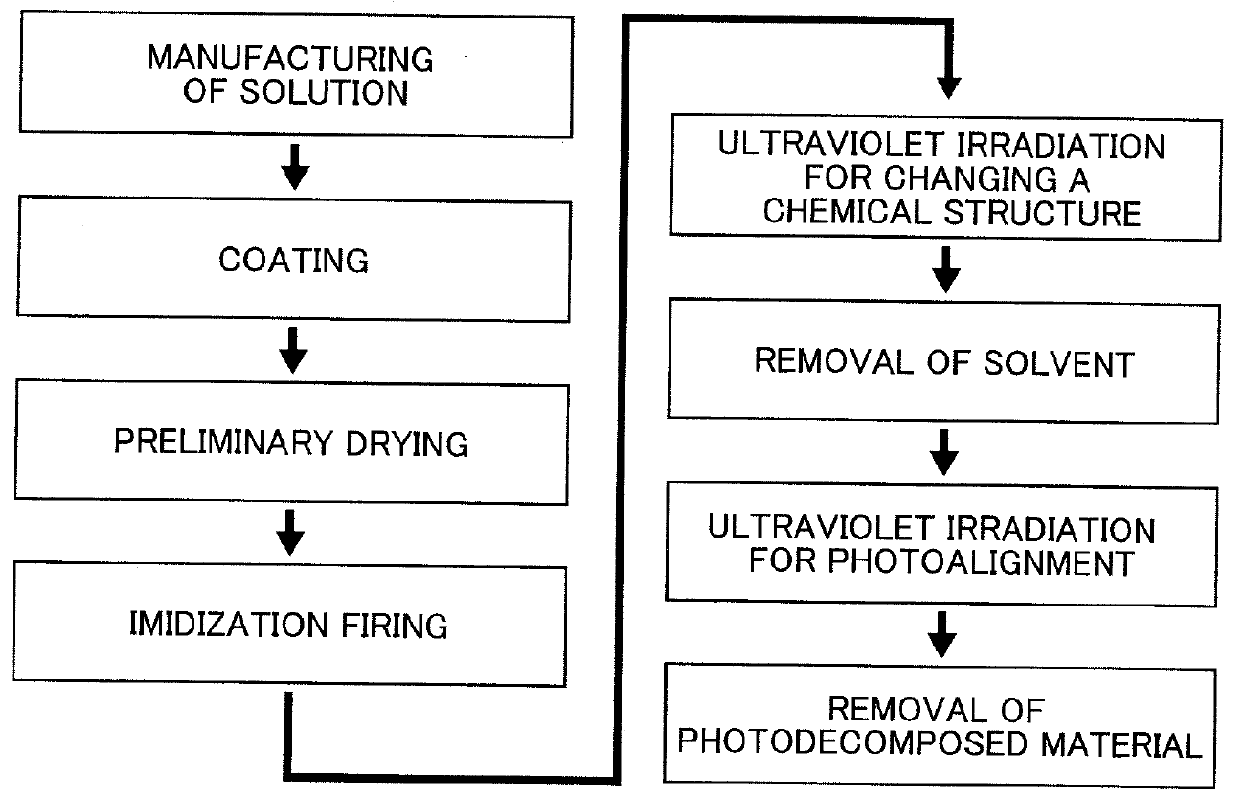
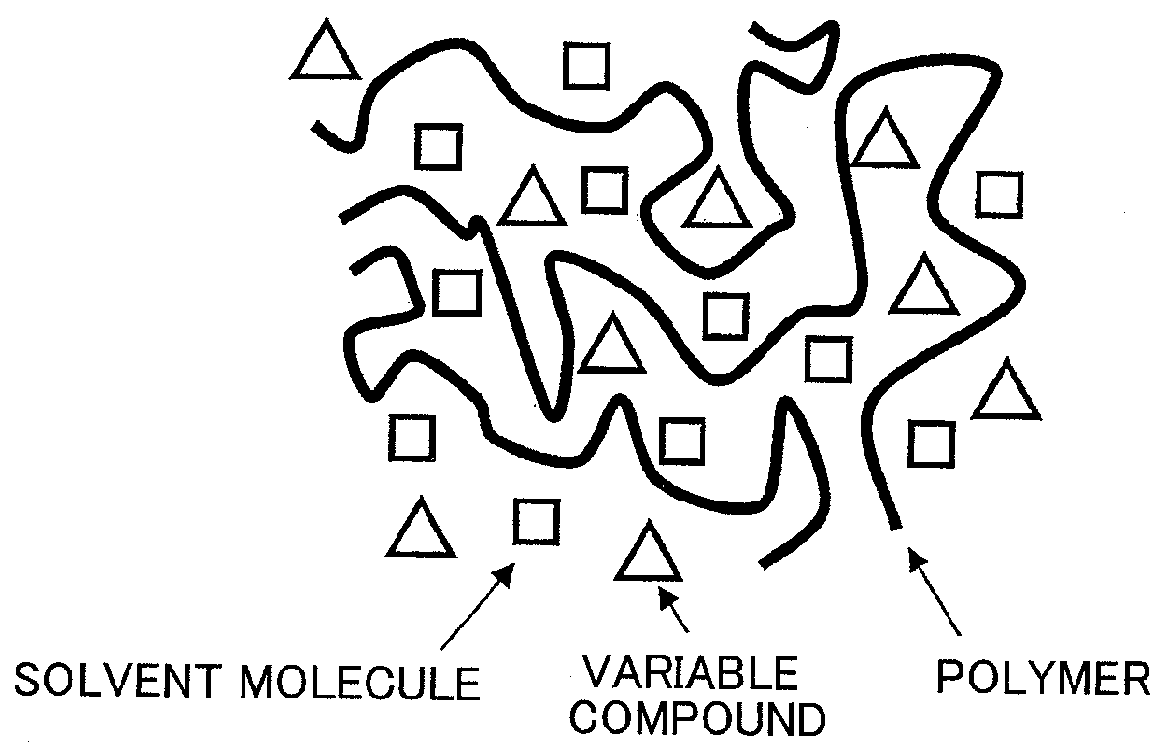
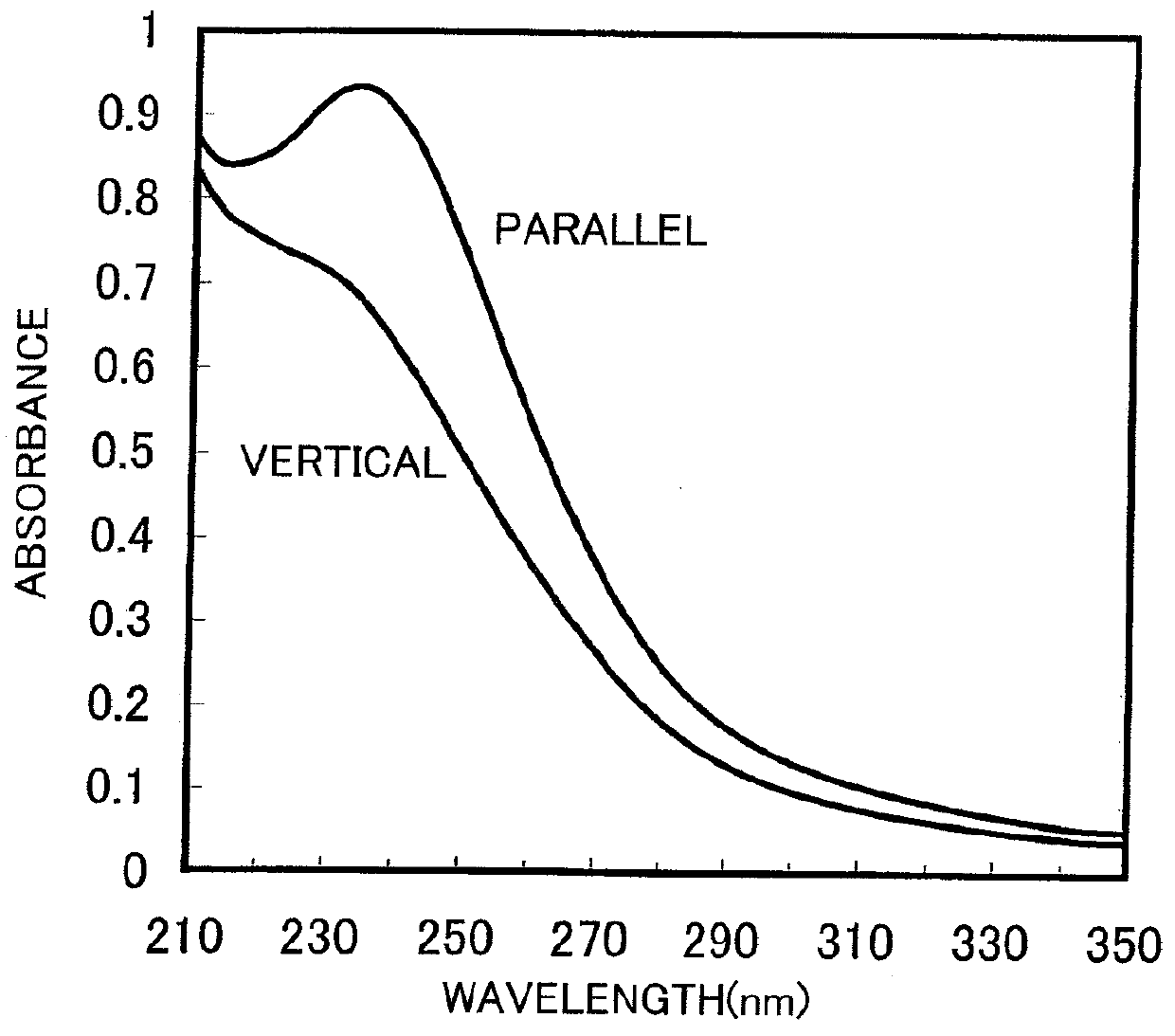
Provided is a solvent for forming an alignment film capable of fabricating a liquid crystal alignment film having high quality, an improved imidization ratio, large surface anisotropy, and a strong anchoring force. The solvent for forming an alignment film including a polymer for a liquid crystal display includes the polymer of the alignment film including polyimide and a variable compound capable of changing a chemical structure for evaporating after imidizing and sintering, which is in a liquid state during a film-forming process of coating, imidizing, and sintering polyamic acid which is a precursor of polyimide.
Owner:JAPAN DISPLAY INC
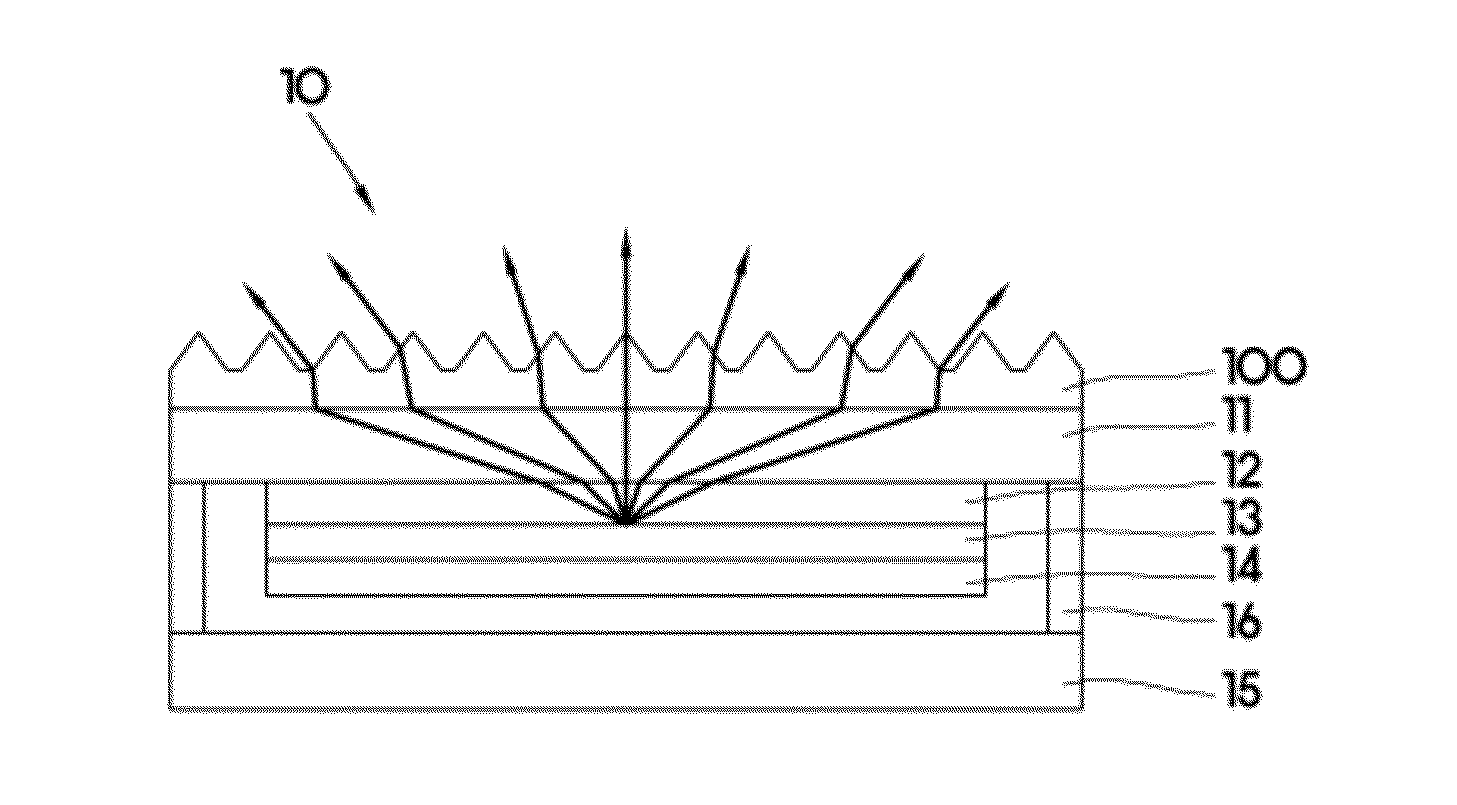
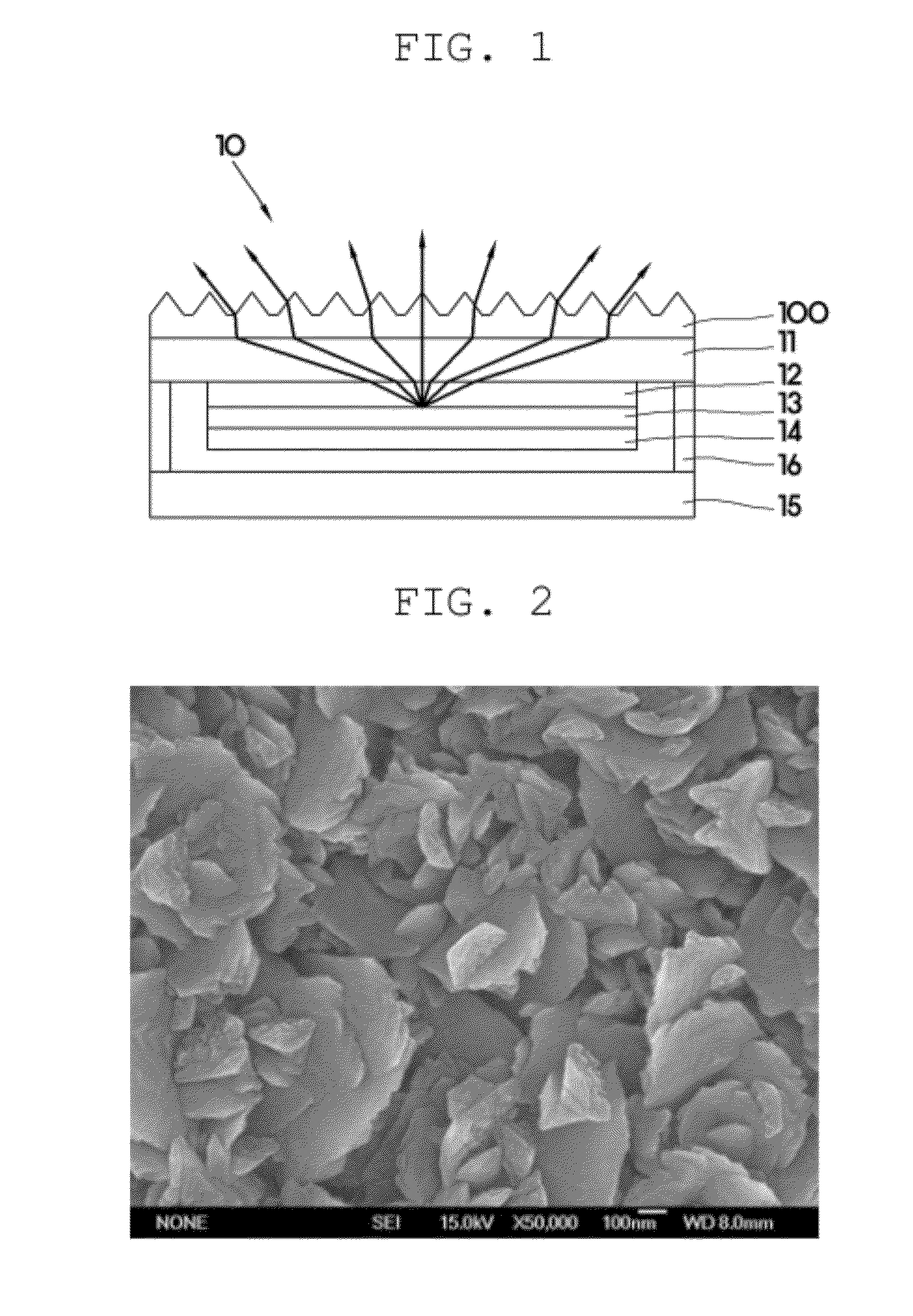
Light extraction substrate for electroluminescent device and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20120261701A1Light extraction efficiency can be improvedHigh transparencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWide bandElectroluminescence
A light extraction substrate for an electroluminescent device and a manufacturing method thereof, in which light extraction efficiency is increased. The light extraction substrate for an electroluminescent device includes a substrate and a light extraction layer formed on the substrate. The light extraction layer contains an oxide that has a wide band gap of 2.8 eV or more. The light extraction layer has a texture on the surface thereof.
Owner:SAMSUNG CORNING PRECISION MATERIALS CO LTD
Preparation method of polyacrylamide emulsion
ActiveCN103232573AHigh molecular chain densityHigh densityNon-fibrous pulp additionPaper/cardboardHydrocarbon solventsPapermaking
The invention discloses a preparation method of a polyacrylamide emulsion. The preparation method comprises the following steps of adding acrylamide, one or more anion monomers, a grafting matrix, an aqueous stabilizer, a molecular weight conditioning agent and an initiator into water, adjusting a pH value to obtain a water phase, adding an emulsifier into a hydrocarbon solvent to obtain an oil phase, dropwisely adding the water phase into the oil phase, carrying out one-step emulsification or multistep emulsification to obtain an emulsion, carrying out displacement deoxygenation on the emulsion by inert gas, and adding the initiator into the emulsion for polymerization initiation to obtain a branched anion polyacrylamide water-in-oil anti-phase emulsion after polymerization is finished. The polyacrylamide emulsion obtained by the preparation method is used for the modern papermaking industry, avoids inorganic filler re-falling after retention, improves inorganic filler actual retention effects, avoids falling-off of dust and lint of a screen cloth, guarantees uniform and stable retention of an inorganic filler in a page, and properly reduces a bentonite use amount.
Owner:JIANGSU FEYMER TECH
Preparation of magnetic silicon dioxide microsphere with metallic ion chelated surface and use thereof
InactiveCN101323454APrevent leakageStrong forceSilicaPeptide preparation methodsProtein targetMicrosphere
The invention relates to a method for preparing magnetic silicon dioxide microspheres with the surfaces chelated with metal ions; the method of the inventioncomprises the following steps of preparation of the magnetic silicon dioxide microspheres, epoxidation of the magnetic silicon dioxide microspheres, carboxylation of the magnetic silicon dioxide microspheres and chelation technique of metal ions. Compared with the existing preparing method, the method of the invention has the advantages of reasonable design, simple operation and large amount of chelation of metal, etc. The magnetic silicon dioxide microspheres with the surfaces chelated with the metal ions, which are prepared by adopting the method, contain cobalt ions, have stronger bonding force with the modified microspheres so as to lead the cobalt ions to be not easy to leak out, and have higher selectivity and proper bonding strength with histidine on the protein, thus leading the magnetic silicon dioxide microspheres with the surfaces chelated with the metal ions to have high selectivity to hexameric histidine tag protein, and being easy to realize the separation and the purification of the target protein; the magnetic silicon dioxide microspheres with the surfaces chelated with the metal ions, which are prepared by adopting the method, can be used for separating the hexameric histidine tag protein.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
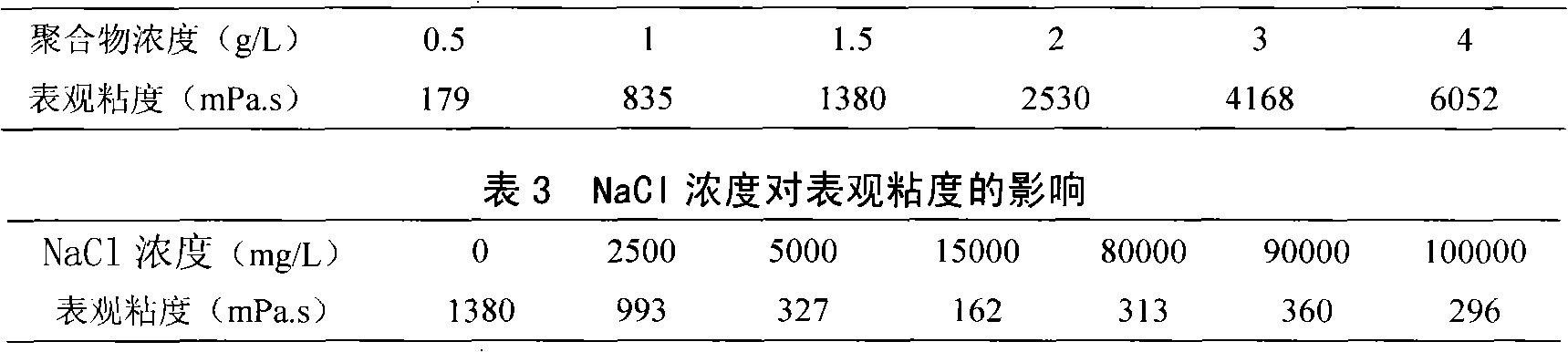
Temperature-resistant water-soluble copolymer, preparation and use thereof
InactiveCN101274974AImprove solution performanceImprove rigidityDrilling compositionSolubilityPersulfate
The invention discloses a copolymer with temperature resistance and water solubility and the preparation method and application thereof, which is characterized in that: 20 portions of acrylic amide, 0.1 to 10 portions of anion monomer or / and cation monomer, 0.05 to 3 portions of fluorine-containing styrene or / and perfluoroalkyl styrene hydrophobic monomer, 0.5 to 60 portions of surface active agent and 50 to 700 portions of deionized water are put into a three-necked reaction bulb; after the solution pH is regulated to be equal to 2.5 to 9 and N2 is connected for 30 minutes, 0.001 to 0.2 portion of an evocating agent of persulfate is added under temperature of 20 to 70 DEG C, reacting for 6 to 36 hours, and PATF is prepared. Then water is used for diluting so as to prepare PATF concentrated solution, thus obtaining a copolymer that has medium molecular weight and water solubility, is high-temperature resistant, has an ability of molecular association and can be used in high temperature and high salinity reservoir. The copolymer is prepared into aqueous solution with a mass concentration of 0.3 to 3g / L and a surface-active-agent concentration of 0.01 to 4mmol / L, which is put in a blending container with a dasher and is stirred even at room temperature to prepare a polymer oil-displacing agent which is high-temperature resistant, high tackifying and anti-sharing and has excellent aging resistance under high salinity and the temperature of 110 DEG C. The prepared oil-displacing polymer has excellent solution properties owing to the supermolecular structure formed by the association between molecules of fluorine-containing cinnamene or / and alkylbenzene hydrophobic groups, thus having favorable application prospects in high temperature and high salinity reservoir exploitation.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
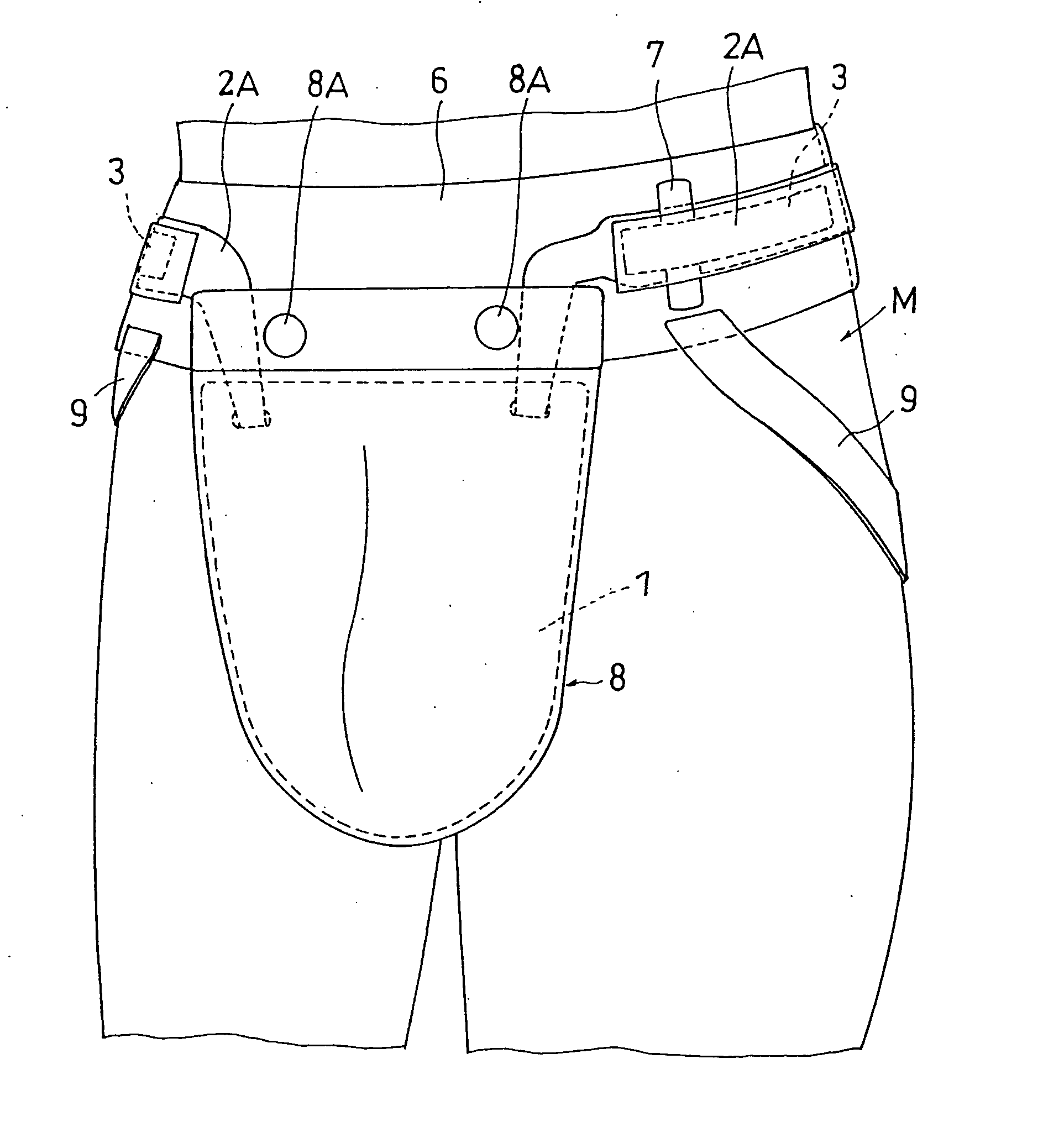
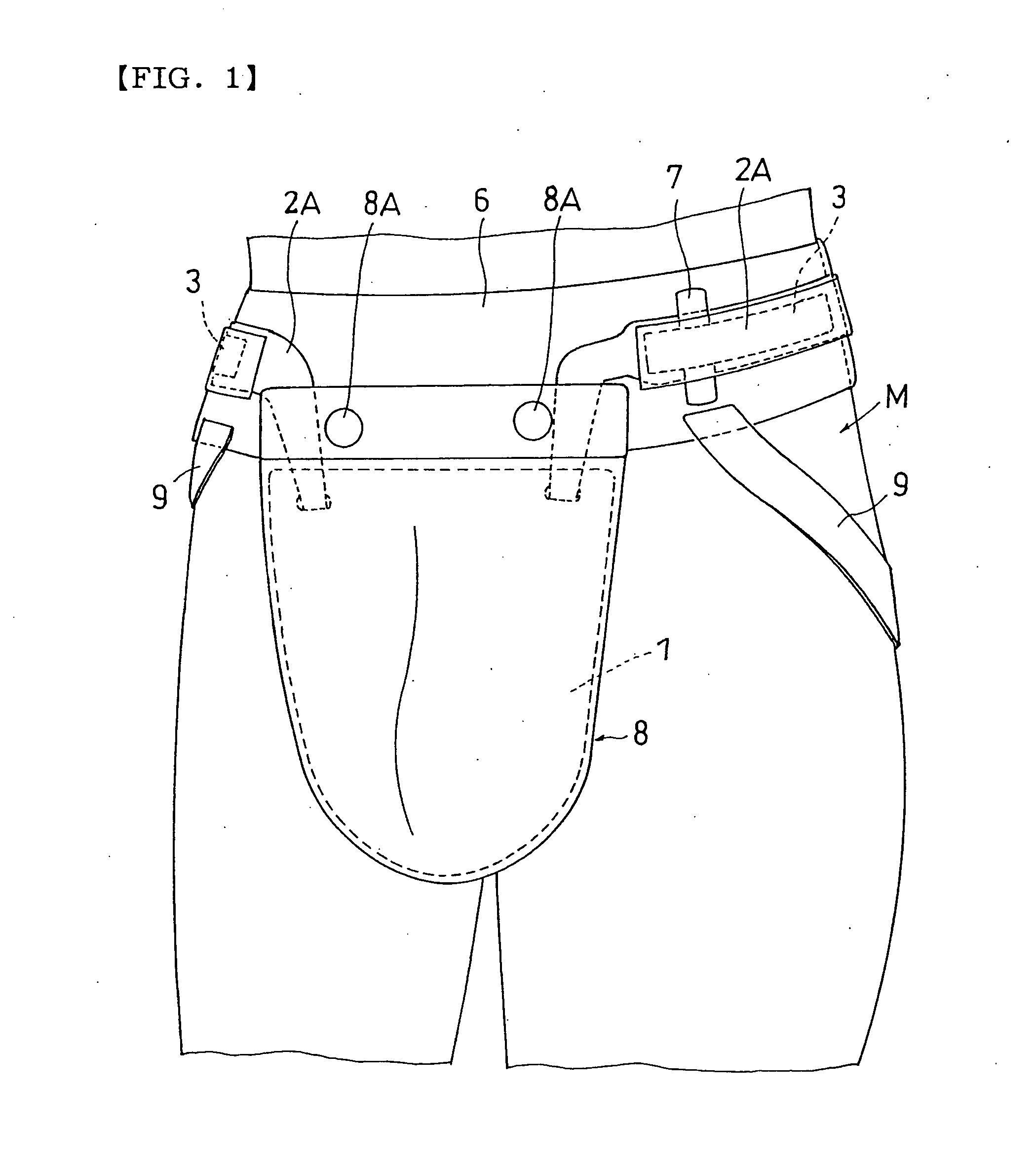
Groin protector for combat sports
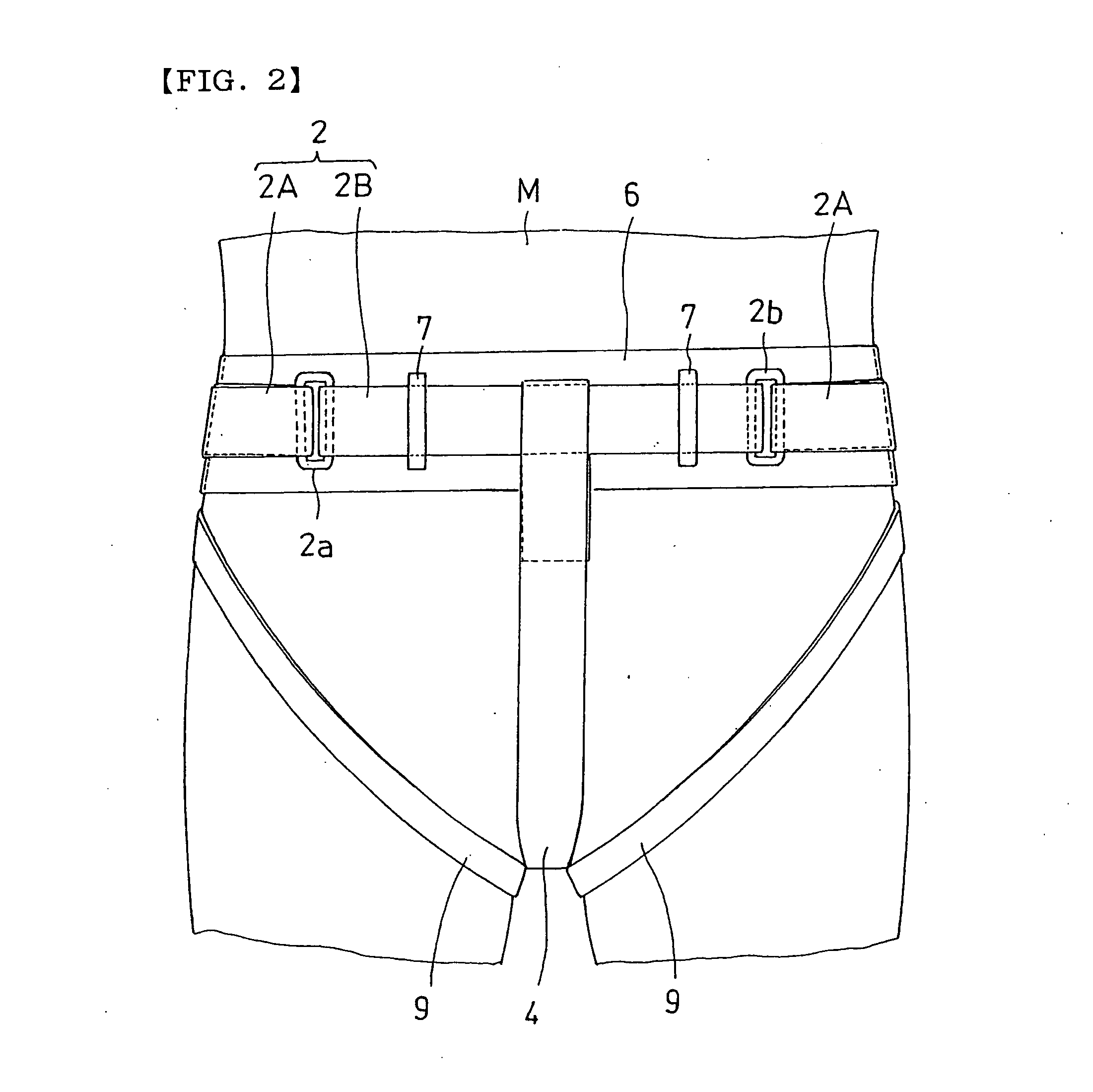
InactiveUS20050177931A1Avoid positioningShort timeSport apparatusProtective garmentEngineeringMechanical engineering
It is an object of the present invention to provide a convenient groin protector for combat sports capable of reliably preventing the position of the plate-like rigid body of the groin protector body from being deviated during a match, and capable of wearing and taking off the groin protector in a short time. The groin protector comprises, for wearing the protector body, a waist belt made of inelastic band-like member which is attached such that the plate-like rigid body 1 is suspended and which is wound around and attached to a hip of the player M, and a surface fastener type belt retaining mechanism 3 which retains so that the waist belt 2 is not loosened in a state in which the waist belt 2 is wound around the hip of the player M and fastened.
Owner:TSUJIMOTO TAKESHI
CsPW/Zr-MCM-41 catalyst prepared in supercritical CO2 environment and application of catalyst
ActiveCN105498845AWide variety of sourcesGood dispersionMolecular sieve catalystsOrganic compound preparationAcroleinMCM-41
The invention discloses a CsPW / Zr-MCM-41 catalyst prepared in a supercritical CO2 environment. The preparation method comprises the following steps: Zr-MCM-41 is taken as the carrier, and 10-60% of Cs modified salts is loaded by adopting the supercritical CO2 impregnation technology; with the utilization of the catalyst, the glycerin conversion rate reaches 65.2-100%, the acrolein selectivity reaches 56.8-85.4%; the invention further discloses application of the CsPW / Zr-MCM-41 catalyst to preparation of acrolein through glycerol selective dehydration. Compared with the prior art, the catalyst prepared by adopting the preparation method has the advantages that the dispersion degree of Cs modified salt on the carrier is high, the acting force between the Cs modified salt and the carrier is strong, the hydrothermal stability is high, the acidity loss possibility is low, and meanwhile, when compared with the conventional product, the obtained product is high in glycerin conversion rate and acrolein selectivity, and long in service life.
Owner:SHANDONG XINGQIANG CHEM IND TECH RES INST CO LTD
Novel method for modifying graphene with polymer
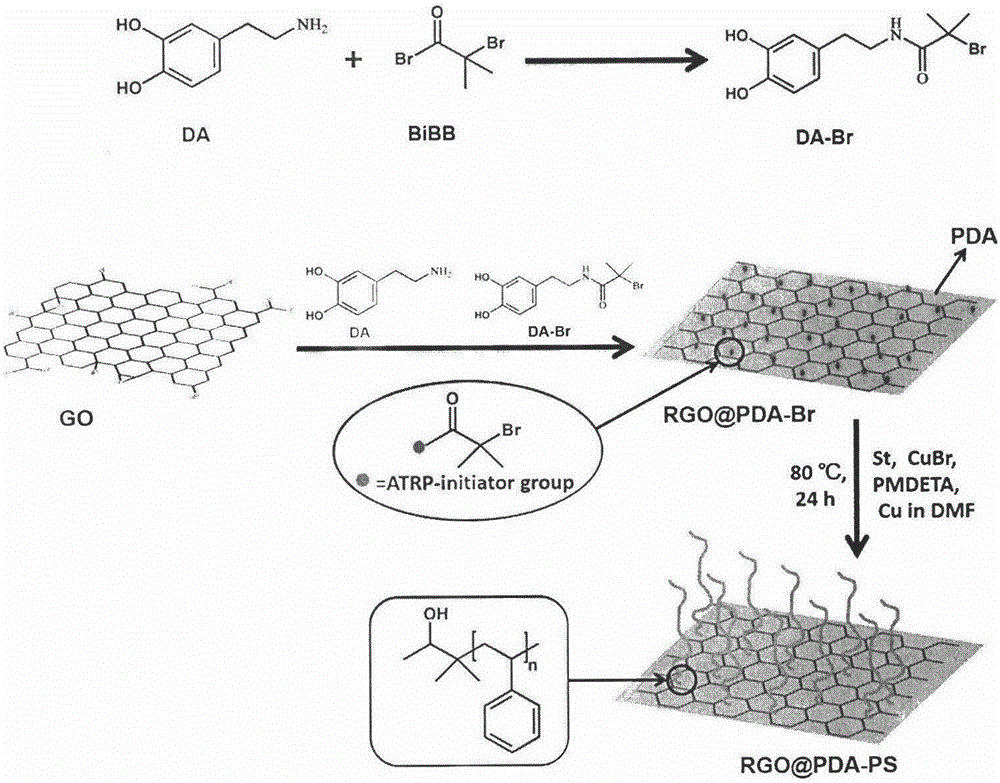
The invention discloses a novel method for modifying graphene with polymer. By introducing polydopamine and combining covalent modification with non-covalent modification, the method increases the stability of the modified product structure under the premise of ensuring the integrity of the graphene structure. Firstly, by utilizing the strong adhesion of dopamine, the dopamine is self-polymerized to form a film on the surface of a graphene sheet, moreover, 2-Bromo-2-methylpropionyl bromide (BiBB) as common initiator for atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP) is grafted on the dopamine by amidation, at the same time, graphene oxide (GO) is partially reduced by the dopamine (DA), and thereby graphene macroinitiator RGO@PDA-Br is obtained. Polymeric monomer is then added, so that the ATRP of the polymeric monomer is initiated on the surface of the graphene, and thereby a polymer-modified graphene material is obtained. By controlling conditions such as monomer concentration and reaction time, the novel method can obtain modified graphene materials with different densities and chain lengths of polymer grafted on the surfaces, meeting the characteristics of controllable / living ATRP. In addition, the feasibility and universality of the novel method for modifying graphene with polymer put forward by the invention are applicable to various monomers suitable for ATRP.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Fluorescent probe and preparation method thereof
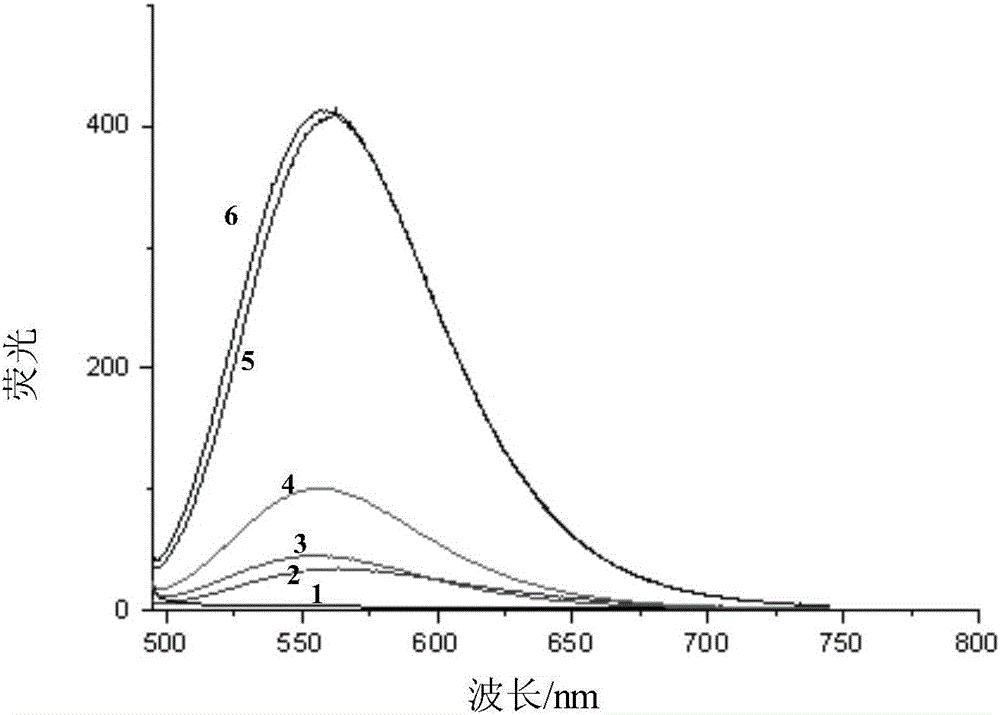
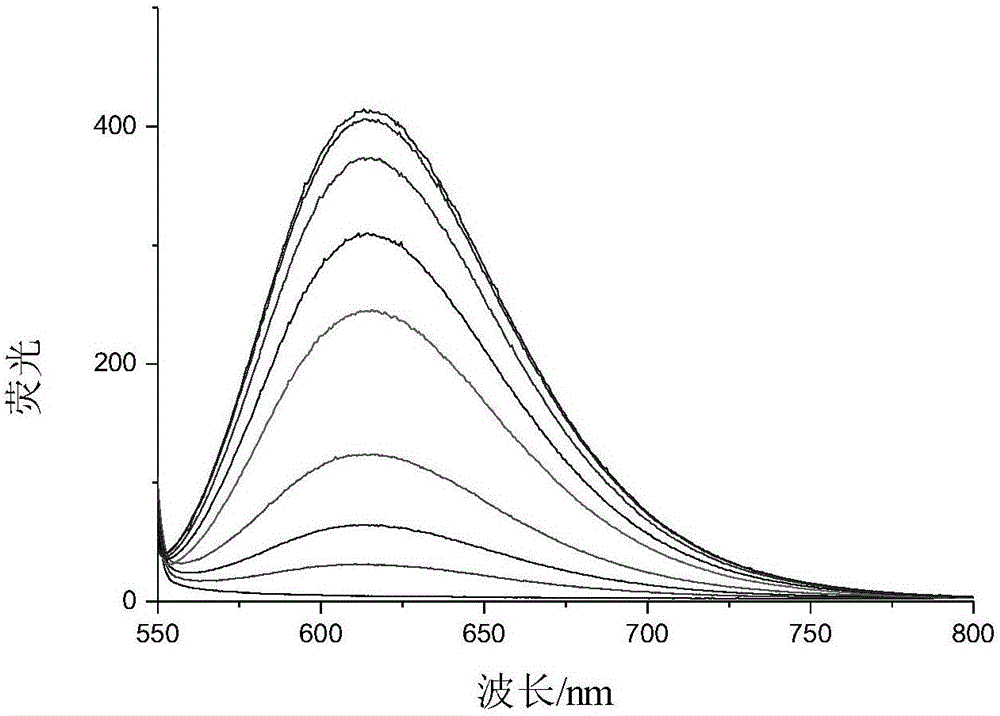
ActiveCN106833623AStrong forceEasy to pile upOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceSolubilityDouble bond
The invention provides a fluorescent probe represented by the formula (I), wherein R1 and R2 are independently selected from H or an aromatic vinyl group, and at least one of R1 and R2 is the aromatic vinyl group; R3 is selected from H, F, Cl, Br, OH, OCH3, N(CH3)2 or C1-C6 alkyl; and R4 is selected from C1-C6 alkyl. Compared with the prior art, because the fluorescent probe provided by the invention has a relatively large electronic conjugated system and plane, the intensity of the intramolecular charge transfer effect can affect the molecular fluorescence emission intensity; when the fluorescent probe and the G-quadruplex generate a specific action, the flexibility of intramolecular rotatable double bonds is restricted, the intramolecular charge transfer effect is enhanced, and the fluorescence is also enhanced significantly; moreover, the fluorescent probe provided by the invention has the advantages of low biotoxicity, phototoxicity and photobleaching property, good light stability, good water solubility and good cell membrane permeability.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Propane dehydrogenation catalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108325523AImprove conversion rateHigh selectivityMaterial nanotechnologyCatalyst carriersMagnesium AluminateChemistry
The invention discloses a propane dehydrogenation catalyst, which is obtained by loading metal platinum on magnesium aluminate spinel carriers, wherein the metal platinum of the catalyst is in a one-dimensional or two-dimensional highly dispersed state on the surface of the carrier; platinum atoms exist in a single atom or sub-nanometer cluster form; the particle diameter of the sub-nanometer cluster is smaller than 1nm. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the propane dehydrogenation catalyst. Compared with a catalyst prepared by the existing method, the obtained propane dehydrogenation catalyst has the advantages that the conversion rate and the selectivity are obviously improved; the stability is high; good application prospects are realized.
Owner:贵研工业催化剂(云南)有限公司
Connector with a moving plate
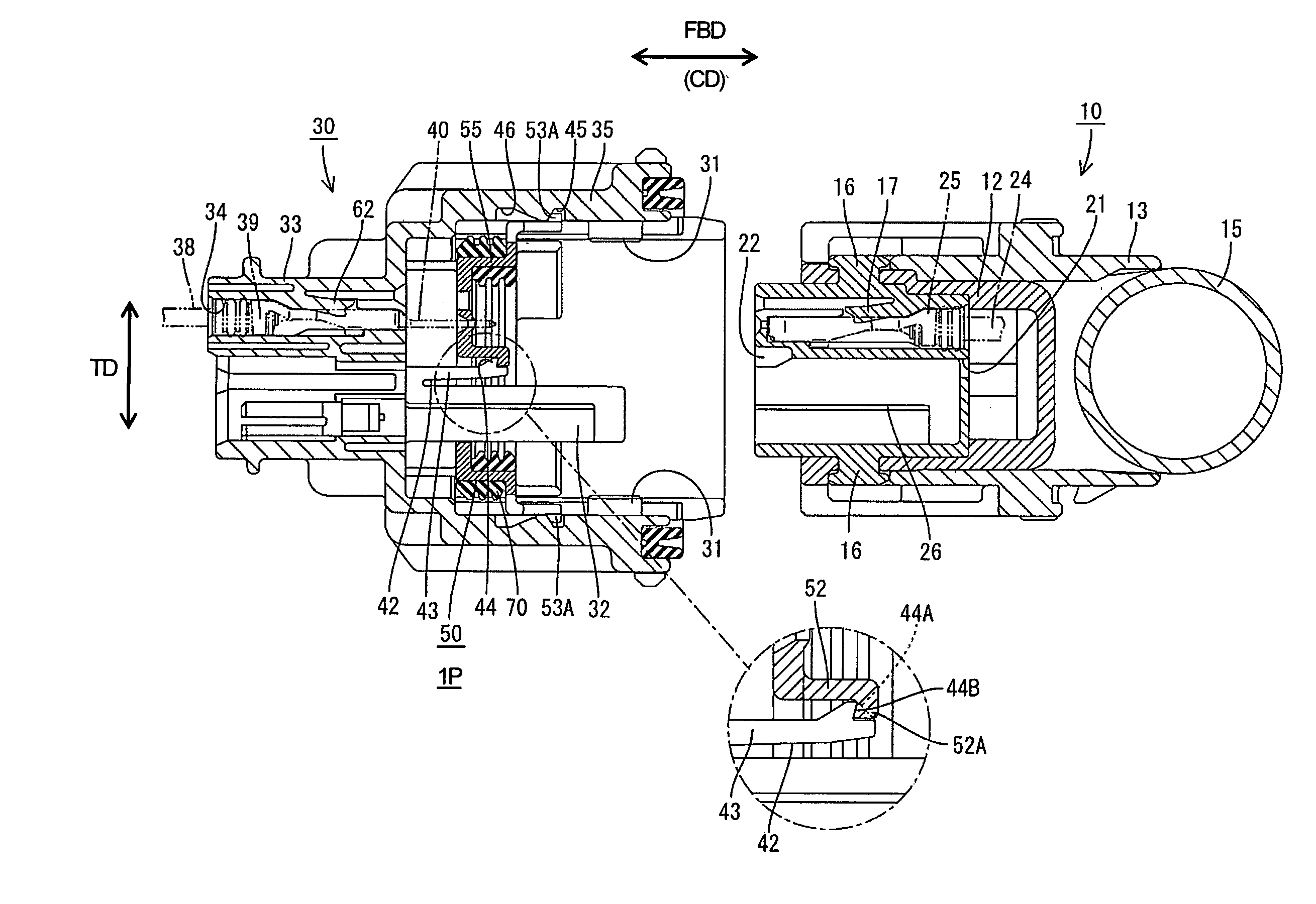
ActiveUS7134901B2Strong forcePrevent inadvertent movementEngagement/disengagement of coupling partsIncorrect coupling preventionEngineeringMechanical engineering
A moving plate (50) is movable between a retained position and a released position in a receptacle (35) of a male housing (30). One receiving portion (52) is provided in a middle part of the front surface of the moving plate (50), and a resiliently deformable latch (42) projects from the back surface of the receptacle (35) so that the leading end of the latch (42) is engageable with the receiving portion (52) through an insertion hole (64) of the moving plate (50). Movement of the moving plate (50) from the retained position to the released position is prevented by the resilient engagement of the latch (42) and the receiving portion (52). At the start of the connection of two housings (10, 30), a releasing portion (22) on the front surface of a female housing (10) contacts the latch (42) to disengage the latch (42) from the receiving portion (52).
Owner:SUMITOMO WIRING SYST LTD
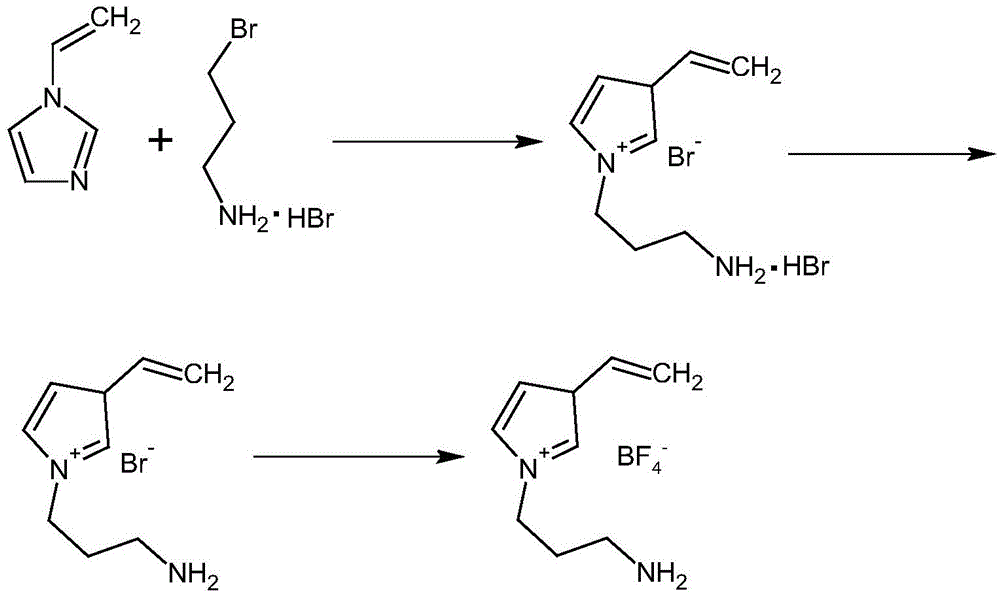
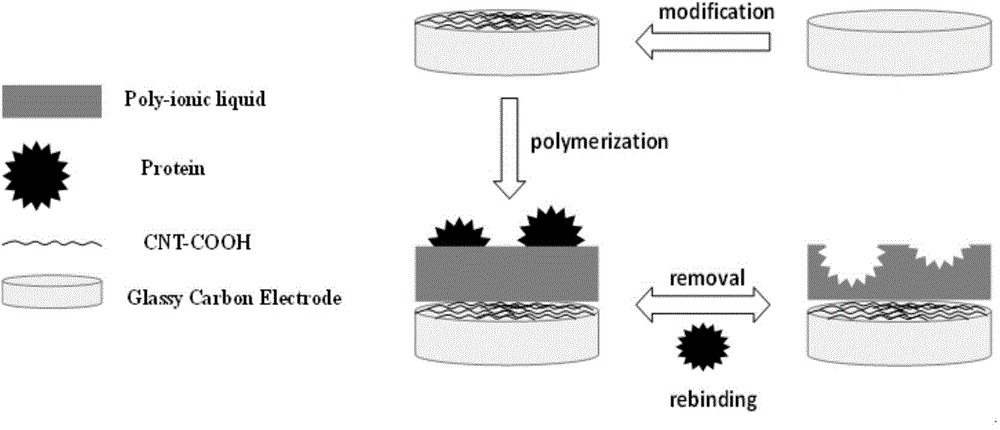
Protein molecular imprinting polyion liquid membrane electrochemical transducer
InactiveCN104142361ALarge specific surface areaGuaranteed stabilityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansBiocompatibility TestingIonic liquid
The invention relates to the technical field of electro-analytical chemistry and protein identification transducers, and discloses a synthesizing method of functionalized ionic liquid and a preparation method and application of a molecular imprinting electrochemical transducer composed of the functionalized ionic liquid, carboxylation multiwalled carbon nanotubes and glassy carbon electrodes. The preparation method of the molecular imprinting electrochemical transducer comprises the steps that the polymerizable amino-functionalized ionic liquid is used as a functional monomer, BSA is used as template protein, N, N'-methylene bisacrylamide is used as a cross-linking agent, an oxidation-reduction system composed of ammonium persulfate and TEMED is used as an initiator, after polymerization, a molecularly imprinted polymer film is formed on the surfaces of the glassy carbon electrodes decorating the carboxylation multiwalled carbon nanotubes, and then the template protein is eluted to obtain the molecular imprinting electrochemical transducer which can identify template protein in a specific mode. The molecular imprinting electrochemical transducer has the advantages of being simple in preparation, low in material cost, high in selectivity, good in biocompatibility, and capable of being used for identifying and detecting protein in aqueous solution.
Owner:SOUTH CENTRAL UNIVERSITY FOR NATIONALITIES
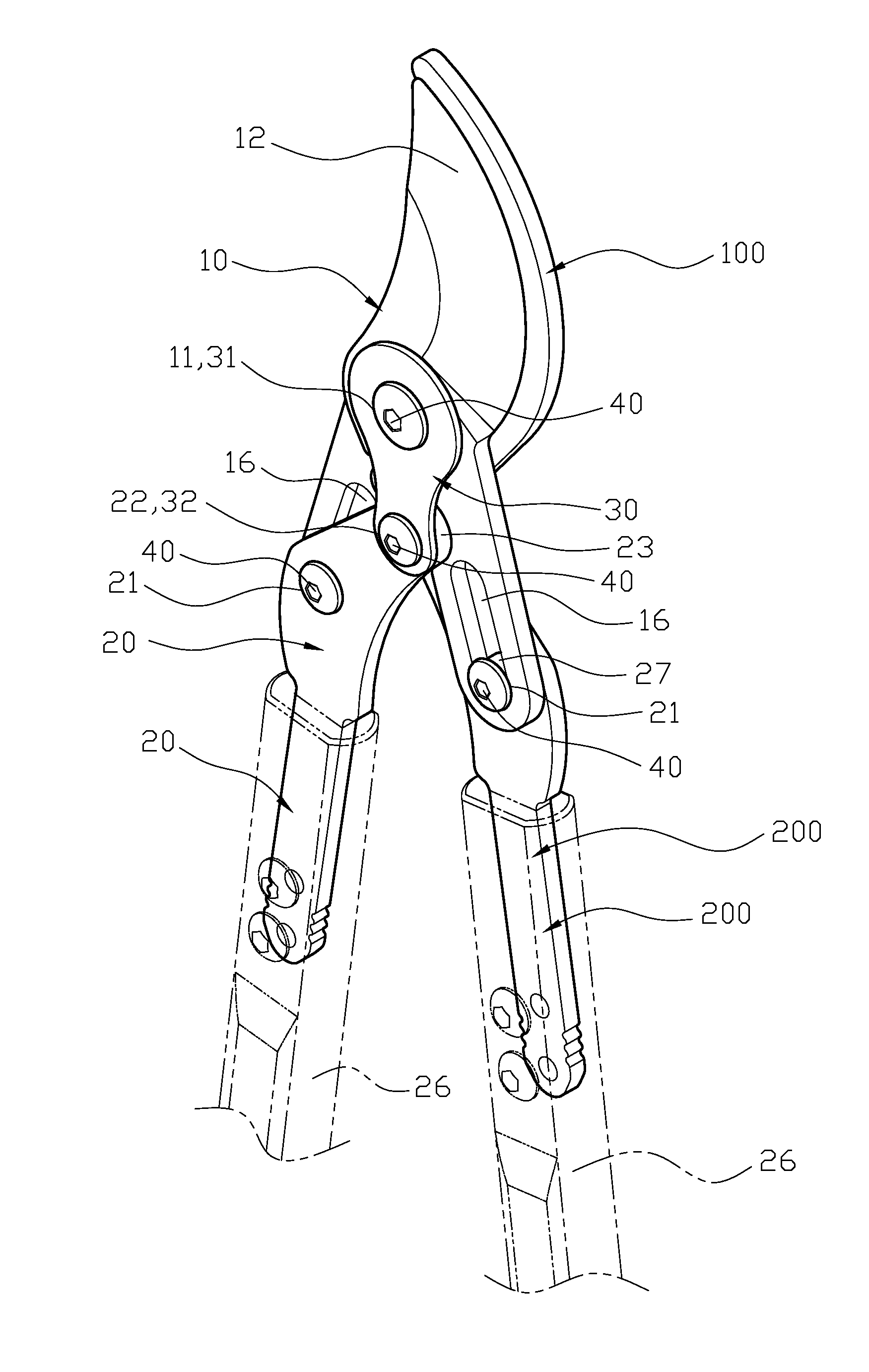
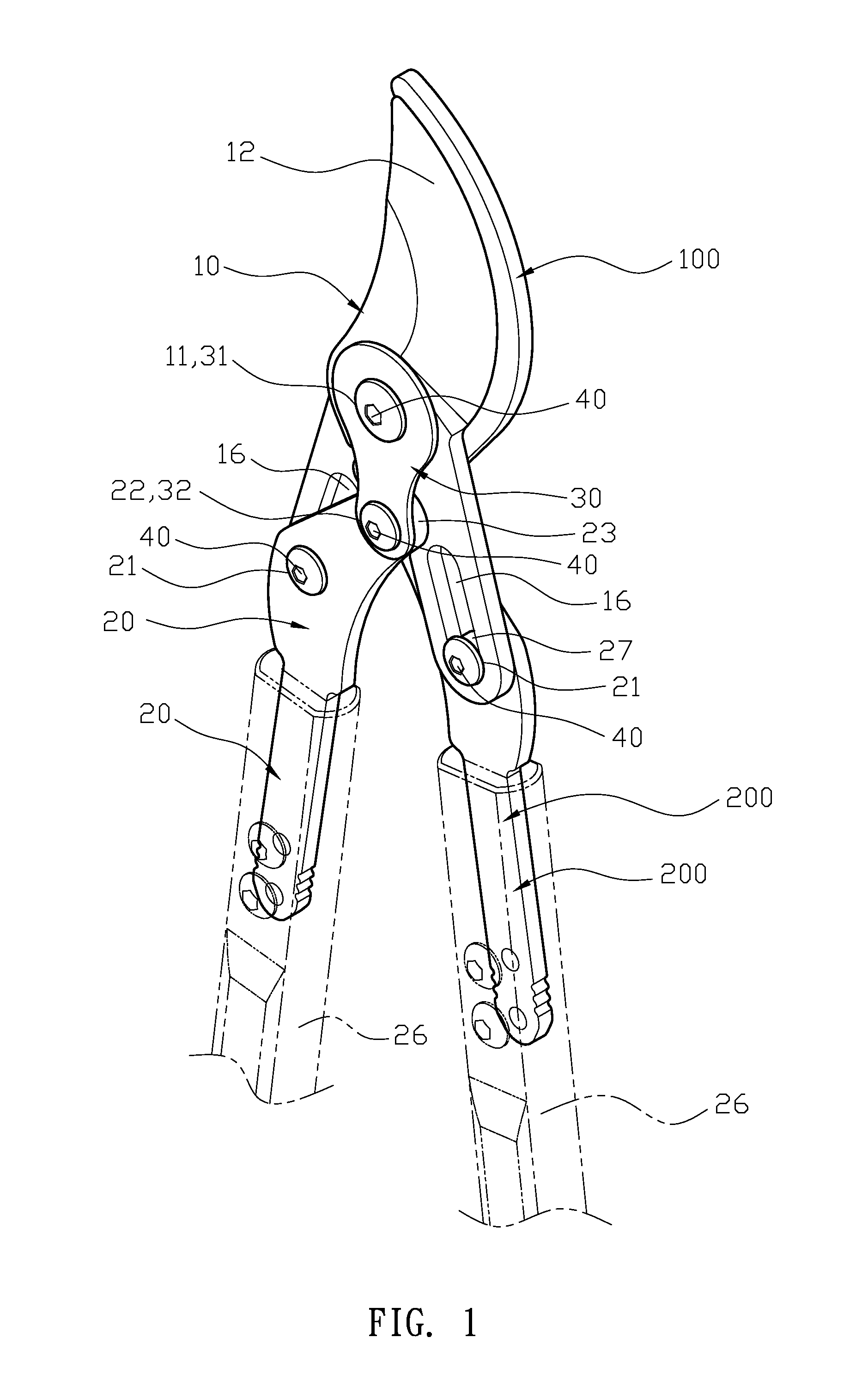
Garden shears
ActiveUS20120186087A1Strong forceIncrease the torque for the blade portionCuttersCutting implementsEngineeringKnife blades
Garden shears includes two corresponding cutting members, two opposing applying arms and two assembling members. Each cutting member has a main pivot aperture at a middle section thereof, a blade portion above the main pivot aperture, a pushing arc and a sliding arc continuously disposed below the main pivot aperture and a protrusion disposed between the pushing arc and the sliding arc, and an adjustable slot at a lower section. Each applying arm has a driving pivot aperture at a middle section, an eccentric pivot aperture at a top section, a rotation portion corresponding to the sliding arc formed at a top edge, a pushing edge formed at a side of the rotation portion, an indentation formed between the rotation portion and the pushing edge, and a handle at a lower section; wherein the assembling member is a flat member and has at least one securing aperture
Owner:HO CHENG GARDEN TOOLS
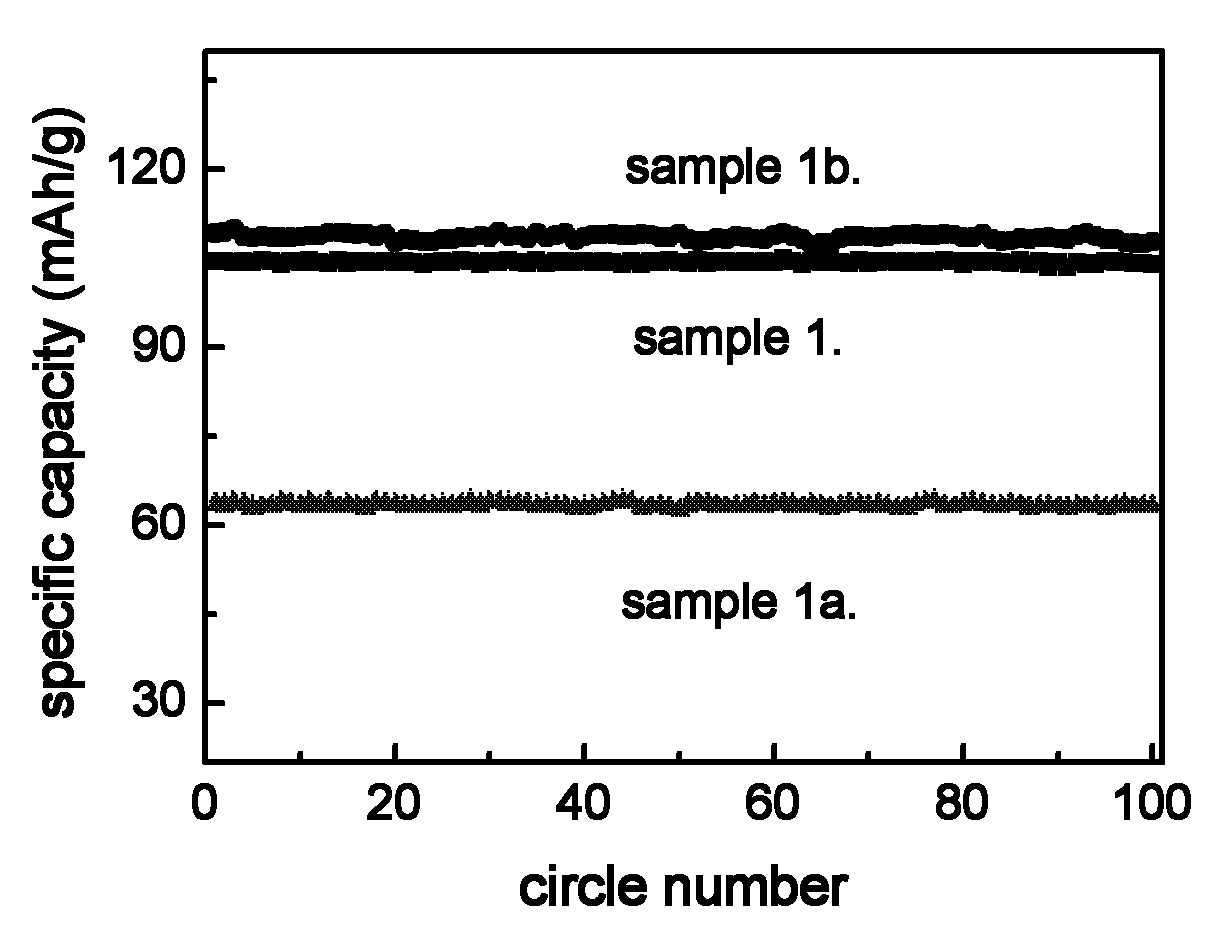
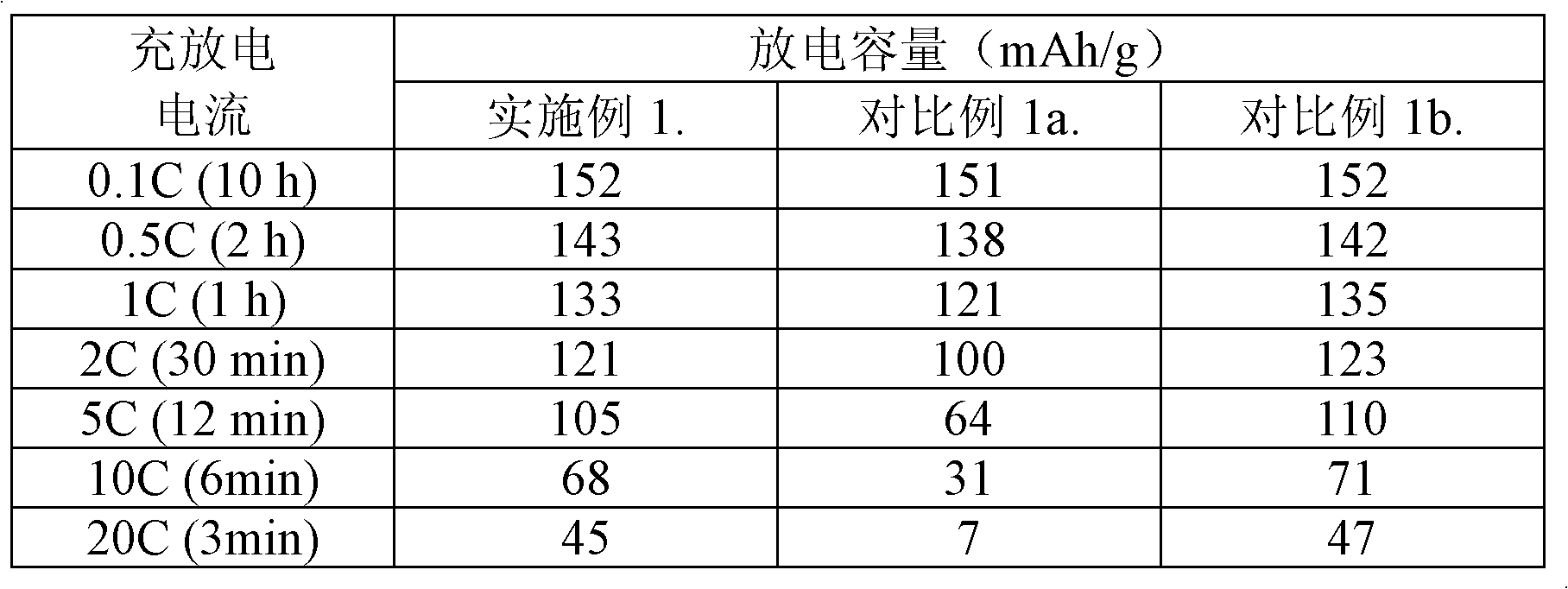
Power battery electrode and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN102104140AStrong forceProcess stabilityElectrode carriers/collectorsNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulator electrodesWater basedPower battery
The invention relates to the technical field of rechargeable lithium ion batteries, in particular to a high-performance power battery electrode and a manufacturing method thereof. The manufacturing method is suitable for manufacturing pole pieces of a positive electrode and a negative electrode of a rechargeable lithium ion battery. The manufacturing method comprises the following steps of: coating a conductive layer without lithium storage activity on a metal foil by a water-based process first and then coating a material with the lithium storage activity on the metal foil by using an oil-system formula to obtain a power battery electrode after drying and rolling the conductive layer. The electrode manufacturing method utilizes the advantages of high acting force and low internal resistance of the water-based process and metal, utilizes the characteristics of stable process and long cycle life of the oil-system formula, reduces the using amount of a bonding agent, can greatly improve the high-rate performance and the cycle life of the battery, and is an ideal power battery electrode manufacturing method.
Owner:CHANGZHOU HECO NEW ENERGY TECH CO LTD
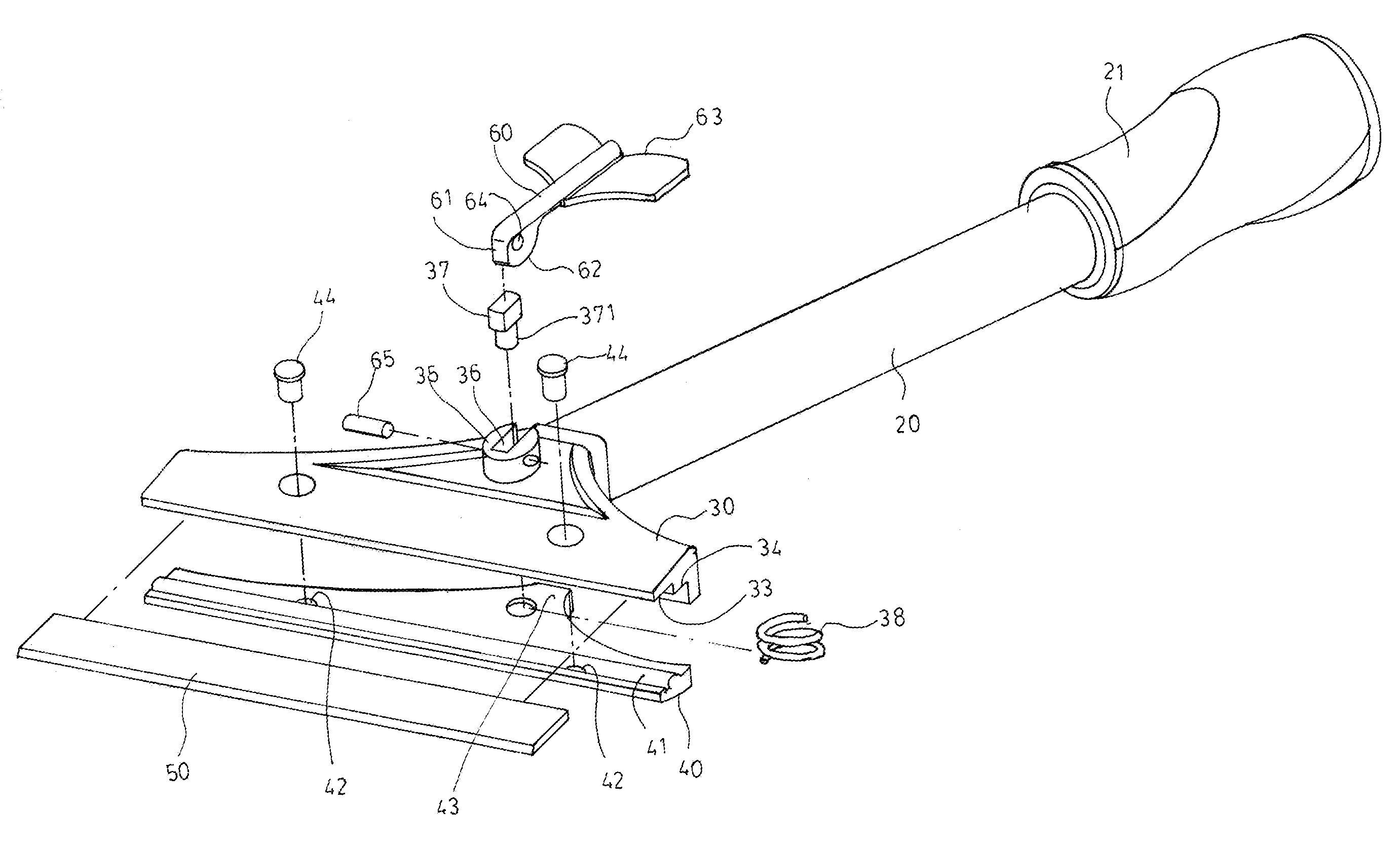
Scraping tool with blade lock assembly
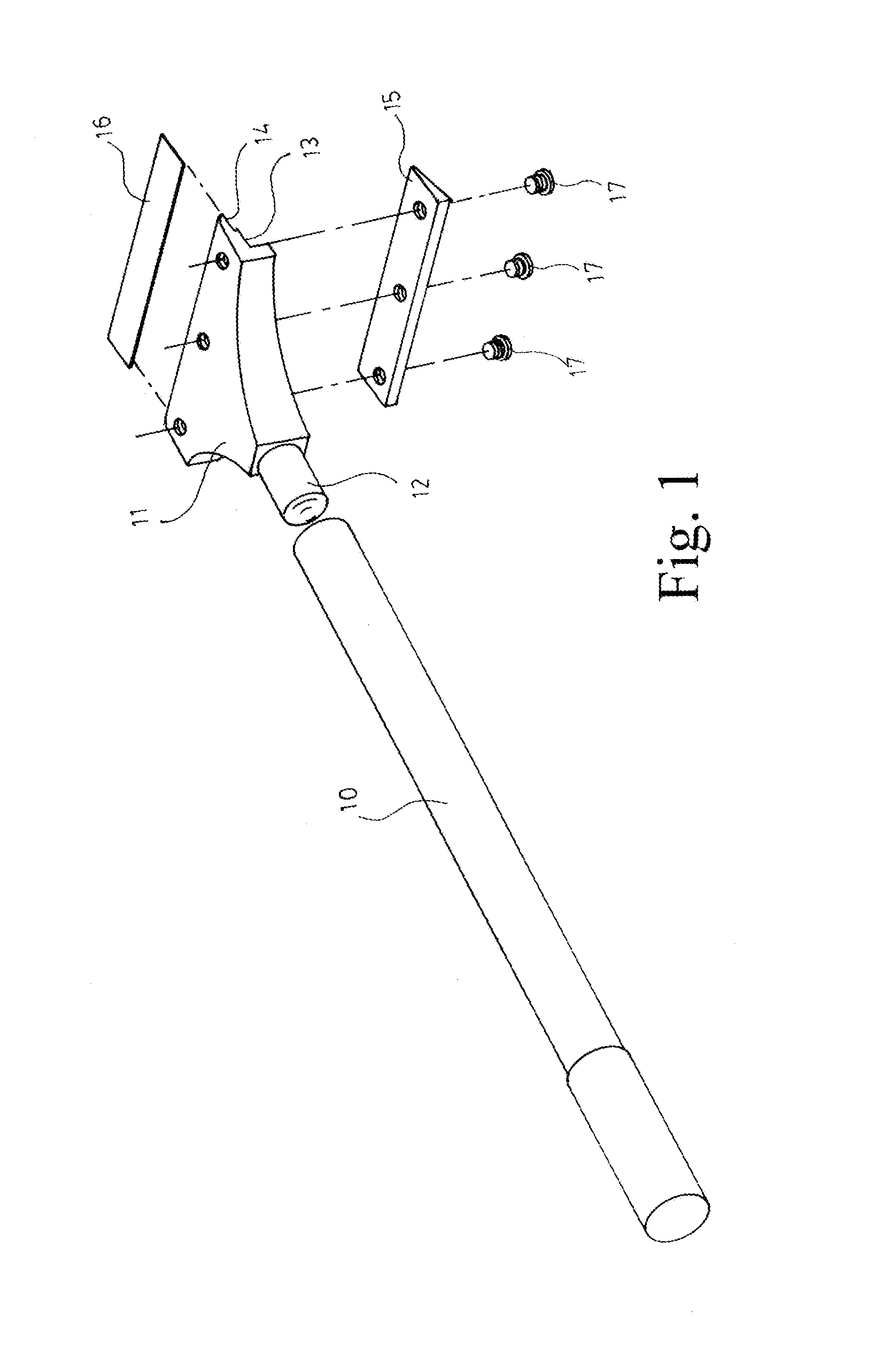
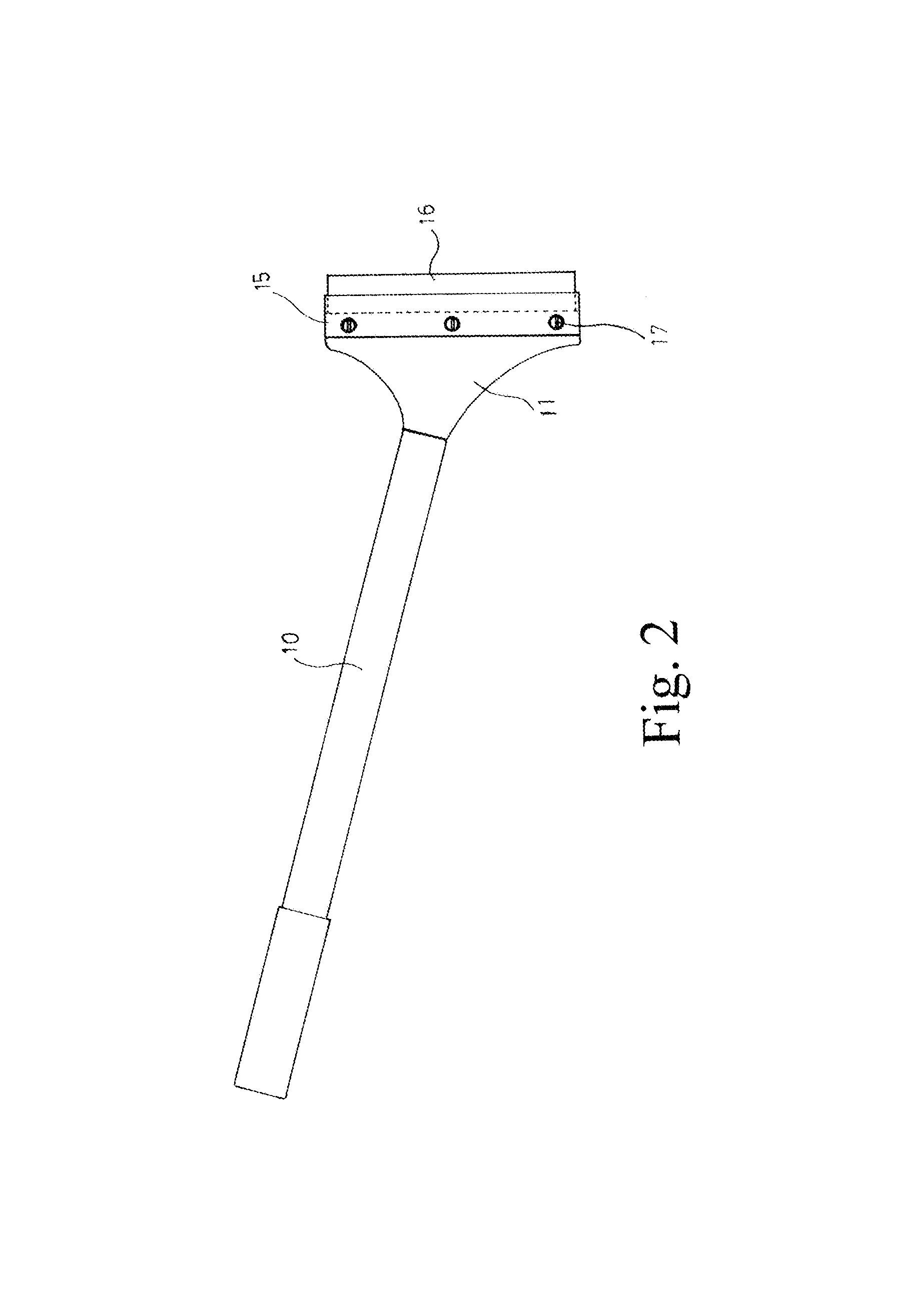
ActiveUS8356415B2Quick assemblyFast replacementLiquid surface applicatorsCarpet cleanersEngineeringKnife blades
The invention is related to a scraping tool that can be assembled and replaced for scraper blade quickly. The scraping tool in general comprises a stick for hand grasp and a scraping section in the front. The invention mainly uses an arm of suitable length extended from the back end of a jaw clamp toward the middle. It uses fasteners to be located inside the groove in the back of the scraping section. The fastener is also used as pivot for the arm to swing back and forth. On the arm in the back of the jaw clamp, there is a control button that provides vertical pushing force in the back of the jaw clamp and allows strong clamping force in the front of the jaw clamp onto the scraper blade to achieve stable assembly and fast replacement for scraper blade.
Owner:LIN WEN CHEN
Exhaust gas purifying catalyst
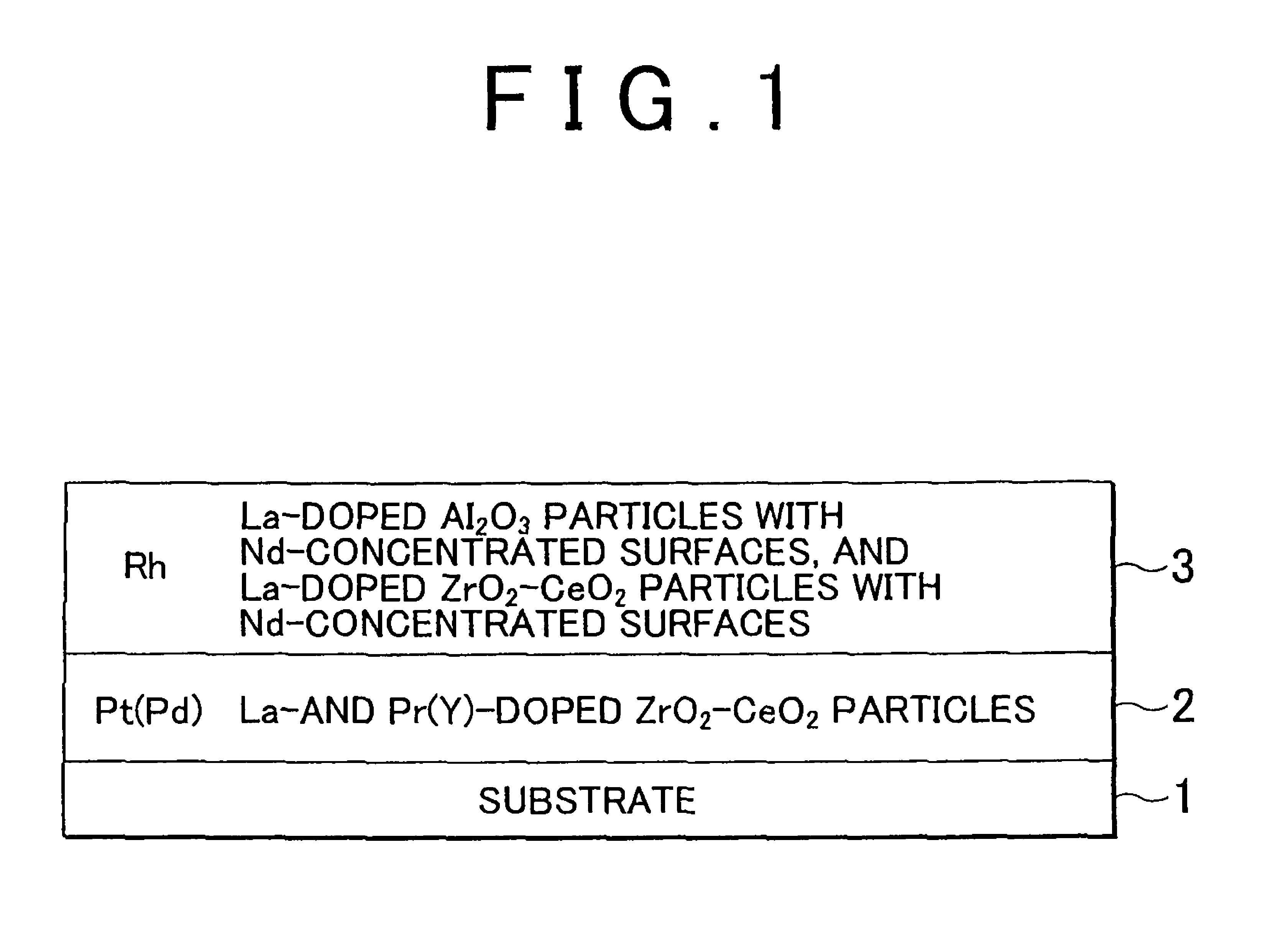
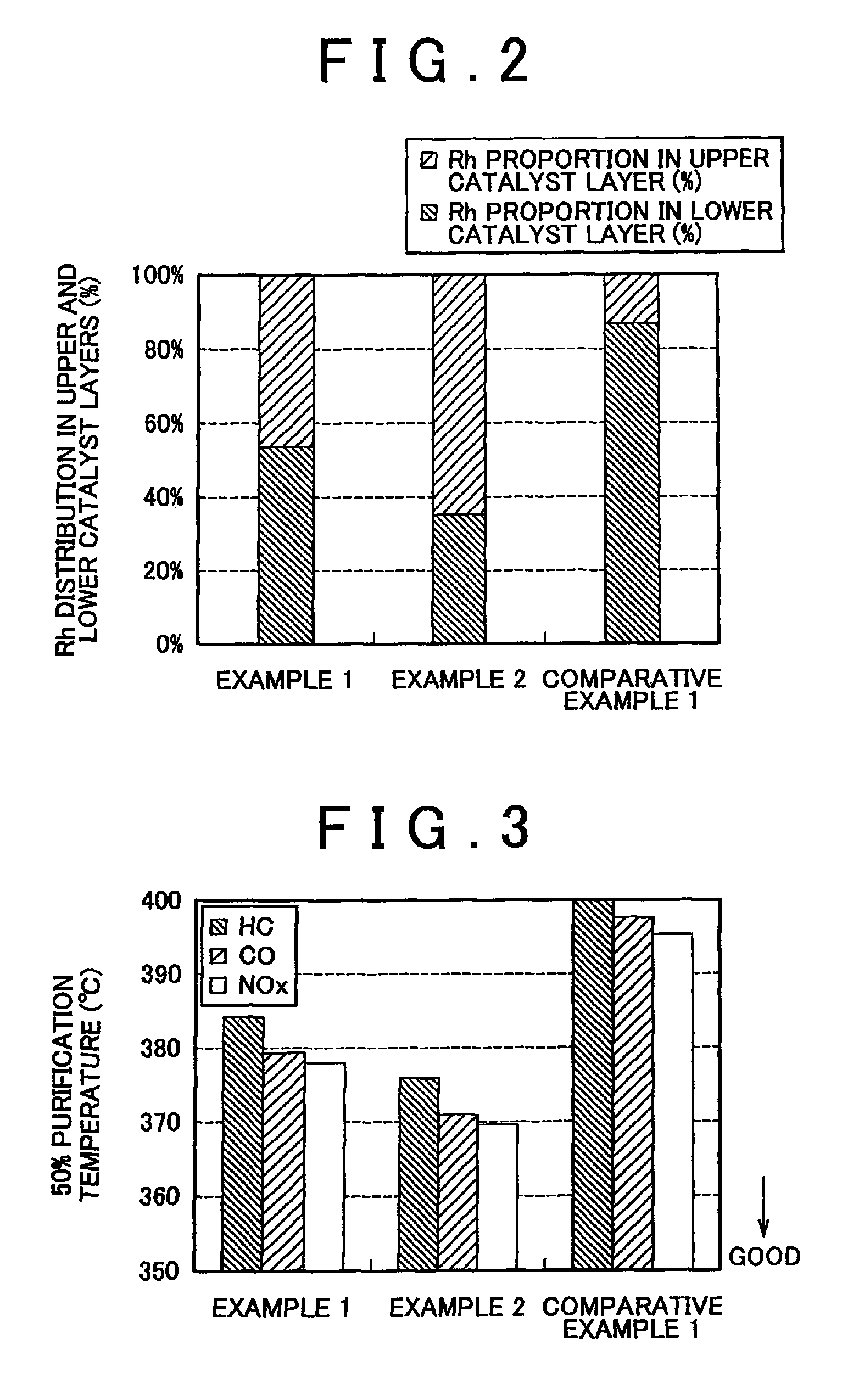
ActiveUS8580705B2Suppresses migration and sinteringImprove exhaust gas purification performanceGas treatmentInternal combustion piston enginesRare-earth elementMixed oxide
An exhaust gas purifying catalyst includes a substrate that defines an exhaust gas passage; a lower catalyst layer formed over the substrate, and an upper catalyst layer formed over the lower catalyst layer. The lower catalyst layer has a lower catalytic precious metal that contains at least one of Pt and Pd, and a lower-layer carrier that supports the lower catalytic precious metal. The upper catalyst layer has an upper catalytic precious metal that contains Rh, and an upper-layer carrier that supports the upper catalytic precious metal. The upper-layer carrier includes an inorganic mixed oxide that contains Ce, Zr, Al, Nd, and at least one element selected from the group consisting of rare earth elements other than Ce and alkaline earth elements. The Nd is unevenly distributed in covering layers that covers surfaces of interior regions within the inorganic mixed oxide.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +2
Nanocrystalline accumulation meso-microporous ZSM-5 catalyst and preparation and application
ActiveCN104525245APropylene selectivity is highLong catalyst lifeMaterial nanotechnologyMolecular sieve catalystsMolecular sieveCrystallite
The invention provides a nanocrystalline accumulation meso-microporous ZSM-5 catalyst and preparation and application thereof. The catalyst is aggregated by small grains with particle sizes of 20-100 nm to an aggregation state with a particle size of 200-2000 nm, the aggregation state forms the catalyst, the specific surface area of the catalyst is 350-420 m<2> / g, and the pore volume of the catalyst is 0.25-0.35 cm<3> / g. According to the invention, a mesoporous-microporous composite nanocrystalline accumulation state ZSM-5 molecular sieve is directly synthesized; under the condition of adding no second template, a solid silicon source is pretreated to generate different degrees of depolymerization, the material ratio of the synthesis system is further adjusted, a sodium salt is added to adjust the growth speed in a crystallization process of the molecular sieve, and meanwhile, a two-stage crystallization method is adopted to promote the generation of a crystal nucleus at a low temperature and promote the growth of a crystal at a high temperature, so as to synthesize a serial grain aggregation state ZSM-5 molecular sieve.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
Hanger
InactiveUS7097144B2Strong attractive forceIncrease air circulationApparel holdersPicture framesEngineeringClothes hanger
A hanger includes a hanger body having a prescribed external peripheral shape on which clothing is hung up. A first magnet is arranged in a projecting manner on a rear side of the hanger body for attaching the hanger to a prescribed suspending place.
Owner:KOHNO TATSUYUKI
Method for fabricating carbon nanotube array
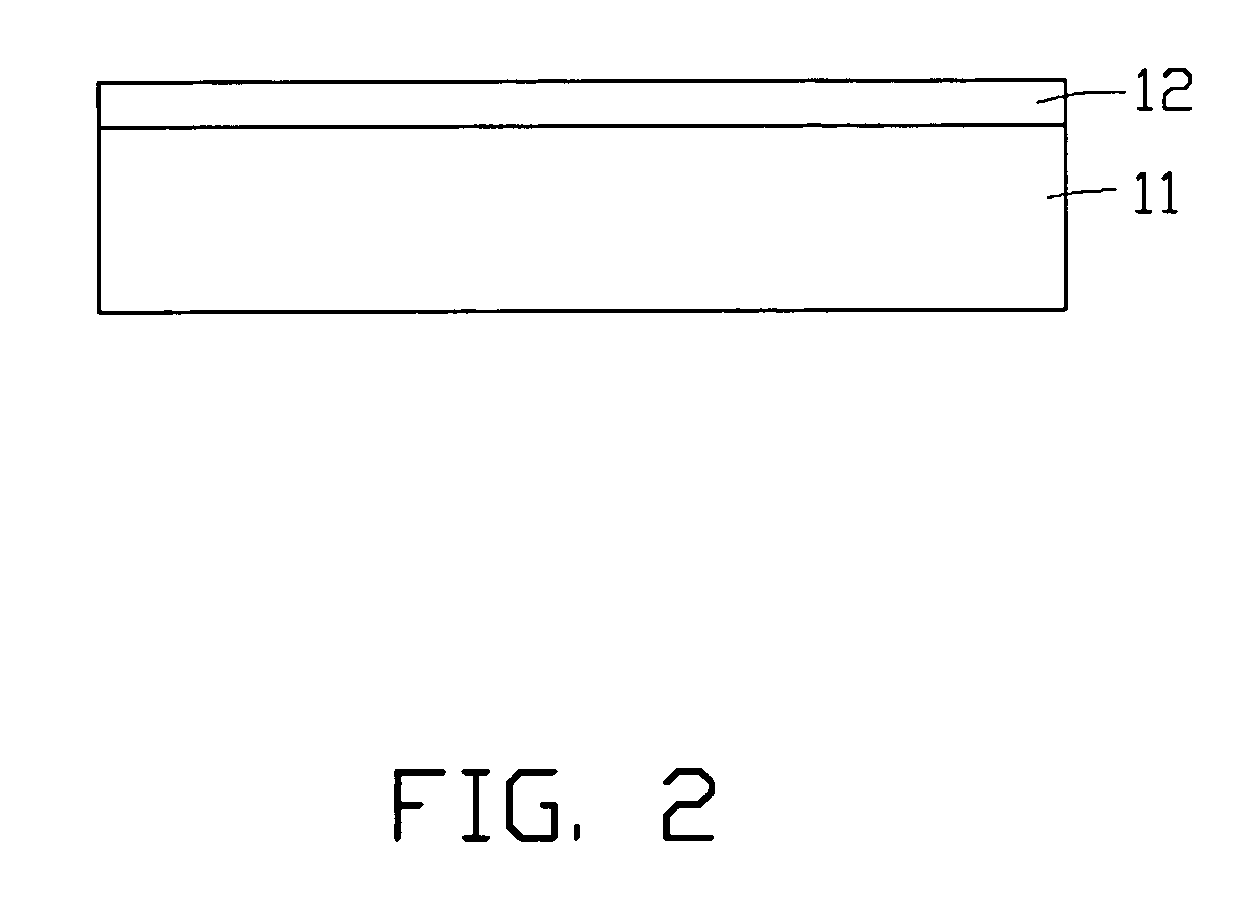
InactiveUS20100227058A1Flat surfaceStrong attractive forceMaterial nanotechnologyChemical vapor deposition coatingCarbon nanotubeNanotube array
A method for fabricating a super-aligned carbon nanotube array includes the following steps: (1) providing a flat and smooth substrate (11); (2) depositing a catalyst layer (12) on the substrate at a rate of less than about 5 nm / s; (3) annealing the catalyst layer at atmosphere; (4) positioning the substrate with the catalyst layer into a furnace; (5) heating the furnace up to a predetermined temperature; and (6) supplying a reaction gas into the furnace, thereby growing a number of carbon nanotubes (22) on the substrate, via the catalyst layer, such that the carbon nanotube array is formed on the substrate.
Owner:BEIJING FUNATE INNOVATION TECH +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com