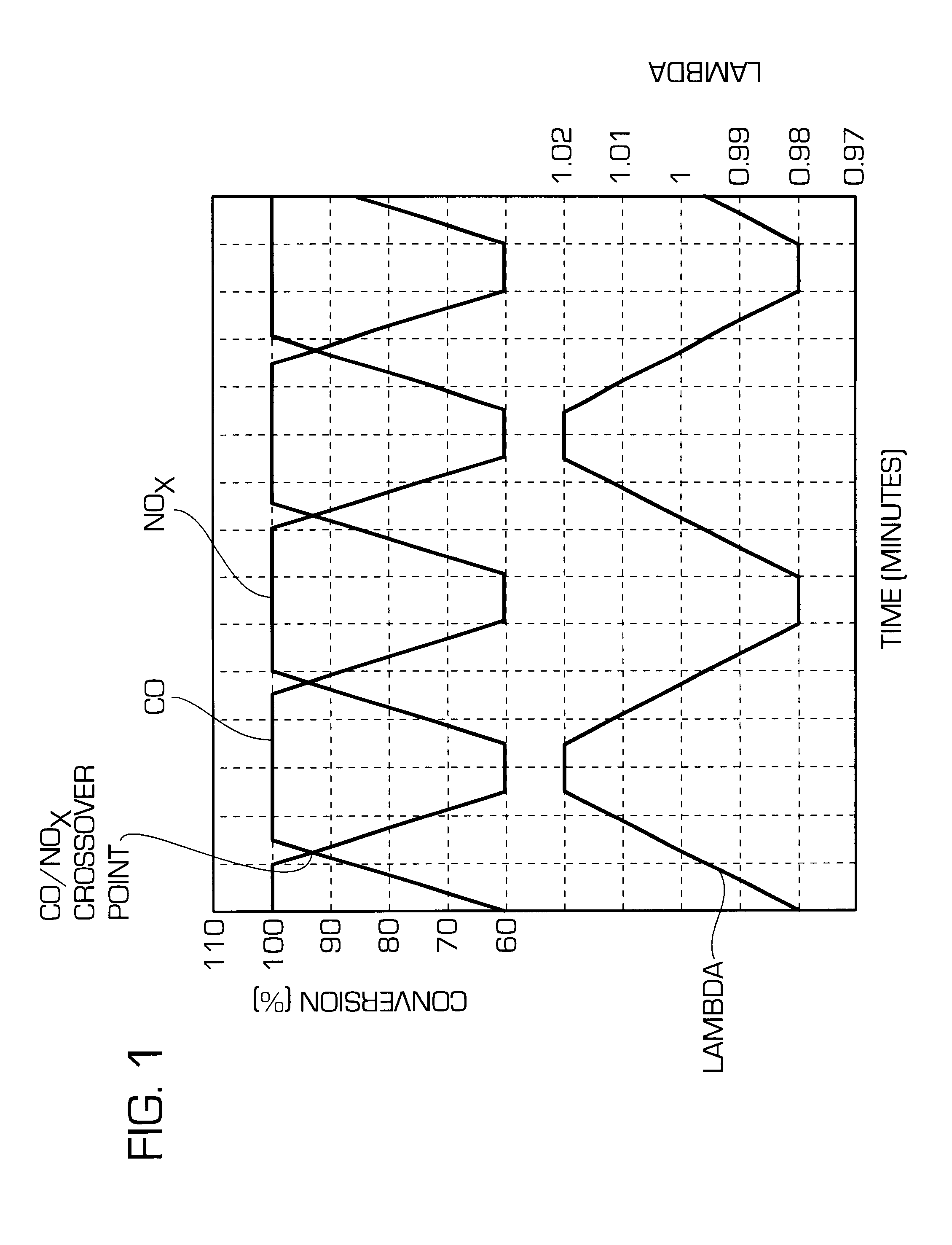
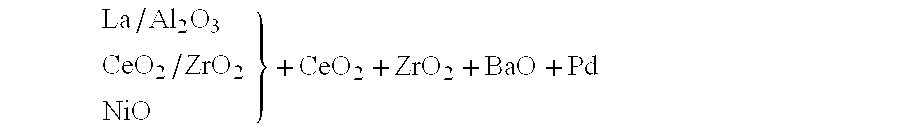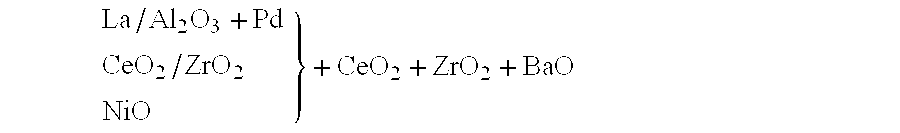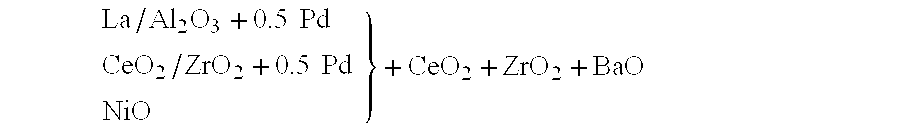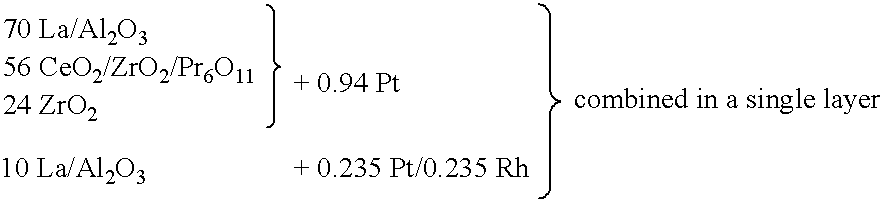Patents
Literature
1012 results about "Mixed oxide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In chemistry, a mixed oxide is a somewhat informal name for an oxide that contains cations of more than one chemical element or cations of a single element in several states of oxidation. The term is usually applied to solid ionic compounds that contain the oxide anion O²⁻ and two or more element cations. Typical examples are ilmenite (FeTiO₃), a mixed oxide of iron (Fe²⁺) and titanium (Ti⁴⁺) cations, the mineral perovskite and oxides sharing the perovskite structure and garnet. The cations may be the same element in different ionization states: a notable example is magnetite Fe₃O₄, which contains the cations Fe²⁺ ("ferrous" iron) and Fe³⁺ ("ferric" iron) in 1:2 ratio. Other notable examples include the ferrites, strontium titanate SrTiO₃ (which, despite its name, contains Ti⁴⁺ cations and not the TiO₃²⁻ anion), yttrium aluminum garnet Y₃Al₅O₁₂, and many more. Sometimes the term is applied loosely to solid solutions of metal oxides rather than chemical compounds...
Application of supported non-metallocene catalyst in ethene polymerization process by slurry method
The invention discloses an application of load non- metallocene catalyst in the slurry process for vinyl polymerying, the load non- metallocene catalyst and catalyst promoter forming the catalytic system, the alkene polymerization comprising: vinyl homopolymerization, combined polymerization of vinyl with propylene, butylenes, hexane, octane or norbornene; the catalyst carrier being chosen from: inorganic oxide of metallic oxide from IIA, IIIA, IVA, and IVB groups, or oxided mixture and mixing oxide; the catalyst promoter being chosen from: methylaluoxane, ethylaluoxane, isobutylaluoxane, trimethylaluminum,triethylaluminum,triisobutylaluminum,methylaluoxane-trimethylaluminum or methylaluoxane-triethylaluminum; the mole proportion between the catalyst promoter and catalyst being Al / Ti= 1:1-500. The inventioin is characterized by the less methylaluoxane consumption, stable reaction, easy-to-control polymerization temperature and non still-sticking phenomenon. The produced polyolefine possesses perfect granual shape, and the maximum polymer clamp density can reach 0.385 g / ml.
Owner:SINOPEC YANGZI PETROCHEM
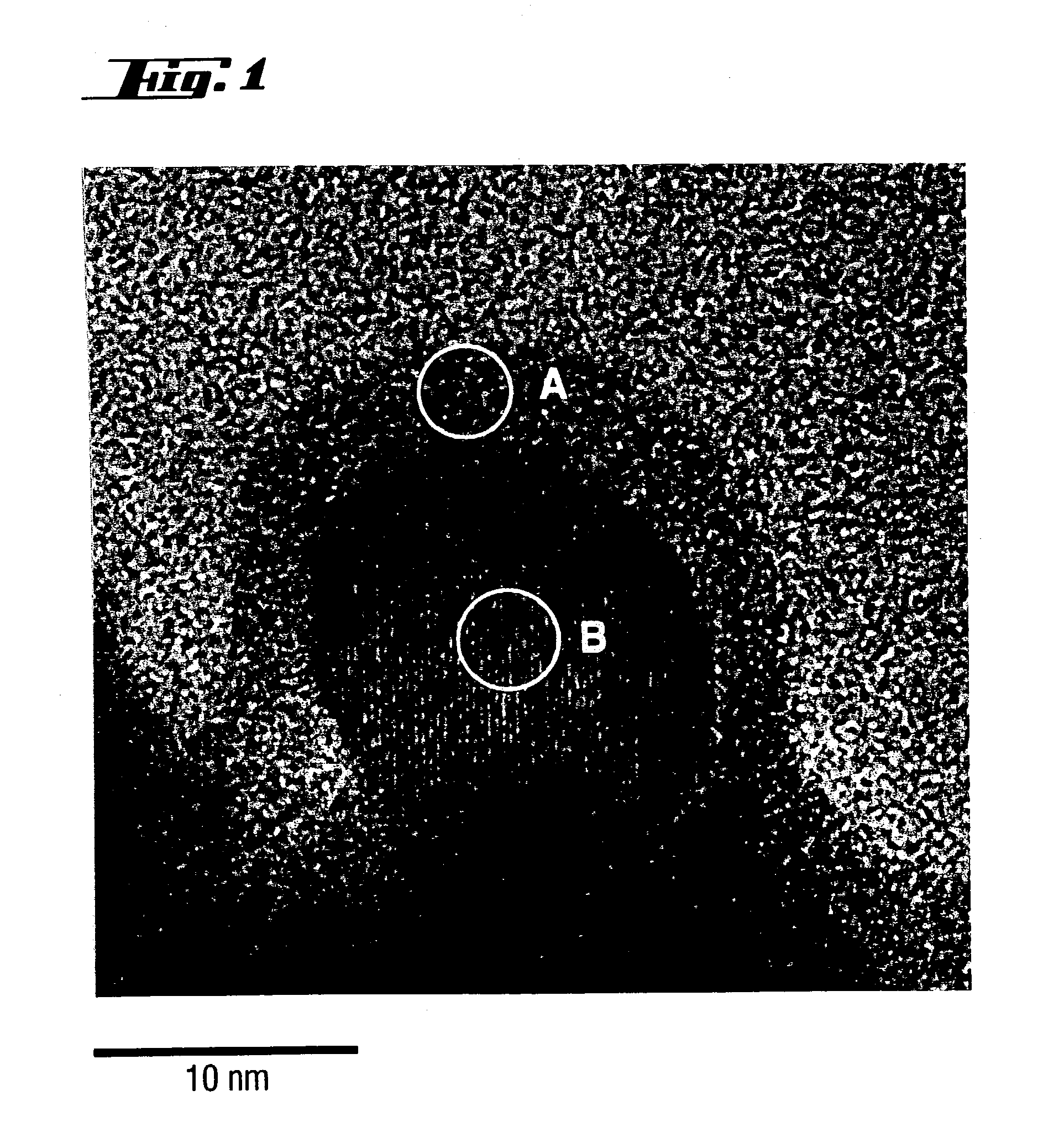
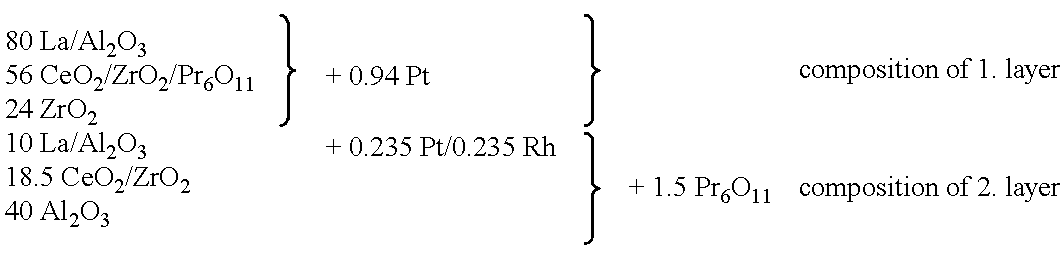
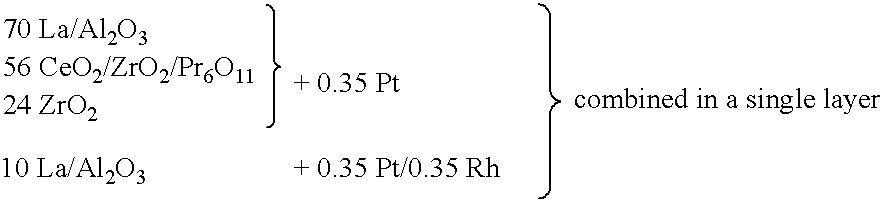
Layered noble metal-containing exhaust gas catalyst and its preparation
InactiveUS6294140B1Shorten recovery timeImprove conversion efficiencyOrganic chemistryNitrogen compoundsCerium(IV) oxideEngineering
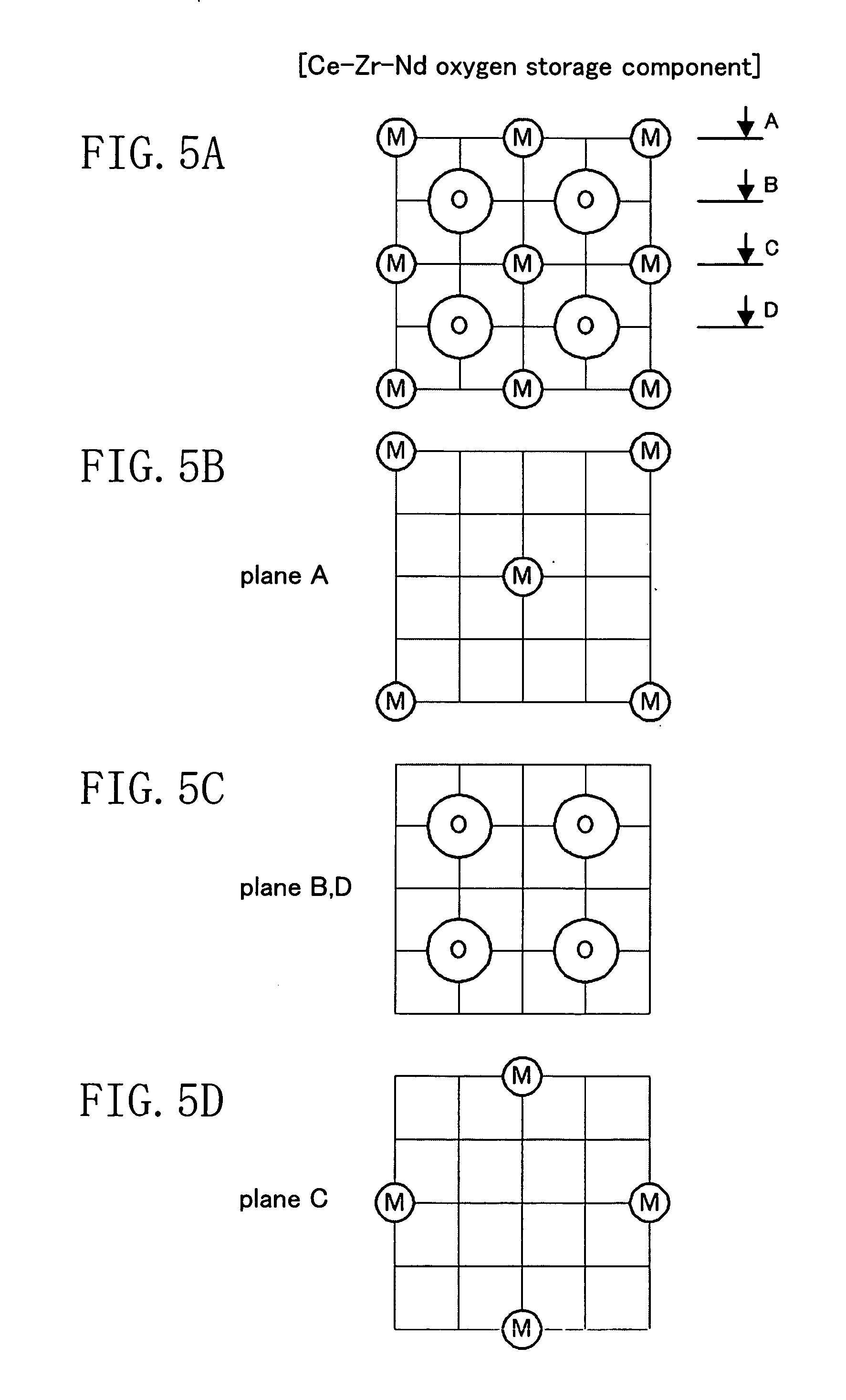
A catalyst for treating exhaust gas from an internal combustion engine includes a carrier body coated with an inner layer and an outer layer. The inner layer includes platinum deposited on a first support material and on a first oxygen storage component, and the outer layer includes platinum and rhodium deposited on a second support material and on a second oxygen storage component. The first and second support materials may be the same or different, and may be selected from the group of: silica, alumina, titania, zirconia, mixed oxides or mixtures thereof, and zirconia-rich zirconia / ceria mixed oxide. The first and second oxygen storage components may include ceria-rich ceria / zirconia mixed oxide compounds, optionally including praseodymia, yttria, neodymia, lanthana or mixtures thereof.
Owner:DMC2 DEGUSSA METALS +1
Exhaust gas treatment catalyst for internal combustion engines with two catalytically active layers on a carrier structure
InactiveUS6348430B1Improve heat resistanceHigh activityInorganic chemistryInternal combustion piston enginesParticulatesPartial oxidation
A catalyst for treating the exhaust gas from internal combustion engines is provided, wherein the catalyst contains two catalytically active layers supported on a support. The first catalytically active layer contains a platinum group metal in close contact with all of the constituents of the first catalytically active layer, wherein the constituents of the first catalytically active layer include particulate aluminum oxide; particulate oxygen storage material, such as cerium oxide, cerium / zirconium and zirconium / cerium mixed oxides, and alkaline earth metal oxides. The second catalytically active layer, which is in direct contact with the exhaust gas, contains particulate aluminum oxide and at least one particulate oxygen storage material, such as cerium oxide, cerium / zirconium and zirconium / cerium mixed oxides. Rhodium is supported on part of the aluminum oxides in the second catalytically active layer or on the particulate oxygen storage material in the second catalytically active layer. By providing the platinum group metal in close contact with all of the constituents of the first catalytically active layer, improved conversion efficiency of the impurities in the exhaust gas can be achieved.
Owner:UMICORE AG & CO KG +1
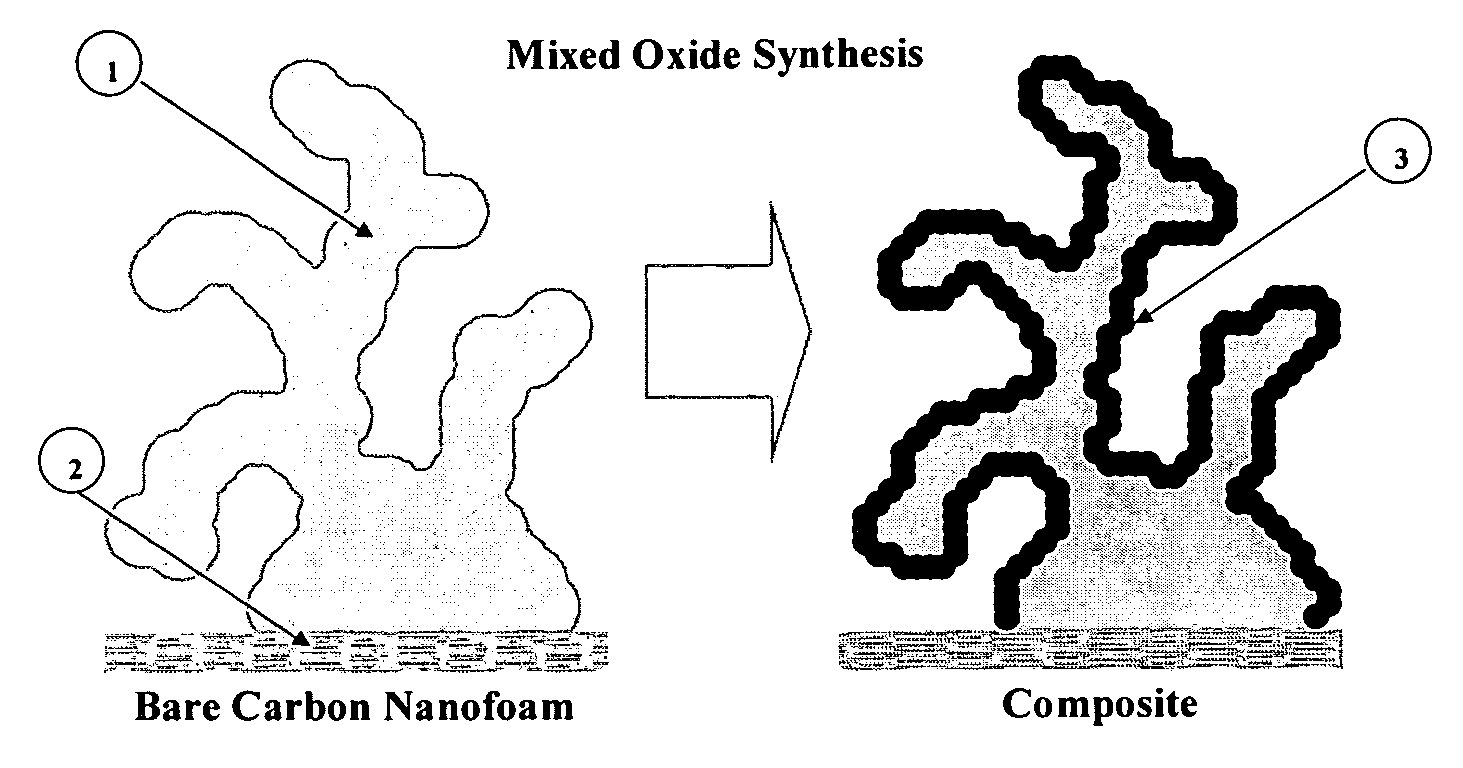
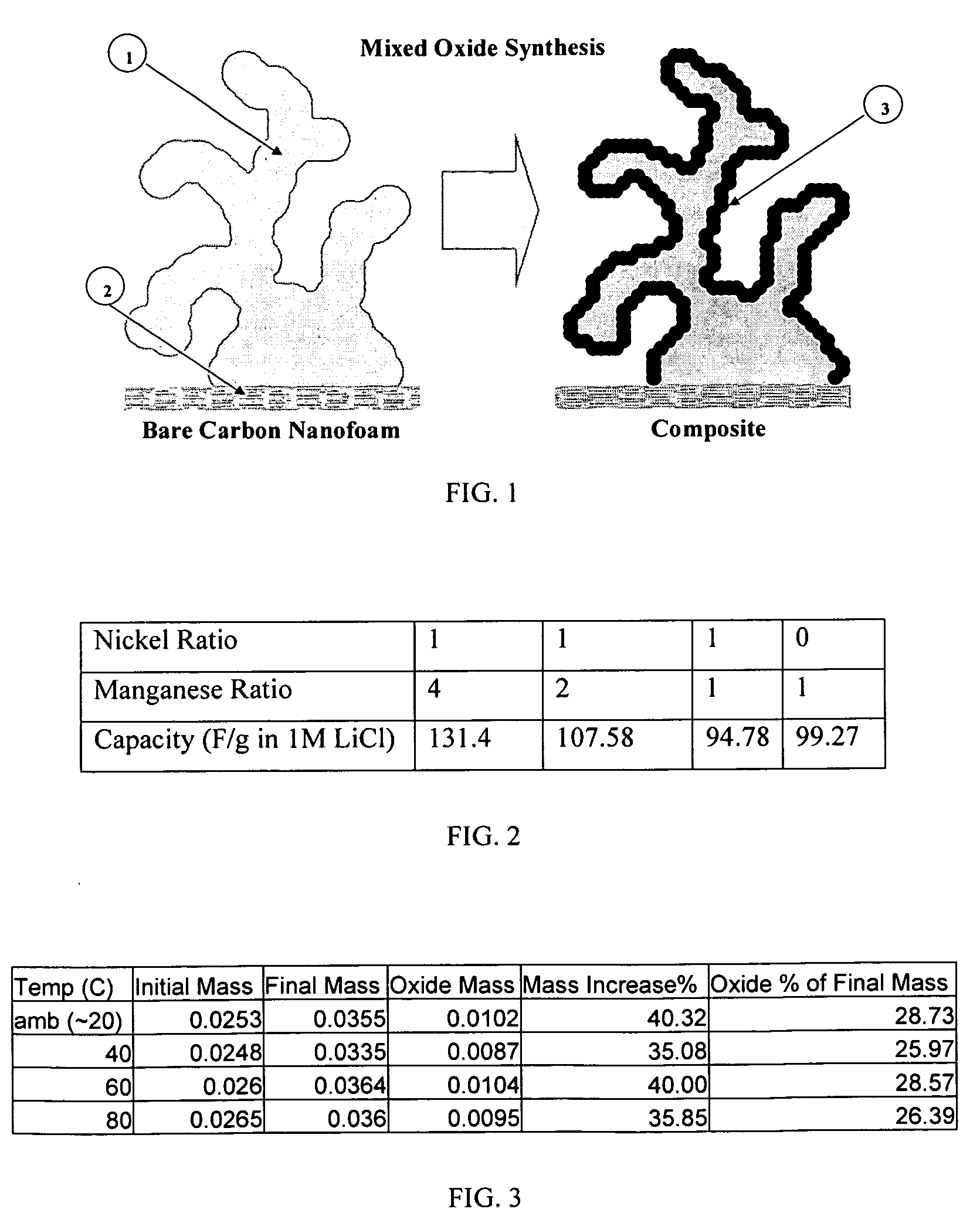
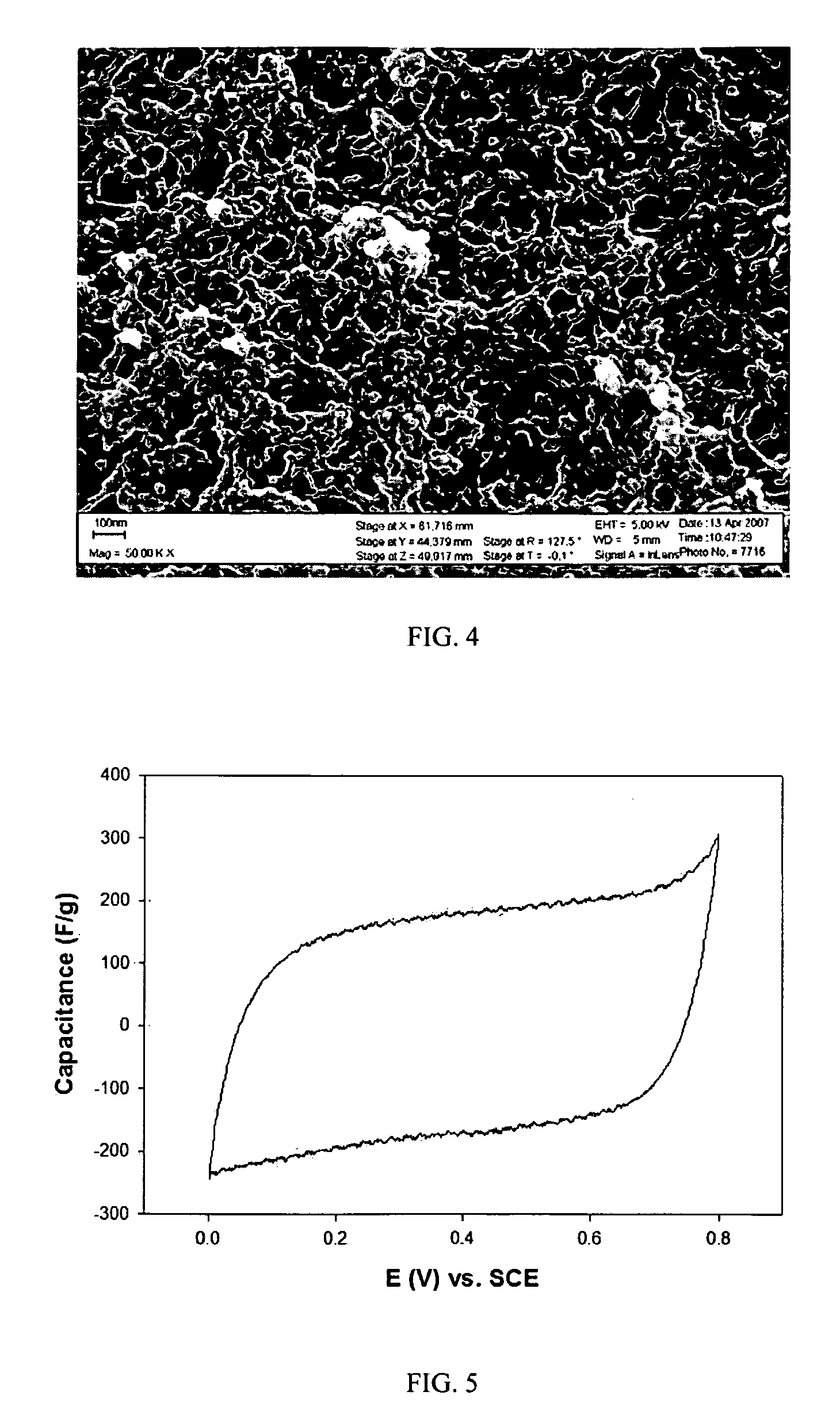
Composite electrode comprising a carbon structure coated with a thin film of mixed metal oxides for electrochemical energy storage
InactiveUS20090185327A1Increase capacityProlong lifeLiquid electrolytic capacitorsFinal product manufactureComposite electrodeMixed oxide
A composite electrode is created by forming a thin conformal coating of mixed metal oxides on a highly porous carbon structure. The highly porous carbon structure performs a role in the synthesis of the mixed oxide coating and in providing a three-dimensional, electronically conductive substrate supporting the thin coating of mixed metal oxides. The metal oxide mixture shall include two or more metal oxides. The composite electrode, a process for producing said composite electrode, an electrochemical capacitor and an electrochemical secondary (rechargeable) battery using said composite electrode are disclosed.
Owner:SEYMOUR FRASER WADE
Monolithic honeycomb structure made of porous ceramic and use as a particle filter
InactiveUS6582796B1Prevent the evaporation of the waterEasy curingInternal combustion piston enginesSilencing apparatusSodium BentoniteOxygen
A monolithic honeycomb-type structure useful in particular as a particle filter for exhaust gases from diesel engines has a number of passages that empty into the end faces of said monolith, but are alternately open and sealed. The monolith consists of a porous refractory material that comprises: 70 to 97% by mass of alpha and / or beta crystallographic-type silicon carbide that has at least one particle size and preferably at least two particle sizes, and 3 to 30% by mass of at least one bonding ceramic phase in the form of a micronic powder or particles that are obtained by atomization, comprising at least one simple oxide, for example, B2O3, Al2O3, SiO2, MgO, K2O, Li2O, Na2O, CaO, BaO, TiO, ZrO2 and Fe2O3 and / or at least one mixed oxide, for example, the alkaline aluminosilicates (of Li, Na, or K) or alkaline-earth aluminosilicates (of Mg, Ca, Sr or Ba), clays, bentonite, feldspars or other natural silico-aluminous materials. The production of the monolith comprises a calcination stage under an oxygen-containing atmosphere at a temperature up to 1650° C., but less than 1550° C.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
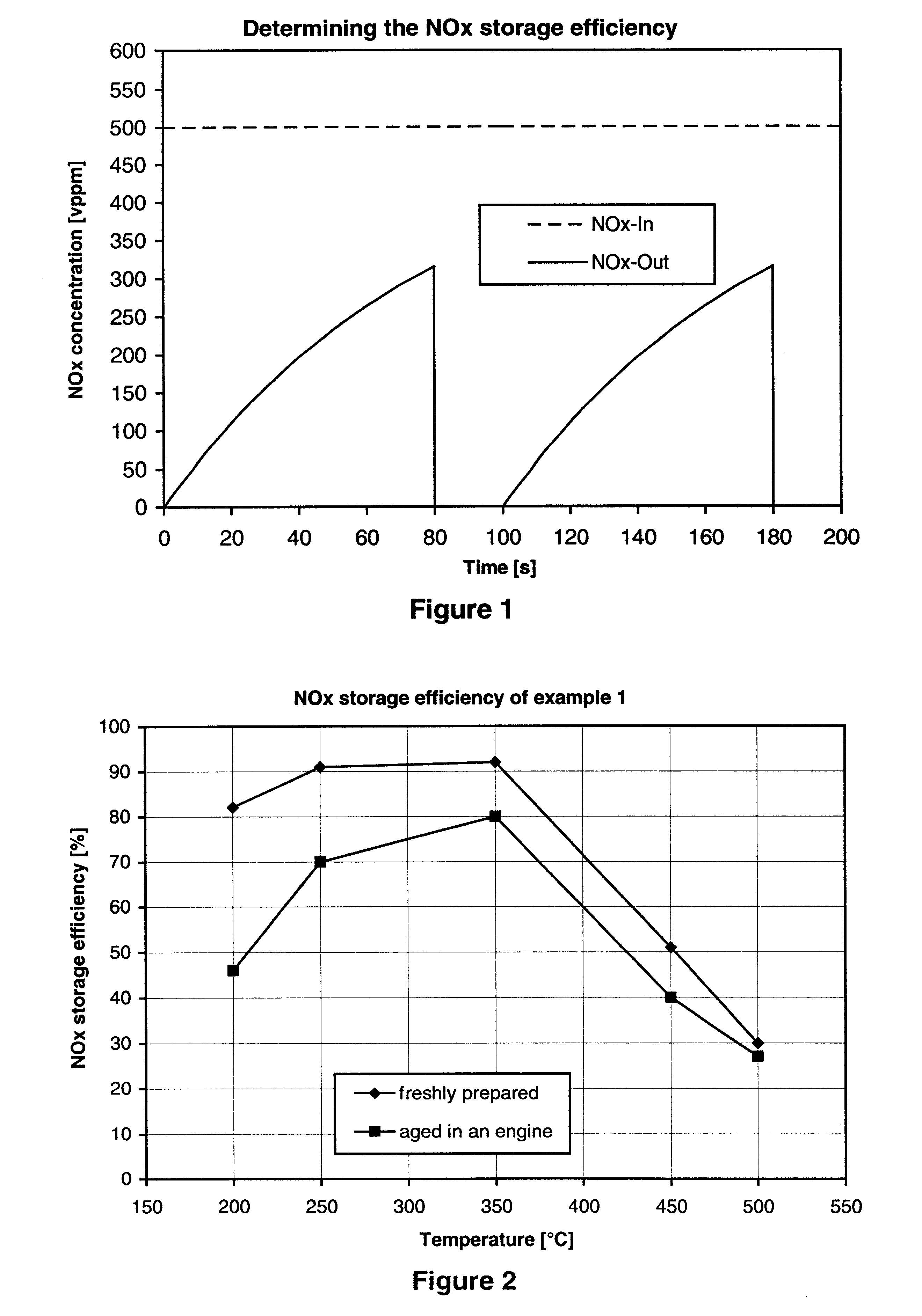
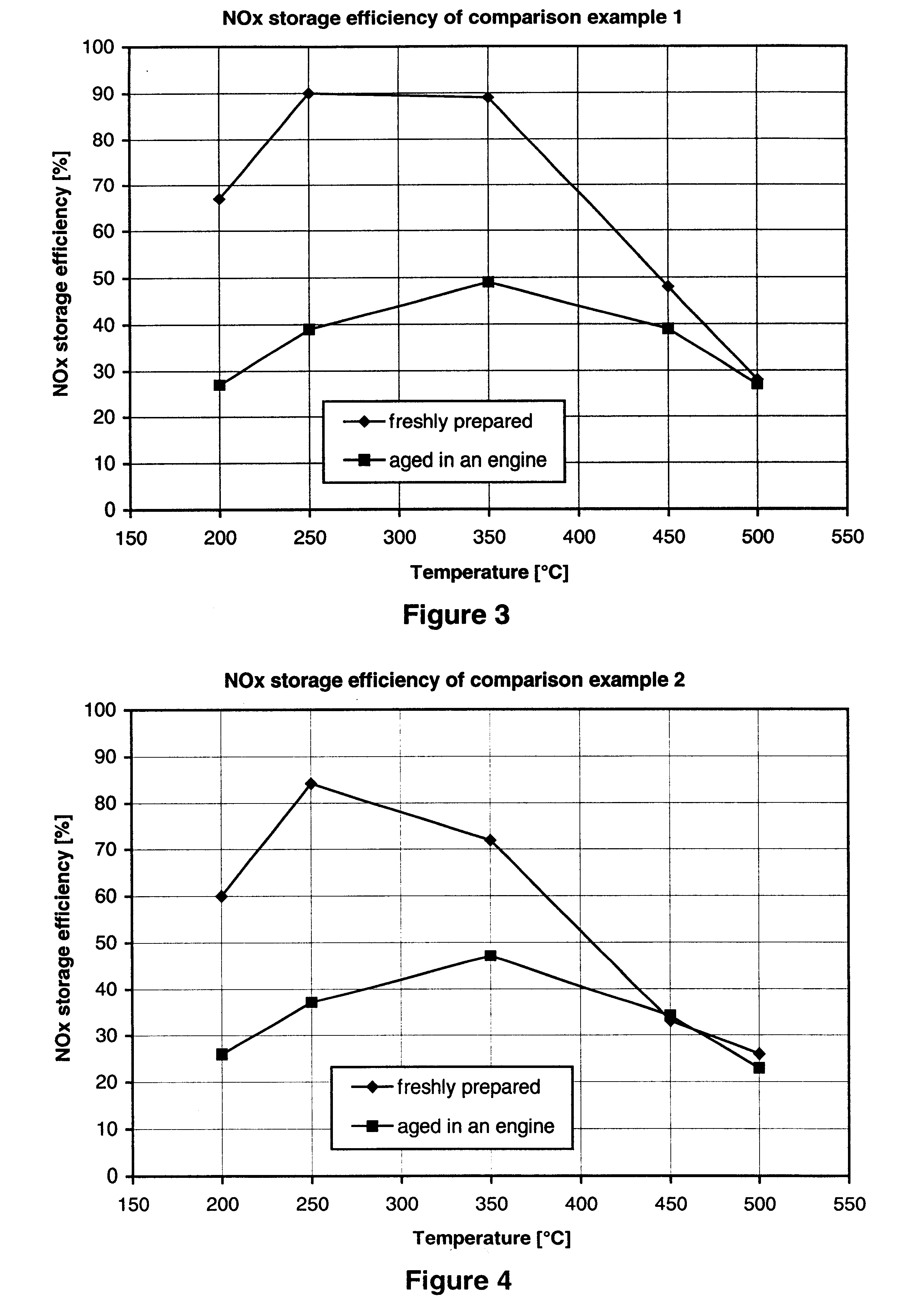
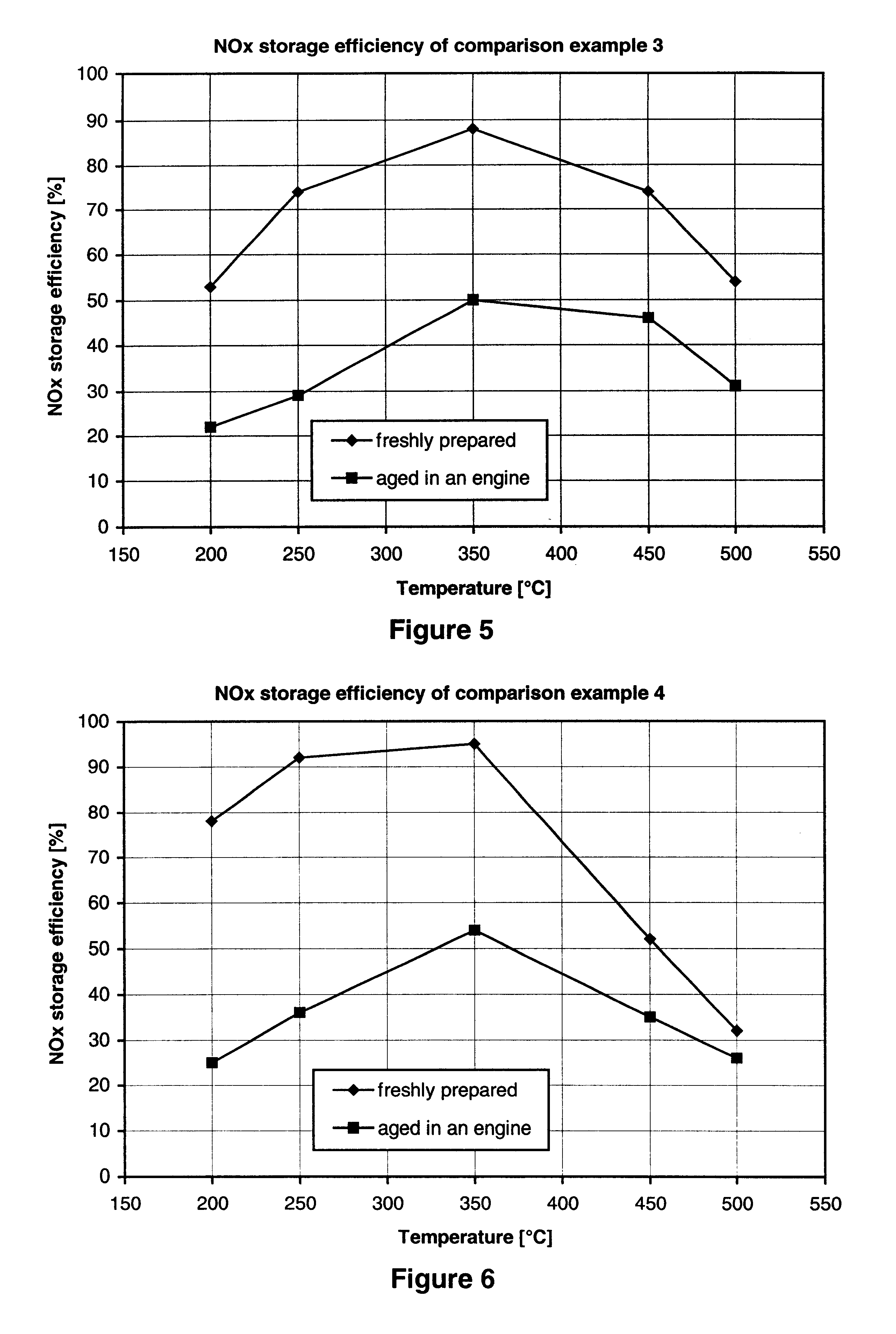
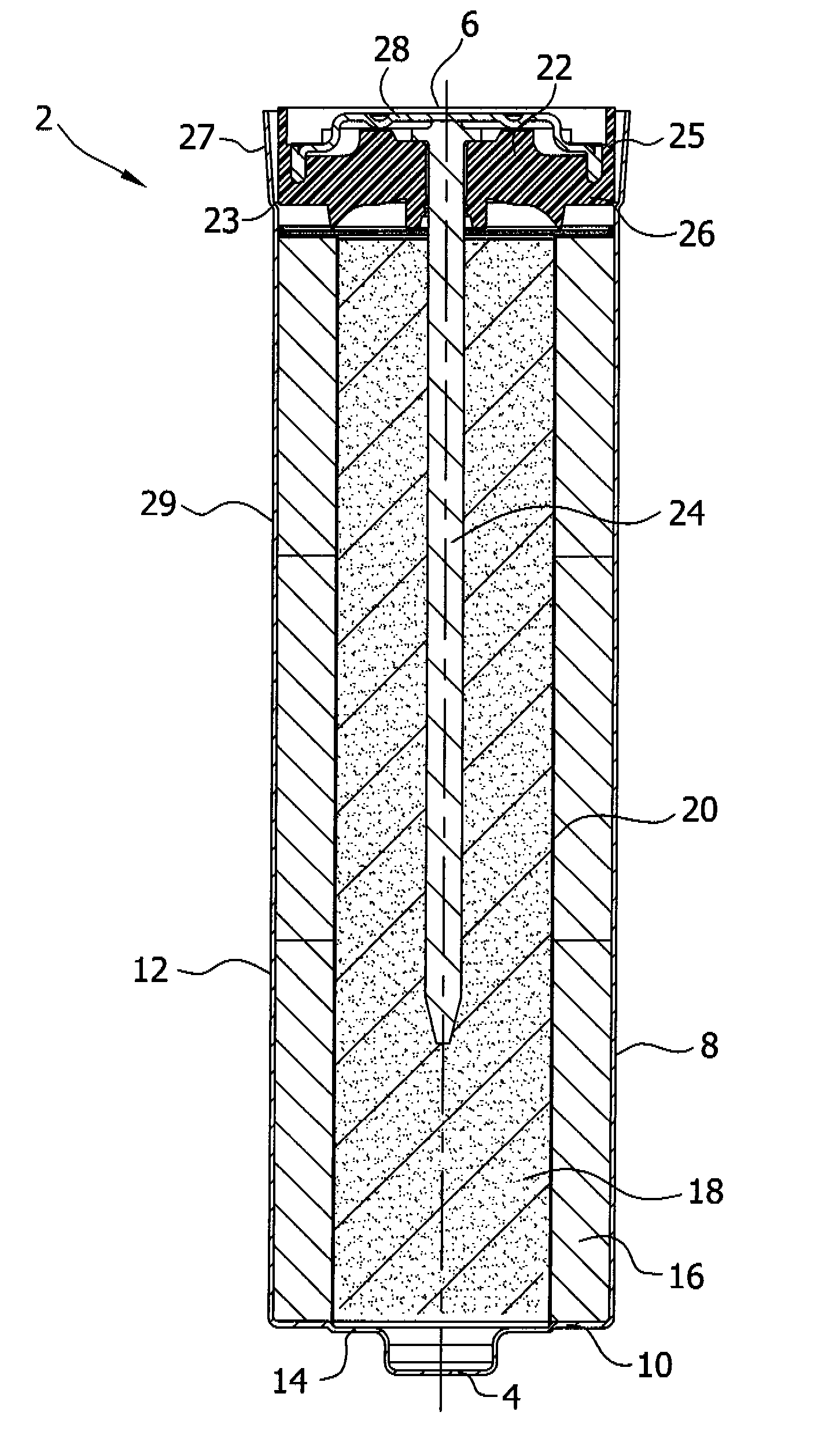
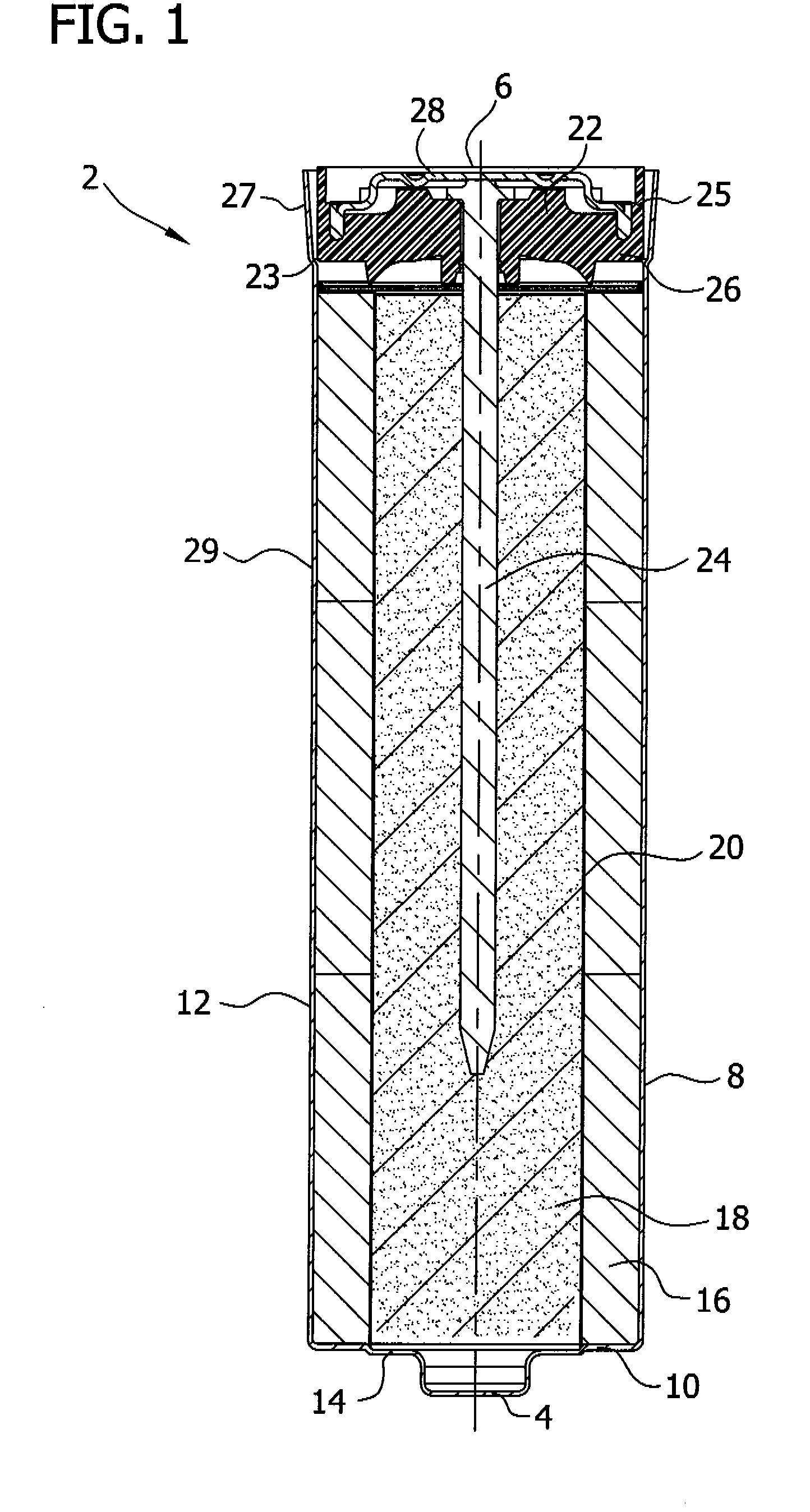
Nitrogen oxide storage material and nitrogen oxide storing catalyst prepared therefrom
InactiveUS6350421B1Determine efficiencyNitrogen compoundsExhaust apparatusAlkaline earth metalCuprate
A nitrogen oxide storage material is disclosed which contains at least one storage component for nitrogen oxides in the form of an oxide, mixed oxide, carbonate or hydroxide of the alkaline earth metals magnesium, calcium, strontium and barium and the alkali metals potassium and caesium on a high surface area support material. The support material can be doped cerium oxide, cerium / zirconium mixed oxide, calcium titanate, strontium titanate, barium titanate, barium stannate, barium zirconate, magnesium oxide, lanthanum oxide, praseodymium oxide, samarium oxide, neodymium oxide, yttrium oxide, zirconium silicate, yttrium barium cuprate, lead titanate, tin titanate, bismuth titanate, lanthanum cobaltate, lanthanum manganate and barium cuprate or mixtures thereof.
Owner:DMC2 DEGUSSA METALS +1
Copper-manganese mixed oxide cathode material for use in alkaline cells having high capacity
ActiveUS20080090138A1Cell seperators/membranes/diaphragms/spacersNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulator electrodesStructural waterMixed oxide
The present invention relates to a copper-manganese mixed oxide cathode material, which is suitable for use in a cathode of an electrochemical cell, and which has the formula MnxCuyOz,.nH2O, wherein the oxidation state of Cu is between about +1 and about +3, the oxidation state of Mn is between about +2 and about +7, x is equal to about 3−y, y is less than about 3, z is calculated or experimentally determined, using means known in the art, based on the values of x and y, as well as the oxidation states of Mn and Cu, and nH2O represents the surface and structural water present in the mixed oxide material. The present invention further relates to an electrochemical cell comprising an anode, a cathode, and a separator disposed between the anode and cathode, and an electrolyte in fluid communication with the anode, the cathode and the separator, wherein the cathode comprises the noted cathode material. The present invention still further relates to such an active cathode material, or an alternative cathode material, wherein the copper-manganese mixed oxide comprises a defect spinel-type structure, which is also suitable for use as a cathode component of an alkaline electrochemical cell.
Owner:ENERGIZER BRANDS
Cationic mixed-oxide dispersion, coating pigment and ink-absorbing medium
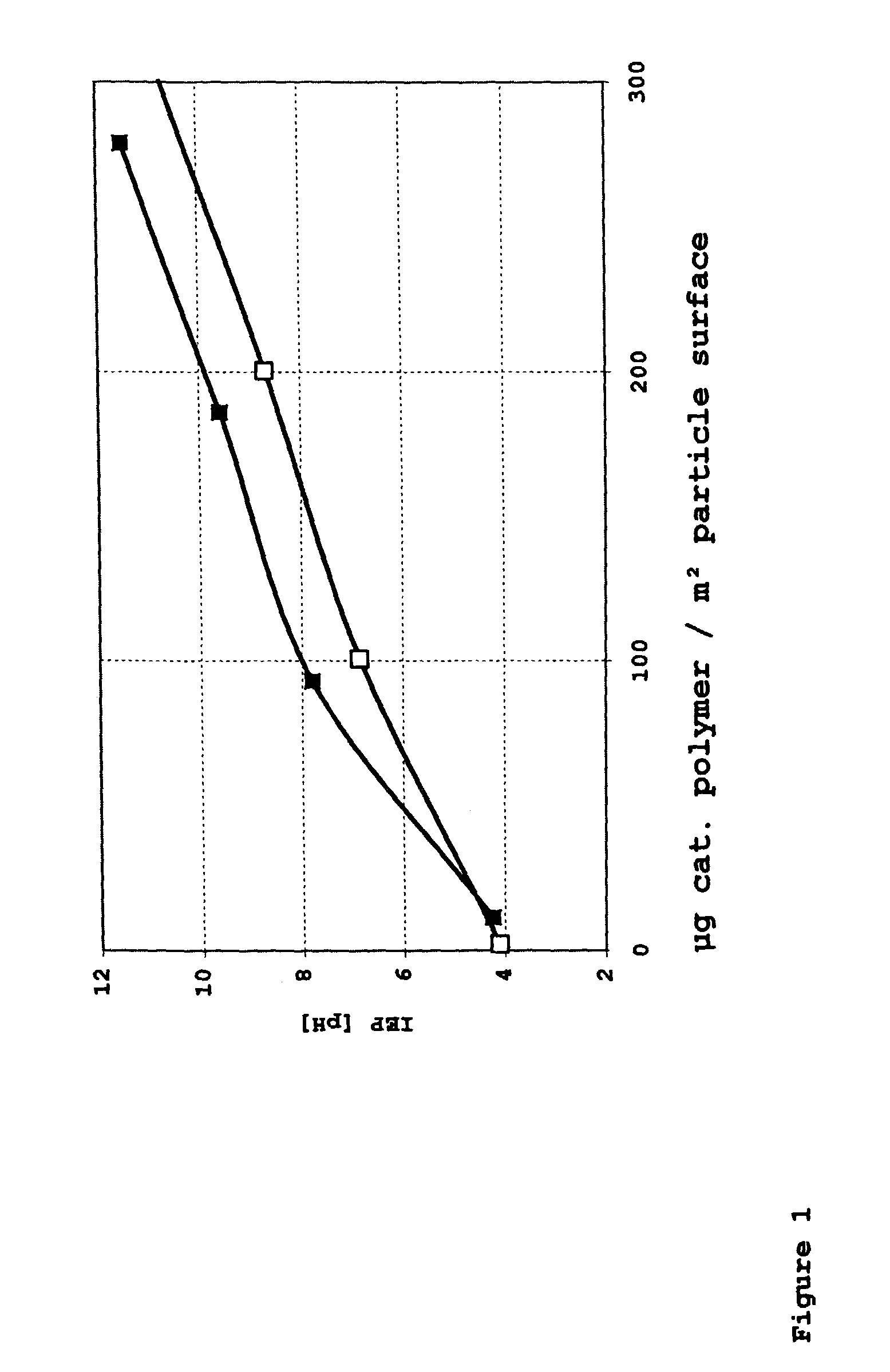
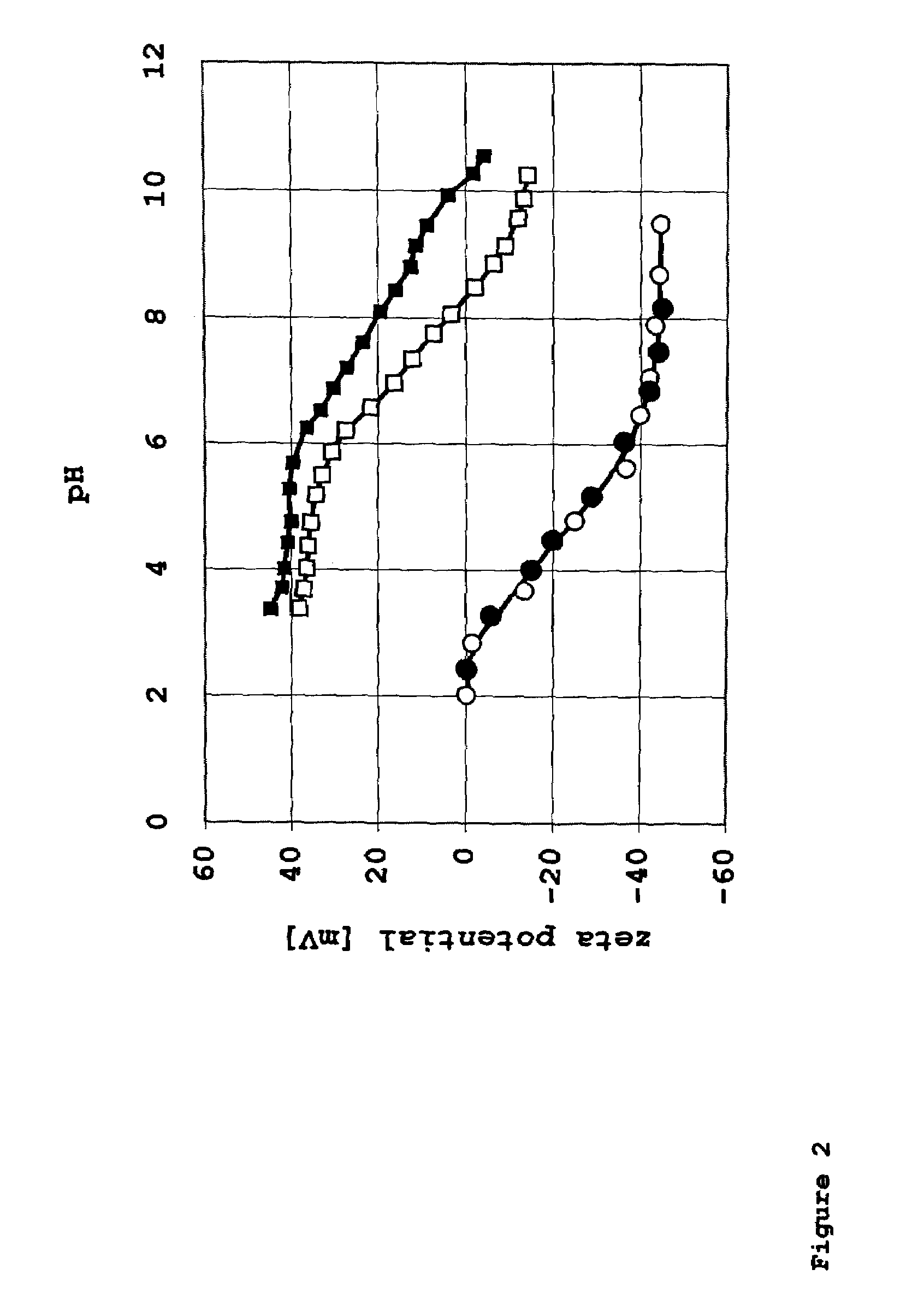
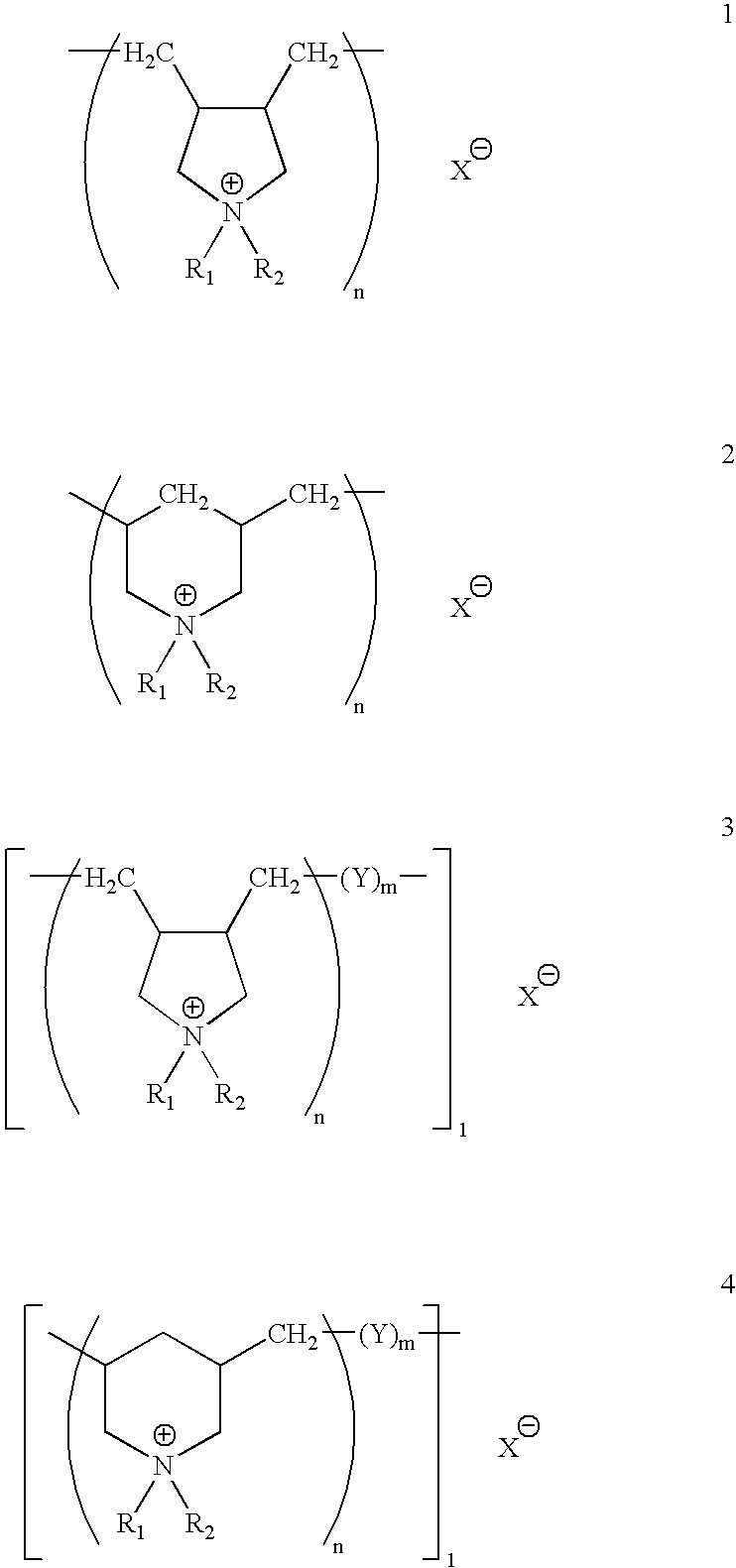
InactiveUS7015270B2Avoid large quantitiesHigh glossCoatings with pigmentsInorganic pigment treatmentZeta potentialMixed oxide
A stable, aqueous dispersion, which includes:silicon dioxide mixed-oxide particles dispersed in at least one water-soluble cationic polymer having a mass average molar mass of less than 100,000 g / mol, said mixed-oxide including aluminum oxide or titanium dioxide,wherein said particles are produced by flame hydrolysis,wherein said particles have a BET specific surface area of 5 to 600 m2 / g and a negative zeta potential,and wherein the dispersion has a positive zeta potential.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Exhaust gas purification catalyst
InactiveUS20060217263A1Improve catalytic conversion effectImprove heat resistanceInternal combustion piston enginesDispersed particle separationHoneycomb likePt element
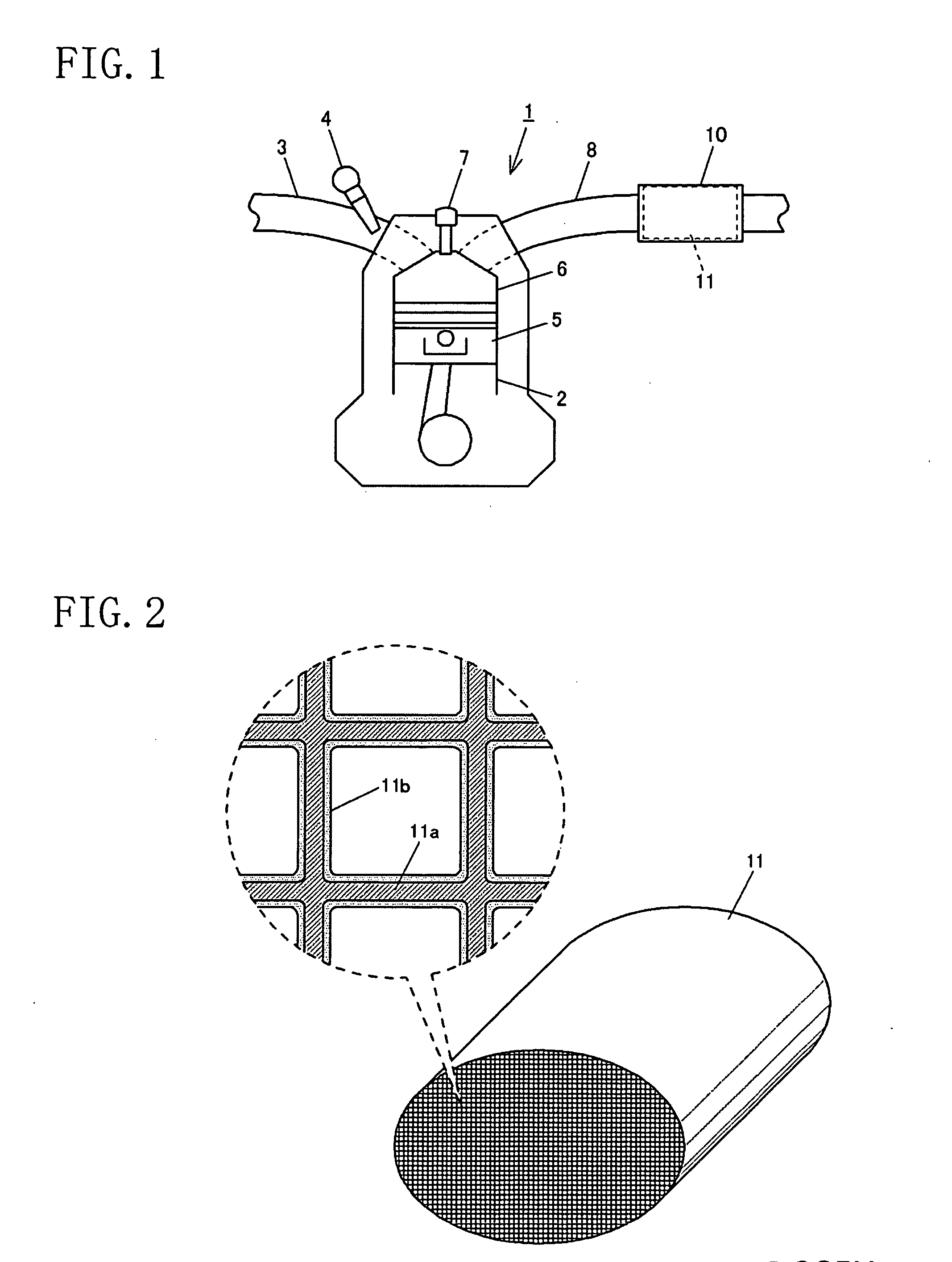
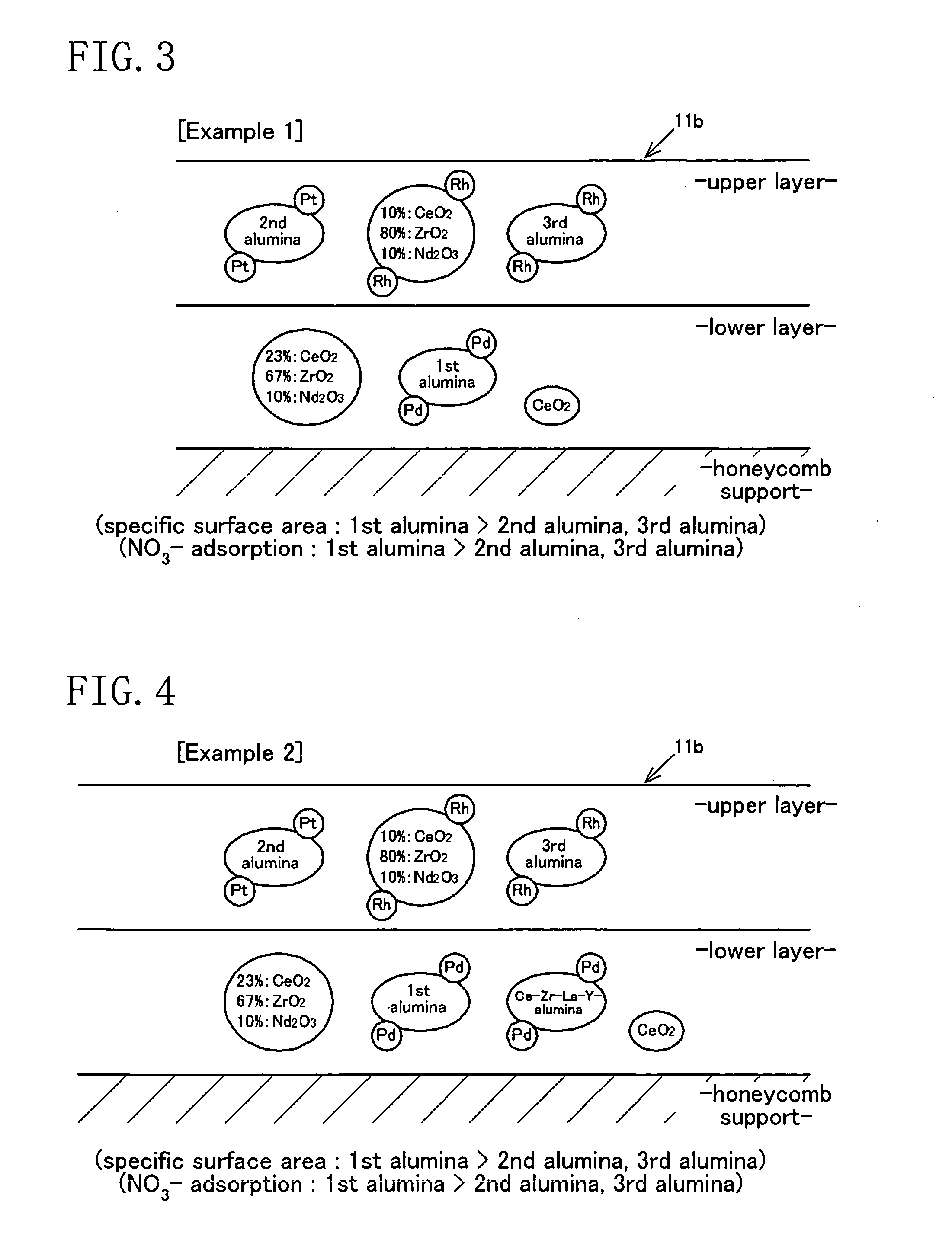
In an exhaust gas purification catalyst in which a catalytic coating containing plural kinds of aluminas and plural kinds of oxygen storage components each carrying a catalytic precious metal is coated on a honeycomb support, the catalytic coating is formed of an upper layer and a lower layer, palladium is carried on a first alumina and a Ce—Zr—La—Y-alumina compound having oxygen storage capacity in the lower layer, platinum is carried on a second alumina in the upper layer, and rhodium is carried on a third alumina and a Ce—Zr—Nd mixed oxide having oxygen storage capacity in the upper layer.
Owner:TOKYO ROKI +1
Silicon-titanium mixed oxide powder prepared by flame hydrolysis, which is surface-enriched with silicon dioxide, and the preparation and use thereof
Silicon-titanium mixed oxide powder prepared by flame hydrolysis, having a ratio by weight of silicon dioxide / titanium dioxide, which is greater on the surface of the primary particles than that within the total primary particle. It is prepared by a flame hydrolysis process, in that a stream consisting of a vaporous titanium dioxide precursor and oxygen or an oxygen-containing gas and hydrogen, and a second stream consisting of a vaporous silicon dioxide precursor and a carrier gas consisting of oxygen, an oxygen-containing gas and / or an inert gas, are guided separately into the reaction chamber of a burner such as is known for the preparation of pyrogenic oxides, and are burnt here, the solid mixed oxide powder and hot gases are subsequently cooled, and the gases are separated from the solid. The powder may be used, for example, for the preparation of sunscreen preparations.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Preparation of iron-managanese compounded oxide/diatomite adsorbant, its using and regenerating method
ActiveCN101024160AImprove adsorption capacityGood arsenic removal effectOther chemical processesWater/sewage treatment by sorptionSorbentManganese oxide
The invention supplies a new type adsorbent--mixed oxide of iron and manganese / diatomite preparation, use and regeneration method, belongs to the treatment of technology. The method used the soluble ferrous permanganate and salt as raw materials, respectively prepared the solutions, after adequate lye into permanganate solution, mixed two salt solutions, by adding diatomite particles, full oscillation, standing aging, neutralize, washing and drying to get the manganese oxide / silicon algae absorbent. The adsorbent is larger than the surface area and good adsorption properties can be used to remove arsenic in water pollutants (especially tervalence arsenic), and the adsorption surface activity of the saturated absorption of pollutants can be directly passed to load manganese oxide compound to regeneration.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Exhaust gas catalyst
InactiveUS6180075B1Favorable degree of conversionExceptional heat and aging resistanceNitrogen compoundsInternal combustion piston enginesZirconium hydrideCerium(IV) oxide
A single-layered three-way catalytic converter containing palladium as the only catalytically active noble metal, with high activity and heat resistance. The catalyst contains, in addition to finely divided, stabilized aluminum oxide, at least one finely divided cerium / zirconium mixed oxide and optionally finely divided nickel oxide as well as highly dispersed amounts of cerium oxide, zirconium oxide and barium oxide. The palladium is distributed largely uniformly throughout the entire catalyst.
Owner:DMC2 DEGUSSA METALS +1
Hydrophilic coatings, methods for depositing hydrophilic coatings, and improved deposition technology for thin films
The invention provides certain embodiments that involve sputtering techniques for applying a mixed oxide film comprising silica and titania. In these embodiments, the techniques involve sputtering at least two targets in a common chamber (e.g., in a shared gaseous atmosphere). A first of these targets includes silicon, while a second of the targets includes titanium. Further, the invention provides embodiments involving a substrate bearing a hydrophilic coating, which can be deposited by sputtering or any other suitable thin film deposition technique. The invention also provides techniques and apparatuses useful for depositing a wide variety of coating types. For example, the invention provides thin film deposition technologies in which sputtering apparatuses or other thin film deposition apparatuses are employed.
Owner:CARDINAL CG
Low visibility laser marking additive
InactiveUS7187396B2Retains laser markabilityReduce total powerRecording apparatusNanotechVisibilityParticulates
Owner:ENGELHARD CORP
Silicon-titanium mixed oxide powder prepared by flame hydrolysis, which is surface-enriched with silicon dioxide, and the preparation and the use thereof
InactiveUS7083769B2Reduce photocatalytic activitySimple preparation processPowder deliveryCosmetic preparationsHydrolysisSilicon dioxide
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Single layer high performance catalyst
InactiveUS6524992B2Improve catalytic performanceLow production costInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusPlatinumMixed oxide
A single layer high performance catalyst containing on an inert carrier body a catalytic coating comprising platinum, rhodium and various oxide materials. The catalyst contains a catalytic coating having at least one first support material selected from the group having a first active alumina, a ceria rich ceria / zirconia mixed oxide and a zirconia component, said at least one first support material being catalyzed with a first part of the total platinum amount of the catalyst, and a second support material catalyzed with the second part of the total platinum amount and with rhodium said second support material being a second active alumina.
Owner:UMICORE AG & CO KG +1
Method for producing a nitrogen oxide storage material and a storage material made with it
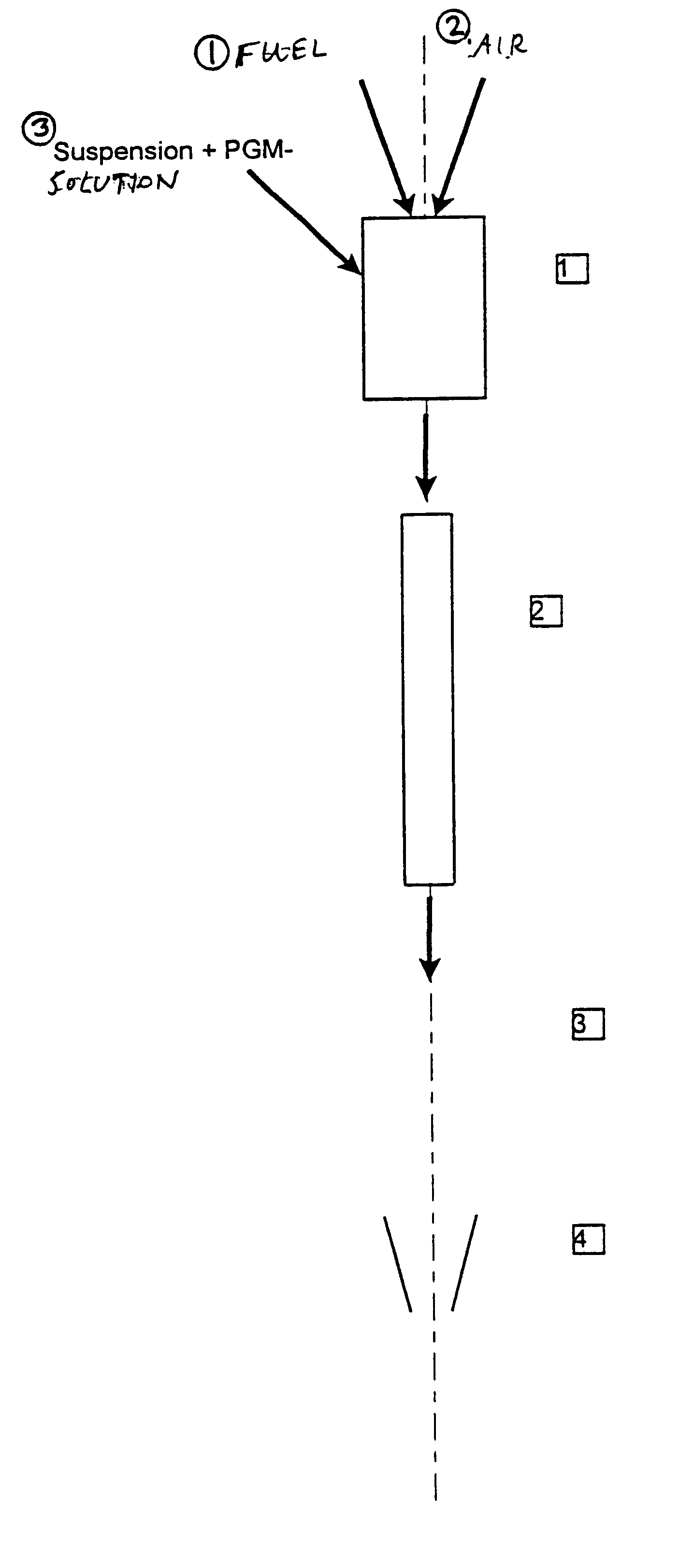
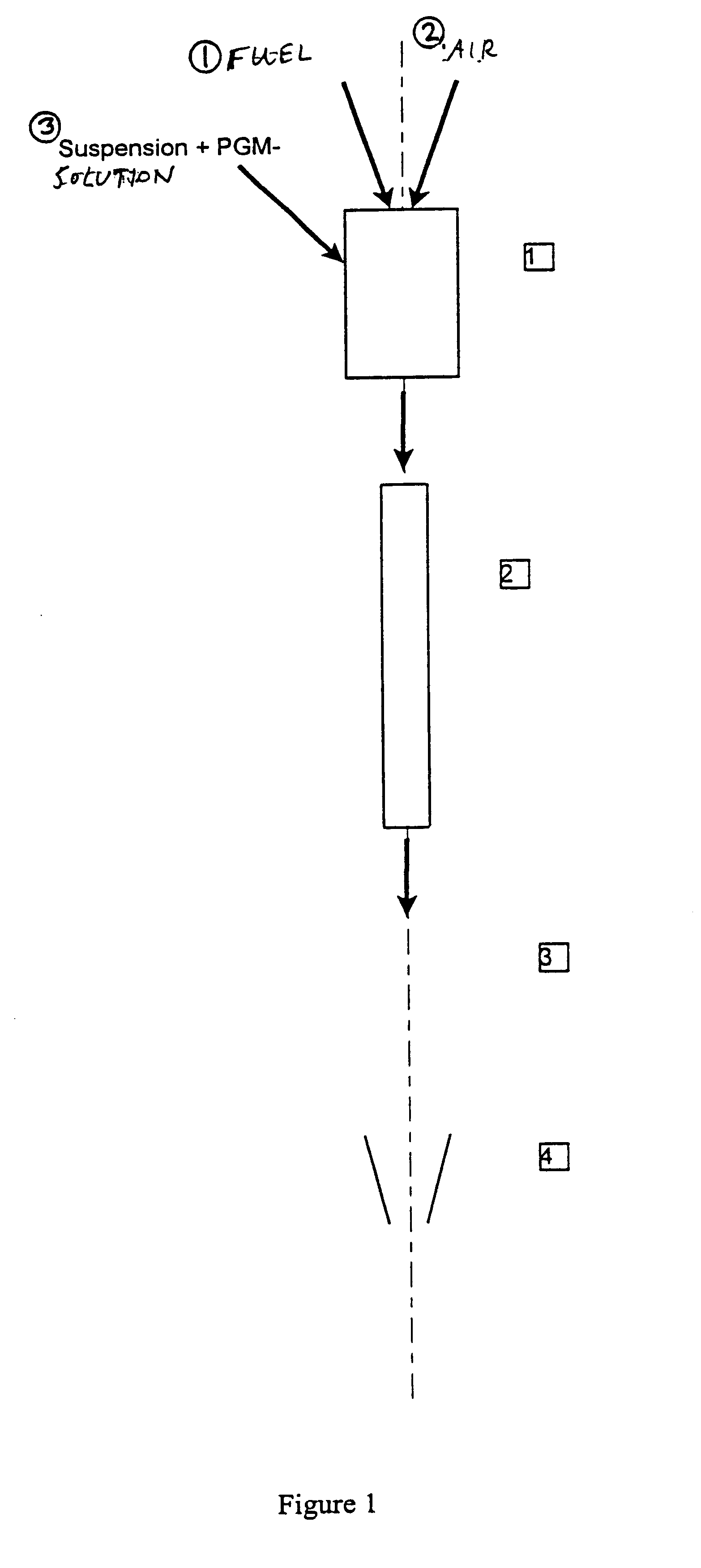
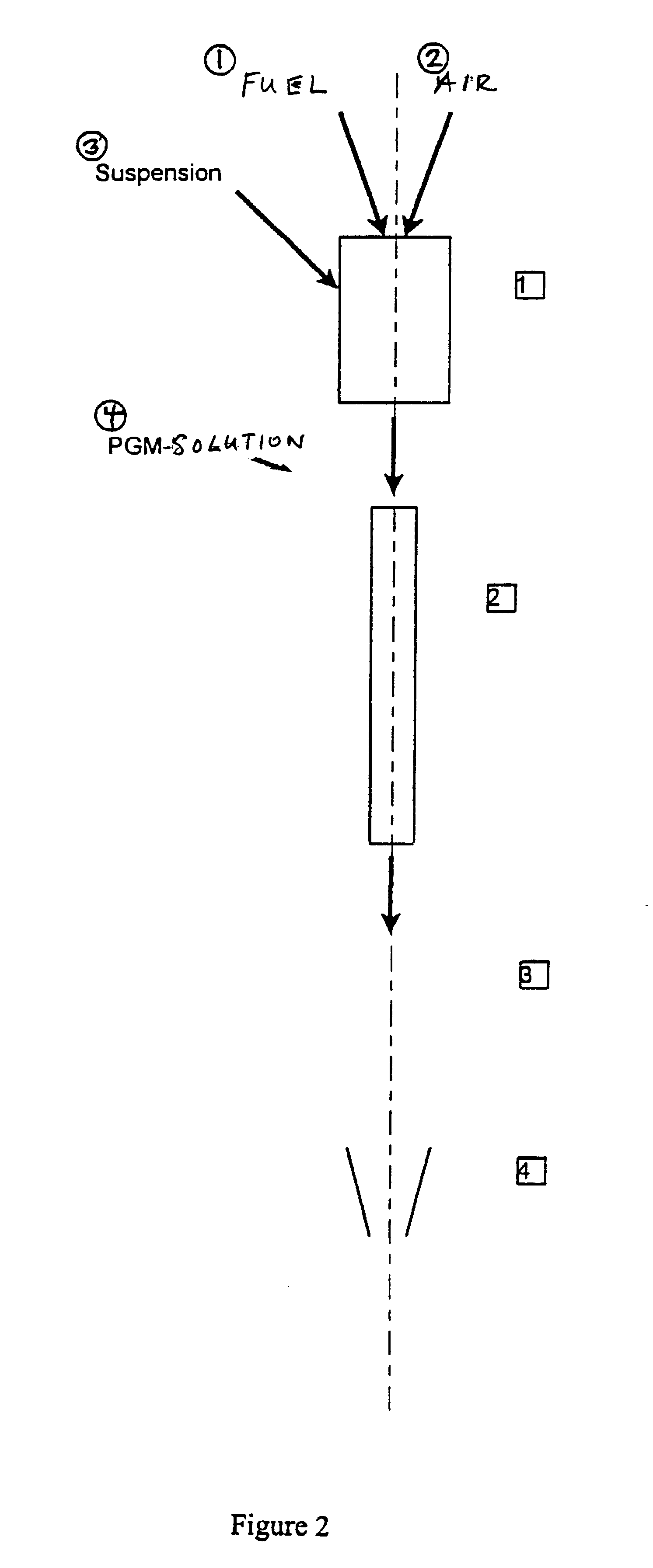
A method for producing a nitrogen oxide storage material that contains at least one storage component in the form of particles of an oxide, carbonate or hydroxide of the elements magnesium, strontium, barium, lanthanum and cerium on a carrier material from the group consisting of doped cerium oxide, cerium / zirconium mixed oxide and aluminum oxide or mixtures of these. The method is carried out by suspending the support material in an aqueous solution of precursors of the storage components, this suspension is then introduced into a hot gas stream, the temperature of which is calculated so that, during a residence time of the suspension in the hot gas stream of less than one minute, the solvent of the suspension is evaporated out and the precursors of the storage components are thermally broken down and converted to the storage components before the storage material that forms in this way is separated from the stream of hot gases.
Owner:UMICORE AG & CO KG +1
Methods and equipment for depositing hydrophilic coatings, and deposition technologies for thin films
The invention provides certain embodiments that involve sputtering techniques for applying a mixed oxide film comprising silica and titania. In these embodiments, the techniques involve sputtering at least two targets in a common chamber (e.g., in a shared gaseous atmosphere). A first of these targets includes silicon, while a second of the targets includes titanium. Further, the invention provides embodiments involving a substrate bearing a hydrophilic coating, which can be deposited by sputtering or any other suitable thin film deposition technique. The invention also provides techniques and apparatuses useful for depositing a wide variety of coating types. For example, the invention provides thin film deposition technologies in which sputtering apparatuses or other thin film deposition apparatuses are employed.
Owner:CARDINAL CG
Removal of particulates from the exhaust gas of internal combustion engines operated with a predominantly stoichiometric air/fuel mixture
ActiveUS8640440B2Sufficient thermal aging stabilityImproved thermal cycling stabilityCombination devicesOrganic chemistryParticulatesExternal combustion engine
Disclosed herein is a catalytically active particulate filter, an exhaust gas cleaning system and a process for cleaning the exhaust gases of predominantly stoichiometrically operated internal combustion engines, which are suitable, as well as the gaseous CO, HC and NOx pollutants, also for removing particulates from the exhaust gas. The particulate filter comprises a filter body and a catalytically active coating consisting of two layers. The first layer is in contact with the incoming exhaust gas, the second layer with the outgoing exhaust gas. Both layers contain alumina. The first layer contains palladium. The second layer contains, in addition to rhodium, an oxygen-storing cerium / zirconium mixed oxide.
Owner:UMICORE AG & CO KG
Supported oxidative dehydrogenation catalyst
The present invention provides a process for the manufacture of an efficient and robust catalyst for the oxidative dehydrogenation of paraffins to olefins, preferably lower C2-4 paraffins. The present invention provides a process for the preparation of an oxidative dehydrogenation catalyst of C2-4 paraffins to olefins comprising comminuting: from 10 to 99 weight % of a mixed oxide catalyst of the formula VxMoyNbzTemMenOp, wherein Me is a metal selected from the group consisting of Ta, Ti, W, Hf, Zr, Sb and mixtures thereof; with from 90 to 1 weight % of an inert matrix selected from oxides of titanium, zirconia, aluminum, magnesium, yttria, lantana, silica and their mixed compositions or a carbon matrix to produce particles having a size from 1 to 100 microns and forming the resulting particles into pellets having a size from 0.1 to 2 mm.
Owner:NOVA CHEM (INT) SA
THERMALLY STABLE DOPED AND UNDOPED POROUS ALUMINUM OXIDES AND NANOCOMPOSITE CeO2-ZrO2 AND Al2O3 CONTAINING MIXED OXIDES
InactiveUS20090023581A1Improve thermal stabilityImproved oxygen storageMaterial nanotechnologyBarium aluminatesDopantMixed oxide
The present invention relates to doped or undoped aluminas having after calcination at 1200° C. for 5-24 hours a pore volume ≧0.5 ml / g and a BET surface area greater then 35 m2 / g. The invention also relates to a method for preparing these aluminas comprising the steps of: a. preparing an aqueous solution of an aluminum salt with optional co-dopants, b. treating the aqueous solution with hydrogen peroxide, c. precipitating the alumina using a base, and d. filtering, drying and calcining the alumina.
Owner:MAGNESIUM ELETRON LTD
Positive Ignition Engine and Exhaust System Comprising Three-Way Catalysed Filter
InactiveUS20140234189A1Nitrogen compoundsInternal combustion piston enginesPorous substratePtru catalyst
A positive ignition engine is disclosed. The engine comprises an exhaust system comprising a filter for filtering particulate matter from the emitted exhaust gas. The filter comprises a porous substrate having inlet surfaces and outlet surfaces. The porous substrate is coated at least in part with a three-way catalyst washcoat comprising a platinum group metal and a plurality of solid particles. The plurality of solid particles comprises at least one base metal oxide and at least one oxygen storage component which is a mixed oxide or composite oxide comprising cerium. The mixed oxide or composite oxide comprising cerium and / or the at least one base metal oxide has a median particle size (D50) less than 1 μm. The platinum group metal platinum and rhodium; palladium and rhodium; platinum, palladium and rhodium; palladium only; or rhodium only. A process for treating exhaust gas using the filter is also disclosed.
Owner:JOHNSON MATTHEY PLC
Selective catalytic reduction of nitrogen oxides in the exhaust gas of diesel engines
InactiveUS20110142737A1High activityGood choiceNitrogen compoundsInternal combustion piston enginesCeriumDiesel engine
A catalyst and a process for selective catalytic reduction of nitrogen oxides in diesel engine exhaust gases with ammonia or a compound decomposable to ammonia are described. The exhaust gas to be cleaned is passed together with ammonia or a compound decomposable to ammonia over a catalyst which comprises a zeolite or a zeolite-like compound containing 1-10% by weight of copper, based on the total weight of the zeolite or of the zeolite-like compound, and a homogeneous cerium-zirconium mixed oxide and / or a cerium oxide. The zeolite used or the zeolite-like compound used is selected from the group consisting of chabazite, SAPO-34, ALPO-34 and zeolite-β.
Owner:UMICORE AG & CO KG
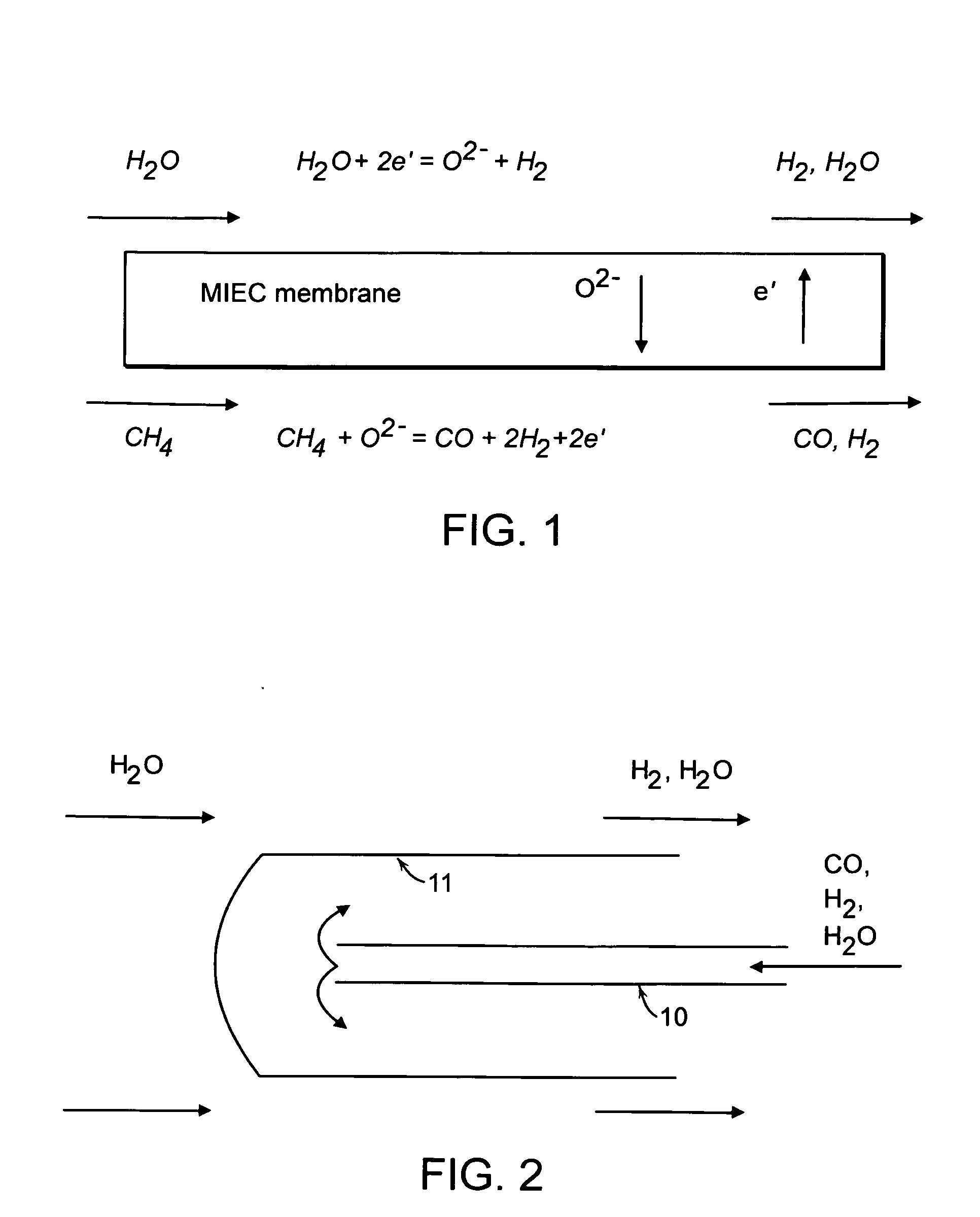
Composite mixed oxide ionic and electronic conductors for hydrogen separation
InactiveUS20060191408A1Efficient separationHigh hydrogen fluxesSemi-permeable membranesMembranesCeramic compositeHydrogen
A mixed ionic and electronic conducting membrane includes a two-phase solid state ceramic composite, wherein the first phase comprises an oxygen ion conductor and the second phase comprises an n-type electronically conductive oxide, wherein the electronically conductive oxide is stable at an oxygen partial pressure as low as 10−20 atm and has an electronic conductivity of at least 1 S / cm. A hydrogen separation system and related methods using the mixed ionic and electronic conducting membrane are described.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
Surface-modified silicon dioxide-titanium dioxide mixed oxides
Pyrogenically prepared surface-modified silicon dioxide-titanium dioxide mixed oxides are prepared by spraying pyrogenically prepared silicon dioxide-titanium dioxide mixed oxides with a surface-modifying agent. The surface-modified pyrogenically prepared silicon dioxide-titanium dioxide mixed oxides can be used in sun protection formulation.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Method for electrowinning of titanium metal or alloy from titanium oxide containing compound in the liquid state
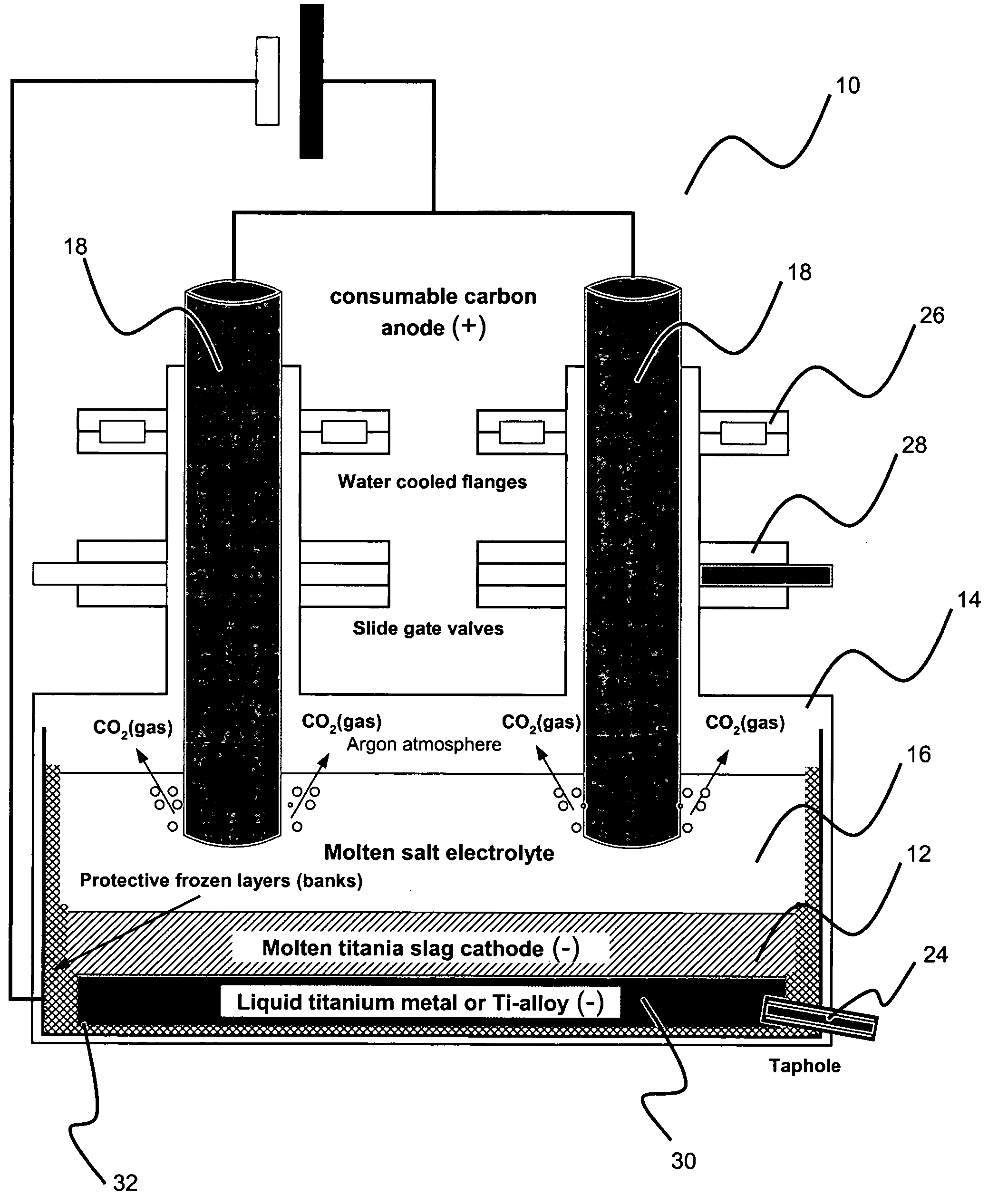
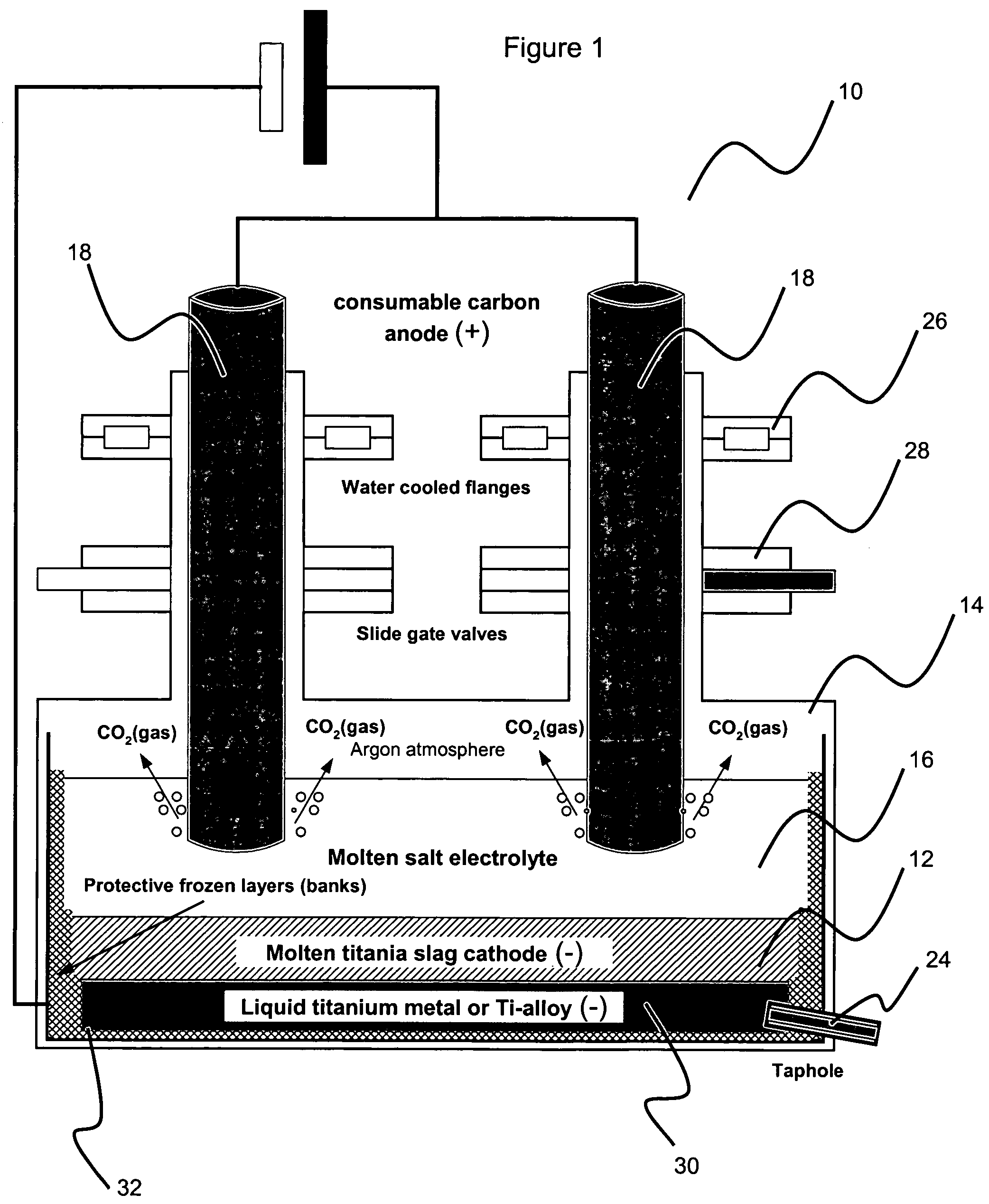
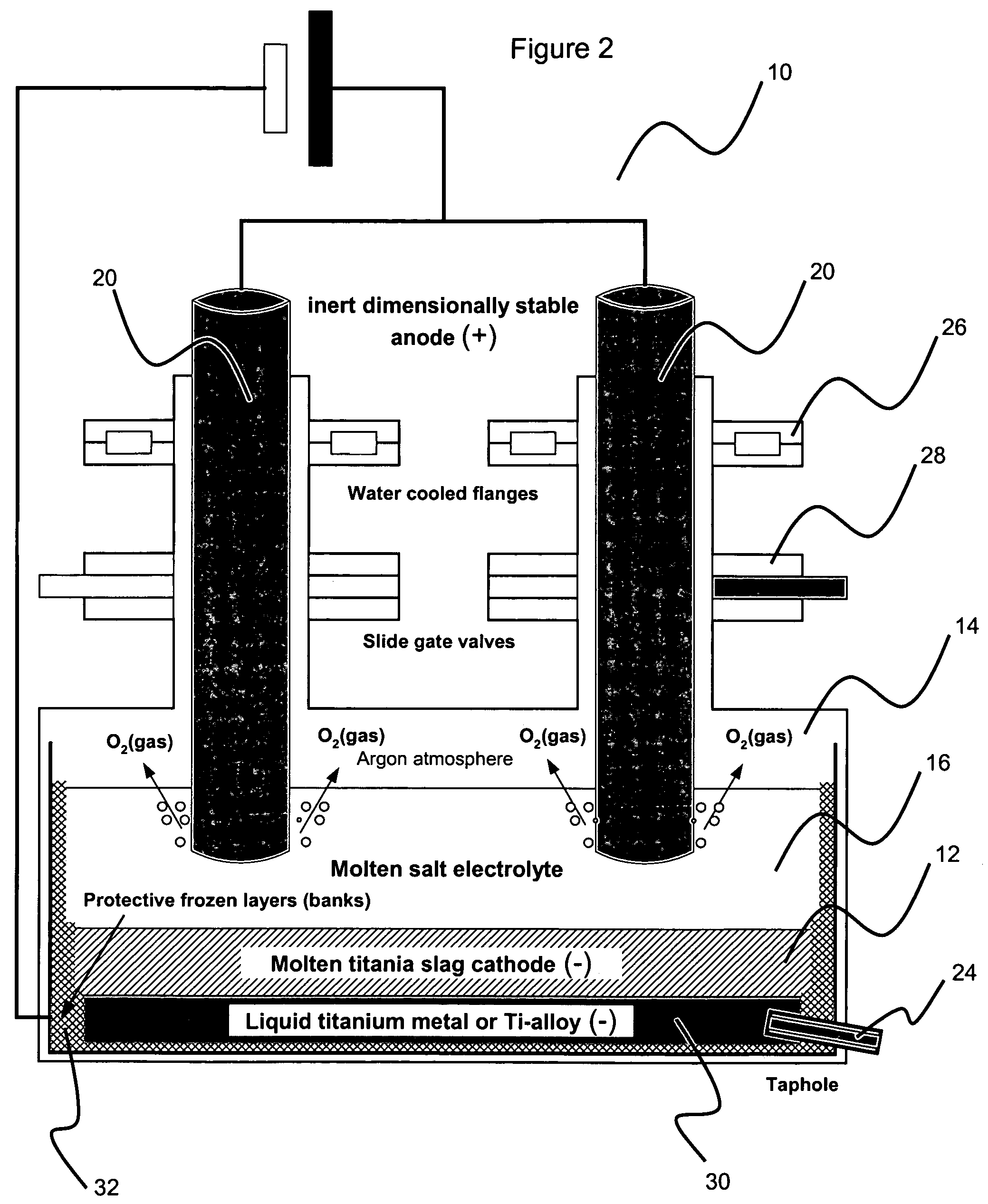
This invention relates to a method for electrowinning of titanium metal or titanium alloys from electrically conductive titanium mixed oxide compounds in the liquid state such as molten titania slag, molten ilmenite, molten leucoxene, molten perowskite, molten titanite, molten natural or synthetic rutile or molten titanium dioxide. The method involves providing the conductive titanium oxide compound at temperatures corresponding to the liquid state, pouring the molten material into an electrochemical reactor to form a pool of electrically conductive liquid acting as cathode material, covering the cathode material with a layer of electrolyte, such as molten salts or a solid state ionic conductor, deoxidizing electrochemically the molten cathode by direct current electrolysis. Preferably, the deoxidizing step is performed at high temperature using either a consumable carbon anode or an inert dimensionally stable anode or a gas diffusion anode. During the electrochemical reduction, droplets of liquid titanium metal or titanium alloy are produced at the slag / electrolyte interface and sink by gravity settling to the bottom of the electrochemical reactor forming, after coalescence, a pool of liquid titanium metal or titanium alloy. Meanwhile carbon dioxide or oxygen gas is evolved at the anode. The liquid metal is continuously siphoned or tapped under an inert atmosphere and cast into dense and coherent titanium metal or titanium alloy ingots.
Owner:QIT FER & TITANE INC
Metallic oxide mixture catalyzer for purifying organic waste gas and method of preparing the same
ActiveCN101138728AKeep aliveImprove performanceDispersed particle separationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsCeriumCordierite
The present invention relates to a catalyst of a metal oxide compound used for organic exhaust gas purification, and a preparation method for the catalyst. The catalyst uses the cordierite honeycomb ceramic intensively pretreated with the nitric acid as a carrier, and an active aluminum oxide coating modified by a mixed oxide of cerium, lanthanum and zirconium, and an active component comprising a plurality of metallic oxide mixtures are loaded on the carrier in a lump. For the catalyst preparation method, heat treatment is conducted on the carrier with the nitric acid, the concentration of which is 5 to 15 percent; after a specific surface area of the carrier is increased, the coating, which comprises and is loaded with the mixed oxide active component, is immersed in a lump. The catalyst is provided with the large specific surface area. The active component is a transition metal oxide mixture, which comprises no noble metal. Moreover, the catalyst is provided with the excellent performance and the low cost, and can be spread and applied easily. The catalyst is provided with the high catalytic combustion efficiency for the organic exhaust gas comprising benzene, toluene, dimethybenzene, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and so on, and the ignition temperature is low. Thus, the catalyst is widely applicable for purification of the industrial organic exhaust gas. The technique of one-time immersion, drying and calcination is adopted, so the manufacture equipment needed is simple.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Titania-alumina mixed oxide hydrodesulfurization catalyst and preparing process thereof
ActiveCN101199935AGuaranteed qualityAssurance controlMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsRefining to eliminate hetero atomsAluminium chlorideHydrodesulfurization
The utility model relates to a synthesis of a titania-alumina mixed oxide material and a catalyst carrier of a supported deep hydrodesulfurization catalyst by taking the compound as the carrier. 1)take the tetrabutyl titanate and the aluminum chloride or the pseudo-boehmite as the raw material, prepare the mesoporous mixed oxide material of TiO2-Al2O3 with the sol-gel method, and use the material as the carrier of the diesel oil deep hydrodesulfurization catalyst; 2)use the dipping method by modifying the active metal variety and the dipping method to get highly dispersed supported mesoporous hydrodesulfurization catalyst of TiO2-Al2O3 compound material after baking; in the diesel oil hydrogenation deep desulfurization reaction, the desulfurization capability is good, and the desulfurization rate can reach 99 percent; if the reaction can be operated under a relative relaxative condition, the sulfur in the diesel oil can be desorbed from 1300ppm to below 15 ppm, or from the 430ppm to below 1ppm; the sulfur content in the product can meet the standard of Europe IV.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
Transparent protective layer for a body
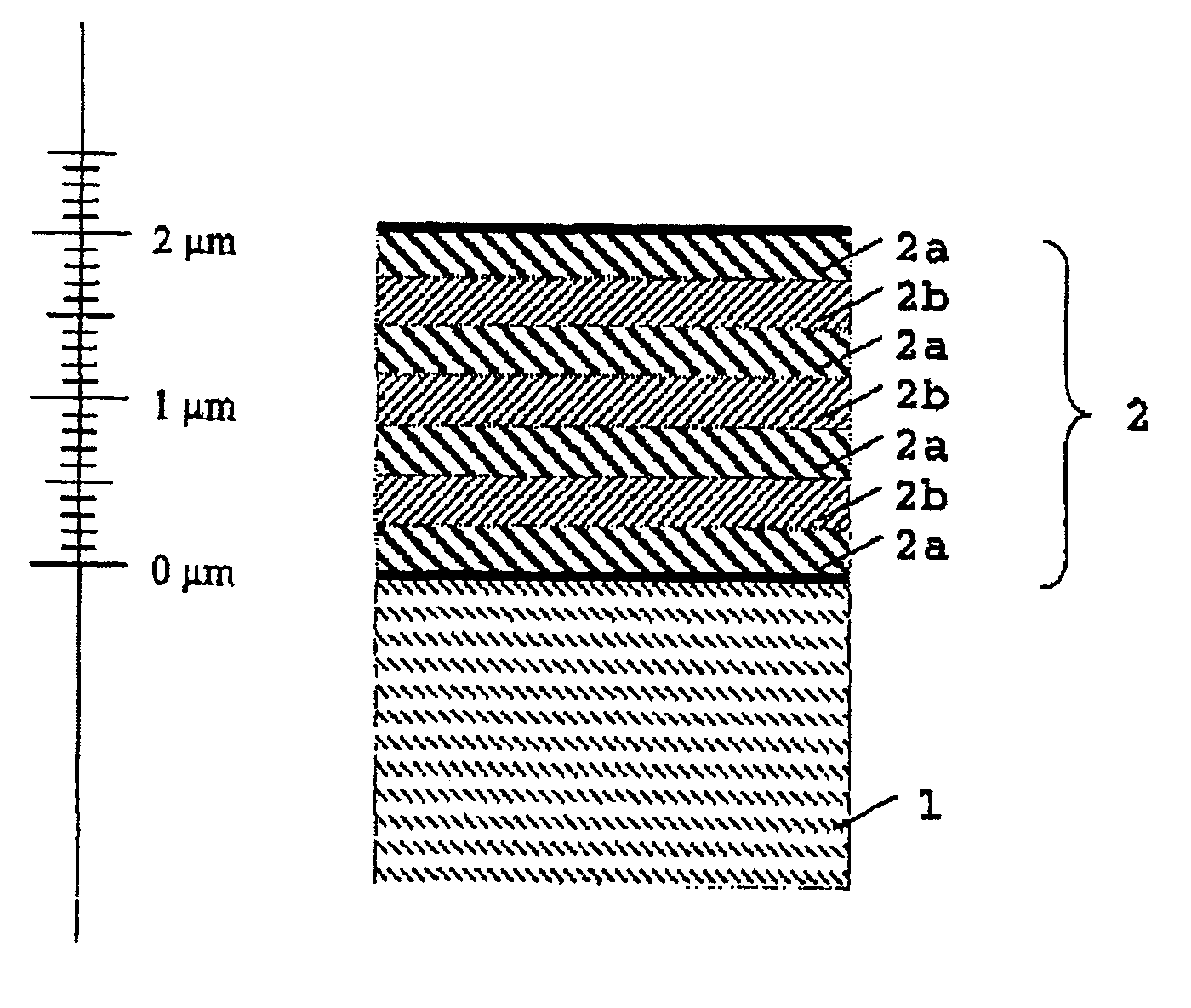
InactiveUS7018727B2Increase resistanceAttractive visual appearanceStoves/ranges topsNatural mineral layered productsMixed oxideTitanium
The invention relates to a transparent protective layer, in particular a scratchproof layer for glass and glass-ceramic, which is able to withstand high temperatures, has a smooth and dense surface, an attractive surface design and is preferably used for coating cooking plates. A protective layer according to the invention comprises at least one crystalline metal oxide layer which has at least one interlayer formed from an amorphous, thermally stable mixed oxide, the interlayer being arranged being sublayers of the metal oxide layer. A further protective layer according to the invention comprises at least one amorphous, thermally stable mixed oxide layer which has at least one interlayer formed from a crystalline metal oxide, the interlayer being arranged between the sublayers of the amorphous mixed oxide layer. The amorphous mixed oxide layer has at least two metallic components. The crystalline metal oxide layers preferably consist of yttrium-stabilized zirconium oxide, and the amorphous mixed oxide layers preferably consist of titanium / aluminum oxide.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
Catalyst for synthesizing methanol by hydrogenating carbon dioxide and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102240553AHigh selectivityImprove conversion rateOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationMixed oxideSlurry
The invention relates to a catalyst for synthesizing methanol by hydrogenating carbon dioxide and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of catalysts. The catalyst for synthesizing the methanol by hydrogenating the carbon dioxide comprises a mixed oxide of one or more of Cu, Zn, La, Ce and M, wherein M is Al, Si, Ti or Zr; the catalyst comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 30-70% of CuO, 10-40% of ZnO, 1-5% of accelerative activators Ln2O3, 1-5% of stabilizers CeO2 and 5-20% of carrier oxides MxOy. The preparation method of the catalyst comprises the following steps of: firstly mashing the carrier oxides MxOy; and then adding active matter components and precipitators into oxide slurry in a parallel flowing manner for coprecipitation. The catalyst disclosed by the invention has the advantages of high specific surface reaching 200 m<2> / g, stable structure, contact compactness among all the components and high synergistic effect, so that the catalyst has higher activity and selectivity; the preparation process of the catalyst has the advantages of simplicity, good repeatability and convenience for industrial production; in addition, by means of the catalyst disclosed by the invention, the conversion rate of the carbon dioxide is high and reaches 35 percent under appropriate reaction conditions, and the selectivity of the methanol is higher and reaches more than 80 percent.
Owner:大连瑞克科技股份有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com