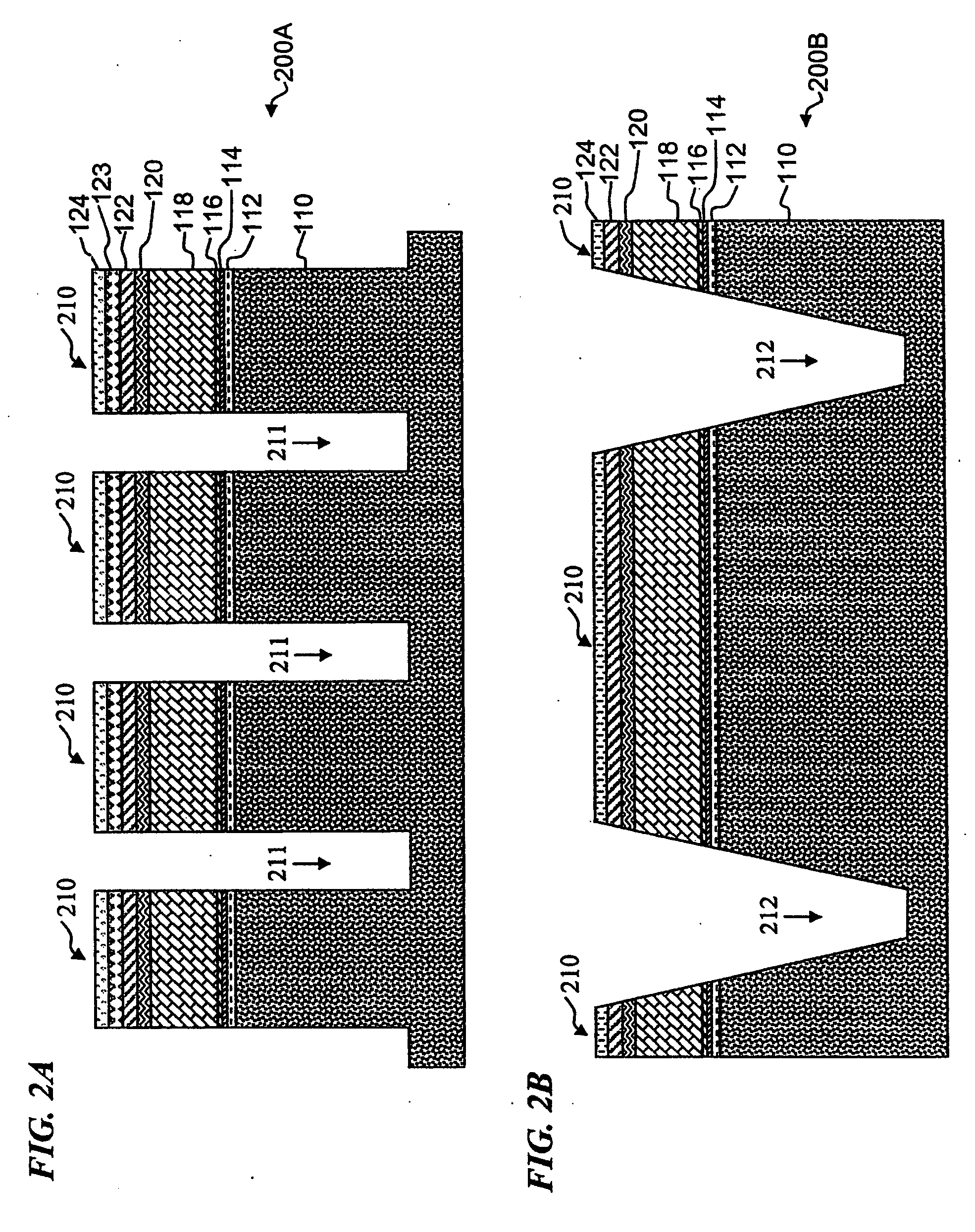
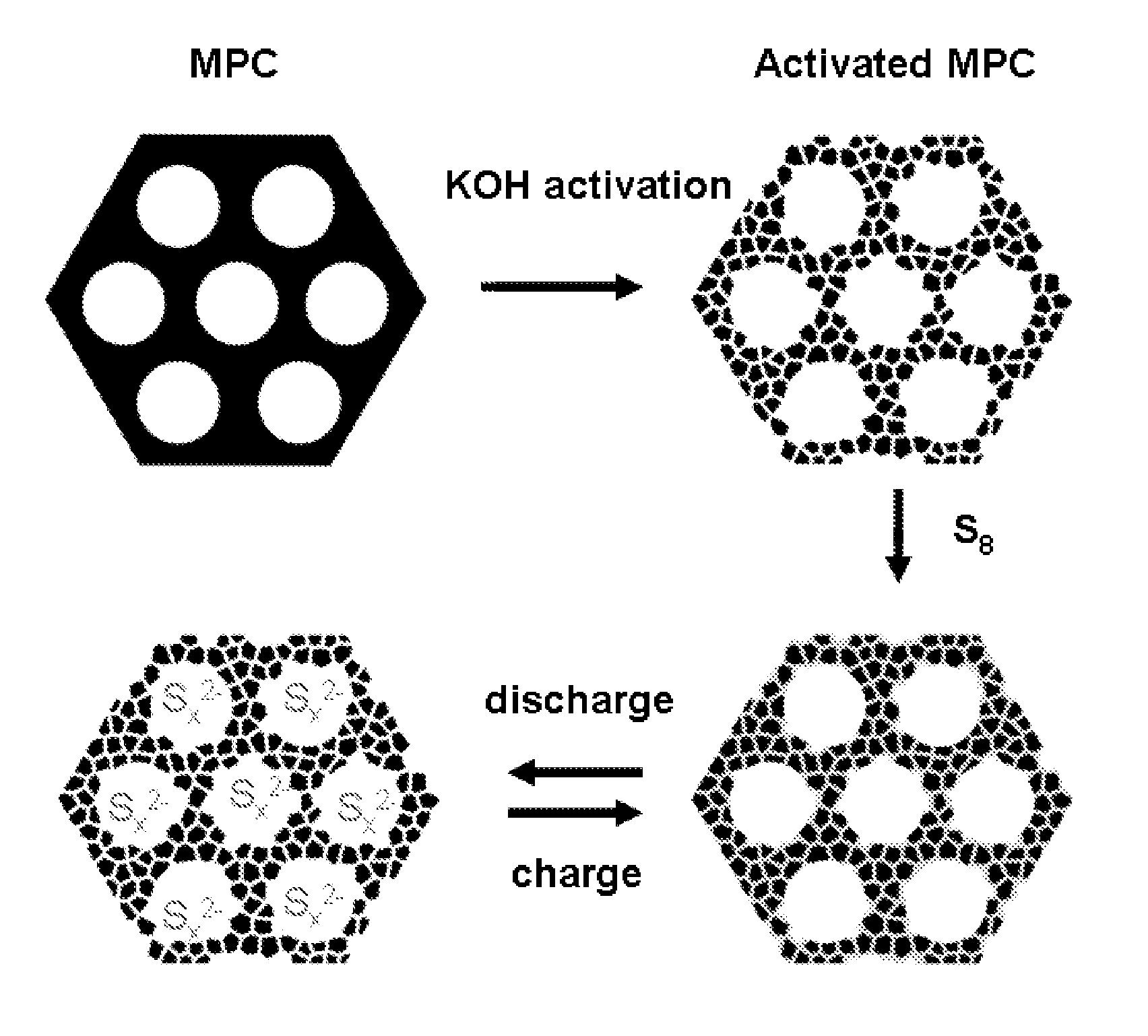
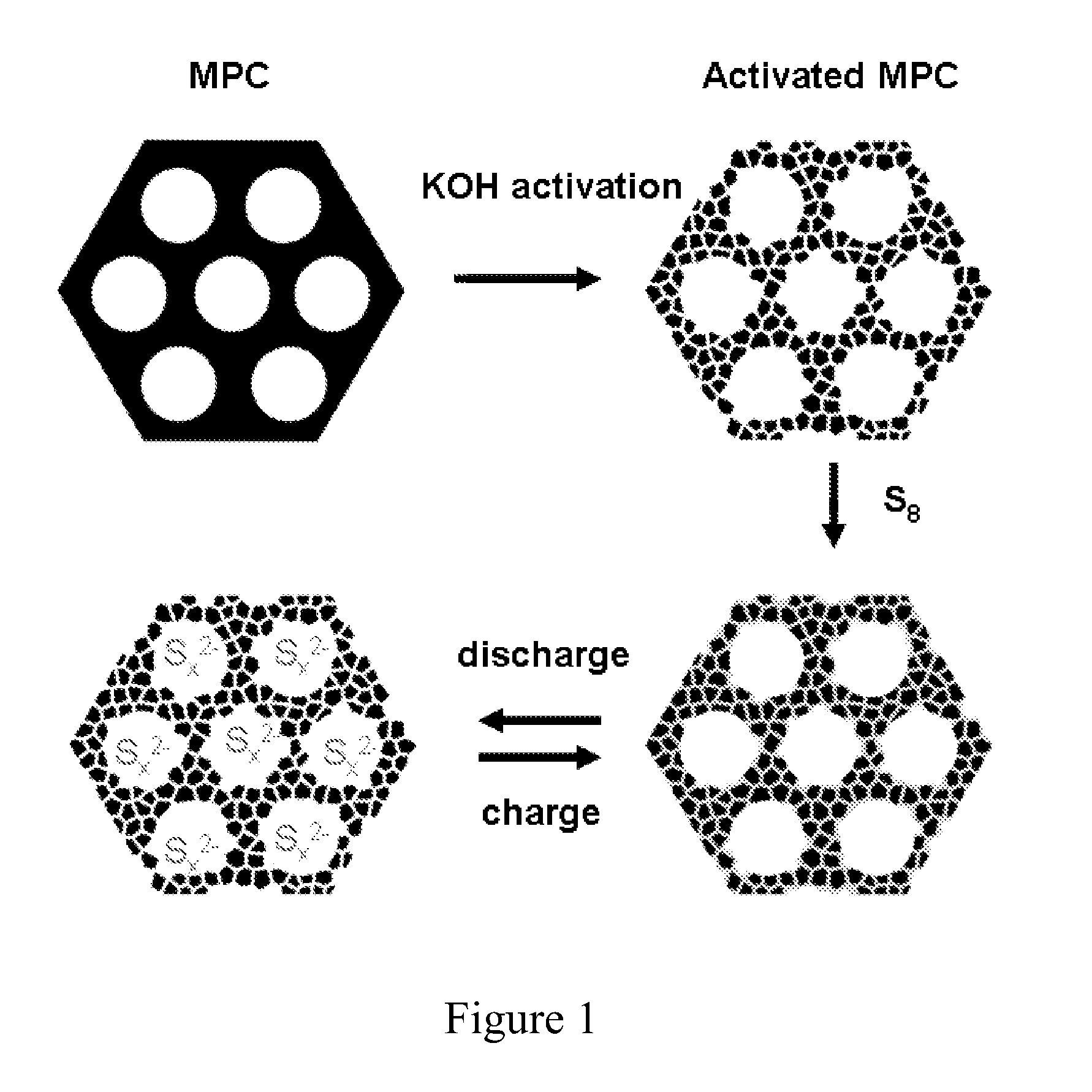
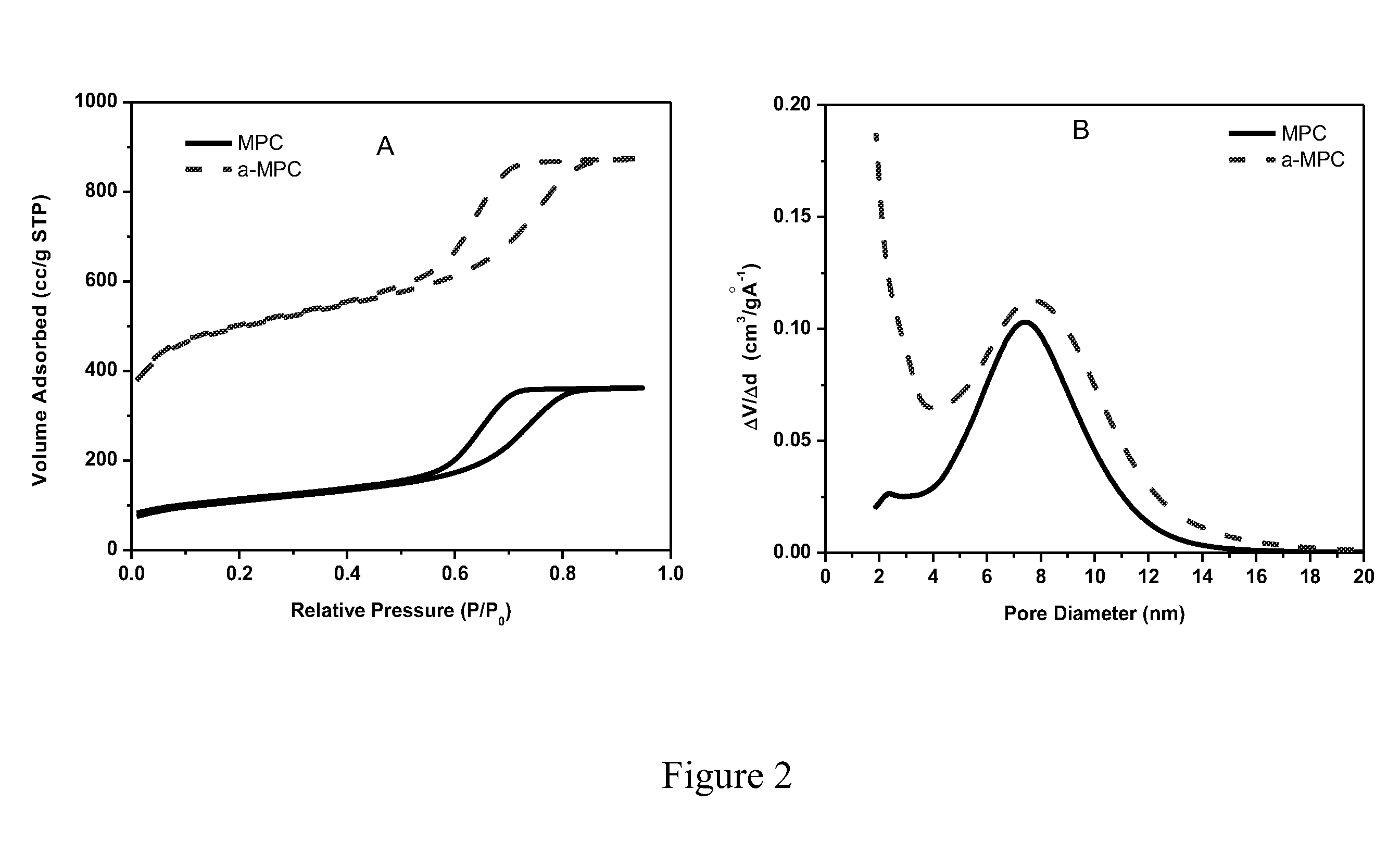
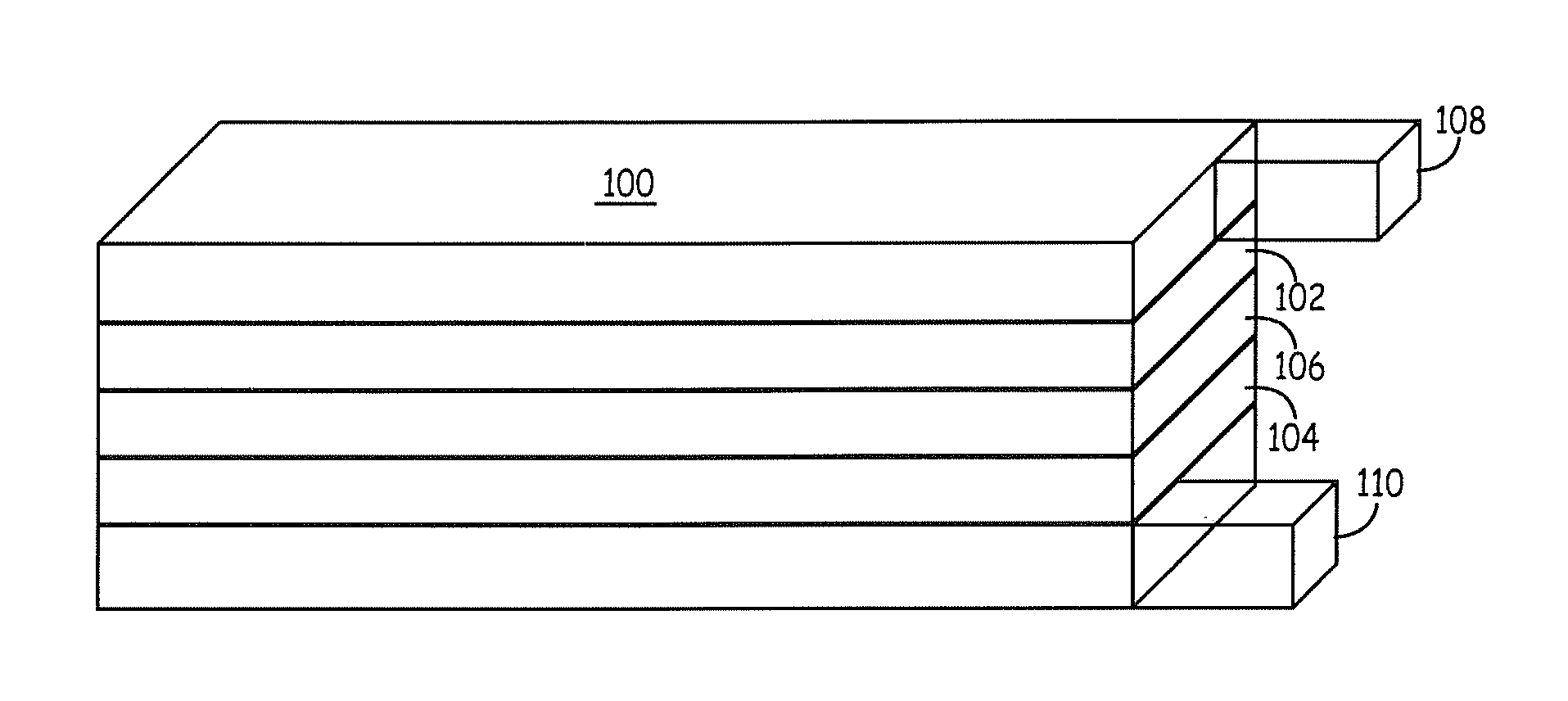
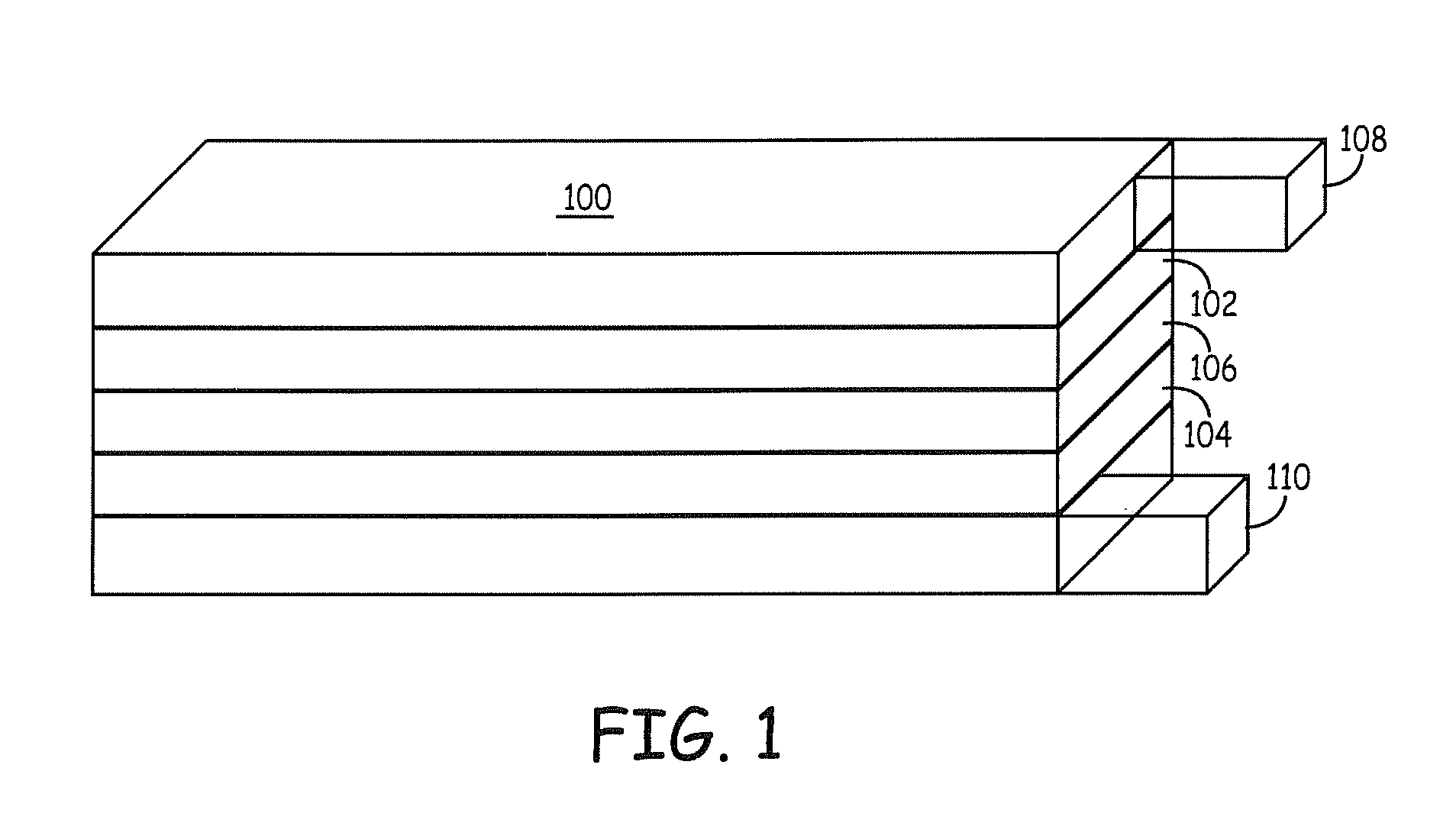
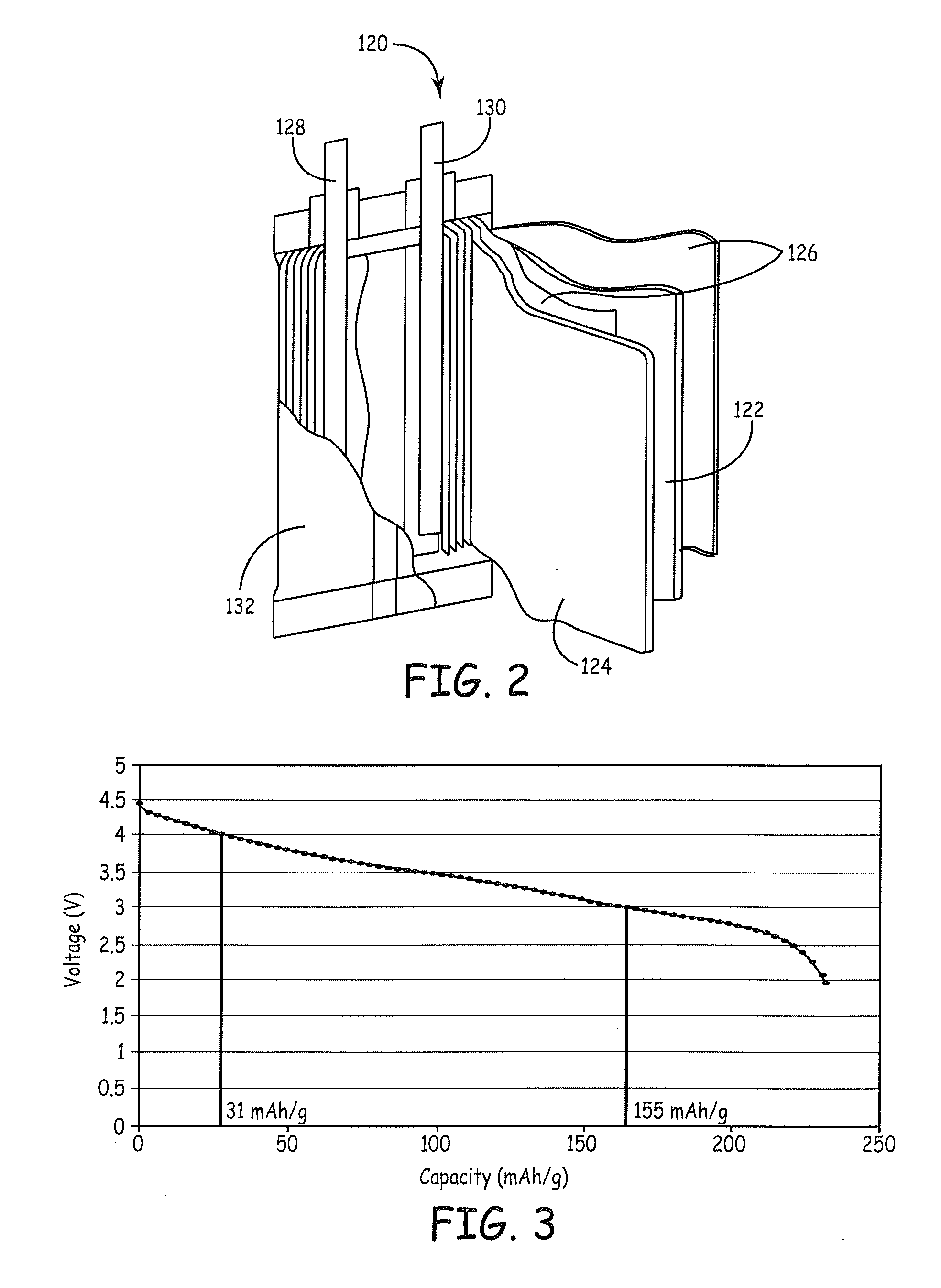
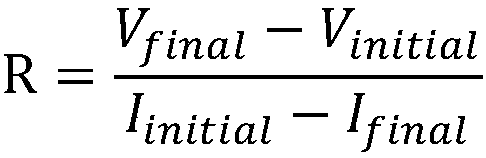Patents
Literature
10645 results about "Cathode material" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cathode materials are comprised of cobalt, nickel and manganese in the crystal structure forming a multi-metal oxide material to which lithium is added.
Graphene-Enhanced cathode materials for lithium batteries
ActiveUS20120058397A1Short timeEasy dischargeNon-metal conductorsMaterial nanotechnologyParticulatesCvd graphene
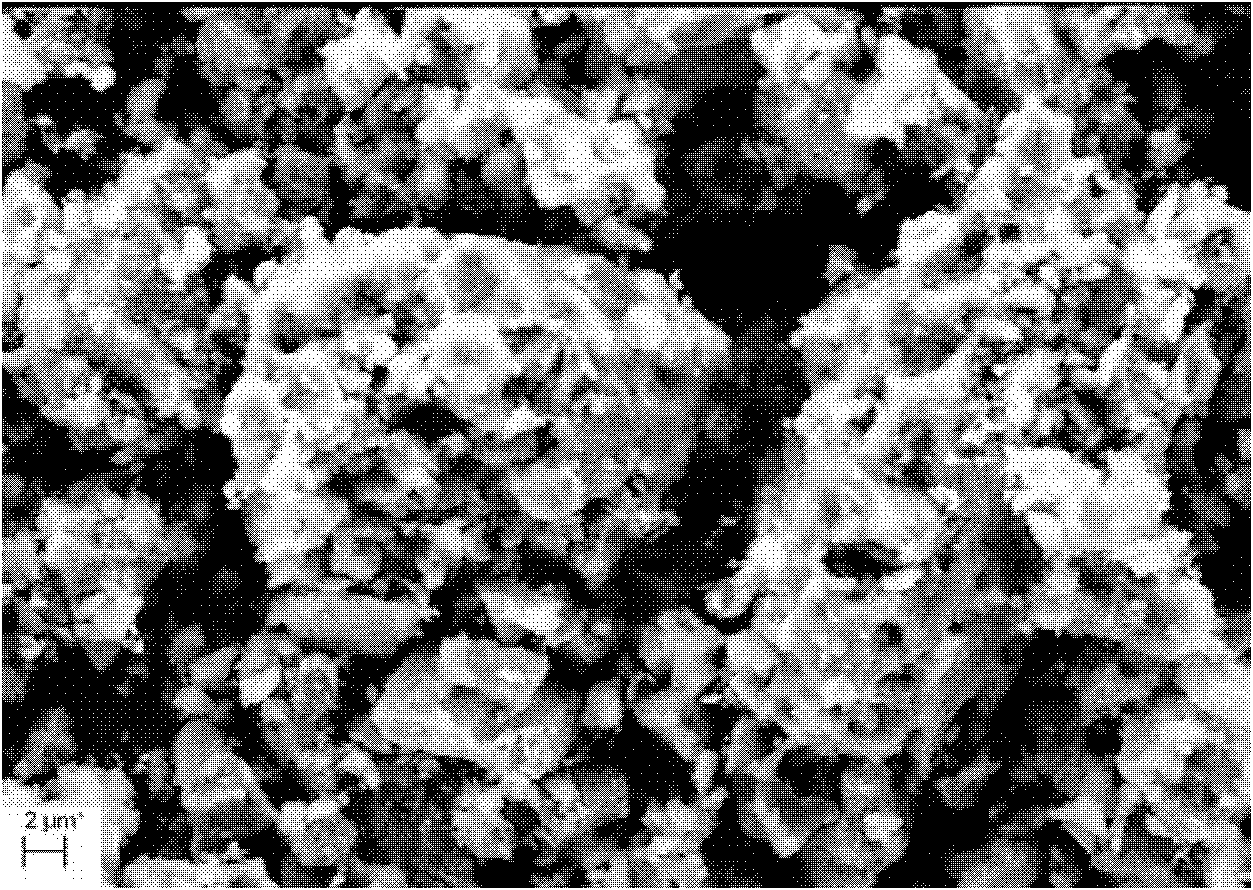
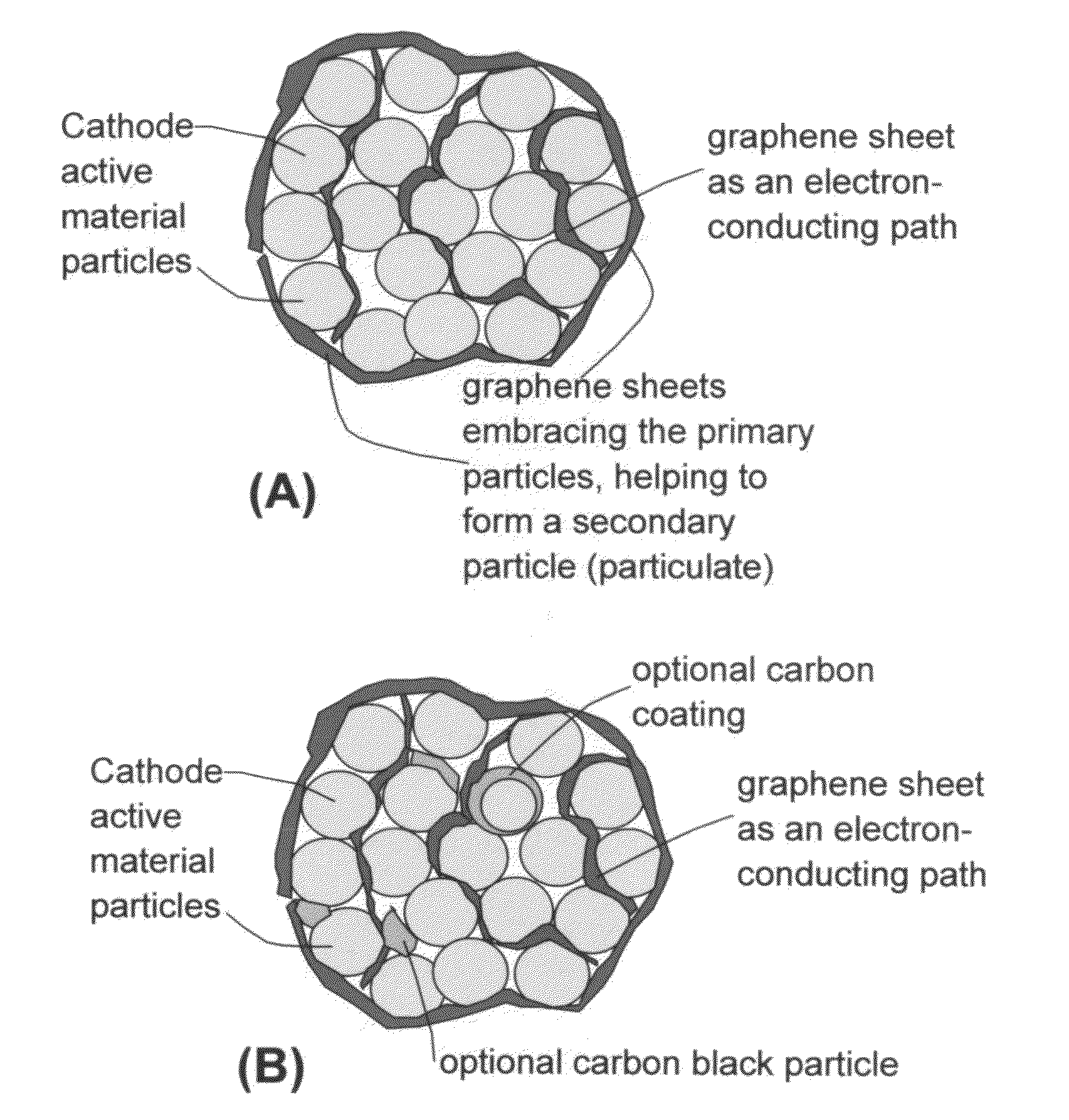
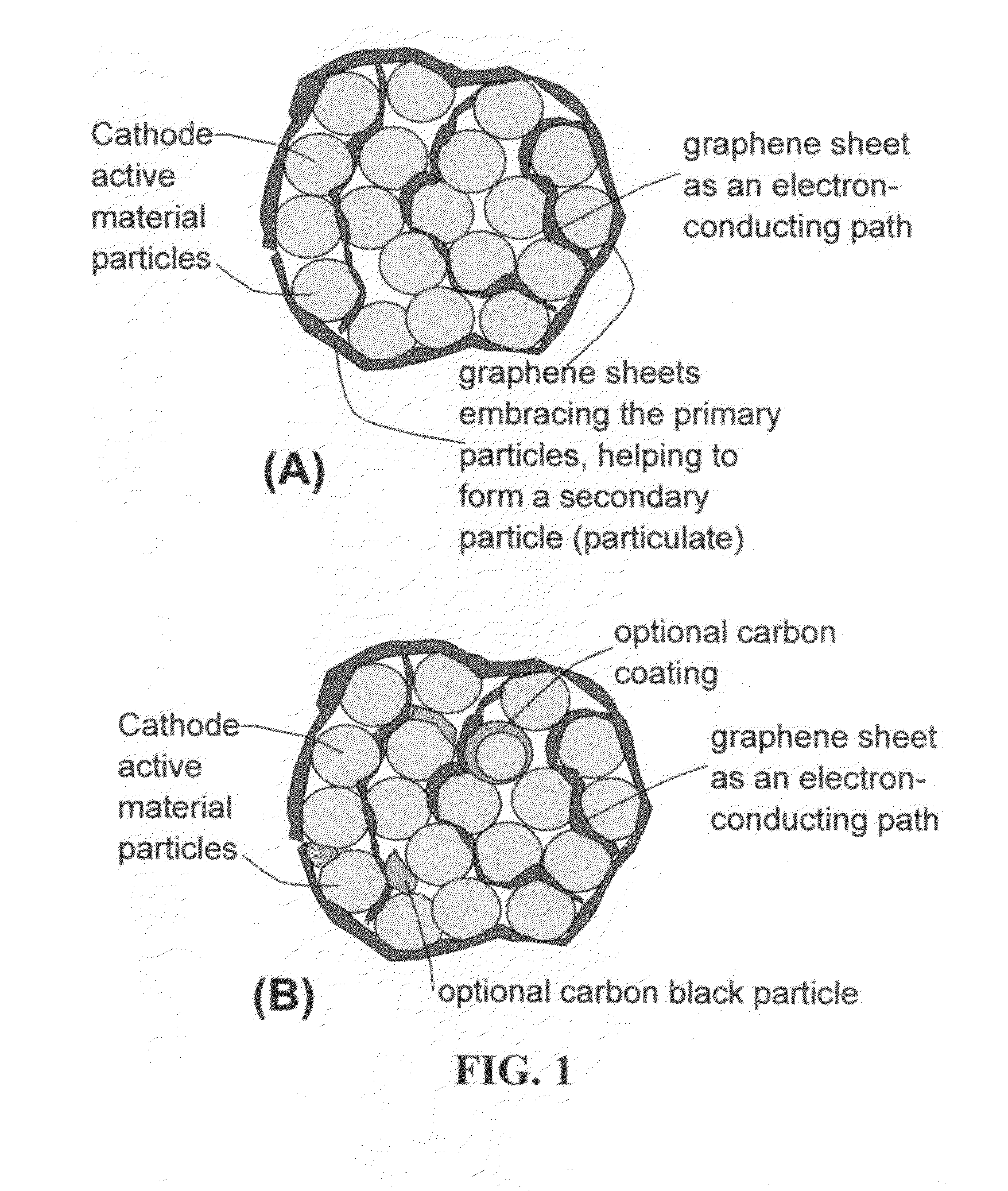
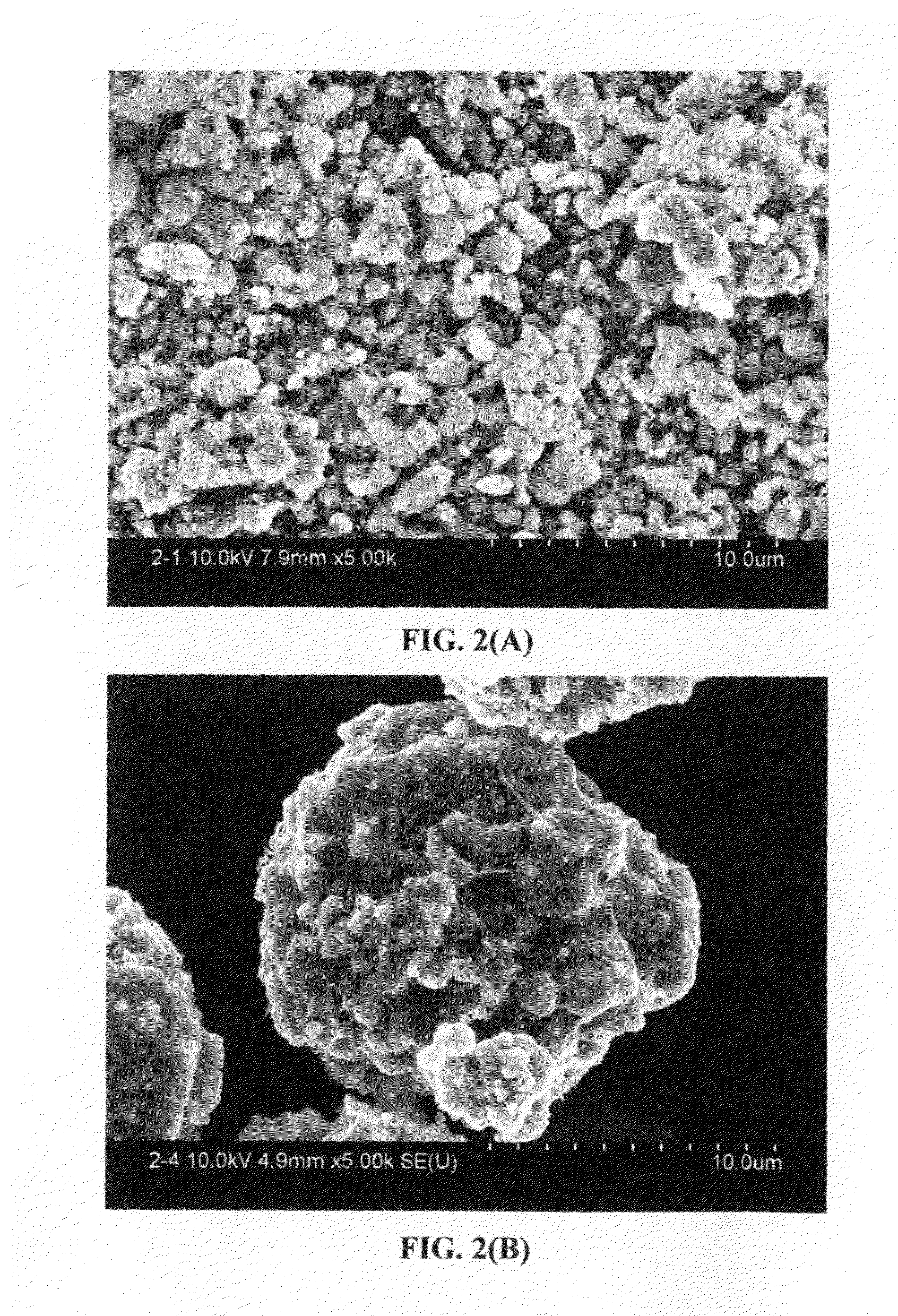
A nano graphene-enhanced particulate for use as a lithium battery cathode active material, wherein the particulate is formed of a single or a plurality of graphene sheets and a plurality of fine cathode active material particles with a size smaller than 10 μm (preferably sub-micron or nano-scaled), and the graphene sheets and the particles are mutually bonded or agglomerated into an individual discrete particulate with at least a graphene sheet embracing the cathode active material particles, and wherein the particulate has an electrical conductivity no less than 10−4 S / cm and the graphene is in an amount of from 0.01% to 30% by weight based on the total weight of graphene and the cathode active material combined.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
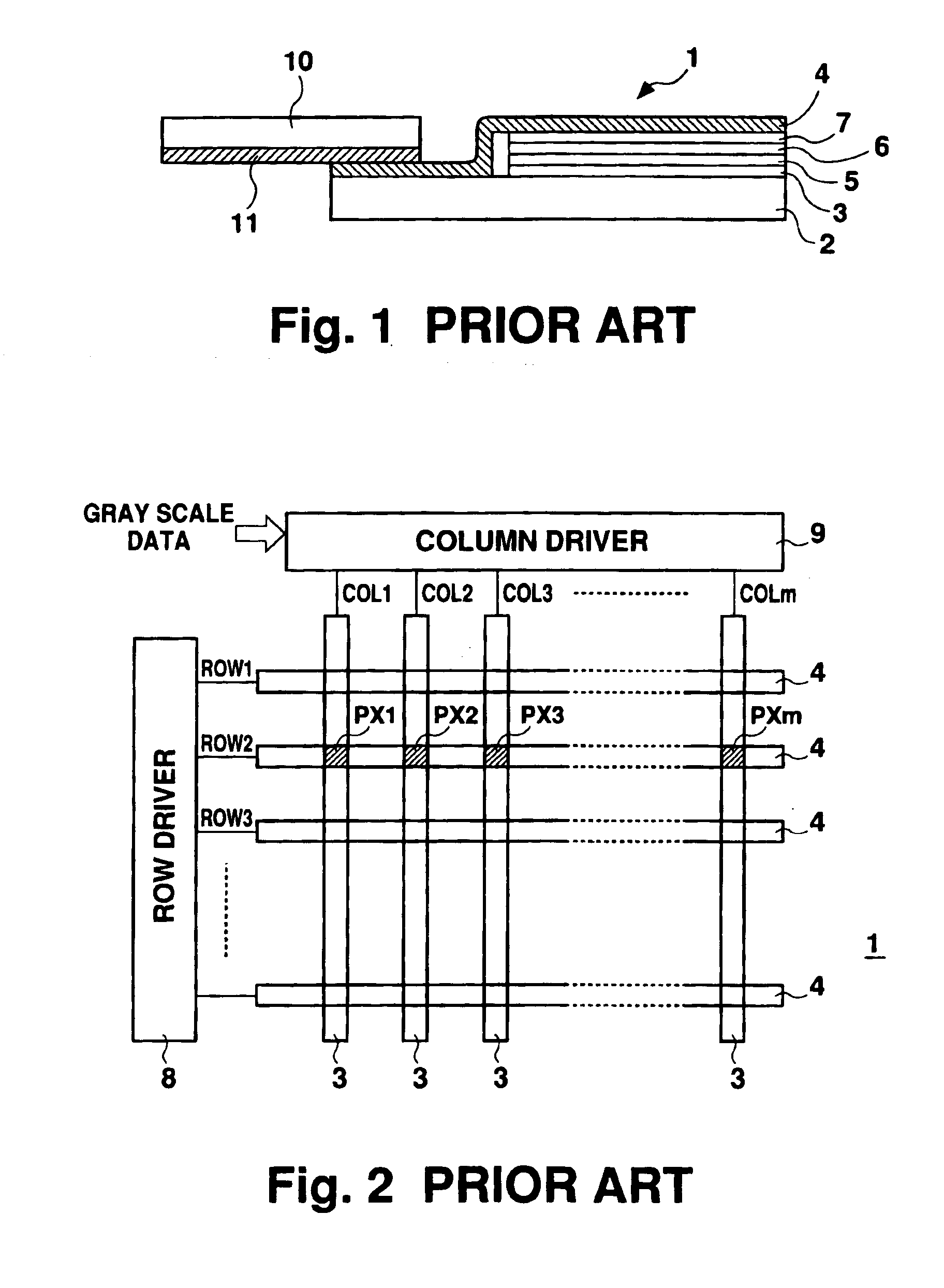
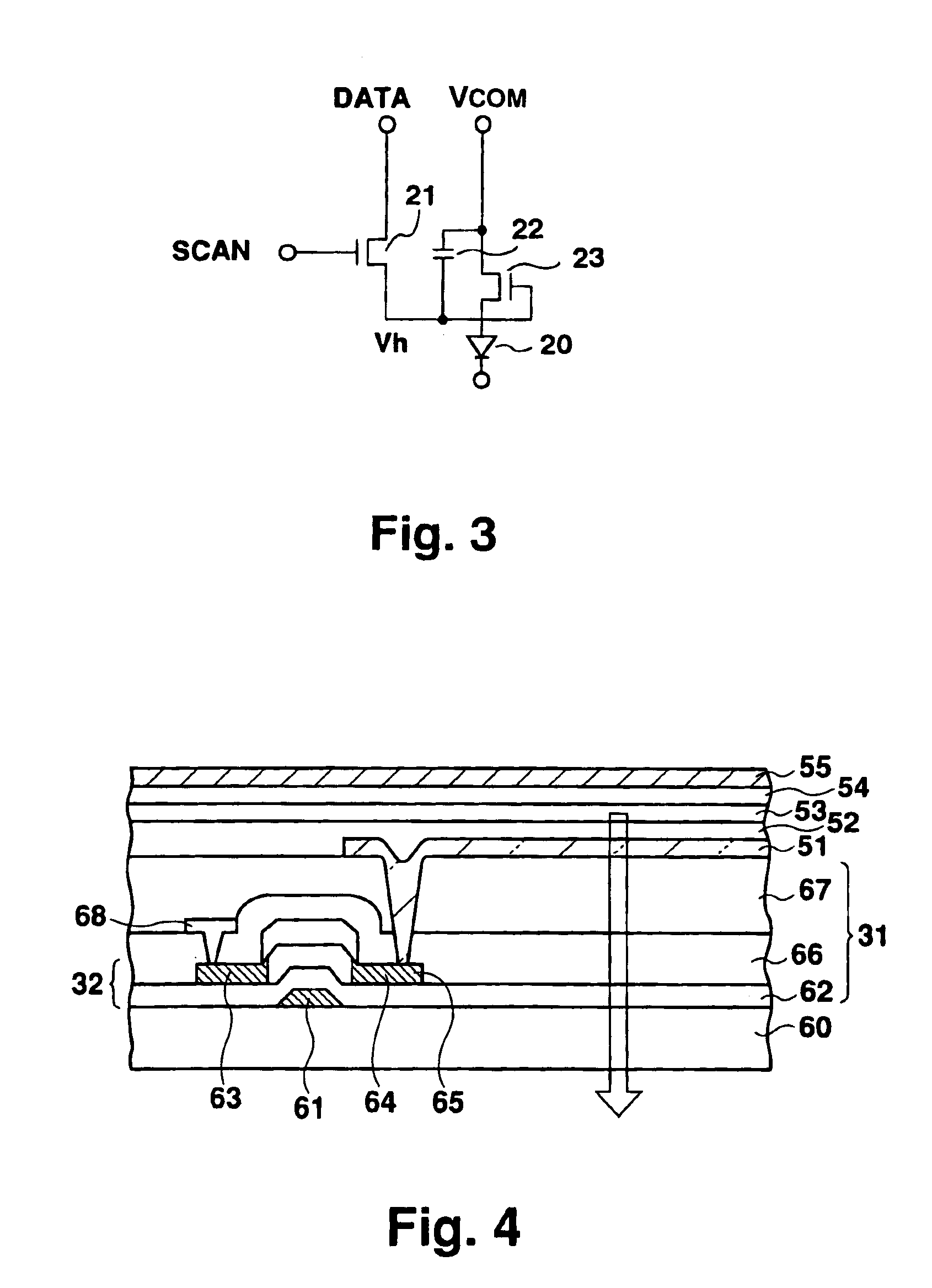
Active-type electroluminescent display
InactiveUS6911960B1Reduce conductor resistanceReduce light intensityDischarge tube luminescnet screensStatic indicating devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceMetallic materials
In an active-type electroluminescent (EL) display, a conductor interconnecting a cathode (55) of an EL panel (30, 40) and a connection terminal of a signal input substrate (35) has a multilayer structure formed of a cathode material and a conductive material used in a thin-film transistor forming step. The conductor may be formed of a conductive material used in a thin film transistor forming step. A metal material for a gate electrode or drain electrode is preferably used as the conductive material. The connection conductor structure can reduce the electrical resistance of the connection conductor, thus preventing a decrease in display intensity of an EL display.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Layered cathode materials for lithium ion rechargeable batteries
ActiveUS7205072B2Improve impedance characteristicsImprove stabilityAlkali metal oxidesNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulator electrodesDopantRechargeable cell
A number of materials with the composition Li1+xNiαMnβCoγM′δO2−zFz (M′=Mg,Zn,Al,Ga,B,Zr,Ti) for use with rechargeable batteries, wherein x is between about 0 and 0.3, α is between about 0.2 and 0.6, β is between about 0.2 and 0.6, γ is between about 0 and 0.3, δ is between about 0 and 0.15, and z is between about 0 and 0.2. Adding the above metal and fluorine dopants affects capacity, impedance, and stability of the layered oxide structure during electrochemical cycling.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC +2
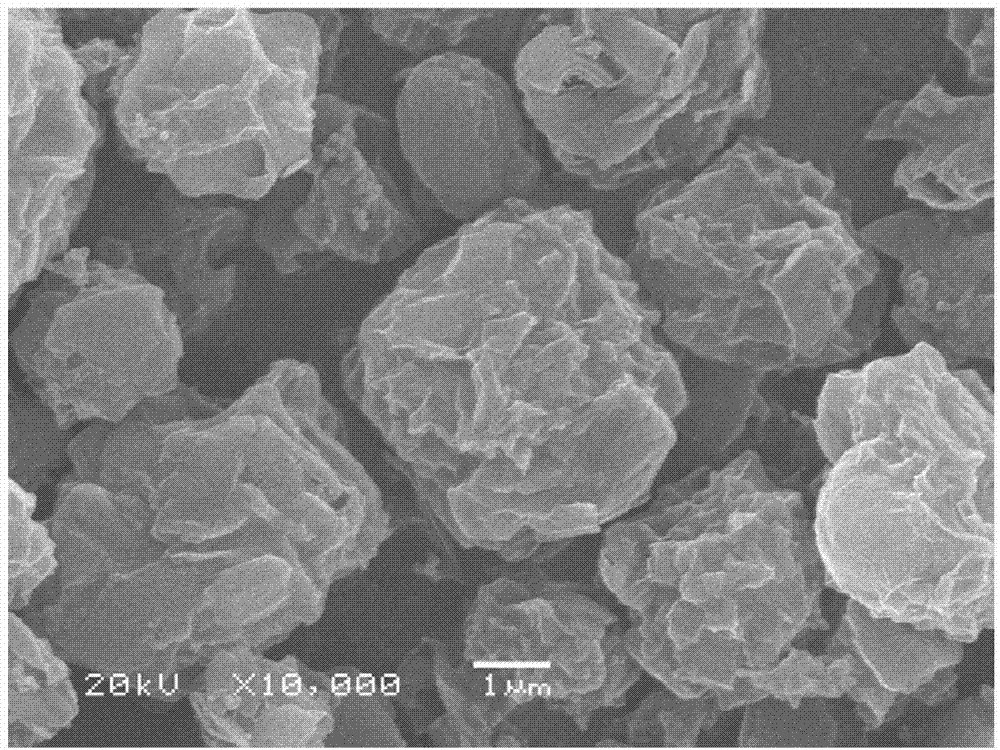
Carbon/silicon/carbon nano composite structure cathode material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a carbon / silicon / carbon nano composite structure cathode material and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of electrochemical power supply technologies. The cathode material consists of a carbon-based conductive substrate, nano silicon and a nano carbon coating layer, wherein the nano silicon is uniformly distributed on the carbon-based conductive substrate; the nano carbon coating layer is arranged on the surface of the nano silicon; the carbon-based conductive substrate is porous carbon, a carbon nanotube or graphene; the nano silicon exists in the state of nanoparticles or nano films; the weight percentage of the nano silicon in the cathode material is 10-90 percent; and the thickness of the nano carbon coating layer is 0.1-10 nanometers. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: depositing nano silicon on the carbon substrate in a reaction space in oxygen-free atmosphere by adopting a chemical vapor deposition process; and coating nano carbon on the surface of the nano silicon by adopting the chemical vapor deposition process. In the obtained carbon / silicon / carbon composite cathode material, the volume change of a silicon electrode material is controlled effectively in the charging and discharging processes, the electrode structure is kept complete, the circulation volume is large, the circulation service life is long, and the electrochemical performance is high.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
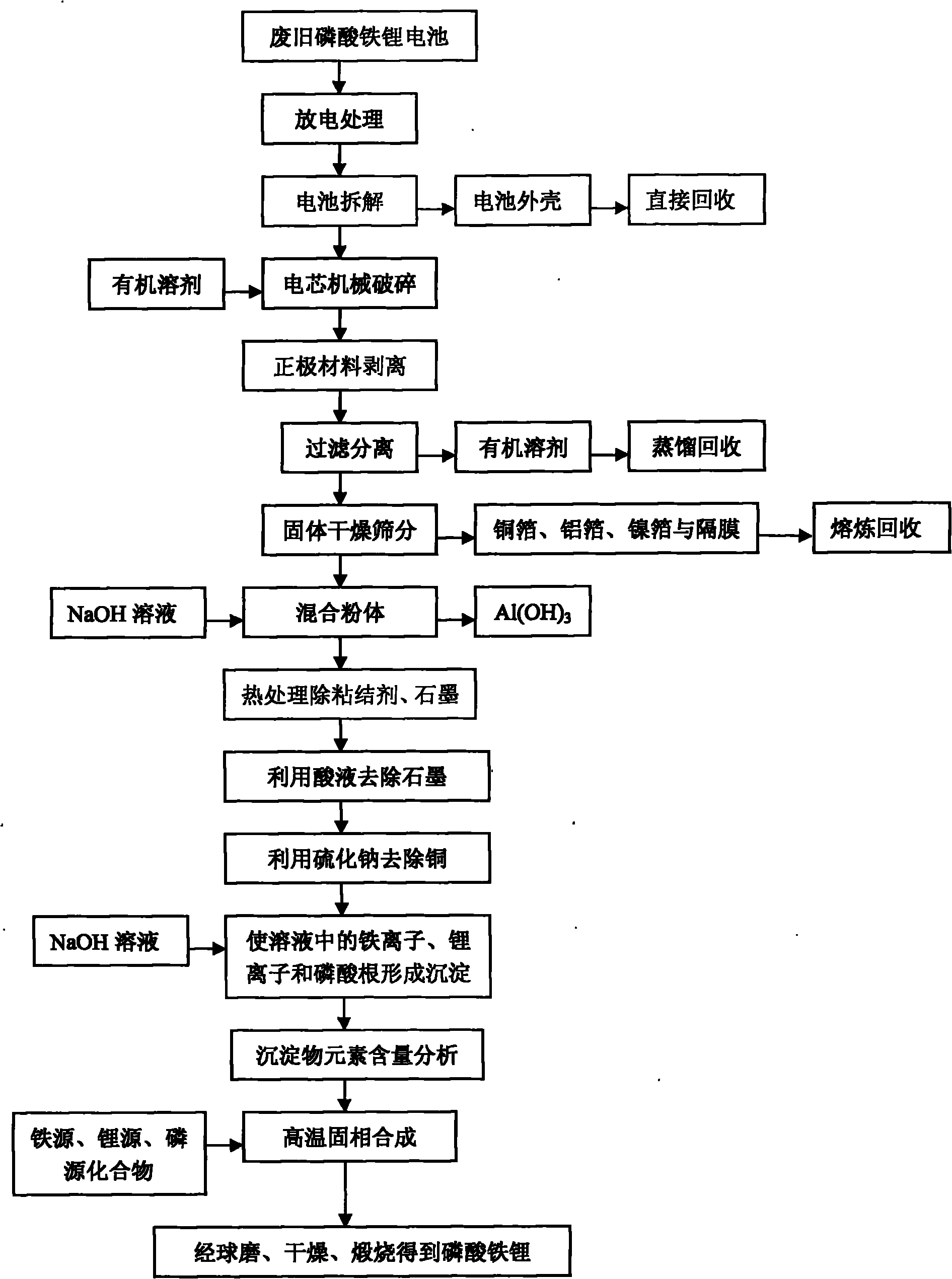
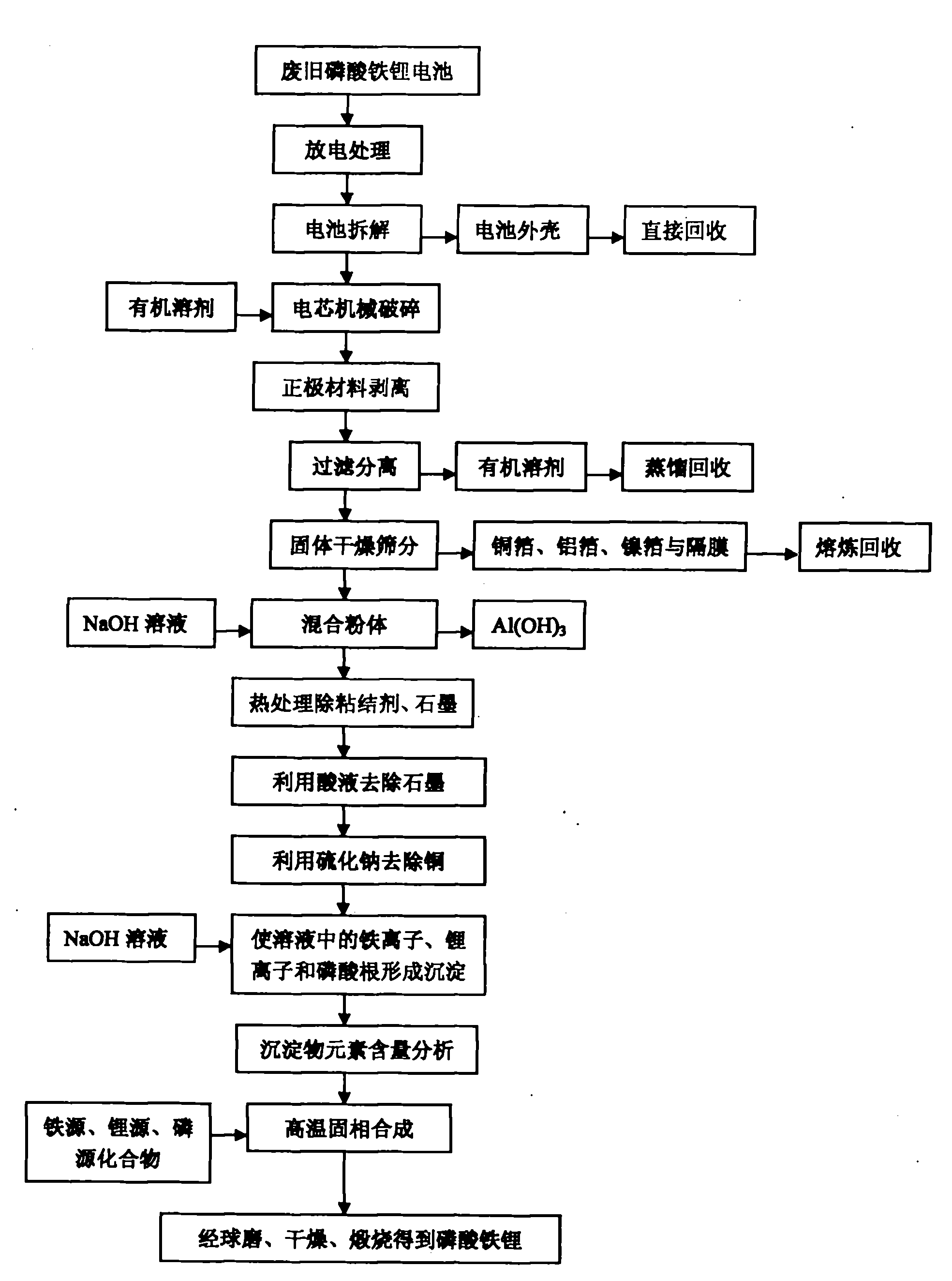
Comprehensive recovering method of waste lithium iron phosphate battery
InactiveCN101847763AImprove performanceLow priceWaste accumulators reclaimingProcess efficiency improvementAdhesiveCalcination
The invention provides a comprehensive recovering method of waste lithium iron phosphate batteries, which has simple and reasonable process, low recovering cost and high added value. The method comprises the following steps: utilizing an organic solvent to dissolve an adhesive on battery cell fragments, and realizing the separation of lithium iron phosphate material and clean aluminum and copper foils through screening, wherein the aluminum and copper foils are recovered by smelting; utilizing a NaOH solution to remove residual aluminum foil scraps in the lithium iron phosphate material, and removing graphite and remaining adhesive by heat treatment; after dissolving the lithium iron phosphate with acid, utilizing sodium sulphide to remove copper ions, and utilizing the NaOH solution or ammonia solution to allow iron, lithium and phosphorus ions in the solution to generate sediments; adding iron source, lithium source or phosphorus source compounds to adjust the molar ratio of iron, lithium and phosphorus; and finally adding a carbon source, and obtaining a lithium iron phosphate cathode material through ball milling and calcination in inert atmosphere. After the treatment of the steps, the recovery rate of valuable metals in the batteries is more than 95%, and the comprehensive recovery rate of the lithium iron phosphate cathode material is more than 90%.
Owner:CHERY AUTOMOBILE CO LTD
Lithium iron phosphate cathode materials with enhanced energy density and power performance
InactiveUS20090155689A1Powerful performanceHigh discharge ratePhosphatesPeroxides/peroxyhydrates/peroxyacids/superoxides/ozonidesFiberPhosphate
The invention is related to a cathode material comprising particles having a lithium metal phosphate core and a pyrolytic carbon deposit, said particles having a synthetic multimodal particle size distribution comprising at least one fraction of micron size particles and one fraction of submicron size particles, said lithium metal phosphate having formula LiMPO4 wherein M is at least Fe or Mn.Said material is prepared by method comprising the steps of providing starting micron sized particles and starting submicron sized particles of at least one lithium metal phosphate or of precursors of a lithium metal phosphate; mixing by mechanical means said starting particles; making a pyrolytic carbon deposit on the lithium metal phosphate starting particles before or after the mixing step, and on their metal precursor before or after mixing the particles; optionally adding carbon black, graphite powder or fibers to the said lithium metal phosphate particles before the mechanical mixing.
Owner:PHOSTECH LITHIUM
Reducing carbon dioxide to products
InactiveUS20110114502A1Provide stabile long-term reduction of carbon dioxideLow costCellsPhotography auxillary processesPtru catalystElectrical battery
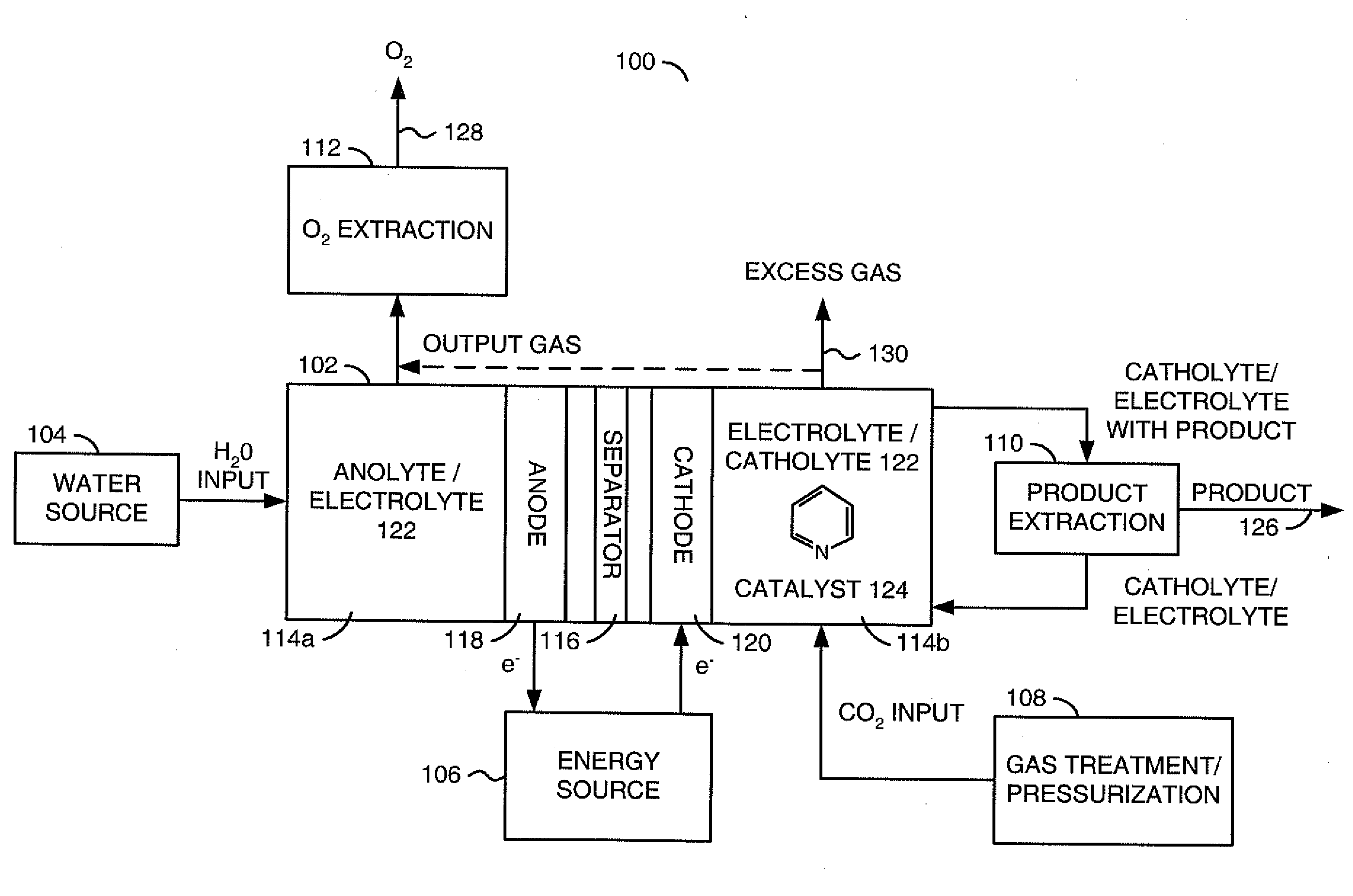
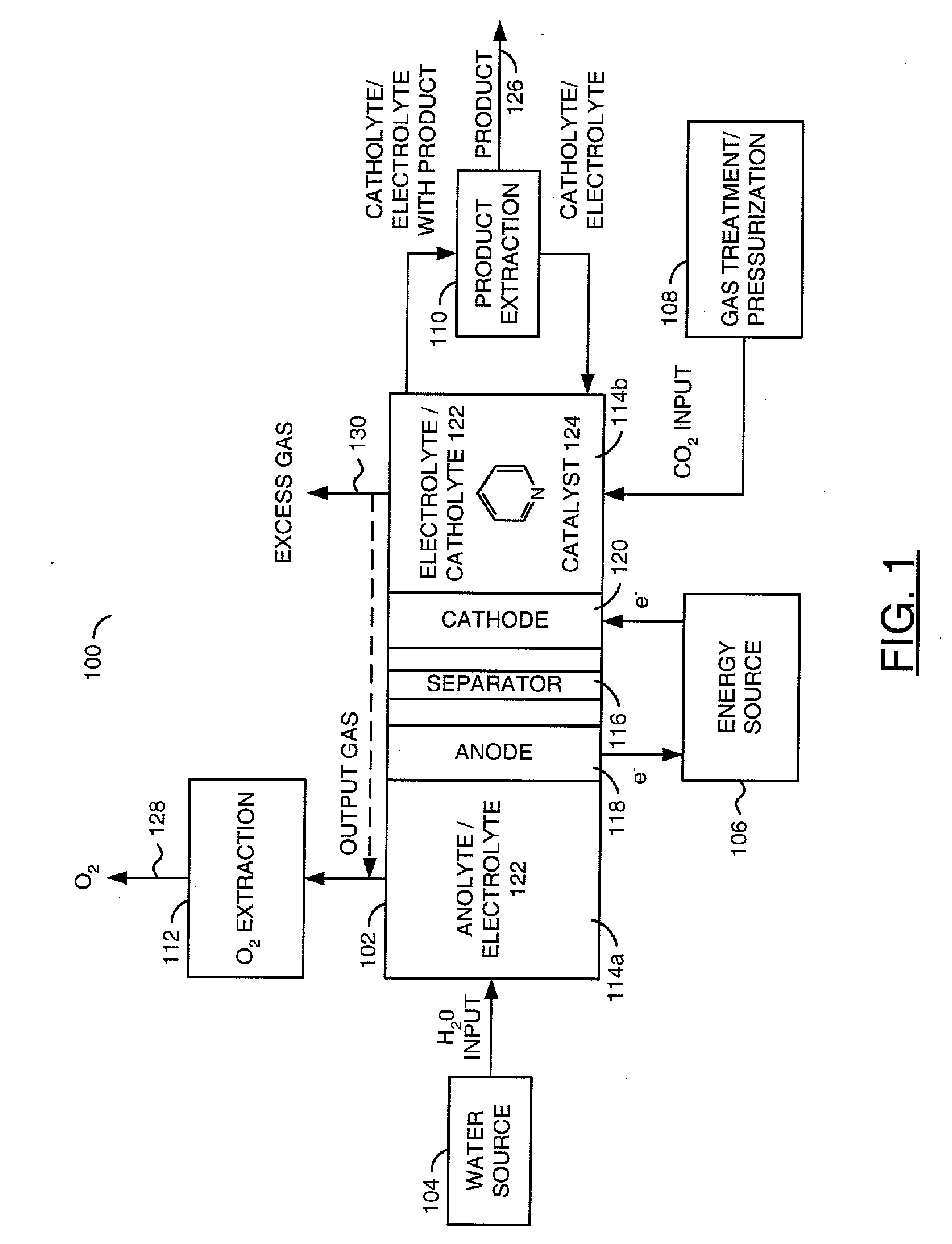
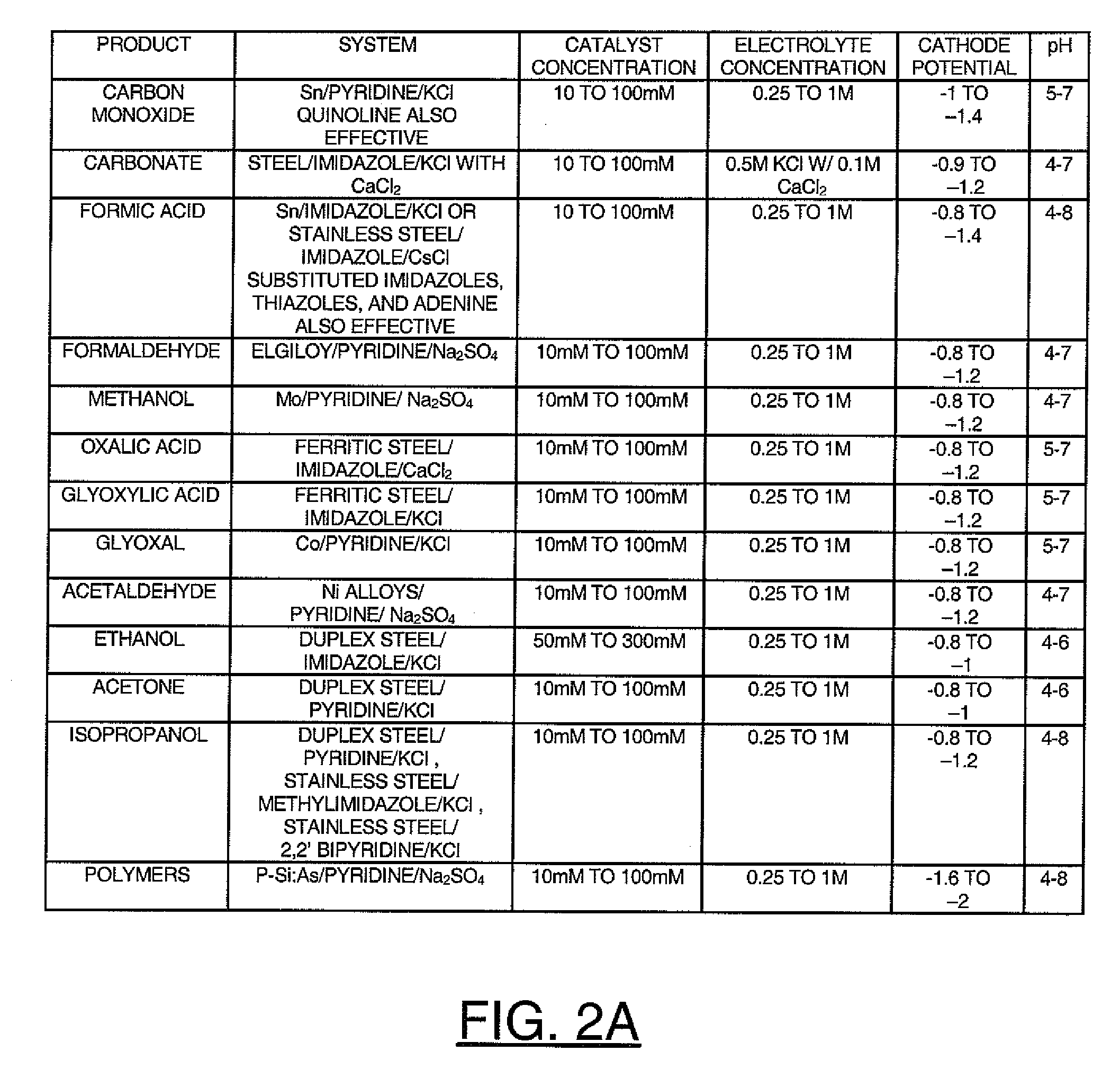
A method for reducing carbon dioxide to one or more products is disclosed. The method may include steps (A) to (C). Step (A) may bubble the carbon dioxide into a solution of an electrolyte and a catalyst in a divided electrochemical cell. The divided electrochemical cell may include an anode in a first cell compartment and a cathode in a second cell compartment. The cathode generally reduces the carbon dioxide into the products. Step (B) may vary at least one of (i) which of the products is produced and (ii) a faradaic yield of the products by adjusting one or more of (a) a cathode material and (b) a surface morphology of the cathode. Step (C) may separate the products from the solution.
Owner:LIQUID LIGHT
Method and apparatus for solid-state microbattery photolithographic manufacture, singulation and passivation
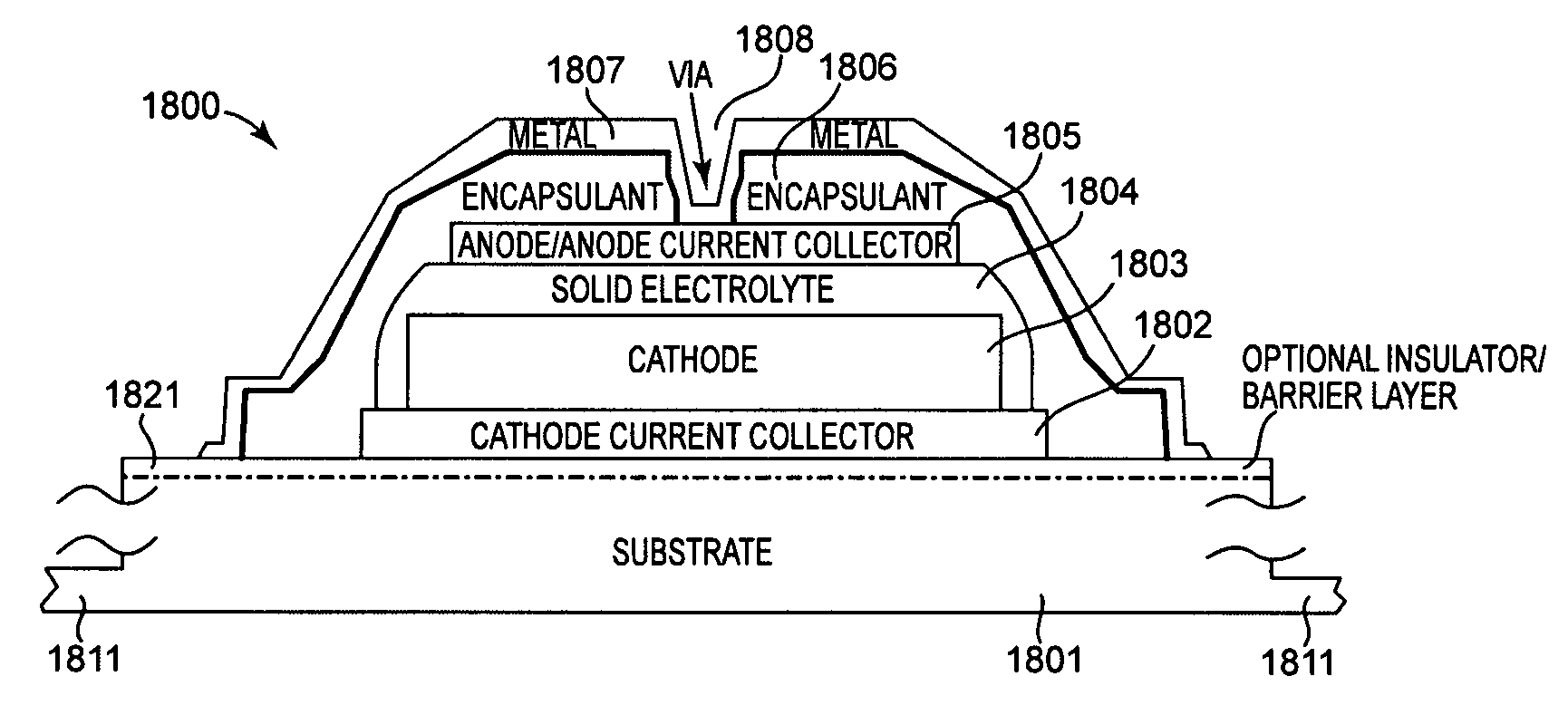
InactiveUS20080032236A1Efficient and economical manufactureReduced number of stepSolid electrolytesDecorative surface effectsChemical treatmentPhotoresist
A method for producing a thin film lithium battery is provided, comprising applying a cathode current collector, a cathode material, an anode current collector, and an electrolyte layer separating the cathode material from the anode current collector to a substrate, wherein at least one of the layers contains lithiated compounds that is patterned at least in part by a photolithography operation comprising removal of a photoresist material from the layer containing lithiated compounds by a process including a wet chemical treatment. Additionally, a method and apparatus for making lithium batteries by providing a first sheet that includes a substrate having a cathode material, an anode material, and a LiPON barrier / electrolyte layer separating the cathode material from the anode material; and removing a subset of first material to separate a plurality of cells from the first sheet. In some embodiments, the method further includes depositing second material on the sheet to cover the plurality of cells; and removing a subset of second material to separate a plurality of cells from the first sheet.
Owner:CYMBET CORP
Sulfur-carbon nanocomposites and their application as cathode materials in lithium-sulfur batteries
ActiveUS20110052998A1Minimize formationEasy to transportAlkaline accumulatorsElectrode thermal treatmentCarbon compositesPorous carbon
The invention is directed in a first aspect to a sulfur-carbon composite material comprising: (i) a bimodal porous carbon component containing therein a first mode of pores which are mesopores, and a second mode of pores which are micropores; and (ii) elemental sulfur contained in at least a portion of said micropores. The invention is also directed to the aforesaid sulfur-carbon composite as a layer on a current collector material; a lithium ion battery containing the sulfur-carbon composite in a cathode therein; as well as a method for preparing the sulfur-composite material.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
THIN-FILM BATTERIES WITH POLYMER AND LiPON ELECTROLYTE LAYERS AND METHOD
InactiveUS20070015061A1Improve environmental resistanceInhibition formationFinal product manufactureElectrode carriers/collectorsLithium metalPolymer gel
A method and apparatus for making thin-film batteries having composite multi-layered electrolytes with soft electrolyte between hard electrolyte covering the negative and / or positive electrode, and the resulting batteries. In some embodiments, foil-core cathode sheets each having a cathode material (e.g., LiCoO2) covered by a hard electrolyte on both sides, and foil-core anode sheets having an anode material (e.g., lithium metal) covered by a hard electrolyte on both sides, are laminated using a soft (e.g., polymer gel) electrolyte sandwiched between alternating cathode and anode sheets. A hard glass-like electrolyte layer obtains a smooth hard positive-electrode lithium-metal layer upon charging, but when very thin, have randomly spaced pinholes / defects. When the hard layers are formed on both the positive and negative electrodes, one electrode's dendrite-short-causing defects on are not aligned with the other electrode's defects. The soft electrolyte layer both conducts ions across the gap between hard electrolyte layers and fills pinholes.
Owner:CYMBET CORP
Graphene/metal oxide composite cathode material for lithium ion battery and preparation
InactiveCN102646817APromote circulationExcellent rate performanceCell electrodesHigh energyIn situ polymerization
The invention belongs to the fields of material synthesis and energy technology, and especially relates to a graphene / metal oxide composite cathode material for lithium ion batteries and a preparation method thereof. Grapheme is dispersed into various metal oxide precursor salt solutions; a graphene / metal oxide compound is obtained directly by a hydrothermal method, or an graphene / metal oxide compound is obtained by a liquid in-situ polymerization method or a coprecipitation process; and the graphene / metal oxide compound is obtained by heat treatment or hydrothermal treatment. In the invention, the novel three-dimensional composite cathode material of graphene-coated metal oxide or graphene-anchored metal oxide is prepared by carrying metal oxide particles with graphene as a carrier. The obtained composite material can be used as a lithium ion battery cathode, which has a high specific capacity, excellent cycle stability and rate capability, and is expected to be used as a lithium ion battery cathode material with a high energy density and a high power density.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Low Cost Solid State Rechargeable Battery and Method of Manufacturing Same
InactiveUS20090092903A1Solid electrolytesElectrode thermal treatmentOptoelectronicsConductive materials
A solid state Li battery and an all ceramic Li-ion battery are disclosed. The all ceramic battery has a solid state battery cathode comprised of a mixture of an active cathode material, an electronically conductive material, and a solid ionically conductive material. The cathode mixture is sintered. The battery also has a solid state battery anode comprised of a mixture of an active anode material, an electronically conductive material, and a solid ionically conductive material. The anode mixture is sintered. The battery also has a solid state separator positioned between said solid state battery cathode and said solid state battery anode. In the solid state Li battery the all ceramic anode is replaced with an evaporated thin film Li metal anode.
Owner:JOHNSON IP HLDG LLC
Thin-film batteries with soft and hard electrolyte layers and method
InactiveUS20070015060A1Improve environmental resistanceInhibition formationFinal product manufactureConductive materialLithium metalPolymer gel
A method and apparatus for making thin-film batteries having composite multi-layered electrolytes with soft electrolyte between hard electrolyte covering the negative and / or positive electrode, and the resulting batteries. In some embodiments, foil-core cathode sheets each having a cathode material (e.g., LiCoO2) covered by a hard electrolyte on both sides, and foil-core anode sheets having an anode material (e.g., lithium metal) covered by a hard electrolyte on both sides, are laminated using a soft (e.g., polymer gel) electrolyte sandwiched between alternating cathode and anode sheets. A hard glass-like electrolyte layer obtains a smooth hard positive-electrode lithium-metal layer upon charging, but when very thin, have randomly spaced pinholes / defects. When the hard layers are formed on both the positive and negative electrodes, one electrode's dendrite-short-causing defects on are not aligned with the other electrode's defects. The soft electrolyte layer both conducts ions across the gap between hard electrolyte layers and fills pinholes.
Owner:CYMBET CORP
Novel composite cathodes, electrochemical cells comprising novel composite cathodes, and processes for fabricating same
The present invention pertains to composite cathodes suitable for use in an electrochemical cell, said cathodes comprising: (a) an electroactive sulfur-containing cathode material, wherein said electroactive sulfur-containing cathode material, in its oxidized state, comprises a polysulfide moiety of the formula —Sm—, wherein m is an integer equal to or greater than 3; and, (b) an electroactive transition metal chalcogenide composition, which encapsulates said electroactive sulfur-containing cathode material, and which retards the transport of anionic reduction products of said electroactive sulfur-containing cathode material, said electroactive transition metal chalcogenide composition comprising an electroactive transition metal chalcogenide having the formula MjYk(OR)l wherein: M is a transition metal; Y is the same or different at each occurrence and is oxygen, sulfur, or selenium; R is an organic group and is the same or different at each occurrence; j is an integer ranging from 1 to 12; k is a number ranging from 0 to 72; and l is a number ranging from 0 to 72; with the proviso that k and l cannot both be 0. The present invention also pertains to methods of making such composite cathodes, cells comprising such composite cathodes, and methods of making such cells.
Owner:SION POWER CORP
Lithium-ion secondary battery
InactiveUS20070026315A1Safer chemistry characteristicLow cathode costPrimary cell to battery groupingFinal product manufactureManganateSpinel
A lithium-ion battery includes a cathode that includes an active cathode material. The active cathode material includes a cathode mixture that includes a lithium cobaltate and a manganate spinel a manganate spinel represented by an empirical formula of Li(1+x1)(Mn1−y1A′y2)2−x2Oz1. The lithium cobaltate and the manganate spinel are in a weight ratio of lithium cobaltate: manganate spinel between about 0.95:0.05 to about 0.55:0.45. A lithium-ion battery pack employs a cathode that includes an active cathode material as described above. A method of forming a lithium-ion battery includes the steps of forming an active cathode material as described above; forming a cathode electrode with the active cathode material; and forming an anode electrode in electrical contact with the cathode via an electrolyte.
Owner:BOSTON POWER INC
Structured electrolyte for micro-battery
InactiveUS20060154141A1Fine surfaceSolid electrolytesFinal product manufactureOptoelectronicsElectrolyte
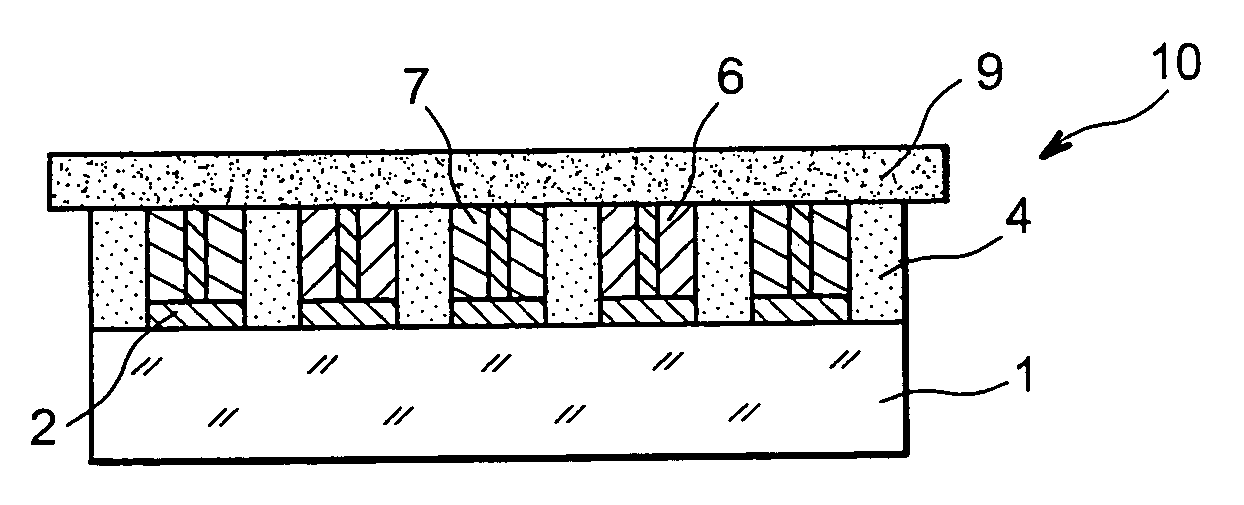
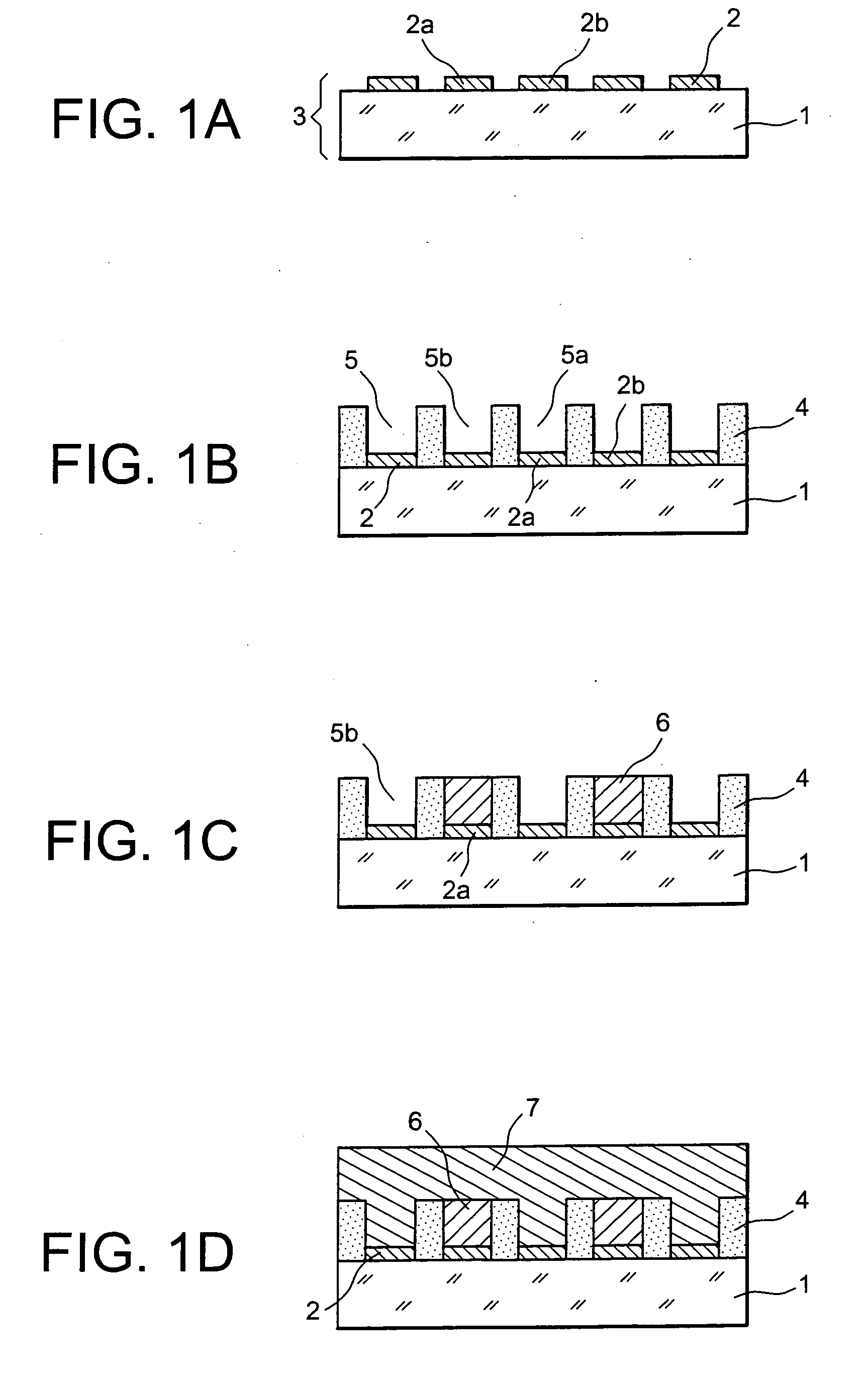
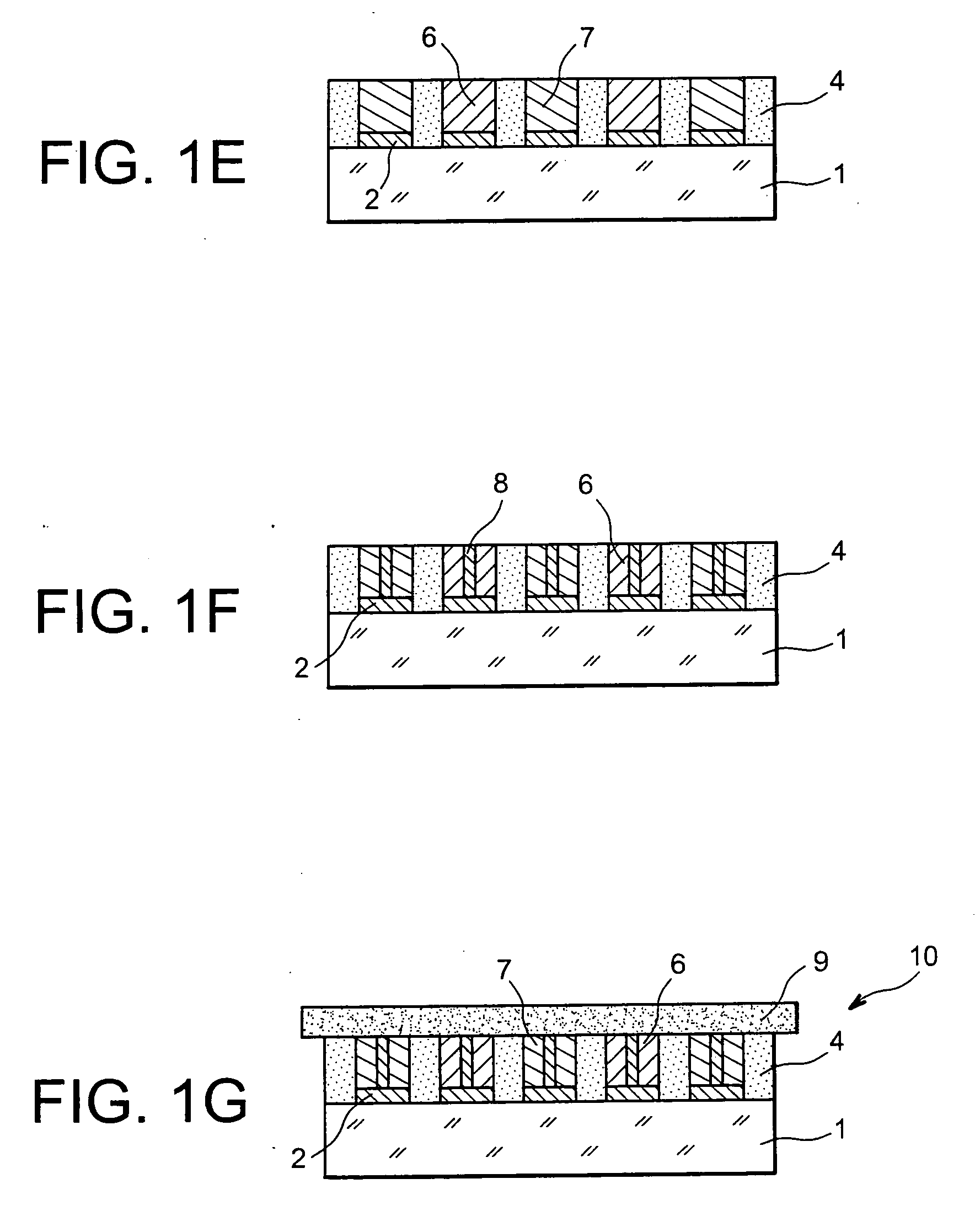
In order to increase the capacity of an “all-solid” type micro-battery, the layer of electrolyte is structured: transversing cavities are created in the flat layer, advantageously at the level of patches of collector material, then filled by anode or cathode material.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Silicon oxide based high capacity anode materials for lithium ion batteries
Silicon oxide based materials, including composites with various electrical conductive compositions, are formulated into desirable anodes. The anodes can be effectively combined into lithium ion batteries with high capacity cathode materials. In some formulations, supplemental lithium can be used to stabilize cycling as well as to reduce effects of first cycle irreversible capacity loss. Batteries are described with surprisingly good cycling properties with good specific capacities with respect to both cathode active weights and anode active weights.
Owner:IONBLOX INC
Active metal/aqueous electrochemical cells and systems
InactiveUS7645543B2Degree of flexibilityWithout performanceFuel and primary cellsAlkaline accumulatorsElectrochemical cellBattery cell
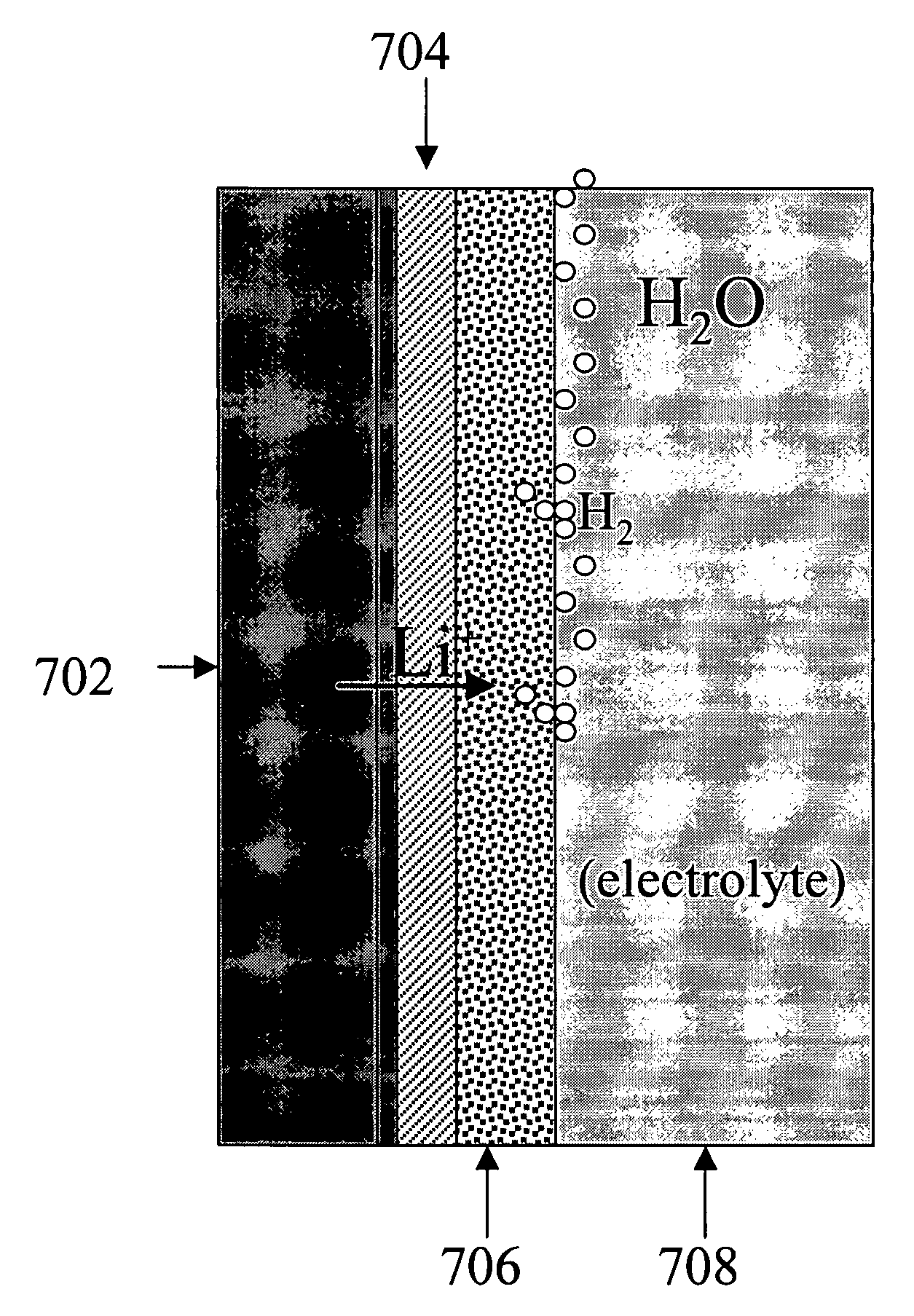
Alkali (or other active) metal battery and other electrochemical cells incorporating active metal anodes together with aqueous cathode / electrolyte systems. The battery cells have a highly ionically conductive protective membrane adjacent to the alkali metal anode that effectively isolates (de-couples) the alkali metal electrode from solvent, electrolyte processing and / or cathode environments, and at the same time allows ion transport in and out of these environments. Isolation of the anode from other components of a battery cell or other electrochemical cell in this way allows the use of virtually any solvent, electrolyte and / or cathode material in conjunction with the anode. Also, optimization of electrolytes or cathode-side solvent systems may be done without impacting anode stability or performance. In particular, Li / water, Li / air and Li / metal hydride cells, components, configurations and fabrication techniques are provided.
Owner:POLYPLUS BATTERY CO INC
Electrochemical method of producing nano-scaled graphene platelets
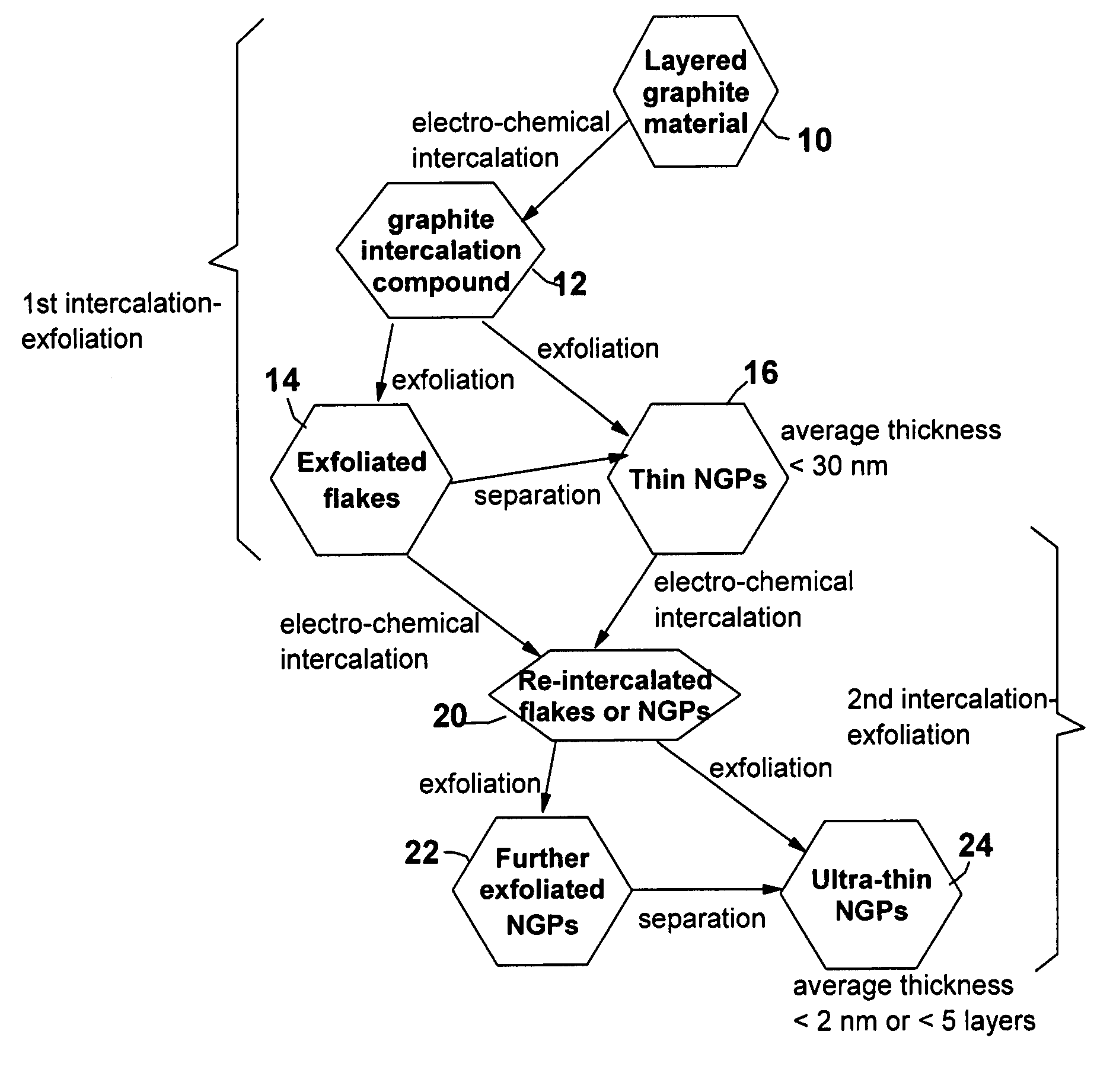
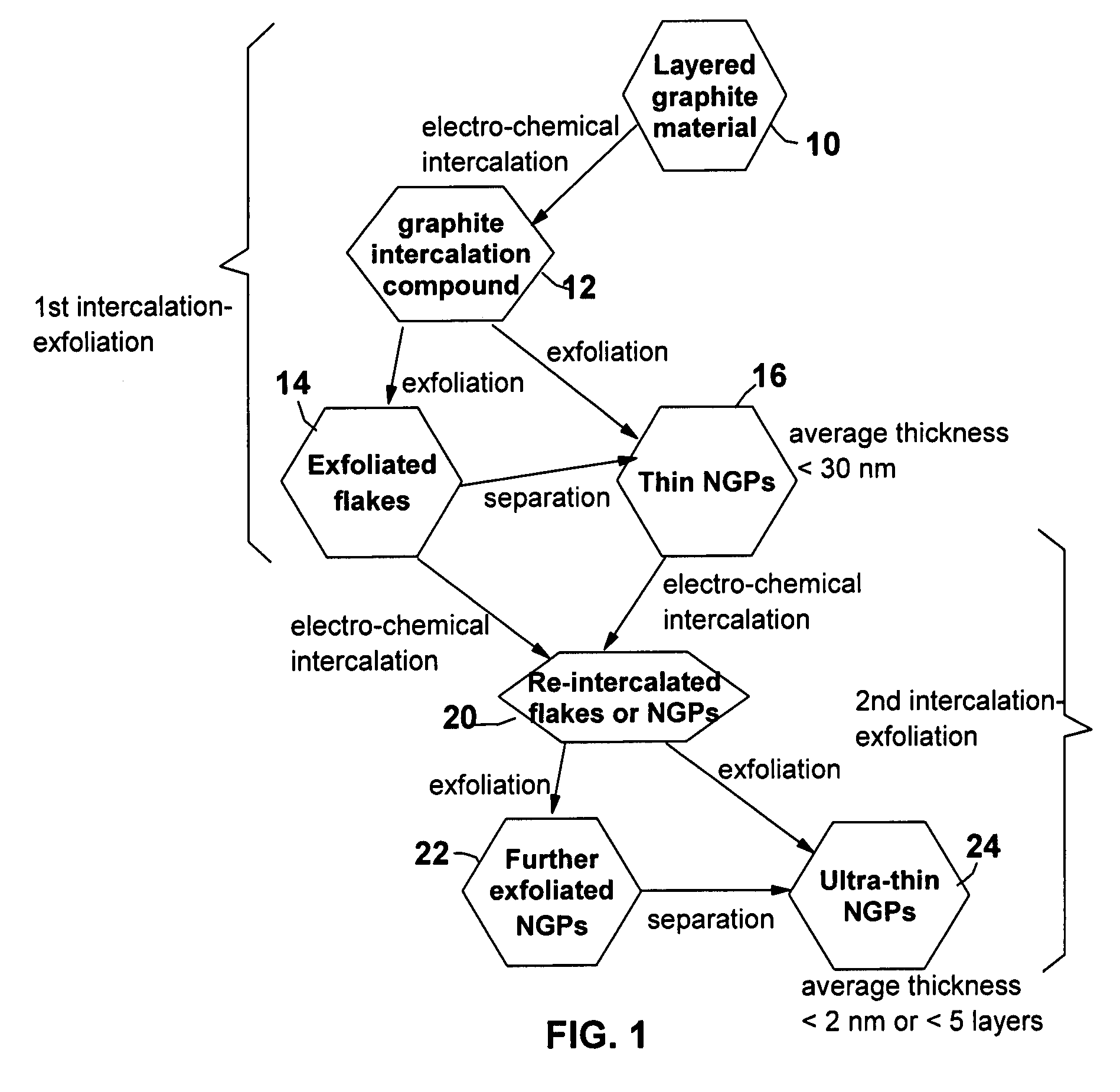
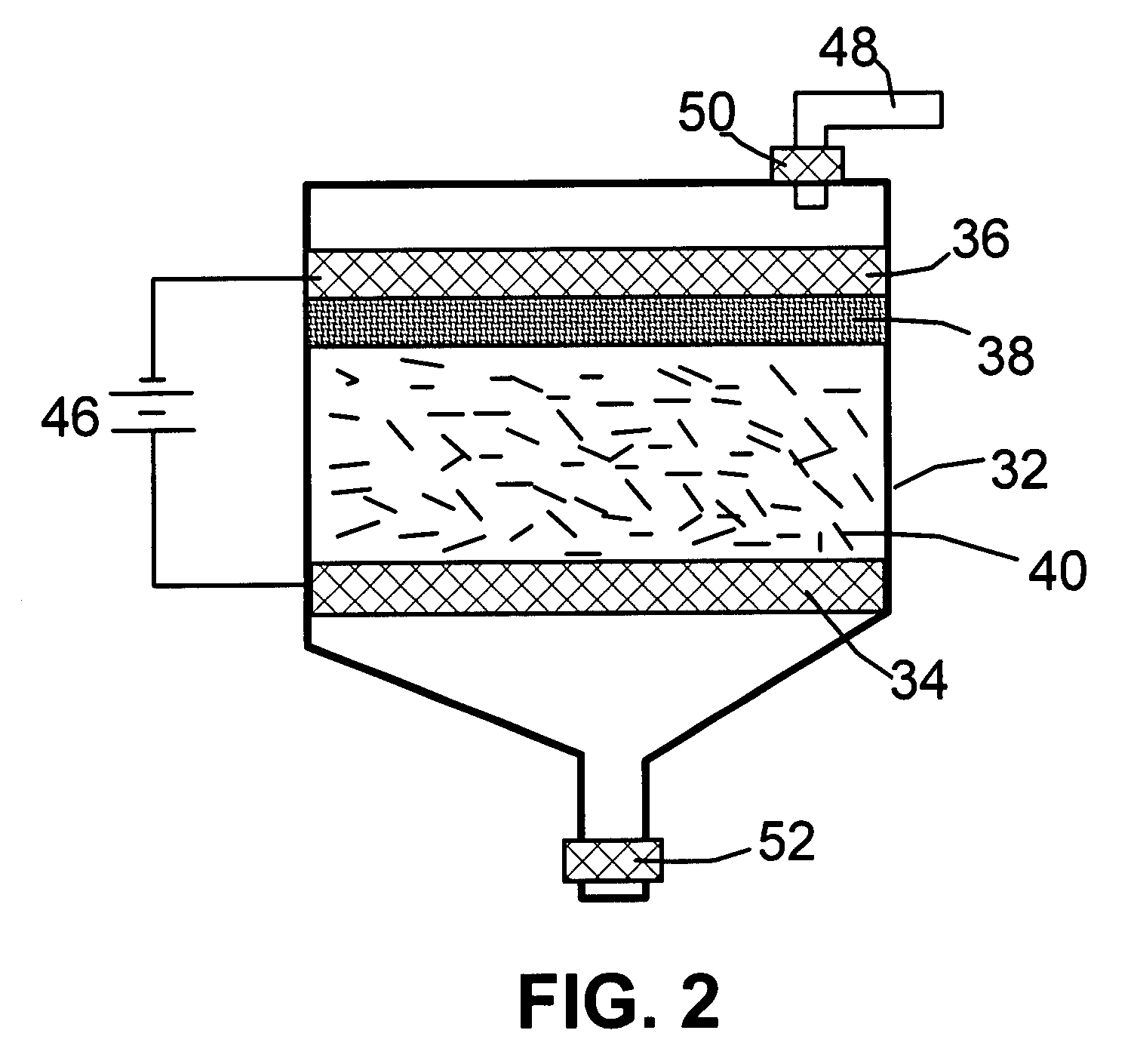
A method of producing nano-scaled graphene platelets with an average thickness smaller than 30 nm from a layered graphite material. The method comprises (a) forming a carboxylic acid-intercalated graphite compound by an electrochemical reaction which uses a carboxylic acid as both an electrolyte and an intercalate source, the layered graphite material as an anode material, and a metal or graphite as a cathode material, and wherein a current is imposed upon the cathode and the anode at a current density for a duration of time sufficient for effecting the electrochemical reaction; (b) exposing the intercalated graphite compound to a thermal shock to produce exfoliated graphite; and (c) subjecting the exfoliated graphite to a mechanical shearing treatment to produce the nano-scaled graphene platelets. Preferred carboxylic acids are formic acid and acetic acid. The exfoliation step in the instant invention does not involve the evolution of undesirable species, such as NOx and SOx, which are common by-products of exfoliating conventional sulfuric or nitric acid-intercalated graphite compounds. The nano-scaled platelets are candidate reinforcement fillers for polymer nanocomposites. Nano-scaled graphene platelets are much lower-cost alternatives to carbon nano-tubes or carbon nano-fibers.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
Binary, ternary and quaternary lithium phosphates, method for the production thereof and use of the same
ActiveUS20040151649A1High specific capacitySimple and inexpensivePhosphatesPeroxides/peroxyhydrates/peroxyacids/superoxides/ozonidesRoom temperatureReducing atmosphere
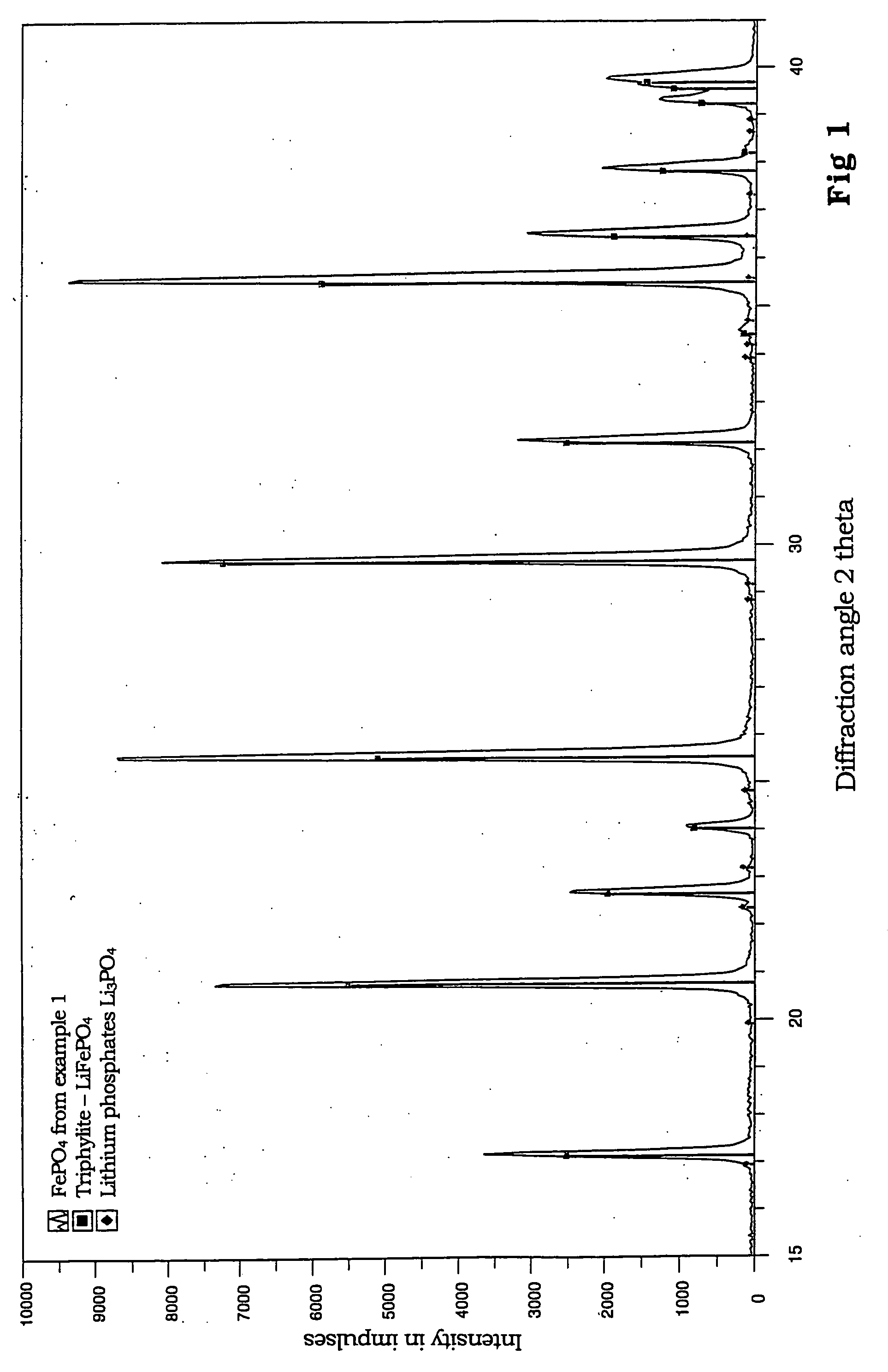
The invention relates to binary, ternary and quaternary lithium phosphates of general formula Li(FexM<1>yM<2>z)PO4 wherein M<1 >represents at least one element of the group comprising Sc, Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Al, Zr, and La; M<2 >represents at least one element of the group comprising Sc, Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Al, Zr, and La; x=between 0.5 and 1, y=between 0 and 0.5, z=between 0 and 0.5, provided that x+y+z=1, or x=0, y =1 and z=0. The said lithium phosphates can be obtained according to a method whereby precursor compounds of elements Li, Fe, M<1 >and / or M<2 >are precipitated from aqueous solutions and the precipitation product is dried in an inert gas atmosphere or a reducing atmosphere at a temperature which is between room temperature and approximately 200° C. and tempered at a temperature of between 300° C. and 1000° C. The inventive lithium phosphates have a very high capacity when used as cathode material in lithium accumulators.
Owner:ZENT FUR SONNENENERGIE & WASSERSTOFF FORSCHUNG BADEN WURTTEMBERG GEMEINNUTZIGE STIFTUNG
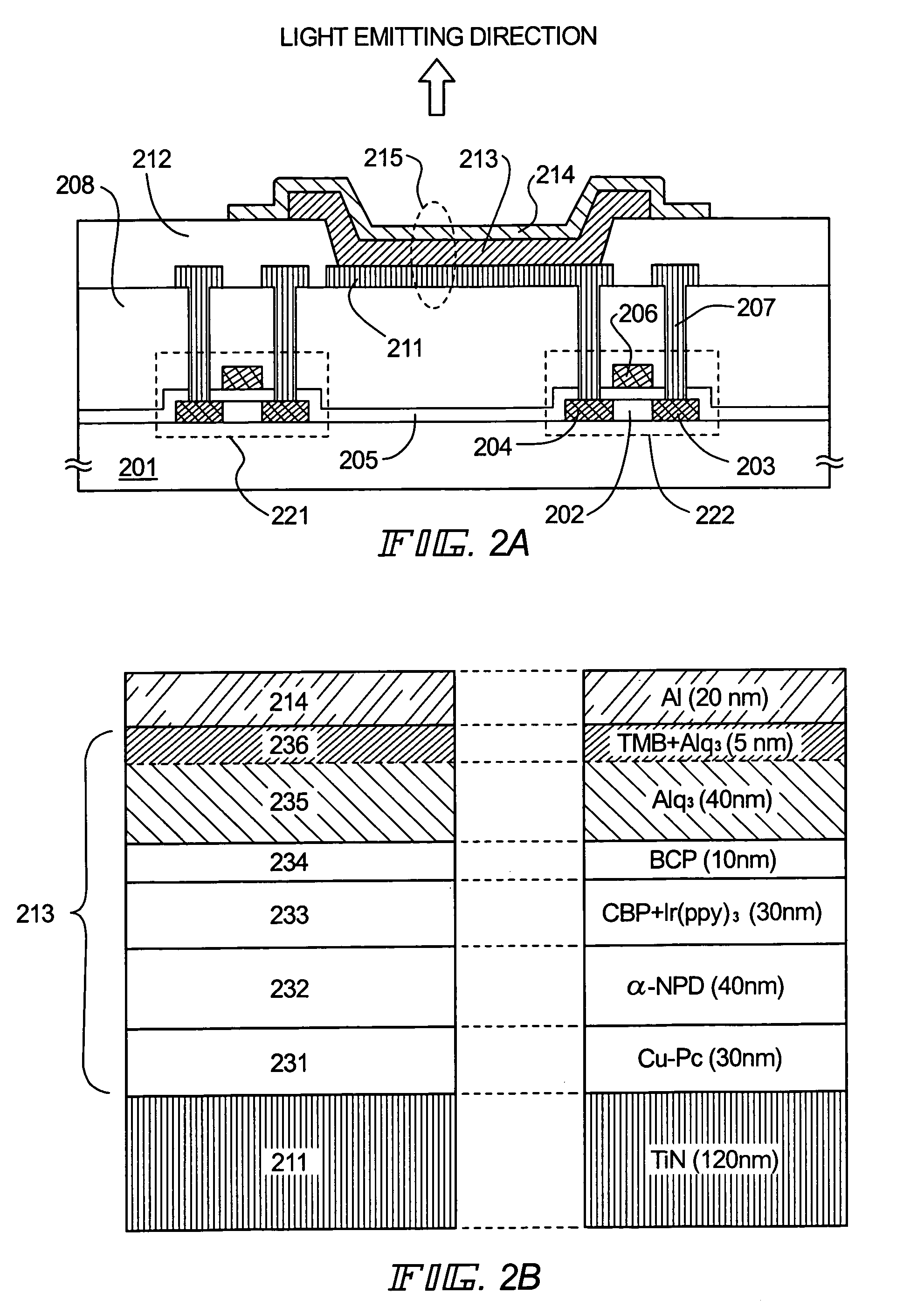
Light emitting device
InactiveUS7141817B2Improve injectionAvoid quenchingSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectron injectionElectron donor
By doping an organic compound functioning as an electron donor (hereinafter referred to as donor molecules) into an organic compound layer contacting a cathode, donor levels can be formed between respective LUMO (lowest unoccupied molecular orbital) levels between the cathode and the organic compound layer, and therefore electrons can be injected from the cathode, and transmission of the injected electrons can be performed with good efficiency. Further, there are no problems such as excessive energy loss, deterioration of the organic compound layer itself, and the like accompanying electron movement, and therefore an increase in the electron injecting characteristics and a decrease in the driver voltage can both be achieved without depending on the work function of the cathode material.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Lithium-ion secondary battery
InactiveUS20080008933A1Safer chemistry characteristicLow cathode costPrimary cell to battery groupingElectrode carriers/collectorsManganateManganese
In one embodiment, an active cathode material comprises a mixture that includes: at least one of a lithium cobaltate and a lithium nickelate; and at least one of a manganate spinel represented by an empirical formula of Li(1+x1)(Mn1−y1A′y1)2−x1Oz1 and an olivine compound represented by an empirical formula of Li(1−x2)A″x2MPO4. In another embodiment, an active cathode material comprises a mixture that includes: a lithium nickelate selected from the group consisting of LiCoO2-coated LiNi0.8Co0.15Al0.05O2, and Li(Ni1 / 3Co1 / 3Mn1 / 3)O2; and a manganate spinel represented by an empirical formula of Li(1+x7)Mn2−y7Oz7. A lithium-ion battery and a battery pack each independently employ a cathode that includes an active cathode material as described above. A method of forming a lithium-ion battery includes the steps of forming an active cathode material as described above; forming a cathode electrode with the active cathode material; and forming an anode electrode in electrical contact with the cathode via an electrolyte. A system comprises a portable electronic device and a battery pack or lithium-ion battery as described above.
Owner:BOSTON POWER INC
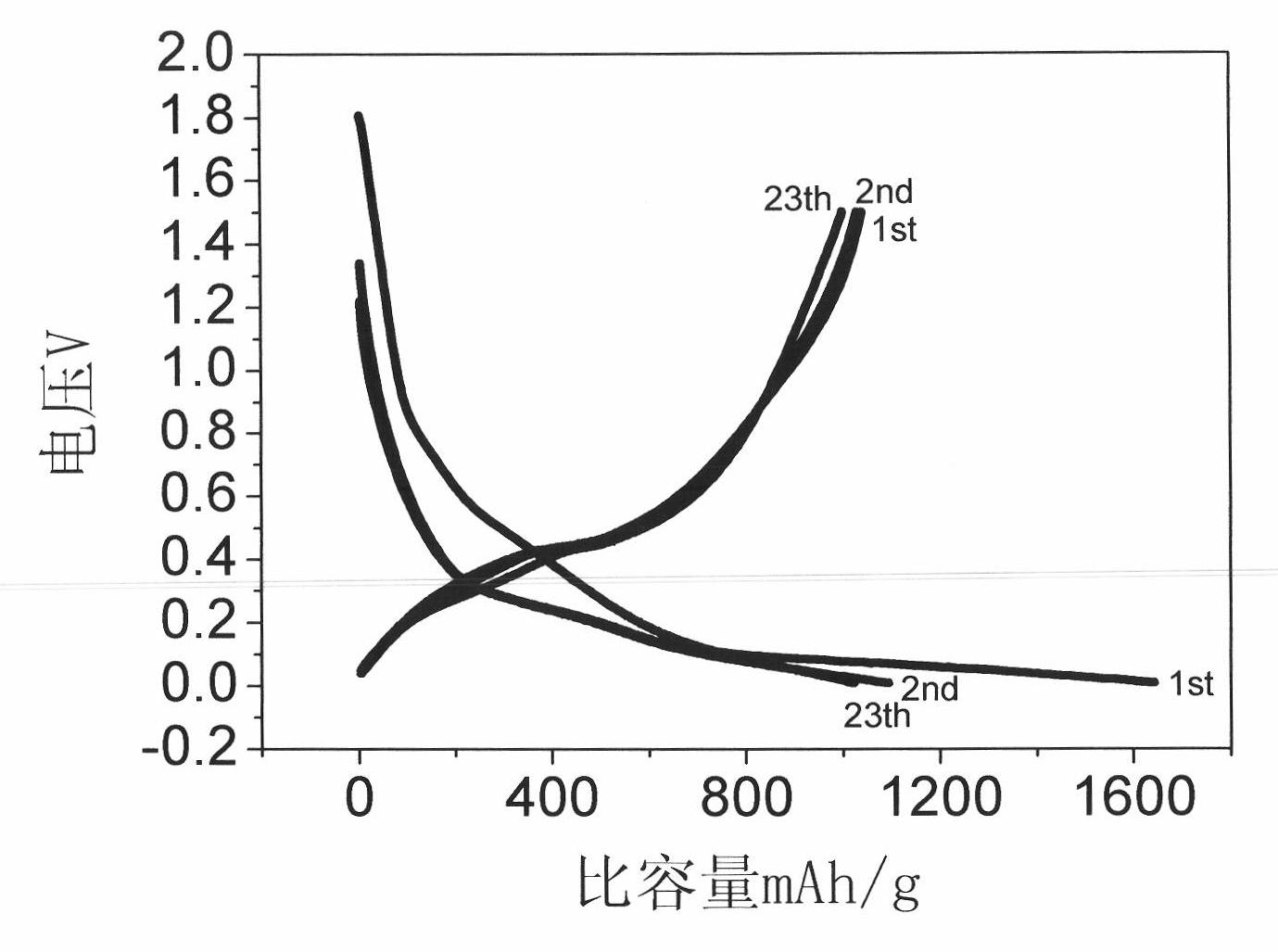
Preparation method of silicon and carbon-coated graphene composite cathode material
ActiveCN103050666ARealize in situ restorationThe preparation process is simple, convenient and practicalMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesCarbon coatedStructural stability
The invention discloses a preparation method of a silicon and carbon-coated graphene composite cathode material. The technical problem to be solved is to enhance the electronic conductivity of the silicon-based cathode material, buffer the volume effect produced in the process of deintercalation of the lithium in the silicon-based cathode material and enhance the structure stability in the circulation process of the material at the same time. The material is prepared by using a spray drying-thermally decomposing treatment process in the invention. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: evenly dispersing nano silicon and graphite micro powder in a dispersion solution of oxidized graphene, carrying out thermal treatment under an inert protection atmosphere after spray drying, subsequently cooling along a furnace to obtain the silicon and carbon-coated graphene composite cathode material. The extra binder does not need to add in the process of manufacturing balls in the invention and the outer oxidized graphene is thermally reduced in situ to graphene in the thermal treatment process of the composite precursor, so that the process is simple and easy to operate; and the practical degree is high. The prepared composite material has the advantages of great reversible capacity, designable capacity, good cycling performance and high-current discharging performance, high tap density and the like.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Graphene/silicon lithium ion battery cathode material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101924211AHigh specific capacityImprove cycle stabilityCell electrodesComposite filmNew energy
The invention discloses a grapheme / silicon composite material for a lithium ion battery cathode material and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the fields of electrochemistry and new energy materials. The method comprises the following steps of: using graphite as a raw material; oxidizing the graphite into oxidized graphite by adopting oxidants of concentrated sulfuric acid and potassium permanganate; then, ultrasonically stripping the oxidized graphite to prepare oxidized graphene; mixing oxidized graphene in different proportions with nano silicon powder; ultrasonically dispersing, filtering or directly drying into a cake / film; and roasting under a reduction atmosphere to prepare self-support graphene / silicon composite film materials in different proportions. Proved by electrochemistry tests, the graphene / silicon composite film material prepared by the method has higher specific capacity and cycle stability, simple preparation method and easy mass production and consequently is an ideal high-energy lithium ion battery cathode material.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING +1
Gradient cathode material for lithium rechargeable batteries
InactiveUS6921609B2Increase capacityImproved cyclabilityAluminium compoundsAlkaline accumulatorsManganesePotassium
A composition suitable for use as a cathode material of a lithium battery includes a core material having an empirical formula LixM′zNi1−yM″yO2. “x” is equal to or greater than about 0.1 and equal to or less than about 1.3. “y” is greater than about 0.0 and equal to or less than about 0.5. “z” is greater than about 0.0 and equal to or less than about 0.2. M′ is at least one member of the group consisting of sodium, potassium, nickel, calcium, magnesium and strontium. M″ is at least one member of the group consisting of cobalt, iron, manganese, chromium, vanadium, titanium, magnesium, silicon, boron, aluminum and gallium. A coating on the core has a greater ratio of cobalt to nickel than the core. The coating and, optionally, the core can be a material having an empirical formula Lix1Ax2Ni1−y1−z1Coy1Bz1Oa. “x1” is greater than about 0.1 a equal to or less than about 1.3. “x2,”“y1” and “z1” each is greater than about 0.0 and equal to or less than about 0.2. “a” is greater than 1.5 and less than about 2.1. “A” is at least one element selected from the group consisting of barium, magnesium, calcium and strontium. “B” is at least one element selected from the group consisting of boron, aluminum, gallium, manganese, titanium, vanadium and zirconium.
Owner:TIAX LLC
Large-capacity high power polymer ferric lithium phosphate power cell and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101409369AImprove securityIncrease capacityElectrode manufacturing processesFinal product manufactureSlurryElectric vehicle
The invention discloses a large-capacity high-power polymer lithium iron phosphate power battery. The weight ratio of anode slurry is as follows: 81 to 85 percent of lithium iron phosphate, 1 to 5.5 percent of superconduction carbon, 0 to 2.5 percent of conductive carbon soot, 0 to 4 percent of conductive black lead, 0 to 2.5 percent of crystalline flake graphite, 0 to 2 percent of carbon nanometer tube as well as 6 to 7.5 percent of polyvinylidene fluoride; the weight ratio of cathode slurry is as follows: 89 to 91 percent of cathode material, 1 to 3.5 percent of superconduction carbon, 0 to 2 percent of conductive carbon soot, 0 to 4 percent of conductive black lead, 2.5 to 3.5 percent of styrene-butadiene rubber as well as 1.5 to 2 percent of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose; the steps for preparing the battery are as follows: preparing slurry, coating the anode and the cathode, rolling and pressing a polar plate, transversely and separately cutting the polar plate, baking the polar plate, welding the polar ears of the anode and the cathode, preparing a battery cell, putting the electric core into a shell and sealing, baking the electric core, injecting liquid into the battery as well as forming the battery and dividing the volume of the battery. The invention relates to a lithium-ion secondary battery which can provide drive energies for electric tools, electric bicycles, motor cars and electric vehicles.
Owner:MCNAIR TECH
Method for preparing porous silicon/carbon composite material by using diatomite as raw material and application
The invention provides a method for preparing a porous silicon / carbon composite material by using diatomite as the raw material, which is characterized by comprising the following steps of: with the diatomite as the raw material, performing simple refinement and purification processing to obtain silicon with a porous structure by means of metallothermic reduction; performing mechanical ball-milling with the carbon materials and / or precursors of carbon, hydro-thermal carbonization, pyrolytic carbonization or chemical vapor deposition to prepare the porous silicon / carbon composite material. Thecomposite material can be directly used as the cathode of the lithium ion battery, or can be mixed with other cathode materials to be used as the cathode materials of the lithium ion battery. Compared with a pure silicon material as the cathode material of the lithium ion battery, the porous silicon / carbon composite material has the advantages that the first reversible capacity and the circulation stability of the material are greatly improved. In the method, the inexpensive and accessible natural minerals are used as the raw materials, thus the cost is low and the preparation method is simple.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
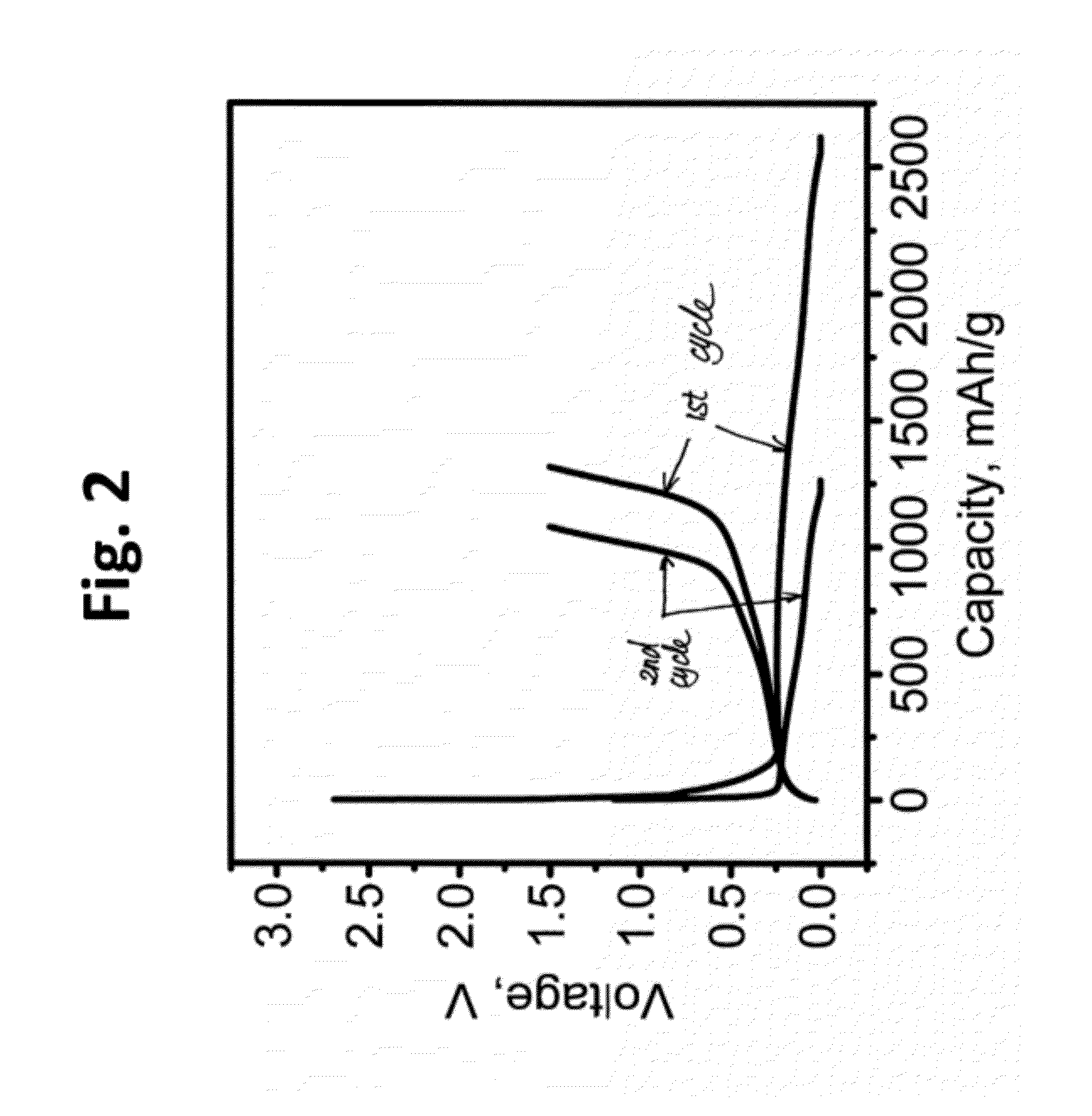
Very Long Cycling of Lithium Ion Batteries with Lithium Rich Cathode Materials
Lithium ion batteries can be activated and then cycled to exploit a moderate fraction of the discharge cycling capacity such that the discharge capacity and average discharge voltage stay within initial values for thousands of cycles. The superior cycling performance has been achieved at relatively high discharge rates and for practical battery formats. Lithium ion battery performance can also be achieved with superior cycling performance with partially activated batteries such that good discharge capacities can be exploited for many thousands of cycles before the discharge capacity and average discharge voltage drops more than 20% from initial values. The positive electrode active material can be a lithium rich metal oxide. The activation of the battery can comprise phase changes of the active materials. As described herein, the phase changes can be manipulated to exploit a reasonable fraction of the available high capacity of the material while providing outstanding cycling stability.
Owner:IONBLOX INC
Manufacturing method of all solid state power lithium ion battery
ActiveCN108232318AReduce interface resistanceImprove securitySolid electrolytesFinal product manufactureHigh energyAdhesive
The invention discloses a manufacturing method of an all solid state power lithium ion battery. The manufacturing method comprises the steps of dissolving an anode active material, a conductive agent,an adhesive and a polymer electrolyte in a solvent, so as to prepare an anode sizing agent, applying the anode sizing agent to an anode current collector, performing thermal treatment and rolling treatment so as to obtain an anode piece; then dissolving a cathode material, a conductive agent, an adhesive and a polymer electrolyte in a solvent, so as to prepare a cathode sizing agent, applying thecathode sizing agent to a cathode current collector, and performing thermal treatment and rolling treatment so as to obtain a cathode piece; dissolving a polymer electrolyte, a filler and lithium salt in a solvent, so as to prepare an electrolyte solution; applying the electrolyte solution to the surface of the anode piece or the cathode piece, and performing thermal treatment to obtain an anodepiece or a cathode piece with an electrolyte layer; and finally, assembling the anode piece and the cathode piece in a winding or superposing manner, so as to prepare the all solid state lithium ion battery. The all solid state lithium battery prepared by the method has the advantages of lower interface resistance, higher energy density, high security and the like.
Owner:SHAANXI COAL & CHEM TECH INST
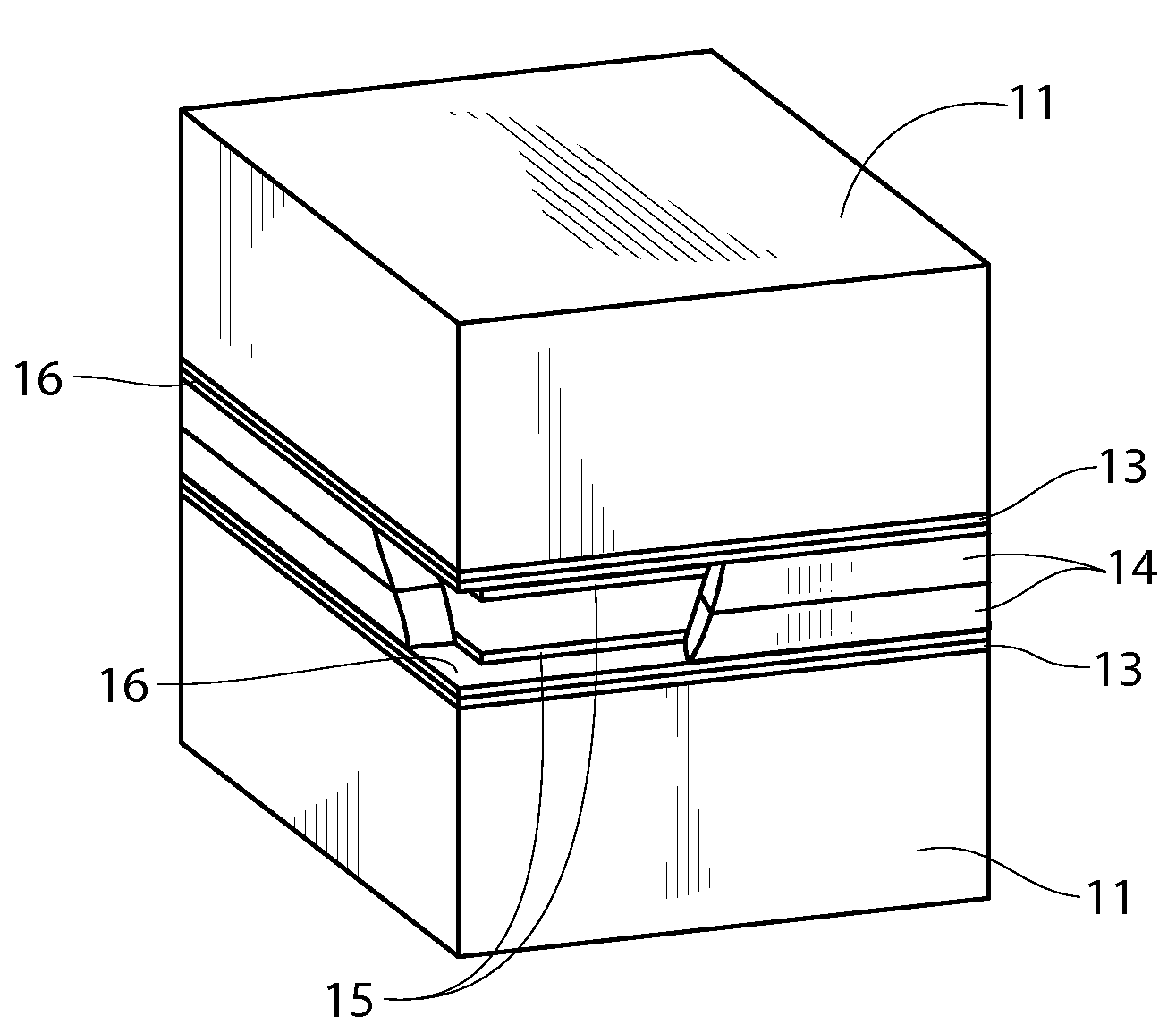
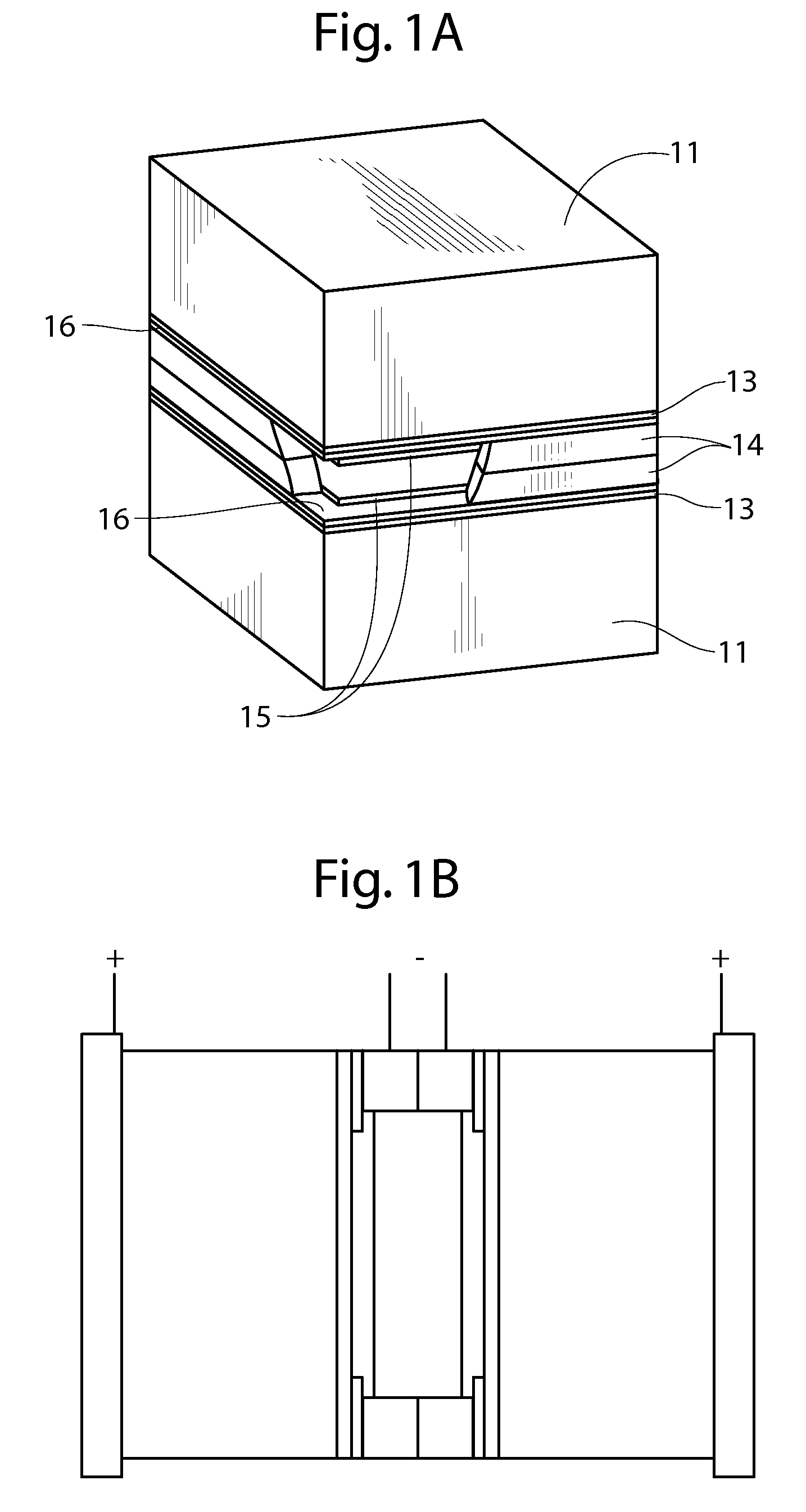
Continuous process for producing electrodes and alkali metal batteries having ultra-high energy densities
ActiveUS20170104204A1Increase energy densityImprove power densityFinal product manufactureElectrode carriers/collectorsTectorial membraneHigh energy
A process for producing an electrode for an alkali metal battery, comprising: (a) Continuously feeding an electrically conductive porous layer to an anode or cathode material impregnation zone, wherein the conductive porous layer has two opposed porous surfaces and contain interconnected conductive pathways and at least 70% by volume of pores; (b) Impregnating a wet anode or cathode active material mixture into the porous layer from at least one of the two porous surfaces to form an anode or cathode electrode, wherein the wet anode or cathode active material mixture contains an anode or cathode active material and an optional conductive additive mixed with a liquid electrolyte; and (c) Supplying at least a protective film to cover the at least one porous surface to form the electrode.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com