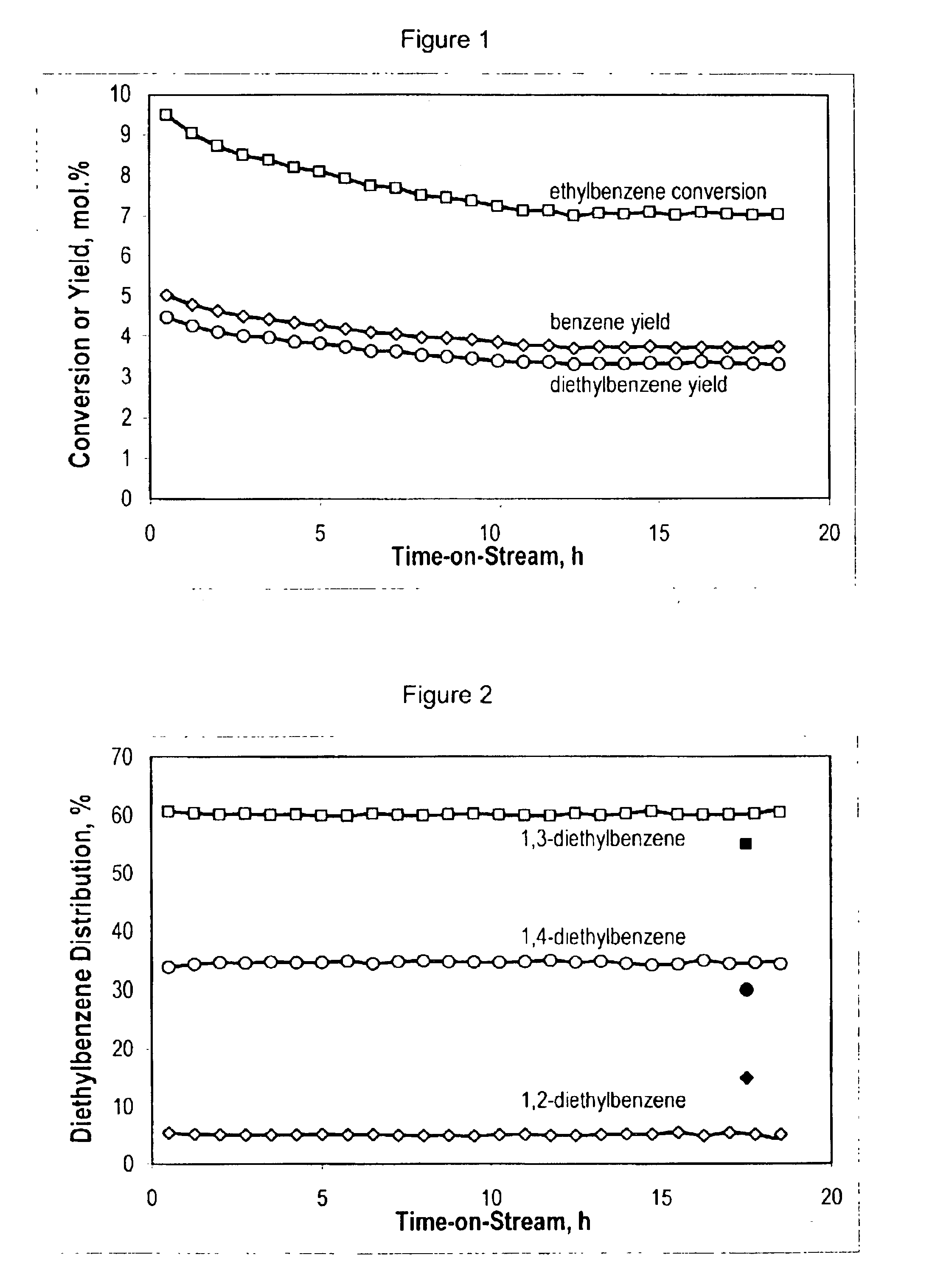
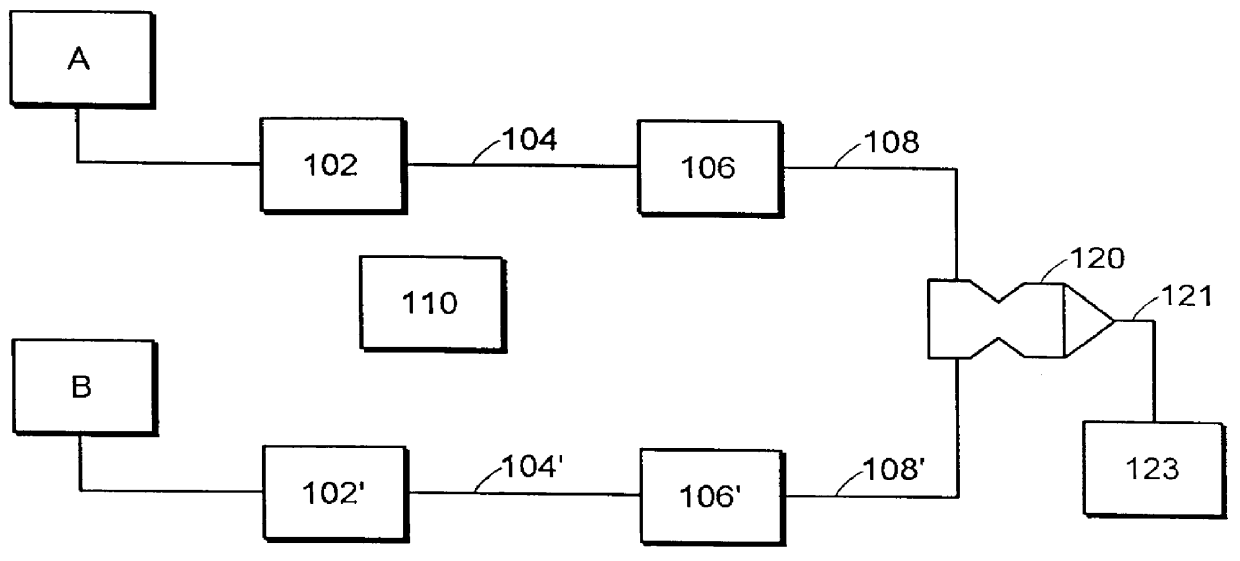
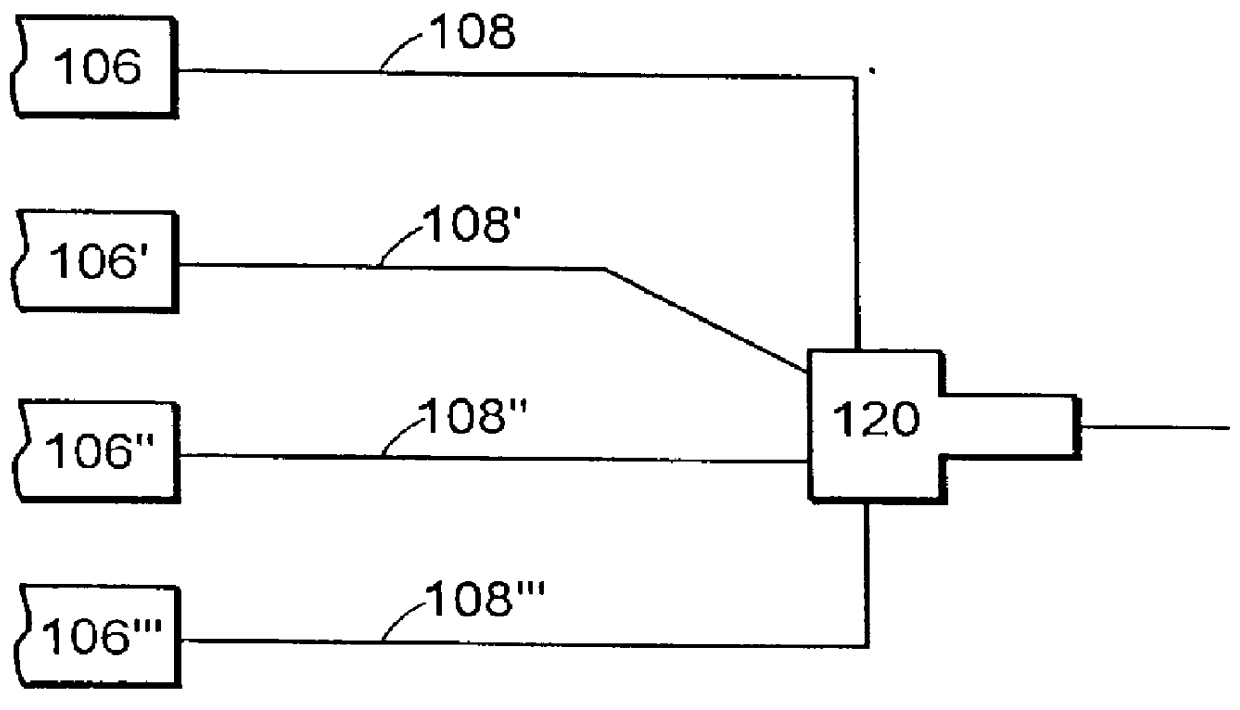
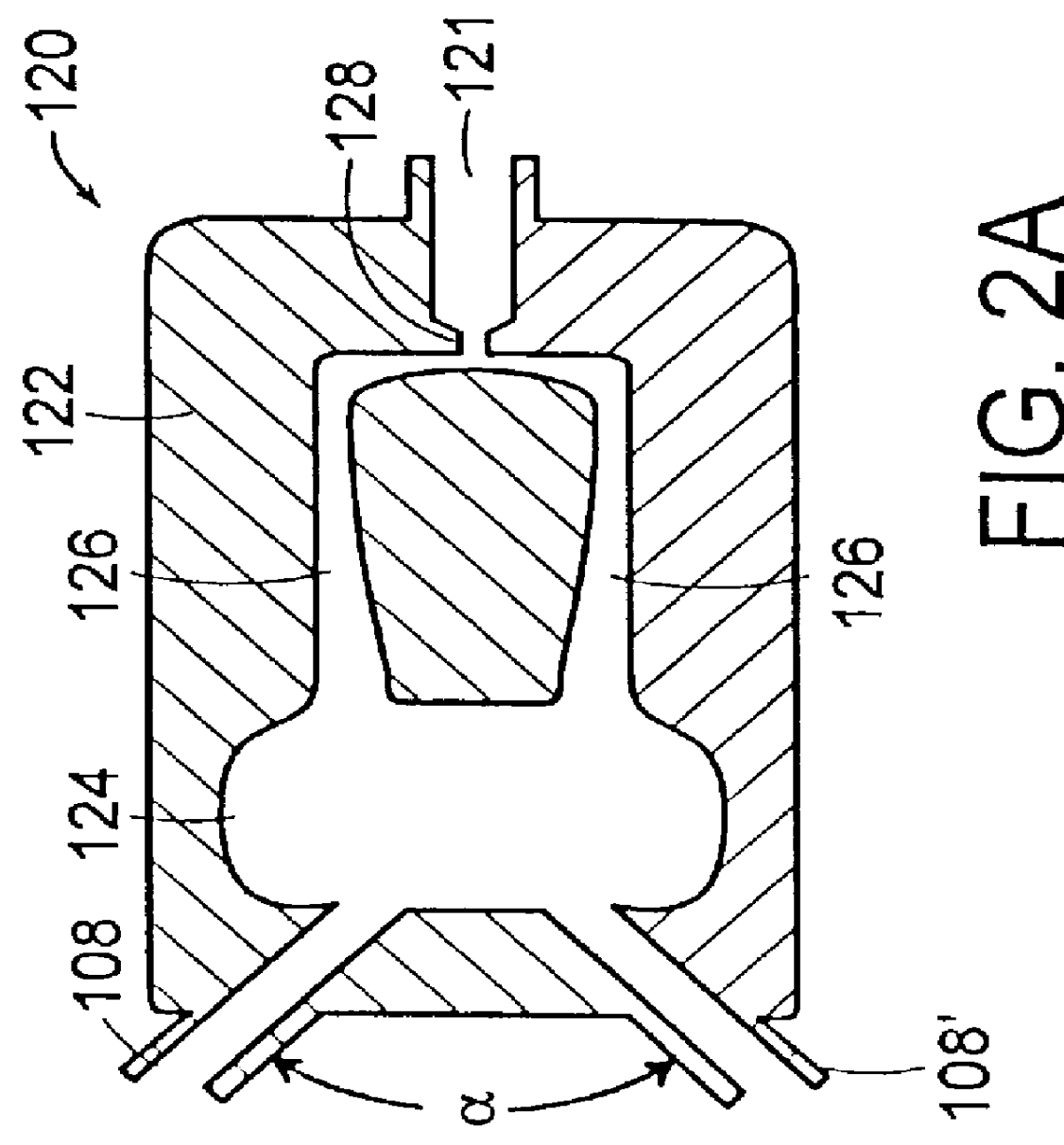
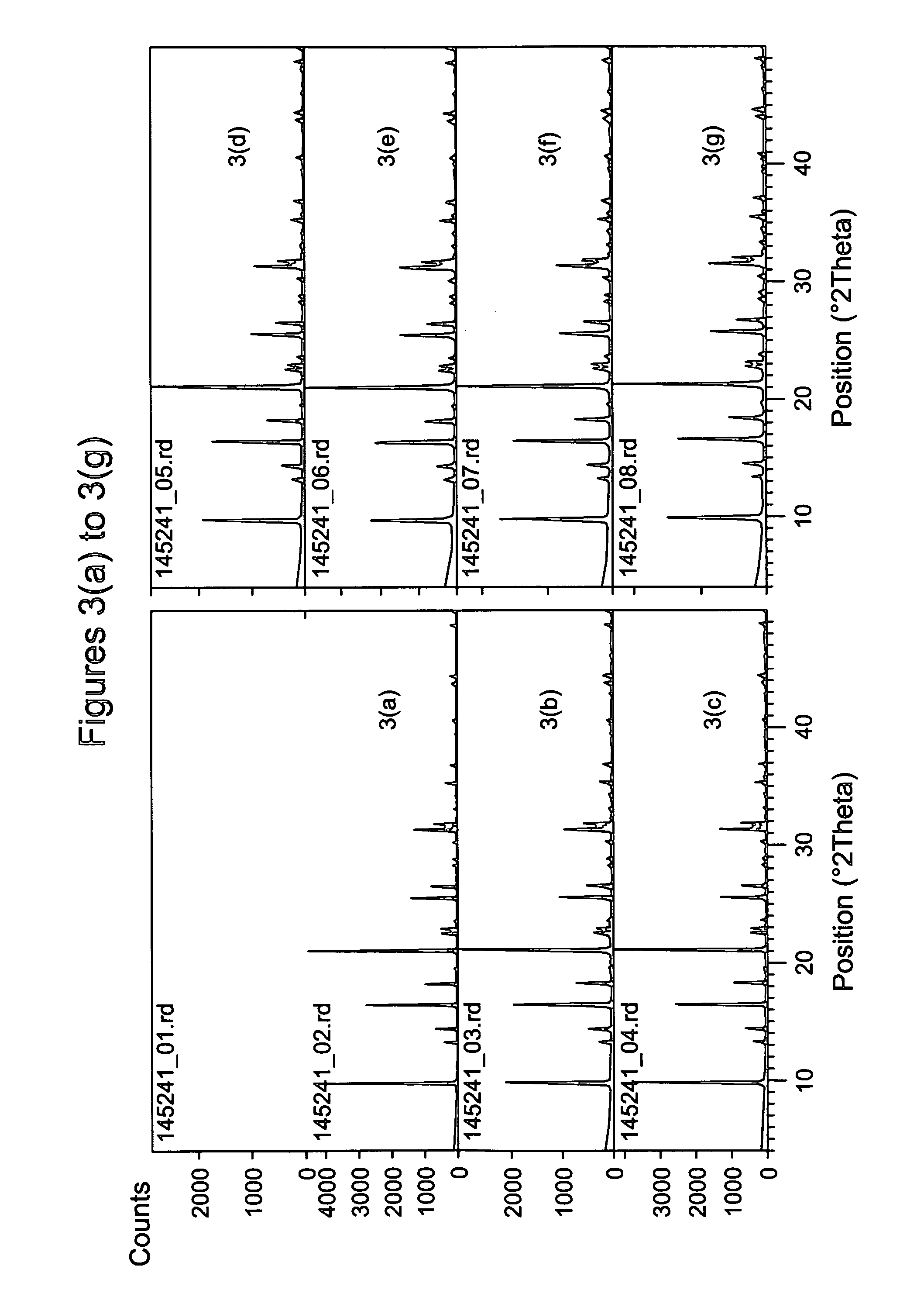
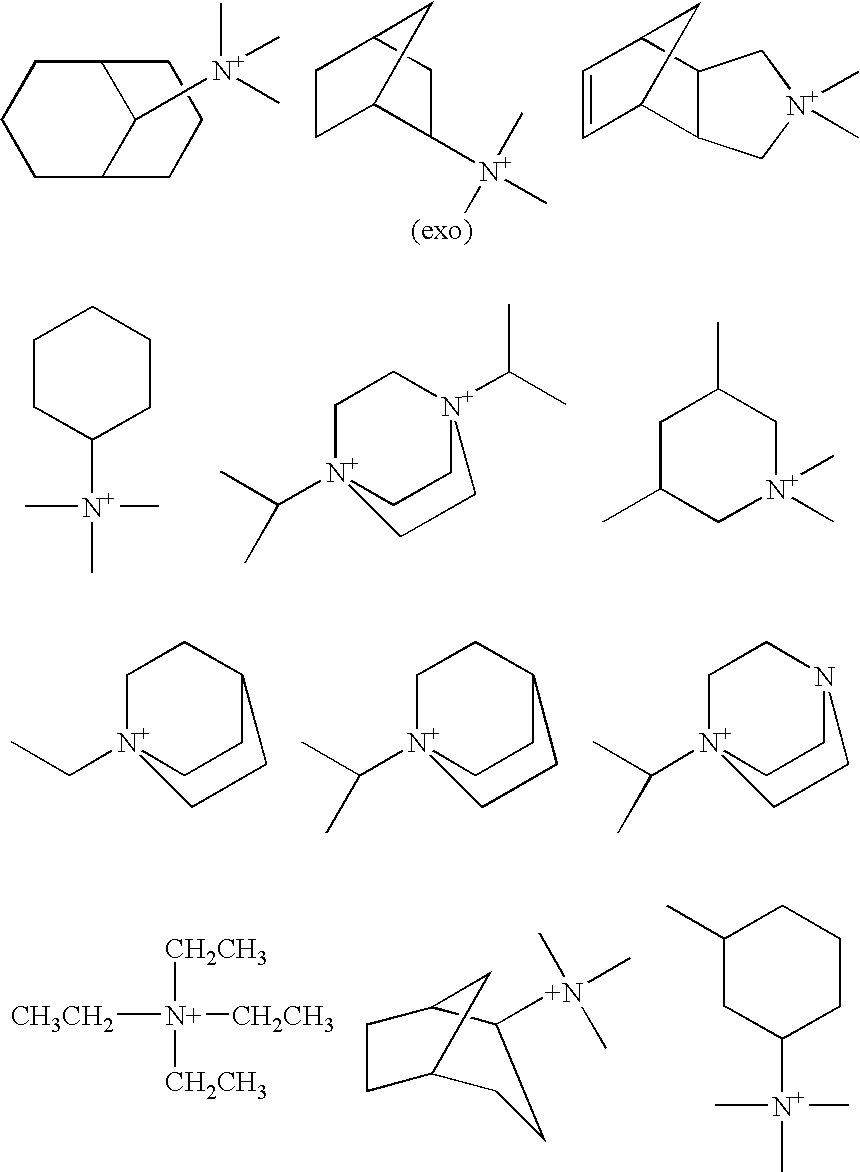
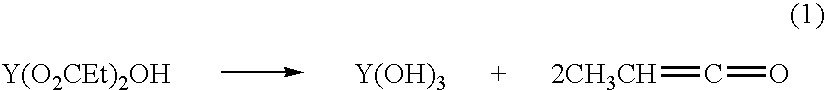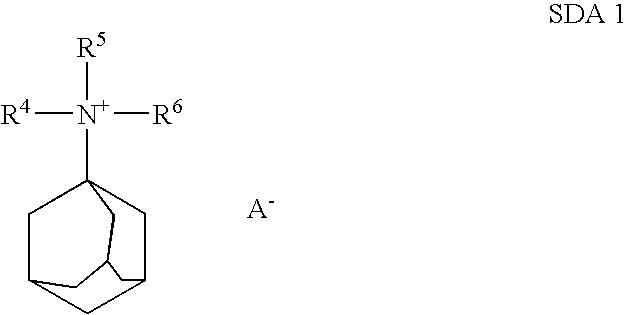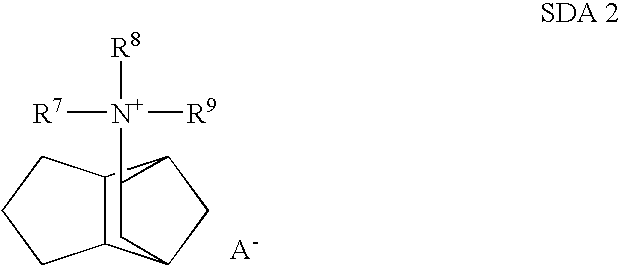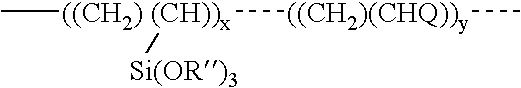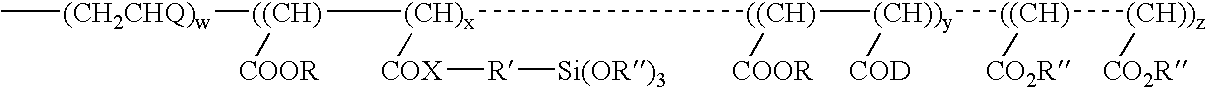Patents
Literature
2047results about "Aluminium compounds" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method of forming mixed rare earth oxynitride and aluminum oxynitride films by atomic layer deposition
InactiveUS20070237699A1Aluminium compoundsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate dielectricRare earth
A method is provided for depositing a gate dielectric that includes at least two rare earth metal elements in the form of an oxynitride or an aluminum oxynitride. The method includes disposing a substrate in a process chamber and exposing the substrate to a gas pulse containing a first rare earth precursor and to a gas pulse containing a second rare earth precursor. The substrate may also optionally be exposed to a gas pulse containing an aluminum precursor. Sequentially after each precursor gas pulse, the substrate is exposed to a gas pulse of an oxygen-containing gas, nitrogen-containing gas or an oxygen- and nitrogen-containing gas. In alternative embodiments, the first and second rare earth precursors may be pulsed together, and either or both may be pulsed together with the aluminum precursor. The first and second rare earth precursors comprise a different rare earth metal element. The sequential exposing steps may be repeated to deposit a mixed rare earth oxynitride or aluminum oxynitride layer with a desired thickness. Purge or evacuation steps may also be performed after each gas pulse.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Copper CHA zeolite catalysts
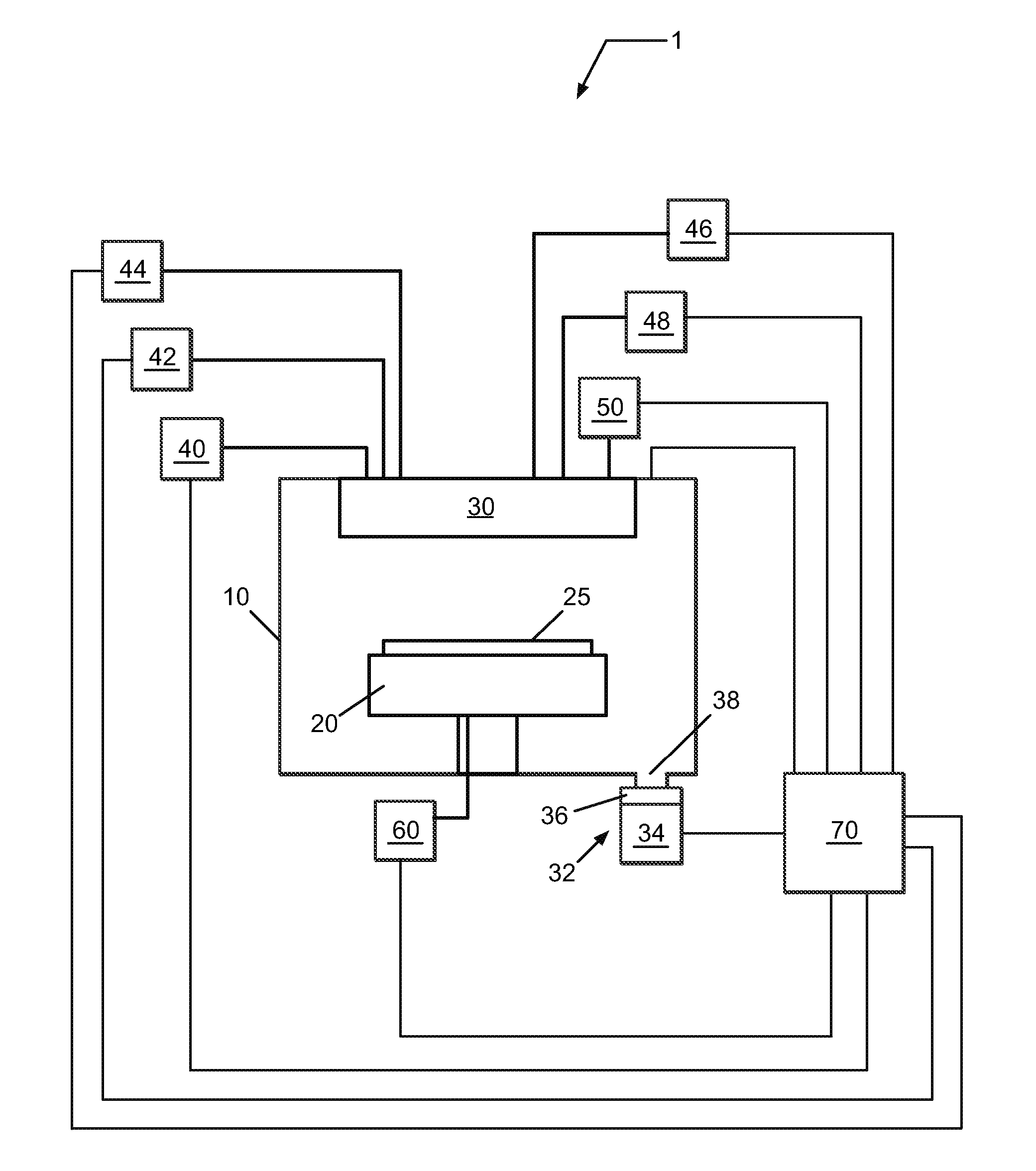
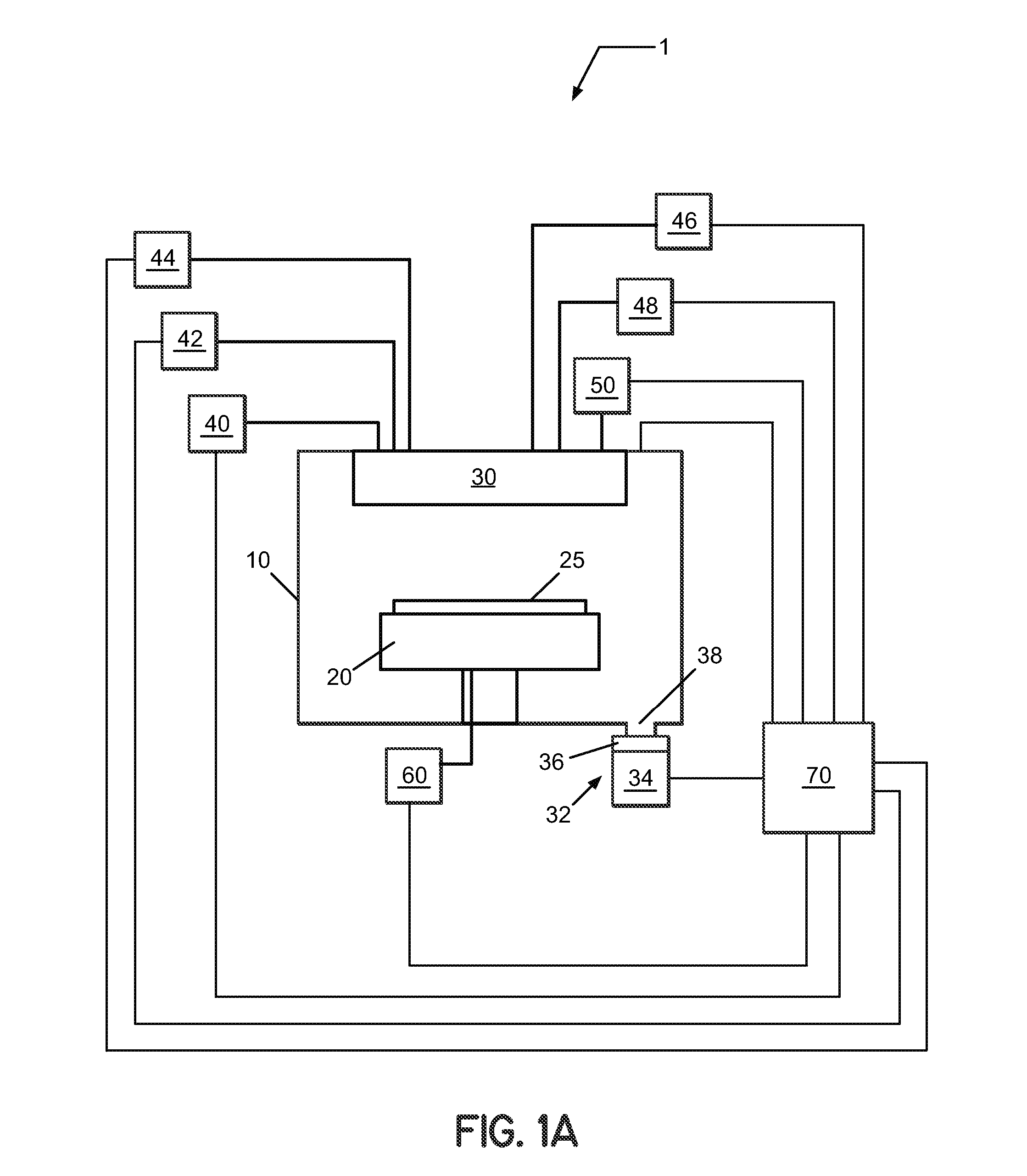
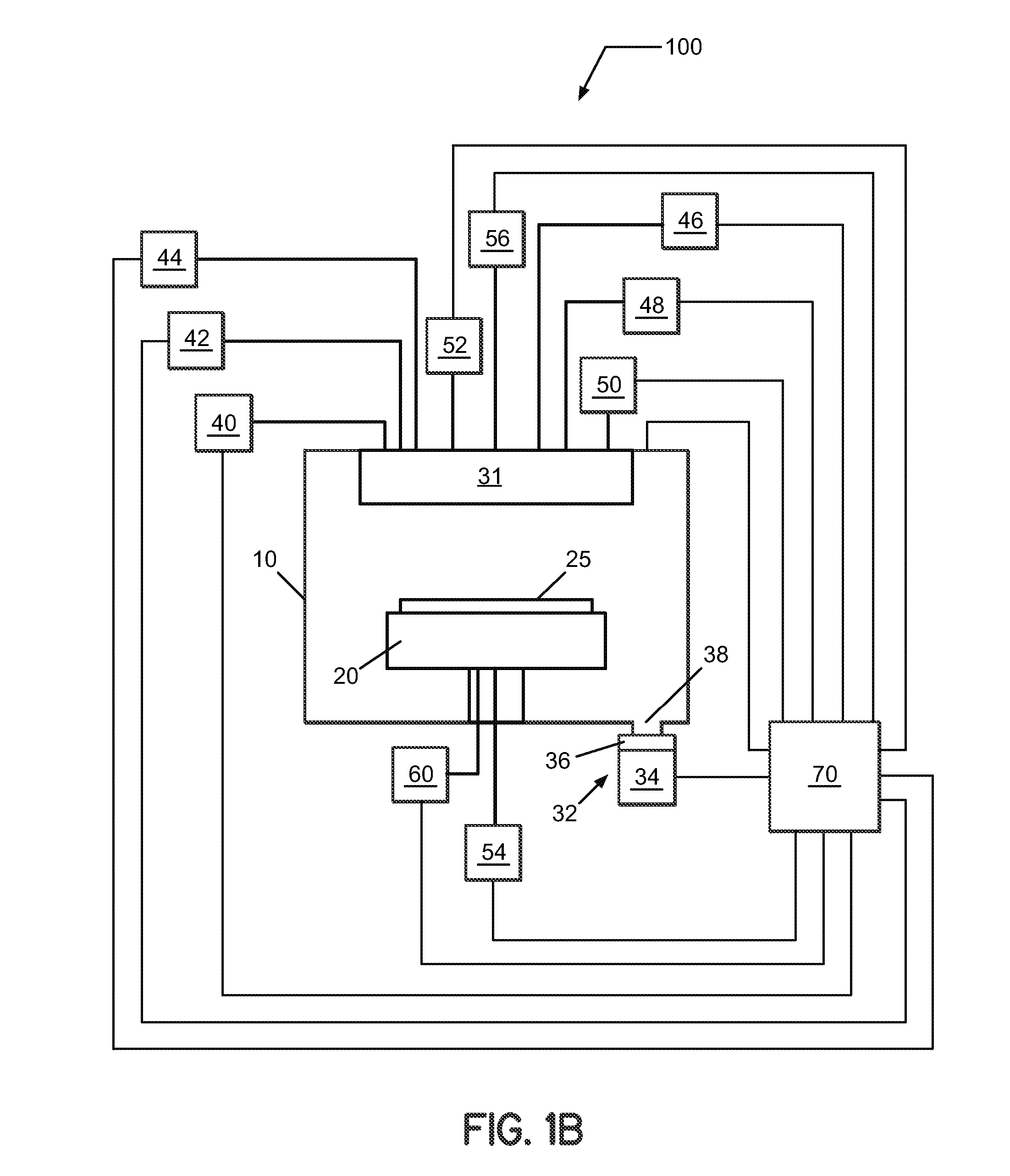
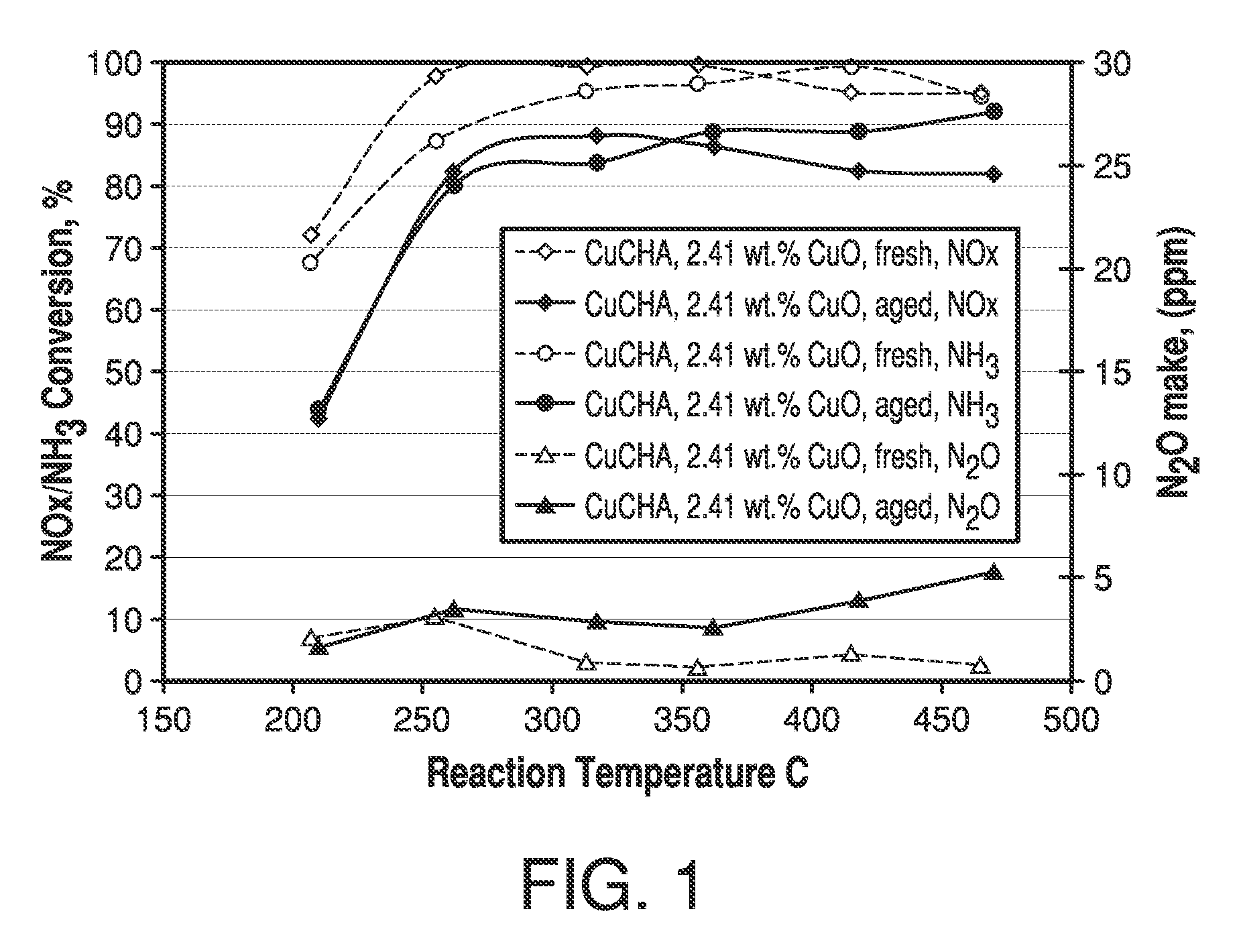
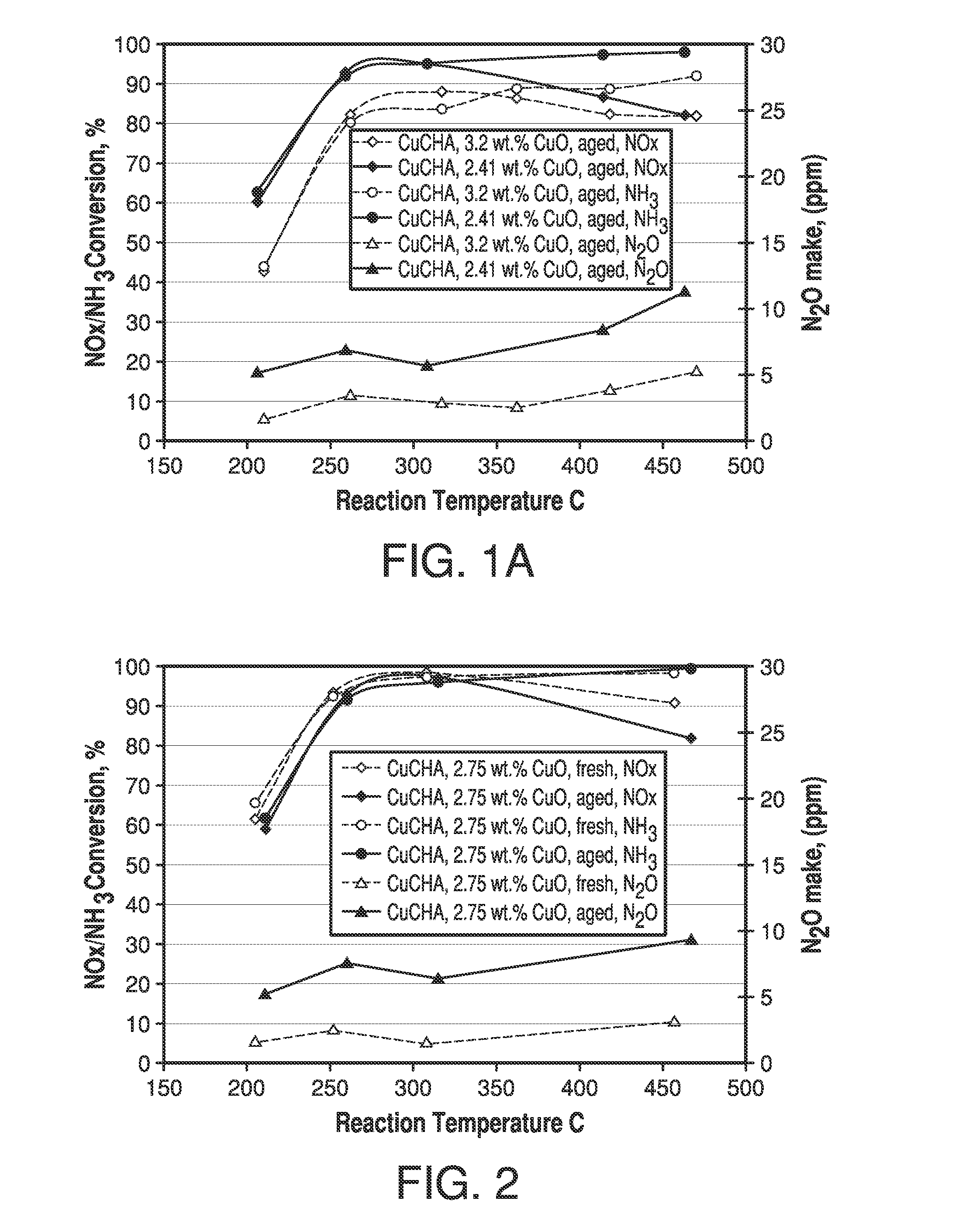
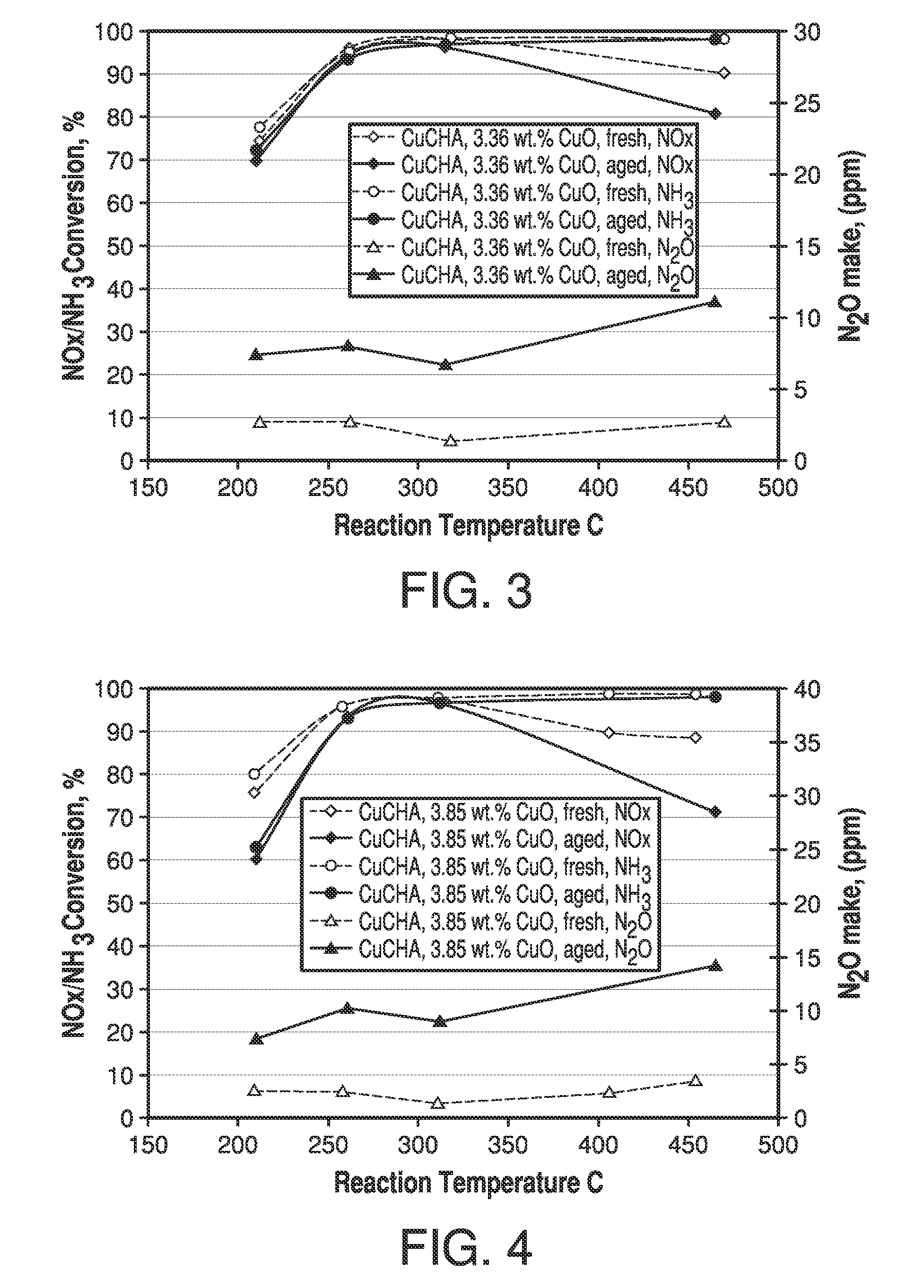
ActiveUS7601662B2Good hydrothermal stabilityHigh catalytic activityCombination devicesAluminium compoundsReaction temperatureCrystal structure
Zeolite catalysts and systems and methods for preparing and using zeolite catalysts having the CHA crystal structure are disclosed. The catalysts can be used to remove nitrogen oxides from a gaseous medium across a broad temperature range and exhibit hydrothermal stable at high reaction temperatures. The zeolite catalysts include a zeolite carrier having a silica to alumina ratio from about 15:1 to about 256:1 and a copper to alumina ratio from about 0.25:1 to about 1:1.
Owner:BASF CORP
Reactive oligomers for isocyanate coatings
InactiveUS6221494B1Extended shelf lifeHigh glossAluminium compoundsSynthetic resin layered productsEpoxyOligomer
The invention is directed to a two-pack solvent-based ambient curable coating composition comprising a binder of a hydroxyl and crosslinking components. The hydroxyl component includes a linear or branched cycloaliphatic moiety-containing reactive oligomer or blend of oligomers with a weight average molecular weight not exceeding 3,000, a polydispersity not exceeding about 1.7 with at least 2 hydroxyl groups, at least 1, on average, being a primary hydroxyl group. The reactive oligomer is formed by the reaction of an oligomeric acid with monofunctional epoxy. The crosslinking component includes one or more of an oligomeric crosslinker containing at least 2 isocyanate groups. The coating composition of the invention is particularly suited in automotive refinish coatings.
Owner:AXALTA COATING SYST IP CO LLC
Mixed-metal oxide particles by liquid feed flame spray pyrolysis of oxide precursors in oxygenated solvents
Liquid feed flame spray pyrolysis of solutions of a metal oxide precursor which is an alkoxide or C1-6 carboxylate and at least one second metal oxide precursor and / or second metal compound dissolved in oxygenated solvent by combustion with oxygen lead to the formation of sub-micron mixed-metal oxide powders not accessible by other processes or by the pyrolysis of metal chlorides or nitrates. The powders have numerous uses in advanced materials applications including particulate solid state lasers, advanced ceramic materials, and as catalysts in organic synthesis and automobile exhaust systems.
Owner:TAL MATERIALS +1
Mixed-metal oxide particles by liquid feed flame spray pyrolysis of oxide precursors in oxygenated solvents
Liquid feed flame spray pyrolysis of solutions of a metal oxide precursor which is an alkoxide or C1-6 carboxylate and at least one second metal oxide precursor and / or second metal compound dissolved in oxygenated solvent by combustion with oxygen lead to the formation of sub-micron mixed-metal oxide powders not accessible by other processes or by the pyrolysis of metal chlorides or nitrates. The powders have numerous uses in advanced materials applications including particulate solid state lasers, advanced ceramic materials, and as catalysts in organic synthesis and automobile exhaust systems.
Owner:TAL MATERIALS +1
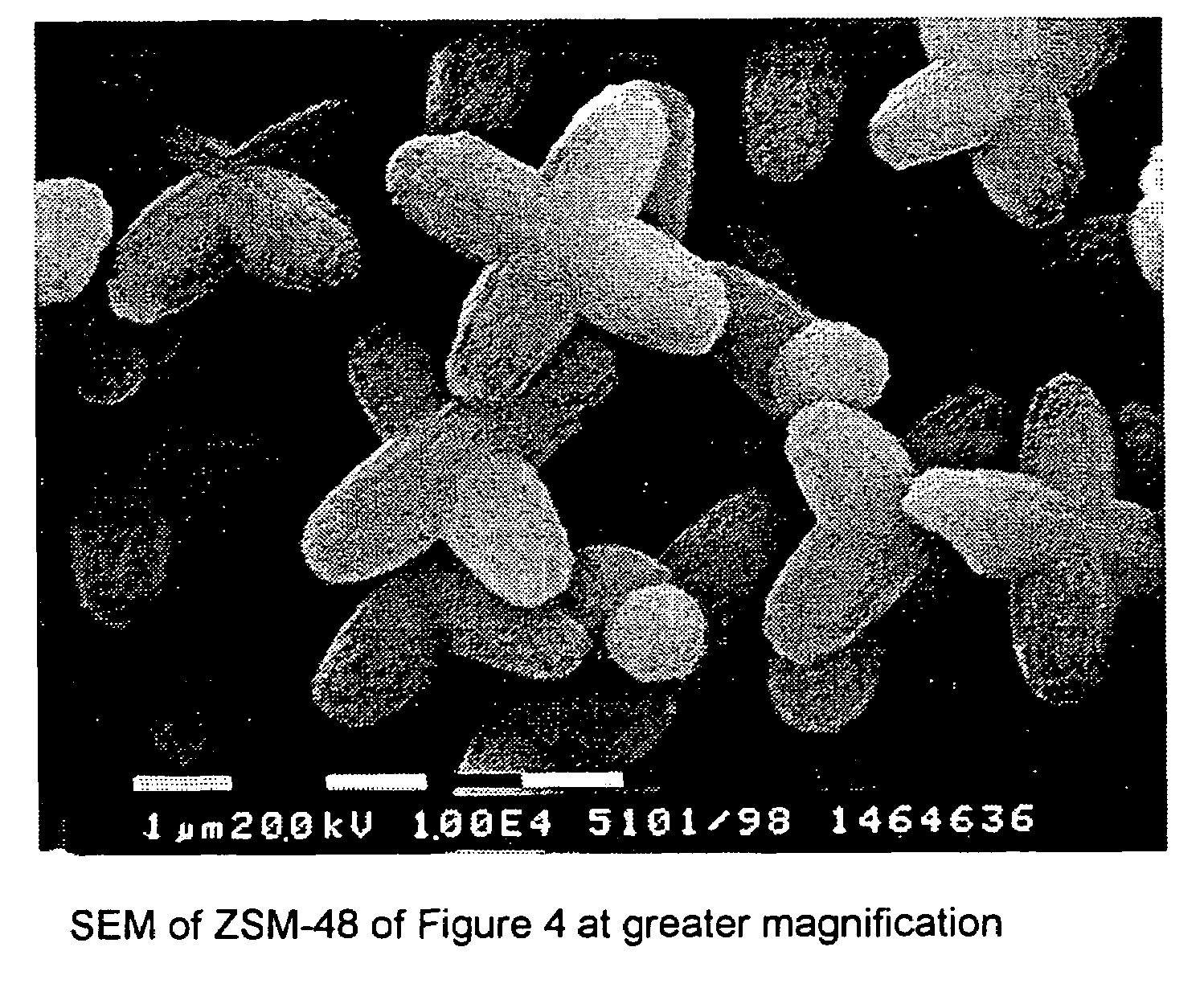
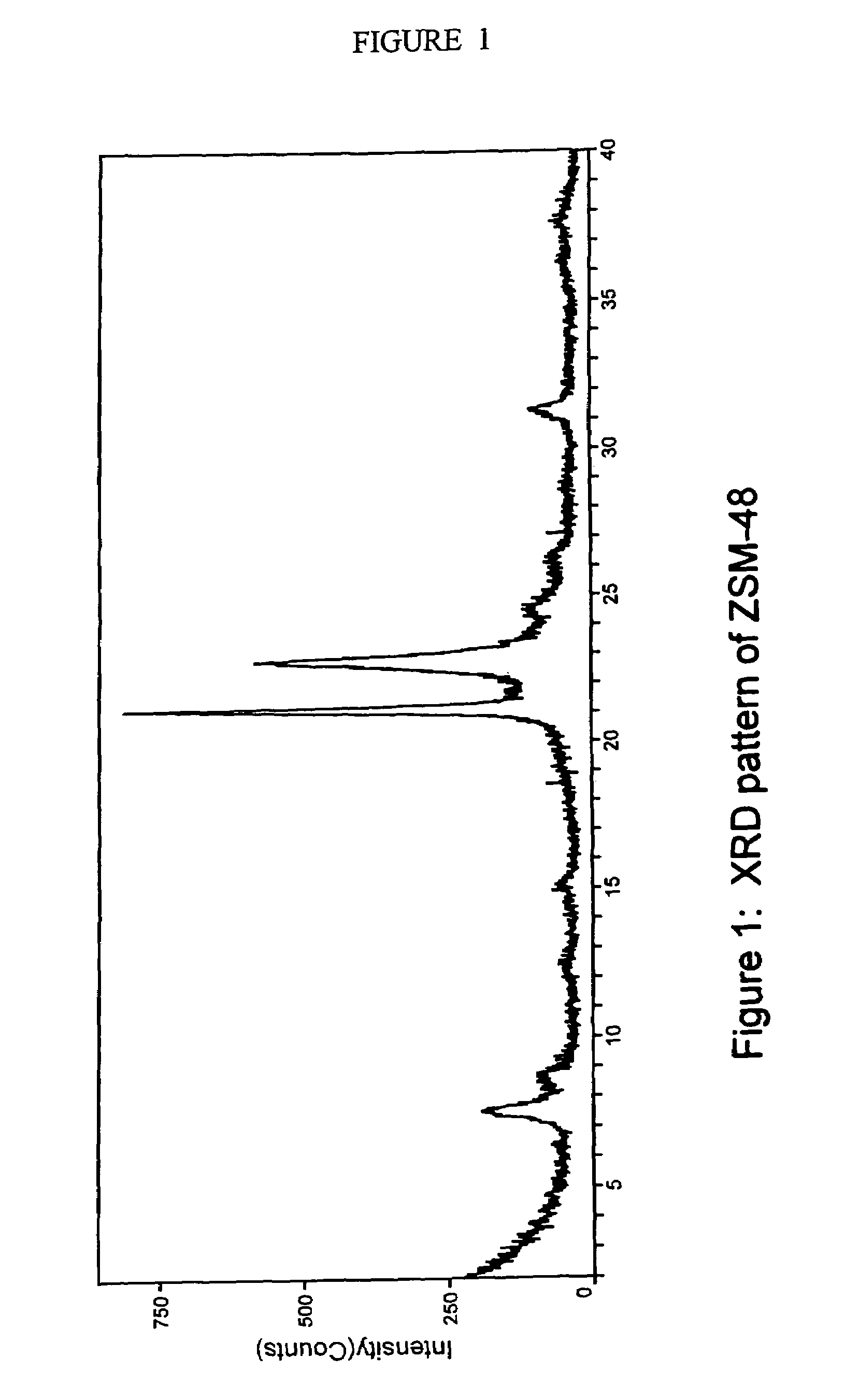
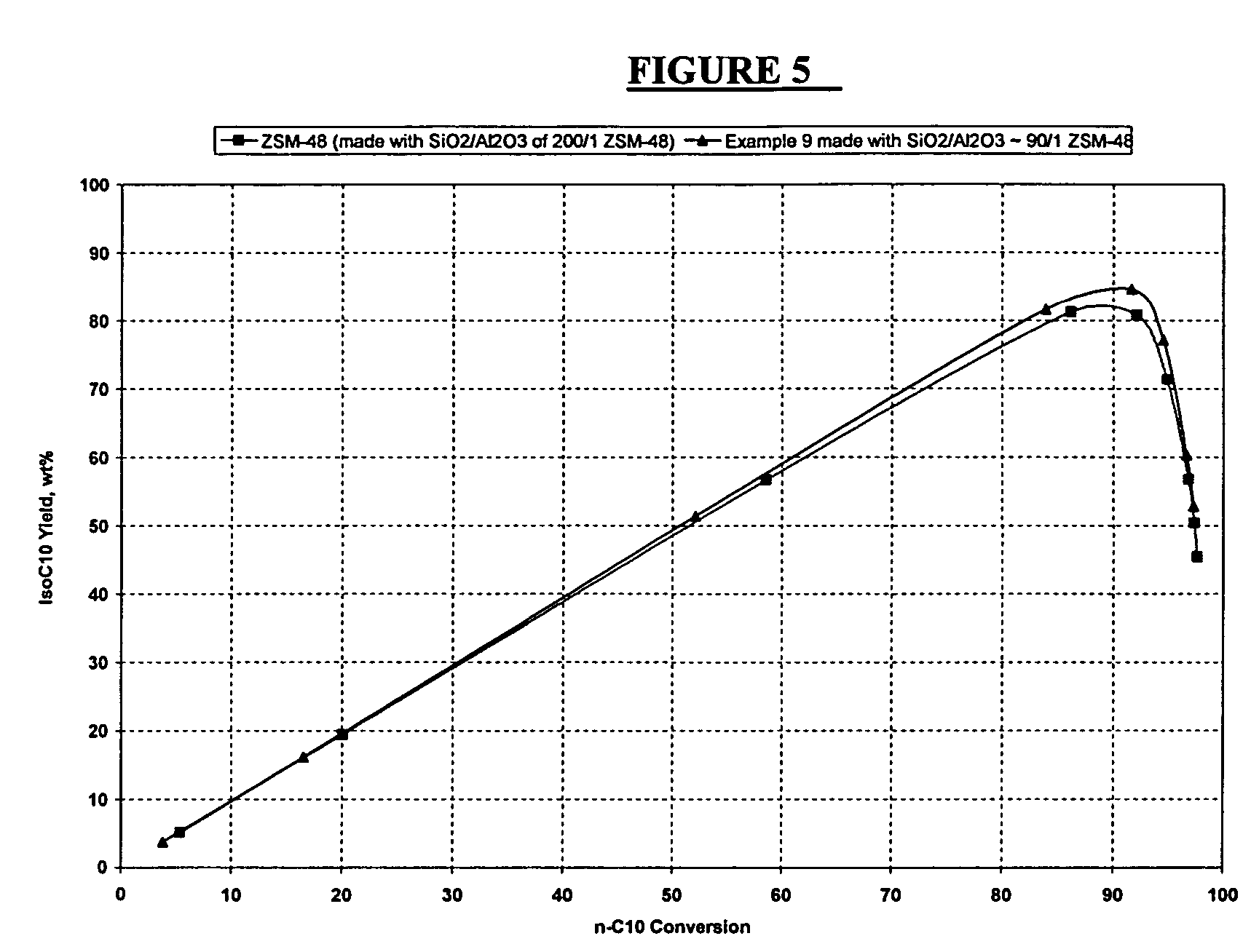
Synthesis of ZSM-48 crystals with heterostructural, non ZSM-48, seeding
ActiveUS6923949B1Suppresses formation of impurityPromotes more aluminum incorporationAluminium compoundsMolecular-sieve and base-exchange compoundsHigh activityZeolite
Pure phase, high activity ZSM-48 crystals having a SiO2 / Al2O3 ratio of less than about 150 / 1, substantially free from ZSM-50 and Kenyaite, and fibrous morphology crystals. The crystals may further have a specific cross morphology. A method for making such crystals using heterostructural, zeolite seeds, other than ZSM-48 and ZSM-50 seeds.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
High activity ZSM-48 and methods for dewaxing
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Abrasive particles having complex shapes and methods of forming same
An abrasive grain is disclosed and may include a body. The body may define a length (l), a height (h), and a width (w). In a particular aspect, the length is greater than or equal to the height and the height is greater than or equal to the width. Further, in a particular aspect, the body may include a primary aspect ratio defined by the ratio of length:height of at least about 2:1. The body may also include an upright orientation probability of at least about 50%.
Owner:SAINT GOBAIN CERAMICS & PLASTICS INC
Method of the preparation of microporous crystalline molecular sieve possessing mesoporous frameworks
InactiveUS7785563B2Facilitate diffusion and adsorptionImprove overall utilizationAluminium compoundsSilicaMolecular sieveChemical treatment
The present invention relates to a method of preparing a microporous crystalline molecular sieve having mesoporous skeleton, comprising following steps: (a) adding a meso-SDA (meso-Structure Directing Agent) into a gel composition of synthesizing molecular sieve, (b) subjecting the mixture obtained in the above step (a) to crystallization by a hydrothermal reaction, a microwave reaction, a dry-gel synthesis, etc., and (c) removing selectively organic materials from the resulted material obtained in the above step (b) by a calcination or a chemical treatment. Molecular sieve having mesoporous skeleton synthesized by the present invention exhibits, as compared with conventional zeolite, a good molecule diffusion ability and a greatly improved catalytic activity.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
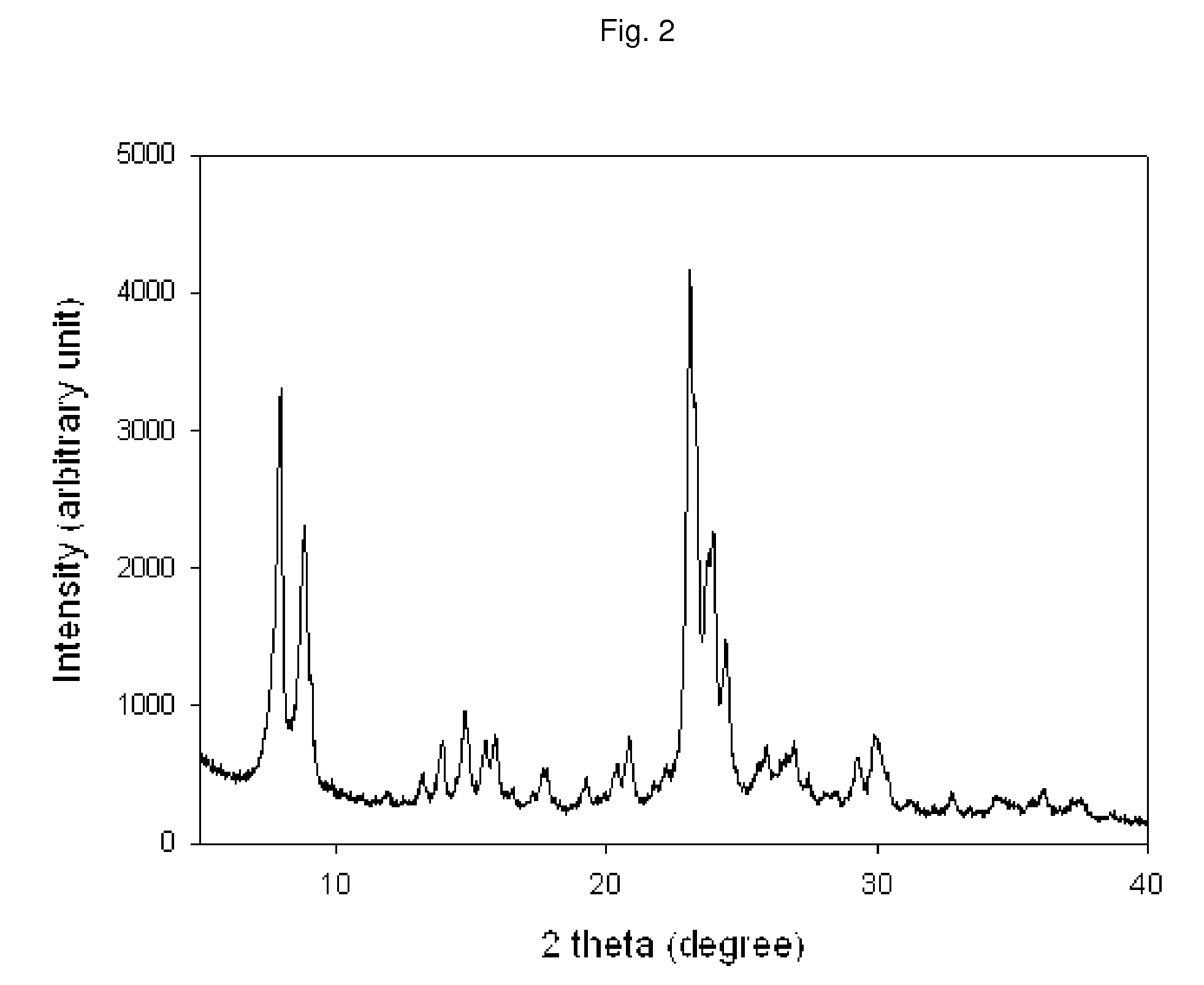
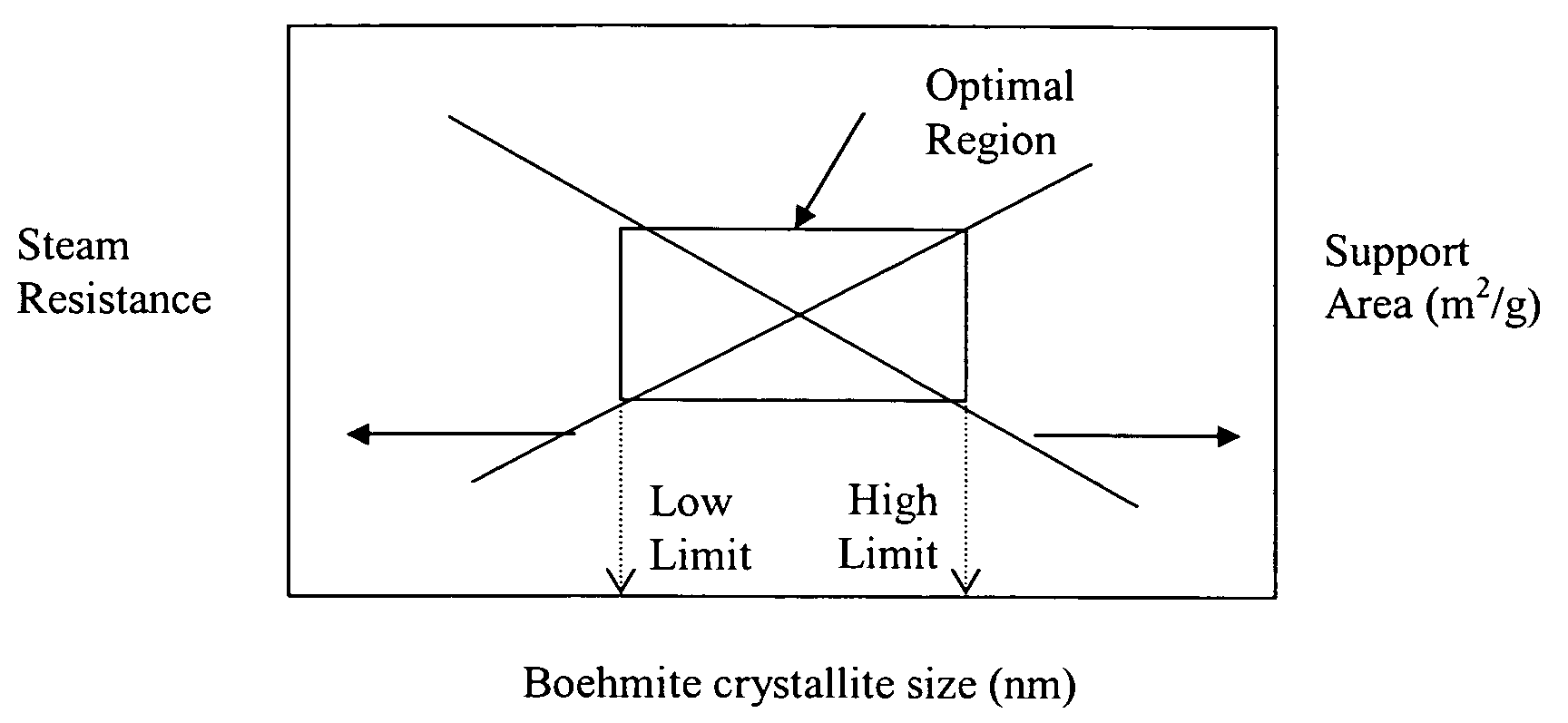
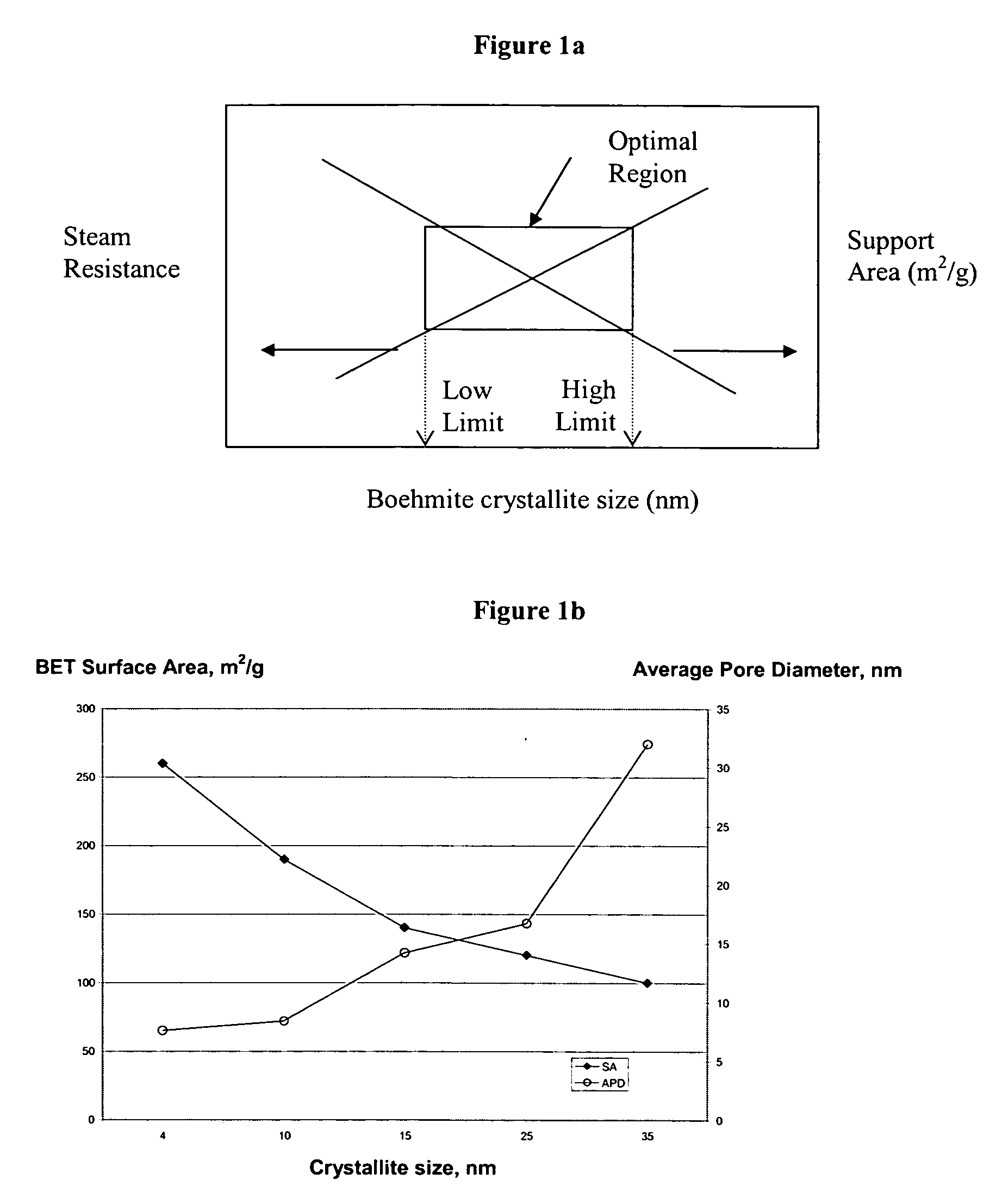
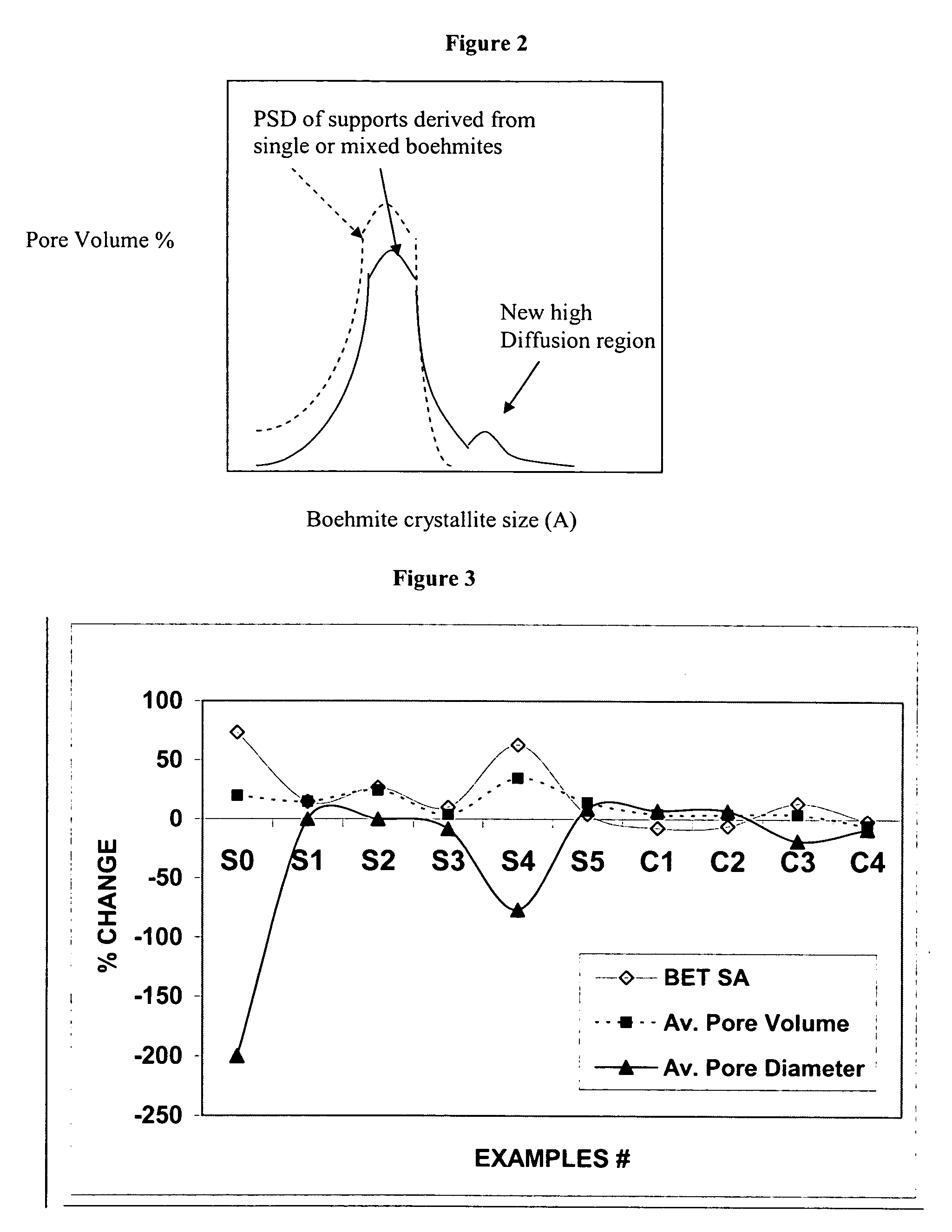
Stabilized boehmite-derived catalyst supports, catalysts, methods of making and using
ActiveUS20050234137A1Good hydrothermal stabilityImprove stabilityMaterial nanotechnologyCatalyst carriersPorosityAluminium hydroxide
A stabilized catalyst support having improved hydrothermal stability, catalyst made therefrom, and method for producing hydrocarbons from synthesis gas using said catalyst. The stabilized support is made by a method comprising treating a crystalline hydrous alumina precursor in contact with at least one structural stabilizer or compound thereof. The crystalline hydrous alumina precursor preferably includes an average crystallite size selected from an optimum range delimited by desired hydrothermal resistance and desired porosity. The crystalline hydrous alumina precursor preferably includes an alumina hydroxide, such as crystalline boehmite, crystalline bayerite, or a plurality thereof differing in average crystallite sizes by at least about 1 nm. The crystalline hydrous alumina precursor may be shaped before or after contact with the structural stabilizer or compound thereof. The treating includes calcining at 450° C. or more. Preferred structural stabilizers can include cobalt, magnesium, manganese, manganese, zirconium, boron, aluminum, barium, silicon, lanthanum, oxides thereof, or combinations thereof.
Owner:CLARIANT INT LTD
Methods to improve heteroatom lattice substitution in large and extra-large pore borosilicate zeolites
InactiveUS6790433B2Controlled catalytic propertyAluminium compoundsMolecular sieve catalystsIron saltsAluminosilicate
The invention, in one embodiment, is a method for preparing crystalline zeolites by (a) contacting a calcined essentially aluminum free borosilicate zeolite with an aqueous acid solution, thereby producing an at least partially deboronated zeolite; (b) contacting said at least partially deboronated zeolite with a solution selected from the group consisting of an aqueous aluminum salt solution, thereby producing an aluminosilicate zeolite; an aqueous gallium salt solution, thereby producing a gallosilicate zeolite; an aqueous iron salt solution, thereby producing a ferrosilicate zeolite; and mixtures thereof; and (c) where the contacting in step (b) occurs at a pH of not greater than about 3.5. In another embodiment, the present invention provides a method for preparing crystalline zeolites by contacting a calcined essentially aluminum free large or extra-large pore borosilicate zeolite with a solution selected from the group consisting of an aqueous aluminum salt solution, thereby producing an aluminosilicate zeolite; an aqueous gallium salt solution, thereby producing a gallosilicate zeolite; an aqueous iron salt solution, thereby producing a ferrosilicate zeolite; and mixtures thereof; and where the contacting occurs at a pH of not greater than about 3.5.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Increased thermal conductivity monolithic zeolite structures
A monolith comprises a zeolite, a thermally conductive carbon, and a binder. The zeolite is included in the form of beads, pellets, powders and mixtures thereof. The thermally conductive carbon can be carbon nano-fibers, diamond or graphite which provide thermal conductivities in excess of about 100 W / m·K to more than 1,000 W / m·K. A method of preparing a zeolite monolith includes the steps of mixing a zeolite dispersion in an aqueous colloidal silica binder with a dispersion of carbon nano-fibers in water followed by dehydration and curing of the binder is given.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Gradient cathode material for lithium rechargeable batteries
InactiveUS6921609B2Increase capacityImproved cyclabilityAluminium compoundsAlkaline accumulatorsManganesePotassium
A composition suitable for use as a cathode material of a lithium battery includes a core material having an empirical formula LixM′zNi1−yM″yO2. “x” is equal to or greater than about 0.1 and equal to or less than about 1.3. “y” is greater than about 0.0 and equal to or less than about 0.5. “z” is greater than about 0.0 and equal to or less than about 0.2. M′ is at least one member of the group consisting of sodium, potassium, nickel, calcium, magnesium and strontium. M″ is at least one member of the group consisting of cobalt, iron, manganese, chromium, vanadium, titanium, magnesium, silicon, boron, aluminum and gallium. A coating on the core has a greater ratio of cobalt to nickel than the core. The coating and, optionally, the core can be a material having an empirical formula Lix1Ax2Ni1−y1−z1Coy1Bz1Oa. “x1” is greater than about 0.1 a equal to or less than about 1.3. “x2,”“y1” and “z1” each is greater than about 0.0 and equal to or less than about 0.2. “a” is greater than 1.5 and less than about 2.1. “A” is at least one element selected from the group consisting of barium, magnesium, calcium and strontium. “B” is at least one element selected from the group consisting of boron, aluminum, gallium, manganese, titanium, vanadium and zirconium.
Owner:TIAX LLC
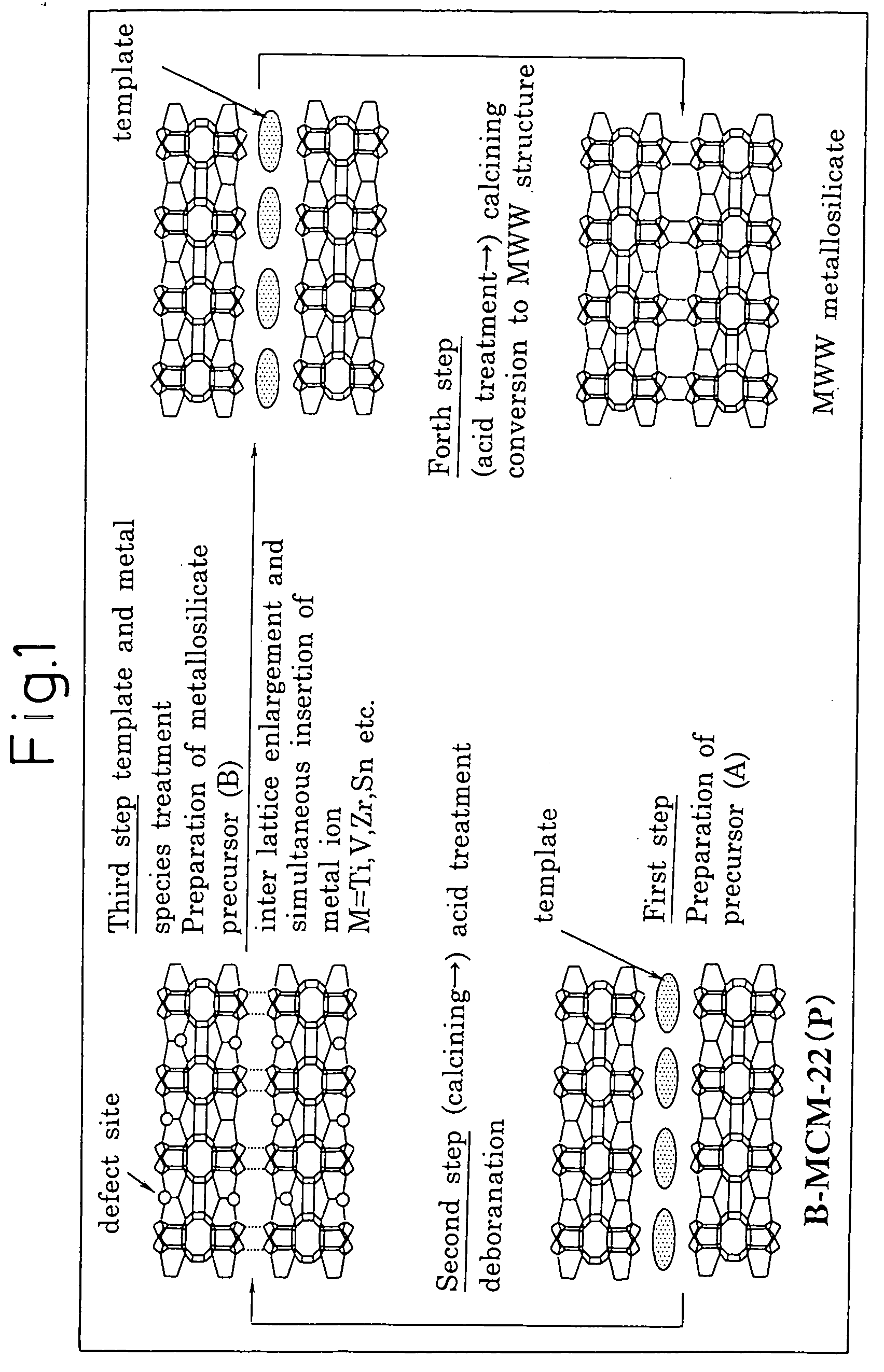
Mww type zeolite substance, precursor substance therefor, and process for producing these substances
ActiveUS20050158238A1Easy to synthesizeRaise the ratioAluminium compoundsMolecular sieve catalystsCompound (substance)Silicon
A process for easily synthesizing a zeolite substance containing an element having a large ionic radius in the framework at a high ratio. This process comprises the following first to fourth steps: First Step: a step of heating a mixture containing a template compound, a compound containing a Group 13 element of the periodic table, a silicon-containing compound and water to obtain a precursor (A); Second Step: a step of acid-treating the precursor (A) obtained in the first step; Third Step: a step of heating the acid-treated precursor (A) obtained in the second step together with a mixture containing a template compound and water to obtain a precursor (B); and Fourth Step: a step of calcining the precursor (B) obtained in the third step to obtain a zeolite substance.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Cycloolefin resin pellets and a process for producing a molded product thereof
InactiveUS6342549B1High transparencyReduce the amount requiredAluminium compoundsSolesVitrificationShell molding
Cycloolefin resin pellets of the present invention comprises a cycloolefin resin pellet and a powdery coating material and / or a liquid coating material, the melting point or the glass transition point of the coating material being 200° C. or lower, and the coating material being adhered onto the surface of the cycloolefin resin pellets, so that the molded product thereof is excellent in transparency.
Owner:TICONA GMBH +1
Catalyst for fluidized catalytic cracking of heavy hydrocarbon oil and method of fluidized catalytic cracking
InactiveUS6916762B2Efficient inactivationReduce the amount requiredCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesAluminium compoundsHydrogenOxide matrix
An FCC catalyst which not only deactivates catalyst poison metals, such as nickel, vanadium and the like, in feedstock oils, inhibits the generation of hydrogen or coke, has excellent cracking activity and bottom oil-treating ability, and can yield a gasoline and LCO fraction in high yields, but also retains the performances on a high level over long and has an improved catalyst life; and an FCC method using the catalyst. The FCC catalyst has a compound of a bivalent metal or of bivalent and trivalent metals showing an XRD pattern of a carbonate of the bivalent metal; an inorganic oxide matrix and the compound dispersed therein; or an inorganic oxide matrix and the compound dispersed therein together with a crystalline aluminosilicate zeolite, and relates to an FCC method in which at least one of the catalysts are used in combination with an FCC catalyst obtained by evenly dispersing a crystalline aluminosilicate zeolite in an inorganic oxide matrix.
Owner:GASOLINEEUM ENERGY CENT FOUND +1
Use of multiple stream high pressure mixer/reactor
InactiveUS6159442AHigh strengthMaintain good propertiesCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesPressurized chemical processStream flowHigh pressure
Owner:MICROFLUIDICS INT
Pressure-sensitive adhesive composition and tapes
InactiveUS6022914AImprove flame retardant performanceReduce viscosityAluminium compoundsNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesHalogenFire retardant
The present invention relates to a pressure-sensitive adhesive composition containing a non-halogen, non-intumescent flame-retardant system comprising at least one flame-retardant agent with the provisos that the flame-retardant system does not comprise Sb2O3 or does not consist only of alumina trihydrate.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Chabazite-containing molecular sieve, its synthesis and its use in the conversion of oxygenates to olefins
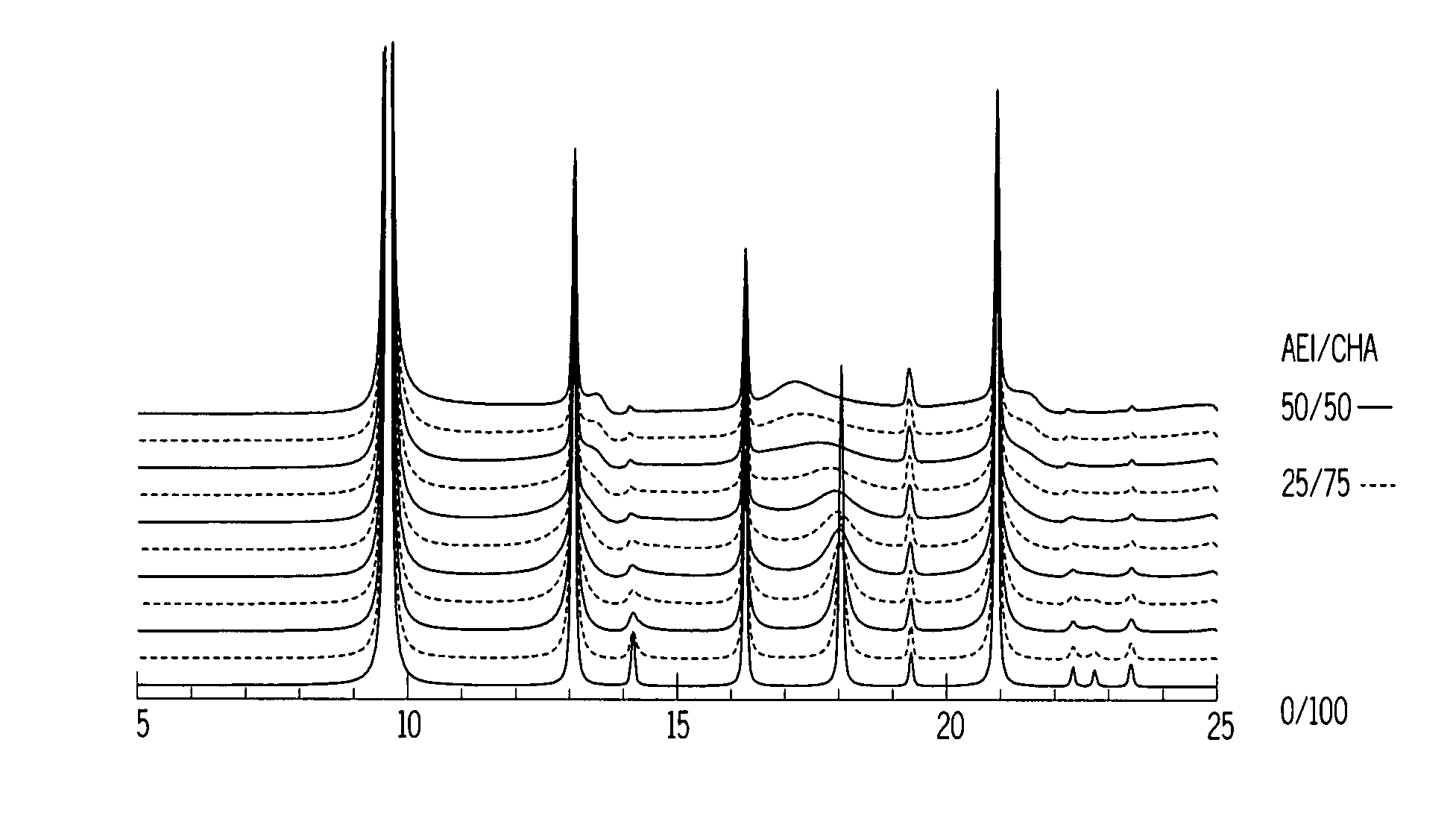
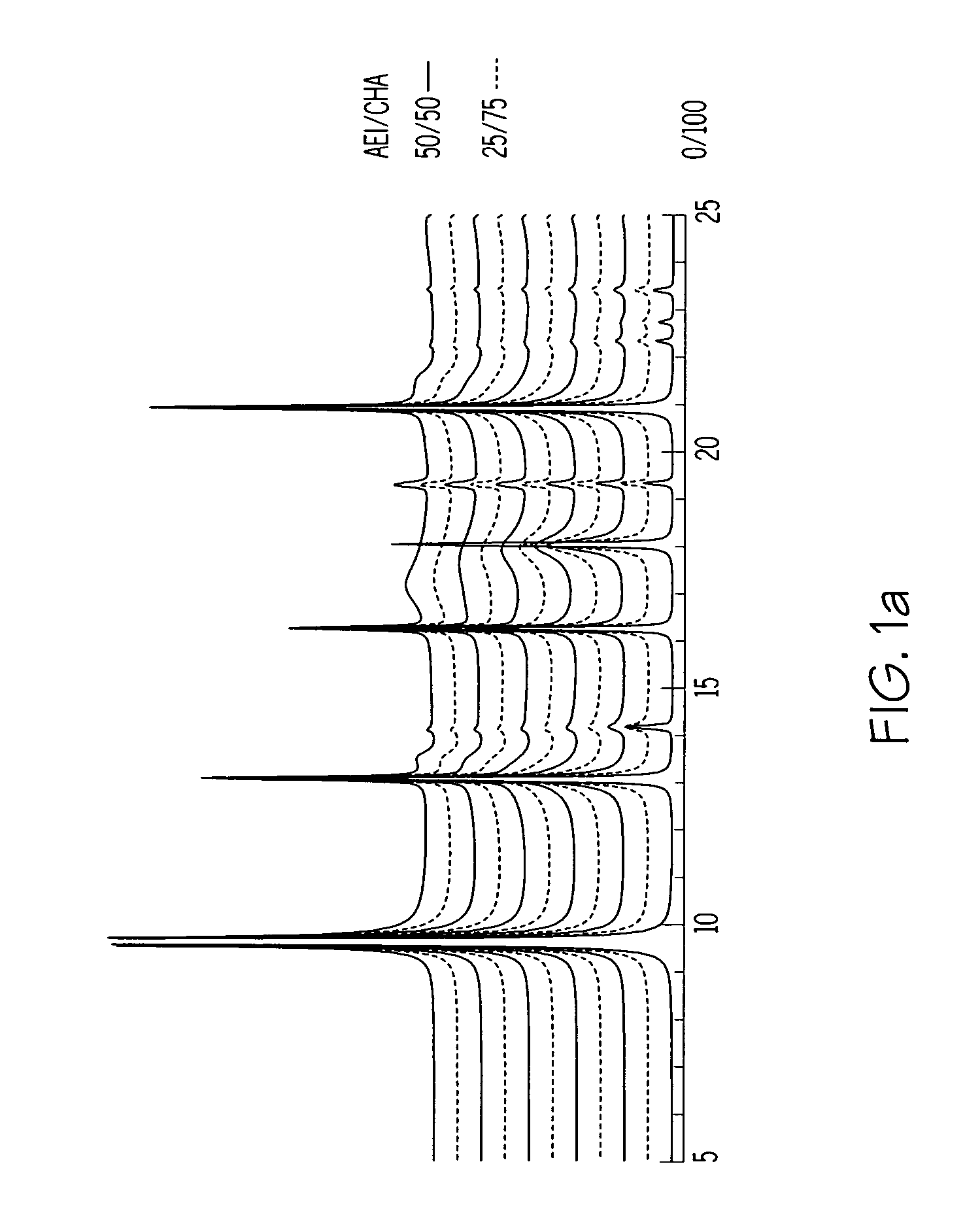
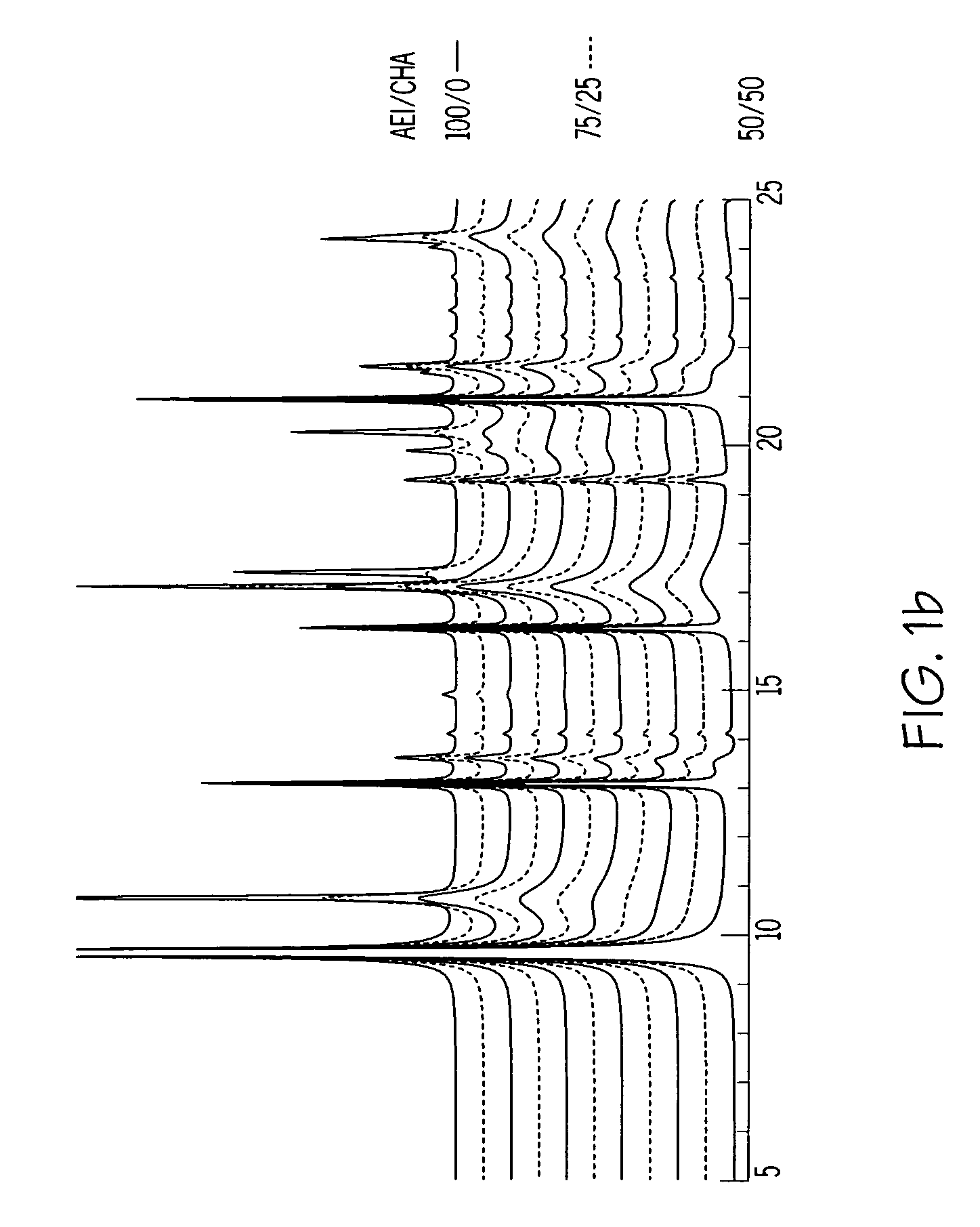
A crystalline material substantially free of framework phosphorus and comprising a CHA framework type molecular sieve with stacking faults or at least one intergrown phase of a CHA framework type molecular sieve and an AEI framework type molecular sieve, wherein said material, in its calcined, anhydrous form, has a composition involving the molar relationship:(n)X2O3:YO2,wherein X is a trivalent element; Y is a tetravalent element; and n is from 0 to about 0.5. The material exhibits activity and selectivity in the conversion of methanol to lower olefins, especially ethylene and propylene.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC +1
Fast luminescent silicon
There are provided mesoporous silica materials containing in their pores stabilized clusters of silicon atom, of size 2 nanometers or less, and capable of photoluminescence to emit fast photons. They are prepared by chemical vapor deposition of silicon or a silicon precursor such as disilane, under soft conditions such as temperature of 100-150 DEG C., into the mesopores of silicate films which have mesoporous channels prepared by growth of the films using a template to control their sizes, but without removing the template residues from the films prior to the chemical vapor deposition. The template residues serve to limit the size of the silicon clusters which conform. The use of the soft conditions on CVD retains the template residues in an intact, substantially unchanged form. The resultant films have clusters of silicon, of 2 nanometer size or less, anchored to the mesopores, and air stable, so that they can be used in optoelectronic devices in conjunction with standard silicon semiconductors.
Owner:THE GOVERNINIG COUNCIL OF THE UNIV OF TORANTO
Medical Device Having Coating With Zeolite Drug Reservoirs
A medical device having a drug-eluting coating that includes a pharmaceutical compound or, more generally, a therapeutic material housed within pores of a zeolite carrier. The zeolite carrier has an open porous structure with reservoirs for holding the therapeutic material. The therapeutic material loaded zeolites may be suspended or dispersed within a bioerodible polymer matrix to provide controlled delivery of the therapeutic material. Zeolite drug carriers may have enhanced or optimally engineered pore sizes for a particular therapeutic material and release profile. Along with a therapeutic material, reservoirs of a zeolite drug delivery system may include a release agent. The release agent may be used to entrap the therapeutic material until such time as a triggering condition is met that prompts the release agent to activate and thereby release the therapeutic material from the zeolite reservoir.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Treatment of CHA-type molecular sieves and their use in the conversion of oxygenates to olefins
A method is disclosed of treating a crystalline material comprising a CHA framework-type molecular sieve, wherein said crystalline material has a composition and involving the molar relationship:(n)X2O3:YO2,where X is a trivalent element, Y is a tetravalent element, and n is less than 0.07, and wherein the crystalline material does not comprise a silicoaluminophosphate, is substantially free of framework phosphorus, or both. The method can comprise treating the crystalline material with steam under conditions such that the prime olefin selectivity of the treated material in an oxygenate conversion process is greater than the prime olefin selectivity of the untreated material in the same process.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Synthesis of chabazite-containing molecular sieves and their use in the conversion of oxygenates to olefins
The synthesis of a crystalline material, in particular, a high silica zeolite, comprising a chabazite-type framework molecular sieve is conducted in the presence of an organic directing agent having the formula: [R1R2R3N—R4]+Q−wherein R1 and R2 are independently selected from hydrocarbyl groups and hydroxy-substituted hydrocarbyl groups having from 1 to 3 carbon atoms, provided that R1 and R2 may be joined to form a nitrogen-containing heterocyclic structure, R3 is an alkyl group having 2 to 4 carbon atoms and R4 is selected from a 4- to 8-membered cycloalkyl group, optionally, substituted by 1 to 3 alkyl groups each having from 1 to 3 carbon atoms; and a 4- to 8-membered heterocyclic group having from 1 to 3 heteroatoms, said heterocyclic group being, optionally, substituted by 1 to 3 alkyl groups each having from 1 to 3 carbon atoms and the or each heteroatom in said heterocyclic group being selected from the group consisting of O, N, and S, or R3 and R4 are hydrocarbyl groups having from 1 to 3 carbon atoms joined to form a nitrogen-containing heterocyclic structure; and Q− is a anion.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Preparation of Molecular Sieves Using a Structure Directing Agent and An N, N, N-Triakyl Benzyl Quaternary Ammonium Cation
Crystalline molecular sieves are prepared using a mixture comprising an organic structure directing agent capable of forming the molecular-sieve and an N,N,N-trialkyl benzyl quaternary ammonium cation.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Selective catalyst for aromatics conversion
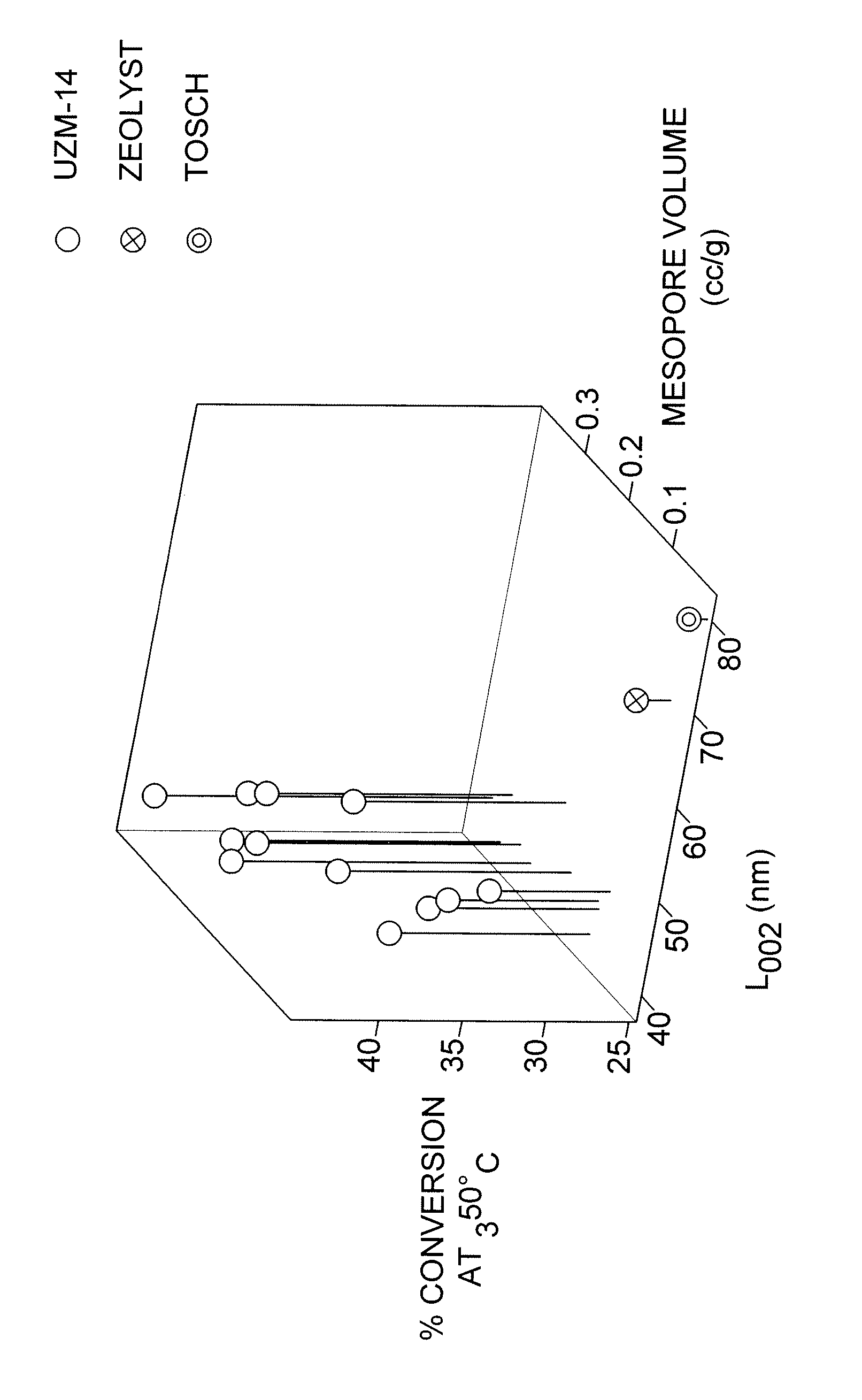
The subject invention comprises a novel UZM-14 catalytic material comprising globular aggregates of crystallites having a MOR framework type with a mean crystallite length parallel to the direction of 12-ring channels of about 60 nm or less and a mesopore volume of at least about 0.10 cc / gram. Catalysts formed from the novel material are particularly effective for the transalkylation of aromatics.
Owner:UOP LLC
Compositions and methods for making stabilized mesoporous materials
InactiveUS20110171121A1Aluminium compoundsFaujasite aluminosilicate zeoliteMesoporous materialAmmonia
Compositions and methods for making stabilized mesoporous materials. Surfactant-treated mesoporous precursor materials can be heat-treated in the presence of steam and / or ammonia in a heat-treating environment. The steam and / or ammonia can be introduced into the heat-treating environment via in situ and / or ex situ sources. Such stabilized mesoporous materials can have increased structural stability.
Owner:RIVE TECH
Zeolite composite, method for making and catalytic application thereof
A catalytic material includes microporous zeolites supported on a mesoporous inorganic oxide support. The microporous zeolite can include zeolite Beta, zeolite Y (including “ultra stable Y”—USY), mordenite, Zeolite L, ZSM-5, ZSM-11, ZSM-12, ZSM-20, Theta-1, ZSM-23, ZSM-34, ZSM-35, ZSM-48, SSZ-32, PSH-3, MCM-22, MCM-49, MCM-56, ITQ-1, ITQ-2, ITQ-4, ITQ-21, SAPO-5, SAPO-11, SAPO-37, Breck-6, ALPO4-5, etc. The mesoporous inorganic oxide can be e.g., silica or silicate. The catalytic material can be further modified by introducing some metals e.g. aluminum, titanium, molybdenum, nickel, cobalt, iron, tungsten, palladium and platinum. It can be used as catalysts for acylation, alkylation, dimerization, oligomerization, polymerization, hydrogenation, dehydrogenation, aromatization, isomerization, hydrotreating, catalytic cracking and hydrocracking reactions.
Owner:ABB LUMMUS GLOBAL INC
Method for making MTT zeolites without an organic template
InactiveUS6099820ALow raw material costMinimize wasteAluminium compoundsMolecular-sieve and base-exchange compoundsSufficient timeX-ray
The invention includes a method for preparing a crystalline zeolite having the X-ray diffraction lines of Table 1. The method includes preparing a template-free reaction mixture including at least one active source of a first oxide selected from the group consisting of an oxide of silicon, germanium or both, optionally at least one active source of a second oxide selected from the group consisting of an oxide of aluminum, boron, gallium, iron or a mixture thereof; and heating the reaction mixture at crystallization conditions for sufficient time to form a crystallized material containing zeolite crystals having the X-ray diffraction lines of Table 1, where said zeolite crystals have a first oxide / second oxide molar ratio greater than 12.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Cathode active material and nonaqueous secondary battery containing the same
InactiveUS6103422ASuppress deterioration of electrode performanceReduce charge and dischargeAluminium compoundsActive material electrodesManganeseCobalt
PCT No. PCT / JP96 / 03738 Sec. 371 Date Jun. 24, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Jun. 24, 1998 PCT Filed Dec. 20, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 23918 PCT Pub. Date Jul. 3, 1997The powdery cathode active material of the present invention for use in a nonaqueous electrolyte secondary battery comprises as the active ingredient a lithium manganese composite oxide and at least one nonmanganese metal element selected from the group consisting of aluminum, magnesium, vanadium, chromium, iron, cobalt, nickel, and zinc, provided that the nonmanganese metal element exists in the surface portions of fine particles constituting the powdery cathode active material. A nonaqueous electrolyte secondary battery comprising such a cathode active material, an anode active material and a nonaqueous electrolytic solution containing a lithium salt has a large charge-and-discharge capacity and a stable charge-and-discharge cycle durability, and can be prepared inexpensively.
Owner:KAO CORP
Method of preventing or reducing aluminosilicate scale in a bayer process
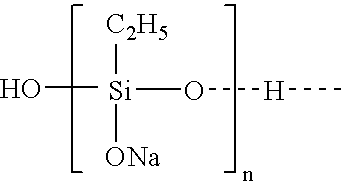
ActiveUS20050010008A2Reduce and eliminate aluminosilicate scalingReduce and even completely prevent formationSilicon organic compoundsAluminium compoundsPlate heat exchangerEnd-group
Abstract of the DisclosureMaterials and a process are provided whereby polymers with the pendant group or end group containing --Si(OR")3 (where R" is H, an alkyl group, Na, K, or NH4) are used to control aluminosilicate scaling in a Bayer process. When materials of the present invention are added to the Bayer liquor before the heat exchangers, they reduce and even completely prevent formation of aluminosilicate scale on heat exchanger walls. The present materials are effective at treatment concentrations that make them economically practical.
Owner:CYTEC TECH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com