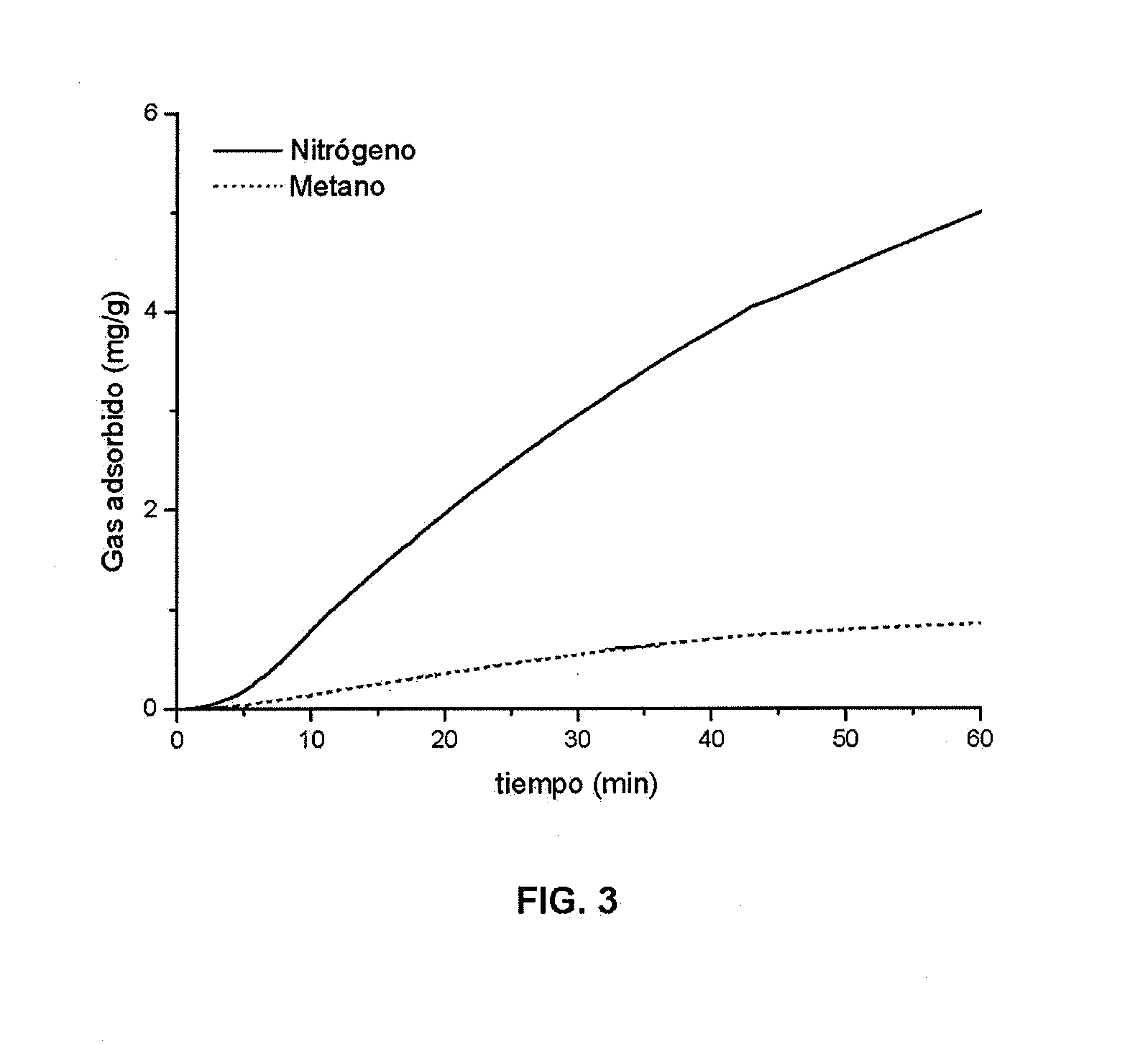
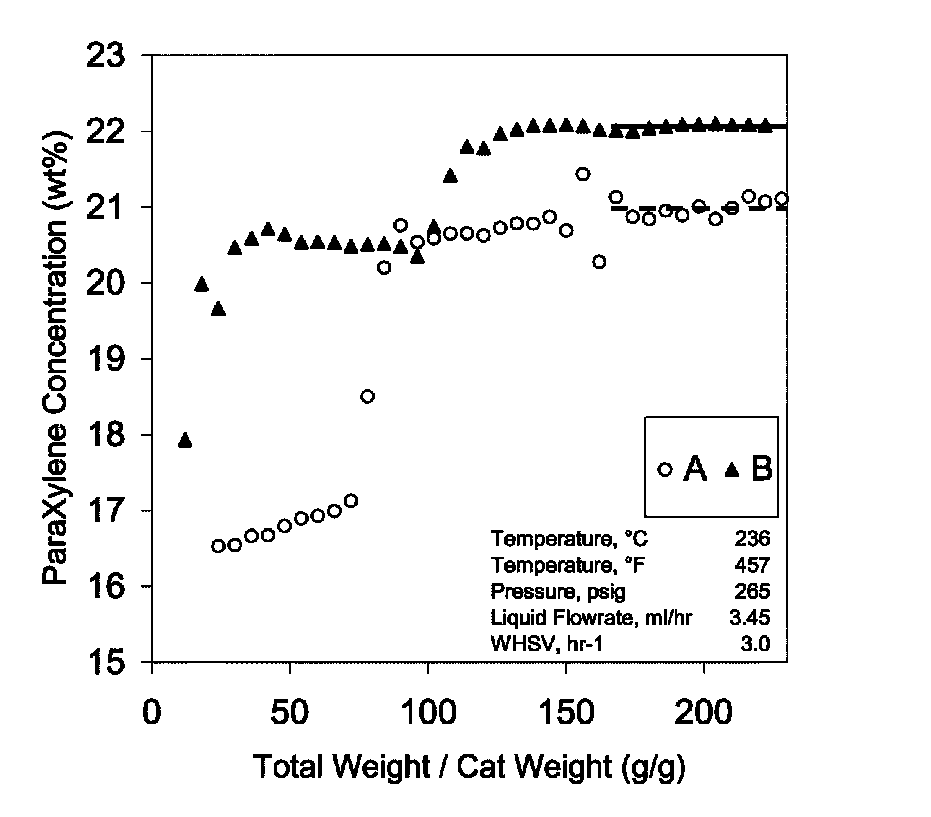
Patents
Literature
1434results about "Molecular-sieve and base-exchange compounds" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
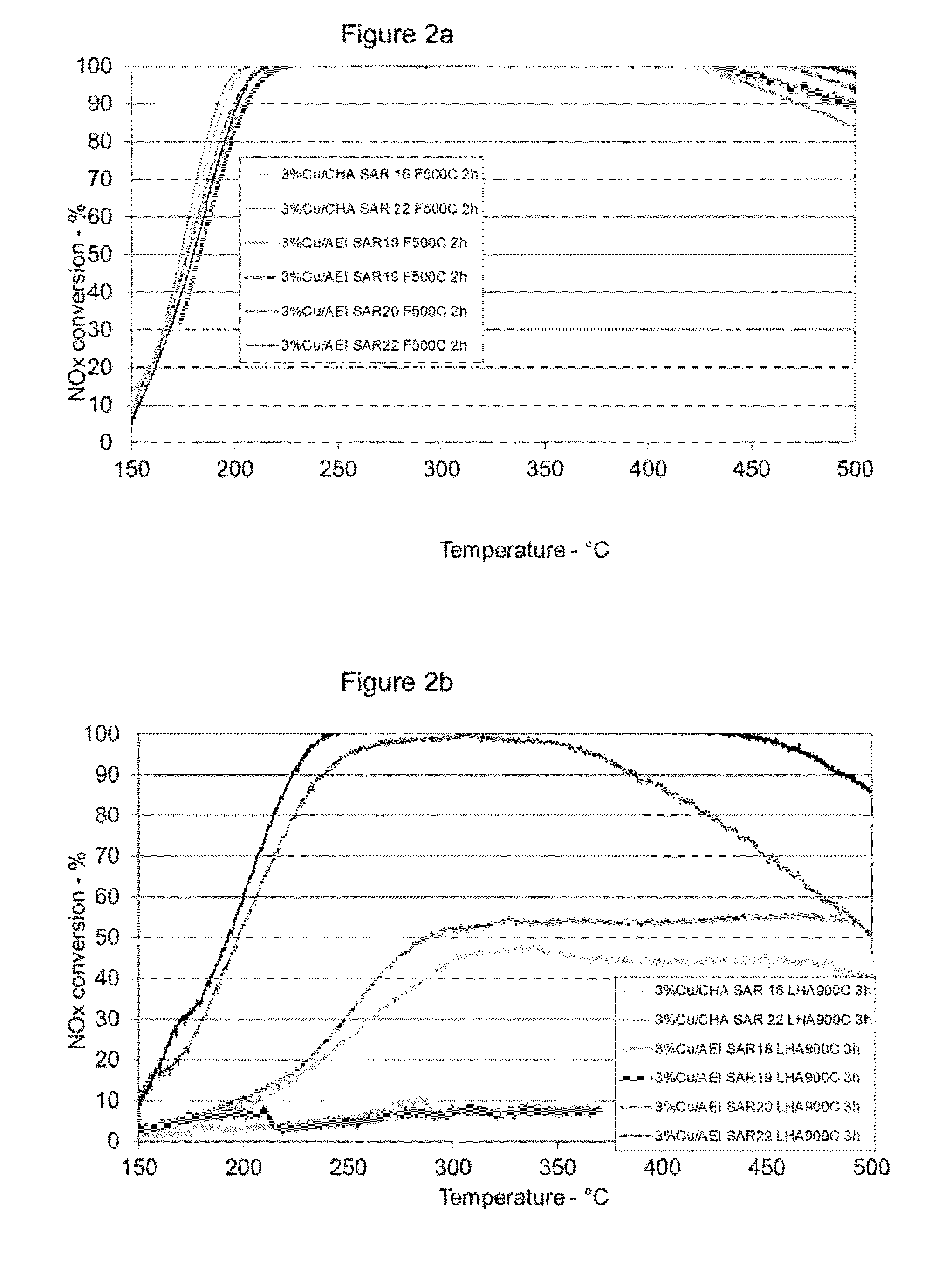
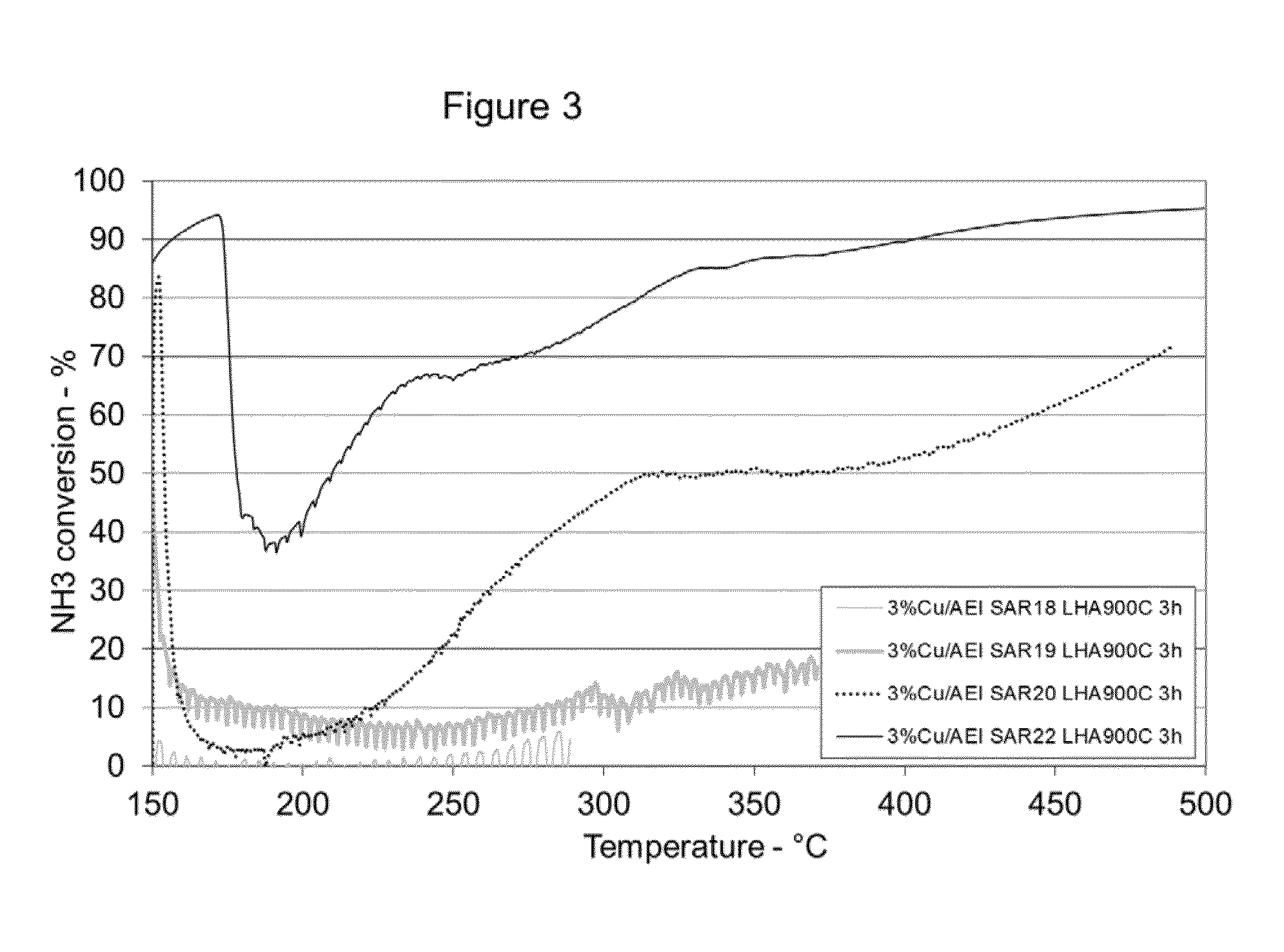
Copper CHA zeolite catalysts
ActiveUS7601662B2Good hydrothermal stabilityHigh catalytic activityCombination devicesAluminium compoundsReaction temperatureCrystal structure
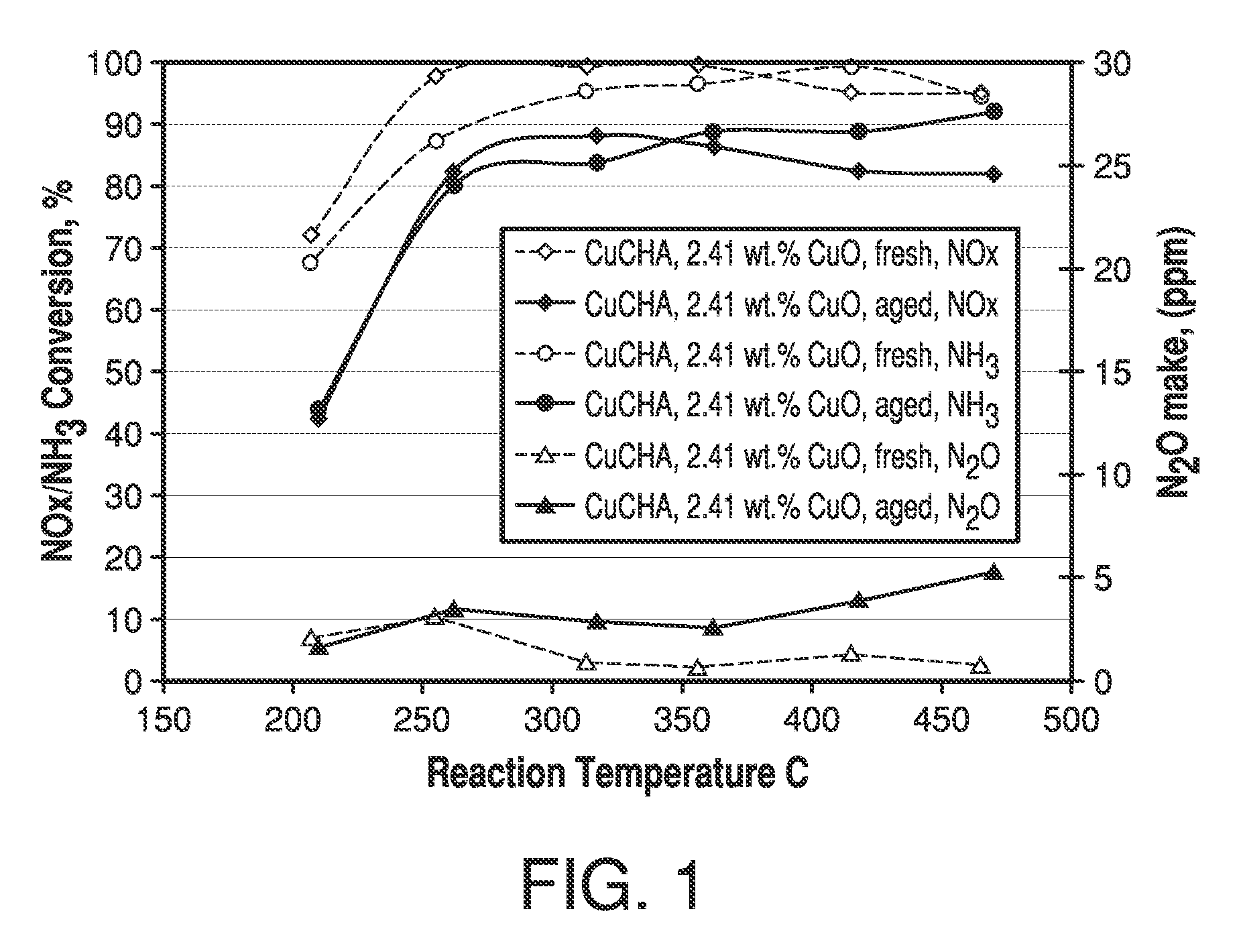
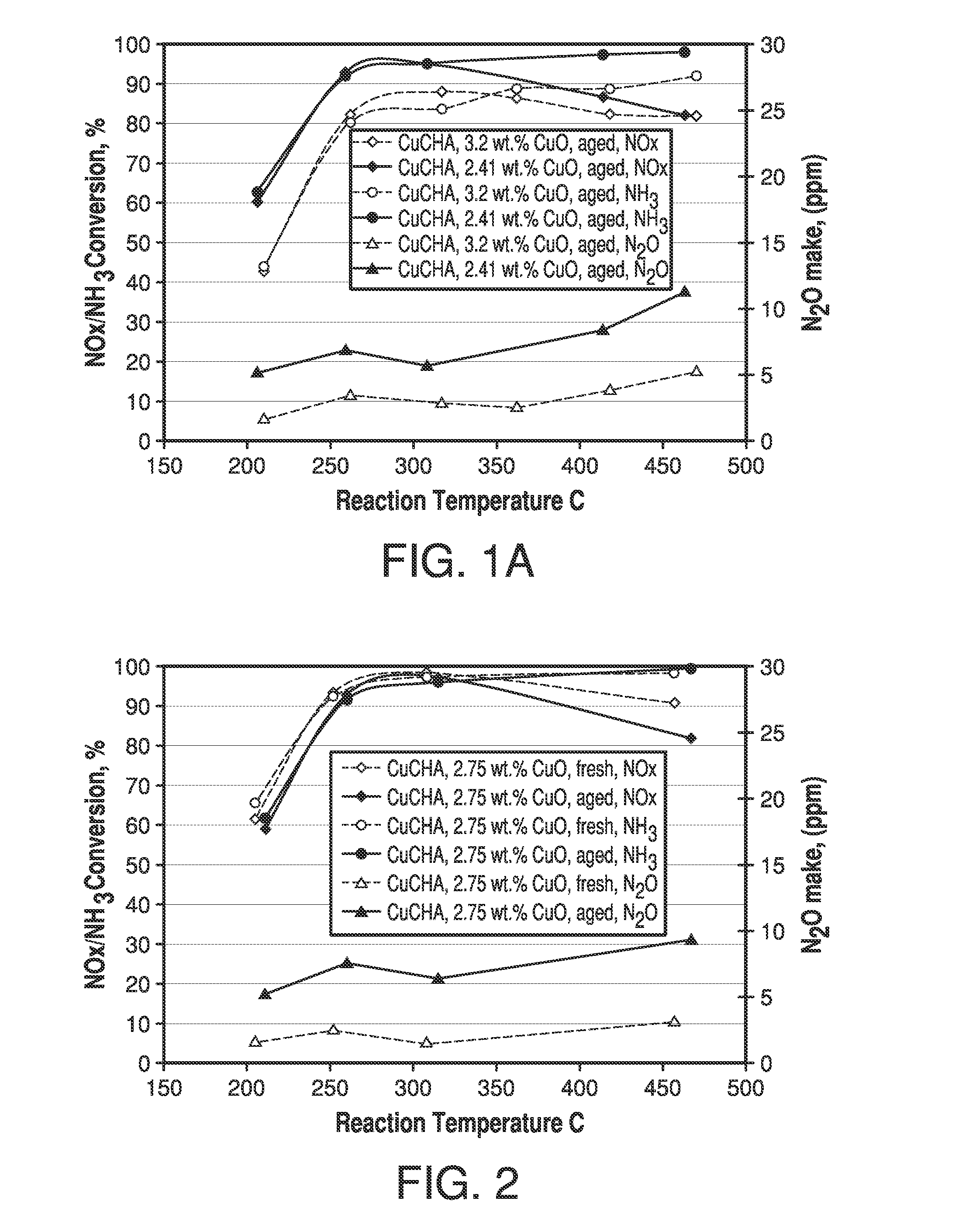
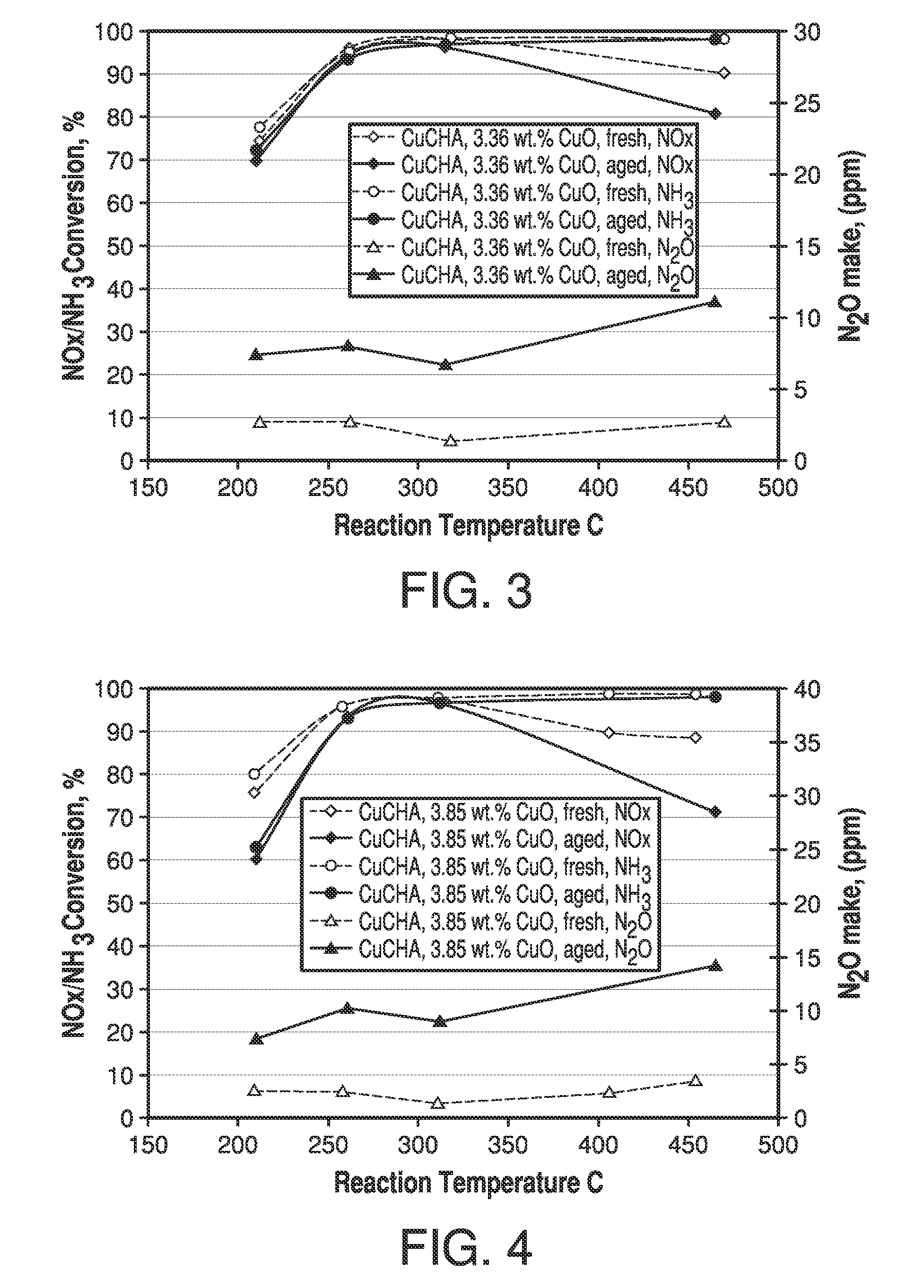
Zeolite catalysts and systems and methods for preparing and using zeolite catalysts having the CHA crystal structure are disclosed. The catalysts can be used to remove nitrogen oxides from a gaseous medium across a broad temperature range and exhibit hydrothermal stable at high reaction temperatures. The zeolite catalysts include a zeolite carrier having a silica to alumina ratio from about 15:1 to about 256:1 and a copper to alumina ratio from about 0.25:1 to about 1:1.
Owner:BASF CORP
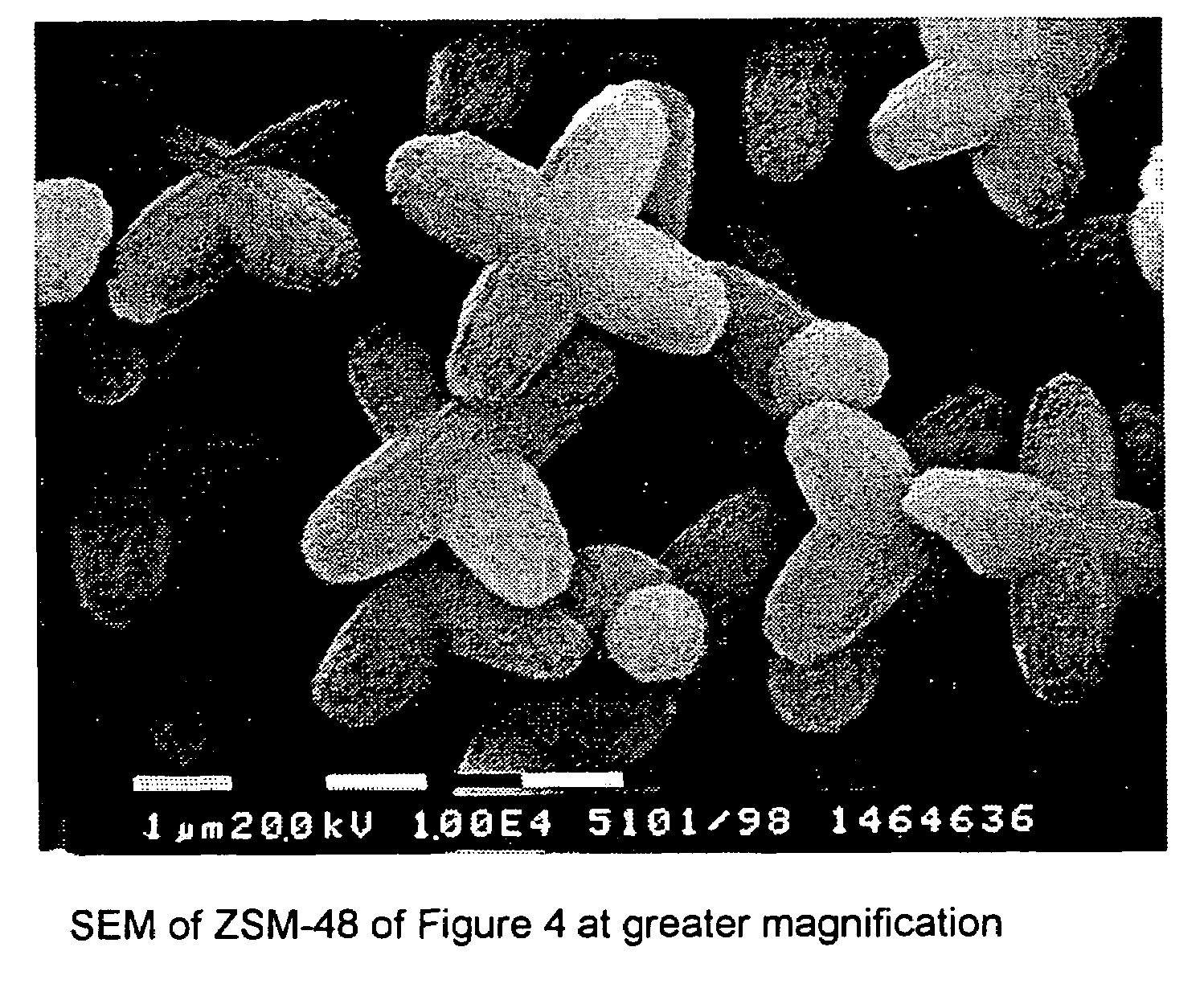
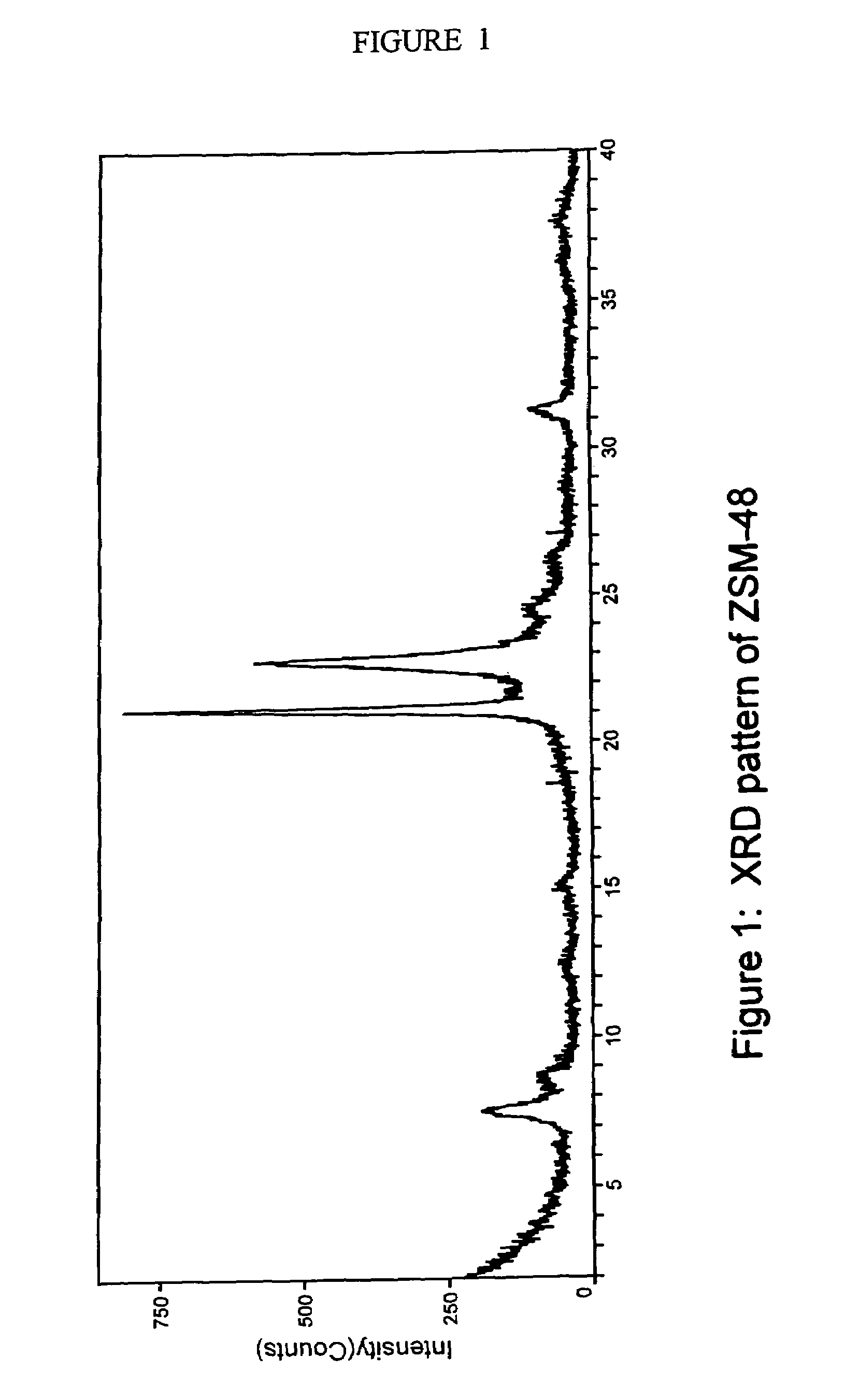
Synthesis of ZSM-48 crystals with heterostructural, non ZSM-48, seeding
ActiveUS6923949B1Suppresses formation of impurityPromotes more aluminum incorporationAluminium compoundsMolecular-sieve and base-exchange compoundsHigh activityZeolite
Pure phase, high activity ZSM-48 crystals having a SiO2 / Al2O3 ratio of less than about 150 / 1, substantially free from ZSM-50 and Kenyaite, and fibrous morphology crystals. The crystals may further have a specific cross morphology. A method for making such crystals using heterostructural, zeolite seeds, other than ZSM-48 and ZSM-50 seeds.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Increased thermal conductivity monolithic zeolite structures
A monolith comprises a zeolite, a thermally conductive carbon, and a binder. The zeolite is included in the form of beads, pellets, powders and mixtures thereof. The thermally conductive carbon can be carbon nano-fibers, diamond or graphite which provide thermal conductivities in excess of about 100 W / m·K to more than 1,000 W / m·K. A method of preparing a zeolite monolith includes the steps of mixing a zeolite dispersion in an aqueous colloidal silica binder with a dispersion of carbon nano-fibers in water followed by dehydration and curing of the binder is given.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Method for preparing mesoporous silica molecular sieve fiber
InactiveCN101387019AIncrease the areaIncrease the apertureInorganic material artificial filamentsMolecular-sieve and base-exchange compoundsFiberNanowire
The present invention discloses a method for preparing a wide aperture mesoporous silica molecular sieve fiber. An industrialized nonionics or cationic surfactant is adopted as a template. An organic or inorganic silicon source is adopted as a precursor. In the state where various auxiliary reagents, such as inorganic salt, alcohol and the like, are added, the fiber is synthesized through the cooperative assembly between a surface active agent and inorganic species and a hydrothermal treatment process. The mesoporous silica molecular sieve fiber is between 3 and 20 nm in aperture, between 0.3 and 2.5 cm^3 / g in pore volume, and between 600 and 1200 cm^2 / g in specific area. The material is easy to obtain, the technical requirements are comparatively simple, and the operation is feasible. The method has a very wide application range in terms of the preparation of composite fortifying fiber and semiconductor porous nanometer tube and nanometer wire in the fields of nanometer microelectrode and aviation material.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
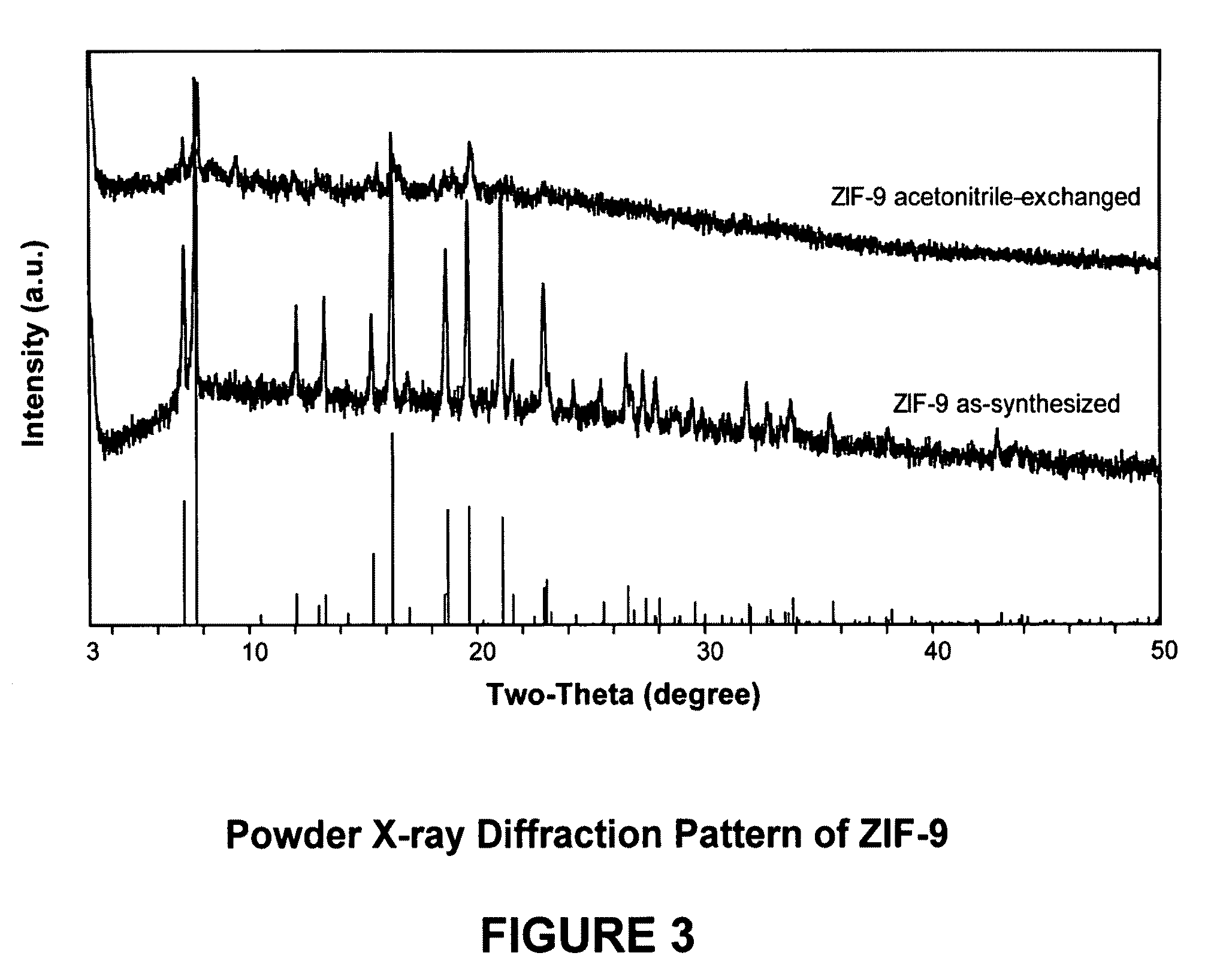
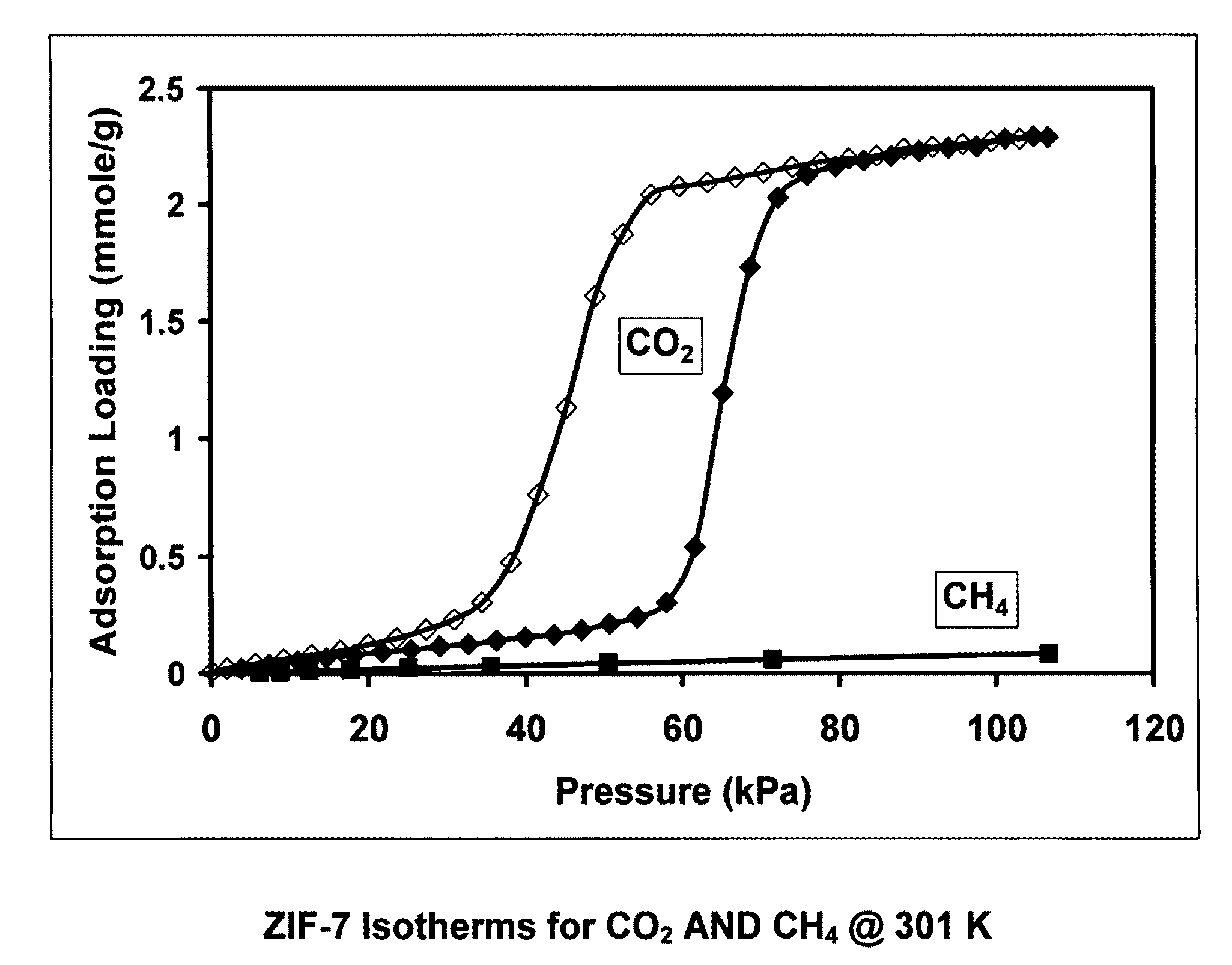
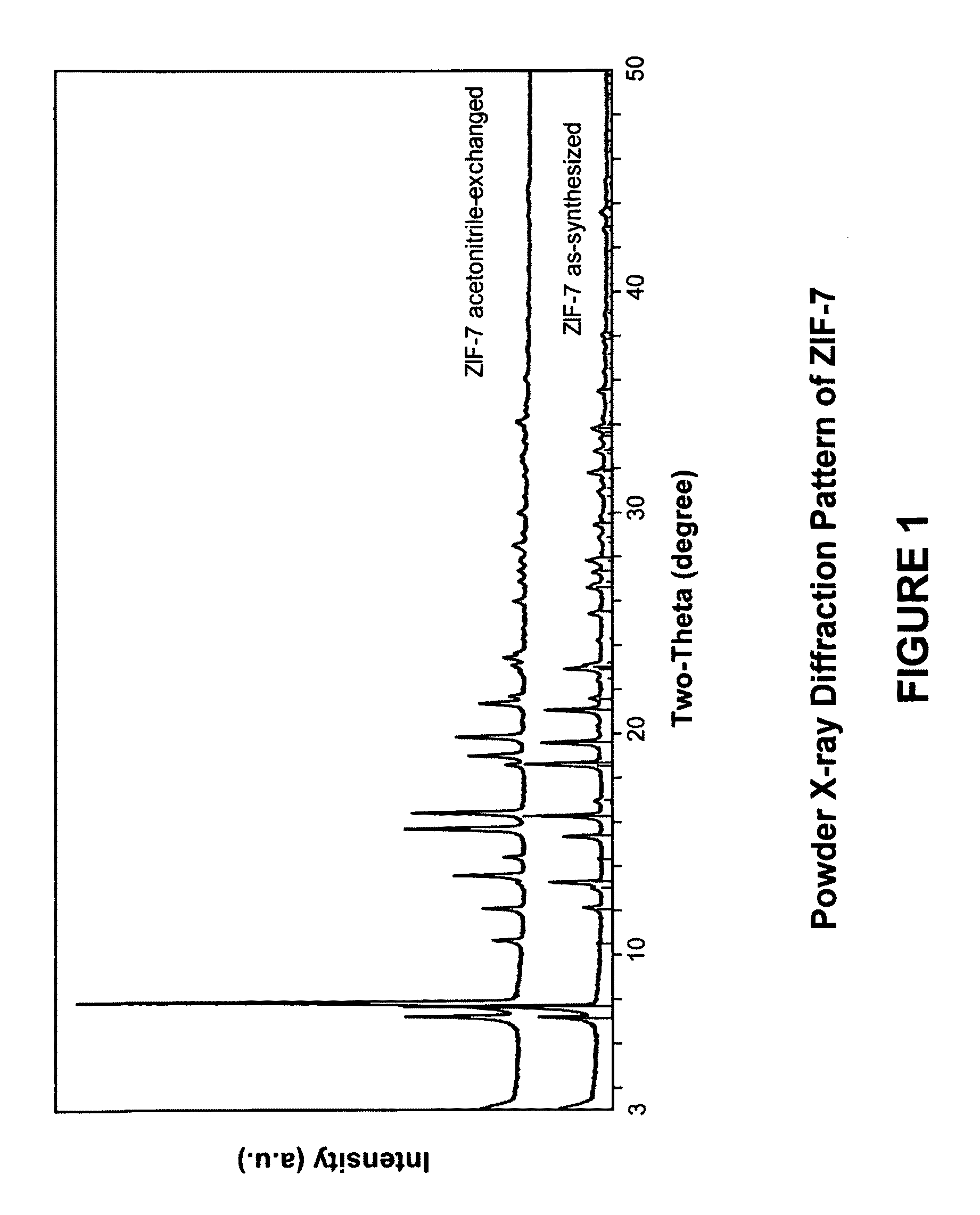
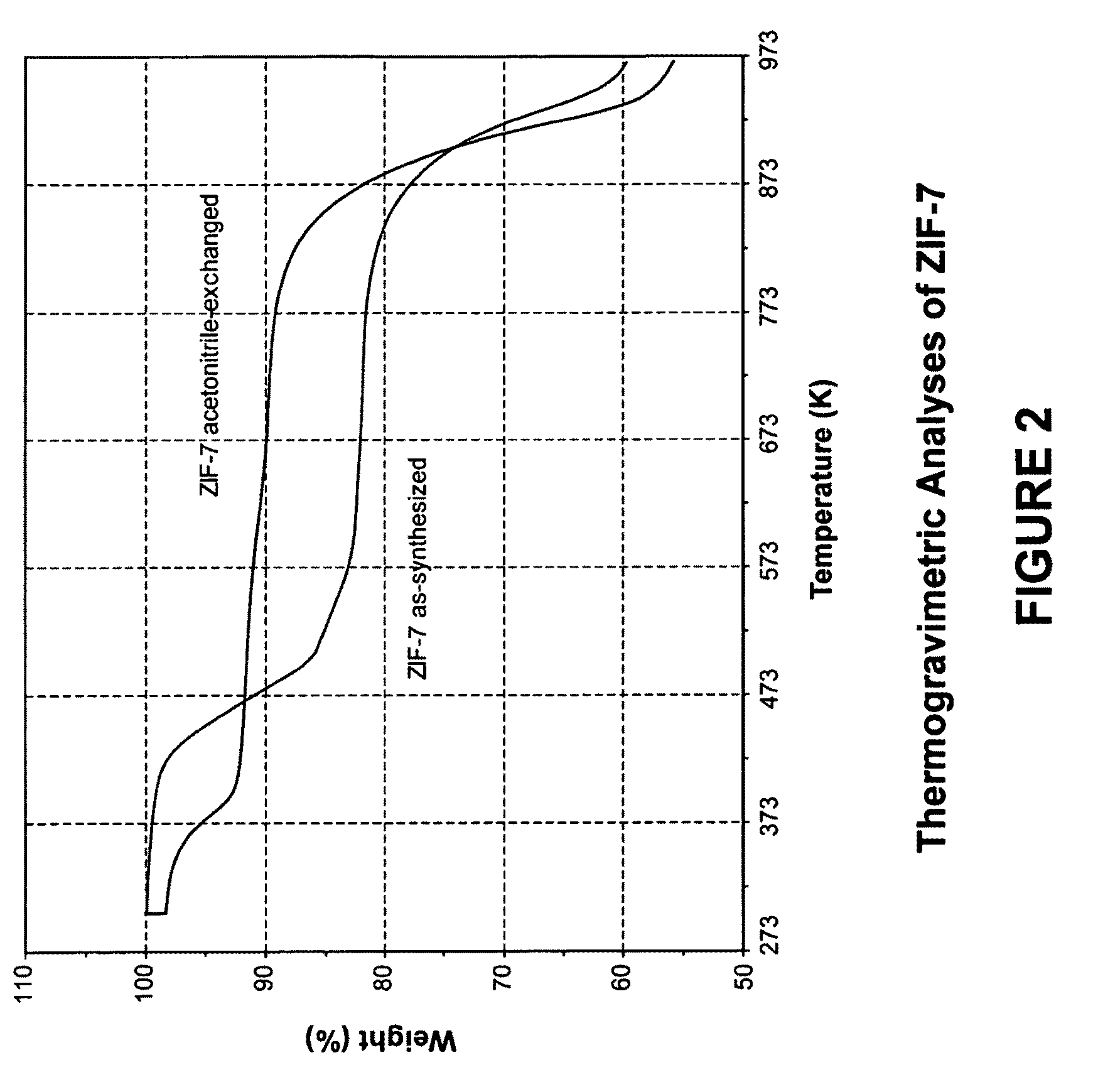
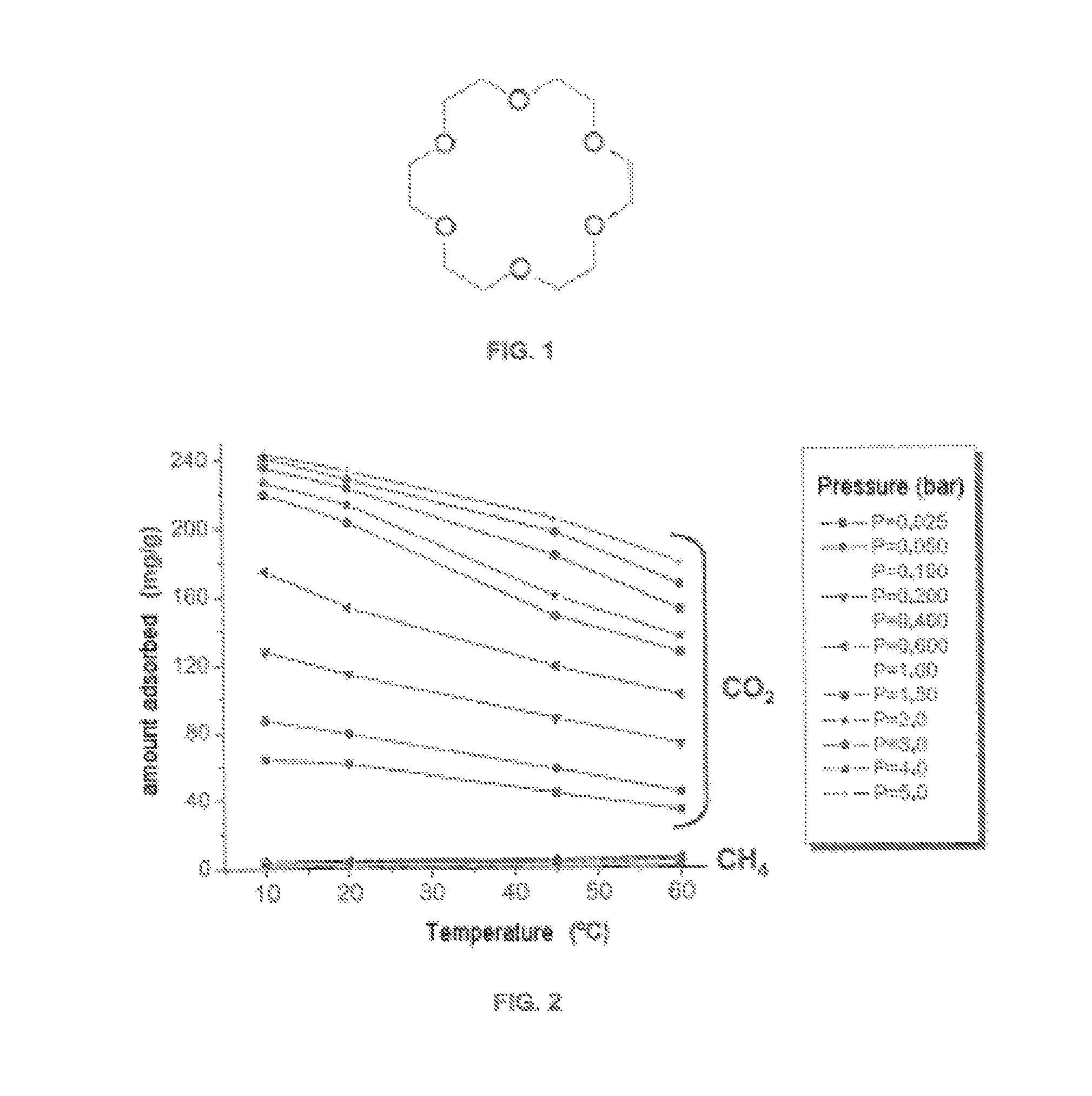
Separation of carbon dioxide from methane utilizing zeolitic imidazolate framework materials
The present invention relates to the selective separation of carbon dioxide (“CO2”) from methane (“CH4”) in streams containing both carbon dioxide and methane utilizing a zeolitic imidazolate framework (“ZIF”) material. Preferably, the stream to be separated is fed to the present process in a substantially gaseous phase. In preferred embodiments, the current invention is utilized in a process to separate carbon dioxide from natural gas streams preferably for sequestration of at least a portion of the carbon dioxide present in the natural gas.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Catalyst for treating exhaust gas
ActiveUS20140271426A1Improve catalytic performanceCombination devicesNitrogen compoundsMolecular sieveSilicon dioxide
Provided is a catalyst composition having an aluminosilicate molecular sieve having an AEI structure and a mole ratio of silica-to-alumina of about 20 to about 30 loaded with about 1 to about 5 weight percent of a promoter metal, based on the total weight of the molecular sieve material. Also provided are method, articles, and systems utilizing the catalyst composition.
Owner:JOHNSON MATTHEY PLC
Catalyst for fluidized catalytic cracking of heavy hydrocarbon oil and method of fluidized catalytic cracking
InactiveUS6916762B2Efficient inactivationReduce the amount requiredCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesAluminium compoundsHydrogenOxide matrix
An FCC catalyst which not only deactivates catalyst poison metals, such as nickel, vanadium and the like, in feedstock oils, inhibits the generation of hydrogen or coke, has excellent cracking activity and bottom oil-treating ability, and can yield a gasoline and LCO fraction in high yields, but also retains the performances on a high level over long and has an improved catalyst life; and an FCC method using the catalyst. The FCC catalyst has a compound of a bivalent metal or of bivalent and trivalent metals showing an XRD pattern of a carbonate of the bivalent metal; an inorganic oxide matrix and the compound dispersed therein; or an inorganic oxide matrix and the compound dispersed therein together with a crystalline aluminosilicate zeolite, and relates to an FCC method in which at least one of the catalysts are used in combination with an FCC catalyst obtained by evenly dispersing a crystalline aluminosilicate zeolite in an inorganic oxide matrix.
Owner:GASOLINEEUM ENERGY CENT FOUND +1
Microporous-mesoporous molecular sieve containing noble metal, preparation method and application to catalytic reduction of p-nitrophenol
InactiveCN103011189AReduce pollutionLow cost of industrializationMolecular sieve catalystsOrganic compound preparationWater bathsDispersity
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular sieve preparation, and particularly relates to an in-situ preparation method for a microporous-mesoporous molecular sieve containing noble metal. The in-situ preparation method comprises the steps as follows: adding a coupling pore-forming agent, a silicon source, an aluminum source or a titanium source, and an alkali source into a water solution of noble metal nano particles in sequence under the water bath condition; and ageing, drying, crystallizing, drying and carrying out high-temperature calcination to obtain the microporous-mesoporous molecular sieve containing the noble metal. The prepared microporous-mesoporous molecular sieve is provided with a hierarchical pore structure; the noble metal nano particles with high dispersity are covered in situ while a mesoporous structure is generated; and a synthetic method is convenient and simple, saves energy and reduces emission. A multifunctional catalyst prepared with the method integrates the advantages of the microporous channels of the molecular sieve, the transgranular meso pores and the intergranular meso pores of the molecular sieve and the noble metal nano particles, and is more suitable for catalytic reactions of sulfur-containing large molecules such as hydrogen desulfurization and the like.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Medical Device Having Coating With Zeolite Drug Reservoirs
A medical device having a drug-eluting coating that includes a pharmaceutical compound or, more generally, a therapeutic material housed within pores of a zeolite carrier. The zeolite carrier has an open porous structure with reservoirs for holding the therapeutic material. The therapeutic material loaded zeolites may be suspended or dispersed within a bioerodible polymer matrix to provide controlled delivery of the therapeutic material. Zeolite drug carriers may have enhanced or optimally engineered pore sizes for a particular therapeutic material and release profile. Along with a therapeutic material, reservoirs of a zeolite drug delivery system may include a release agent. The release agent may be used to entrap the therapeutic material until such time as a triggering condition is met that prompts the release agent to activate and thereby release the therapeutic material from the zeolite reservoir.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
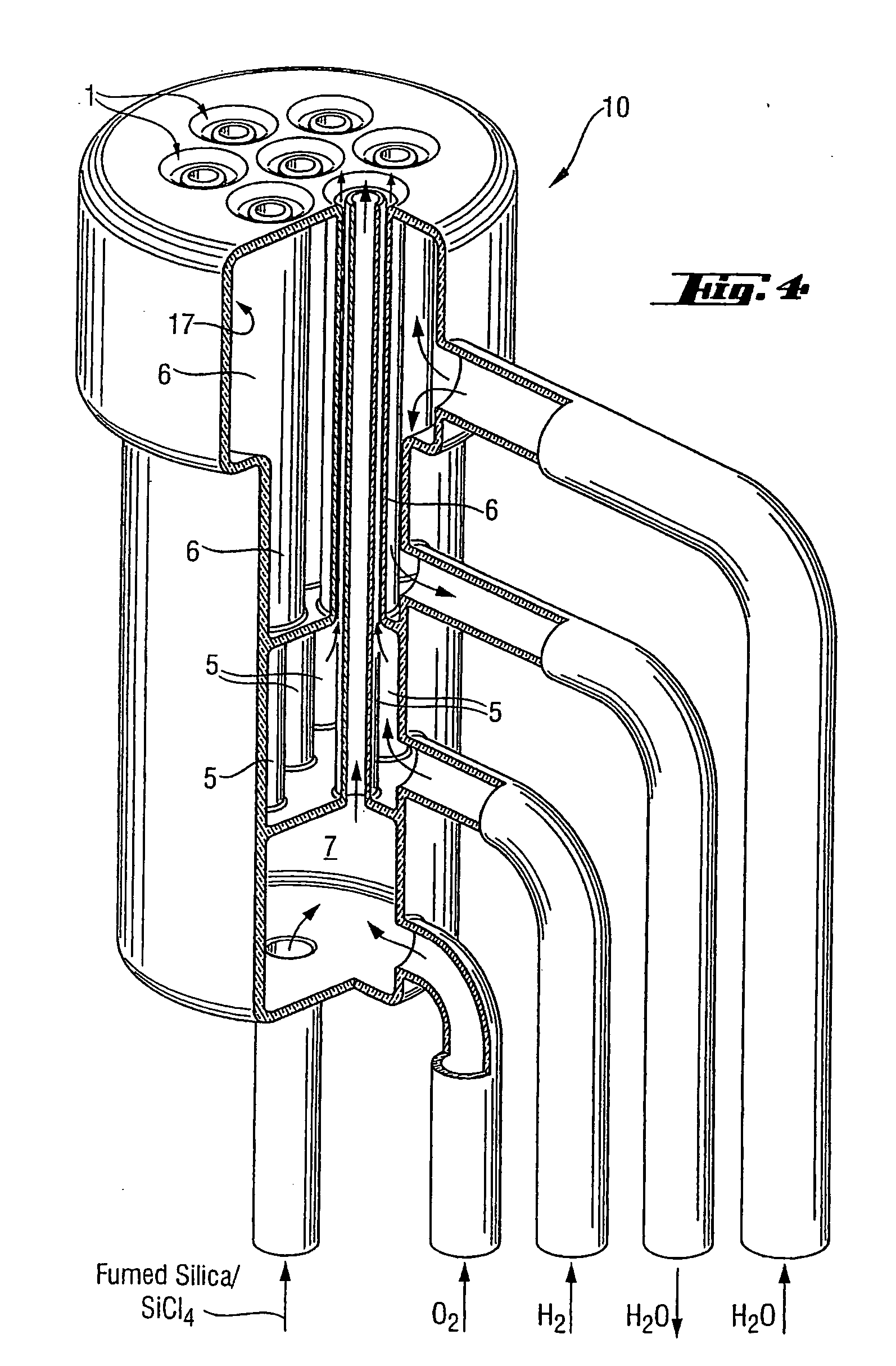
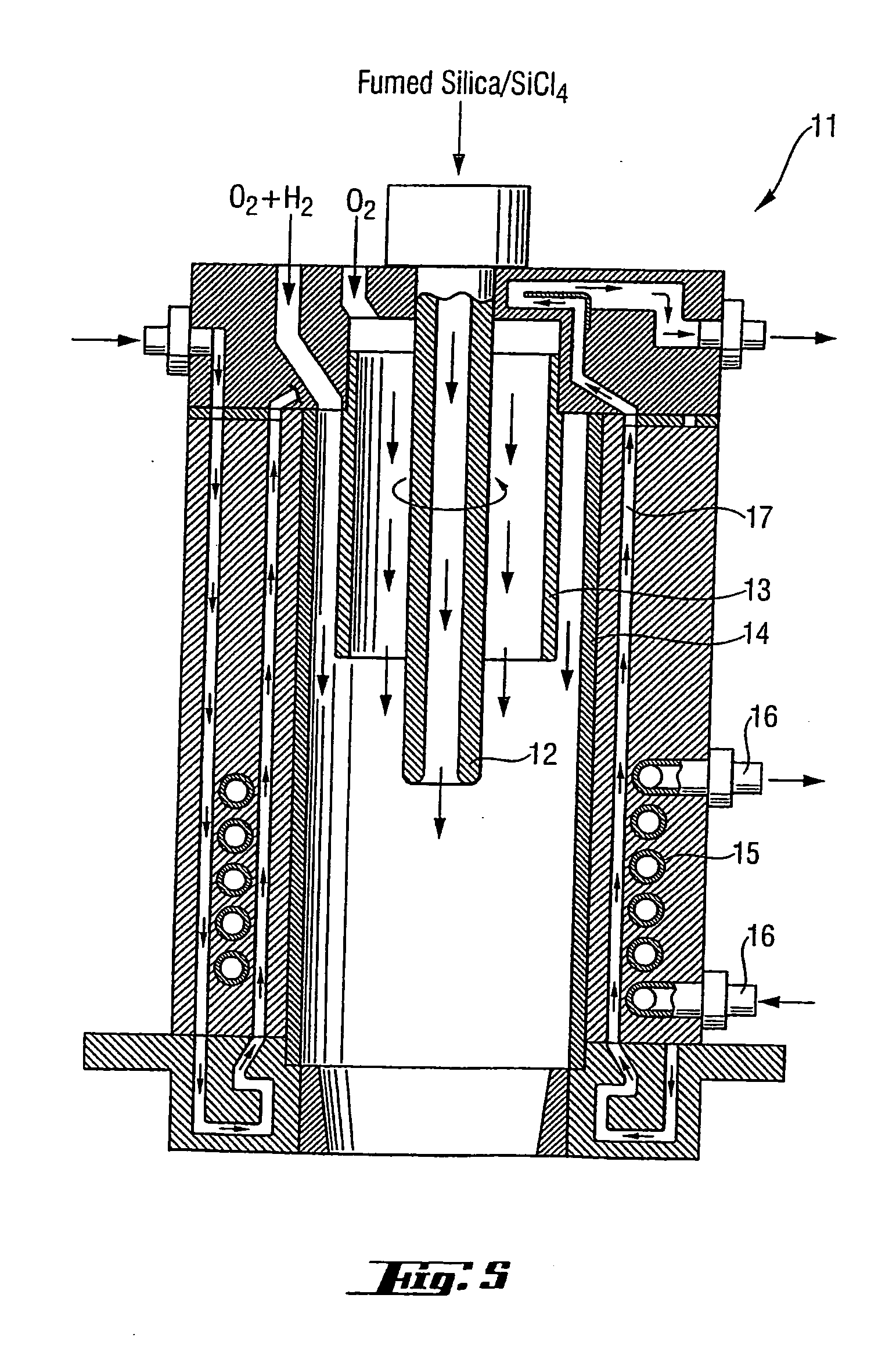
High-purity silica powder, and process and apparatus for producing it
Use of a flame hydrolysis apparatus for preparing fumed silica particles or a plasma torch apparatus for sintering fumed silica particles to fused silica particles is capable of producing highly pure silica with non-silicon metal impurities less than 500 pb, when at least an inner nozzle is constructed of a silicon-containing material having a low level of non-silicon metal impurities. Preferably, all surfaces in the respective apparatus which contact silica are of similar construction. The silica contains a low level of impurities as produced, without requiring further purification.
Owner:WACKER CHEM GMBH
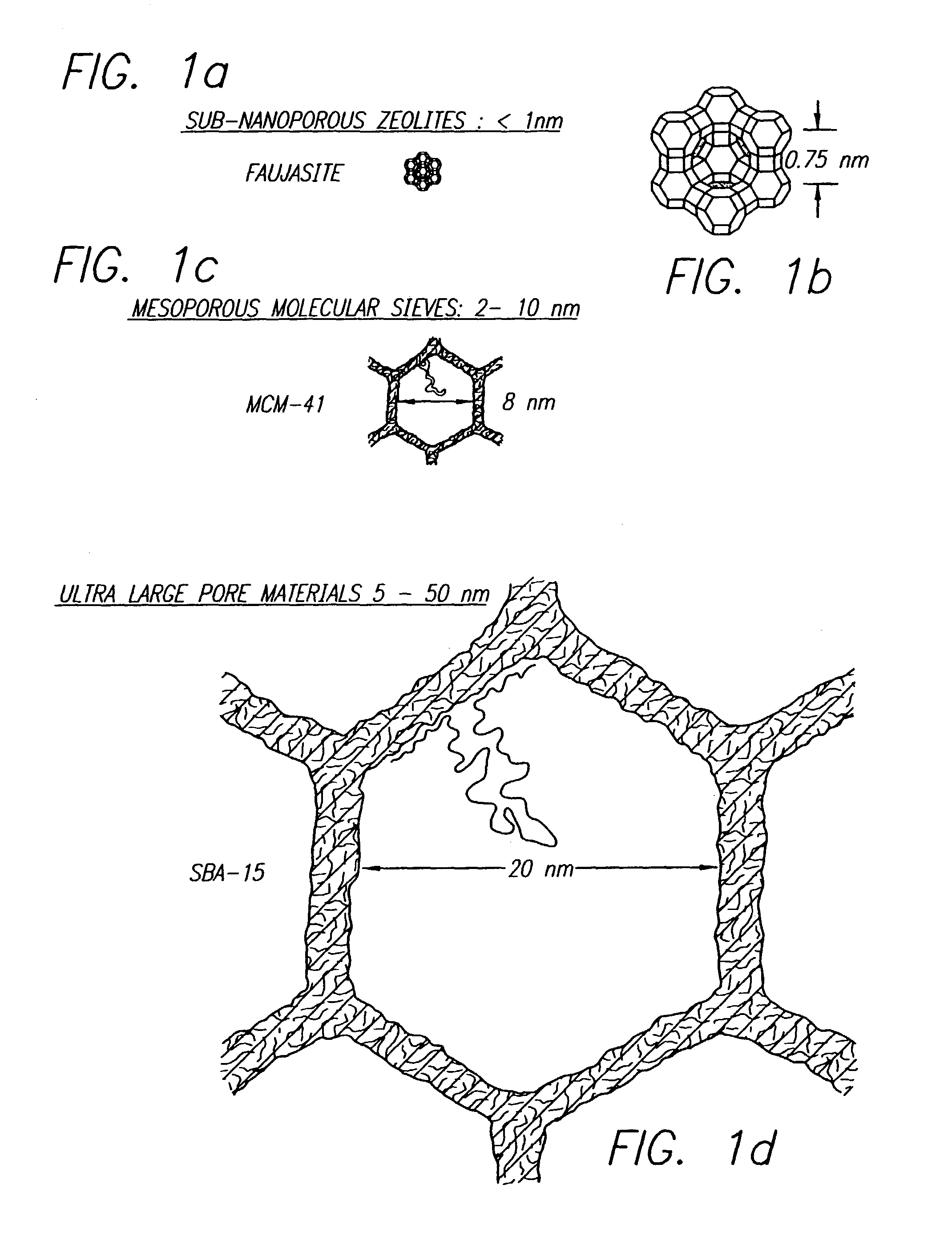
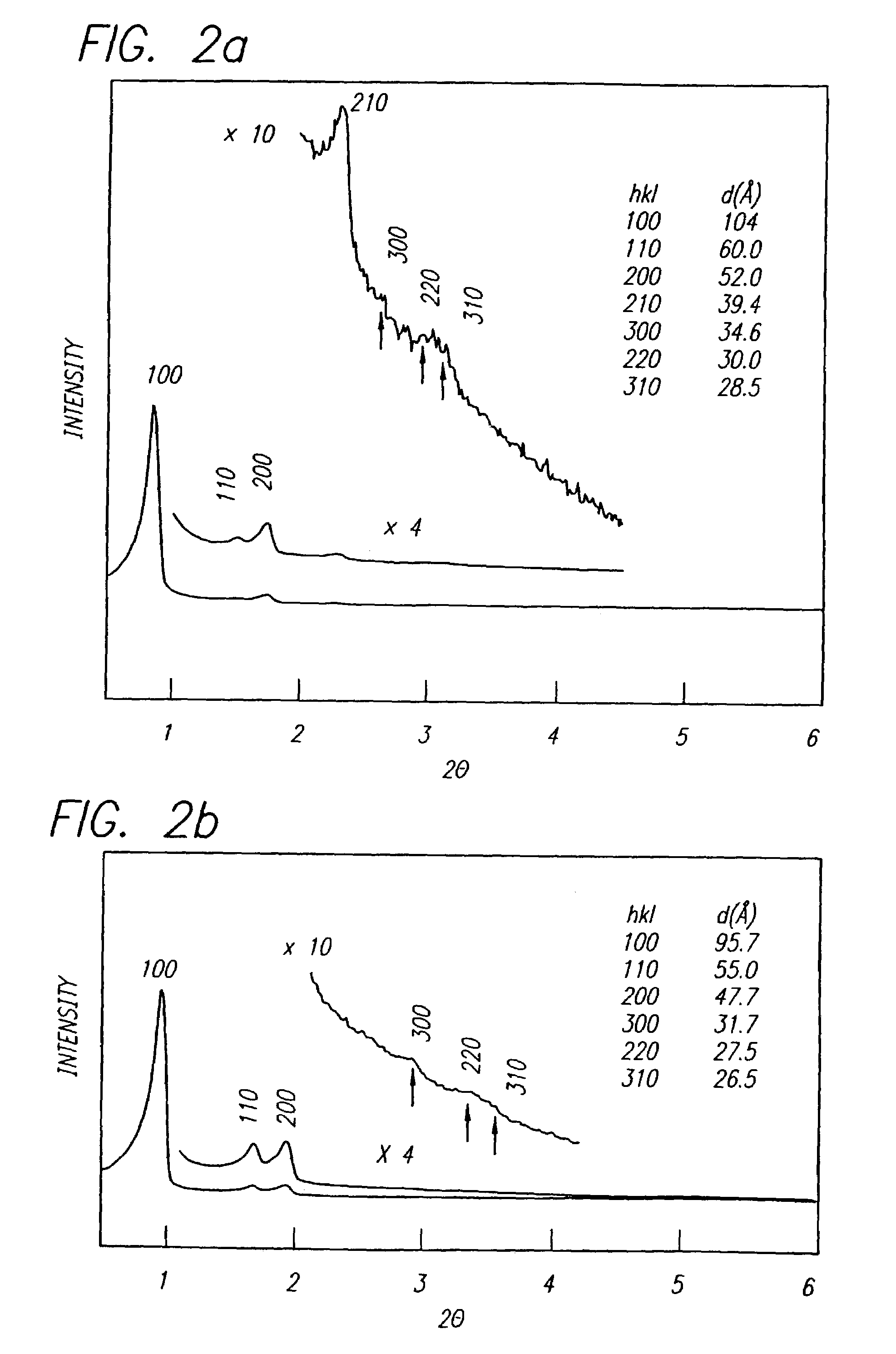
Block copolymer processing for mesostructured inorganic oxide materials
InactiveUS7176245B2High BET surface areaIncrease surface areaMolecular-sieve and base-exchange compoundsCation exchangersMesoporous materialCopolymer
Owner:SBA MATERIALS
Gasoline sulfur reduction in fluid catalytic cracking
InactiveUS6852214B1Reduce sulfur contentLow sulfurCatalytic crackingMolecular sieve catalystsOxidation stateGasoline
The sulfur content of liquid cracking products, especially the cracked gasoline, of the catalytic cracking process is reduced by the use of a sulfur reduction additive comprising a porous molecular sieve which contains a metal in an oxidation state above zero within the interior of the pore structure of the sieve. The molecular sieve is normally a large pore size zeolite such as USY or zeolite beta or an intermediate pore size zeolite such as ZSM-5. The metal is normally a metal of Period 4 of the Periodic Table, preferably zinc or vanadium. The sulfur reduction catalyst may be used in the form of a separate particle additive or as a component of an integrated cracking / sulfur reduction catalyst.
Owner:MOBIL OIL CORP +1
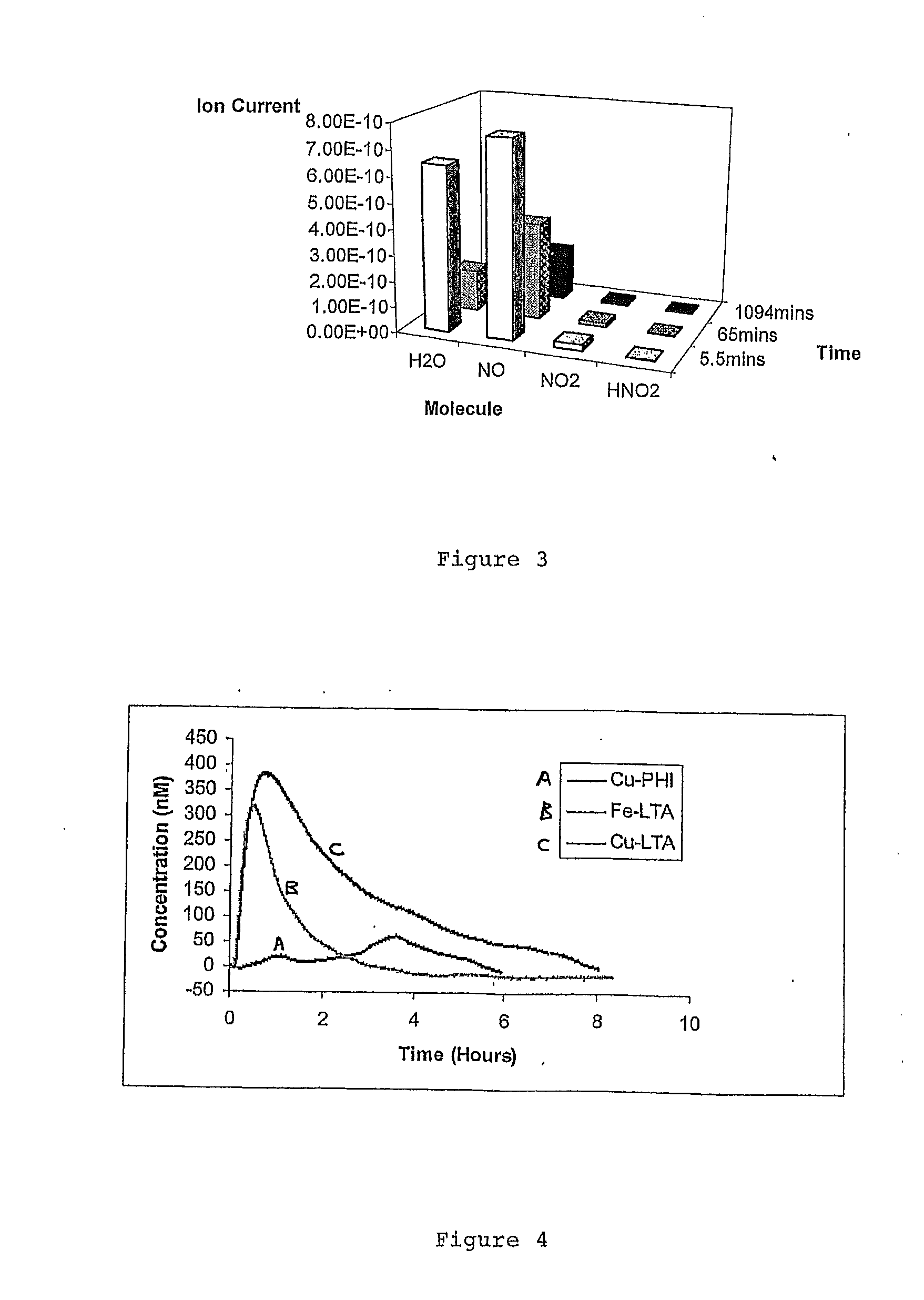
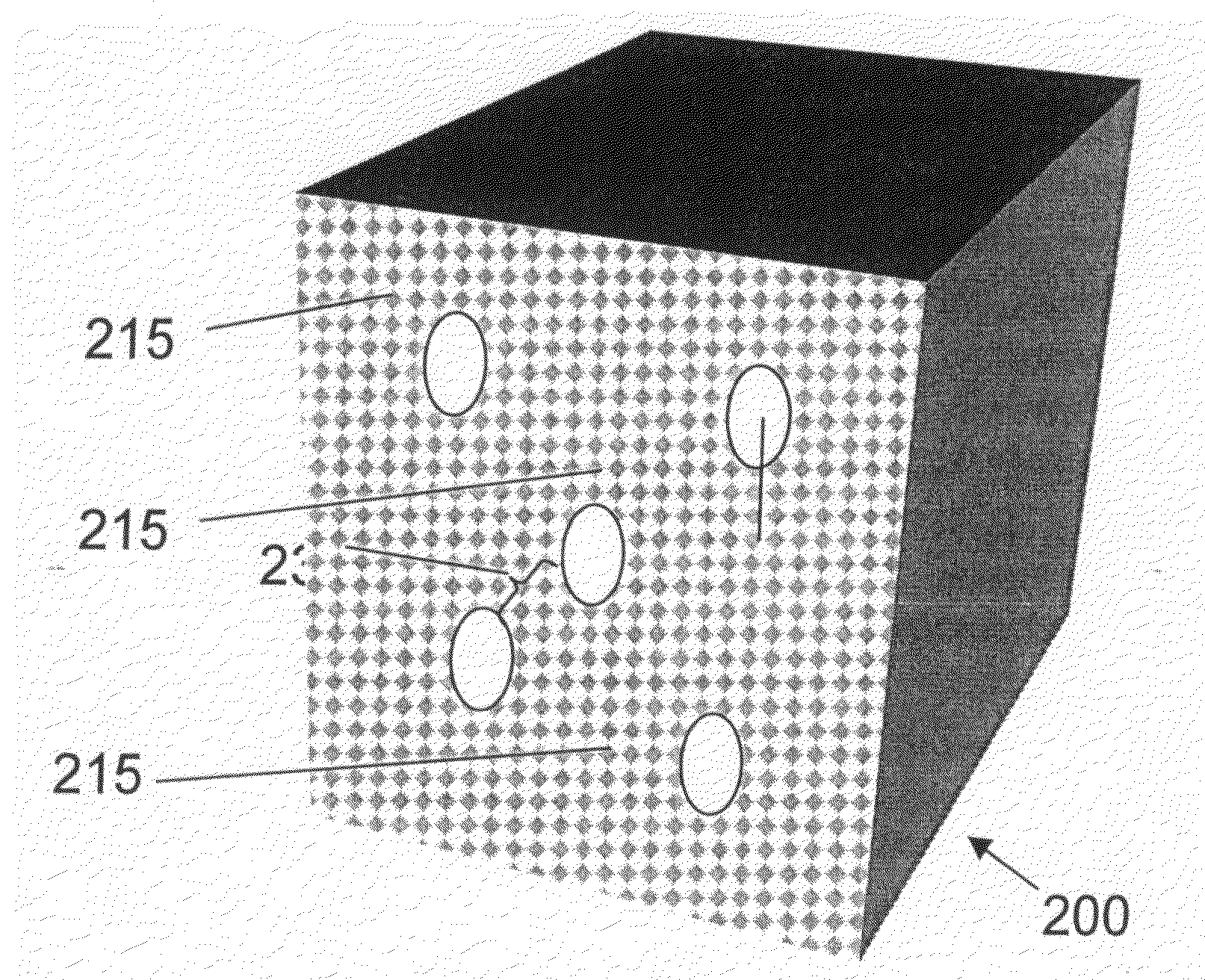
Zeolites for delivery of nitric oxide
ActiveUS20060269620A1Reduce restenosisAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsNitric oxideChemistry
Zeolite composite, method for making and catalytic application thereof
A catalytic material includes microporous zeolites supported on a mesoporous inorganic oxide support. The microporous zeolite can include zeolite Beta, zeolite Y (including “ultra stable Y”—USY), mordenite, Zeolite L, ZSM-5, ZSM-11, ZSM-12, ZSM-20, Theta-1, ZSM-23, ZSM-34, ZSM-35, ZSM-48, SSZ-32, PSH-3, MCM-22, MCM-49, MCM-56, ITQ-1, ITQ-2, ITQ-4, ITQ-21, SAPO-5, SAPO-11, SAPO-37, Breck-6, ALPO4-5, etc. The mesoporous inorganic oxide can be e.g., silica or silicate. The catalytic material can be further modified by introducing some metals e.g. aluminum, titanium, molybdenum, nickel, cobalt, iron, tungsten, palladium and platinum. It can be used as catalysts for acylation, alkylation, dimerization, oligomerization, polymerization, hydrogenation, dehydrogenation, aromatization, isomerization, hydrotreating, catalytic cracking and hydrocracking reactions.
Owner:ABB LUMMUS GLOBAL INC
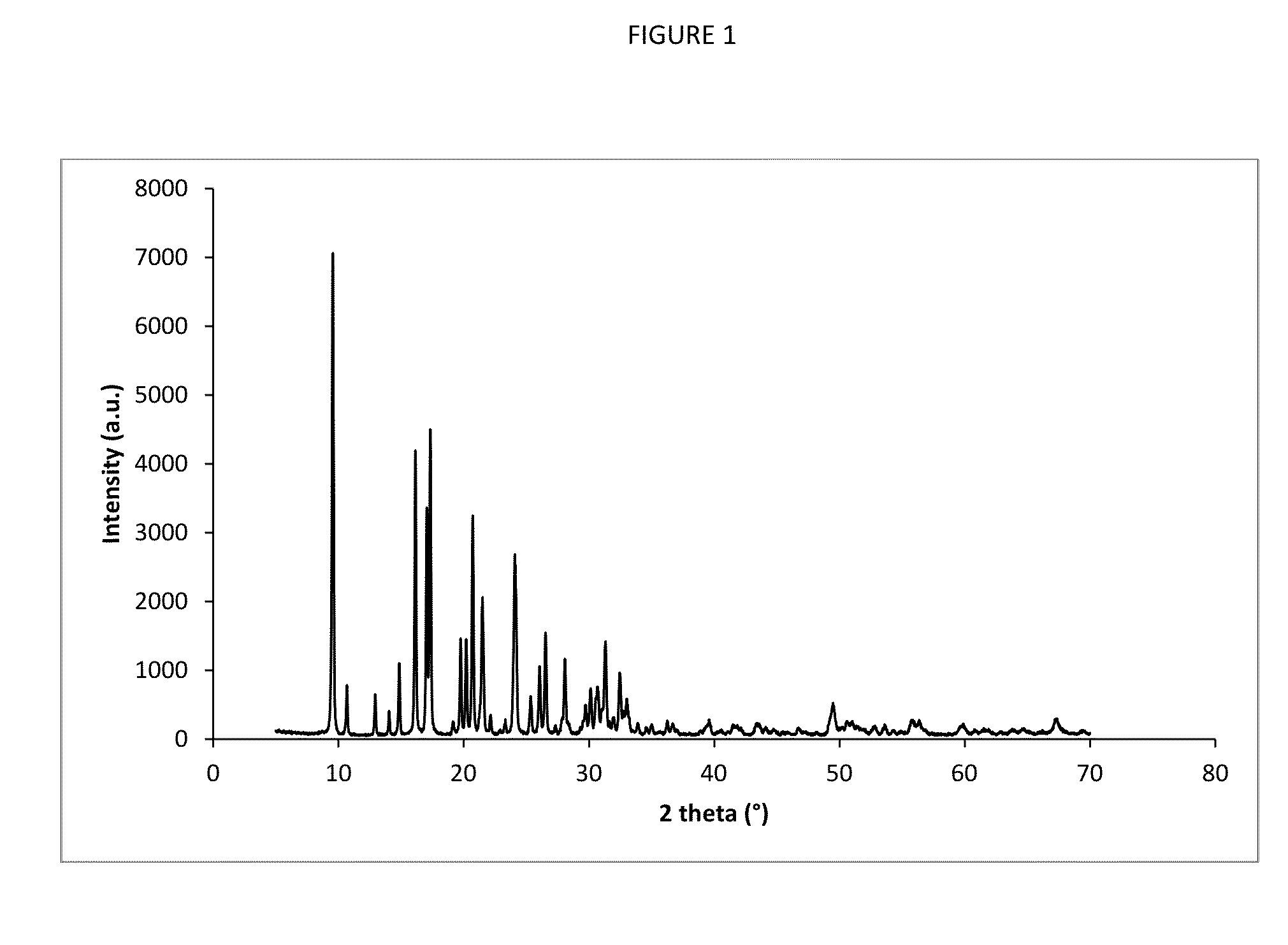
Method for making MTT zeolites without an organic template
InactiveUS6099820ALow raw material costMinimize wasteAluminium compoundsMolecular-sieve and base-exchange compoundsSufficient timeX-ray
The invention includes a method for preparing a crystalline zeolite having the X-ray diffraction lines of Table 1. The method includes preparing a template-free reaction mixture including at least one active source of a first oxide selected from the group consisting of an oxide of silicon, germanium or both, optionally at least one active source of a second oxide selected from the group consisting of an oxide of aluminum, boron, gallium, iron or a mixture thereof; and heating the reaction mixture at crystallization conditions for sufficient time to form a crystallized material containing zeolite crystals having the X-ray diffraction lines of Table 1, where said zeolite crystals have a first oxide / second oxide molar ratio greater than 12.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Hollow-structured mesoporous silica material and preparation process
A hollow-structured mesoporous silica material composed of hollow silica particles that have a shell having radial-arrayed channels, and a process for its preparation. The thin-shell type of mesoporous materials with different morphologies are prepared by growing and synthesizing mesoporous silica on the surface of calcium carbonate nanoparticles with different shapes as inorganic templates, and then removing the inorganic templates. The hollow-structure mesoporous silica material can be used in many fields such as the preparation of catalyst, pesticide and optical fiber.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH +1
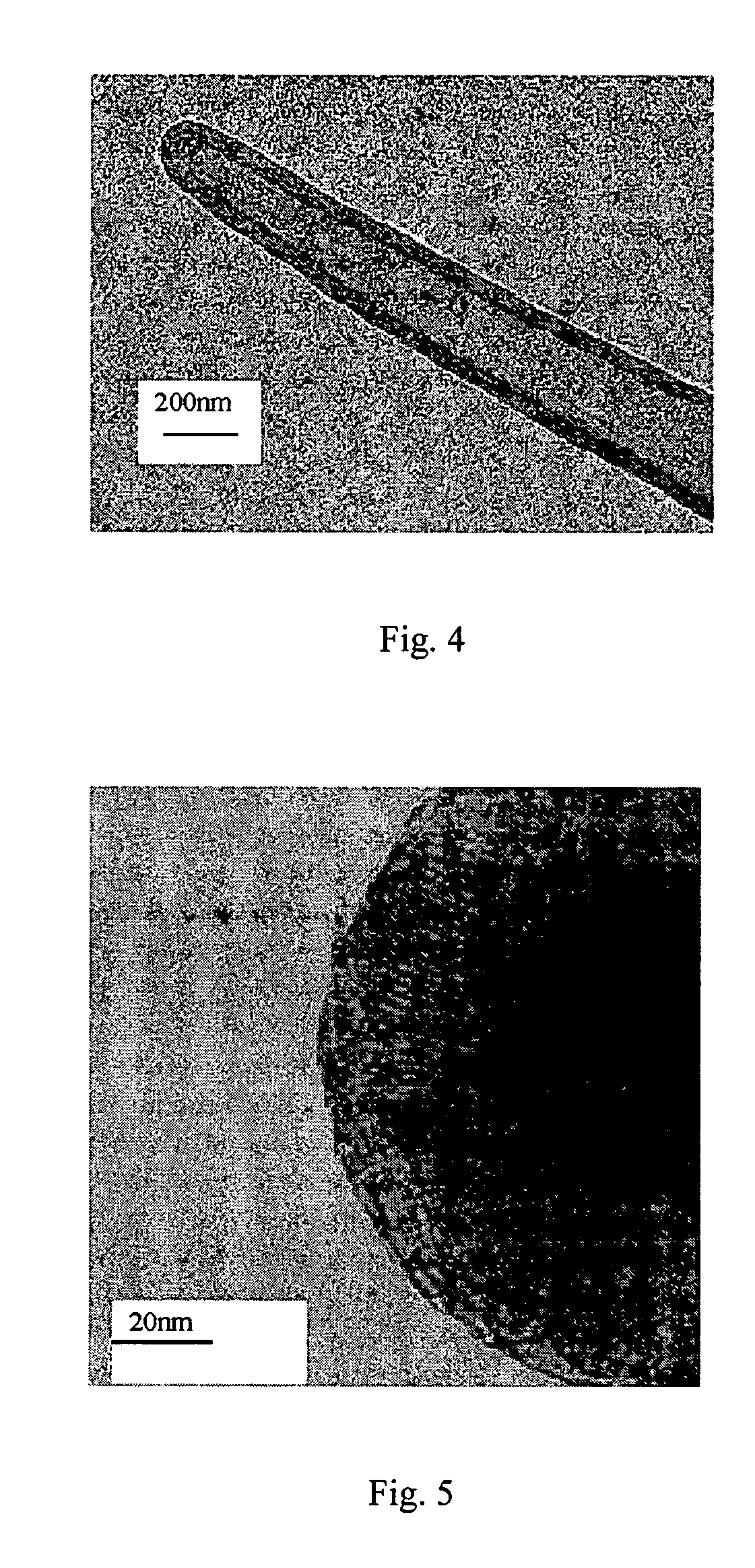
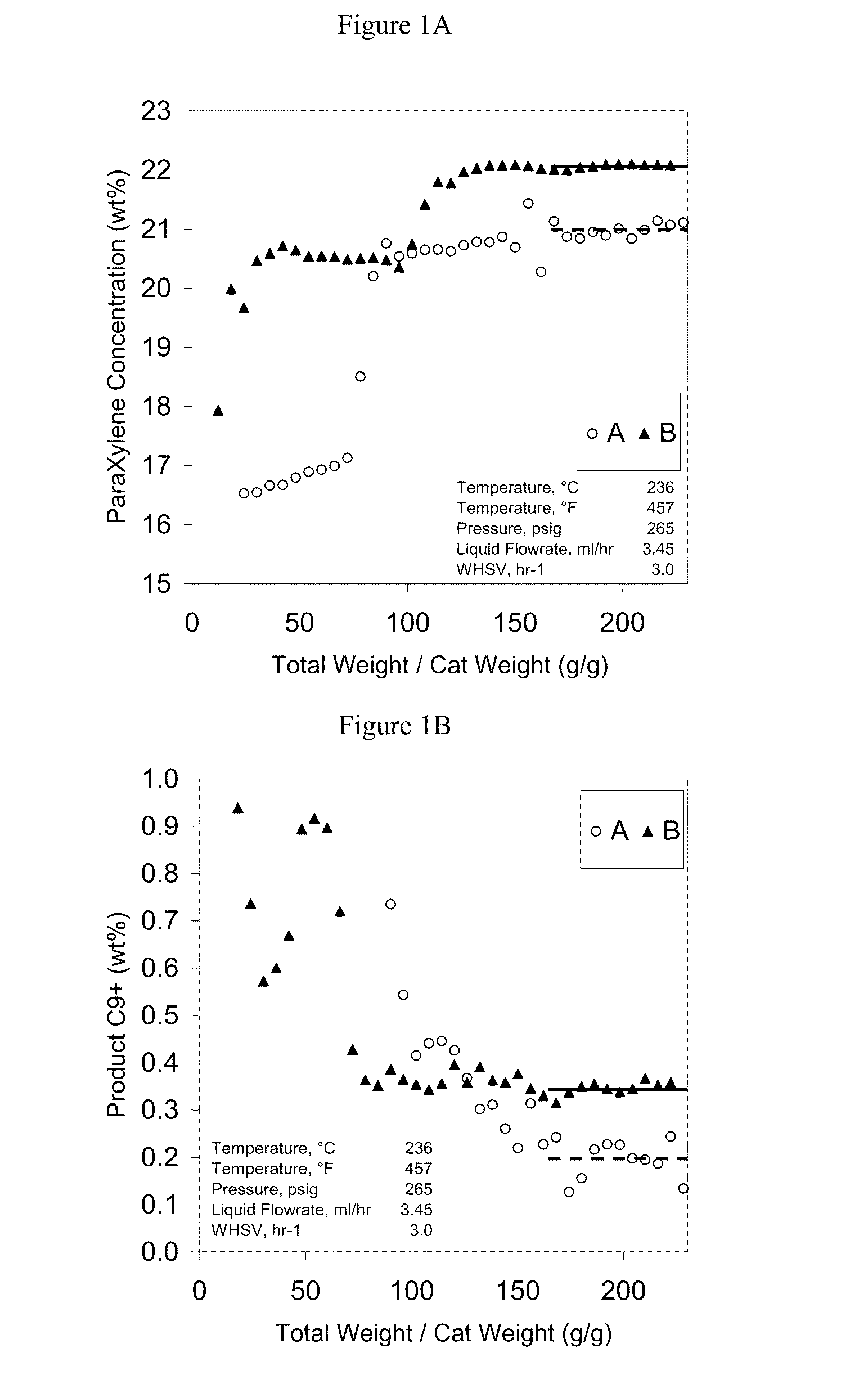
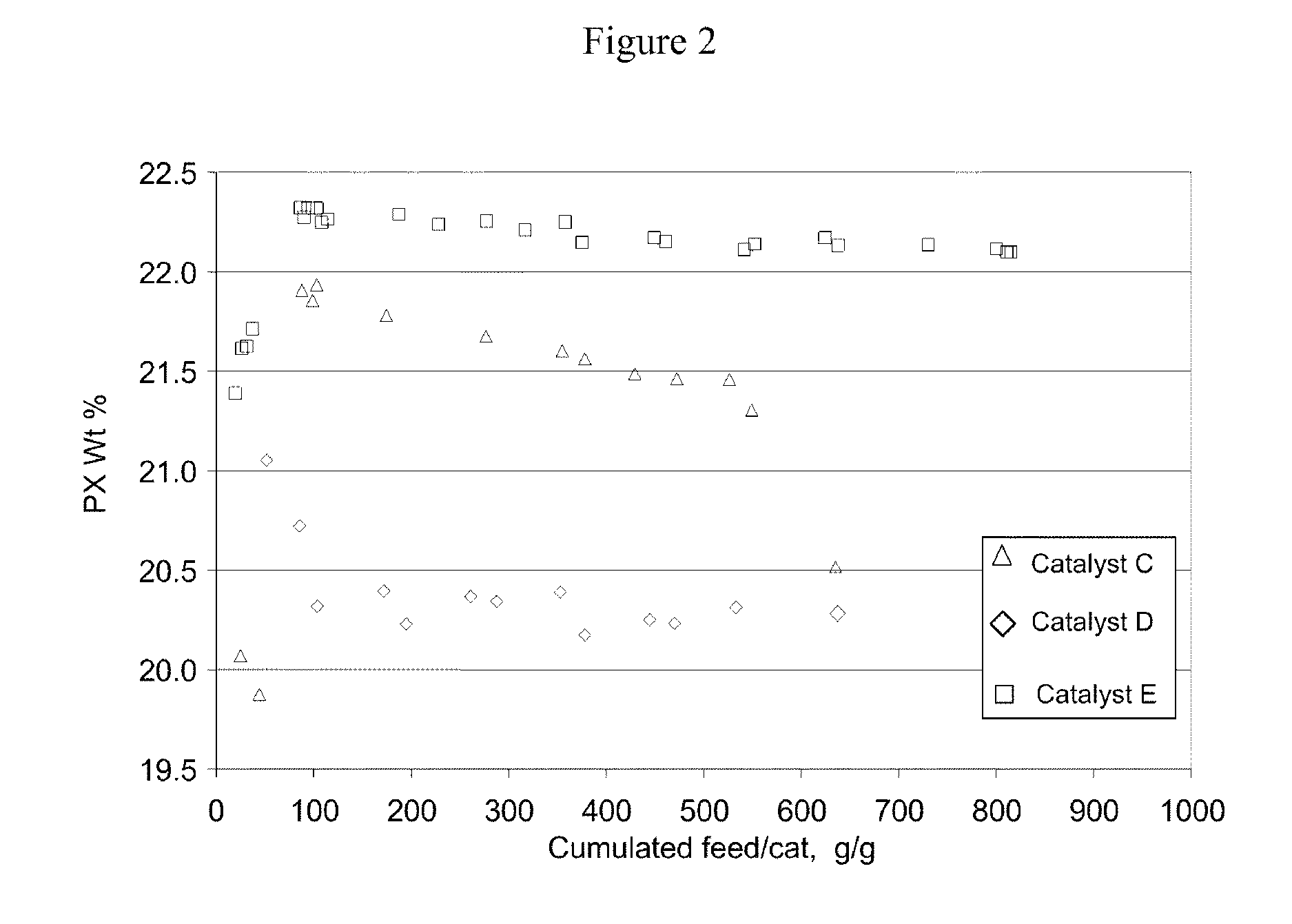
Binderless adsorbents with improved mass transfer properties and their use in the adsorptive separation of para-xylene
ActiveUS7812208B2Improve performanceImprove mass transfer effectOther chemical processesMolecular-sieve and base-exchange compoundsProduction rateSorbent
Owner:UOP LLC
Modification method of titanium silicone molecular sieve and its application
InactiveCN1555923AHigh activityHigh selectivityMolecular sieve catalystsMolecular-sieve and base-exchange compoundsMolecular sieveTitanium
A process for modifying Ti-Si molecular sieve TS-1 with MFI structure includes proportionally adding TS-1 to the aqueous solution of metal salt, laying aside for 6-100 hr, evaporating water by water both at 30-100 deg.C, drying at 110-200 deg.C for 1-20 hr, programmed heating to 200-800 deg.C within 1-12 hr, and calcining at this temp for 2-20 hr. It can be used in epoxidizing reaction of propylene to increase the conversion rate of H2O2 and the selectivity to epoxy propane.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH +1
Separation of carbon dioxide from methane utilizing zeolitic imidazolate framework materials
The present invention relates to the selective separation of carbon dioxide (“CO2”) from methane (“CH4”) in streams containing both carbon dioxide and methane utilizing a zeolitic imidazolate framework (“ZIF”) material. Preferably, the stream to be separated is fed to the present process in a substantially gaseous phase. In preferred embodiments, the current invention is utilized in a process to separate carbon dioxide from natural gas streams preferably for sequestration of at least a portion of the carbon dioxide present in the natural gas.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
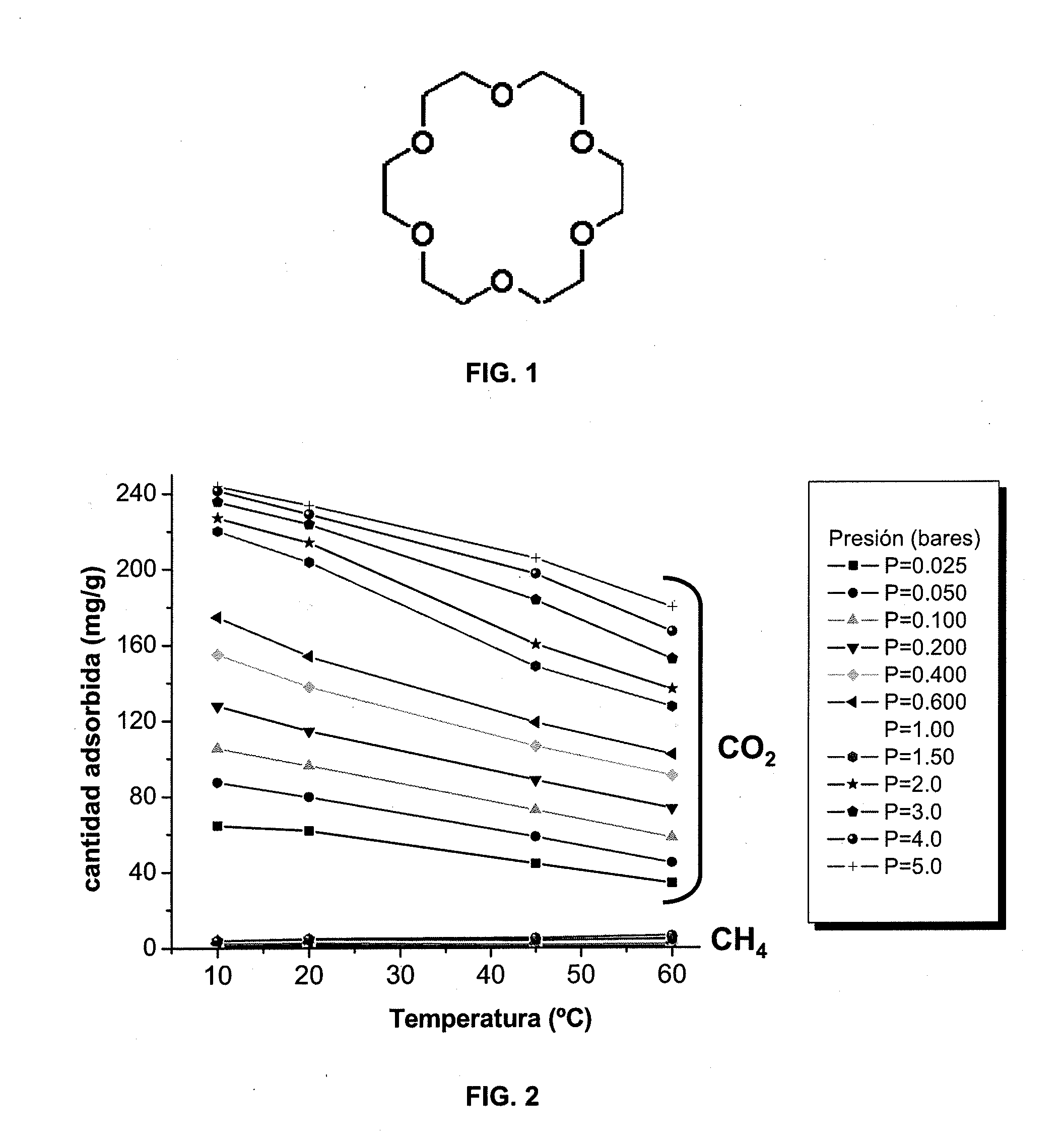
Use of a microporous crystalline material of zeolitic nature with rho structure in natural gas processing
The present invention describes the use of isostructural zeolites with rho zeolitic structure in processes of adsorption and separation of the various components of natural gas.
Owner:CONSEJO SUPERIOR DE INVESTIGACIONES CIENTIFICAS (CSIC) +1
Methods and compositions for directed microwave chemistry
InactiveUS7351590B2Immobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsArtificial enzymeChemical measurement
The present invention concerns a novel means by which specific chosen reactions can be accelerated through the use of a new type of artificial enzyme. The invention allows specific reactions to occur at an accelerated rate, even in the presence of other non-chosen molecules, which may be very similar in structure to the chosen reactant. The reactions may be stoichiometric or catalytic.
Owner:MILESTONE SRL
Silicon dioxide mesoporous material and its preparing method
The mesoporous silica material consists of hollow silica grains with radically radial arranged hole canal in the wall. The present invention also provides the preparation process of the said mesoporous silica material, and the preparation process includes adopting calcium carbonate in different forms as inorganic template; growing and synthesizing mesoporous material on the surface and subsequent eliminating the inorganic template to obtain thin shell type mesoporous material in different forms. The present invention also provides the application of the mesoporous silica material in preparing catalyst, pesticide and optical fiber.
Owner:XIAMEN NANOTECH +1
Zeolites for Delivery of Nitric Oxide
ActiveUS20100331968A1Reduce restenosisAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsEngineeringNitric oxide
There is described zeolites containing releasably adsorbed nitric oxide, methods of preparing the zeolites, methods of releasing the nitric oxide into a solution or into air and uses of the zeolites in therapy.
Owner:THE UNIV COURT OF THE UNIV OF GLASGOW
Methods for making mesostructured zeolitic materials
ActiveUS20080138274A1Avoid associated costsReduce time costAluminium compoundsMolecular sieve catalystsSlurryCrystallinity
A quantity of solution sufficient to dissolve a pH controlling substance and / or substantially dissolve a surfactant without substantial excess solution is controlled under a set of time and temperature conditions to transform an inorganic material having long-range crystallinity to a mesostructure having long-range crystallinity. The method employs concentrated conditions that have a consistency similar to a thick slurry. The economic viability of scaling up such thick slurry methods is improved relative to prior more dilute methods of transforming an inorganic material to a mesostructure.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Crystalline MWW-type titanosilicate catalyst for producing oxidized compound, production process for the catalyst, and process for producing oxidized compound by using the catalyst
InactiveUS20040092757A1Material nanotechnologyPreparation by oxidation reactionsDouble bondOxidizing agent
A crystalline titanosilicate catalyst which is usable as a catalyst in the oxidation reaction of a compound having a carbon-carbon double bond and at least one other functional group, a process for producing the catalyst, and a process for producing an oxidized compound by an oxidation reaction using the catalyst. It has been found that a crystalline titanosilicate having a structural code of MWW effectively functions as a catalyst in an oxidation reaction of a compound having a carbon-carbon double bond and at least one other functional group wherein the carbon-carbon double bond of the compound is oxidized by using a peroxide as an oxidizing agent, thereby to highly selectively provide an intended oxidized compound.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Increased thermal conductivity monolithic zeolite structures
A monolith comprises a zeolite, a thermally conductive carbon, and a binder. The zeolite is included in the form of beads, pellets, powders and mixtures thereof. The thermally conductive carbon can be carbon nano-fibers, diamond or graphite which provide thermal conductivities in excess of about 100 W / m·K to more than 1,000 W / m·K. A method of preparing a zeolite monolith includes the steps of mixing a zeolite dispersion in an aqueous colloidal silica binder with a dispersion of carbon nano-fibers in water followed by dehydration and curing of the binder is given.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Method of producing alkylbenzene and catalyst used therefor
InactiveUS20120000819A1Increase added valueInhibit productionAluminium compoundsMolecular sieve catalystsAlkaneAcid strength
A method that efficiently produces an alkylbenzene with a high added value from a 1.5-cyclic aromatic hydrocarbon while suppressing excessive hydrocracking and nuclear hydrogenation, and preventing a decrease in catalytic activity due to deposition of carbon during a hydrocracking reaction, and a catalyst used therefor, are disclosed. A method of producing an alkylbenzene includes causing a hydrocarbon oil feedstock containing an alkylbenzene content of less than 20 vol %, a bicyclic aromatic hydrocarbon content of less than 30 vol %, and a 1.5-cyclic aromatic hydrocarbon content of 25 vol % or more to come in contact with a hydrocracking catalyst that includes a solid acid having a maximum acid strength of Brönsted acid of 110 kJ / mol or more and less than 140 kJ / mol.
Owner:GASOLINEEUM ENERGY CENT FOUND +1
Xylene isomerization process and catalyst therefor
InactiveUS8697929B2Reduce investmentReduce operating costsHydrocarbon by isomerisationAluminium compoundsIsomerizationProcess conditions
The invention concerns a xylenes isomerization process for the production of equilibrium or near-equilibrium xylenes. The process utilizes a catalyst comprising HZSM-5 or MCM-49 and process conditions including a temperature of less than 295° C. and a pressure sufficient to maintain the xylenes in liquid phase. In embodiments, the process can be operated in a continuous mode with ppm levels of dissolved H2 in the feed and in other embodiments in a cyclic mode without the H2 in feed but with periodic regenerations using a feed having low ppm levels of H2.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Use of a microporous crystalline material of zeolitic nature with RHO structure in natural gas processing
The present invention describes the use of isostructural zeolites with rho zeolitic structure in processes of adsorption and separation of the various components of natural gas.
Owner:CONSEJO SUPERIOR DE INVESTIGACIONES CIENTIFICAS (CSIC) +1
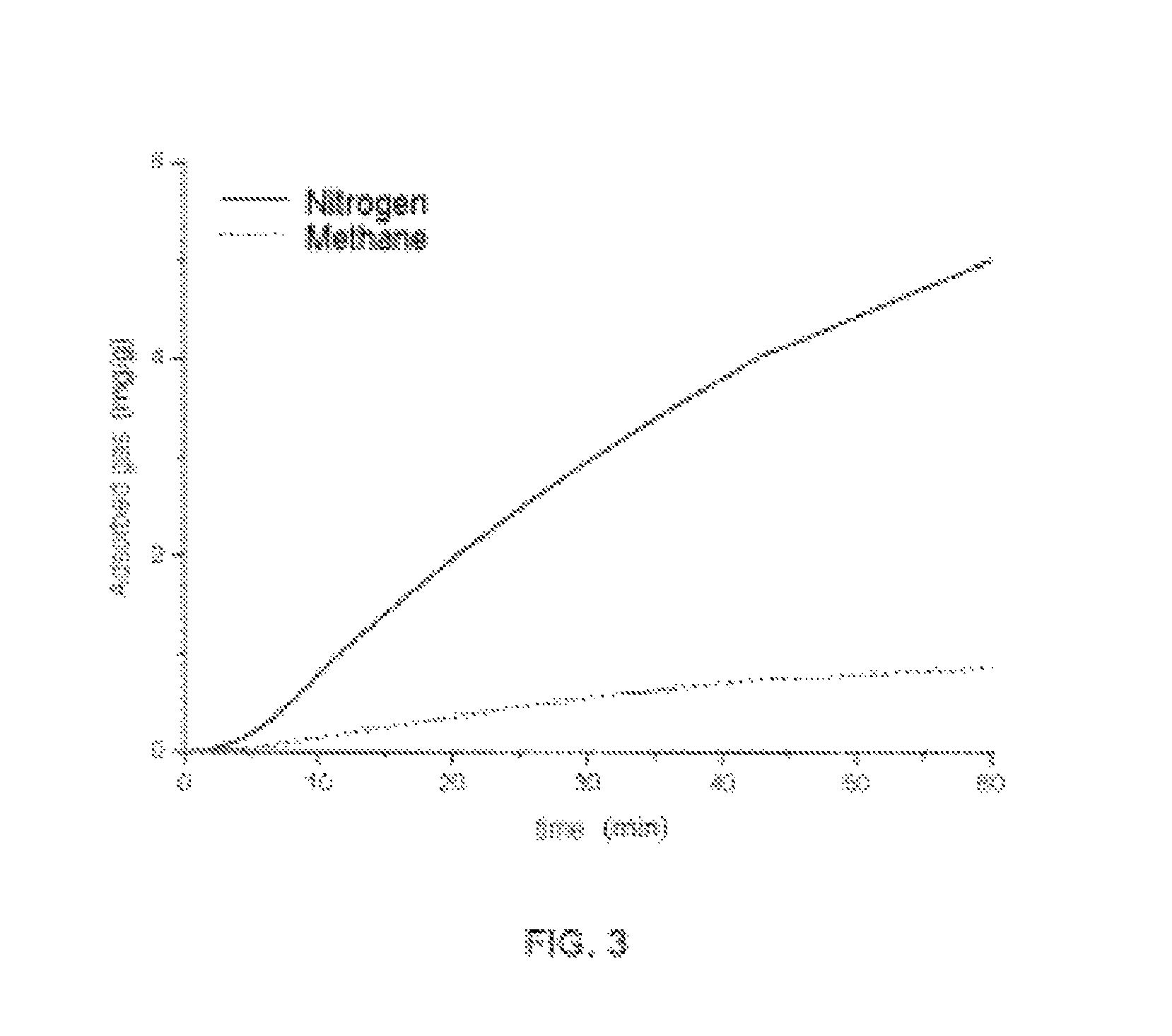
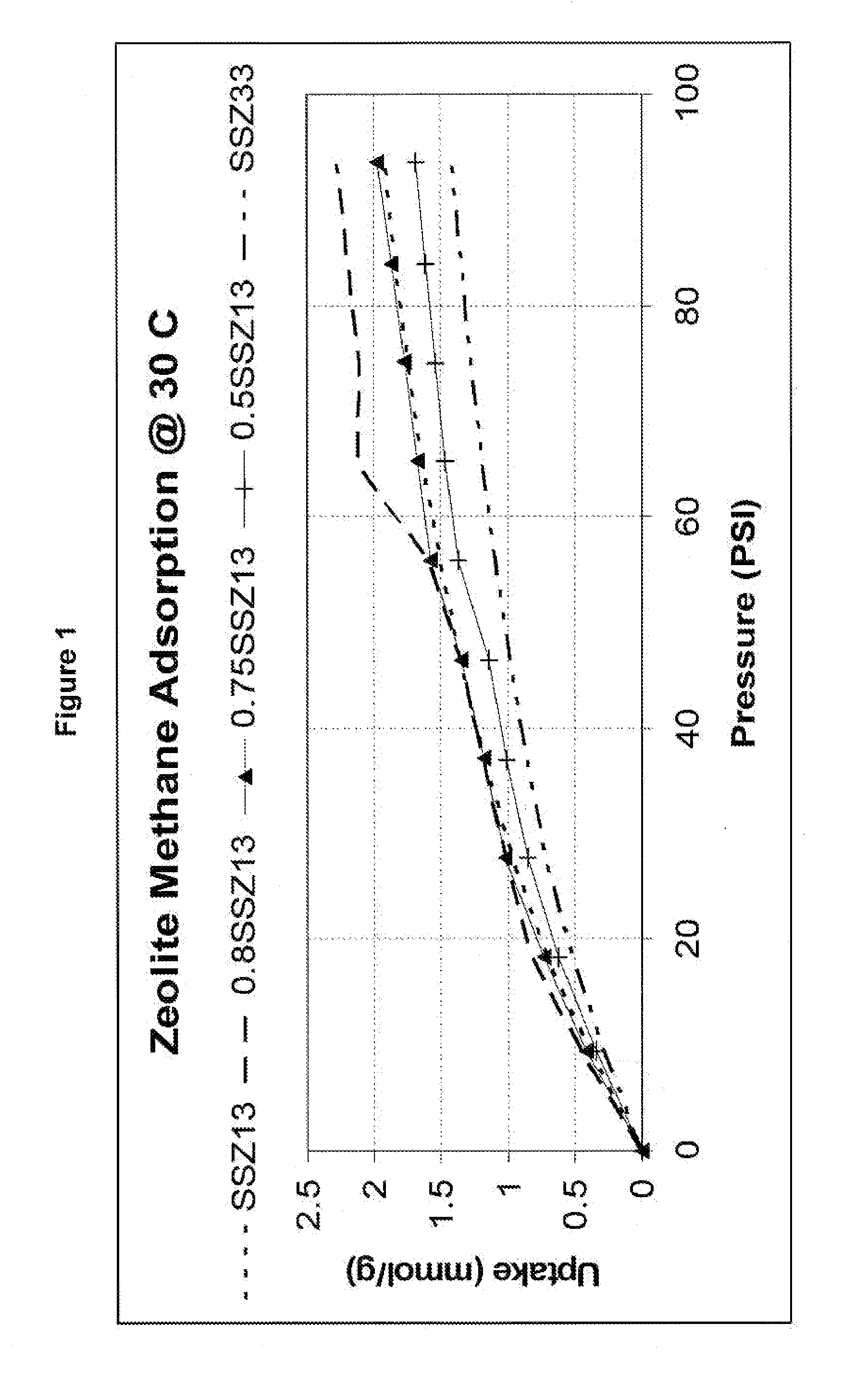
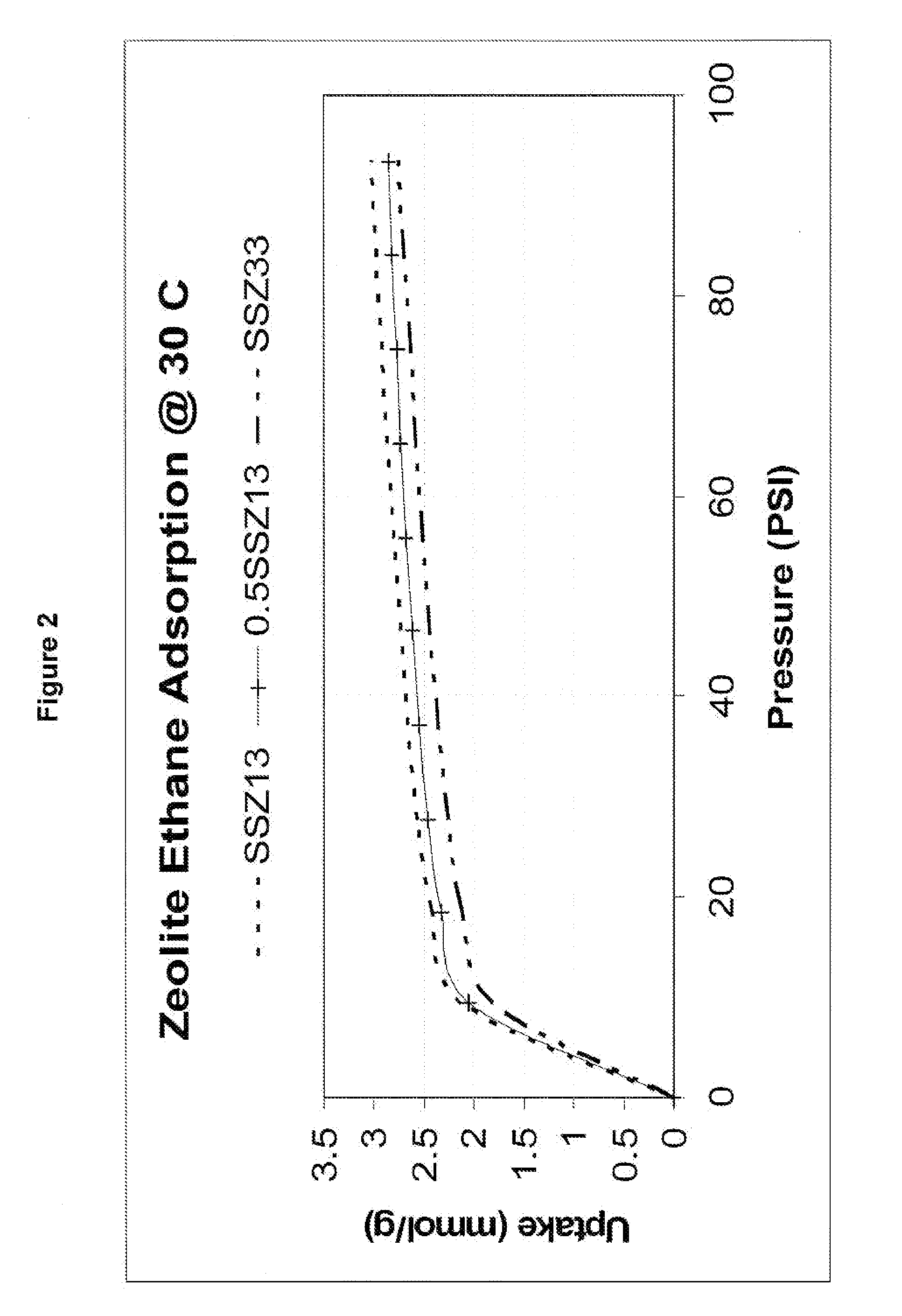
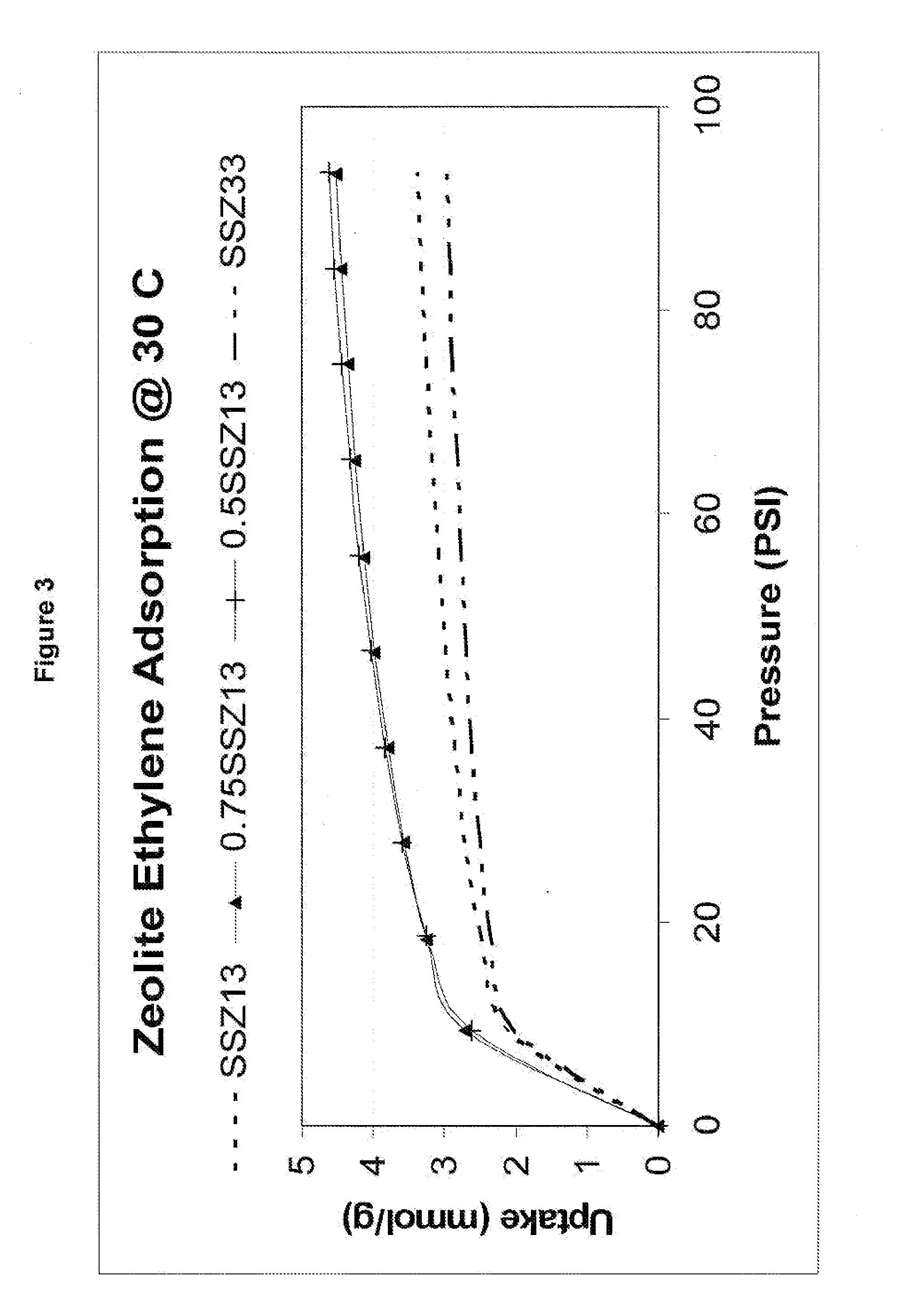
Treatment of cold start engine exhaust
ActiveUS20080159936A1Emission reductionAluminium compoundsOrganic chemistryInternal combustion engineMole ratio
The present invention relates to a process for reducing cold start emissions in an exhaust gas stream (such as from an internal combustion engine) by contacting the exhaust stream with a combination of molecular sieves comprising (1) a small pore crystalline molecular sieve or mixture of molecular sieves having pores no larger than 8 membered rings selected from the group consisting of SSZ-13, SSZ-16, SSZ-36, SSZ-39, SSZ-50, SSZ-52 and SSZ-73 molecular sieve and having a mole ratio at least 10 of (a) an oxide of a first tetravalent element to (b) an oxide of a trivalent element, pentavalent element, second tetravalent element which is different from said first tetravalent element or mixture thereof and (2) a medium-large pore crystalline molecular sieve having pores at least as large as 10 membered rings selected from the group consisting of SSZ-26, SSZ-33, SSZ-64, zeolite Beta, CIT-1, CIT-6 and ITQ-4 and having a mole ratio of at least 10 of (a) an oxide of a first tetravalent element to (b) an oxide of a trivalent element, pentavalent element, second tetravalent element which is different from said first tetravalent element or mixture thereof.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com