Patents
Literature
196 results about "Natural-gas processing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Natural-gas processing is a complex industrial process designed to clean raw natural gas by separating impurities and various non-methane hydrocarbons and fluids to produce what is known as pipeline quality dry natural gas.
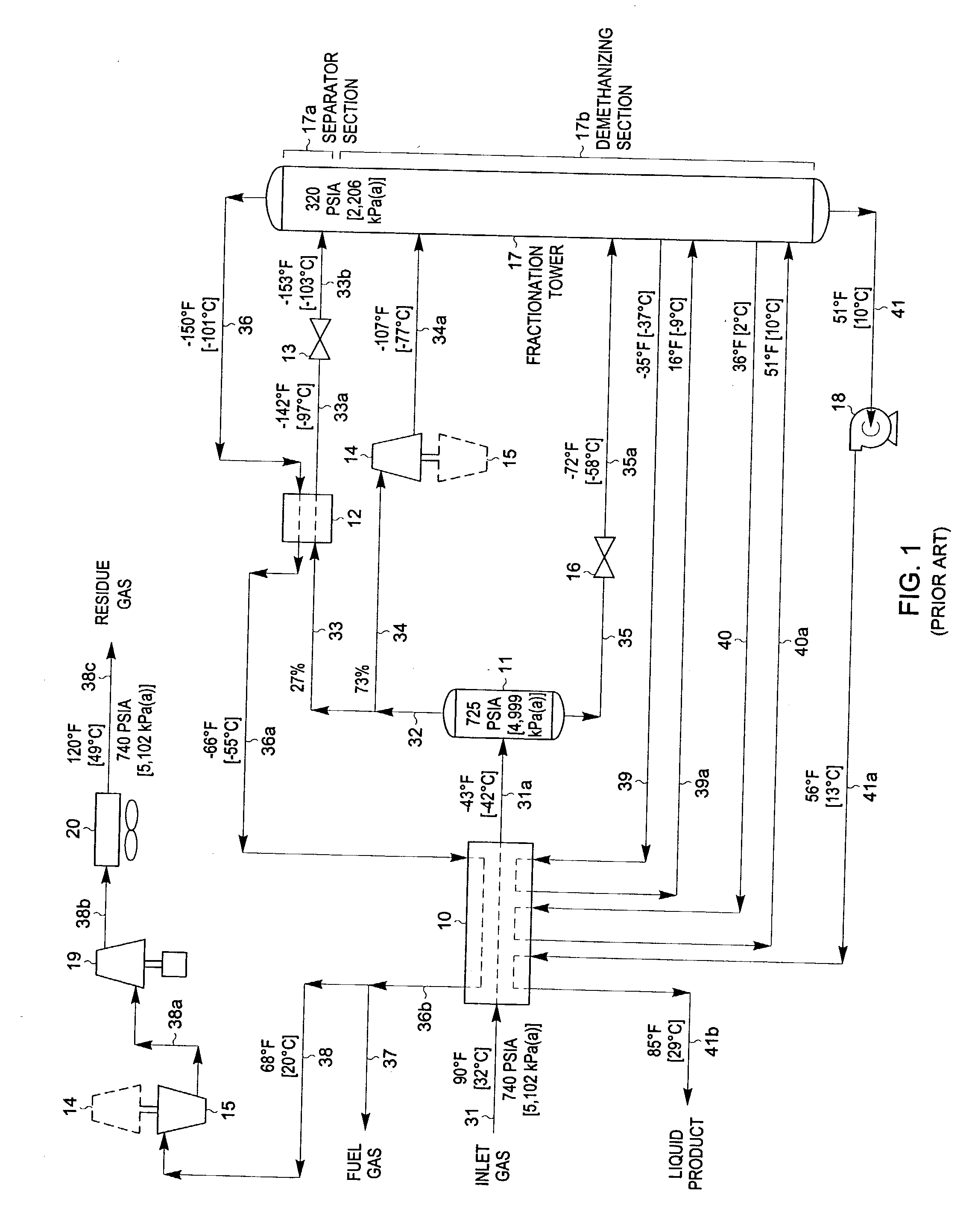
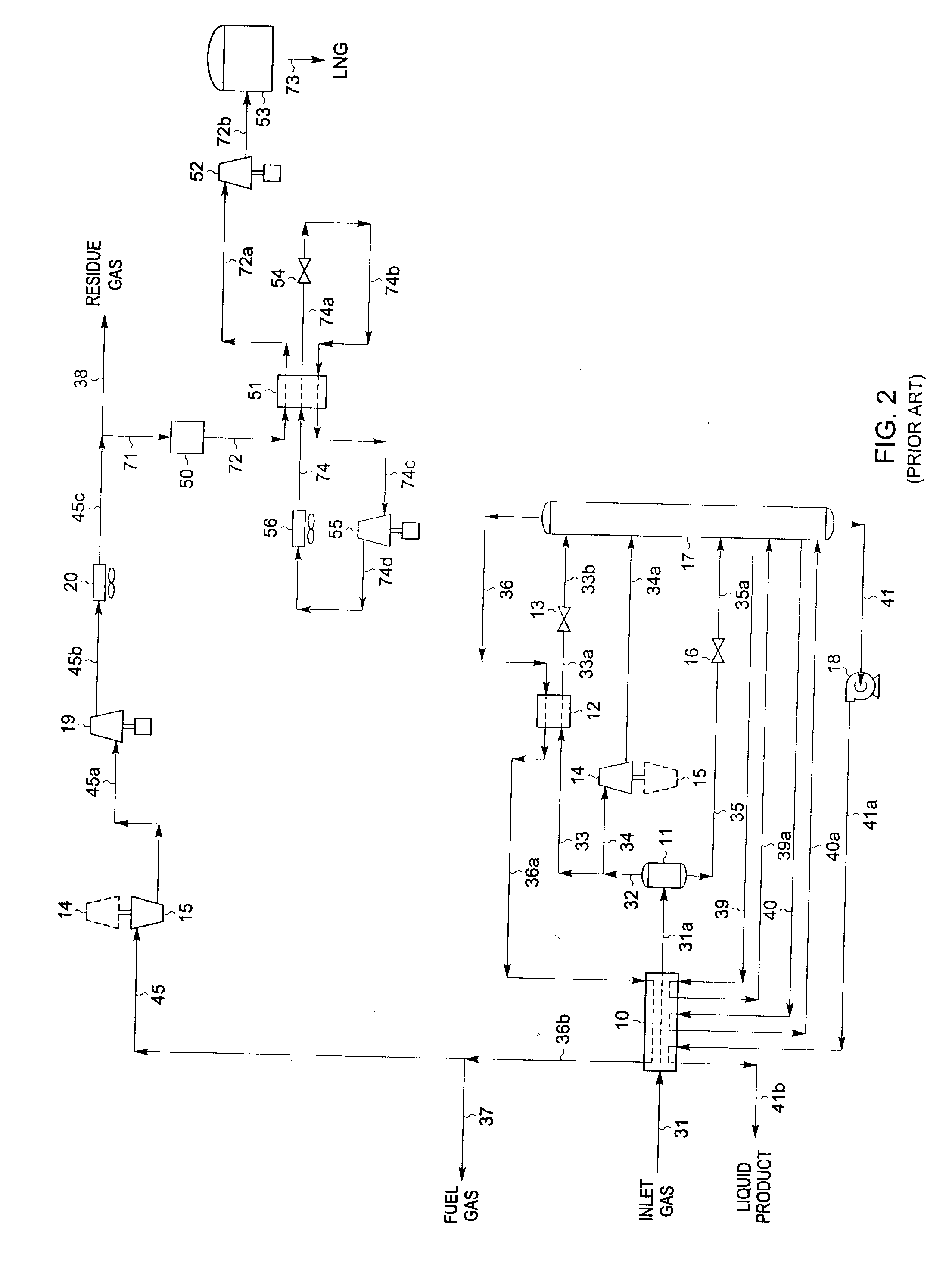
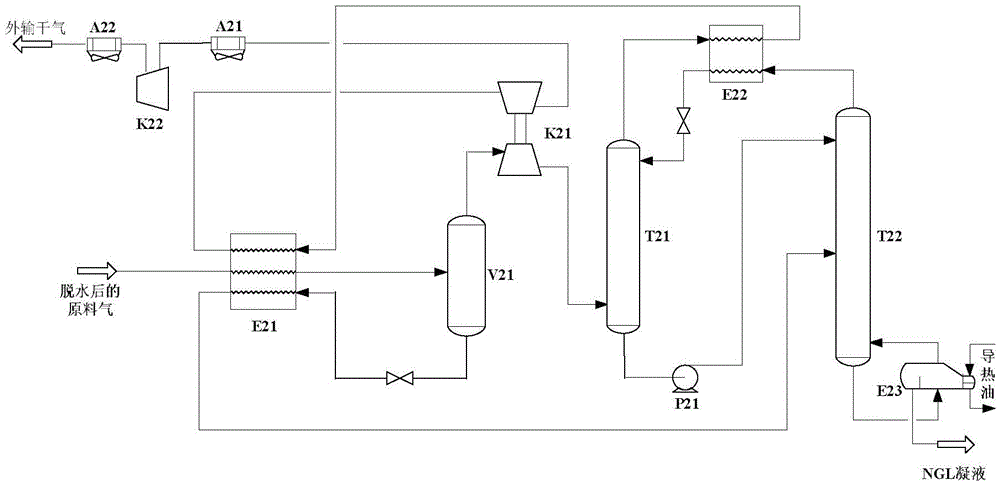
LNG production in cryogenic natural gas processing plants
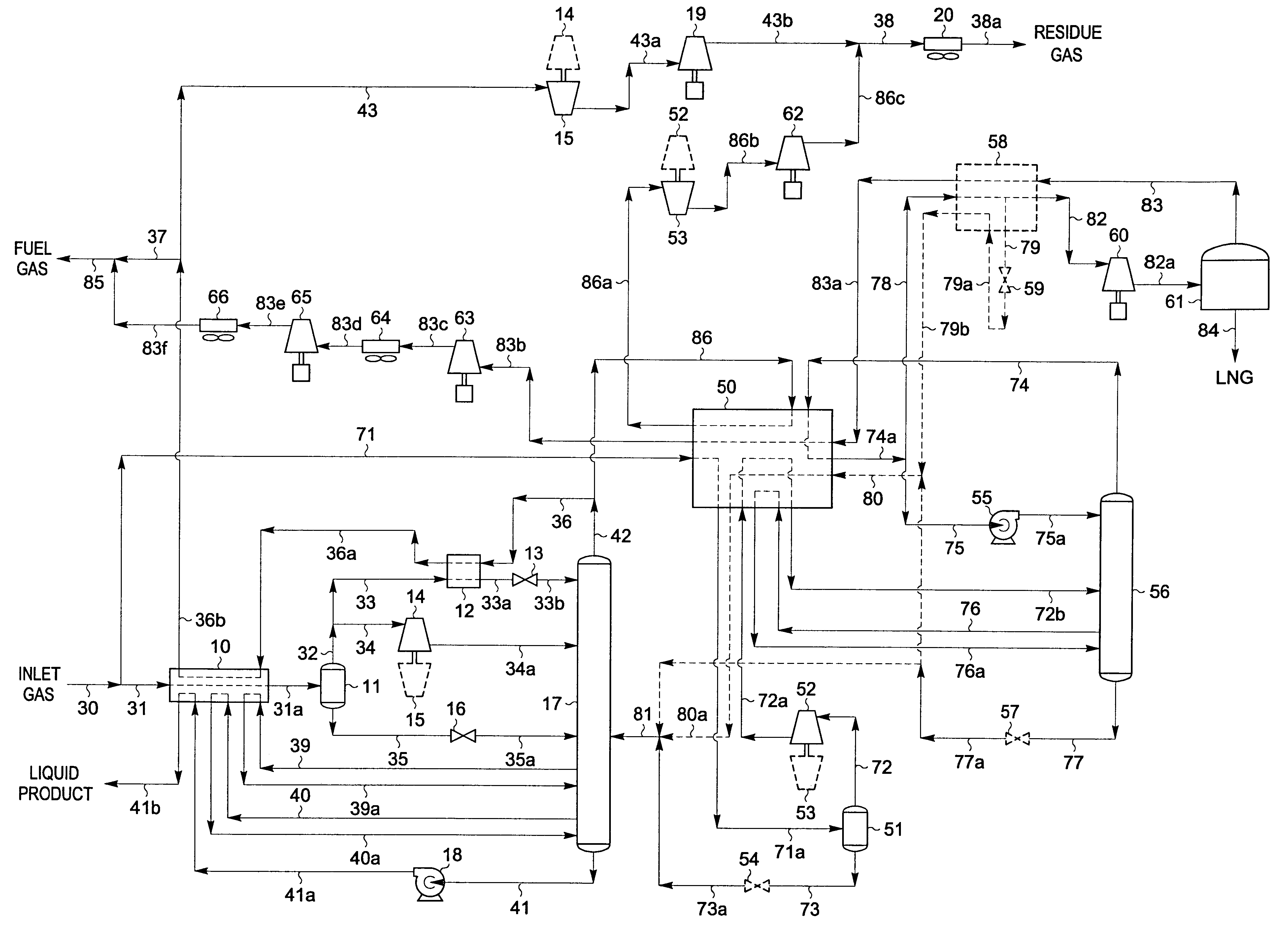
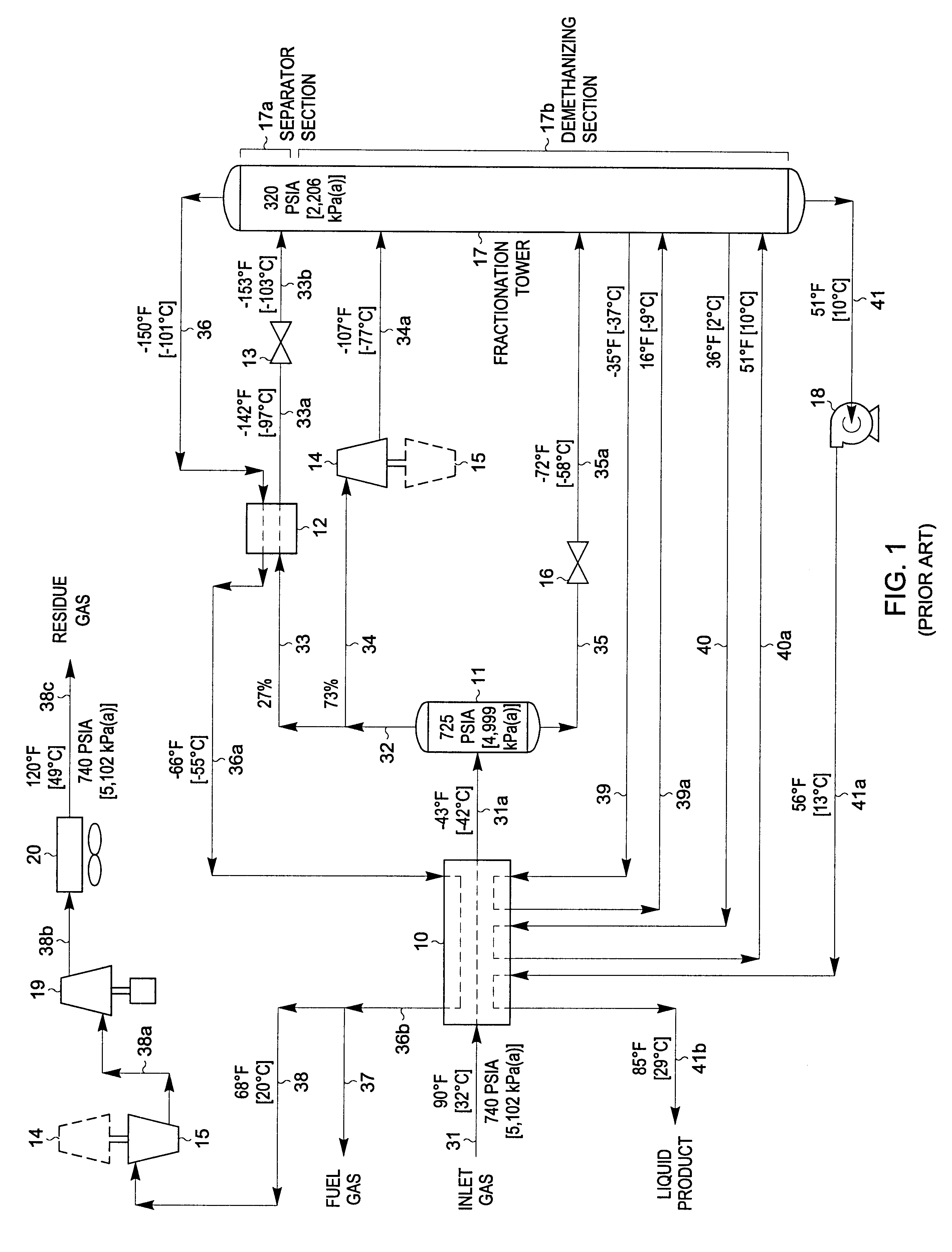
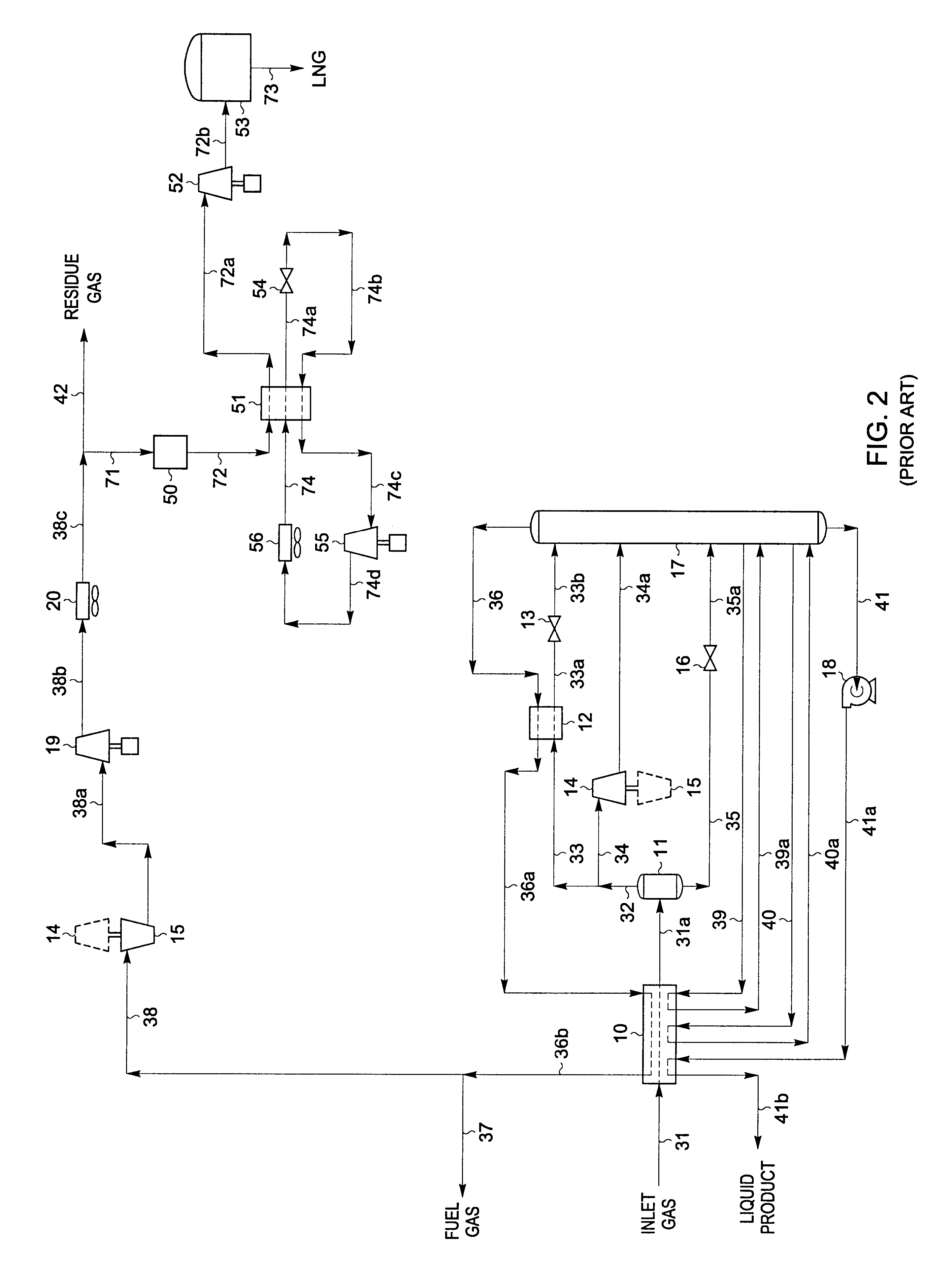
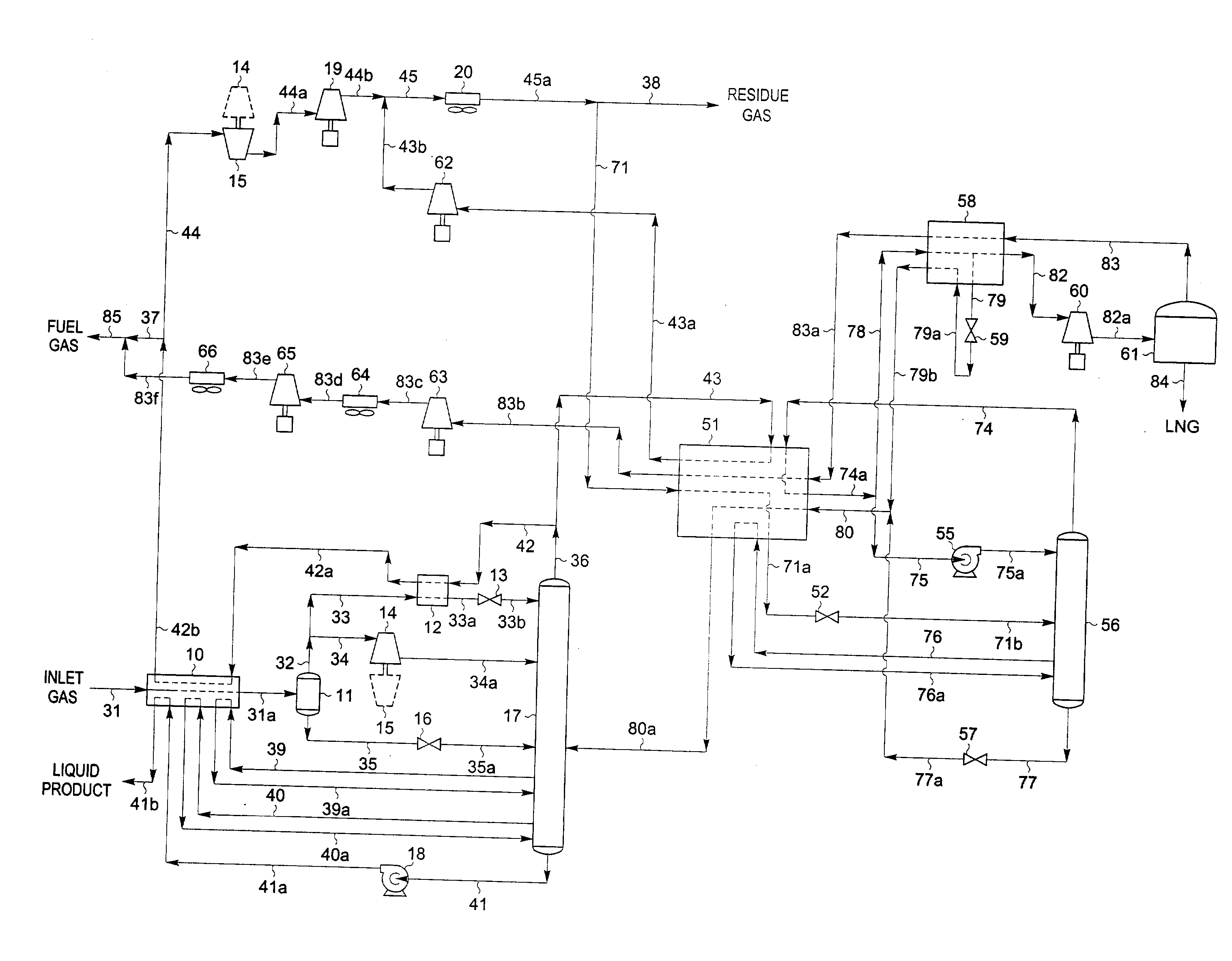
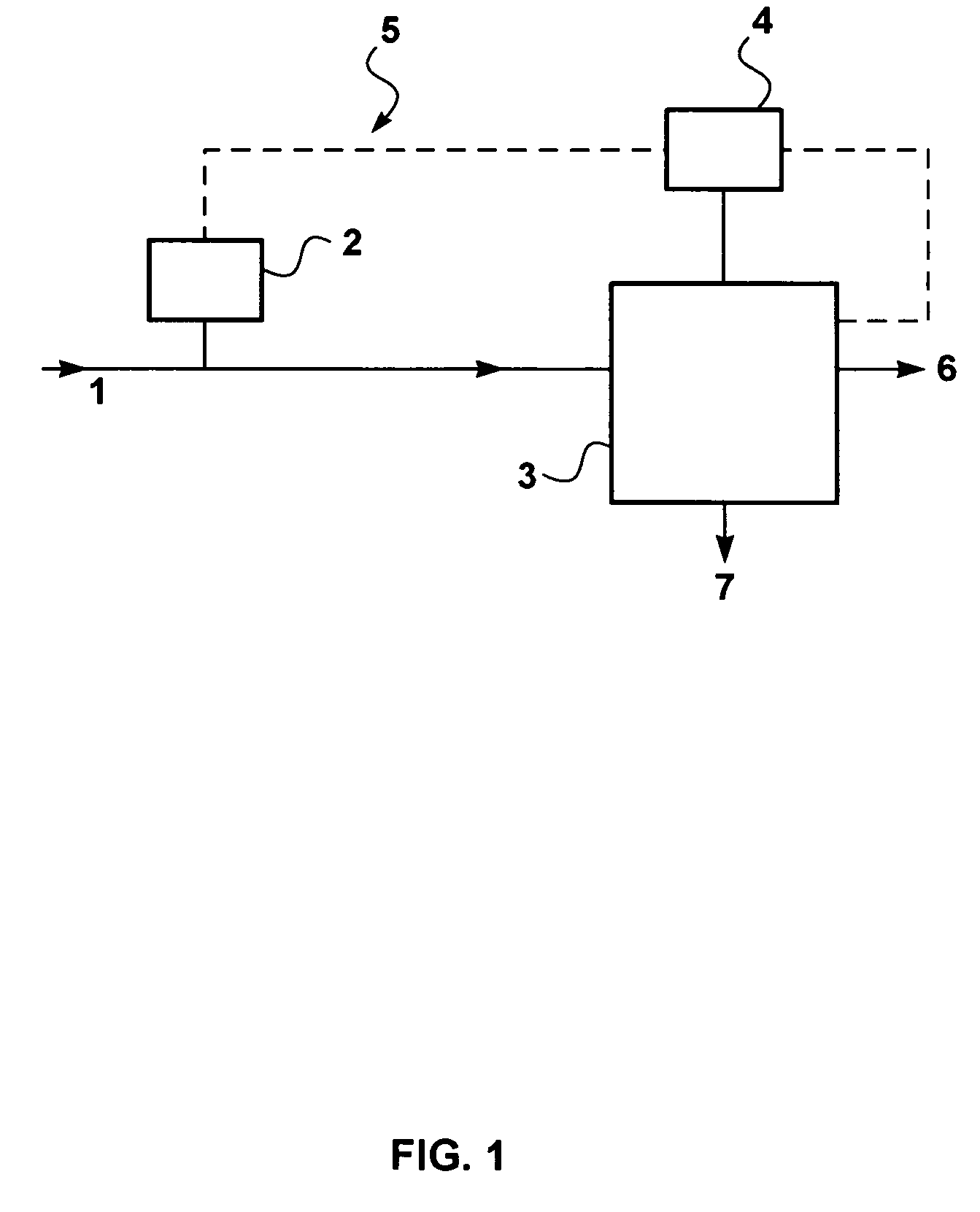
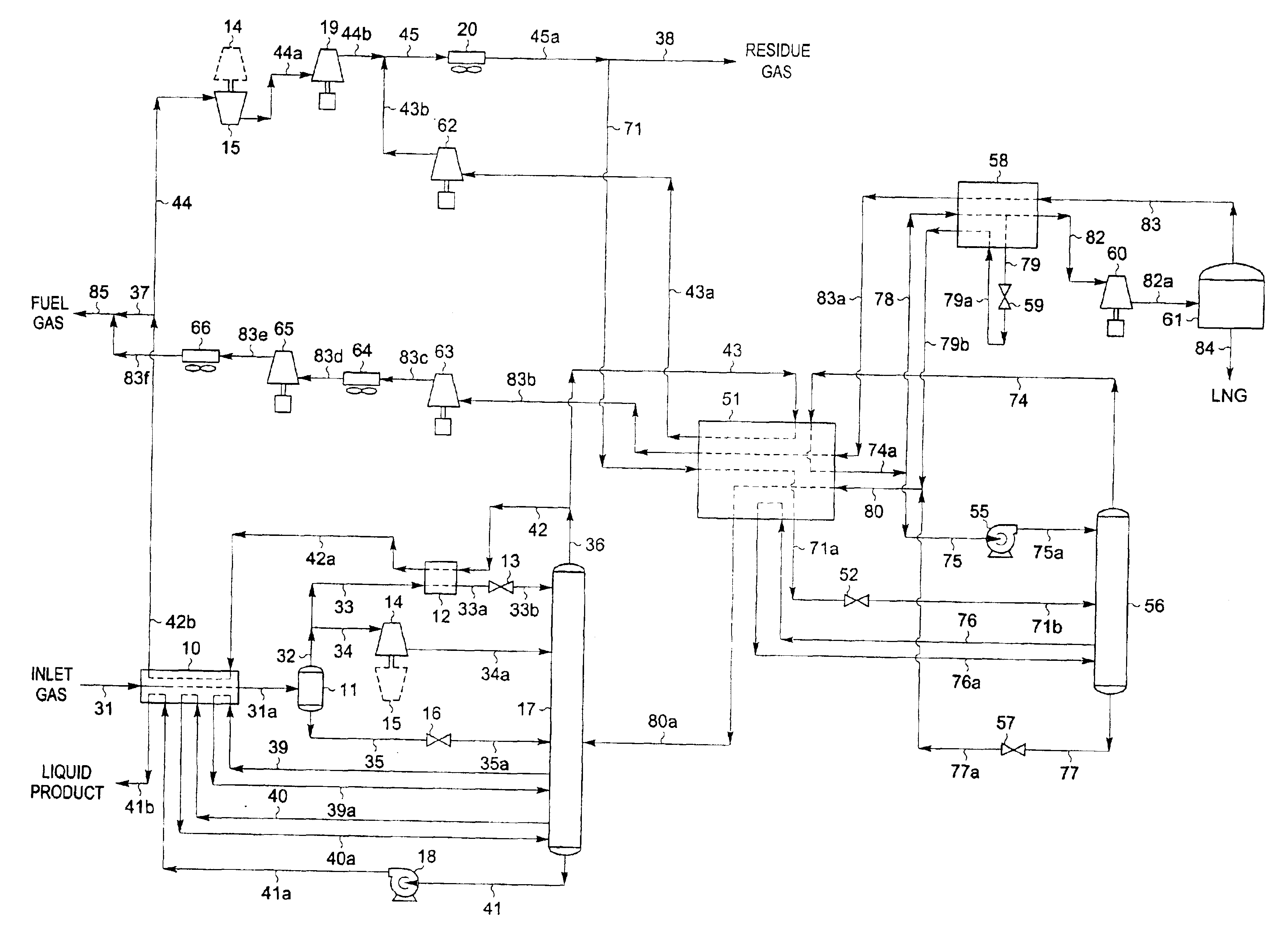
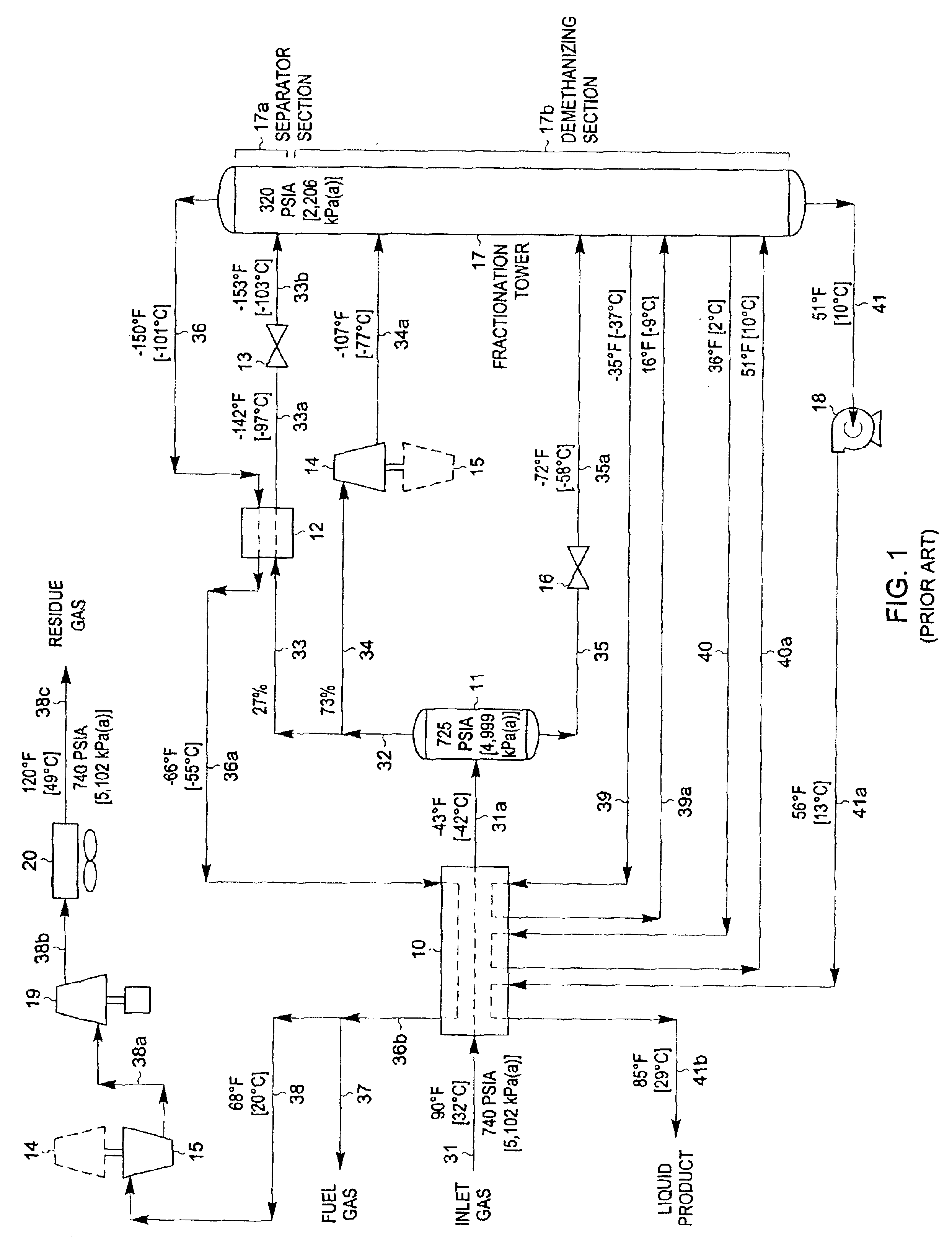
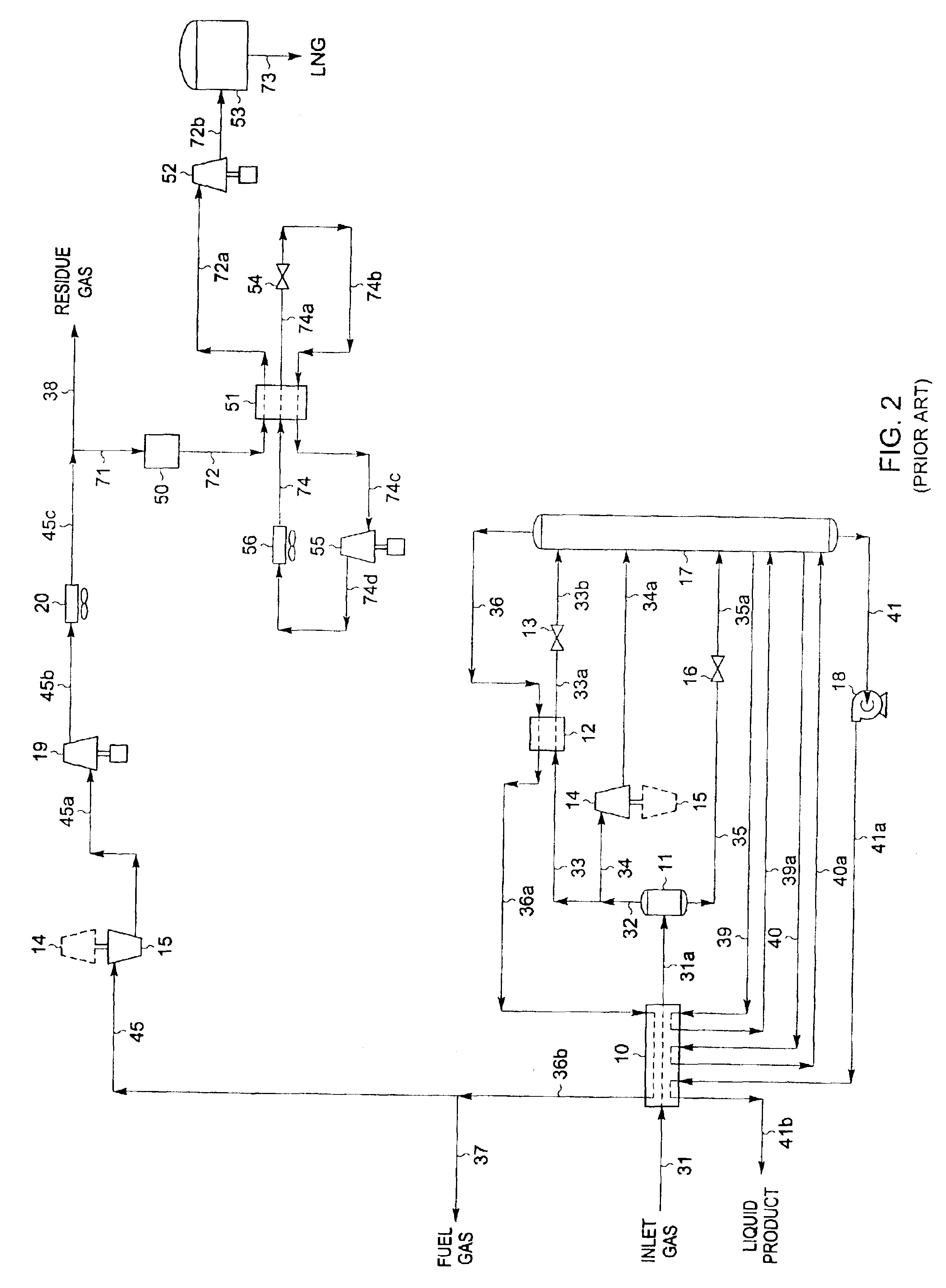
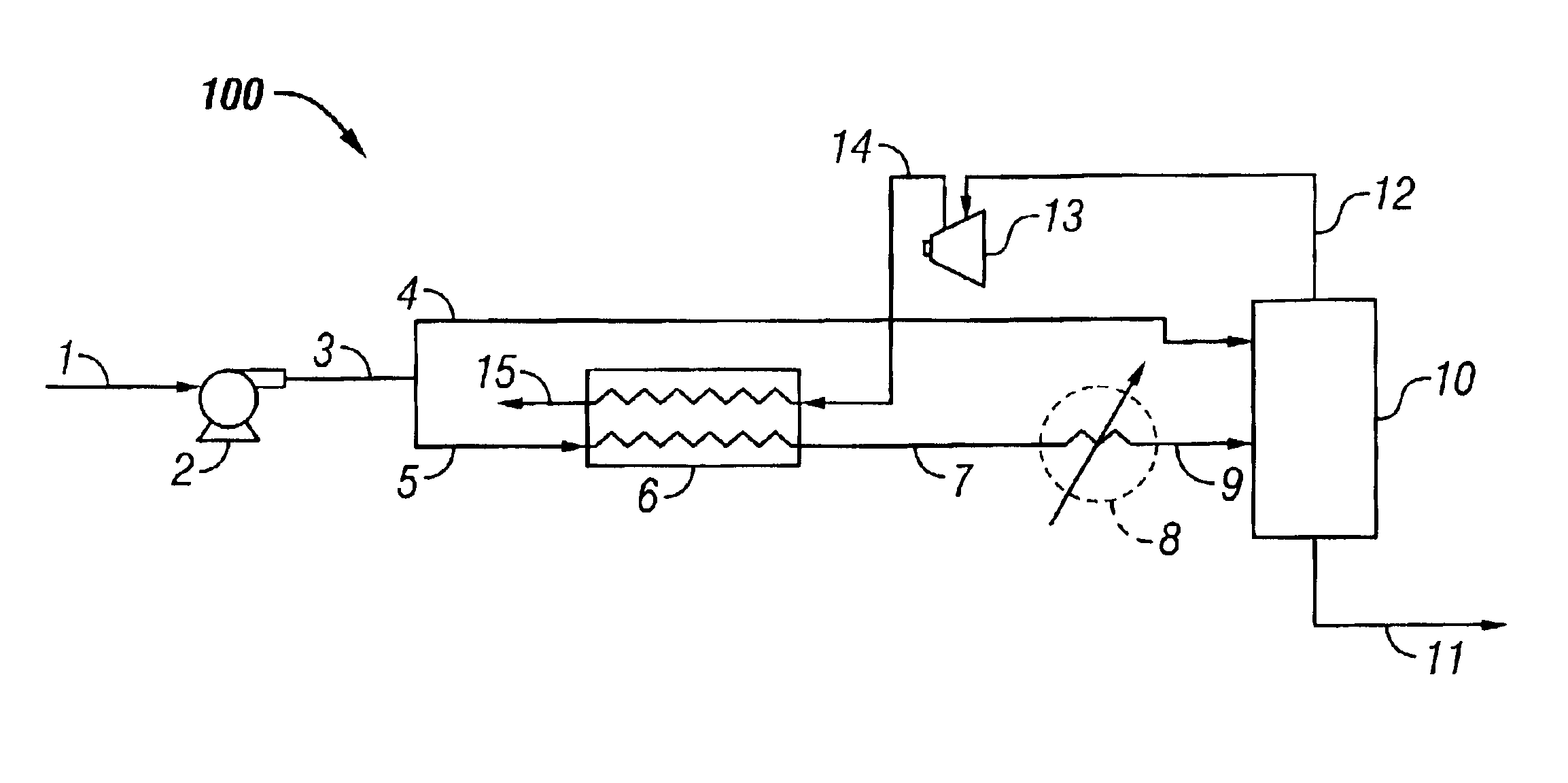
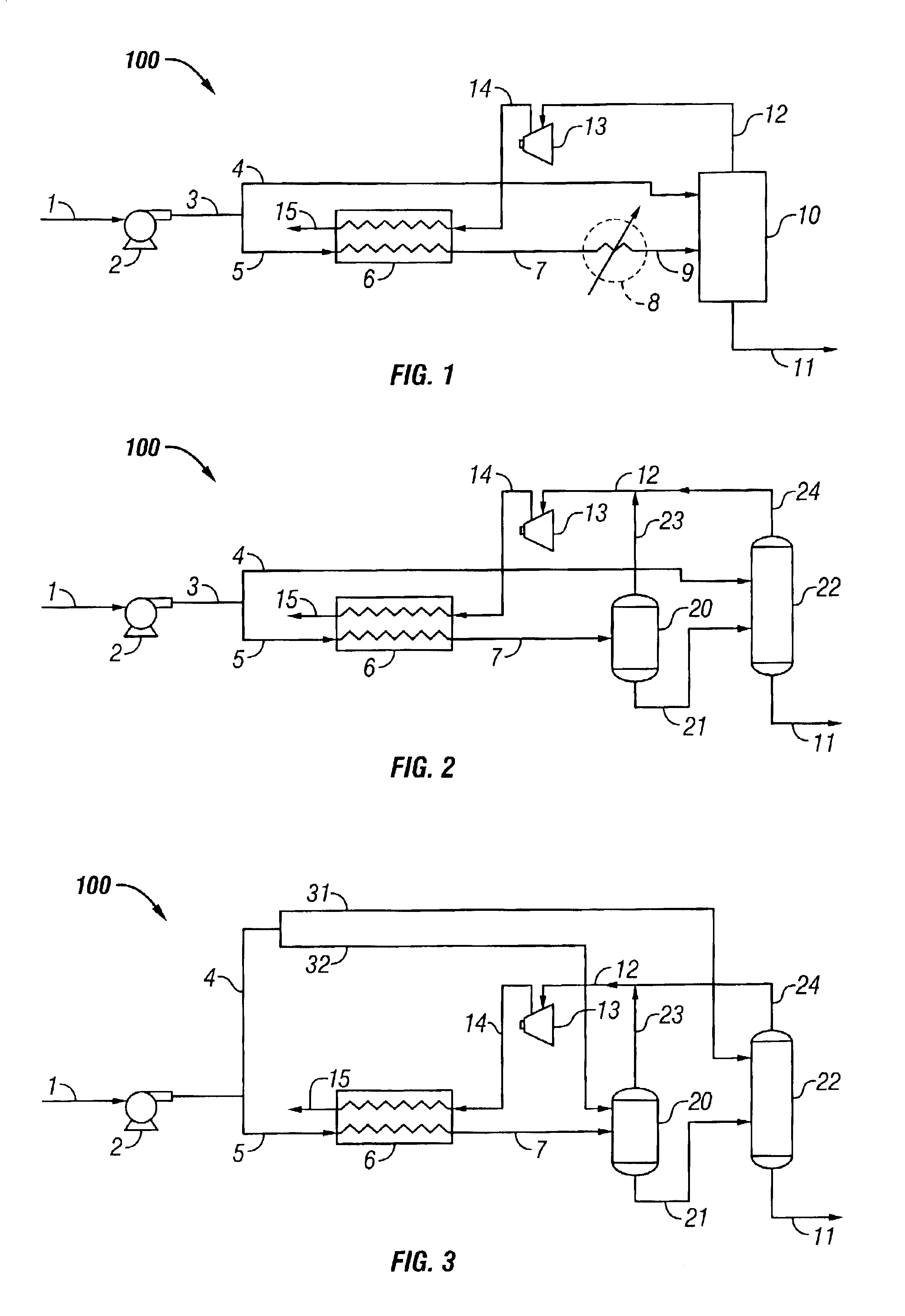
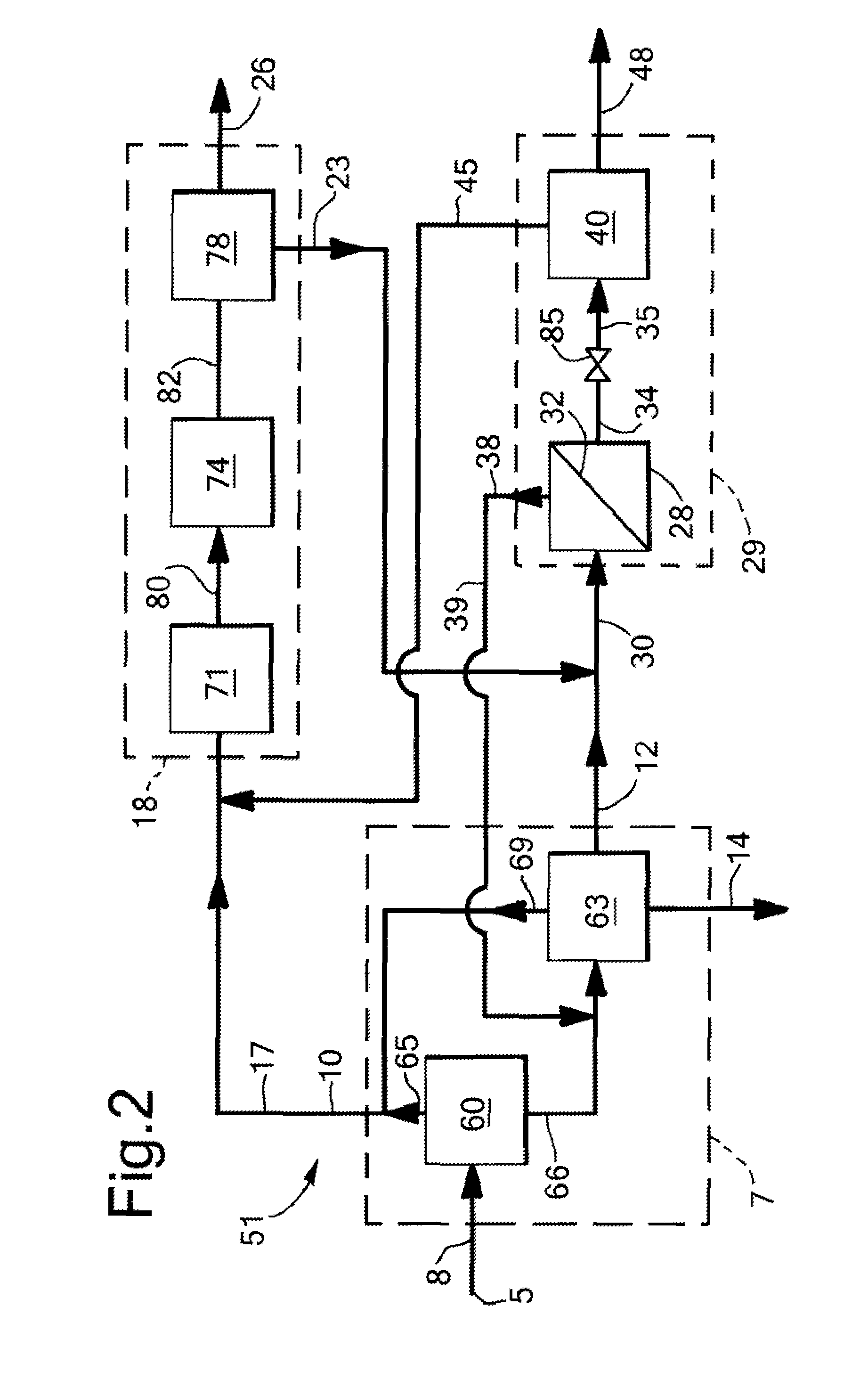
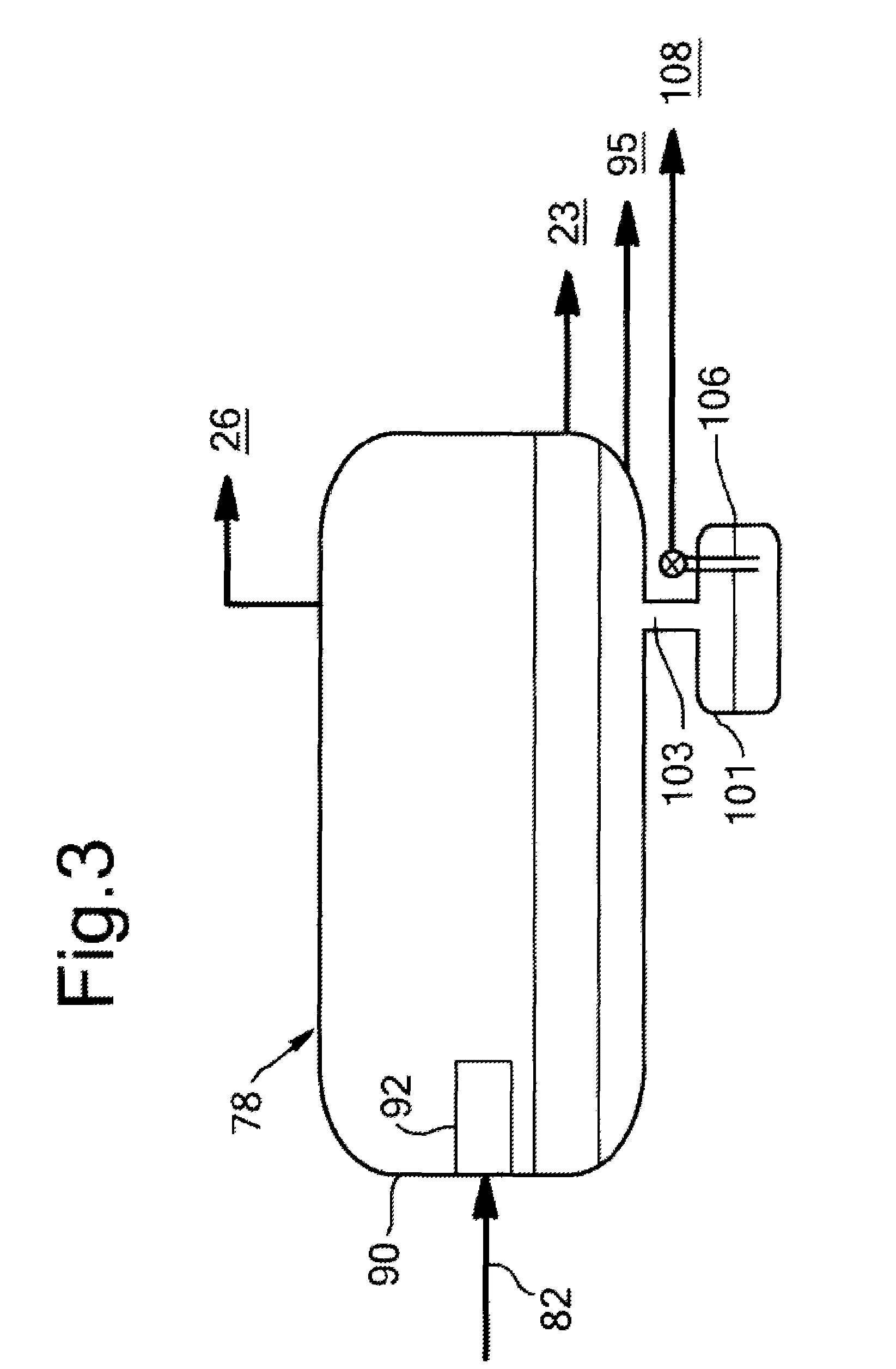
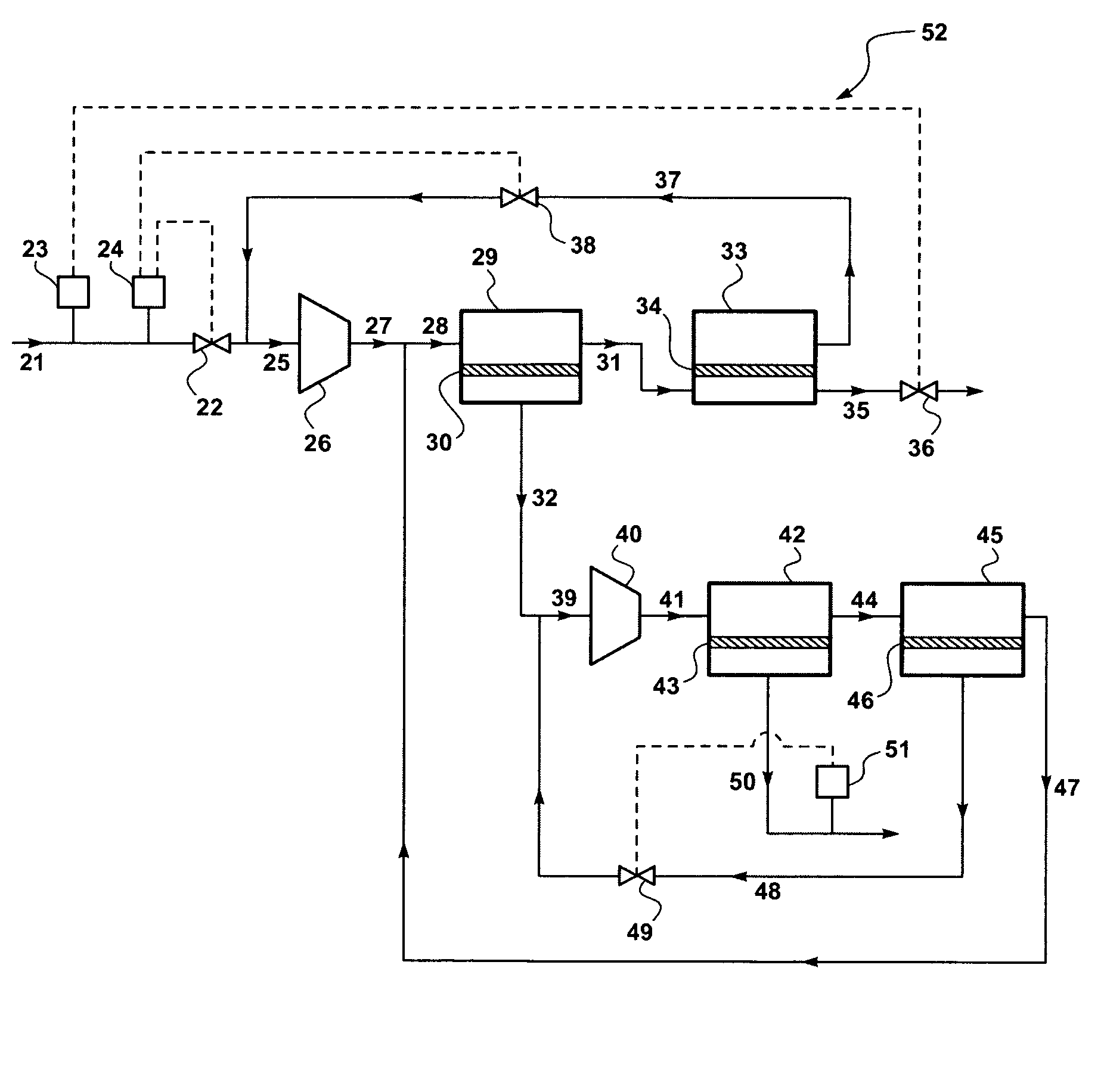
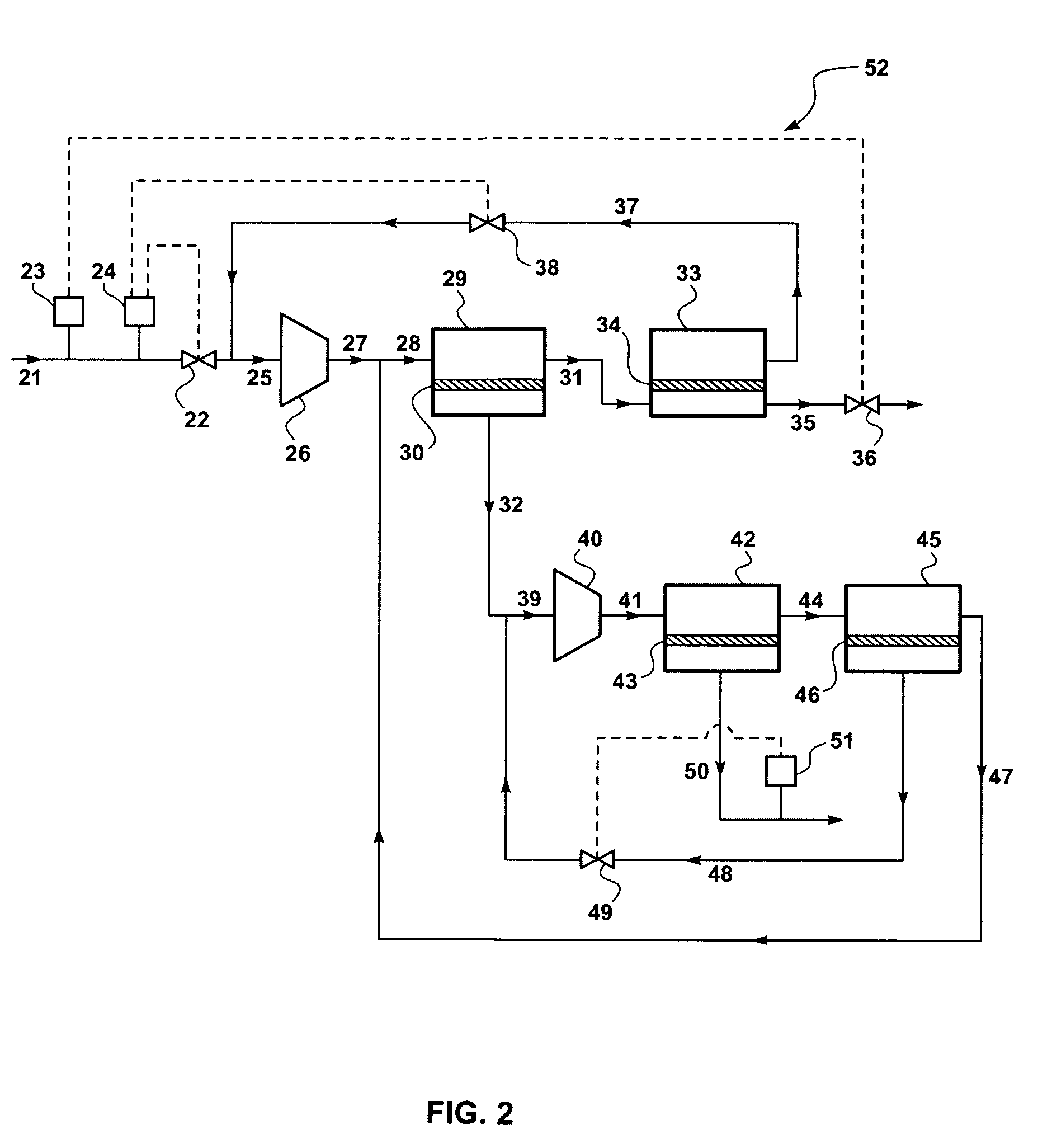
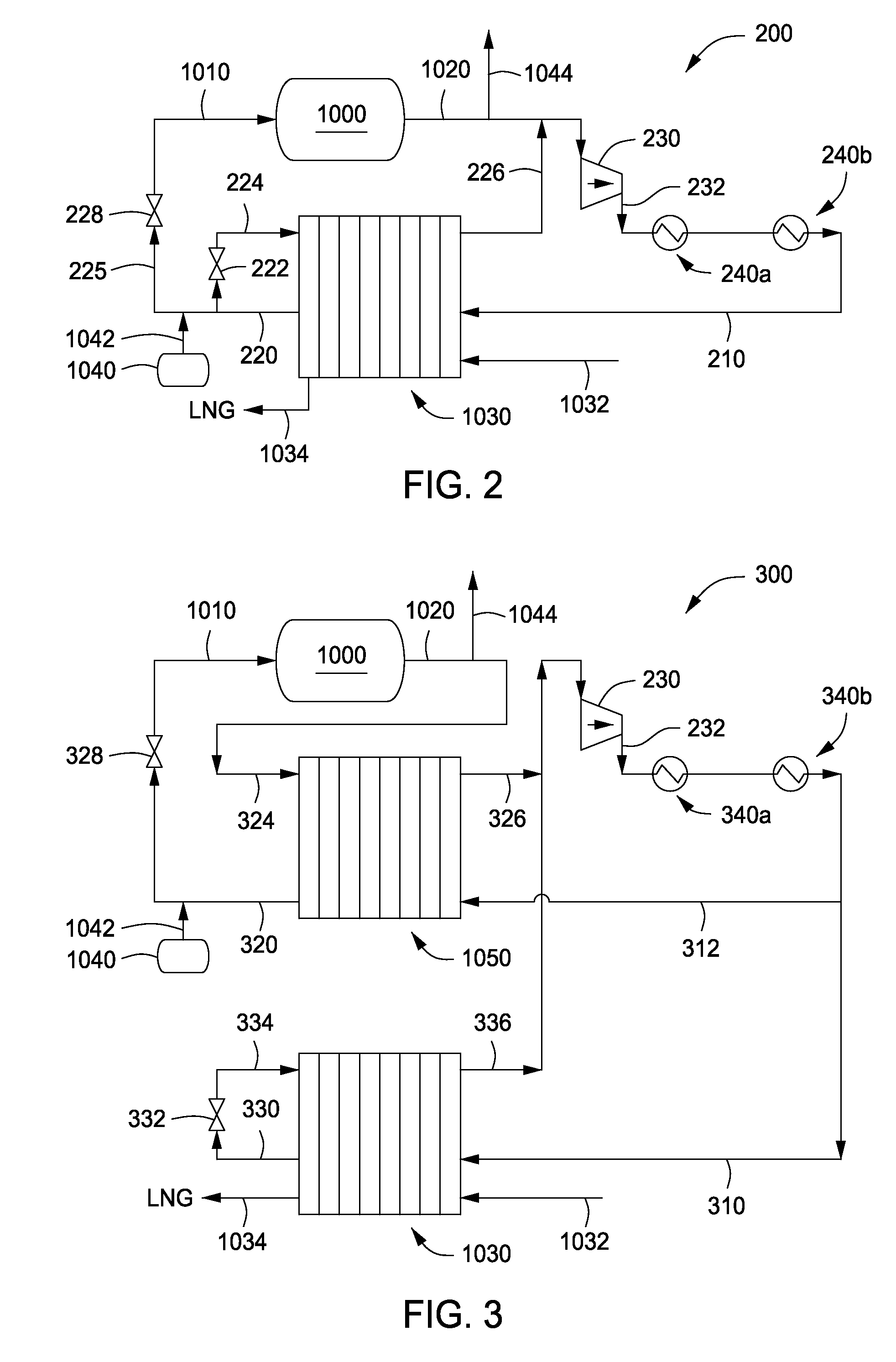
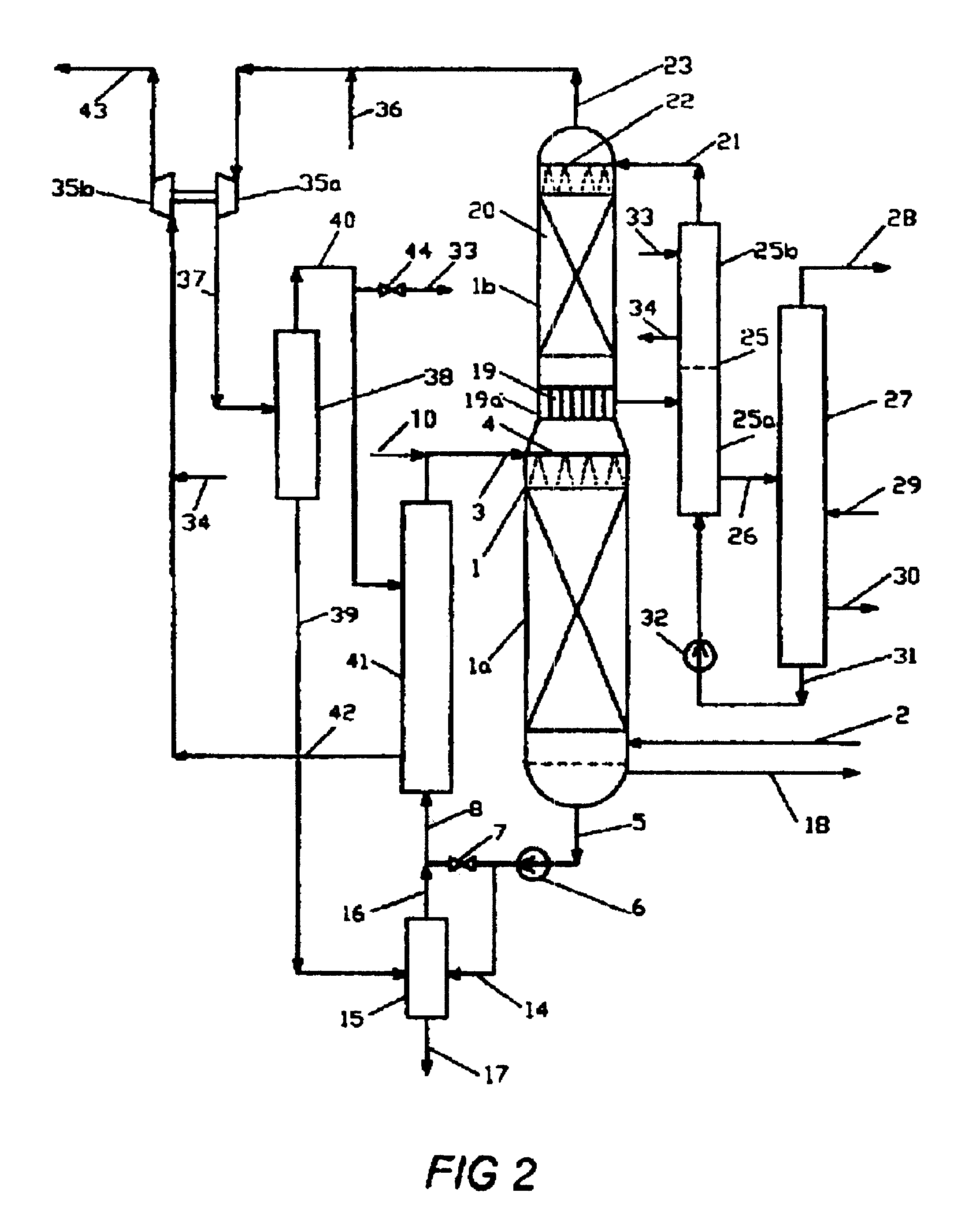
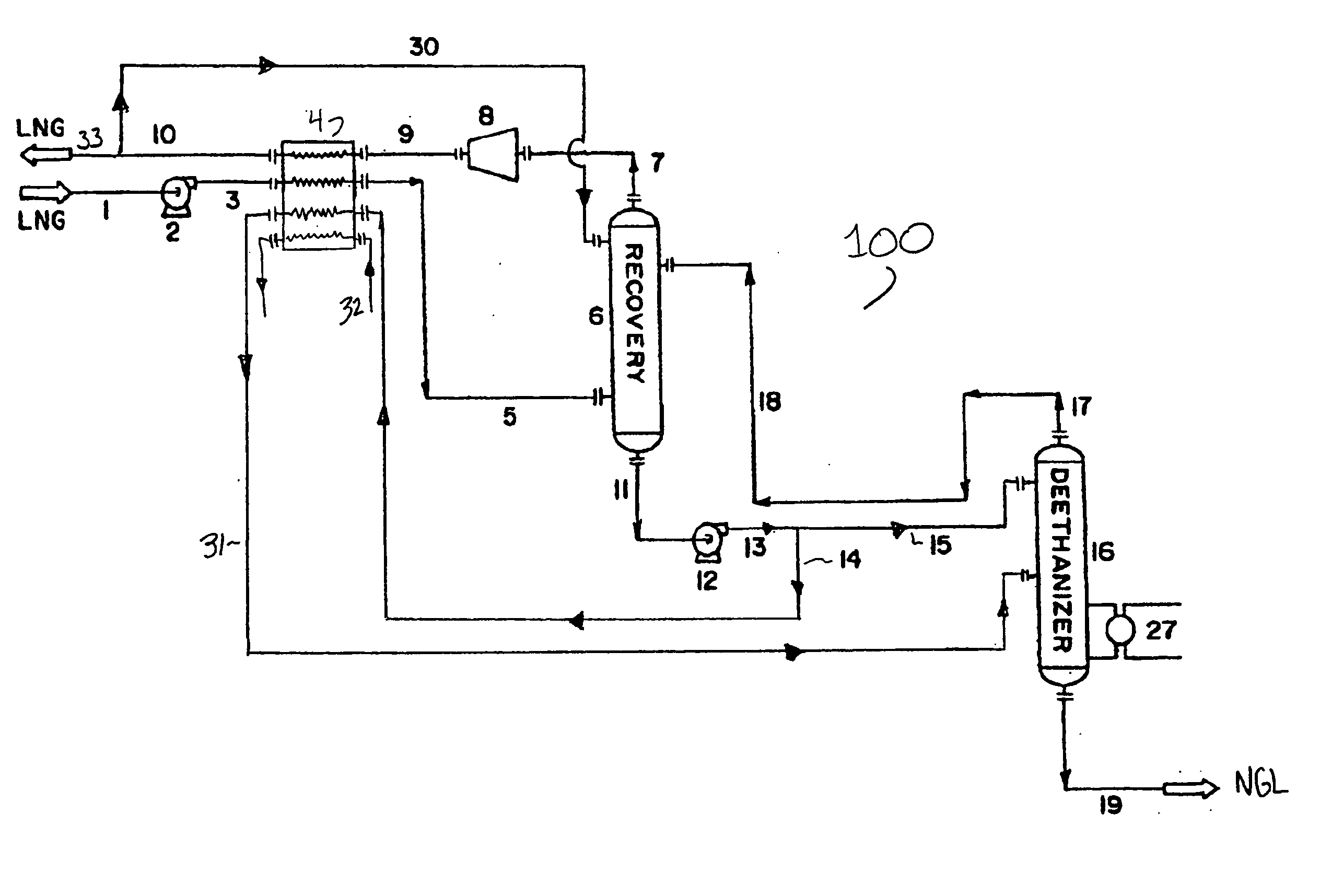
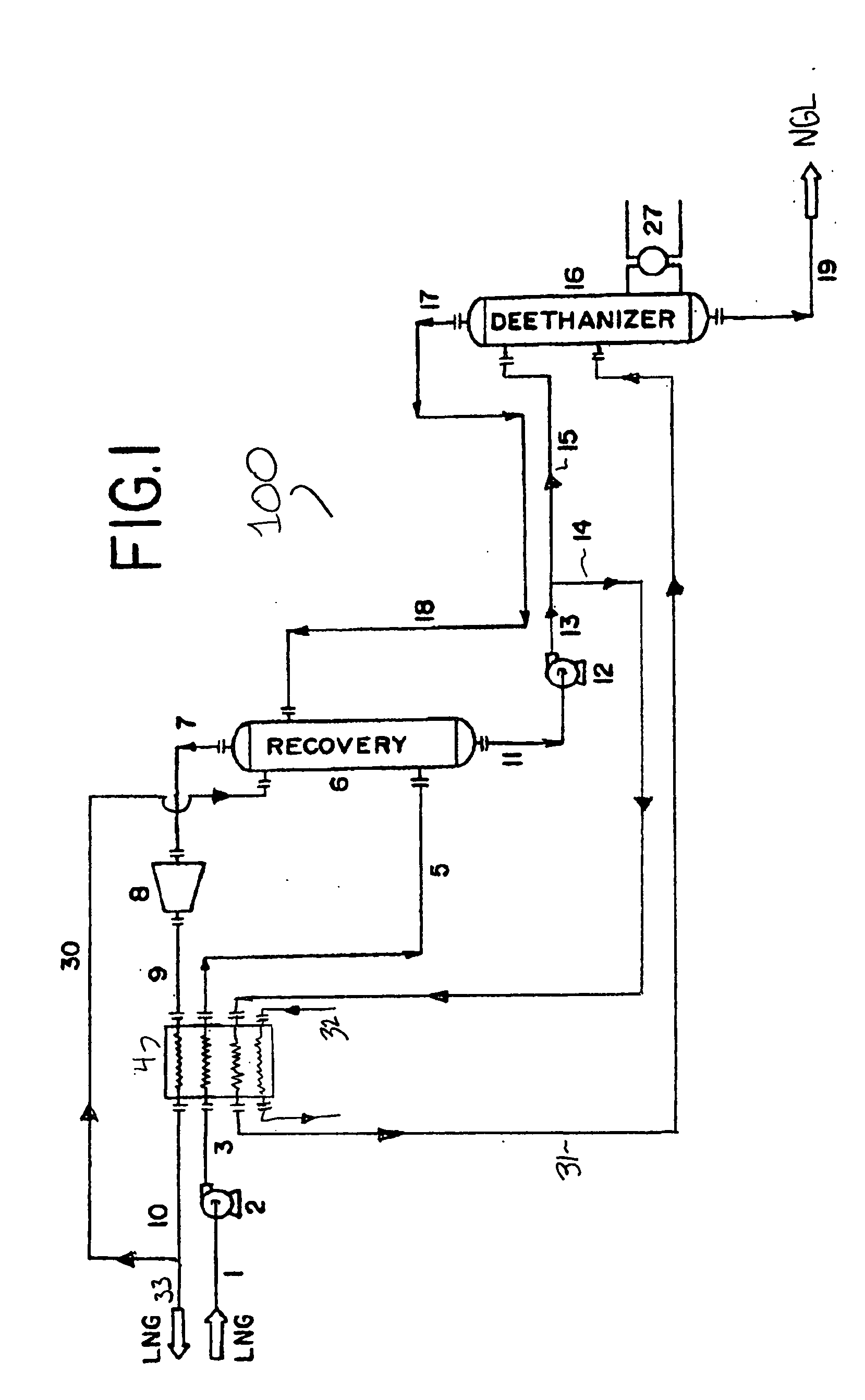
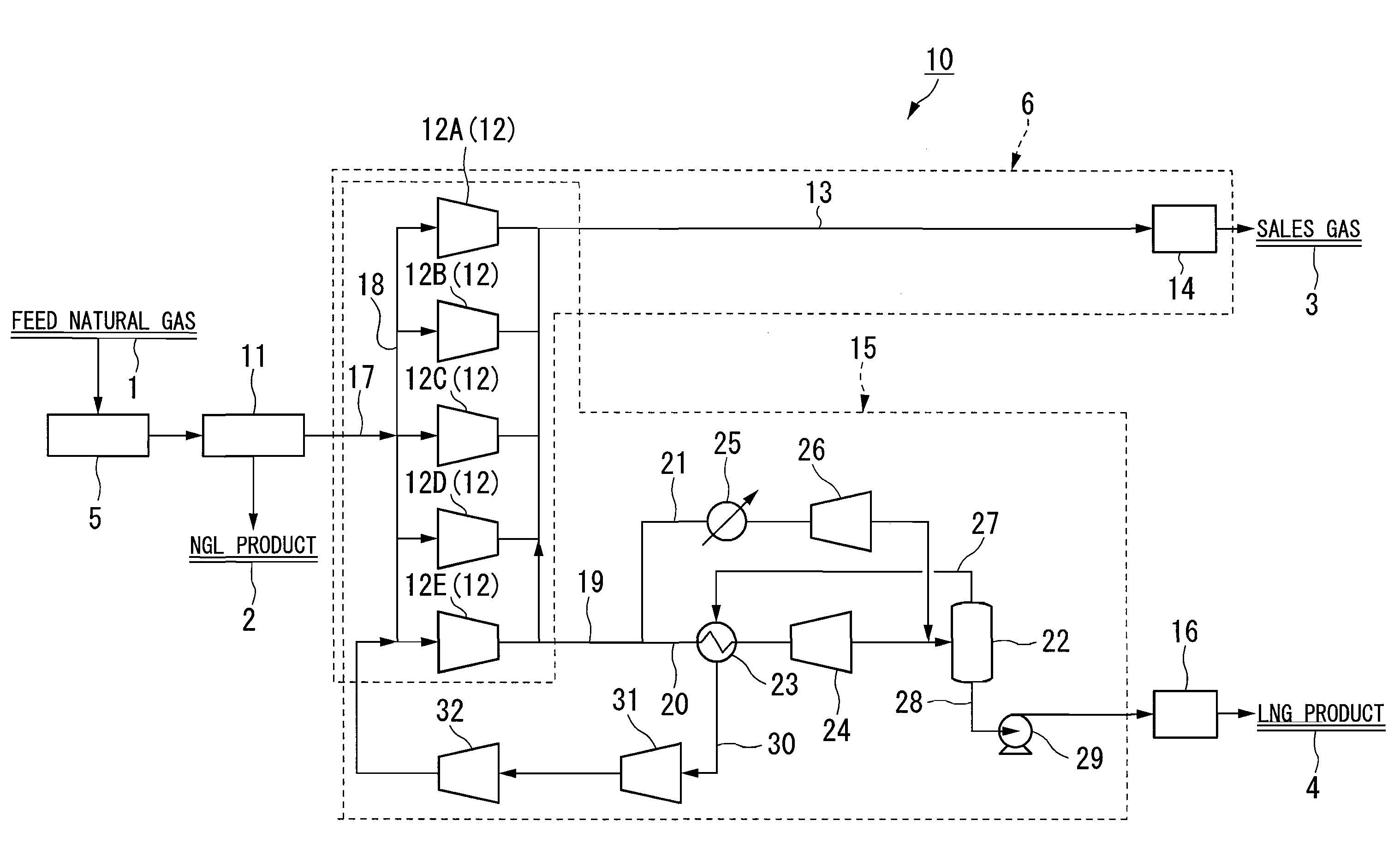
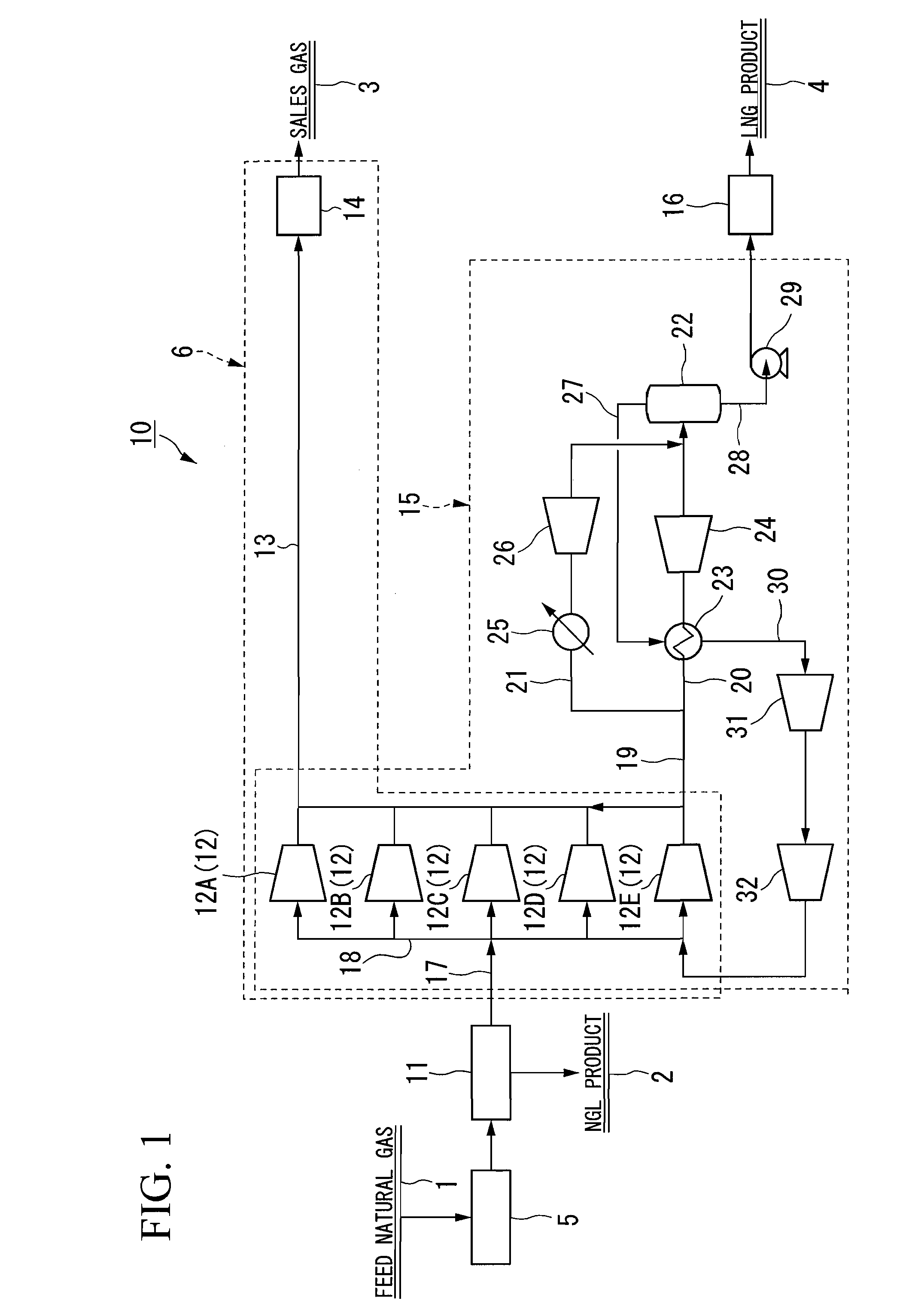
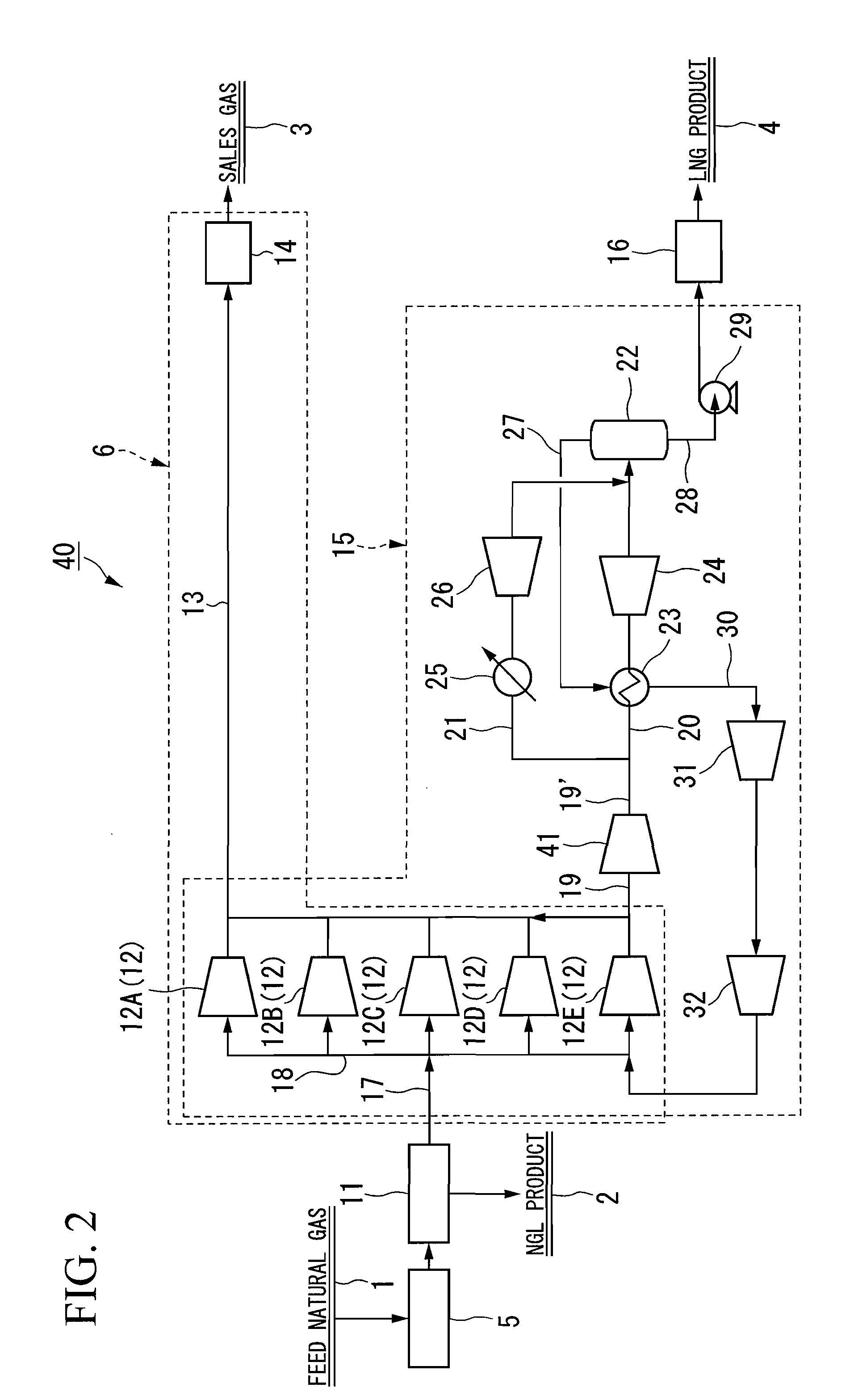
A process for liquefying natural gas in conjunction with processing natural gas to recover natural gas liquids (NGL) is disclosed. In the process, the natural gas stream to be liquefied is taken from one of the streams in the NGL recovery plant and cooled under pressure to condense it. A distillation stream is withdrawn from the NGL recovery plant to provide some of the cooling required to condense the natural gas stream. The condensed natural gas stream is expanded to an intermediate pressure and supplied to a mid-column feed point on a distillation column. The bottom product from this distillation column preferentially contains the majority of any hydrocarbons heavier than methane that would otherwise reduce the purity of the liquefied natural gas, and is routed to the NGL recovery plant so that these heavier hydrocarbons can be recovered in the NGL product. The overhead vapor from the distillation column is cooled and condensed, and a portion of the condensed stream is supplied to a top feed point on the distillation column to serve as reflux. A second portion of the condensed stream is expanded to low pressure to form the liquefied natural gas stream.
Owner:ORTLOFF ENGINEERS
LNG production in cryogenic natural gas processing plants
A process for liquefying natural gas in conjunction with processing natural gas to recover natural gas liquids (NGL) is disclosed. In the process, the natural gas stream to be liquefied is taken from one of the streams in the NGL recovery plant and cooled under pressure to condense it. A distillation stream is withdrawn from the NGL recovery plant to provide some of the cooling required to condense the natural gas stream. A portion of the condensed stream is expanded to an intermediate pressure and then used to provide some of the cooling required to condense the natural gas stream, and thereafter routed to the NGL recovery plant so that any heavier hydrocarbons it contains can be recovered in the NGL product. The remaining portion of the condensed stream is expanded to low pressure to form the liquefied natural gas stream.
Owner:ORTLOFF ENGINEERS
Method for separating hydrocarbon-containing gas mixtures using hydrocarbon-resistant membranes
A method of separating or concentrating hydrocarbon-containing gas mixtures such as hydrogen from hydrocarbons, carbon dioxide from hydrocarbons, nitrogen from hydrocarbons, and hydrocarbons from one another using a selectively permeable membrane. The method is well suited to separate hydrocarbon-containing mixtures such as those generated by petroleum refining industries, petrochemical industries, natural gas processing, and the like. The membranes exhibit extremely good resistance to plasticization by hydrocarbon components in the gas mixture under practical industrial process conditions.
Owner:LAIR LIQUIDE SA POUR LETUDE & LEXPLOITATION DES PROCEDES GEORGES CLAUDE
Natural gas treatment process for stimulated well
InactiveUS20070125537A1Reduce concentrationCombination devicesAuxillary pretreatmentHigh concentrationNatural-gas processing
A process and equipment for treating natural gas produced by a well that has recently been stimulated, and that contains an undesirably high concentration of the fracturing gas used to stimulate the well. The process involves treating the gas by membrane separation, and provides for control of treatment parameters to compensate for the changing concentration of fracturing gas in the produced gas, as well as changes in gas flow rate.
Owner:MEMBRANE TECH & RES
LNG production in cryogenic natural gas processing plants
InactiveUS6889523B2Improve efficiencyConsiderable capital and operating costSolidificationLiquefactionCompressed natural gasNatural-gas processing
A process for liquefying natural gas in conjunction with processing natural gas to recover natural gas liquids (NGL) is disclosed. In the process, the natural gas stream to be liquefied is taken from one of the streams in the NGL recovery plant and cooled under pressure to condense it. A distillation stream is withdrawn from the NGL recovery plant to provide some of the cooling required to condense the natural gas stream. A portion of the condensed stream is expanded to an intermediate pressure and then used to provide some of the cooling required to condense the natural gas stream, and thereafter routed to the NGL recovery plant so that any heavier hydrocarbons it contains can be recovered in the NGL product. The remaining portion of the condensed stream is expanded to low pressure to form the liquefied natural gas stream.
Owner:ORTLOFF ENGINEERS
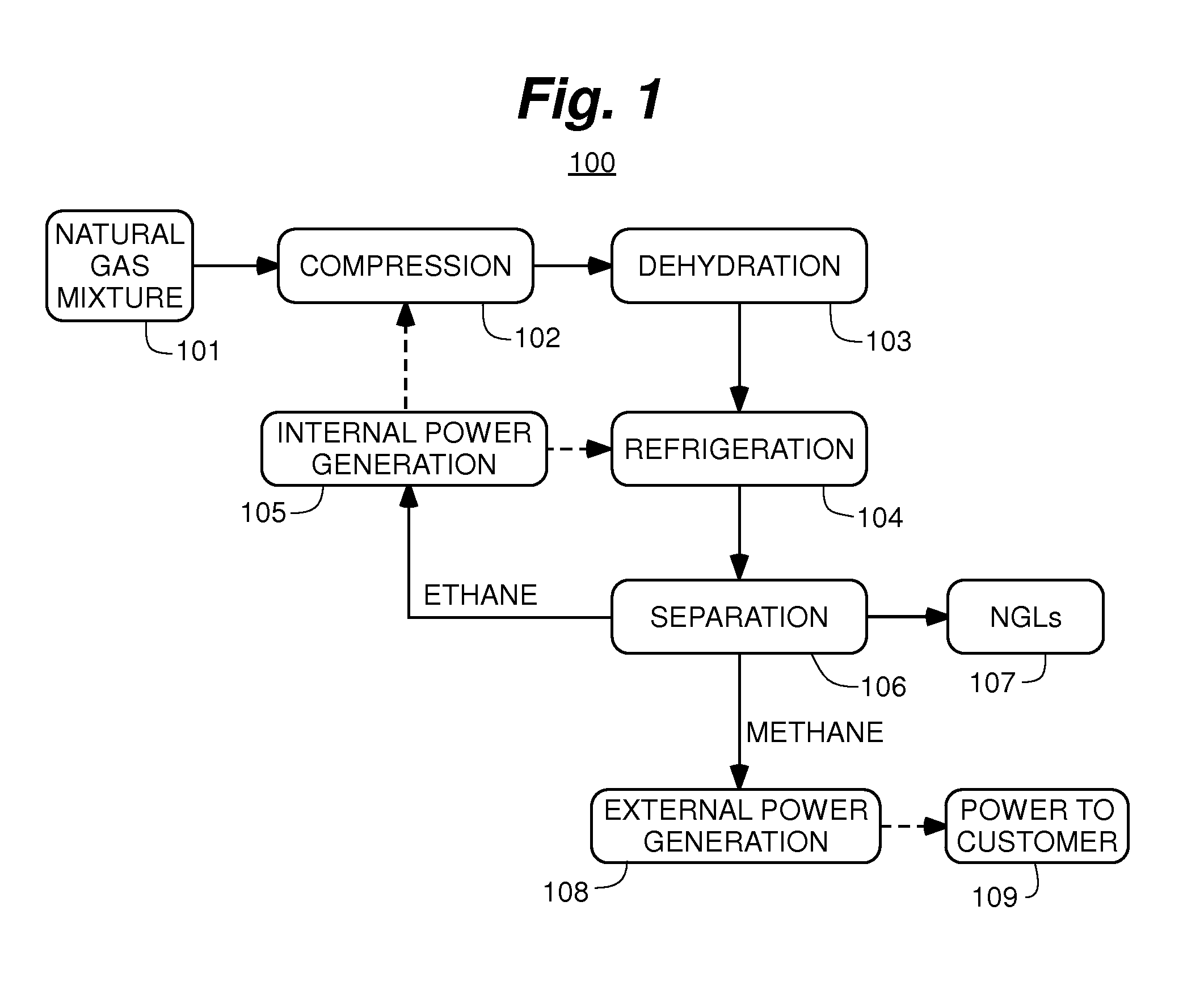
Systems and methods for separating alkane gases with applications to raw natural gas processing and flare gas capture
InactiveUS20140366577A1Reduce stepsHigh quality separationSolidificationLiquefactionAlkaneNatural-gas processing
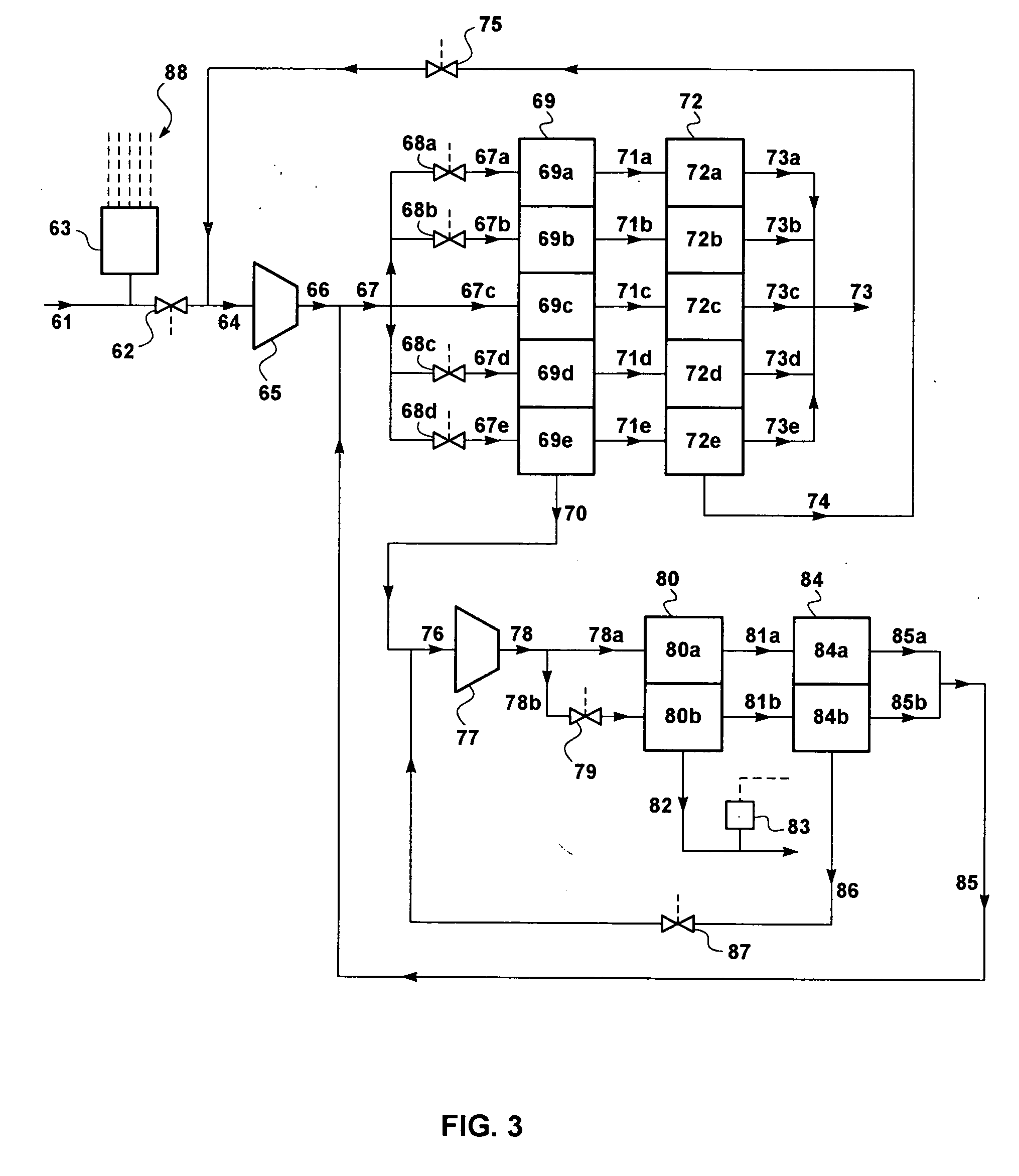
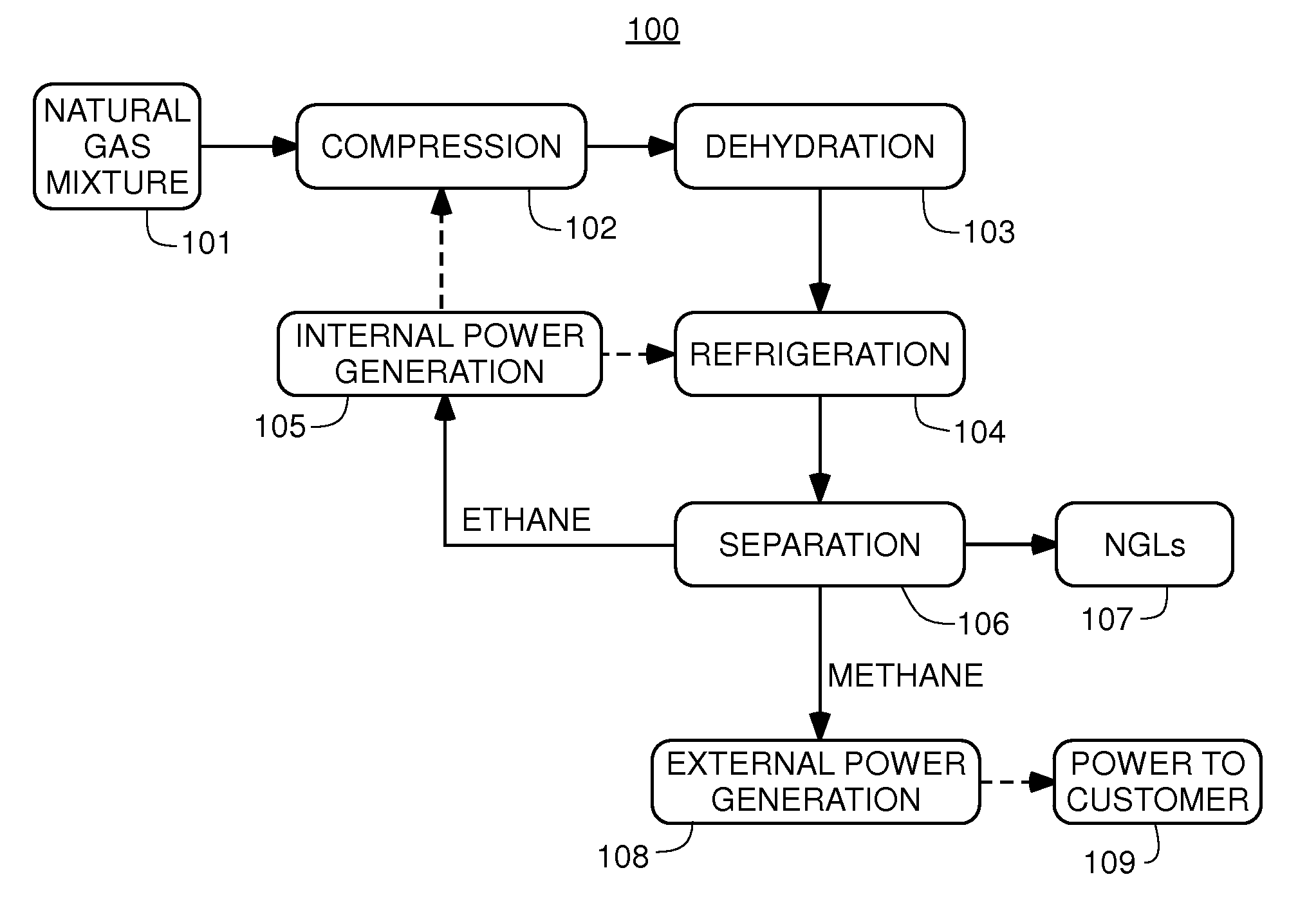
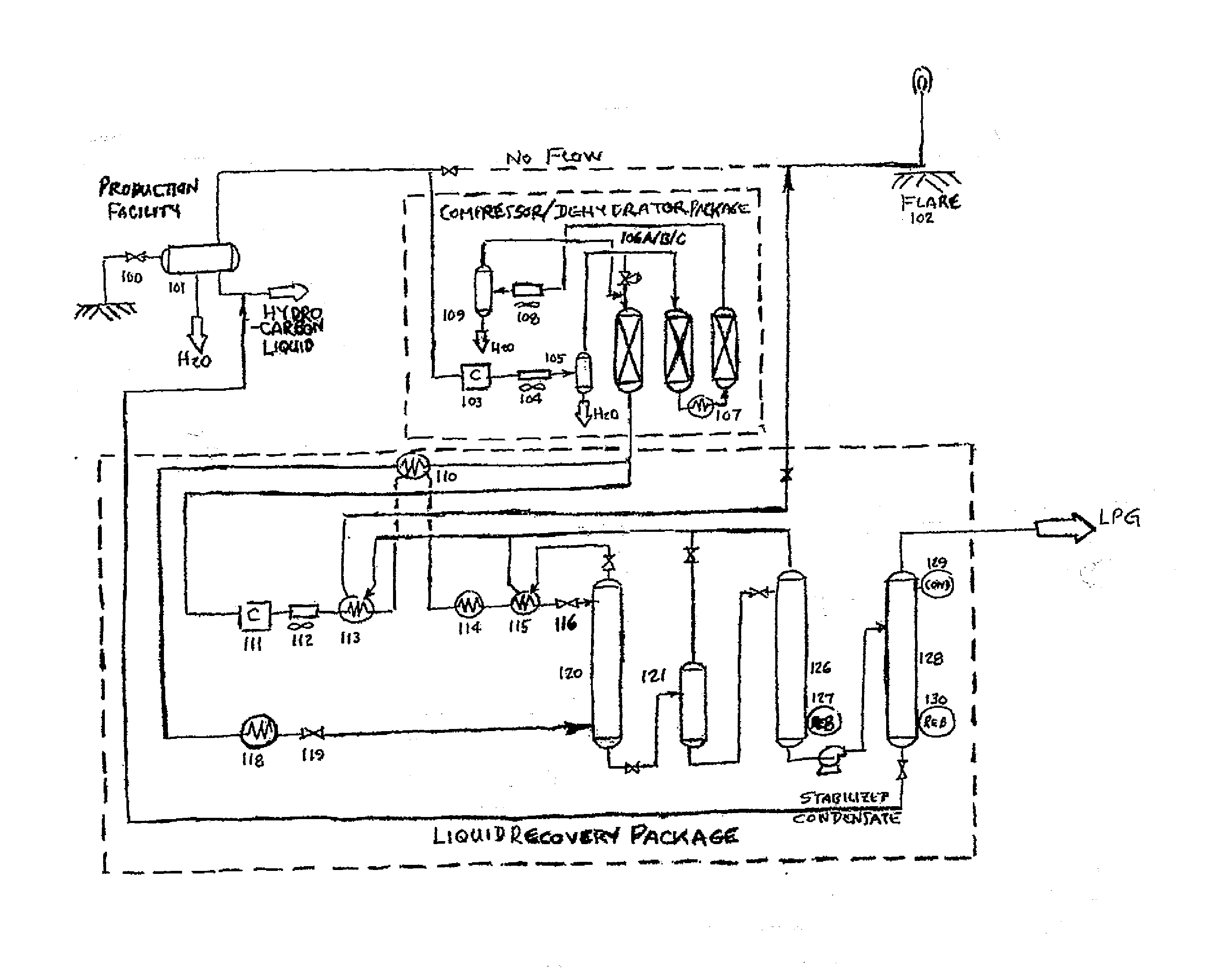
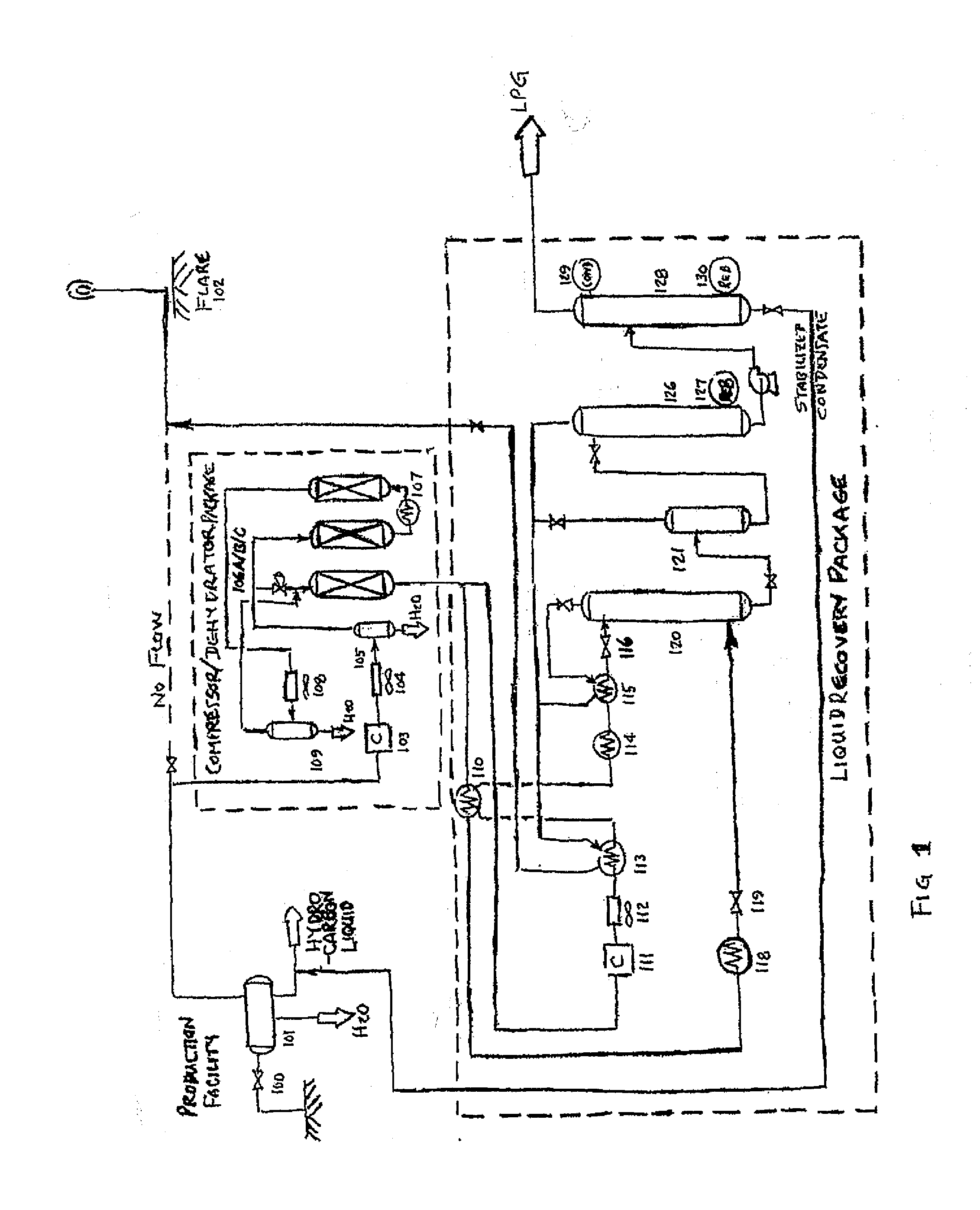
The present invention is a field-deployable system for separating methane and natural gas liquids (NGLs) from a raw gas stream comprising a compressor; a dehydrator; a refrigerator having one or more stages; and a separation subsystem adapted to separate the raw gas stream into three product streams including a methane stream that is at least 80% methane, an ethane-rich stream, and a NGLs stream having a vapor pressure of no more than 250 psia at 38° C. The methane stream is sufficiently lean to be useable in existing natural gas engines without modification. The NGLs stream has a sufficiently low vapor pressure to be transportable in standard propane containers. The ethane-rich stream may be utilized within the system itself to power its own operations. The system can be utilized to reduce flaring from liquids-rich gas production sites to an absolute minimum, produce natural gas liquids for transport, and provide dry methane gas suitable for use in portable field generators.
Owner:PIONEER ENERGY
Use of a microporous crystalline material of zeolitic nature with rho structure in natural gas processing
The present invention describes the use of isostructural zeolites with rho zeolitic structure in processes of adsorption and separation of the various components of natural gas.
Owner:CONSEJO SUPERIOR DE INVESTIGACIONES CIENTIFICAS (CSIC) +1
Liquid natural gas processing
ActiveUS6941771B2Avoid the needLower energy requirementsSolidificationLiquefactionRefluxNatural-gas processing
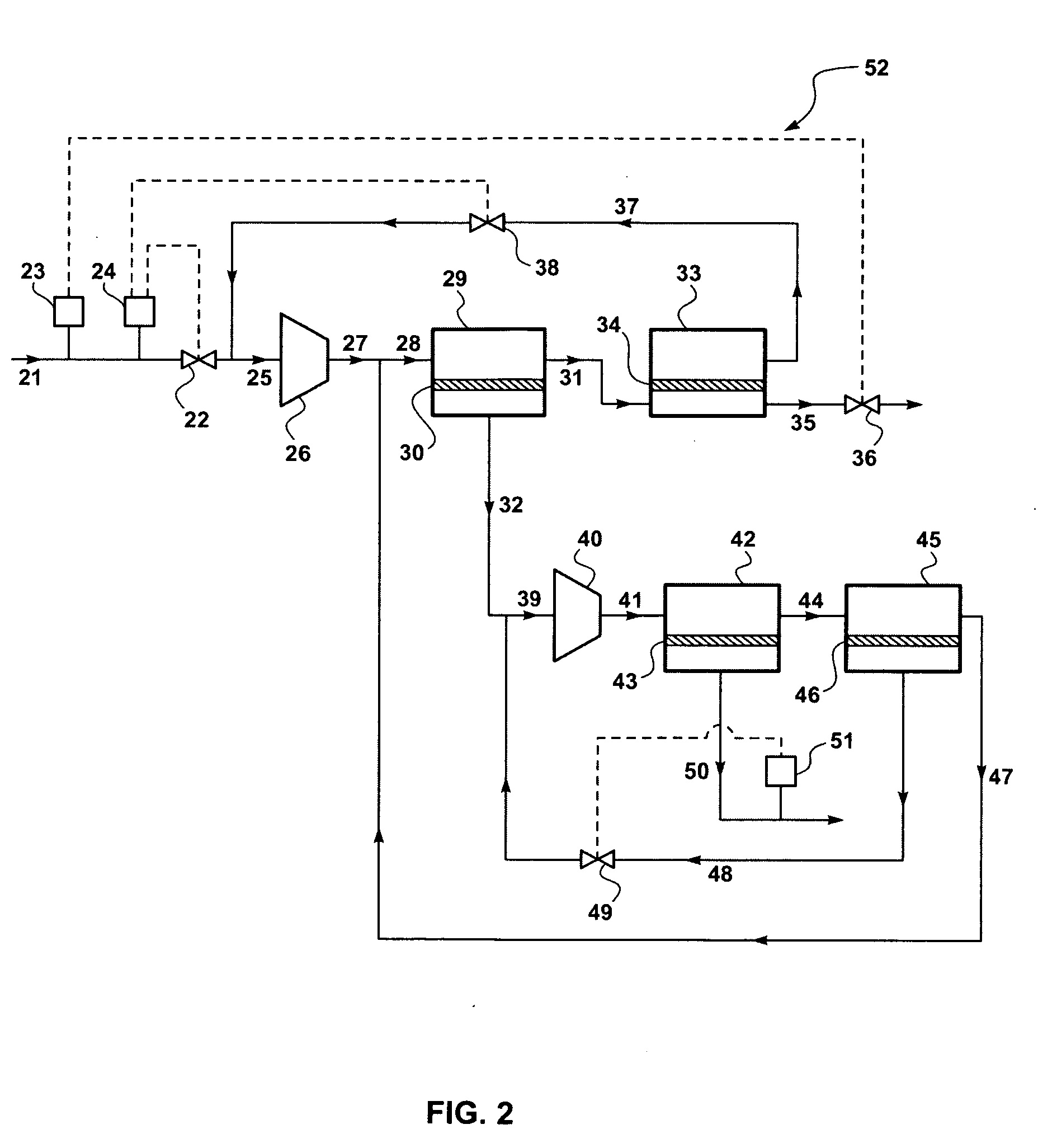
A process for the recovery of natural gas liquids (NGL) (ethane, ethylene, propane, propylene and heavier hydrocarbons) from liquefied natural gas (LNG) is disclosed. The LNG feed stream is split with at least one portion used as an external reflux, without prior treatment, to improve the separation and recovery of the natural gas liquids (NGL).
Owner:HOWE BAKER ENGINEERS LTD
Use of a microporous crystalline material of zeolitic nature with RHO structure in natural gas processing
The present invention describes the use of isostructural zeolites with rho zeolitic structure in processes of adsorption and separation of the various components of natural gas.
Owner:CONSEJO SUPERIOR DE INVESTIGACIONES CIENTIFICAS (CSIC) +1
Supersonic condensation and cyclone separation device
InactiveCN101619918AAchieve separationReduce the temperatureSolidificationLiquefactionCycloneNatural-gas processing
The invention provides a supersonic condensation and cyclone separation device, which leads air flow to generate powerful rotation in a blade-guiding manner at an entrance; then, a laval nozzle is used for coordinating with the separation device to lead the air flow to reach a supersonic speed and reduce temperature thereof greatly, thus condensing components with higher dew points and achieving the separation between the gas phase and the liquid phase under the action of the centrifugal force generated by the rotation of the air flow; and a highly-efficient liquid trap and a cyclone-recovering booster are arranged at the tail part of the nozzle. Compared with the existing supersonic separating device, the supersonic separation device of the invention has higher efficiency of separation and cyclone recovery under the same working conditions of low flow rate, for the device has the advantages that the flow channel of the device in a high-speed flow field area is smooth, the fractional resistance of the wall surface is low and the device is provided with the cyclone recovering booster suitable for the conditions of low flow rate. Since quite a lot of inland gas fields has low single-well flow rate in China, the device of the invention has wide application prospect in the field of natural gas treatment for the inland gas fields in China.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Composite Perfluorohydrocarbon Membranes, Their Preparation and Use
InactiveUS20070256969A1Improved uniform pore structureSimple and cost-effective and industrially feasibleSemi-permeable membranesMembranesArylNatural-gas processing
Composite porous hydrophobic membranes are prepared by forming a perfluorohydrocarbon layer on the surface of a preformed porous polymeric substrate. The substrate can be formed from poly(aryl ether ketone) and a perfluorohydrocarbon layer can be chemically grafted to the surface of the substrate. The membranes can be utilized for a broad range of fluid separations, such as microfiltration, nanofiltration, ultrafiltration as membrane contactors for membrane distillation and for degassing and dewatering of fluids. The membranes can further contain a dense ultra-thin perfluorohydrocarbon layer superimposed on the porous poly(aryl ether ketone) substrate and can be utilized as membrane contactors or as gas separation membranes for natural gas treatment and gas dehydration.
Owner:POROGEN
Method for reducing the mercury content of natural gas condensate and natural gas processing plant
InactiveUS20100147745A1Avoid typingMembranesGas treatmentNatural-gas condensateNatural-gas processing
A method for reducing the mercury content of natural gas condensate, comprising the steps of providing a nanofiltration membrane having a feed side and a permeate side; contacting the natural gas condensate with the feed side of the membrane; and obtaining a mercury-depleted natural gas condensate at the permeate side of the membrane; and a natural gas processing plant comprising a condensate workup section including a nanofiltration membrane separation unit for reducing the mercury content of natural gas condensate.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
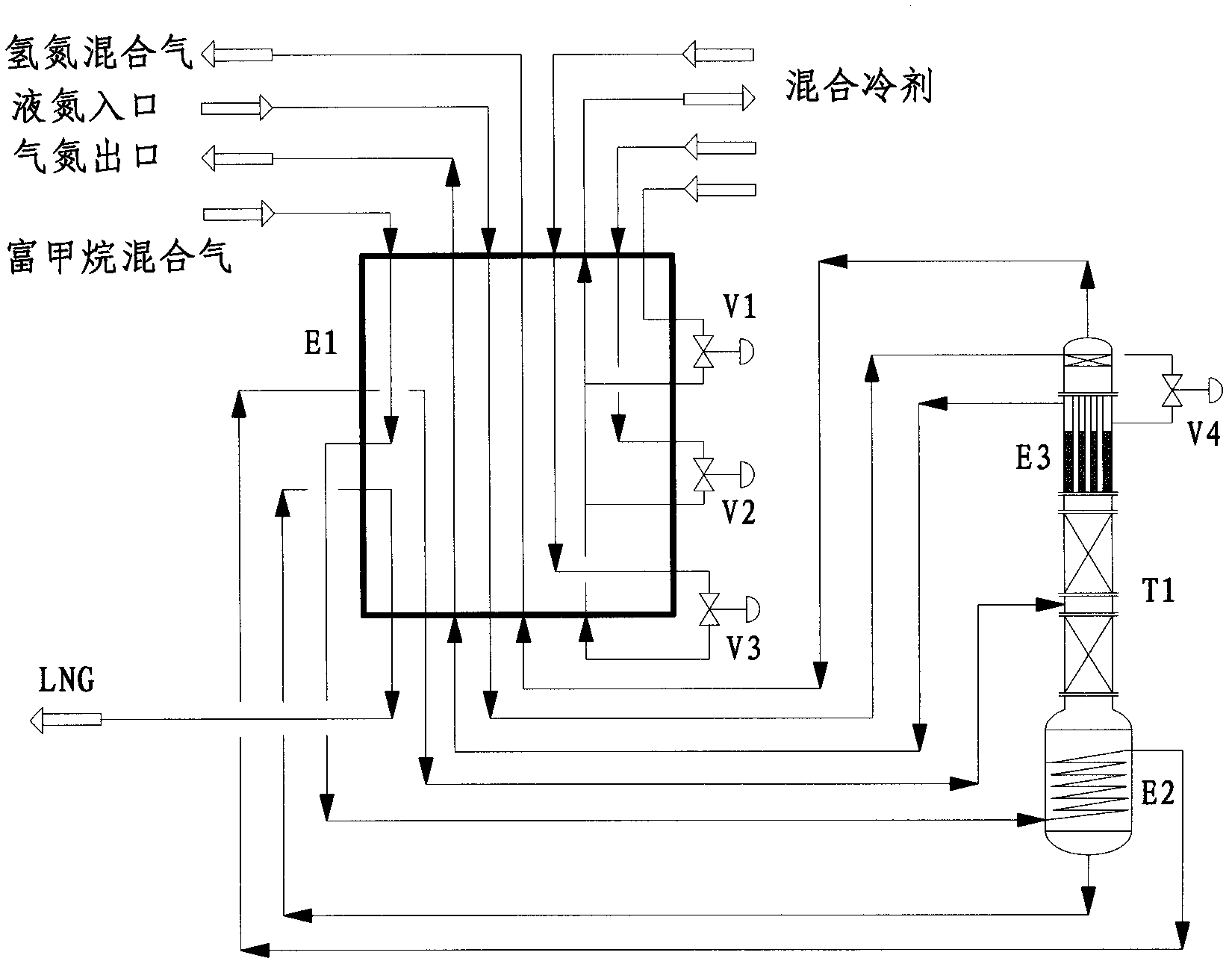
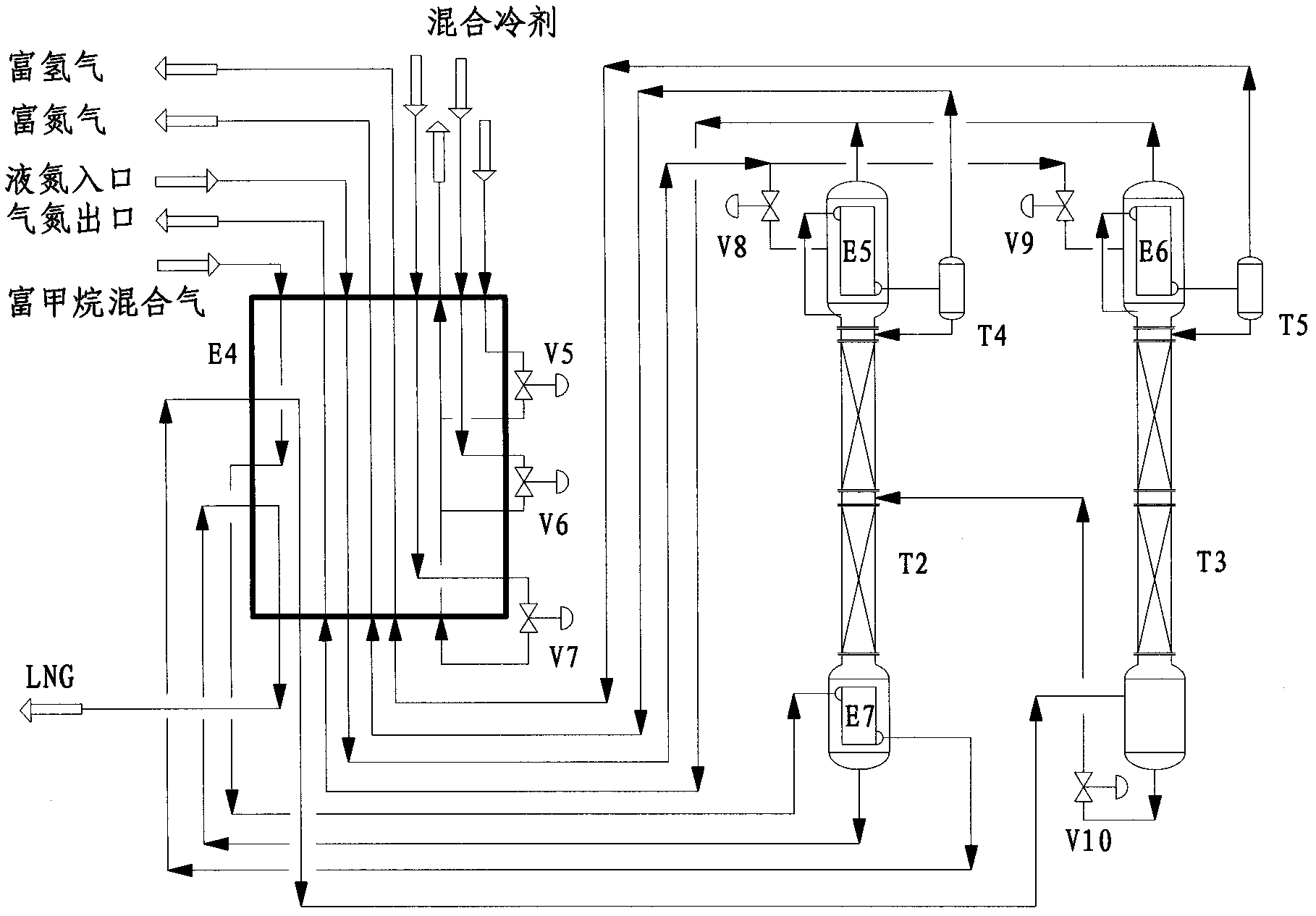
Industrial arts for dehydrogenation and denitrogen and de-carbon monoxide from high methane gas and liquefied natural gas production
Disclosed is industrial arts for dehydrogenation, denitrogen and de-carbon monoxide from high methane gas and liquefied natural gas production. The industrial arts comprise two parts which are low temperature liquefaction and rectification separation. The low temperature liquefaction part is finished in a cold box through cooling provided by a mixed cryogen. A single tower procedure or a double tower procedure is adopted by the rectification separation part to remove hydrogen, nitrogen and carbon monoxide. Methane component in high methane mixed gas with the hydrogen and the nitrogen is liquefied sequentially through the cold box, rectifying tower bottom reboiler and the cold box, and the high methane mixed gas with the hydrogen and the nitrogen enters into a rectification separation system, and then the hydrogen, the nitrogen and the carbon monoxide are removed. Hydrogen content in obtained liquefied natural gas (LNG) products is less than or equal to 2000 ppm, nitrogen content is less than or equal to 4%, and carbon monoxide content is less than or equal to 6%. The invention further provides a natural gas liquefaction art of the high methane gas with the hydrogen, the nitrogen and the carbon monoxide. The hydrogen, the nitrogen and the carbon monoxide are removed, and meanwhile the LNG with a better separating effect compared with a traditional industrial art is obtained, and process route is advanced. Compared with the traditional industrial art, power consumption of the system can be reduced by 20%.
Owner:XINDI ENERGY ENG TECH
Natural gas treatment process for stimulated well
InactiveUS7537641B2Combination devicesAuxillary pretreatmentHigh concentrationNatural-gas processing
A process and equipment for treating natural gas produced by a well that has recently been stimulated, and that contains an undesirably high concentration of the fracturing gas used to stimulate the well. The process involves treating the gas by membrane separation, and provides for control of treatment parameters to compensate for the changing concentration of fracturing gas in the produced gas, as well as changes in gas flow rate.
Owner:MEMBRANE TECH & RES
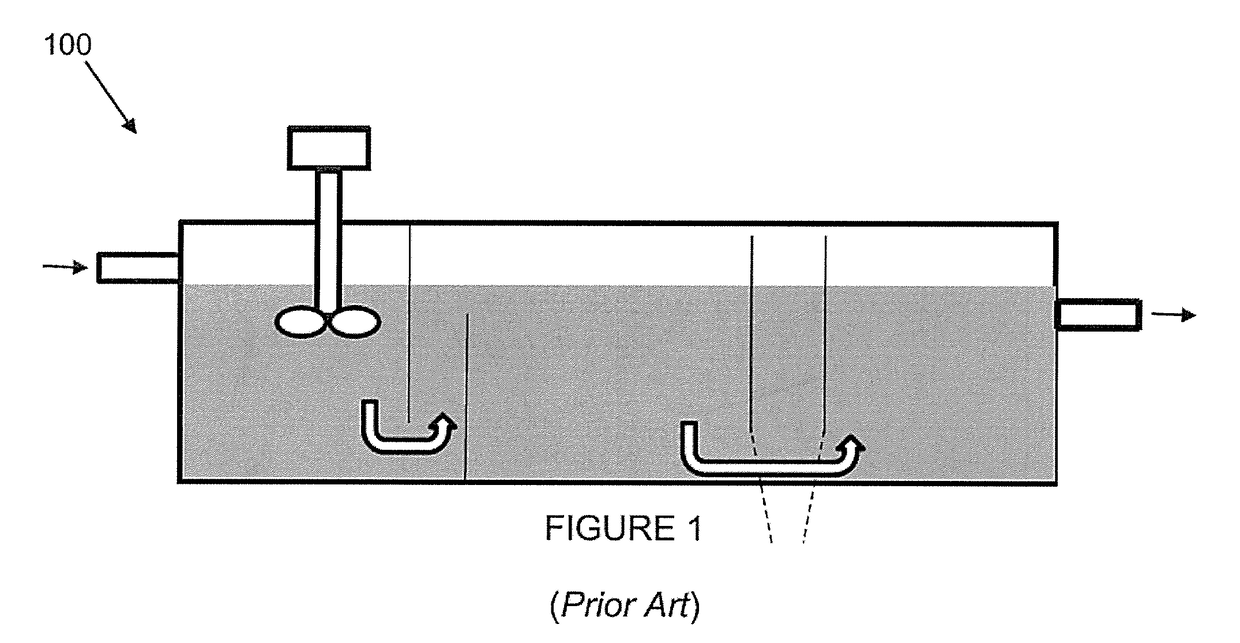
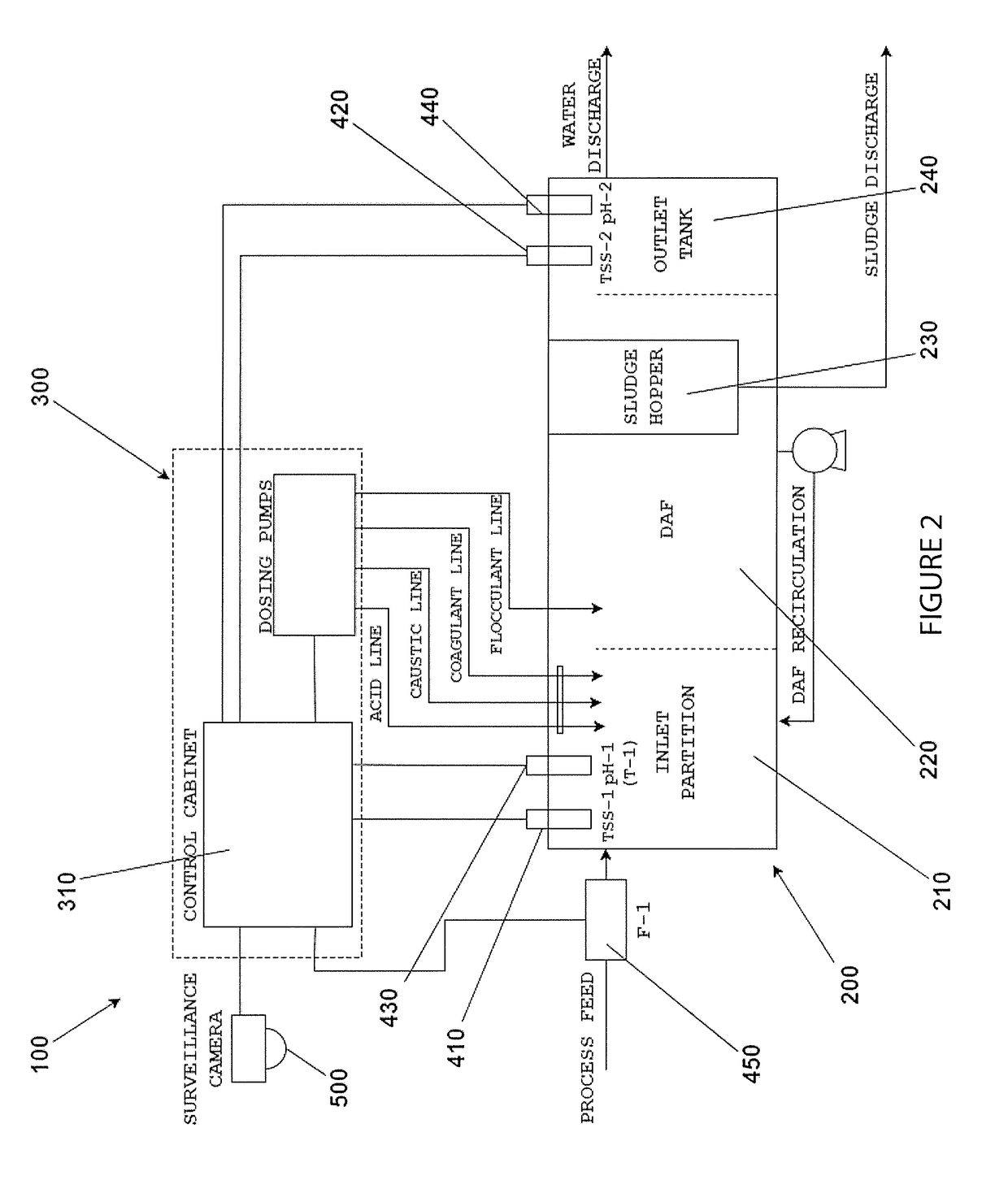
Water treatment system and method
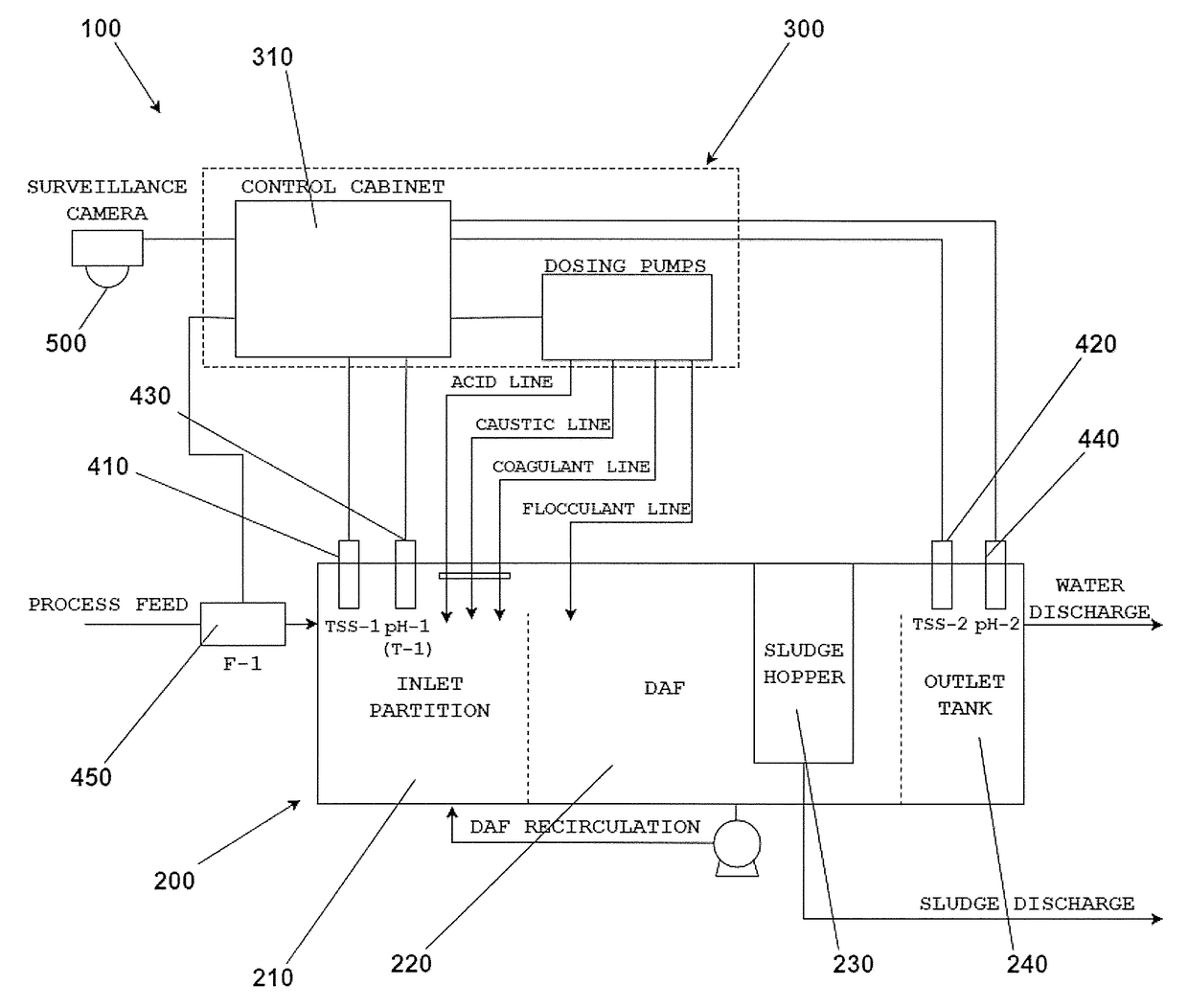
ActiveUS20170297929A1Discharge costReduce and even eliminate non-complianceWater treatment parameter controlNature of treatment waterWater treatment systemNatural-gas processing
Disclosed herein is a water treatment system for connection to a water treatment plant (e.g. a dissolved air flotation device). The plant may have an inlet for the receipt of feed water (e.g. waste water) and an outlet for the discharge of treated water. The treatment system may comprise a first sensor disposed such that it is in fluidity communication with the feed water, and a second sensor disposed such that it is in fluidity communication with the treated water. The first and second sensors may be configured to sense parameters of the feed and treated water. The system may further comprise a first applicator (e.g. a pump) that is configured to discharge a treatment source (e.g. a chemical source) to the plant to treat the feed water. The disclosed system may be used to treat waste water (e.g. the treatment of effluent from oil refineries, petrochemical and chemical plants, natural gas processing plants, paper mills and general water treatment). The system has analogous applications in other processing methods that also use DAF, or very similar, systems, such as the processing of mineral ores and other such solid extraction processing methods.
Owner:WATERWERX TECH PTY LTD
Pump-free LNG gas-filling system and liquefied natural gas processing method
InactiveCN103672394AIncrease profitReduce filling energy consumption to zero energy consumptionPipeline systemsContainer discharging methodsNatural-gas processingGas phase
The invention discloses a pump-free LNG gas-filling system and a liquefied natural gas processing method. The pump-free LNG gas-filling system includes an LNG low-temperature storage tank; an upper gas phase of the LNG low-temperature storage tank is provided with a first pipeline and a second pipeline, a lower liquid phase of the LNG low-temperature storage tank is provided with a third pipeline and a fourth pipeline, the first pipeline is provided with a first valve, the second pipeline is provided with a second valve, the third pipeline is provided with a third valve, and the fourth pipeline is provided with a fourth valve; the second pipeline and the third pipeline are communicated with a liquid discharging port through a liquid discharging pipeline, the liquid discharging port is provided with an eighth valve, and positions, corresponding to the second pipeline and the third pipeline, of the liquid discharging pipeline are respectively provided with a second emergency shut-off valve and a third emergency shut-off valve. The liquefied natural gas processing method is provided. With adopting of technical forms of a liquid adding pipeline, a system gas phase pipeline and system liquid discharging and pressurized pipelines, car filling energy dissipation is reduced to be zero energy dissipation, a low-temperature pump and other devices are not required to be increased, and using cost and maintenance cost of the low-temperature pump and other devices are saved.
Owner:QINGDAO JIENENG HIGH&NEW TECH
Natural gas treatment process
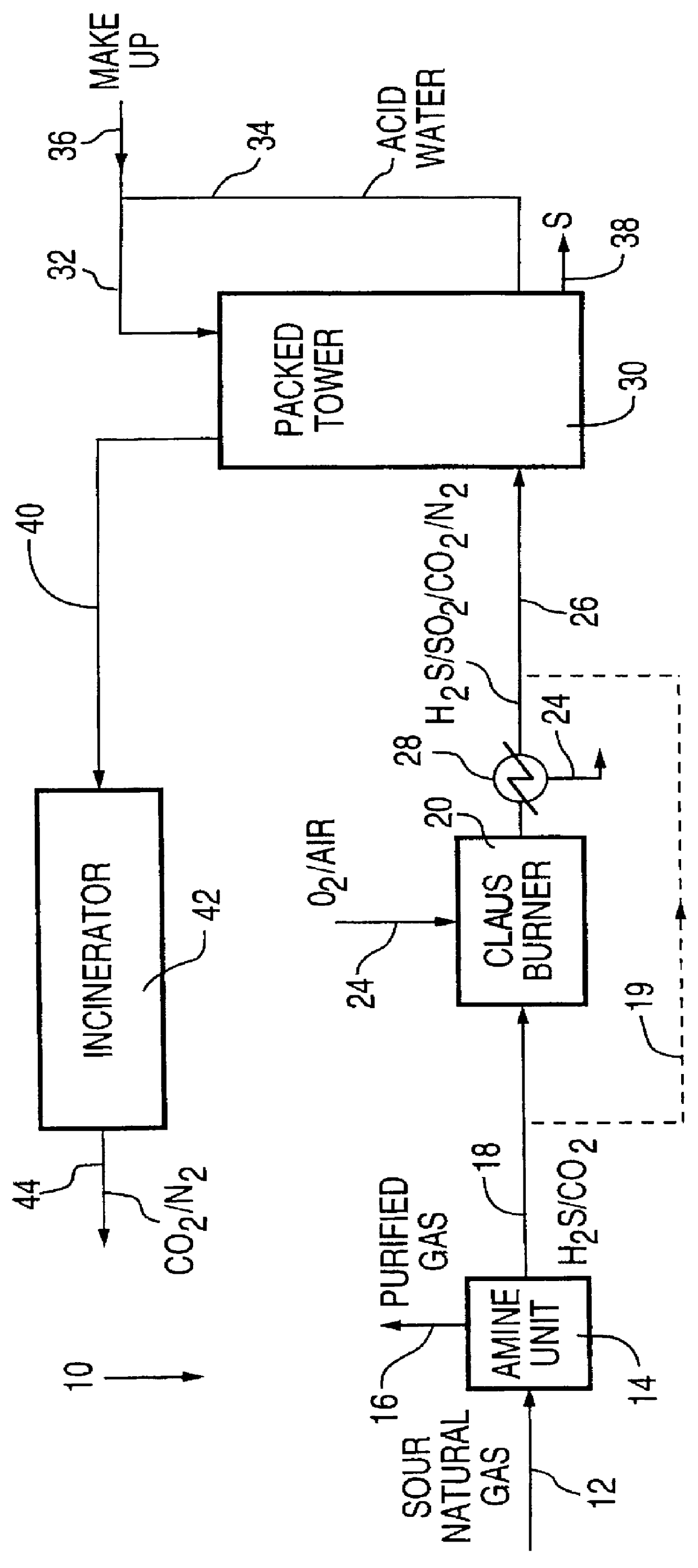
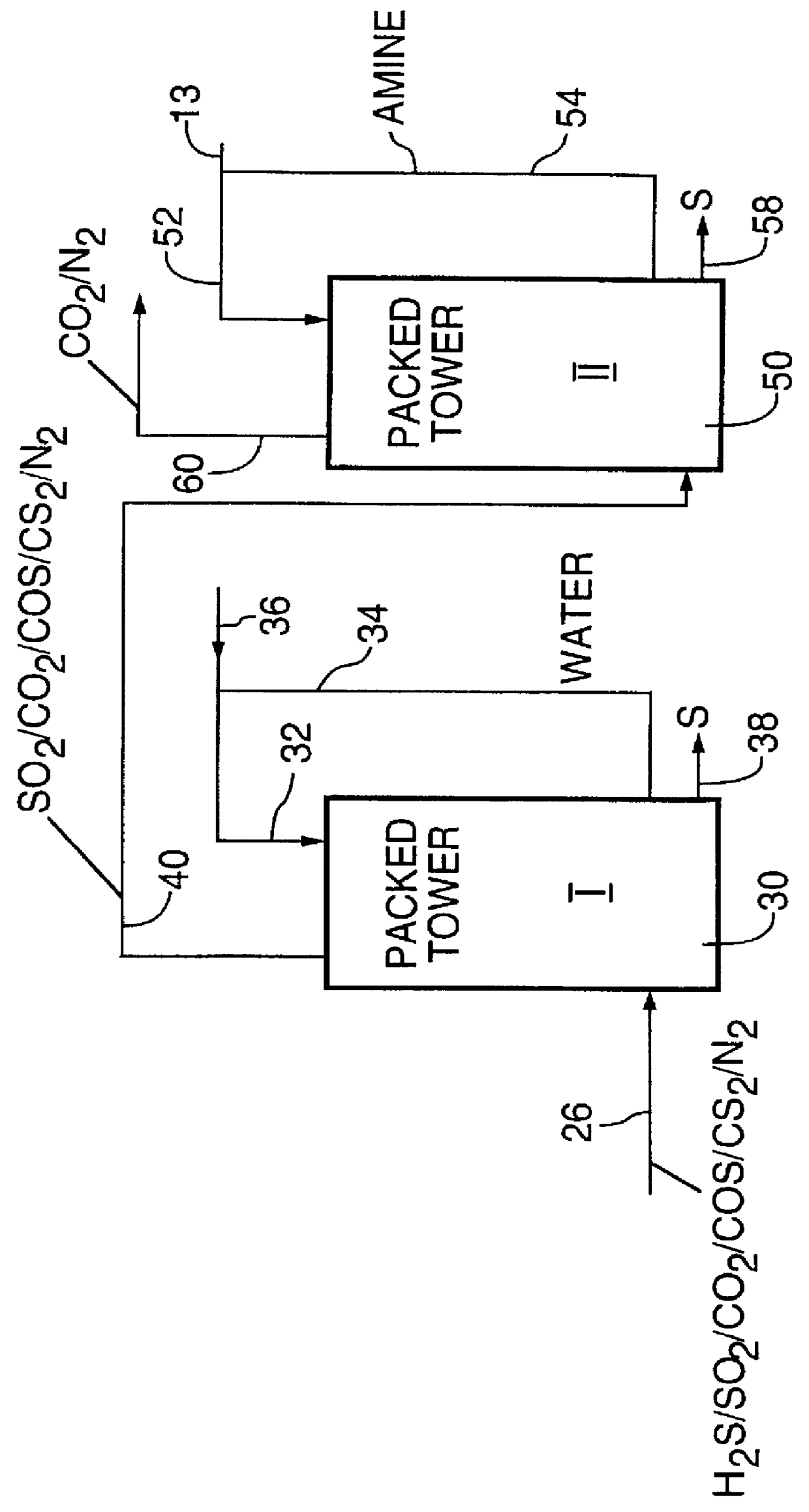
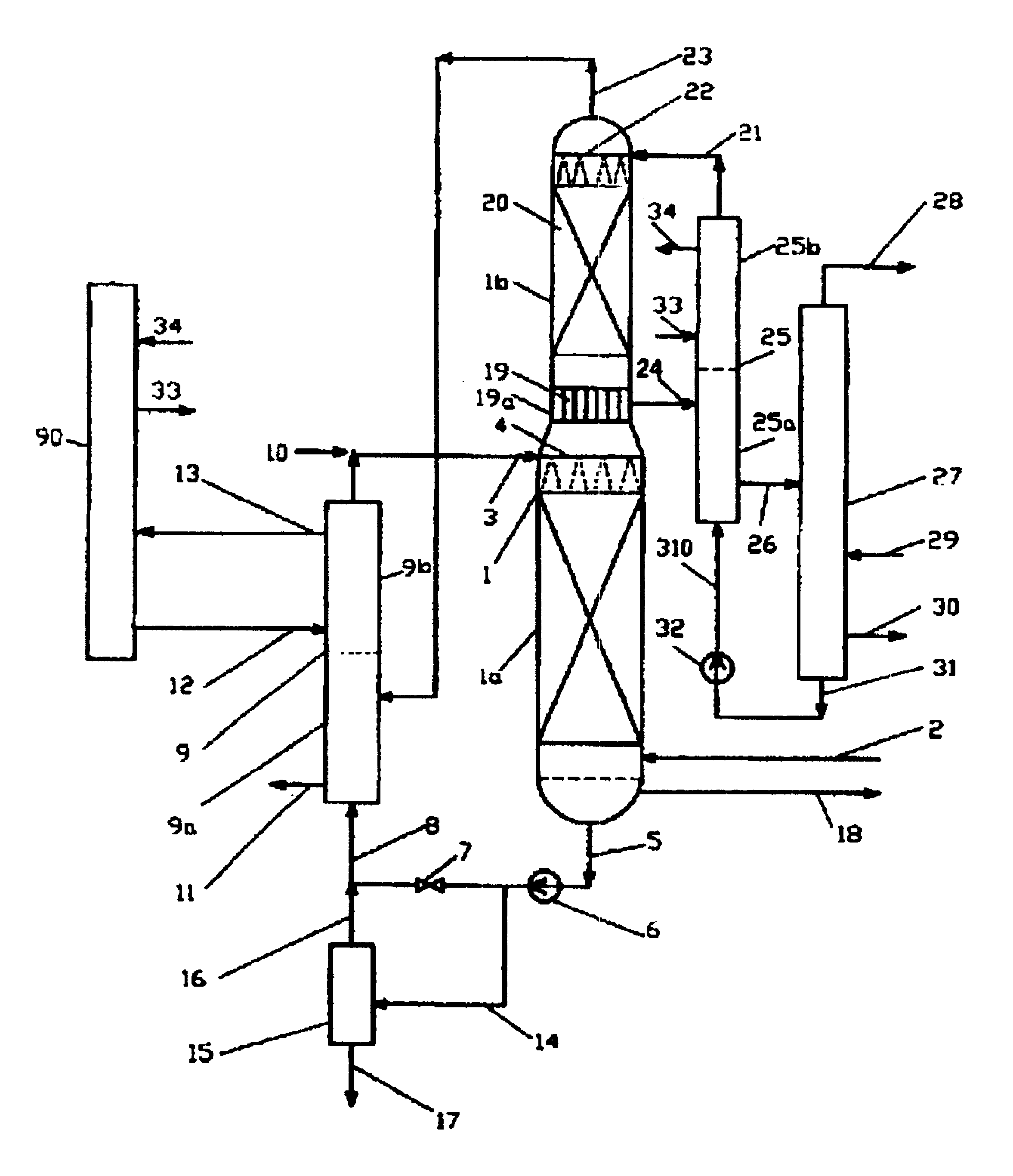
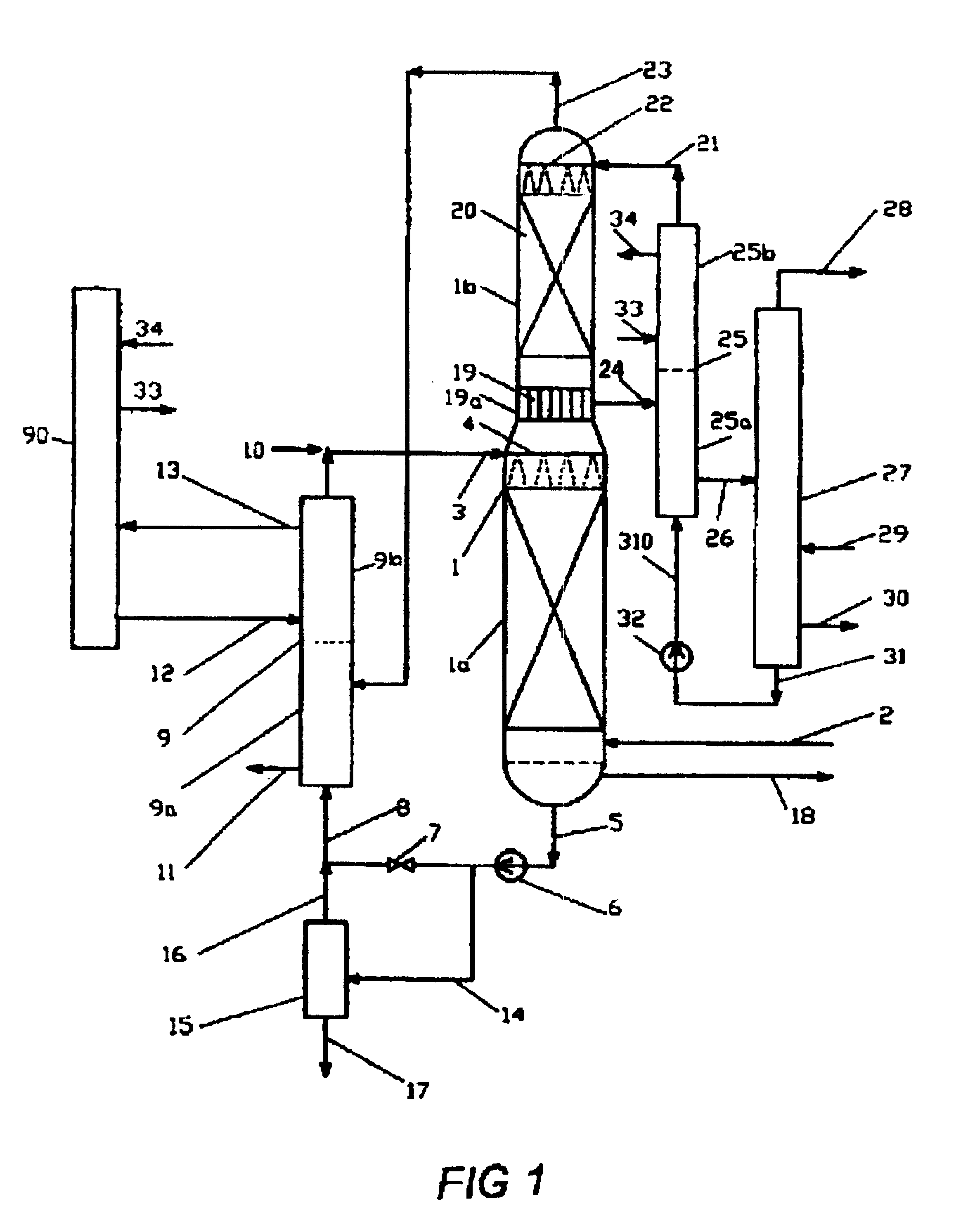
PCT No. PCT / CA97 / 00536 Sec. 371 Date Jul. 15, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Jul. 15, 1998 PCT Filed Jul. 28, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO98 / 04337 PCT Pub. Date Feb. 5, 1998Hydrogen sulfide is removed from gas streams by reaction with sulfur dioxide in an autogeneously-formed aqueous acid medium according to the equation: SO2+2H2S->2H2O+3S the sulfur being removed from the aqueous phase. Carbonyl sulfide and / or carbon disulfide is removed from gas streams by hydrolysis to hydrogen sulfide in the presence of a weak organic base catalyst, such as quinoline, with the hydrogen sulfide reacting with sulfur dioxide to form sulfur.
Owner:APOLLO ENVIRONMENTAL SYST
Condensed liquid recycling method for high-pressure natural gas
ActiveCN104807288AImprove separation efficiencyImprove operational stabilitySolidificationLiquefactionRecovery methodCompressed natural gas
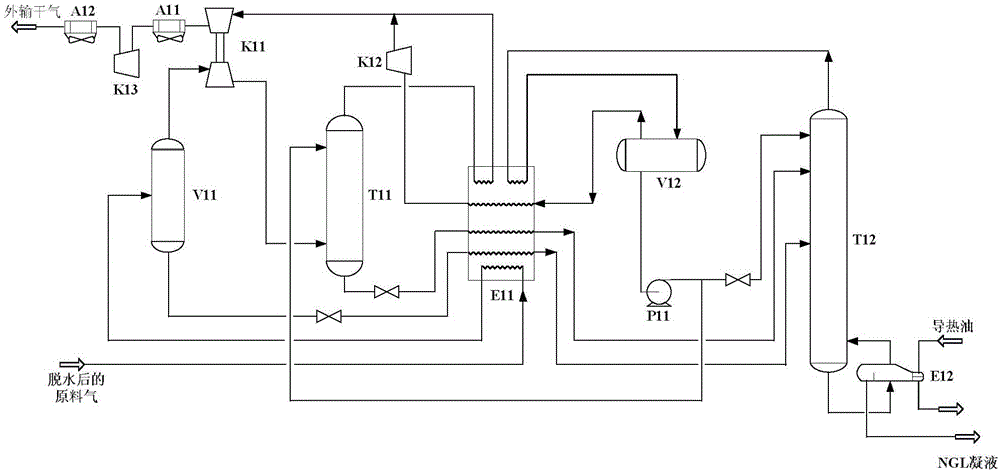
The invention discloses a condensed liquid recycling method for high-pressure natural gas, and relates to the technical field of natural gas processing technologies. According to the method, on the basis of an expansion machine refrigeration-twin tower technology, low-content propane liquid hydrocarbon is used as an absorbent; a high-pressure absorption tower is arranged; by adoption of a high-pressure and low-temperature absorption and gasification refrigeration theory, propane and condensed liquid heavier than propane in a gas phase from the outlet of an expansion machine are recycled; in the process, a cold box adopts a multi-strand high-efficiency plate fin type heat exchanger; a deethanization tower adopts three strands of material feeding, so that the high-pressure natural gas condensed liquid recycling method including expansion machine refrigeration, high-pressure absorption and condensed water fractionation is realized. According to the method, the compression power of an external air conveying pressurizer and the energy consumption of a device system are reduced, the separation effect and the operation stability of an absorption tower are improved, the system cold and heat utilization rate and the propane recycling rate are improved, and the economical benefit of device operation is enhanced.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
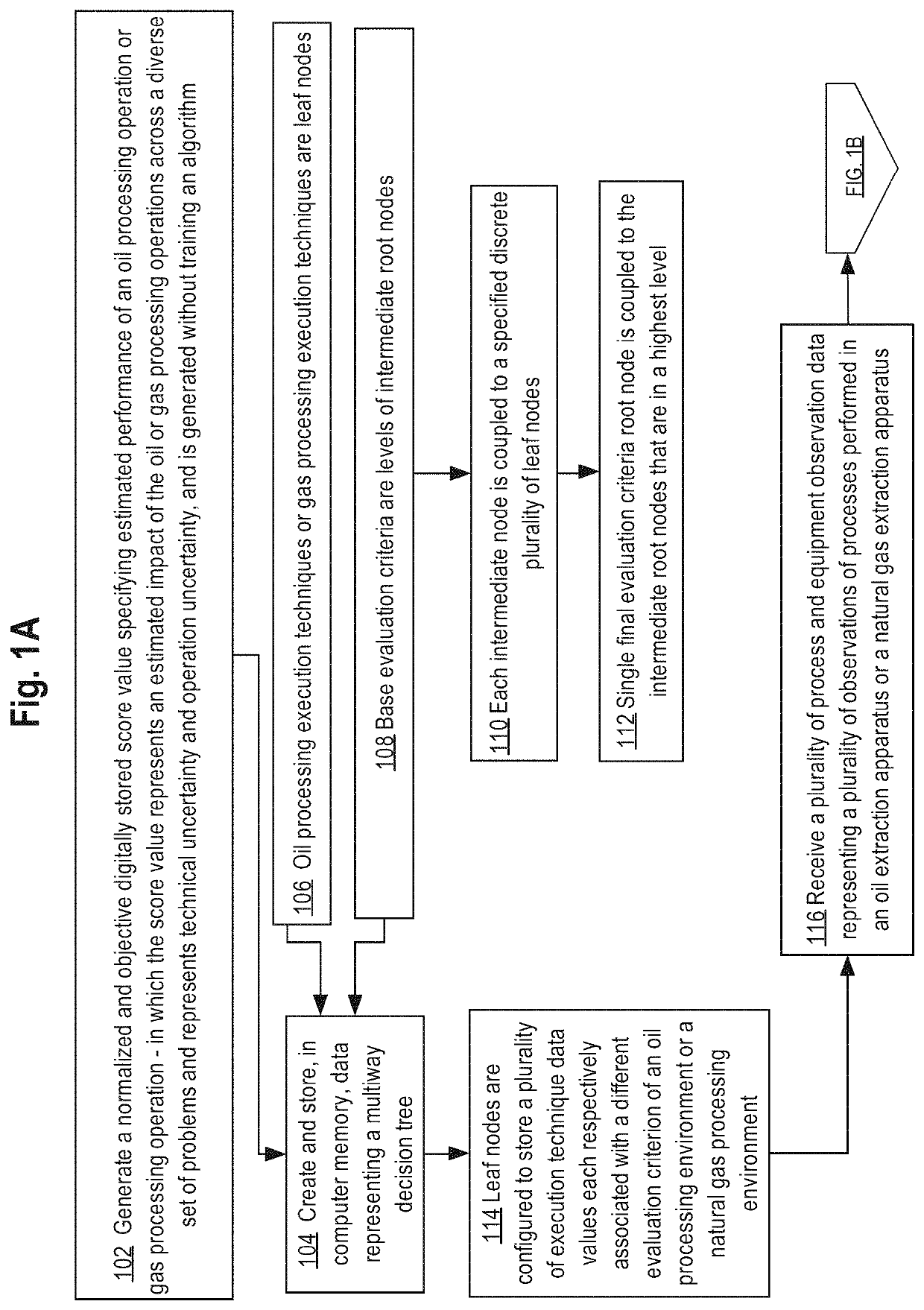
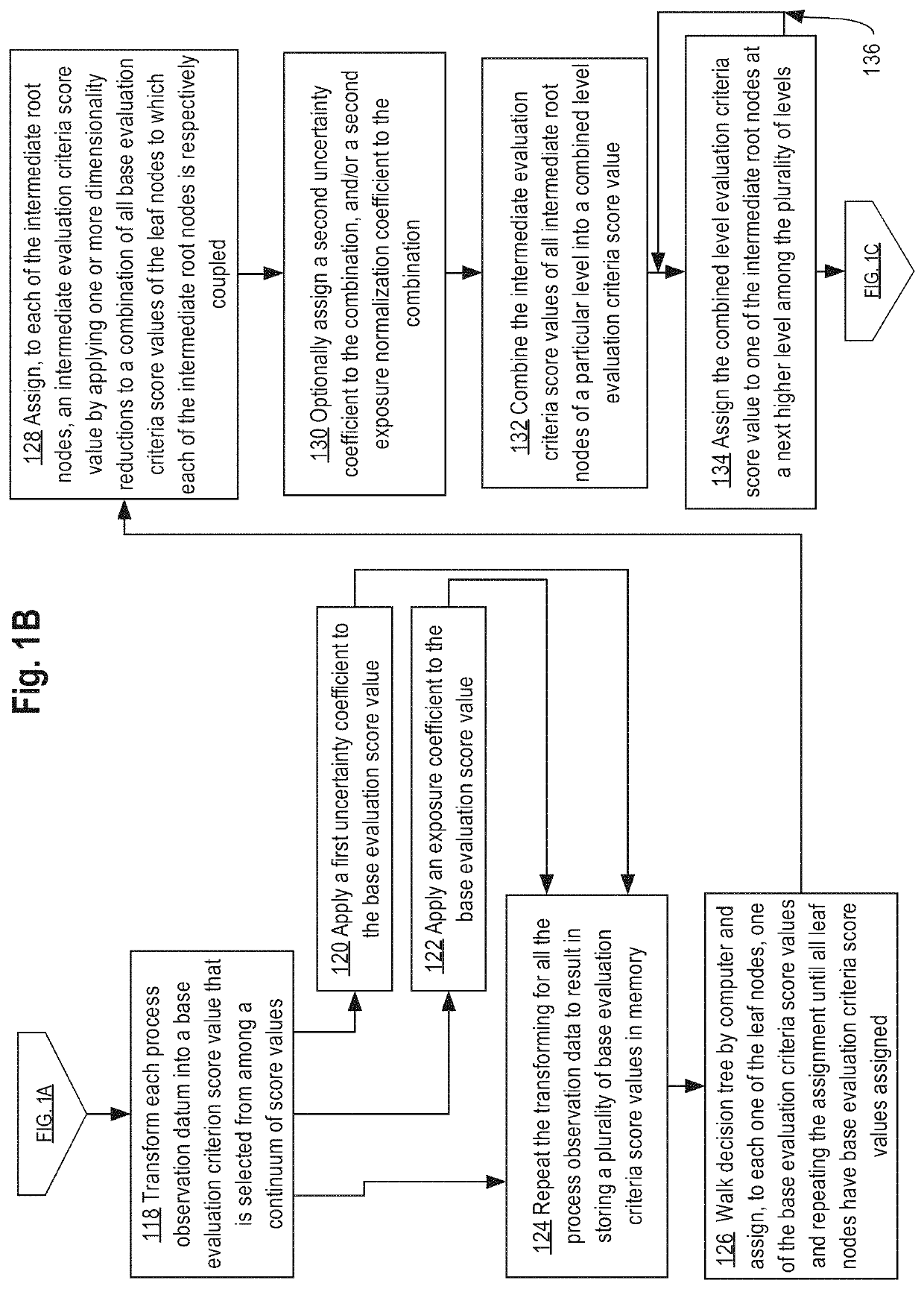
Computer-implemented impact analysis of energy facilities
ActiveUS10671772B2Technology managementDesign optimisation/simulationEnergy facilitiesNatural-gas processing
A data processing method for execution using a programmed computer to generate an objective score value specifying an estimated impact of an oil or gas processing operation comprises: receiving a plurality of data associated with the oil or gas processing operation; identifying, using the plurality of data, a plurality of events that may occur during the oil or gas processing operation; for each event of the plurality of events, determining a relative weighting of potential impact of the event for the oil or gas processing operation using local conditions and a master event profile for the event; for each event of the plurality of events, determining an effectiveness of one or more control efforts; for each event of the plurality of events, determining a score using the relative weighting of the potential impact of the event and the effectiveness of the one or more control efforts; determining the objective digitally stored score value for the oil or gas processing operation using the score for each event of the plurality of events and benchmarking the objective digitally stored score value to a plurality of objective digitally stored score values for other oil or gas processing operations.
Owner:INDEPENDENT ENERGY STANDARDS CORP
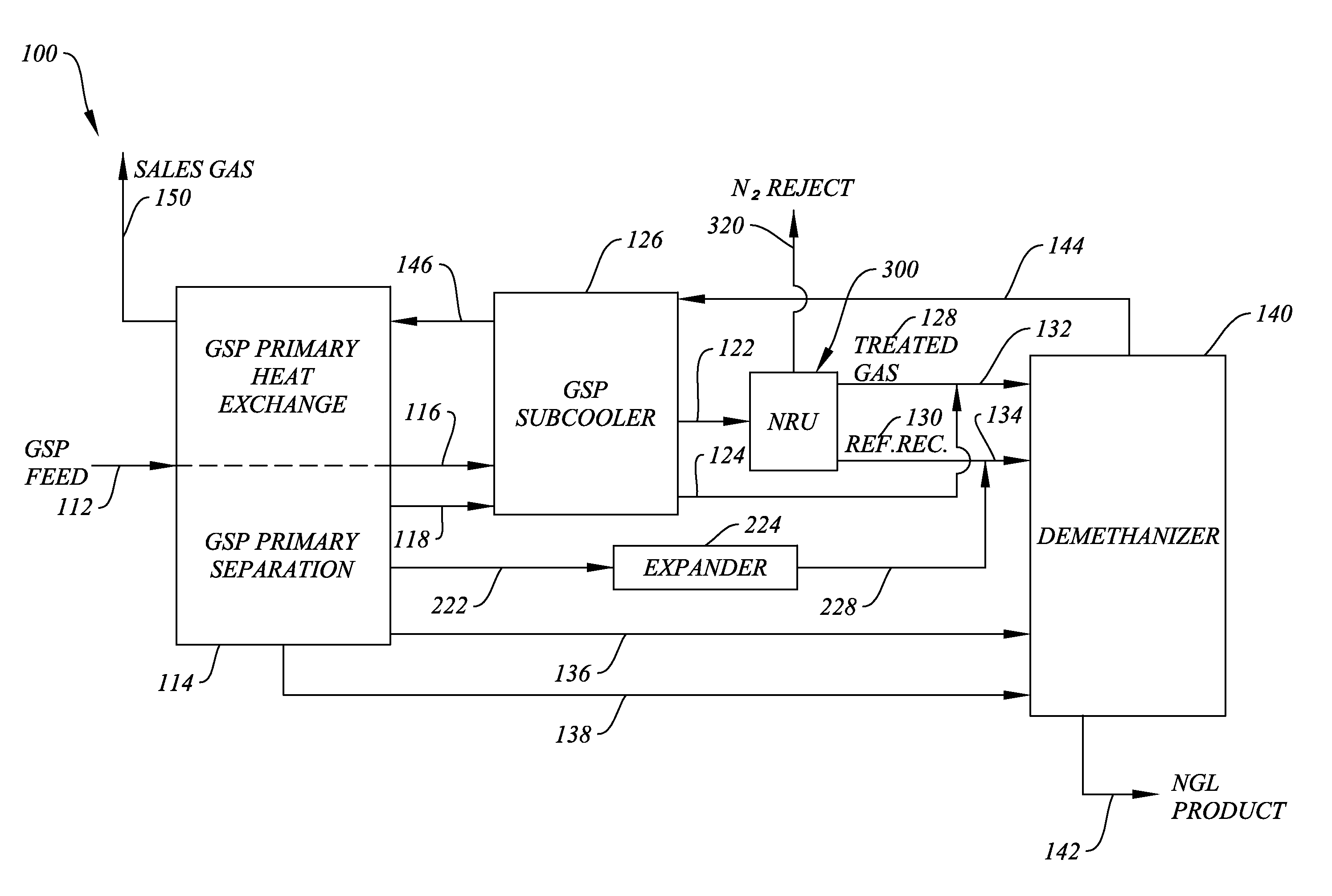
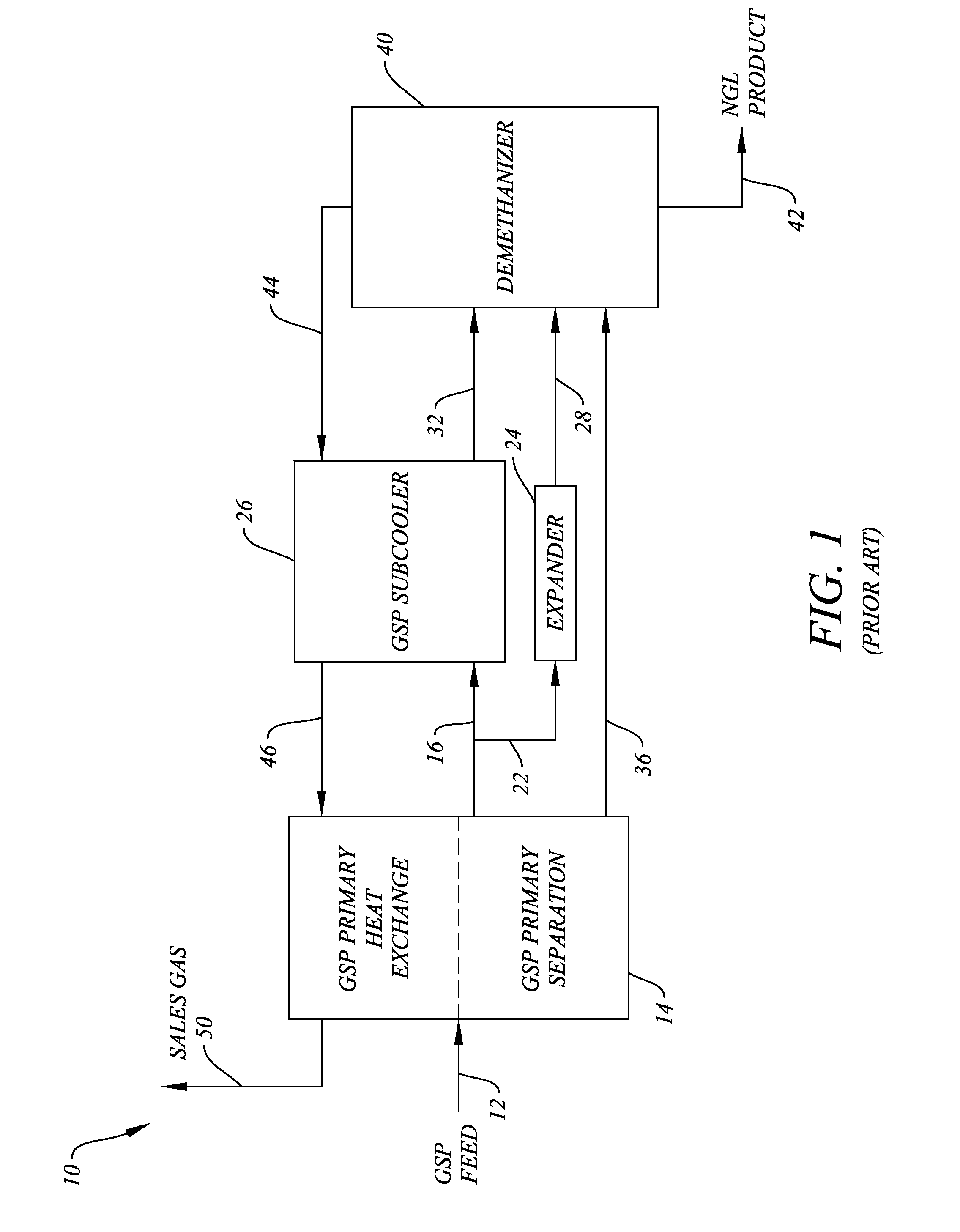
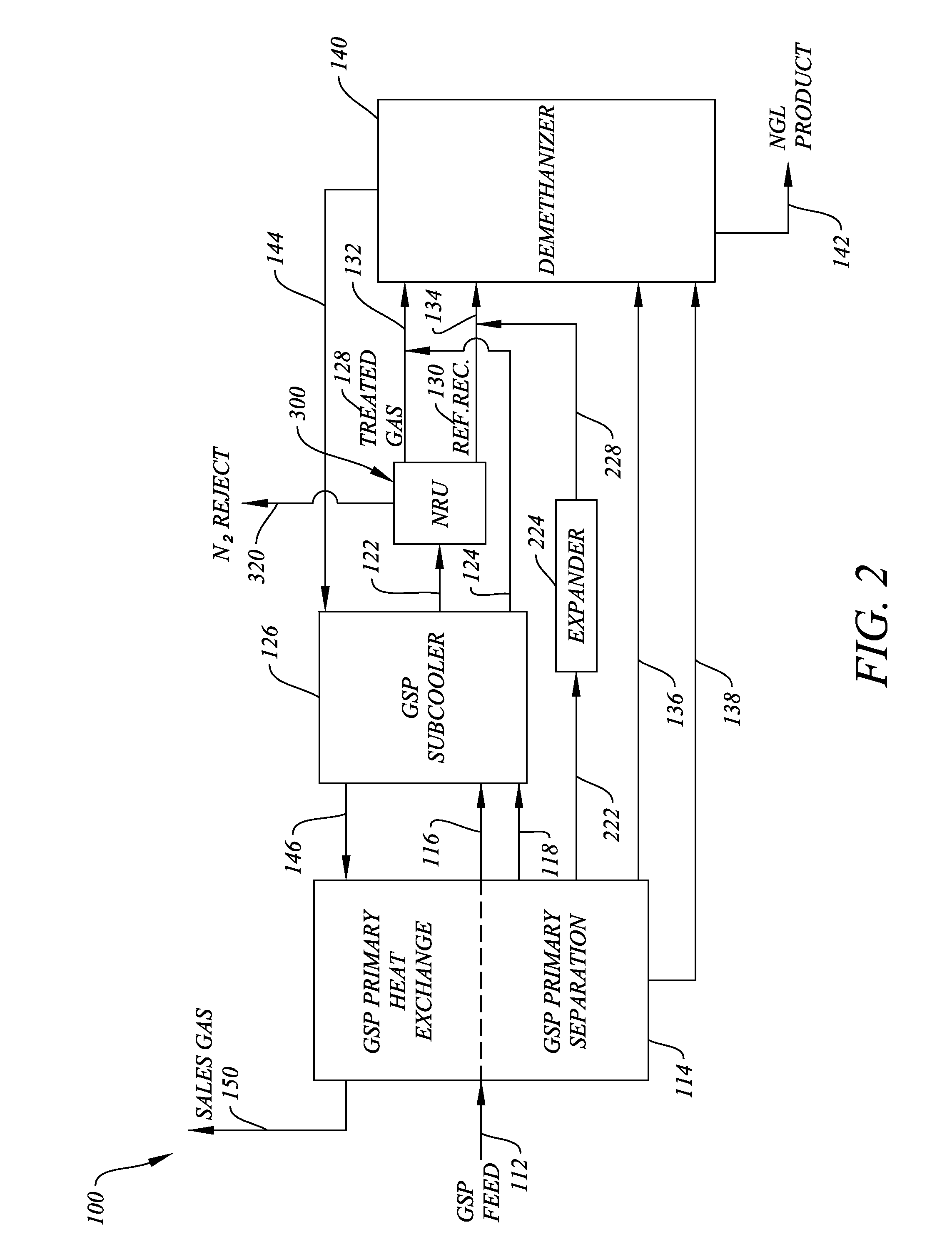
System and Method for Removing Excess Nitrogen from Gas Subcooled Expander Operations
ActiveUS20140013797A1Facilitate economically efficient removalNitrogen contentSolidificationLiquefactionNatural-gas processingPipeline transport
A system and method for removing nitrogen from an intermediate stream in a gas subcooled process operation that processes natural gas into a sales gas stream and a natural gas liquids stream. The system and method of the invention are particularly suitable for use with gas subcooled process operations where the sales gas stream exceeds pipeline nitrogen specifications by up to about 3%, such as for reducing the nitrogen content of sales gas streams to levels permissible for pipeline transport.
Owner:BCCK HLDG CO
Method for recovering ethane in high-pressure natural gases
InactiveCN105037069AHigh recovery rateHigh energy consumptionLiquid hydrocarbon mixture recoveryGaseous fuelsCompressed natural gasNatural-gas processing
The invention discloses a method for recovering ethane in high-pressure natural gases, relating to the technical field of natural gas processing technology. The method is characterized by combining high-pressure and low-temperature absorption, partial low-temperature gas supercooling, an externally transported gas reflux process and refrigeration with an expansion machine and dividing both the supercooled gas in a low-temperature separator and externally transported gas reflux into two parts, wherein one part of the supercooled gas and the externally transported gas reflux enter a high-pressure absorption tower and the other part of the supercooled gas and the externally transported gas reflux enter a demethanizer to improve the ethane recovery rate which can be adjusted according to the target value of the recovery rate. The method has the beneficial effects that the operating pressures of the high-pressure absorption tower and the demethanizer can be independently arranged, thus reducing the compression power of an externally transported gas booster set and the heat load of a reboiler of the demethanizer; the method is suitable for devices with feed gas pressures more than 7.0MPa for recovering ethane in the natural gases and has the characteristics of high recovery rate, low system energy consumption, and the like.
Owner:PETROCHINA PLANNING & ENG INST +1
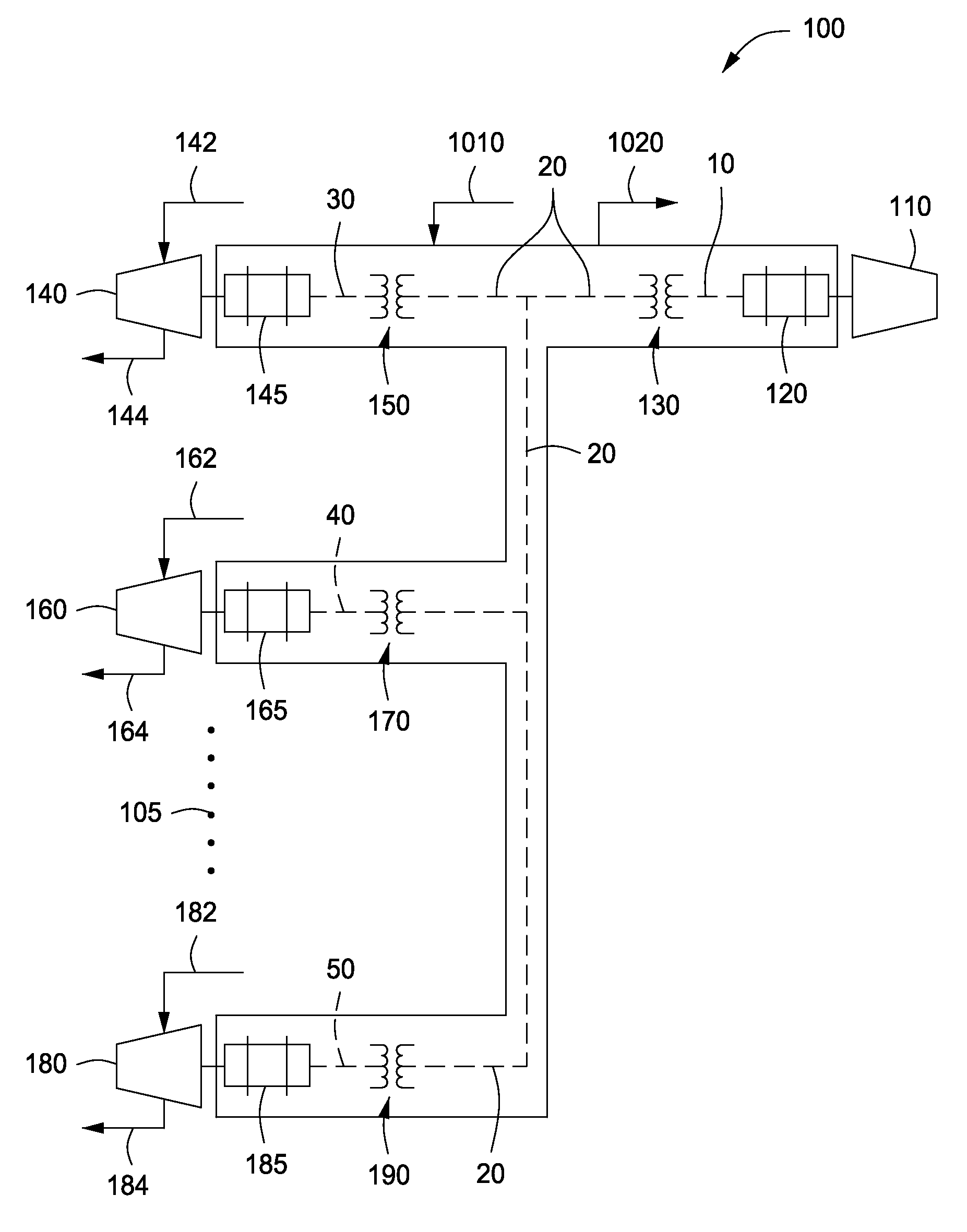
Superconducting System For Enhanced Natural Gas Production
InactiveUS20120289407A1Small footprintImprove efficiencySolidificationLiquefactionMain processing unitElectricity
Provided is a natural gas processing facility for the liquefaction or regasification of natural gas. The facility includes a primary processing unit, e.g., refrigeration unit, for warming natural gas or chilling natural gas to at least a temperature of liquefaction. The facility also has superconducting electrical components integrated into the facility. The superconducting electrical components incorporate superconducting material so as to improve electrical efficiency of the facility by at least one percent over what would be experienced through the use of conventional electrical components. The superconducting electrical components may be one or more motors, one or more generators, one or more transfonners, switch gears, one or more electrical transmission conductors, variable speed drives, or combinations thereof.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Comprehensive natural gas processing
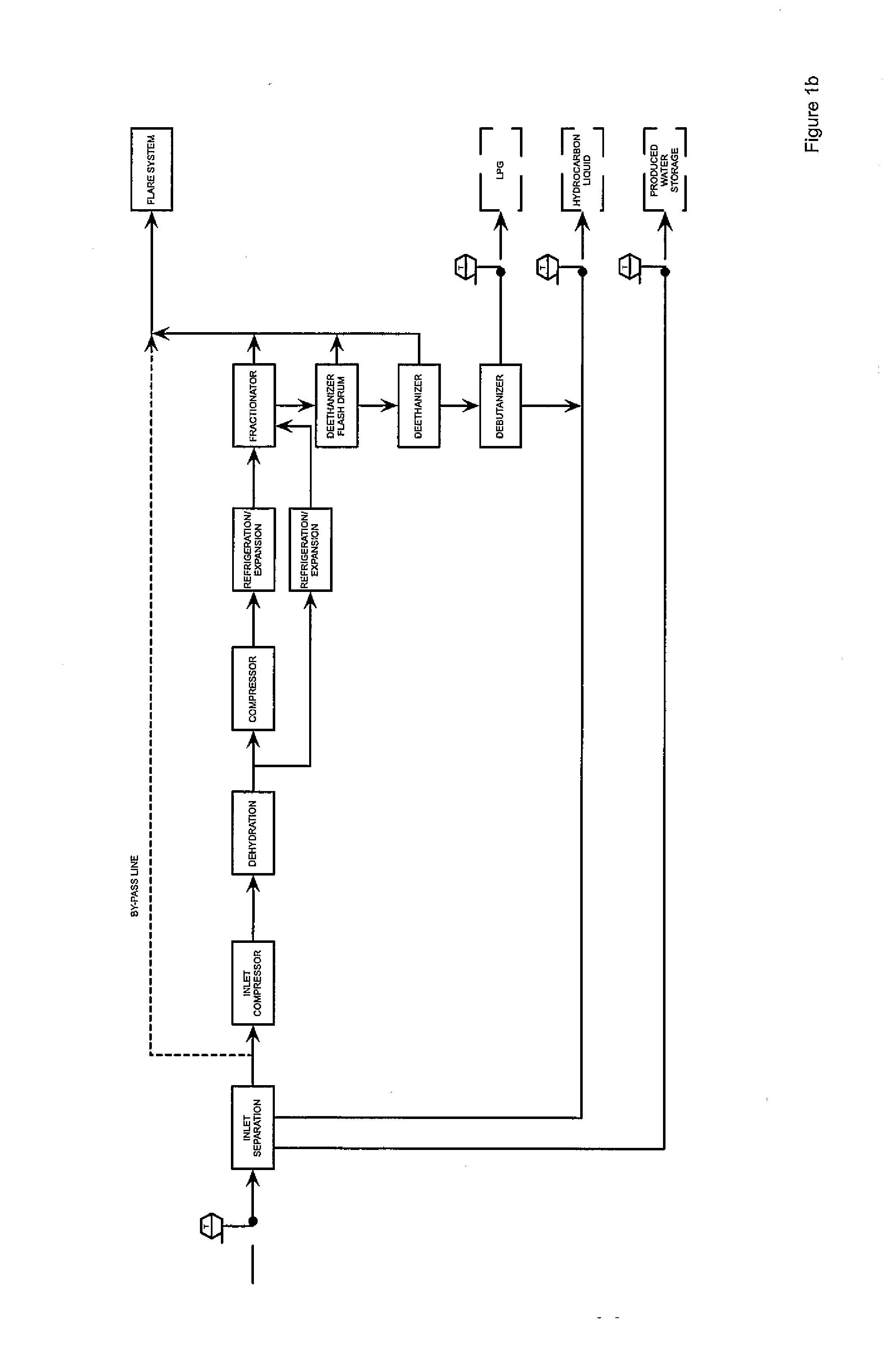
InactiveUSRE39826E1Efficient and cost-effective comprehensive processingLow costSolidificationLiquefactionNatural-gas processingTransport medium
The present invention related to a process and an apparatus for efficient and cost-effective comprehensive processing of natural gas, including the removal of moisture and the recovery of the higher hydrocarbons components (C2+). The said apparatus comprises the following major components: an integrated natural gas processor with a dehydration section and a higher hydrocarbons absorption section; a heat transport medium cooler; an absorbent cooler; a fractional distiller for separating the light oil from the heavy oil absorbent; an inhibitor regenerator; and a refrigeration unit. The present invention provides a low-cost natural gas comprehensive processorprocessing that is universally applicable to both terrestrial and off-shore natural gas exploitation. The said apparatus also provides an efficient and cost-effective natural gas dehydrator when the dehydration section is used independently without incorporating the absorption section.
Owner:LU YINGZHONG
Processing and Transport of Stranded Gas to Conserve Resources and Reduce Emissions
ActiveUS20150007981A1Save resourcesEmission reductionSolidificationLiquefactionProduction rateNatural-gas processing
A method of gas production from a field containing natural gas processing particularly for transport of stranded gas to conserve resources and reduce emissions includes extracting gas a gas supply from a plurality of individual gas wells in the field and initially at the individual gas wells providing a recovery unit having a production capacity matching that of the well for carrying out liquid recovery from the gas supply and compression of the natural gas. When a production rate of the well declines to a low level, typically to about 20% of the original,the recovery unit is removed for redeployment either at a central plant or at other wells which are still at the high production and is substituted by a dehydration system and gas compressor arranged to fill portable pressure vessels typically on trucks for transporting the compressed natural gas to a main pipe line.
Owner:SHOMODY RONALD GRANT +1
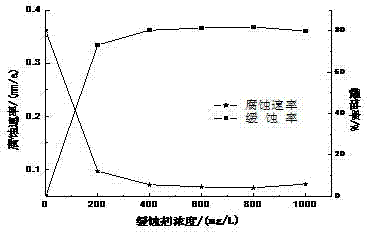
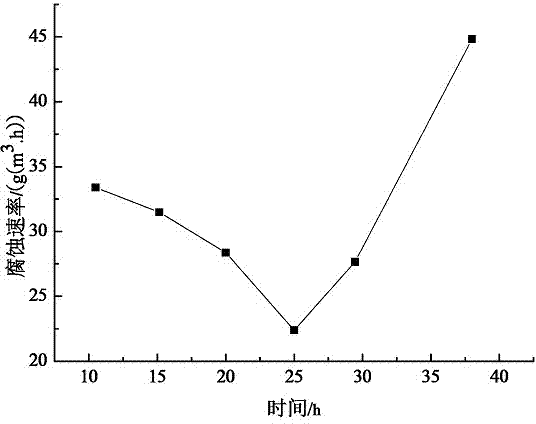
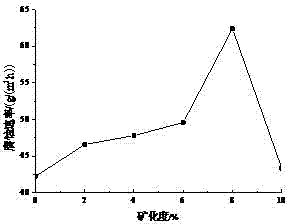
Imidazoline corrosion inhibitor, synthetic method and application thereof
The invention relates to an imidazoline corrosion inhibitor, a synthetic method and application thereof, and is applicable to boiler anticorrosion in natural gas processing plant. The imidazoline corrosion inhibitor comprises main agent of rosin, and additives of bis(beta-aminoethyl) amineand N,N-dimethyl acetamide. In addition, on the basis of synthesis of imidazoline corrosion inhibitor, guanyl with closing-opening performance under the action of CO2 / N2 is introduced, so as to on the one hand improve the corrosion inhibition performance of on CO2, and on the other hand recycle the inhibitor. Finally, under simulated field conditions, when the dosage of the corrosion inhibitor is at 400 mg / L, the inhibition rate reaches 80%, and the corrosion rate and corrosion inhibition efficiency are good. The corrosion inhibitor mainly inhibits the cathodic hydrogen evolution reduction reaction as well as anodic metal dissolution effect, and belongs to a mixed type corrosion inhibitor focusing on anodic inhibition. The corrosion inhibitor provided by the invention has the advantages of low cost, simple and efficient usage mode, low toxicity, no stimulation, no odor and reduction of pollution on water and environment.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
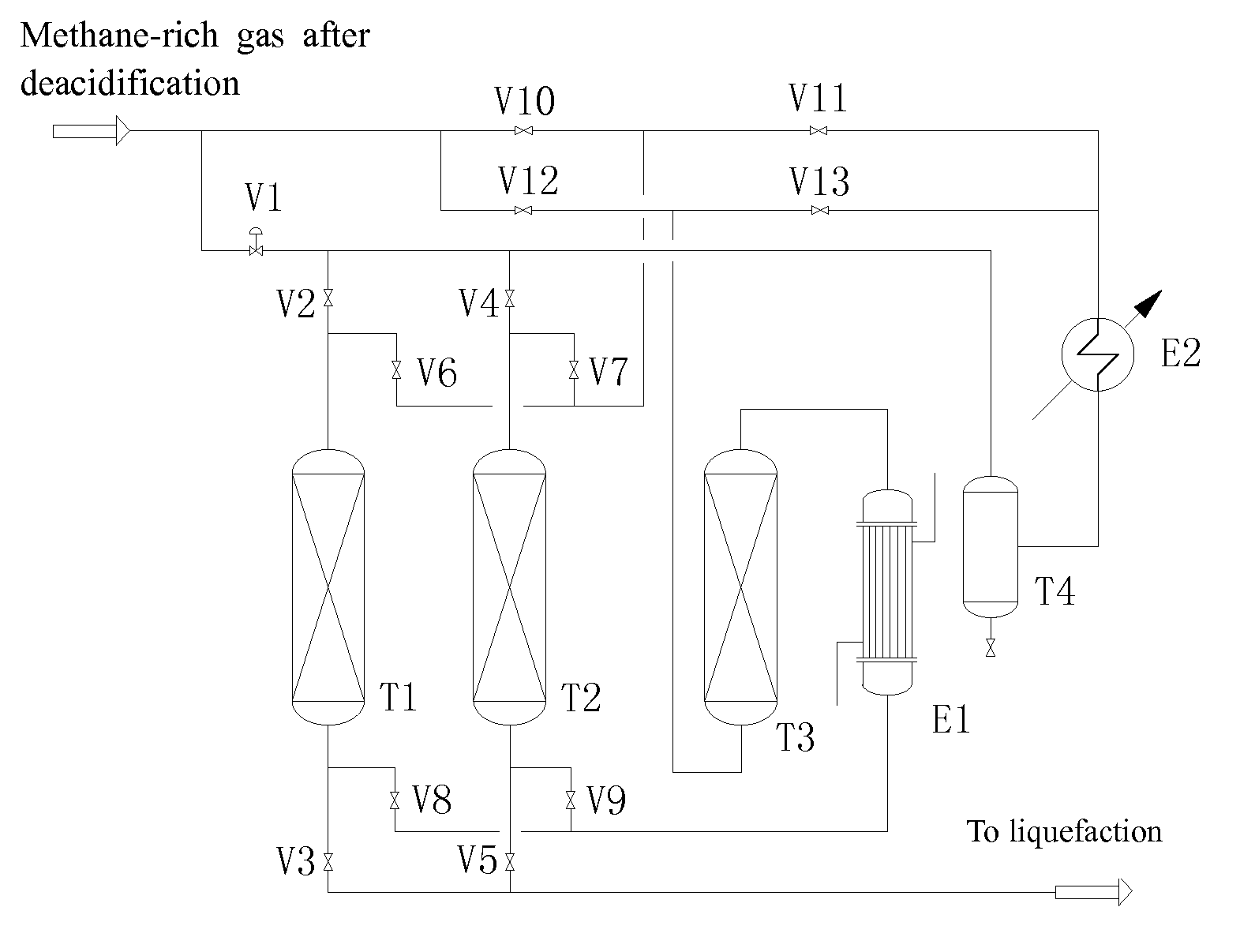
Water removal and heavy-hydrocarbon removal process in liquefied natural gas production from mixed gas rich in methane
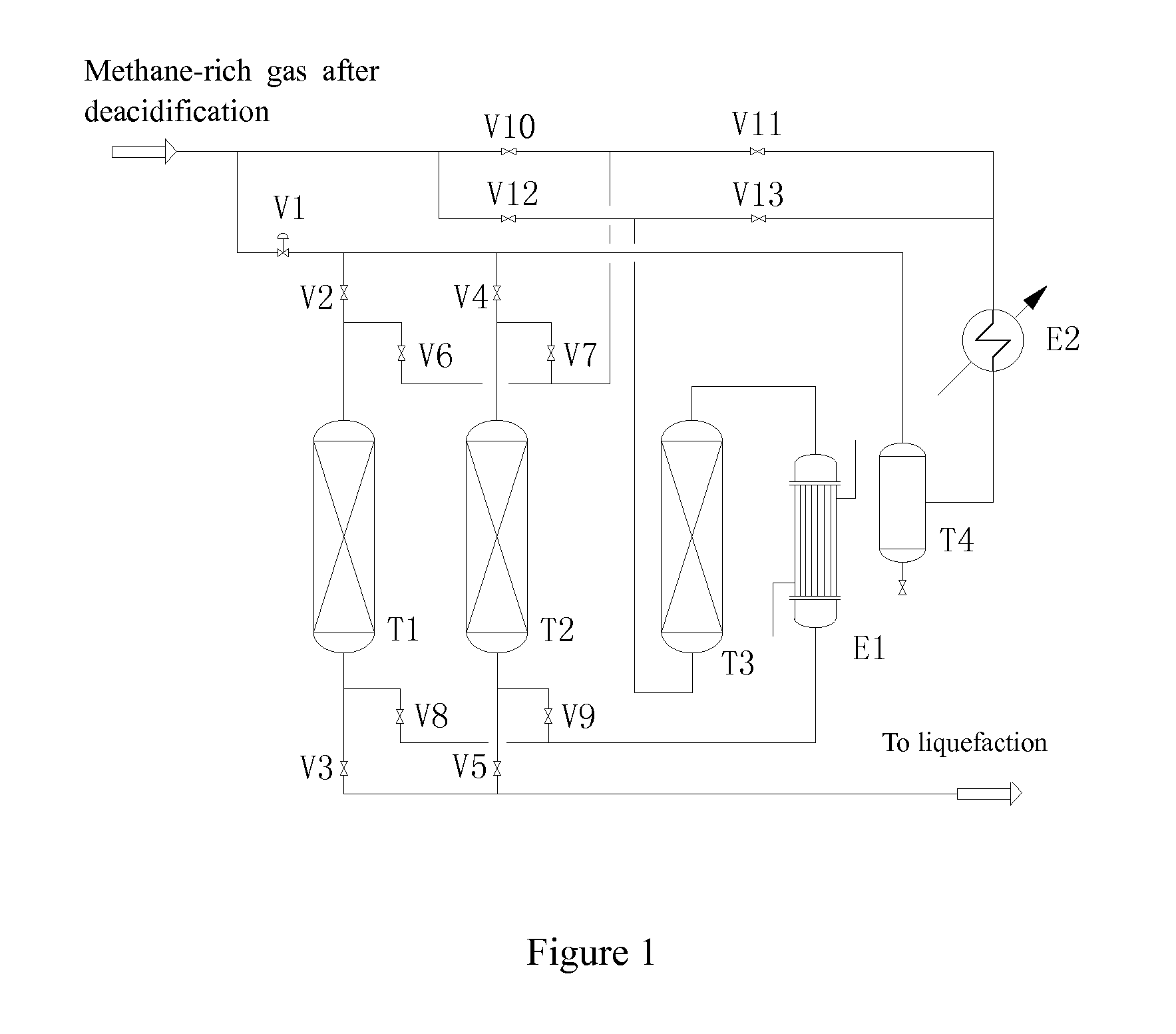
A process for dehydrating and removing heavy hydrocarbons in the production of liquefied natural gas from a methane-rich gas mixture is disclosed, wherein the methane-rich gas mixture subjected to deacidification treatment is divided into two streams, i.e. the first stream and the second stream, wherein the first stream used as a system process gas is introduced into a drying procedure, and the second stream used as regenerating gas is introduced into a regenerating procedure; the first stream is subjected to a drying treatment, and the moisture and the heavy hydrocarbons are simultaneously removed from the first stream in a composite adsorbent bed(s) of a drying tower, wherein the moisture is removed such that the dew point at normal pressure is ≦−76° C. and the heavy hydrocarbon components of C6 and higher are removed such that the content of these components is ≦217 ppm; and the second stream is used as a regenerating gas in the regenerating procedure of the above-mentioned drying tower, subjected to a regenerating process, and then returned as a part of the system process gas. Comparing to those conventional processes, the present invention can achieve good purifying effect, lower equipment investment and late-stage energy consumption of the system, increase utilization ratio of feed gas, and the operation target of each unit becomes more clear and easy to control. The present invention further relates to an apparatus for carrying out the process.
Owner:XINDI ENERGY ENG TECH
Inline pilot with flame detection device and method thereof
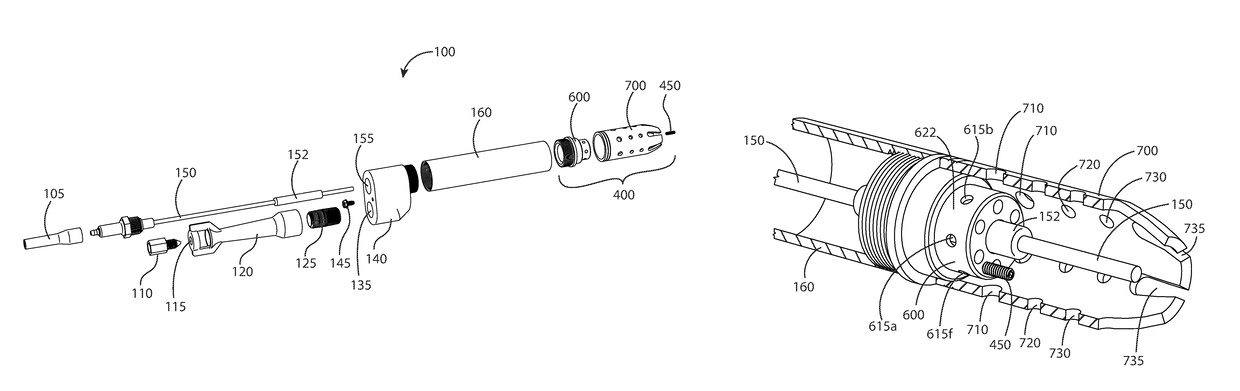
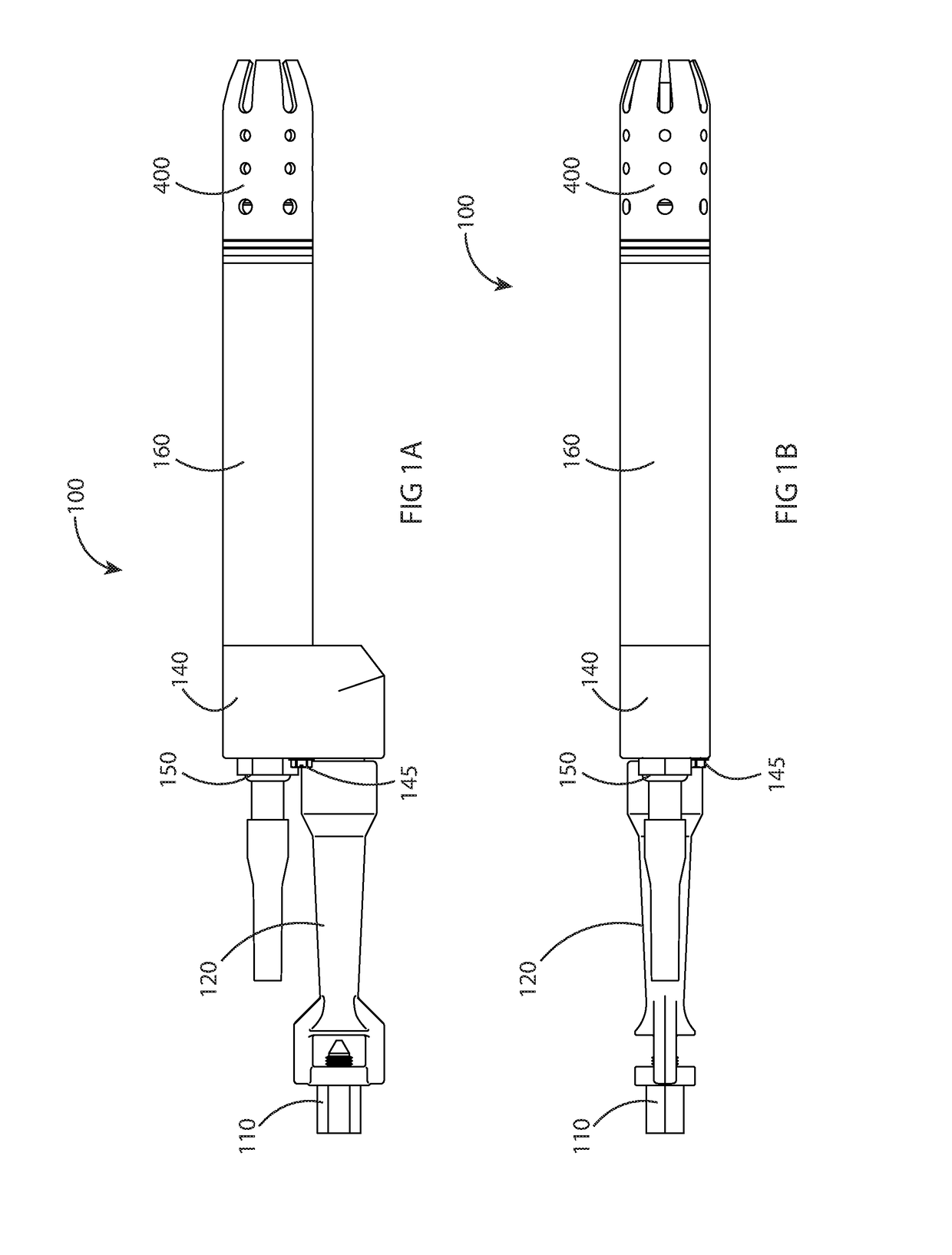
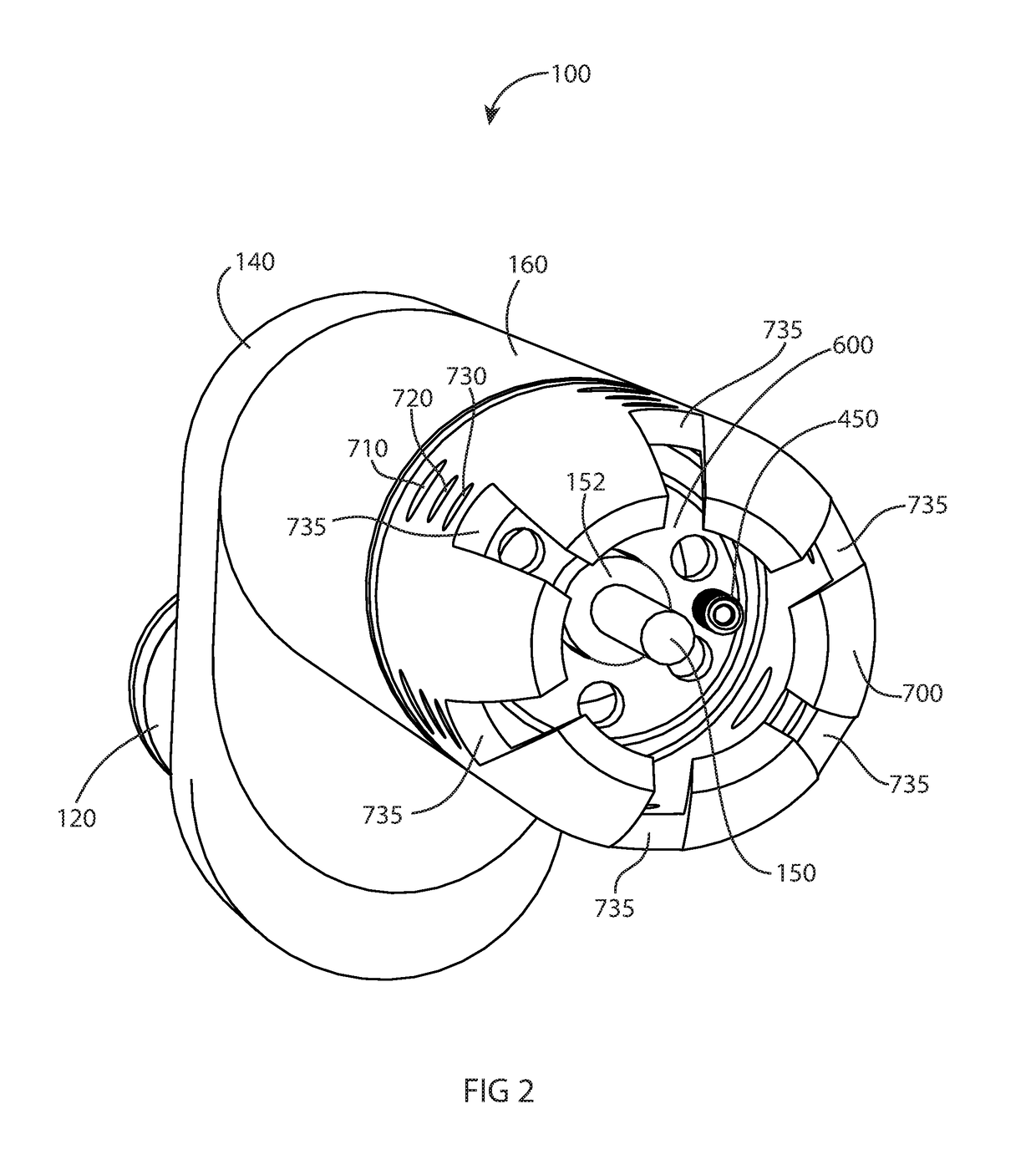
ActiveUS10101028B2Robust detectionSmooth connectionBurner ignition devicsPilot flame ignitersCombustionNatural-gas processing
A novel inline pilot assembly and method of flame detection for use with combustion applications for oil or gas processing is provided wherein the pilot assembly includes a pilot novel assembly with a unique placement of fuel and induction holes to improve flame stability, promote flame anchoring near the diffuser, and discourage the pilot flame front from migrating forward away from the diffuser.
Owner:PROFIRE ENERGY
Liquid natural gas processing
InactiveUS20060260356A1Reduce capital investmentWeaken energySolidificationLiquefactionRefluxNatural-gas processing
A process for the recovery of natural gas liquids (NGL) from liquefied natural gas (LNG) is disclosed. The LNG feed stream is subjected to a two stage separation process where the bottoms from the first stage separation containing C2+ hydrocarbons is split into two portions, with one portion being heated and used as a reflux during the second stage separation to recover the NGL product.
Owner:HOWE BAKER ENGINEERS LTD
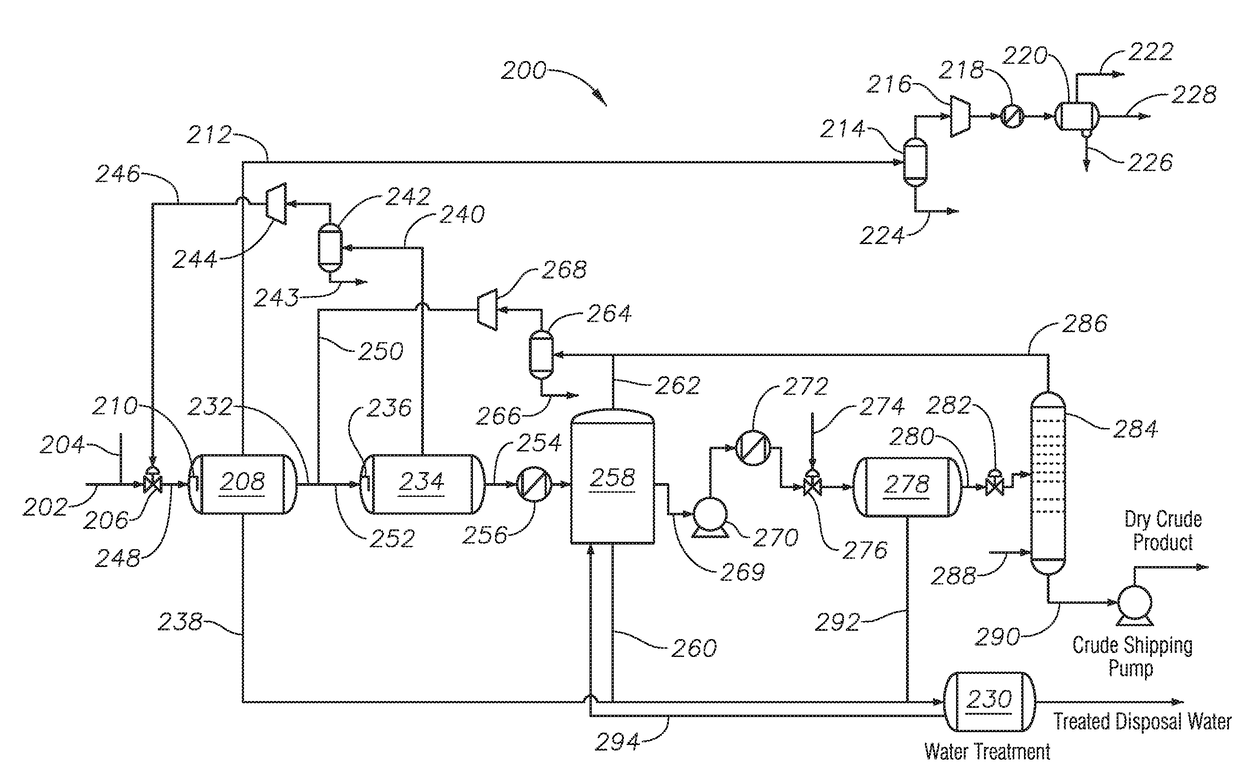
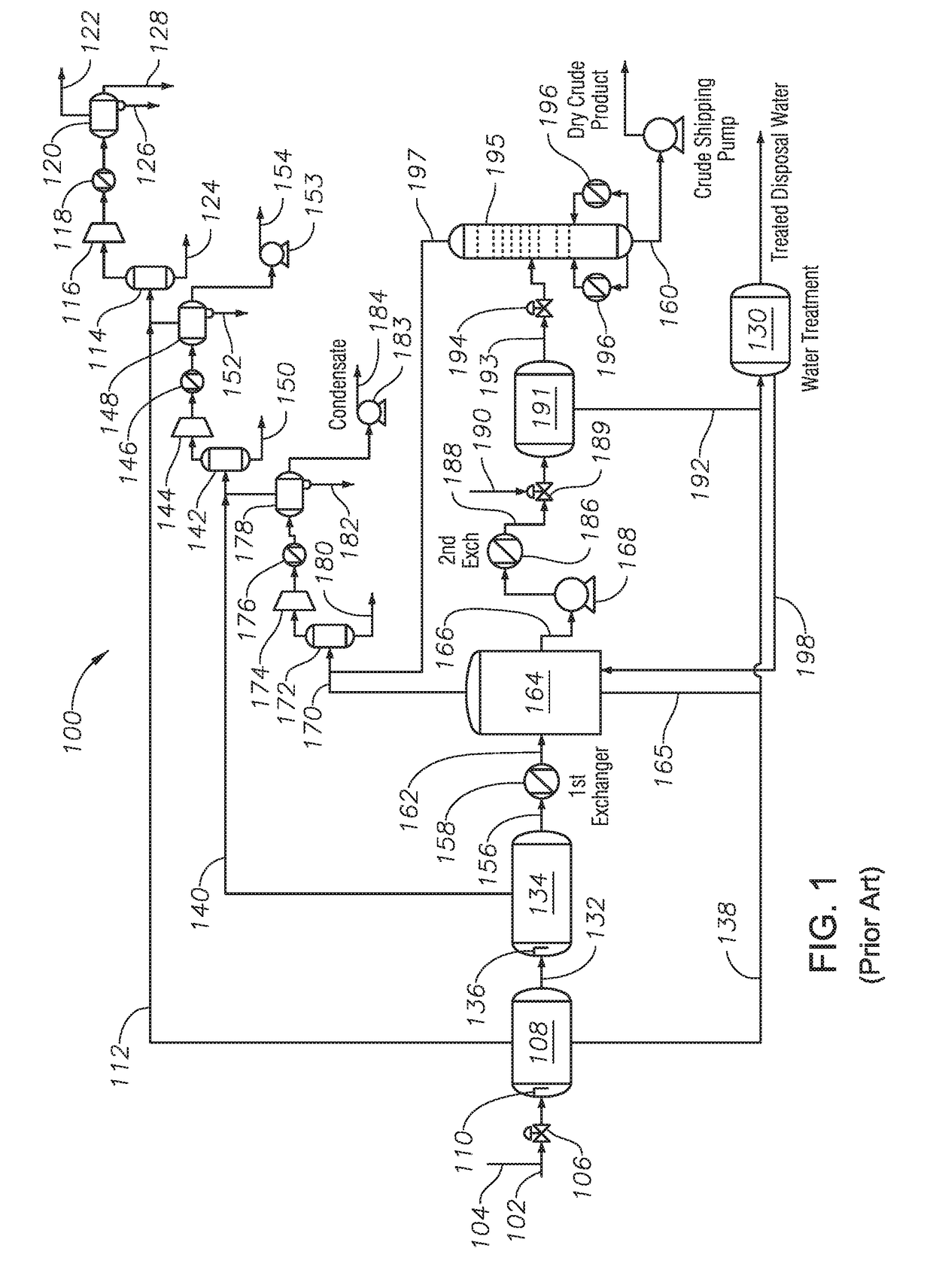
Integrated Gas Oil Separation Plant for Crude Oil and Natural Gas Processing
ActiveUS20180066194A1Low costReduce expenditureDewatering/demulsification with electric/magnetic meansLiquid hydrocarbon mixture recoveryNatural-gas processingOil separation
Systems and methods of integrated gas oil separation are disclosed. Systems include a high pressure production trap (HPPT), a low pressure production trap (LPPT), a low pressure degassing tank (LPDT), a first knockout drum (KOD) fluidly coupled to the LPDT and operable to accept an atmospheric pressure off-gas from the LPDT, an atmospheric pressure compressor fluidly coupled to the first KOD and operable to compress the atmospheric pressure off-gas to introduce the atmospheric pressure off-gas from the LPDT into the LPPT inlet feed stream, a second KOD fluidly coupled to the LPPT and operable to accept a low pressure off-gas from the LPPT, and a low pressure compressor fluidly coupled to the second KOD and operable to compress the low pressure off-gas to introduce the low pressure off-gas from the LPPT into the crude oil inlet feed stream.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
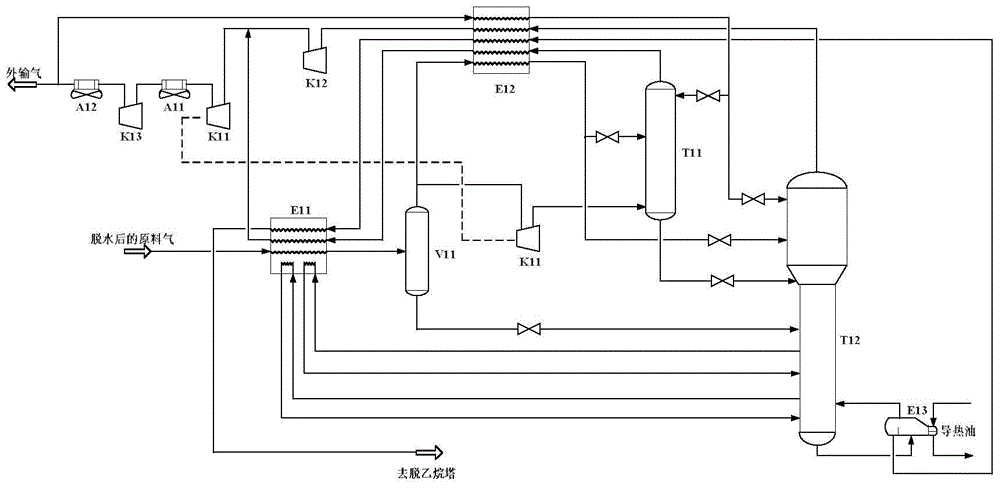
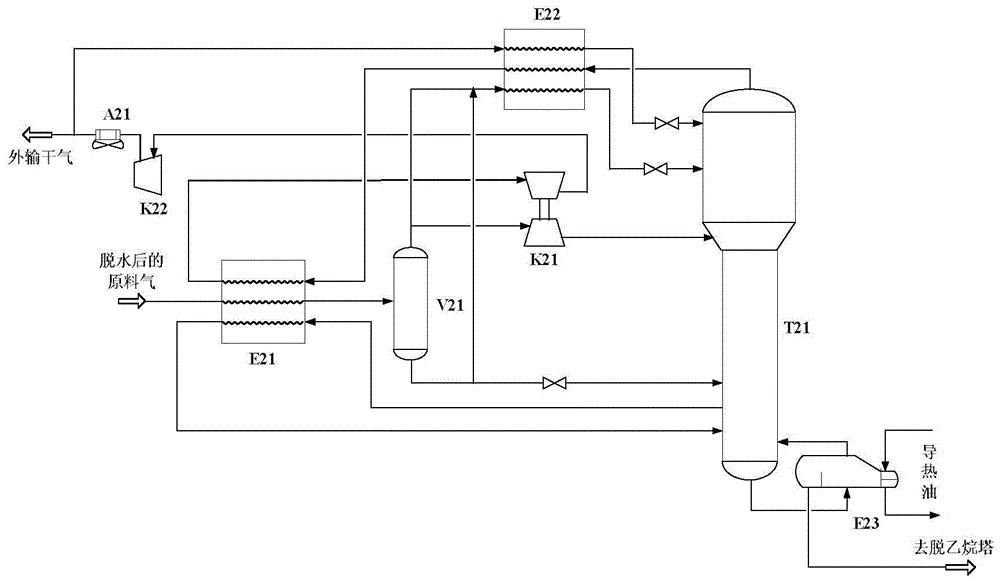
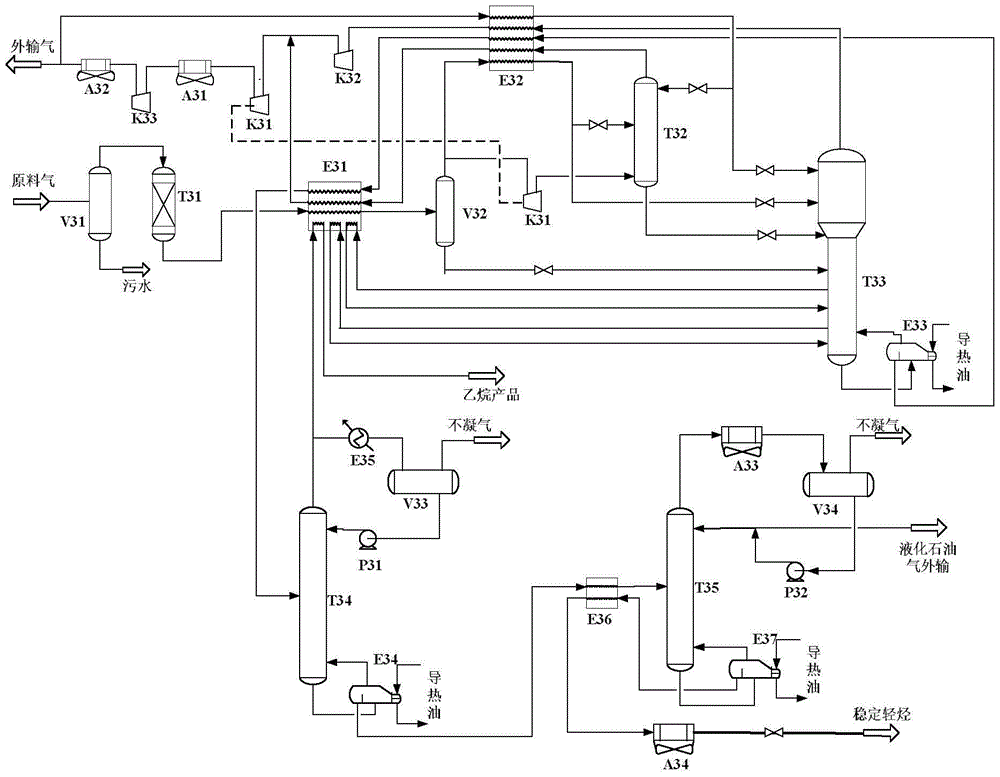
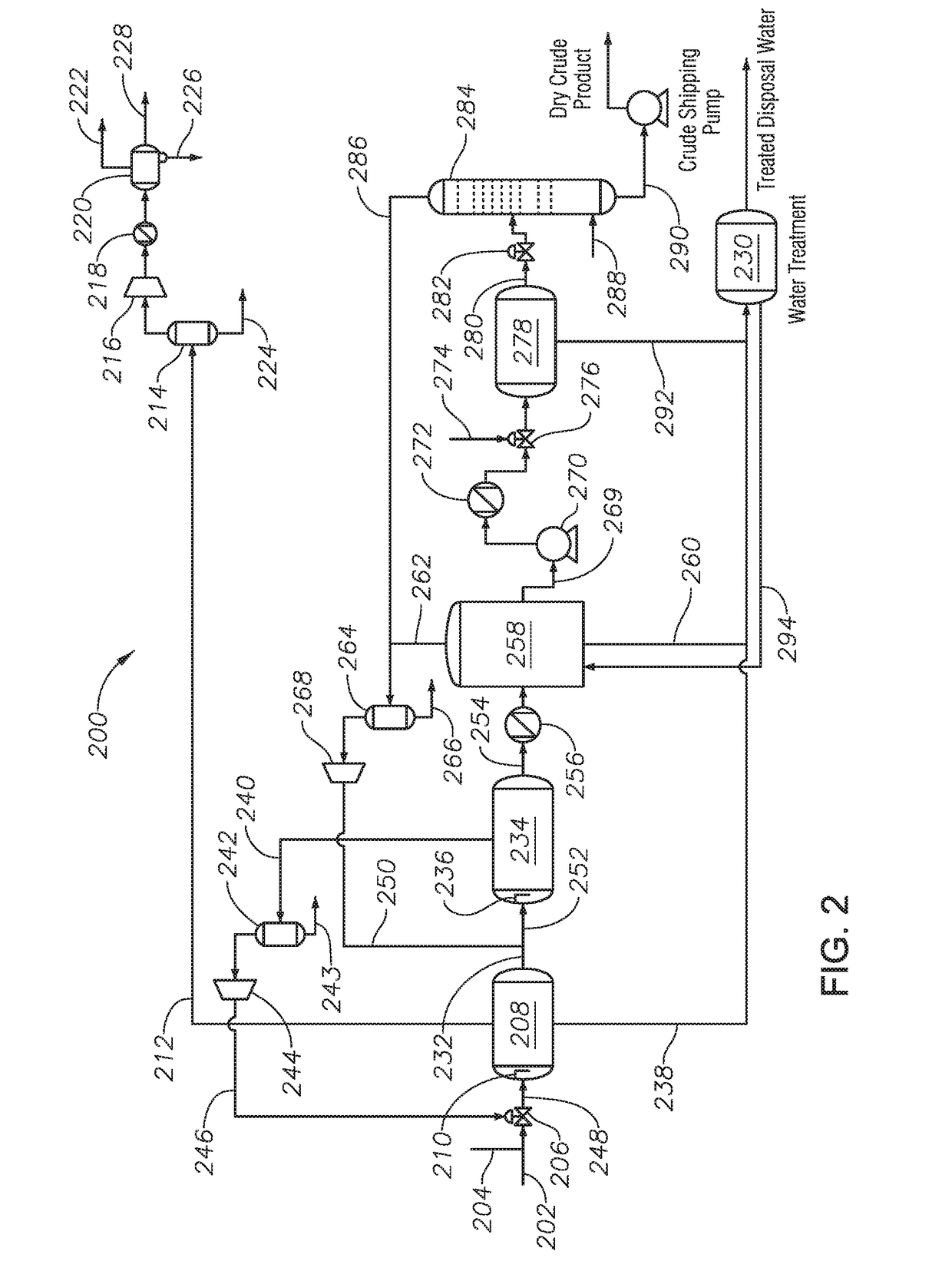
Natural gas processing method
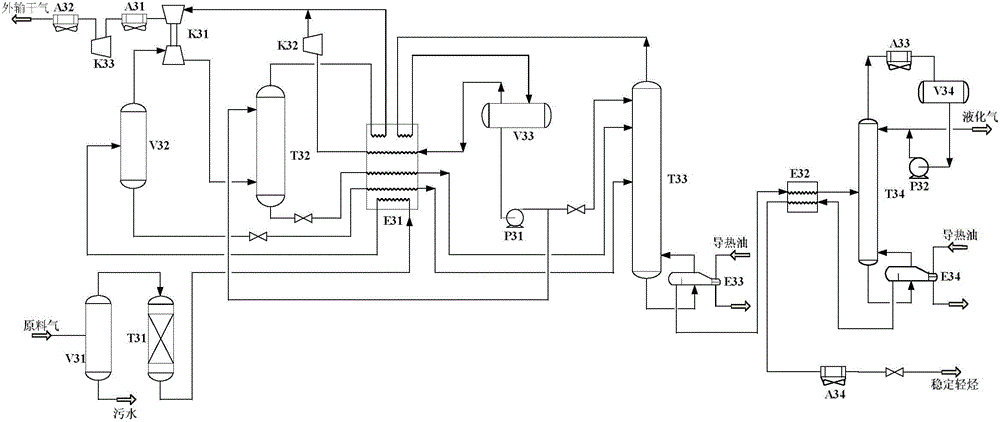
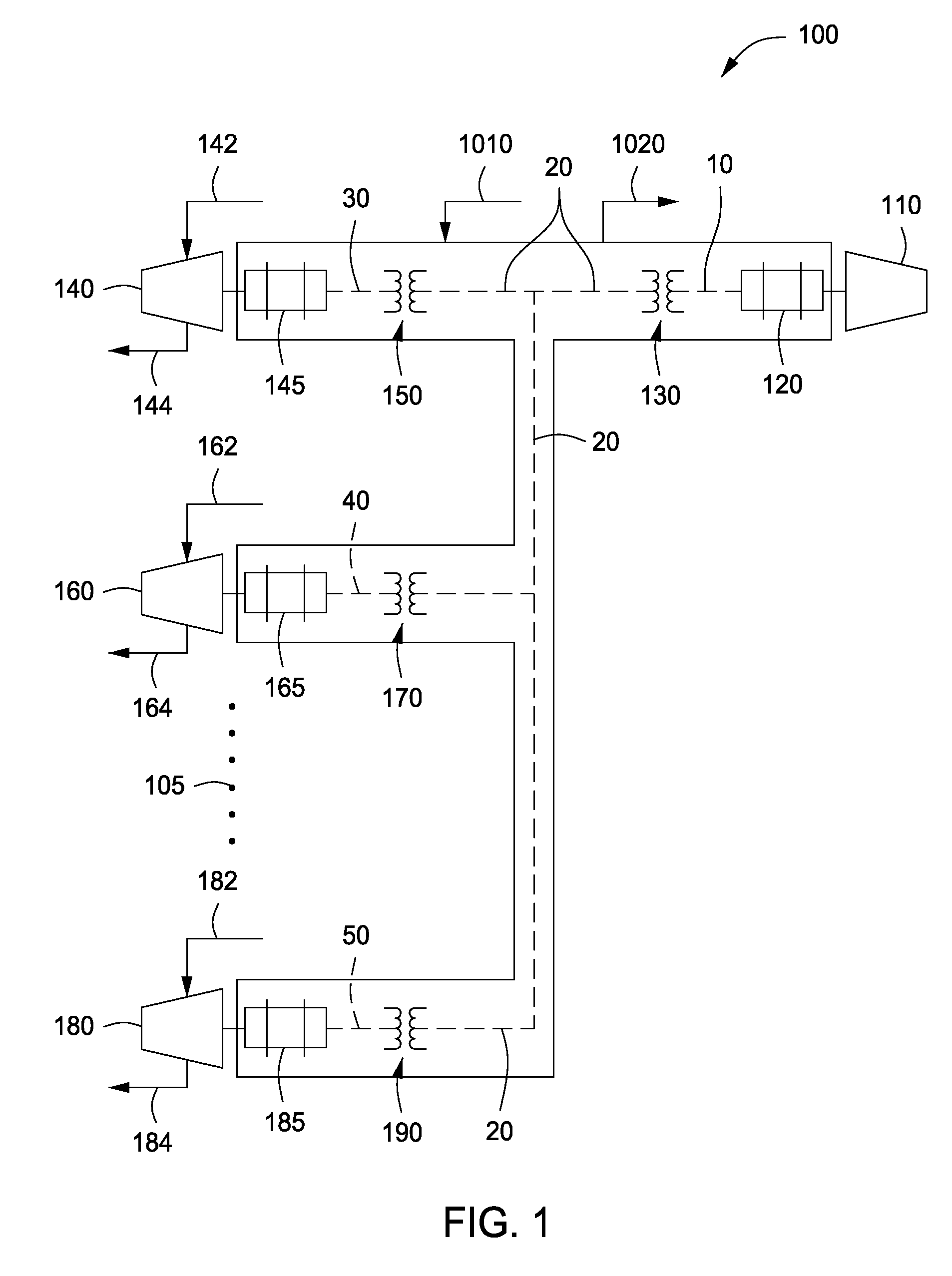
A natural gas processing method includes: a pretreatment process of obtaining a treated natural gas; an NGL recovery process of cooling the treated natural gas obtained in the pretreatment process to recover an NGL product composed of ethane and heavier hydrocarbons and to separate a lean gas; a sales gas production process of compressing a part of the lean gas separated in the NGL recovery process to obtain a high-pressure gas; and a natural gas liquefying process of cooling the high-pressure gas after the high-pressure gas is obtained by compressing the lean gas separated in the NGL recovery process, to thereby obtain the LNG product. In the natural gas processing method, a gas compressor used in the sales gas production process is used as a gas compressor in the natural gas liquefying process.
Owner:JGC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com