Patents
Literature
1096957 results about "Materials science" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The interdisciplinary field of materials science, also commonly termed materials science and engineering, is the design and discovery of new materials, particularly solids. The intellectual origins of materials science stem from the Enlightenment, when researchers began to use analytical thinking from chemistry, physics, and engineering to understand ancient, phenomenological observations in metallurgy and mineralogy. Materials science still incorporates elements of physics, chemistry, and engineering. As such, the field was long considered by academic institutions as a sub-field of these related fields. Beginning in the 1940s, materials science began to be more widely recognized as a specific and distinct field of science and engineering, and major technical universities around the world created dedicated schools of the study, within either the Science or Engineering schools, hence the naming.
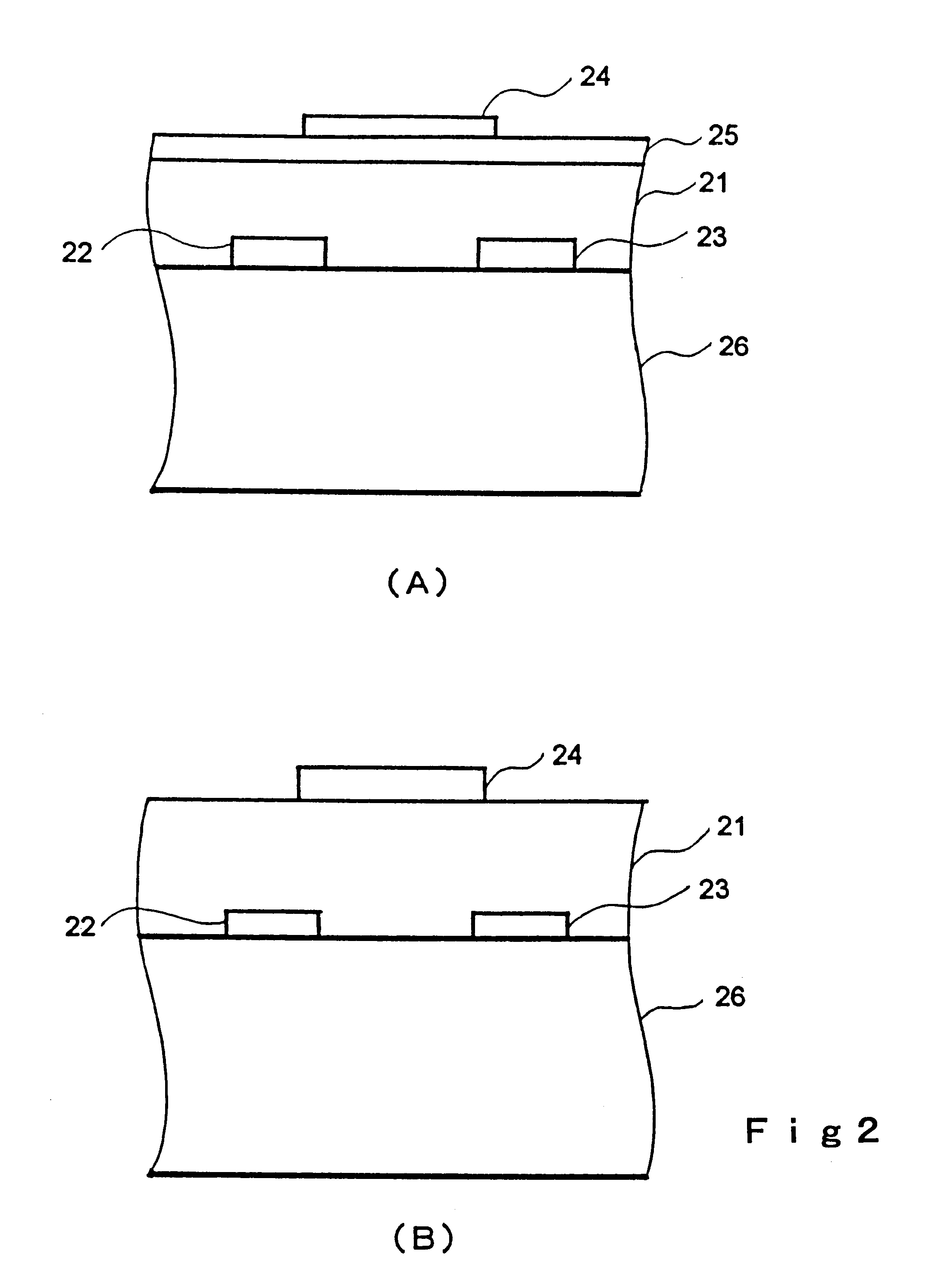
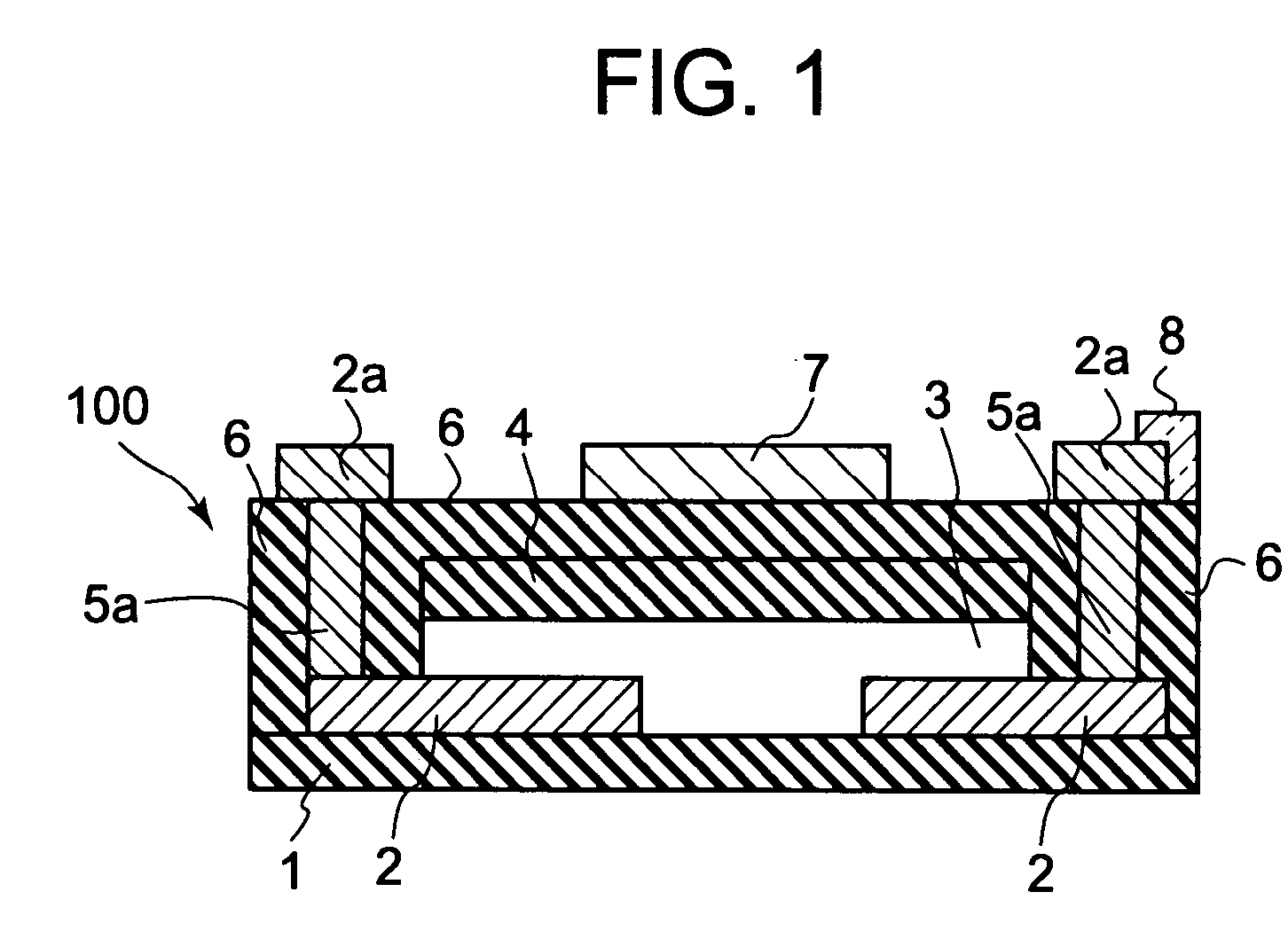
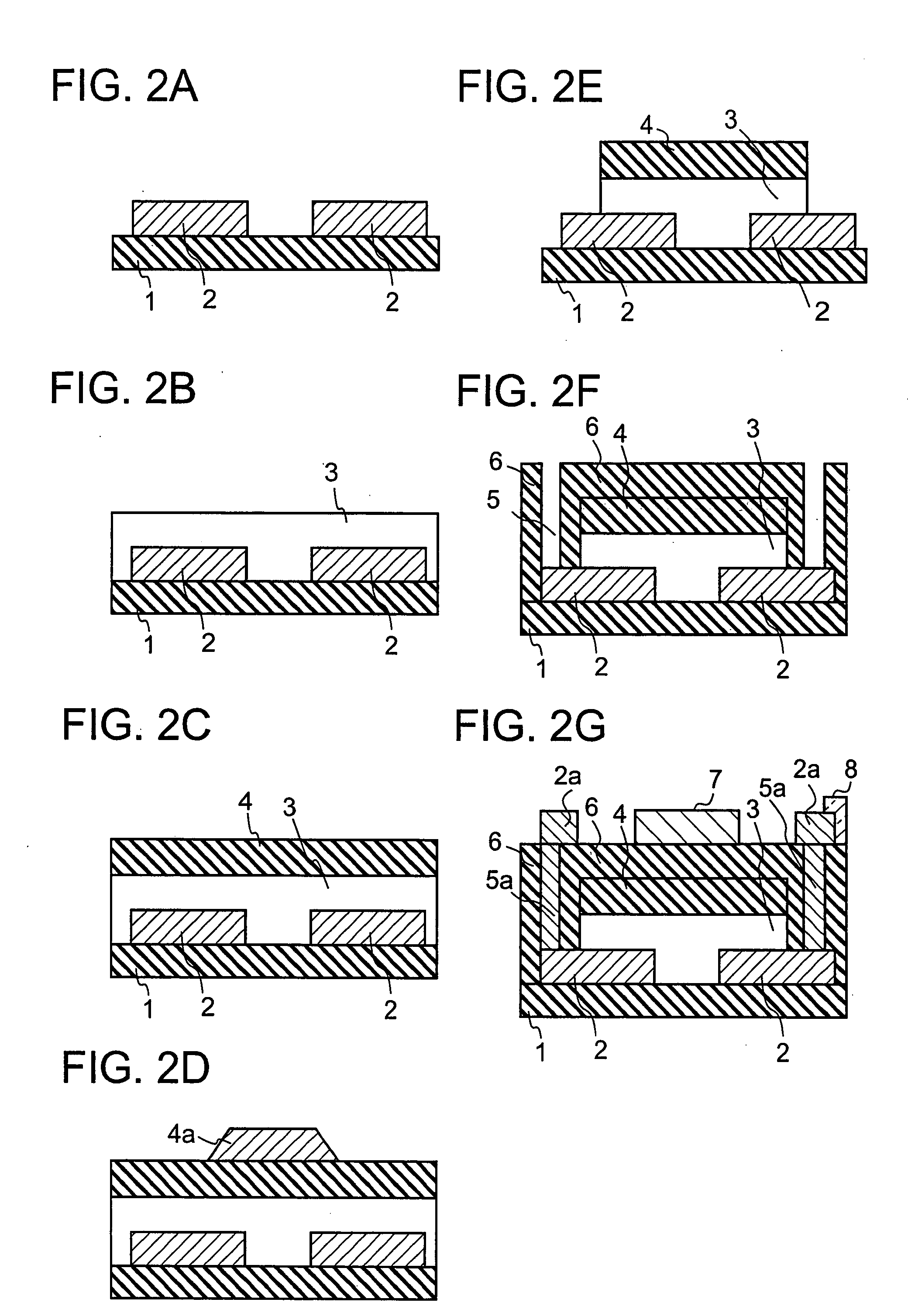
Semiconductor device, manufacturing method, and electronic device
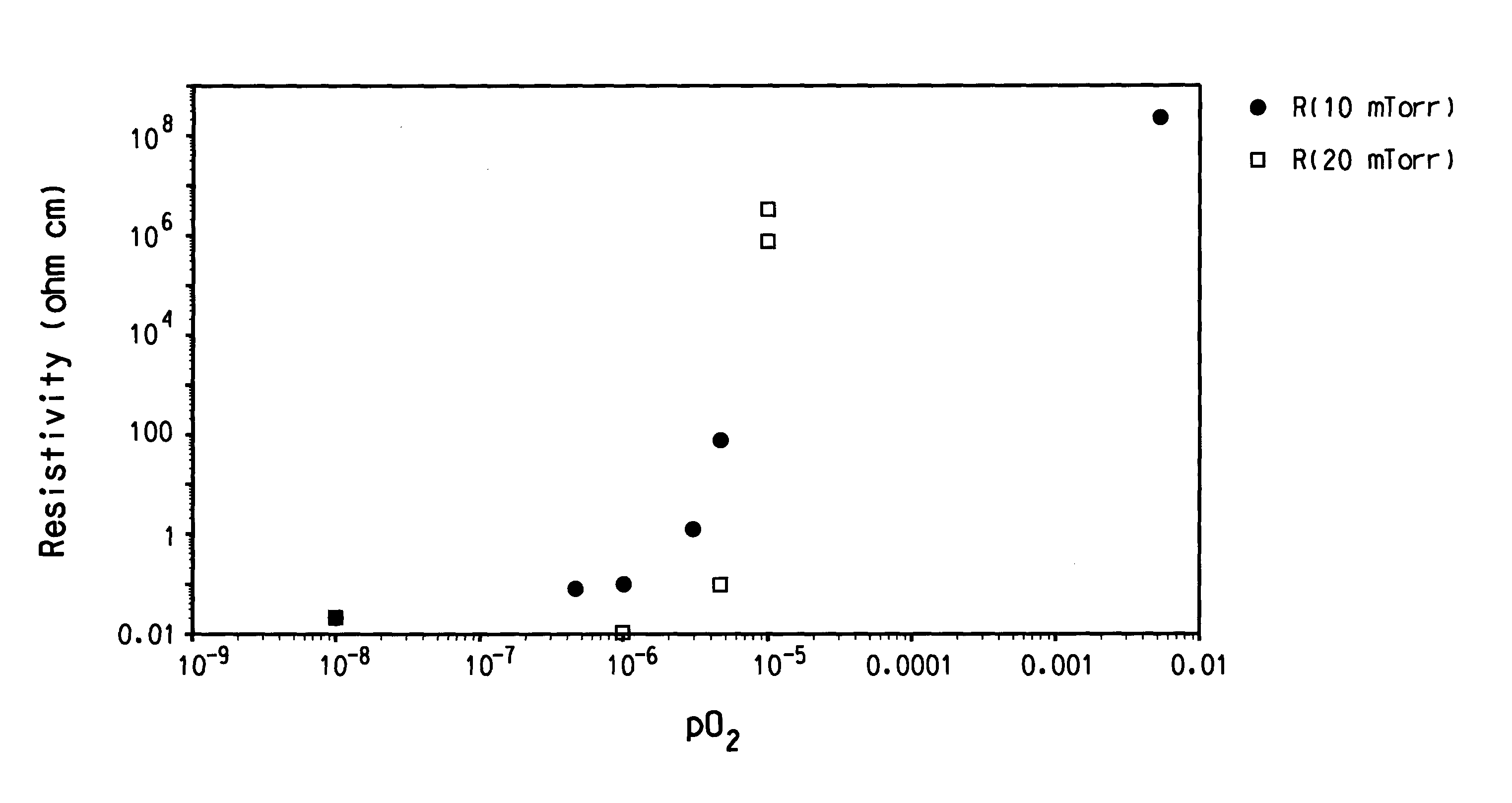
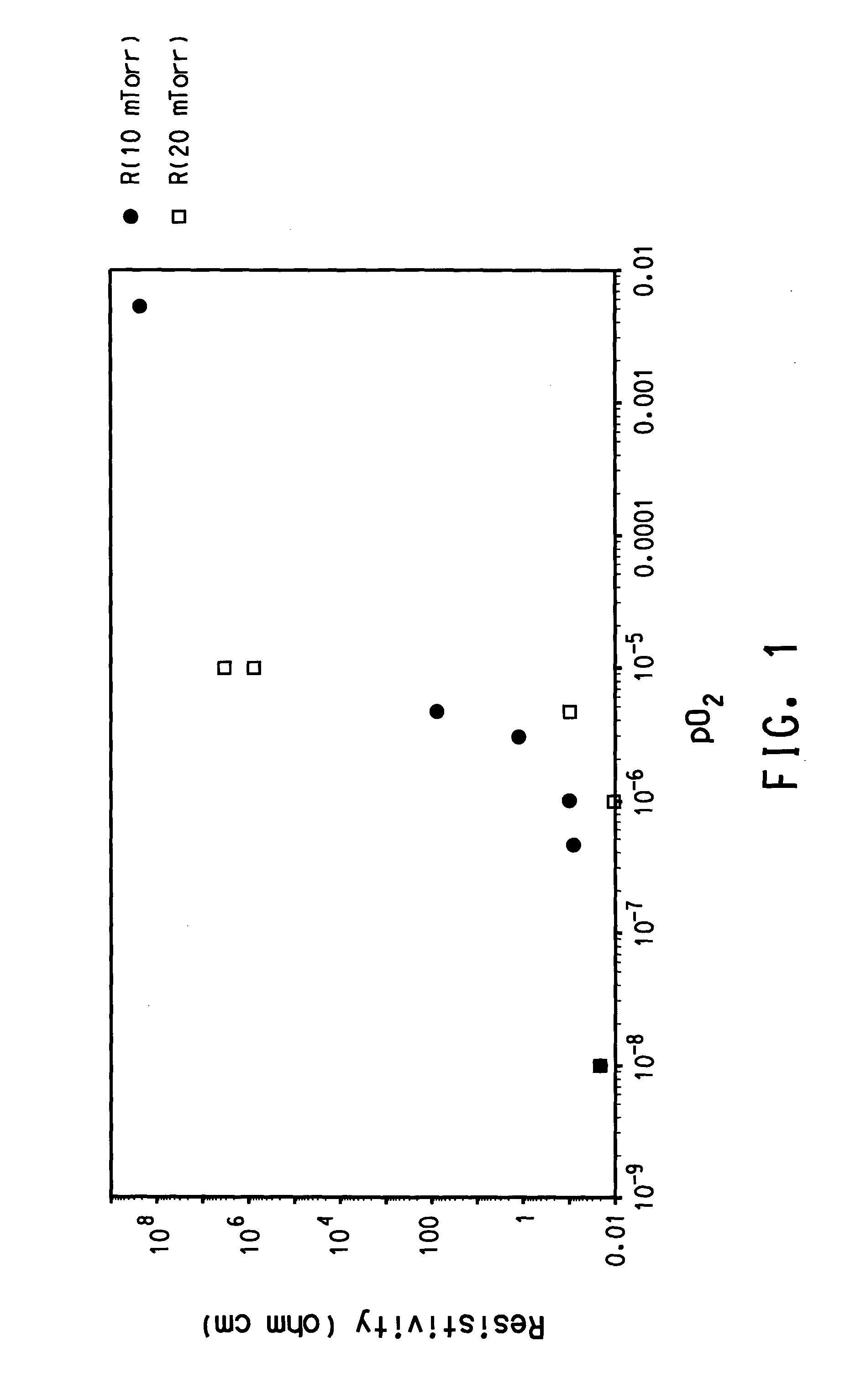
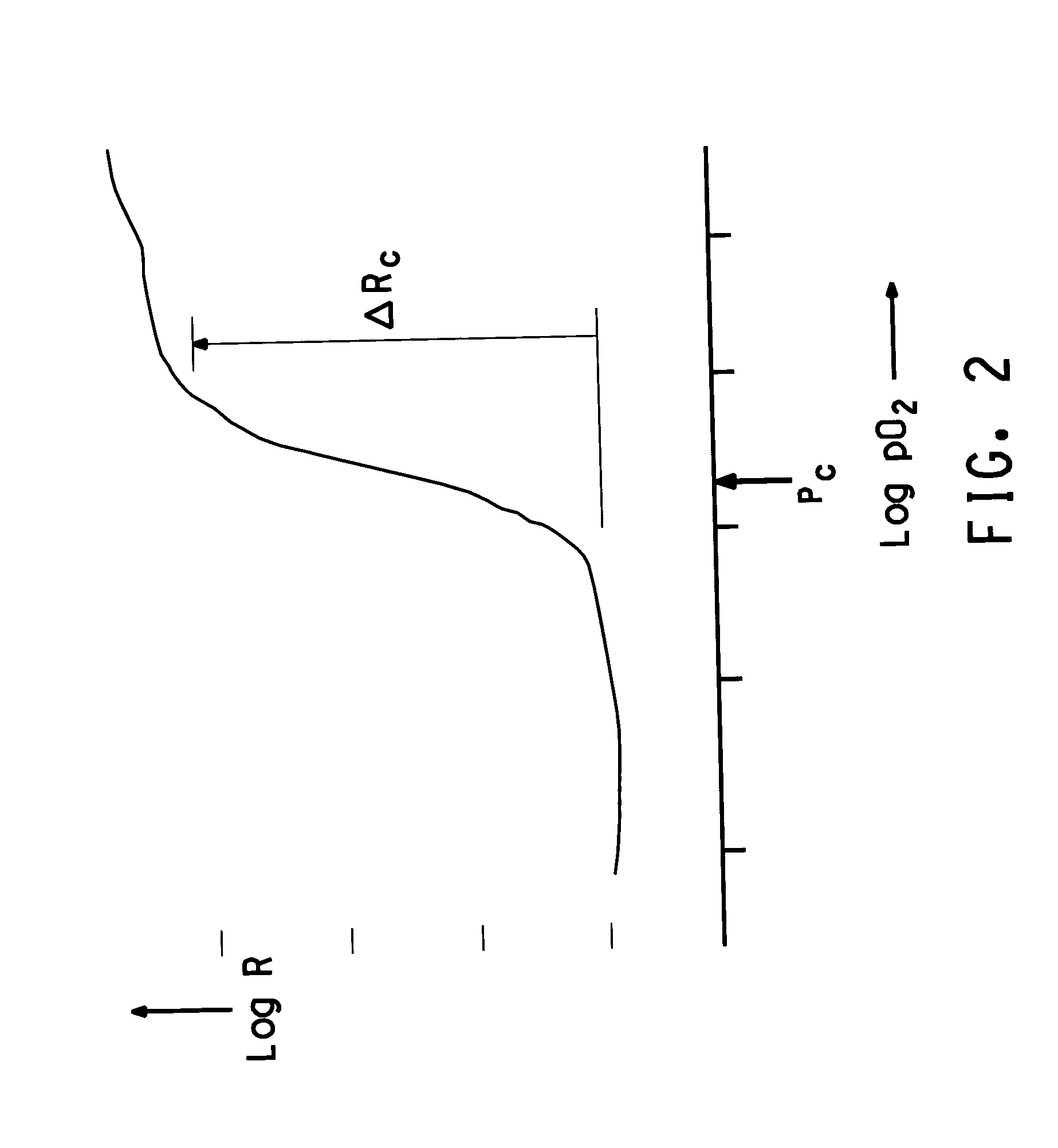
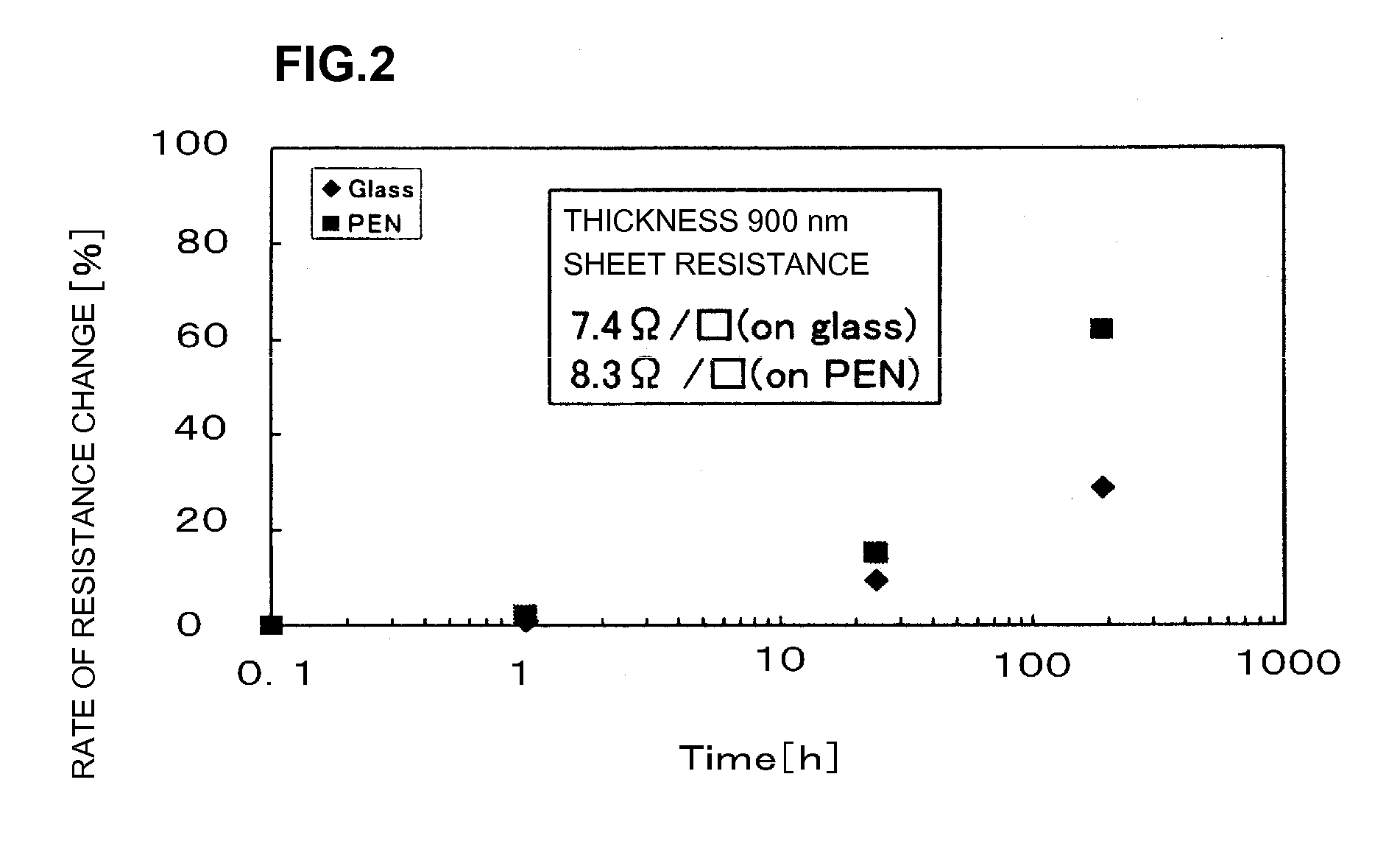
ActiveUS20060244107A1Stabilize element propertyEasy to manufactureTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSurface levelIntrinsic resistance
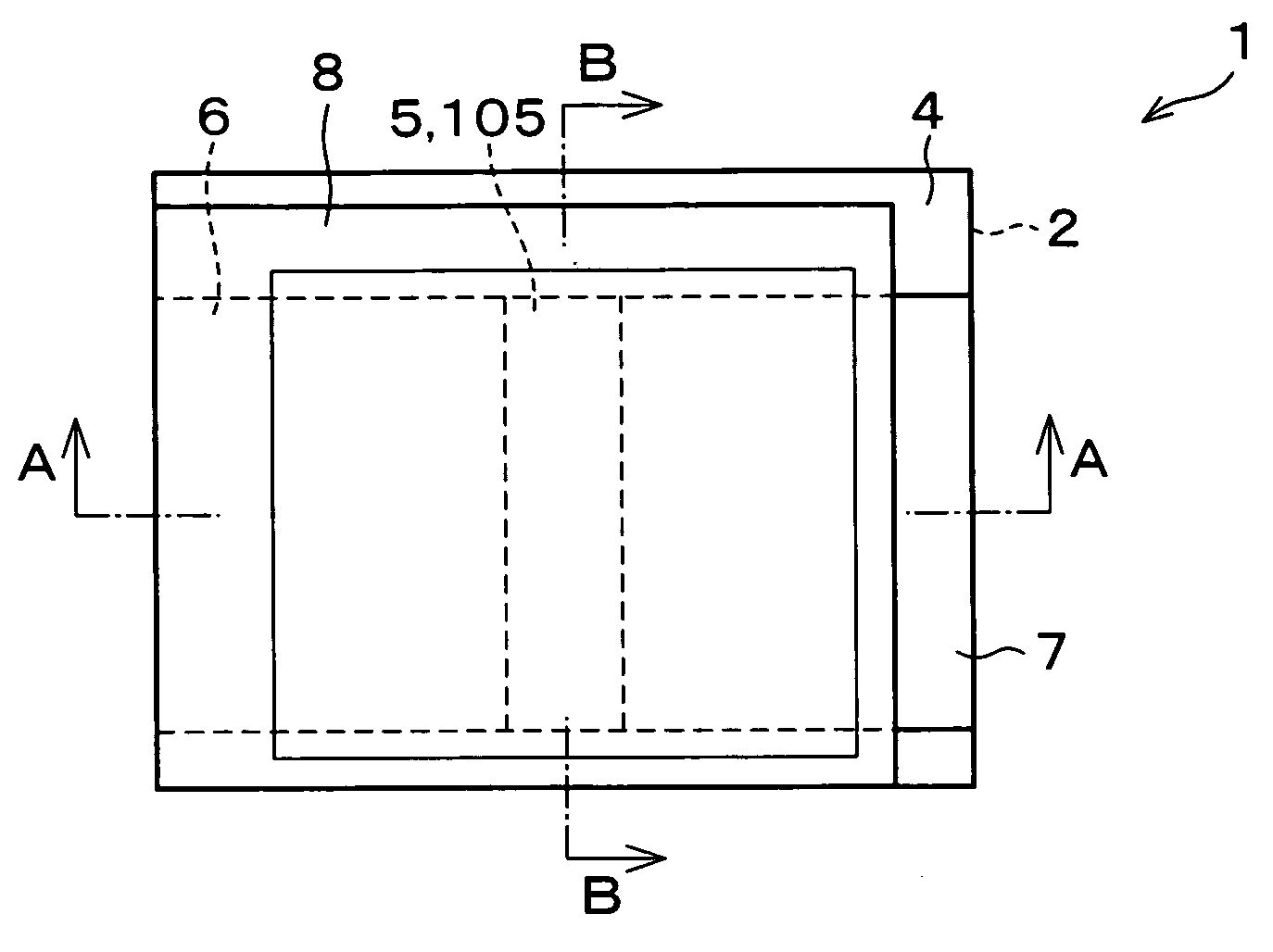
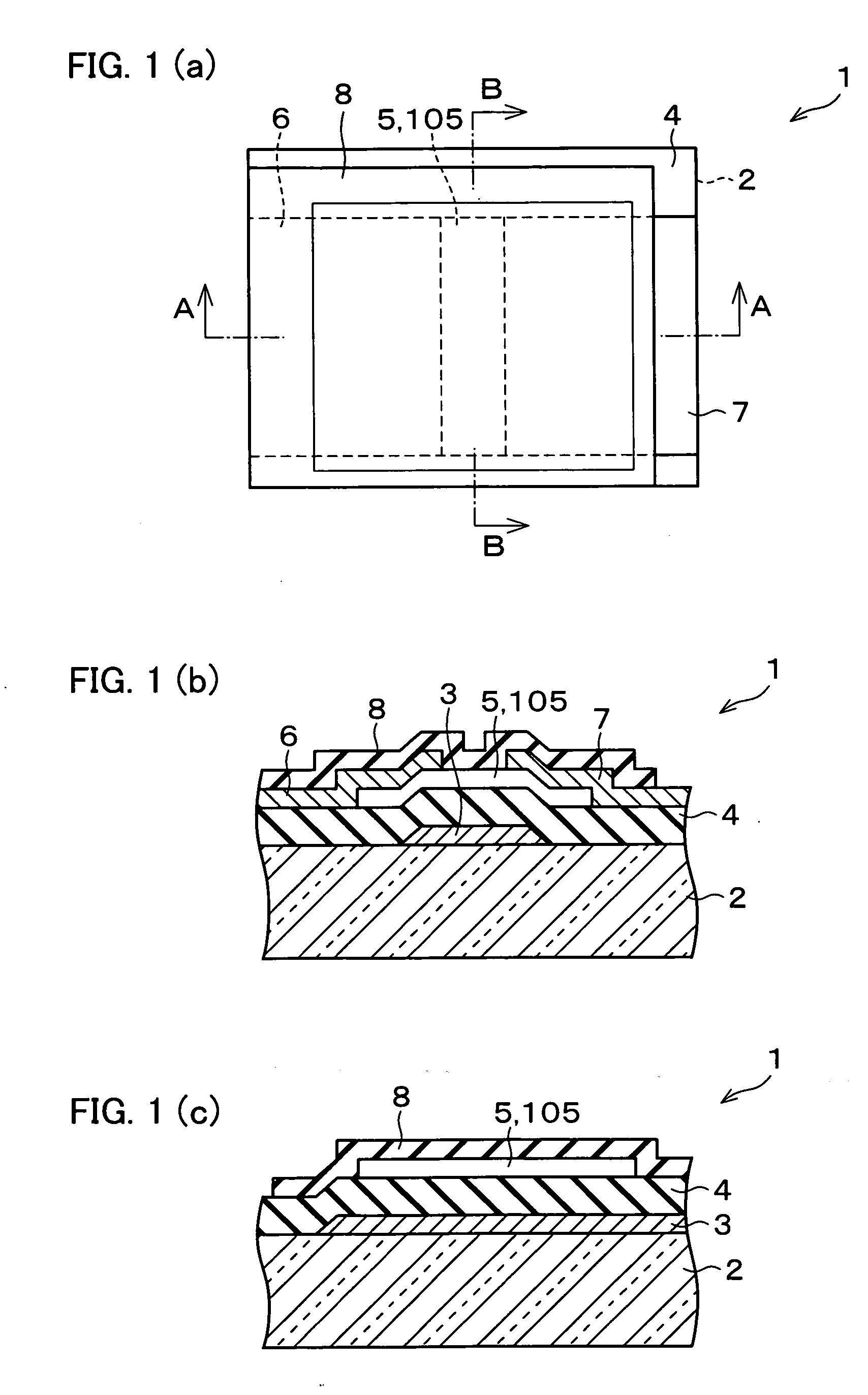
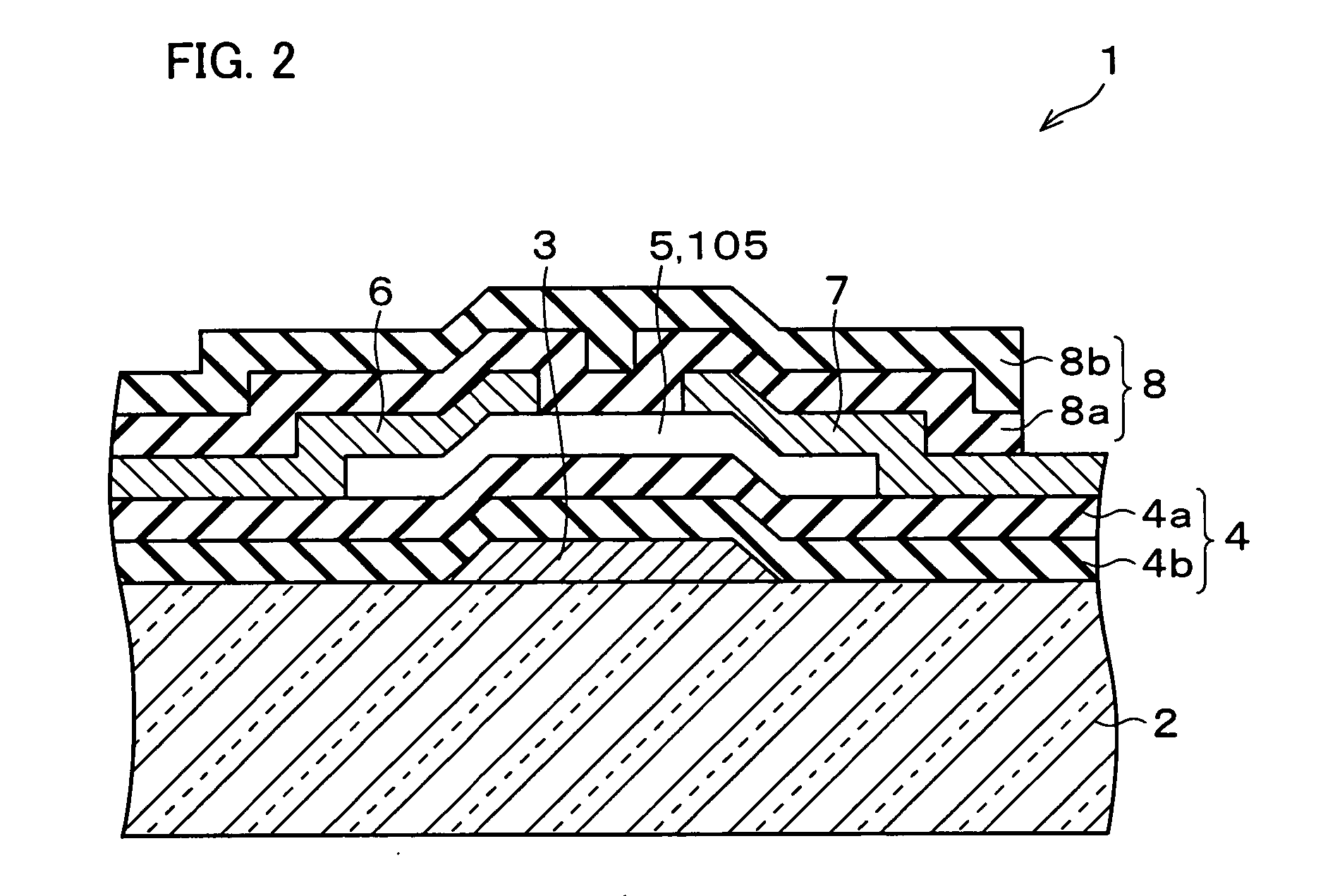
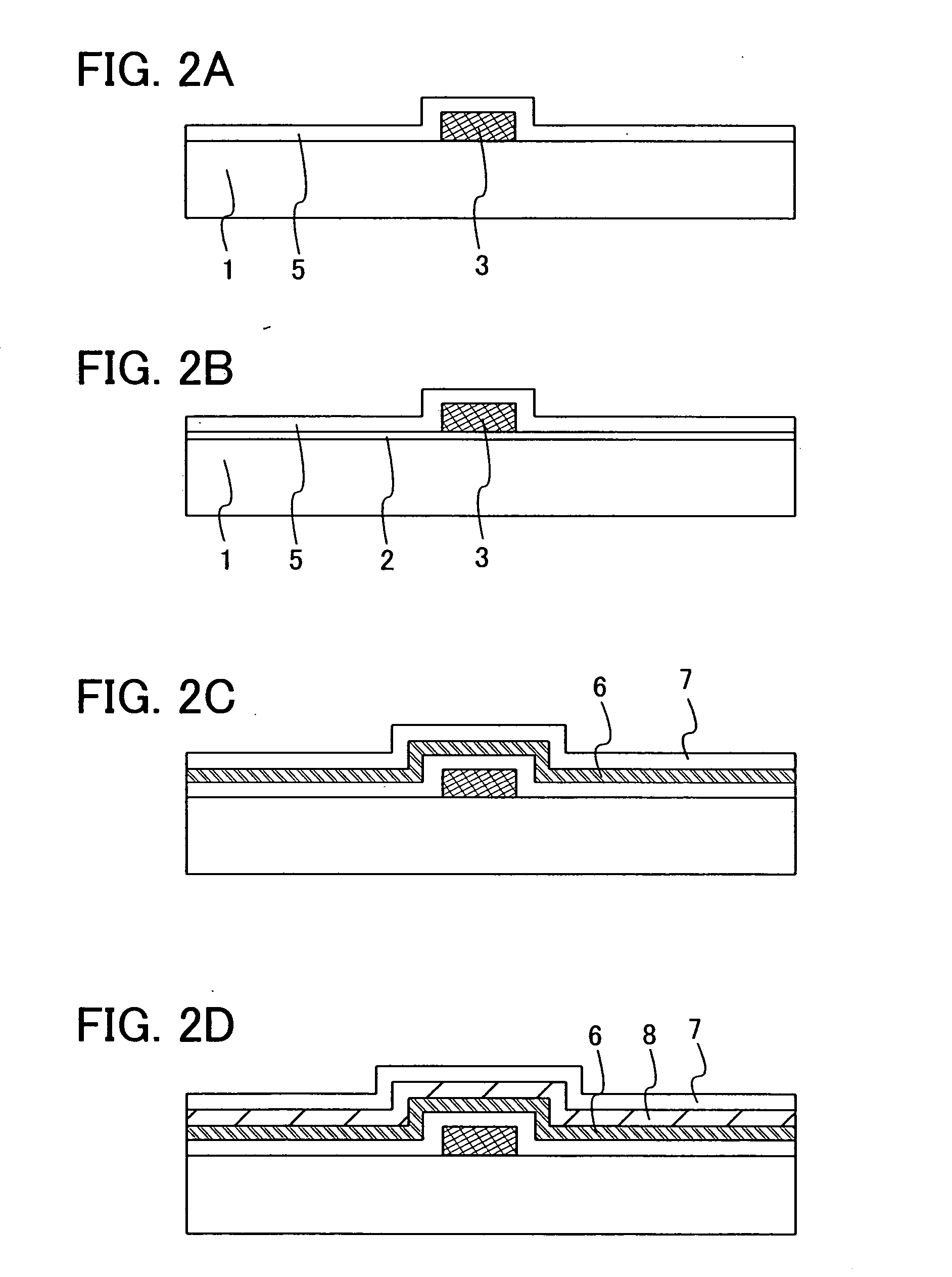
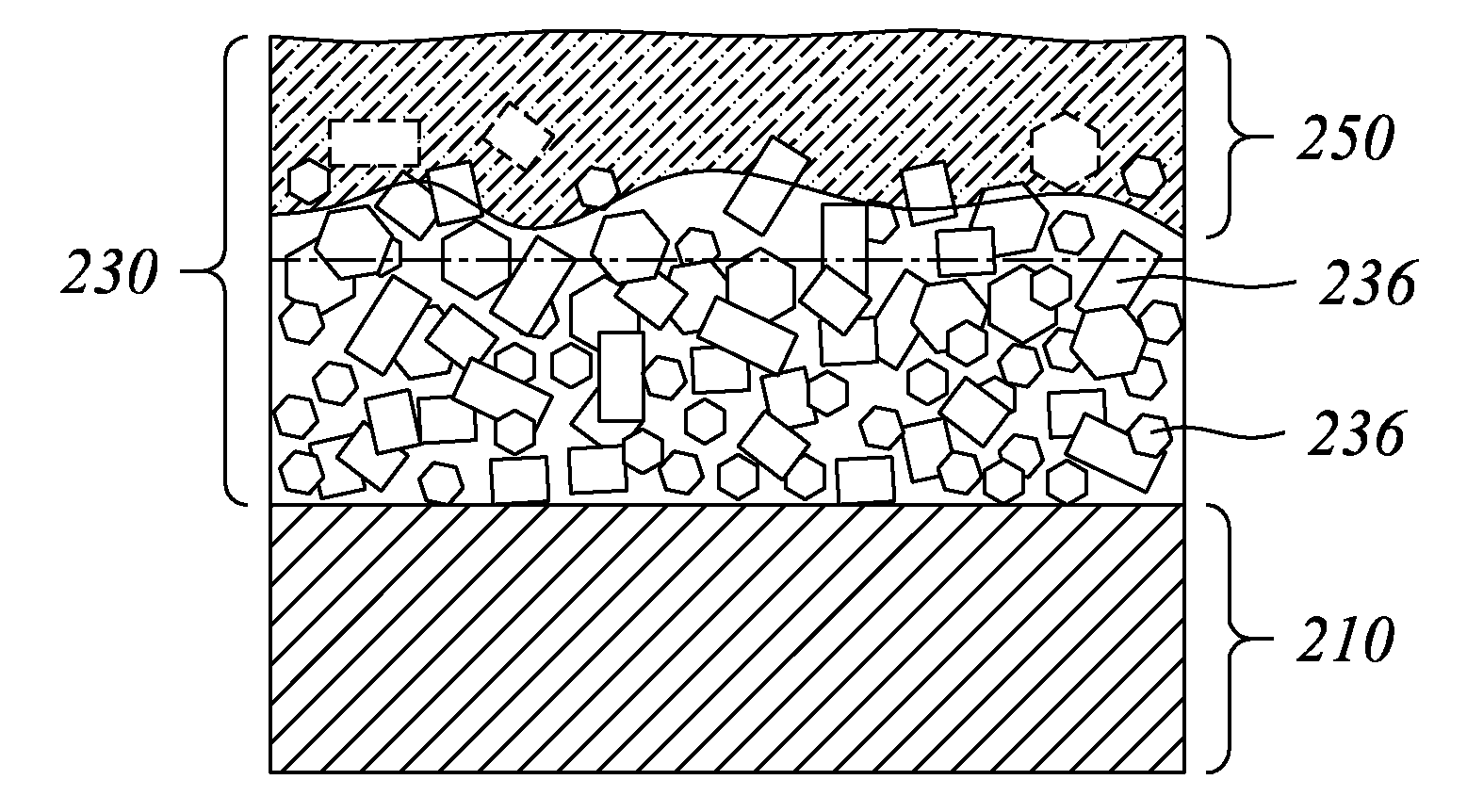
In a thin film transistor (1), a gate insulating layer (4) is formed on a gate electrode (3) formed on an insulating substrate (2). Formed on the gate insulating layer (4) is a semiconductor layer (5). Formed on the semiconductor layer (5) are a source electrode (6) and a drain electrode (7). A protective layer (8) covers them, so that the semiconductor layer (5) is blocked from an atmosphere. The semiconductor layer (5) (active layer) is made of, e.g., a semiconductor containing polycrystalline ZnO to which, e.g., a group V element is added. The protective layer (8) thus formed causes decrease of a surface level of the semiconductor layer (5). This eliminates a depletion layer spreading therewithin. Accordingly, the ZnO becomes an n-type semiconductor indicating an intrinsic resistance, with the result that too many free electrons are generated. However, the added element works on the ZnO as an accepter impurity, so that the free electrons are reduced. This decreases a gate voltage required for removal of the free electrons, so that the threshold voltage of the thin film transistor (1) becomes on the order of 0V. This allows practical use of a semiconductor device which has an active layer made of zinc oxide and which includes an protective layer for blocking the active layer from an atmosphere.
Owner:SHARP KK +2
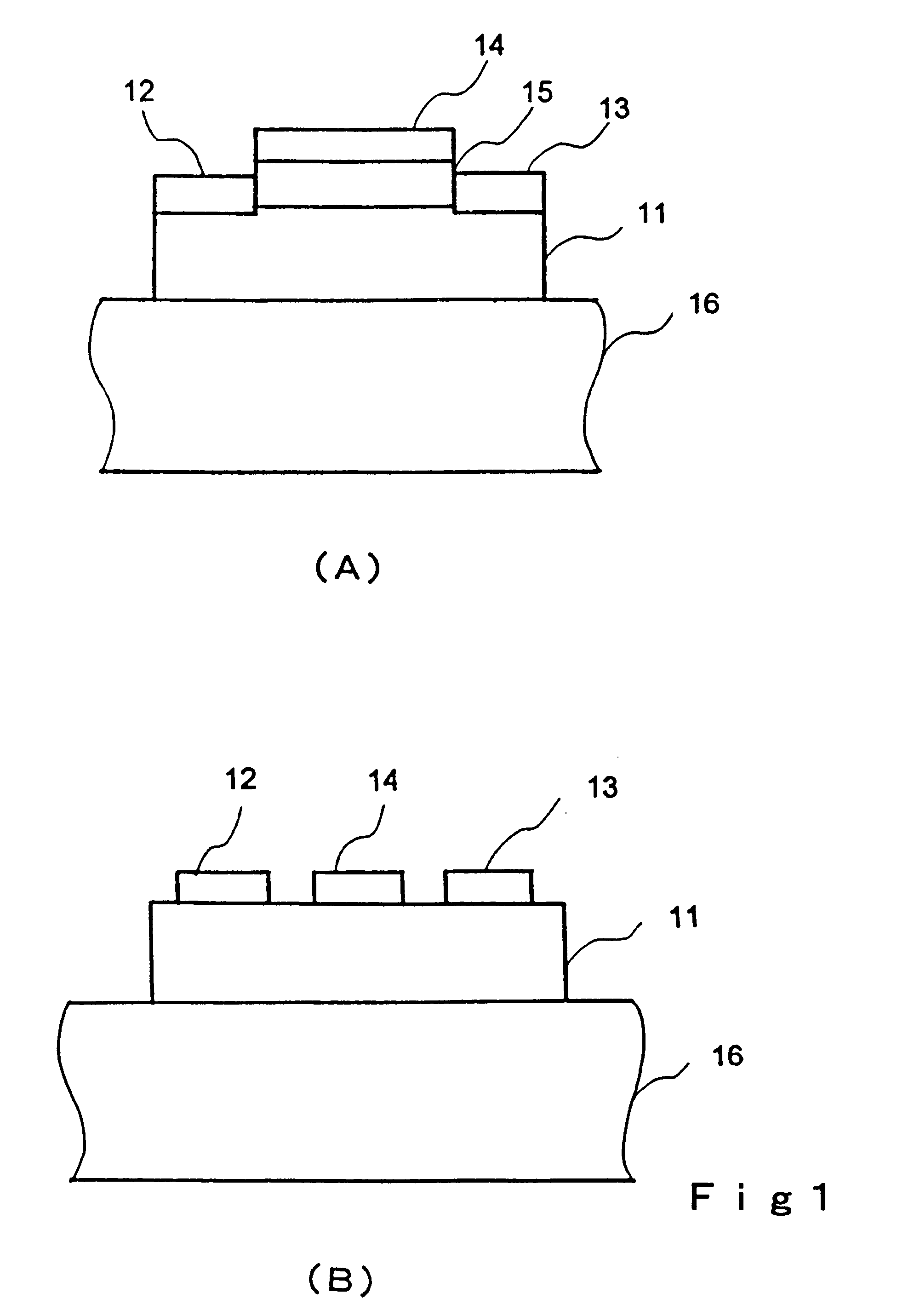
Transistor and semiconductor device
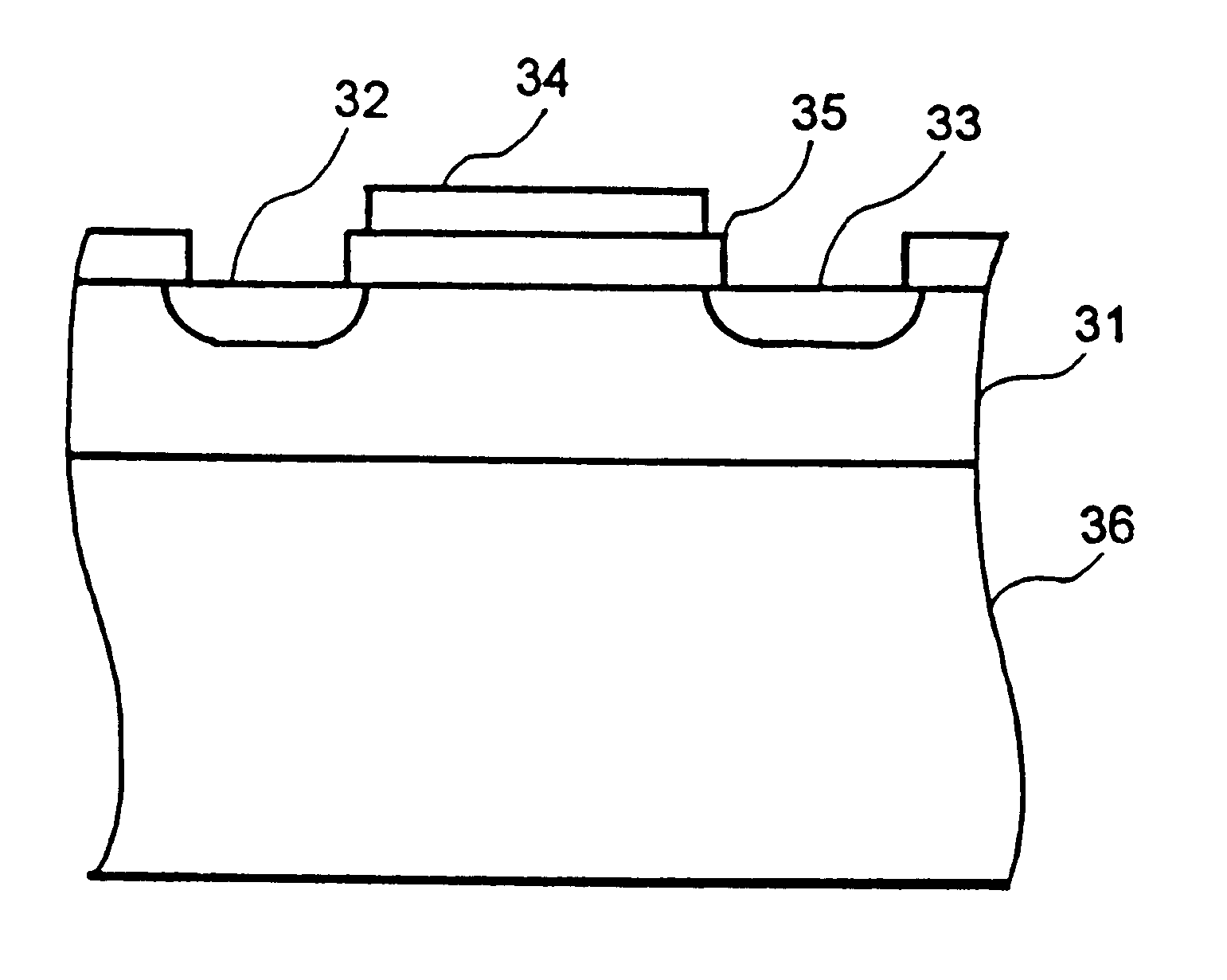
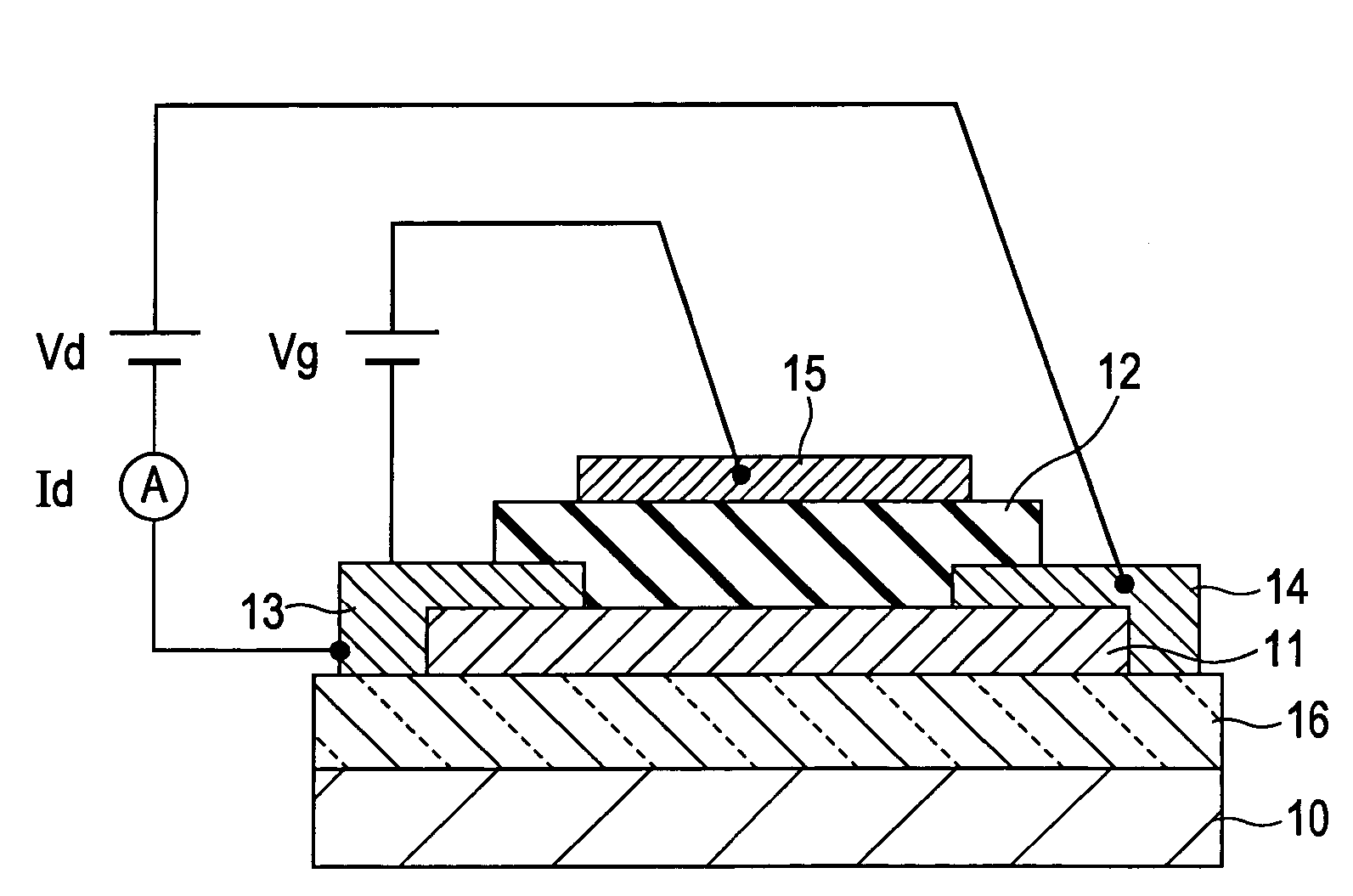
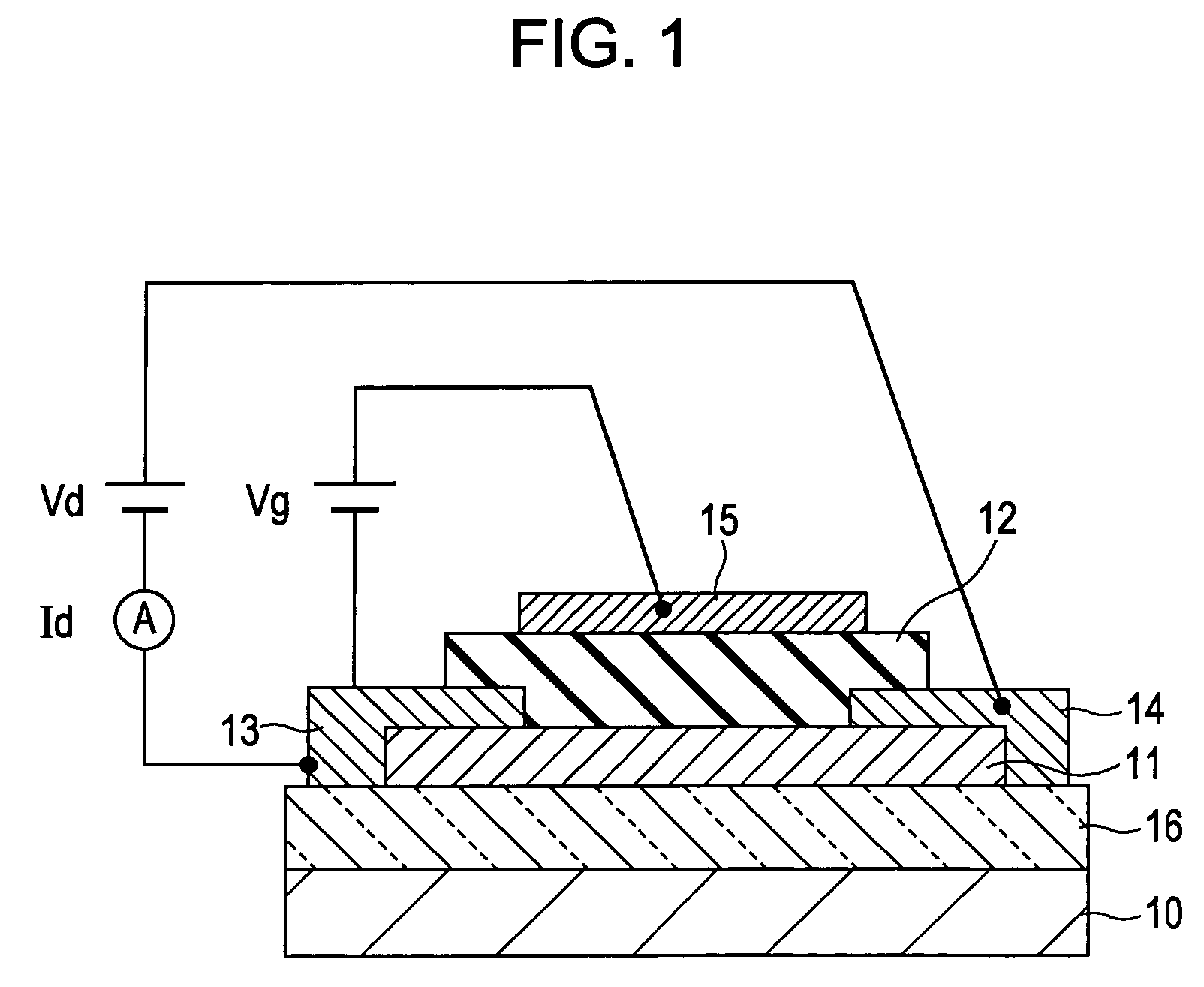
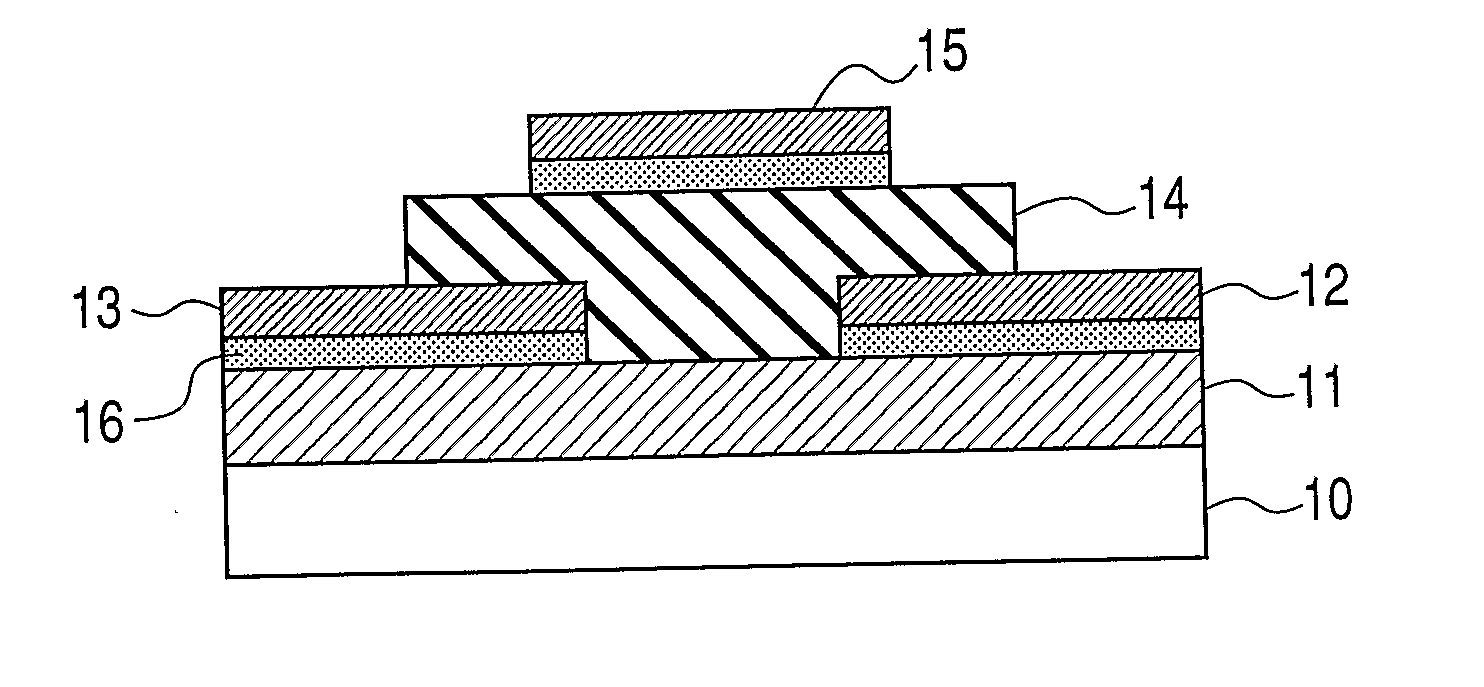
A transistor is provided, which is entirely and partially transparent by the use of a transparent channel layer made of zinc oxide or the like. A channel layer 11 formed of a transparent semiconductor such as zinc oxide ZnO. A transparent electrode is used for all of a source 12, a drain 13 and a gate 14, or a part of them. As the transparent electrode, a transparent conductive material such as conductive ZnO doped with, for example, group III elements is used. As a gate insulating layer 15, a transparent insulative material such as insulative ZnO doped with elements capable of taking a valence of one as a valence number or group V elements is used. If a substrate 16 must be transparent, for example, glass, sapphire, plastic or the like can be used as a transparent material.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
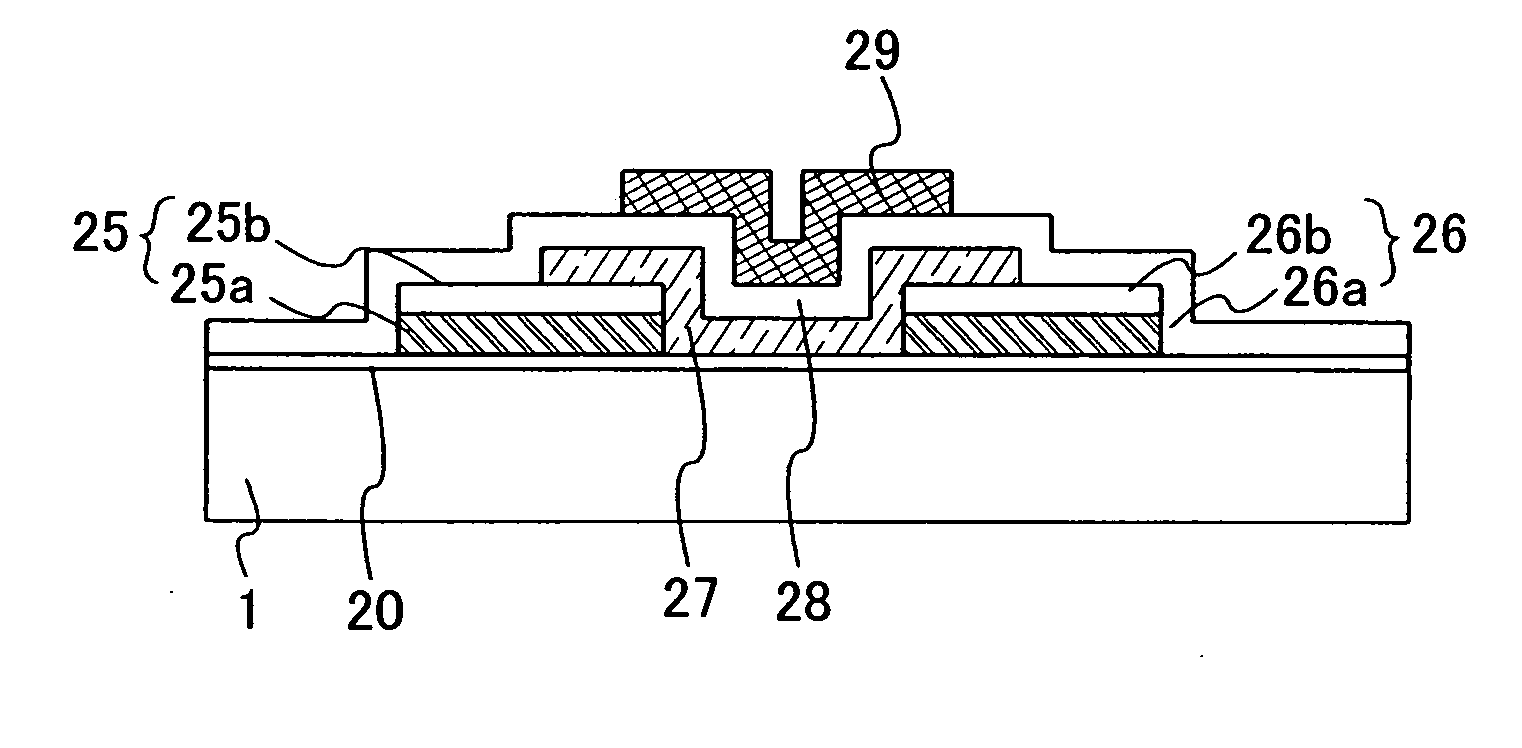
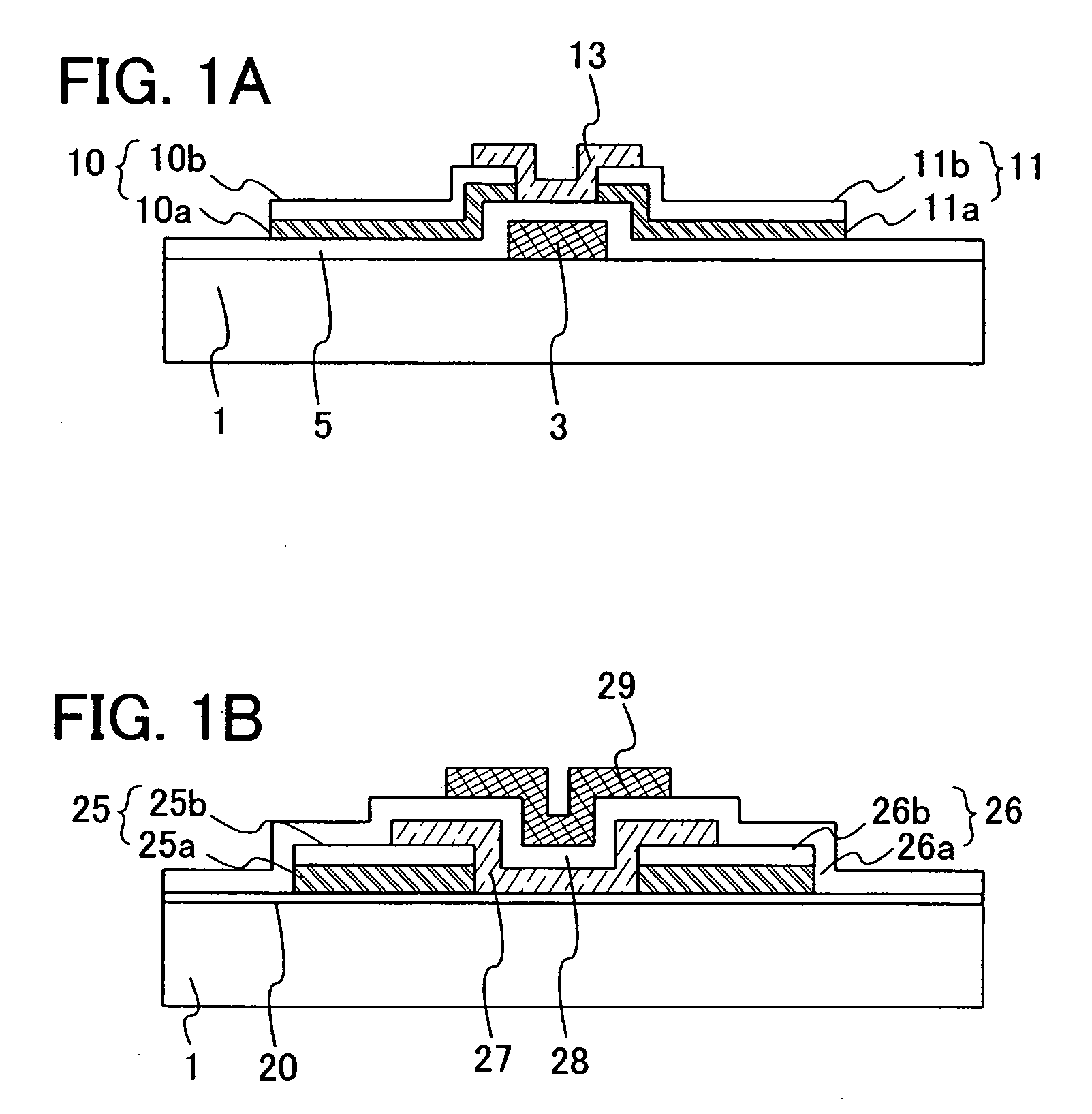
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20070108446A1Low resistance of wireLower resistanceTransistorElectroluminescent light sourcesAlloySilicon oxide
To provide a semiconductor device in which a defect or fault is not generated and a manufacturing method thereof even if a ZnO semiconductor film is used and a ZnO film to which an n-type or p-type impurity is added is used for a source electrode and a drain electrode. The semiconductor device includes a gate insulating film formed by using a silicon oxide film or a silicon oxynitride film over a gate electrode, an Al film or an Al alloy film over the gate insulating film, a ZnO film to which an n-type or p-type impurity is added over the Al film or the Al alloy film, and a ZnO semiconductor film over the ZnO film to which an n-type or p-type impurity is added and the gate insulating film.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Color el display and method for producing the same
ActiveUS20080129195A1Quality improvementHigh color purityDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsDisplay deviceEngineering
One embodiment of the present invention is a color EL display characterized in that at least color filters, a thin film transistor circuit, an organic EL layer, and a common electrode are laminated in this order on a transparent substrate. Another embodiment of the invention is a method for producing a color EL display comprising the steps of forming color filters or a transparent substrate; forming a thin film transistor circuit; forming an organic EL layer; and forming a common electrode, wherein process temperatures of the steps of forming the thin film transistor circuit and subsequent steps are 200° C. or less.
Owner:TOPPAN PRINTING CO LTD
Transparent oxide semiconductor thin film transistors
This invention relates to novel, transparent oxide semiconductor thin film transistors (TFT's) and a process for making them.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
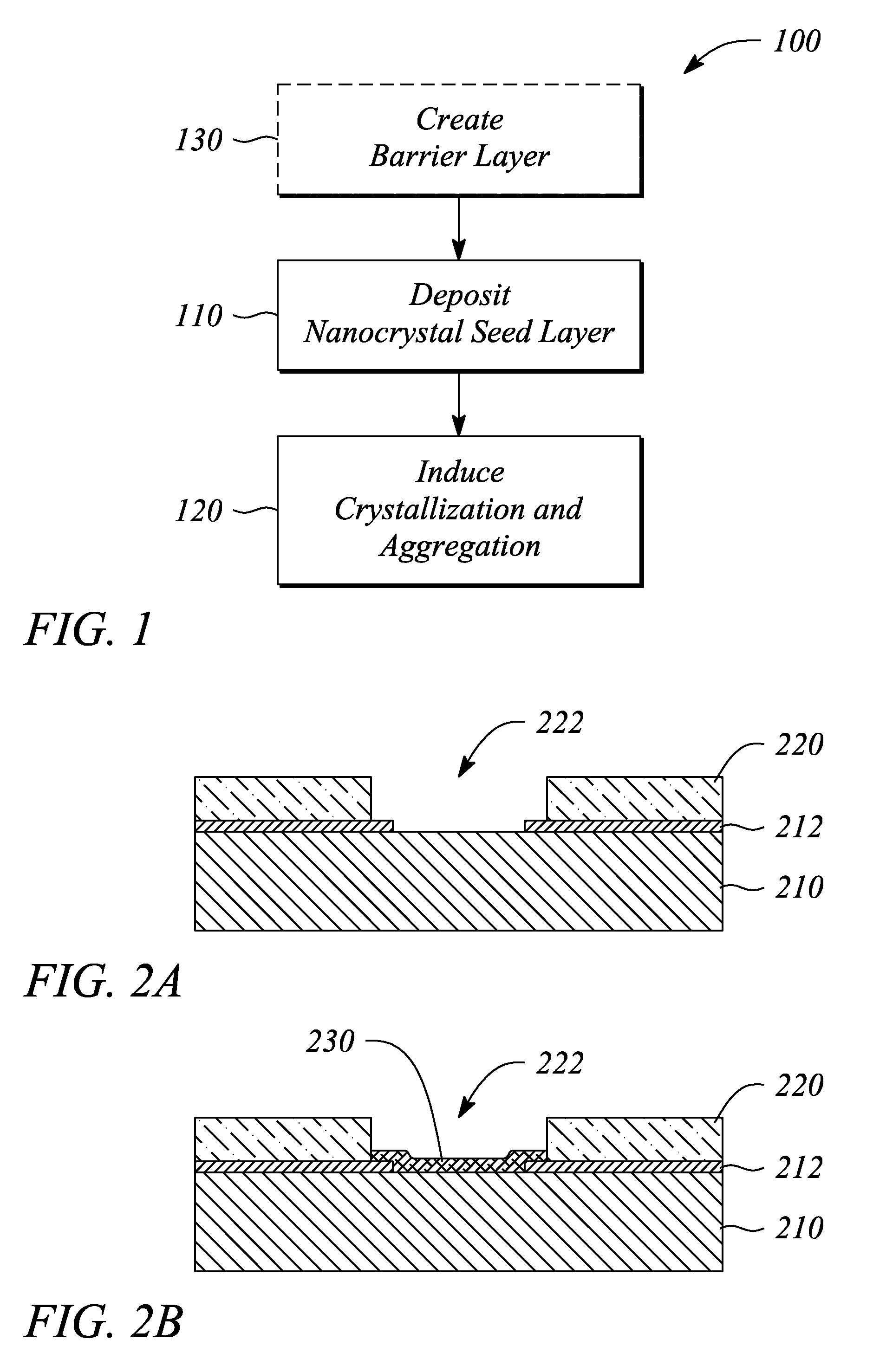
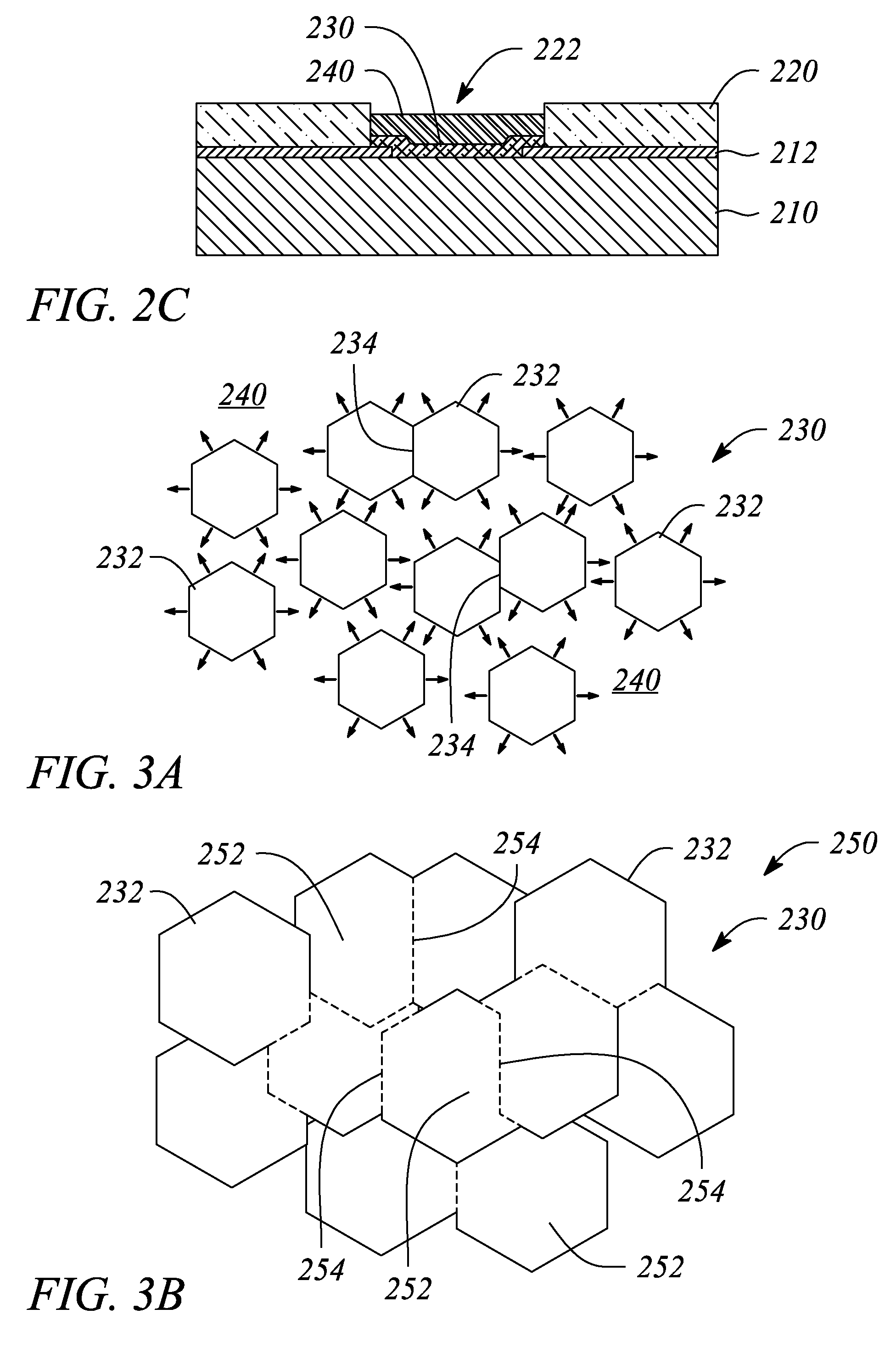
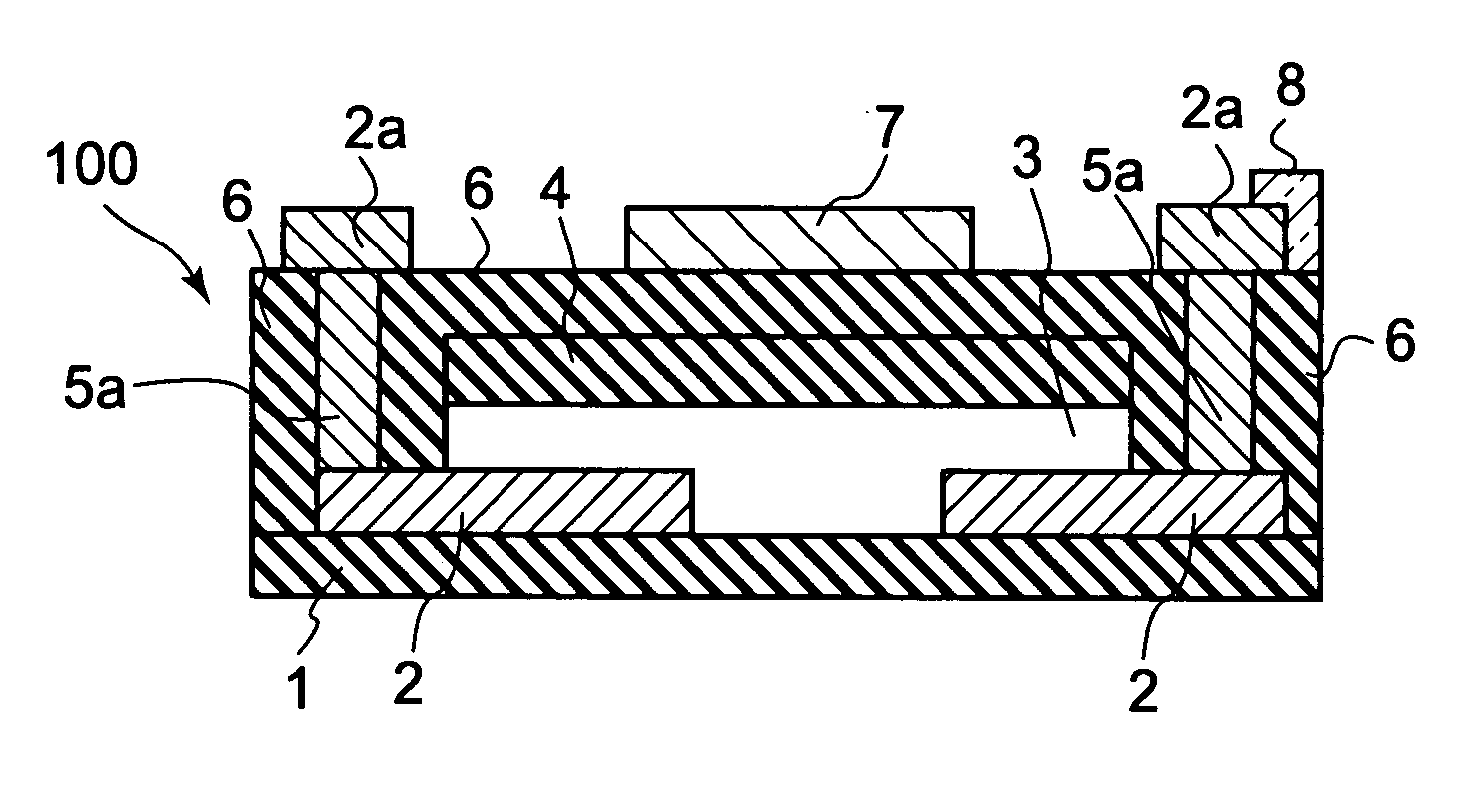
Fused nanocrystal thin film semiconductor and method
A thin film semiconductor and a method of its fabrication use induced crystallization and aggregation of a nanocrystal seed layer to form a merged-domain layer. The nanocrystal seed layer is deposited onto a substrate surface within a defined boundary. A reaction temperature below a boiling point of a reaction solution is employed. A thin film metal-oxide transistor and a method of its production employ the thin film semiconductor as a channel of the transistor. The merged-domain layer exhibits high carrier mobility.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
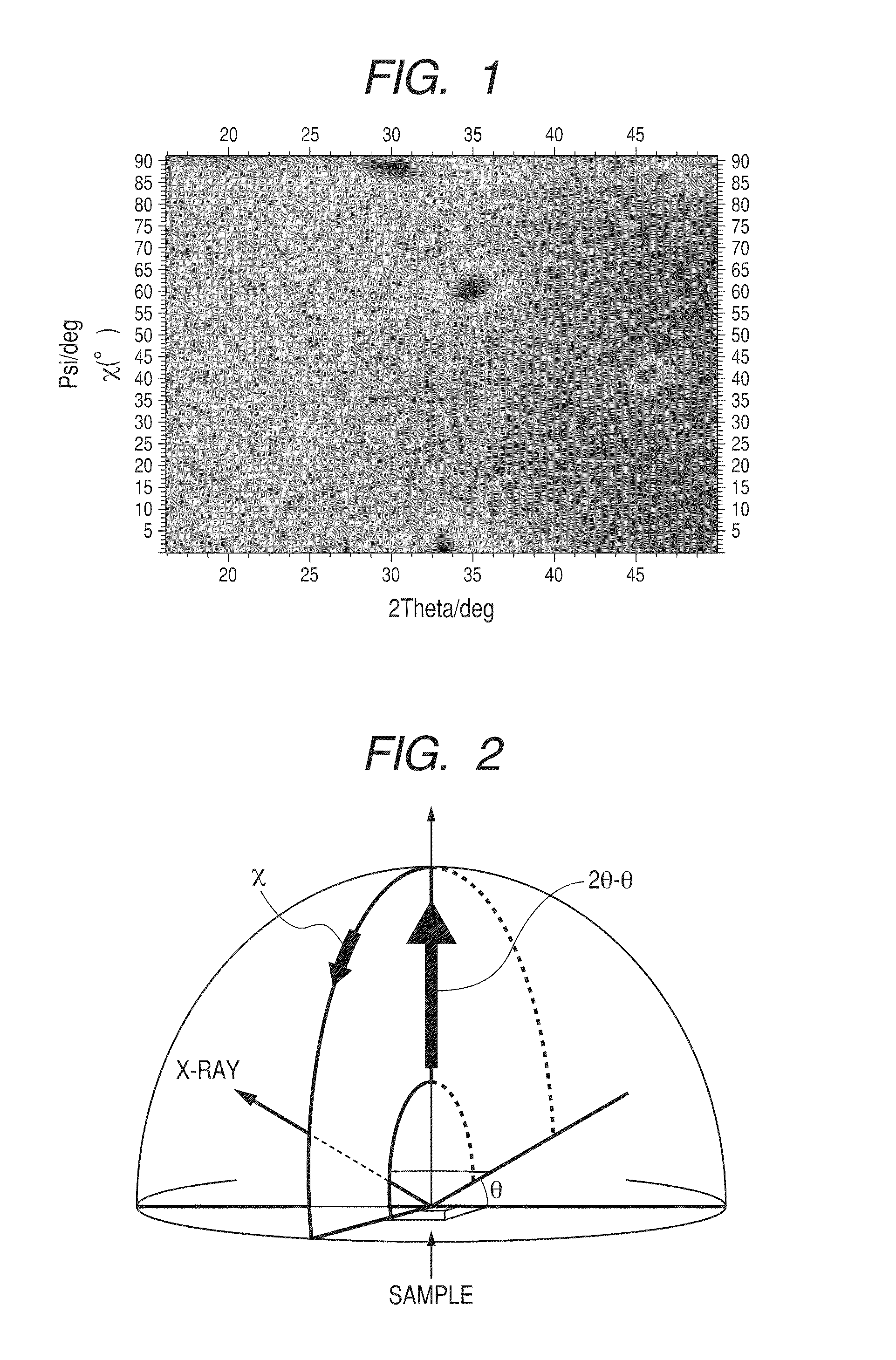
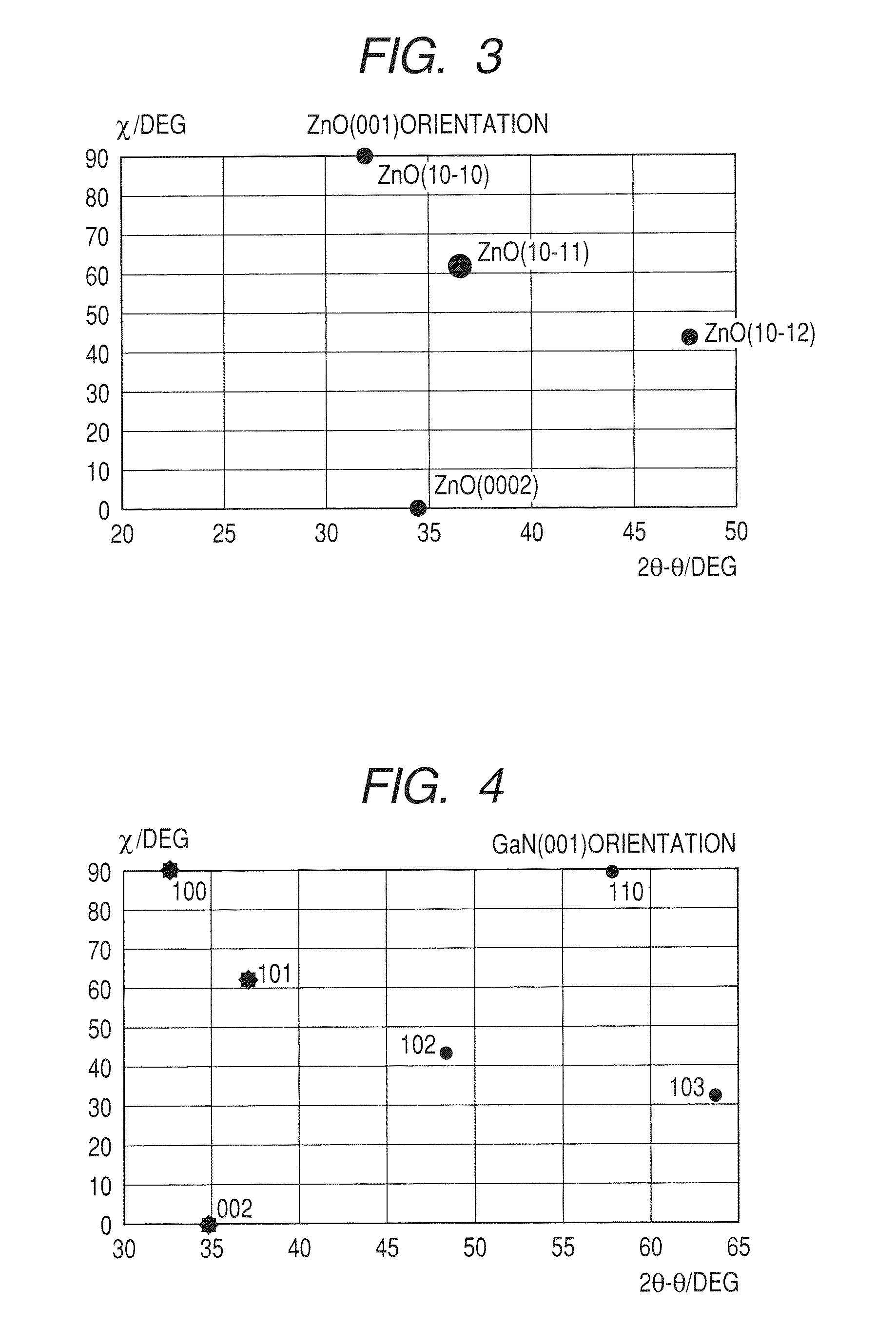
Semiconductor device including active layer made of zinc oxide with controlled orientations and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20070187678A1Improve heat resistanceImprove propertiesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesZincActive layer
A semiconductor device includes an oxide semiconductor thin film layer primarily including zinc oxide having at least one orientation other than (002) orientation. The zinc oxide may have a mixed orientation including (002) orientation and (101) orientation. Alternatively, the zinc oxide may have a mixed orientation including (100) orientation and (101) orientation.
Owner:KOICHI IND PROMOTION CENT +1
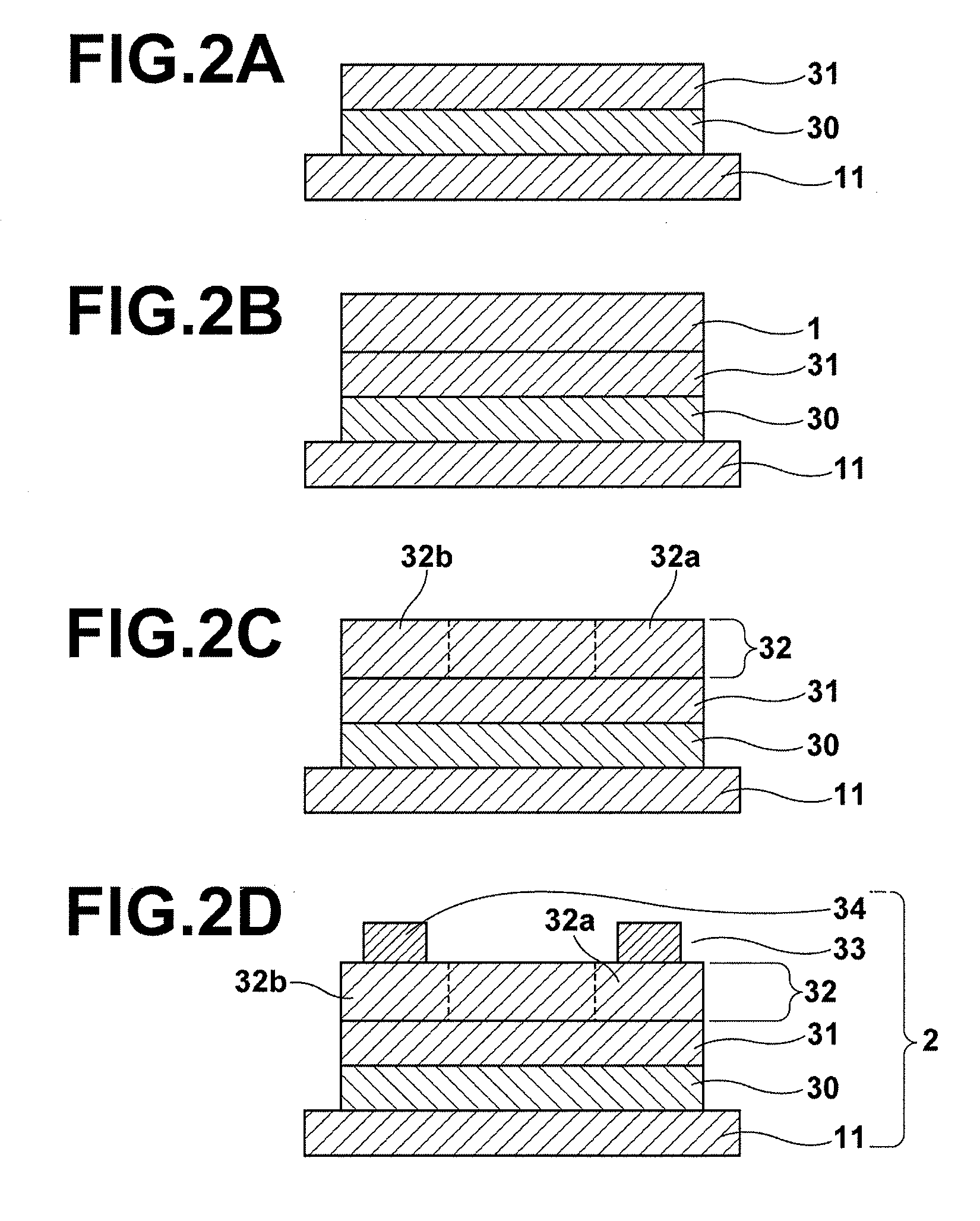
Process for producing oriented inorganic crystalline film, and semiconductor device using the oriented inorganic crystalline film
ActiveUS20090152506A1Orientation can be controlledLow costFrom gel stateFrom solid stateOrganic solventDevice material
In a process for producing an oriented inorganic crystalline film, a non-monocrystalline film containing inorganic crystalline particles is formed on a substrate by a liquid phase technique using a raw-material solution which contains a raw material and an organic solvent, where the inorganic crystalline particles have a layered crystal structure and are contained in the raw material. Then, the non-monocrystalline film is crystallized by heating the non-monocrystalline film to a temperature equal to or higher than the crystallization temperature of the non-monocrystalline film so that part of the inorganic crystalline particles act as crystal nuclei.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
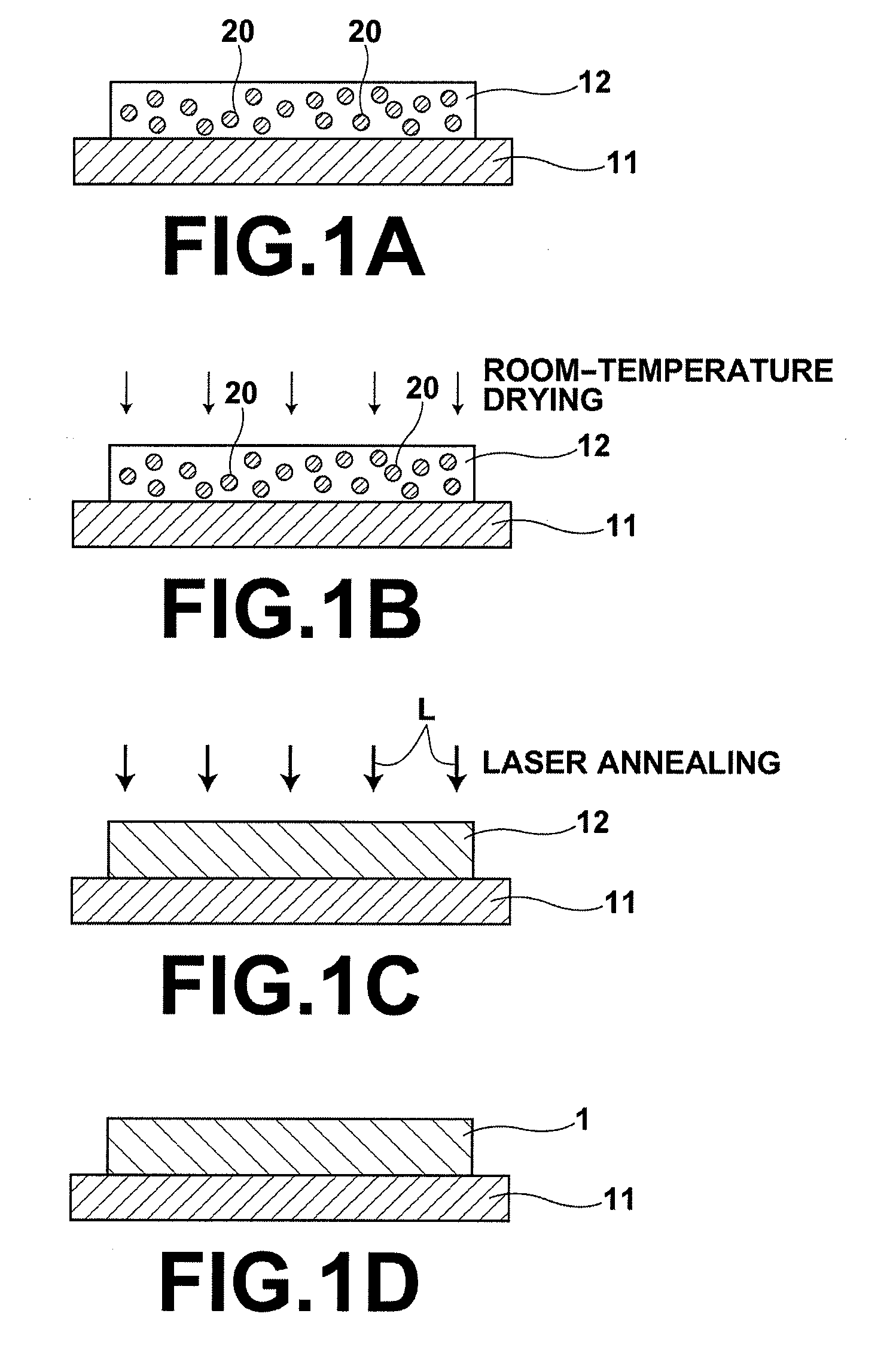
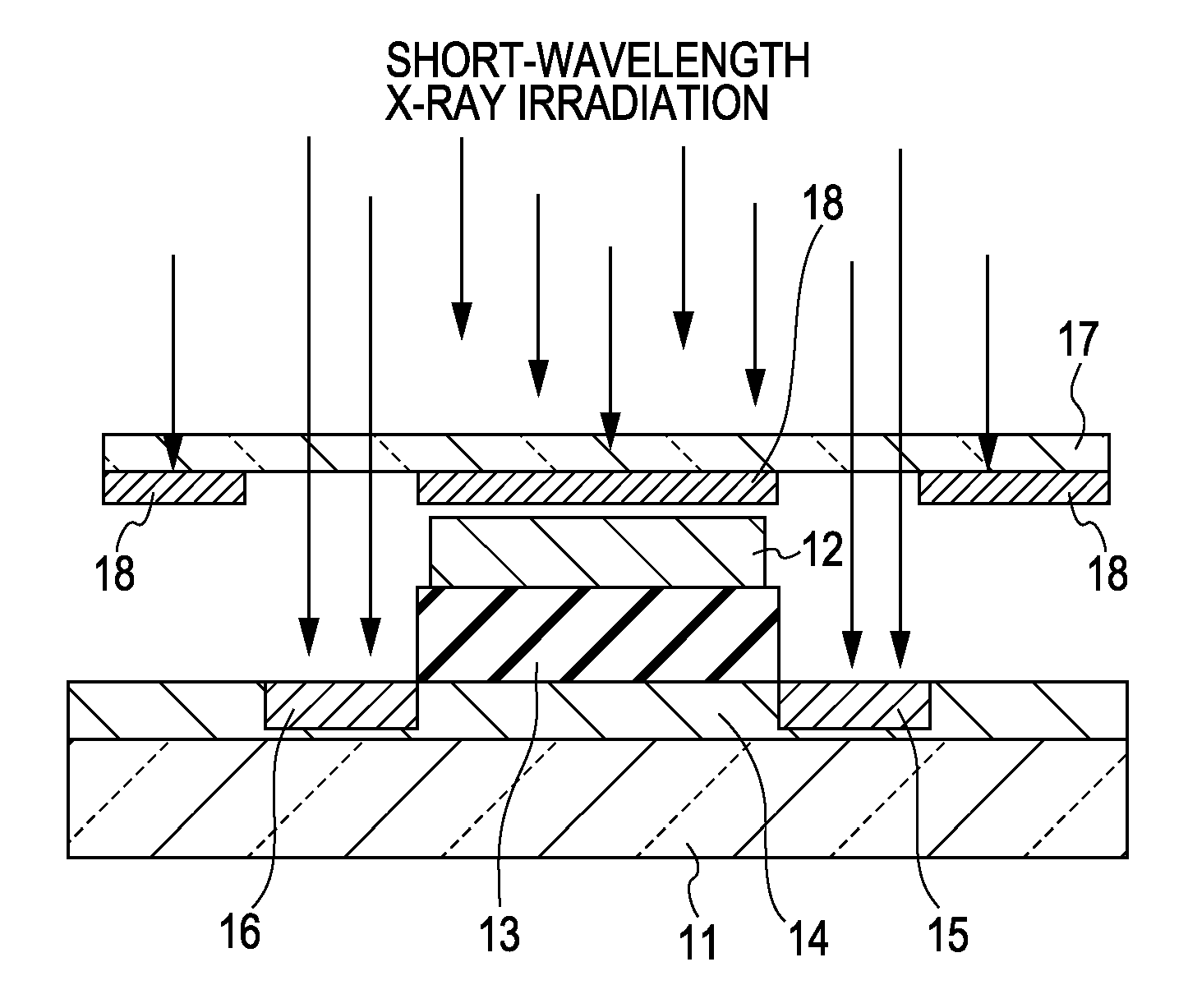
Method of fabricating oxide semiconductor device
InactiveUS20070054507A1Efficient solutionReduce conductivitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSemiconductorMaterials science
A method for fabricating a device using an oxide semiconductor, including a process of forming the oxide semiconductor on a substrate and a process of changing the conductivity of the oxide semiconductor by irradiating a predetermined region thereof with an energy ray.
Owner:CANON KK
Transparent conductive film and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20080050595A1Improve economyConductive layers on insulating-supportsSynthetic resin layered productsRocking curveFull width at half maximum
A ZnO-based transparent conductive film has practicable moisture resistance, desired characteristics of a transparent conductive film, and excellent economy. The transparent conductive film is produced by growing ZnO doped with a group III element oxide on a substrate and has a region with a crystal structure in which a c-axis grows along a plurality of different directions. The transparent conductive film produced by growing ZnO doped with a group III element oxide on a substrate has a ZnO (002) rocking curve full width at half maximum of about 13.5° or more.ZnO is doped with a group III element oxide so that the ratio of the group III element oxide in the transparent conductive film is about 7% to about 40% by weight.The transparent conductive film is formed on the substrate with a SiNx thin film provided therebetween.The transparent conductive film is formed on the substrate by a thin film formation method with a bias voltage applied to the substrate.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
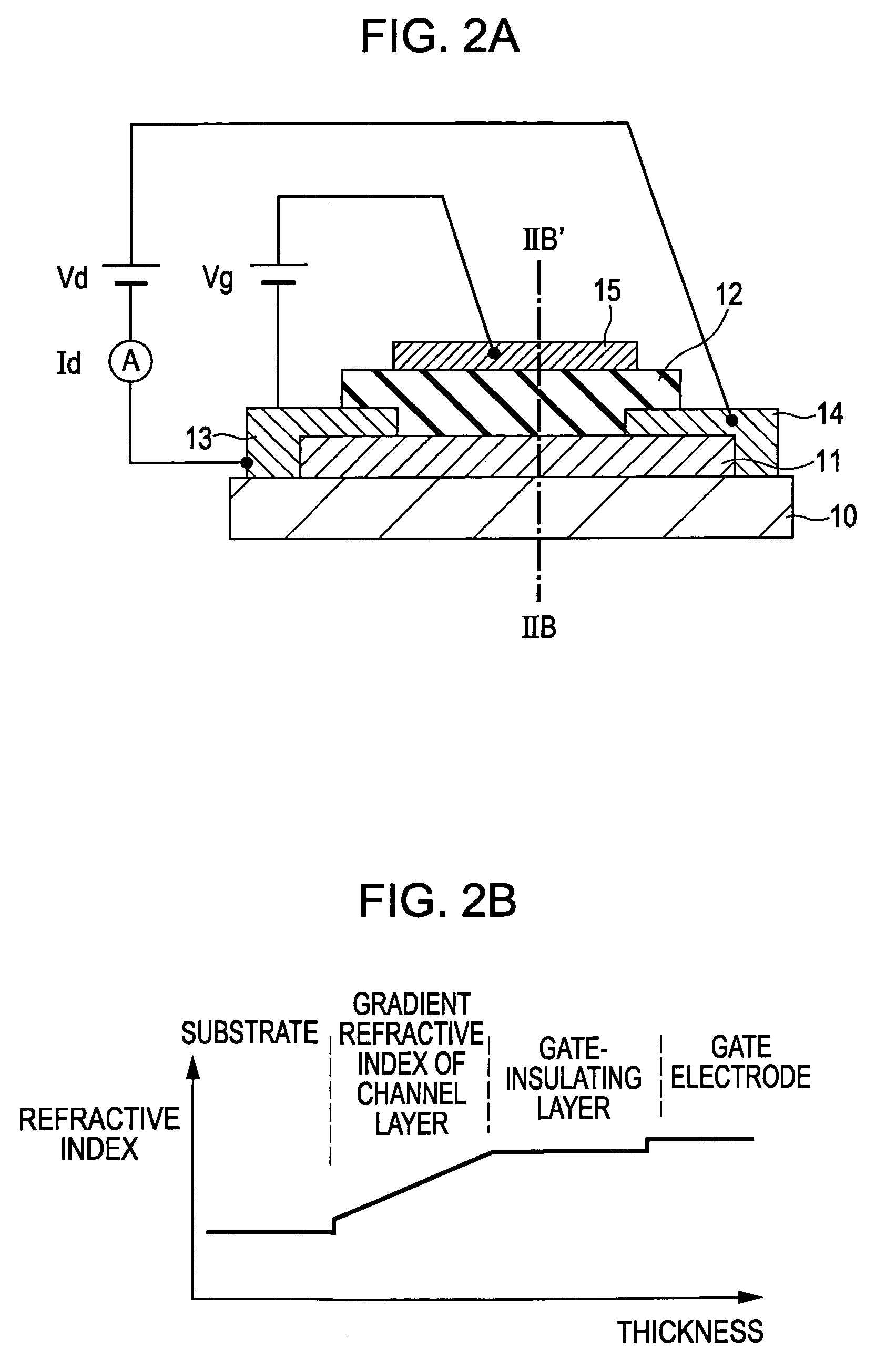
Thin-film transistor and thin-film diode having amorphous-oxide semiconductor layer
ActiveUS7453087B2High light transmittanceHigh transparencyTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingThin-film diodeRefractive index
A thin-film transistor including a channel layer being formed of an oxide semiconductor transparent to visible light and having a refractive index of nx, a gate-insulating layer disposed on one face of the channel layer, and a transparent layer disposed on the other face of the channel layer and having a refractive index of nt, where there is a relationship of nx>nt. A thin-film transistor including a substrate having a refractive index of no, a transparent layer disposed on the substrate and having a refractive index of nt, and a channel layer disposed on the transparent layer and having a refractive index of nx, where there is a relationship of nx>nt>no.
Owner:CANON KK
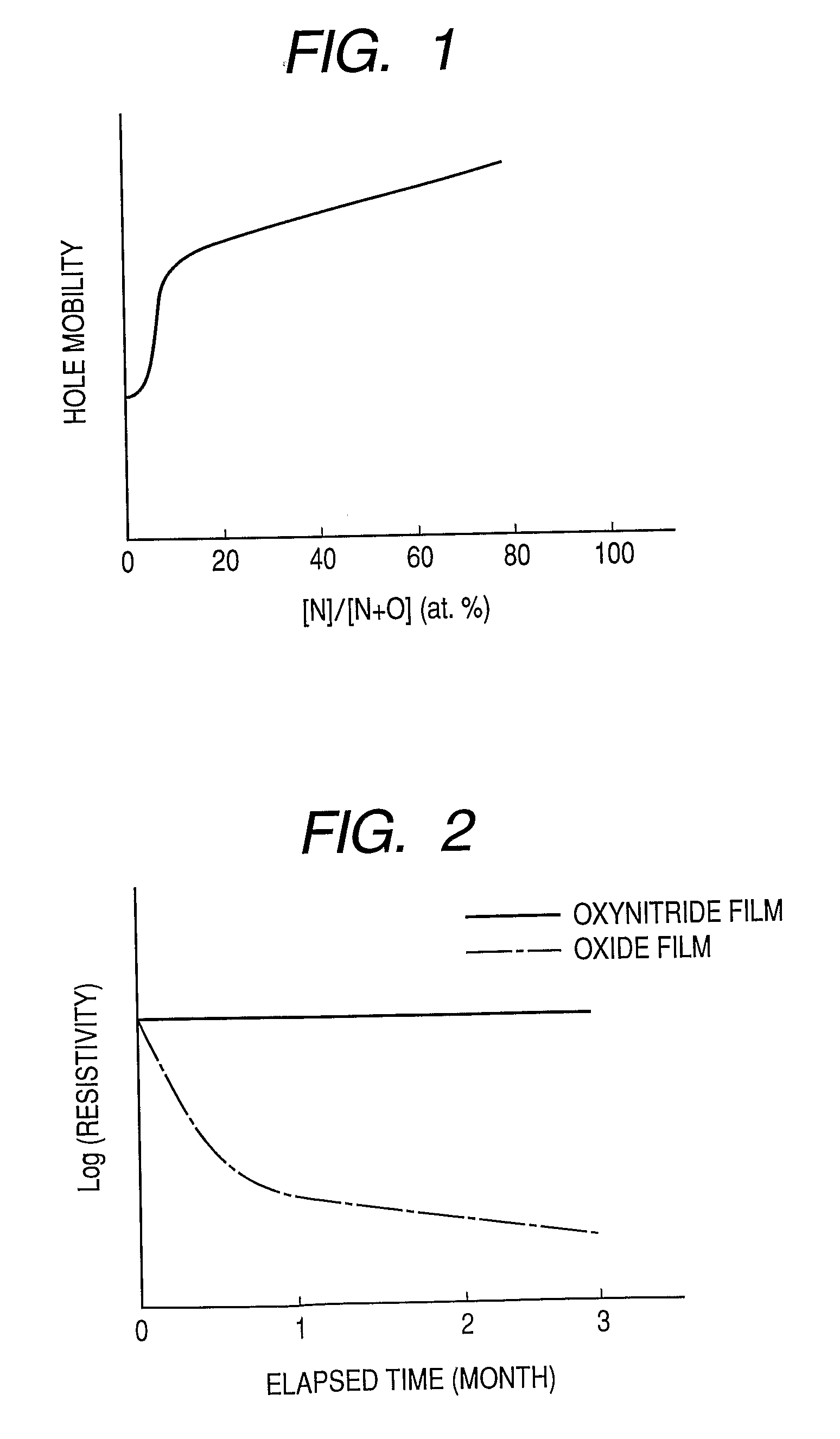
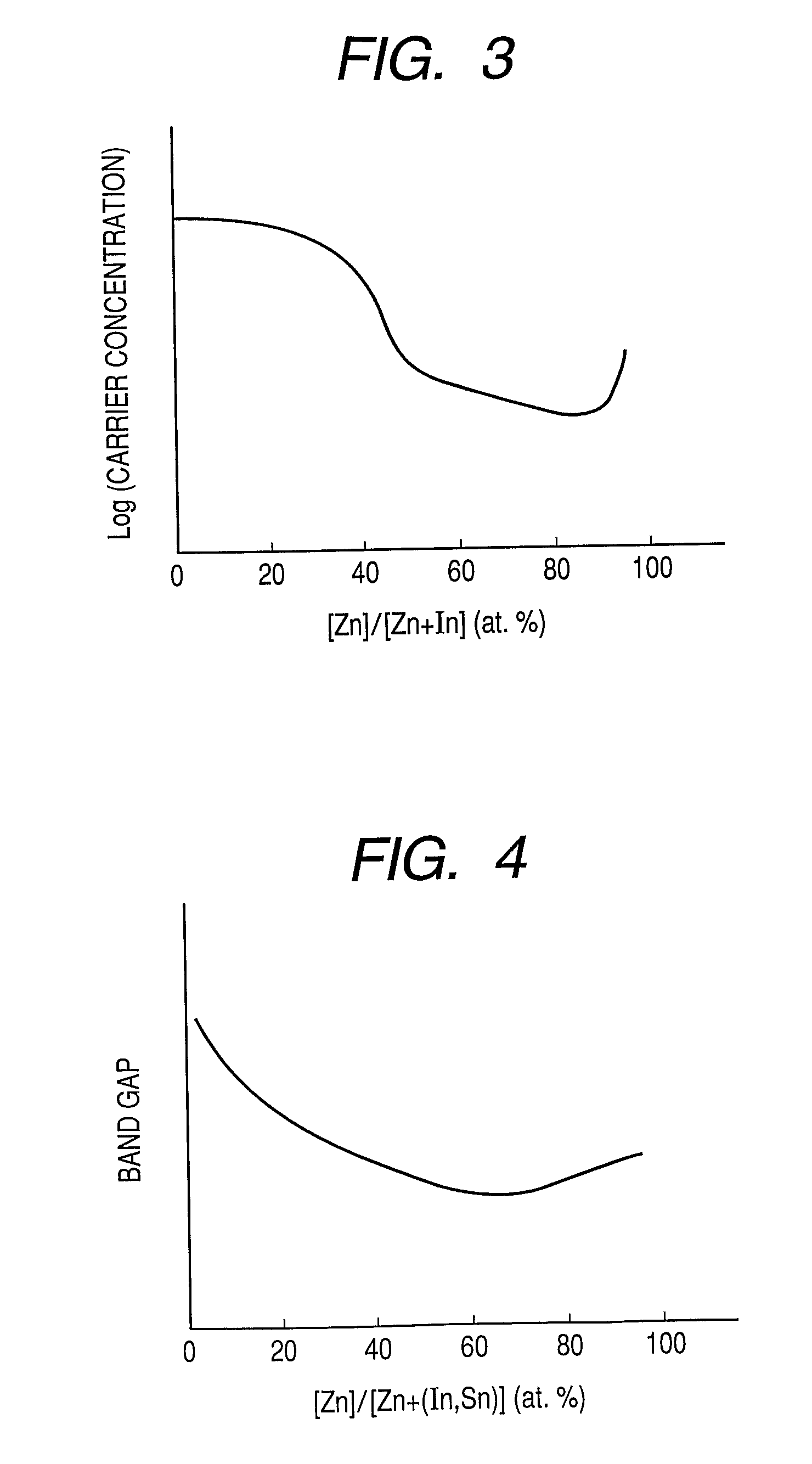
Oxynitride semiconductor
ActiveUS20100109002A1High mobility and environmental stabilityImprove mobilitySemiconductor devicesNitrogen oxideOxygen
Provided is an oxynitride semiconductor comprising a metal oxynitride. The metal oxynitride contains Zn and at least one element selected from the group consisting of In, Ga, Sn, Mg, Si, Ge, Y, Ti, Mo, W, and Al. The metal oxynitride has an atomic composition ratio of N, N / (N+O), of 7 atomic percent or more to 80 atomic percent or less.
Owner:CANON KK
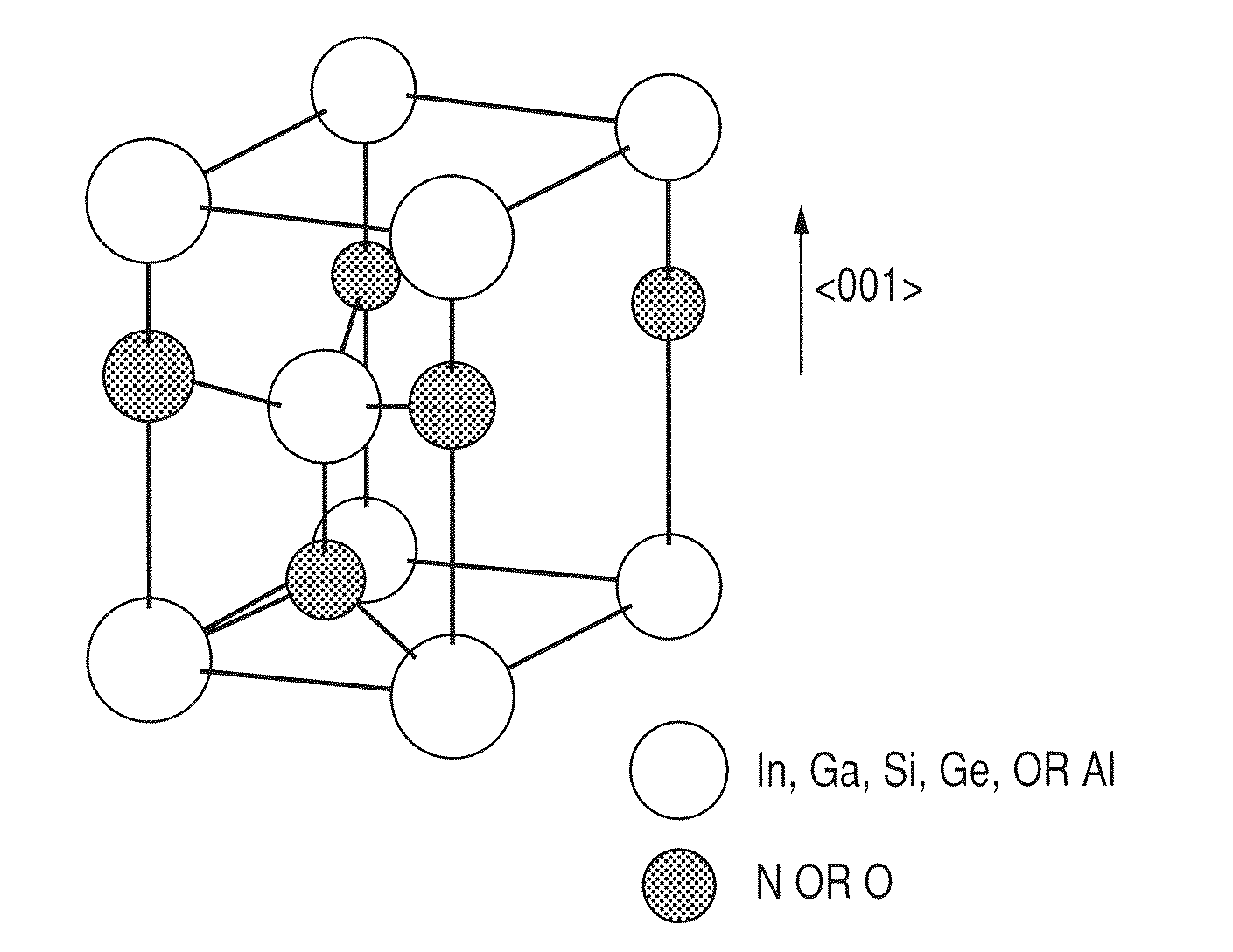
Substrate for growing wurtzite type crystal and method for manufacturing the same and semiconductor device
ActiveUS20100092800A1Low costHigh crystallinityPolycrystalline material growthVacuum evaporation coatingNitrideSemiconductor
A laminated structure comprises a first layer comprising a crystal with six-fold symmetry, and a second layer comprising a metal oxynitride crystal formed on the first layer, wherein the second layer comprises at least one element selected from the group consisting of In, Ga, Si, Ge and Al, N, O and Zn, as main elements, and wherein the second layer has in-plane orientation.
Owner:CANON KK
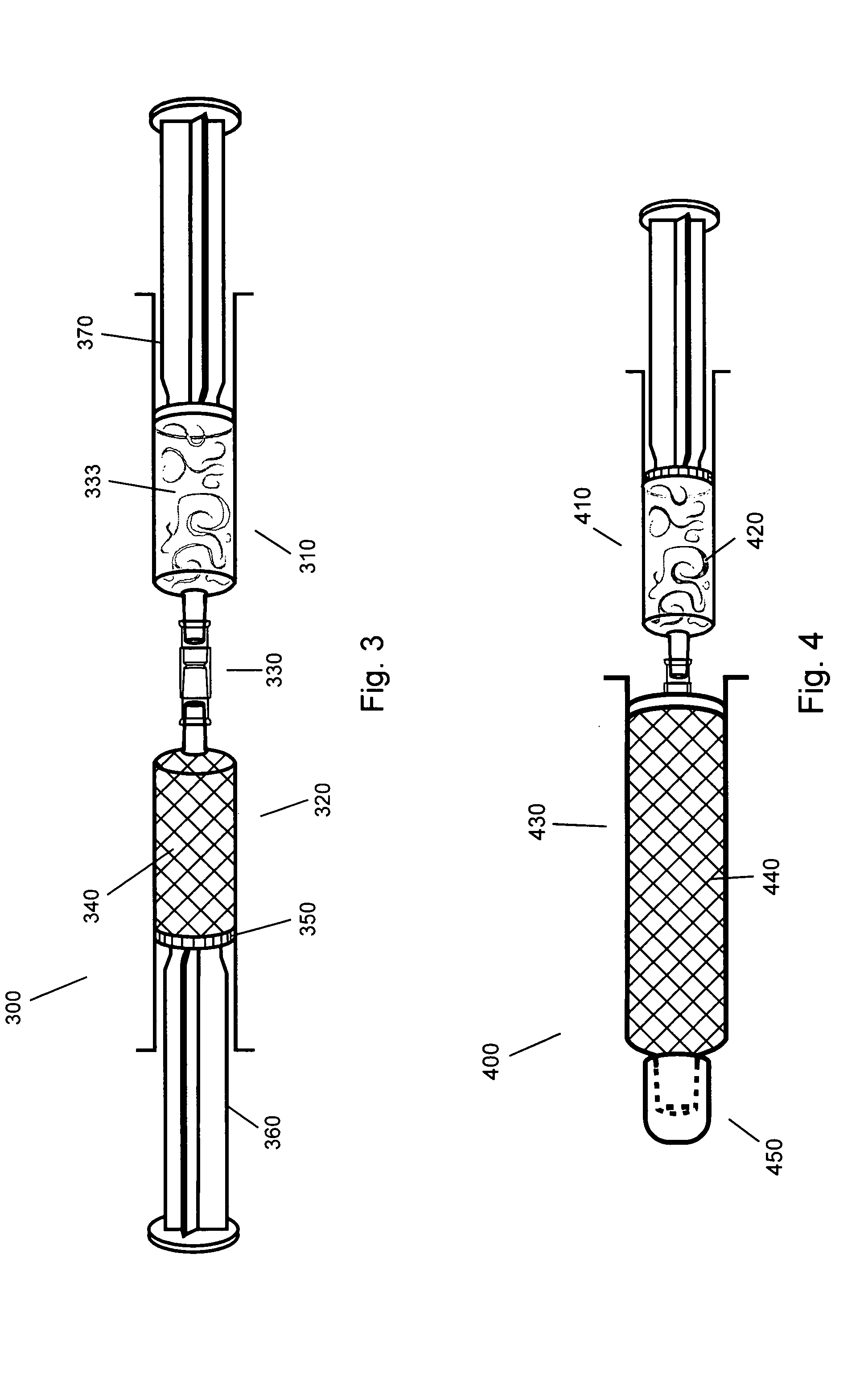
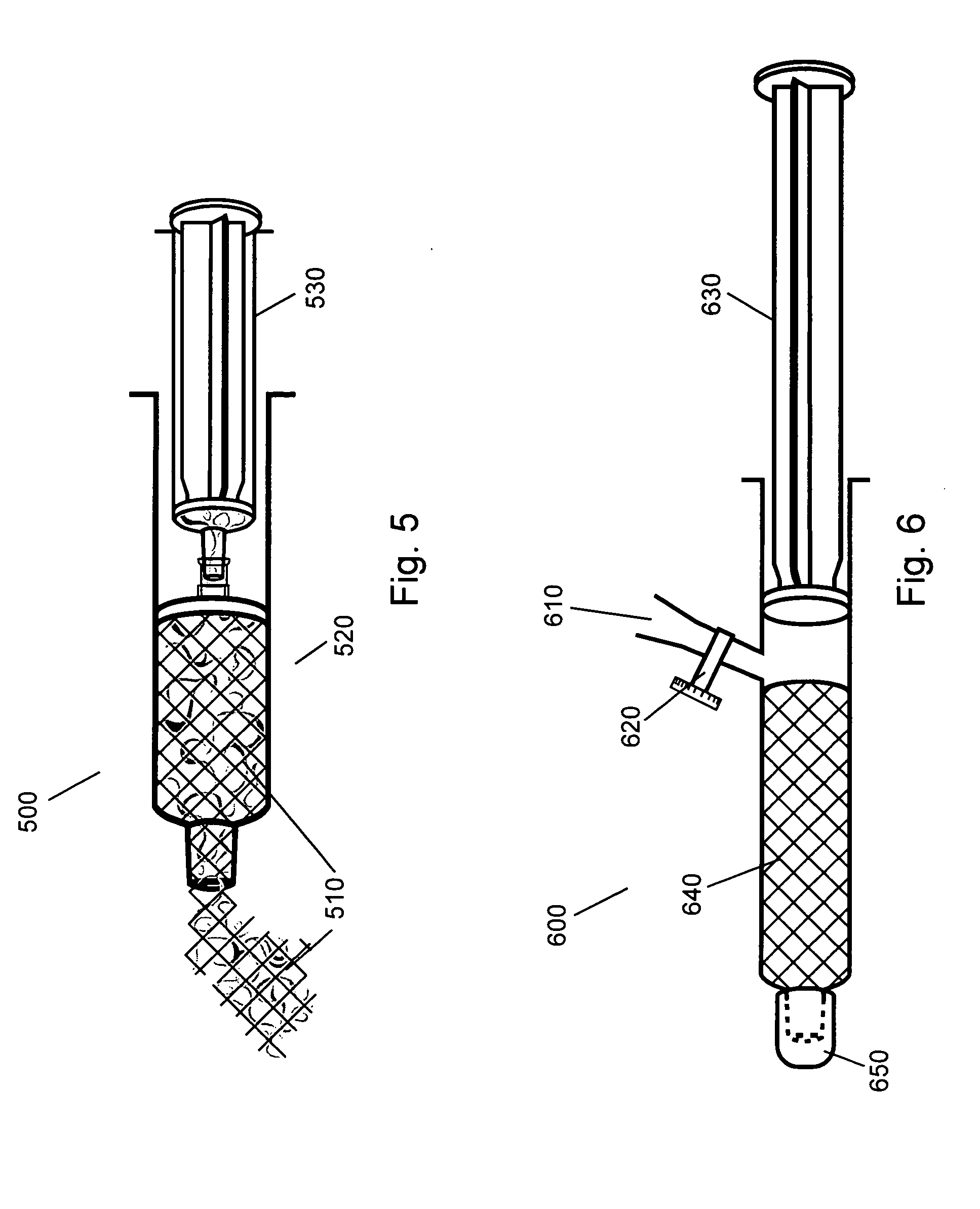
Smoking article incorporating a conductive substrate
The present invention provides a conductive substrate useful for Joule heating, such as in an electronic smoking article. Particularly, the invention provides a resistive heating element formed of a conductive substrate. The conductive substrate comprises an electrically conductive material and a carbonaceous additive, such as a binder material. The conductive substrate is carbonized in that it is subjected to calcining conditions to effectively reduce the carbonaceous additive to its carbon skeleton. It has been found that such carbonized substrate has surprisingly improved resistance properties in relation a substrate of the same formulation that is not carbonized. The carbonized substrate can include an aerosol precursor material. The formed resistive heating element can be included in an electronic smoking article to simultaneously provide resistive heating and aerosol formation with a single, unitary component.
Owner:RAI STRATEGIC HLDG INC
Organic electroluminescent device having an azatriphenylene derivative
ActiveUS20090115316A1Promote resultsReduce the driving voltageOrganic chemistryDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectricityEngineering
Azatriphenylene derivatives and their use in the electron-transporting layer of an electroluminescent device that comprises an anode, a spaced-apart cathode, and at least one electron-transporting layer disposed between the spaced-apart anode and cathode. Such EL devices provide lower drive voltage, improved power efficiency, and longer operational lifetime.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Analyte sensor method of making the same
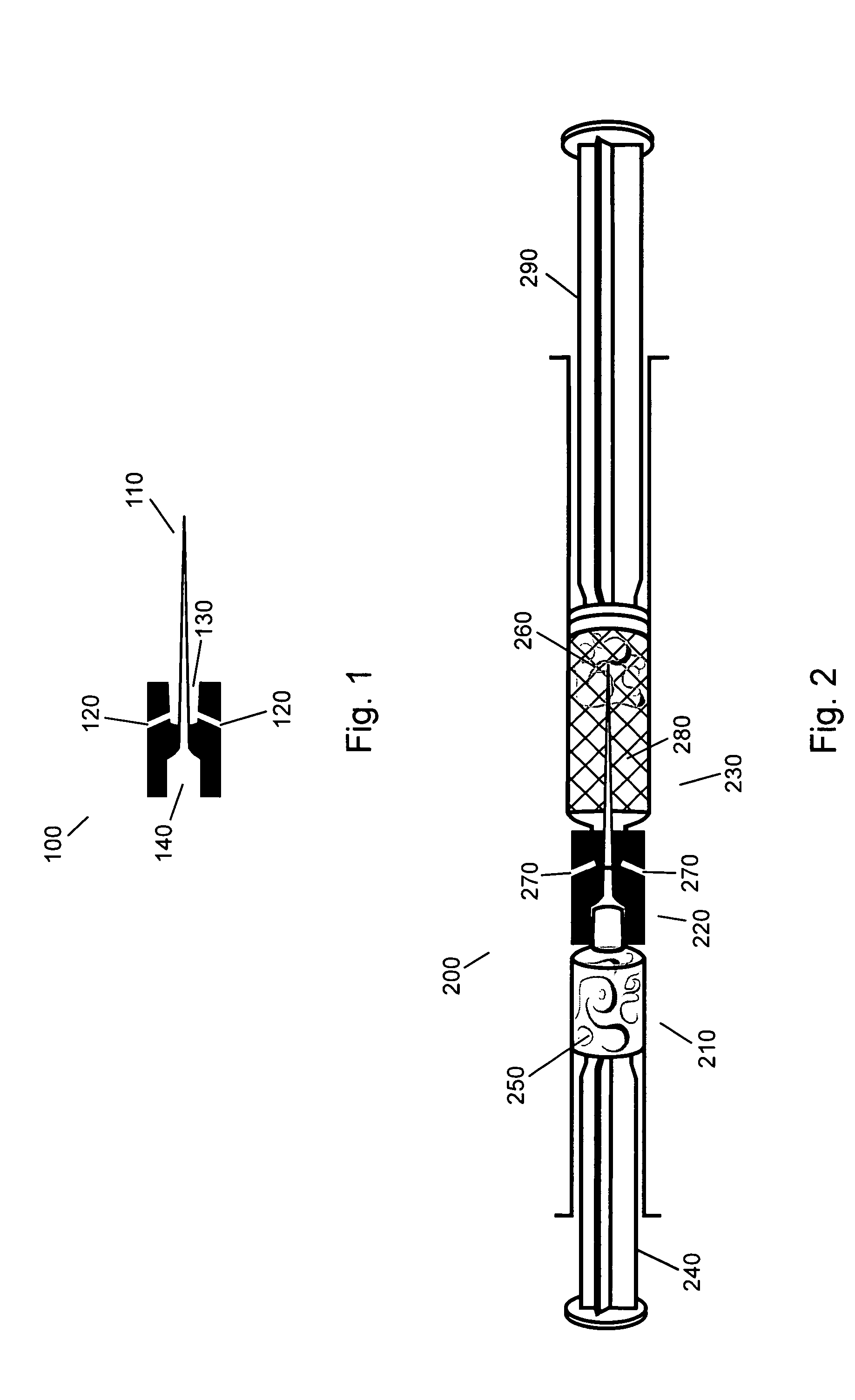
A sensor and method of making the same for implantation in a body that includes a substrate with notches cut in the substrate to form a necked down region in the substrate; and at least one sensor electrode formed from one or more conductive layers. Preferably, the thickness of the substrate ranges from approximately 25μ to 350μ, but the thickness of the substrate can range from 5μ to 750μ. The sensor may be incorporated in to a sensor assembly includes a slotted needle having a slot. The notches creating the necked down region allow the substrate to slide into the slotted needle, which that has the slot narrow enough to permit passage of the necked down region. However, a non-necked down region of the substrate is prevented from pulling out of the slotted needle through the slot. The slot of the slotted needle may also permit the necked down region of the substrate to slide down the slot.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Hemostatic fibrous material
InactiveUS20120004636A1Promote blood clottingPromoting blood clottingBiocideDiagnosticsFiberMolecular materials
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
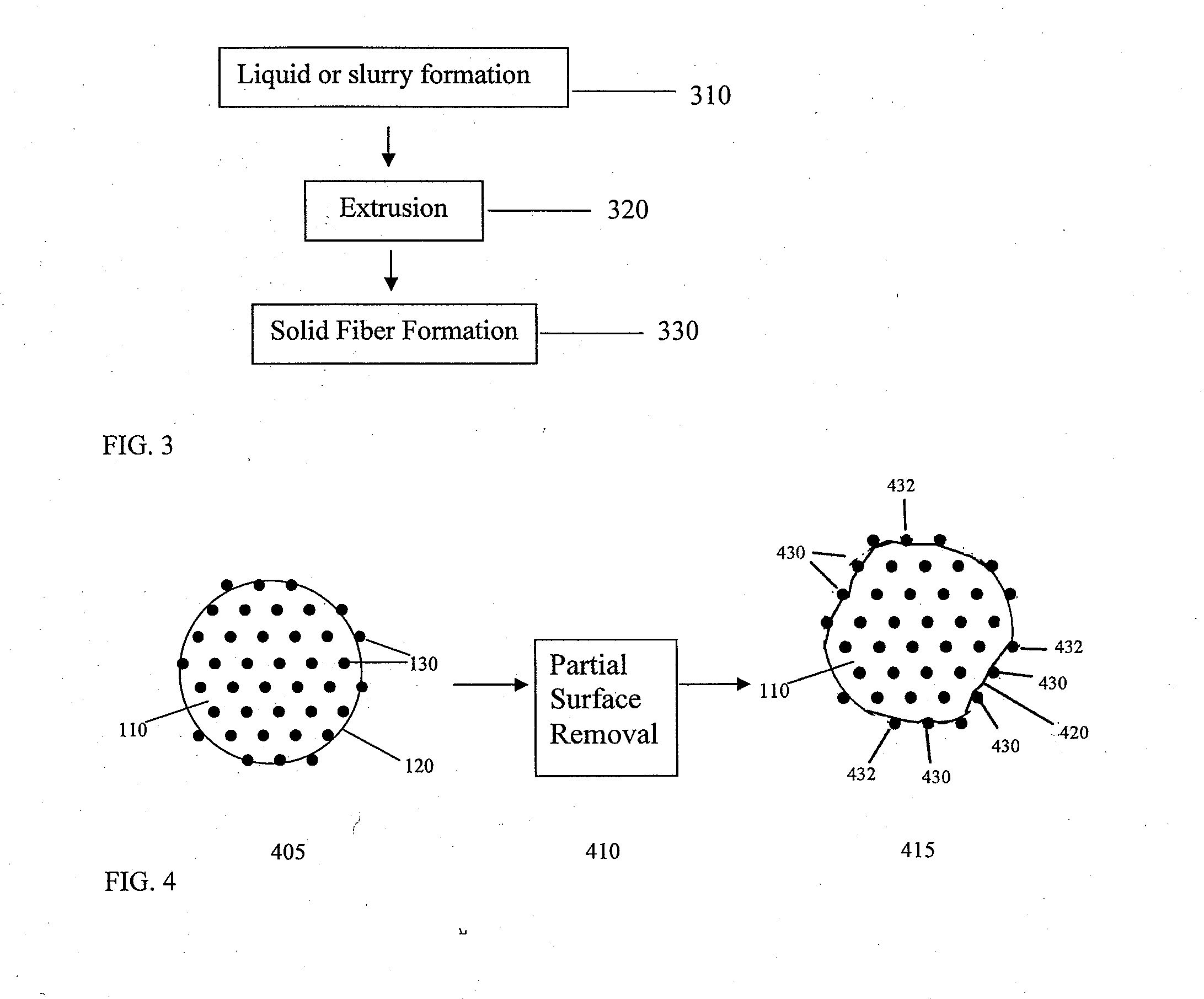
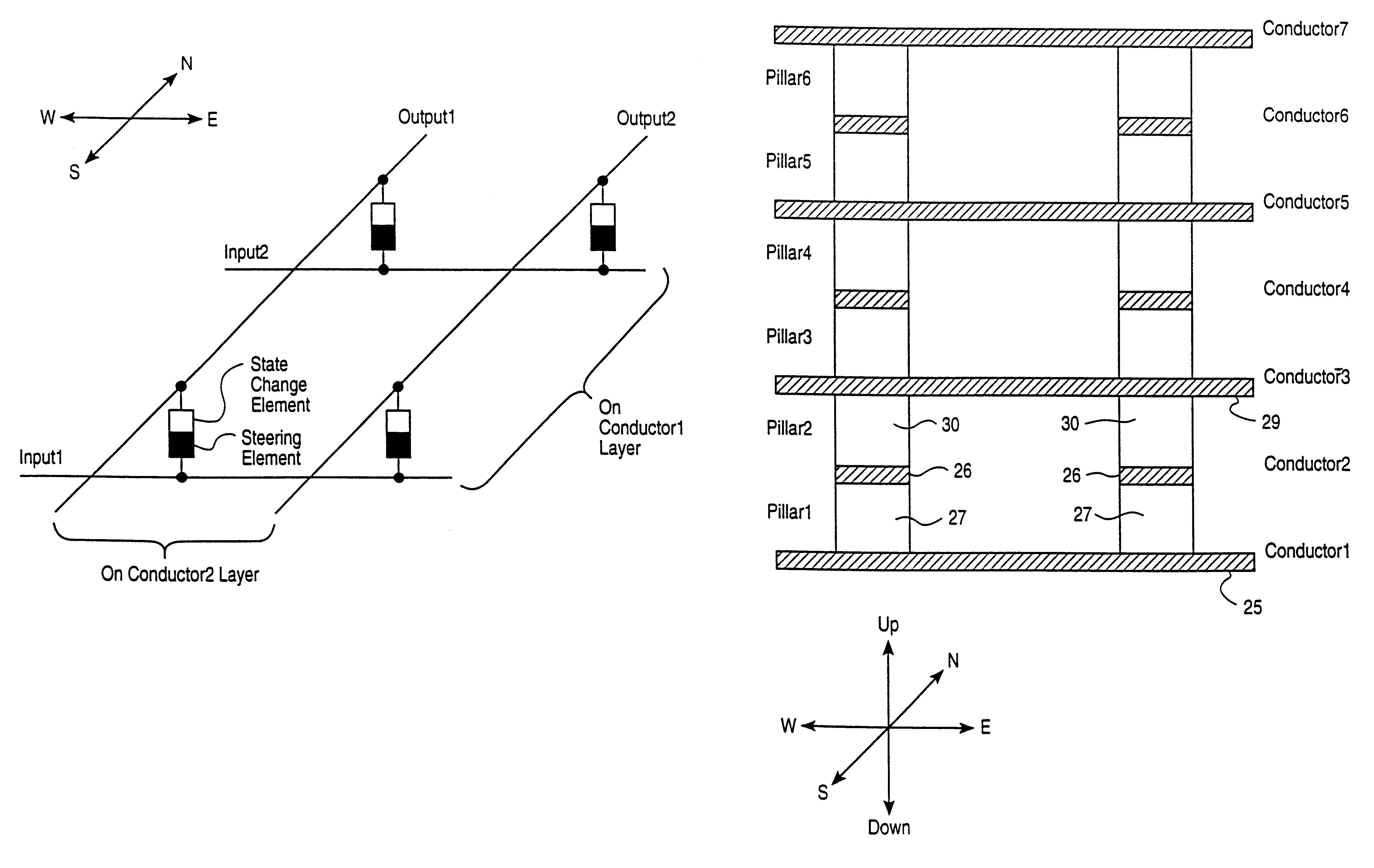
Vertically stacked field programmable nonvolatile memory and method of fabrication
A very high density field programmable memory is disclosed. An array is formed vertically above a substrate using several layers, each layer of which includes vertically fabricated memory cells. The cell in an N level array may be formed with N+1 masking steps plus masking steps needed for contacts. Maximum use of self alignment techniques minimizes photolithographic limitations. In one embodiment the peripheral circuits are formed in a silicon substrate and an N level array is fabricated above the substrate.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Gel suitable for implantation and delivery system
InactiveUS20050186240A1Readily and quickly rehydratableFacilitates cellular ingrowthPowder deliveryProsthesisHigh concentrationSolvation
The invention concerns a dried form of a porous polymer gel material which may be rehydrated and placed under pressure or compression to induce solvation, thereby forming a high concentration gel, in the form of an injectable viscous putty or dough, which may be implantated in the body.
Owner:KENSEY NASH CORP
Long wearable soft contact lens
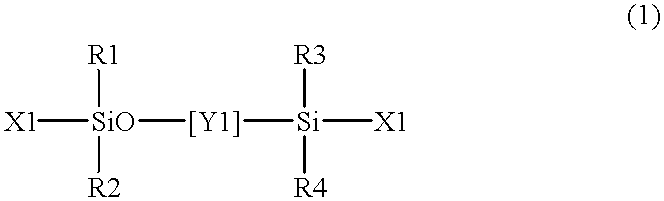
The present invention relates to a soft contact lens, and provides a contact lens which shows small and stable contact angle to water at its surface in water as well as in air, little deposition in wearing, high oxygen permeability, no adhesion of lens to a cornea and superior extended-wearing characteristics. The present invention provides a hydrogel soft contact lens which has contact angle at a lens surface in a range of 10-50° by the captive bubble method in water and 30-90° by the sessile drop method in air, oxygen permeability of not less than 30 and water content of not less than 5%, and also a hydrogel soft contact lens consisting of a polymer comprising a hydrophilic siloxanyl monomer shown by a specified general formula.
Owner:COOPERVISION INT LTD
Absorbent articles comprising nanoparticles
Owner:NANO MET ZERO
Tissue-derived mesh for orthopedic regeneration
An implant including a substantially cohesive aggregate comprising bone-derived particles. Cohesiveness is maintained by a member of mechanical interlocking, engagement of adjacent bone-derived particles with one another through engagement with a binding agent, thermal bonding, chemical bonding, or a matrix material in which the bone-derived particles are retained. The aggregate is shaped as a one-dimensional or two-dimensional body.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Surgical sealing surfaces and methods of use
ActiveUS7220951B2Fast transferHighly stable current-limitingDielectric heatingSurgical instruments for heatingOmni directionalSwitching time
Various embodiments provide compositions that exhibit positive temperature coefficient of resistance (PTCR) properties for use in thermal interactions with tissue—including thermal sensing and I2R current-limiting interactions. Embodiments also provide tissue-engaging surfaces having PTCR materials that provide very fast switching times between low resistance and high, current-limiting resistance. One embodiment provides a matrix for an electrosurgical energy delivery surface comprising a PTCR material and a heat exchange material disposed within an interior of the matrix. The PTCR material has a substantially conductive state and a substantially non-conductive state. The heat exchange material has a structure configured to have an omni-directional thermal diffusivity for exchanging heat with the PTCR material to cause rapid switching of the PTCR material between the conductive state and non-conductive state. Preferably, the structure comprises a graphite foam having an open cell configuration. The matrix can be carried by tissue contacting surfaces of various electrosurgical devices.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Bi-phasic compressed porous reinforcement materials suitable for implant
ActiveUS8389588B2Efficient use ofHigh and low porosity zoneBone implantSkeletal disorderFluid migrationUltimate tensile strength
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Bioabsorbable Polymer, Bioabsorbable Composite Stents
InactiveUS20080249608A1Simple and inexpensive to manufactureVarying of ductilityStentsSurgeryMetallic materialsMedical device
Biocompatible materials may be configured into any number of implantable medical devices including intraluminal stents. The biocompatible material may comprise metallic and non-metallic materials in hybrid structures. In one such structure, a device may be fabricated with one or more elements having an inner metallic core that is biodegradable with an outer shell formed from a polymeric material that is biodegradable. Additionally, therapeutic agents may be incorporated into the microstructure or the bulk material.
Owner:CORDIS CORP
Fabrication of biocompatible polymeric composites
InactiveUS6147135ASure easyImprove performanceSuture equipmentsCosmetic preparationsFiberPolymer science
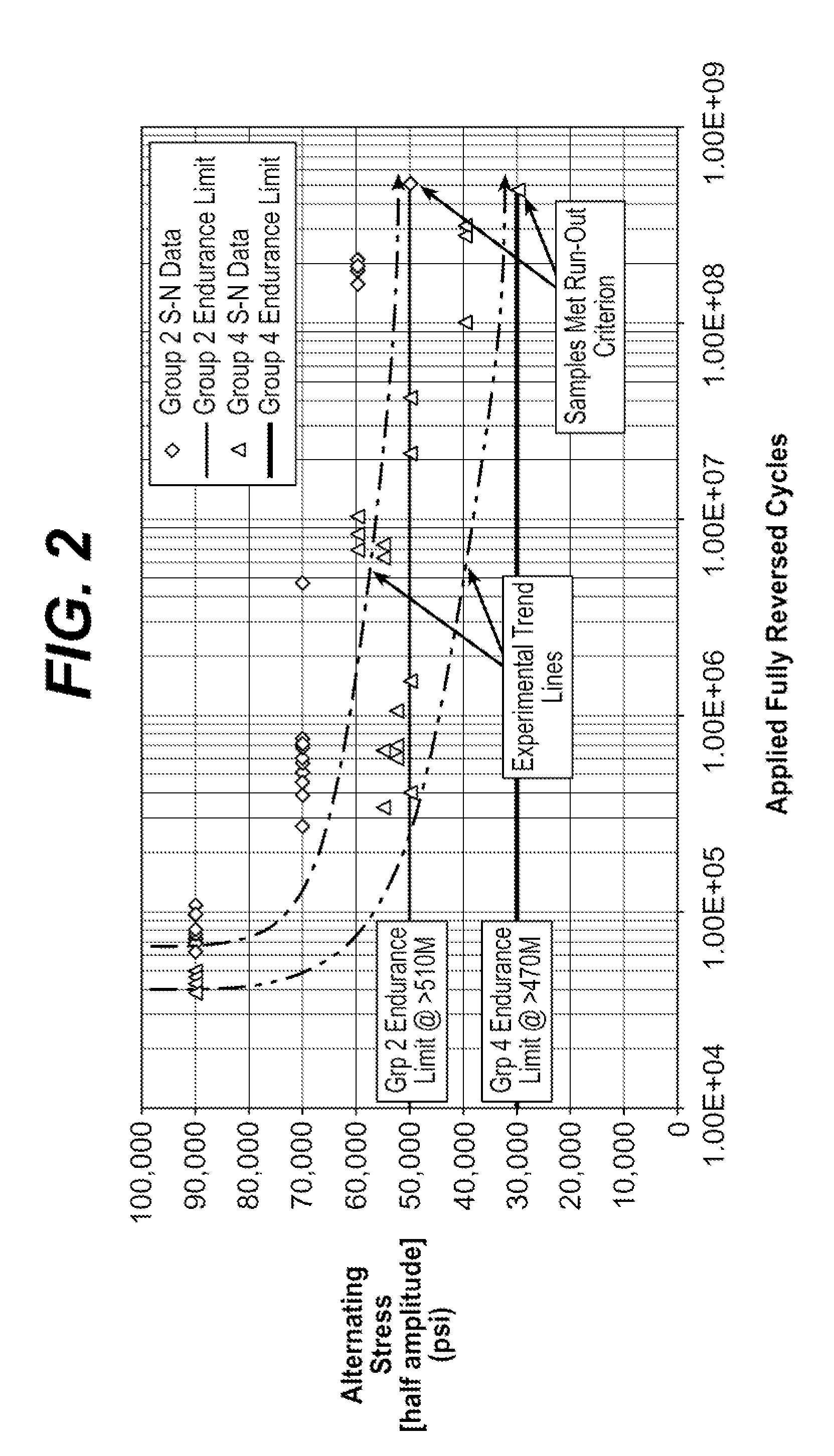
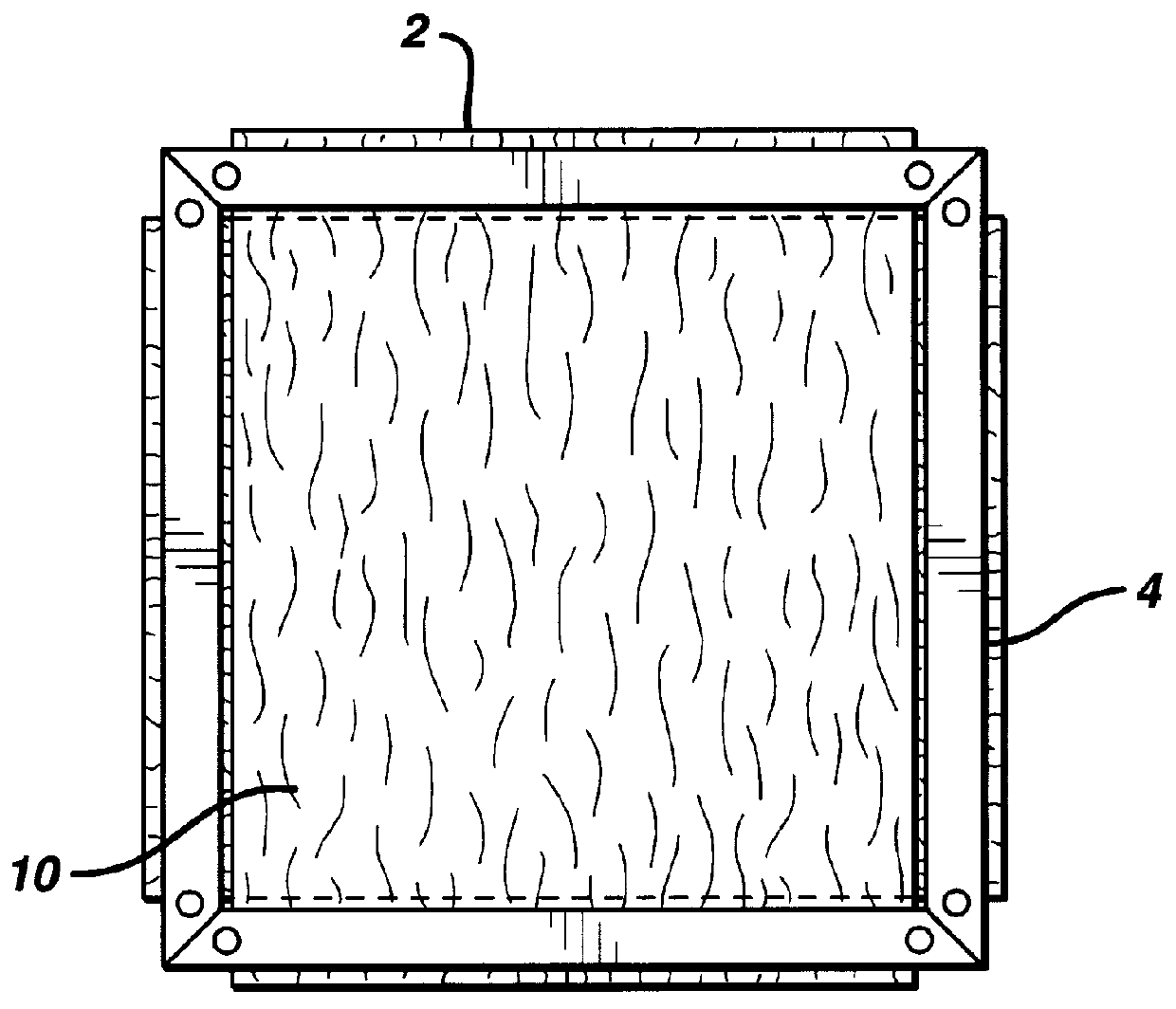
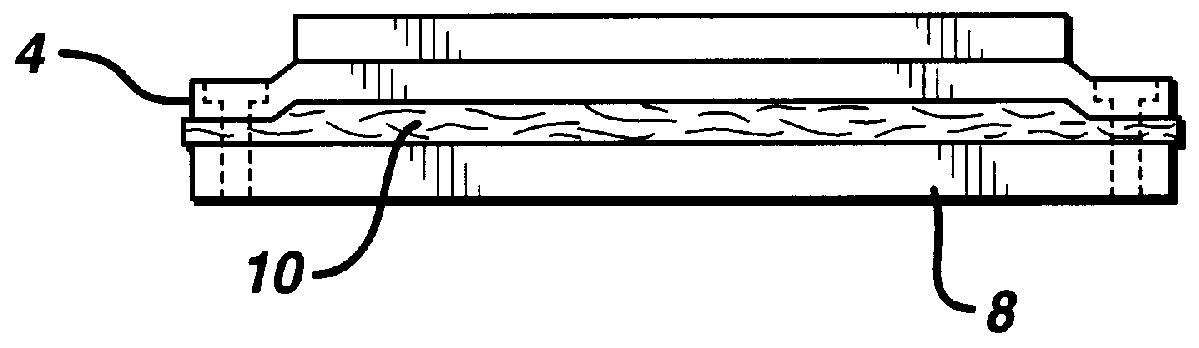
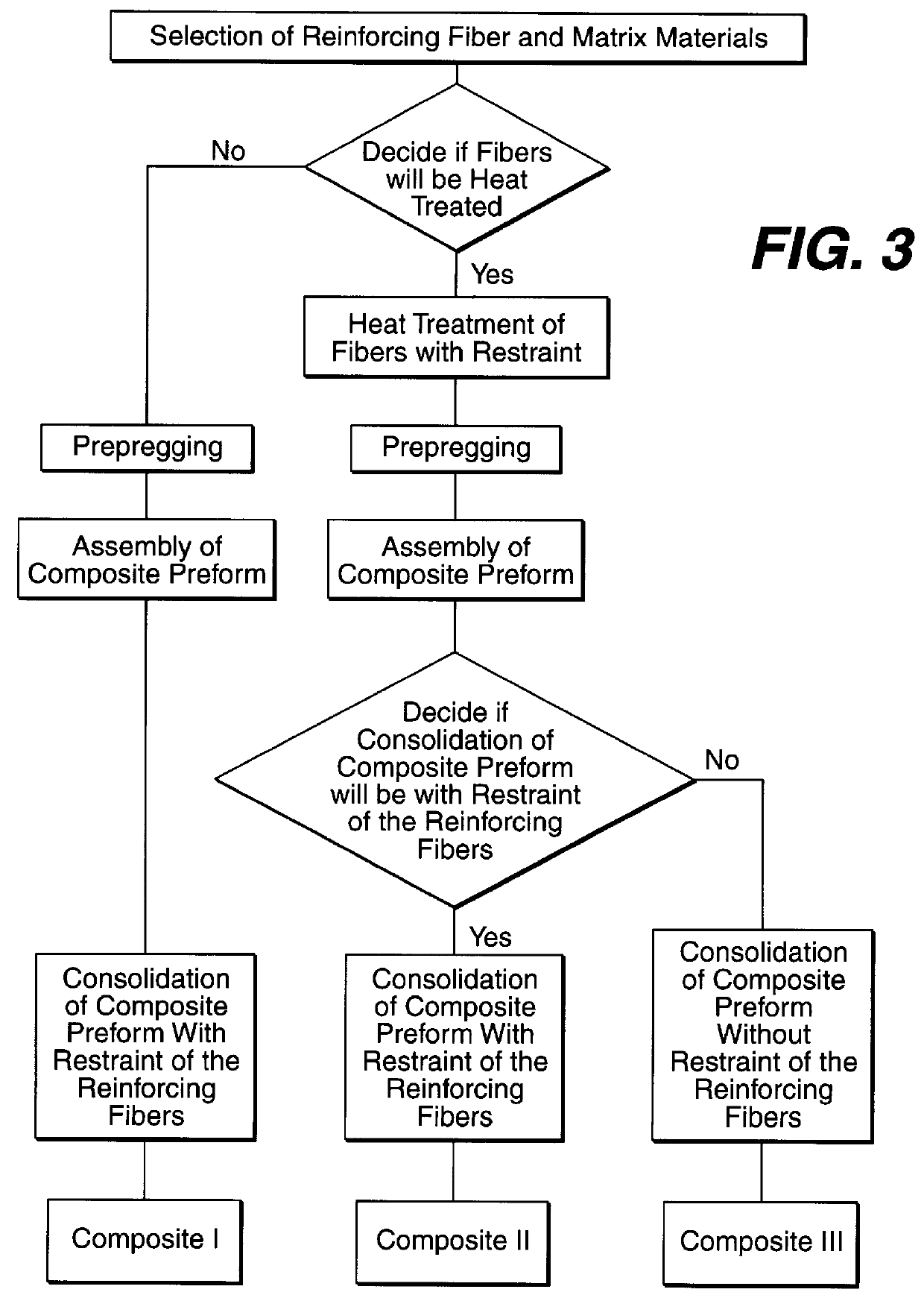
Composite materials formed from biocompatible polymer fibers and biodegradable polymers are disclosed. The heat treatment conditions for the reinforcing fibers are described so that the mechanical properties of the fibers can be retained during composite consolidation process. The processing conditions and set-ups to consolidations are constrained to the temperatures lower than fiber heat treatment temperatures. The reinforcing fibers are restrained under tension so that the minimum relaxation occurs during consolidation process.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Shielded optical probe having an electrical connector
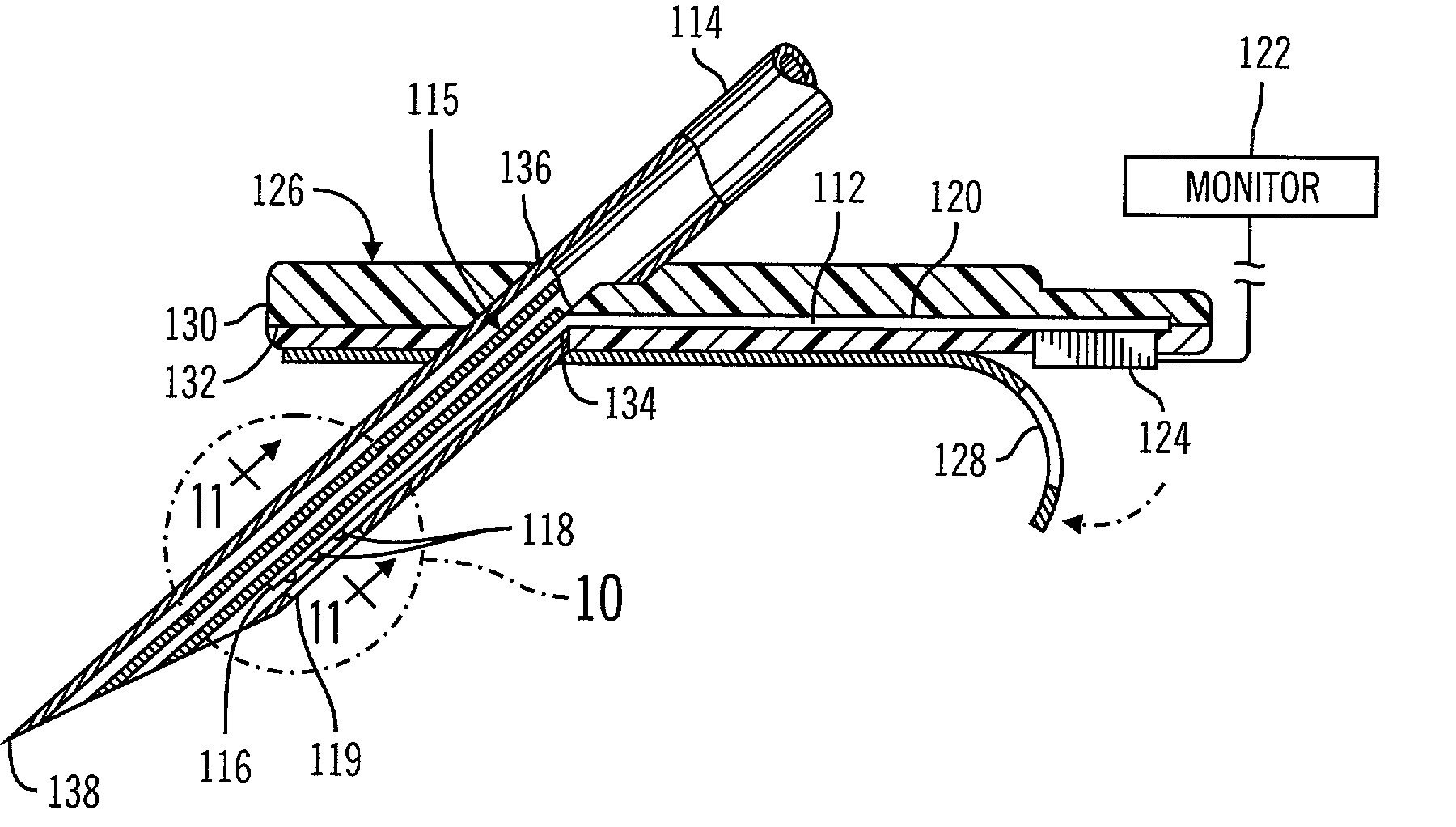
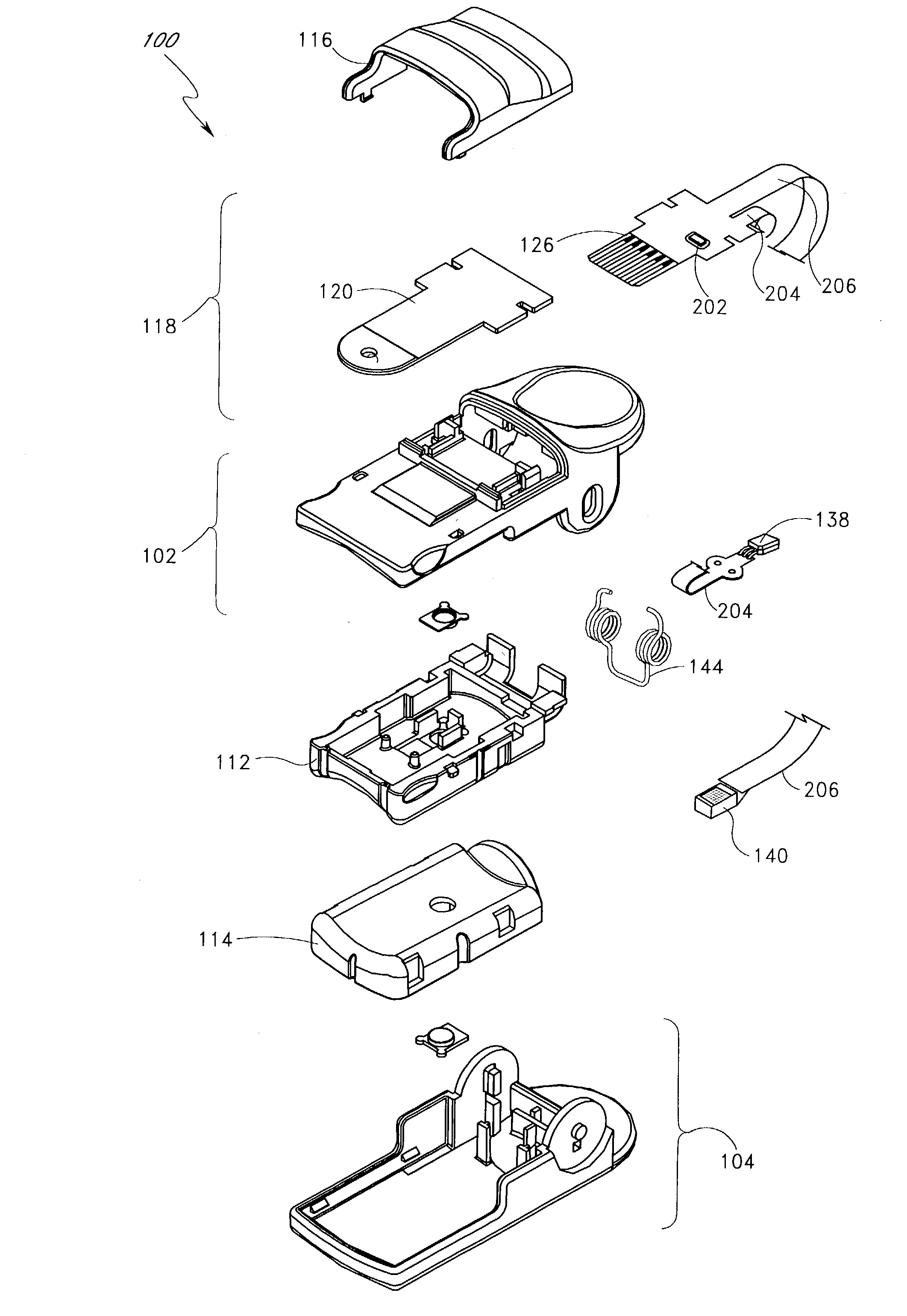
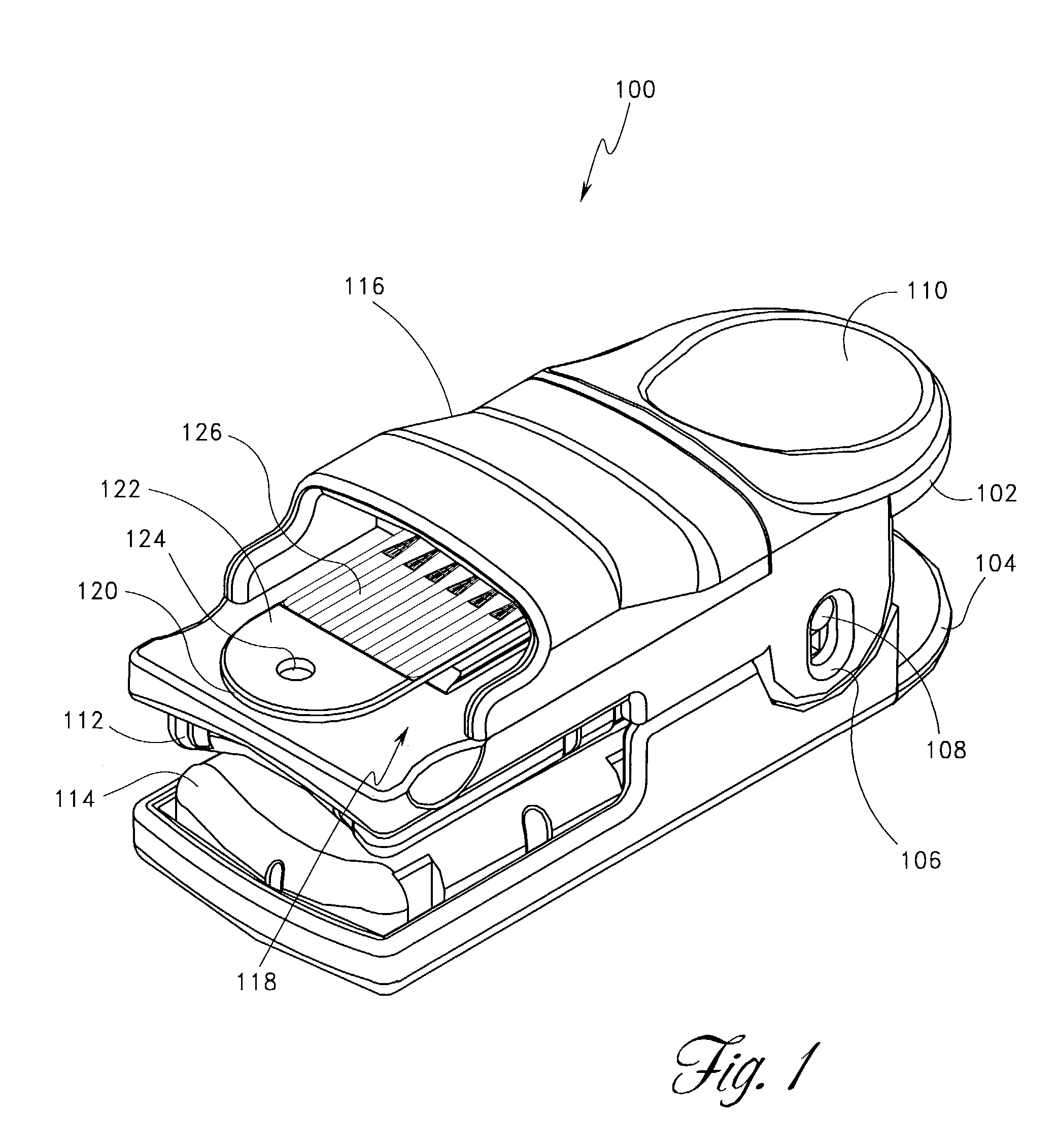
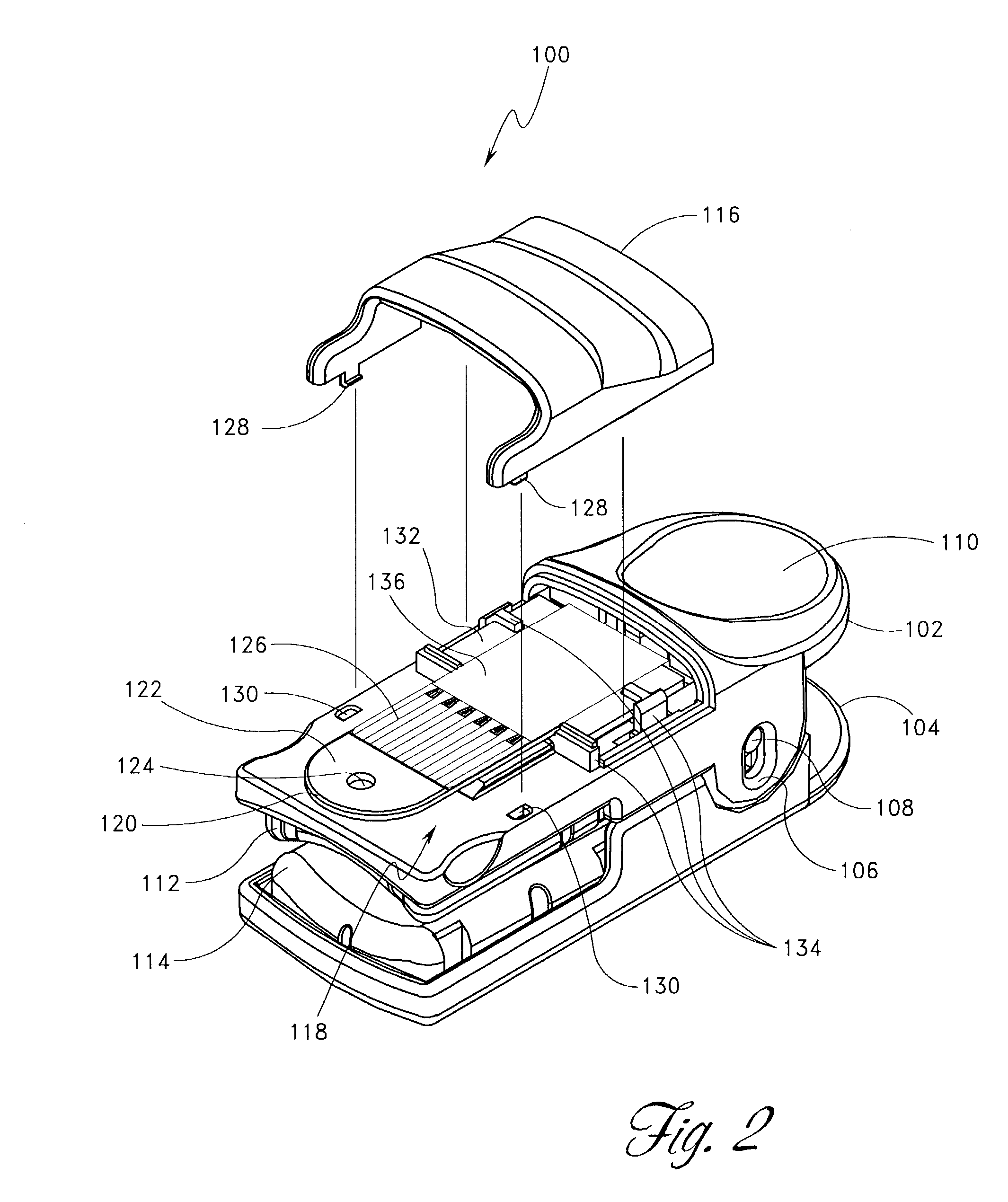
InactiveUS7132641B2Eliminate needEasy to adaptRotary current collectorInvestigating moving sheetsElectrical connectionEngineering
A noninvasive optical probe has an electrical connector for connecting the optical probe to a cable connector. According to one embodiment, the electrical connector includes a durable flexible tab suspended between the housing of the optical probe and a protective cover. The electrical connector also advantageously forms, according to various embodiments, a flexible, plugable, lockable, removable, and sealable electrical connection.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
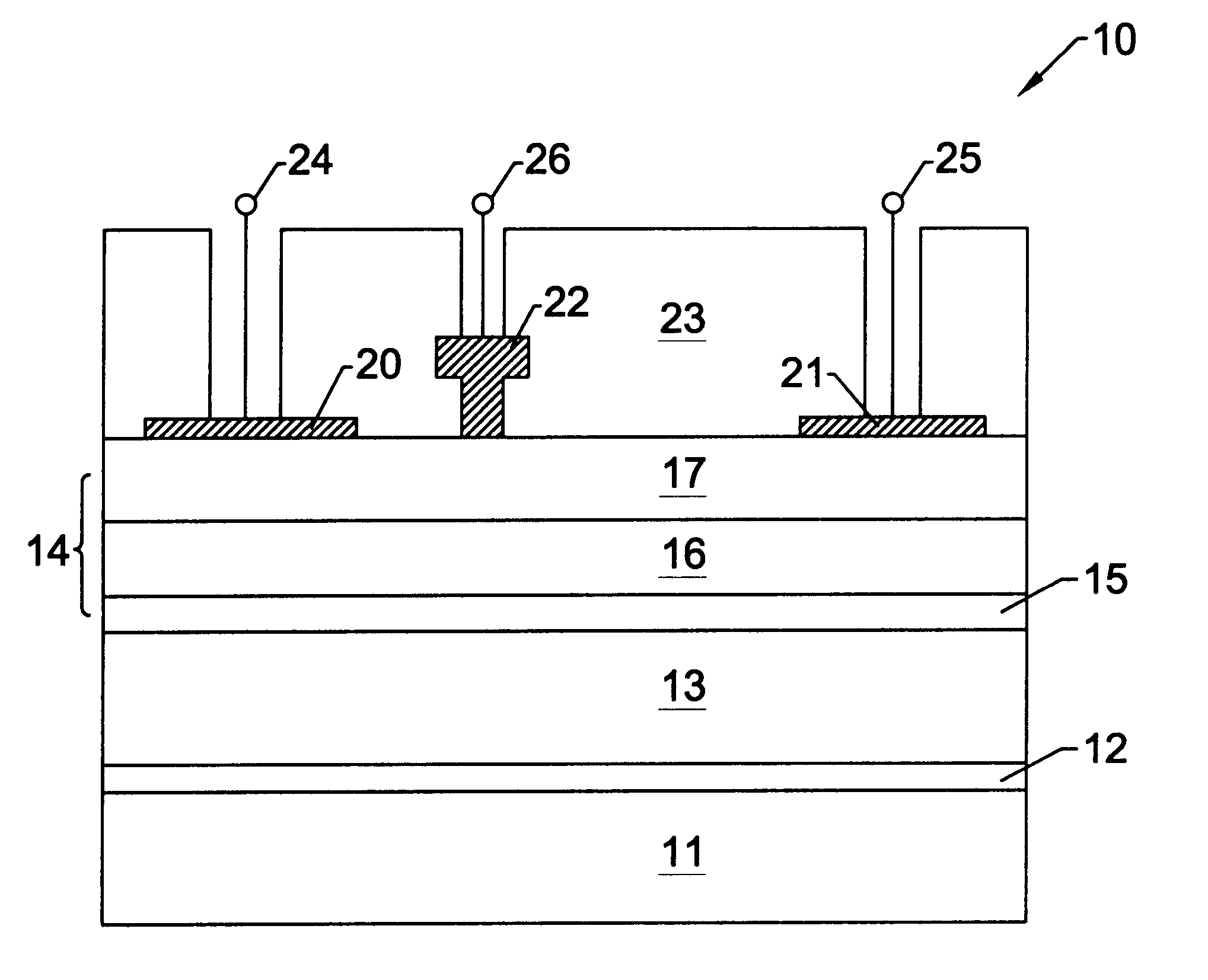
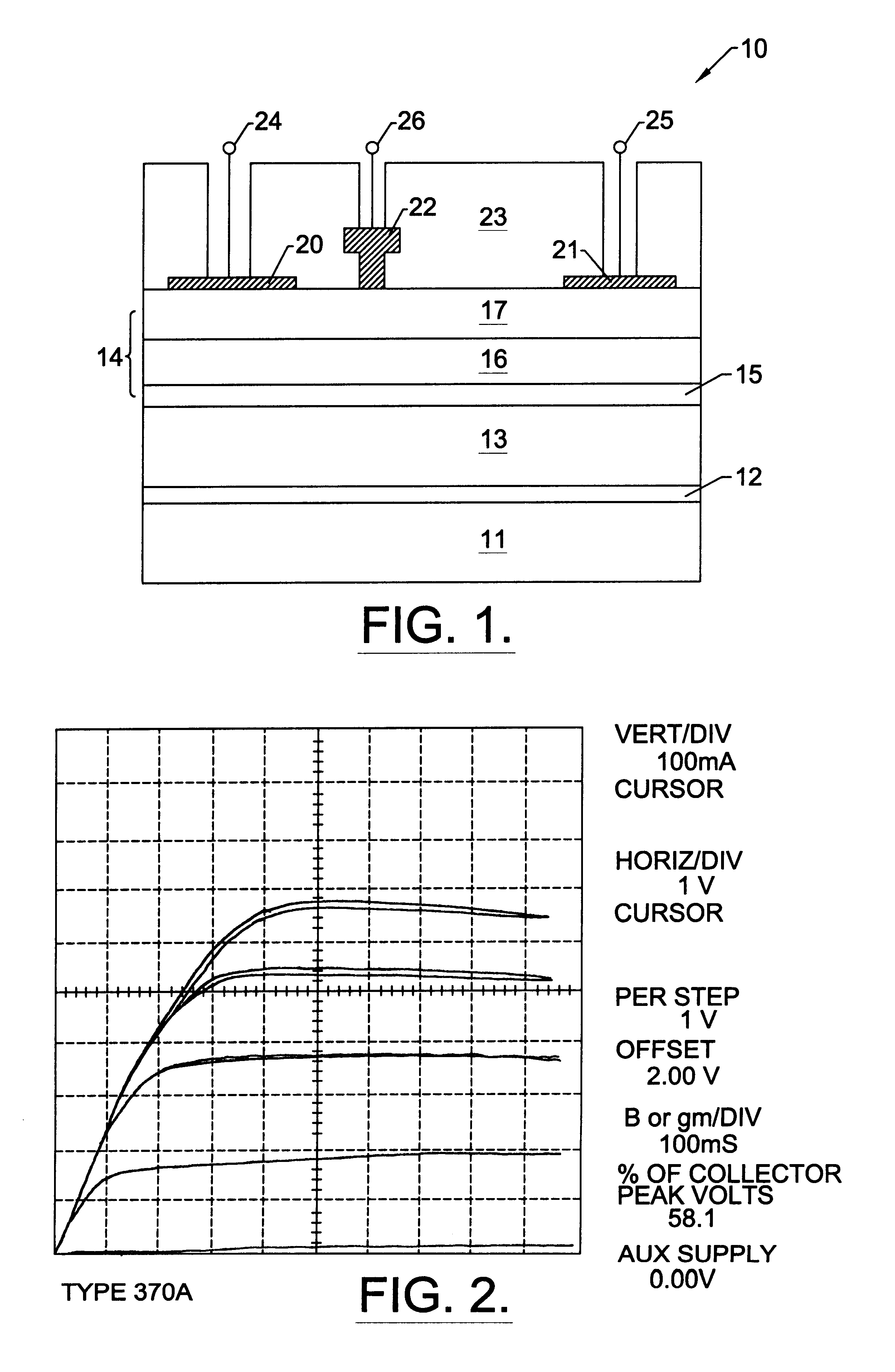
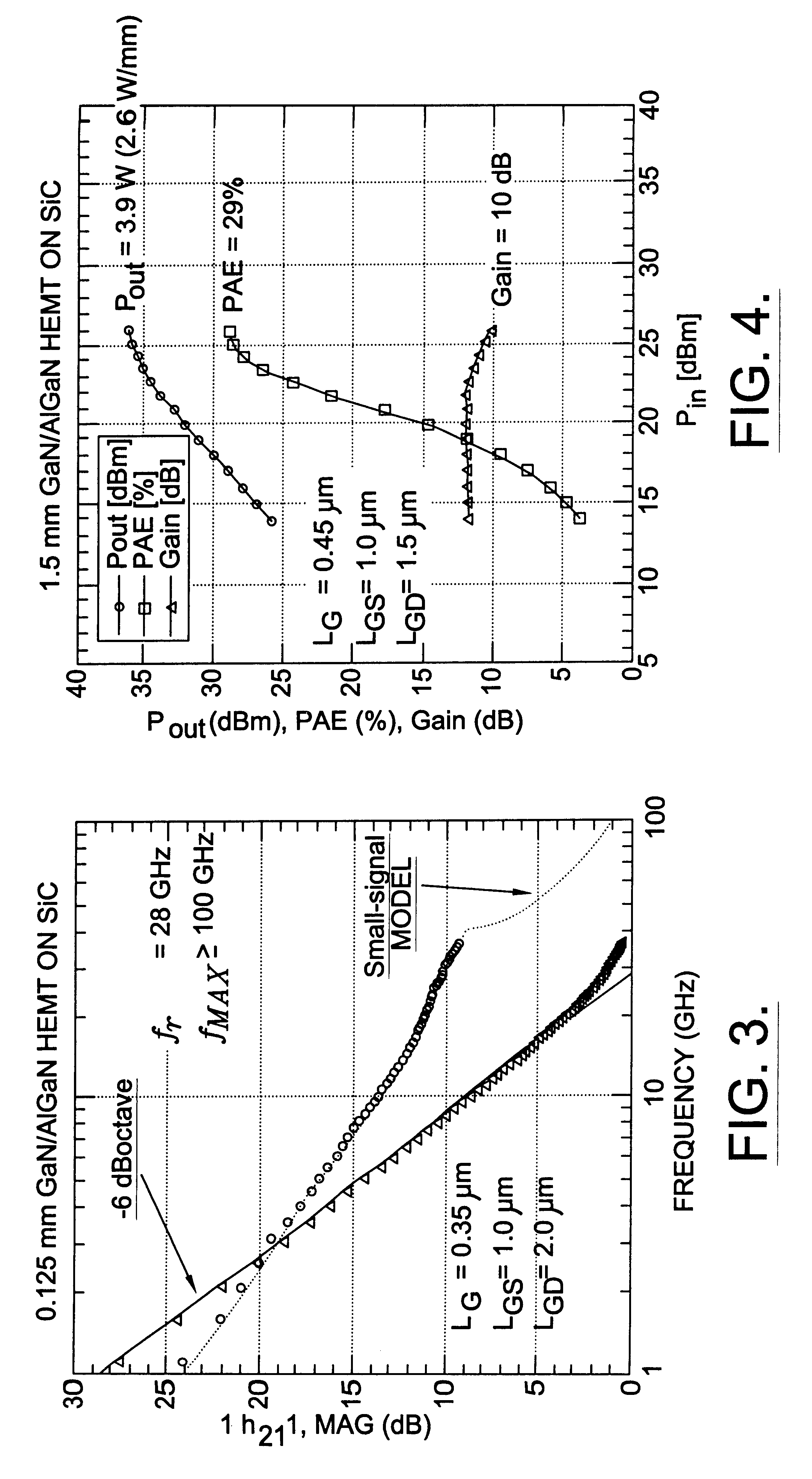
Nitride based transistors on semi-insulating silicon carbide substrates
InactiveUS6316793B1Quality improvementImprove thermal conductivitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGallium nitrideMaterials science
A high electron mobility transistor (HEMT) is disclosed that includes a semi-insulating silicon carbide substrate, an aluminum nitride buffer layer on the substrate, an insulating gallium nitride layer on the buffer layer, an active structure of aluminum gallium nitride on the gallium nitride layer, a passivation layer on the aluminum gallium nitride active structure, and respective source, drain and gate contacts to the aluminum gallium nitride active structure.
Owner:WOLFSPEED INC
Selectively absorbable/biodegradable, fibrous composite constructs and applications thereof
A family of selectively absorbable / biodegradable, fibrous composite constructs includes different combinations of biostable and absorbable / biodegradable yarns assembled as initially interdependent, load-bearing components, transitioning to exhibit independent functional properties during in vivo end-use. The family of constructs consists of two groups, one group is made of fiber-reinforced composites of high compliance, absorbable matrices of segmented polyaxial copolyesters reinforced with multifilament yarn constructs, which are combinations of ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene fibers and at least one absorbable / biodegradable fiber selected from silk fibers and multifilament yarns made from linear segmented, l-lactide copolyesters and poly (3-hydroxyalkanoates, are useful in orthopedic, maxillofacial, urological, vascular, hernial repair and tissue engineering applications. The second group is made of coated and uncoated, warp-knitted mesh constructs for use in hernial, vascular, and urological tissue repair and tissue engineering.
Owner:POLY MED
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com