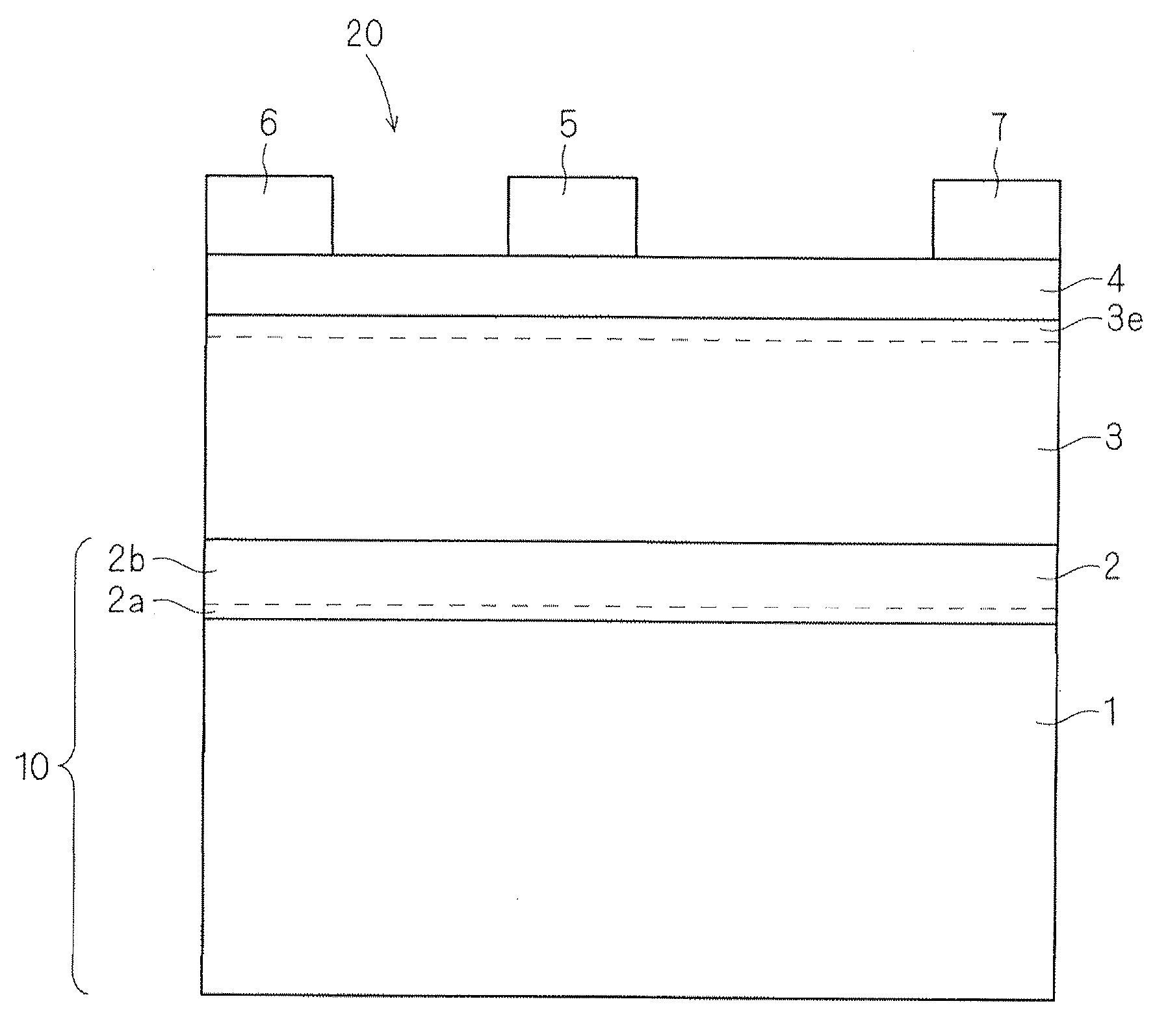
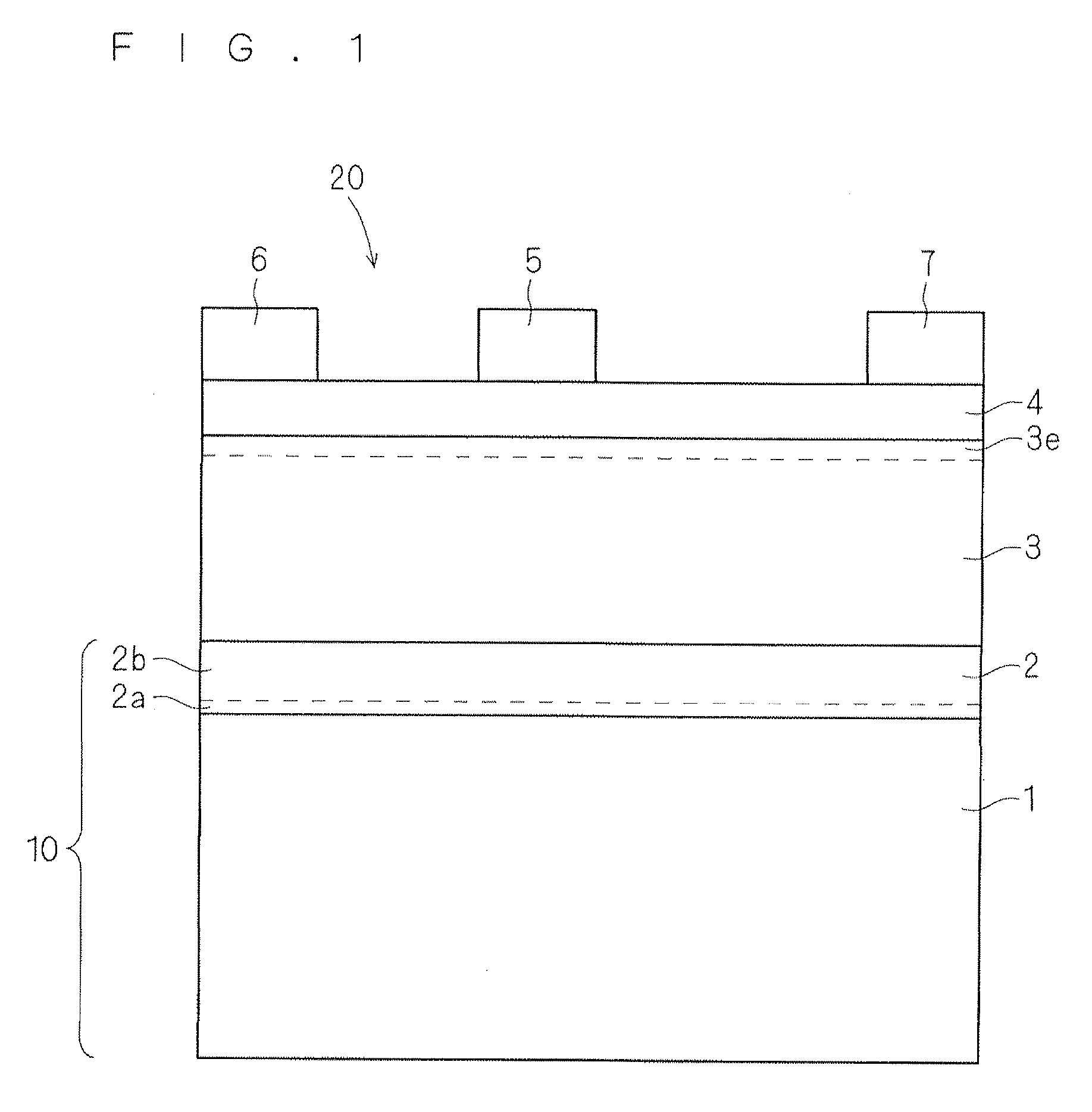
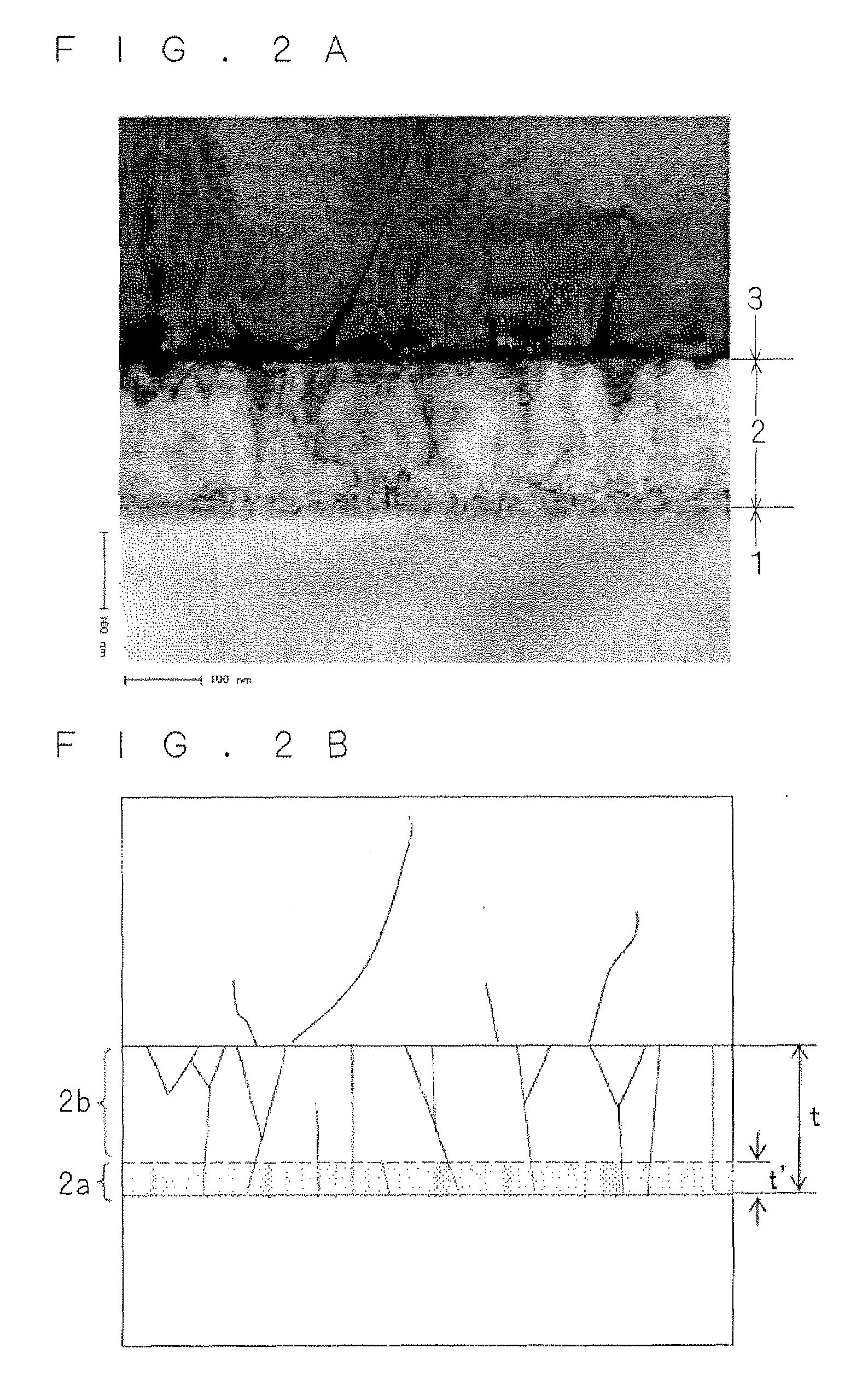
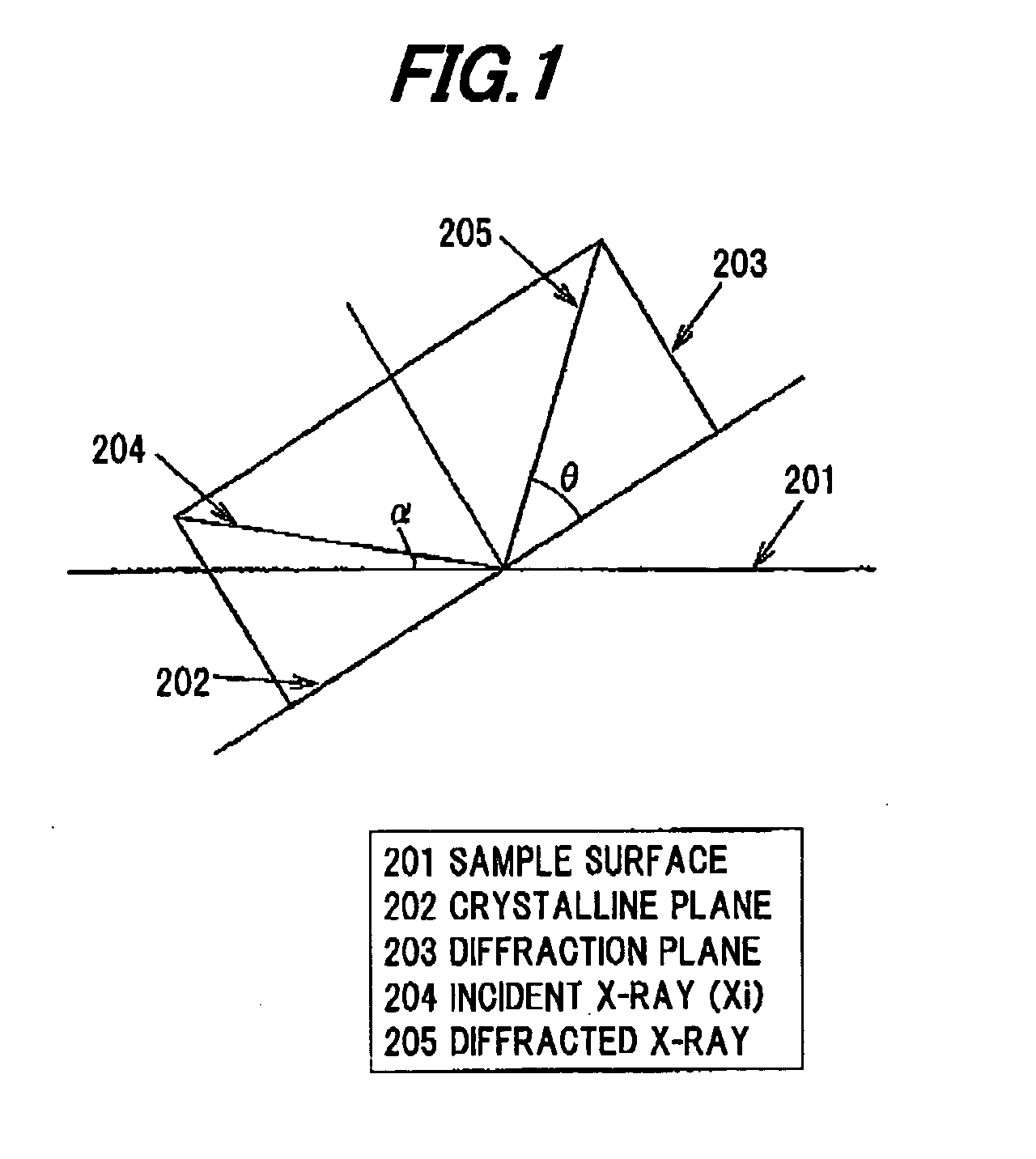
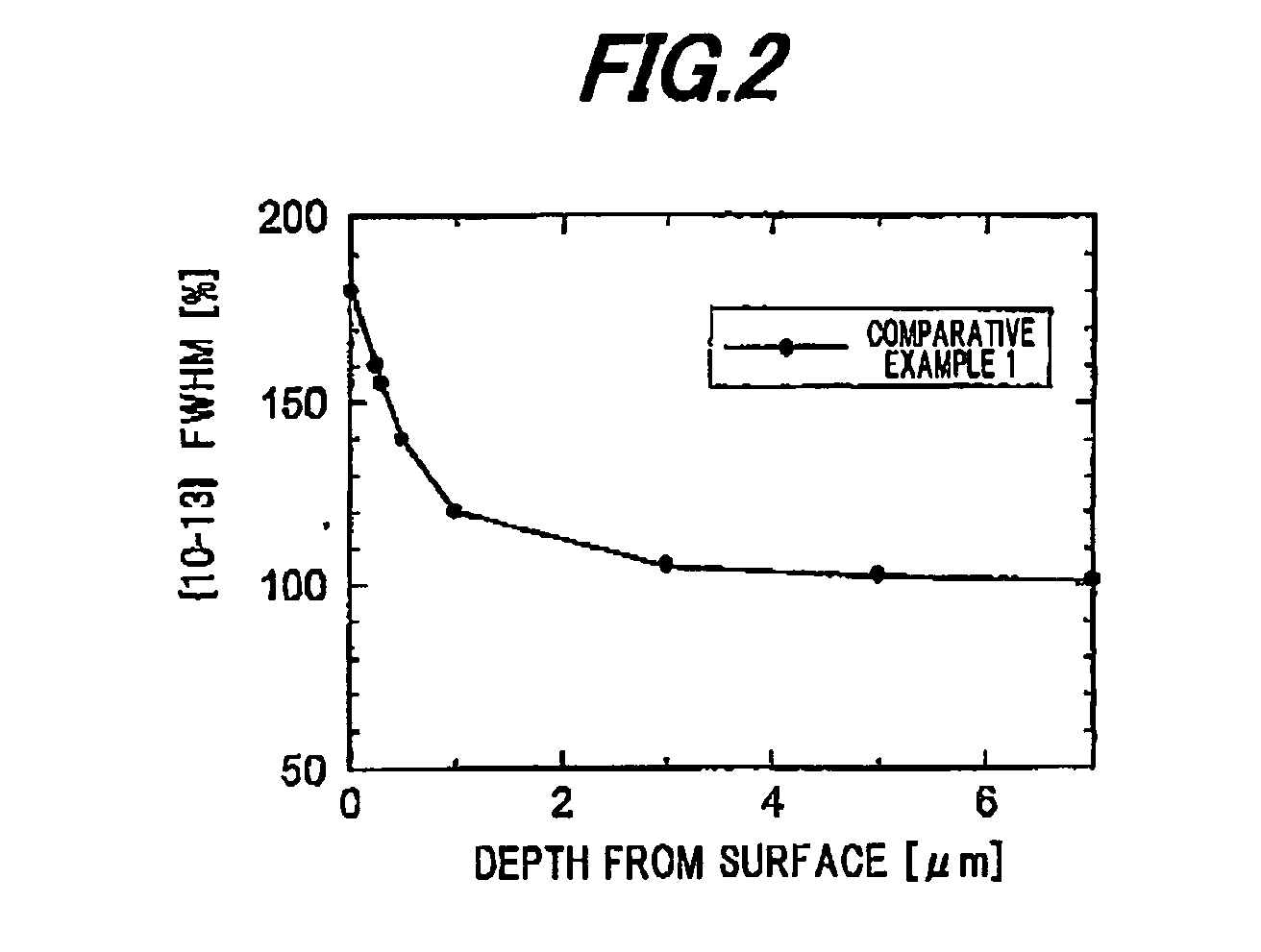
Patents
Literature
153 results about "Rocking curve" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
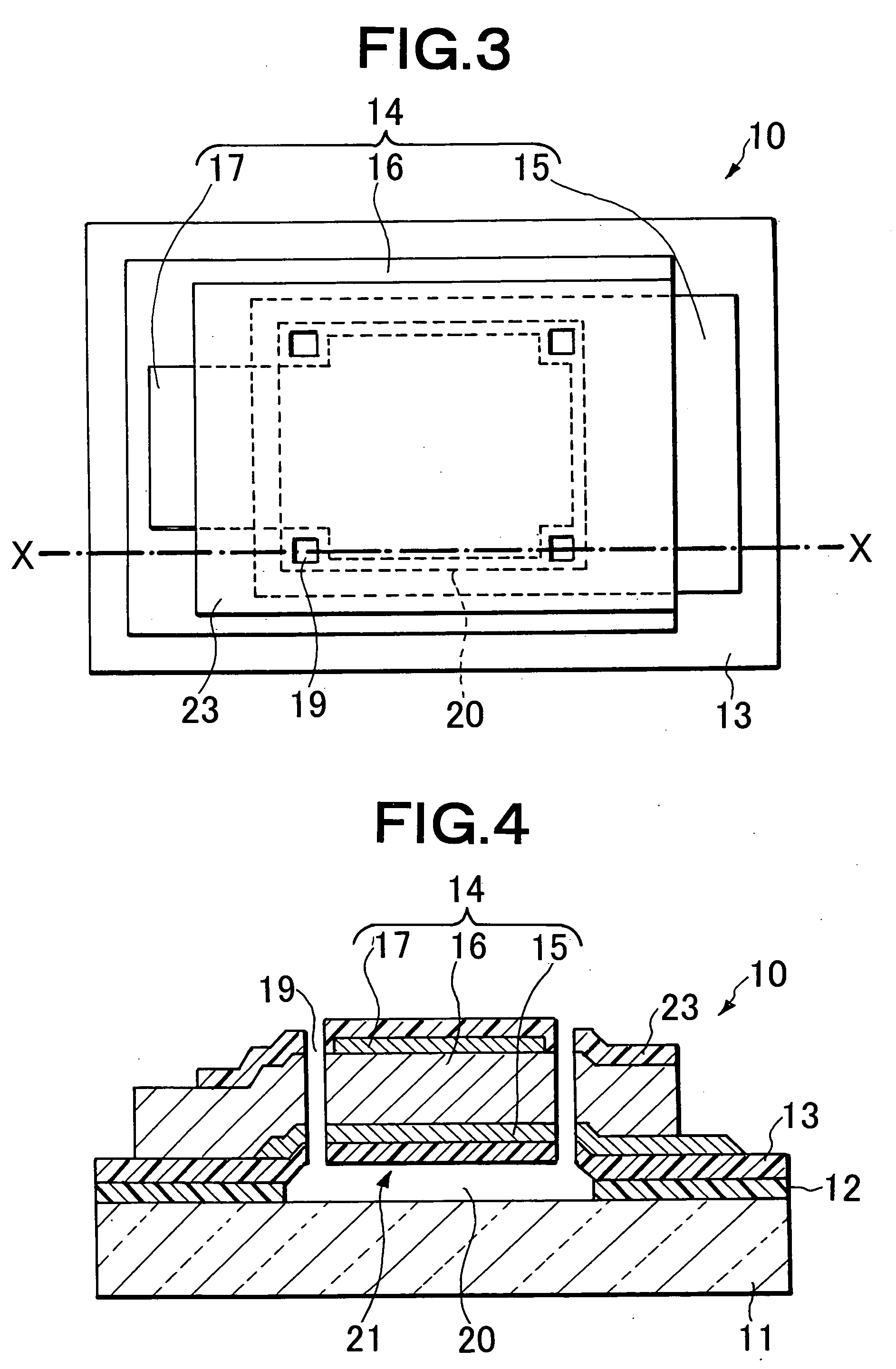
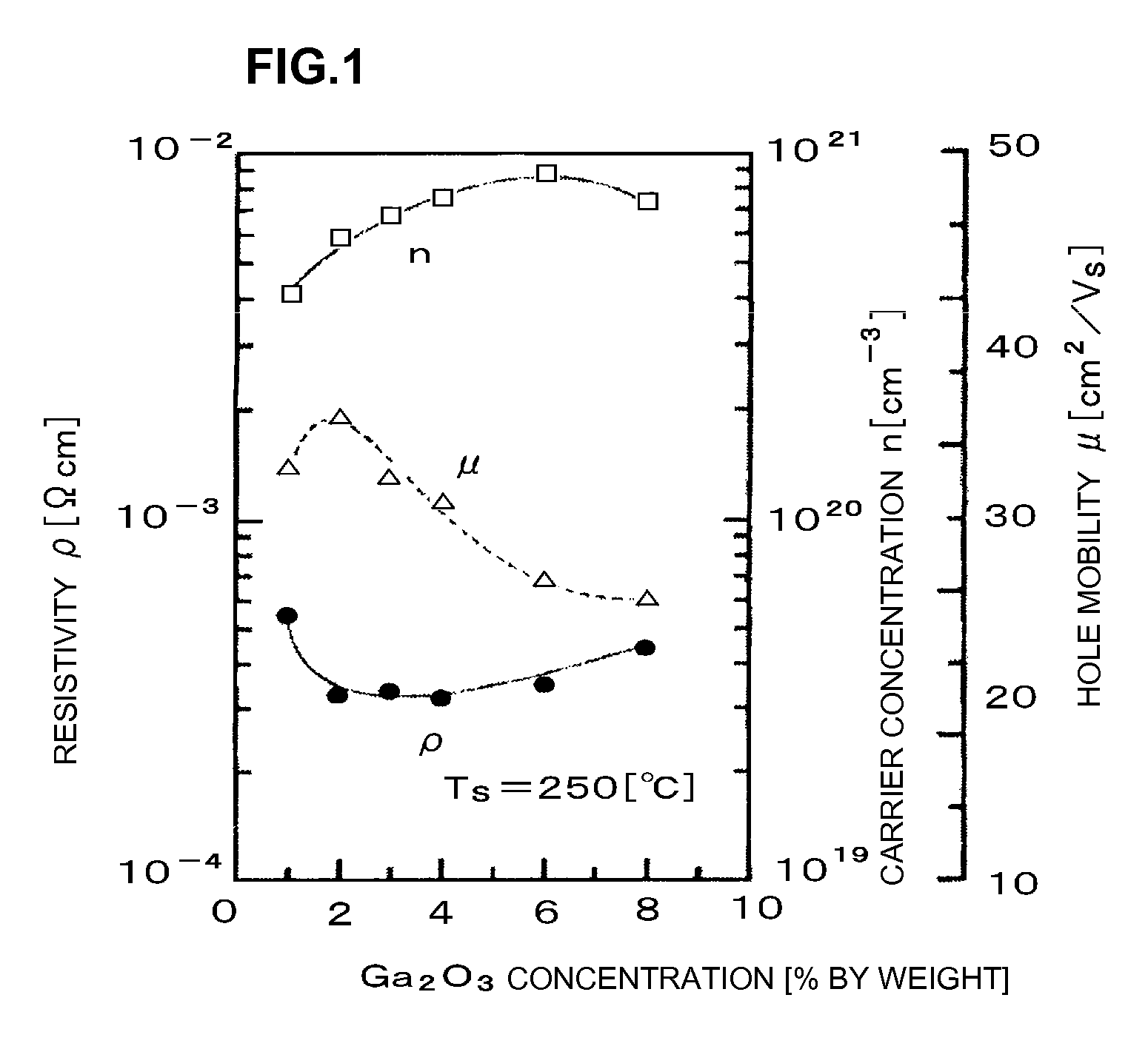
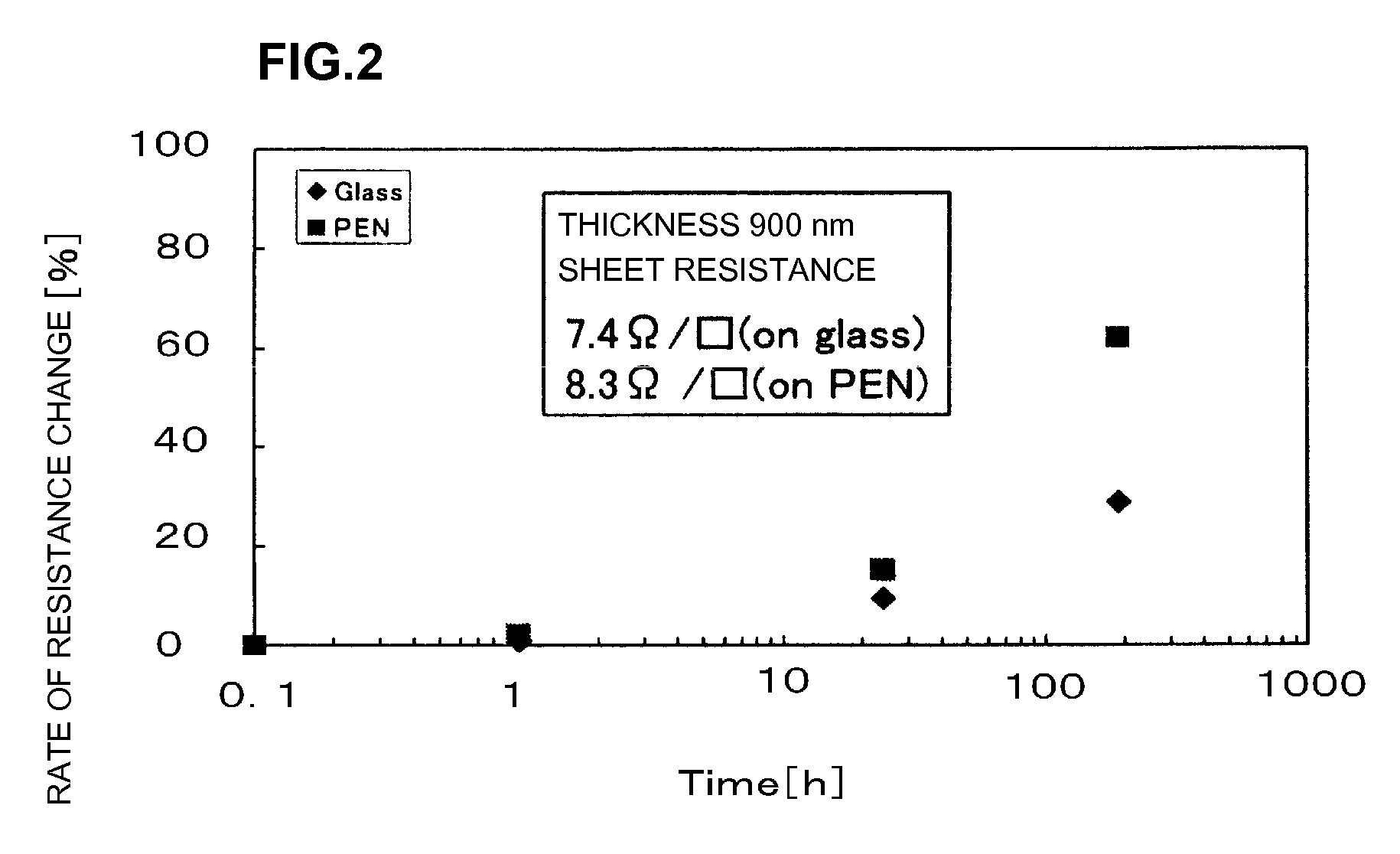
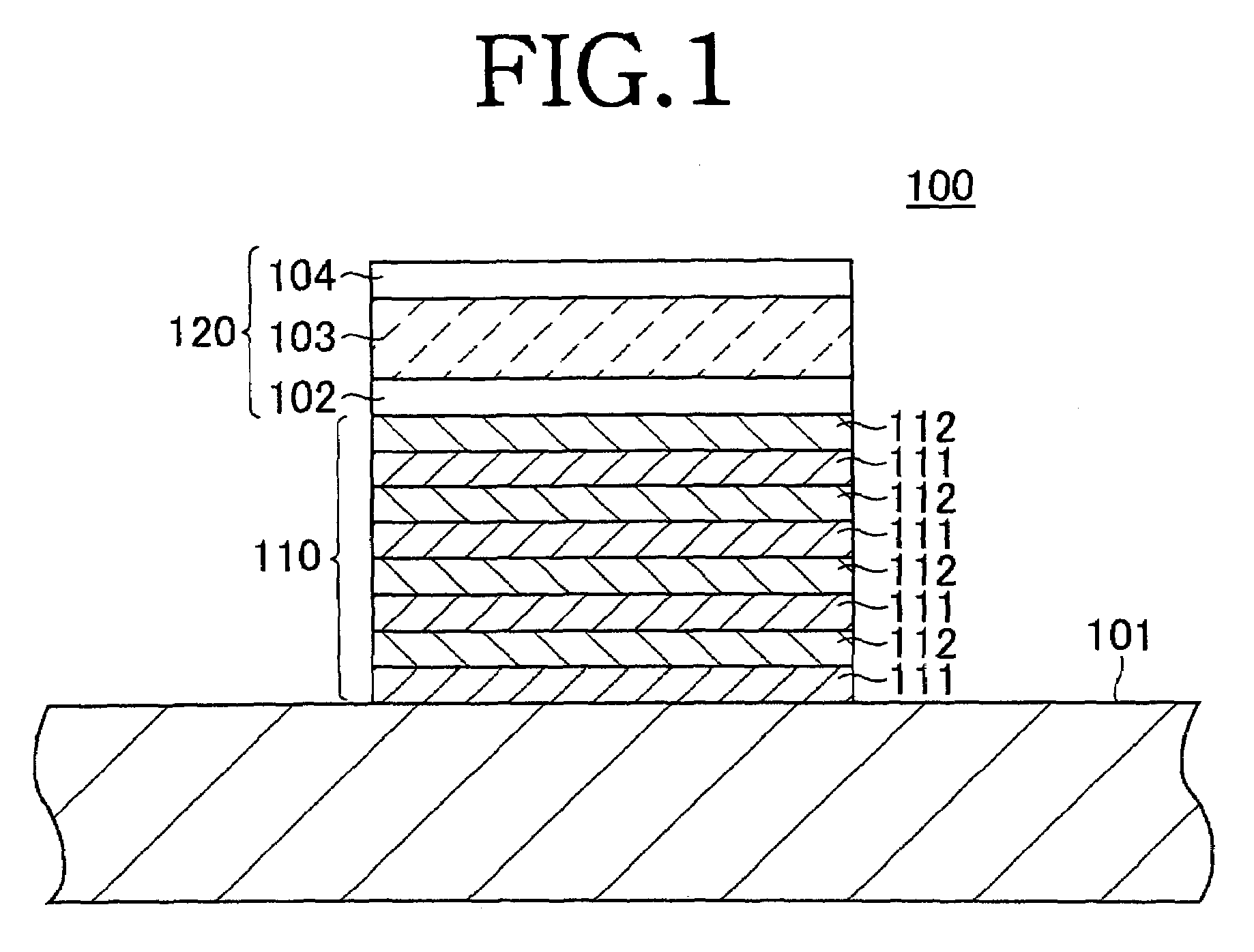
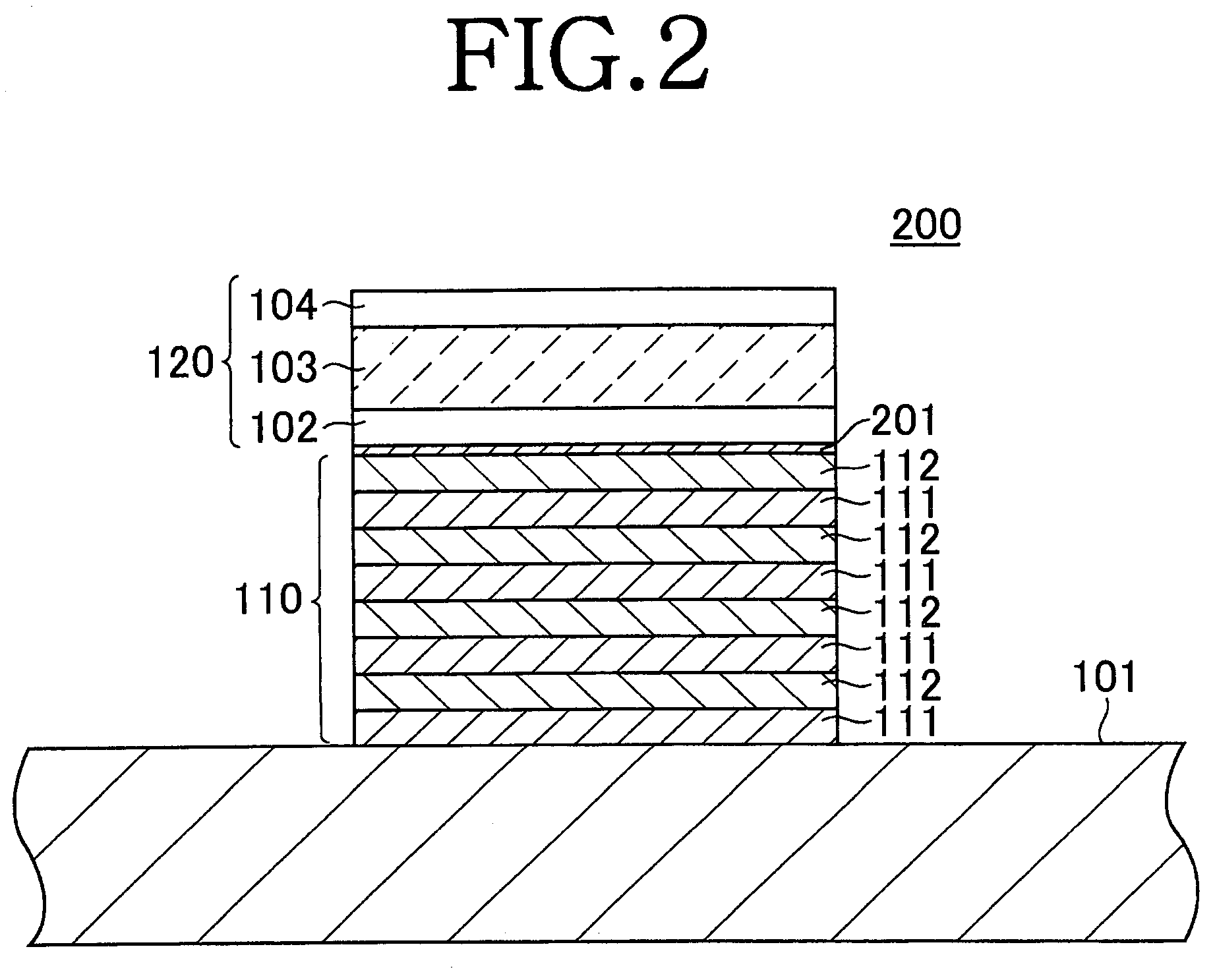
Transparent conductive film and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20080050595A1Improve economyConductive layers on insulating-supportsSynthetic resin layered productsRocking curveFull width at half maximum
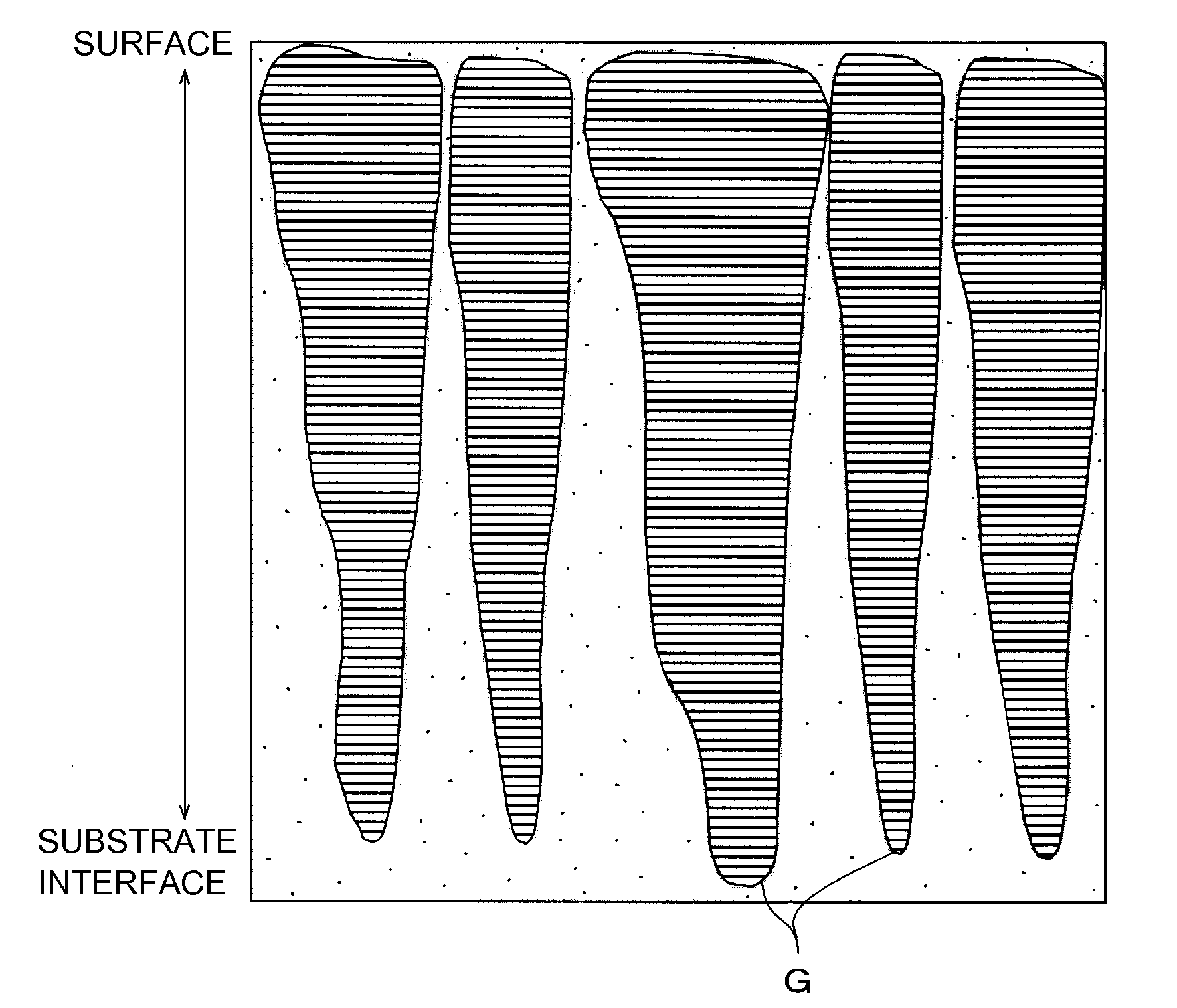
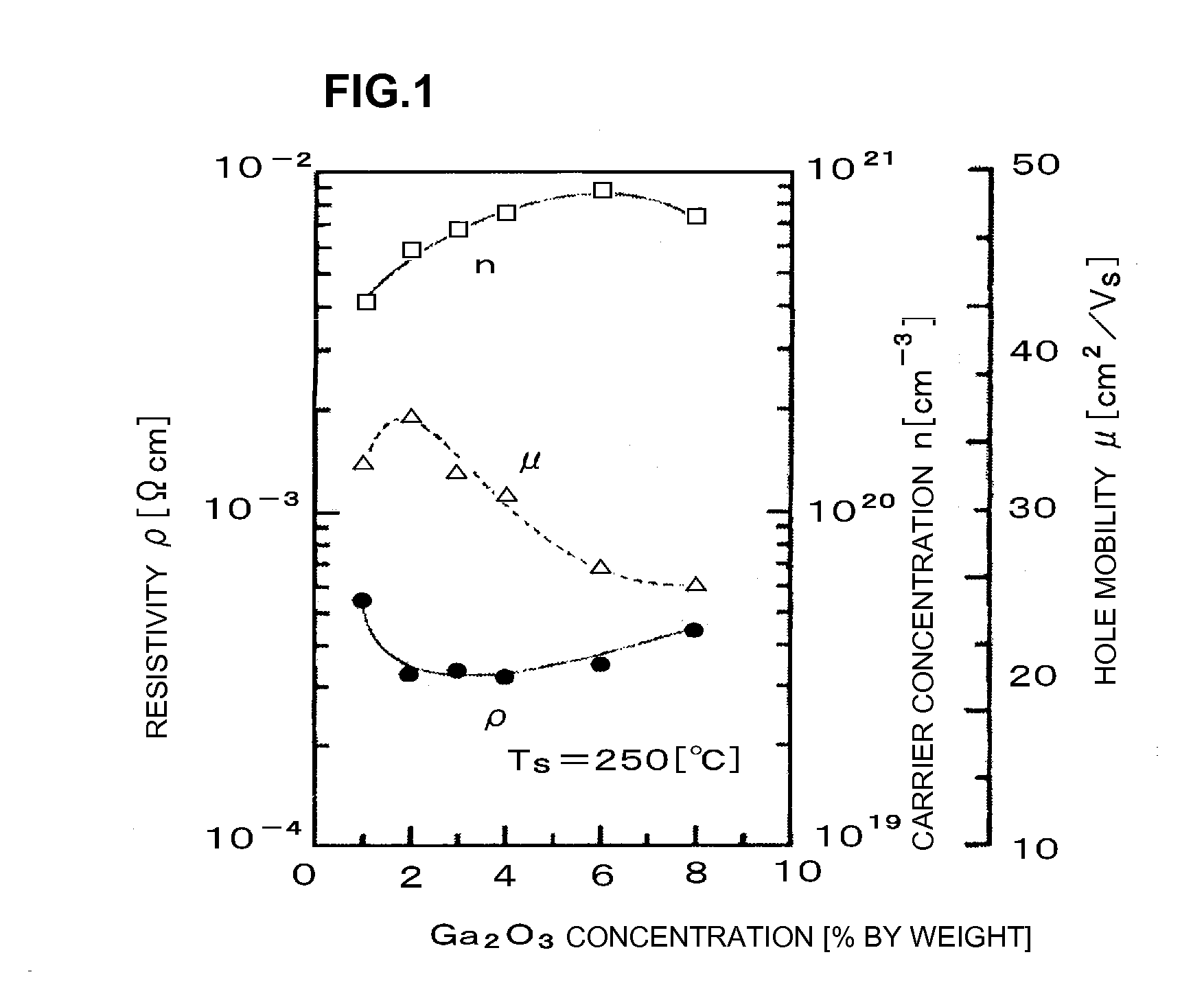
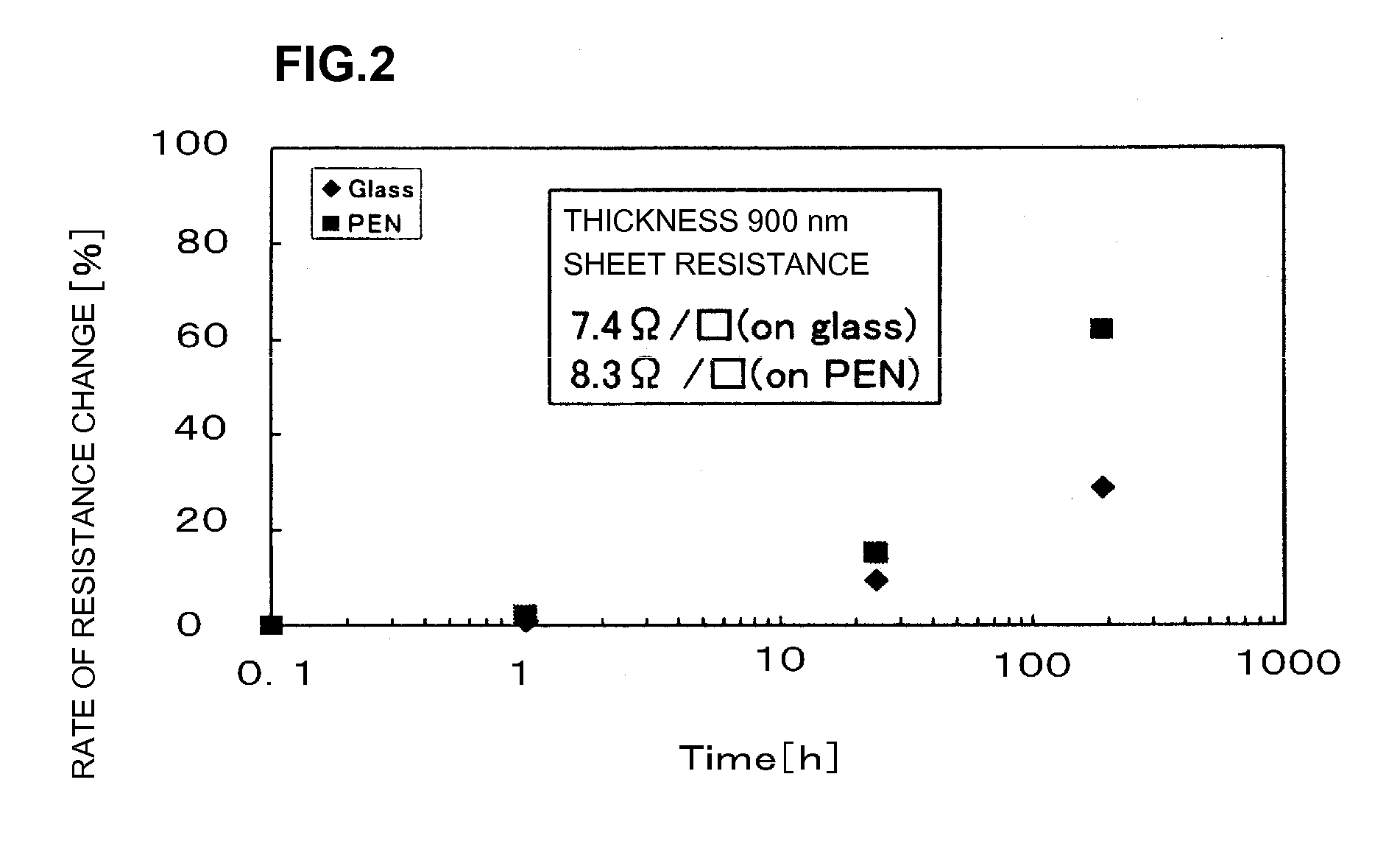
A ZnO-based transparent conductive film has practicable moisture resistance, desired characteristics of a transparent conductive film, and excellent economy. The transparent conductive film is produced by growing ZnO doped with a group III element oxide on a substrate and has a region with a crystal structure in which a c-axis grows along a plurality of different directions. The transparent conductive film produced by growing ZnO doped with a group III element oxide on a substrate has a ZnO (002) rocking curve full width at half maximum of about 13.5° or more.ZnO is doped with a group III element oxide so that the ratio of the group III element oxide in the transparent conductive film is about 7% to about 40% by weight.The transparent conductive film is formed on the substrate with a SiNx thin film provided therebetween.The transparent conductive film is formed on the substrate by a thin film formation method with a bias voltage applied to the substrate.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Nitride semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same
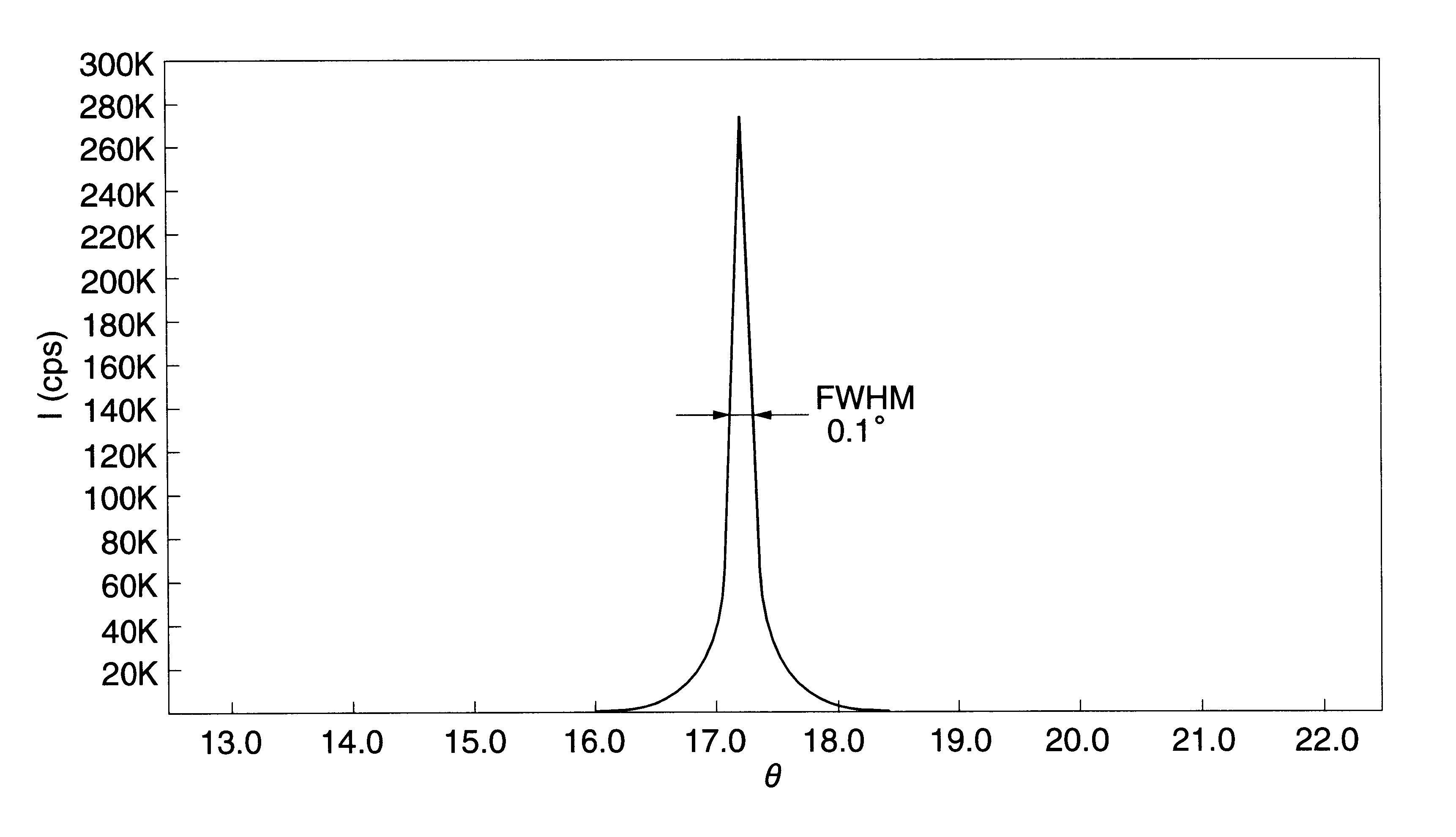
A nitride semiconductor device of high quality and excellent crystallinity and the method of manufacturing the same, wherein a nitride series compound semiconductor having at least an element belonging to the group IIIA and nitrogen is grown directly on a substrate, X-ray diffraction peaks of the nitride series compound semiconductor consist only of the peaks from the C-face of the hexagonal system, and the half width of an X-ray rocking curve at (0002) peak in the C-surface is 0.2 degrees of less, and wherein the method includes a step of introducing an organic metal compound at least containing a group IIIA element and a plasma activated nitrogen source into a reaction vessel to grow a nitride series compound semiconductor on the surface of a substrate, in which the ratio for the amount of the group IIIA element and nitrogen atom supplied (ratio for the number of atoms) is group IIIA element: nitrogen atom=1:50,000 to 1:1,000,000.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
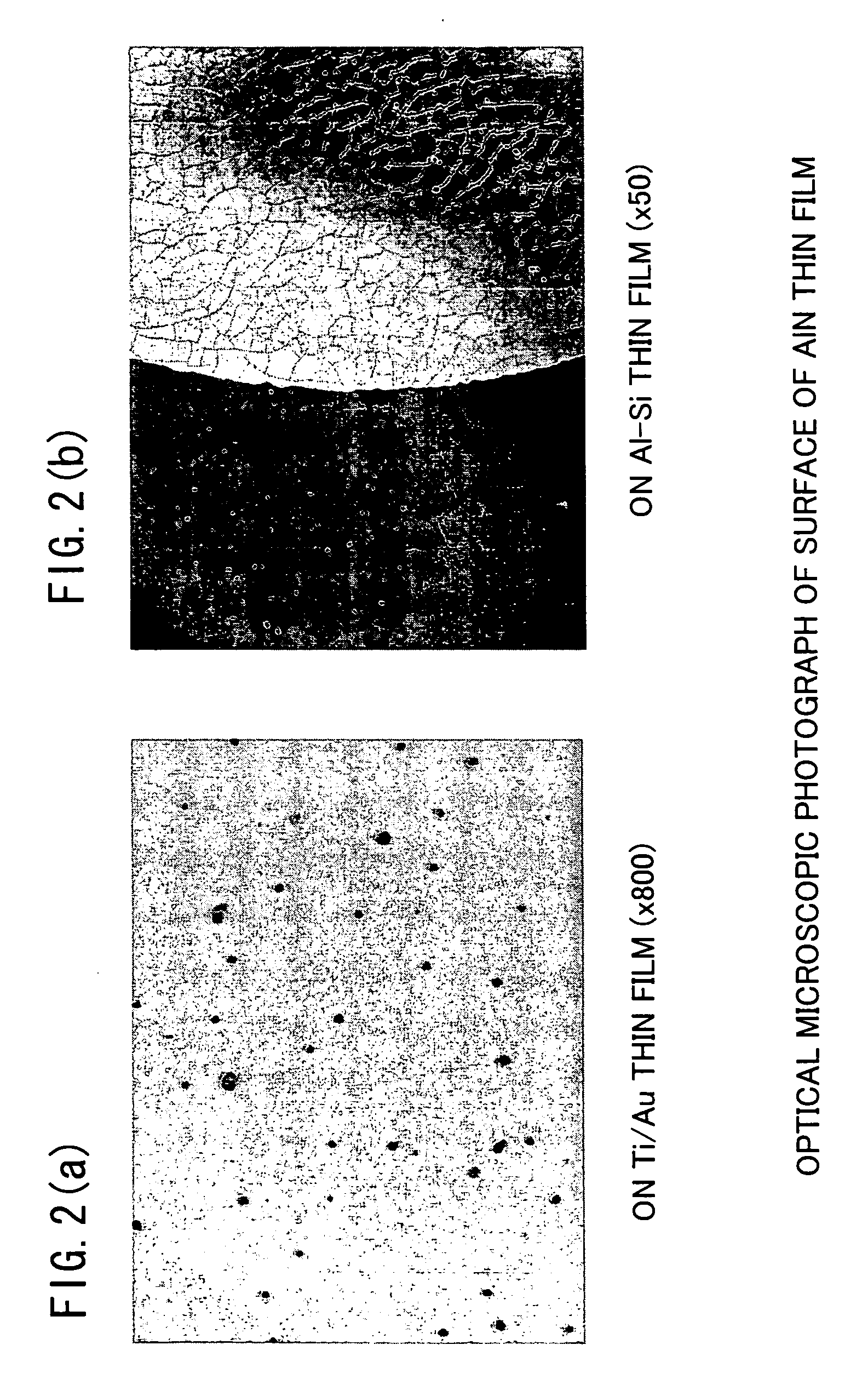
Aluminum nitride thin film, composite film containing the same and piezoelectric thin film resonator using the same
ActiveUS20070080611A1Improve featuresHigh crystallinityPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesRocking curveComposite film
A piezoelectric thin film resonator has a substrate and a piezoelectric layered structure including a lower electrode, piezoelectric aluminum nitride thin film with c-axis orientation and upper electrode formed on the substrate in this order. The lower electrode are made of a metal thin film including a layer containing ruthenium as a major component having a full-width half maximum (FWHM) of a rocking curve of a (0002) diffraction peak of ruthenium of 3.0° or less. The piezoelectric aluminum nitride thin film formed on the lower electrode has a full-width half maximum (FWHM) of a rocking curve of a (0002) diffraction peak of 2.0° or less.
Owner:MEMS SOLUTIONS INC
Transparent conductive film and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS7867636B2Improve economyConductive layers on insulating-supportsSynthetic resin layered productsRocking curveCrystal structure
A ZnO-based transparent conductive film is produced by growing ZnO doped with a group III element oxide on a substrate and has a region with a crystal structure in which a c-axis grows along a plurality of different directions. The transparent conductive film produced by growing ZnO doped with a group III element oxide on a substrate has a ZnO (002) rocking curve full width at half maximum of about 13.5° or more. ZnO is doped with a group III element oxide so that the ratio of the group III element oxide in the transparent conductive film is about 7% to about 40% by weight. The transparent conductive film is formed on the substrate with a SiNx thin film provided therebetween. The transparent conductive film is formed on the substrate by a thin film formation method with a bias voltage applied to the substrate.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Substrate for epitaxy and method of preparing the same
ActiveUS20060054075A1Quality improvementInhibited DiffusionPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMOSFETRocking curve
The substrate is used for opto-electric or electrical devices and comprises a layer of nitride grown by means of vapor phase epitaxy growth wherein both main surfaces of the nitride substrate are substantially consisting of non N-polar face and N-polar face respectively and the dislocation density of the substrate is 5×105 / cm2 or less. Therefore, the template type substrate has a good dislocation density and a good value of FWHM of the X-ray rocking curve from (0002) plane less than 80, so that the resulting template type substrate is very useful for the epitaxy substrate from gaseous phase such as MOCVD, MBE and HVPE, resulting in possibility of making good opto-electric devices such as Laser Diode and large-output LED and good electric devices such as MOSFET.
Owner:AMMONO SP Z O O (PL) +1
Aluminum nitride thin film, composite film containing the same and piezoelectric thin film resonator using the same
ActiveUS7482737B2Improvement factorImprove sound qualityPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyImpedence networksRocking curveComposite film
A piezoelectric thin film resonator has a substrate and a piezoelectric layered structure including a lower electrode, piezoelectric aluminum nitride thin film with c-axis orientation and upper electrode formed on the substrate in this order. The lower electrode are made of a metal thin film including a layer containing ruthenium as a major component having a full-width half maximum (FWHM) of a rocking curve of a (0002) diffraction peak of ruthenium of 3.0° or less. The piezoelectric aluminum nitride thin film formed on the lower electrode has a full-width half maximum (FWHM) of a rocking curve of a (0002) diffraction peak of 2.0° or less.
Owner:MEMS SOLUTIONS INC
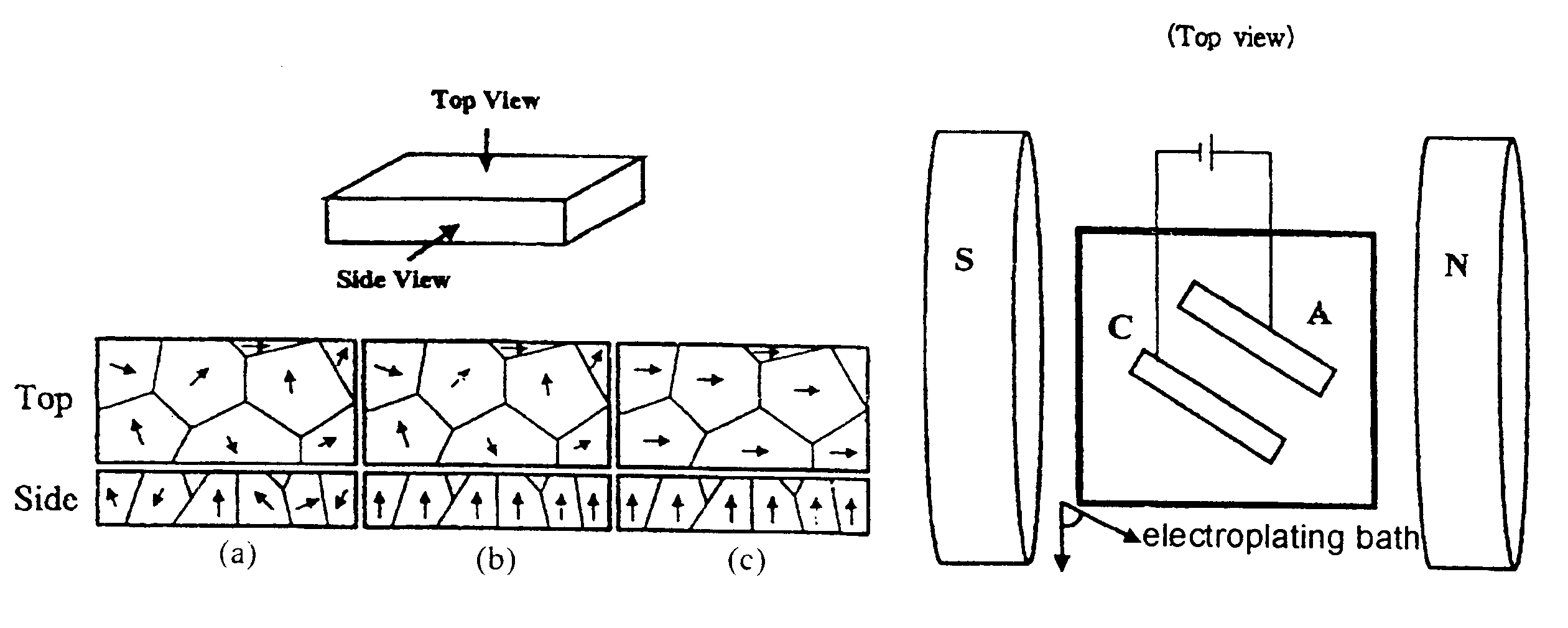
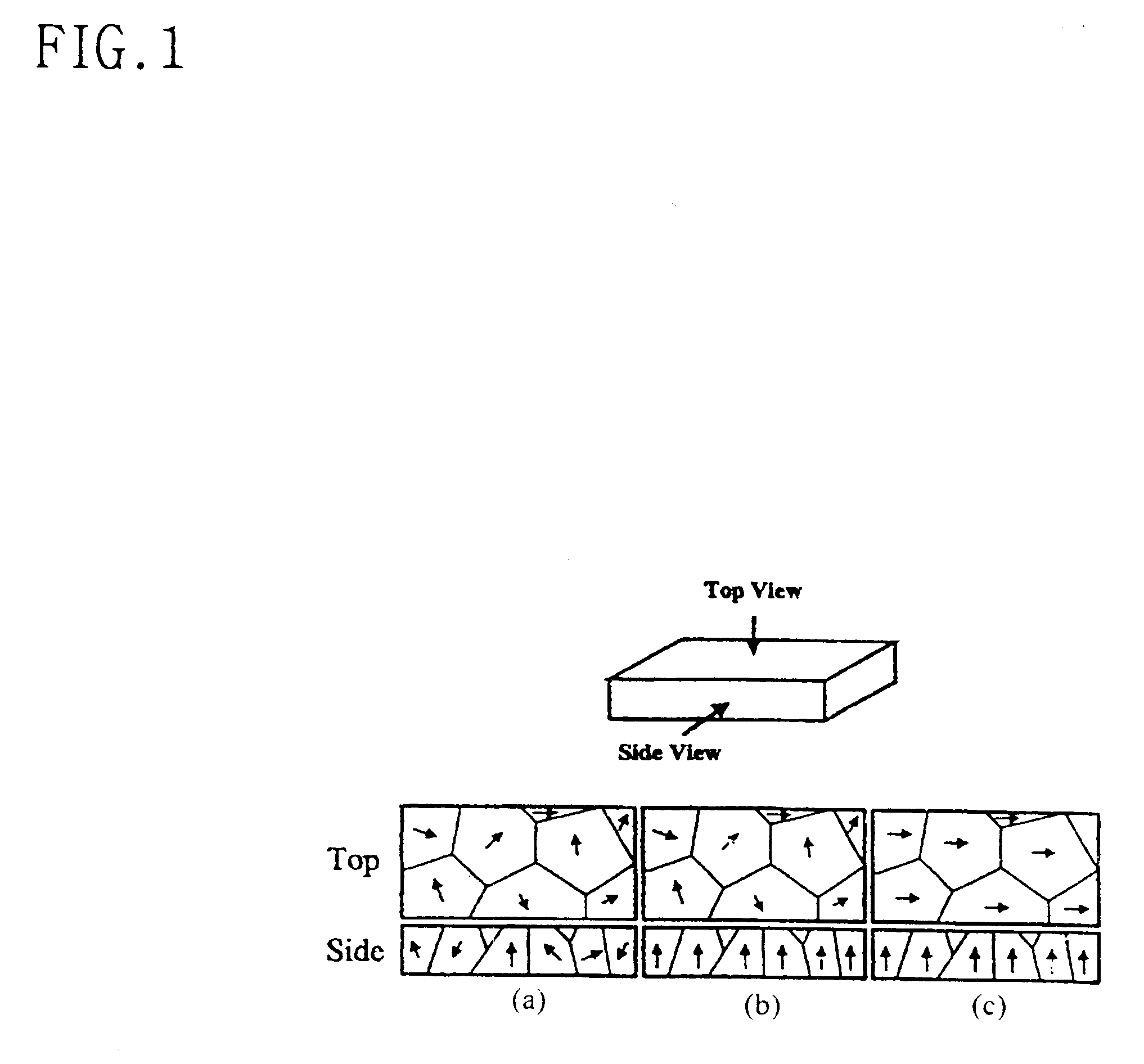
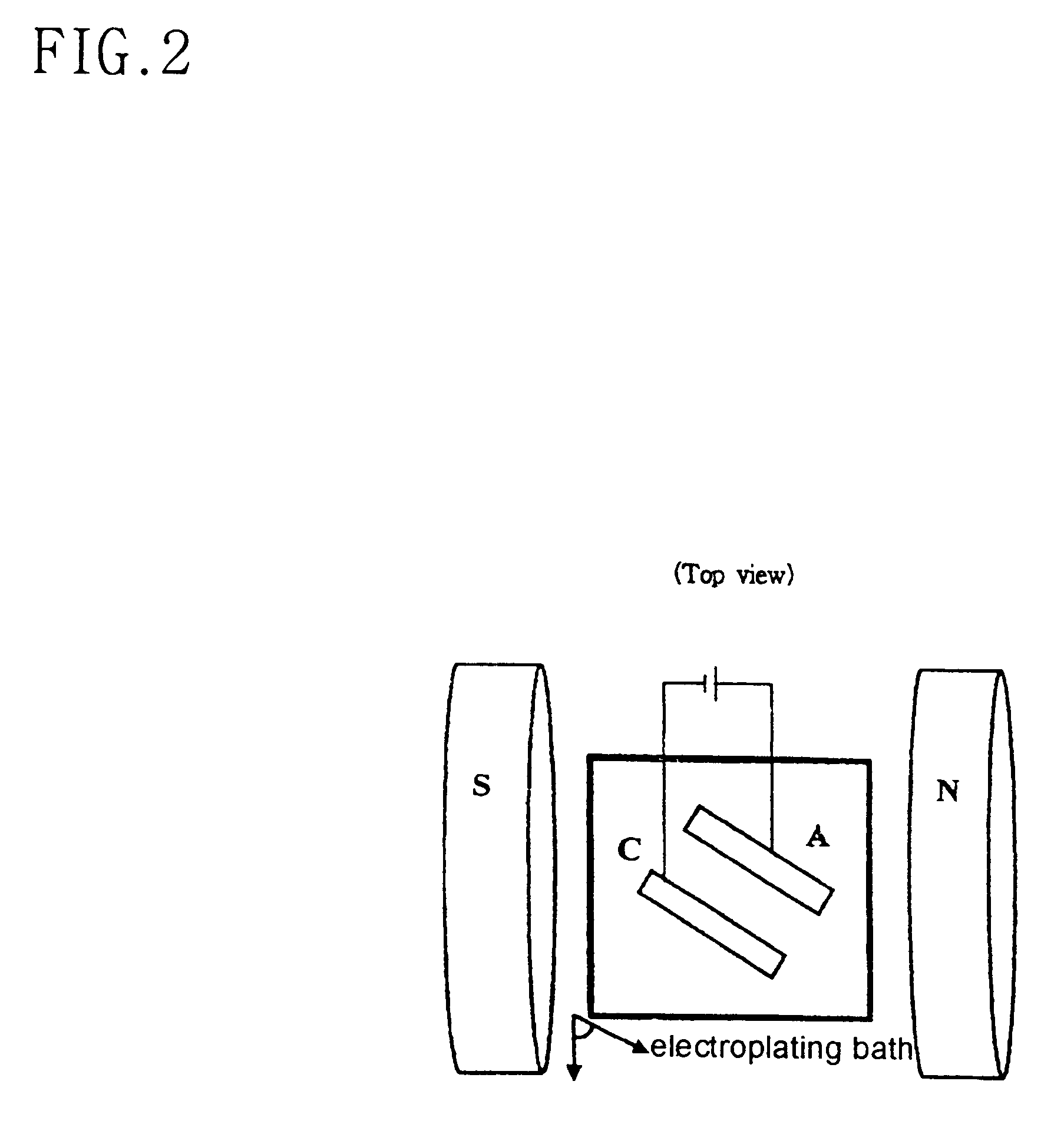
Electroplating process for preparing a Ni layer of biaxial texture
Disclosed is an Ni-plated layer of biaxial texture, which is formed by electroplating. In the Ni-plated layer,peaks measured on a theta-rocking curve have a FWHM of 7° or less in terms of the misorientation on the c-axis; and peaks measured on phi-scan have a FWHM of 21° or less in terms of the misorientation on the plane formed by the a-axis and the b-axis. Also, a process of electroplating a Ni layer are disclosed. The process comprises forming a Ni-plated layer of biaxial texture under a magnetic field by electroplating and subjecting the Ni-plated layer to thermal treatment to develop the biaxial texture. This electroplating process is expected to give a significant contribution to the development of the electroplating technology and to replace the vacuum deposition used for the preparation of thin film magnetic materials or thin film piezoelectric materials.
Owner:KOREA INST OF MASCH & MATERIALS
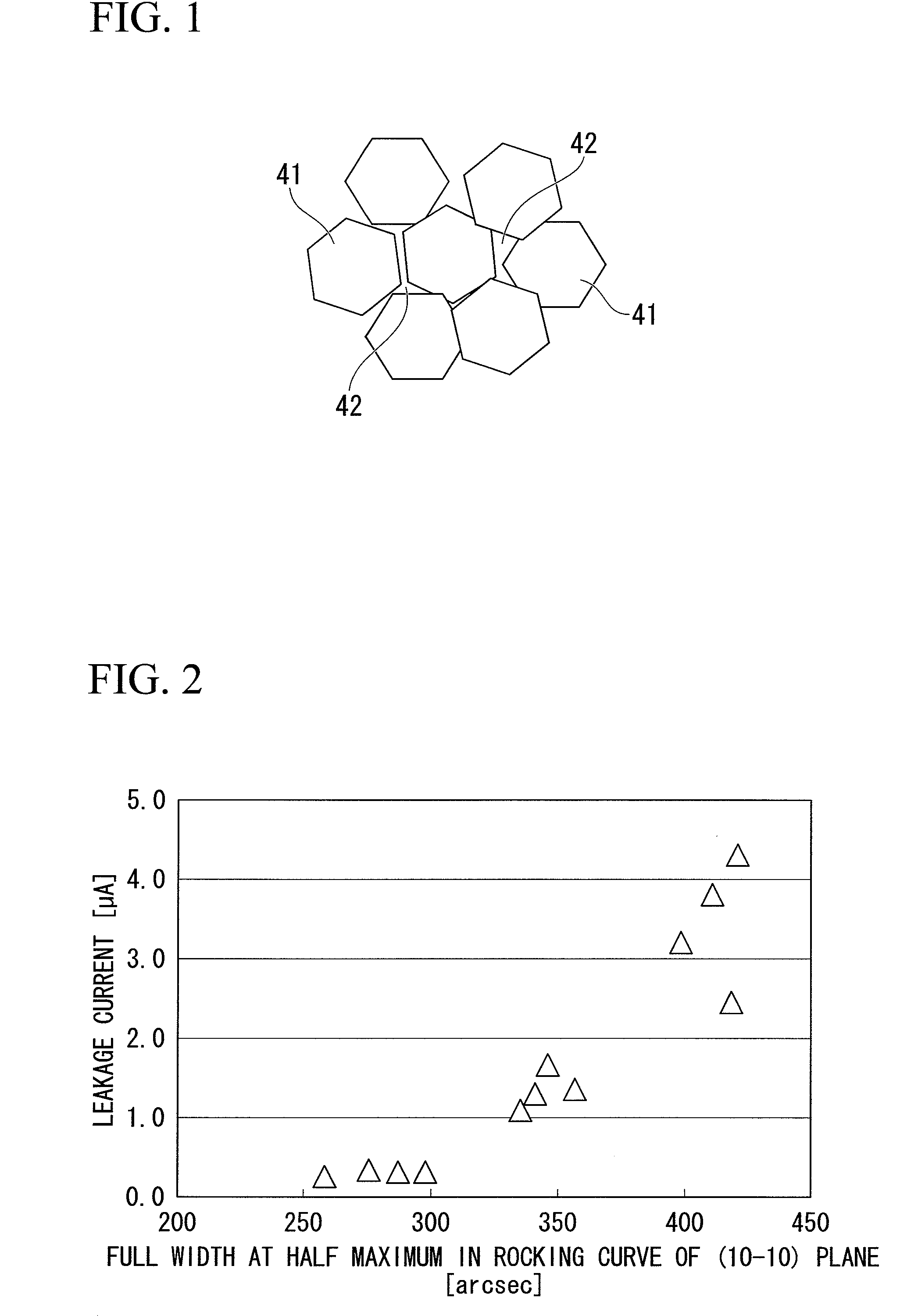
Group-iii nitride compound semiconductor device and production method thereof, group-iii nitride compound semiconductor light-emitting device and production method thereof, and lamp
InactiveUS20090194784A1Improve in-plane uniformityLower Level RequirementsSolid-state devicesVacuum evaporation coatingRocking curveInter layer
A group-III nitride compound semiconductor device of the present invention comprises a substrate, an intermediate layer provided on the substrate, and a base layer provided on the intermediate layer in which a full width at half maximum in rocking curve of a (0002) plane is 100 arcsec or lower and a full width at half maximum in rocking curve of a (10-10) plane is 300 arcsec or lower. Also, a production method of a group-III nitride compound semiconductor device of the present invention comprises forming the intermediate layer by using a sputtering method.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Substrate for epitaxy and method of preparing the same
ActiveUS7387677B2Quality improvementFrom gel stateFrom normal temperature solutionsMOSFETRocking curve
The substrate is used for opto-electric or electrical devices and comprises a layer of nitride grown by means of vapor phase epitaxy growth wherein both main surfaces of the nitride substrate are substantially consisting of non N-polar face and N-polar face respectively and the dislocation density of the substrate is 5×105 / cm2 or less. Therefore, the template type substrate has a good dislocation density and a good value of FWHM of the X-ray rocking curve from (0002) plane less than 80, so that the resulting template type substrate is very useful for the epitaxy substrate from gaseous phase such as MOCVD, MBE and HVPE, resulting in possibility of making good opto-electric devices such as Laser Diode and large-output LED and good electric devices such as MOSFET.
Owner:AMMONO SP Z O O (PL) +1
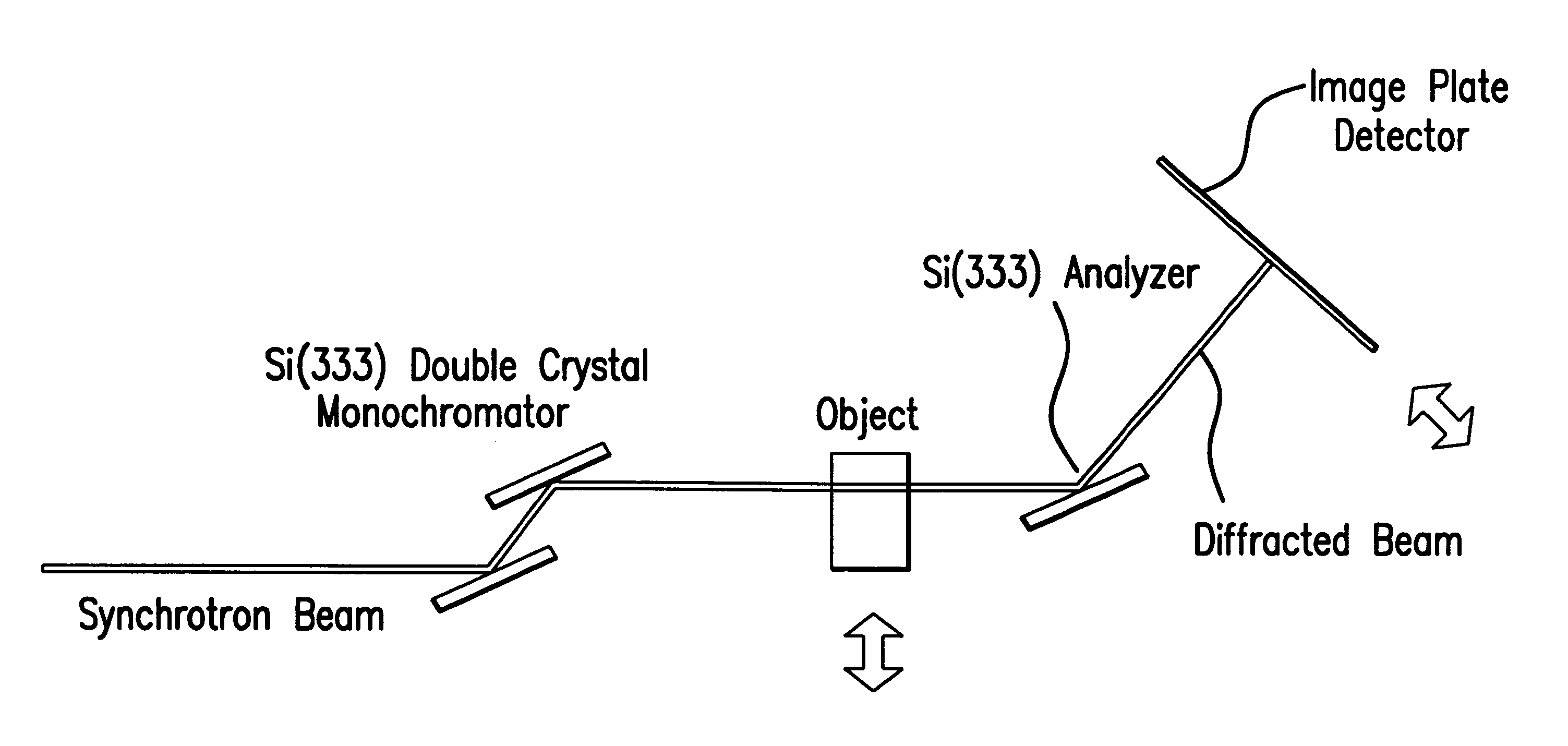
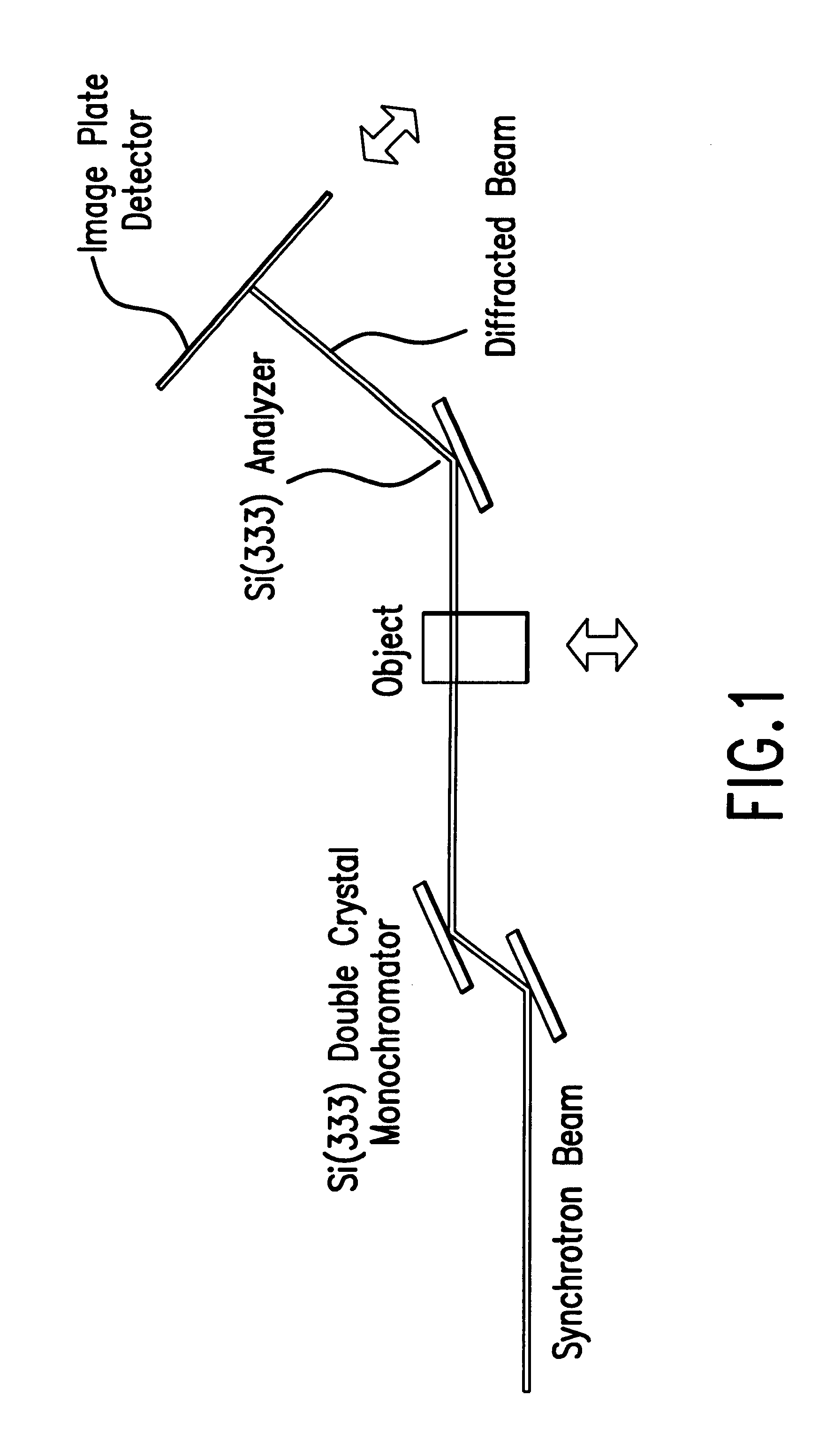
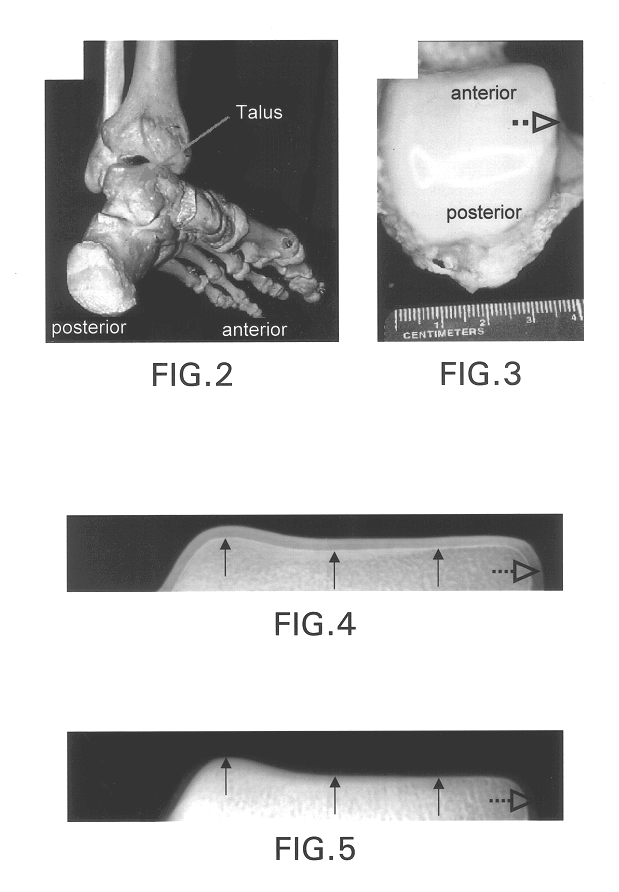
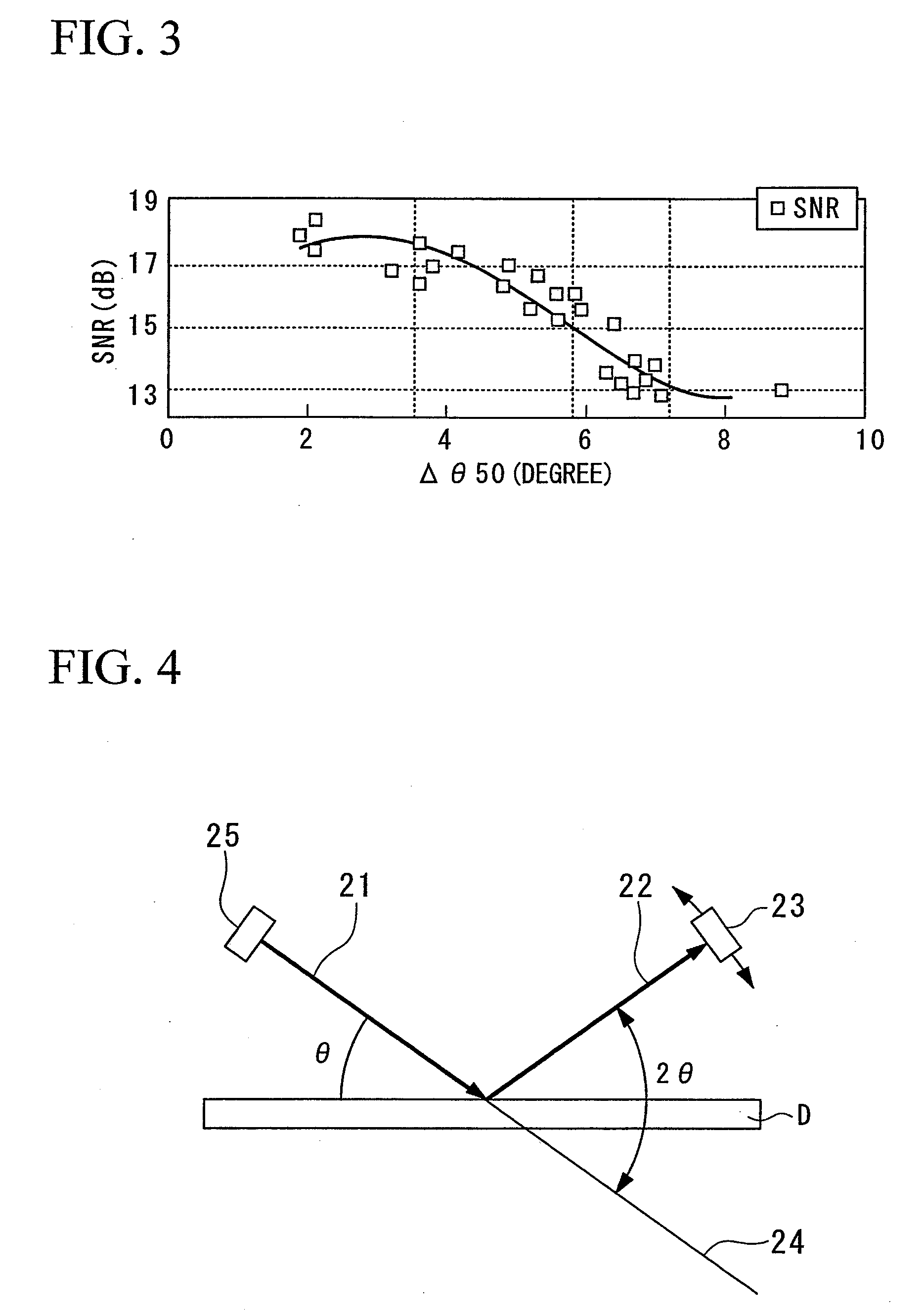
Diffraction enhanced x-ray imaging of articular cartilage
InactiveUS6577708B2Imaging devicesX-ray spectral distribution measurementRocking curveAngle of incidence
A method and system for detecting an image of an object, particularly a soft tissue material. A generated x-ray beam is transmitted through the soft tissue material. A transmitted beam is directed at an angle of incidence upon a crystal analyzer. An image of the object is detected from a beam diffracted from the crystal analyzer either at or near a peak of a rocking curve of the crystal analyzer. The method and system of this invention is particularly useful for analyzing images of cartilage.
Owner:ILLINOIS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY +2
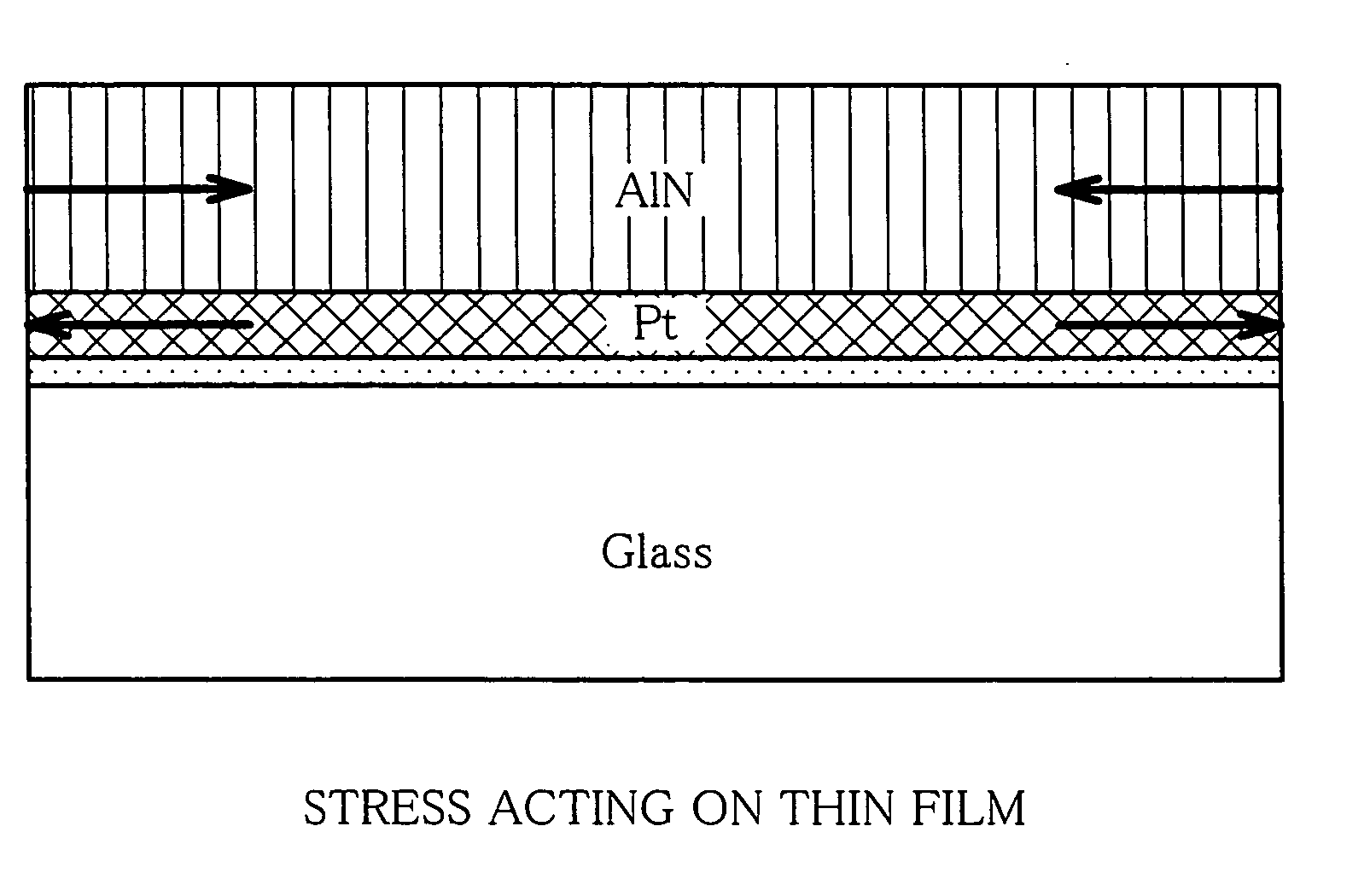
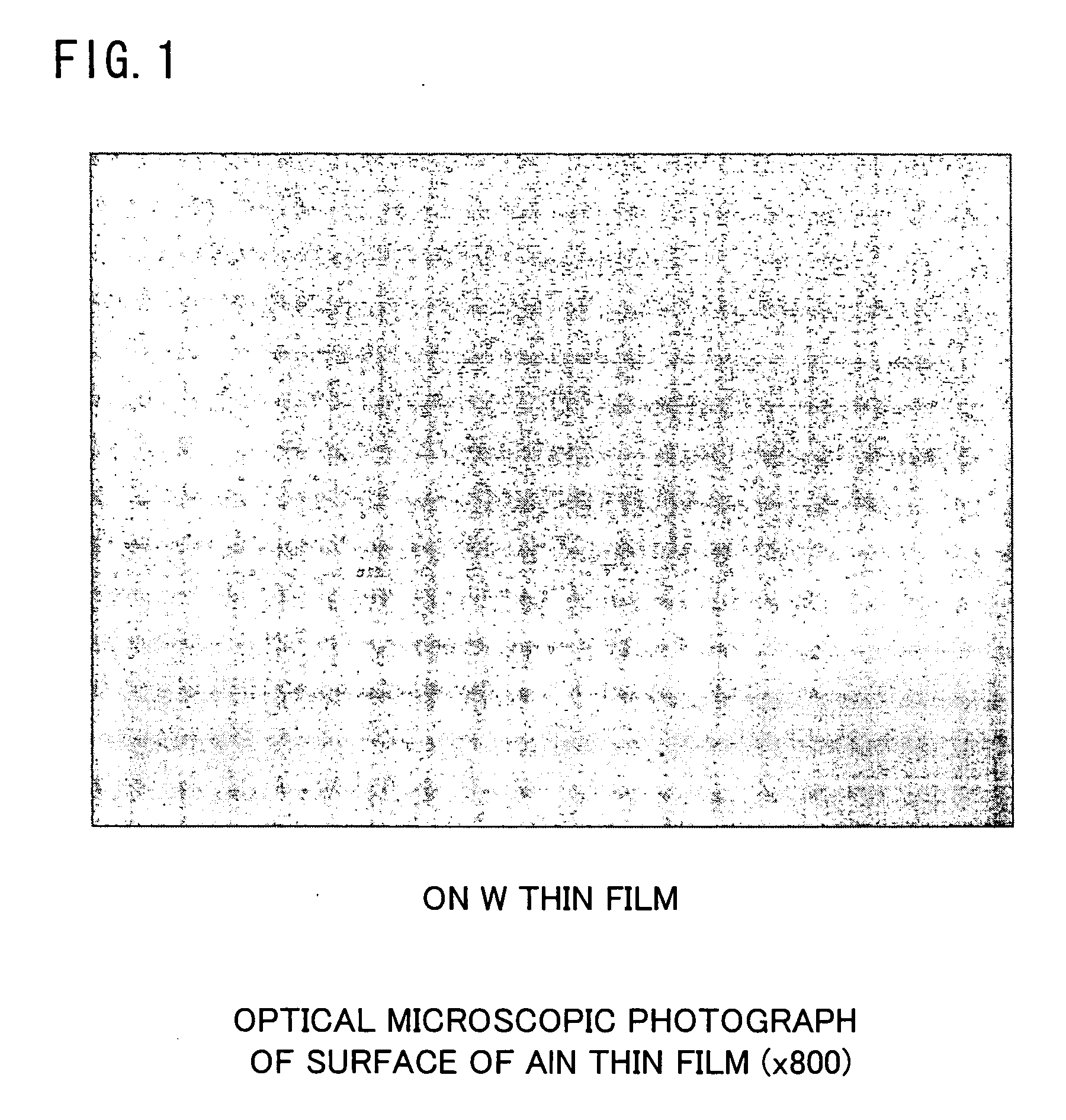
Piezoelectric device comprising ultrahighly-orientated aluminum nitride thin film and its manufacturing method
InactiveUS20050236710A1Improve performancePiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsRocking curveFull width
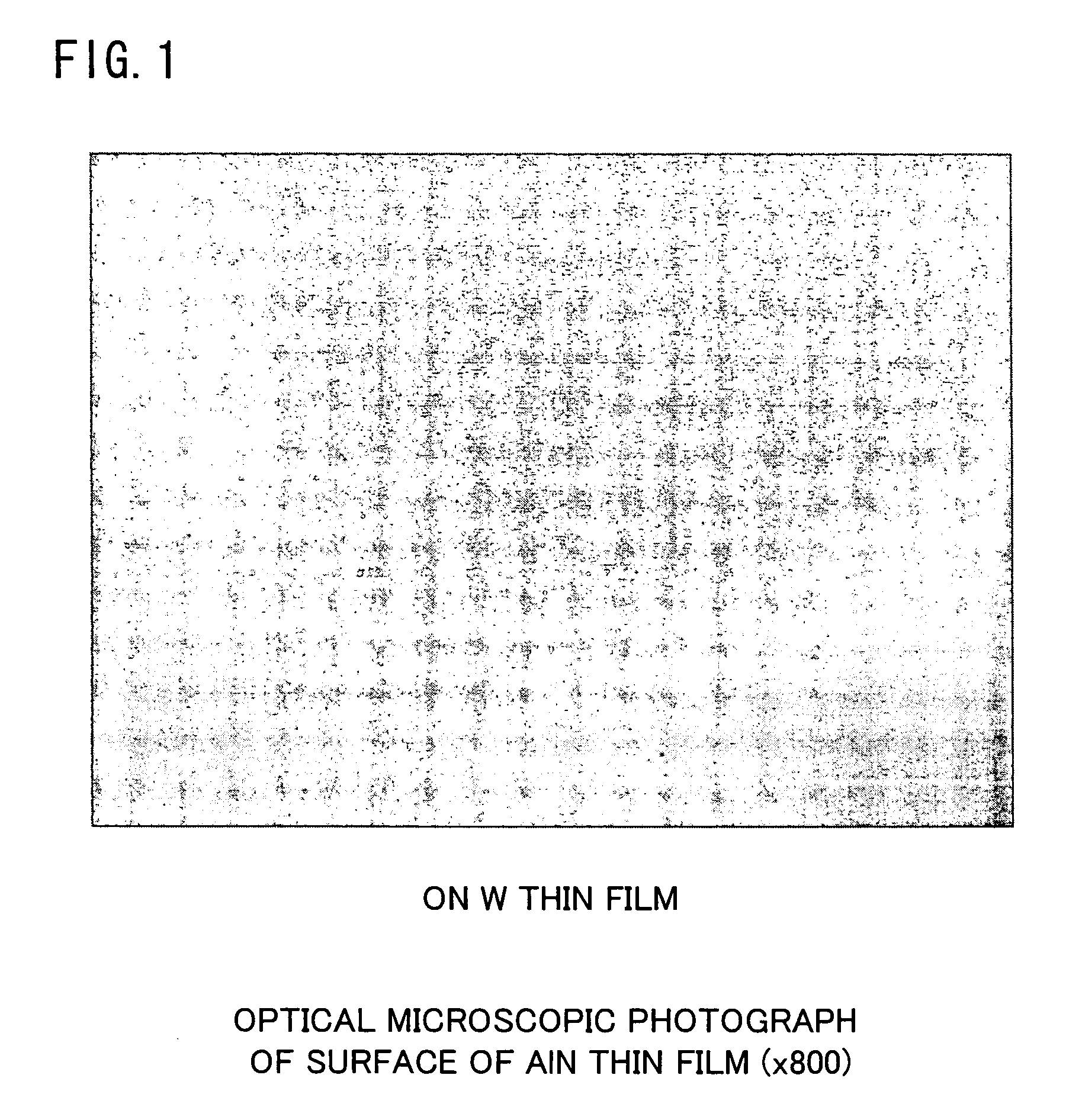
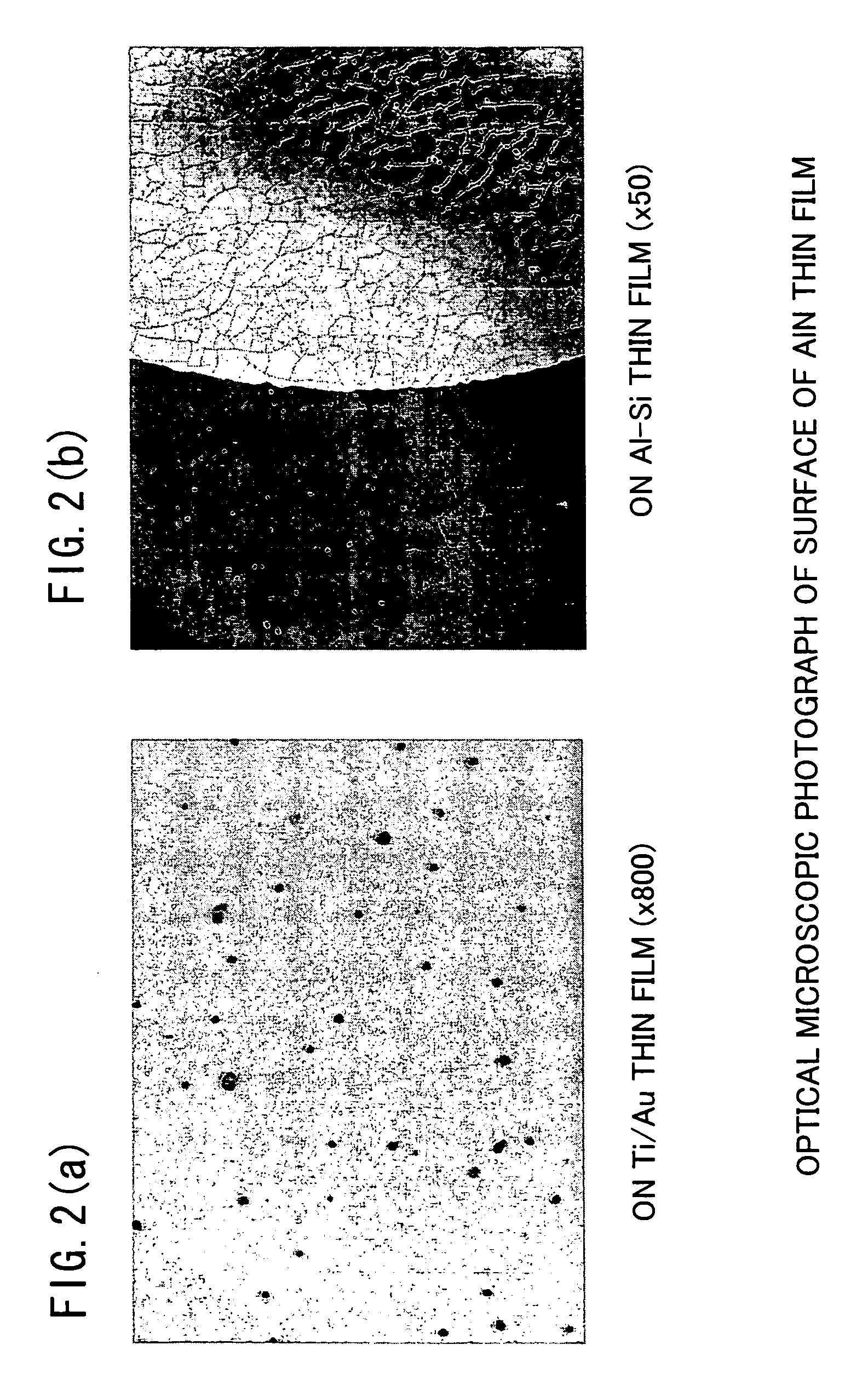
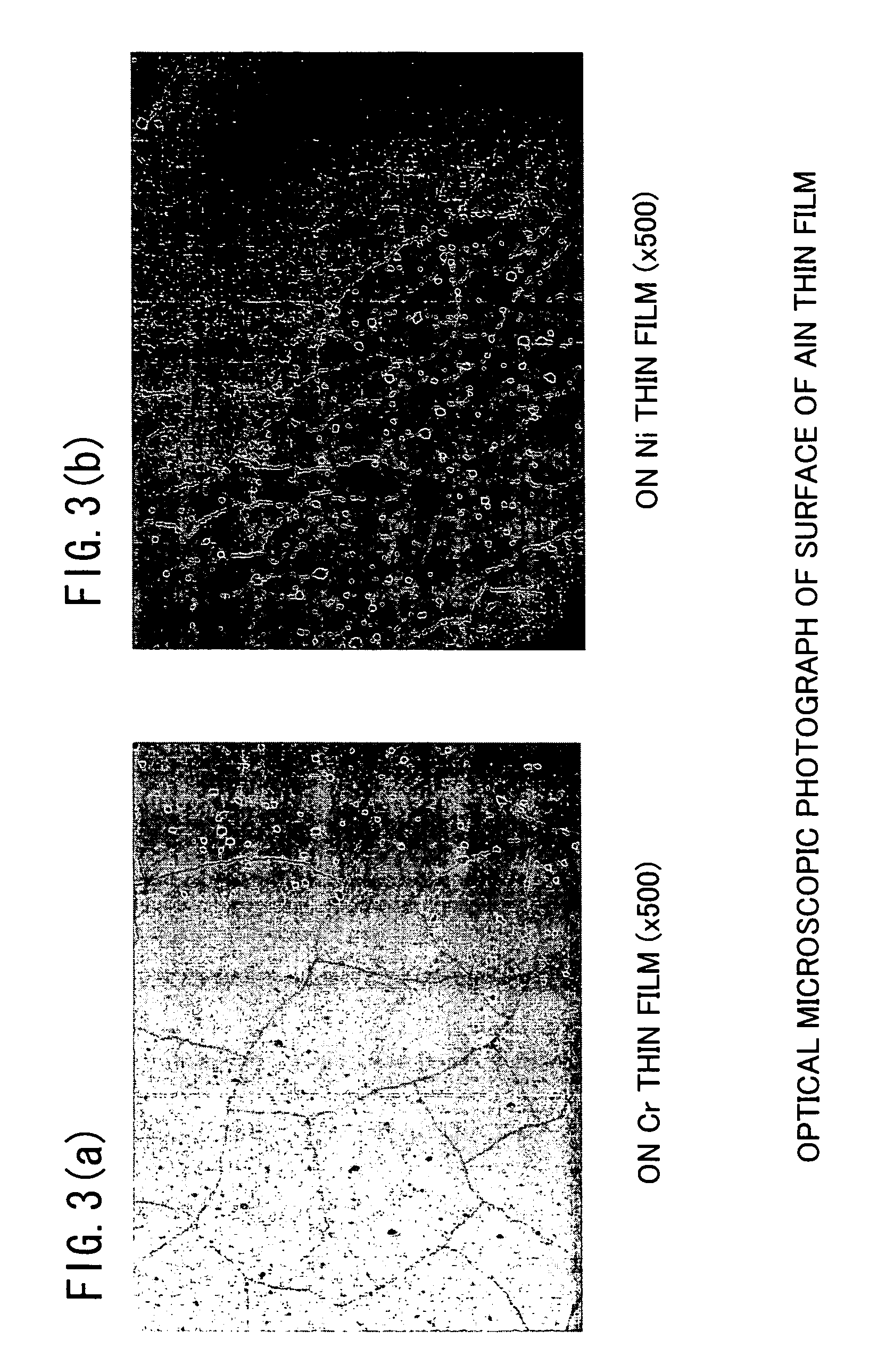
The present invention has an objective to provide a high performance piezoelectric element in which is formed an aluminum nitride thin film free from hillocks, cracks, and peeling which exhibits superhigh c-axis orientation, by forming a bottom electrode from a W layer with no intervening adhesive layer on a glass or other cheap substrate. The piezoelectric element of the present invention is a piezoelectric element using a superhigh-oriented aluminum nitride thin film characterized in that the piezoelectric element is free from hillocks, cracks, and peeling and includes a stack structure in which a bottom electrode, a piezoelectric body thin film, and a top electrode are sequentially formed on a substrate; the bottom electrode is made of an oriented W layer of which a (111) plane of W is parallel to a surface of the substrate; and the piezoelectric body thin film is formed of a c-axis-oriented aluminum nitride thin film having a rocking curve full width half maximum (RCFWHM) not exceeding 2.5°.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
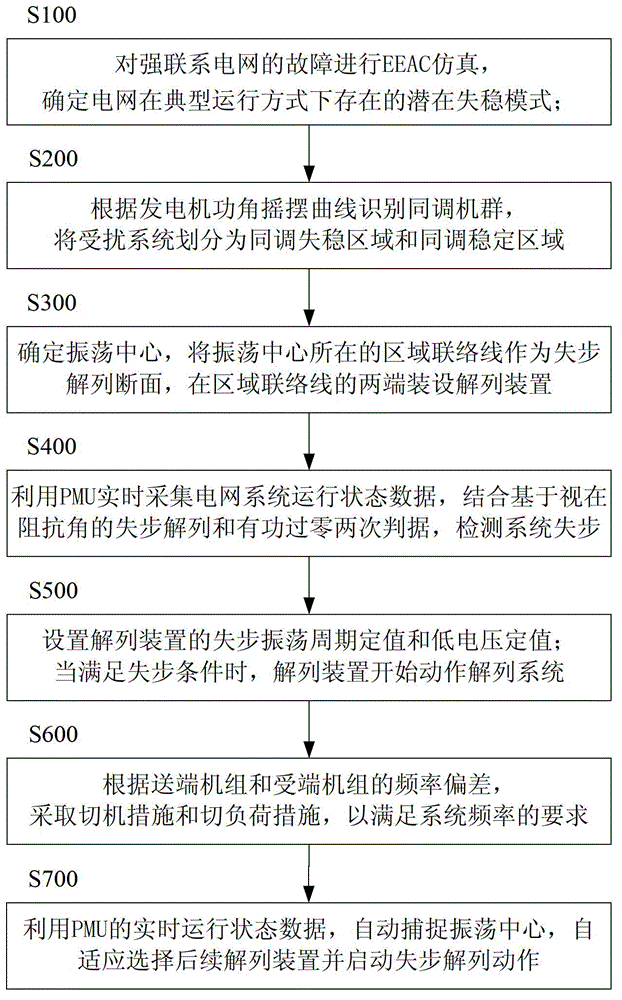
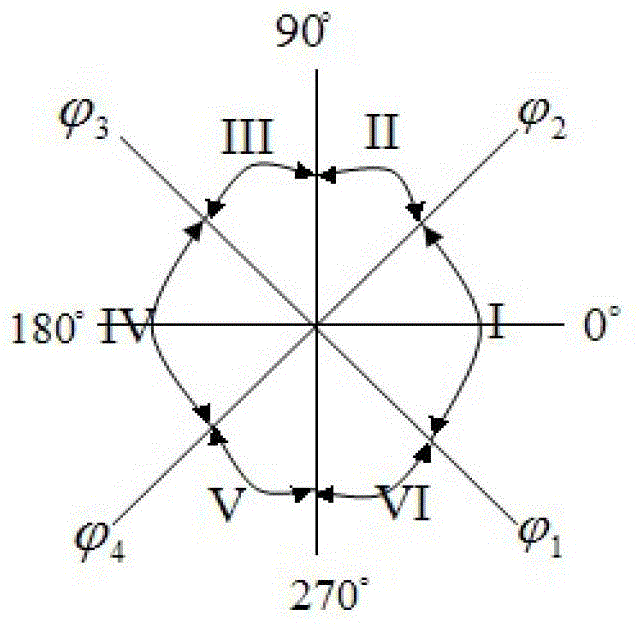
Strong-connection power grid out-of-step disconnection method
InactiveCN103199527AAvoid destabilizing accidentsAc network circuit arrangementsRocking curveVoltage amplitude
The invention relates to a strong-connection power grid out-of-step disconnection method. The theory of an extended equal area criterion (EEAC) dominant mode is regarded as a basis, perturbed trajectories rocking curves are used for recognizing perturbed system coherent generators, and coherent areas can be divided further. Out-of-step disconnection criteria applicable to a strong-connection power grid and based on sections are selected and composed of u cosine phi criteria and voltage amplitude criteria, the combination criteria can judge out-of-step of the strong-connection power grid effectively, and the time and the positions of oscillation centers can be captured. The position of a disconnection point is confirmed according to out-of-step sections formed by junctors where the oscillation centers are located. Correct disconnection time and disconnection range are selected for setting devices, and a disconnection command action device is started after a certain requirement is met. Effective generator shedding and load shedding measures are taken according to power shortage of a subsystem after disconnection. The strong-connection power grid out-of-step disconnection method is applicable to out-of-step disconnection schemes of the strong-connection power grid, damage accidents on stability of the strong-connection power grid can be avoided, and reliable guarantee is provided for safe and stable operation of the strong-connection power grid.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIVERSITY OF ELECTRIC POWER +1
Dielectric film structure, piezoelectric actuator using dielectric element film structure and ink jet head
InactiveUS7059711B2Excellent dielectric propertiesImprove ferroelectric propertiesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyCeramicsDielectricIn plane
The present invention provides a dielectric film structure having a substrate and a dielectric film provided on the substrate and in which the dielectric film has (001) face orientation with respect to the substrate, and in which a value u in the following equation (1) regarding the dielectric film is a real number greater than 2:u=(Cc / Ca)×(Wa / Wc) (1)where, Cc is a count number of a peak of a (00l′) face of the dielectric film in an Out-of-plane X ray diffraction measurement (here, l′ is a natural number selected so that Cc becomes maximum); Ca is a count number of a peak of a (h′00) face of the dielectric film in an In-plane X ray diffraction measurement (here, h′ is a natural number selected so that Cc becomes maximum); Wc is a half-value width of a peak of the (00l′) face of the dielectric film in an Out-of-plane rocking curve X ray diffraction measurement; and Wa is a half-value width of a peak of the (h′00) face of the dielectric film in an In-plane rocking curve X ray diffraction measurement.
Owner:CANON KK
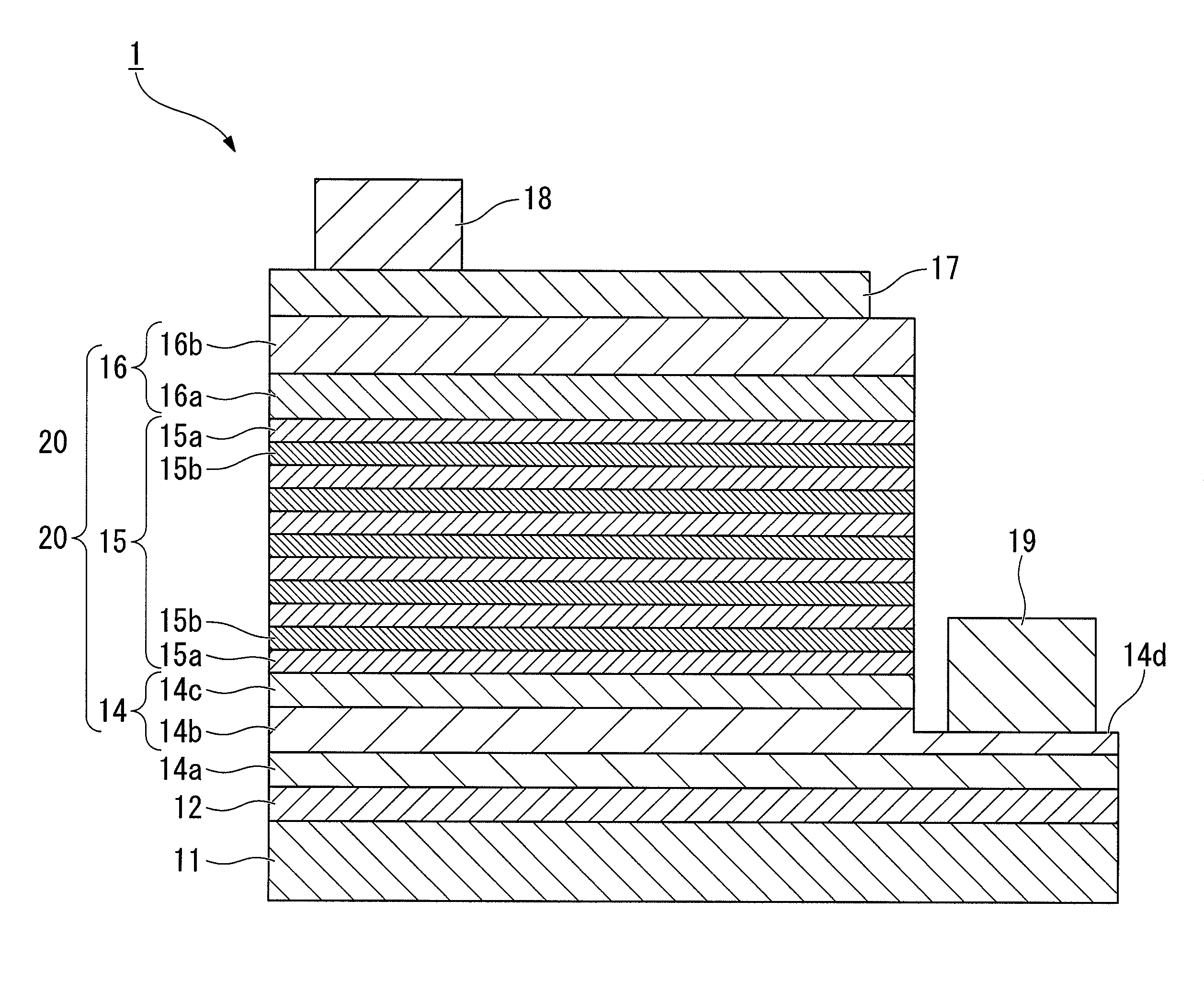
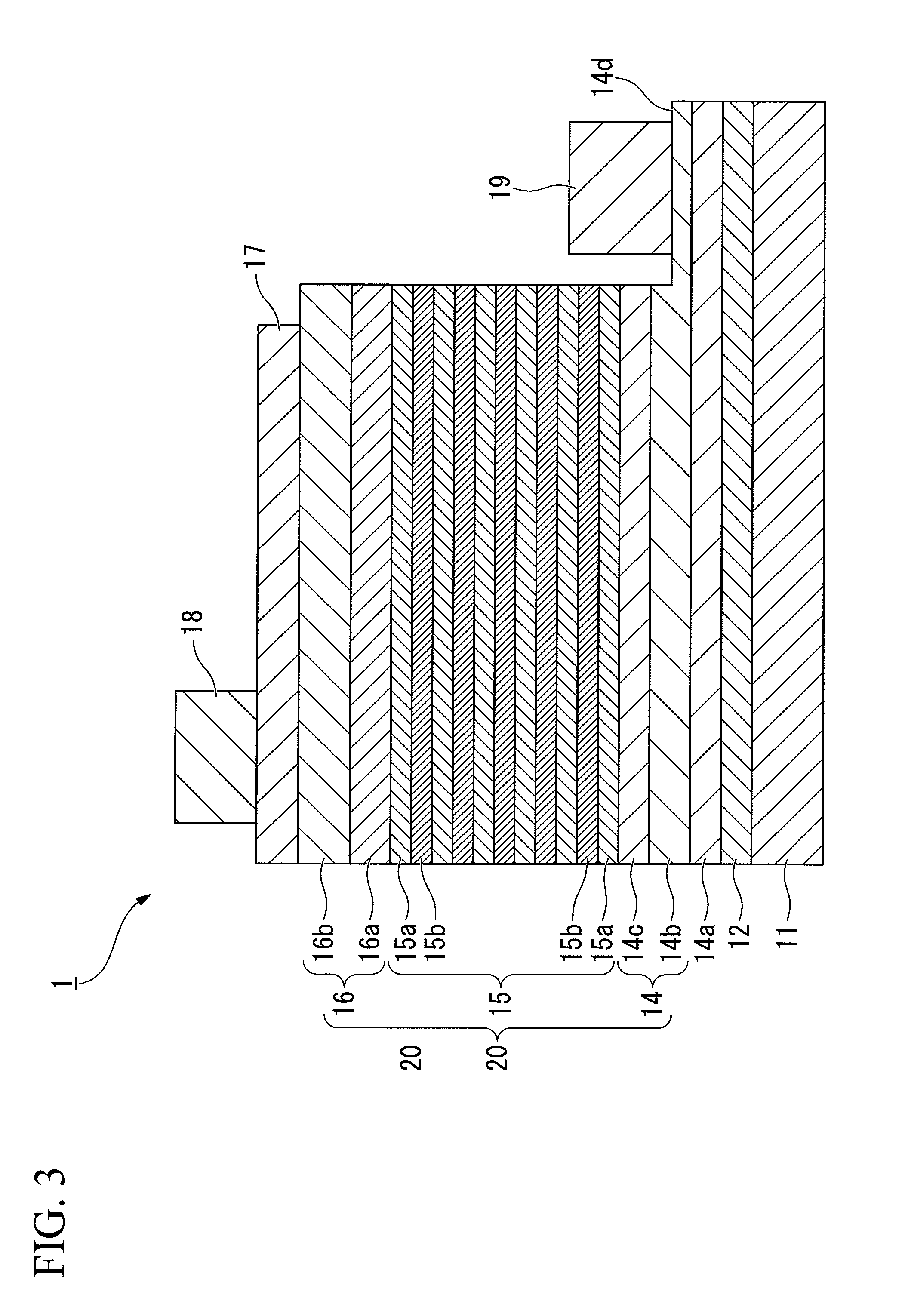
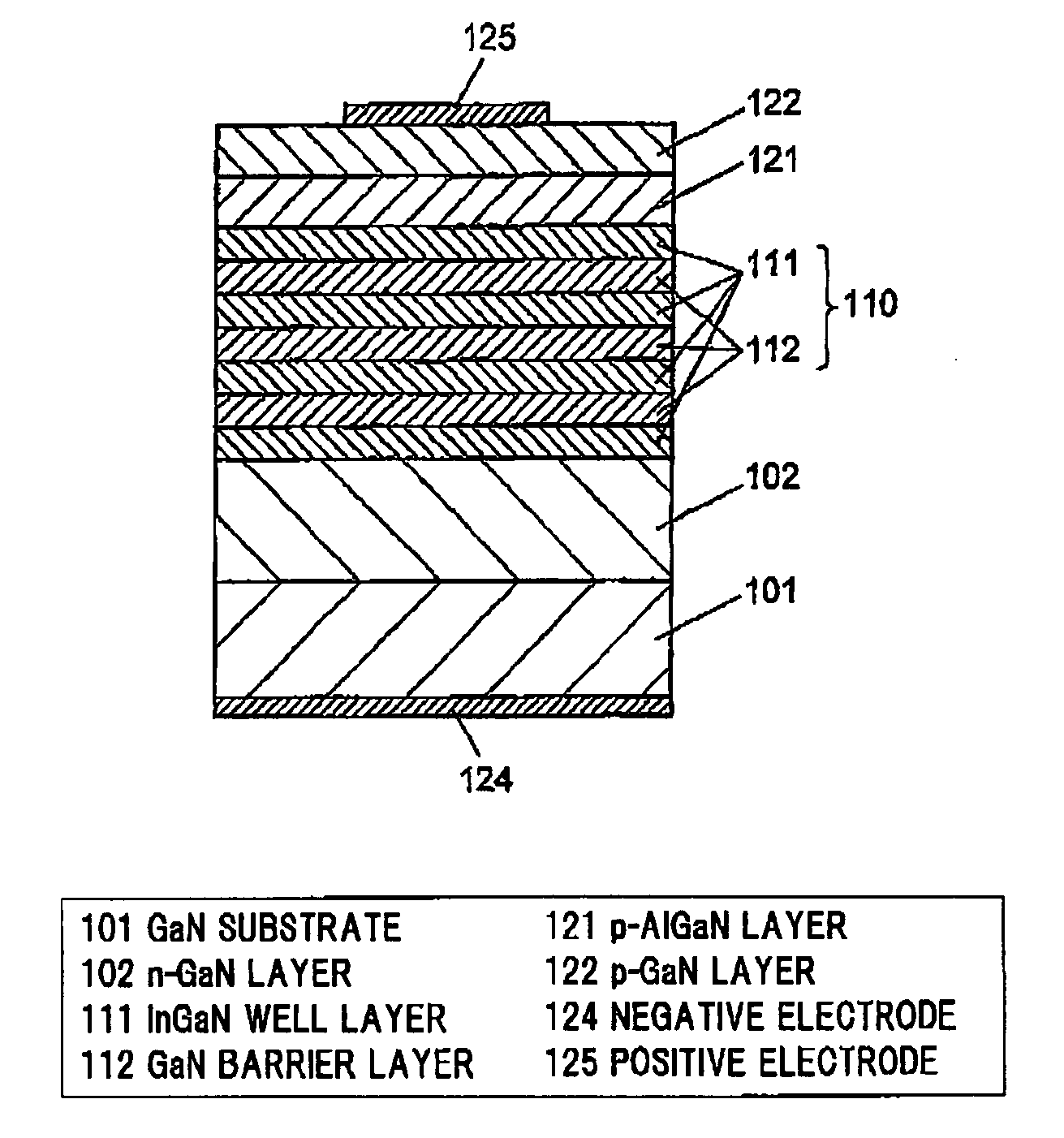
Method for manufacturing group iii nitride semiconductor light emitting element, group iii nitride semiconductor light emitting element and lamp
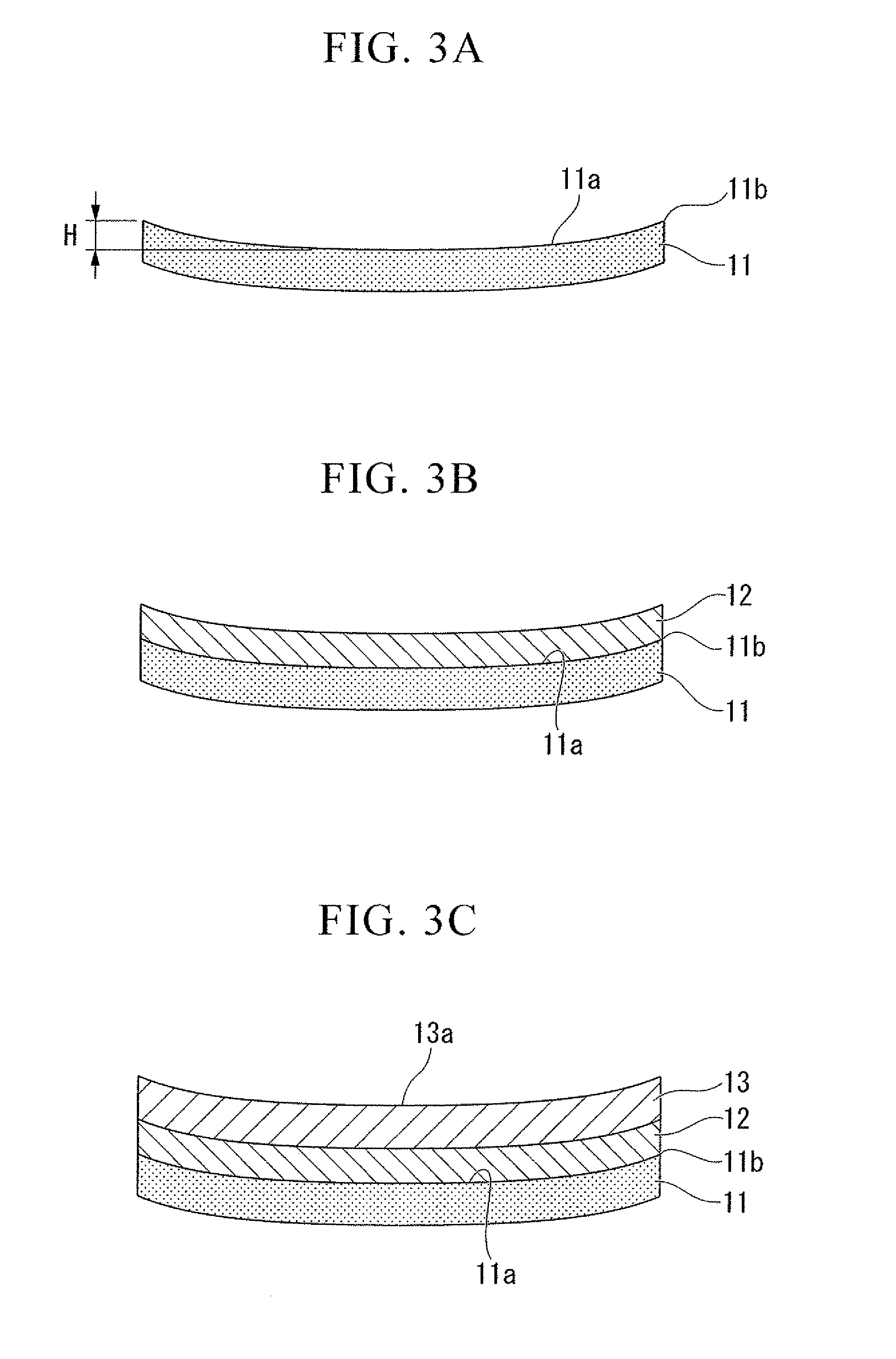
ActiveUS20110163349A1High crystallinityStable emission wavelengthSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRocking curveX-ray
The present invention provides a method for manufacturing a group III nitride semiconductor light emitting element, with which warping can be suppressed upon the formation of respective layers on the substrate, a semiconductor layer including a light emitting layer of excellent crystallinity can be formed, and excellent light emission characteristics can be obtained; such a group III nitride semiconductor light emitting element; and a lamp. Specifically disclosed is a method for manufacturing a group III nitride semiconductor light emitting element, in which an intermediate layer, an underlayer, an n-type contact layer, an n-type cladding layer, a light emitting layer, a p-type cladding layer, and a p-type contact layer are laminated in sequence on a principal plane of a substrate, wherein a substrate having a diameter of 4 inches (100 mm) or larger, with having an amount of warping H within a range from 0.1 to 30 μm and at least a part of the edge of the substrate warping toward the principal plane at room temperature, is prepared as the substrate; the X-ray rocking curve full width at half maximum (FWHM) of the (0002) plane is 100 arcsec or less and the X-ray rocking curve FWHM of the (10-10) plane is 300 arcsec or less, in a state where the intermediate layer has been formed on the substrate and where thereafter the underlayer and the n-type contact layer are formed on the intermediate layer; and furthermore the n-type cladding layer, the light emitting layer, the p-type cladding layer, and the p-type contact layer are formed on the n-type contact layer.
Owner:TOYODA GOSEI CO LTD
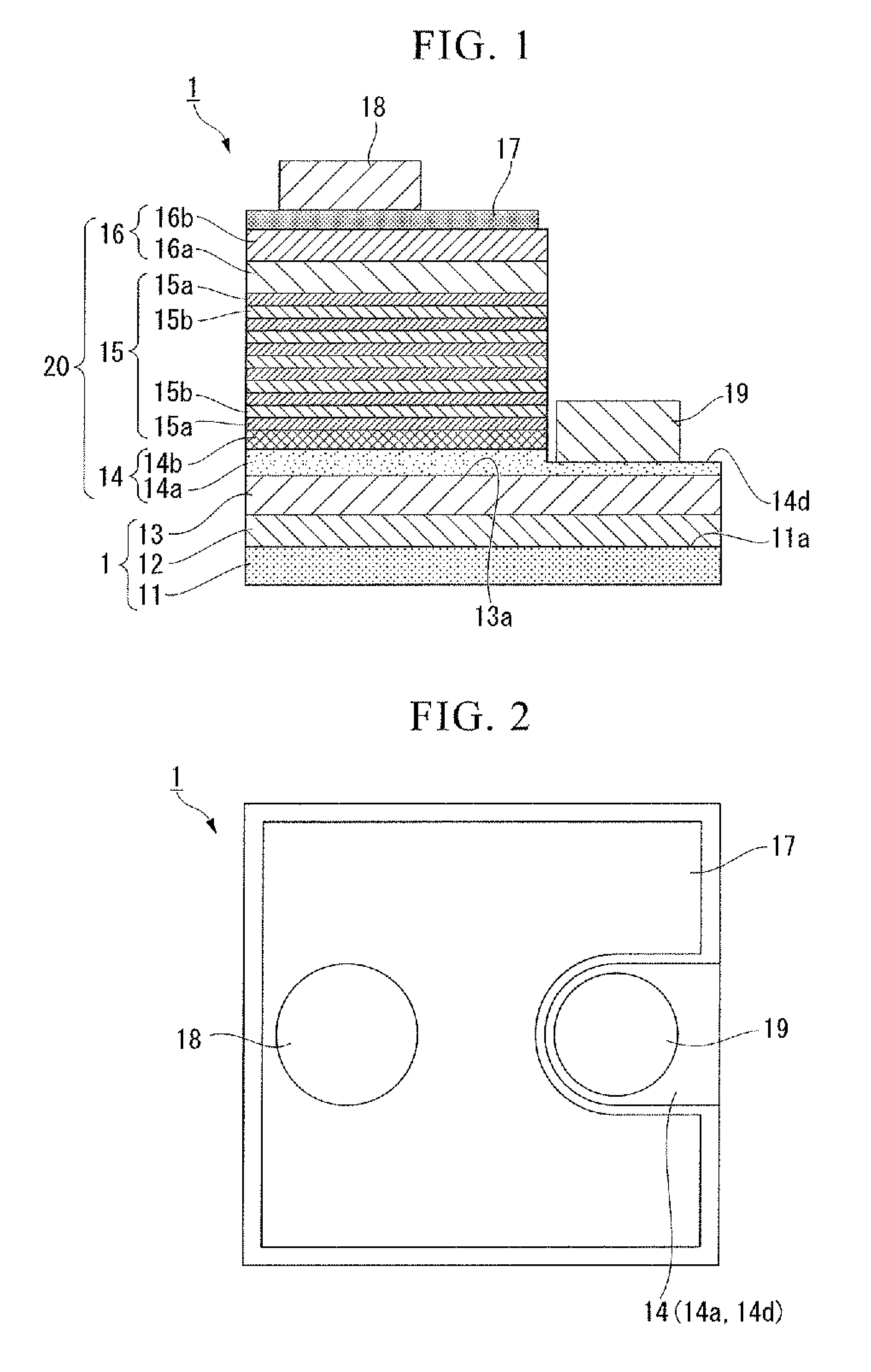
Highly crystalline aluminum nitride multi-layered substrate and production process thereof
InactiveUS20050059257A1Reduce dislocation densityHigh crystallinityPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsRocking curveCrystal orientation
A highly crystalline aluminum nitride multi-layered substrate comprising a single-crystal α-alumina substrate, an aluminum oxynitride layer and a highly crystalline aluminum nitride film as the outermost layer which are formed in the mentioned order, wherein the aluminum oxynitride layer has a threading dislocation density of 6.3×107 / cm2 or less and a crystal orientation expressed by the half-value width of its rocking curve of 4,320 arcsec or less; and a production process thereof.
Owner:TOKYO INST OF TECH +1
Magnetic recording medium, production process thereof, and magnetic recording and reproducing apparatus
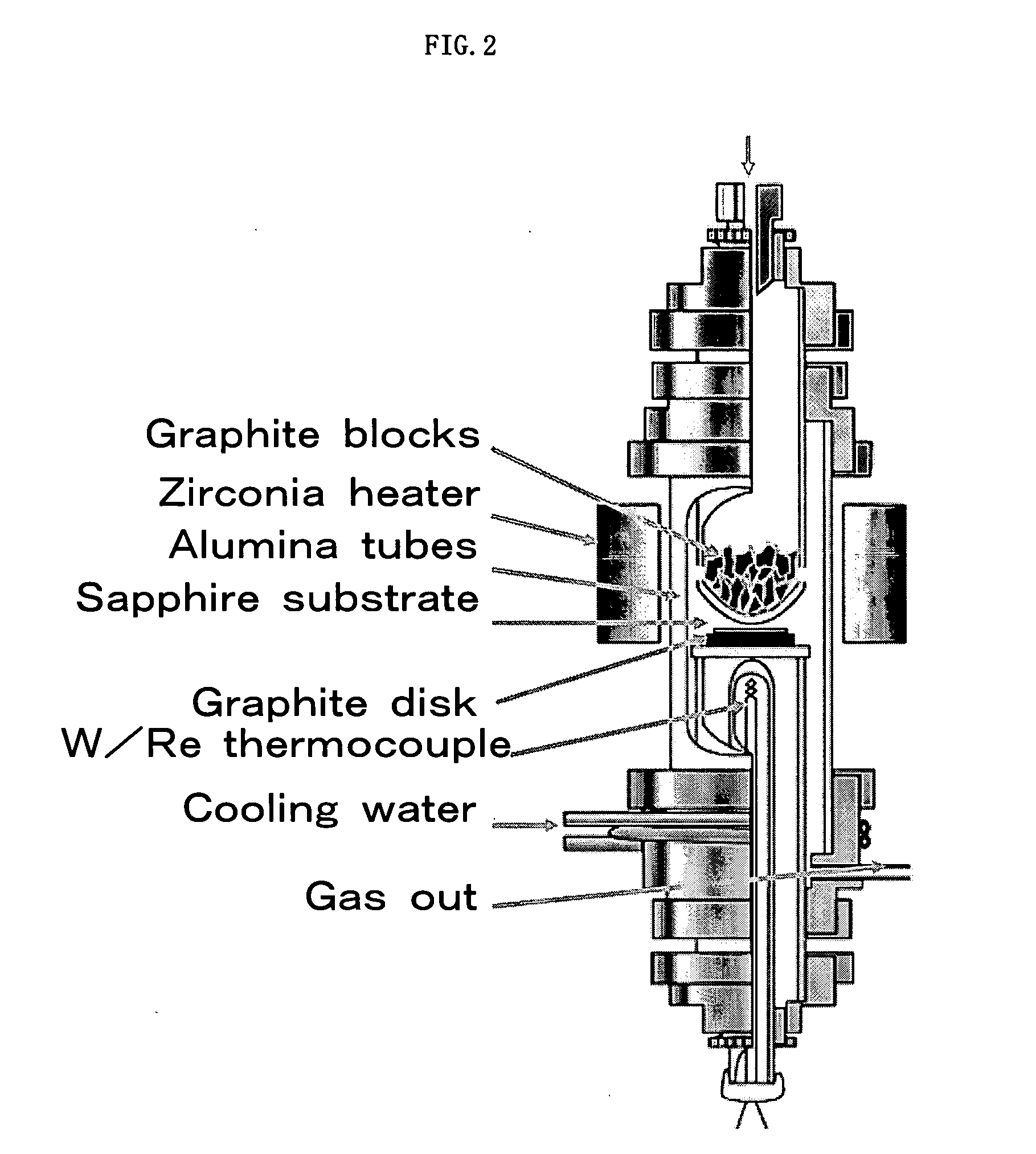
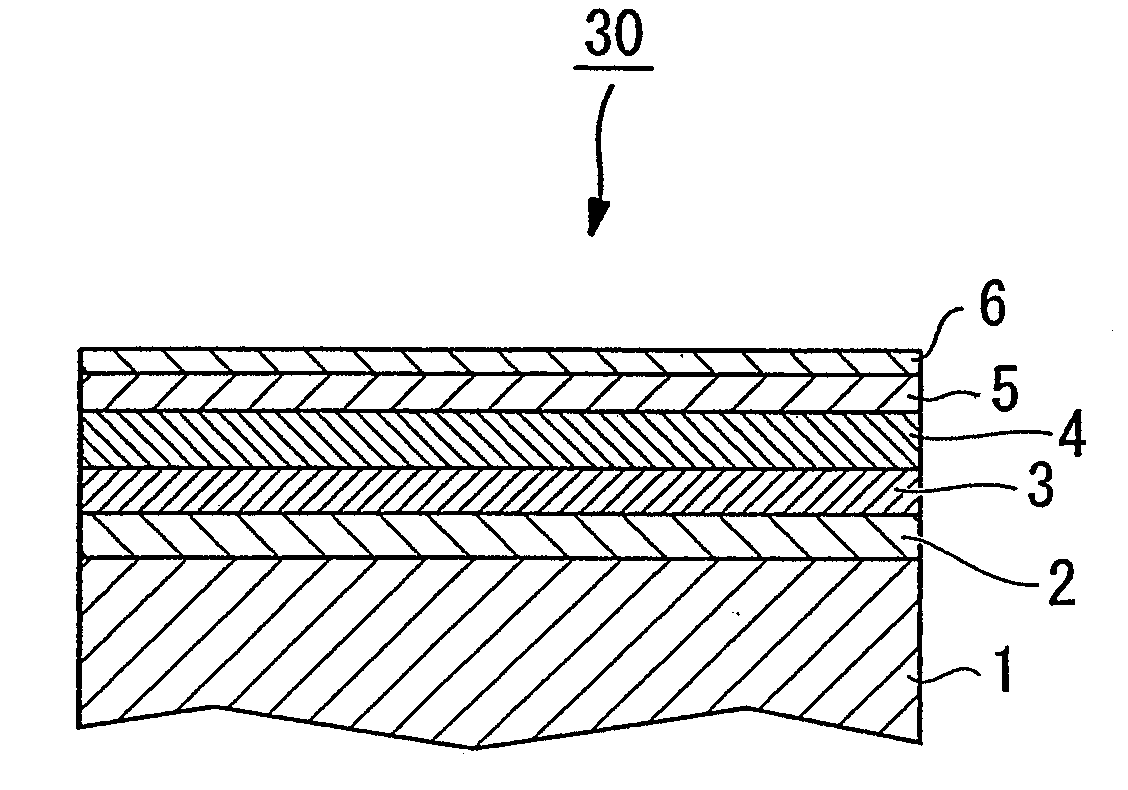
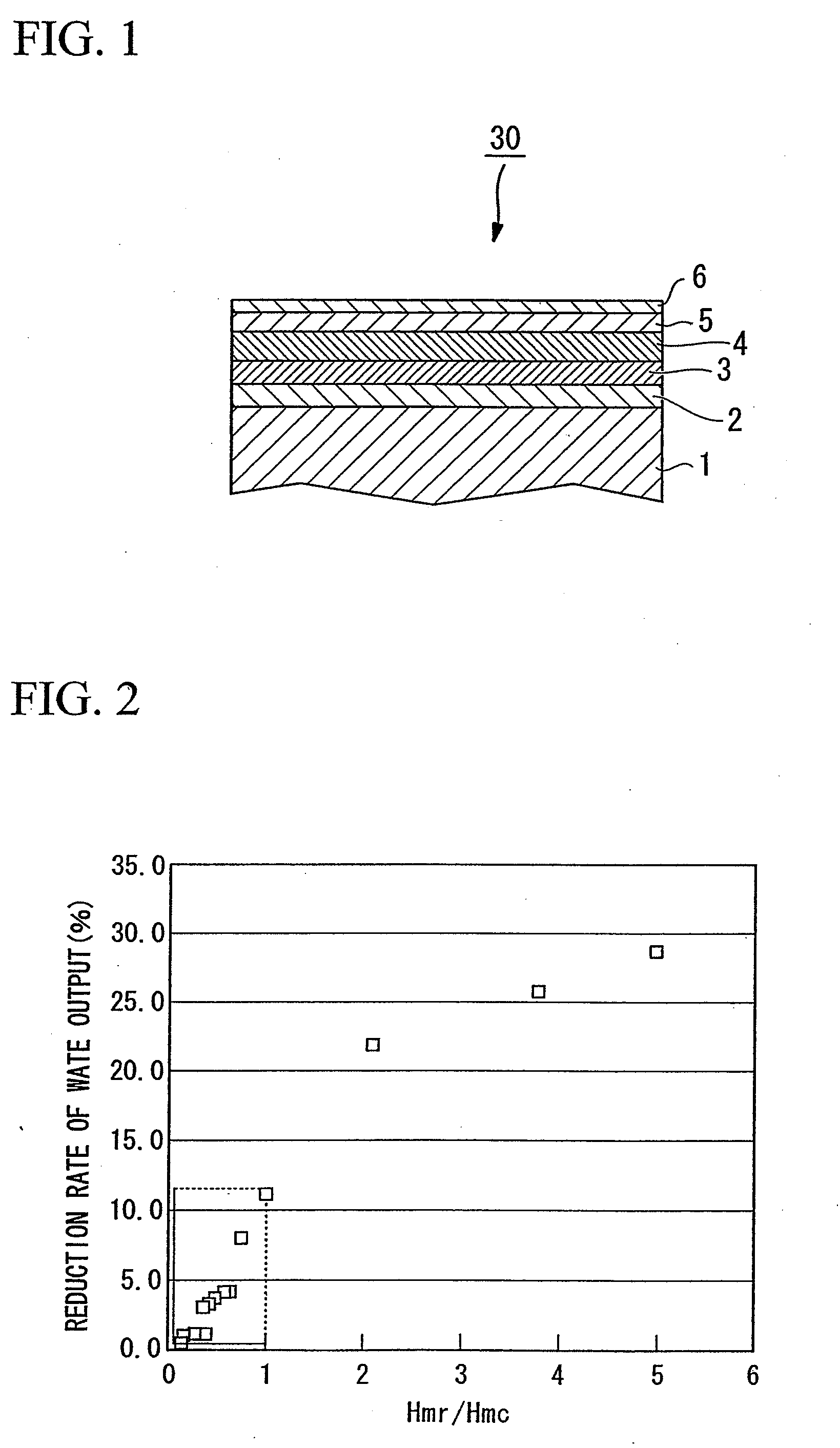
InactiveUS20090142625A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioImprove recording densityDifferent record carrier formsMagnetic materials for record carriersColloidal silicaRocking curve
The present invention provides a magnetic recording medium which enables improvement of the layer quality of magnetic layer grown on the surface of a soft magnetic underlayer by conducting excellent control of crystal orientation by imparting an optimal half-width of the Rocking curve (Δθ50), as well as obtainment of SNR that suppresses generation of TA and enables realization of high-density recording. The magnetic recording medium includes a soft magnetic underlayer, an orientation control layer, a perpendicular magnetic recording layer, and a protective layer, which are disposed on top of a non-magnetic substrate; wherein the magnetic anisotropy ratio (Hmr / Hmc) of the soft magnetic underlayer is 1 or less, and Δθ50 is 1 to 6 degrees. The soft magnetic underlayer is formed on the primary surface of the non-magnetic substrate where the primary surface has been polished one substrate at a time by a sheet-type texture processing device using polishing tape and a slurry containing colloidal silica abrasive grain.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Out-of-step solution method with self-adaptive function
ActiveCN103337831AAvoid destabilizing accidentsAvoid sabotage accidentsEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionPhase sequence/synchronism indicationTransient stateRocking curve
An out-of-step solution method with a self-adaptive function relates to an emergency protection method that can complete automatic switching in case of abnormality of an AC and DC grid, in particular to an out-of-step solution method with the self-adaptive function, which is used for out-of-step fleet solution of a strong connection grid system. The method comprises the following steps: performing EEAC simulation for failures of the strong connection grid, so as to determine a potential instability mode; obtaining a power angle rocking curve of a generator according to transient simulation, so as to identify coherence fleet, wherein affected system is divided into a coherence instability region and a coherence stable range; determining a center of oscillation and installing a solution device; real-timely acquiring running state data of the grid system by utilizing a PMU, so as to detect whether the system is out of step; setting the solution conditions, automatically capturing the center of oscillation, selecting the solution device in a self-adaptive manner, and starting the solution operation. Due to the adoption of the method, in case the system is out of step, automatic solution is ensured while respective synchronicity of the solved subsystems is ensured, and accordingly, safe and stable operation of the grid is ensured.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
Film bulk acoustic wave resonator
ActiveUS7173361B2Improved acoustic multilayerImprove featuresPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyImpedence networksThin-film bulk acoustic resonatorRocking curve
A film bulk acoustic wave resonator of the invention includes a substrate; a resonant structure provided on the substrate constituted by a lower electrode, a piezoelectric film and an upper electrode; and an acoustic multilayer of a plurality of reflective films provided between the substrate and the resonant structure. At least one of the reflective films of the acoustic multilayer has a specified crystal plane orientation, and an X-ray rocking curve full width at half maximum that is preferably not greater than 10 degrees, and more preferably is not greater than 3 degrees. This makes it possible to obtain better resonance characteristics than in the case of the prior art, by increasing the efficiency with which bulk waves propagating towards the substrate are reflected.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
High crystalline quality synthetic diamond
ActiveCN101443476AAvoid applying elastic strainPolycrystalline material growthFrom chemically reactive gasesRocking curveX-ray
The invention relates to a single crystal CVD diamond material, wherein the extended defect density as characterised by X-ray topography is less than 400 / cm2 over an area of greater than 0.014 cm2. The invention further relates to a method for producing a CVD single crystal diamond material according to any preceding claim comprising the step of selecting a substrate on which to grow the CVD single crystal diamond, wherein the substrate has at least one of a density of extended defects as characterised by X-ray topography of less than 400 / cm2 over an area greater than 0.014 cm2; an optical isotropy of less than 1x10-5 over a volume greater than 0.1 mm3; and a FWHM X-ray rocking curve width for the (004) reflection of less than 20 arc seconds.
Owner:EHLEMENT SIKS TECHZ PTI
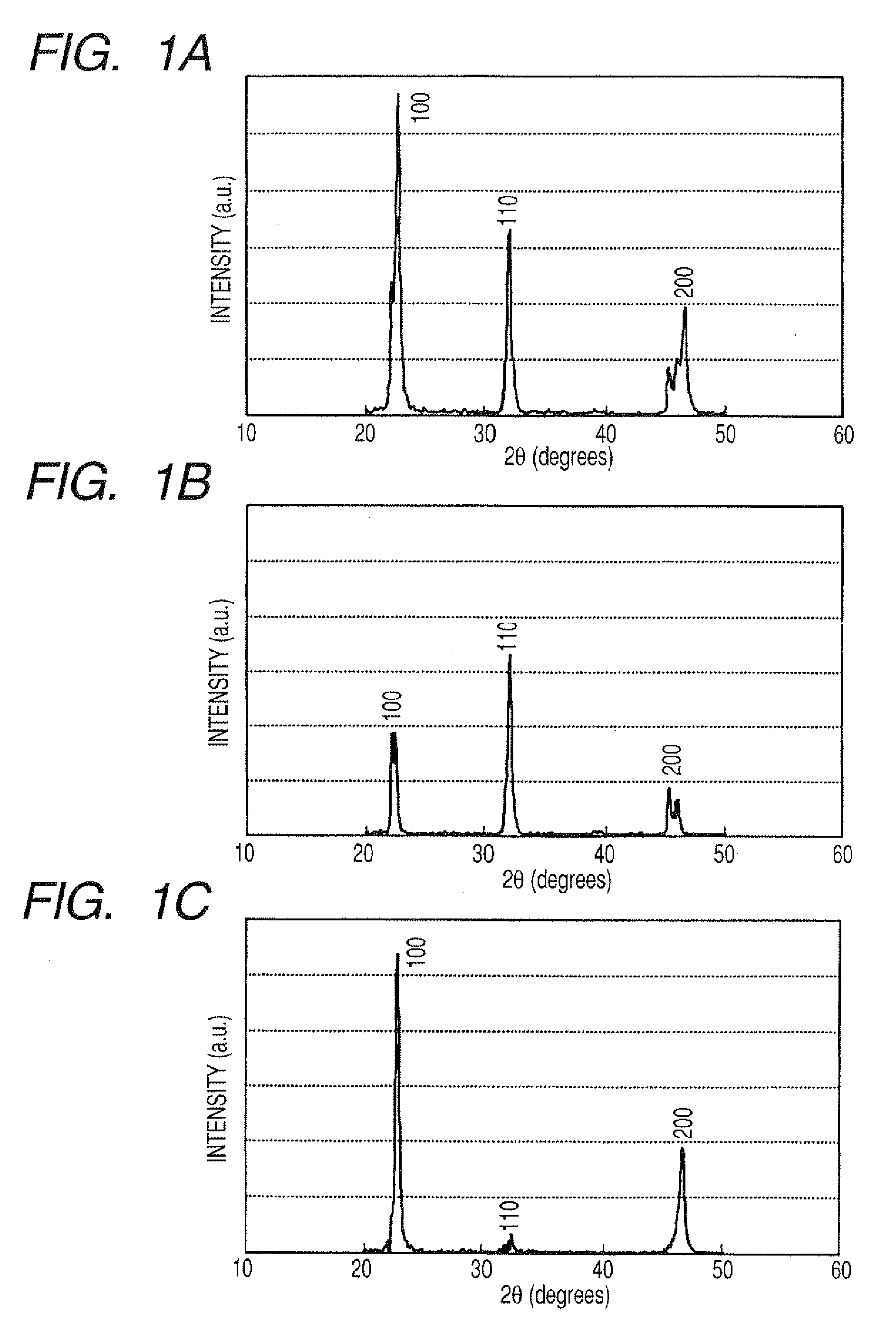
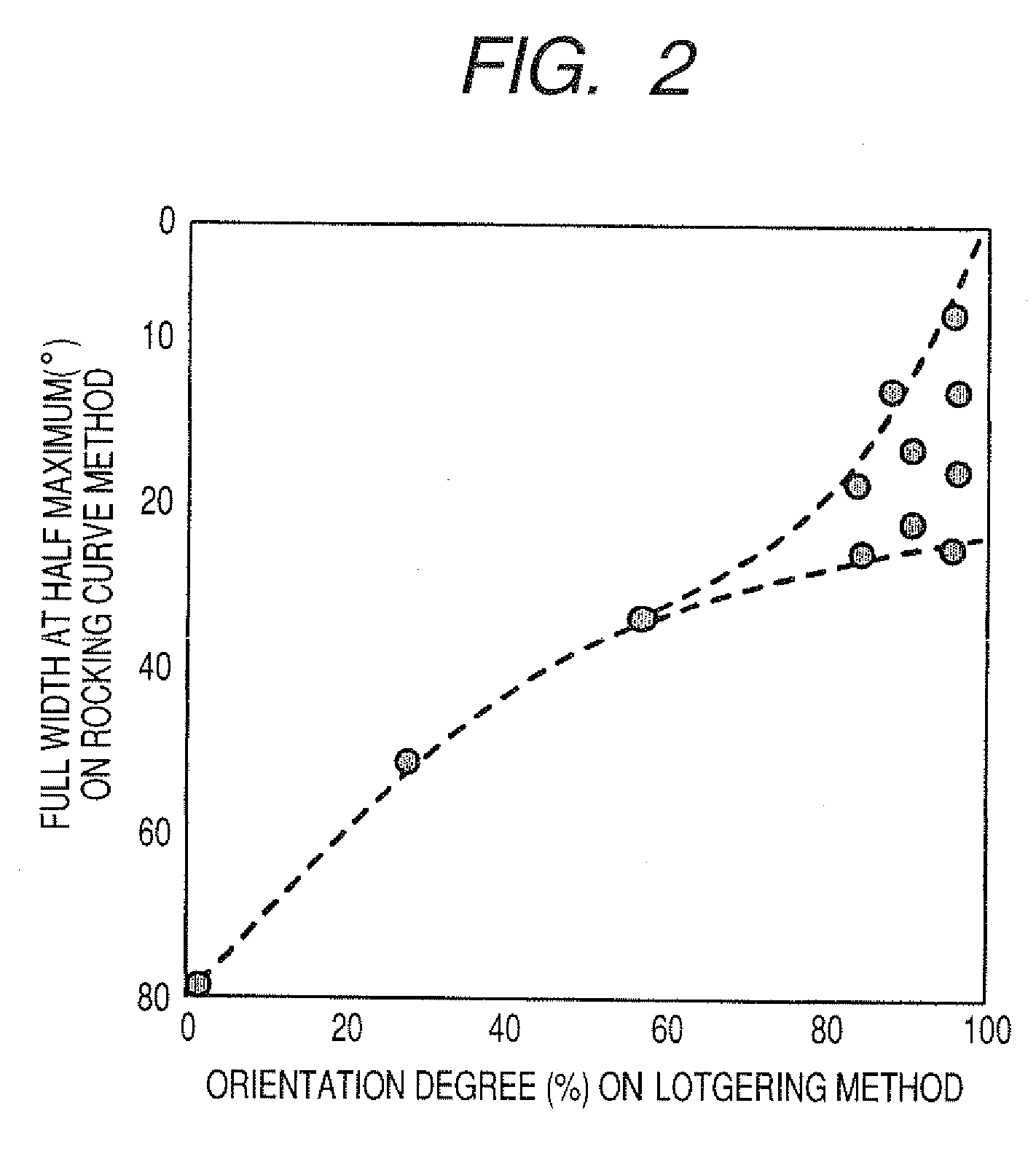
Method of manufacturing crystal oriented ceramics
InactiveUS20090121374A1Excellent piezoelectric propertiesIncreased Curie temperatureRocking curveFull width at half maximum
A method of manufacturing a crystal oriented ceramics is disclosed. The method comprises preparing step, mixing step, shaping step and sintering method. At least one of anisotropically shaped powder, used as raw material, and a compact, formed by shaping step, is selected to have an orientation degree of 80% or more with a full width at half maximum (FWHM) of 15° or less according to a rocking curve method. A microscopic powder, having an average grain diameter one-third or less that of anisotropically shaped powder, is prepared for mixing therewith to prepare raw material mixture. The raw material mixture is shaped into the compact so as to allow oriented planes of anisotropically shaped powder to be oriented in a nearly identical direction. In a sintering step, anisotropically shaped powder and microscopic powder are sintered with each other to obtain the crystal oriented ceramics.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Epitaxial substrate, semiconductor device substrate, and HEMT device
ActiveUS20100051961A1Preferable crystal qualityImprove featuresSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesRocking curveDevice material
A buffer layer formed of Inx1Aly1Gaz1N formed on a base, with an upper part of the buffer layer containing columnar polycrystalline including a grain boundary existing in a direction substantially perpendicular to a surface of the base. The number of grain boundaries in the lower part of the buffer layer is greater than that in the upper part, and a full width at half maximum of an X-ray rocking curve of the upper part is 300-3000 seconds, RMS of the surface of the buffer layer is 0.2 nm-6 nm, and the ratio of the grain boundary width of the crystal grain of the upper part in a direction parallel to the base surface to the formation thickness of the buffer layer is 0.5-1.5.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Molecular beam epitaxy growth of ternary and quaternary metal chalcogenide films
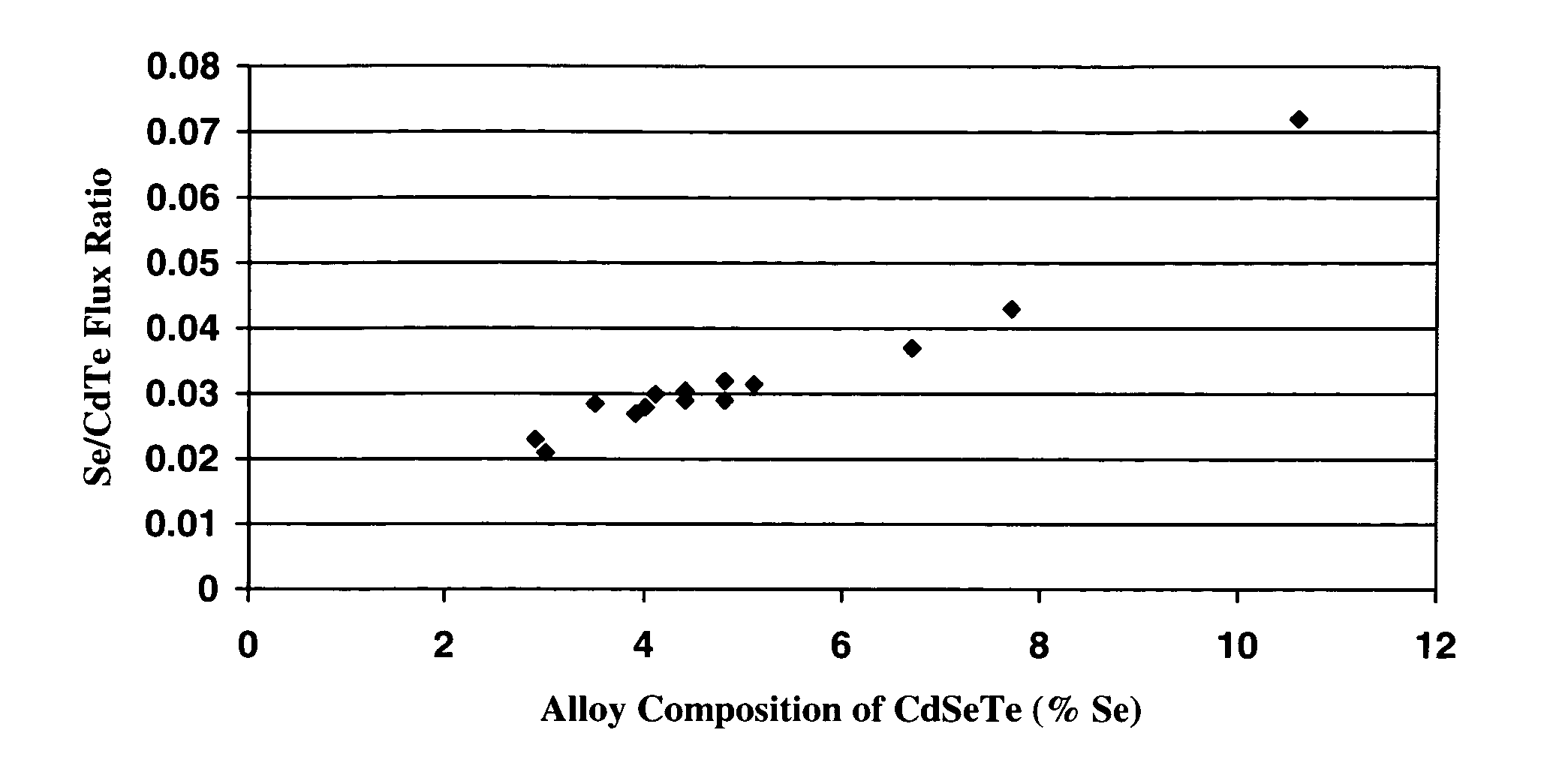
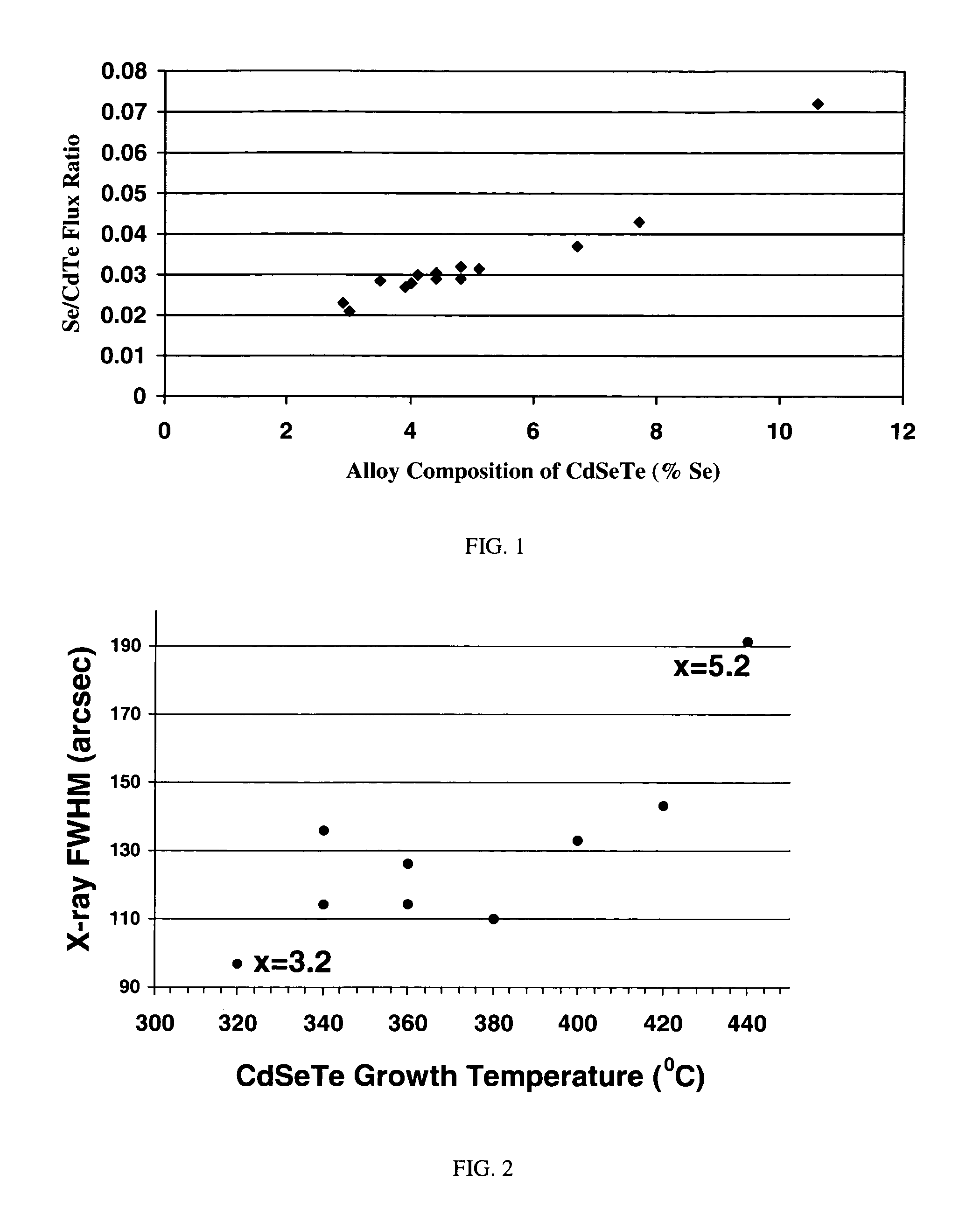
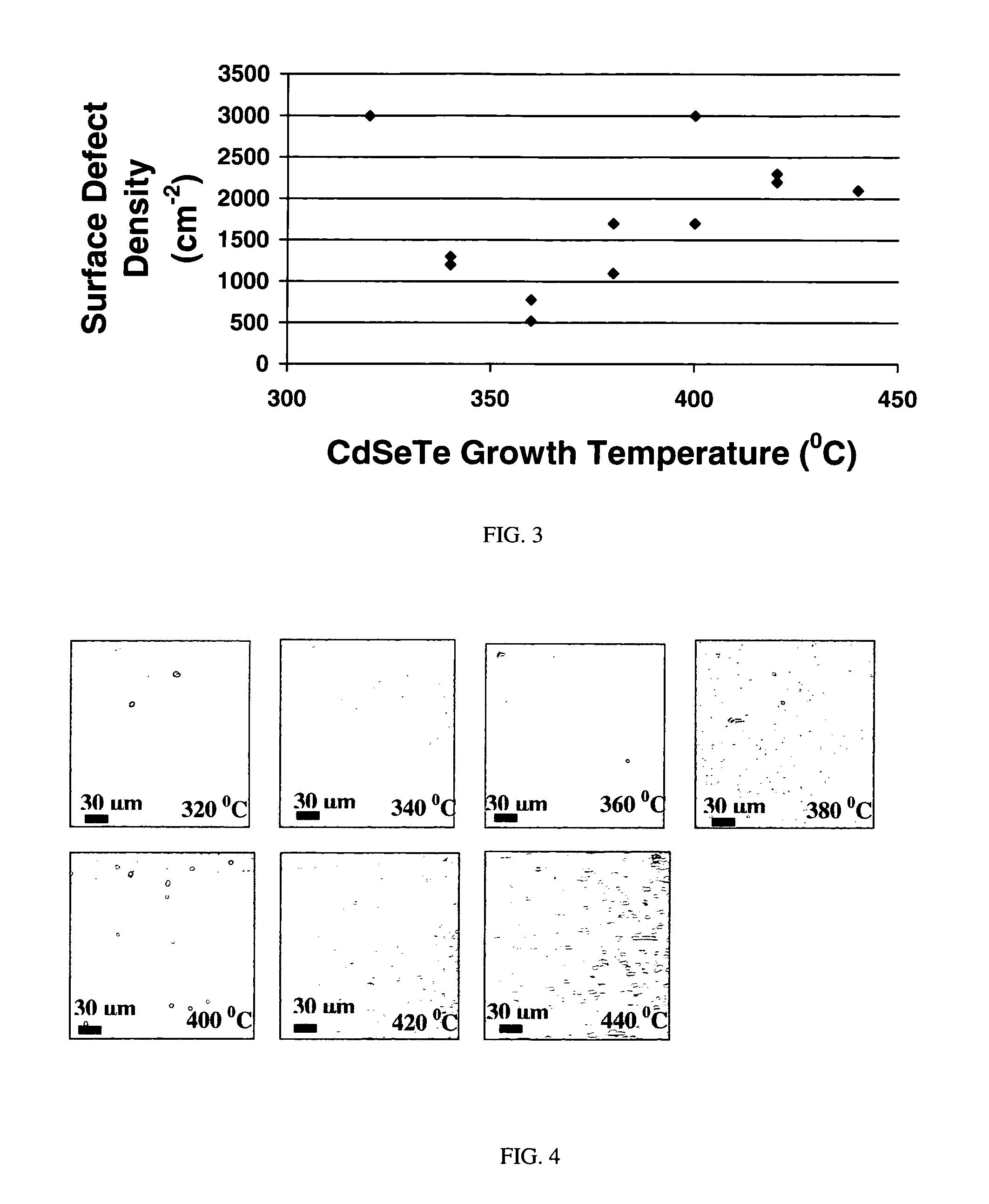
InactiveUS7518207B1Improve surface morphologyReduce surface defect densitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationRocking curveSulfur
The ternary alloy CdSexTe1-x(2 1 1) and the quaternary alloy Cd1-zZnzSexTe1-x have been grown on Si(2 1 1) substrates using molecular beam epitaxy (MBE). The growth of CdSeTe is facilitated using a compound CdTe effusion source and a Se effusion source while the growth of CdZnSeTe is facilitated using a compound CdTe effusion source, a compound ZnTe effusion source, and an elemental Se source. The alloy compositions (x) and (z) of CdSexTe1-x ternary compound and Cd1-zZnzSexTe1-x are controlled through the Se / CdTe and ZnTe / CdTe flux ratios. The rate of Se incorporation is higher than the rate of Te incorporation as growth temperature increases. As-grown CdSeTe with 4% Se and CdZnSeTe with 4% Zn+Se, which is substantially lattice matched to long-wavelength infrared HgCdTe materials, exhibits excellent surface morphology, low surface defect density (less than 500 cm2), and a narrow X-ray rocking curve (a full-width at half maximum of 103 arcsec).
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Carbon-based material, electrode catalyst, oxygen reduction electrode catalyst, gas diffusion electrode, aqueous solution electrolytic device, and production method for carbon-based material
ActiveCN103974900AImprove performanceMaterial nanotechnologyActive material electrodesRocking curveElectrolysis
Provided is a carbon-based material having high catalytic activity. This carbon-based material comprises a graphene doped with a metal atom and at least one type of non-metallic atom selected from a nitrogen atom, a boron atom, a sulfur atom, and a phosphorous atom. The ratio, for the carbon-based material, between the maximum peak intensity derived from an inactive metal compound and a metal crystal, and the (002) surface peak intensity in a rocking curve obtained by x-ray diffraction measurement using a CuKalpha ray is no more than 0.1.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP +1
Substrate for epitaxial growth
ActiveUS6869702B2Improve crystal qualityCrystalline qualityPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRocking curveFull width at half maximum
A substrate for epitaxial growth allowing formation of an Al-containing group III nitride film having high crystal quality is provided. A nitride film containing at least Al is formed on a 6H—SiC base by CVD at a temperature of at least 1100° C., for example. The substrate for epitaxial growth allowing formation of an Al-containing group III nitride film having high crystal quality is obtained by setting the dislocation density of the nitride film to not more than 1×1011 / cm2, the full width at half maximum of an X-ray rocking curve for (002) plane to not more than 200 seconds and the full width at the half maximum of the X-ray rocking curve for (102) plane to not more than 1500 seconds.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Method for growing AIN or AlGaN film
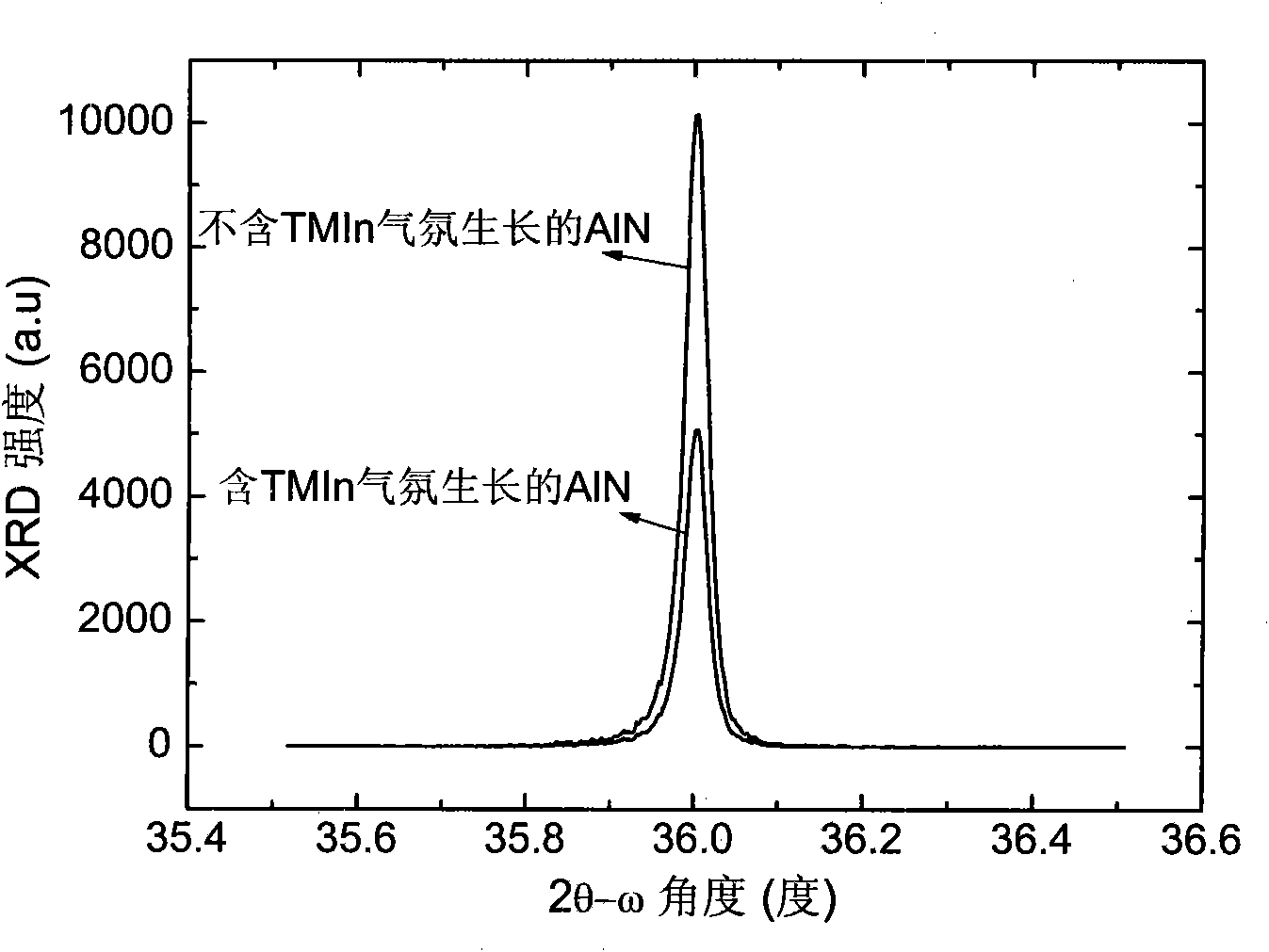
InactiveCN101603172AImprove crystal qualityImprove flatnessChemical vapor deposition coatingRocking curveActive agent
The invention provides a method for growing an AIN or AlGaN film, and the method is described as follows: proper TMIn is led into and used as active agent to improve the crystal quality and the surface planeness of the AIN or AlGaN film during using the metal organic chemical gas phase deposition method to grow AIN or AlGaN film. The method comprises the following steps: generally using hydrogen as carrier gas and taking TMGa, TMAl and NH3 respectively as a Ga source, an Al source and an N source; leading the TMIn and other raw materials into a reaction chamber together at the same time to grow under the temperature of 1050-1200 DEG C, wherein the flow of the TMIn is usually 40-400sccm. The surface roughness of a sample is shown by adopting an atomic power micro method and the crystal quality of the sample is shown by adopting X-ray to diffract tricrystal rocking curve peak half-width, the result shows that: compared the AIN and AlGaN sample prepared by the method with the sample grown by adopting the prior art, the surface roughness is lowered obviously, and the crystal quality is improved.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Piezoelectric thin film element and piezoelectric thin film device
ActiveUS20110175488A1Solve the large leakage currentSmall leak currentPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyImpedence networksRocking curveX-ray
To provide a piezoelectric thin film on a substrate, having an alkali-niobium oxide-based perovskite structure expressed by a composition formula (K1−xNax)yNbO3, wherein the composition ratio x of the piezoelectric thin film expressed by (K1−xNax)yNbO3 is in a range of 0.4≦x≦0.7, and a half width of a rocking curve of (001) plane by X-ray diffraction measurement is in a range of 0.5° or more and 2.5° or less.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
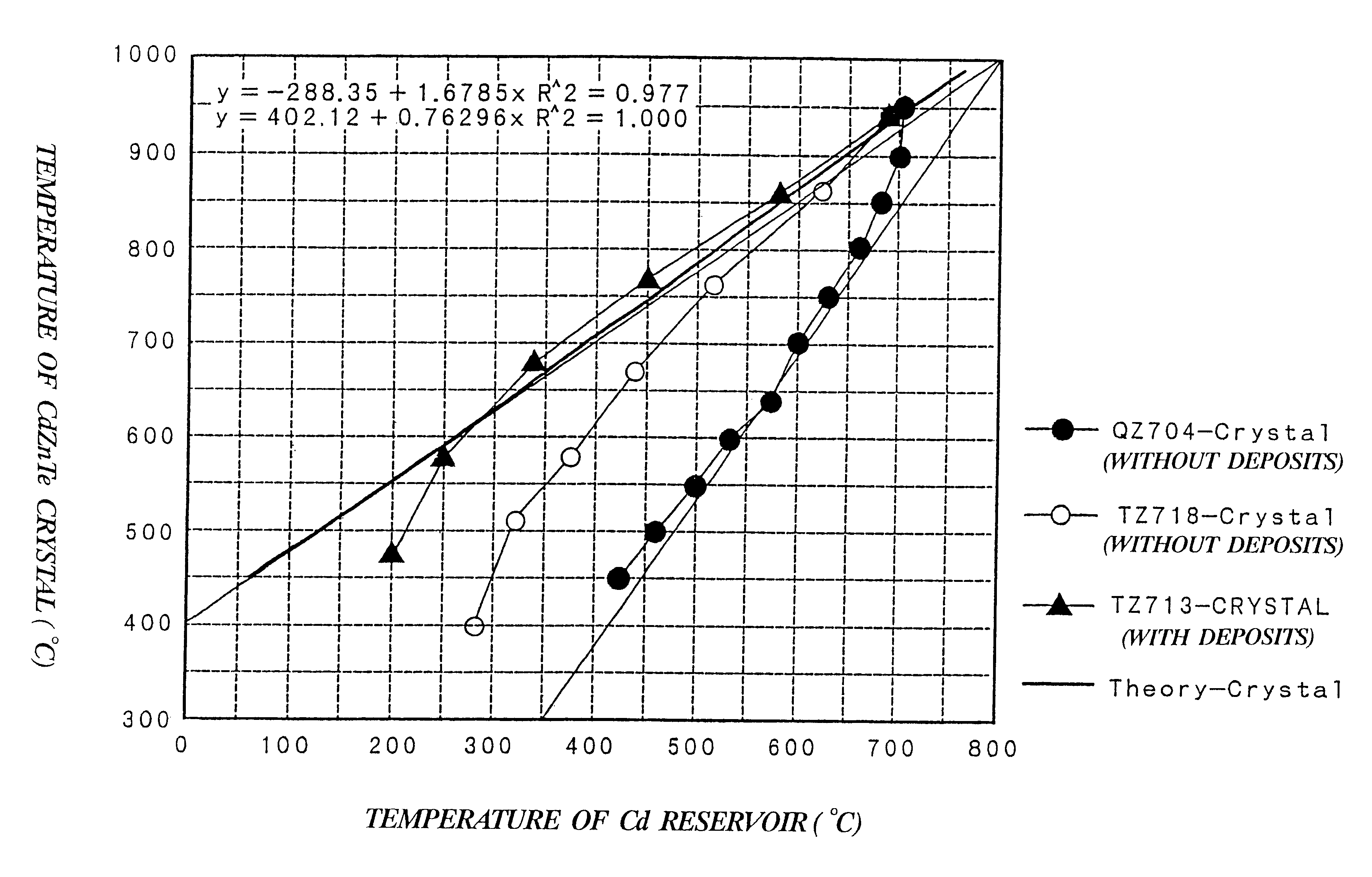
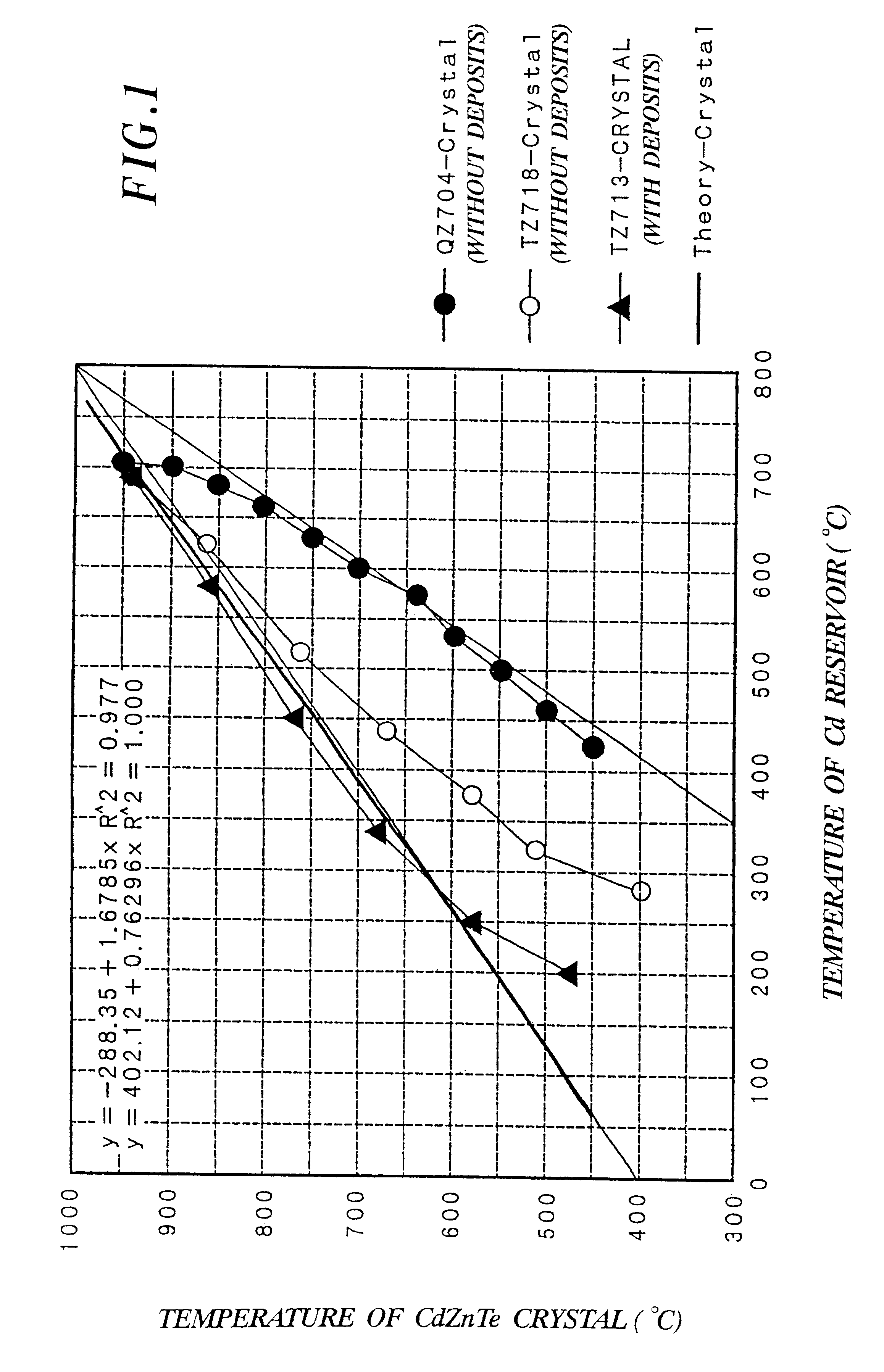
CdTe crystal or CdZnTe crystal and method for preparing the same
InactiveUS6299680B1Maintain good propertiesDeposits having Te or Cd are reducedSelenium/tellurium compundsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRocking curveX-ray
An object of the present invention is to reduce the etch pit density (EPD) and the full-width-half-maximum (FWHM) value of the double crystal X-ray rocking curve, and to provide a CdTe crystal or a CdZnTe crystal which does not include deposits having Cd or Te and the process for producing the same. After a CdTe crystal or a CdZnTe crystal was grown, while the temperature of the crystal is from 700 to 1050° C., the Cd pressure is adjusted so as to keep the stoichiometry of the crystal at the above temperature. The crystal is left for time t which is determined so that each of a diameter L(r) of the crystal and a length L(z) thereof satisfies the following equation 1:Then, when the crystal is cooled, the temperature of the crystal is decreased within a range in which the temperature of the crystal and that of a Cd reservoir satisfy the following equation 2:
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING & METALS CO LTD
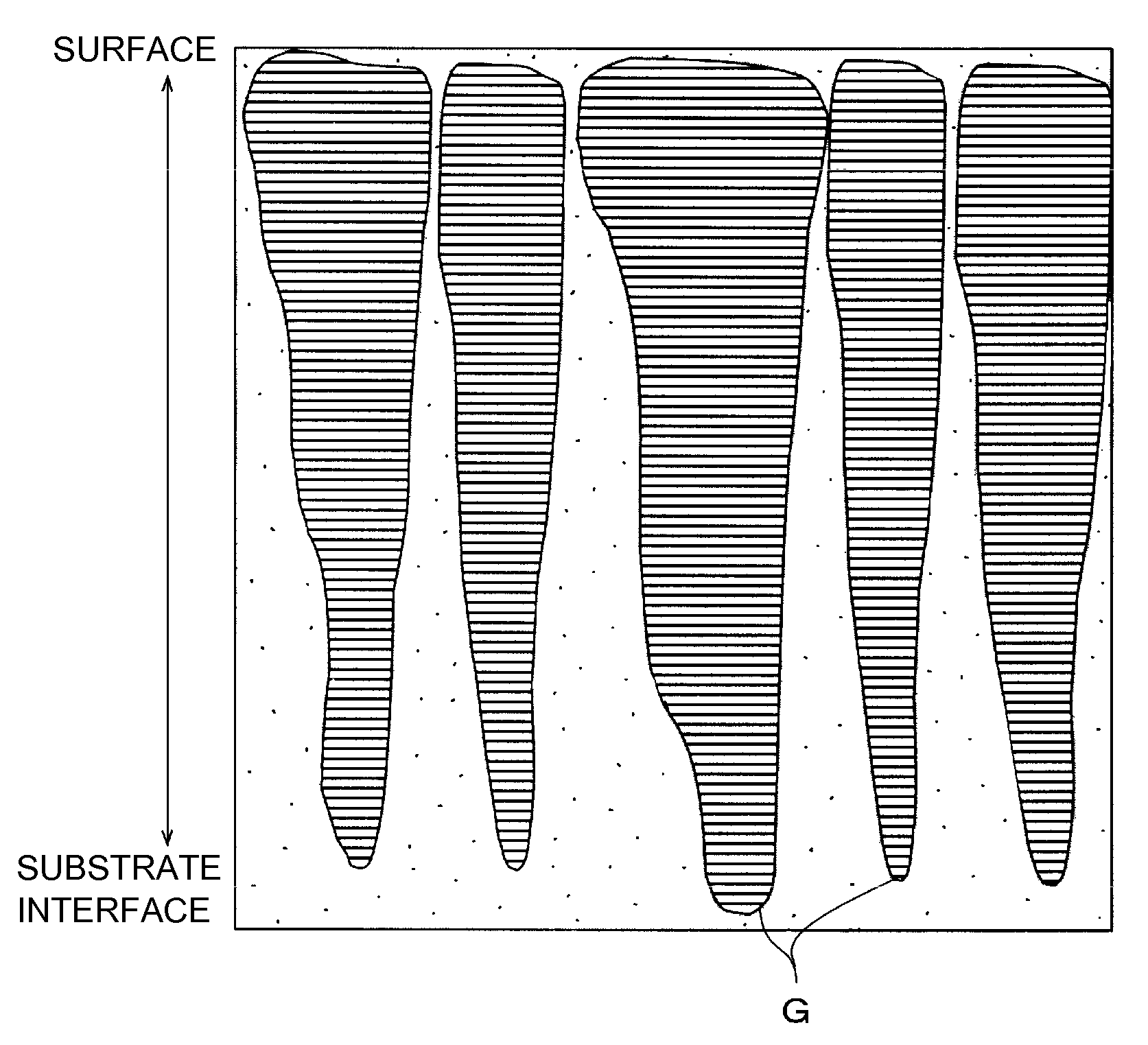
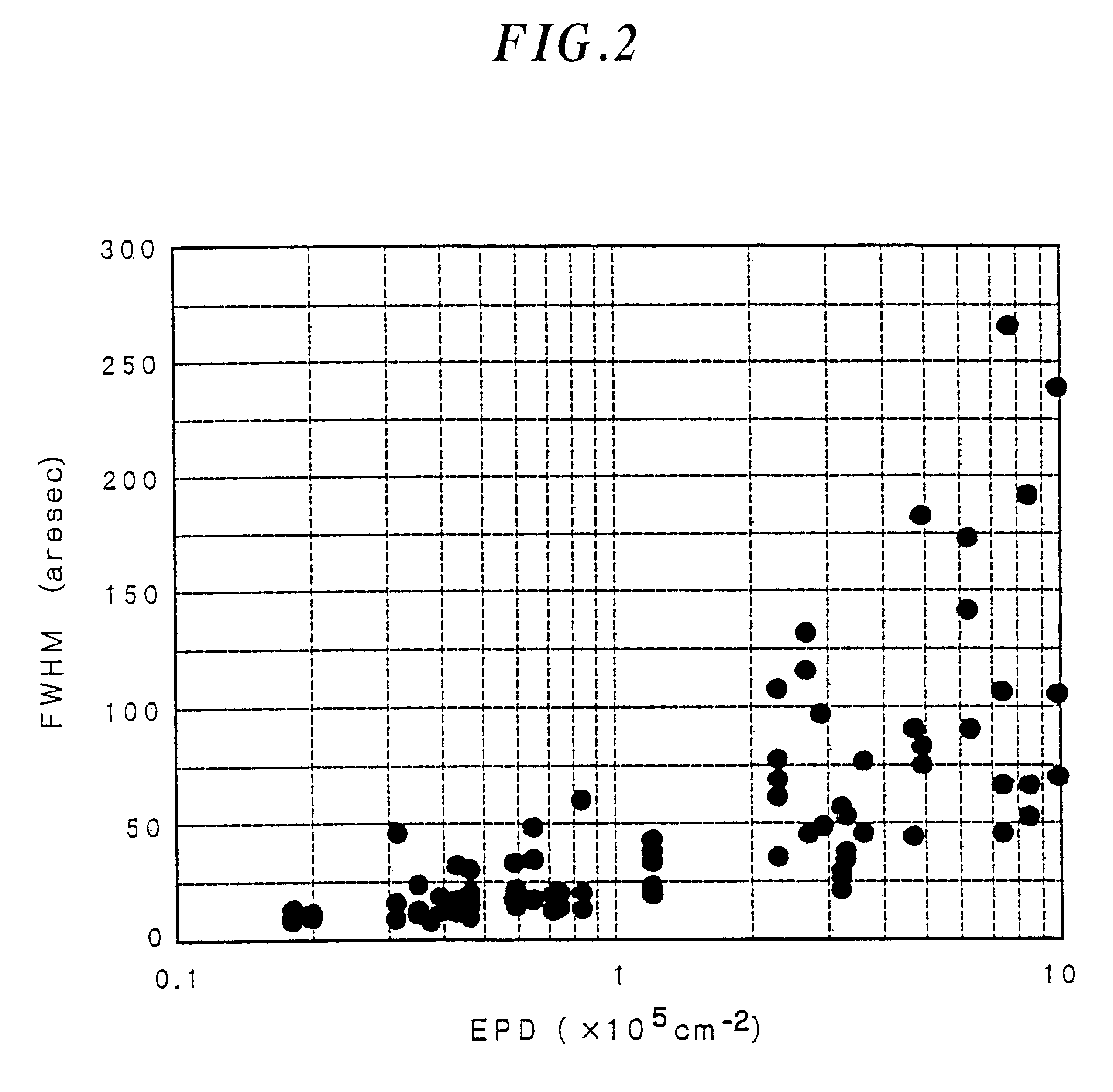
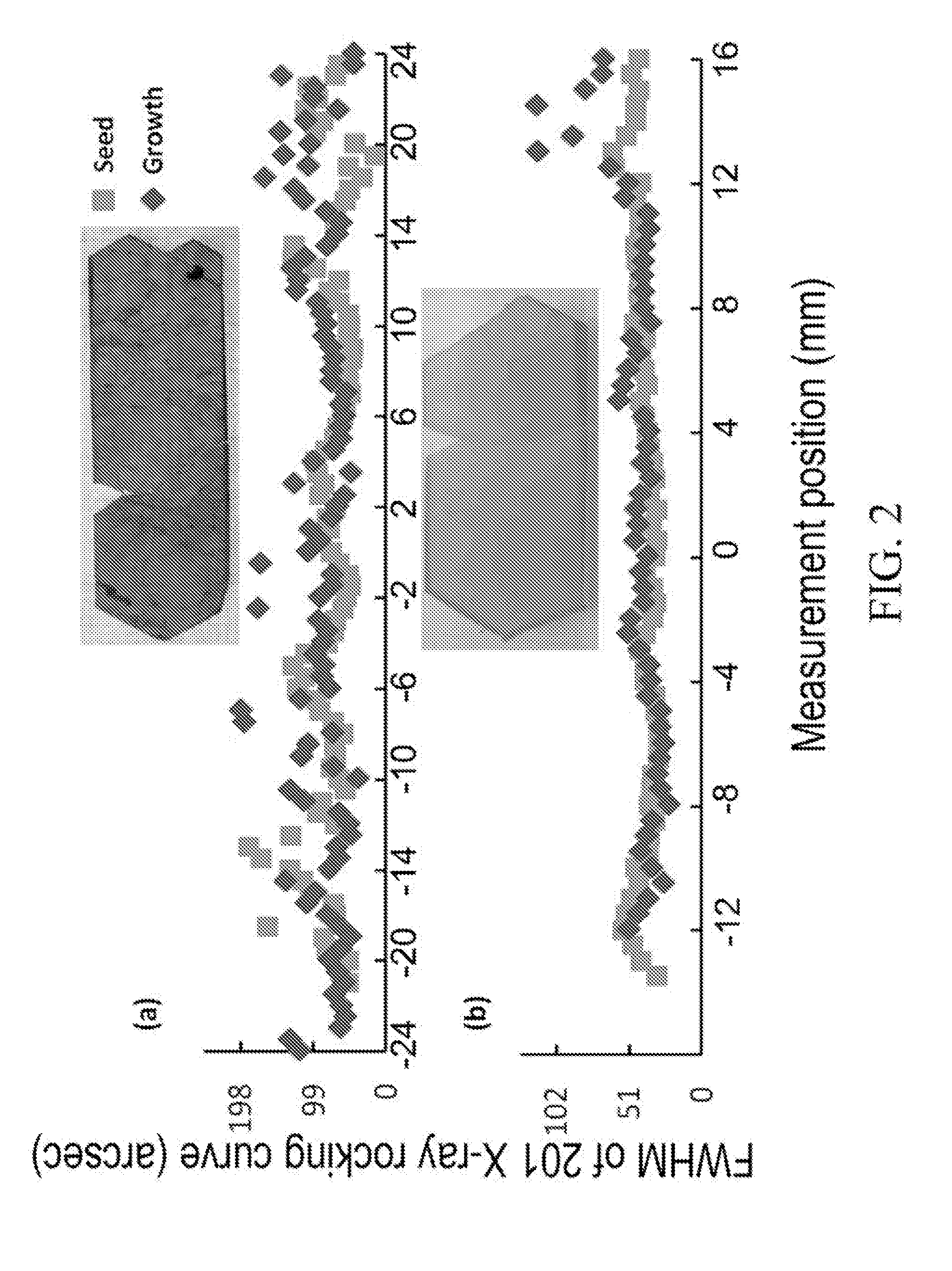
Seed selection and growth methods for reduced-crack group iii nitride bulk crystals
ActiveUS20160215410A1Polycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsRocking curveBulk crystal
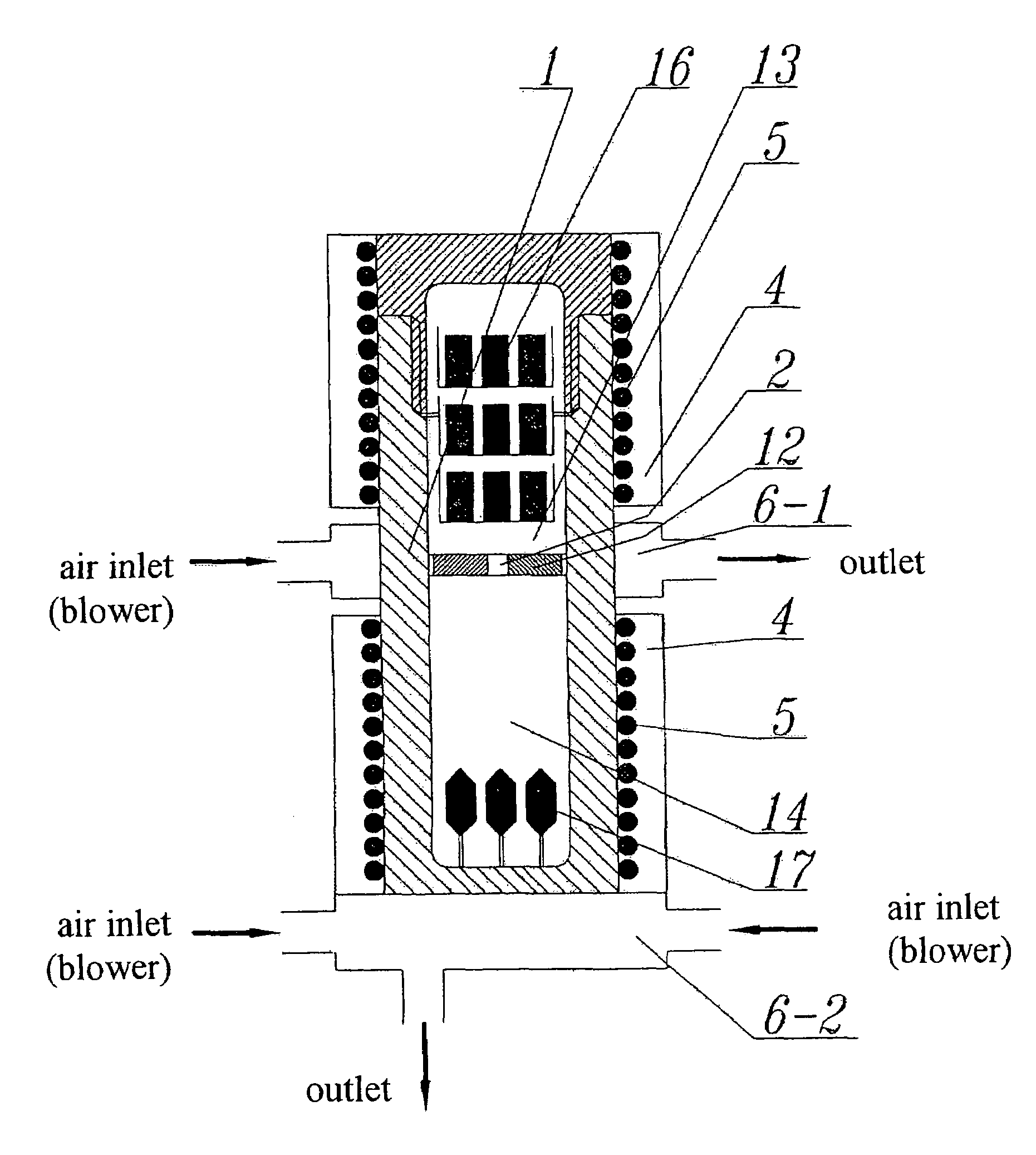
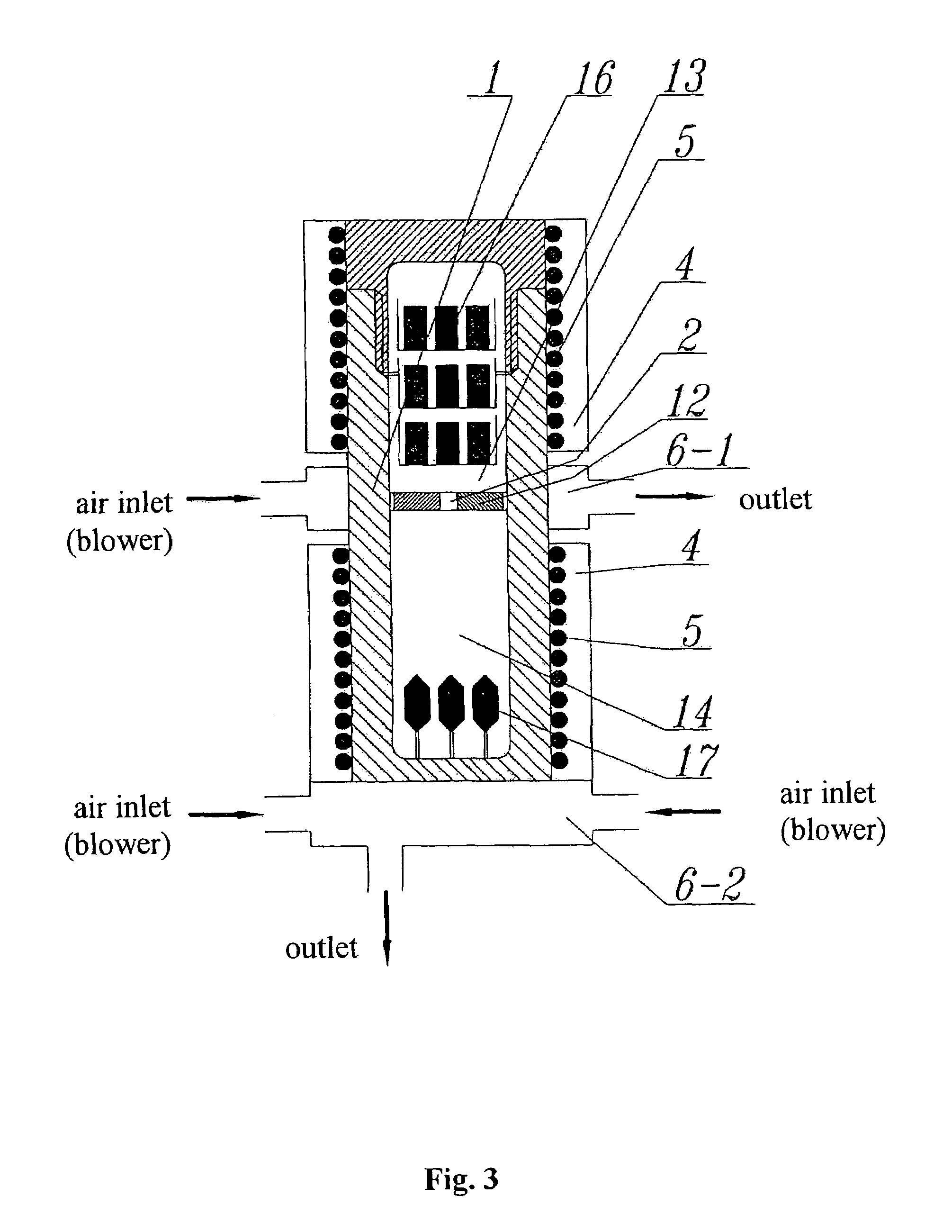
In one instance, the invention provides a method of growing bulk crystal of group III nitride using a seed crystal selected by (a) measuring x-ray rocking curves of a seed crystal at more than one point, (b) quantifying the peak widths of the measured x-ray rocking curves, and (c) evaluating the distribution of the quantified peak widths. The invention also includes the method of selecting a seed crystal for growing bulk crystal of group III nitride.The bulk crystal of group III nitride can be grown in supercritical ammonia or a melt of group III metal using at least one seed selected by the method above.
Owner:SIXPOINT MATERIALS
Piezoelectric device comprising ultrahighly-oriented aluminum nitride thin film and its manufacturing method
InactiveUS7233094B2Improve performancePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsRocking curveFull width
The present invention has an objective to provide a high performance piezoelectric element in which is formed an aluminum nitride thin film free from hillocks, cracks, and peeling which exhibits superhigh c-axis orientation, by forming a bottom electrode from a W layer with no intervening adhesive layer on a glass or other cheap substrate. The piezoelectric element of the present invention is a piezoelectric element using a superhigh-oriented aluminum nitride thin film characterized in that the piezoelectric element is free from hillocks, cracks, and peeling and includes a stack structure in which a bottom electrode, a piezoelectric body thin film, and a top electrode are sequentially formed on a substrate; the bottom electrode is made of an oriented W layer of which a (111) plane of W is parallel to a surface of the substrate; and the piezoelectric body thin film is formed of a c-axis-oriented aluminum nitride thin film having a rocking curve full width half maximum (RCFWHM) not exceeding 2.5°.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Nitride semiconductor substrate, production method therefor and nitride semiconductor device
ActiveUS20110248281A1Suppress mutationImprove crystal qualityPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRocking curveSurface layer
A nitride semiconductor substrate includes two principal surfaces including an upper surface that is a growth face and a lower surface on its opposite side. An FWHM in a surface layer region at depths of from 0 to 250 nm from the upper surface is narrower than an FWHM in an inner region at depths exceeding 5 μm from the upper surface, where the FWHMs are obtained by X-ray rocking curve measurement using diffraction off a particular asymmetric plane inclined relative to the upper surface.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com