Patents
Literature
402results about "Imaging devices" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
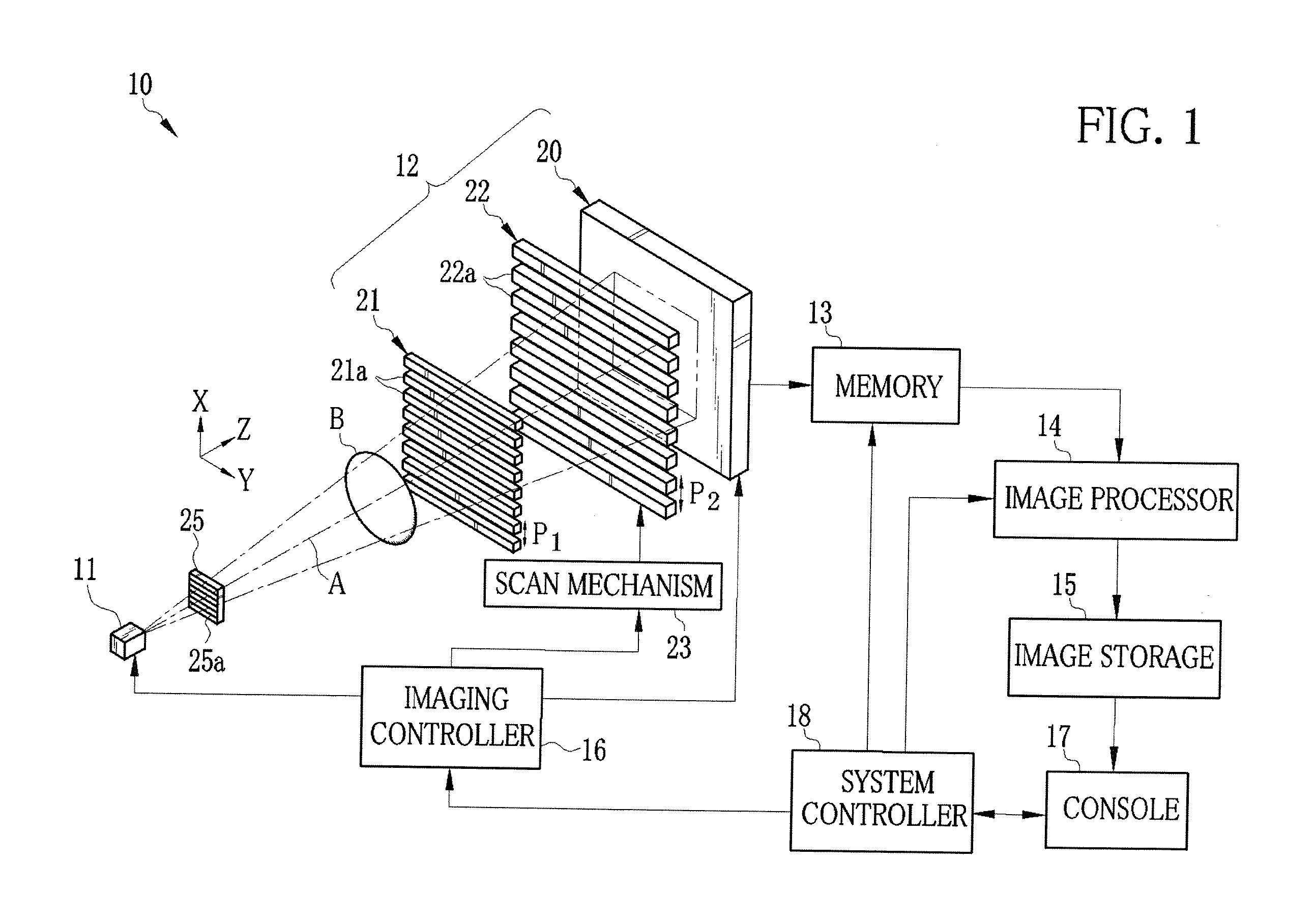
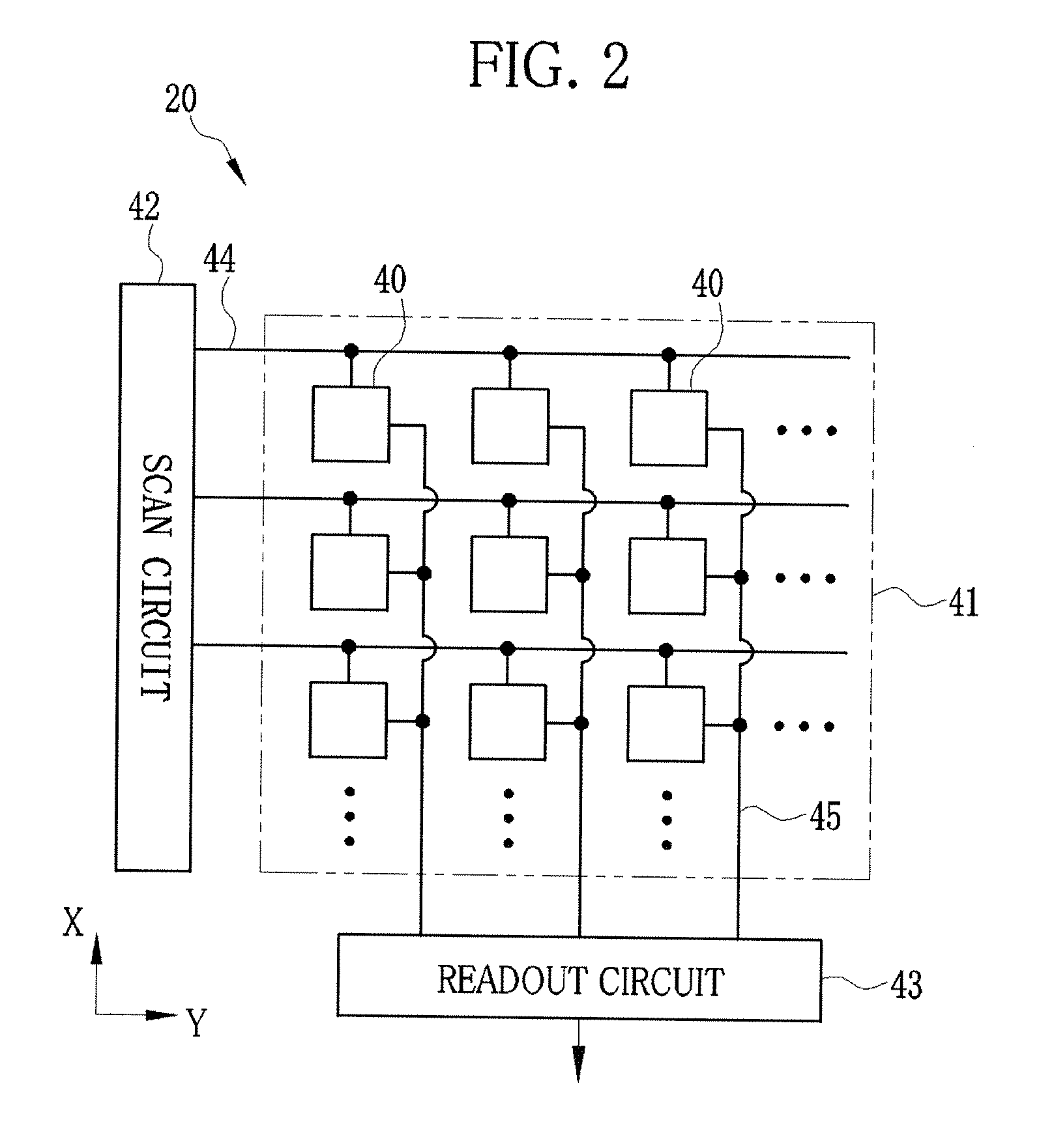
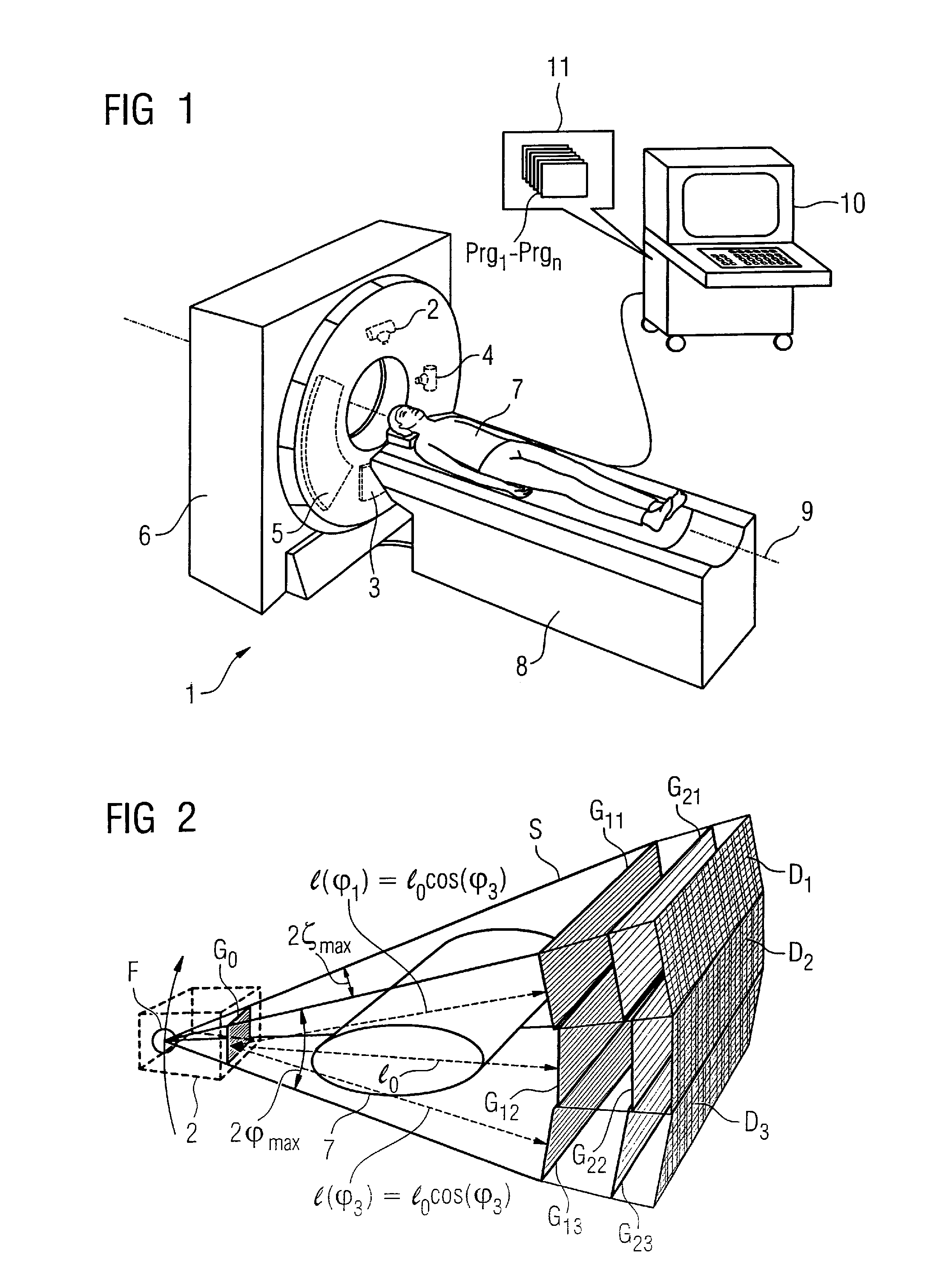
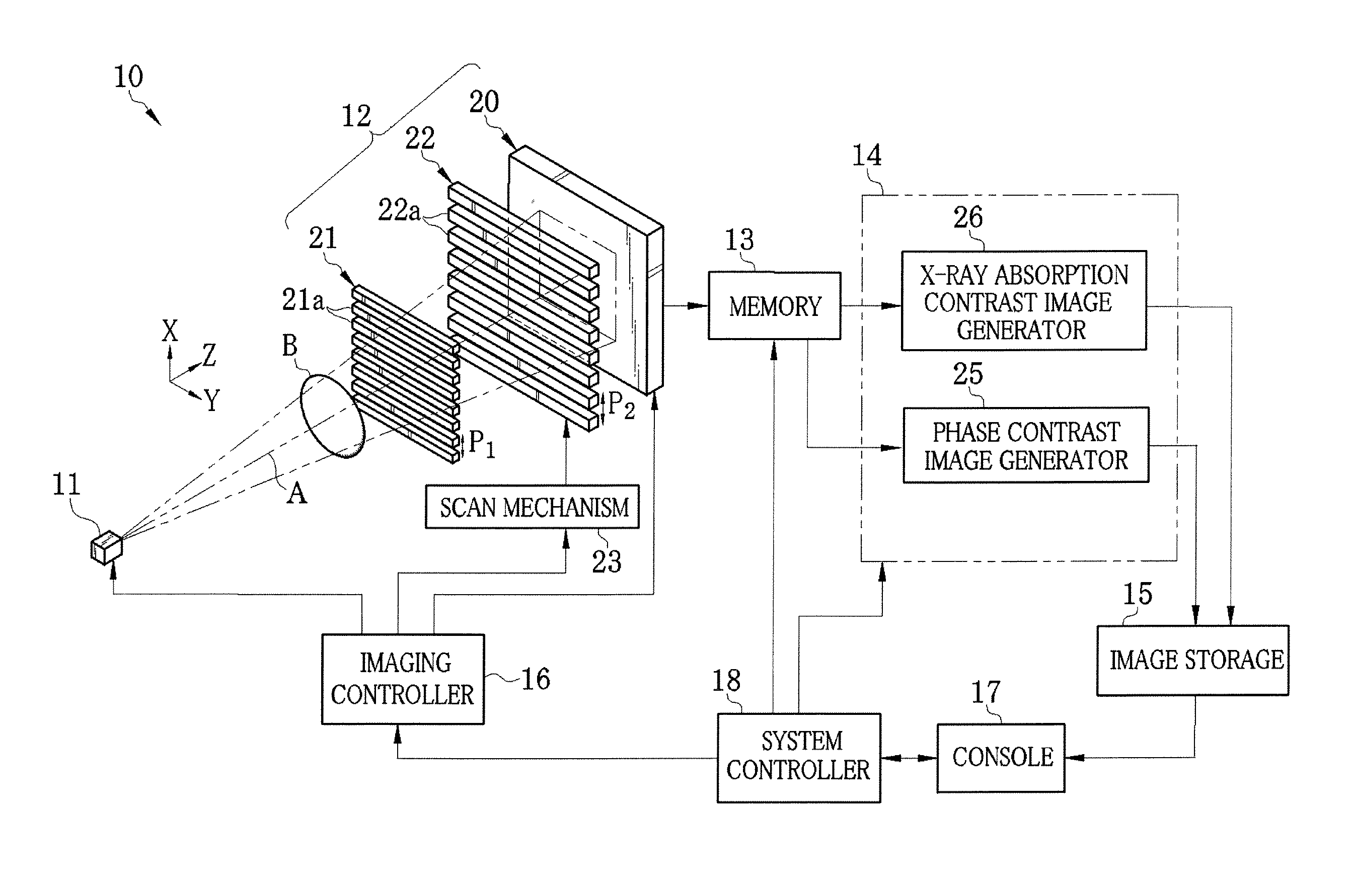
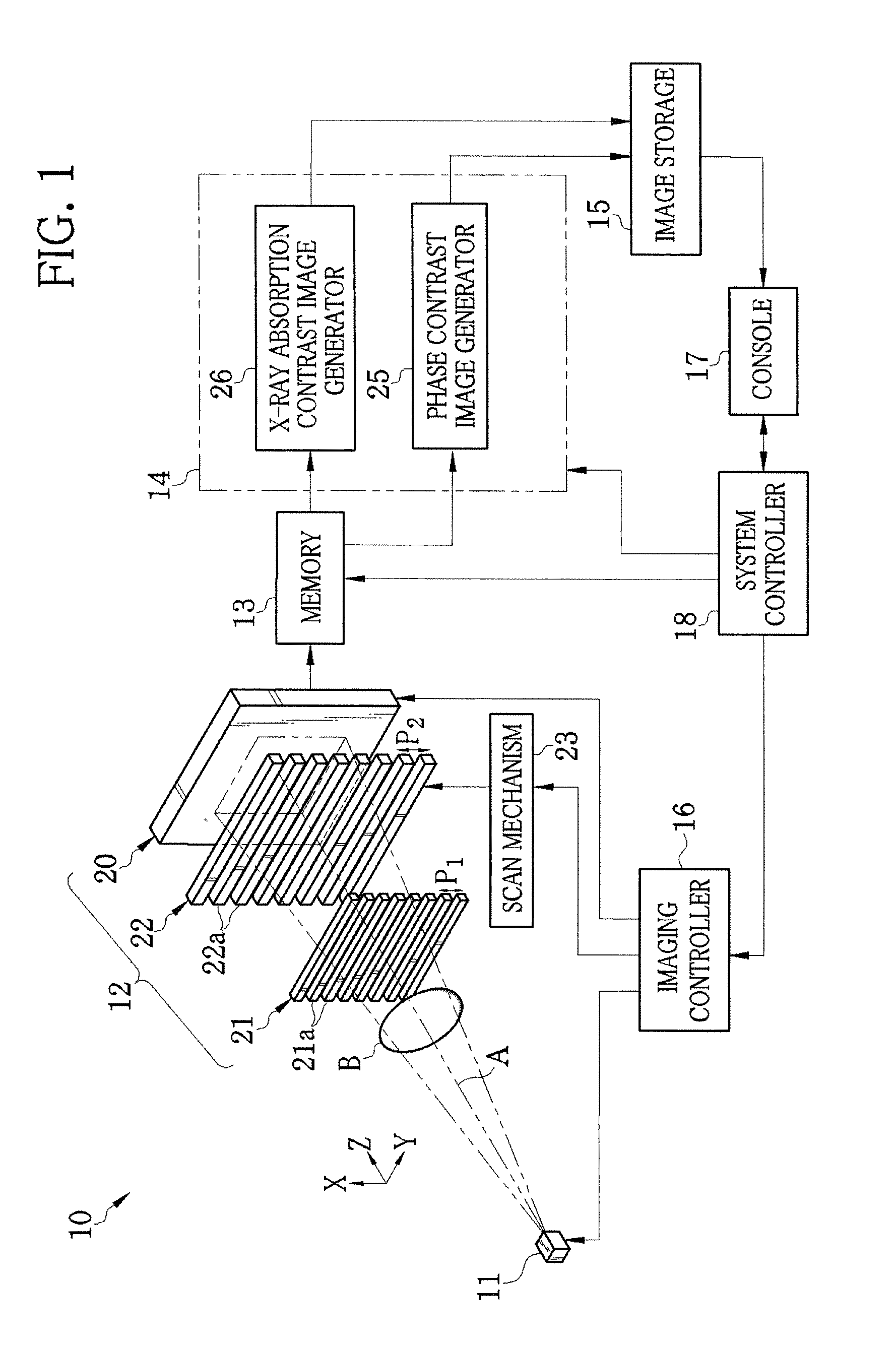
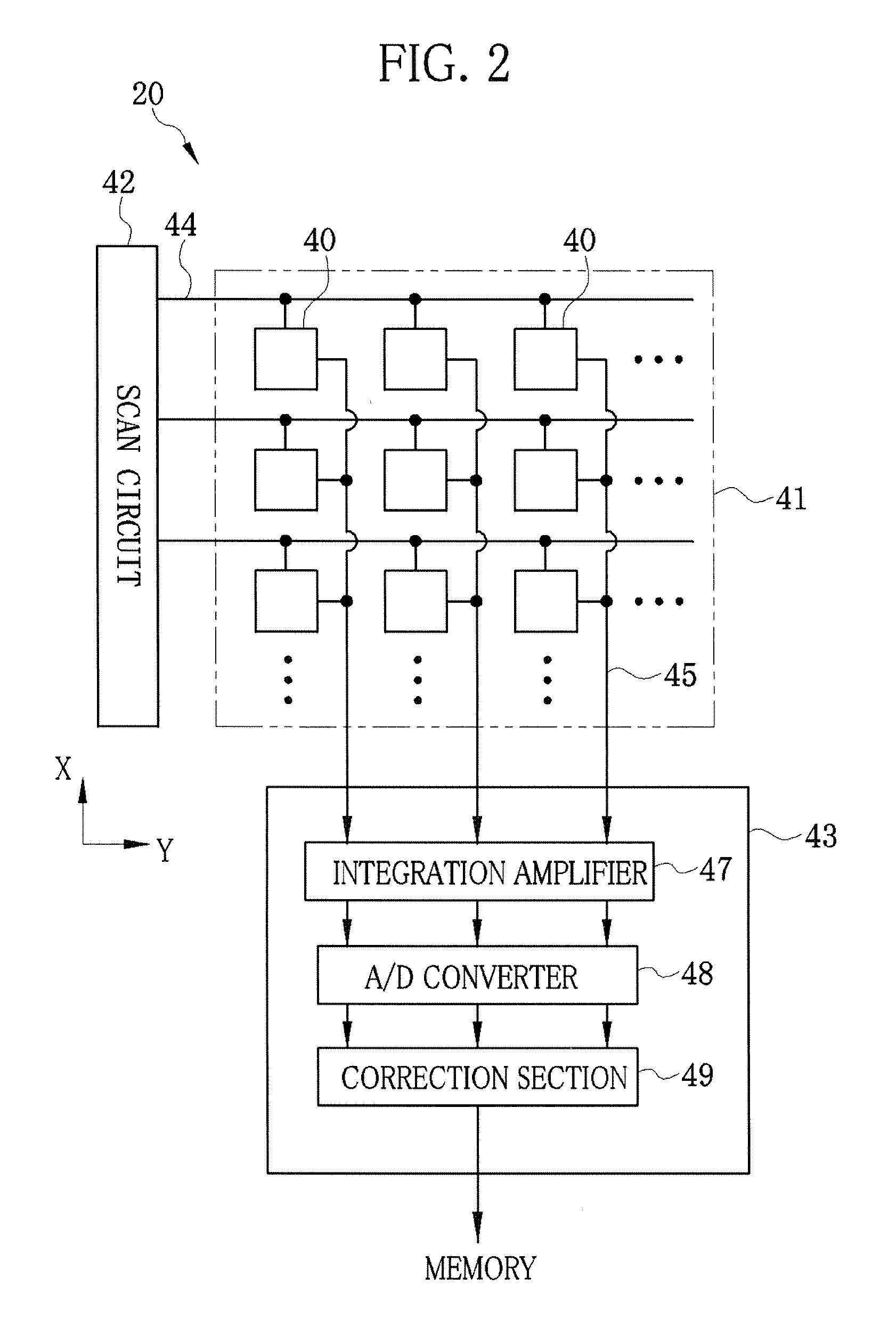
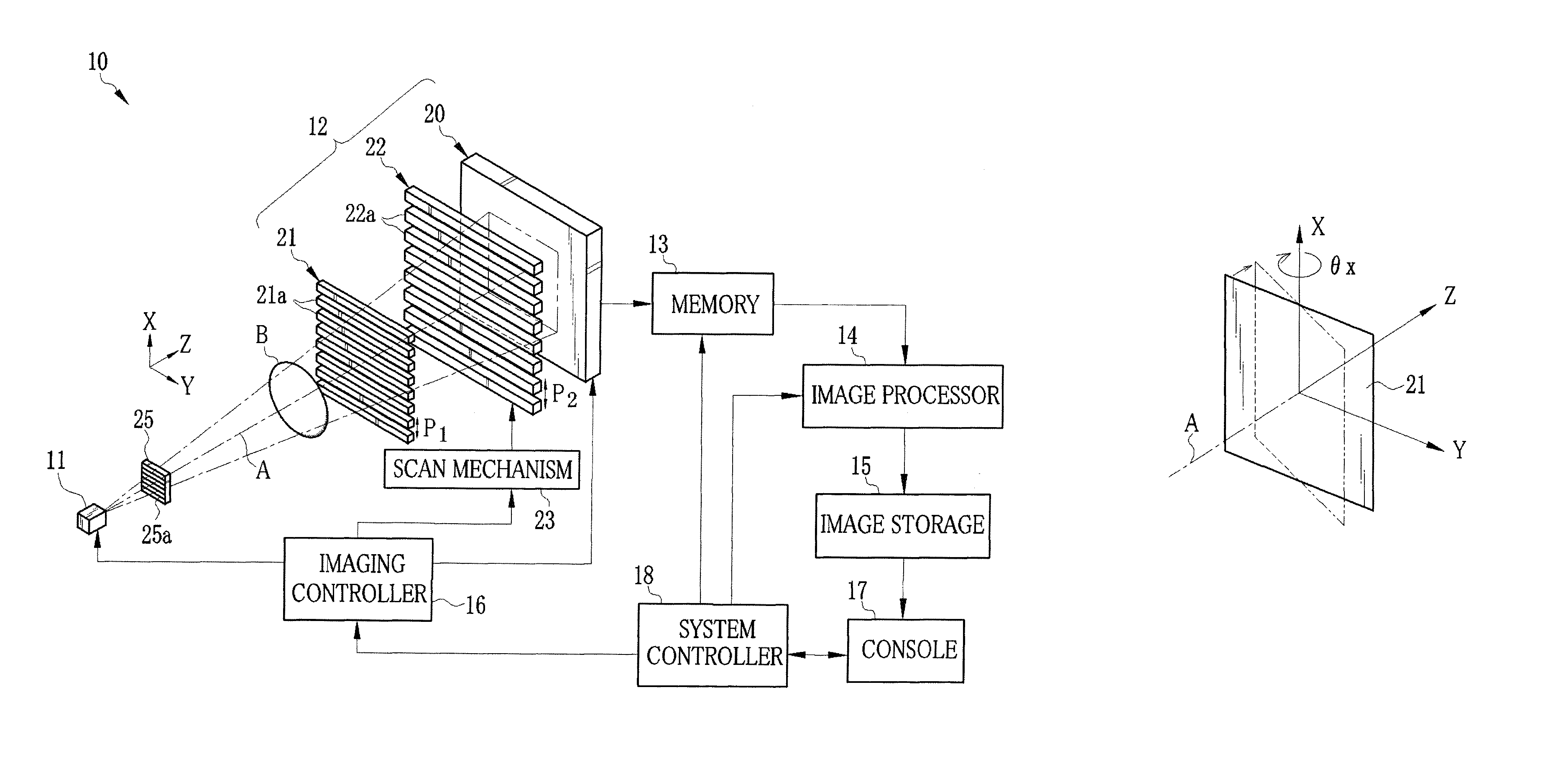
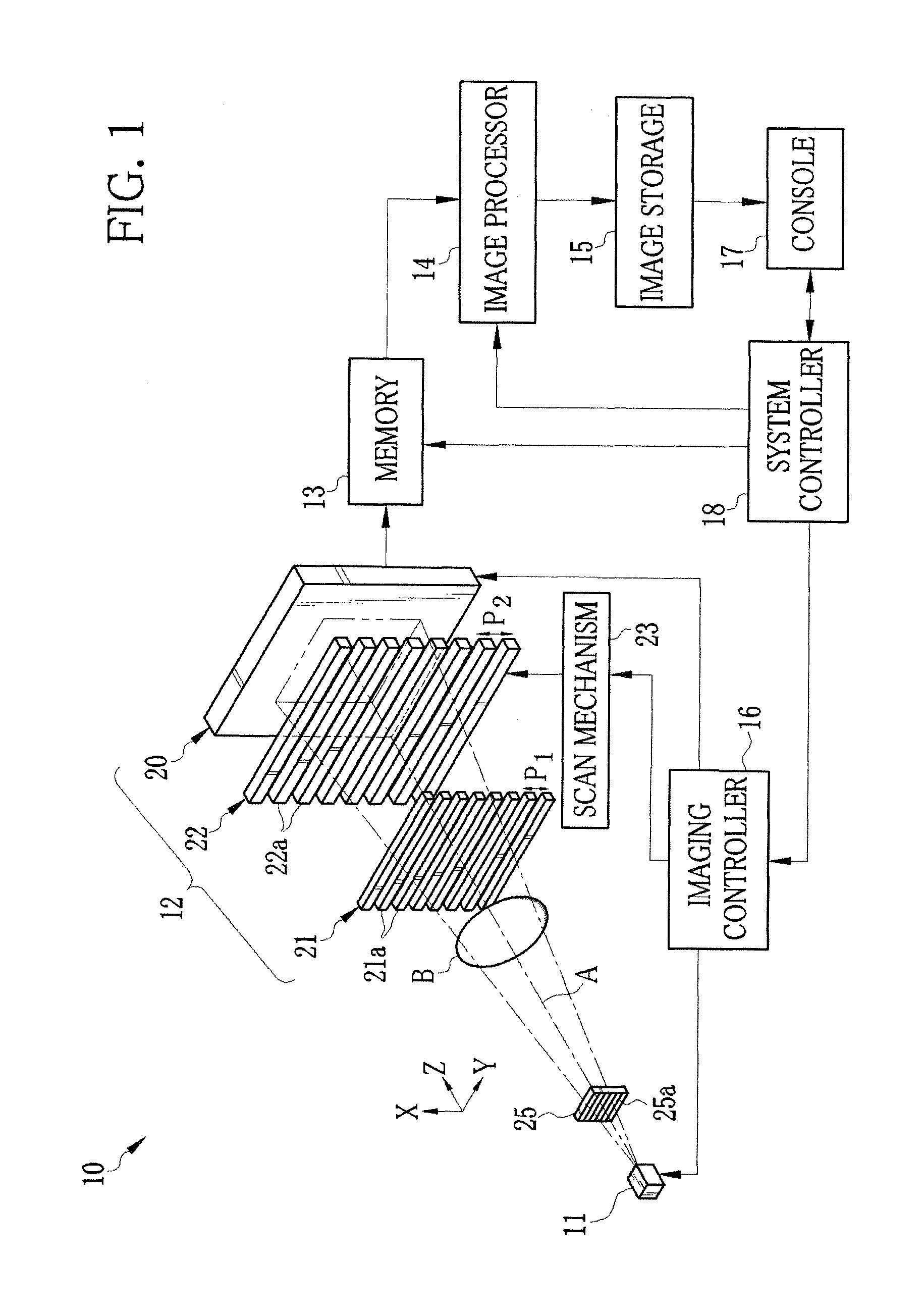
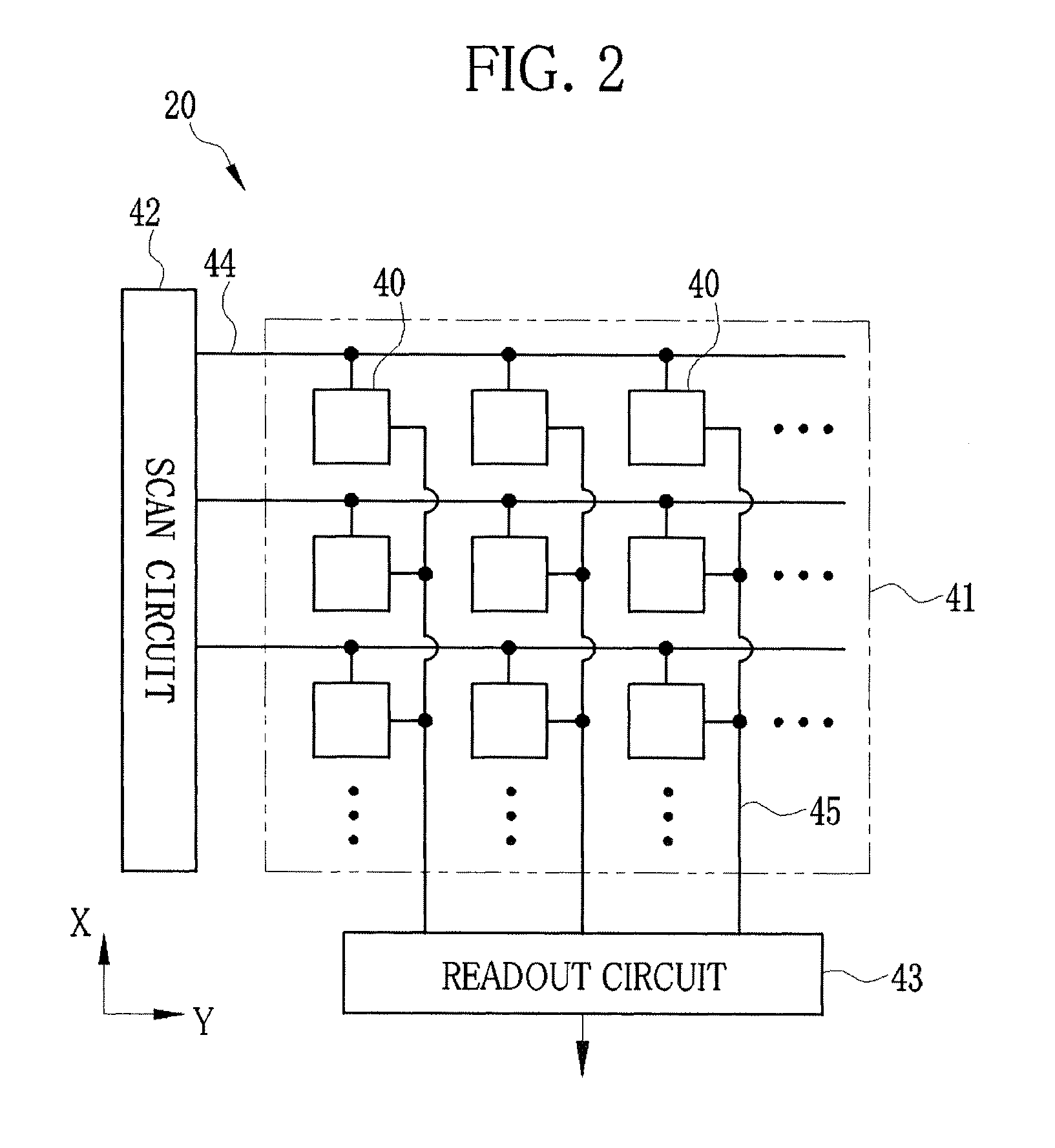
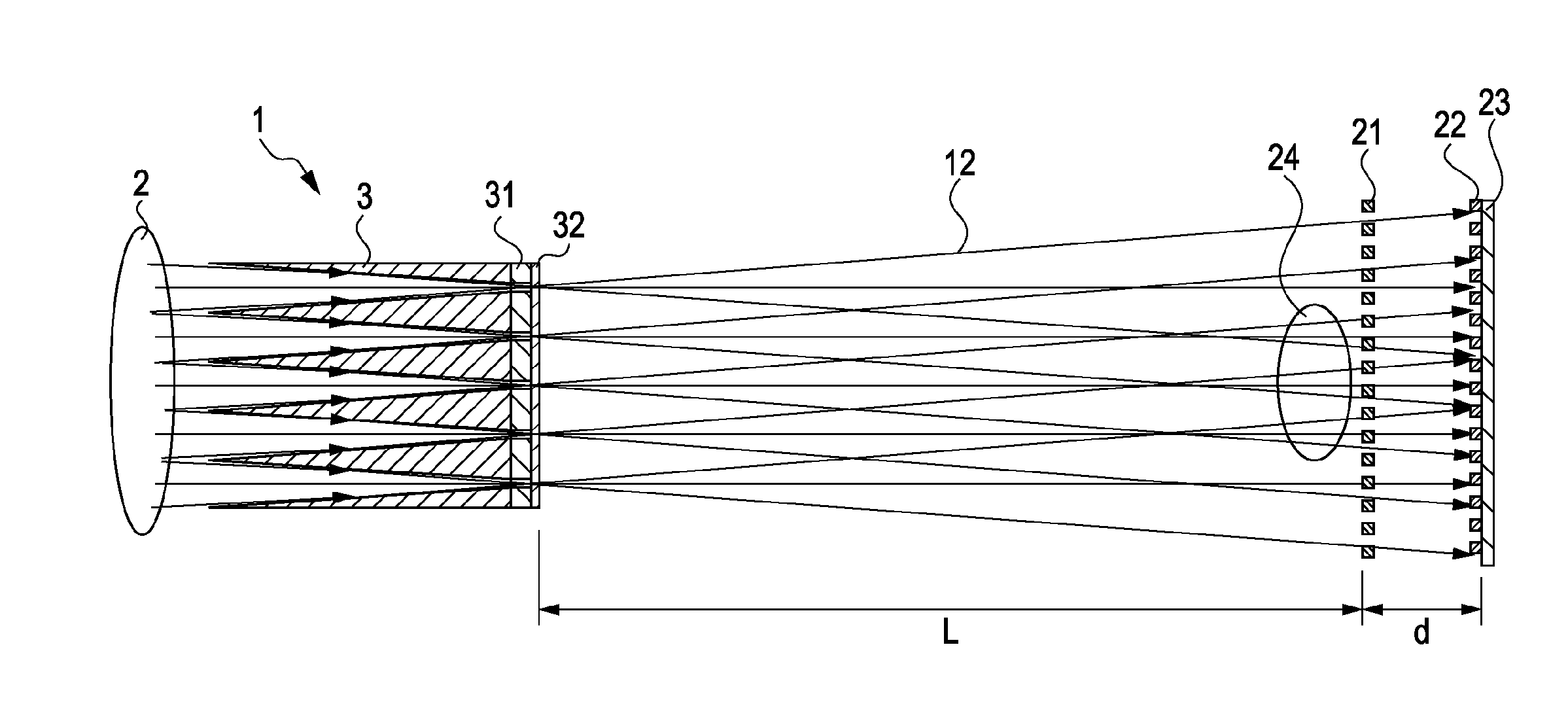
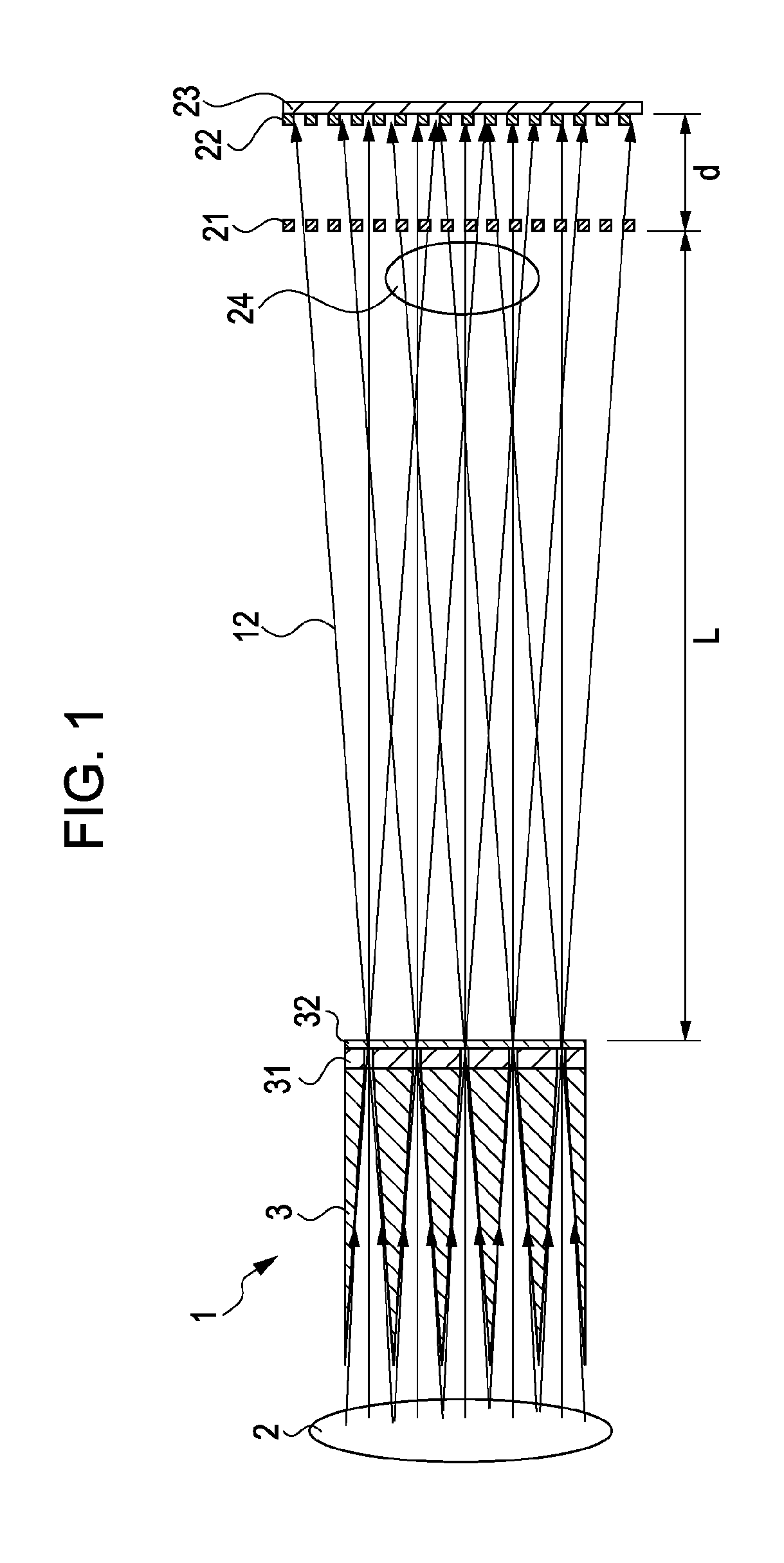
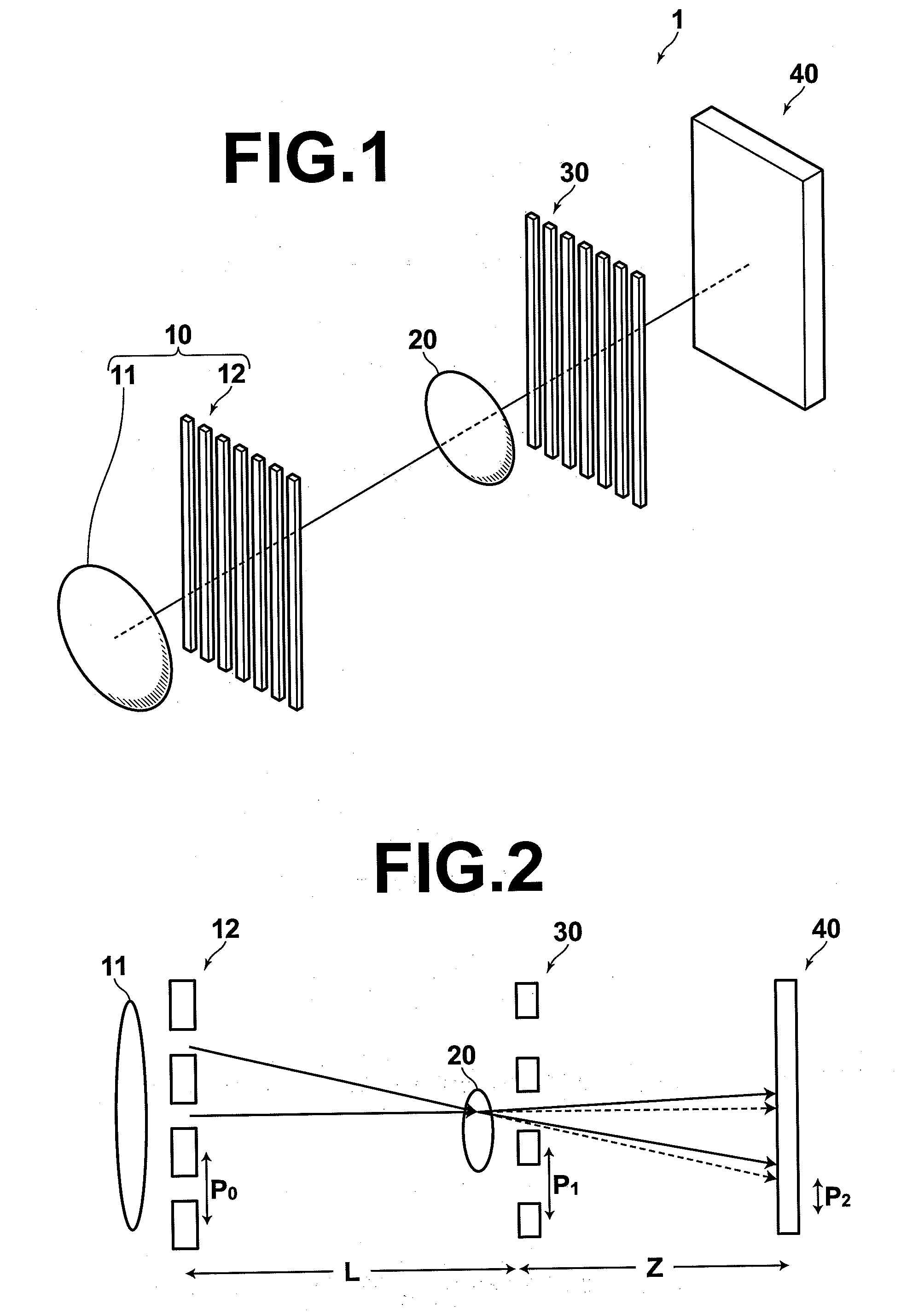
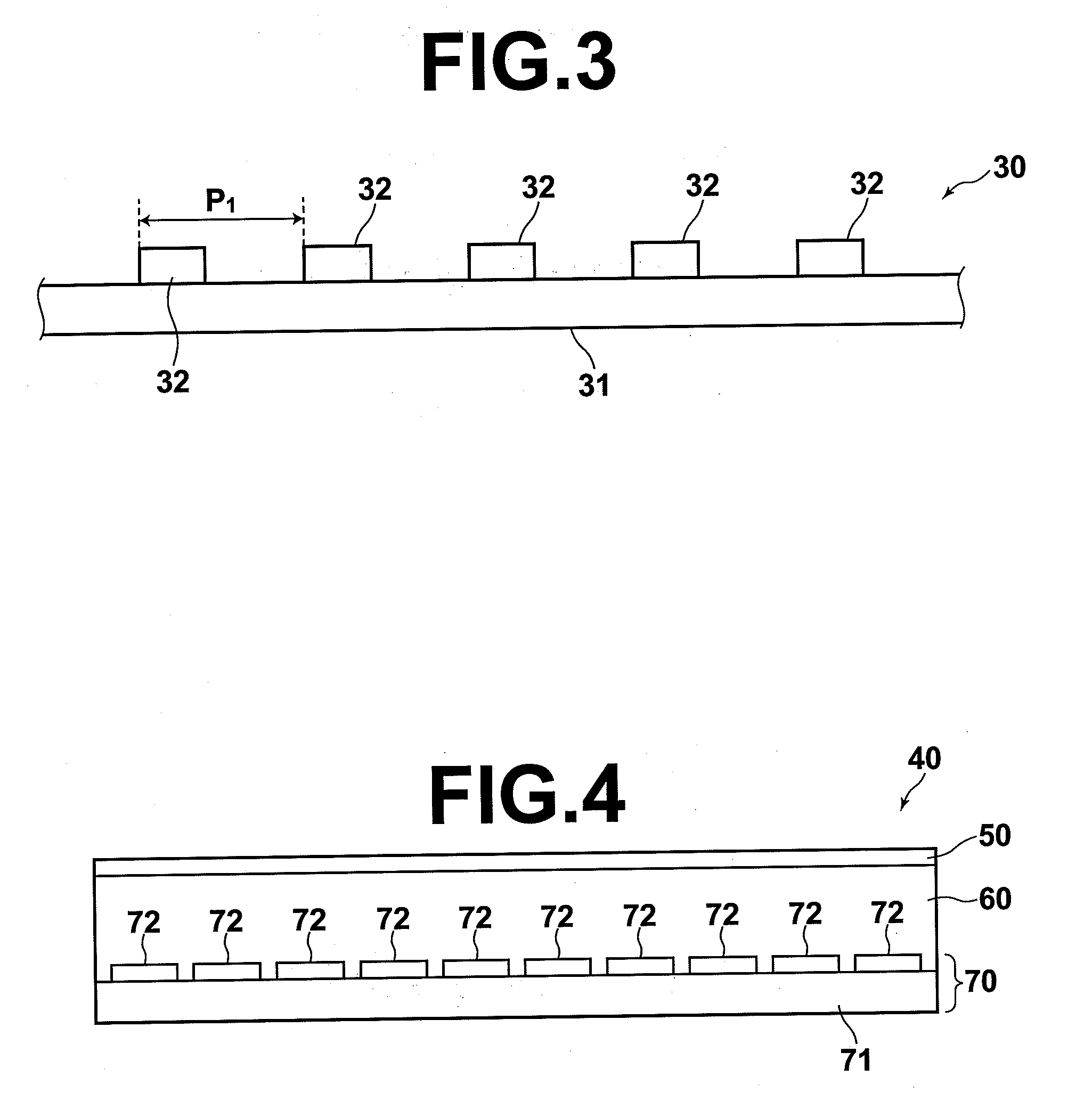
X-ray imaging system and imaging method
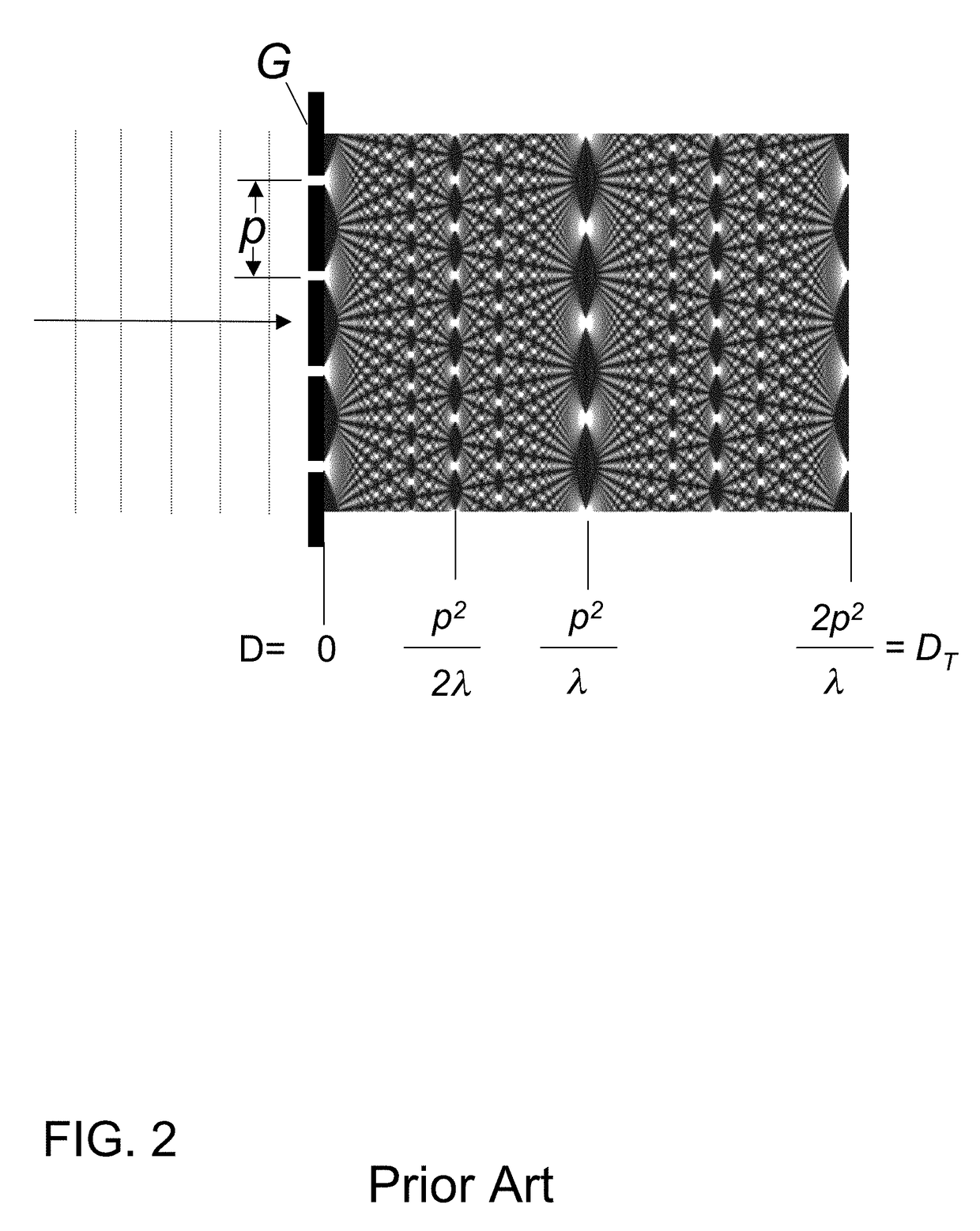
ActiveUS7180979B2Easy constructionImaging devicesHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionImage contrastImage detection
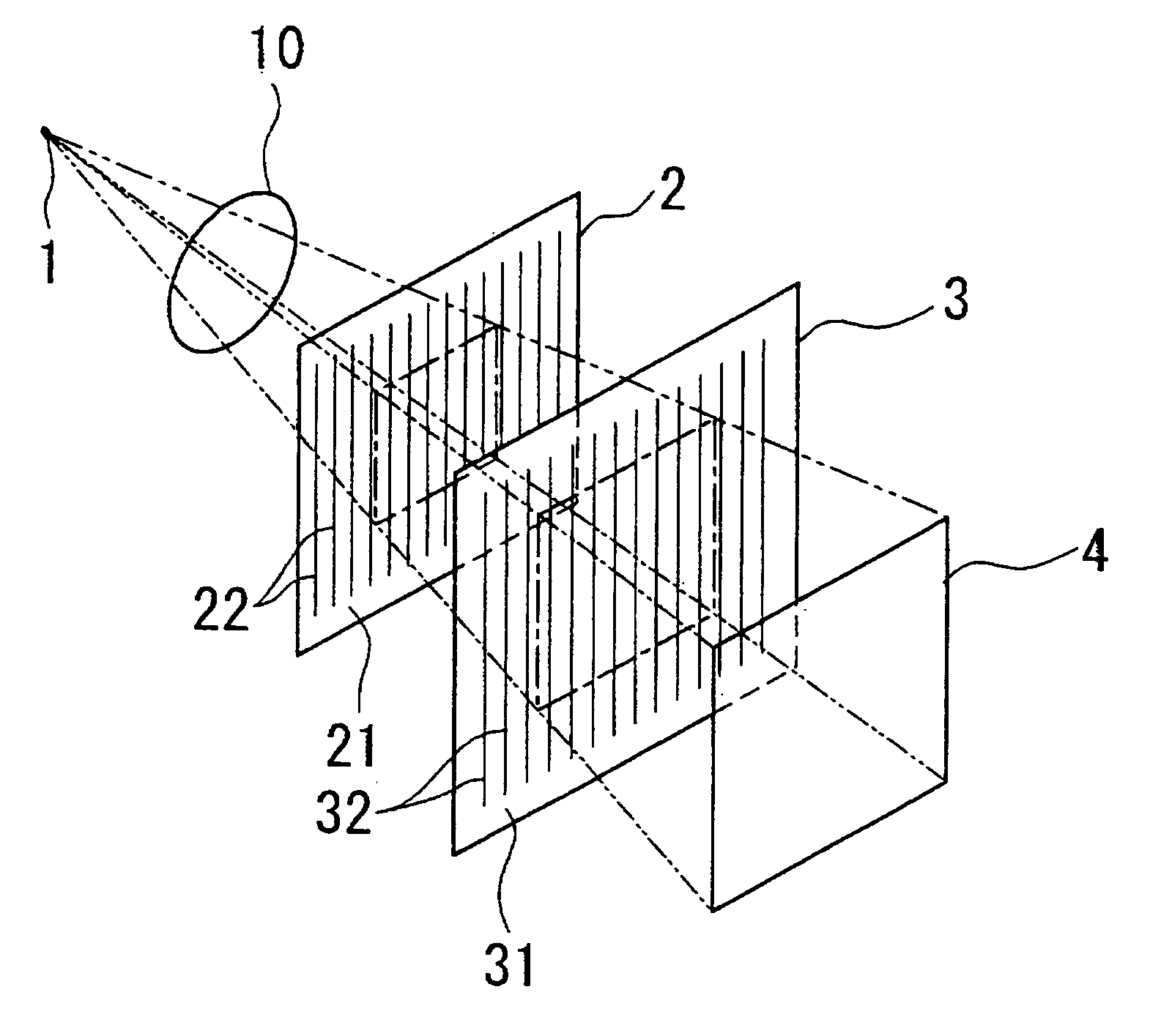
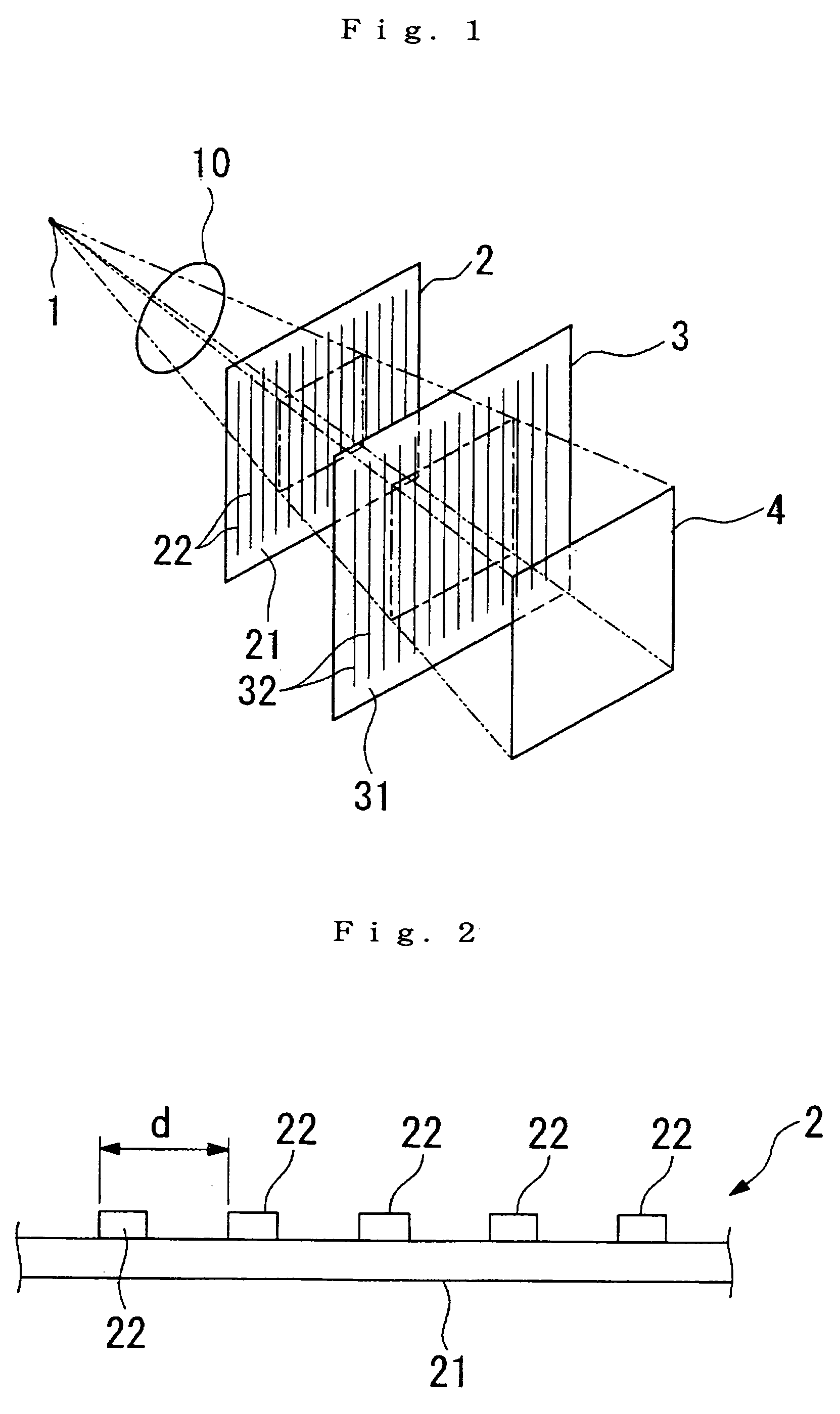
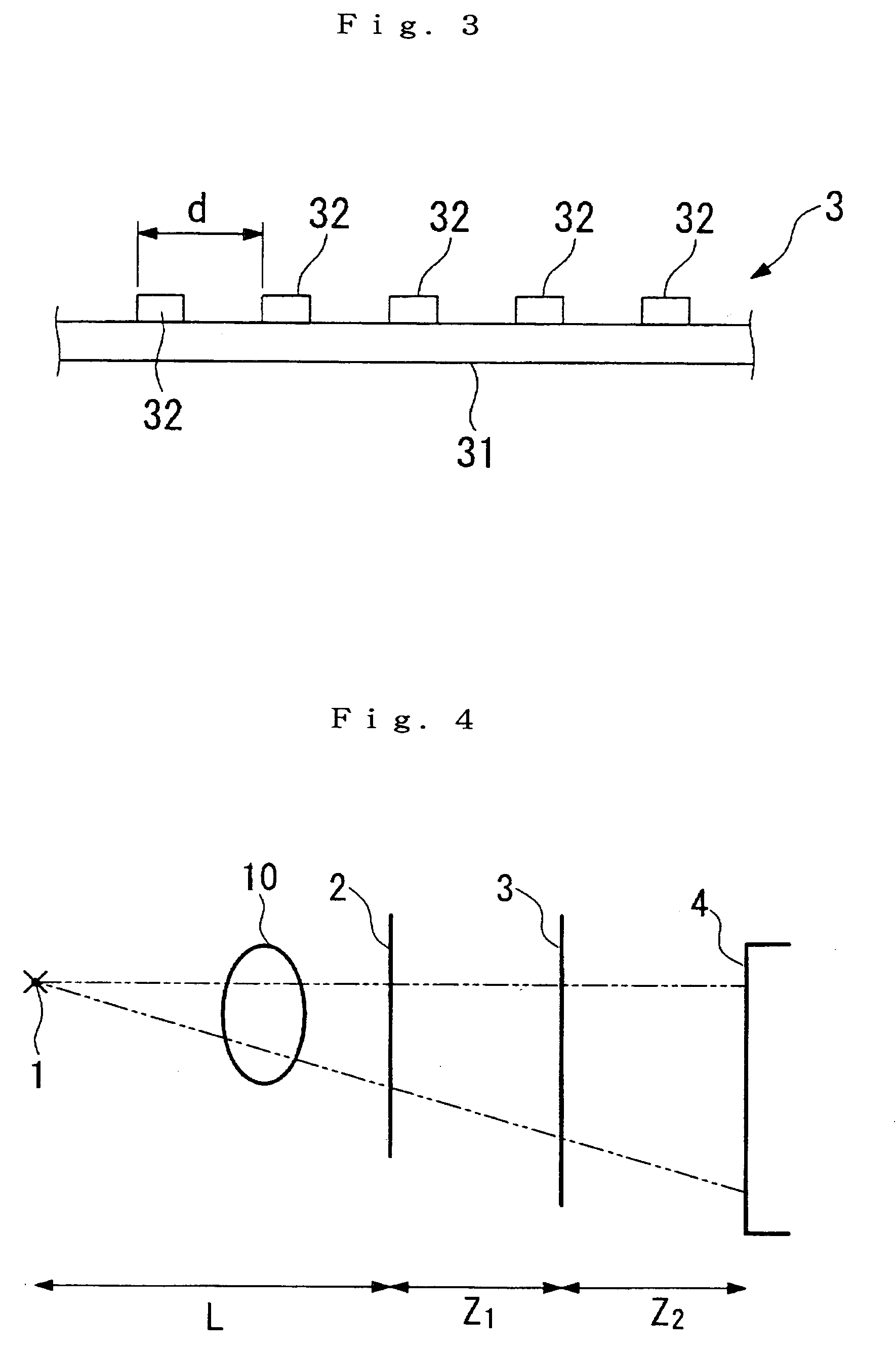
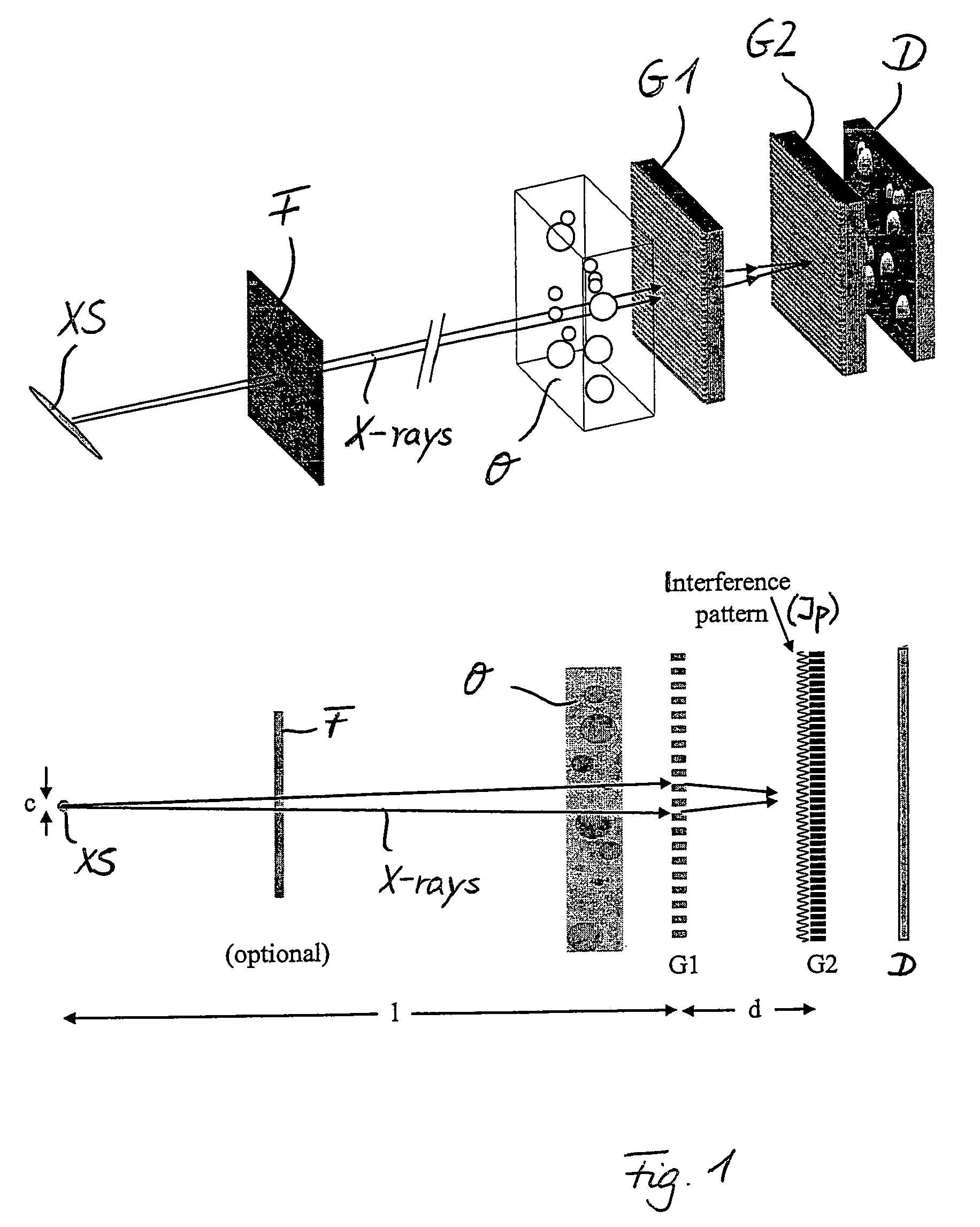
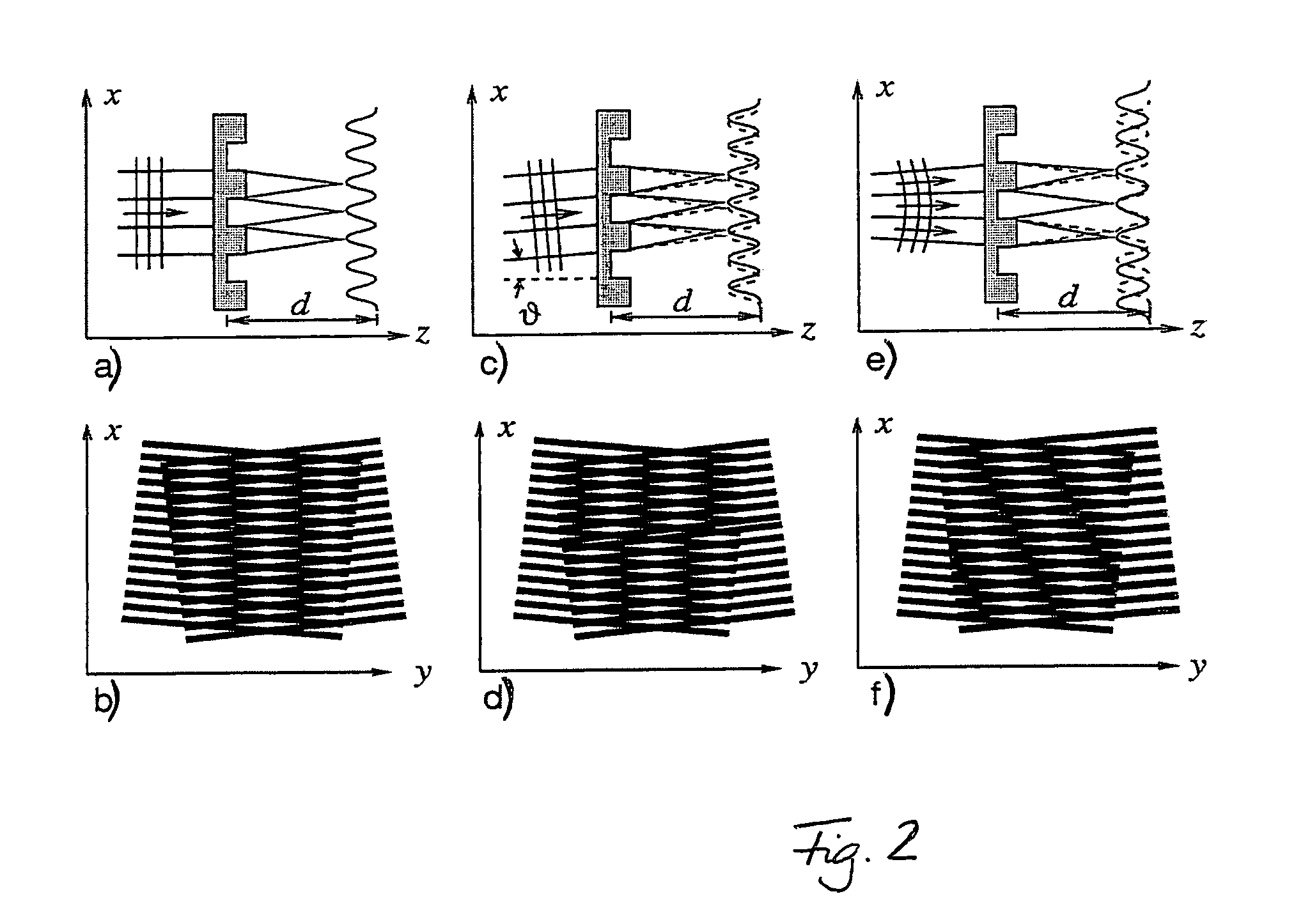
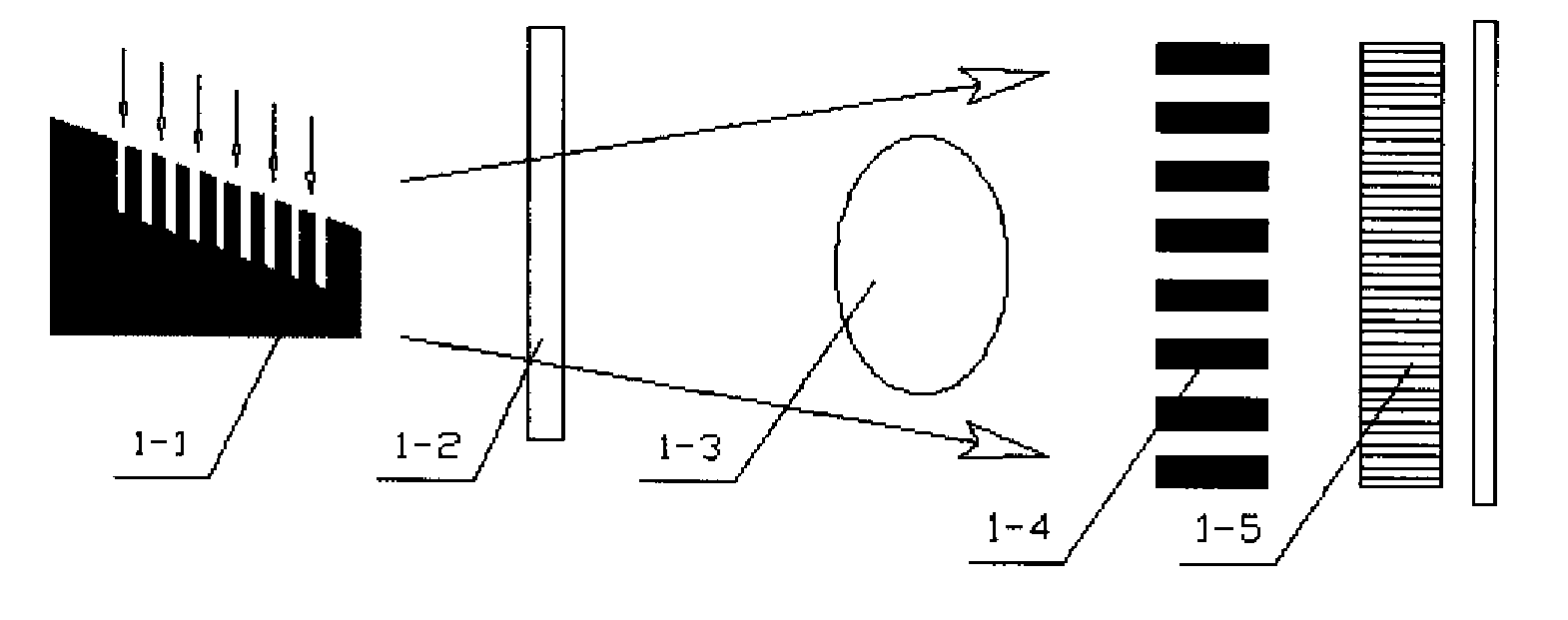
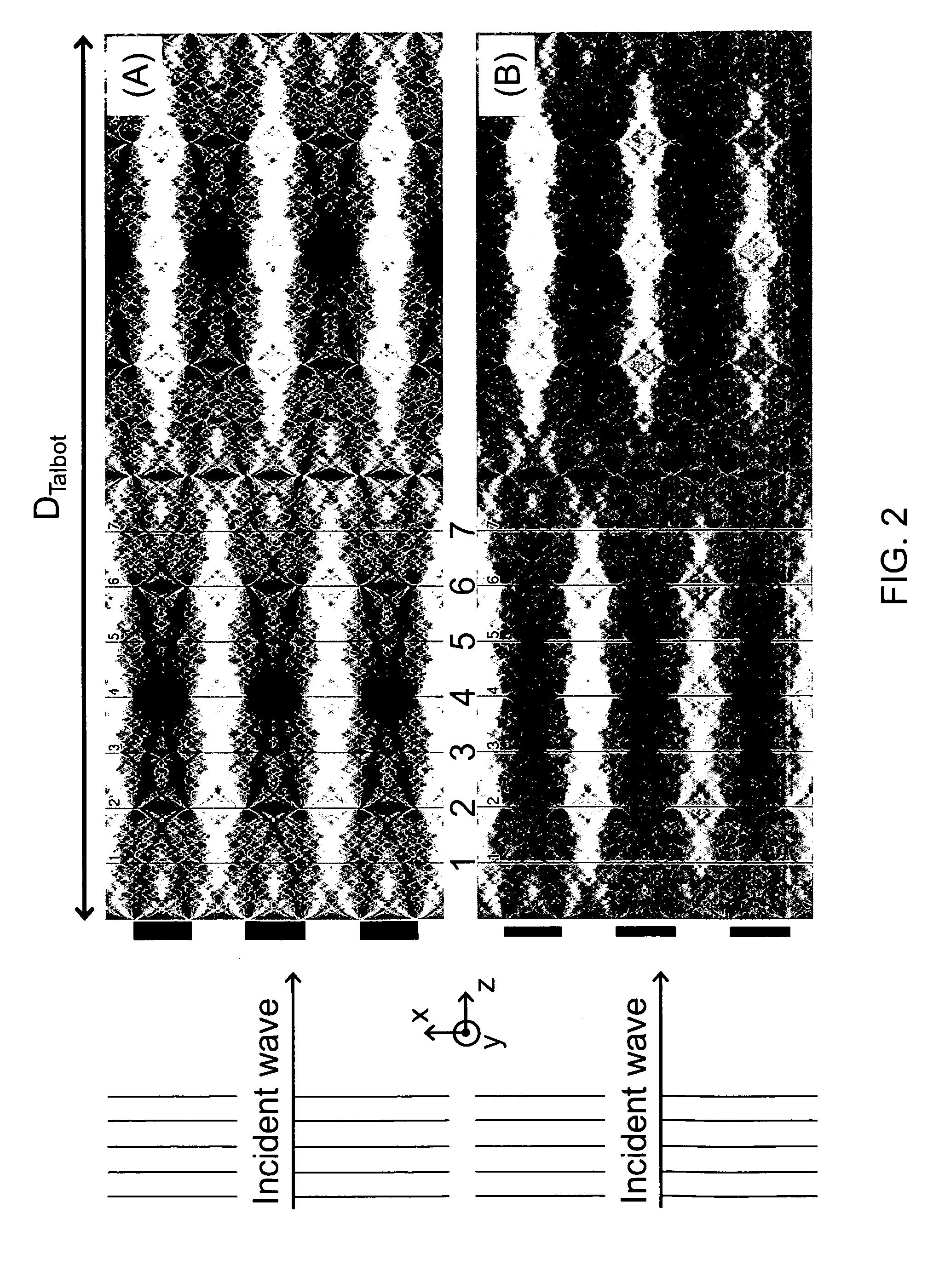
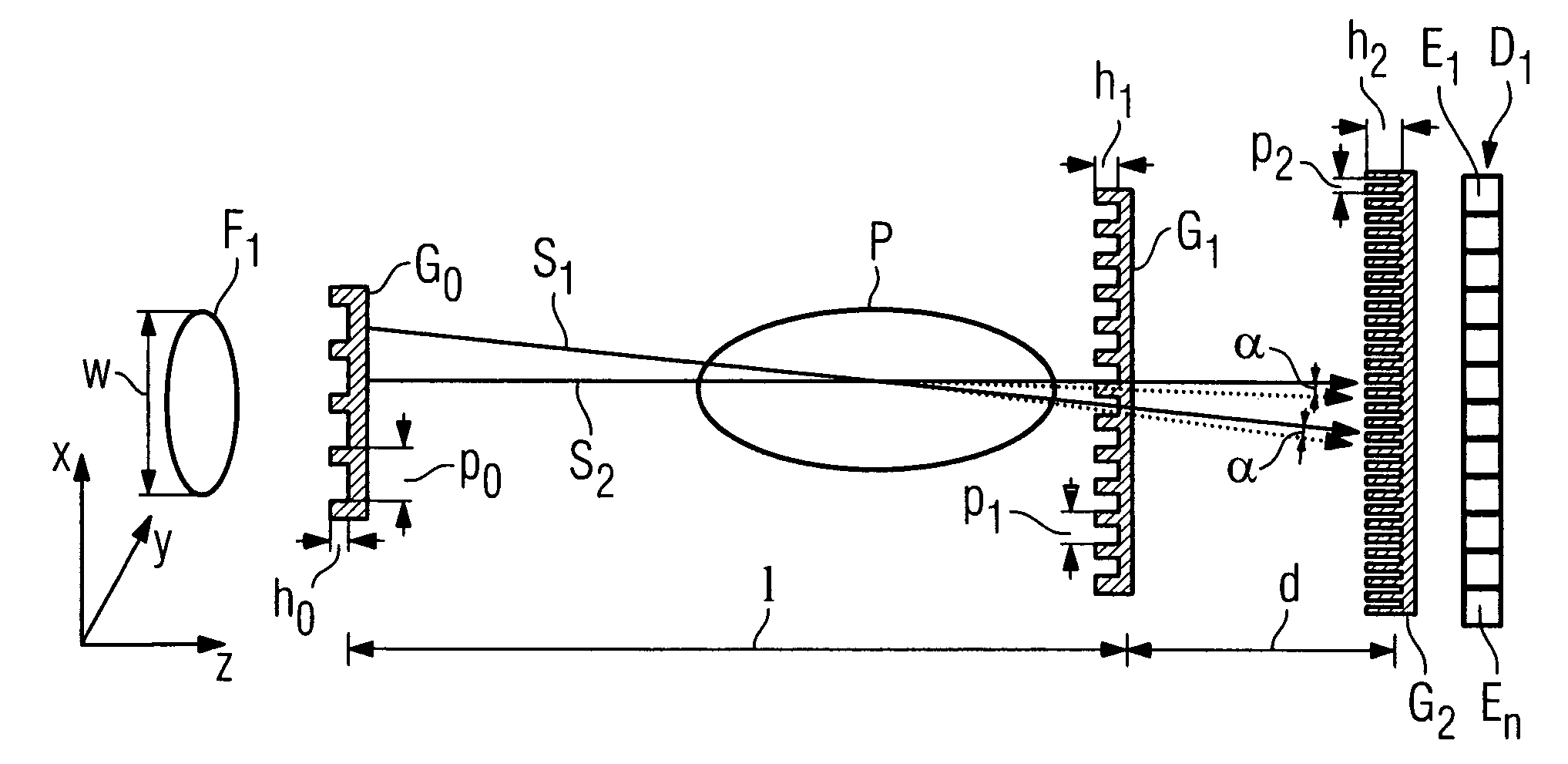
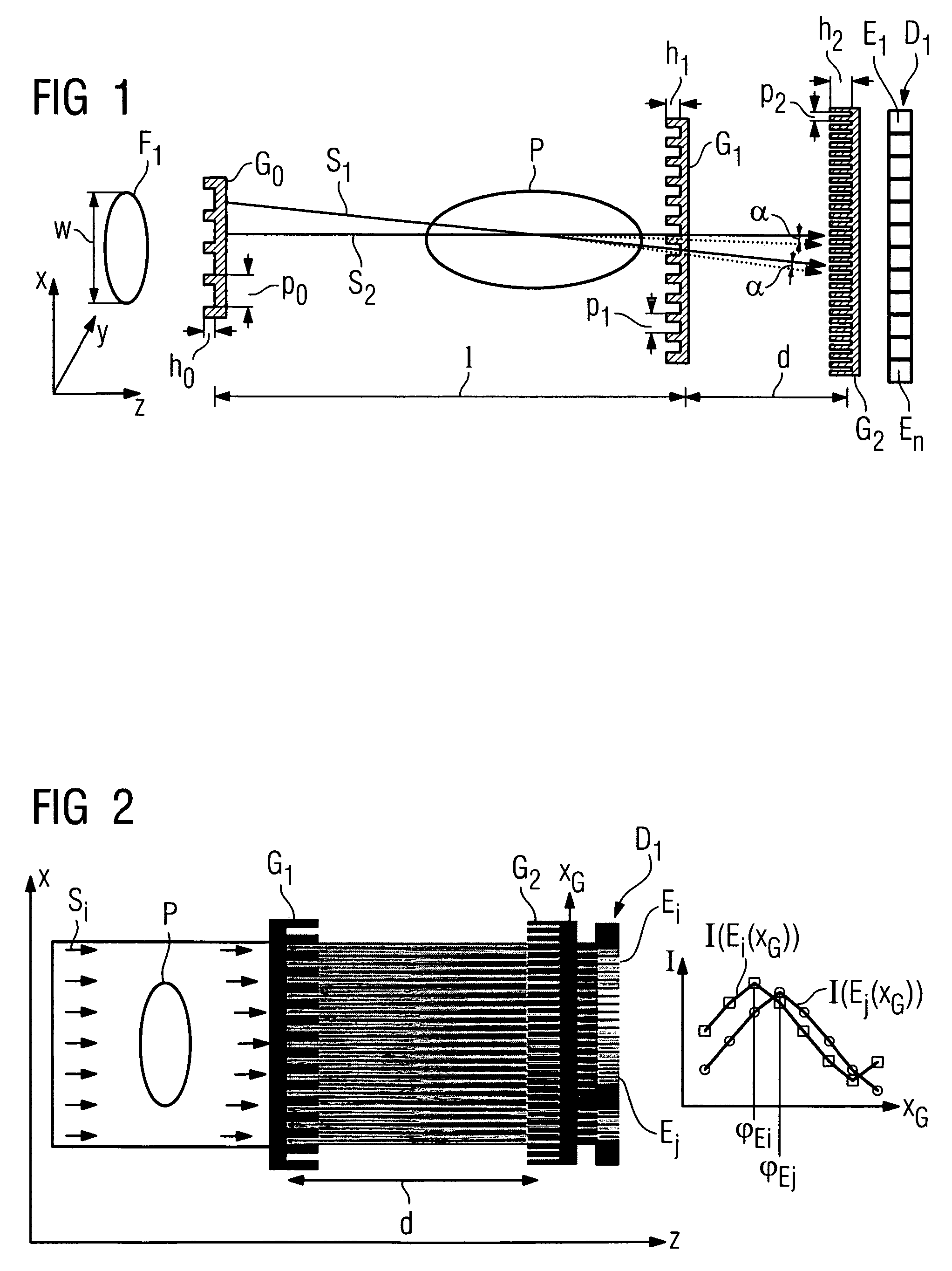
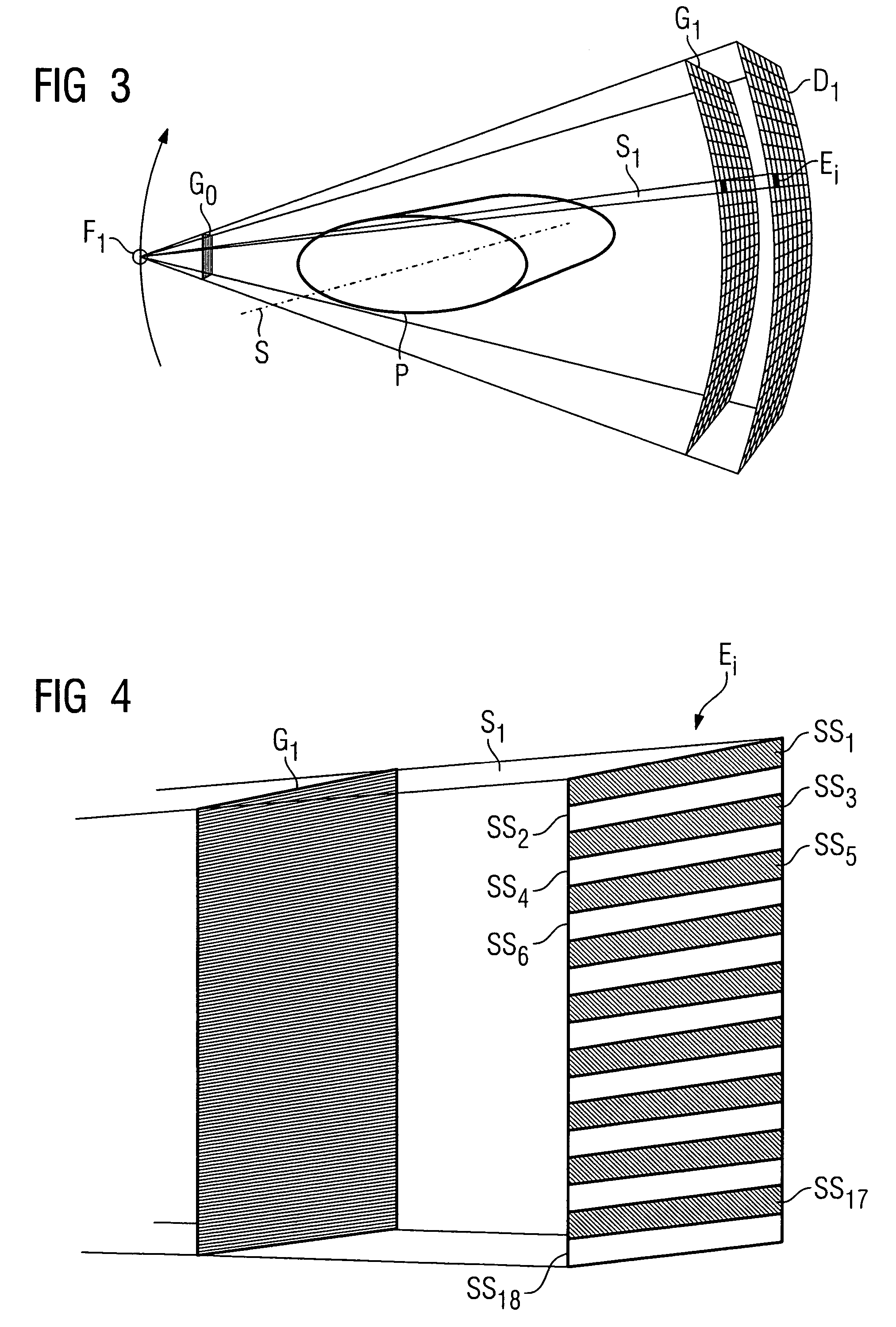
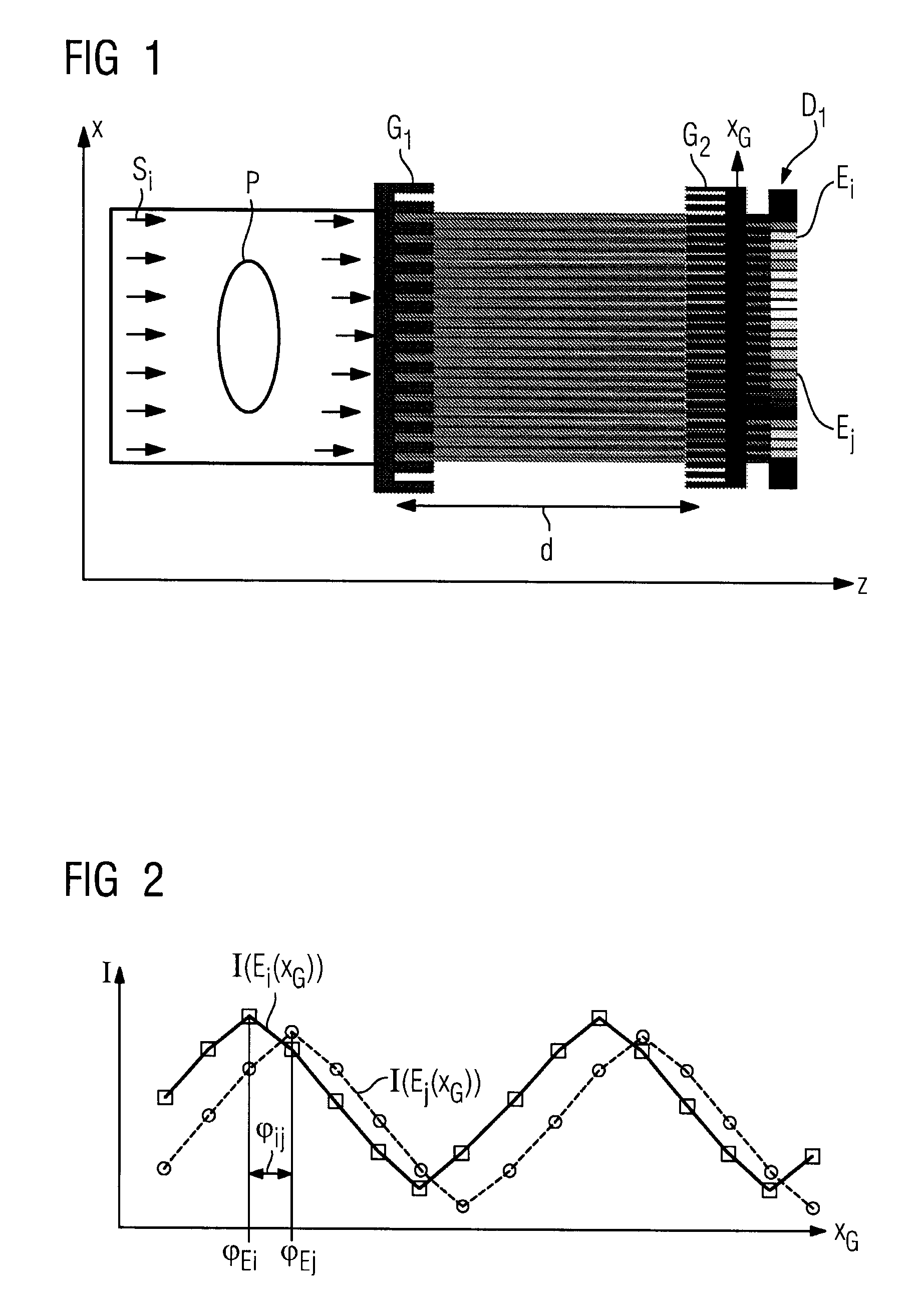
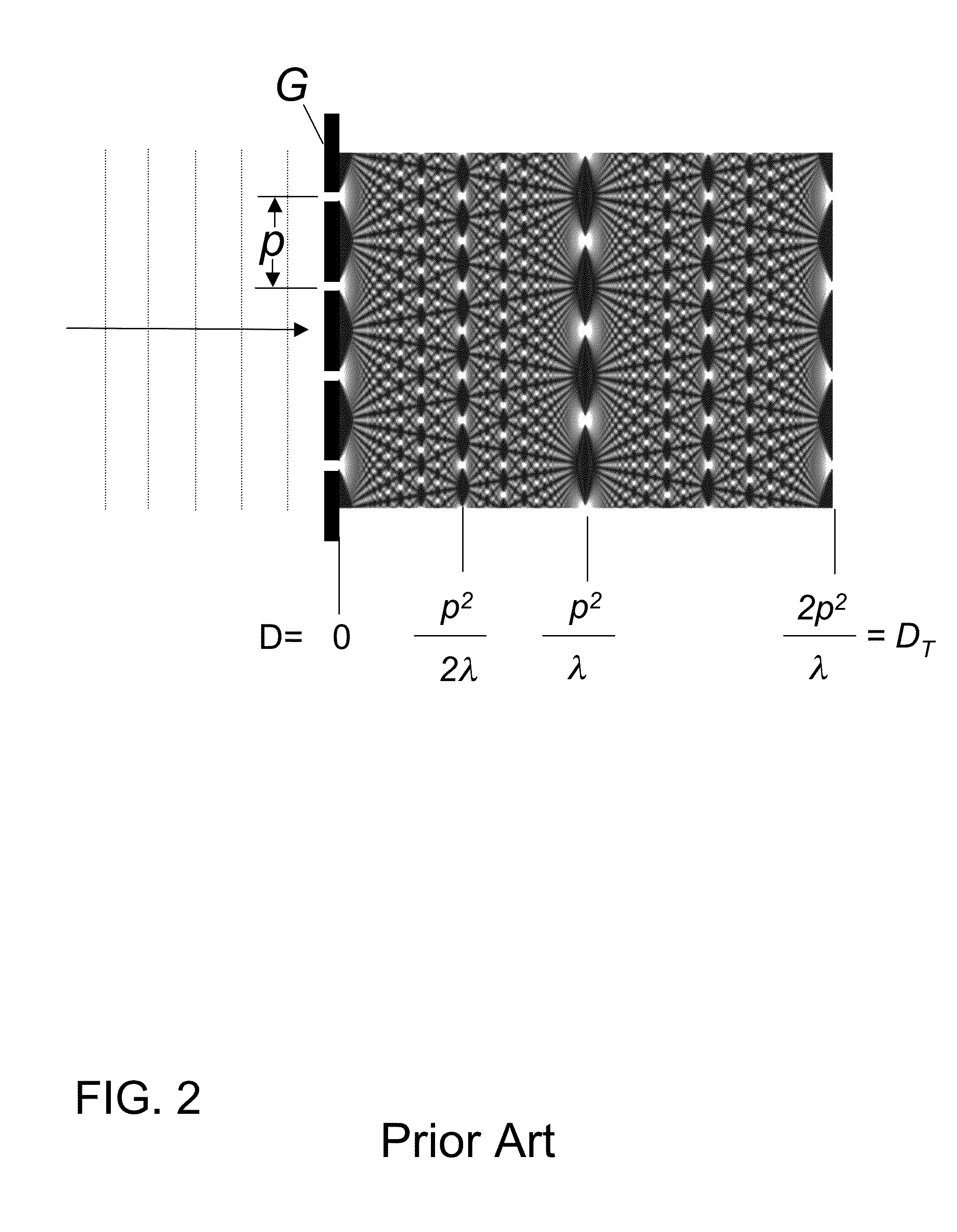
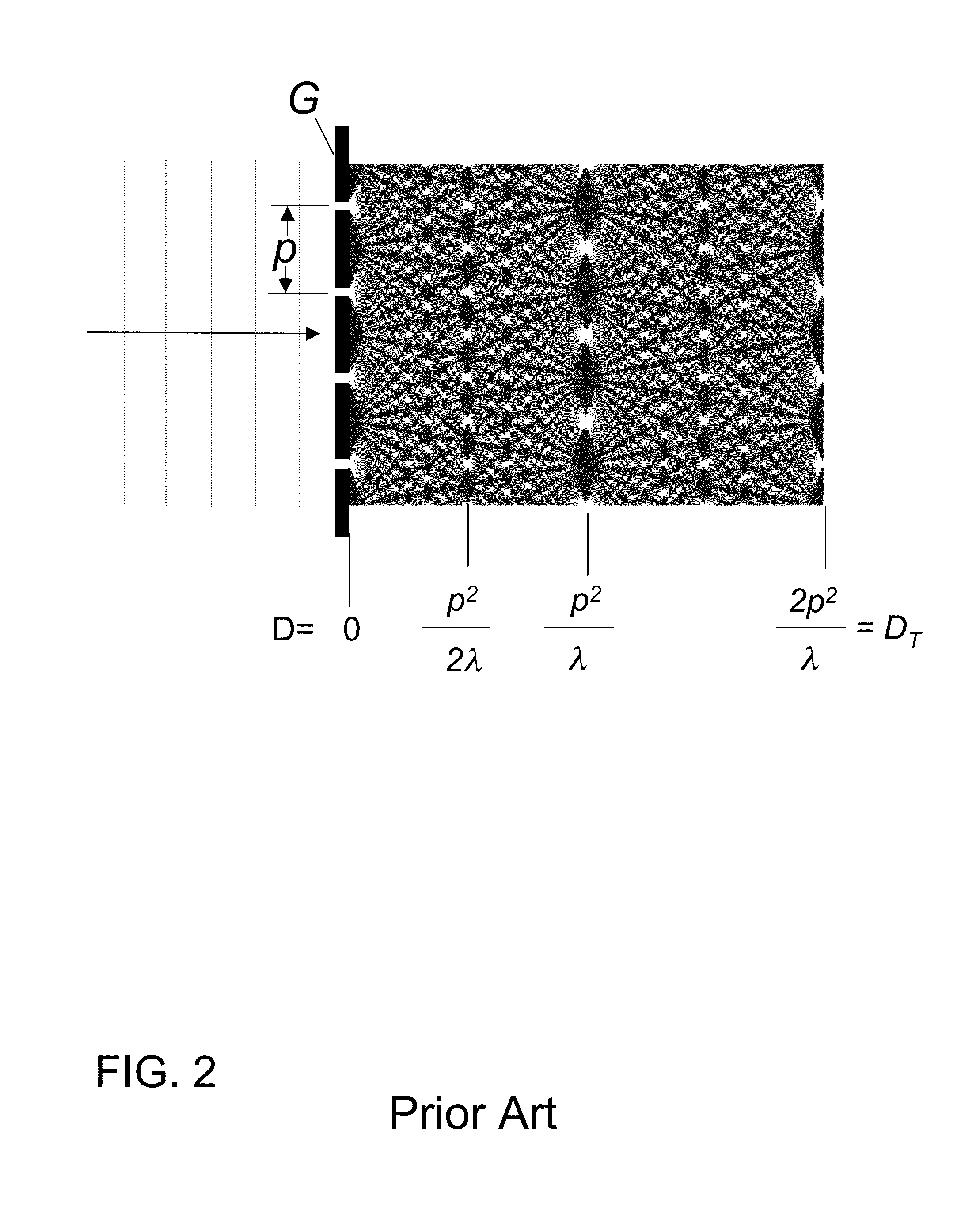
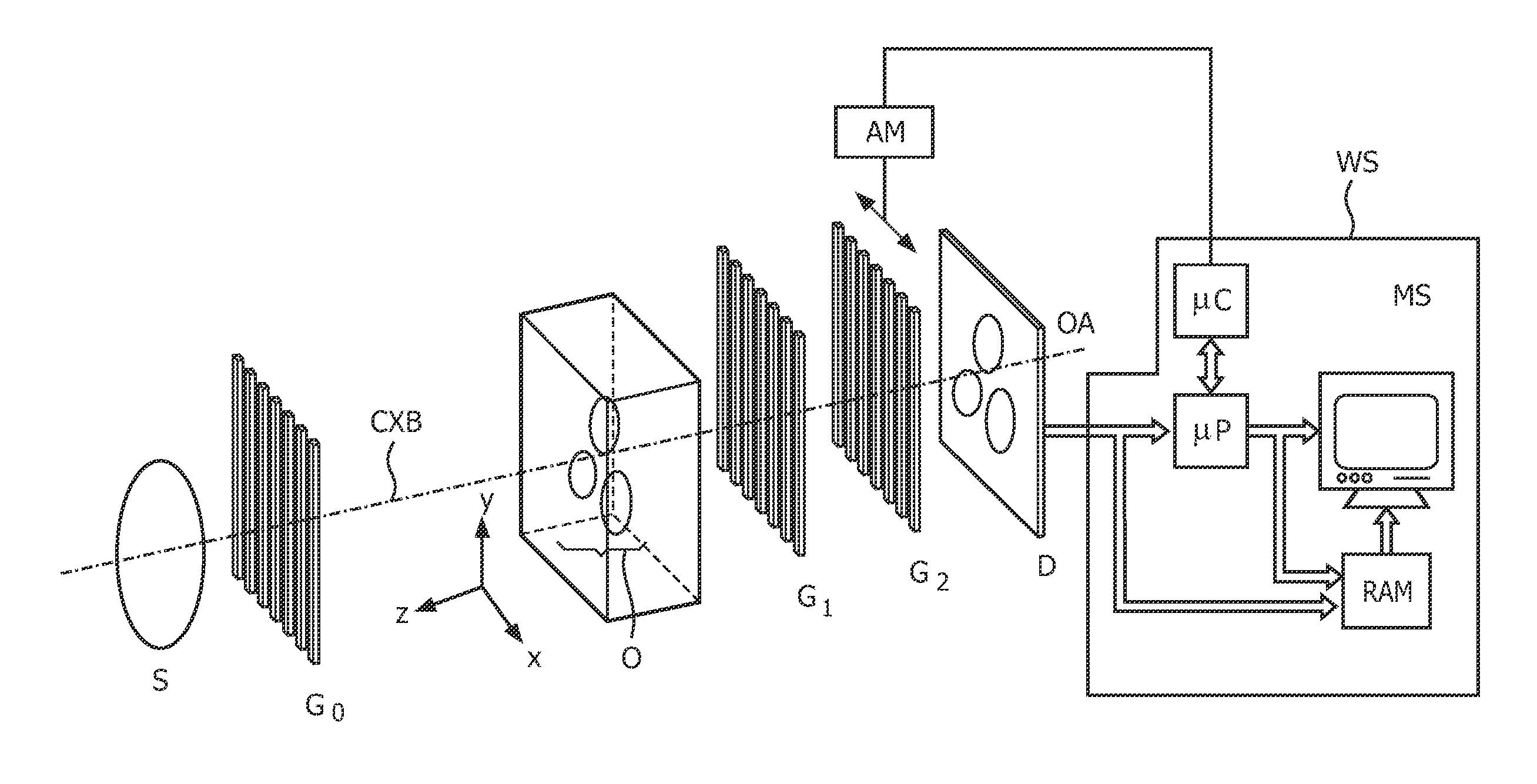
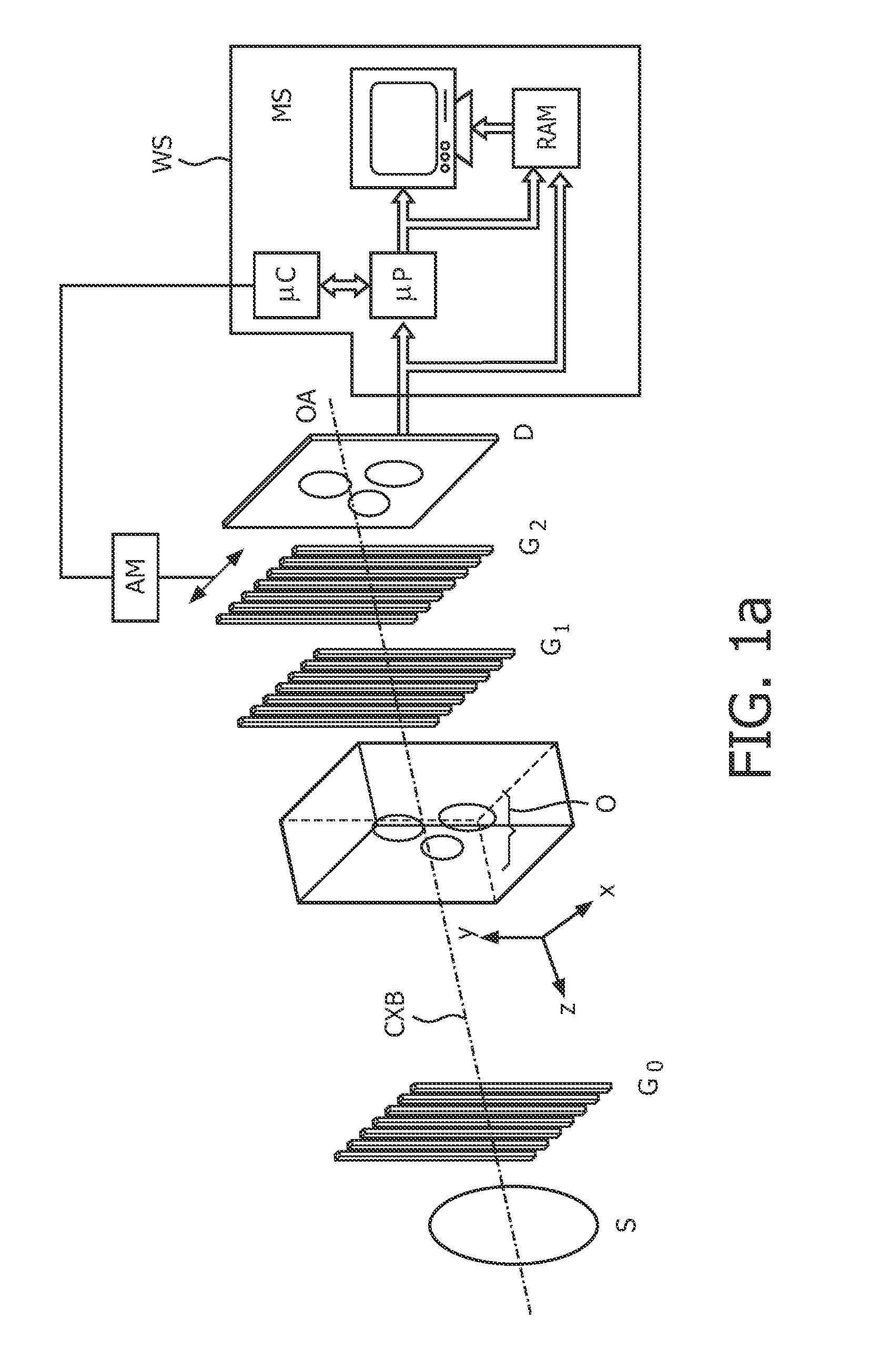
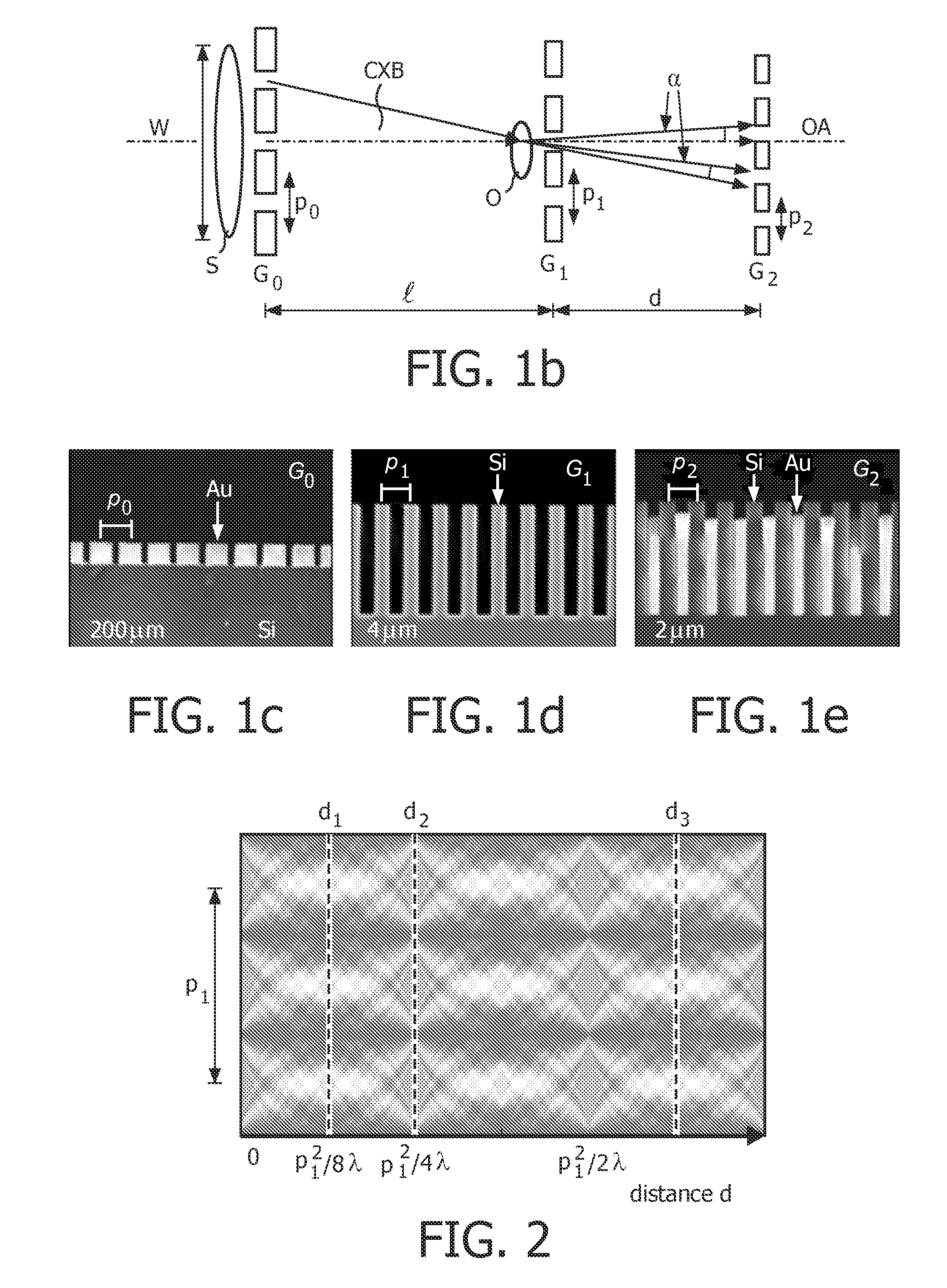
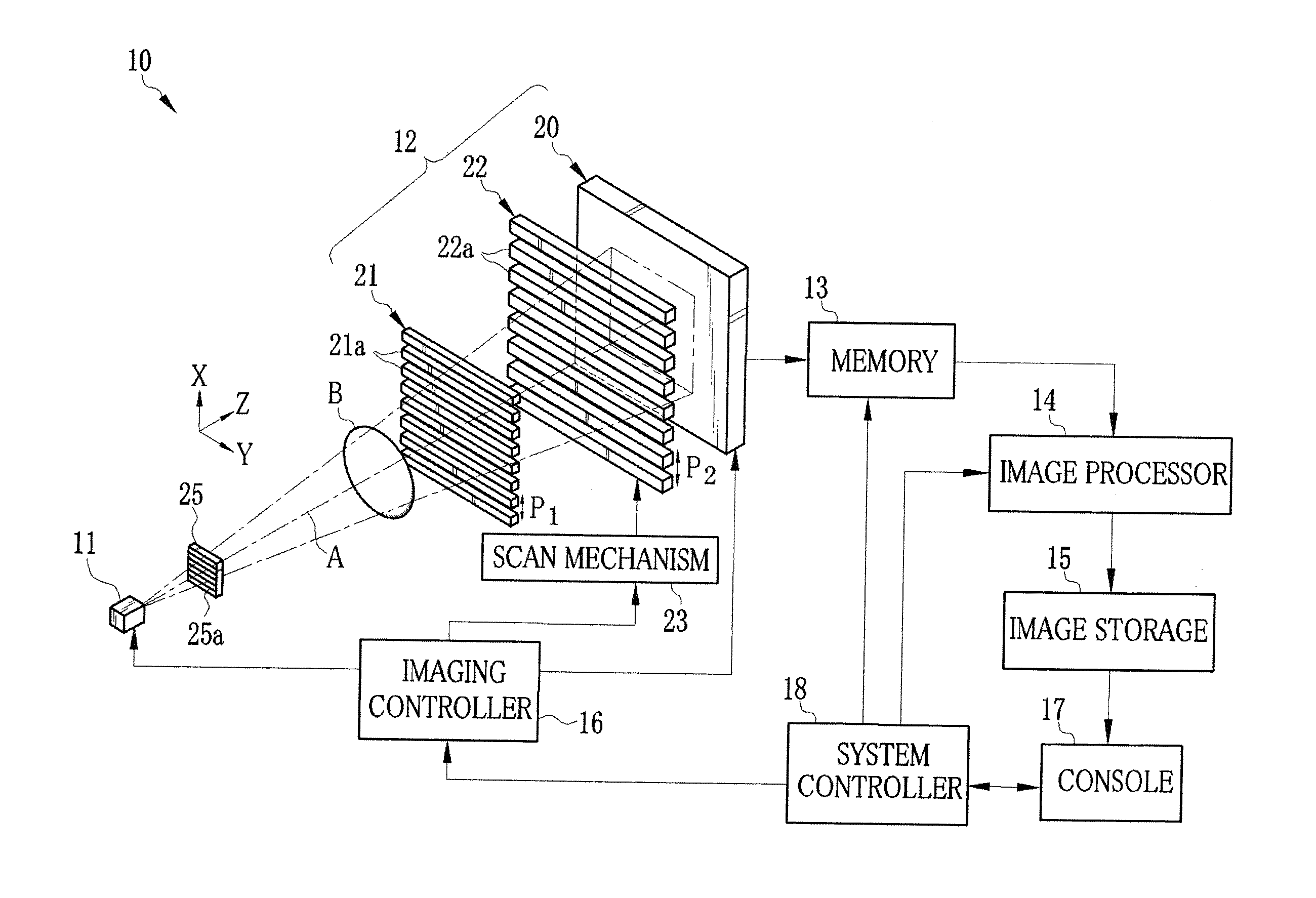
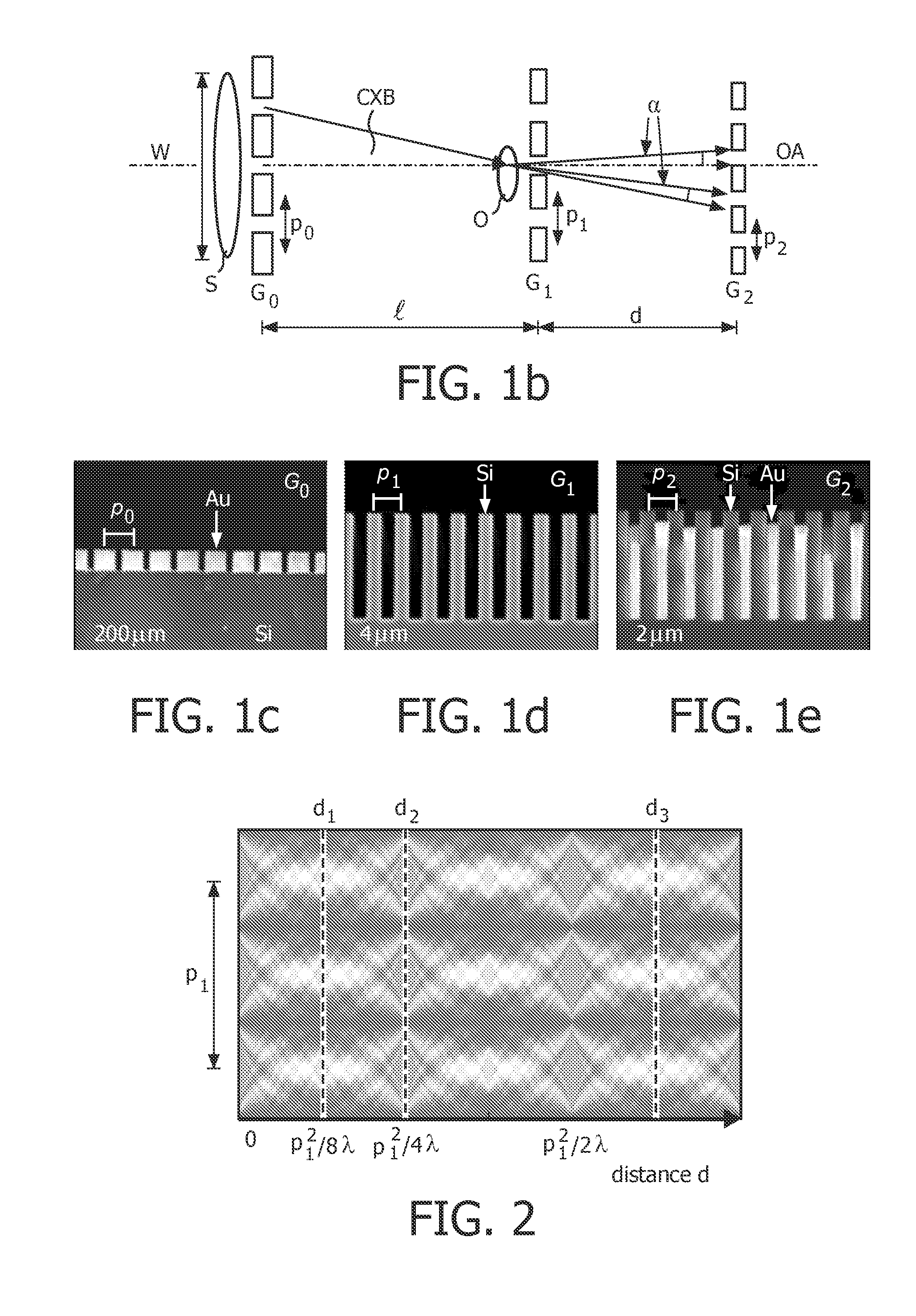
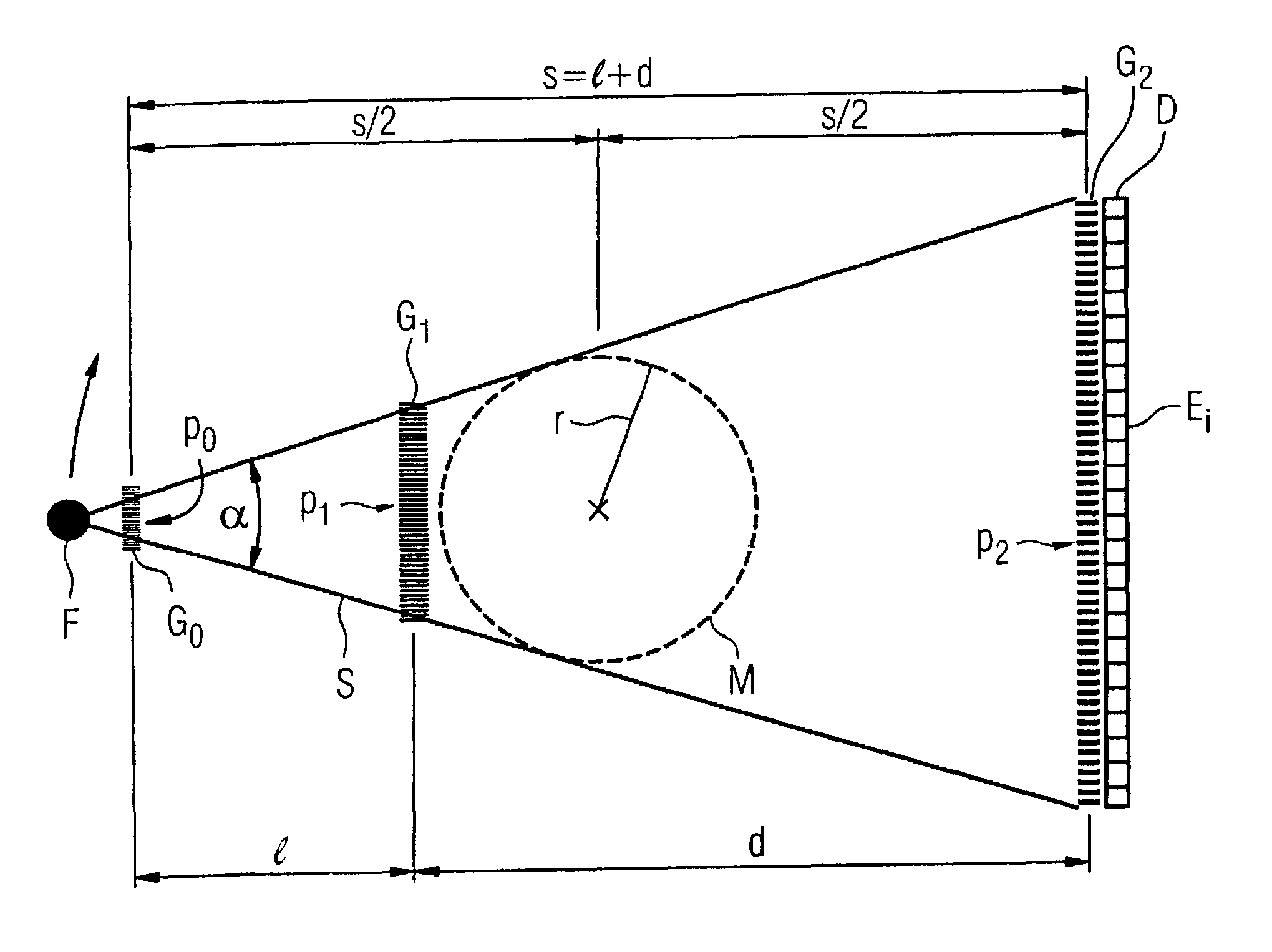
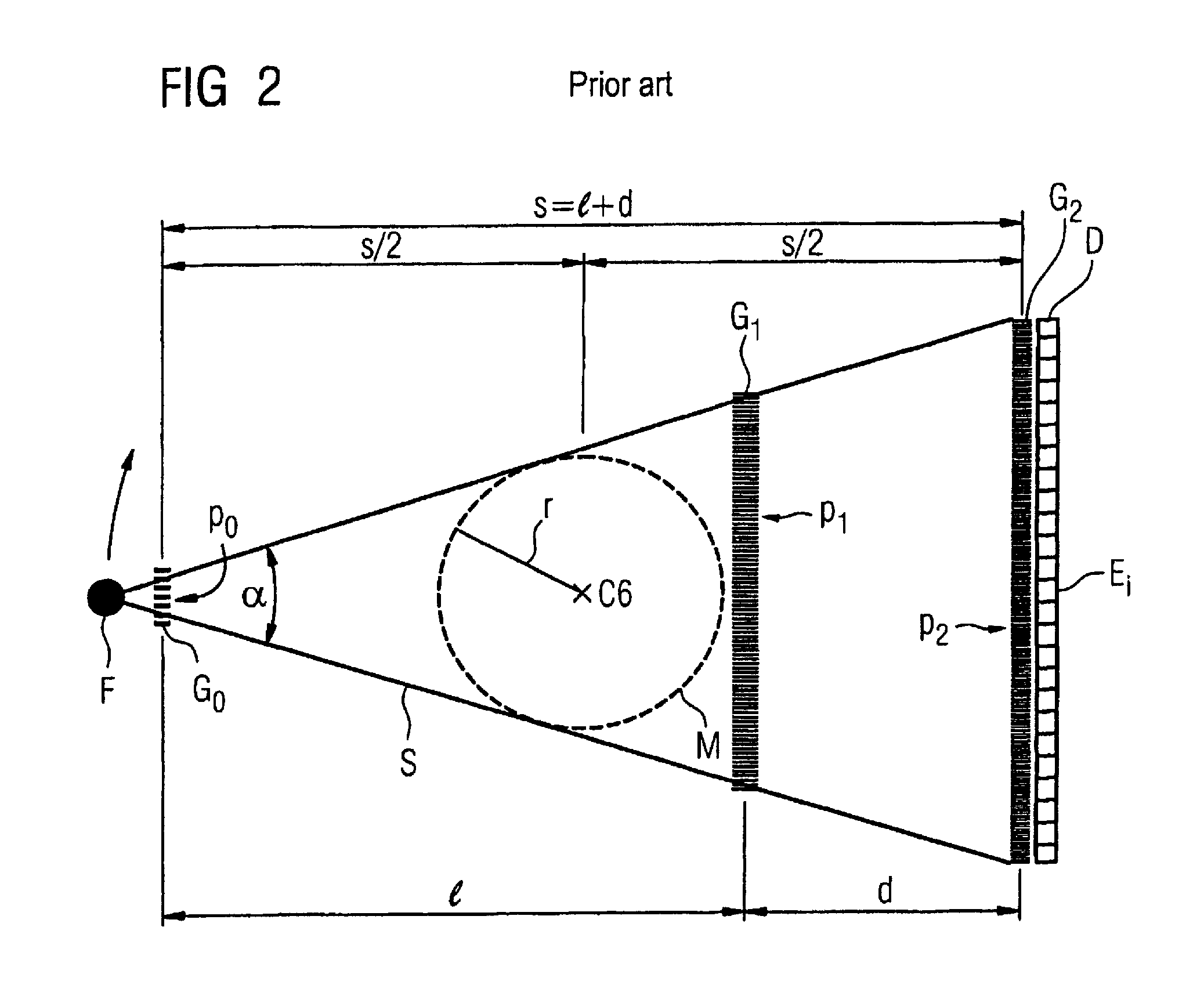
The present invention provides an apparatus capable of X-ray imaging utilizing phase of X-rays. An X-ray imaging apparatus equipped with first and second diffraction gratings and an X-ray image detector are described. The first diffraction grating generates a Talbot effect and a second diffraction grating diffracts X-rays diffracted by the first diffraction grating. An image detector is provided to detect the X-rays diffracted by the second diffraction grating. In this manner, image contrasts caused by changes in phase of X-rays due to a subject arranged in front of the first diffraction grating or between the first diffraction grating and the second diffraction grating can be achieved.
Owner:MOMOSE ATSUSHI
Interferometer for quantitative phase contrast imaging and tomography with an incoherent polychromatic x-ray source
ActiveUS7889838B2Little effortAlleviate scattering artifactImaging devicesTomographyHard X-raysTransmission geometry
Owner:PAUL SCHERRER INSTITUT
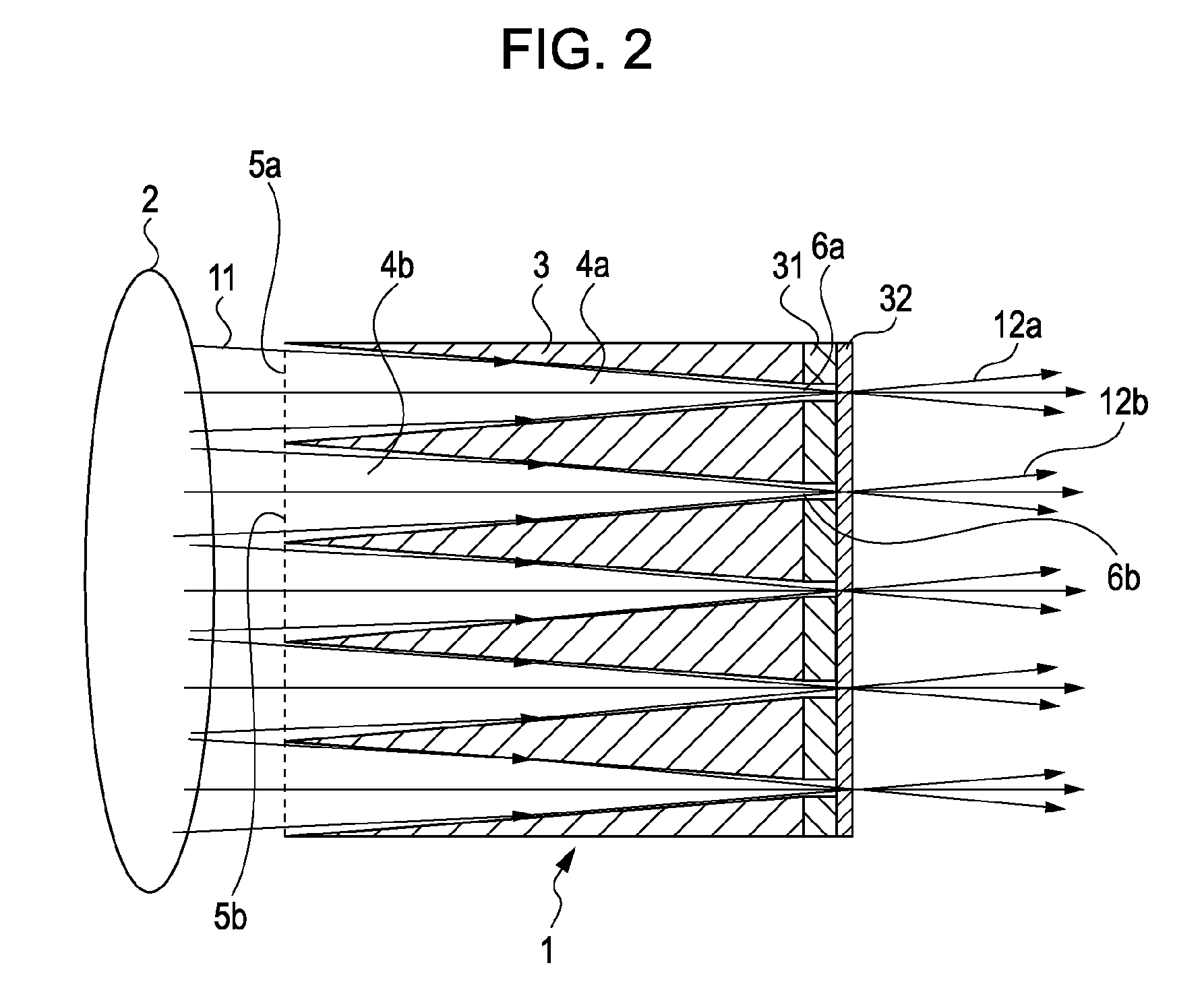
X-ray imaging system and imaging method
ActiveUS20050286680A1Easy constructionImaging devicesHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionSoft x rayImage contrast
The object of the present invention is to provide an apparatus capable of X-ray imaging utilizing phase of X-rays with a simple construction. The X-ray imaging apparatus of the present invention is equipped with first and second diffraction gratings and an X-ray image detector. The first diffraction grating is constructed to generate the Talbot effect using X-rays irradiated at the first diffraction grating. The second diffraction grating is configured so as to diffract the X-rays diffracted by the first diffraction grating. The X-ray image detector is configured so as to detect the X-rays diffracted by the second diffraction grating. By diffracting X-rays diffracted by the first diffraction grating, the second diffraction grating is capable of forming image contrast caused by changes in phase of X-rays due to the subject arranged in front of the front surface of the first diffraction grating or between the first diffraction grating and the second diffraction grating. The X-ray image detector is capable of detecting X-rays creating image contrast.
Owner:MOMOSE ATSUSHI
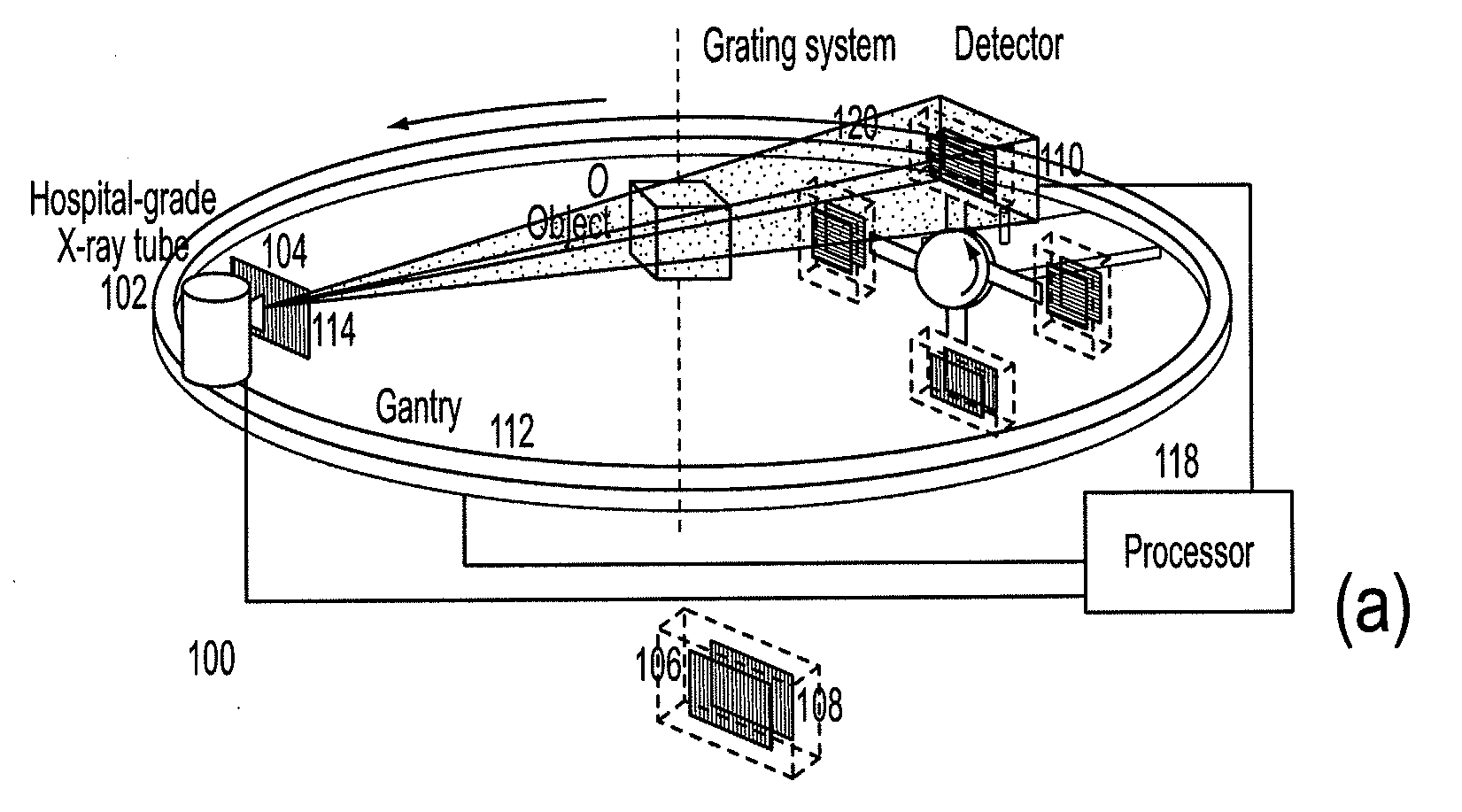
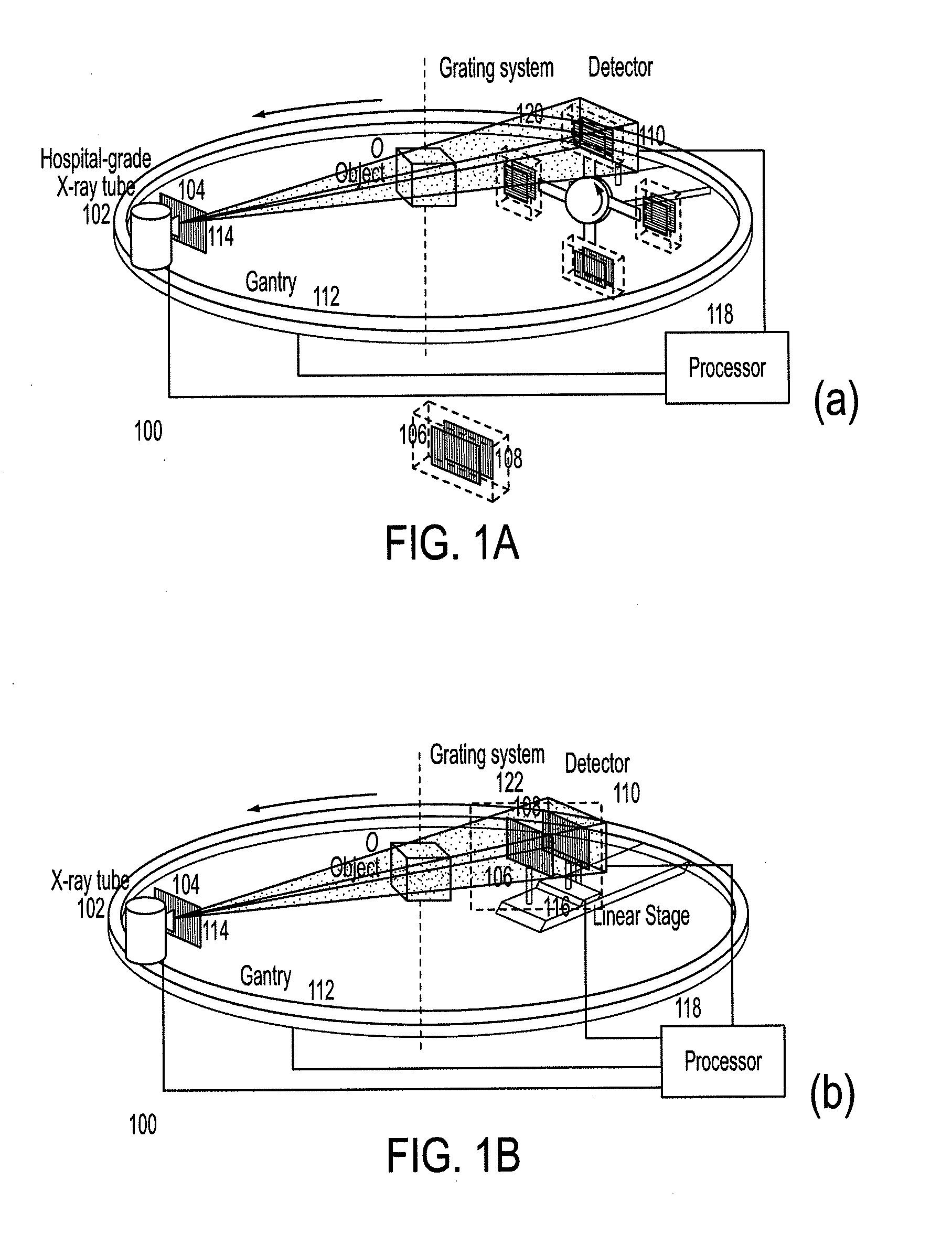
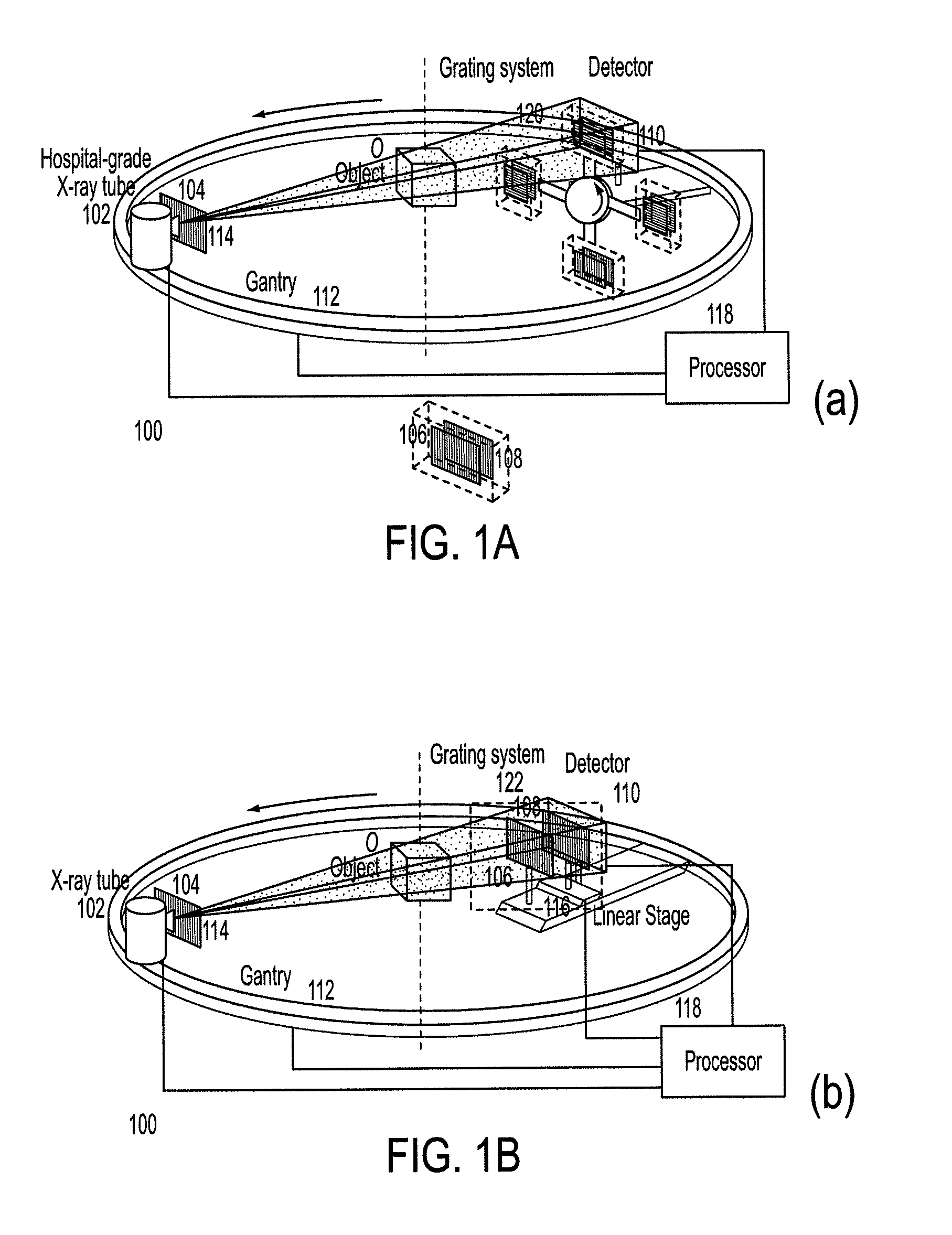
Methods and apparatus for differential phase-contrast fan beam ct, cone-beam ct and hybrid cone-beam ct
ActiveUS20100220832A1Improve spatial resolutionIncrease doseImaging devicesRadiation/particle handlingHybrid systemPhase grating
A device for imaging an object, such as for breast imaging, includes a gantry frame having mounted thereon an x-ray source, a source grating, a holder or other place for the object to be imaged, a phase grating, an analyzer grating, and an x-ray detector. The device images objects by differential-phase-contrast cone-beam computed tomography. A hybrid system includes sources and detectors for both conventional and differential-phase-contrast computed tomography.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Differential interference phase contrast X-ray imaging system
InactiveUS8073099B2High radiant fluxPhoton energy is highImaging devicesX-ray tube electrodesHigh energyPhotoconductive detector
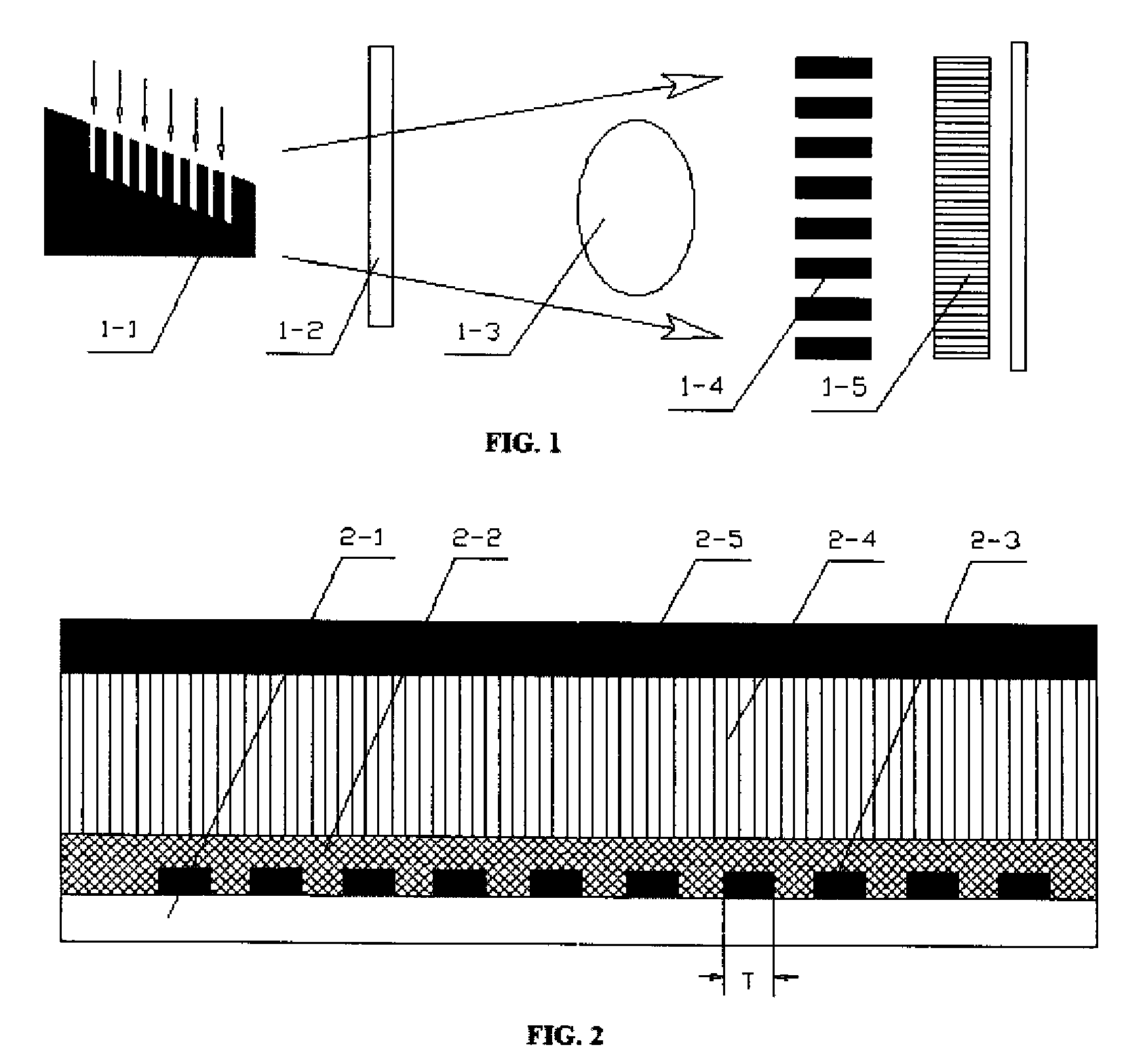
A differential phase-contrast X-ray imaging system is provided. Along the direction of X-ray propagation, the basic components are X-ray tube, filter, object platform, X-ray phase grating, and X-ray detector. The system provides: 1) X-ray beam from parallel-arranged source array with good coherence, high energy, and wider angles of divergence with 30-50 degree. 2) The novel X-ray detector adopted in present invention plays dual roles of conventional analyzer grating and conventional detector. The basic structure of the detector includes a set of parallel-arranged linear array X-ray scintillator screens, optical coupling system, an area array detector or parallel-arranged linear array X-ray photoconductive detector. In this case, relative parameters for scintillator screens or photoconductive detector correspond to phase grating and parallel-arranged line source array, which can provide the coherent X-rays with high energy.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Methods and apparatus for differential phase-contrast fan beam CT, cone-beam CT and hybrid cone-beam CT
ActiveUS7949095B2Increase doseImprove spatial resolutionImaging devicesRadiation/particle handlingPhase gratingHybrid system
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
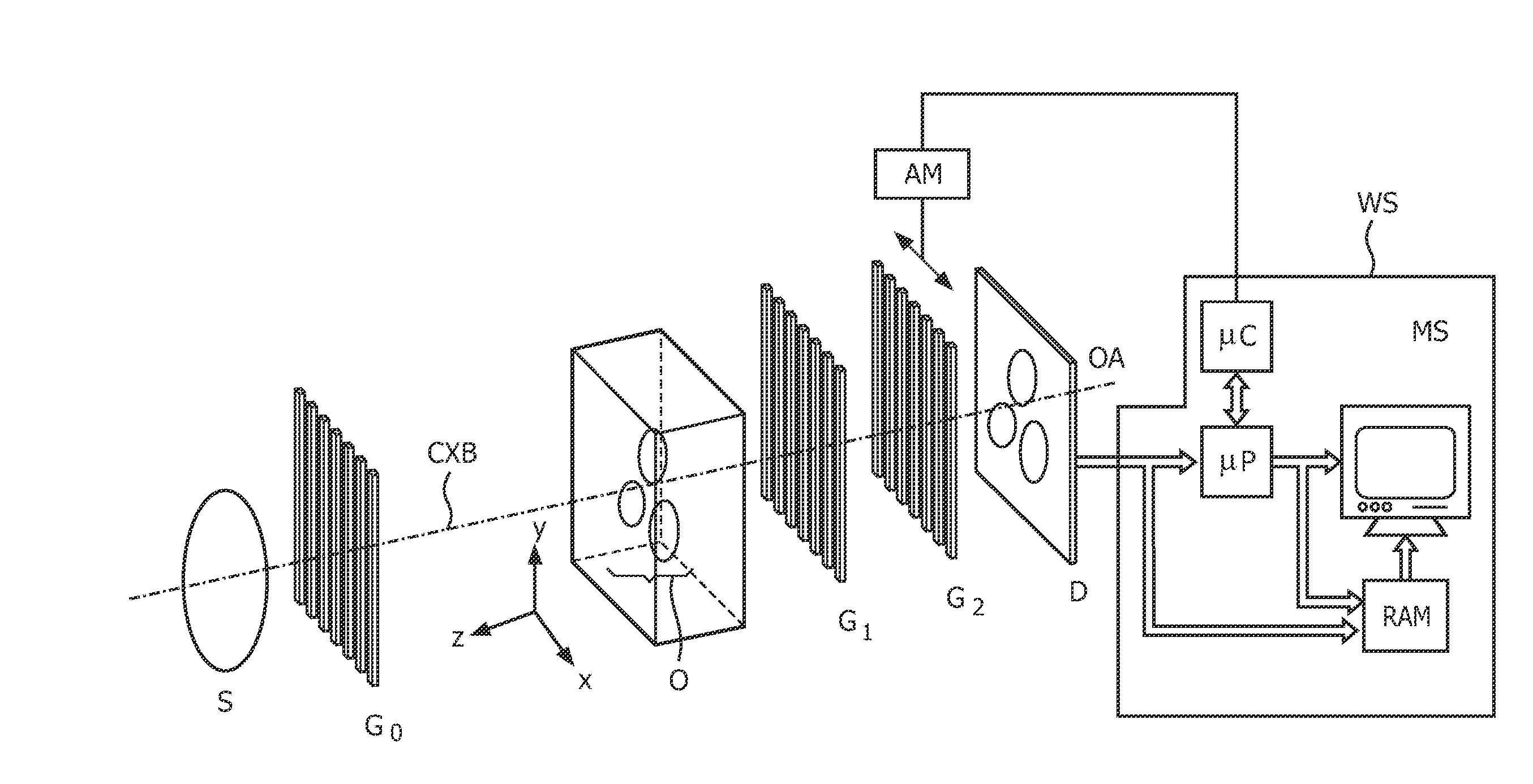
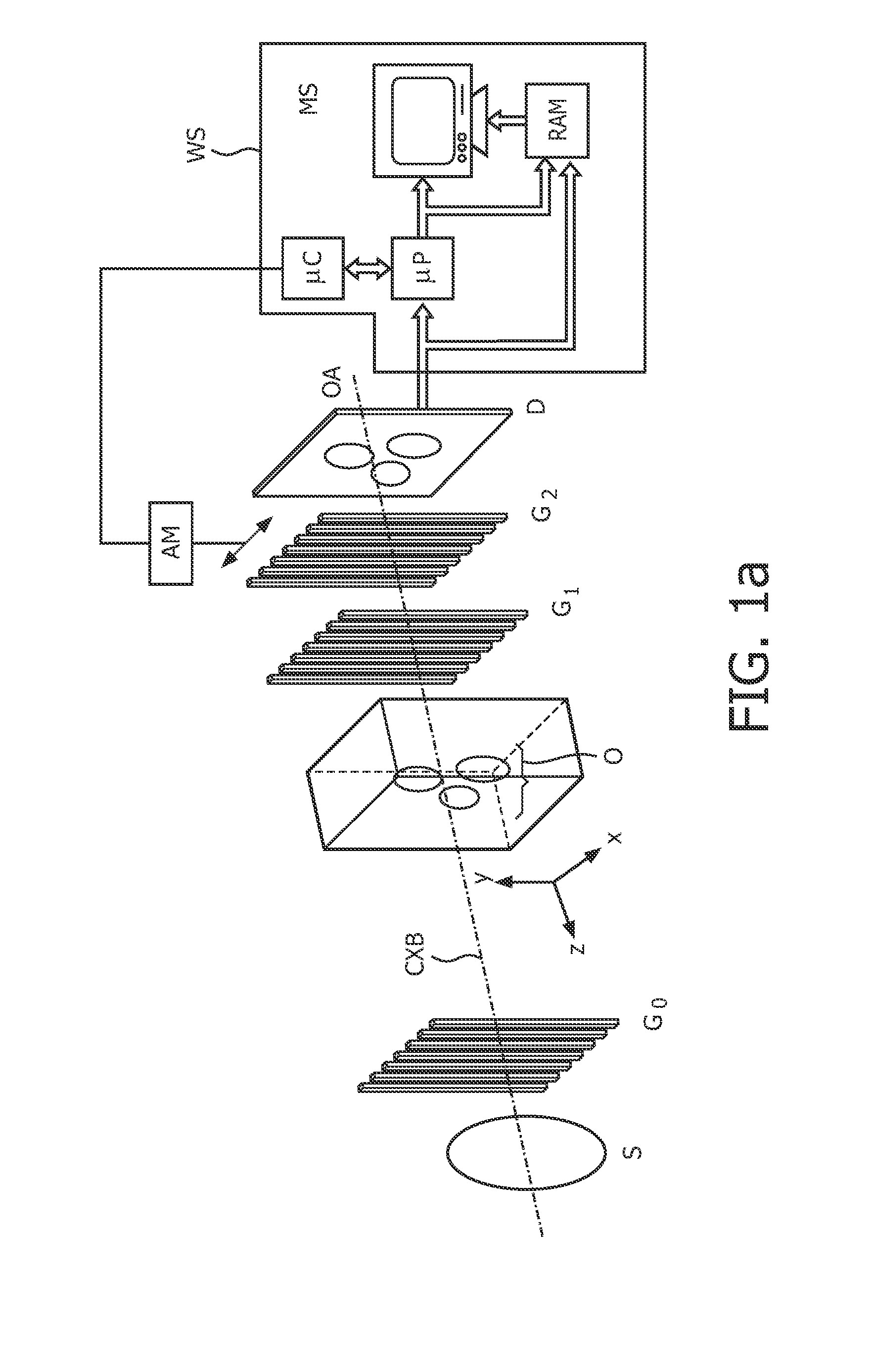
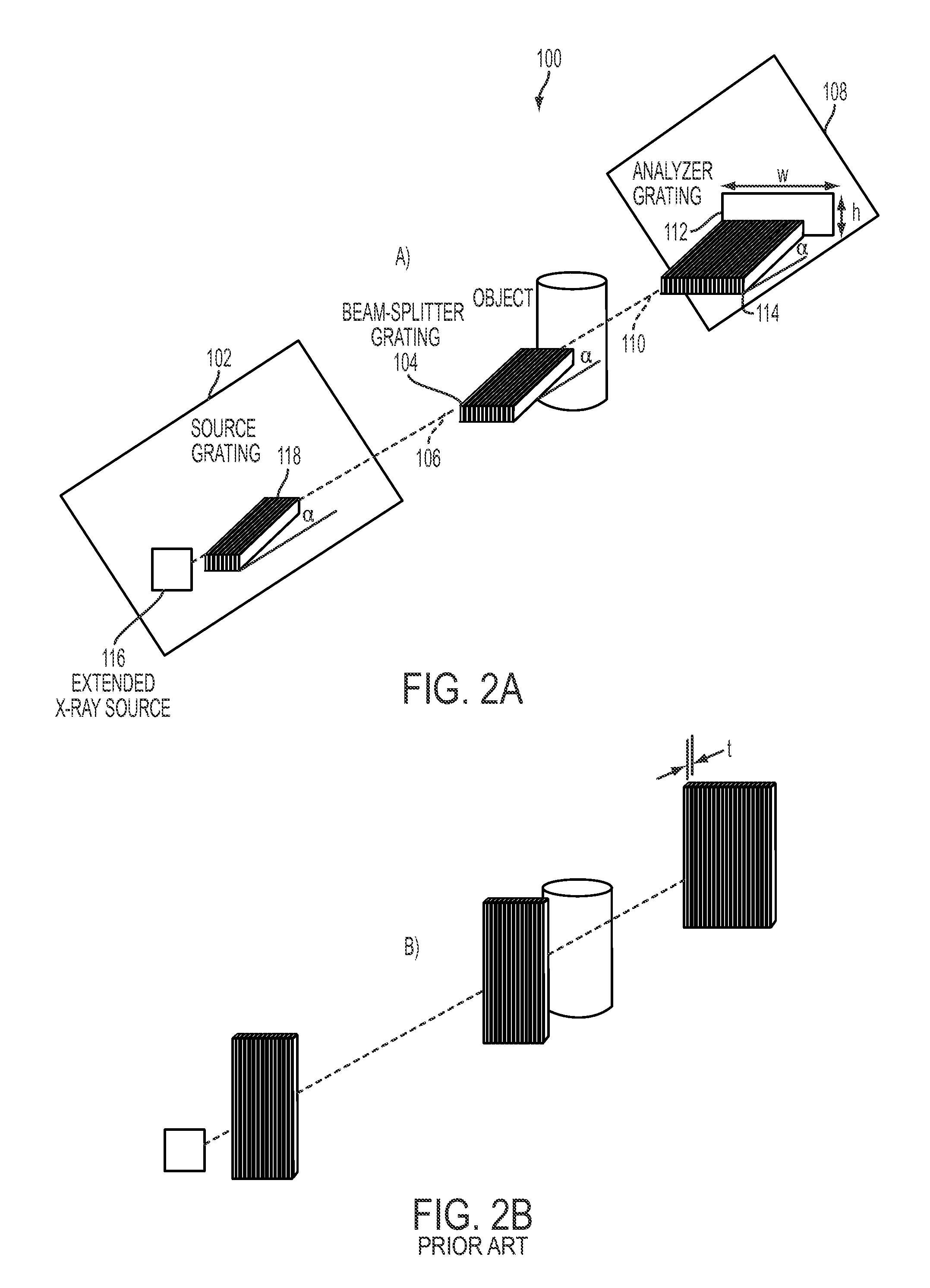
Interferometer device and method
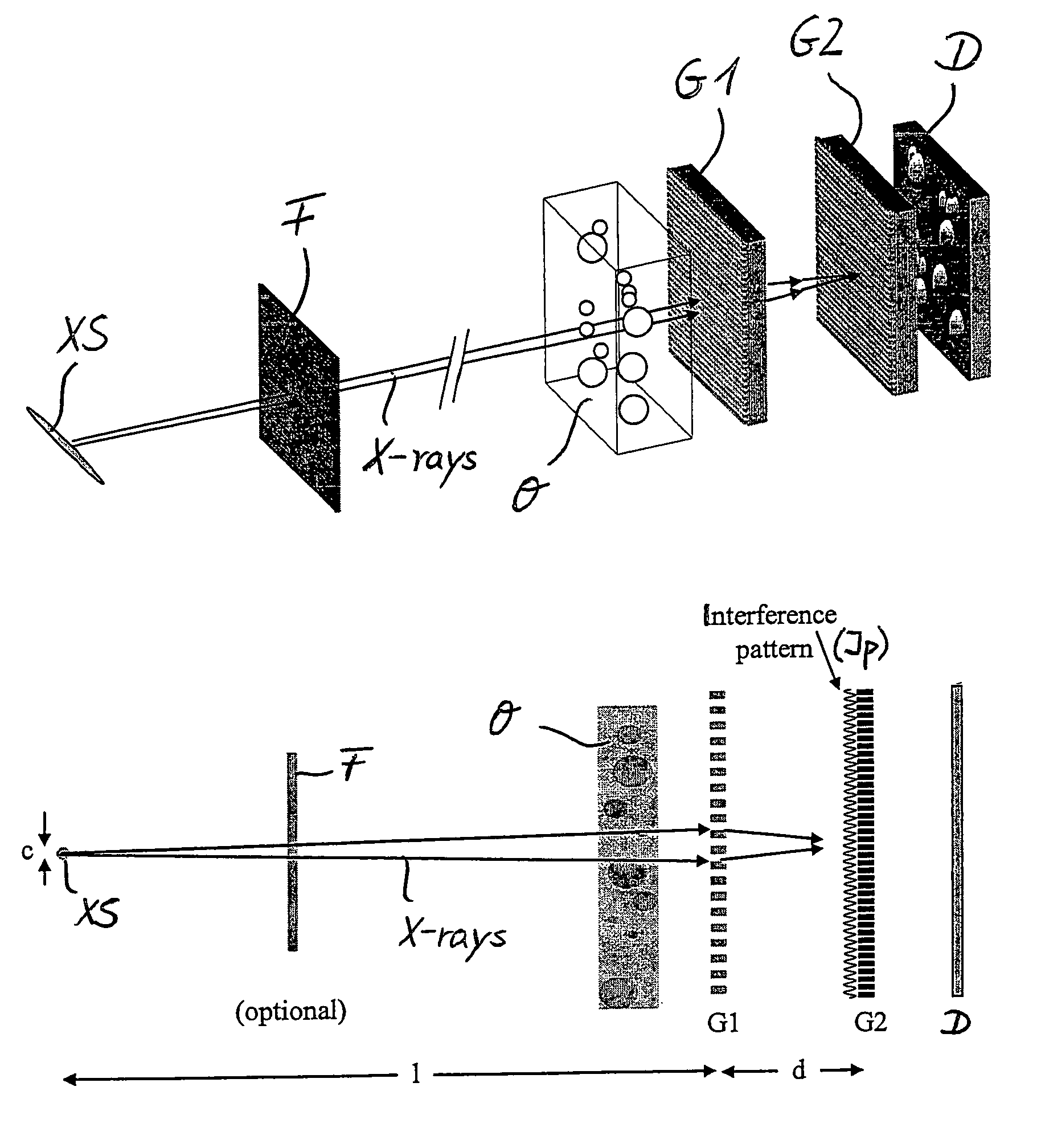
The present invention discloses an interferometer device and method. In embodiments, the device comprises an electromagnetic radiation source emitting radiation having a first mean wavelength λLE; a phase grating having a first aspect ratio; an absorption grating having a second aspect ratio; and a detector. The electromagnetic radiation source, the phase grating, the absorption grating and the detector are radiatively coupled with each other. The absorption grating is positioned between the detector and the phase grating; the electromagnetic radiation source is positioned in front of the source grating; and wherein the phase grating is designed such to cause a phase shift that is smaller than π on the emitted radiation. Additional and alternative embodiments are specified and claimed.
Owner:CSEM CENT SUISSE DELECTRONIQUE & DE MICROTECHNIQUE SA RECH & DEV
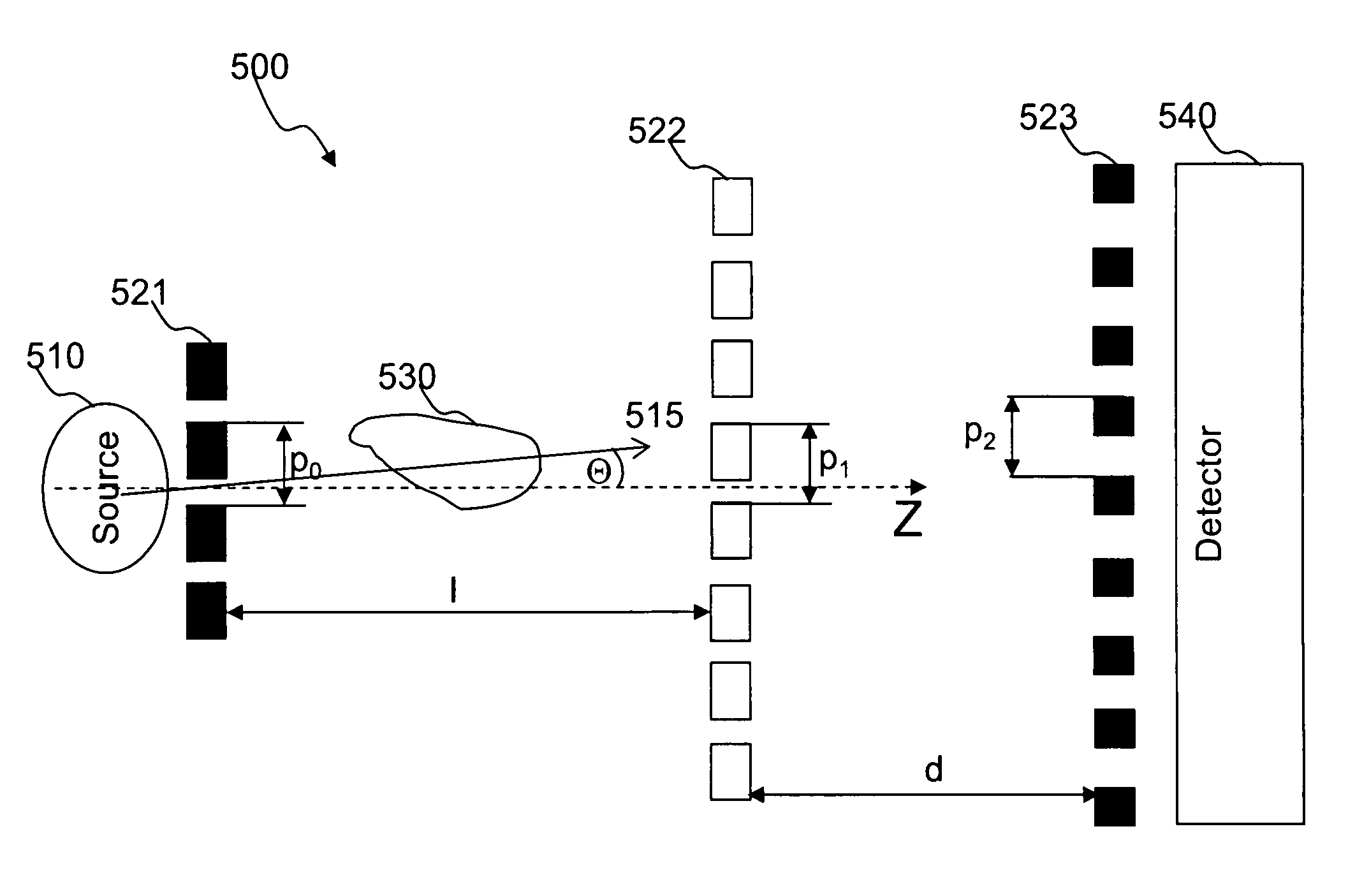
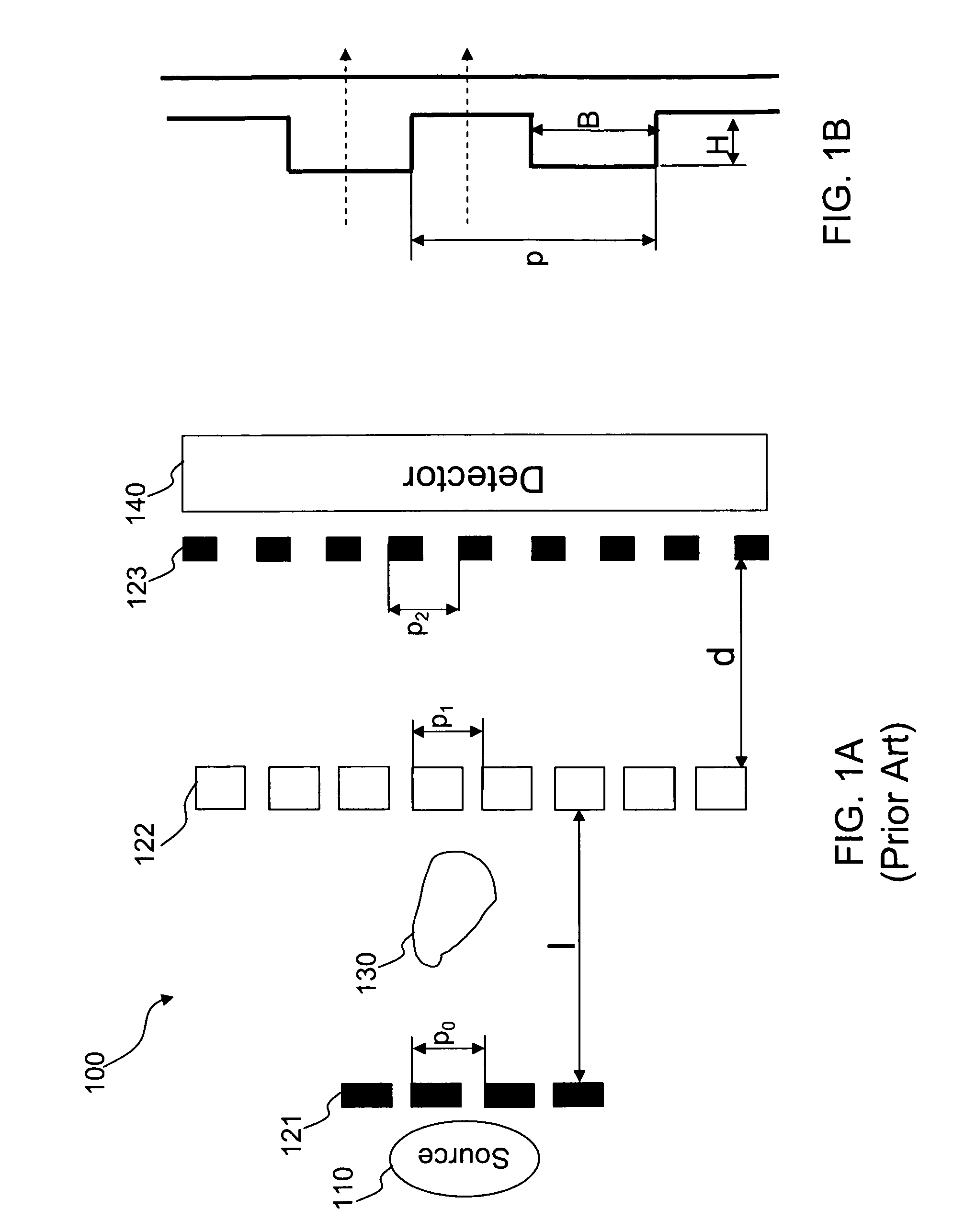
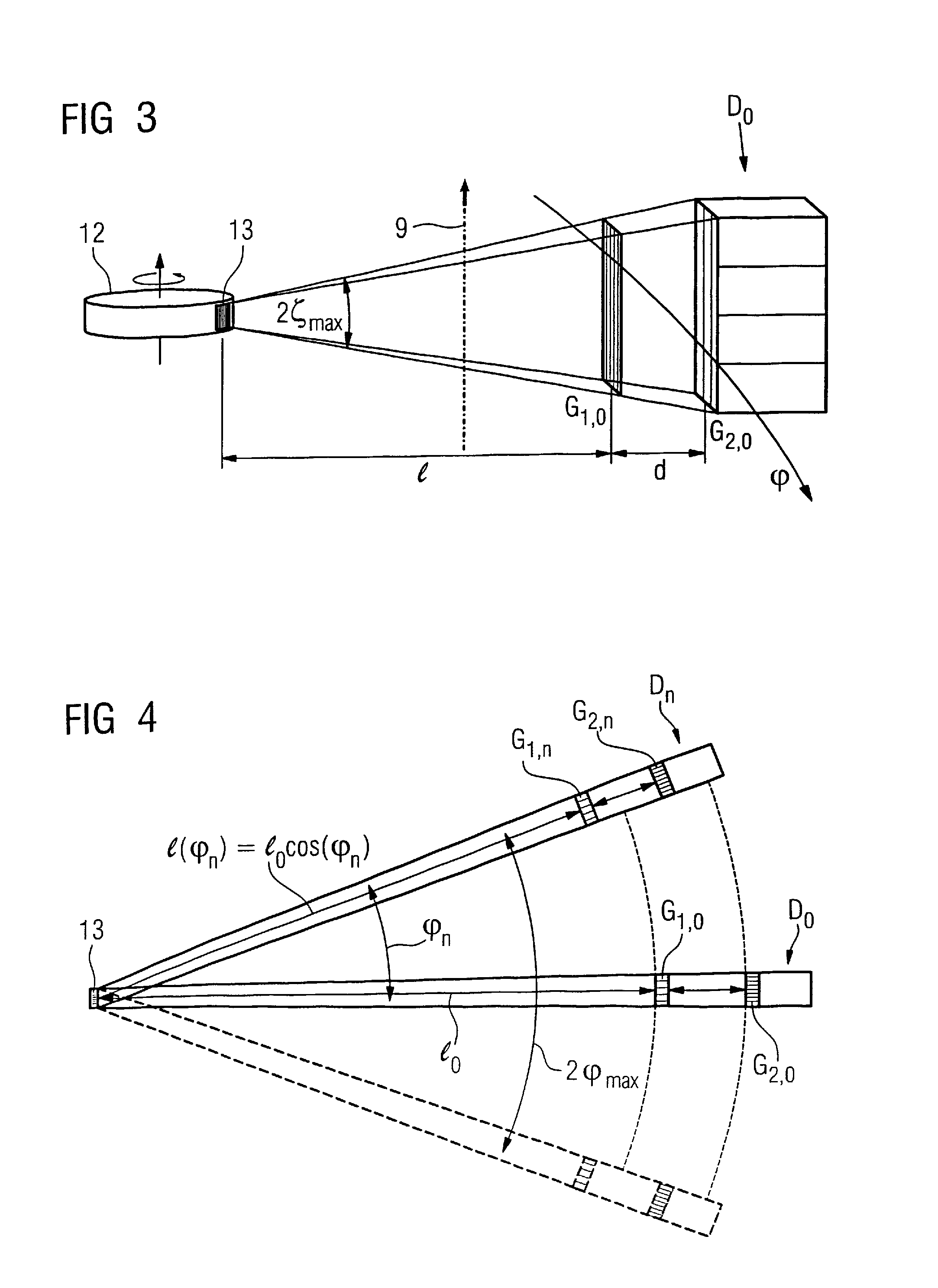
Focus/detector system of an x-ray apparatus for generating phase contrast recordings
InactiveUS7492871B2Improve stabilitySimple structureImaging devicesMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPhase gratingBeam source
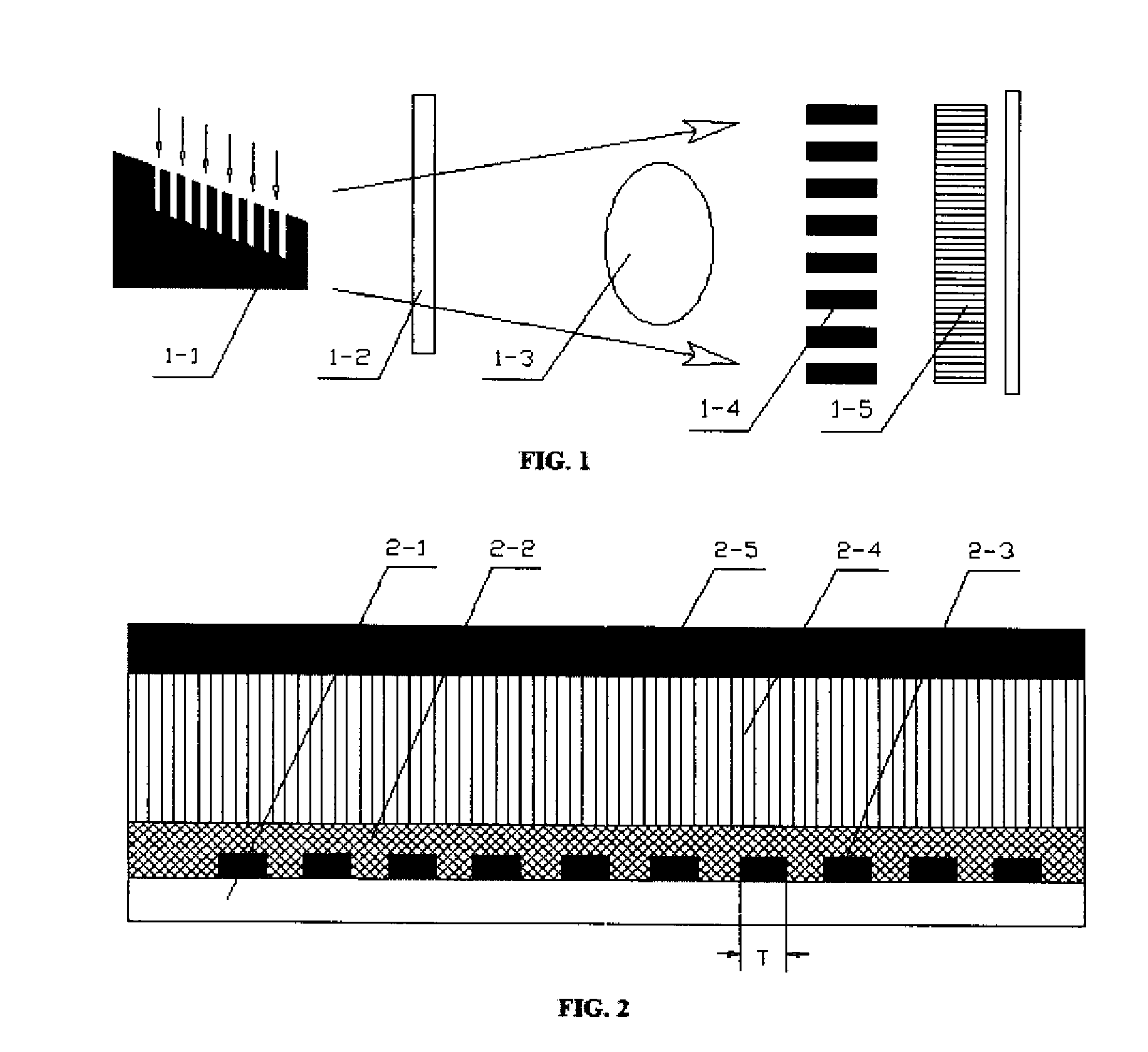
A focus / detector system of an X-ray apparatus and a method for generating projective or tomographic phase contrast recordings, are disclosed. In an embodiment of the system, the system includes a beam source equipped with a focus and a focus-side source grating, arranged in the beam path and generates a field of ray-wise coherent X-rays, a grating / detector arrangement having a phase grating and grating lines arranged parallel to the source grating for generating an interference pattern, and a detector having a multiplicity of detector elements arranged flat for measuring the position-dependent radiation intensity behind the phase grating. Finally, the detector elements are formed by a multiplicity of elongate scintillation strips, which are aligned parallel to the grating lines of the phase grating and have a small period, whose integer multiple corresponds to the average large period of the interference pattern which is formed by the phase grating.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH +1
Optimized x-ray energy for high resolution imaging of integrated circuits structures
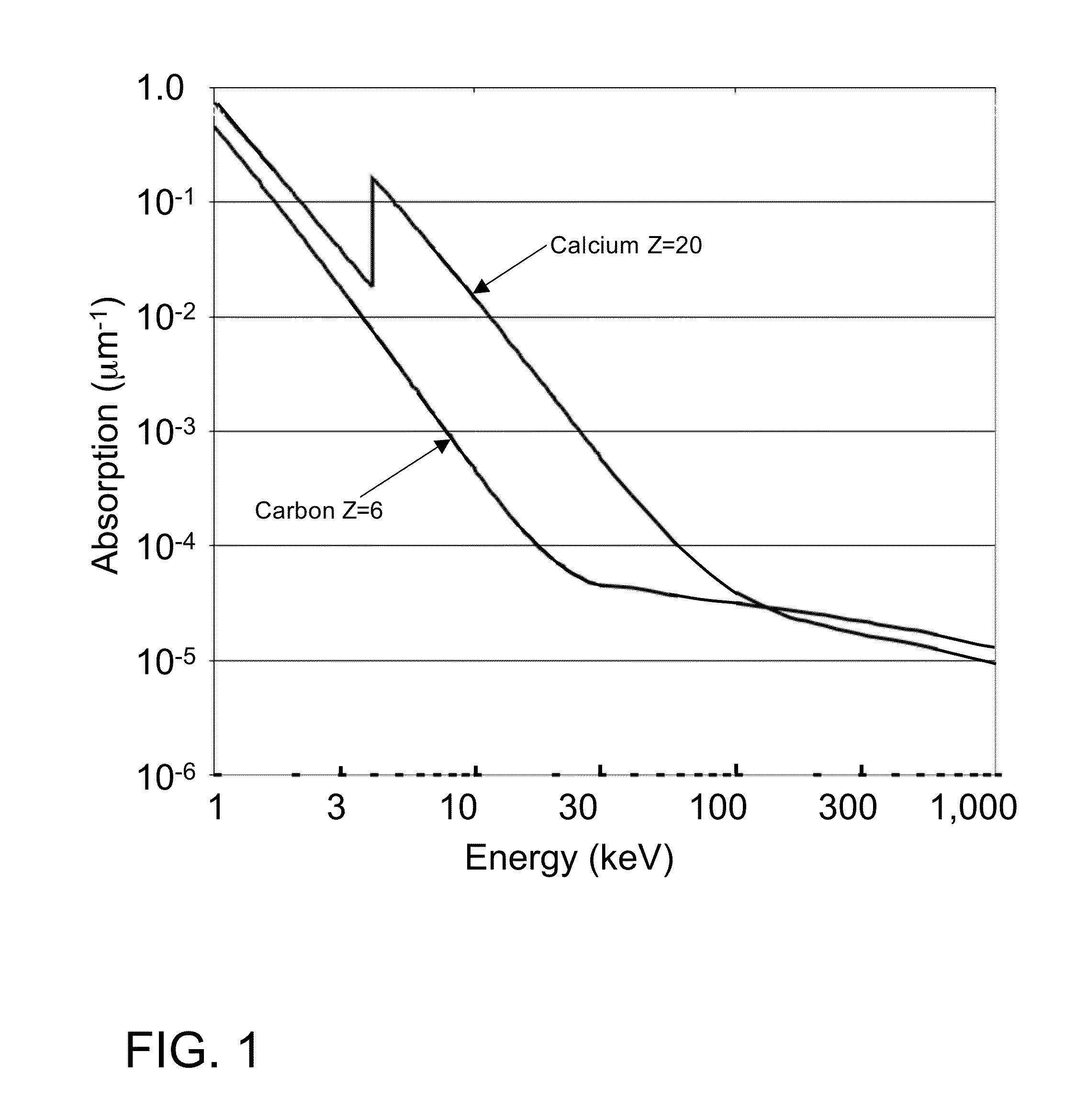
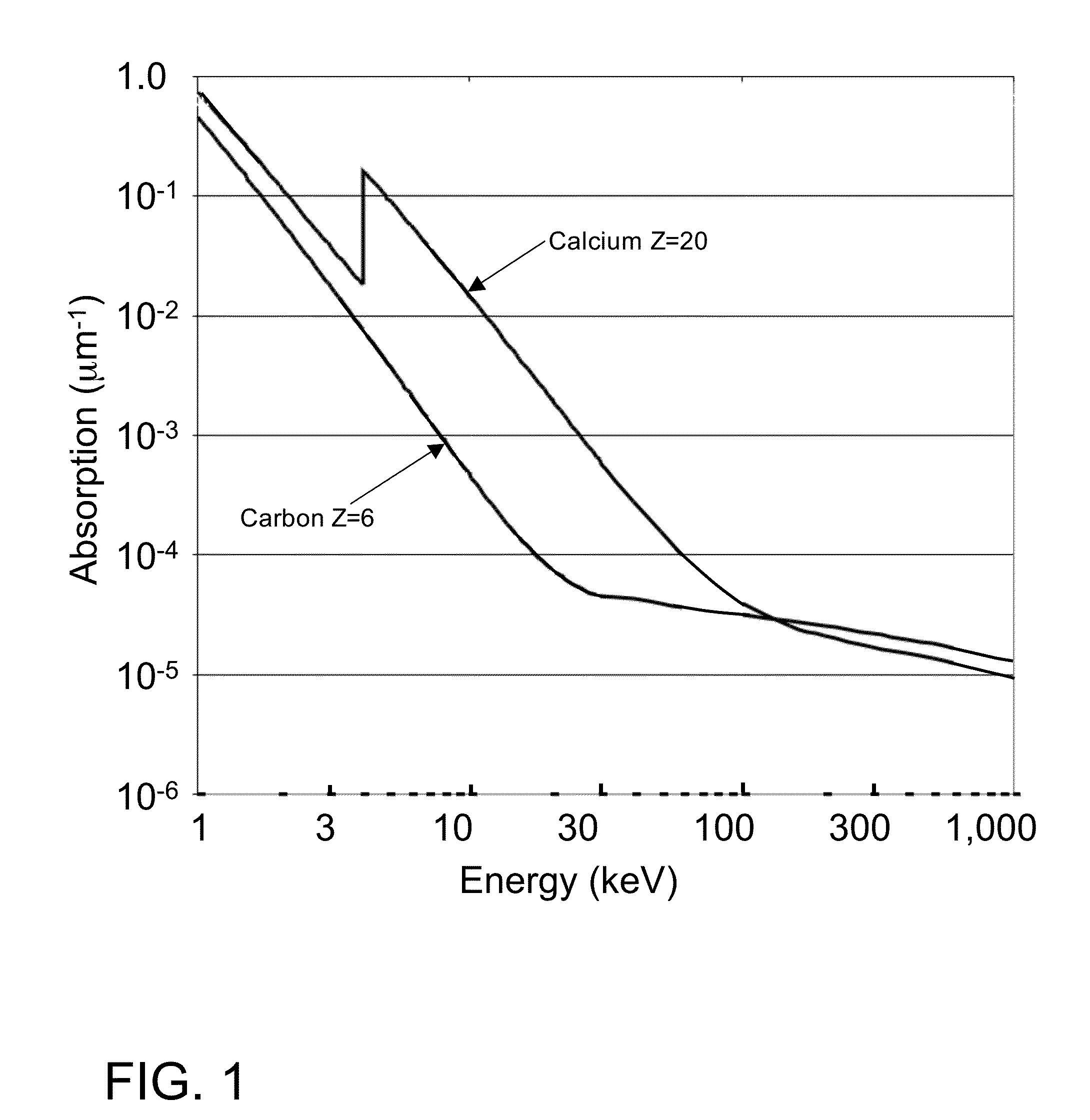
ActiveUS7394890B1Increase contrastImprove throughputImaging devicesX-ray spectral distribution measurementHigh resolution imagingX-ray
An x-ray imaging system uses particular emission lines that are optimized for imaging specific metallic structures in a semiconductor integrated circuit structures and optimized for the use with specific optical elements and scintillator materials. Such a system is distinguished from currently-existing x-ray imaging systems that primarily use the integral of all emission lines and the broad Bremstralung radiation. The disclosed system provides favorable imaging characteristics such as ability to enhance the contrast of certain materials in a sample, to use different contrast mechanisms in a single imaging system, and to increase the throughput of the system.
Owner:CARL ZEISS X RAY MICROSCOPY
Focus detector arrangement and method for generating contrast x-ray images
ActiveUS7817777B2Improve utilizationRaise the ratioImaging devicesRadiation/particle handlingSoft x rayX-ray
In a focus detector arrangement and method for an x-ray apparatus for generating projection or tomographic phase-contrast images of an examination subject, a beam of coherent x-rays is generated by an anode that has areas of different radiation emission characteristics arranged in bands thereon, that proceed parallel to grid lines of a phase grid that is used to generate the phase-contrast images.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
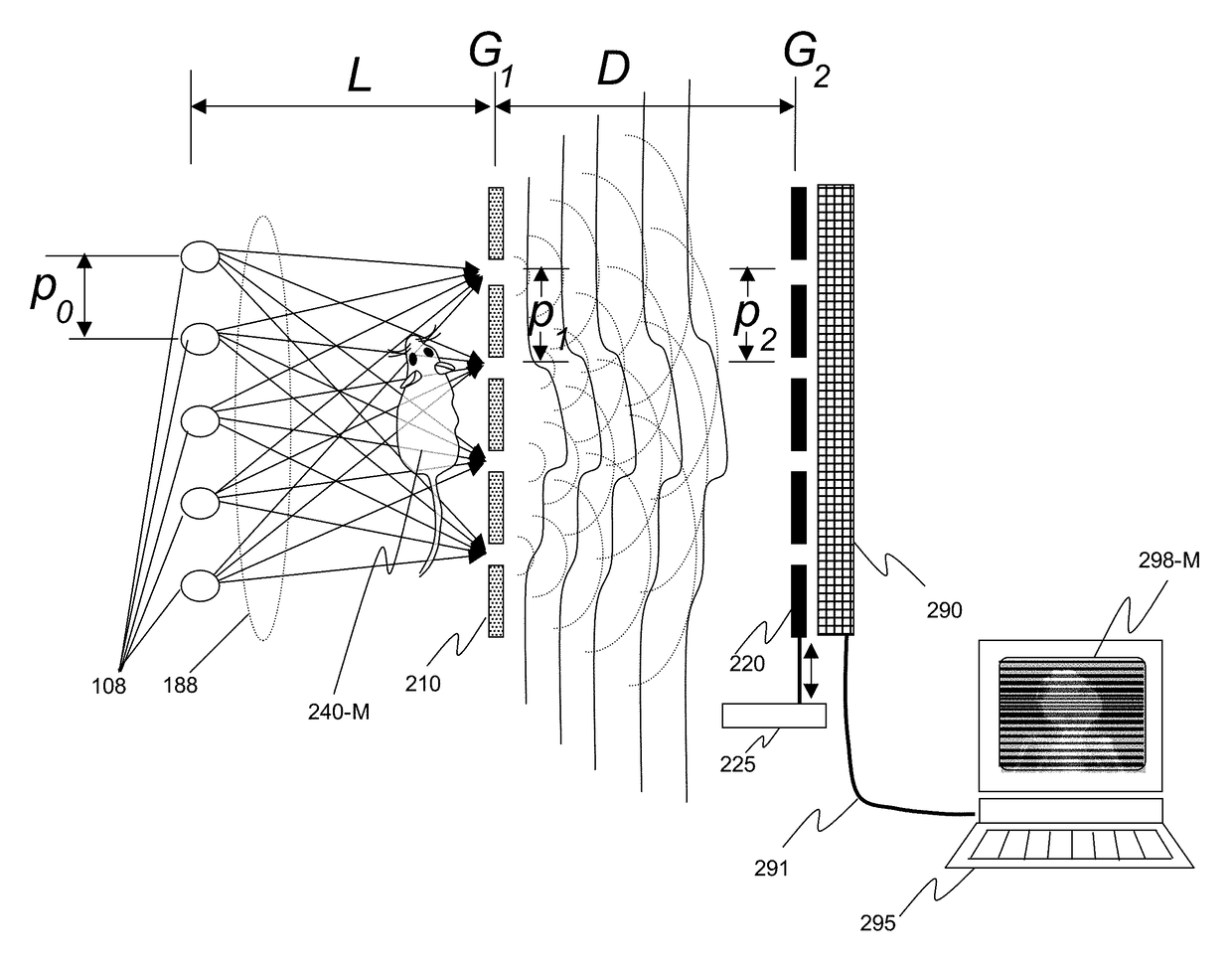
X-ray interferometric imaging system
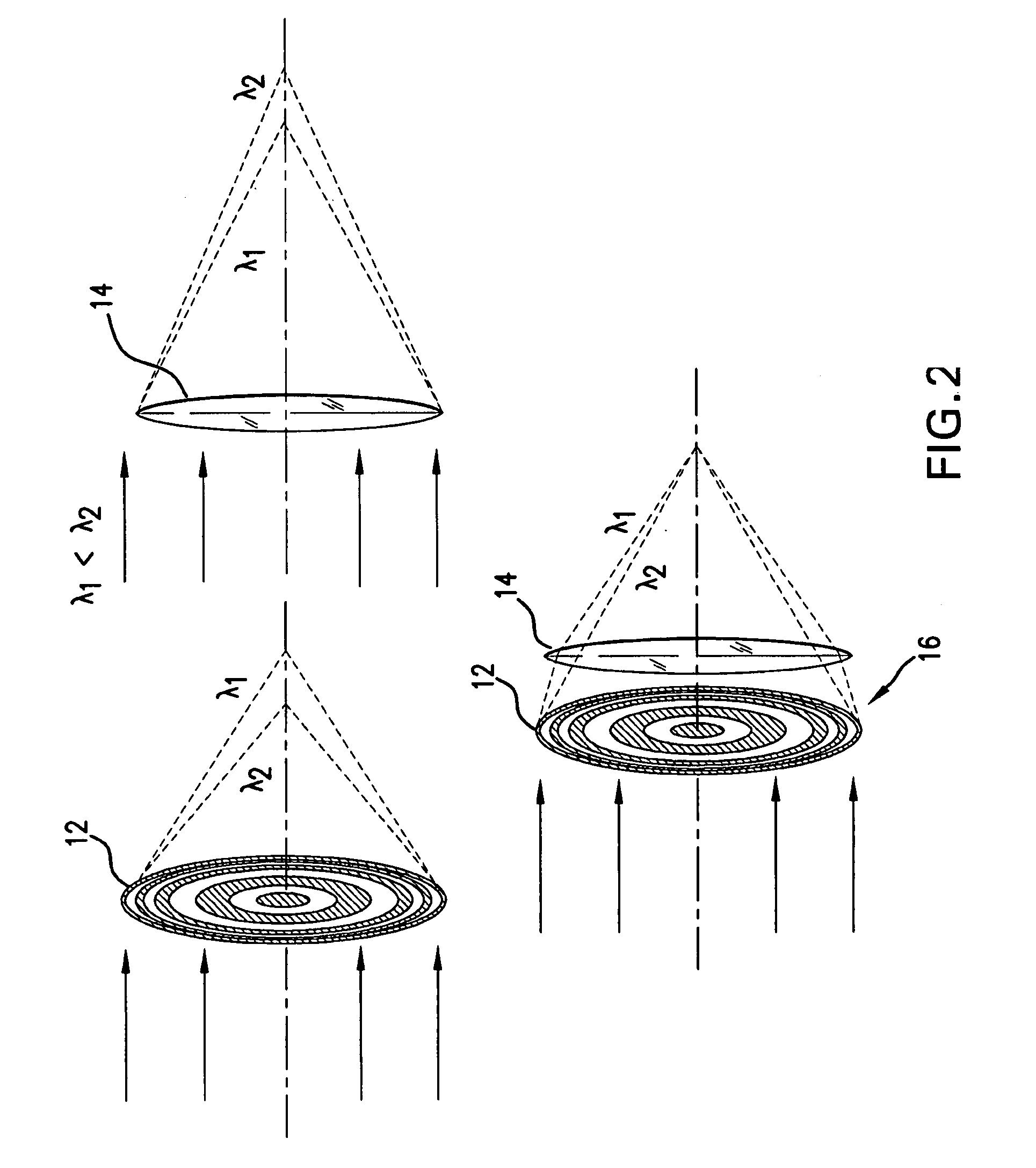
ActiveUS20150243397A1Increase brightnessLarge x-ray powerImaging devicesHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionPhysicsSoft x ray
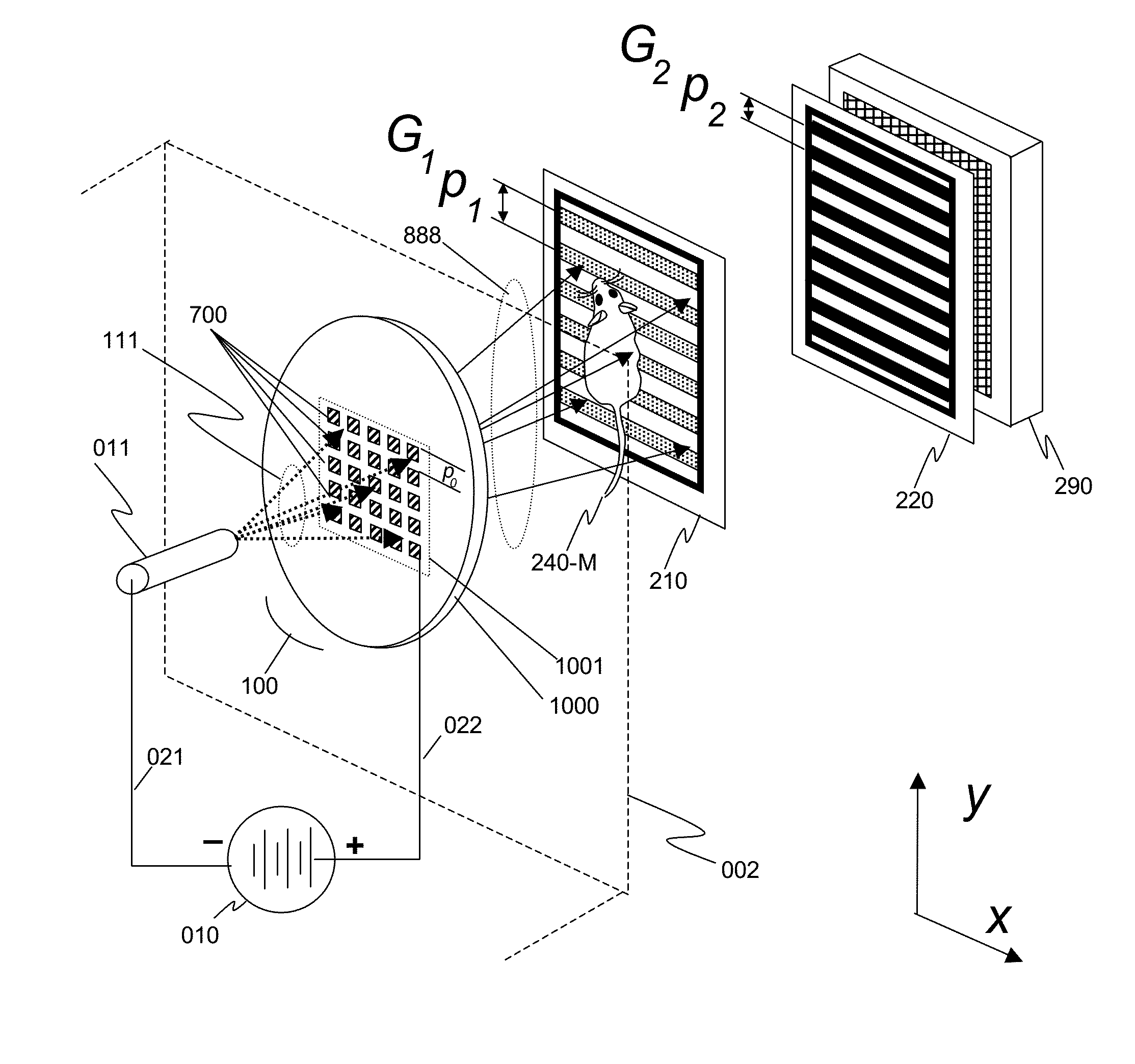
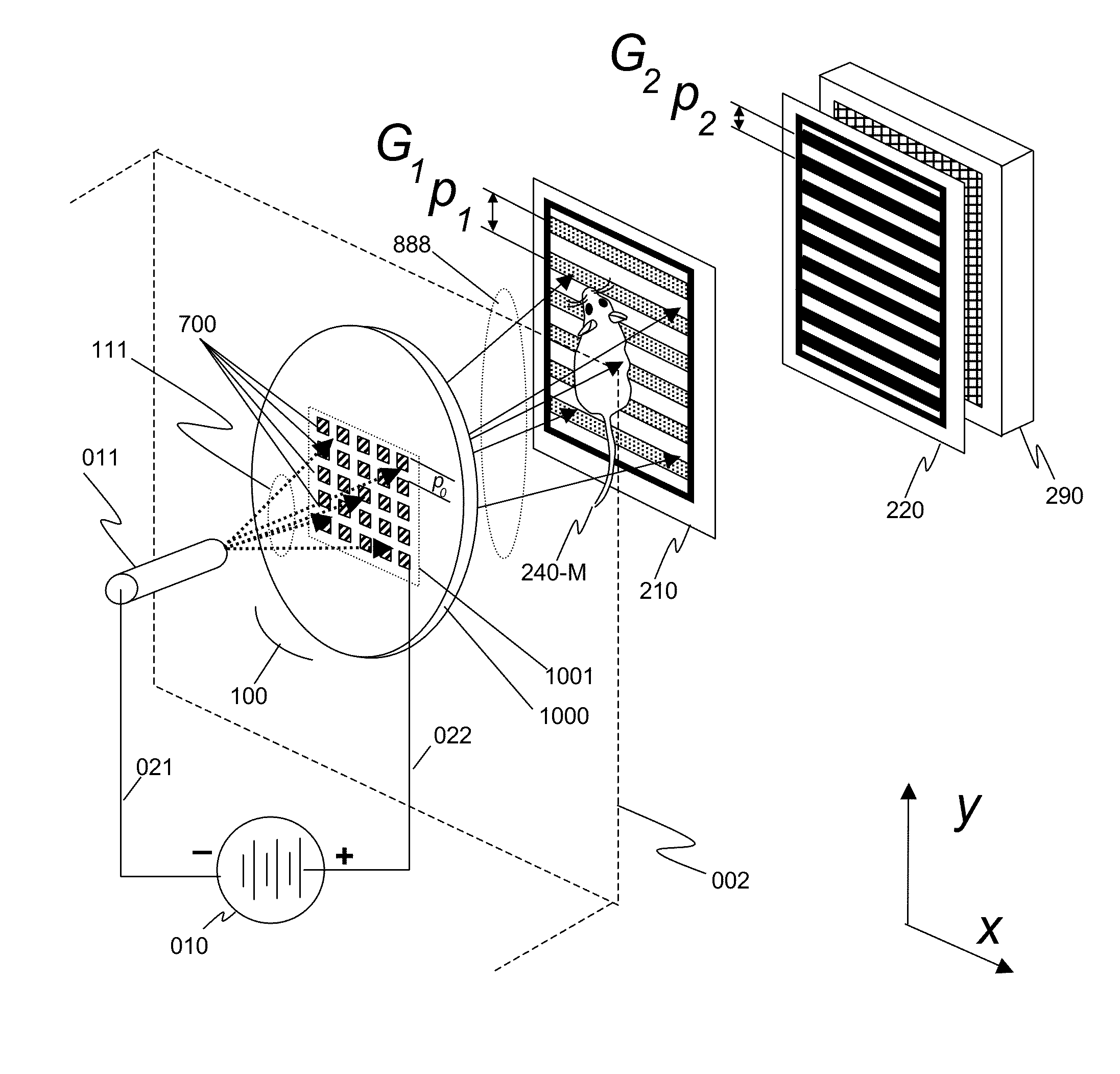
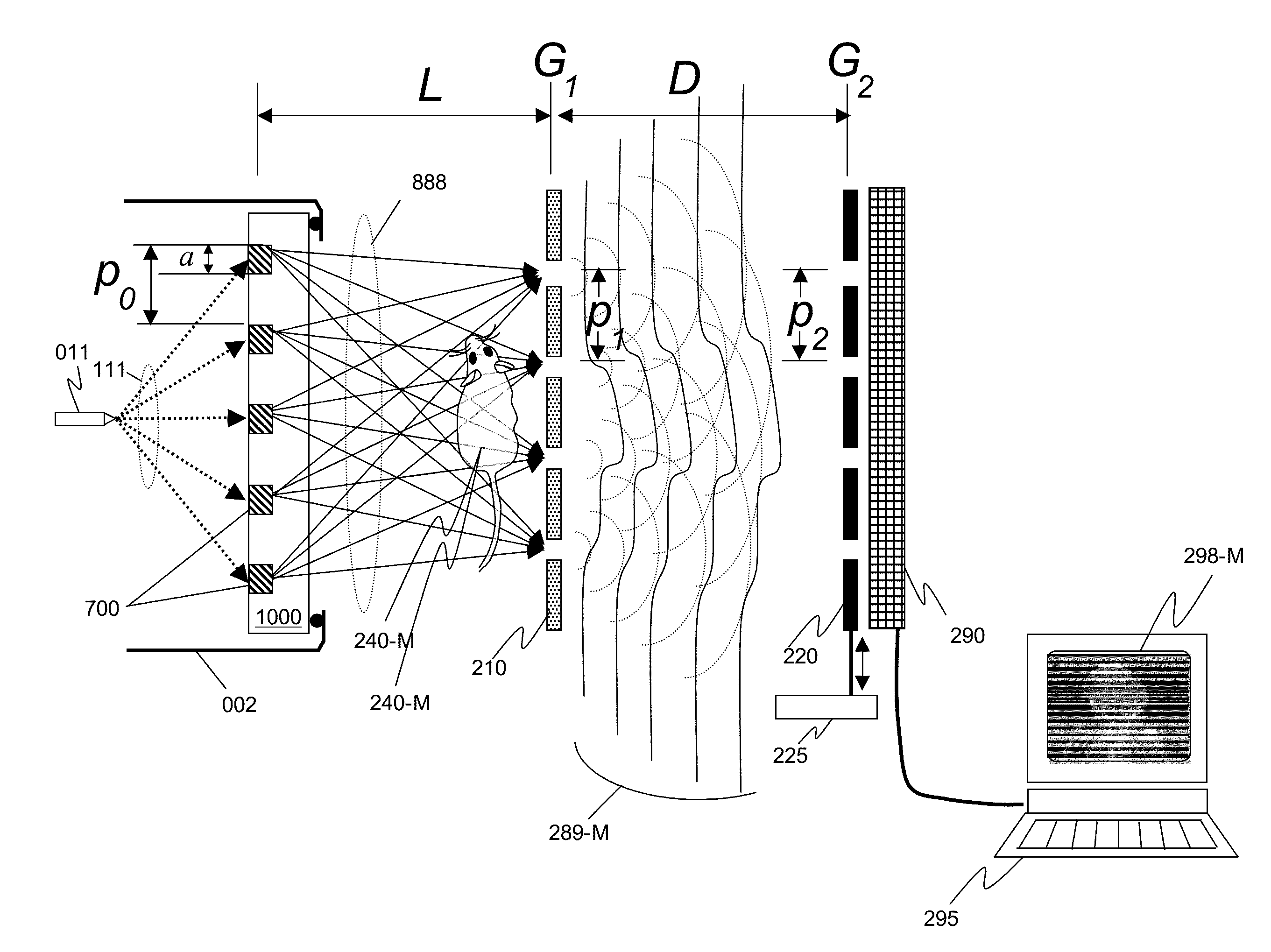
An x-ray interferometric imaging system in which the x-ray source comprises a target having a plurality of structured coherent sub-sources of x-rays embedded in a thermally conducting substrate. The system additionally comprises a beam-splitting grating G1 that establishes a Talbot interference pattern, which may be a π phase-shifting grating, and an x-ray detector to convert two-dimensional x-ray intensities into electronic signals. The system may also comprise a second analyzer grating G2 that may be placed in front of the detector to form additional interference fringes, a means to translate the second grating G2 relative to the detector. The system may additionally comprise an antiscattering grid to reduce signals from scattered x-rays. Various configurations of dark-field and bright-field detectors are also disclosed.
Owner:SIGRAY INC
X-ray interferometric imaging system
InactiveUS20150117599A1Increase brightnessLarge x-ray powerImaging devicesMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSoft x rayGrating
We disclose an x-ray interferometric imaging system in which the x-ray source comprises a target having a plurality of structured coherent sub-sources of x-rays embedded in a thermally conducting substrate. The system additionally comprises a beam-splitting grating G1 that establishes a Talbot interference pattern, which may be a π phase-shifting grating, and an x-ray detector to convert two-dimensional x-ray intensities into electronic signals. The system may also comprise a second analyzer grating G2 that may be placed in front of the detector to form additional interference fringes, and a means to translate the second grating G2 relative to the detector.In some embodiments, the structures are microstructures with lateral dimensions measured on the order of microns, and with a thickness on the order of one half of the electron penetration depth within the substrate. In some embodiments, the structures are formed within a regular array.
Owner:SIGRAY INC
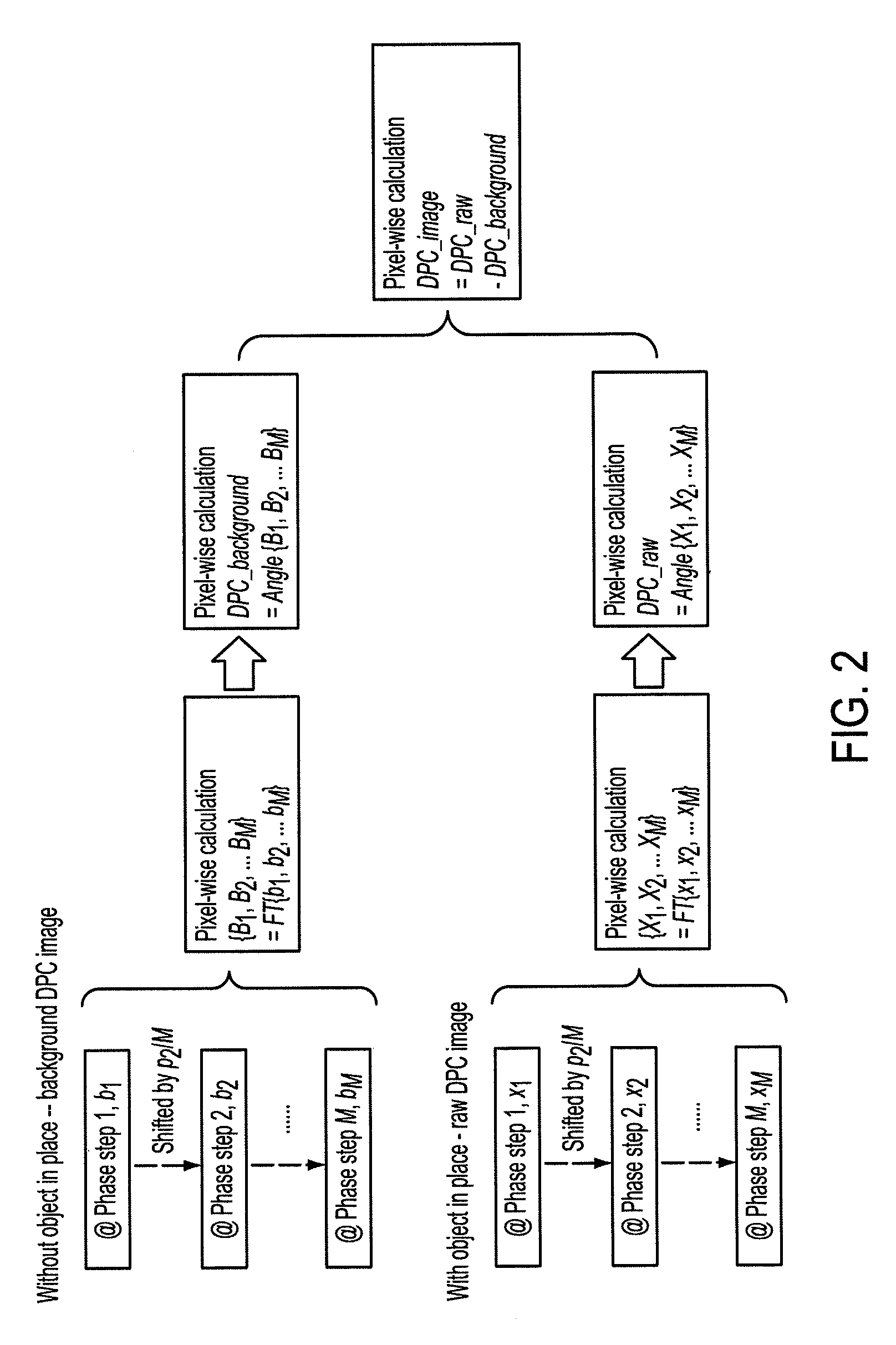
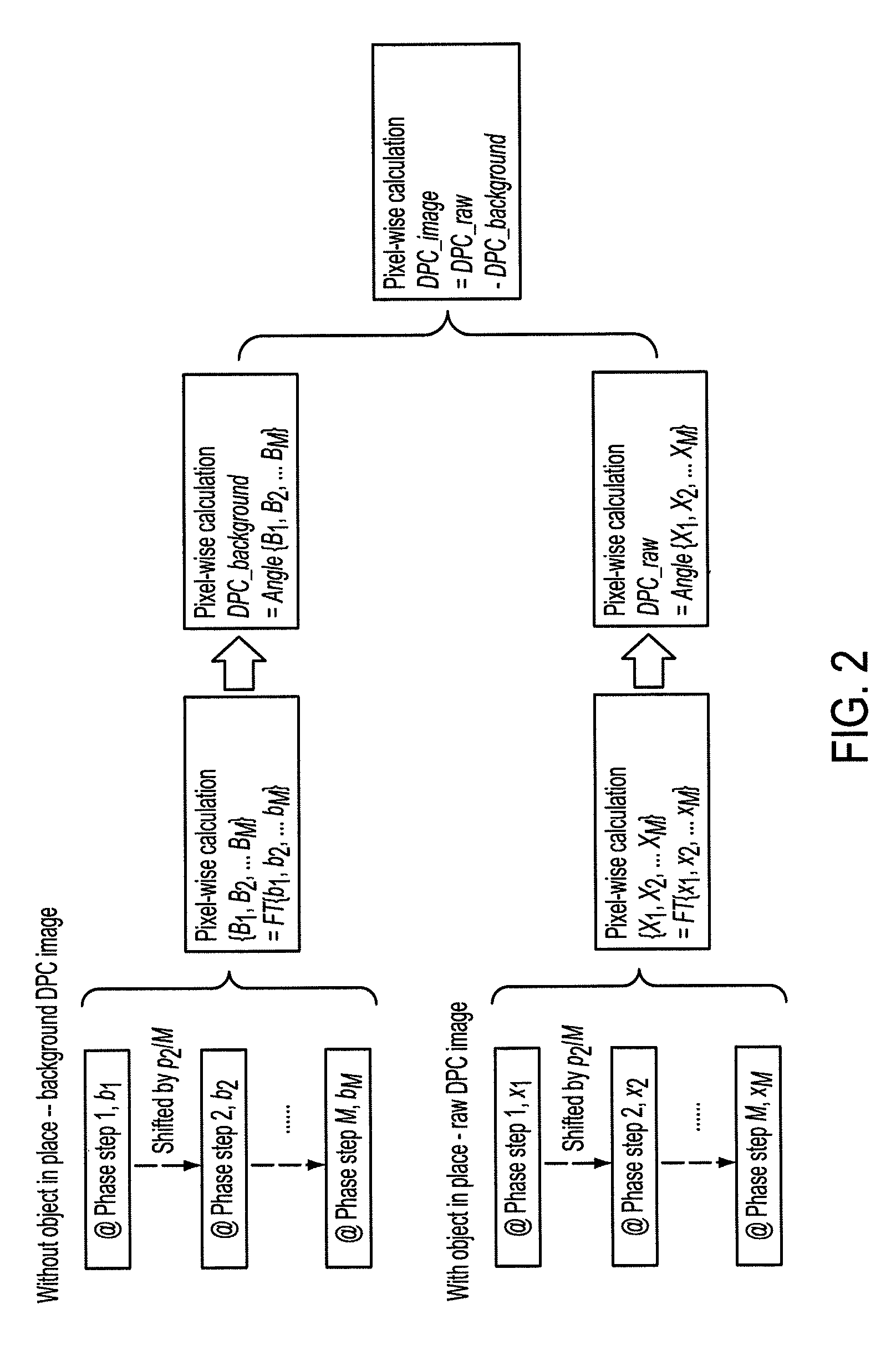
Correction method for differential phase contrast imaging
ActiveUS8855265B2Reduce impactImprove image qualityImaging devicesHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionHard X-raysBeam splitter
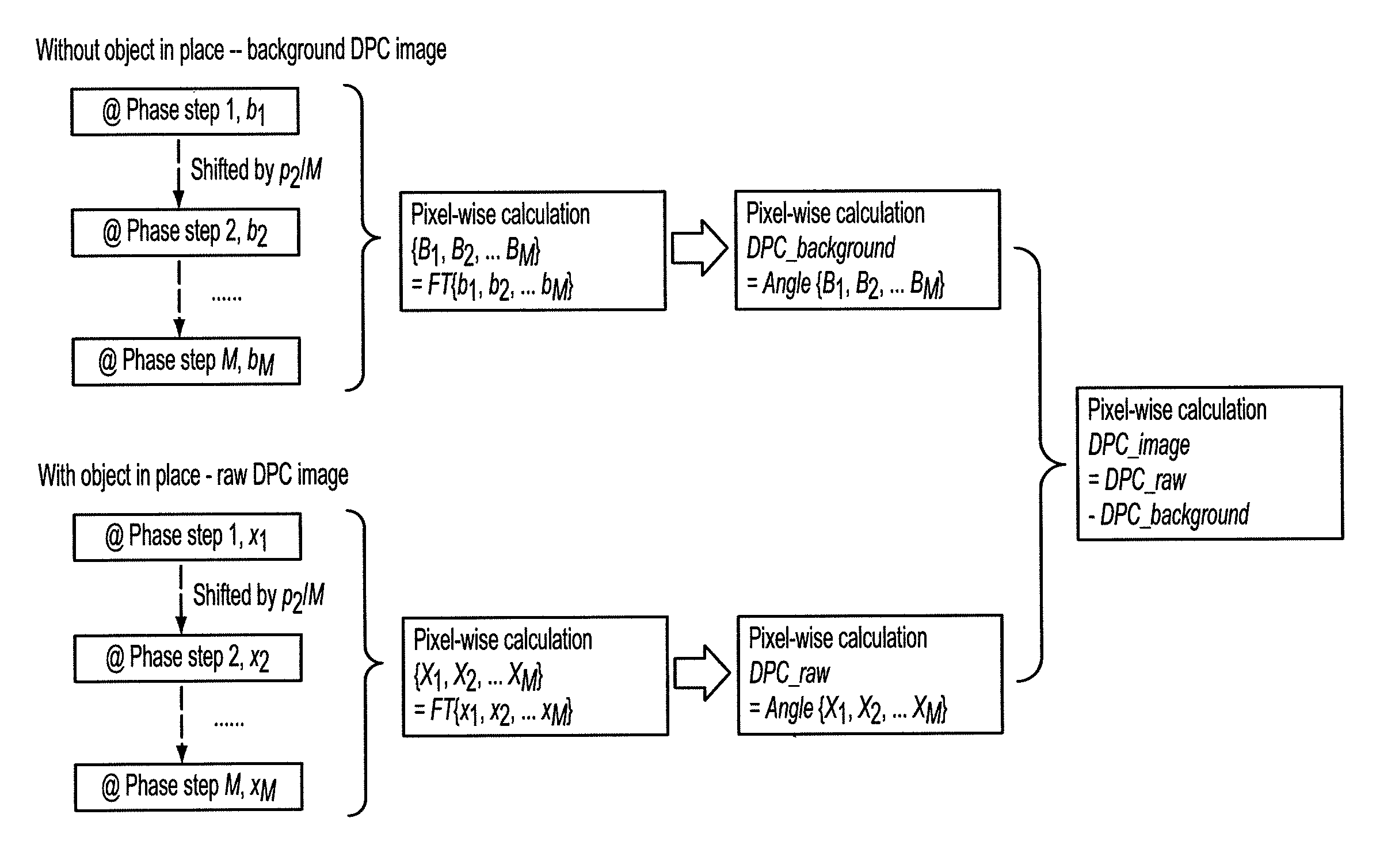
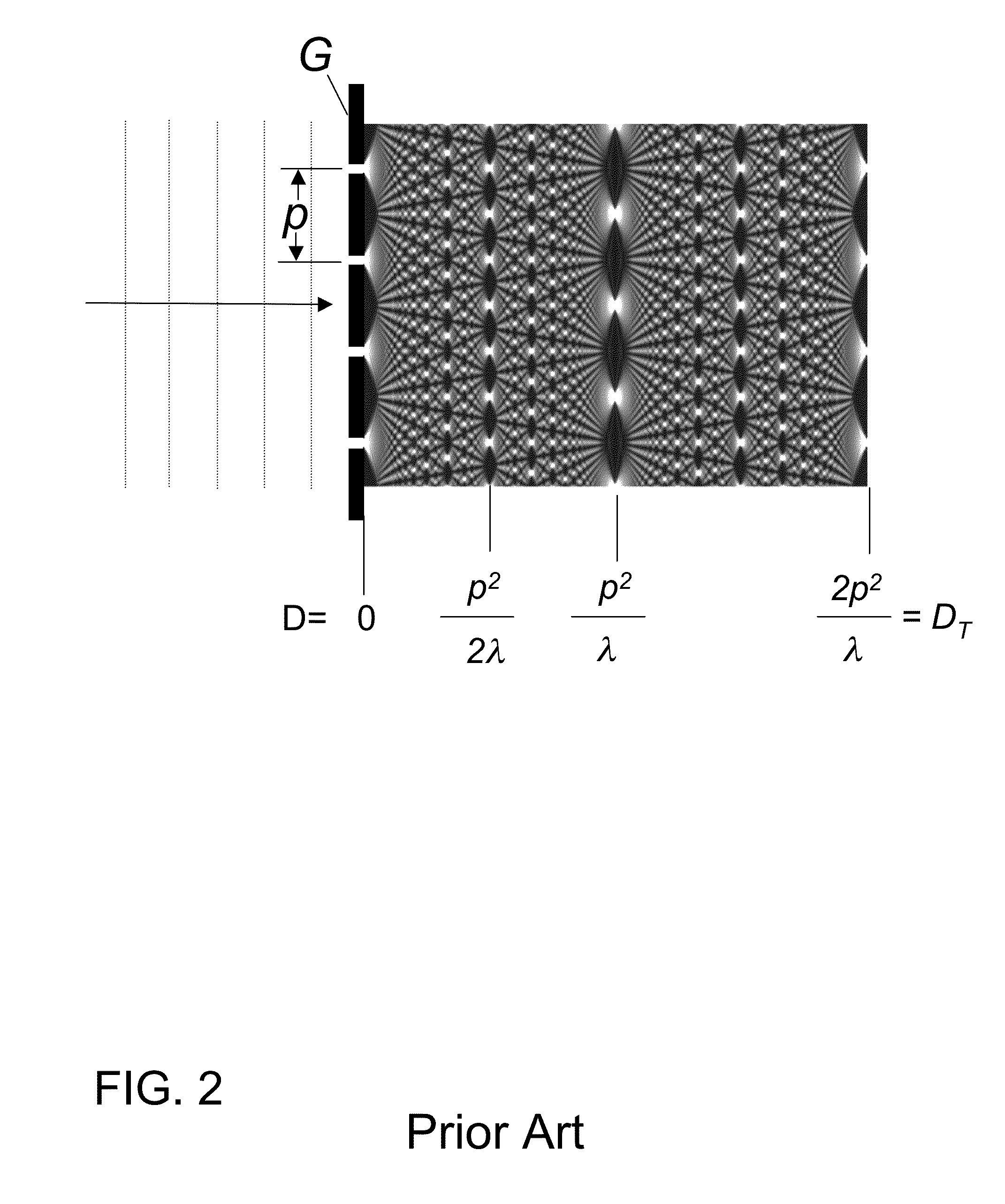
The present invention generally refers to a correction method for grating-based X-ray differential phase contrast imaging (DPCI) as well as to an apparatus which can advantageously be applied in X-ray radiography and tomography for hard X-ray DPCI of a sample object or an anatomical region of interest to be scanned. More precisely, the proposed invention provides a suitable approach that helps to enhance the image quality of an acquired X-ray image which is affected by phase wrapping, e.g. in the resulting Moiré interference pattern of an emitted X-ray beam in the detector plane of a Talbot-Lau type interferometer after diffracting said X-ray beam at a phase-shifting beam splitter grating. This problem, which is further aggravated by noise in the obtained DPCI images, occurs if the phase between two adjacent pixels in the detected X-ray image varies by more than π radians and is effected by a line integration over the object's local phase gradient, which induces a phase offset error of π radians that leads to prominent line artifacts parallel to the direction of said line integration.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
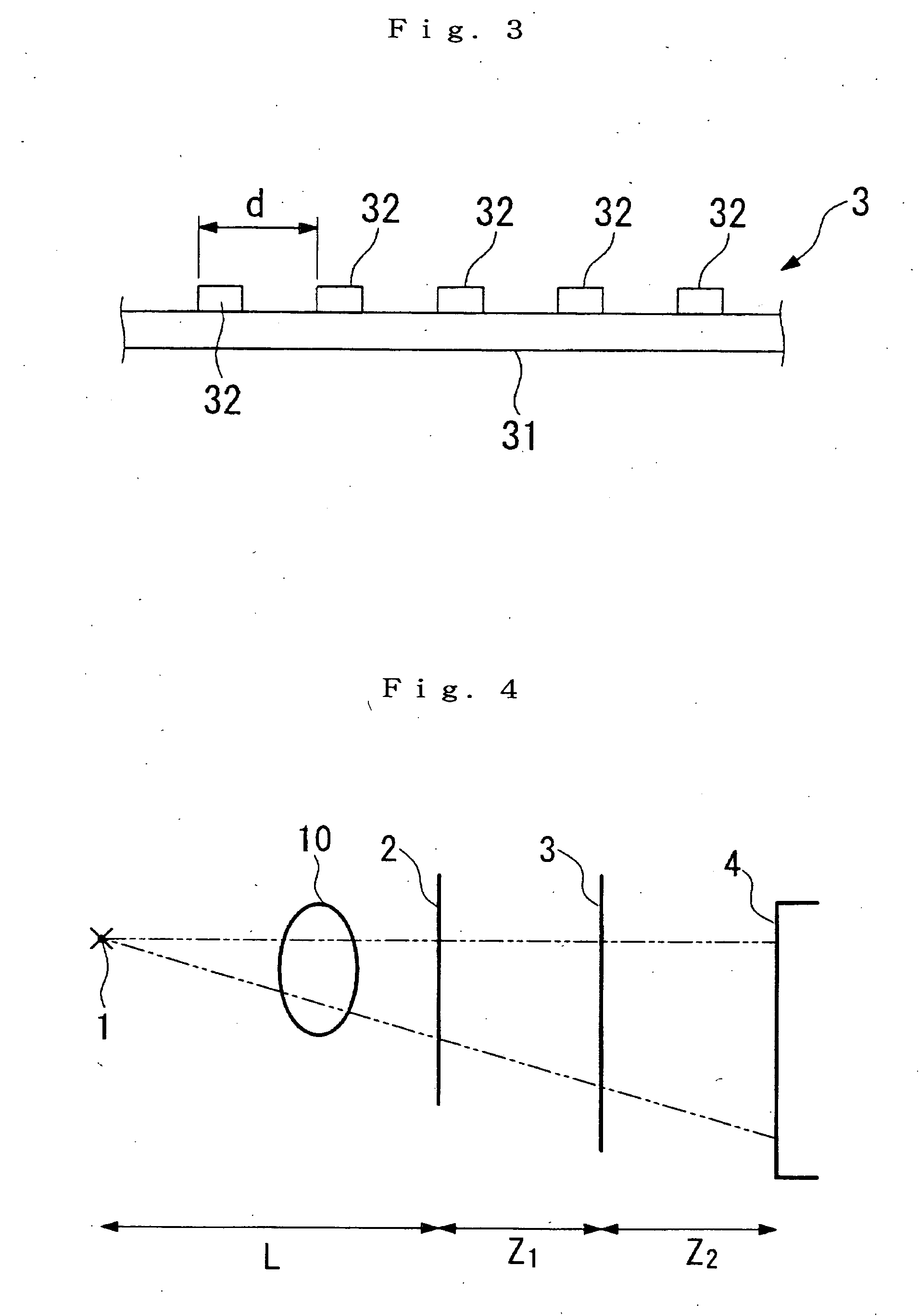
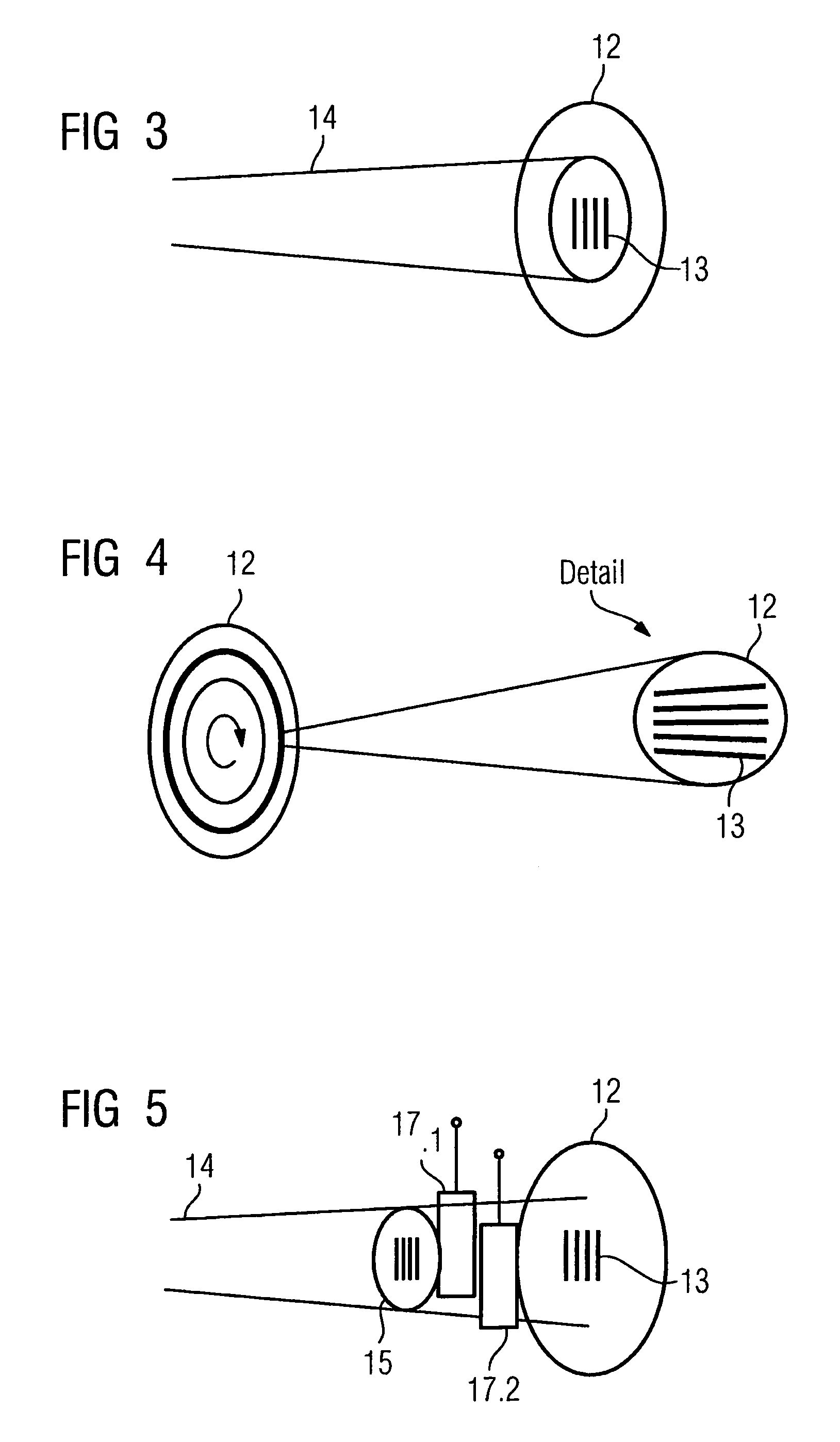
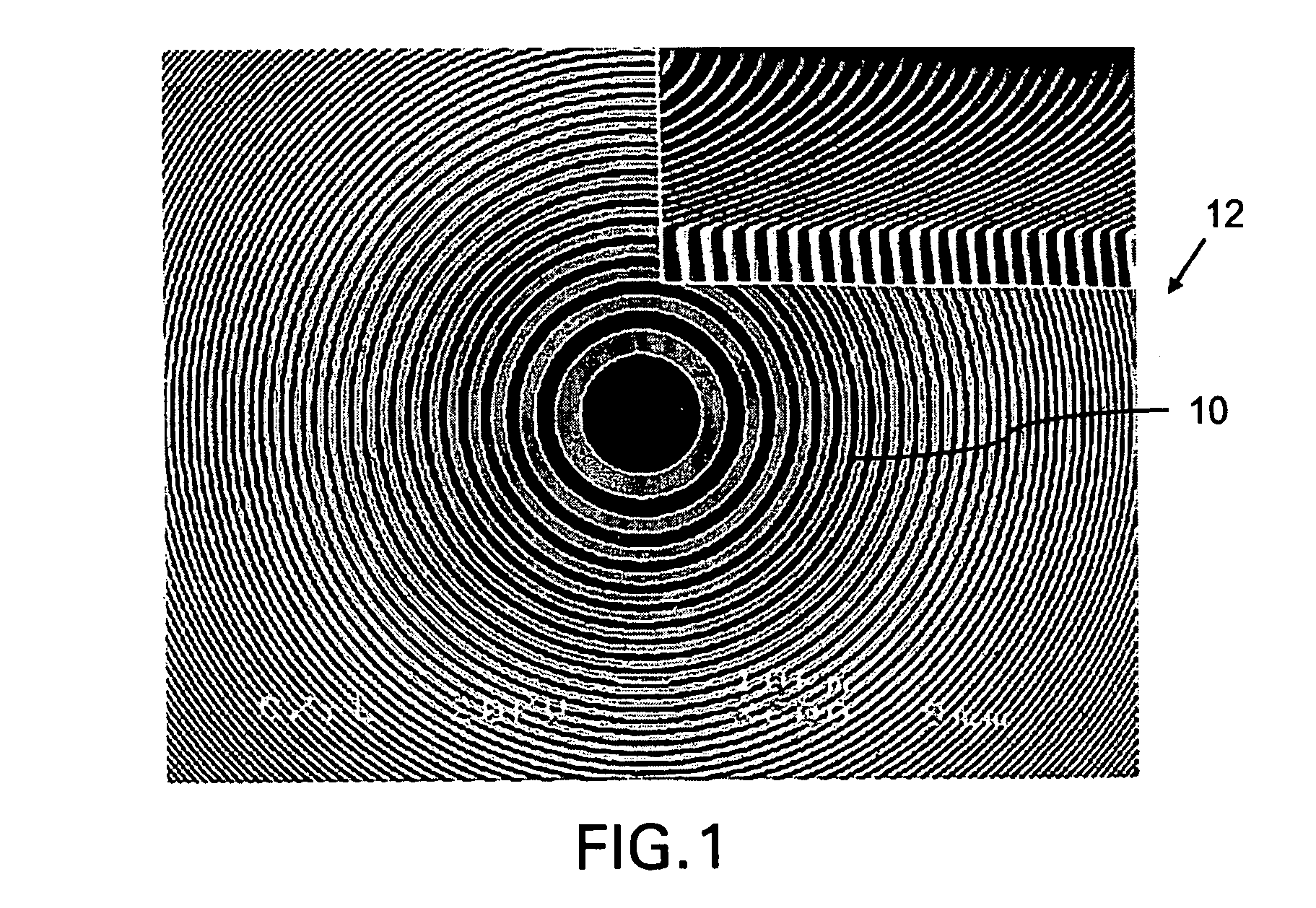
Diffraction grating and alignment method thereof, and radiation imaging system
InactiveUS20110243300A1Improve image qualityEasy to adjustImaging devicesHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionRadiation imagingX-ray
An X-ray imaging system includes first to third absorption gratings. Initially, the third absorption grating is disposed in a Z axis orthogonal to a detection surface of a FPD, and the position of the third absorption grating is adjusted in θx and θy directions based on a dose of X-rays having passed through the third absorption grating. Then, the first absorption grating is disposed in the Z axis so as to produce a moiré pattern. The position of the first absorption grating is adjusted in the θx and θy directions so that a frequency of the moiré pattern detected by the FPD becomes uniform. Then, the position of the first absorption grating is adjusted in a Z or θz direction so that the FPD loses the detection of the moiré pattern. After that, the second absorption grating is aligned in a like manner as the first absorption grating.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Correction method for differential phase contrast imaging
ActiveUS20120099702A1Good estimateImprove image qualityImaging devicesHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionHard X-raysBeam splitter
The present invention generally refers to a correction method for grating-based X-ray differential phase contrast imaging (DPCI) as well as to an apparatus which can advantageously be applied in X-ray radiography and tomography for hard X-ray DPCI of a sample object or an anatomical region of interest to be scanned. More precisely, the proposed invention provides a suitable approach that helps to enhance the image quality of an acquired X-ray image which is affected by phase wrapping, e.g. in the resulting Moiré interference pattern of an emitted X-ray beam in the detector plane of a Talbot-Lau type interferometer after diffracting said X-ray beam at a phase-shifting beam splitter grating. This problem, which is further aggravated by noise in the obtained DPCI images, occurs if the phase between two adjacent pixels in the detected X-ray image varies by more than π radians and is effected by a line integration over the object's local phase gradient, which induces a phase offset error of π radians that leads to prominent line artifacts parallel to the direction of said line integration.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
X-ray method for the measurement, characterization, and analysis of periodic structures
ActiveUS20150260663A1Lightweight productionIncrease brightnessImaging devicesX-ray tube electrodesSoft x rayGrating
Periodic spatial patterns of x-ray illumination are used to gather information about periodic objects. The structured illumination may be created using the interaction of a coherent or partially coherent x-ray source with a beam splitting grating to create a Talbot interference pattern with periodic structure. The object having periodic structures to be measured is then placed into the structured illumination, and the ensemble of signals from the multiple illumination spots is analyzed to determine various properties of the object and its structures. Applications to x-ray absorption / transmission, small angle x-ray scattering, x-ray fluorescence, x-ray reflectance, and x-ray diffraction are all possible using the method of the invention.
Owner:SIGRAY INC
X-ray CT system for x-ray phase contrast and/or x-ray dark field imaging
ActiveUS7983381B2Technical requirementPractical operationImaging devicesRadiation/particle handlingSoft x rayGrating interferometer
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH +1
X-ray CT system to generate tomographic phase contrast or dark field exposures
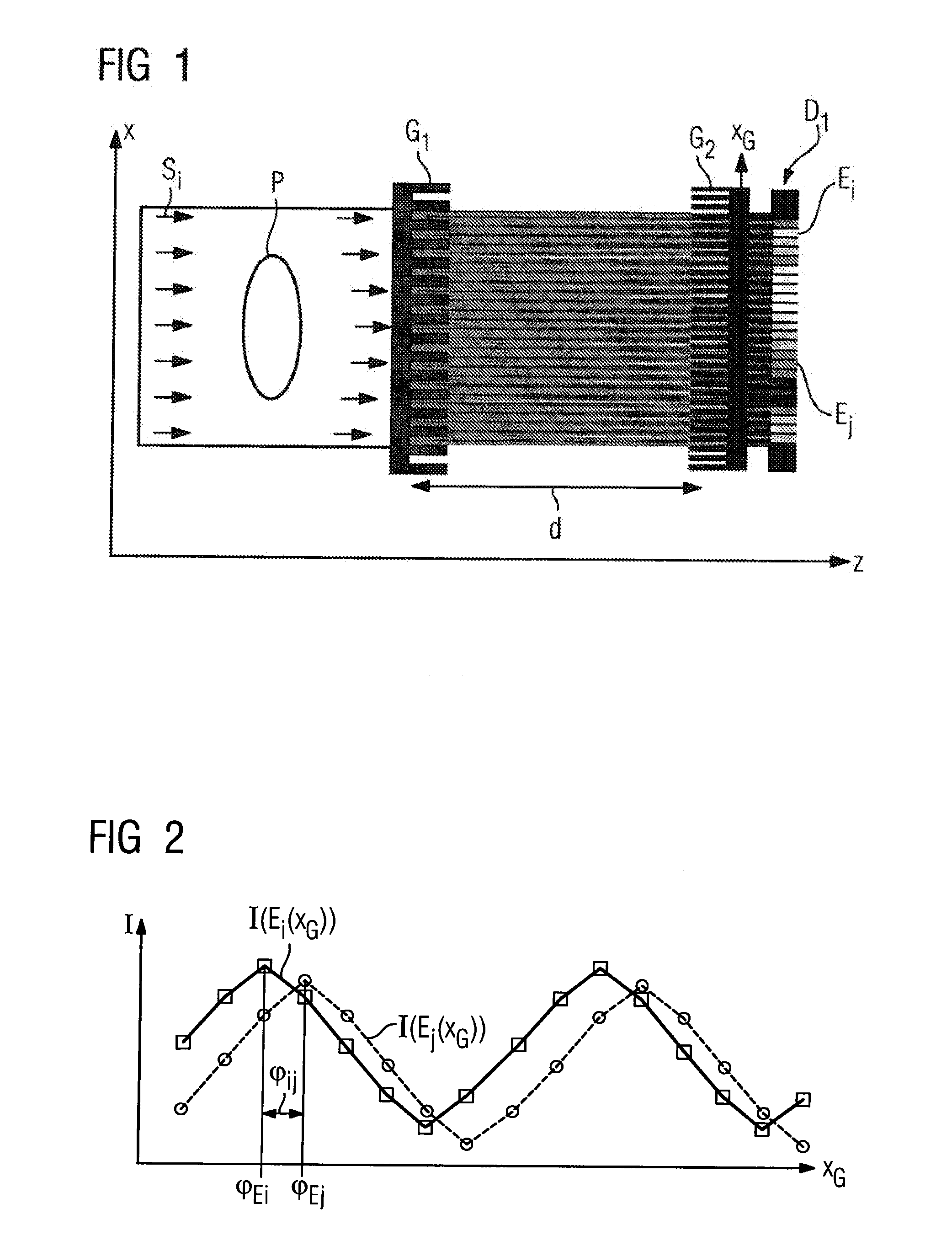
InactiveUS8009796B2Easy to measureImprove measurement resultsImaging devicesMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationGrating interferometerPhase grating
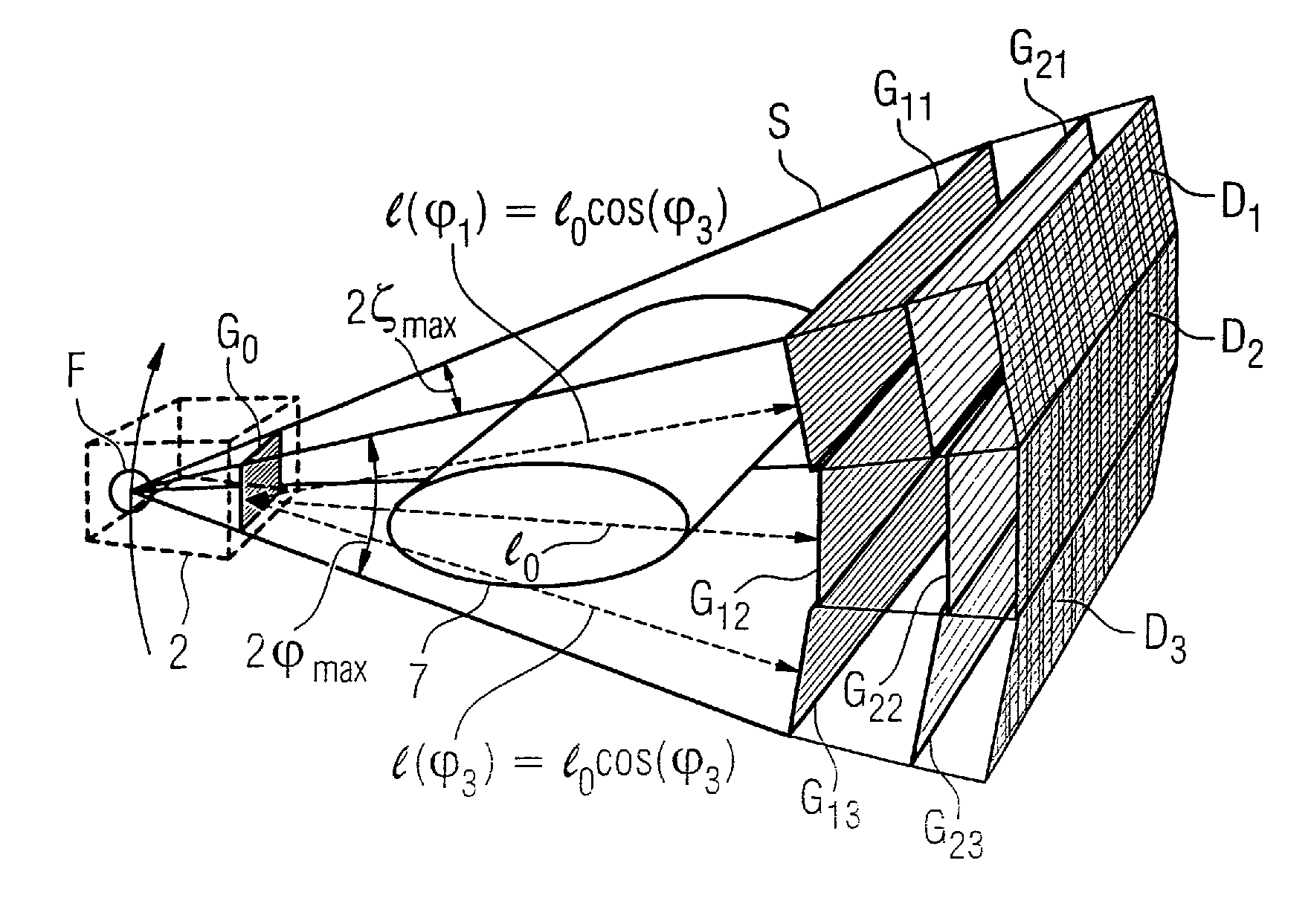
An x-ray CT system that generates tomographic phase contrast or dark field exposures, has at least one grating interferometer with three grating structures arranged in series in the radiation direction, with a modular design of the second and third grating structures. The distance between the first grating structure of the x-ray source and the second grating structure (fashioned as a phase grating) of the respective grating / detector modules is adapted, depending on the fan angle, corresponding to a period of the grating structure of the x-ray source projected onto the grating detector module at a respective fan angle (φi).
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH +1
X-ray interferometric imaging system
ActiveUS9719947B2Lightweight productionIncrease brightnessImaging devicesX-ray tube electrodesSoft x rayGrating
Owner:SIGRAY INC
Differential Interference Phase Contrast X-ray Imaging System
InactiveUS20100091947A1Photon energy is highWide emission angleImaging devicesX-ray tube electrodesPhotoconductive detectorHigh energy
A differential phase-contrast X-ray imaging system is provided. Along the direction of X-ray propagation, the basic components are X-ray tube, filter, object platform, X-ray phase grating, and X-ray detector. The system provides: 1) X-ray beam from parallel-arranged source array with good coherence, high energy, and wider angles of divergence with 30-50 degree. 2) The novel X-ray detector adopted in present invention plays dual roles of conventional analyzer grating and conventional detector. The basic structure of the detector includes a set of parallel-arranged linear array X-ray scintillator screens, optical coupling system, an area array detector or parallel-arranged linear array X-ray photoconductive detector. In this case, relative parameters for scintillator screens or photoconductive detector correspond to phase grating and parallel-arranged line source array, which can provide the coherent X-rays with high energy.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Focus detector arrangement and method for generating contrast x-ray images
ActiveUS20090154640A1Improved dose utilizationRaise the ratioImaging devicesRadiation/particle handlingSoft x rayX-ray
In a focus detector arrangement and method for an x-ray apparatus for generating projection or tomographic phase-contrast images of an examination subject, a beam of coherent x-rays is generated by an anode that has areas of different radiation emission characteristics arranged in bands thereon, that proceed parallel to grid lines of a phase grid that is used to generate the phase-contrast images.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
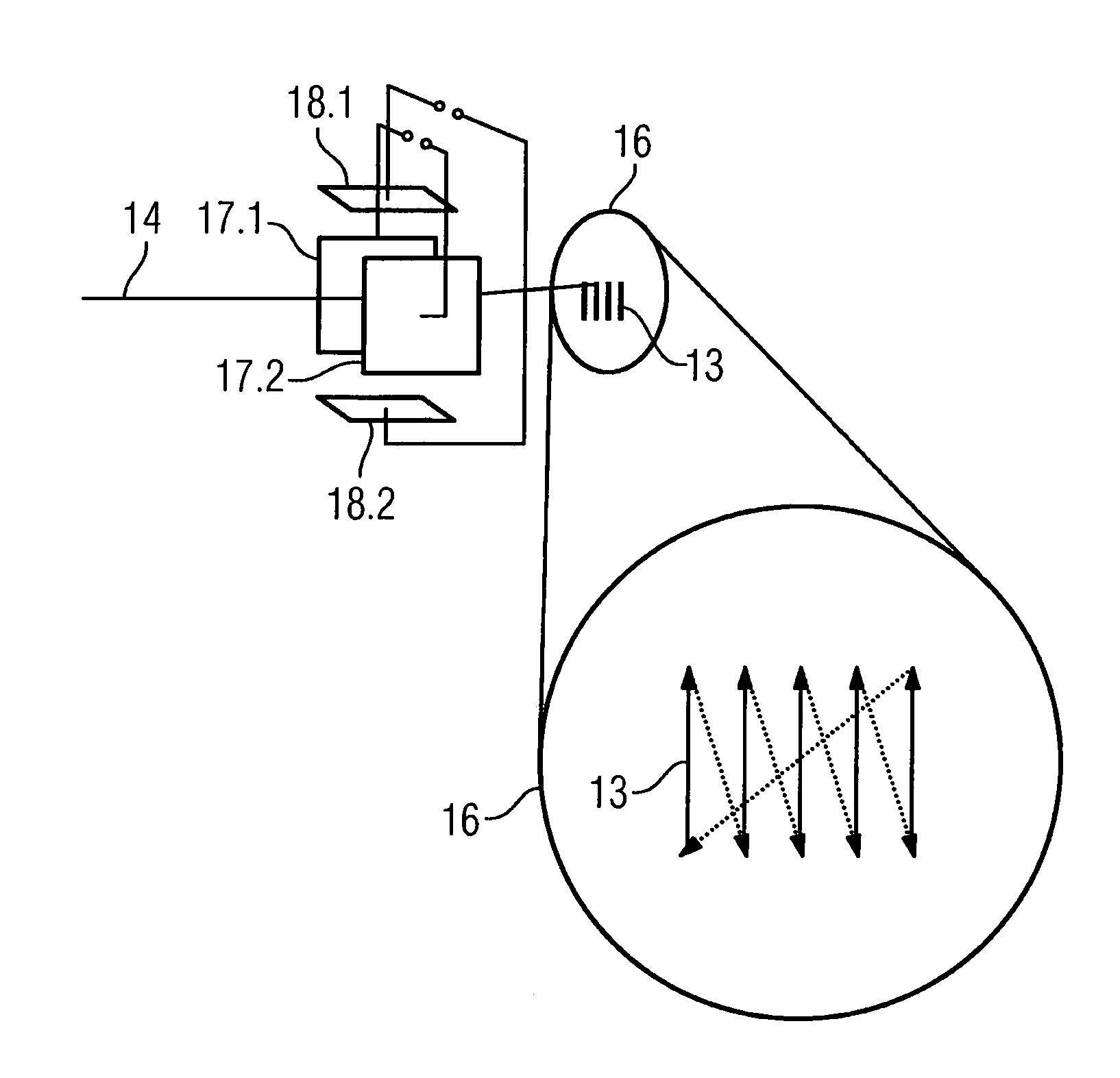
Radiation imaging system and method
InactiveUS20110243302A1Eliminate the effects ofEnhance the imageImaging devicesRadiation/particle handlingGratingAbsorption contrast
A radiation imaging system includes an X-ray source, first and second absorption gratins disposed in a path of X-rays emitted from the X-ray source, and an FPD. The second absorption grating is stepwise slid in an X direction relatively against the first absorption grating. Whenever the second absorption grating is slid, the FPD captures a fringe image and produces image data. A correction section corrects the image data for spatial variation of X-ray transmittance of the first and second absorption gratings. A phase contrast image generator produces a phase contrast image from the corrected image data. An X-ray absorption contrast image generator calculates a value related to an average of the corrected image data on a pixel-by-pixel basis, and produces an X-ray absorption contrast image from the value.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
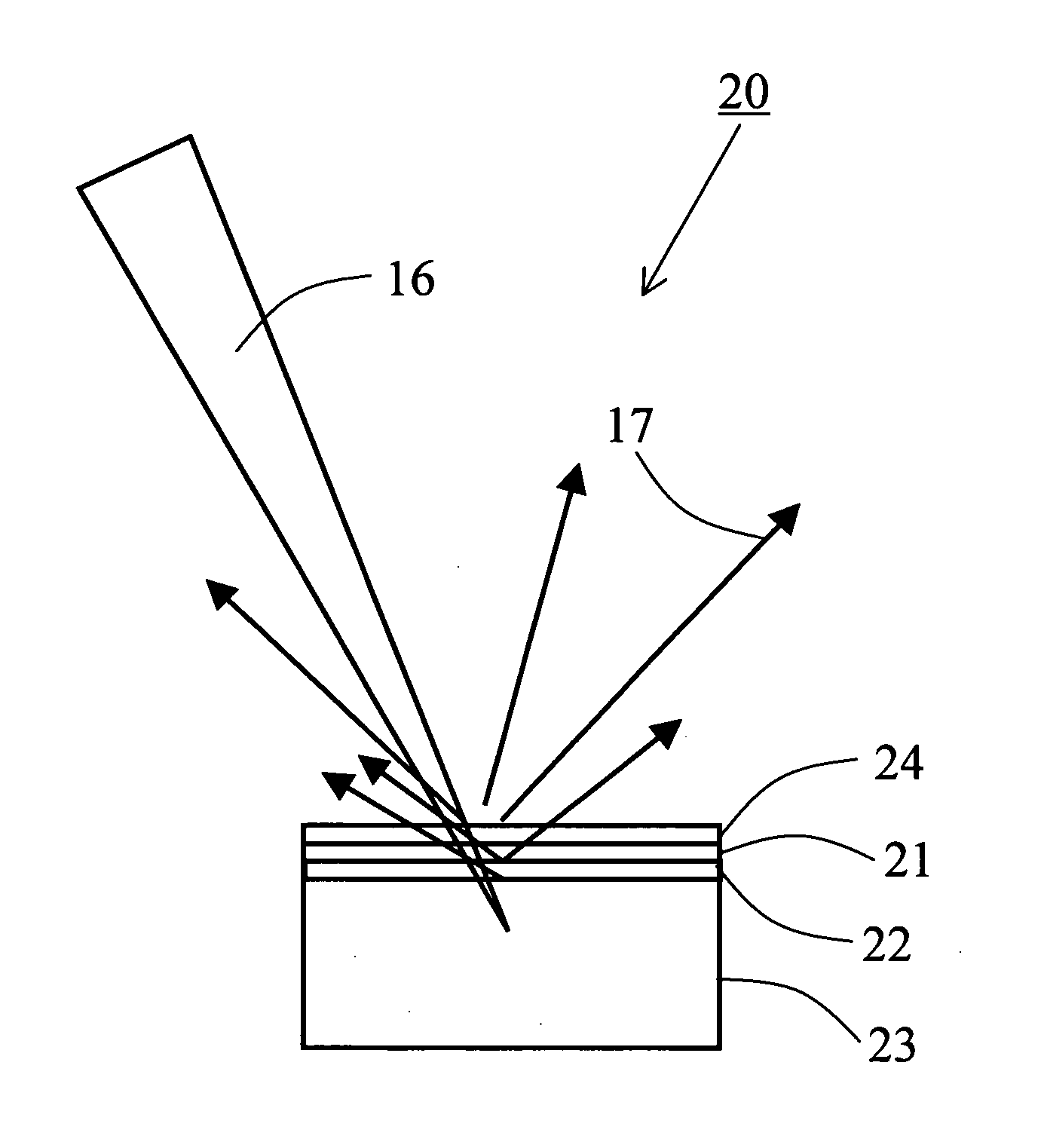
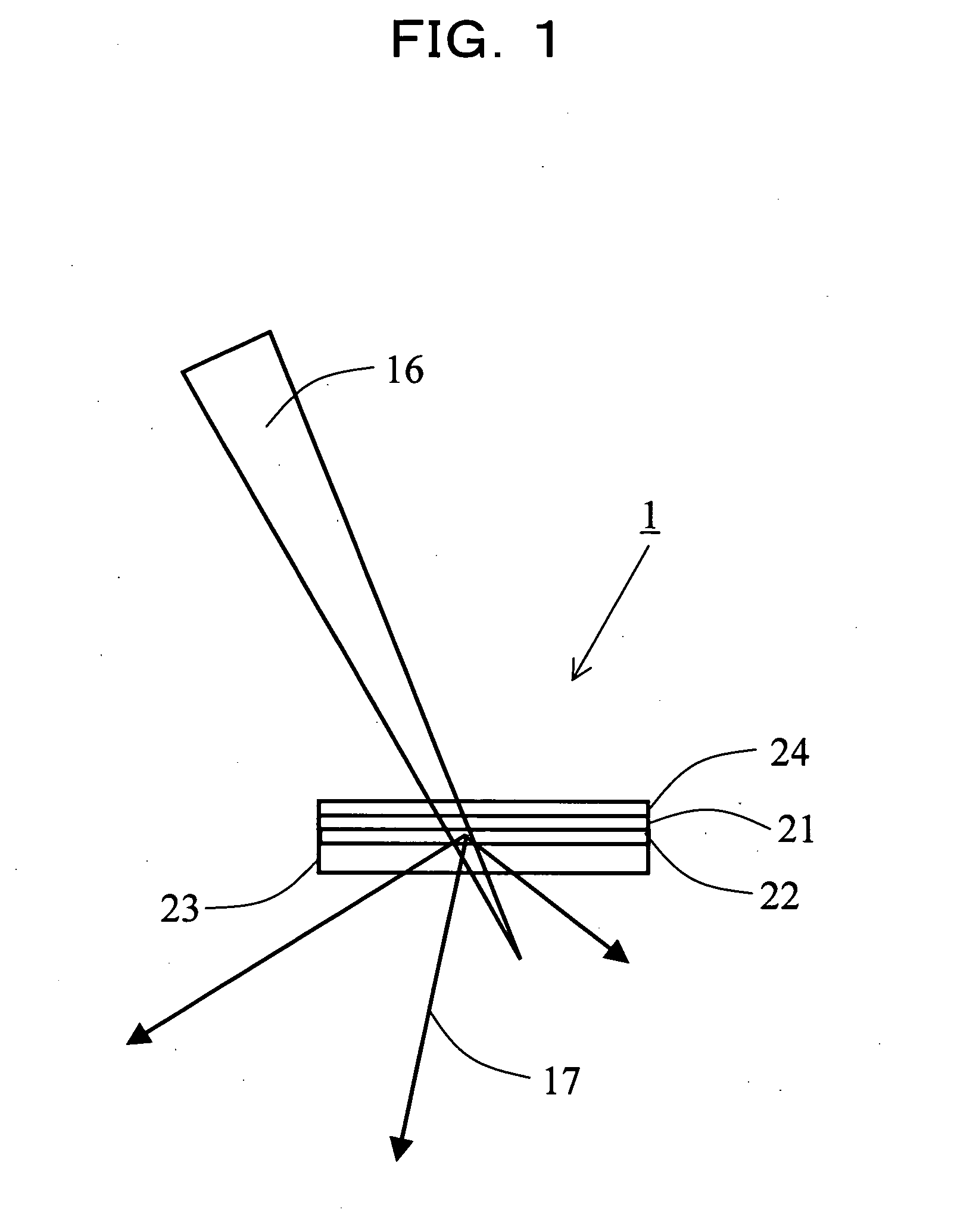
X-Ray Target and Apparatuses Using the Same
InactiveUS20070248215A1Highly convenientElectron beam absorptivityX-ray tube laminated targetsImaging devicesFluorescenceHigh intensity
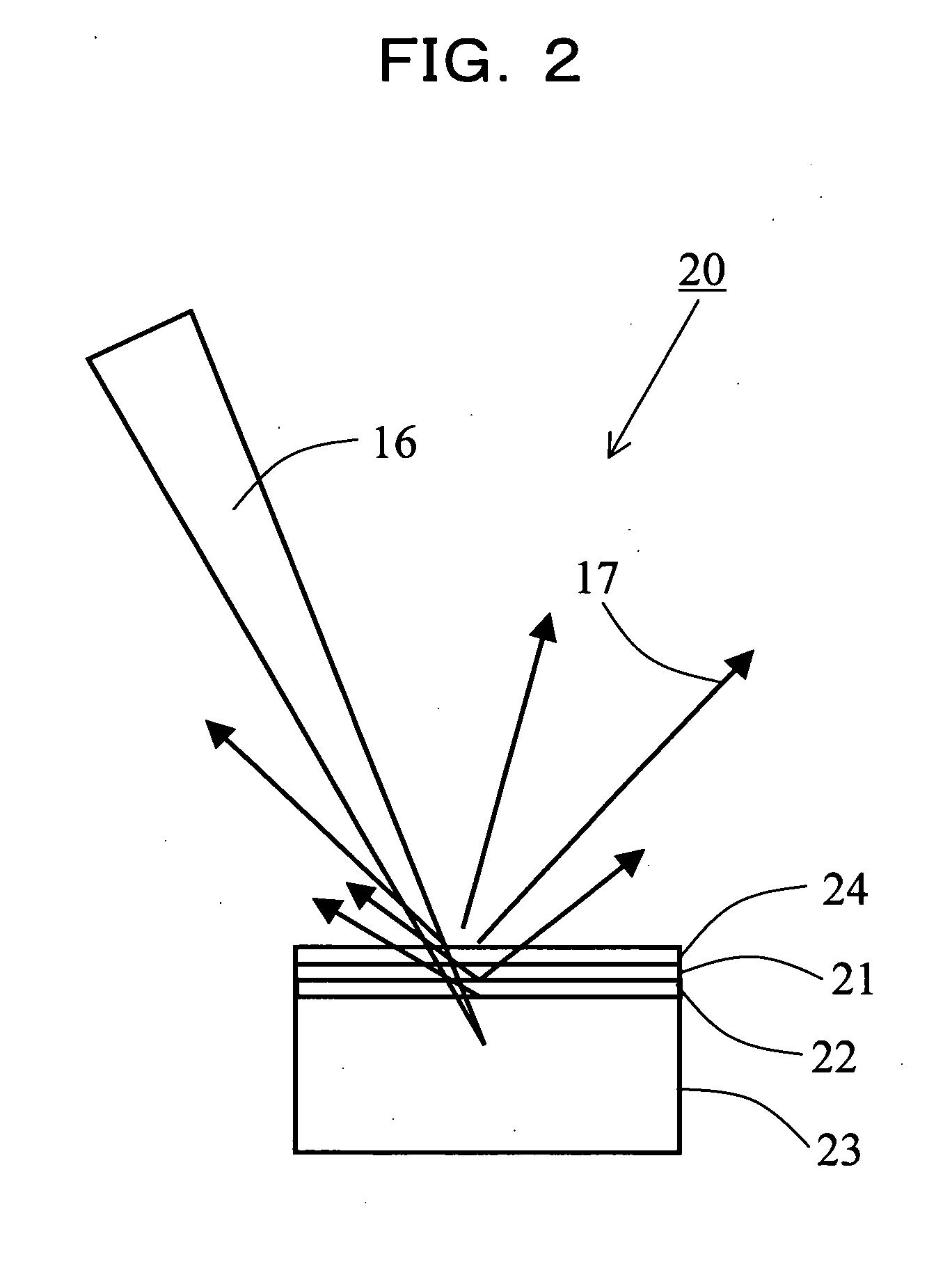
Disclosed are an X-ray target having a micro focus size and capable of producing X-rays of high intensity, and apparatuses using such an X-ray target. The X-ray target (1) has a structure in which a first cap layer (21), a target layer (22), and a second cap layer (23) are successively laminated, wherein the first and second cap layers (21and 23) are each composed of a material which is lower in electron beam absorptivity than that of which the target layer (22) is composed. An X-ray generator using the X-ray target (1) can generate highly intense and nanofocus (several nm) X-rays (17). Using the X-ray generator, an X-ray microscope allows obtaining a high resolution transmission image, an X-ray diffraction apparatus allows obtaining an X-ray diffraction image of a very small area, and a fluorescent X-ray analysis apparatus allows making the fluorescent X-ray analysis of a minute area.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
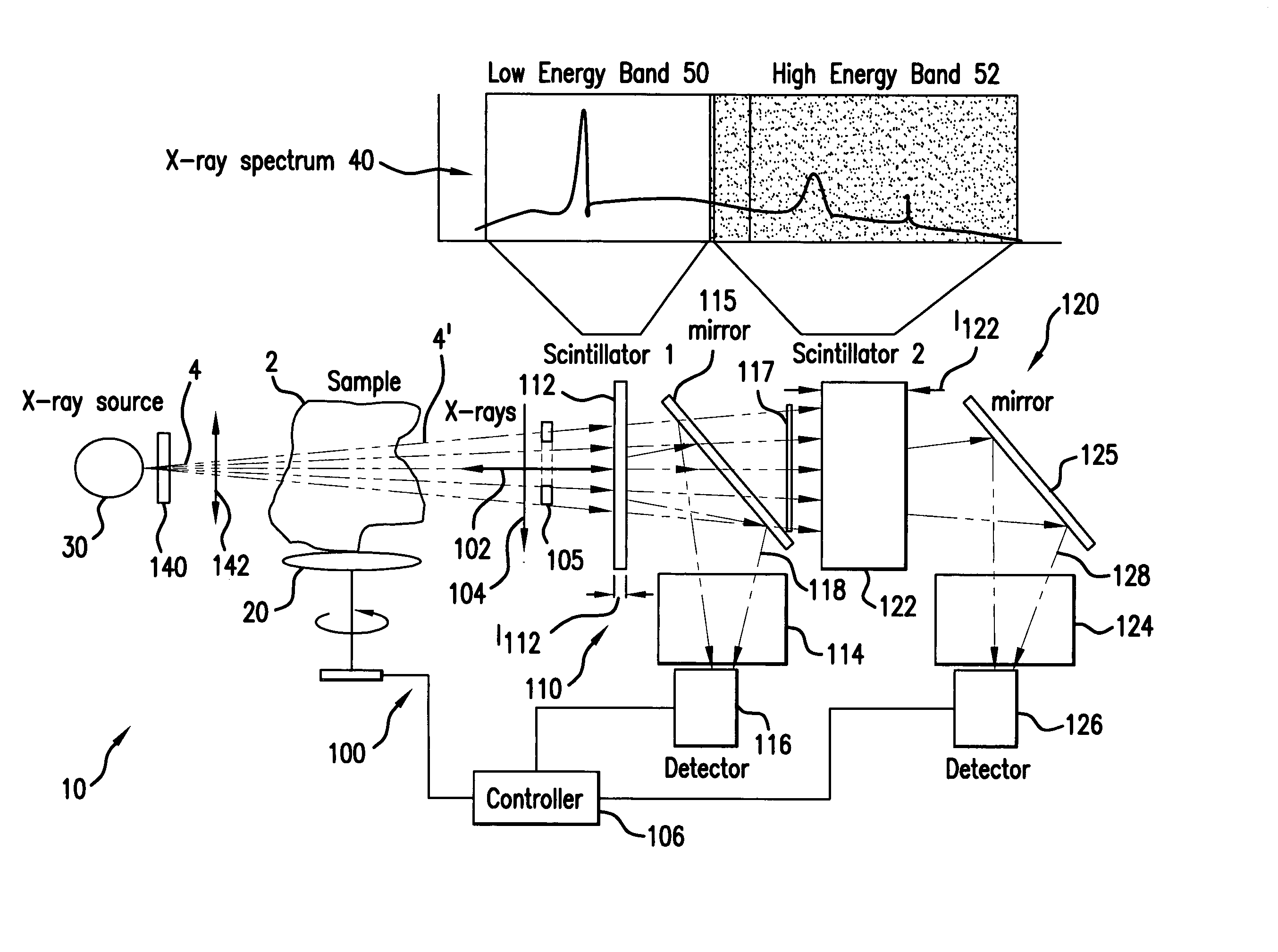
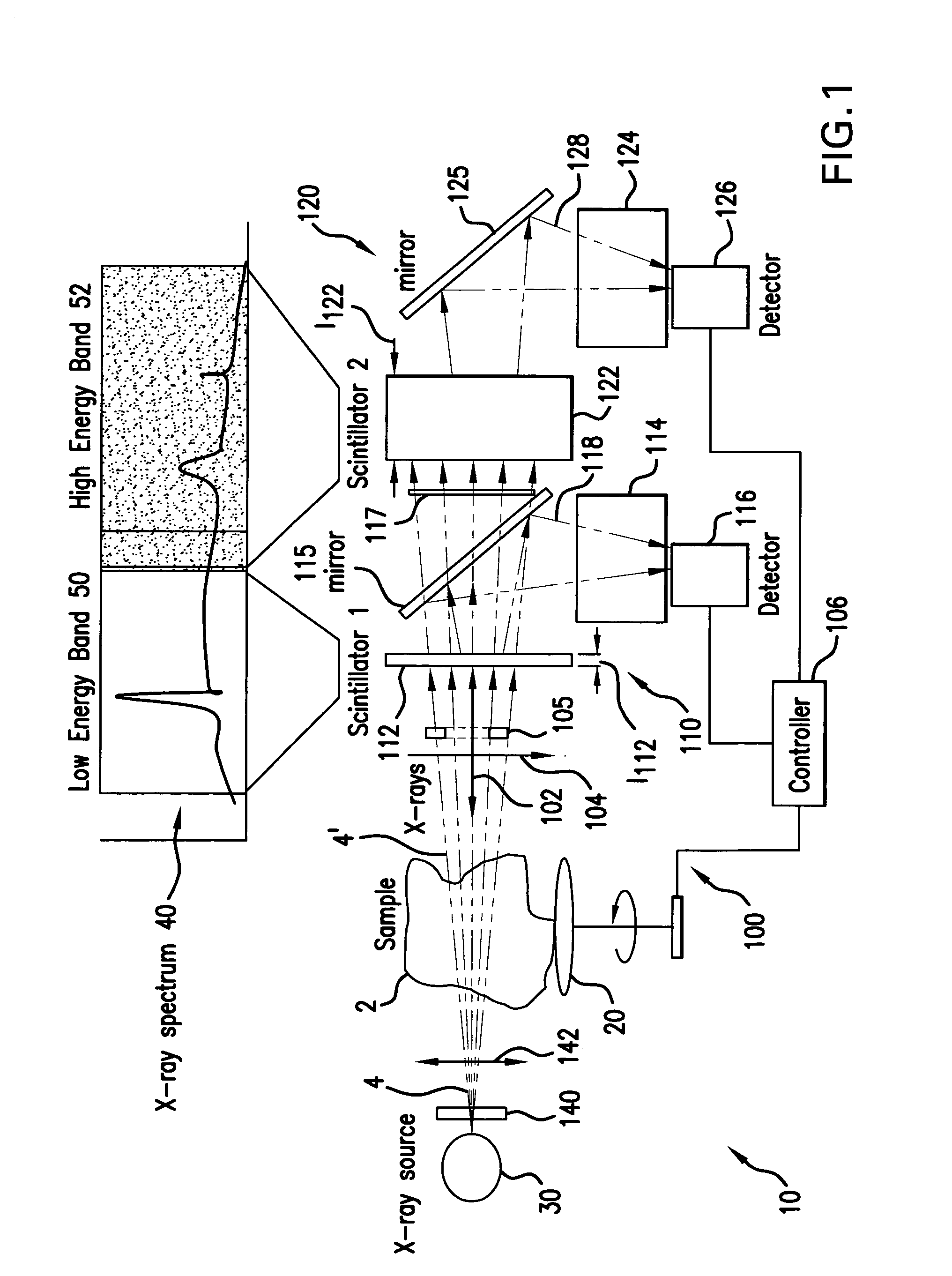
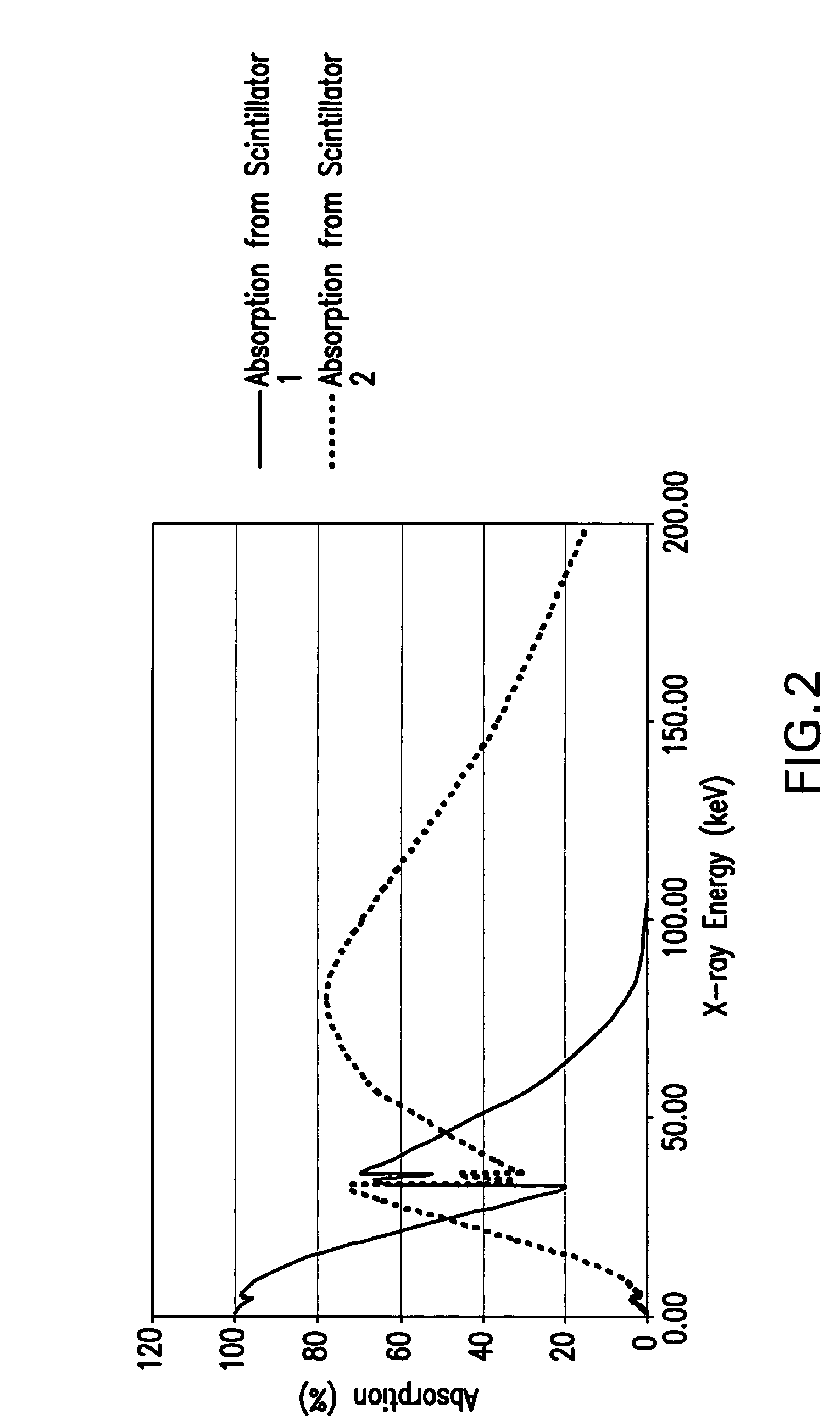
Dual-band detector system for x-ray imaging of biological samples
ActiveUS7286640B2Ease of evaluationFacilitate implementation and deploymentImaging devicesSolid-state devicesImage resolutionImage contrast
A digital dual-band detector functions as an imaging platform capable of extracting hard and soft tissue images, for example. The detector has a first detector system comprising a first scintillator for converting x-rays from a sample to an first optical signal, and a first detector for detecting the first optical signal in combination with a second detector system comprising a second scintillator for converting x-rays from the sample and passing through the first scintillator to a second optical signal, and a second detector for detecting the second optical signal. The detector can facilitate the implementation and deployment of recent developments and can permit low cost practical deployment in clinical applications as well as biomedical research applications where significant improvement in spatial resolution and image contrast is required.
Owner:CARL ZEISS X RAY MICROSCOPY
Diffraction grating and alignment method thereof, and radiation imaging system
InactiveUS8755487B2Easy to adjustImprove image qualityImaging devicesX-ray spectral distribution measurementRadiation imagingX-ray
An X-ray imaging system includes first to third absorption gratings. Initially, the third absorption grating is disposed in a Z axis orthogonal to a detection surface of a FPD, and the position of the third absorption grating is adjusted in θx and θy directions based on a dose of X-rays having passed through the third absorption grating. Then, the first absorption grating is disposed in the Z axis so as to produce a moiré pattern. The position of the first absorption grating is adjusted in the θx and θy directions so that a frequency of the moiré pattern detected by the FPD becomes uniform. Then, the position of the first absorption grating is adjusted in a Z or θz direction so that the FPD loses the detection of the moiré pattern. After that, the second absorption grating is aligned in a like manner as the first absorption grating.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
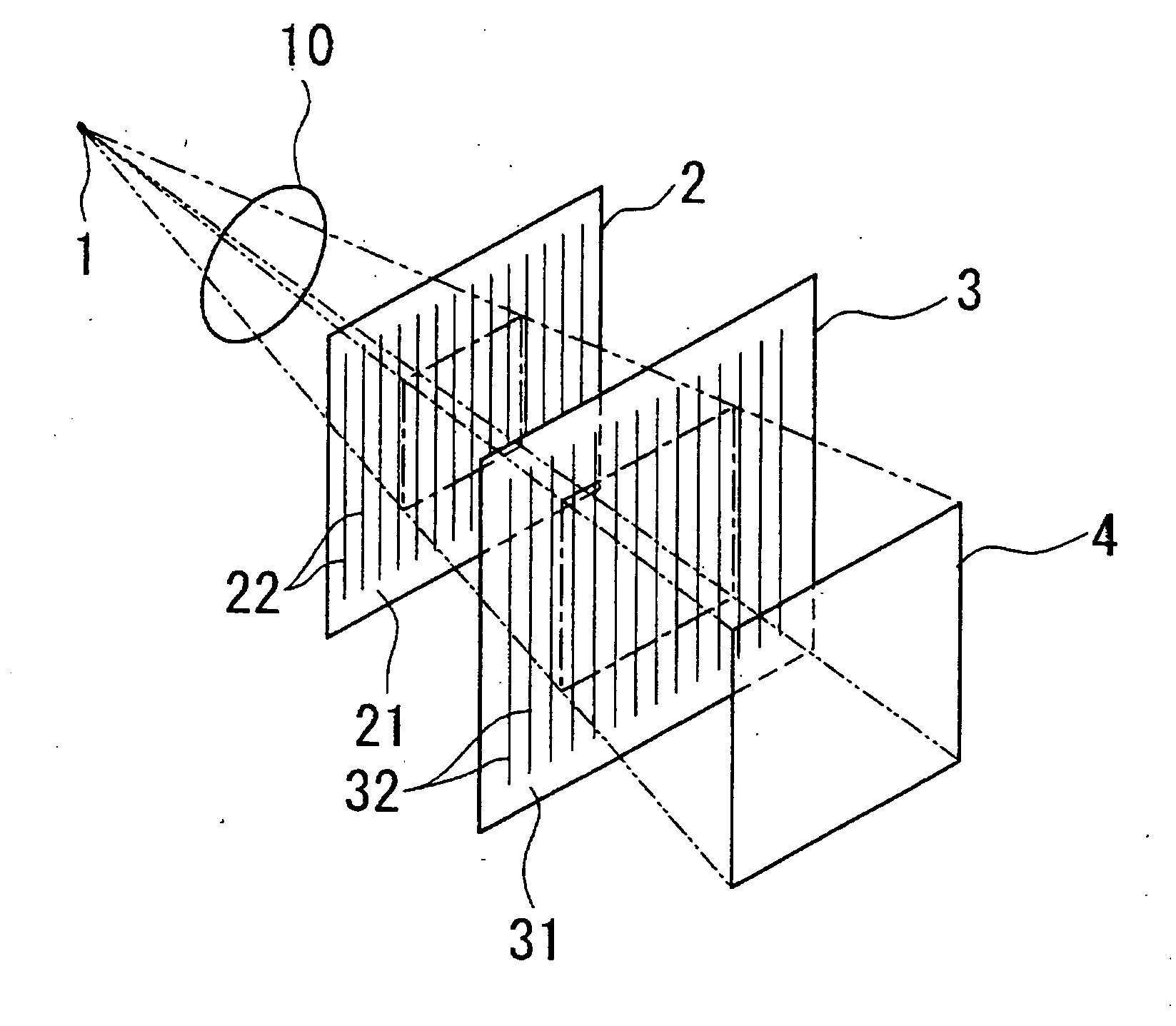
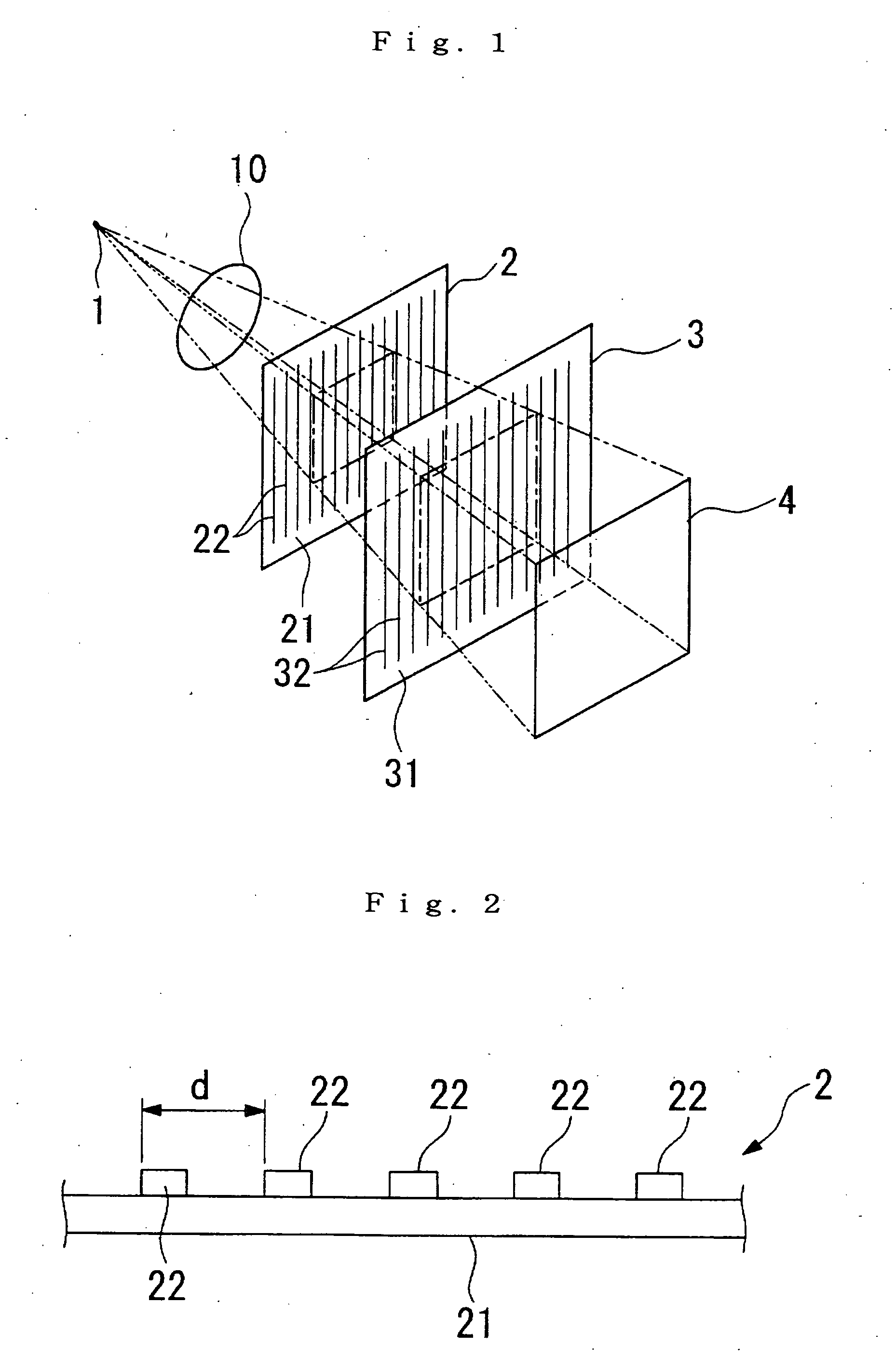
Source grating for talbot-lau-type interferometer
InactiveUS20100260315A1High X-ray transmittanceSufficient quantityImaging devicesX-ray spectral distribution measurementGratingX-ray
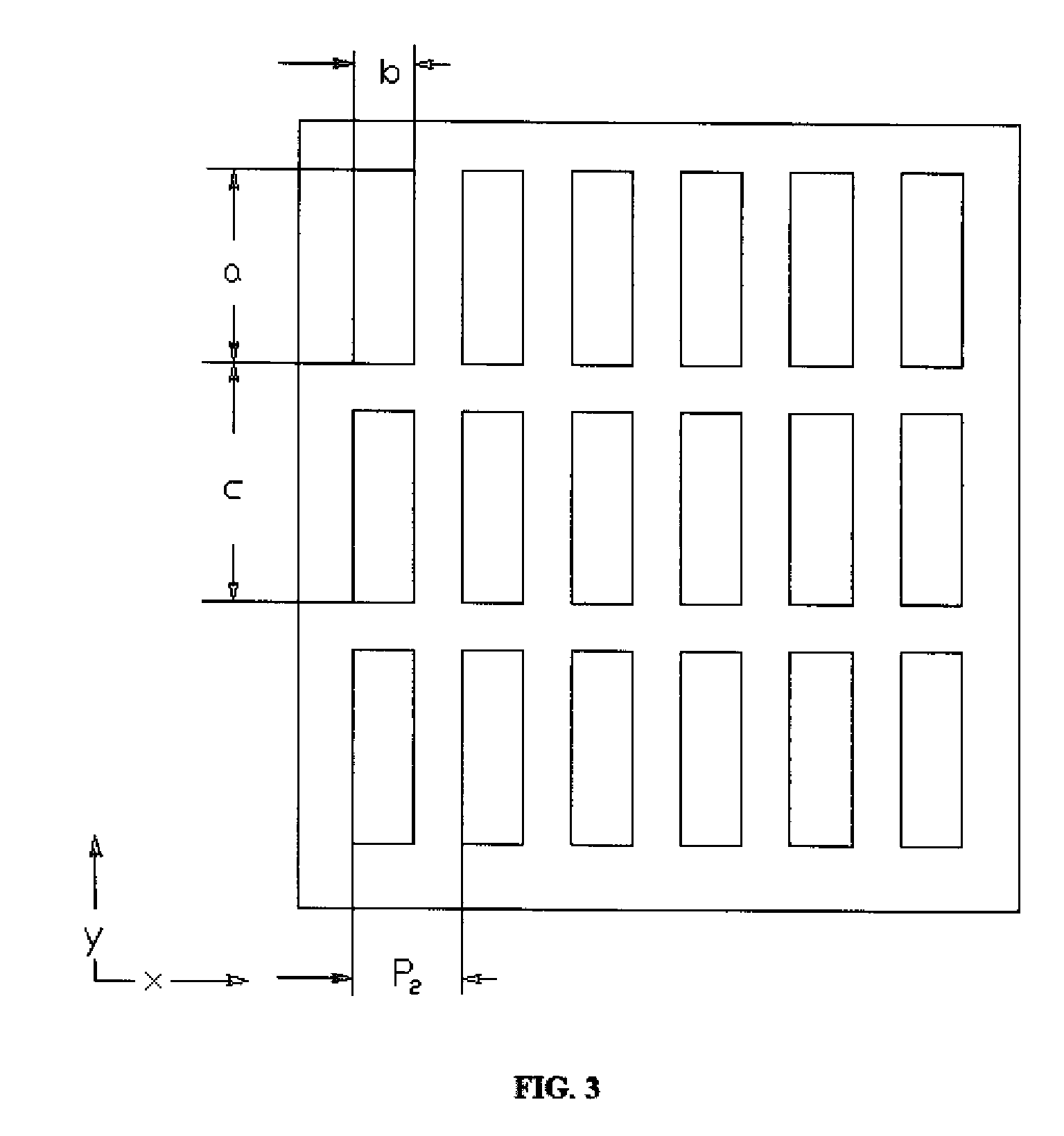
A source grating for a Talbot-Lau-type interferometer includes a plurality of channels having incident apertures provided on a side irradiated with X-rays and exit apertures provided on an opposite side of the side irradiated with the X-rays; the exit apertures of the channels have an aperture area smaller than an aperture area of the incident apertures; and the exit apertures of the channels are arranged so that interference fringes of Talbot self-images formed by X-rays exiting from the exit apertures of the adjacent channels are aligned with each other.
Owner:CANON KK
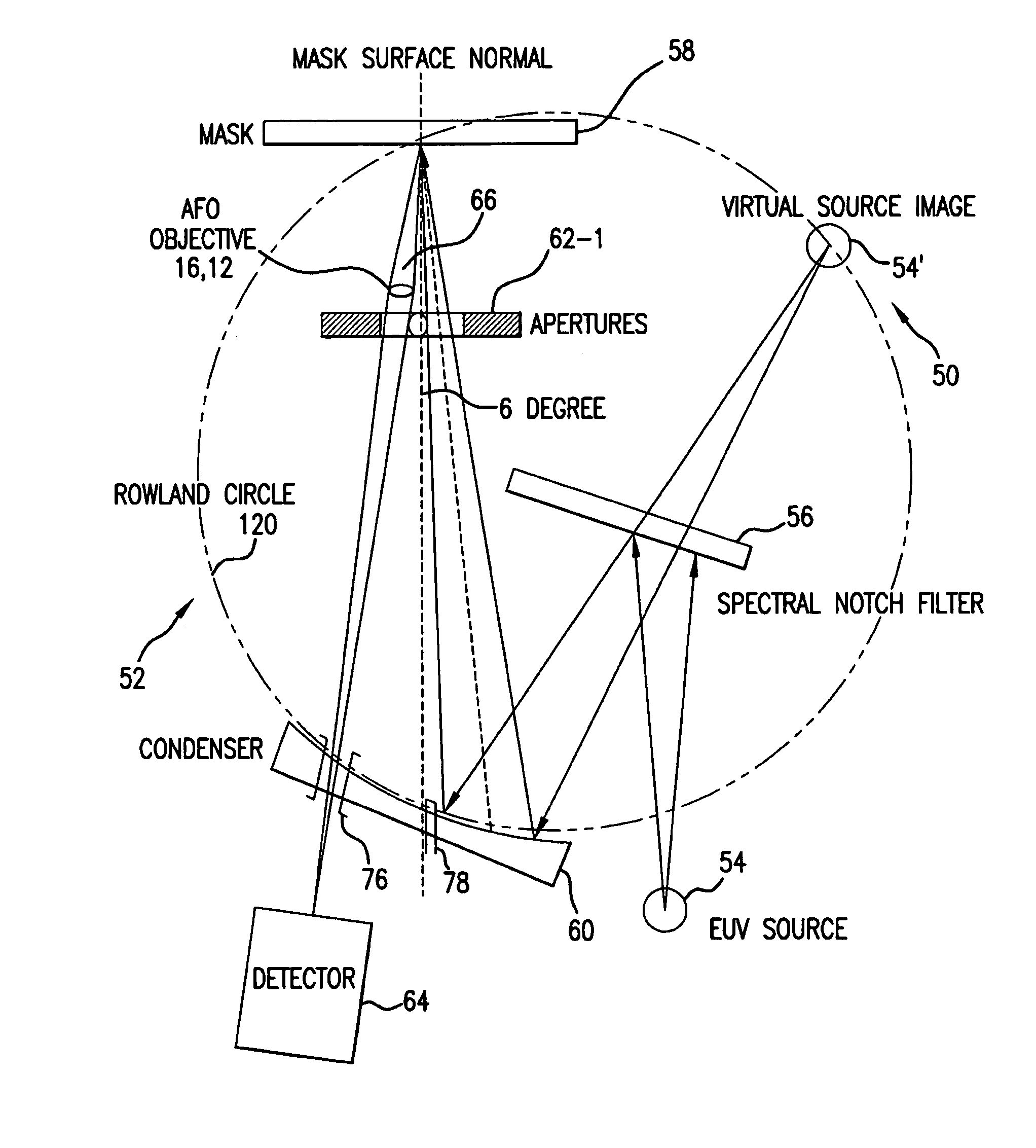
Short wavelength metrology imaging system
ActiveUS7268945B2Easy to implementEasy to switchImaging devicesNanoinformaticsHigh resolution imagingSystems design
An extreme ultraviolet (EUV) AIM tool for both the EUV actinic lithography and high-resolution imaging or inspection is described. This tool can be extended to lithography nodes beyond the 32 nanometer (nm) node covering other short wavelength radiation such as soft X-rays. The metrology tool is preferably based on an imaging optic referred to as an Achromatic Fresnel Optic (AFO). The AFO is a transmissive optic that includes a diffractive Fresnel zone plate lens component and a dispersion-correcting refractive lens component. It retains all of the imaging properties of a Fresnel zone plate lens, including a demonstrated resolution capability of better than 25 nanometers and freedom from image distortion. It overcomes the chromatic aberration of the Fresnel zone plate lens and has a larger usable spectral bandwidth. These optical properties and optical system designs enable the development of the AFO-based AIM tool with improved performance that has advantages compared with an AIM tool based on multilayer reflective mirror optics in both performance and cost.
Owner:CARL ZEISS X RAY MICROSCOPY
Differential phase contrast x-ray imaging system and components
A differential phase contrast X-ray imaging system includes an X-ray illumination system, a beam splitter arranged in an optical path of the X-ray illumination system, and a detection system arranged in an optical path to detect X-rays after passing through the beam splitter.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Rotational X ray device for phase contrast imaging
InactiveUS8565371B2Reduce lossesImaging devicesMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSoft x rayPhase grating
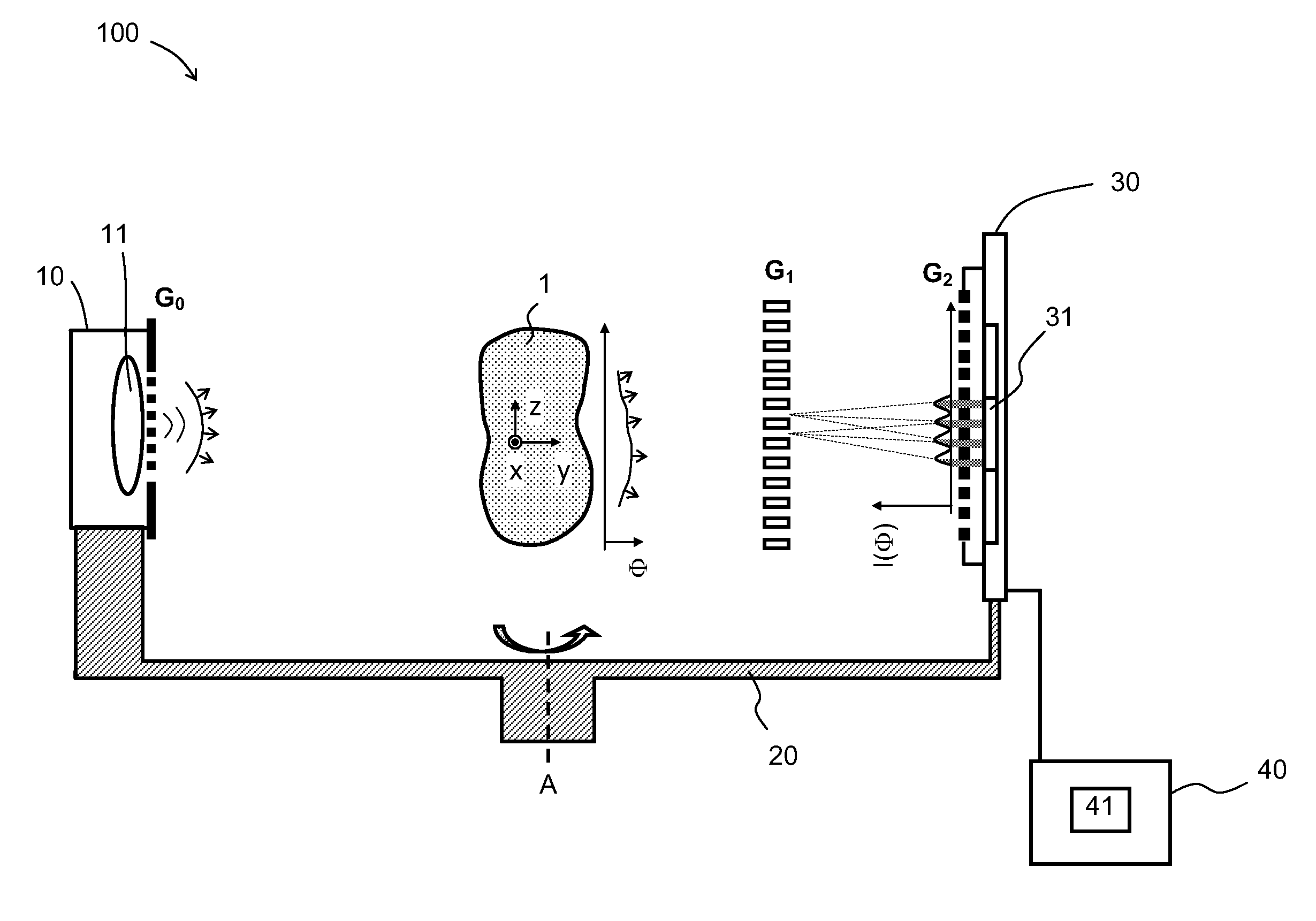
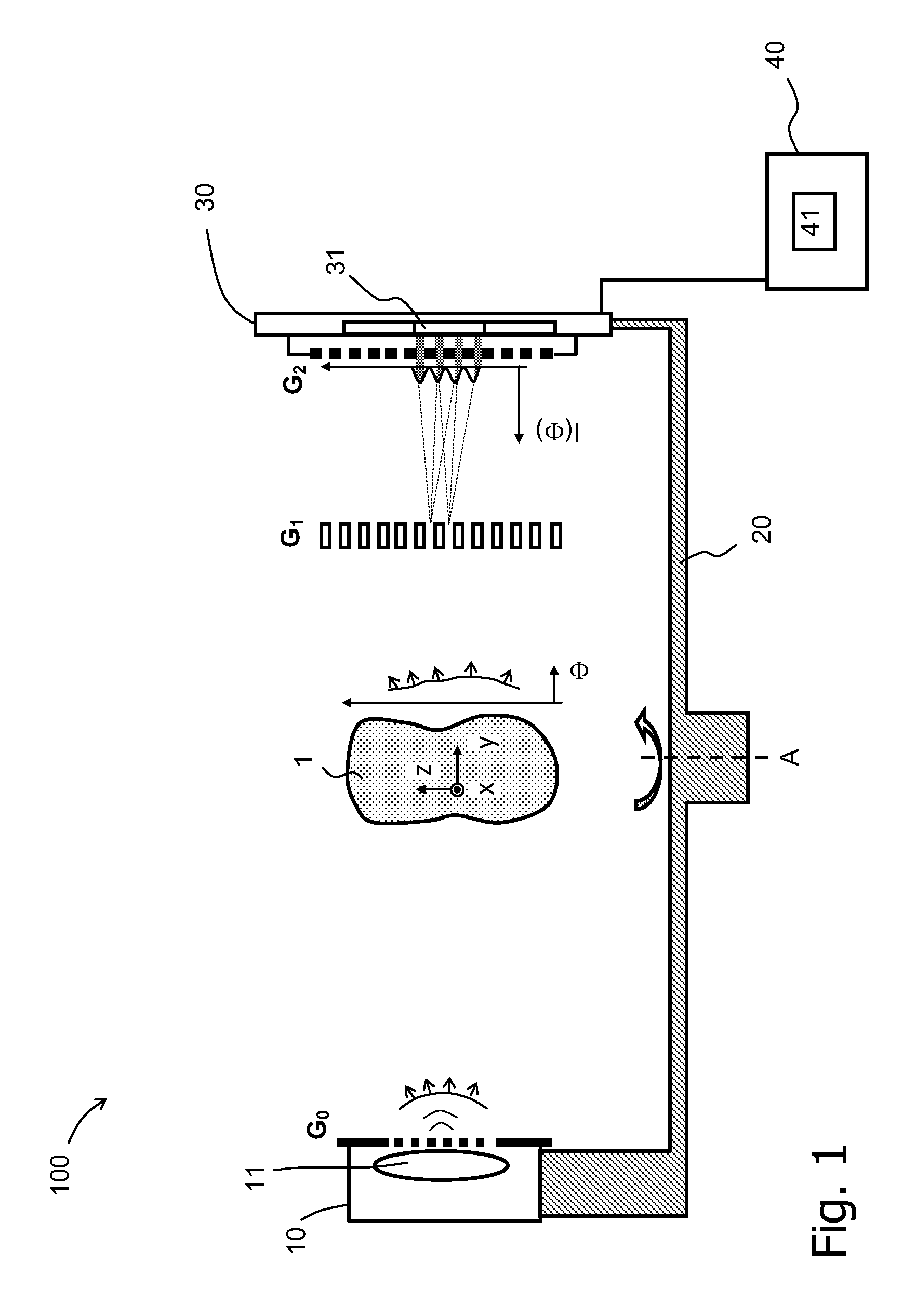
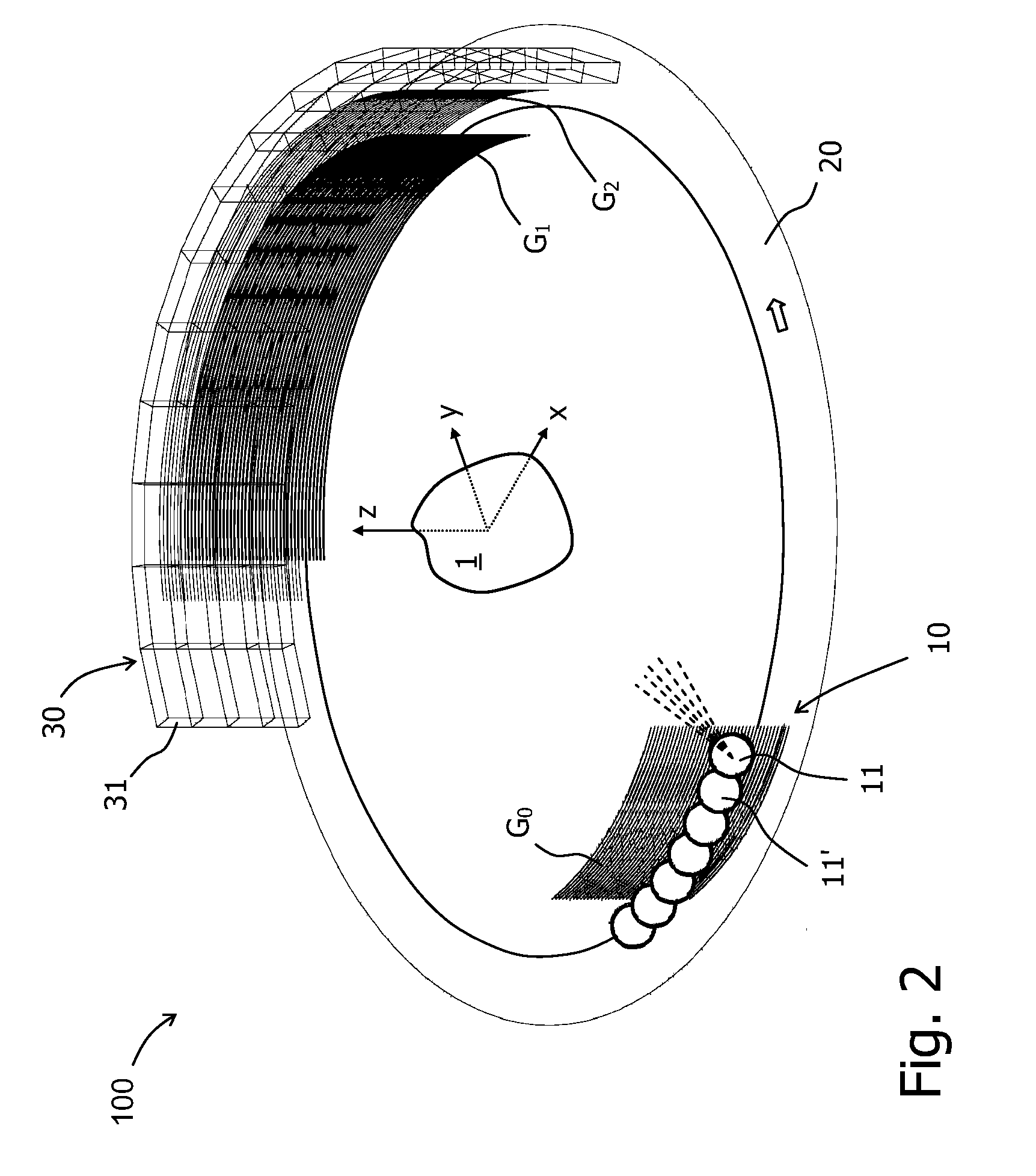
The invention relates to a rotational X-ray device (100), for example a CT scanner, for generating phase contrast images of an object (1). In a particular embodiment of the device (100), a plurality of X-ray sources (11), an X-ray detector (30), and an analyzer grating (G2) are attached to a rotatable gantry (20), while a ring-shaped phase grating (G1) is stationary. The X-ray sources are disposed such that X-rays first pass an object under study before traversing the phase grating (G1) and subsequently the analyzer grating (G2). This is achieved by either shifting the X-ray sources axially with respect to the ring-shaped phase grating (G1) or by disposing the X-ray sources in the interior of the ring. Moreover, the phase grating (G1) and the analyzer (G2) shall have spatially varying relative phase (and / or periodicity), for example realized by line grids that are tilted with respect to each other. During the rotation of the gantry (20), the synchronized activation of X-ray sources (11) allows to generate projection images of an object (1) from the same viewing angle with different relative positions (and therefore phases) between the phase grating (G1) and the analyzer (G2).
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Radiation image detector and phase contrast radiation imaging apparatus
InactiveUS20090110144A1Simple structureEasy to manufactureImaging devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansElectricityFluence
A phase contrast radiation imaging apparatus is includes a radiation source, a diffraction grating, and a radiation image detector. The radiation image detector is equipped with a charge generating layer that generates electric charges when irradiated with radiation, and charge collecting electrodes that collect the electric charges. The charge collecting electrodes are linear electrode groups, constituted by linear electrodes which are arranged at a constant period and are electrically connected to each other, provided to have different phases from each other. Thereby, use of a conventional amplitude diffraction grating is obviated.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com