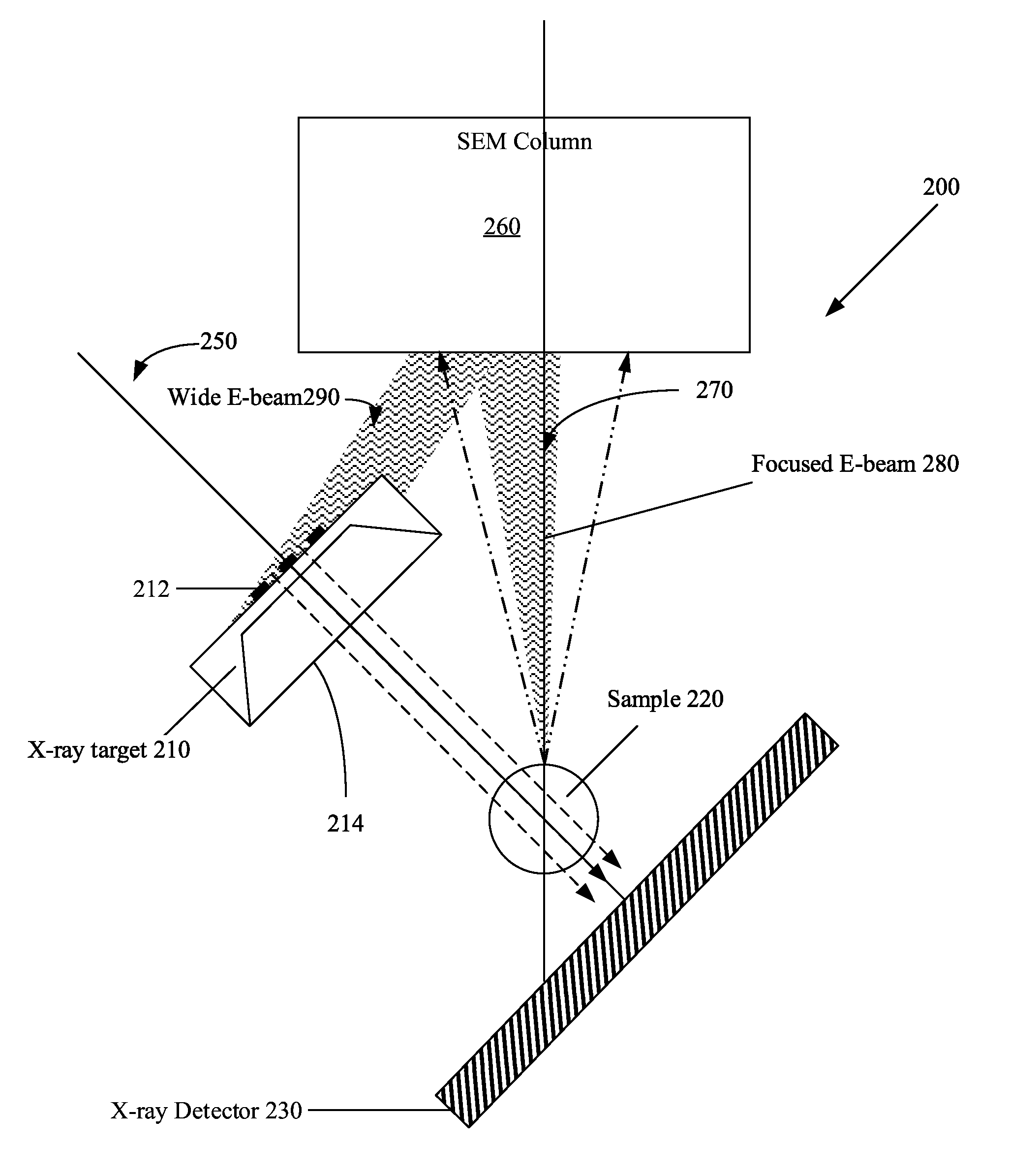
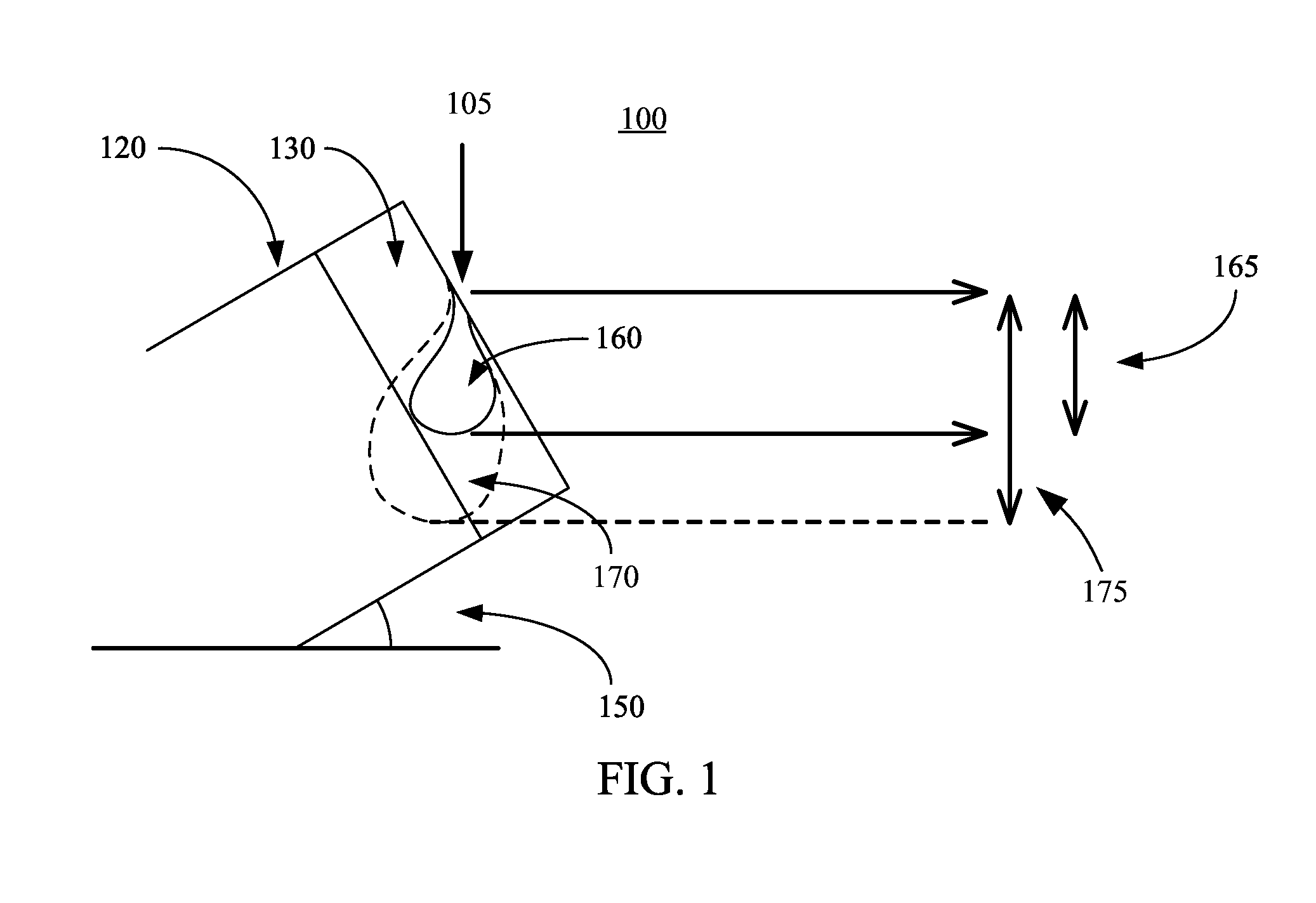
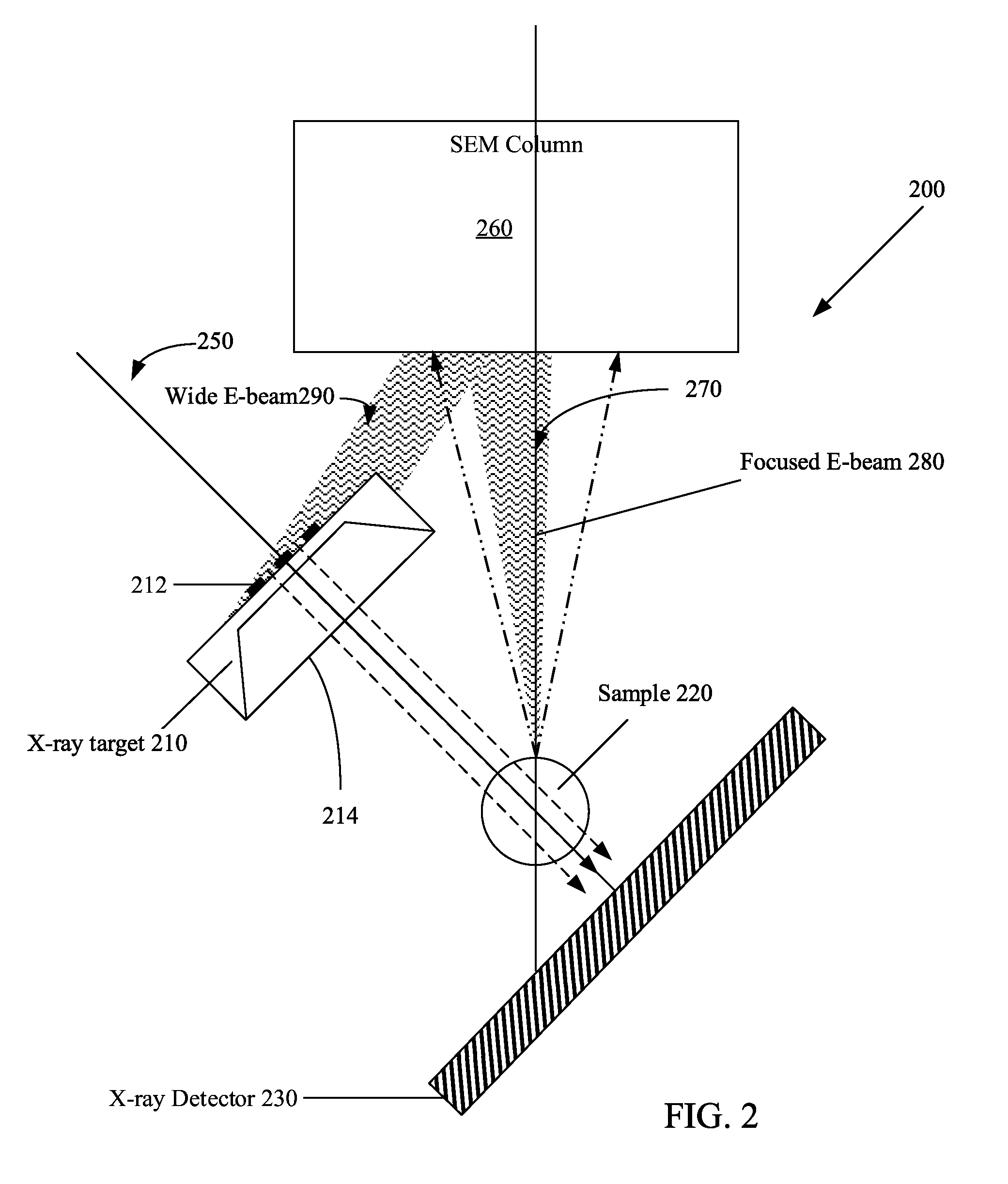
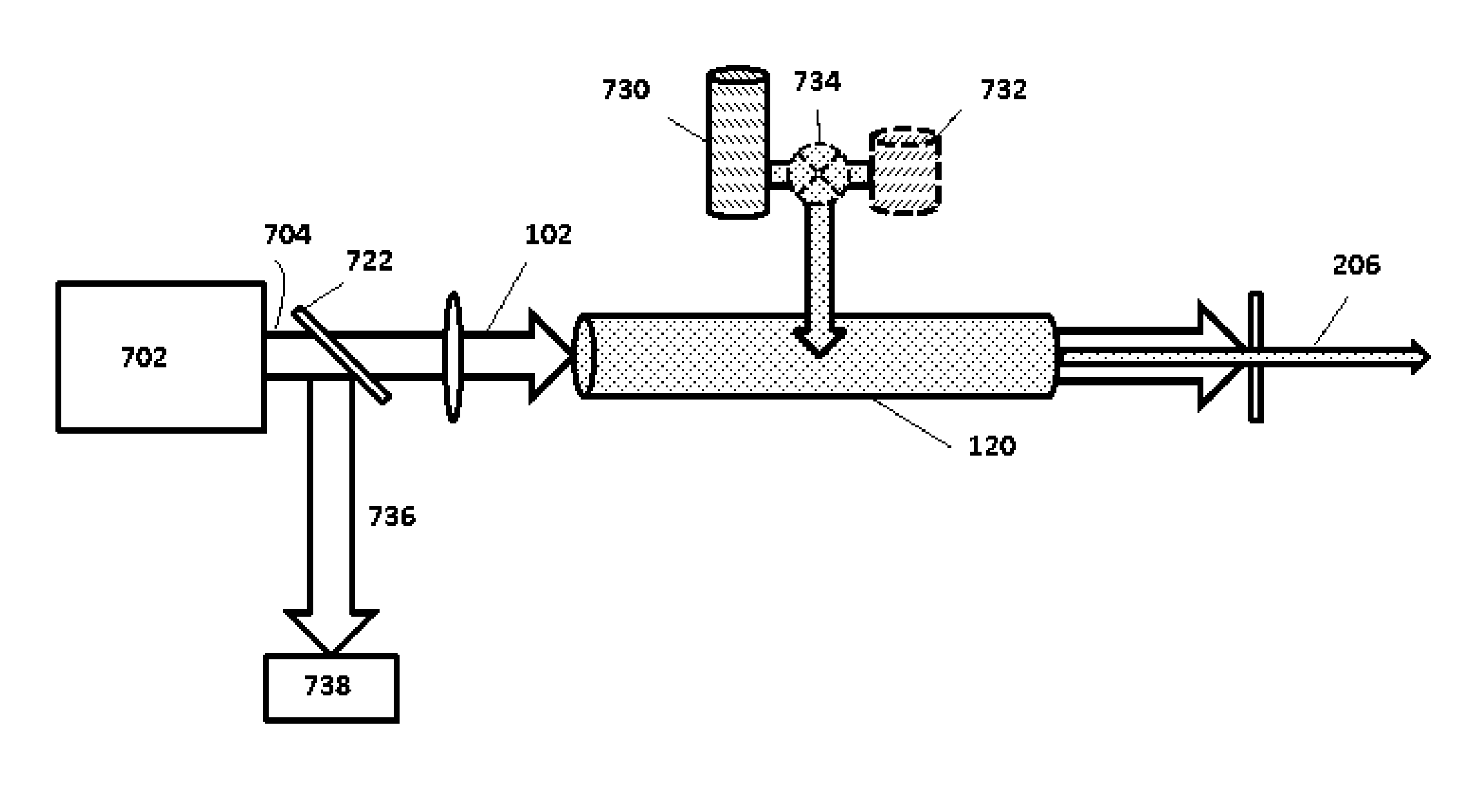
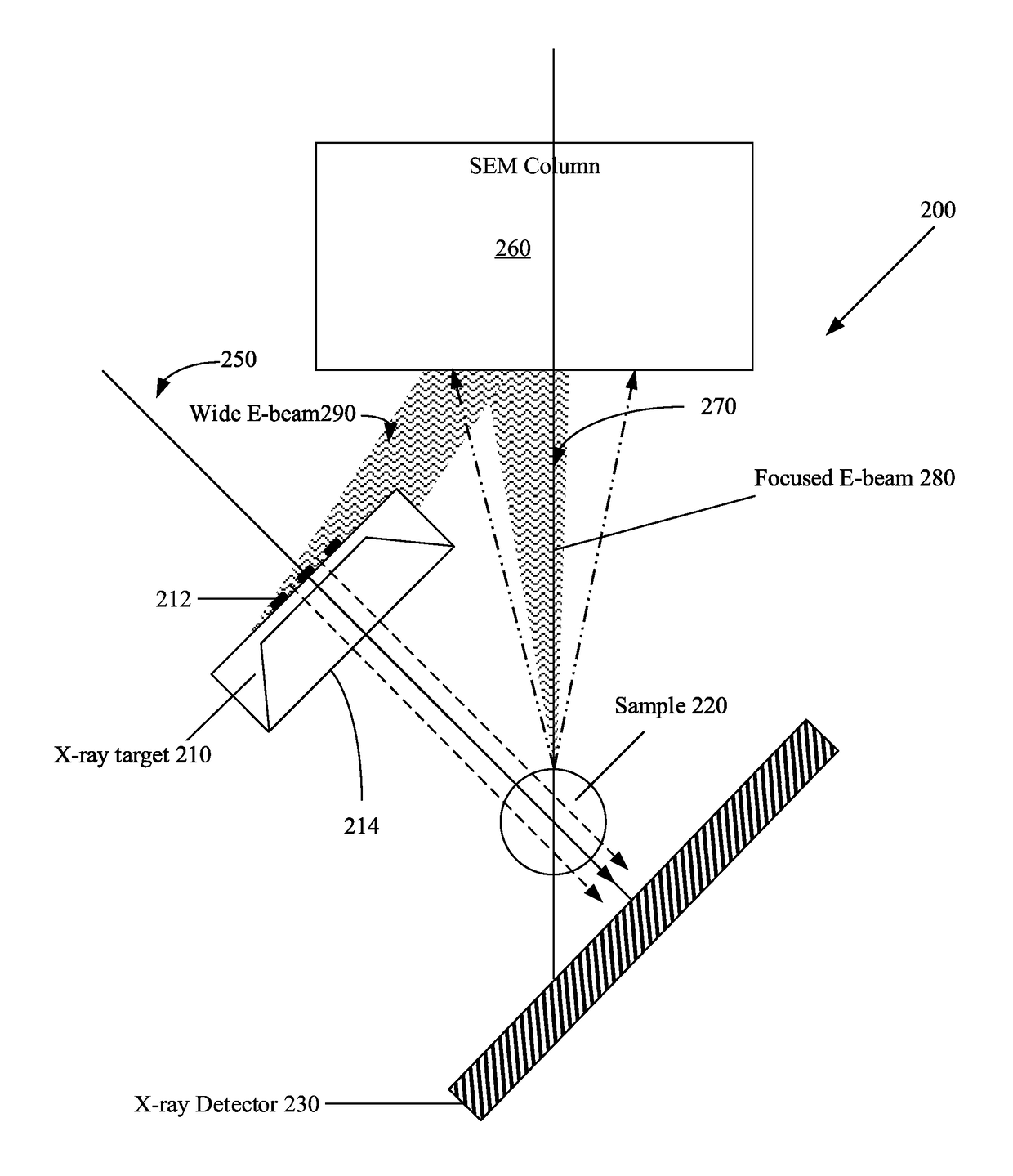
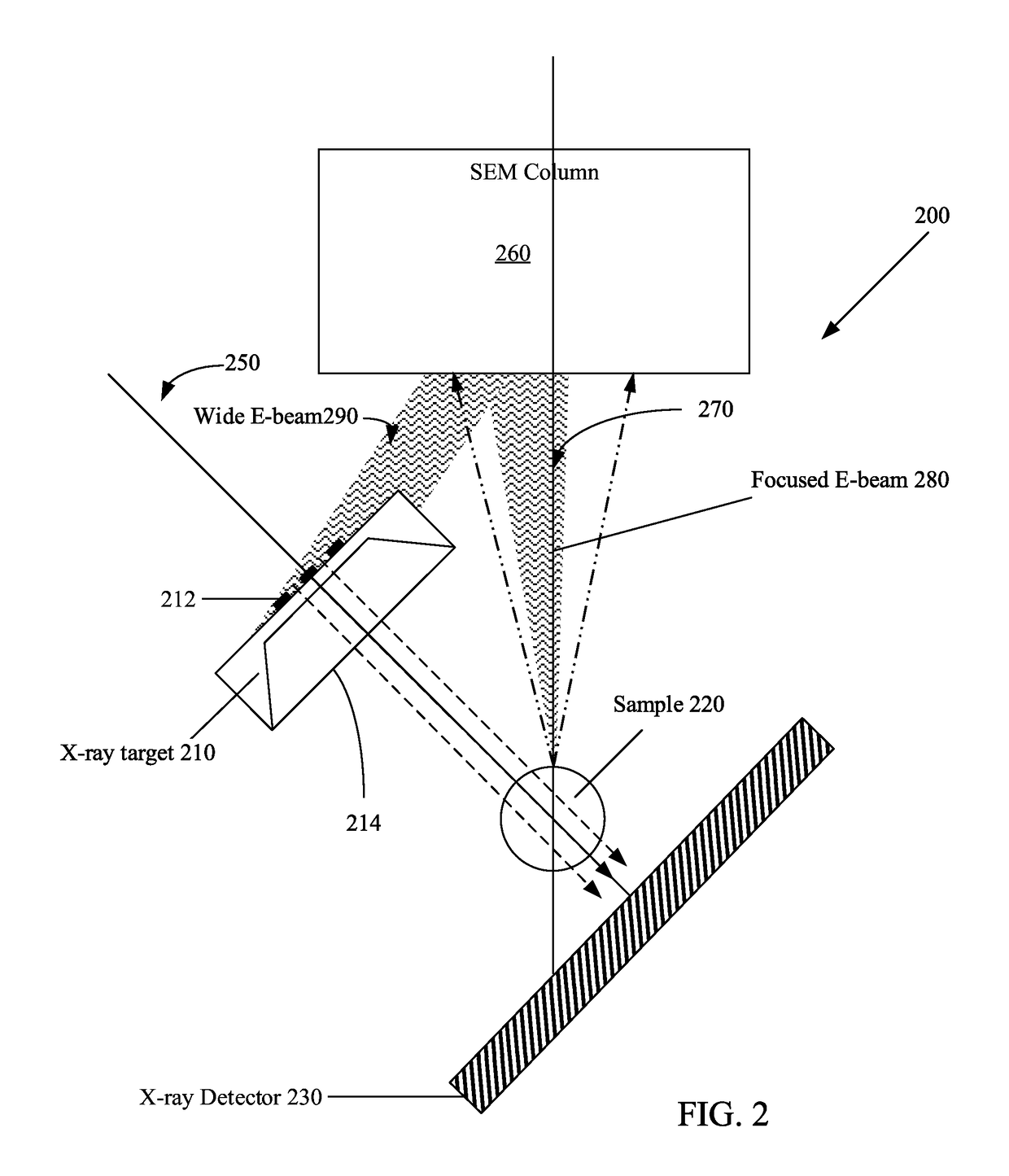
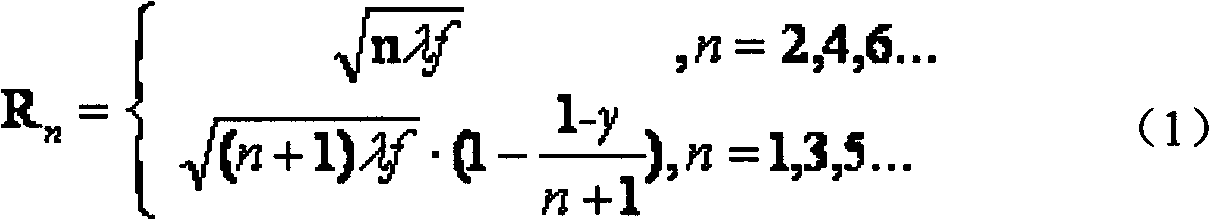Patents
Literature
108 results about "Hard X-rays" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
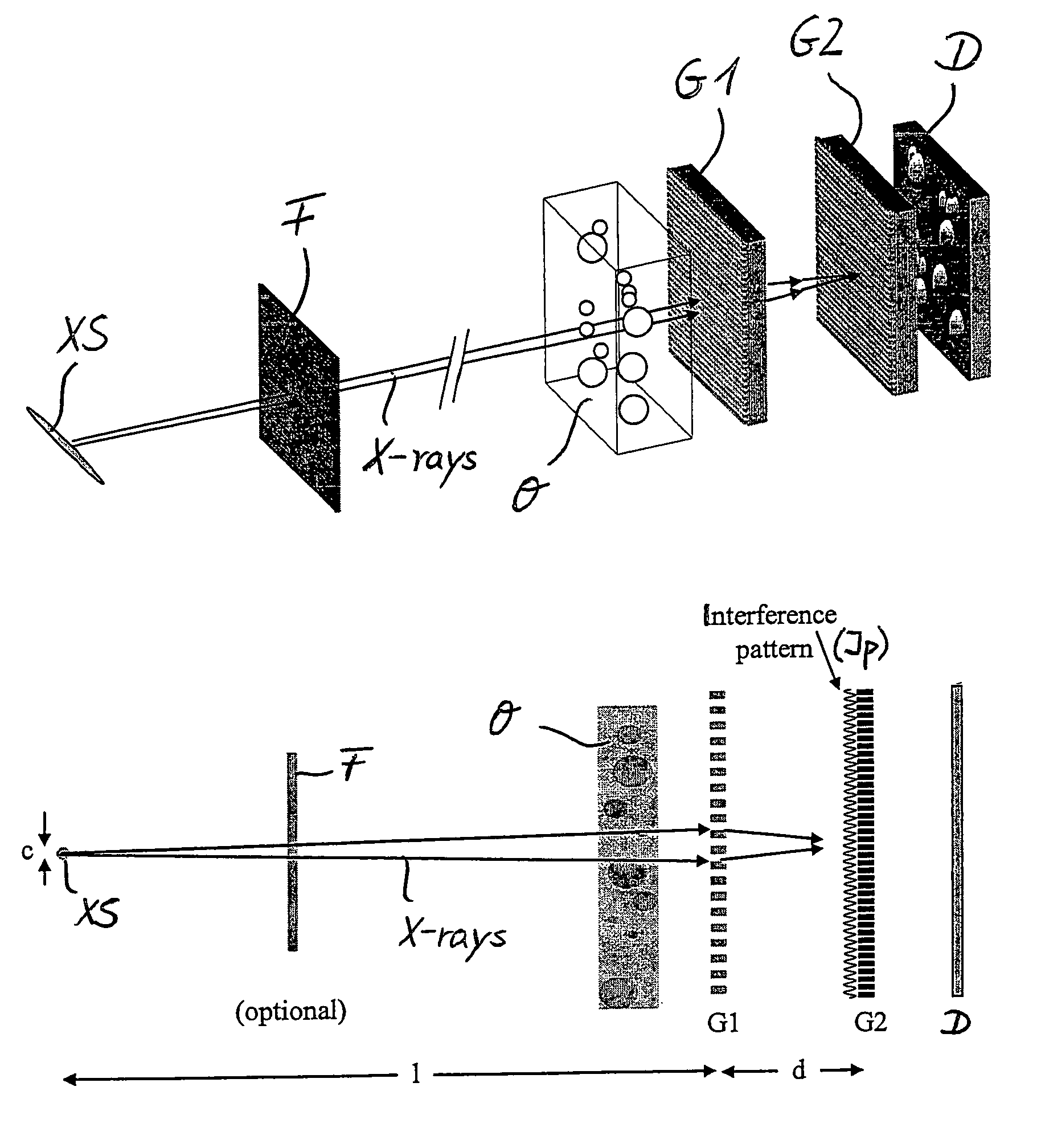
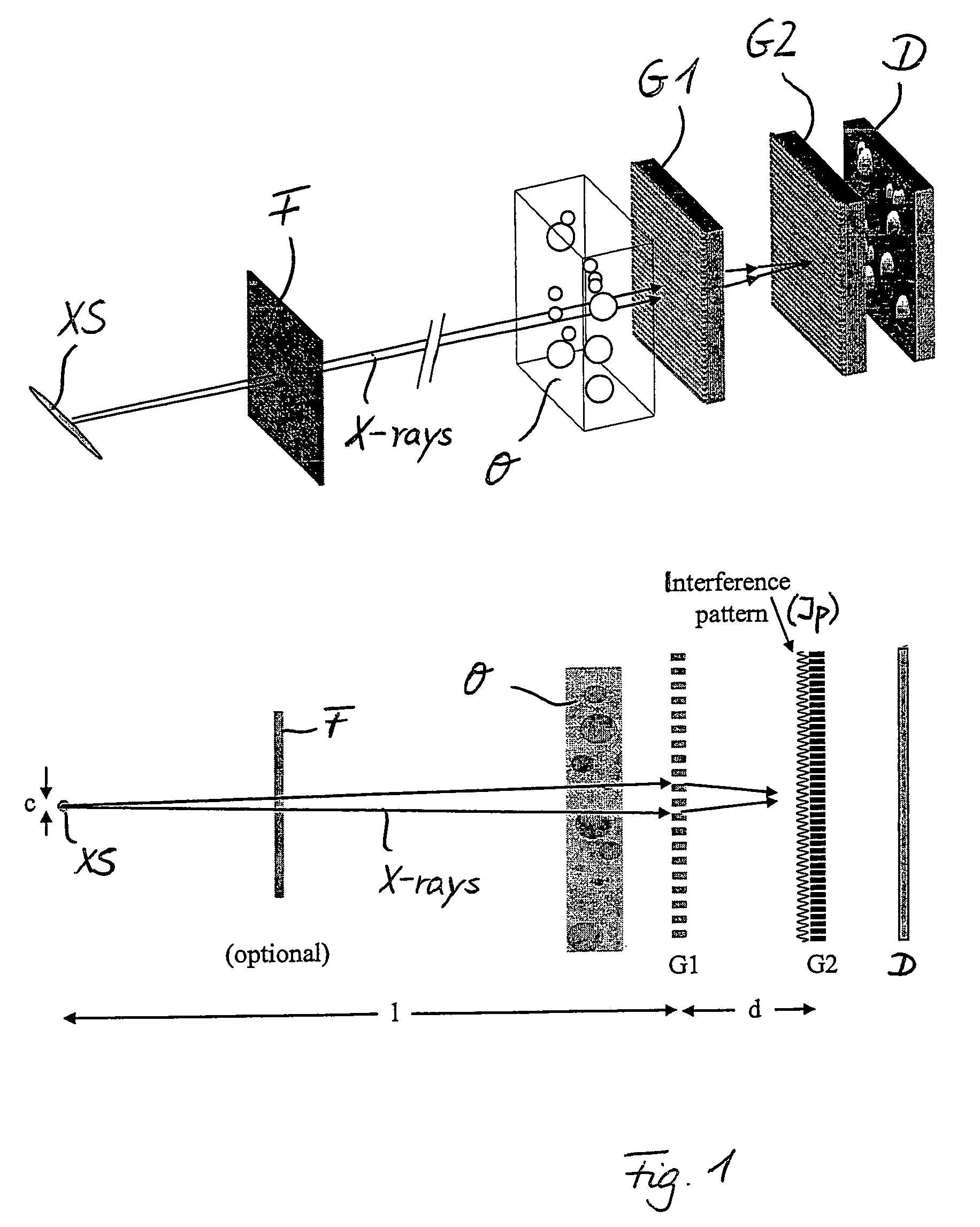
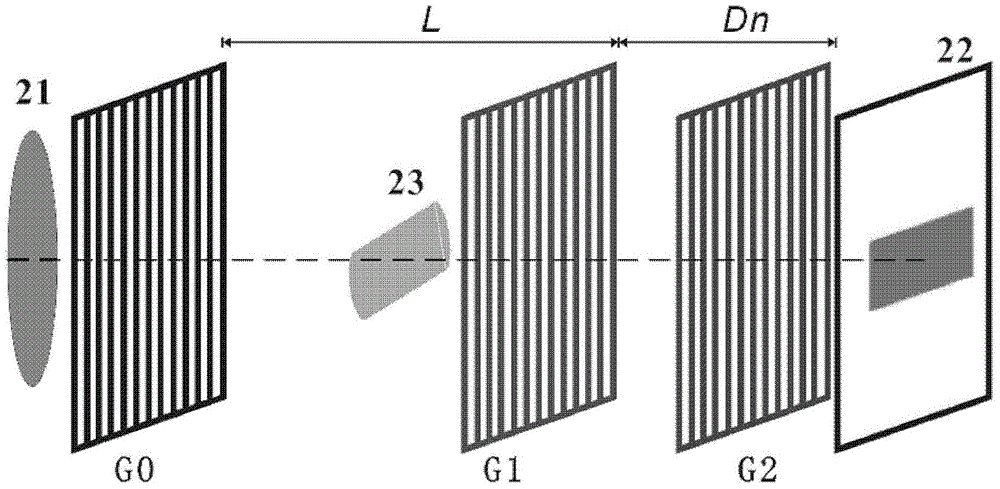
Interferometer for quantitative phase contrast imaging and tomography with an incoherent polychromatic x-ray source
ActiveUS7889838B2Little effortAlleviate scattering artifactImaging devicesTomographyHard X-raysTransmission geometry
Owner:PAUL SCHERRER INSTITUT
Correction method for differential phase contrast imaging
ActiveUS8855265B2Reduce impactImprove image qualityImaging devicesHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionHard X-raysBeam splitter
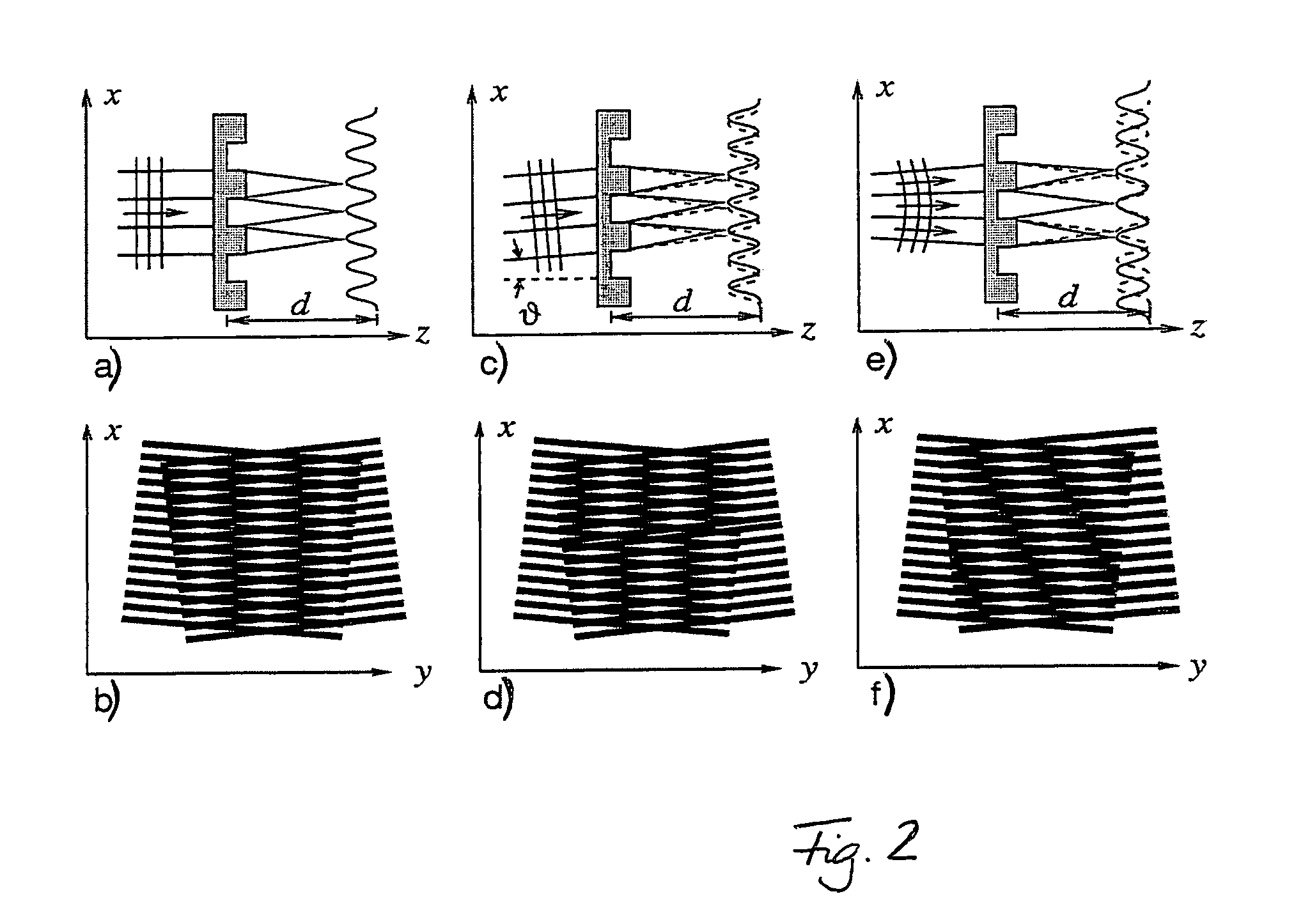
The present invention generally refers to a correction method for grating-based X-ray differential phase contrast imaging (DPCI) as well as to an apparatus which can advantageously be applied in X-ray radiography and tomography for hard X-ray DPCI of a sample object or an anatomical region of interest to be scanned. More precisely, the proposed invention provides a suitable approach that helps to enhance the image quality of an acquired X-ray image which is affected by phase wrapping, e.g. in the resulting Moiré interference pattern of an emitted X-ray beam in the detector plane of a Talbot-Lau type interferometer after diffracting said X-ray beam at a phase-shifting beam splitter grating. This problem, which is further aggravated by noise in the obtained DPCI images, occurs if the phase between two adjacent pixels in the detected X-ray image varies by more than π radians and is effected by a line integration over the object's local phase gradient, which induces a phase offset error of π radians that leads to prominent line artifacts parallel to the direction of said line integration.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Correction method for differential phase contrast imaging
ActiveUS20120099702A1Good estimateImprove image qualityImaging devicesHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionHard X-raysBeam splitter
The present invention generally refers to a correction method for grating-based X-ray differential phase contrast imaging (DPCI) as well as to an apparatus which can advantageously be applied in X-ray radiography and tomography for hard X-ray DPCI of a sample object or an anatomical region of interest to be scanned. More precisely, the proposed invention provides a suitable approach that helps to enhance the image quality of an acquired X-ray image which is affected by phase wrapping, e.g. in the resulting Moiré interference pattern of an emitted X-ray beam in the detector plane of a Talbot-Lau type interferometer after diffracting said X-ray beam at a phase-shifting beam splitter grating. This problem, which is further aggravated by noise in the obtained DPCI images, occurs if the phase between two adjacent pixels in the detected X-ray image varies by more than π radians and is effected by a line integration over the object's local phase gradient, which induces a phase offset error of π radians that leads to prominent line artifacts parallel to the direction of said line integration.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Lobster eye X-ray imaging system and method of fabrication thereof
ActiveUS7231017B2Raise the ratioHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectrode and associated part arrangementsHard X-raysBackscatter X-ray
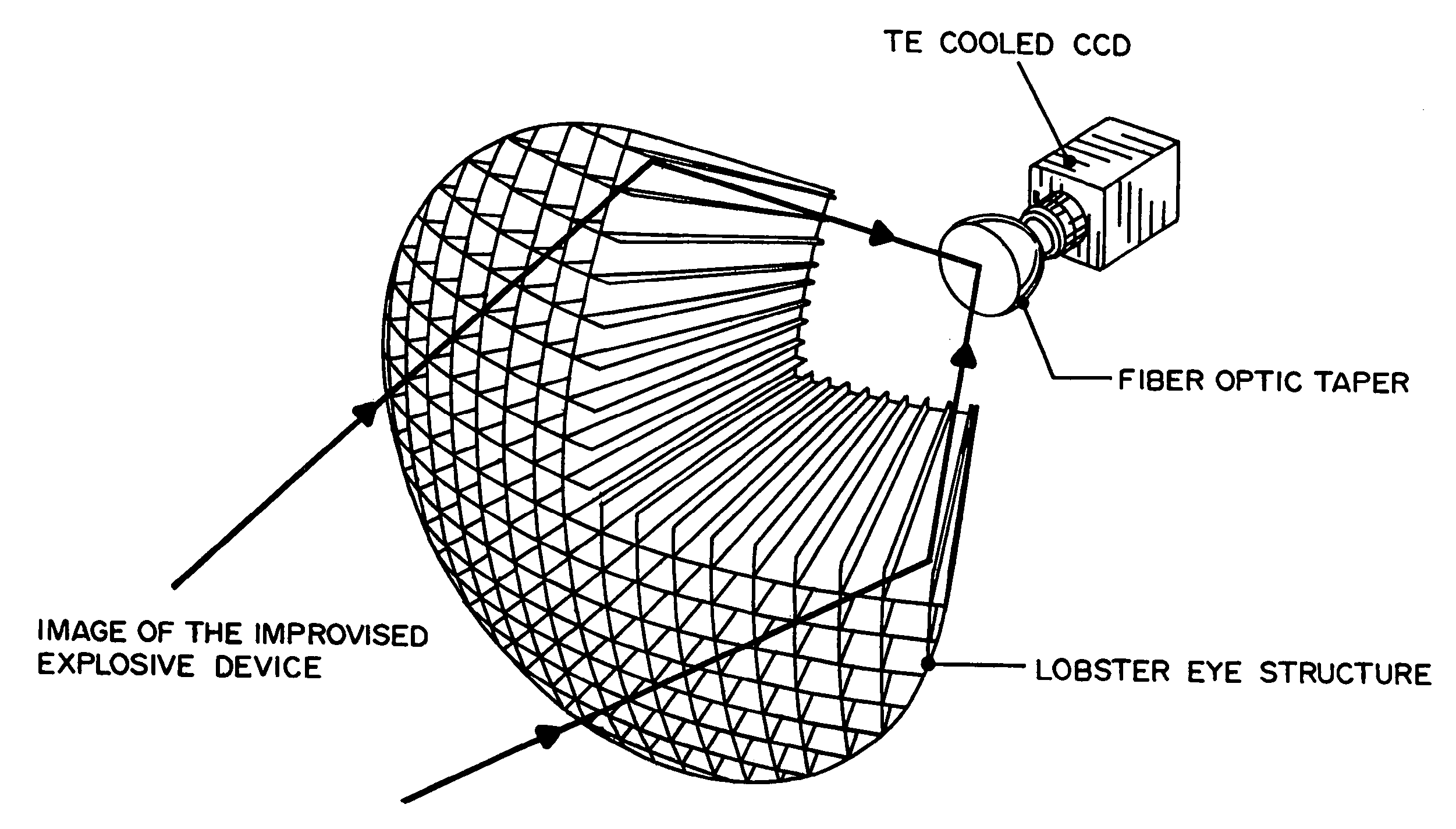
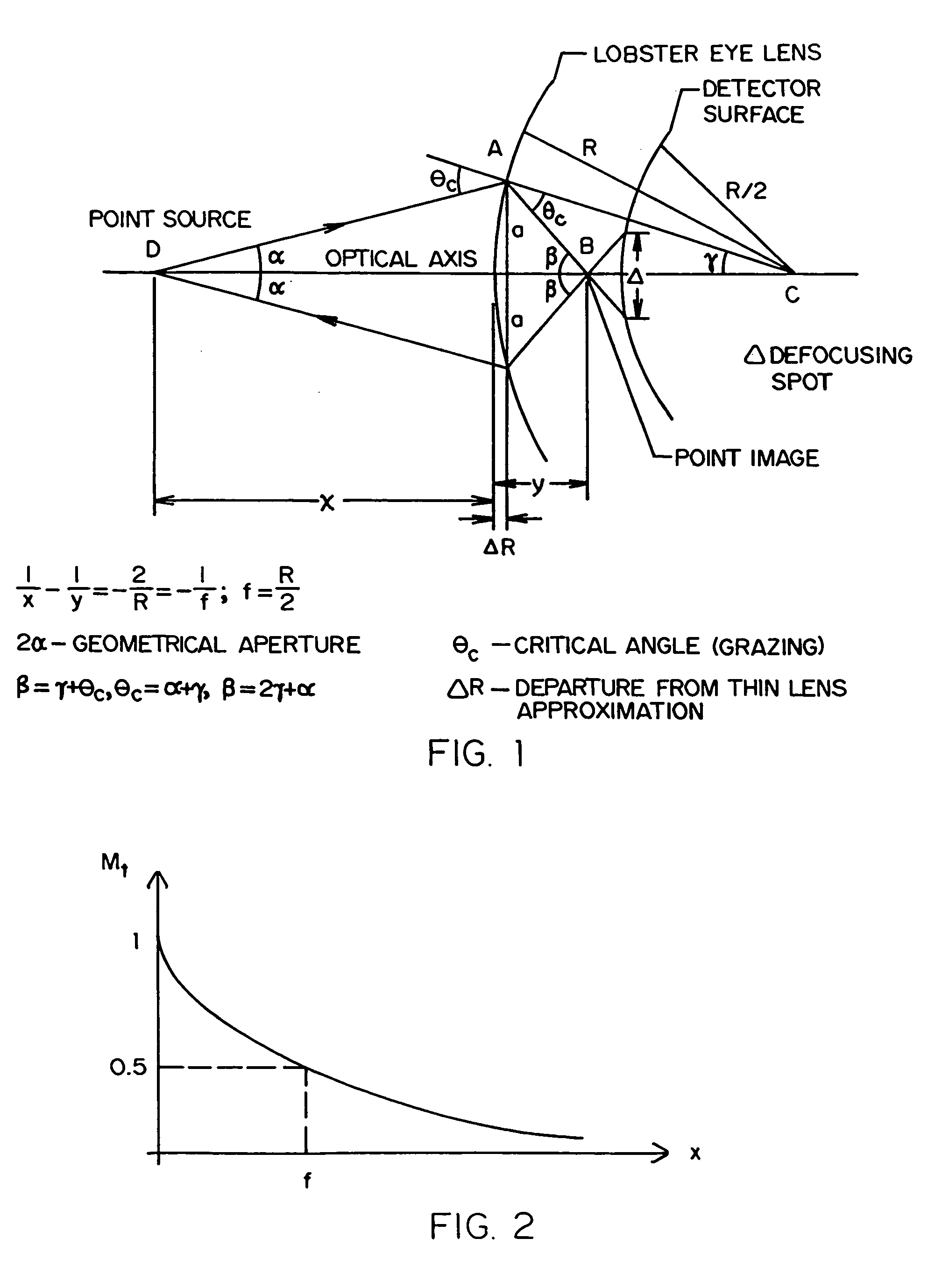
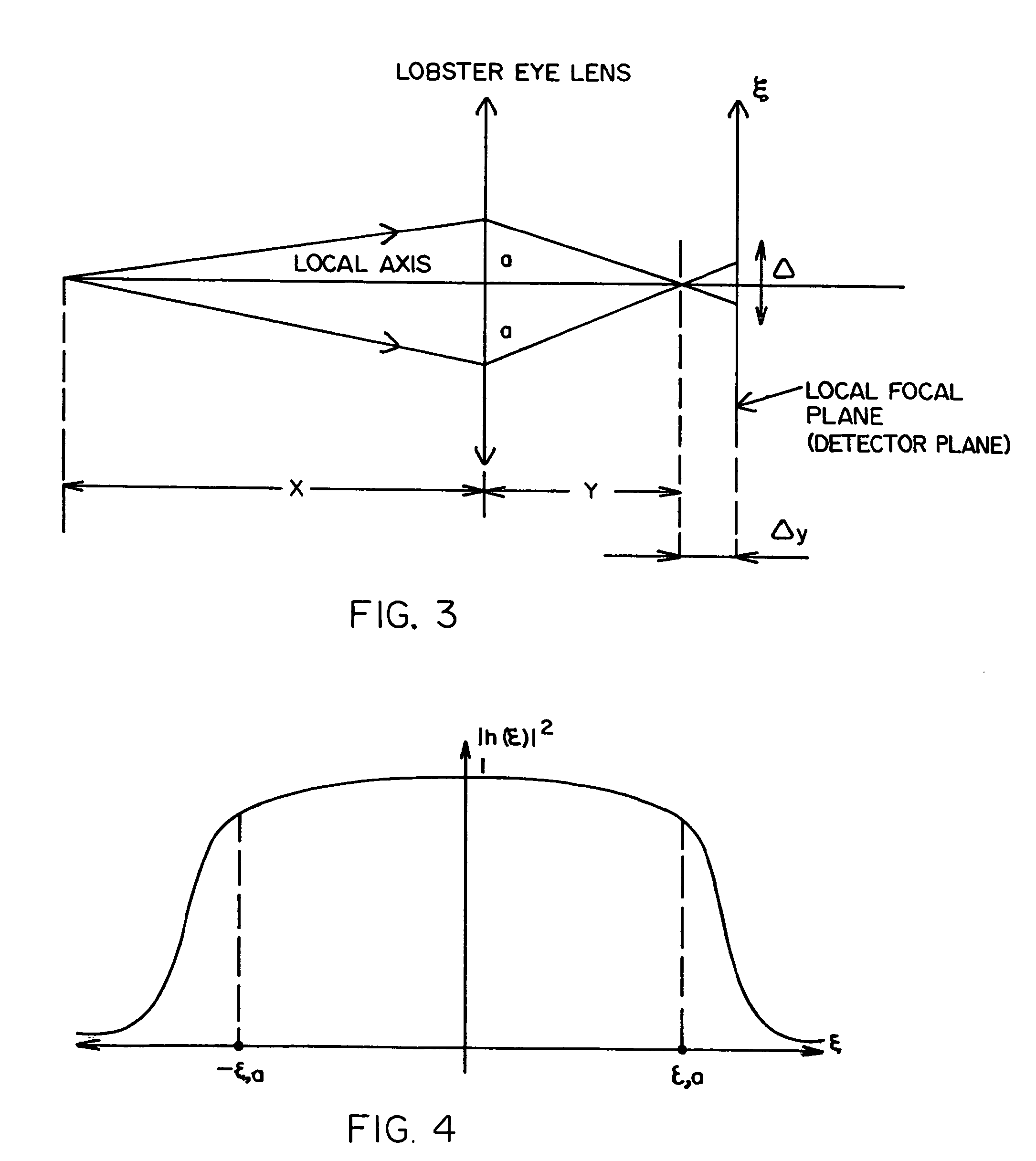
A Lobster Eye X-ray Imaging System based on a unique Lobster Eye (LE) structure, X-ray generator, scintillator-based detector and cooled CCD (or Intensified CCD) for real-time, safe, staring Compton backscatter X-ray detection of objects hidden under ground, in containers, behind walls, bulkheads etc. In contrast to existing scanning pencil beam systems, Lobster Eye X-Ray Imaging System's true focusing X-ray optics simultaneously acquire ballistic Compton backscattering photons (CBPs) from an entire scene irradiated by a wide-open cone beam from one or more X-ray generators. The Lobster Eye X-ray Imaging System collects (focuses) thousands of times more backscattered hard X-rays in the range from 40 to 120 keV (or wavelength λ=0.31 to 0.1 Å) than current backscatter imaging sensors (BISs), giving high sensitivity and signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and penetration through ground, metal walls etc. The collection efficiency of Lobster Eye X-ray Imaging System is optimized to reduce emitted X-ray power and miniaturize the device. This device is especially advantageous for and satisfies requirements of X-ray-based inspection systems, namely, penetration of the X-rays through ground, metal and other material concealments; safety; and man-portability. The advanced technology disclosed herein is also applicable to medical diagnostics and military applications such as mine detection, security screening and a like.
Owner:MERCURY MISSION SYST LLC
Low dose single step grating based X-ray phase contrast imaging
InactiveCN102325498ASmall doseImage quality is not degradedMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationRadiation diagnosticsHard X-raysGrating
Phase sensitive X-ray imaging methods can provide substantially increased contrast over conventional absorption based imaging, and therefore new and otherwise inaccessible information. The use of gratings as optical elements in hard X-ray phase imaging overcomes some of the problems that have impaired the wider use of phase contrast in X-ray radiography and tomography. So far, to separate the phase information from other contributions detected with a grating interferometer, a phase-stepping approach has been considered, which implies the acquisition of multiple radiographic projections. Here,an innovative, highly sensitive X-ray tomographic phase contrast imaging approach is presented based on grating interferometry, which extracts the phase contrast signal without the need of phase stepping. Compared to the existing phase step approach, the main advantage of this new method dubbed 'reverse projection' is the significantly reduced delivered dose, without degradation of the image quality. The new technique sets the pre-requisites for future fast and low dose phase contrast imaging methods, fundamental for imaging biological specimens and in-vivo studies.
Owner:INST OF HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
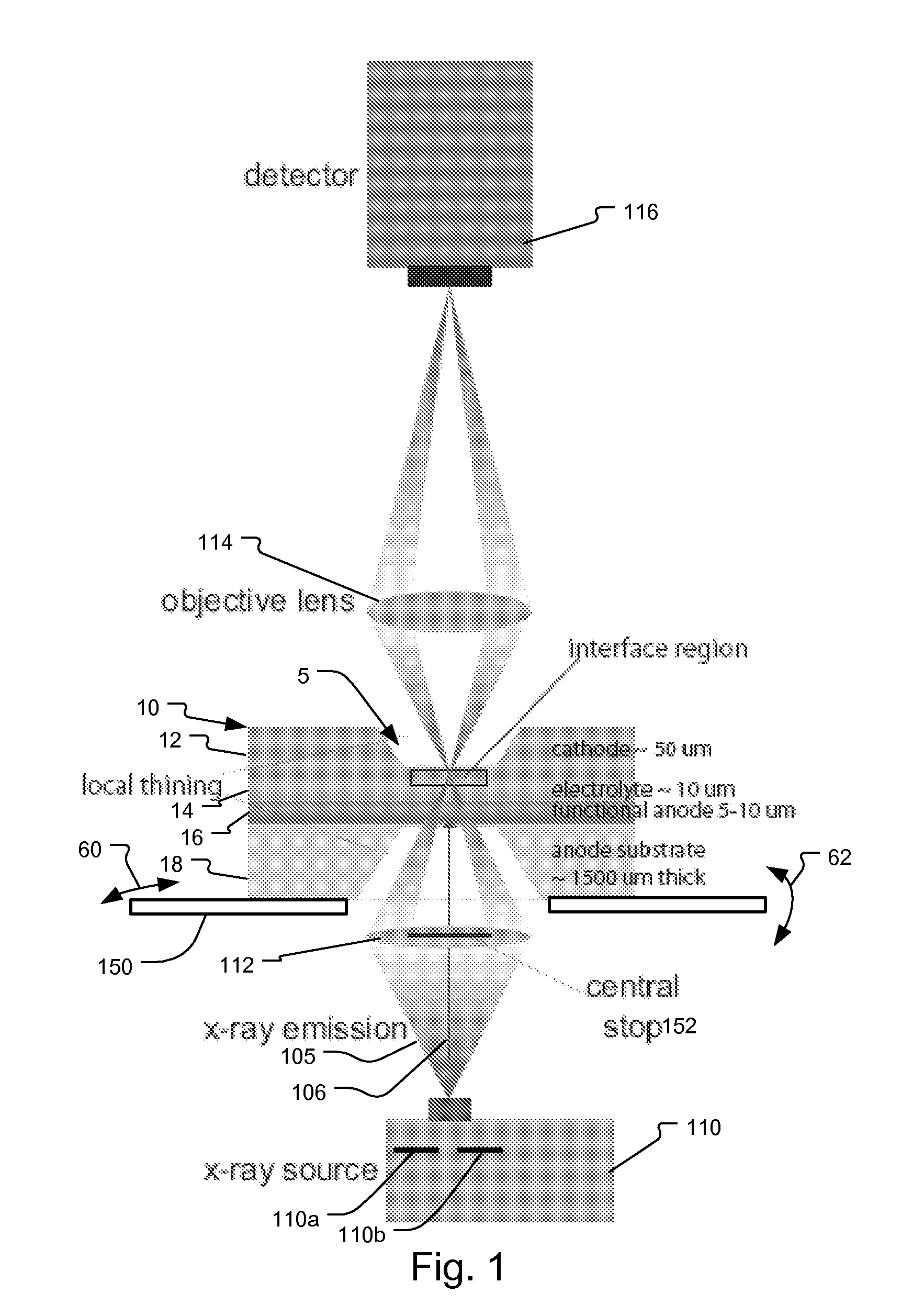
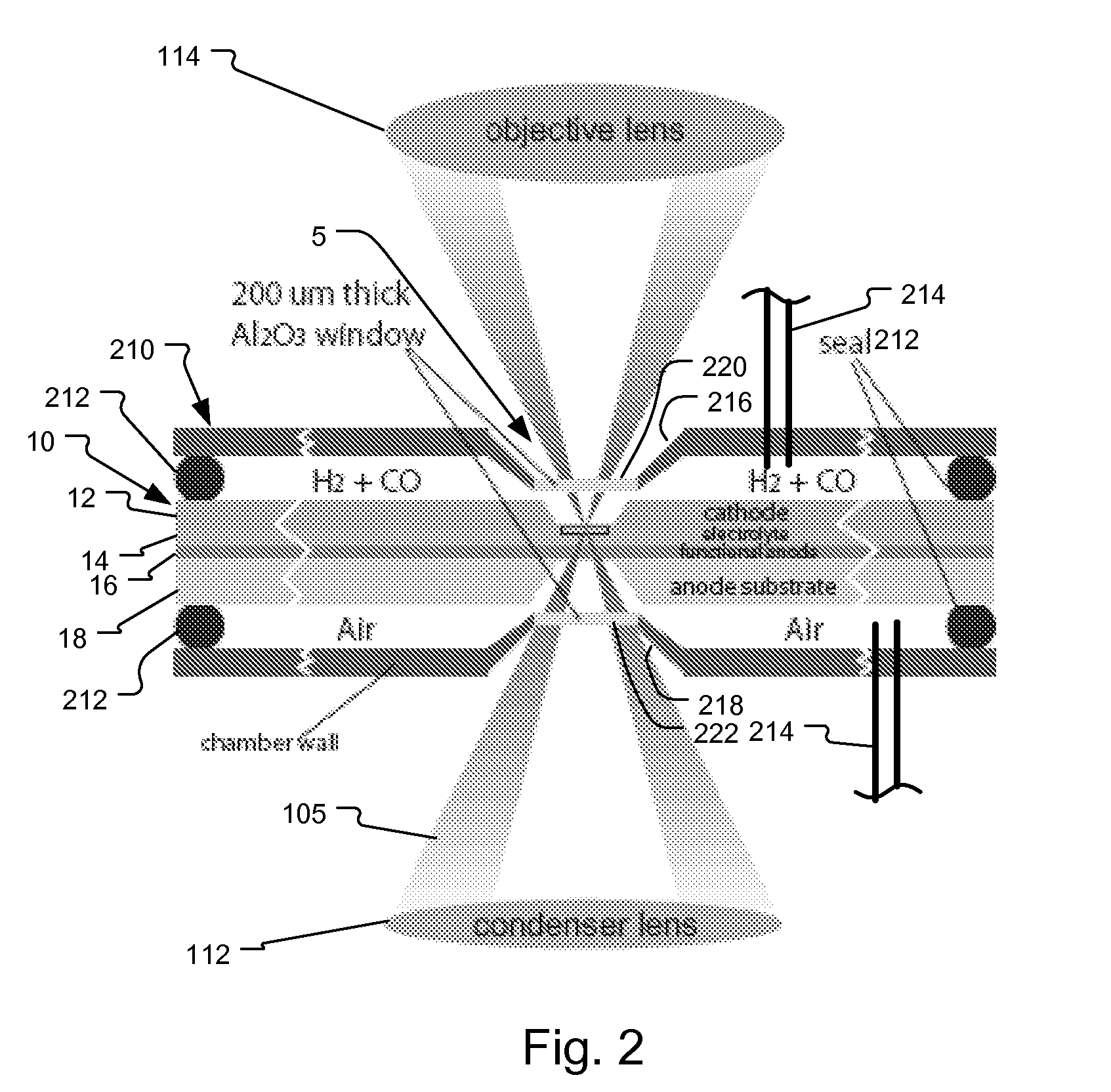
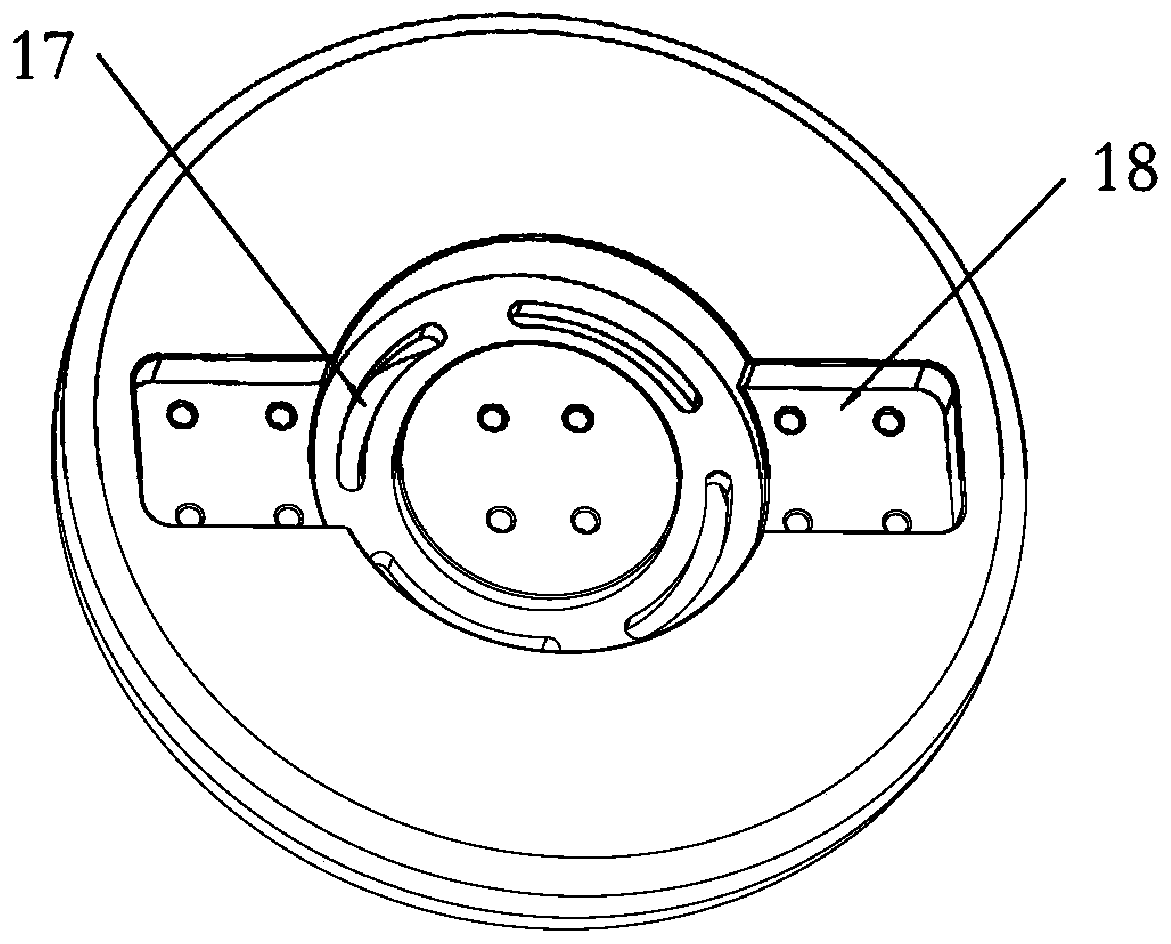
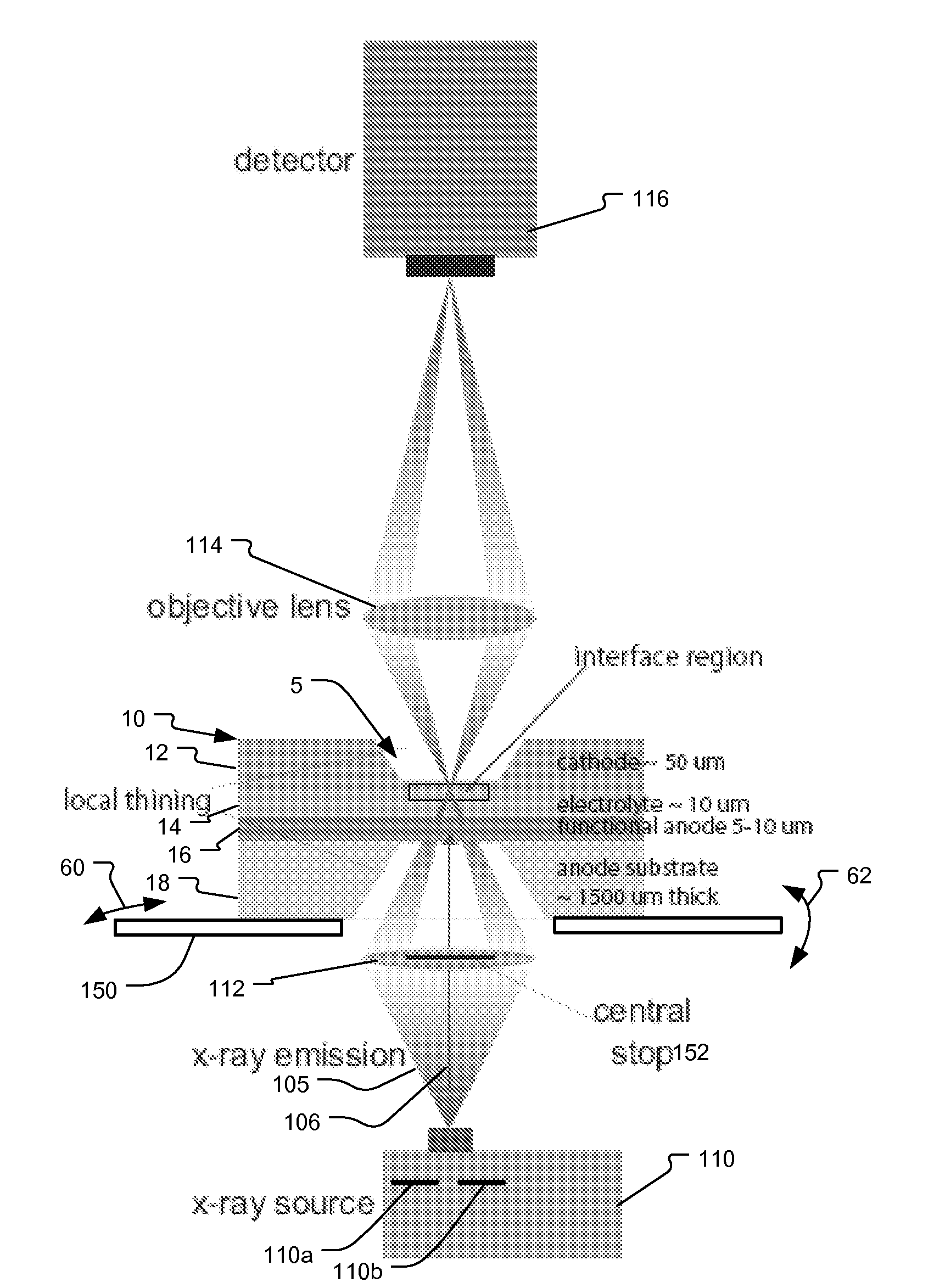
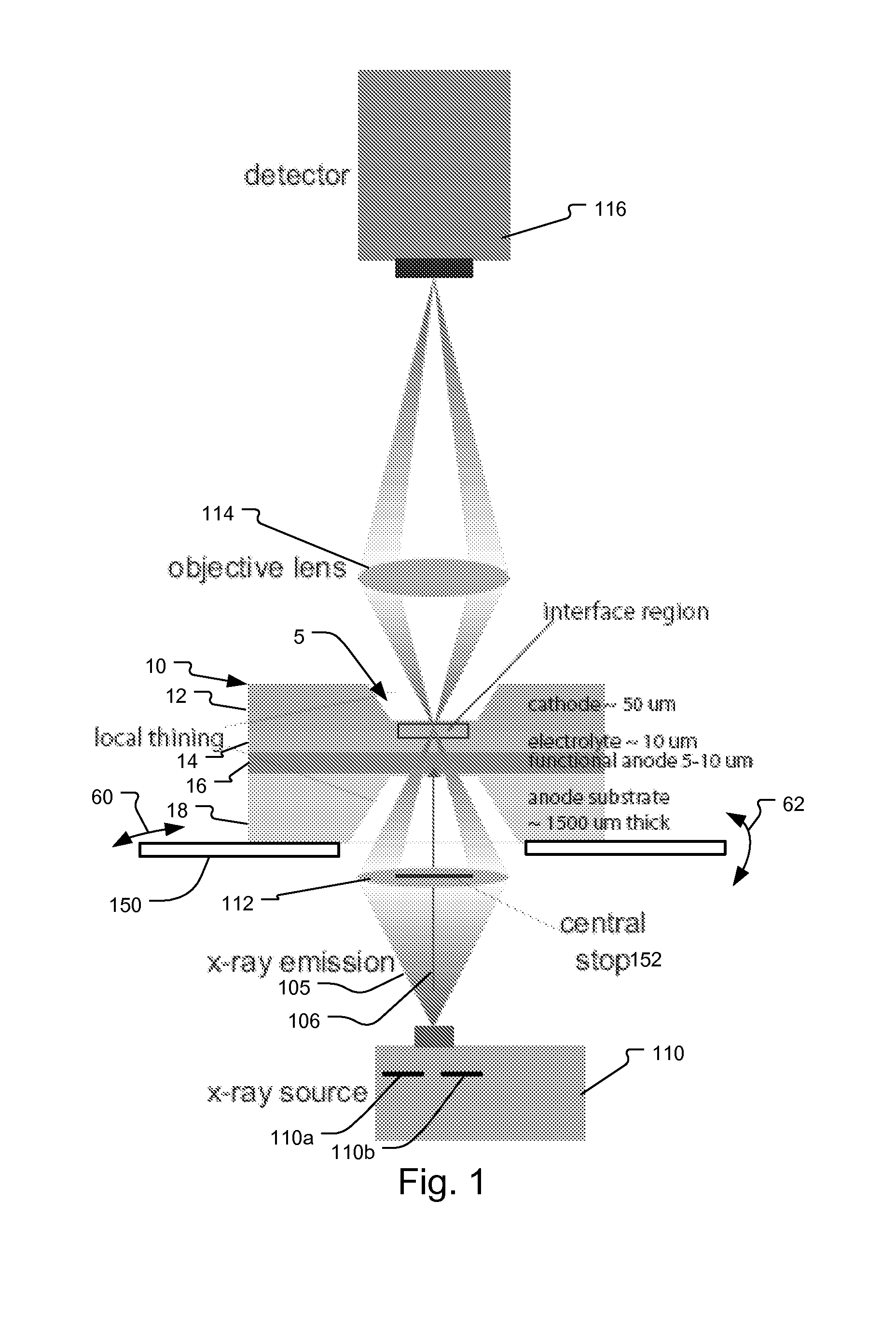
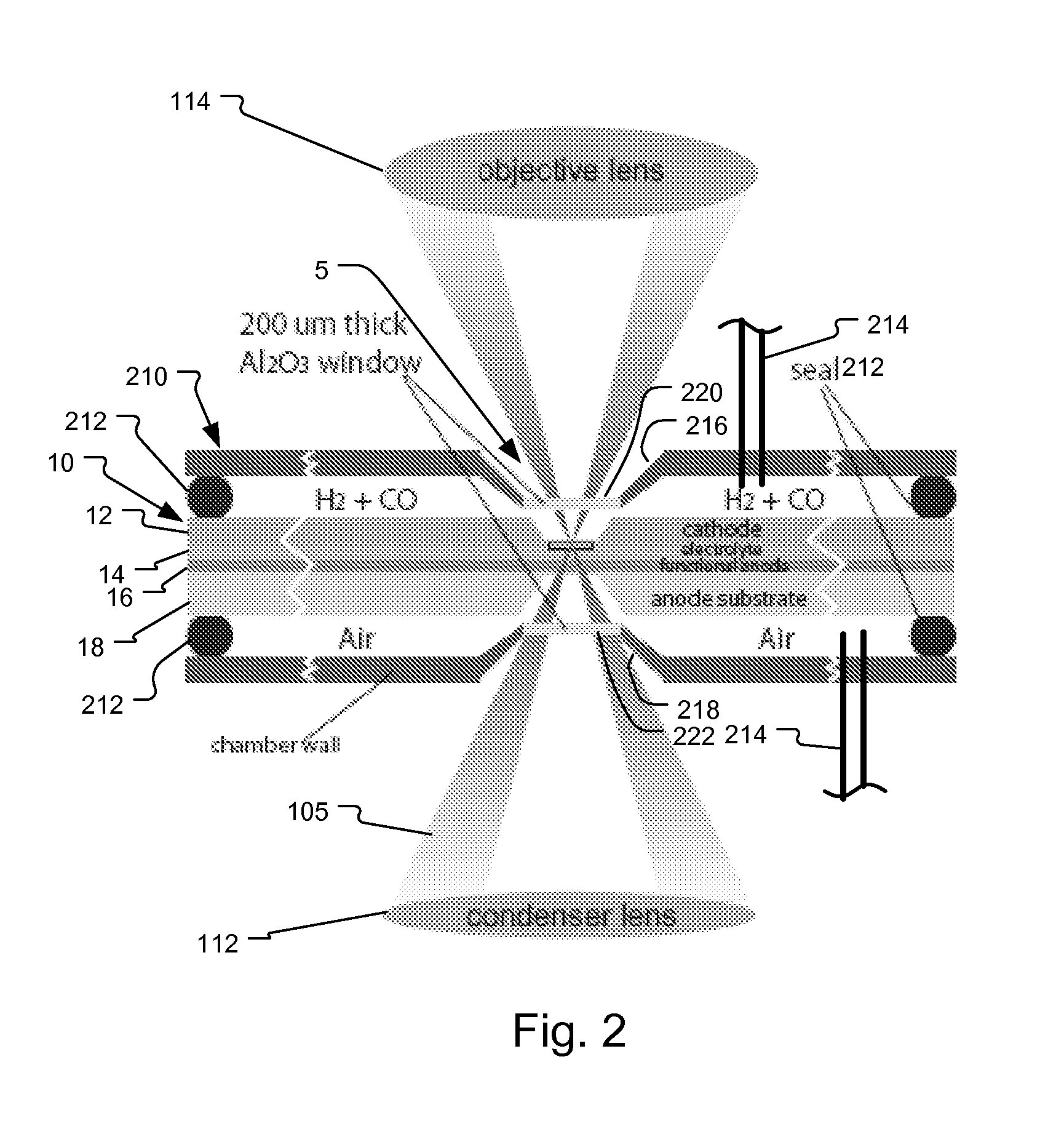
System and method for fuel cell material x-ray analysis
ActiveUS7499521B2Shorten development timeImprove reliabilityRadiation/particle handlingUsing wave/particle radiation meansHard X-raysMetrology
An imaging technology for fuel cells is based on x-ray microscopy. A metrology system images the electro-chemical interaction areas of solid-oxide fuel cells (SOFC) in-situ. This system takes advantage of both the penetrating power and elemental absorption contrast of hard x-ray radiation to image the internal interaction areas in a SOFC. The technology can further take advantage of the strong dependence of the x-ray absorption on material type and energy to distinguish the four major material types: cathode, electrolyte, air, and low-Z contaminants such as sulfur.
Owner:CARL ZEISS X RAY MICROSCOPY
Heating stage and heating stage device for X-ray microprobes and experimental method of heating stage device
ActiveCN106483148AEasy to centerHeating evenlyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX ray microprobeHard X-rays
The invention discloses a heating stage for X-ray microprobes. The heating stage comprises a heating stage body, a heater and a sample holder; an incident window and a transmitting window are coaxially and correspondingly arranged on the front wall and the rear wall of the heating stage body respectively, and the bottom of the heating stage body can be mounted on a sample positioning platform; the sample holder is sleeved in the heater in high heating area ratio; each of the heater and the sample holder is provided with a light transmission hole, and the light transmission hole is coaxial with the incident window and the transmitting window. The heating stage for the X-ray microprobes can be operated vertically, and temperature gradient of samples is small; in addition, the heating stage has the advantages of high light transmission, vacuum chamber, easiness in alignment, good temperature uniform of the samples, wide sample type and shape adaptability, high operation temperature limit and the like. In addition, the invention further discloses a heating stage device and an experimental method thereof. The heating stage device is high in back-scattered fluorescent detection efficiency, sufficient rotatable angle and detection angle, overall atmosphere protection and vacuum environment are provided for the samples. The heating stage, the heating stage device and the experimental method are especially suitable for hard X-ray microprobes.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF APPLIED PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
X-ray grating phase-contrast imaging device and method
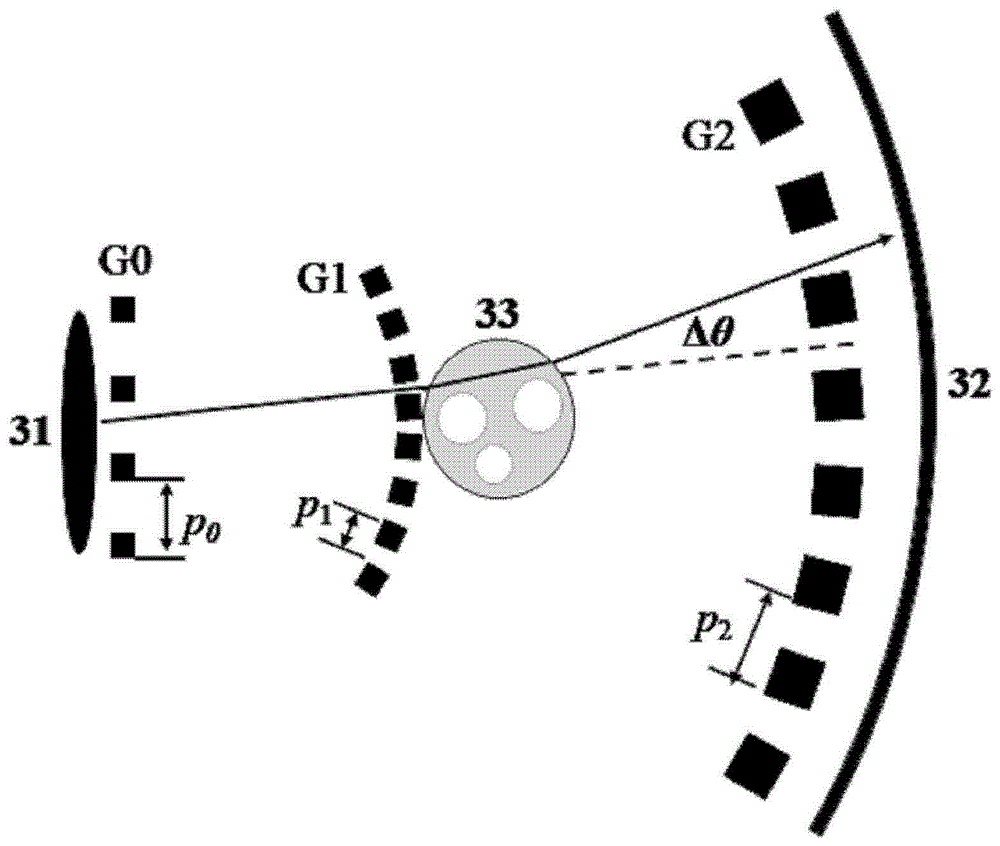
InactiveCN104622492AHigh image contrastReduce radiation doseMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationRadiation diagnosticsGratingHard X-rays
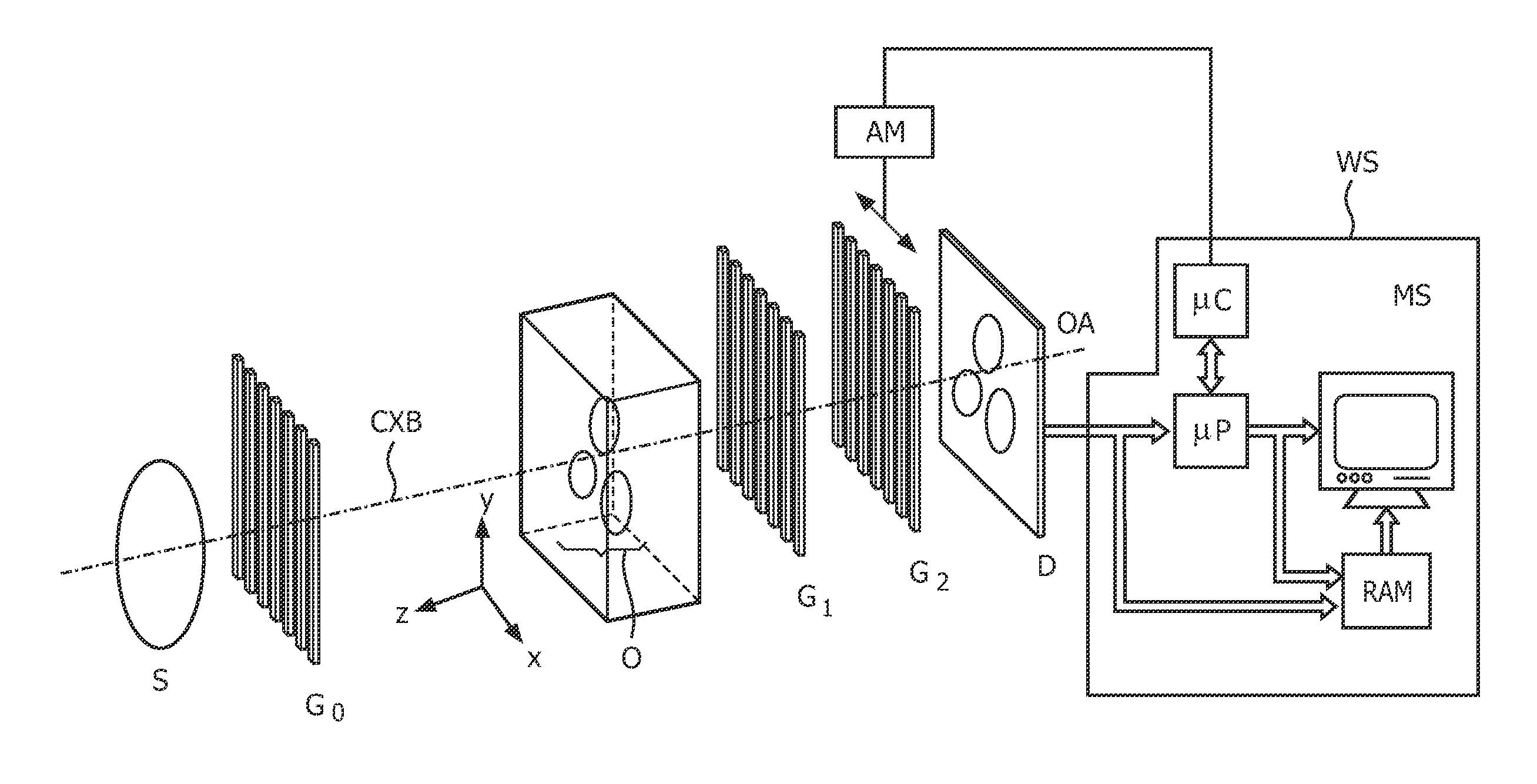
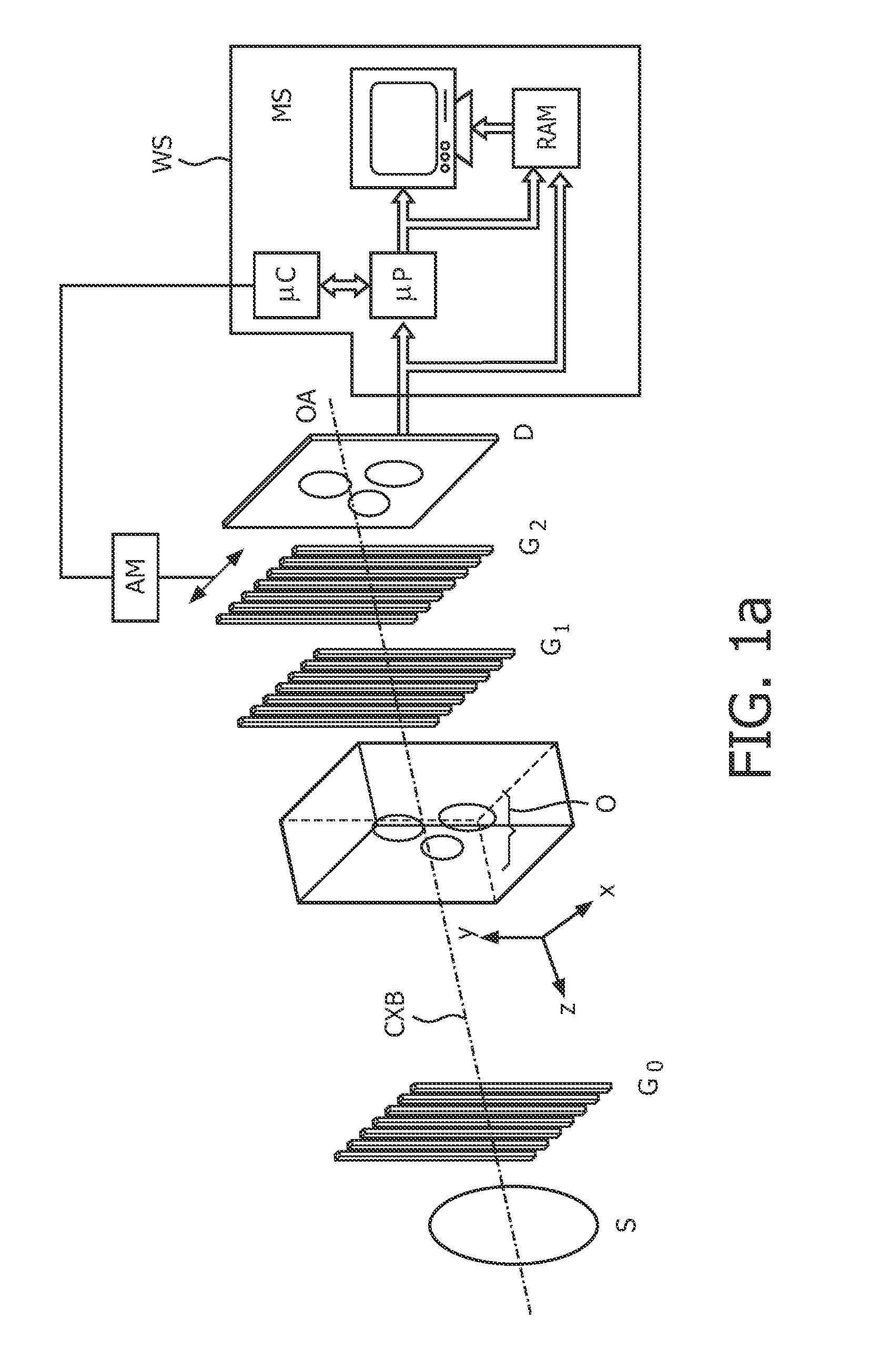
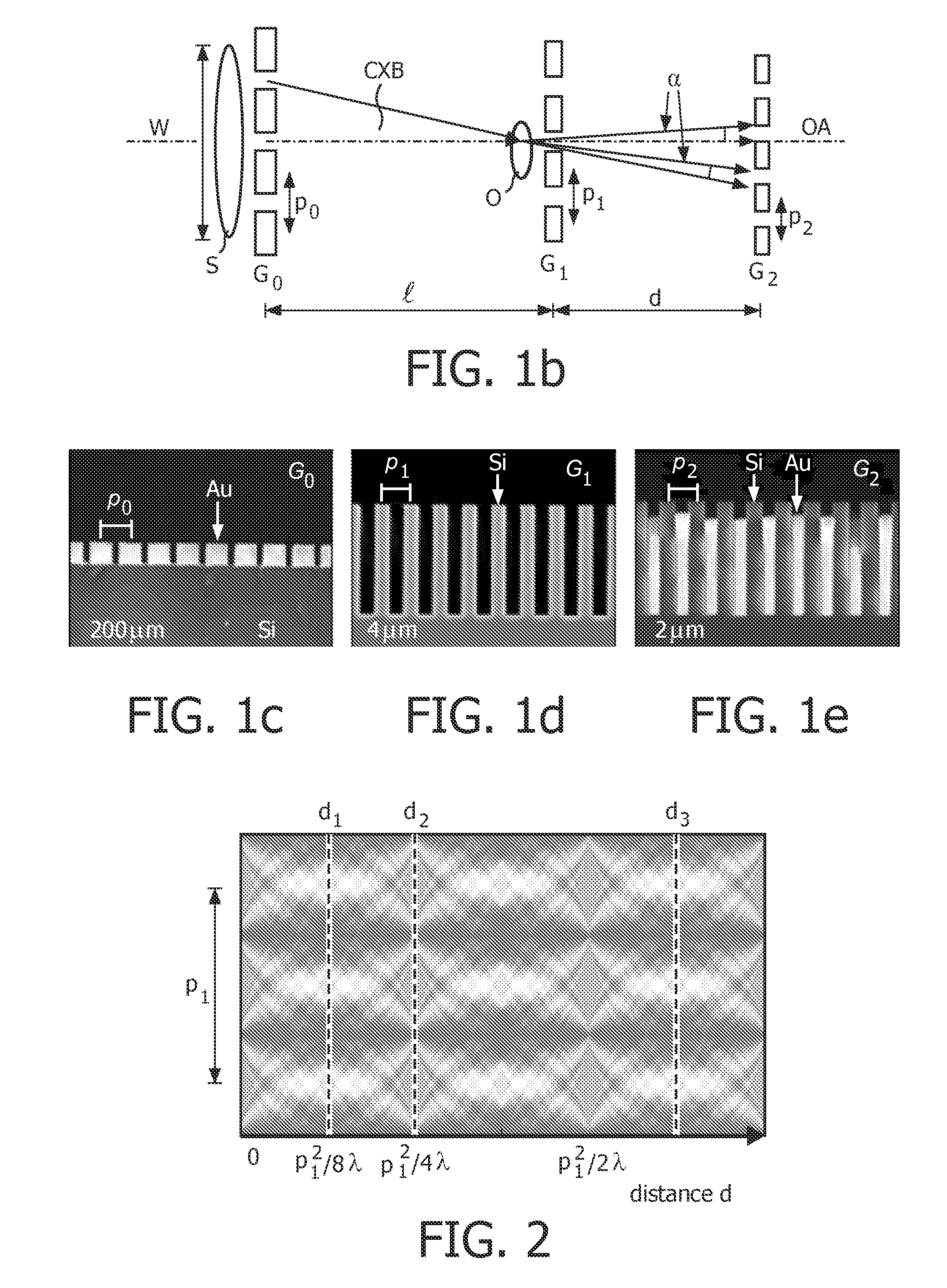
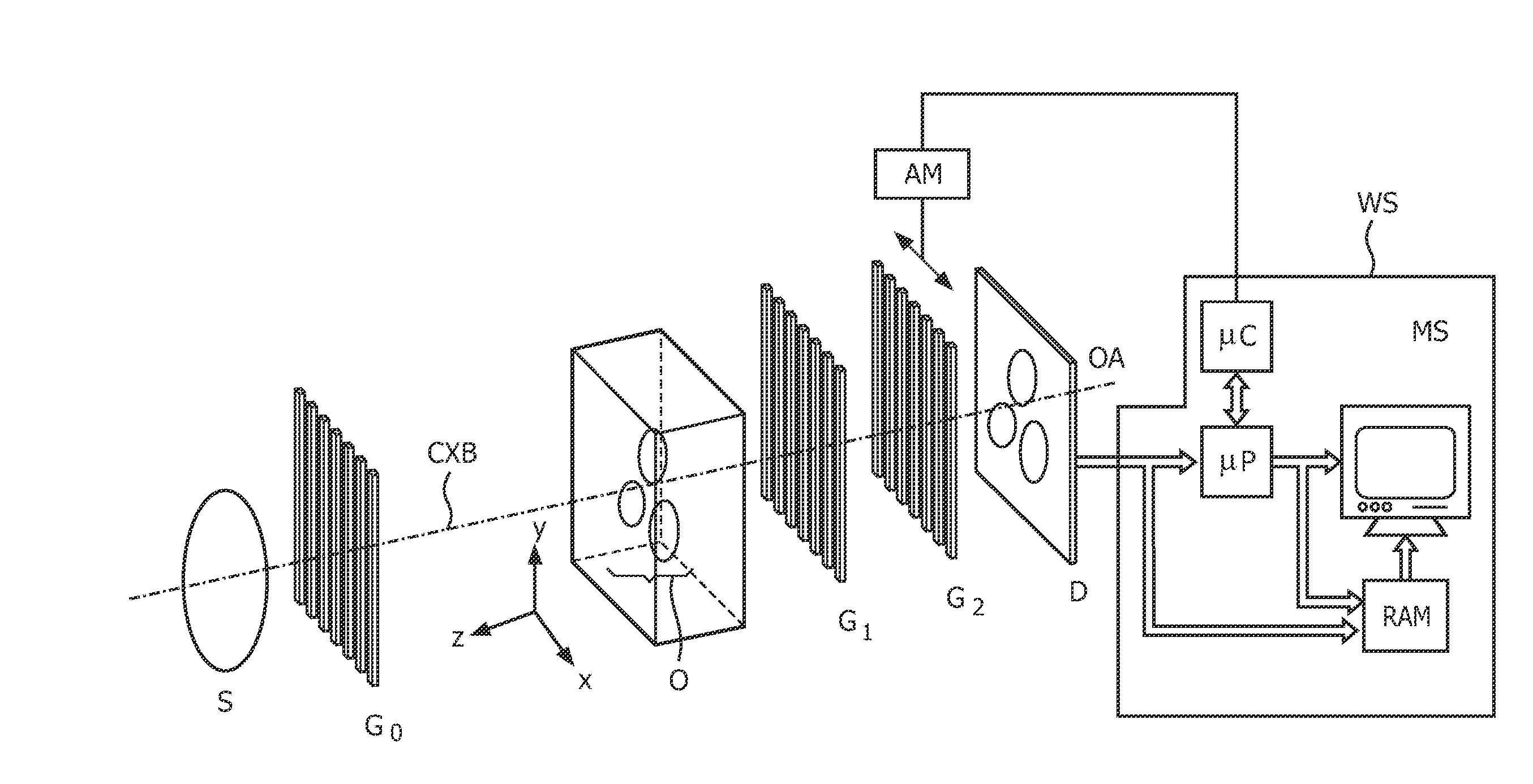
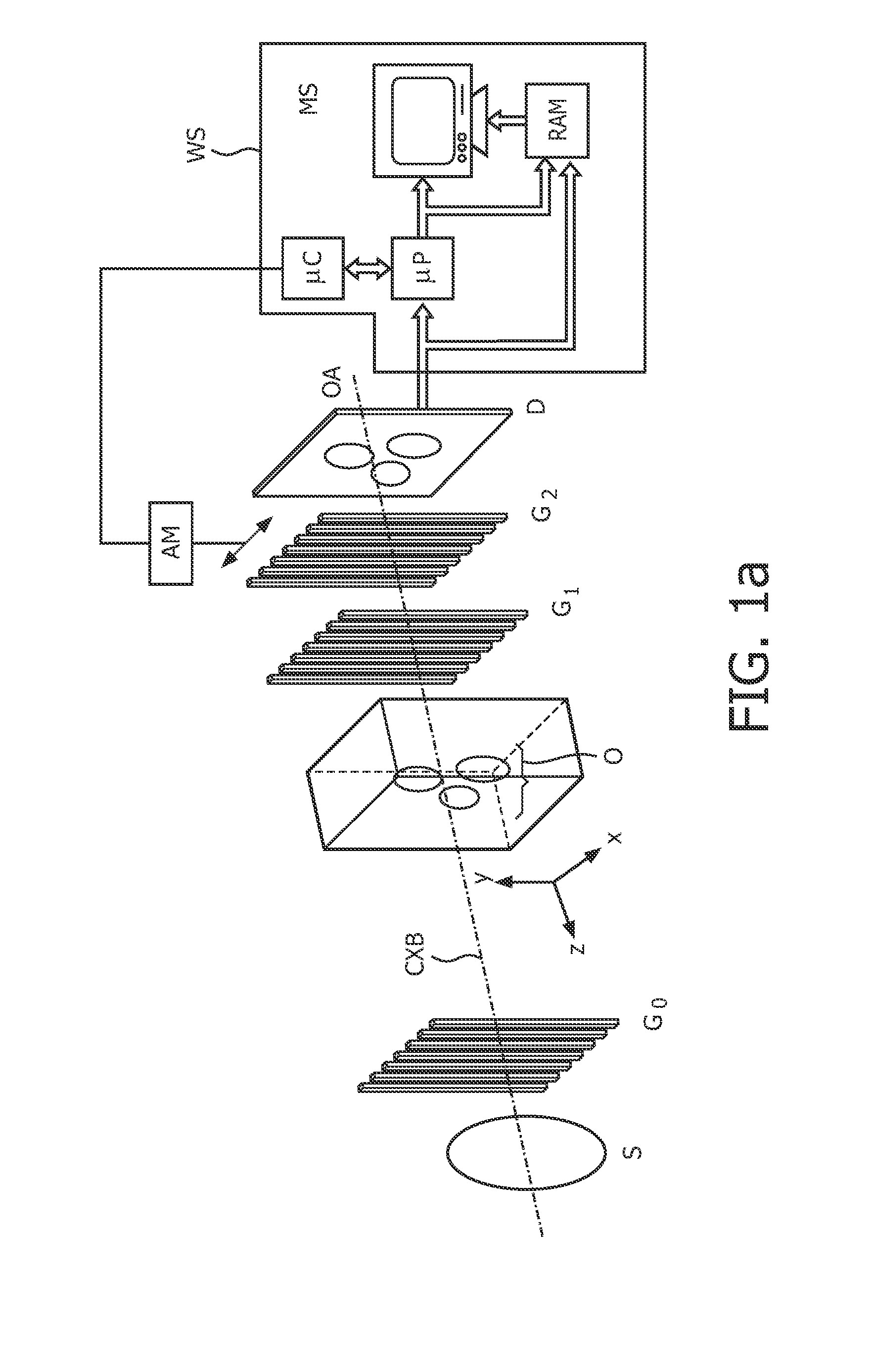
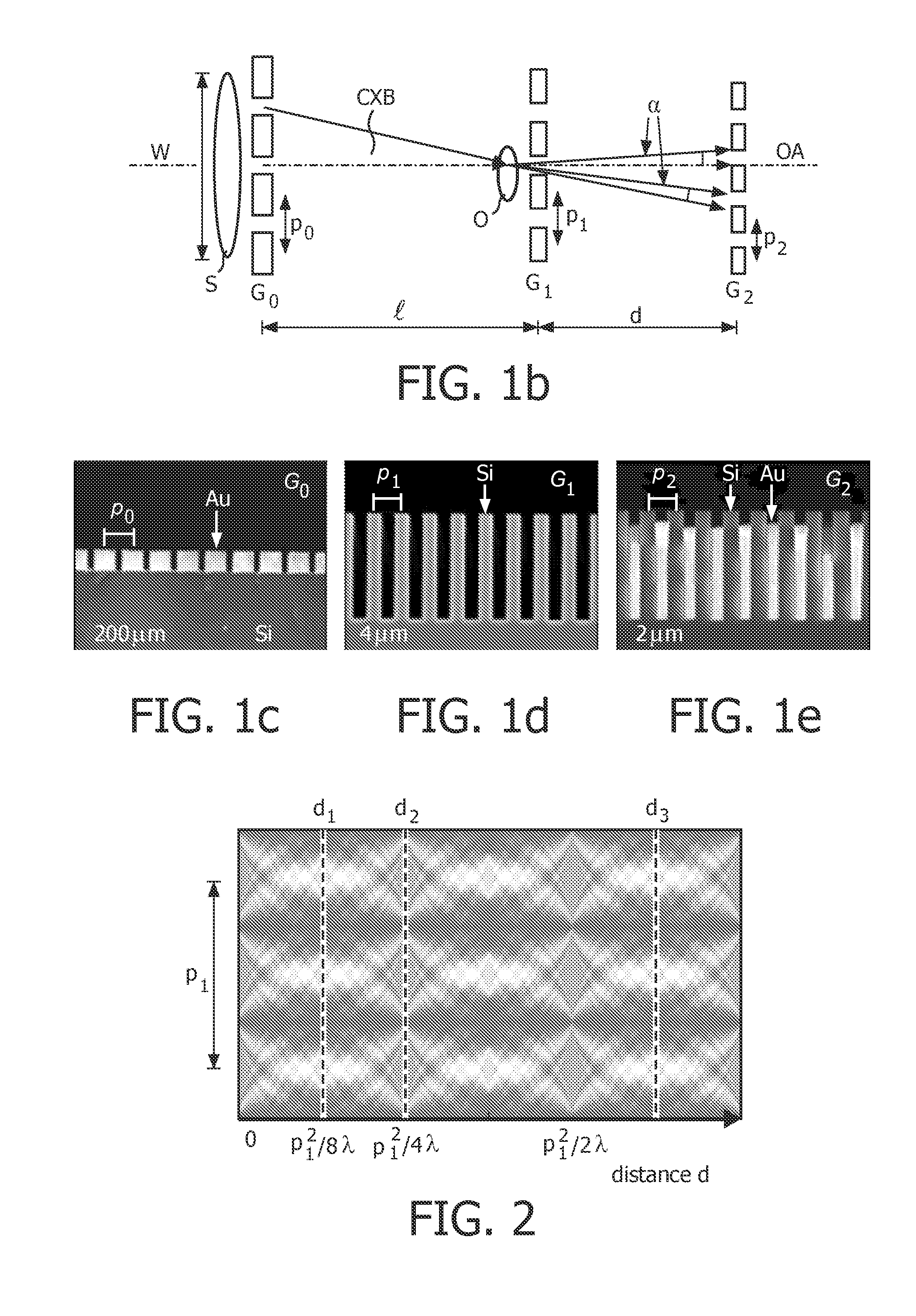
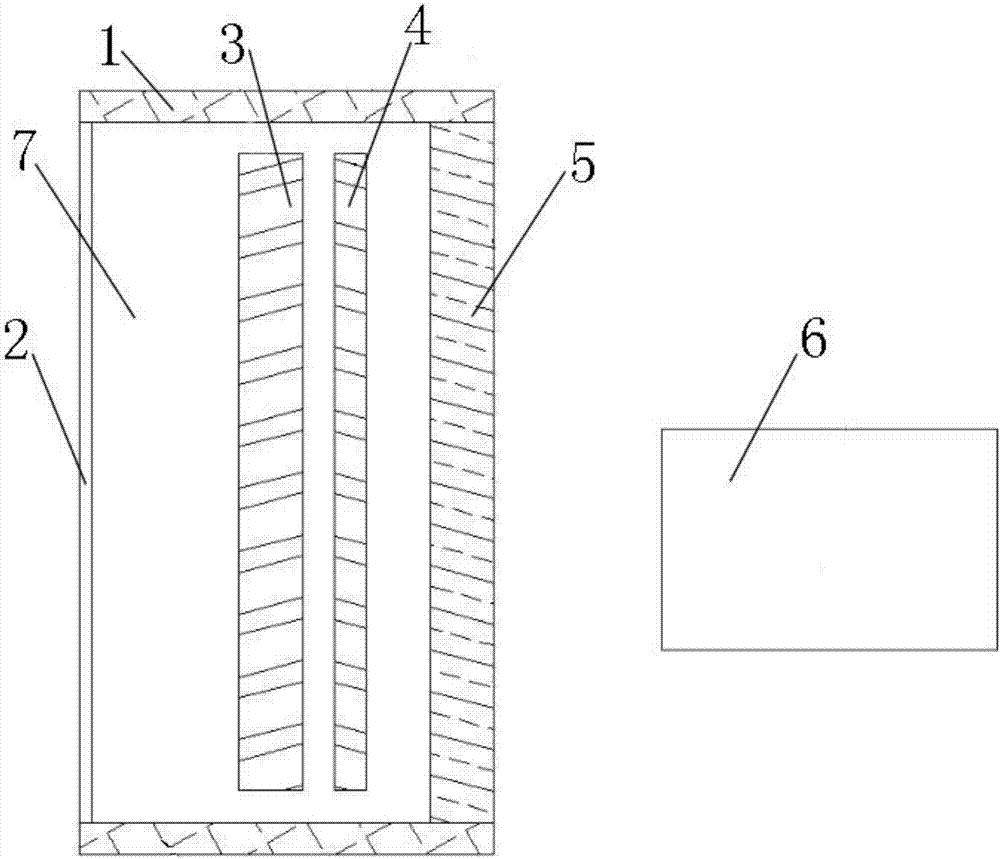
A hard X-ray grating phase-contrast imaging apparatus with large field-of-view, high contrast and low dose and the method thereof. The apparatus includes a source emitter (31), a source grating (G0), a beam splitting grating (G1), an analyzer grating (G2) and a detector (32). The source grating (G0), the beam splitting grating (G1), the analyzer grating (G2) and the detector (32) are orderly arranged in the transmission path of the source emitter (31). The period of the beam splitting grating (G1) is 30-50μm and the aspect ratio is not greater than 20. The apparatus can provide a high image contrast and a low radiation dose and realize a phase-contrast imaging with high energy and a large field-of-view by increasing the grating period, improving the duty ratio of the beam splitting grating (G1) and increasing the distance from an object to the analyzer grating (G2). The apparatus can also utilize the conventional polychromatic x-ray light source and available grating manufacture process, and be suitable for clinical use.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Device and method for generating femtosecond time-resolved X-ray source
InactiveCN102185250ASimple and fast operationWave amplification devicesHard X-raysFemto second laser
The invention provides a device for generating a femtosecond time-resolved X-ray source, comprising a femtosecond laser, a reflector, a focusing optical element as well as a target material and an ultrasound gas nozzle in a vacuum target chamber, wherein the femtosecond laser is used for outputting laser pulses with the pulse widths at the order of femtosecond and the contrast ratio of lasers is between 10-9 and 10-8; the focusing optical element is used for receiving the laser pulses and navigating the laser pulses to the focusing area of the focusing optical element, and the average strength of lasers in the focusing area is at least 5*10<16>W / cm<2>; and the target material is changed to a cluster through the ultrasound gas nozzle, and interacts with the laser pulses in the focusing area to generate femtosecond X-rays, and a gas is an inert gas. The device is simple in operation, and the formed ultrafast single-color hard X-ray source can help the application of X-rays driven by a single laser in the femtosecond time resolution become possible.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
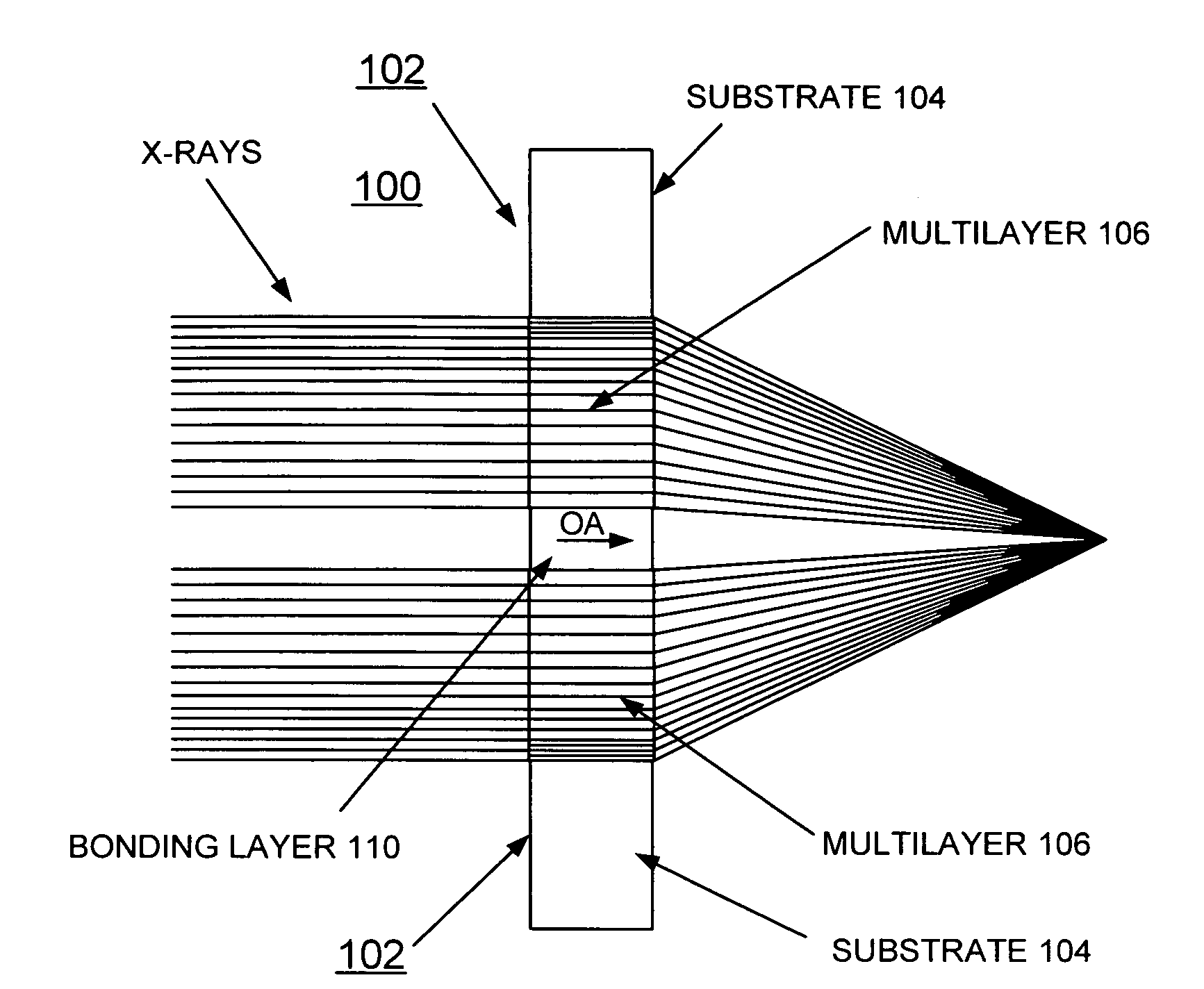
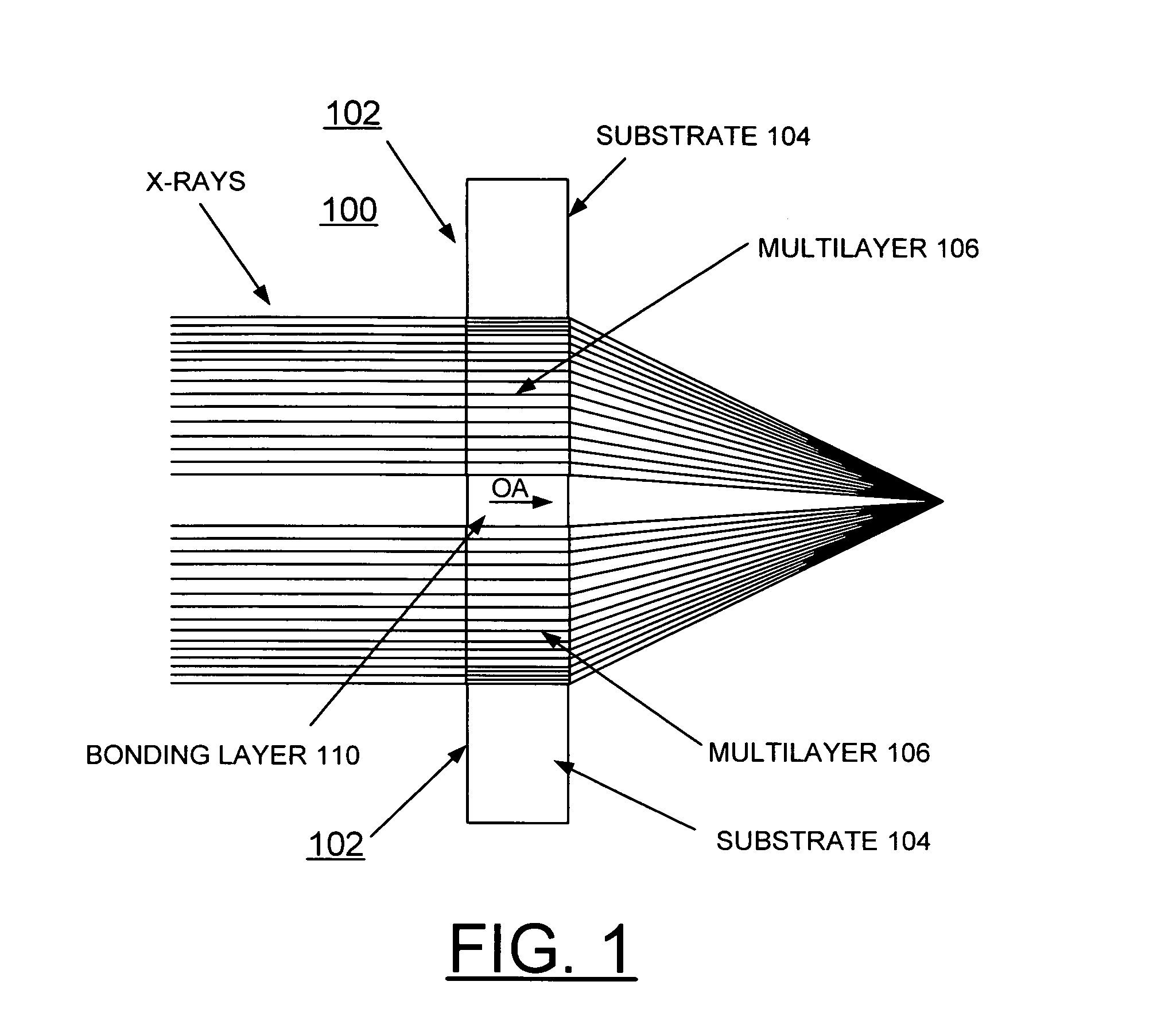
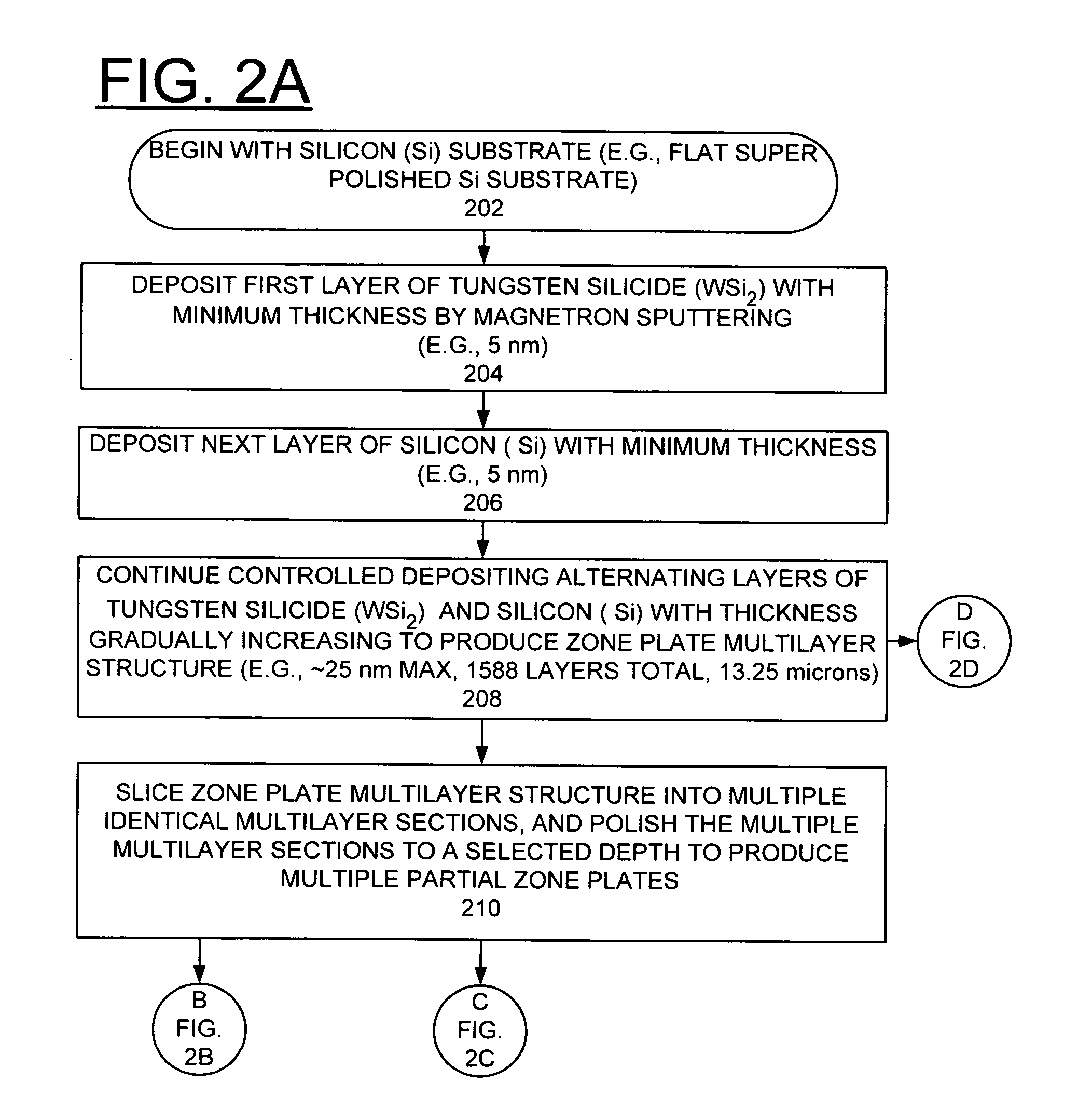
Method of making and structure of Multilayer Laue Lens for focusing hard x-rays
InactiveUS20080137810A1High diffraction efficiencyImprove efficiencyNanoinformaticsHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionHard X-raysTransmission geometry
A zone plate multilayer structure includes a substrate carrying a plurality of alternating layers respectively formed of tungsten silicide (WSi2) and silicon (Si). The alternating layers are sequentially deposited precisely controlling a thickness of each layer from a minimum thickness of a first deposited layer adjacent the substrate to a maximum thickness of a last deposited layer. The first minimum thickness layer has a selected thickness of less than or equal to 5 nm with the thickness of the alternating layers monotonically increasing to provide a zone plate multilayer structure having a thickness of greater than 12 μm (microns). The x-rays are diffracted in Laue transmission geometry by the specific arrangement of silicon and tungsten silicide.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
New X ray tube, and fabricating method
New type X ray tube is capable of generating X beam of rays with high spatial coherence, large dose, and large emission angle. Anode in extended electron beam or ion beam bomb structure, or structured electron beam or non-structured ion beam bomb is adopted in the invention to generate parallel-arranged linear array of emitter of X ray. Modes in structured electron or ion beam emitter, or structured grid, or electron or ion beam scan are adopted to realize emitter of X ray. Parallel-arranged periodic structure composed of high Z metal strips with narrow enough line width is adopted for structured anode. The disclosed X ray tube is workable under mode of continuous operation, or mode of pulse operation; and capable of outputting hard X ray or soft X ray. The invention is applicable to fundamental research in areas of biology, medical science, and material science etc. or in use for areas of disease diagnosis, industrial non-destructive inspection, online test etc.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Apparatus and method for substrate neutralization and glass substrate charging prevention
InactiveCN1835653ABroaden the range of static electricity removalEliminate static electricityElectric discharge tubesStatic indicating devicesHard X-raysLength wave
A neutralizing method and a neutralizing apparatus for effectively neutralizing an insulating member in a simple and efficient way are disclosed. A hard X-ray generating device radiates a hard X-ray on the obverse surface of the insulating member from the direction perpendicular to the obverse surface of the insulating member. The hard X-ray generating apparatus radiates a hard X-ray having the wavelength of not less than 0.05 AA but less than 1 AA. The hard X-ray ionizes the air on the obverse surface of the insulating member and neutralizes the charge on the obverse surface of the insulating member, while at the same time neutralizing the charge on the reverse surface of the insulating member by the X-ray transmitted through the insulating member.
Owner:ORMON CORP
High aspect ratio x-ray targets and uses of same
ActiveUS20150303021A1Simple structureEasy to useX-ray tube laminated targetsRadiation/particle handlingSoft x rayHard X-rays
An x-ray target, a method of using the x-ray target, and a computer program product with instructions for carrying out a method of using the x-ray target. The x-ray target includes a substrate made from a soft x-ray producing material and a high aspect ratio structure made from a hard x-ray producing material. The hard x-ray producing material is embedded in the substrate, formed on the substrate, cantilevered out from the edge of the substrate, or any combination thereof. The high aspect ratio structure comprises a plurality of high aspect ratio structures arranged in one or more grids or arrays, and the high aspect ratio structures in one of the one or more grids or arrays are arranged to form a Hadamard matrix structure.
Owner:FEI CO
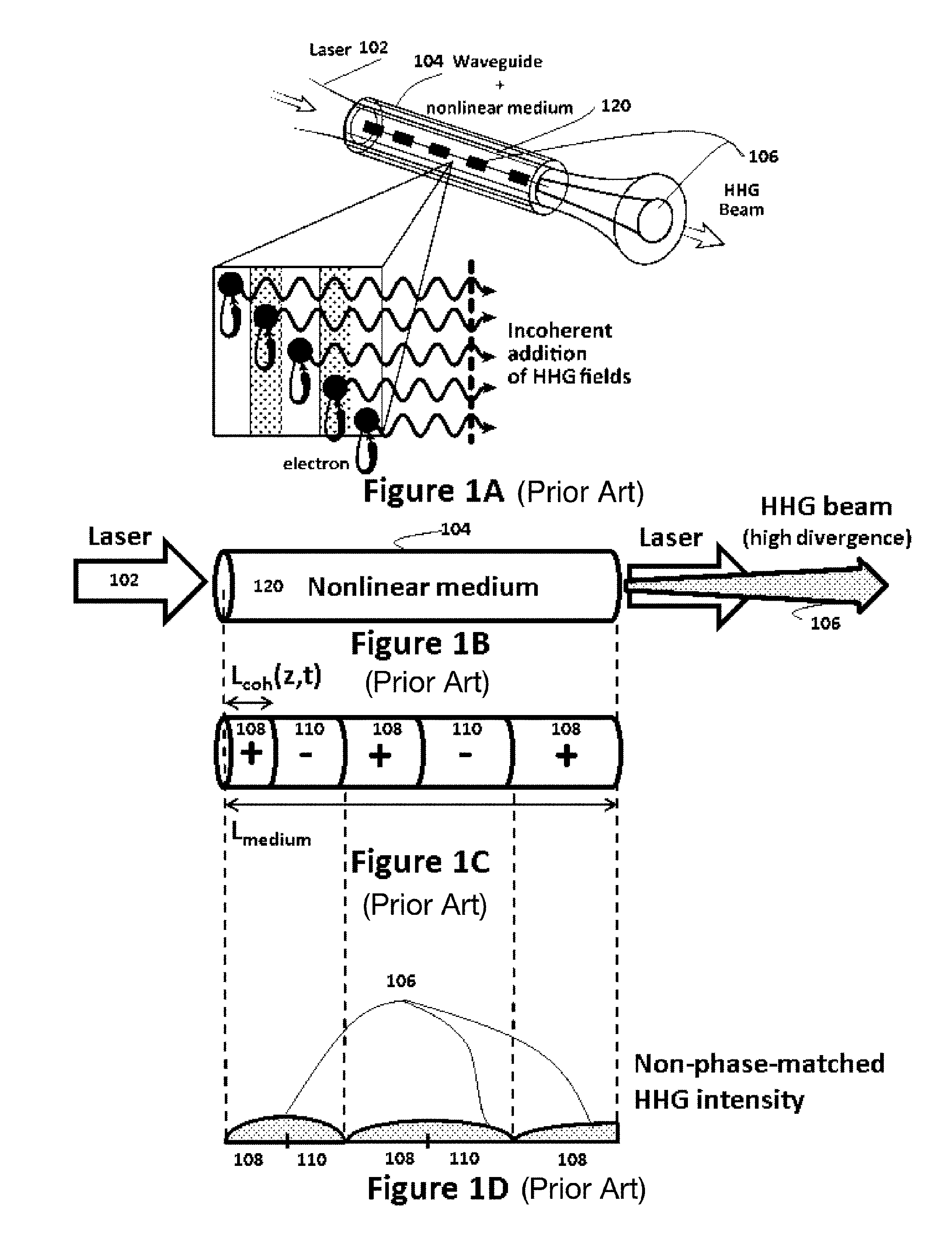
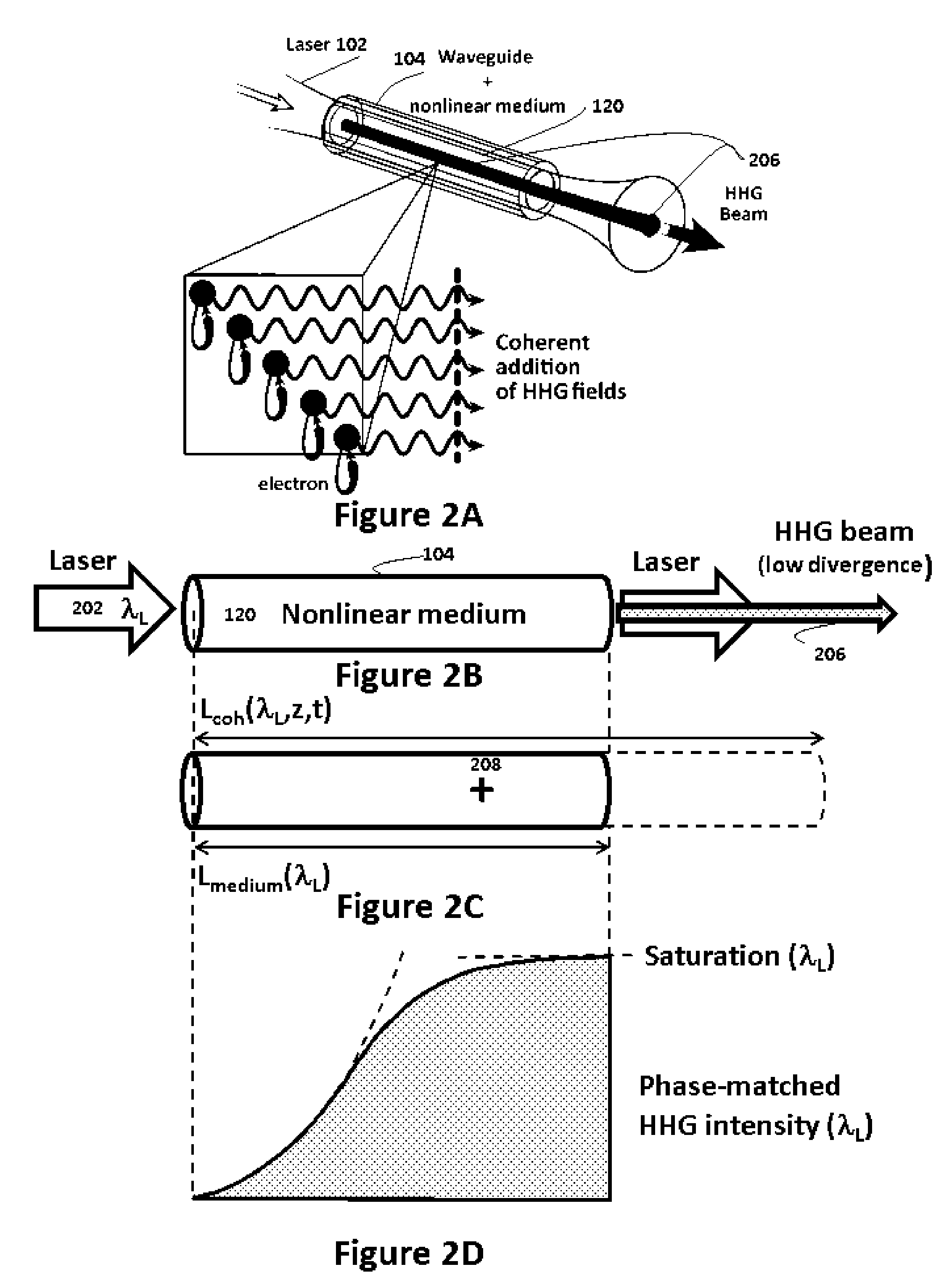
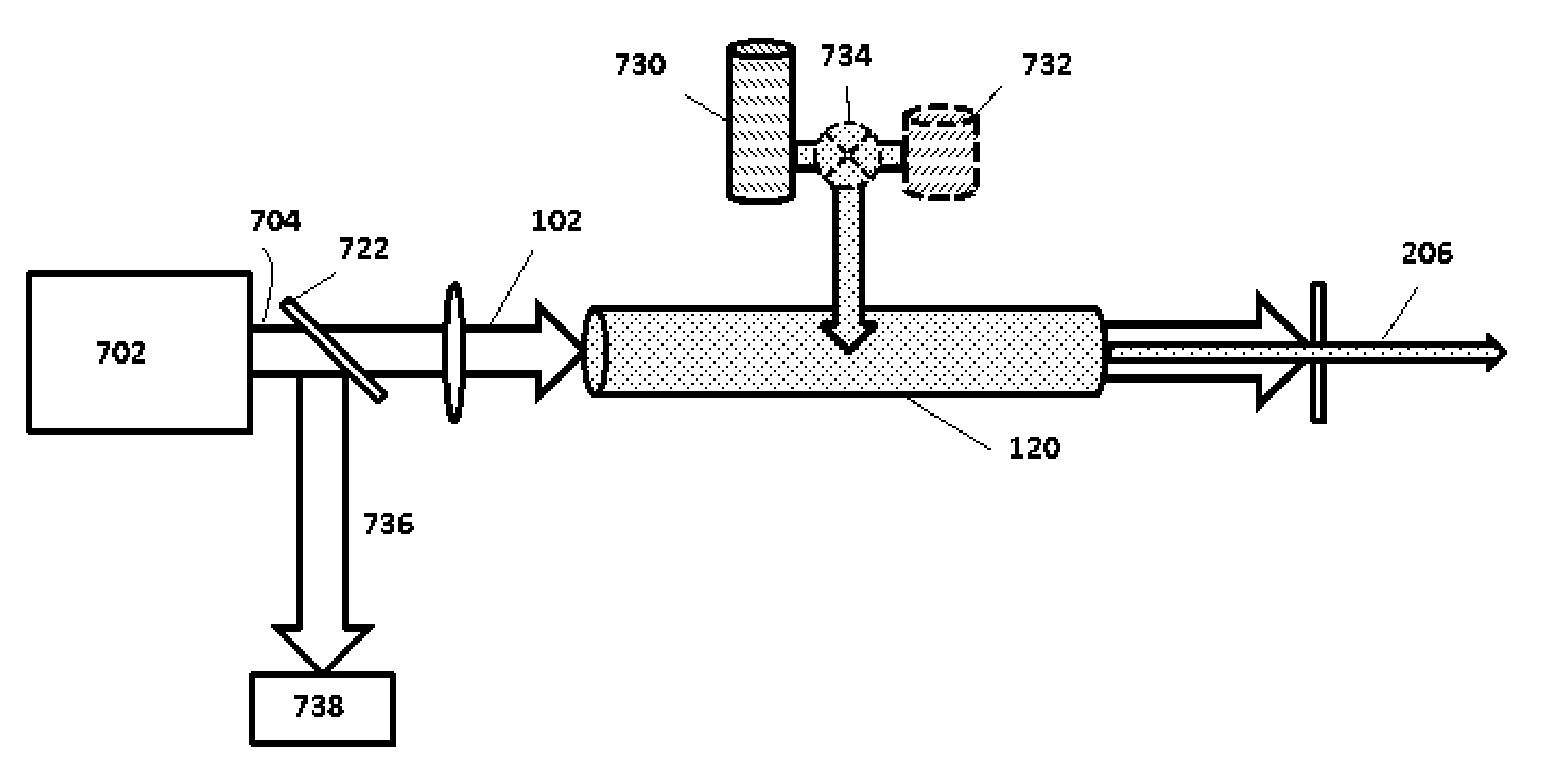
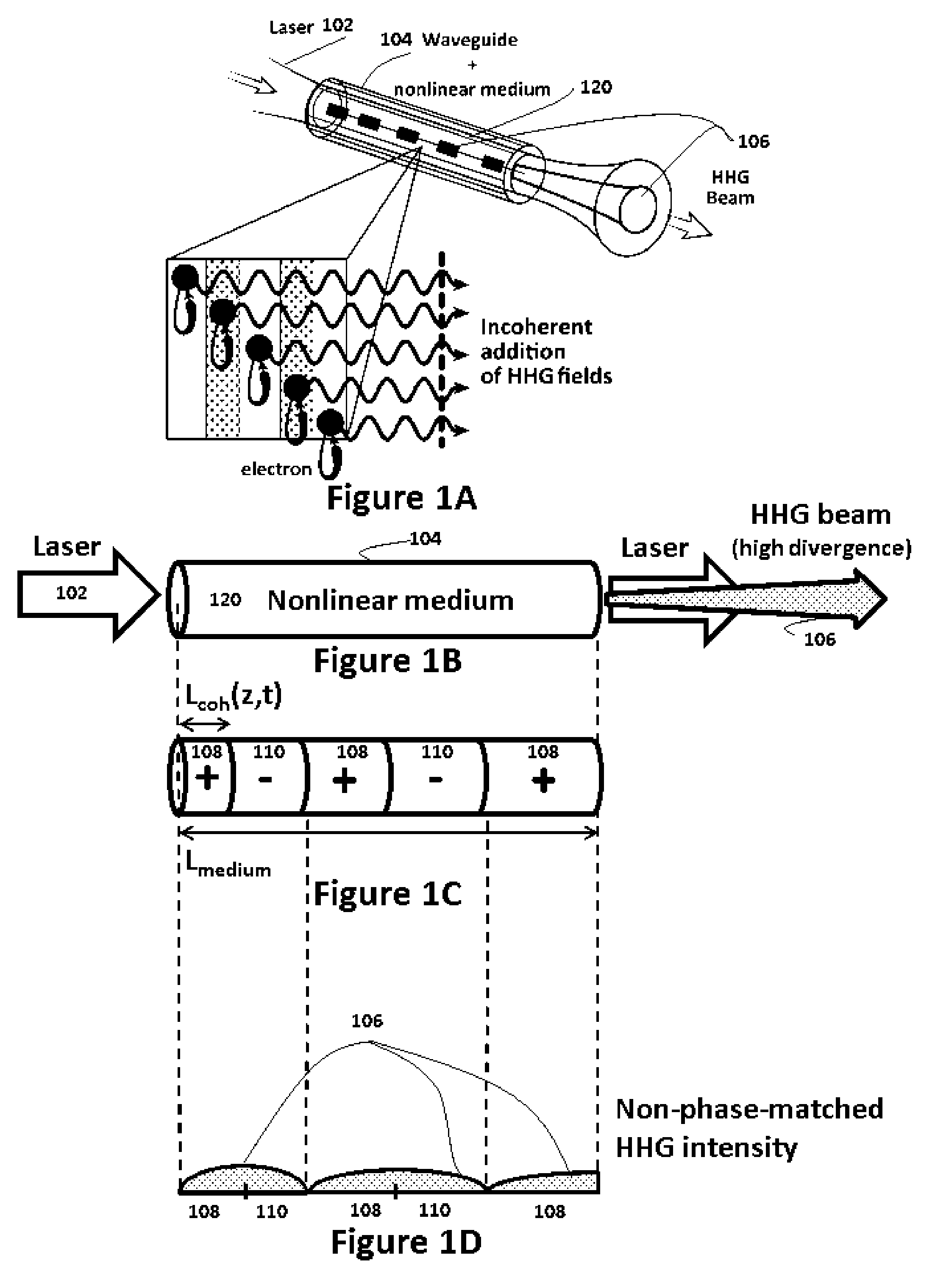
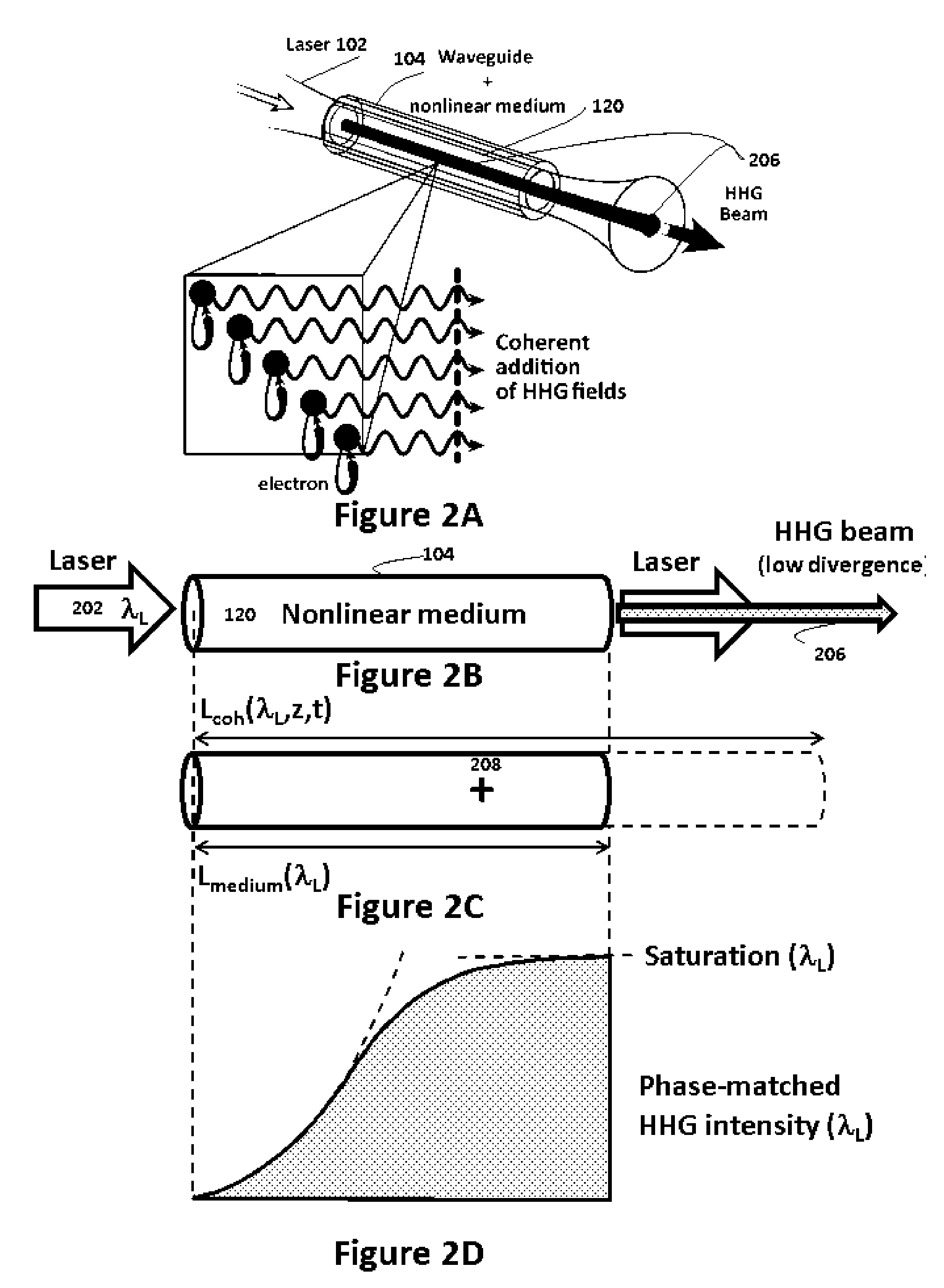
Phase-matched generation of coherent soft and hard X-rays using IR lasers
ActiveUS8462824B2Improve coherenceMaximum efficiencyActive medium materialX-ray apparatusHard X-raysHigher order harmonics
Phase-matched high-order harmonic generation of soft and hard X-rays is accomplished using infrared driving lasers in a high-pressure non-linear medium. The pressure of the non-linear medium is increased to multi-atmospheres and a mid-IR (or higher) laser device provides the driving pulse. Based on this scaling, also a general method for global optimization of the flux of phase-matched high-order harmonic generation at a desired wavelength is designed.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Phase-matched Generation of Coherent Soft and Hard X-rays Using IR Lasers
ActiveUS20110007772A1Great spatial coherenceMinimize phase mismatchActive medium materialX-ray tube with very high currentHard X-raysHigher order harmonics
Phase-matched high-order harmonic generation of soft and hard X-rays is accomplished using infrared driving lasers in a high-pressure non-linear medium. The pressure of the non-linear medium is increased to multi-atmospheres and a mid-IR (or higher) laser device provides the driving pulse. Based on this scaling, also a general method for global optimization of the flux of phase-matched high-order harmonic generation at a desired wavelength is designed.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Optical broad band element and process for its production
A process for the production of optical broad band elements for the ultra violet to hard x-ray wavelength range, especially the extreme ultra violet wavelength range is described. A set from series of layers made of at least two materials in relation to the layer sequence is designed and numerical optimization of the the layer thicknesses and of the cap layer thickness is performed. The materials are chosen in such a way that two successive layers interact with each other as little as possible or controllably. The set can be formed from MO2C— and Si-layers. The numerical optimization takes into account interlayers of a certain thickness and composition.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
High aspect ratio x-ray targets and uses of same
ActiveUS9934930B2Easy to useX-ray tube electrodesCathode ray concentrating/focusing/directingSoft x rayHard X-rays
An x-ray target, a method of using the x-ray target, and a computer program product with instructions for carrying out a method of using the x-ray target. The x-ray target includes a substrate made from a soft x-ray producing material and a high aspect ratio structure made from a hard x-ray producing material. The hard x-ray producing material is embedded in the substrate, formed on the substrate, cantilevered out from the edge of the substrate, or any combination thereof. The high aspect ratio structure comprises a plurality of high aspect ratio structures arranged in one or more grids or arrays, and the high aspect ratio structures in one of the one or more grids or arrays are arranged to form a Hadamard matrix structure.
Owner:FEI CO
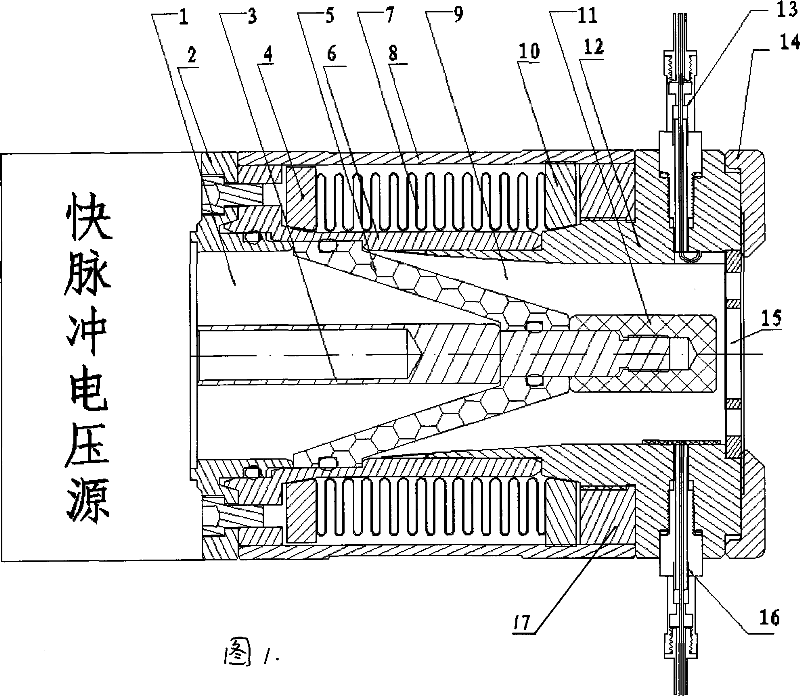
Repeat frequency fast pulse hard x-ray generator
InactiveCN101042976AAdjustable ray energyAdjustable intensityX-ray tube vessels/containerX-ray tube with very high currentHard X-raysVacuum chamber
A repetitive frequency fast pulse hard X-ray generator, diode of the invention is constructed by fixed supporting tubular and sliding supporting tubular, they are connected tightly by the bellows, and grooved rail is set on the bell socket part, rotating otter cylinder is set at the outer to drive the sliding supporting tubular move along the grooved rail; cathode connecting bar is set at the axis in cavity, the front end is cathode target; conical packing ring is set in the cavity of diode to divide the cavity into fore vacuum chamber and back oil recess; anode assembly are fixed at the fore and outer end of the diode. The invention designs the diode to be an active structure, that resolves the technique puzzle of stability of power source, vacuum tightness of diode, axiality of dynamic and static supporting, flexible adjustment on-line; on the precondition of not destroying the vacuum, adjusting aspect ratio flexibly can be realized, the current detecting detector is built; it possesses advantages of flexible structure, repeatable frequency or running for one time, and the pulse width, intensity and power spectrum can be adjustable continuously, it compensates for defects of current technique, and it provides ideal field of radiation for development and application of new type rapid response detector, building fast pulse hard X-ray metering standard, physical mechanism research of diode and pulse ray dynamic imaging technique.
Owner:NORTHWEST INST OF NUCLEAR TECH
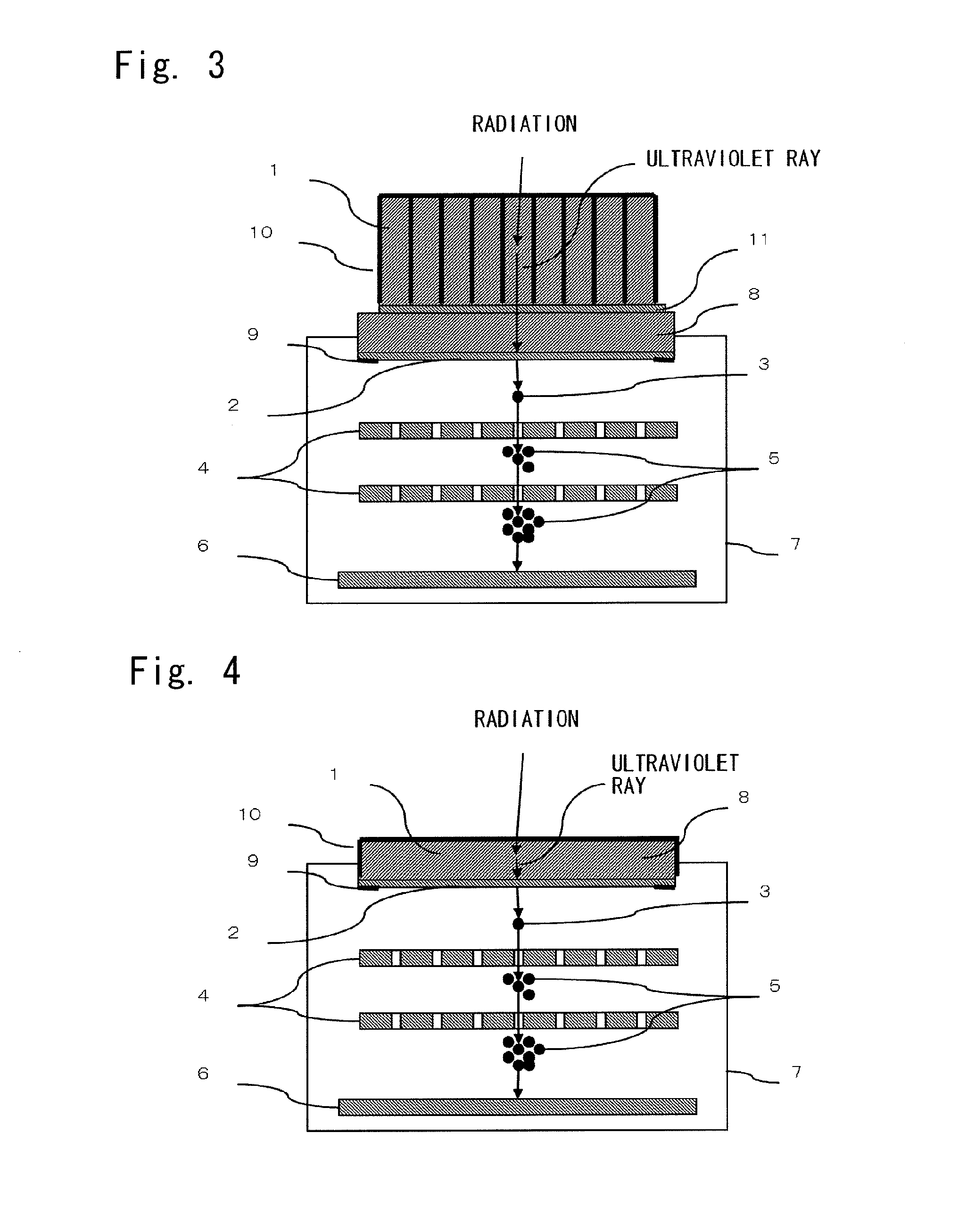
Radiographic image detector
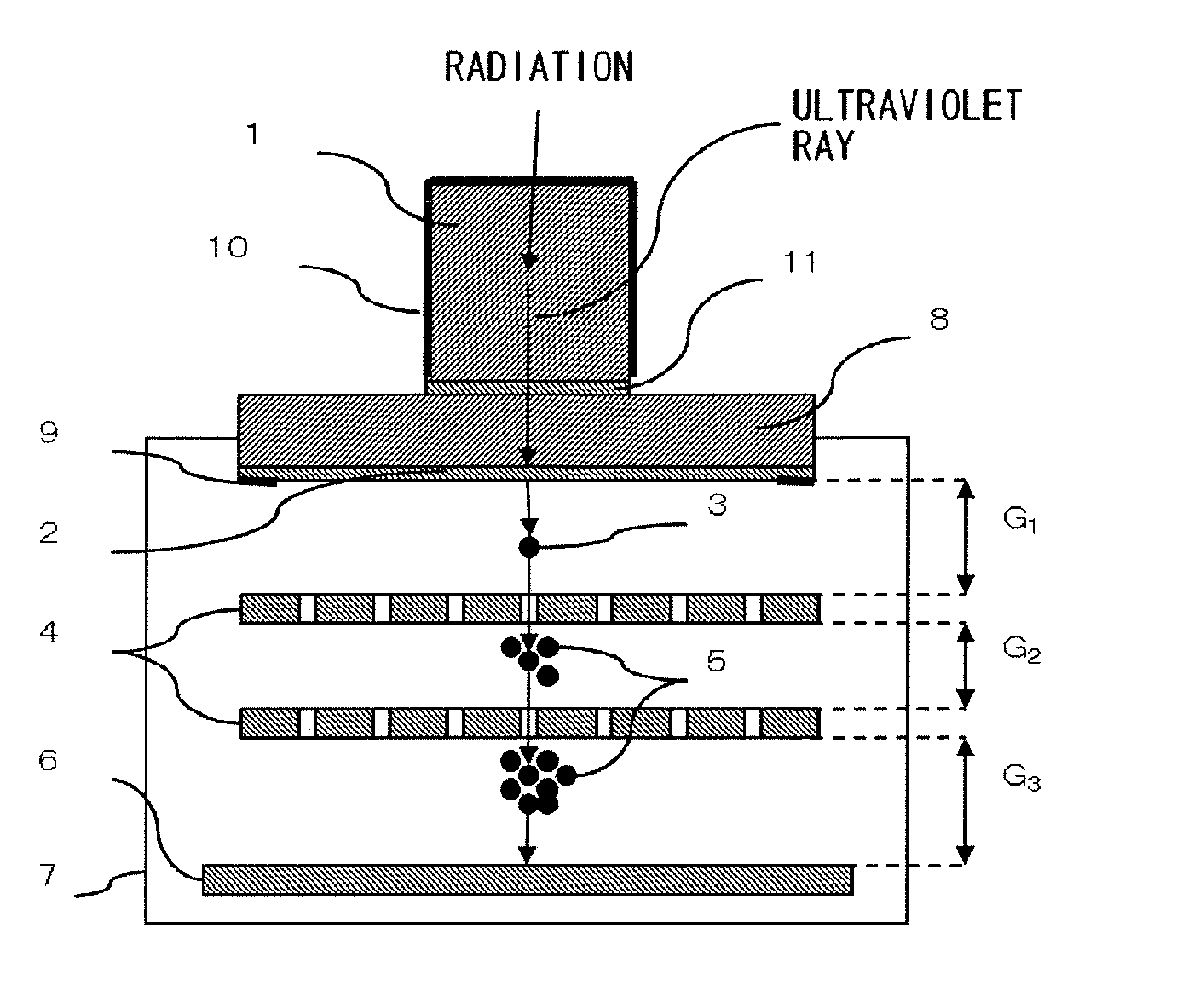
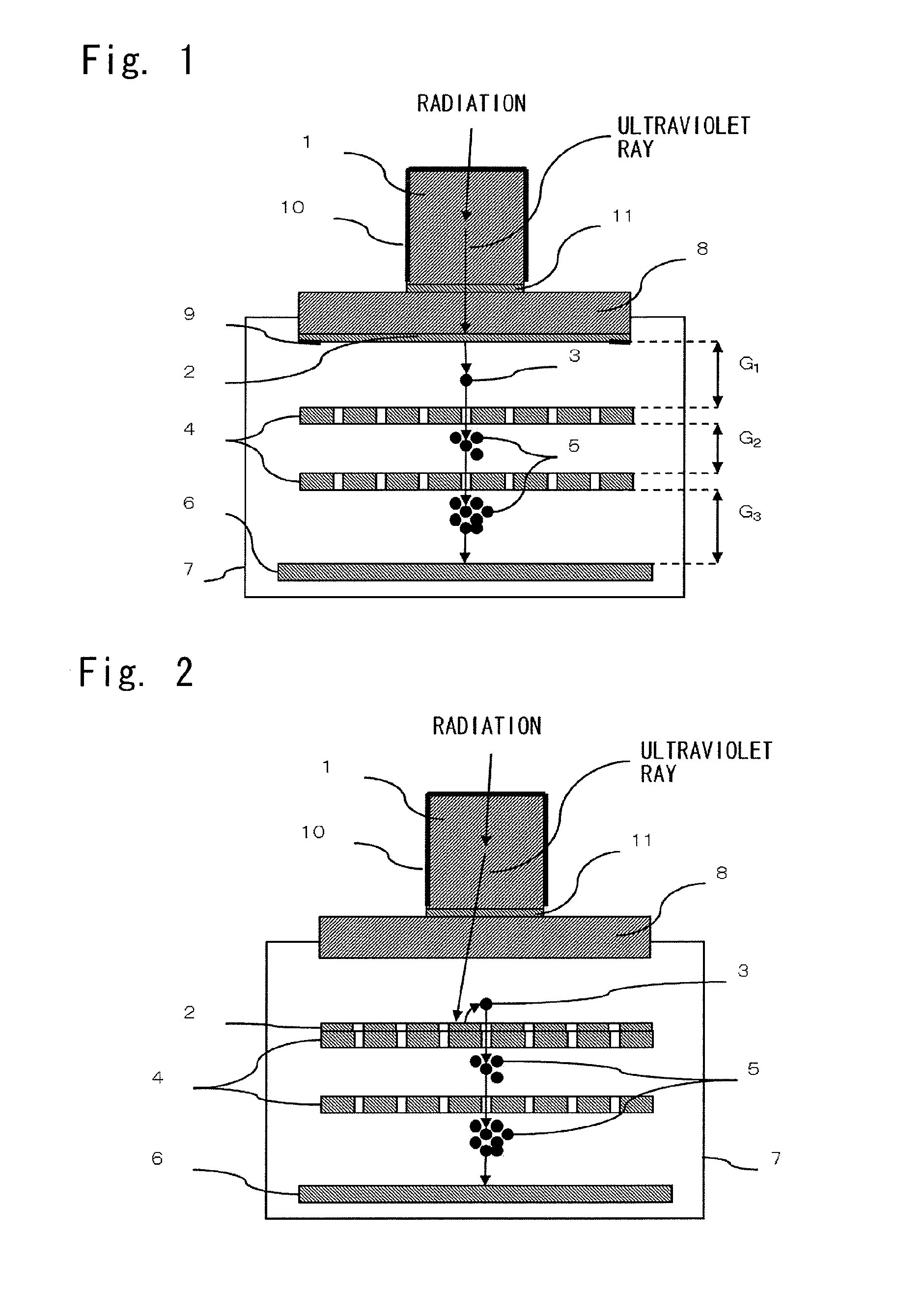
InactiveUS20120018642A1High sensitivityExcellent in position resolutionCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesSolid-state devicesHard X-raysLanthanum fluoride
[Problems to be Solved] It is an object of the present invention to provide a novel radiographic image detector which can detect radiation, such as hard X-rays or γ-rays, with high sensitivity and which is excellent in position resolution and count rate characteristic.[Means to Solve the Problems] A radiographic image detector comprises a combination of a scintillator, such as a lanthanum fluoride crystal containing neodymium, for converting incident radiation into ultraviolet rays; and a gas multiplication ultraviolet image detector for converting ultraviolet rays into electrons, amplifying such electrons by use of a gas electron avalanche phenomenon, and detecting the electrons. The radiographic image detector is characterized in that the gas multiplication ultraviolet image detector is basically constituted by a photoelectric conversion substance, such as cesium iodide or cesium telluride, for converting ultraviolet rays into electrons; a gas electron multiplier for amplifying electrons by use of the gas electron avalanche phenomenon; and a pixel electrode having an amplification function and a detection function.
Owner:TOKUYAMA CORP +3
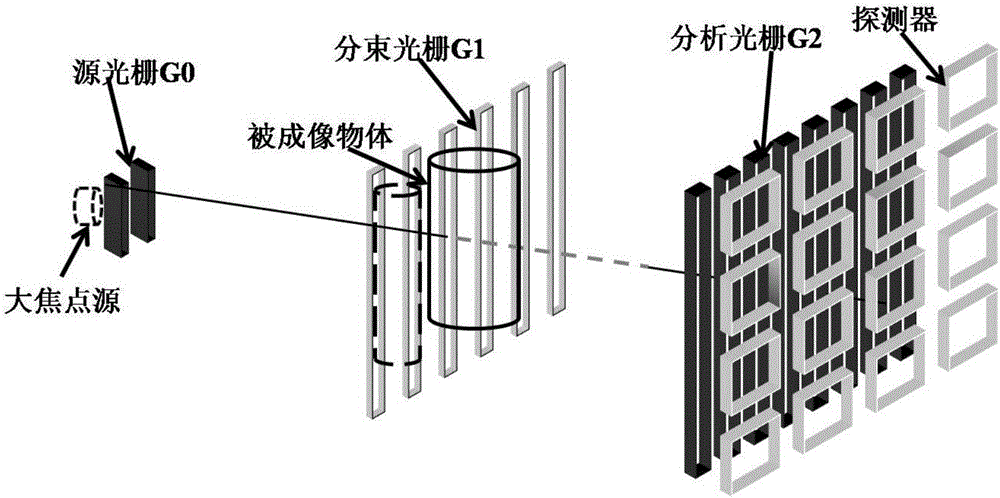
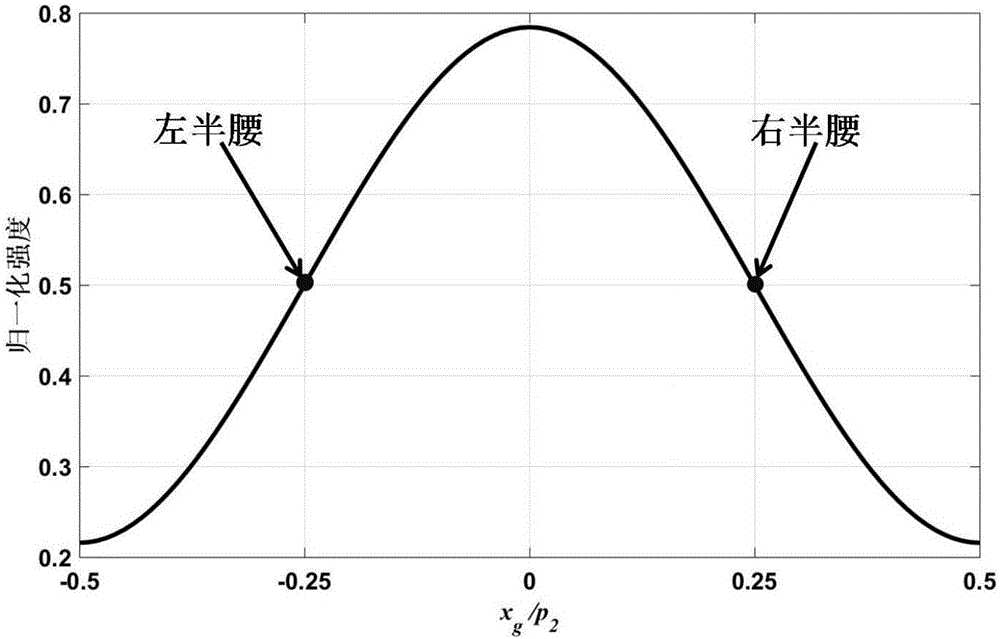
Novel method for extracting information of one-shot hard X-ray grating interferometer
ActiveCN105852895AOvercome limitationsRapid radiation doseRadiation diagnostic device controlComputerised tomographsHard X-raysGrating
The invention discloses a novel method for extracting information of a one-shot hard X-ray grating interferometer. The novel method comprises the following steps that 1, any grating is moved, so that the hard X-ray grating interferometer works at the left half position or the right half position of a light intensity changing curve; 2, a background projection image and a projection image of an imaged object are obtained; 3, the normalized projection image of the imaged object is obtained and subjected to logarithm taking processing; 4, according to the logarithm result, an expression is constructed to carry out Fourier transform; 5, according to the Fourier transform result, inverse Fourier transform is utilized for extracting absorption and phase shift signals of the imaged object. According to the method, a tedious grating scanning procedure is abandoned, the image acquiring procedure of the hard X-ray grating interferometer is simplified, fast and low-radiation-dosage hard X-ray phase contrast imaging can be achieved, therefore, the imaging efficiency is improved, and a new way is provided for low-radiation-dosage clinical medical imaging.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
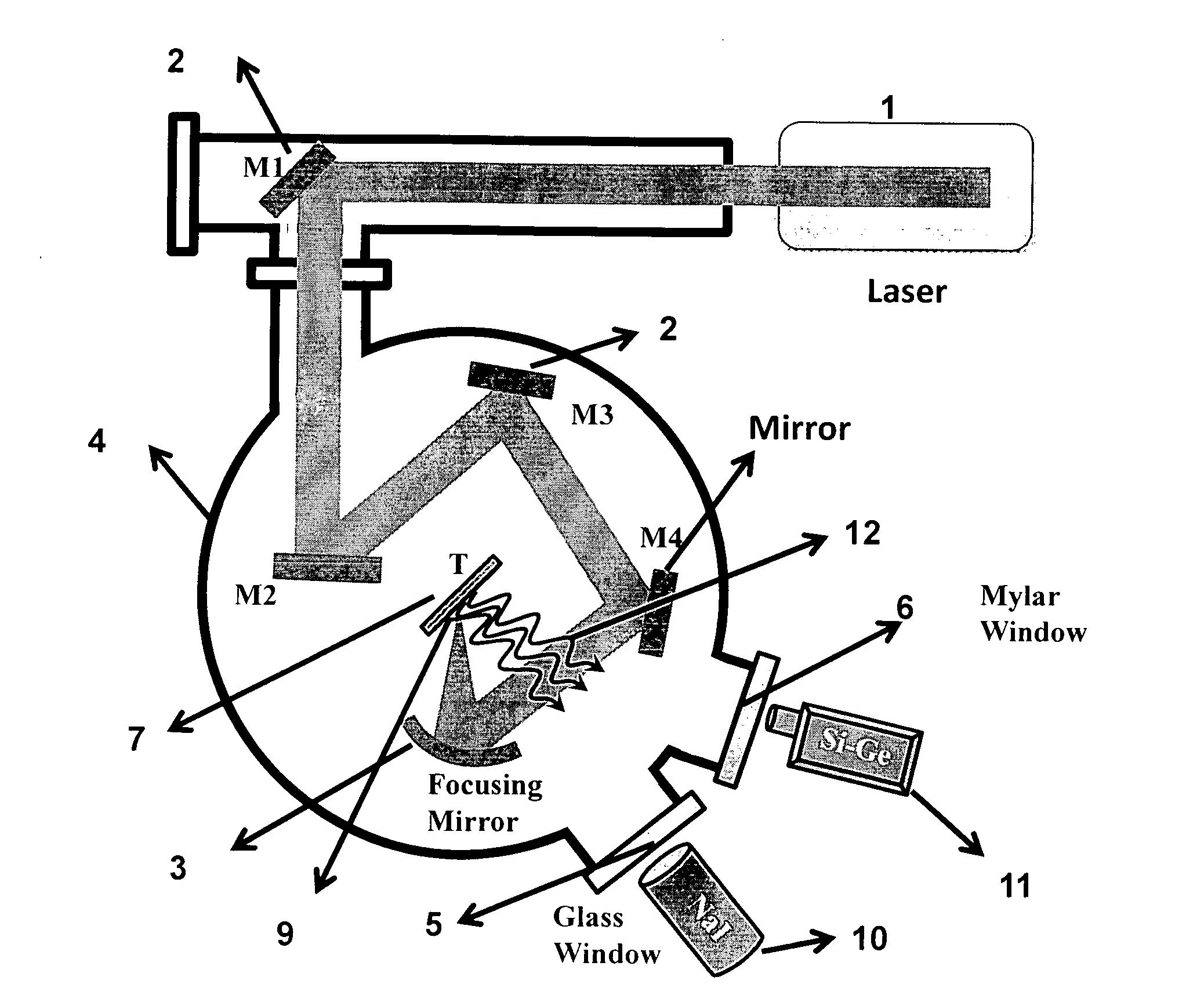
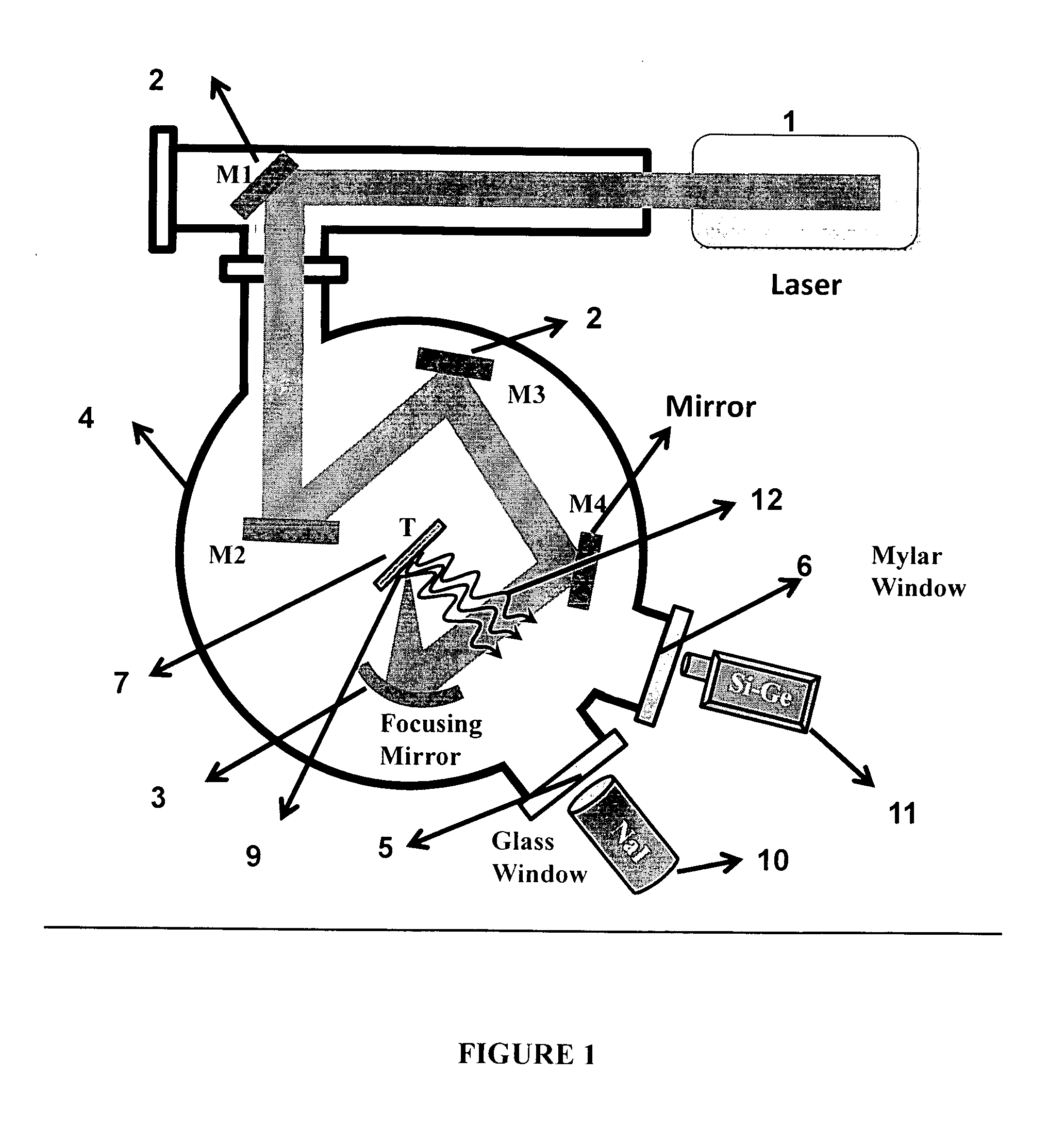
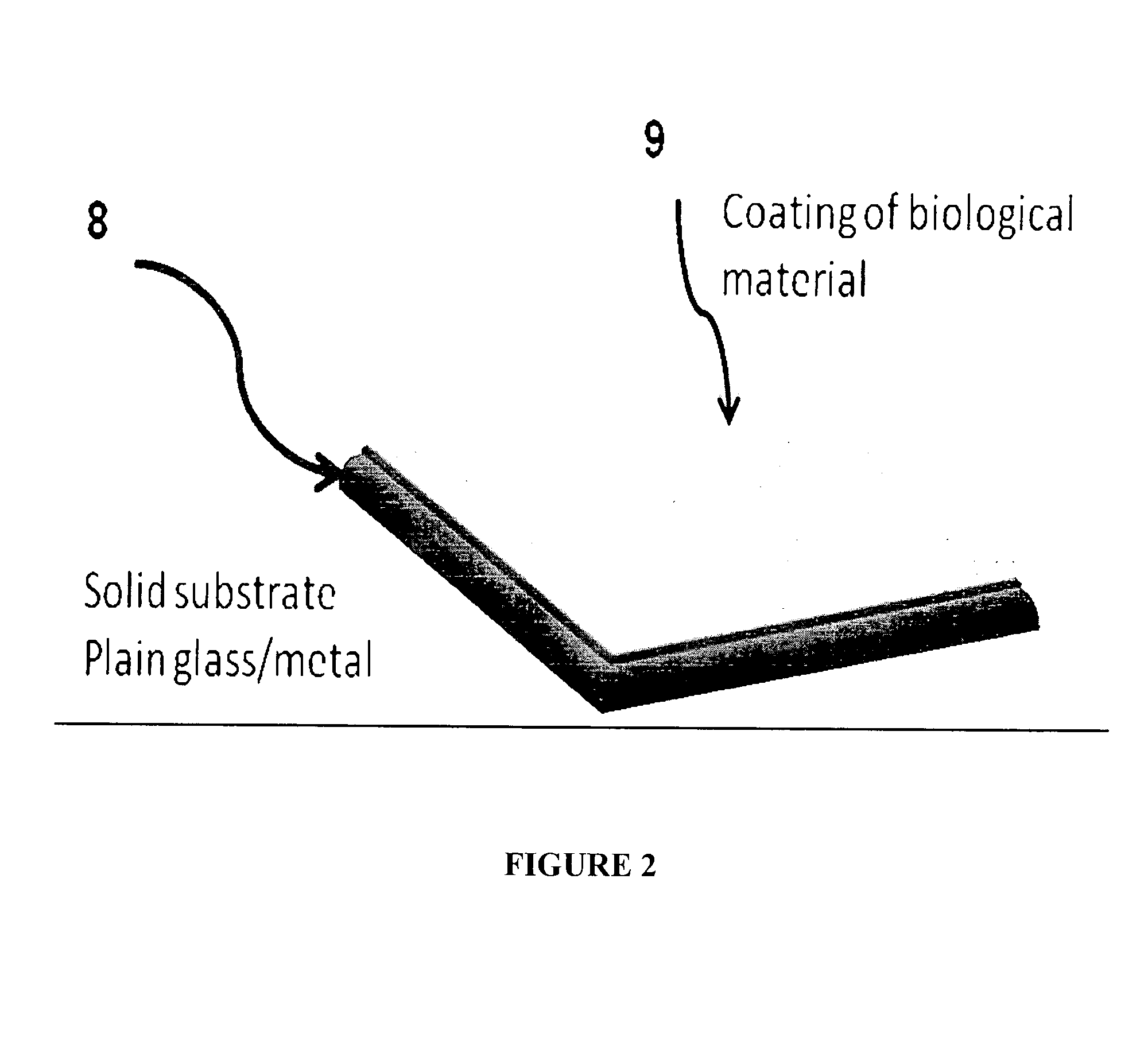
Biological laser plasma x-ray point source
InactiveUS20120228523A1Enhances X-ray yieldImprove emission characteristicsX-ray tube electrodesX-ray apparatusHard X-raysPlankton
The invention provides targets coated with structured biological materials, which are employed in laser produced plasma systems. The biological materials selected from cells of microbial, protozoan or plankton origin are applied on a portion of a solid target, like polished glass plate which then form a target system that absorbs the intense laser pulses, generates hot dense plasma and results in the emission of the X-rays. The method of coating structured biomaterial decreases the usable laser intensity required for producing the hot plasma, while increasing the X-ray yield. The coatings are easy to prepare and it is possible to vary the nature and shape of the cellular material in order to control / regulate the interaction with the light and thereby optimize the resultant plasma generation and X-ray emission. The increase in temperature of the plasma and the increase in yield demonstrate that the method is suitable for enhancing the emission yield in the Ultra Violet, Extreme Ultra violet, x-ray and the hard x-ray regimes.
Owner:TATA INSTITUTE OF FUNDAMENTAL RESEARCH
Graphite material, method for producing same, carbon material for battery electrodes, and battery
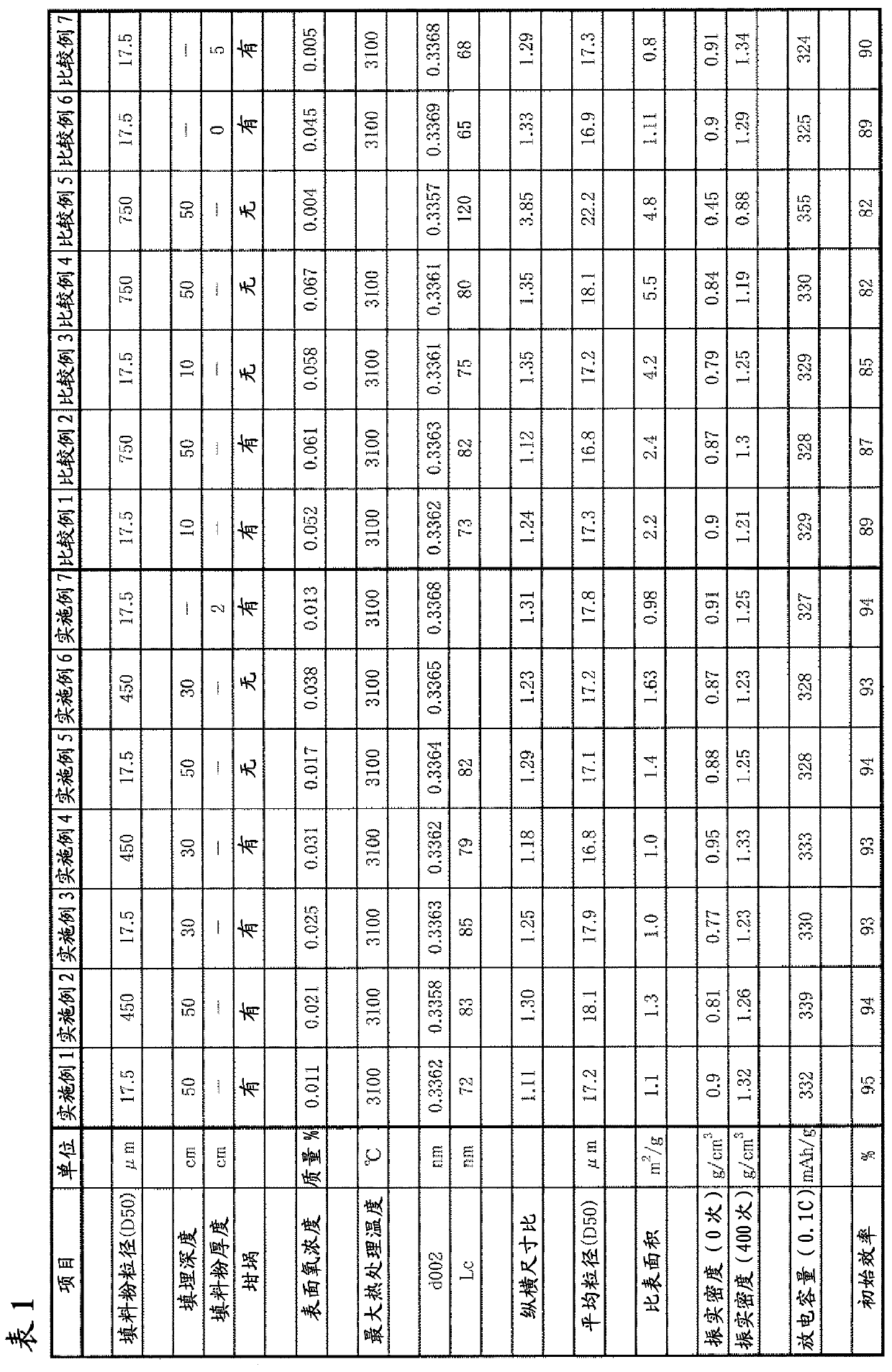
InactiveCN103328378AImprove initial efficiencyIncrease capacityGraphiteCell electrodesCurrent loadHard X-rays
The present invention provides: a graphite material which is suitable as an electrode material for nonaqueous electrolyte secondary batteries; a method for producing the graphite material; a carbon material for battery electrodes; and an excellent secondary battery which has an extremely small irreversible capacity,while maintaining charge / discharge cycle characteristics, large-current load characteristics and discharge capacity at high levels. A graphite material, wherein the oxygen amount (a) (mass%) in the region from the particle surface to 40 nm in the depth direction is within the range of 0.010<= a <= 0.04 as determined by the peak intensity of O1s obtained by HAX-PES measurement using a hard X-ray of 7,940 eV, can be used as a carbon material for battery electrodes that have excellent initial efficiency and small irreversible capacity, while maintaining large-current load characteristics, cycle characteristics and discharge capacity at high levels.
Owner:RESONAC HOLDINGS CORPORATION
Flashing optical fiber panel and preparation method
ActiveCN105293905AHigh resolutionImprove detection efficiencyX-ray/infra-red processesConversion screensFiberHard X-rays
The present invention discloses a flashing optical fiber panel and a preparation method, the preparation method comprises the following steps: 1, weighing each raw material according to the raw material composition, uniformly mixing all the raw materials and uniformly grinding to obtain a mixture; 2, pouring the mixture into a crucible, and putting the crucible into a reducing atmosphere glass melting furnace to prepare a glass melt; 3, leaking the glass melt to form a glass rod, placing the glass rod into a 500-700 DEG C muffle furnace for insulation, cooling with the furnace and naturally cooling for annealing; 4, cutting the annealed glass, grinding the surface, polishing, and processing into a sample, namely a flashing glass core rod; and 5, using the flashing glass as a core material for preparing the flashing optical fiber panel, matching the core material with leather material glass to pull into optical fiber, arranging the optical fiber, and molding by hot melt pressing to prepare a flashing optical fiber panel blank, and optically processing the flashing optical fiber panel blank to prepare the desired size flashing optical fiber panel; the flashing optical fiber panel achieves the low radiation dose and high-resolution imaging detection of hard X-rays and other high-energy rays.
Owner:CHINA BUILDING MATERIALS ACAD
Advanced multilayered Laue lens for hard X-ray focusing
InactiveCN103021496AOvercoming the inefficiency of high-order diffractionIncreased focus resolutionHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionHard X-raysDiffraction efficiency
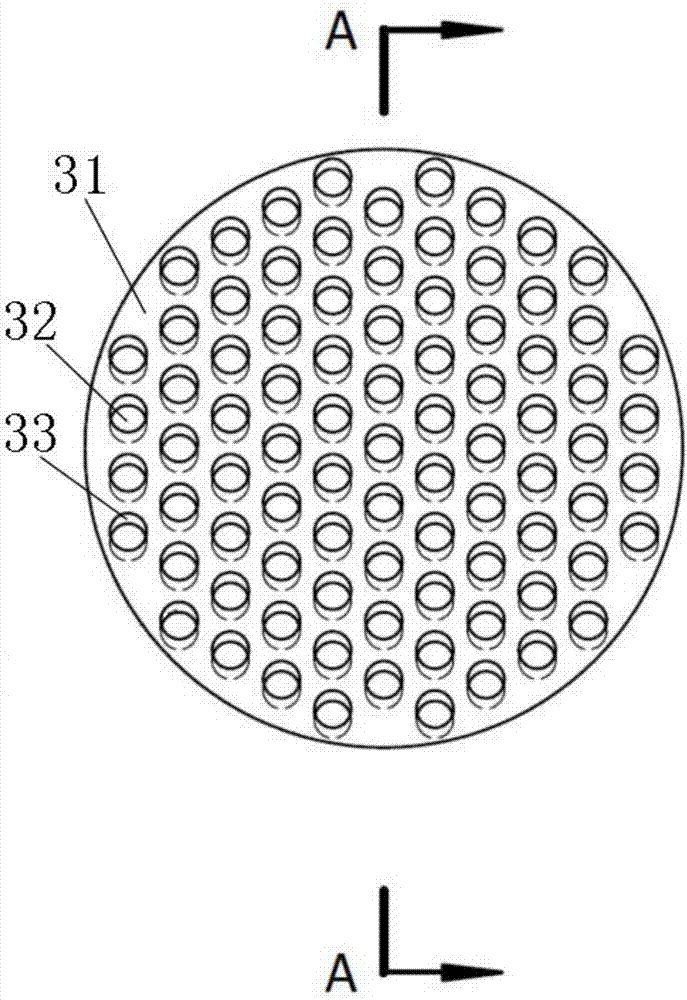
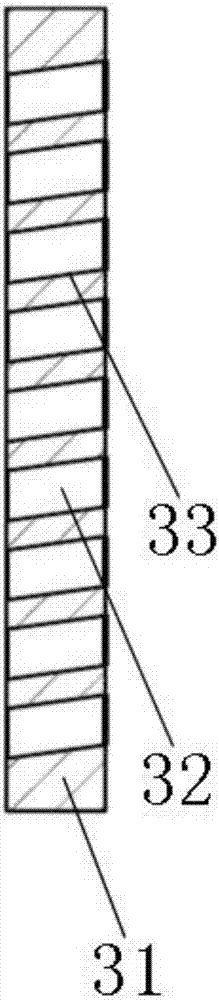
The invention relates to an advanced multilayered Laue lens for hard X-ray focusing. The proper depth t of the cross section can be selected by changing the thickness ratio (gamma=dA / (dA+dB), A is an absorbing layer, B is a spacing layer) of two materials of a local grating of the multilayered Laue lens, and the efficiency of the advanced diffraction can greatly enhanced, so that the advanced diffraction can be efficiently utilized, and further, the focusing resolution ratio of the hard X-ray is enhanced. Compared with the traditional multilayered Laue lens, the invention provides an effective method for realizing the high-efficiency nanoscale hard X-ray focusing, which utilizes the advanced diffraction of the Laue lens to focus the hard X-ray, and overcomes the problem of the low advanced diffraction efficiency of the traditional wave zone plate by changing the thickness ratio of the different materials in the Laue lens structure.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Multichannel hard X-ray imaging detector with time gating function
PendingCN107402401ASimple structureScientific and reasonable designRadiation intensity measurementHard X-raysOptoelectronics
The invention discloses a hard X-ray imaging detector which settles the problems of low time resolution, low space resolution, small visual field and incapability of satisfying a detecting requirement in hard X-ray detection. The hard X-ray imaging detector comprises a sealed vacuum chamber, a multichannel hard X-ray detecting optical cathode, a microchannel board and a pulse high-voltage power supply, wherein the vacuum chamber is mainly composed of a detector frame, a ray filtering window and a fluorescent screen, and the multichannel hard X-ray detecting optical cathode and the multichannel board are arranged in the vacuum chamber. The pulse high-voltage power supply supplies working voltage to the multichannel hard X-ray detecting optical cathode and the multichannel board, and supplies loading voltage to a space between the multichannel hard X-ray detecting optical cathode and the microchannel board and a space between the microchannel board and the fluorescent screen. The hard X-ray imaging detector has advantages of simple structure, scientific and reasonable design, and high convenience in use. The hard X-ray imaging detector can effectively improve time resolution, space resolution and object space resolution in detecting the hard X-ray. Furthermore the hard X-ray imaging detector has a time gating function and furthermore has a large detecting visual field.
Owner:LASER FUSION RES CENT CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
X-Ray Monitoring Optical Elements
ActiveUS20150092925A1Good surface conductivityRadiation/particle handlingX-ray apparatusSoft x rayHard X-rays
An X-ray article and method for analyzing hard X-rays which have interacted with a test system. The X-ray article is operative to diffract or otherwise process X-rays from an input X-ray beam which have interacted with the test system and at the same time provide an electrical circuit adapted to collect photoelectrons emitted from an X-ray optical element of the X-ray article to analyze features of the test system.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
Multidimensional alignment apparatus for hard x-ray focusing with two multilayer laue lenses
InactiveUS7597475B1Precise alignmentGuaranteed smooth progressRadiation/particle handlingNanoinformaticsSoft x rayHard X-rays
A multidimensional alignment apparatus is provided for multidimensional aligning of two linear multilayer Laue lenses (MLLs) for two-dimensional hard X-ray focusing. The multidimensional alignment apparatus precisely aligns and ensures stability of two linear MLLs performing hard x-ray focusing. The multidimensional alignment apparatus includes a base, a lower stages group controlling a first upstream MLL, an upper stages group positioned over the lower stages group controlling a second downstream MLL and an upper stage support attached to the base. The lower stages group provides five degrees of freedom precision positioning adjustment for the first upstream MLL. The second downstream MLL is mounted on the upper stages group with three degrees of freedom adjustment capability.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
Bremsstrahlung reflection triode
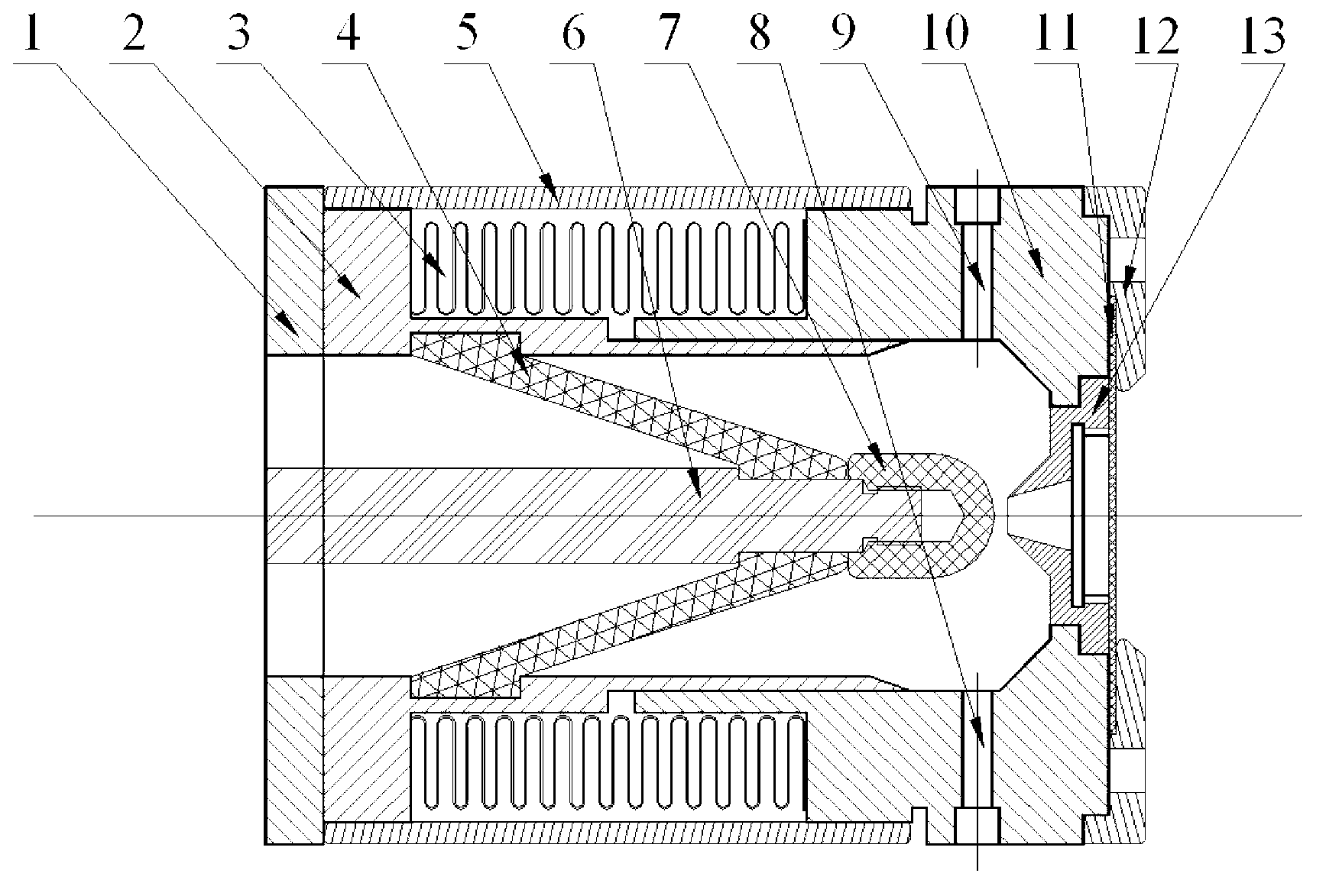
ActiveCN110047721ATake advantage ofLower average energyX-ray tube electrodesCathode ray concentrating/focusing/directingHard X-raysStrong pulse
The invention relates to a bremsstrahlung reflection triode for generating strong pulse hard X rays. The problems that the gap potentials of two cathodes and anodes of an existing bremsstrahlung reflection triode are inconsistent, and a radiation field cannot be fully utilized are solved. The triode comprises a reflection triode cavity, an anode base, an anode, cathodes, transverse cover plates, aforward cover plate, an insulation plate fixing nut, an insulation plate transition piece and an insulation plate. The part, connected with the insulation plate, of the reflection triode cavity is acylinder, the part, away from the insulation plate, of the reflection triode cavity is transited into a closed cavity, and two parallel flat plates are arranged on the opposite surfaces of the closedcavity; the two cathodes are respectively arranged on the two flat plates of the closed cavity; the anode is positioned between the two cathodes; the anode is arranged on the anode base, the anode base is installed on a water line inner cylinder through the insulation plate transition piece, and the insulation plate transition piece is fixed through the insulation plate fixing nut. The transversecover plates are arranged on the two flat plates of the closed cavity respectively, and the forward cover plate is arranged at the axial tail end of the closed cavity.
Owner:NORTHWEST INST OF NUCLEAR TECH
System and Method for Fuel Cell Material X-Ray Analysis
ActiveUS20080165924A1Shorten development timeImprove reliabilityRadiation/particle handlingUsing wave/particle radiation meansMetrologyHard X-rays
An imaging technology for fuel cells is based on x-ray microscopy. A metrology system images the electrochemical interaction areas of solid-oxide fuel cells (SOFC) in-situ. This system takes advantage of both the penetrating power and elemental absorption contrast of hard x-ray radiation to image the internal interaction areas in a SOFC. The technology can further take advantage of the strong dependence of the x-ray absorption on material type and energy to distinguish the four major material types: cathode, electrolyte, air, and low-Z contaminants such as sulfur.
Owner:CARL ZEISS X RAY MICROSCOPY
Vacuum diode with high current, small focal spot and long service life
ActiveCN103077875AIncrease beam intensityShort pulse timeX-ray tube electrodesX-ray tube vessels/containerHard X-raysElectron
The invention relates to a vacuum diode with high current, small focal spot and long service life. The original diode in a repetition frequency fast-pulse hard X-ray generator is modified, the structure and the material of movable cathode and anode assemblies are improved, a cathode head is made of tungsten nickel copper alloy materials and is seated on a movable support, a conical hole structure inwards forming a sharp end bulge is used for emitting electrons and is aligned with X rays, and an anode target is made of metal tantalum materials and is fixedly arranged on a copper core wire through screw threads. The conical annular cathode structure is improved, the radius of sent plasmas is favorably controlled, dense plasmas can be conveniently obtained, the self pinching condition in the electronic beam transporting process is met, submillimeter beam spots are formed, and the detailed imaging requirement of the pulse imaging field is met.
Owner:NORTHWEST INST OF NUCLEAR TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com