Patents
Literature
1575 results about "Image detector" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Robotic surgical device
InactiveUS20050096502A1Minimize traumaShorten preoperative preparation timeEndoscopesLaproscopesRobotic armDistal portion
Described herein is a robotic surgical device configured for performing minimally invasive surgical procedures. The robotic surgical device comprises an elongated body for insertion into a patient's body through a small incision. In one variation, the elongated body houses a plurality of robotic arms. Once the distal portion of the elongated body is inserted into the patient body, the operator may then deploy the plurality of robotic arms to perform surgical procedures within the patient's body. An image detector may be positioned at the distal portion of the elongated body or on one of the robotic arms to provide visual feedback to the operator of the device. In another variation, each of the robotic arms comprises two or more joints, allowing the operator to maneuver the robotic arms in a coordinated manner within a region around the distal end of the device.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
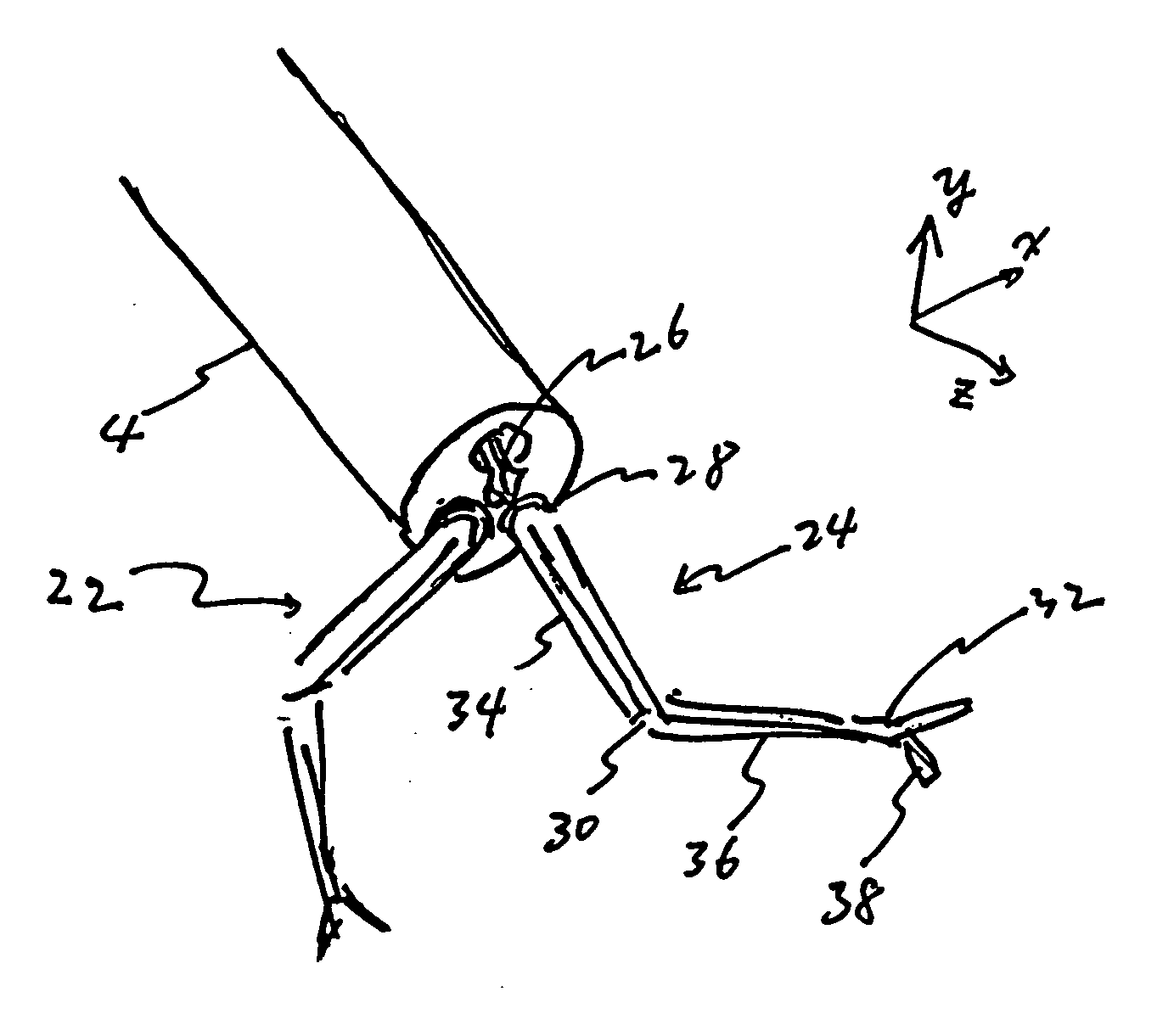
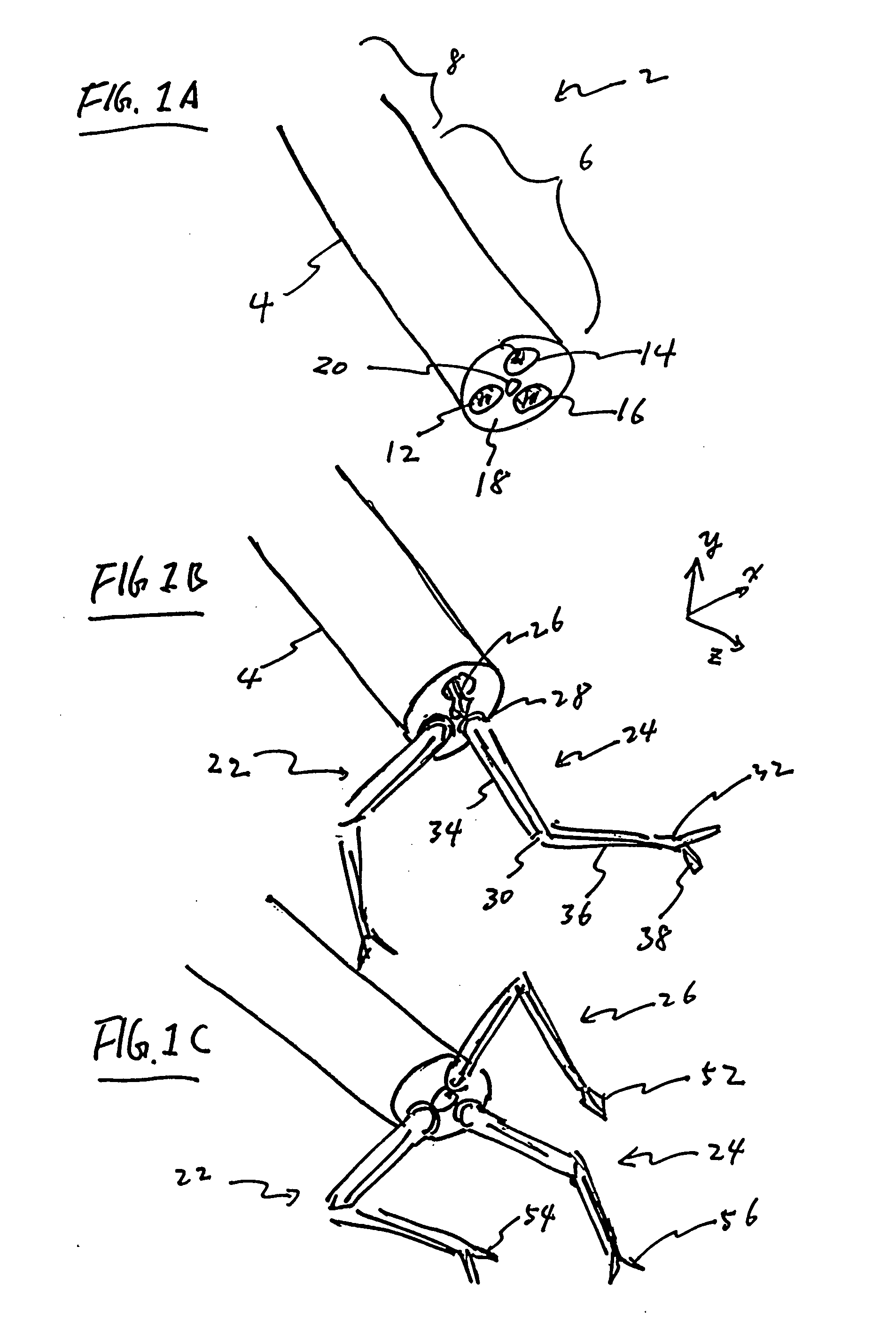
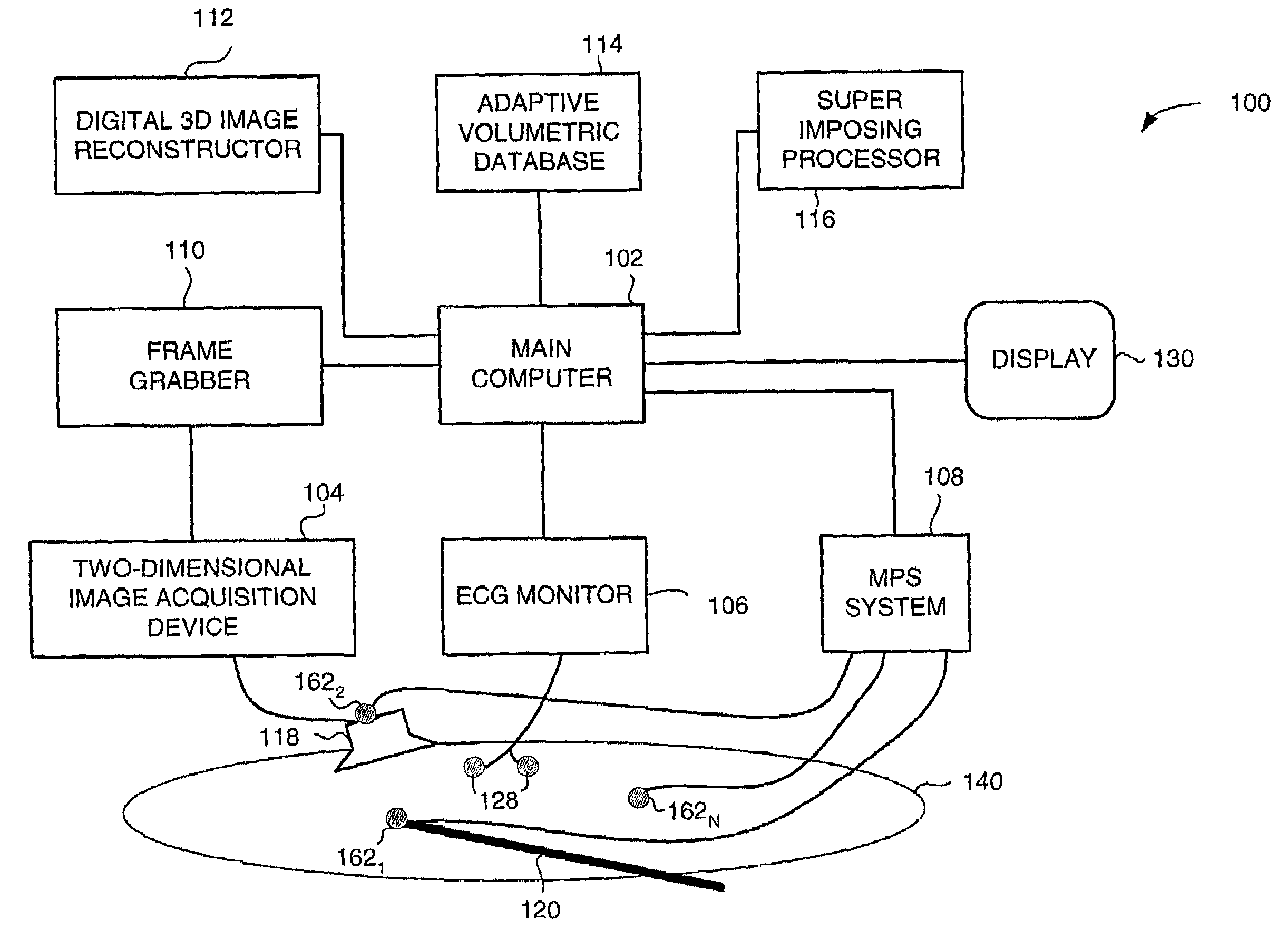
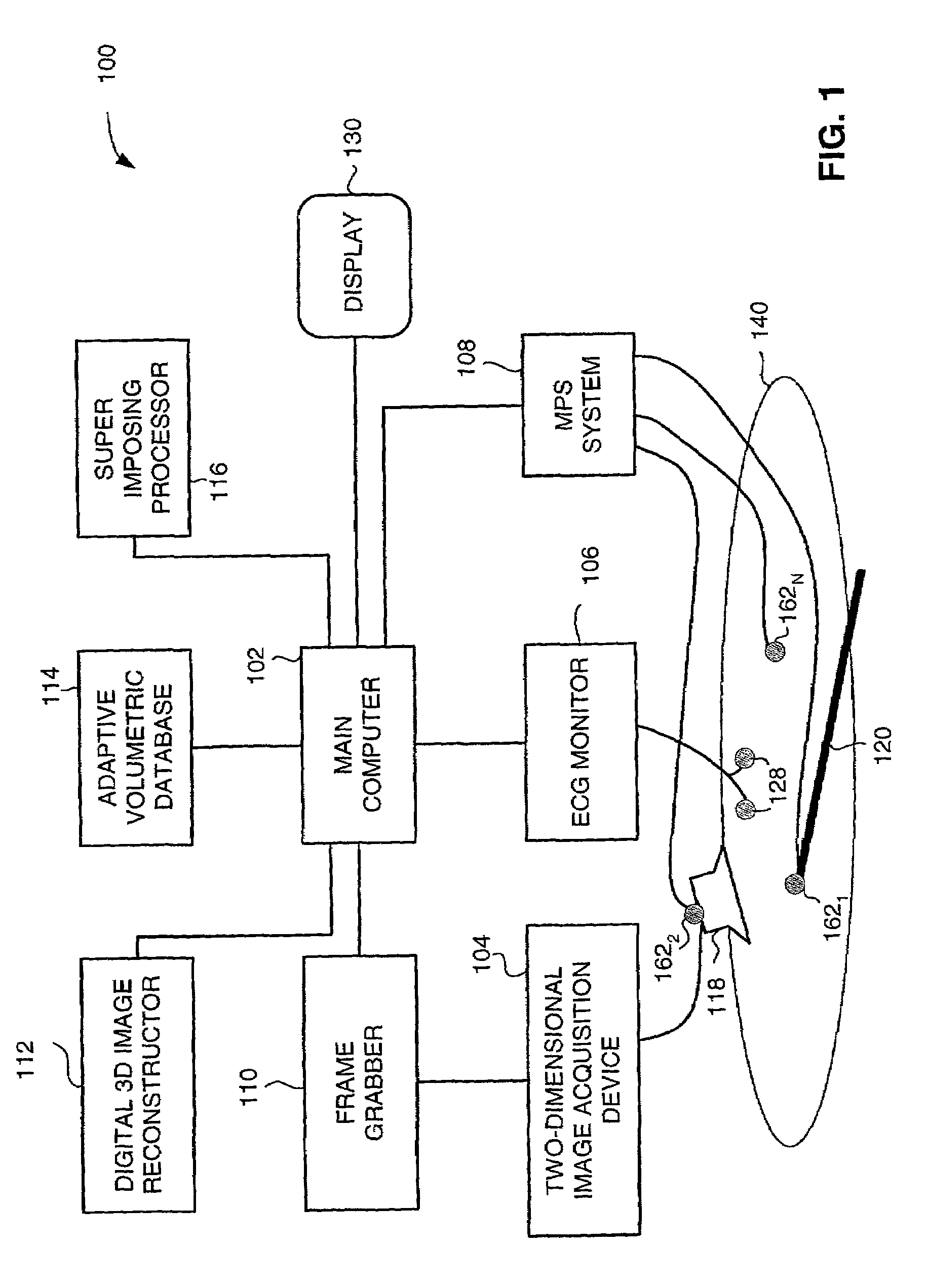
Method and apparatus for real time quantitative three-dimensional image reconstruction of a moving organ and intra-body navigation
InactiveUS7343195B2Operating tablesUsing subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic vibration meansImage detectionMedical imaging
Medical imaging and navigation system including a processor, a medical positioning system (MPS), a two-dimensional imaging system and an inspected organ monitor interface, the MPS including an imaging MPS sensor, the two-dimensional imaging system including an image detector, the processor being coupled to a display unit and to a database, the MPS being coupled to the processor, the imaging MPS sensor being firmly attached to the image detector, the two-dimensional imaging system being coupled to the processor, the image detector being firmly attached to an imaging catheter.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL INT HLDG SARL
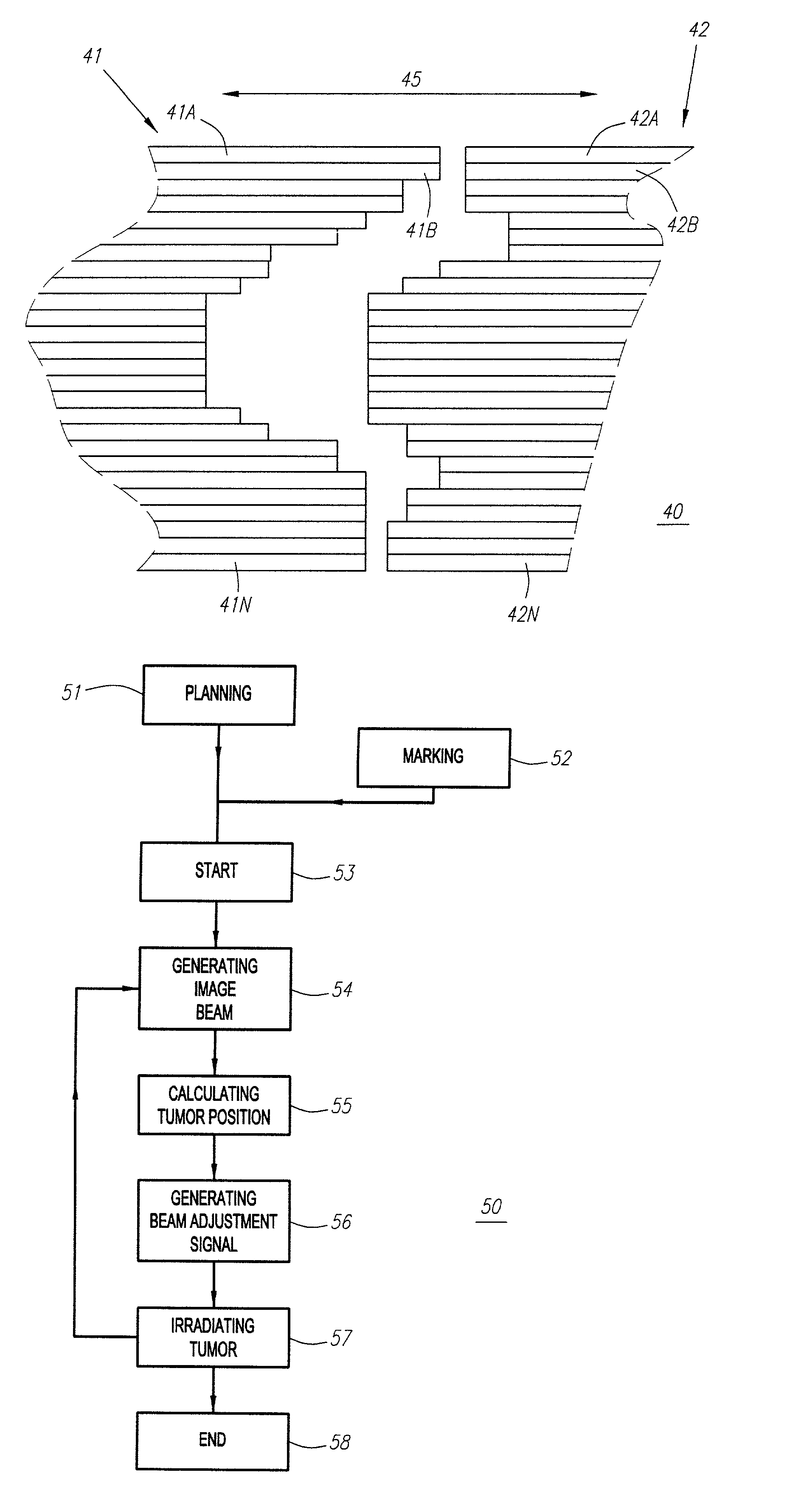
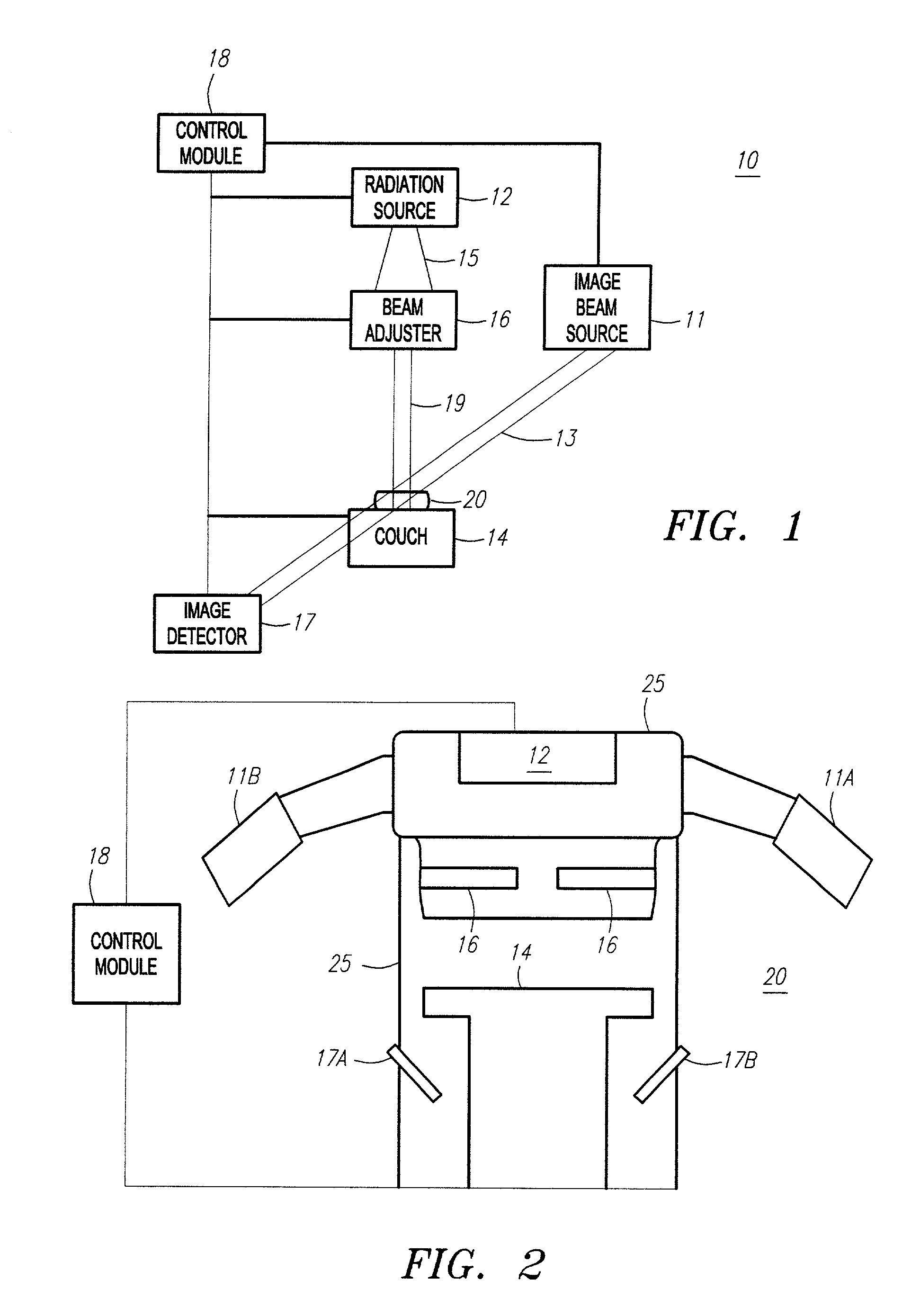
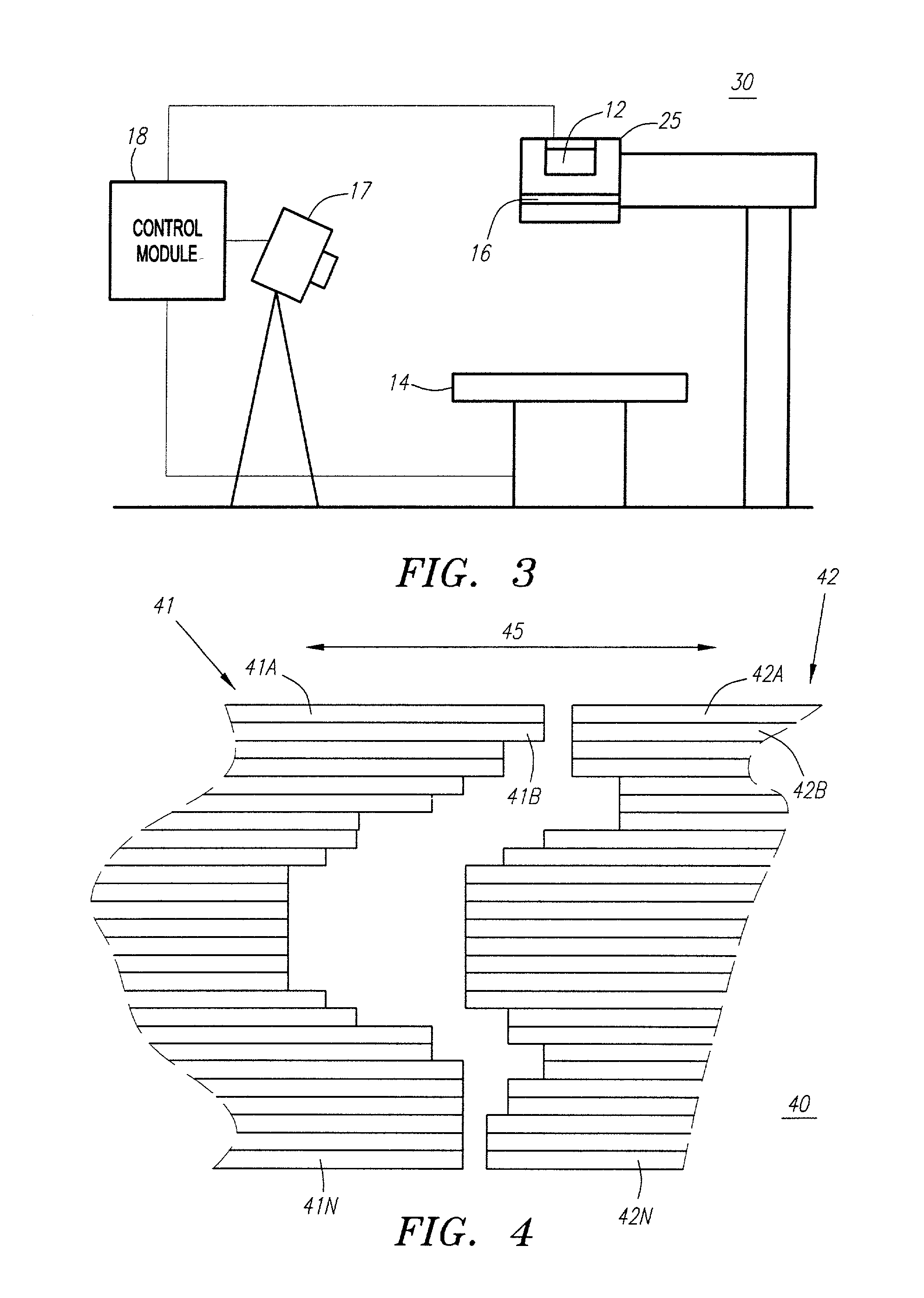
Method and apparatus for irradiating a target
An apparatus (10) for irradiating a target includes a radiation source (12) for generating a radiation beam and a multiple leaf beam adjuster (16) for collimating and adjusting the shape of the radiation beam from the radiation source (12) that would be projected on the target. An image detector (17) detects generates an image signal of the target. In response to the image signal, a control module (18) generate a beam adjustment signal for controlling the beam adjuster (16), thereby enabling the radiation beam from the radiation source (12) to track the movement of the target.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
Apparatus and method for capturing still images and video using coded aperture techniques
ActiveUS20060157640A1Television system detailsBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsGraphicsImaging processing
A system is described for capturing images comprising: a display for displaying graphical images and text; a plurality of apertures formed in the display; an image detector array configured behind the display and configured to sense light transmitted through the apertures in the display, the light reflected from a subject positioned in front of the display; and image processing logic to generate image data using the light transmitted through the apertures, the image data representing an image of a subject.
Owner:REARDEN
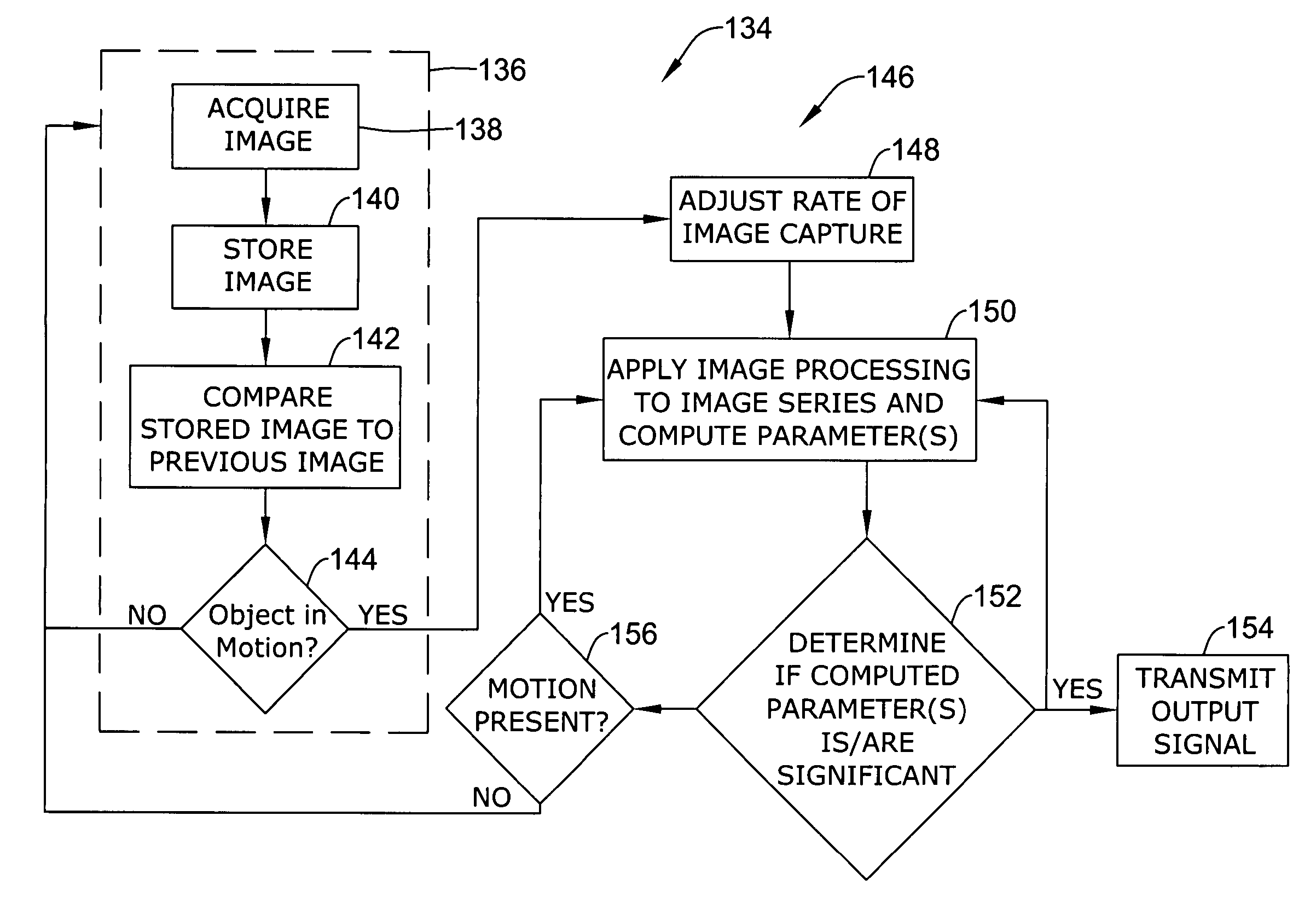
Monitoring devices
Monitoring systems, devices, and methods for monitoring one or more objects within an environment are disclosed. An illustrative monitoring device in accordance with the present invention can include an image detector, an on-board image processor, and communication means for transmitting an imageless signal to a remote location. The image processor can be configured to run one or more routines that can be used to determine a number of parameters relating to each object detected. In some embodiments, the monitoring device can be configured to run an image differencing routine that can be used to initially detect the presence of motion. Once motion is detected, the monitoring device can be configured to initiate a higher rate mode wherein image frames are processed at a higher frame rate to permit the image processor to compute higher-level information about the moving object.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Device, image processing device and method for optical imaging
ActiveUS20110228142A1Short focal lengthShorten build lengthTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesImaging processingGrating
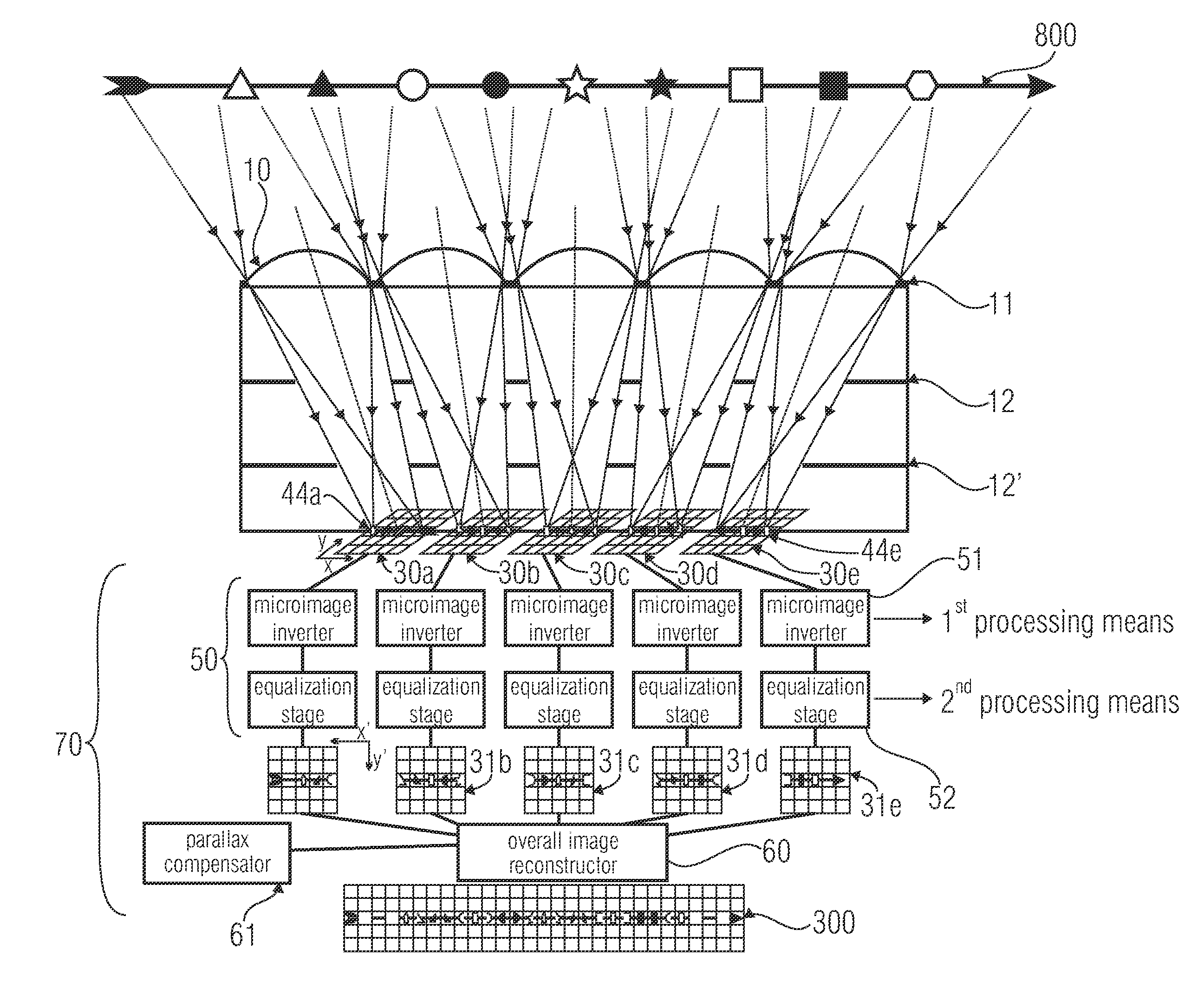
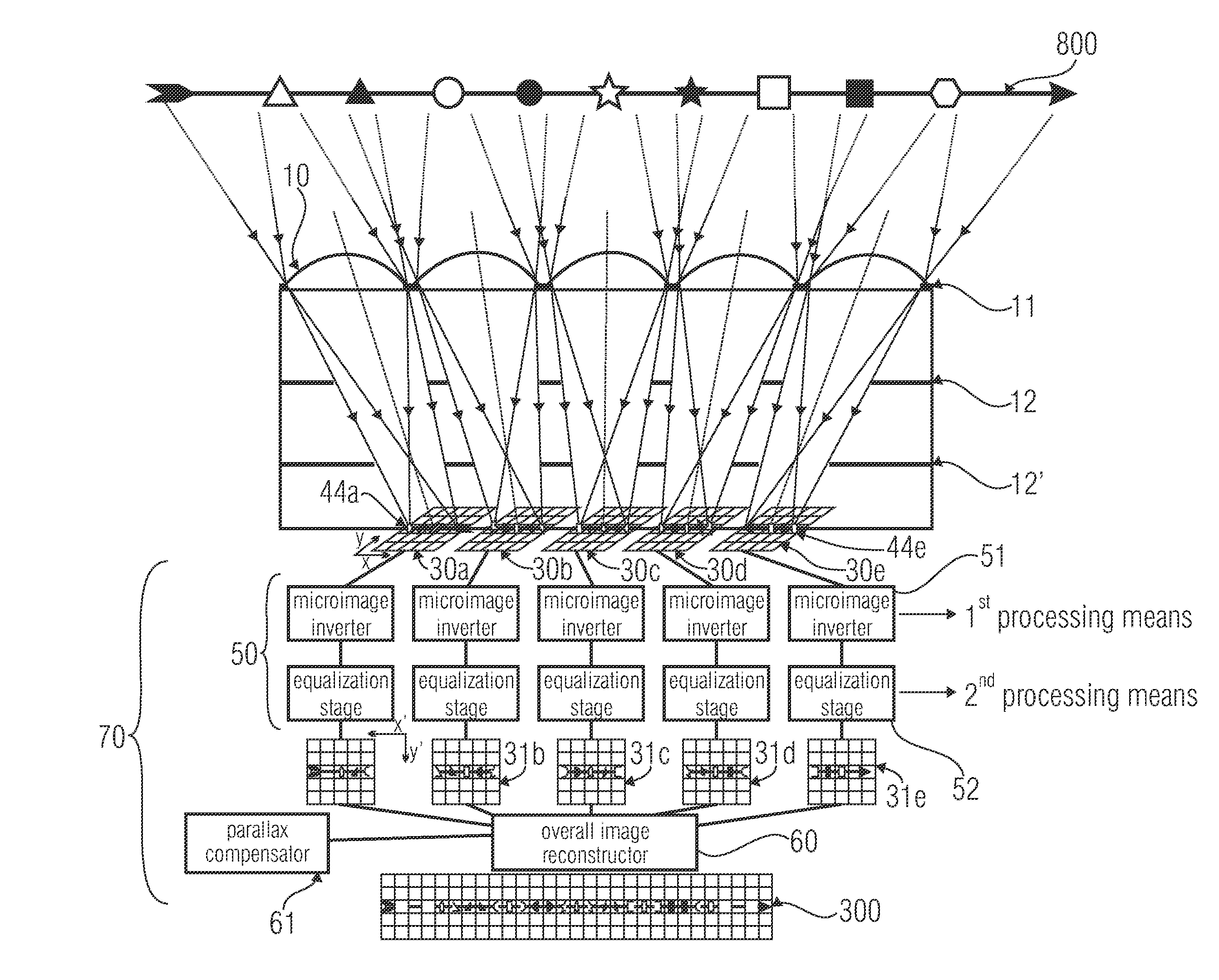
An optical device for imaging is disclosed having at least one micro lens field with at least two micro lenses and one image sensor with at least two image detector matrices. The at least two image detector matrices each include a plurality of image detectors and there is an allocation between the image detector matrices and the micro lenses, so that each micro lens together with an image detector matrix forms an optical channel. The center points of the image detector matrices are shifted laterally by different distances, with respect to centroids, projected onto the image detector matrices, of the micro lens apertures of the associated optical channels, so that the optical channels have different partially overlapping detection areas and so that an overlapping area of the detection areas of two channels is imaged onto the image detector matrices offset with respect to an image detector raster of the image detector matrices. Further, an image processing device and a method for optical imaging are described.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Speckle-image-based optical position transducer having improved mounting and directional sensitivities
InactiveUS6642506B1Reduce sensitivityAvoid smearingSlide gaugesMaterial analysis by optical meansImage detectionRelative motion
A speckle readhead includes a light source that outputs light towards an optically rough surface. Light scattered from this surface contains speckles. The scattered light is imaged onto an image detector, captured and stored. Subsequently, a second image is captured and stored. The two images are repeatedly compared at different offsets in a displacement direction. The comparison having the highest value indicates the amount of displacement between the readhead and the surface that occurred between taking the two images. An optical system of the readhead includes a lens and an aperture. The aperture can be round, with a diameter chosen so that the average size of the speckles is approximately equal to, or larger than, the dimensions of the elements of the image detector. The dimension of the aperture in a direction perpendicular to the direction of displacement can be reduced. Thus, the imaged speckles in that direction will be greater than the dimension of the image detector elements in that direction. Such a readhead is relatively insensitive to lateral offsets. The lens can be a cylindrical lens that magnifies the relative motion along the direction of displacement but does not magnify relative motions in the direction perpendicular to the direction of displacement. The optical system can also be telecentric. Thus, the readhead is relatively insensitive to both separation and relative motions between the readhead and the surface. The light source can be modulated to prevent smearing the speckles across the image detector. The light source can be strobed to freeze the image.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Endoscopy device with removable tip
The present invention provides an endoscope for in vivo imaging the cells, tissue, organs or body cavities of humans or other animals to observe and locate, diagnosis and / or treat disease. Illumination sources, image detectors, sensors may be provided alone or in combination on the removable tip allowing functional alterations or optimization for a particular procedure. Endoscope features such as an instrument channel supporting tissue sampling, suction, treatment, micro-surgery, optical computed tomography, confocal microscopy, laser or drug treatments, injections, gene-therapy, marking, implanting or other medical techniques are maintained.
Owner:PERCEPTRONIX MEDICAL
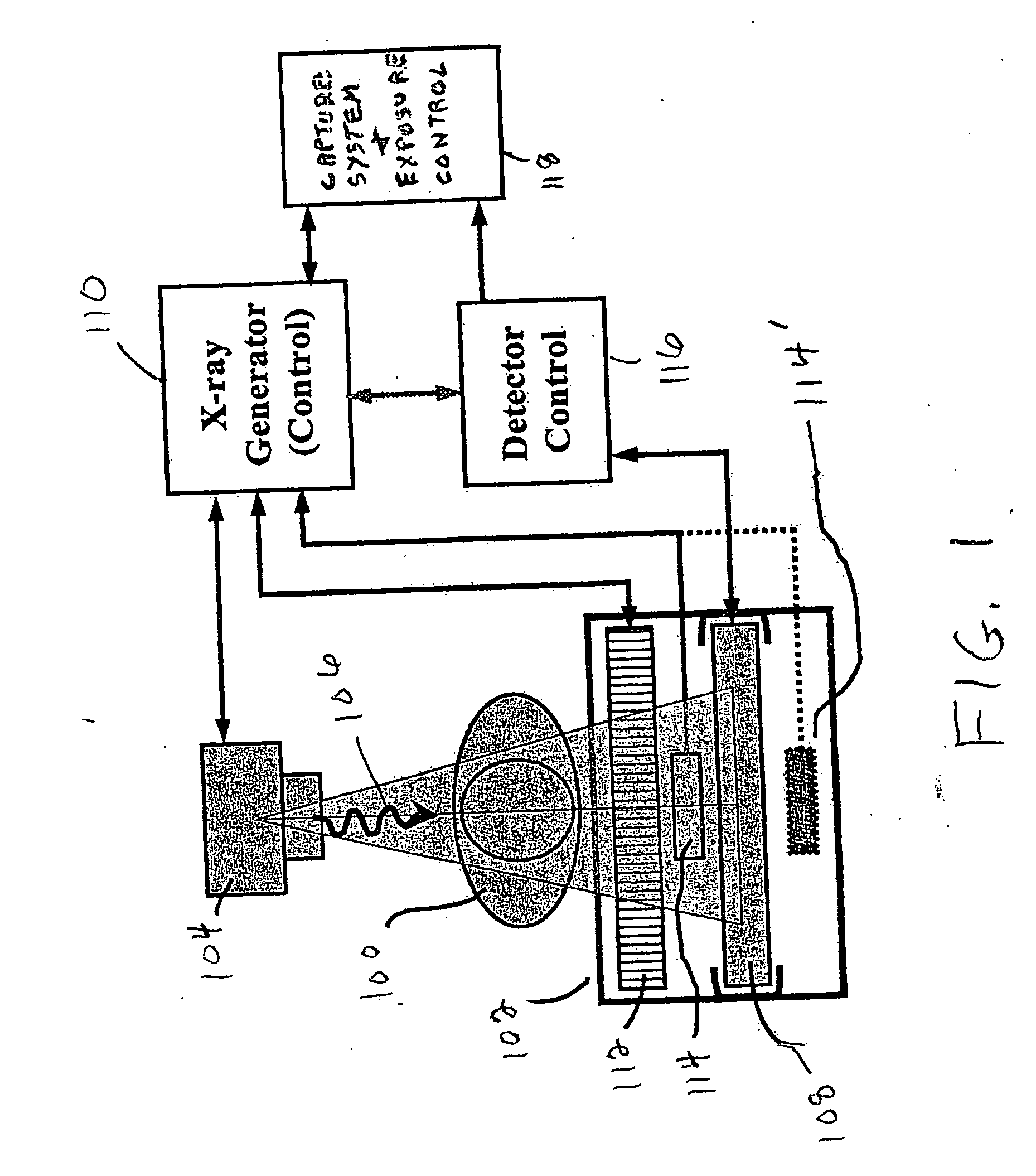
X-ray imaging system and imaging method
ActiveUS7180979B2Easy constructionImaging devicesHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionImage contrastImage detection
The present invention provides an apparatus capable of X-ray imaging utilizing phase of X-rays. An X-ray imaging apparatus equipped with first and second diffraction gratings and an X-ray image detector are described. The first diffraction grating generates a Talbot effect and a second diffraction grating diffracts X-rays diffracted by the first diffraction grating. An image detector is provided to detect the X-rays diffracted by the second diffraction grating. In this manner, image contrasts caused by changes in phase of X-rays due to a subject arranged in front of the first diffraction grating or between the first diffraction grating and the second diffraction grating can be achieved.
Owner:MOMOSE ATSUSHI
Compact and durable encasement for a digital radiography detector
A digital radiography detector includes a housing having first and second spaced planar members and four side walls defining a cavity. A radiographic image detector assembly is mounted within the cavity for converting a radiographic image to an electronic radiographic image. The detector assembly includes a detector array mounted on a stiffener. A shock absorbing elastomer assembly is located within the cavity for absorbing shock to the detector array / stiffener in directions perpendicular to and parallel to the detector array / stiffener.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
System for determination of a location in three dimensional space
InactiveUS6141104AReduce the impact of interferenceNarrow downInput/output for user-computer interactionPosition fixationThree-dimensional spaceMathematical correlation
An optical improvement for angular position sensors, which may be used to determine the spatial coordinates of a small source of light (or other energy) in a 3-dimensional volume. Such sensors normally include a linear photosensitive image detector such as a photodiode array or a charge-coupled device (CCD). An irregular pattern of parallel slits is described which increases the amount of light gathered while avoiding the undesirable characteristics of lens optics for this application. One optimal type of irregular pattern is the uniformly redundant array. A mathematical correlation function together with a polynomial interpolation function can determine the displacement of the image on the detector and thereby the location of the source relative to one angular dimension. Given the locations and orientations of several sensors in a 3-dimensional coordinate system and given the angles measured by each, the location of the point source can be computed.
Owner:IMAGE GUIDED TECH
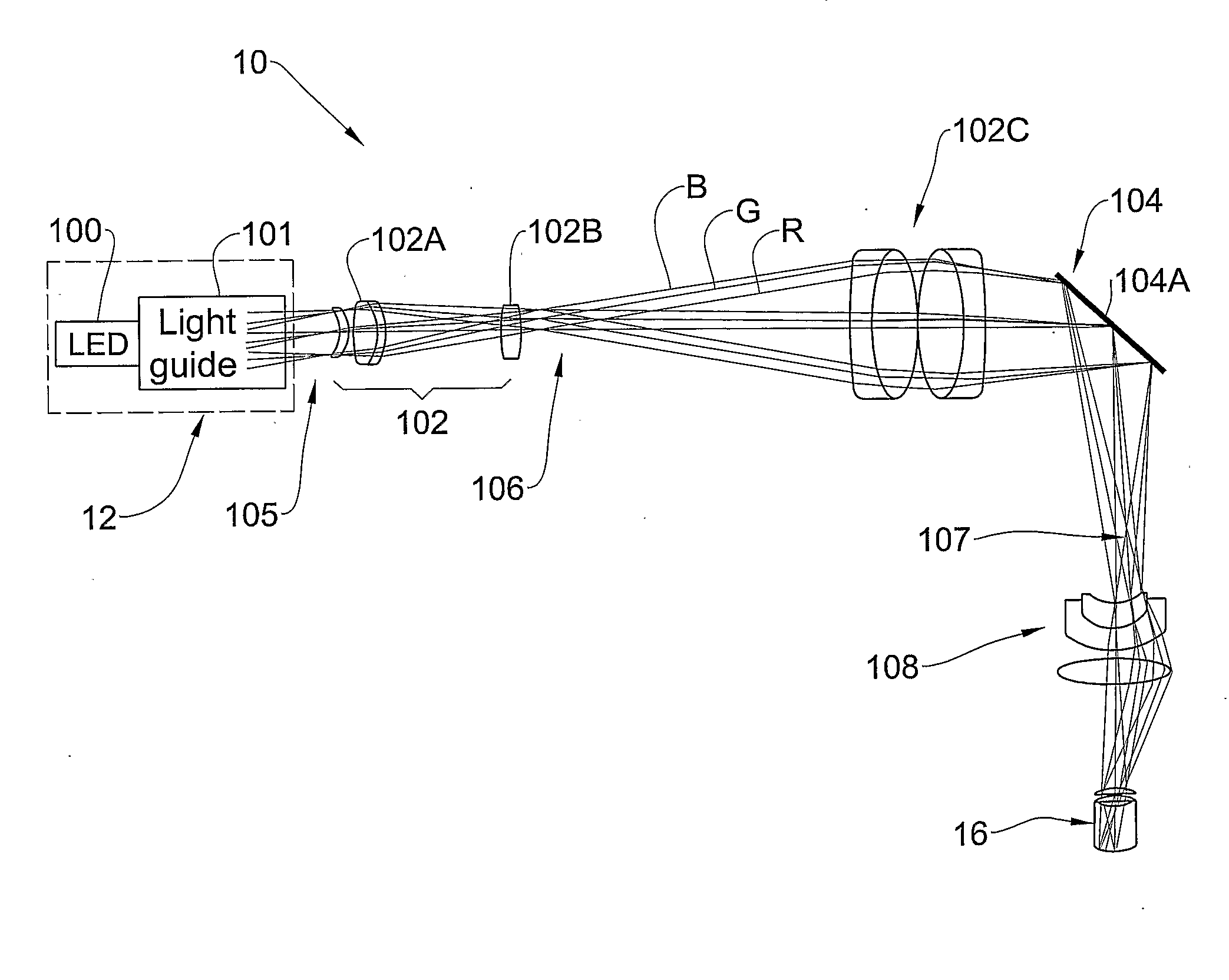
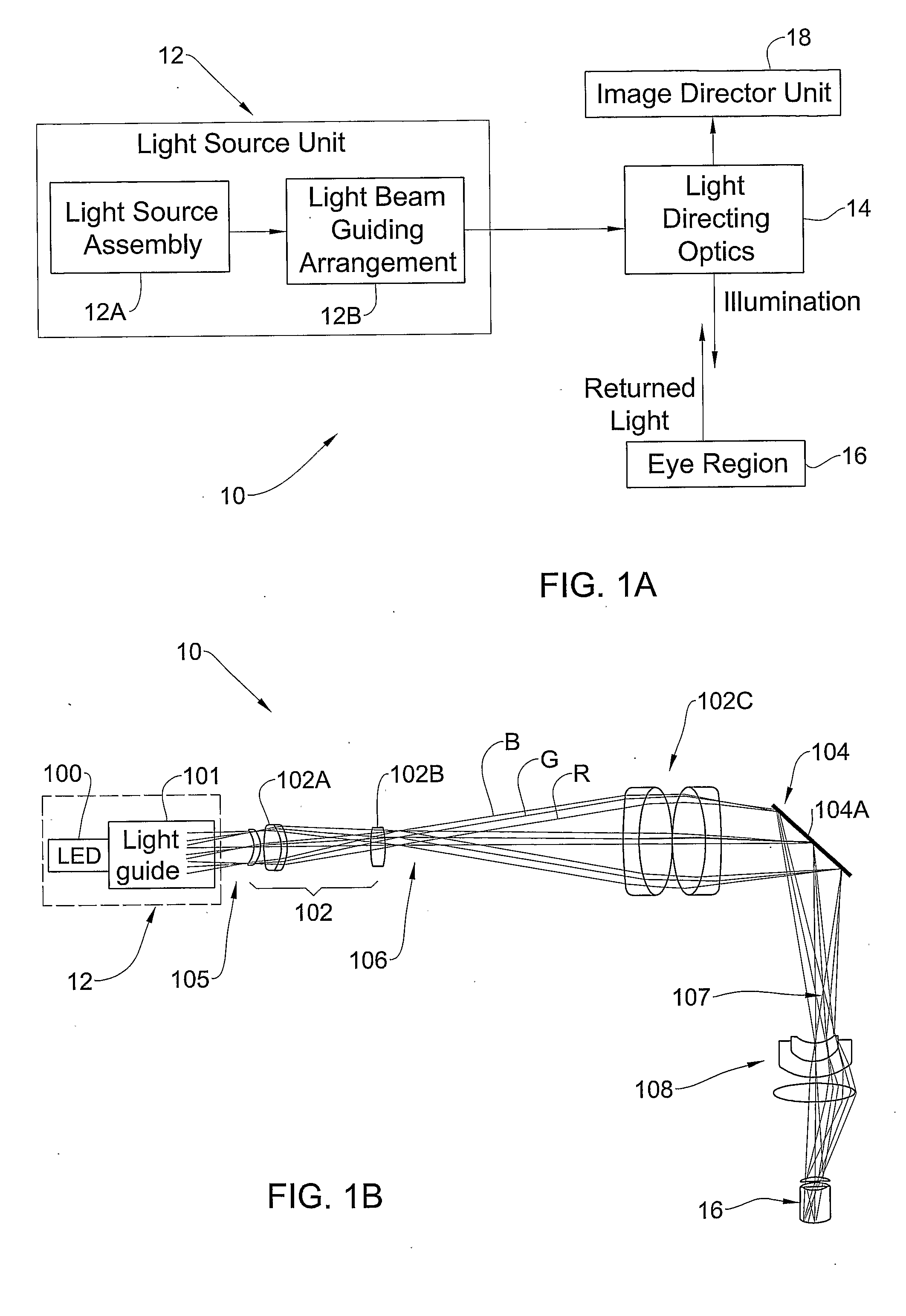
Integrated Retinal Imager And Method
ActiveUS20090153797A1Enhance the imageEfficient couplingMechanical apparatusLight guides for lighting systemsImaging qualityExposure control
A system and method are presented for use in imaging the patient's retina. A light source unit is provided including a light emitting diode (LED) arrangement comprising multiple LEDs of different wavelength ranges. A light guide arrangement is used with the LEDs arrangement and is configured for coupling light from the LEDs and providing output light beams of a desired shape. The illuminating light is directed towards a region on the retina, and light returned from the illuminated region is collected and directed to an image detector unit. The invention enables the use of LED light at high intensity as required in the eye retina imaging, while maintaining the required high-quality imaging. Also, the invention provides for simultaneous or quasi-simultaneous as well as high-speed imaging in FA and ICG imaging procedures, thereby satisfying a long felt need in ophthalmology. Also, the invention provides for automated illumination or light exposure control to optimize overall light exposure to the patient eye and best acquired image quality in terms of brightness, contrast and image signal-to-noise ratio.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and apparatus for three-dimensional microscopy with enhanced resolution
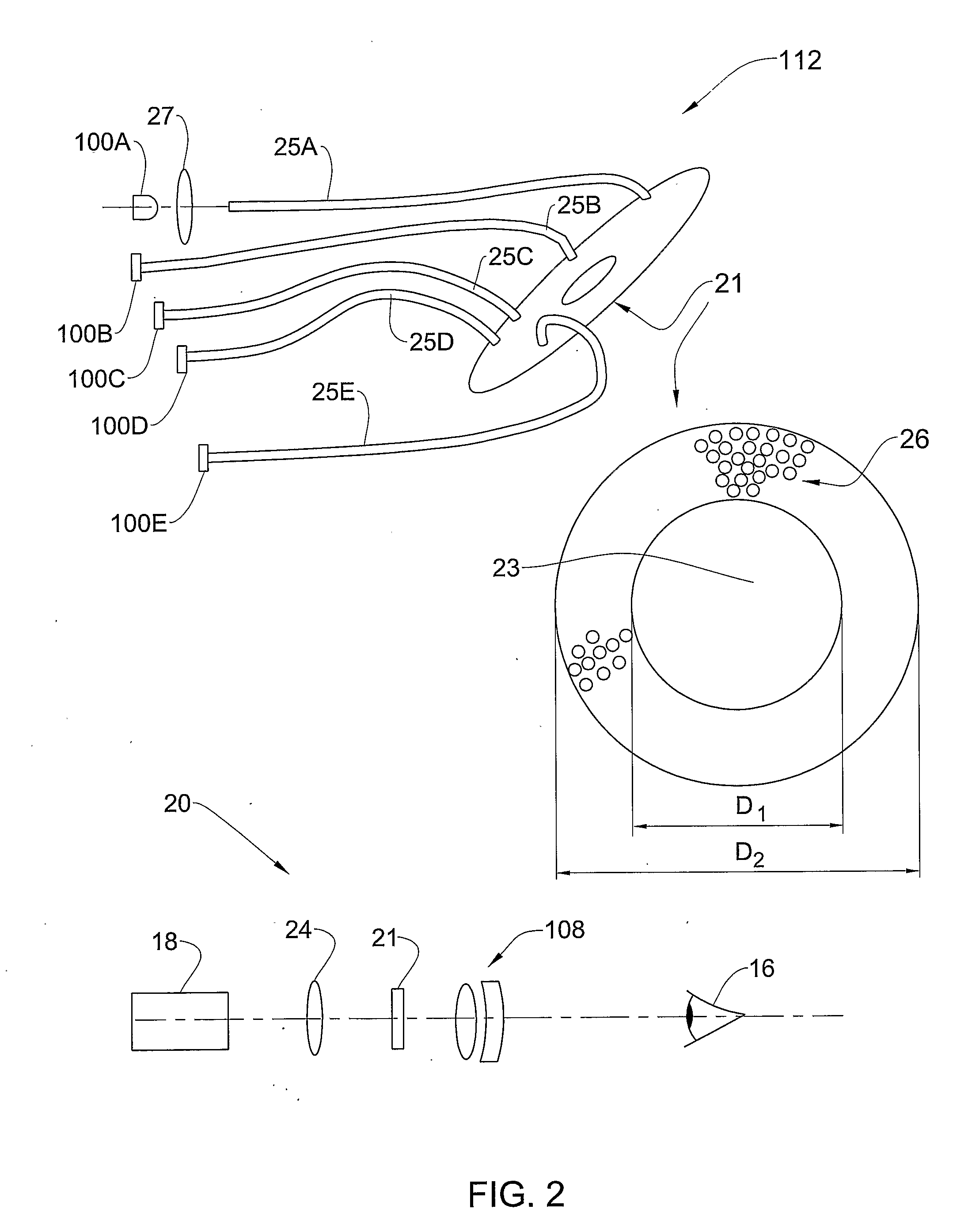
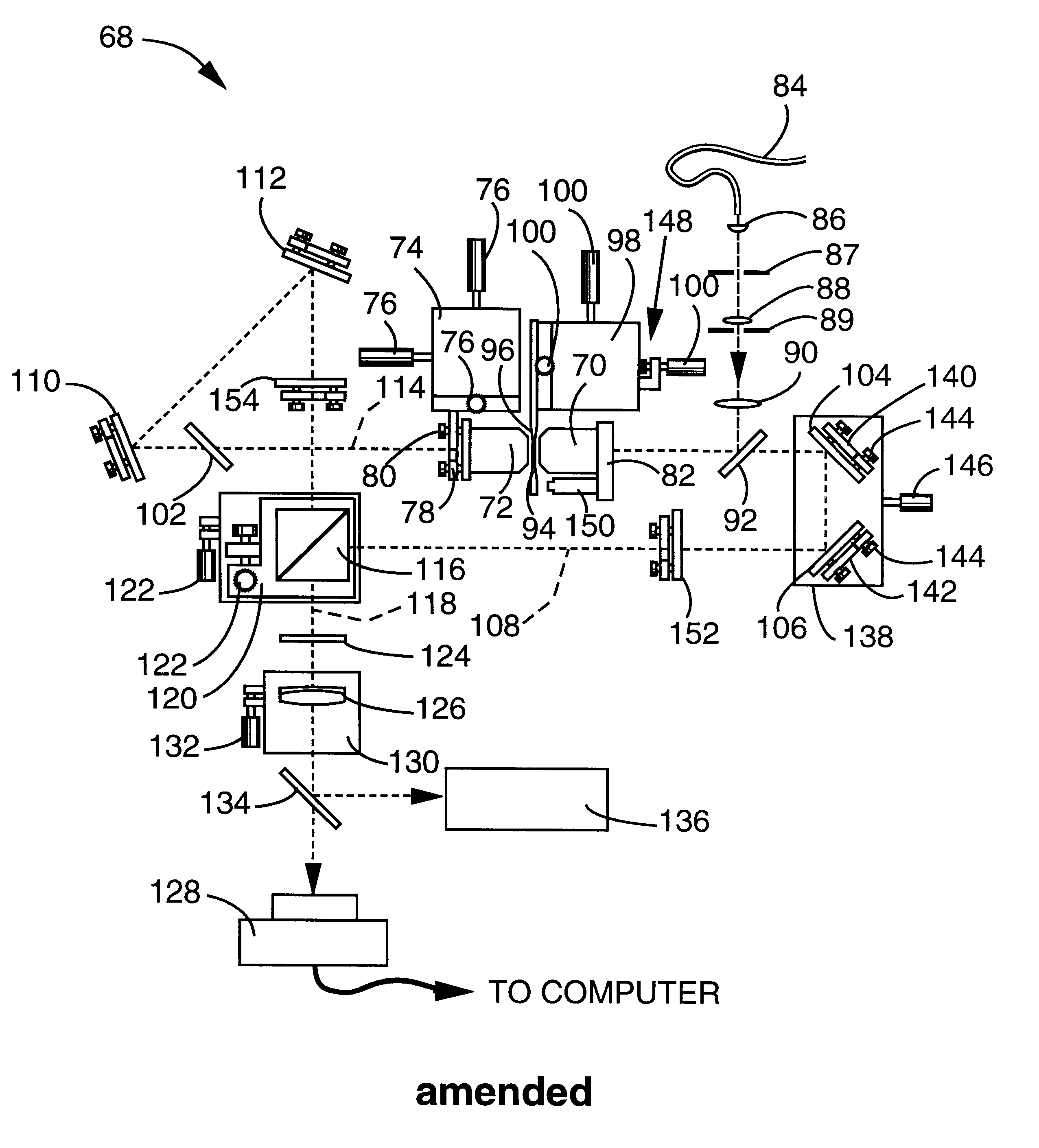
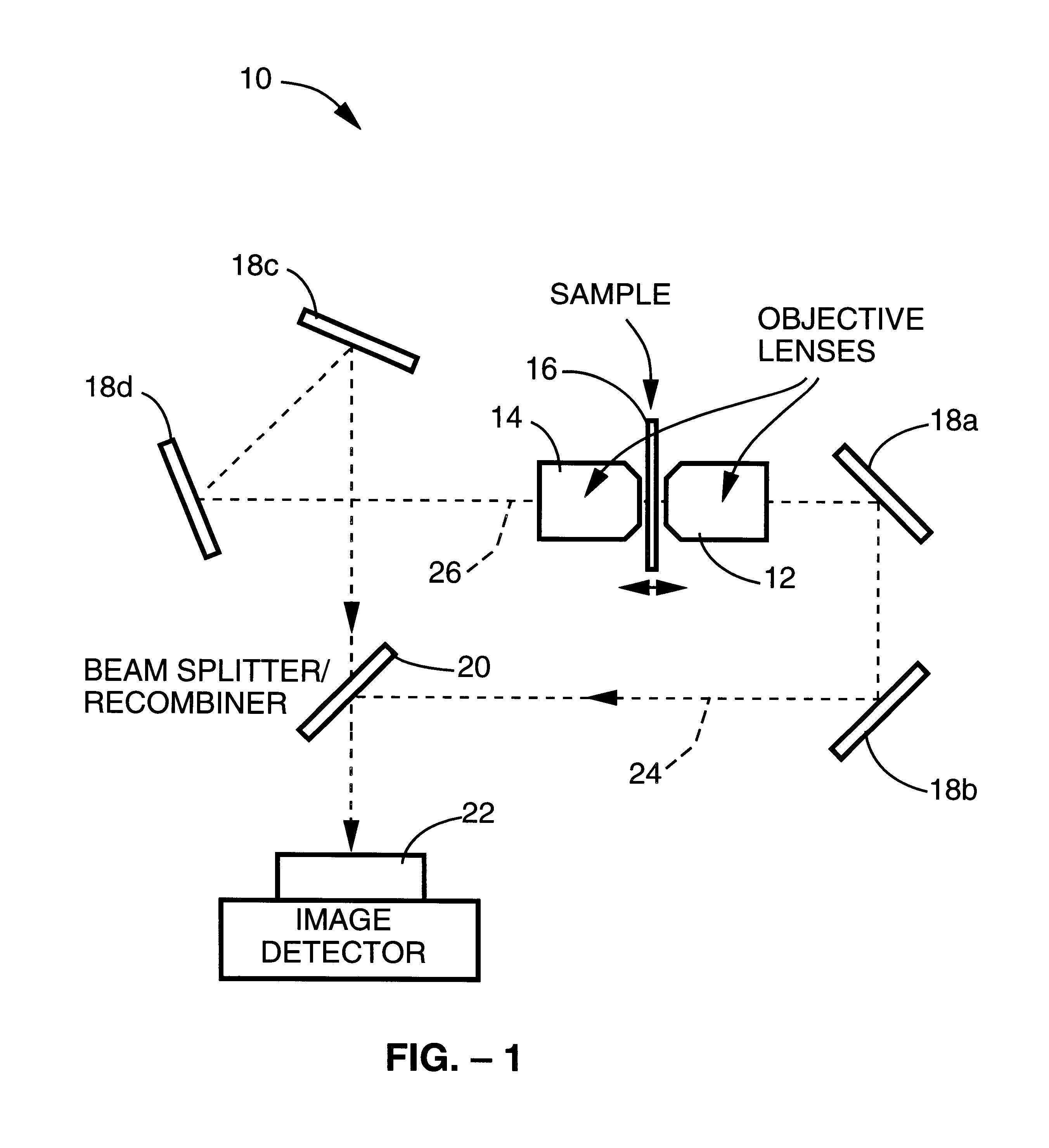
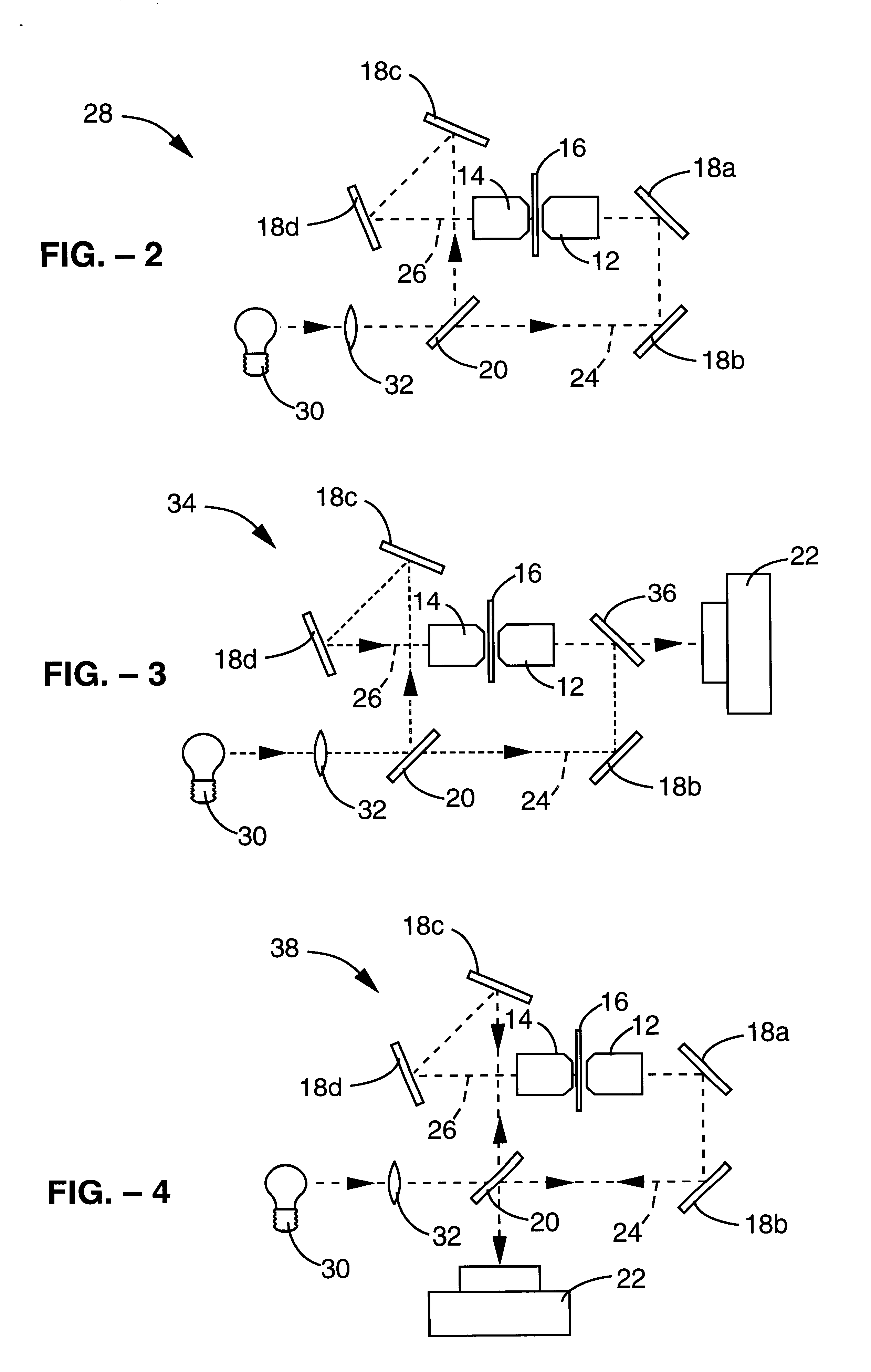
InactiveUSRE38307E1Add depthImprove resolutionMicroscopesColor/spectral properties measurementsOphthalmologyImage resolution
A method and apparatus for three dimensional optical microscopy is disclosed which employs dual opposing objective lenses about a sample and extended incoherent illumination to provide enhanced depth or Z.Iadd.-.Iaddend.direction resolution. In a first embodiment, observed light from both objective lenses are brought into coincidence on an image detector and caused to interfere thereon by optical path length adjustment. In a second embodiment, illuminating light from an extended incoherent light source is detected to the sample through both objective lenses and caused to interfere with a section of the sample by adjusting optical path lengths. Observed light from one objective lens is then recorded. In a third embodiment, which combines the first two embodiments, illuminating light from an extended incoherent light source is directed to the sample through both objective lenses and caused to interfere within a section of the sample by adjusting optical path lengths. The observed light from both lenses is caused to interfere on the image detector by the same optical path length adjustment. .Iadd.In a fourth embodiment of the invention, further spatial structure is introduced into the illumination light. Computational processing is used to enhance lateral or XY resolution as well as depth or Z resolution..Iaddend.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
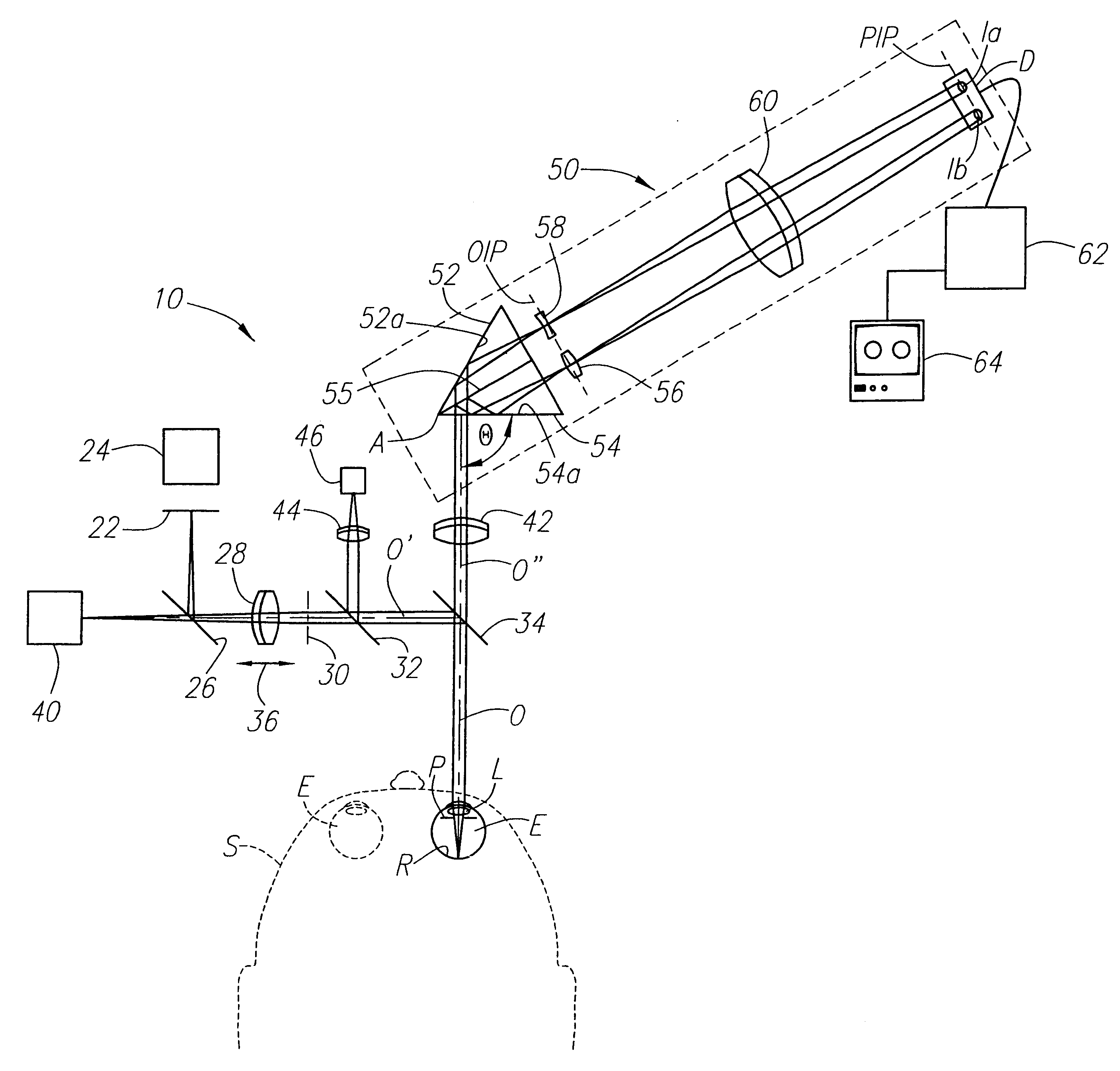
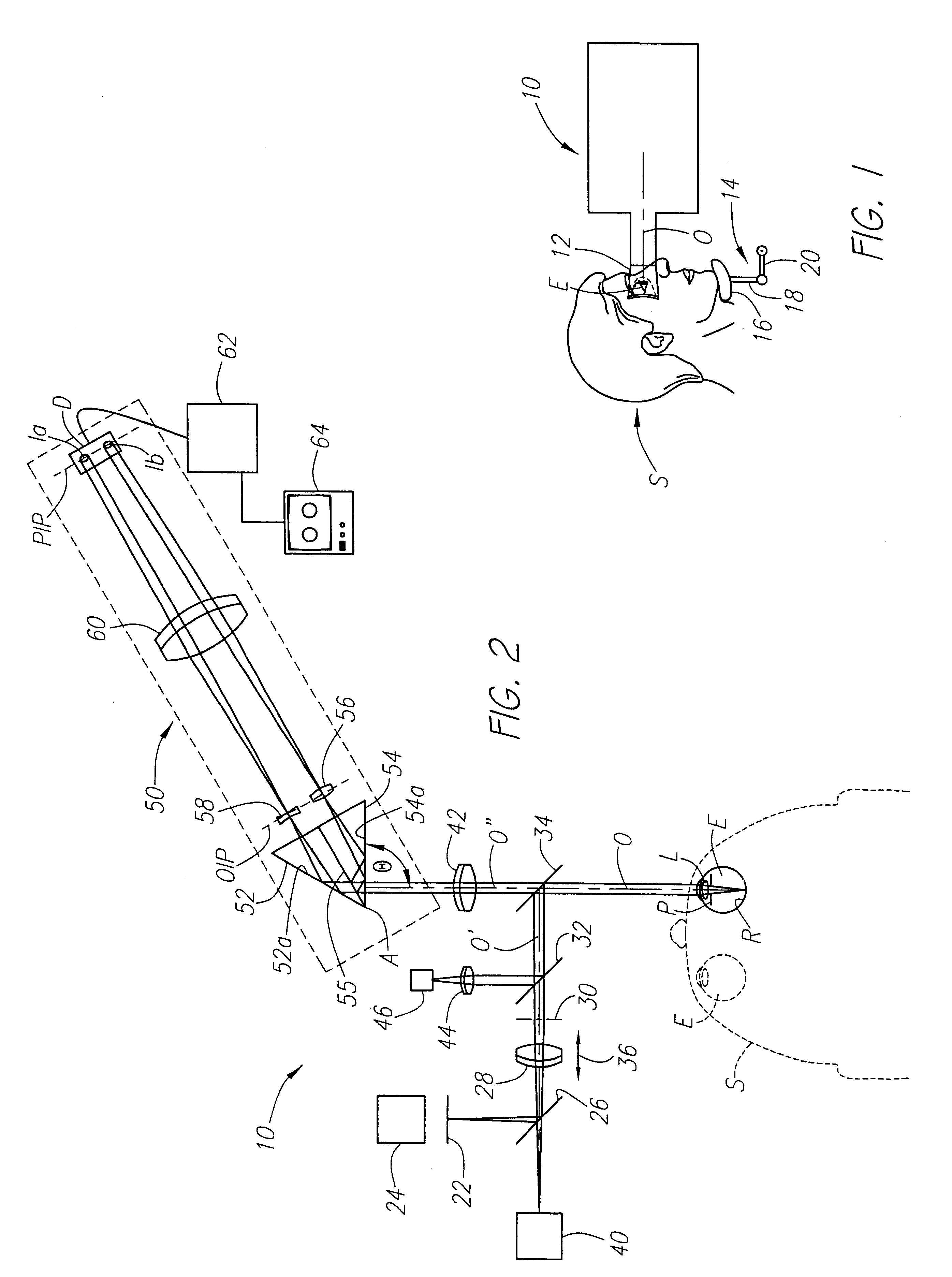
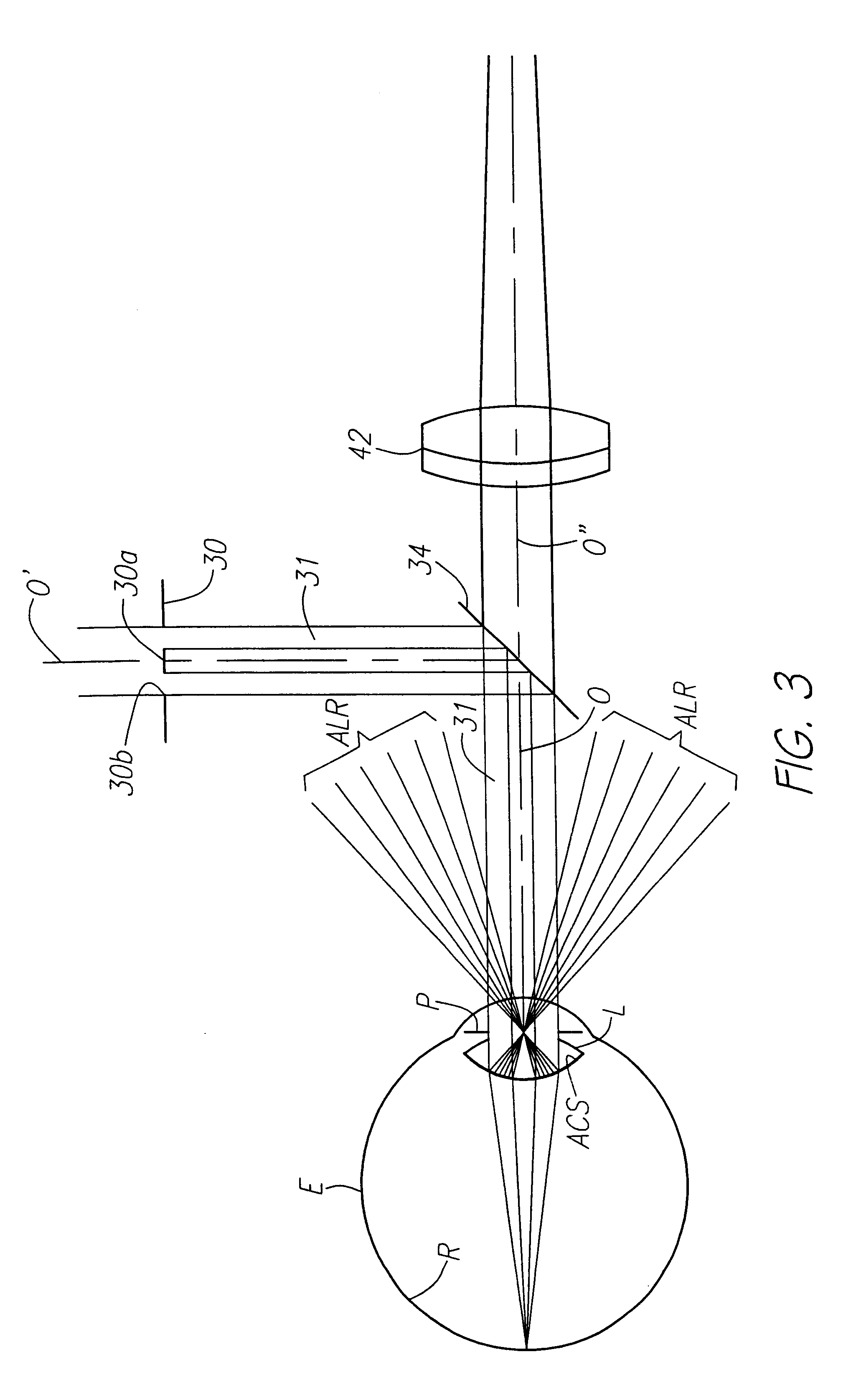
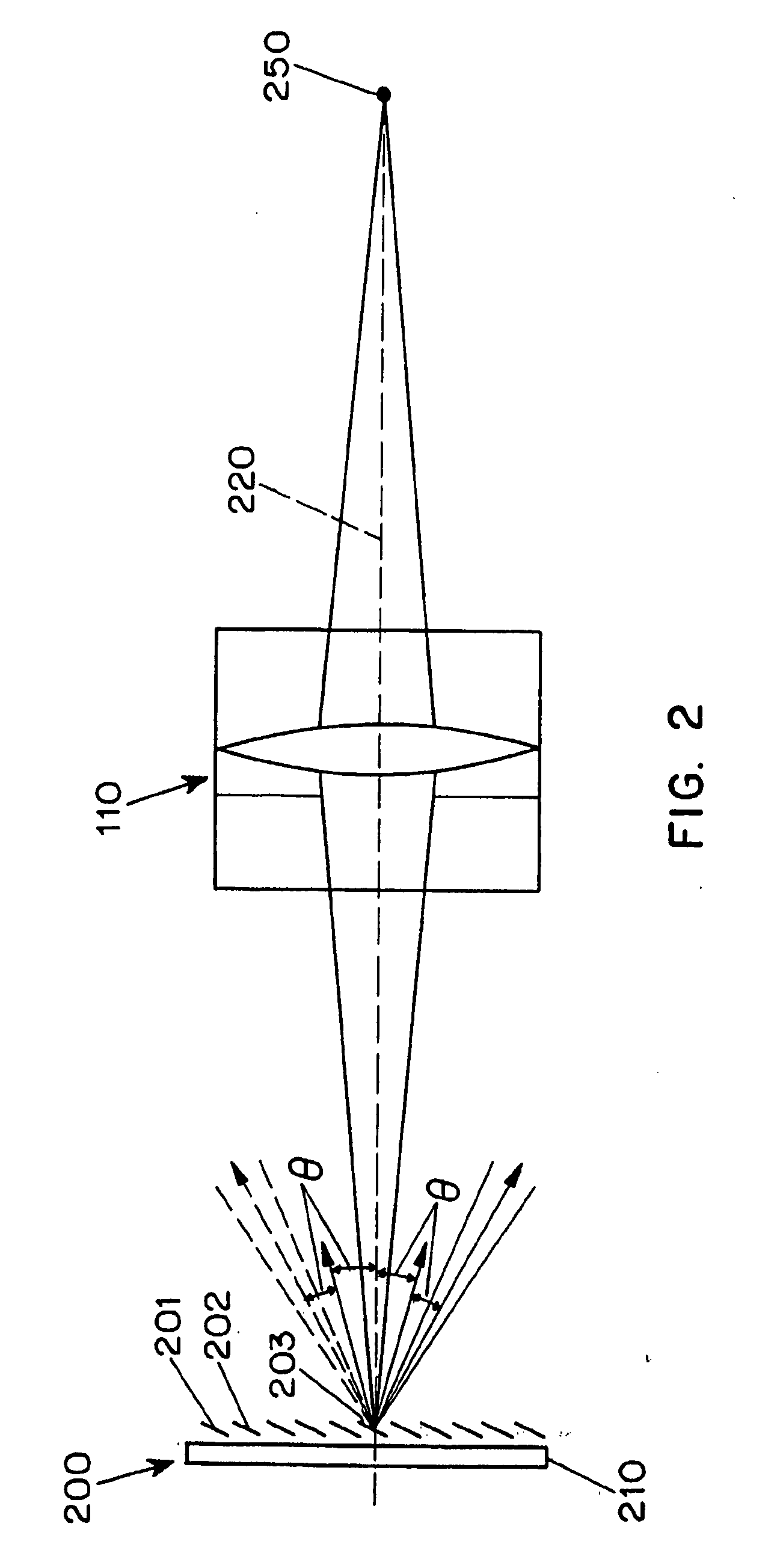
Method and apparatus for measuring optical aberrations of the human eye
InactiveUS6439720B1Quickly and accurately measuringMaximize accuracyRefractometersSkiascopesLight spotImage detection
An apparatus for measuring optical aberrations of the human eye wherein the person positions his or her eye on an optical axis of the apparatus and looks at an illuminated target on the optical axis that is visible to the eye for allowing the eye to focus on the target and establish a position of the eye. A collimating lens on the optical axis is movable along the optical axis for adjusting the apparent optical distance between the eye and the target. A light source directs a predetermined light beam along the optical axis into the eye and onto the retina of the eye as a spot of light. A lens reimages the light scattered from the light spot on the eye retina into a wavefront curvature sensor that forms two oppositely defocused images on an image detector, and a computer processes and analyzes the two defocused images for measuring the optical aberrations of the eye.
Owner:AOPTIX TECH
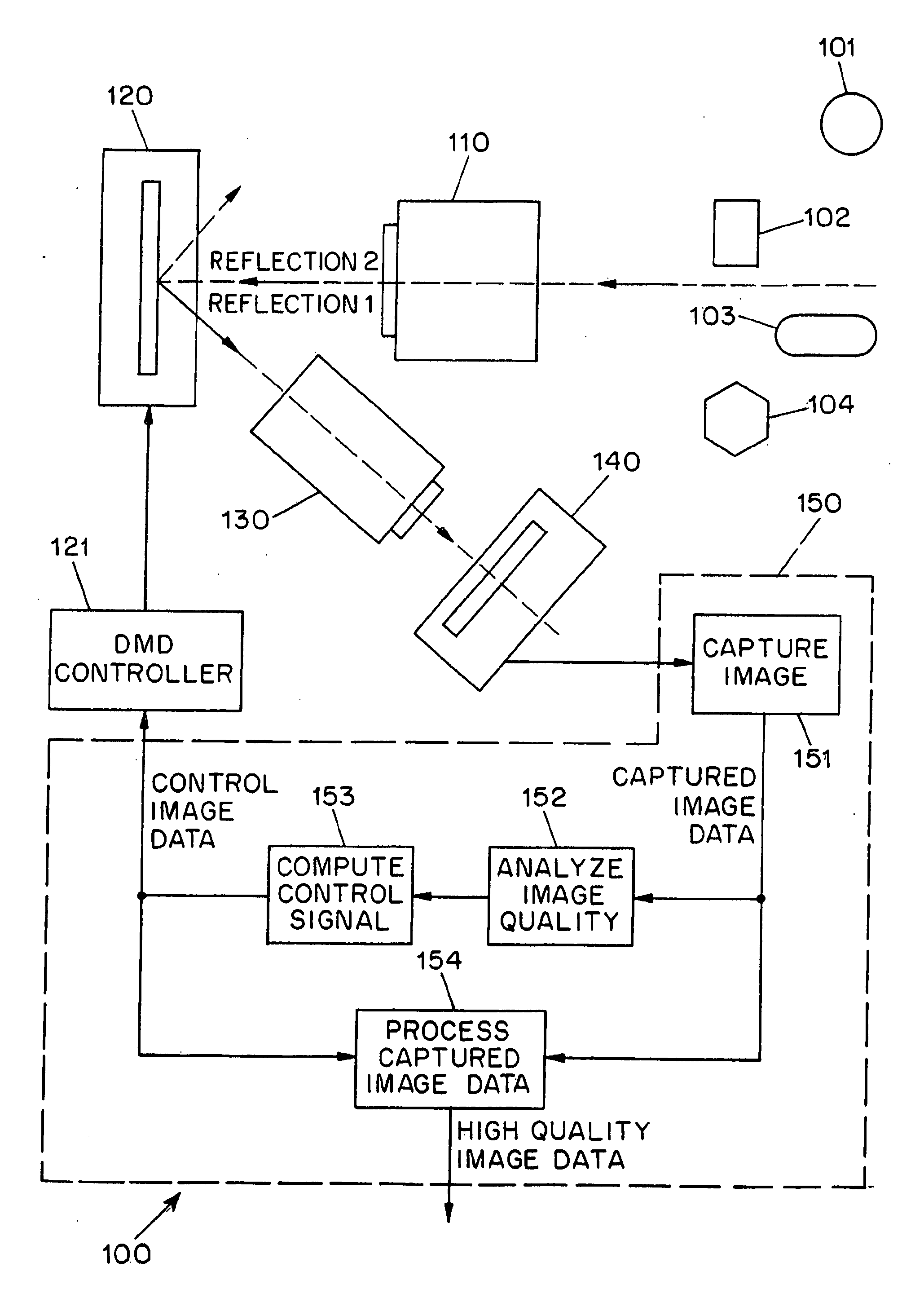
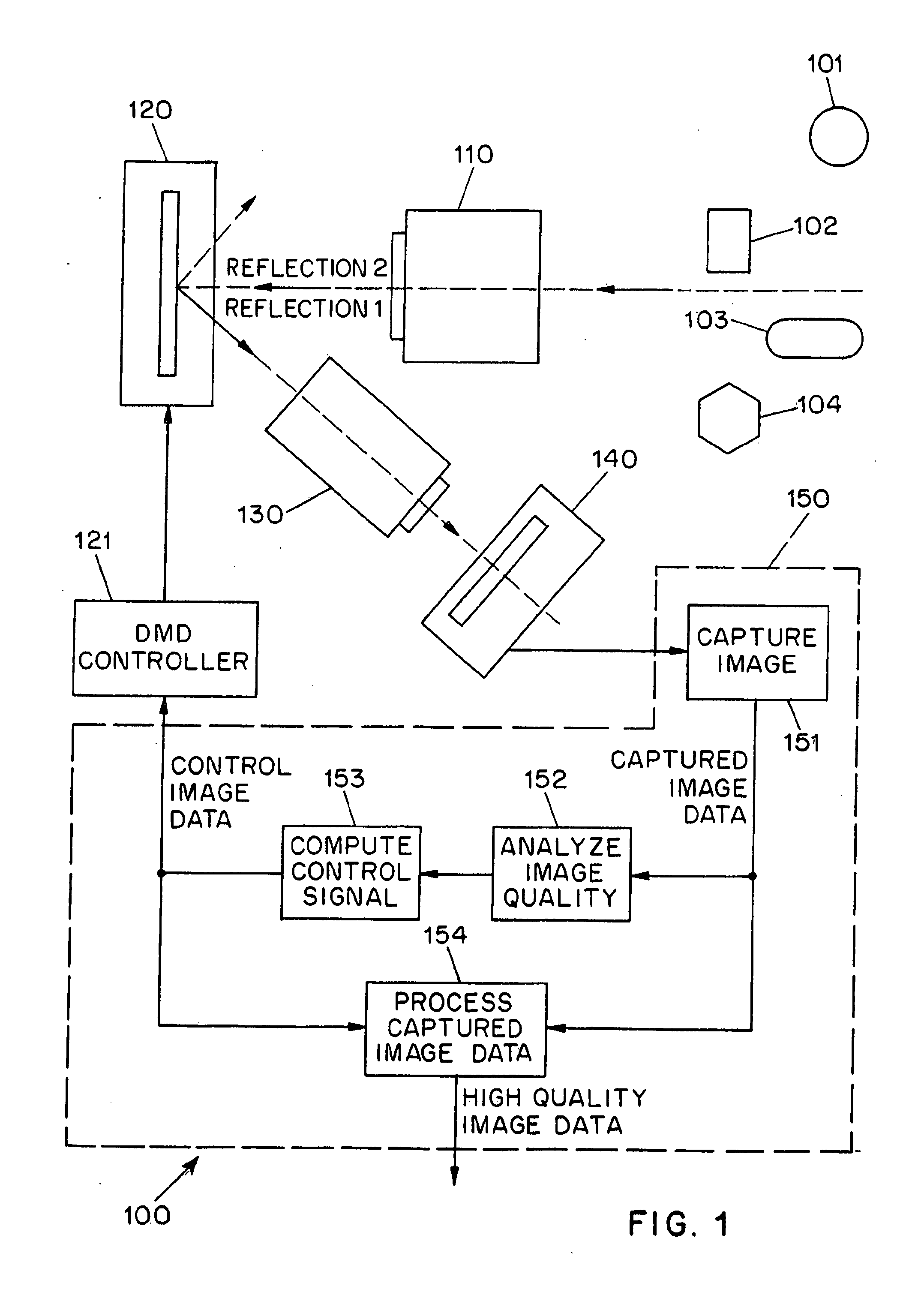
Adaptive imaging using digital light processing
ActiveUS20110211077A1High imageIncrease rangeTelevision system detailsColor television detailsDigital signal processingAdaptive imaging
A system (100) for the adaptive imaging of a scene includes a digital light processing apparatus (150) adapted for controllably reflecting an image of the scene in at least a first direction to thereby reflect an intensity modulated image of the scene along at least the first direction, an image detector (140) for detecting the intensity modulated image of the scene and generating corresponding image data, and an image data processor (154) for processing the image data into control data and providing the control data to the digital light processing (150) apparatus for control thereof.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
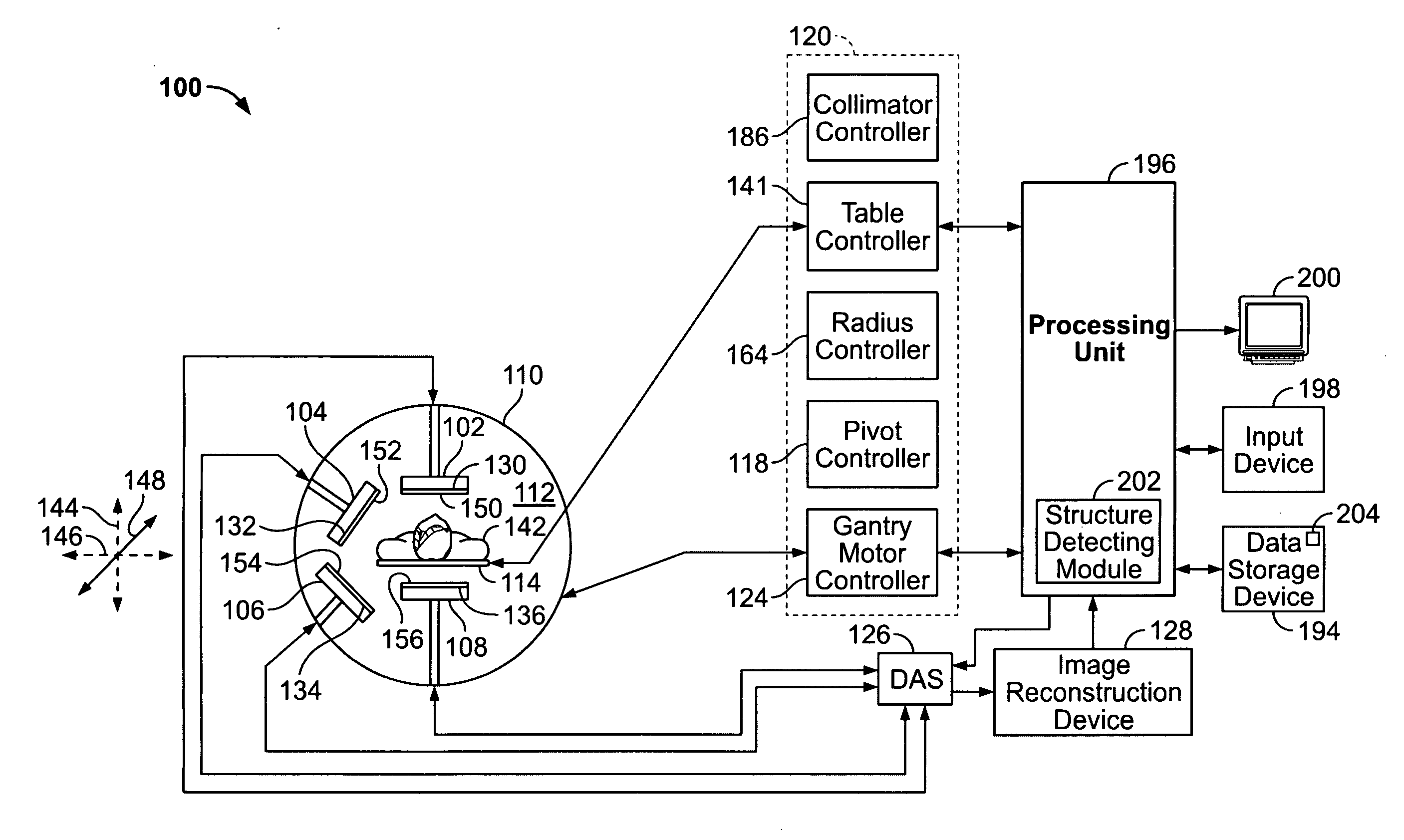
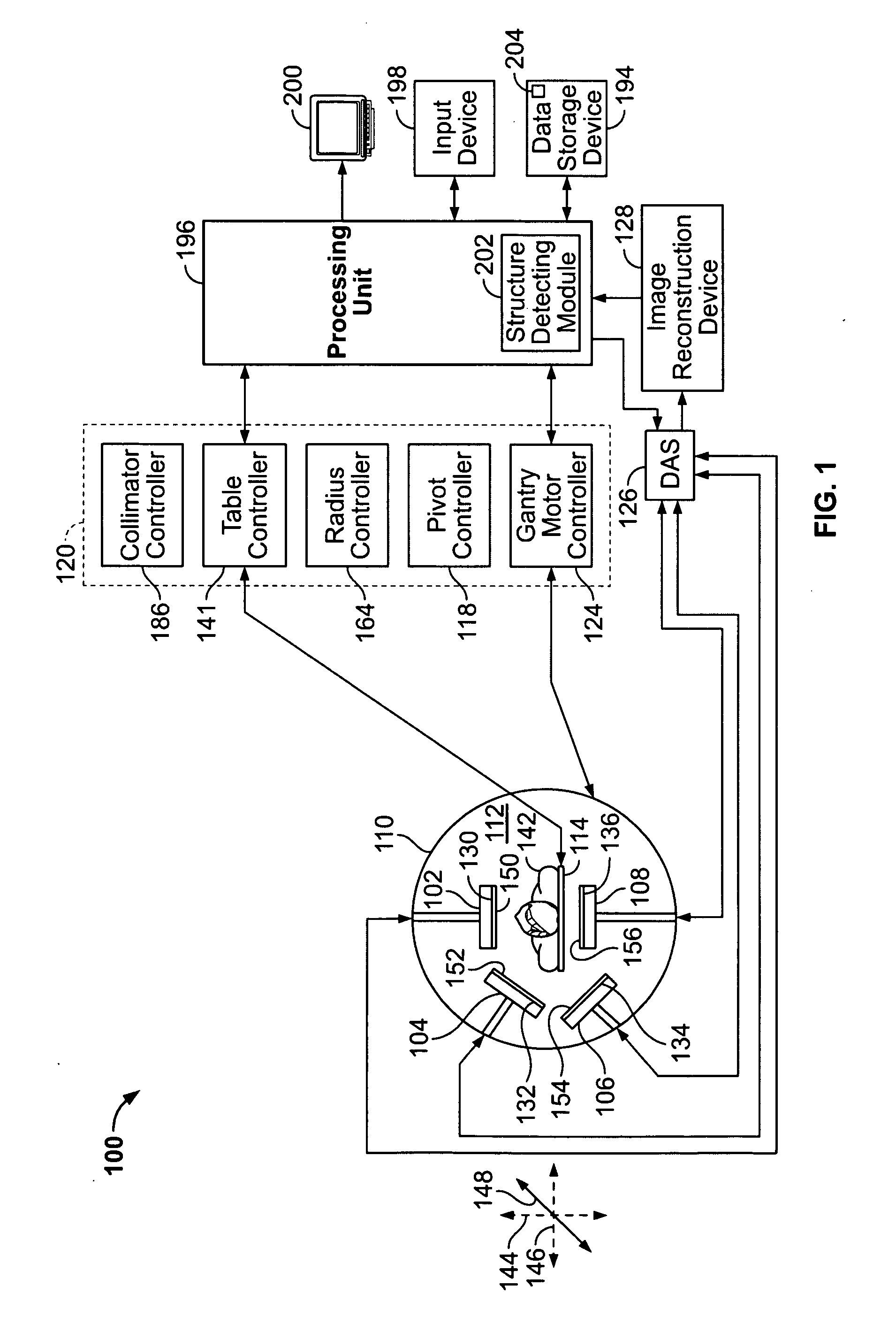
Method and apparatus for imaging with imaging detectors having small fields of view
ActiveUS20080029704A1Handling using diaphragms/collimetersMaterial analysis by optical meansData acquisitionComputer science
An apparatus for imaging a structure of interest comprises a plurality of imaging detectors mounted on a gantry. Each of the plurality of imaging detectors has a field of view (FOV), is independently movable with respect to each other, and is positioned to image a structure of interest within a patient. A data acquisition system receives image data detected within the FOV of each of the plurality of imaging detectors.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE ISRAEL
Submicron thermal imaging method and enhanced resolution (super-resolved) ac-coupled imaging for thermal inspection of integrated circuits
ActiveUS20020126732A1Simple and inexpensive temperature measurementImprove spatial resolutionRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansImage resolutionImage detection
Methods and apparatus for non-contact thermal measurement which are capable of providing sub micron surface thermal characterization of samples, such as active semiconductor devices. The method obtains thermal image information by reflecting a light from a surface of a device in synchronous with the modulation of the thermal excitation and then acquiring and processing an AC-coupled thermoreflective image. The method may be utilized for making measurements using different positioning techniques, such as point measurements, surface scanning, two-dimensional imaging, and combinations thereof. A superresolution method is also described for increasing the resultant image resolution, based on multiple images with fractional pixel offsets, without the need to increase the resolution of the image detectors being utilized. The thermoreflective method provides a spatial resolution better than current infrared cameras, operates within a wide temperature range, and is capable of a thermal resolution on the order of 10 mK.degree..
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Laser doppler perfusion imaging with a plurality of beams
InactiveUS20050187477A1High strengthImprove signal-to-noise ratioScattering properties measurementsIndication/recording movementLight beamLaser light
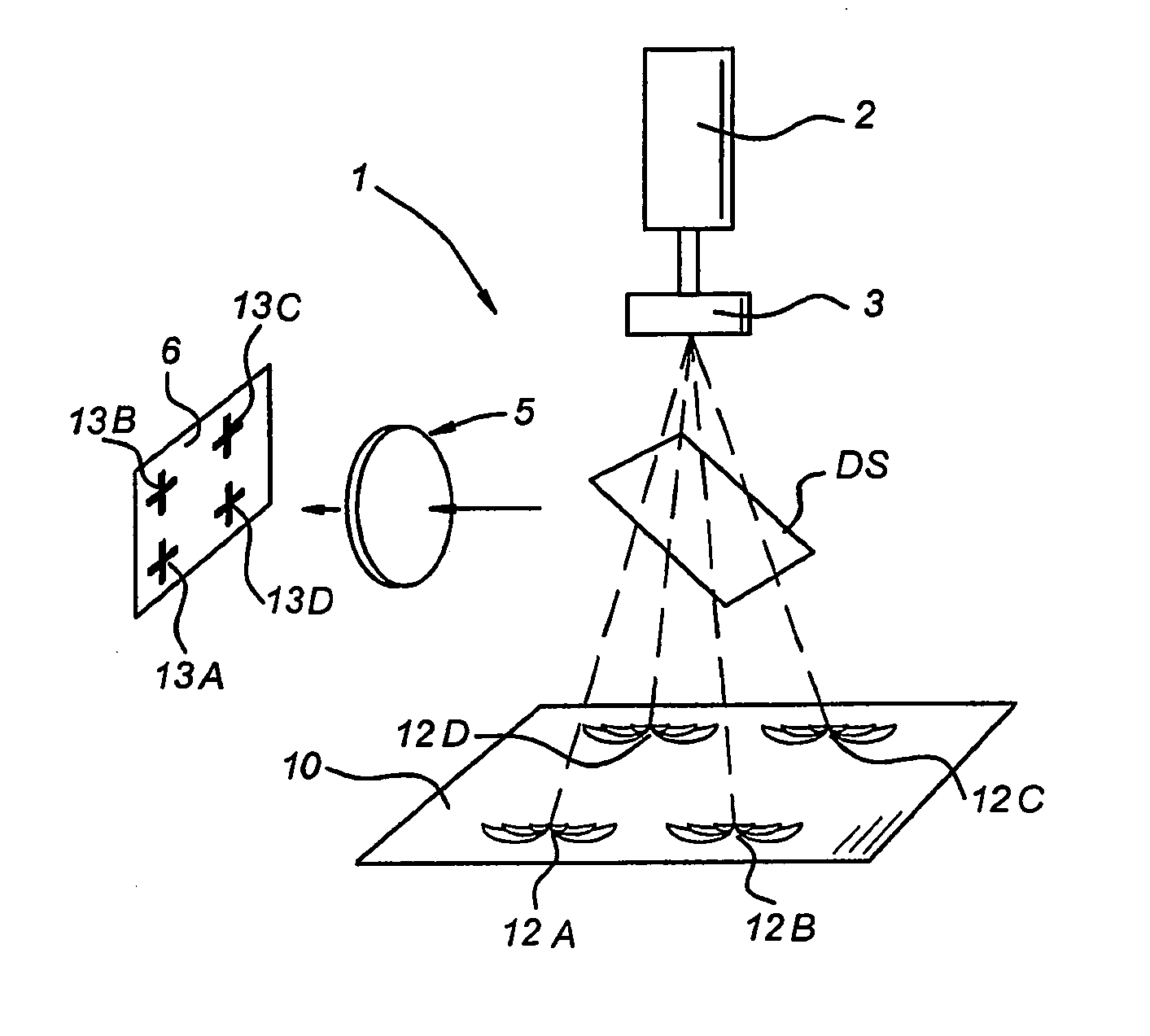
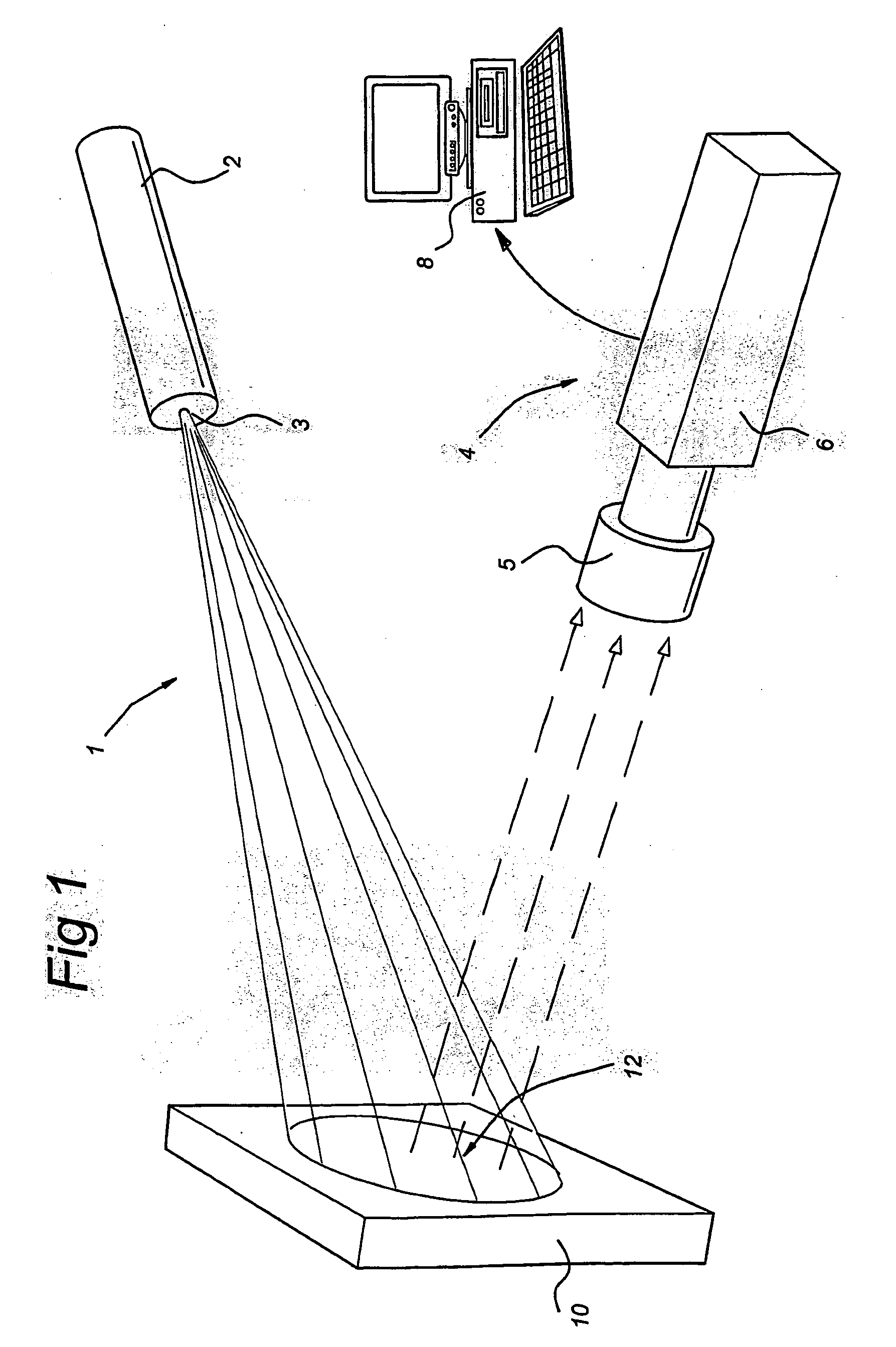
Laser Doppler Perfusion Imaging system including a laser light source (2), an image detector (4), and signal detector (6); the laser light source (2), in use, being arranged for illuminating a selected area of interest (12) on a sample (10) for determining perfusion related data of the sample (10), the image detector, in use, being arranged for capturing an image of the sample (10), and the signal detector (6), in use, being arranged for detecting a laser Doppler signal from the selected area of interest (12) on the sample (10), wherein the laser light source (2) comprises optical means (3) for creating a laser beam comprising a plurality of beams.
Owner:PERIMED
Portable Imaging Apparatus
The present invention relates to a portable imaging apparatus for imaging an internal area of an object, such as a body cavity, organ or passage of a human or animal. The imaging apparatus comprises an endoscope and a hand holdable image-viewing device releasably connectable to a proximal end of the endoscope. The endoscope comprises an image capture optical pathway and an illumination optical pathway. The image-viewing device comprises an image detector optically couplable to the image capture optical pathway, a display in communication with the detector and a light source optically couplable to the illumination optical pathway. In use, light is transmitted from the light source to the distal end of the endoscope via the illumination optical pathway and illuminates the internal area to be viewed. An optical image of the internal area is transmitted from the distal end of the endoscope to the image-viewing device via the optical image pathway and detected by the detector. A virtually instant visual display of the image is provided on the display of the image-viewing device. A method for using the portable imaging apparatus is also disclosed.
Owner:SOLAR INT PRODS
Method of and system for producing digital images of objects with subtantially reduced speckle-noise patterns by illuminating said objects with spatially and/or temporally coherent-reduced planar laser illumination
InactiveUS20020043561A1Reducing speckle-noise patternSemiconductor laser arrangementsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSystems designHand held
Methods of and systems for illuminating objects using planar laser illumination beams having substantially-planar spatial distribution characteristics that extend through the field of view (FOV) of image formation and detection modules employed in such systems. Each planar laser illumination beam is produced from a planar laser illumination beam array (PLIA) comprising an plurality of planar laser illumination modules (PLIMs). Each PLIM comprises a visible laser diode (VLD, a focusing lens, and a cylindrical optical element arranged therewith. The individual planar laser illumination beam components produced from each PLIM are optically combined to produce a composite substantially planar laser illumination beam having substantially uniform power density characteristics over the entire spatial extend thereof and thus the working range of the system. Preferably, each planar laser illumination beam component is focused so that the minimum beam width thereof occurs at a point or plane which is the farthest or maximum object distance at which the system is designed to acquire images, thereby compensating for decreases in the power density of the incident planar laser illumination beam due to the fact that the width of the planar laser illumination beam increases in length for increasing object distances away from the imaging optics. Advanced high-resolution wavefront control methods and devices are disclosed for use with the PLIIM-based systems in order to reduce the power of speckle-noise patterns observed at the image detections thereof. By virtue of the present invention, it is now possible to use both VLDs and high-speed CCD-type image detectors in conveyor, hand-held and hold-under type imaging applications alike, enjoying the advantages and benefits that each such technology has to offer, while avoiding the shortcomings and drawbacks hitherto associated therewith.
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR
Optical system
ActiveUS8203702B1Reduce frictionEnormous difference potential speedAngle measurementAdditive manufacturing apparatusBeam divergencePiston
Method / system locate external articles using source, detector (PSD), entrance aperture, and magnifying / reducing afocal element—expanding FOR>90°, or refining precision. Between (1) source or detector and (2) aperture, at least one plural-axis-rotatable mirror addresses source / detector throughout FOR. ½- to 15-centimeter mirror enables ˜25 to ˜45 μradian beam divergence. Aperture, afocal element, and mirror(s) define source-detector path. Mirror(s) rotate in refractory- (or air / magnetic-) bearing mount; or mirror array. Auxiliary optics illuminate mirror back, monitoring return to measure (null-balance feedback) angle. To optimize imaging, auxiliary radiation propagates via splitters toward array (paralleling measurement paths), then focusing on imaging detector. Focal quality is developed as a PSF, optimized vs. angle; stored results later recover optima. Mirror drive uses magnet(s) on mirror(s). “Piston” motion yields in-phase wavefronts, so array dimensions set diffraction limit. Also: destructive reply; scaling optimizes acceleration vs. thickness; passive systems.
Owner:ARETE ASSOCIATES INC
Device, image processing device and method for optical imaging
ActiveUS8629930B2Short focal lengthReduction of building lengthTelevision system detailsColor television detailsImaging processingGrating
An optical device for imaging is disclosed having at least one micro lens field with at least two micro lenses and one image sensor with at least two image detector matrices. The at least two image detector matrices each include a plurality of image detectors and there is an allocation between the image detector matrices and the micro lenses, so that each micro lens together with an image detector matrix forms an optical channel. The center points of the image detector matrices are shifted laterally by different distances, with respect to centroids, projected onto the image detector matrices, of the micro lens apertures of the associated optical channels, so that the optical channels have different partially overlapping detection areas and so that an overlapping area of the detection areas of two channels is imaged onto the image detector matrices offset with respect to an image detector raster of the image detector matrices. Further, an image processing device and a method for optical imaging are described.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
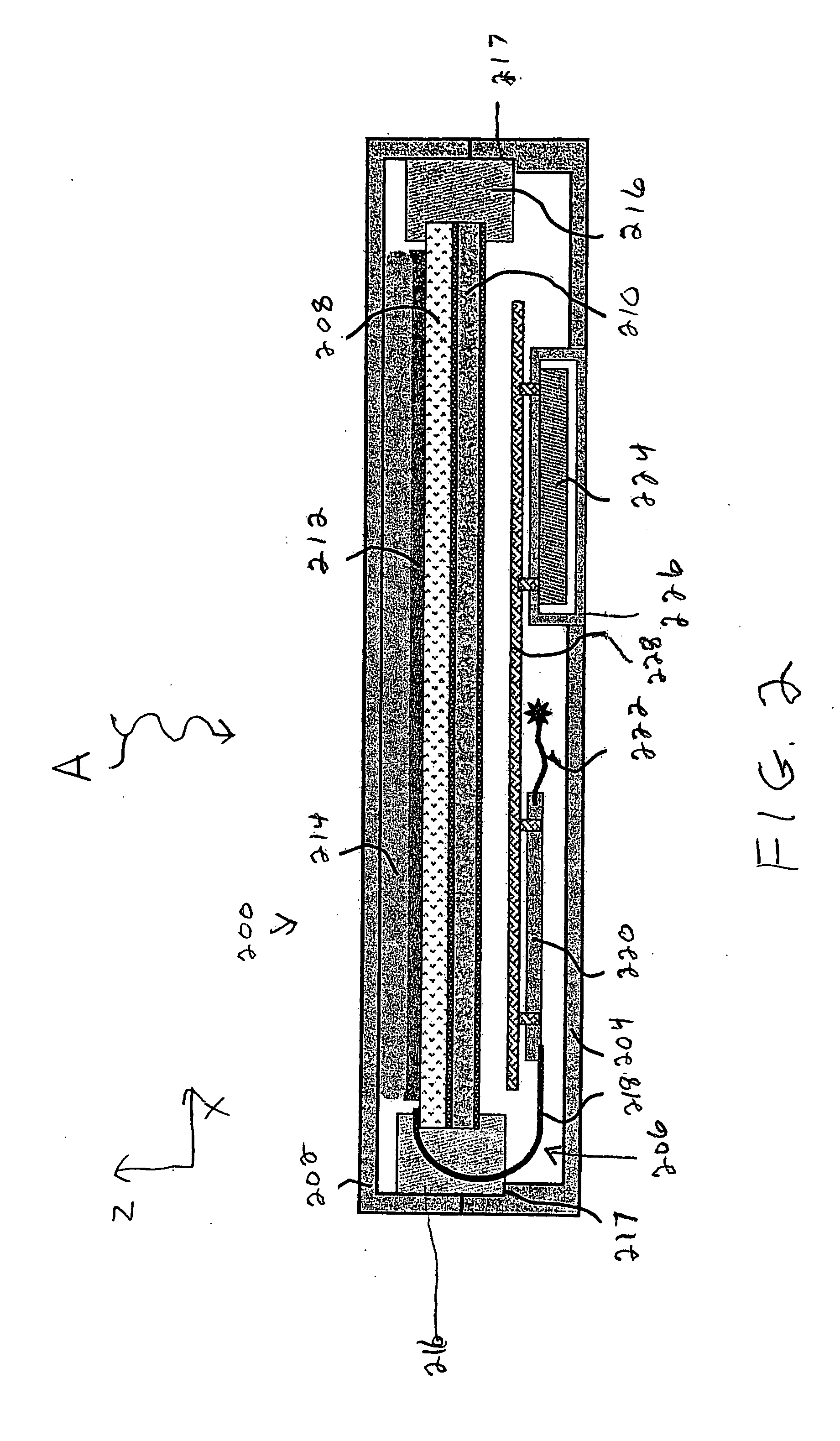
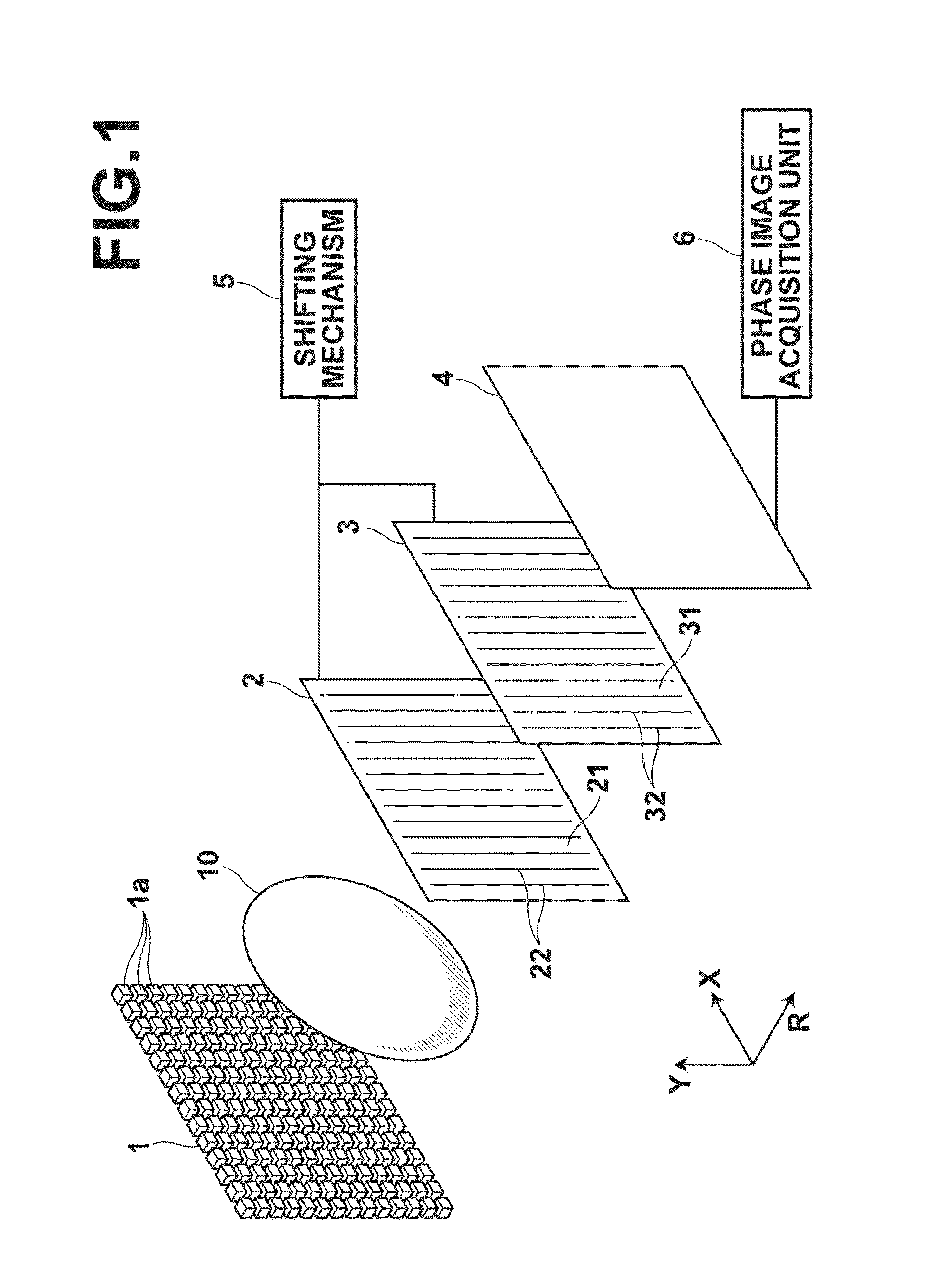
Radiation phase contrast imaging apparatus
InactiveUS20100246765A1Cost of apparatus can be reducedLow costRadiation/particle handlingMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationGratingElectron source
A radiation phase contrast imaging apparatus, including a radiation emission unit having a plurality of electron sources for emitting electron beams, and a target for emitting radiation through collision of electron beam emitted from each electron source, a first grating in which grating structures for diffracting radiation are disposed periodically, a second grating in which grating structures for transmitting and shielding radiation are disposed periodically, and a radiation image detector for detecting radiation transmitted through the second grating, in which the first and second gratings are disposed in an optical axis direction of the radiation so as to be able to substantially superimpose each image of the first grating formed based on radiation corresponding to each electron source on a surface of the second grating, and the radiation corresponding to each electron source forms each phase image of the same subject on the radiation image detector.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
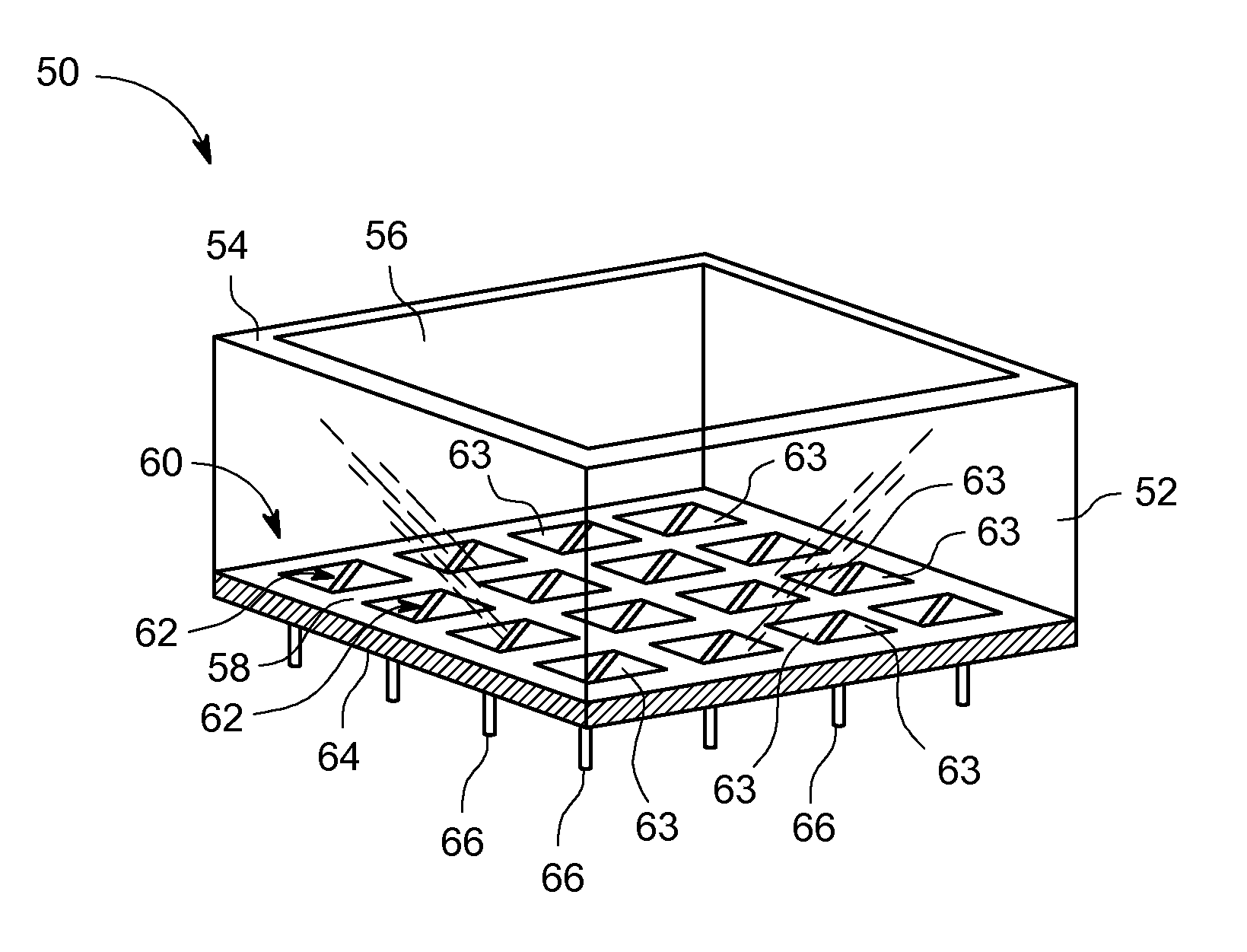
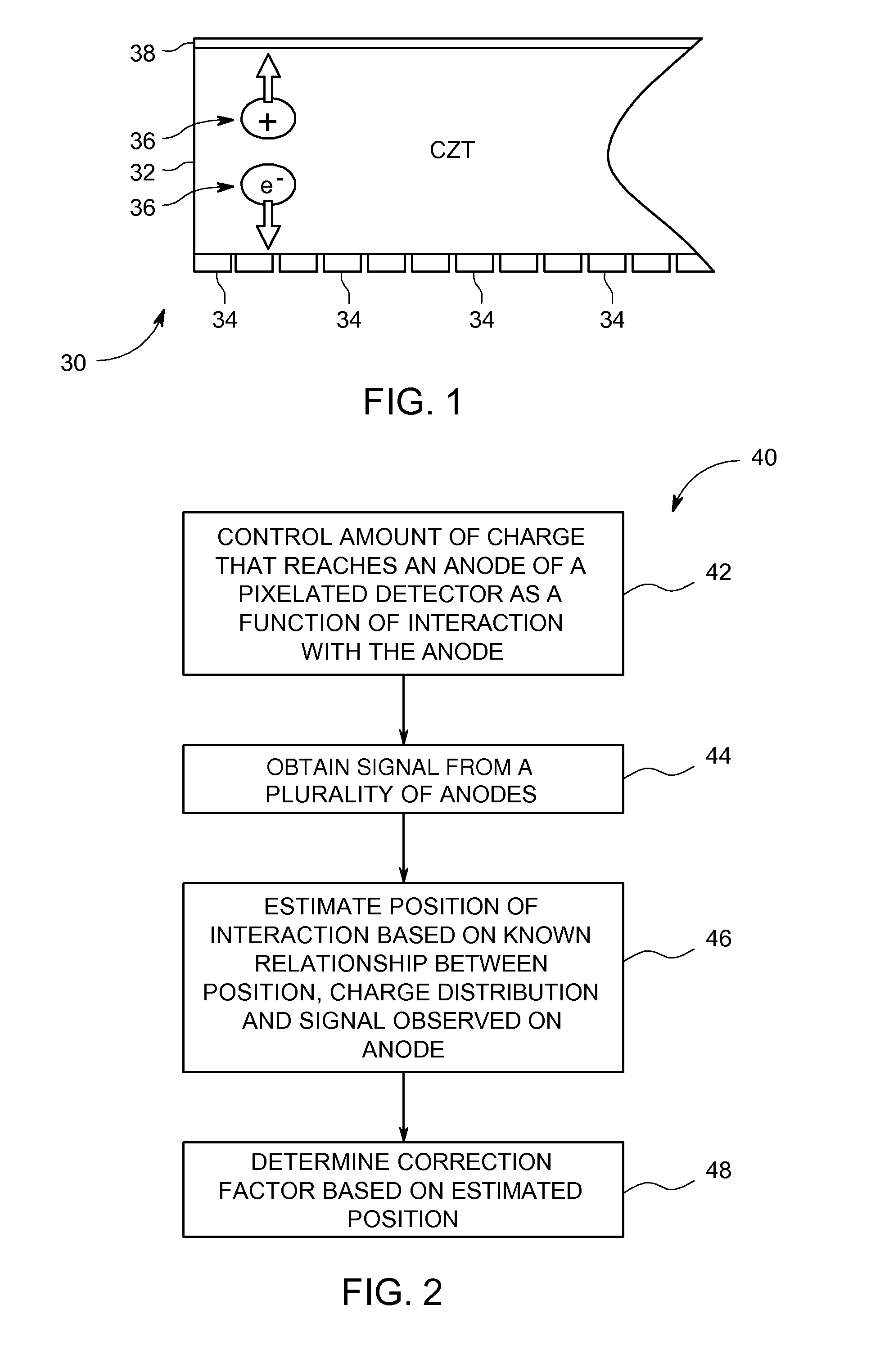
Systems and methods for providing a shared charge in pixelated image detectors
InactiveUS20110155918A1Material analysis by optical meansRadiation intensity measurementPixel basedComputer science
Systems and methods for providing a shared charge in pixelated image detectors are provided. One method includes providing a plurality of pixels for a pixelated solid state photon detector in a configuration such that a charge distribution is detected by at least two pixels and obtaining charge information from the at least two pixels. The method further includes determining a position of an interaction of the charge distribution with the plurality of pixels based on the obtained charge information.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST ISRAEL
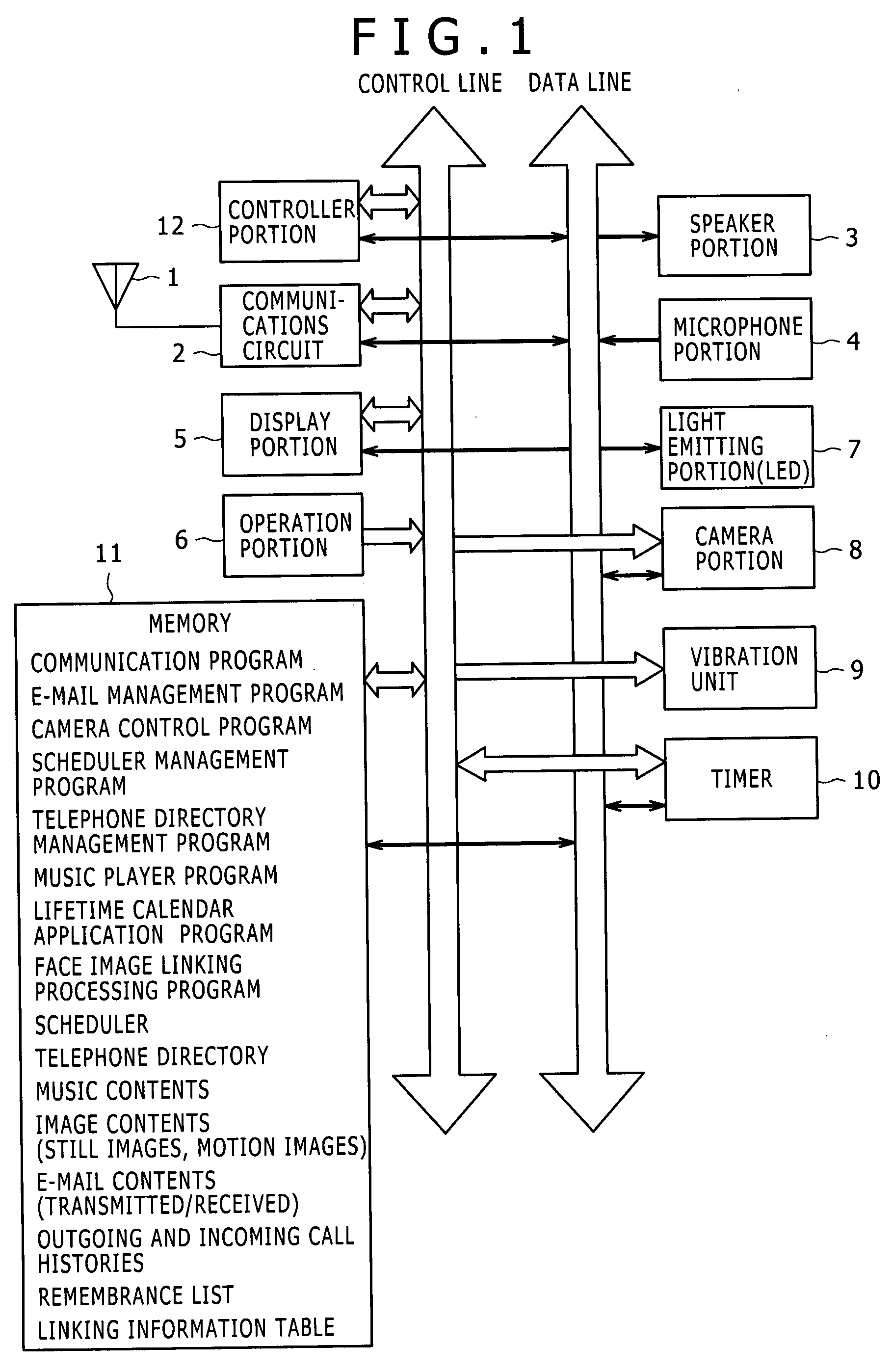
Information processing apparatus, information processing method, information processing program, and mobile terminal device
ActiveUS20070268309A1Special service for subscribersCharacter and pattern recognitionImage detectorImage content
An information processing apparatus includes a face image extractor portion, a matching image detector portion, a linking processing portion, a communication address information acquiring portion, and a controller portion. The face image extractor portion extracts a face image of a person in a still image content. The matching image detector portion detects from a memory containing or storing face images and communication address information of respective users the matching face image matching with the extracted face image, which has been extracted by the face image extractor portion. When the matching face image matching with the extracted face image, which has been extracted by the face image extractor portion, is detected by the matching image detector, the linking processing portion performs a linking process to link the extracted face image and communication address information corresponding to the extracted face image and stored in the memory. When the person is selected from the still image content, the communication address information acquiring portion acquires from the memory the communication address information linked by the linking process to the face image of the selected person. The controller portion controls a communication section to make a telephone call to a telephone number corresponding to the communication address information acquired by the communication address information acquiring portion or that performs display control to display on a display portion a creation screen for an e-mail piece having an input e-mail address corresponding to the communication address information.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
Systems and methods for detecting and analyzing polymers
InactiveUS7351538B2Easy to detectEasy to identifyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsWide fieldLinear arrays
A detection system and methods for improving the ability of the detection system to recognize labels that are disposed on a polymer. Embodiments of the invention include schemes for selecting emitters and labels used within the system in a manner that allows an increase in the number of distinct labels that can be used together in a system. In other embodiments, the detection system and methods are directed to identifying portions of a detection signal that may be associated with extra labels residing within a detection zone. In other embodiments, the detection system and methods relate to using wide field imaging detectors while reducing out of focus noise contributions to detection signals of the system. Still, other embodiments relate to the use of linear array detectors to detect labels.
Owner:U S GENOMICS INC
Method and apparatus for measuring optical aberrations of the human eye
InactiveUS20020047992A1Measure quickly and accuratelyQuickly and accurately measuringRefractometersSkiascopesLight spotImage detection
An apparatus for measuring optical aberrations of the human eye wherein the person positions his or her eye on an optical axis of the apparatus and looks at an illuminated target on the optical axis that is visible to the eye for allowing the eye to focus on the target and establish a position of the eye. A collimating lens on the optical axis is movable along the optical axis for adjusting the apparent optical distance between the eye and the target. A light source directs a predetermined light beam along the optical axis into the eye and onto the retina of the eye as a spot of light. A lens reimages the light scattered from the light spot on the eye retina into a wavefront curvature sensor that forms two oppositely defocused images on an image detector, and a computer processes and analyzes the two defocused images for measuring the optical aberrations of the eye.
Owner:AOPTIX TECH
Hand held device and methods for examining a patient's retina
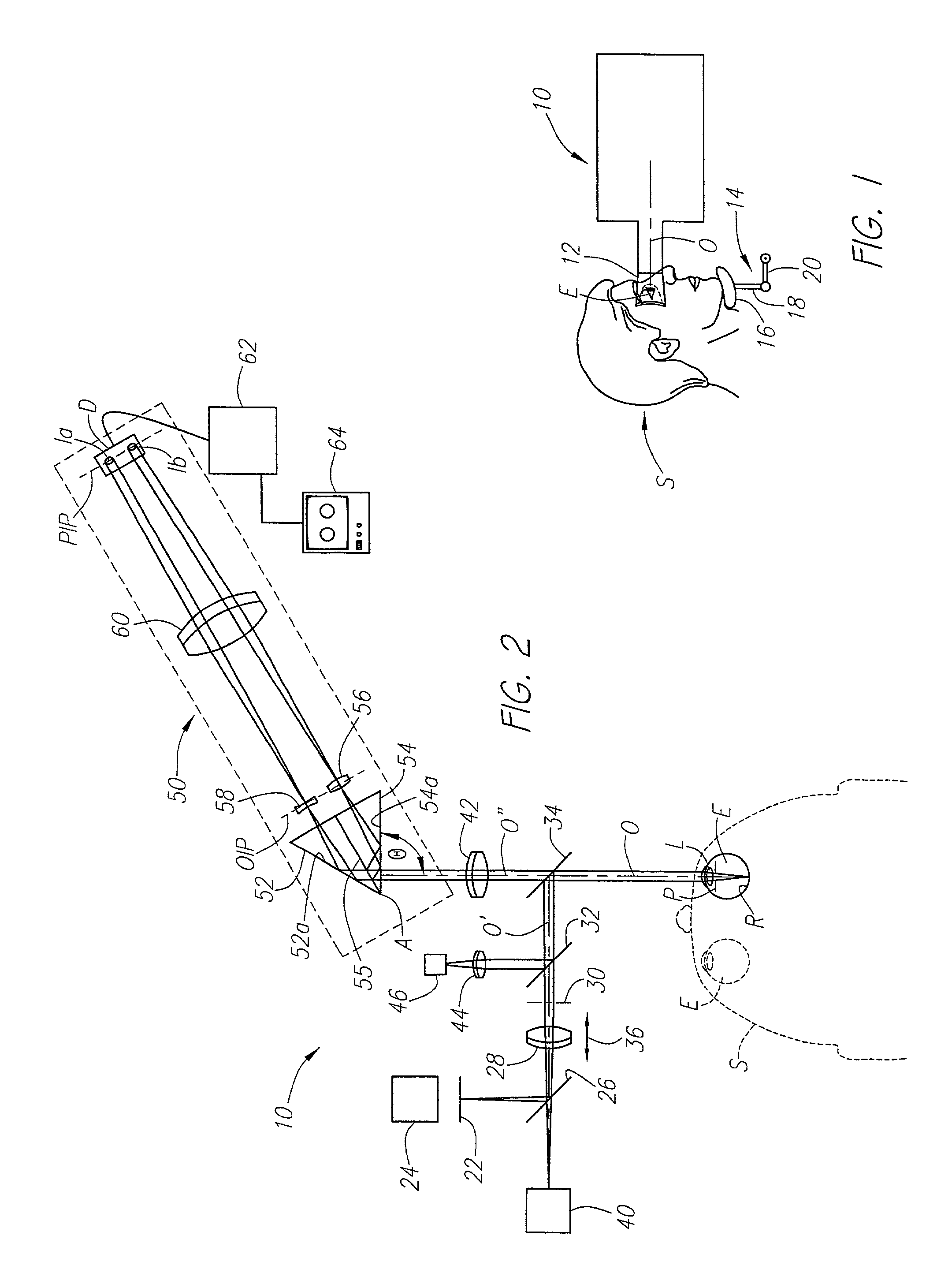
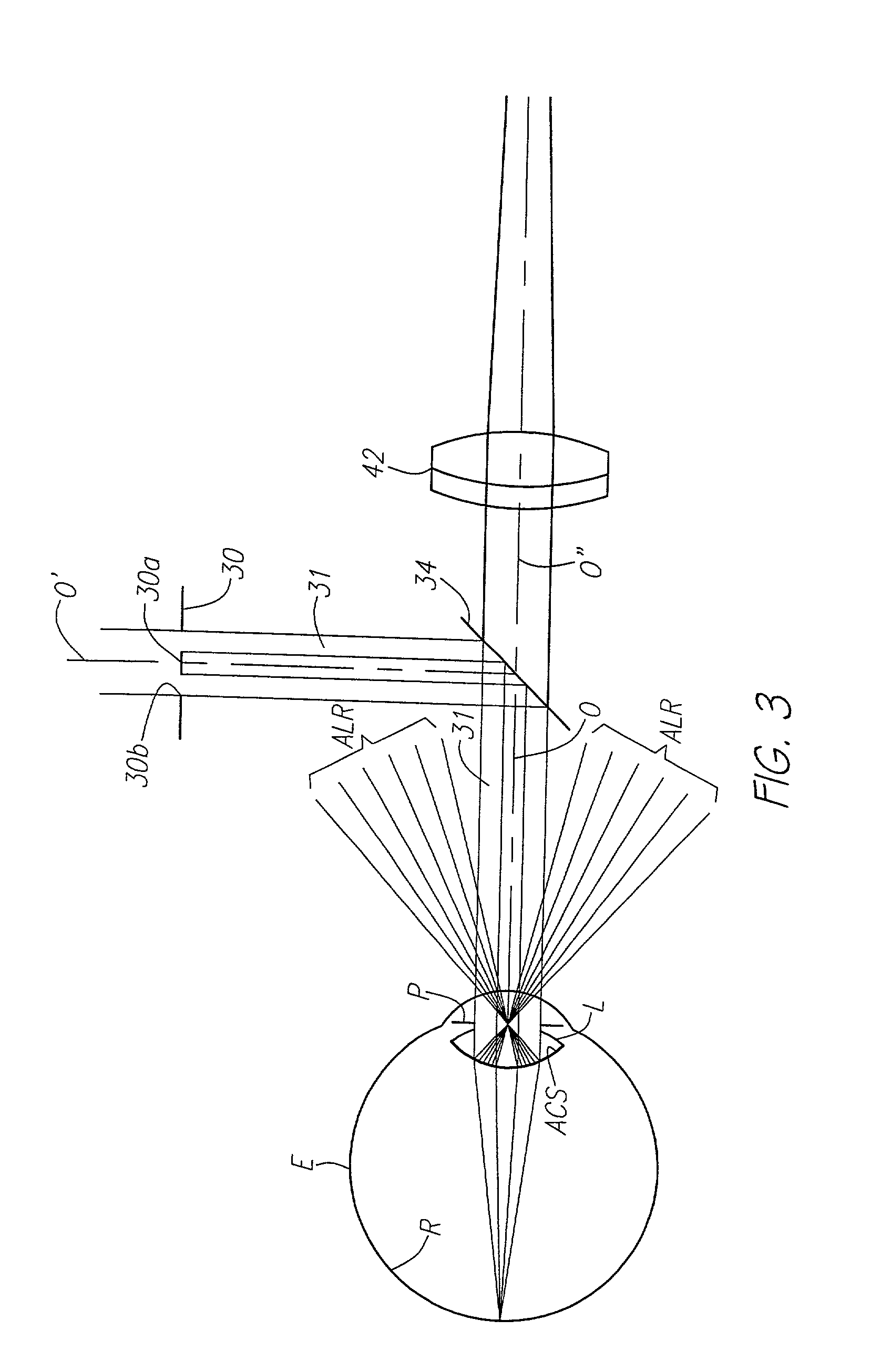
A hand held device for examining a patient's retina. In one example, the device generates visible or non-visible illuminating beams having desired spectral content. The illuminating beams are then polarized to generate polarized light beam(s) that are directed towards the patient's retina. At the patient's eye, a portion of the polarized beam is partially reflected by the cornea and travels back to the device, and another portion of the polarized beam enters the eye through the undilated pupil, illuminates the patient's retina, and generates a reflected retinal image (generally de-polarized) which also travels back to the device. The device receives the retinal image and transmits certain portions of the retinal image on through to an image detector (i.e., CCD or CMOS); and the device deflects the received polarized corneal reflections away from the image capture device. Hence, the image capture device receives retinal images but does not receive the polarized corneal reflected light.
Owner:OCUTRONICS
Systems and methods for detecting and analyzing polymers
InactiveUS20060078915A1Easy to detectEasy to identifyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsWide fieldSystem identification
A detection system and methods for improving the ability of the detection system to recognize labels that are disposed on a polymer. Embodiments of the invention include schemes for selecting emitters and labels used within the system in a manner that allows an increase in the number of distinct labels that can be used together in a system. In other embodiments, the detection system and methods are directed to identifying portions of a detection signal that may be associated with extra labels residing within a detection zone. In other embodiments, the detection system and methods relate to using wide field imaging detectors while reducing out of focus noise contributions to detection signals of the system. Still, other embodiments relate to the use of linear array detectors to detect labels
Owner:U S GENOMICS INC
3-d imaging using telecentric defocus
An apparatus for obtaining 3-D surface contour image data of a tooth has a double telecentric optical system disposed to form an image of the surface of the tooth onto an image detector array. A focus adjustment mechanism is actuable to adjust the position of either or both the double telecentric optical system and the image detector array along an optical axis to each of a sequence of focus positions. A control logic processor is in control signal communication with the focus adjustment mechanism to adjust focus position, and is in image data communication with the image detector array for receiving image data obtained by the image detector array and with a memory for storing the received image data corresponding to each of the sequence of focus positions. The control logic processor is further responsive to stored instructions for computing 3-D surface contour image data from the image data.
Owner:DENTAL IMAGING TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com