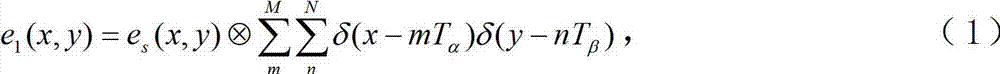Patents
Literature
58 results about "Talbot effect" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
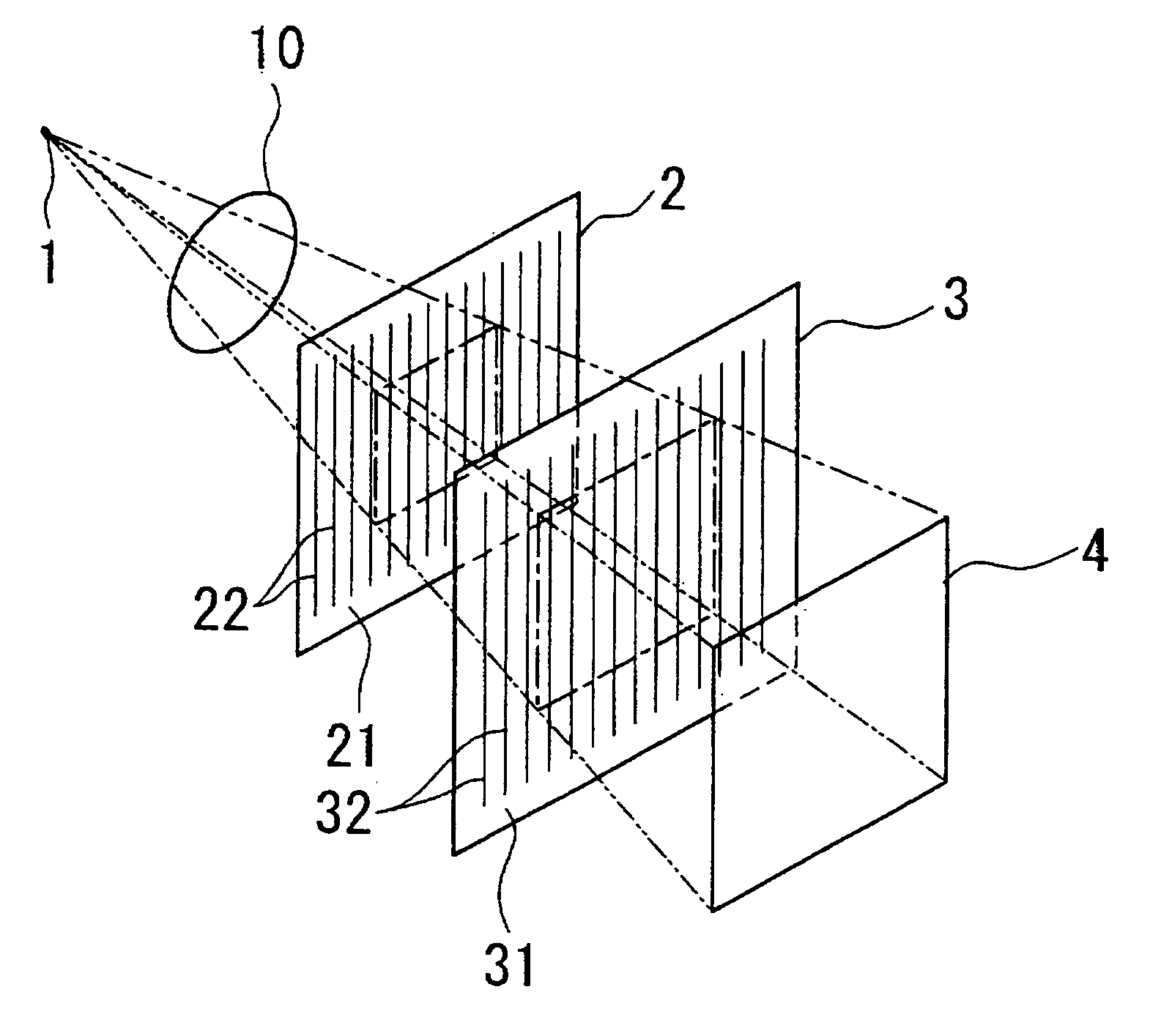
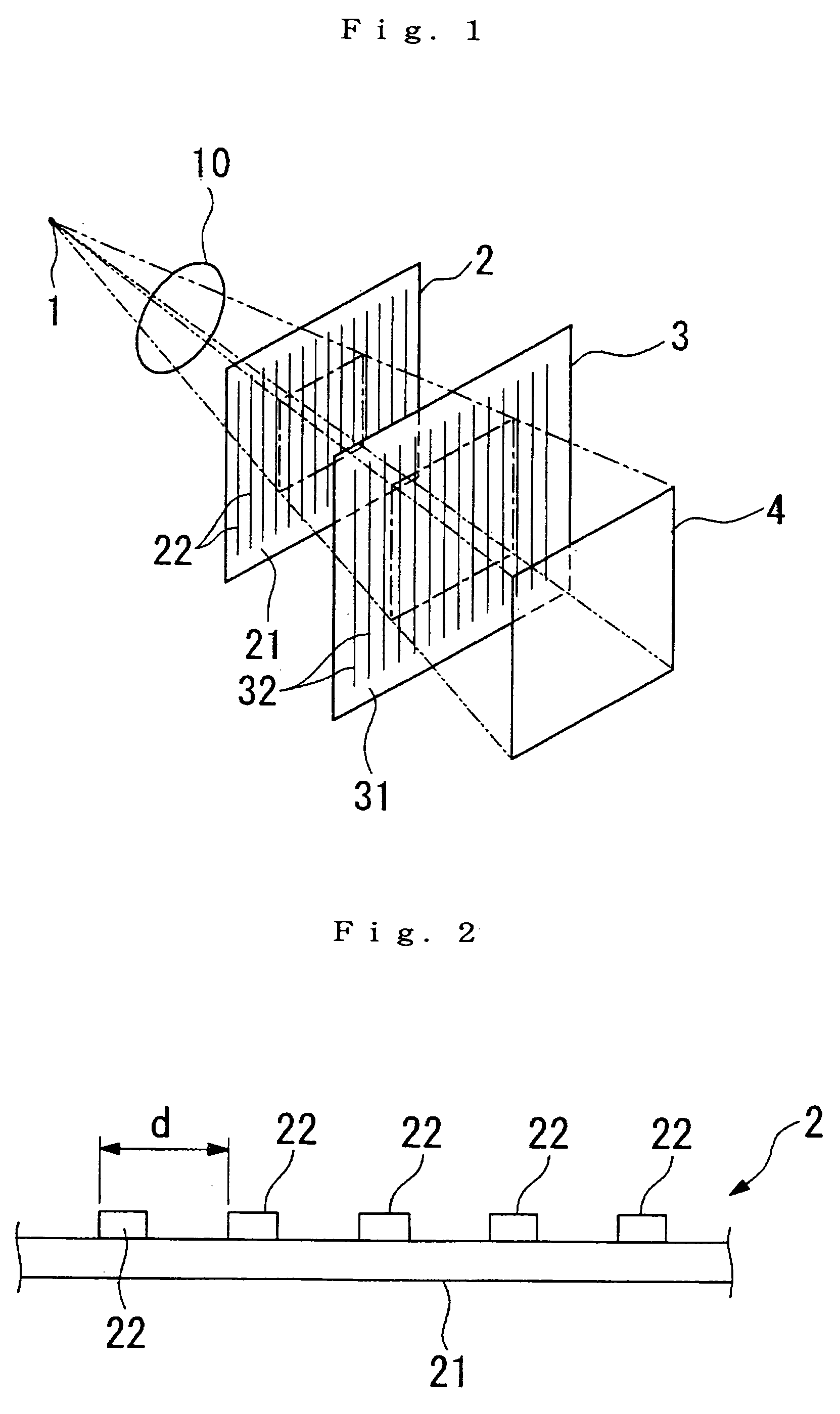
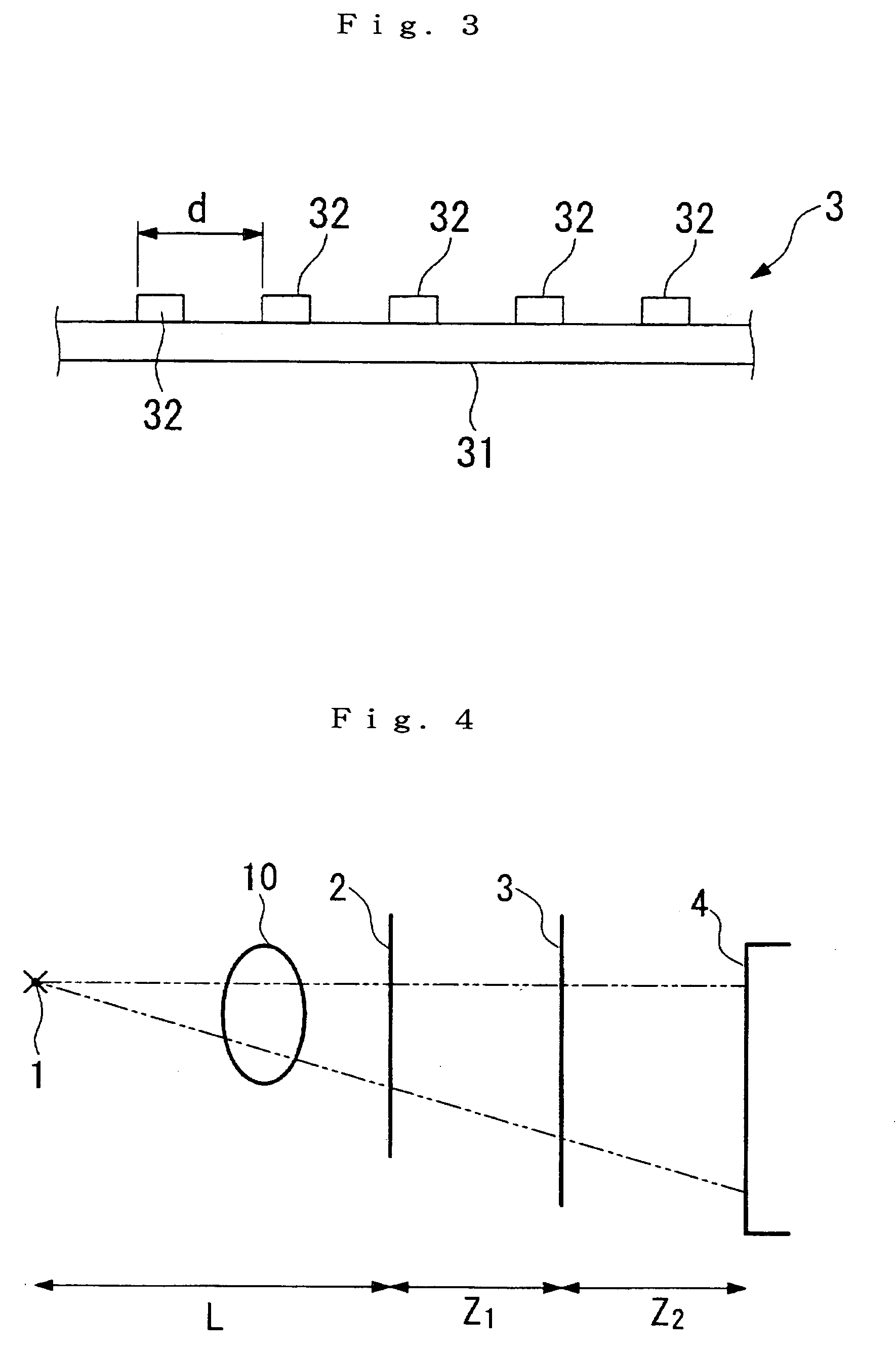
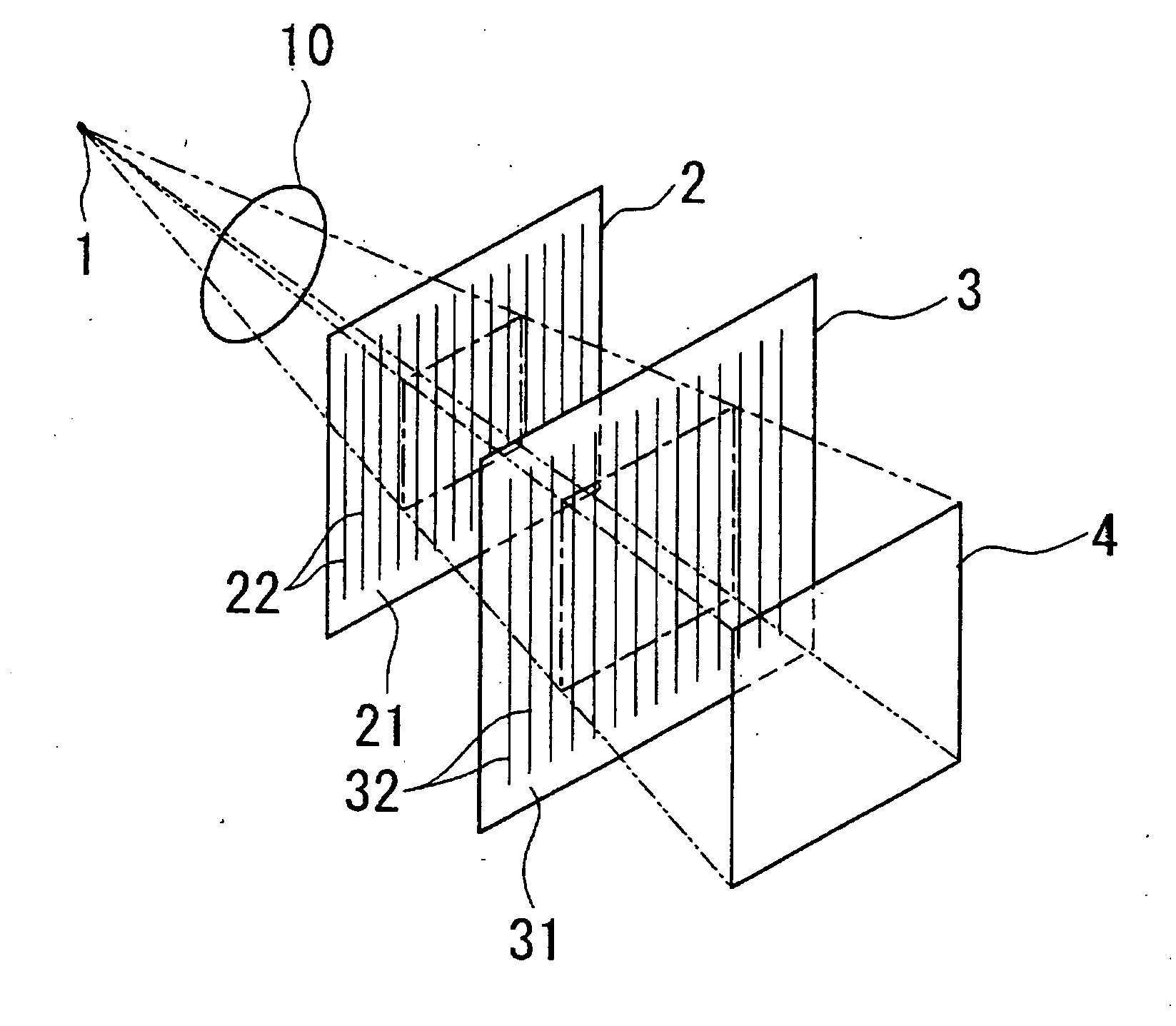
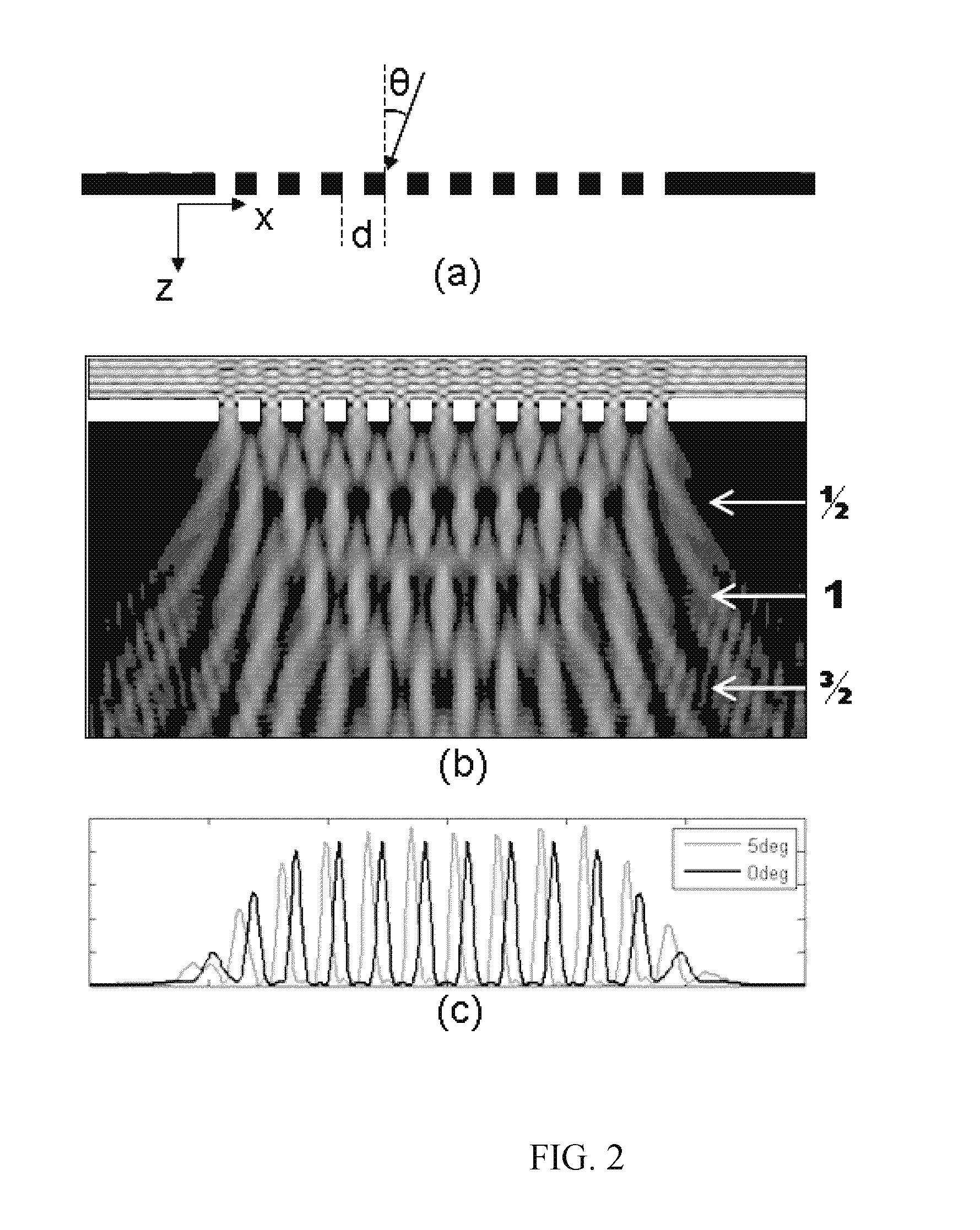
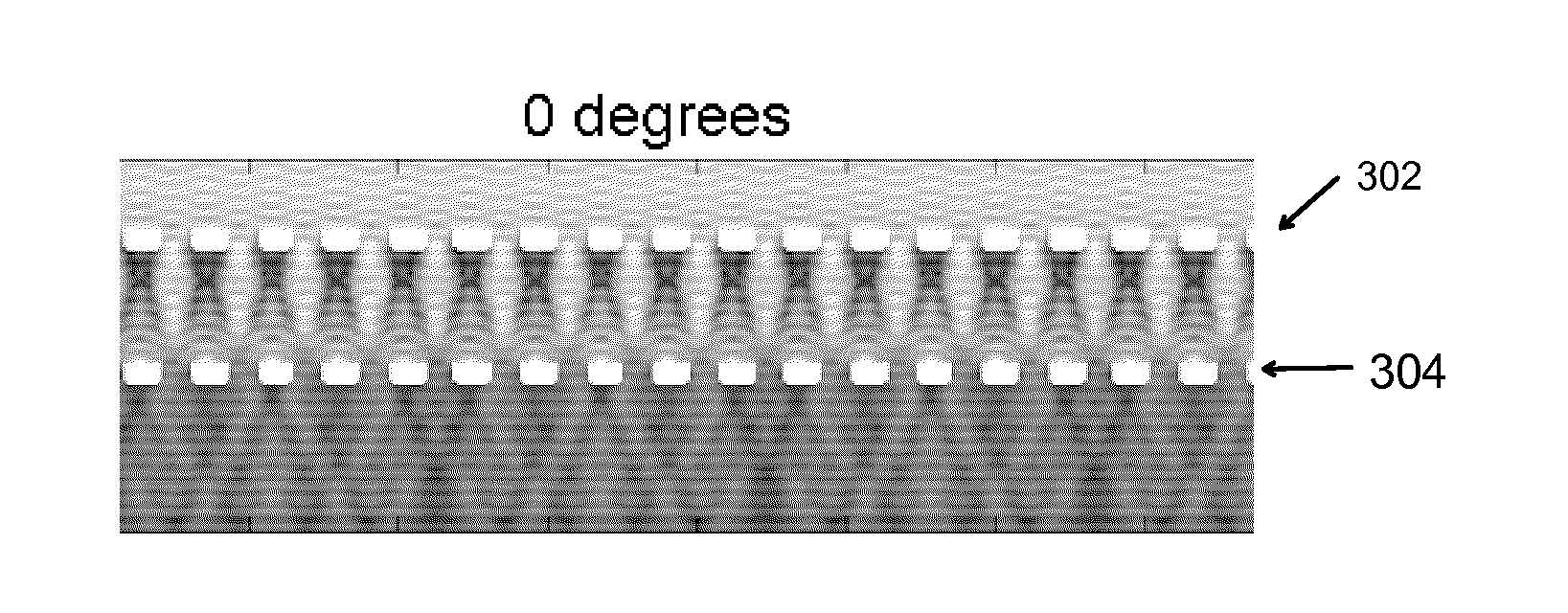
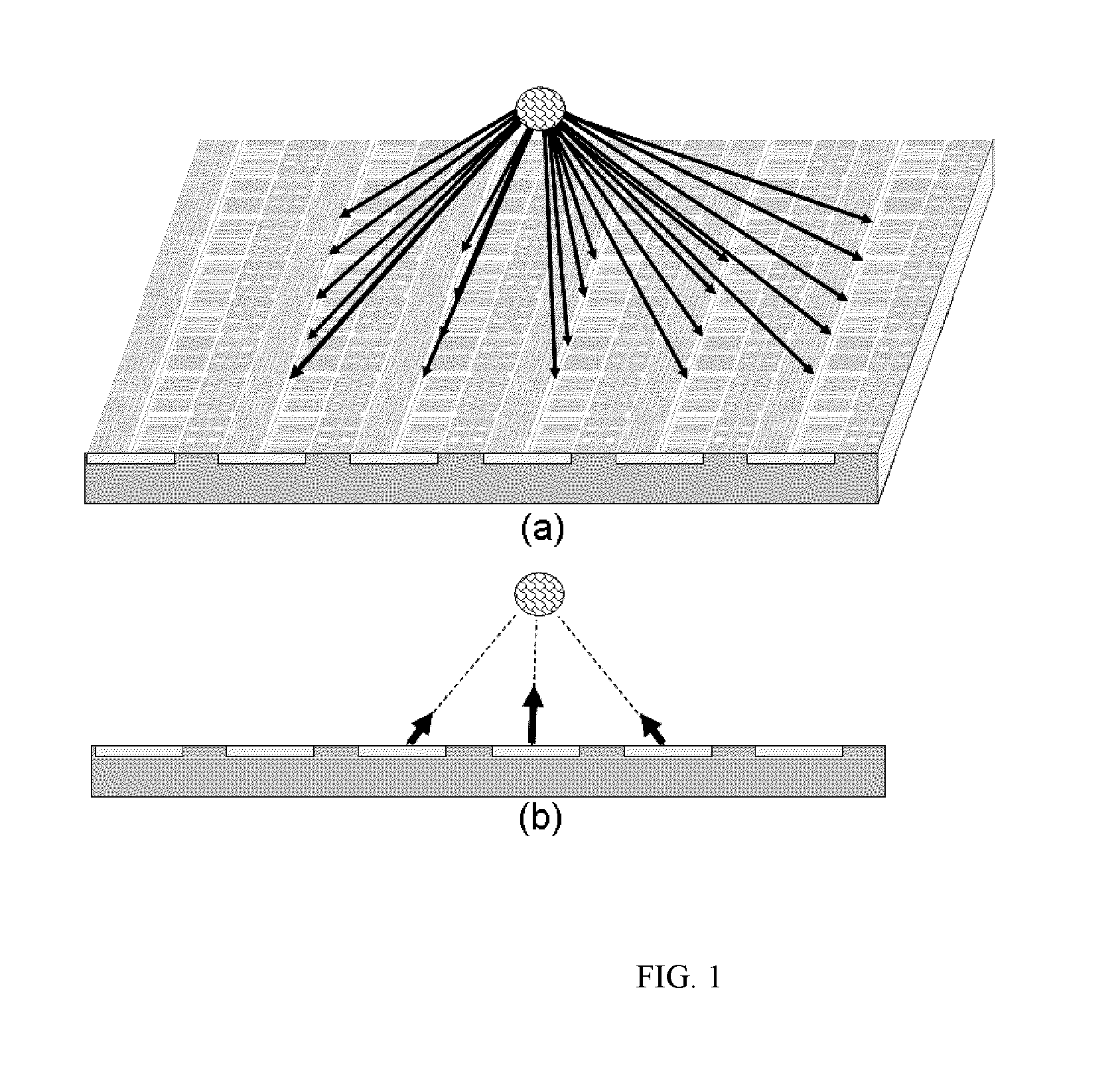
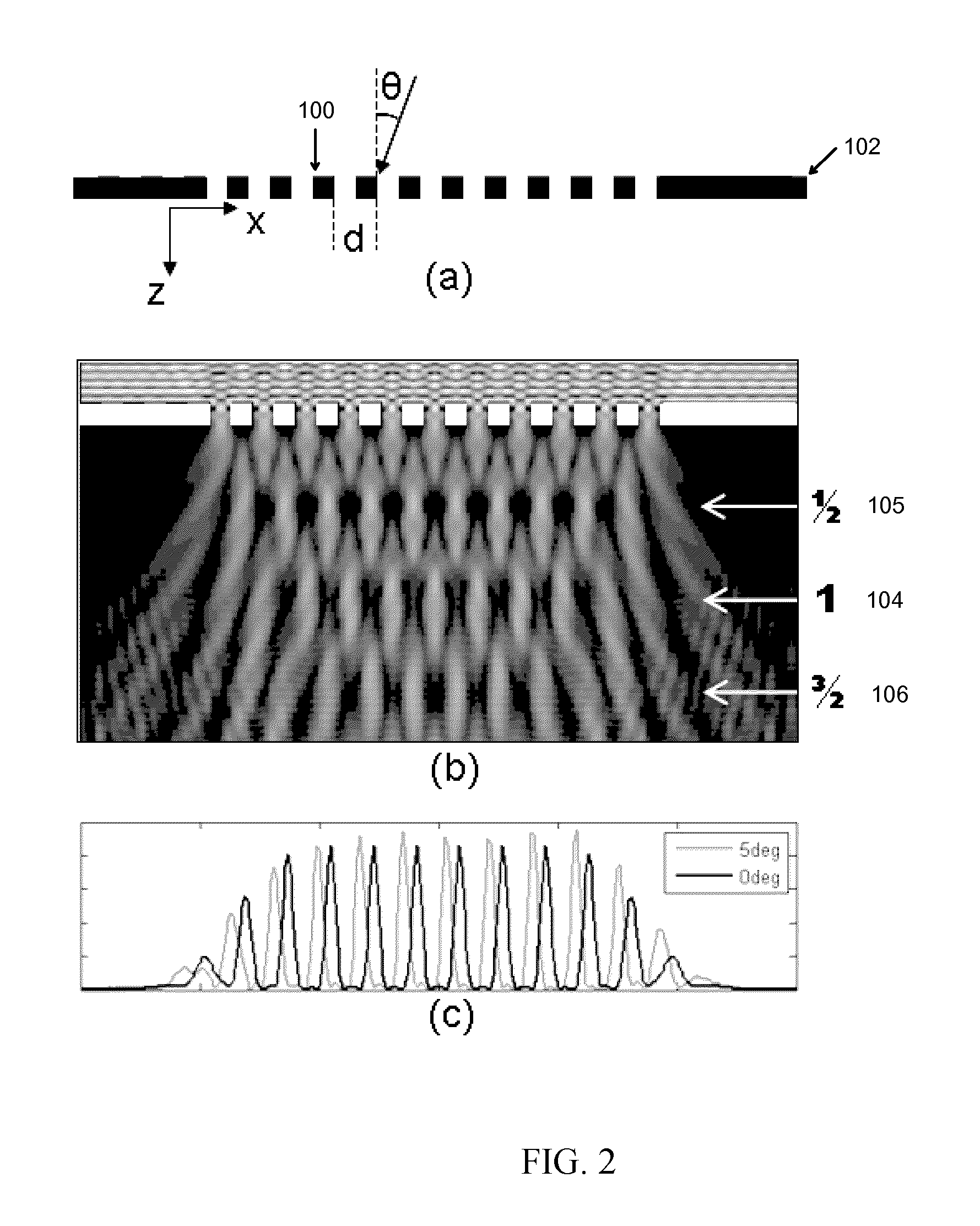
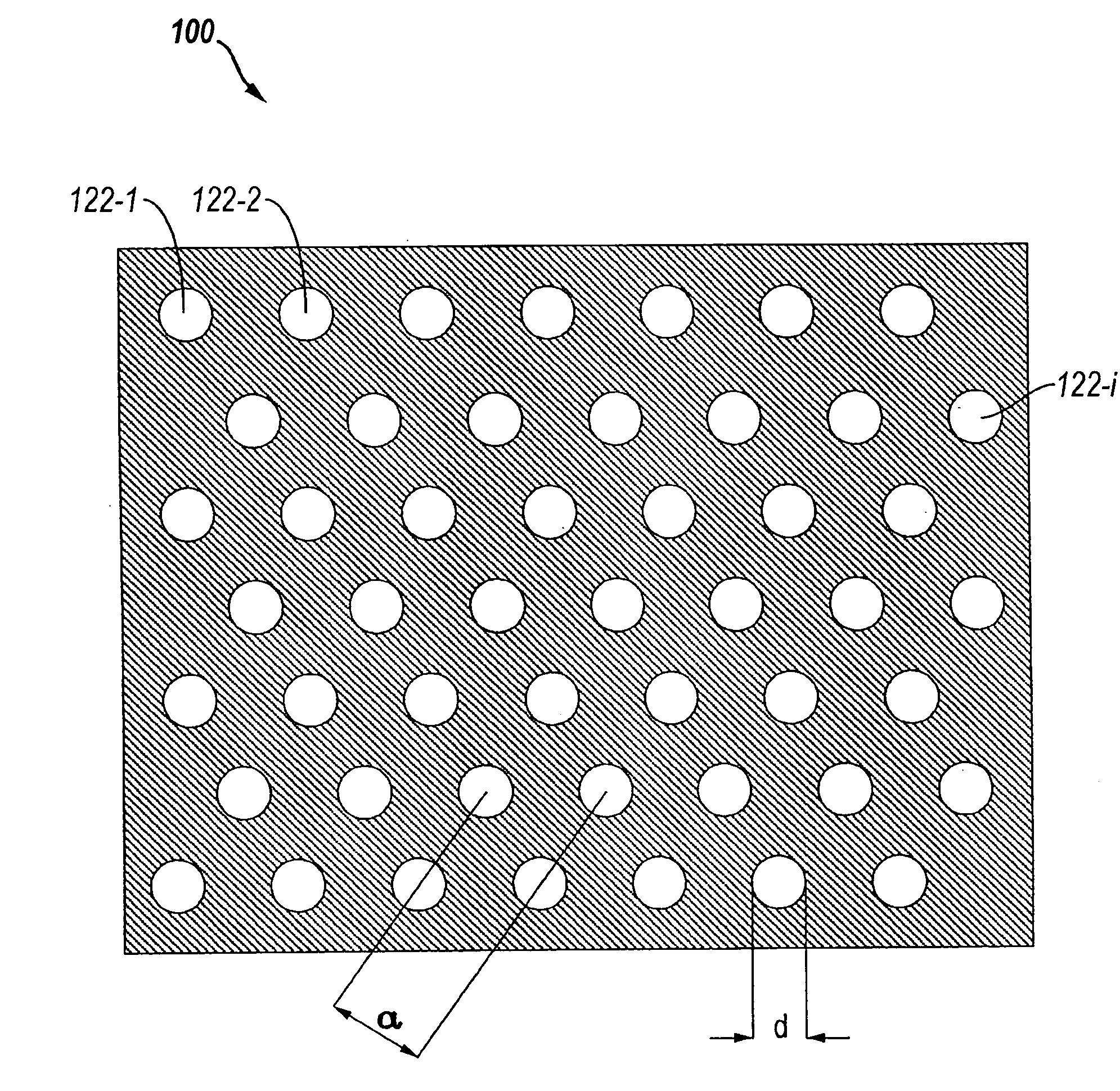
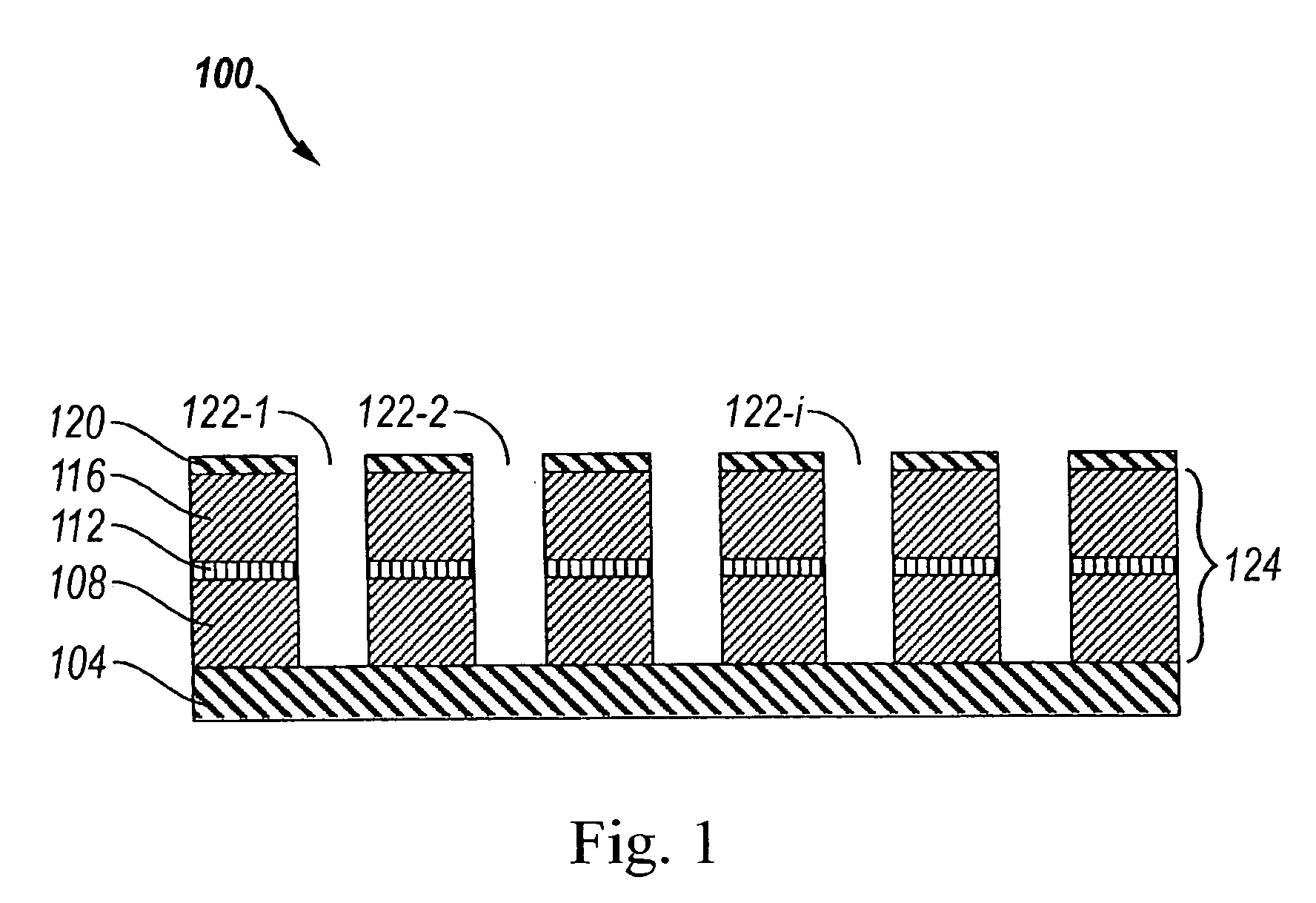
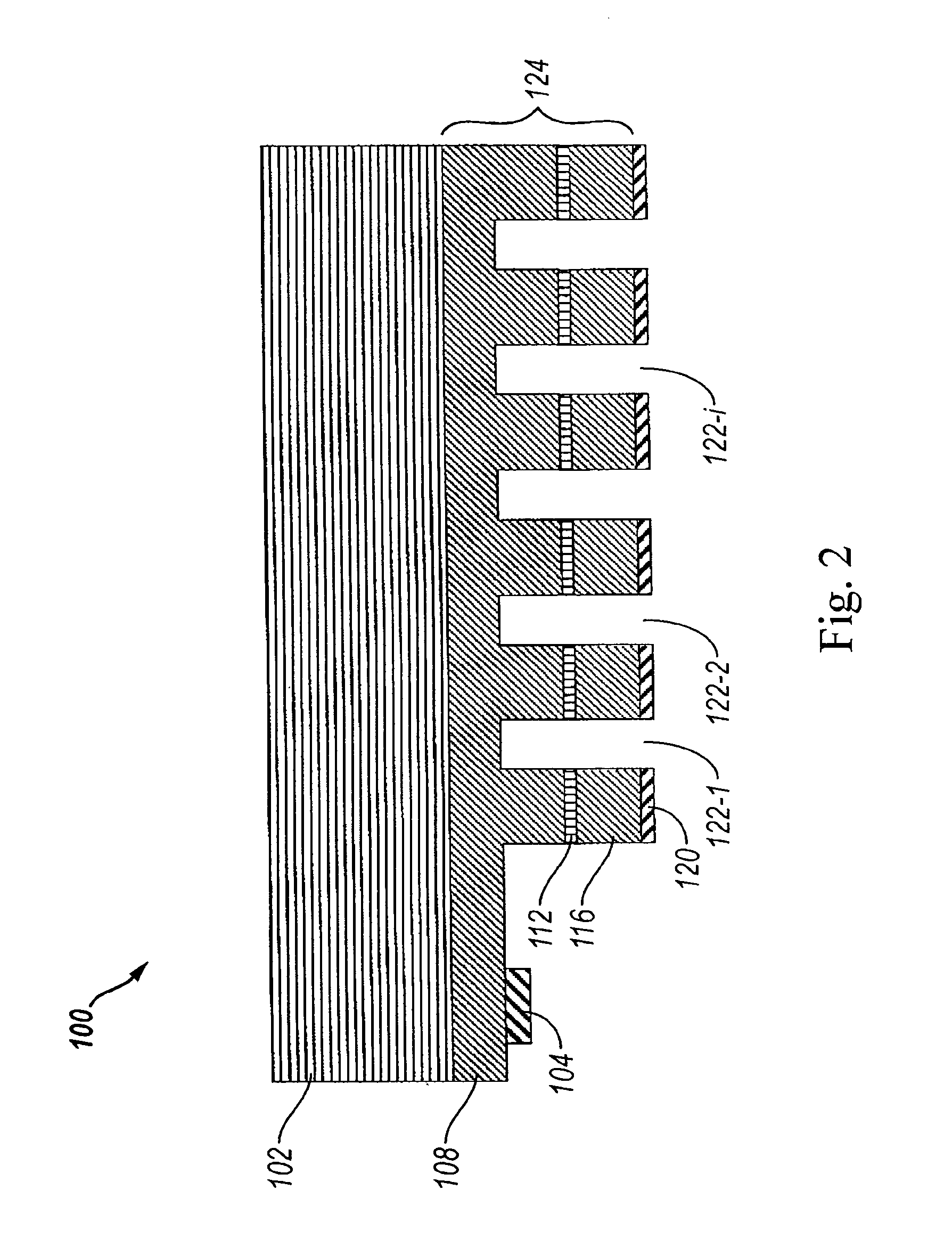
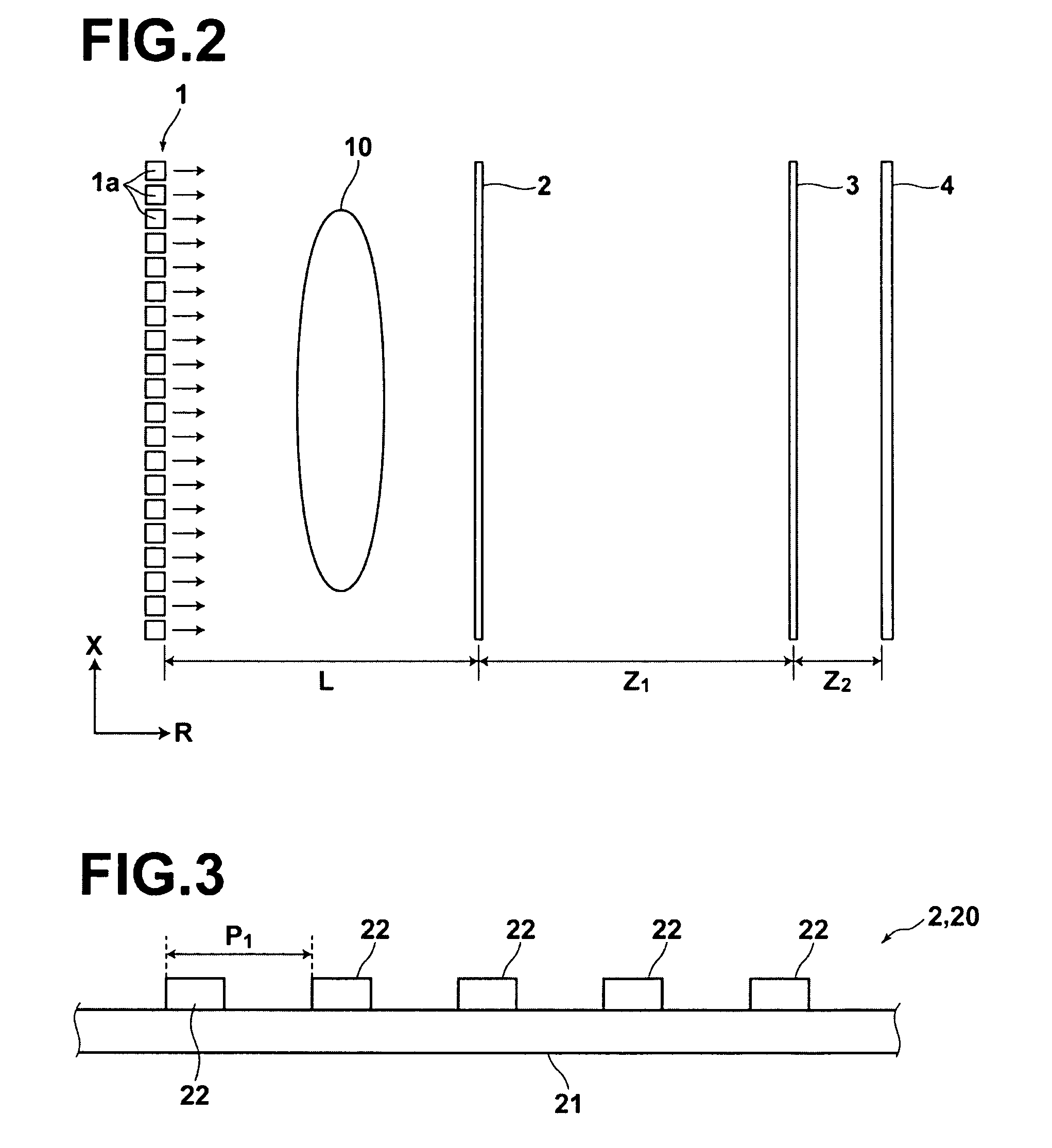
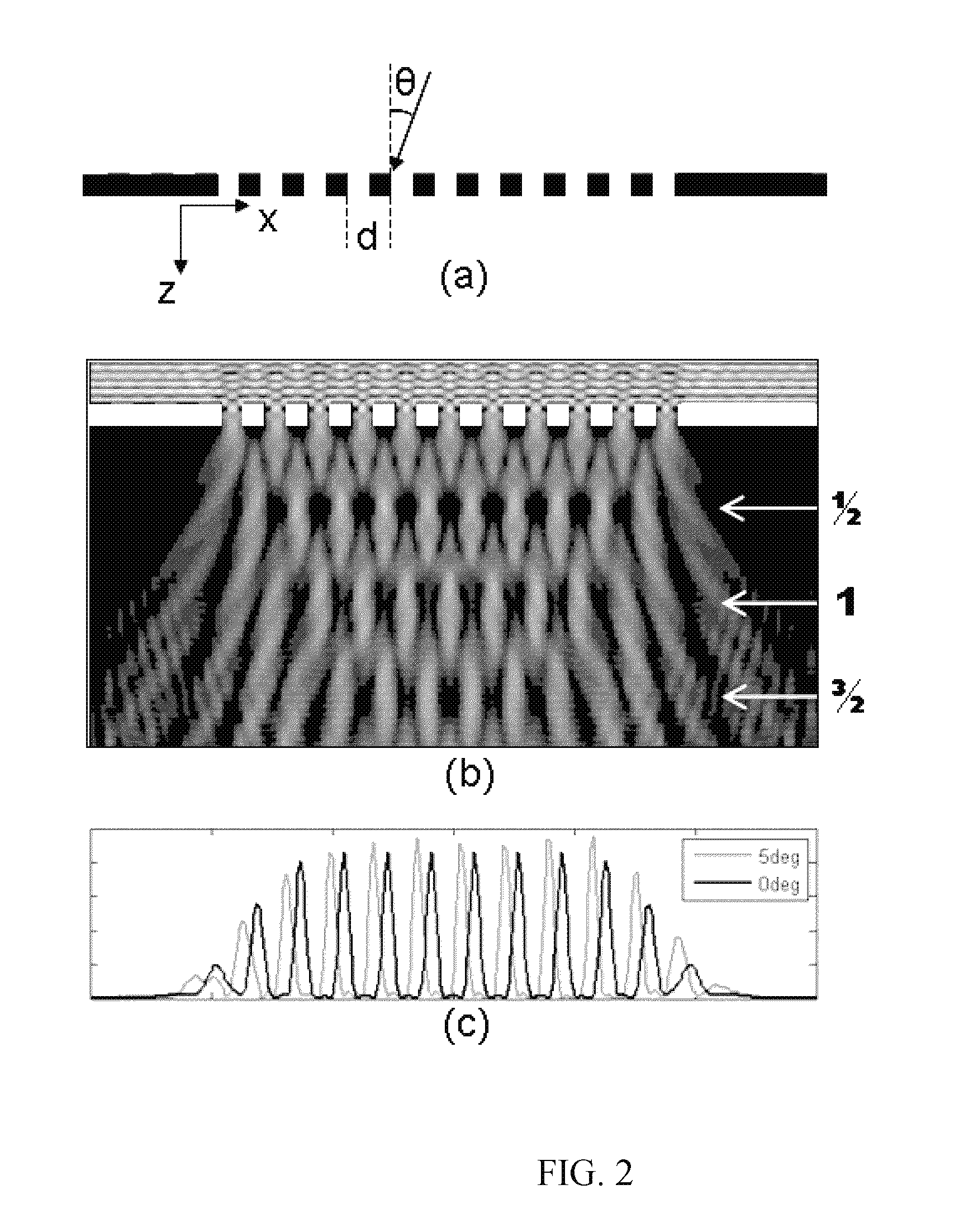
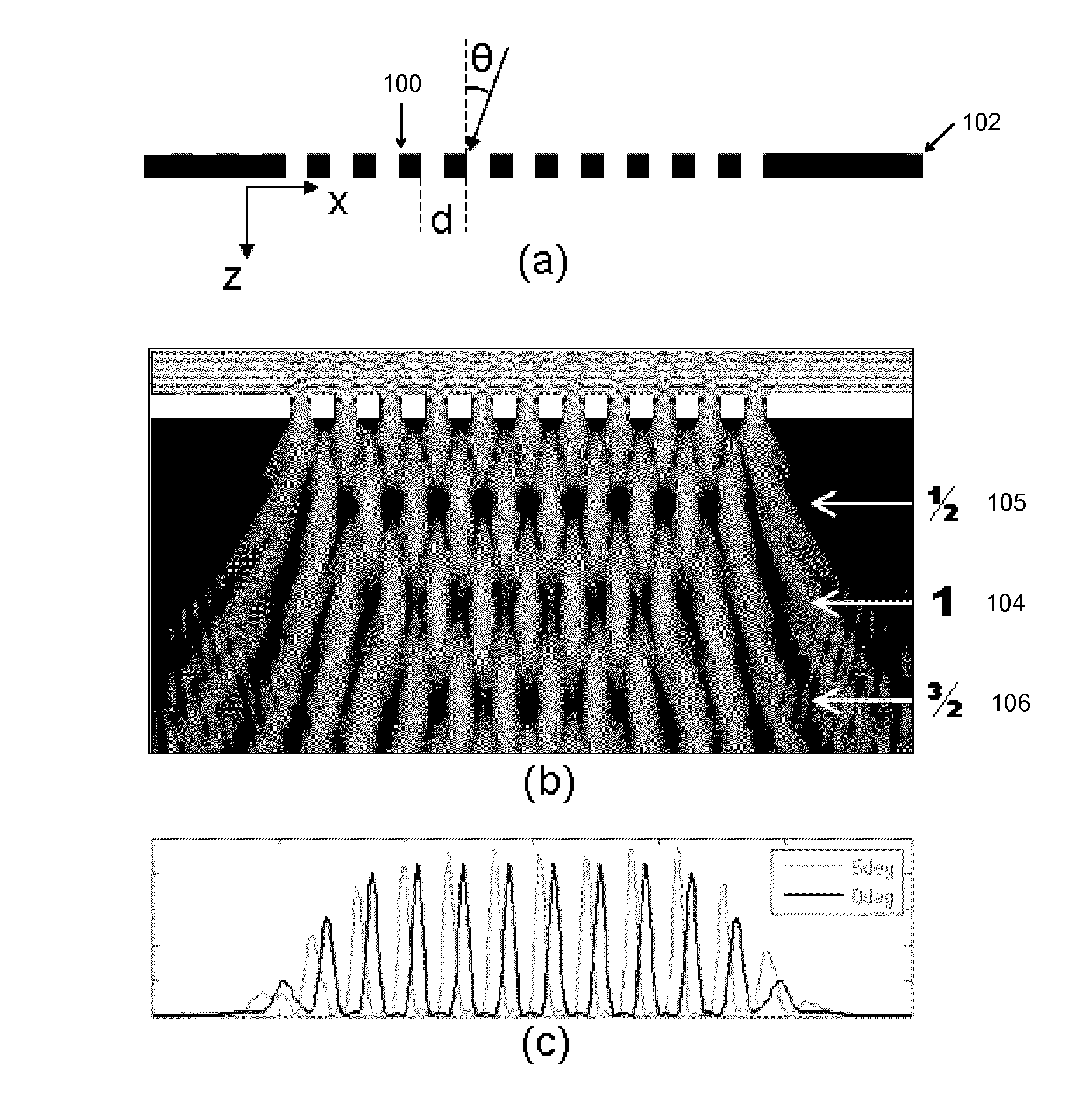
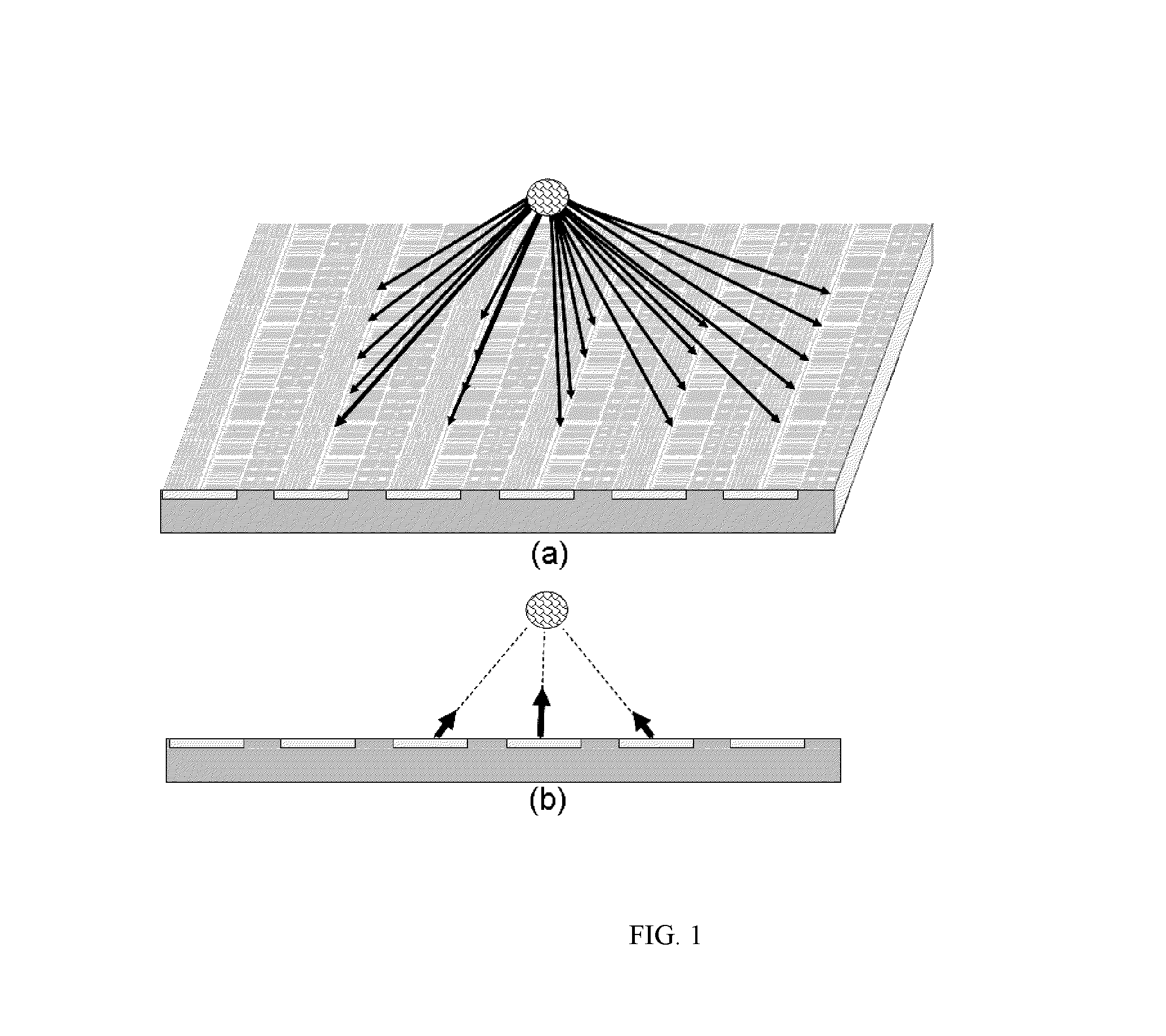
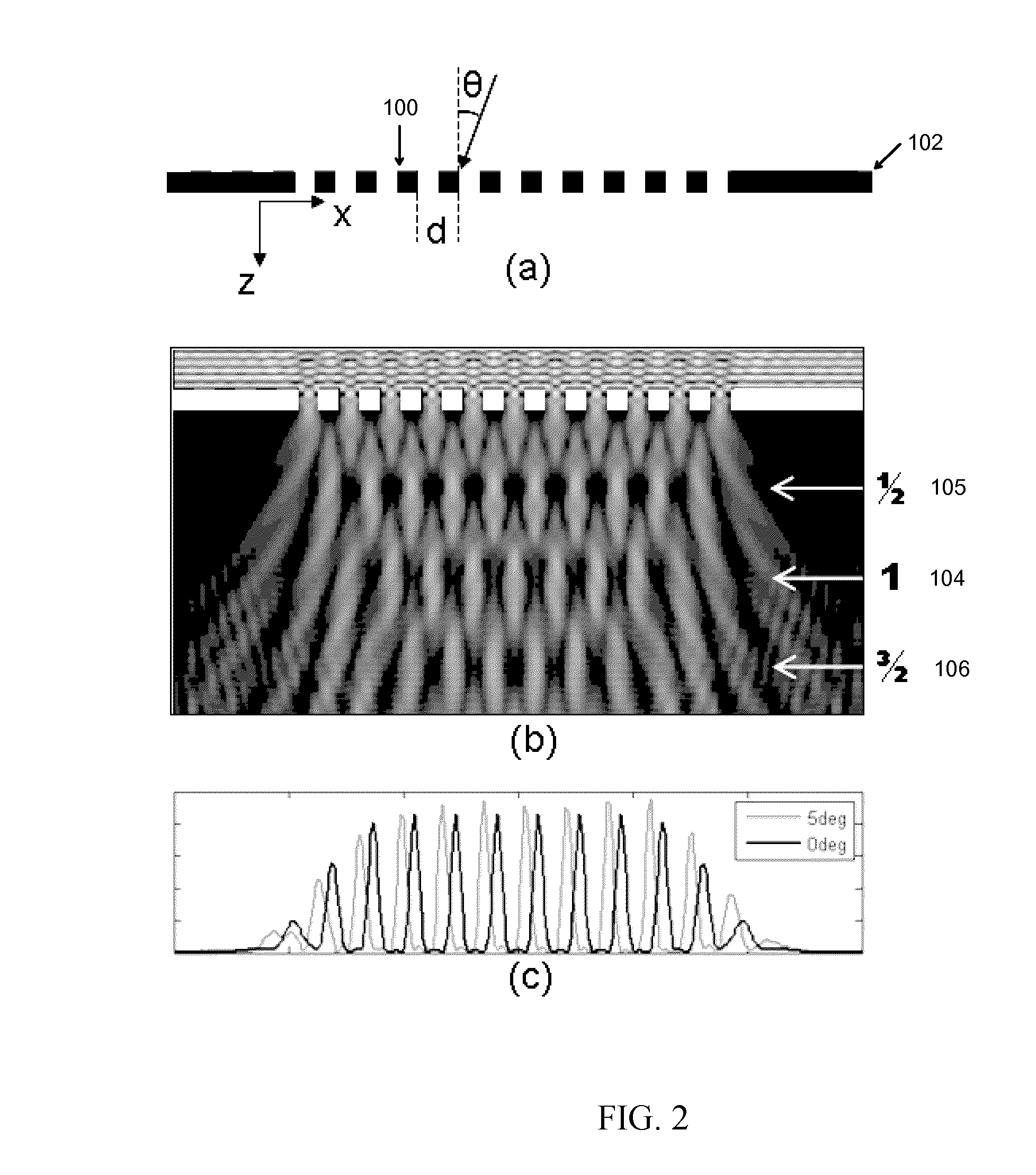
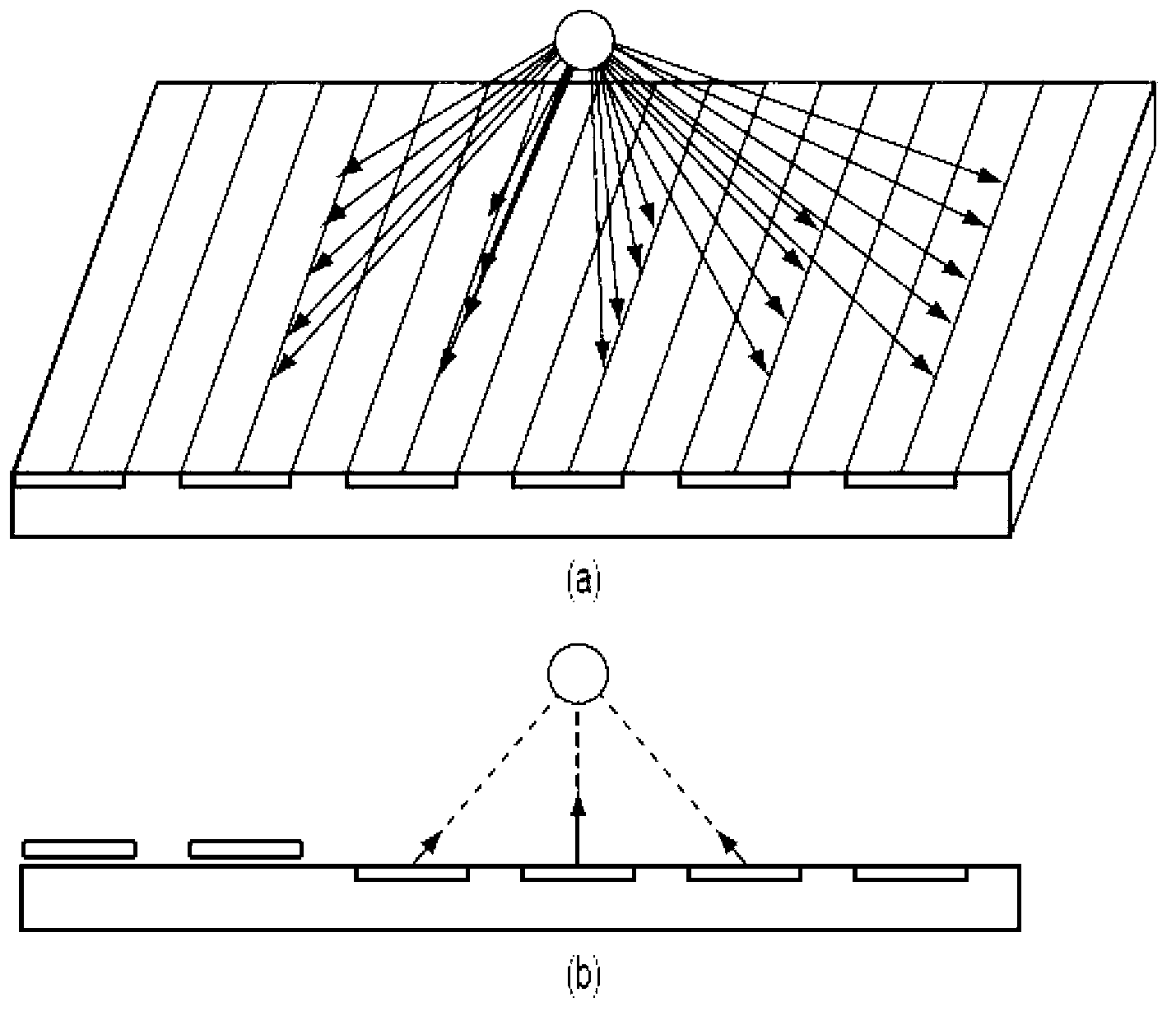
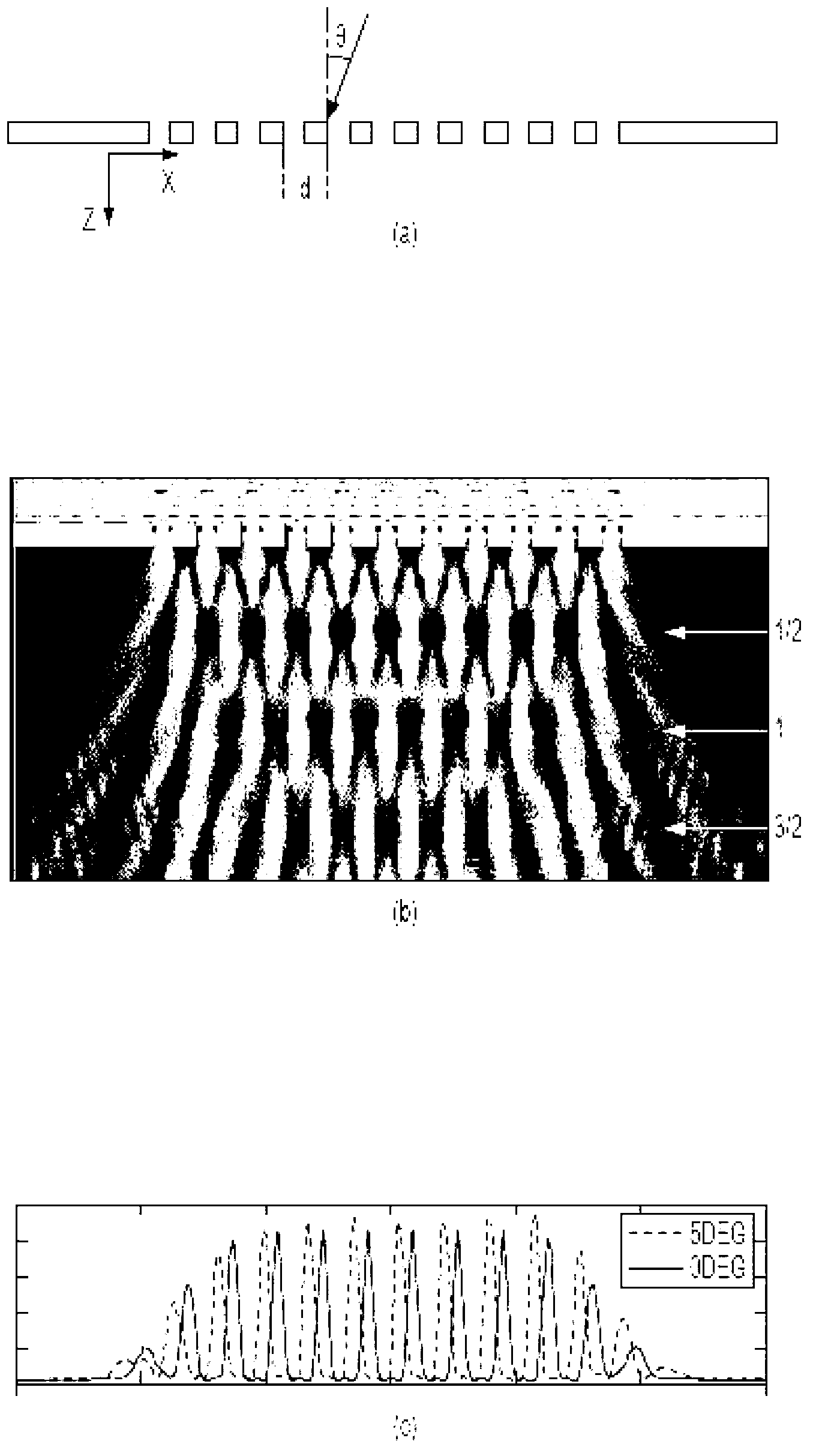
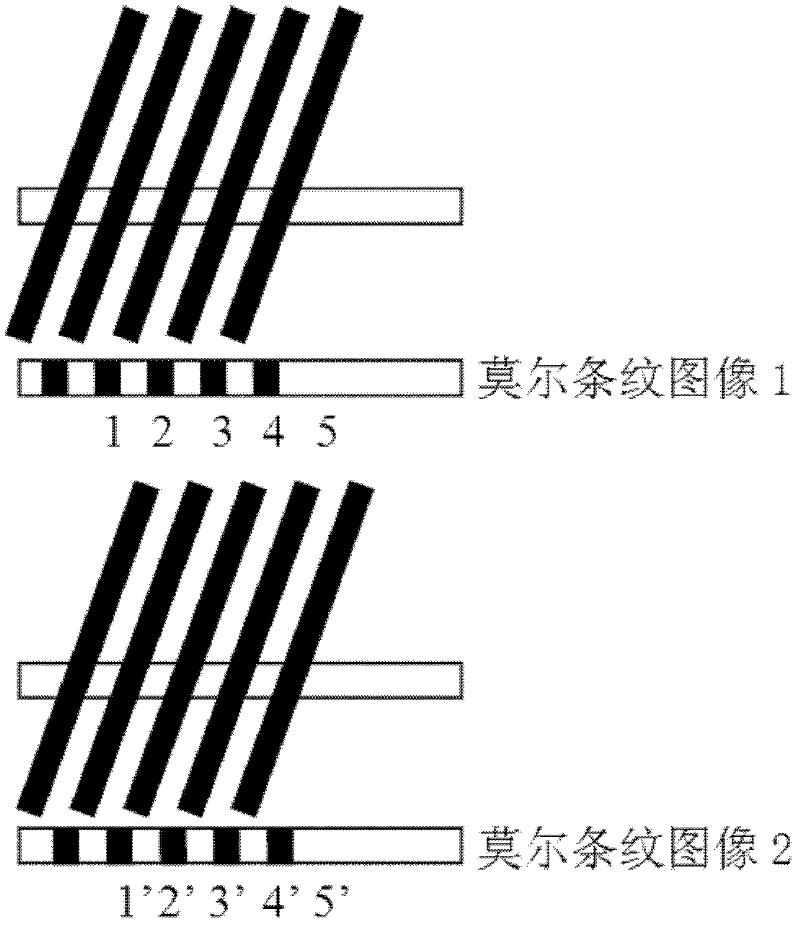
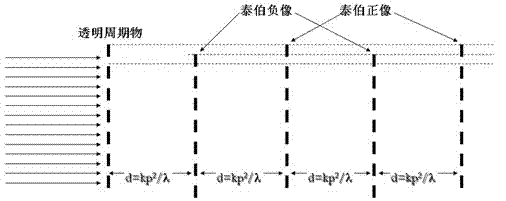
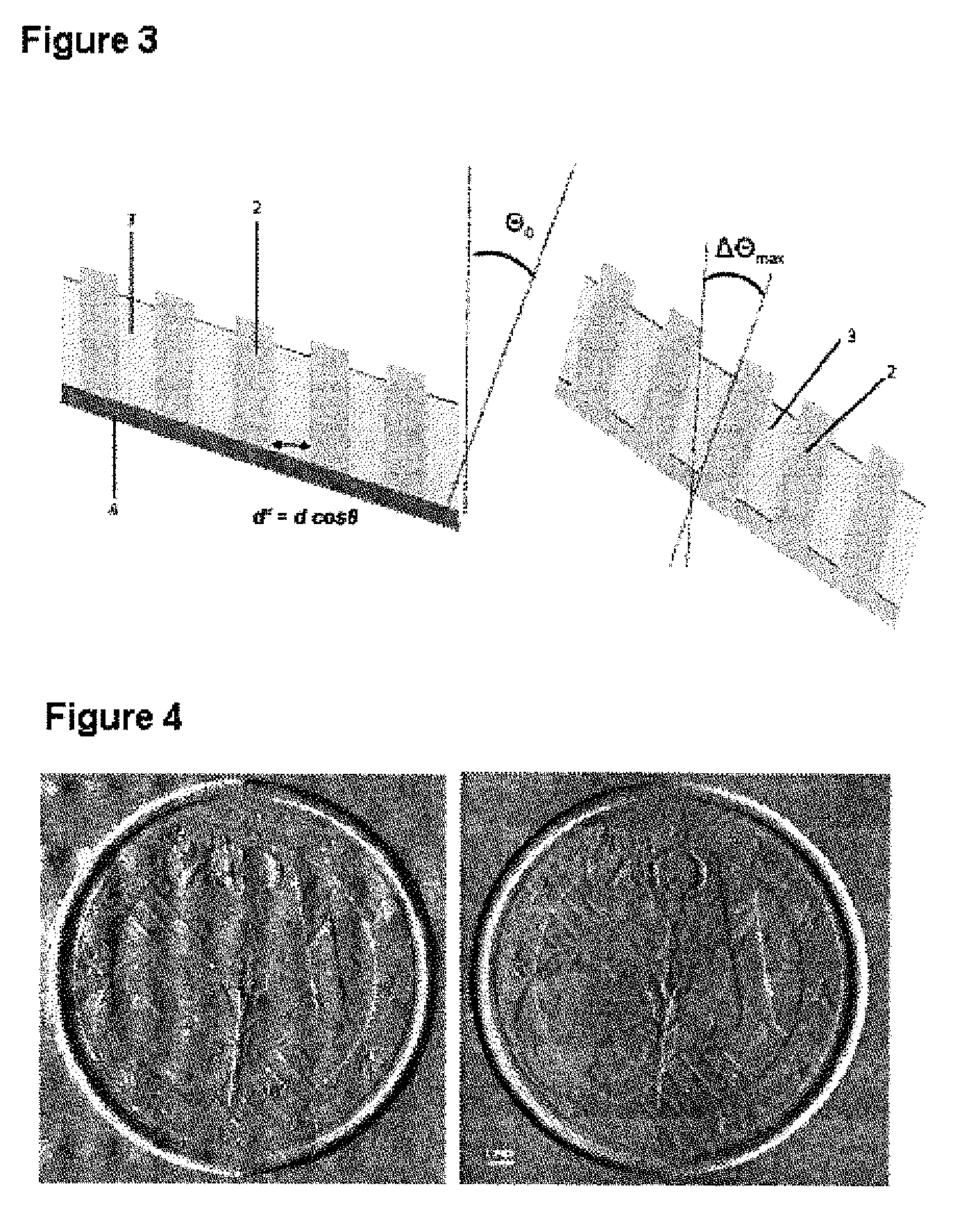
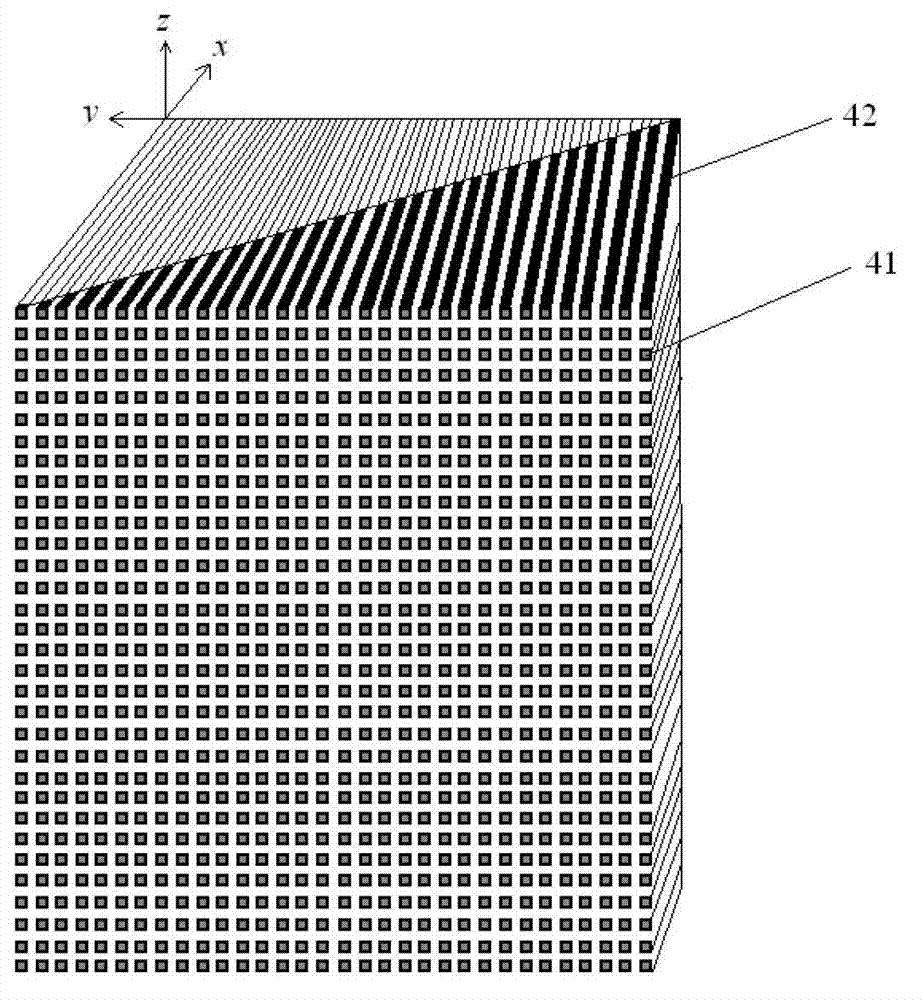
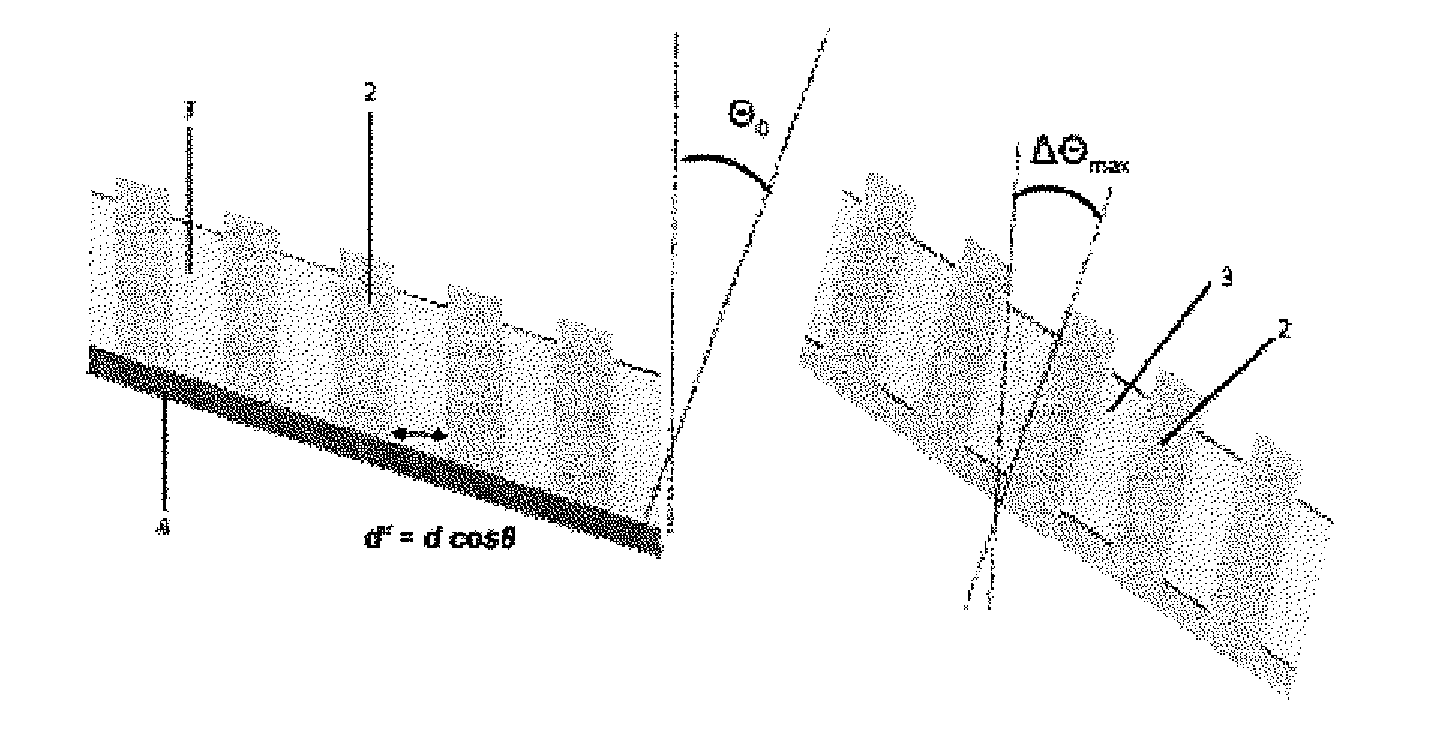
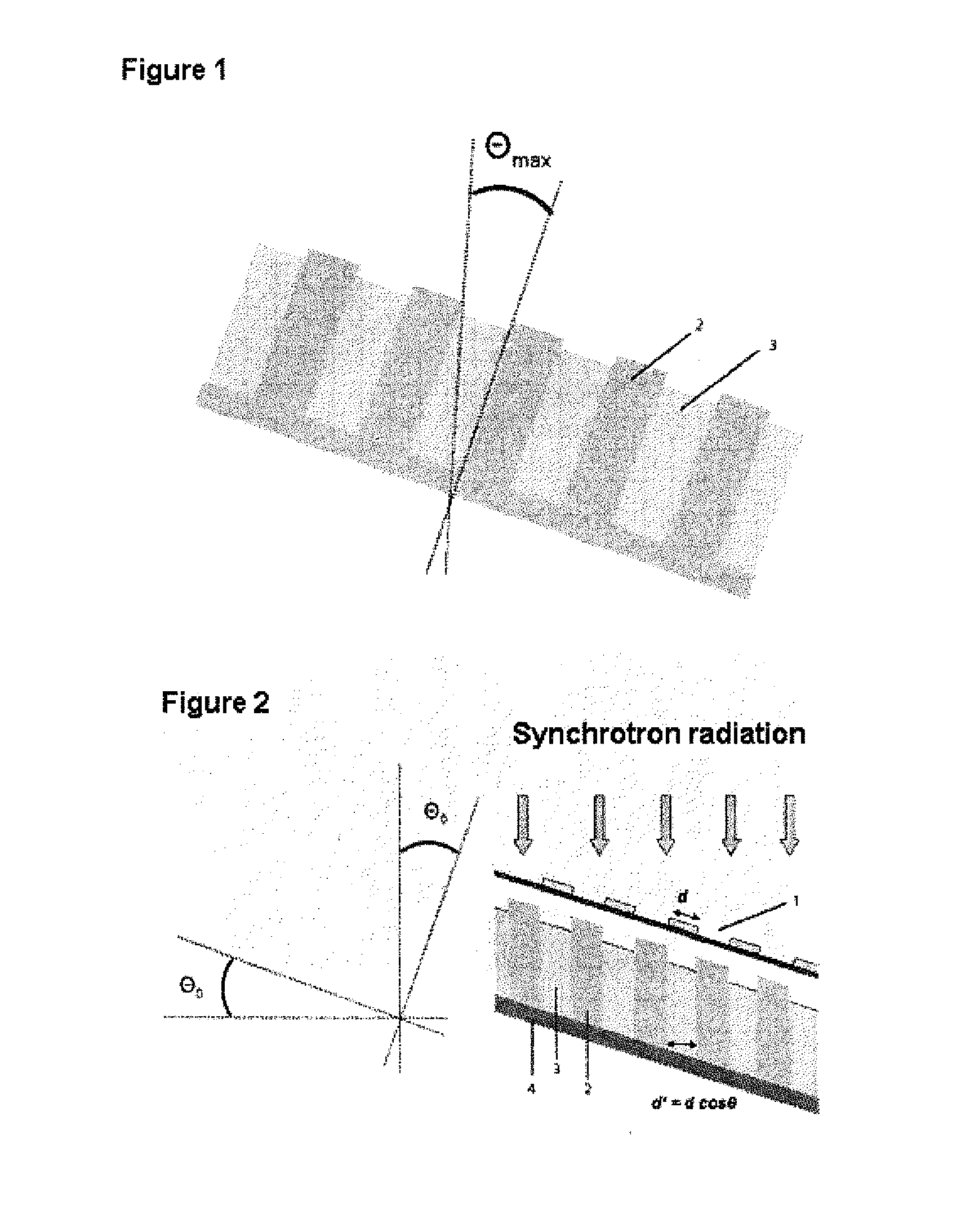
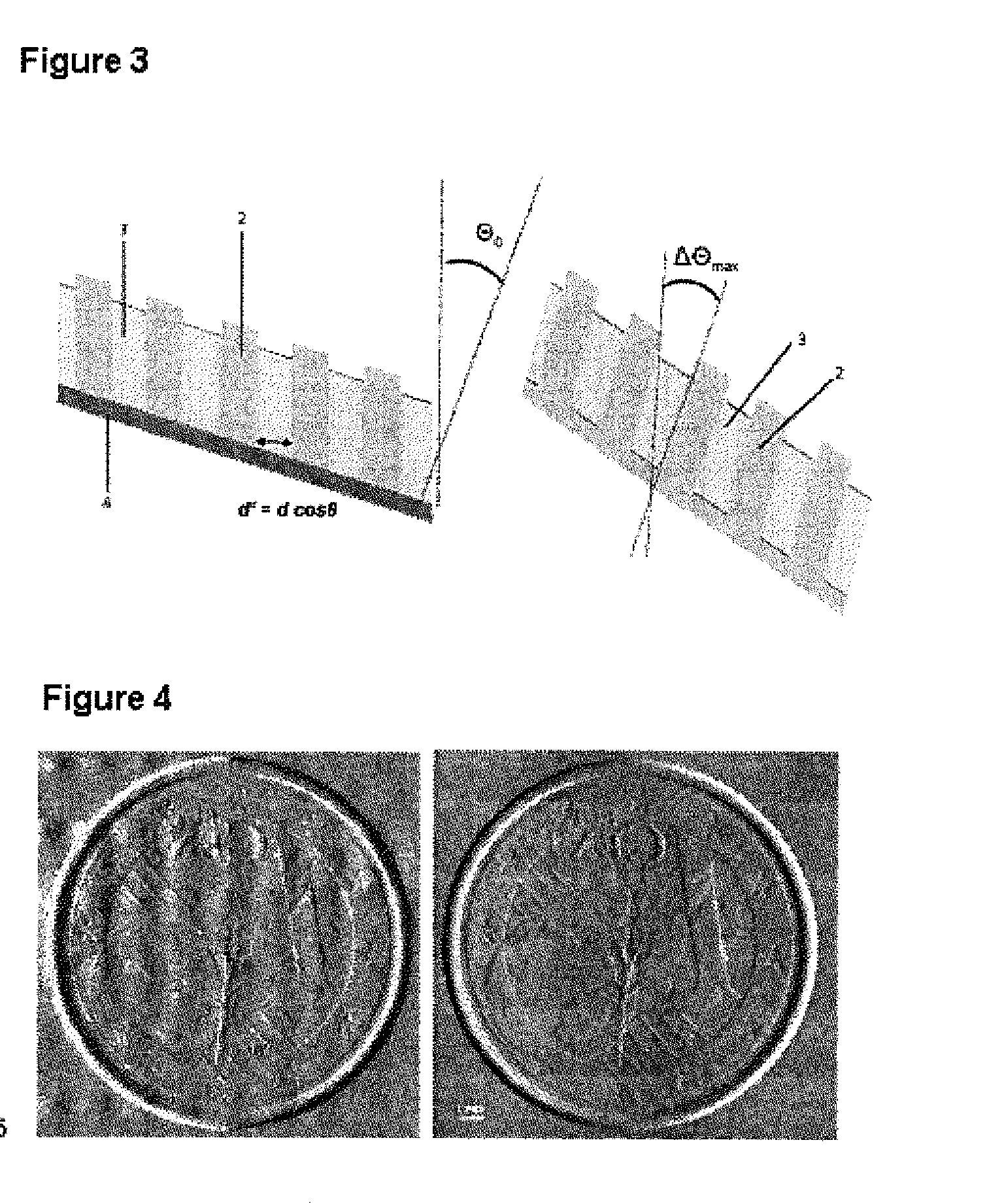
The Talbot effect is a near-field diffraction effect first observed in 1836 by Henry Fox Talbot. When a plane wave is incident upon a periodic diffraction grating, the image of the grating is repeated at regular distances away from the grating plane. The regular distance is called the Talbot length, and the repeated images are called self images or Talbot images. Furthermore, at half the Talbot length, a self-image also occurs, but phase-shifted by half a period (the physical meaning of this is that it is laterally shifted by half the width of the grating period).
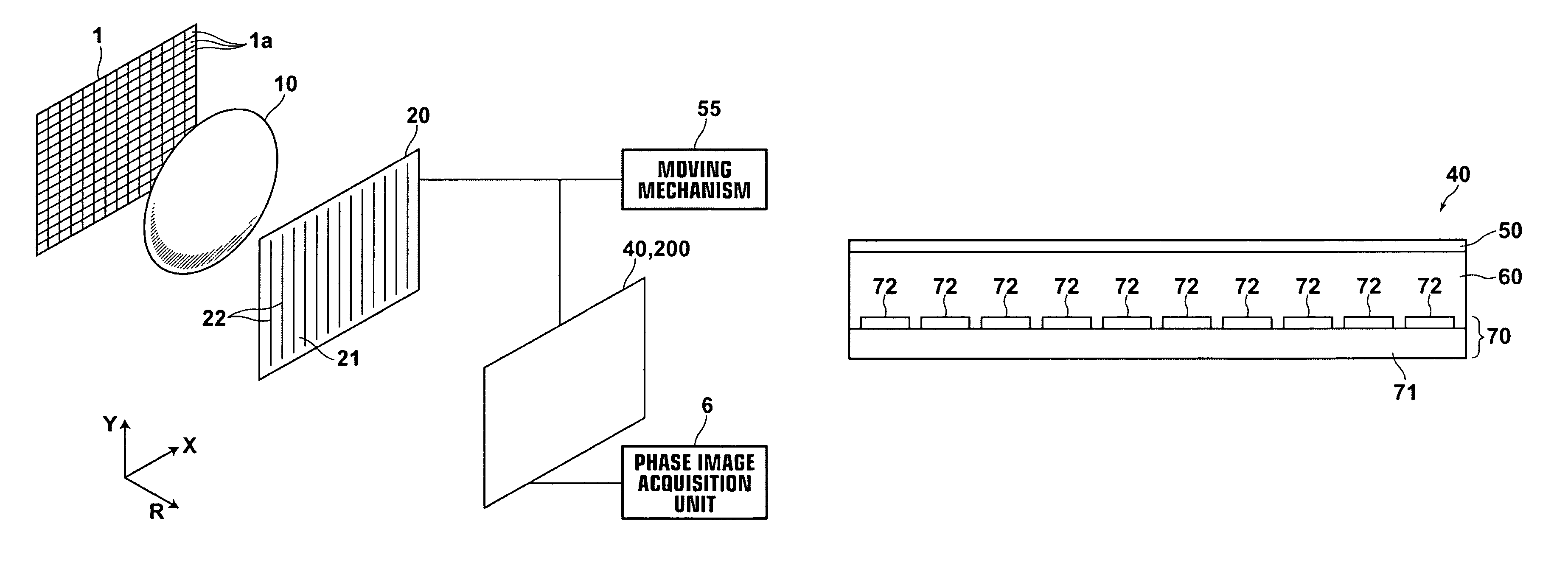
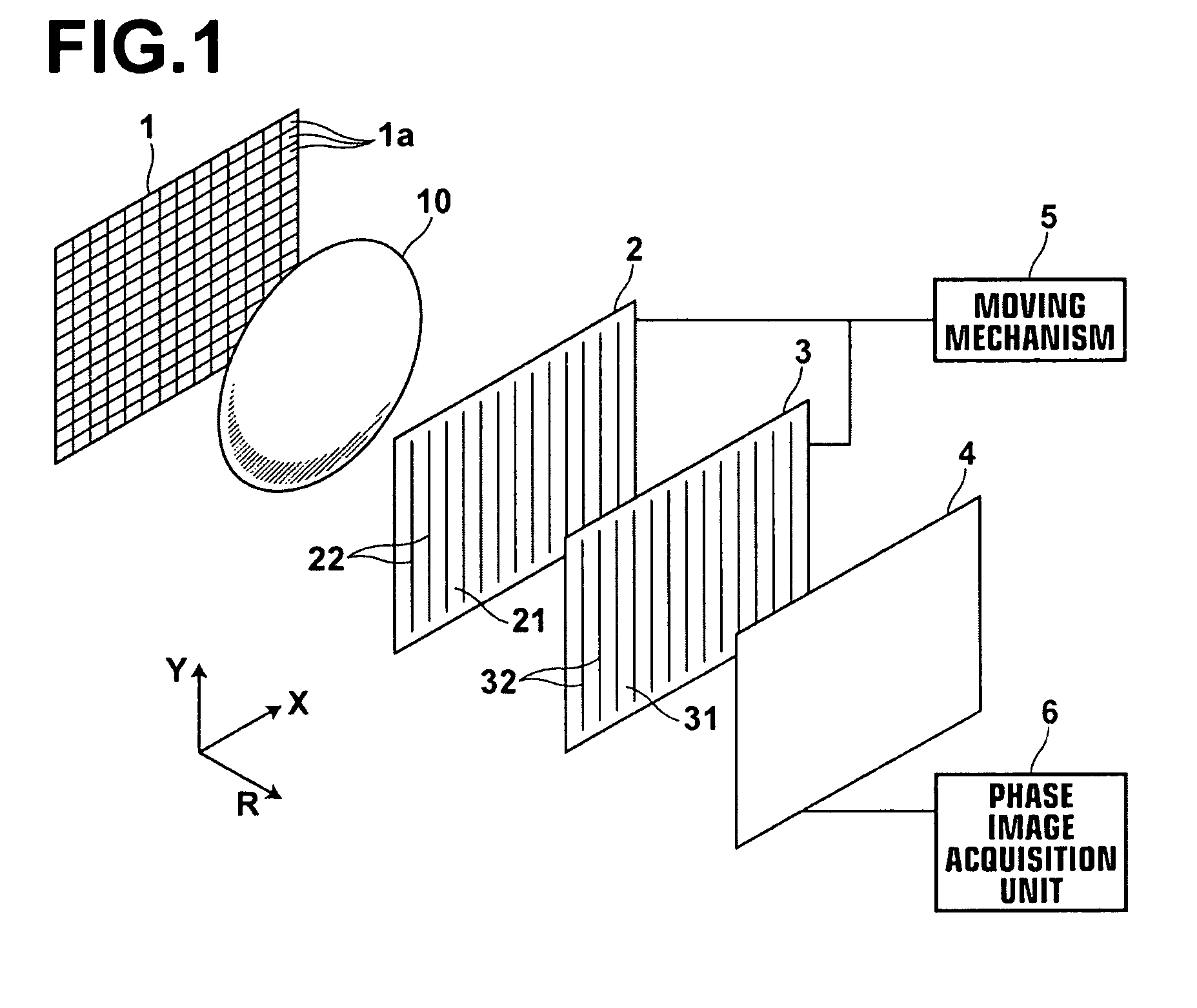
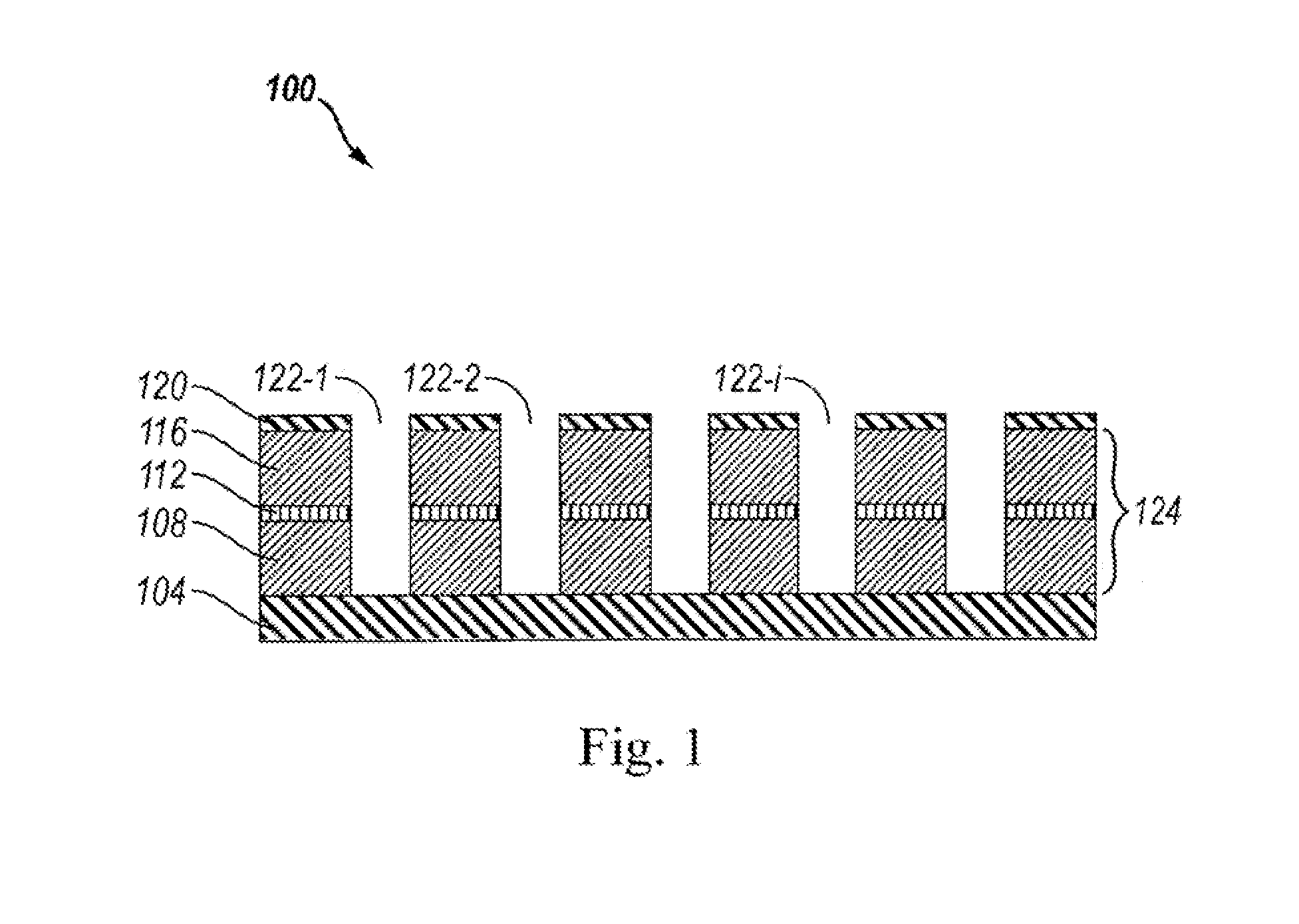
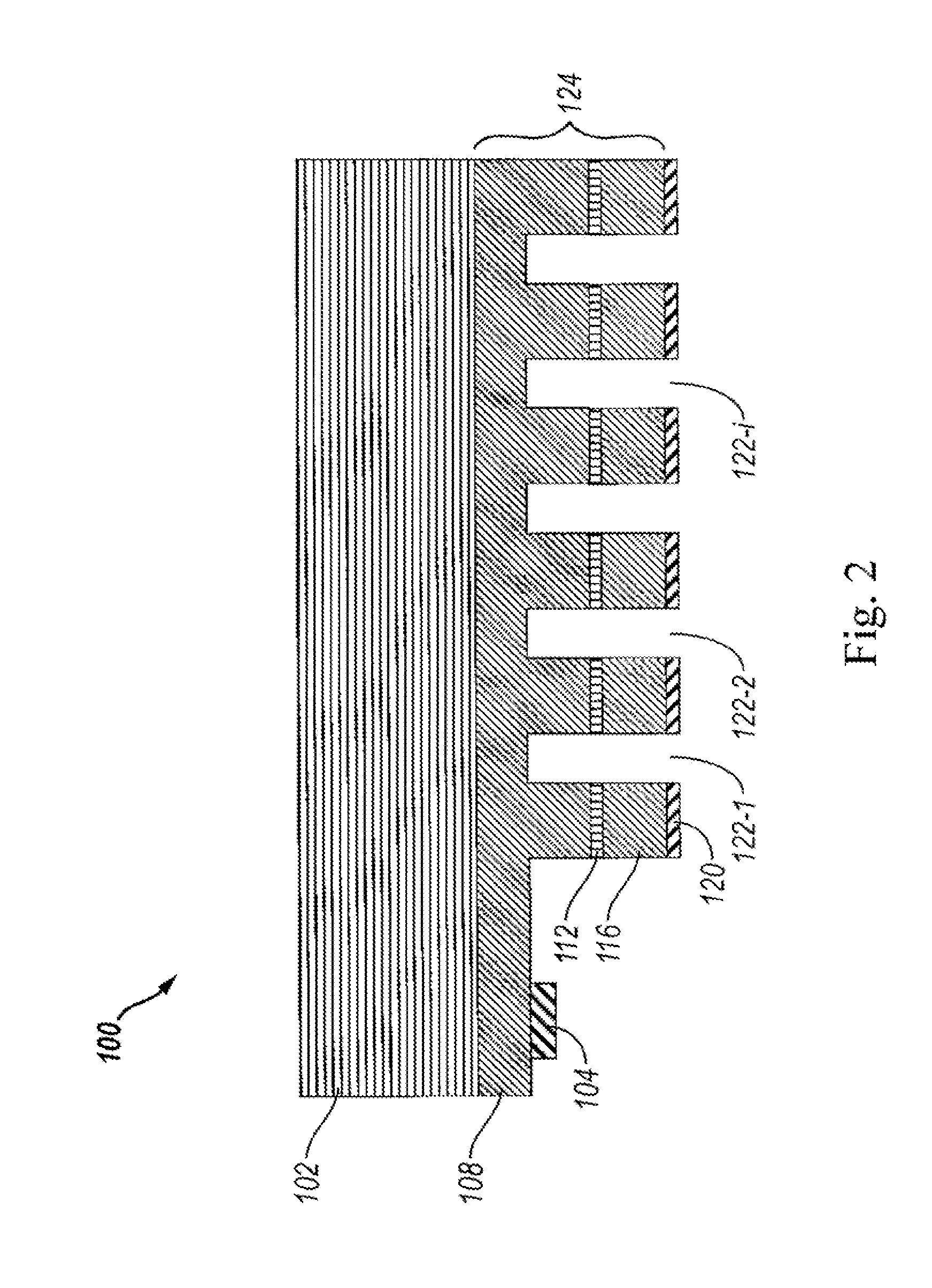
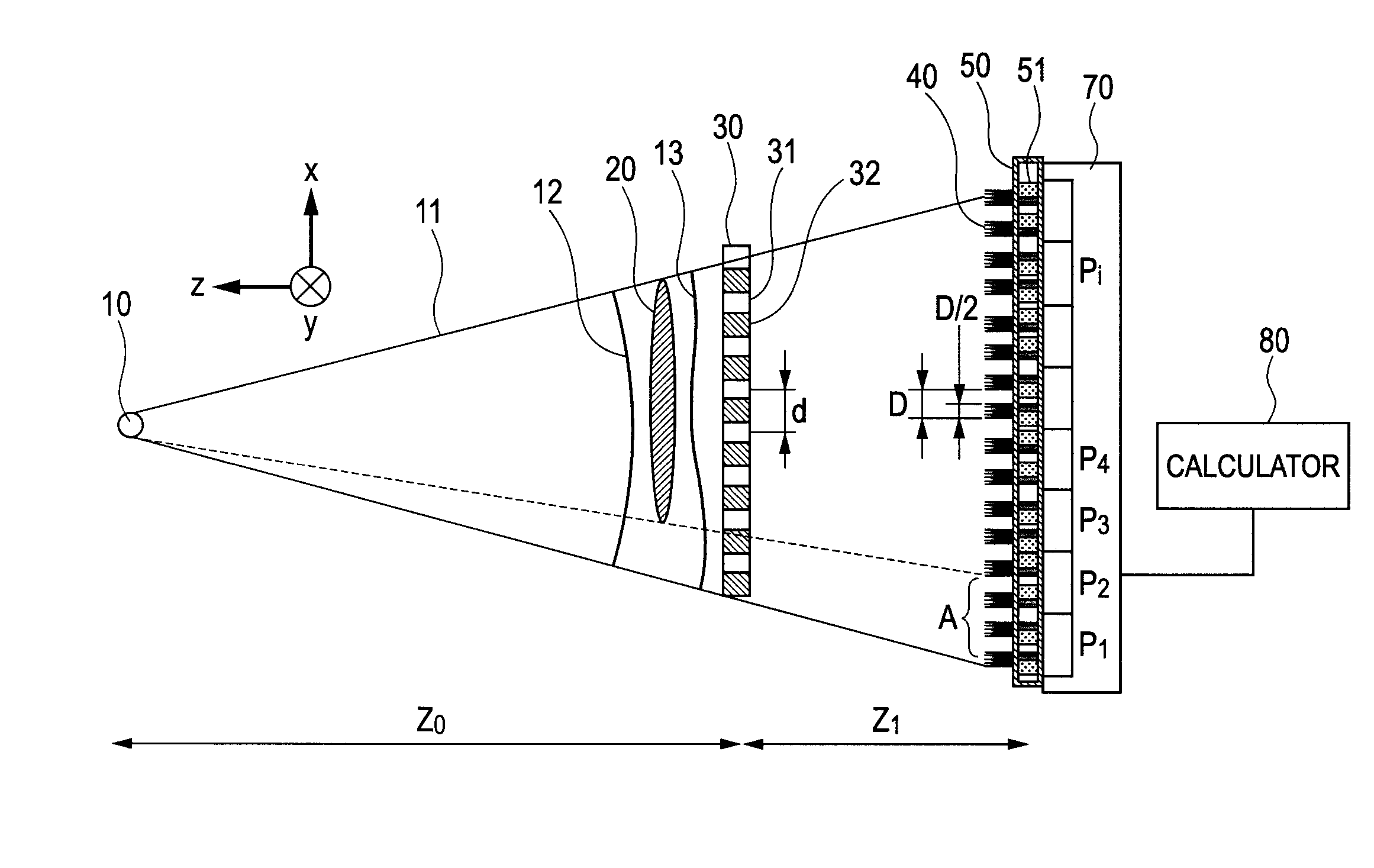
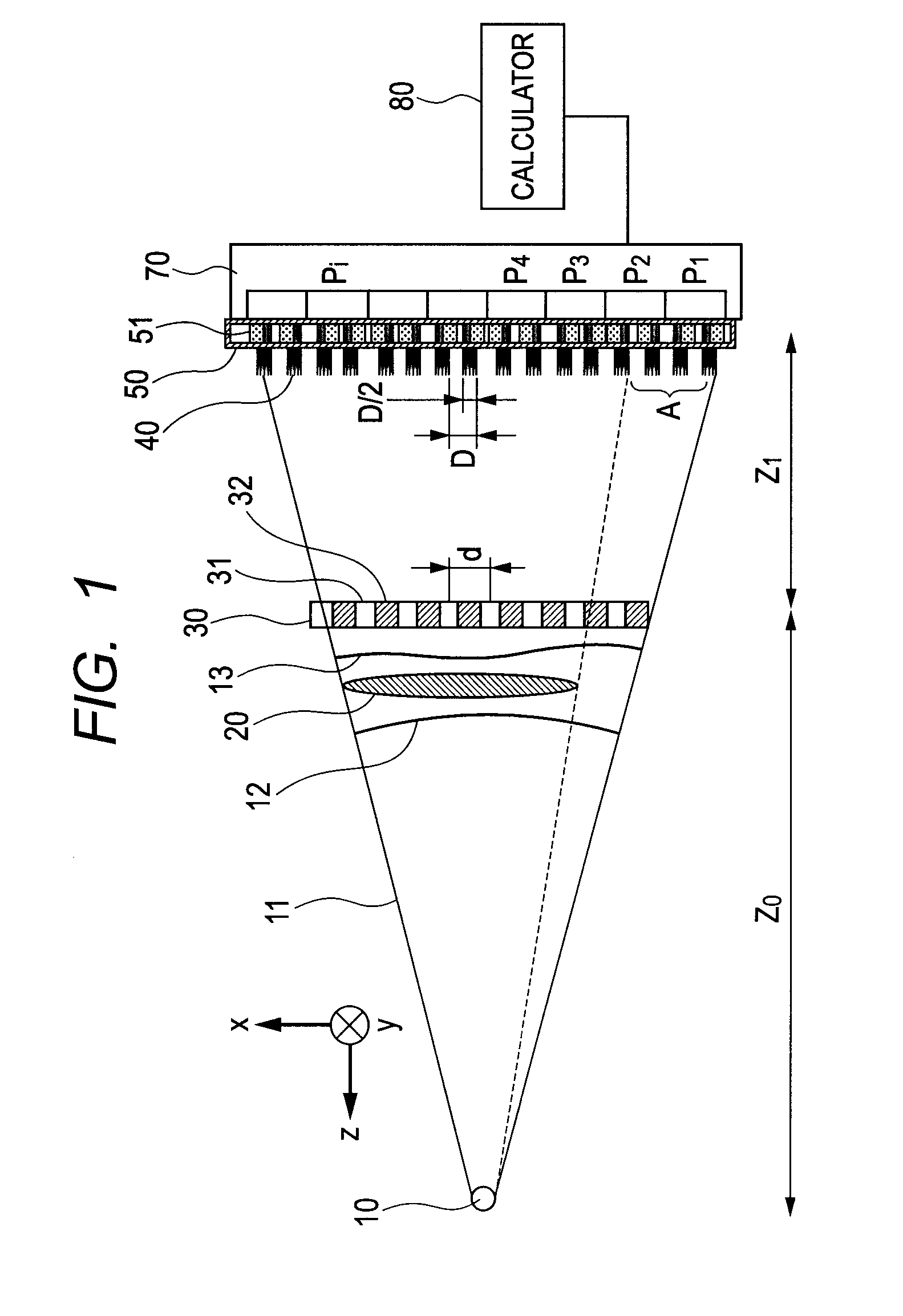
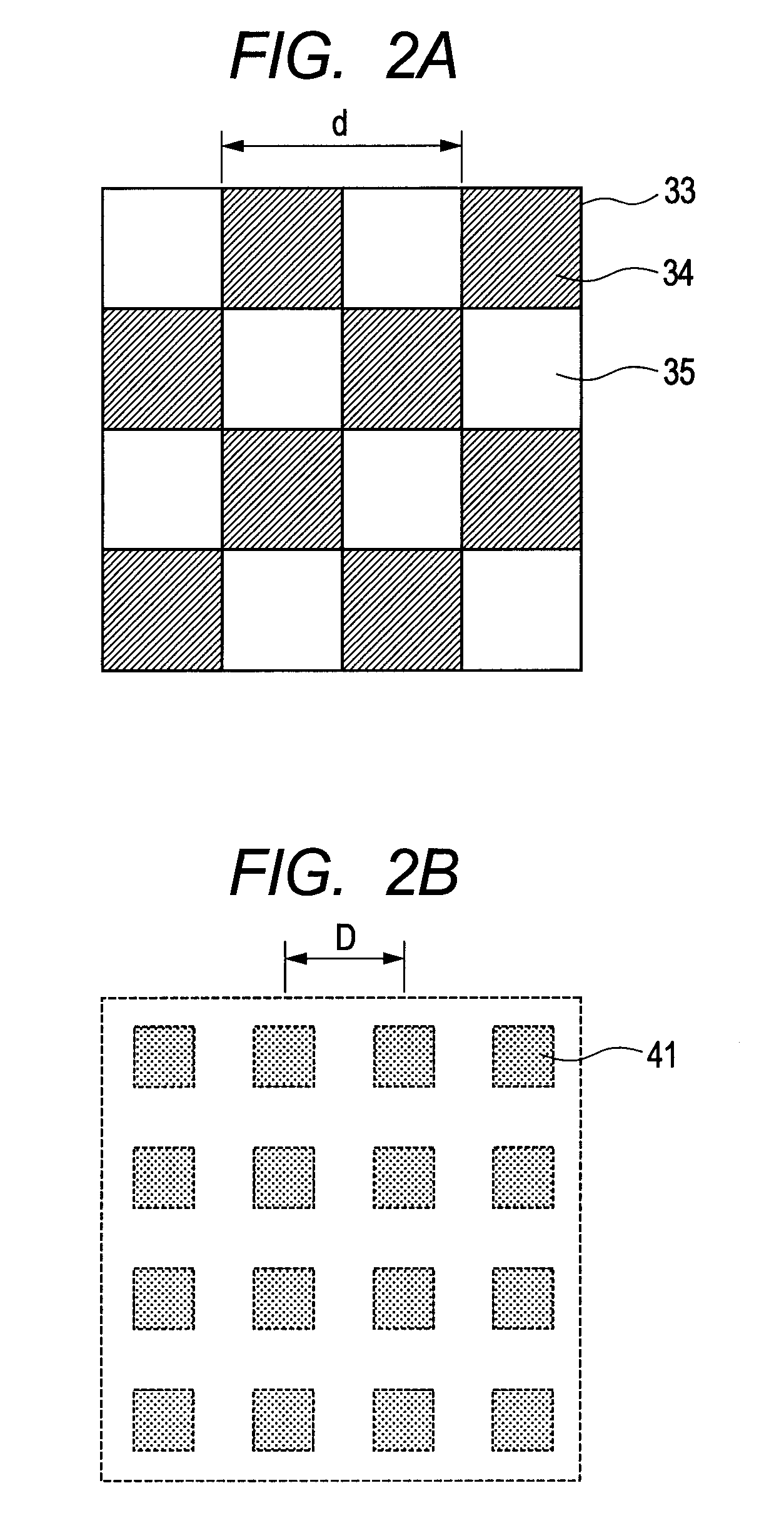
X-ray imaging system and imaging method
ActiveUS7180979B2Easy constructionImaging devicesHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionImage contrastImage detection
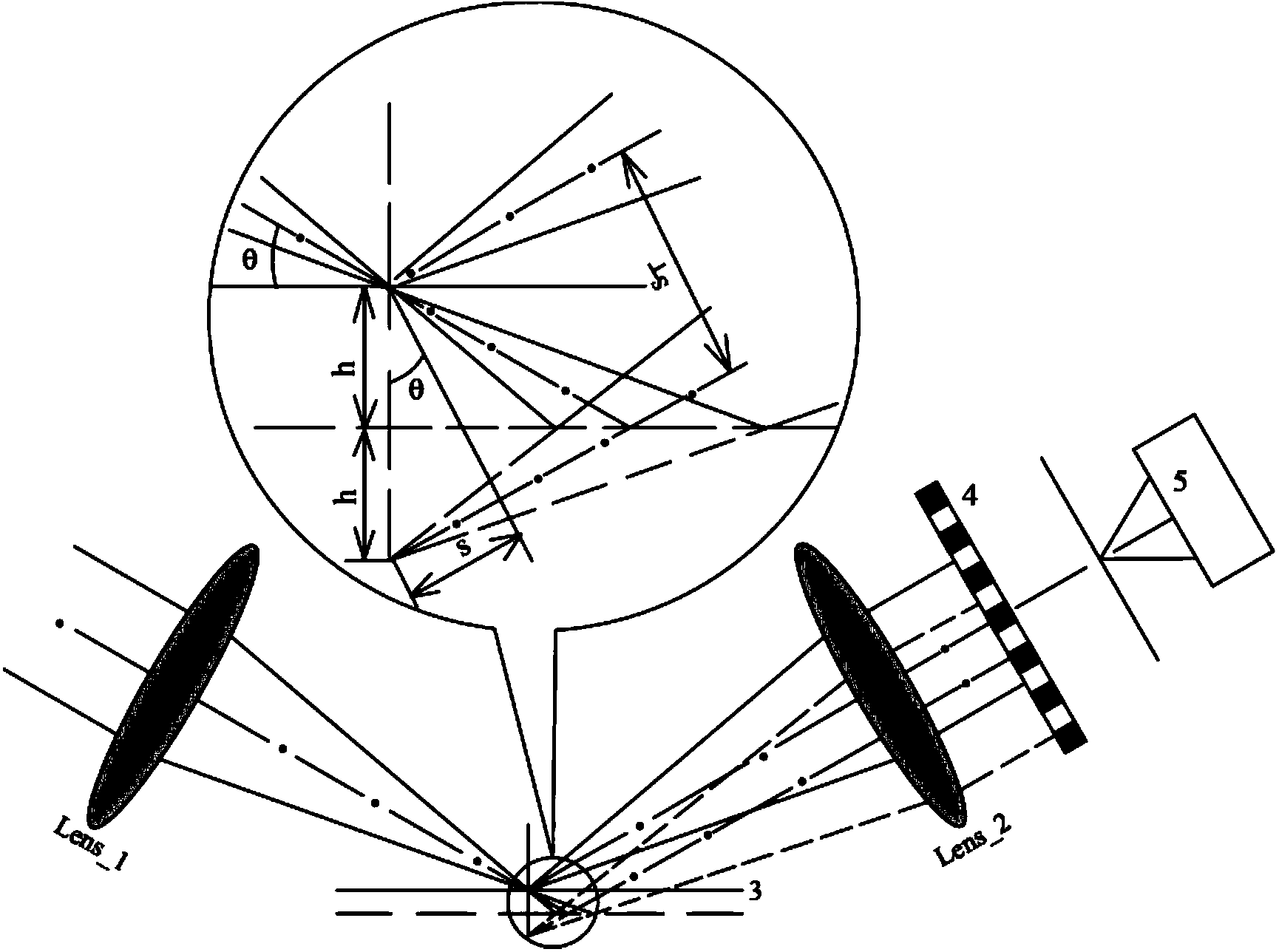
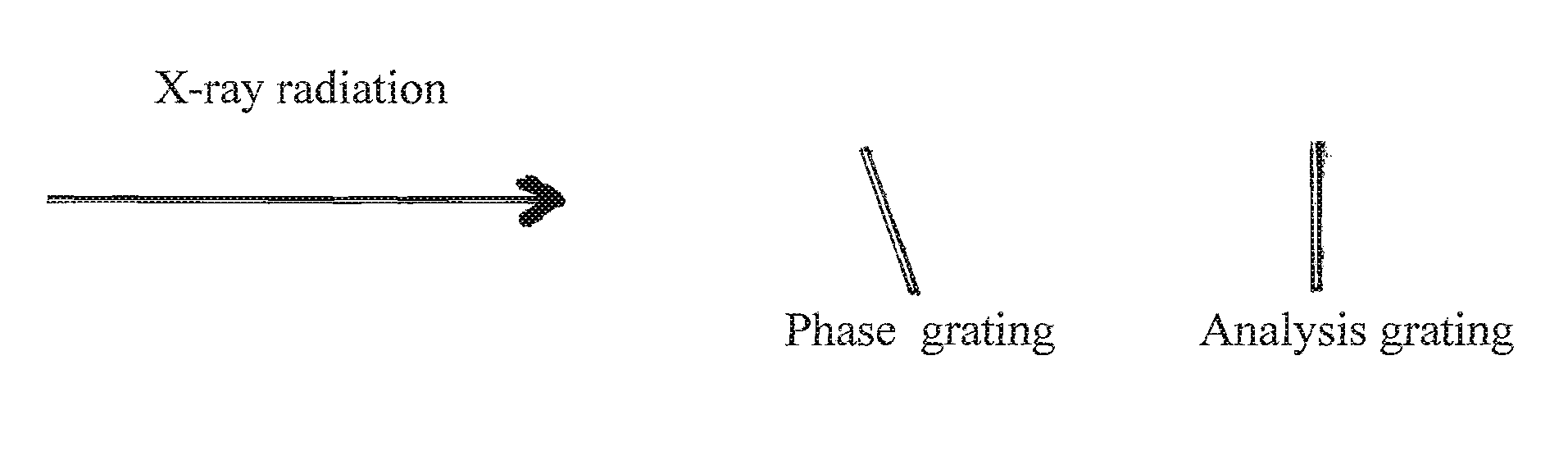
The present invention provides an apparatus capable of X-ray imaging utilizing phase of X-rays. An X-ray imaging apparatus equipped with first and second diffraction gratings and an X-ray image detector are described. The first diffraction grating generates a Talbot effect and a second diffraction grating diffracts X-rays diffracted by the first diffraction grating. An image detector is provided to detect the X-rays diffracted by the second diffraction grating. In this manner, image contrasts caused by changes in phase of X-rays due to a subject arranged in front of the first diffraction grating or between the first diffraction grating and the second diffraction grating can be achieved.
Owner:MOMOSE ATSUSHI
X-ray imaging system and imaging method
ActiveUS20050286680A1Easy constructionImaging devicesHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionSoft x rayImage contrast
The object of the present invention is to provide an apparatus capable of X-ray imaging utilizing phase of X-rays with a simple construction. The X-ray imaging apparatus of the present invention is equipped with first and second diffraction gratings and an X-ray image detector. The first diffraction grating is constructed to generate the Talbot effect using X-rays irradiated at the first diffraction grating. The second diffraction grating is configured so as to diffract the X-rays diffracted by the first diffraction grating. The X-ray image detector is configured so as to detect the X-rays diffracted by the second diffraction grating. By diffracting X-rays diffracted by the first diffraction grating, the second diffraction grating is capable of forming image contrast caused by changes in phase of X-rays due to the subject arranged in front of the front surface of the first diffraction grating or between the first diffraction grating and the second diffraction grating. The X-ray image detector is capable of detecting X-rays creating image contrast.
Owner:MOMOSE ATSUSHI
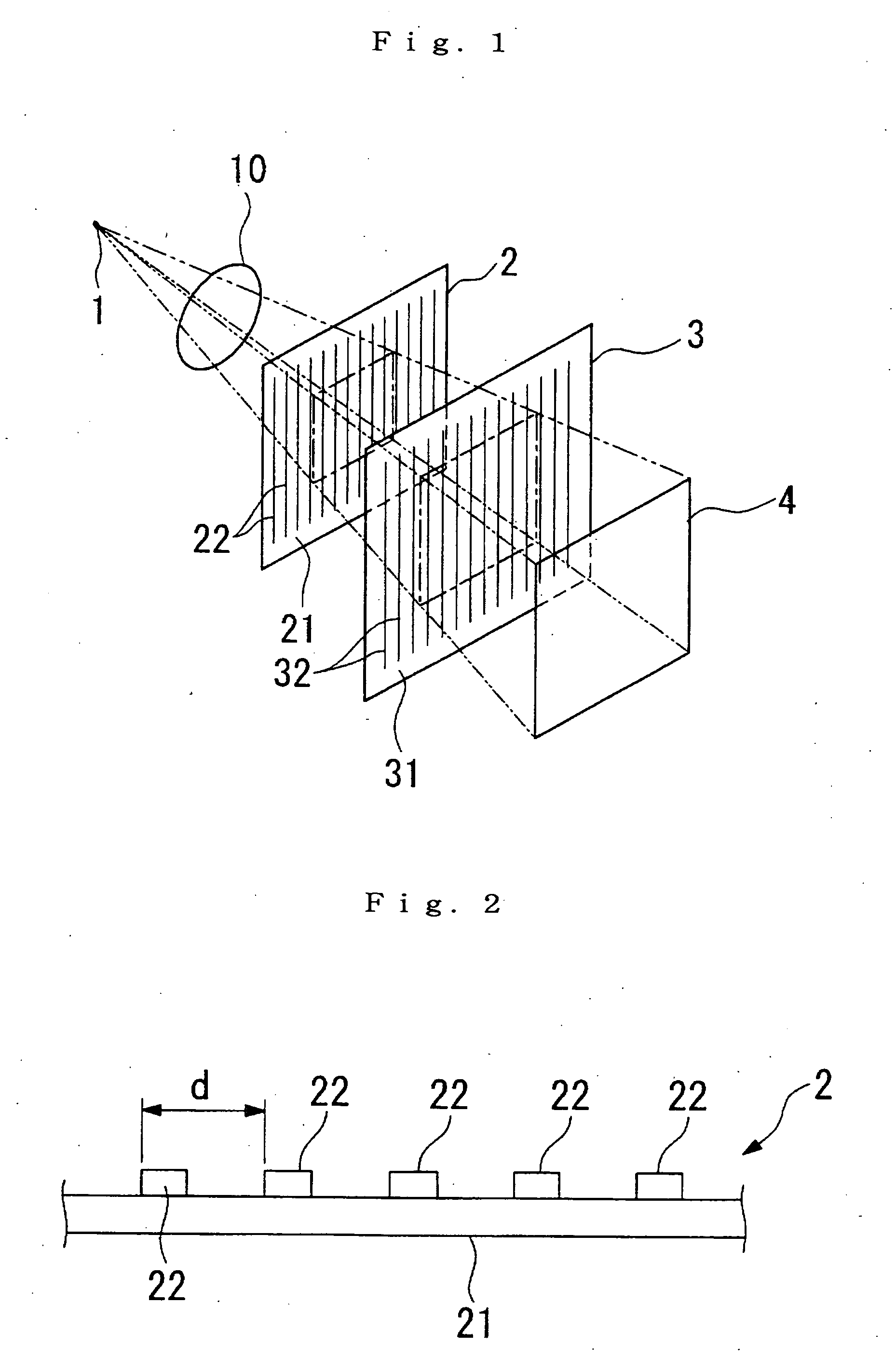
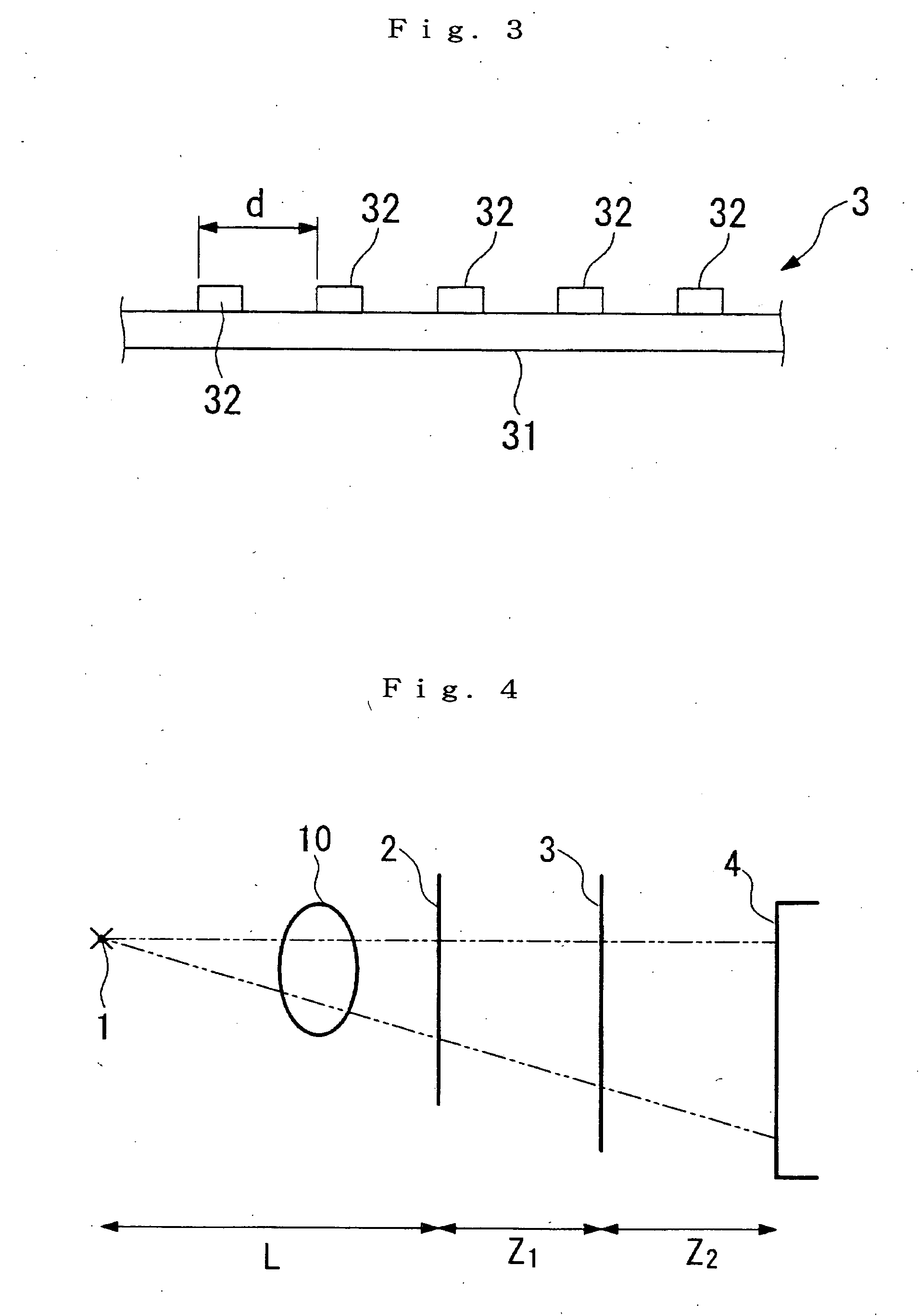
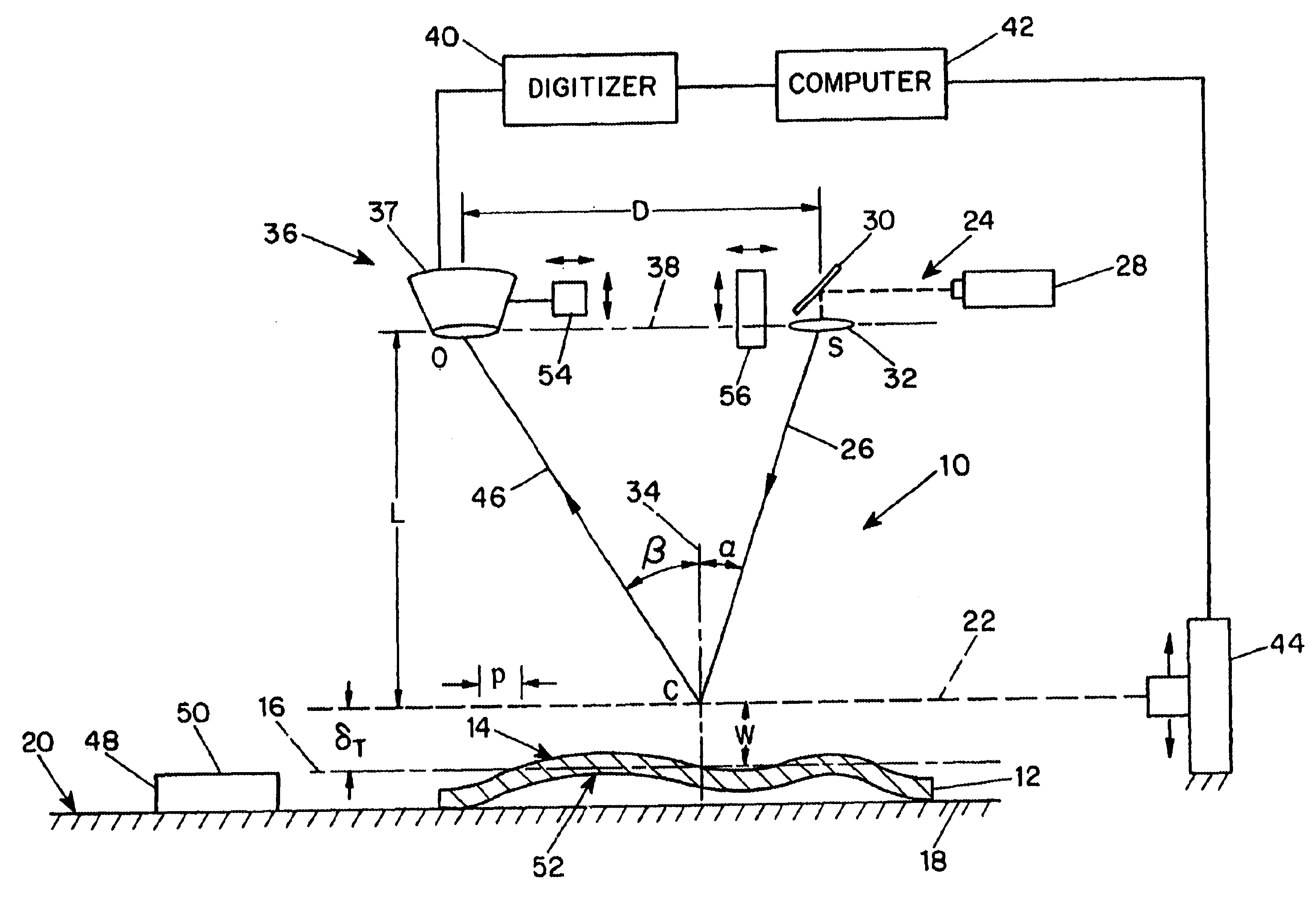
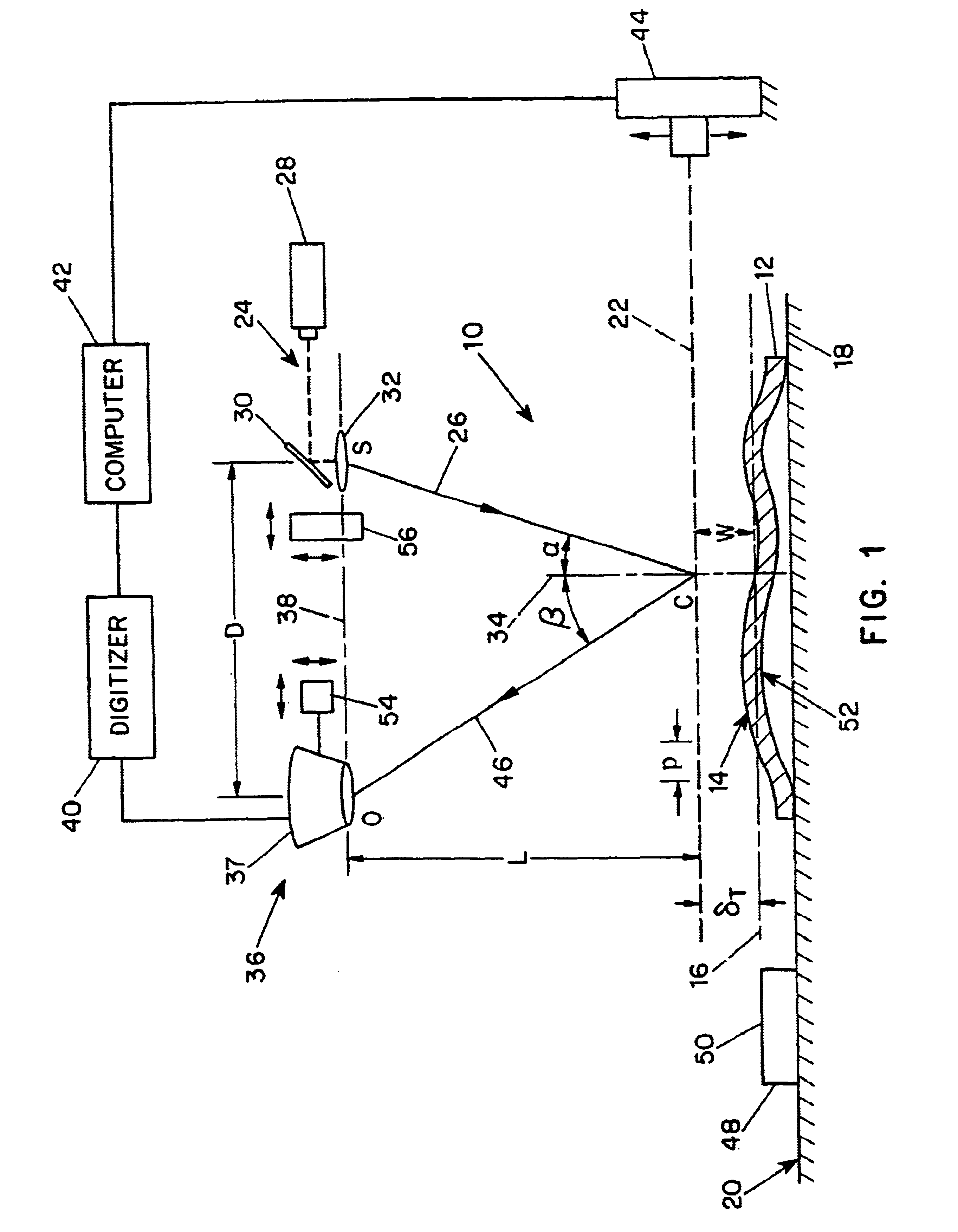
Shadow moire surface measurement using Talbot effect
InactiveUS6731391B1Sufficient diameterAdjustable distanceMaterial analysis by optical meansUsing optical meansTalbot effectSurface measurement
A method and apparatus for surface measurement using the shadow moire effect with the Talbot effect. The apparatus includes a specimen mount to receive a specimen having a surface to be measured, and a reference grating mounted adjacent to the specimen mount so as to be substantially parallel to a mean surface plane of the specimen. The reference grating is mounted in such a manner that the distance between the reference grating and the mean surface plane of the specimen can be adjusted to a Talbot distance deltaT. The apparatus also includes a light source to illuminate the specimen through the grating and a detector positioned to detect the moire fringes produced by the grating due to variation of the surface of the specimen.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Light field image sensor, method and applications
ActiveUS20120091372A1Accurate predictionThe implementation process is simpleSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansTalbot effectAngle–sensitive pixel
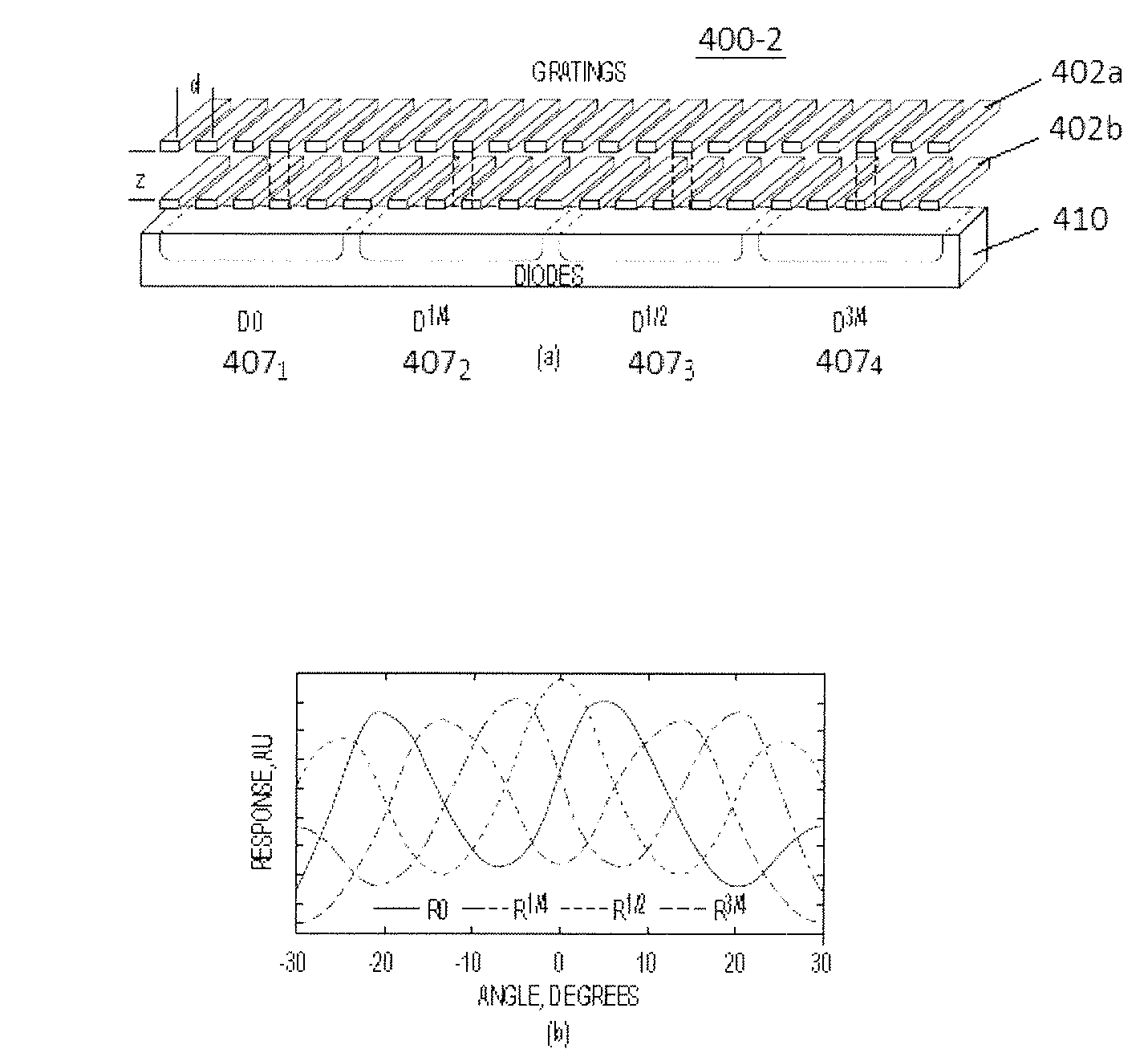
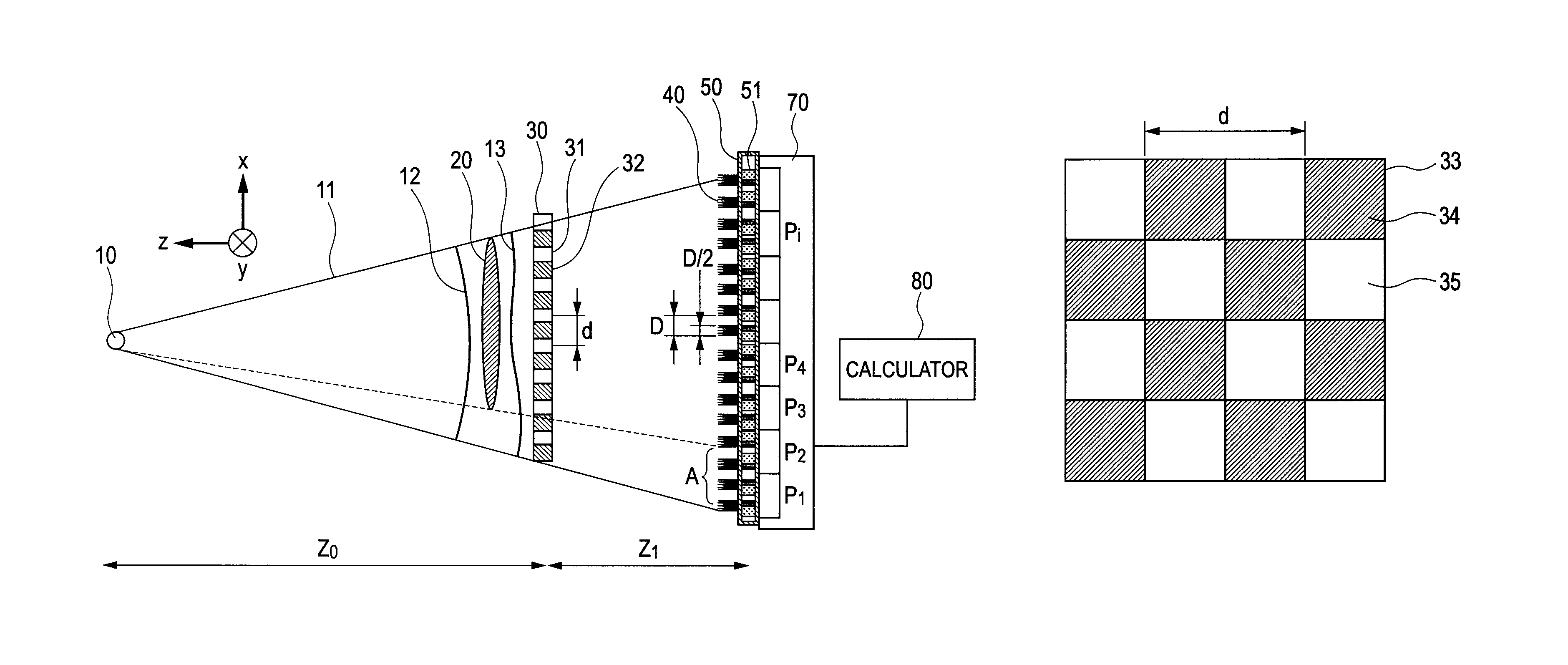
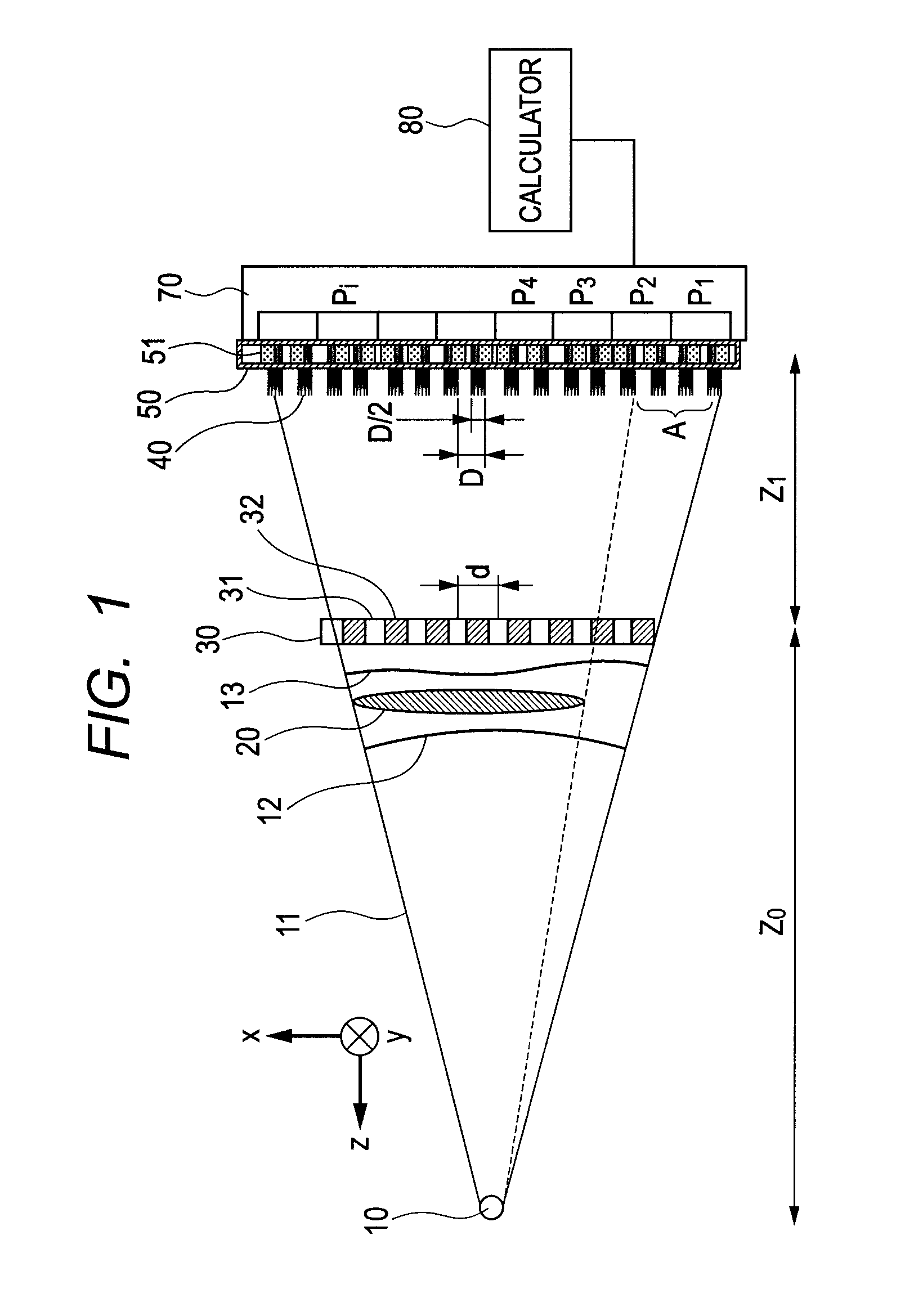
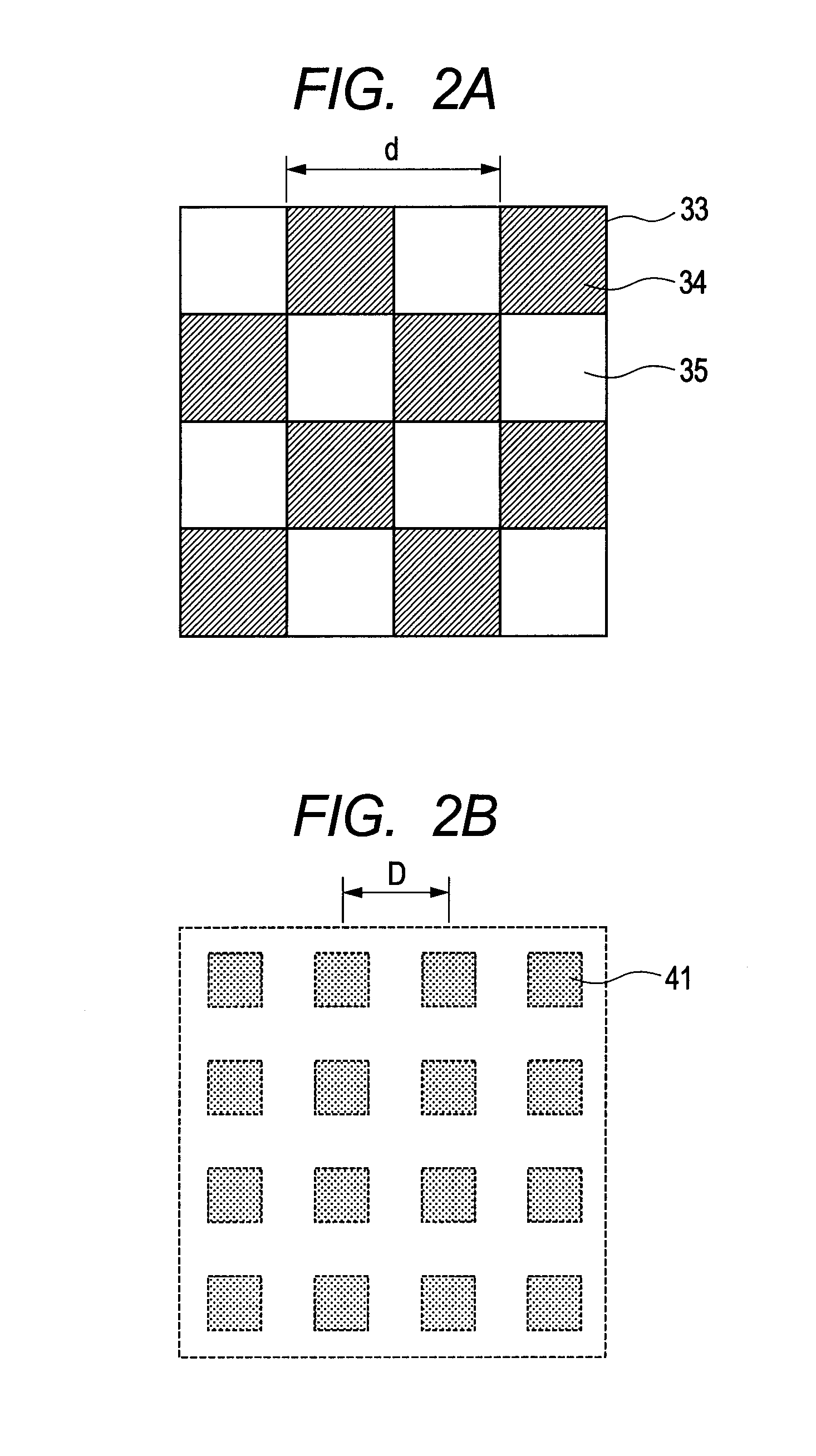
An angle-sensitive pixel (ASP) device that uses the Talbot effect to detect the local intensity and incident angle of light includes a phase grating disposed above a photodiode assembly or a phase grating disposed above an analyzer grating that is disposed above a photodiode assembly. When illuminated by a plane wave, the upper grating generates a self-image at a selected Talbot depth. Several such structures, tuned to different incident angles, are sufficient to extract local incident angle and intensity. Arrays of such structures are sufficient to localize light sources in three dimensions without any additional optics.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Light field image sensor, method and applications
ActiveUS20110174998A1Accurate predictionThe implementation process is simpleBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsInstruments for comonautical navigationTalbot effectAngle–sensitive pixel
An angle-sensitive pixel (ASP) device that uses the Talbot effect to detect the local intensity and incident angle of light includes two local diffraction gratings stacked above a photodiode. When illuminated by a plane wave, the upper grating generates a self-image at a selected Talbot depth. The second grating, placed at this depth, blocks or passes light depending upon incident angle. Several such structures, tuned to different incident angles, are sufficient to extract local incident angle and intensity. Arrays of such structures are sufficient to localize light sources in three dimensions without any additional optics.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
LED including photonic crystal structure
InactiveUS7279718B2Increase transmit powerMore energySolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesManufacturing technologyLateral overgrowth
A photonic crystal light emitting diode (“PXLED”) is provided. The PXLED includes a periodic structure, such as a lattice of holes, formed in the semiconductor layers of an LED. The parameters of the periodic structure are such that the energy of the photons, emitted by the PXLED, lies close to a band edge of the band structure of the periodic structure. Metal electrode layers have a strong influence on the efficiency of the PXLEDs. Also, PXLEDs formed from GaN have a low surface recombination velocity and hence a high efficiency. The PXLEDs are formed with novel fabrication techniques, such as the epitaxial lateral overgrowth technique over a patterned masking layer, yielding semiconductor layers with low defect density. Inverting the PXLED to expose the pattern of the masking layer or using the Talbot effect to create an aligned second patterned masking layer allows the formation of PXLEDs with low defect density.
Owner:LUMILEDS
Radiation phase image radiographing apparatus
InactiveUS8139711B2Reduce the spread angleSmall sizeImaging devicesX-ray spectral distribution measurementTalbot effectRadiography
A radiation phase image radiographing apparatus, including a radiation emission unit having multiple radiation sources for emitting radiation onto a subject, the radiation sources being distributed such that radiation emitted from each of the radiation sources and transmitted through the subject forms a part of a projected image of the subject, a first diffraction grating configured to be exposed to the radiation emitted from the multiple radiation sources of the radiation emission unit and to produce a Talbot effect by the exposure, a second diffraction grating for diffracting the radiation diffracted by the first diffraction grating, and a radiation image detector for detecting the radiation diffracted by the second diffraction grating.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
LED including photonic crystal structure
InactiveUS7642108B2Increase transmit powerMore energySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingManufacturing technologyPhotonic crystal structure
A photonic crystal light emitting diode (“PXLED”) is provided. The PXLED includes a periodic structure, such as a lattice of holes, formed in the semiconductor layers of an LED. The parameters of the periodic structure are such that the energy of the photons, emitted by the PXLED, lies close to a band edge of the band structure of the periodic structure. Metal electrode layers have a strong influence on the efficiency of the PXLEDs. Also, PXLEDs formed from GaN have a low surface recombination velocity and hence a high efficiency. The PXLEDs are formed with novel fabrication techniques, such as the epitaxial lateral overgrowth technique over a patterned masking layer, yielding semiconductor layers with low defect density. Inverting the PXLED to expose the pattern of the masking layer or using the Talbot effect to create an aligned second patterned masking layer allows the formation of PXLEDs with low defect density.
Owner:LUMILEDS
Light field image sensor with an angle-sensitive pixel (ASP) device
ActiveUS8809758B2Accurate predictionThe implementation process is simplePhotometrySolid-state devicesPhase gratingAngular degrees
An angle-sensitive pixel (ASP) device that uses the Talbot effect to detect the local intensity and incident angle of light includes a phase grating disposed above a photodiode assembly or a phase grating disposed above an analyzer grating that is disposed above a photodiode assembly. When illuminated by a plane wave, the upper grating generates a self-image at a selected Talbot depth. Several such structures, tuned to different incident angles, are sufficient to extract local incident angle and intensity. Arrays of such structures are sufficient to localize light sources in three dimensions without any additional optics.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Light field image sensor, method and applications
ActiveUS8530811B2Accurate predictionThe implementation process is simpleBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsInstruments for comonautical navigationTalbot effectAngle–sensitive pixel
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Light field image sensor, method and applications
An angle-sensitive pixel (ASP) device that uses the Talbot effect to detect the local intensity and incident angle of light includes a phase grating disposed above a photodiode assembly or a phase grating disposed above an analyzer grating that is disposed above a photodiode assembly. When illuminated by a plane wave, the upper grating generates a self-image at a selected Talbot depth. Several such structures, tuned to different incident angles, are sufficient to extract local incident angle and intensity. Arrays of such structures are sufficient to localize light sources in three dimensions without any additional optics.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
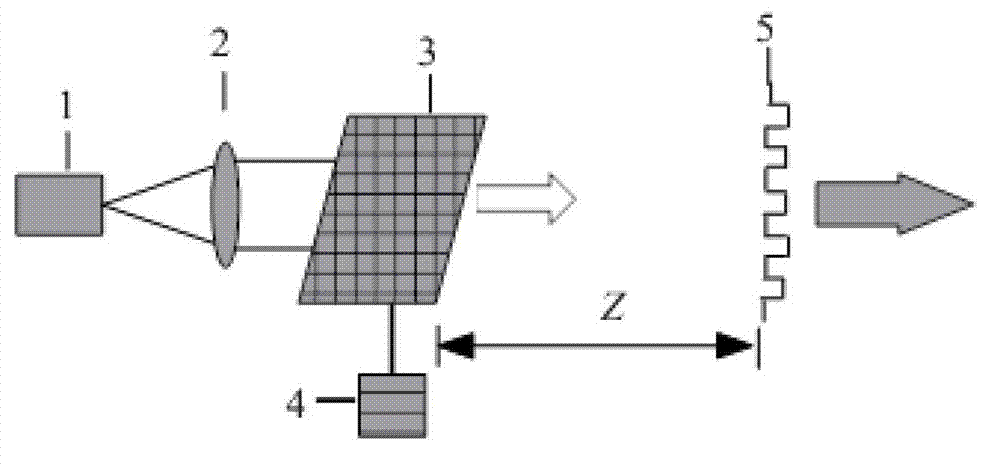
Multi-source parallel confocal micro detection system
InactiveCN101666620AApplicable measurement requirementsMeet the measurementUsing optical meansImage resolutionTalbot effect
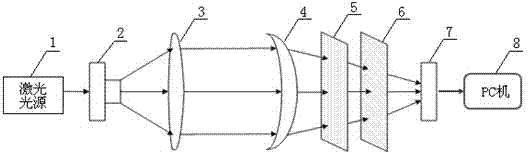
The invention relates to a multi-source parallel confocal micro detection system comprising a plurality of lasers, the light outlet of the lasers is provided with a beam combiner, a collimating lens is arranged in front of the light outlet of the beam combiner, the light outlet of the beam combiner is on the focal point on one side of the collimating lens, and the other side of the collimating lens is provided with a microlens array; a spectroscope, a first telephotolens and a second telephotolens are arranged in front of the light path of the microlens array, and one side of the reflecting surface of the spectroscope is provided with an area array CCD. The multi-source parallel confocal micro detection system also comprises a movable workbench on which a liner scale is fixed, and the liner scale is arranged on the light path of the second telephotolens; and a detected object surface is arranged on the workbench and moves along with the workbench. The invention adopts lasers with various wavelengths to build the synthesized light source of the parallel confocal detection system, overcomes the influence of the Talbot effect on the premise of ensuring laser parallel confocal system resolution and measuring speed and realizes large-range and high-precision measurement so as to extend the application range of the parallel confocal detection system.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
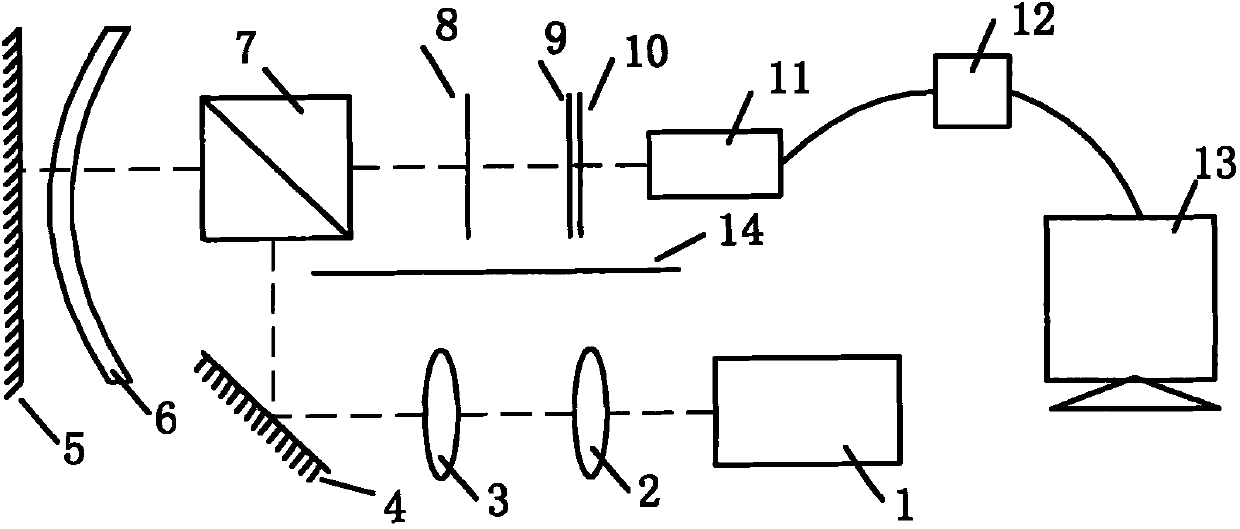
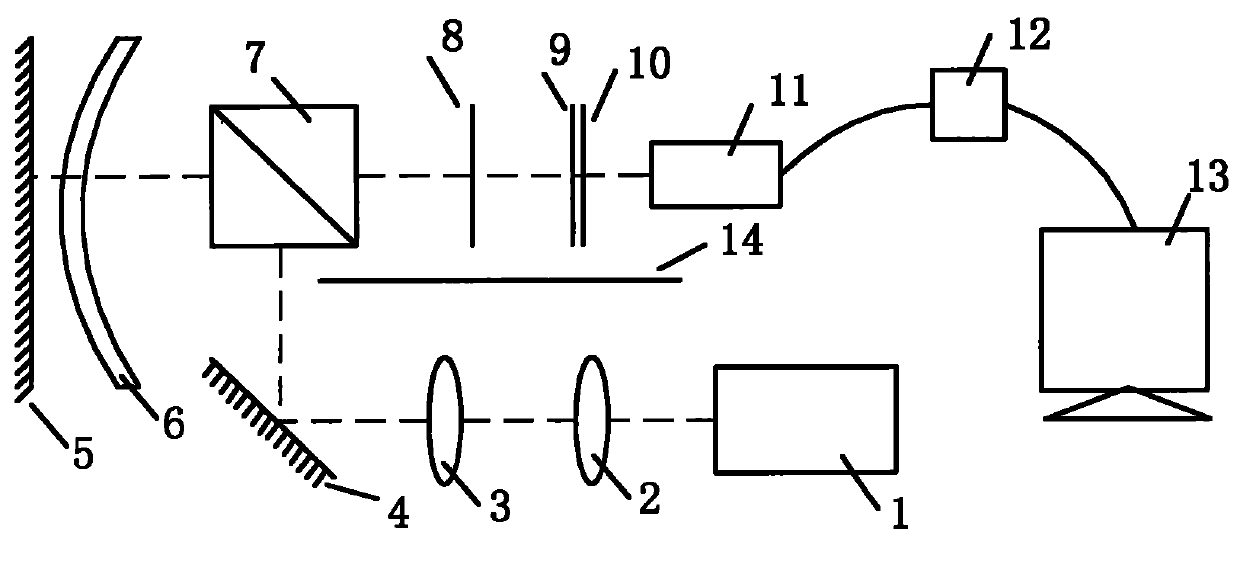
Talbot effect-based aspheric surface detection system
InactiveCN101995230ARealize high-precision detectionHigh precisionUsing optical meansAspheric lensPrism
The invention discloses a Talbot effect-based aspheric surface detection system, which comprises a semiconductor laser, a micro objective, an autocollimator objective, a first reflector, a second reflector, an aspheric mirror to be detected, a dispersion prism, a first optical grating, a second optical grating, a frosted glass plate, a charge coupled device (CCD) camera, an image acquisition card and a computer. A light beam emitted from the semiconductor laser is collimated and expanded by the micro objective and the autocollimator objective, is incident into a certain sampling position of the aspheric mirror to be detected after being turned by the first reflector and the dispersion prism, and is incident into the first optical grating by the dispersion prism after being reflected by the second reflector to form a Talbot image at a Talbot distance thereof; simultaneously, the second optical grating is arranged at the position of the Talbot image, and the Talbot image of the first optical grating and the second optical grating form a Moire fringe; the CCD camera and the image acquisition card acquires the displacement of the Moire fringe; and the computer reconstructs an aspheric surface by wavefont fitting. The Talbot effect-based aspheric surface detection system has a simple structure, and can realize the high-accuracy detection of the aspheric mirrors with large apertures or relatively steeper surfaces.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
LED Including Photonic Crystal Structure
InactiveUS20080070334A1Increase transmit powerMore energySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotonic crystal structureLateral overgrowth
A photonic crystal light emitting diode (“PXLED”) is provided. The PXLED includes a periodic structure, such as a lattice of holes, formed in the semiconductor layers of an LED. The parameters of the periodic structure are such that the energy of the photons, emitted by the PXLED, lies close to a band edge of the band structure of the periodic structure. Metal electrode layers have a strong influence on the efficiency of the PXLEDs. Also, PXLEDs formed from GaN have a low surface recombination velocity and hence a high efficiency. The PXLEDs are formed with novel fabrication techniques, such as the epitaxial lateral overgrowth technique over a patterned masking layer, yielding semiconductor layers with low defect density. Inverting the PXLED to expose the pattern of the masking layer or using the Talbot effect to create an aligned second patterned masking layer allows the formation of PXLEDs with low defect density.
Owner:LUMILEDS
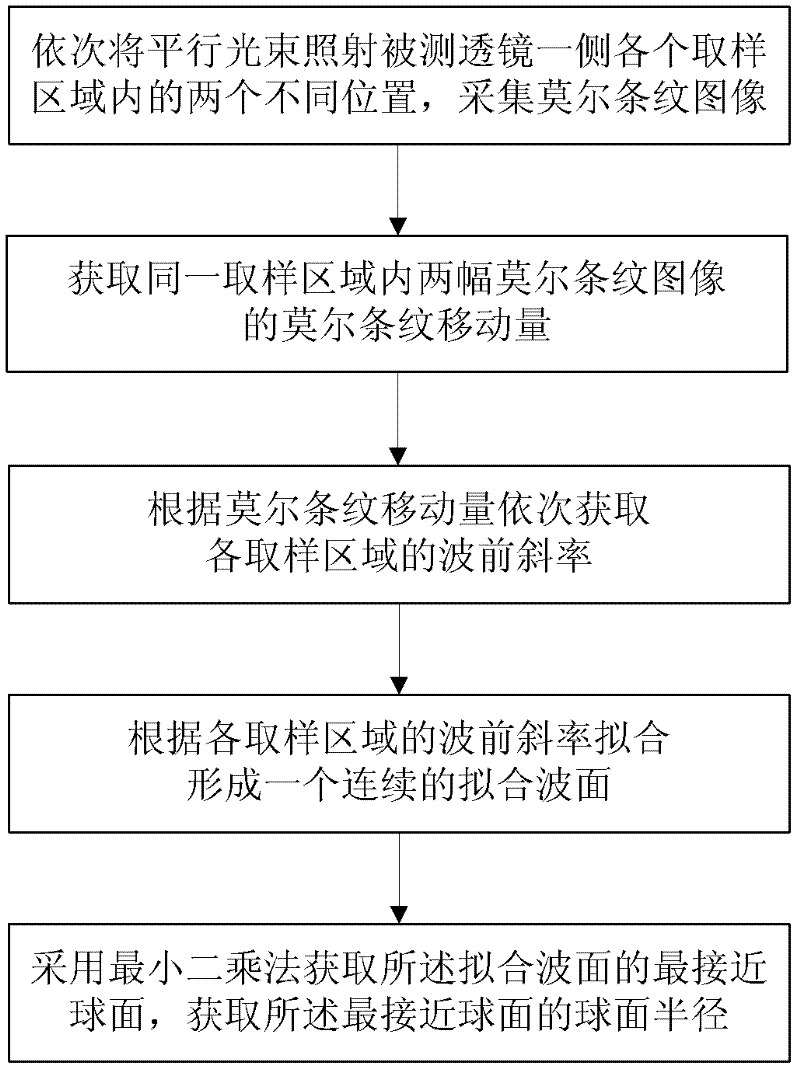
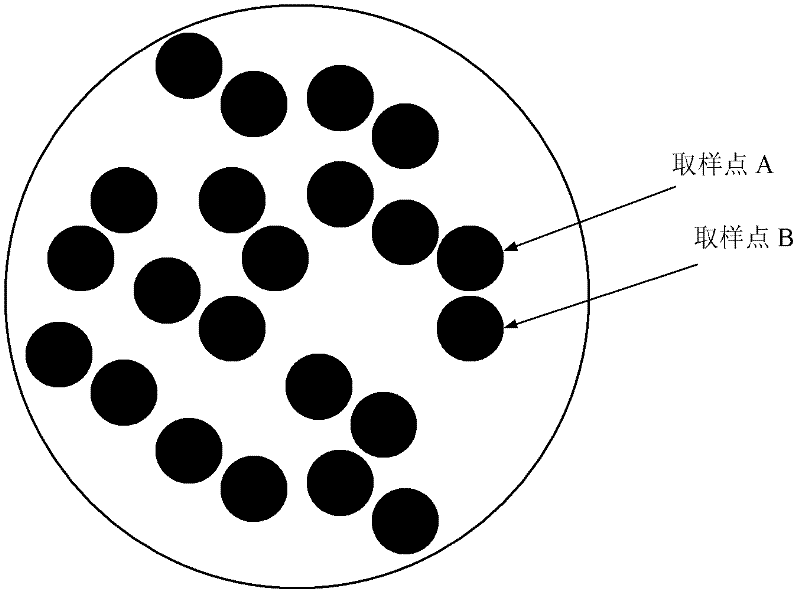
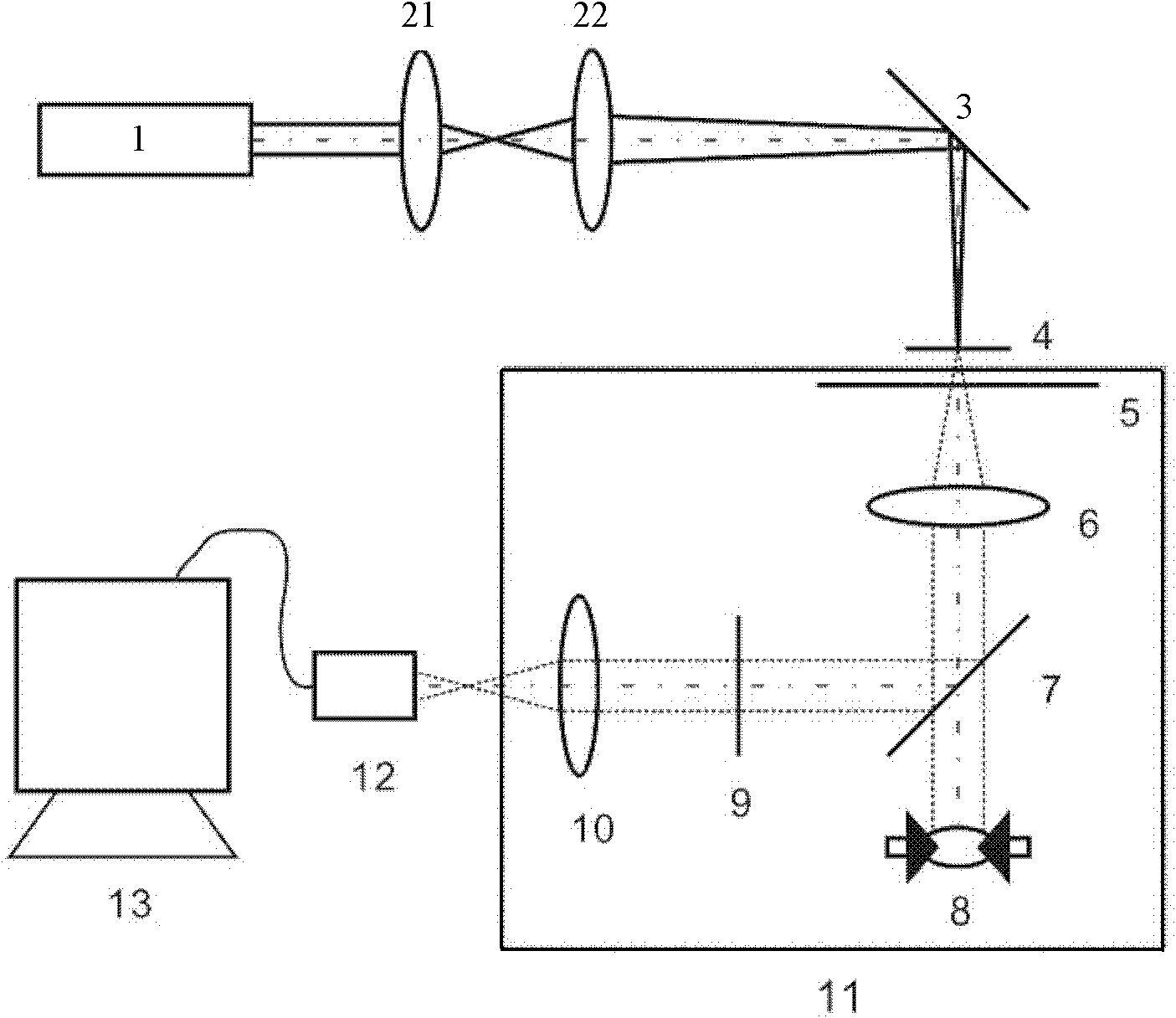
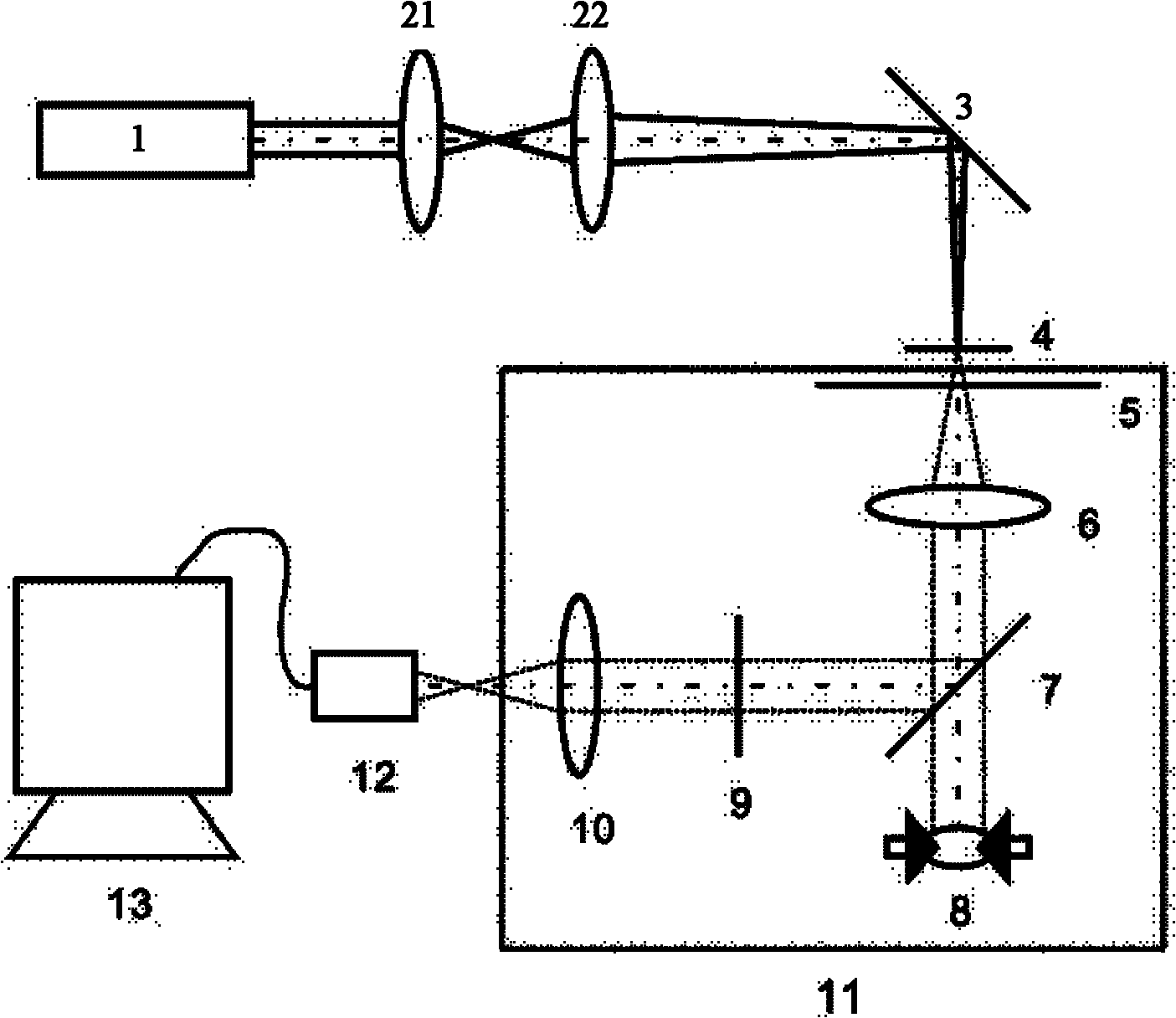
Method and device for measuring focal distance of long-focal-length and large-aperture lens
InactiveCN102331336ASolve measurement difficultiesSolve the accuracy problemUsing optical meansTesting optical propertiesImaging processingLight beam
The invention discloses a method and a device for measuring a focal distance of a long-focal-length and large-aperture lens. The method comprises the following implementation steps of: (1) irradiating sampling points on one side of a lens to be tested by parallel light beams in sequence and acquiring a moire fringe image of a Talbot effect of transmitted light; (2) acquiring moire fringe movementamount of a plurality of groups of moire fringe images of two sampling points with distance less than diameter of the parallel light beams; (3) acquiring wave front slope of two corresponding sampling point regions of the lens to be tested in sequence according to the moire fringe movement amount; (4) fitting each wave front slope to form a continuous fitting wave surface; and (5) acquiring the closest spherical surface of the fitting wave surface by using the least square method to acquire the spherical radius of the closest spherical surface. The device comprises a parallel light beam transmission unit, a moire fringe generation unit, an image acquisition unit and an image processing unit. Through the method and the device, the focal distance measurement of the long-focal-length and large-aperture lens can be effectively realized; and the method and the device have the advantages of high measurement accuracy, high adaptability and easiness and convenience in operation.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Device and method for preparing long-periodic fiber bragg grating by femtosecond laser Talbot effect
InactiveCN104698531AImprove efficiencyReduce processing timeCladded optical fibreOptical waveguide light guideLong-period fiber gratingFemto second laser
The invention discloses a device for preparing a long-periodic fiber bragg grating by femtosecond laser Talbot effect and a method for preparing the long-periodic fiber bragg grating by femtosecond laser Talbot effect, and belongs to the technical field of manufacturing of a fiber sensor. The device comprises a femtosecond laser light source, first and second collimating diaphragms, an achromatic half-wave plate, a polarization splitting prism, a shutter, a reflecting mirror, first and second convex lenses, a cylindrical lens, first and second precise moving platforms, a phase grating, a to-be-processed fiber, an electric controlled three-dimensional precise moving platform, a broadband light source, a spectrograph and a computer. Based on the Talbot effect, the femtosecond laser is used for irradiating the phase grating and forming stable bright and dark alternated light intensity distribution at a preset score Talbot distance place behind the grating; the femtosecond laser is linearly focused and irradiated on the to-be-processed fiber through the cylindrical lens, and the to-be-processed fiber and the femtosecond laser are mutually acted to generate non-linear absorption; the refractive index is periodically changed, and thereby the long-periodic fiber bragg grating is prepared. The device and method have the advantages of being simple in structure, high in utilization rate of the femtosecond laser, short in processing time, and low in manufacturing cost.
Owner:SHANDONG JIAOTONG UNIV
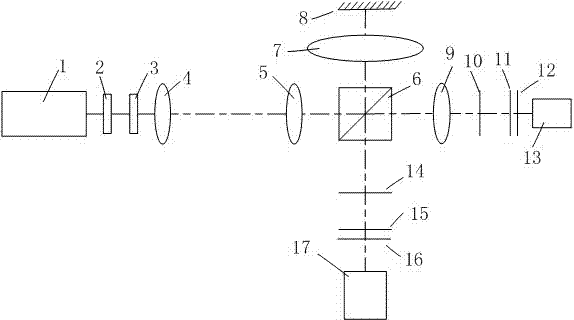
Focal power detecting system of multifocal lens based on Talbot effect
InactiveCN103115753AAchieve one-time measurementReal-time processingTesting optical propertiesPhase differenceLaser light
The invention relates to a focal power detecting system of a multifocal lens based on Talbot effect. A laser device sends out laser light sources which can form parallel light through beam expanding and collimation of a spatial filter and a collimating lens, and the parallel light sequentially passes through a main Ronchi grating and an auxiliary Ronchi grating which have an included angle after passing through a multifocal lens which needs to be measured. Distortion Moire fringes containing focal power information of the measured lens are obtained on a receiving screen, and the focal power information of the measured lens is obtained by using a personal computer (PC) to perform image processing and computing on the distortion Moire fringes obtained on the receiving screen. Light rays pass through a lens with different focal power, and the lens enables the light rays to generate phase differences, so that corresponding distortion Moire fringes are generated. Furthermore, a focal power information parameter of the measured lens is obtained by processing the Moire fringes, and therefore measurement of the multifocal lens is achieved. One-time measurement of the multifocal lens is achieved, and real-time processing of a computer can automatically work out the focal power information of the lens, and therefore efficiency is improved. Furthermore, the focal power detecting system of the multifocal lens based on the Talbot effect is simple in light path construction, and therefore stability of the system is improved.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
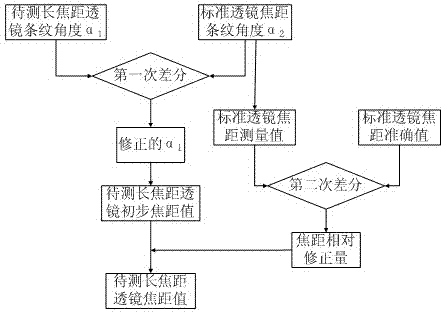
Compound differential type long-focus measuring device based on Talbot effect
ActiveCN102252824AAccurate correctionHigh measurement accuracyTesting optical propertiesLong-focus lensBeam splitter
The invention discloses a compound differential type long-focus measuring device based on a Talbot effect. The light of a laser source runs through a polaroid, a lambda / 4 wave plate, a microscope objective and a collimating mirror, to be divided into two beams by a beam splitter prism, wherein one beam is incident to a standard lens, a first grating and a second grating, to form moire fringes on first ground glass, the first CCD (Charge Coupled Device) is used for collecting the fringes and inputting the fringes to a computer so as to calculate the angle alpha 1 of the fringes, to get a standard lens focus; the other beam is incident to a long-focus lens to be measured, reflected by a reflector and then incident to third and fourth gratings, to form moire fringes on second ground glass, and a second CCD is used for collecting the fringes and inputting the fringes to the computer so as to calculate the angle alpha 2 of the fringes; the alpha 1 and alpha 2 are subjected to differential treatment and the alpha 1 is corrected to obtain a long-focus value; and the standard lens focus and the known standard value thereof are subjected to differential treatment and the long-focus value to be measured is corrected to obtain a focus value of the long-focus lens to be measured finally. According to the device disclosed by the invention, the external interference is eliminated by adopting the two differential treatments, and the high precision measurement for the long-focus lens can be realized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Novel holographic optical tweezers system based on Talbot effect
InactiveCN102162908AReduce calculationLow powerRadiation/particle handlingMicroscopesImaging analysisOptical axis
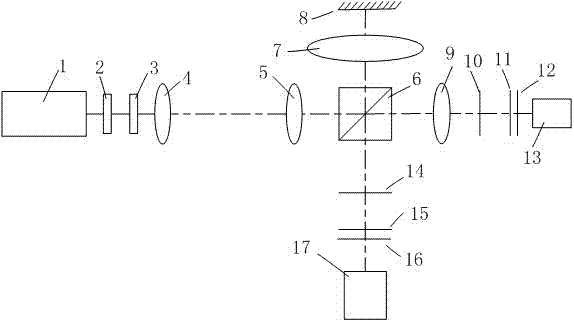
The invention relates to laser holographic optical tweezers, and provides a novel holographic optical tweezers system based on the Talbot effect with a simple structure and high operability. The novel holographic optical tweezers system comprises a laser, a first lens, a second lens, a reflector, a holographic element, an inverted microscope, a CCD image sensor and a computer, wherein the two lens are sequentially arranged between the laser beam output end of the laser and the reflector in tandem; the laser and the two lenses have the same optical axis; the focuses of the two lenses are in coincidence with each other when the two lenses are placed in the initial positions; the focus position of the laser beam can be controlled by micro-adjusting the distance between the two lenses so as to make the focus point of the laser beam located on the holographic element; a particle is placed on the object stage of the inverted microscope; the particle can be arranged in a Talbot self-imaging position of the holographic element by adjusting the distance between the object stage of the inverted microscope and the holographic element; and the information output end of the CCD image sensor isconnected with the computer for image analysis and processing.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Measuring method for micro-lens array focal length based on Newton method and Talbot effect
InactiveCN102788683AEasy to operateLow costTesting optical propertiesClassical mechanicsFocal position
A measuring method for micro-lens array focal length based on the Newton method and the Talbot effect belongs to the field of optical detection. The Talbot effect of Ronchi grating is utilized, Talbot self-imaging cycle with parallel light passing through the Ronchi grating is consistent to grating cycle, and a start point board is placed at a focus of object space of a micro-lens to be detected. The start point board is adjusted and focal object distance of the start point board is ensured by a micro-moving table. Out-of-focus of the start point board can be calculated according to changes of the Talbot self-imaging cycle of grating, and curvature radius of the micro-lens before the micro-lens exits spherical wave is image distance of imaging of the micro-lens. Measurement of focal length of the micro-lens can be achieved according to position relation of the image distance and focus image distance and by combining the Newton method. The measuring method is simple and easy to implement and has high measuring precision.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Focus detection method based on grating Talbot effect
InactiveCN104238284ASimple structureImprove anti-interference abilityUsing optical meansPhotomechanical exposure apparatusTalbot effectPhase change
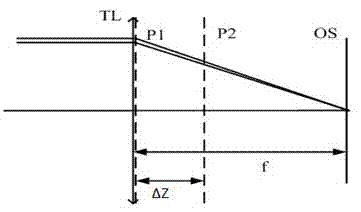
The invention relates to a focus detection method based on a grating Talbot effect. The method is used for detecting the position of a silicon chip of a photoetching machine system in real time to complete the high-accuracy leveling and focusing of the silicon chip. By virtue of a detection system, the high-accuracy focus detection of the silicon chip of a photoetching machine is completed according to the self-imaging phase change of the grating Talbot effect due to the fact that the silicon chip is out of focus. When the silicon chip is positioned on a focal plane, grating forming wave-front is planar wave-front. When the silicon chip is out of focus, the imaging wave-front is spherical wave-front. The focus detection method is higher in anti-interference capacity and better in technological adaptability.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
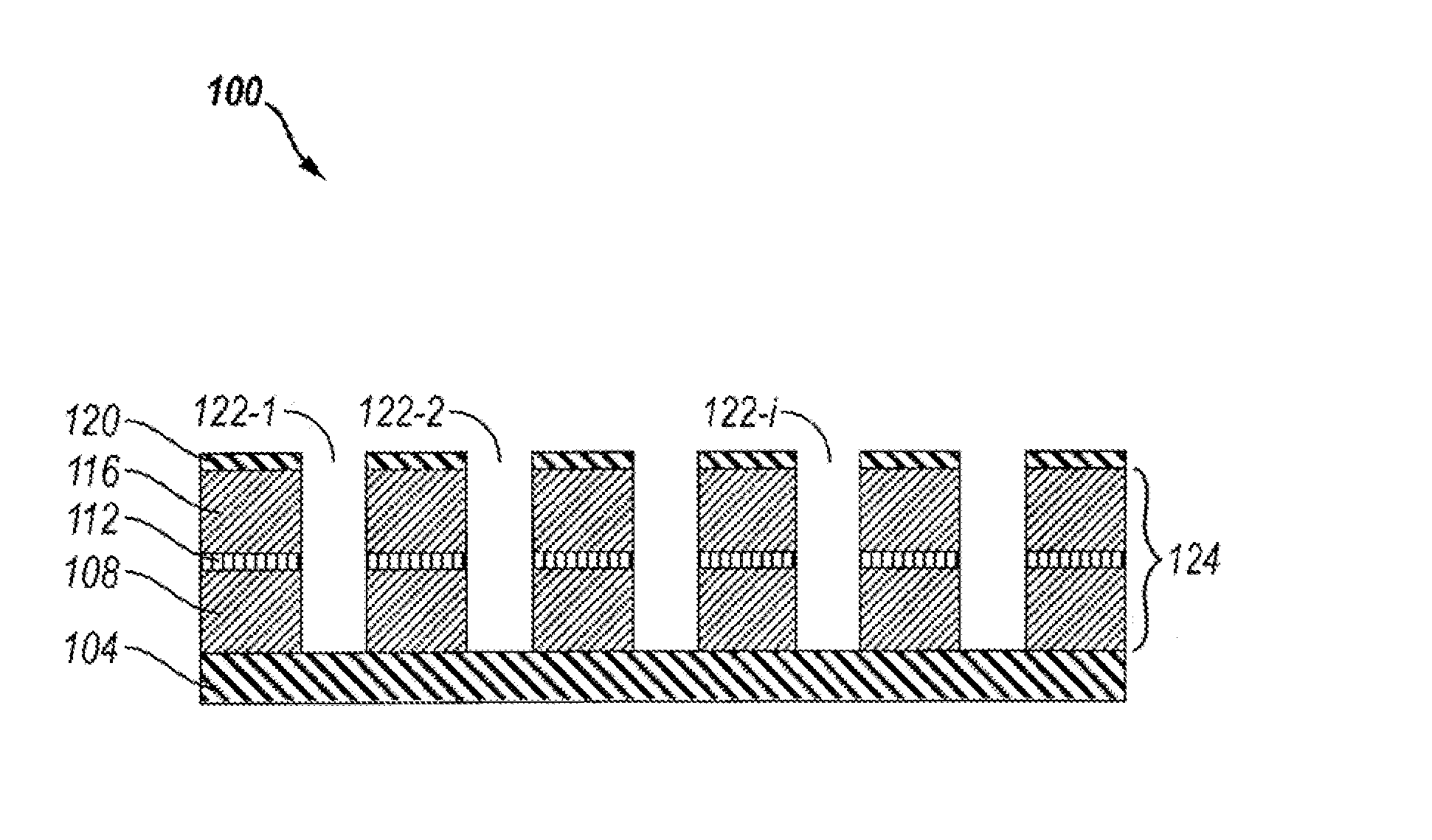
Inclined phase grating structures
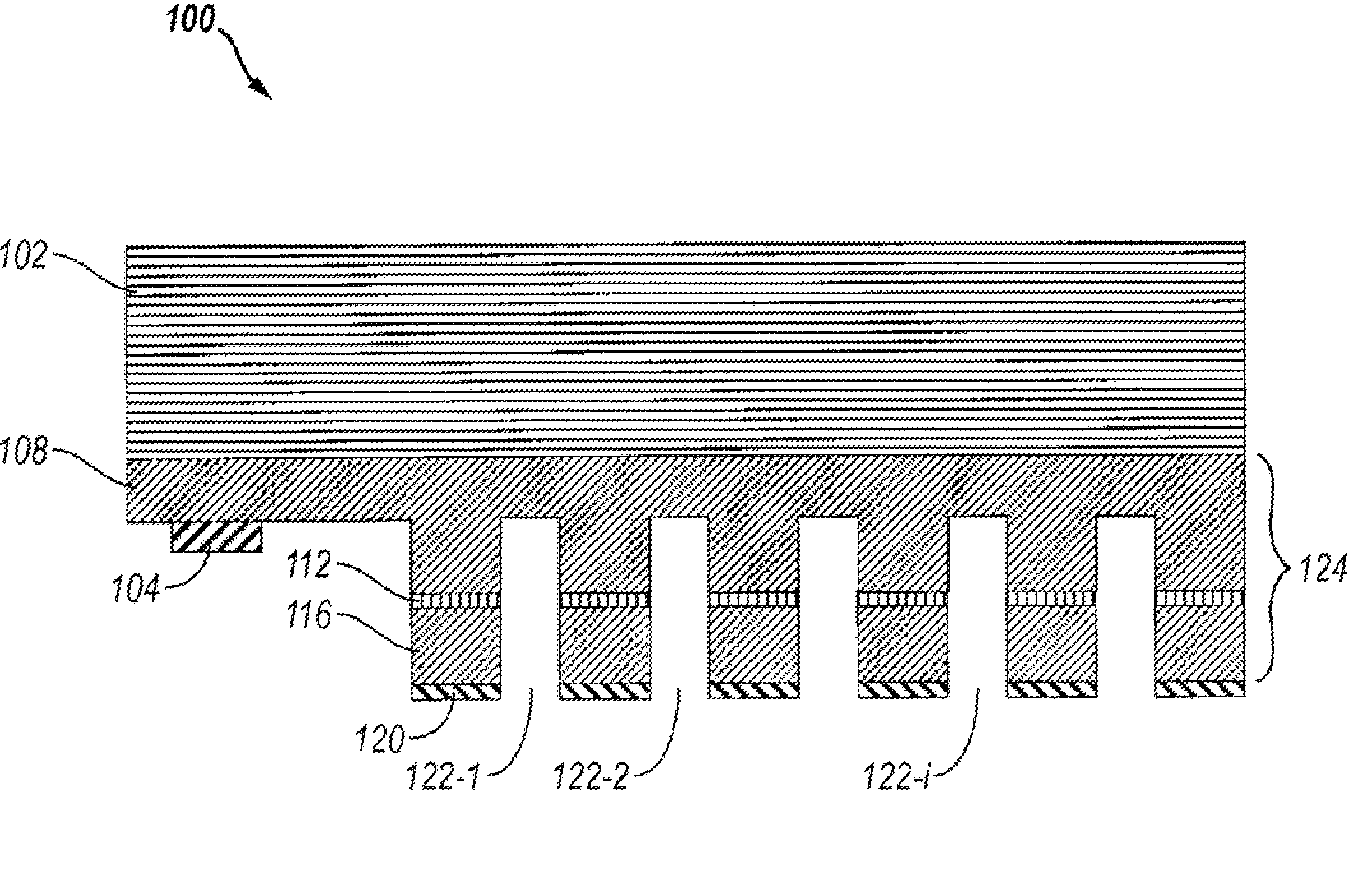
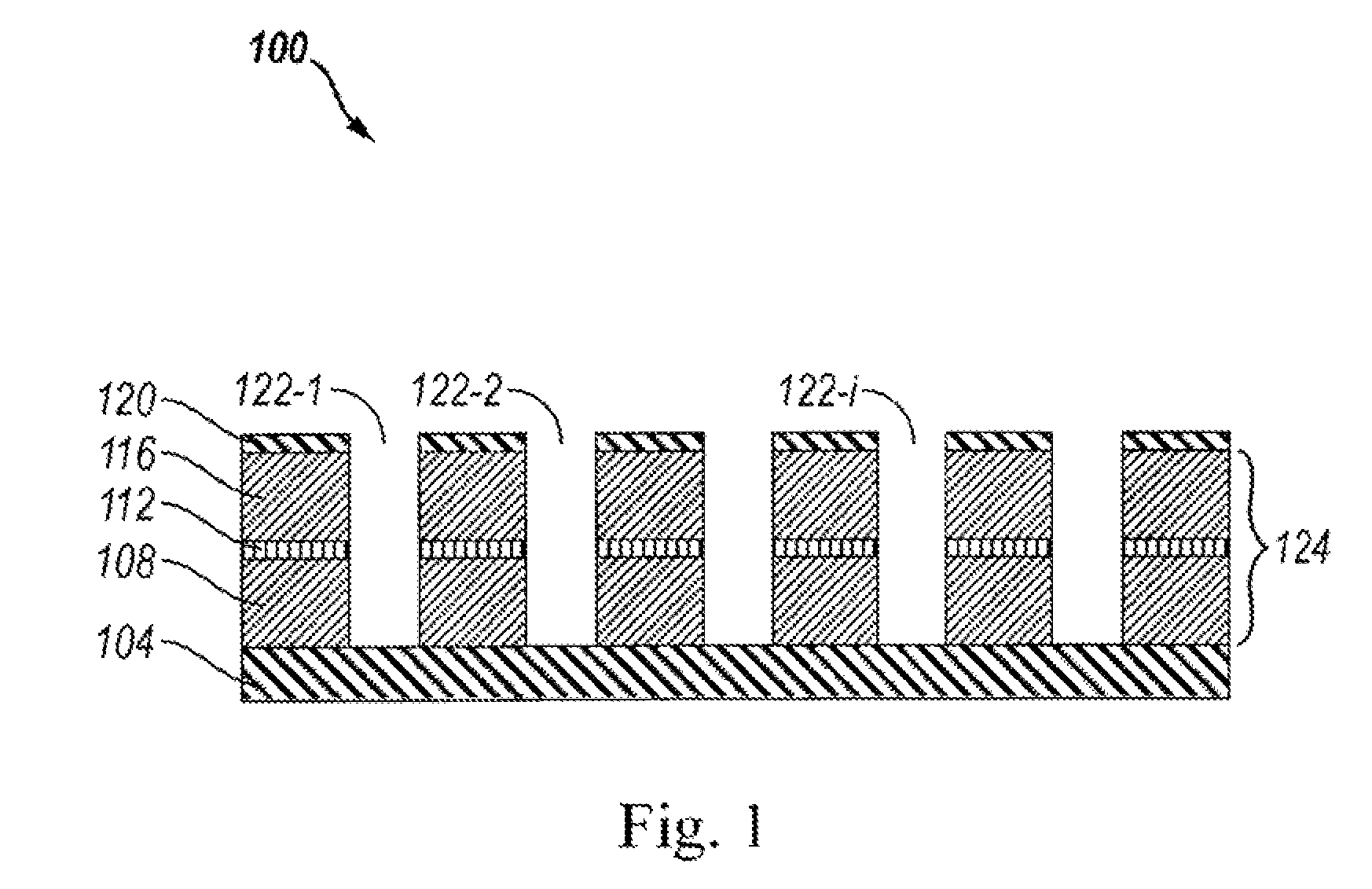
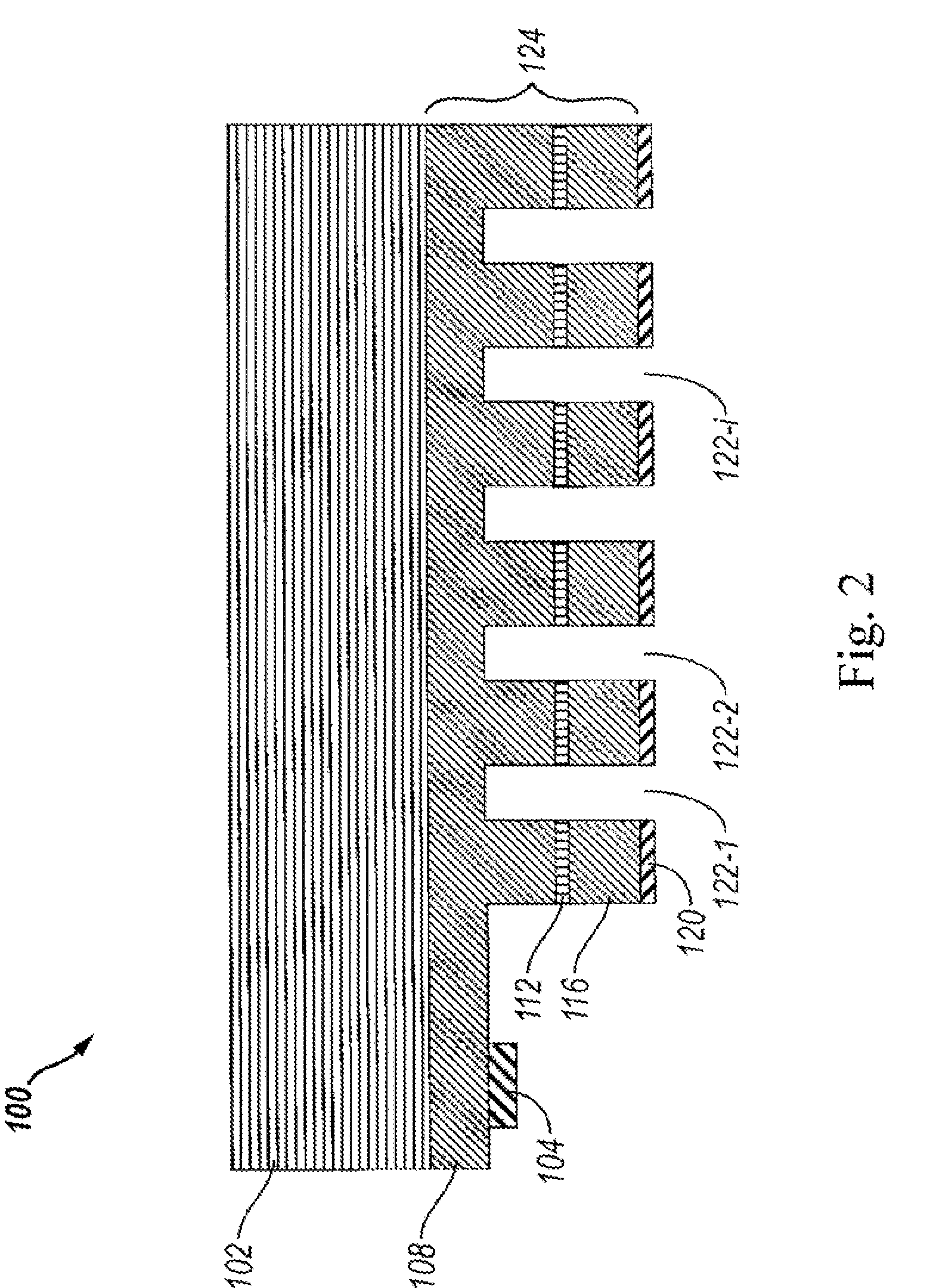
ActiveUS9480447B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationComputerised tomographsGrating interferometerPhase grating
Grating interferometer comprising inclined phase grating structures, method for increasing the definition of phase contrast images of interferometers or in applications which are based on the Talbot effect, using inclined phase grating structures, phase gratings wherein the grating structures are positioned at angles on the substrate of the phase grating, method for producing grating structures which are positioned at angles on the substrate of the phase grating, and corresponding uses.
Owner:KARLSRUHER INST FUR TECH
X-ray imaging apparatus
InactiveUS8995613B2Reduce impactImprove qualityImaging devicesHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionSoft x rayX-ray
An X-ray imaging apparatus which takes an image of an object to be detected, comprises: a first grating to form a periodic bright-dark pattern by a Talbot effect, based on an X-ray from an X-ray source; a second grating, disposed at a position where the bright-dark pattern is formed, to block a part of the bright-dark pattern; a detector to detect an X-ray intensity distribution of the X-ray which passed through the second grating; and a calculator to calculate phase information of the X-ray based on the detected X-ray intensity distribution, wherein the second grating includes a first region having a first blocking pattern and a second region having a second blocking pattern, and a direction in which the first blocking pattern blocks a bright section of the bright-dark pattern is different from a direction in which the second blocking pattern blocks the bright section of the bright-dark pattern.
Owner:CANON KK
X-ray imaging apparatus
InactiveUS20120263274A1Reduce the impactImprove qualityImaging devicesHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionX-rayTalbot effect
An X-ray imaging apparatus which takes an image of an object to be detected, comprises: a first grating to form a periodic bright-dark pattern by a Talbot effect, based on an X-ray from an X-ray source; a second grating, disposed at a position where the bright-dark pattern is formed, to block a part of the bright-dark pattern; a detector to detect an X-ray intensity distribution of the X-ray which passed through the second grating; and a calculator to calculate phase information of the X-ray based on the detected X-ray intensity distribution, wherein the second grating includes a first region having a first blocking pattern and a second region having a second blocking pattern, and a direction in which the first blocking pattern blocks a bright section of the bright-dark pattern is different from a direction in which the second blocking pattern blocks the bright section of the bright-dark pattern.
Owner:CANON KK
Laser scanning side lobe suppression device of phased array
InactiveCN102866394AImprove machining accuracyEasy to implementWave based measurement systemsImaging conditionLaser array
The invention discloses a laser scanning side lobe suppression device of a phased array. The suppression device comprises a master oscillation laser and a phase compensation plate, a beam expanding collimator and an optical phased array scanner are arranged between the master oscillation laser and the phase compensation plate in sequence, and the optical phased array scanner is also connected with a controller; the distance between the output end of the optical phased array scanner and the phase compensation plate can meet the self-imaging conditions of fractional Talbot effect; and the phase of the phase compensation plate corresponds to the phase of the Fresnel diffraction propagated from an optical field of a laser array to an optical field in the fractional Talbot distance. The laser scanning side lobesuppression device of the phased array disclosed by the invention is used for outputting non-mechanical scanning beams with high beam quality in a phased array laser radar transmission system, has the advantages of simple structure, stable and reliable performance, rapid high-resolution non-mechanical laser scanning and the like, is specially suitable for the fields such as laser scanning radars and laser communications, and has significant meaning for development of compact, light and high-quality laser scanning system.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
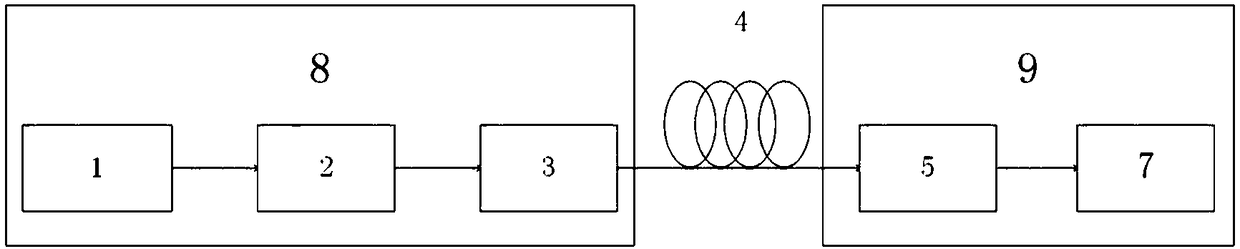
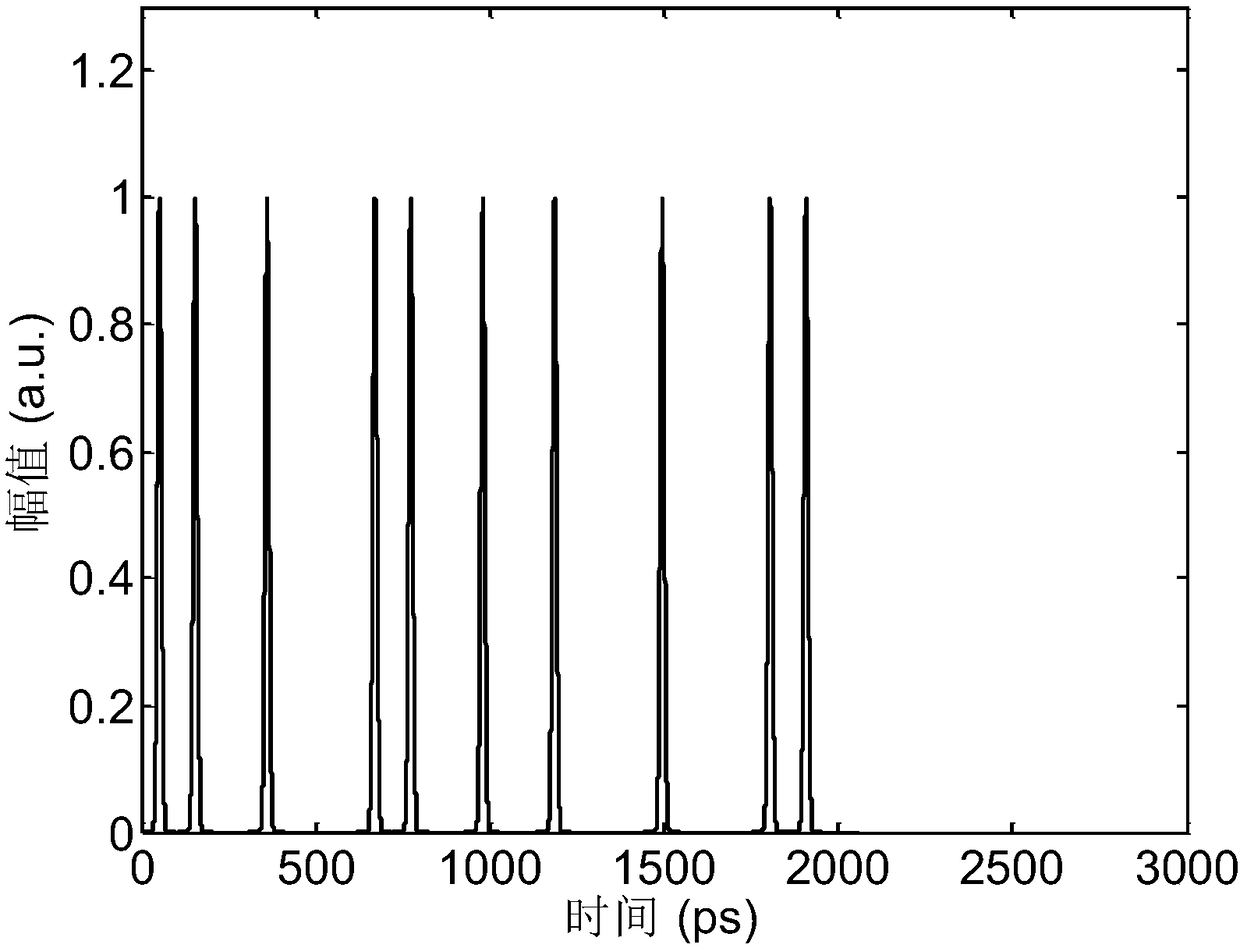
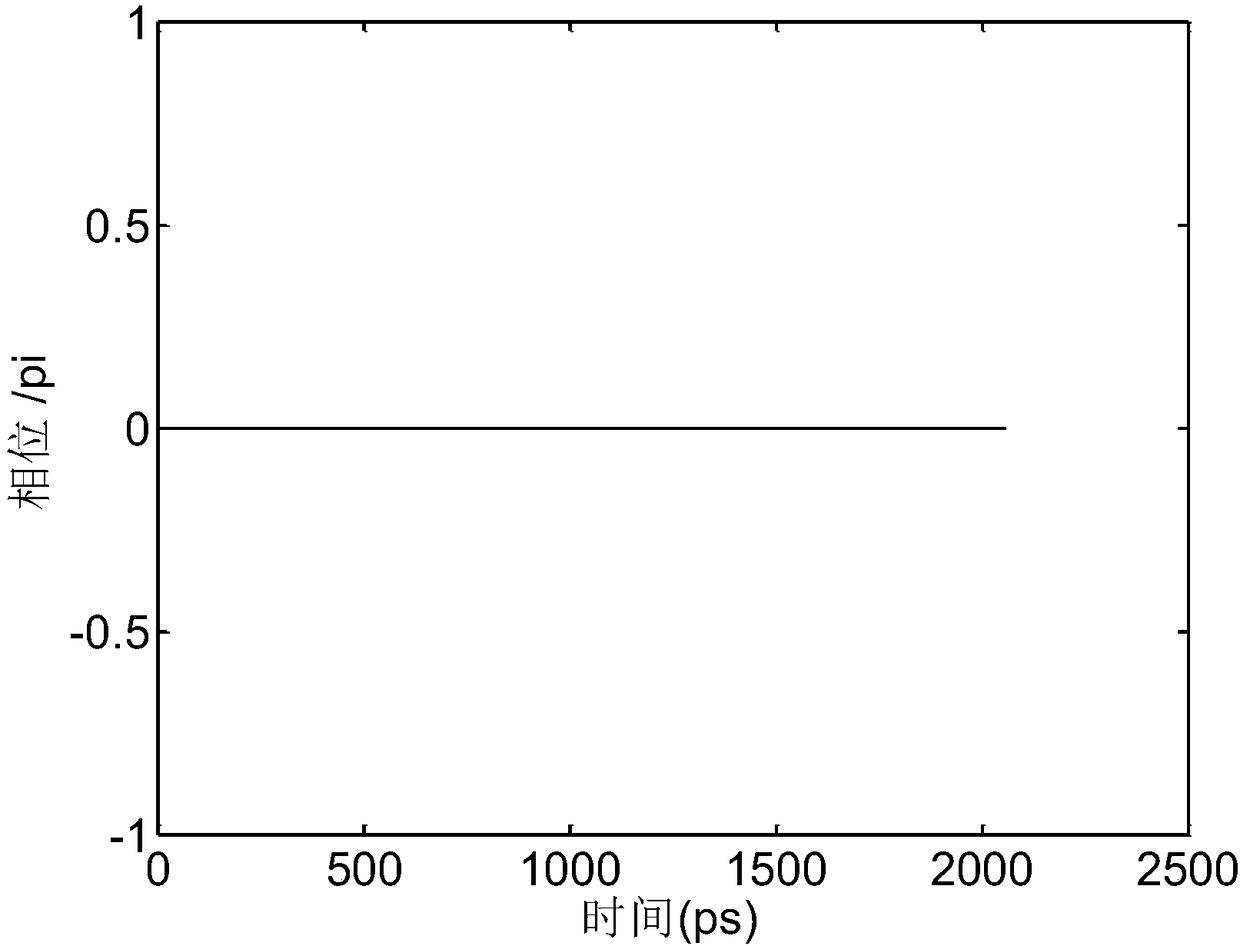
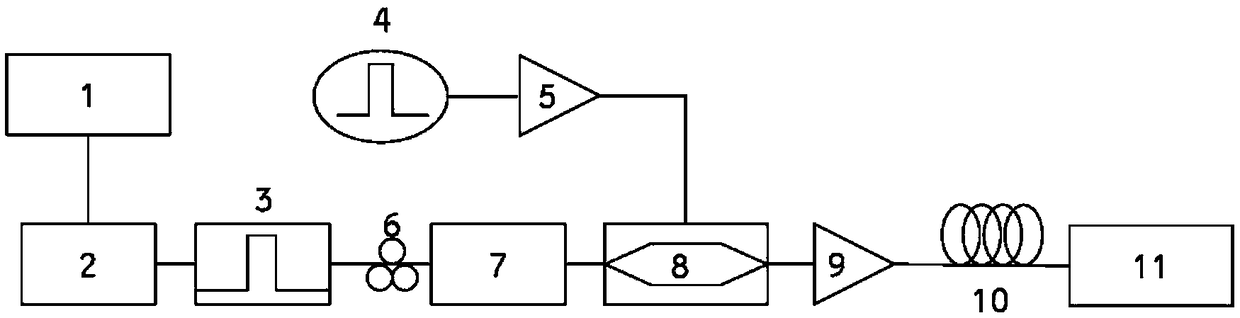
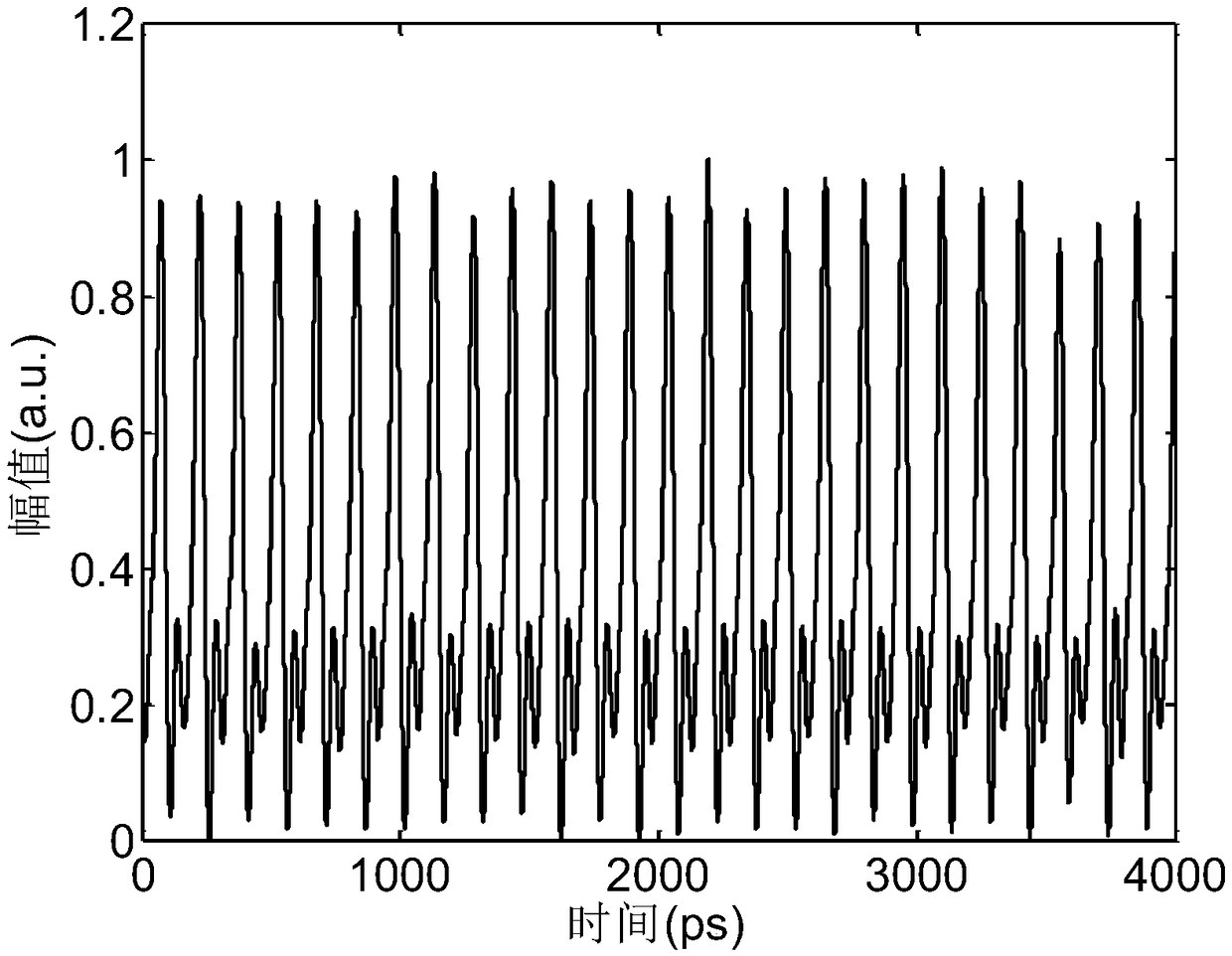
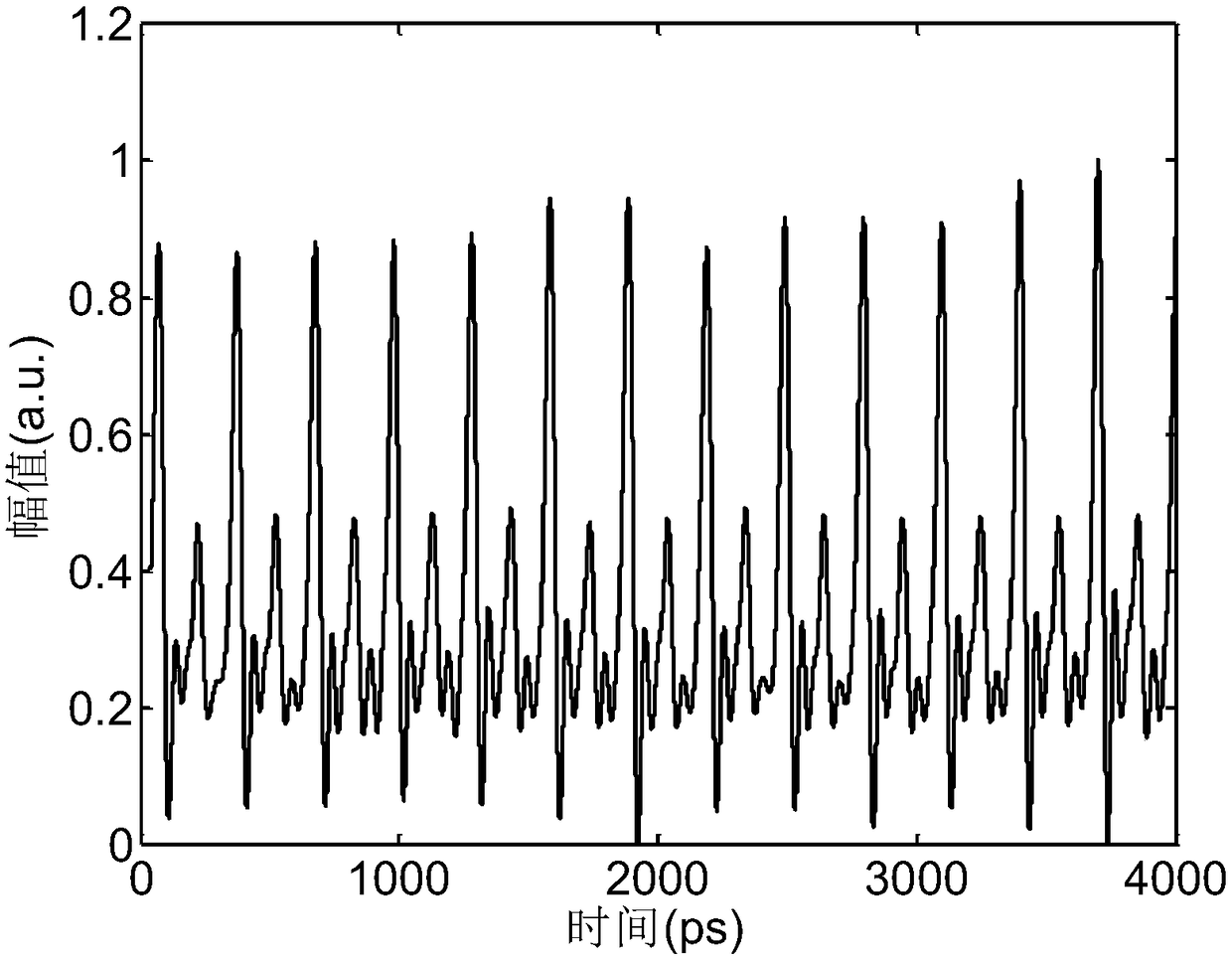
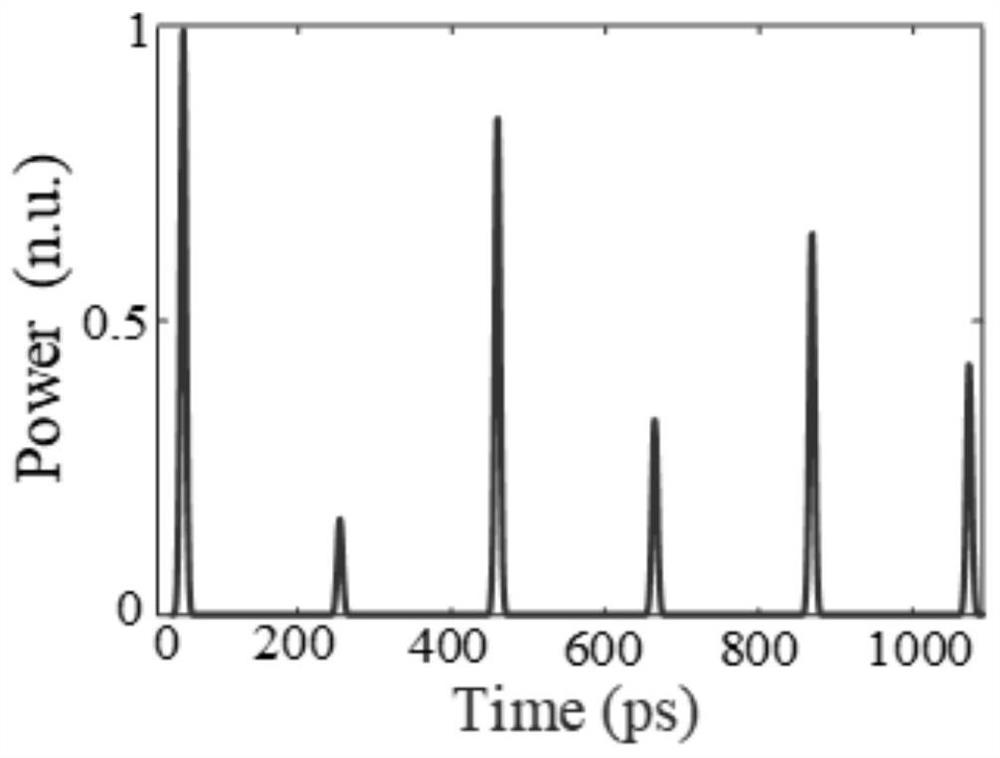
Encryption and decryption communication device and secure communication system based on time domain Talbot effect
ActiveCN108599870AReduce lossTo achieve the effect of confidential communicationElectromagnetic transmission optical aspectsComputer hardwareTime domain
The invention discloses an encryption and decryption communication device and a secure communication system based on a time domain Talbot effect, belonging to the technical field of optical communication. The encryption communication device comprises an active mode-locked laser, an intensity modulator and a positive dispersion device; and the decryption communication device comprises a negative dispersion device and an optical detector. According to the scheme of the invention, a dispersive medium with arbitrary dispersion is utilized, so that the optical signal pulse can be changed into a disordered signal without carrying information, an original signal can be obtained by inverse dispersion demodulation at the output end, the effect of secure communication can be achieved, and moreover,the technical scheme is simple and the cost is low.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Time domain Talbot effect based time domain stealth system
ActiveCN108710248AGood temporal stealth effectActive medium shape and constructionLight demodulationTime domainTime range
The invention belongs to the technical field of optical communication and discloses a time domain Talbot effect based time domain stealth system. The time domain stealth system comprises a signal generating device and a stealth device, the signal generating device is used for generating optical pulses and modulating signals, and the stealth device is used for realizing time domain stealth throughintroduction of a chromatic dispersion value according with an equation as shown in the specification. By introduction of a time domain average effect of the time domain Talbot effect to a time domainstealth conception, energy of pulse sequences with modulated intensity information is redistributed to realize average in a certain time range, and thus, obtained output light looks the same as output light of a light source, and time domain stealth is realized.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Inclined phase grating structures
ActiveUS20130148780A1Improve image qualityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationComputerised tomographsGrating interferometerPhase grating
Grating interferometer comprising inclined phase grating structures, method for increasing the definition of phase contrast images of interferometers or in applications which are based on the Talbot effect, using inclined phase grating structures, phase gratings wherein the grating structures are positioned at angles on the substrate of the phase grating, method for producing grating structures which are positioned at angles on the substrate of the phase grating, and corresponding uses.
Owner:KARLSRUHER INST FUR TECH
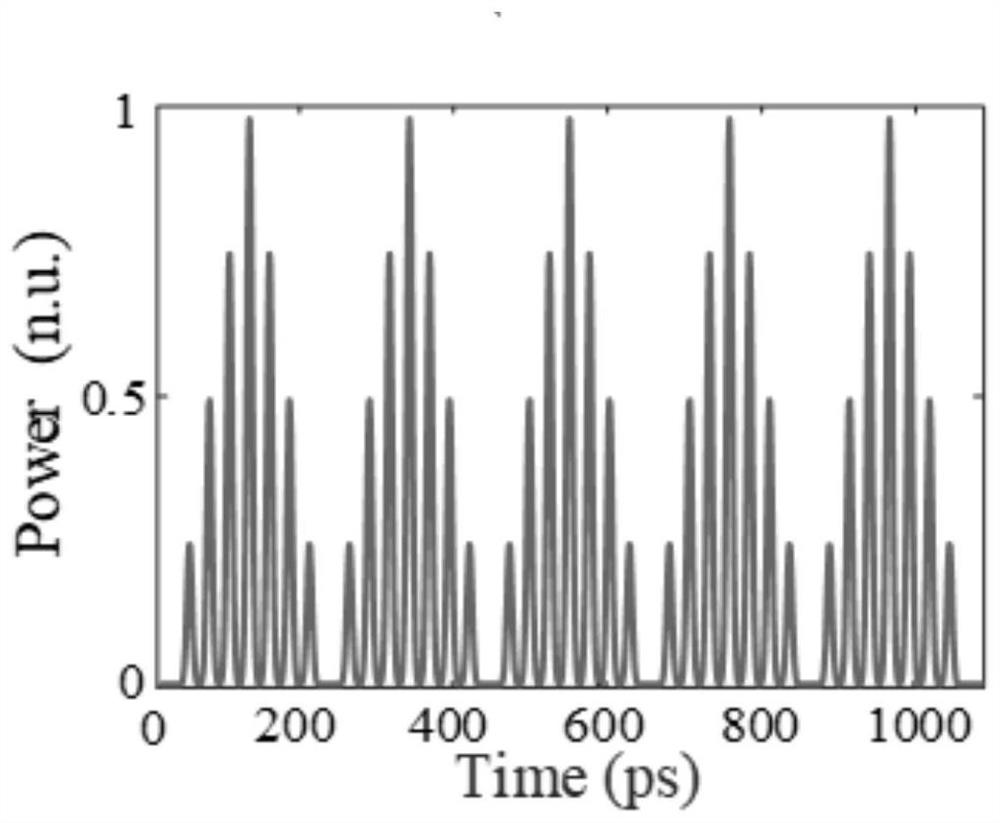
Arbitrary waveform generation device and method based on integer-order time domain Talpot effect
InactiveCN111769875AReduce complexitySolve the difficult bottleneck of high-rate signalElectromagnetic transmittersPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsContinuous lightLine width
The invention relates to the field of signal processing and signal generation, in particular to an arbitrary waveform generation device based on an integer-order time domain Talbot effect. A radio frequency signal generator is connected with a push-pull Mach-Zehnder modulator; a Gaussian light pulse sequence generated by the narrow-linewidth continuous light laser and a periodic analog radio frequency signal generated by the radio frequency signal generator are simultaneously added into the push-pull Mach-Zehnder modulator; the periodic analog radio frequency signal is sampled by the Gaussianoptical pulse sequence to obtain a periodic optical pulse sequence of the instantaneous frequency of the periodic analog radio frequency signal; the periodic light pulse sequence enters a dispersion optical fiber of which the first-order dispersion coefficient meets an integer-order time domain Talpot effect; and an optical pulse sequence is output through the dispersion optical fiber. According to the invention, the expected ideal output time waveform is generated according to the relationship between the output optical pulse sequence and the input periodic analog radio frequency signal.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com