Patents
Literature
4012 results about "Angular degrees" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The angular degree (symbolized deg or °) is a unit of plane angular measure used in some engineering applications, and by most lay people. There are 360 angular degrees in a complete circle.
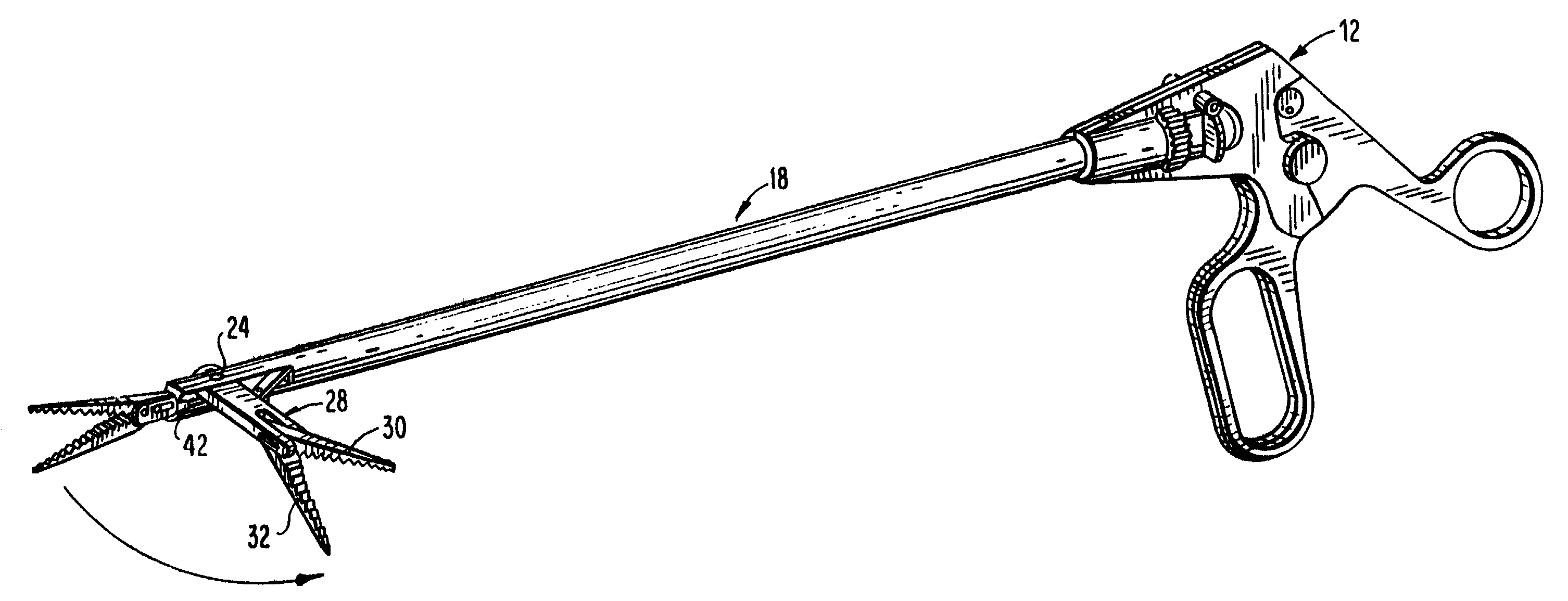
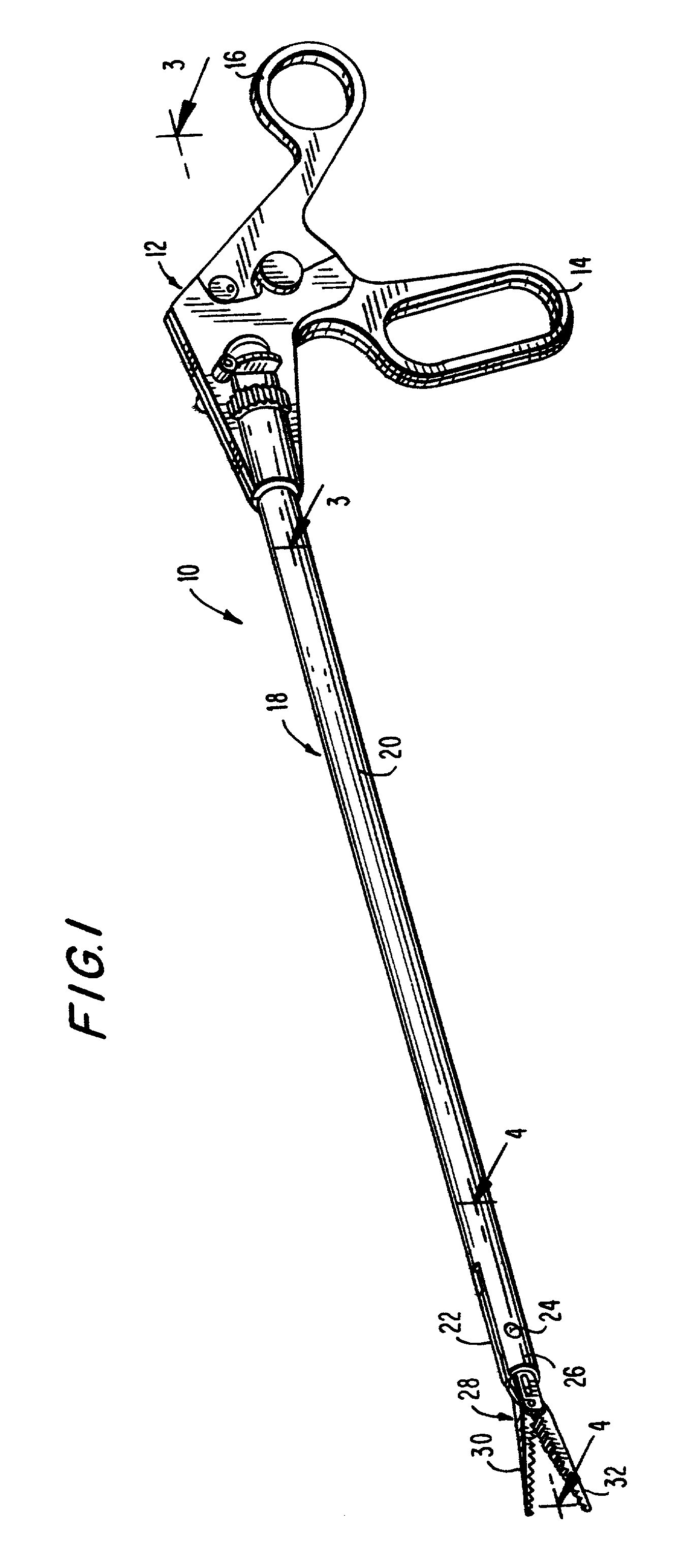
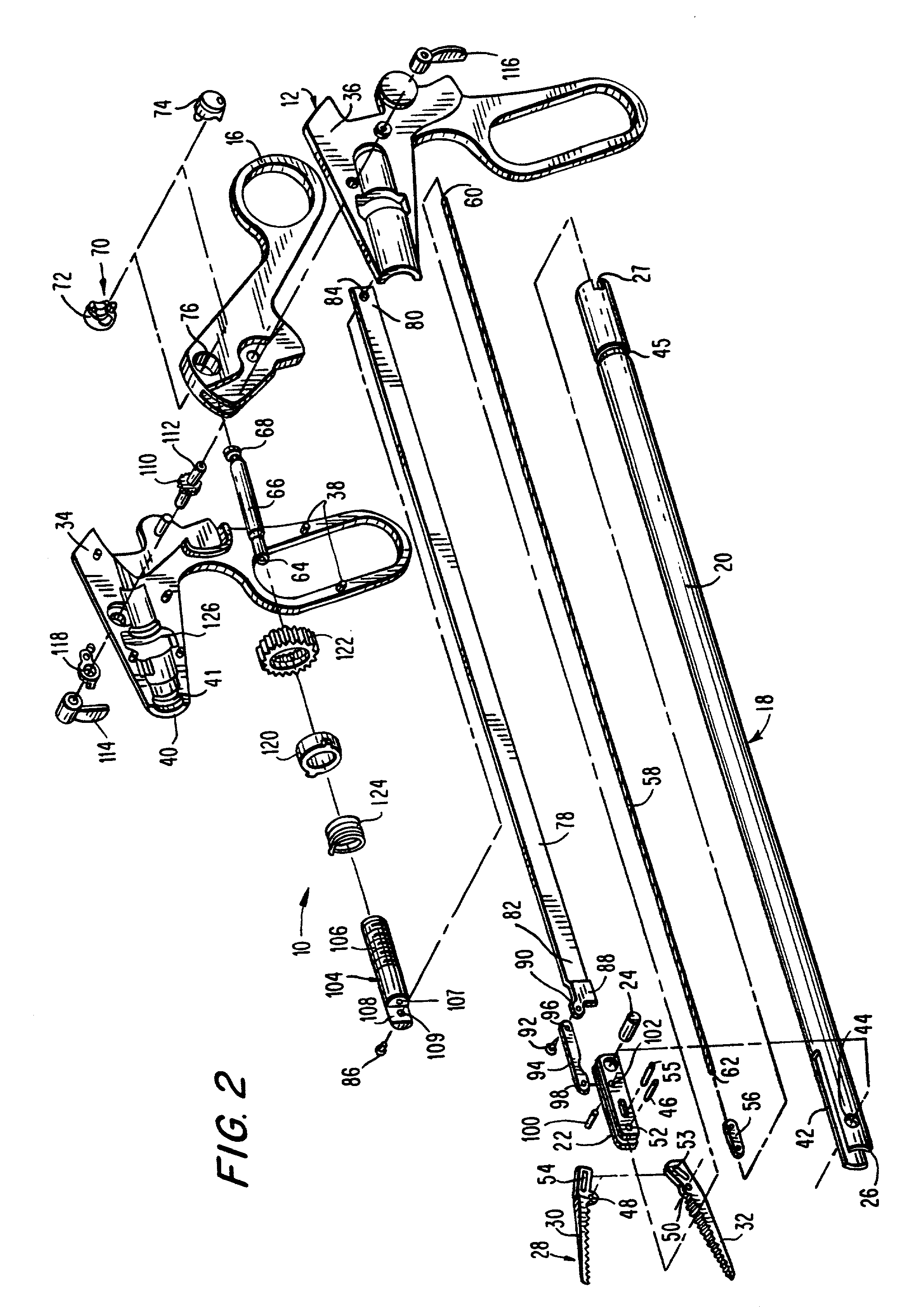
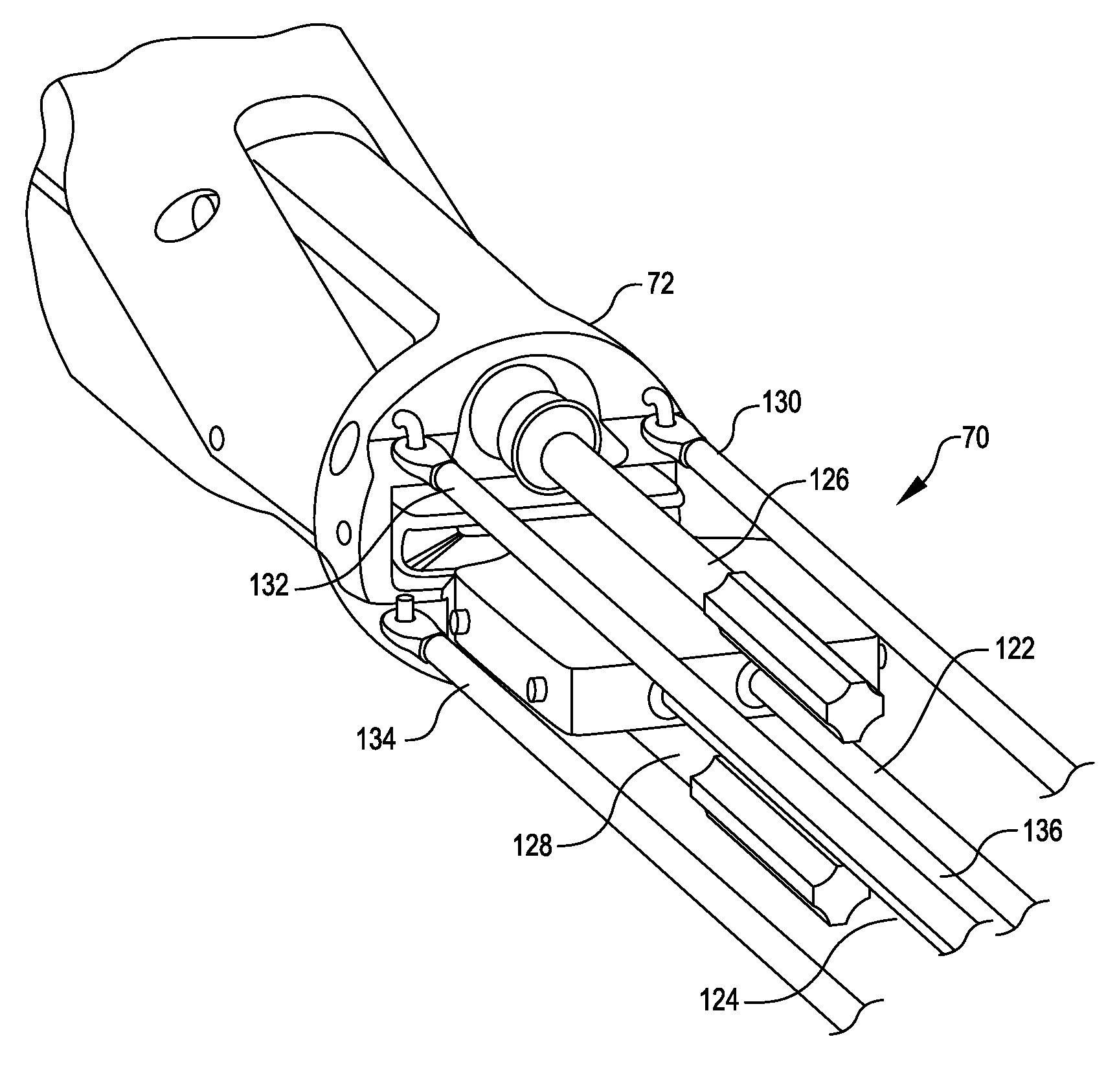
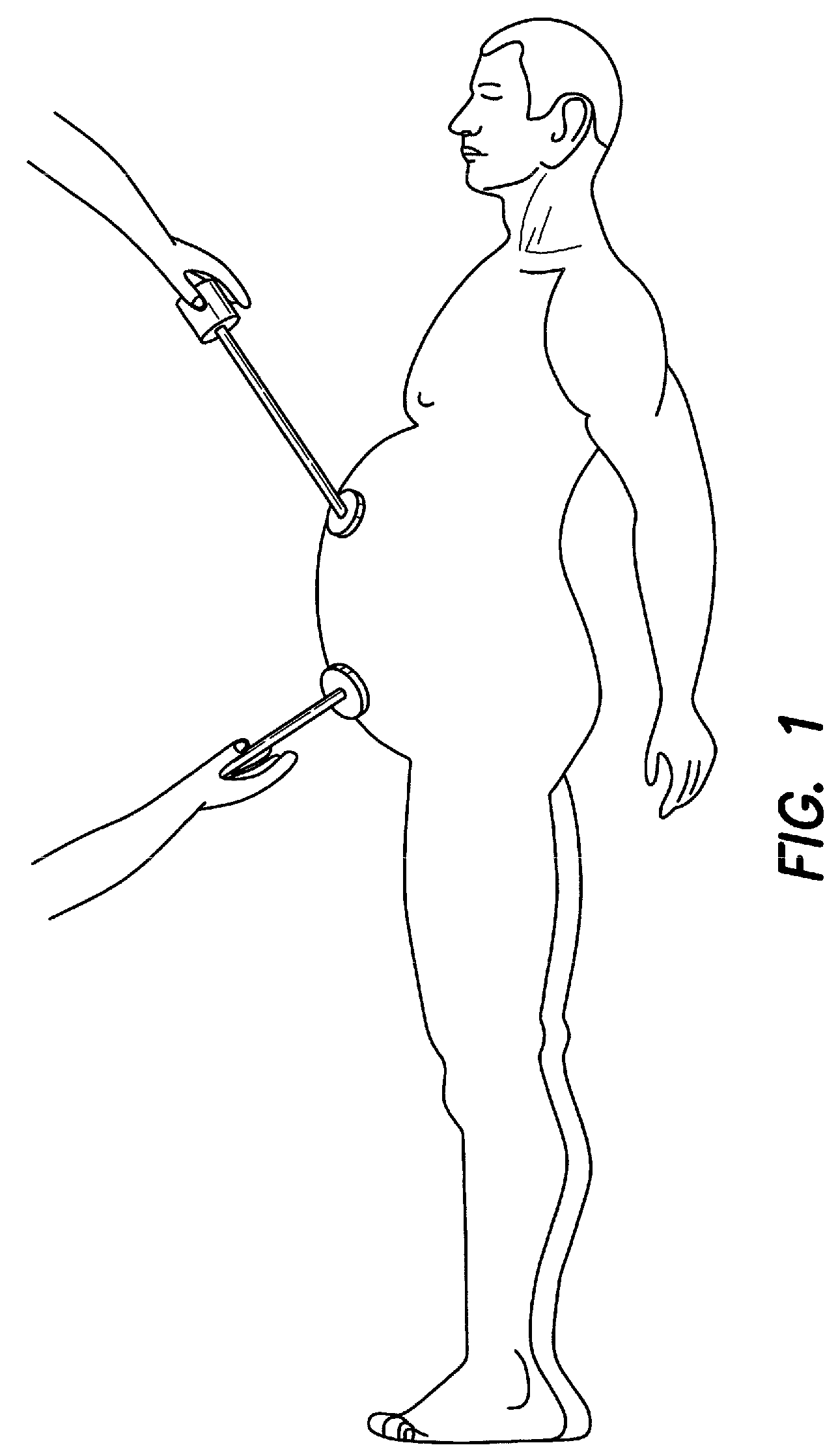
Articulating endoscopic surgical apparatus
InactiveUS7087071B2Vaccination/ovulation diagnosticsSurgical instruments for heatingInjection portDistal portion
A surgical instrument is provided for use in endoscopic or laparoscopic procedures. The instrument includes a handle portion, an endoscopic portion extending from the handle portion, an articulating section pivotably connected to a distal end portion of the endoscopic portion, and a retractor assembly operatively associated with the articulating section. Structure is provided for manipulating the articulating section relative to the longitudinal axis of the endoscopic portion within an angular degree of rotation. An injection port may also be provided to deliver fluids through the endoscopic portion to the operative site.
Owner:UNITED STATES SURGICAL CORP
Surgical tool with a two degree of freedom wrist
ActiveUS8852174B2Amount of maneuverabilityShorten the lengthYielding couplingDiagnosticsDrive shaftAngular degrees
Surgical tools having a two degree-of-freedom wrist, wrist articulation by linked tension members, mechanisms for transmitting torque through an angle, and minimally invasive surgical tools incorporating these features are disclosed. An elongate intermediate wrist member is pivotally coupled with a distal end of an instrument shaft so as to rotate about a first axis transverse to the shaft, and an end effector body is pivotally coupled with the intermediate member so as to rotate about a second axis that is transverse to the first axis. Linked tension members interact with attachment features to articulate the wrist. A torque-transmitting mechanism includes a coupling member, coupling pins, a drive shaft, and a driven shaft. The drive shaft is coupled with the driven shaft so as to control the relative orientations of the drive shaft, the coupling member, and the driven shaft.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
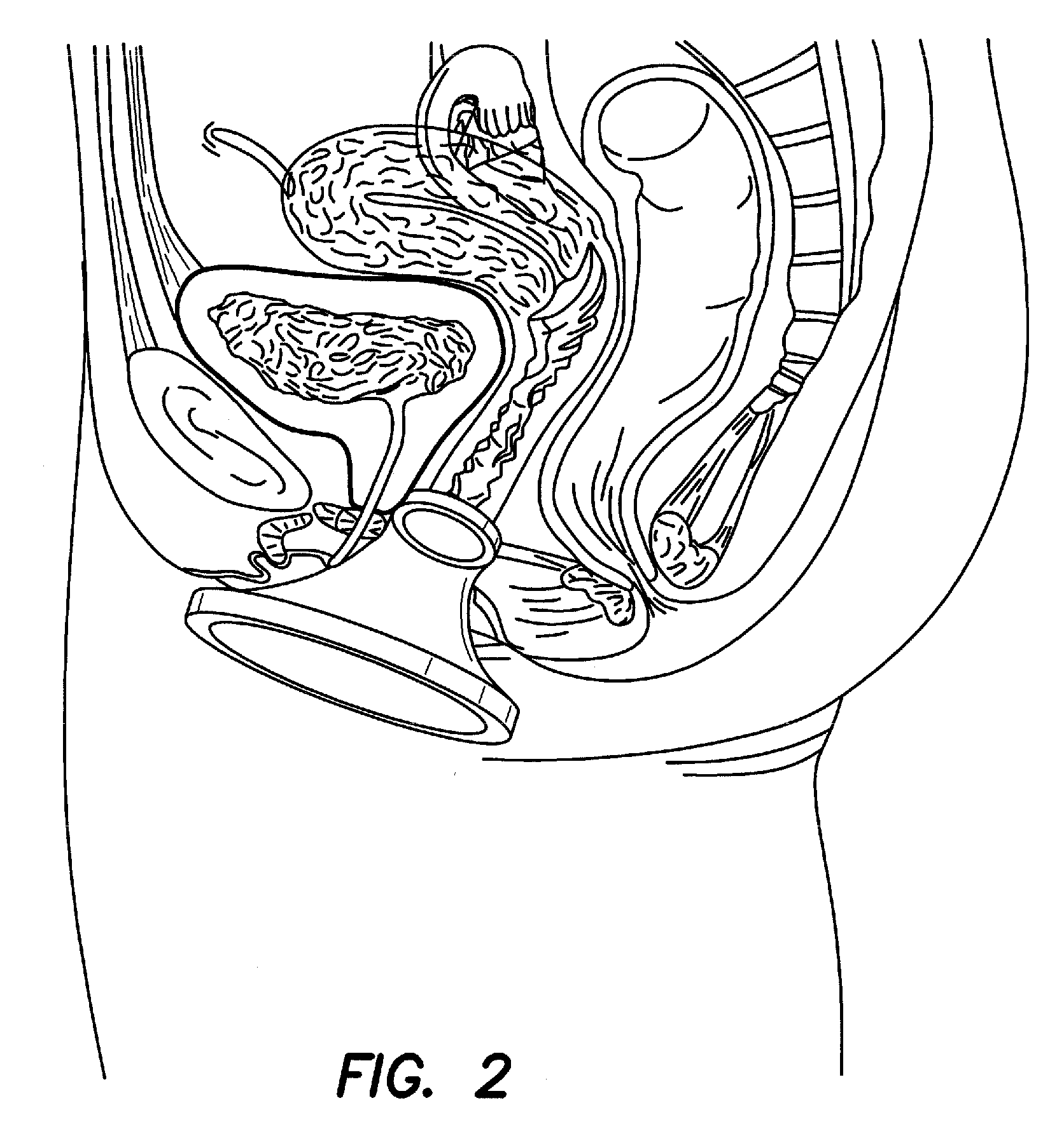
Surgical instrument access device
ActiveUS20090187079A1Easy to foldFacilitates folding the distal ringCannulasSurgical needlesAngular degreesEngineering
Embodiments of an access device system useful for single or limited port procedures comprises a retractor and a gel cap removably coupled to the retractor. The gel cap comprises a gel pad that acts as an artificial body wall, through which instruments may be inserted into a body cavity, either directly or through one or more trocars. The gel pad permits flexible instrument placement, as well as translational and angular degrees of freedom for the instruments while maintaining a gas tight seal.
Owner:APPL MEDICAL RESOURCES CORP
Cone beam CT scanning
A CBCT system is described that includes a radiation source for emitting a cone beam of radiation in a beam direction towards an object, a detector for detecting the cone beam of radiation, and a positioner for moving the radiation source and the object according to a scanning trajectory. The system is operated according to a sampling pattern that includes intersections of the scanning trajectory and a reconstruction trajectory, wherein motion of the radiation source is substantially confined to a spherical shell. The positioner moves the radiation source at a speed higher than a highest speed of the object by a factor of at least 10. The largest angular discrepancy between any vector in a range of the scanning trajectory and the nearest sample of the scanning trajectory does not exceed 10°, preferably 6° and more preferably 3°.
Owner:EIN GAL MOSHE
Method and device for head tracking
InactiveUS20050256675A1Accurate judgmentEasy accessInput/output for user-computer interactionTelevision system detailsClassical mechanicsDisplay device
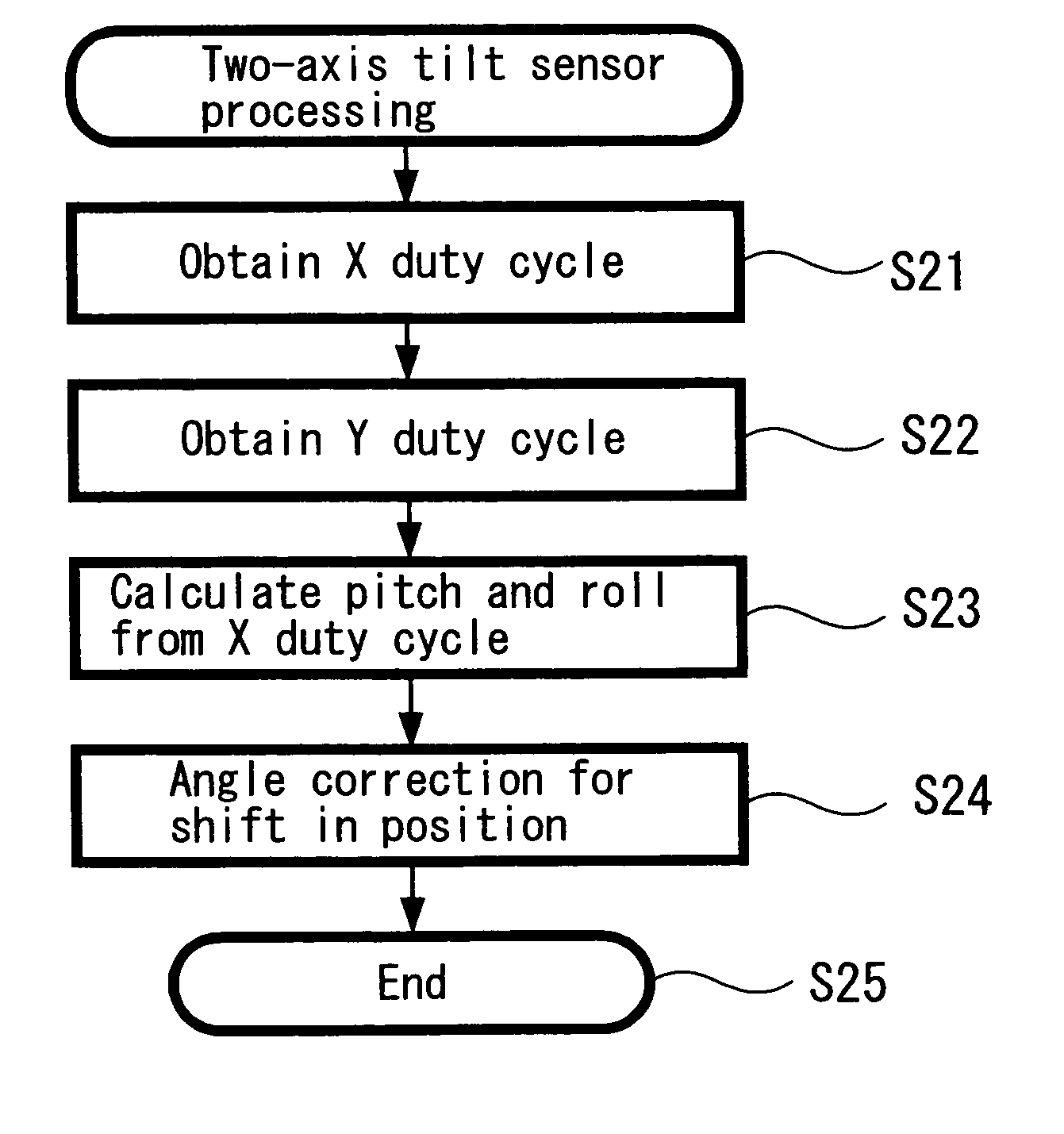
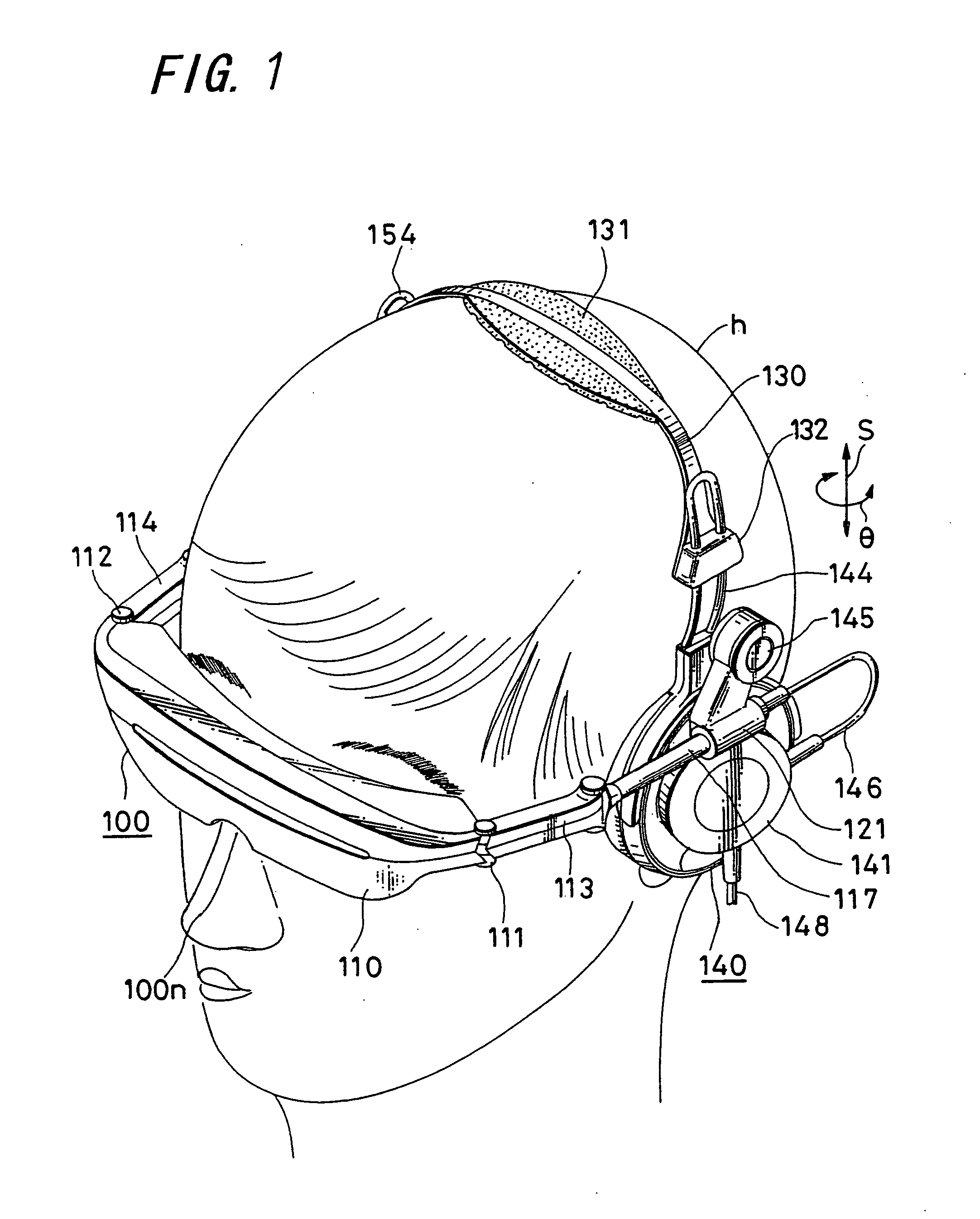
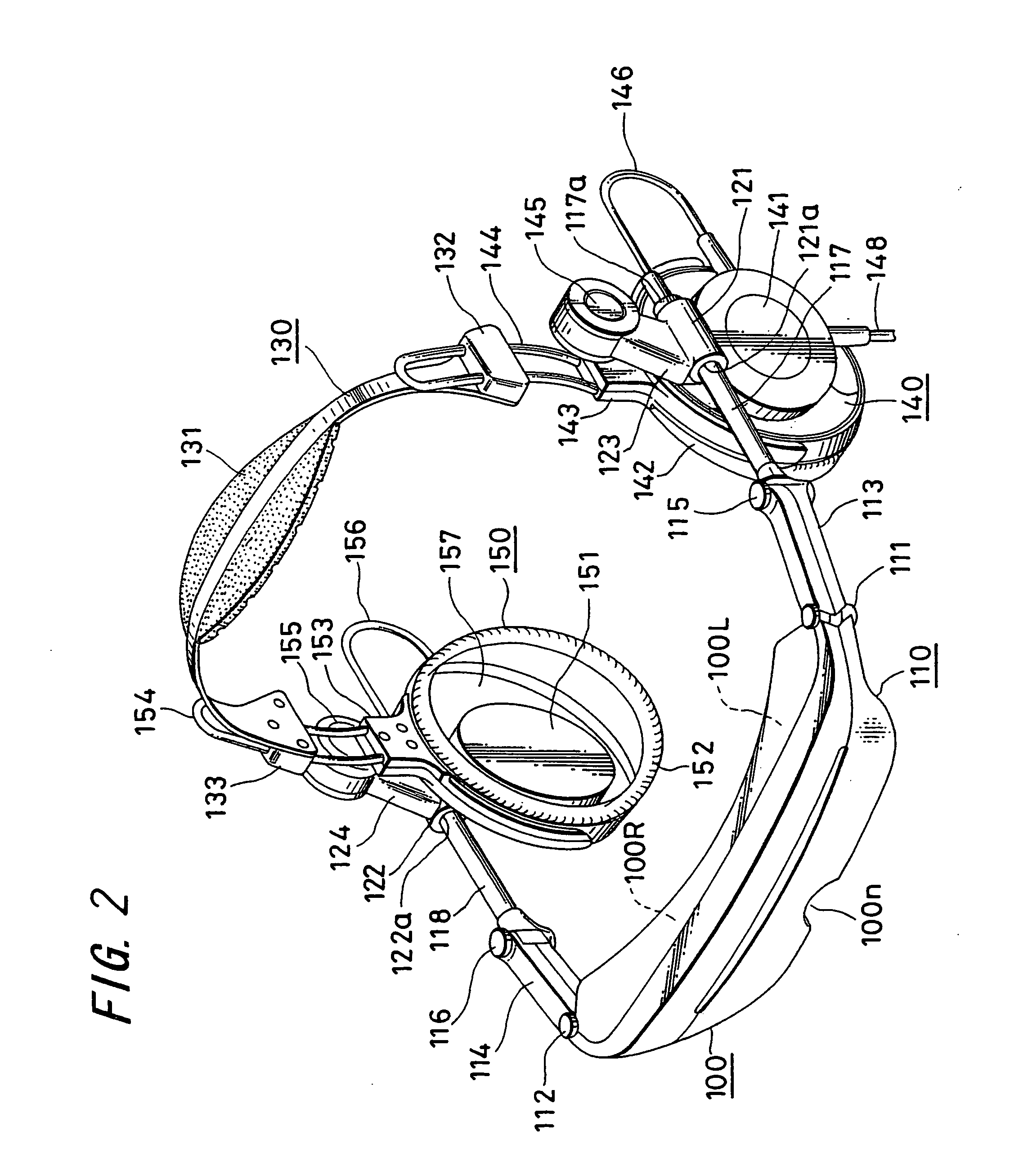
When the three-dimensional direction the head faces is detected by three axes, that is, a yaw angle that is an angle turning around an erect axis erected on the horizontal surface of the head, and a pitch angle and a roll angle that are angles formed by the above erect axis and two axes perpendicular thereto, a gyro sensor 11 which detects the yaw angle from the integral value of the acceleration, a tilt sensor 12 which detects the inclination of a plane that intersects the direction of the erect axis at right angles, and calculation element 14 which calculates the pitch angle and the roll angle from the output of a tilt sensor are provided, so that the direction that the head faces can be detected with a simple detecting structure including the two sensors, in a head mounted display or the like.
Owner:SONY CORP
Optical tracking apparatus using six degrees of freedom
InactiveUS8077914B1Improve robustnessAccurate trackingAcquiring/recognising eyesEye diagnosticsAngular degreesLight-emitting diode
This invention discloses an optical object tracking method and system with to up to six degrees of freedom: three translational and three angular coordinates. In the preferred embodiment, the system includes two near-infra-red light sources (e.g., light emitting diode), two cameras, and a digital signal processor. The system performs to tasks: object locking and tracking. For object locking and tracking, a single camera and two off-axis light sources are engaged. For more precise object tracking, two spatially-separate cameras and a single diode are used. In another embodiment, a third camera may be used to separate the locking and tracking tasks. The light sources may have different light wavelengths and may operate in a sequential mode. The cameras may be sensitive over different spectral ranges and may also differ in terms of field-of-view and resolution. The invention describes a method based on capturing images of light reflections at the camera focal plane and analyzing them, through mathematical mapping, for known locations of light sources and cameras. Invention can be adopted for the tracking of an eyeball. The related method determines an object location and orientation or a gaze vector and a point-of-regard.
Owner:KAPLAN ARKADY
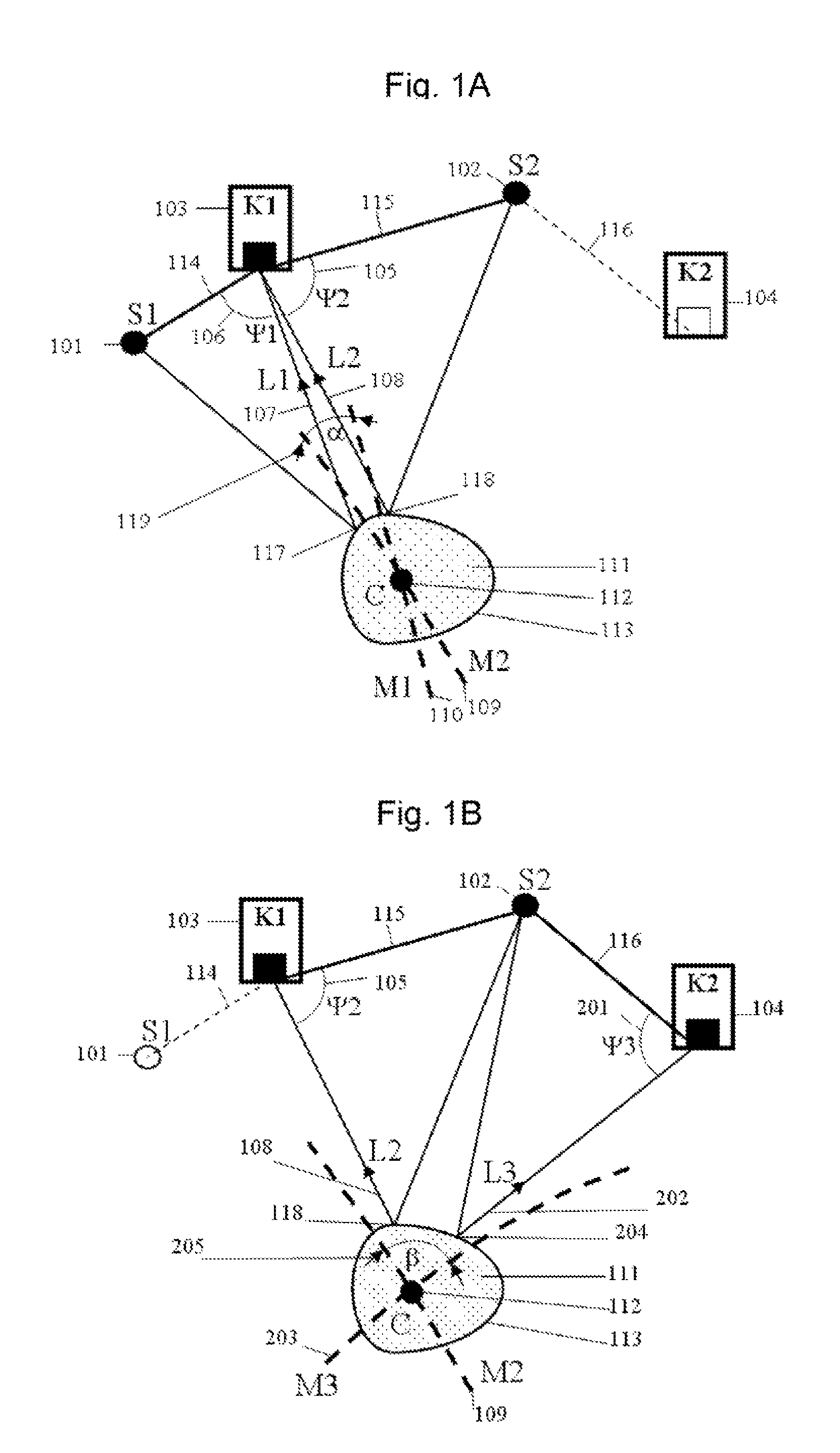
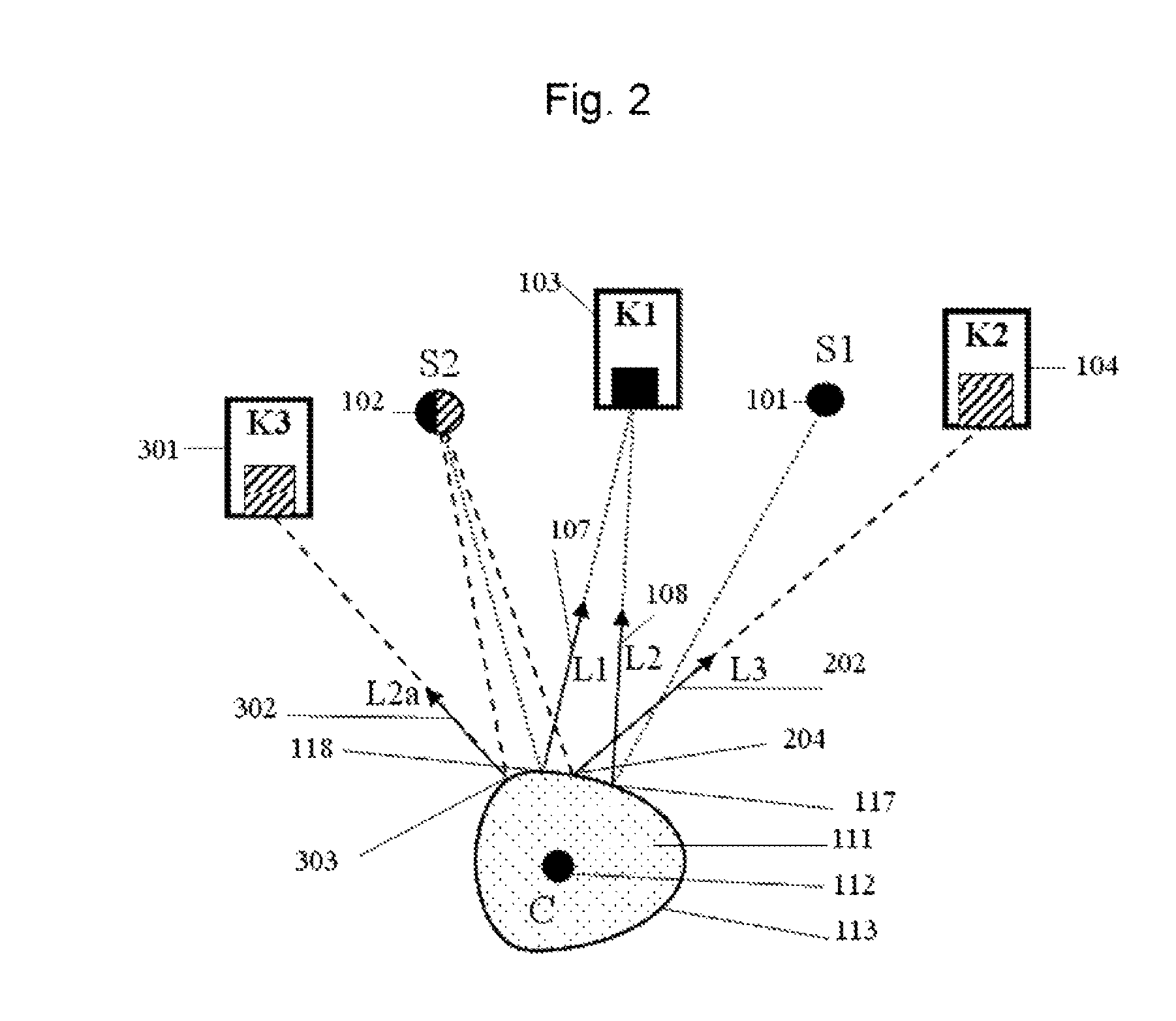
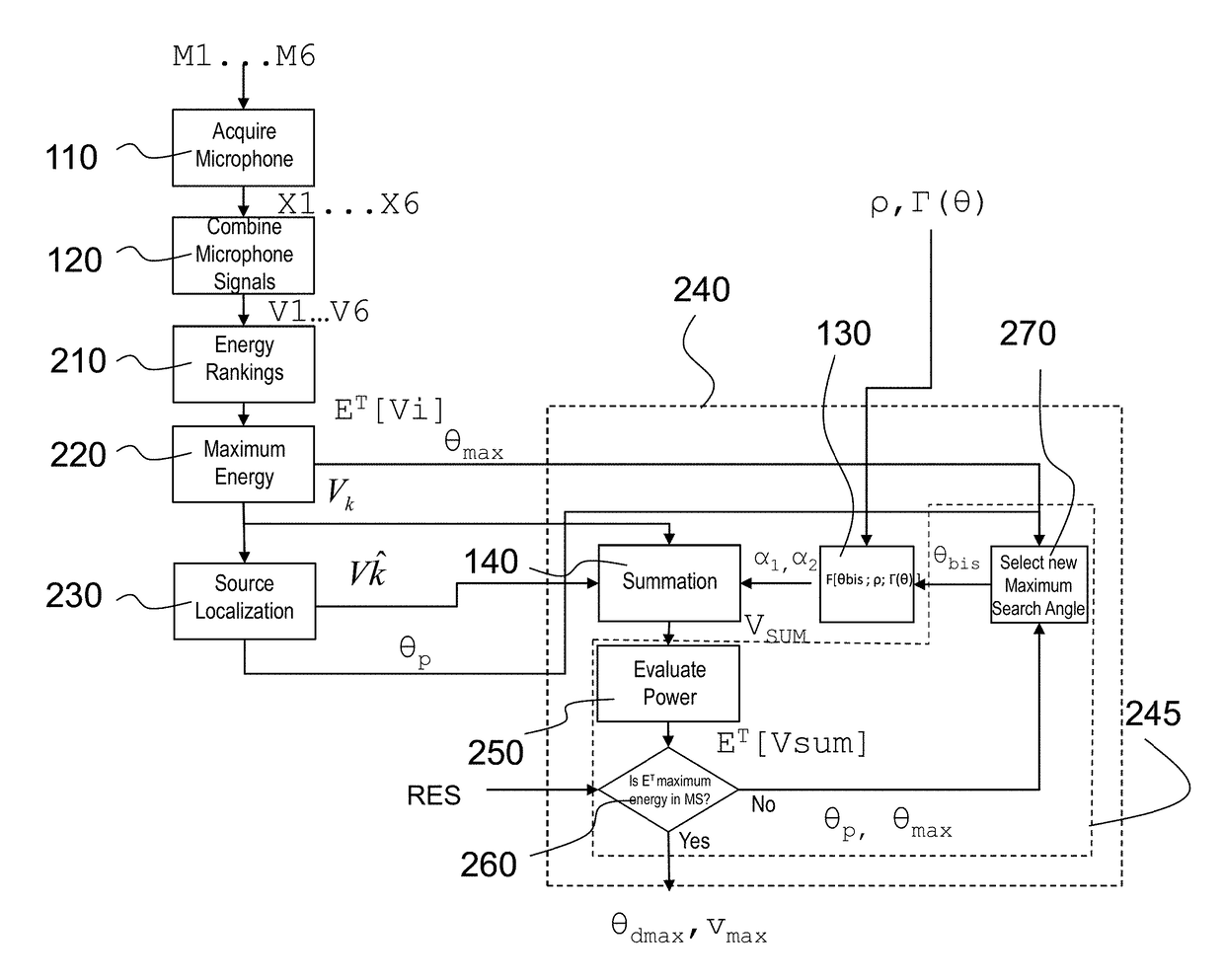
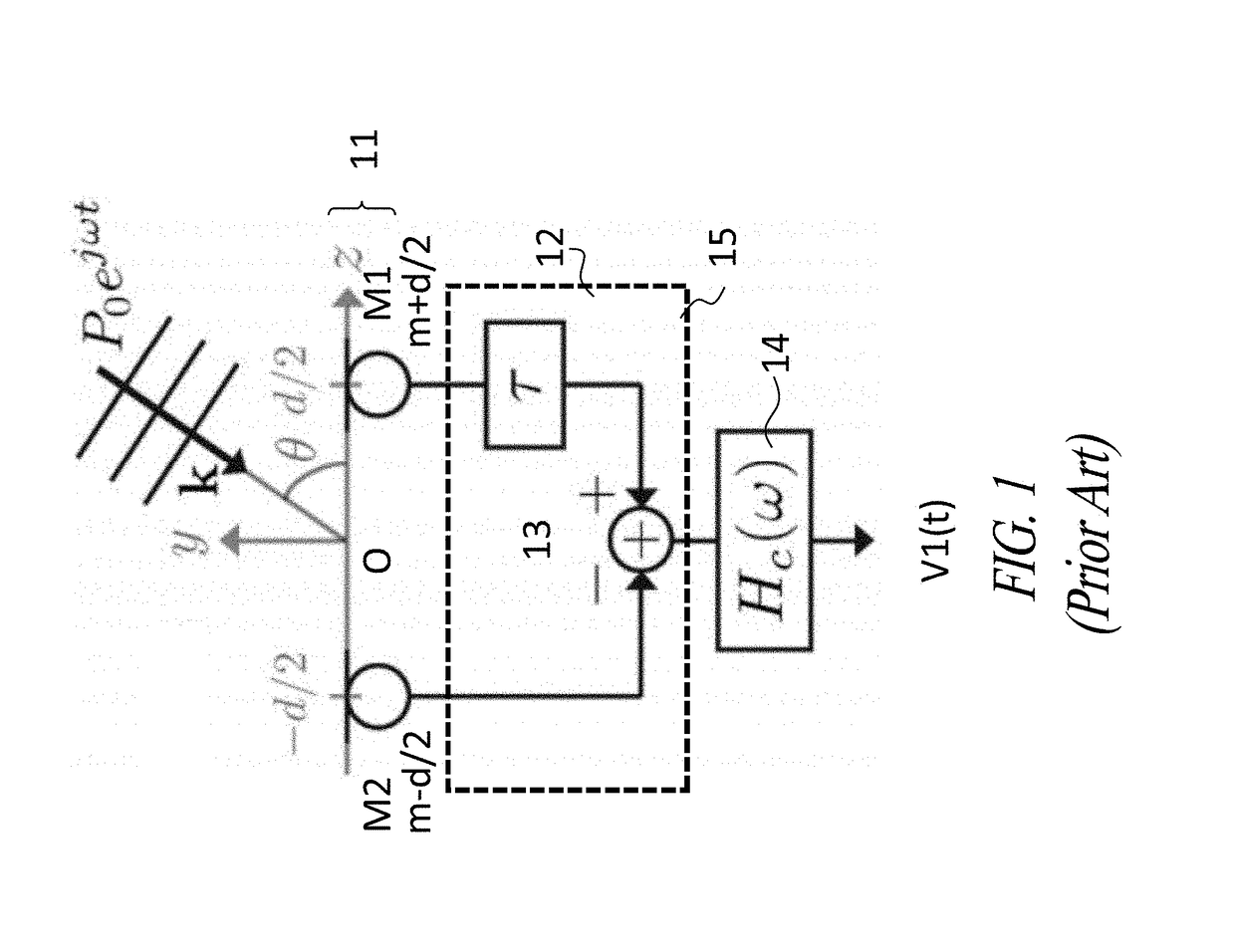
Beamforming method based on arrays of microphones and corresponding apparatus
A beamforming method employs a plurality of microphones arranged in an array with respect to a reference point. The method includes acquiring microphone signals from the microphones and combining the microphone signals (x1 . . . xM) to obtain Virtual Microphones, combining the microphone signals to obtain a pair of directional Virtual Microphones having respective signals determining respective patterns of radiation with a same origin corresponding to the reference point and rotated at different pattern direction angles, defining a separation angle between them, obtaining a sum radiation signal of a sum Virtual Microphone with a sum radiation pattern, associating a respective weight to the signals of the pair of directional Virtual Microphones, obtaining respective weighted signals of radiation and summing the weighted signals, computing respective weights as a function of a determined pattern direction angle of the pattern of radiation of the pair of directional Virtual Microphones and of the separation angle.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
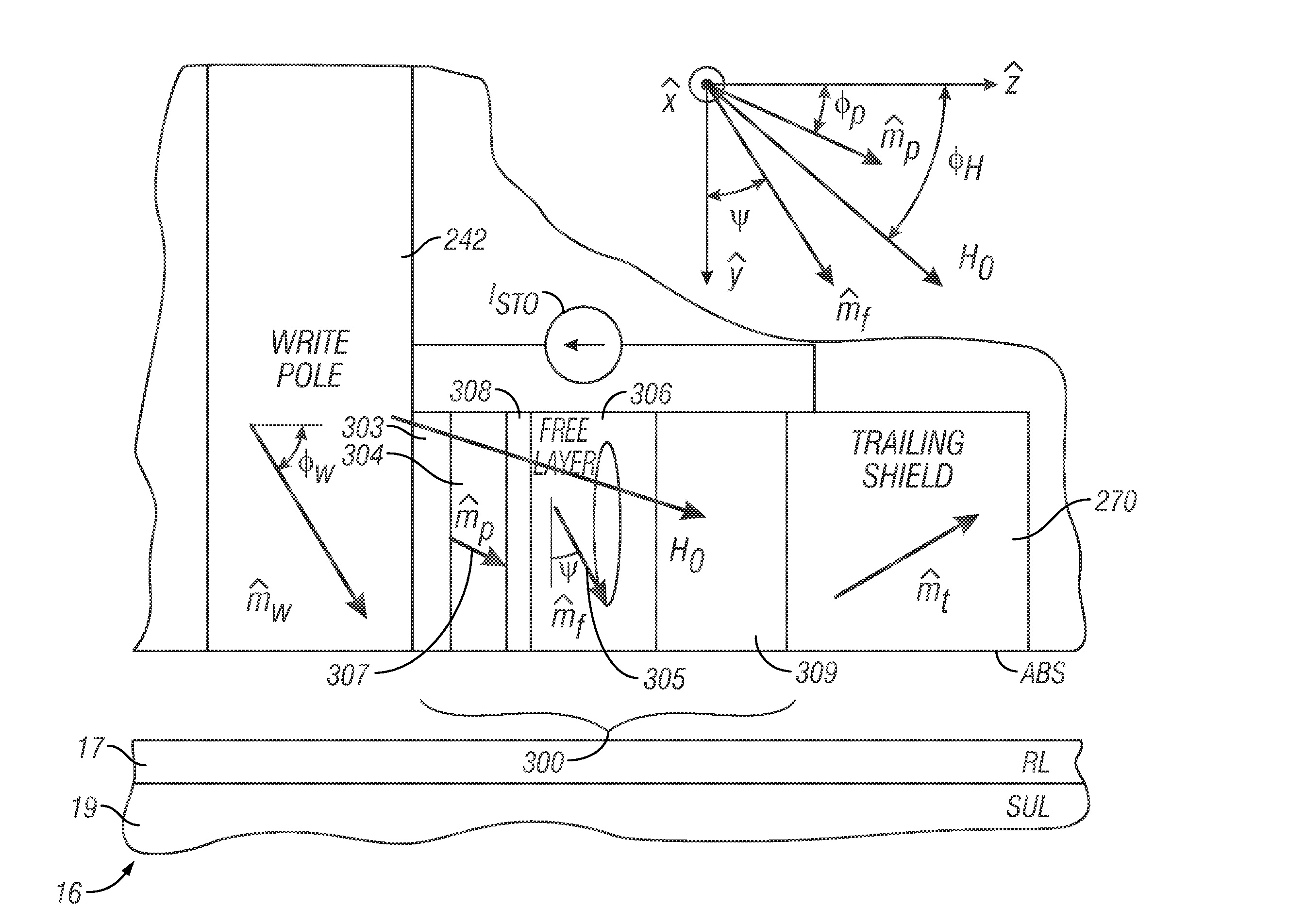
Perpendicular magnetic recording write head and system with improved spin torque oscillator for microwave-assisted magnetic recording
ActiveUS7982996B2Record information storageManufacture of flux-sensitive headsPower flowSpin torque oscillators
A microwave-assisted magnetic recording (MAMR) write head and system has a spin-torque oscillator (STO) located between the write pole of the write head and a trailing shield that alters the write field from the write pole. The STO is a stack of layers whose planes lie generally parallel to the X-Y plane of an X-Y-Z coordinate system, the stack including a ferromagnetic polarizer layer, a free ferromagnetic layer, and a nonmagnetic electrically conductive spacer between the polarizer layer and the free layer. In the presence of the write field from the write pole the polarizer layer has its magnetization oriented at an angle between 20 and 80 degrees, preferably between 30 and 70 degrees, with the Z-axis. In the presence of a direct electrical current through the STO stack, the free layer magnetization rotates or precesses about the Z-axis with a non-zero angle to the Z-axis.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Single port access system
ActiveUS20100094227A1Easy to foldFacilitates folding the distal ringCannulasInfusion syringesAngular degreesSurgical department
Embodiments of a surgical access system useful for single or limited port procedures comprise a trocar comprising a fixation cannula, a retractor, and a gel cap removably coupled to the retractor. The gel cap comprises a gel pad that acts as an artificial body wall, through which instruments may be inserted into a body cavity, either directly or through one or more trocars. The fixation cannula comprises a retainer and a bolster, which together, capture the artificial body wall therebetween, thereby fixing the trocar thereto. The gel pad permits flexible instrument placement, as well as translational and angular degrees of freedom for the instruments while maintaining a gas tight seal.
Owner:APPL MEDICAL RESOURCES CORP
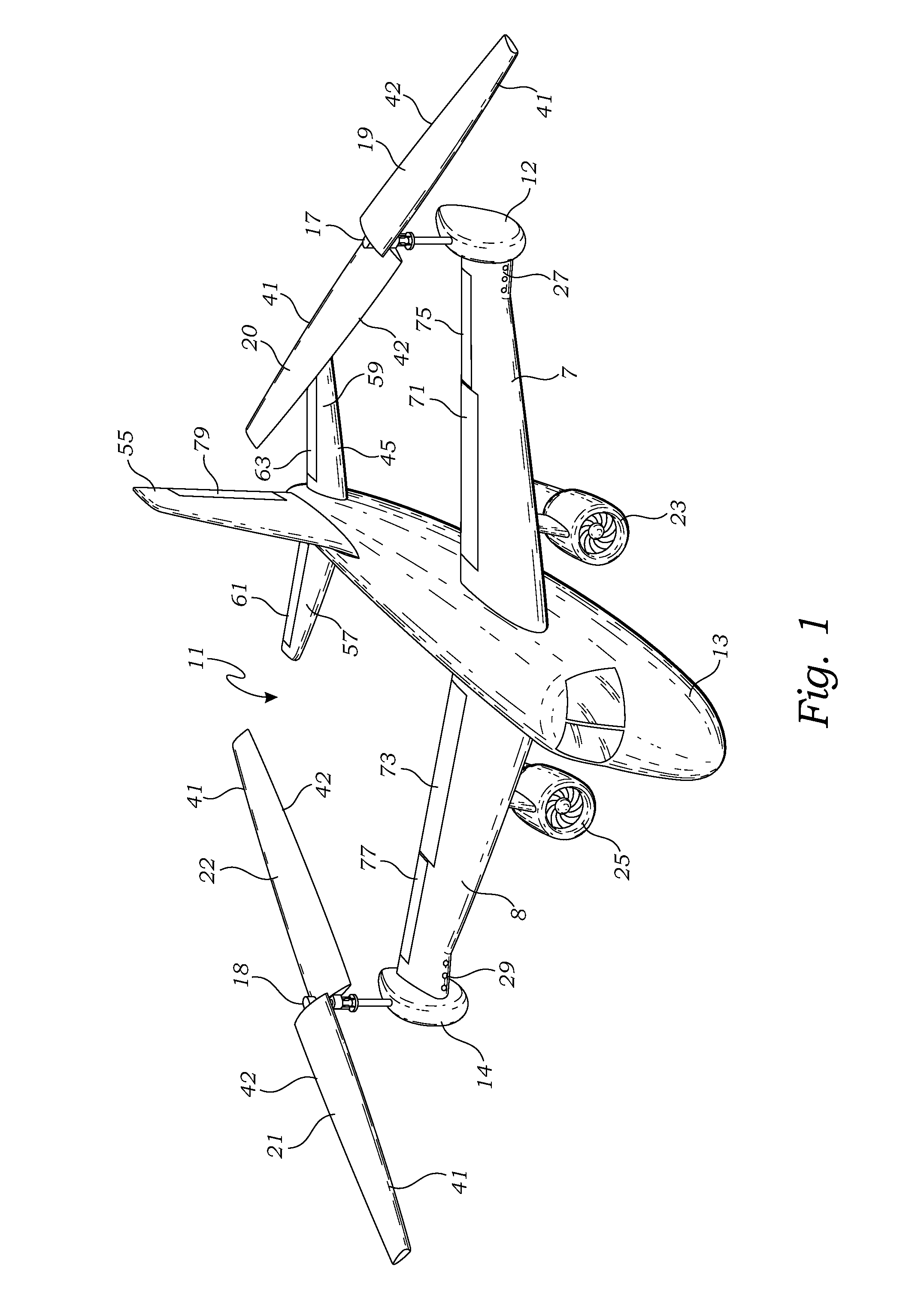
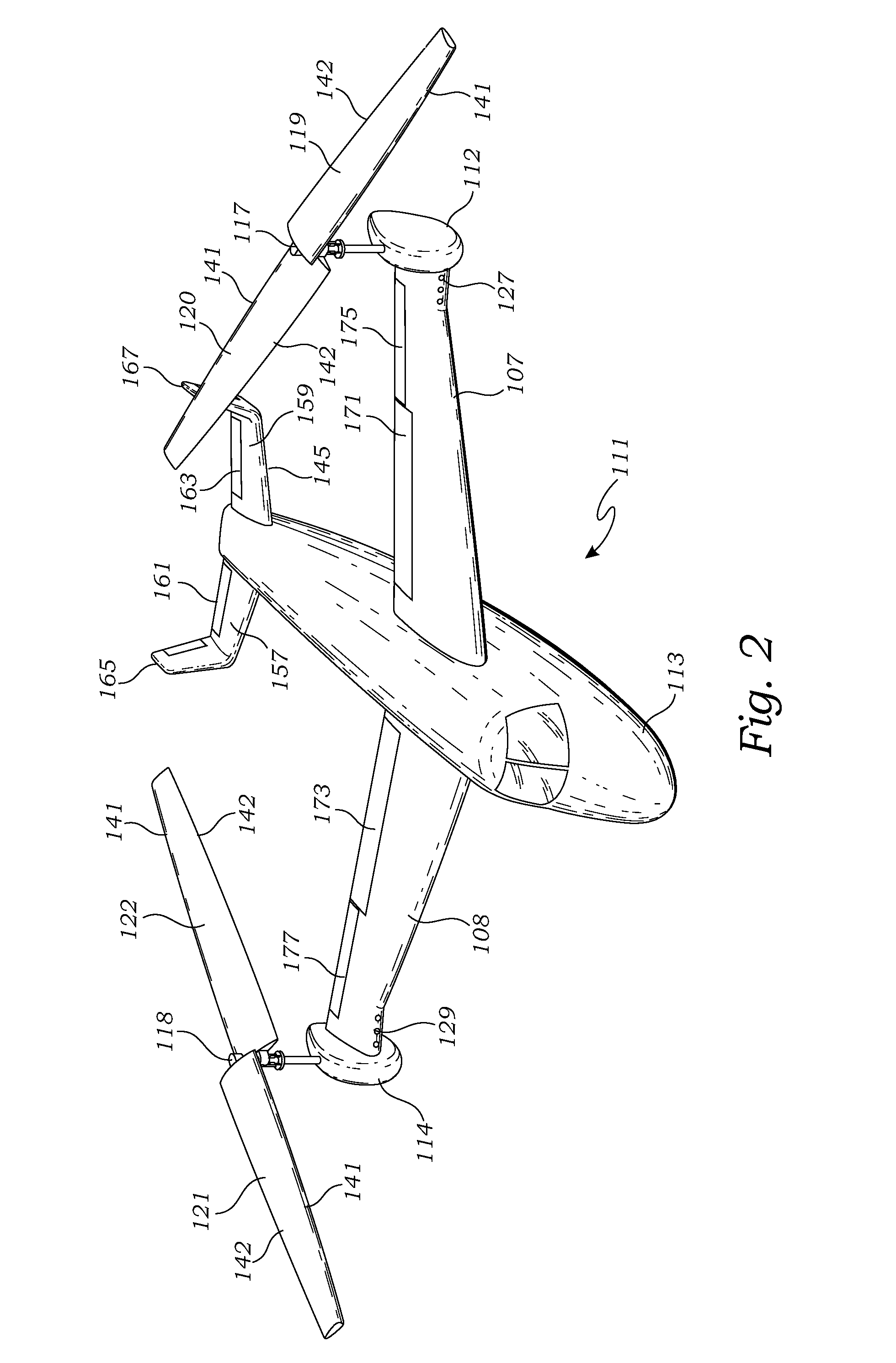
Rotor for a dual mode aircraft
A rotor for use on an aircraft has a plurality (N) of rotor blades mounted on a plurality (N) of concentric masts. Each of the rotor blades has a rounded leading edge and a tapered trailing edge. The plurality (N) of concentric masts each operably mount one of the plurality of rotor blades at N different elevations. A locking element selectively locks or unlocks the concentric masts together in a plane of rotation, enabling the angle between any two rotor blades to be variable from 0-360 degrees during flight. A feathering hinge is operably attached to each blade for changing the pitch of each blade with respect to the plane of rotation as controlled by a pitch control mechanism.
Owner:HONG JIANHUI +1
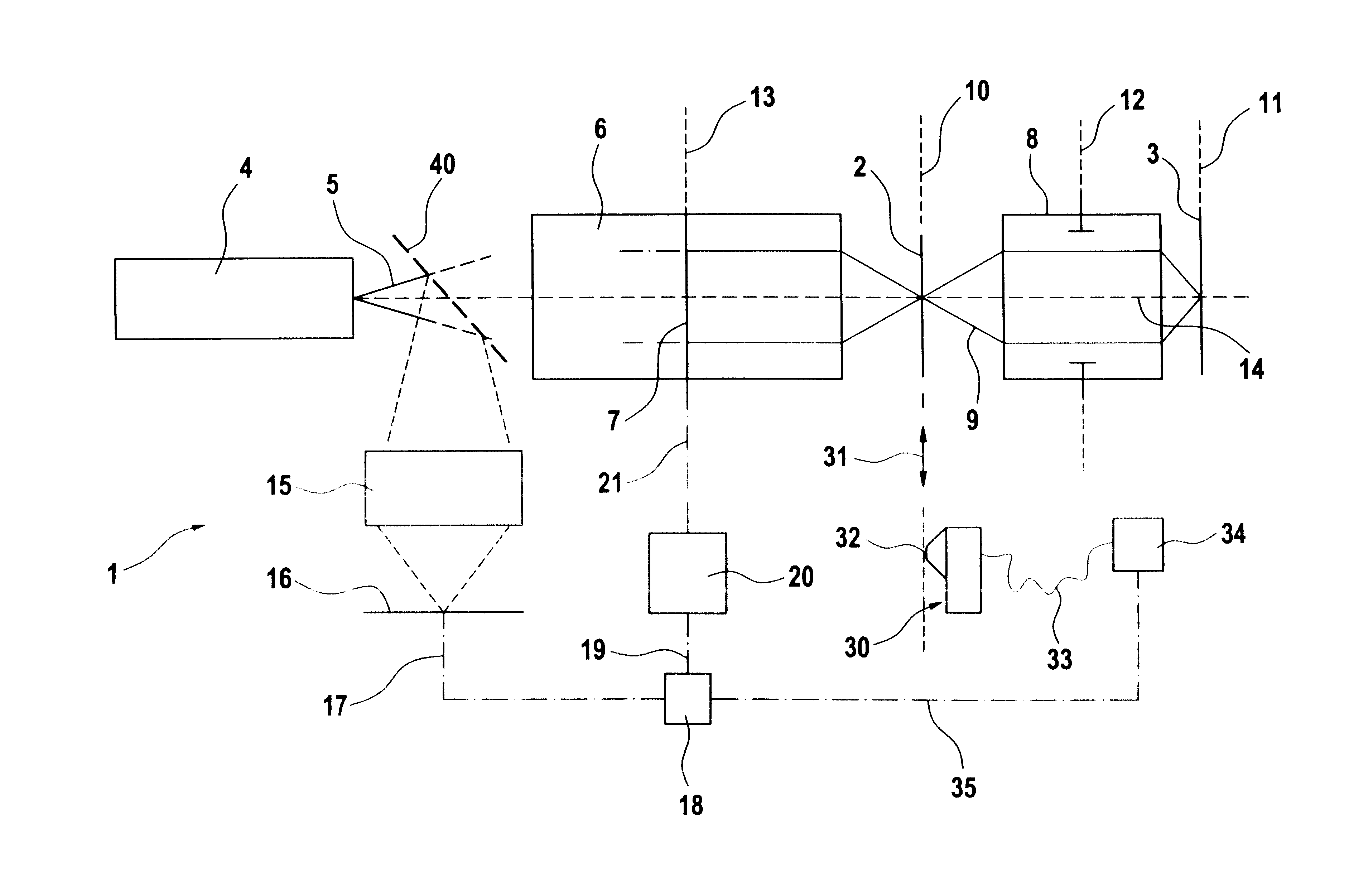
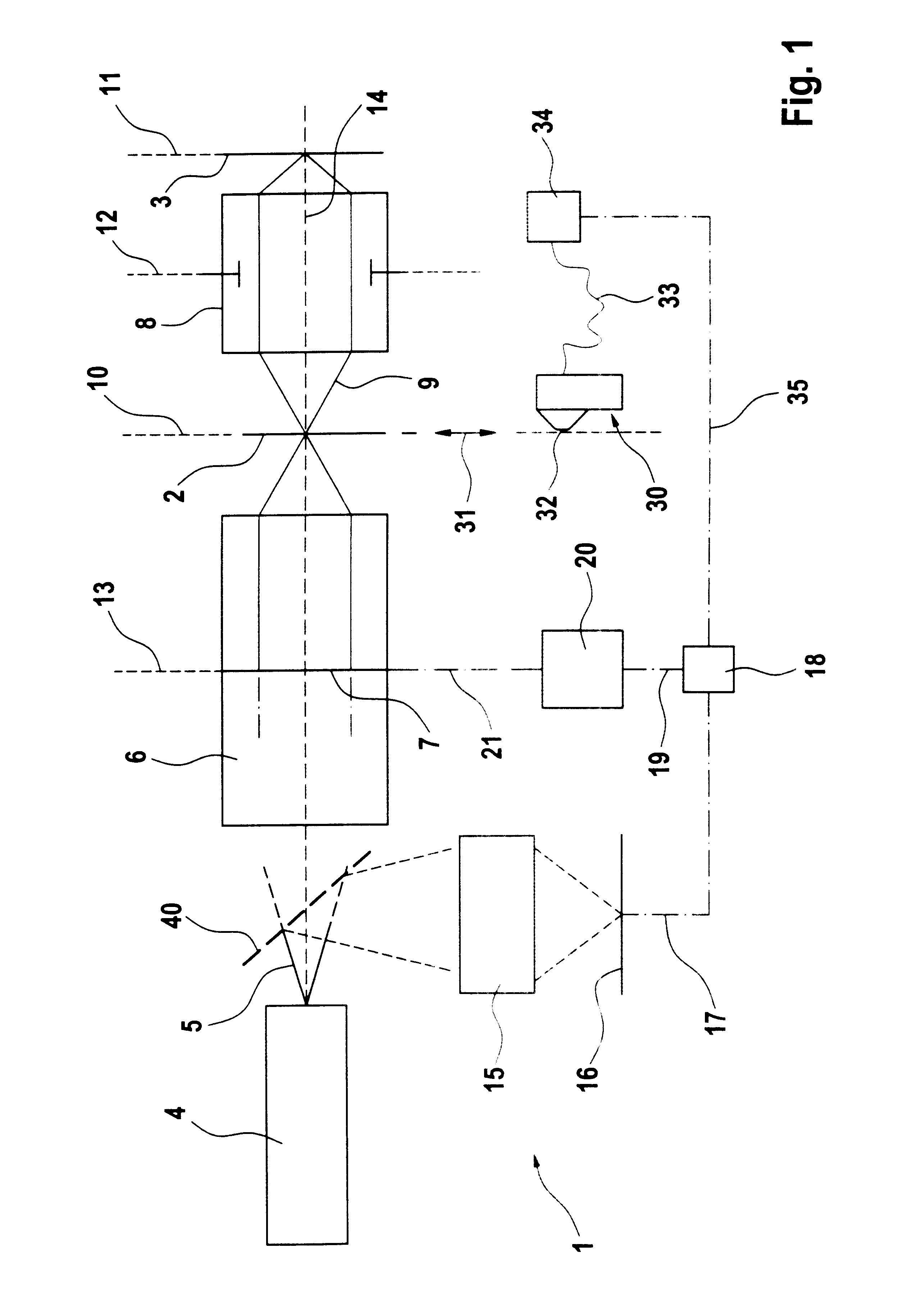
Projection exposure device
InactiveUS6535274B2Facilitates defined and definedEasy to set upElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingProjection opticsLithographic artist
A projection exposure device, in particular for micro-lithography, serves to produce an image of an object in an image plane positioned in an object plane. This happens with the aid of a light source emitting projection light and illumination optics positioned in the ray path between the light source and the object plane. In addition projection optics positioned in the ray path between the object plane and the image plane serve to guide the projection light. A filter (7) is positioned in a filter plane which lies in the vicinity of a pupil plane between the light source and the object plane. This has a moveable filter element (22') which has at least in certain areas (24) for the projection light a transmission factor which is greater than zero and less than 100%. The moveable filter element (22') is moveable in the filter plane and has a distribution of the transmission factor over the filter face, in such a way that the intensity distribution of the projection light perpendicular to the optical axis (14) in the ray path after the filter (7) changes with the movement of the filter element (22'). With such a filter (7) an illumination angle distribution can be adapted to a pre-set value (FIG. 5).
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH +1
Flying Vehicle Guiding System And Flying Vehicle Guiding Method
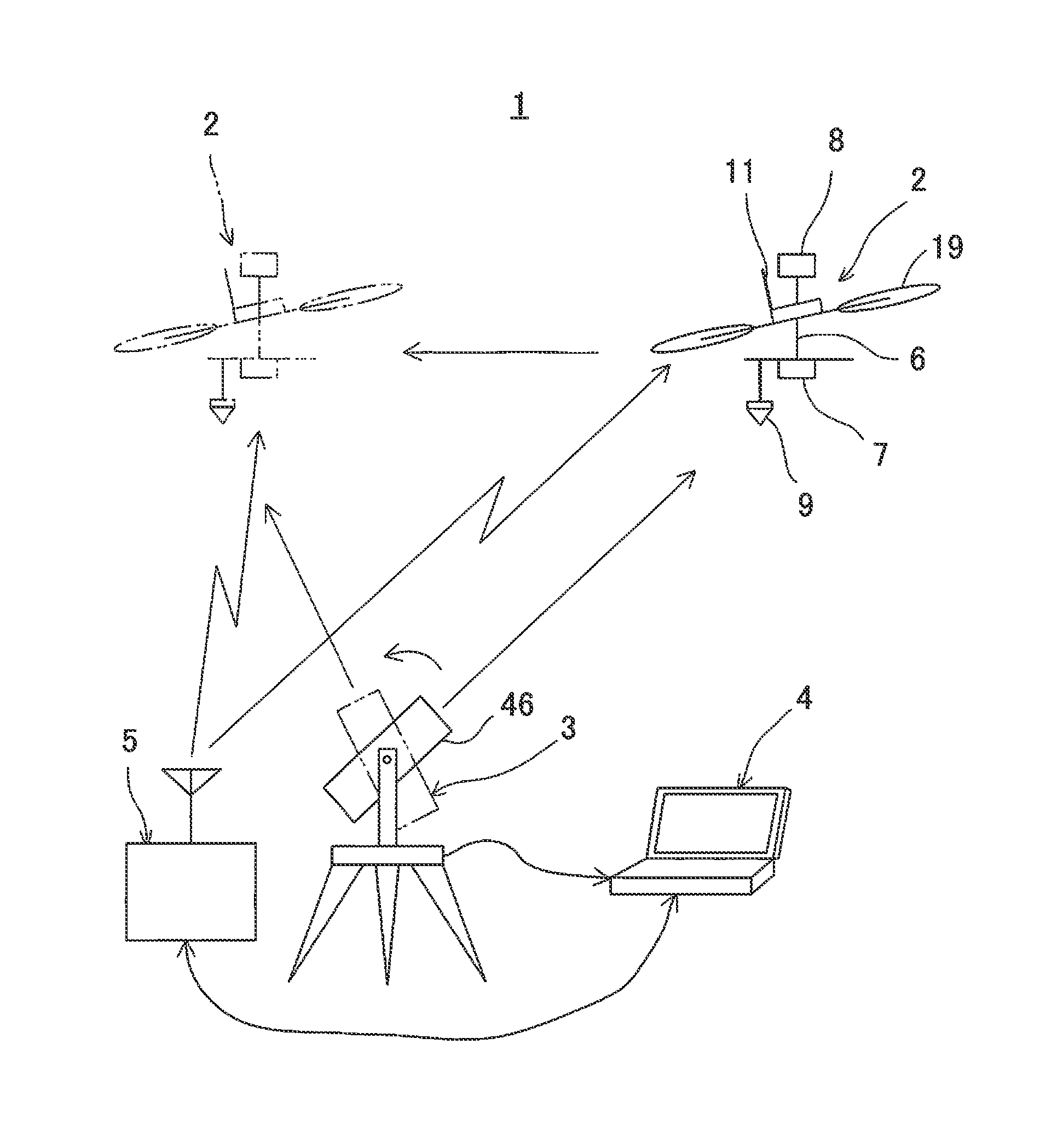
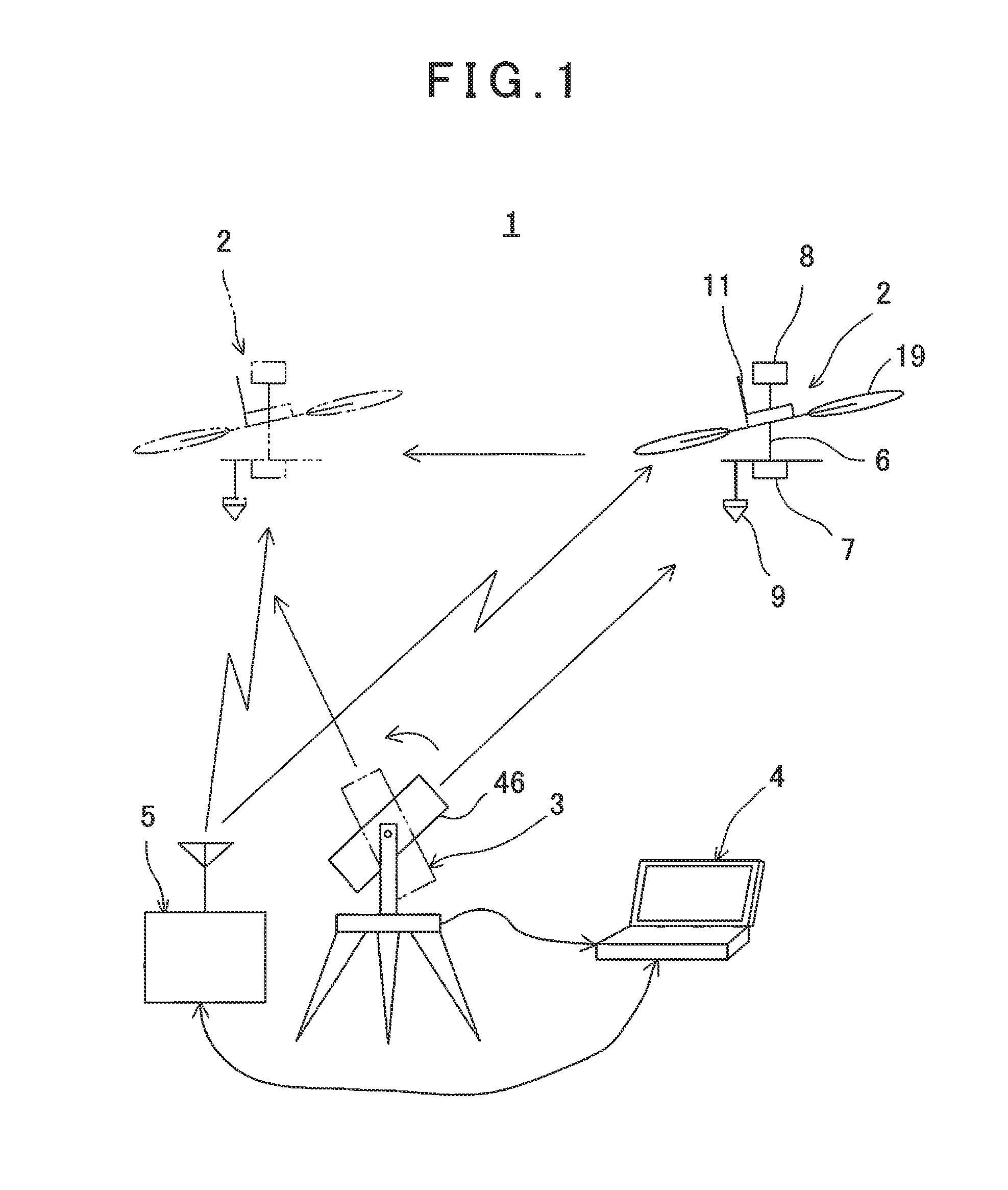
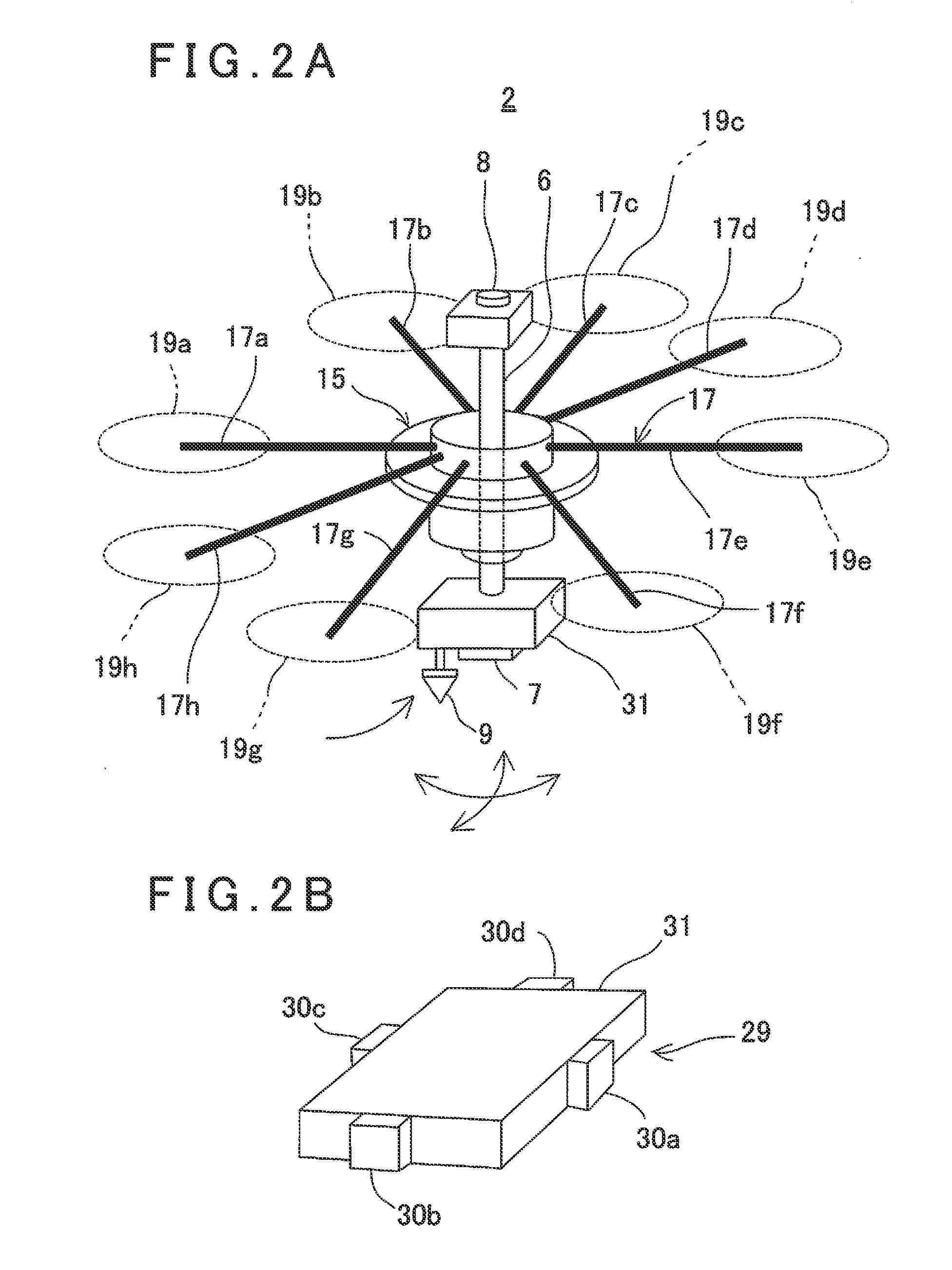
ActiveUS20140371952A1Improve image processing capabilitiesOperational securityDigital data processing detailsPhotogrammetry/videogrammetrySurvey instrumentFlight vehicle
A flying vehicle guiding system, which comprises a remotely controllable flying vehicle system, a surveying instrument being able to measure distance, angle, and track, and a ground base station for controlling a flight of the flying vehicle system based on measuring results by the surveying instrument, wherein the flying vehicle system has a retro-reflector as an object to be measured, wherein the surveying instrument has a non-prism surveying function for performing distance measurement and angle measurement without a retro-reflector, a prism surveying function for performing distance measurement and angle measurement with respect to the retro-reflector, and a tracking function for tracking the retro-reflector and for performing distance measurement and angle measurement, wherein the surveying instrument performs non-prism measurement on a scheduled flight area, the ground base station sets a safe flight area based on the results of the non-prism measurement, and controls so that the flying vehicle system flies in the safe flight area based on the results of tracking measurement by de surveying instrument.
Owner:KK TOPCON
Handheld camera stabilizer with integration of smart device
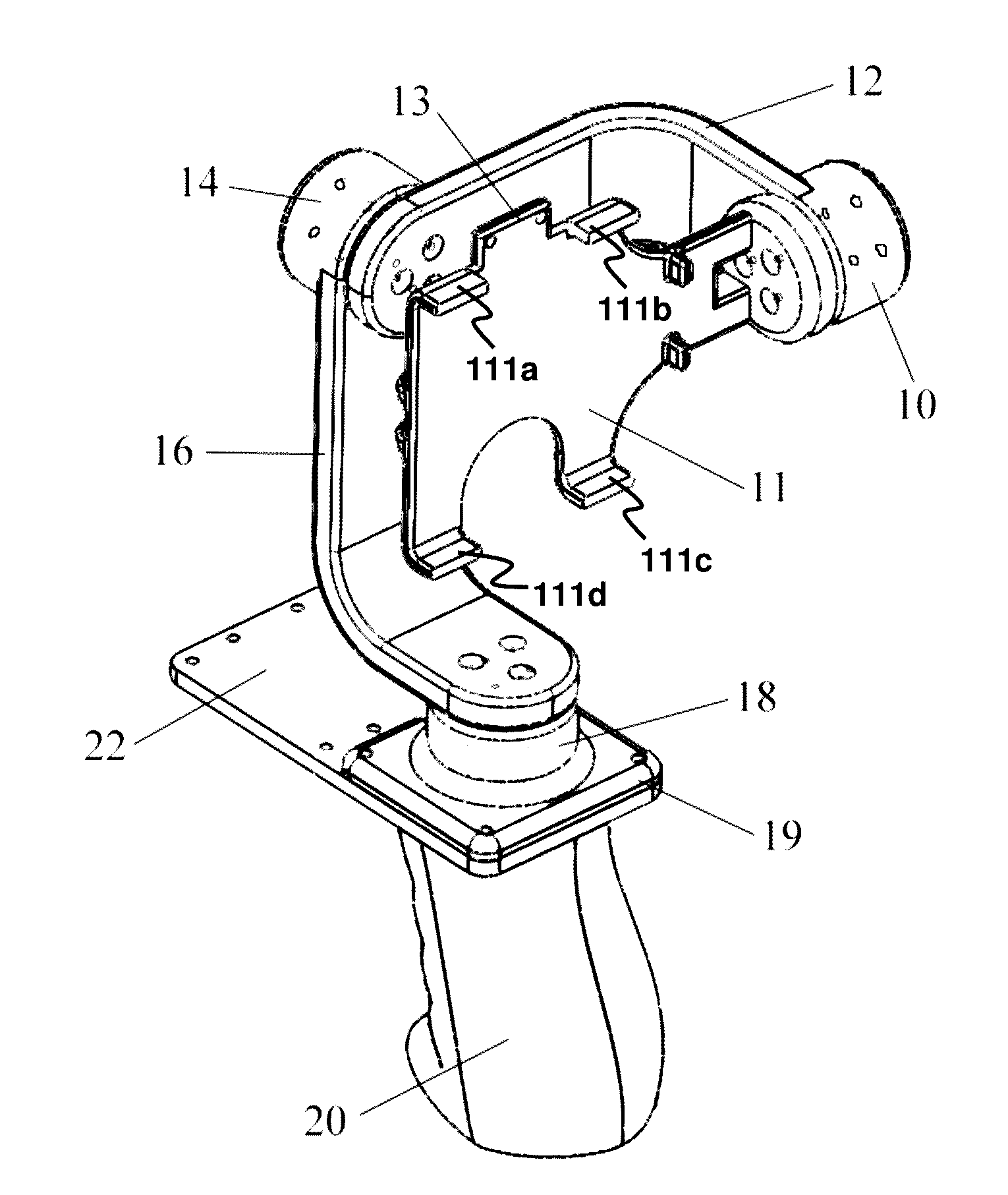
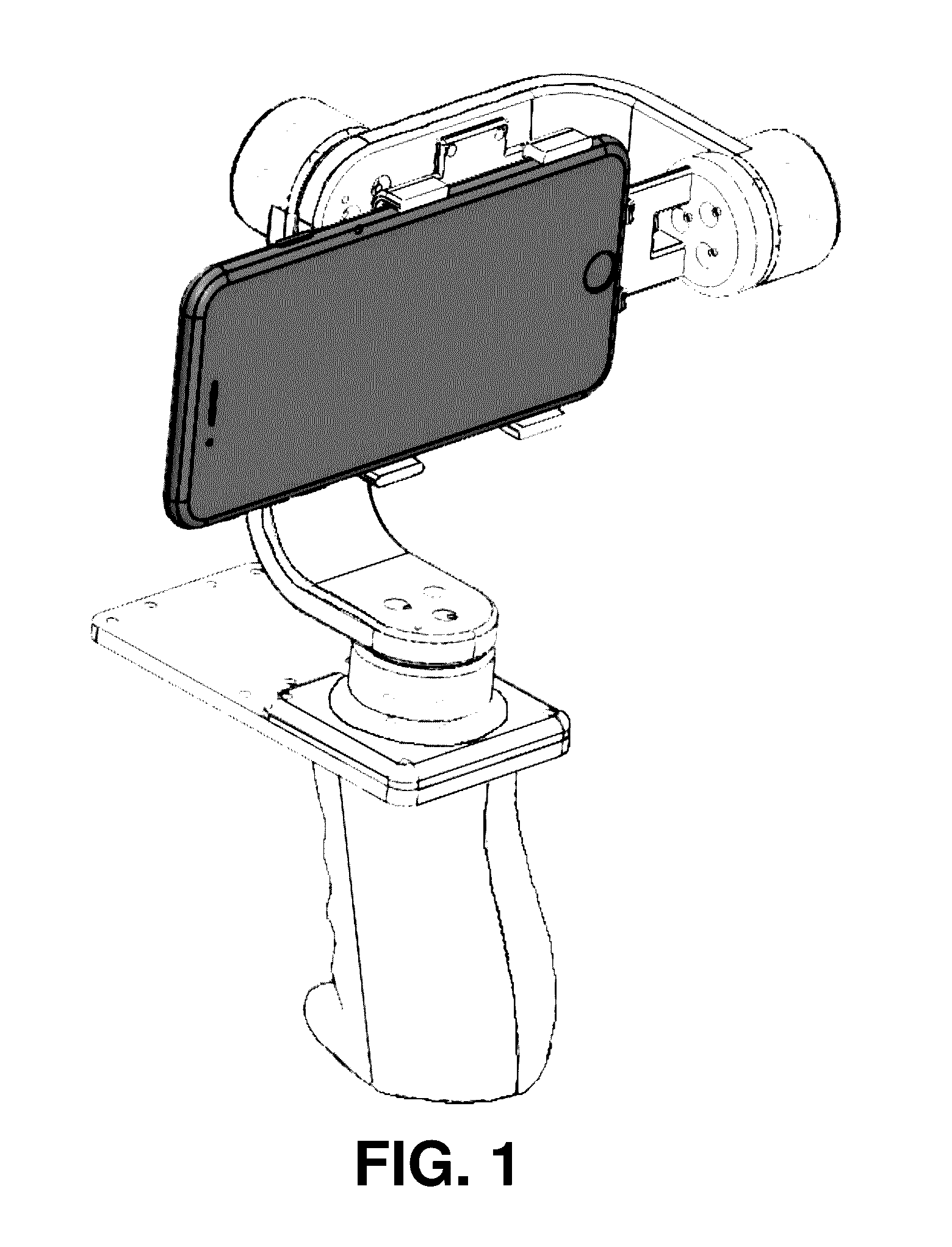
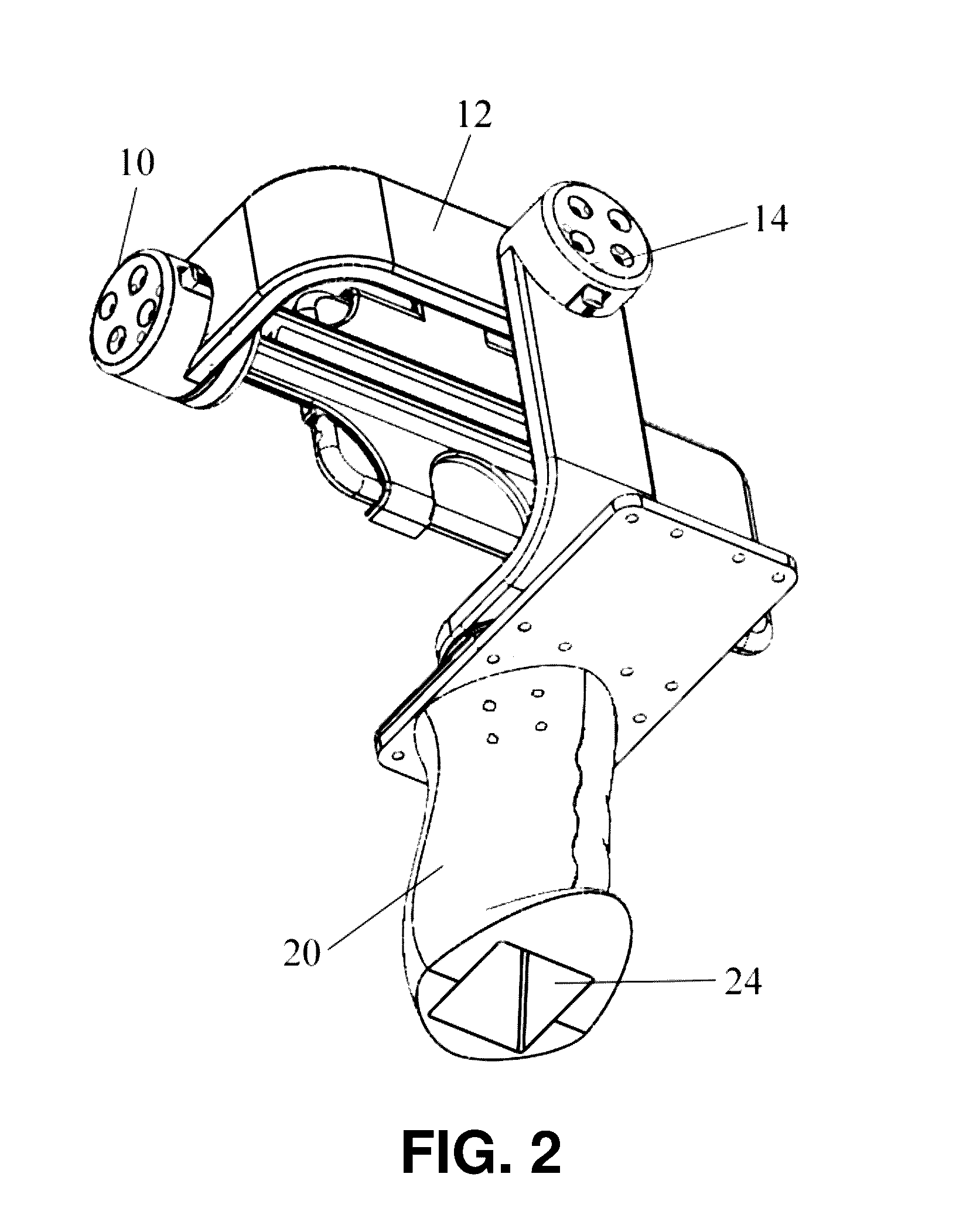
InactiveUS20160381271A1Television system detailsColor television detailsAngular velocityAngular degrees
A handheld stabilizer for automatically stabilizing a camera device, such as a smartphone, when the camera device is mounted on the stabilizer is provided. The stabilizer comprises a camera device mount for holding the camera device, a plurality of motors collectively arranged to cause the camera device mount to be rotatable about three predetermined substantially-orthogonal axes, an inertial-measurement unit (IMU) sensor for measuring an angle and an angular velocity experienced by the camera device about each of the three axes, and a controller. By means of the IMU sensor, an attitude of the camera device is measured. The controller is configured to estimate an attitude error of the camera device according to the measured attitude, and to automatically control the plurality of motors in response to the attitude error so as to controllably rotate the camera device about each of the three axes to counter the attitude error.
Owner:DELTRON INTELLIGENCE TECH LTD
Surgical instrument access device
ActiveUS8343047B2Easy to foldFacilitates folding the distal ringCannulasSurgical needlesAngular degreesEngineering
Embodiments of an access device system useful for single or limited port procedures includes a retractor and a gel cap removably coupled to the retractor. The gel cap includes a gel pad that acts as an artificial body wall, through which instruments may be inserted into a body cavity, either directly or through one or more trocars. The gel pad permits flexible instrument placement, as well as translational and angular degrees of freedom for the instruments while maintaining a gas tight seal.
Owner:APPL MEDICAL RESOURCES CORP
Wearable pulse oximetry device
ActiveUS20140200423A1Diagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Pulse oximetry
A pulse oximetry device that is mounted on a wrist strap and fixates an area above a distal end of the ulna with a dome shaped structure. This area is used as measuring area. The measurement is carried out by a detector positioned above the fixated area, that detects light emitted by light sources having different wave lengths that are located at a periphery of the fixated area. Hence, the reflections are measured at neither a reflection mode nor a transmission mode, but are at an angle between 20° and 160° from the emitted light. This mode, termed trans-illumination, allows achieving an excellent signal to noise ratio that for the first time enables continuous and reliable measurement of oximetry data on the wrist.
Owner:OXITONE MEDICAL
Vibration actuator having magnetic circuit elastically supported by a spiral damper with increased compliance
InactiveUS6377145B1Improve seismic performanceStable characteristicsTransducer detailsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesAngular degreesCoil spring
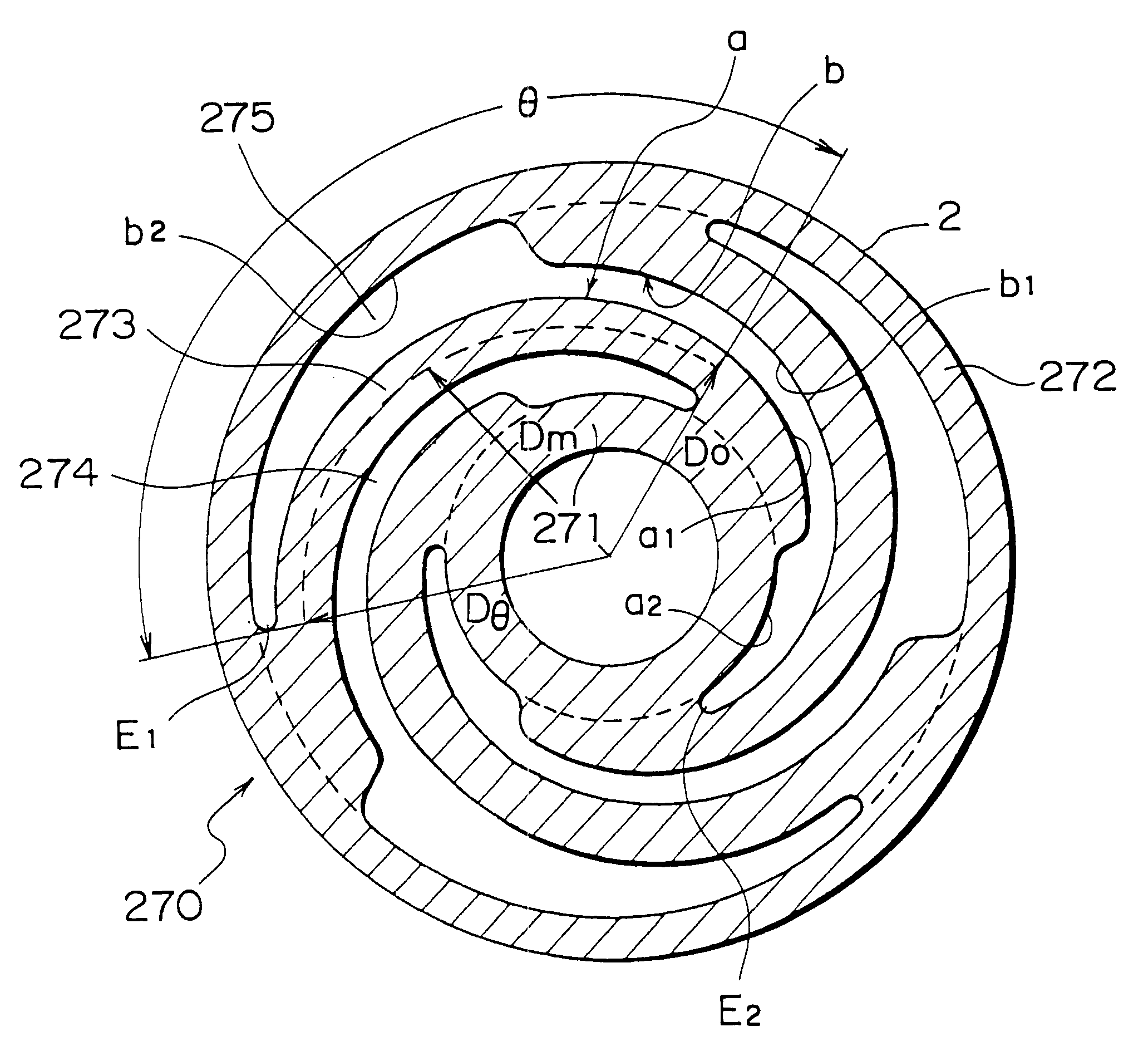
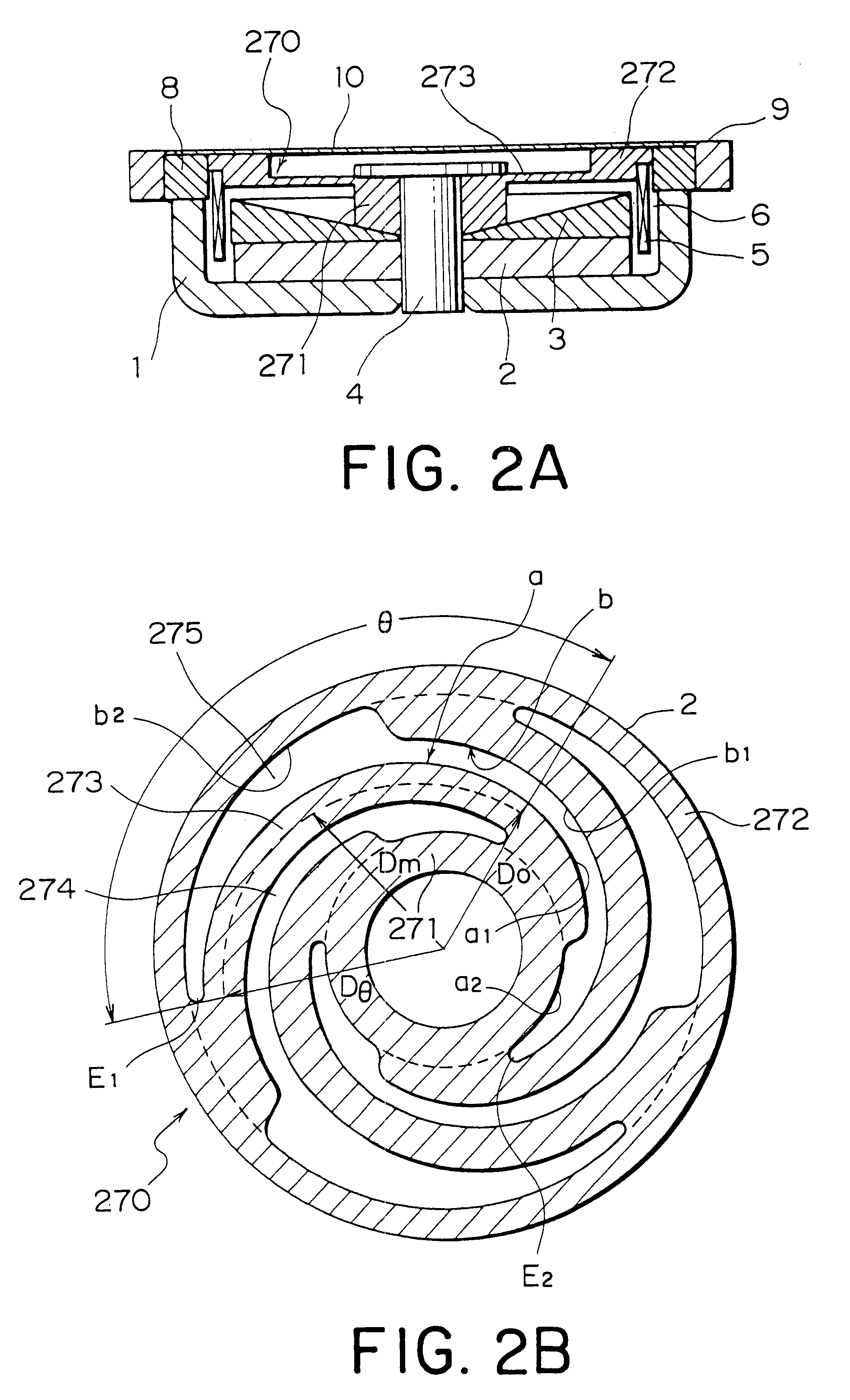
A vibration actuator includes an electromechanical transducer having a magnetic circuit (1-4) and a driving coil (5), a support frame (9), and a damper (270) elastically supporting the magnetic circuit onto the support frame to flexibly damp the vibration of the magnetic circuit when a driving AC current is supplied to the coil (5). The damper (270) comprises inner and outer ring portions (271, 272) and a plurality of spiral spring portions (273) determined by a plurality of spiral slits (274, 275) formed in the damper. In order to reduce the spiral spring portion determined by the adjacent two spiral slits in its compliance, each of the spiral spring portions has an effective spring length determined by an effective angle (theta) which is determined as an angle (by angular degree) from an inner end of the inner spiral slit to an outer end of the outer spiral slit defining each respective spiral spring portion around a center of the damper. The effective angle is 55 angular degree or more. In a preferable example, the effective spring length is determined by a product (r.theta) of an average radius (r) value by the unit of "mm" and the effective angle (theta) value by unit of the angular degree. The effective spring length is selected to 320 or more, and preferably 400 or more.
Owner:TOKIN CORP
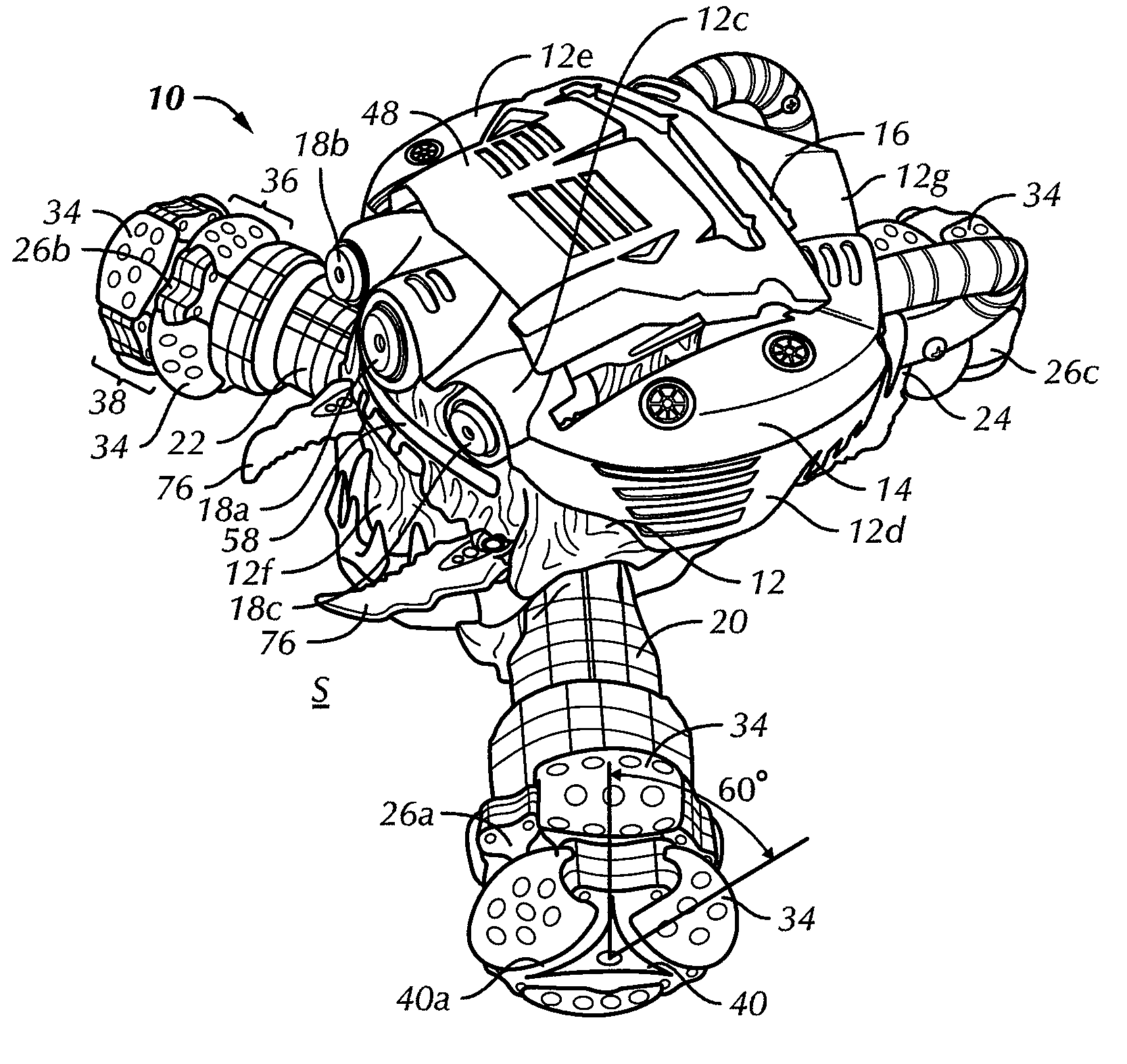
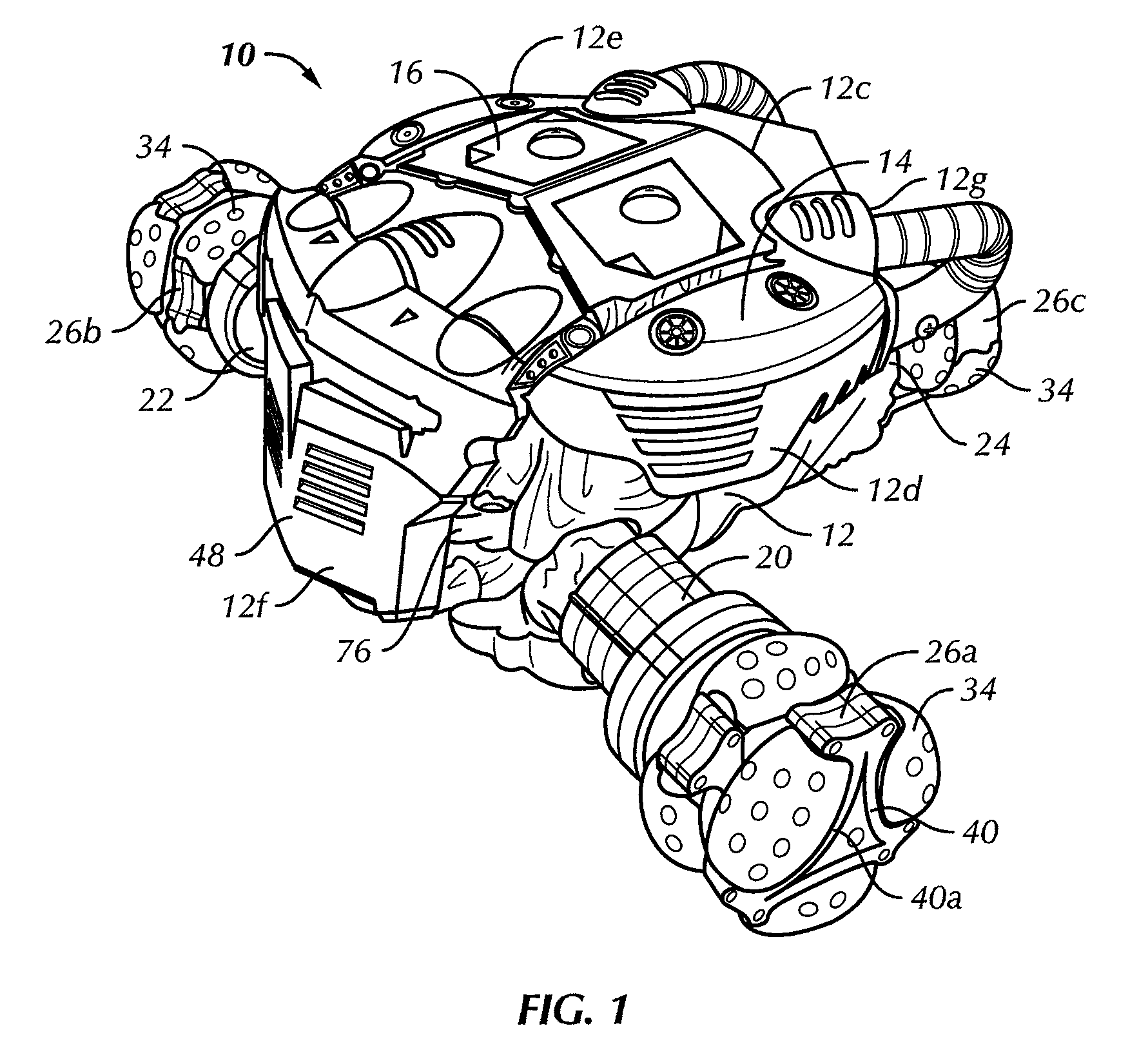
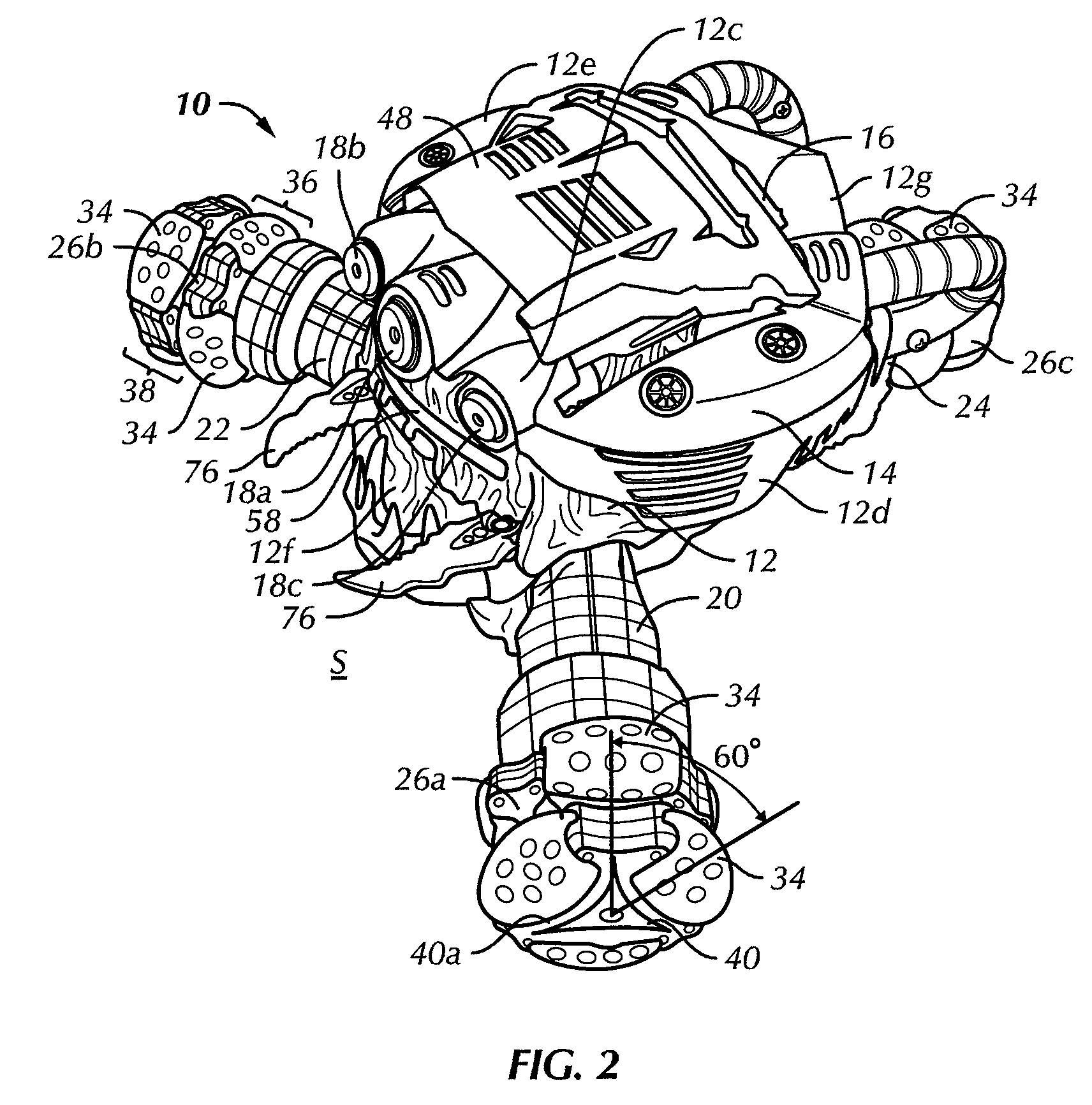
Multi-mode three wheeled toy vehicle
Owner:MATTEL INC
Spinal implant measuring system and method
A method for measuring a spinal implant comprises the steps of: providing a device including a gauge configured to measure an angle in a measuring plane and extending to an engagement surface; disposing the engagement surface with a first selected position of an implant or an anatomy, the first selected position being disposed at a first orientation; calibrating the gauge to a zero angle measurement at the first orientation; disposing the engagement surface with a second selected position of the implant or the anatomy, the second selected position being disposed at a second orientation; and measuring an angle of the second orientation relative to the first orientation such that the gauge determines the angle relative to the zero angle measurement. Various devices are disclosed.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Method for autonomously localizing robots on basis of laser radar
ActiveCN107991683AAdd iterative optimizationEasy alignmentNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsElectromagnetic wave reradiationPoint cloudRadar
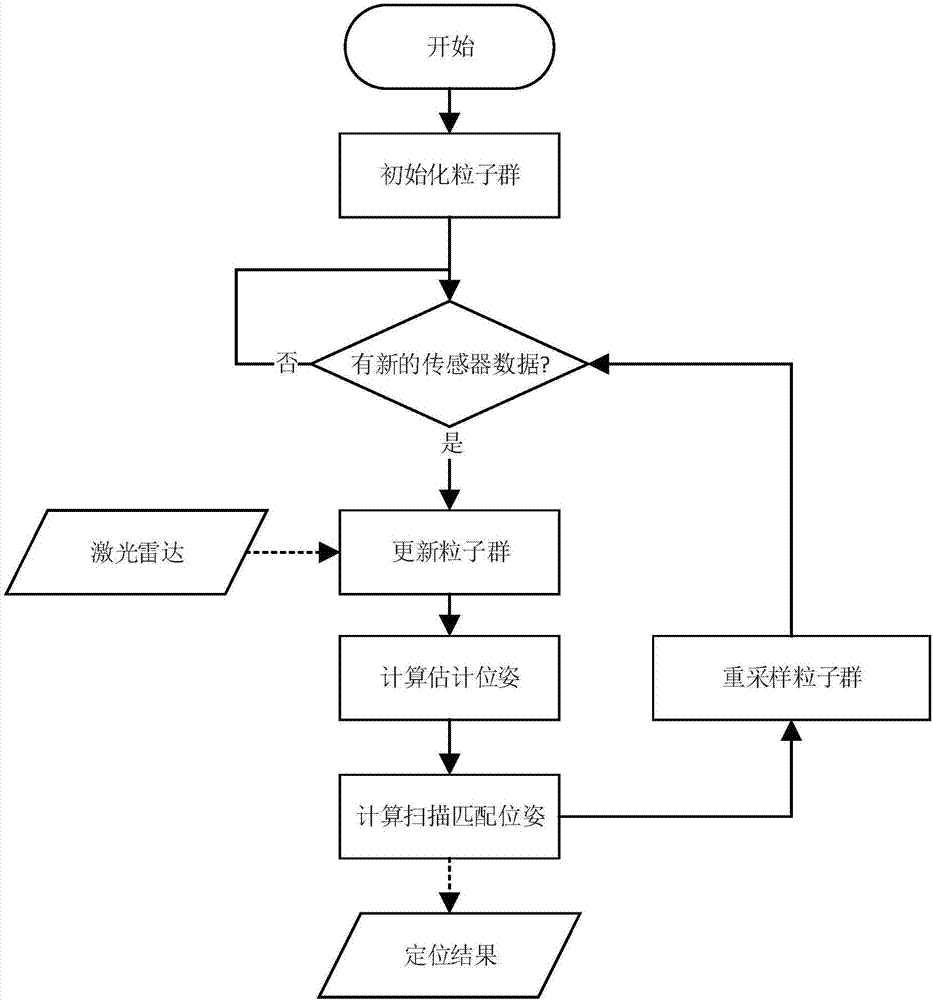
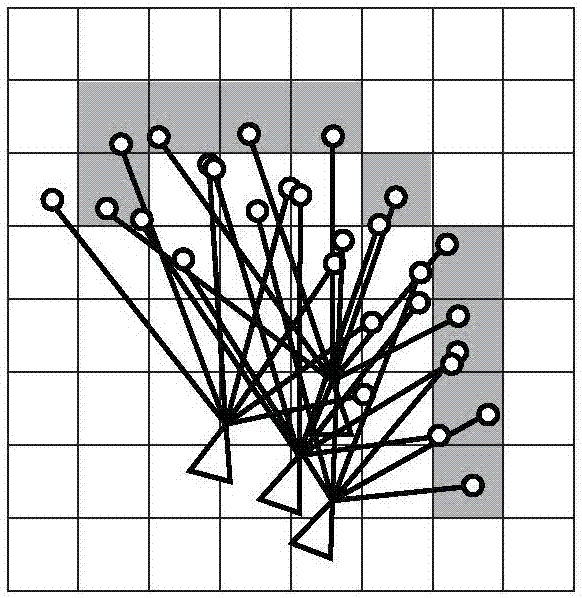
The invention discloses a method for autonomously localizing robots on the basis of laser radar. The method includes randomly generating N particles to form particle swarms around initial locations ofthe robots, and updating the particle swarms according to robot real-time movement distances and real-time rotation angles measured by sensors of the robots at current operation moments of the robots; computing the superposition quantity of point cloud of the laser radar and obstacles of maps for each particle to use the superposition quantity as a score of the particle, computing weighted position and posture average values of the particle swarms by the aid of the score, which is used as a weight, of each particle and utilizing the weighted position and posture average values as AMCL (adaptive Monte Carlo localization) estimation positions and posture; utilizing the AMCL estimation positions and posture as initial values, acquiring scanned and matched positions and posture by the aid ofscanning and matching algorithms on the basis of Gauss-Newton iterative processes and utilizing the scanned and matched positions and posture as the optimal positions and posture of the robots at thecurrent operation moments; re-sampling the particle swarms by the aid of AMCL algorithms to ultimately obtain the global optimal positions and posture of the robots during operation. The global optimal positions and posture of the robots are used as localization results. The method has the advantage that the localization convergence rate can be greatly increased, and the localization precision andthe localization stability can be greatly enhanced.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
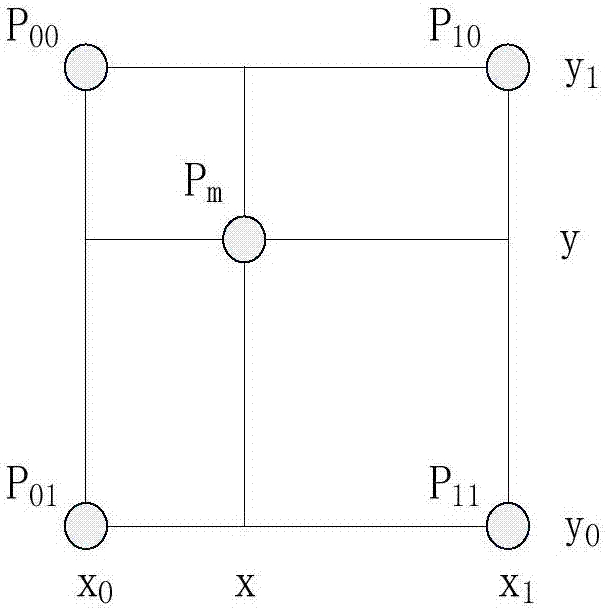
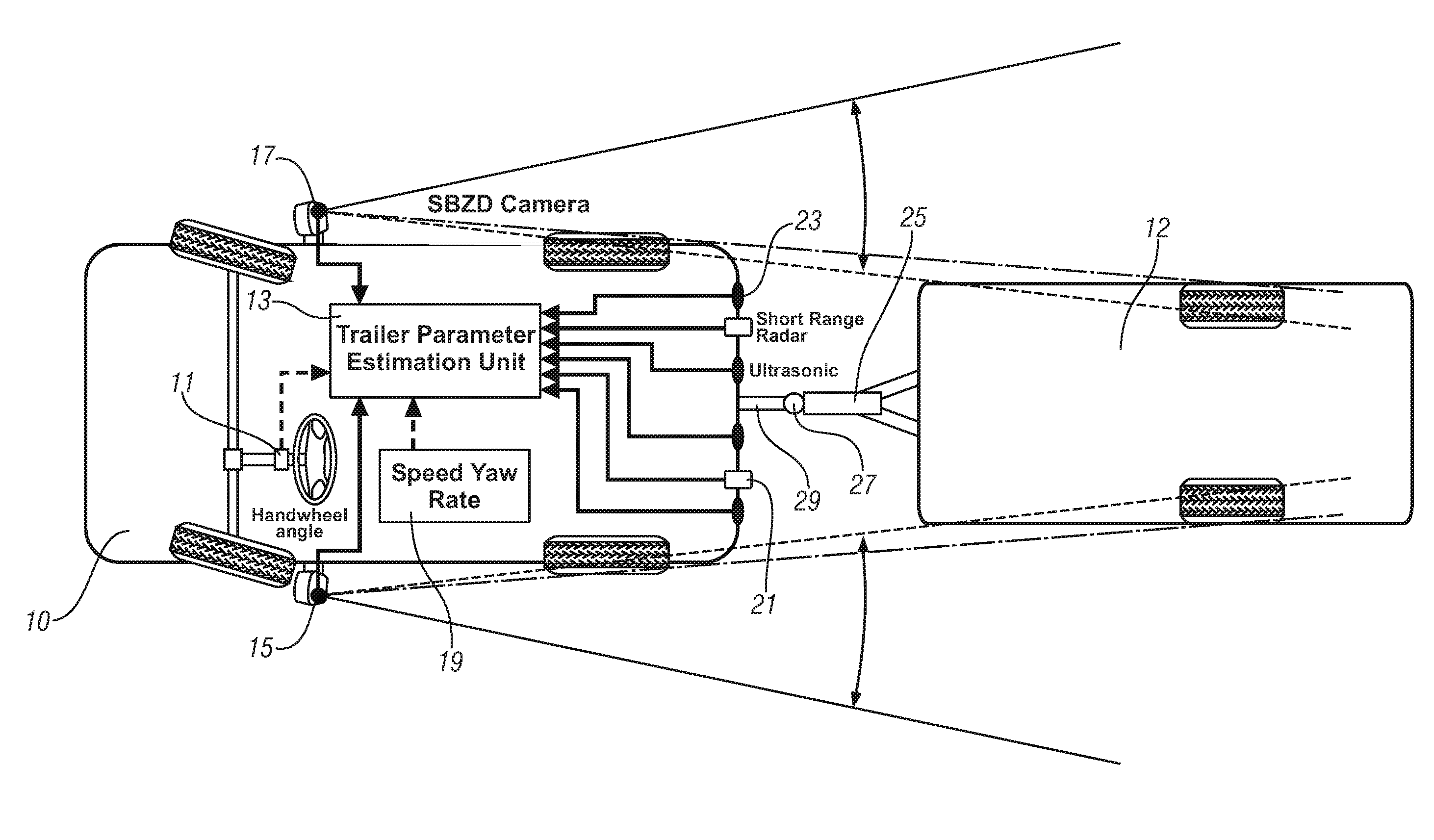
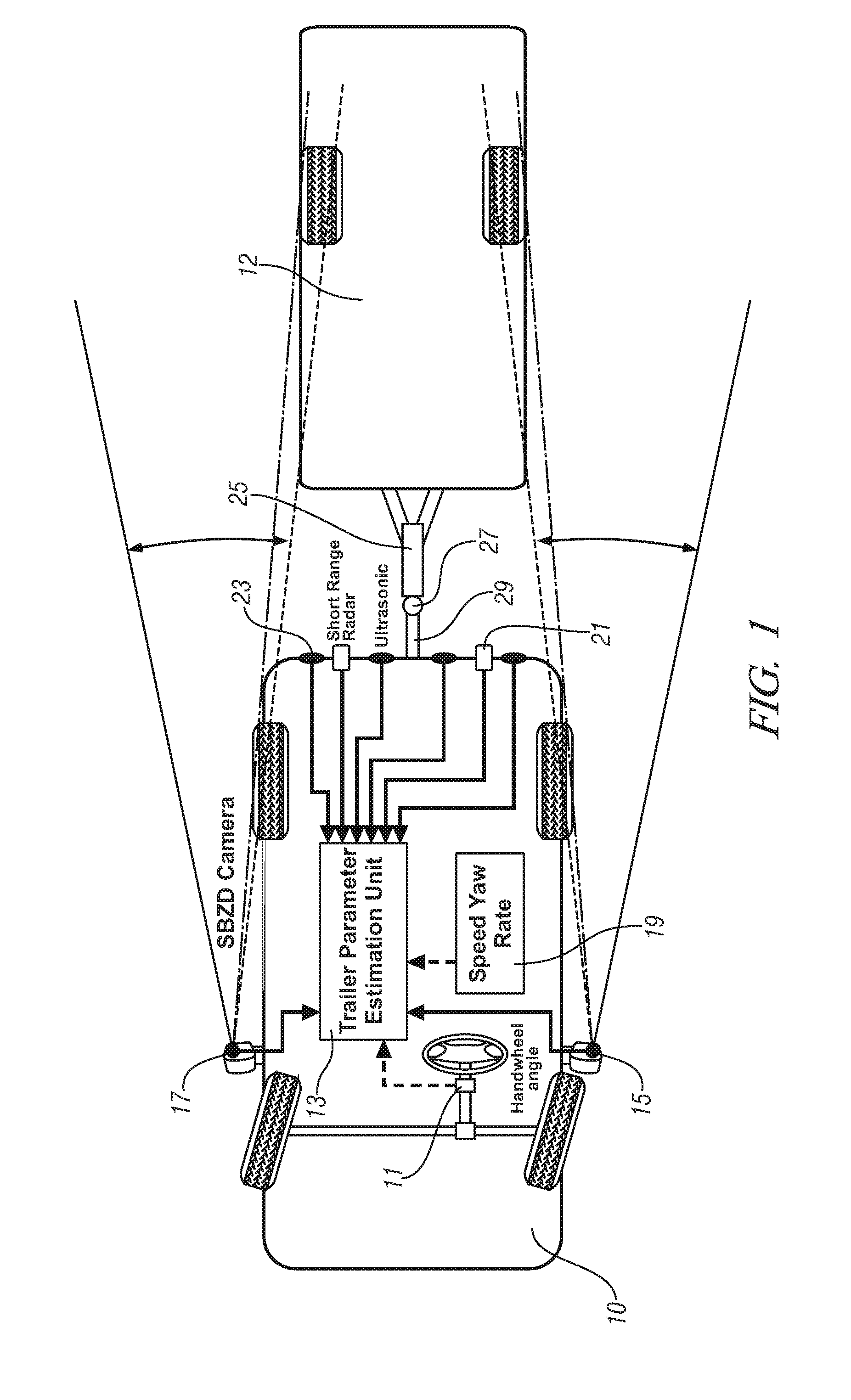
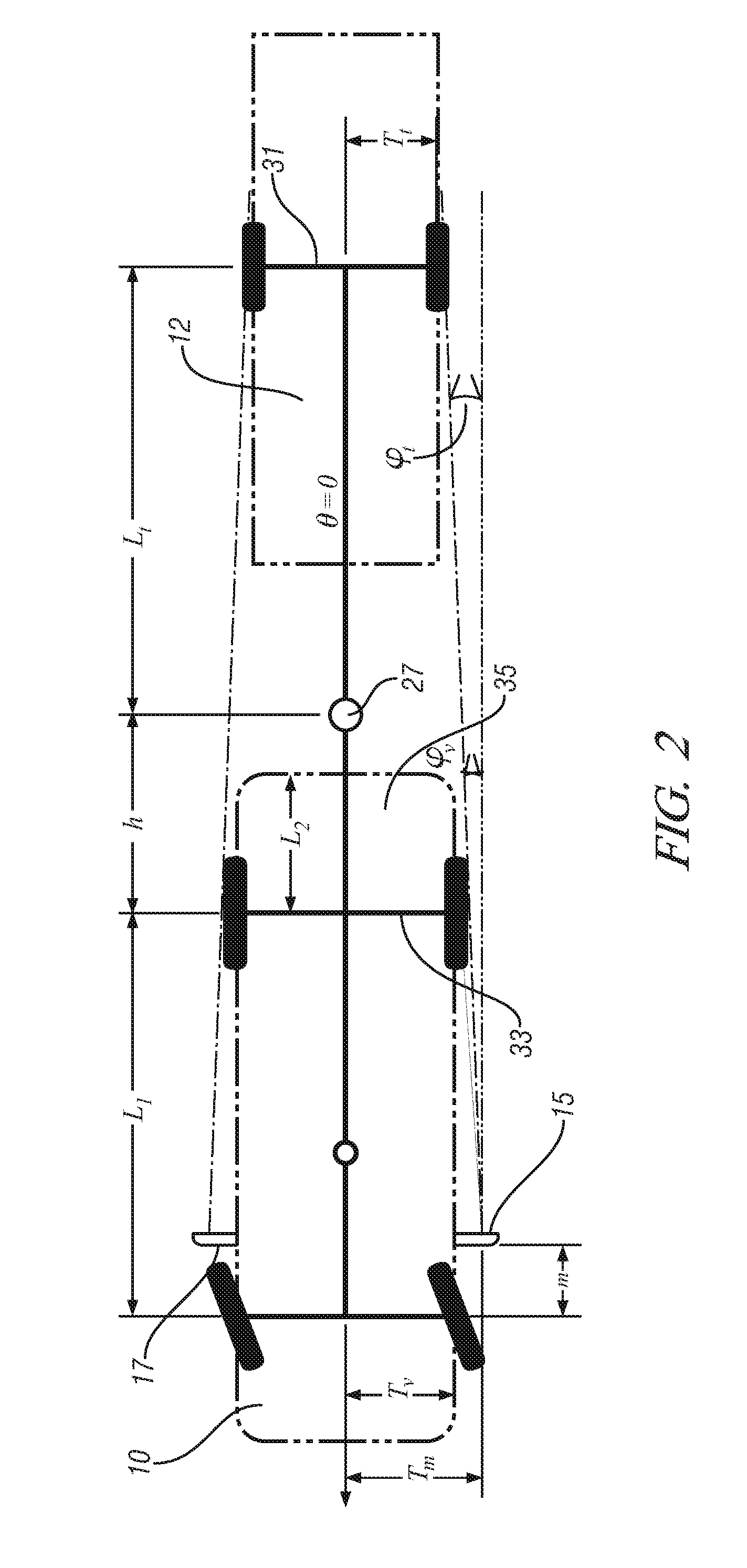
Trailer articulation angle estimation
A method for operating a vehicle includes acquiring position information including an azimuth angle between a non-contacting sensor and a wheeled axle of an attached trailer, determining a trailer tongue length correlated to the position information, determining a track width of the attached trailer correlated to the position information, and calculating a trailer hitch articulation angle corresponding to the trailer tongue length and the track width of the attached trailer.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Motorized venetian blind system
Owner:LUTRON TECH CO LLC
Apparatus and method for solar heat gain reduction in a window assembly
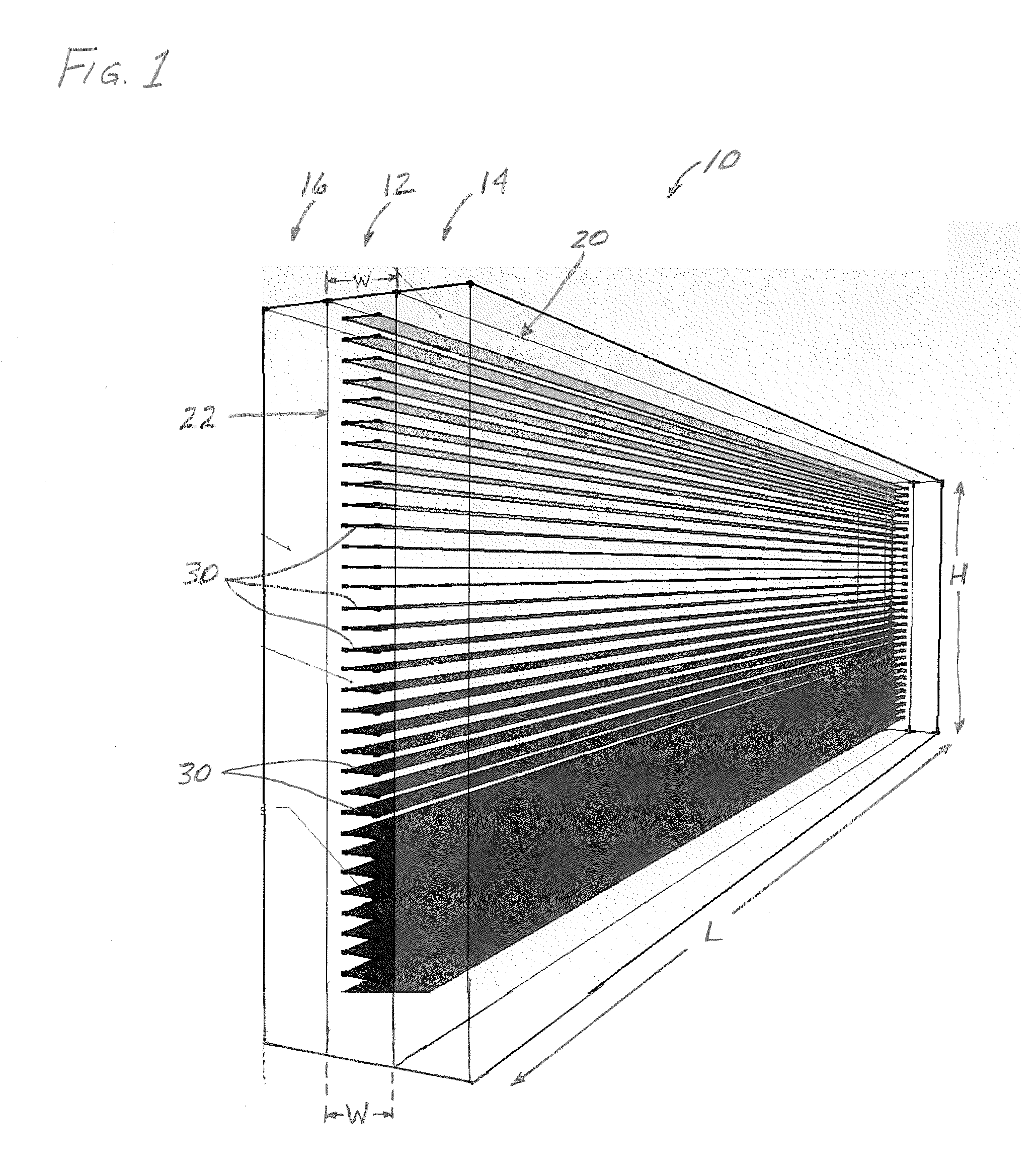
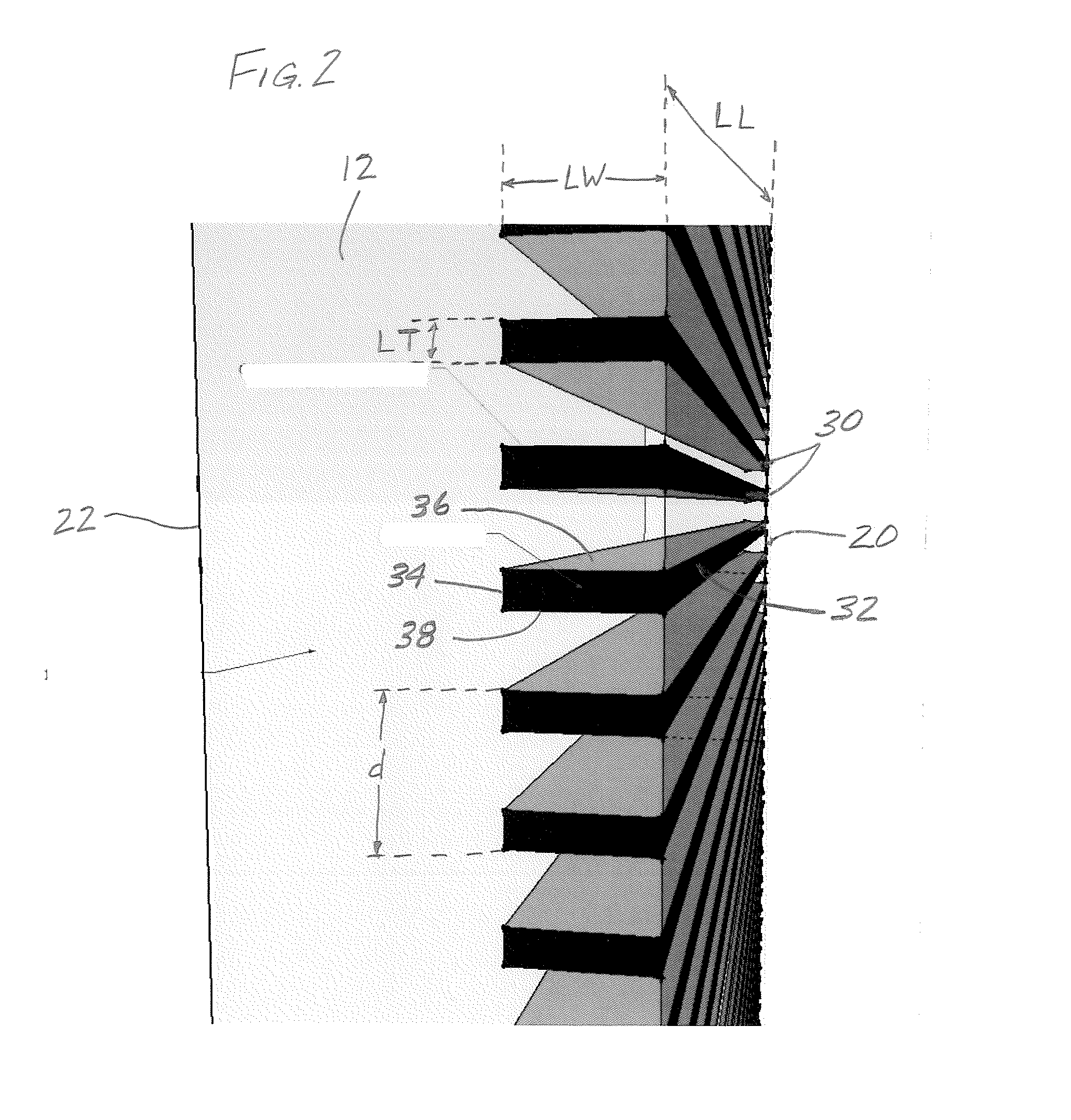
InactiveUS20110088324A1Avoid spreadingLight protection screensUnits with parallel planesHorizonWindow shutter
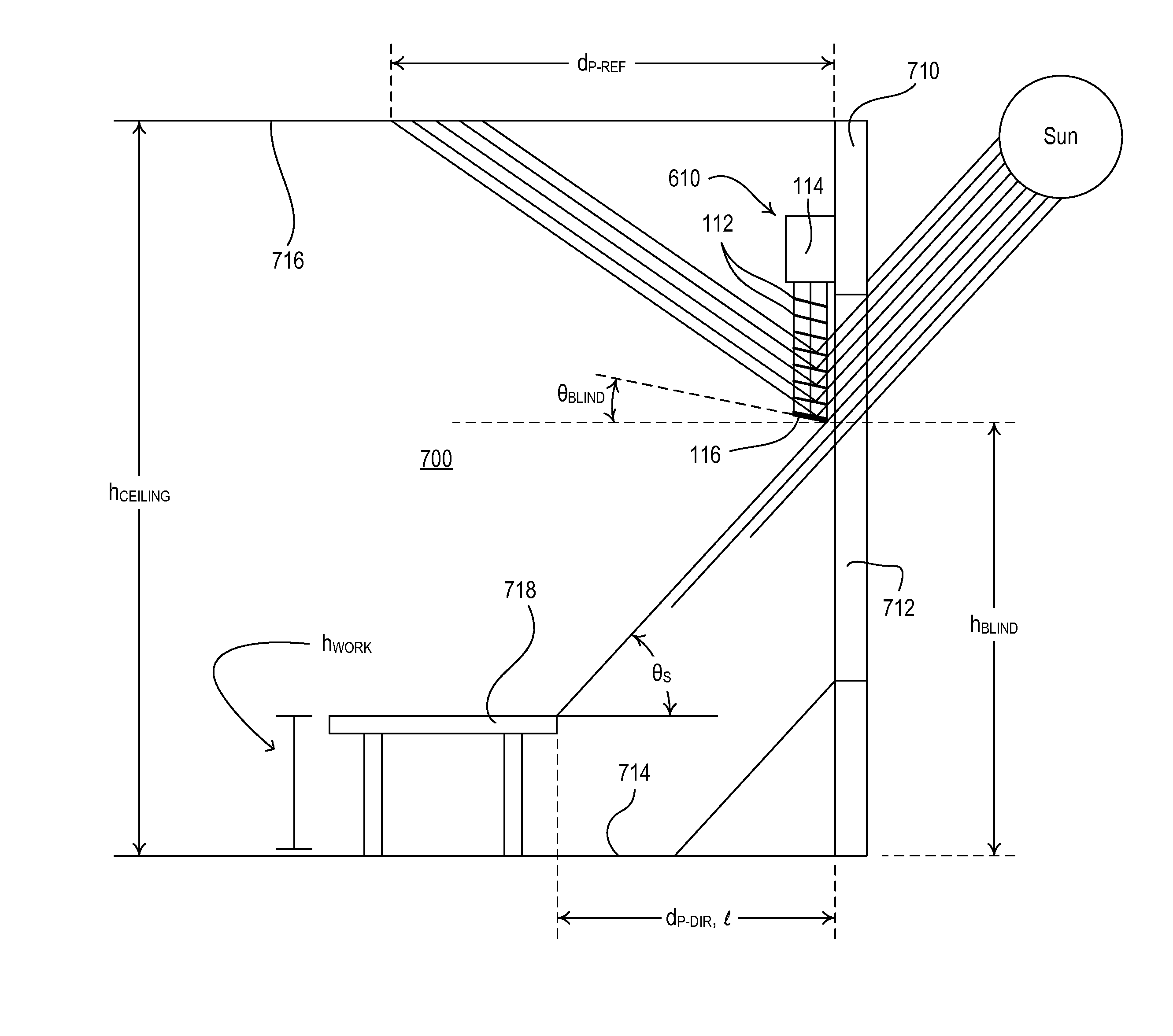
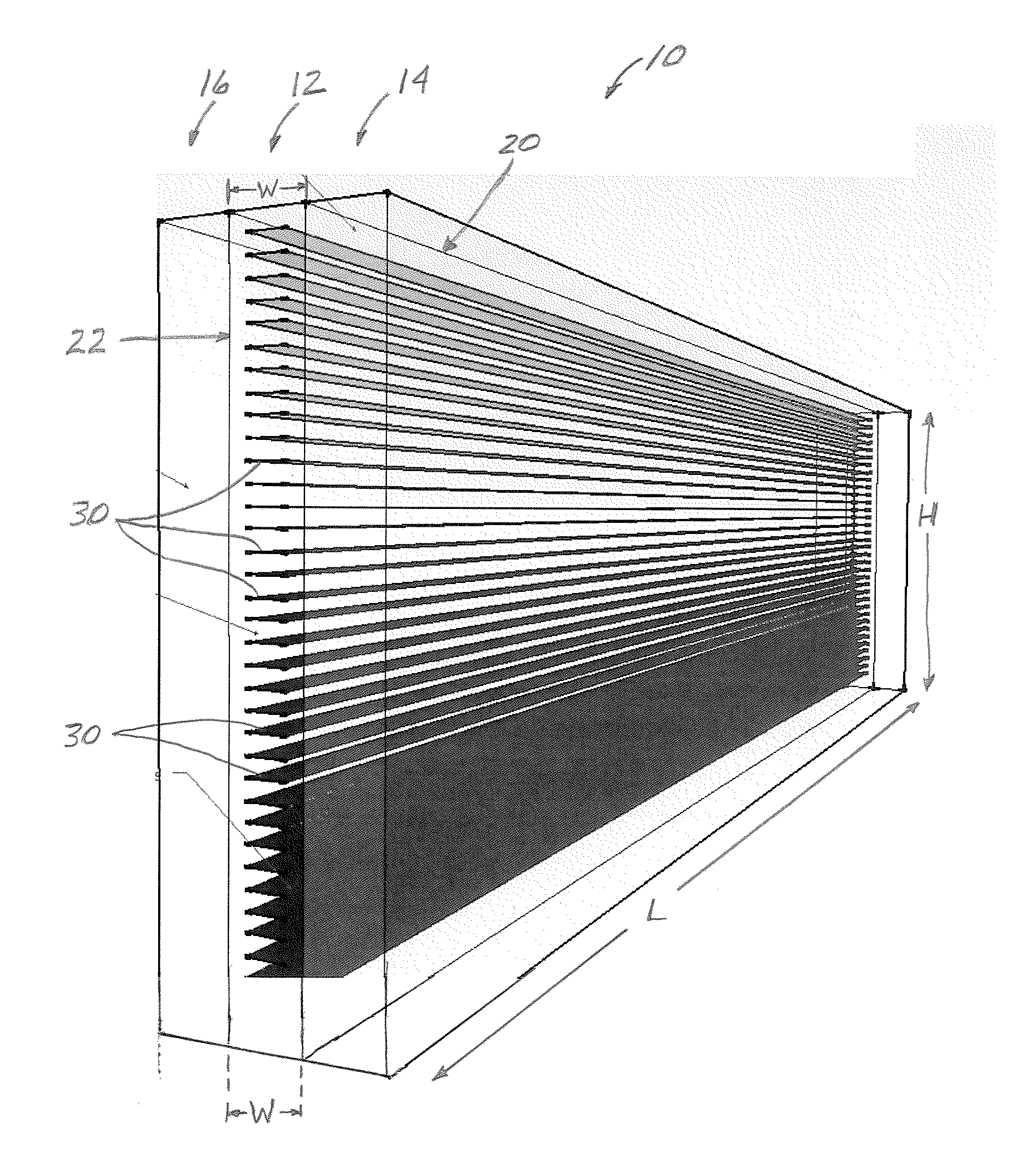
A window assembly having at least one pane is presented for use in a building. Positioned within the pane are a plurality of spaced-apart micro-louvers which extend substantially across the length of the pane. The micro-louvers are positioned to block transmission of direct sunlight through the pane when the sun is at a selected angle above the horizon or higher. The angle at and above which direct light is blocked can be selected to be approximately 30 or 45 degrees above the horizon, for example. The angle can be selected based on the latitude of the location of the window assembly, the time of day during which direct sunlight is blocked, etc. The micro-louvers may have reflective surfaces, be colored as desired, be opaque or translucent.
Owner:WESSEL ROBERT B
Wearable 7-degree-of-freedom upper limb movement rehabilitation training exoskeleton
InactiveCN102119902AEasy to analyzeEasy to formulateChiropractic devicesMedial rotationAngular degrees
The invention provides a wearable 7-degree-of-freedom upper limb movement rehabilitation training exoskeleton which comprises a supporting rod and an exoskeleton training device which are fixed on a base, wherein the exoskeleton training device is formed by connecting a shoulder adduction / abduction joint, a shoulder flexion / extension joint, a shoulder medial rotation / lateral rotation joint, an elbow flexion / extension joint, an elbow medial rotation / lateral rotation joint, a wrist adduction / abduction joint and a wrist flexion / extension joint in series. The joints are directly driven by a motor, wherein the shoulder and elbow rotating joints are additionally provided with a spur-gear set, the structure is simple, and the response speed is high. Compared with the prior art, the exoskeleton provided by the invention has more degrees of freedom of movement and can adapt to standing and sitting training. The length of an exoskeleton rod can be adjusted according to the height of a patient, thereby ensuring the wearing comfort. A spacing structure is adopted by the joints, thereby improving the safety. Angle and moment sensors at the joint points can acquire kinematic and dynamic data of each joint in real time, thereby being convenient for physical therapists to subsequently analyze and establish a training scheme to achieve an optimal rehabilitation effect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
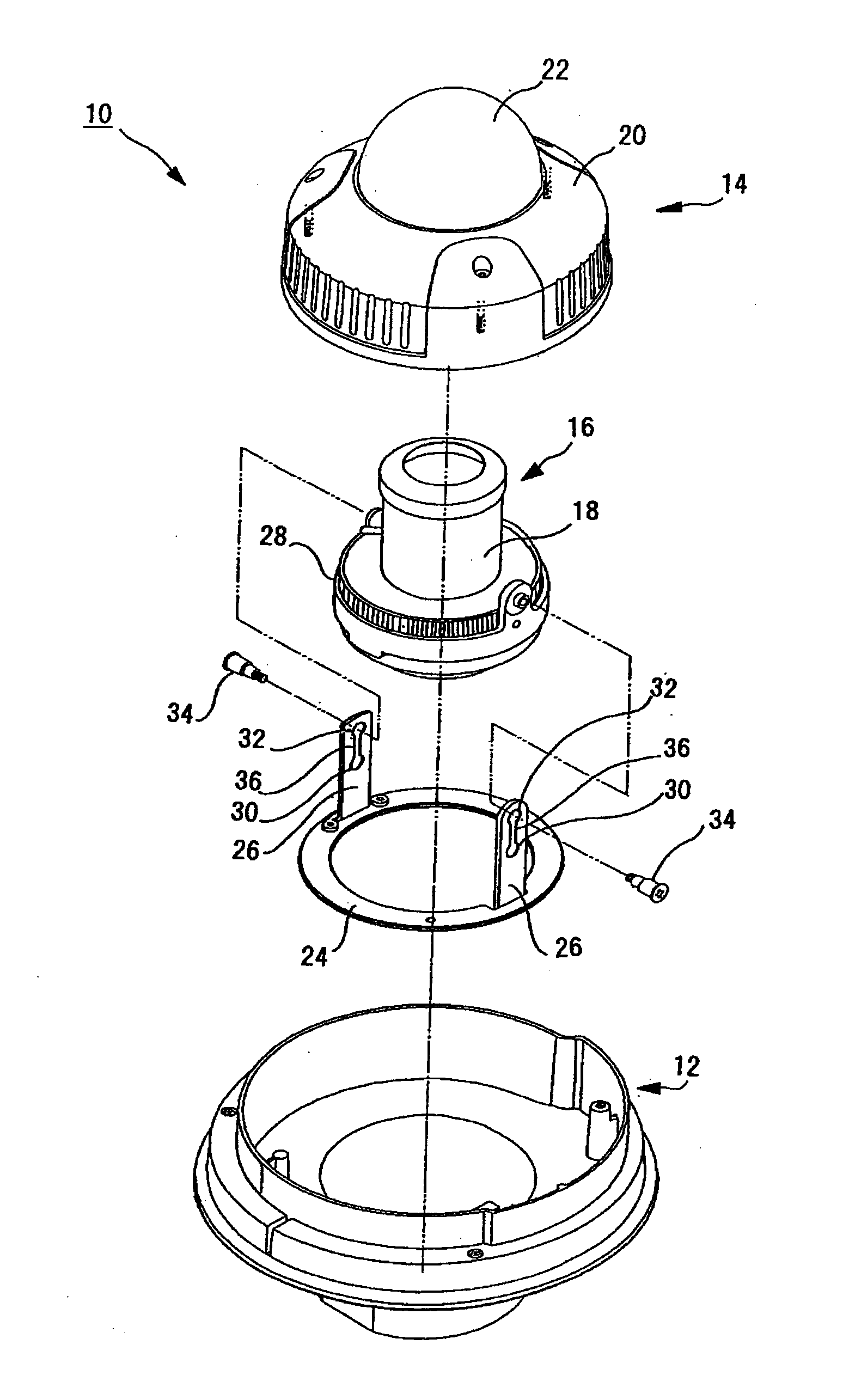
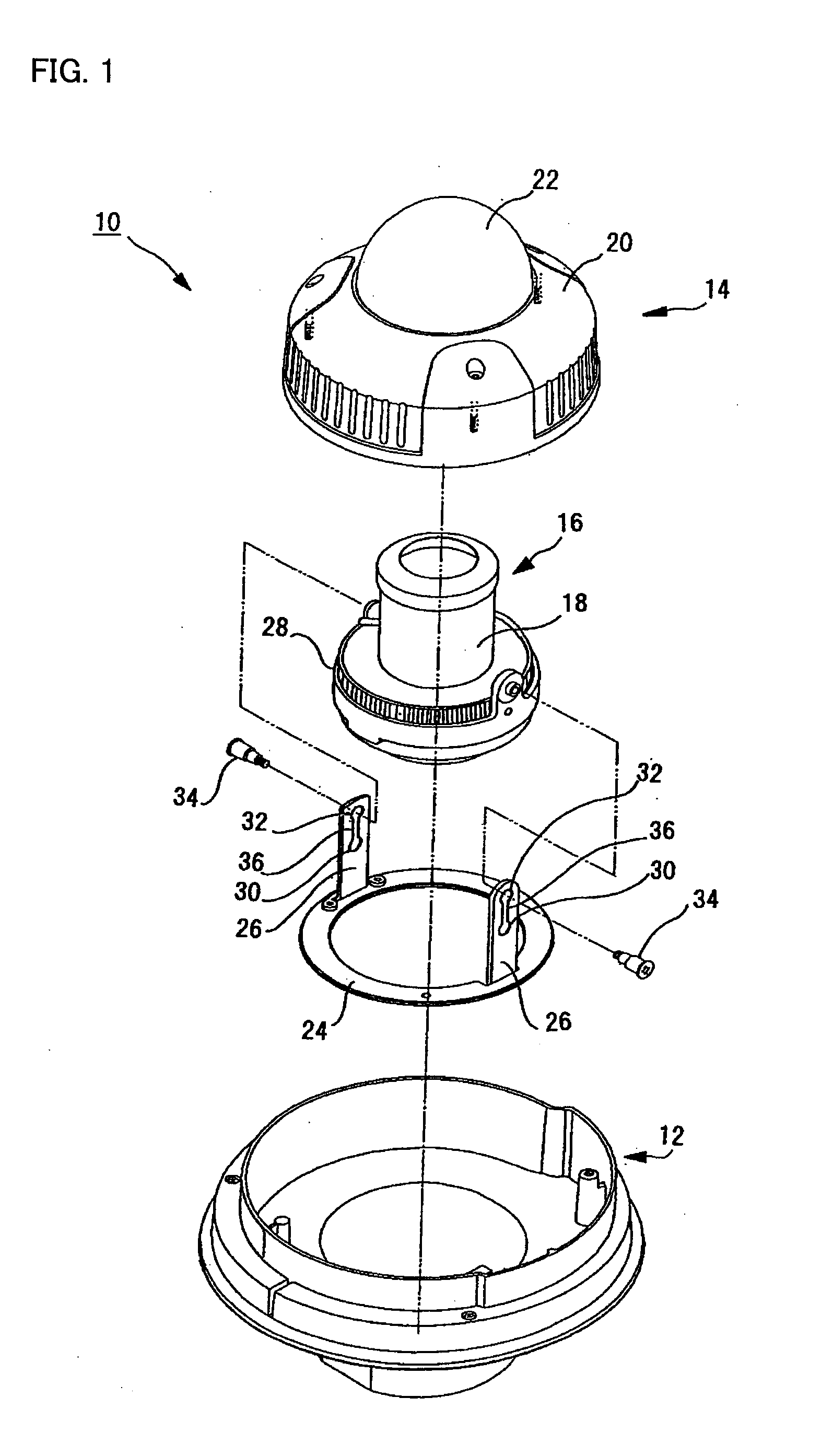
Dome Type Camera
InactiveUS20080231699A1Enhance the imageTelevision system detailsPrintersElevation angleCentre of rotation
A lens (16) is rotatably provided inside a dome cover (22). The lens (16) is supported so that the center of rotation can be moved from the center of a dome to a position apart therefrom in the zenith direction. A lens moving mechanism for moving the lens (16) according to a rotation in the tilt direction of the lens (16) may be provided. The lens moving mechanism may be a cam structure. The cam structure is set so that the rotation axis of the lens (16) is held at the center of the dome in a predetermined center hold angle range corresponding to the direction of an elevation angle, and that the rotation axis of the lens (16) is moved from the center of the dome in the zenith direction at angles lower than the center hold angle range. Good images can be obtained even when shooting in the direction of a depression angle.
Owner:PANASONIC I PRO SENSING SOLUTIONS CO LTD
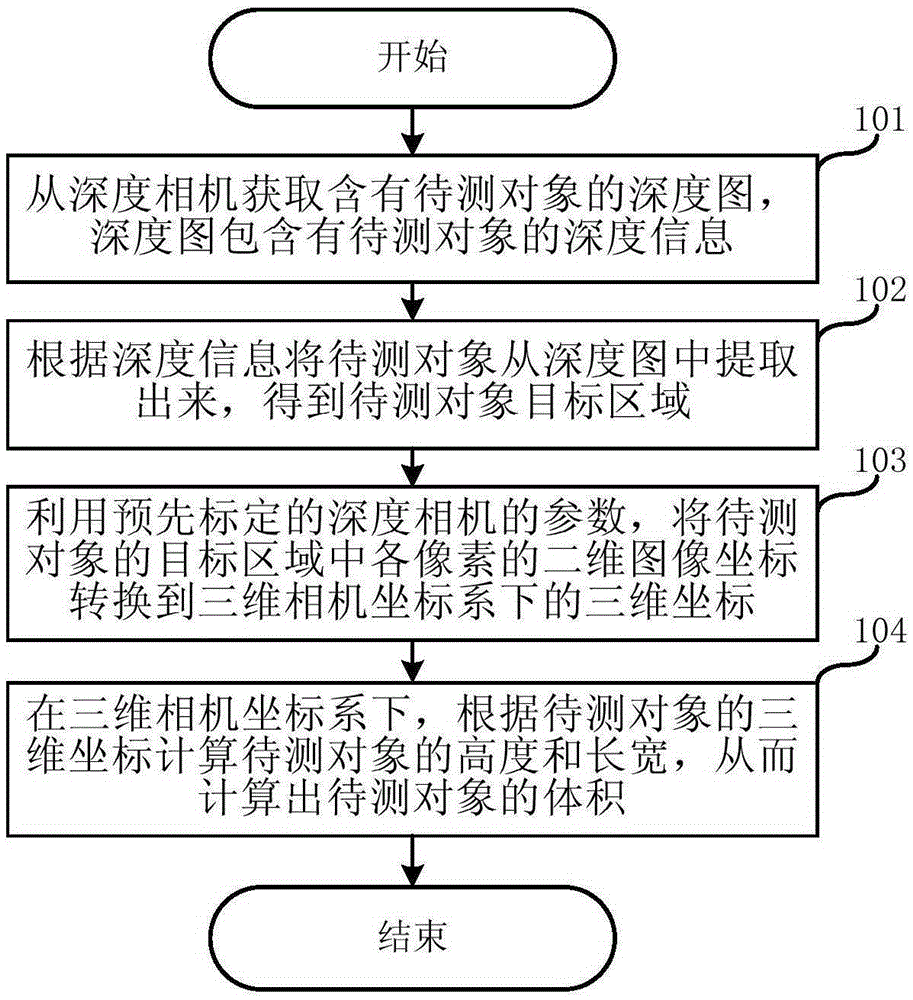
Volume measurement method and system based on depth camera
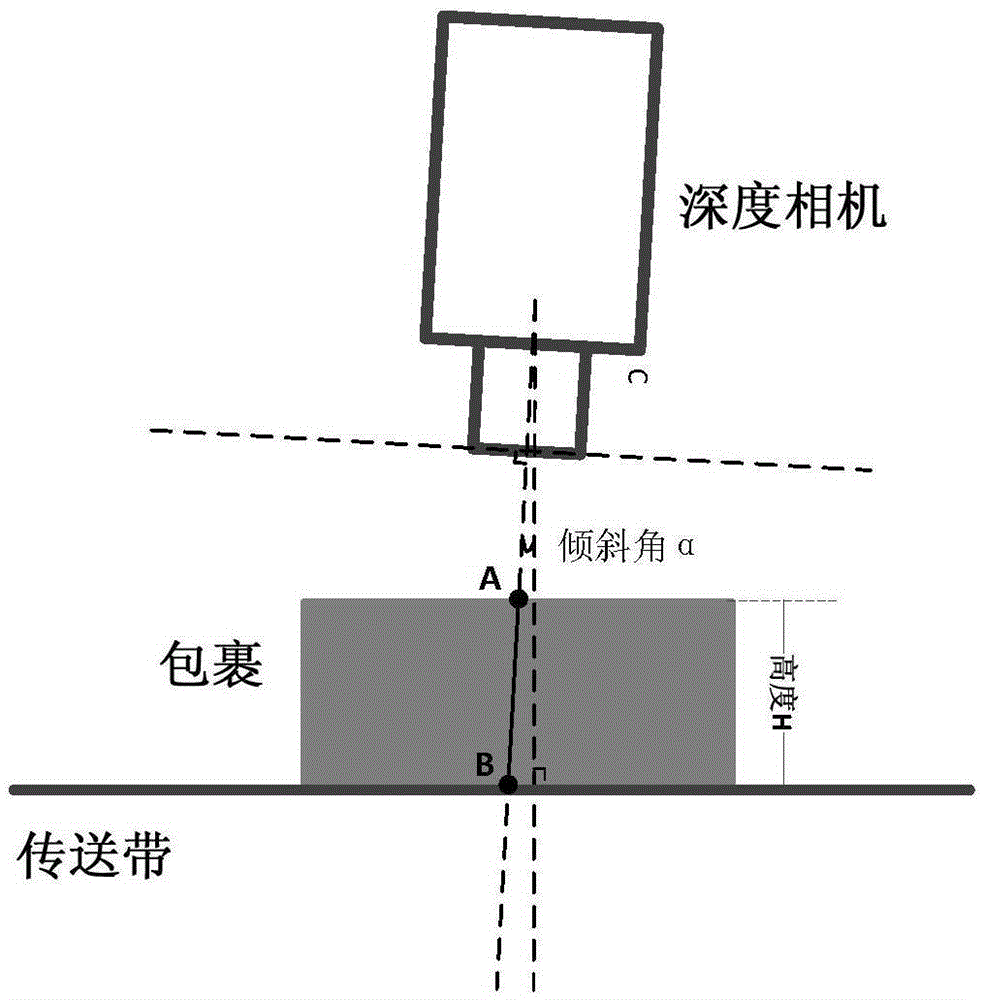
ActiveCN106839975AHigh measurement accuracyNot affected by camera angleUsing optical meansAngular degreesComputer vision
The invention relates to the technical field of computer vision, and discloses a volume measurement method and system based on a depth camera. The method includes the steps: acquiring depth images with objects to be measured from the depth camera; extracting the objects to be measured from the depth images according to depth information to obtain target areas of the objects to be measured; converting two-dimensional image coordinates of pixels in the target areas of the objects to be measured to three-dimensional coordinates under a three-dimensional camera coordinate system by the aid of pre-calibrated parameters of the depth camera; calculating heights and lengths and widths of the objects to be measured according to the three-dimensional coordinates of the objects to be measured under the three-dimensional camera coordinate system, and calculating volumes of the objects to be measured. The depth images comprise depth information of the objects to be measured. The method is high in measuring accuracy and simple and convenient to use and can not be affected by shooting angles and heights, and mounting heights and angles of the camera cannot be calibrated.
Owner:HANGZHOU HIKVISION DIGITAL TECH
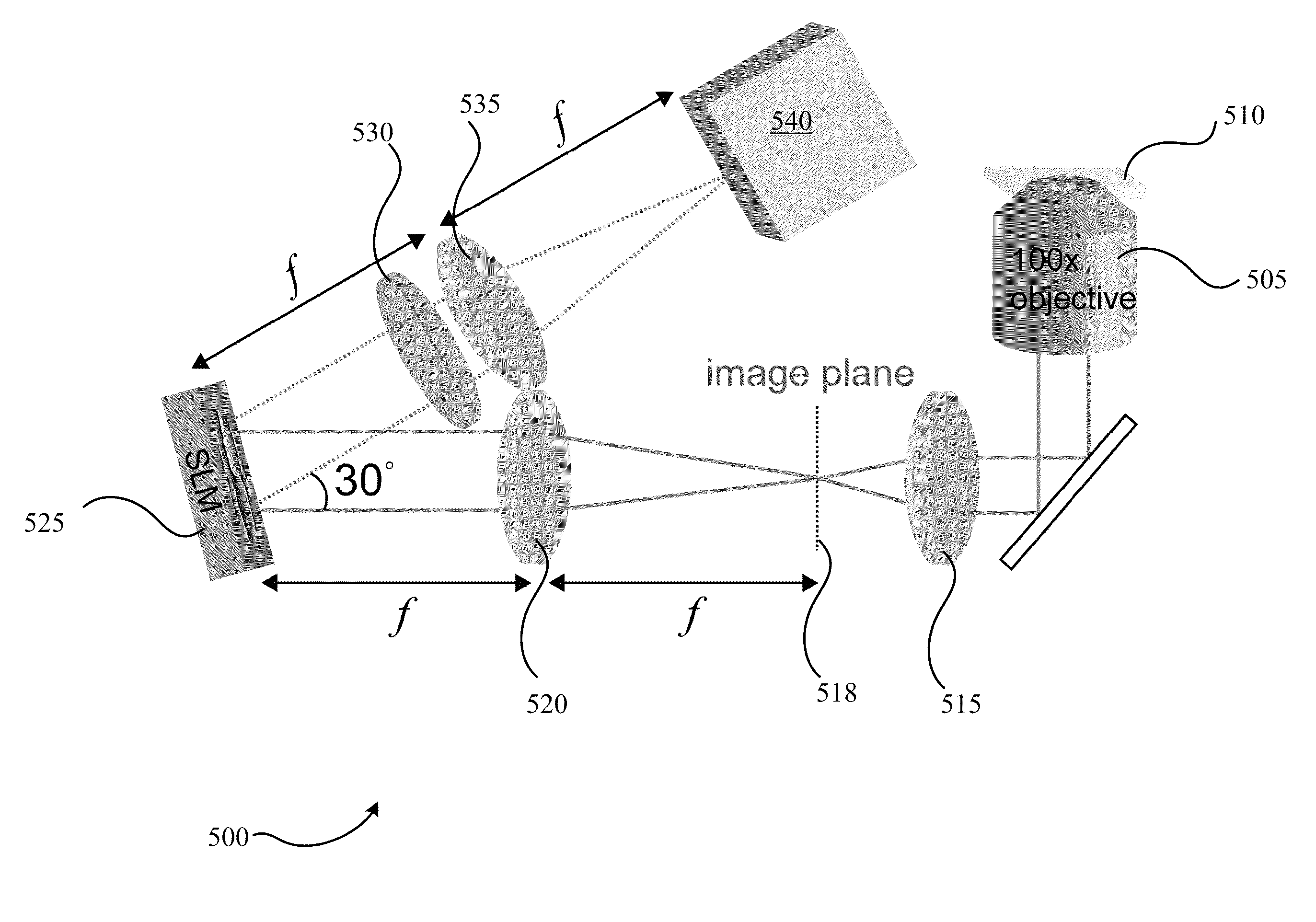
Three-dimensional single-molecule fluorescence imaging beyond the diffraction limit using a double-helix point spread function
Embodiments of the present invention can resolve molecules beyond the optical diffraction limit in three dimensions. A double-helix point spread function can be used to in conjunction with a microscope to provide dual-lobed images of a molecule. Based on the rotation of the dual-lobed image, the axial position of the molecule can be estimated or determined. In some embodiments, the angular rotation of the dual-lobed imaged can be determined using a centroid fit calculation or by finding the midpoints of the centers of the two lobes. Regardless of the technique, the correspondence between the rotation and axial position can be utilized. A double-helix point spread function can also be used to determine the lateral positions of molecules and hence their three-dimensional location.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF +1
360-degree camera head for unmanned surface sea vehicle
InactiveUS20120154521A1Increase relative motionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsImaging processingMarine engineering
A camera head for use in a marine environment having a cylindrical watertight housing, top and bottom plate members closing the cylindrical housing, and a plurality of ports through the vertical wall of the housing and positioned at a regular angular intervals. A transparent pane is sealed over each port, retained in place by compression against a gasket or O-ring by a compression member. A corresponding plurality of cameras are fixedly positioned behind the ports and the angular field of view of each camera is selected to be greater than the angular interval between the ports such that a continuous 360-degree view of the marine environment is always visible. Six 72-degree FOV cameras spaced at regular 60-degree intervals are preferred. The housing contains cooling / ventilation as well as power and image processing and control systems so as to be self contained.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Determination of the three-dimensional location of a target viewed by a camera
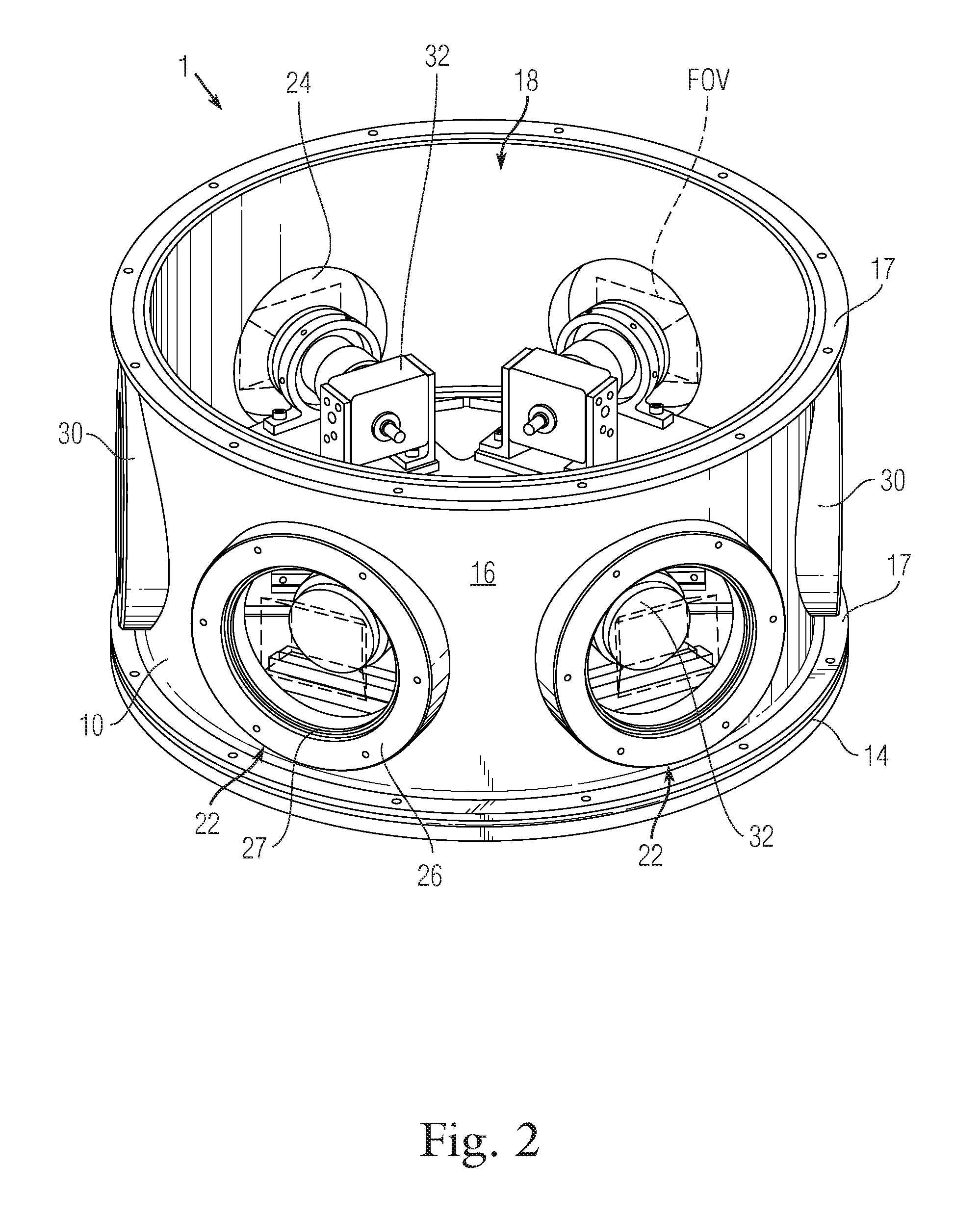
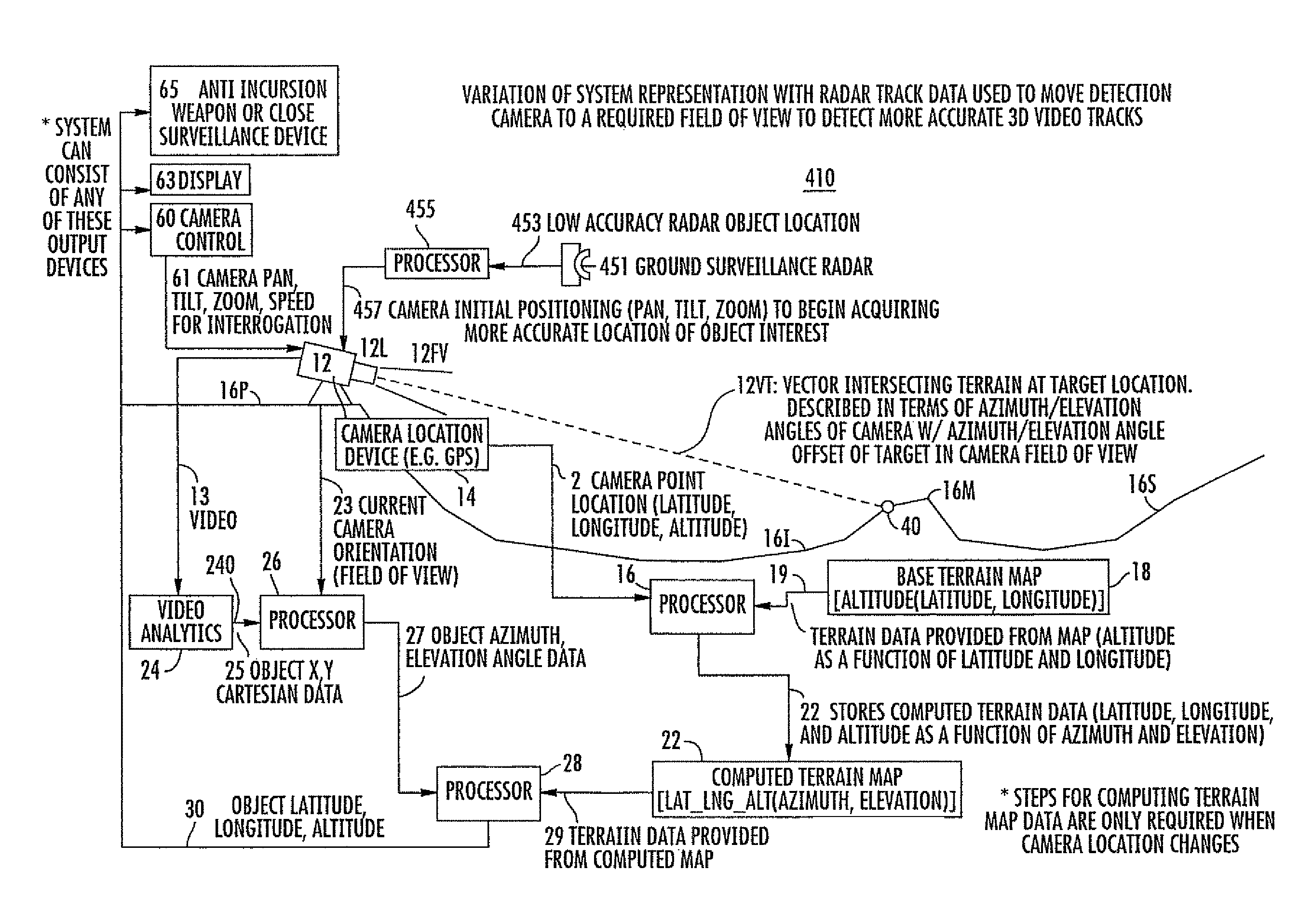
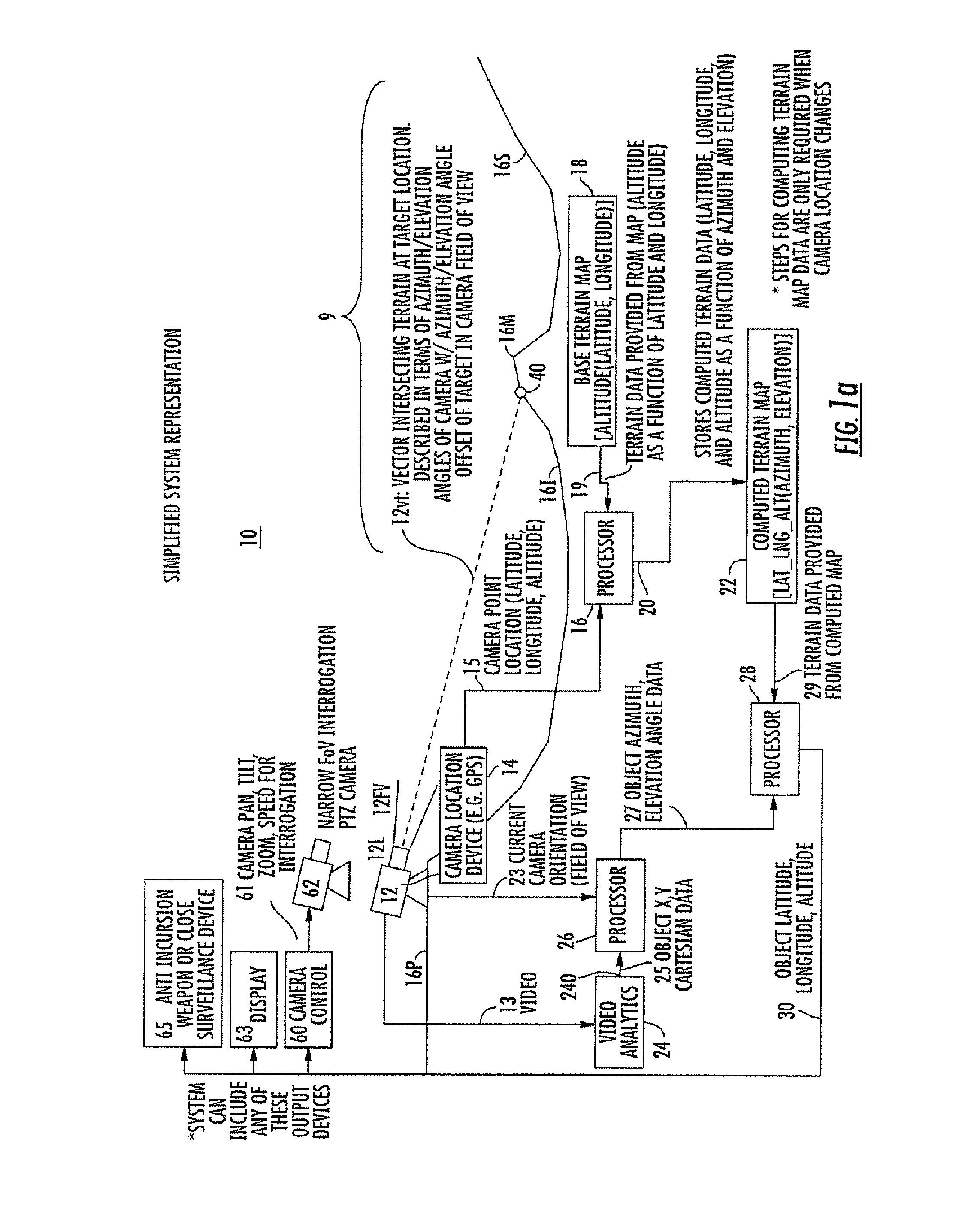
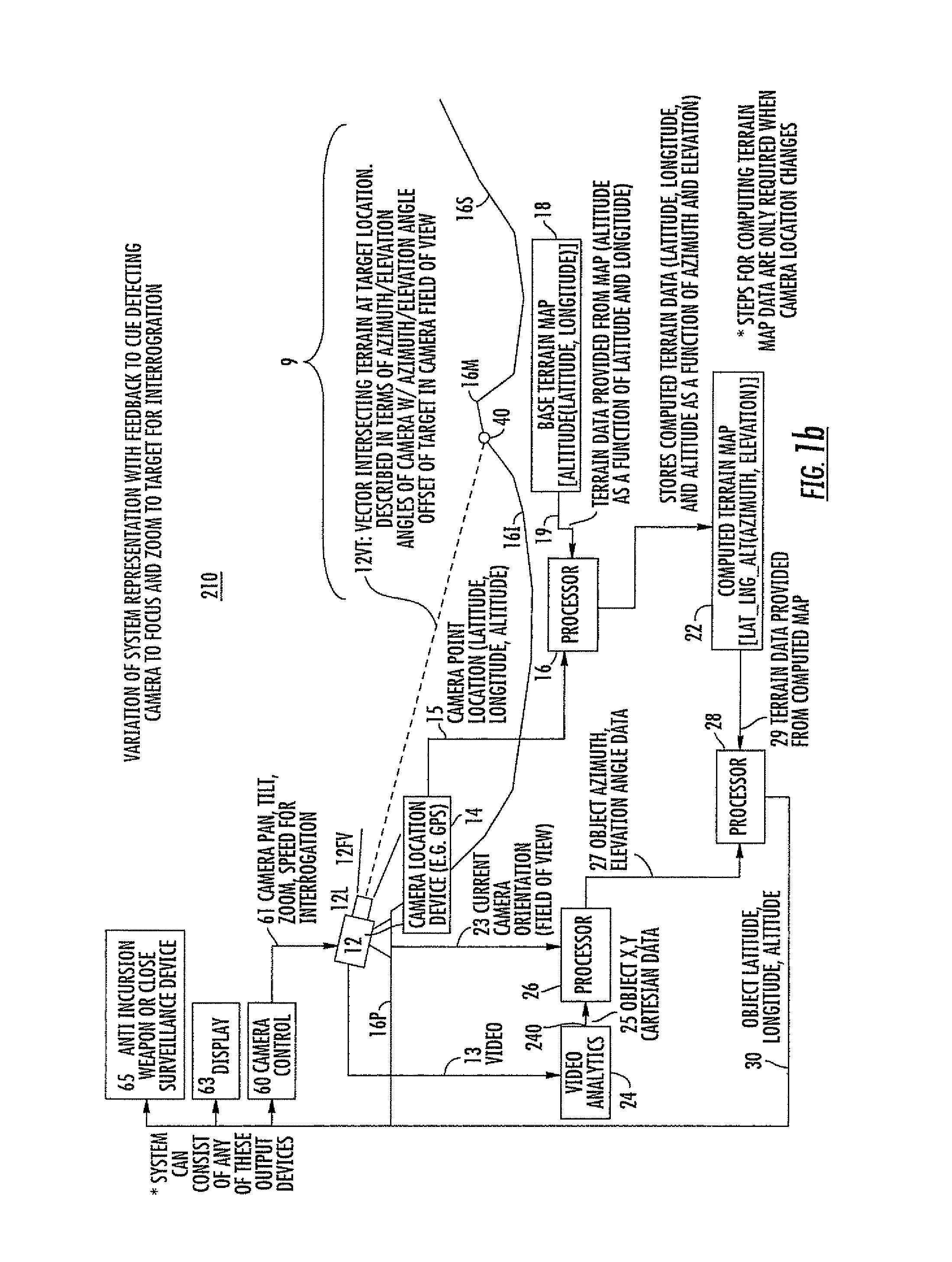
ActiveUS8049658B1Improve accuracyPosition fixationCharacter and pattern recognitionTerrainElevation angle
A method for determining, in three dimensions, the location of a moving ground object observed in a region by a video camera. A terrain map supplies altitude for the latitude and longitude of each terrain point. The terrain information is combined with camera location, field of view, and orientation to produce a computed terrain map relative to the camera. A video analytics step processes the video and locates moving target(s) in two Cartesian coordinates. The coordinates are processed with the camera information to produce target location in terms of azimuth and elevation angle. The computed map information is combined with the angular target location to produce latitude, longitude, and altitude of the target. The target location information is used for further investigation or to attack the target. Also, a method for determining the third dimension of a 2-D radar track to cue a camera or fuse with camera data.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Vision measuring method for spaced round geometrical parameters
InactiveCN1566900AHigh measurement accuracyHigh degree of automationTelevision system detailsColor television detailsObservational errorThree-dimensional space
This invention belongs to measuring technique field and relates to improvement for space round geometry parameters non-contact measuring method. This invention can calculate eh real three dimensional coordinates of round fringe by use of polar line restriction and calculate space round geometry parameters based on space round optimal fit. This invention reduces the measuring error caused by shape distortion of space round perspective projecting and increases the measuring accuracy of round geometry parameters based on the optical method. When the surface of space round to be measured is angle more than fifty degrees, the repeatability accuracy 3sigma of space round geometry center is superior to minus or plus 0.01 mm.
Owner:HUANGSHI BANGKE TECH CO LTD
Numerically controlled drilling and milling processing method for runner of blisk of engine
InactiveCN101733618AImprove processing efficiencyShorten the manufacturing cyclePositioning apparatusNumerical controlAngular degreesEngineering
The invention provides a numerically controlled drilling and milling processing method for a runner of a blisk of an engine. The main technical flow before drilling and milling the runner comprises the following steps: lathing each surface of a blank, performing nondestructive testing, lathing inner and outer cavities of the blisk, finely milling a needed periphery and an axial benchmark, drilling and boring an angular datum hole, drilling and milling the runner and inspecting. A part and a fixture are in peripheral seam allowance fit to limit a radial degree of freedom of the part; an end face gland and a central pull bar axially limit an axial degree of freedom of the part; and a precise positioning pin angularly limits an angular degree of freedom of the part. The method has the advantages that: by applying the drilling and milling processing method to a part machining process of the blisk of the engine having the material removing rate of over 90 percent, the method improves the processing efficiency, shortens the manufacturing period of the product, and provides a new technical means for removing a large amount of remainder materials of the blisk; and the processing of a high-temperature alloy, a titanium alloy and other difficult-to-process materials shows that the material is more difficult to process, the removing rate is bigger and the effect is more obvious.
Owner:SHENYANG LIMING AERO-ENGINE GROUP CORPORATION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com