Patents
Literature
1510 results about "Beam direction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
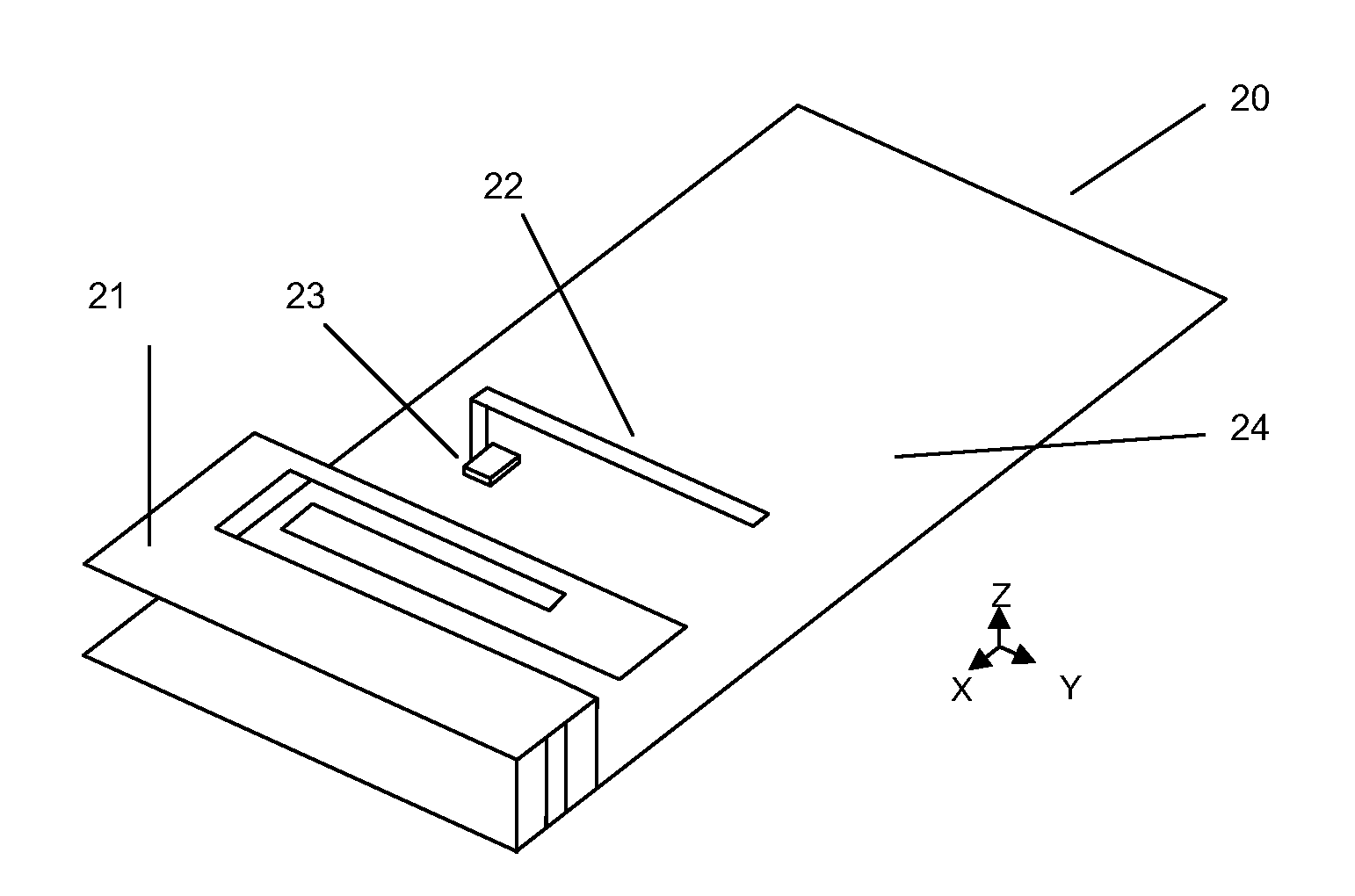
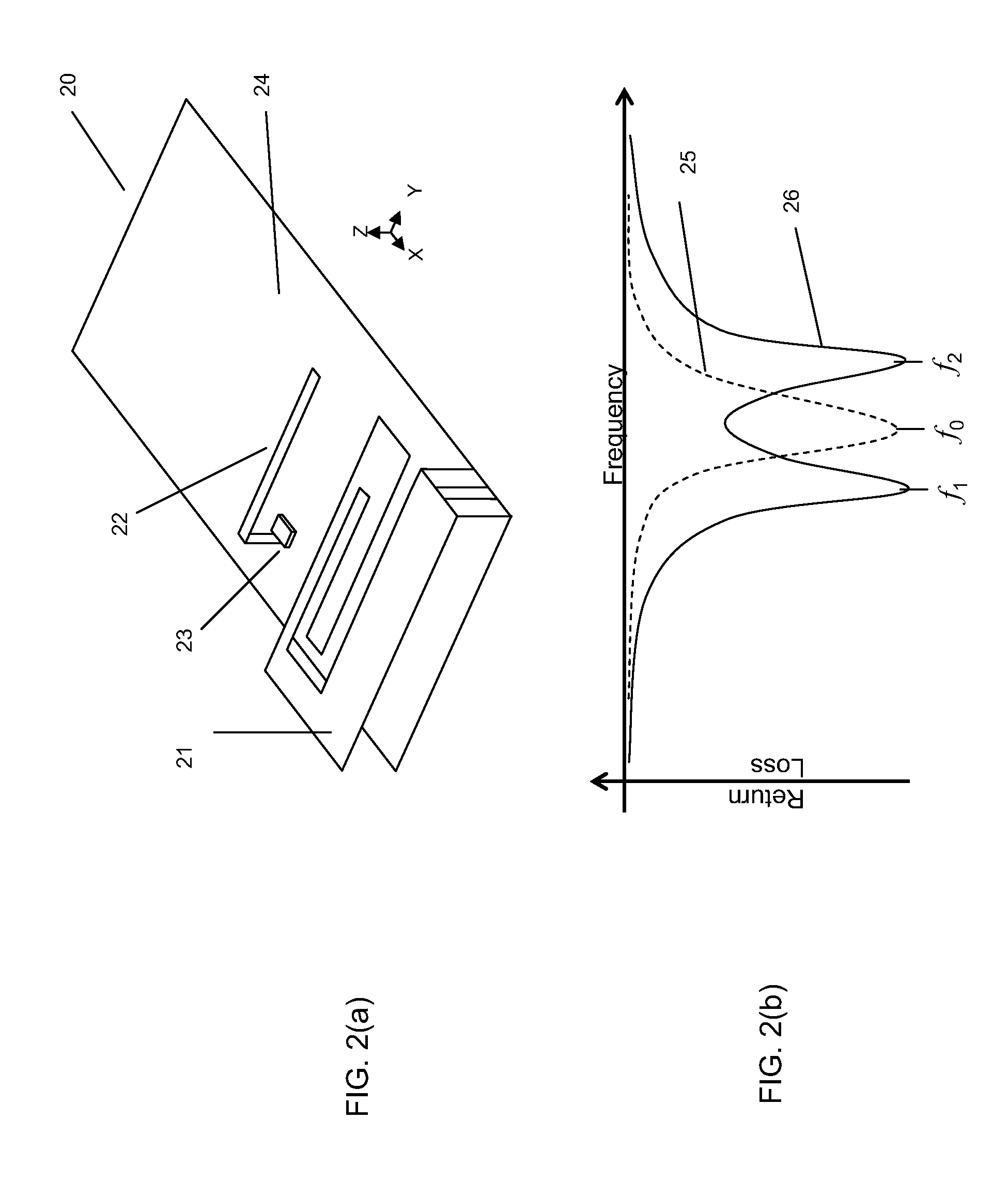
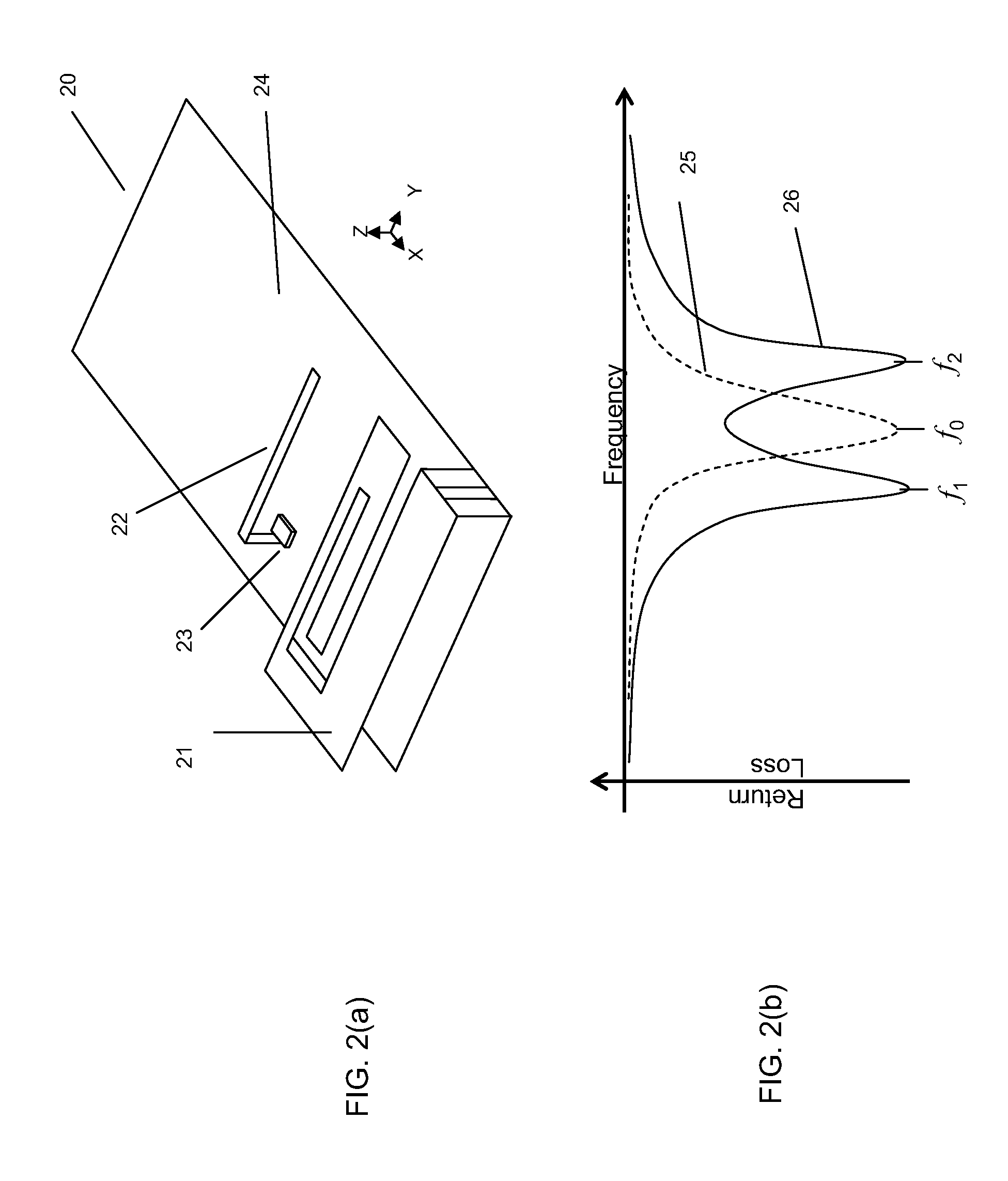
Beam scanning antennas with plurality of antenna elements for scanning beam direction
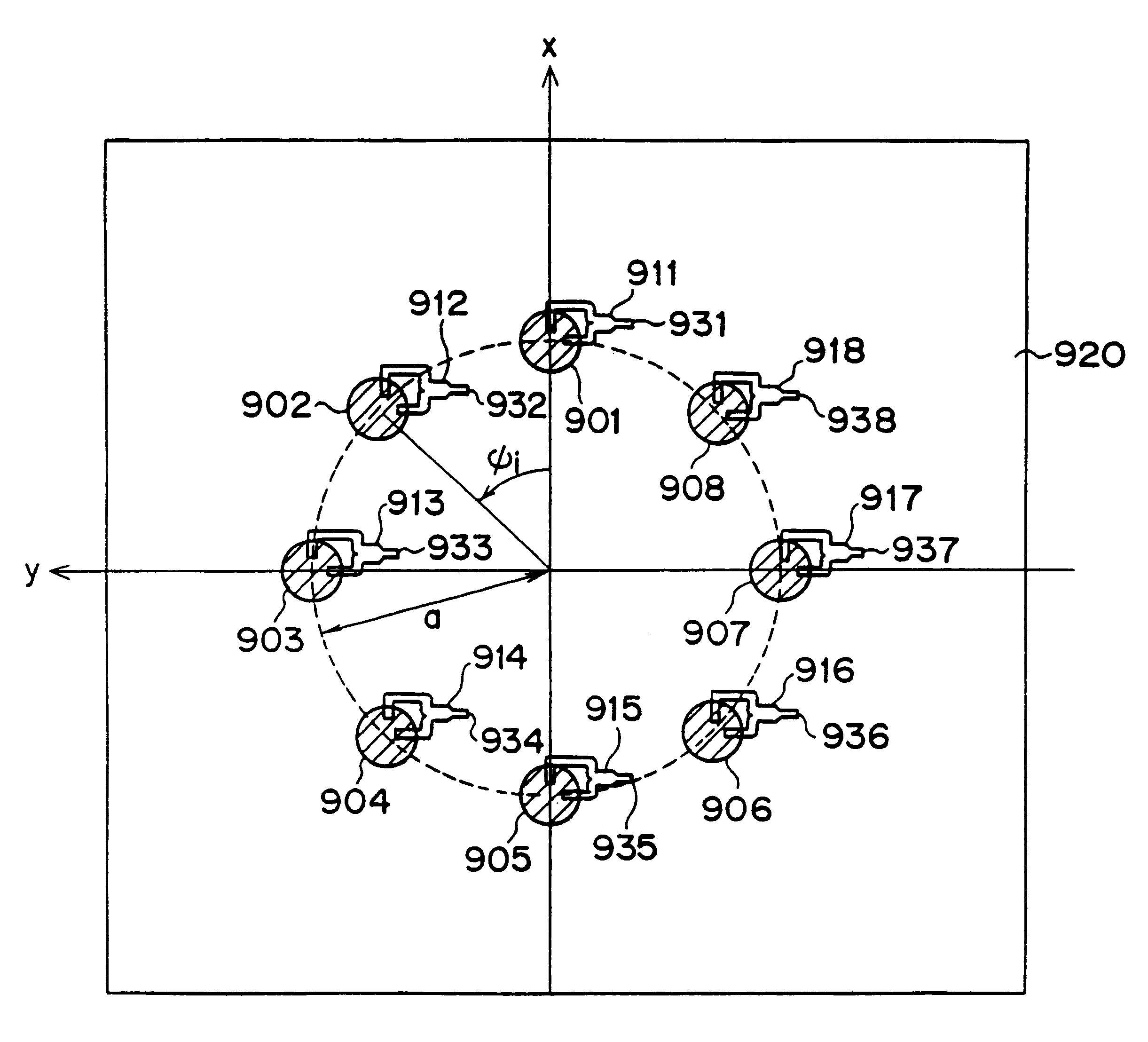
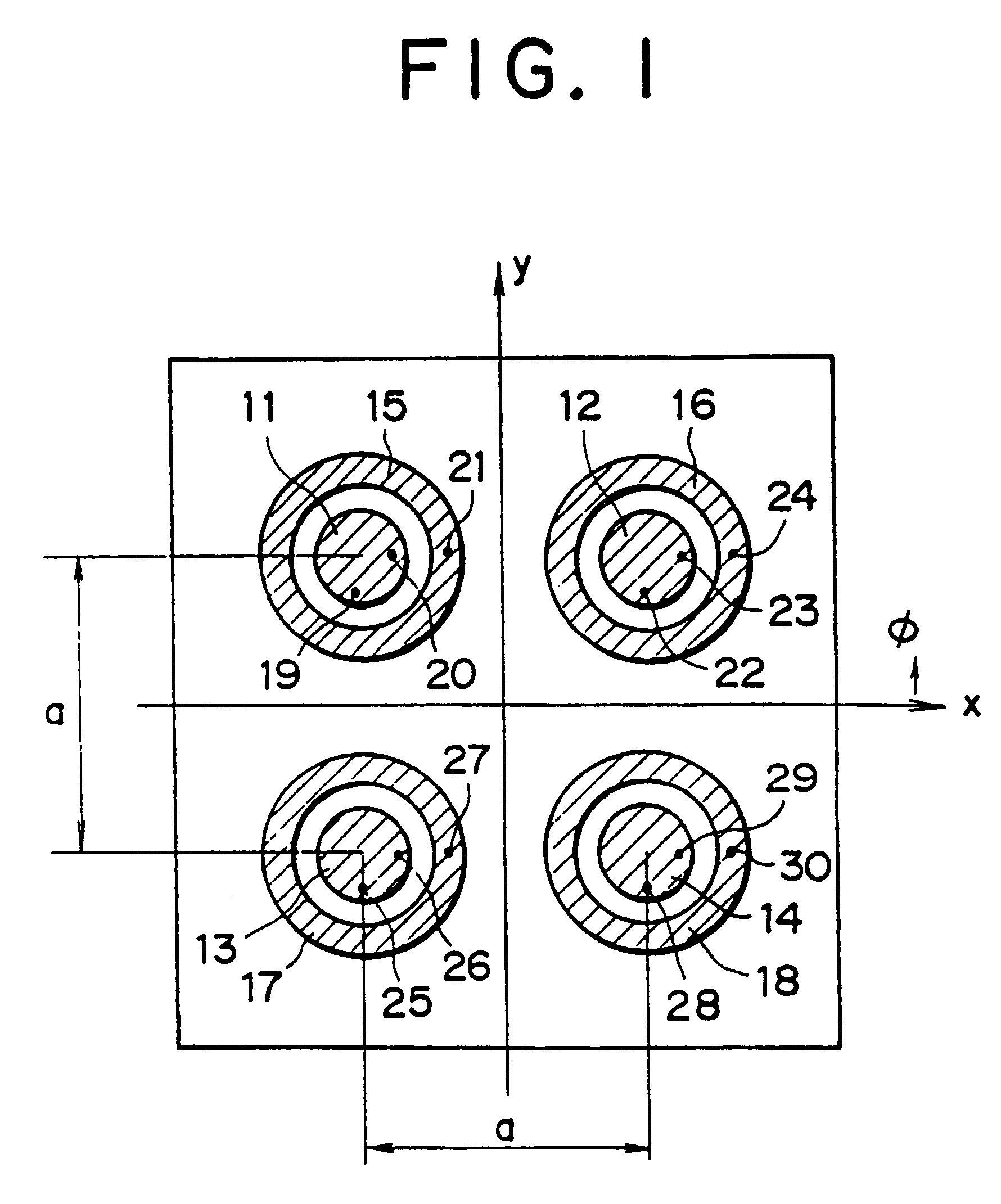
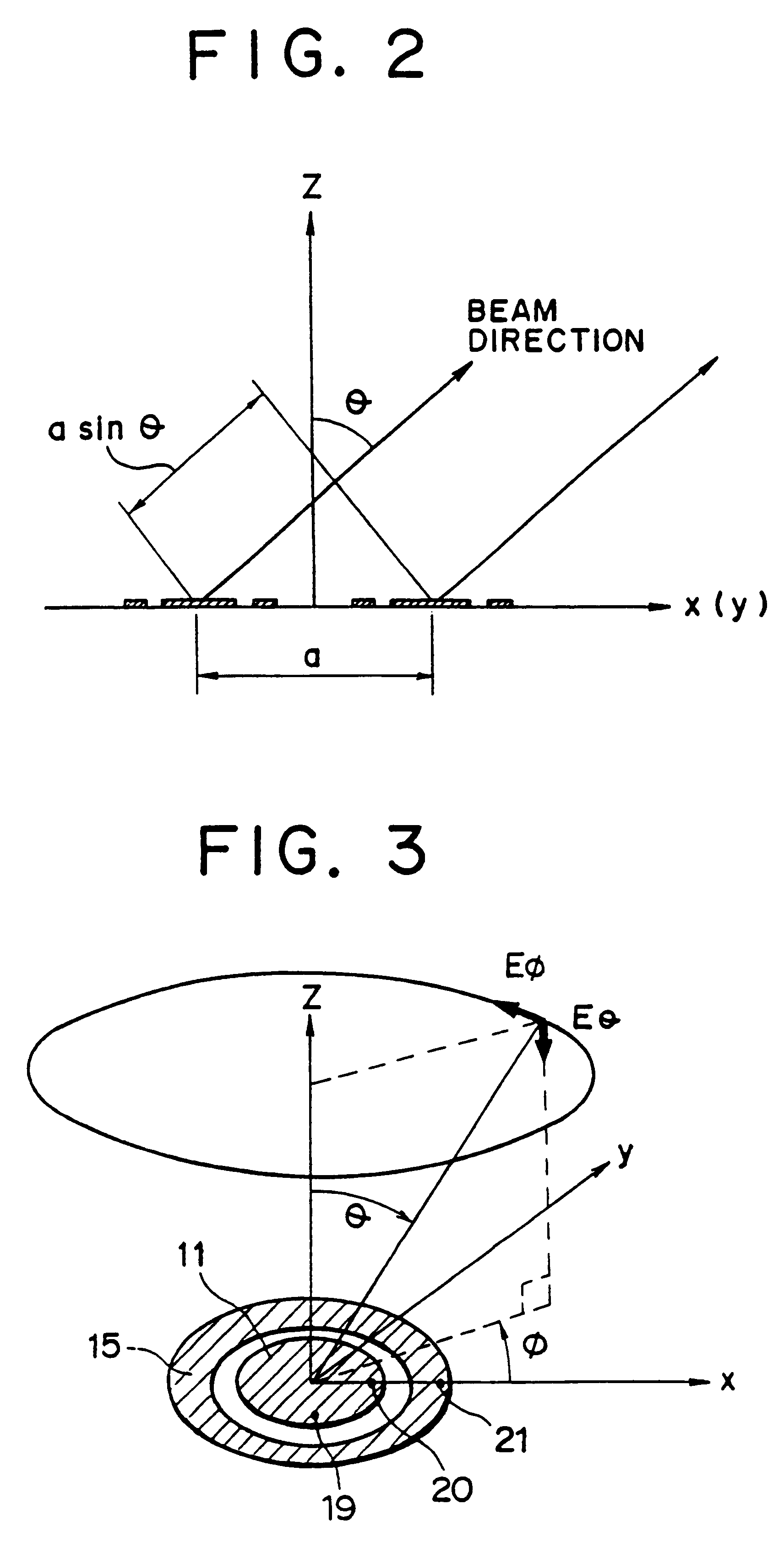
An array antenna is formed of a plurality of antenna elements, each of which scans a beam in the direction of an angle theta to a boresight of the antenna and electrically varies the direction of a rotation angle phi of the beam. The antenna elements are disposed so that the optical path difference of radio waves transmitted or received by two adjacent antenna elements in the directions of a plurality of direction angles phi on the plane tilted for an angle theta to the boresight of the antenna is nearly a multiple of the wave length of the radio waves.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
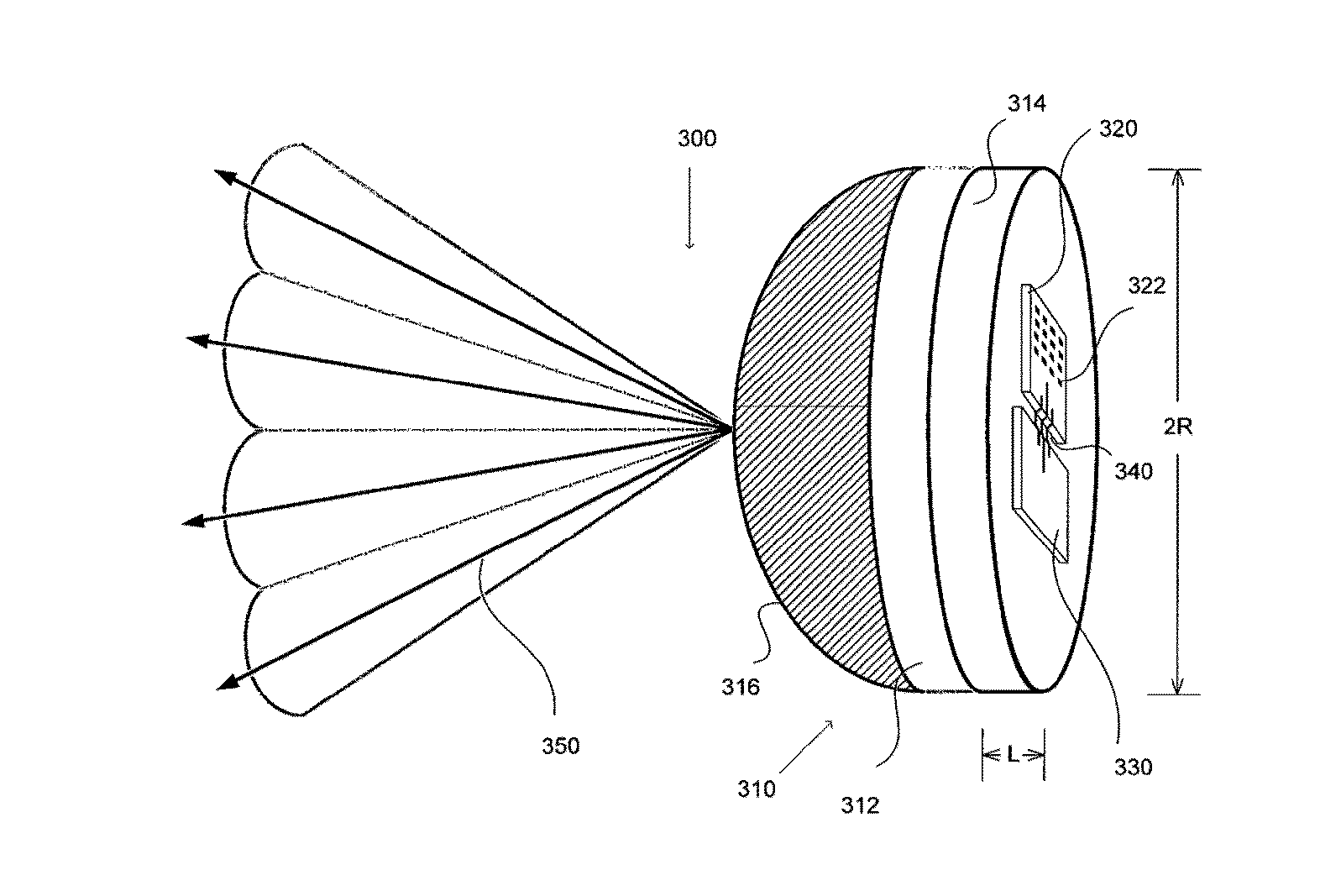
Lens antenna with electronic beam steering capabilities
InactiveUS20150116154A1Improve directivityImprove radiation efficiencyWaveguide hornsAntenna gainRadio relay
The invention discloses a lens antenna with high directivity intended for use in radio-relay communication systems, said antenna providing the capability of electronic steering of the main radiation pattern beam by switching between horn antenna elements placed on a plane focal surface of the lens. Electronic beam steering allows antenna to automatically adjust the beam direction during initial alignment of transmitting and receiving antennas and in case of small antenna orientation changes observed due to the influence of different reasons (wind, vibrations, compression and / or extension of portions of the supporting structures with the temperature changes, etc.). The technical result of the invention is the increase of the antenna directivity with simultaneously provided capability of scanning the beam in a continuous angle range and also the increase of the antenna radiation efficiency and, consequently, the increase of the lens antenna gain. This result is achieved by the implementation of horn antenna elements with optimized geometry.
Owner:OBSHCHESTVO S OGRANICHENNOJ OTVETSTVENNOSTYU RADIO GIGABIT
System and method of relay communication with electronic beam adjustment
ActiveUS20140227966A1Avoid the needSimple procedureAntenna supports/mountingsRadio transmissionTransceiverHigh-gain antenna
The invention relates to millimeter-wave point-to-point communication systems. A system comprises two separated millimeter-wave transceivers which provide high throughput data transmission and reception in frequency duplex mode and use high gain antennas capable of electronic scanning in some continuous angle range provided by the control module that implement control algorithms for antenna radiation pattern. Also a method based on the exploitation of scanning antennas of initial beam directions fine adjustment and subsequent beam directions tracking and readjustment when needed is proposed.The proposed system and method provide automatic recovery of failed connection in case of relay station orientation change due to influence of various external factors (wind, vibration, different intensity of heating of the bracing mountings at different time of a day and others) and can be used in backhaul systems of base station sites for mobile networks.
Owner:OBSHCHESTVO S OGRANICHENNOJ OTVETSTVENNOSTYU RADIO GIGABIT
End-to-end service quality monitoring method and system in a radio network
ActiveUS20110096678A1Prevent data security threatGuaranteed continuous availabilityError preventionTransmission systemsQuality of serviceRadio networks
The present invention discloses a method and a system for service quality monitoring in a network comprising radio interfaces. The measurements are end-to-end measurements between the end user and chosen network element. The measurements are implemented using monitoring stations which can monitor the traffic passively or actively by transmitting test signals. The antenna beam directions of the monitoring stations can be controlled. The performance server works as a counterpart of the active tests. A reporting suite may define the performed measurements and it also collects the measurement data from different monitoring stations. Monitoring data from several corporate intranets can also be collected to an external server through internet connection.
Owner:7SIGNAL OY
Apparatus and method for adaptive beam-forming in wireless communication system
ActiveUS20130039345A1Effectively performing beam-formingImprove performanceError preventionNetwork topologiesCommunications systemTelecommunications
Apparatuses and methods for maintaining an optimal beam direction in a wireless communication system are provided. The method for operating a receiving node in a wireless communication system includes, determining a first transmission beam is determined as a preferred transmission beam using a plurality of reference signals transmitted by a transmitting node, generating preferred transmission beam information, transmitting the preferred transmission beam information to the transmitting node, receiving transmissions from the transmitting node via the first transmission beam, and determining whether a change of a transmission beam is necessary. When the change of the transmission beam is determined to be necessary, generating a beam change request and transmitting the beam change request to the transmitting node.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Cone beam CT scanning
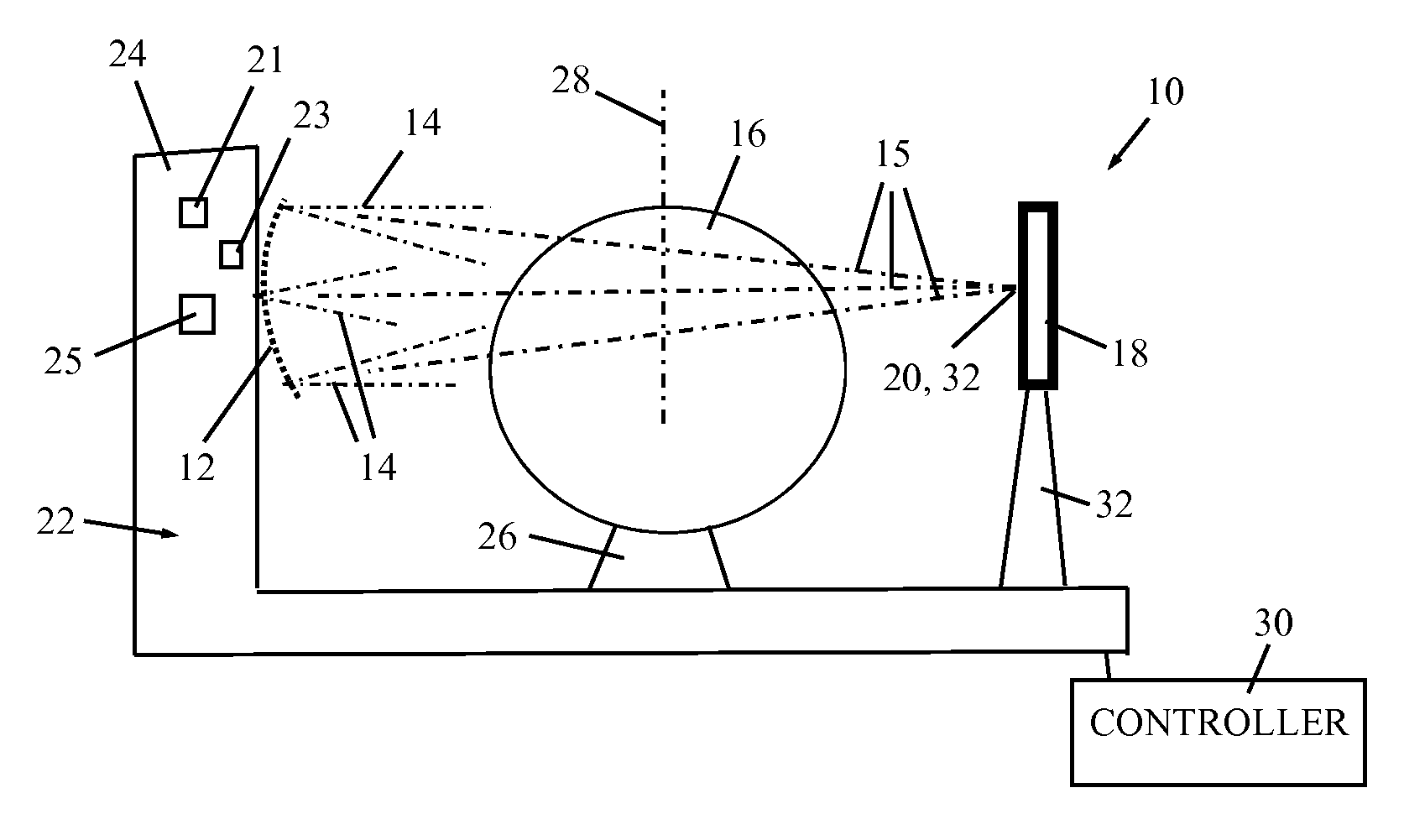
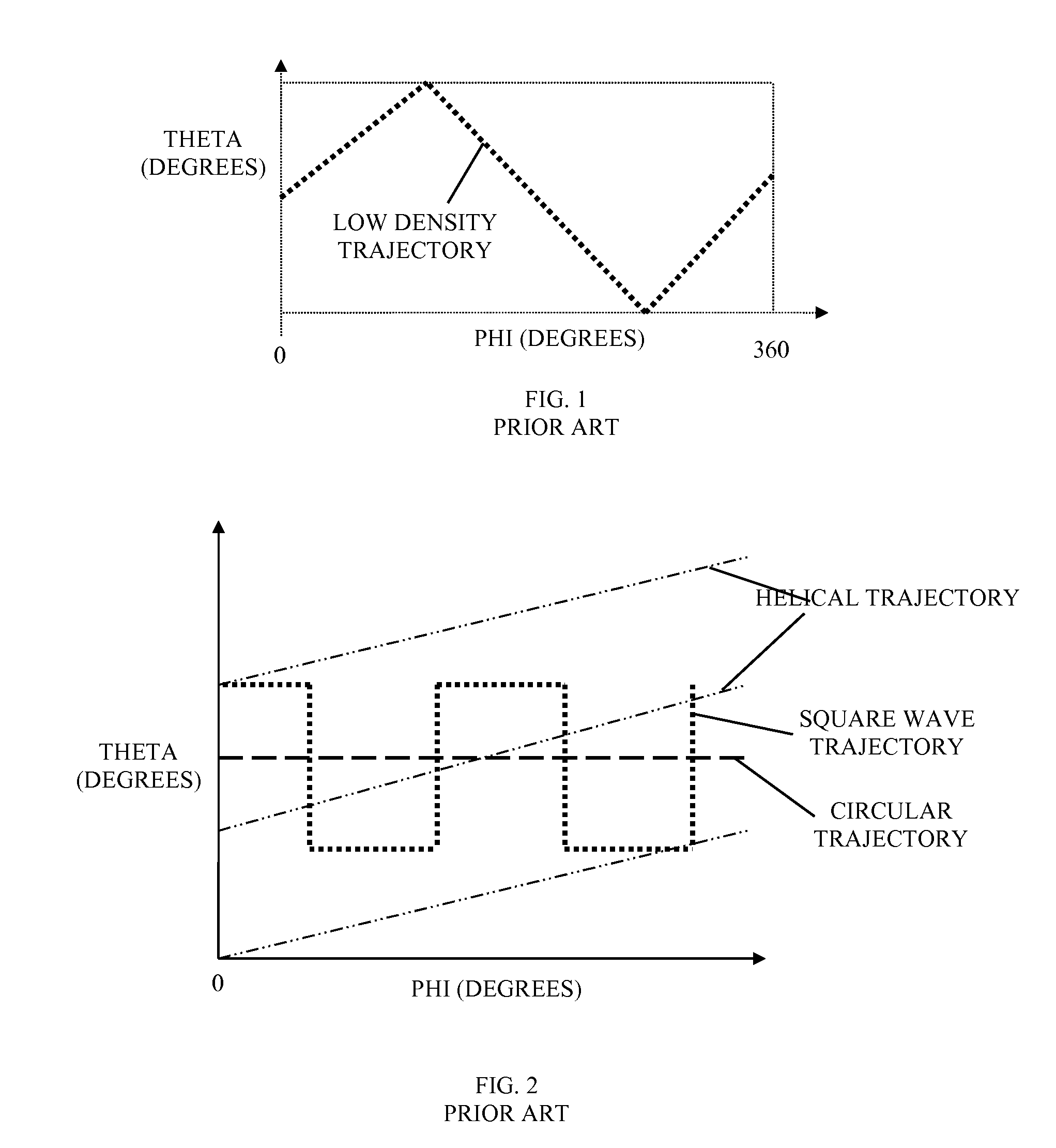
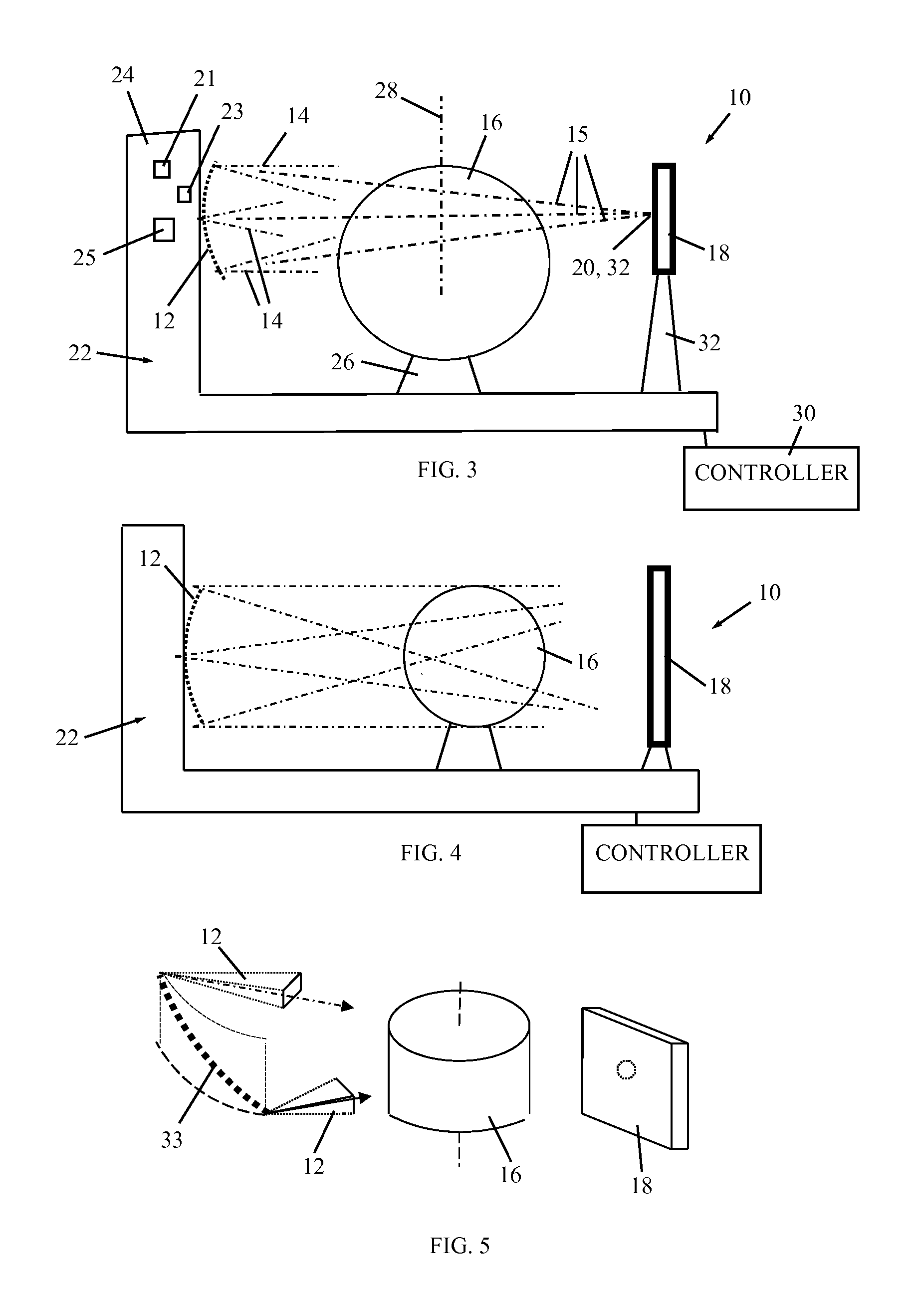
A CBCT system is described that includes a radiation source for emitting a cone beam of radiation in a beam direction towards an object, a detector for detecting the cone beam of radiation, and a positioner for moving the radiation source and the object according to a scanning trajectory. The system is operated according to a sampling pattern that includes intersections of the scanning trajectory and a reconstruction trajectory, wherein motion of the radiation source is substantially confined to a spherical shell. The positioner moves the radiation source at a speed higher than a highest speed of the object by a factor of at least 10. The largest angular discrepancy between any vector in a range of the scanning trajectory and the nearest sample of the scanning trajectory does not exceed 10°, preferably 6° and more preferably 3°.
Owner:EIN GAL MOSHE
Method And Software For Irradiating A Target Volume With A Particle Beam And Device Implementing Same
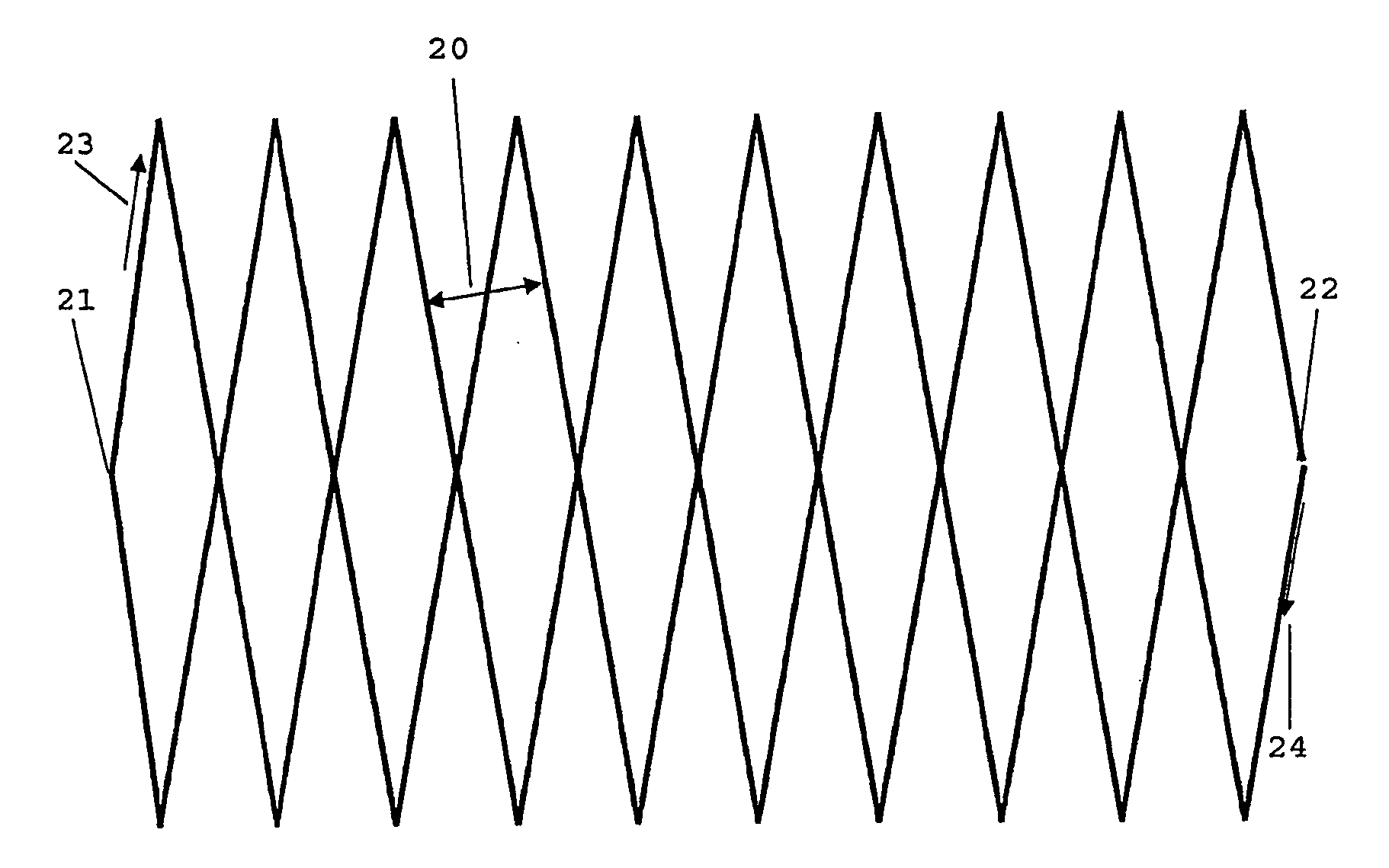
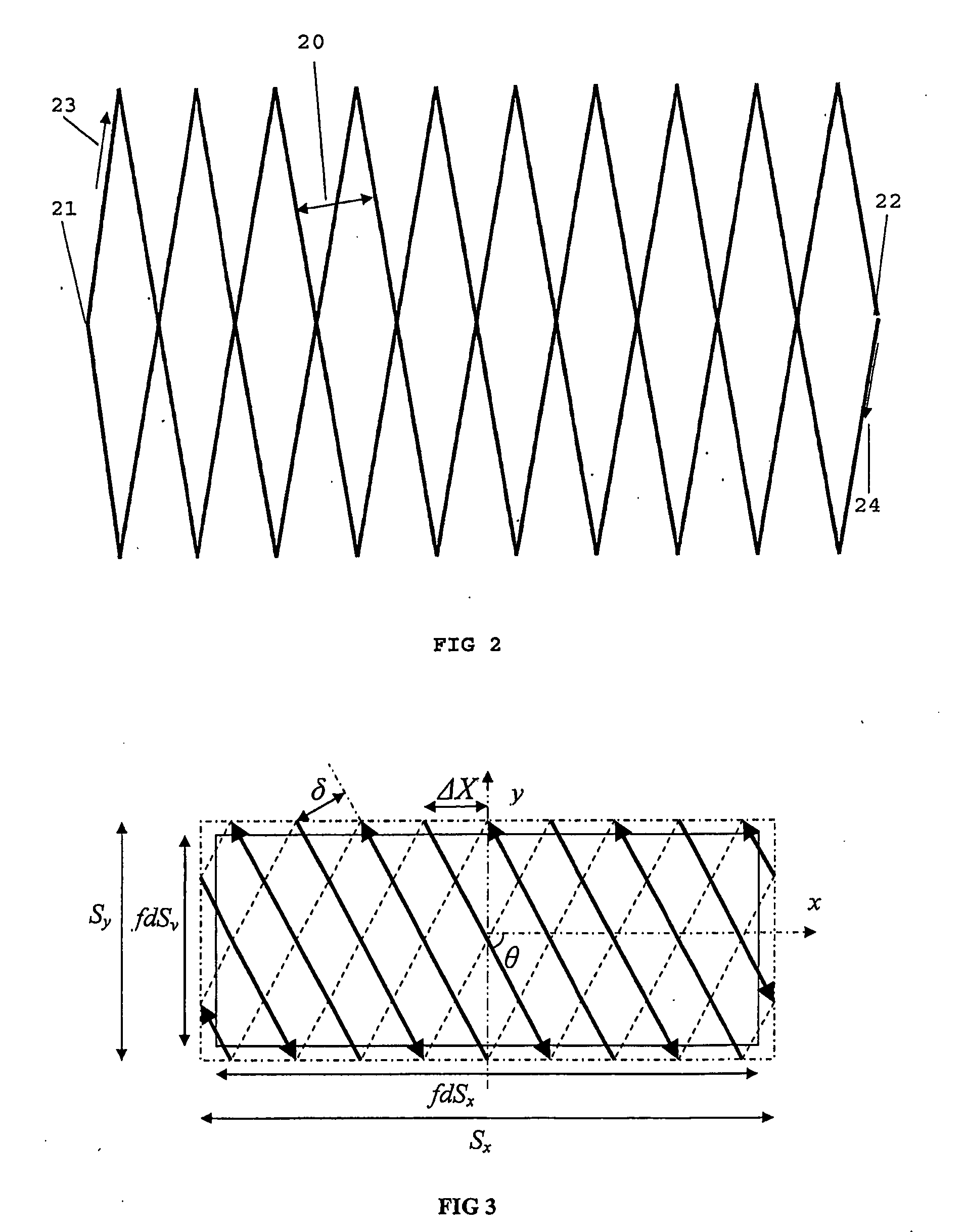
The present invention is related to a method for treating or irradiating a target volume with a particle beam produced by an accelerator, comprising the steps of: deflecting said particle beam with the help of scanning means in two orthogonal (X, Y) directions, thereby constituting an irradiation plane perpendicular to the direction (Z) of the beam, defining in the irradiation plane a scanning field which circumscribes the area of intersection of target volume and irradiation plane and scanning said scanning field by drawing scan lines which form a scan pattern comprising interleaved frames of triangle waves. The scan pattern is preferably continuous and represents contiguous rhombi figures. The invention is equally related to a device and a software program or sequencer implementing the method.
Owner:ION BEAM APPL
Wireless communication method
ActiveUS20070243878A1Prevent throughput degradationReduce the amount requiredSite diversityCode division multiplexData rateBeam direction
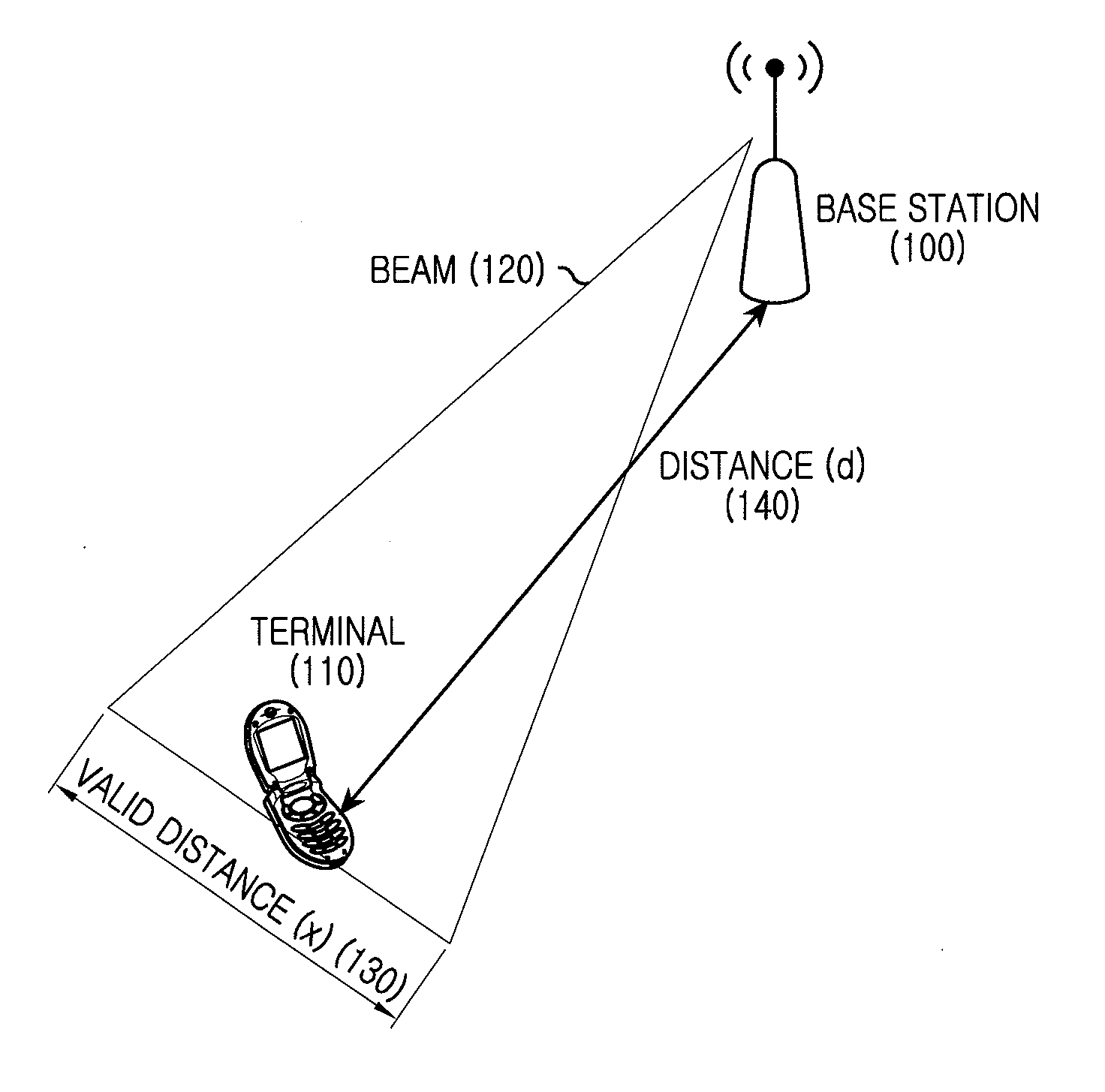
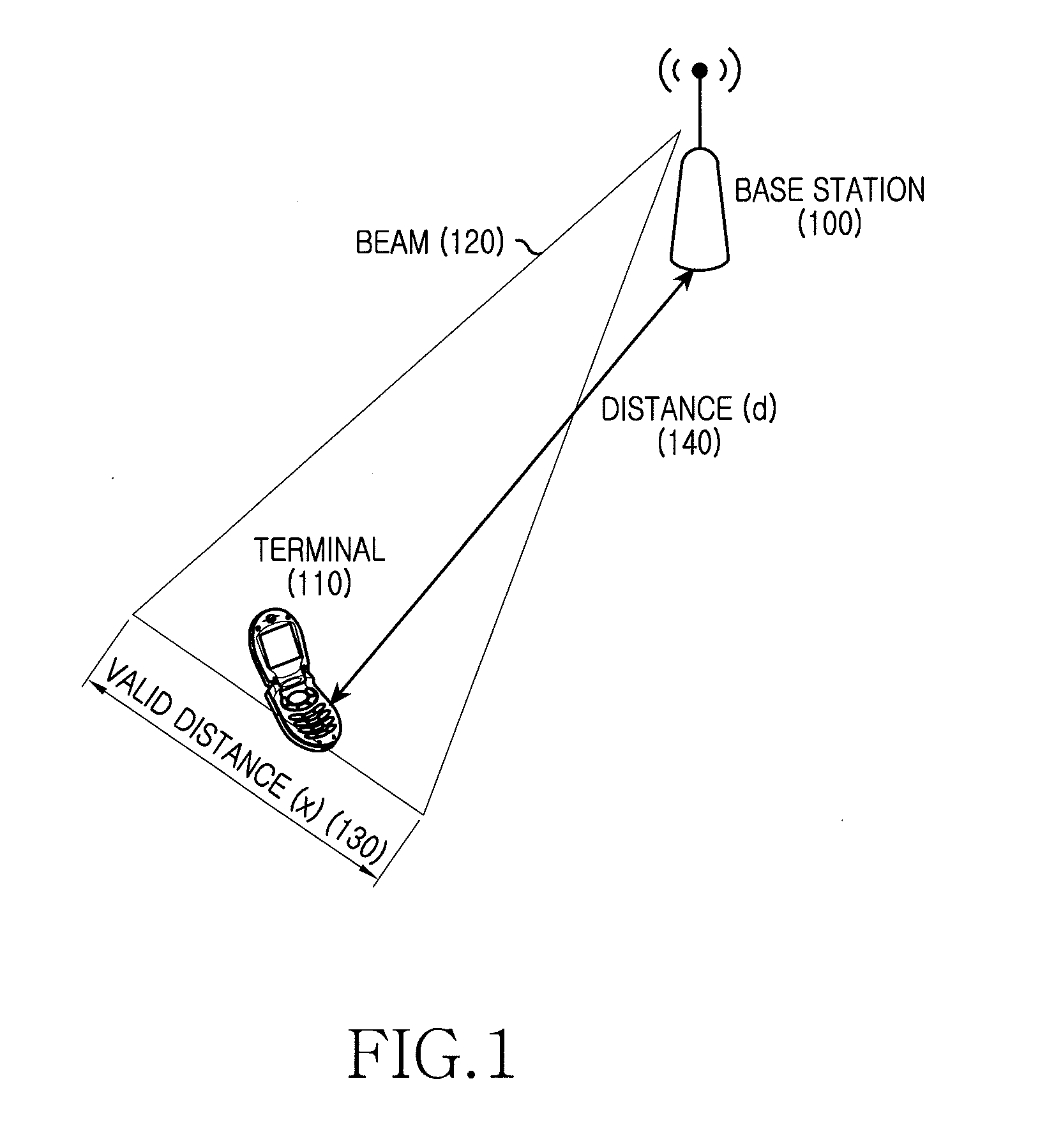
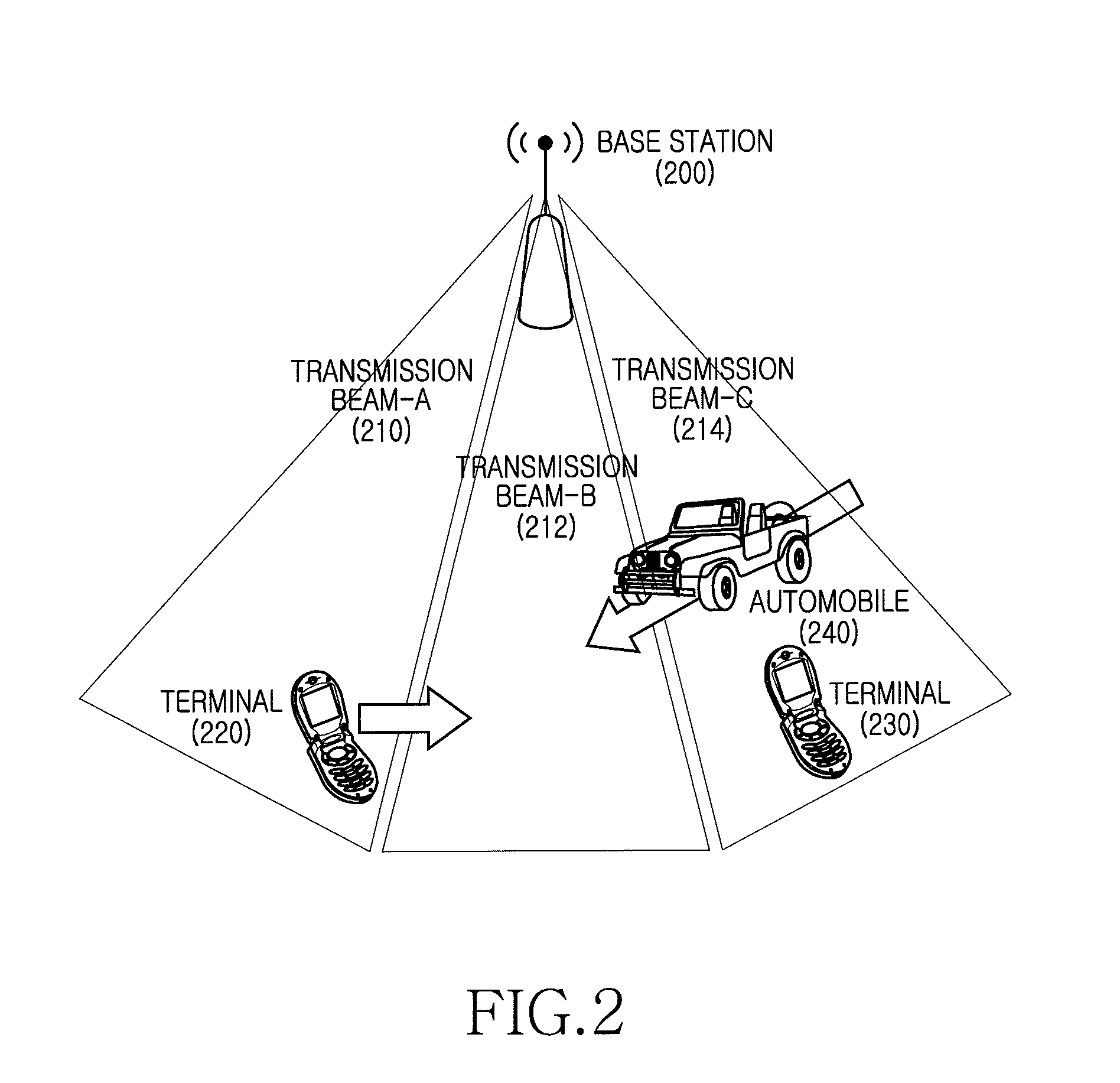
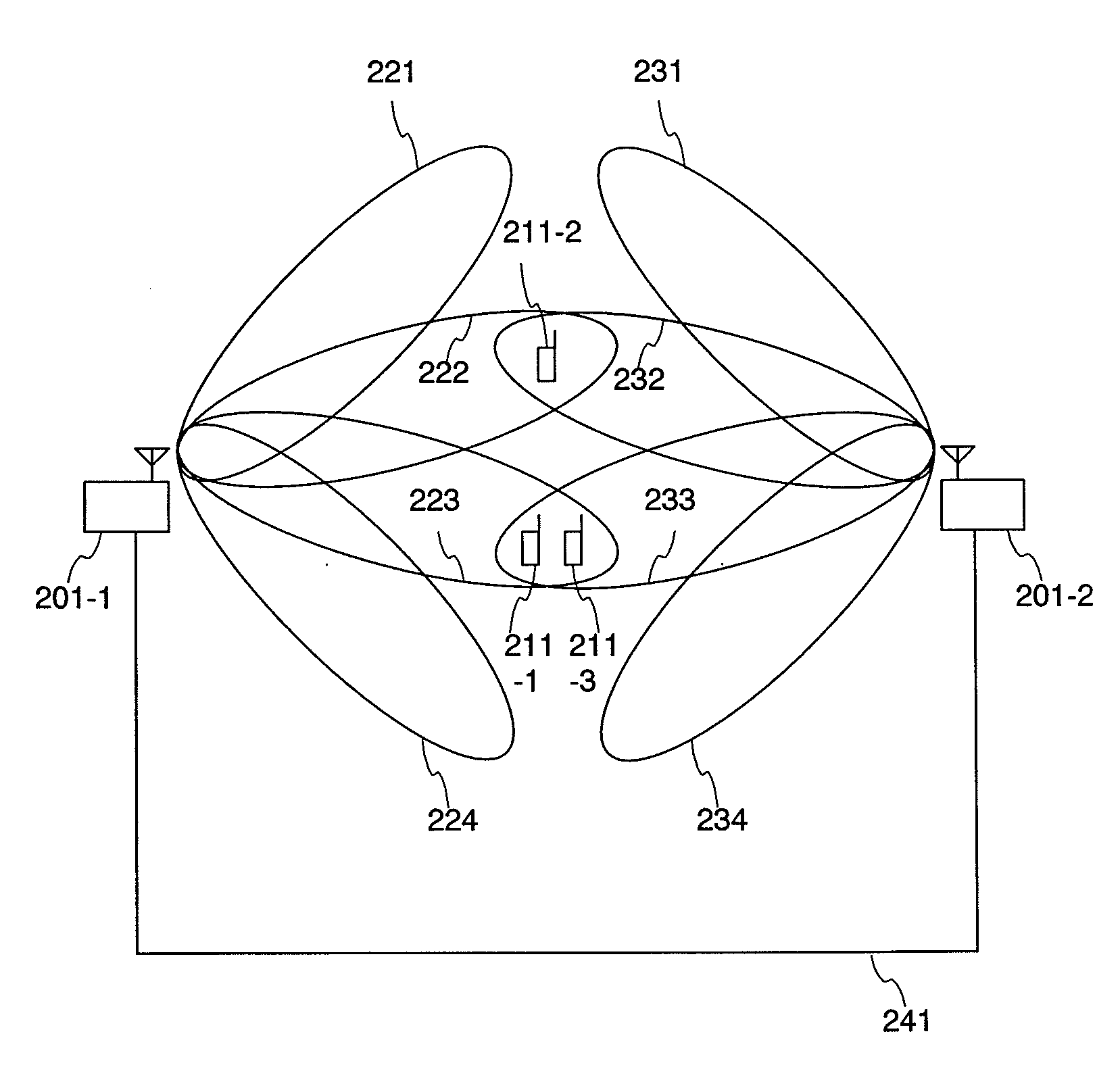
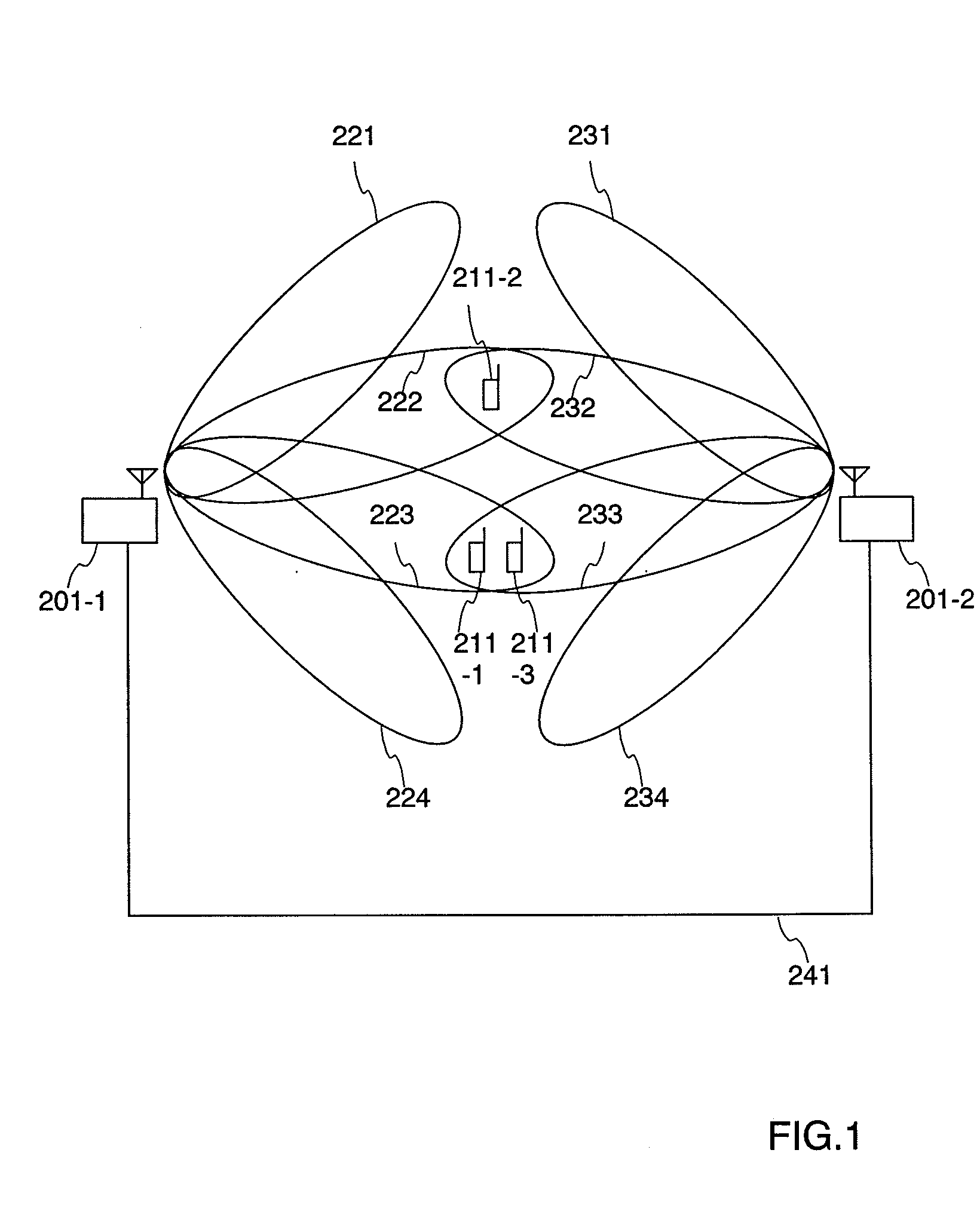
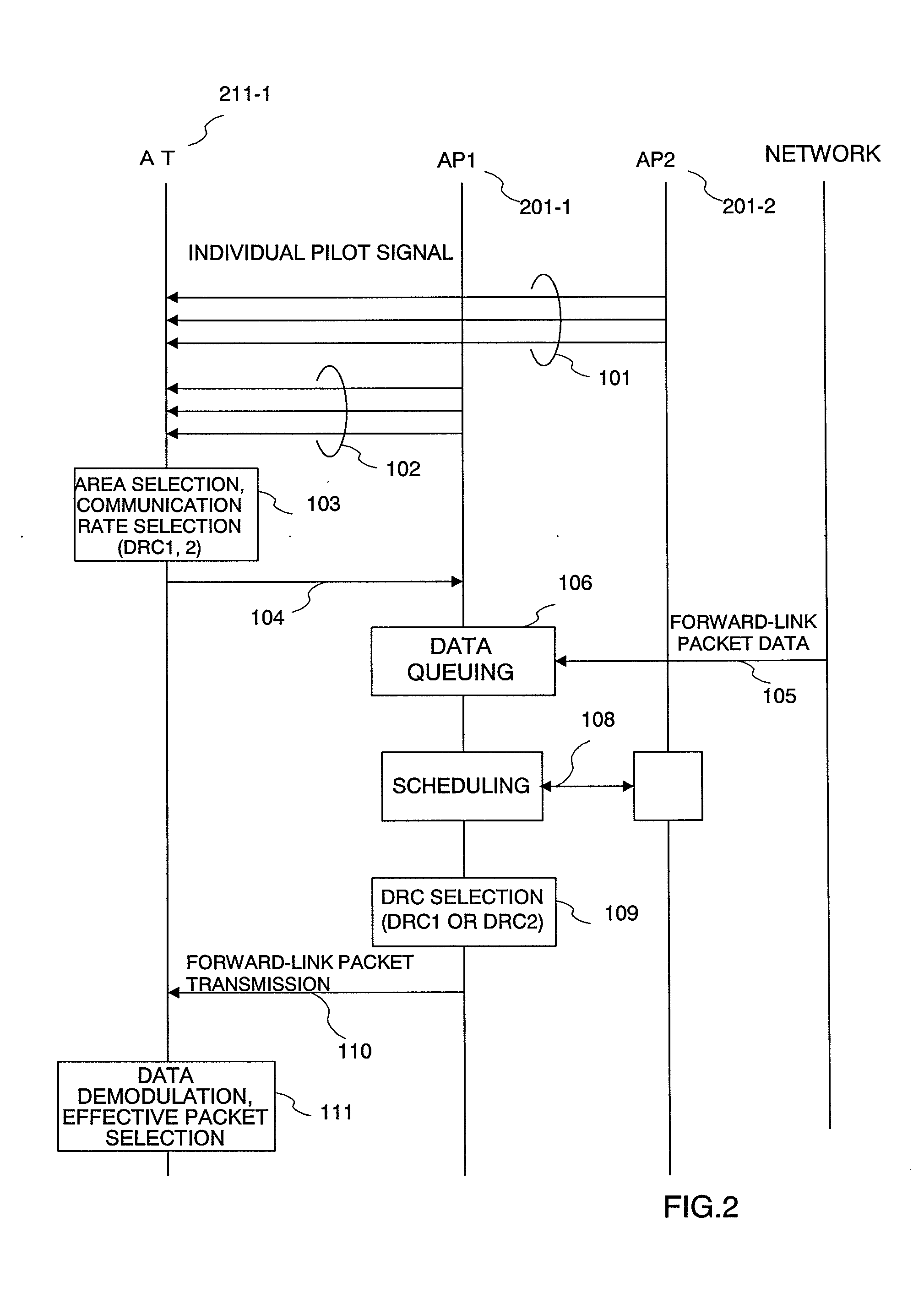
A terminal 211 measures pilot signals transmitted in directional (beam) patterns from an adjacent cell and an own cell, and estimates reception qualities with the presence (high) / absence (low) of the interference from the adjacent cell. The terminal 211 requests data rate request values (DRC1, DRC2) corresponding to the reception qualities with the presence / absence of the interference to the base station 201. The base station 201 shares beam direction schedule with an adjacent cell base station, and confirms the presence / absence of interference to the terminal 211 for each slot. In accordance with the presence / absence of the interference, the base station 201 selects a suitable one of the two values of the data rates requested from the terminal 211, and modulates the data and transmits it.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Antenna and method for steering antenna beam direction
ActiveUS7911402B2Simultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsBeam directionEngineering
An antenna comprising an IMD element, and one or more parasitic and active tuning elements is disclosed. The IMD element, when used in combination with the active tuning and parasitic elements, allows antenna operation at multiple resonant frequencies. In addition, the direction of antenna radiation pattern may be arbitrarily rotated in accordance with the parasitic and active tuning elements.
Owner:KYOCERA AVX COMPONENTS (SAN DIEGO) INC
Apparatus and method for beam locking in wireless communication system
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Radio communication method in a wireless local network
ActiveUS7729662B2Raise the ratioConvenient timeSpatial transmit diversityWireless commuication servicesCommunication qualityTransceiver
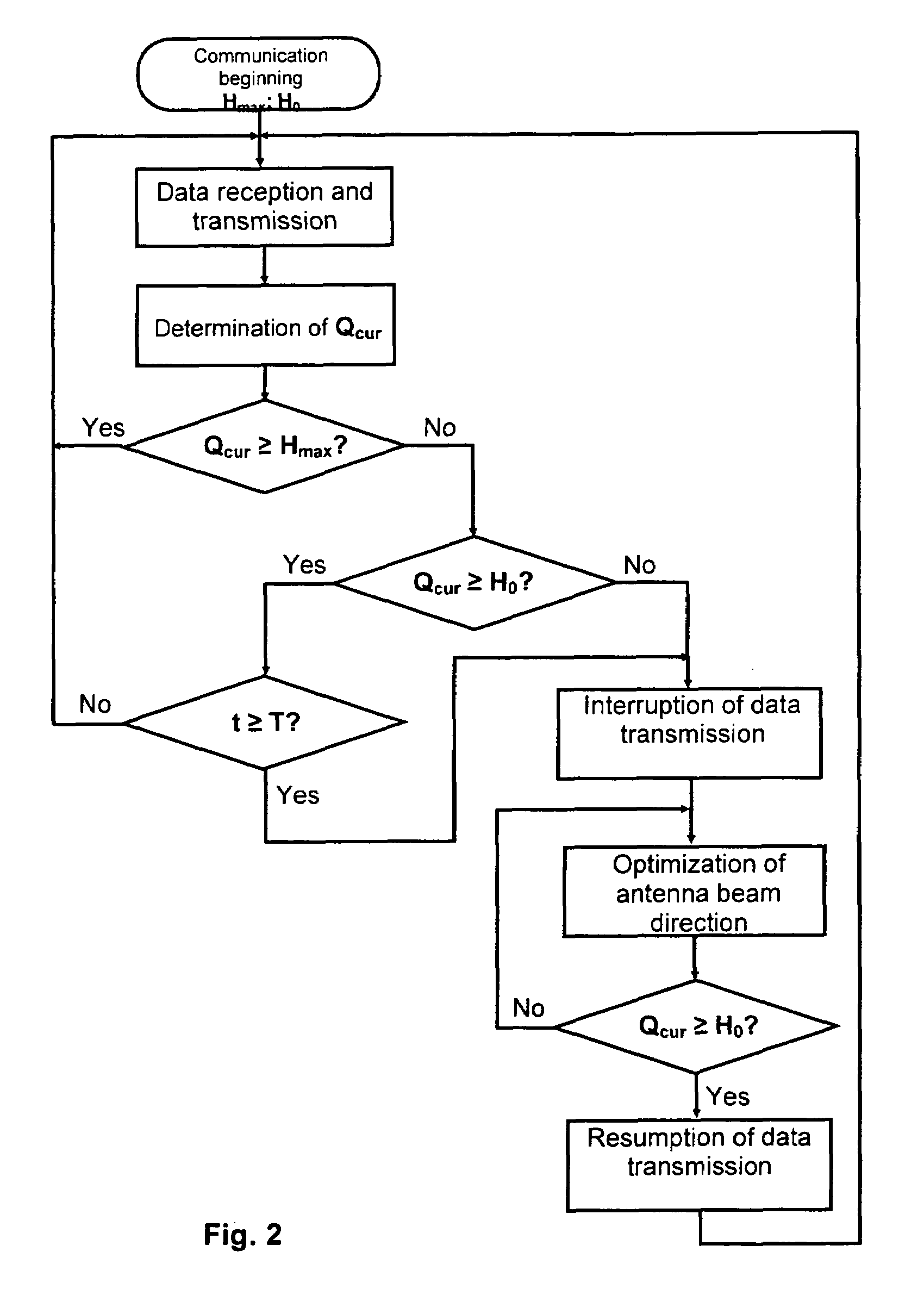
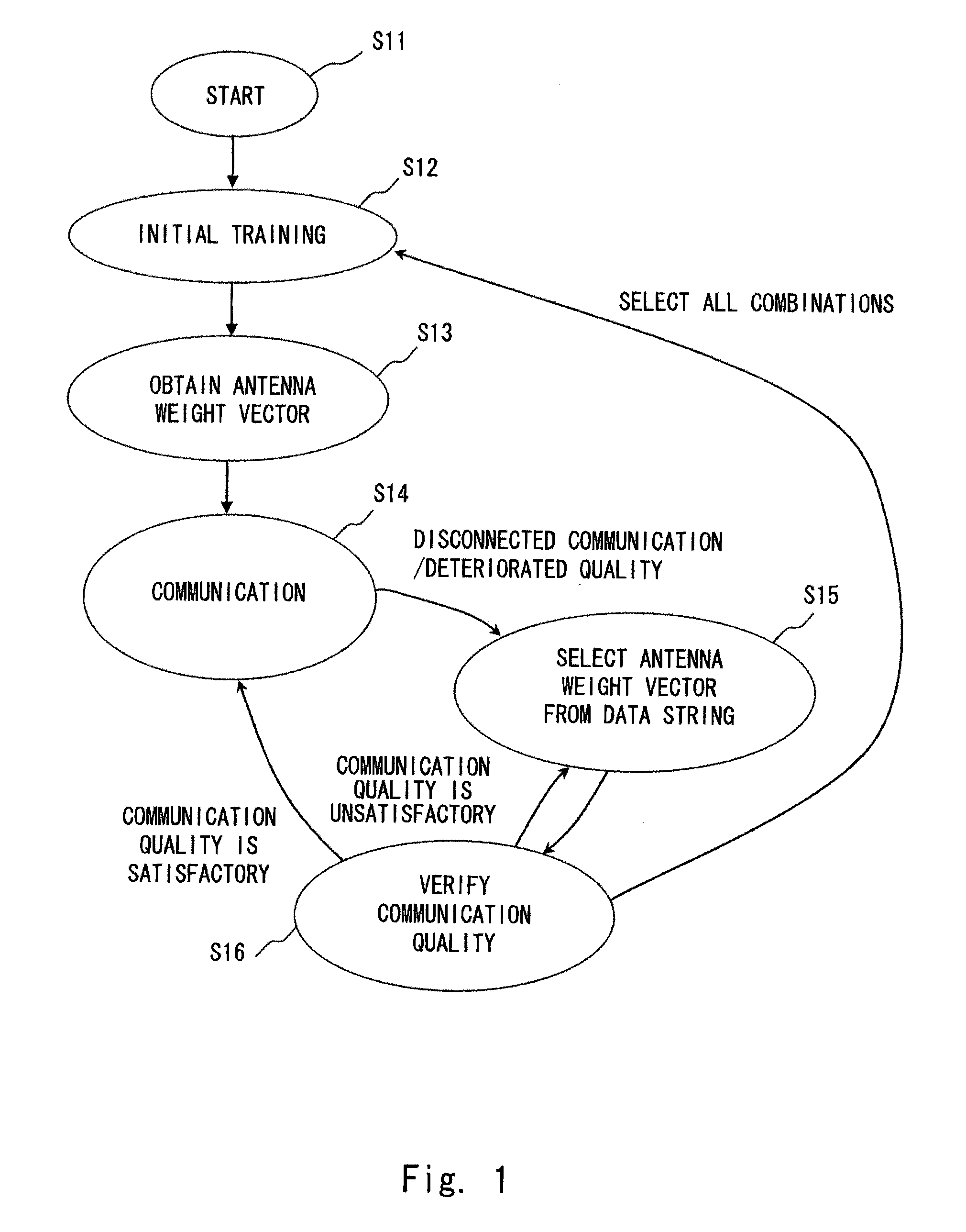
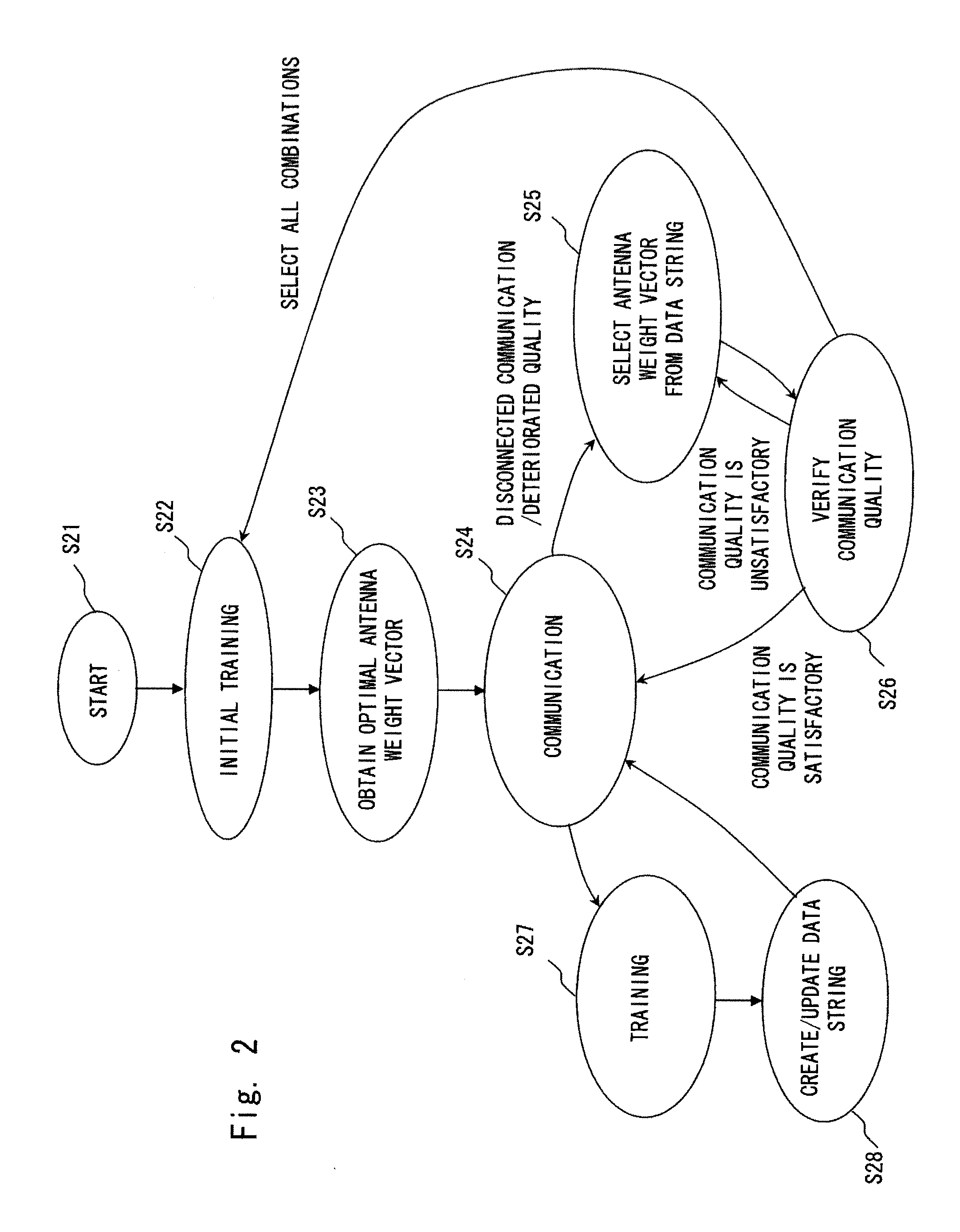
A method for radio communication in a wireless local area network including at least one transceiver equipped with an antenna with a controlled directivity pattern, according to which, in addition to the assignment in advance of the threshold value of communication quality H0 corresponding to the minimum pre-specified communication quality, the current value of communication quality Qcur is periodically determined based on the signal being received, the threshold value of the communication quality Hmax (corresponding to the pre-specified maximum communication quality) is also additionally assigned in advance. With the current value of communication quality Qcur being grater than or equal to the upper threshold value Hmax, the information exchange is continued, while with the current communication quality value Qcur being less than the upper threshold value Hmax, but greater than or equal to the lowest threshold value H0, the information exchange is also continued and the procedure for the optimization of antenna beam direction is carried out after a pre-specified time interval T.
Owner:AIRGAIN INC
Beam-oriented pixellated scintillators for radiation imaging
ActiveUS7692156B1Improved performance characteristicsImprove spatial resolutionSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansHigh resolution imagingImage resolution
The present invention provides radiation detectors and methods, including radiation detection devices having beam-oriented scintillators capable of high-performance, high resolution imaging, methods of fabricating scintillators, and methods of radiation detection. A radiation detection device includes a beam-oriented pixellated scintillator disposed on a substrate, the scintillator having a first pixel having a first pixel axis and a second pixel having a second pixel axis, wherein the first and second axes are at an angle relative to each other, and wherein each axis is substantially parallel to a predetermined beam direction for illuminating the corresponding pixel.
Owner:RADIATION MONITORING DEVICES
Control method of wireless communication system, wireless communication system, transmitting apparatus, and receiving apparatus
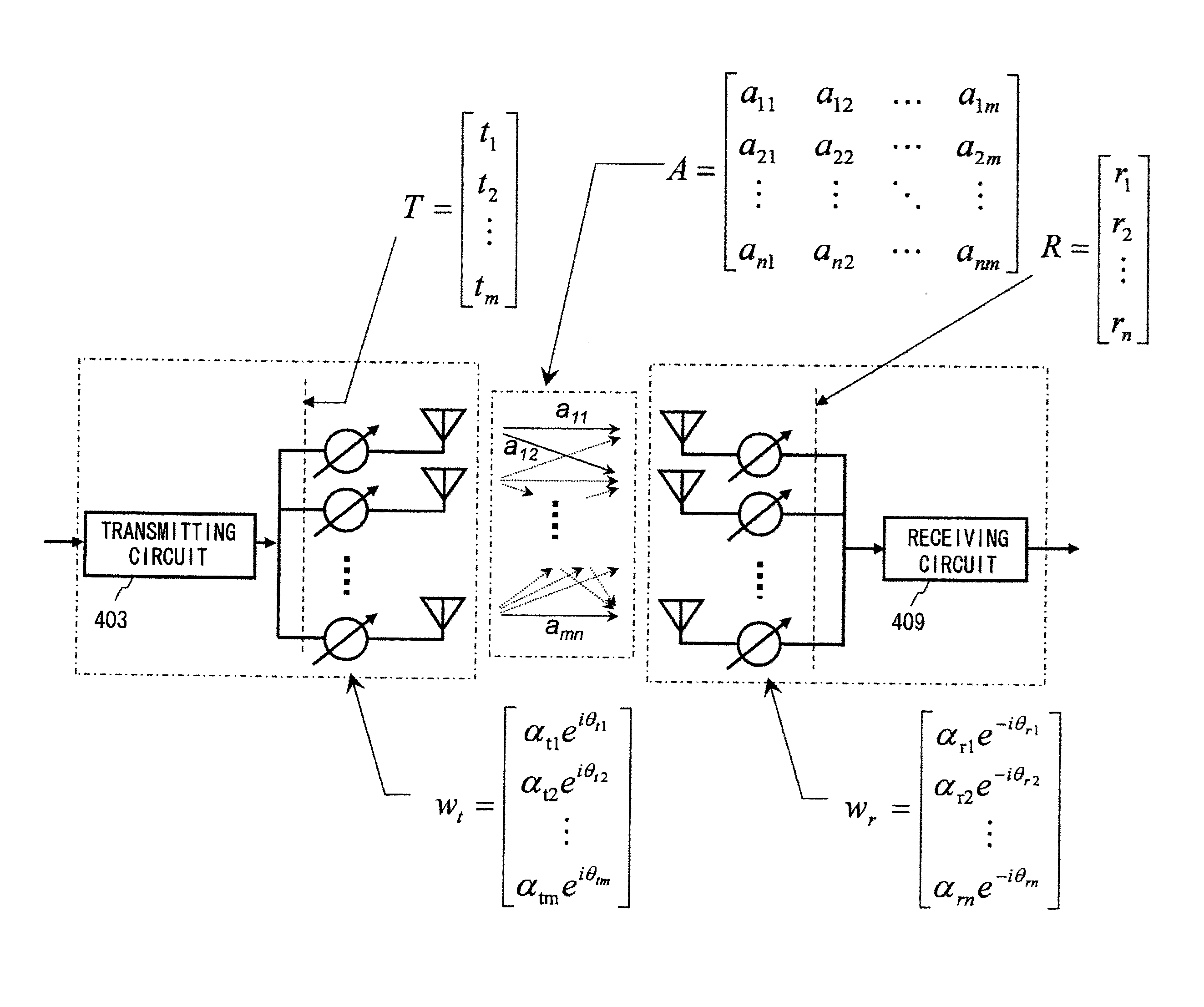
ActiveUS20110105032A1Improve communication qualityShort timeSpatial transmit diversityRadio transmission for post communicationSingular value decompositionCommunications system
A channel response matrix is obtained by performing a training process between a transmitter 401 and a receiver 402 to obtain optimal signal phases of the antenna array. Next, a singular-value decomposition (SVD) process is performed to decompose the channel response matrix into a correlation matrix and eigenvalues. Next, a diagonal matrix having square roots of the eigenvalues as its components is obtained. Next, all but one of diagonal components included in the diagonal matrix are replaced with zeros, and optimal setting of the amplitudes and phases of signals to be applied to the antenna array (antenna weight vector) for use in wireless communication between the transmitter and the receiver is obtained based on a channel response matrix that is reconstructed by using the component-replaced diagonal matrix. In this way, when wireless communication is implemented by performing beam forming, the time necessary to find and set a beam direction can be reduced.
Owner:NEC CORP
Method and apparatus for treatment by ionizing radiation
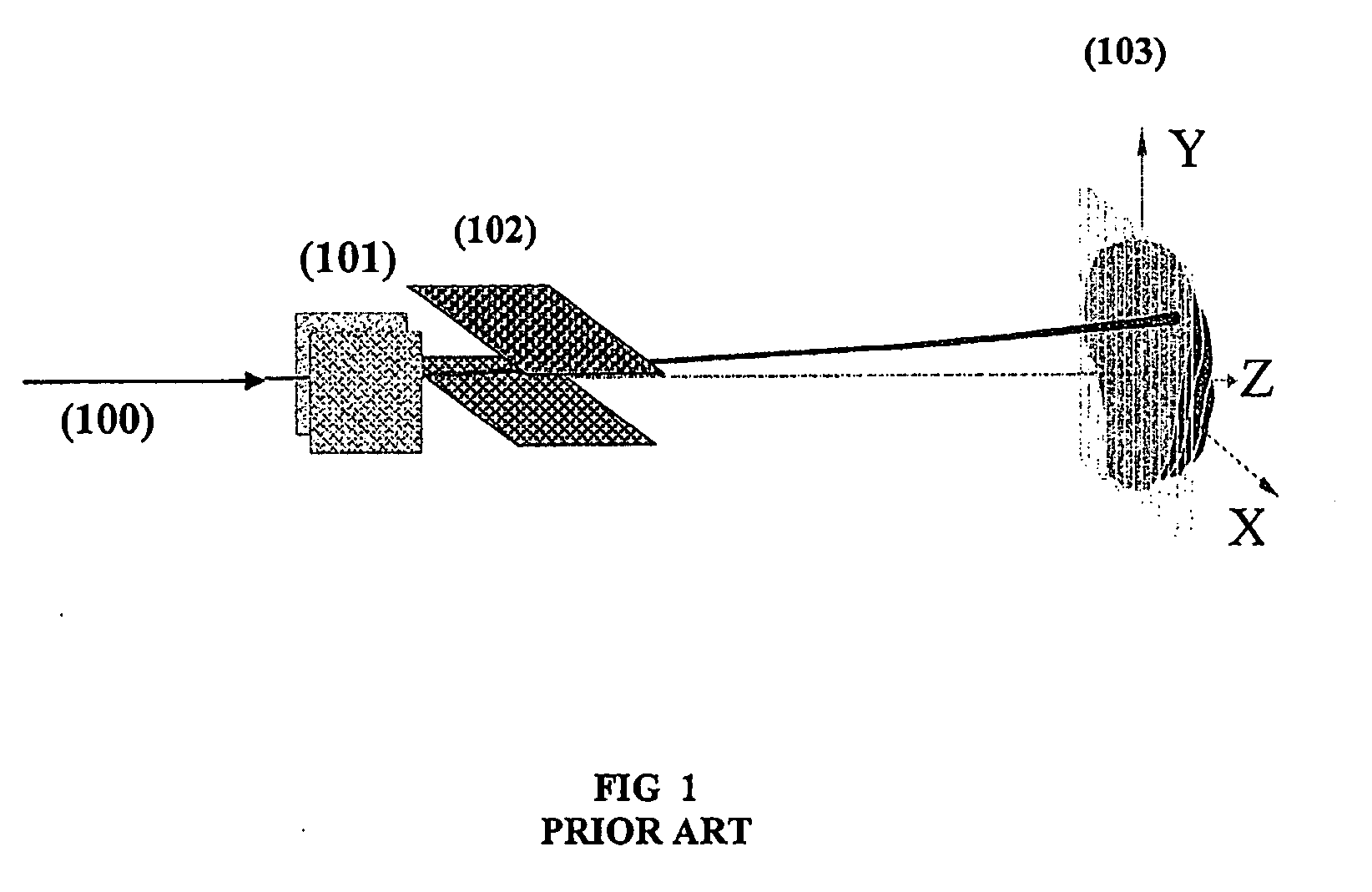
ActiveUS20050089141A1Improve accuracyEasy to operateMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingBeam directionLight beam
A radiation therapy / surgery device optimised to meet the needs of the Neurosurgeon is provided, i.e. one for the treatment of tumours in the brain. It combines the qualities of a good penumbra and accuracy, simple prescription and operation, together with high reliability and minimal technical support. The device comprises a rotateable support, on which is provided a mount extending from the support out of the plane of the circle, and a radiation source attached to the mount via a pivot, the pivot having an axis which passes through the axis of rotation of the support, the radiation source being aligned so as to produce a beam which passes through the co-incidence of the rotation axis and the pivot. It will generally be easier to engineer the apparatus if the rotateable support is planar, and more convenient if the rotateable support is disposed in an upright position. The rotation of the rotateable support will be eased if this part of the apparatus is circular. A particularly preferred orientation is one in which the radiation source is spaced from the rotateable support, to allow it to pivot without fouling the latter. It is thus preferred that the mount extends transverse to the support. In this way, the pivot axis is spaced from the rotateable support providing free space in which the radiation source can pivot. Another way of expressing this preference is to state that the pivot axis is located out of the plane of the rotateable support. To simplify the geometry of the device and the associated arithmetic, it is preferred both that the pivot axis is substantially perpendicular to the rotation axis, and that the beam direction is perpendicular to the pivot axis. It is preferred that the radiation source is a linear accelerator. The output of the radiation source is preferably collimated to conform to the shape of the area to be treated.
Owner:ELEKTA AB
Antenna and method for steering antenna beam direction
ActiveUS20090224991A1Simultaneous aerial operationsIndividually energised antenna arraysBeam directionCombined use
An antenna comprising an IMD element, and one or more parasitic and active tuning elements is disclosed. The IMD element, when used in combination with the active tuning and parasitic elements, allows antenna operation at multiple resonant frequencies. In addition, the direction of antenna radiation pattern may be arbitrarily rotated in accordance with the parasitic and active tuning elements.
Owner:KYOCERA AVX COMPONENTS (SAN DIEGO) INC
Apparatus and method for beam locking in a wireless communication system
ActiveUS20130017836A1Radio transmissionWireless communicationMeasurement deviceCommunications system
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Wideband interference cancellation using DSP algorithms
ActiveUS7362257B2Easy to detectFunction increaseCommunication jammingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionDiscriminatorFrequency spectrum
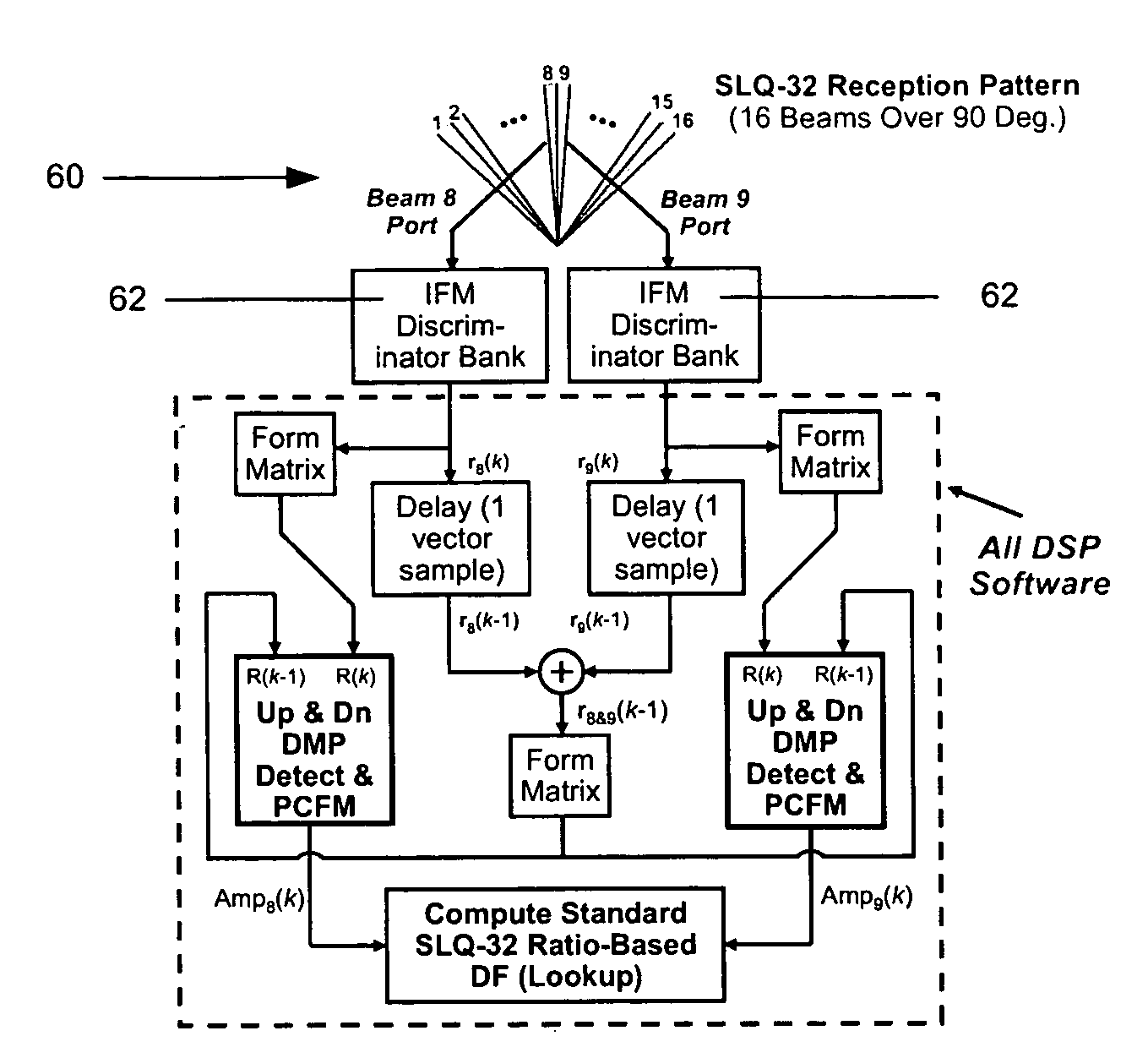
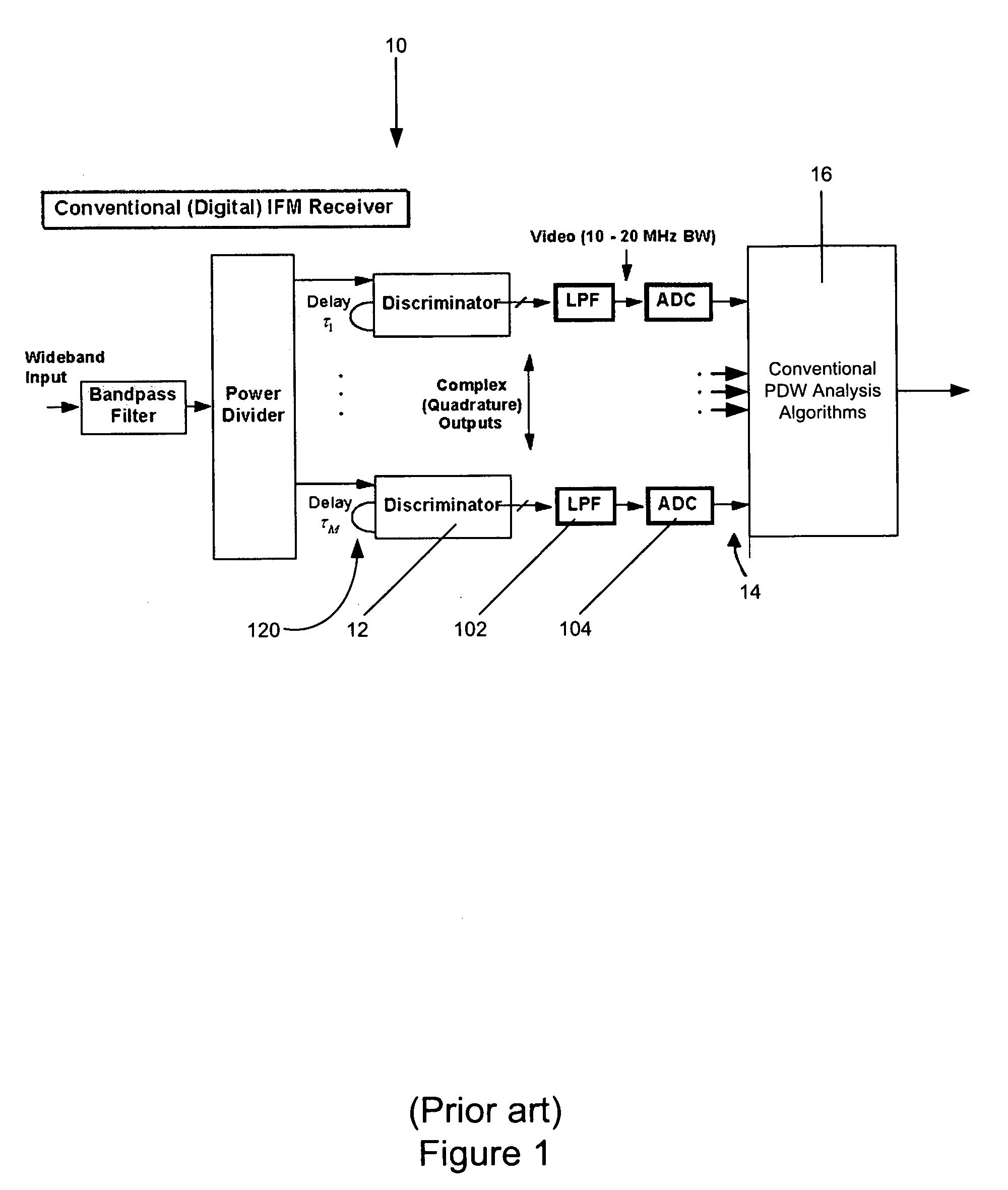
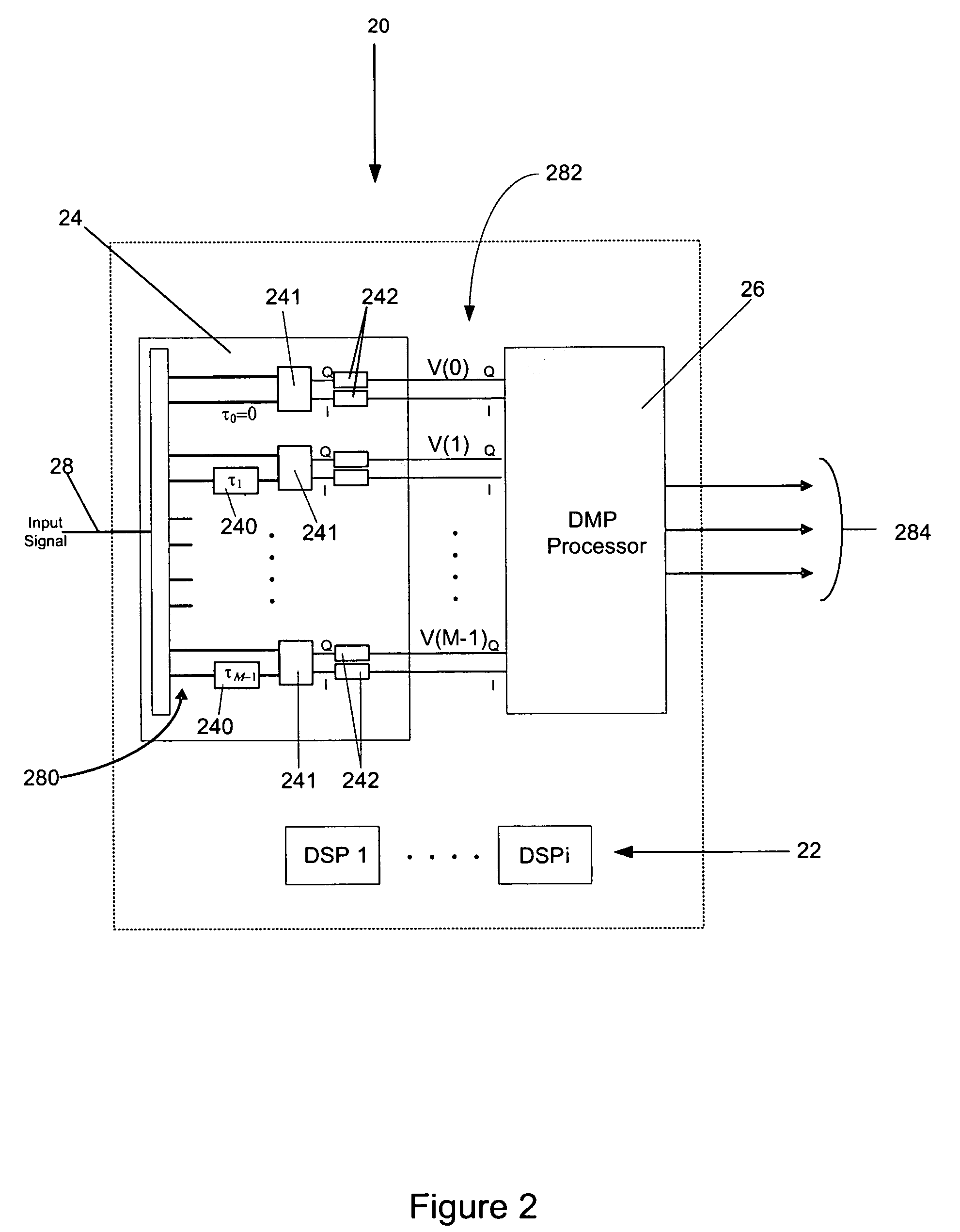
A method and system is provided for detecting and characterizing pulsed threat radar emitters through heavy in-band interference. System includes an advanced digital signal processing method provides spatial and temporal interference cancellation, super-resolution direction-finding, and high resolution spectrum analysis techniques. The system receives the digitized output of a discriminator bank and produces highly accurate threat pulse radio frequency estimates. The invention further provides a two-channel configuration for a DF subsystem, to perform adjacent-beam direction-finding through severe interference environments. The invention provides increased sensitivity, increased frequency accuracy, and up to 40 dB of increased interference look-through capability in ES system but remains transparent to ES system functioning and to ES system operators.
Owner:RADIX TECH
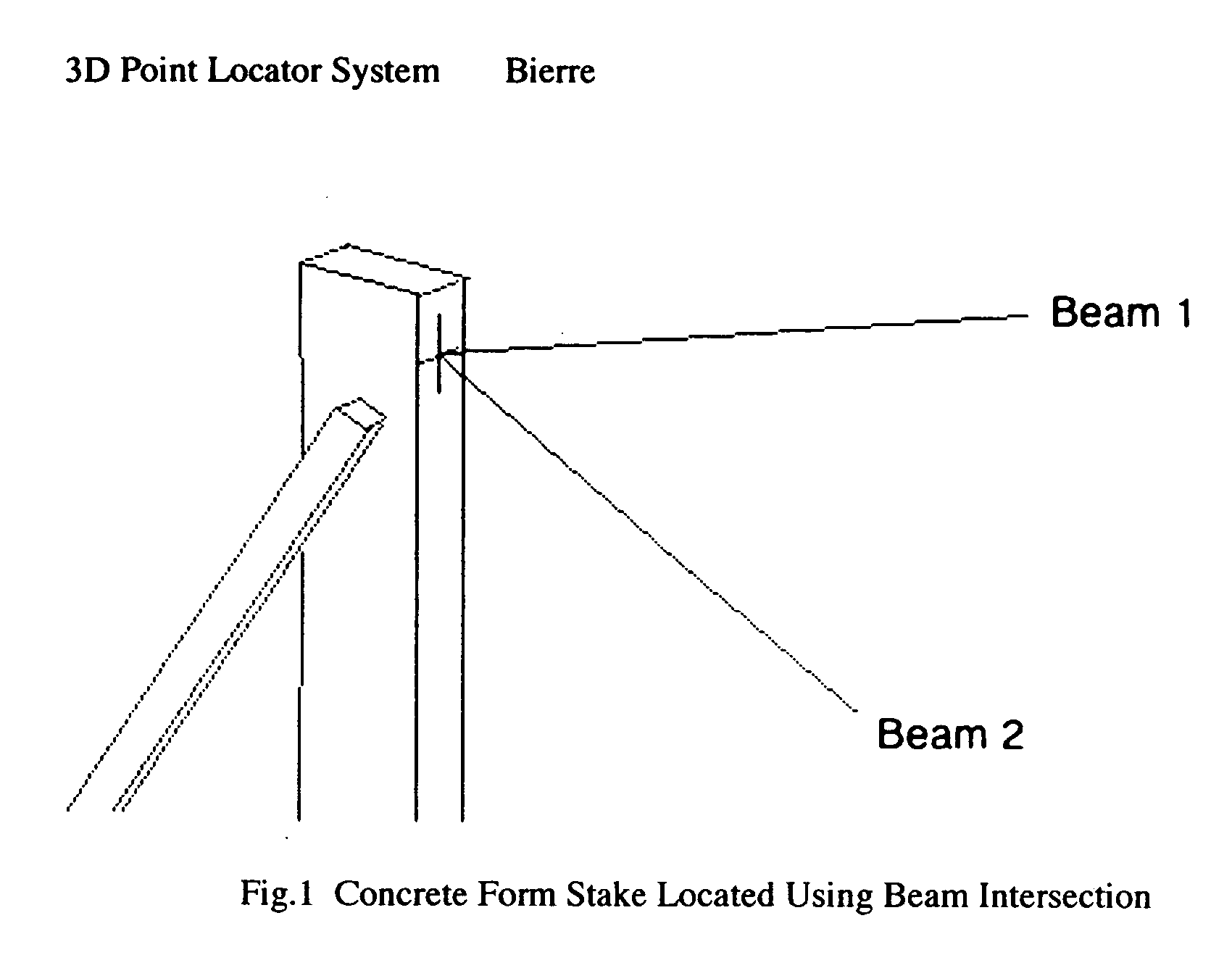
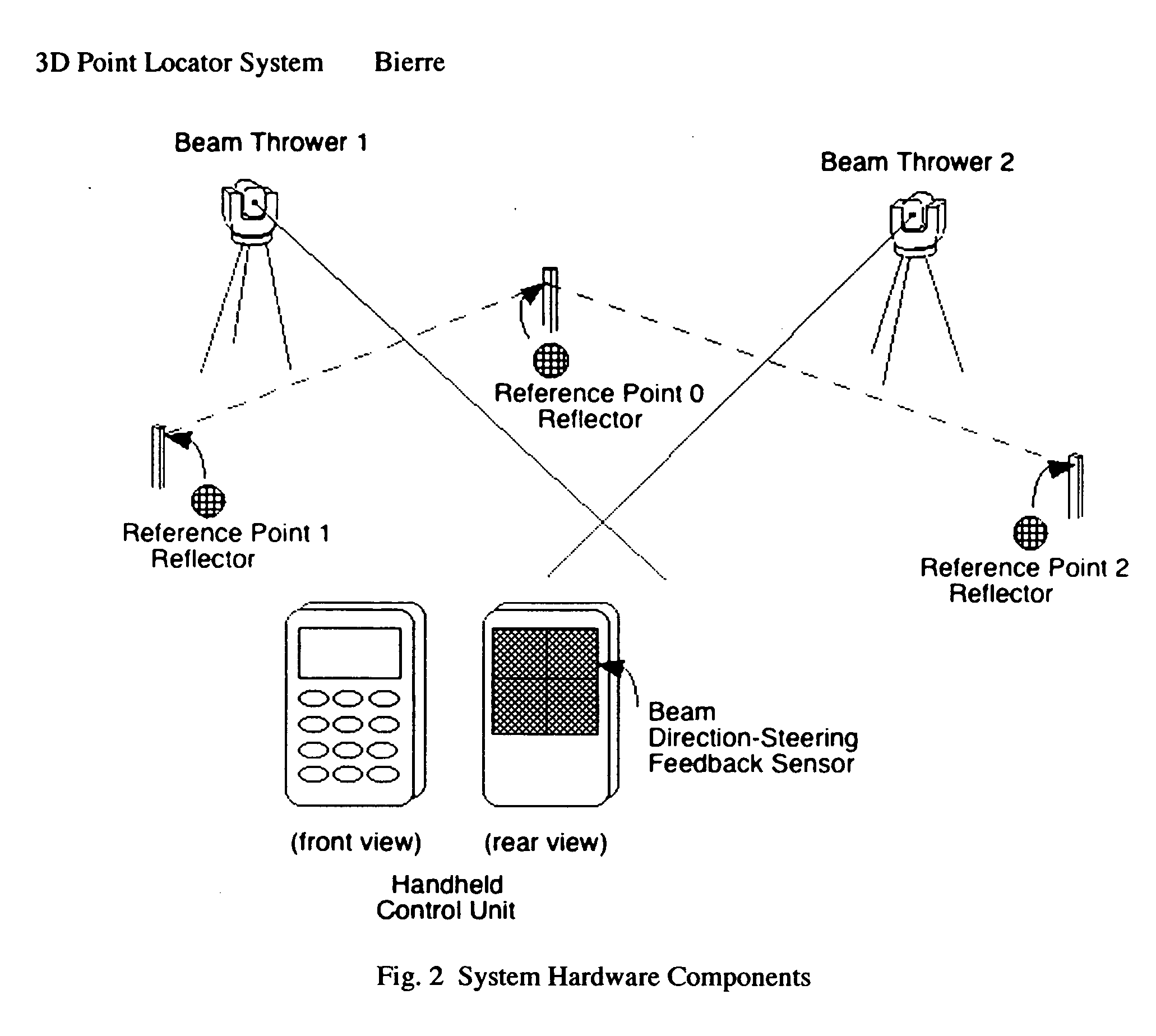
3D point locator system
InactiveUS20050102063A1DistanceReduce distanceComputer controlSimulator controlOperational systemSurvey instrument
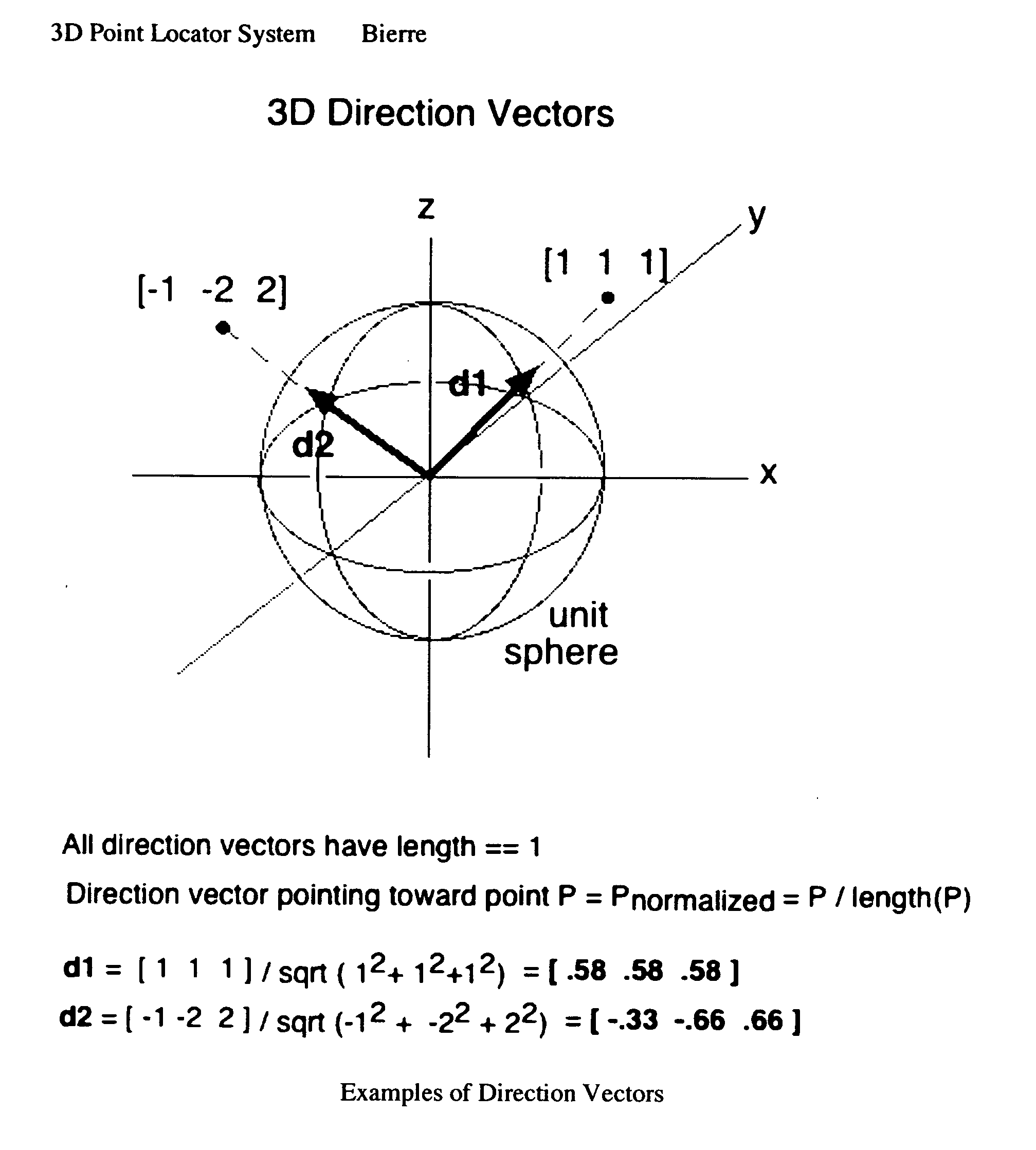
An automated system and method of geometric 3D point location. The invention teaches a system design for translating a CAD model into real spatial locations at a construction site, interior environment, or other workspace. Specified points are materialized by intersecting two visible pencil light beams there, each beam under the control of its own robotic ray-steering beam source. Practicability requires each beam source to know its precise location and rotational orientation in the CAD-based coordinate system. As an enabling sub-invention, therefore, an automated system and method for self-location and self-orientation of a polar-angle-sensing device is specified, based on its observation of three (3) known reference points. Two such devices, under the control of a handheld unit downloaded with the CAD model or pointlist, are sufficient to orchestrate the arbitrary point location of the invention, by the following method: Three CAD-specified reference points are optically defined by emplacing a spot retroreflector at each. The user then situates the two beam source devices at unspecified locations and orientations. The user then trains each beam source on each reference point, enabling the beam source to compute its location and orientation, using the algorithm of the sub-invention. The user then may select a CAD-specified design point using the handheld controller, and in response, the handheld instructs the two beam sources to radiate toward the currently selected point P. Each beam source independently transforms P into a direction vector from self, applies a 3×3 matrix rotator that corrects for its arbitrary rotational orientation, and instructs its robotics to assume the resultant beam direction. In consummation of the inventive thread, the pair of light beams form an intersection at the specified point P, giving the worker visual cues to precisely position materials there. This design posits significant ease-of-use advantages over construction point location using a single-beam total station. The invention locates the point effortlessly and with dispatch compared to the total station method of iterative manual search maneuvering a prism into place. Speed enables building features on top of point location, such as metered plumb and edge traversal, and graphical point selection. The invention eliminates the need for a receiving device to occupy space at the specified point, leaving it free to be occupied by building materials. The invention's beam intersection creates a pattern of instantaneous visual feedback signifying correct emplacement of such building materials. Unlike surveying instruments, the invention's freedom to situate its two ray-steering devices at arbitrary locations and orientations, and its reliance instead on the staking of 3 reference points, eliminates the need for specialized surveying skill to set up and operate the system, widening access to builders, engineers, and craftspeople.
Owner:BIERRE PIERRE
Methods for measuring and transmitting downlink signals and apparatuses therefor
ActiveUS20130279356A1Lower performance requirementsImprove performanceError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommunications systemBeam direction
A method in which a User Equipment (UE) measures a downlink signal in a wireless communication system is disclosed. The method includes receiving information about a Beam Direction Pattern (BDP) of the downlink signal and measuring the downlink signal based on the information about the BDP. The information about the BDP includes an index of a subframe in which the downlink signal is to be transmitted using a specific BDP and includes an identifier (ID) of the specific BDP. The BDP of the downlink signal is switched according to the subframe index based on the information about the BDP.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC +1
Directional carrier sense medium access for wireless nodes
ActiveUS7321580B1Easy to useImprove performanceError preventionTransmission systemsTransceiverNetwork packet
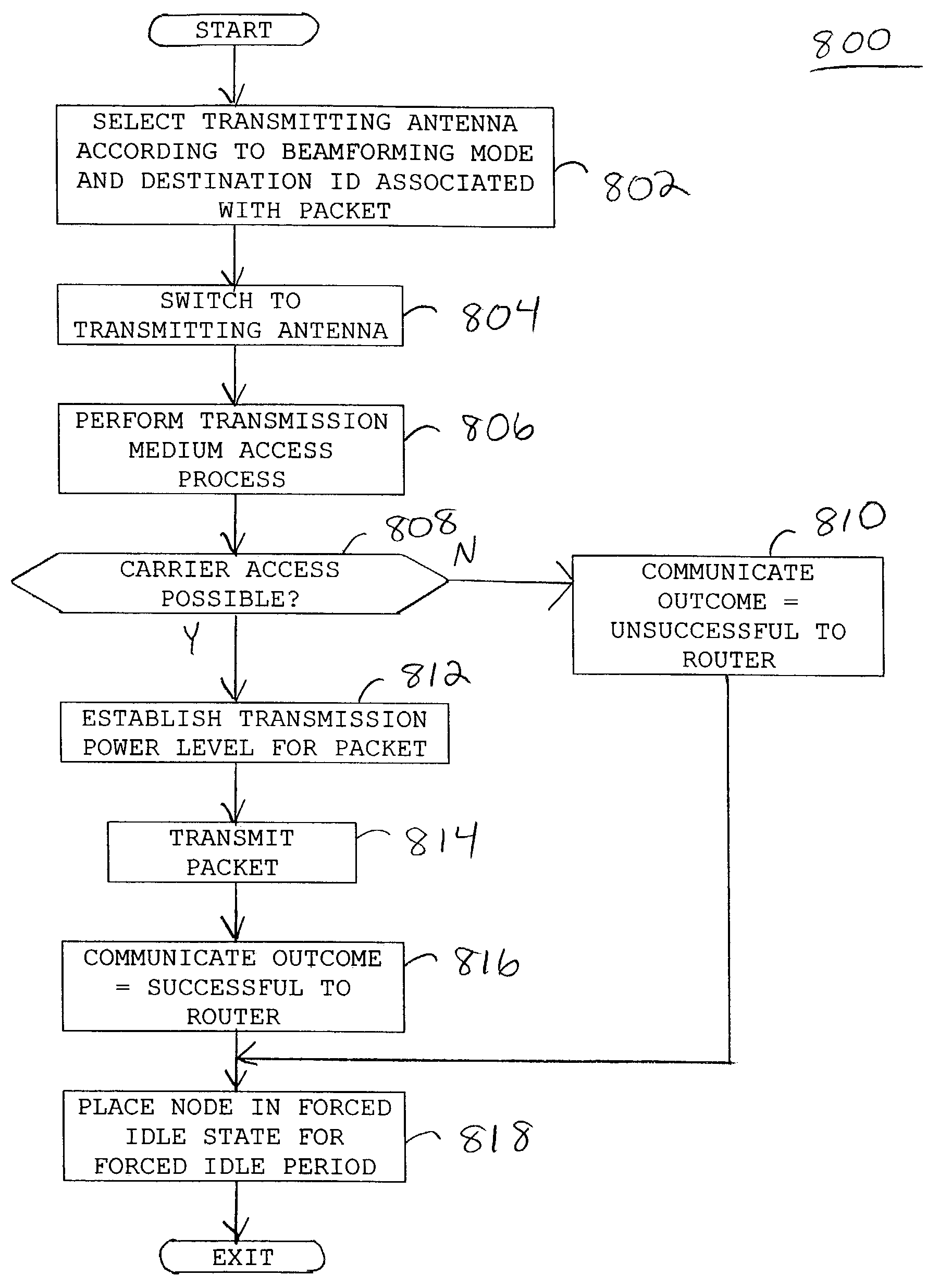
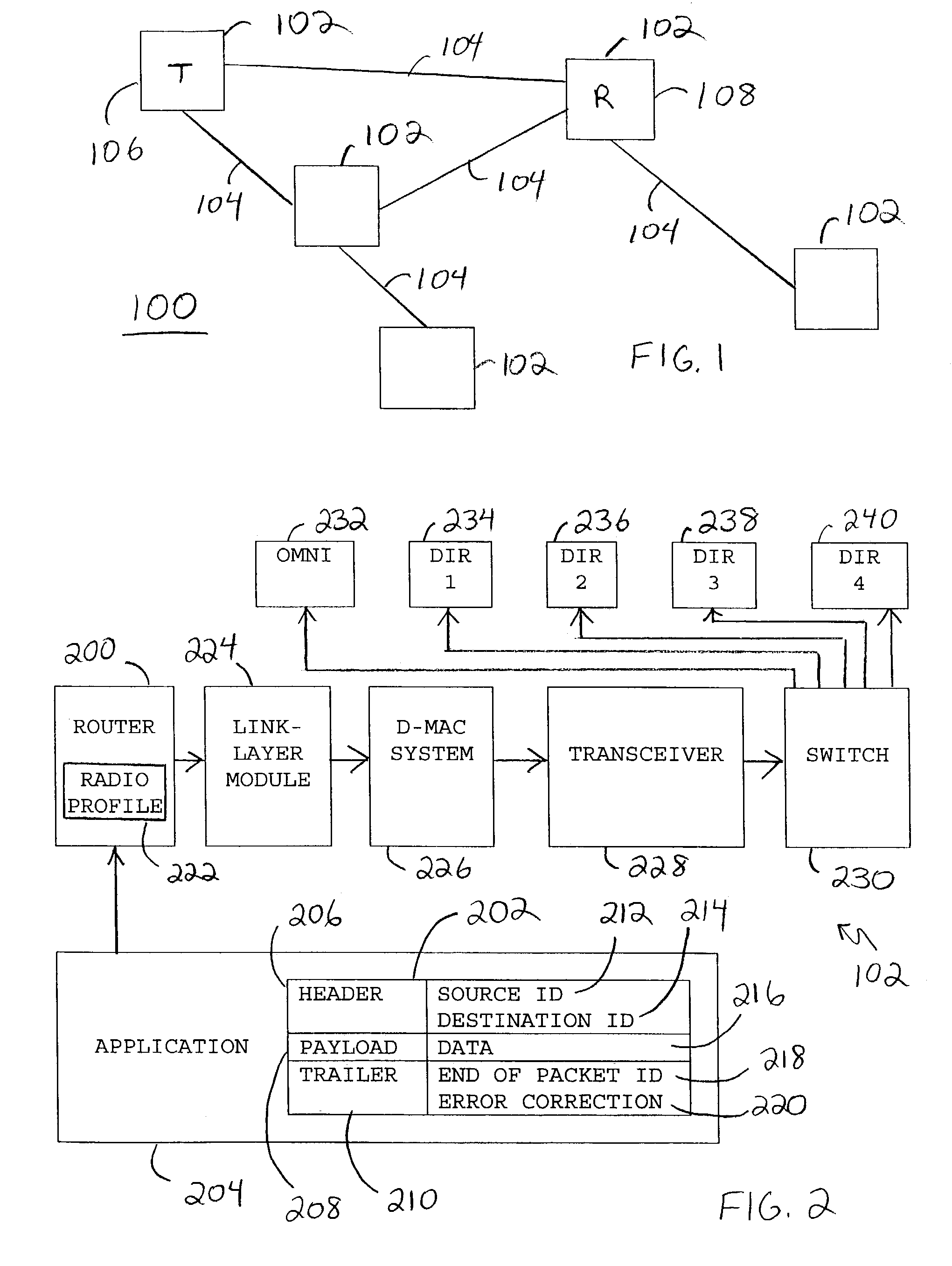
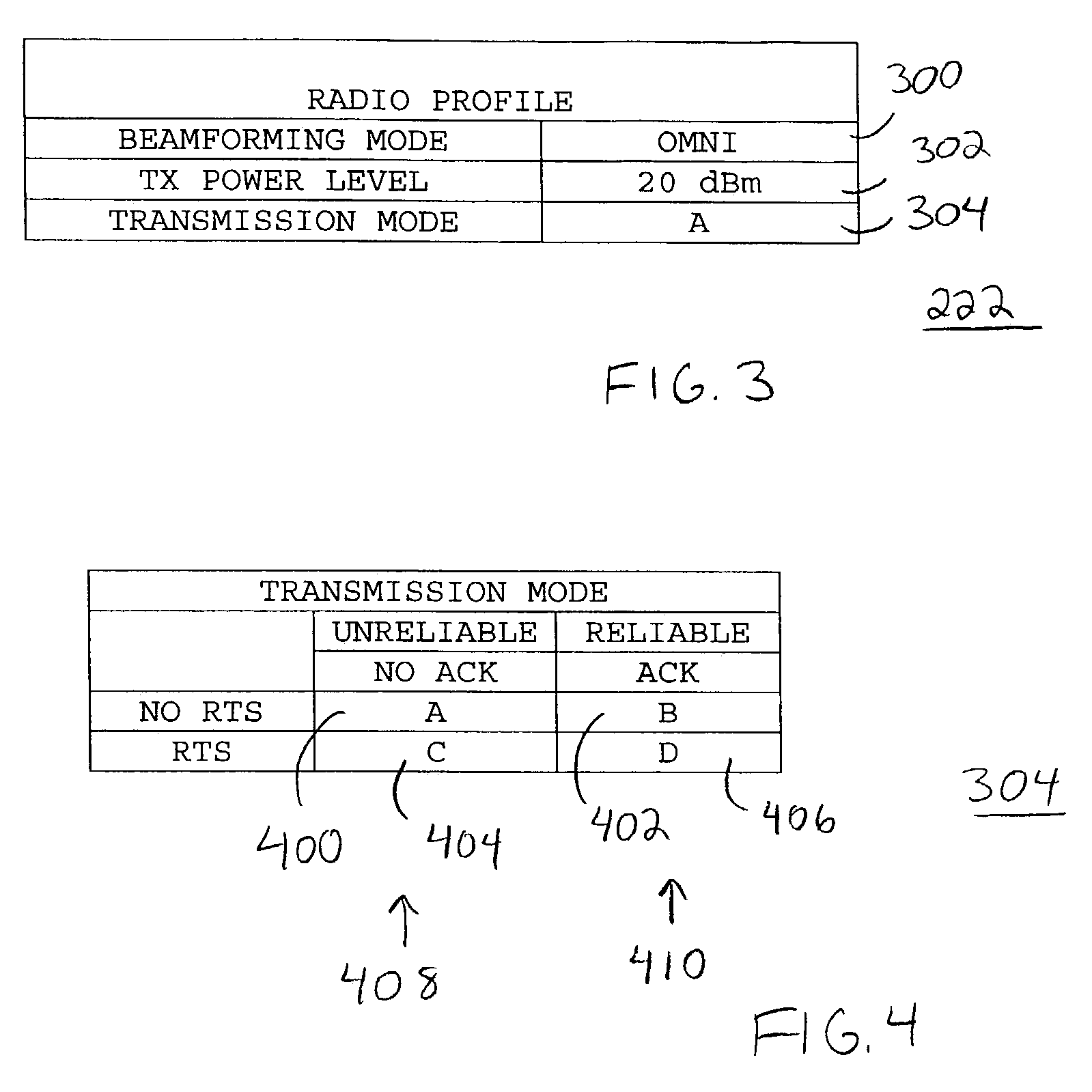
A method (508) and system (226) provide directional medium access control for wireless nodes (102) in a wireless network (100), each of the nodes (102) having a transceiver (228) and a plurality of antennas (232, 234, 236, 238, 240) in selective communication with the transceiver (228). Packets (202) are transmitted from a transmitting node (106) of the nodes (102) when a channel (104) is sensed as being free in a beam direction of a selected one of the antennas (232, 234, 236, 238, 240), and in accordance with a pre-determined transmission mode (304) for the data packet (202). The transmitting node (106) is periodically placed in a forced idle state, thereby being prevented from transmitting data packets (202), but being able to receive and respond to data packets (202) from other nodes (102).
Owner:USTA TECH LLC
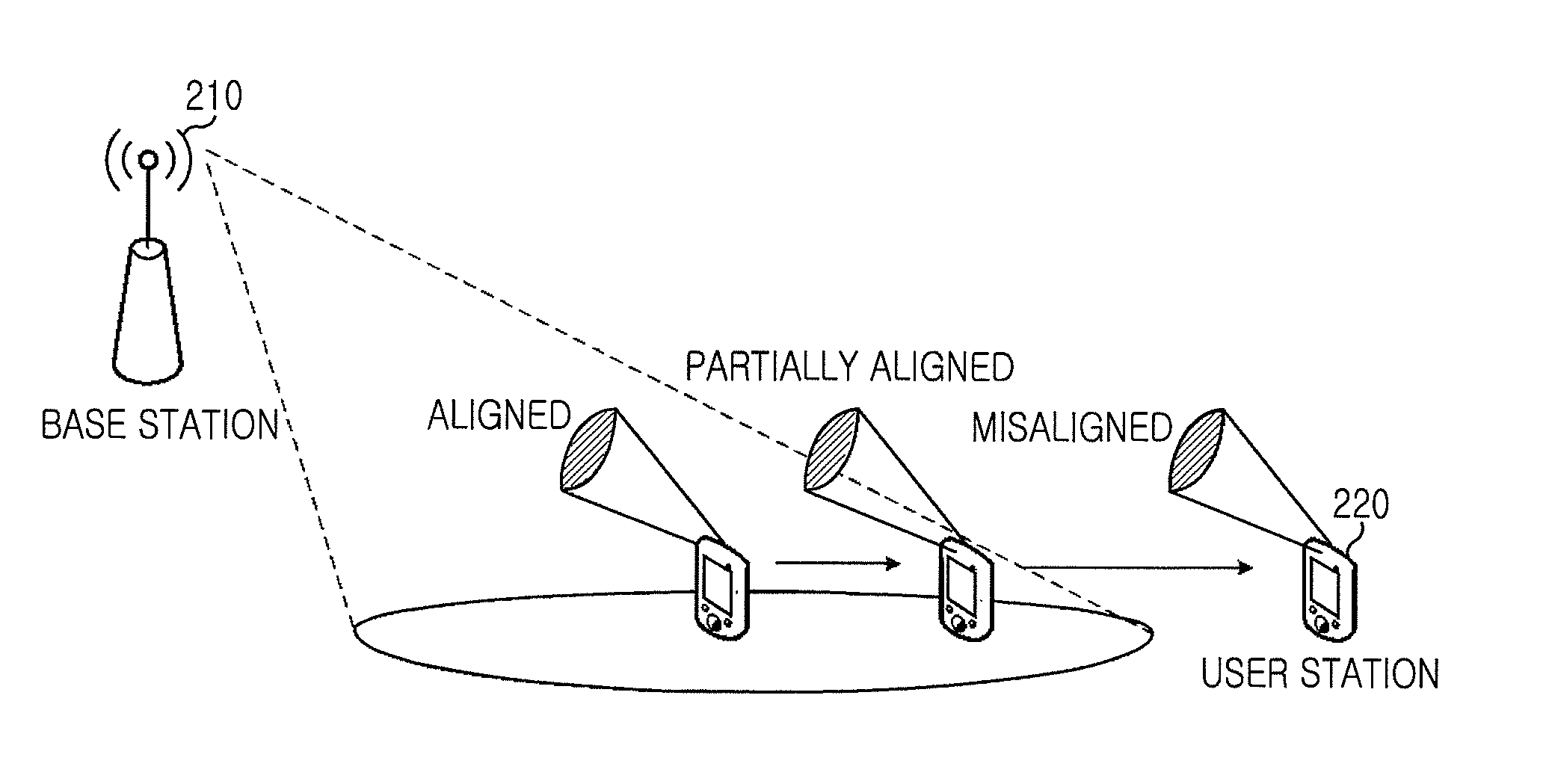
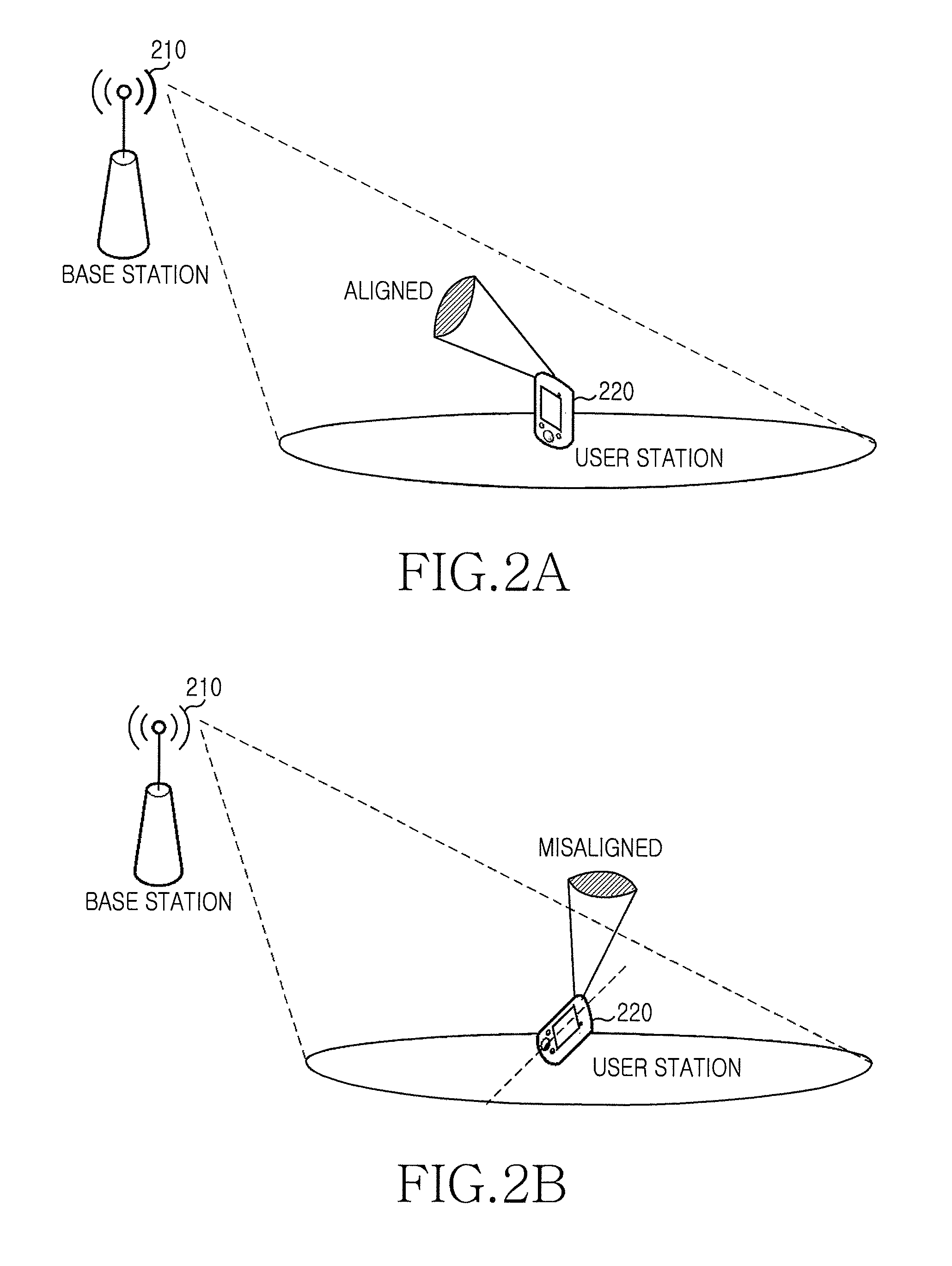
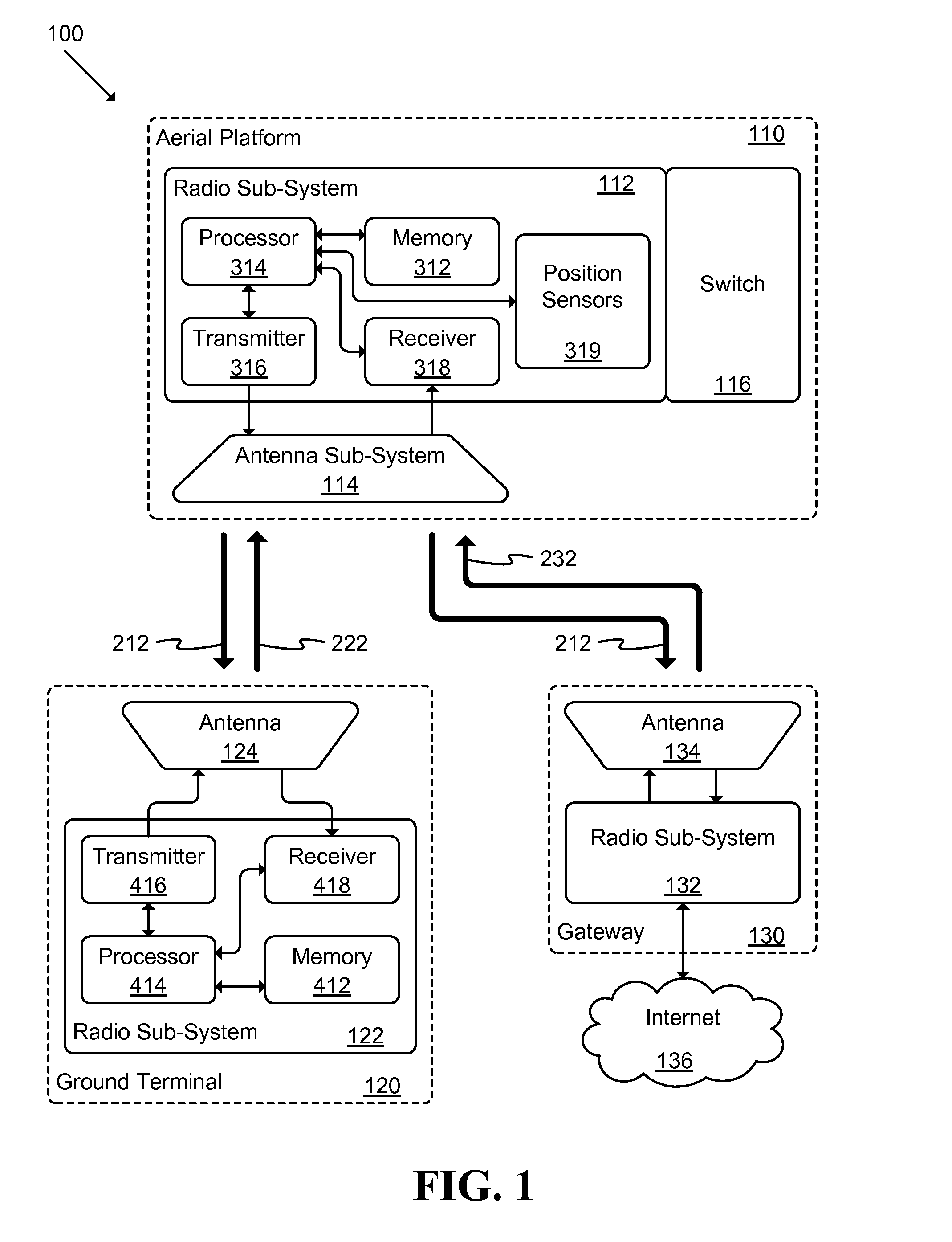
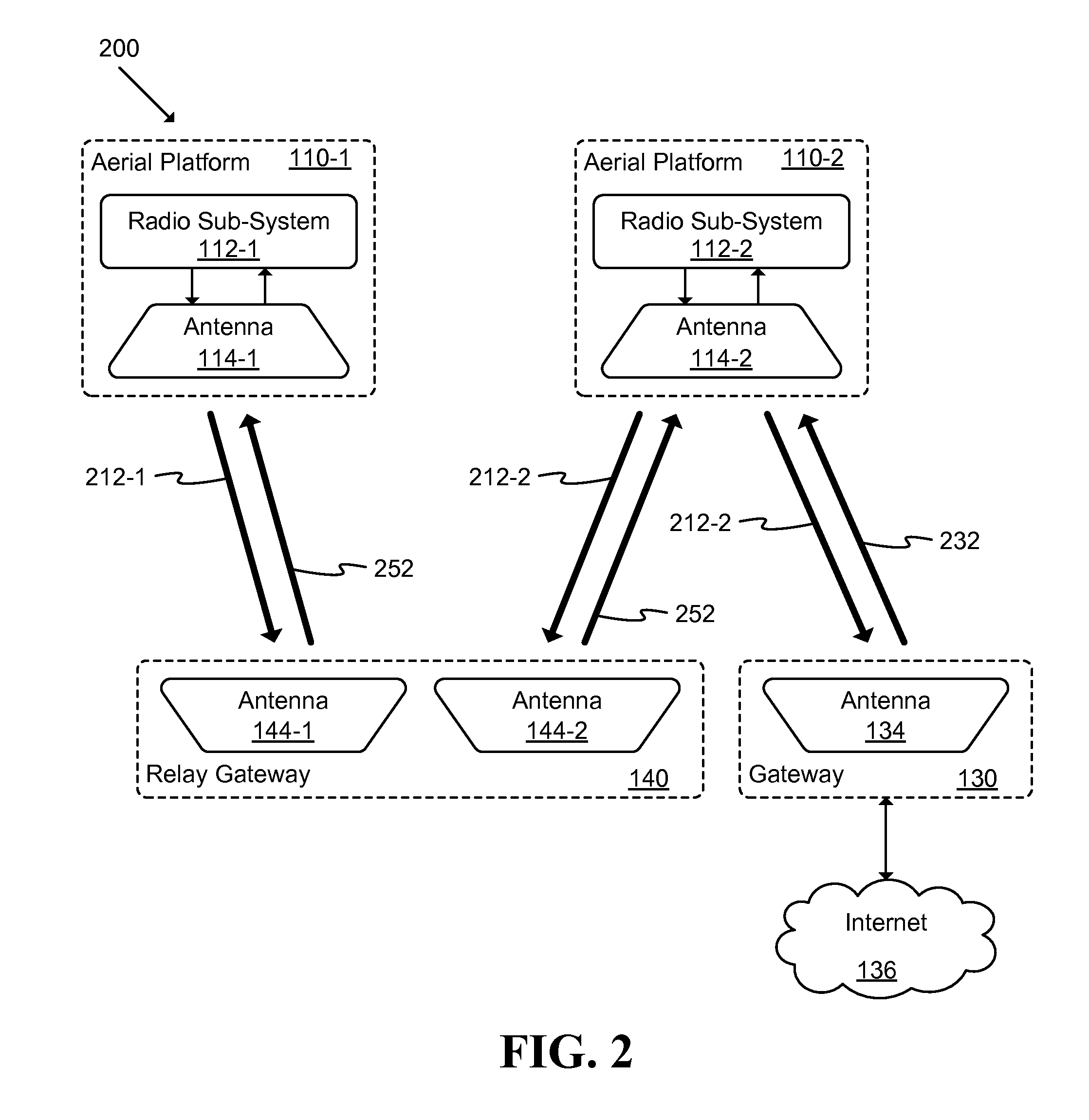
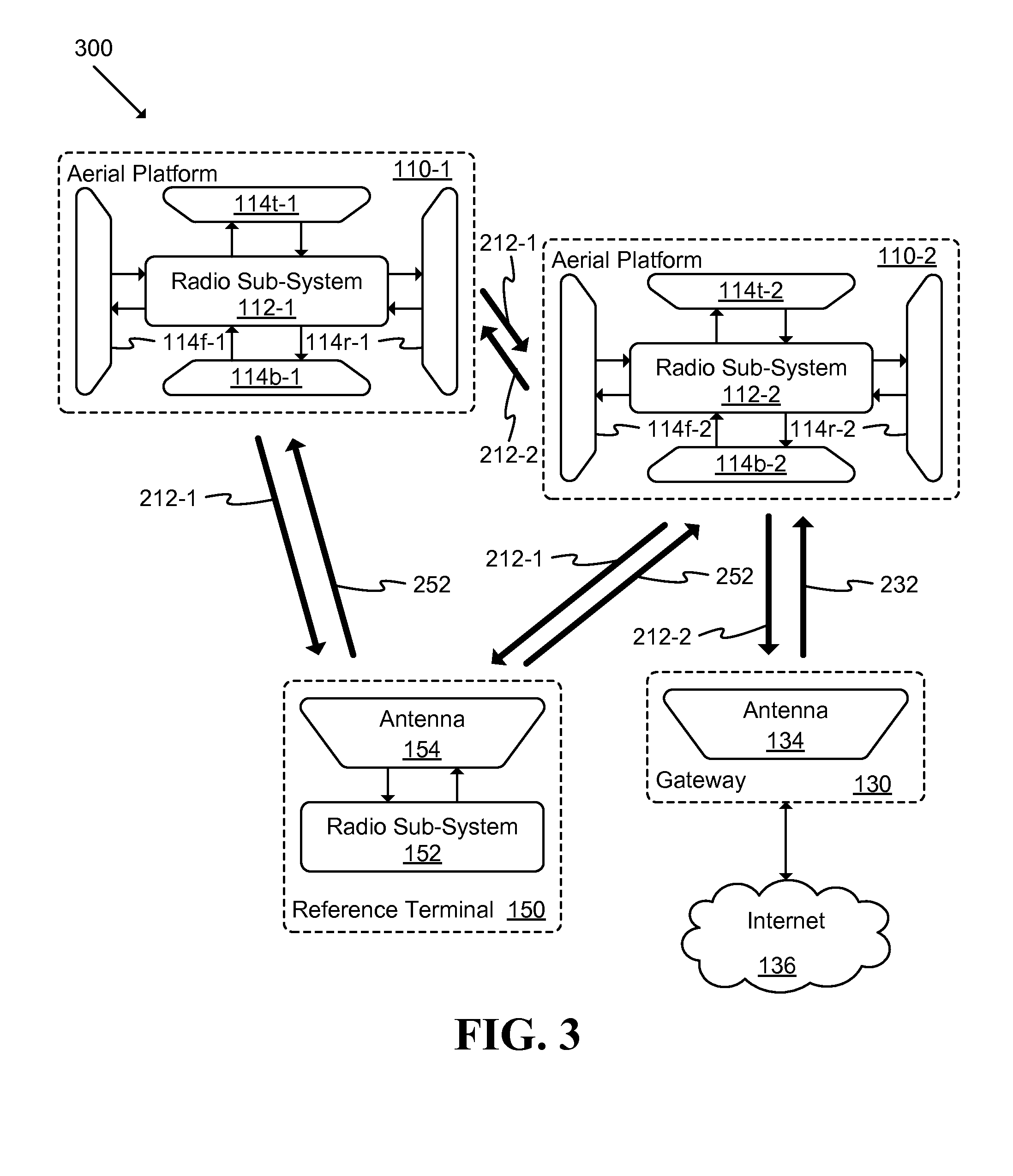
Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Communication Using Distributed Antenna Placement and Beam Pointing
A communication system is described. The system includes: at least one gateway able to provide broadband connectivity, a set of ground terminals, and a set of aerial platforms, where at least one aerial platform is able to communicate with at least one gateway using radio frequencies, each aerial platform is able to communicate with ground terminals using radio frequencies, and each aerial platform is able to communicate with each other aerial platform using radio frequencies. An automated method for determining a beam direction for communication among UAVs includes: dividing a space around the UAV into multiple sub-regions, and, iteratively: selecting a sub-region from among the multiple sub-regions; pointing a signal toward the sub-region; and determining whether a signal is received from another UAV, until all sub-regions from among the multiple sub-regions have been selected.
Owner:BRIDGEWEST FINANCE LLC
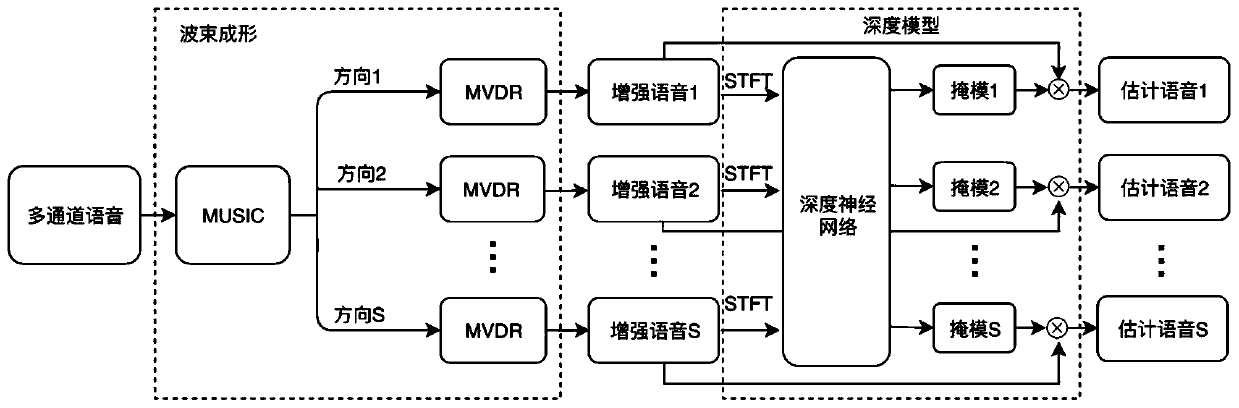
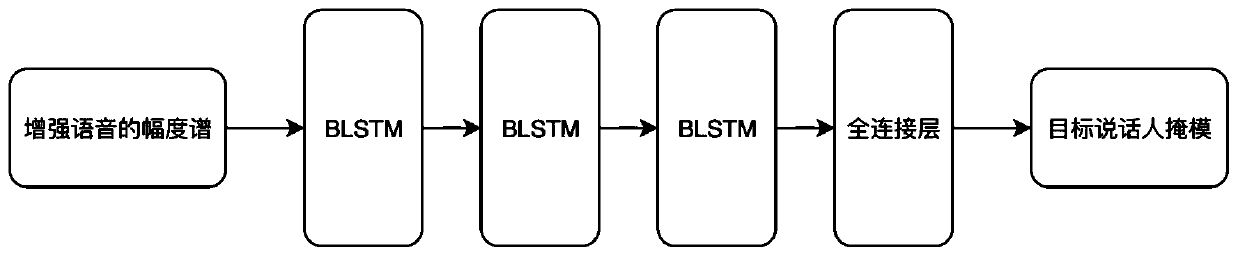
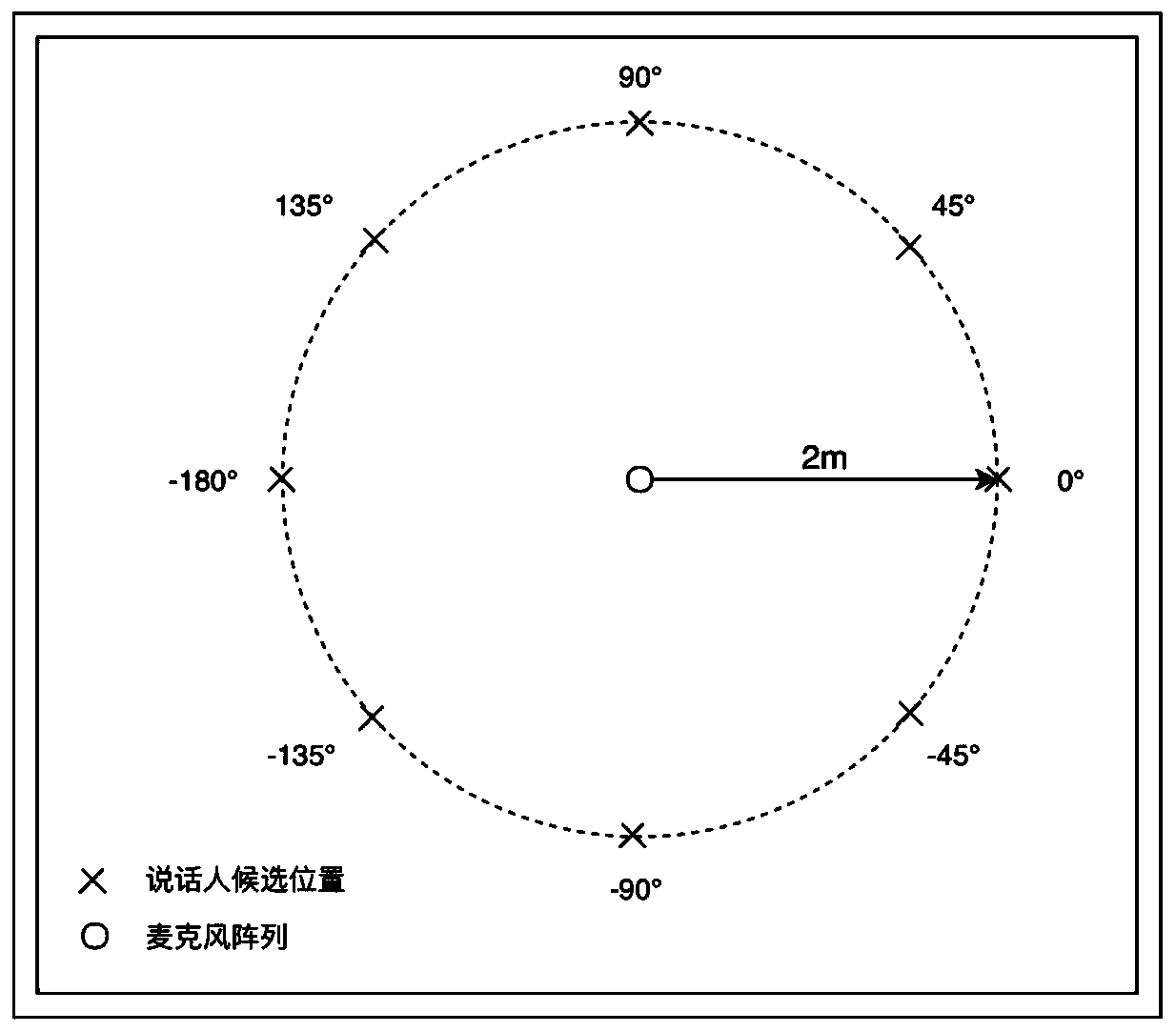
Multi-speaker speech separation method and system based on beam forming
The invention discloses a multi-speaker speech separation method and system. The method comprises the following steps : acquiring mixed voice signals, obtaining multichannel multi-speaker mixed voicesignals, and scanning the multi-channel multi-speaker mixed voice signals to obtain MUSIC energy spectra; obtaining S peak values from the MUSIC energy spectra, wherein each peak value corresponds toa beam direction; respectively enhancing S beams to obtain mixed voice in S directions; performing short-time Fourier transform on the mixed voice corresponding to each direction to obtain short-timeFourier amplitude spectra of the S target speaker voice, and respectively inputting the short-time Fourier amplitude spectra into a depth neural network to estimate a phase sensing mask correspondingto each target speaker; and performing element-by-element multiplication between the phase sensing mask of each target speaker and amplitude spectra of the corresponding mixed speech to obtain the amplitude spectrum of the target speaker, and the time domain signal of the target speaker is recovered by inverse short-time Fourier transform using the phase spectrum of the corresponding mixed speech.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
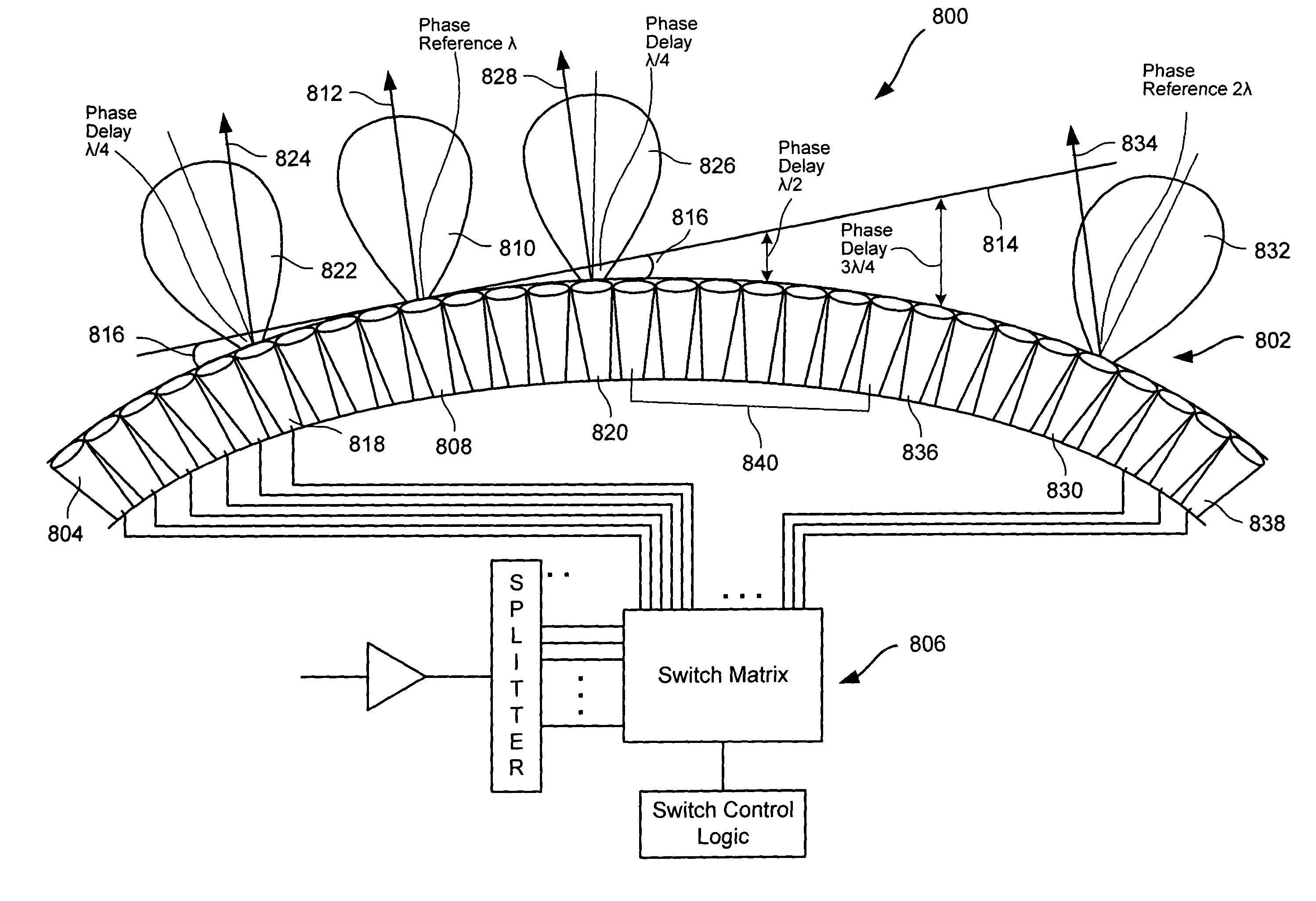
High-gain conformal array antenna
ActiveUS6961025B1Antenna adaptation in movable bodiesIndividually energised antenna arraysControl signalBeam direction
An antenna array system comprising a plurality of antenna elements organized in an array and configured to form a non-planar shaped antenna array surface. The antenna array system further comprises switching circuitry configured to switch each of the plurality of antenna elements on or off based on control signals. In one embodiment, the antenna array system is configured such that the antenna beam direction can be steered in a first direction by switching on a first set of antenna elements, and the antenna beam direction can be steered in a second direction by switching on a second set of antenna elements. In one embodiment, the second set of antenna elements can include one or more antenna elements from the first set of antenna elements, or the second set of antenna elements may not include any antenna elements from the first set.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Method for manufacturing organic electroluminescent display device
InactiveCN1489419AImprove directivityUniform film thicknessElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesBeam directionEngineering
A vapor-depositing mask is disposed adjacent a surface of a substrate disposed in a vacuum chamber, vapor-depositing beams containing an organic EL material are generated by a vapor-depositing beam generator, the vapor-depositing beams pass through openings in the vapor-depositing mask, and the organic EL material is vapor-deposited in a predetermined region on the surface of the substrate. The vapor-depositing beams are guided through a plurality of vapor-depositing beam passing pipes provided in the vapor-depositing beam generator. Alternatively, the vapor-depositing beams generated by the vapor-depositing beam generator are guided through a vapor-depositing beam direction adjusting board having a plurality of vapor-depositing beam passing holes. This enhances directional uniformity of the vapor-depositing beams, thereby enabling making each film thickness of organic EL material layers uniform and thus enhancing precision of forming patterns of the layers.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
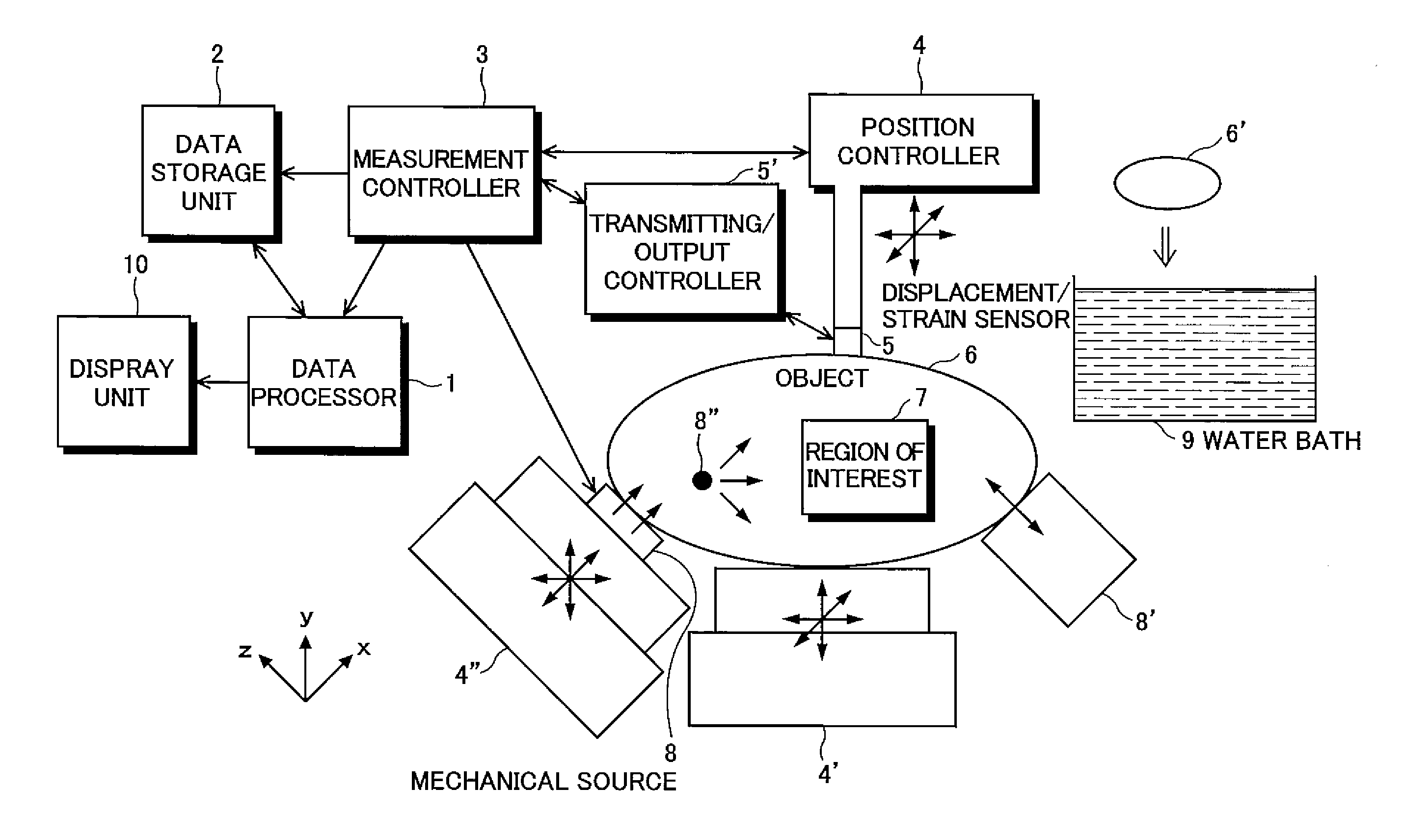
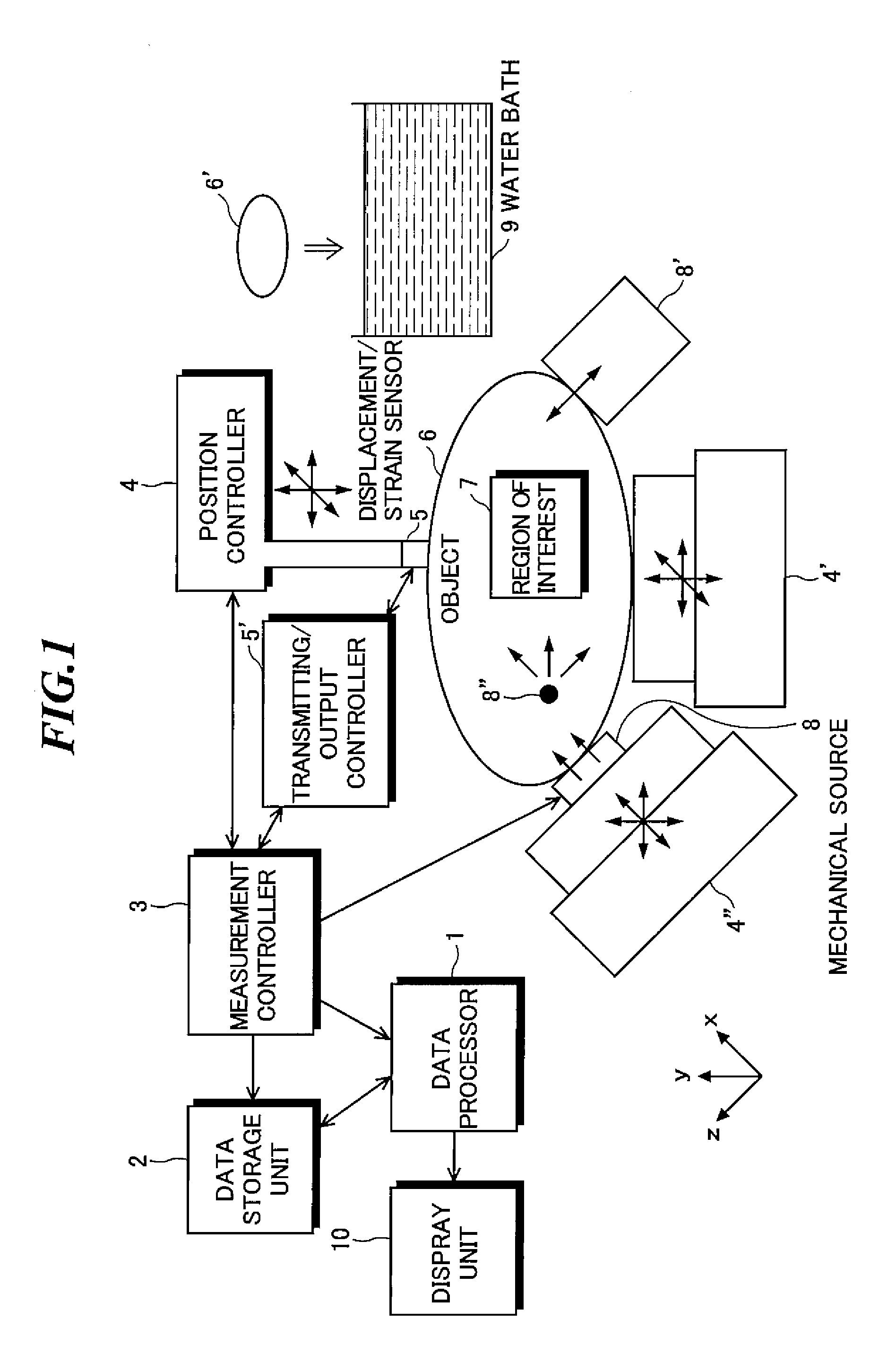
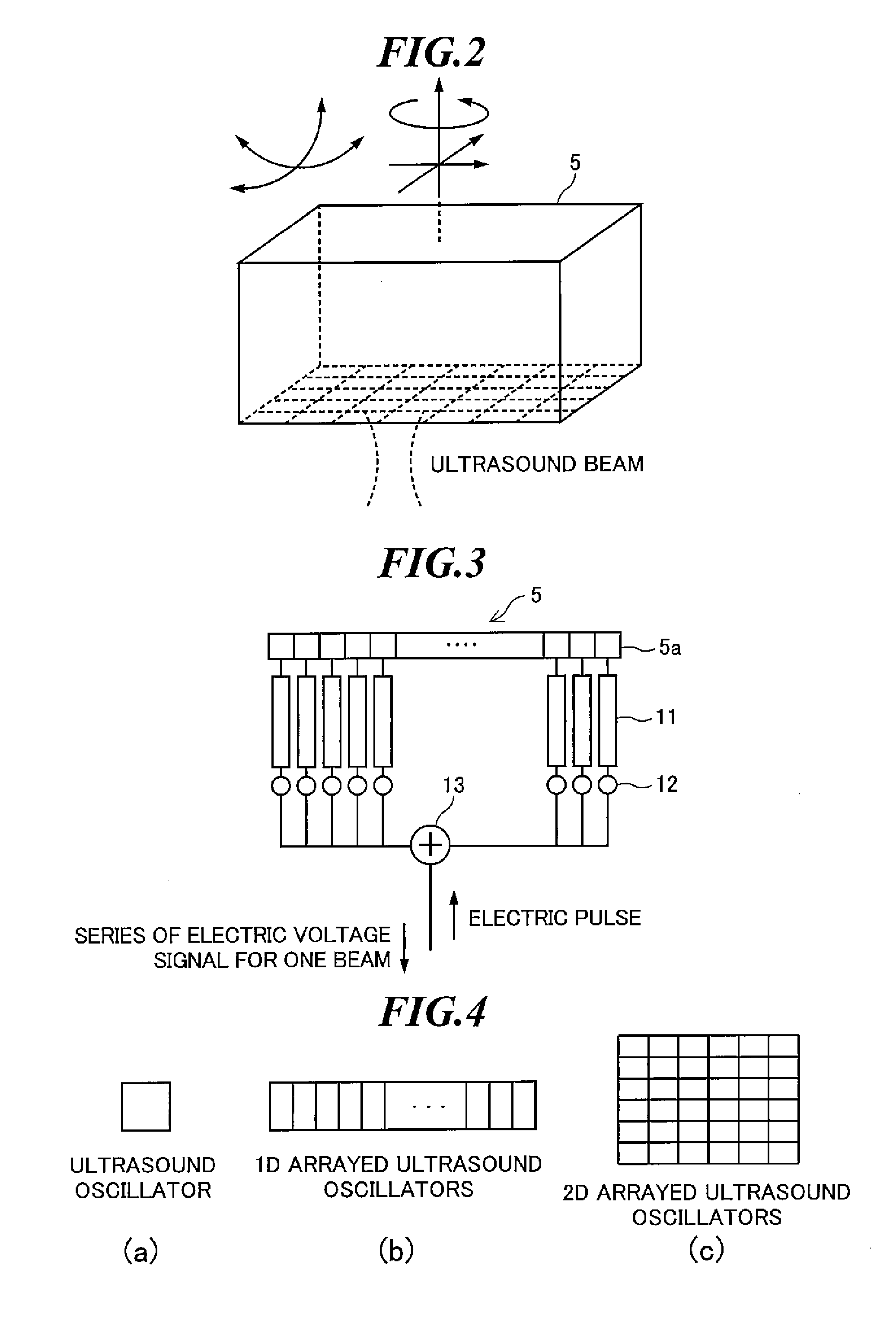
Imaging method, displacement measurement method and apparatus
ActiveUS20130046175A1Short timeAccurate displacementOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsFrequency vectorSteering angle
A displacement measurement method for achieving, at each position of interest, high accuracy measurement of a displacement, a velocity and a strain in an actually generated beam direction by measuring the beam direction angle from ultrasound echo data. The method includes the steps of: generating an ultrasound echo data frame through scanning an object in a lateral direction with an ultrasound steered beam having one steering angle; calculating both a beam direction and a frequency in the beam direction based on an azimuth angle φ=tan−1(fy / fx), a polar angle θ=cos−1[fz / (fx2+fy2+fz2)1 / 2], and a frequency (fx2+fy2+fz2)1 / 2 in the case where first spectral moments calculated from local ultrasound echo data at plural different temporal phases are expressed by a three-dimensional frequency vector (fx, fy, fz); and calculating a displacement component in the beam direction at each position of interest generated between plural different temporal phases.
Owner:SUMI CHIKAYOSHI
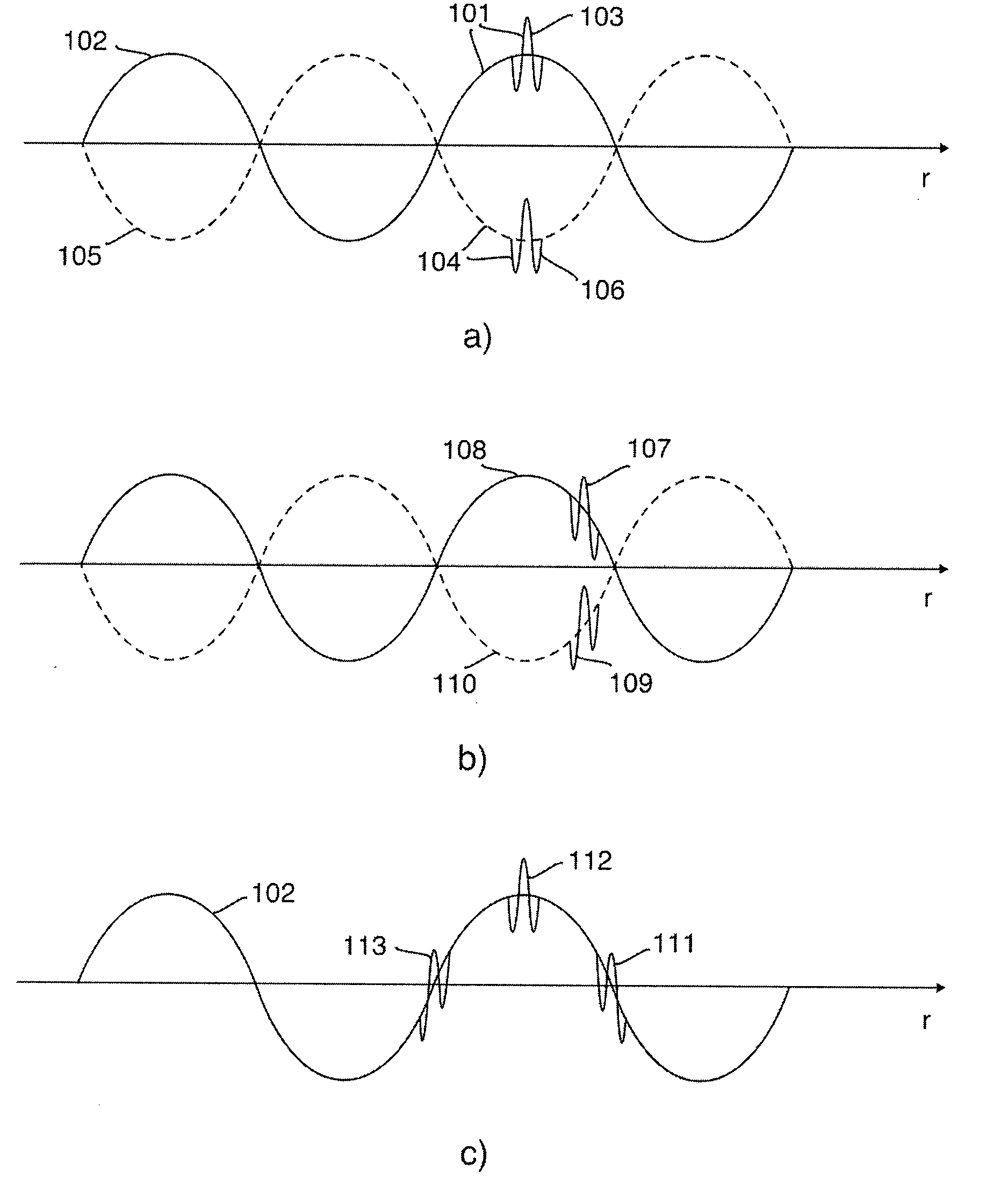
Nonlinear Elastic Wave Measurement and Imaging with Two-Frequency Elastic Wave Pulse Complexes
ActiveUS20100036244A1Fast timeSimple processOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsBeam directionTransducer
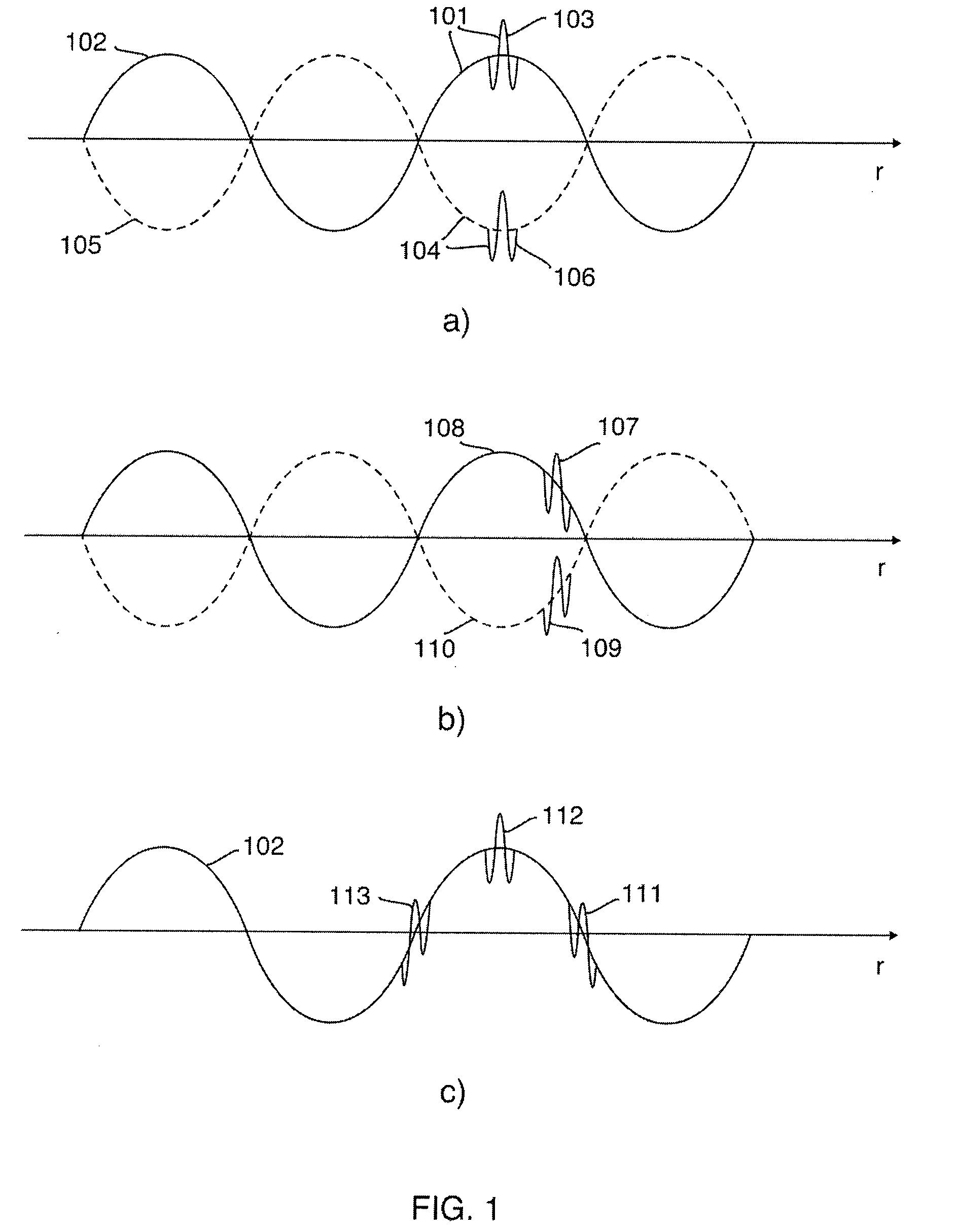
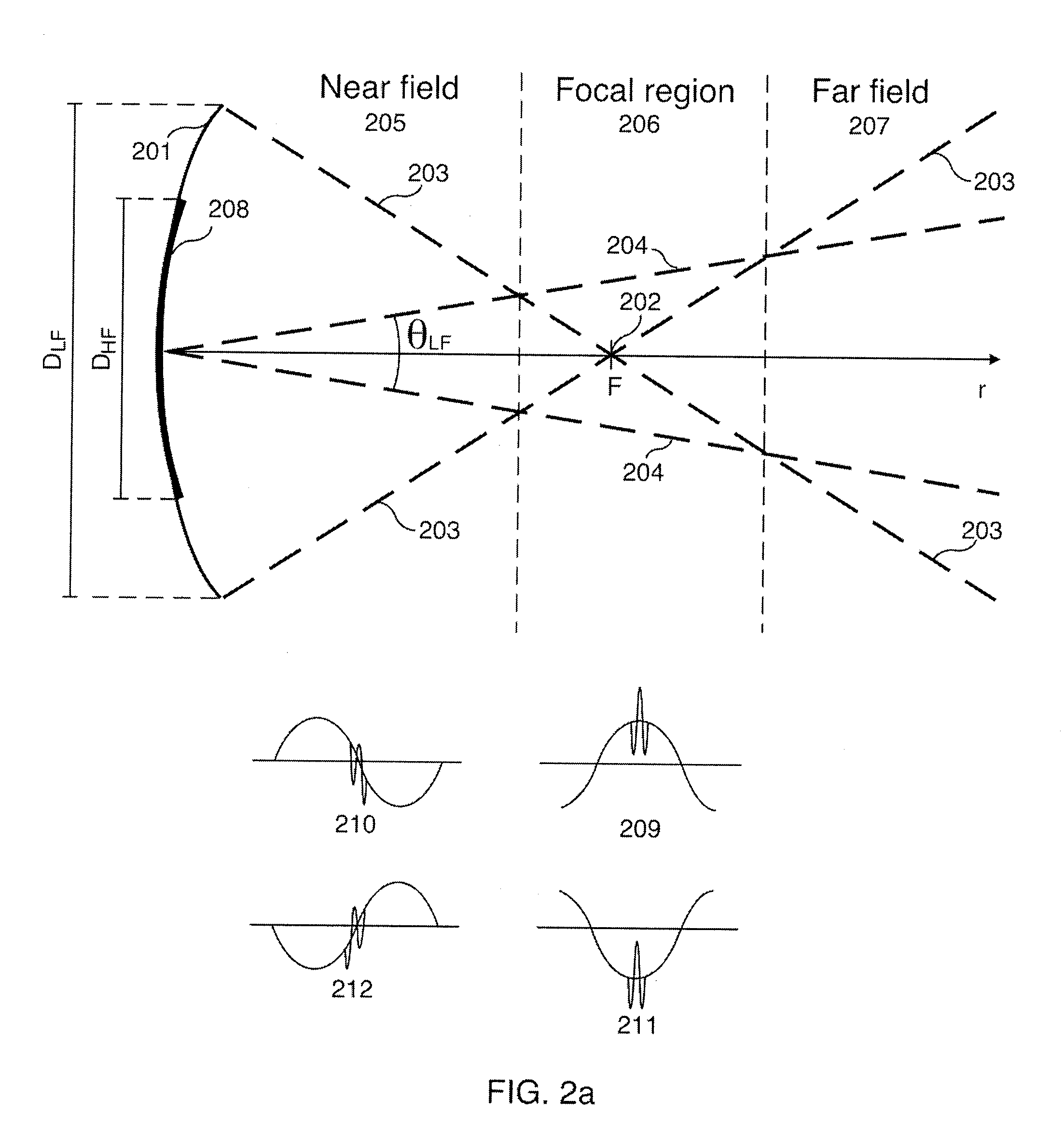
Methods and instruments for suppression of multiple scattering noise and extraction of nonlinear scattering components with measurement or imaging of a region of an object with elastic waves, where elastic wave pulse complexes are transmitted towards said region where said pulse complexes are composed of a high frequency (HF) and a low frequency (LF) pulse with the same or overlapping beam directions and where the HF pulse is so close to the LF pulse that it observes the modification of the object by the LF pulse at least for a part of the image depth. The frequency and / or amplitude and / or phase of said LF pulse relative to said HF pulse varies for transmitted pulse complexes in order to nonlinearly manipulate the object elasticity observed by the HF pulse along at least parts of its propagation, and where received HF signals are picked up by transducers from one or both of scattered and transmitted components of the transmitted HF pulses. Said received HF signals are processed to form measurement or image signals for display, and where in the process of forming said measurement or image signals said received HF signals are one or both of delay corrected with correction delay in the fast time (depth-time), and pulse distortion corrected in the fast time, and combined in slow time to form noise suppressed HF signals or nonlinear scattering HF signals that are used for further processing to form measurement or image signals. The methods are applicable to elastic waves where the material elasticity is nonlinear in relation to the material deformation.
Owner:SURF TECH AS
Staged wireless resource management method based on dynamic cell group in cellular system
InactiveCN101400135AGuaranteed performanceReduce distractionsNetwork planningTime domainWireless resource management
The invention discloses a classification wireless resource management method based on a dynamic district group, suitable for cellular communication system. Adjacent districts constitute a district group according to interference relationships between adjacent districts, a plurality of districts belonging to the same district group are joined up to perform wireless resource management, reducing interference between the districts and increasing performance of the edge users, ensuring requirement of service quality. Structure of the district group is updated periodically according to the interference change between the districts. The wireless resource management method in the invention is a classification method. The district group may unifiedly manage the resource distribution of a plurality of districts inwards, also manage the resource distribution of the edge of the district. The districts in the district group are joined up in a centralized mode, also in a distributing mode. The wireless resources distributed in the district group comprise time, frequency and space, the joining mode includes combining time domain and frequency domain, combining beam direction and power.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Multi-beam source
ActiveUS8183543B2Reduce various aberration effectReduce the spread angleThermometer detailsStability-of-path spectrometersBeam splitterBeam source
A multi-beam source for generating a plurality of beamlets of energetic electrically charged particles. The multi-beam source includes an illumination system generating an illuminating beam of charged particles and a beam-forming system being arranged after the illumination system as seen in the direction of the beam, adapted to form a plurality of telecentric or homocentric beamlets out of the illuminating beam. The beam forming system includes a beam-splitter and an electrical zone device, the electrical zone having a composite electrode composed of a plurality of substantially planar partial electrodes, adapted to be applied different electrostatic potentials and thus influencing the beamlets.
Owner:IMS NANOFABTION
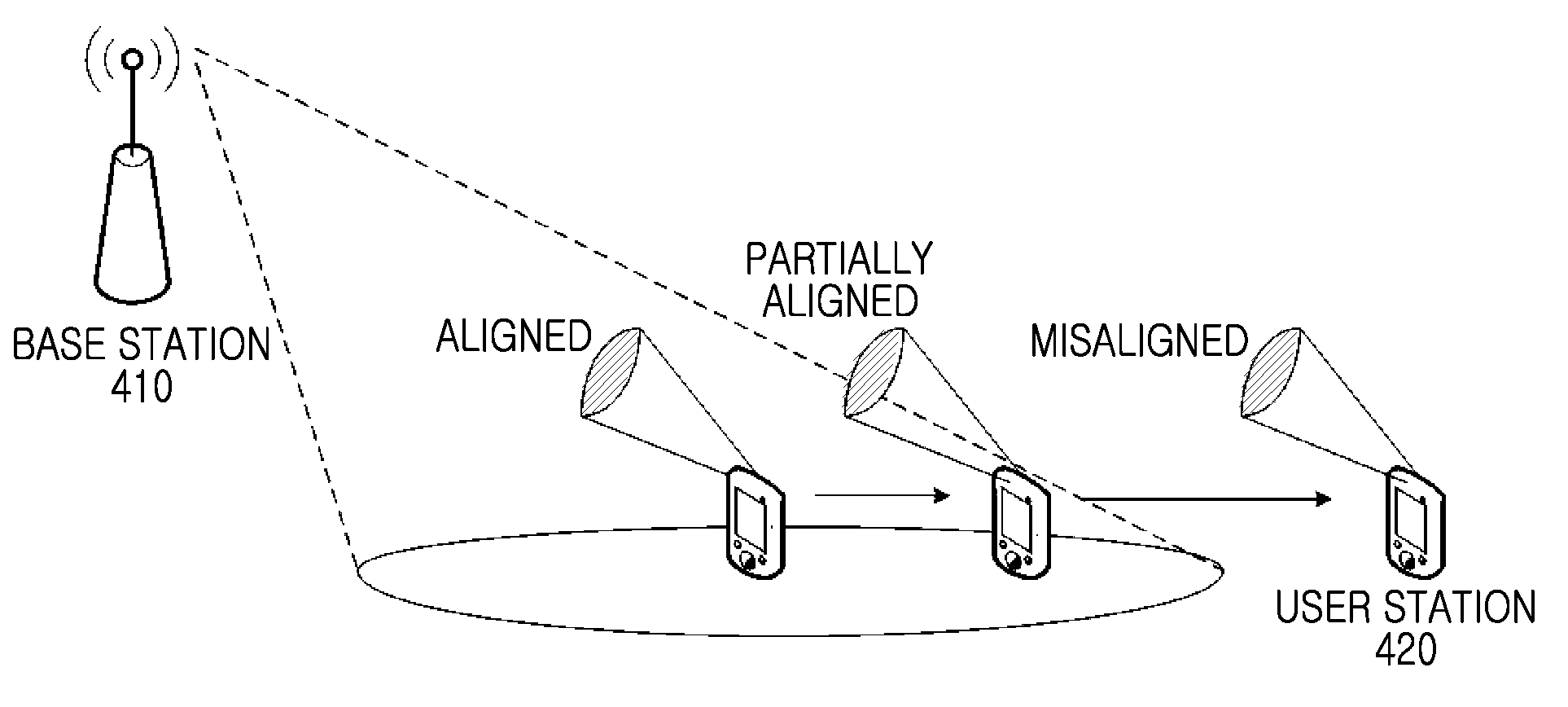
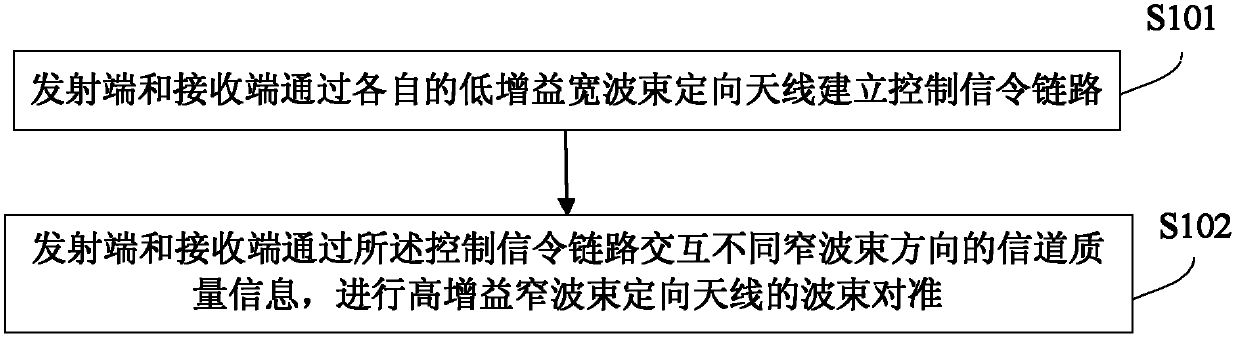
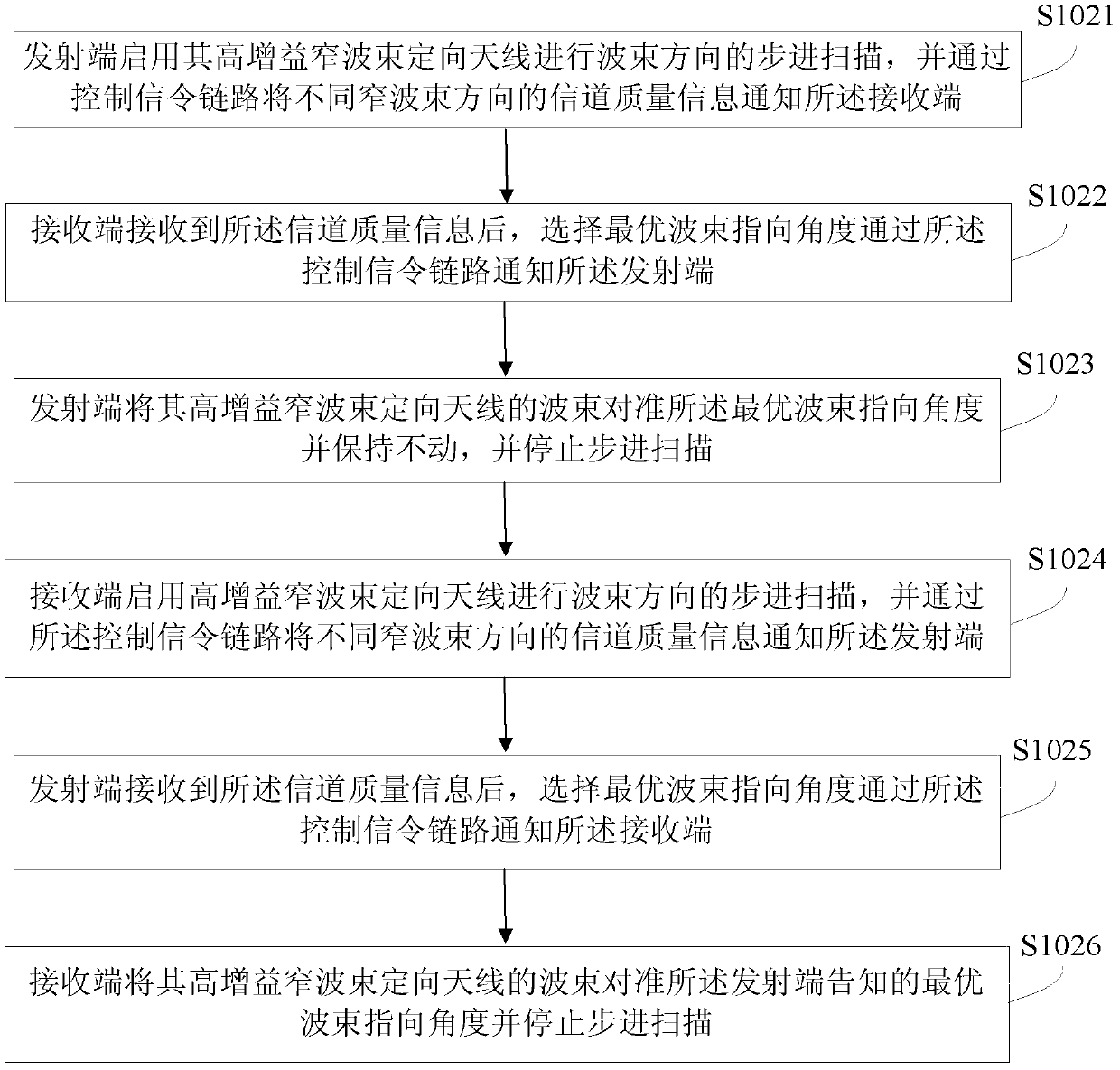
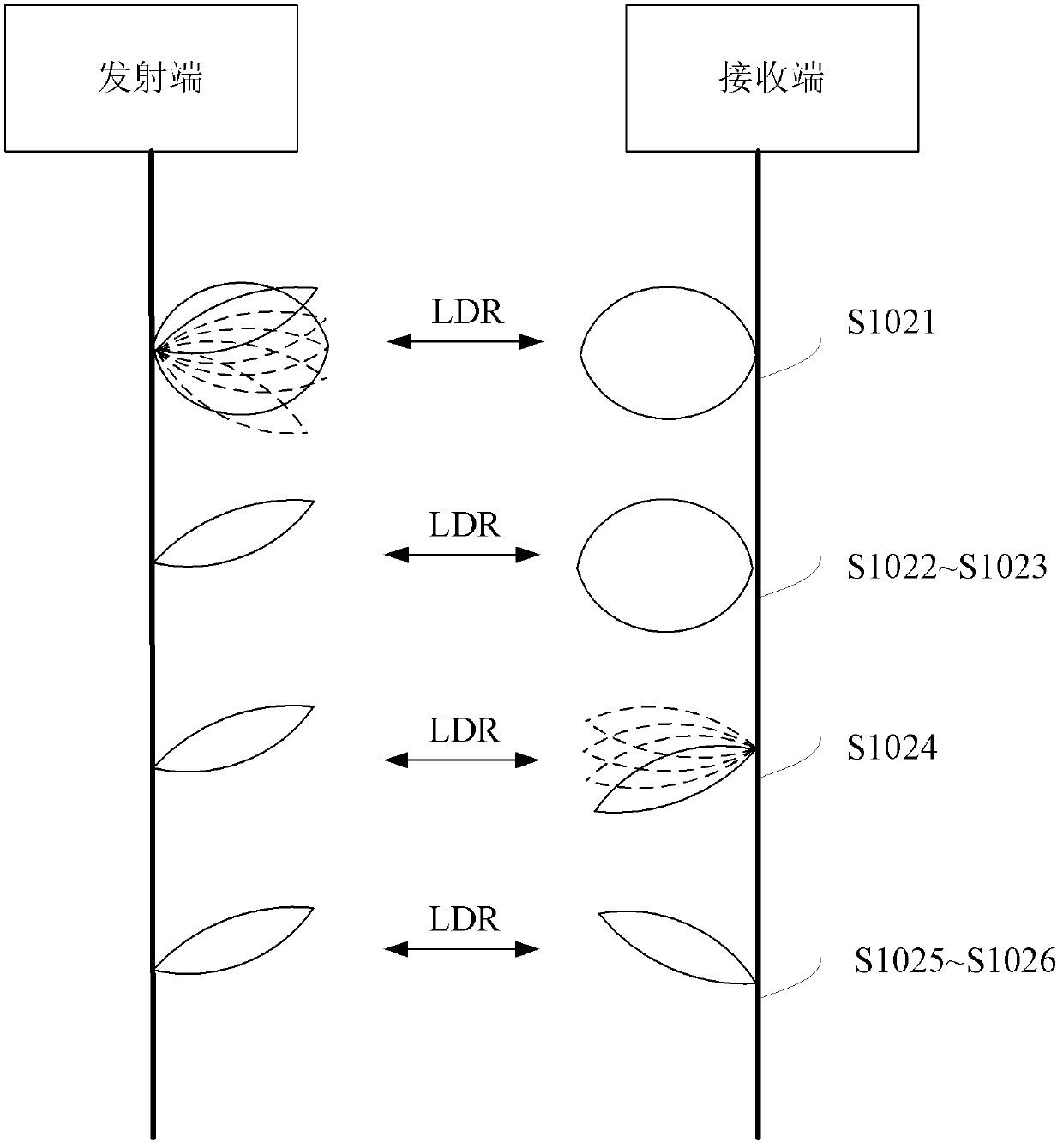
Wave beam alignment method, device and system for millimeter wave communication system
InactiveCN103378892AGuaranteed to continueShorten the timeSpatial transmit diversityMillimeter wave communication systemsControl signal
The invention discloses a wave beam alignment method, device and system for a millimeter wave communication system. The wave beam alignment device is provided with a high-gain narrow-wave-beam directional antenna and a low-gain wide-wave-beam directional antenna, and comprises a link establishment module and a wave beam alignment module, wherein the link establishment module for establishing a control signaling link with an opposite terminal through the low-gain wide-wave-beam directional antenna, and the wave beam alignment module is used for interacting channel quality information in the different narrow-wave-beam directions with the opposite terminal through the control signaling link and performing wave beam alignment of the high-gain narrow-wave-beam directional antenna with the opposite terminal. If the device serves as a transmitting device, the opposite terminal serves as a receiving device; or if the device serves as the receiving device, the opposite terminal serves as the transmitting device. The system comprises the transmitting device and the receiving device. The wave beam alignment method, device and system can ensure continuity of a link between the transmitting device and the receiving device during wave beam direction scanning, meanwhile the total scanning times is decreased from N2 to 2N, and the time for establishing data transmission connection is greatly shortened.
Owner:ZTE CORP
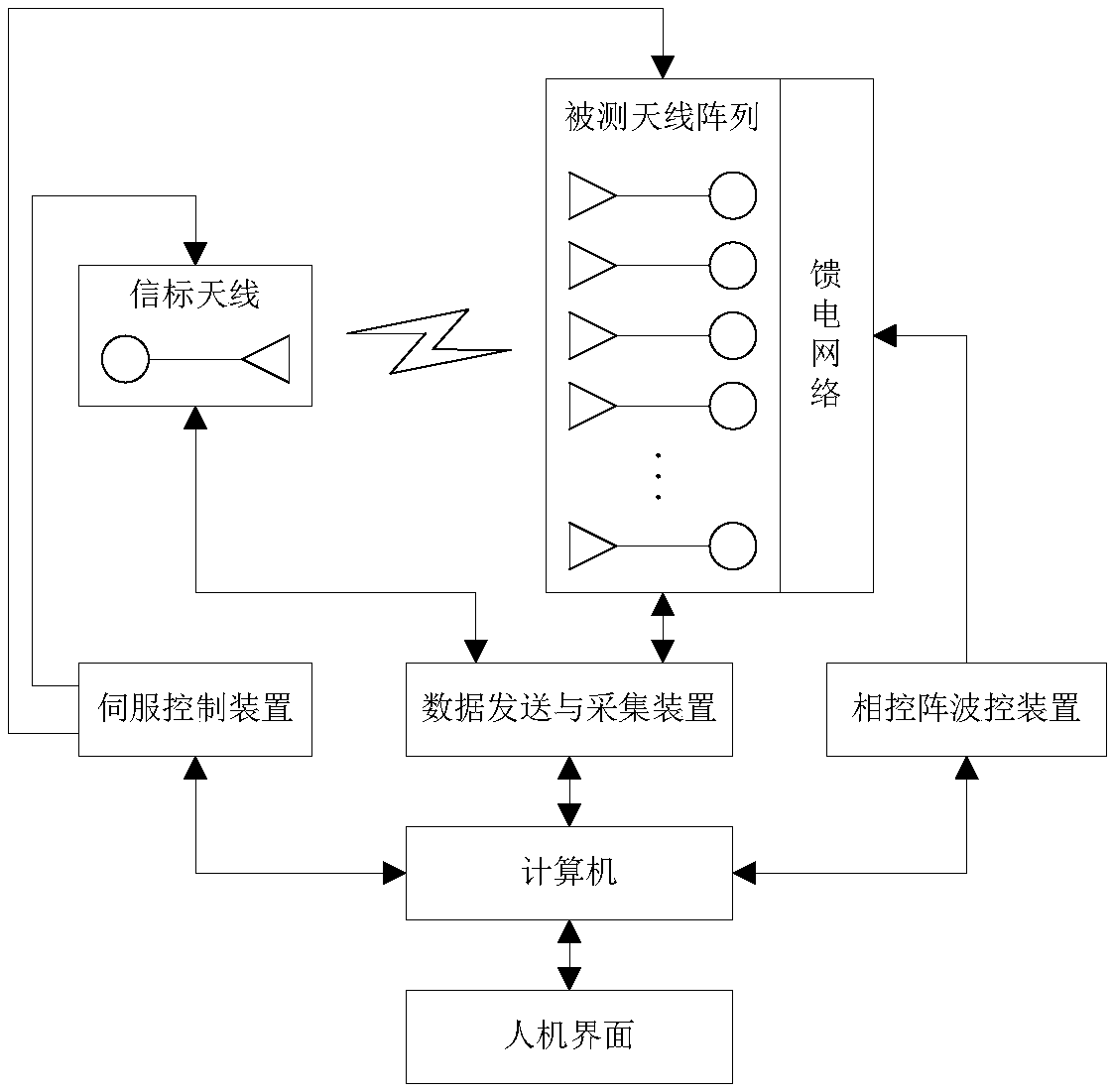
Large-scale MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) antenna array far field calibration system
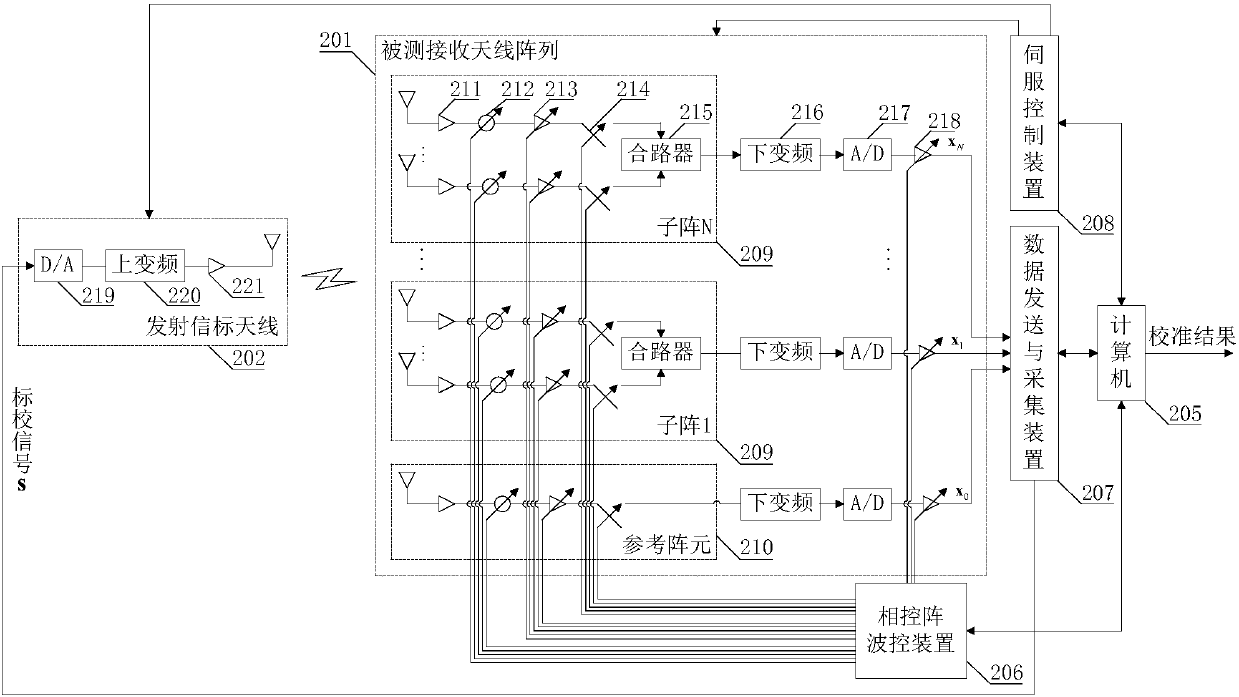
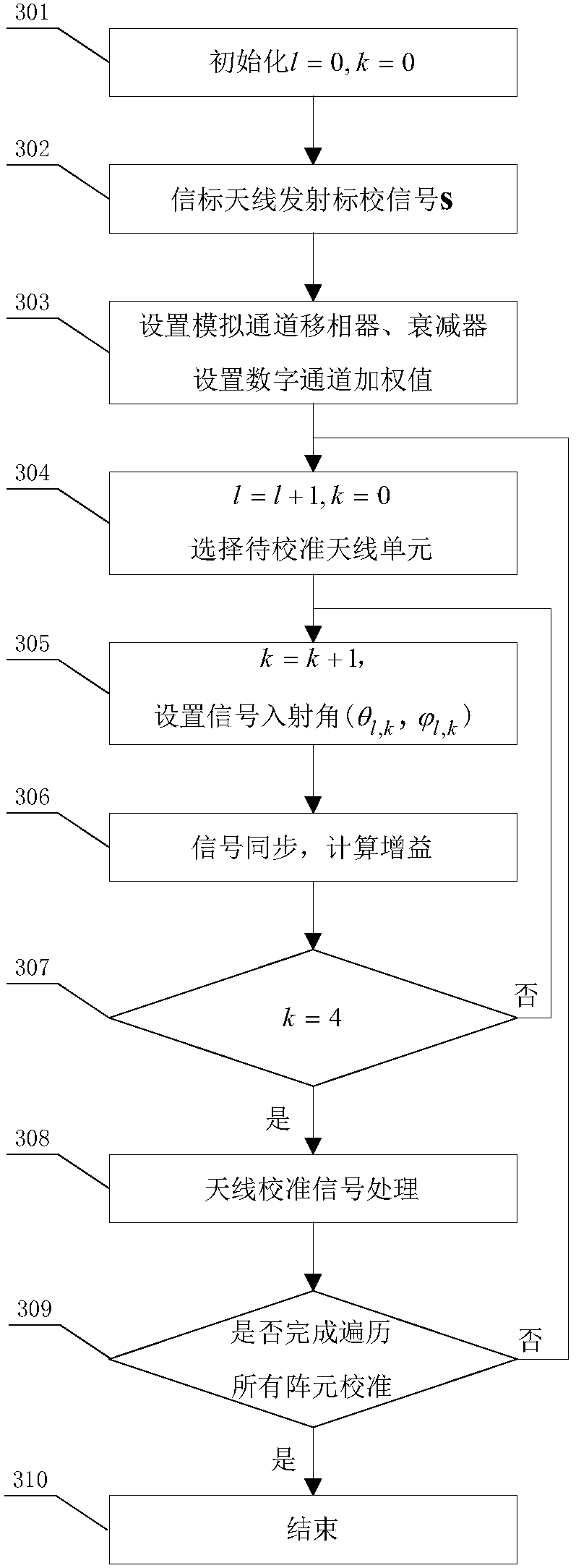
InactiveCN108155958AImprove calibration efficiencyAvoid mutual interferenceTransmitters monitoringSpatial transmit diversityCalibration resultArray element
The invention discloses a large-scale MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) antenna array far field calibration system. The calibration accuracy of a wave beam direction error caused by an array element position error and an amplitude phase error in an antenna array under test can be effectively increased by the calibration system. The calibration system is implemented by the following technical scheme: a server control device controls the relative position between the antenna array under test and a beacon antenna, and changes a wave beam incident angle from a transmitting beacon antenna to areceiving antenna array under test or a wave beam departure angle from a transmitting antenna array under test to a receiving beacon antenna; a phased array wave control device controls all phase shifters, attenuators, switches and digital weighting of a feed network of the antenna array under test; a data transmitting and acquiring device controls digital signals transmitted by the transmitting antenna array under test and the transmitting beacon antenna, and acquires digital signals received by the receiving antenna array under test and the receiving beacon antenna; and the array element positioning error and the amplitude phase error of the antenna array under test are calculated on the basis of a digital domain signal processing algorithm, and a calibration result of the antenna arrayunder test is output.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com