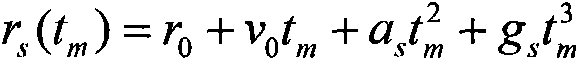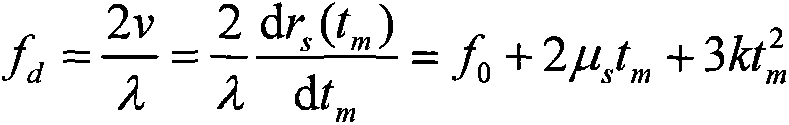Patents
Literature
253 results about "Slow time" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
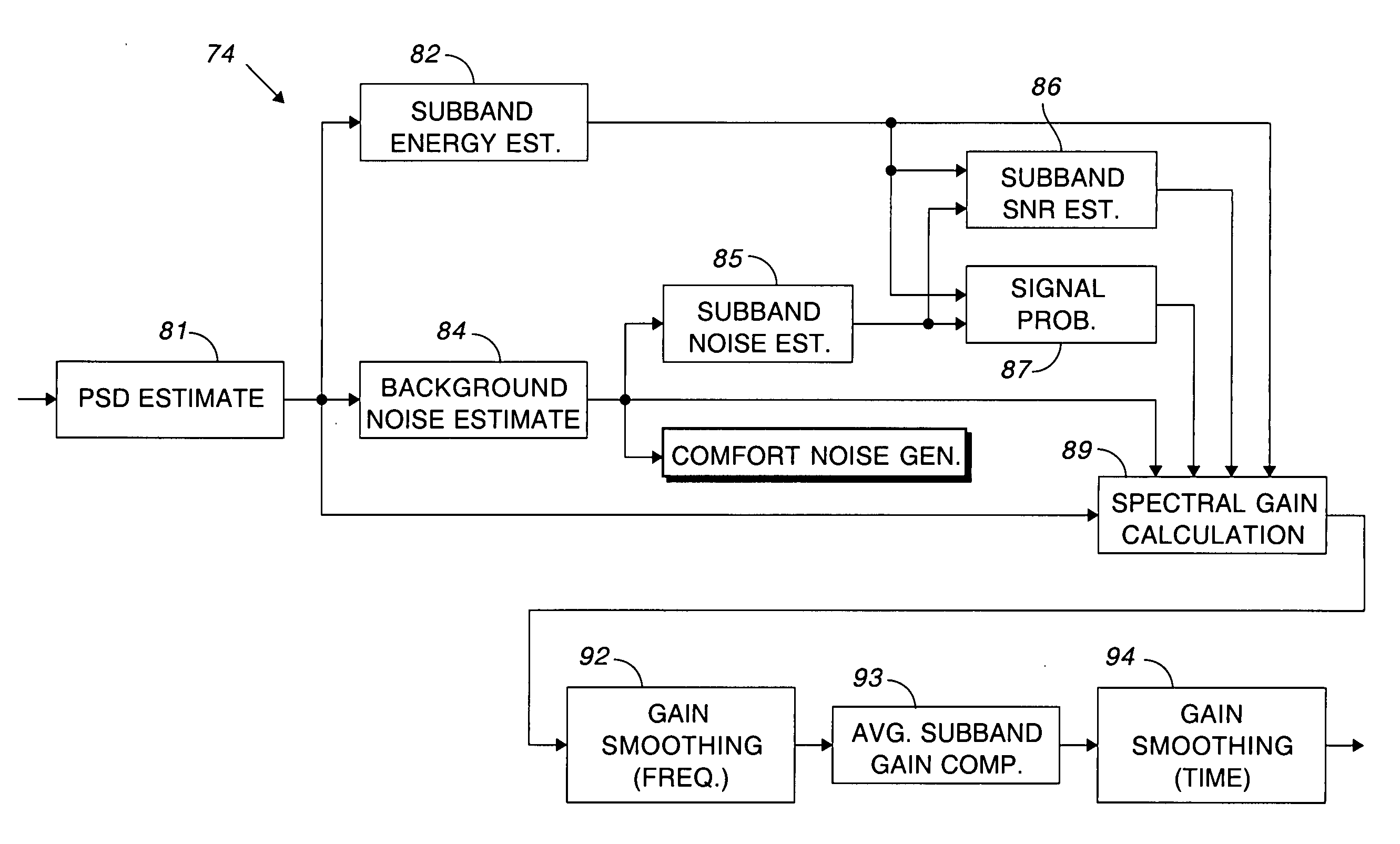
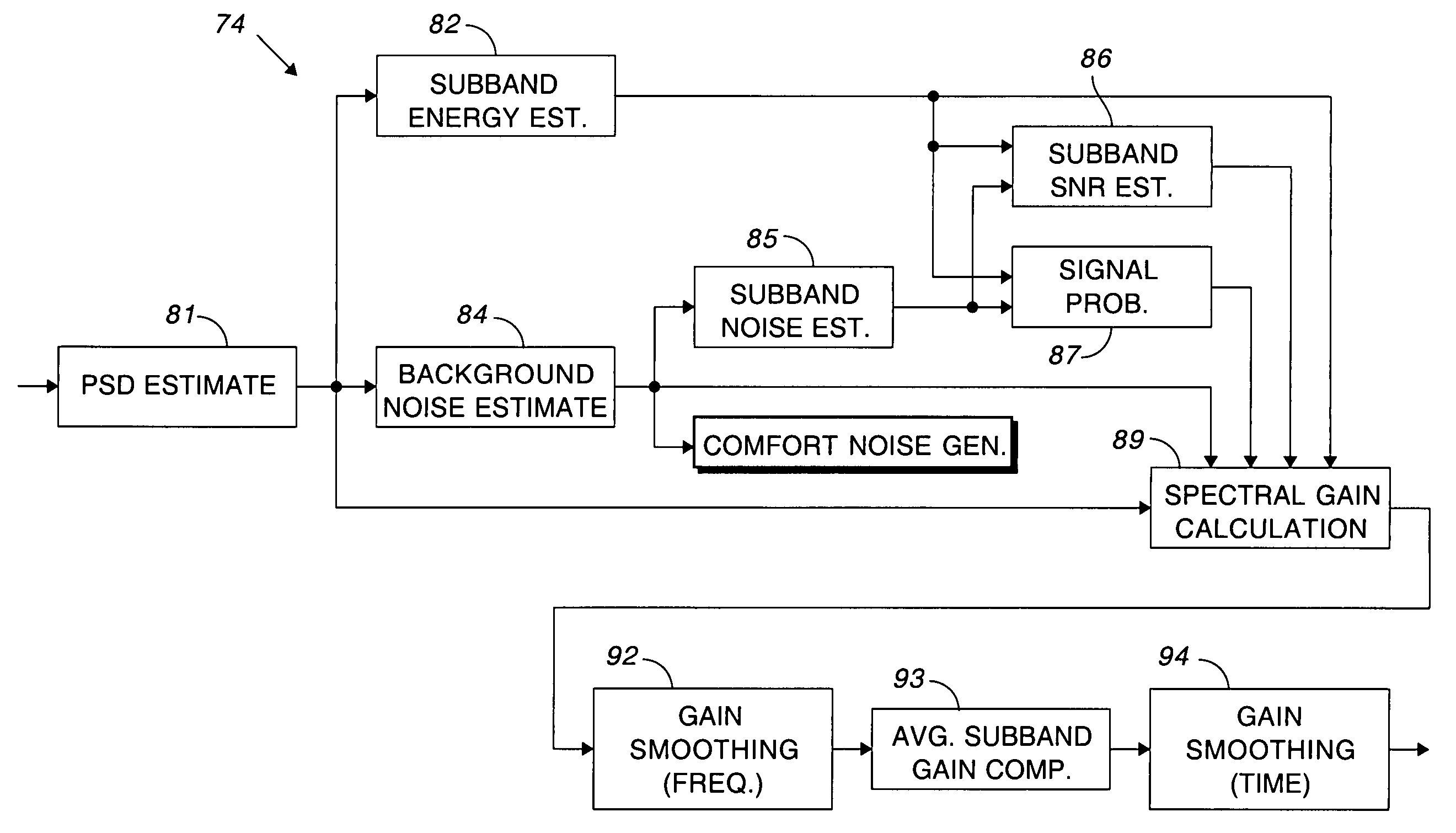
Comfort noise generator using modified doblinger noise estimate
ActiveUS20050278171A1Generate efficientlyEliminates noise pumpingSpeech analysisTime domainComfort noise
A background noise estimate based upon a modified Doblinger noise estimate is used for modulating the output of a pseudo-random phase spectrum generator to produce the comfort noise. The circuit for estimating noise includes a smoothing filter having a slower time constant for updating the noise estimate during noise than during speech. Comfort noise is smoothly inserted by basing the amount of comfort noise on the amount of noise suppression. A discrete inverse Fourier transform converts the comfort noise back to the time domain and overlapping windows eliminate artifacts that may have been produced during processing.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
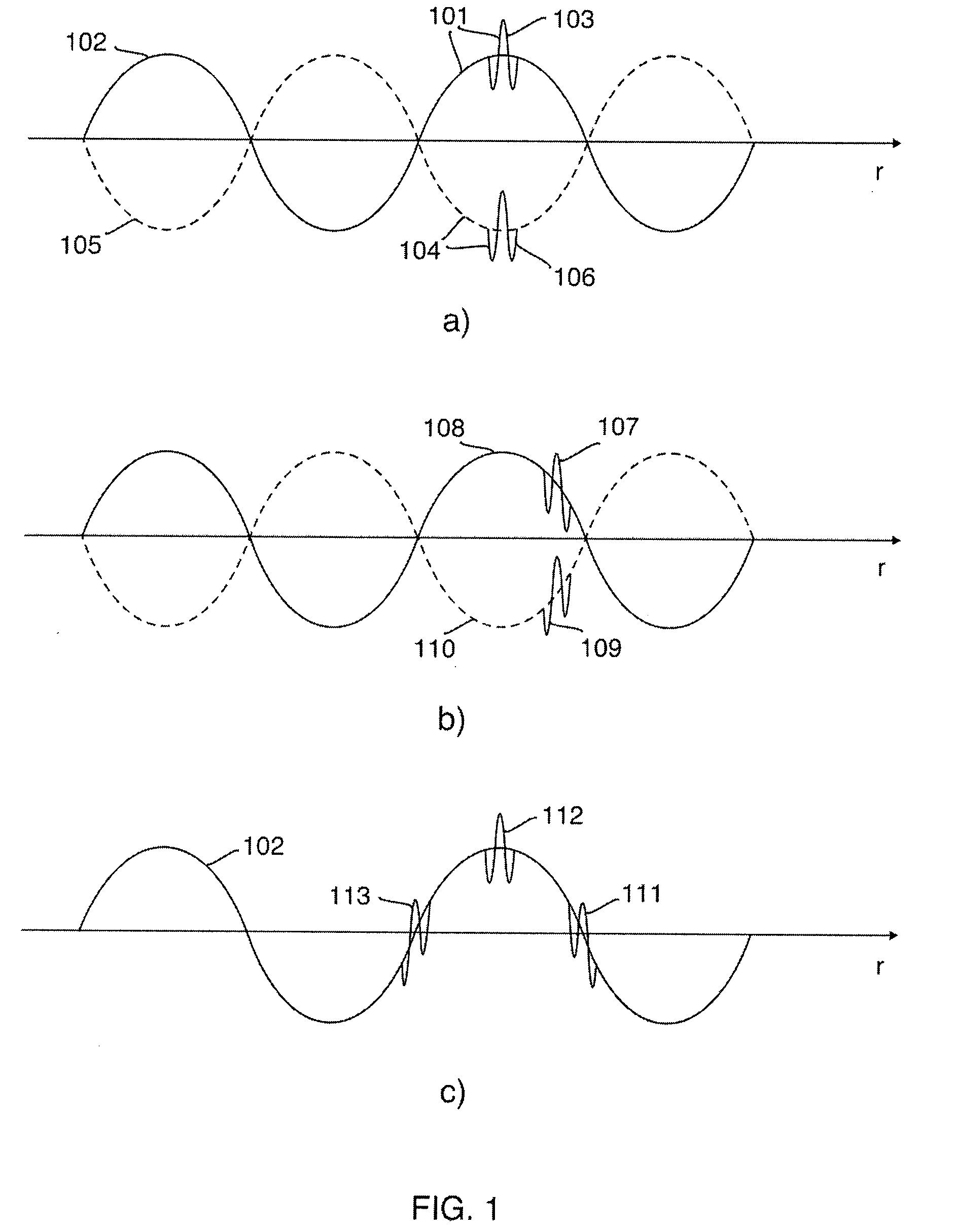
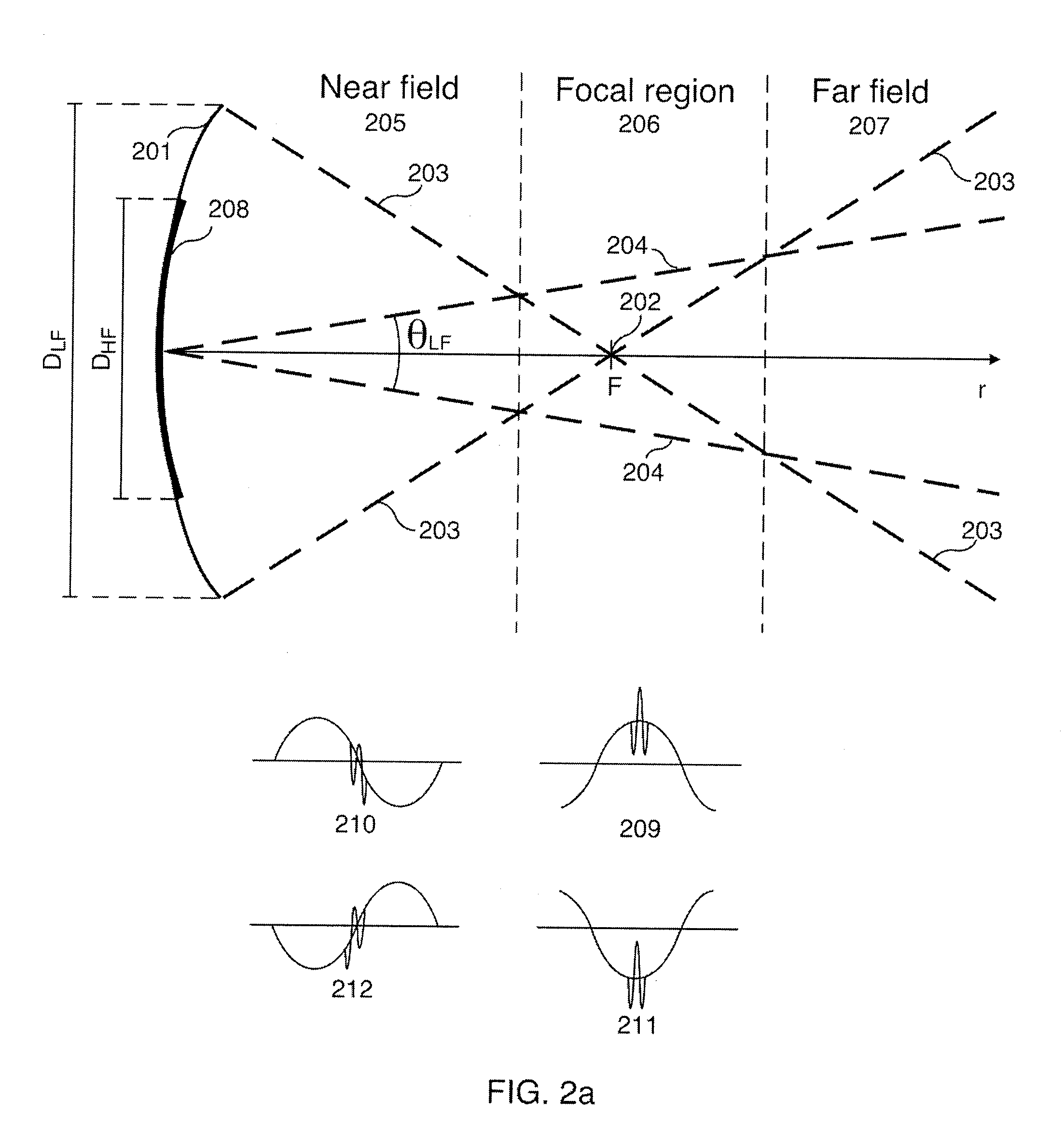
Nonlinear Elastic Wave Measurement and Imaging with Two-Frequency Elastic Wave Pulse Complexes
ActiveUS20100036244A1Fast timeSimple processOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsBeam directionTransducer
Methods and instruments for suppression of multiple scattering noise and extraction of nonlinear scattering components with measurement or imaging of a region of an object with elastic waves, where elastic wave pulse complexes are transmitted towards said region where said pulse complexes are composed of a high frequency (HF) and a low frequency (LF) pulse with the same or overlapping beam directions and where the HF pulse is so close to the LF pulse that it observes the modification of the object by the LF pulse at least for a part of the image depth. The frequency and / or amplitude and / or phase of said LF pulse relative to said HF pulse varies for transmitted pulse complexes in order to nonlinearly manipulate the object elasticity observed by the HF pulse along at least parts of its propagation, and where received HF signals are picked up by transducers from one or both of scattered and transmitted components of the transmitted HF pulses. Said received HF signals are processed to form measurement or image signals for display, and where in the process of forming said measurement or image signals said received HF signals are one or both of delay corrected with correction delay in the fast time (depth-time), and pulse distortion corrected in the fast time, and combined in slow time to form noise suppressed HF signals or nonlinear scattering HF signals that are used for further processing to form measurement or image signals. The methods are applicable to elastic waves where the material elasticity is nonlinear in relation to the material deformation.
Owner:SURF TECH AS
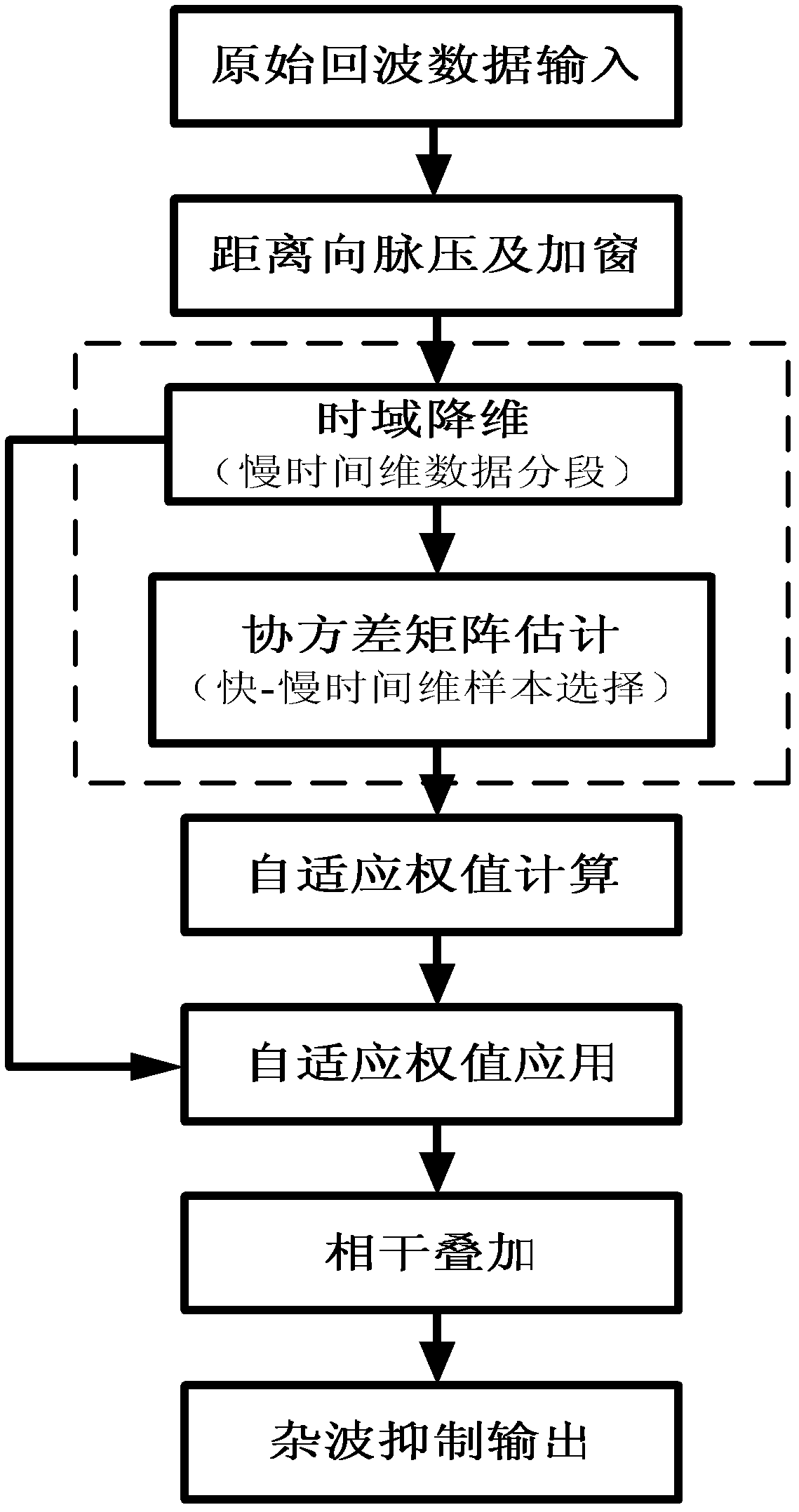
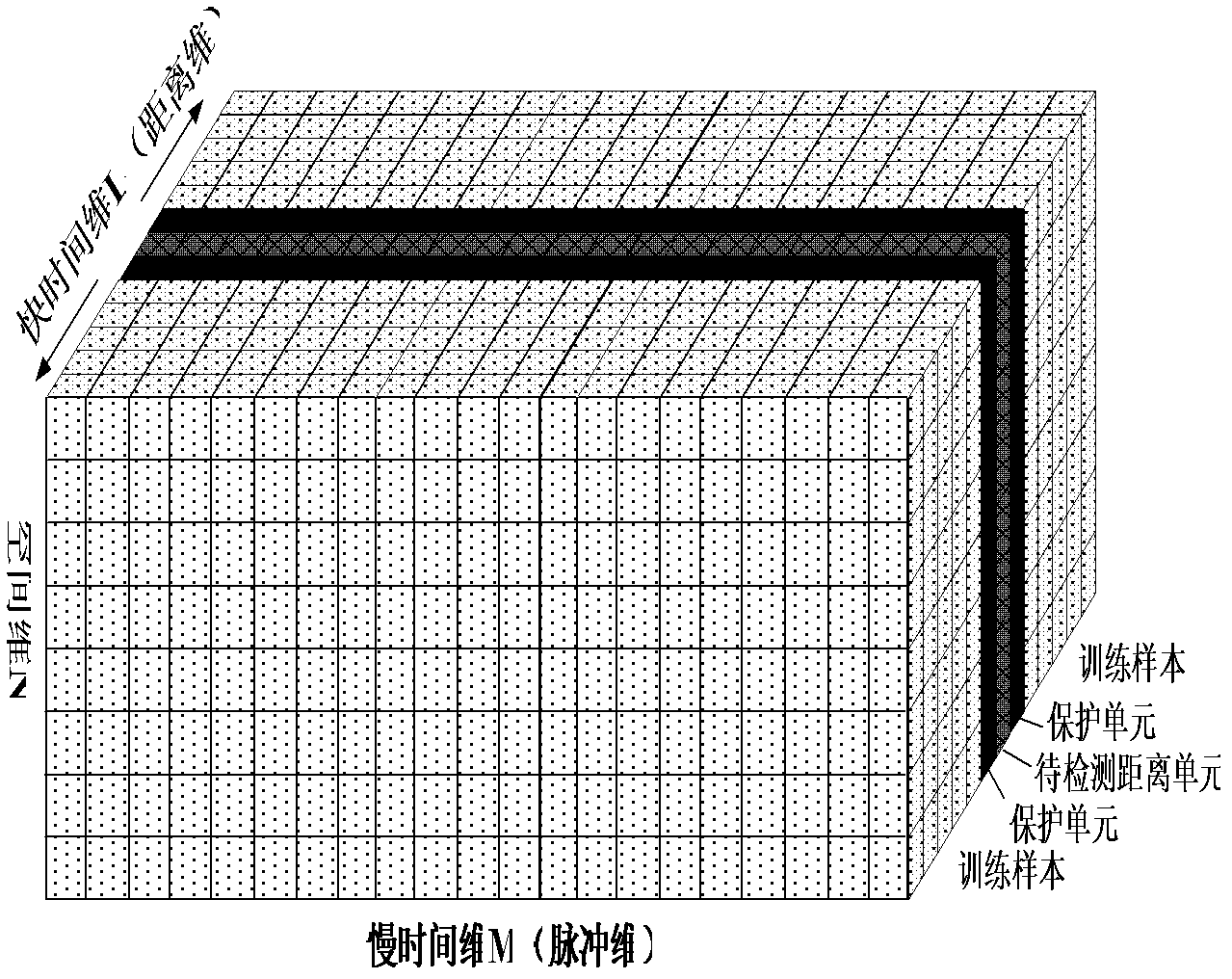
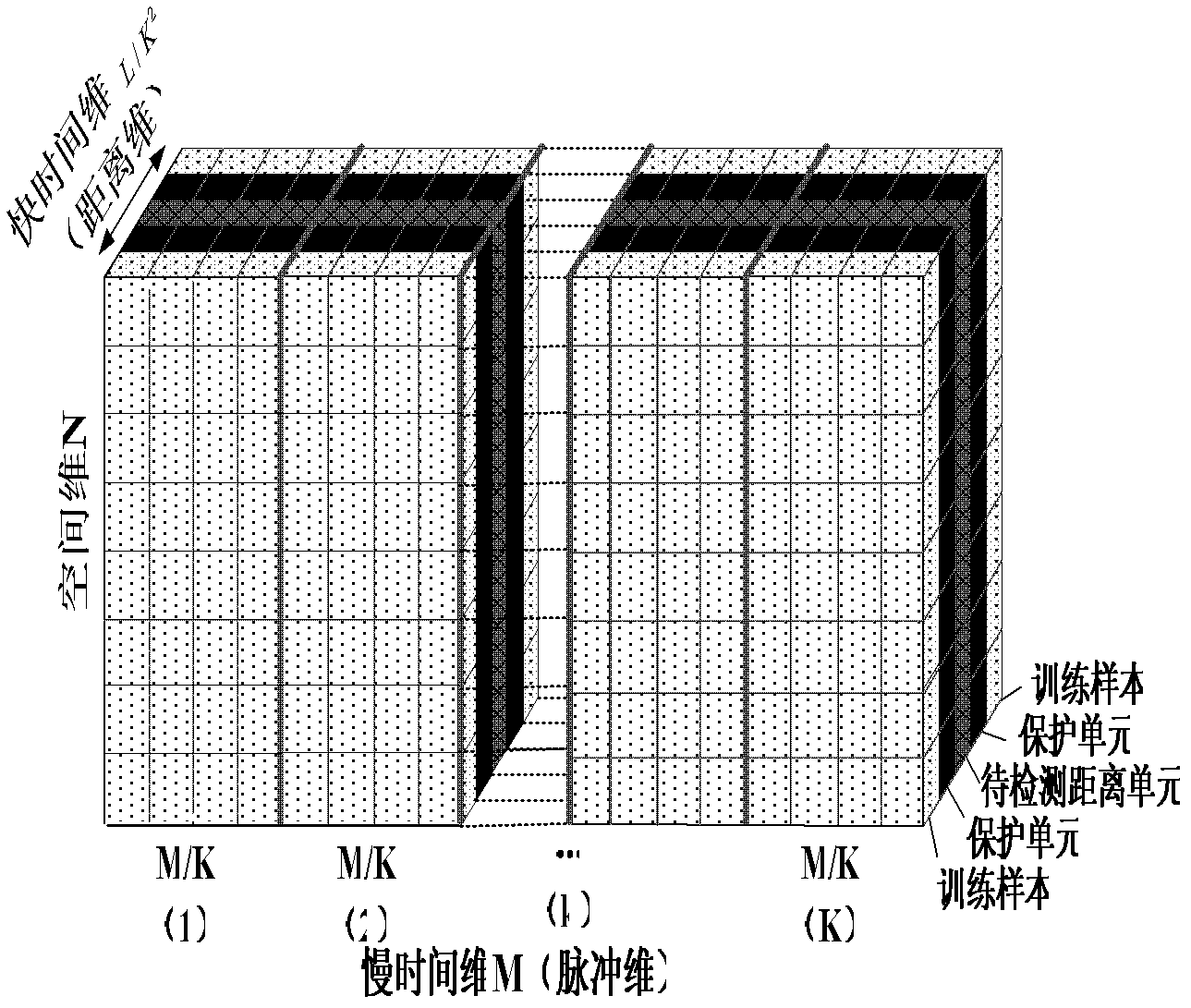
Sample-training-based non-stationary clutter suppression method of vehicle-mounted radar
InactiveCN103018727ASolve the problem of clutter distance dependenceImproved clutter suppression performanceWave based measurement systemsTime domainRadar
The invention discloses a sample-training-based non-stationary clutter suppression method of a vehicle-mounted radar, which relates to vehicle-mounted radar technology. The method comprises the steps of estimation of a clutter covariance matrix based on combined time-dimension sample training strategies, application of a self-adaptive weight, and coherence stack to output signals. The method specifically comprises the following steps of: inputting raw echo data; compressing and windowing pulses in a distance dimension; segmenting slow-time-dimension data; selecting quick-slow time dimension training samples; estimating the clutter covariance matrix; calculating and applying the self-adaptive weight; and carrying out coherence stack on the output signals. According to the method, the sample training strategies are changed under an STAP (space-time adaptive processing) time domain dimension reducing structure in light of the clutter range dependence of the vehicle-mounted radar, thus the estimation precision of the clutter covariance matrix can be effectively improved, and the clutter suppression performance of a main lobe is improved as well. The sample-training-based non-stationary clutter suppression method shows high robustness in engineering application, and is particularly applicable to detection on a slow moving object.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Radar slightly-moving target detection method based on Radon-linear canonical ambiguity function
ActiveCN103344949AEfficient accumulationFlexible matchingWave based measurement systemsTarget signalPulse pressure
The invention relates to a radar slightly-moving target detection method based on a Radon-linear canonical ambiguity function (RLCAF) and belongs to the technical field of radar signal processing and detection. The radar slightly-moving target detection method based on the RLCAF comprises the following steps that (1) demodulation and pulse pressure are conducted on a radar echo in the distance direction so that in-pulse accumulation can be completed; (2) the type of a target to be detected is predicted, and parameters are initialized; (3) the distance and Doppler migration are compensated through the RLCAF and signal energy of a slightly-moving target is accumulated; (4) the parameters are traversed and searched, an RLCAF domain detection unit figure is established, and constant false-alarm detection is conducted; (5) target moving parameters are estimated and moving trace points are output. According to the radar slightly-moving target detection method based on the RLCAF, the advantages of an ambiguity function and the advantages of linear canonical transformation are combined, non-uniform velocity translational motion target signals or turning target signals can be flexibly matched and accumulated in a clutter background, the signal-to-clutter ratio is improved, range migration can be compensated through the extraction of a target observation value in a distance-slow-time plane, phase-coherent accumulation for a long time is completed, the detection capacity of radar to the slightly-moving target is improved, and therefore the radar slightly-moving target detection method based on the RLCAF is wide in applicability.
Owner:NAVAL AVIATION UNIV
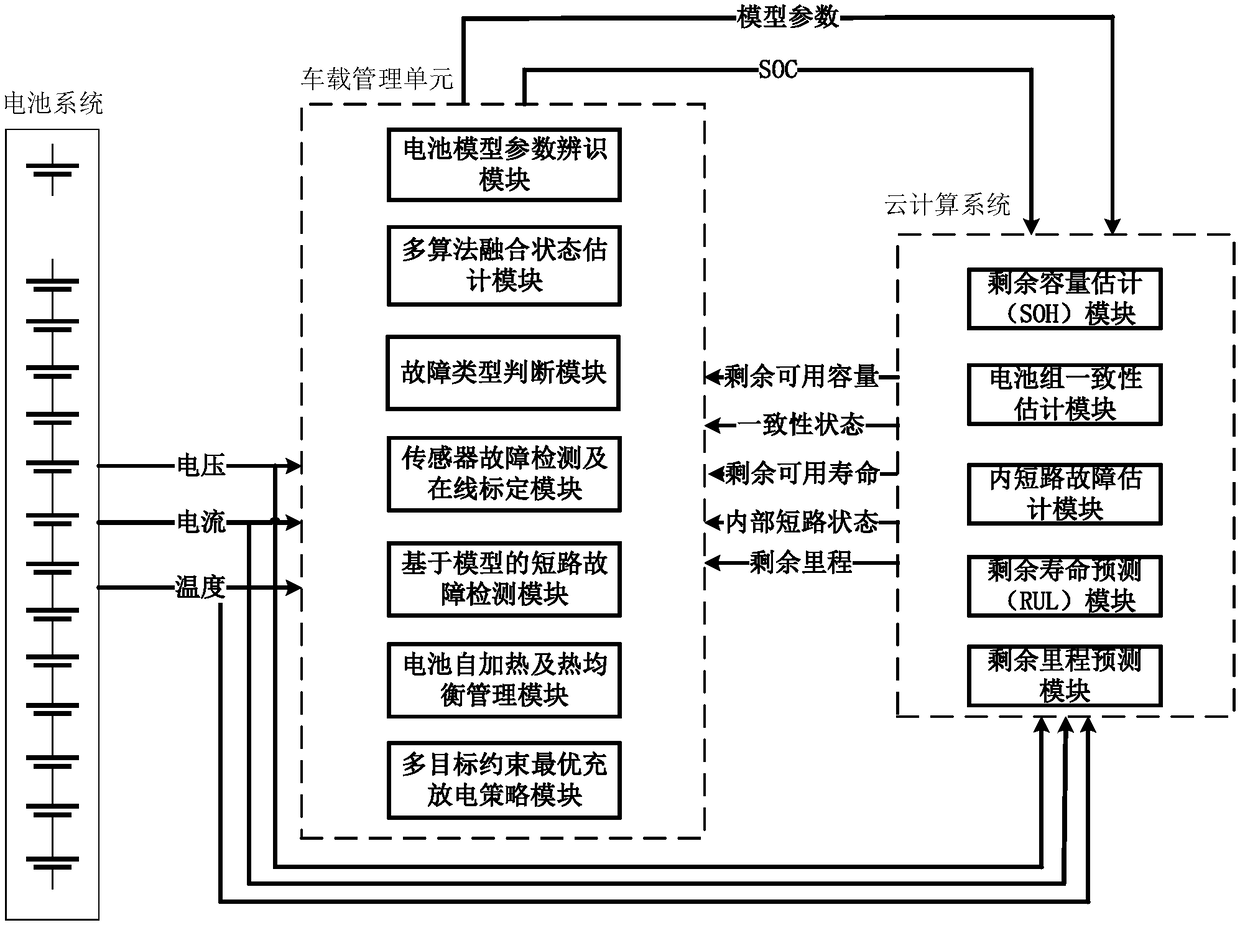
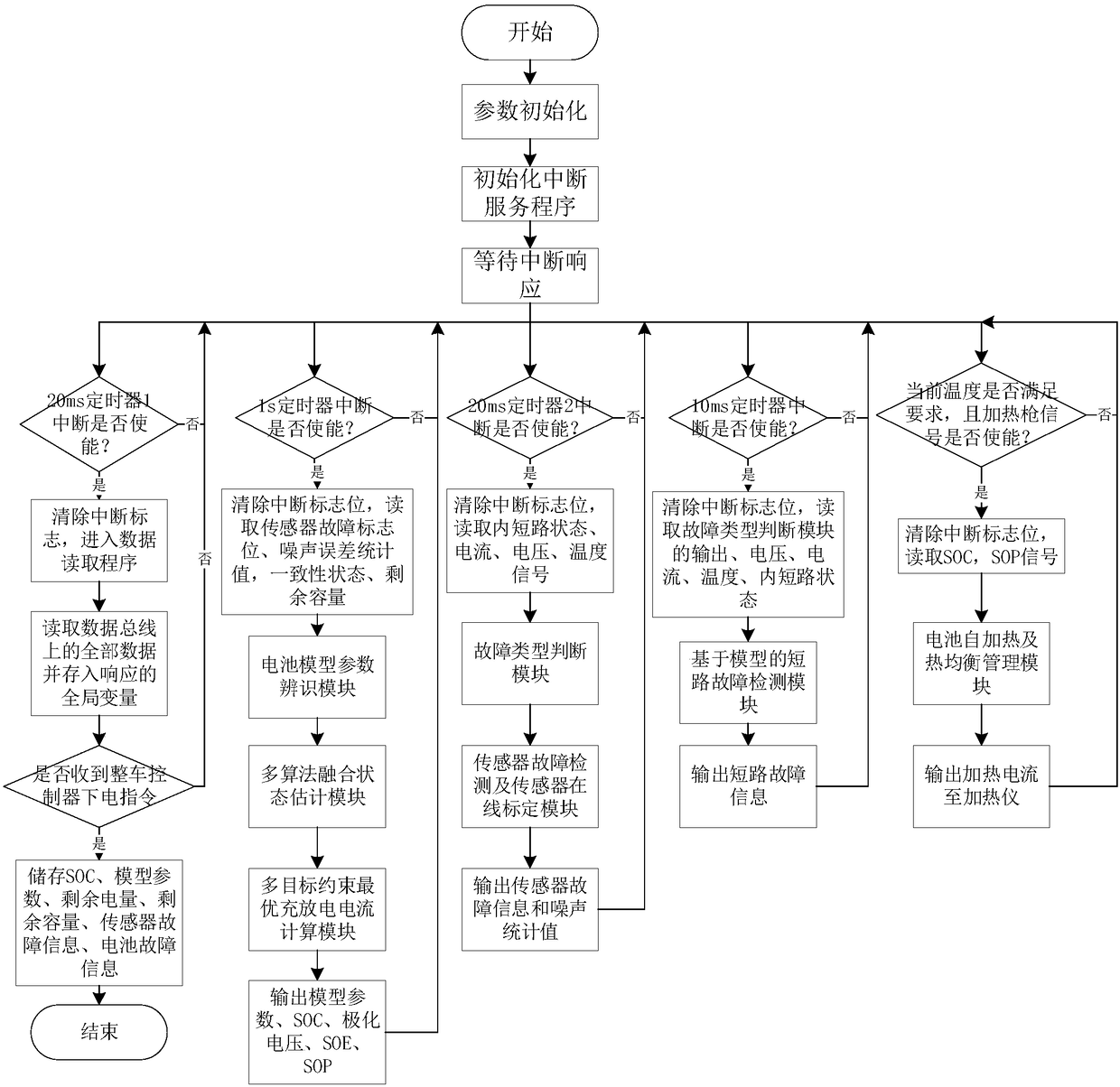
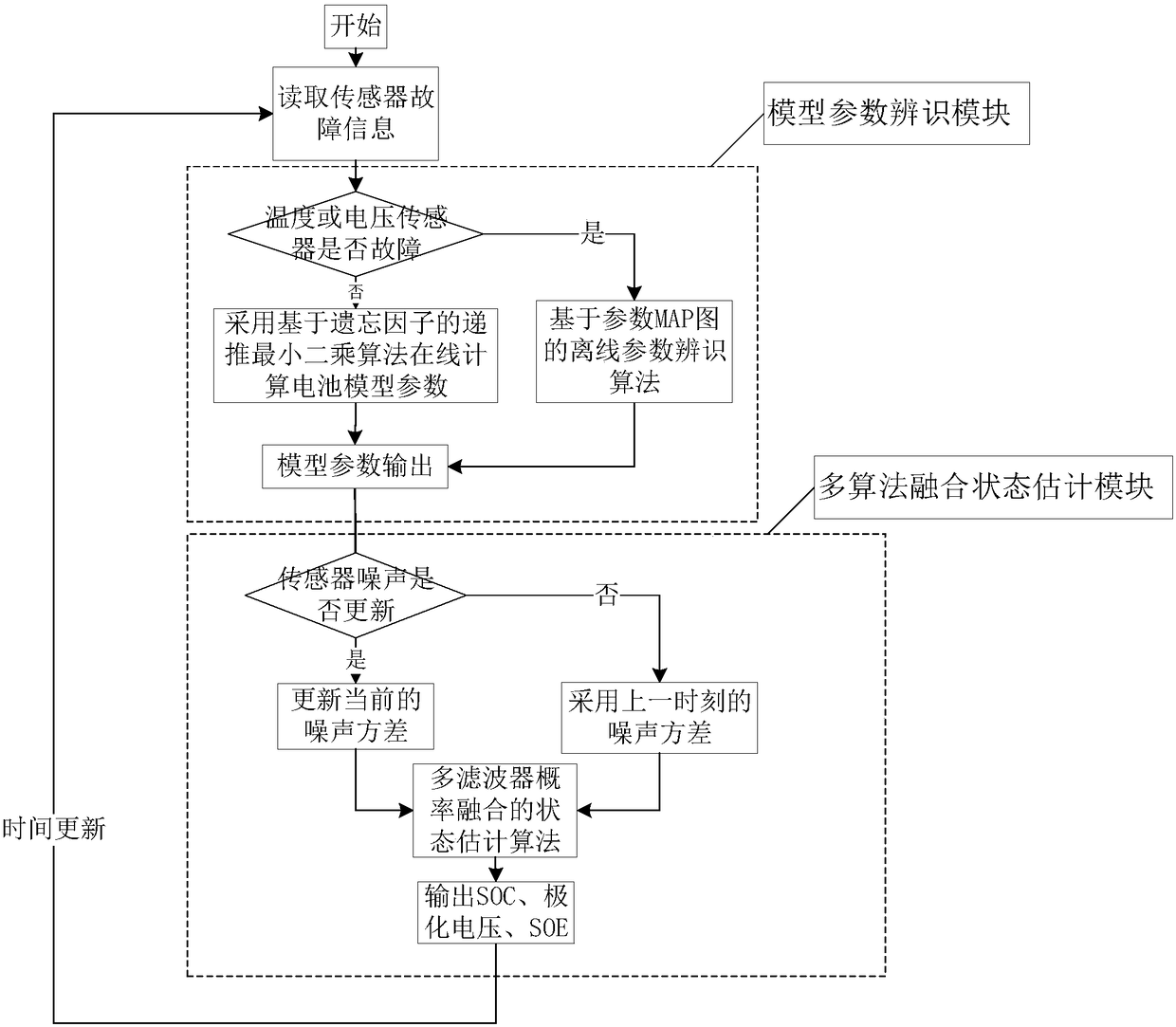
Battery management system
The invention relates to a battery management system which comprises a vehicle-mounted battery management unit and a cloud calculation system based on battery historical data. The vehicle-mounted battery management unit conducts battery model parameter identification through voltage, current and temperature which are measured by a battery information acquisition unit, conducts state SOC and SOE estimation through identified parameters and achieves functions of multi-objective optimization charging and discharging capacity SOP estimation, battery short-circuit fault detection, sensor fault detection, sensor online calibration and battery self-heating and heat equilibrium and the like on the basis of model parameters. The characteristics that a cloud server is large in memory space and highin computing power are used for achieving online battery capacity estimation, namely the section of health SOH estimation, and battery pack consistency estimation and remaining mileage prediction areconducted through the model parameters and SOC information. The inner short-circuit condition of parameter slow time varying is estimated. The remaining useful life (RUL) is predicted through the historical charging data. Calculation results are transmitted back to the vehicle-mounted battery management unit through wireless transmission.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
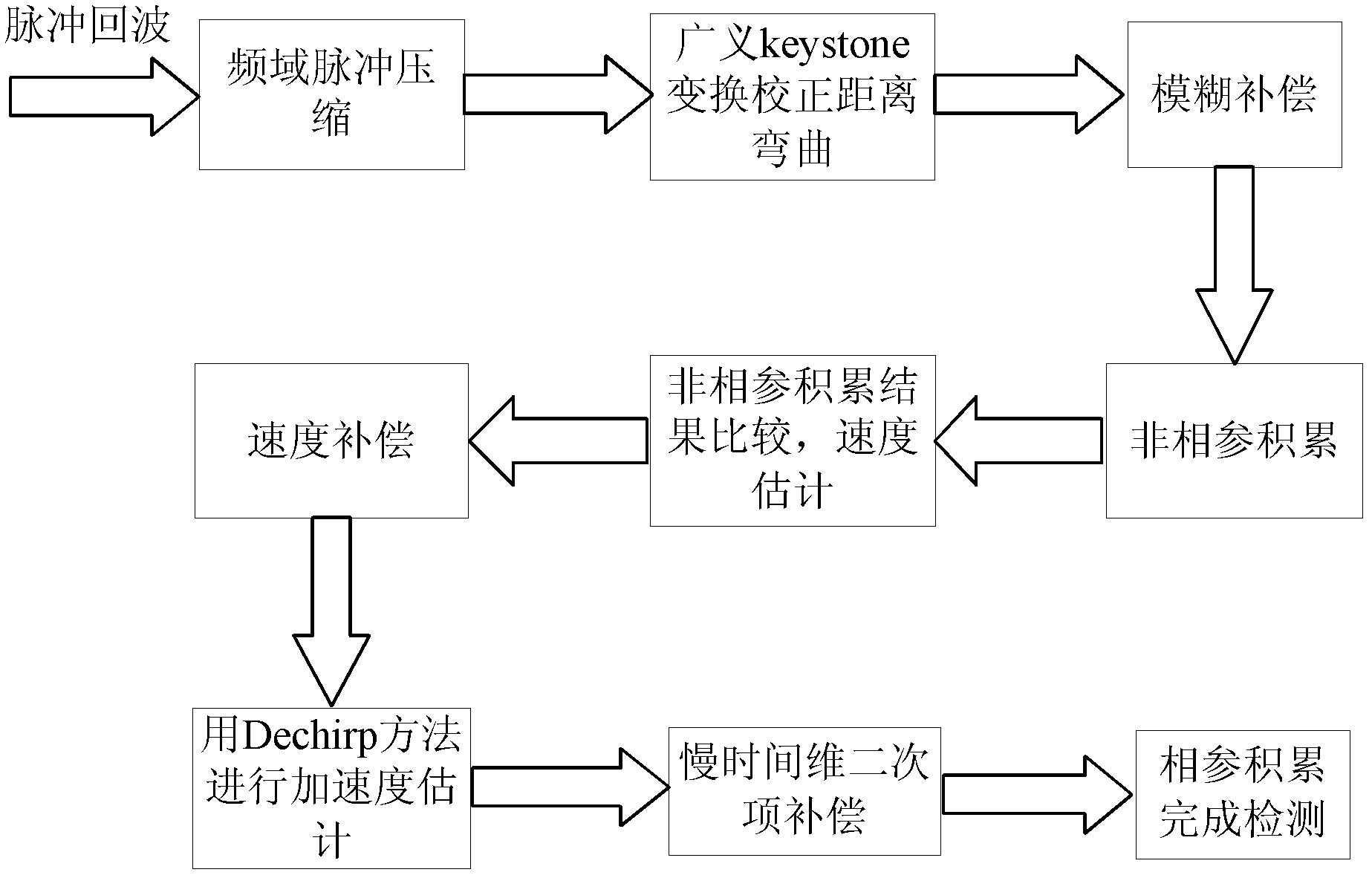
Radar detection method based on generalized keystone transformation and non-coherent accumulation
The invention discloses a radar detection method based on generalized keystone transformation and non-coherent accumulation, wherein the method mainly solves the detection problem of a high speed and highly accelerated target in a strong Gaussian white noise background. The method is implemented by the following steps: (1) generating radar target multiple-pulse echoes with Gaussian white noise added, and performing frequency domain pulse compression; (2) correcting range curvature of the pulse-compressed echoes by using the generalized keystone transformation; (3) performing fuzzy compensation on the curvature-corrected echoes by using a fuzzy factor; (4) performing non-coherent accumulation on the fuzzy-compensated echoes, and performing velocity compensation and slow time dimensional quadratic term compensation on the echoes by using a target velocity obtained in the non-coherent accumulation; (5) performing coherent accumulation on the slow time dimensional quadratic term compensated echoes to obtain the target to be detected. The method provided in the invention can eliminate effects of the range curvature and migration of the echoes on energy accumulation, can reduce computation of velocity search, and can be used in the detection of the target in the strong Gaussian white noise background.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
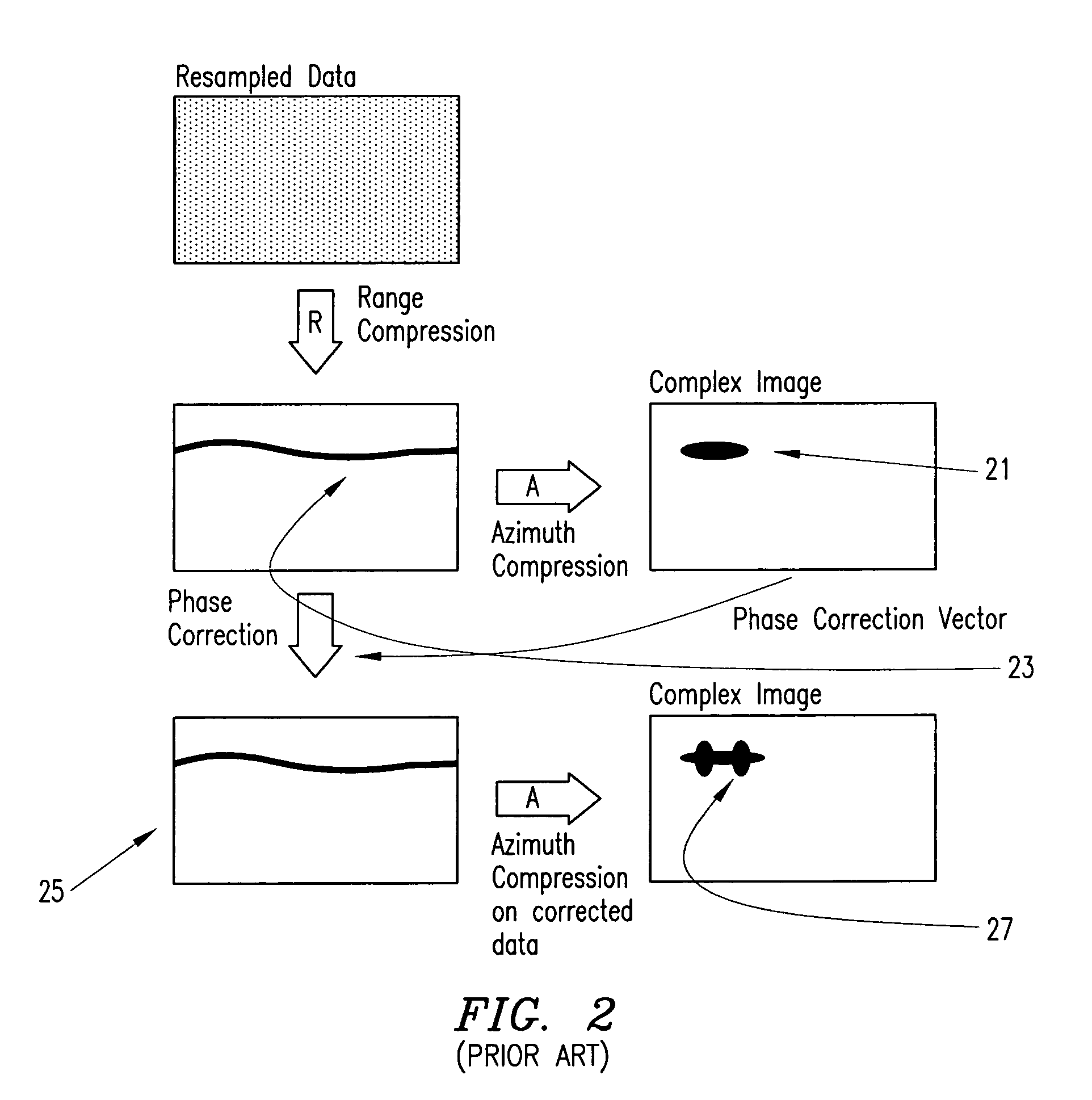
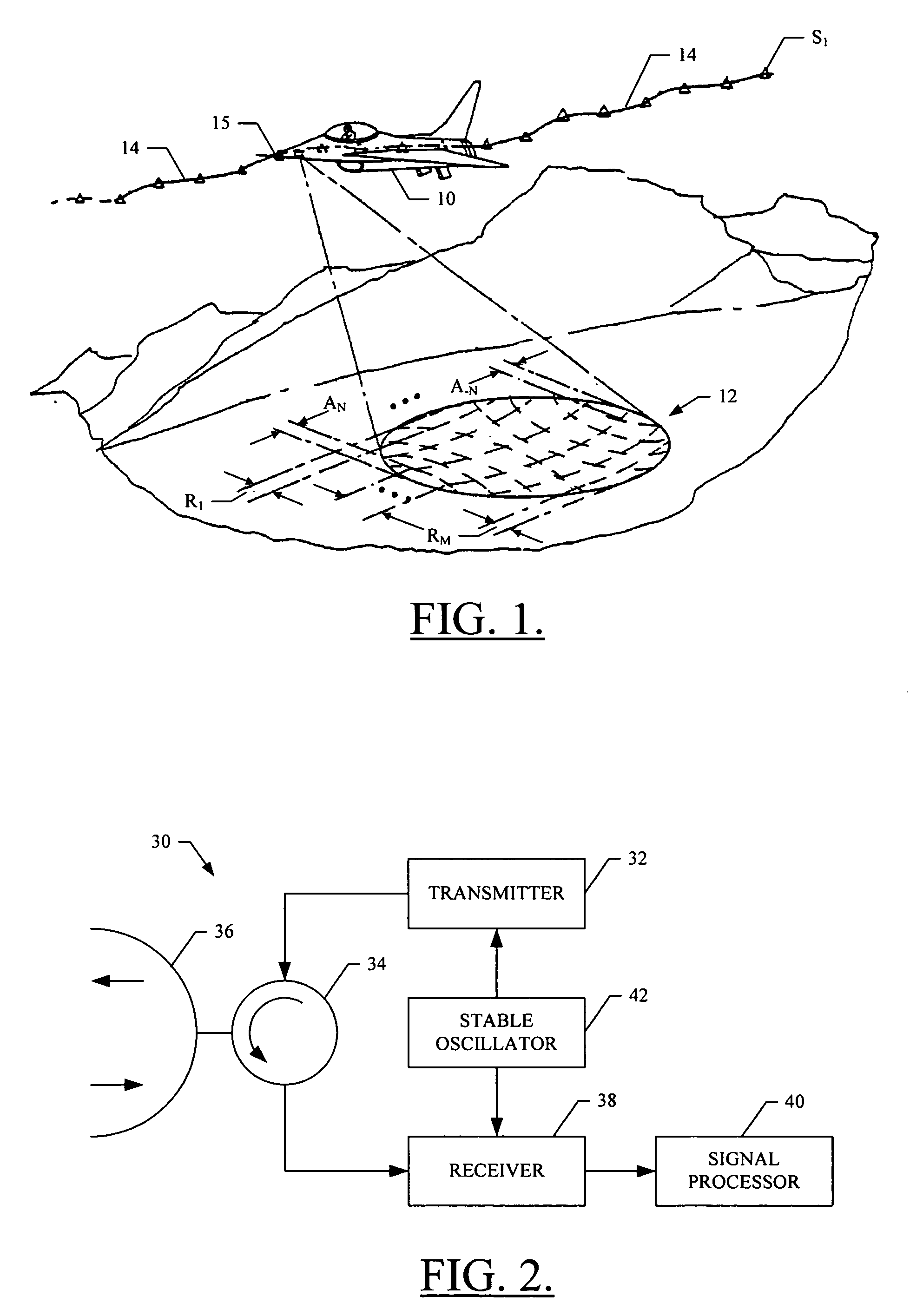
Correction of motion measurement errors beyond the range resolution of a synthetic aperture radar
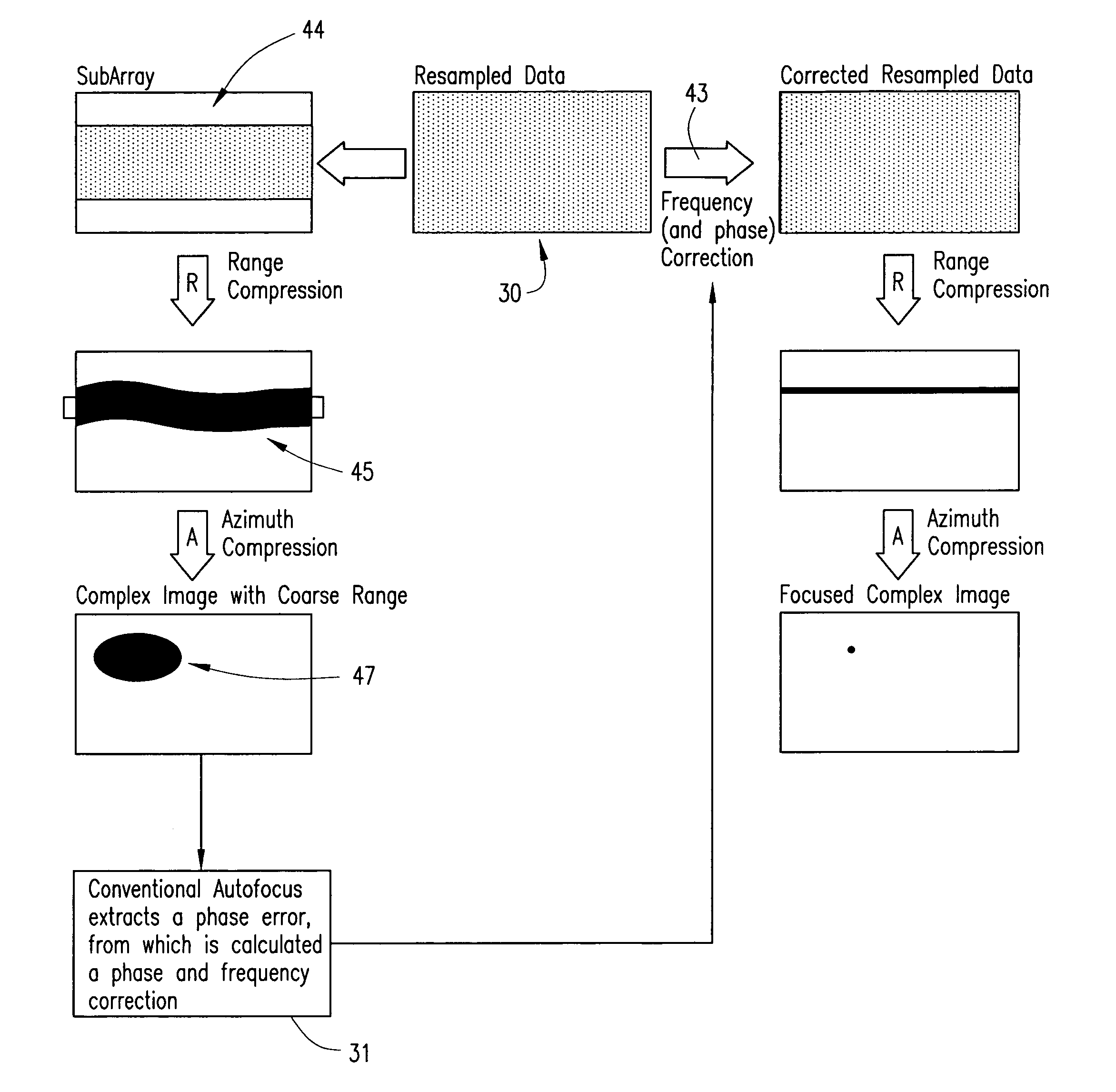
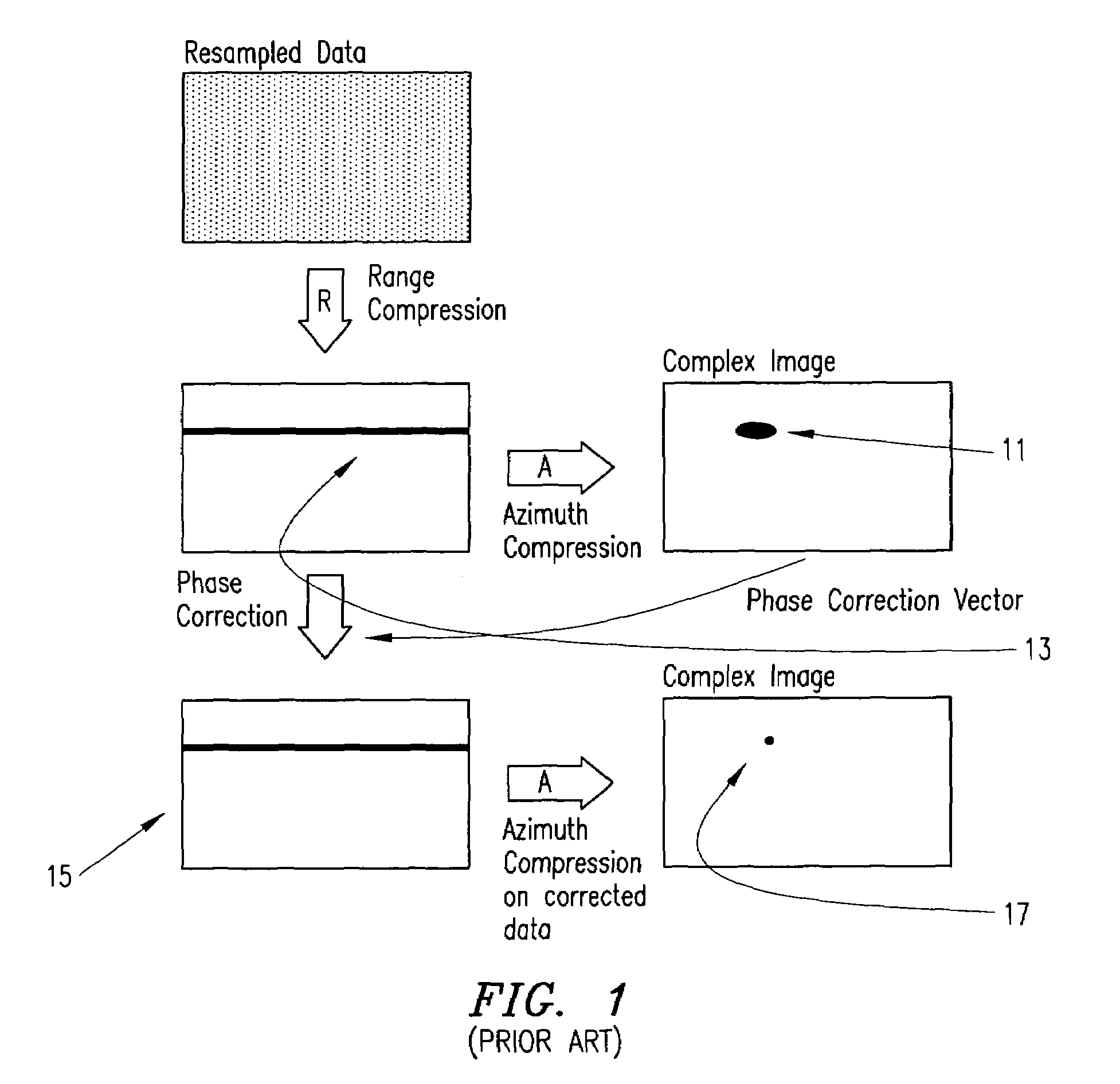
Motion measurement errors that extend beyond the range resolution of a synthetic aperture radar (SAR) can be corrected by effectively decreasing the range resolution of the SAR in order to permit measurement of the error. Range profiles can be compared across the slow-time dimension of the input data in order to estimate the error. Once the error has been determined, appropriate frequency and phase correction can be applied to the uncompressed input data, after which range and azimuth compression can be performed to produce a desired SAR image.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
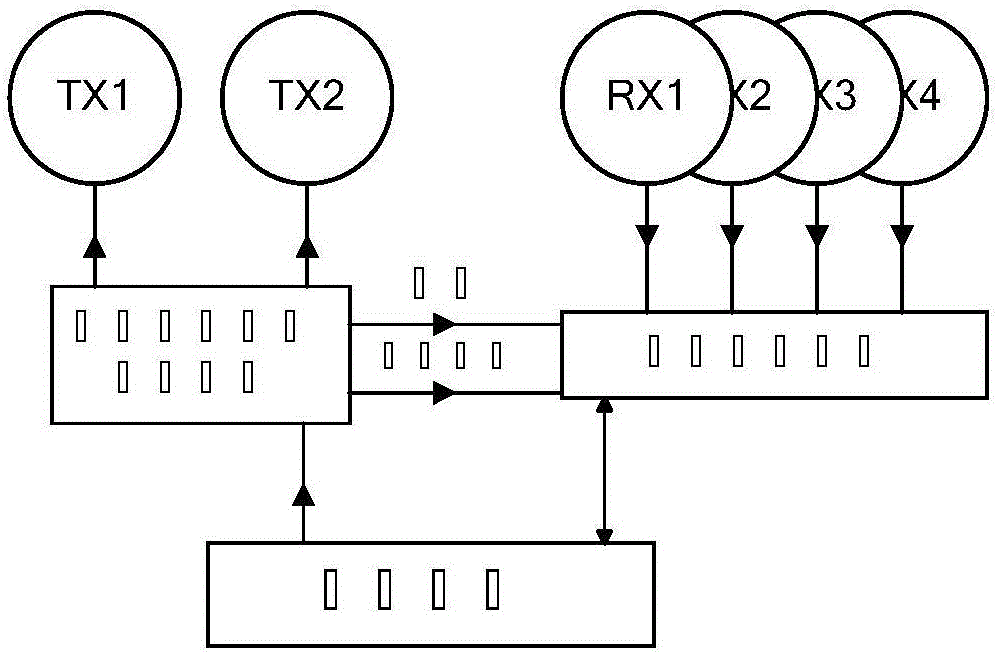
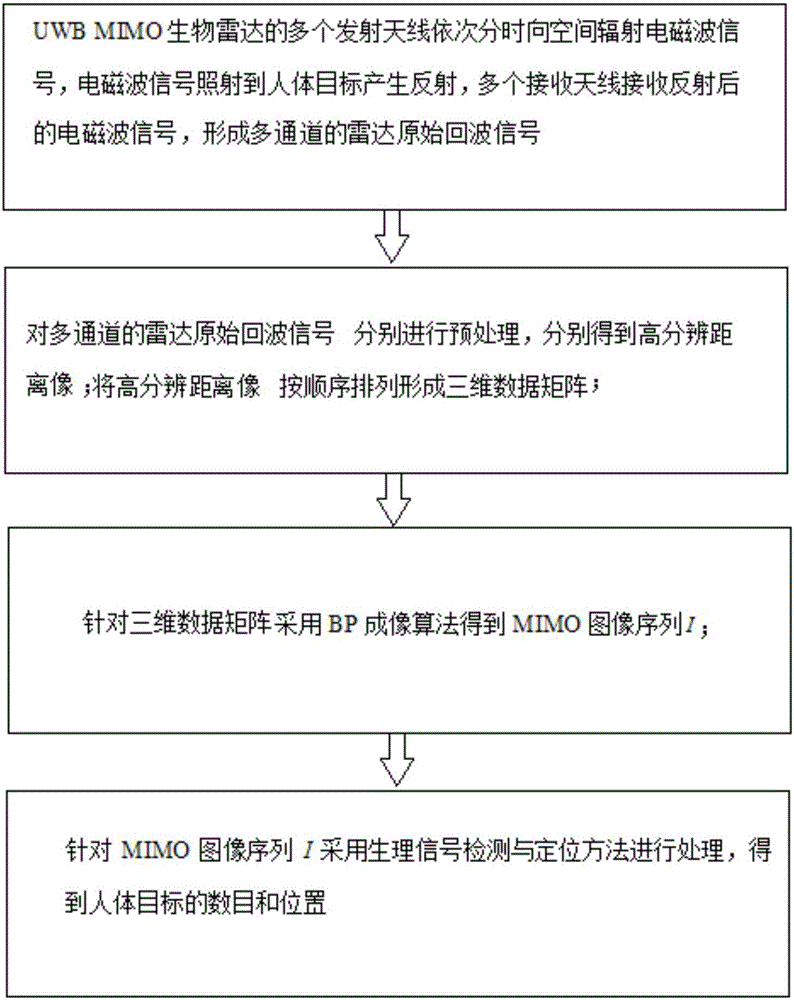
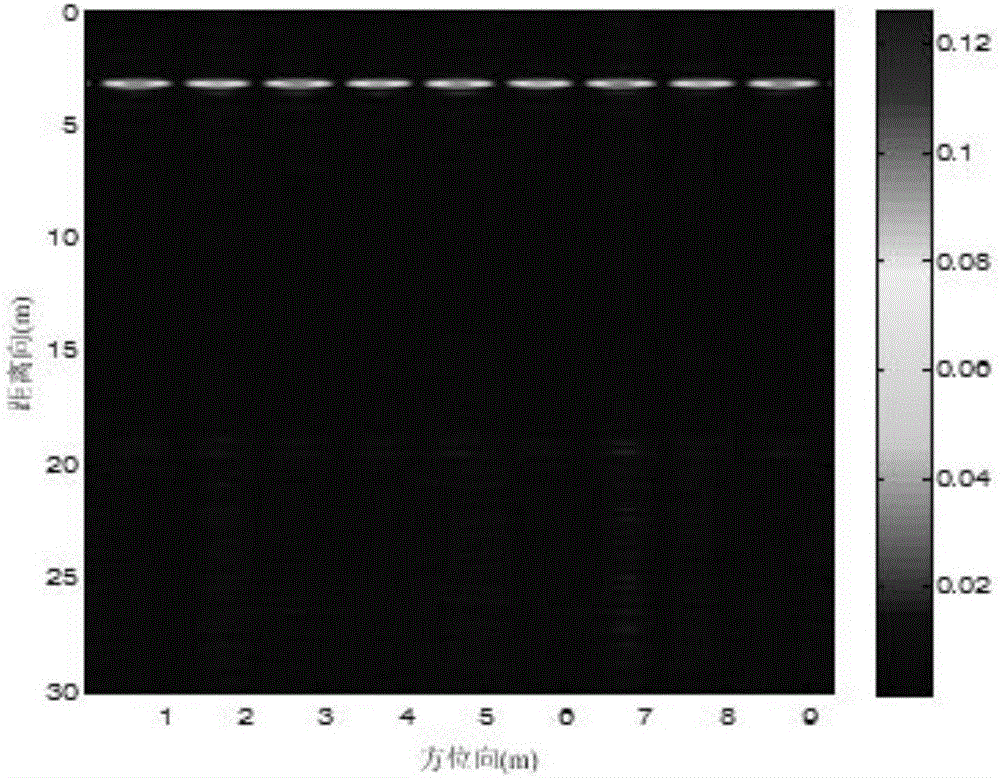
Static human target recognizing and positioning method based on UWB (Ultra Wideband) MIMO (Multiple-Input Multiple-Output) bio-radar
ActiveCN106054156AEasy to identifyPrecise positioningRadio wave reradiation/reflectionUltra-widebandHuman body
The invention discloses a static human target recognizing and positioning method based on UWB (Ultra Wideband) MIMO (Multiple-Input Multiple-Output) bio-radar. A distance-slow time-multi-channel three-dimensional data matrix is formed by preprocessing original echo signals of radar, so that the spatial separation degree of physical sign signals and surrounding clutter of human body is effectively improved; and the physical sign signals of the human body are detected and positioned via a physical signal detection and positioning algorithm, so that the human target recognizing and positioning performance of the bio-radar can be effectively improved.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Improved algorithm based on parameter estimation and compensation of quadratic phase function
ActiveCN108761404ARich spatial informationEasy accessRadio wave reradiation/reflectionInformation processingImproved algorithm
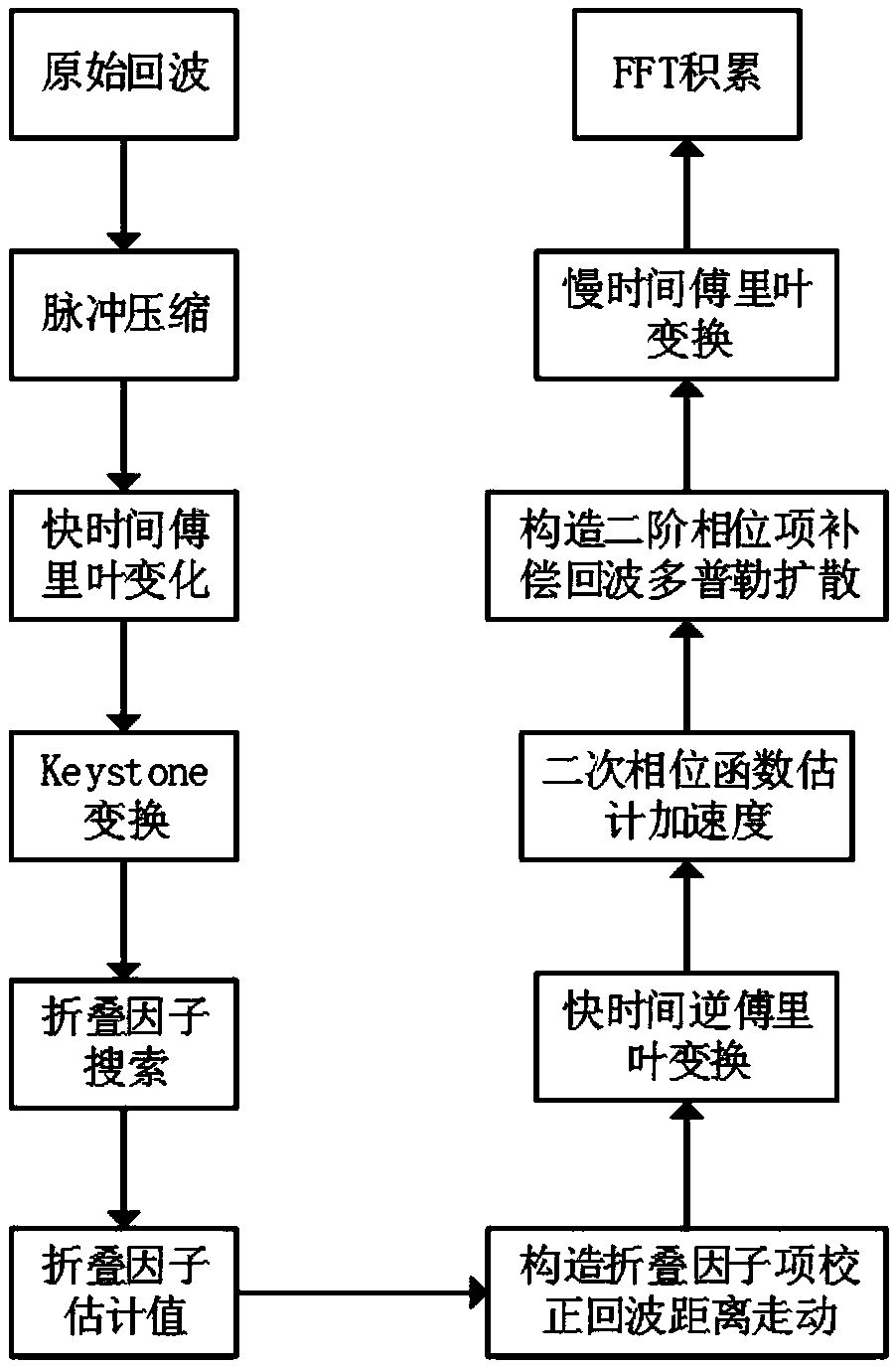
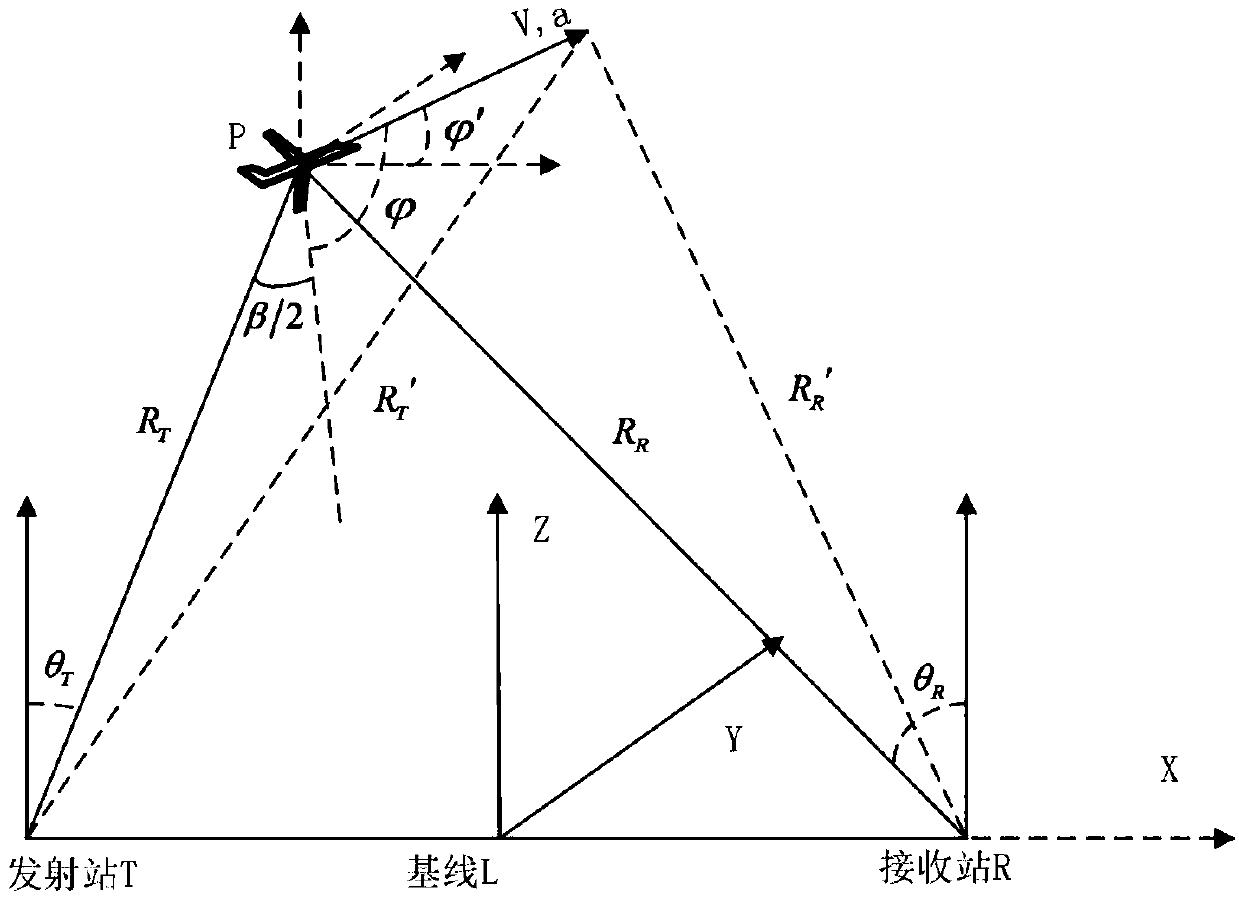
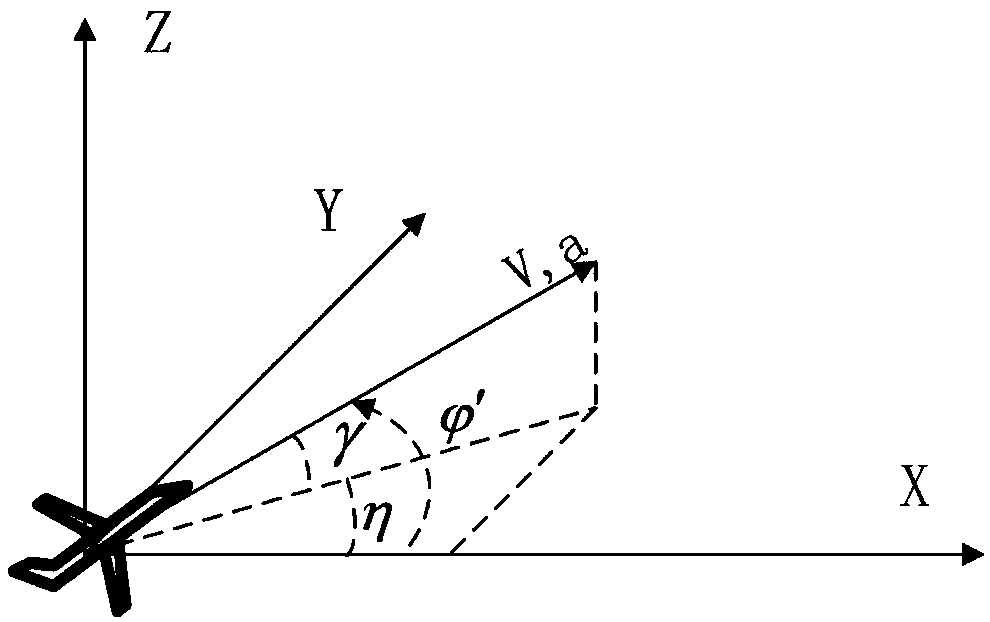
The invention discloses an improved algorithm based on parameter estimation and compensation of a quadratic phase function, and belongs to the technical field of signal and information processing. Thealgorithm performs range walk correction on slow time-range frequency domain echo signal considering range walk and Doppler diffusion through Keystone transform, and then eliminates a coupling relation between the range frequency f and the slow time tn in a second-order phase item corresponding to the acceleration in a narrow-band condition; meanwhile, a folding factor corresponding to the blindspeed is searched, a folding factor compensation item is constructed to correct the range walk caused by the blind speed; then the target acceleration is estimated by using the quadratic phase function, and a second-order phase item corresponding to the acceleration is constructed to compensate Doppler diffusion of the echo signal; and finally, long-term phase-coherent accumulation is performed soas to realize high-speed weak target detection of bistatic radar. The method disclosed by the invention is high in operation speed, stable in performance and applicable to detection of weak targets with a low signal-to-noise ratio and difficultly estimated target parameters.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Laser wavelength control unit with piezoelectric driver
InactiveUS6650666B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingActive medium materialElectric dischargeVibration control
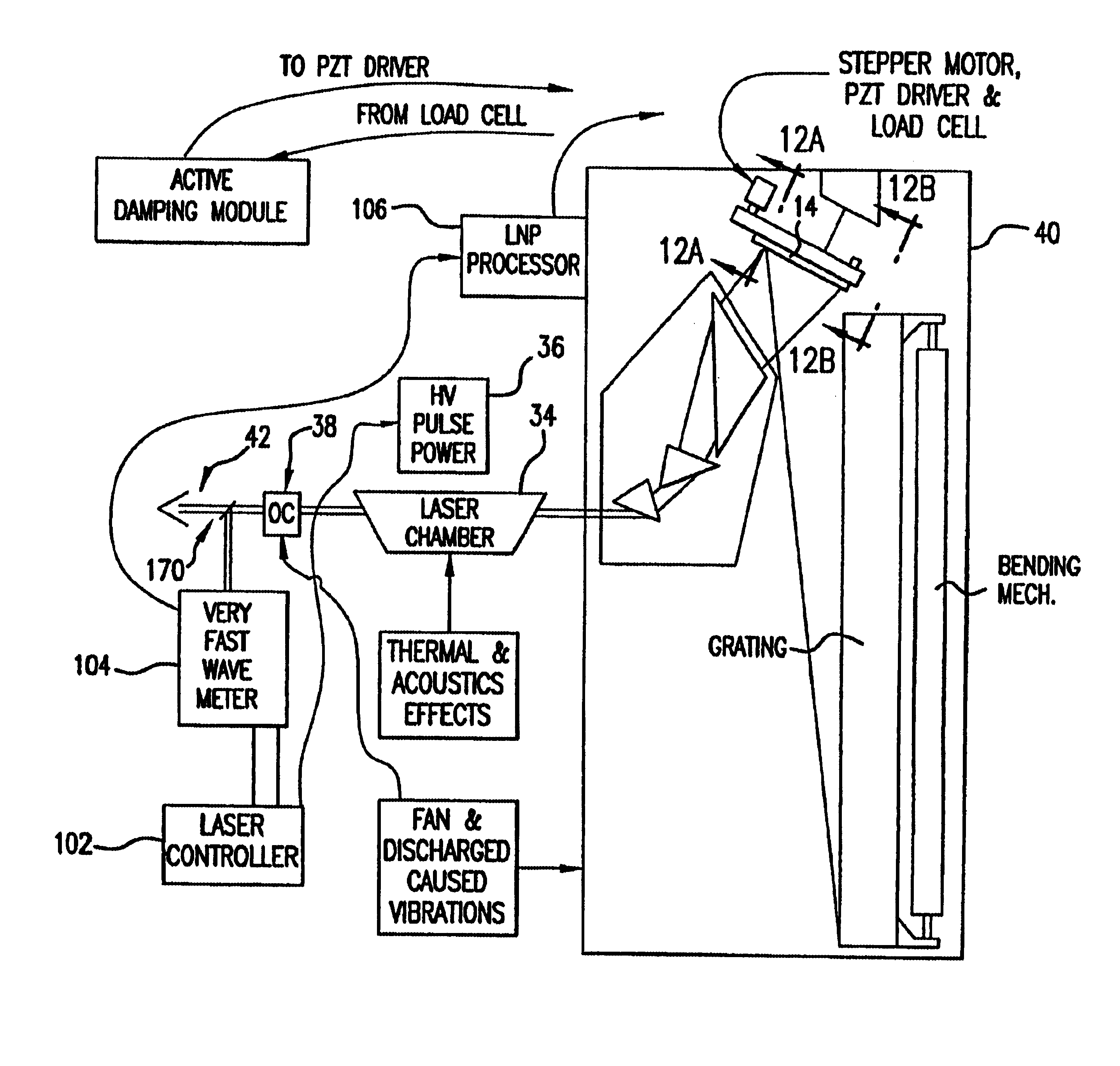
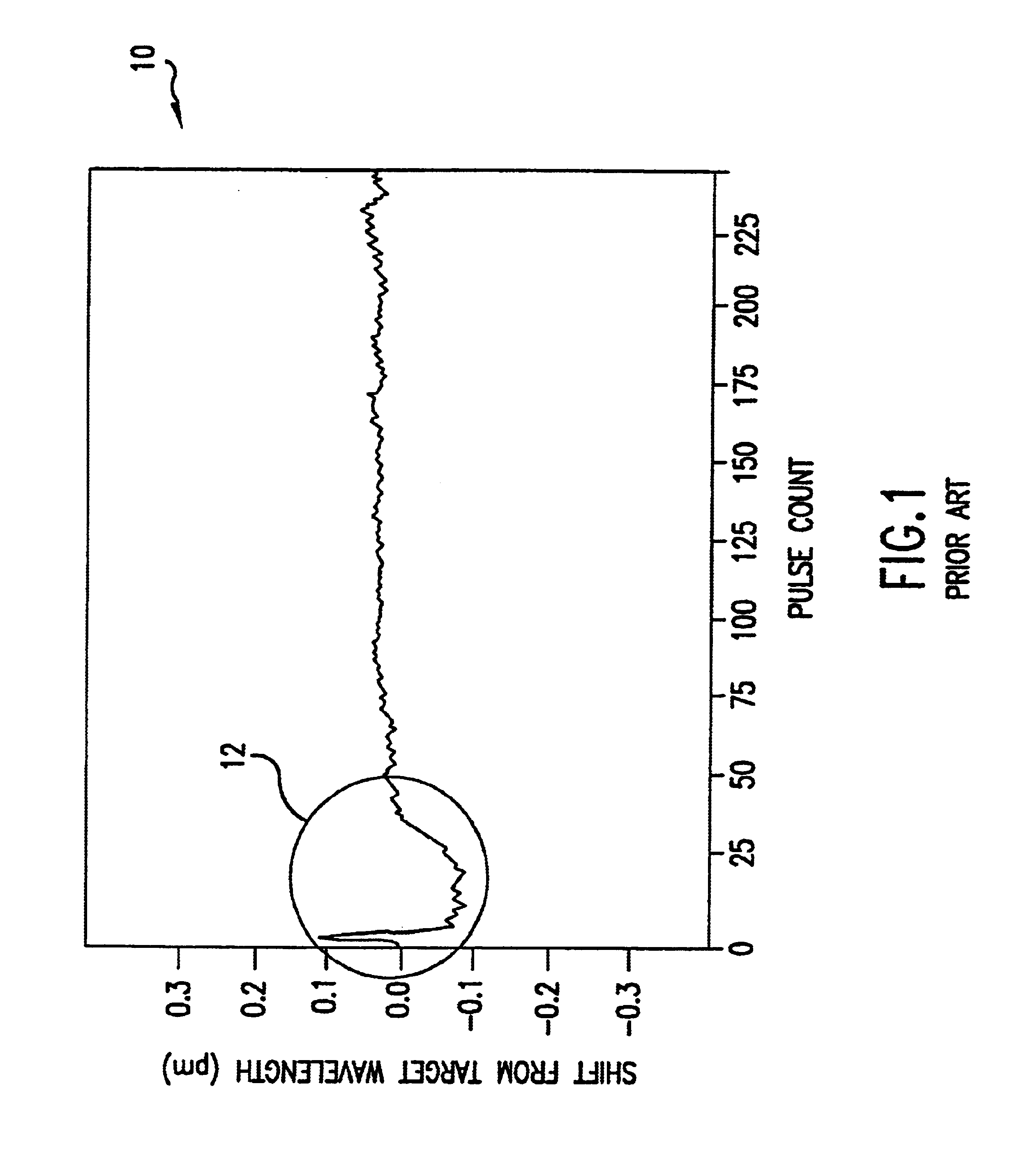
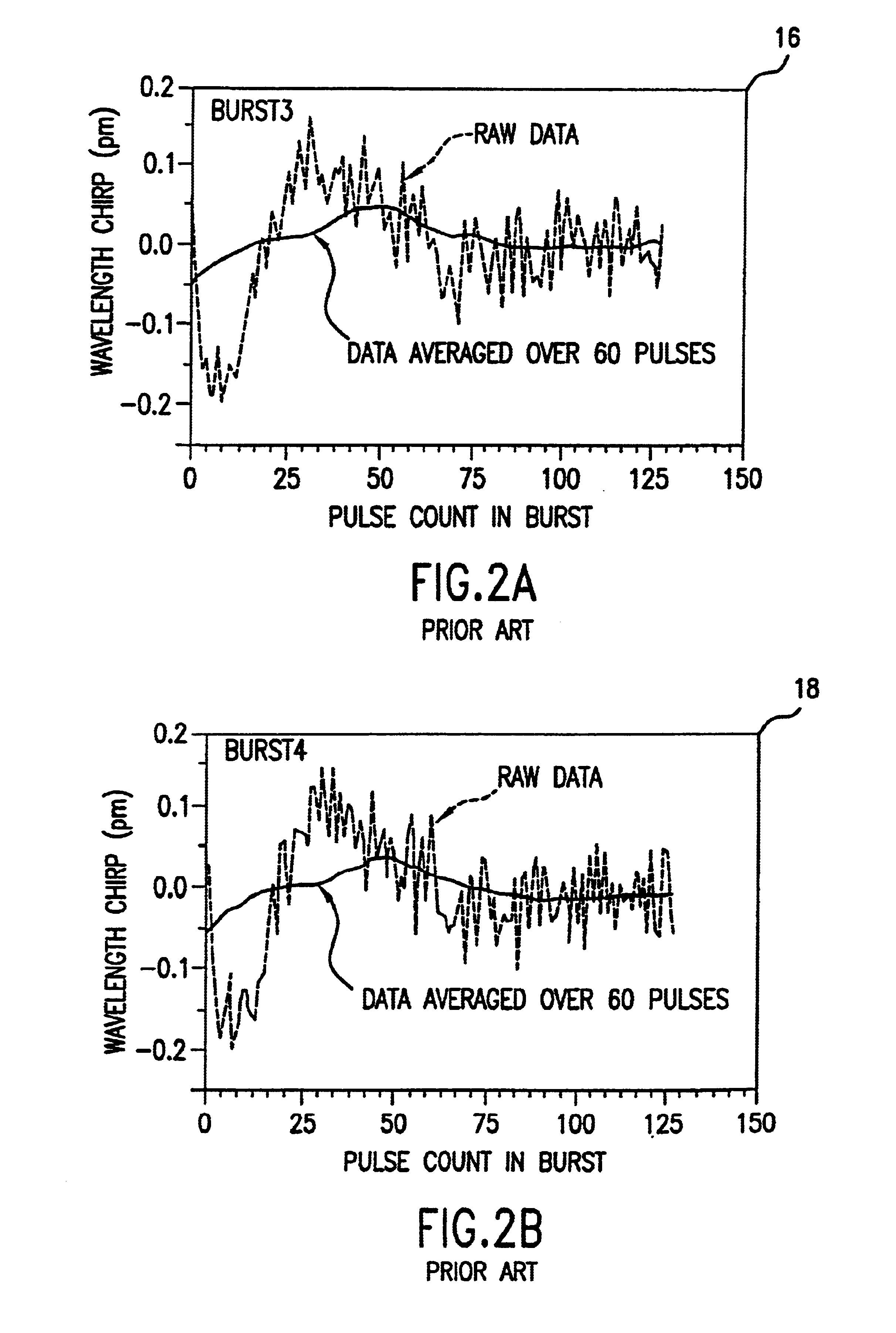
An electric discharge laser with fast wavelength correction. Fast wavelength correction equipment includes at least one piezoelectric drive and a fast wavelength measurement system and fast feedback response times. In a preferred embodiment, equipment is provided to control wavelength on a slow time frame of several milliseconds, on a intermediate time from of about one to five milliseconds and on a very fast time frame of a few microseconds. Preferred techniques include a combination of a relatively slow stepper motor and a very fast piezoelectric driver for tuning the laser wavelength using a tuning mirror. A preferred control technique is described (utilizing a very fast wavelength monitor) to provide the slow and intermediate wavelength control with the combination of a stepper motor and a piezoelectric driver. Very fast wavelength control is provided with a piezoelectric load cell in combination with the piezoelectric driver. Preferred embodiments provide (1) fast feedback control based on wavelength measurements, (2) fast vibration control, (3) active damping using the load cell and an active damping module, (4) transient inversion using feed forward algorithms based on historical burst data. A preferred embodiment adapts the feed forward algorithms to current conditions. Another preferred embodiment measures tuning mirror position to permit wavelength pretuning and active wavelength tuning.
Owner:CYMER INC
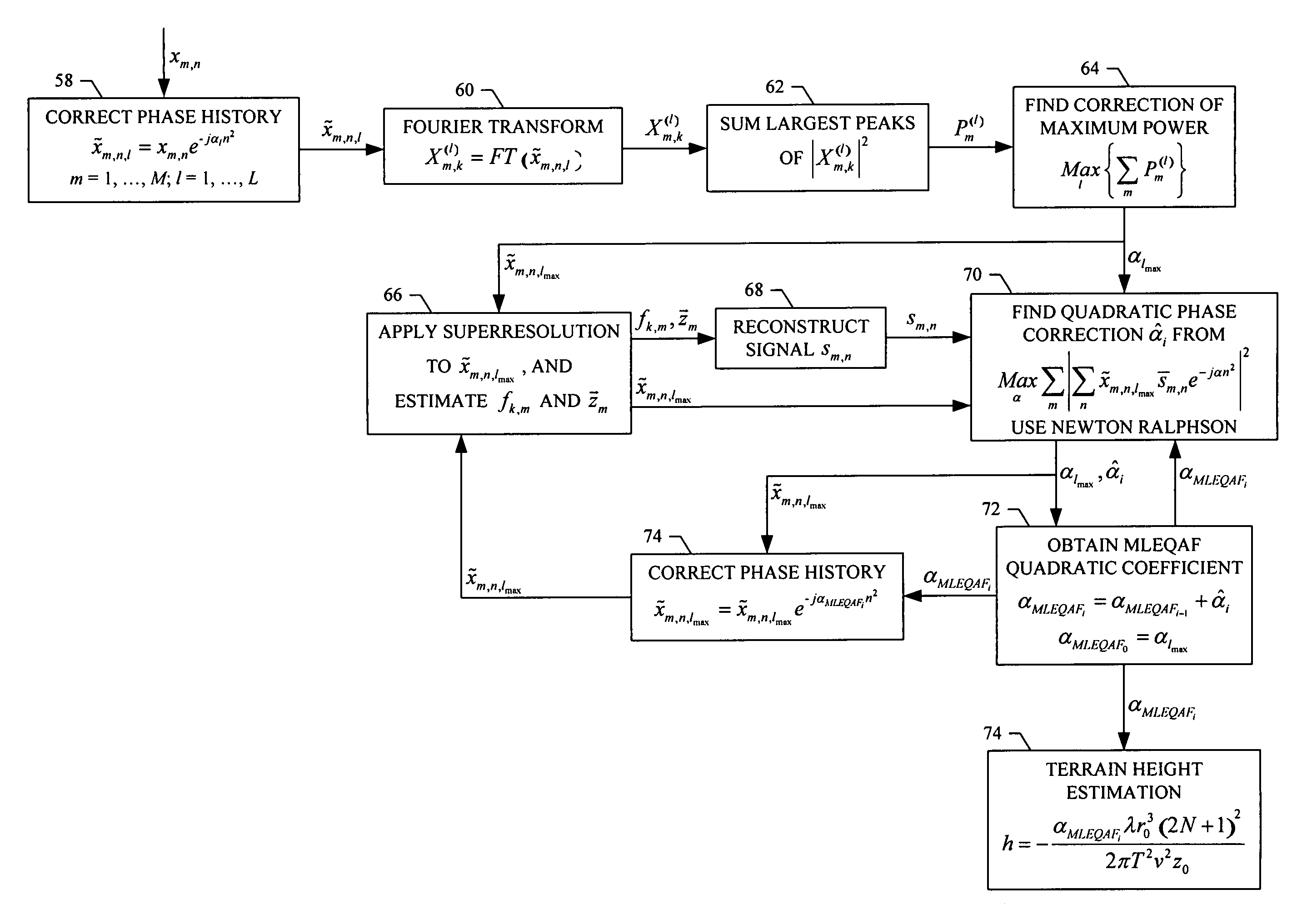
System, method and computer program product for reducing quadratic phase errors in synthetic aperture radar signals
InactiveUS7064702B1Reducing quadratic phase errorReduce errorsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSynthetic aperture sonarEnvironmental geology
A method is provided for reducing quadratic phase errors in synthetic aperture radar signals from a plurality of range lines where each range line includes a plurality of azimuth positions. The method includes receiving a plurality of slow-time samples representing radar signals for a plurality of azimuth positions for a plurality of range lines. A plurality of corrected samples and an initial quadratic phase error coefficient are identified based upon the slow-time samples. The corrected samples are processed according to a superresolution signal processing technique to thereby obtain a plurality of estimated Doppler frequencies for a plurality of point scatterers at each range line, after which a true signal for each range line is reconstructed based upon the plurality of estimated Doppler frequencies. A correction to the initial quadratic phase error coefficient is then obtained based upon the corrected samples, the true signals and the initial quadratic phase error coefficient.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Method for detecting weak target by radar
InactiveCN102901956AOvercoming the defect of false track of the targetSolve the distance to walkWave based measurement systemsTime domainTrack-before-detect
The invention relates to radar target detection technology. The invention discloses a method for detecting a weak target by a radar, aiming at the defects that the method for detecting the weak target in the prior art causes distance walking due to the increment of accumulation time and the target false track is formed by aggregation effect in the traditional dynamic programming-track before detect (DP-TBD) algorithm. The method comprises the steps of A. carrying out pulse compression on each frame of radar return data along the rapid time dimension; B. carrying out keystone conversion on each frame of compressed signal in the frequency domain; C. converting each frame of processed signal into time domain, and carrying out the phase-coherent accumulation of slow time dimension; D. removing weak points from the sequence; E. carrying out direction weight-based DP-TBD treatment on the K frames of signals which are processed in the above steps, wherein K is a positive integer and is set according to radar parameters. The method not only can be used for detecting the weak target, but also can accurately recover the trace of the target.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
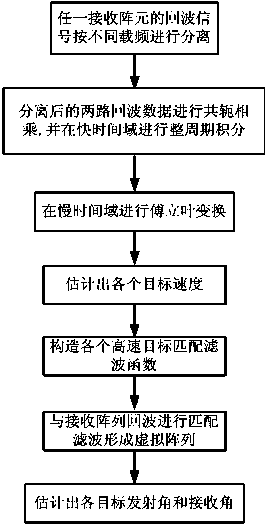
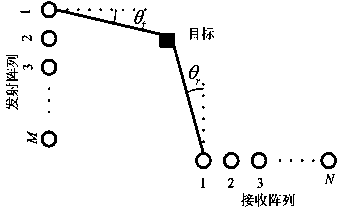
Bistatic MIMO radar high-speed movement target parameter estimation method based on dual-frequency transmission
ActiveCN103823217AAvoid estimationThe estimation algorithm is difficult to effectively form a virtual array due to the high-speed and high-maneuvering movement of the targetRadio wave reradiation/reflectionDual frequencyTime domain
The invention discloses a bistatic MIMO radar high-speed movement target parameter estimation method based on dual-frequency transmission. Echo signals of high-speed high-mobility targets are received through a receiving array of bistatic MIMO radar, and the echo signals of the receiving array are divided according to different carrier frequencies; conjugate multiplication is conducted on the two routes of echo data obtained through division, and whole cycle integration is conducted in a rapid time domain; Fourier conversion is conducted on the integrated data in a slow time domain, and each target speed is estimated; high-speed target matching filtering functions are set up; matching filtering is conducted on the echo signals of the receiving array to form a virtual array; the transmission angle of each target and the receiving angle of the target are estimated. The range walk of the high-speed targets is corrected according to the characteristic of the echo signals of the dual-frequency transmission MIMO radar, the problem that the parameter estimation performance is influenced by unstable factors such as Doppler spread and RCS rapid fluctuation is solved, and MIMO radar parameter estimation under the high-speed high-mobility targets is achieved.
Owner:常熟紫金知识产权服务有限公司
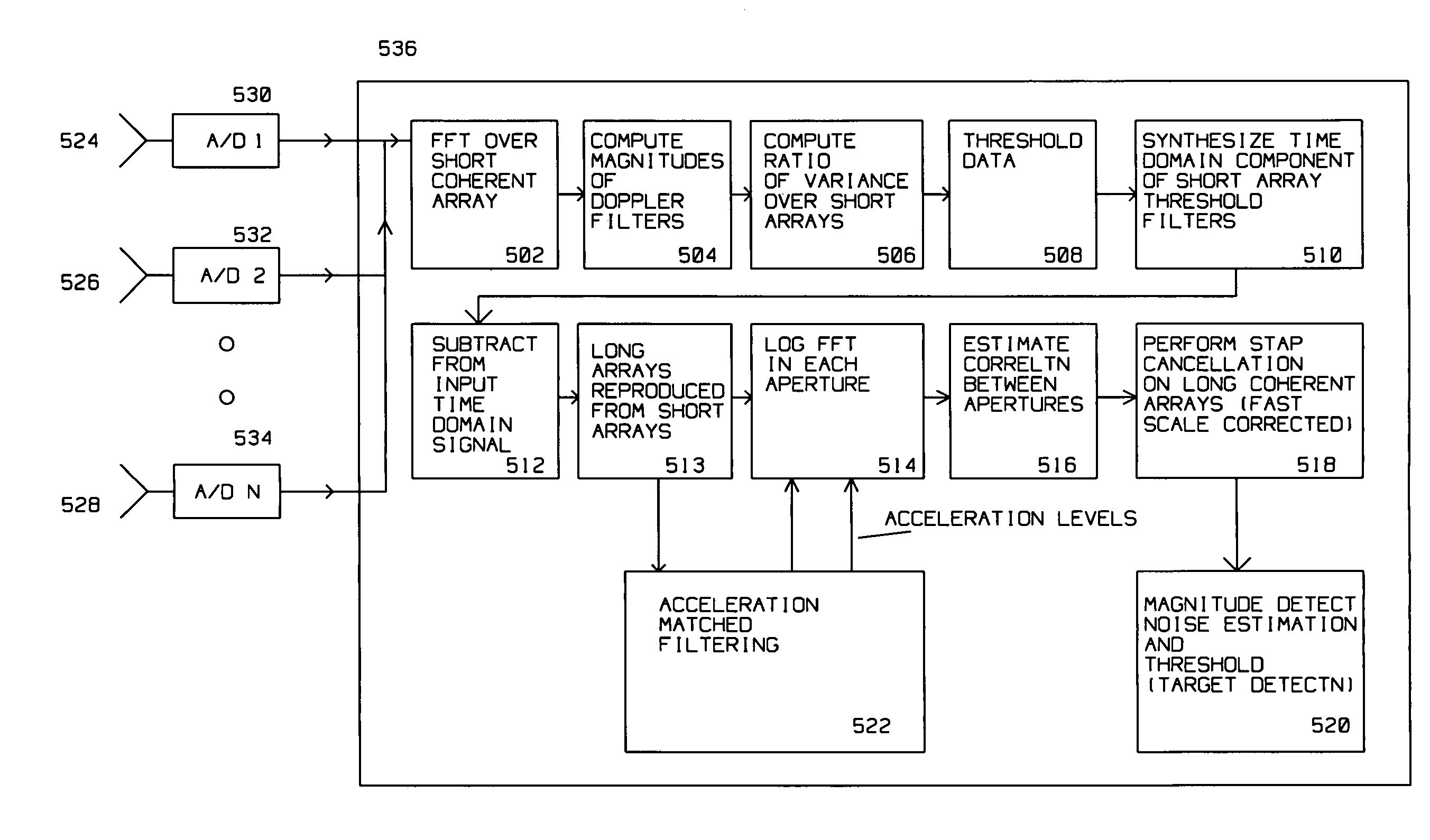
Fast and slow time scale clutter cancellation
Target detection in the presence of non stationary clutter is improved by a radar receiver on a moving platform for detecting a target using a plurality of short coherent arrays and a plurality of long coherent arrays synthesized from the short coherent arrays overlapping the target. The target is obscured by slow scale clutter and fast scale clutter in the vicinity of the target. The radar receiver has a plurality of subapertures overlapping to acquire radar returns reflected from the target during the arrays, an analog to digital converter for each of the subapertures to convert the radar returns into digital radar returns for a plurality of range bins covering the target, the slow scale clutter and the fast scale clutter; and a digital computer for performing steps of SAR image creation, further enhanced by thresholding short array magnitude data, computing a time domain component of threshold filters using the thresholded short array magnitude data then coherently subtracting the time domain component of threshold filters from the short arrays, and using the result to synthesize long coherent arrays. A Space Time Adaptive Algorithm (STAP) is applied to the long coherent arrays thus obtained to suppress slow and stationary clutter. The short coherent arrays are between 10 and 400 milliseconds long. The long coherent arrays are between 400 and 4000 milliseconds long.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Comfort noise generator using modified Doblinger noise estimate
ActiveUS7649988B2Slow constantSuppression amountTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsSpeech analysisFourier transform on finite groupsEngineering
A background noise estimate based upon a modified Doblinger noise estimate is used for modulating the output of a pseudo-random phase spectrum generator to produce the comfort noise. The circuit for estimating noise includes a smoothing filter having a slower time constant for updating the noise estimate during noise than during speech. Comfort noise is smoothly inserted by basing the amount of comfort noise on the amount of noise suppression. A discrete inverse Fourier transform converts the comfort noise back to the time domain and overlapping windows eliminate artifacts that may have been produced during processing.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
Phase-coherent accumulation detection method applied to three-order maneuvering target
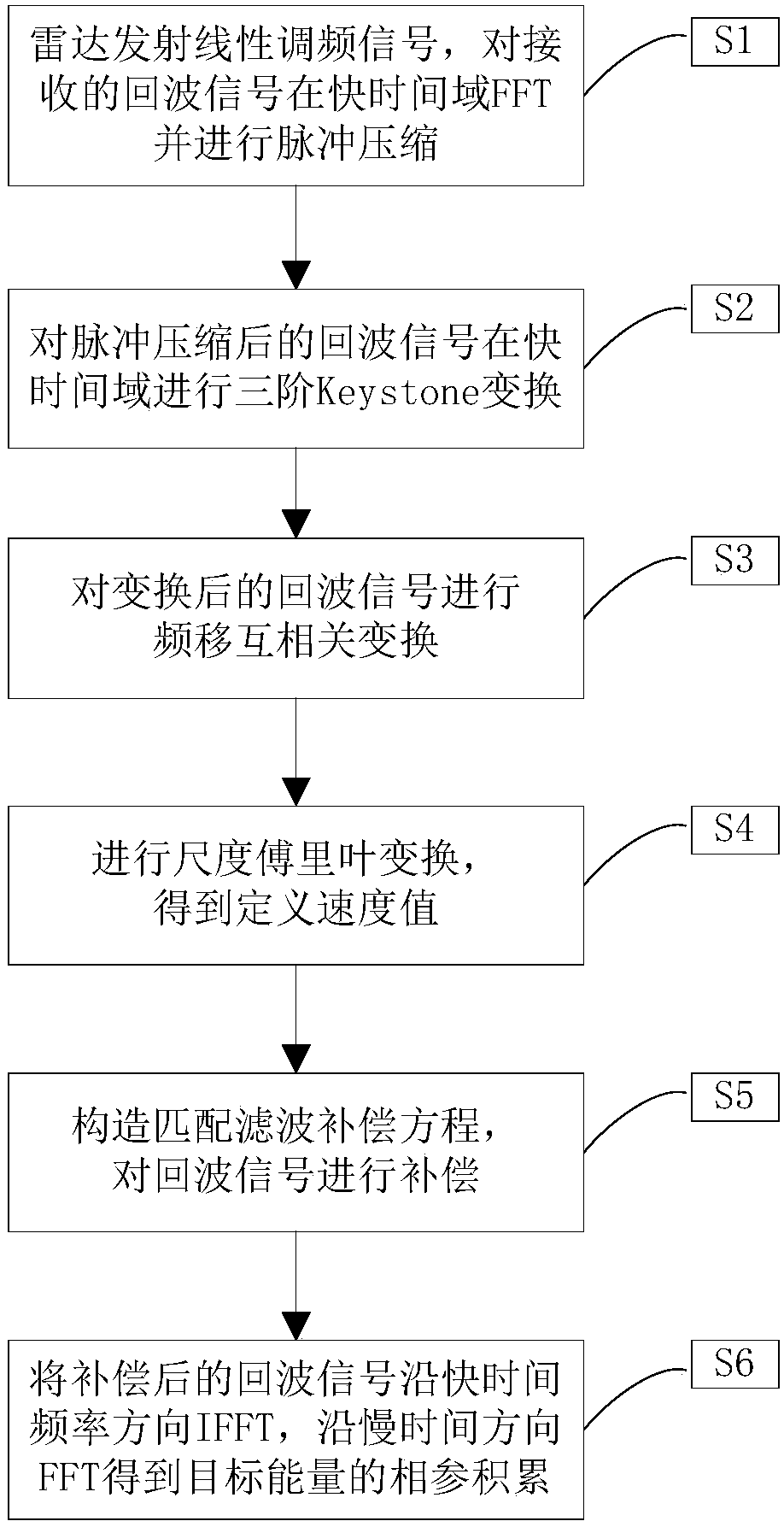
ActiveCN108549067AEasy to detectImprove real-time performanceWave based measurement systemsFrequency shiftFourier transform
The invention provides a phase-coherent accumulation detection method applied to a three-order maneuvering target, belonging to the technical field of radar signals. The method comprises the followingsteps: carrying out fast-time frequency domain pulse compression on an echo signal, and carrying out three-order Keystone conversion so as to correct three-order range migration of a target; carryingout frequency shift mutual correlation and scale Fourier transform, so as to obtain a defined speed value; eliminating first-order range walk by virtue of the cooperation of a fast-time frequency domain matched filtering equation constructed by the defined speed, combining an accelerated speed with a jerk of the searched target by virtue of a two-dimensional matched filtering equation, and compensating and eliminating second-order range walk and Doppler spreading effect of the target; and detecting the phase-coherent accumulation of the energy of the target by virtue of slow time fast Fouriertransform. According to the method, phase-coherent accumulation is realized by virtue of the range and phase information of the target echo to eliminate the range migration and the Doppler migrationeffect of the three-order maneuvering target, so that the detection performance of radar can be remarkably improved, and the practicability is strong.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
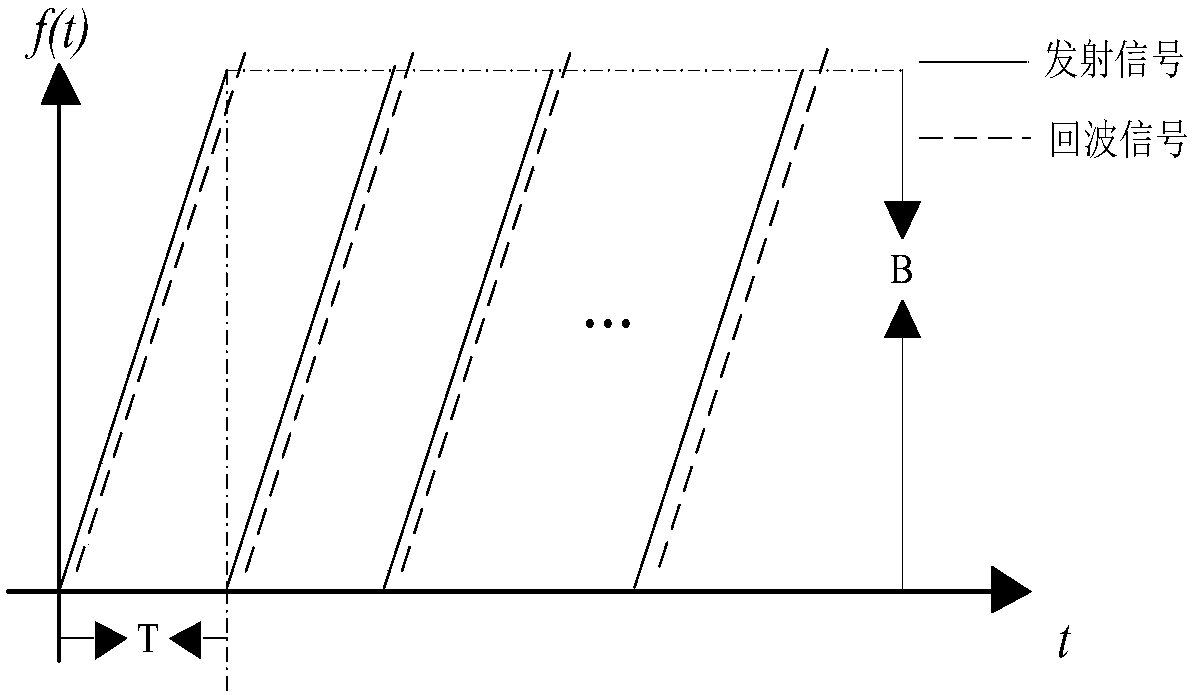
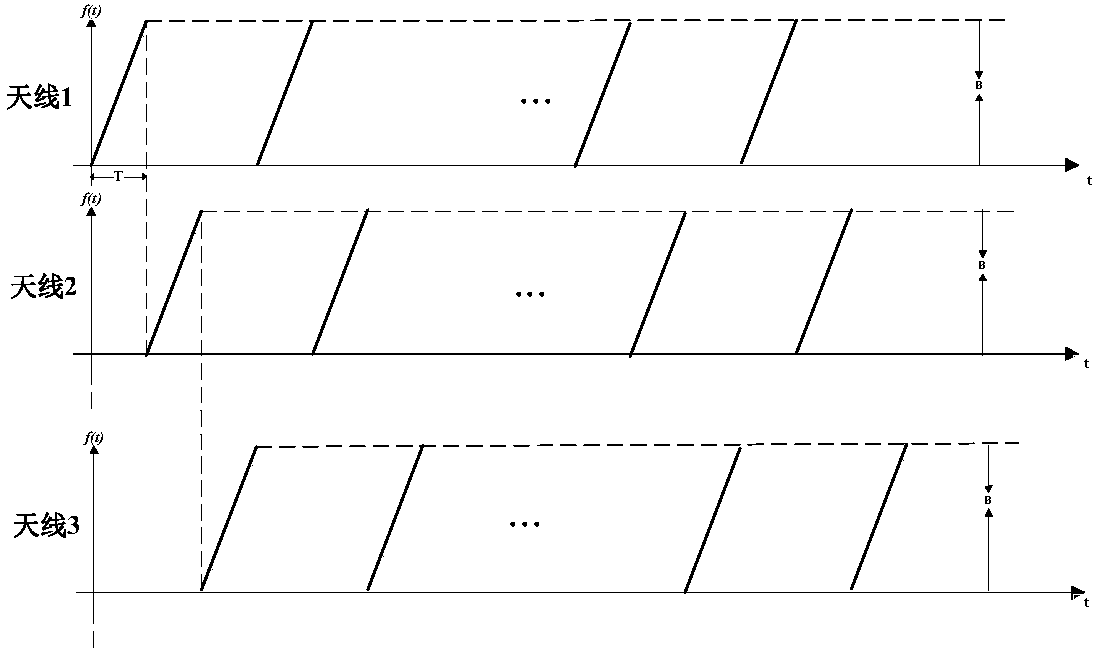
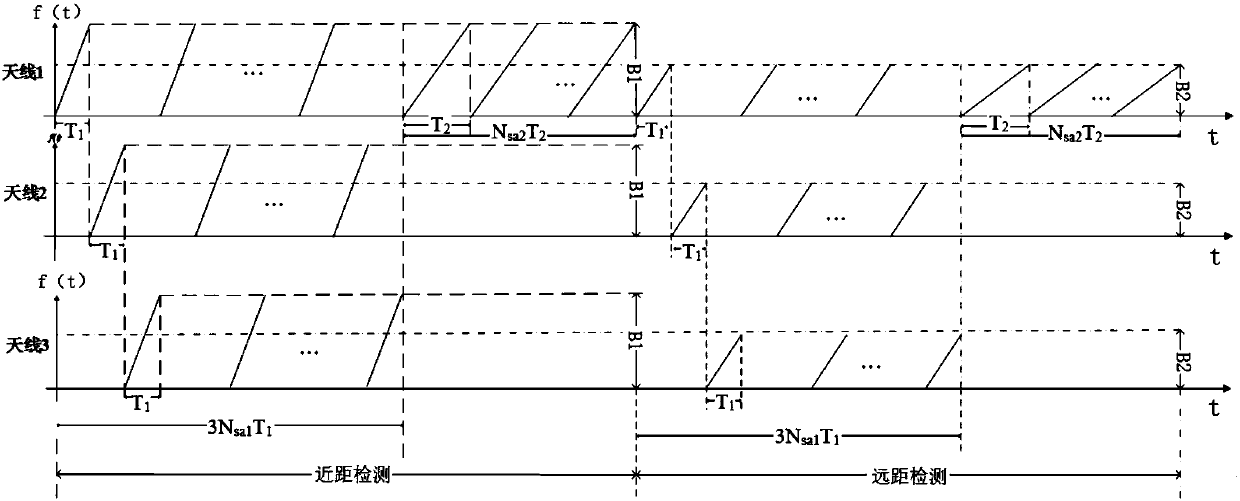
Saw-tooth wave distance measuring and speed measuring method based on 77GHz millimeter wave radar
InactiveCN107688178ARealize multi-target ranging and speed measurementReduce detection errorRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFast Fourier transformVirtual array
The invention provides a saw-tooth wave distance measuring and speed measuring method based on a 77GHz millimeter wave radar. The saw-tooth wave distance measuring and speed measuring method comprisesthe following steps: a. transmitting same frequency modulation continuous saw-tooth wave transmitting signals by Nt transmitting antennas in sequence and forming a virtual array; b. receiving echo signals of the transmitting signals by Nt receiving antennas and forming a virtual array YV which belongs to CNtNr*Ns*Nsa1, wherein Ns is equal to fsT and Nsa1 is a transmitting period; c. carrying outwindowing FFT (Fast Fourier Transform) on each transmitting period and a receiving signal of each antenna to obtain YVF which belongs to CNtNr*NqFFT*Nsa1, wherein NqFFT is a rapid time dimension FFT point number; d. carrying out slow time dimension FFT on receiving signals of different distance units of each receiving antenna to obtain YVFF which belongs to CNtNr*NqFFT*NsFFT, wherein NsFFT is a slow time dimension FFT point number; e. carrying out phase compensation on each distance-speed unit of the YVFF to obtain YVFFC which belongs to CNtNr*NqFFT*NsFFT; f. carrying out beam forming on all the distance-speed units to obtain Z which belongs to CNqFFT*NsFFT; g. carrying out constant false alarm CFAR detection on data obtained by the beam forming to obtain a constant false alarm detection result; h. substituting the constant false alarm detection result into an equation to obtain a speed v and a distance parameter r.
Owner:上海莫吉娜智能信息科技有限公司
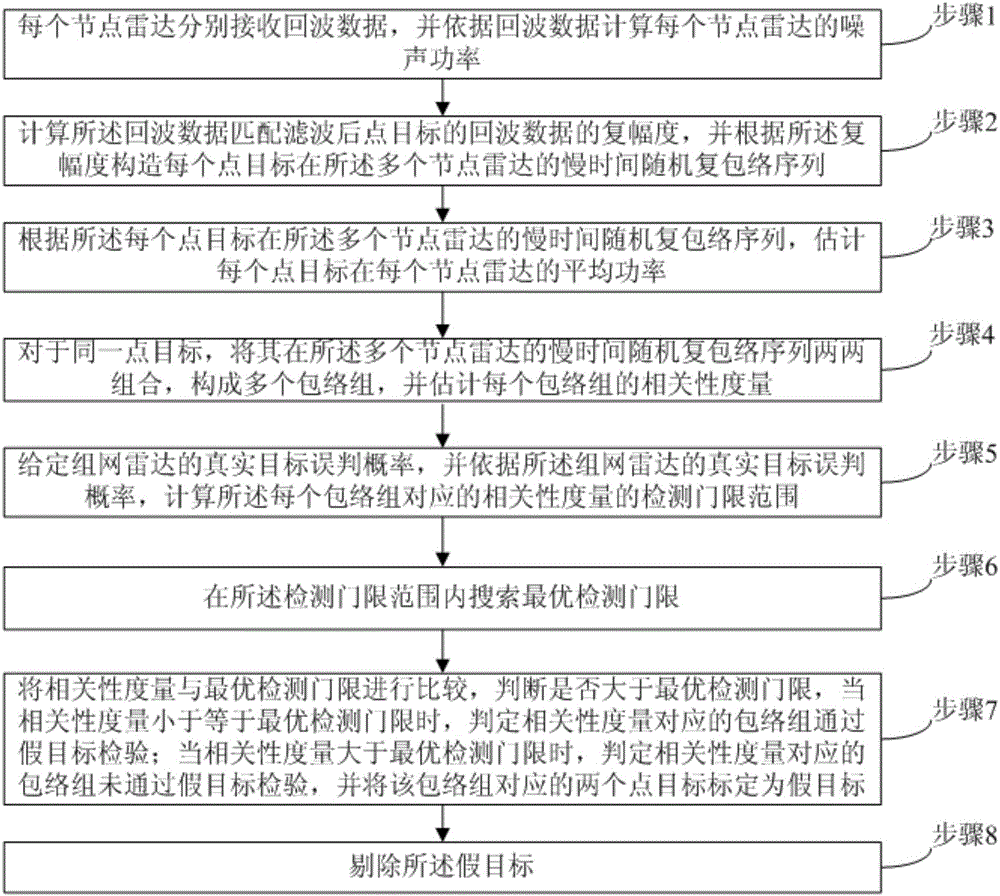
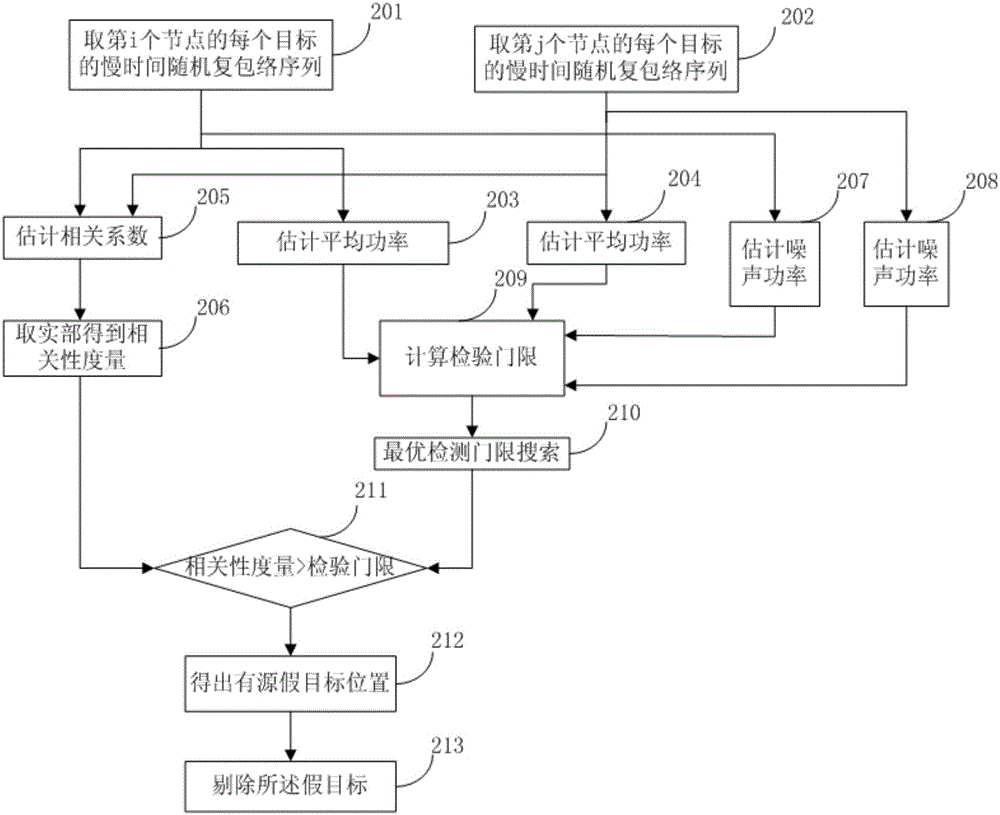
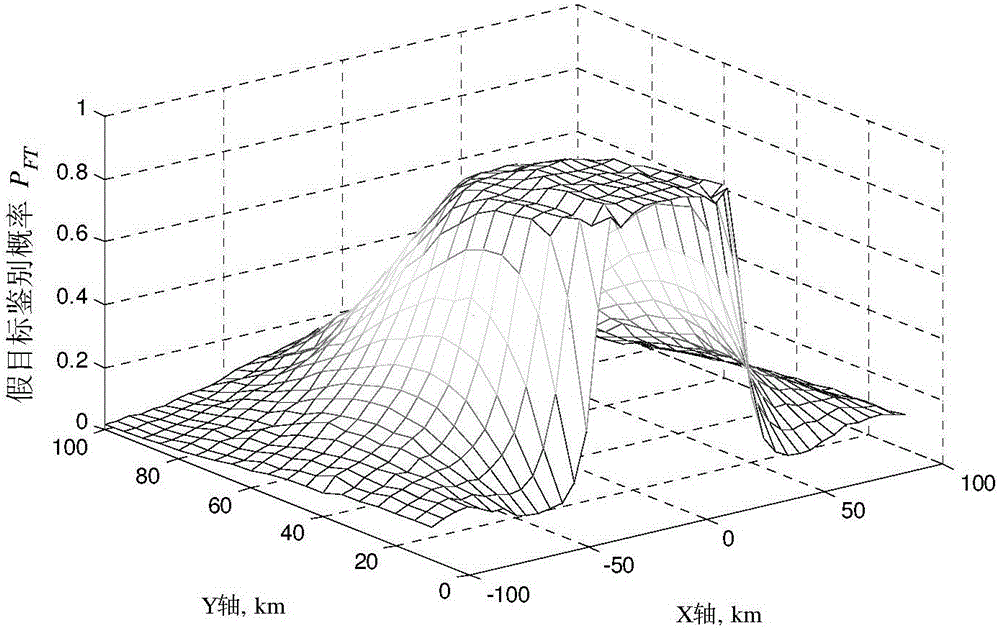
Signal-level fusion networking radar anti-cheating interference method under object signal correlation
ActiveCN104991232AIncrease usageEffective against deceptive interferenceWave based measurement systemsNODALPattern recognition
The invention proposes a signal-level fusion networking radar anti-cheating interference method under object signal correlation, and the method can achieve the effective discrimination of false targets generated by different cheating interferences. The method comprises the steps: 1, enabling each junction radar to receive echo data and calculate a corresponding noise power; 2, building slow-time random complex envelope sequences of each point target at a plurality of junction radars; 3, estimating the mean power of each point target at each junction radar; 4, enabling the slow-time random complex envelope sequences of the same point target at the plurality of junction radars to be combined in a paired manner to form a plurality of envelope groups, and estimating a correlation tolerance; 5, calculating a detection threshold range; 6, searching an optimal detection threshold; 7, judging whether the correlation tolerance is greater than the optimal detection threshold or not: judging that the envelope groups pass through false target examination if the correlation tolerance is not greater than the optimal detection threshold, or else, marking two corresponding point targets as false targets; 8, eliminating the false targets.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
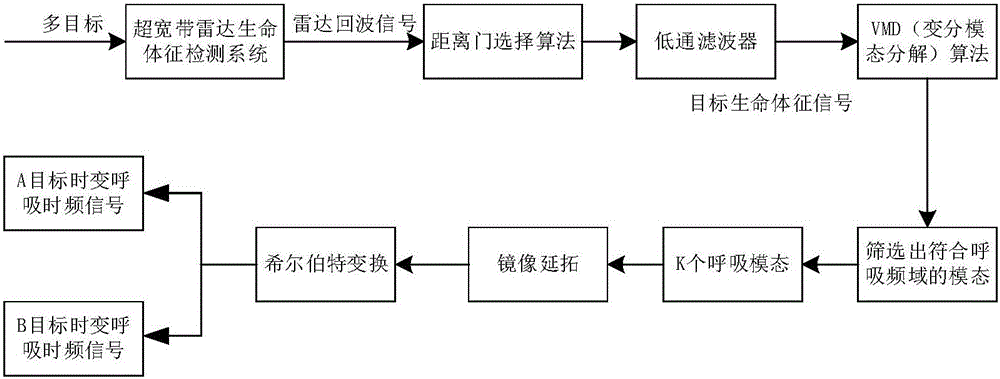
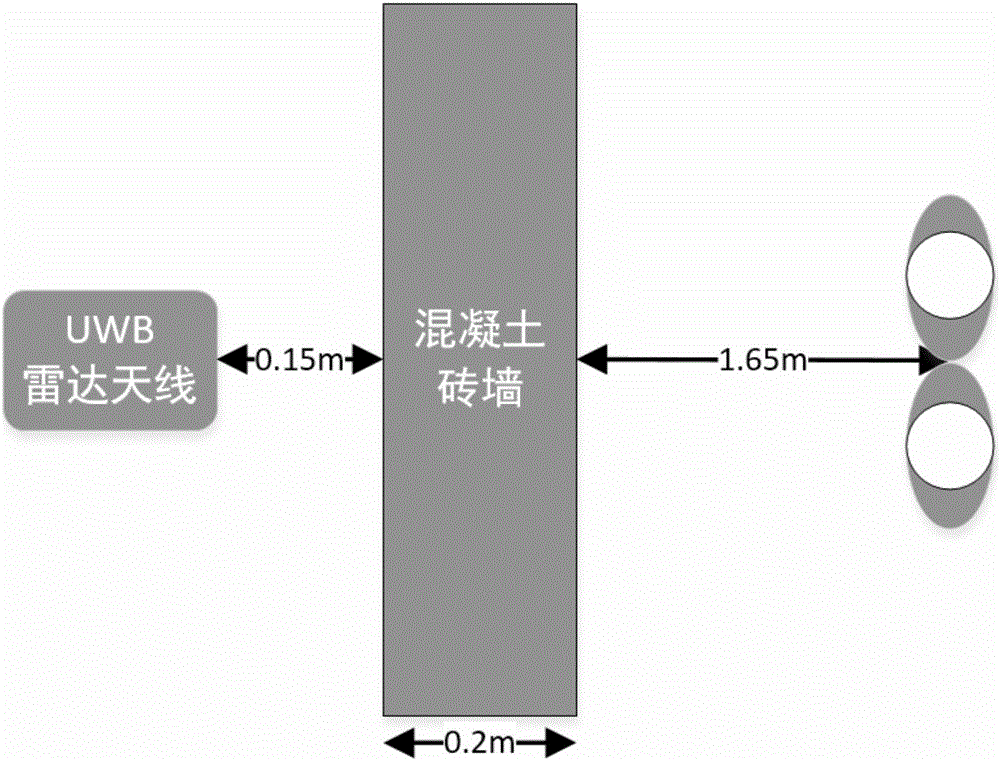
Multi-person through-wall time varying breathing signal detection method based on VMD
ActiveCN106019271ARealize synchronous trackingEliminate distractionsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionDecompositionLow-pass filter
The invention discloses a multi-person through-wall time varying breathing signal detection method based on VMD, comprising the steps of: an ultra wide band emission antenna emitting narrow pulse, through human thoracic cavity micro-doppler vibration, echo being received by a receiving antenna, and performing slow time sampling on ultra wide band radar echo to obtain a through-wall human body echo signal matrix; calculating the variance of each distance door through a distance door selection algorithm, the one with a largest variance being a distance door where a multi-person target exists, and employing a low pass filter to eliminate high frequency interference and superfluous frequency components; utilizing a VMD algorithm to perform mode decomposition on filtered signals, and iterating sub-signals to obtain effective information meeting the number and frequency band of breathing; and performing Hilbert transformation and time frequency treatment to obtain dynamic instantaneous information including smooth breathing characteristics. The method can effectively eliminate interference harmonic wave of different breathing components, remove metope interference, and enhance weak breathing signals, and has the characteristics of strong interference immunity and accurate time varying tracking characteristics.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
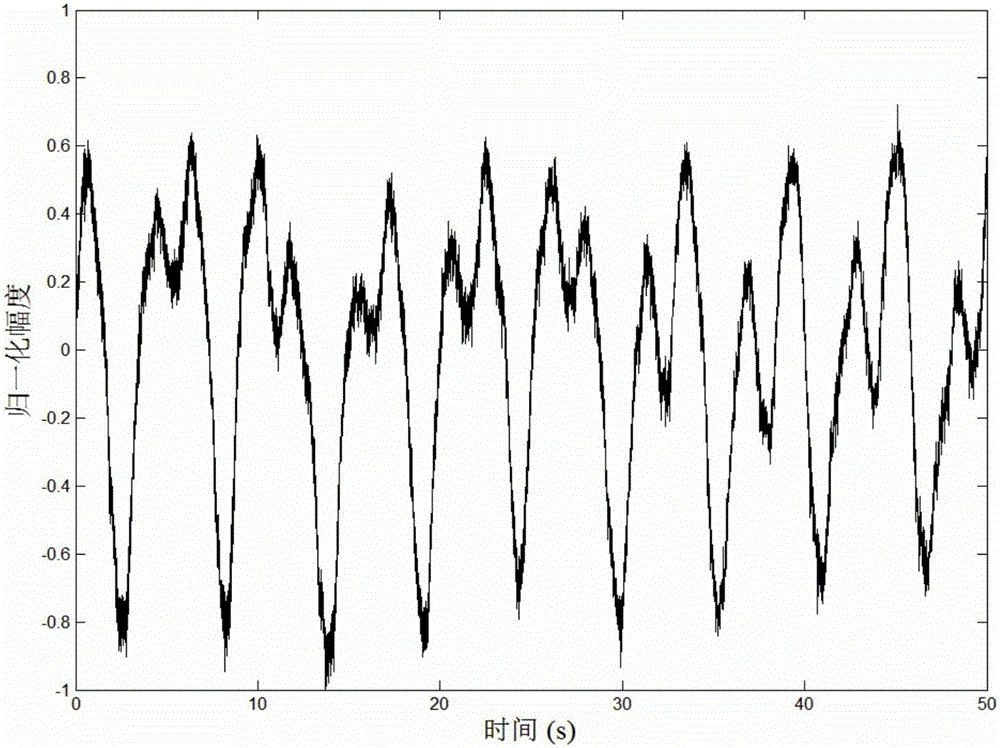
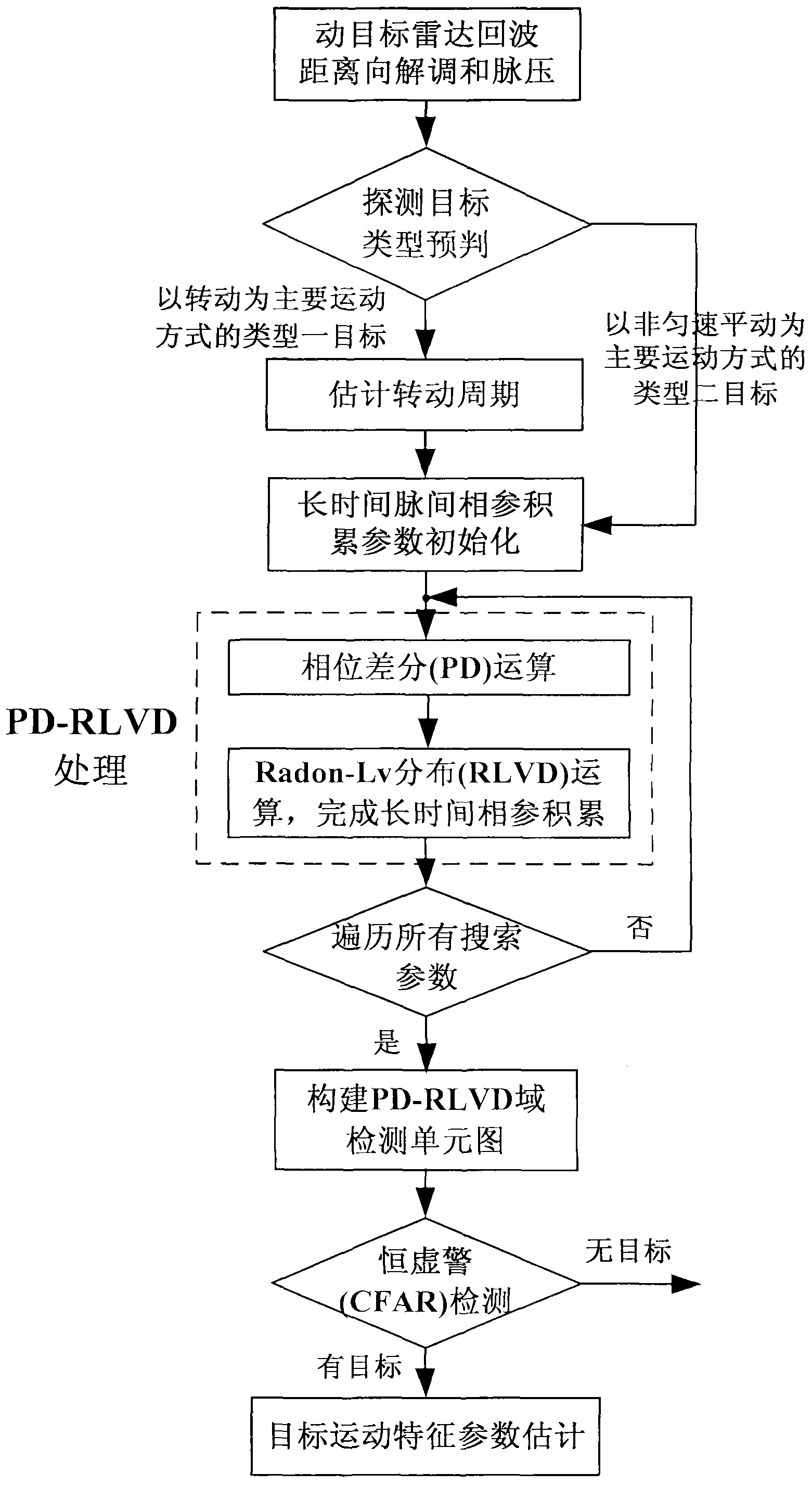
Method for detecting radar weak moving target based on PD (Phase Differentiation) RLVD (Radon-Lv Distribution)
ActiveCN103399310ACoherent accumulation implementationImprove estimation accuracyWave based measurement systemsTarget signalRadar signal processing
The invention relates to a method for detecting a radar weak moving target based on PD (Phase Differentiation) RLVD (Radon-Lv Distribution), and belongs to the technical field of radar signal processing and detecting. The method comprises the following steps: first, performing PD operation on a demodulated and pulsed radar echo, and reducing the order of a cubic phase signal related to slow time to obtain a secondary phase signal; then, performing RLVD operation to finish long-time phase-coherent accumulation, including Radon-instantaneous auto-correlation operation, scaling treatment and Radon-Fourier transform; finally, establishing a PD-RLVD domain detection unit figure, performing constant false-alarm detection and estimating a target movement parameter. By the method, a target observation value is extracted from a distance-slow time plane to compensate distance migration to finish the long-time phase-coherent accumulation; an additional parameter is not required to be set to match a moving target signal, high-order phase signal energy can be accumulated, and a peak value corresponds to modulation frequency and secondary modulation frequency; therefore, the method is suitable for detecting a uniformly accelerated or high-order complex moving target under a strong clutter background.
Owner:NAVAL AERONAUTICAL UNIV
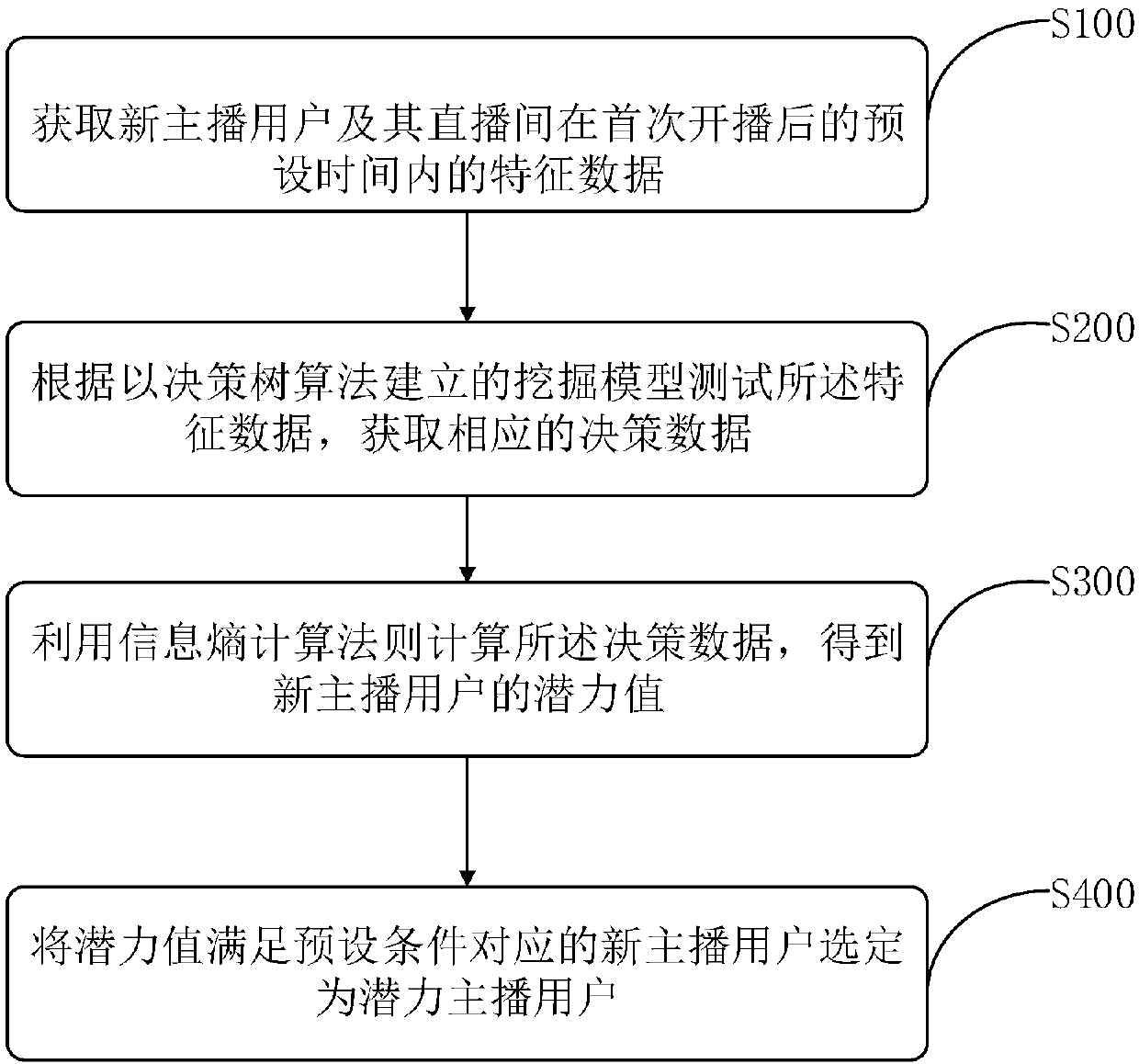
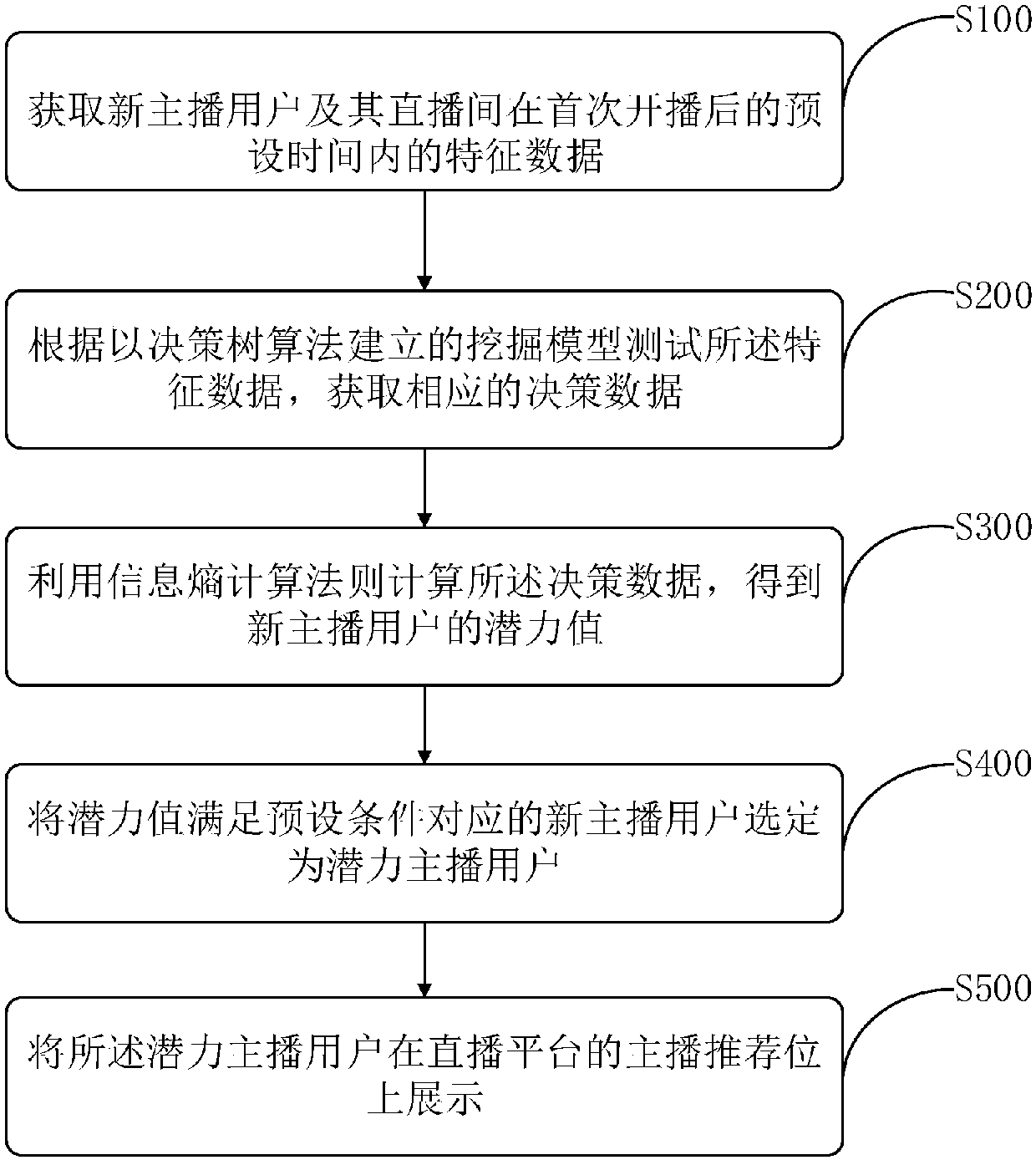
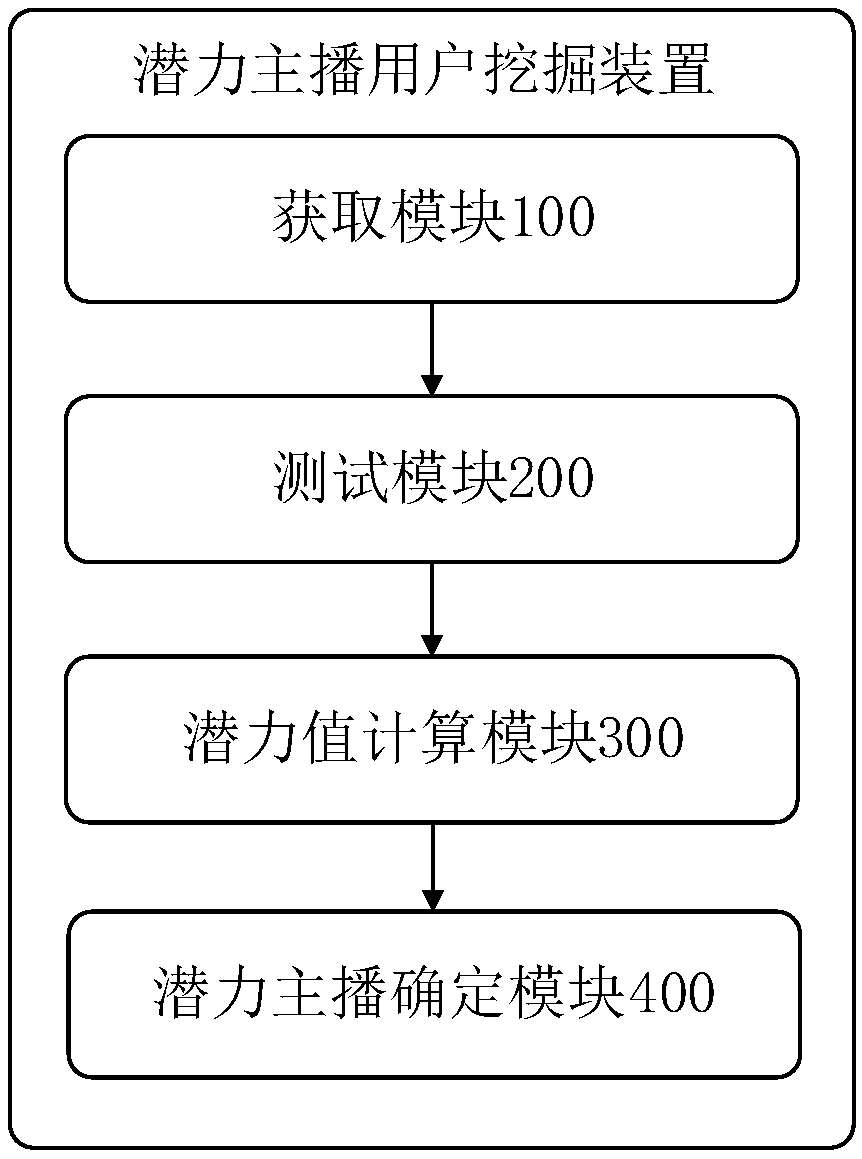
Mining method and device of potential anchor user, and server
ActiveCN107666615AIncrease exposureAvoid churnData miningSelective content distributionData dredgingModel testing
The invention relates to the field of data mining of internet broadcasting, in particular to a mining method and device of a potential anchor user, and a server. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring feature data of new anchor users and direct broadcasting rooms of the new anchor users within preset time after first-time broadcasting starting; testing the feature data according to amining model established based on a decision tree algorithm and obtaining corresponding decision-making data; calculating the decision-making data by using an information entropy computing rule to obtain potential values of the new anchor users; and selecting the new anchor user with the potential value meeting a preset condition as a potential anchor user. According the invention, a new potentialanchor user is discovered by a direct broadcasting platform automatically and fast with a high coverage rate; and thus problems of slow time effectiveness, low coverage rate, and high subjectivity during the existing manual potential anchor user discovery are solved.
Owner:GUANGZHOU HUYA INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
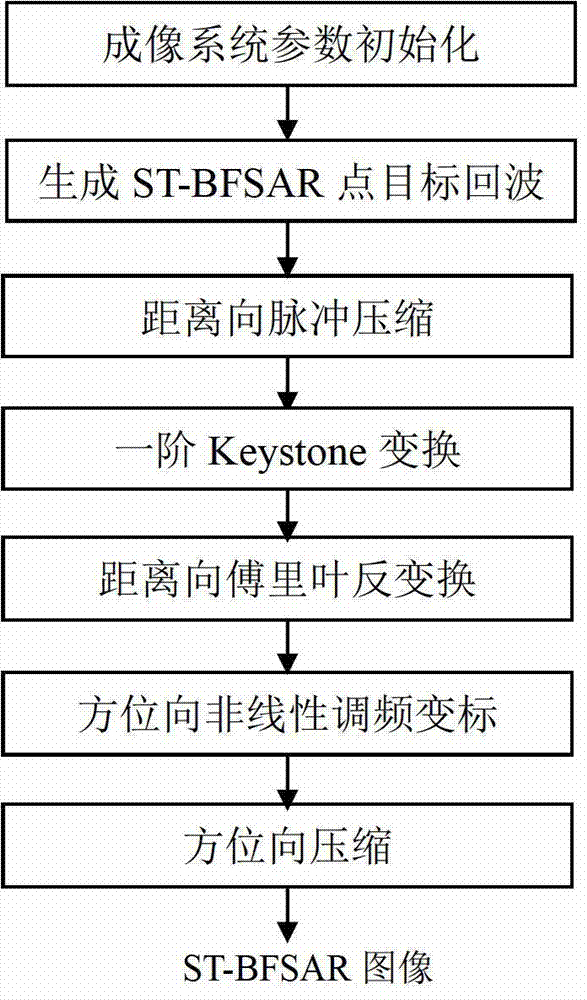
Method for imaging stationary transmitter bistatic foresight synthetic aperture radar (ST-BFSAR)
ActiveCN102778681AEliminate voidsAchieve precise focusRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadarSynthetic aperture radar
The invention discloses a method for imaging a stationary transmitter bistatic foresight synthetic aperture radar (ST-BFSAR). The method comprises the following specific steps: after obtaining a target echo, rectifying a two-dimensional space variant of a distance migration of the ST-BFSAR by using first-order Keystone transform, wherein an object which has a same bistatic distance sum at a slow time zero moment is moved to a same distance gate during the operation; and after the distance migration rectification is accomplished, balancing the Doppler chirp scaling of an object in the same distance gate by using a non-linear chirp scaling variant object so as to eliminate the space variant of the Doppler chirp scaling along a directional bit and accomplishing the directional bit compression, so that the precise focusing of the ST-BFSAR is realized, and the problem that the two-dimensional space variant during the data treatment of the ST-BFSAR cannot be solved by using a traditional SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) imaging method and an existing bistatic foresight SAR imaging method is solved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Onboard InSAR data processing method based on BP algorithm and time-varying baseline
ActiveCN103487809AReduce elevation errorRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPhase filterPhase difference
The invention discloses an onboard InSAR data processing method based on a BP algorithm and a time-varying baseline, and belongs to the field of radar imaging and InSAR signal processing. According to the onboard InSAR data processing method based on the BP algorithm and the time-varying baseline, the BP imaging algorithm is used for obtaining complex image data of double antennas, an interferometric phase representing the landform elevation is obtained through phase difference processing, phase filtering processing and phase unwrapping processing, and an accurate digital landform elevation is obtained through an elevation inversion method of the time-varying baseline. According to the BP imaging algorithm, an imaging area is divided into grids, and coherent accumulation in the azimuth direction is carried out on data obtained through pulse compression processing in the distance direction pulse by pulse to obtain high-accuracy complex image data according to motion tracks of phase centers of the antennas. According to the elevation inversion method of the time-varying baseline, parameters of the time-varying baseline change along the imaging grids in the azimuth direction point by point, namely, the parameters of the time-varying baseline change along the slow time, and the parameters of the time-varying baseline are determined by the space positions, at each moment, of the phase centers of the two antennas, and comprise the length of the time-varying baseline and the dip angle of the time-varying baseline.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
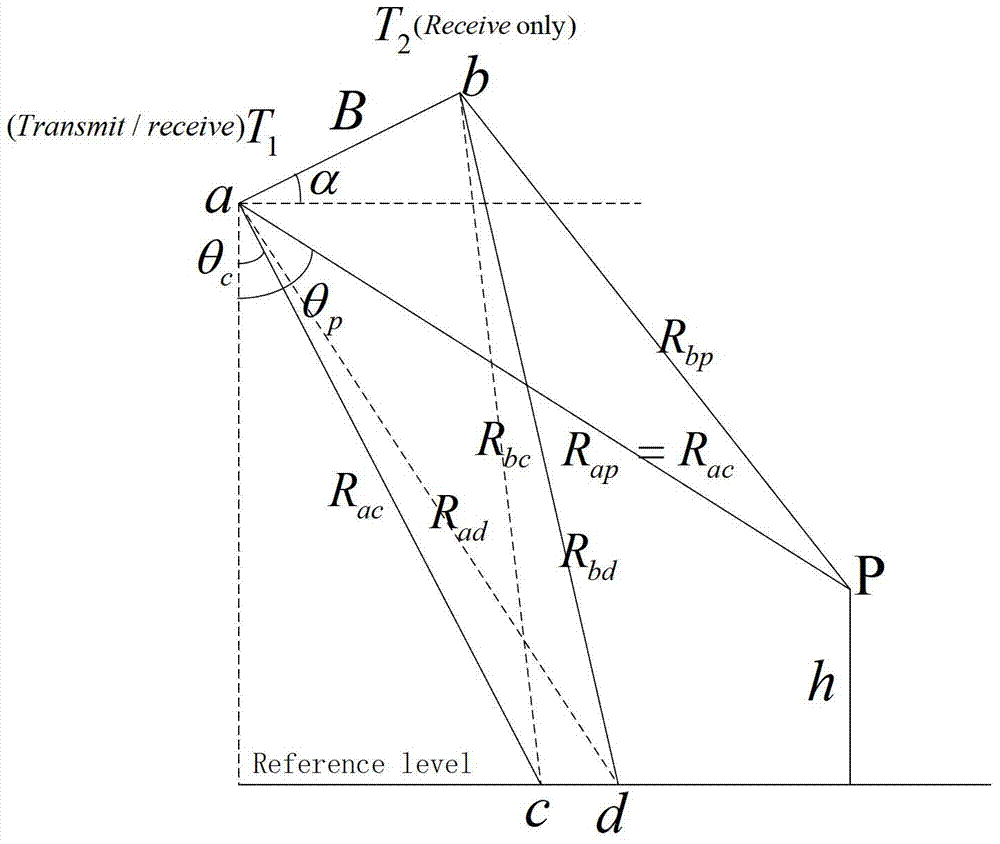
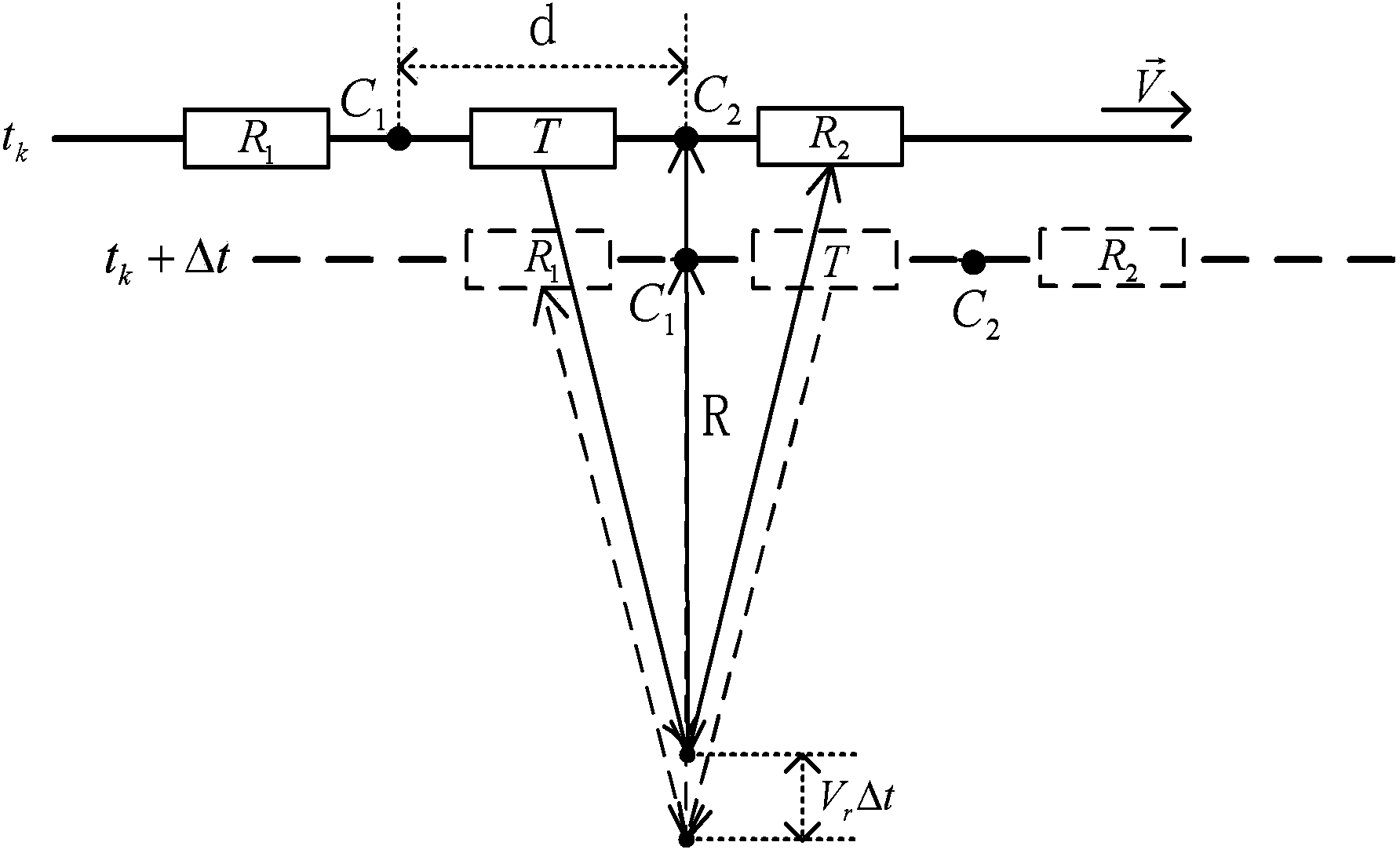
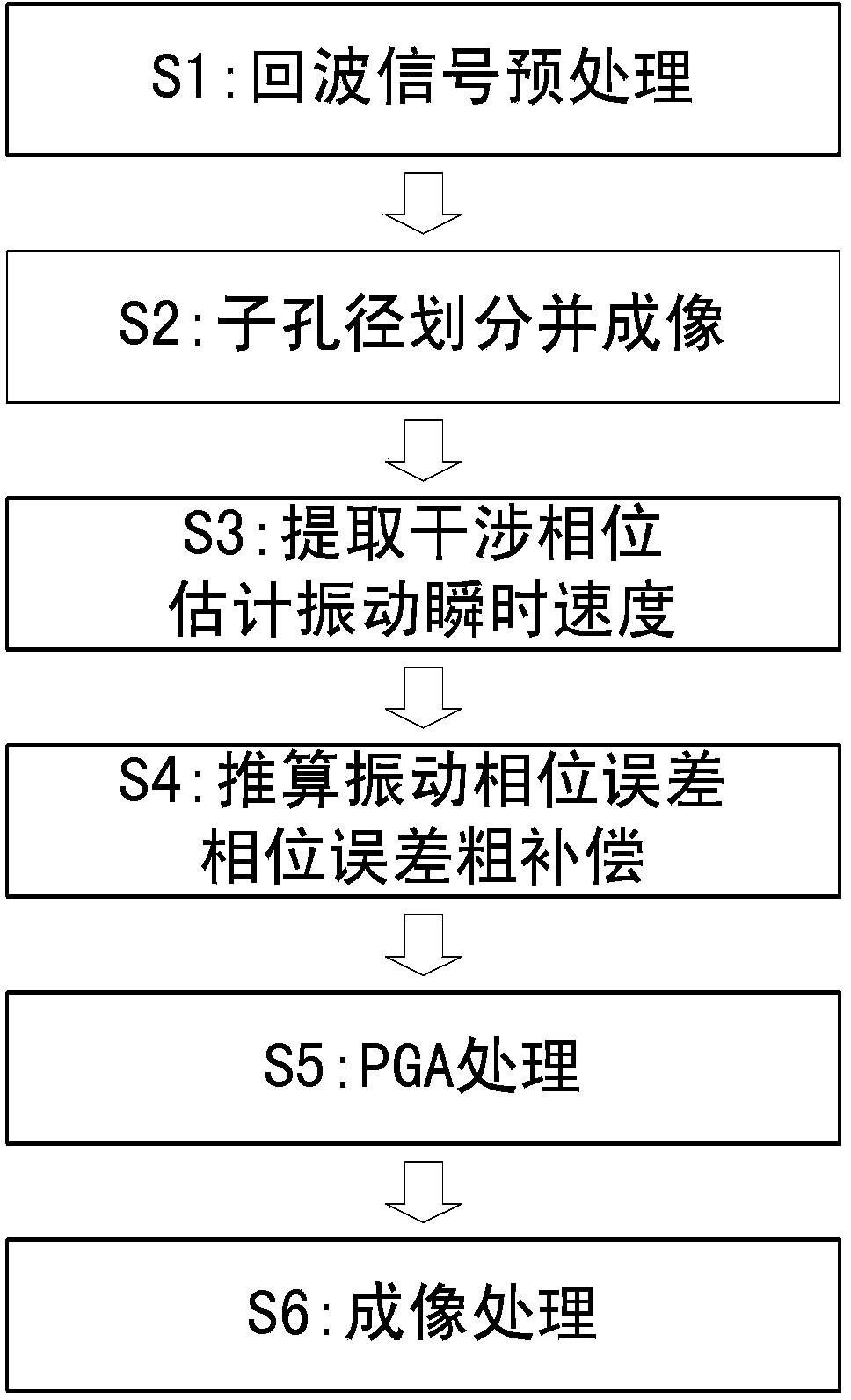
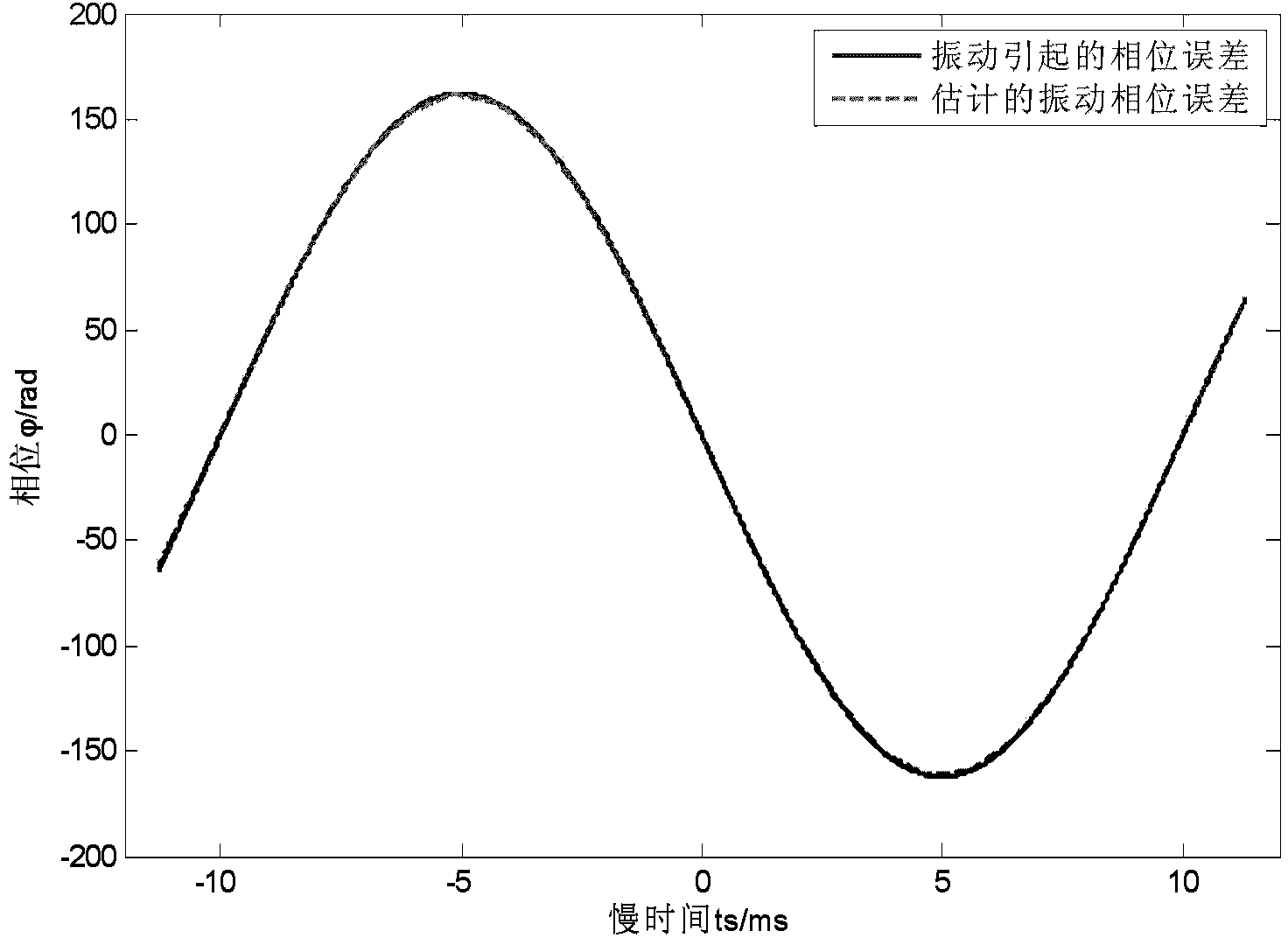
Onboard SAL imaging method adopting along-track interference to inhibit platform vibration
ActiveCN103728621AReduce vibrationReduce constraints on isolated strong pointsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionHigh resolution imagingSlow time
The invention discloses an onboard SAL imaging method adopting along-track interference to inhibit the platform vibration. The method comprises the steps: pre-processing an echo signal, dividing a slow time subaperture and imaging the subaperture; processing an image of the subaperture by means of the interference, extracting an interferometric phase, and estimating the instantaneous speed of a platform in vibration; calculating a phase error caused by the vibration, and performing coarse compensation on the phase error; processing the phase-compensated data by means of PGA (Programmable Gain Amplifier) treatment to obtain a final imaging result. Based on an along-track multi-detector observing structure, the onboard SAL vibration inhibition and imaging method can effectively inhibit influences caused by the platform vibration, and realizes the high-resolution imaging of an onboard SAL azimuth.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Multi-ship target SAR and ISAR hybrid imaging method of airborne radar
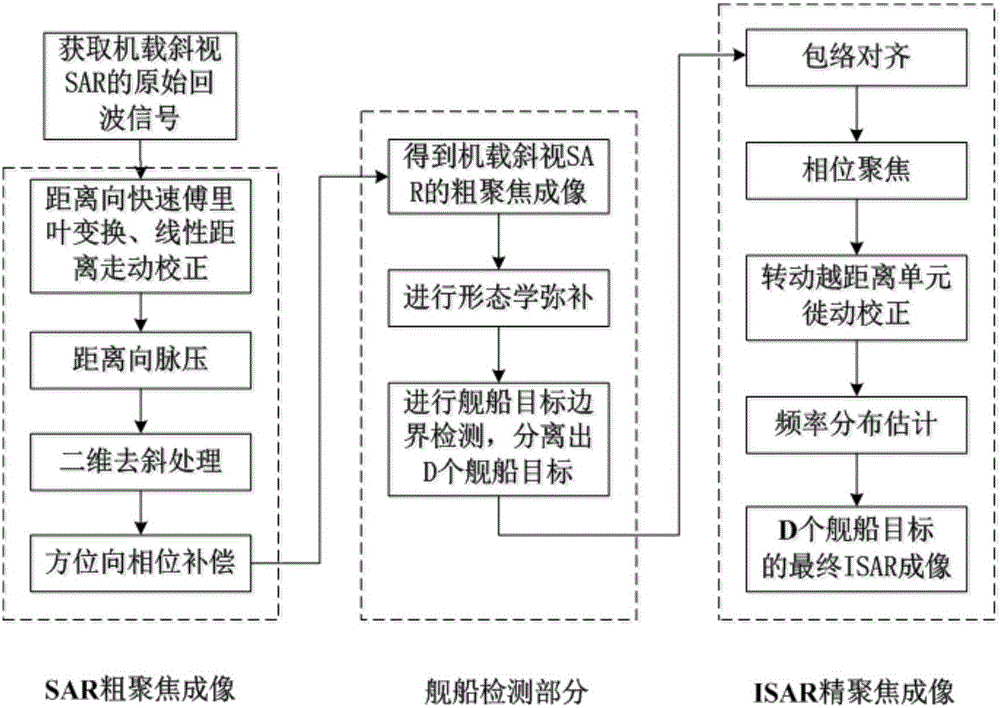
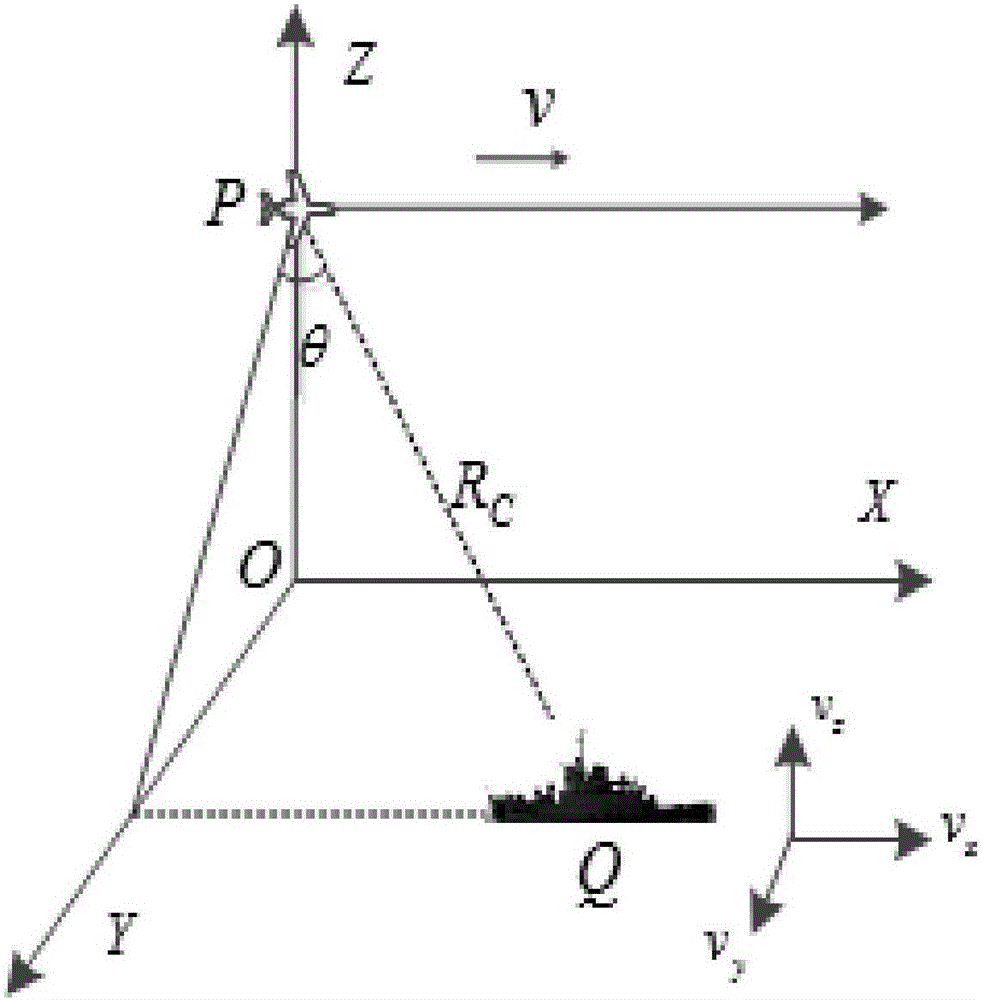
The invention discloses a multi-ship target SAR and ISAR hybrid imaging method of an airborne radar. The method is characterized in that a geometric model of an airborne squint SAR to sea surface ship target imaging is established and an instantaneous slant distance R(ta) expression of a sea surface ship target; the airborne squint SAR emits a chirp signal so as to acquire original echo signal s(t; ta) of the airborne squint SAR, and range direction FFT, linear distance walking correction and range direction pulse pressure are successively performed on the s(t; ta) so as to acquire the original echo signal of the airborne squint SAR after pulse pressure; then two-dimensional de-sloping processing and azimuth direction phase compensation are successively performed on the original echo signal so as to acquire coarse focus imaging S0 of the airborne squint SAR, and then morphological offset is performed so as to acquire an airborne SAR binary image S2 after the morphological offset; ship target boundary detection is performed on the S2 so as to extract D ship targets, and then envelope alignment, phase focusing, rotated migration though resolution cell correction and frequency distribution estimation corresponding to intermediate time of orientation slow time ta are successively performed so as to acquire final ISAR imaging of the D ship targets.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
LFMCW radar detection moving human body target method based on human body model
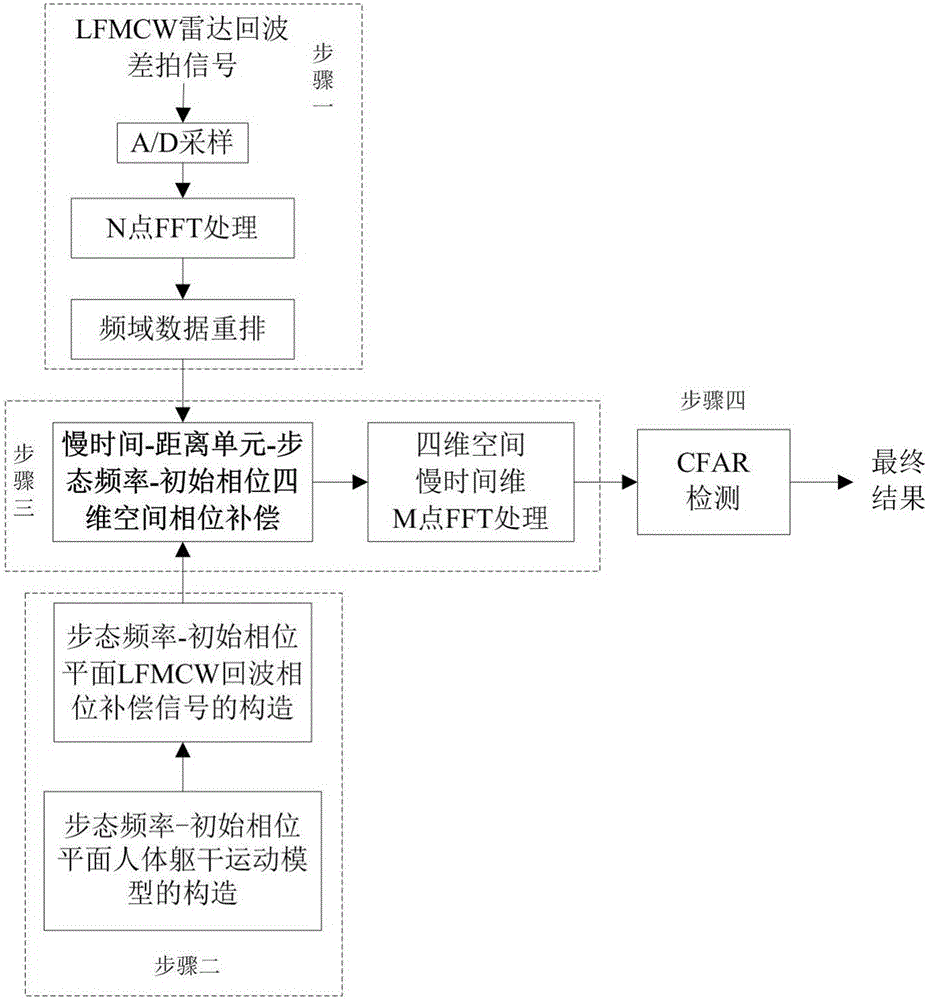
ActiveCN106291524AImprove detection signal-to-noise ratioInhibition of DiffusionSpecial data processing applicationsInformaticsHuman bodyDistance to target
The invention provides an LFMCW radar detection moving human body target method based on a human body model. The method comprises the steps that analog-to-digital conversion is carried out on an LFMCW radar echo beat signal; FFT processing is carried out on each PRI echo beat datum to acquire the LFMCW radar echo beat signal frequency domain data when a human body slowly moves, and rearranging is carried out in a slow time-distance domain two-dimensional plane; a Boulic human body walking model is constructed; according to the human body moving gait frequency and an initial phase range, a number of human body trunk moving models with different parameters are constructed on a gait frequency-initial phase two-dimensional plane; an LFMCW radar echo nonlinear phase compensation signal is reconstructed, and phase compensation is carried out on the rearranged data; FFT processing is carried out to acquire a four-dimensional space processing result; whether a target is in a distance unit is judged through constant false-alarm detection processing; and the information of distance, velocity and gait frequency of the target are acquired in the presence of the target. According to the invention, the signal-to-noise ratio of LFMCW radar detection is improved, and the human body target detection performance in strong ground clutter is improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Micro-motion target scattering point track association method based on distance-instant Doppler image
ActiveCN105259553AOvercome the shortcomings of poor correlation effectTrack correlation error is smallRadio wave reradiation/reflectionNutationHigh resolution imaging
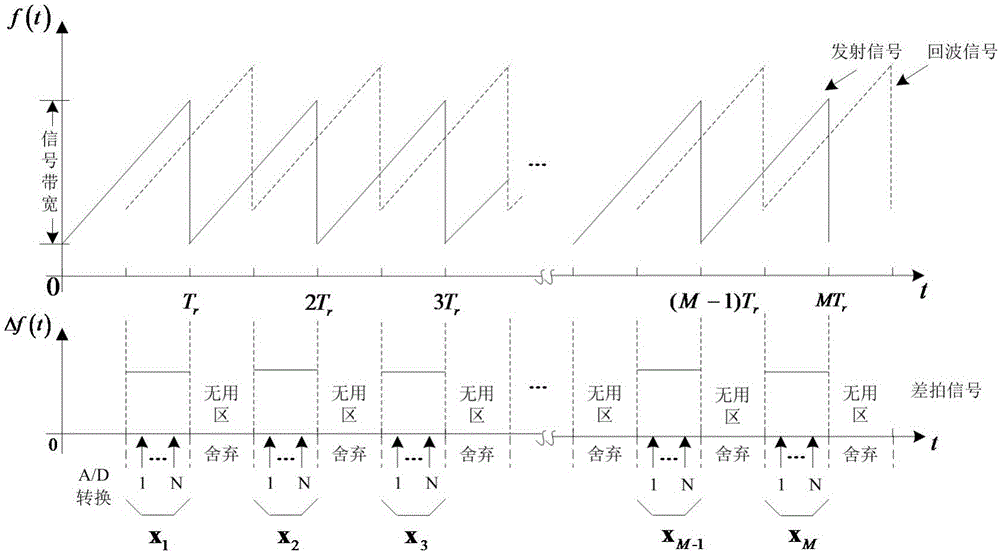
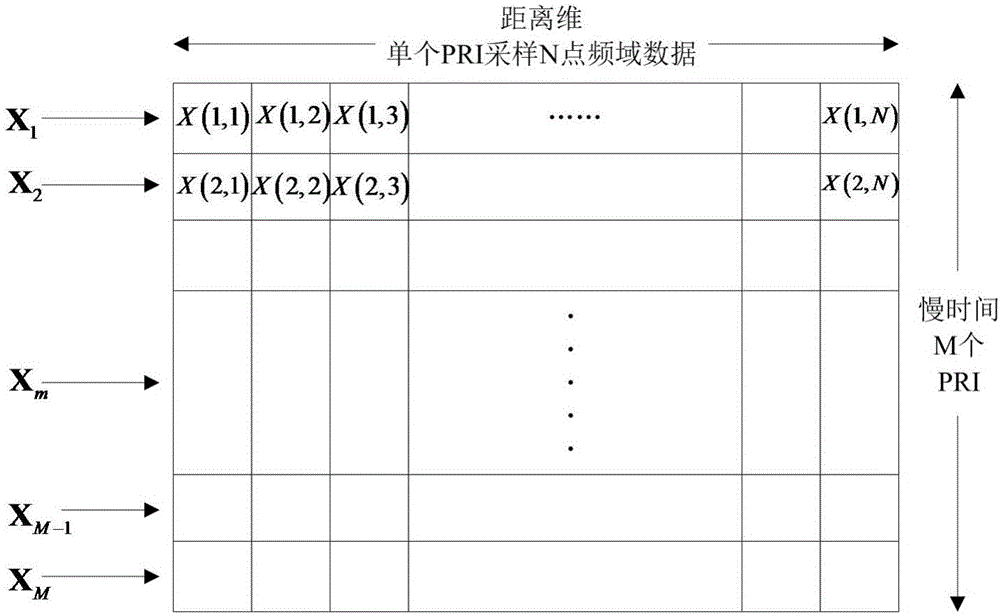
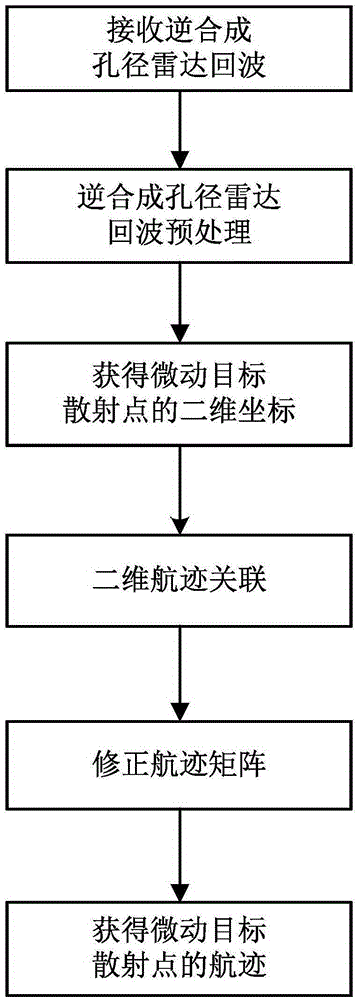
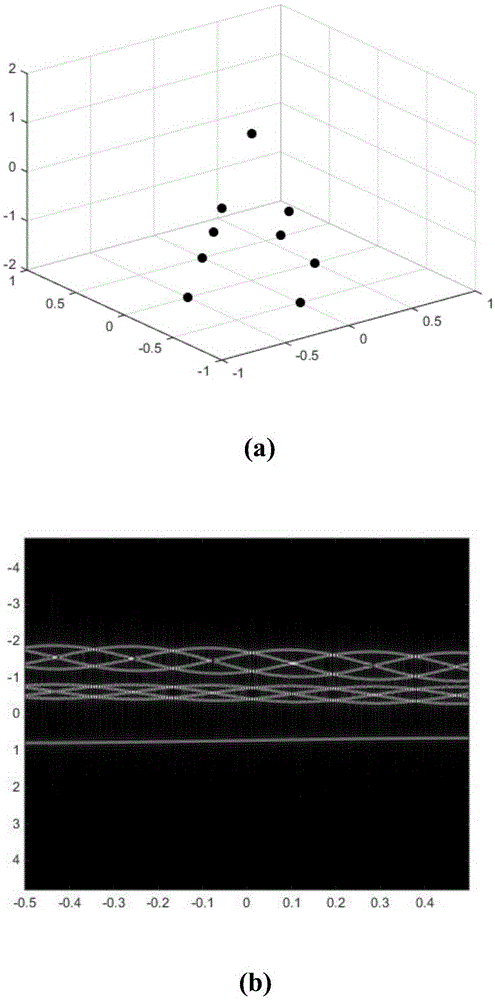
The invention discloses a micro-motion target scattering point track association method based on a distance-instant Doppler image. The method comprises the following steps of (1) receiving an inverse synthetic aperture radar echo; (2) carrying out inverse synthetic aperture radar echo pretreatment; (3) through the distance-instant Doppler image, acquiring a two-dimension coordinate of a micro-motion target scattering point; (4) carrying out two-dimension track association; (5) using a rooting multiple signal classification Root-MUSIC method to correct a track matrix; (6) acquiring a track association result of the micro-motion target scattering point. A domain associated to the scattering point is converted into a slow time-distance-instant Doppler domain with a high separability from a distance-slow time domain; separability of the micro-motion target scattering point is enhanced; for complex motion forms of spinning, processional motion, nutation and the like, advantages that universality is possessed, track association precision is high, an association error is small and so on are achieved; forceful guarantee can be provided for subsequent high-resolution imaging and target feature extraction.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Discrete repetitive controller on basis of power attraction law and control method of discrete repetitive controller
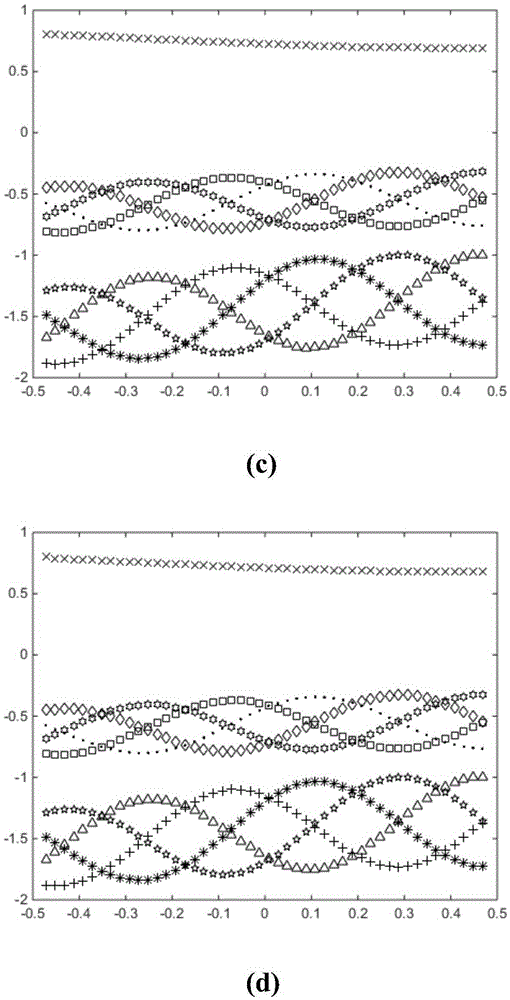
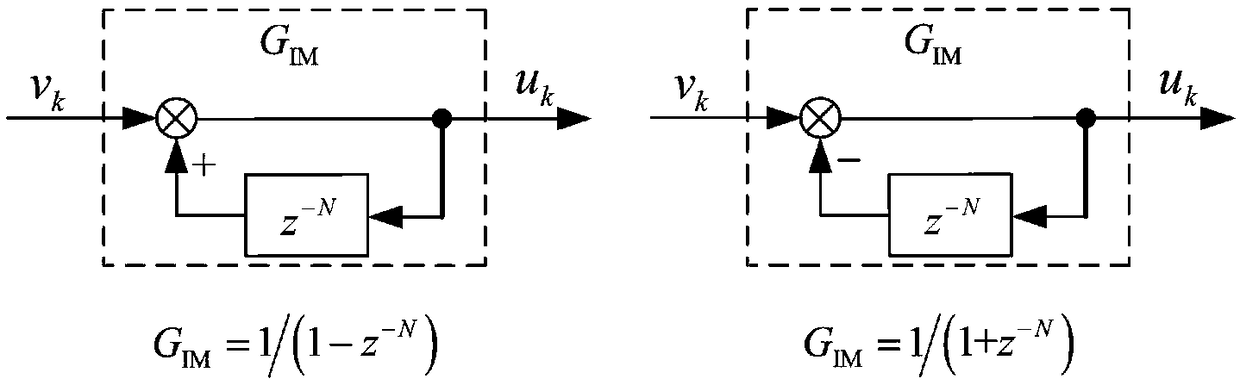
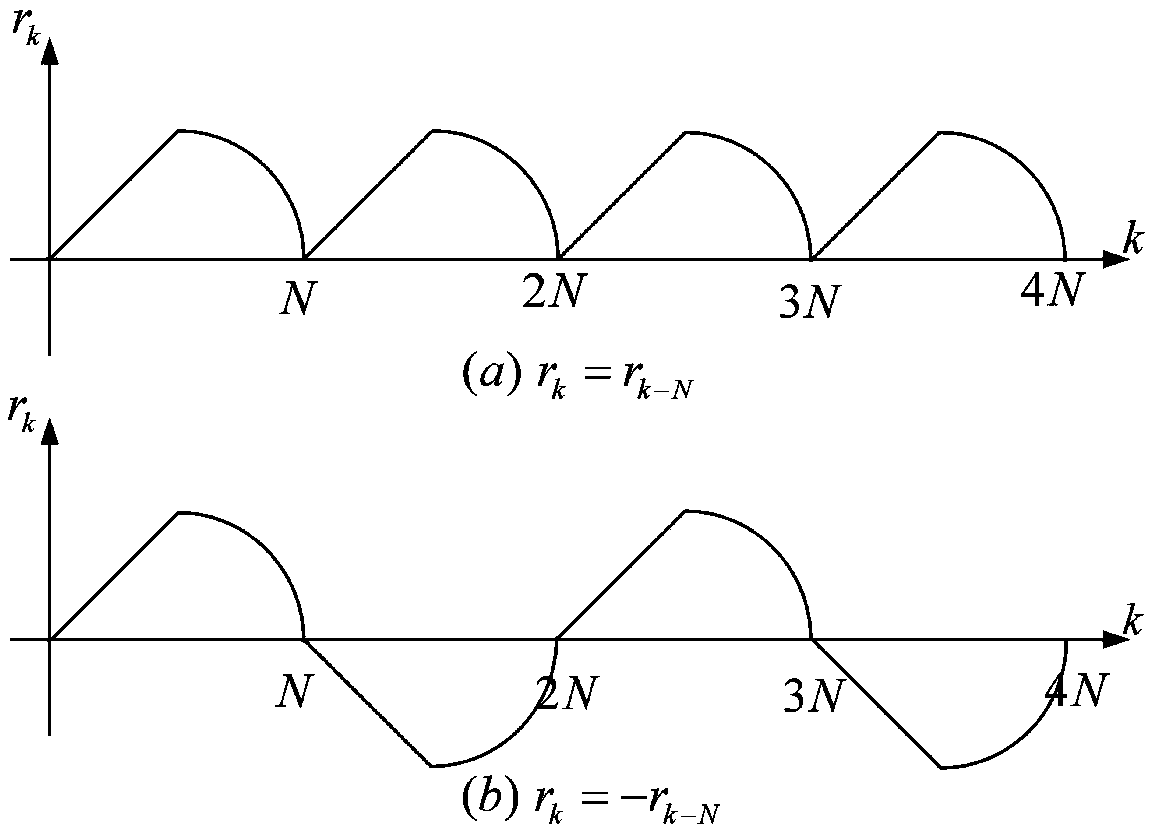
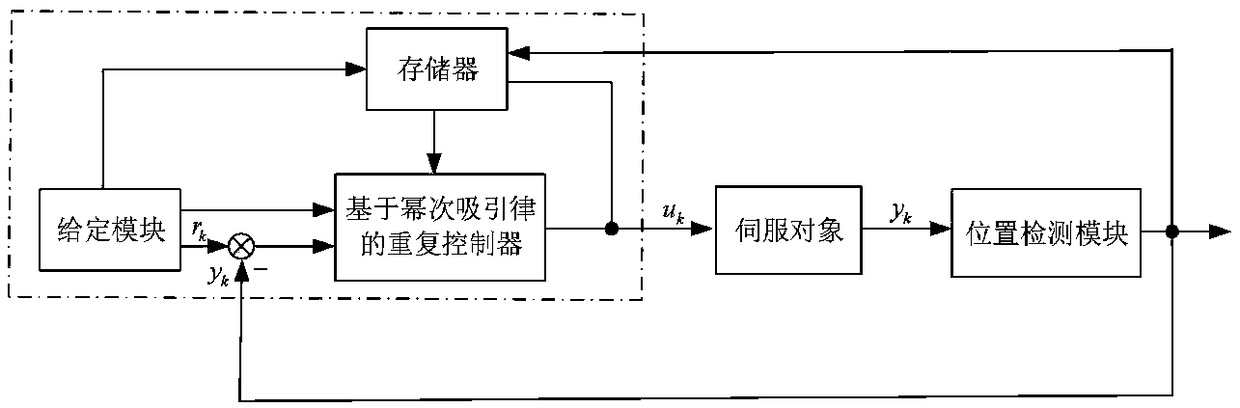
ActiveCN108646574AFast Track Error ConvergenceSuppression of Periodic Interference SignalsAdaptive controlRepetitive controlSlow time
The invention relates to a discrete repetitive controller on the basis of a power attraction law and a control method of the discrete repetitive controller. A given link generates periodic symmetric reference signals; a periodic feedback link is created; an ideal dynamic error is created on the basis of the power attraction law; according to the ideal dynamic error,an e / n signal conversion moduleis constructed,and an output signal of the e / n signal conversion module is used as a correction amount of the discrete repetitive controller; an output signal of the repetitive controller is calculated to serve as input of a servo object,so that a servo system changes along with the reference signals. Specific controller parameter setting work can be performed according to indexes representing a system convergence process,and a power monotone reduction region,a power absolute attraction layer and a steady-state error band boundary which represent a tracking error convergence process are provided. The discrete repetitive controller with time-domain design,good control precision,complete suppression of periodic interference signals and effective elimination of slow time-varying non-periodicinterference signals on the basis of the power attraction law and the control method of the discrete repetitive controller are provided.
Owner:TAIZHOU UNIV +1
Non-linear time-varying process fault monitoring method based on high efficiency recursion kernel principal component analysis
ActiveCN107632592AImplement fault monitoringReduce false alarm rateElectric testing/monitoringDecompositionCharacteristic space
The invention discloses a non-linear time-varying process fault monitoring method based on high efficiency recursion kernel principal component analysis and belongs to the fault detection and diagnosis technology field. The method comprises steps that data having non-linear and slow time-varying characteristics and containing faults is acquired from a Tennessee Eastman process simulator, a Gauss kernel function is utilized to project the acquired normal data to the high-dimensional characteristic space and is centralized, an initial offline monitoring model is established, and a kernel densityestimation function is employed to determine control limit; secondly, when new process data is acquired, through introducing a first-order interference theory method, a model is directly updated based on a characteristic value and a characteristic vector acquired in the offline model, the new data is projected to the updated kernel space and the residual error space to calculate T2 and SPE statistics; when the corresponding control limit is surpassed, occurrence of a monitoring fault is determined, otherwise, the whole process operates normally. The method is advantaged in that two problems are mainly solved, 1), a problem of relatively high false alarm rate generated during fault monitoring in the non-linear time-varying process of kernel principal component analysis is solved; and 2), aproblem of relatively high load existing in a recursion algorithm based on characteristic constant decomposition is solved.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
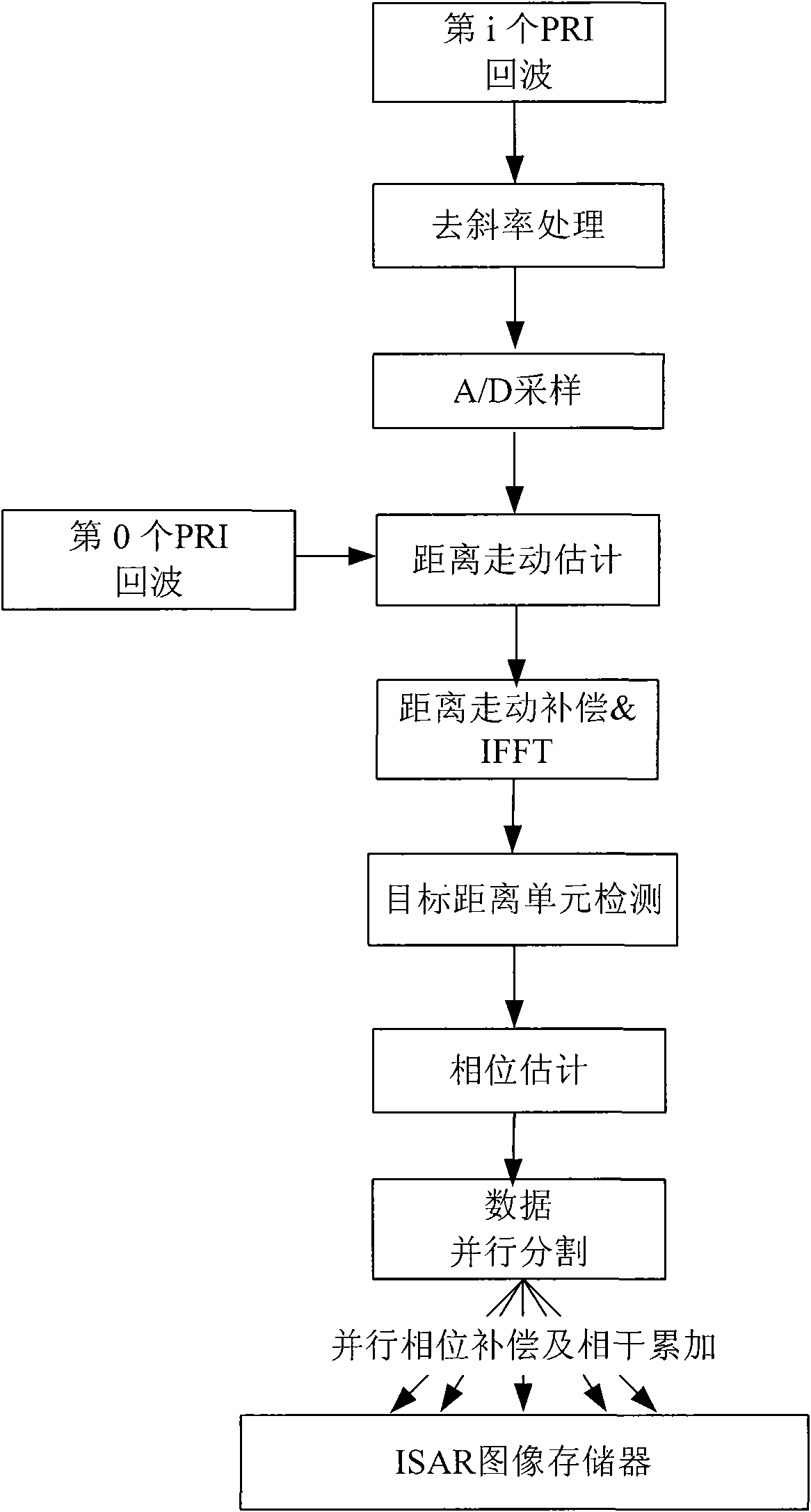
Parallel real-time imaging processing method for inverse synthetic aperture radar
InactiveCN101592733AImprove computing efficiencyTo achieve the purpose of real-time imagingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionInterferometric synthetic aperture radarDecomposition
The invention provides a parallel imaging processing method for real-time imaging of an inverse synthetic aperture radar (ISAR). Aiming at the real-time requirement of the ISAR on the imaging of a high-speed moving target, the method adopts parallel processing technology, designs a parallel processing system structure aiming at ISAR imaging, and performs corresponding parallel decomposition on an ISAR algorithm. The method realizes an ISAR imaging algorithm having causality relative to slow time through a reasonable algorithm design to make data acquisition and imaging processing simultaneously performed; and compared with the conventional ISAR imaging serial processing algorithm, the method can greatly improve the operating efficiency of the ISAR imaging so as to realize real real-time processing to facilitate practical application of the ISAR in projects.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com