Patents
Literature
462 results about "Causality" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Causality (also referred to as causation, or cause and effect) is efficacy, by which one process or state, a cause, contributes to the production of another process or state, an effect, where the cause is partly responsible for the effect, and the effect is partly dependent on the cause. In general, a process has many causes, which are also said to be causal factors for it, and all lie in its past. An effect can in turn be a cause of, or causal factor for, many other effects, which all lie in its future. Some writers have held that causality is metaphysically prior to notions of time and space.
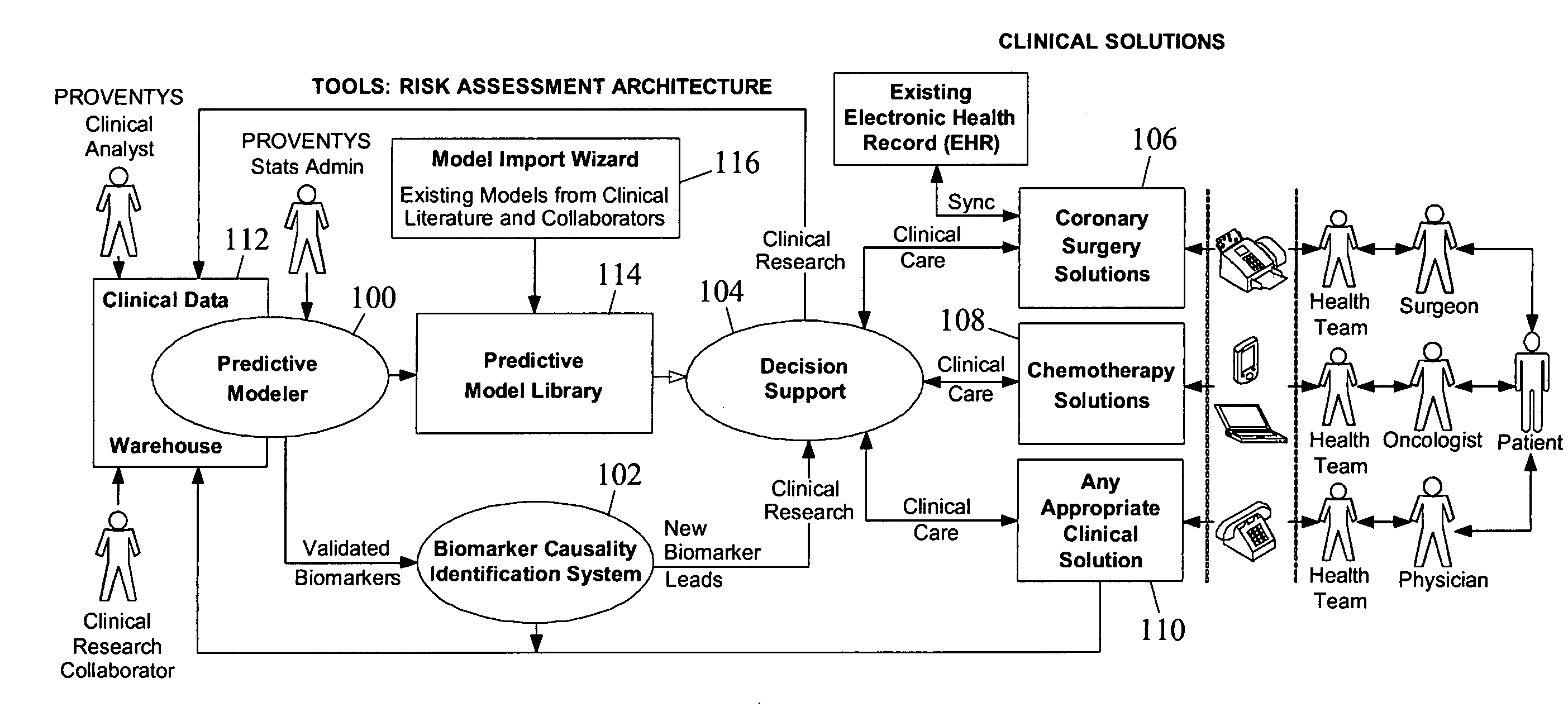
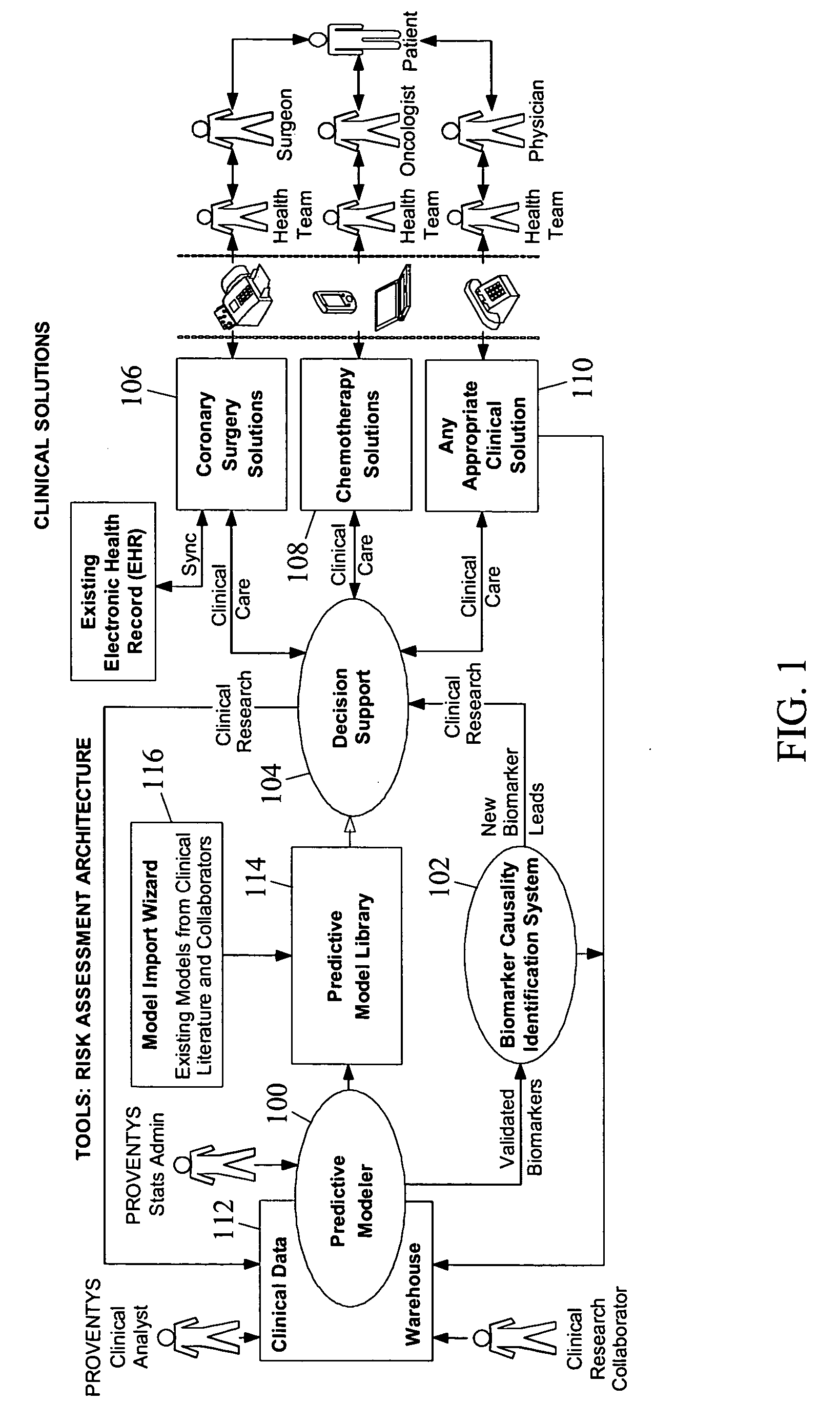
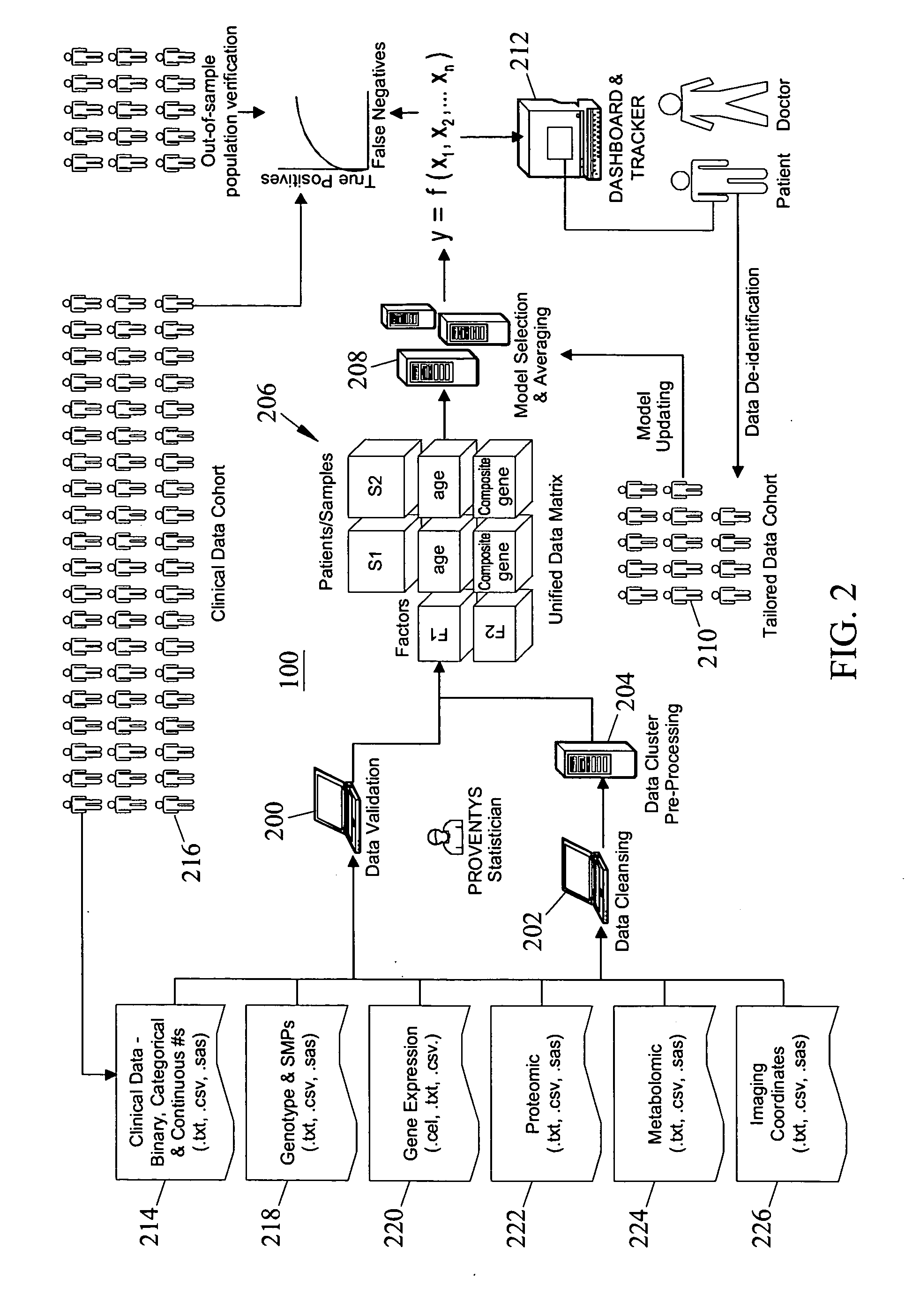
Methods, system, and computer program products for developing and using predictive models for predicting a plurality of medical outcomes, for evaluating intervention strategies, and for simultaneously validating biomarker causality
InactiveUS20060173663A1Medical simulationAnalogue computers for chemical processesEvaluated interventionsOrganism
Methods, systems, and computer program products for developing and using predictive models for predicting medical outcomes and for evaluating intervention strategies, and for simultaneously validating biomarker causality are disclosed. According to one method, clinical data from different sources for a population of individuals is obtained. The clinical data may include different physical and demographic factors regarding the individuals and a plurality of different outcomes for the individuals. Input regarding a search space including models linking different combinations of the factors and at least one of the outcomes is received. In response to receiving the input, a search for models in the search space based on predictive value of the models with regard to the outcome is performed. The identified models are processed to produce a final model linking one of the combinations of factors to the outcome. The final model indicates a likelihood that an individual having the factors in the final model will have the outcome.
Owner:PROVENTYS
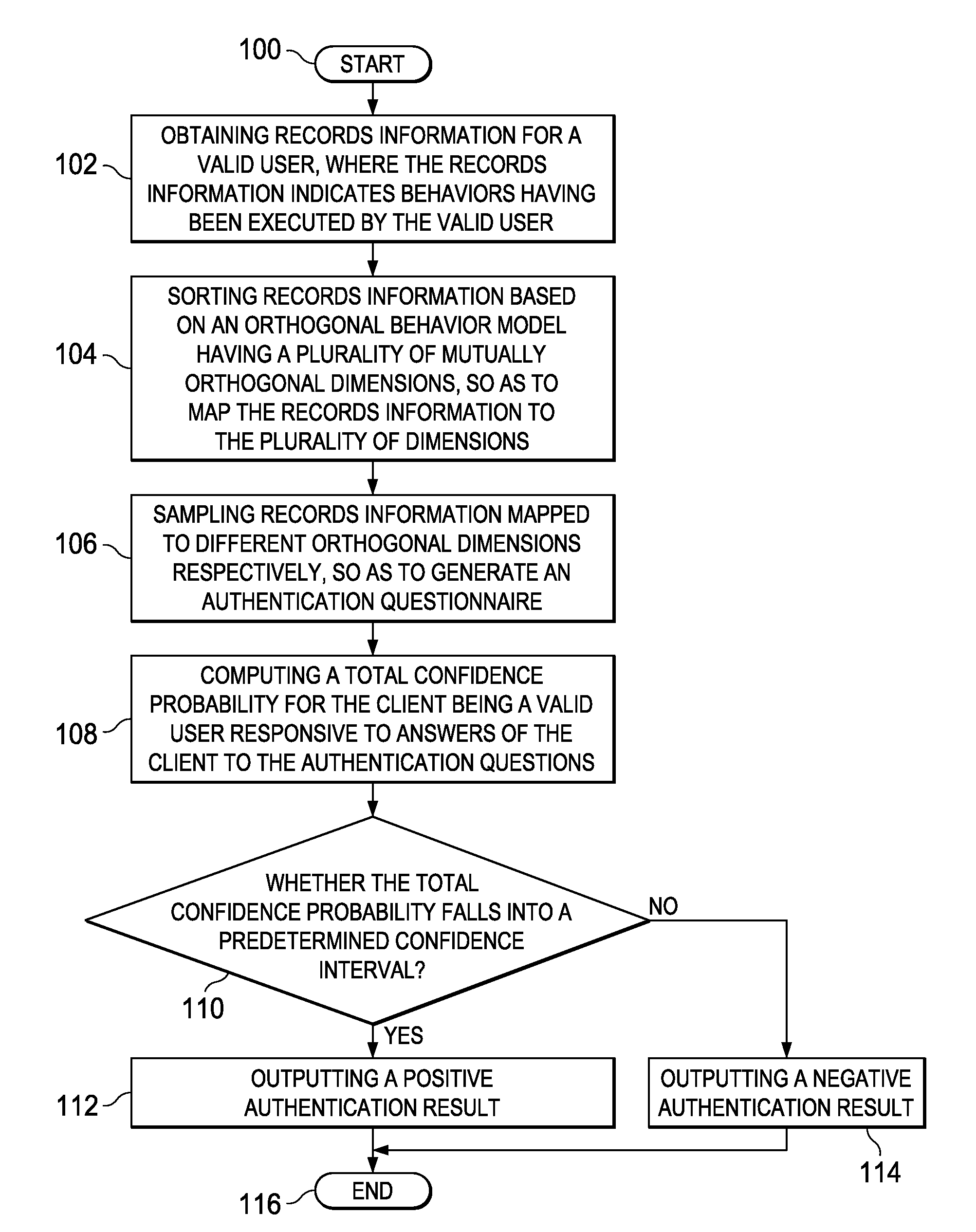
Authentication method and apparatus
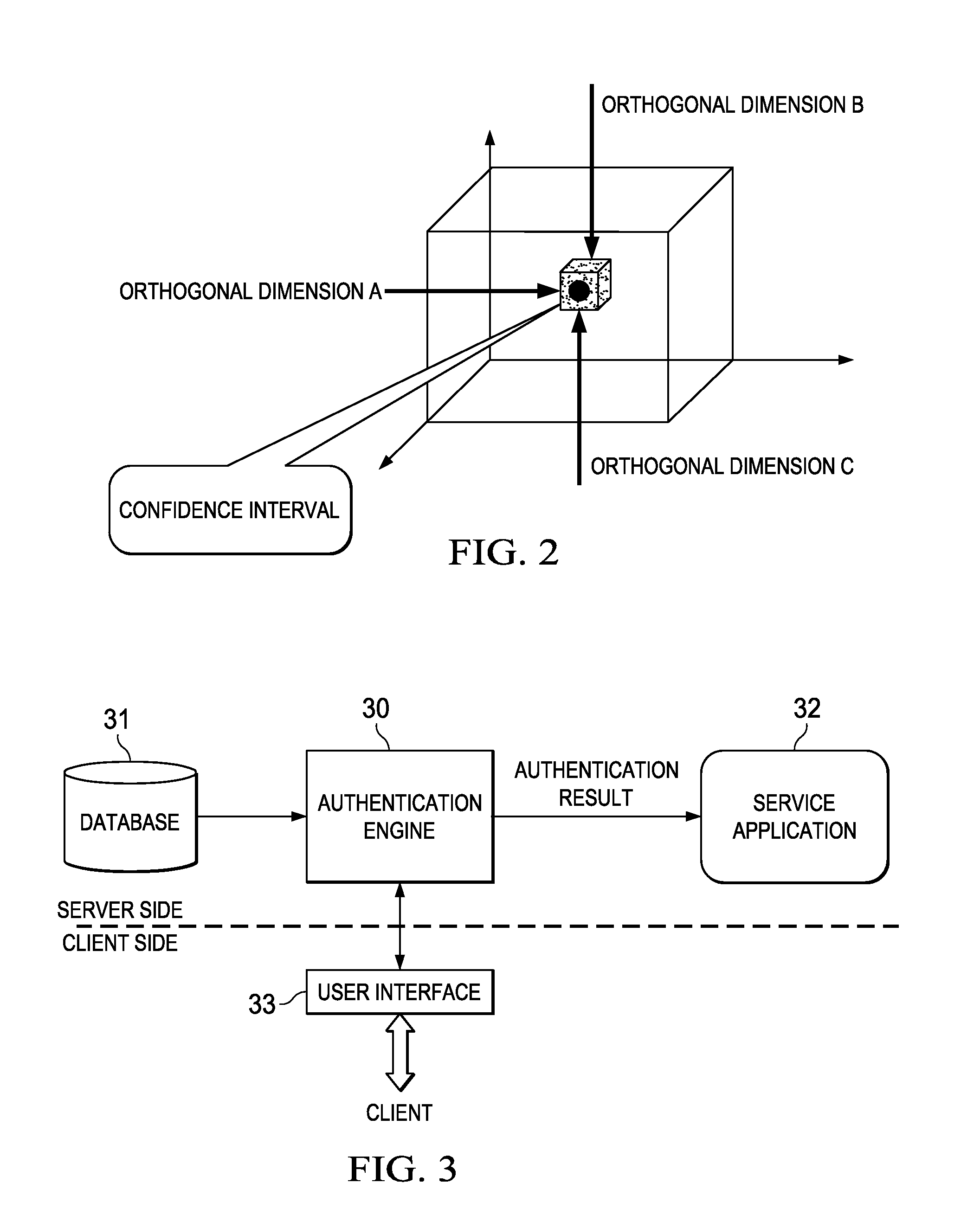
InactiveUS8495718B2More reliableMore securityDigital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsConfidence intervalCausality
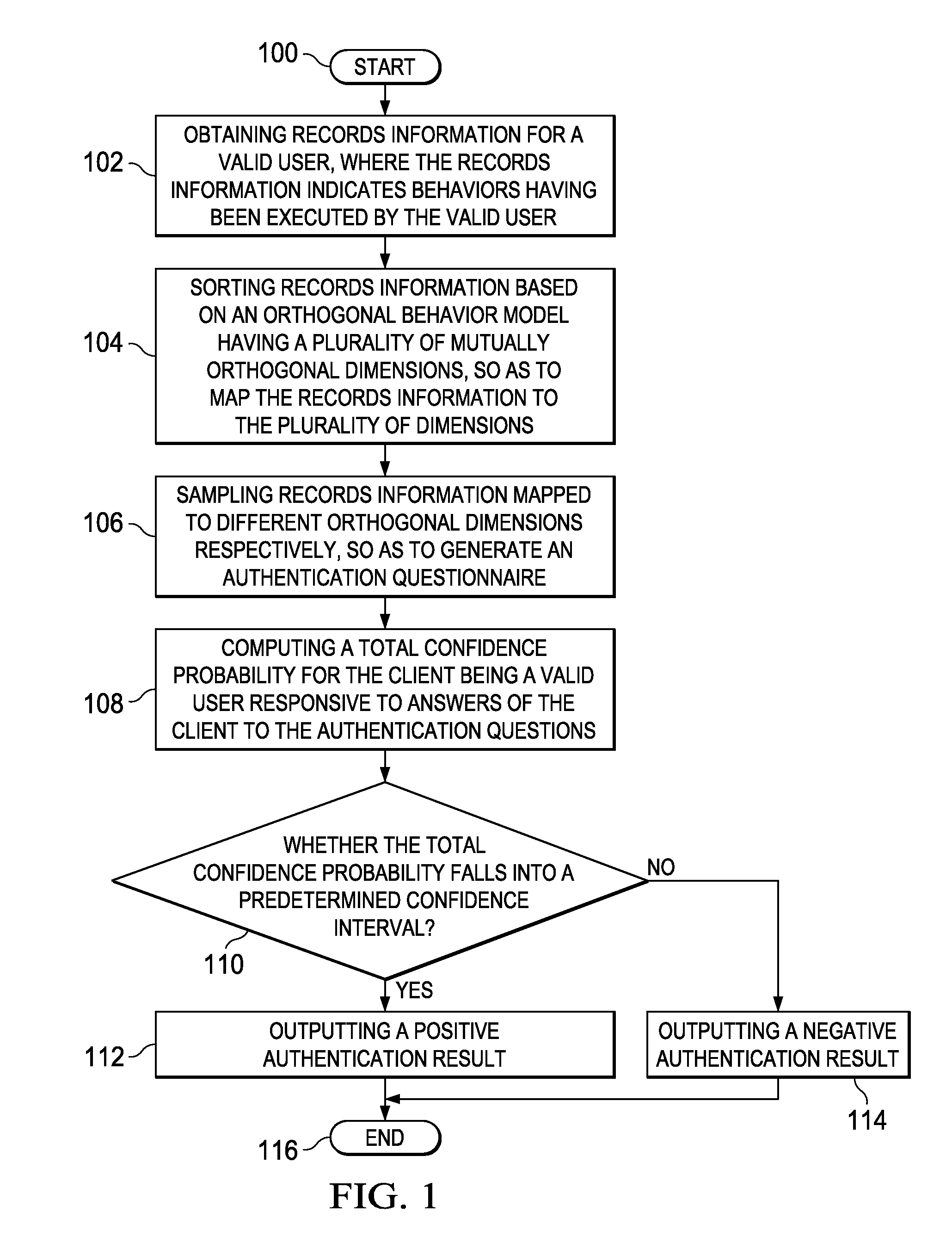
An identity authentication method is provided. The method comprises obtaining records information of a valid user, where the records information indicates behaviors having been executed by the valid user; mapping, based on an orthogonal behavior model having multiple mutually orthogonal dimensions, records information to the multiple dimensions, wherein behaviors indicated by records information mapped to different dimensions do not overlap therebetween and have no logical cause and effect relationship; sampling records information mapped to different dimensions, respectively, so as to generate an authentication questionnaire including a plurality of authentication questions; computing, responsive to answers of a client to the authentication questionnaire, a total confidence P for the client being a valid user; outputting a positive authentication result, responsive to the total confidence probability P falling into a confidence interval; and outputting a negative authentication result, responsive to the total confidence probability P failing to fall into a confidence interval. The present invention further provides a corresponding identity authentication apparatus.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
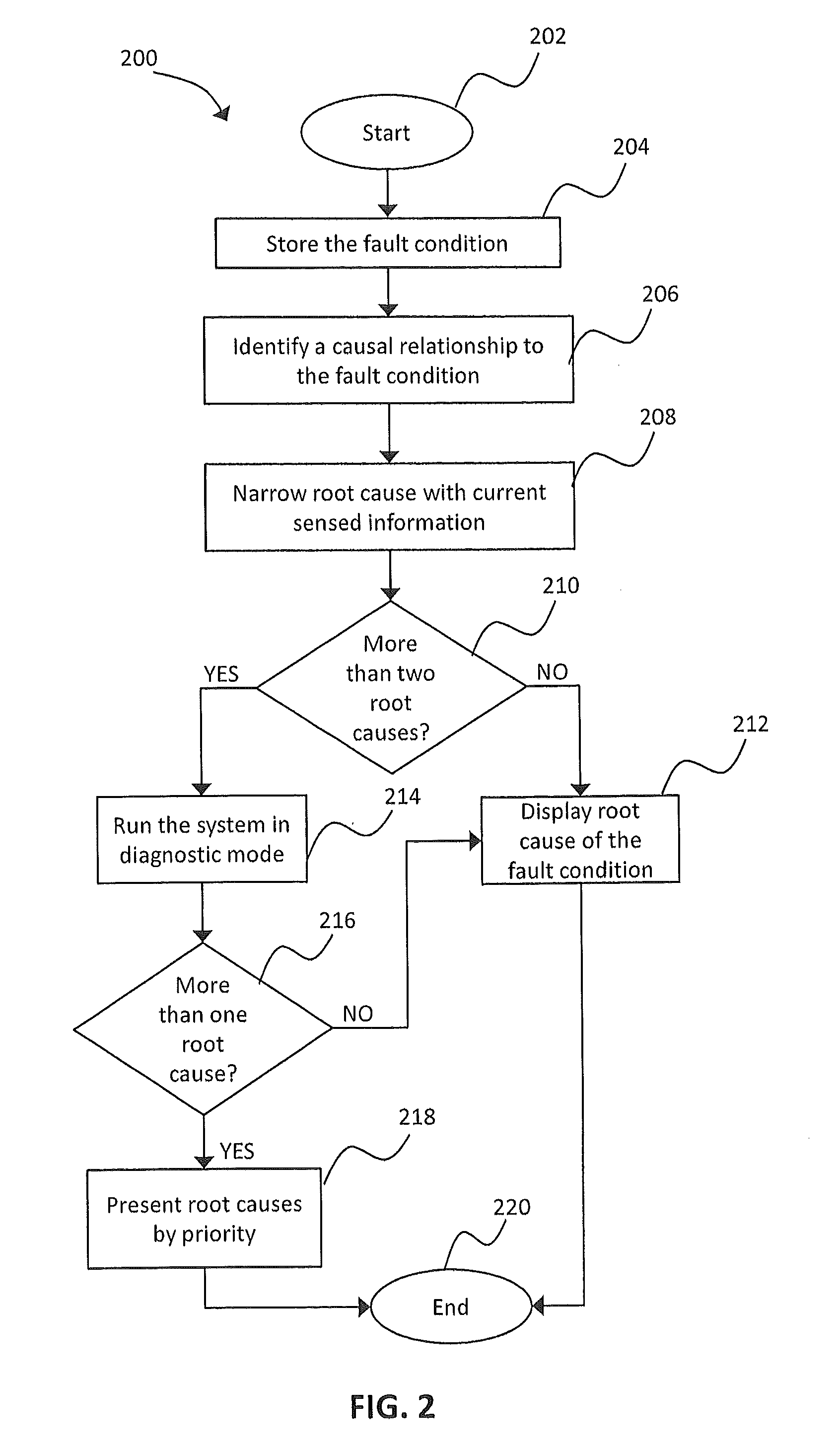
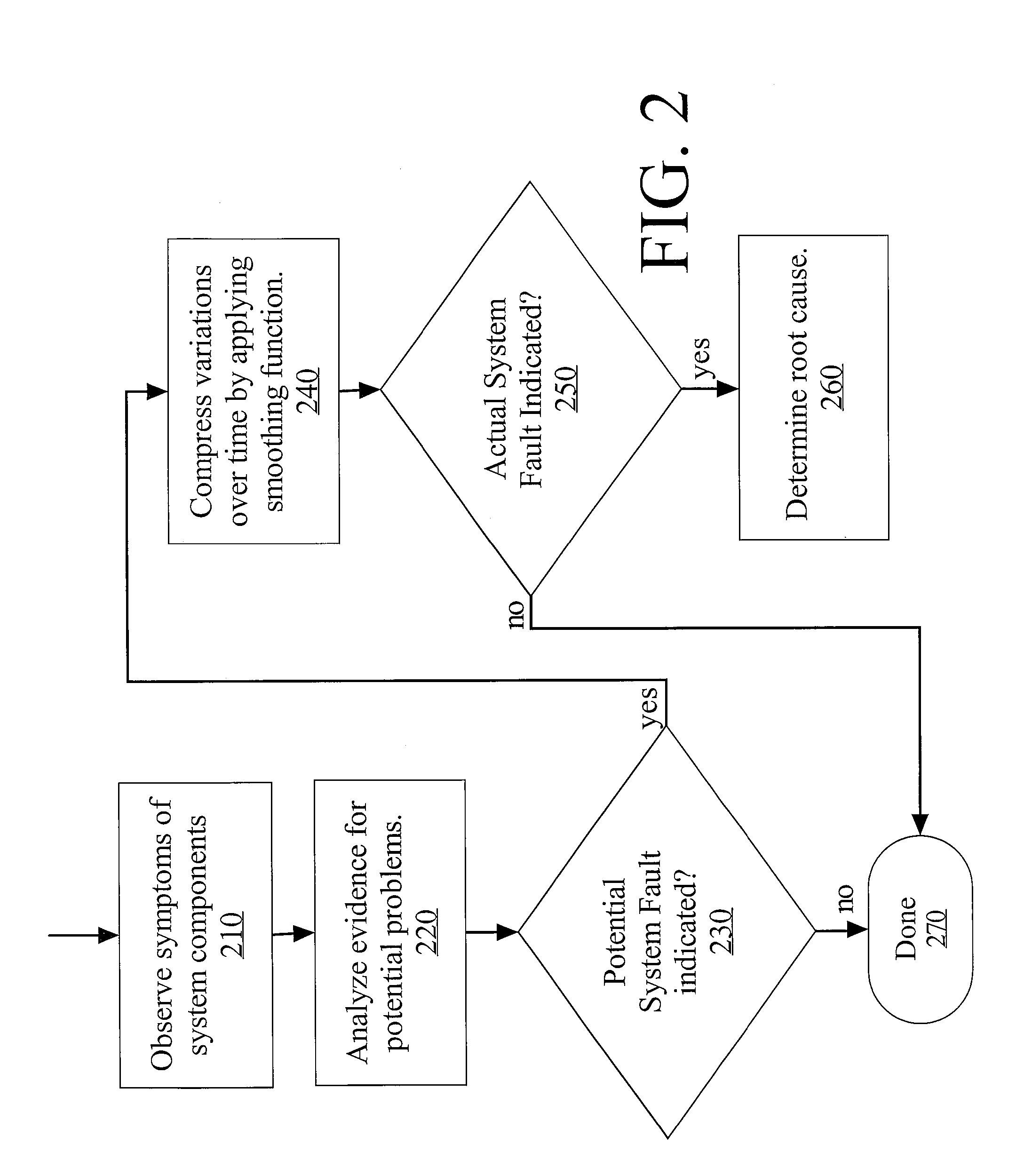
HVAC System Fault Root Cause Self-Determination
A method for self-determining a root cause of a system fault in a heating, ventilation, and cooling (HVAC) system includes receiving a fault message indicative of a fault condition in an operating characteristic of the HVAC system; determining a causal relationship between the fault condition and a predetermined list of root causes associated with the fault condition; receiving information indicative of operating conditions of the HVAC system; and eliminating at least one root cause that is unrelated to the fault condition in response to the receiving of the information.
Owner:CARRIER CORP
System and Method for Reducing Driving Risk With Hindsignt
ActiveUS20070271105A1Readily apparentRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesCommerceDriving riskRelevant information
Owner:DRIVECAM
Robotic microscopy systems
ActiveUS7139415B2High through-put analysisHigh analysisMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorCharacter and pattern recognitionCausalityLiving cell
The invention comprises a robotic microscope system and methods that allow high through-put analysis biological materials, particularly living cells, and allows precise return to and re-imaging of the same field (e.g., the same cell) that has been imaged earlier. This capability enables experiments and testing hypotheses that deal with causality over time intervals which are not possible with conventional microscopy methods.
Owner:THE J DAVID GLADSTONE INST A TESTAMENTARY TRUST ESTABLISHED UNDER THE WILL OF J DAVID GLADS
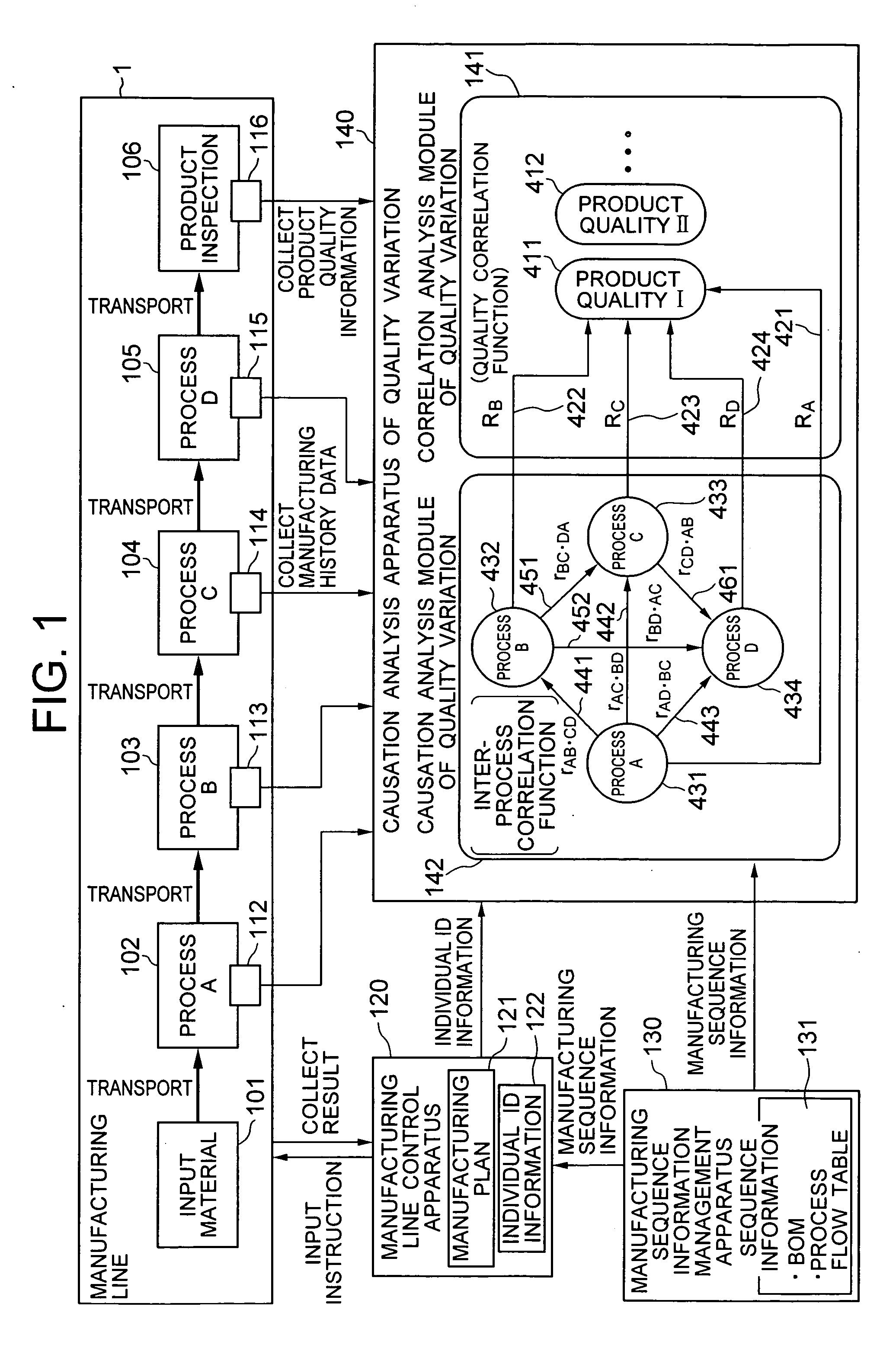
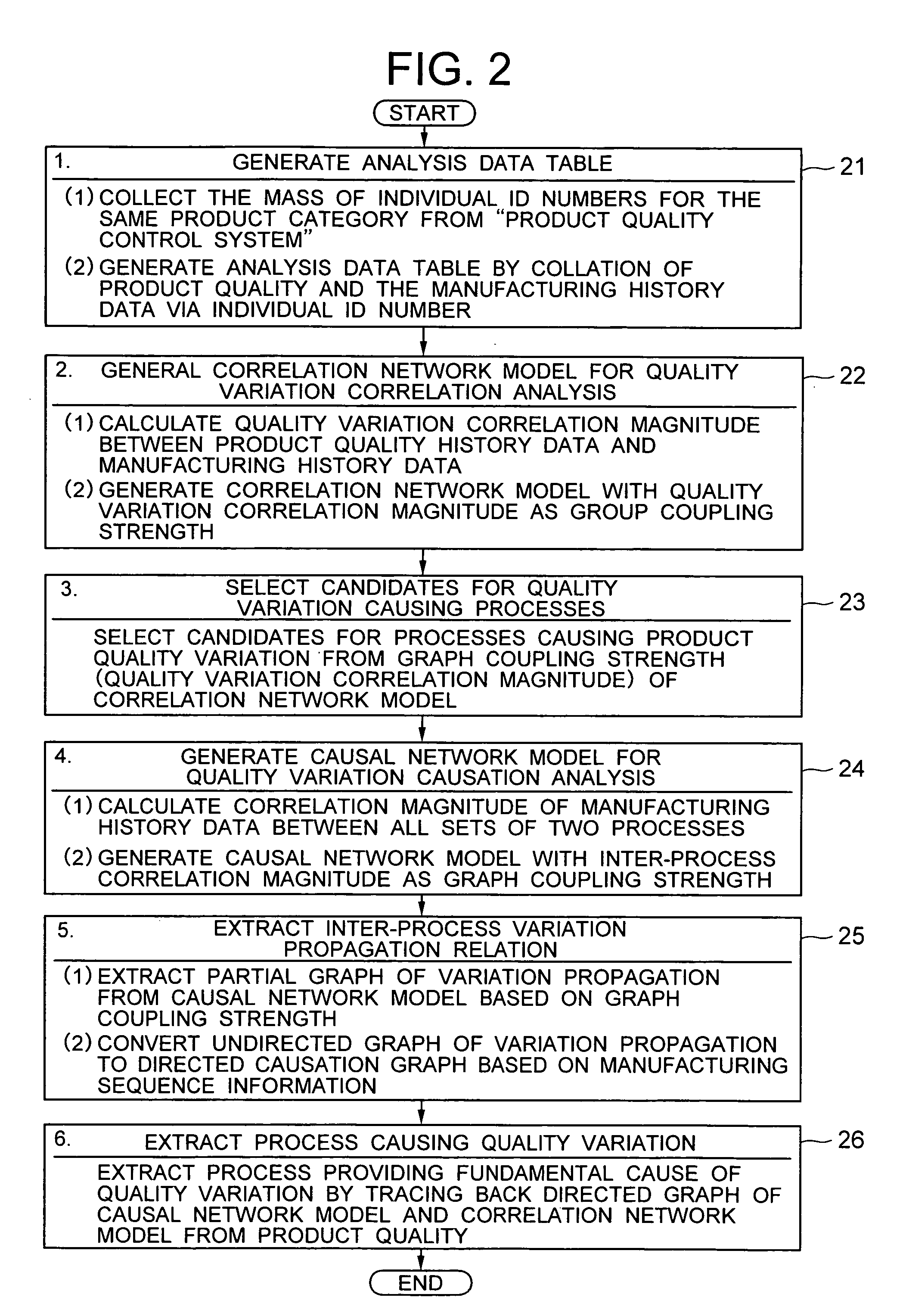
Quality control system for manufacturing industrial products
InactiveUS20060047454A1Quality improvementResourcesSpecial data processing applicationsManufacturing technologyProgram planning
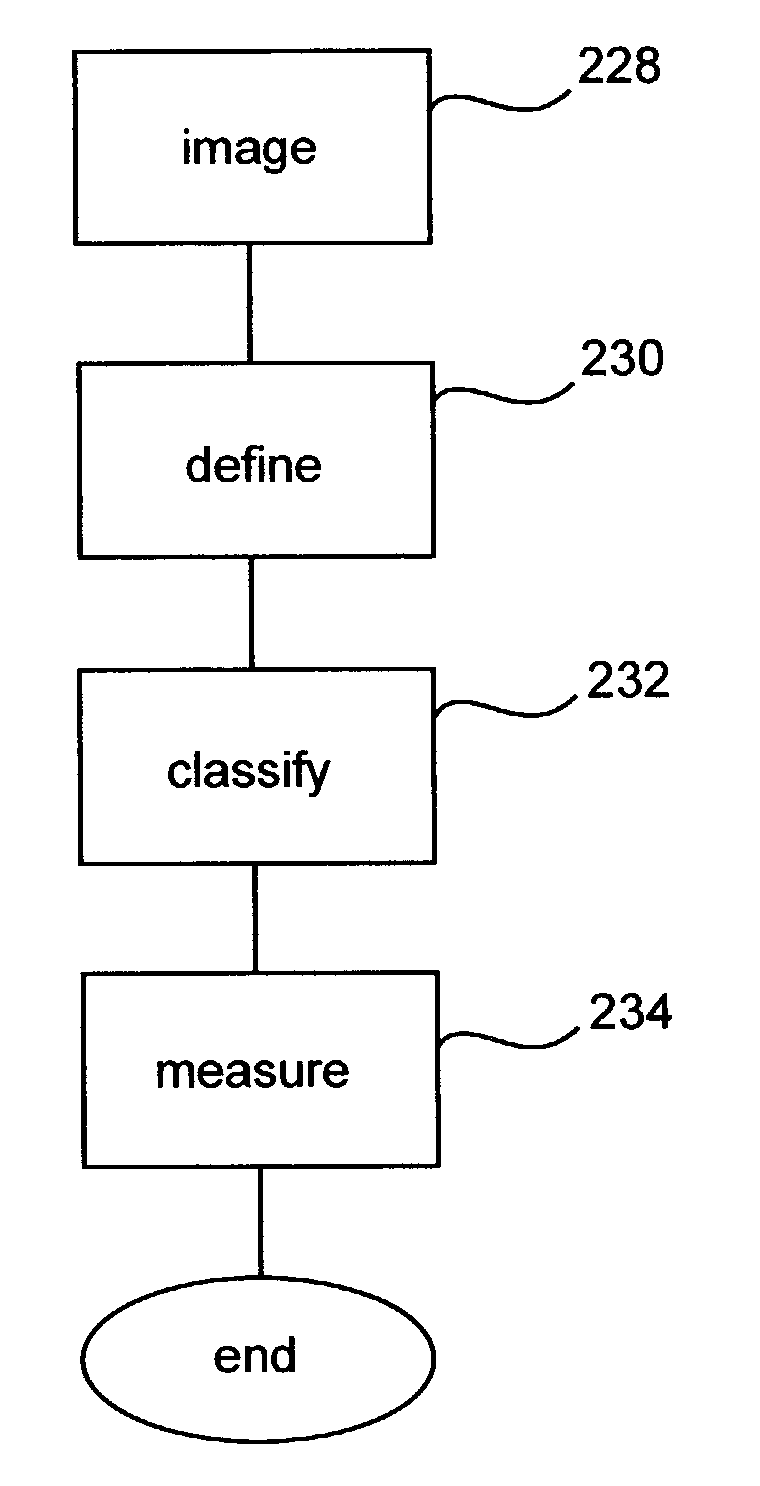
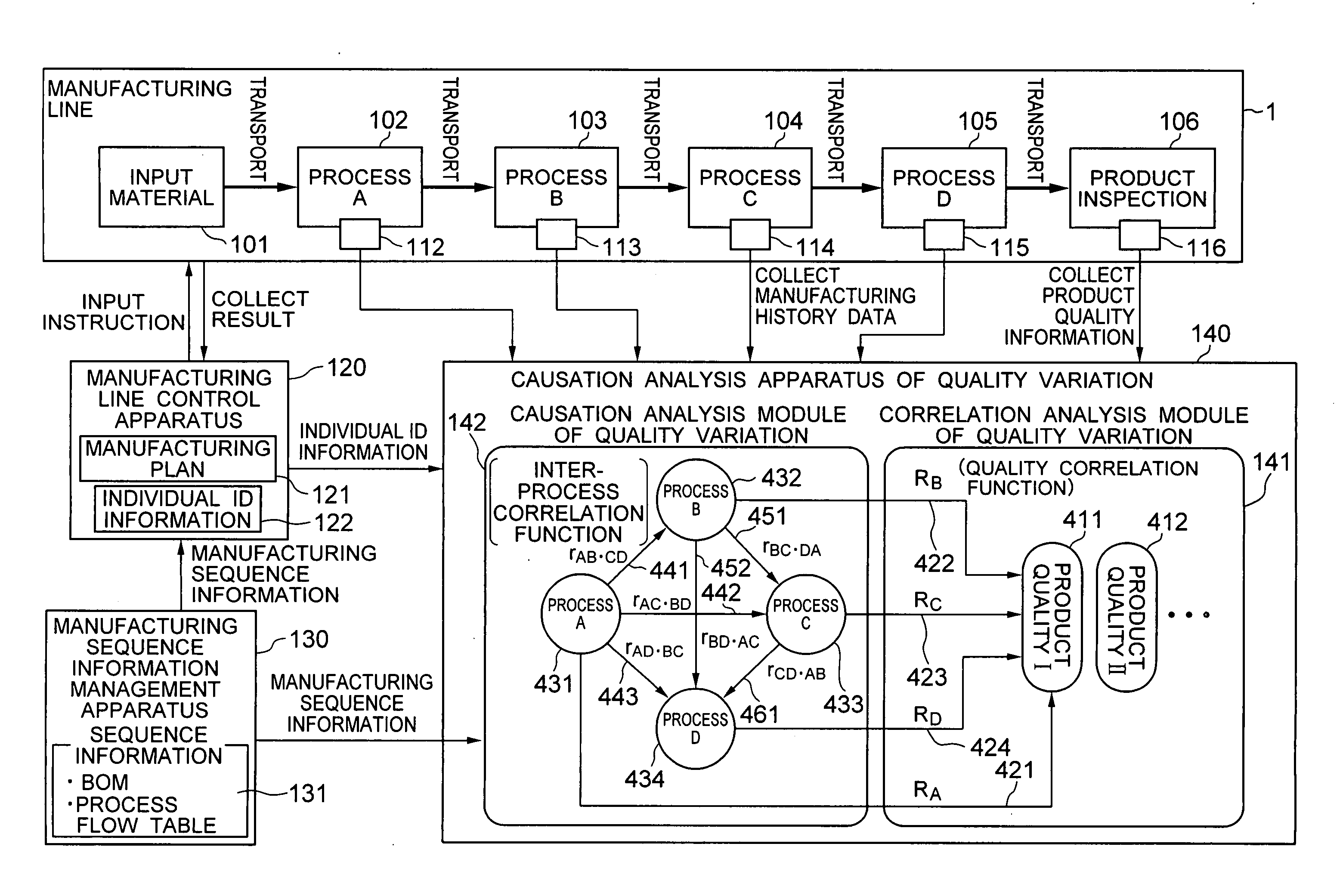
In a quality control system for manufacturing industrial products, the product quality history and the manufacturing process history are collected and collated to calculate the correlation magnitude between the two histories. The candidates for the cause of quality variation hidden in the manufacturing processes are listed, and the correlation magnitude between all combinations of the variates of the manufacturing process history are calculated. Further, by utilizing the manufacturing sequence history used for an input plan, a causation connecting structure model between the manufacturing processes of the manufacturing line is automatically generated and automatically analyzed thereby to automatically extract the fundamental cause of quality variation from the candidates for the cause of quality variation. By doing so, the cause of quality variation of industrial products manufactured through a complicated process can be traced in a complicated connecting structure in the manufacturing history data.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
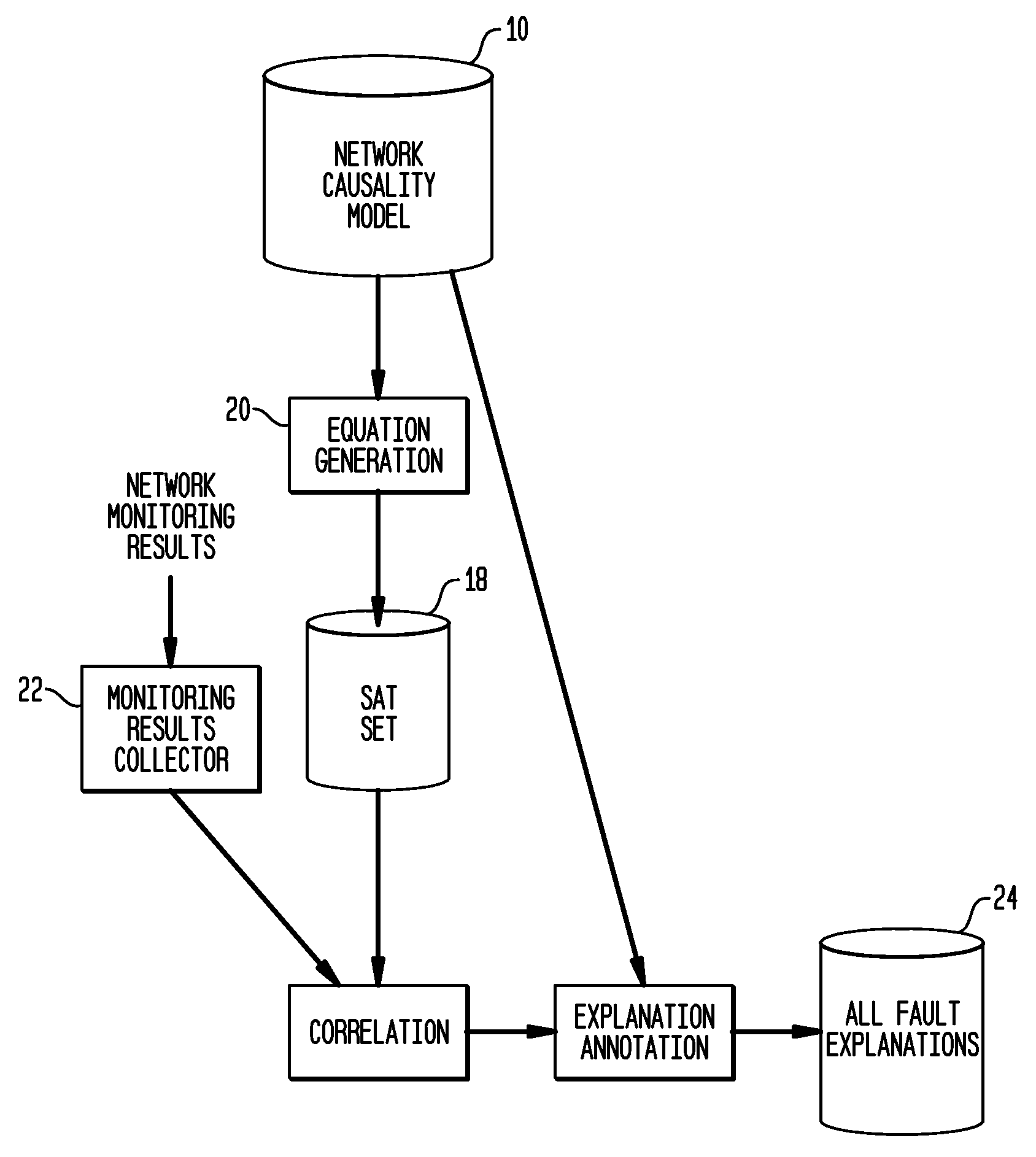
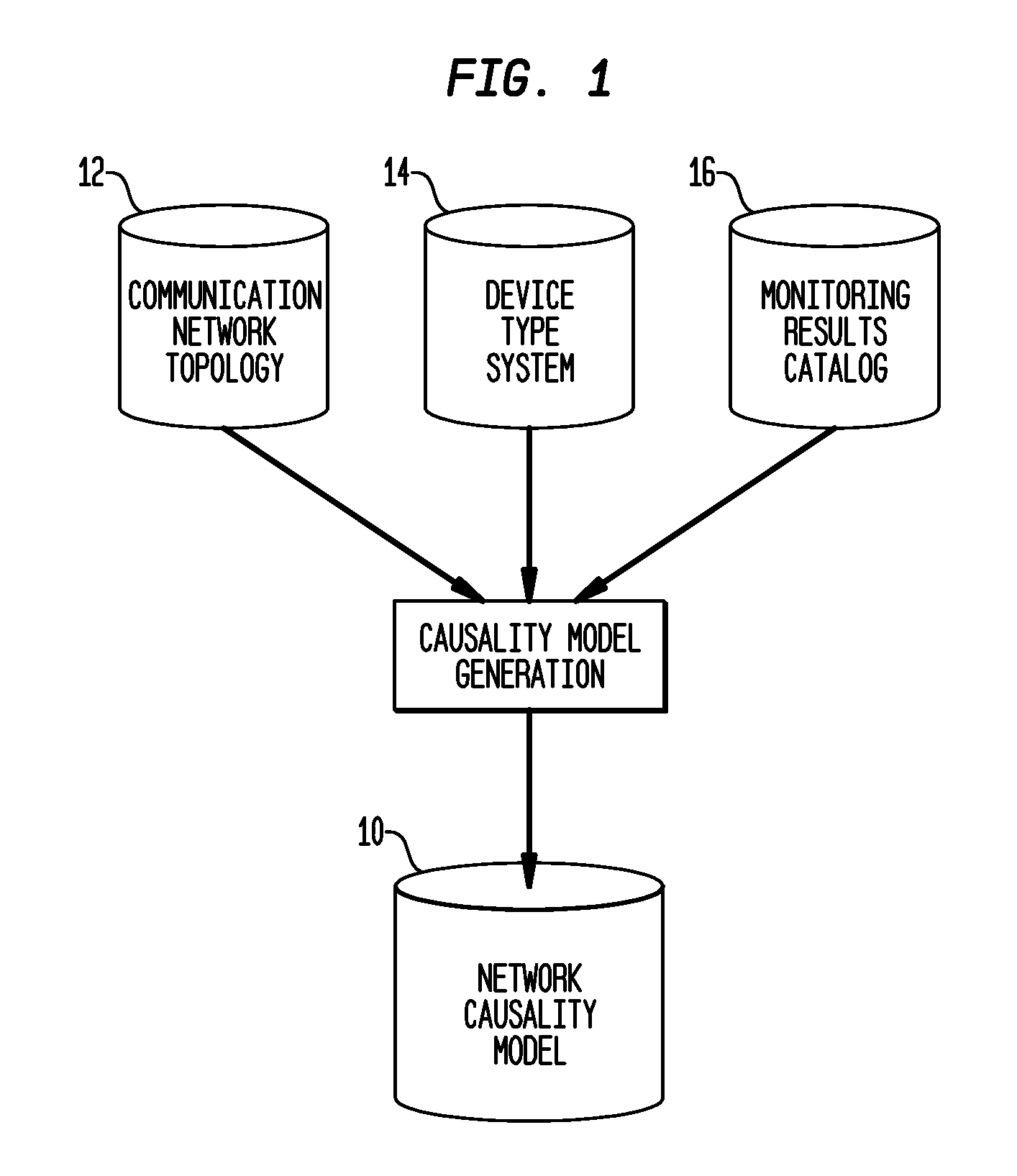
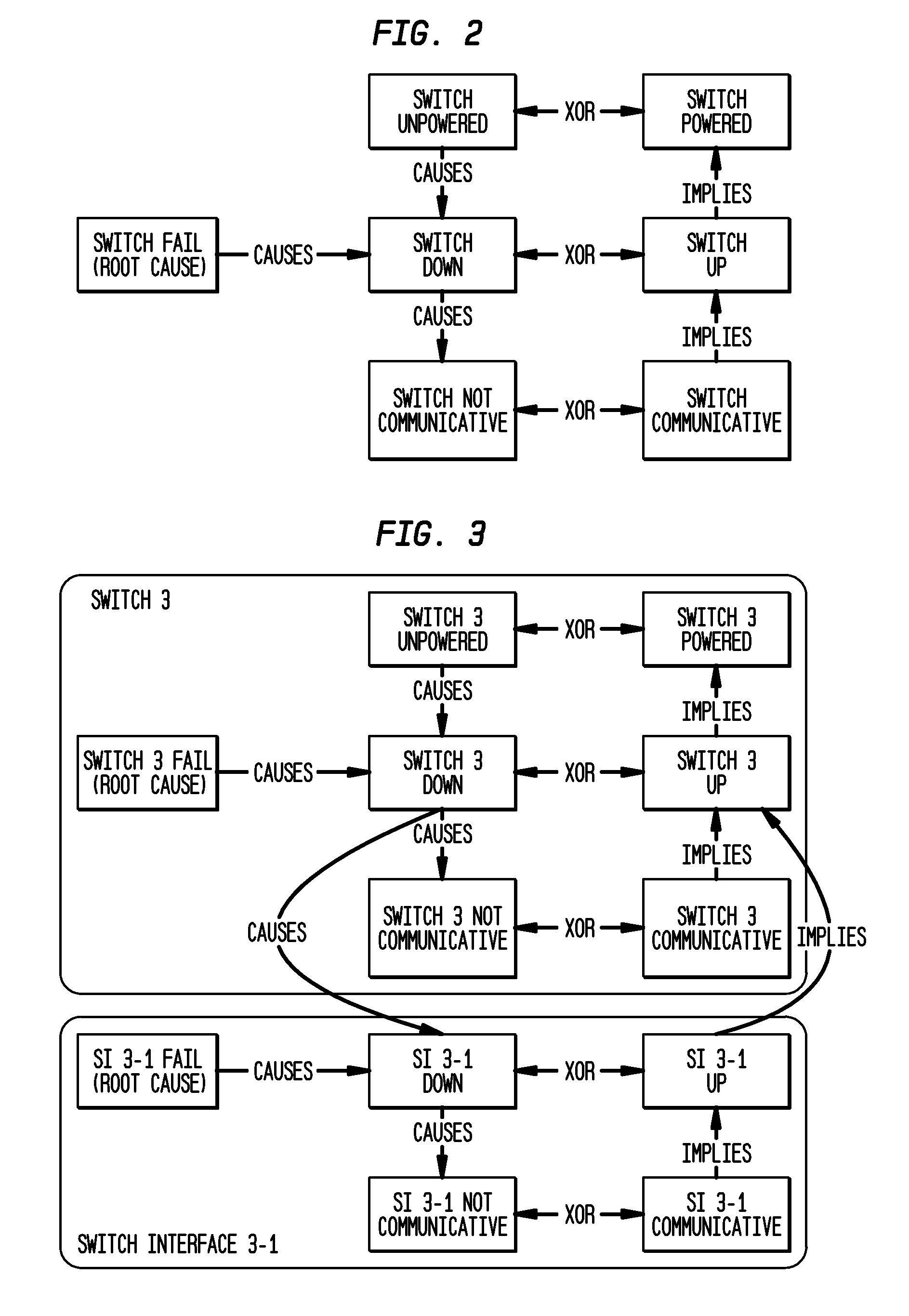
Computing diagnostic explanations of network faults from monitoring data
InactiveUS20100115341A1Digital computer detailsNon-redundant fault processingDisease causationCausality
A system and method for network fault diagnosis in a network having network elements is presented. The method comprises creating a network causality model, generating Boolean expressions from the network causality model, converting the Boolean expressions into SAT sets, receiving network monitoring results, correlating these monitoring results with the SAT sets, and enumerating all possible diagnostic explanations of potential faults, properly annotated. Creating a network causality model can comprise creating, for each network element, an element-specific causality model, stitching together all network elements using the element-specific causality models and a network topology, retrieving monitoring state and propagation information, and generating the network causality model using the stitched together network elements and the monitoring state and propagation information. Stitching together network elements can comprise adding causes and implies dependency between appropriate network elements and / or adding and connecting reachable and not-reachable states. The network causality model can comprise network element states.
Owner:TT GOVERNMENT SOLUTIONS
Rule engine-based method and system for monitoring exceptional service of bank
The invention provides a rule engine-based method and a rule engine-based system for monitoring exceptional service of bank. The method mainly comprises the followings steps: defining and describing operational risk factors of bank service flows, products and service units; determining a lost data and risk data collecting frame to analyze important lost data to determine a cause-and-effect relationship between loss events and risk factors; determining a key risk indicator (KPI); measuring a possible loss amount and a risk probability; measuring the effectiveness of the current management and control method, and making a more effective management and control scheme; deciding and implementing an efficiency and phase equilibrium-based management and control system; and effectively monitoring risk early warning indexes, risk reports aiming at senior management and the risk management and control method. Operational risks of commercial banks are comprehensively monitored, and risks are ensured to be controlled. The system is divided according to logical levels and comprises a service data layer, a data acquisition layer, a data storage layer, a risk processing layer, a risk management layer and an information presentation layer.
Owner:BEIJING YINFENG XINRONG TECH DEV
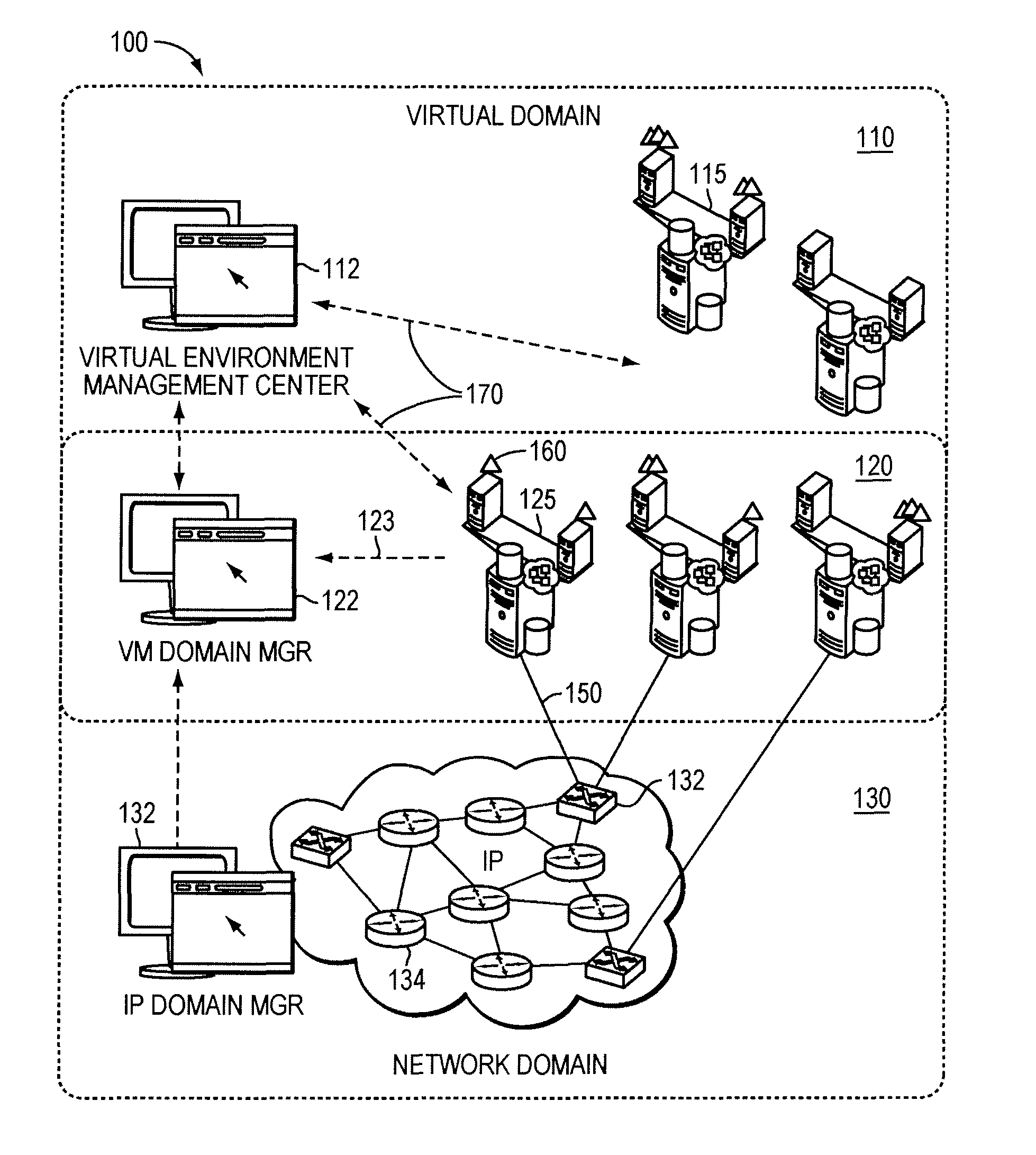
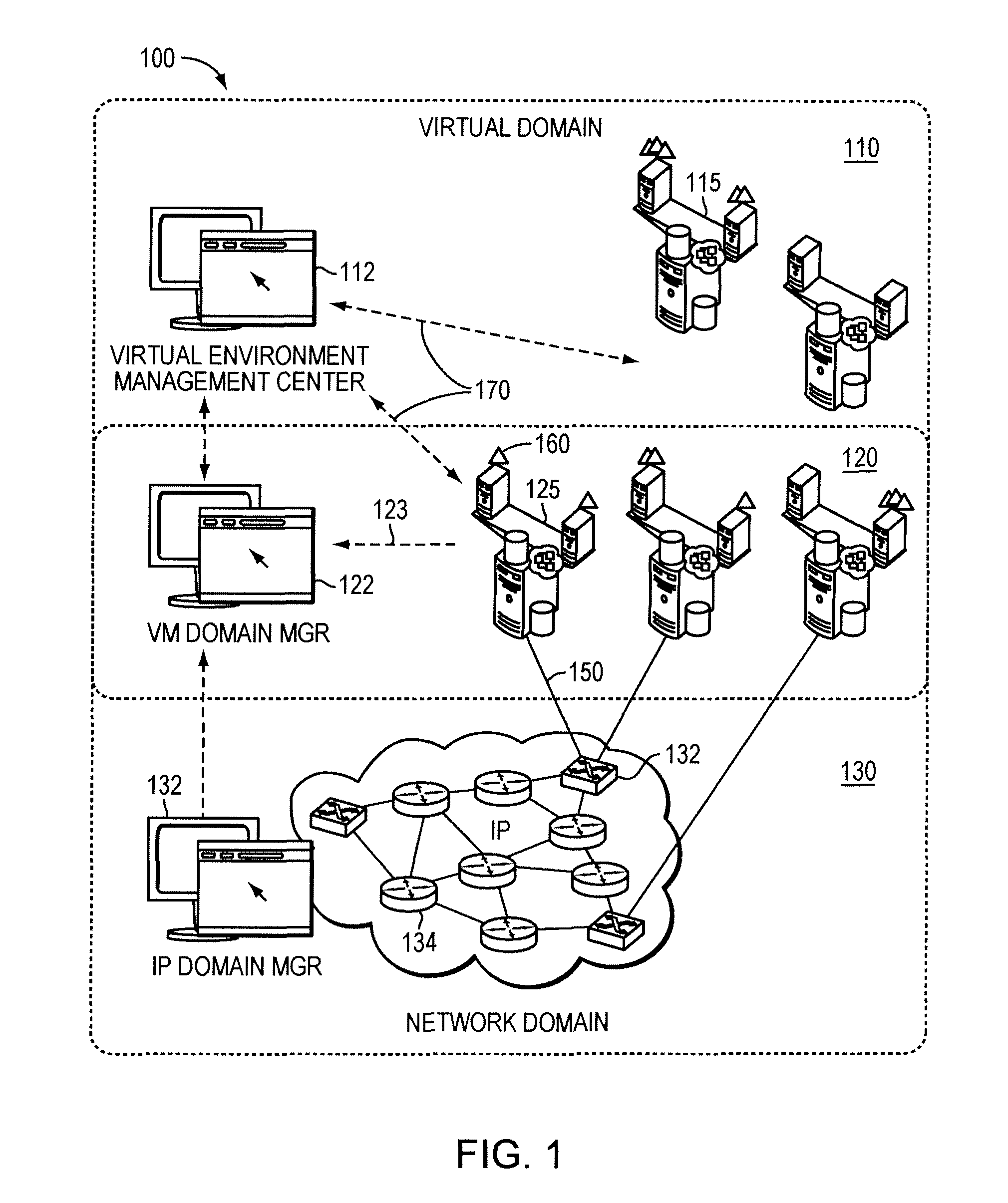
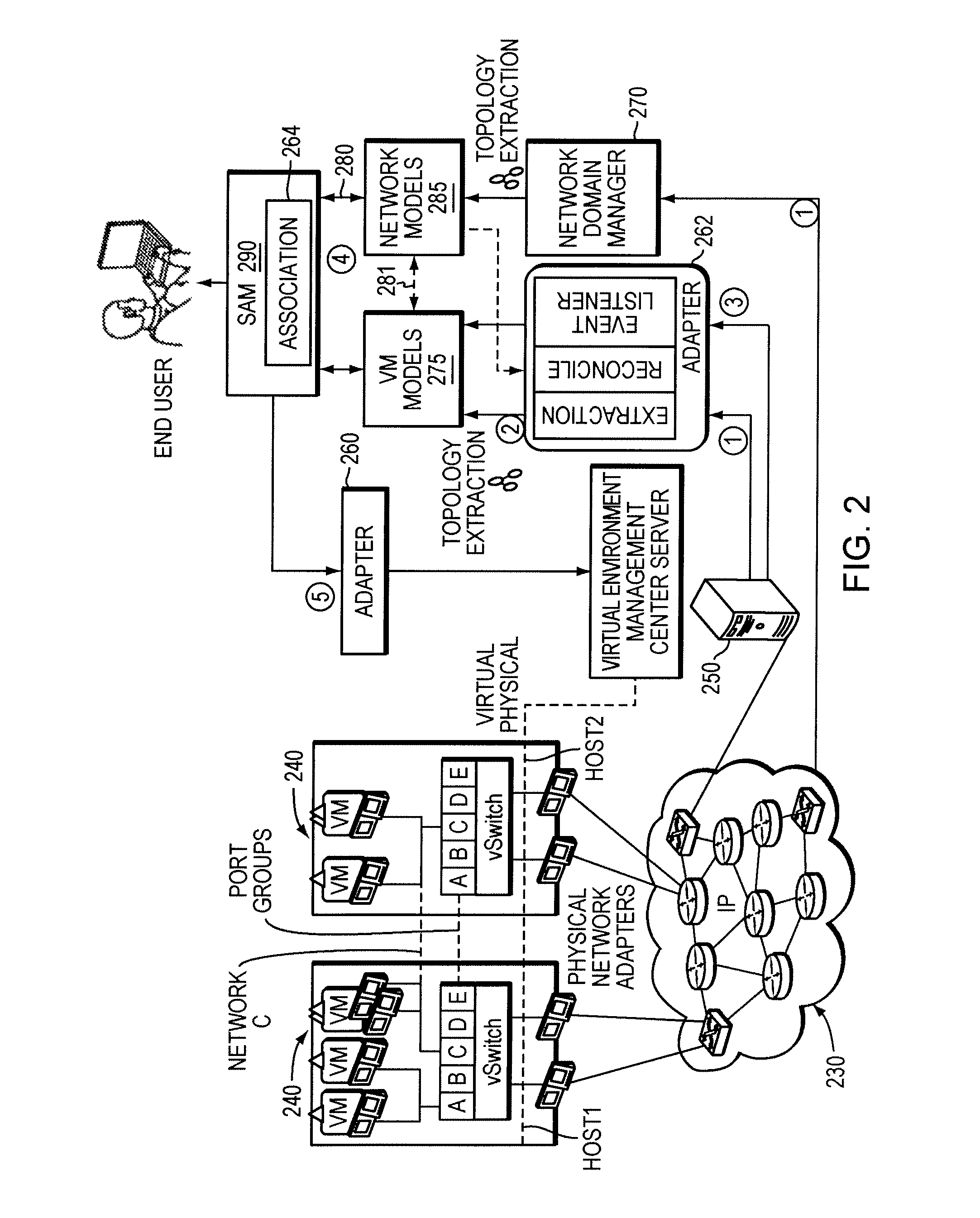
System and method for managing a virtual domain environment to enable root cause and impact analysis
ActiveUS8031634B1Improve intelligenceEasy to analyzeData switching by path configurationRoot causeCausality
A virtual domain management system is provided which associates application, physical and virtual domains to enable propagation of events, symptoms and other information across the domains. The virtual domain manager collects events and symptom information across multiple domains by correlating domain topology models. Using a causality matrix and codebook technology the virtual domain manager uses the information to perform root cause and impact analysis across domains. Information from the analysis may be fed back into the domains to enhance domain management.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
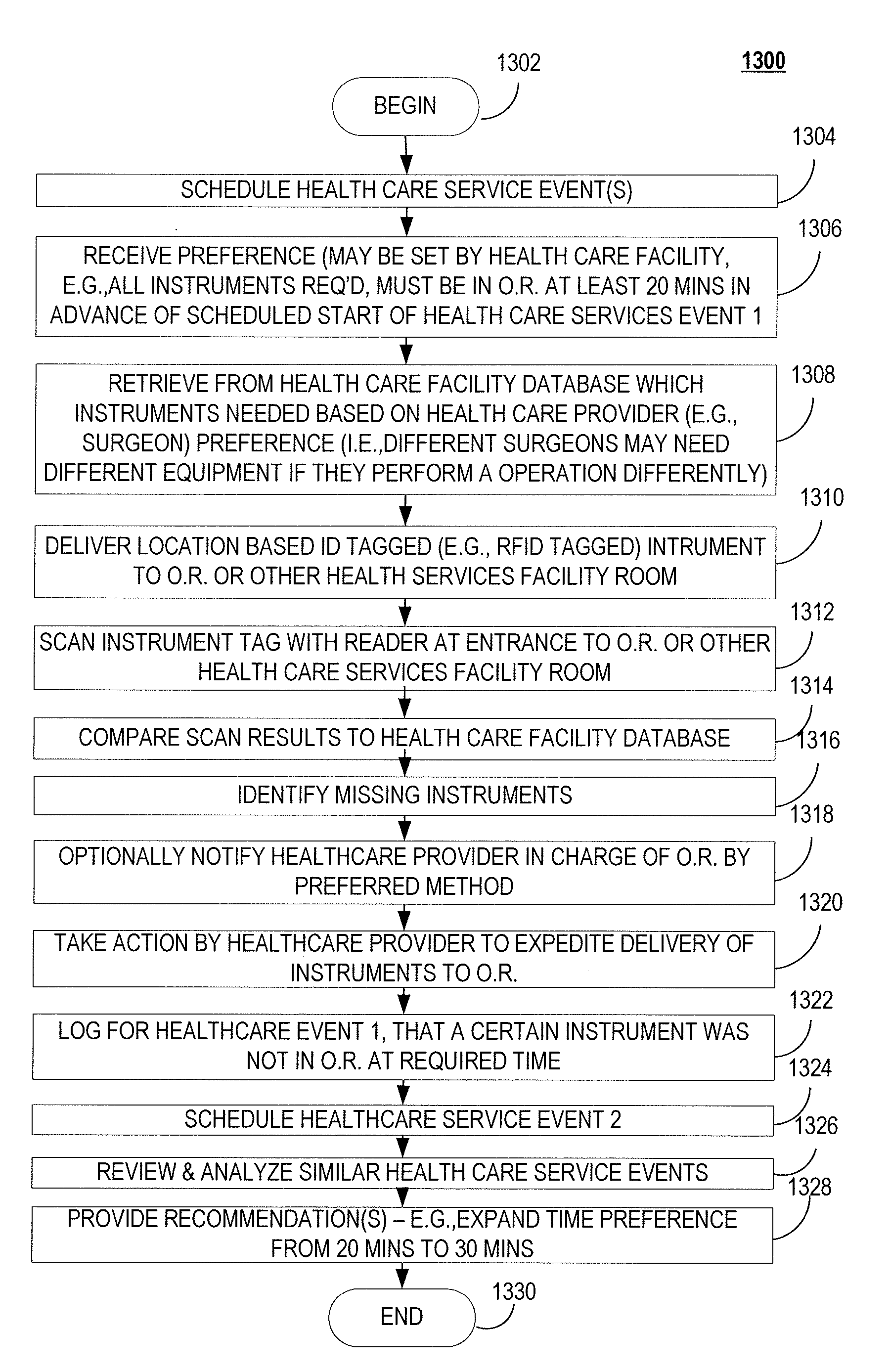
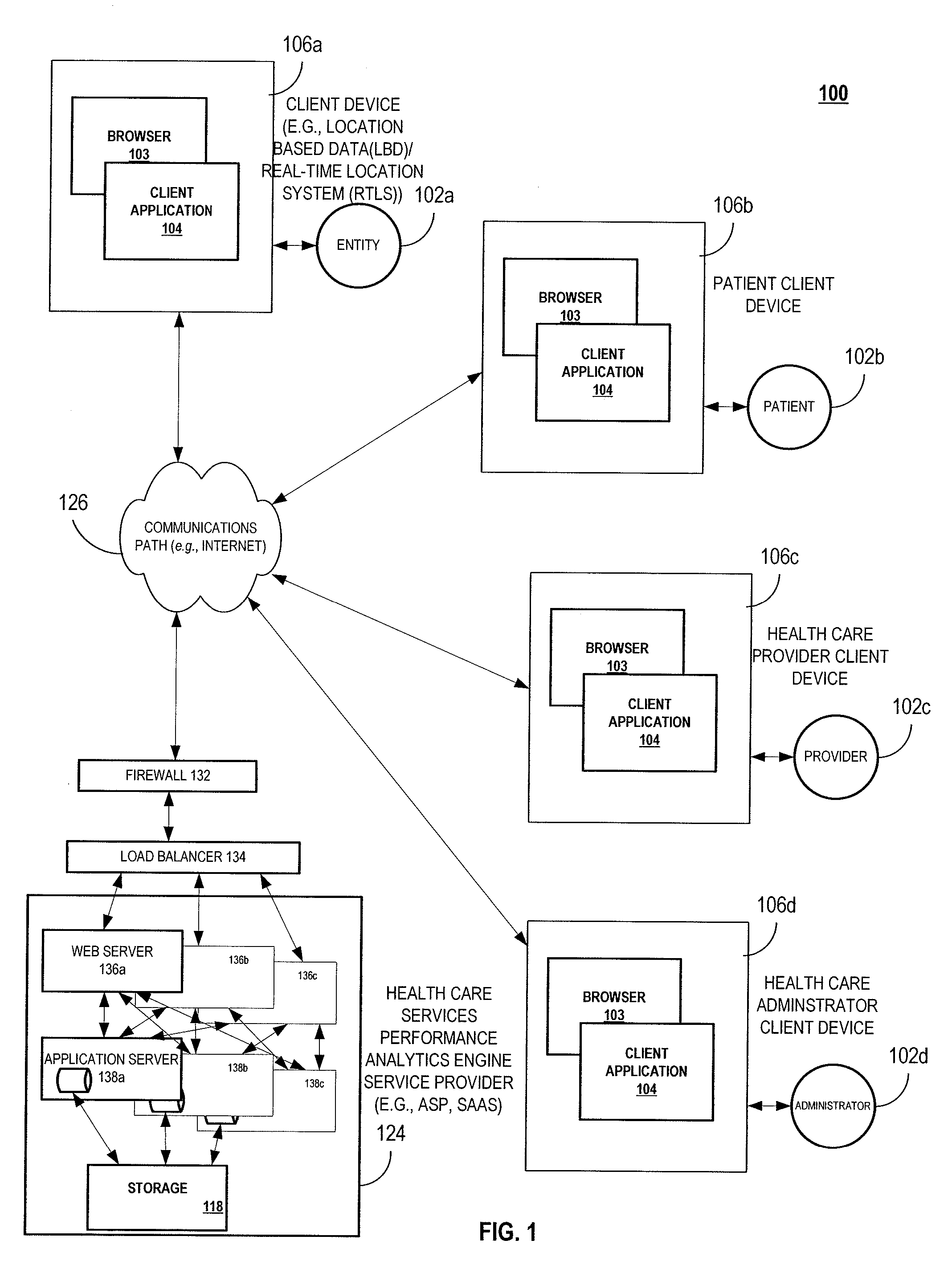
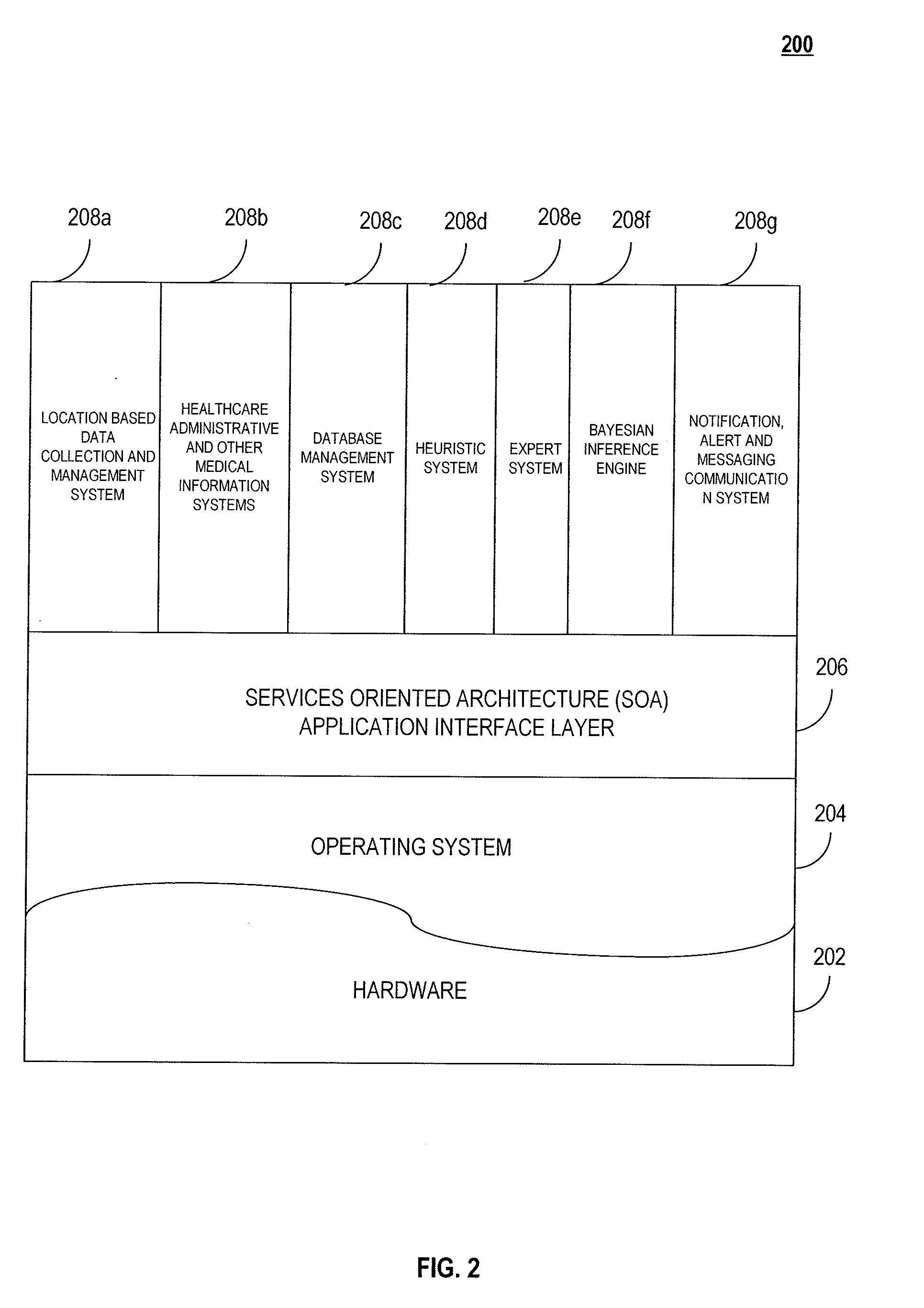
System, method and computer program product for providing health care services performance analytics
InactiveUS20090099862A1Maximize useContinually improvingData processing applicationsTherapiesCourse of actionCausality
A system, method and computer program product for improving the delivery of healthcare services may include, e.g., but not limited to, in an exemplary embodiment, a) capturing data associated with at least one health care services event, wherein said data comprises at least one aspect of said at least one health care services event; b) categorizing, into at least one category, said at least one aspect of said at least one health care services event; c) analyzing said data associated with said categorized health care services event comprising: i) determining a correlation between said at least one aspect of said data to said at least one category, and ii) determining any cause and effect relationship between said at least one aspect and said at least one category; and d) recommending at least one course of action based on said at least one aspect having said correlation and said cause and effect relationship to said at least one category, is disclosed.
Owner:HEURISTIC ANALYTICS
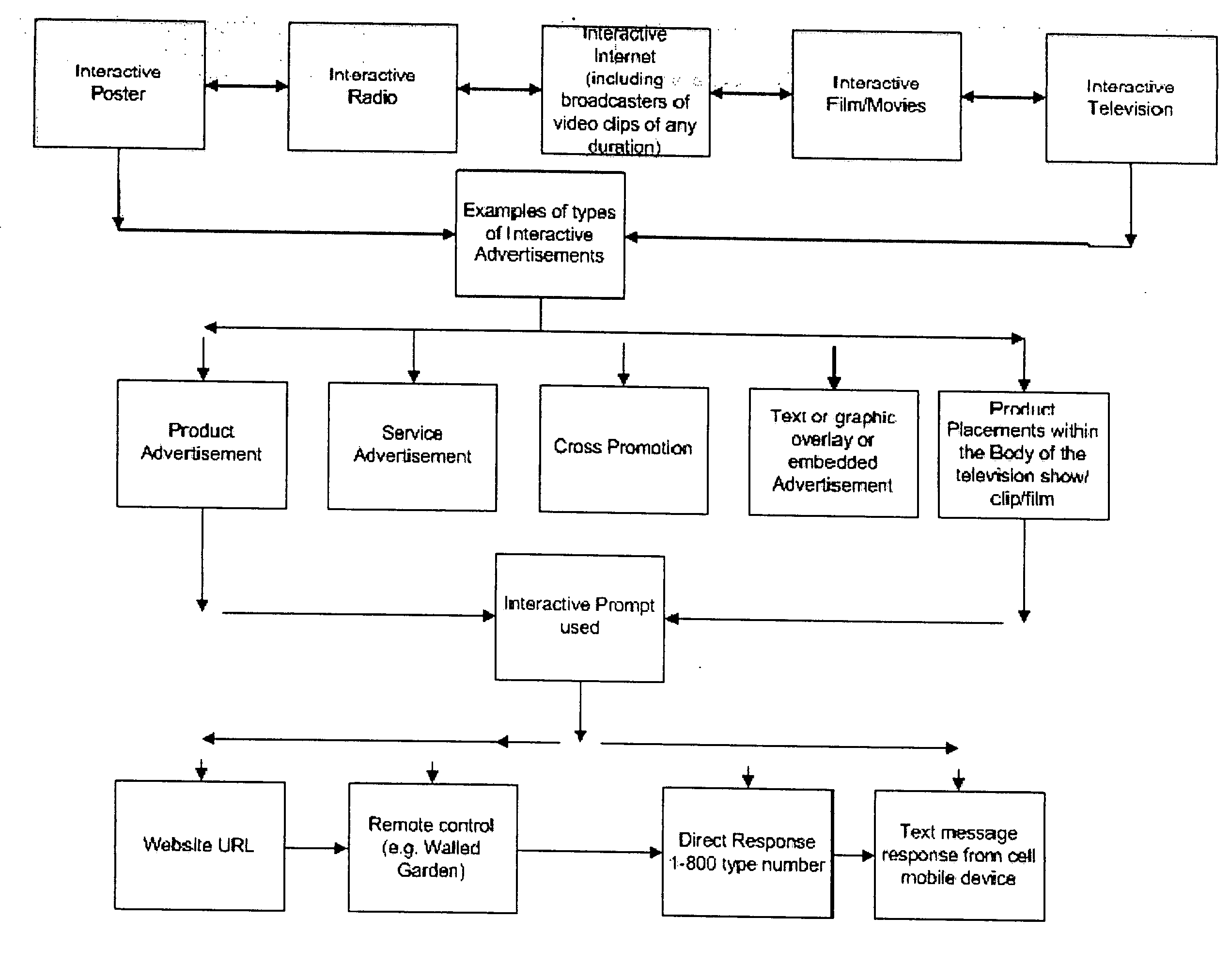
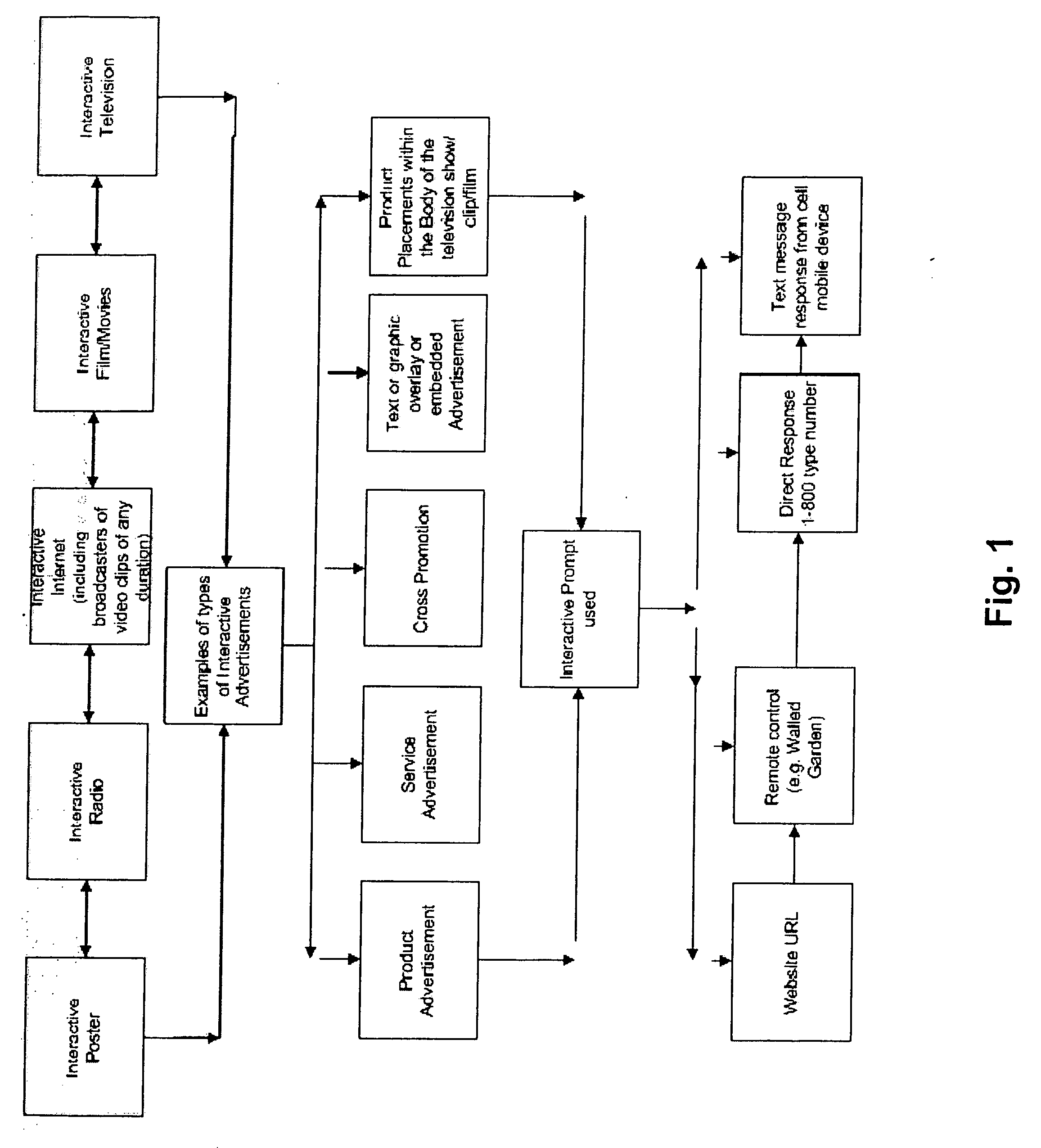
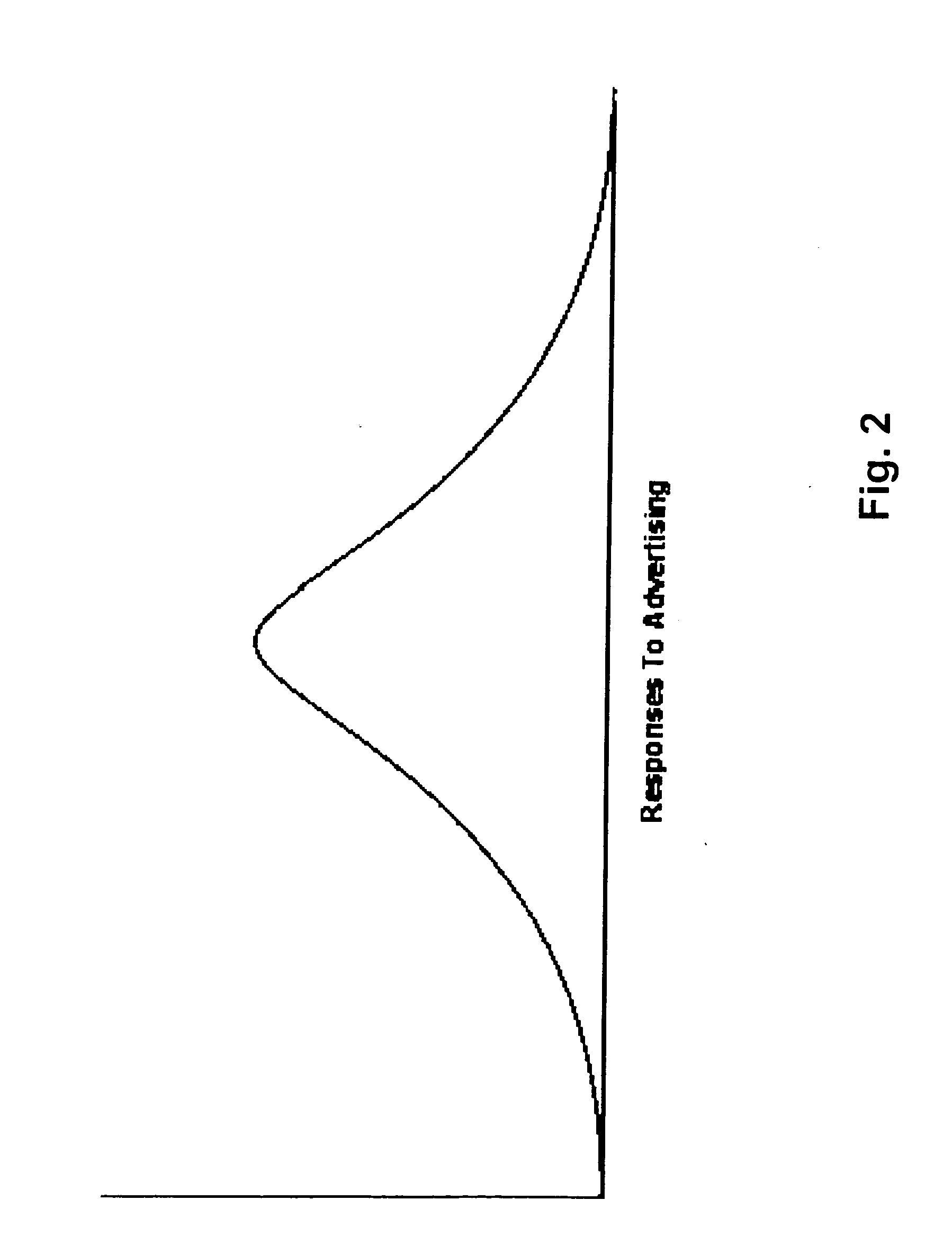
Method for determining, correlating and examining the causal relationships between media program and commercial content with response rates to advertising and product placement
ActiveUS20090210290A1Promote resultsHigh response rateDiscounts/incentivesAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsCausalitySpecific time
A method of determining correlations and causality between media program content and consumer responsiveness involves identifying and storing media and commercial program time occurrence and content information and consumer media reviewing actions which occur in connection with the media and commercial program time occurrence and content information. The information is correlated to obtain and assign responsiveness probability values corresponding to type and intensity of consumer response for each of the media and commercial program time occurrence and content information. These responsiveness probability values are then applied to a second media program to place product advertising at a specific time within specific content therein as determined by the responsiveness probability values thus facilitating creation of new ads and modification of existing ones and further, directing placement of those advertisements within any and all broadcast and Internet media programming.
Owner:ELLIOT SEBASTIAN
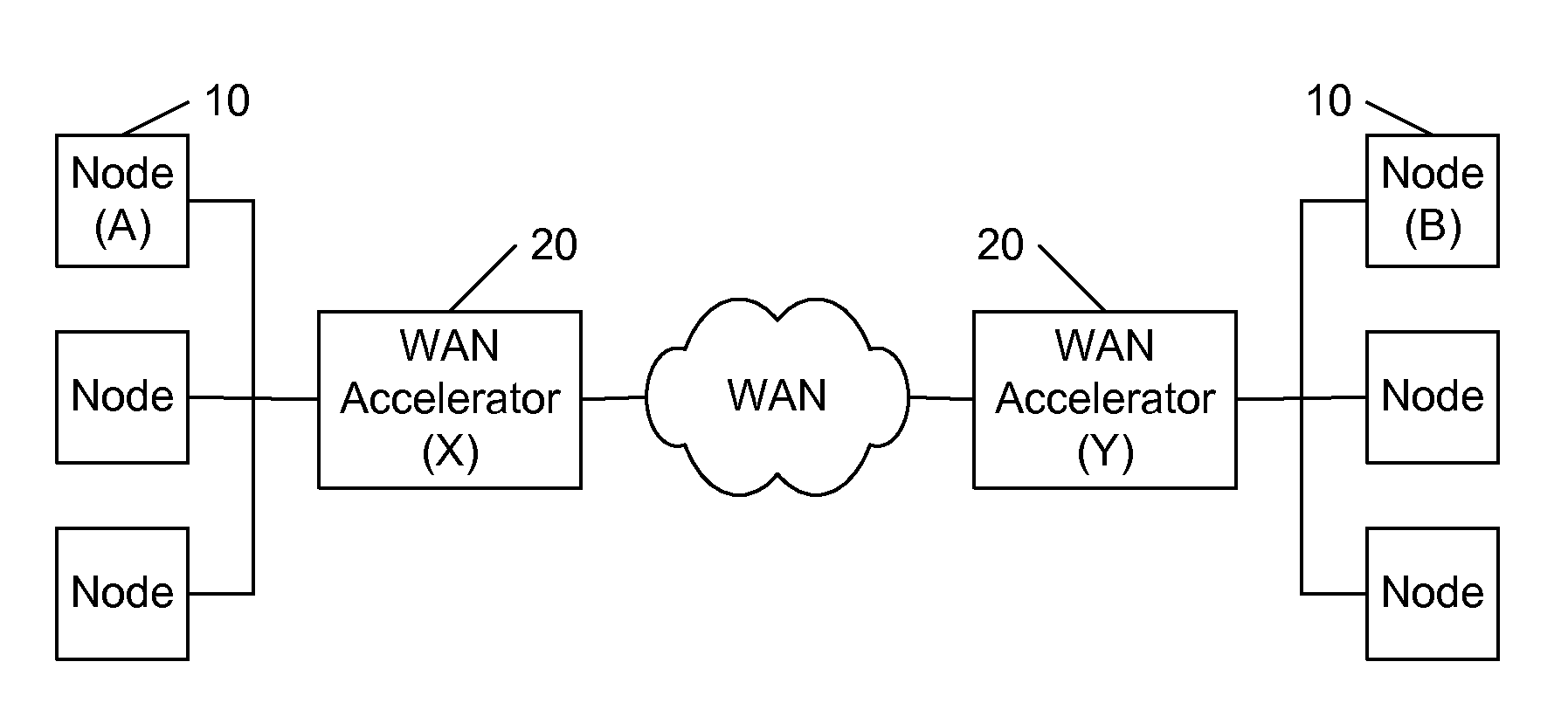
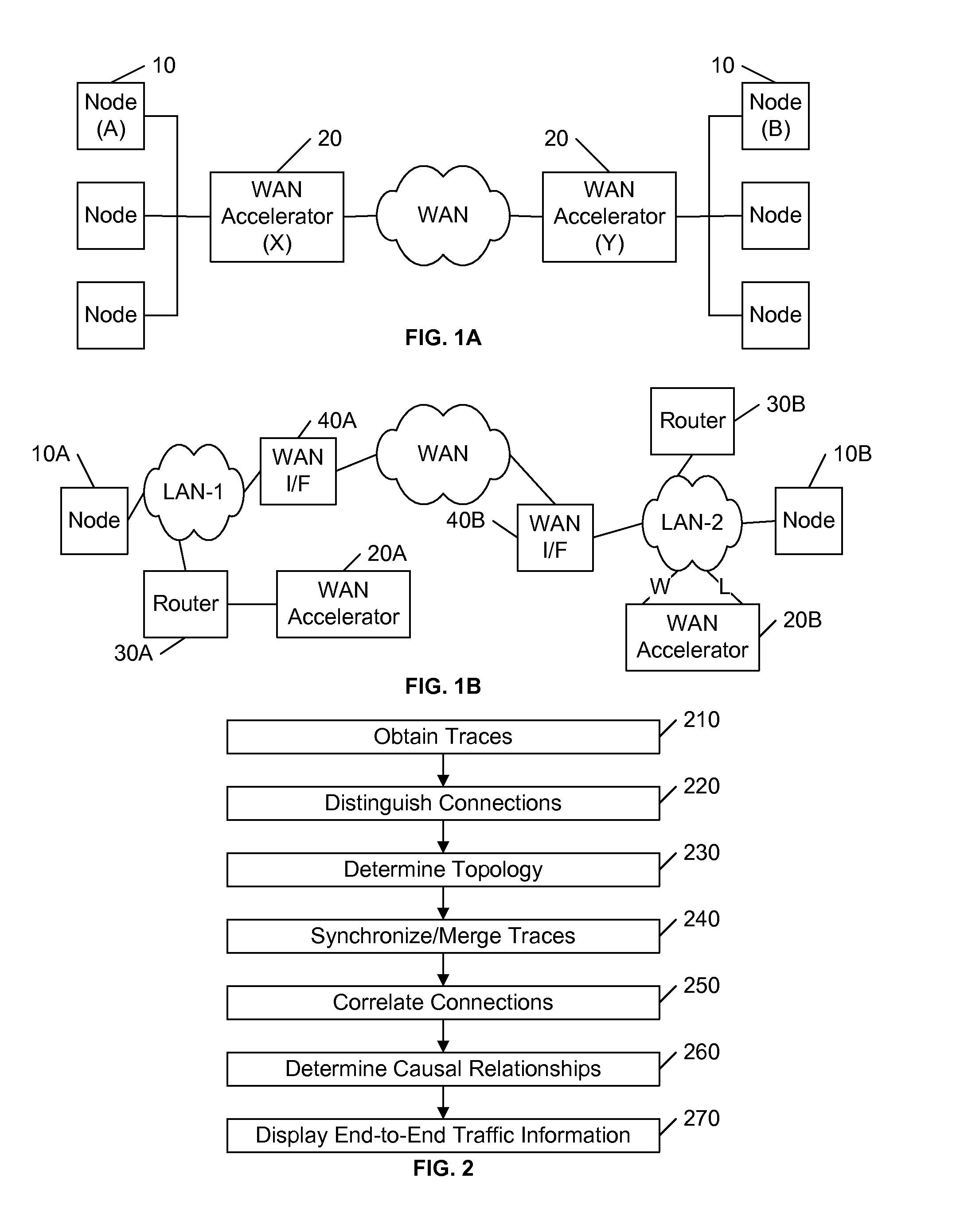
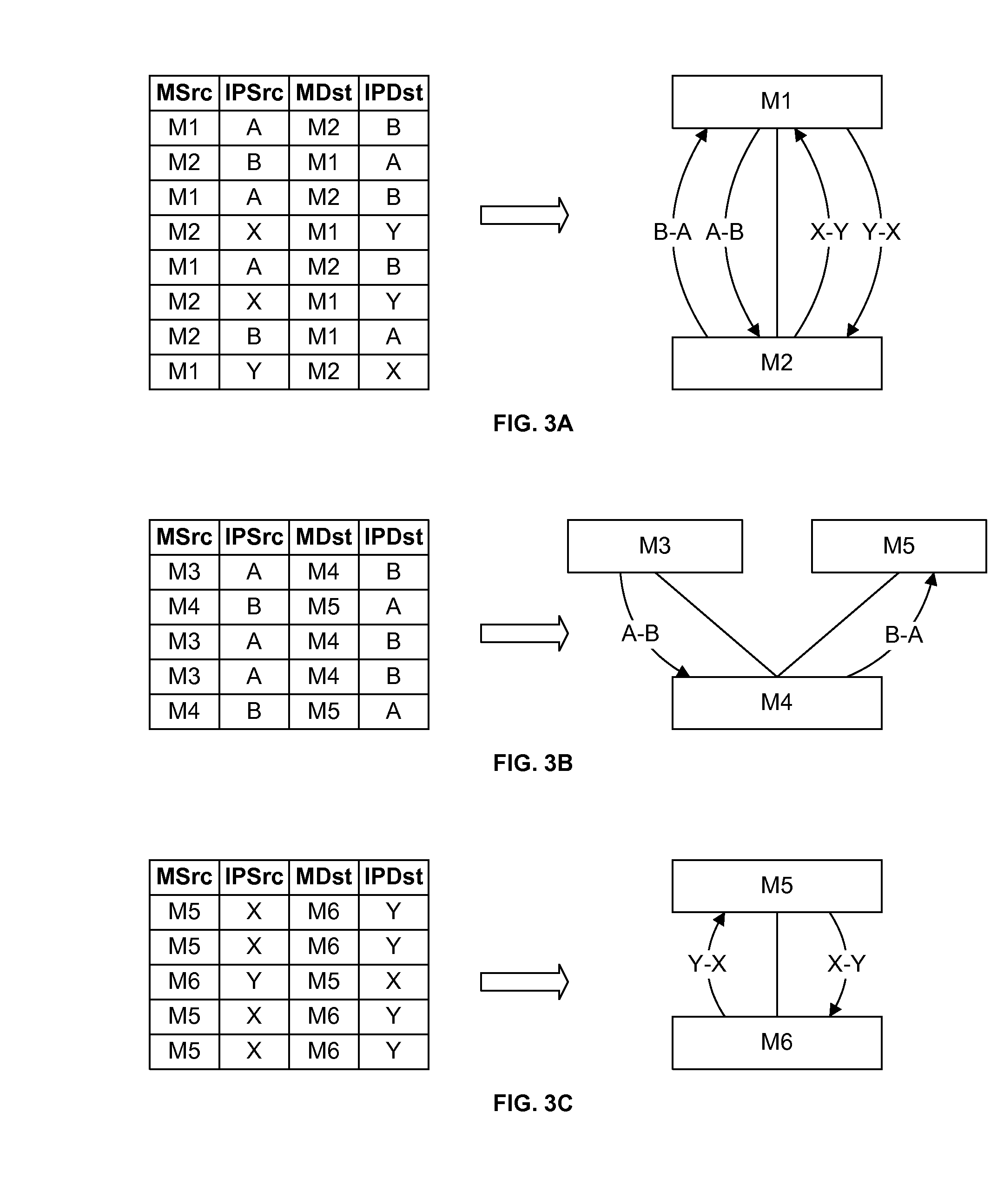
End-to-end analysis of transactions in networks with traffic-altering devices
ActiveUS20100128623A1Facilitate effective network analysisFacilitate diagnosticsError preventionTransmission systemsCausalityReal-time computing
In a network that includes intermediary nodes, such as WAN accelerators, that transform messages between nodes, an end-to-end path of the messages is determined. The determined end-to-end path is used in subsequent analyses of message traces, to identify timing and other factors related to the performance of the network relative to the propagation of these messages, including the propagation of the transformed messages. A variety of techniques are presented for determining the path of the messages, depending upon the characteristics of the collected trace data. Upon determining the message path, the traces are synchronized in time and correlations between the connections along the path are determined, including causal relationships. In a preferred embodiment, a user identifies an application process between or among particular nodes of a network, and the system provides a variety of formats for viewing statistics related to the performance of the application on the network.
Owner:RIVERBED TECH LLC
System and method for debugging computer program based on execution history
ActiveUS8935673B1Easy to debugEasy to navigateMemory loss protectionNuclear monitoringCode spaceSystem of record
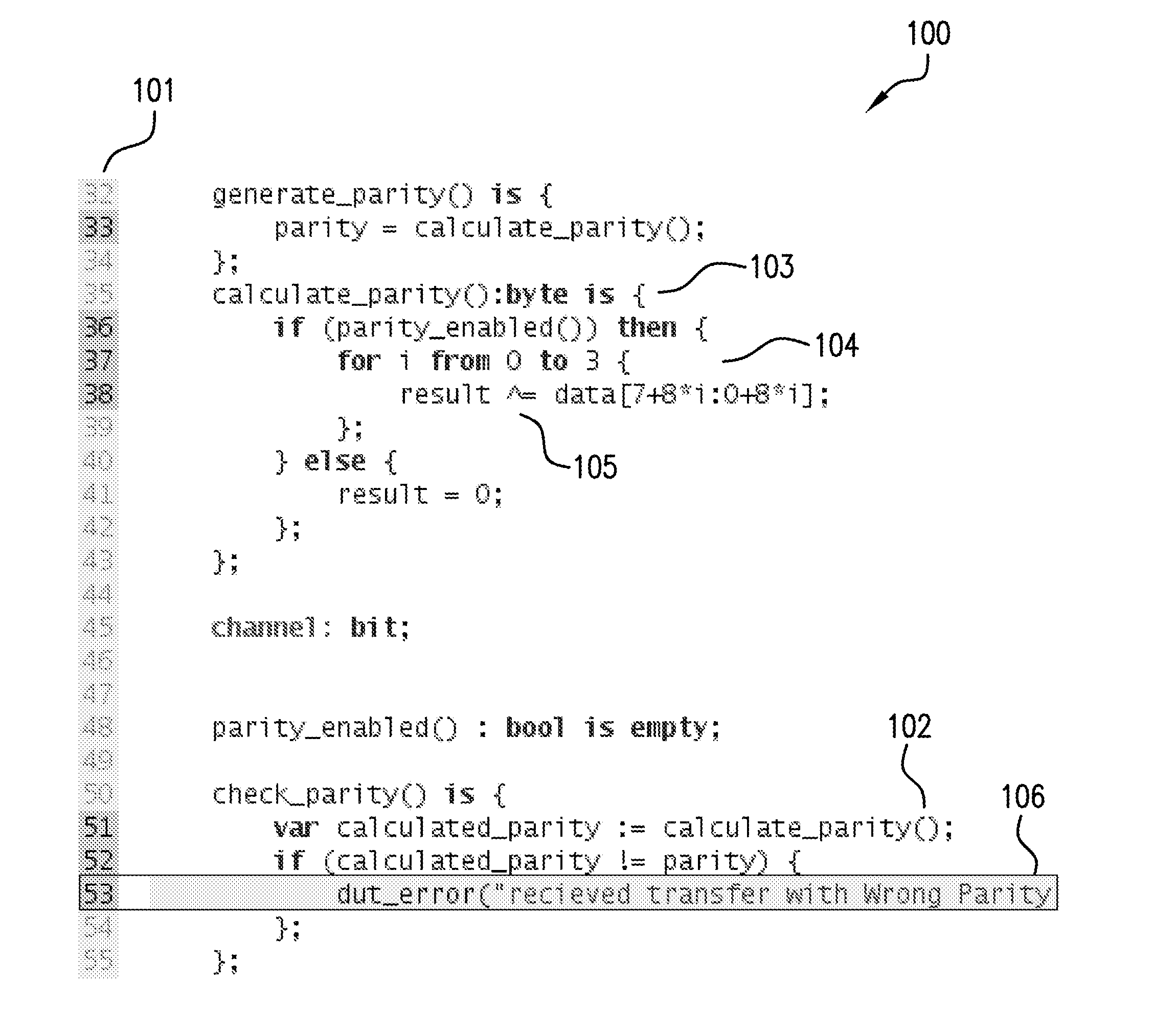
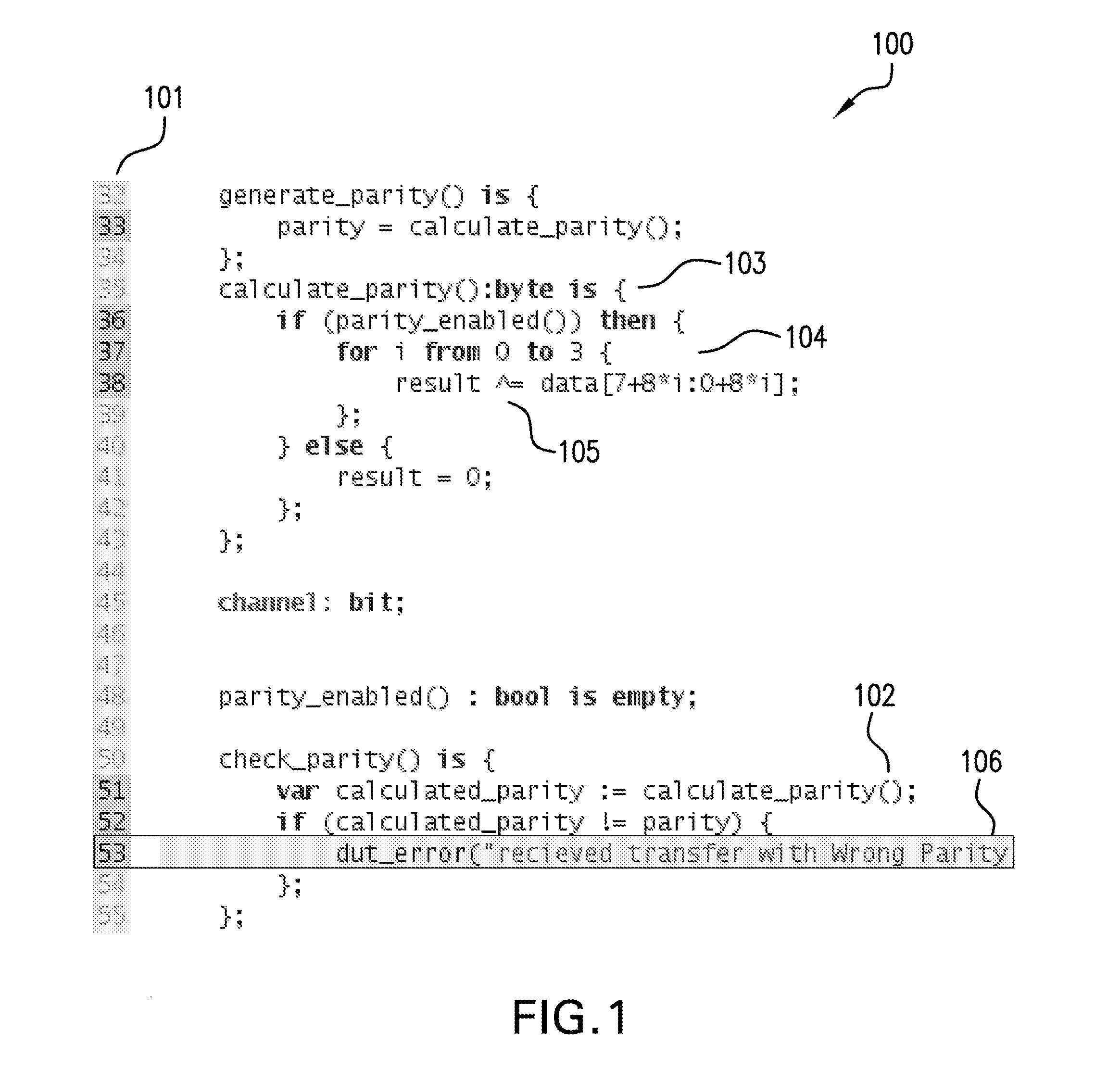
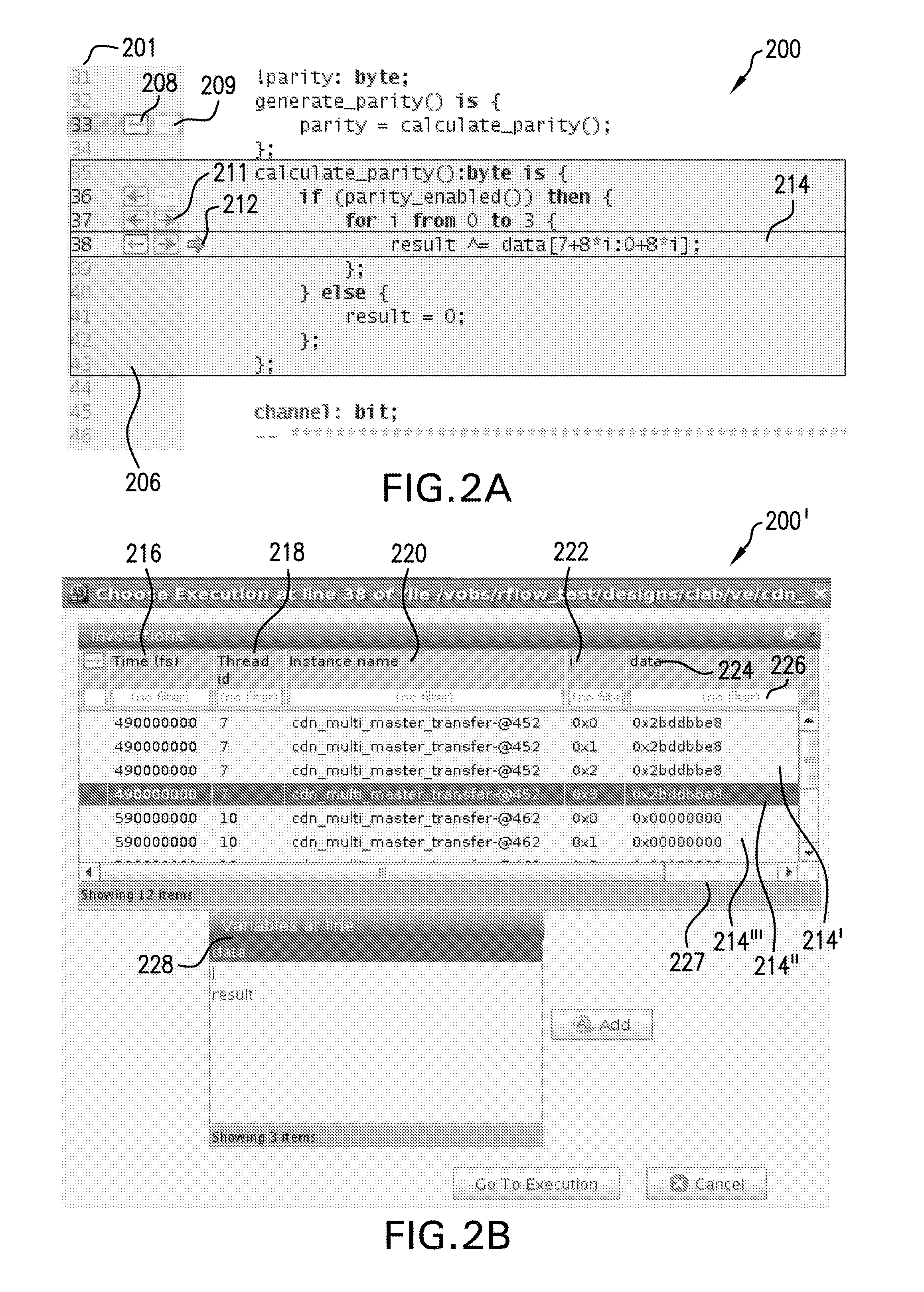
A system and method are provided for enhanced navigation along execution time and code space in a debugger to assist a user in remediating errors, streamlining, or reverse engineering a computer program and the source code thereof. Snapshots of system states are recorded, a causality tree of commands is constructed through execution of the program to be debugged, and an intelligent display of system states captured during runtime and indexed or cross-referenced by time are displayed to the user in an intelligent manner to aid the user with certain debugging tasks. Additionally, further features in assisting the user to locate a root cause of an error or unexpected value and remediate that cause are also provided.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
Method and apparatus for efficient problem resolution via incrementally constructed causality model based on history data
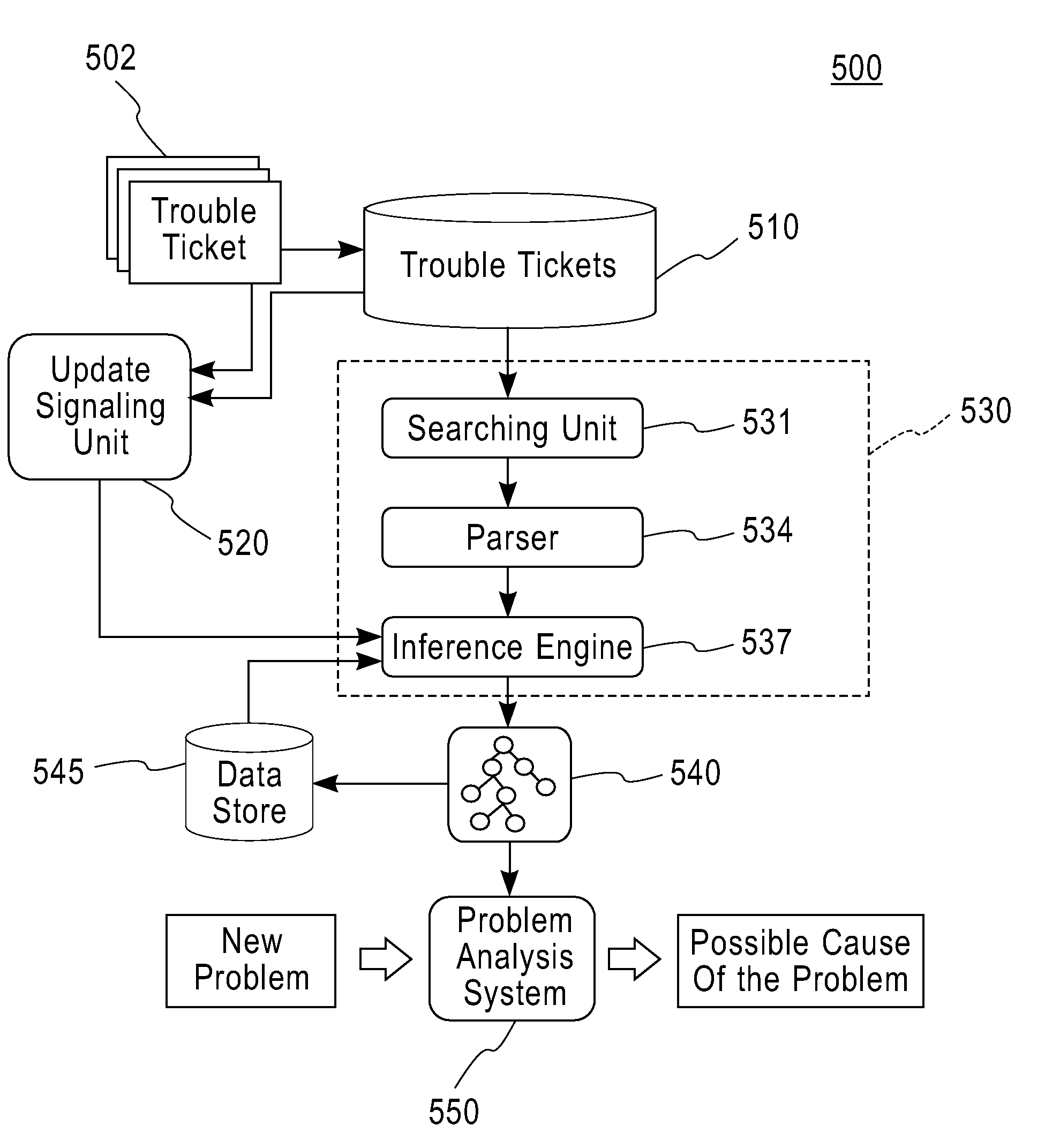
InactiveUS20090055684A1Readily apparentDetecting faulty hardware by remote testNon-redundant fault processingSystems managementDisease causation
A system for problem resolution in network and systems management includes a database of trouble ticket data including information fields for checked components and affected components, an automated model builder system that processes the trouble ticket data to construct a causality model to represent causality information between system components identified in the checked component and affected component fields of the trouble ticket data, and an automated problem analysis system that receives information indicative of a problem event and determines a cause of the problem event using the causality model.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and apparatus for constructing, using and reusing components and structures of an artifical neural network
A method and apparatus for constructing a neuroscience-inspired artificial neural network (NIDA) or a dynamic adaptive neural network array (DANNA) or combinations of substructures thereof comprises one of constructing a substructure of an artificial neural network for performing a subtask of the task of the artificial neural network or extracting a useful substructure based on one of activity, causality path, behavior and inputs and outputs. The method includes identifying useful substructures in artificial neural networks that may be either successful at performing a subtask or unsuccessful at performing a subtask. Successful substructures may be implanted in an artificial neural network and unsuccessful substructures may be extracted from the artificial neural network for performing the task. The method and apparatus supports constructing, using and reusing components and structures of a neuroscience-inspired artificial neural network dynamic architecture in software and a dynamic adaptive neural network array.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
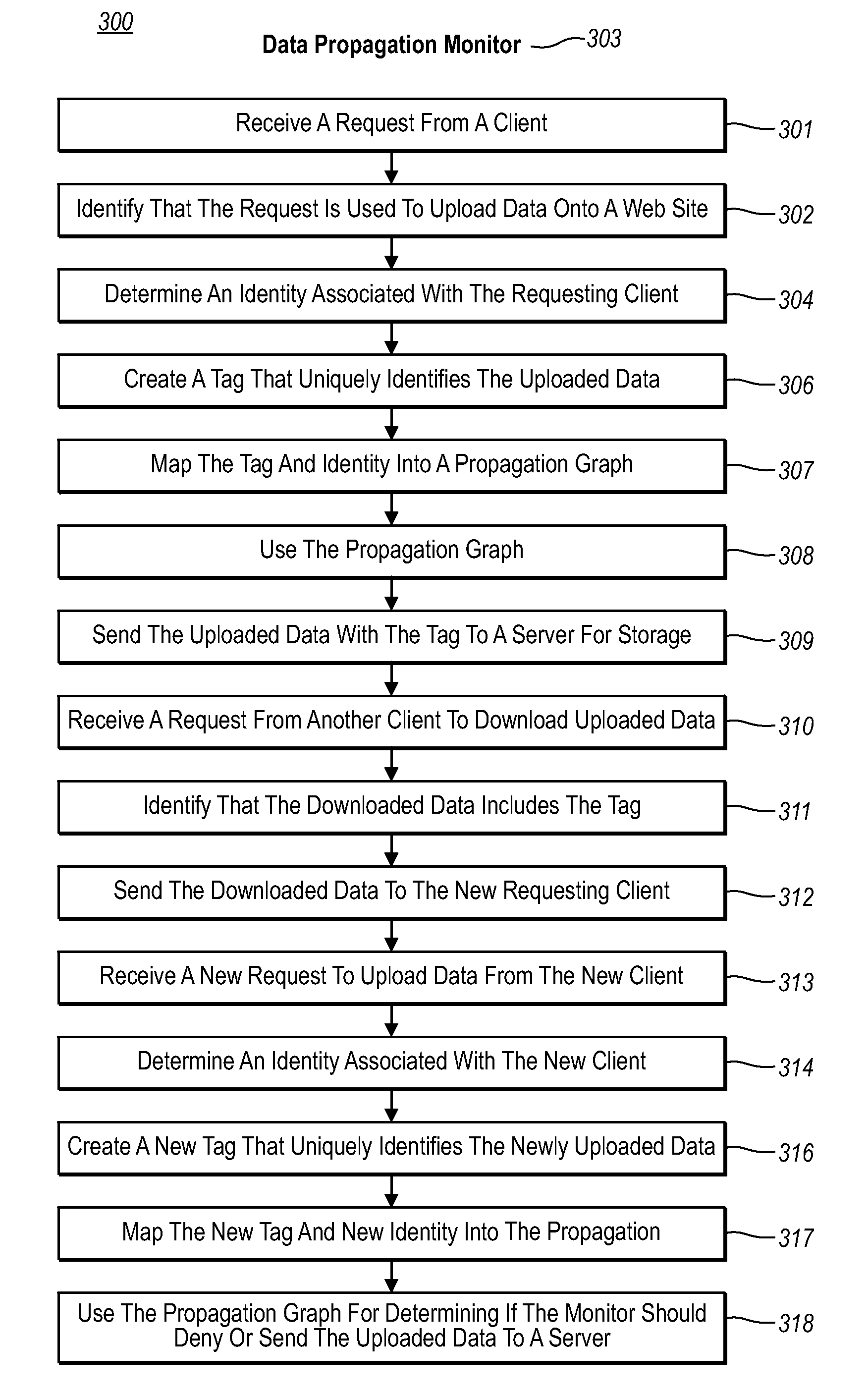
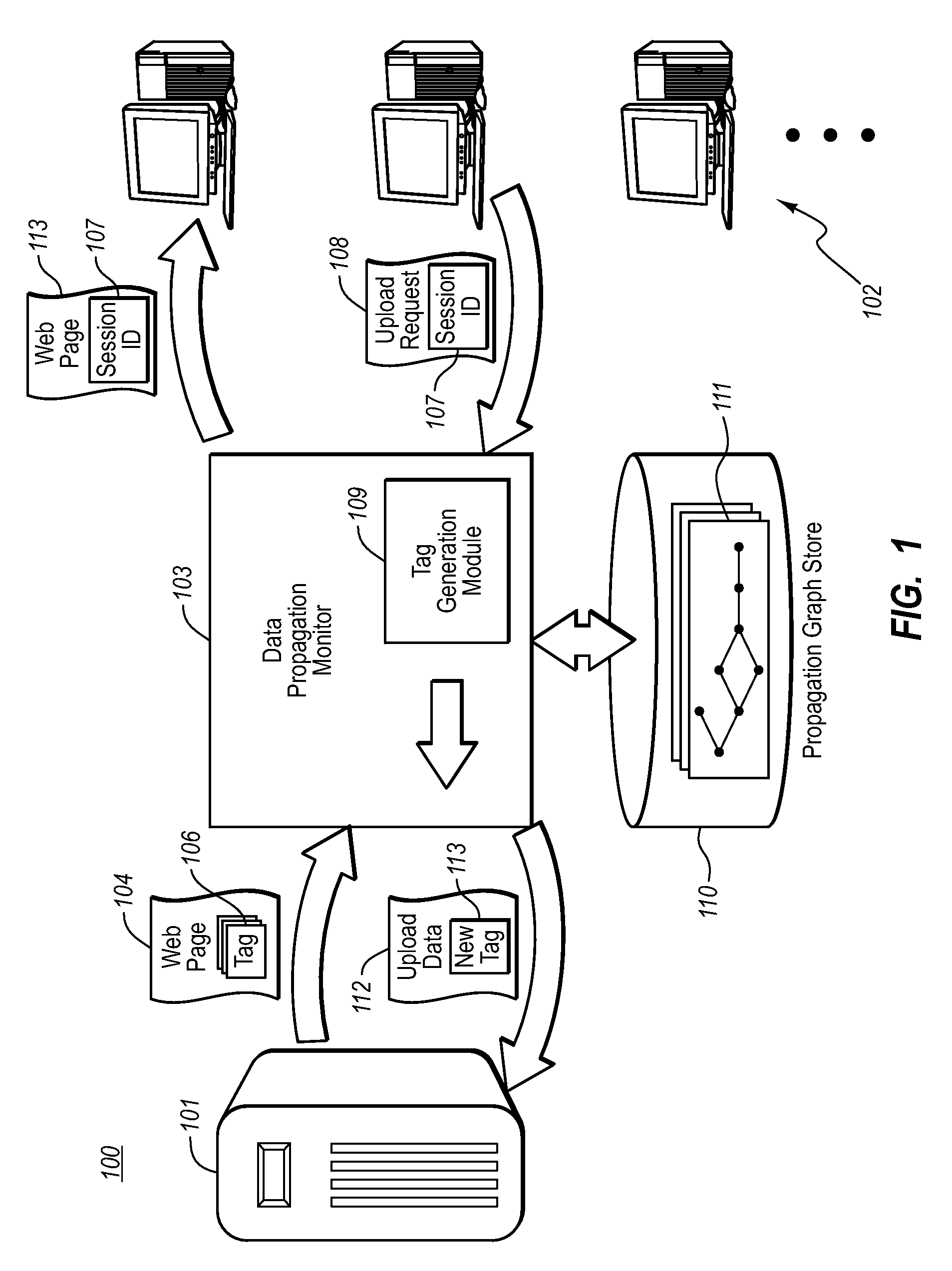
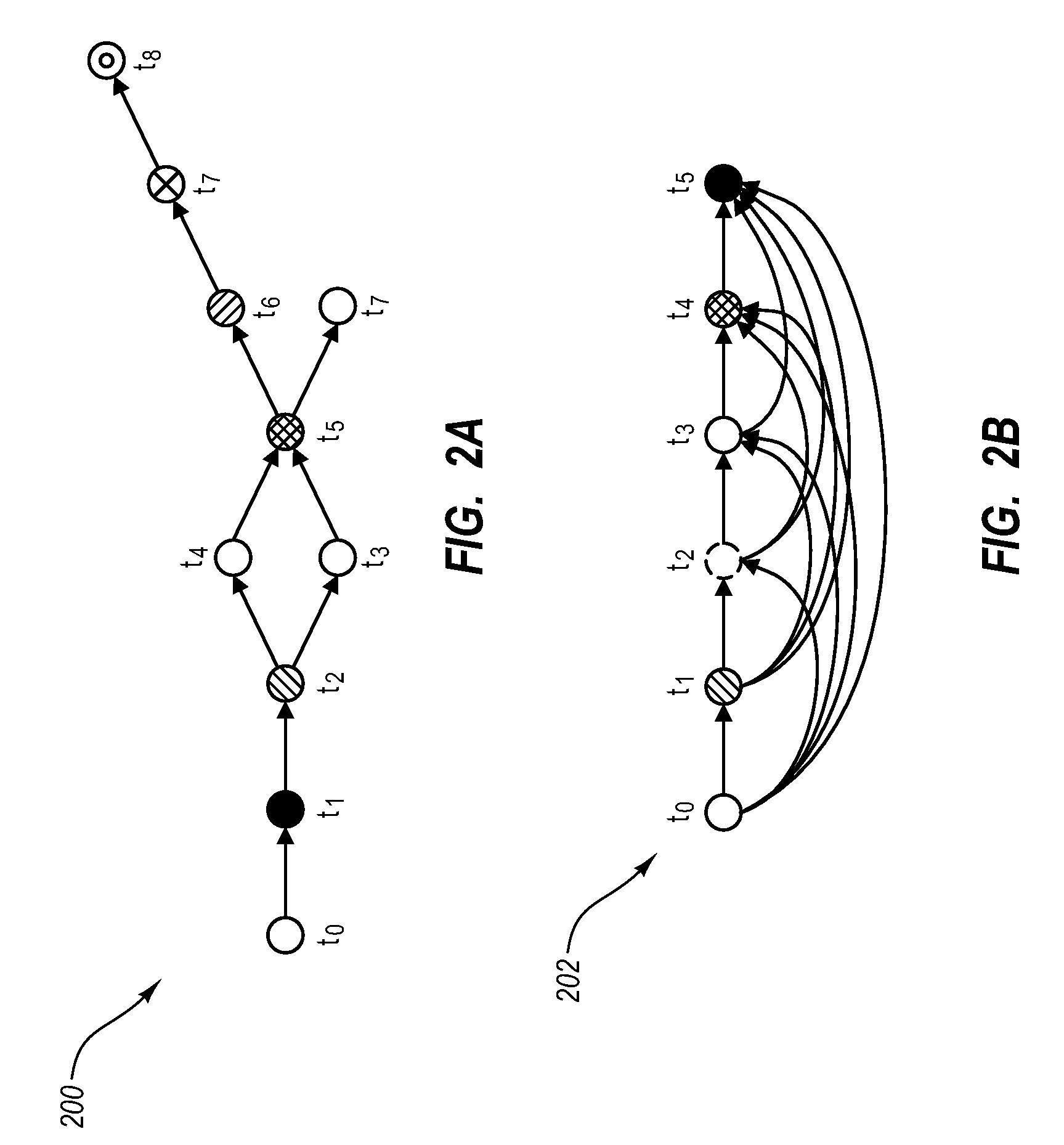
Detecting data propagation in a distributed system
Embodiments gather historical information about data propagation by monitoring requests to and replies from a server. When a request is received from a client system to upload code onto a web site, a user identity associated with the client system is determined and a tag that uniquely identifies the uploaded data is created and mapped with the user identity into a propagation graph. The propagation graph includes nodes and edges associated with a number of client systems that made similar requests such that each node of the propagation graph corresponds to both a tag and user identity of a client system and edges within the propagation graph represent causality links between the nodes. The propagation graph can then be used for finding long propagation chains, which can be useful for detecting worm-like propagation activity.
Owner:ZHIGU HLDG
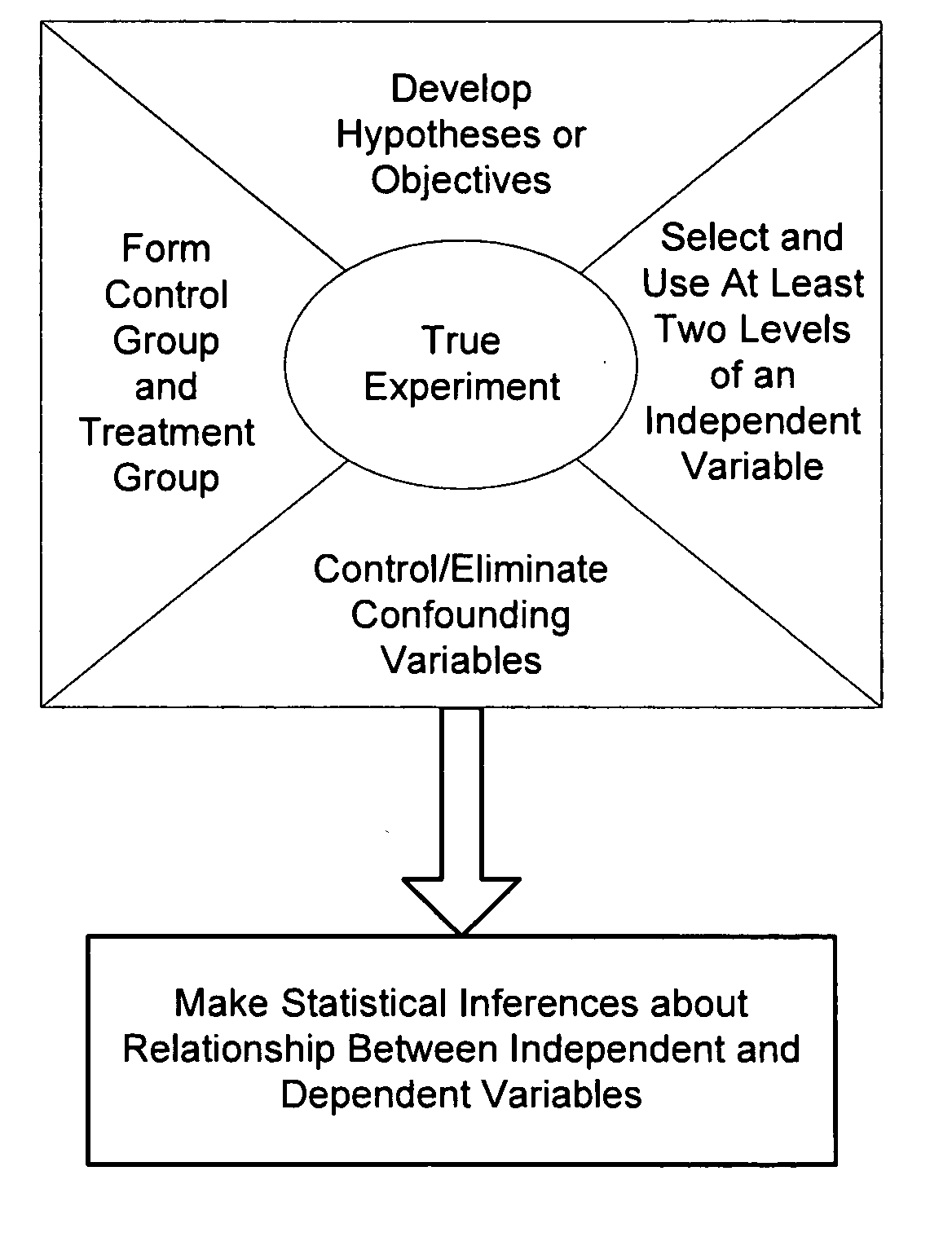
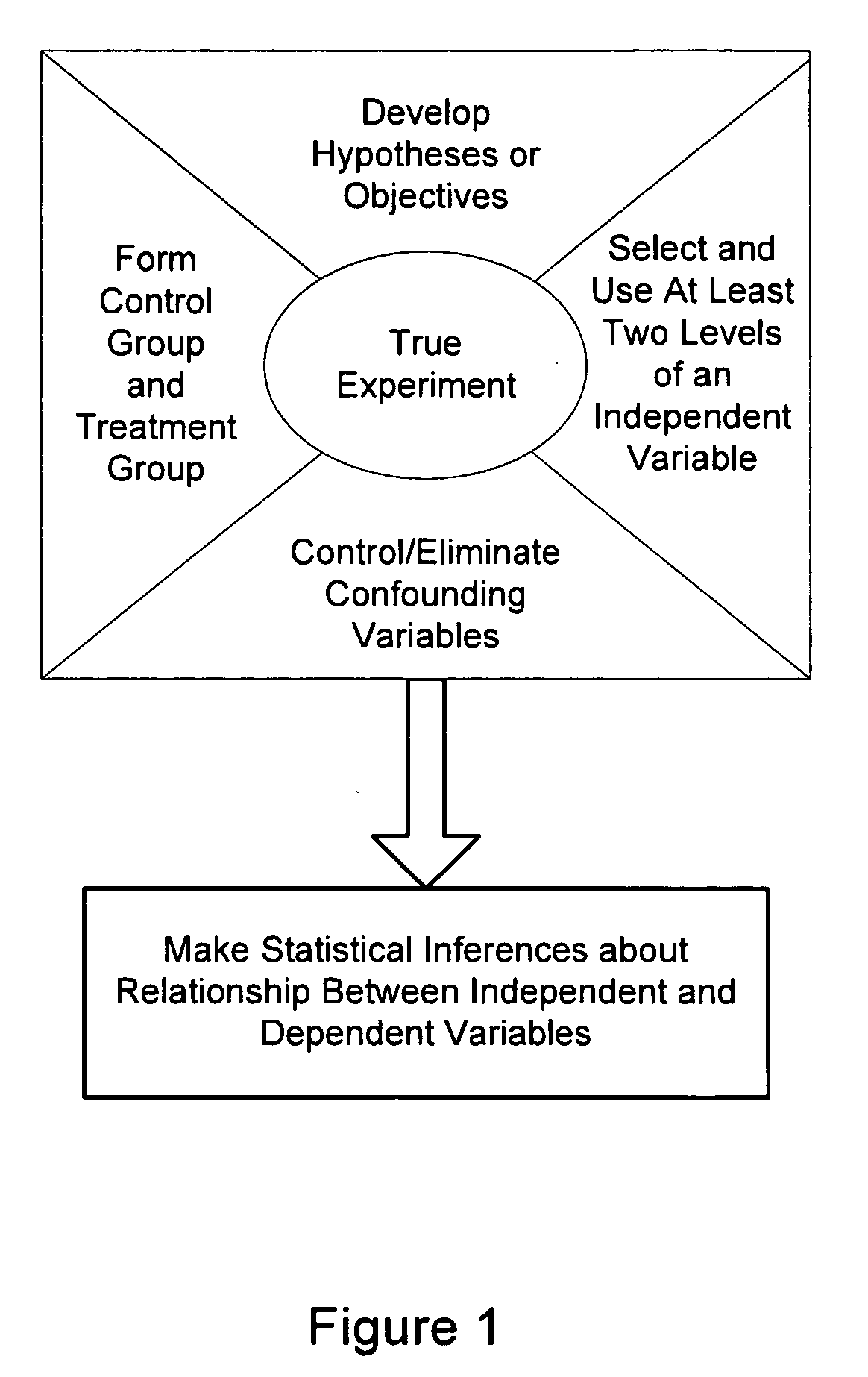
Systems and methods for designing experiments
InactiveUS20070156382A1Reduce the impactReduce impactNatural language data processingProgram controlRandomizationCausality
Methods and systems for designing an experiment using a computer to determine whether the experiment is a true experiment are described. These approaches allow a user who is unsophisticated in the complexities of true experimental design to design and deploy an experiment that produces substantially confound-free results and can be used to determine and quantify any causal relationship between independent and dependent variables. The computer may select one or more independent and / or dependent variables of the experiment or may assist the user in selection of independent and / or dependent variables. Formation of control and treatment groups, randomization and / or blocking to reduce the effects of confounding variables may be performed by the computer with or without input from the user.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Data mining by retrieving causally-related documents not individually satisfying search criteria used
ActiveUS7386439B1Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalDocument preparationElectronic information
This patent describes a method and apparatus to automatically and accurately winnow down arbitrarily large amounts of electronic information created by a particular population of actors to only those subsets of particular interest by having a causal relationship, even when retrieved documents containing this information do not individually satisfy the search criteria used. An actor in this context is defined as any entity, single or aggregate, capable of creating, distributing, modifying, or receiving digital information. Once identified, this subset of information may, for example, be processed, analyzed, redacted, or destroyed, depending on the context of the system's use.
Owner:ERNST & YOUNG U S LLP
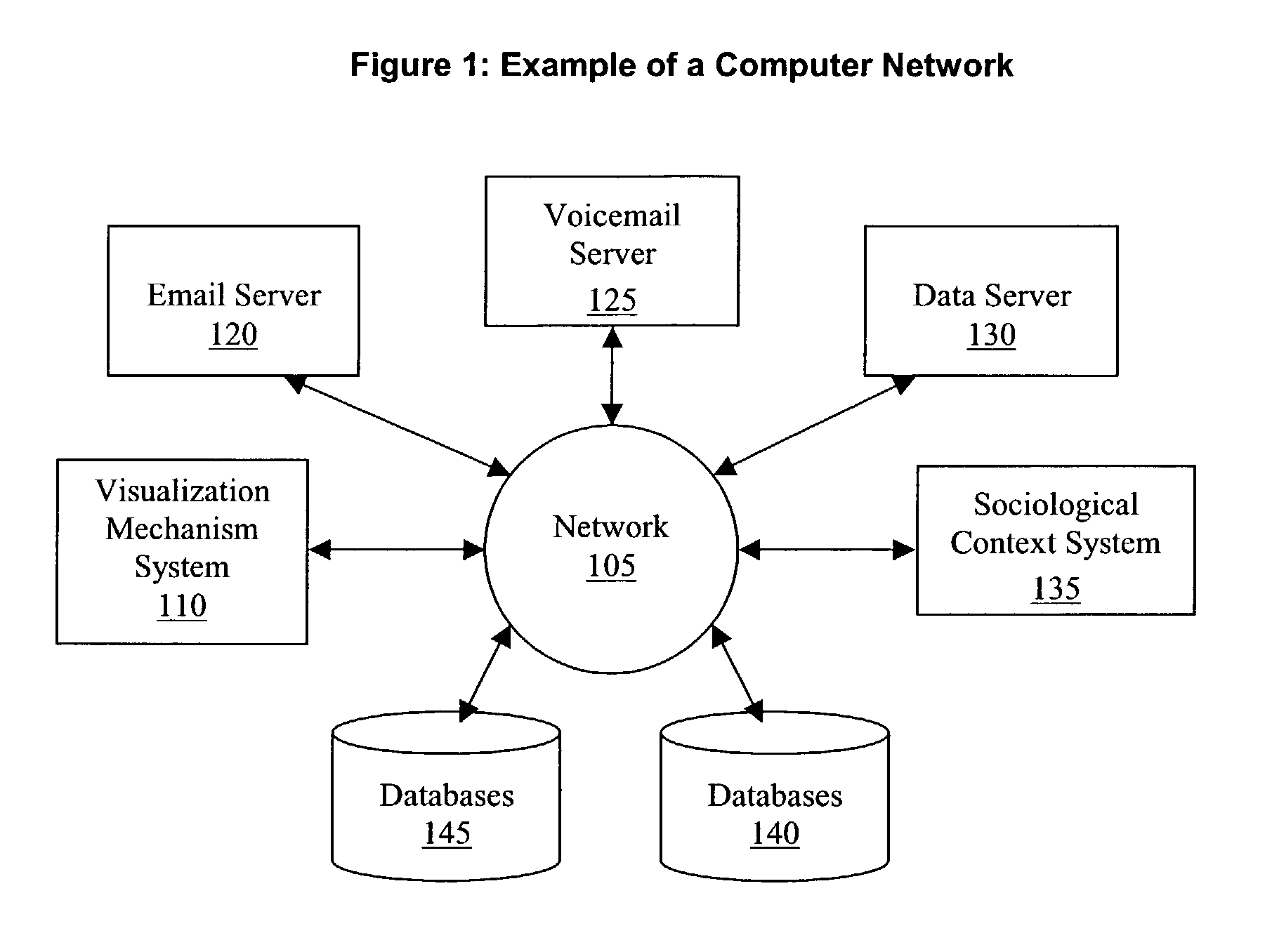
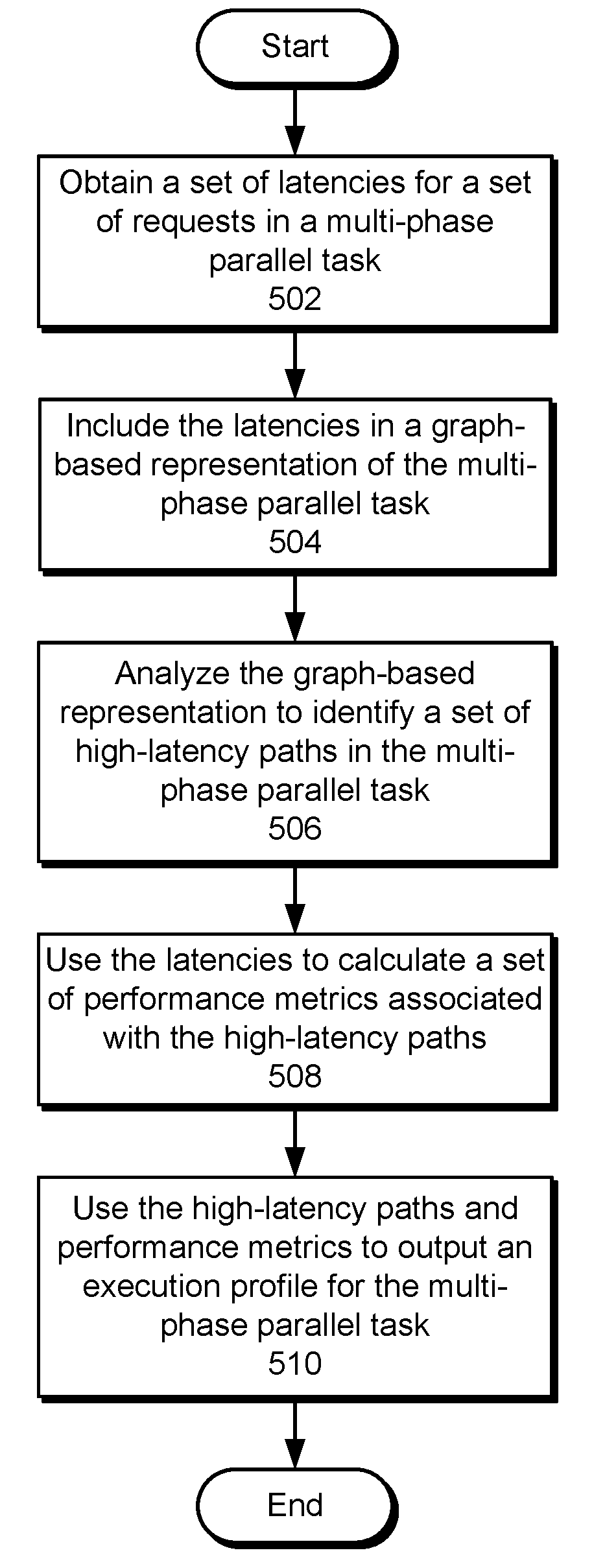
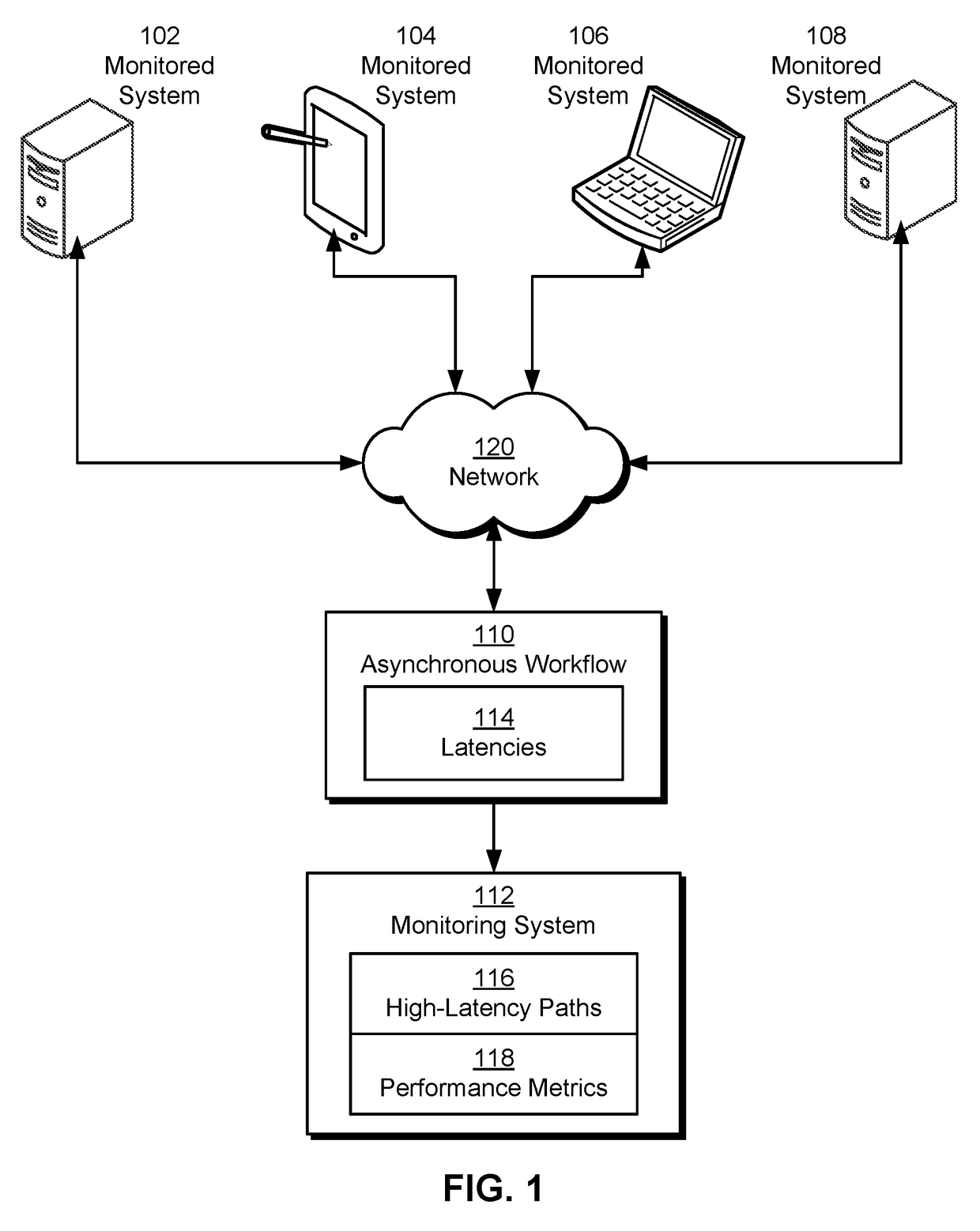
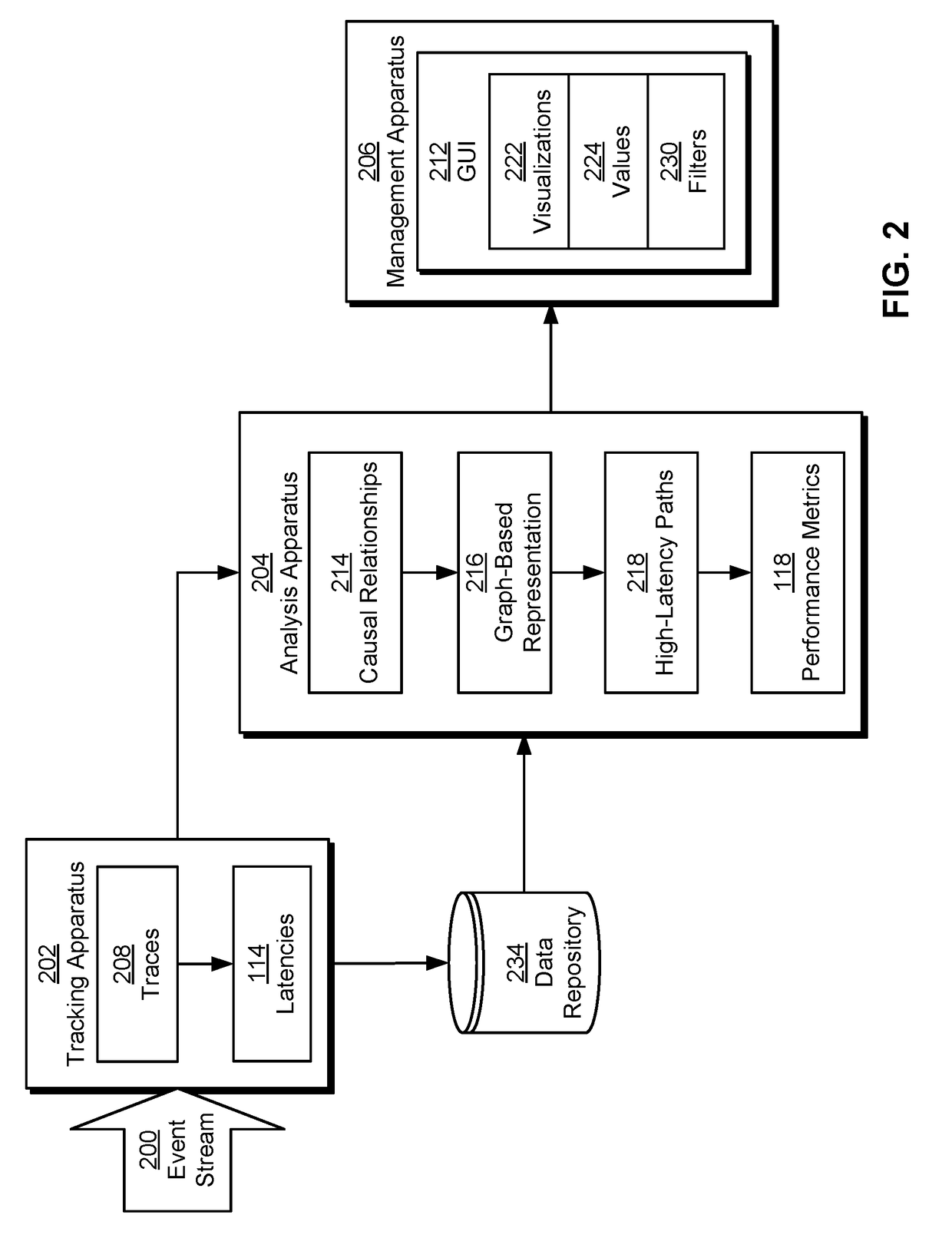
Automatically detecting latency bottlenecks in asynchronous workflows
The disclosed embodiments provide a system for processing data. During operation, the system generates, from a set of traces of an asynchronous workflow, a graph-based representation of the asynchronous workflow. Next, the system uses a set of causal relationships in the asynchronous workflow to update the graph-based representation. The system then analyzes the updated graph-based representation to identify a set of high-latency paths in the asynchronous workflow. Finally, the system uses the set of high-latency paths to output an execution profile for the asynchronous workflow, wherein the execution profile includes a subset of tasks associated with the high-latency paths in the asynchronous workflow.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
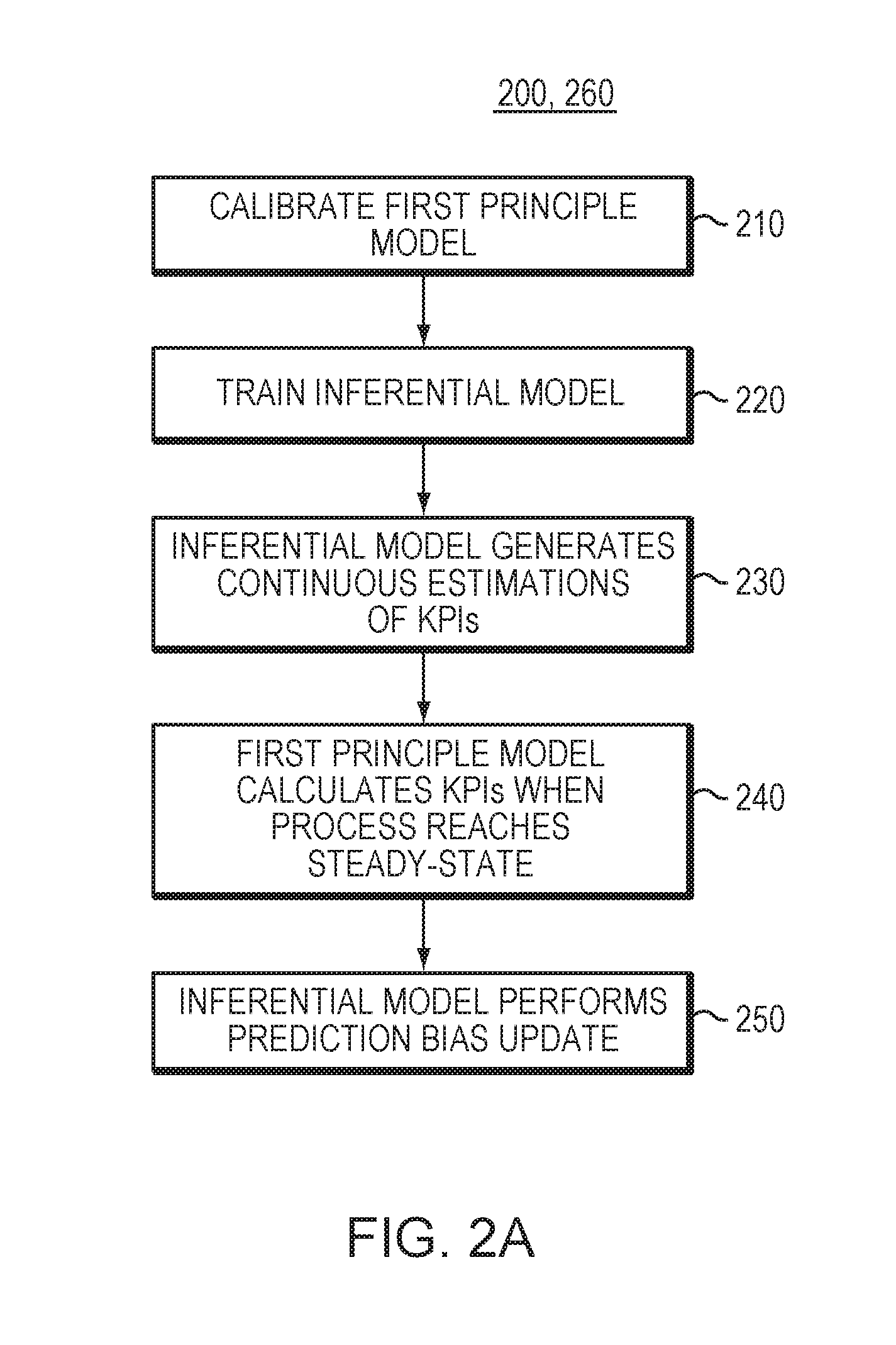
Computer System And Method For Causality Analysis Using Hybrid First-Principles And Inferential Model
ActiveUS20160320768A1Reduce riskReduce economic lossProgramme controlComputer controlData variabilityFirst principle
The present invention is directed to computer-based methods and system to perform root-cause analysis on an industrial process. The methods and system load process data for an industrial process from a historian database and build a hybrid first-principles and inferential model. The methods and system then executes the hybrid model to generate KPIs for the industrial process using the loaded process variables. The methods and system then selects a subset of the KPIs to represent an event occurring in the industrial process, and divides the data for the subset into multiple subset of time series. The system and methods select time intervals from the time series based on the data variability in the selected time intervals and perform a cross-correlation between the loaded process variables and the selected time interval, resulting in a cross-correlation score for each loaded process variable. The methods and system then select precursor candidates from the loaded process variables based on the cross-correlation scores and execute a parametric model for performing quantitative analysis of the selected precursor candidates, resulting in a strength of correlation score for each precursor candidate. The methods and system select root-cause variables from the selected precursor candidates based on the strength of correlation scores for analyzing the root-cause of the event.
Owner:ASPENTECH CORP
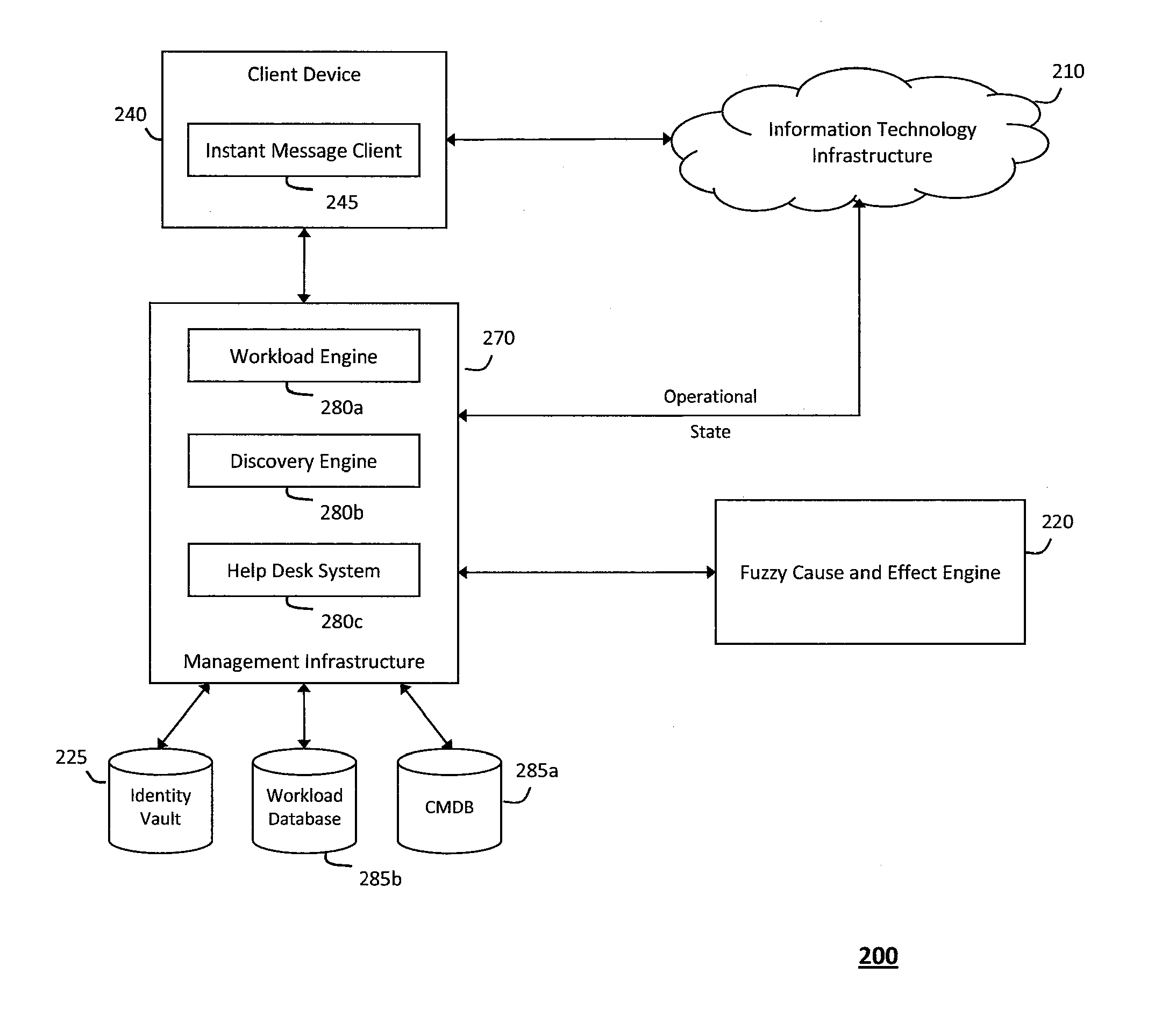
System and method for determining fuzzy cause and effect relationships in an intelligent workload management system
InactiveUS20120130936A1Determine relationshipEnable agilityFuzzy logic based systemsKnowledge representationKnowledge sourcesPotential effect
The system and method for determining fuzzy cause and effect relationships in an intelligent workload management system described herein may combine potential causes and effects captured from various different sources associated with an information technology infrastructure with substantially instantaneous feedback mechanisms and other knowledge sources. As such, fuzzy correlation logic may then be applied to the combined information to determine potential cause and effect relationships and thereby diagnose problems and otherwise manage interactions that occur in the infrastructure. For example, information describing potential causes and potential effects associated with an operational state of the infrastructure may be captured and combined, and any patterns among the information that describes the multiple potential causes and effects may then be identified. As such, fuzzy logic may the be applied to any such patterns to determine possible relationships among the potential causes and the potential effects associated with the infrastructure operational state.
Owner:MICRO FOCUS SOFTWARE INC
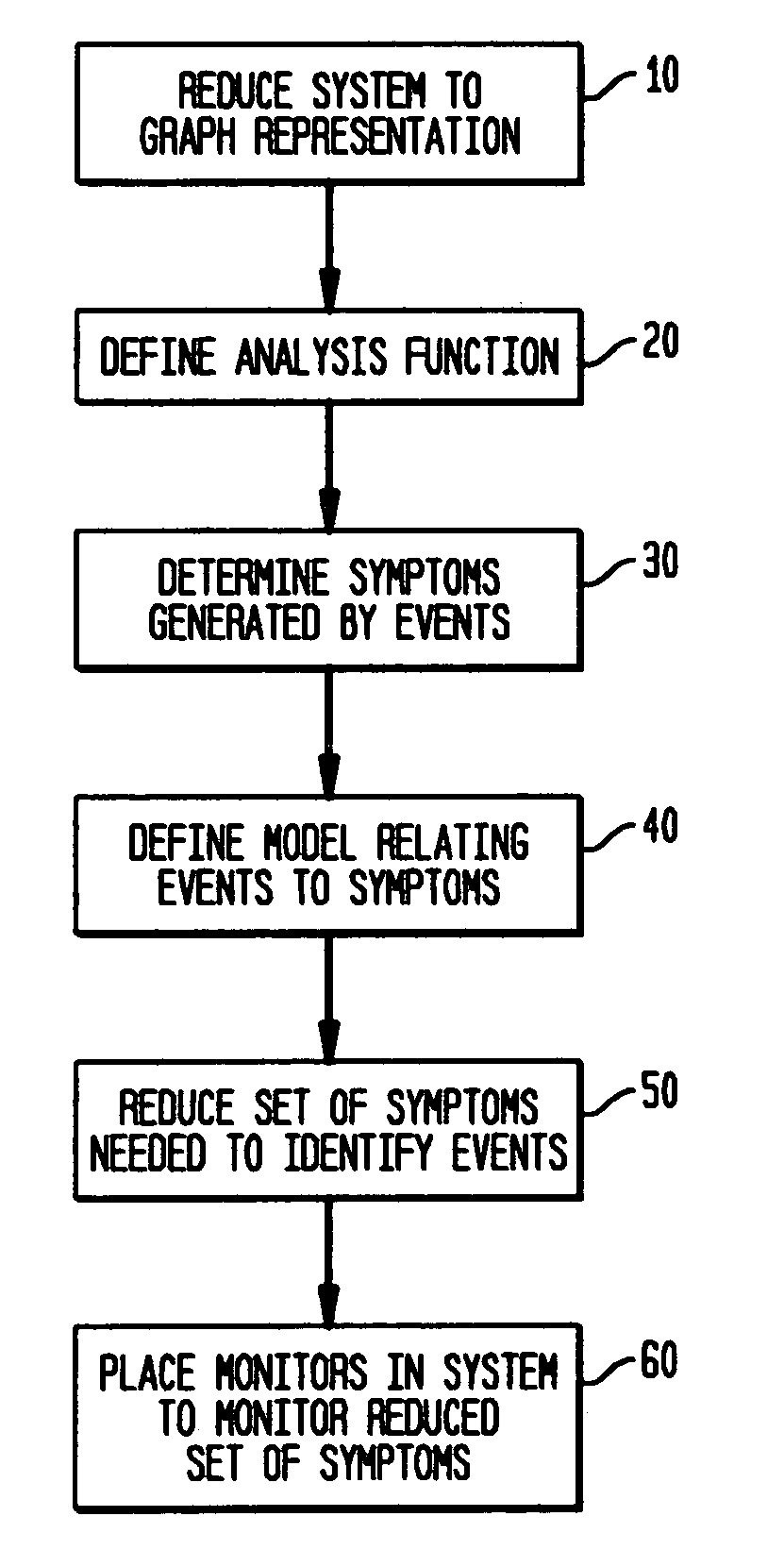
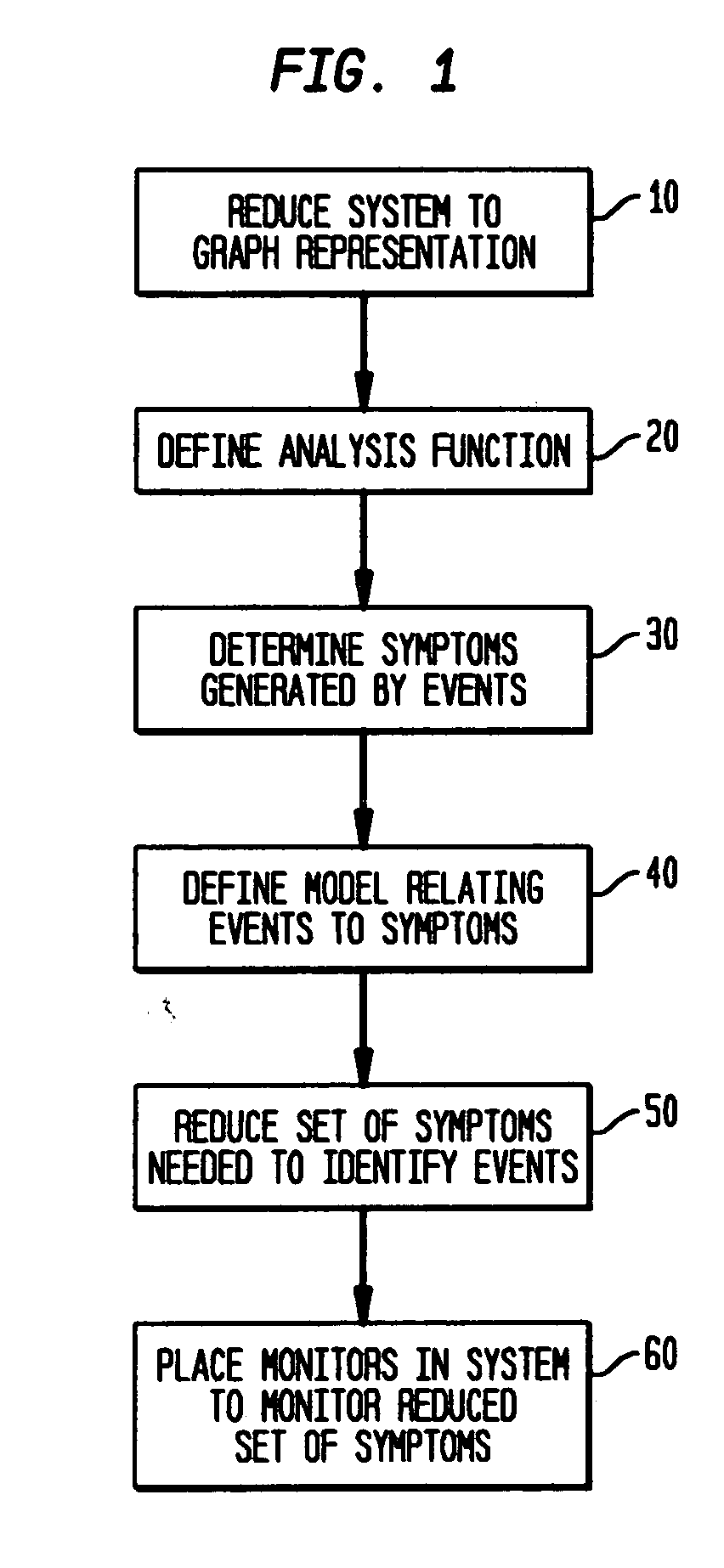
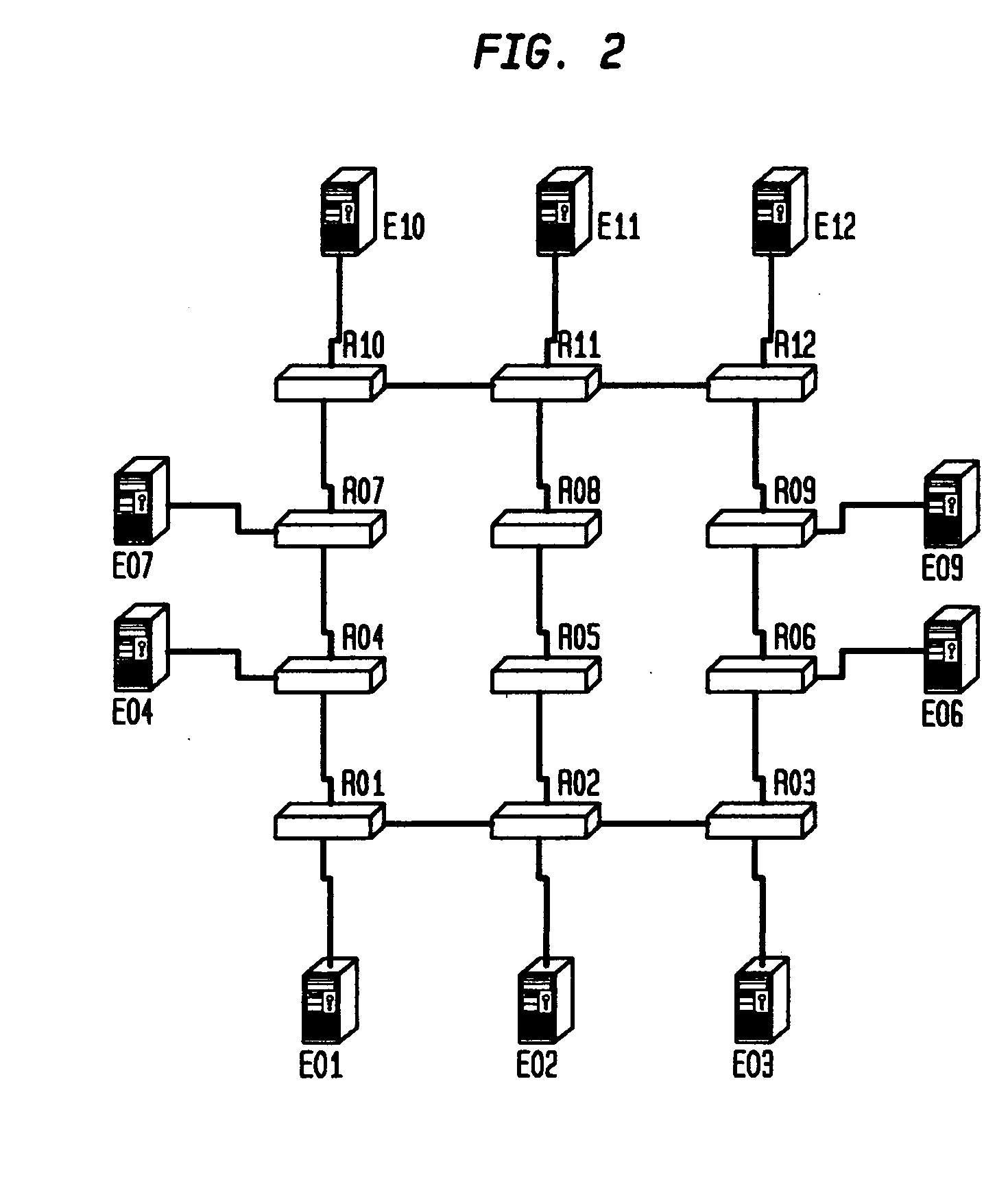
Method and apparatus for determining monitoring locations in distributed systems
ActiveUS20050210133A1Reduce in quantityError detection/correctionDigital computer detailsReduced modelHandling system
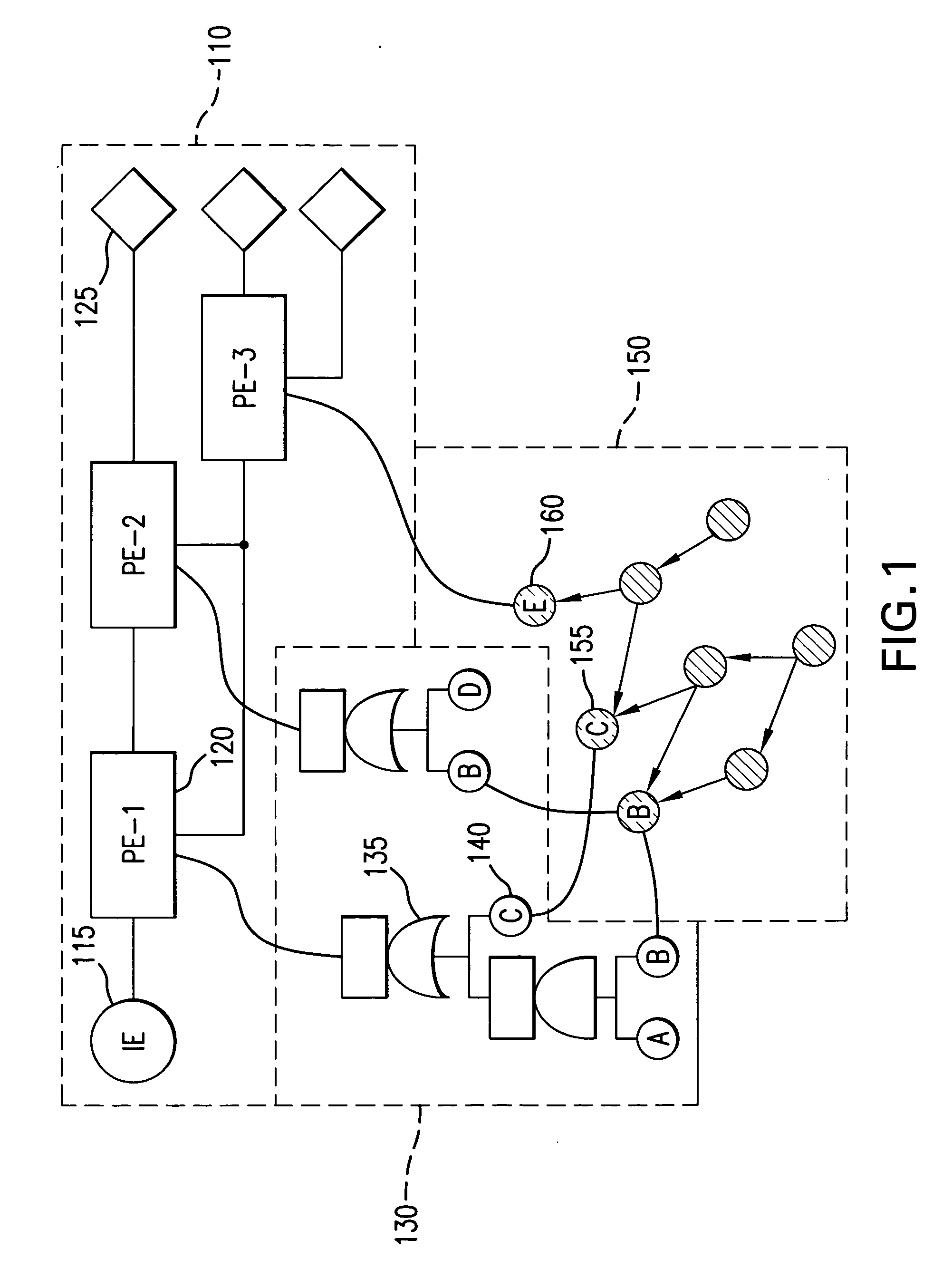
A method and apparatus for determining the number and location of monitoring entities in a distributed system is disclosed. The method comprising the steps of automatically generating a causality mapping model of the dependences between causing events at the nodes of the distributed system and the detectable events associated with a subset of the nodes, the model suitable for representing the execution of at least one system operation, reducing the number of detectable events in the model, wherein the reduced number of detectable events is suitable for substantially representing the execution of the at least one system operation; and placing at least one of the at least one monitoring entities at selected ones of the nodes associated with the detectable events in the reduced model. In another aspect, the processing described herein is in the form of a computer-readable medium suitable for providing instruction to a computer or processing system for executing the processing claimed.
Owner:VMWARE INC
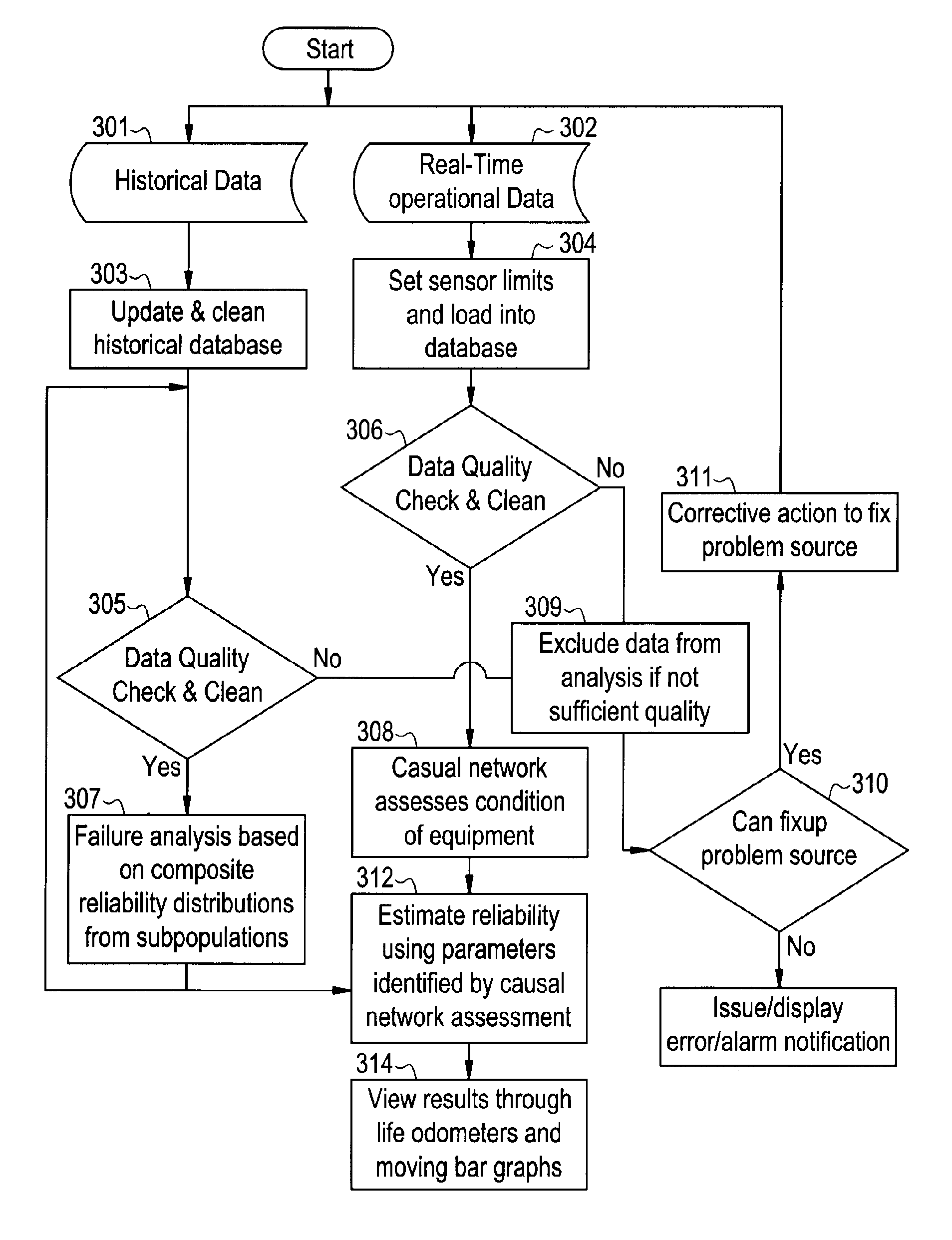
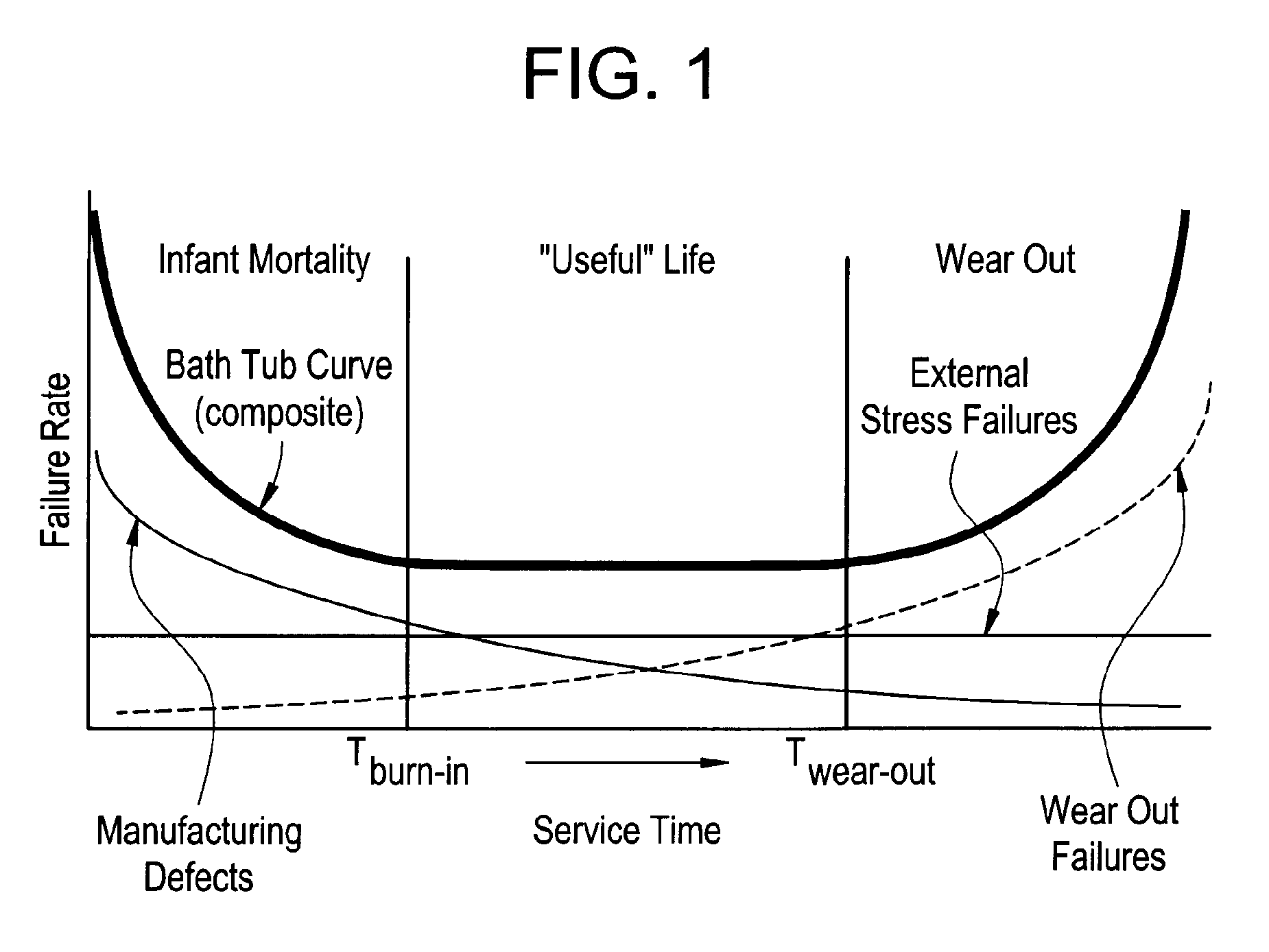
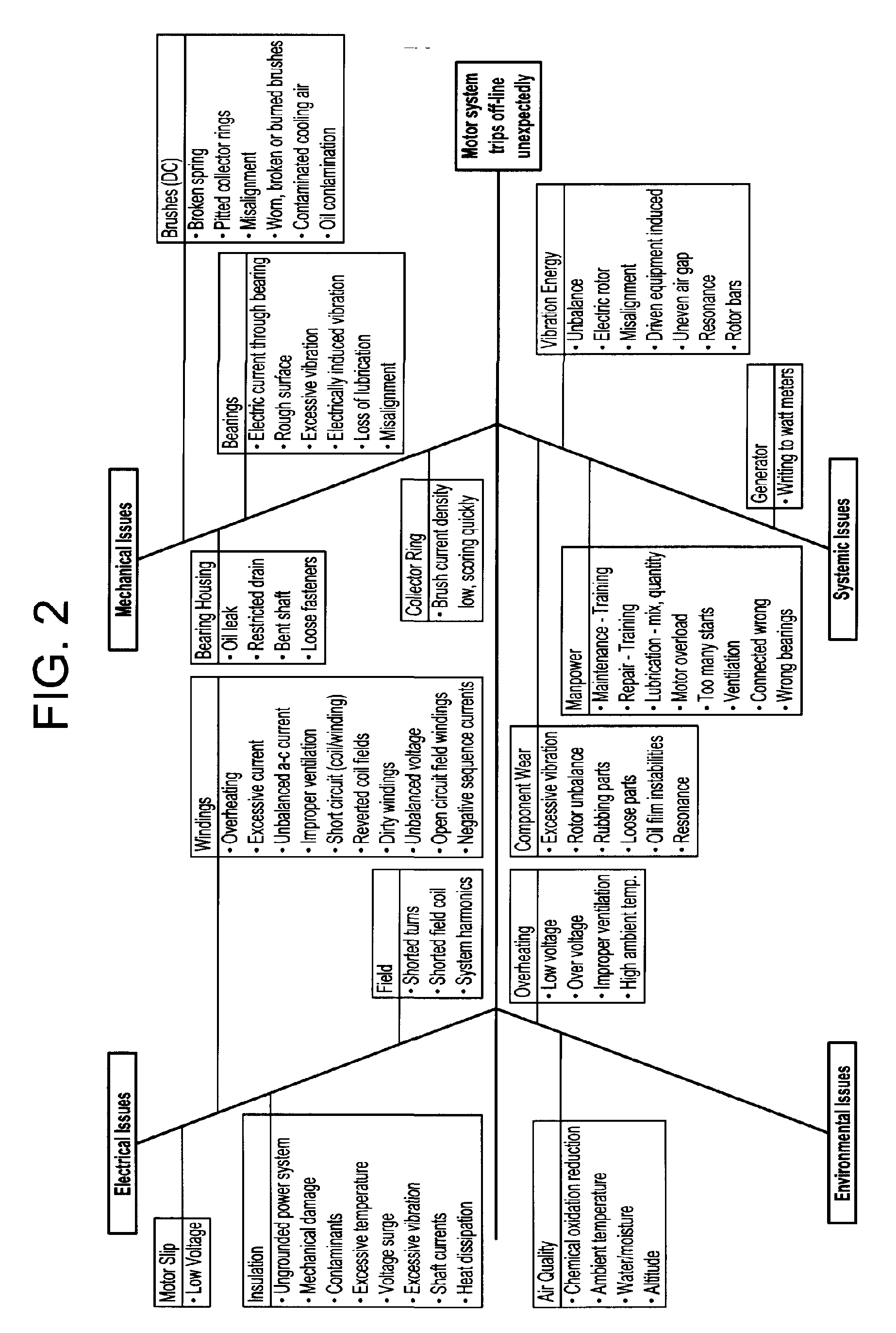
Method and system for predicting remaining life for motors featuring on-line insulation condition monitor
A method for determining reliability and a remaining time before failure with statistical confidence for a motor system includes acquiring historical motor data in a computer system, obtaining operational parameter data, uploading the operational parameter data to the computer system, performing failure analysis, developing a causal network, and performing an integrated causal network and reliability analysis of the motor system. The historical motor data corresponds to the motor system. The operational parameter data is obtained from sensors at the motor system. The sensors include a tan delta sensor. The failure analysis is performed based on a composite of reliability probability distributions corresponding to predetermined sub-populations of historical motor system failure causes. The causal network is developed for modeling reliability of one or more motor system components and assessing motor system component condition based on the causal network. Results from the performing failure analysis are integrated with results from the assessing motor system component condition based on the causal network to compute a quantitative value for a time remaining before failure with an ascertained statistical confidence.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
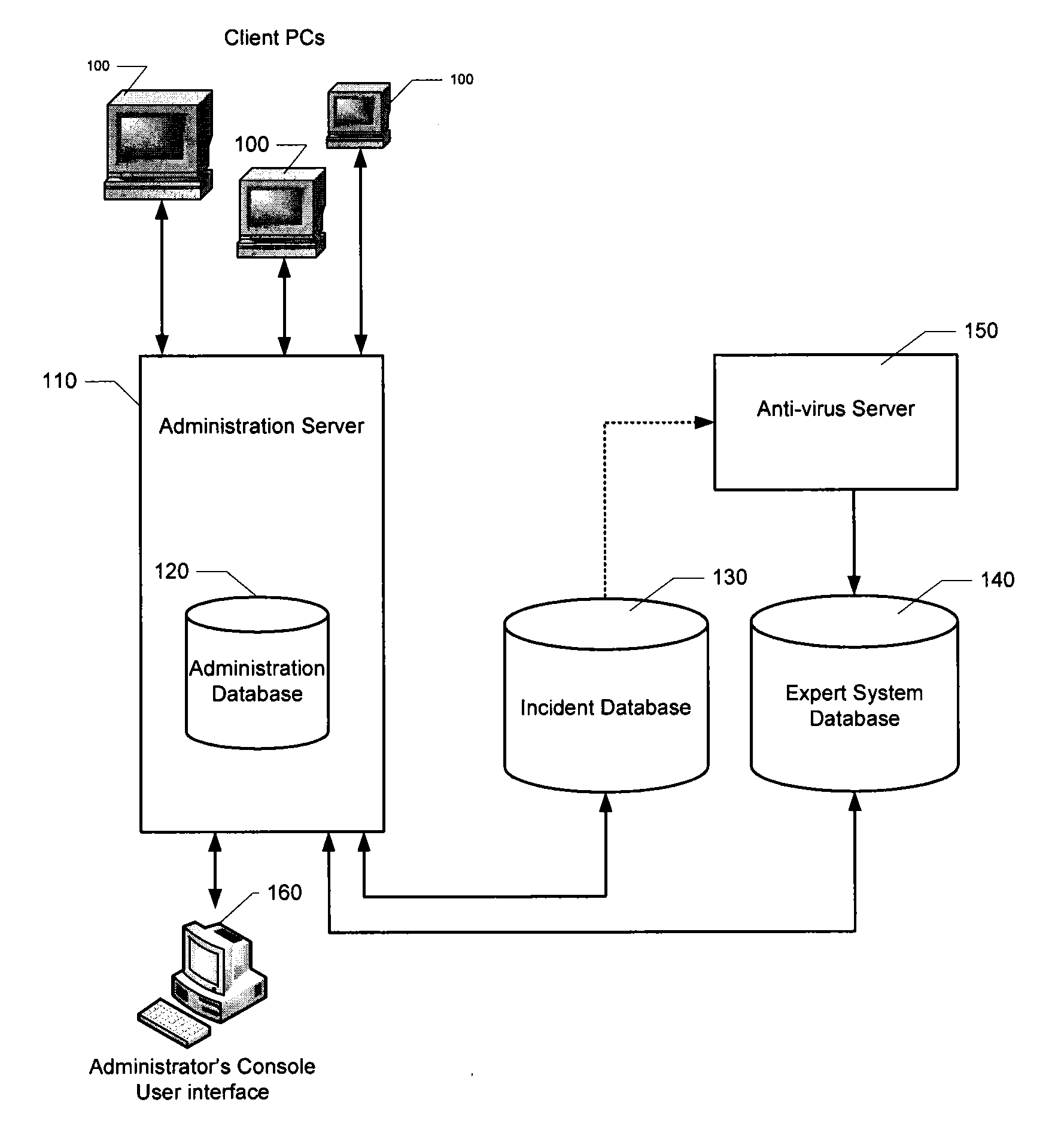
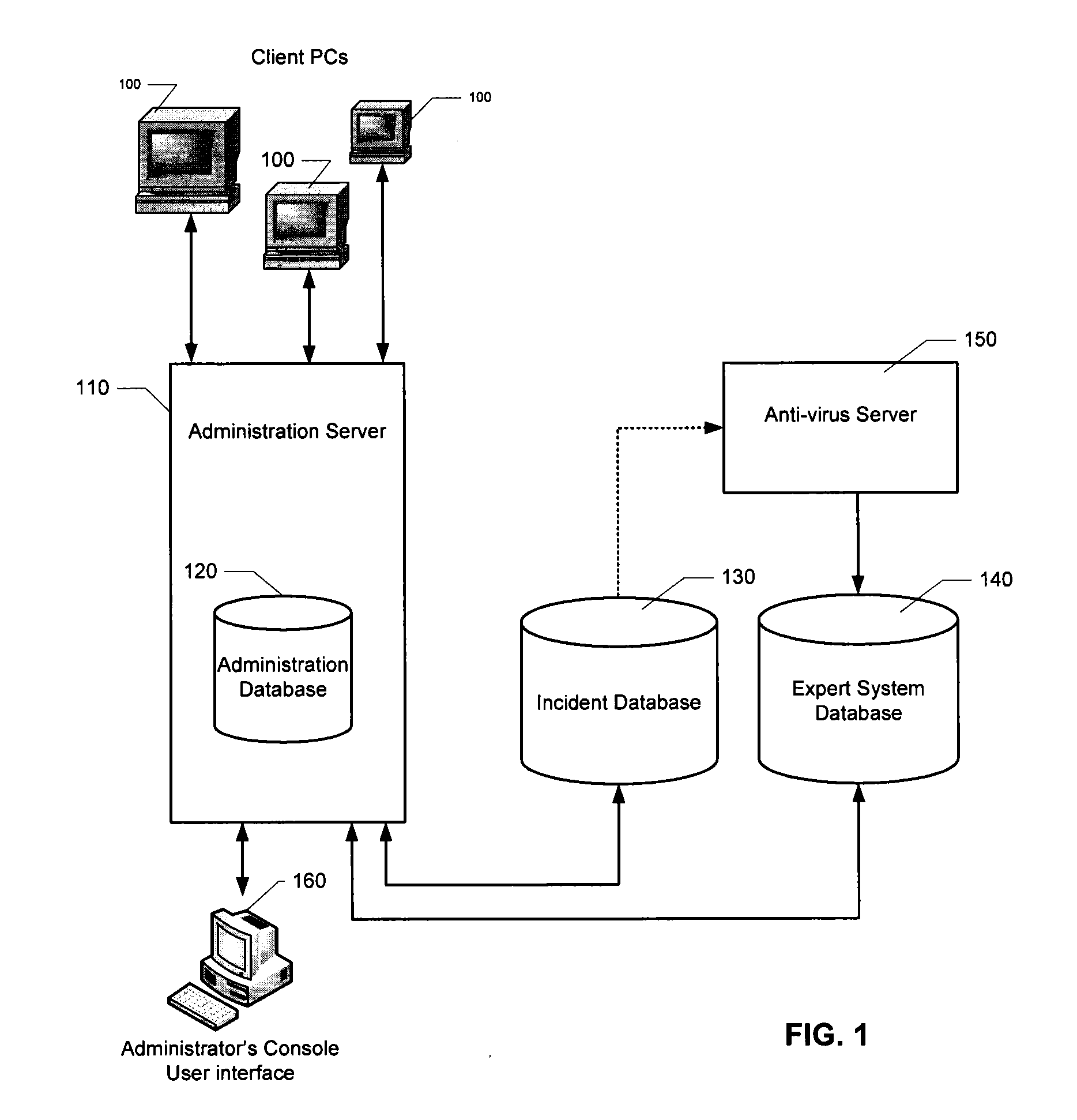
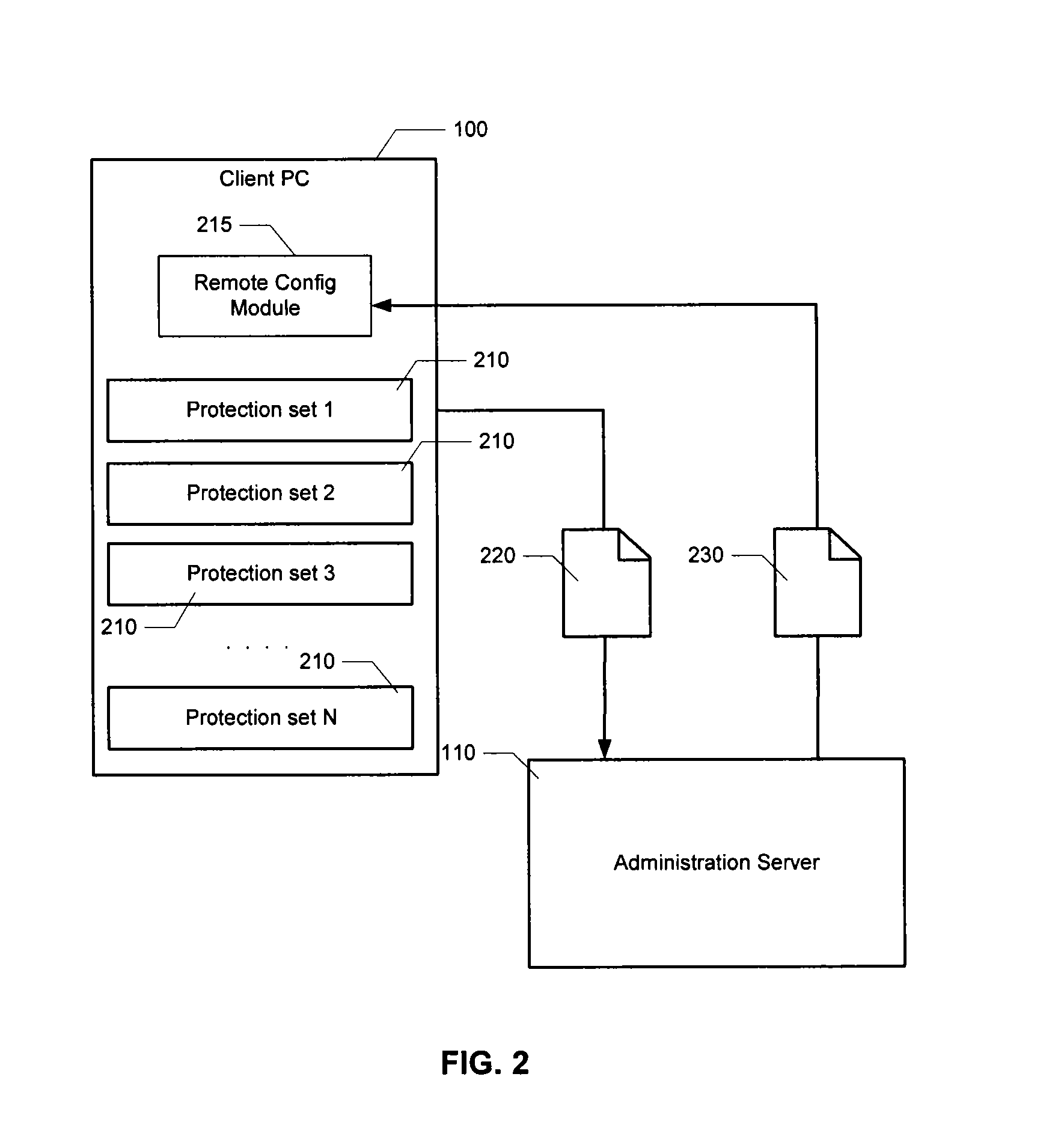
Automatic analysis of security related incidents in computer networks
ActiveUS20130055399A1Reduce time spent on investigatingEasy to detectMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionEvent levelChain of events
Solutions for responding to security-related incidents in a computer network, including a security server, and a client-side arrangement. The security server includes an event collection module communicatively coupled to the computer network, an event analysis module operatively coupled to the event collection module, and a solution module operatively coupled to the event analysis module. The event collection module is configured to obtain incident-related information that includes event-level information from at least one client computer of the plurality of client computers, the incident-related information being associated with at least a first incident which was detected by that at least one client computer and provided to the event collection module in response to that detection. The event analysis module is configured to reconstruct at least one chain of events causally related to the first incident and indicative of a root cause of the first incident based on the incident-related information. The solution module is configured to formulate at least one recommendation for use by the at least one client computer, the at least one recommendation being based on the at least one chain of events, and including corrective / preventive action particularized for responding to the first incident.
Owner:AO KASPERSKY LAB
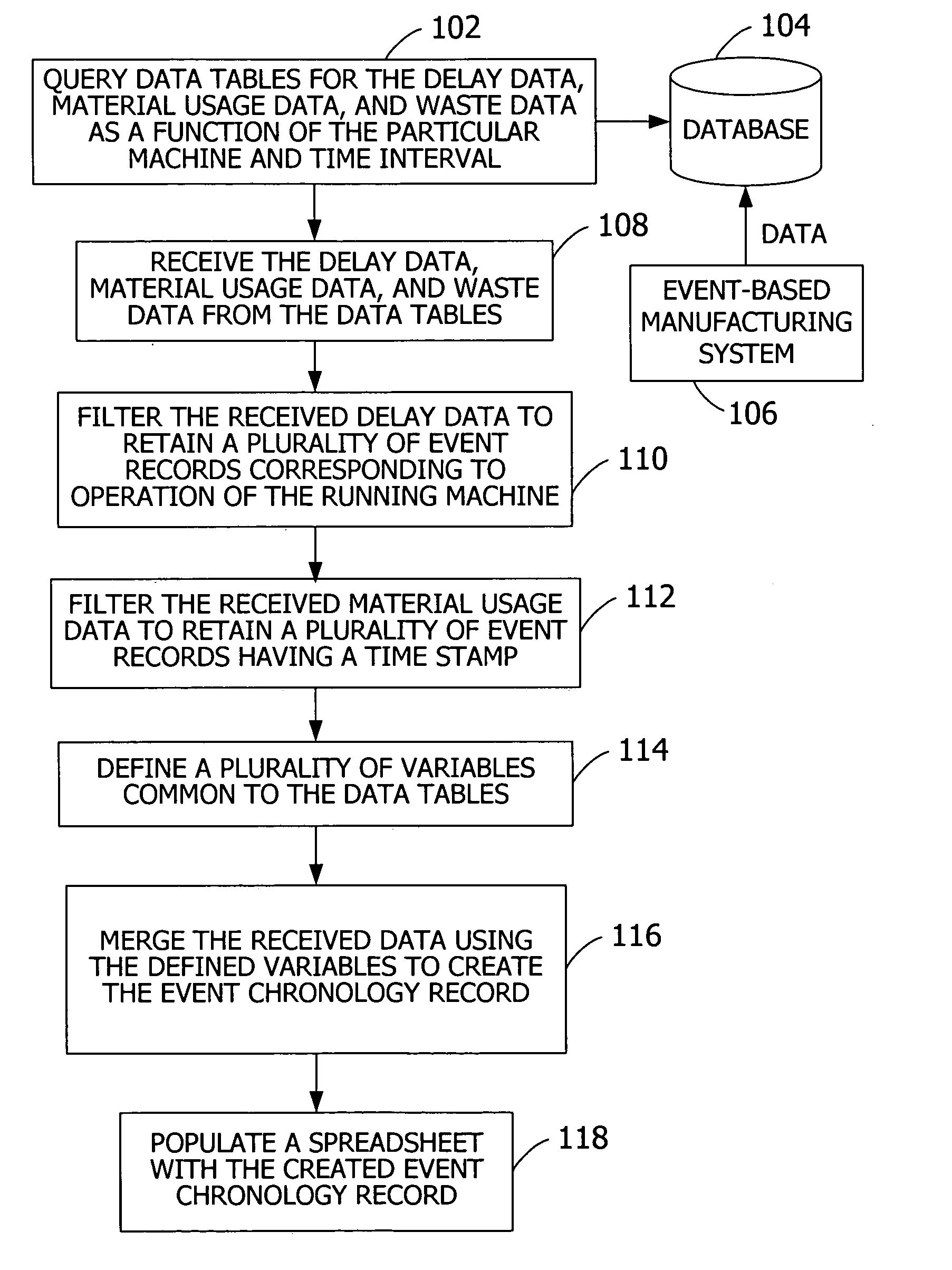
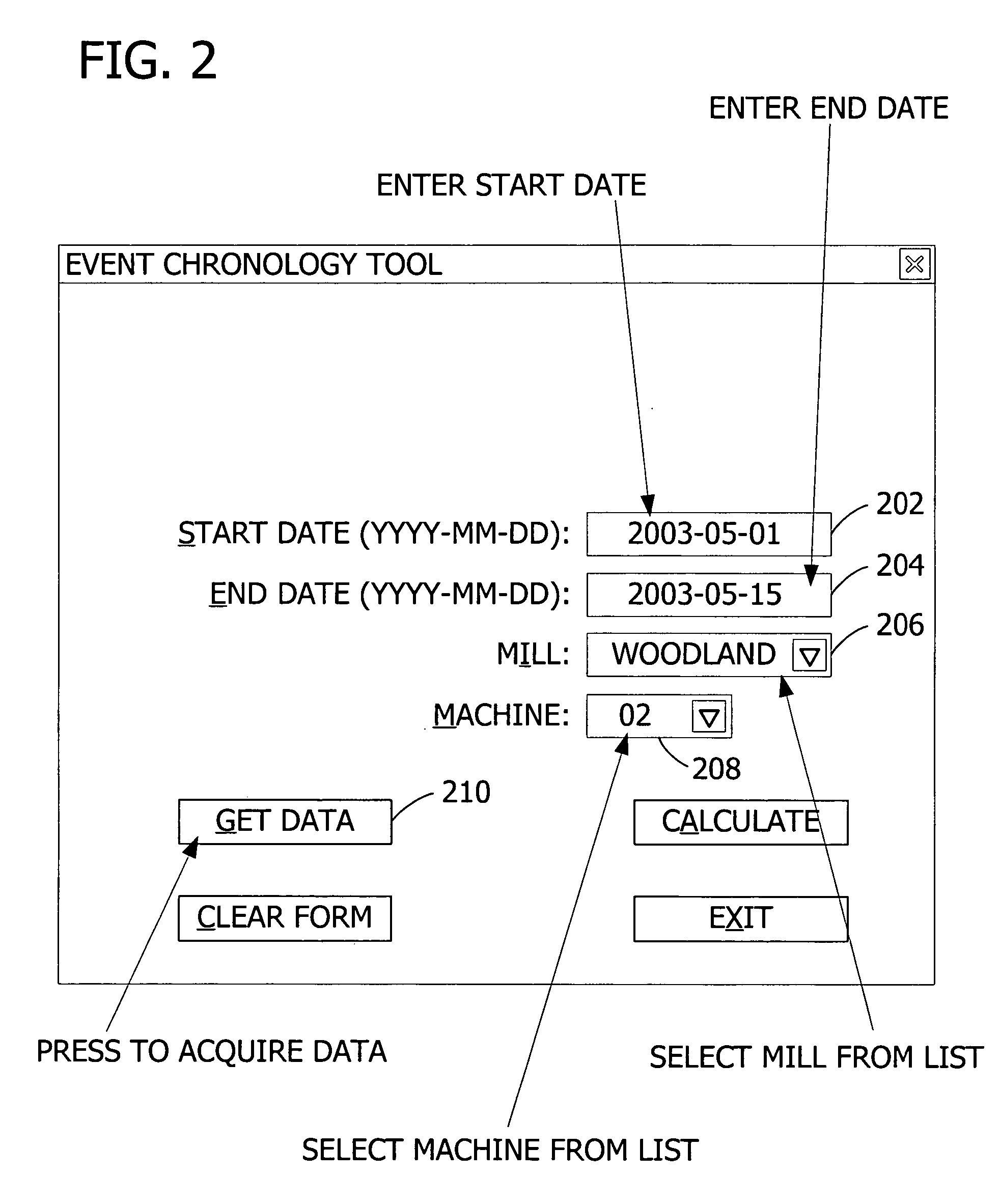
Generating a reliability analysis by identifying causal relationships between events in an event-based manufacturing system
ActiveUS20050278052A1Increase the probability of failureEase of evaluationProgramme controlElectric testing/monitoringHigh probabilityDependability
Analyzing an event chronology record to permit identification of periods of a production sequence that correspond to a high probability of failure. Systems and methods include receiving an event chronology for a particular machine in the production sequence and for a particular time interval. A reliability analysis system accesses process flow information to determine whether a particular event in the event chronology is related to a subsequent adverse event within a predefined event window.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
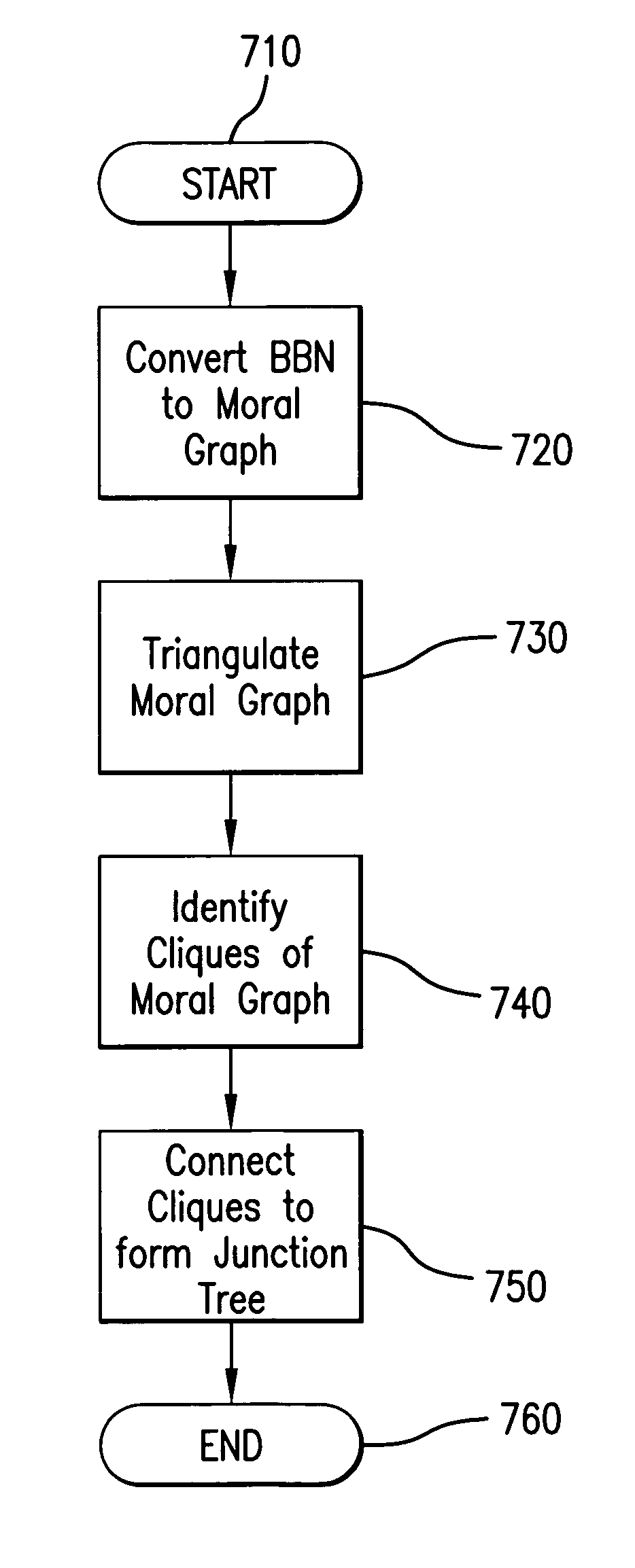
System and methods for assessing risk using hybrid causal logic
A hybrid causal framework applies properties of probabilistic models, such as Bayesian belief networks, to causal logic models, such as fault trees and event sequence diagrams. The probabilistic model establishes a joint probability distribution of causal relationships between events and conditions in the logic models. The probability of the events and conditions are found by propagating probabilities from the probabilistic model through the logic models.
Owner:MARYLAND UNIV OF
Method and apparatus for dealing with accumulative behavior of some system observations in a time series for bayesian inference with a static bayesian network model
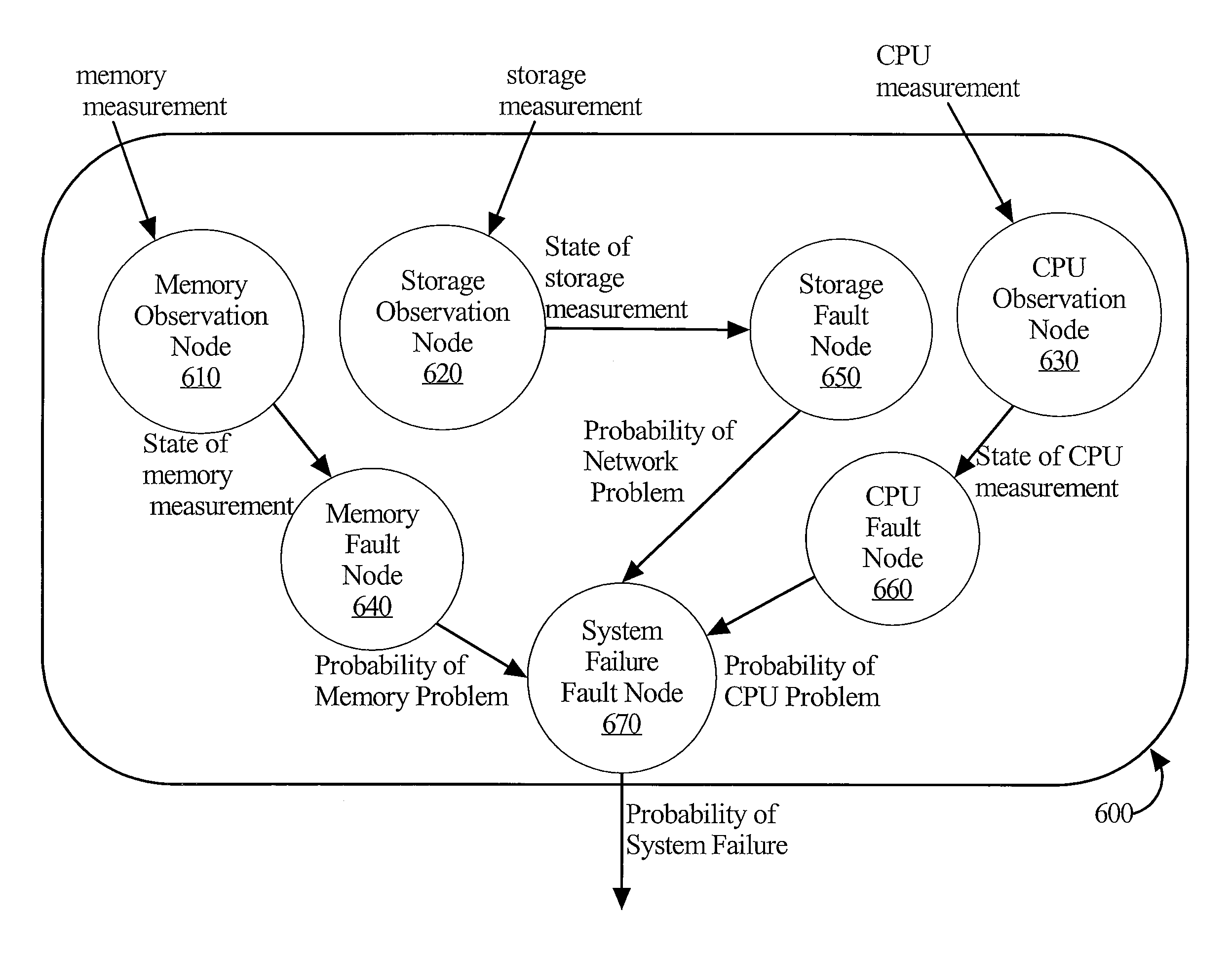
ActiveUS20120005534A1Reliability/availability analysisNon-redundant fault processingProbit modelNetwork model
A method and apparatus are provided for determining the probability that one or more problems have occurred within a complex multi-host system. A probabilistic model representing the cause / effect relationships among potential system problems identifies the probability that a problem occurred in the system based at least on system measure states that are input into the probabilistic model. System measure states may be determined based on an aggregation of system measurement values taken periodically. Aggregating system measurement values may be performed over system measurement values that were taken during a recent time interval. A rolling count aggregation function may be used for this purpose. A rolling count function counts the number of system measurement values taken within the recent time interval that lie within a particular range of values. A system measure state may be determined based on whether the rolling count exceeds a threshold associated with the system measure.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
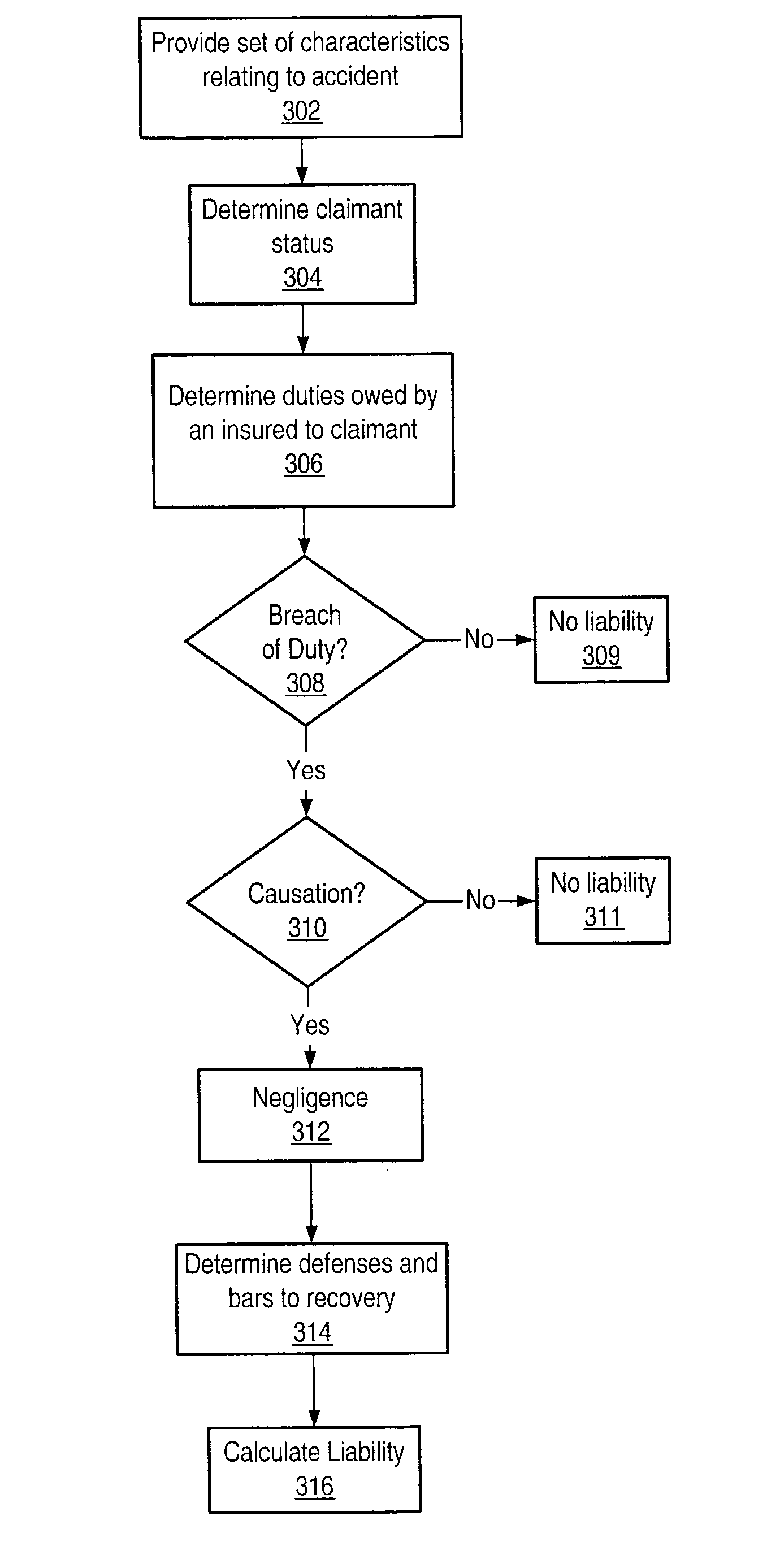
Computerized method and system for determining causation in premises liability for an accident
Computer-implemented methods and systems for determining causation of a dangerous condition in premises liability for an accident are provided. In one embodiment, a set of characteristics of the accident may be provided to a computer system. In some embodiments, a cause in fact of a claimant's harm may be determined from at least one of the characteristics. In certain embodiments, a proximate cause of the claimant's harm may be determined from at least one of the characteristics.
Owner:COMP SCI A OF NV
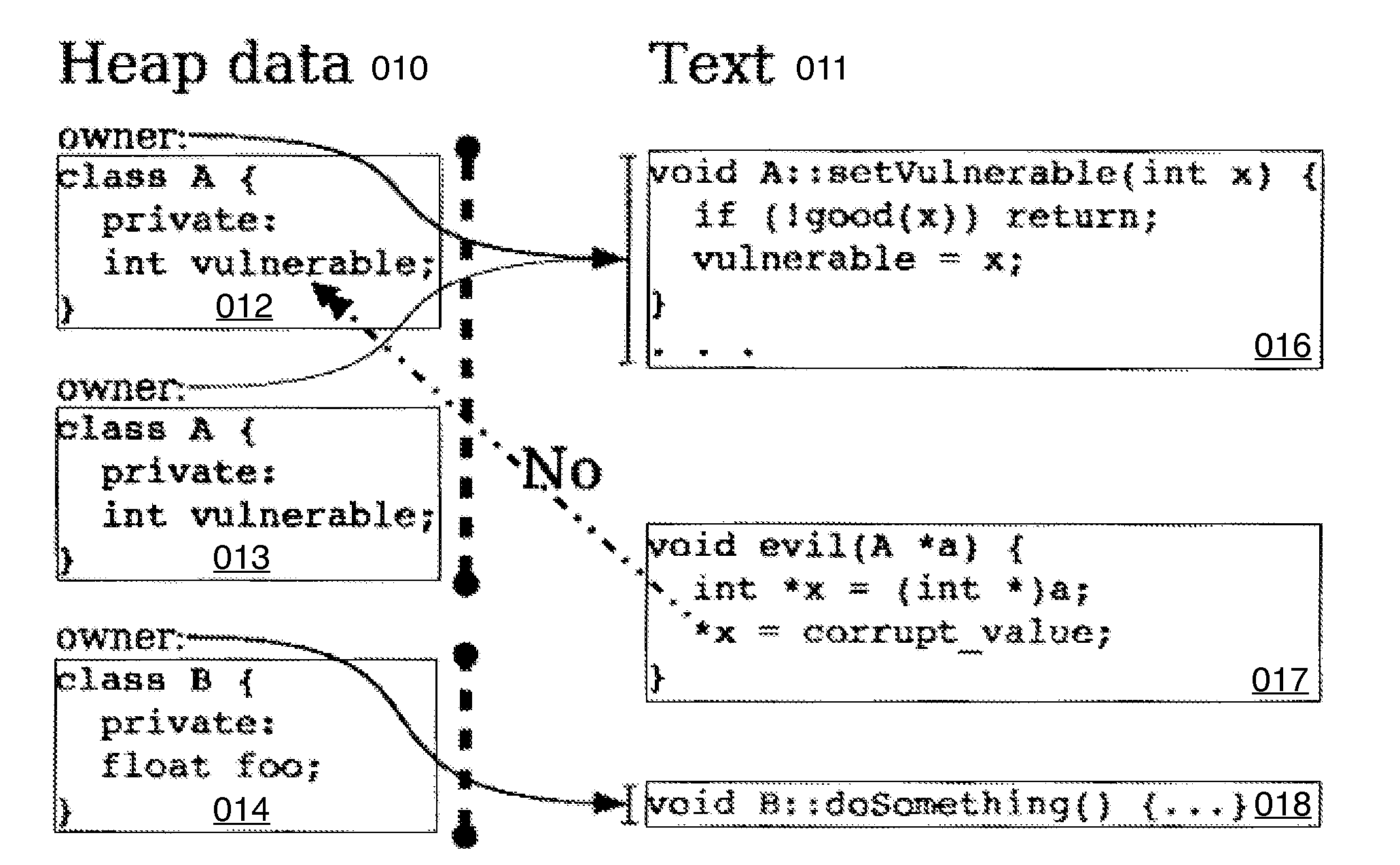
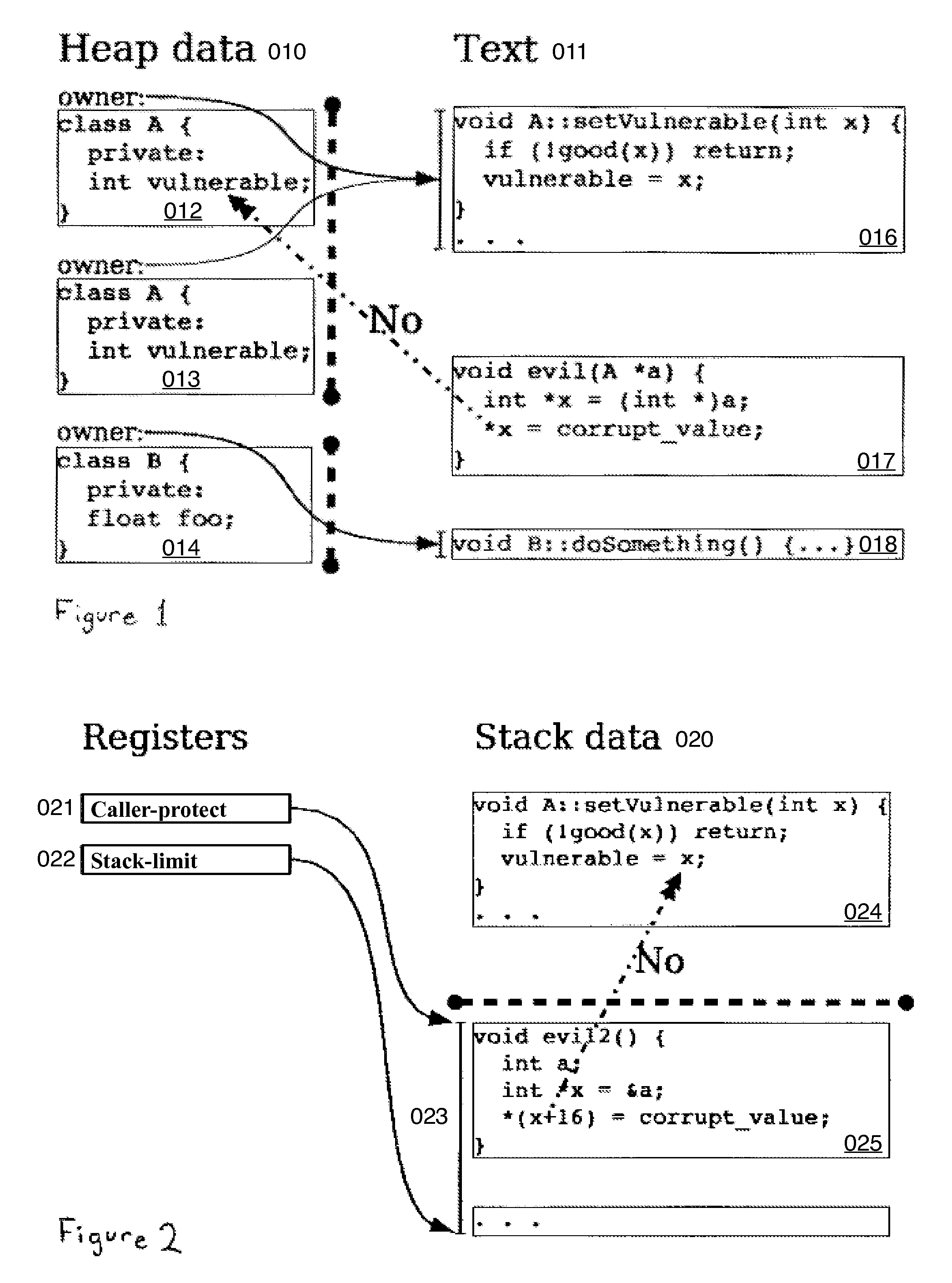
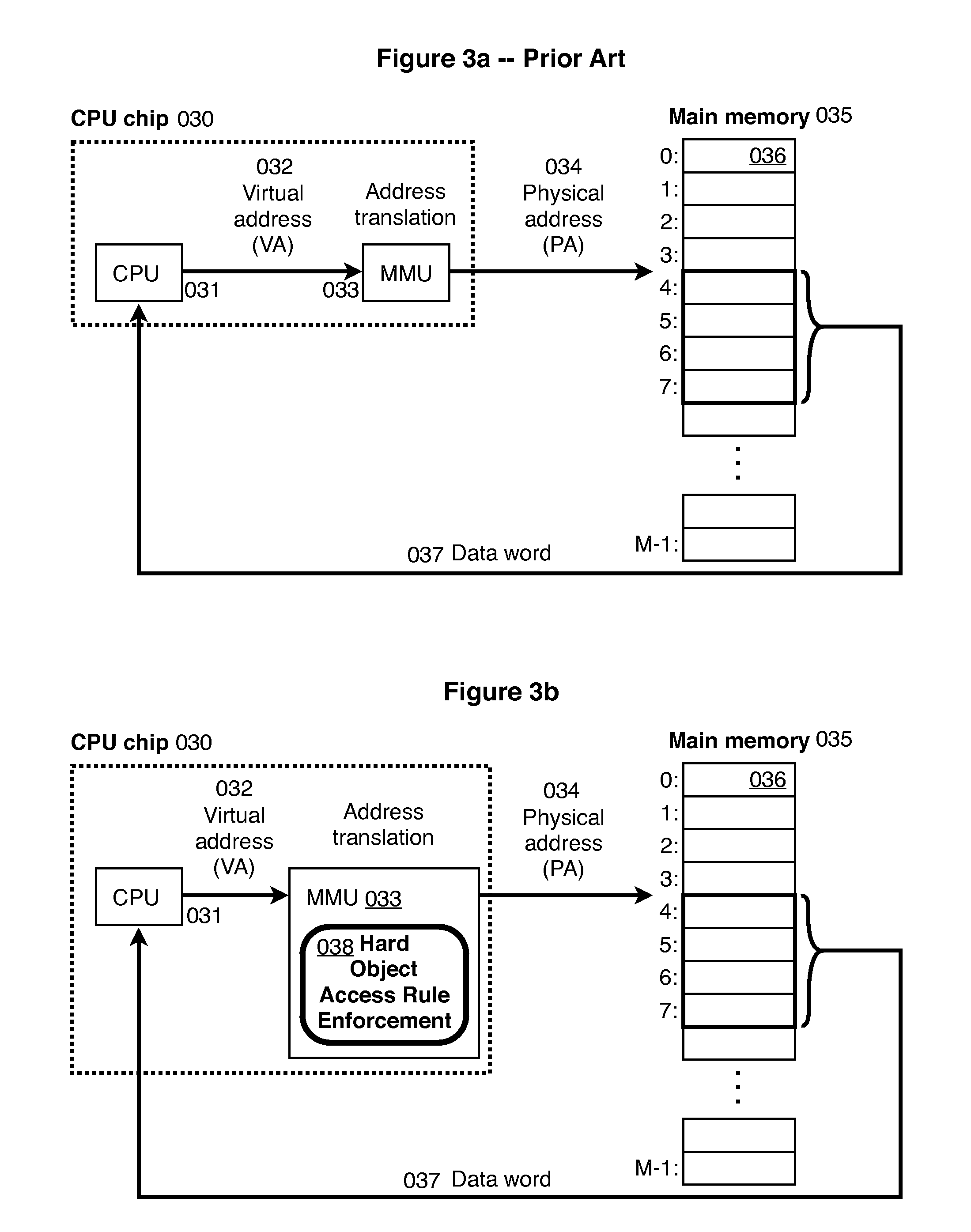
Hard object: constraining control flow and providing lightweight kernel crossings
InactiveUS20120151184A1Specific access rightsGeneral purpose stored program computerSemanticsSystem call
A method providing simple fine-grain hardware primitives with which software engineers can efficiently implement enforceable separation of programs into modules and constraints on control flow, thereby providing fine-grain locality of causality to the world of software. Additionally, a mechanism is provided to mark some modules, or parts thereof, as having kernel privileges and thereby allows the provision of kernel services through normal function calls, obviating the expensive prior art mechanism of system calls. Together with software changes, Object Oriented encapsulation semantics and control flow integrity in hardware are enforced.
Owner:WILKERSON DANIEL SHAWCROSS +1
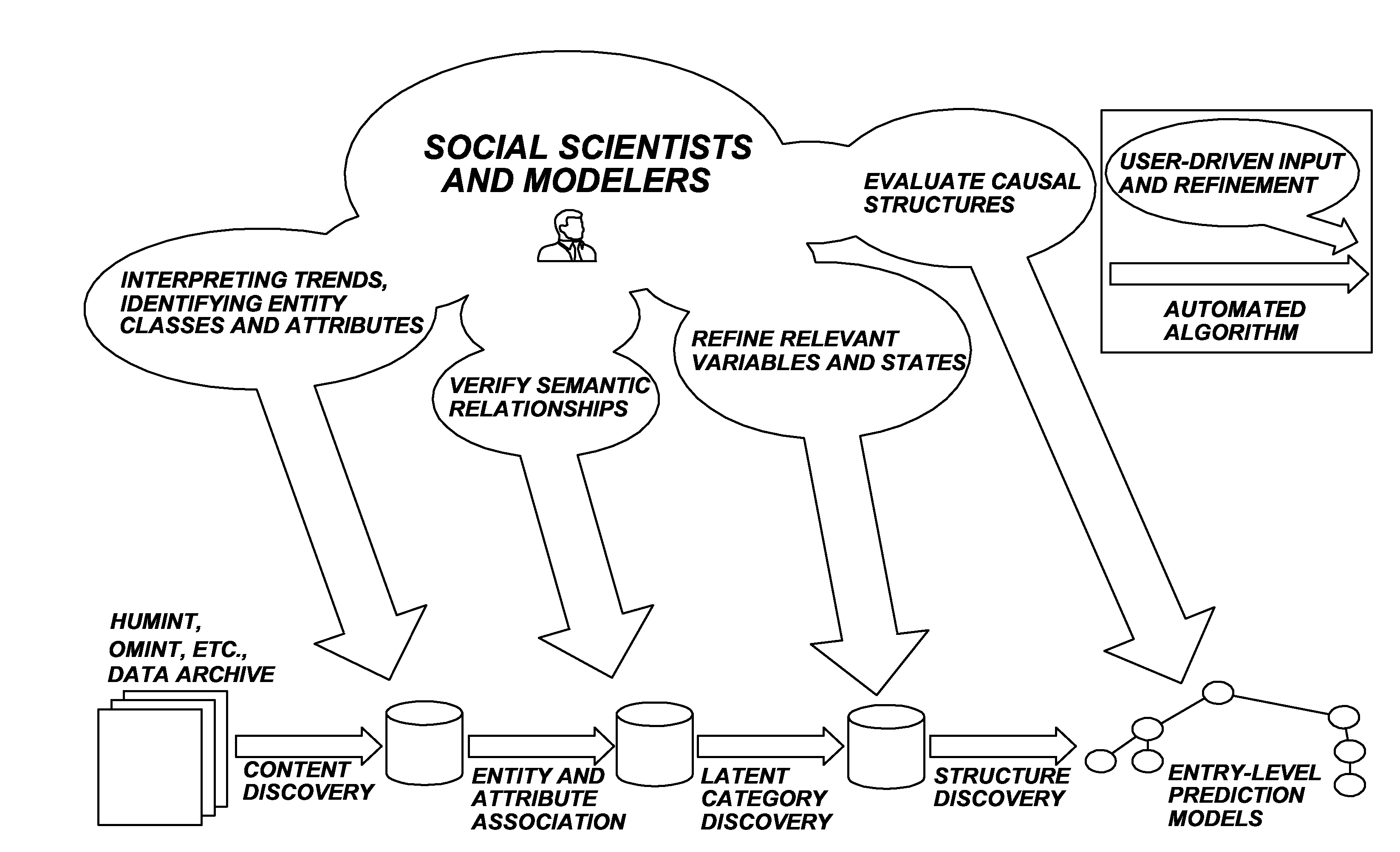
Method and apparatus for creating a predicting model
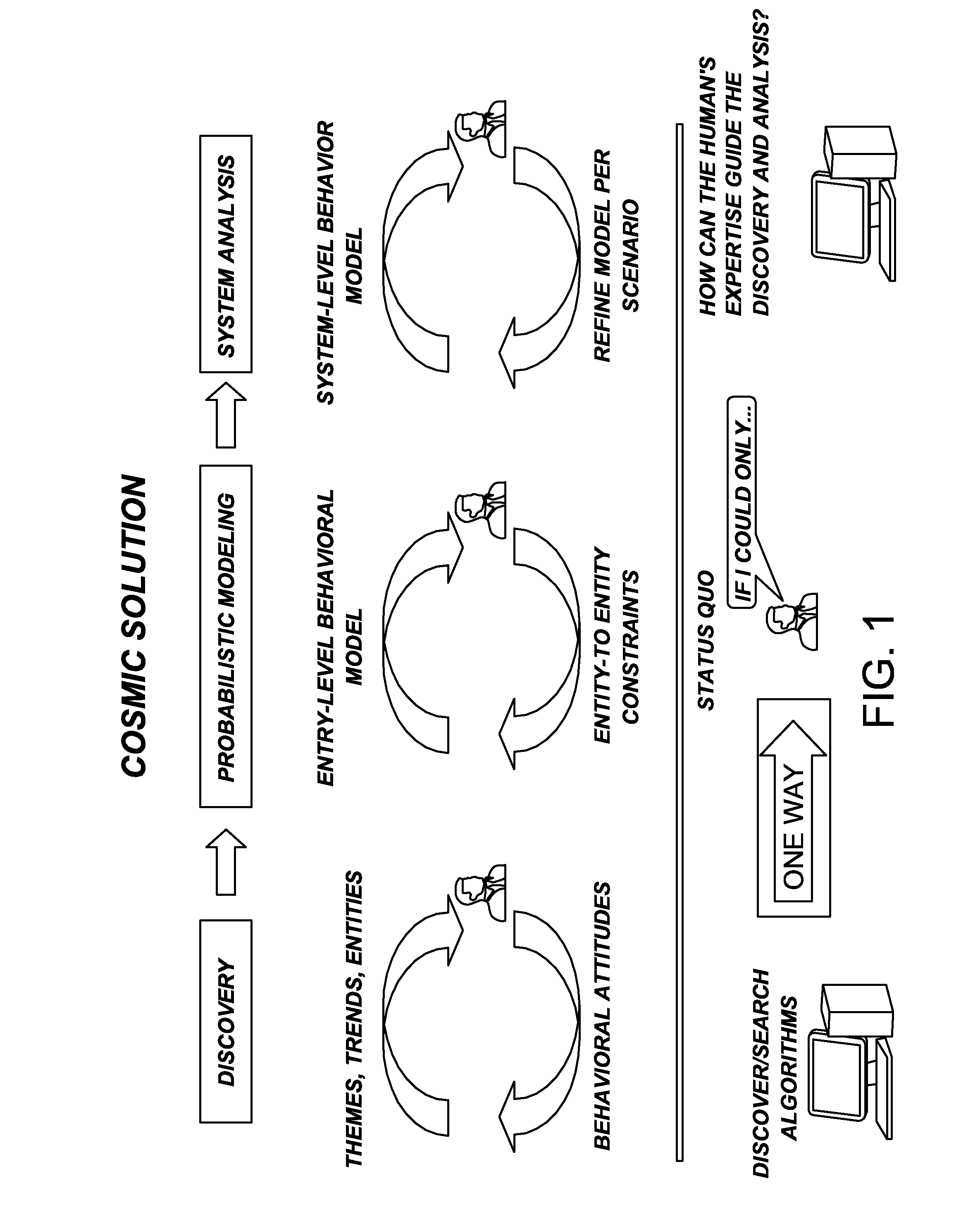
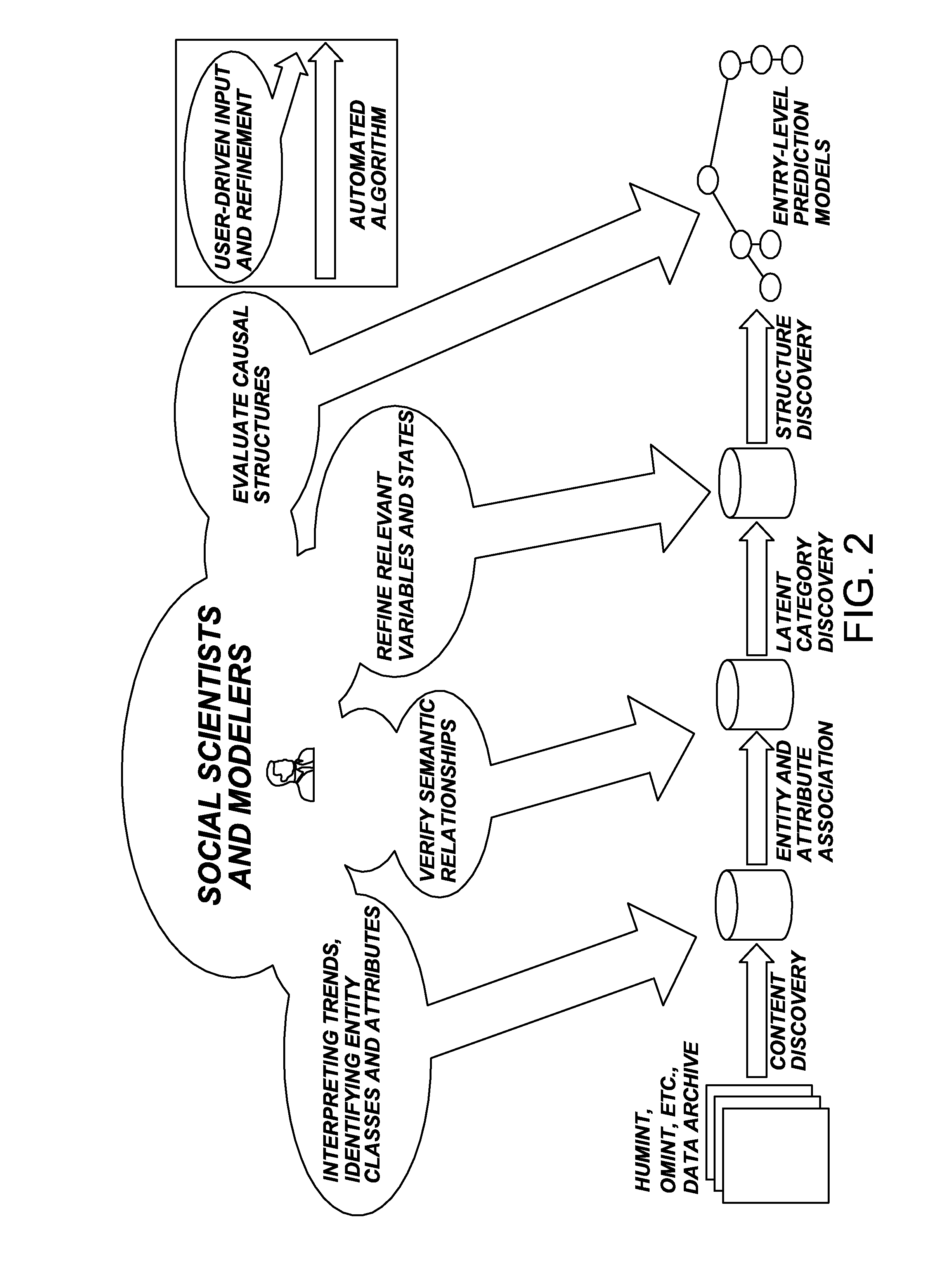
ActiveUS20120323558A1Accurately predicting behaviorIncrease capacitySemantic analysisProbabilistic networksNODALHypothesis
A method for creating a predictive model is disclosed herein, including the steps of determining trends and patterns in electronic data, using at least a first machine language algorithm, refining the determination of the algorithm, searching for social models that describe the identified trends and patterns using at least a second machine language algorithm, verifying causal links, constructing at least one model about human node behavior and interactions, utilizing the social models to do at least one of the following: validate hypotheses, predict future behavior, and examine hypothetical scenarios, and automatically updating predictions when new data is introduced.
Owner:DECISIVE ANALYTICS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com