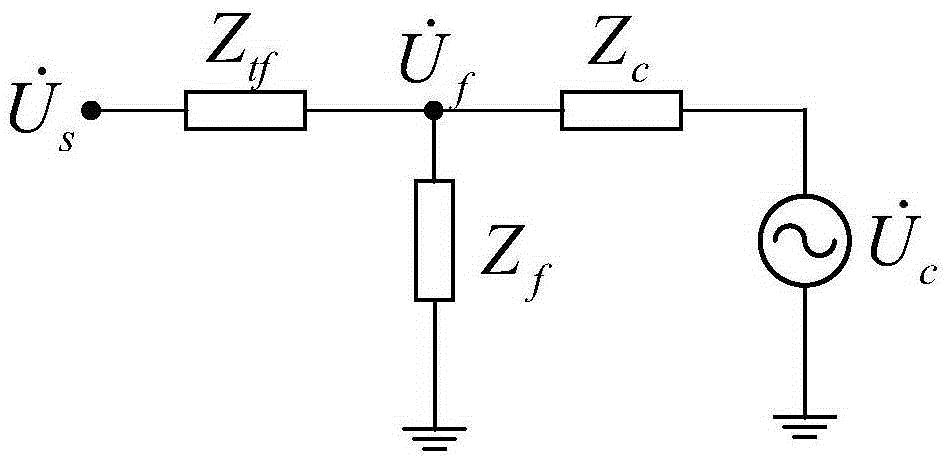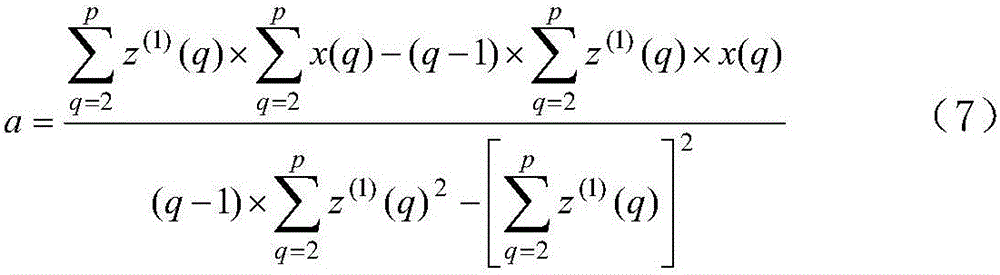Patents
Literature
176 results about "Sub populations" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A subset of a population is called a sub-population. If different sub-populations have different properties, so that the overall population is heterogeneous, the properties and responses of the overall population can often be better understood if the population is first separated into distinct sub-populations.
Methods for detecting genome-wide sequence variations associated with a phenotype
InactiveUS20040002090A1Microbiological testing/measurementFermentationSub populationsGenetic risk factor
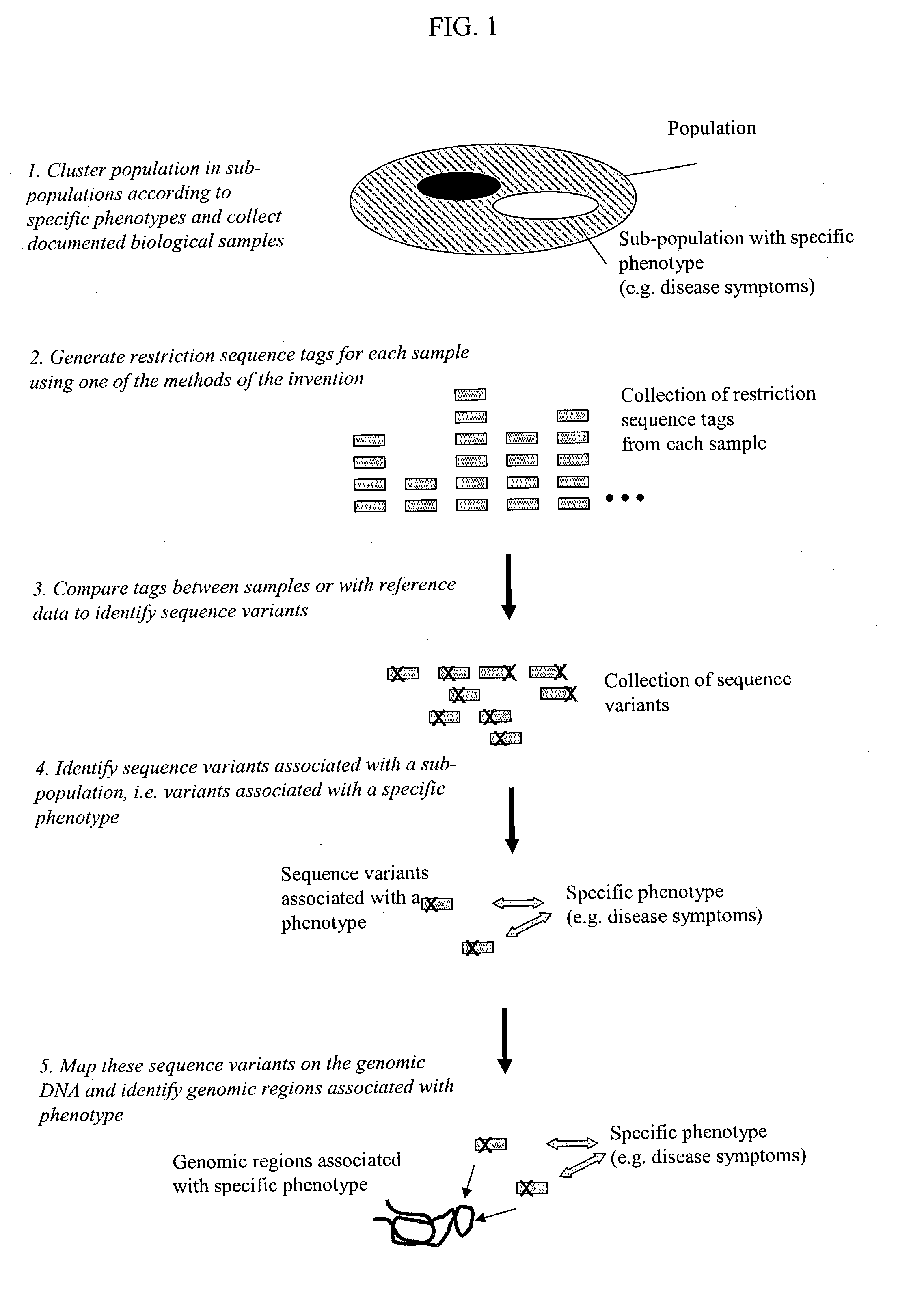
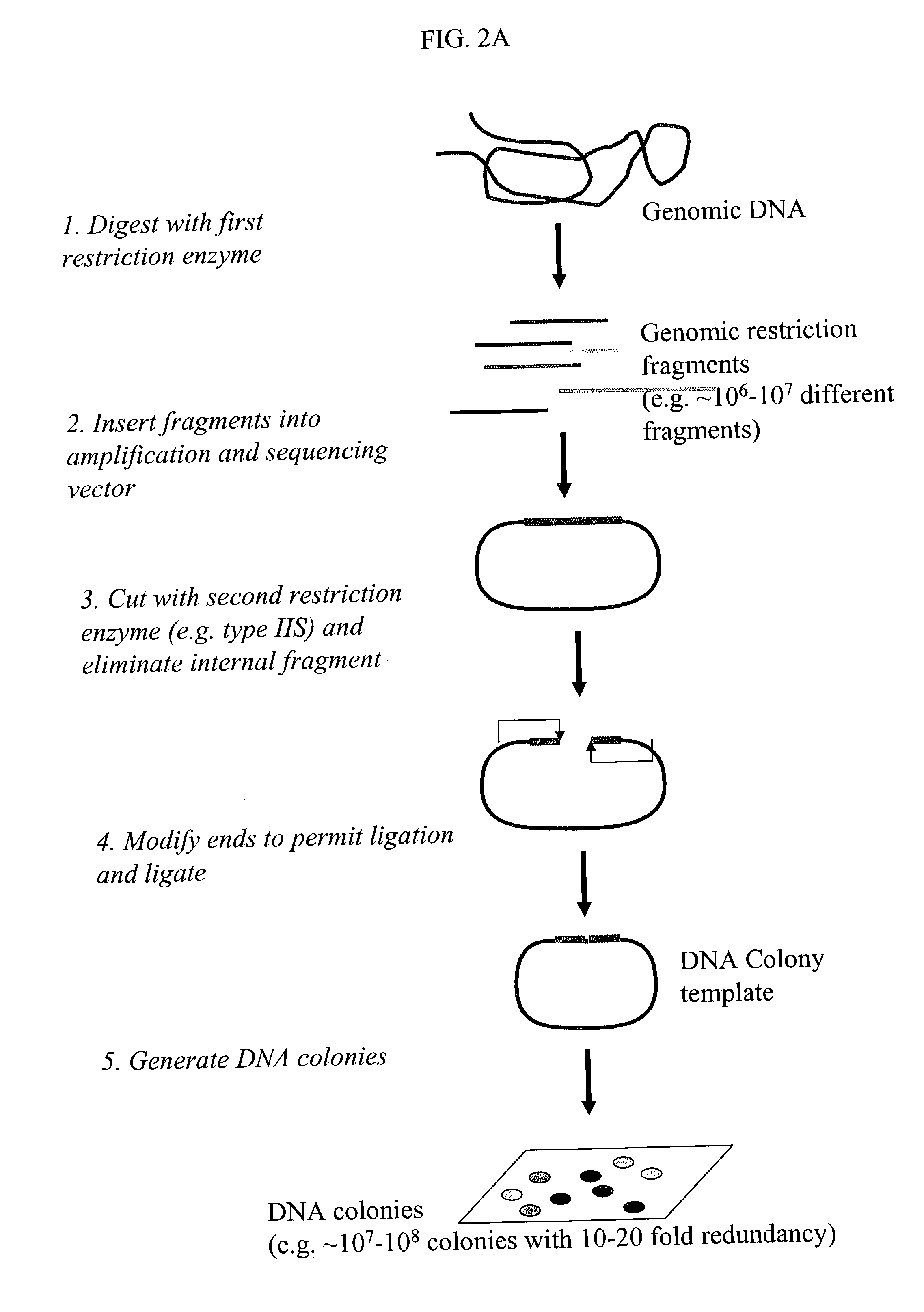
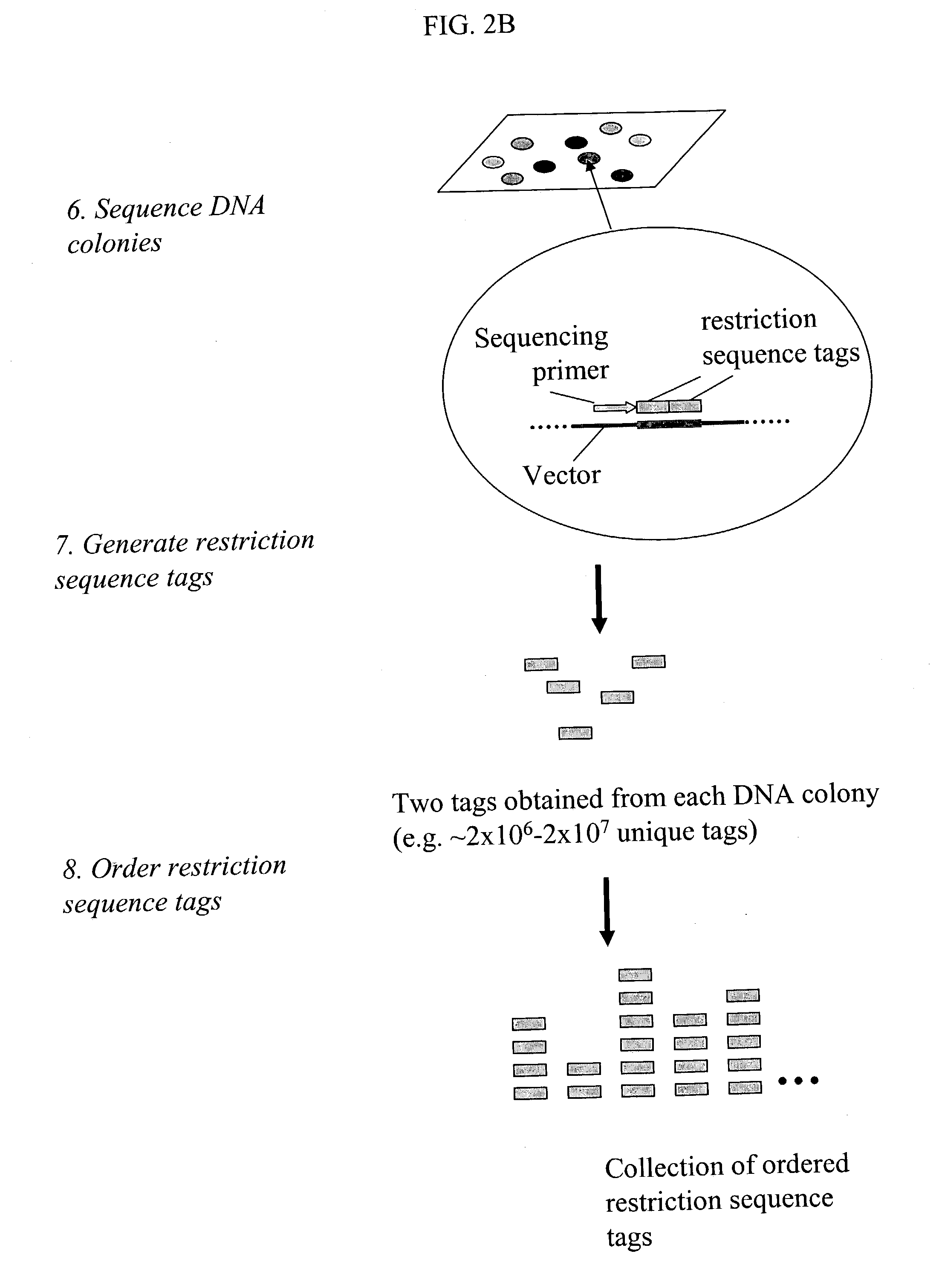
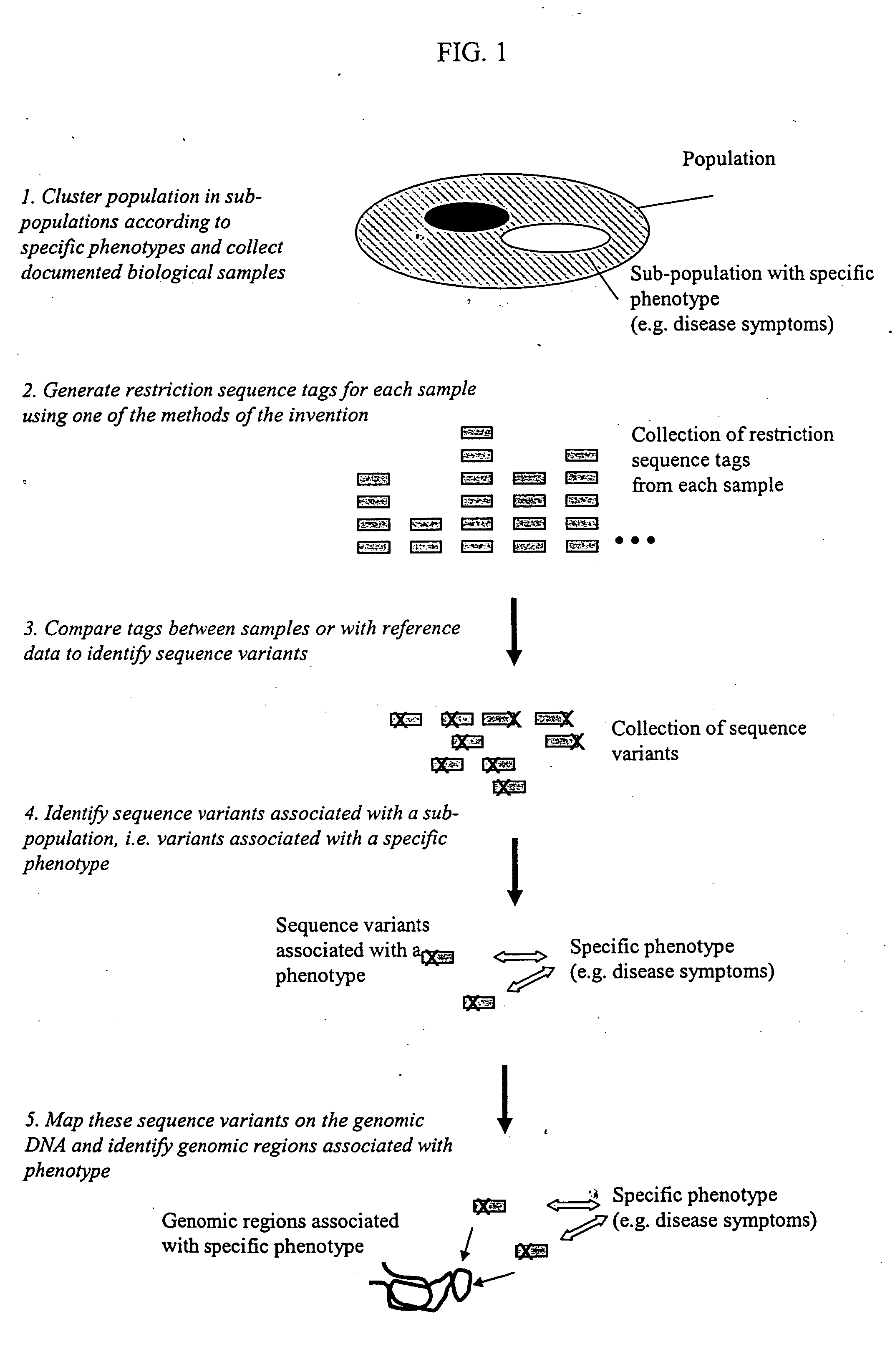
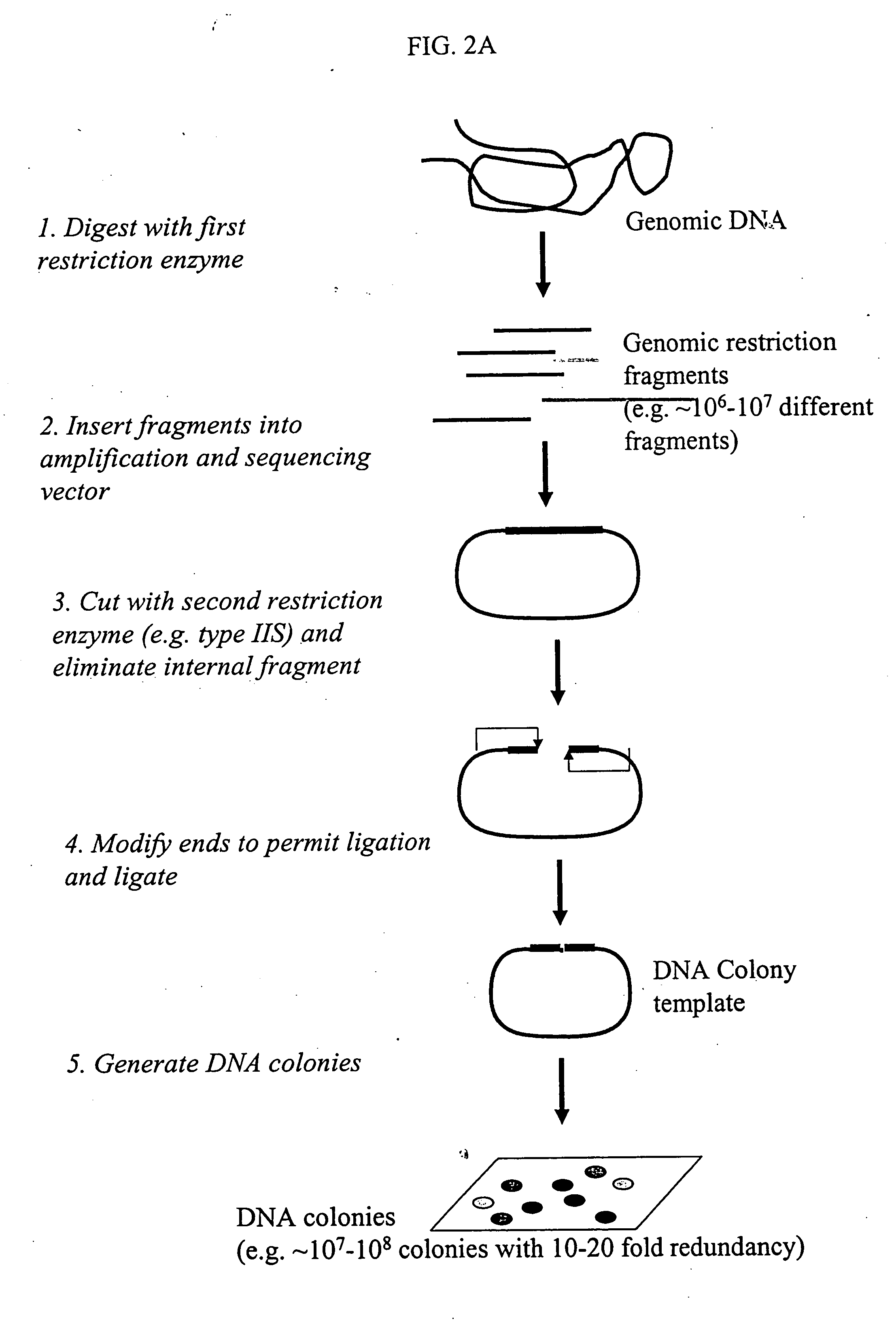
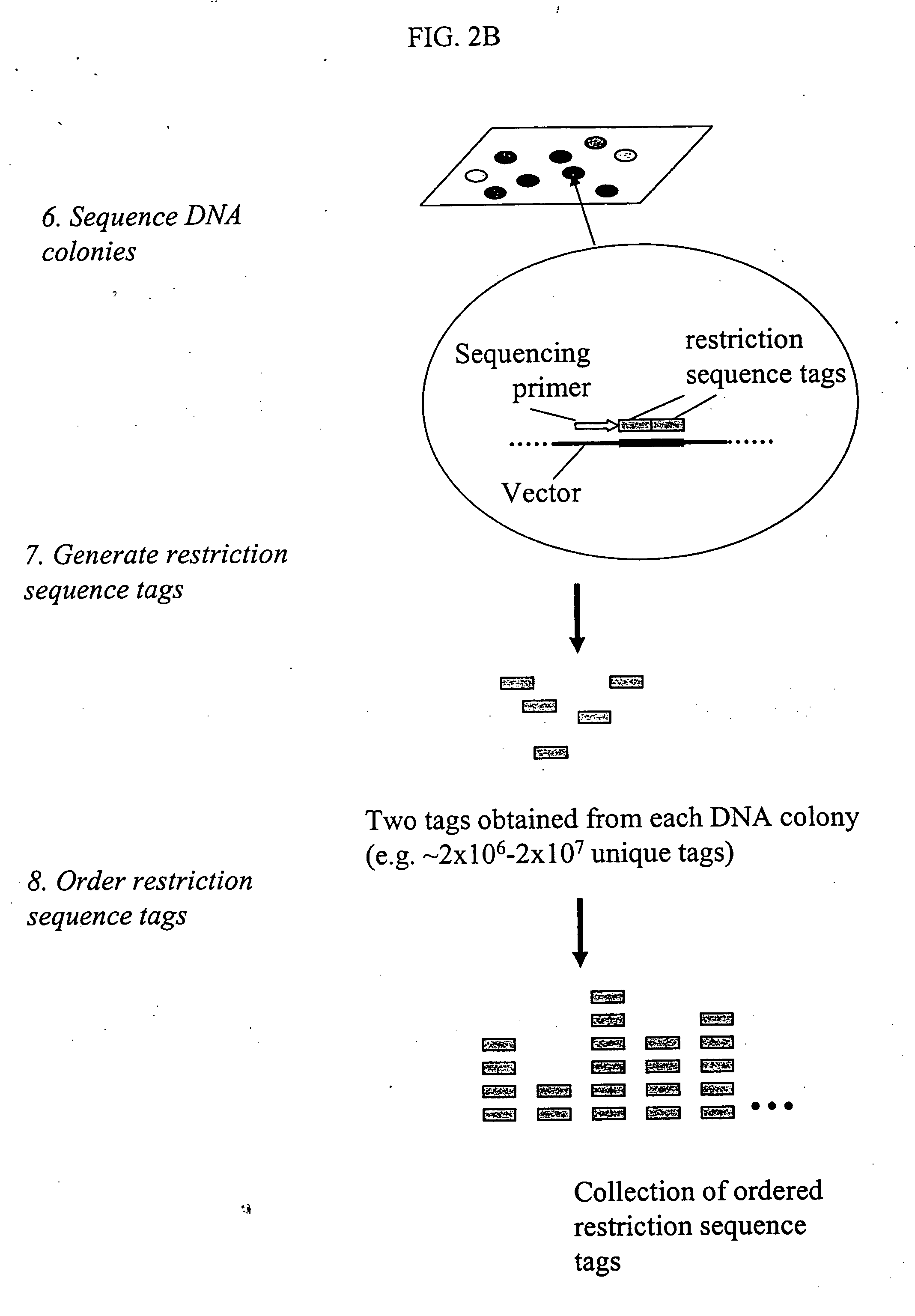
The invention provides methods for determining genome-wide sequence variations associated with a phenotype of a species in a hypothesis-free manner. In the methods of the invention, a set of restriction fragments for each of a sub-population of individuals having the phenotype are generated by digesting nucleic acids from the individual using one or more different restriction enzymes. A set of restriction sequence tags for the individual is then determined from the set of restriction fragments. The restriction sequence tags for the sub-population of organisms are compared and grouped into one or more groups, each of which comprising restriction sequence tags that comprise homologous sequences. The obtained one or more groups of restriction sequence tags identify the sequence variations associated with the phenotype. The methods of the invention can be used for, e.g., analysis of large numbers of sequence variants in many patient samples to identify subtle genetic risk factors.
Owner:SOLEXA
Aggregating and pooling health related information in a communication system with feedback
InactiveUS7305348B1Office automationComputer-assisted diets prescription/deliveryHealth related informationCommunications system
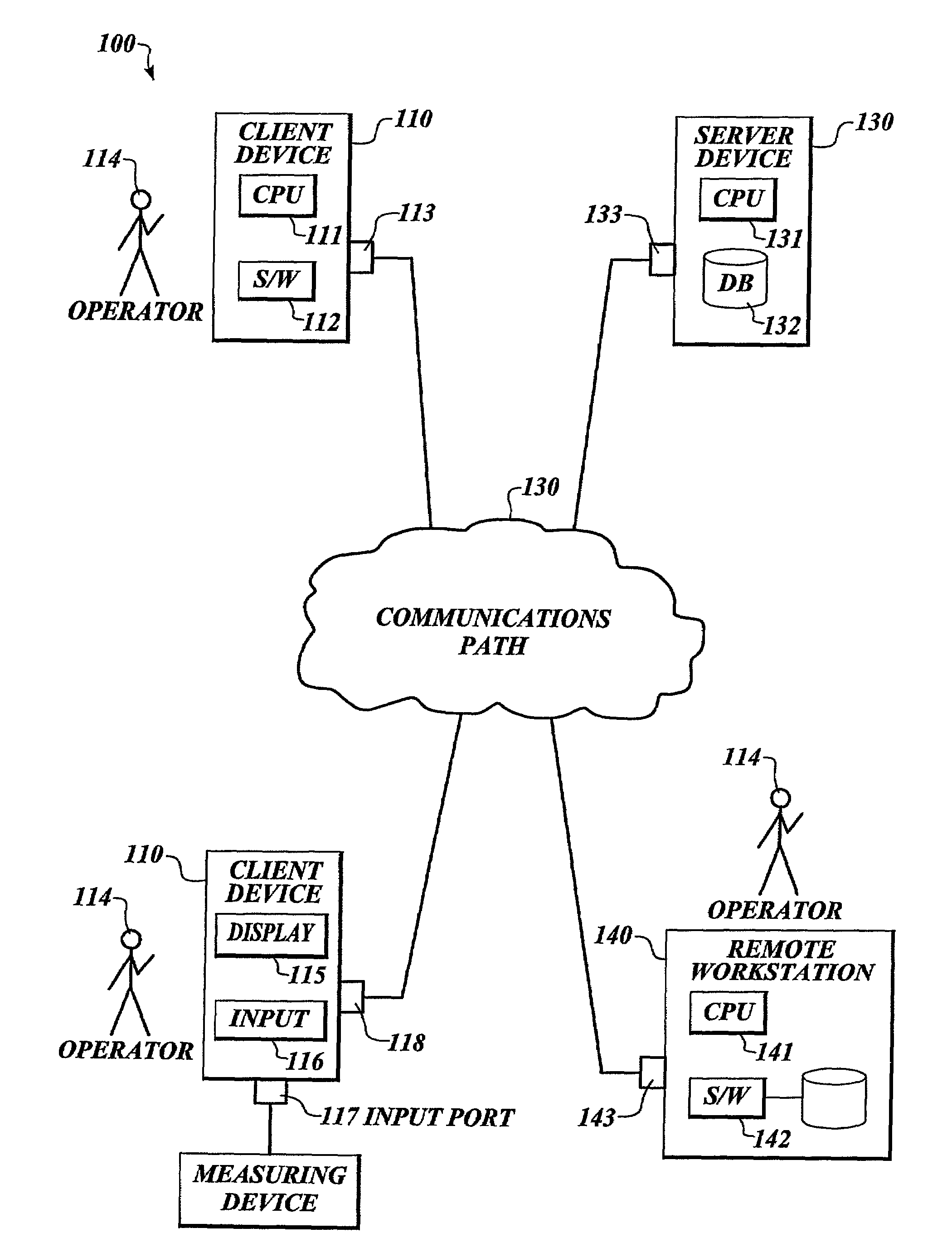
The invention provides a method and system for aggregating and pooling information with feedback in a computer communication system. A communication system includes a server device and a set of client devices. Each client device collects information from an associated individual (whether by asking questions of those individuals, or accepting data input from peripheral devices), and transmits that data to a server device. The server device, or some other device at its behest, determines statistical information with regard to that data (such as aggregate, correlation, dispersion, or other measures), and provides that information to a communication channel for distribution to the individuals. The communication channel can include either (1) a broadcast communication channel that members of an affinity group can display, or (2) redistributing the determined statistical measures to associated individuals using the client devices. The statistical measure (such as an aggregate or sum) can be computed and distributed for the entire population, or can be computed and compared for selected sub-populations as a contest.
Owner:HEALTH HERO NETWORK
Deterministic High-Density Single-Cell Trap Array
ActiveUS20130078163A1Meet needsReduce shearBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHigh densityShear stress
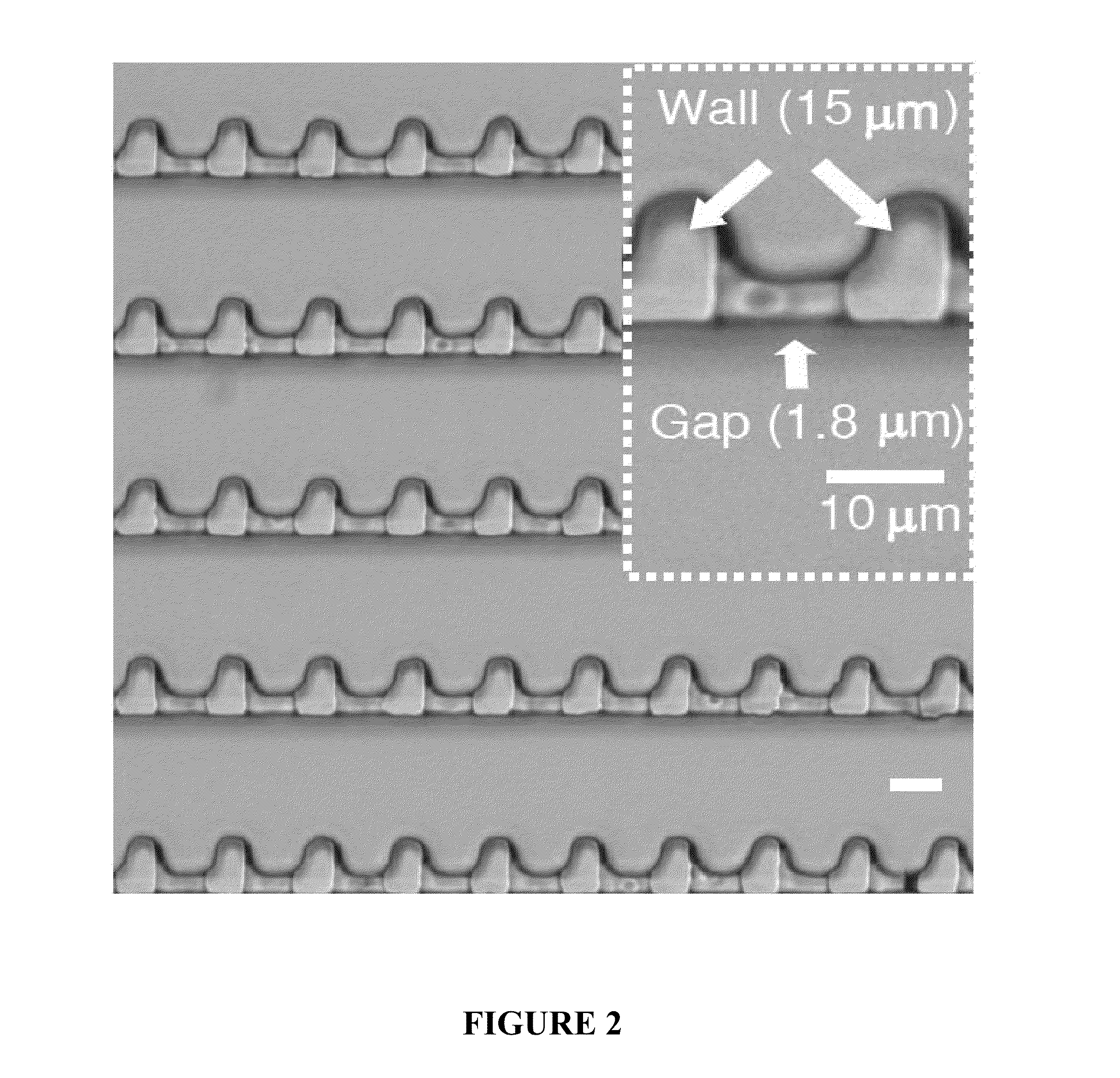
A microfluidic platform for single-cell capture, stimulation, and imaging. It passively traps 4,000 single cells on a 4.5 mm2 footprint in 30 seconds, with a single-cell loading efficiency of 95%. The array format and optimized geometry allows for easy, robust and efficient single-cell loading, while maintaining captured cells in a low shear stress environment for long-term studies. Because cells are captured sequentially, the system is adequate for rare cell samples. Trapped cells can be exposed to various environmental conditions and chemical stimulus and their dynamic response can be monitored over time. The information gained from high-throughput, single-cell time lapsed imaging presents new opportunities in quantifying cellular responses, as averaged information by other measurement methods eliminates sub-population phenotypes.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Method and system for predicting remaining life for motors featuring on-line insulation condition monitor
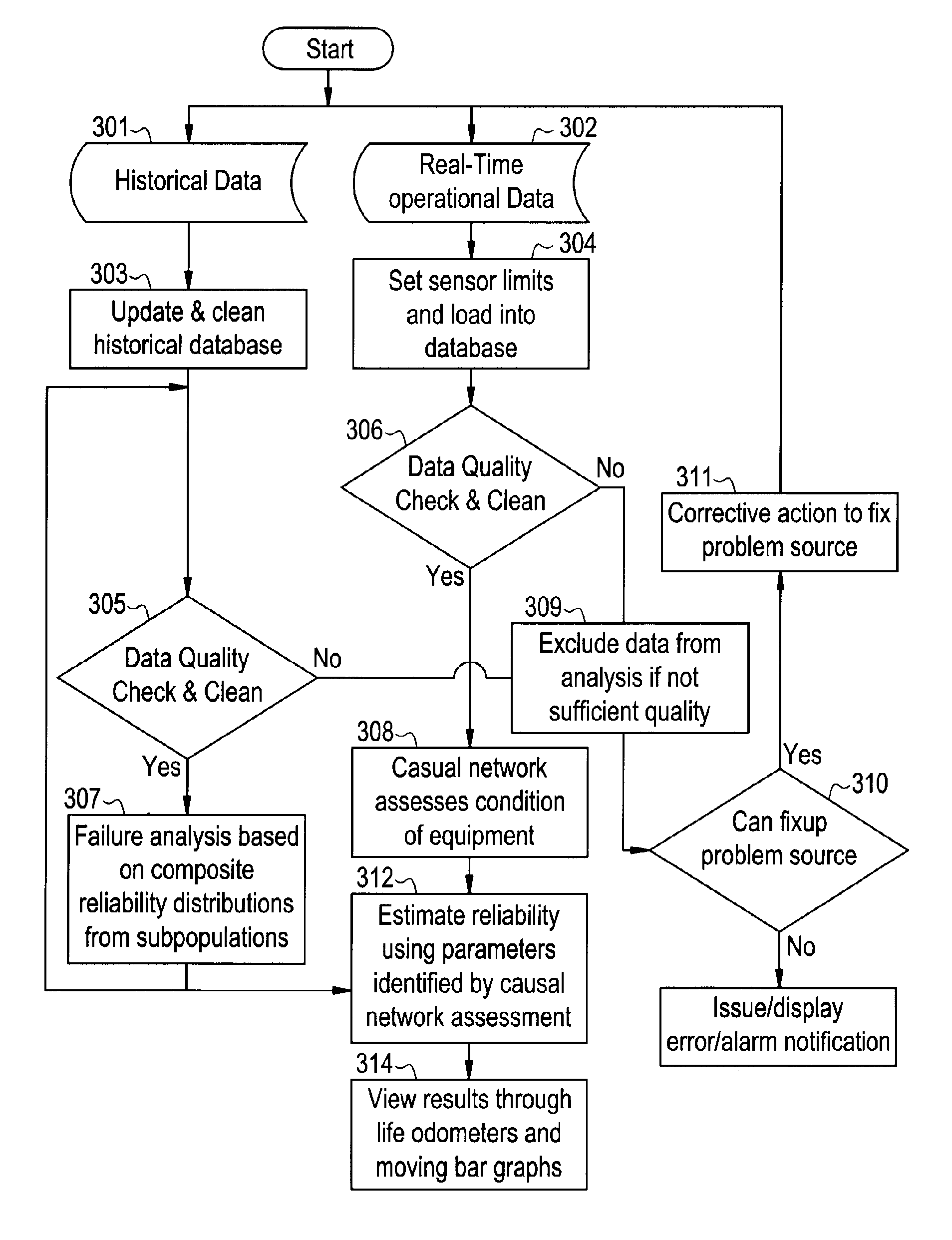
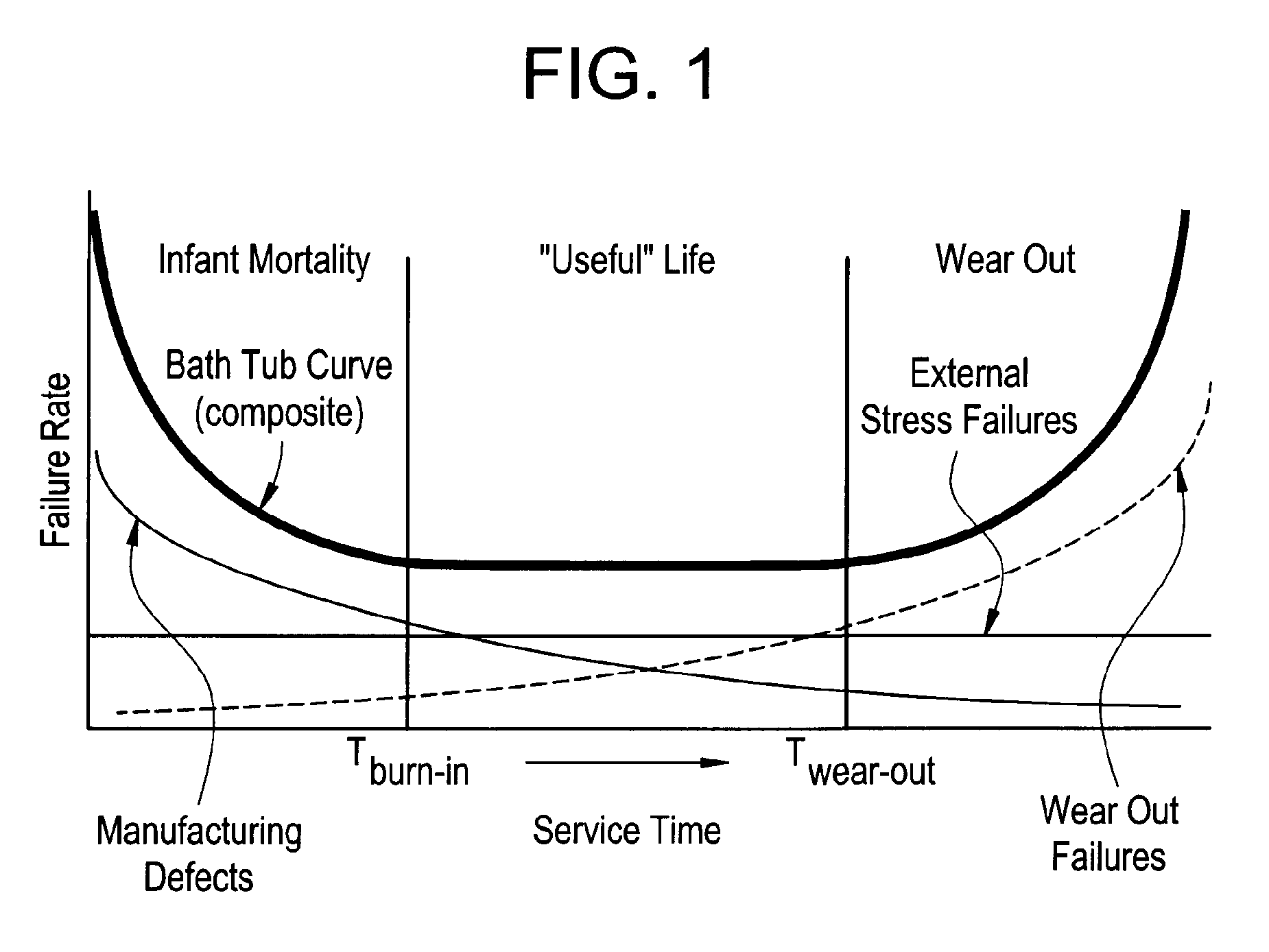
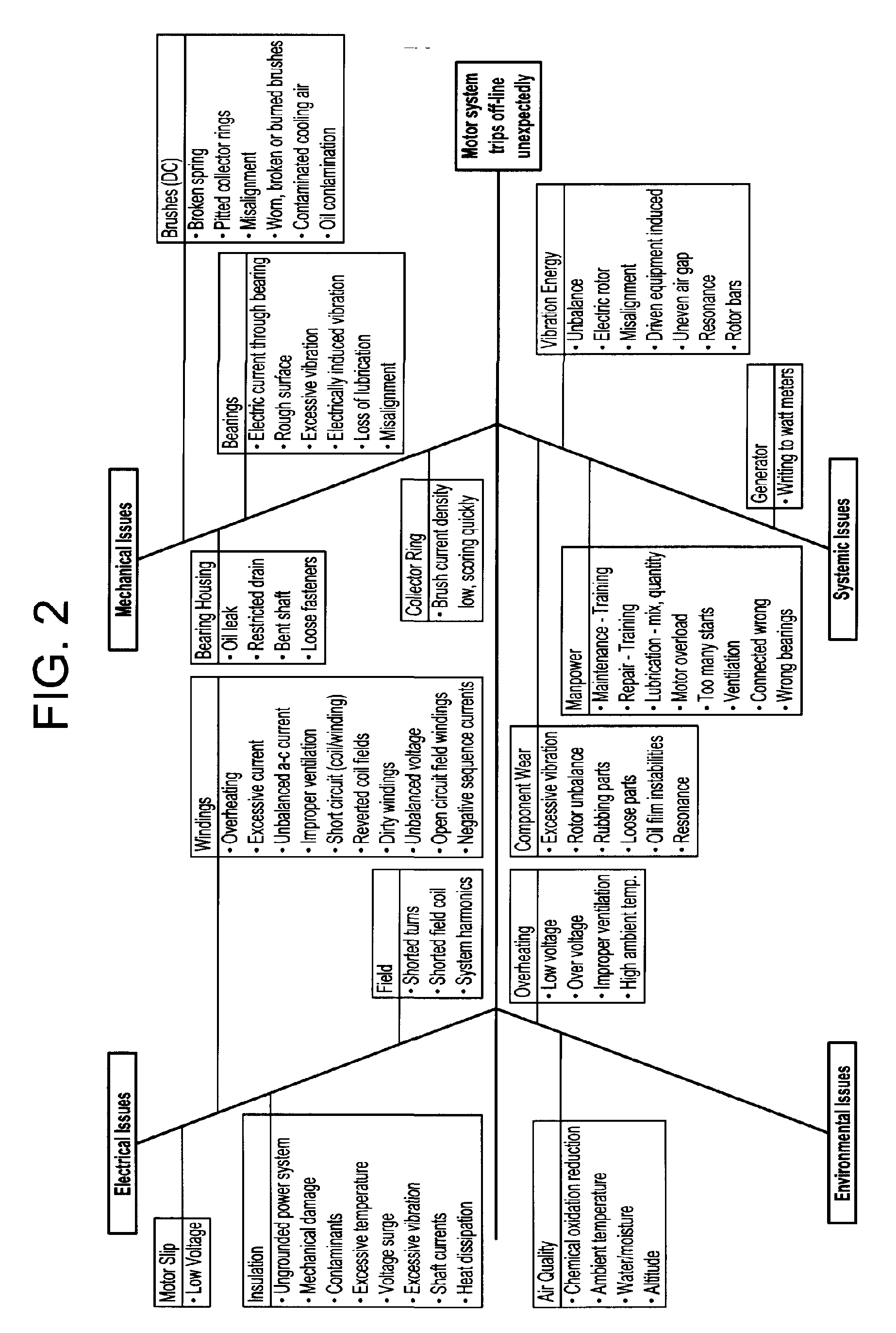
A method for determining reliability and a remaining time before failure with statistical confidence for a motor system includes acquiring historical motor data in a computer system, obtaining operational parameter data, uploading the operational parameter data to the computer system, performing failure analysis, developing a causal network, and performing an integrated causal network and reliability analysis of the motor system. The historical motor data corresponds to the motor system. The operational parameter data is obtained from sensors at the motor system. The sensors include a tan delta sensor. The failure analysis is performed based on a composite of reliability probability distributions corresponding to predetermined sub-populations of historical motor system failure causes. The causal network is developed for modeling reliability of one or more motor system components and assessing motor system component condition based on the causal network. Results from the performing failure analysis are integrated with results from the assessing motor system component condition based on the causal network to compute a quantitative value for a time remaining before failure with an ascertained statistical confidence.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
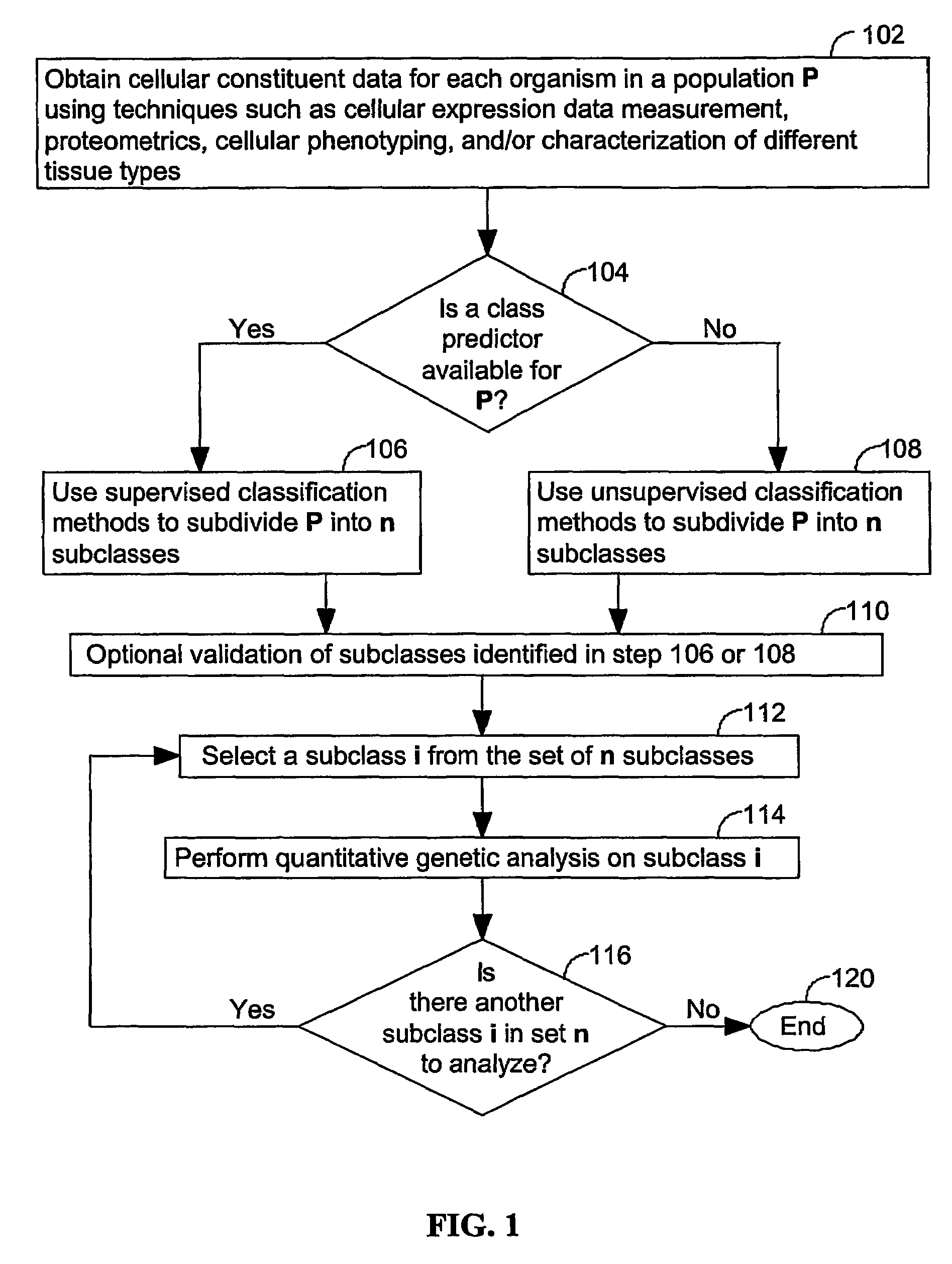
Computer systems and methods for subdividing a complex disease into component diseases
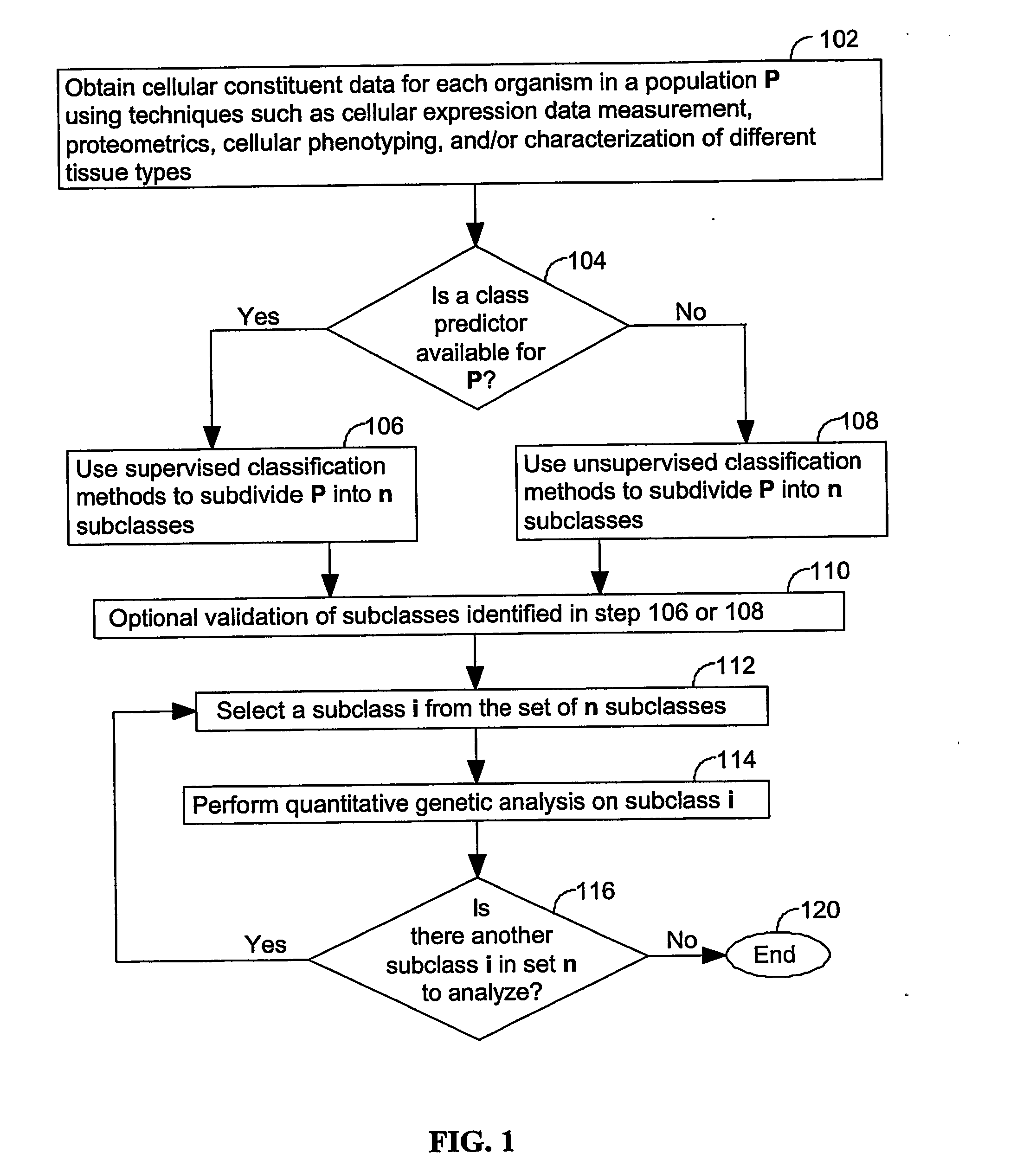
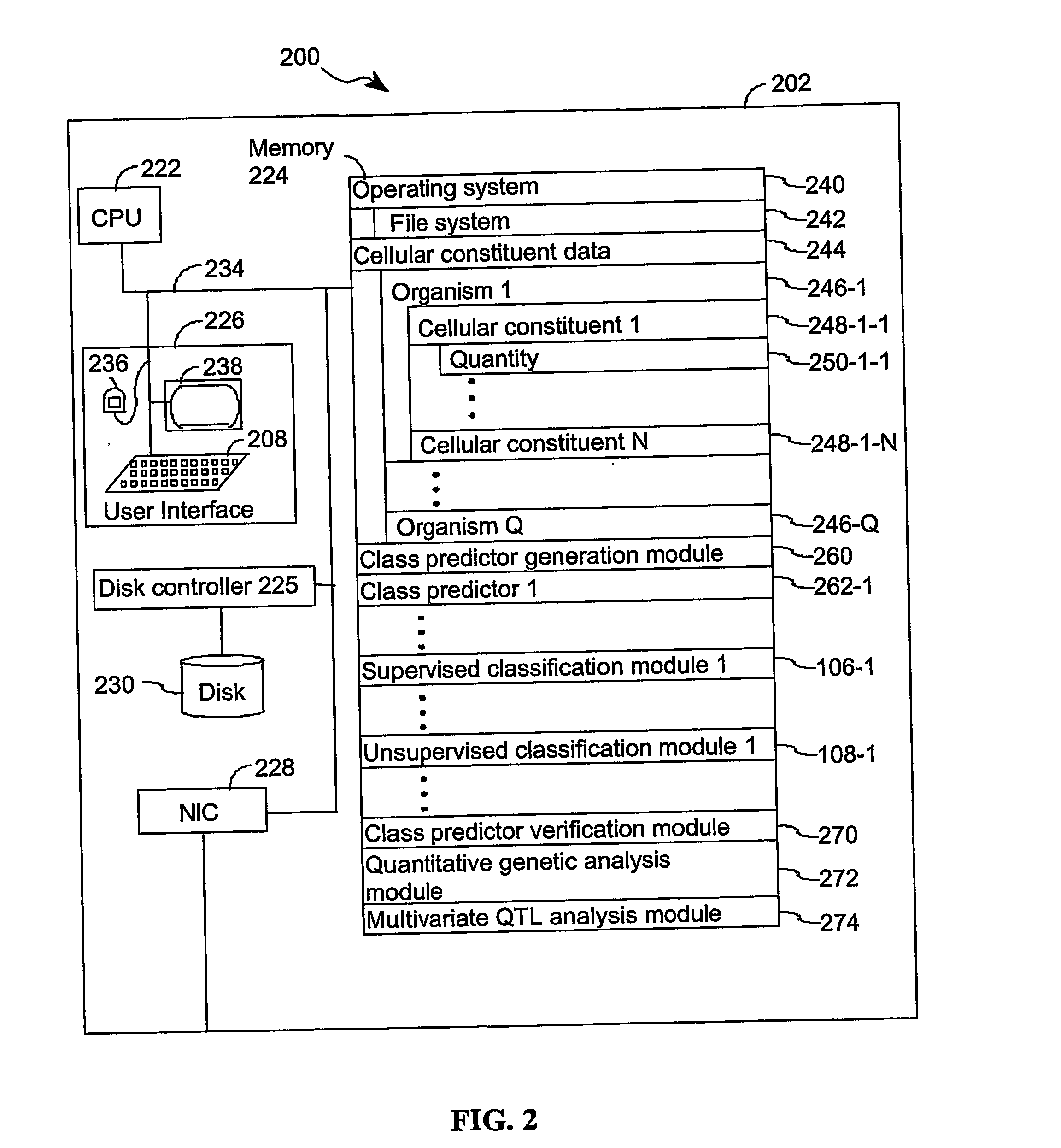
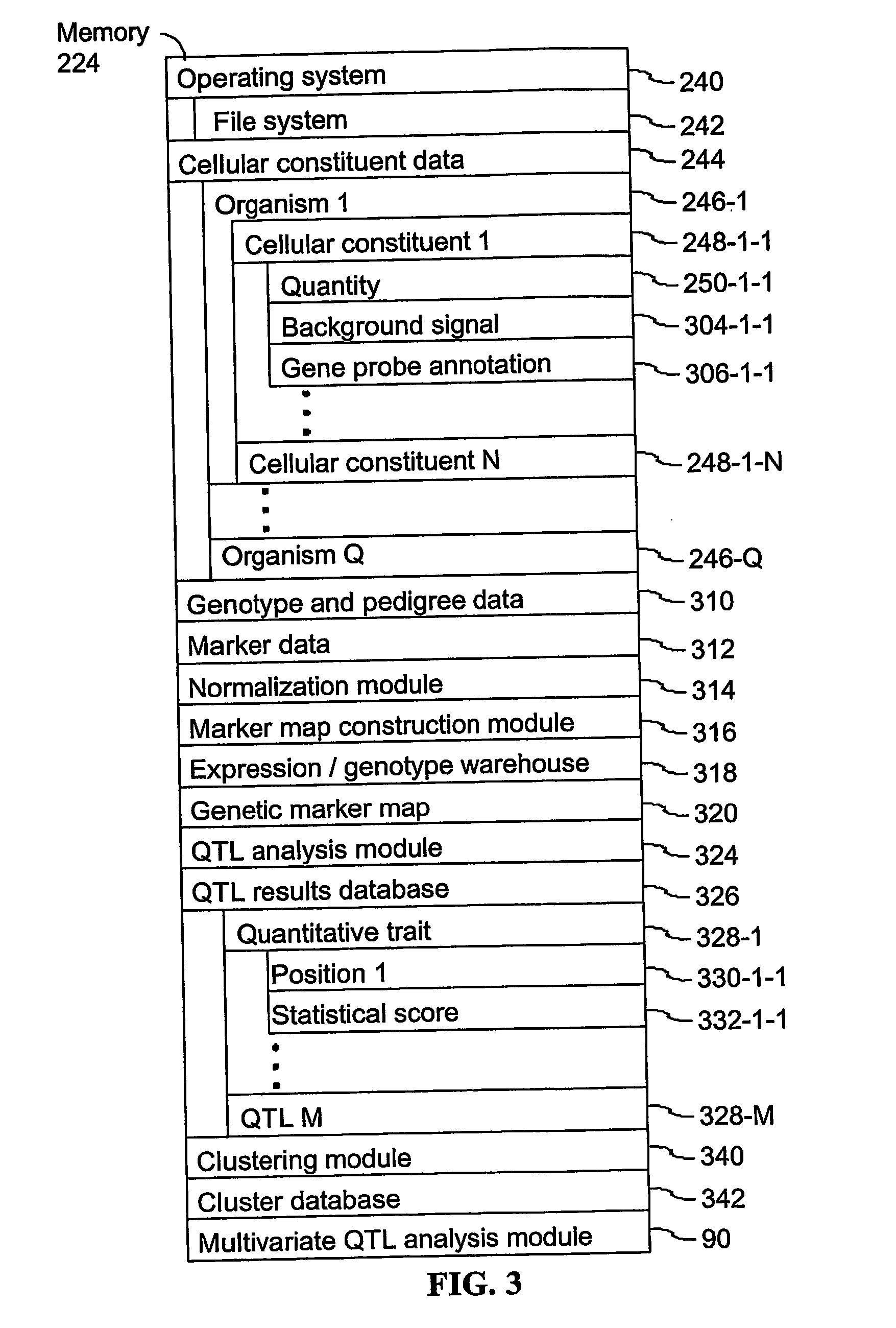
ActiveUS20060122816A1Low heterogeneityImprove accuracy and reliabilityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAnalogue computers for chemical processesBiological bodyQuantitative trait locus
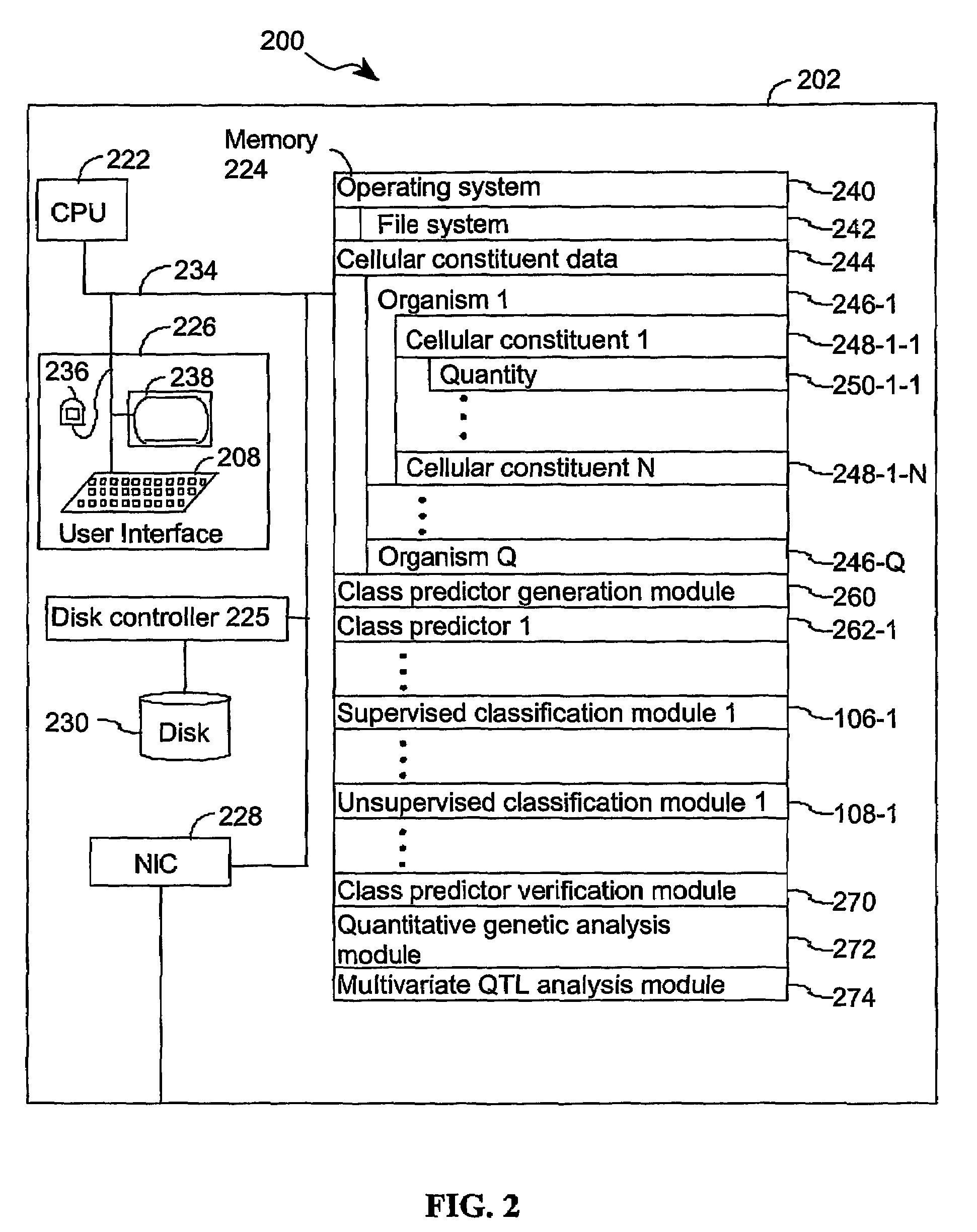
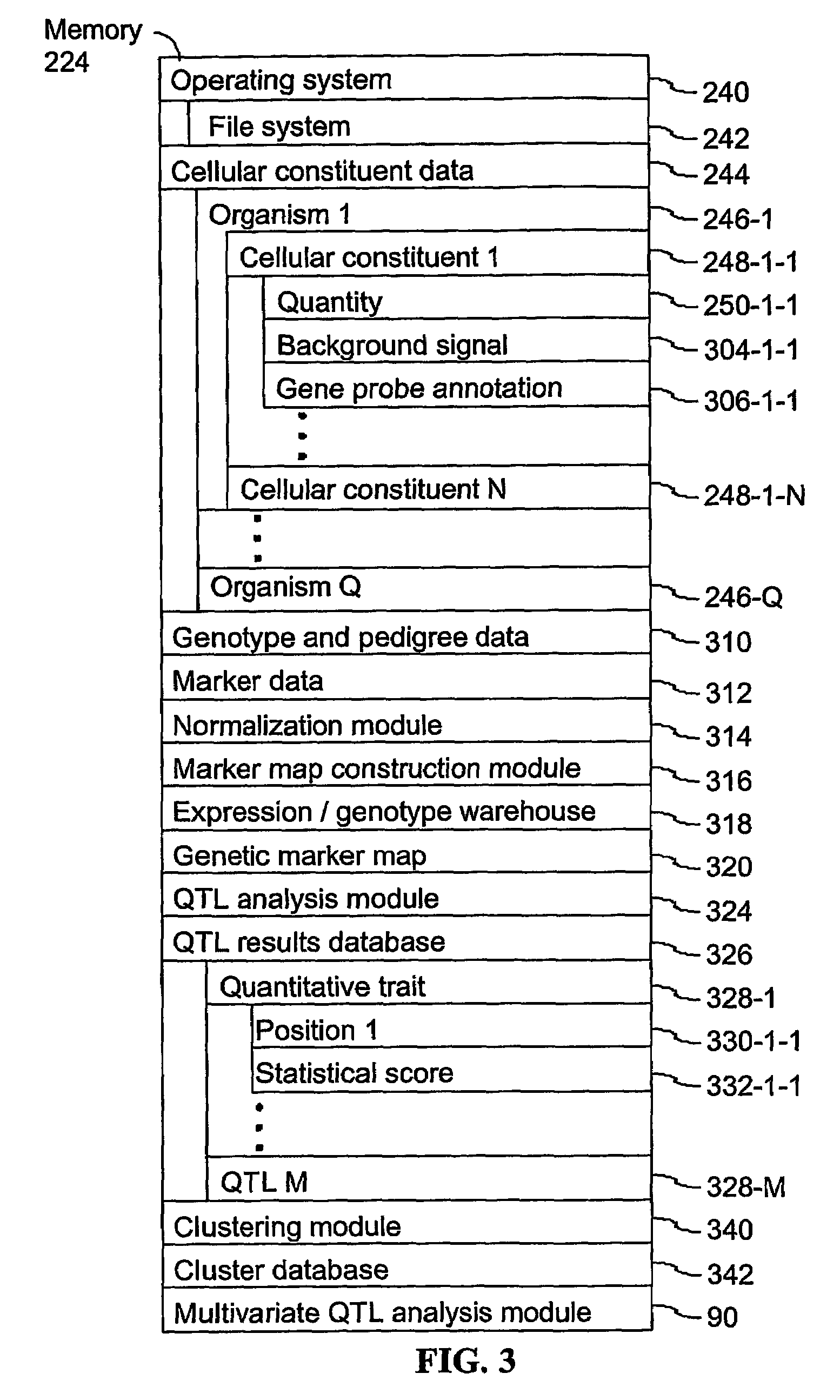
A method for identifying a quantitative trait loci for a complex trait that is exhibited by a plurality of organisms in a population. The population is divided into a plurality of sub-populations using a classification scheme. Depending on what is known about the population, either a supervised or unsupervised classification is used. The classification scheme is derived from a plurality of cellular constituent measurements obtained from each organism in the population. For each sub-population in the plurality of sub-populations, a quantitative genetic analysis is performed on the sub-population in order to identify one or more quantitative trait loci for the complex trait.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Methods for identifying multiple epitopes in selected sub-populations of cells
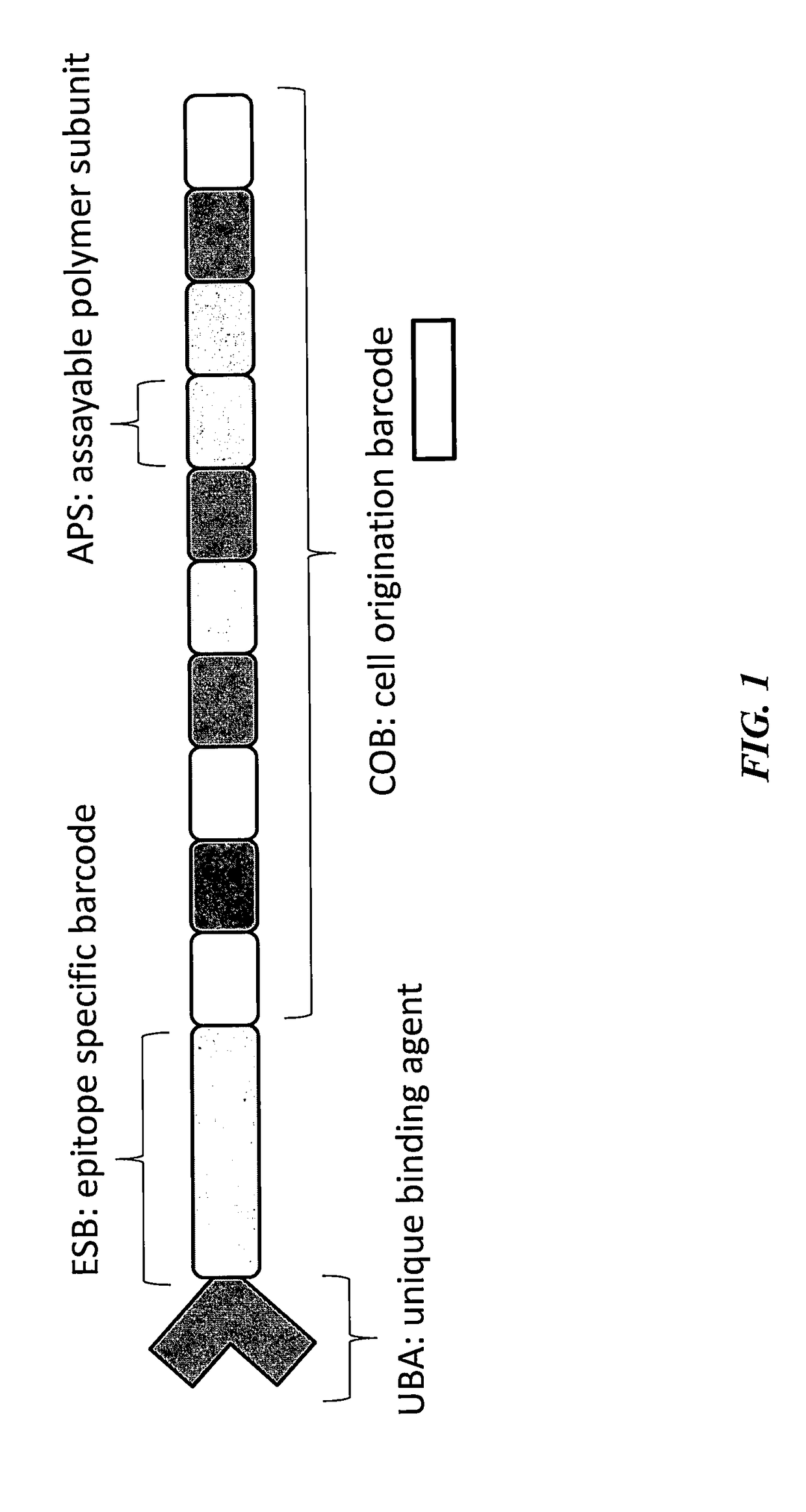
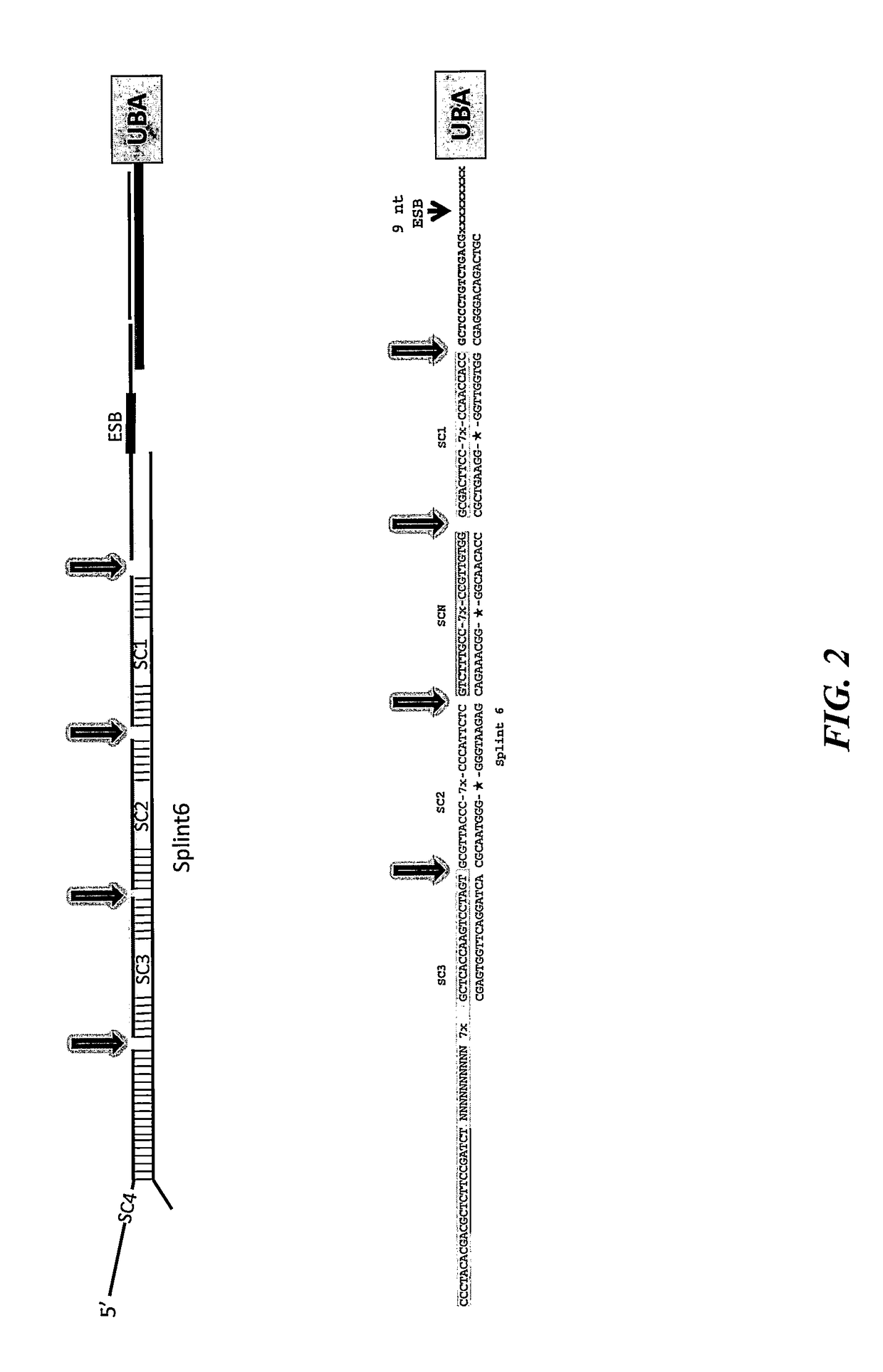
InactiveUS20180320241A1Maximize probabilityInhibition formationMicrobiological testing/measurementAssay labelsEpitope specificitySub populations
A method for identifying a sub-population within a mixed population of cells is disclosed. The method involves contacting the mixed population of cells with at least one unique binding agent, wherein the at least one unique binding agent is designed to bind to a target molecule present in the sub-population, and wherein the at least one unique binding agent is attached to an epitope specific barcode that represents the identity of the target molecule. The method further involves sequentially attaching two or more assayable polymer subunits to the epitope specific barcode to create unique cell origination barcodes that represent the identities of individual cells to which the at least one unique binding agent has bound; and decoding the epitope specific barcode and cell origination barcodes, thereby identifying the sub-population within the mixed population of cells.
Owner:ROCHE SEQUENCING SOLUTIONS INC
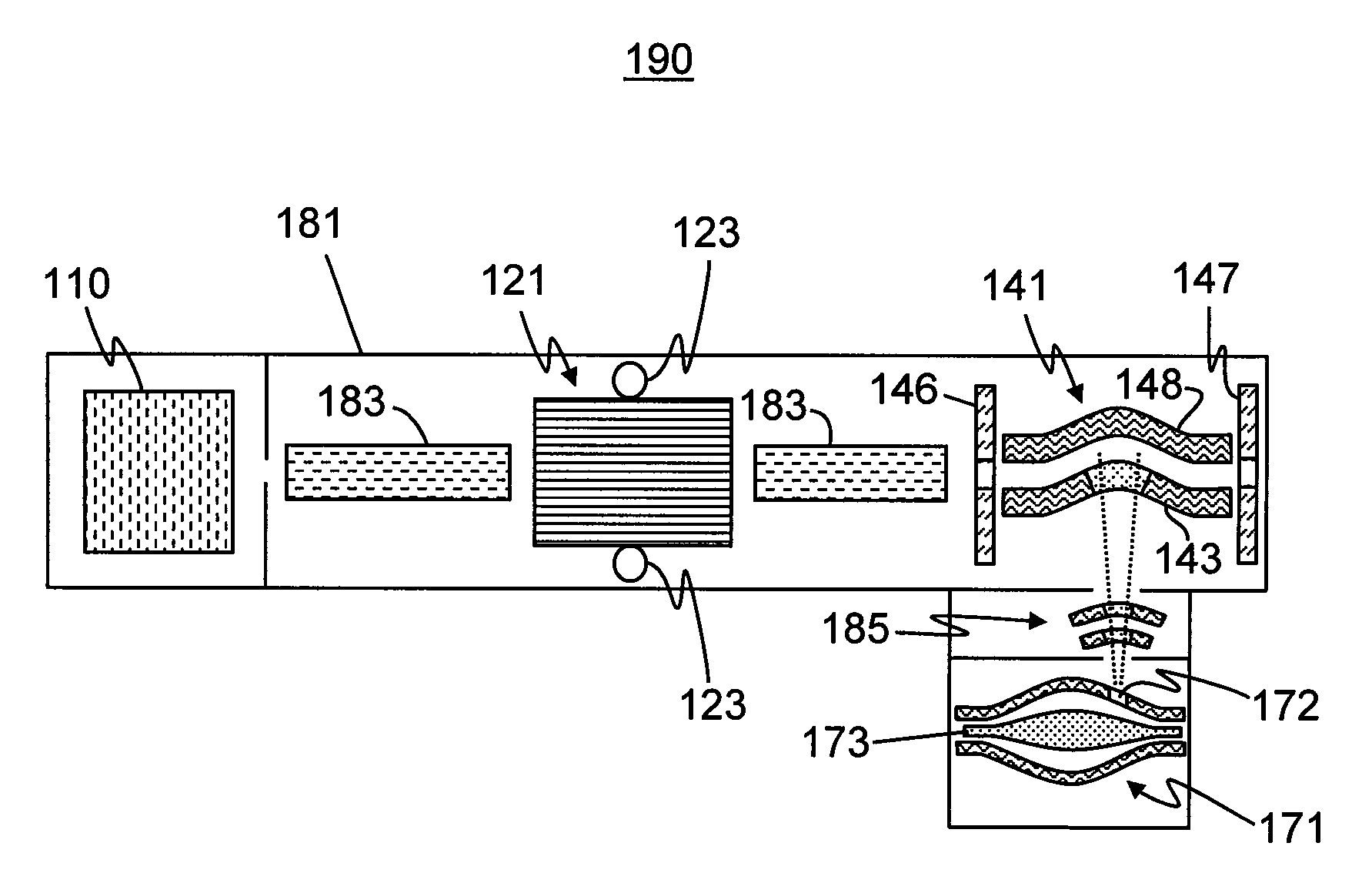
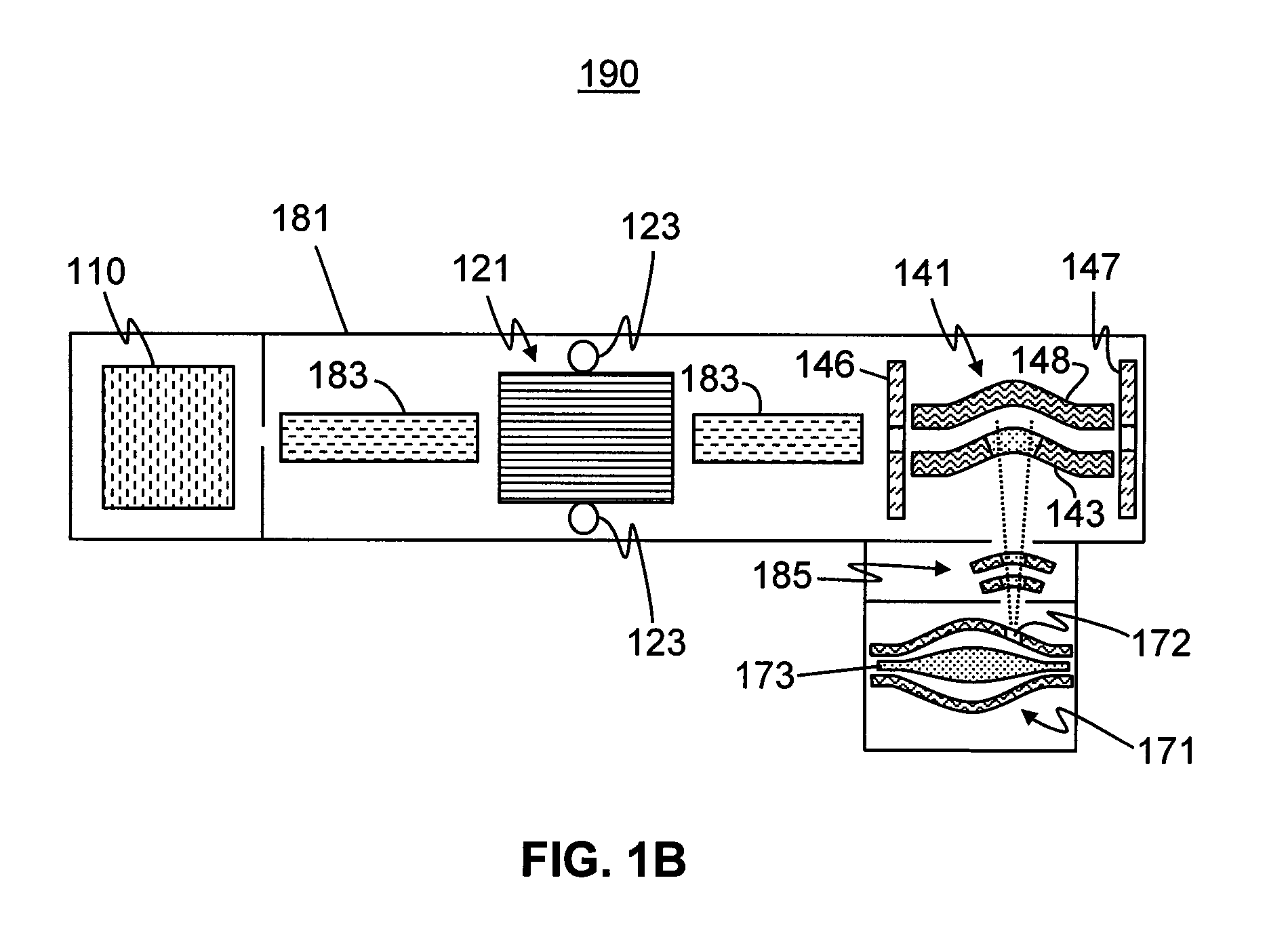
Methods for Data-Dependent Mass Spectrometry of Mixed Biomolecular Analytes
ActiveUS20160268112A1Data-acquisition redundancy is either totally eliminated or significantly reducedRich relevant informationBiological testingSpectrometer combinationsAnalyteSub populations
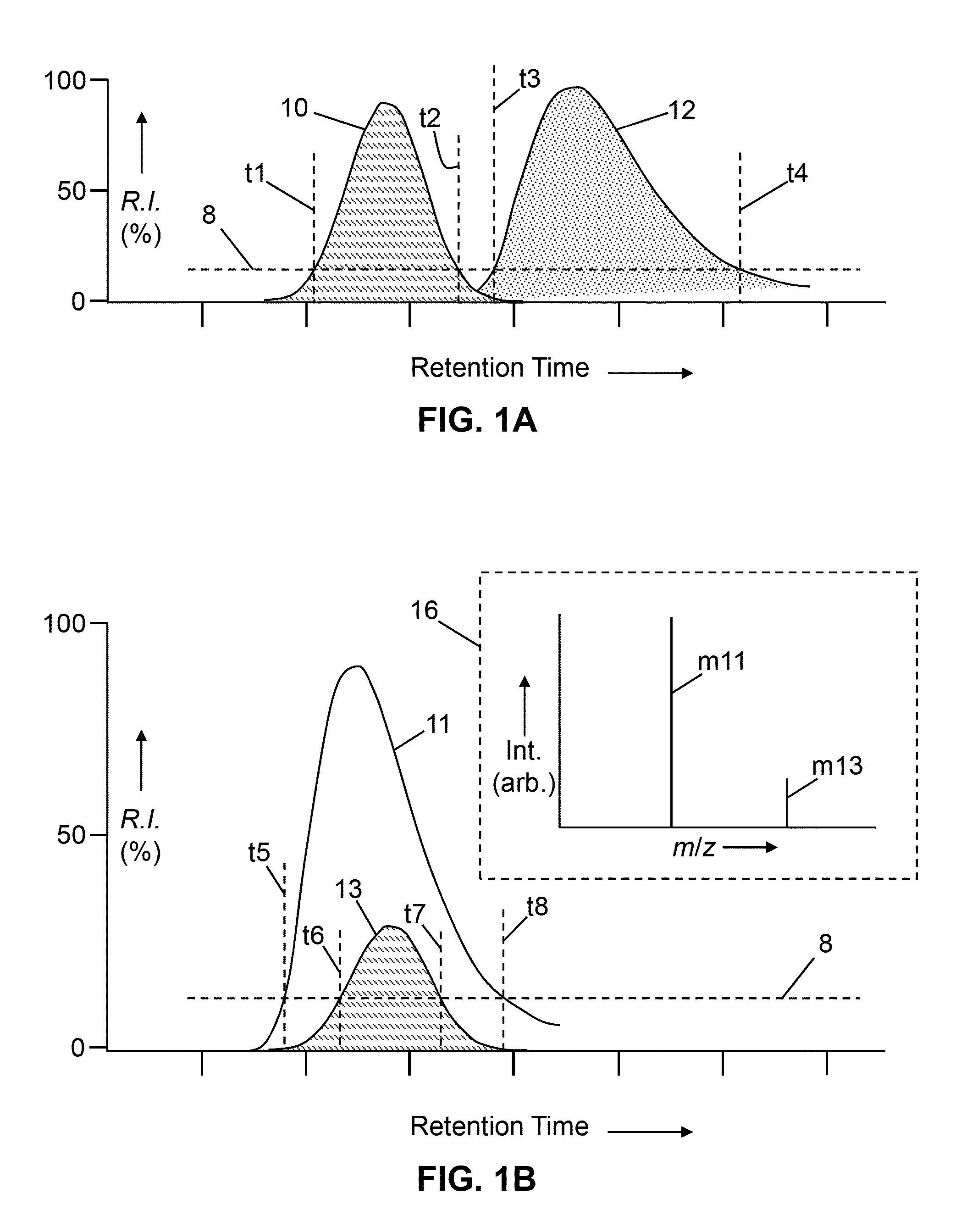
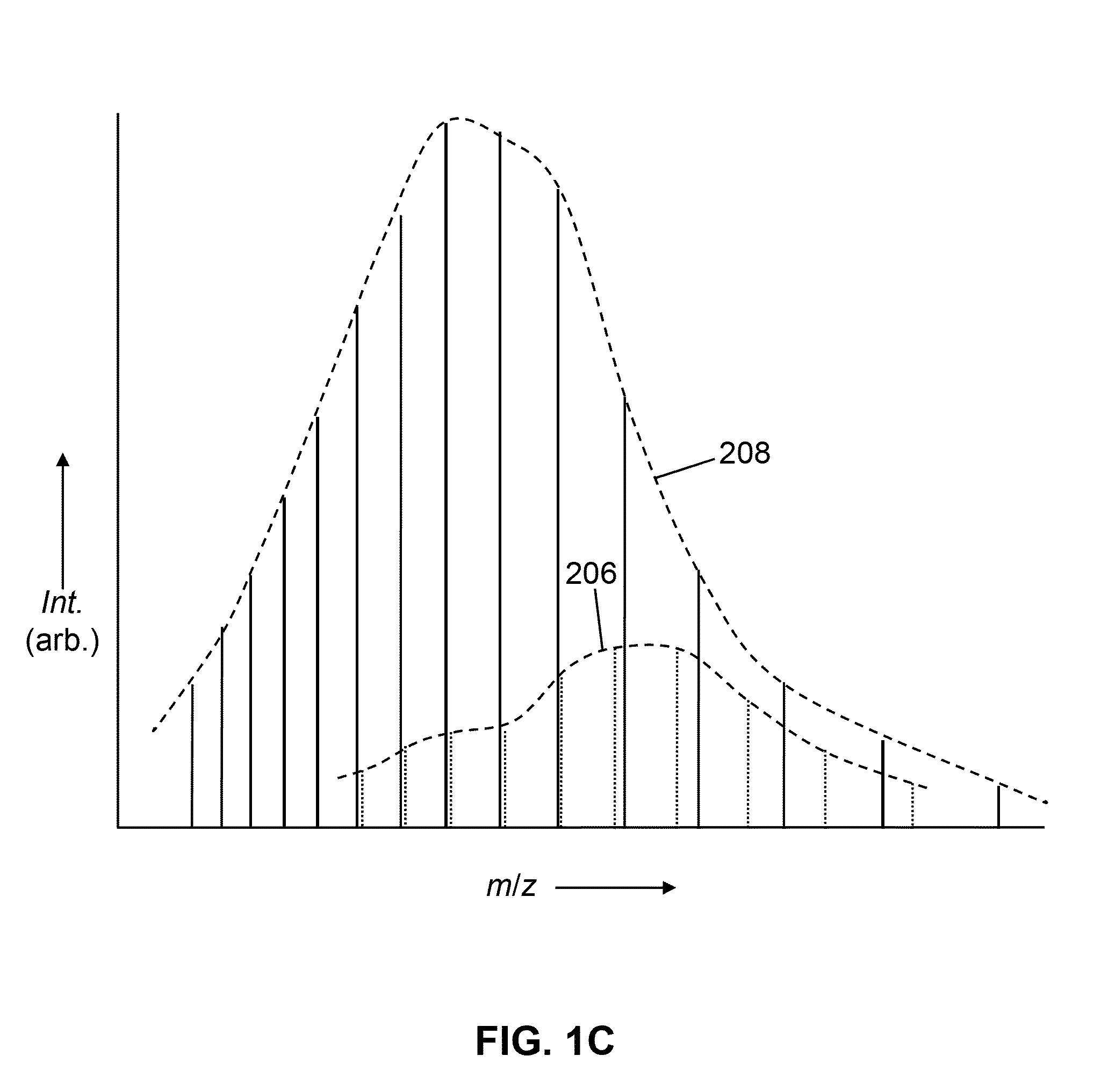
A method for mass spectral analysis of a sample containing a plurality of biomolecule species comprises: (a) mass analyzing a plurality of first-generation ion species generated from a sample portion; (b) automatically recognizing, for each of at least one biomolecule species, a respective subset of m / z ratios corresponding to respective first-generation ion species generated from the each biomolecule species; (c) selecting, from each recognized subset, a single representative m / z ratio; (d) isolating a sub-population of ions having each representative m / z ratio from ions having other m / z ratios; and (e) fragmenting each isolated sub-population of ions so as to generate second-generation ion species.
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
Job-shop scheduling method based on multi-population evolution mechanism
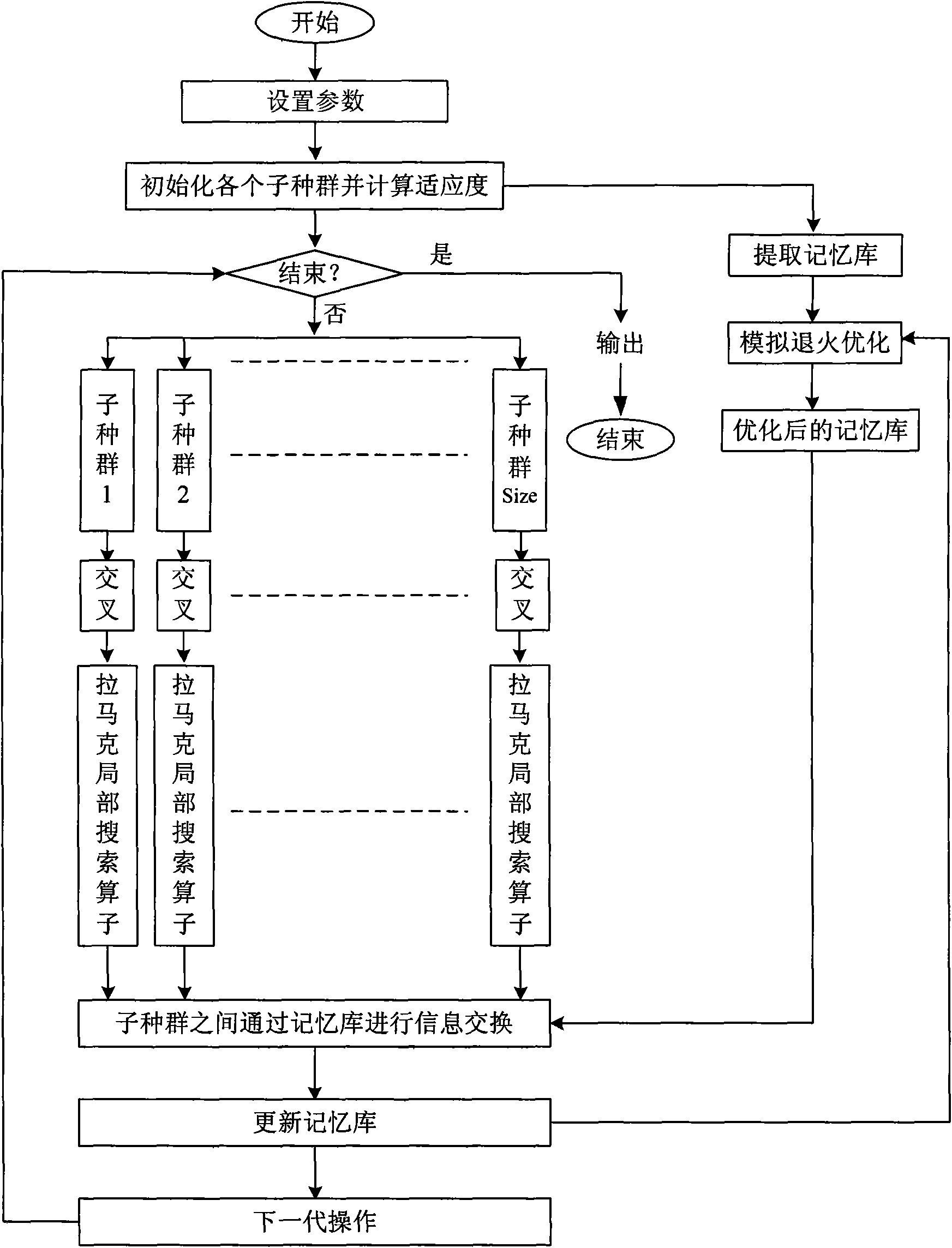
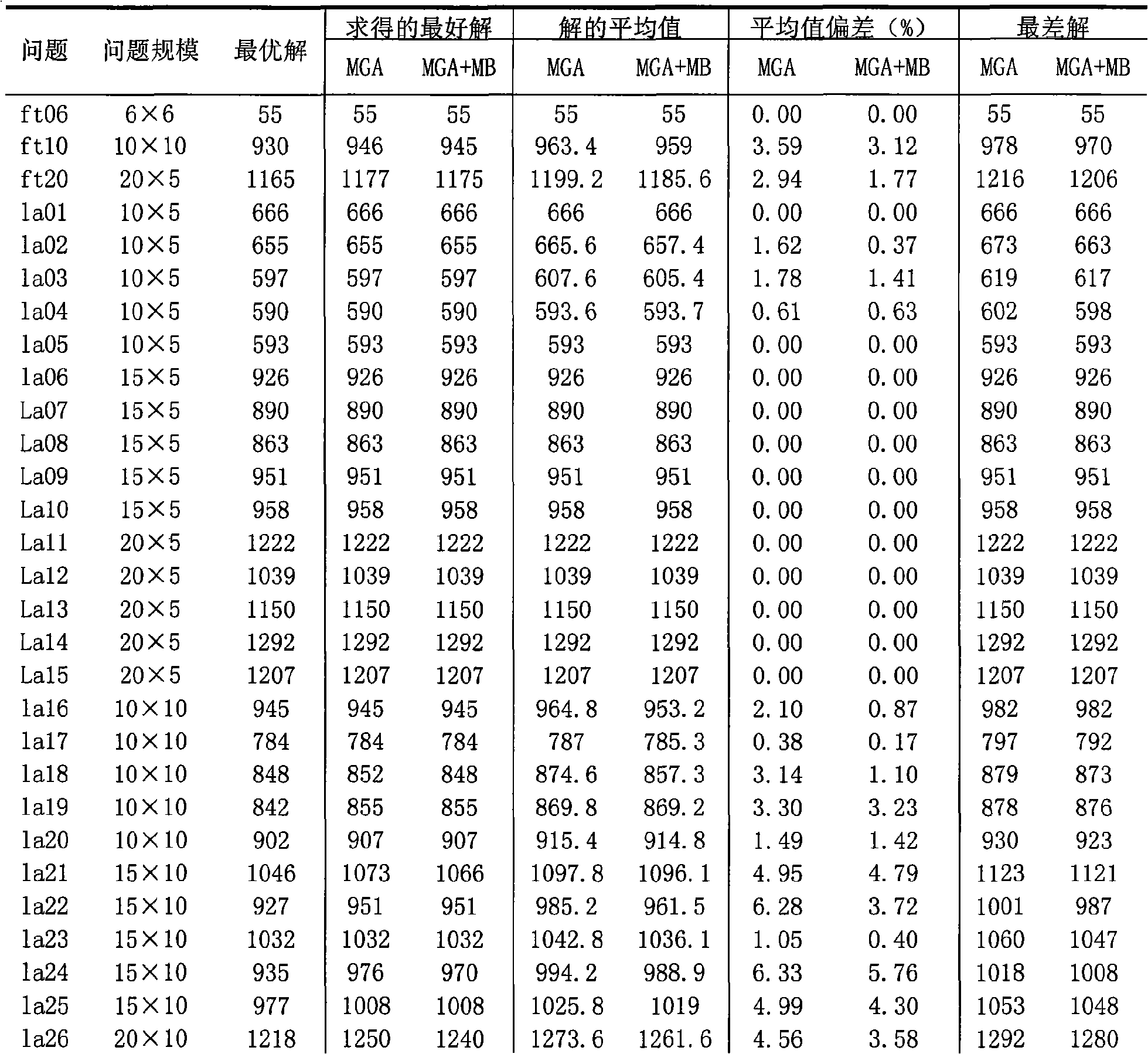
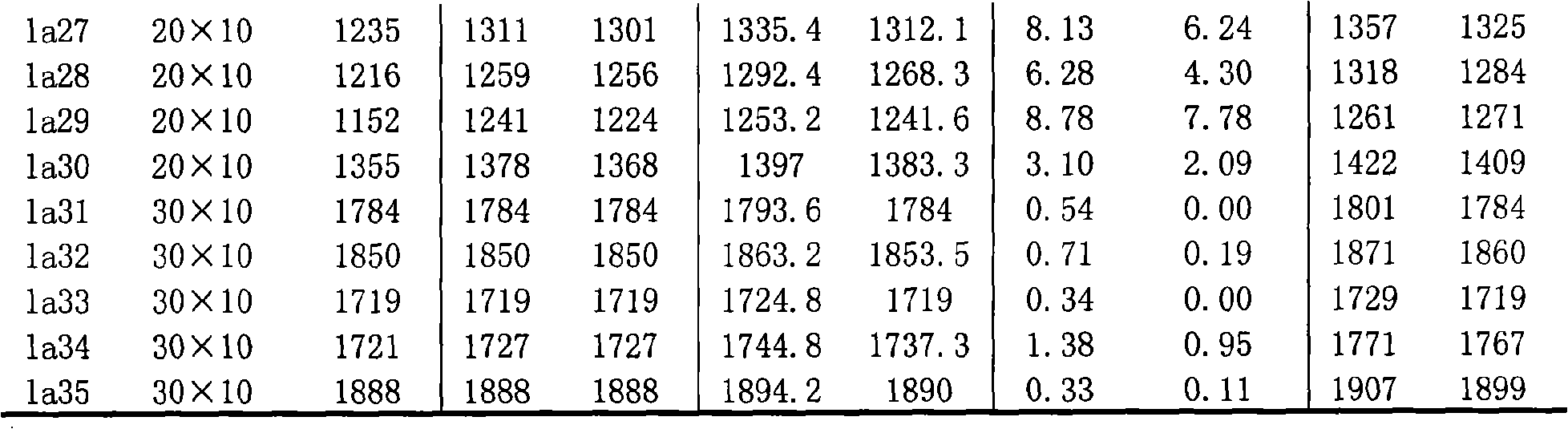
InactiveCN101630380AAvoid excessive competitionDiversity guaranteedGenetic modelsResourcesLocal optimumSub populations
The invention discloses a job-shop scheduling method based on multi-population evolution mechanism, which pertains to the computer field and mainly solves the problem that the present job-shop scheduling method of multi-population genetic algorithm is easy to be trapped into local optimization and poor local search ability. The method comprises the steps of (1) setting parameters and initializing the population; (2) evaluating the chromosomes and the initial memory bank of the population, optimizing the initial memory bank by means of the simulated annealing algorithm; (3) judging whether the termination condition is satisfied, if so, outputting the currently obtained optimal scheduling plan; otherwise, continuing step 4; (4) carrying out the crossover and mutation operation on the chromosomes in each sub-population; (5) communicating the sub-population with the memory bank; and (6) updating the memory bank and optimizing the memory bank by means of the simulated annealing algorithm, and then returning to step (3). The job-shop scheduling method of the invention can obtain the job-shop scheduling plan with high quality, shorten the production time and can be used for selecting the job-shop scheduling plan.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Population mixture modeling with an indeterminate number of sub-populations
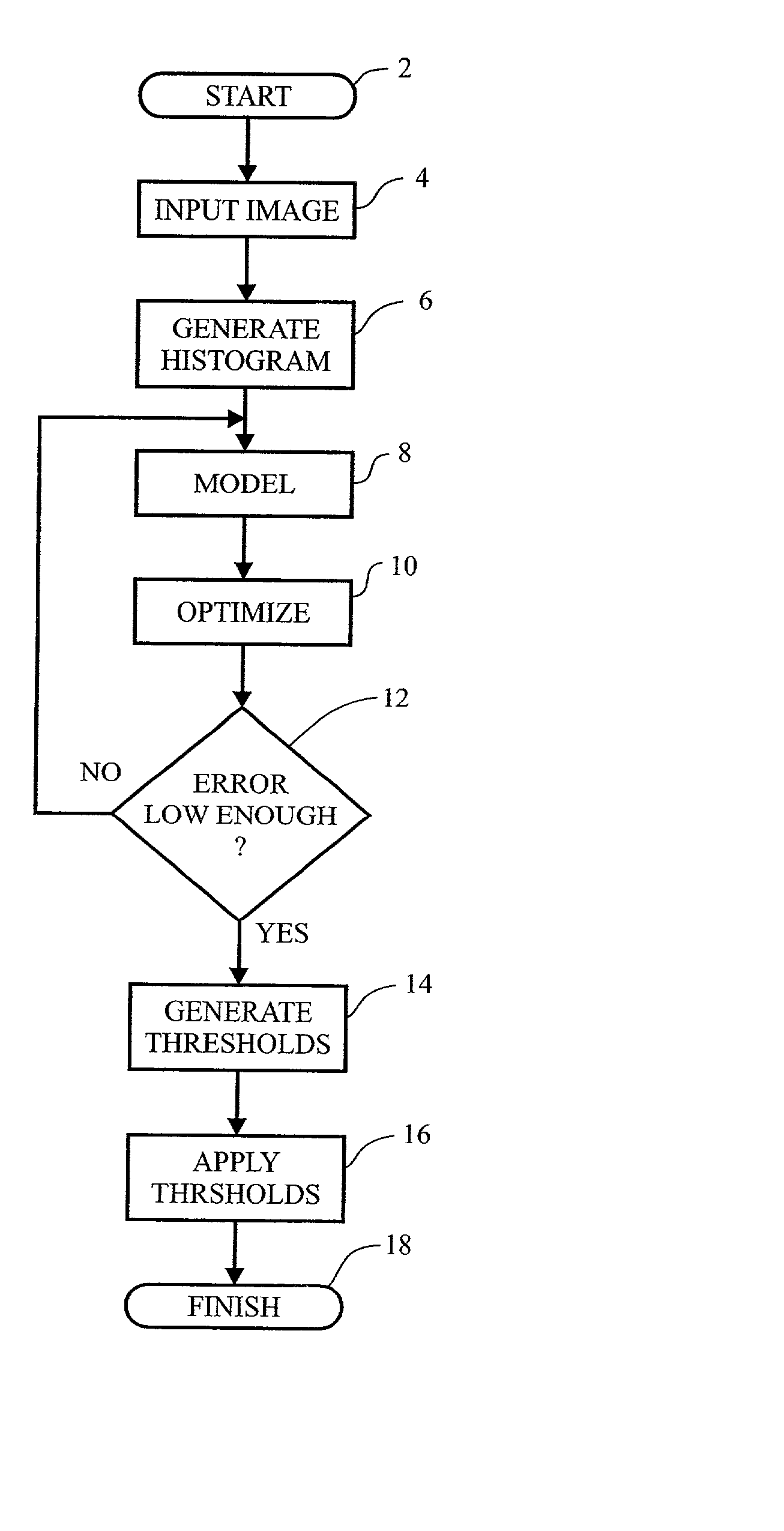
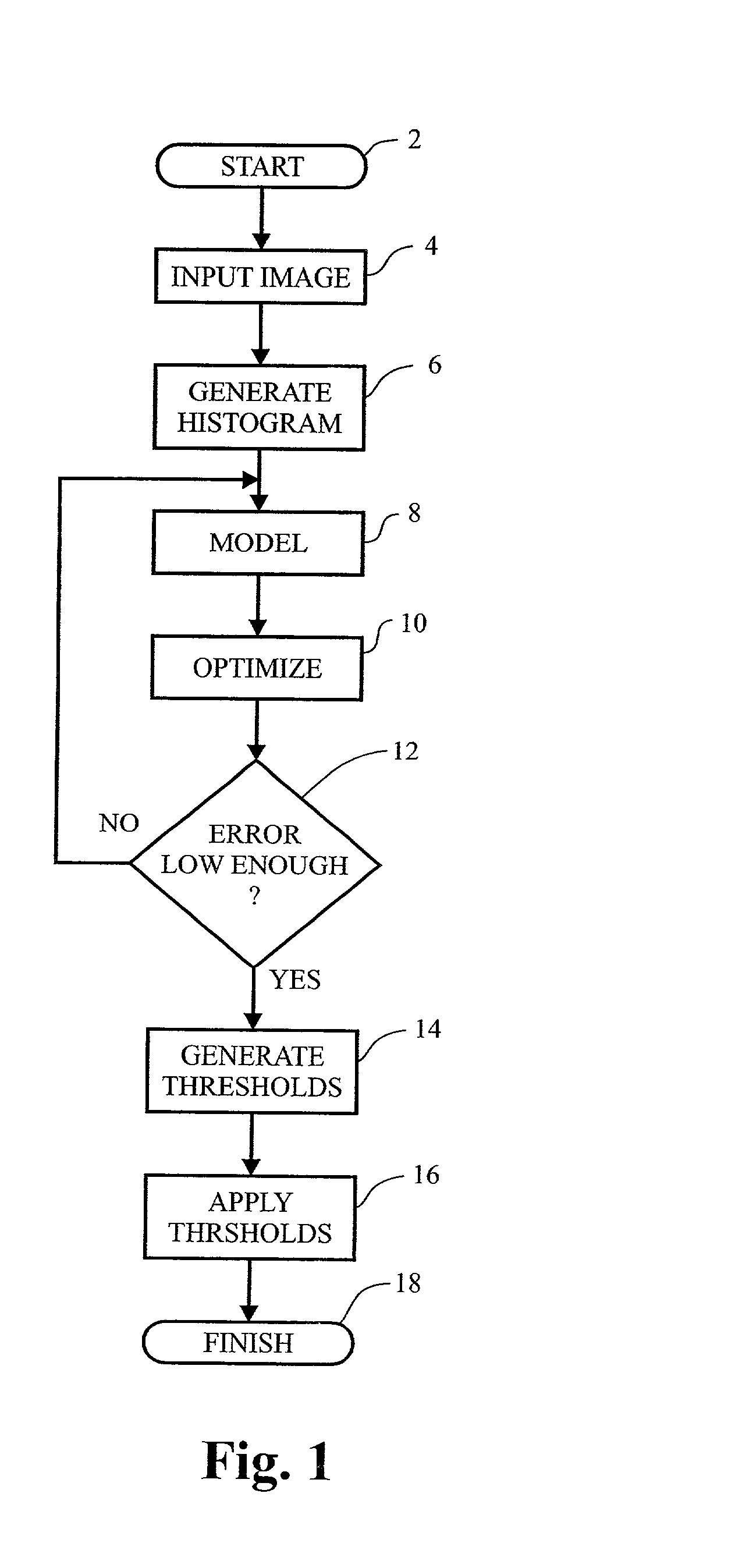
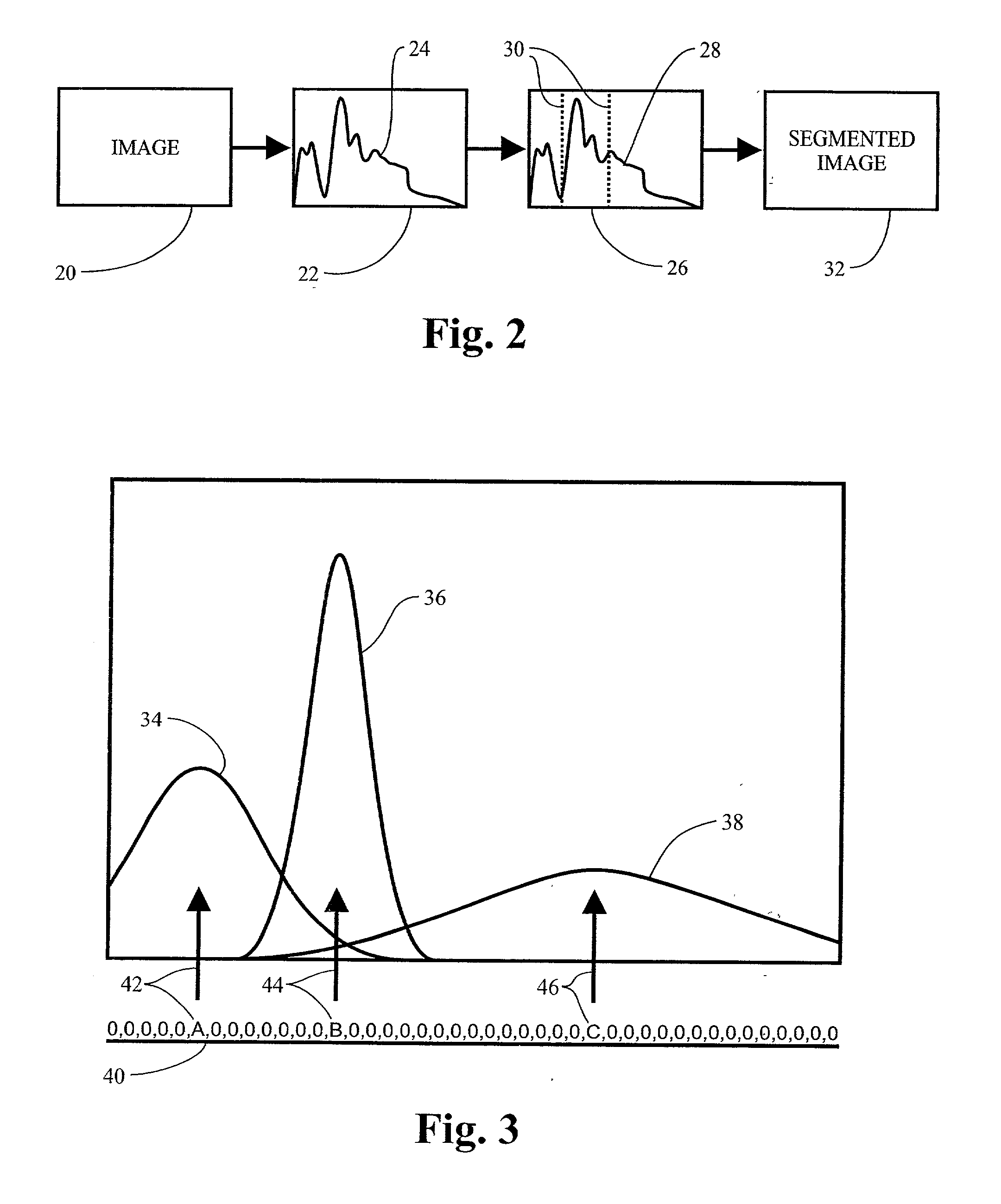
A method and apparatus for determining the best fit of a population mixture model to data. In the digital imaging area, the use of histogram data is employed. A plurality of sub-population functions are defined and then optimized to fit the data. An objective function is employed, which is based upon the parameters of the underlying functions. The number of underlying functions is added to the parameter mix, such that no a priori knowledge of the number of sub-populations is required. In an illustrative embodiment, a genetic algorithm is used to evolve the objective function to an optimal fit of the data. Once an optimal fit is found, through comparison with stopping criteria in a fitness function, the data is segmented according to threshold determined based of classification error in the data.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
Multi-objective power flow optimization method of VSC-HVDC (voltage source converter-high voltage direct current) containing alternating-current/direct-current system
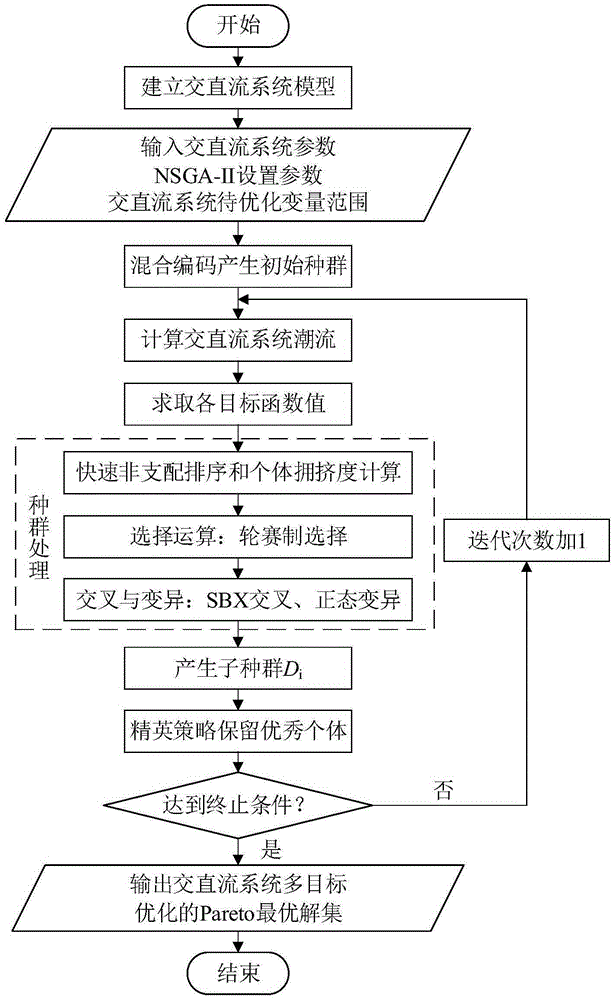
InactiveCN105321003AQuick adjustment abilityFlexible adjustment performanceForecastingPower flowSub populations
The invention discloses a multi-objective power flow optimization method of a VSC-HVDC (voltage source converter-high voltage direct current) containing alternating-current / direct-current system, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: establishing a model, selecting to-be-optimized variables and optimization objectives, and determining constraint conditions; setting an initial variable, and giving a to-be-optimized variable range; under the condition of taking the to-be-optimized variables as population individuals in the optimization process, in a hybrid encoding mode, randomly generating an initial population according to the to-be-optimized variable range; calculating the power flow of the alternating-current / direct-current system by using an alternate iterating algorithm; getting the corresponding optimization objective function value of each individual in the population; carrying out rapid non-dominated sorting on the individuals in the population, calculating a virtual fitness, and through selection, crossing and variation processing, generating sub-populations; retaining excellent individuals in parent individuals by using an elitist strategy; judging whether algorithm termination conditions are satisfied, if so, turning to a step 9), and completing optimization; otherwise, turning to the step 4); completing the optimization process, and outputting results. The method has the advantages of scientificity, strong applicability, good effect, and the like.
Owner:NORTHEAST DIANLI UNIVERSITY +1
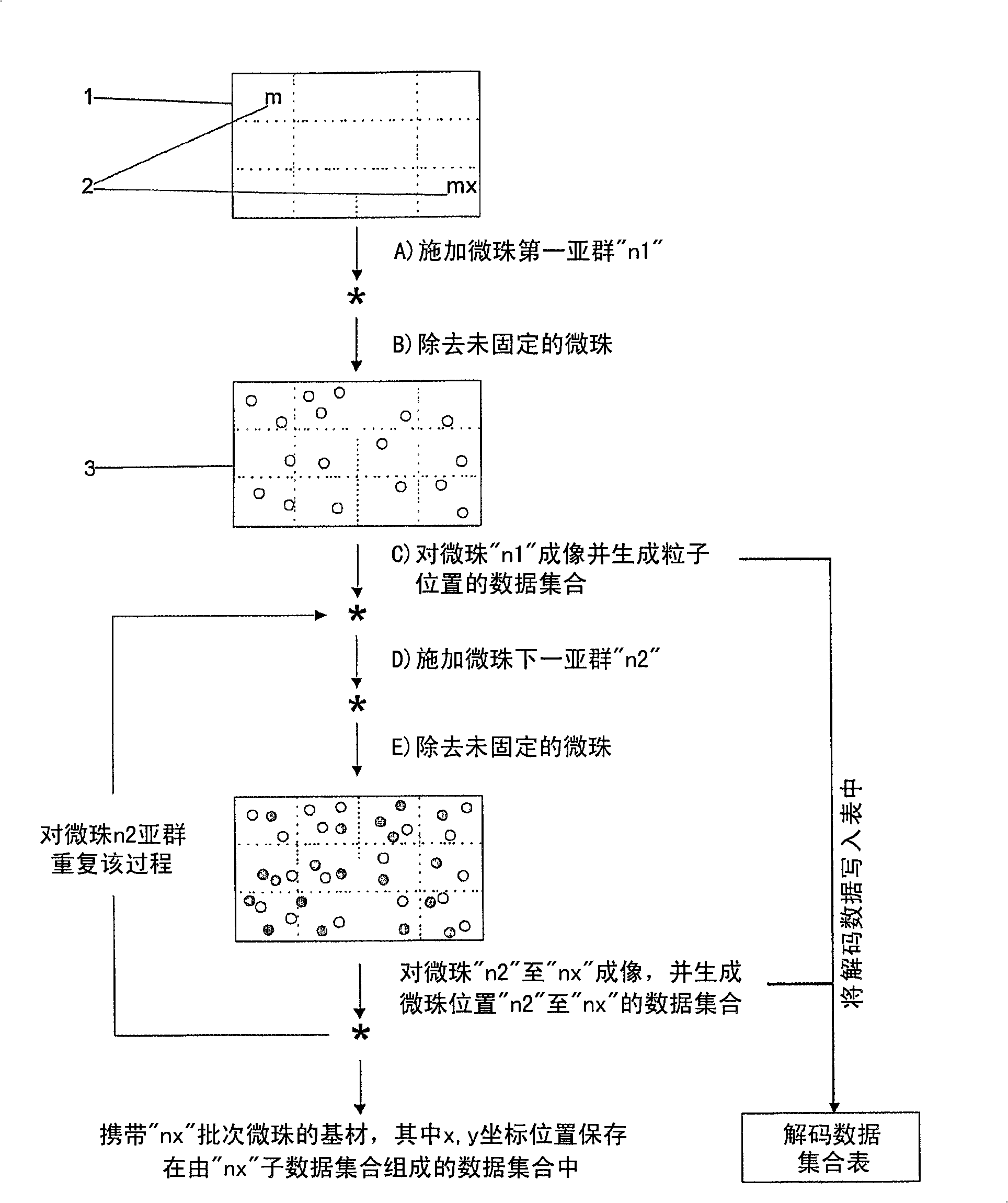
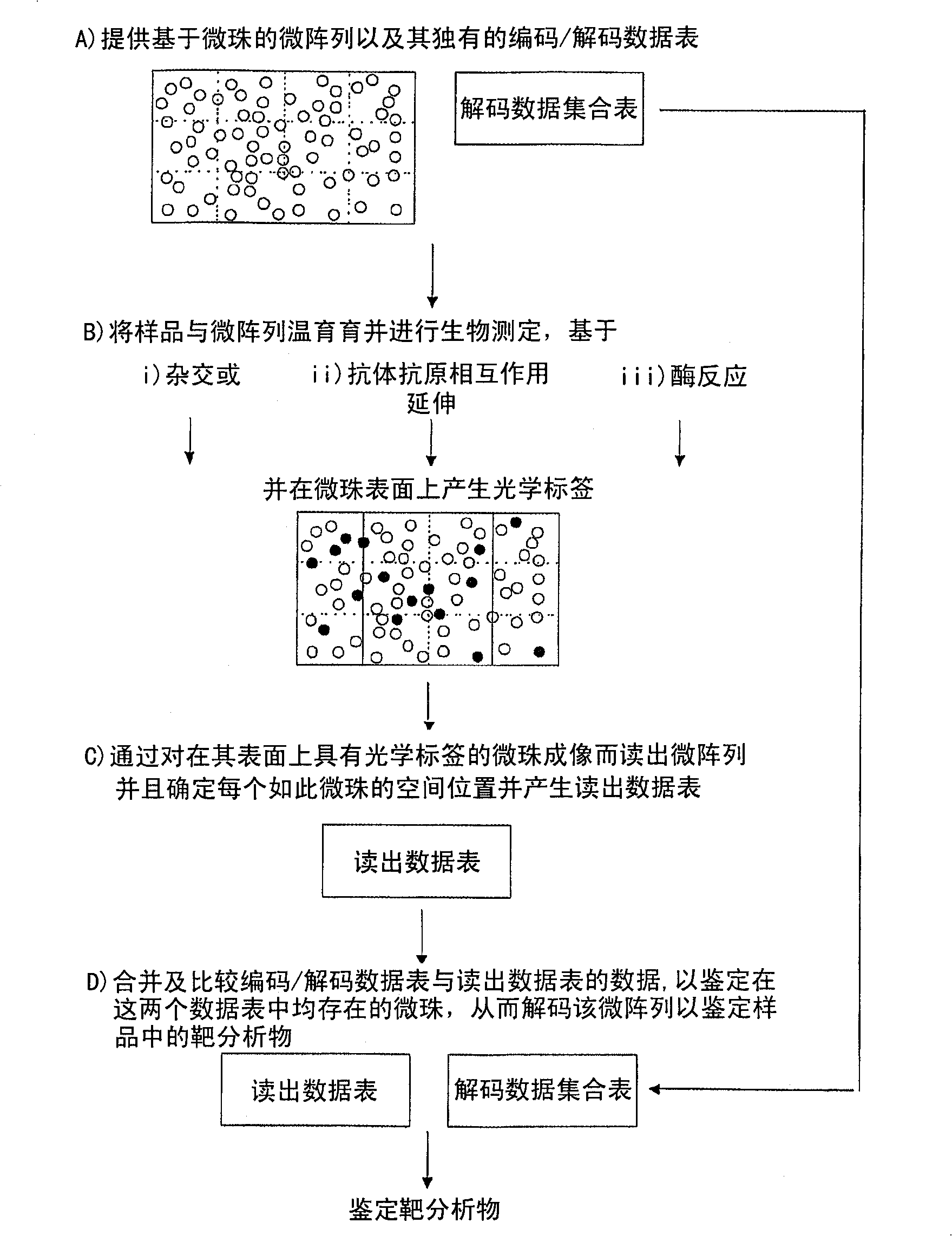
A microarray system and a process for producing microarrays
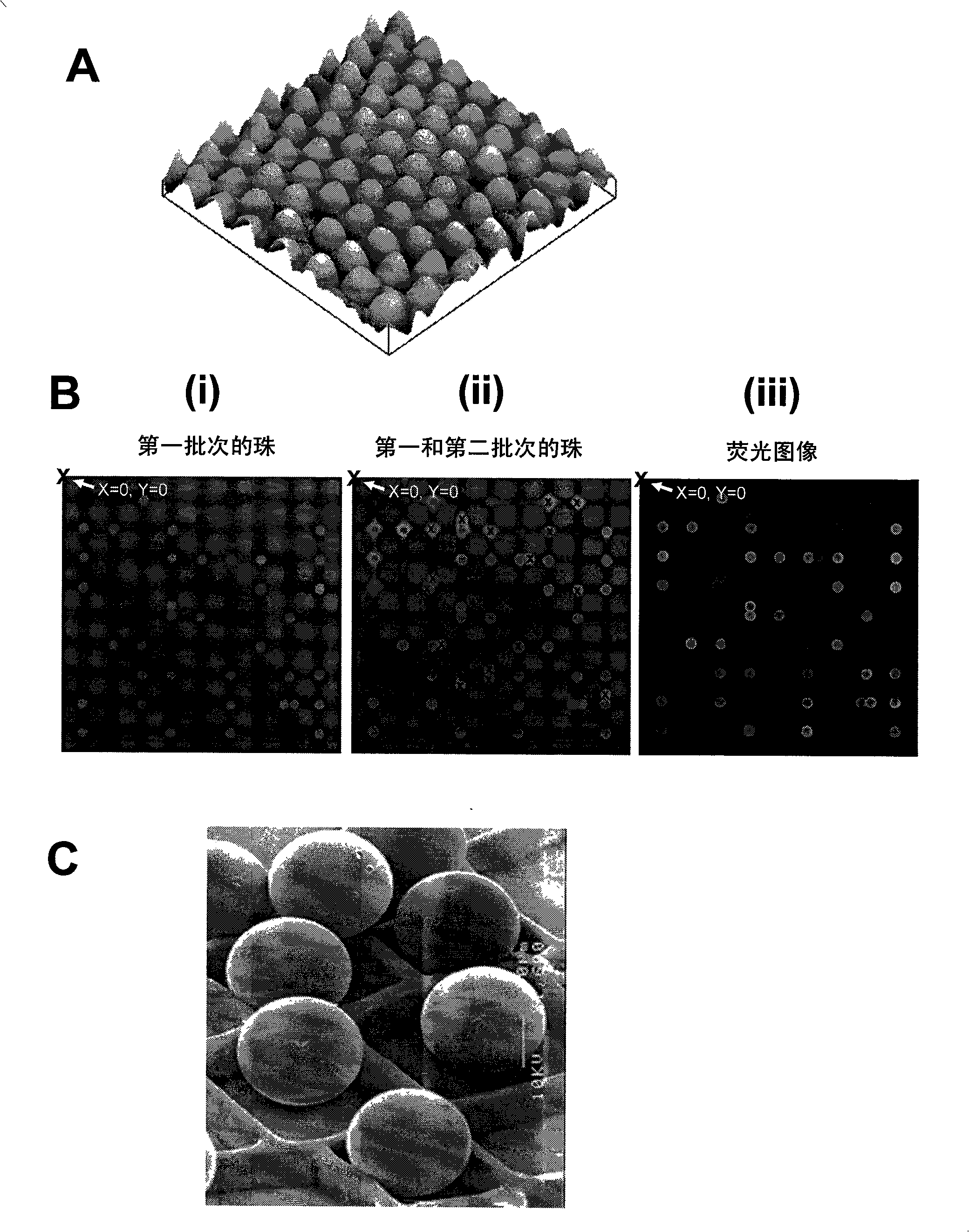
The present invention provides a process for making a micro-array. The process comprises the step of depositing a population of microbeads on a substrate having at least one fiducial. The population being comprised of at least two sub-populations, preferably multiple sub-populations, each comprising a known active agent capable of specific binding with at least one target analyte. The said subpopulations are deposited sequentially and at discrete periods of each other. The process also comprises the step of making images of the substrate after deposition of each subpopulation. The images are then compared using the fiducial as a reference to thereby determine the location of each microbead and to identify the subpopulation, and its known active agent, based on differences between each image. Also disclosed in a system for using the microarray.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
Method for allocating graticule resource based on paralleling genetic algorithm
InactiveCN101324854AQuality improvementHigh speedResource allocationGenetic modelsQuality of serviceAlgorithm
The invention relates to a grid resource allocation method based on a parallel genetic algorithm. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, the information is initialized in a main thread, such as task collection, machine collection, an execution time matrix E of the task, and mapping of a sub-task to the machine, etc.; then a plurality of sub threads are generated and mapped to different processors, an initializing sub-population is independently generated by each sub thread, evolutionary computation is performed in parallel, the optimum individual of each generation is transferred to the main thread, the main thread performs comparison, and the optimum individual is retained; when the predetermined generation arrives, the transfer operation between the sub-groups is performed; and the operation of the main thread and all the sub-groups cannot be finished until the termination conditions are met. The genetic algorithm is taken as the most effective heuristic global stochastic searching method, and the solution of the NP problem can be performed. The quality and the speed for the algorithm for solving are improved by the parallel genetic algorithm proposed according to the natural parallelism of the genetic algorithm, and the method is an effective grid energy resource optimization method and favorable for improving the service quality of the grid.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
System and method for selectively classifying a population
InactiveUS8010295B1Data processing applicationsMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological conditionRisk status
Owner:IB SECURITYHOLDERS
Computer systems and methods for subdividing a complex disease into component diseases
ActiveUS7653491B2Low heterogeneityImprove accuracy and reliabilityRead-only memoriesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansQuantitative trait locusSub populations
A method for identifying a quantitative trait loci for a complex trait that is exhibited by a plurality of organisms in a population. The population is divided into a plurality of sub-populations using a classification scheme. Depending on what is known about the population, either a supervised or unsupervised classification is used. The classification scheme is derived from a plurality of cellular constituent measurements obtained from each organism in the population. For each sub-population in the plurality of sub-populations, a quantitative genetic analysis is performed on the sub-population in order to identify one or more quantitative trait loci for the complex trait.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Methods for detecting genome-wide sequence variations associated with a phenotype
InactiveUS20070015200A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingSub populationsGenetic risk factor
The invention provides methods for determining genome-wide sequence variations associated with a phenotype of a species in a hypothesis-free manner. In the methods of the invention, a set of restriction fragments for each of a sub-population of individuals having the phenotype are generated by digesting nucleic acids from the individual using one or more different restriction enzymes. A set of restriction sequence tags for the individual is then determined from the set of restriction fragments. The restriction sequence tags for the sub-population of organisms are compared and grouped into one or more groups, each of which comprising restriction sequence tags that comprise homologous sequences. The obtained one or more groups of restriction sequence tags identify the sequence variations associated with the phenotype. The methods of the invention can be used for, e.g., analysis of large numbers of sequence variants in many patient samples to identify subtle genetic risk factors.
Owner:SOLEXA
Stem cells obtained from pulp of deciduous or permanent teeth and of dental germ, able to produce human bone tissue
ActiveUS20090035376A1Cell dissociation methodsPowder deliveryCell-Extracellular MatrixSub populations
In this invention is described a method that foresees the isolation of a new subpopulation of stem cells derived form dental pulp, whose differentiation is osteoblasts lead to the subsequent production and employment of a bone tissue, called LAB (Living Autologous Bone). Specifically, the invention describes: 1) the isolation of stem cells from the pulp of deciduous and permanent teeth and of dental germs, obtained from human subjects; 2) the growth of these cells in vitro, under specific conditions that allow the isolation of a cellular sub-population, which, after differentiation in osteoblasts, is able to produce in vitro an extracellular matrix, identical to that detectable in bone tissue; 3) the use of this selected and differentiated cell population in order to produce autologous bone tissue in vitro, containing vital osteoblasts; 4) the preservation of the LAB under conditions which guarantee cellular vitality; 5) the use of the LAB in donor patients to reconstruct bone tissue, as required in the daily practice in dentistry, maxillo-facial surgery and orthopedics.
Owner:CARINCI FRANCESCO +5
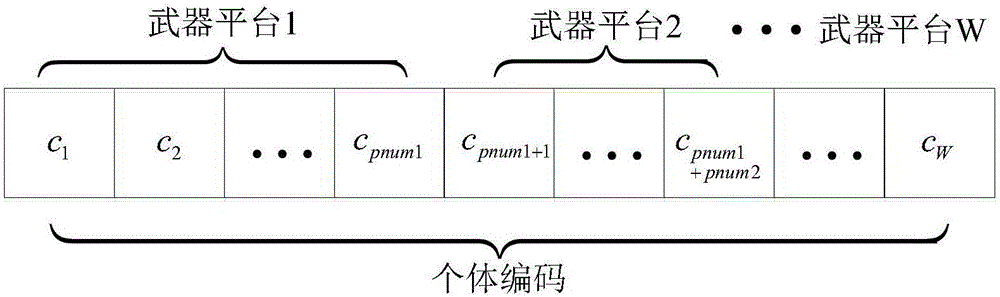
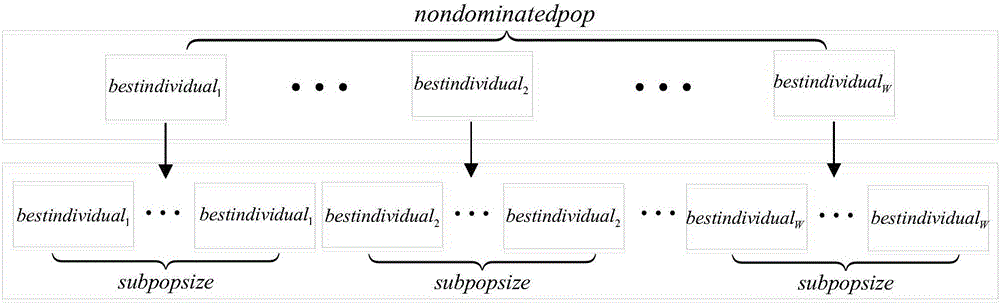
Mass weapon target assignment method based on multiple-target clonal evolutionary algorithm
InactiveCN106599537AStrong Feasible Solution Search CapabilityFull searchSpecial data processing applicationsInformaticsSub populationsAlgorithm
The invention provides a mass weapon target assignment method based on a multiple-target clonal evolutionary algorithm, and belongs to the technical field of computer simulation and method optimization. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, according to the amount of weapons, a plurality of initial sub-populations are generated, the pareto optimal solutions of all sub-populations are calculated, and a dominant population is formed by the optimal solutions; secondly, an algorithm clones all individuals in the dominant population by a cloning mechanism to form a plurality of new sub-populations; and finally, the algorithm gives three special evolution operators and carry out evolution on the individuals by the three evolution operators. By use of the method, a corresponding evolution operator and a corresponding evolution method are designed by aiming at a mass weapon target assignment problem, the mass weapon target assignment problem can be effectively solved, the integral pareto optimal solution can be obtained under the environment of mass weapons and targets, and the method has a good convergence effect.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Computer Network-Interfaced Method for Health Care Provider Active Reach Into Diverse Sub-Population Communities
InactiveUS20140365234A1Improving overall community aspectFacilitates inclusionFinanceTelemedicineSub populationsPublic health
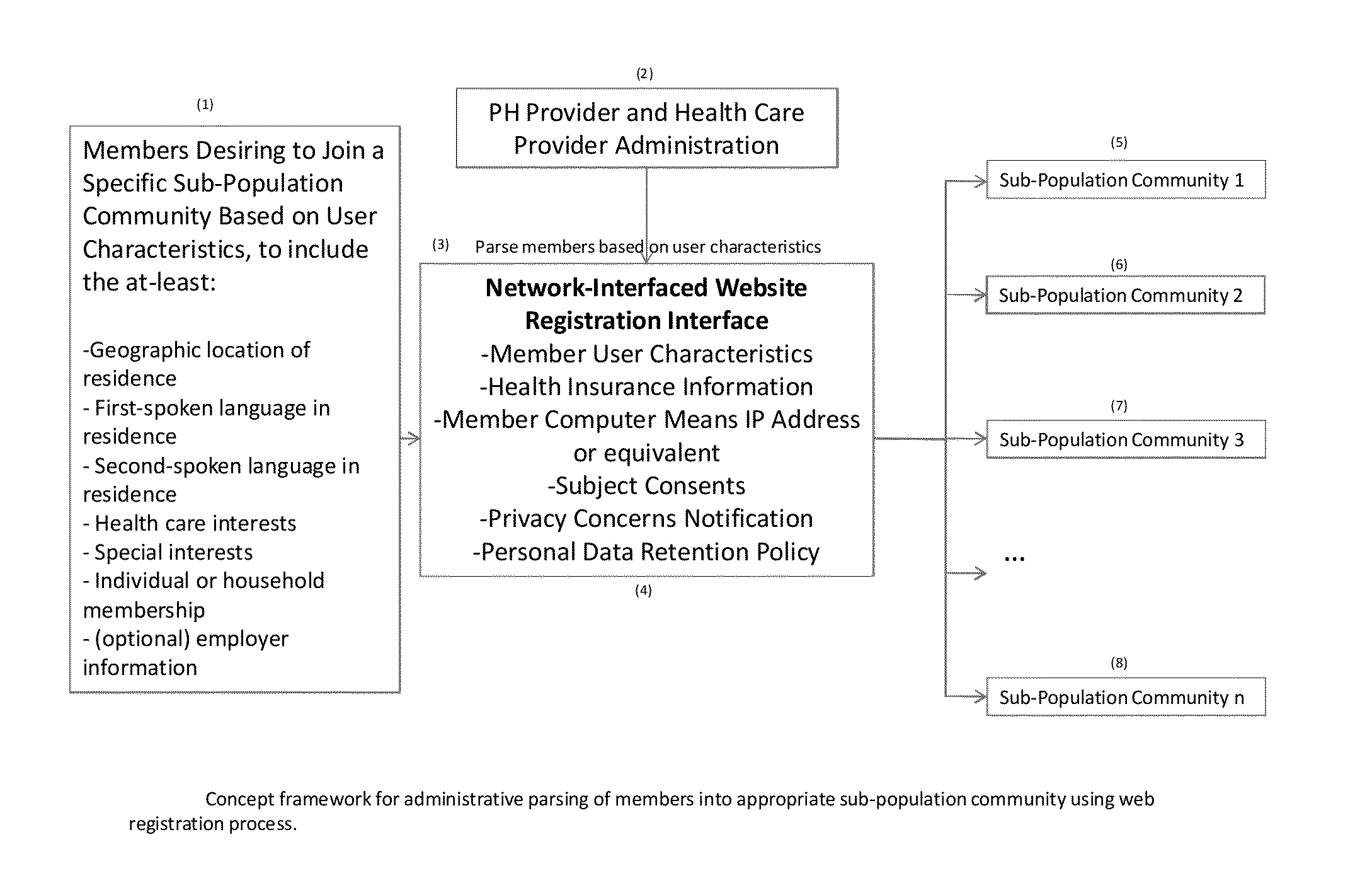
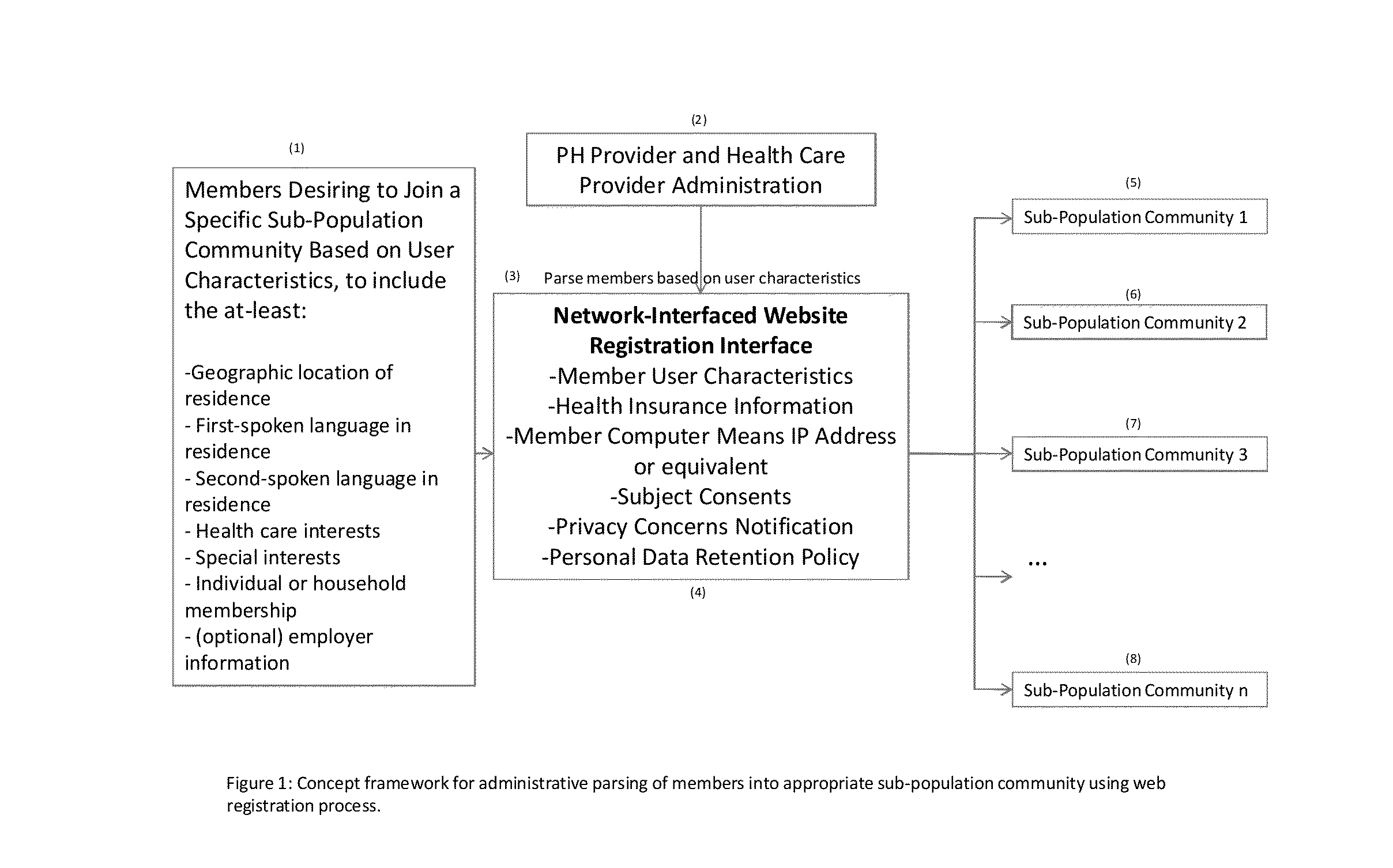
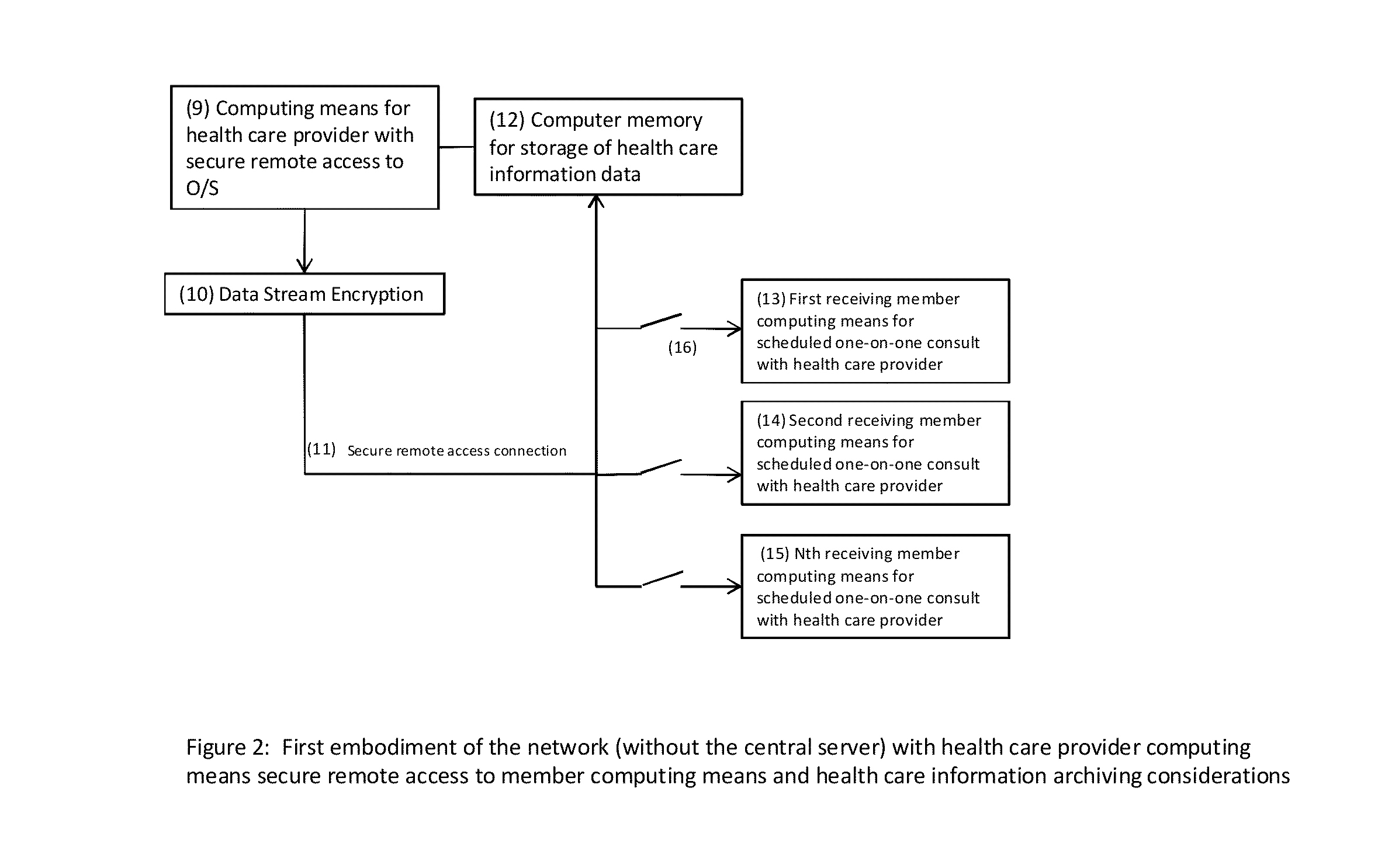
A computer network-interfaced method for public health and health care provider active reach into diverse sub-population communities for the purpose of reducing health care treatment gaps of the population-at-large; comprising a network of computing means for health care provider administrators, a network-interfaced web software registration process requiring member user characteristics and health insurance information to parse members into sub-population communities; provider secure remote access control of network-interfaced computing means of sub-population community members during scheduled consultations, and production, broadcast and storage of protocol-driven life-episodes for actively screening member health care needs and improving social inclusion of sub-population community members.
Owner:COMMUNITY PURSUITS
Determining cell cycle phase data
InactiveUS20060247862A1Solve low usageRapid and versatileAcquiring/recognising microscopic objectsBiological testingSub populationsComputer science
A method of determining cell cycle phase data for cells comprising at least one luminescent reporter capable of emitting radiation, the at least one luminescent reporter comprising a first luminescent reporter which is capable of being indicative of at least one cell cycle phase, said method comprising: storing classification information for classifying individual cells into different cell cycle phases using an automated classification process; receiving image data created by detecting radiation emitted by said at least one luminescent reporter; analyzing said image data to identify object areas in the image data which correspond to individual cells; analyzing said image data, on the basis of said identified object areas, to determine, for a selected cell, one or more measurements including a measurement of a parameter relating to at least a cytoplasmic component of the cell; and applying said classification information to said measurements to classify the selected cell into a selected one of a plurality of sub-populations of cells, each sub-population having cells in a different cell cycle phase.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE LTD
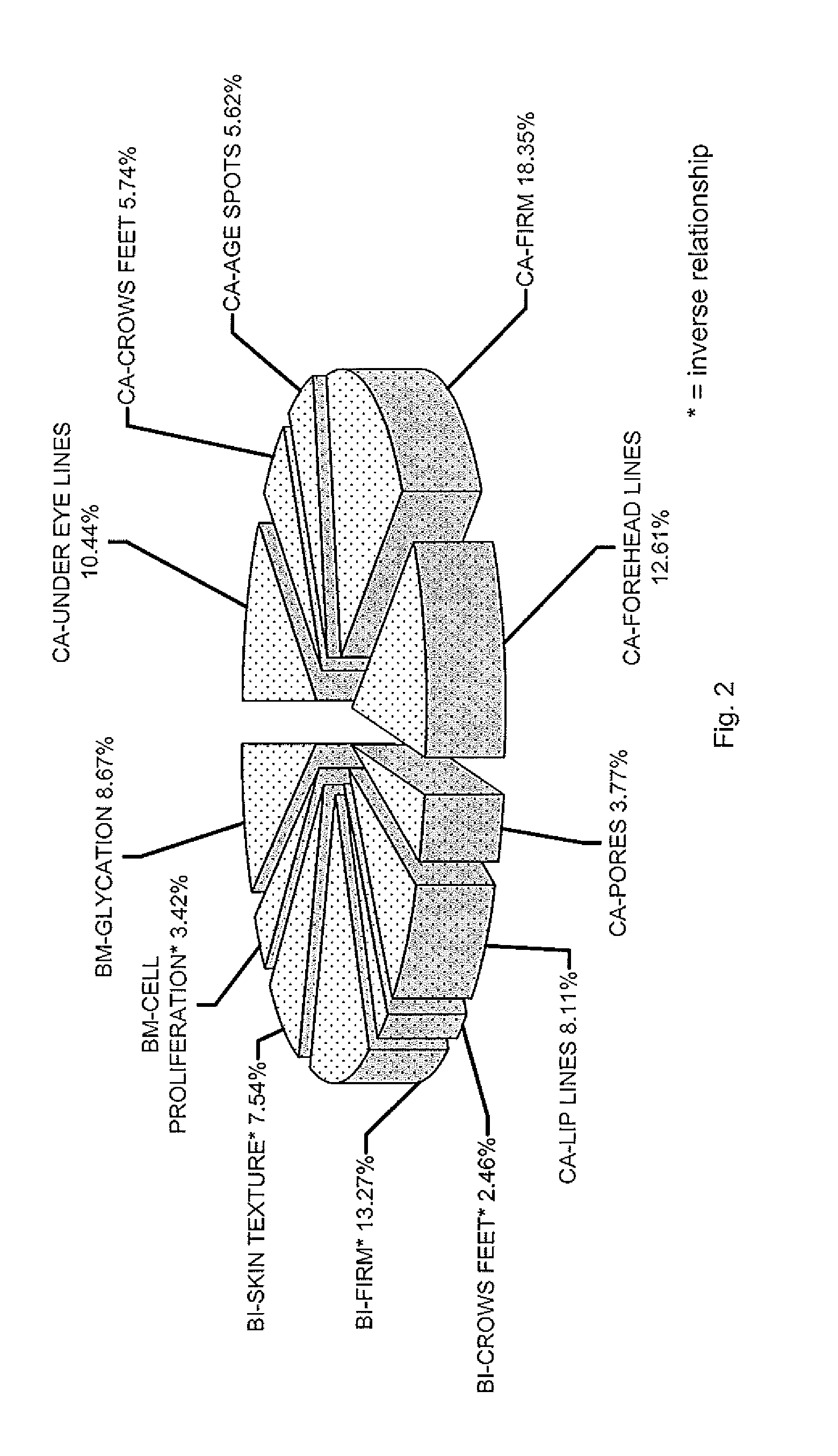
Objective Model Of Apparent Age, Methods And Use
ActiveUS20110202480A1Reduce rateUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsComputer-assisted medical data acquisitionSub populationsMedicine
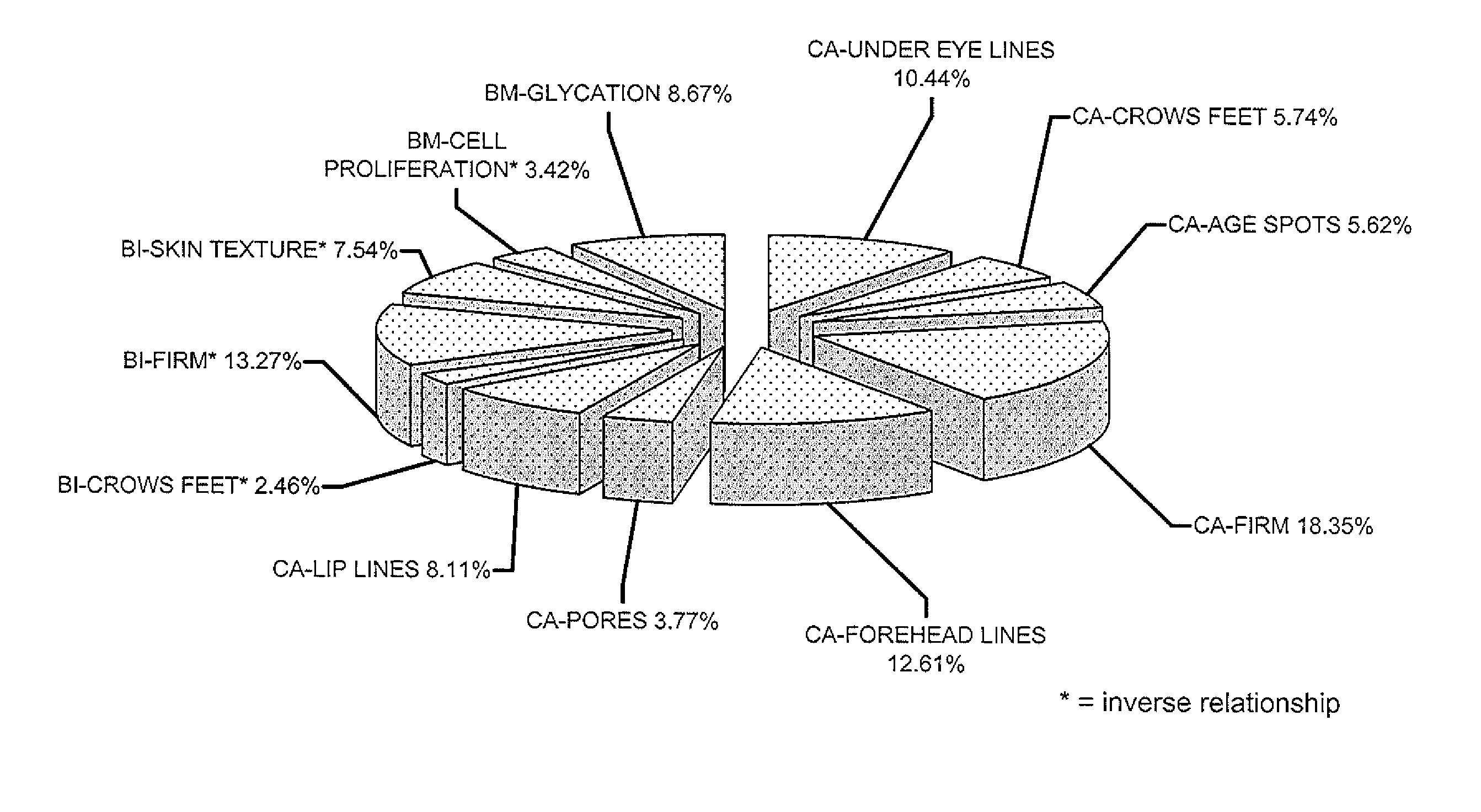
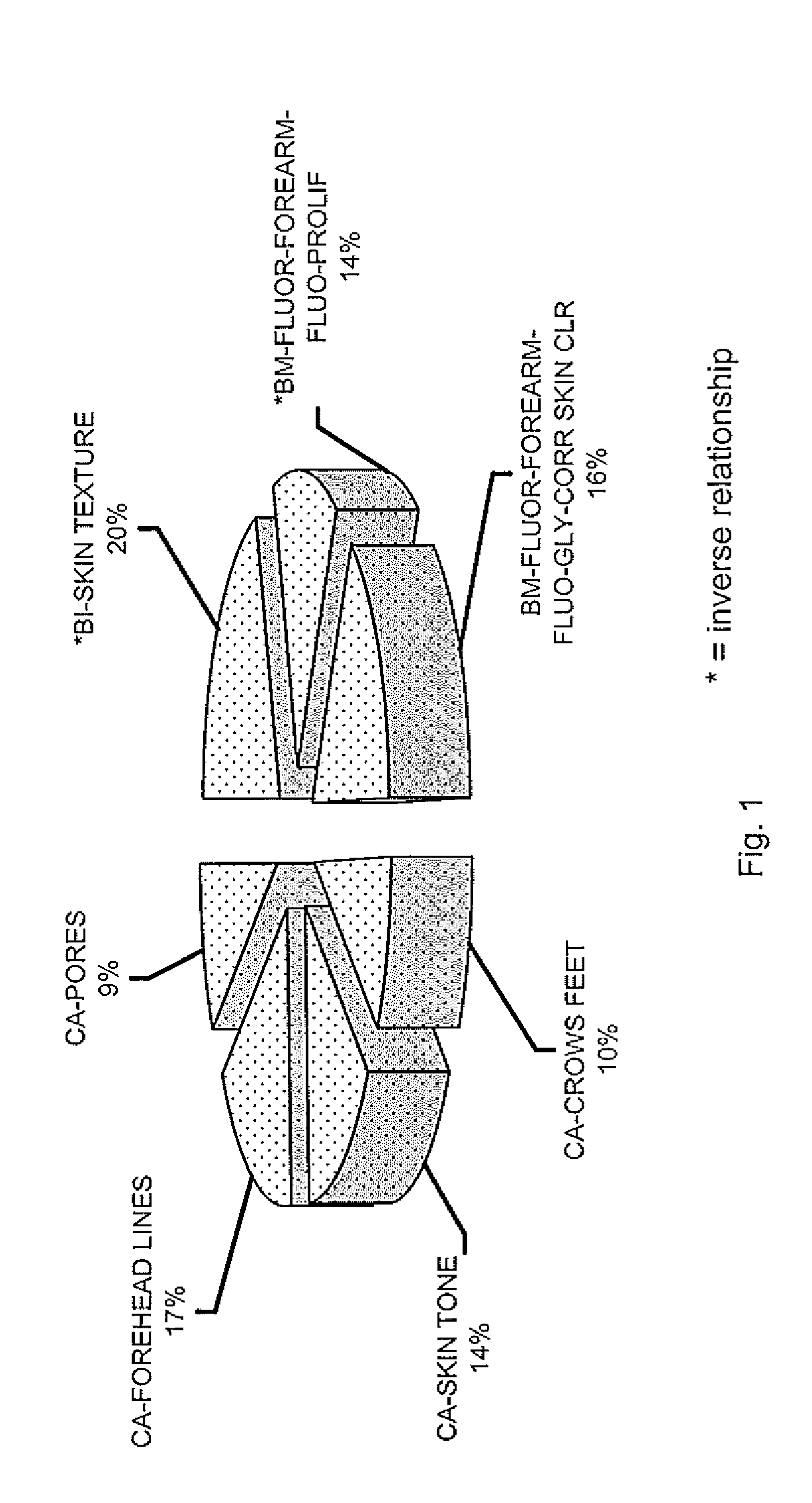
Methods of developing equations for objectively assigning or predicting an apparent age are disclosed. Advantageously, the equations of objective apparent age may be based on a relatively small number of critical parameters combined in a way that accounts for all or most of the apparent skin aging in a defined population or sub-population. Despite the relatively small data collection requirements, the present invention includes an objective model of apparent age that is useful for evaluation of products, useful for predicting treatment outcomes and useful for predicting the effects of deteriorative factors. The formalization of an Objective Apparent Age Score allows one to identify the biophysical and biochemical parameters that mostly influence an individual's apparent age, and can be used to select specific anti-aging treatments with increased chances of visible success. The Objective Apparent Age Score may also be used to support marketing claims.
Owner:ELC MANAGEMENT LLC
Distribution network reconstruction method employing parallel genetic algorithm based on undirected spanning tree
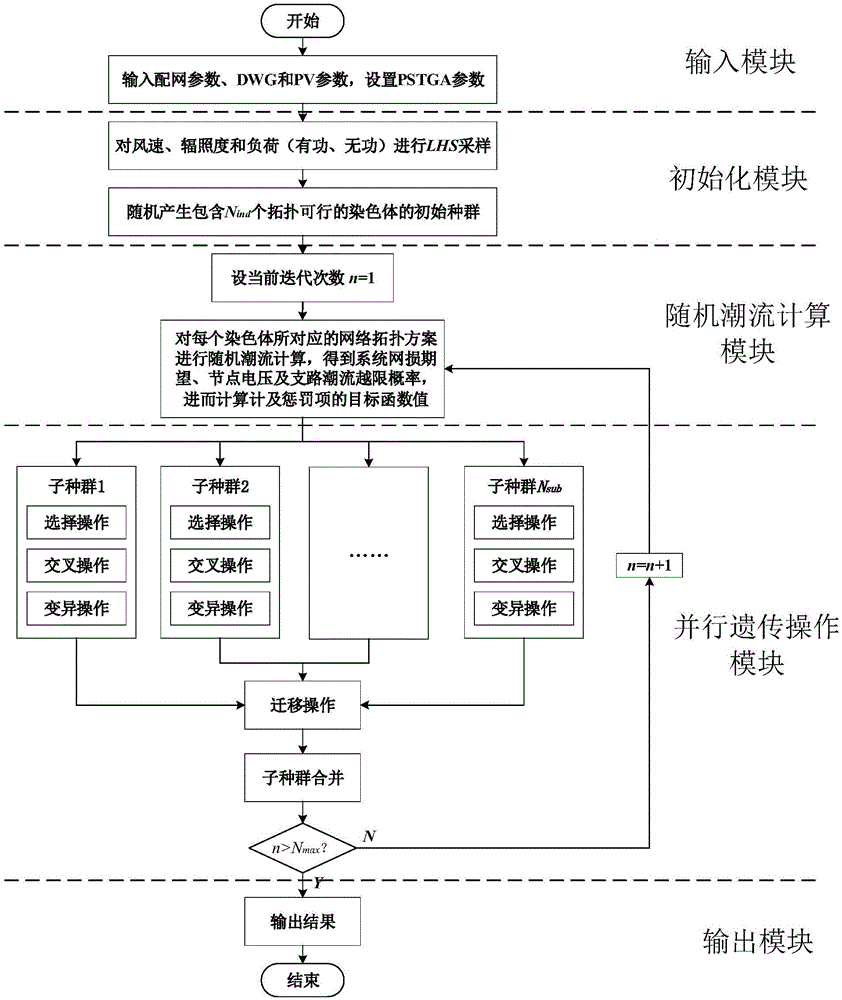
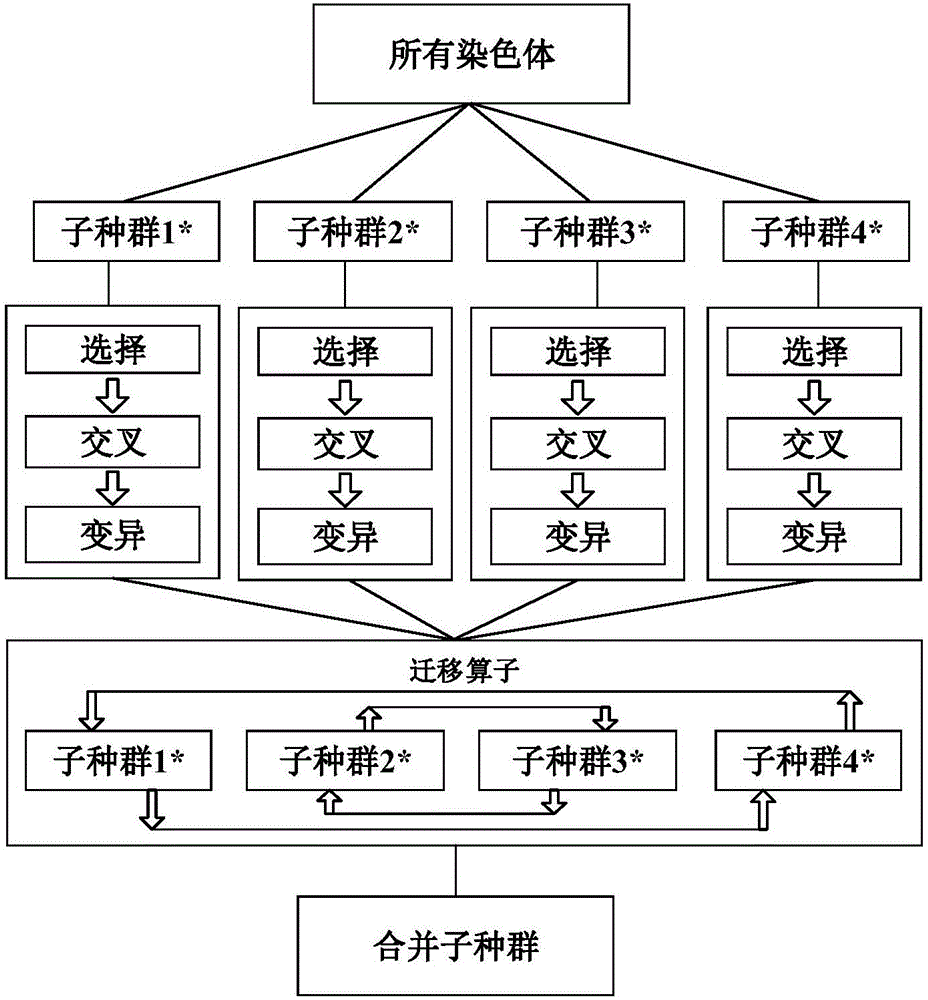
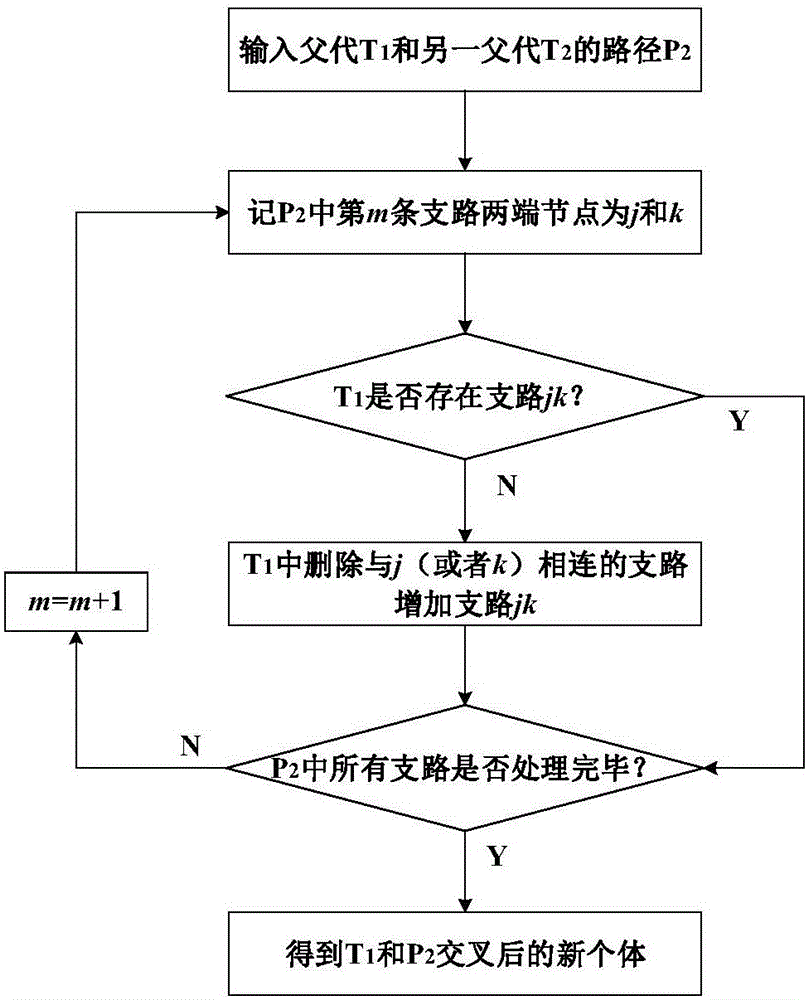
InactiveCN106340873ATroubleshoot refactoring issuesReduce lossGeometric CADSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsSub populationsReconstruction method
The invention relates to a distribution network reconstruction method employing a parallel genetic algorithm based on an undirected spanning tree. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining parameters; performing Monte Carlo simulation sampling; randomly generating an initial population with feasible topology, and setting an initial value of iteration frequency n as 1; performing load flow calculation; calculating a target function value, determining whether constraint conditions are satisfied, if not, returning to the step for re-generating the initial population, and if yes, dividing an existing population into multiple sub populations for performing parallel genetic operation; generating one random permutation P from 1 to Nsub, and establishing a mapping relation between a target sub population i and a source sub population pi, wherein P=[p1, p2,..., pNsub]; replacing the worst individual of each target sub population with an optimal individual of one corresponding source sub population; and determining whether the iteration frequency n reaches requirements, if not, adding one to the iteration frequency and returning to the step of load flow calculation, and if yes, outputting a distribution network reconstruction scheme. Compared to the prior art, the method has the advantages of high calculation efficiency, high integration, close connection with reality and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV +1
Compositions and Methods for Characterizing Breast Cancer
InactiveUS20130059903A1Increase estrogen receptor expressionImprove the level ofOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementSub populationsCD44
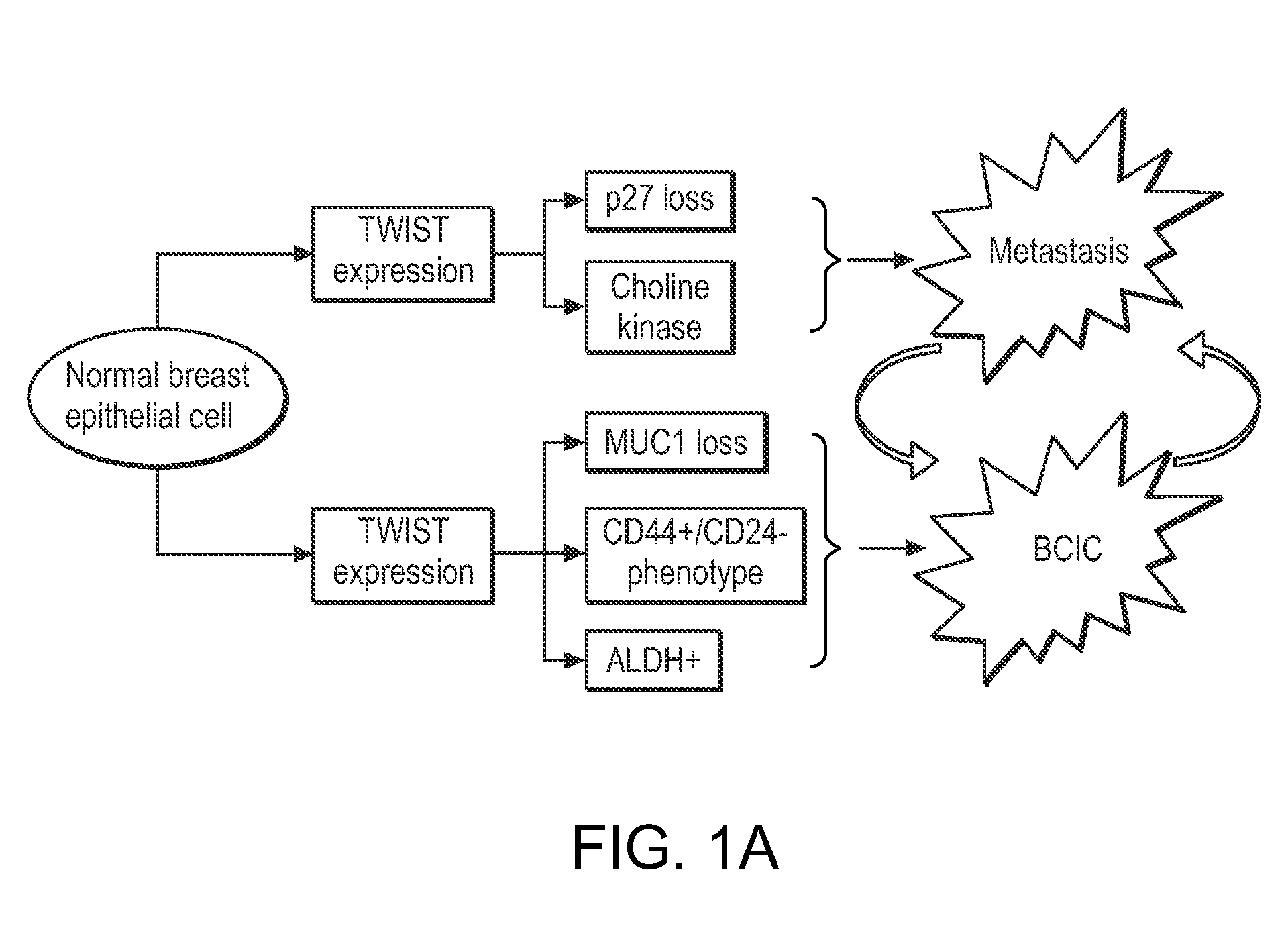
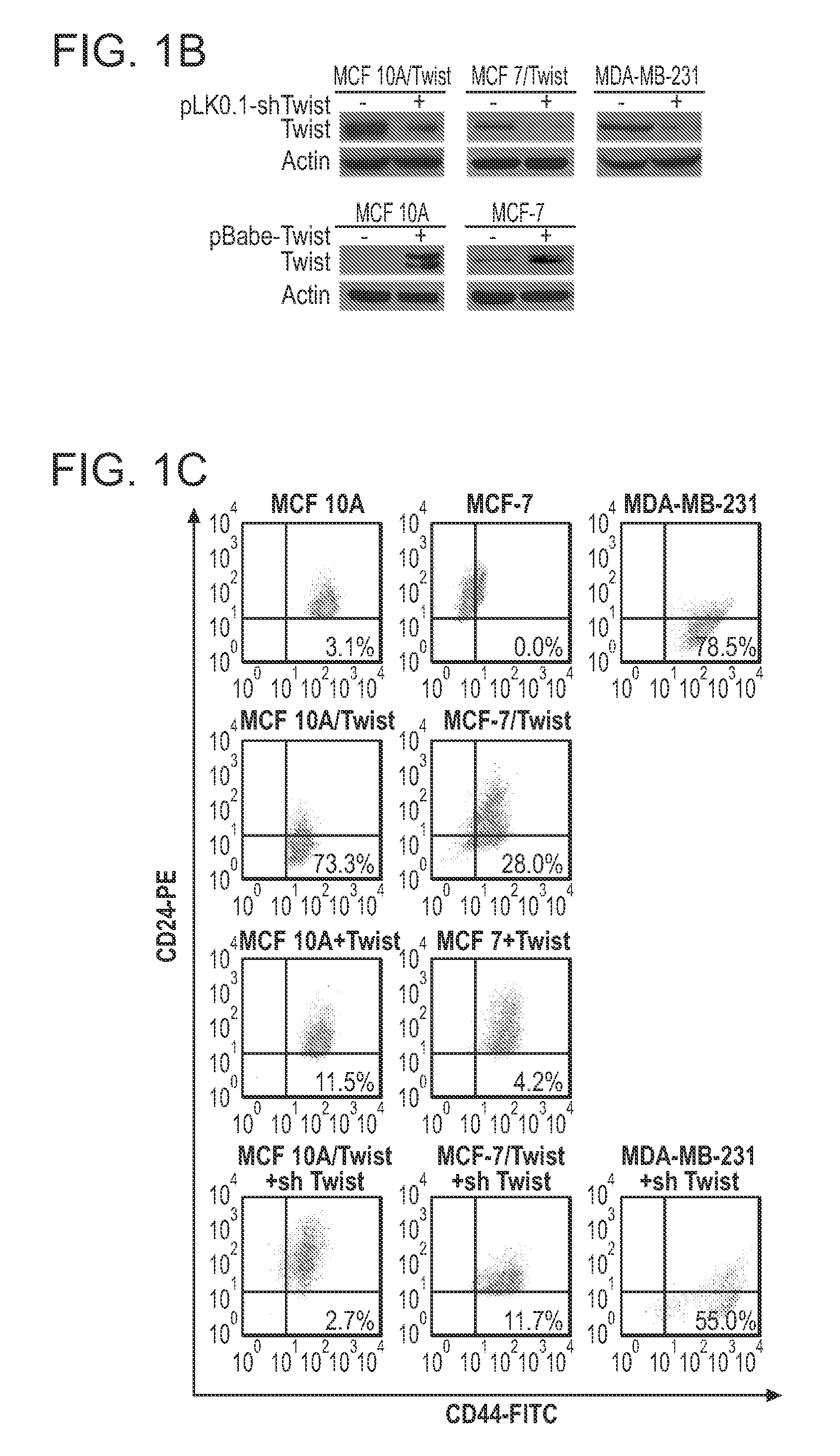
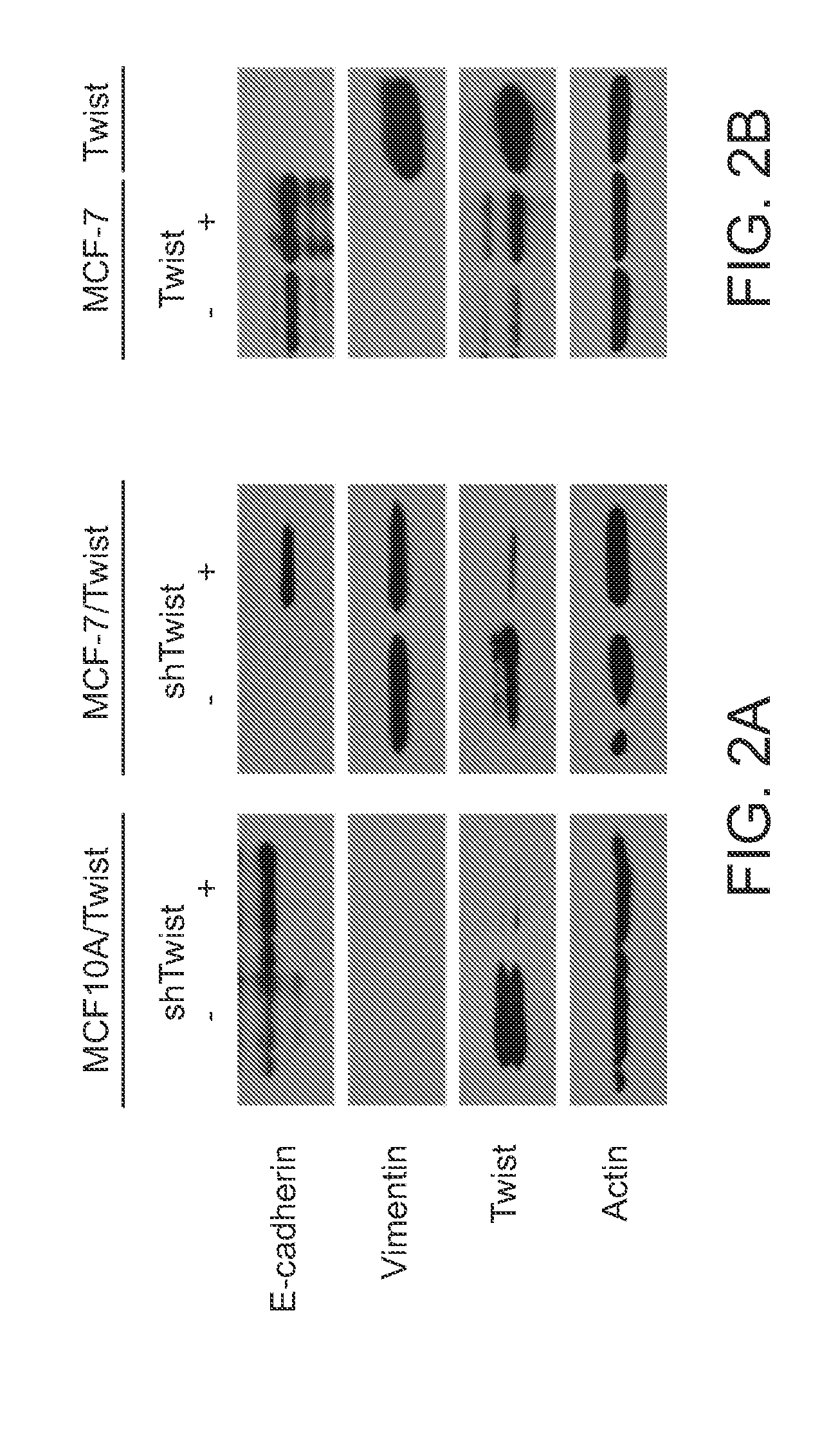
The invention provides compositions and methods for characterizing breast cancer stem In particular, the invention provides for the identification of cells expressing Twist and CD44 that express little or virtually undetectable levels of CD24 (i.e. a Twist+ / CD44+ / CD24− / low cell sub-population). The presence of such cells in a breast cancer specimen identifies the breast cancer as having increased metastic potential. Such cancers are identified as requiring aggressive therapies. Accordingly, the invention provides biomarkers suitable for identifying, diagnosing, and monitoring treatment of a subject with breast cancer.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Self-adaptive multi-object evolution method adopting constraint cloud workflow scheduling
ActiveCN106845642AEasy to handleFast convergenceOffice automationGenetic algorithmsSub populationsCloud workflow
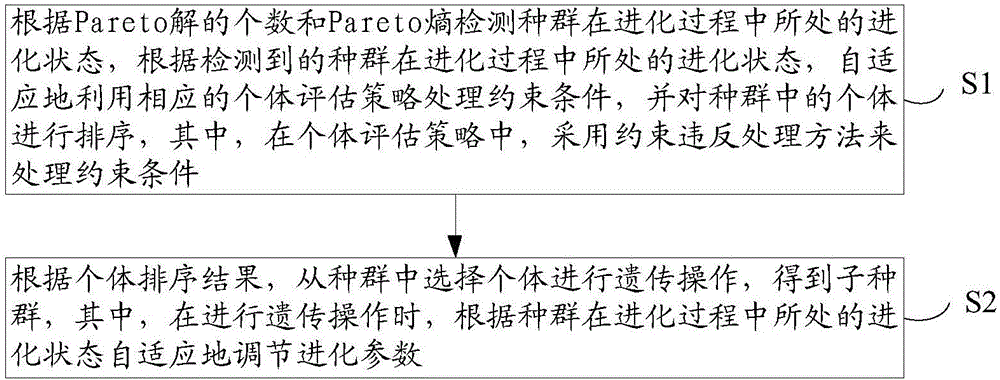
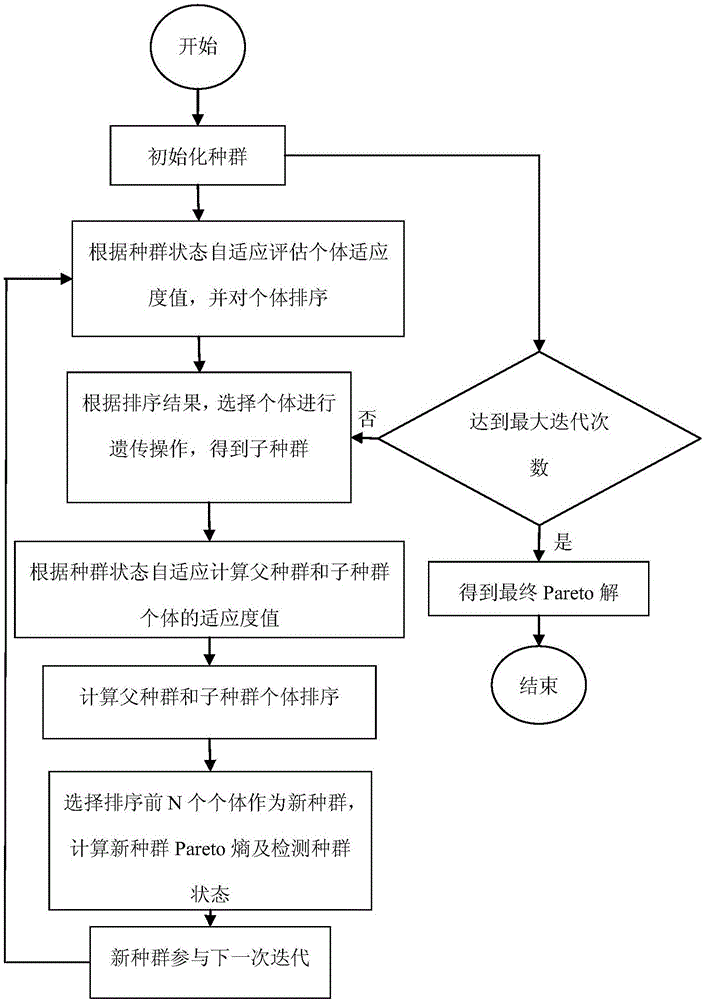
The invention provides a self-adaptive multi-object evolution method adopting constraint cloud workflow scheduling. The overall detection and local mining capability of the multi-object evolution method can be improved. The multi-object evolution method comprises the steps that S1, the evolution states of populations in the evolution process are detected according to the number of Pareto solutions and Pareto entropies, and corresponding individual evaluation strategy processing constraint conditions are self-adaptively utilized to sort individuals in the populations according to the detected evolution states of the populations in the evolution process, wherein a constraint violation processing method is adopted to process the constraint conditions in individual evaluation strategies; S2, according to individual sorting results, individuals are selected from the populations to perform genetic manipulation, and sub-populations are obtained, wherein genetic manipulation parameters are self-adaptively adjusted according to the evolution states of the populations in the evolution process during genetic manipulation. The self-adaptive multi-object evolution method is suitable for solving the multi-object evolution problem having constraints and can be applied to the technical field of workflow scheduling in a cloud computing environment.
Owner:北京明易达科技股份有限公司
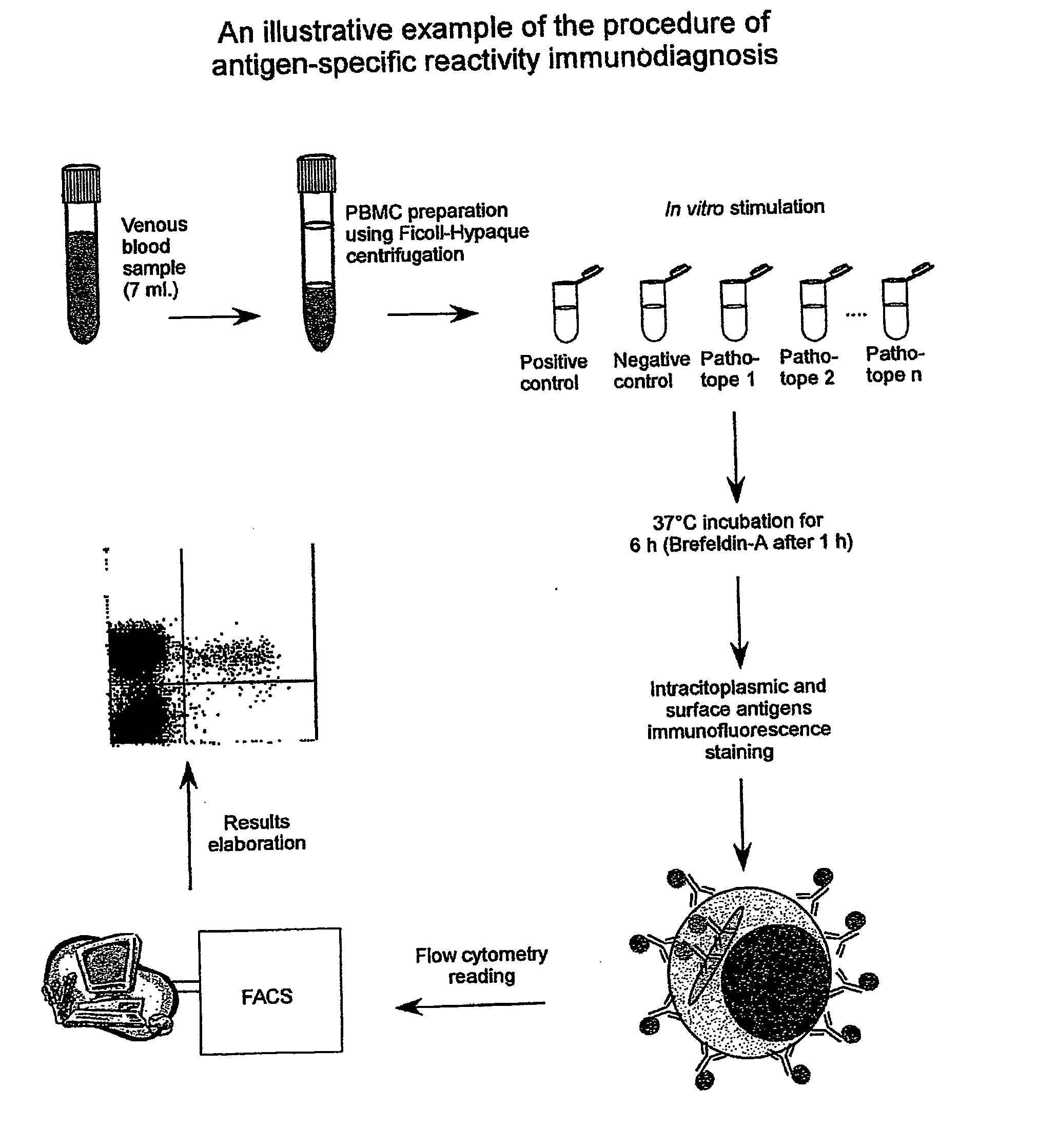
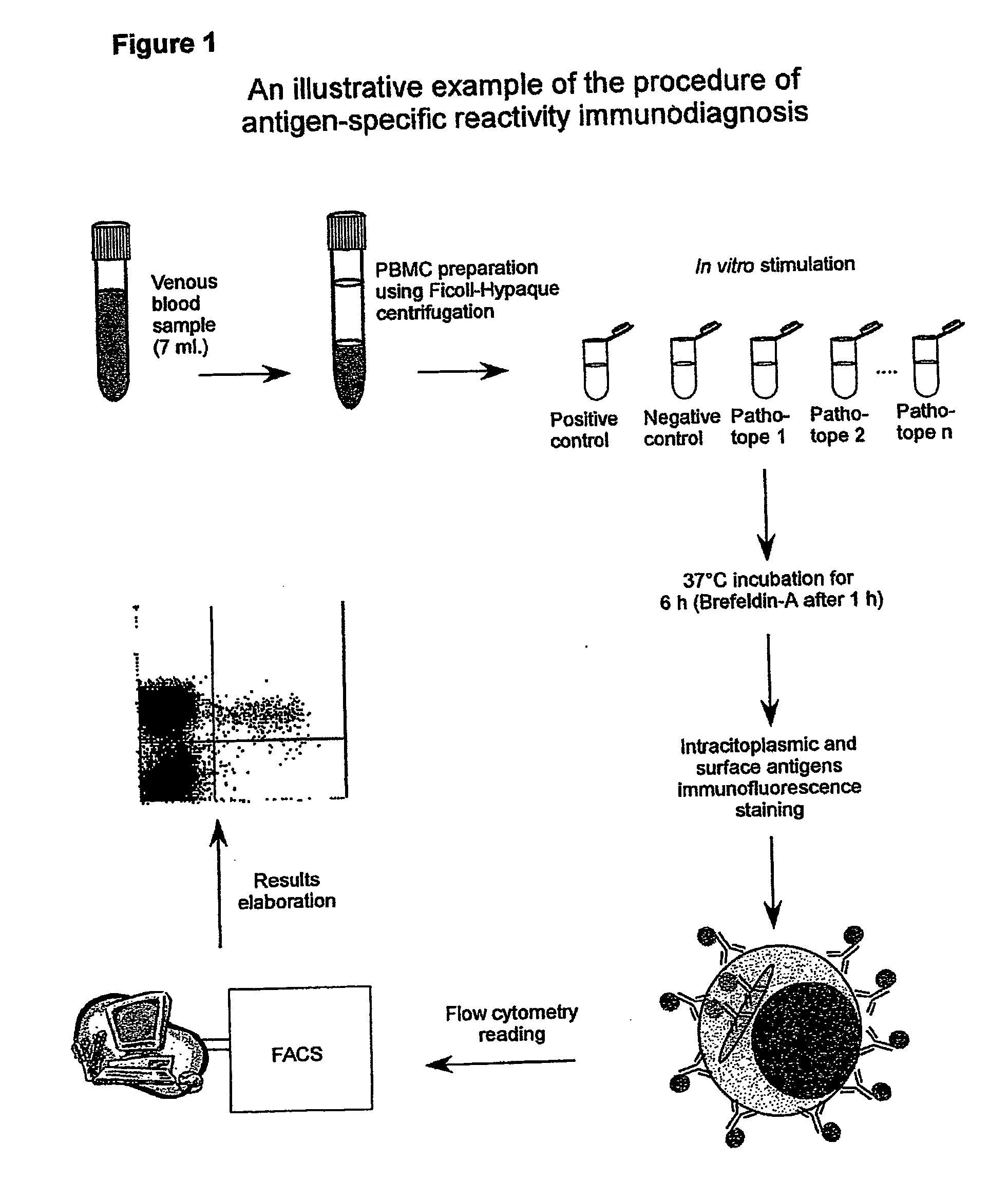
Method and diagnostic tests based on flow cytometric analysis of antigen-specific t lymphocytes
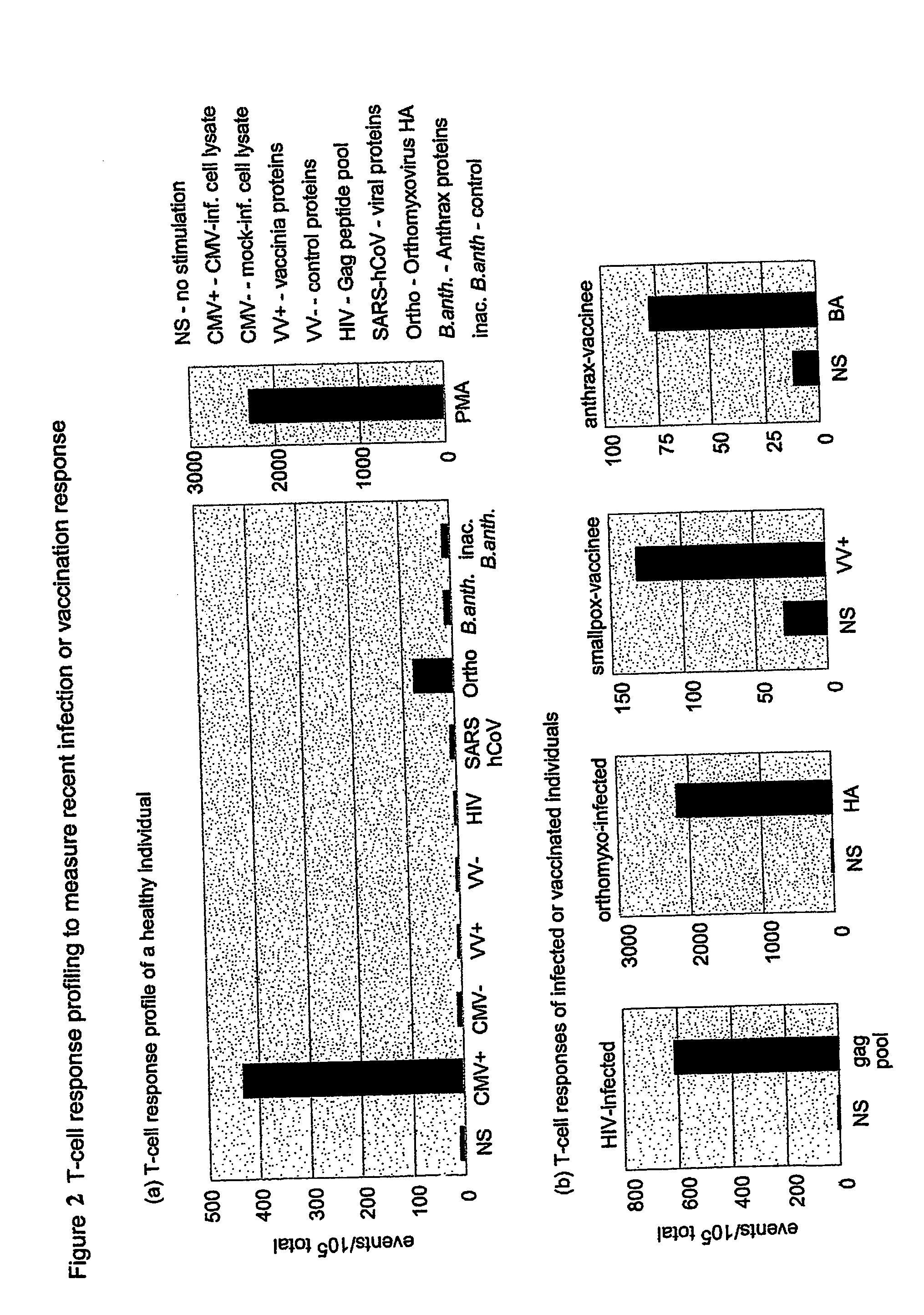
The present invention provides a method for the immuno-diagnosis of diseases with different aetiology (infectious diseases, tumors etc) by measurement of the T cell response J, B and NK lymphocytes) induced by a set of diseasespecific antigens. The method is based on the quantitative determination of antigenspecific T lymphocytes (referred as Ag-Sp), stimulated by using a newly devised pathology-specific antigen or epitope compositions which represent further embodiments of the invention. After stimulation, the selective measurement of the Ag-Sp T lymphocytes is performed by: A) monoclonal antibodies recognizing membrane structures of T lymphocytes and of their sub-populations; B) monoclonal antibodies binding to cytokines accumulating at intracellular level after the stimulation with the antigen; or C) mixtures of A) and B). The flow cytometric detection of the presence of markers of differentiation on T lymphocytes and of intracytoplasmic cytokines allows the acquisition of both qualitative and quantitative results. The invention also provides diagnostic kits for performing the method of the invention.
Owner:INST NAT PER LE MALATTIE INFETTIVE LAZZARO SPALLANZANI IRCCS
Processing method and processing device based on multiple sequence alignment genetic algorithm
InactiveCN102622535AParsimonious classificationImprove processing efficiencyGenetic modelsSpecial data processing applicationsLocal optimumSub populations
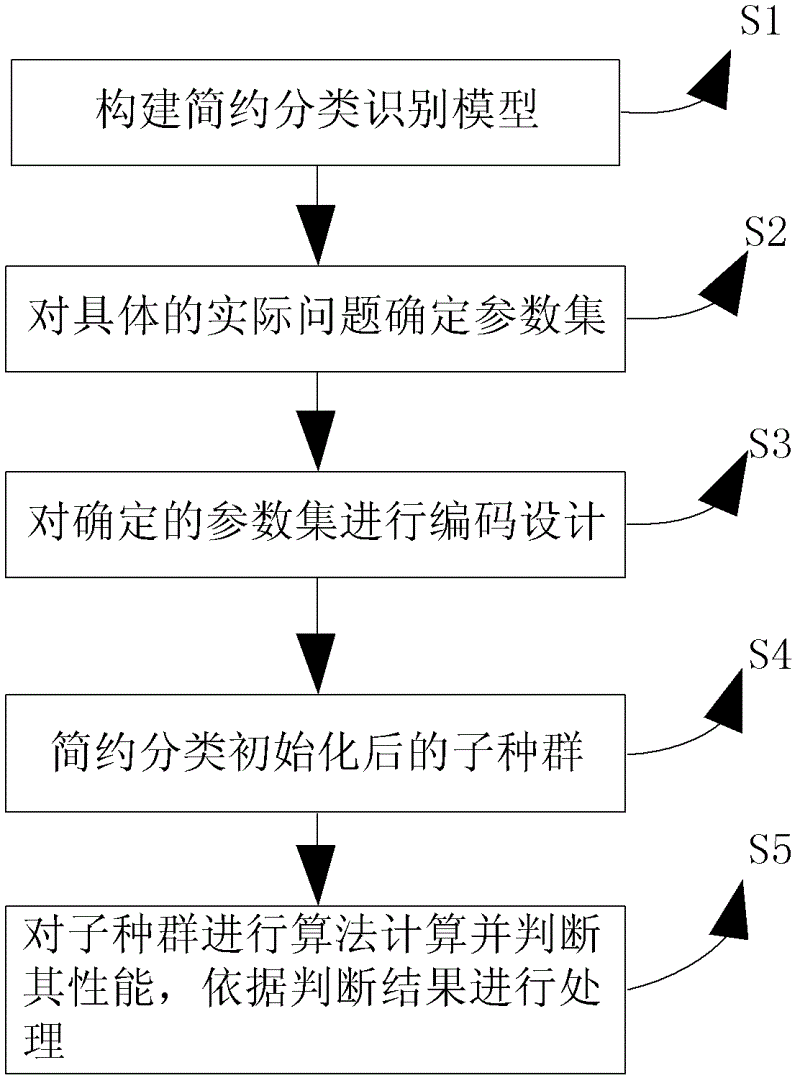
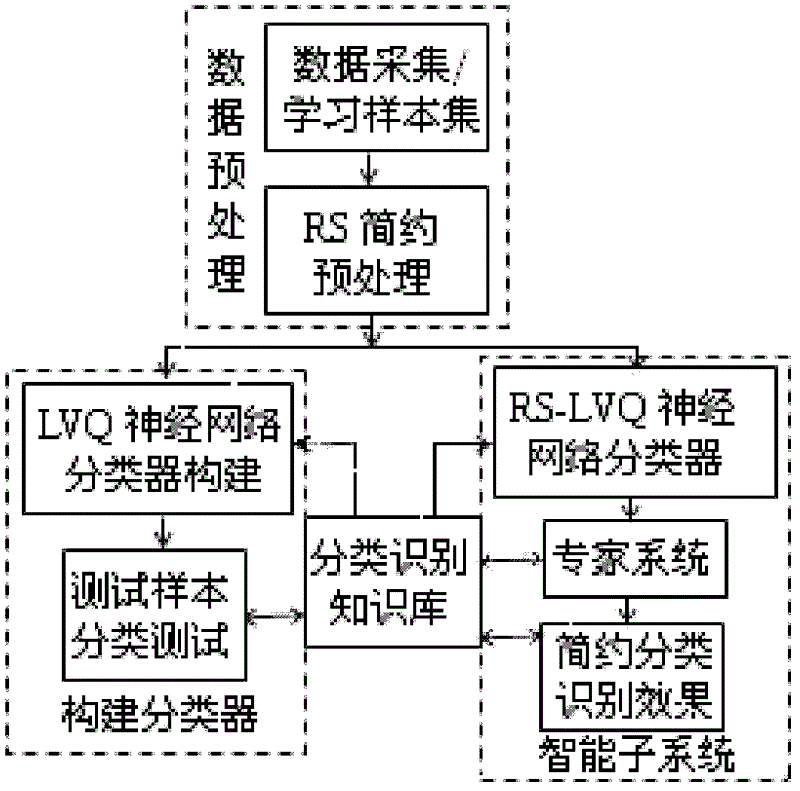
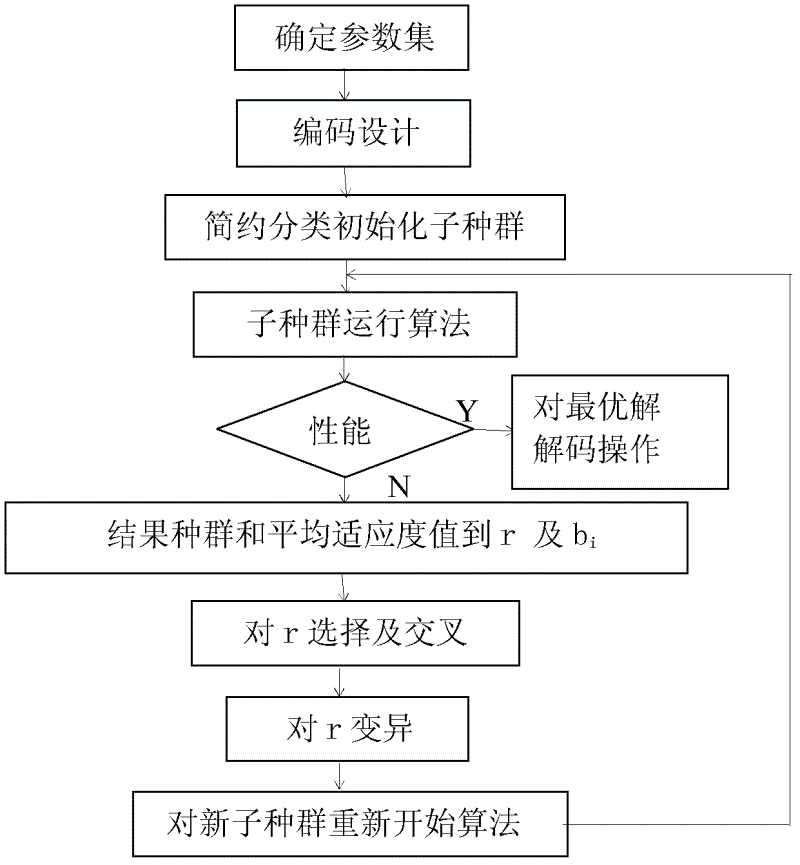
The invention provides a processing method and a processing device based on a multiple sequence alignment genetic algorithm. The processing method includes: building a brief classification identification model, determining a parameter set for special practical problems, performing code design on the determined parameter set, briefly classifying an initialized sub population, performing arithmetic calculation for the sub population and judging performance of the sub population, and processing the sub population according to judging results. The scheme is favorable for efficient comparison identification, overcomes shortcomings that the genetic algorithm is slow in convergence and apt to fall into local optimum and shortcomings that the existing attribute reduction algorithm is high in calculation complexity, not suitable for scale data reduction, not enough in describing of attribute collection and the like, and improves processing efficiency.
Owner:SHANGHAI DIANJI UNIV
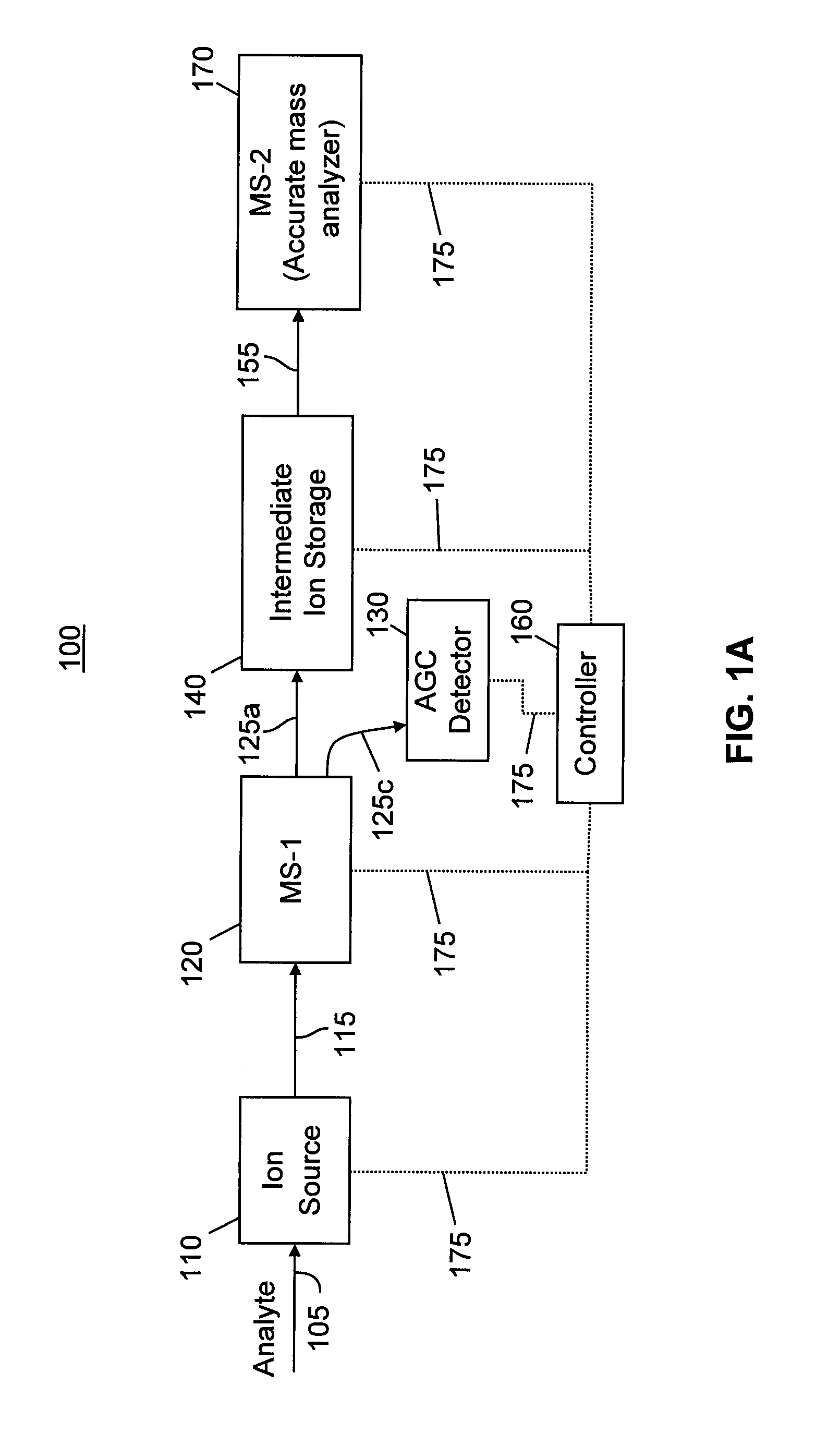
Acquisition and Analysis of Mixed Ion Populations in a Mass Spectrometer
ActiveUS20120049056A1Increase the collision energyAvoid performanceComponent separationIsotope separationChromatographic separationSub populations
A method of obtaining and analyzing a mass spectrum of a sample comprising components is characterized by: setting values of a first energy level and a second energy level; chromatographically separating the components; ionizing a portion of the separated components to create precursor ions; introducing a first portion of the precursor ions into a collision or reaction cell and generating a first sub-population of ions corresponding to the first energy level; introducing a second portion of the precursor ions into the cell and generating a second sub-population of ions corresponding to the second energy level; transferring a mixture of the first and second sub-populations of ions into a mass analyzer; producing an analysis of the ions of the mixture; varying the value of at least one of the first and the second energy levels according to a pre-determined cyclical variation; repeating various above steps; and analyzing the time-variation of the analyses.
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
Stem cells obtained from pulp of deciduous or permanent teeth and of dental germ, able to produce human bone tissue
In this invention is described a method that foresees the isolation of a new subpopulation of stem cells derived form dental pulp, whose differentiation is osteoblasts lead to the subsequent production and employment of a bone tissue, called LAB (Living Autologous Bone). Specifically, the invention describes: 1) the isolation of stem cells from the pulp of deciduous and permanent teeth and of dental germs, obtained from human subjects; 2) the growth of these cells in vitro, under specific conditions that allow the isolation of a cellular sub-population, which, after differentiation in osteoblasts, is able to produce in vitro an extracellular matrix, identical to that detectable in bone tissue; 3) the use of this selected and differentiated cell population in order to produce autologous bone tissue in vitro, containing vital osteoblasts; 4) the preservation of the LAB under conditions which guarantee cellular vitality; 5) the use of the LAB in donor patients to reconstruct bone tissue, as required in the daily practice in dentistry, maxillo-facial surgery and orthopedics.
Owner:POLO TECH PIEMONTESE SRL
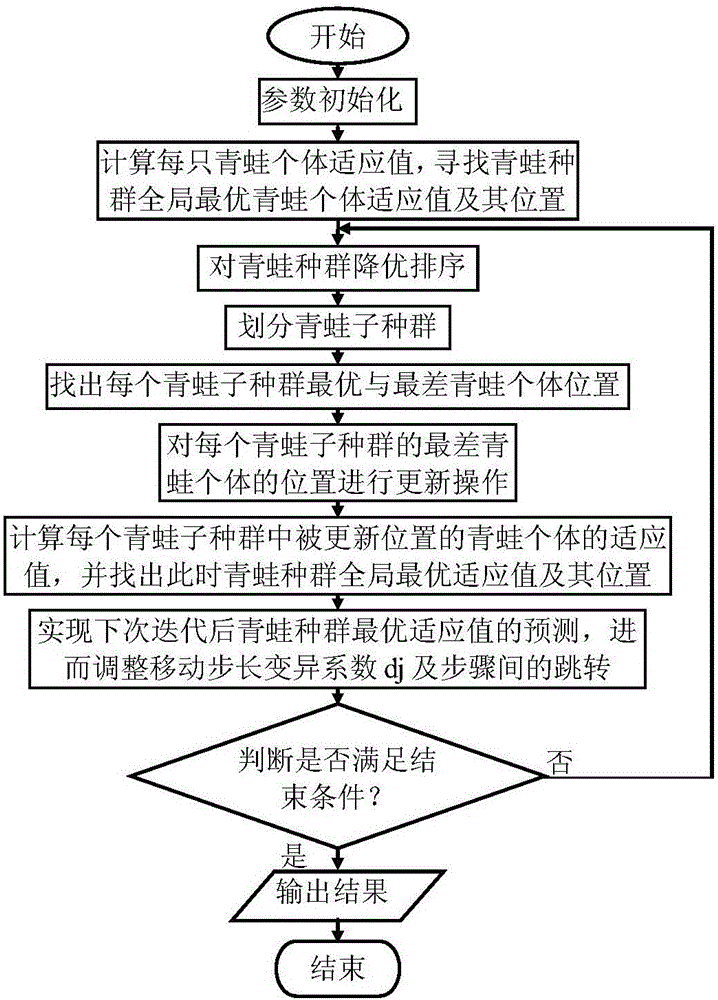
Method for improving standard shuffled frog leaping algorithm
InactiveCN105786759AImprove operational efficiencySimple mode of operationComplex mathematical operationsLocal optimumSub populations
The invention discloses a method for improving a standard shuffled frog leaping algorithm.The method comprises the steps of initializing parameters; calculating the adaptive value of each frog individual, and finding the adaptive value and position of the global optimum frog individual of a frog population; conducting optimum drawdown ranking on the frog population; conducting dividing for obtaining frog sub-populations; finding the positions of the optimum and the worst frog individual of each frog sub-population; conducting updating operation on the position of the worst frog individual of each frog sub-population; calculating the adaptive value of the frog individual with the position updated in each frog sub-population, and finding the global optimum adaptive value and the position of the frog population at this moment; implementing prediction of the global optimum adaptive value of the frog population obtained after iteration is completed next time, and furthermore adjusting the movement step-length variable coefficient dj and skip among steps; judging whether the ending conditions are met or not.By means of the method, the defects that at the later stage, the convergence rate of the standard shuffled frog leaping algorithm is severely lowered, convergence precision is insufficient, and the algorithm is prone to getting into local optimum are overcome.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
A dynamic task perception-oriented cloud manufacturing collaborative task scheduling method
InactiveCN109816243AImproving Performance in Solving Task Scheduling ProblemsOptimal Scheduling SchemeGenetic modelsForecastingSub populationsBiogeography
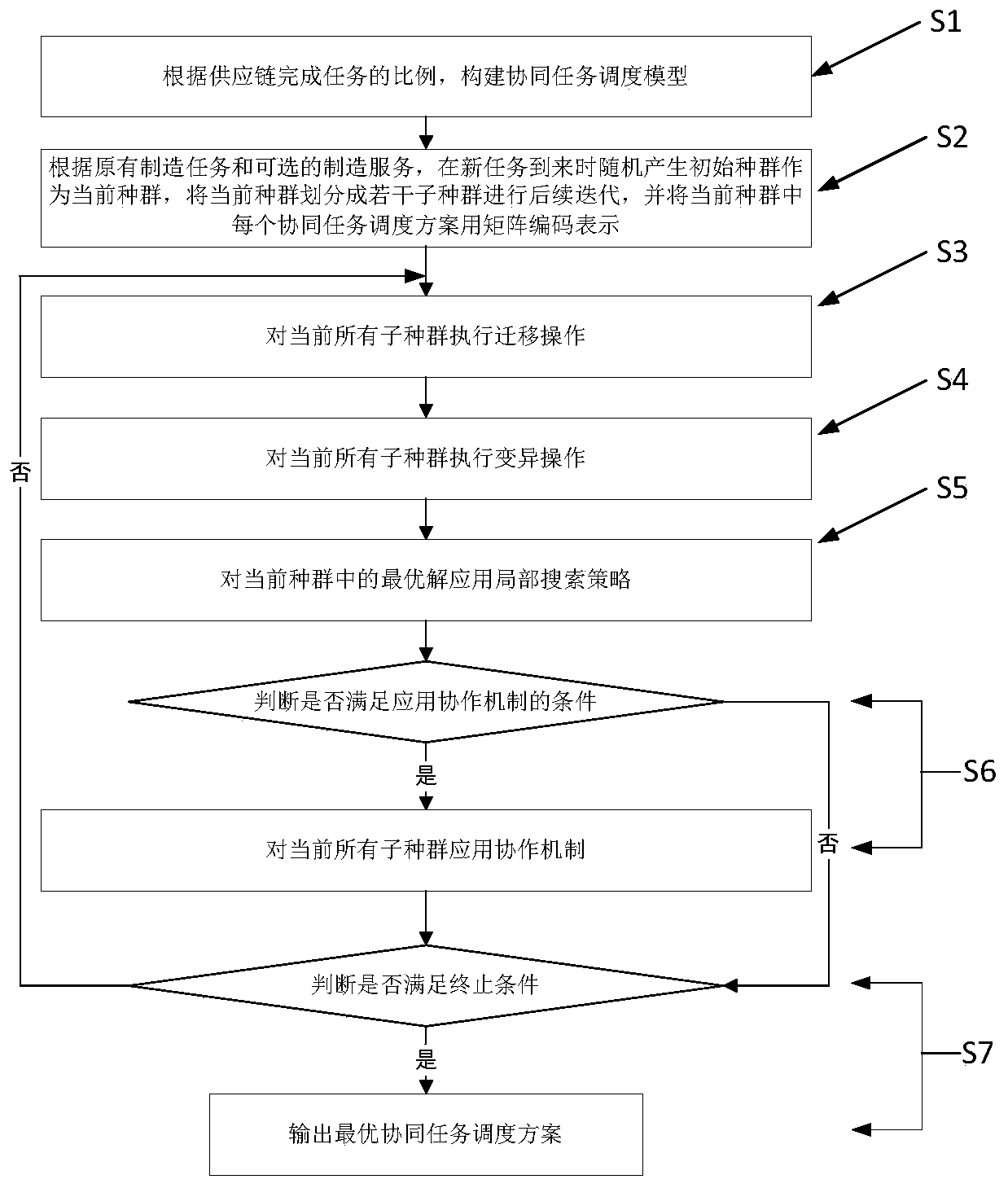
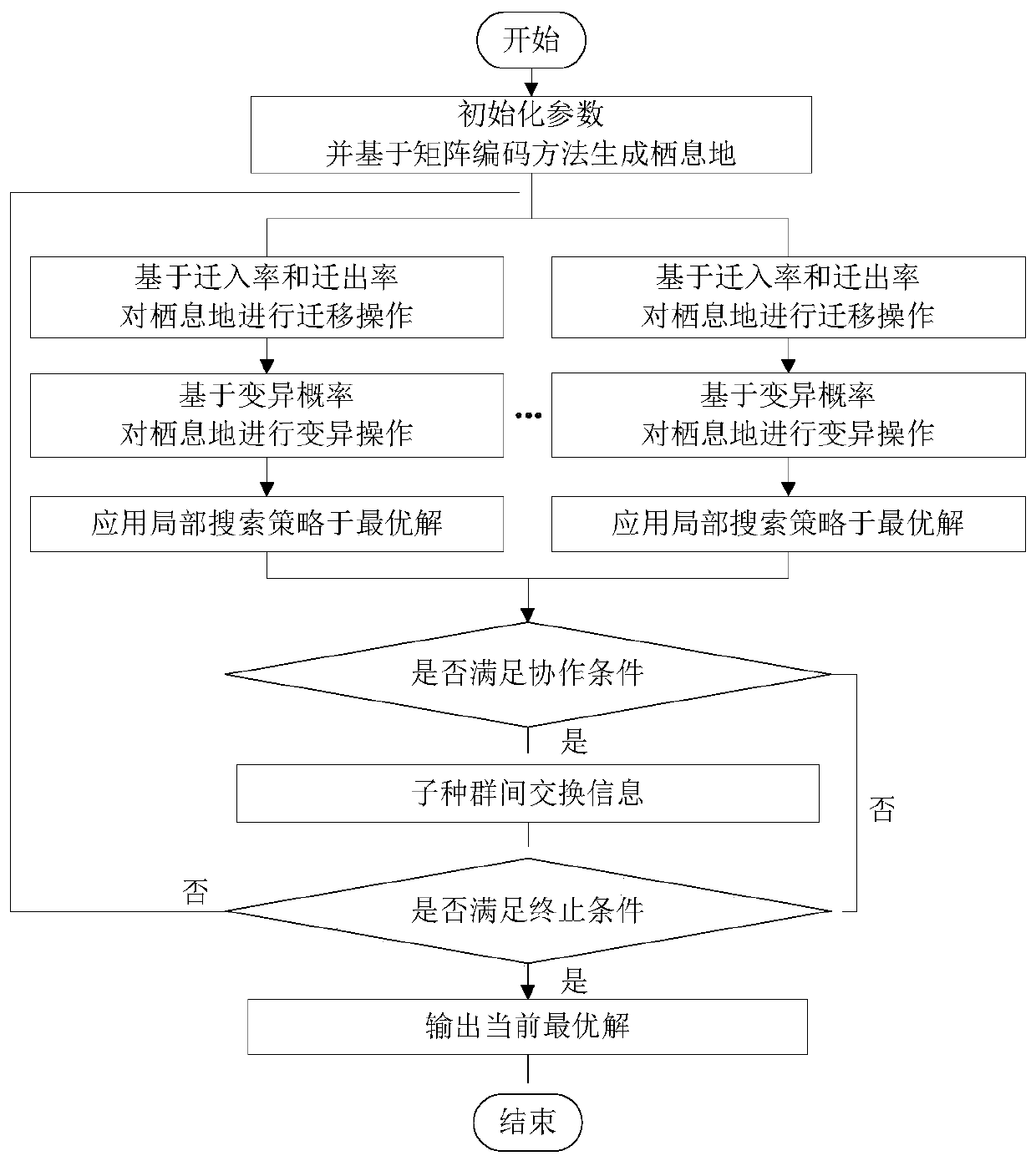
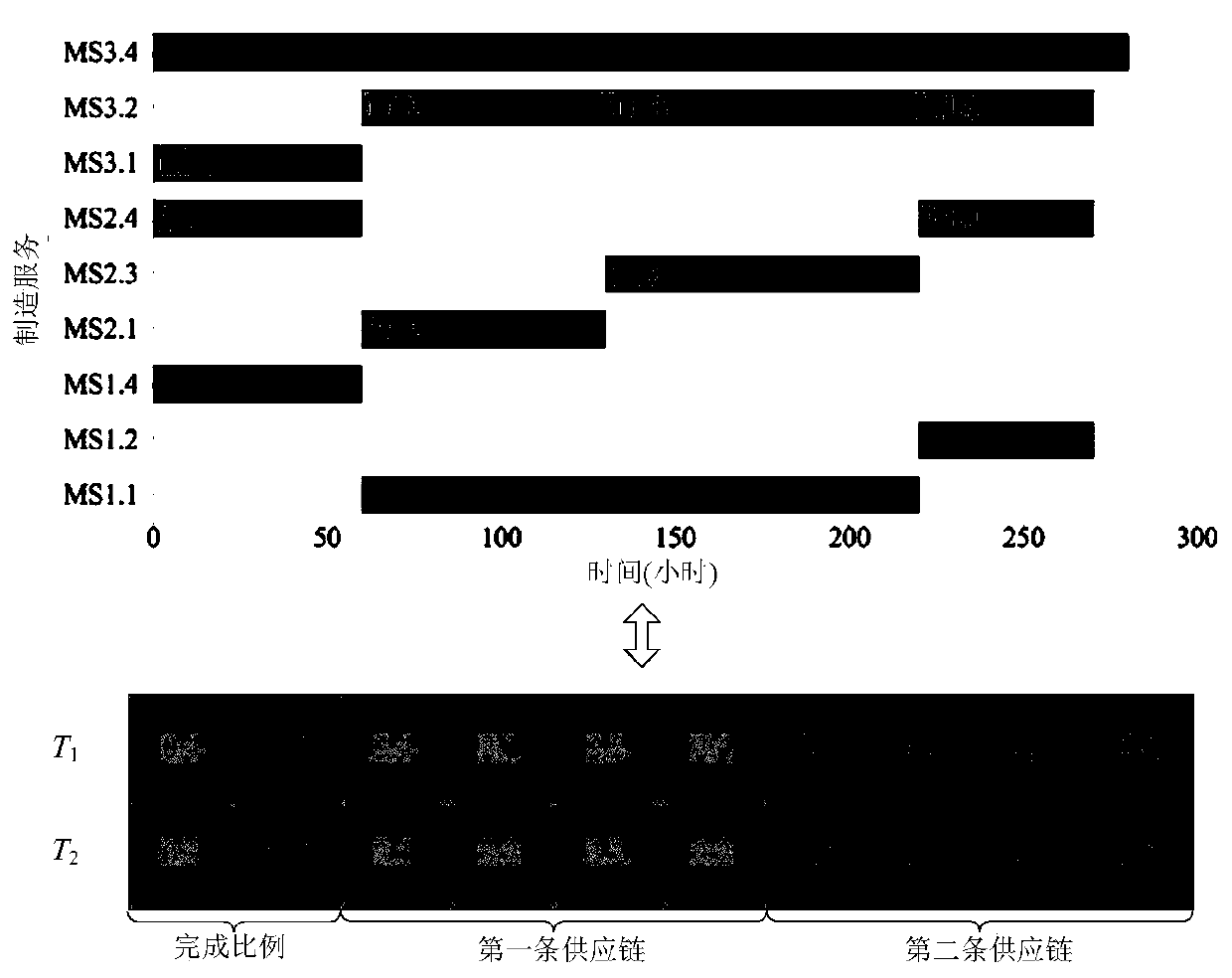
The invention discloses a dynamic task perception-oriented cloud manufacturing collaborative task scheduling method, which comprises the following steps of firstly, constructing a collaborative task scheduling model according to the proportion of tasks completed by a supply chain; generating an initial population as a current population when a new task arrives according to an original manufacturing task and an optional manufacturing service, dividing the current population into a plurality of sub-populations for subsequent iteration, and representing each collaborative task scheduling scheme in the current population by using matrix coding; and finally, solving is performed through an improved multi-population biogeography optimization algorithm, and fusing a multi-population strategy, a local search strategy and a cooperation mechanism, so that the task scheduling problem solving performance of the algorithm is improved. According to the method, a better scheduling scheme can be obtained in the scheduling stage and the re-scheduling stage.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF FINANCE & ECONOMICS
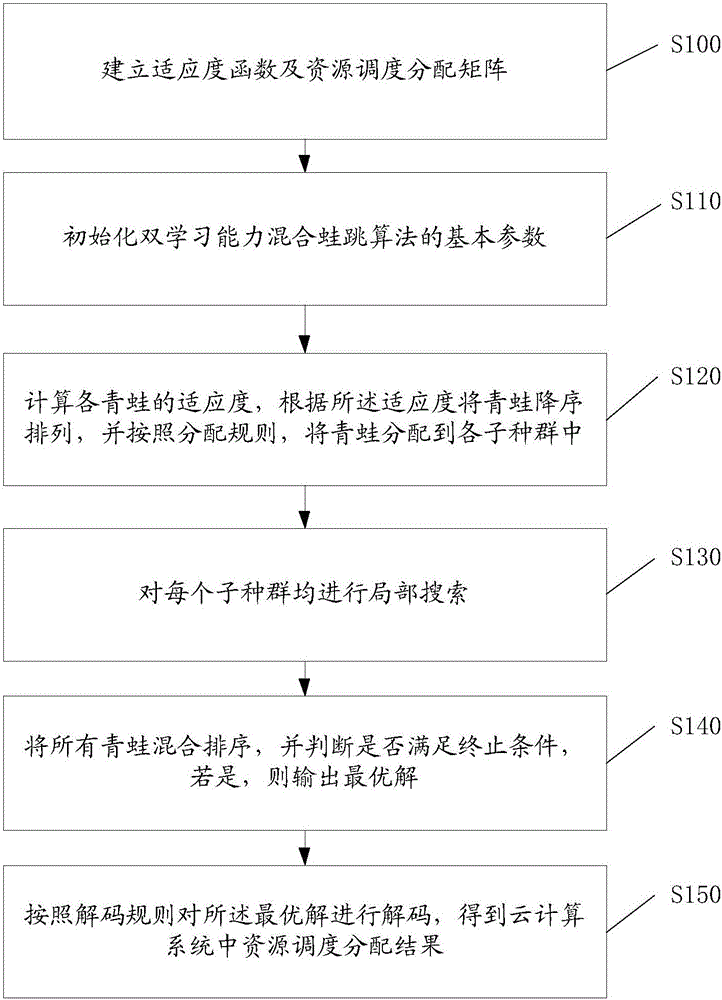
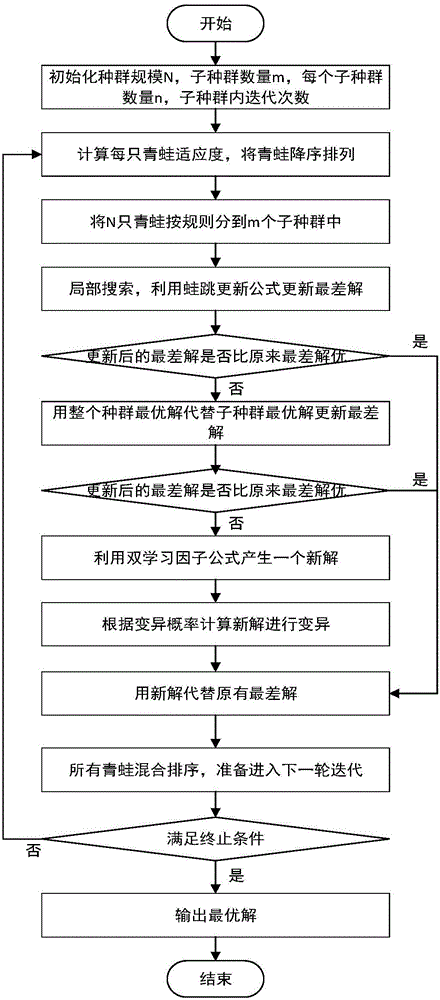
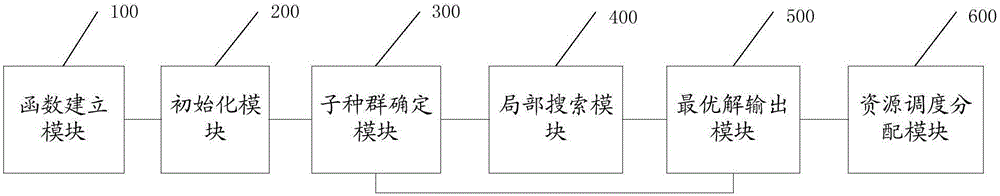
Resource scheduling method and system in cloud computing system
The invention discloses a resource scheduling method in a cloud computing system. According to the method, the position of an updating frog is computed by the aid of a leapfrog updating formula when each sub-population is locally searched, the fitness of the updating frog is computed to judge whether the fitness of the updating frog is superior to that of the worst frog or not, the position of the updating frog replaces that of the worst frog if the fitness of the updating frog is superior to that of the worst frog, the position of the optimal frog in the whole population replaces that of the worst frog if not, whether the fitness of the updated frog is superior to that of the worst frog or not is judged, the position of the updated frog replaces that of the worst frog if the fitness of the updated frog is superior to that of the worst frog, a new step length is generated by a double learning factor formula if not, the new step length is mutated according to mutation probability to obtain the position of the updated frog and replace the position of the worst frog, and the fitness of the updated frog is computed. The method can achieve good performances in optimal time span and load balance for task scheduling. The invention further discloses a resource scheduling system in the cloud computing system.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com