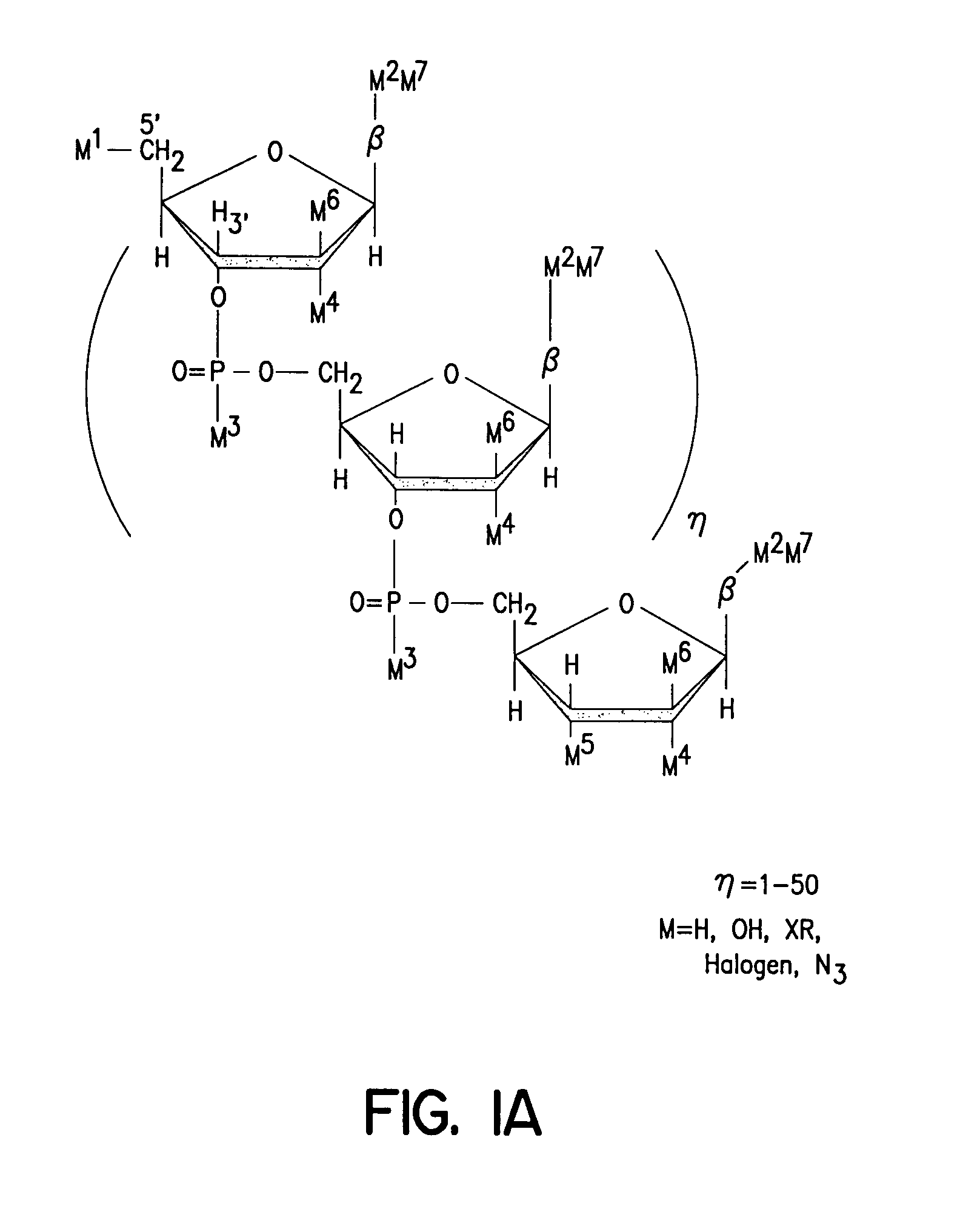
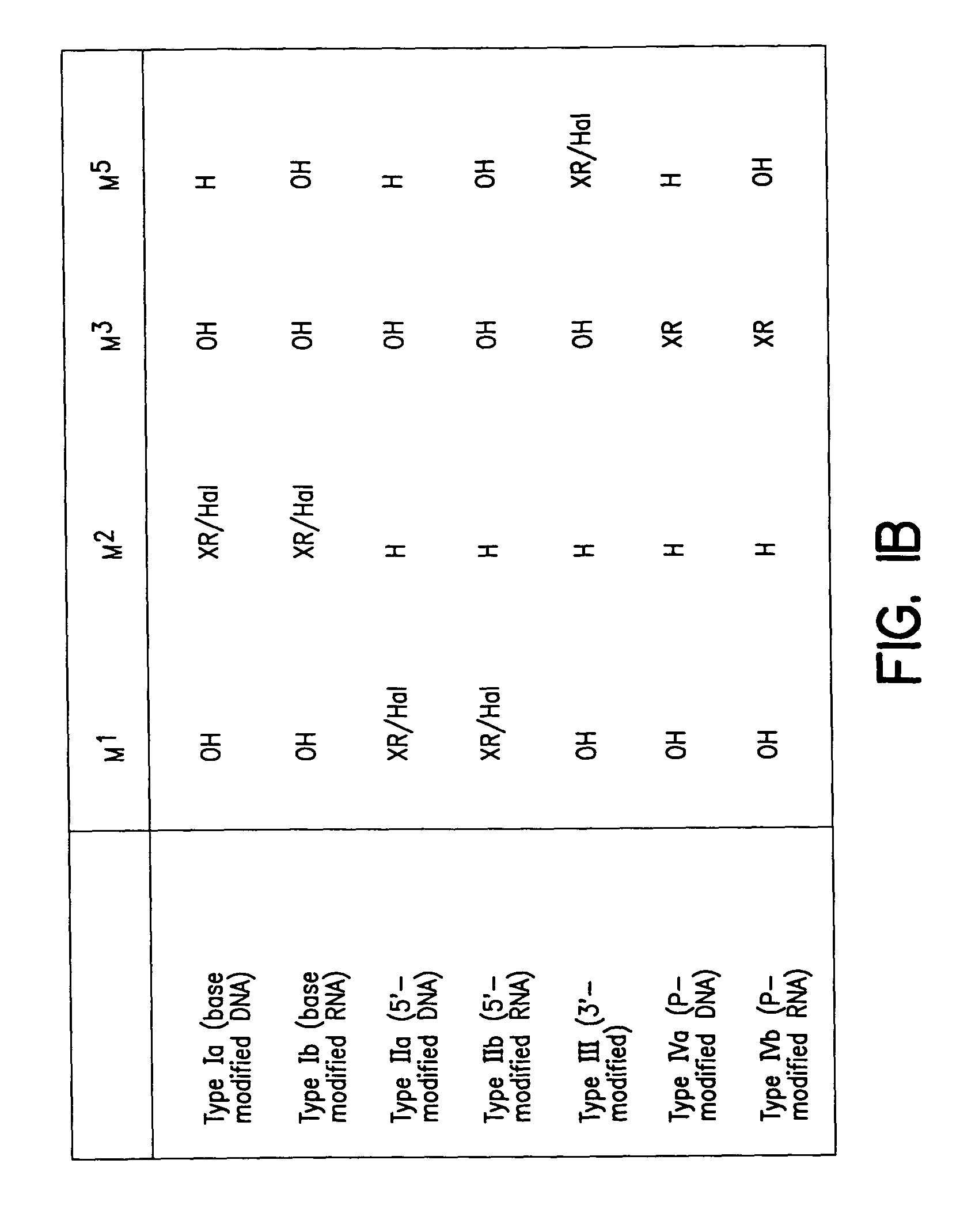
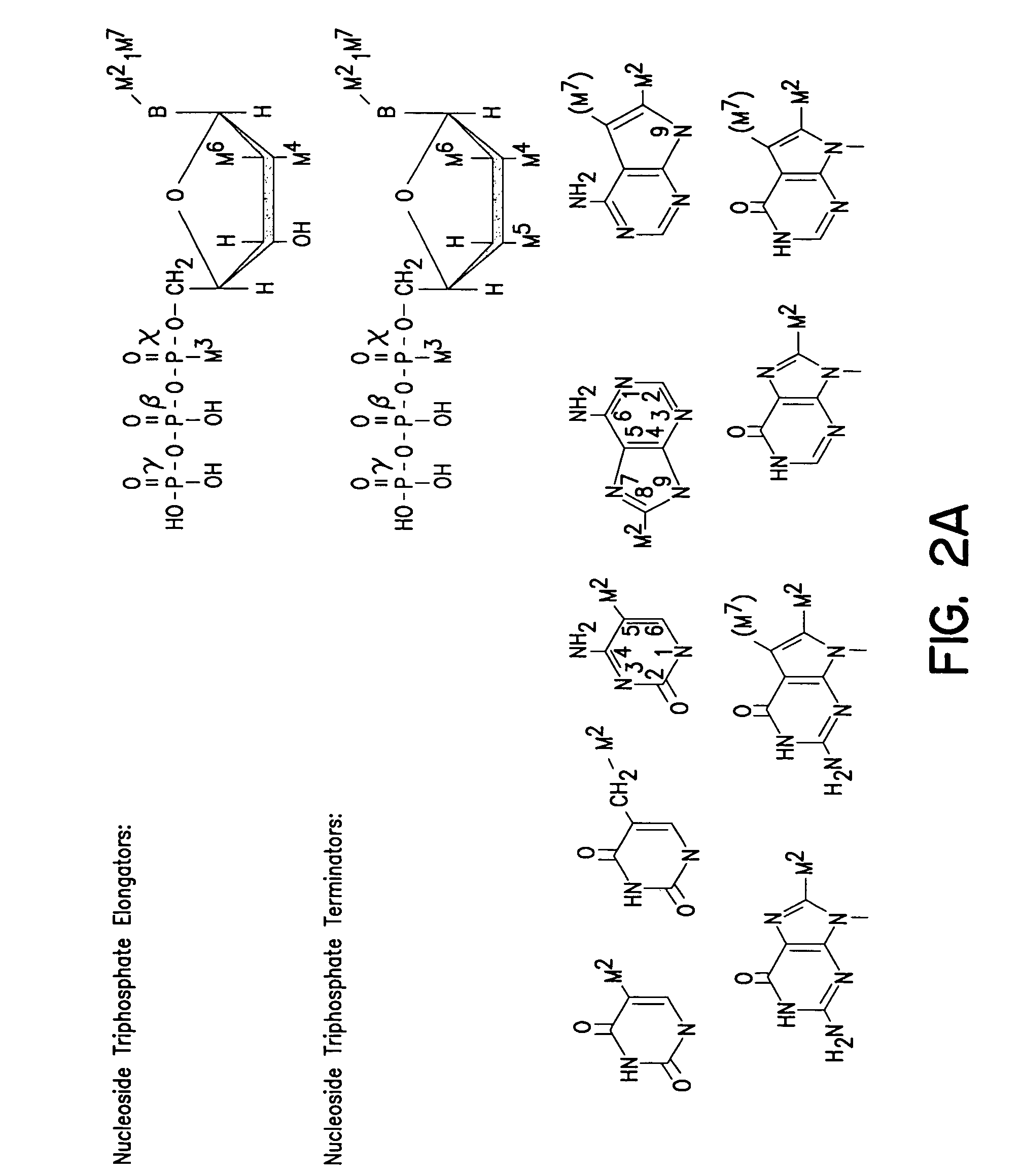
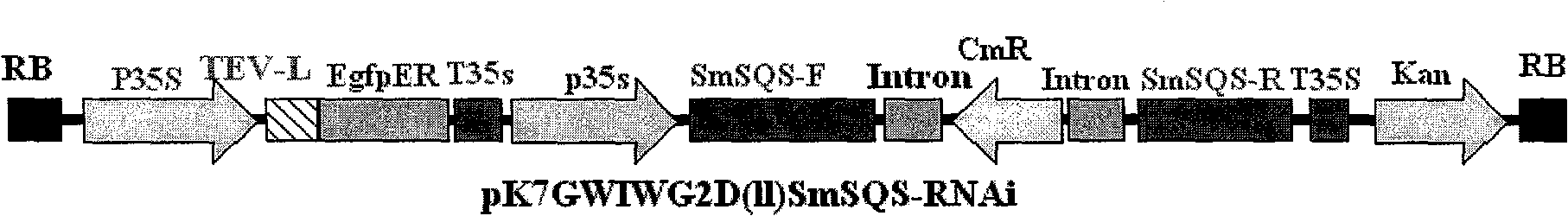Patents
Literature
165 results about "Homologous sequence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
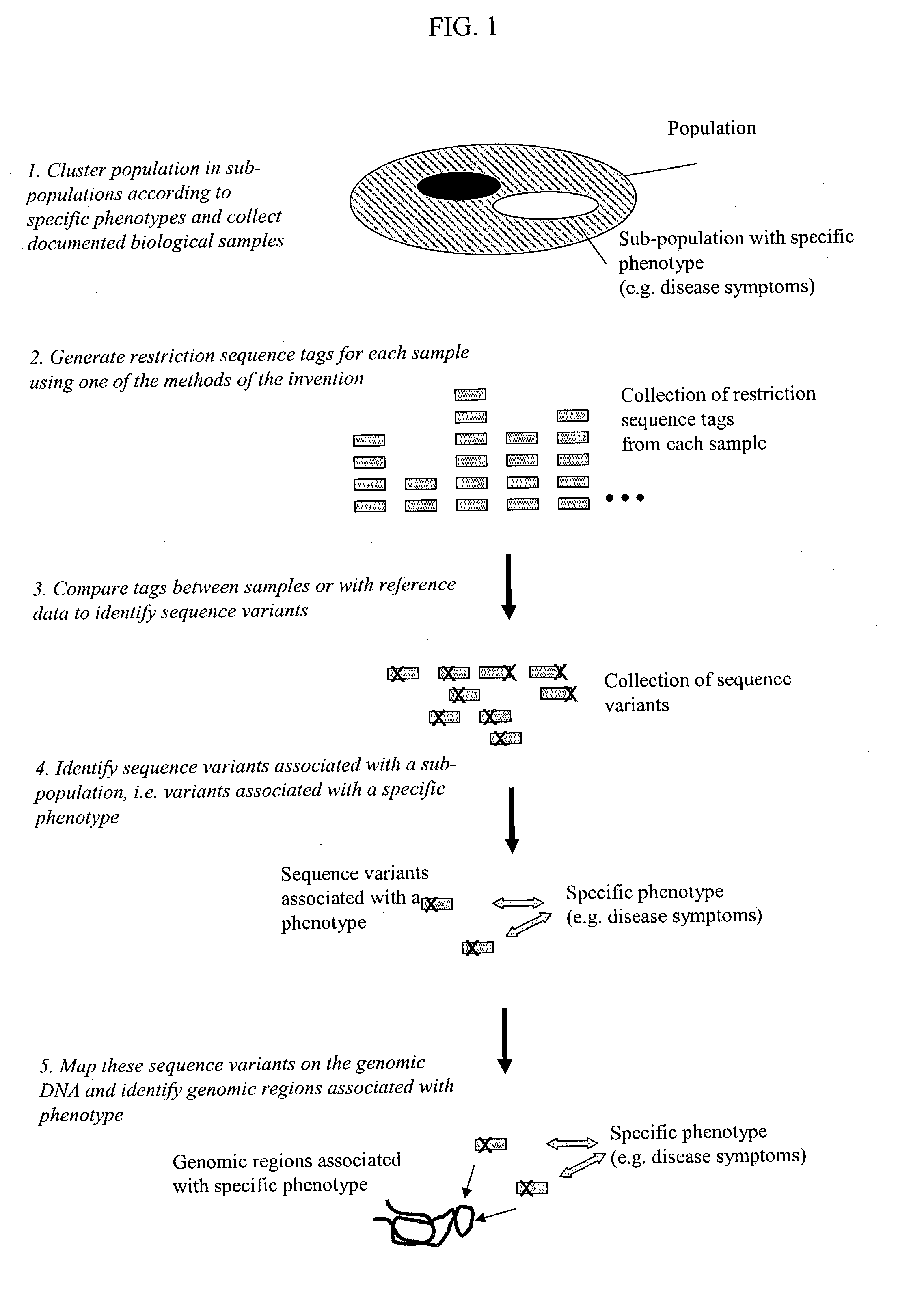
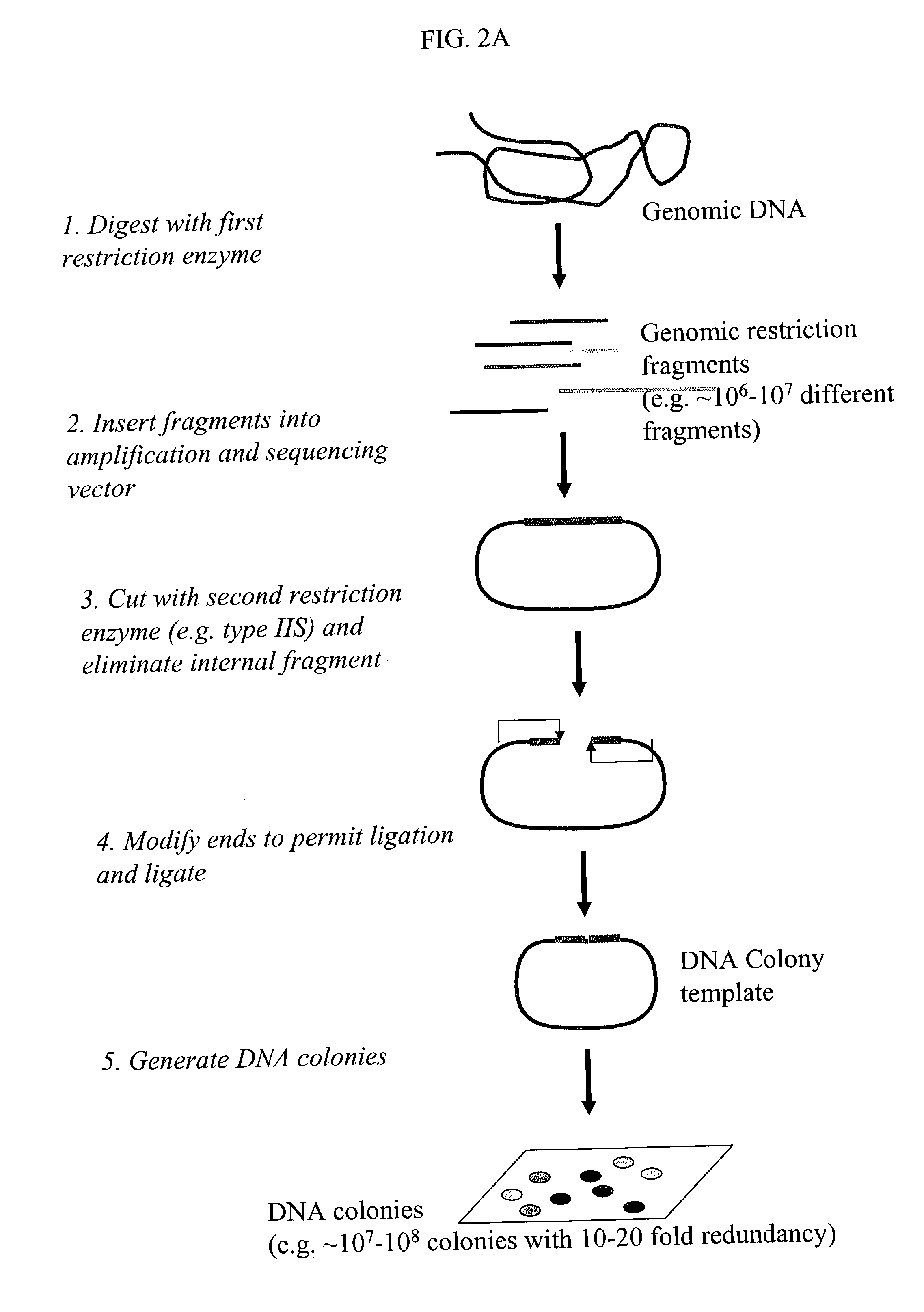
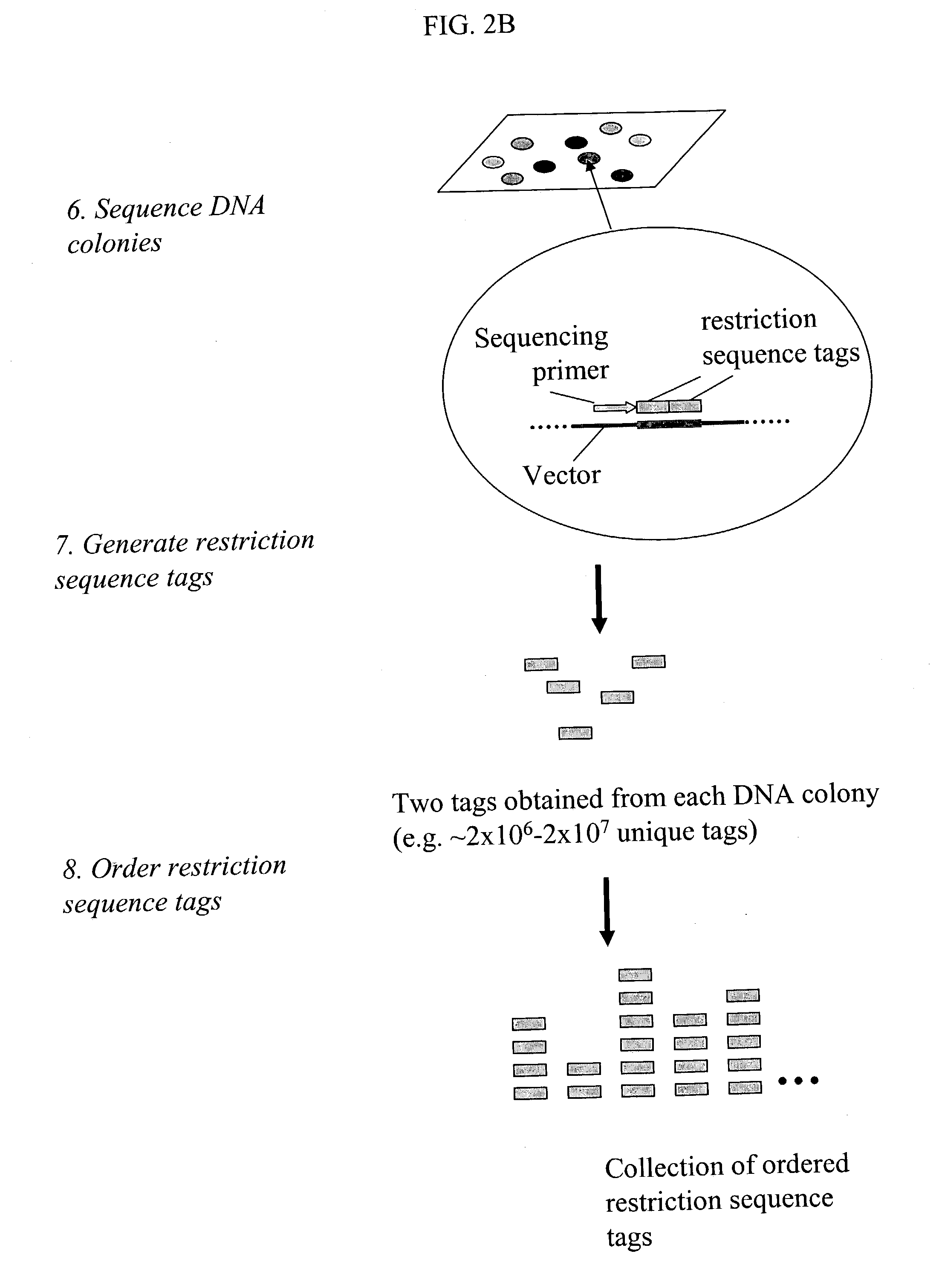
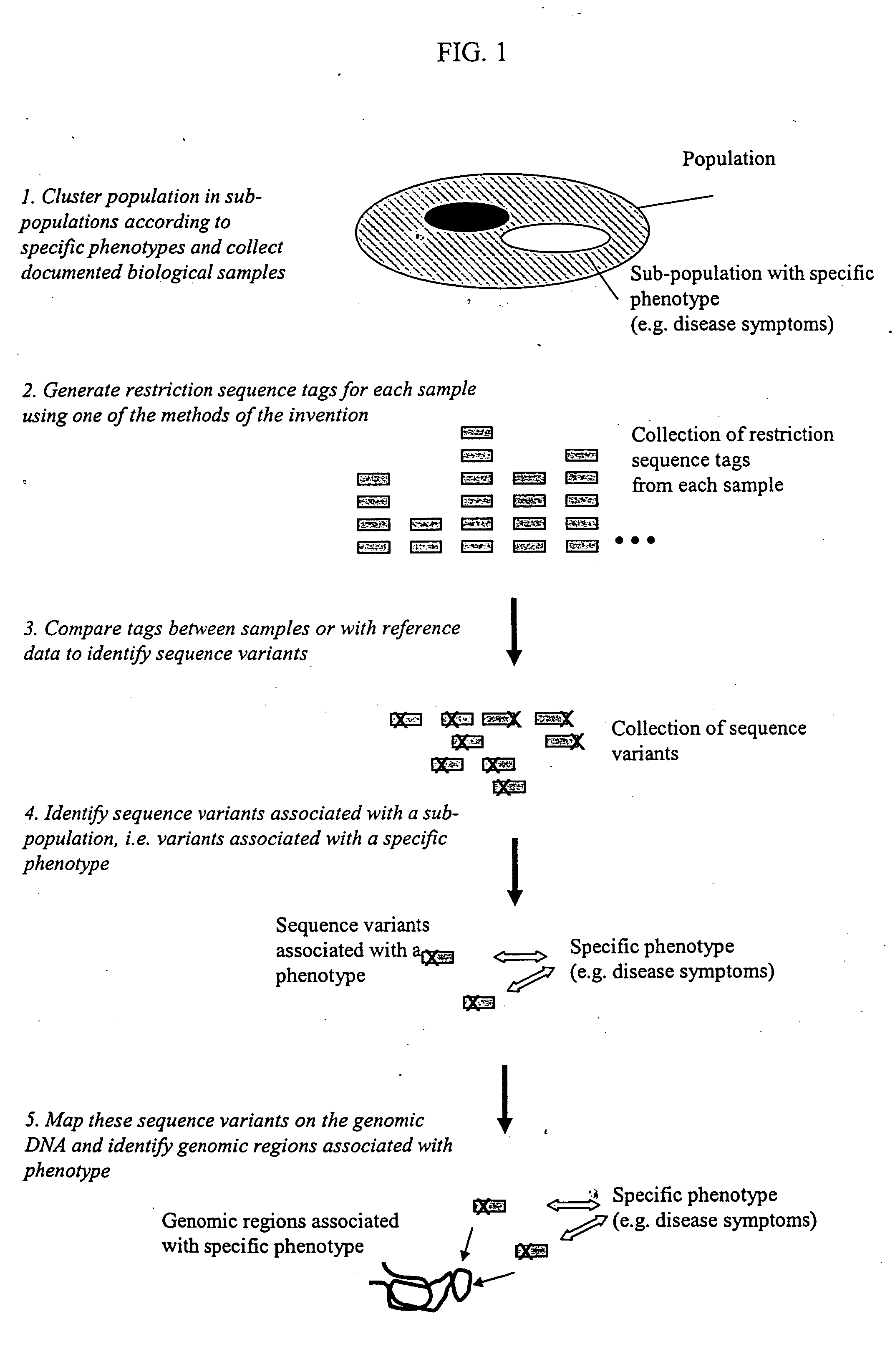
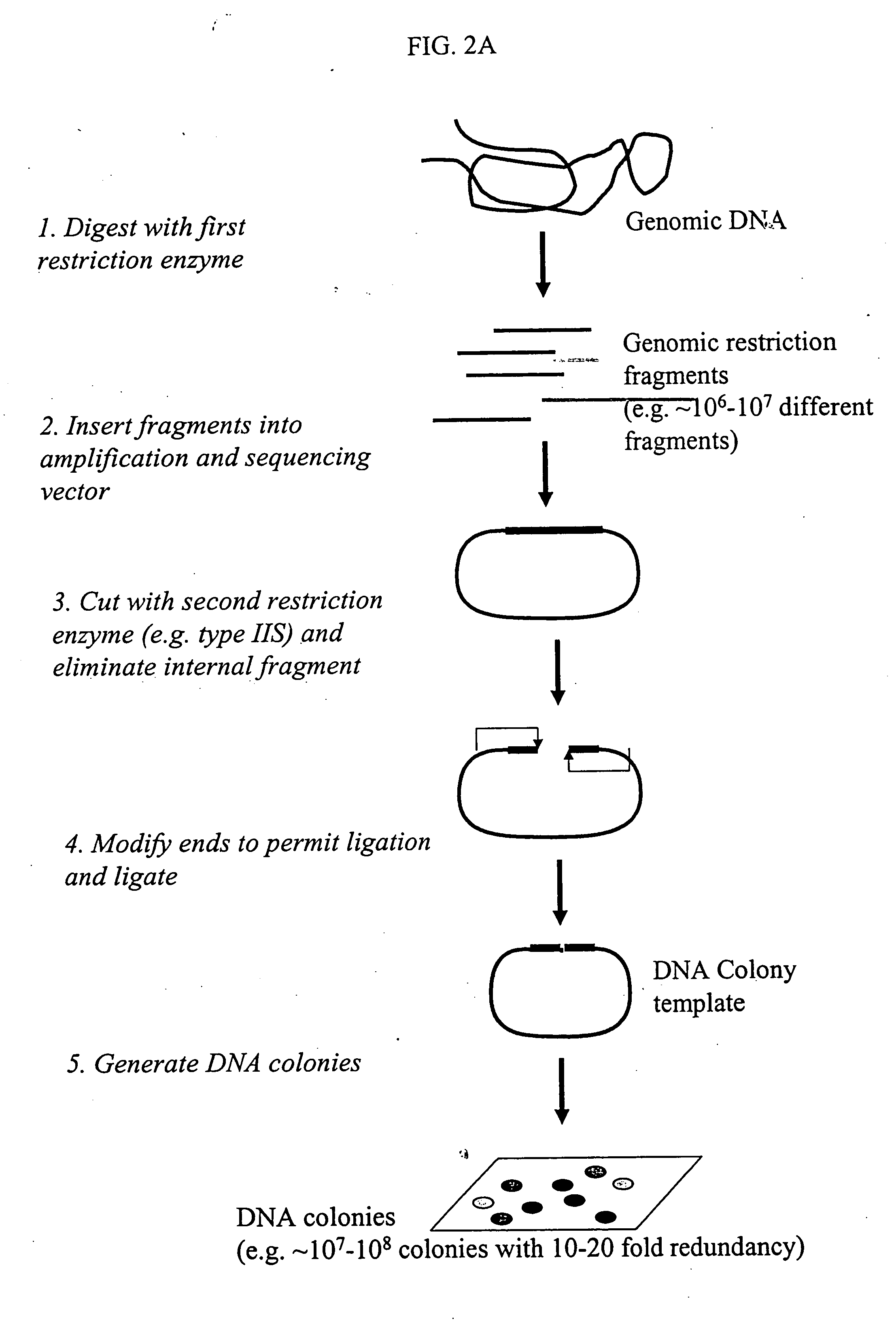
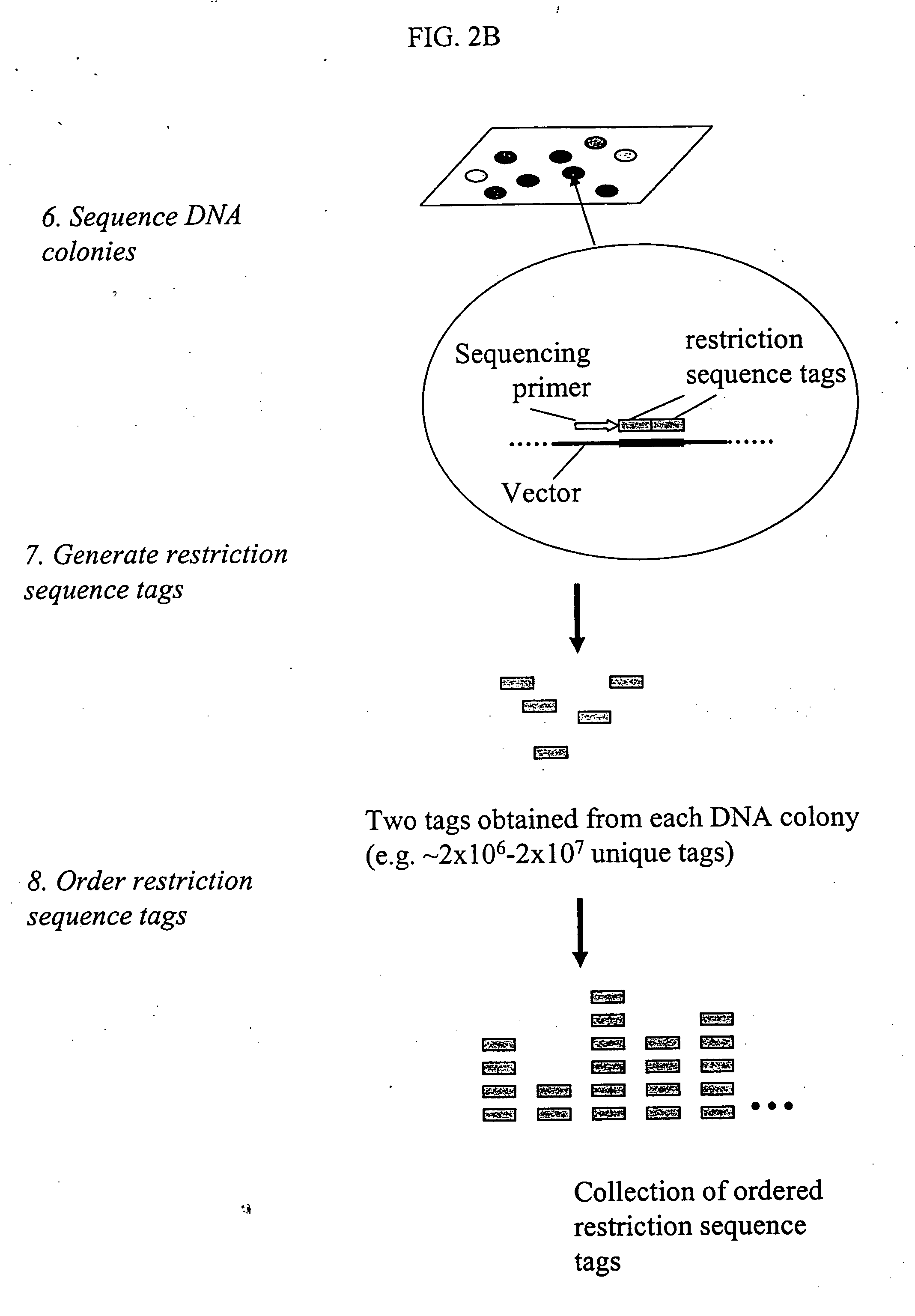
Methods for detecting genome-wide sequence variations associated with a phenotype
InactiveUS20040002090A1Microbiological testing/measurementFermentationSub populationsGenetic risk factor
The invention provides methods for determining genome-wide sequence variations associated with a phenotype of a species in a hypothesis-free manner. In the methods of the invention, a set of restriction fragments for each of a sub-population of individuals having the phenotype are generated by digesting nucleic acids from the individual using one or more different restriction enzymes. A set of restriction sequence tags for the individual is then determined from the set of restriction fragments. The restriction sequence tags for the sub-population of organisms are compared and grouped into one or more groups, each of which comprising restriction sequence tags that comprise homologous sequences. The obtained one or more groups of restriction sequence tags identify the sequence variations associated with the phenotype. The methods of the invention can be used for, e.g., analysis of large numbers of sequence variants in many patient samples to identify subtle genetic risk factors.
Owner:SOLEXA
Method of sequencing genomes by hybridization of oligonucleotide probes
InactiveUS6018041ASugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMammalian genomeHomologous sequence
The conditions under which oligonucleotides hybridize only with entirely homologous sequences are recognized. The sequence of a given DNA fragment is read by the hybridization and assembly of positively hybridizing probes through overlapping portions. By simultaneous hybridization of DNA molecules applied as dots and bound onto a filter, representing single-stranded phage vector with the cloned insert, with about 50,000 to 100,000 groups of probes, the main type of which is (A,T,C,G)(A,T,C,G)N8(A,T,C,G), information for computer determination of a sequence of DNA having the complexity of a mammalian genome are obtained in one step. To obtain a maximally completed sequence, three libraries are cloned into the phage vector, M13, bacteriophage are used: with the 0.5 kb and 7 kbp insert consisting of two sequences, with the average distance in genomic DNA of 100 kbp. For a million bp of genomic DNA, 25,000 subclones of the 0.5 kbp are required as well as 700 subclones 7 kb long and 170 jumping subclones. Subclones of 0.5 kb are applied on a filter in groups of 20 each, so that the total number of samples is 2,120 per million bp. The process can be easily and entirely robotized for factory reading of complex genomic fragments or DNA molecules.
Owner:HYSEQ
Exogenous gene knocking-in and integrating system on basis of CRISPR/Cas9, method for establishing exogenous gene knocking-in and integrating system and application thereof
ActiveCN106191116ANucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionTarget geneIntegrated systems
The invention provides an exogenous gene knocking-in and integrating system on the basis of CRISPR / Cas9, a method for establishing the exogenous gene knocking-in and integrating system and application thereof. The exogenous gene knocking-in and integrating system comprises vectors with report / donor functions and Cas9 expression vectors. Each report / donor vector comprises two target gent homologous arms and an exogenous sequence fragment positioned between the two target gene homologous arms; homologous sequences, which are positioned on a target gene, of the two target gene homologous arms of each report / donor vector are respectively positioned on two sides of a target sequence of the target gene and are connected with the target sequence of the target gene; the exogenous sequence fragments comprise promoters, resistant genes, shorn peptide sequences, report genes and polyA tails which are sequentially arrayed, two SSA repair homologous sequences of each resistant gene are inserted into the resistant gene, and the target sequence of each target gene is inserted in a space between the two corresponding SSA repair homologous sequences. The exogenous gene knocking-in and integrating system, the method and the application have the advantages that exogenous genes can be integrated with endogenous gene sequences in an efficient site-directed and accurately targeted manner, and double-chromosome allelic gene double-knocking-in can be efficiently carried out.
Owner:成都中科奥格生物科技有限公司
Method and kit for the detection and/or quantification of homologous nucleotide sequences on arrays
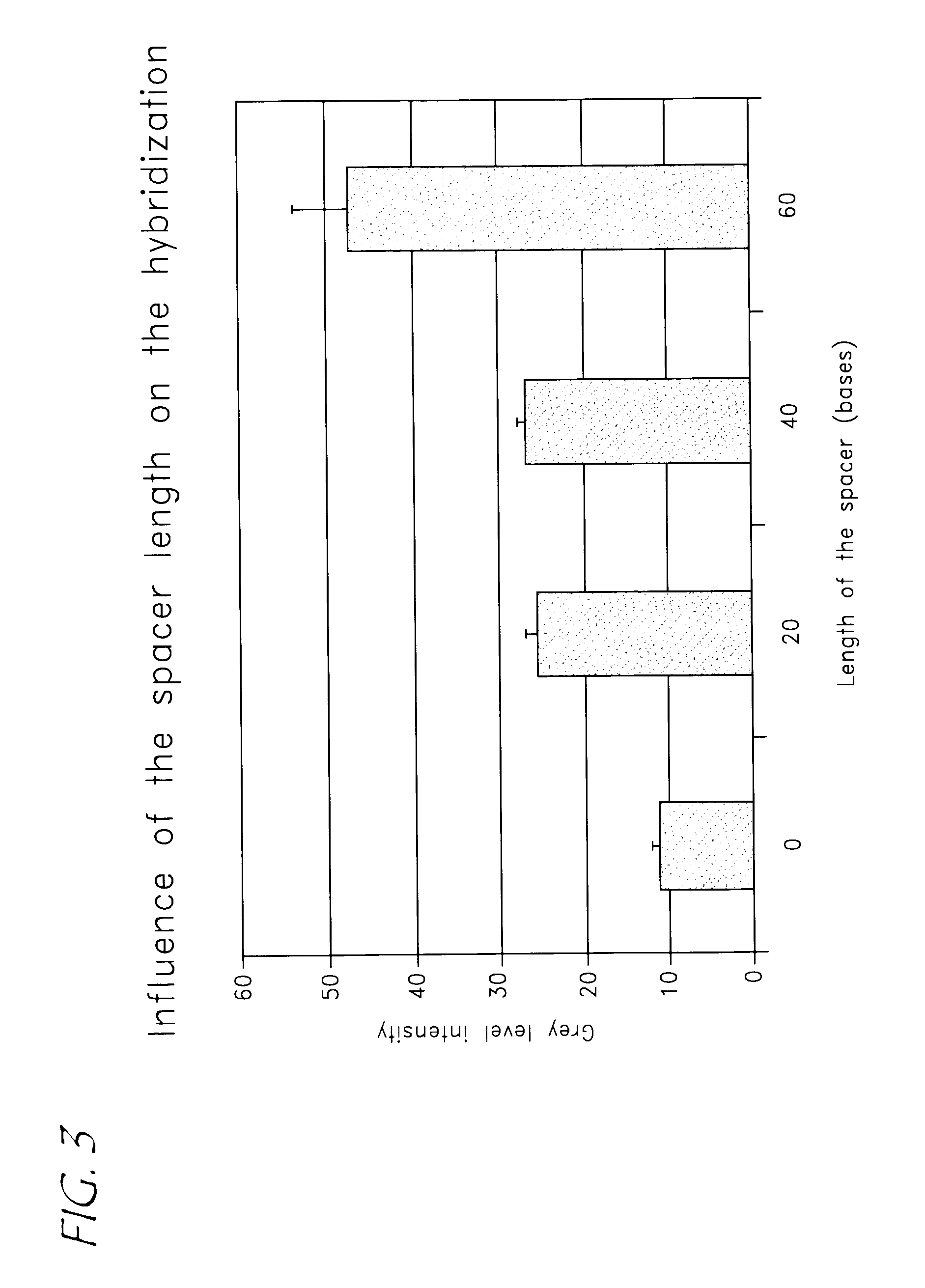
InactiveUS20050272044A1Easy to identifyHighly versatileSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological bodyHomologous sequence
The invention relates to a method and a kit for the specific identification and / or quantification of one or several among at least 7 organisms or parts thereof, in a biological sample being possibly contaminated by at least 4 other organisms, by detecting at least one nucleotide sequence specific of each of the organisms possibly present in said biological sample, wherein said nucleotide sequence is homologous with at least 4 other nucleotide sequences. The method comprises the steps of: amplifying the nucleotide sequences specific of said organisms into target amplified nucleotide sequences using at least 2 different primer pairs, each one being capable of amplifying at least 4 of said homologous nucleotide sequences from other organisms and having an homology higher than 85% with each of the said amplified homologous nucleotide sequences to be amplified; providing an array onto which single-stranded capture nucleotide sequences are arranged at pre-determined locations, said single-stranded capture nucleotide sequences being covalently bound to an insoluble support, via a spacer which is at least 6.8 nm in length, and wherein said capture nucleotide sequences comprise a nucleotide sequence of about 10 to 50 bases which is able to specifically bind to one target amplified sequence without binding to said other amplified homologous nucleotide sequences and presenting an homology lower than 85% with the other capture nucleotide sequences of the said other amplified homologous sequences, contacting said target amplified sequences with the array in one solution under conditions allowing hybridization of the target amplified sequences to complementary capture nucleotide sequences present on the array; and detecting and quantifying signals present on specific locations on the array; wherein the intensities of the signals in specific locations allows identification of the organisms.
Owner:EPPENDORF ARRAY TECH SA
Upland cotton SNP marker and application thereof
InactiveCN105349537AImprove detection efficiencyImprove work efficiencyNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementAgricultural scienceHomologous sequence
The invention discloses an upland cotton SNP marker and application thereof, and belongs to the field of upland cotton SNP marker development. The upland cotton SNP marker is obtained by developing a single-copy SNP marker of an upland cotton genome via chip hybridization and homologous sequence comparison, and picking out SNP markers in a linkage disequilibrium recession distance via linkage disequilibrium analysis. The SNP marker provided by the invention can be applied to analysis of genetic diversity and group structure, or to germplasm identification of upland cotton, is single-copy, and has no remarkable linkage disequilibrium among markers, so that the efficiency of detection, adopting the SNP marker, during analysis of genetic diversity, group structure or fingerprint identification can be greatly improved, and the work efficiency is higher.
Owner:INST OF COTTON RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method of sequencing of genomes by hybridization of oligonucleotide probes
InactiveUS6451996B1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMammalian genomeHomologous sequence
The conditions under which oligonucleotides hybridize only with entirely homologous sequences are recognized. The sequence of a given DNA fragment is read by the hybridization and assembly of positively hybridizing probes through overlapping portions. By simultaneous hybridization of DNA molecules applied as dots and bound onto a filter, representing single-stranded phage vector with the cloned insert, with about 50,000 to 100,000 groups of probes, the main type of which is (A,T,C,G)(A,T,C,G)N8(A,T,C,G), information for computer determination of a sequence of DNA having the complexity of a mammalian genome are obtained in one step. To obtain a maximally completed sequence, three libraries are cloned into the phage vector, M13, bacteriophage are used: with the 0.5 kb and 7 kbp insert consisting of two sequences, with the average distance in genomic DNA of 100 kbp. For a million bp of genomic DNA, 25,000 subclones of the 0.5 kbp are required as well as 700 subclones 7 kb long and 170 jumping subclones. Subclones of 0.5 kb are applied on a filter in groups of 20 each, so that the total number of samples is 2,120 per million bp. The process can be easily and entirely robotized for factory reading of complex genomic fragments or DNA molecules.
Owner:COMPLETE GENOMICS INC
Method and system for detection of phenotype genes and analysis of biological information
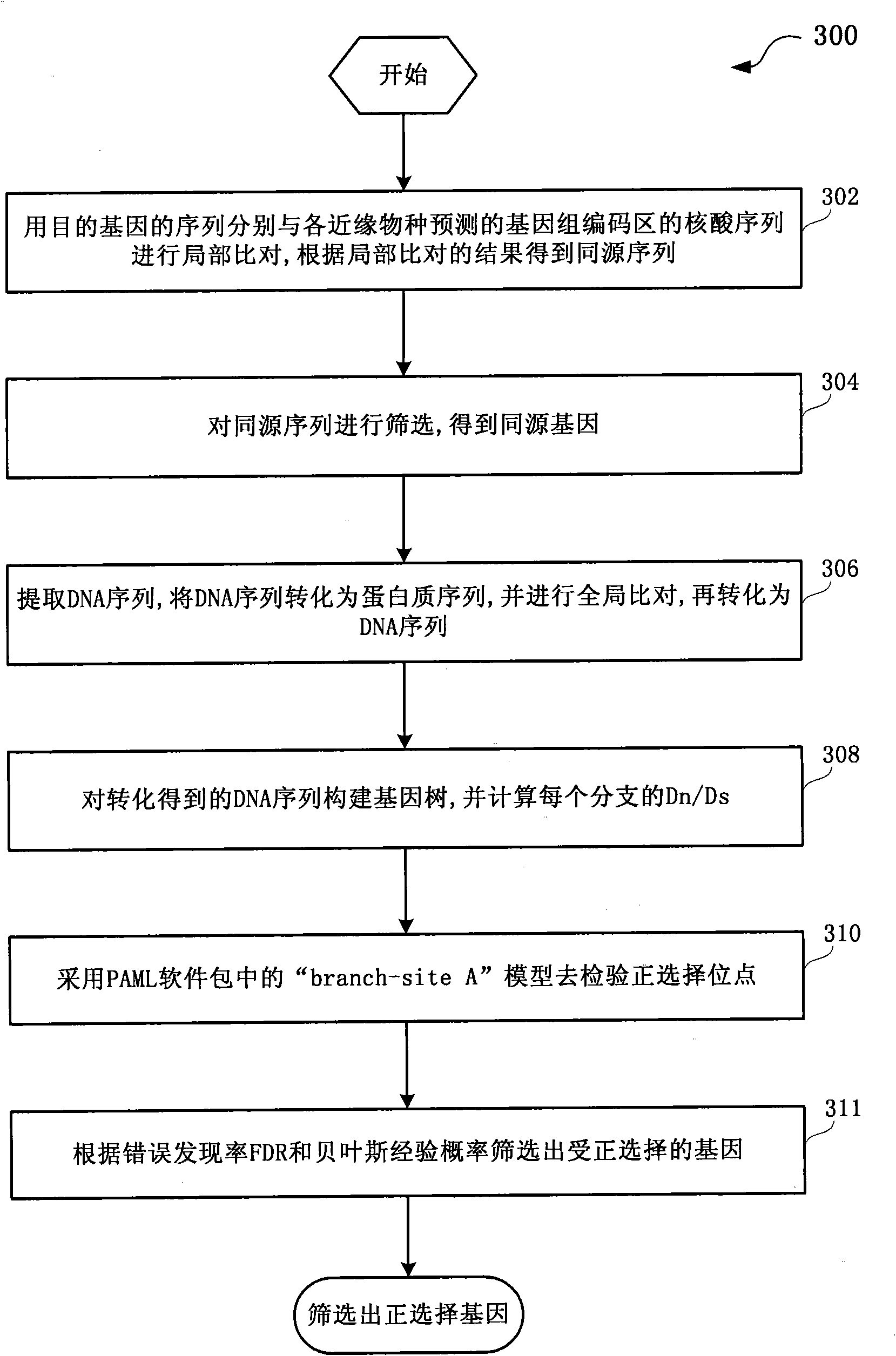
ActiveCN101930502AReduce misleadingEasy to handleMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsNucleotideData information
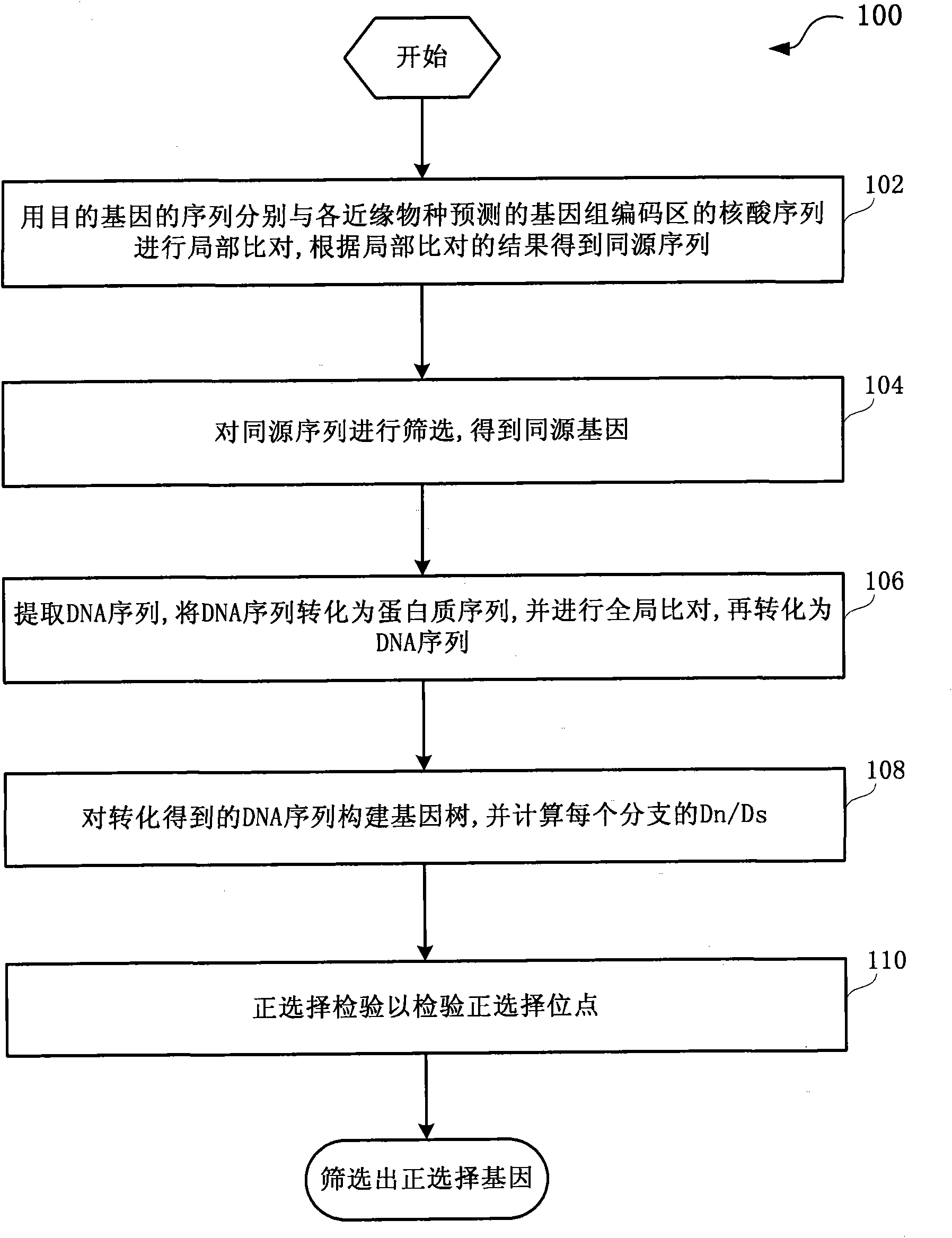
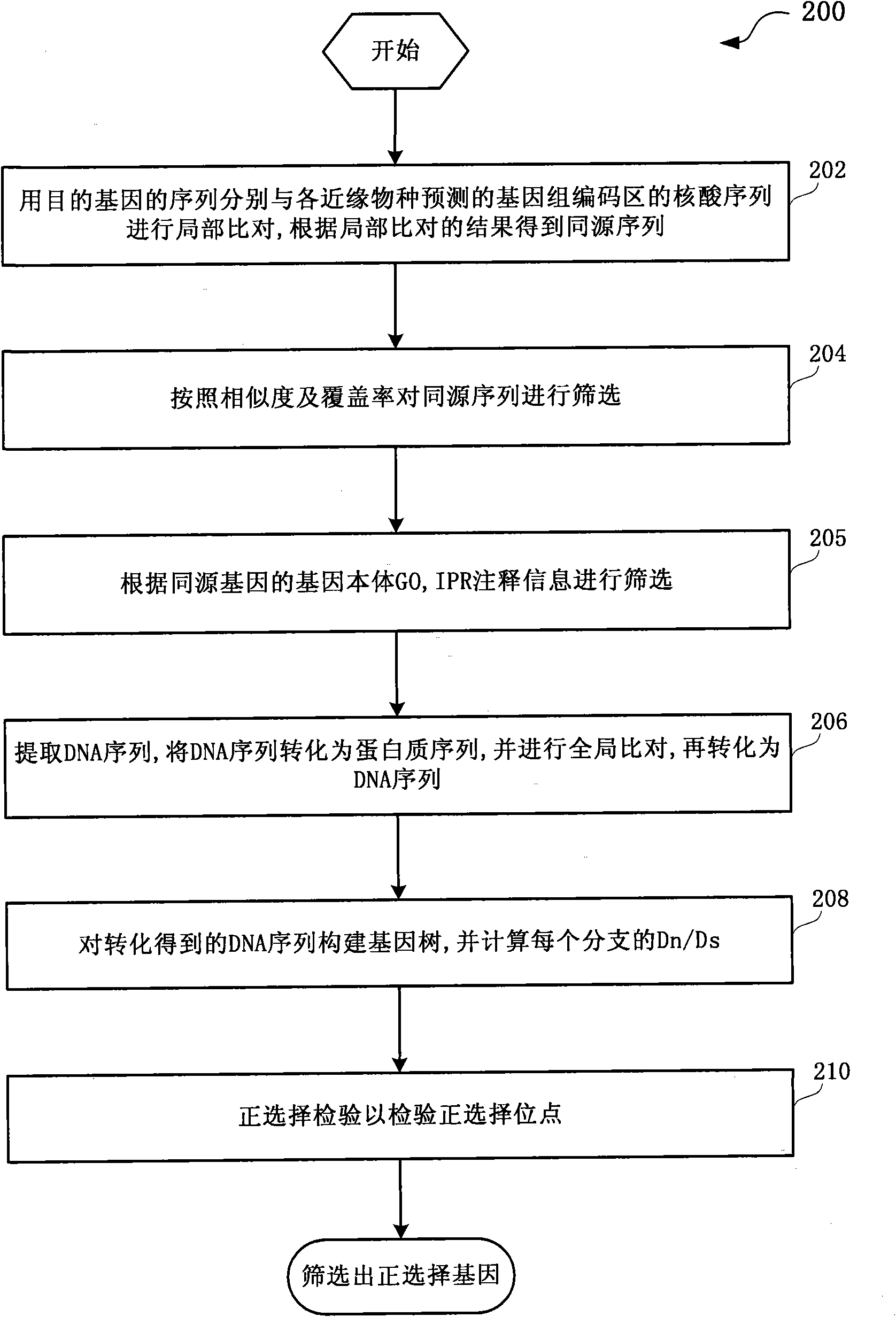
The invention discloses a method and a system for detection of phenotype genes and analysis of biological information. The method comprises the following steps of: performing local comparison between the sequence of target genes and nucleotide sequences of predicted genome coding regions of all allied species respectively, and obtaining a homologous sequence according to the local comparison results; screening the homologous sequence to obtain the homologous genes; extracting a DNA sequence from the homologous genes, converting the DNA sequence into a protein sequence, performing the overall comparison, and then converting the protein sequence into the DNA sequence; constructing a gene tree for the DNA sequence obtained by conversion, and working out Dn / Ds of each branch; and performing positive selection detection and detecting positive selection loci. The method and the system provided by the invention have the advantages of quickly processing a large amount of data information and discovering more accurate information, reducing misguiding of pseudogenes on analysis of biological information and helping to acquire the biological information to explain more biological problems.
Owner:BGI TECH SOLUTIONS
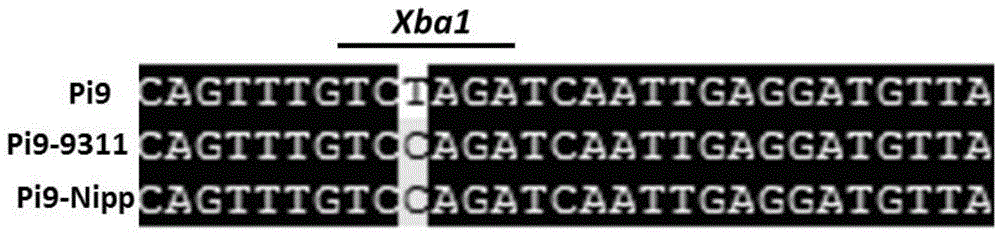
Anti-rice blast gene Pi9 specific CAPS marker Pi9caps and application thereof
InactiveCN104630364ALimited applicabilityAccelerate the progress of breedingMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationRice plantsHomologous sequence
The invention discloses an anti-rice blast gene Pi9 specific CAPS marker Pi9caps and application thereof. The invention discloses a method for identifying or auxiliarily identifying whether rice contains anti-rice blast gene Pi9 and / or whether rice has rice blast resistance, which comprises the following steps: detecting 40804th nucleotide from the 5' terminal of 75-1-127BAC12.1 sequence or homologous sequence thereof in chromosome 6 of rice to be detected, and identifying according to the kind of the 40804th nucleotide the 5' terminal of the 75-1-127BAC12.1 sequence or homologous sequence thereof in chromosome 6 of rice. The anti-rice blast gene Pi9 specific CAPS marker Pi9caps can accurately judge whether the selected rice plant contains the anti-rice blast gene Pi9, and thus, has important application meanings in accelerating the anti-rice blast rice species breeding progress.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
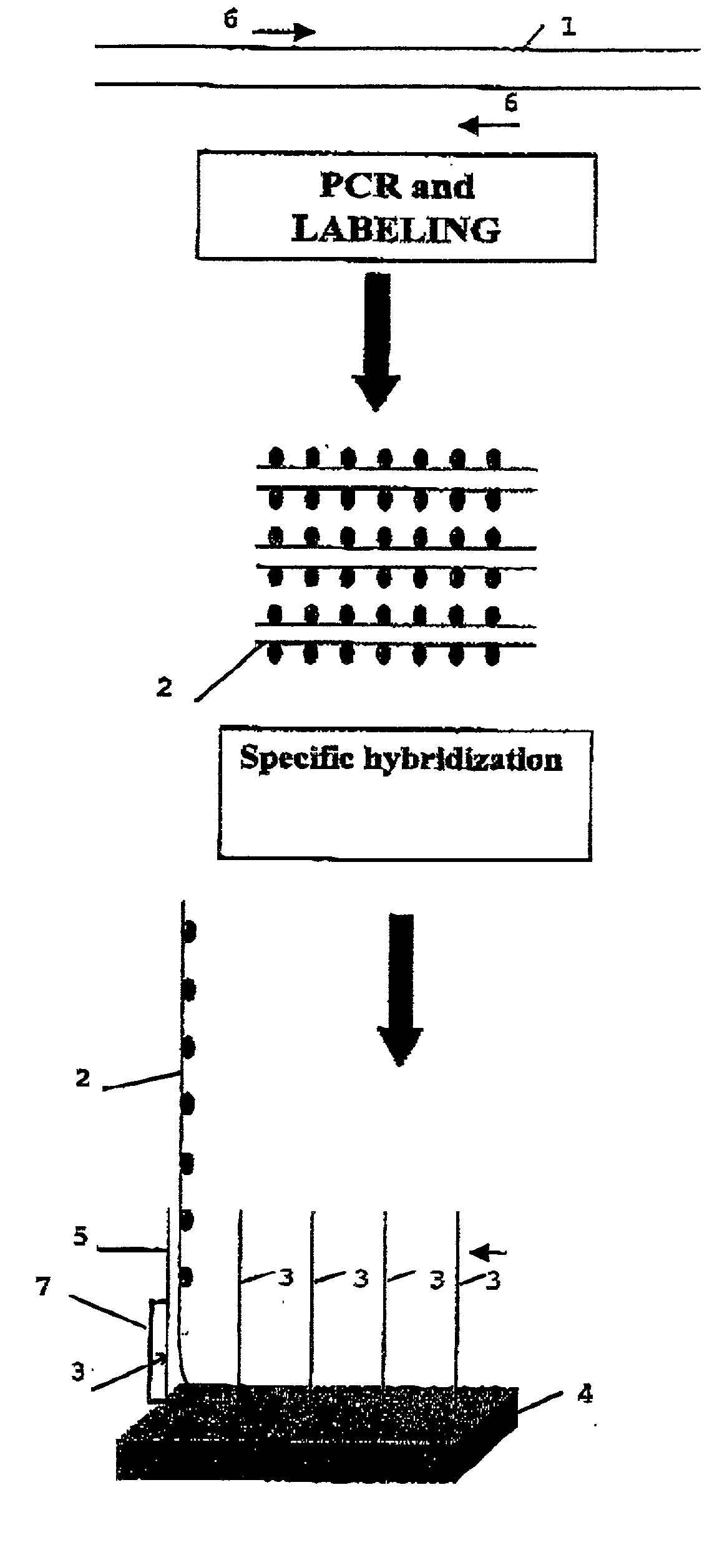
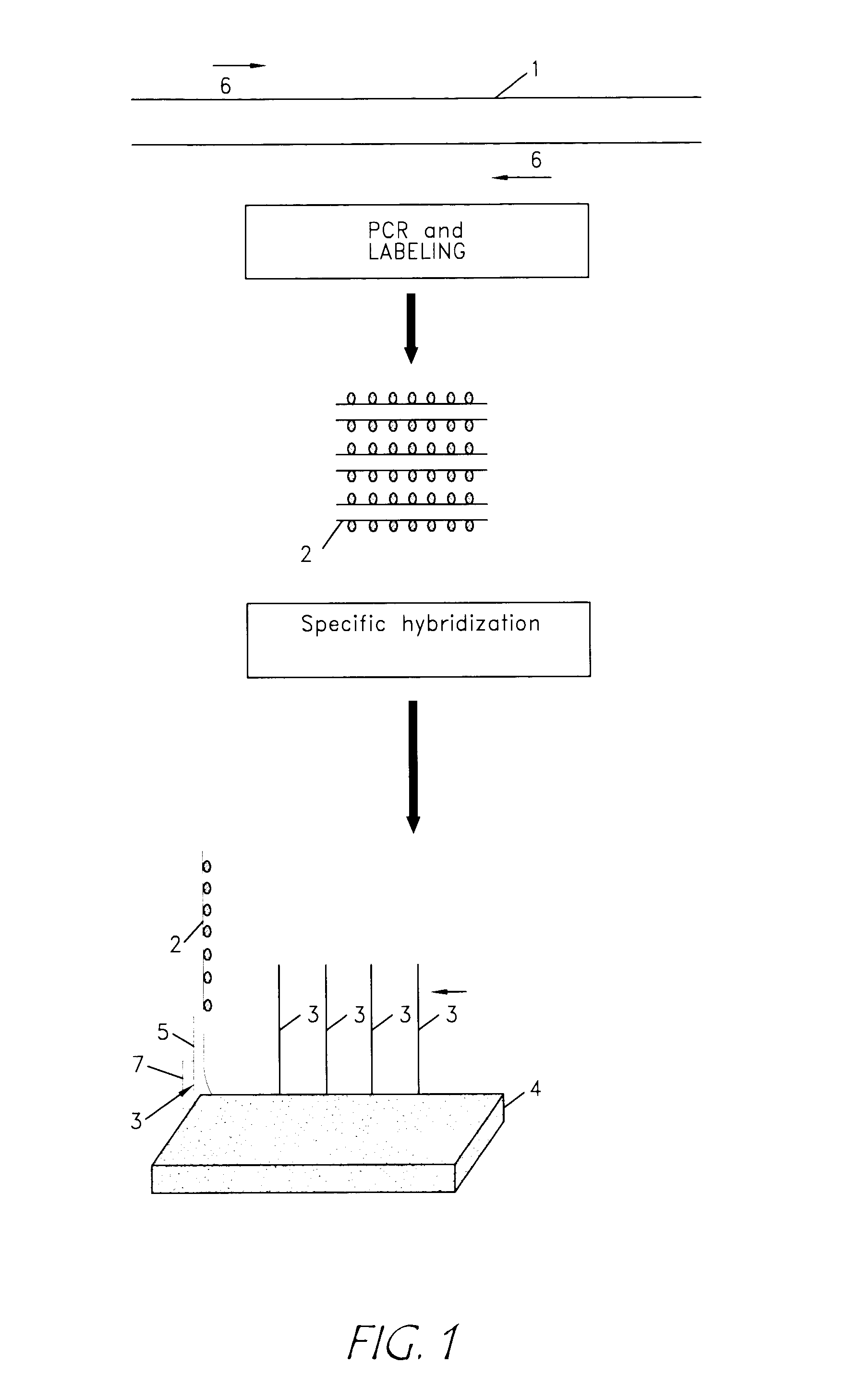
Identification of biological (micro) organisms by detection of their homologous nucleotide sequences on arrays
InactiveUS20020106646A1Easy to identifySimple technologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiological bodyHomologous sequence
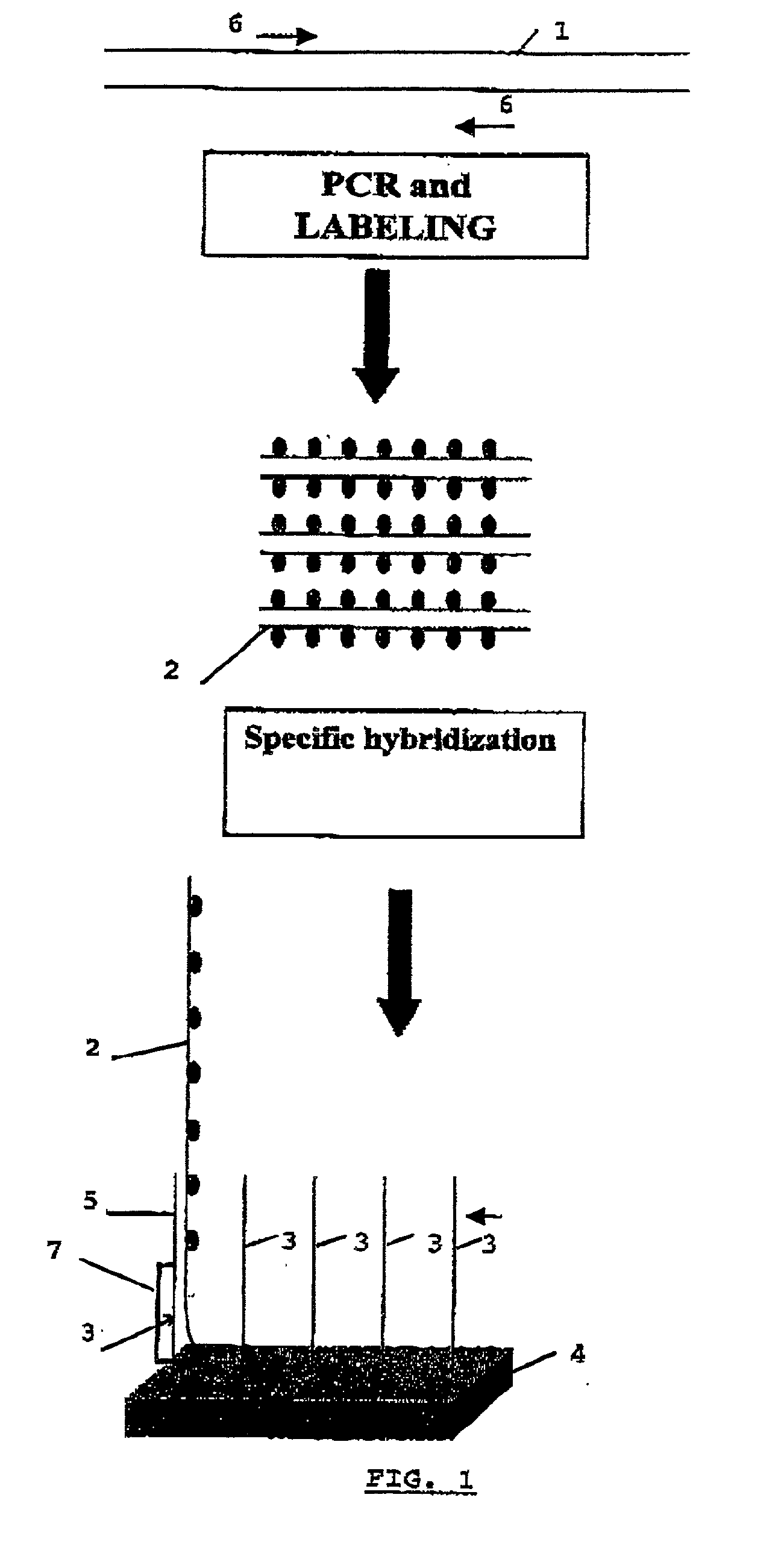
The present invention is related to an identification and / or quantification method of a biological (micro)organism or part of it (possibly present in a biological sample) by a detection of its nucleotide sequence among at least 4 other homologous sequences and comprising the steps of: possibly extracting original nucleotide sequences (1) from the (micro)organism; amplifying or copying with a unique pair of primer(s), at least part of original nucleotide sequences (1) into target nucleotide sequences (2) to be detected; possibly labelling said target nucleotide sequences (2); putting into contact the labelled target nucleotide sequences (2) with single stranded capture nucleotide sequences (3) bound by a single predetermined link to an insoluble solid support (4), preferably a non porous solid support, discriminating the binding of a target nucleotide sequence (2) specific of an organism or part of it by detecting, quantifying and / or recording a signal resulting from a hybridization by complementary base pairing between the target nucleotide sequence (2) and its corresponding capture nucleotide sequence (3), wherein said capture nucleotide sequence (3) being bound to the insoluble solid support (4) at a specific location according to an array, said array having a density of at least 4 different bound single stranded capture nucleotide sequences / cm2 of solid support surface and wherein the binding between the target nucleotide sequence and its corresponding capture nucleotide sequence forms (will result in) said signal at the expected location, the detection of a single signal allowing a discrimination of the target nucleotide sequence specific of an organism or part of it from homologous nucleotide sequences.
Owner:EPPENDORF ARRAY TECH SA
Selective Inhibition of TLR4 Signaling
InactiveUS20100069297A1Enough disruptionCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsPeptide/protein ingredientsHomologous sequenceBiological activation
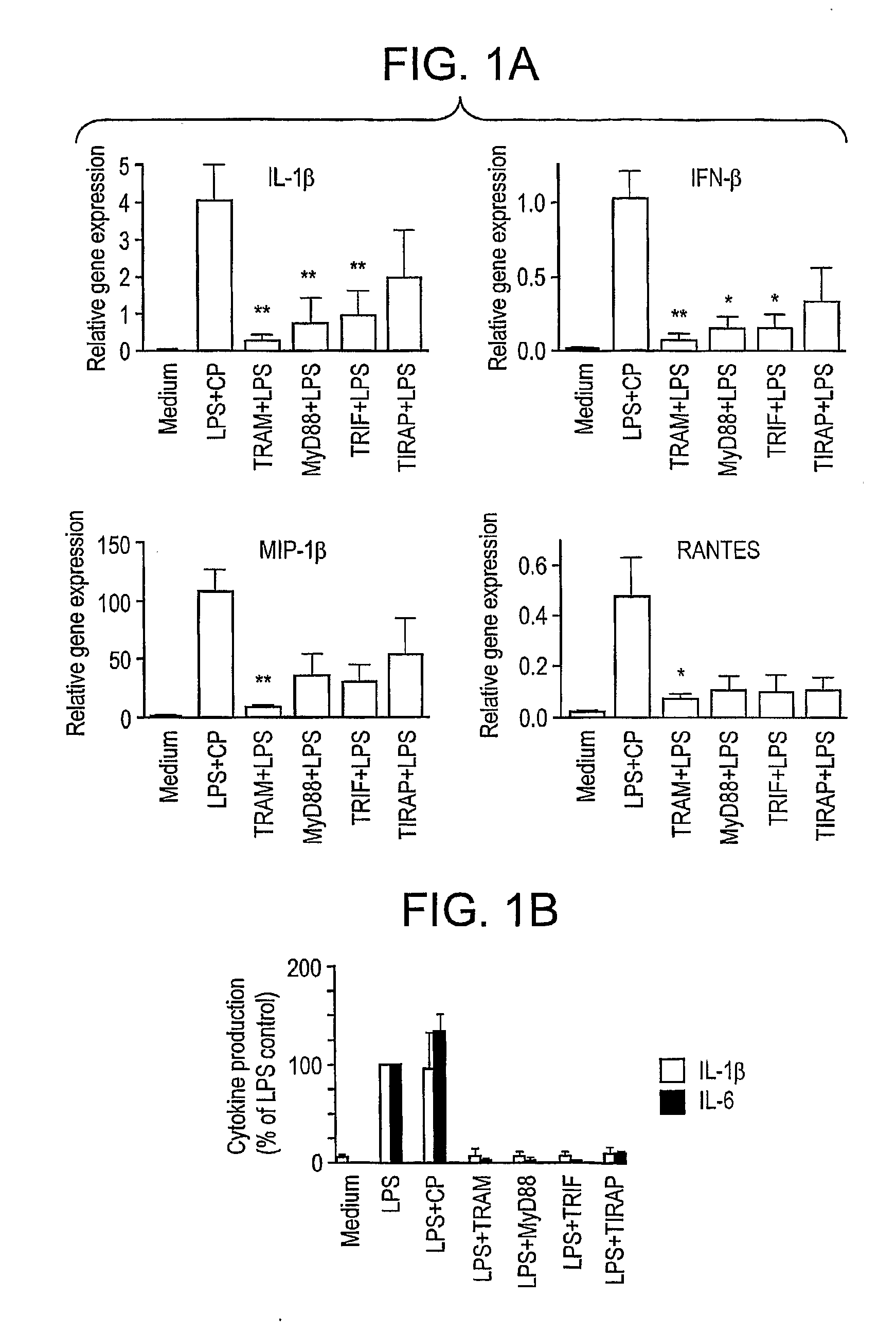
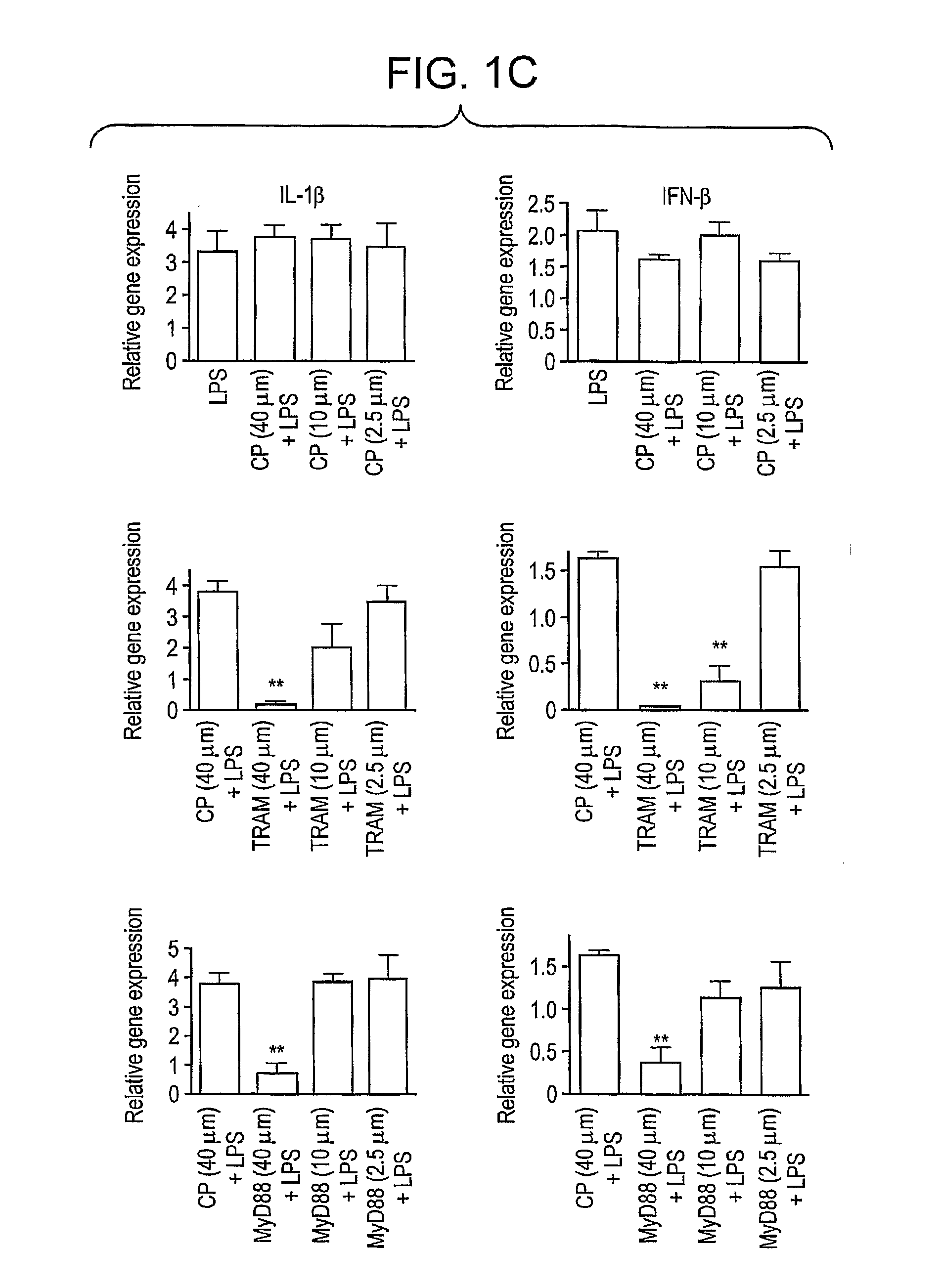
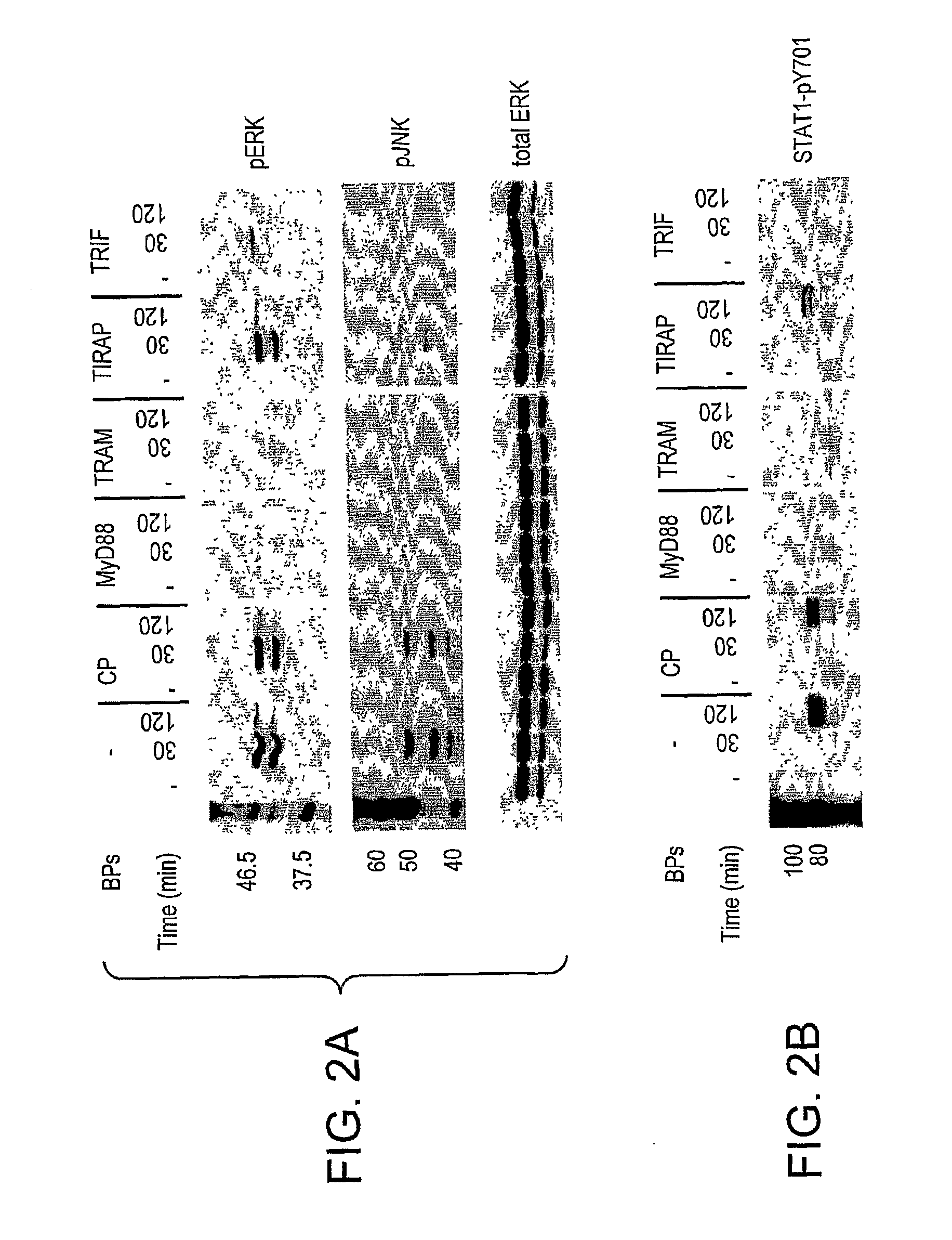
Blocking peptides comprised of the 14 amino acids that correspond to the sequences of the BB-loops of the four known TIR domain-containing adapter proteins (i.e. MyD88, TRAM, TIRAP, and TRIF) and homologous sequences of four TLRs (TLR2, TLR4, TLR1, and TLR6) are described. Adapter BB loop peptides disrupted TLR4, but not TLR2 signaling. TLR2 and TLR4 blocking peptides inhibited TLR4- and TLR2-mediated activation of ERK and cytokine induction, however, these peptides did not inhibit activation of p38. These peptides can be used to treat or prevent an immune or inflammatory response associated with a condition related to TLR4 signaling.
Owner:MARYLAND UNIV OF
Methods for detecting genome-wide sequence variations associated with a phenotype
InactiveUS20070015200A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingSub populationsGenetic risk factor
The invention provides methods for determining genome-wide sequence variations associated with a phenotype of a species in a hypothesis-free manner. In the methods of the invention, a set of restriction fragments for each of a sub-population of individuals having the phenotype are generated by digesting nucleic acids from the individual using one or more different restriction enzymes. A set of restriction sequence tags for the individual is then determined from the set of restriction fragments. The restriction sequence tags for the sub-population of organisms are compared and grouped into one or more groups, each of which comprising restriction sequence tags that comprise homologous sequences. The obtained one or more groups of restriction sequence tags identify the sequence variations associated with the phenotype. The methods of the invention can be used for, e.g., analysis of large numbers of sequence variants in many patient samples to identify subtle genetic risk factors.
Owner:SOLEXA
Banana wilt bacterium molecule detecting genes and detecting method thereof
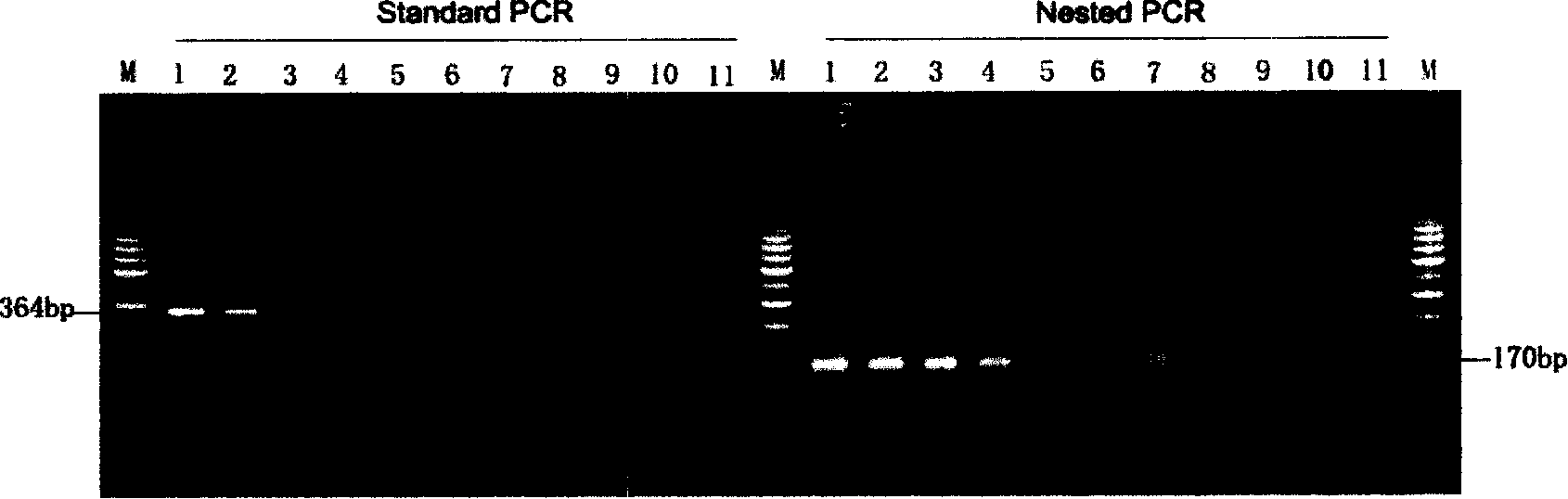
InactiveCN101205558AMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationFusarium oxysporumHomologous sequence
The invention discloses a fusarium oxysporum f.sp.cubense molecular detecting gene and detecting method thereof, which is especially applicable to high sensitive quick molecular detection of fusarium oxysporum f.sp.cubense. The detecting gene is a specific 404bp sequence of the fusarium oxysporum f.sp.cubense, and homologous sequences are not found in a Genbank database. A pair of primers FOC-F / FOC-R is designed to specifically amplify 364bp specific amplified products on pure DNA of the fusarium oxysporum f.sp.cubense, germ-carrying tissues and soils. The invented detecting gene and primers can be used for detecting the fusarium oxysporum f.sp.cubense in banana germ carrying tissues and soils quickly, sensitively and specifically in productive practice; meanwhile, can be used for the early diagnosis for field fusarium oxysporum f.sp.cubense and the monitoring and identification of germs.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION FAAS
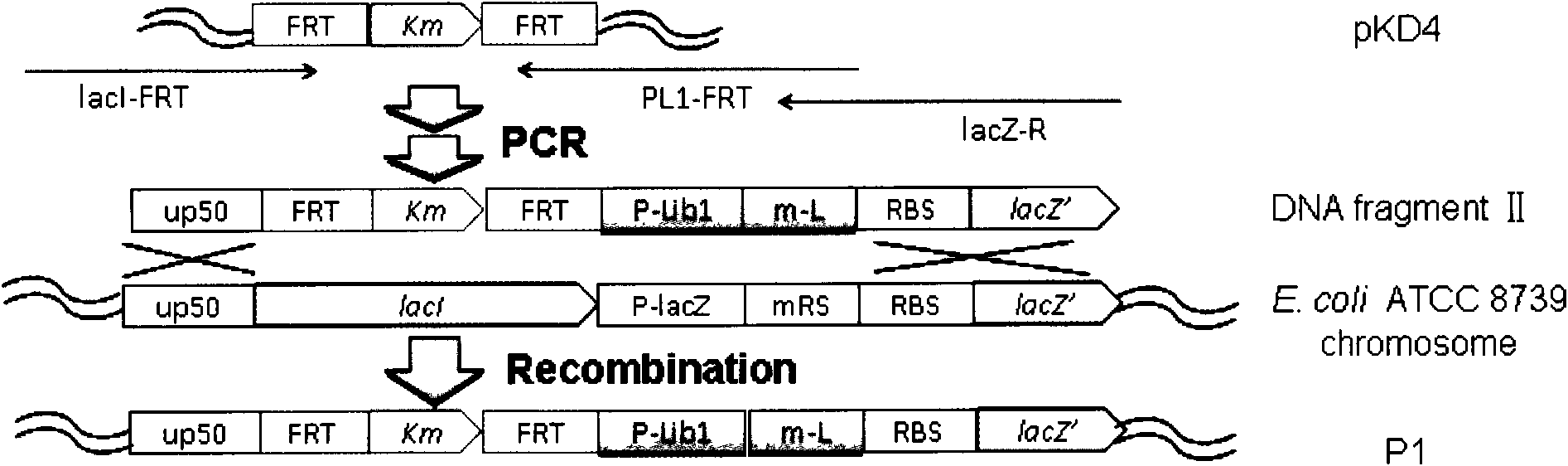
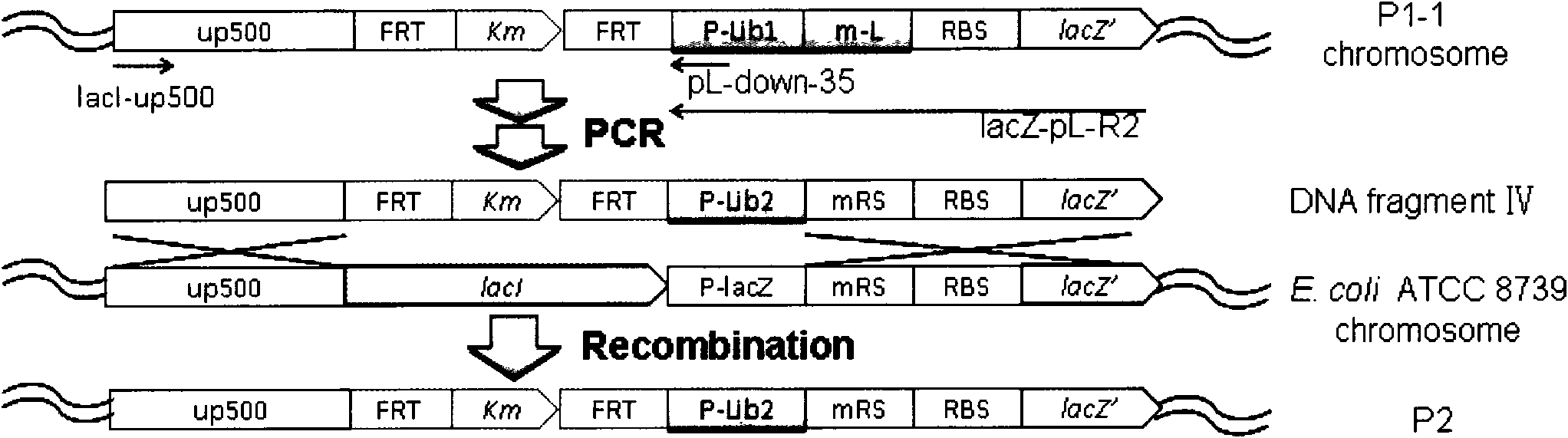
Method for regulating gene expression intensity on microbial chromosome by using artificial regulatory element and its library
The invention discloses a method for regulating the expression intensity of genes on microorganism chromosomes by using artificial regulatory elements and libraries thereof. The method for regulating the gene expression intensity on the microbial chromosome by using the artificial regulatory element and its library provided by the present invention includes the following steps: amplify a DNA fragment by PCR, which includes the upstream sequence of the original regulatory region of the gene to be regulated on the microbial chromosome A homologous fragment containing 40-3000 bases, resistance marker gene, artificial regulatory element library or an artificial regulatory element with specific expression strength, homologous to the sequence downstream of the start codon of the gene to be regulated on the microbial chromosome A fragment containing 40-3000 bases; the DNA fragment is electrotransformed into the microorganism, and the original regulatory region of the gene to be regulated on the microbial chromosome is replaced by an artificial regulatory element library or an artificial regulatory element with a specific expression intensity .
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
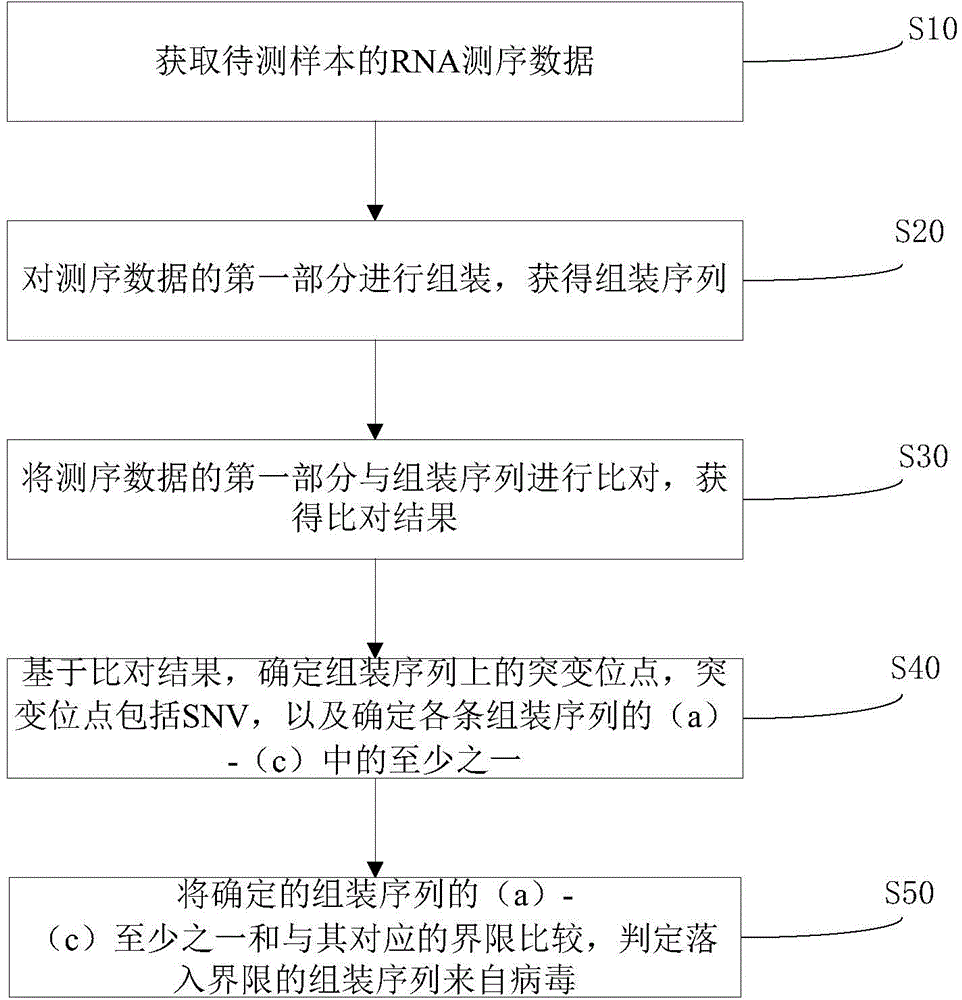
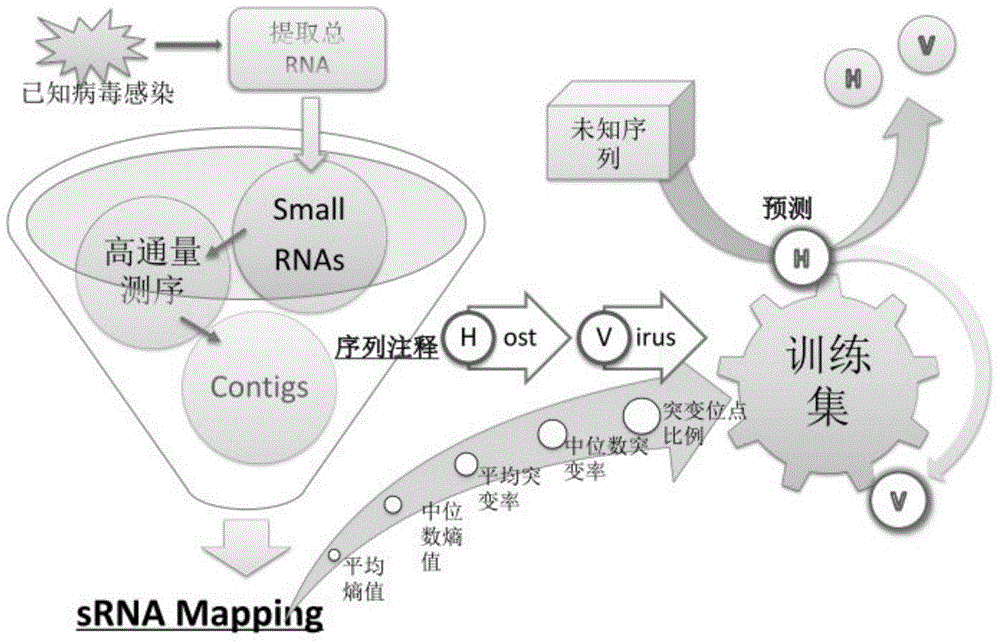
Virus identification method and device
ActiveCN106033502AImprove the detection rateImprove accuracyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAgricultural scienceHomologous sequence
The invention discloses a virus identification method comprising the following steps: obtaining RNA sequencing data of a to-be-tested sample; assembling the first portion of the sequencing data so as to obtain assemble sequences; comparing the first portion of the sequencing data with the assemble sequences so as to obtain a comparison result; determining mutation sites on the assemble sequences according to the comparison result, and determining at least one of the following assemble sequences a-c: a, at least one from the group formed by average entropy and median entropy, and mutation site proportion; b, at least one from the group formed by the average mutation rate and median mutation rate, and the mutation site proportion; c, mutation site proportion; comparing at least one from the assemble sequences a-c with the corresponding boundary, and determining the assemble sequence falling into the boundary to be from virus. The invention also discloses a virus identification device; the virus identification method and / or device can accurately predict whether an unknown sequence is a virus sequence or not without depending on the homologous sequence alignment.
Owner:深圳华大因源医药科技有限公司
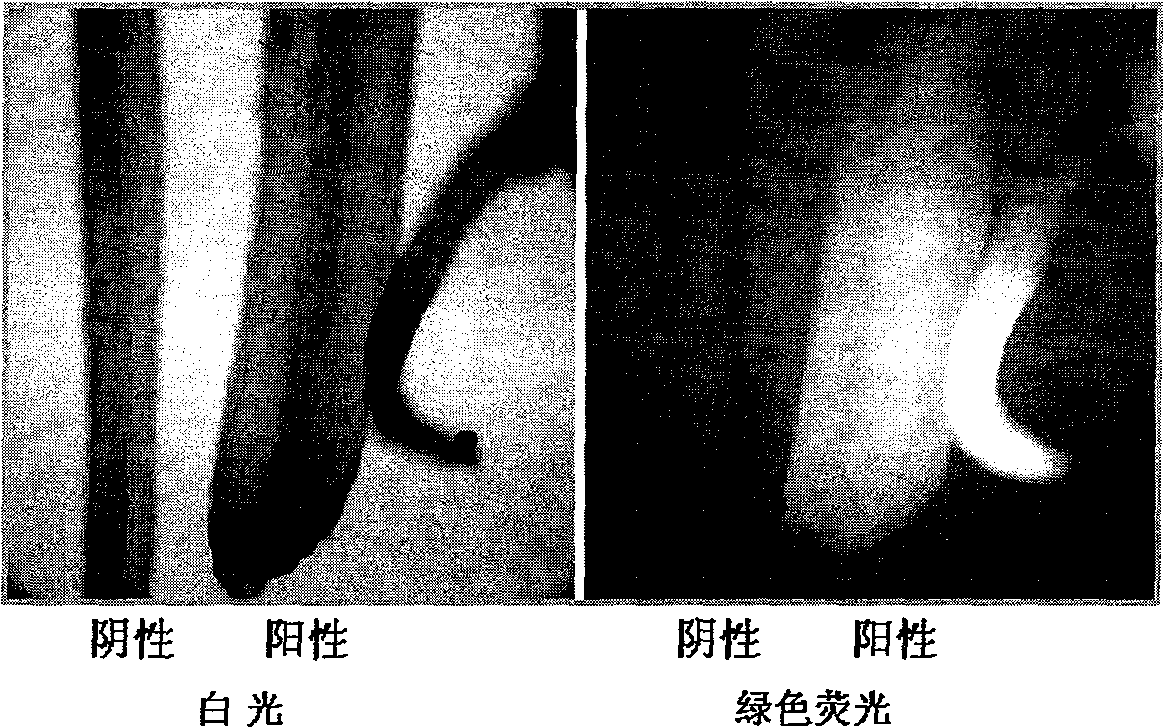
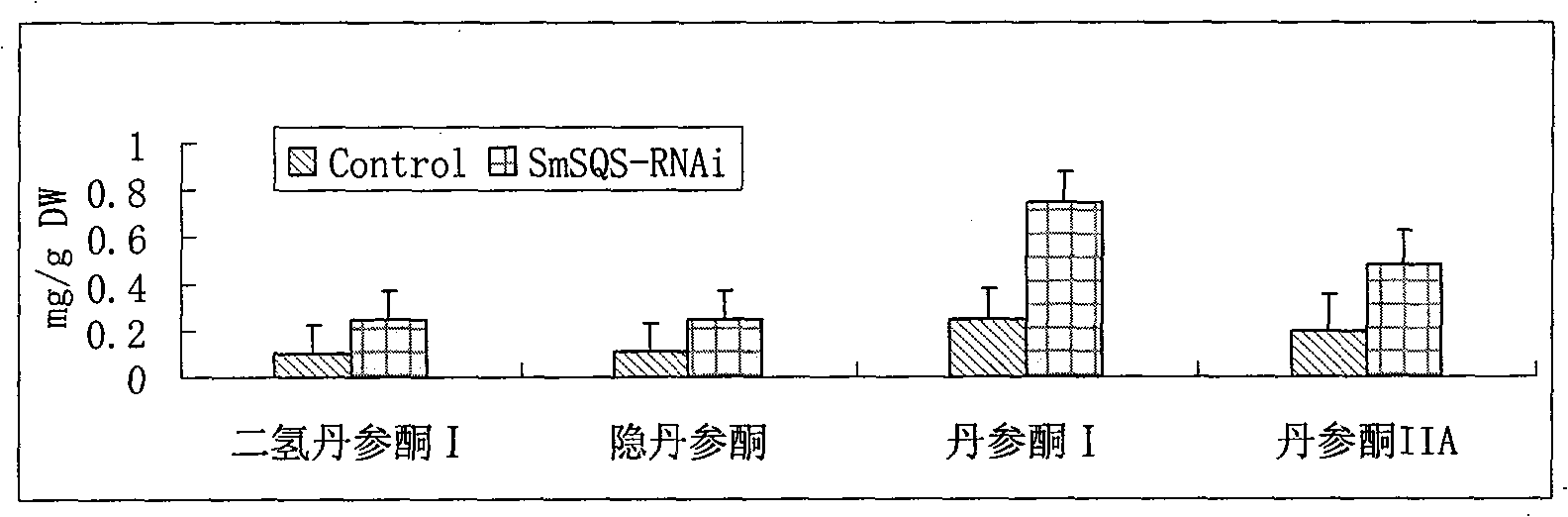
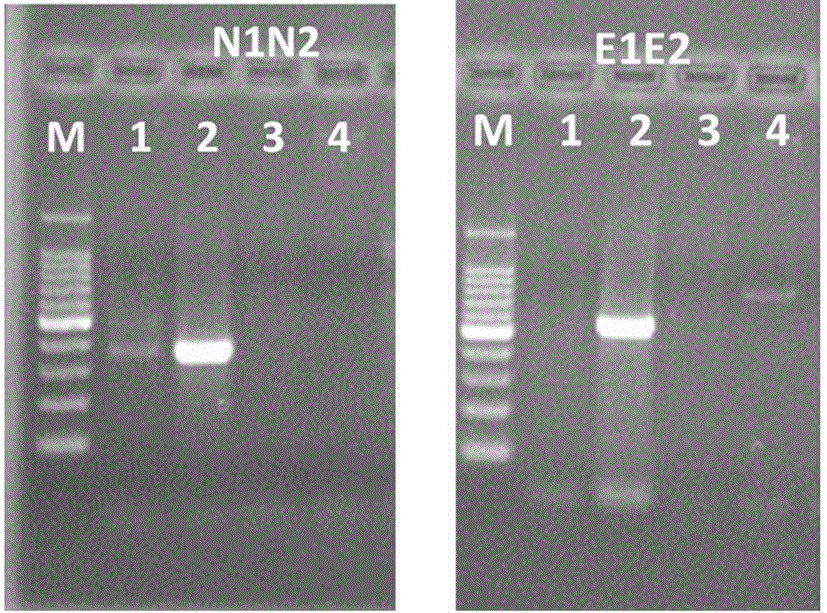
Salvia miltrorrhiza squalene synthase (SmSQS) gene and encoding protein and application thereof
InactiveCN101928717AIncrease contentHigh substance contentBacteriaTransferasesSalvia miltiorrhizaNucleotide
The invention discloses a squalene synthase gene and an encoding protease and application thereof. The gene is cloned from salvia miltrorrhiza by the homology cloning technology for the first time, and fills a gap of cloning and separating the squalene synthase gene from the traditional precious Chinese herbal medicine salvia miltrorrhiza in China. The provided squalene synthase gene has a nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1, a homologous sequence in which one or more nucleotides are added, substituted, inserted or deleted or a nucleotide sequence of allele thereof and derivatives. The protein encoded by the gene has an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.2, or a homologous sequence in which one or more amino acids are added, substituted, inserted or deleted. The provided squalene synthase gene can improve the content of triterpenoid saponin components in plants through biotechnology, and can improve the content of diterpene (tanshinone) substances in the salvia miltrorrhiza by the RNAi technology simultaneously. The squalene synthase gene has good application prospect on research and industrialization of medicinal plant secondary metabolic engineering.
Owner:INST OF CHINESE MATERIA MEDICA CHINA ACAD OF CHINESE MEDICAL SCI
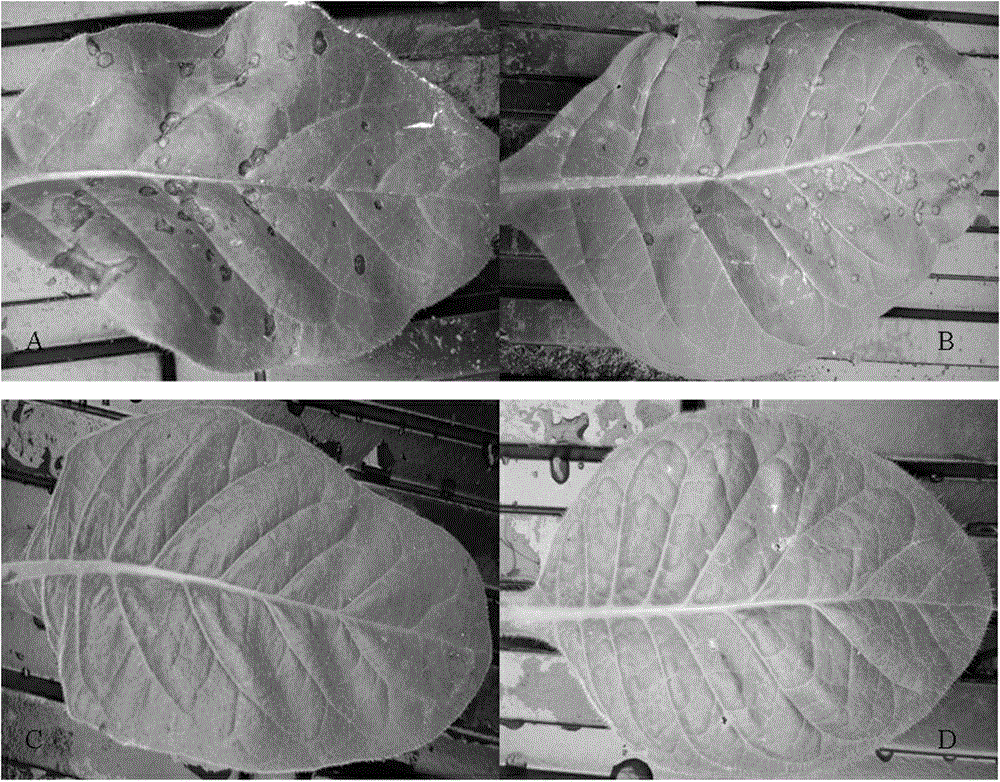
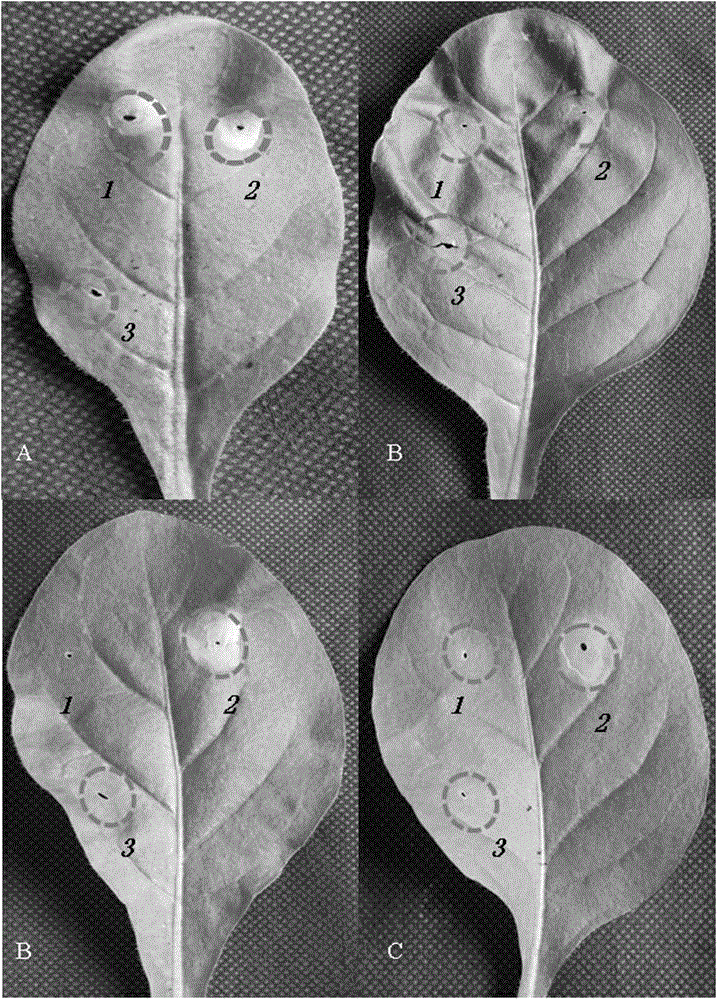
Tobacco mosaic virus resistant N'au gene and cloning method and application thereof
The invention relates to isolation cloning and breeding application of a tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) resistant N'au gene. A nucleotide sequence of the TMV resistant N'au gene is shown as SEQ ID NO.1, and amino acid of polypeptide coded by the TMV resistant N'au gene is shown as SEQ ID NO.2. A non-transgenic TMV-resistant tobacco variety can be obtained by trans-breeding an N'au gene contained in germplasm resources into a TMV-sensitive main planting tobacco variety through a conventional breeding means. The N'au gene in the main planting tobacco variety has a homologous sequence high in nucleotide rate, so that short introgression fragment single plants carrying the N'au gene can be obtained easily through conventional breeding so as to obtain a TMV-resistant variety low in linkage drag. The gene can resist strains U1 and Cg of TMV at the same time. The novel antiviral gene N'au has great application prospect in cultivation of TMV-resistant tobacco.
Owner:YUNNAN ACAD OF TOBACCO AGRI SCI
Identification of biological (micro) organisms by detection of their homologous nucleotide sequences on arrays
InactiveUS7205104B2Easy to identifyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiological bodyHomologous sequence
A method for identifying or quantifying an organism by a detecting its nucleotide sequence among at least 4 other homologous sequences comprising amplifying nucleic acids from the organism to generate target nucleotide sequences to be detected; contacting the target nucleotide sequences with single stranded capture nucleotide sequences bound by a single predetermined link to an insoluble solid support and discriminating the binding of a target nucleotide sequence specific of an organism with a signal resulting from a hybridization by complementary base pairing between the target nucleotide sequence and its corresponding capture nucleotide sequence is disclosed. The capture nucleotide sequence is bound to the insoluble solid support at a specific location on an array having a density of at least 4 different bound single stranded capture nucleotide sequences / cm2. The location of the signal on the array allows identification or quantification of the organism.
Owner:EPPENDORF ARRAY TECH SA
Marine microalgae chloroplast expression vector and application thereof
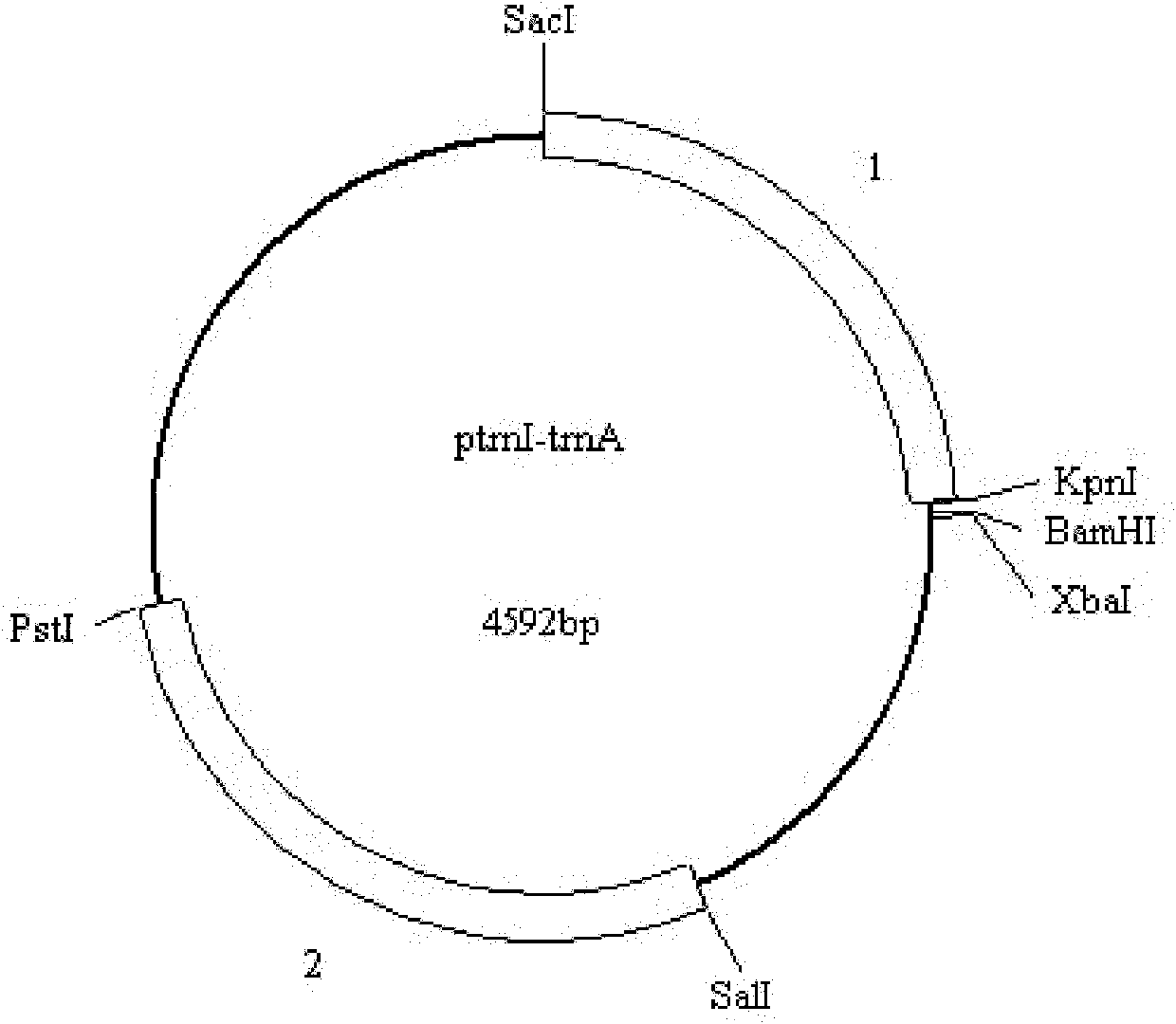
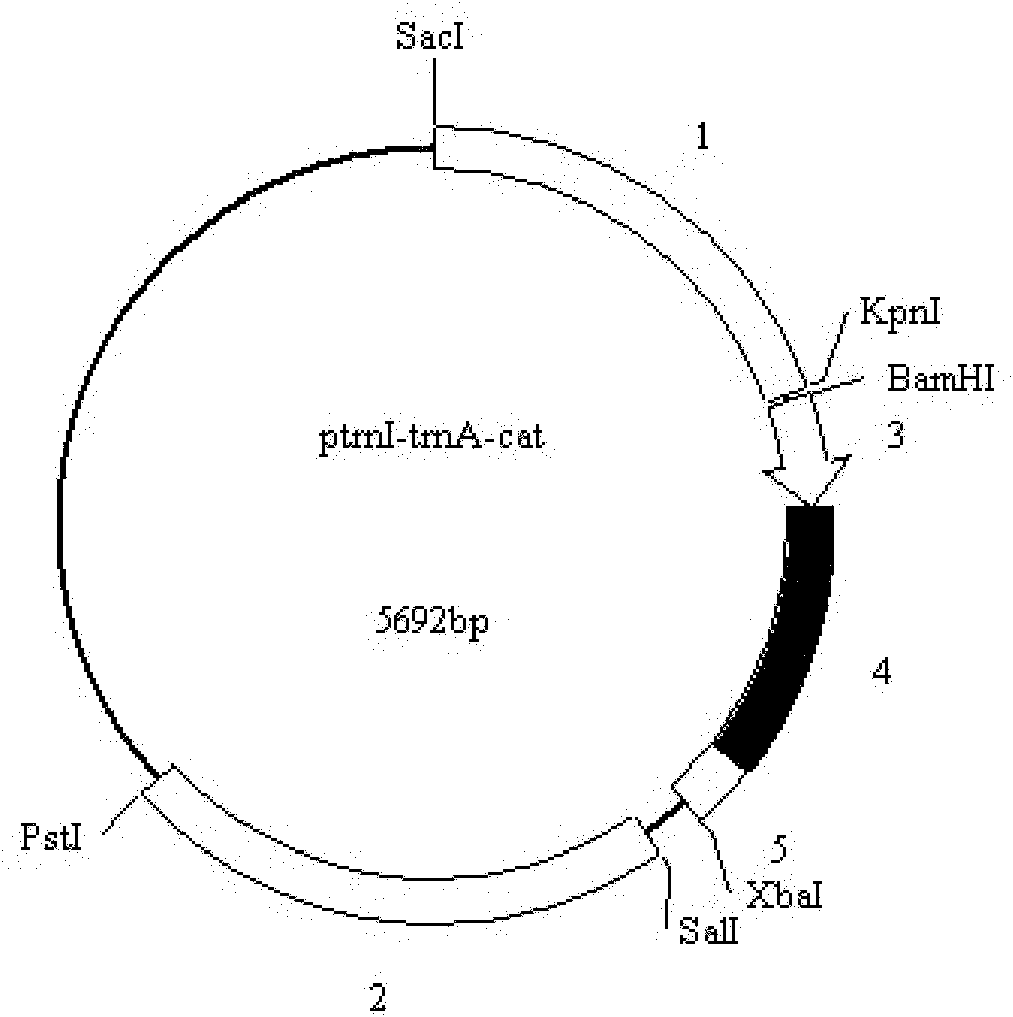
InactiveCN101948871AEasy wayLower conversion costsUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyChloroplast
The invention discloses a marine microalgae chloroplast expression vector and application thereof. The marine microalgae chloroplast expression vector contains a homologous recombinant sequence I, a target gene expression case and a homologous recombinant sequence II, wherein the target gene expression case is positioned between the homologous recombinant sequence I and the homologous recombinant sequence II; 1st to 972nd bp of the homologous recombinant sequence I are 3' part of rns, and 973rd to 1,097th bp are 5' part of trnI; and 1st to 196th bp of the homologous recombinant sequence II are 3' part of trnA, and 197th to 1,483rd bp are 5' part of rnl. The homologous recombinant sequence ensures that the expression vector can be induced into the marine microalgae chloroplast genome by an electric shock method, which is advantageous to the way of inducing the vector into the chloroplast genome, greatly reduces conversion cost, and provides technical support for realizing that marine microalgae chloroplast is used as a bioreactor to produce high value-added products.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Mitochondrial genome library based on high-throughput sequencing and building method thereof
ActiveCN105907748AGuaranteed Accurate AmplificationSensitive and accurate mutation detectionNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman DNA sequencingHomologous sequence
The invention relates to a mitochondrial genome library based on high-throughput sequencing and a building method thereof. The building method comprises the following steps of S1, performing one-step PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification of mitochondria full-length DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) in total DNA; S2, crushing the mitochondria full-length DNA to obtain DNA fragments; S3, performing tail end restoration on the DNA fragments to obtain flat tail end DNA fragments; S4, adding A to the end 3' of the flat tail end DNA fragments to obtain the A-added DNA fragments; S5, adding a connector to the end 3' of the A-added DNA fragments to obtain connector-added DNA fragments; S6, performing front LM-PCR on the connector-added DNA fragments; S7, performing post PCR on the LM-PCR product. The building method of the mitochondrial genome library has the advantages that the mitochondrial full-length DNA is obtained through further PCR amplification from the total DNA, so that the precise amplification of the human mitochondrial genome can be guaranteed; the pollution mixing by the homologous sequence of the human genome is avoided, so that the mutation detection is more sensitive and accurate.
Owner:GUANGZHOU JIAJIAN MEDICAL TESTING CO LTD
Solid phase sequencing of biopolymers
InactiveUS7803529B1Easy to determineSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiopolymerSpectroscopy
This invention relates to methods for detecting and sequencing target nucleic acid sequences, to mass modified nucleic acid probes and arrays of probes useful in these methods, and to kits and systems which contain these probes. Useful methods involve hybridizing the nucleic acids or nucleic acids which represent complementary or homologous sequences of the target to an array of nucleic acid probes. These probes comprise a single-stranded portion, an optional double-stranded portion and a variable sequence within the single-stranded portion. The molecular weights of the hybridized nucleic acids of the set can be determined by mass spectroscopy, and the sequence of the target determined from the molecular weights of the fragments. Nucleic acids whose sequences can be determined include DNA or RNA in biological samples such as patient biopsies and environmental samples. Probes may be fixed to a solid support such as a hybridization chip to facilitate automated molecular weight analysis and identification of the target sequence.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV +1
Application and seamless cloning method of DNA exonuclease
PendingCN107760706AImprove digestion efficiencyFlexible site selectionVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliHomologous sequence
The invention provides application of DNA exonuclease to DNA recombinant seamless cloning and provides a kit capable of being used for DNA recombinant seamless cloning. The DNA exonuclease is T5 exonuclease, T7 exonuclease, exonuclease III or Lambda exonuclease or a mixture thereof. The invention further provides a seamless cloning method applying the DNA exonuclease, which comprises the followingsteps: linearizing a vector through a PCR method or restriction endonuclease digestion; introducing homologous sequences that are respectively homologous to the two ends of the vector at the two endsof a target gene fragment through PCR to obtain an amplified target gene fragment; after the treated target fragment and the treated linearized vector are mixed, adding the DNA exonuclease and a reaction solution for temperature bath to obtain a vector and fragment mixture; converting an echerichia coli receptive cell by using the obtained vector and fragment mixture. The application and the method provided by the invention have the following advantages that the site selection can be flexibly performed, and the gene cloning can be performed in any position of the vector; the vector construction can be quickly, simply and conveniently completed within 10 minutes; meanwhile, the cloning is accurate and efficient.
Owner:NOVOPROTEIN SCI INC
Lawsonia intracellularis proteins, and related methods and materials
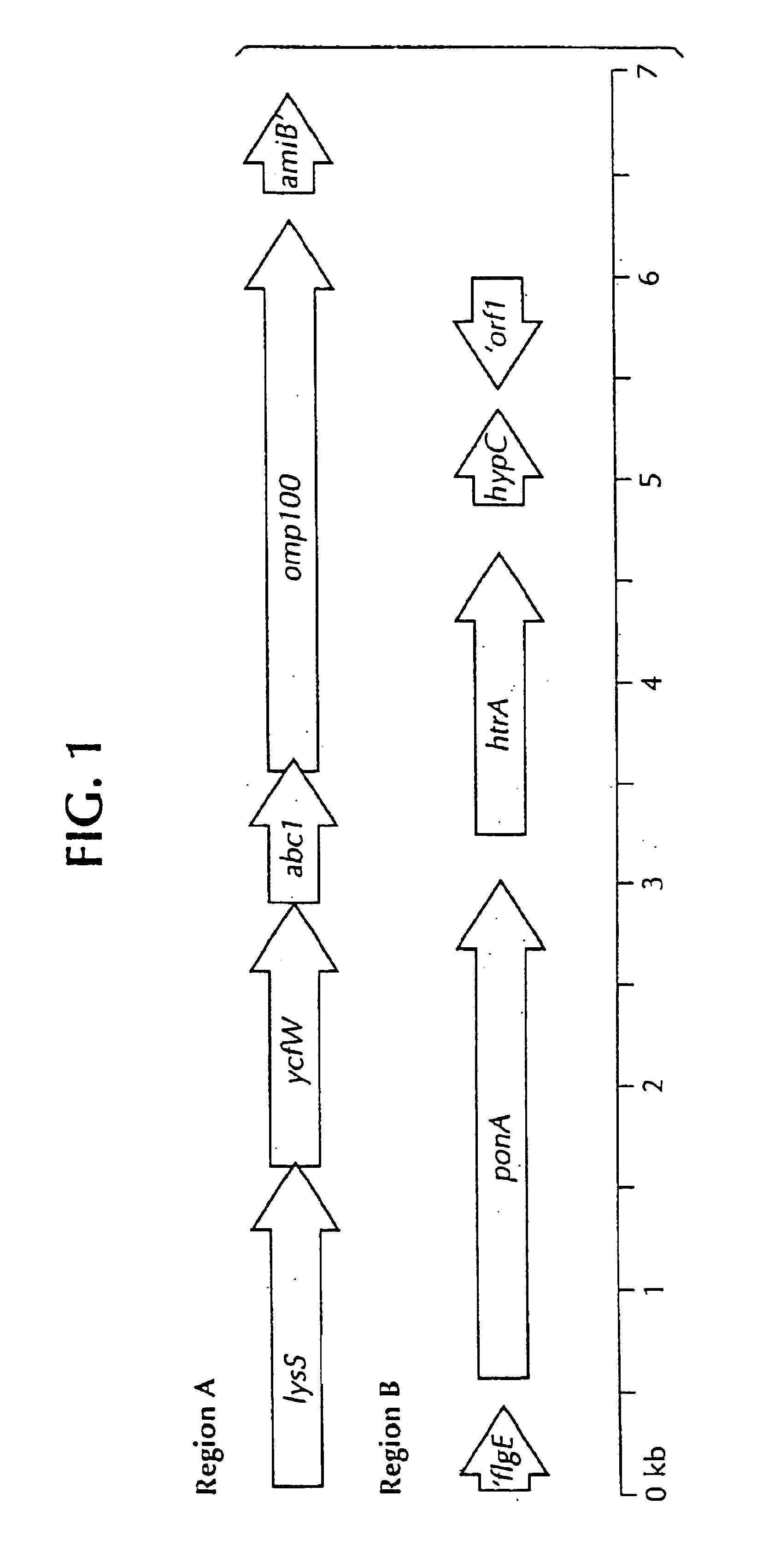
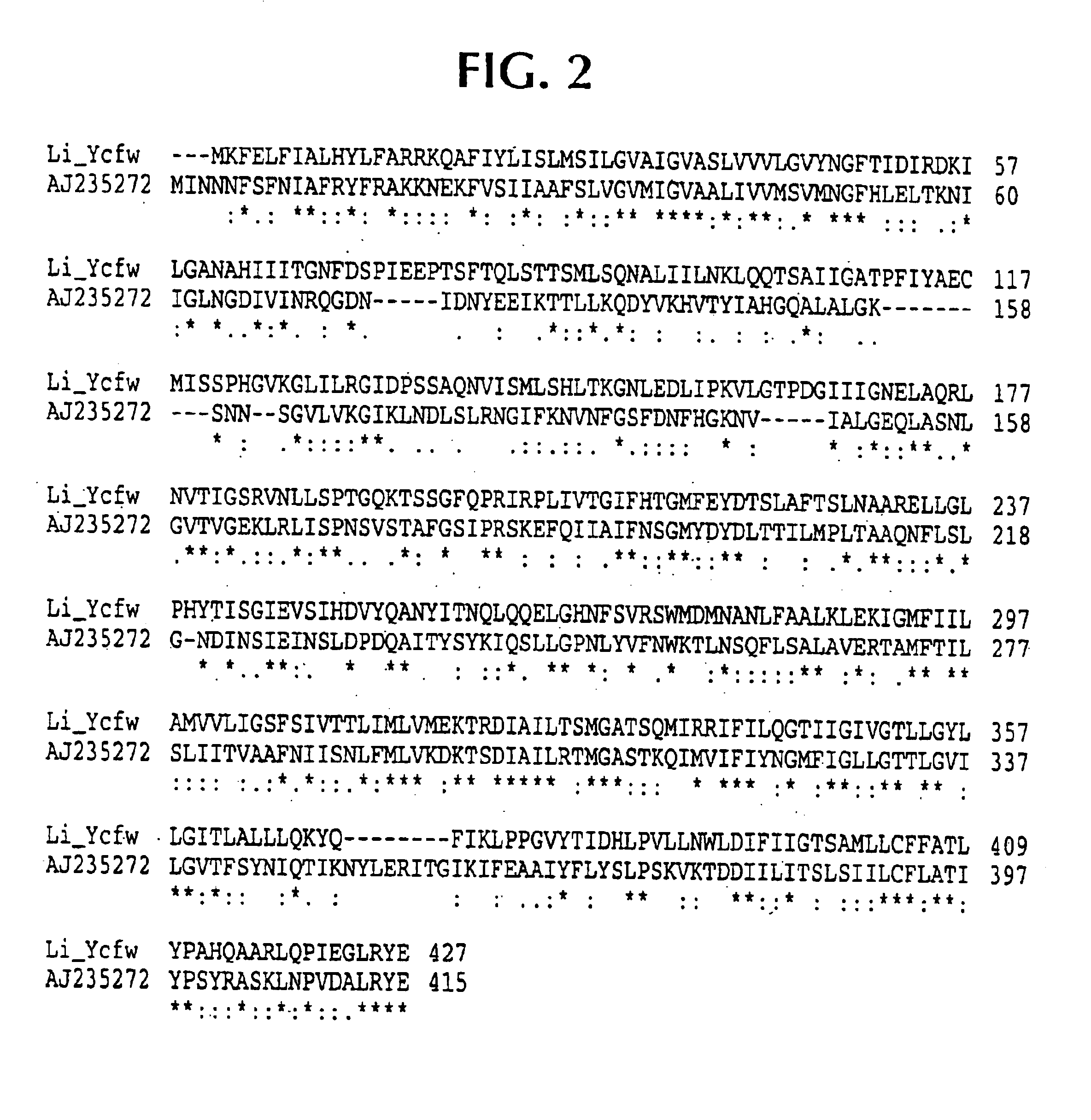
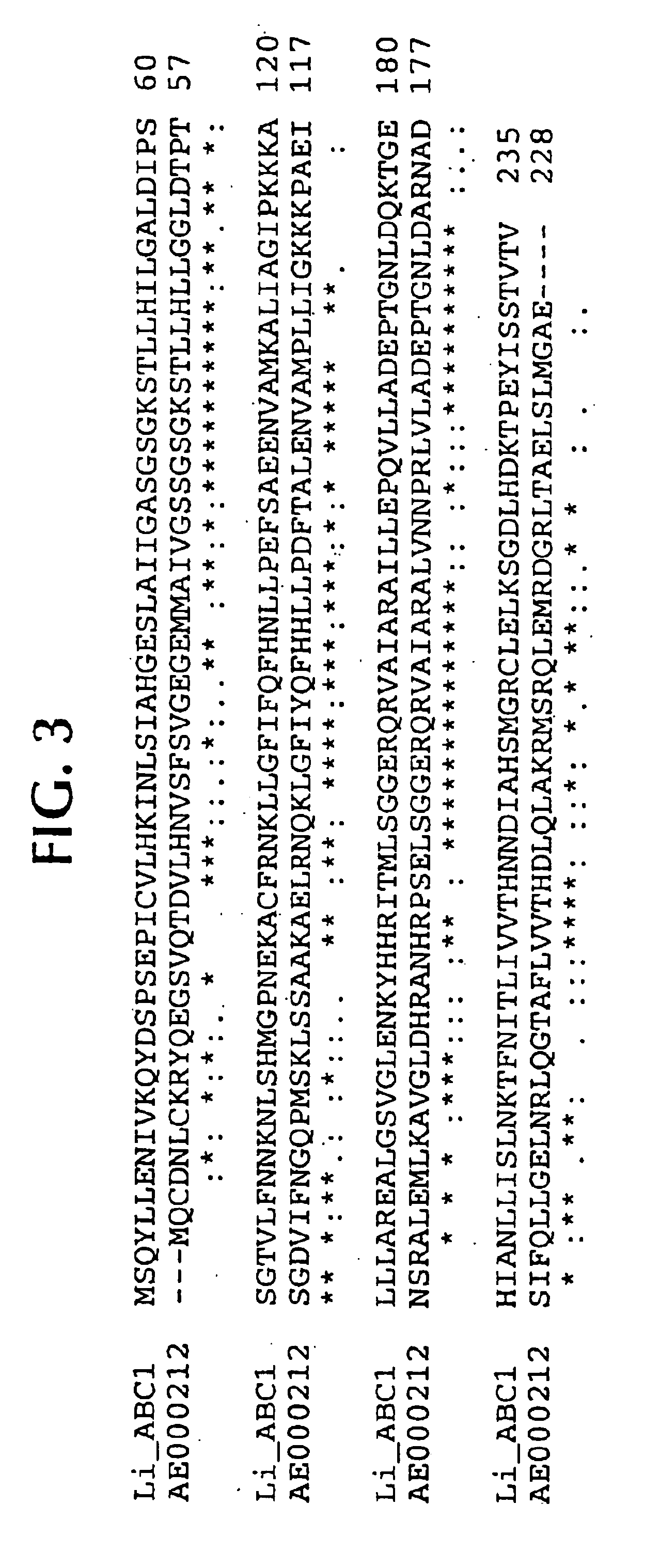
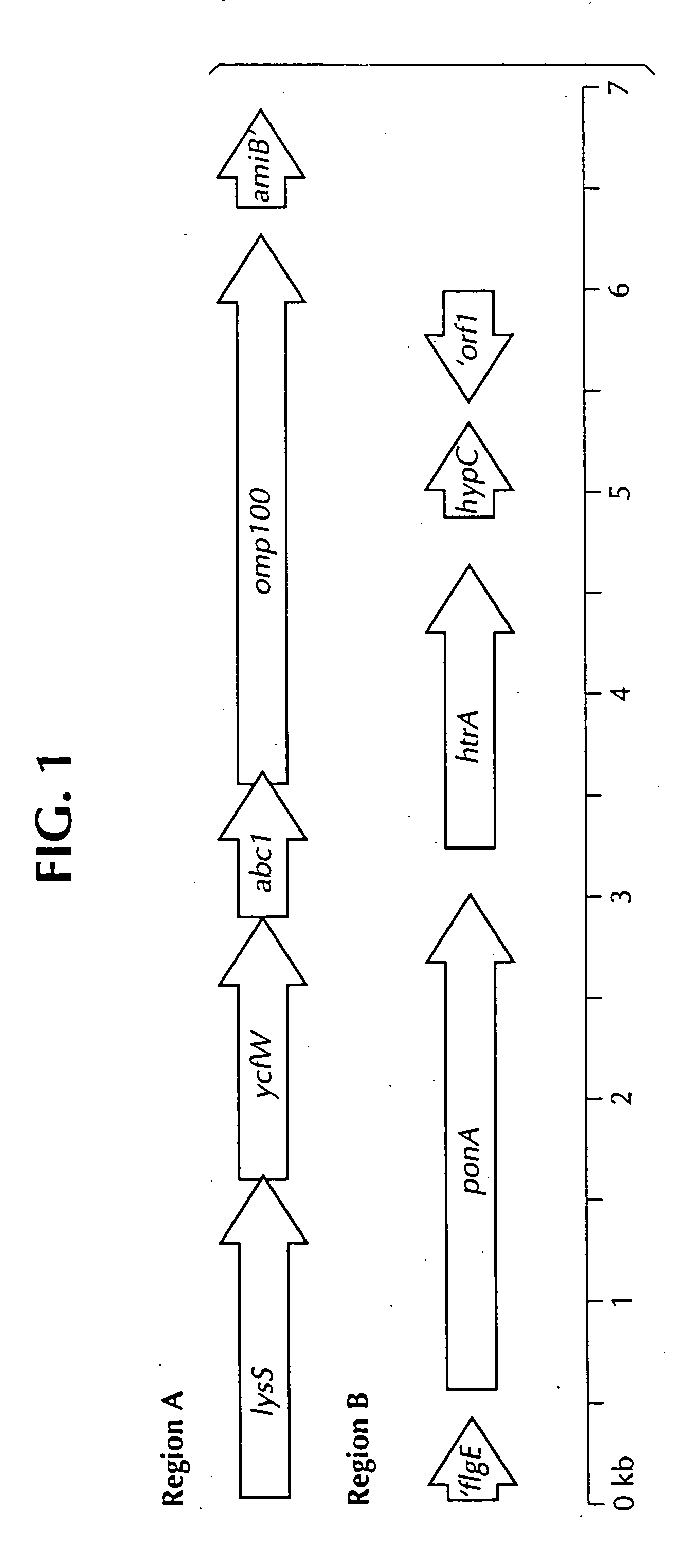
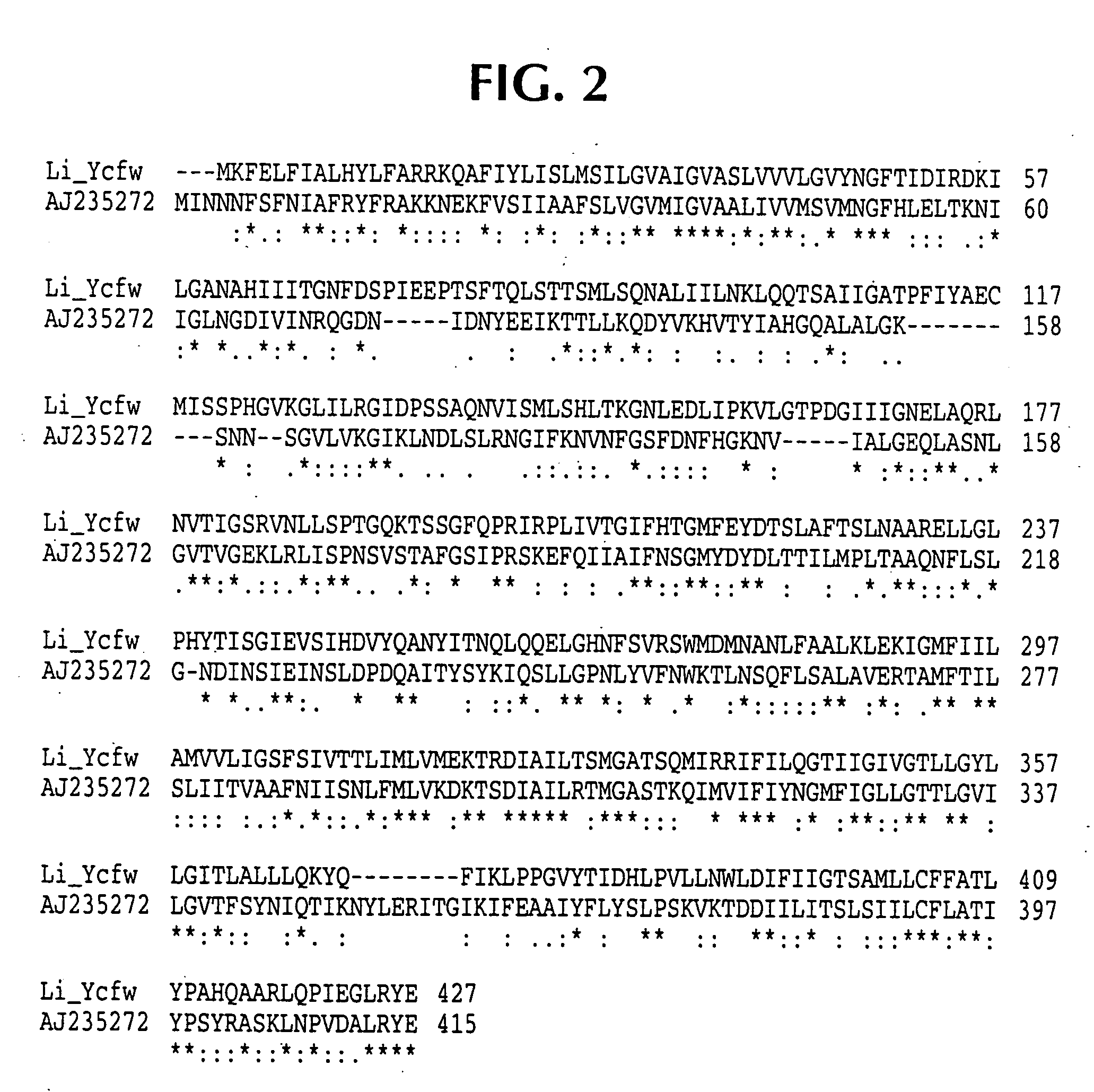
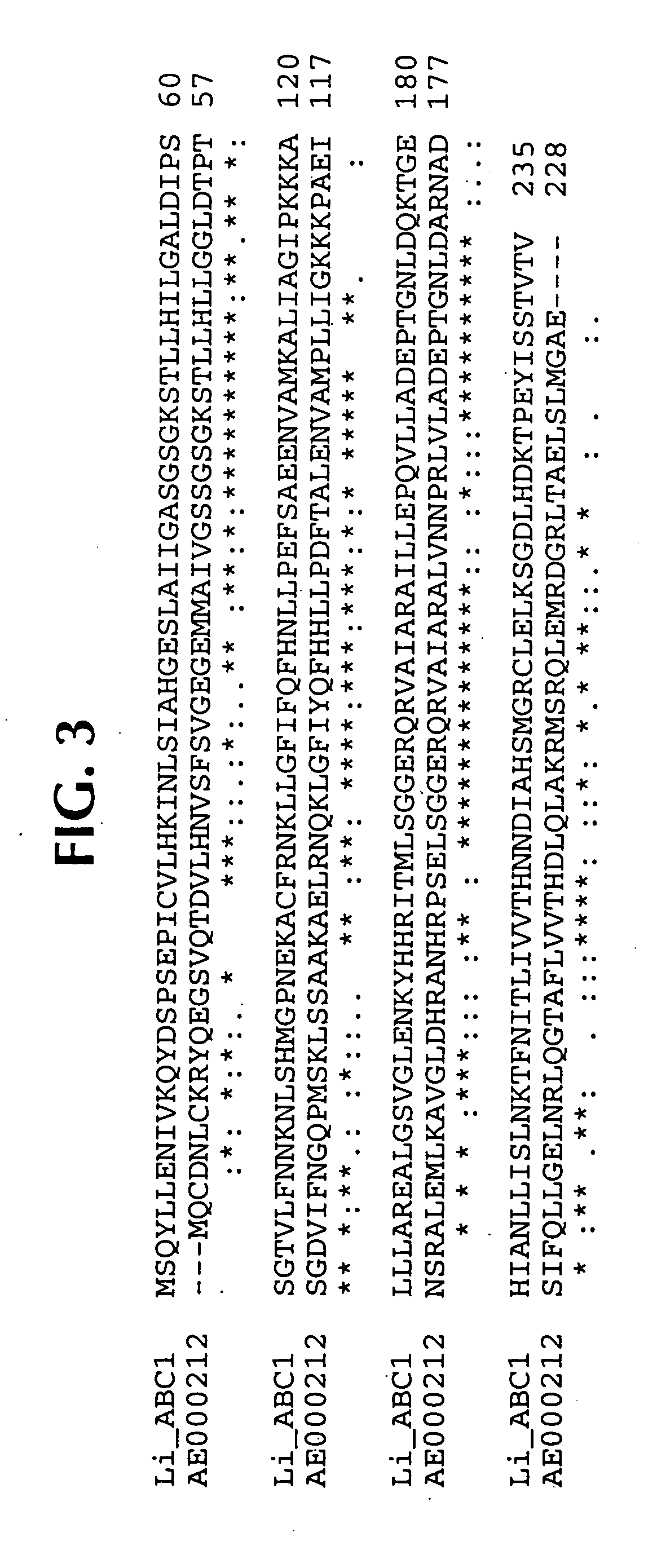
Isolated polynucleotide molecules contain a nucleotide sequence that encodes a L. intracellularis HtrA, PonA, HypC, LysS, YcfW, ABC1, or Omp100 protein, a substantial portion of the sequences, or a homologous sequence. Related polypeptides, immunogenic compositions and assays are described.
Owner:ROSEY EVERETT
Reverse detection for identification and/or quantification of nucleotide target sequences on biochips
InactiveUS20030157528A1Efficient discriminationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNucleotide sequencingHomologous Sequences
The present invention relates to a method for the identification and / or the quantification of one or more target nucleotide sequences (3) present homologous to each other and being possibly present in a sample and discrimination from possibly homologous sequences, by using two sets of nucleotide sequences (1 and 2), wherein a first set of nucleotide sequences possibly labelled (1) bind specifically to said target nucleotide sequences (3) in a first step and are detected and / or quantified through hybridisation with a second set of capture nucleotide sequences (2) having at least a part of sequence complementary to the possibly labelled nucleotide sequence (1) of the first set of nucleotide sequences, said capture nucleotide sequence (2) being immobilised upon the surface (4) of a solid support according to an array of at least 4 discrete regions / cm2, each of said discrete regions being bonded with one species of capture nucleotide sequences (2), and wherein the identification and quantification of the binding between the possibly labelled nucleotide sequence (1) and their corresponding capture nucleotide sequence (2) is correlated with the identification and the quantification of a target nucleotide sequence (3) present in the sample.
Owner:EPPENDORF ARRAY TECH SA
Wolfberry lycopene epsilon-cyclase gene and recombinant vector comprising gene
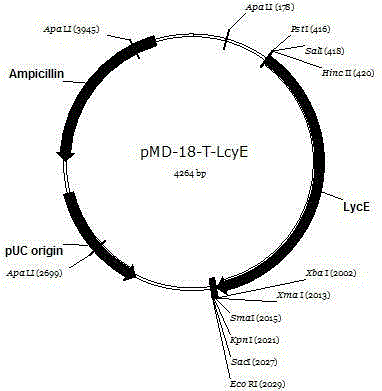
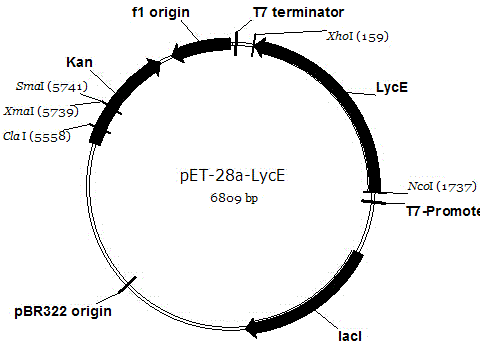
The invention relates to a wolfberry lycopene epsilon-cyclase gene and a recombinant vector comprising the gene. The gene is selected from one of the following nucleotide sequences: 1) a nucleotide sequence shown in a sequence SEQ ID NO.1; and 2) a homologous sequence or an allelic gene thereof and a derivative nucleotide sequence thereof in which 70% of one or more nucleotides are added, replaced, inserted or deleted in the nucleotide sequence shown in the sequence SEQ ID NO. 1. By extracting the total RNA of fresh wolfberry leaves, a wolfberry lycopene epsilon-cyclase gene Lm LcyE is cloned by using a 3'RACE technology, and an obtained complete genome sequence is 1569. An escherichia coli expression vector pET28a-LmLcyE is constructed, the enzymatic activity of cloned wolfberry isopentenyl pyrophosphate isomerase gene Lm LcyE encoding is identified by using an escherichia coli heterologous expression system, and the wolfberry lycopene epsilon-cyclase gene Lm LcyE can catalyze lycopene for cyclizing the lycopene into delta carotene, so that metabolism flows downstream, thereby improving the content of alpha-carotenoid.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for establishing saccharomyces integrated gene mutation library based on in vivo homologous recombination
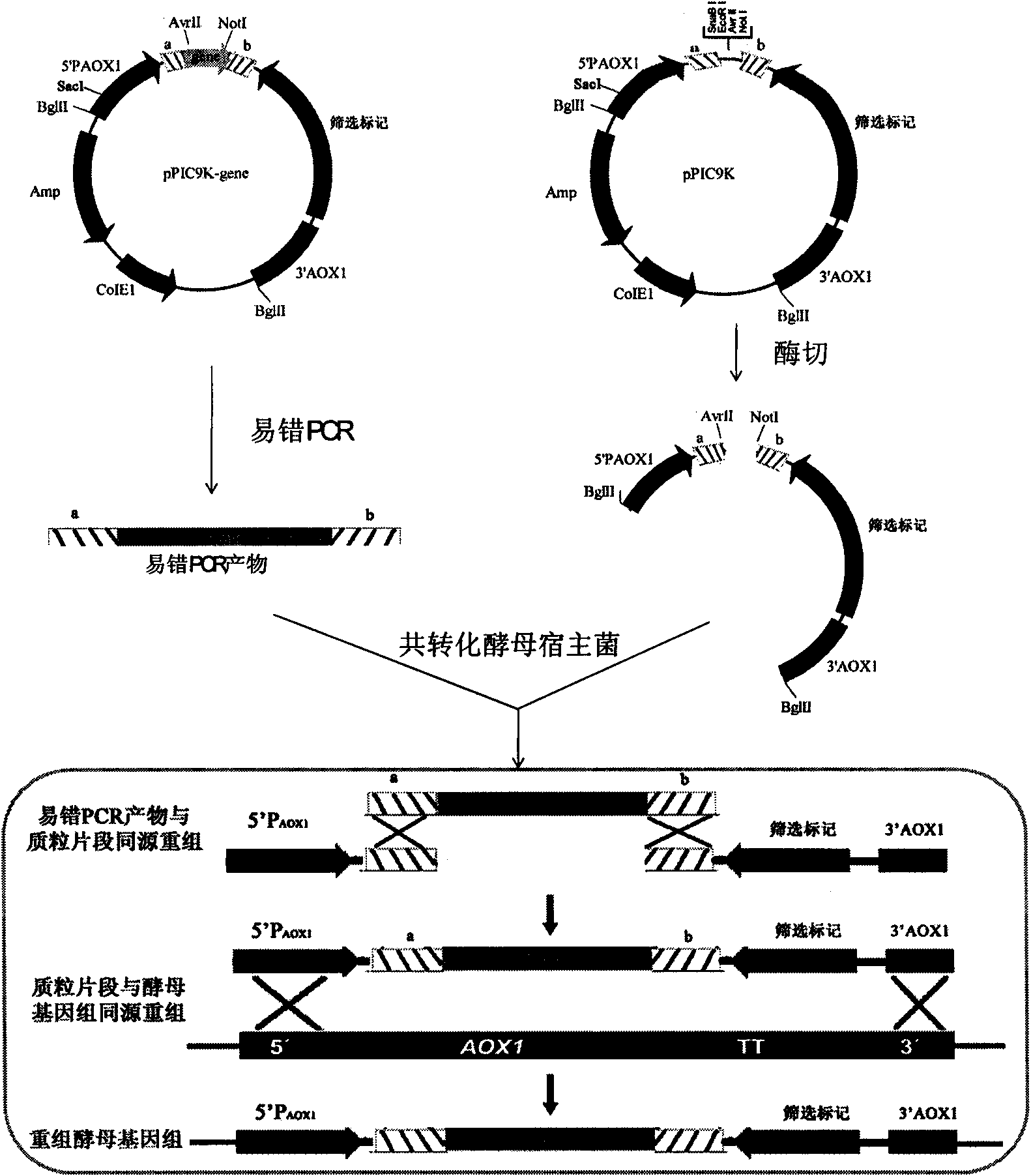
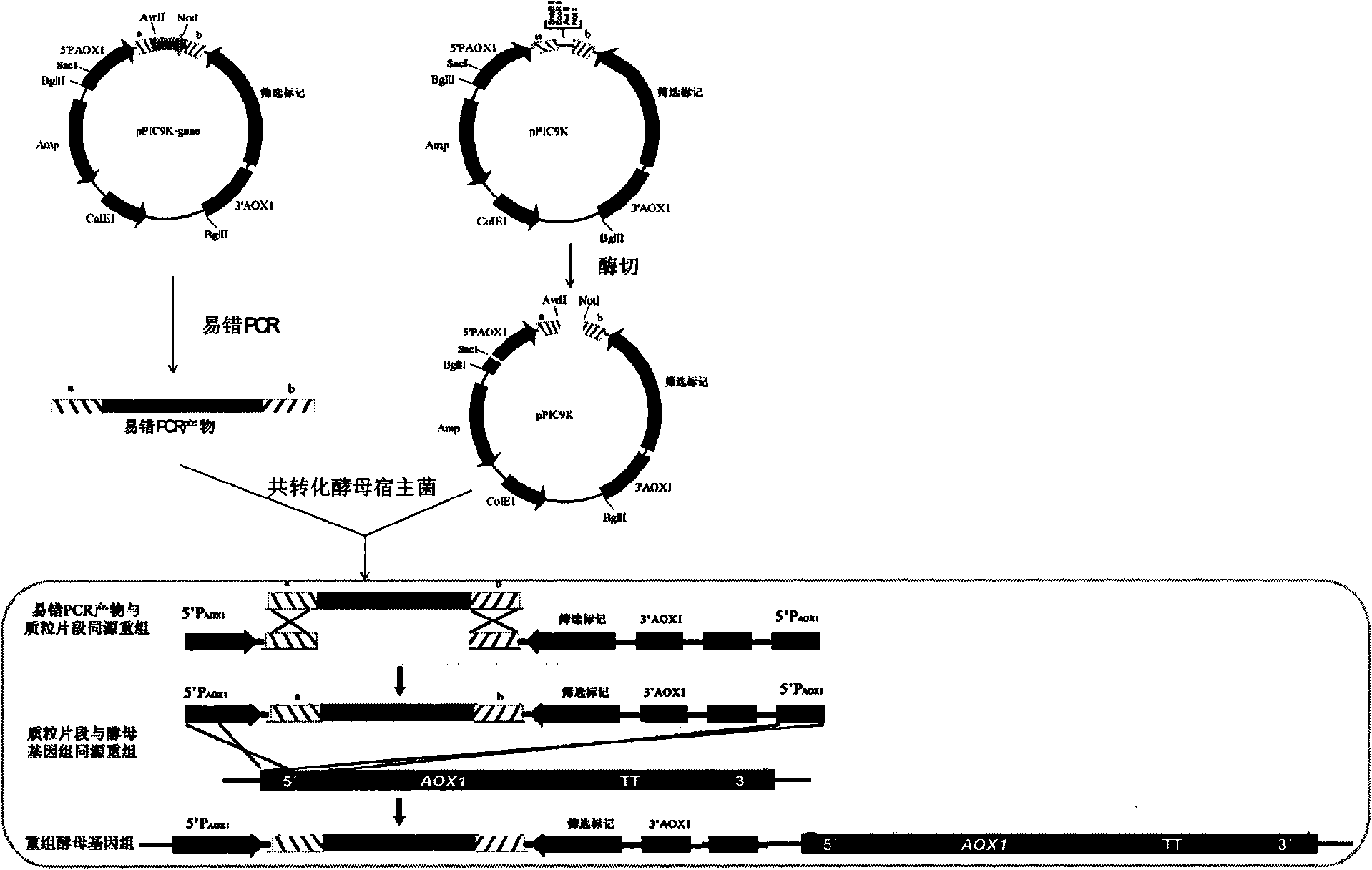
ActiveCN101550605AImprove efficiencyEasy to operateStable introduction of DNAMicroorganism based processesIn vivoProtein engineering
A method for establishing a saccharomyces integrated gene mutation library based on in vivo homologous recombination belongs to the fields of protein engineering, molecular biology technology and genetic engineering. The method comprises the steps of establishing the recombination expression plasmid of the target gene, designing long primer fragment by taking the recombination expression plasmid as a template, amplifying error-prone PCR to obtain the mutated gene with the expression carrier 20-70bp homologous sequence at two ends, respectively carrying out the enzyme tangential linearization to the homologous region of two ends of the mutated gene of the expression carrier and the homologous region of the gene group, mixing the error-prone PCR amplified outcome and the linearized expression carrier by a definite molar ratio and carrying out electro-transformation of the saccharomyces, and integrating the exogenous mutation target gene into the saccharomyces gene group, thus obtaining gene mutation library. The method has high efficiency and convenient operation, shortens the library establishment period from 1-2 weeks to 3 days, needs any sub-cloning steps for library establishment, reduces the loss of content and richness of the gene mutation, has generalization and can be used for various target genes capable of being expressed in the saccharomyces.
Owner:金湖县农副产品营销协会
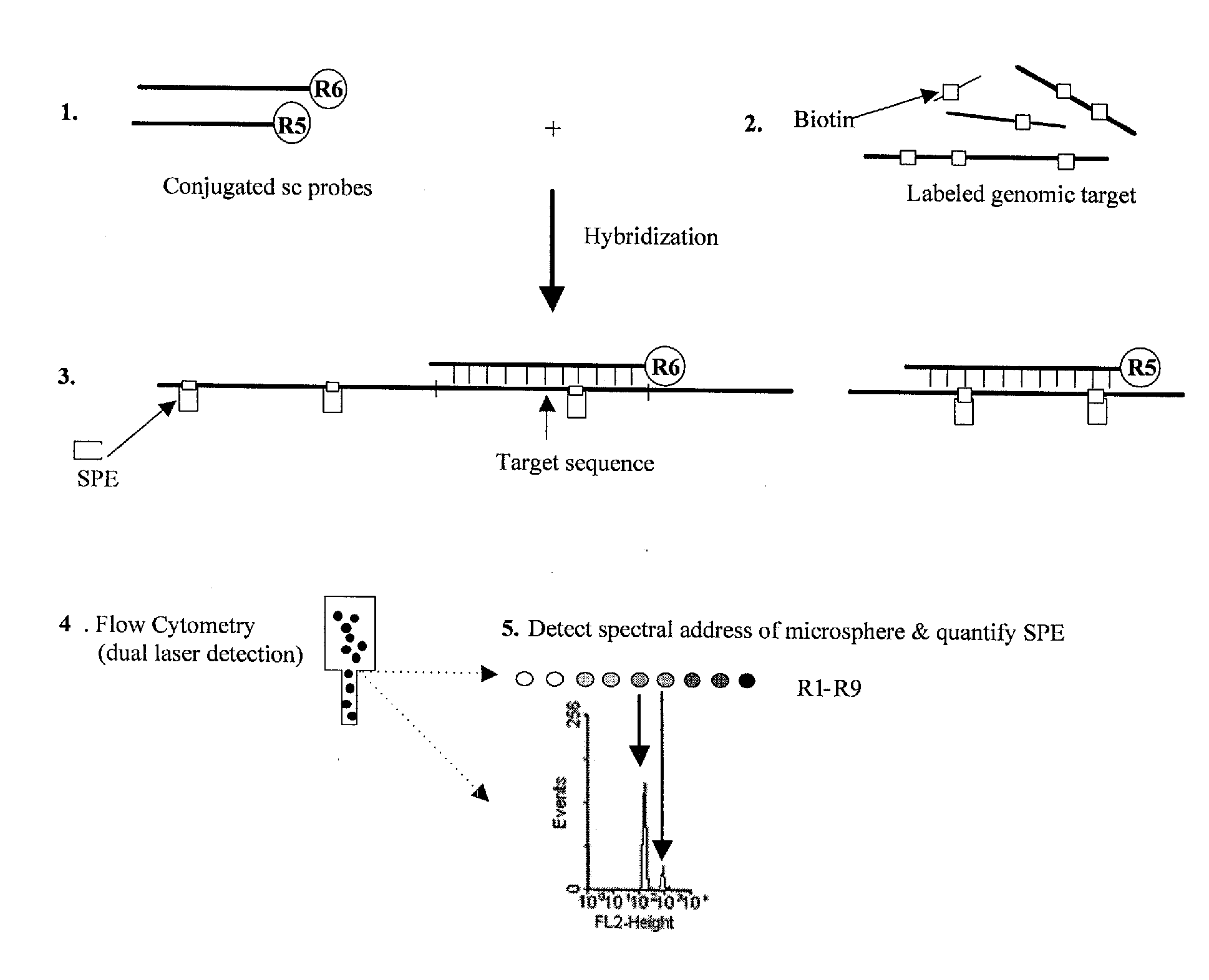
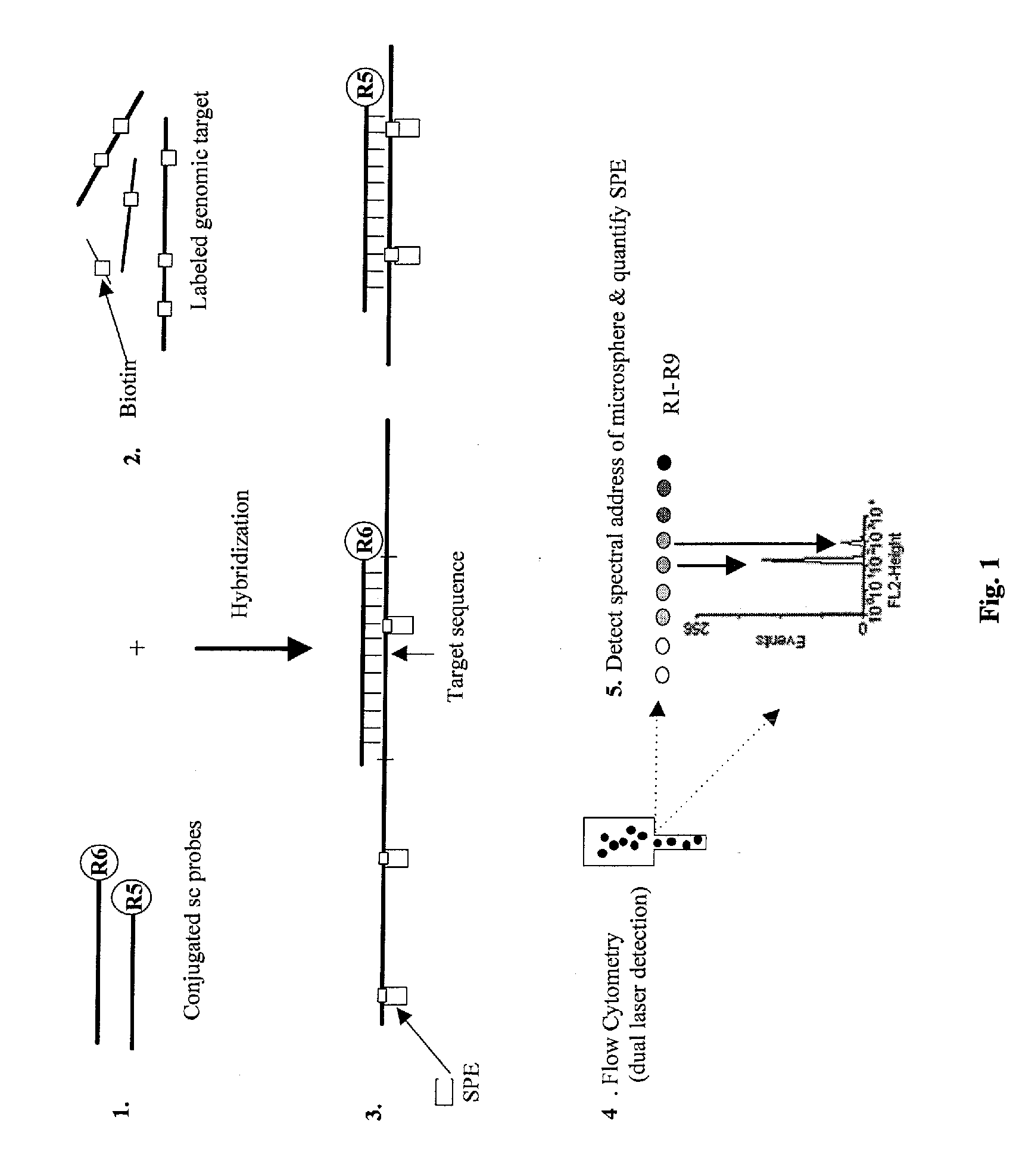
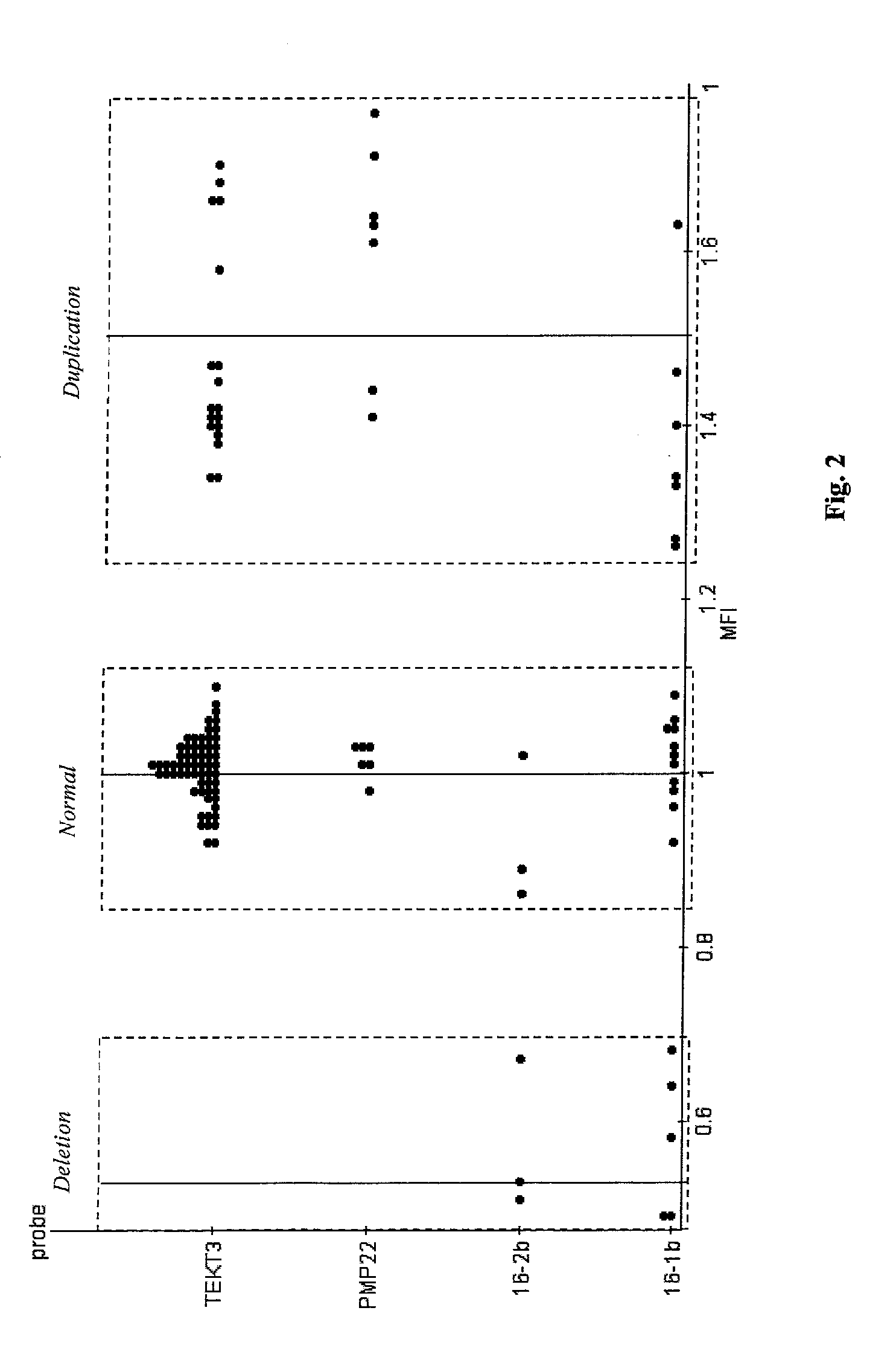
Quantification of microsphere suspension hybridization and uses thereof
InactiveUS20090136918A1Improve accuracyStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingDiseaseBiotin-streptavidin complex
A novel suspension hybridization assay was used to determine nucleic acid copy number by flow cytometry. The assay was validated with low copy (lc) products ranging in length from 100 to 2304 bp conjugated to spectrally-distinct polystyrene microspheres. In the example provided herein, these conjugated microspheres were used as multiplex hybridization probes to detect homologous sequences in genomic DNA extracted from cytogenetic cell pellets and labeled with biotin-dUTP. Hybridization was detected with phycoerythrin-labeled streptavidin and analyzed by flow cytometry. Copy number differences were distinguishable by comparing the mean fluorescence intensities of test probes with a diploid reference probe in genomic DNA of patient samples and abnormal cell lines. The assay is capable of distinguishing a single allele and three alleles at a test locus from a biallelic reference sequence, regardless of chromosomal context. The assay is an improvement on previous methods which require prior amplification of locus-specific target DNA because, lc probes provide adequate specificity and sensitivity for accurate copy number determination of homologous targets. Because of its high sensitivity and accuracy, the assay is useful for determination of nucleic acid copy number for a variety of applications, including determination of genomic copy number in humans, animal models of disease and in solution, measurement of transcript levels, forensic DNA analysis, and quality control analysis in agriculture.
Owner:CHILDRENS MERCY HOSPITAL
Identification and/or quantification method of nucleotide sequence (s) elements specific of genetically modified plants on arrays
InactiveUS20070117106A1Easy to identifyMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological bodyHomologous sequence
The present invention is related to an identification and / or quantification method of several organisms among many other ones possibly present in the analyzed sample having homologous sequence(s) by the determination of the genetic map of the organism. The method combines a limited number of amplifications of target sequence(s) using common primer pairs and the recording upon an array for the presence of single signals resulting from the binding between the capture sequence(s) and their corresponding target sequence(s) and correlating the presence of said detected target sequence(s) to the identification of some genetic specific sequence(s) of said (micro)organism(s) referred as genetic elements and from there to the identification of the organism. The method and device according to the invention allow the easy identification / detection of a sequence specific of an organism among other homologous sequence(s) and possibly its quantification. The identification of the various targets from the initial organism if obtained after their binding on specific capture probes present on a support or substrate preferably in the form of an array. The identification of the amplified targets is obtained directly, after washing of possible contaminants (unbound sequence(s)), by detecting and possibly recording for one target, a single spot signal at one specific location, wherein said capture nucleotide sequence was previously bound and said identification of a target is not a result of a complex pattern of spots upon the microarray to be analyzed in order to identify one target as proposed in the system of the state of the art.
Owner:EPPENDORF ARRAY TECH SA
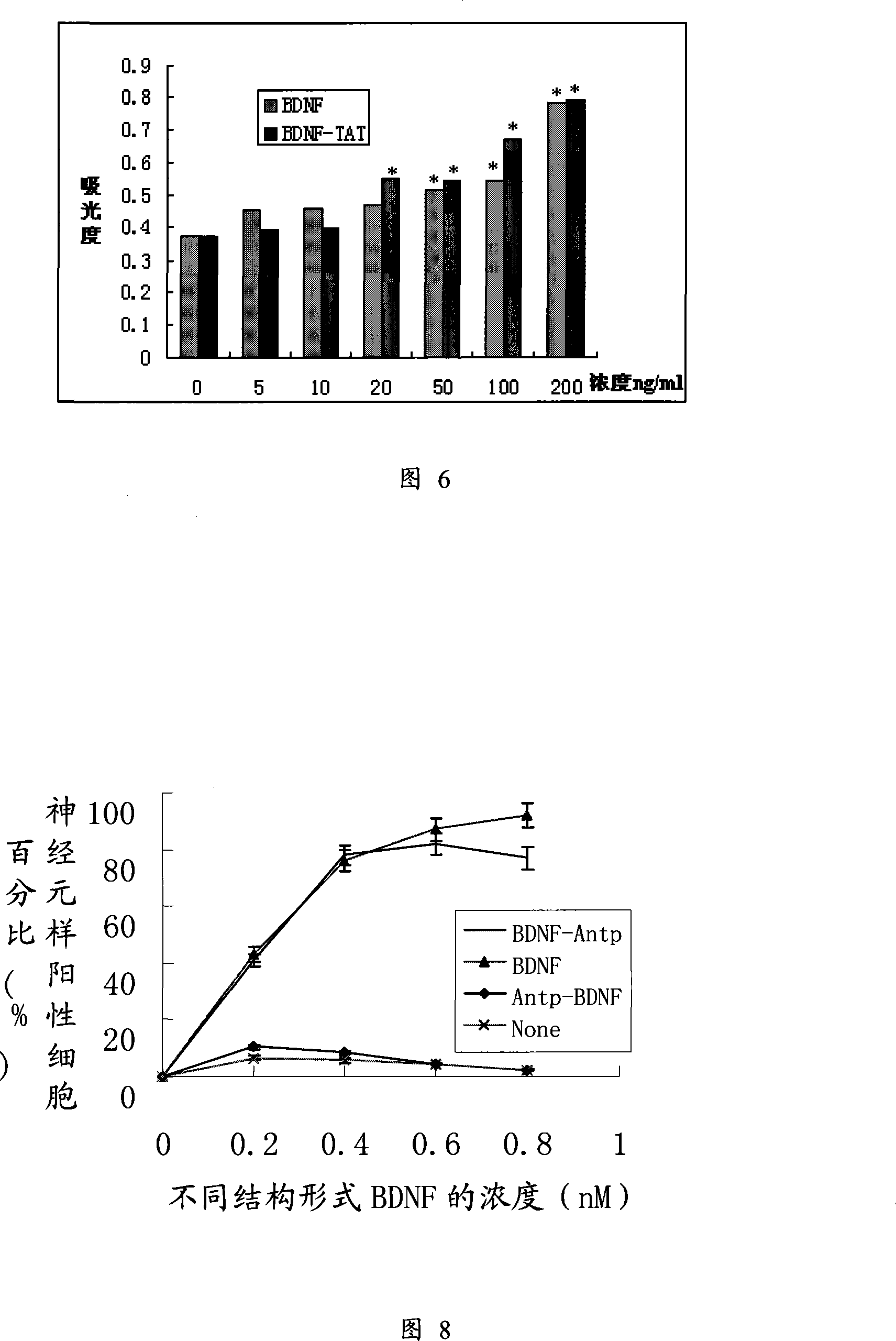
Fusion protein penetrating blood-brain barrier with nerve nourishment gene and encoding gene and uses thereof
InactiveCN101157730AExert biological activityCorrect N-terminal conformationPeptide/protein ingredientsHybrid peptidesNervous systemCell membrane
The present invention discloses a clone of a neurotrophic factor fusion protein gene containing a protein transduction domain, the expression and the purification of the protein, the biological activity of the fusion protein, and the effect for penetrating a cell membrane, particularly for the blood-brain barrier in vivo. The fusion protein comprises a first area which has at least 75 percent of a homologous sequence with a neurotrophic factor and a second area which has at least 75 percent of a homologous sequence with an amino acid sequence of the protein transduction domain, and the second area is positioned at a carboxyl-terminal of the first area; the present invention can carry out the replacement, deletion or addition of the amino acid residues under the premise of not changing the characteristics of the fusion protein. The fusion protein can be used as a drug for the treatment of a plurality of neurodegenerative disorders in central nervous system and the peripheral neuropathies by peripheral routes for drug delivery.
Owner:ZHUJIANG HOSPITAL SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIV
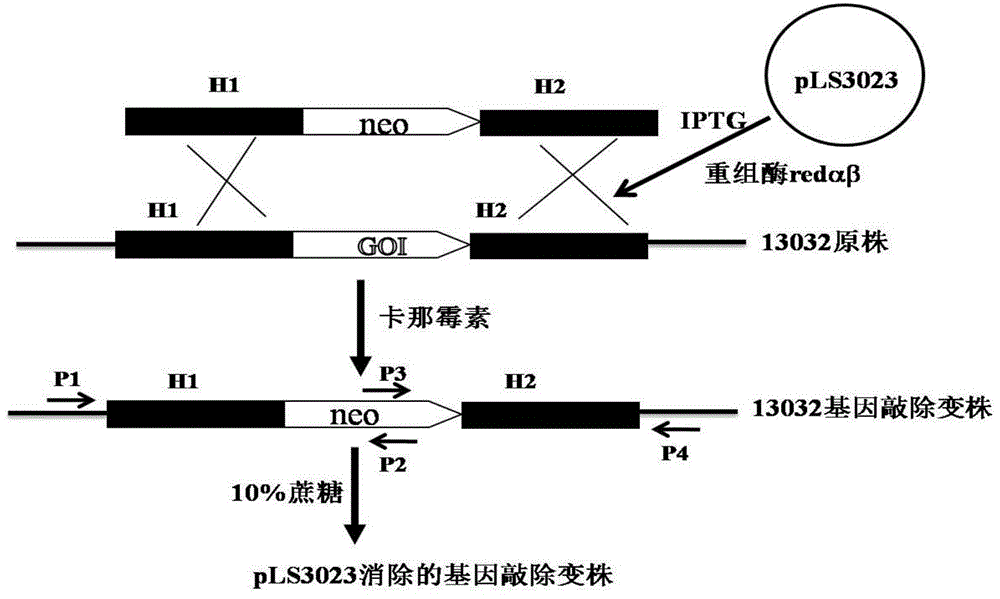
Recombineering-mediated gene knockout method of corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 13032
InactiveCN104561077AMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionSaccharumThiogalactosides
The invention relates to a recombineering-mediated gene knockout method of corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 13032. The gene knockout method comprises the following specific implementation steps: obtaining a DNA fragment which is provided with 500-bp homologous sequences on two sides aiming at genes to be knocked out and a kanamycin resistance gene in the middle through a polymerase chain reaction amplification; carrying out electrotransformation on the DNA fragment into a corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 13032 cell in which recombinase is induced to express by isopropyl-Beta-D-thiogalactopyranoside, and enabling the kanamycin resistance gene to replace the target gene through the resistance selection of kanamycin to obtain gene knockout strains; finally, cultivating mutant strains in a solid medium containing cane sugar to eliminate plasmids containing recombinase genes. The gene knockout method adopts simple PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) and electrotransformation supplemented by the resistance selection of kanamycin, is free of operating steps, such as gene cloning in molecular biology and other certain operating steps, and simple and rapid, and has important application in the aspects of researching gene functions and producing amino acid.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com