Patents
Literature
114 results about "Exonuclease III" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Exonuclease III (ExoIII) is an enzyme that belongs to the exonuclease family. ExoIII catalyzes the stepwise removal of mononucleotides from 3´-hydroxyl termini of double-stranded DNA. A limited number of nucleotides are removed during each binding event, resulting in coordinated progressive deletions within the population of DNA molecules.
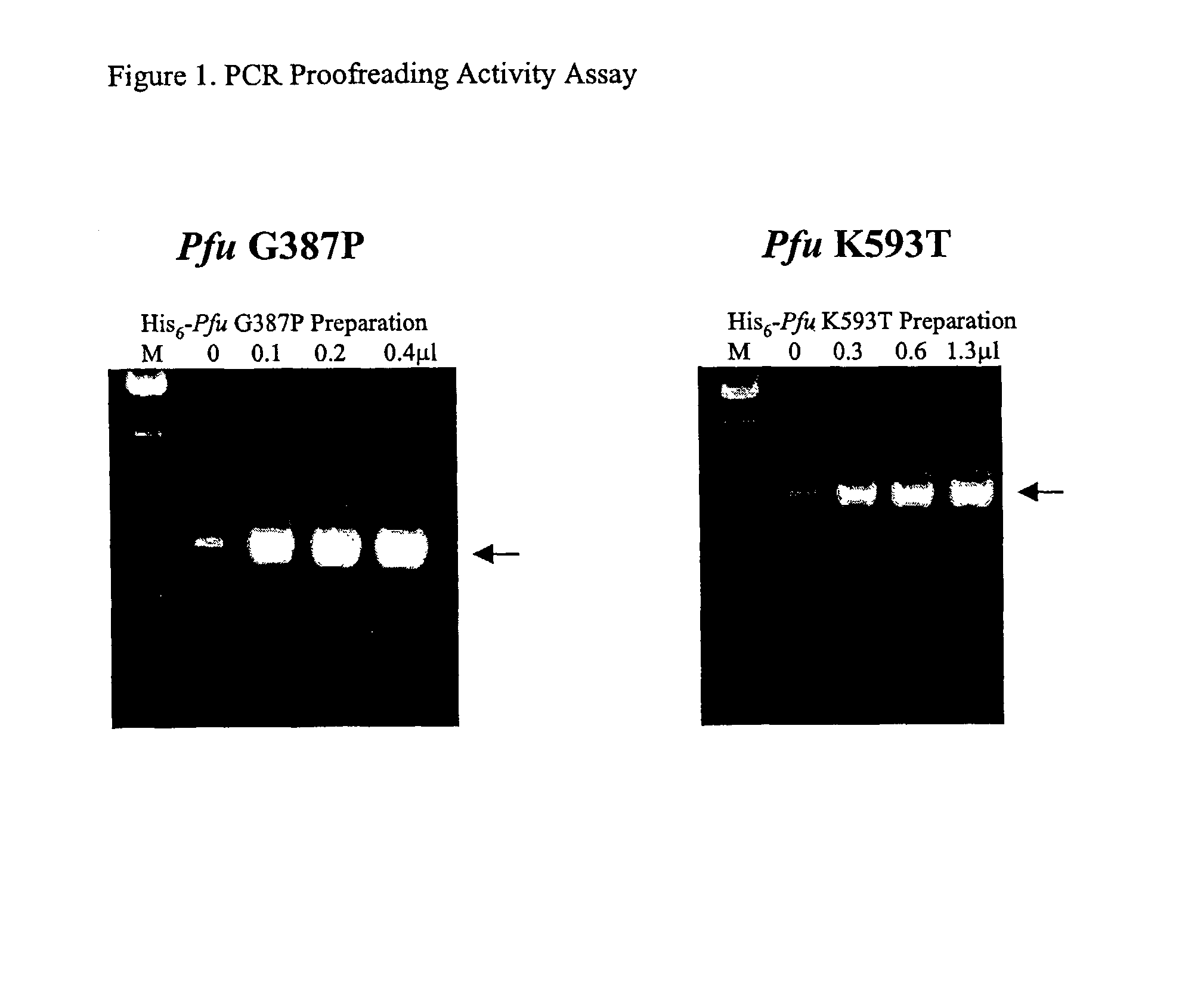
High fidelity DNA polymerase compositions and uses therefor
The subject invention relates to compositions comprising an enzyme mixture which comprises a first enzyme and a second enzyme, where the first enzyme comprises a DNA polymerization activity and the second enzyme comprises an 3′-5′ exonuclease activity and a reduced DNA polymerization activity. The invention also relates to the above compositions in kit format and methods for high fidelity DNA synthesis using the subject compositions of the invention.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
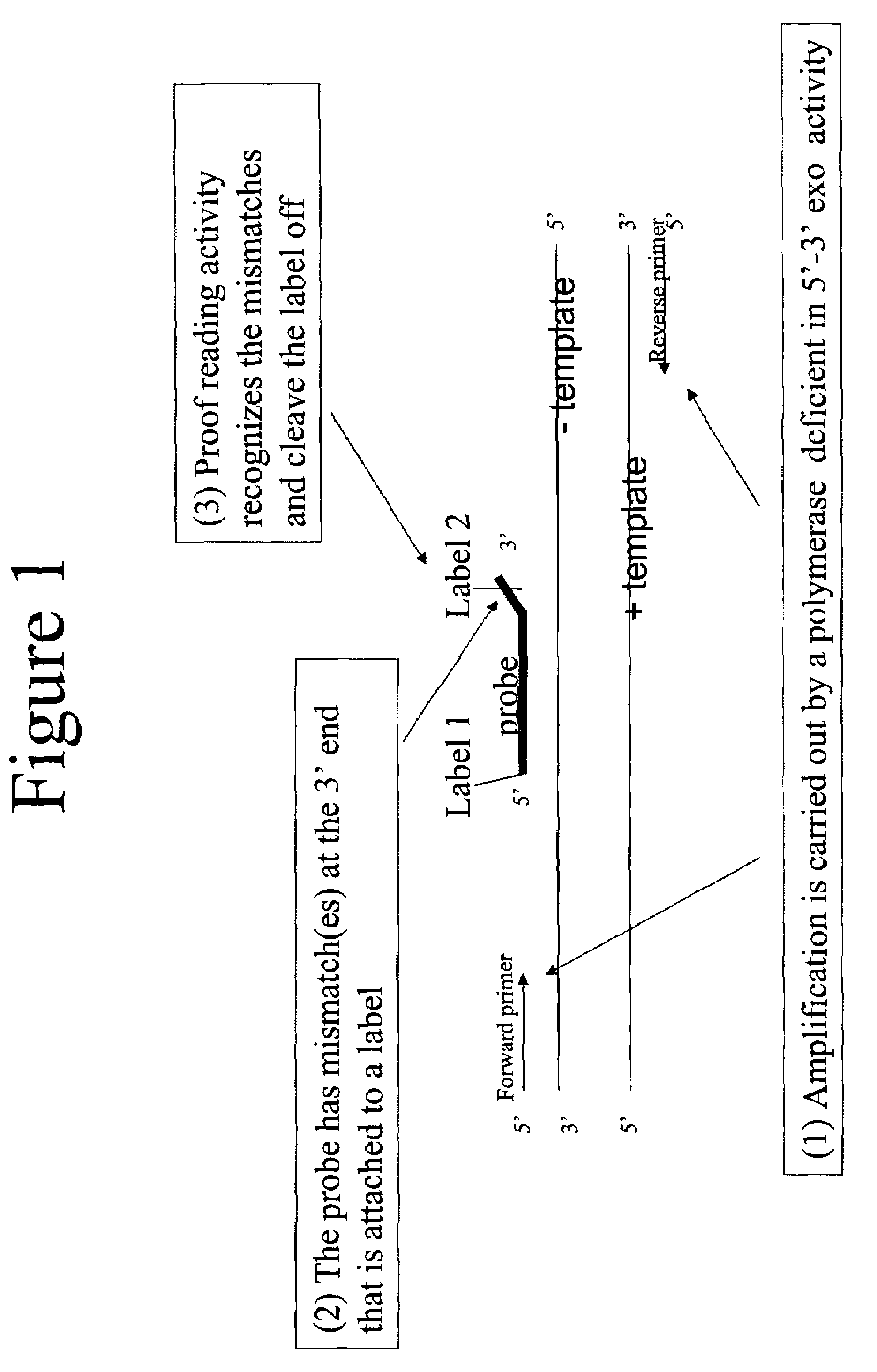
Quantitative amplification with a labeled probe and 3' to 5' exonuclease activity
This invention provides methods and kits for performing a quantitative amplification reaction. The method employs a polymerase enzyme and an enzyme having a 3′ to 5′ exonuclease activity that cleaves the 3′ oligonucleotide of the probe.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
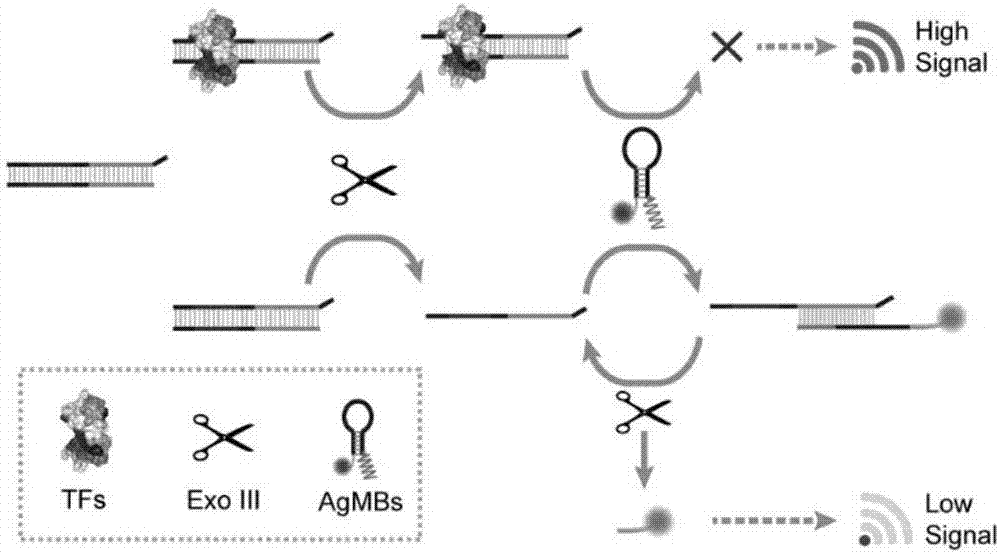
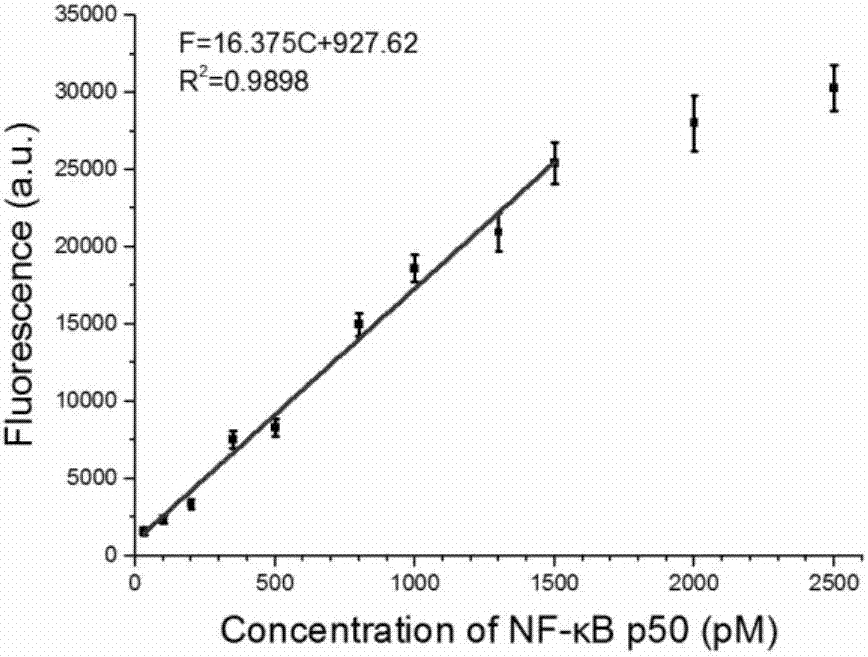
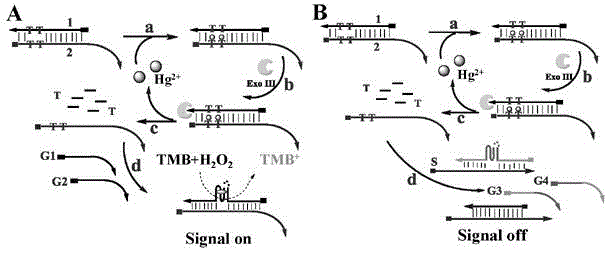
Transcription factor detection method based on DNA-Ag nanoclusters molecular beacons and exonuclease III cycle signal amplification
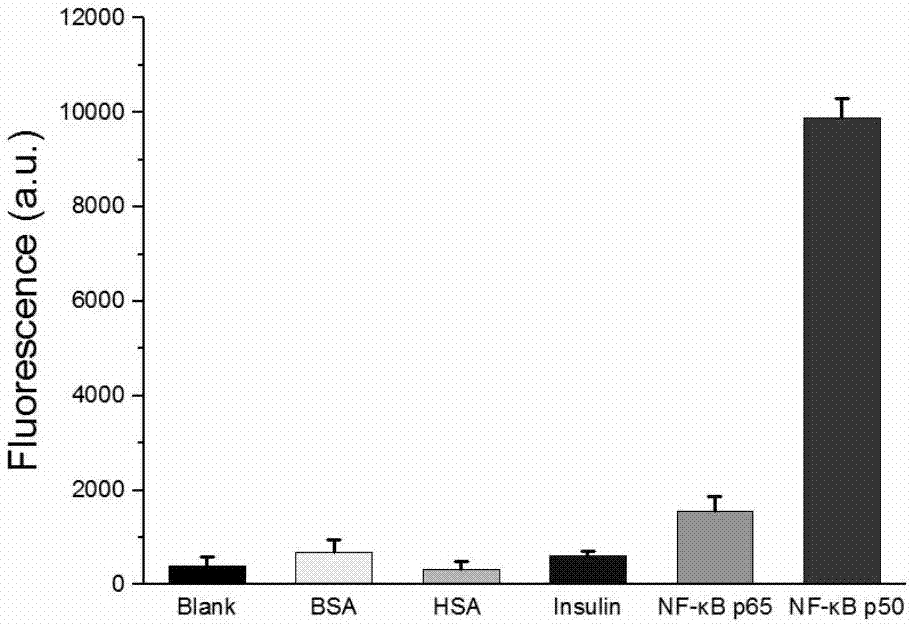
The invention discloses a transcription factor detection method based on DNA-Ag nanoclusters molecular beacons and exonuclease III cycle signal amplification. The novel nanomaterial DNA-Ag nanoclusters molecular beacon is applied as a fluorescent probe to transcription factor detection for the first time. Also, based on the characteristic that fluorescence adjustment of DNA-Ag nanoclusters molecular beacons is carried out by an enzyme cleavable DNA fragment, exonuclease III is added to participate in signal transformation and also participate in enhancement of the detection signal. The transcription factor detection method provided by the invention has the advantages of no label, high selectivity, low cost and high sensitivity, and can realize high throughput detection of transcription factors in biological samples.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
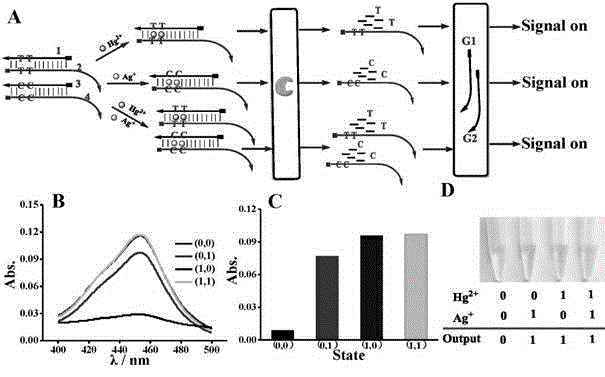
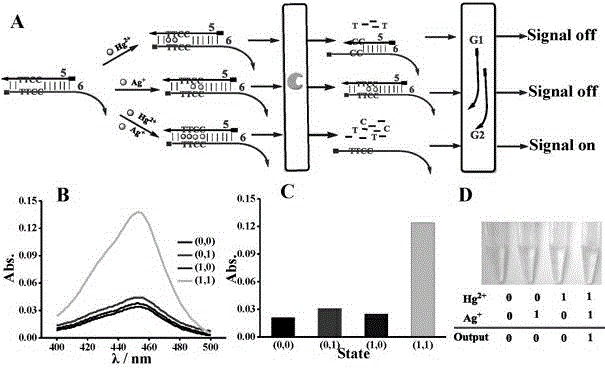
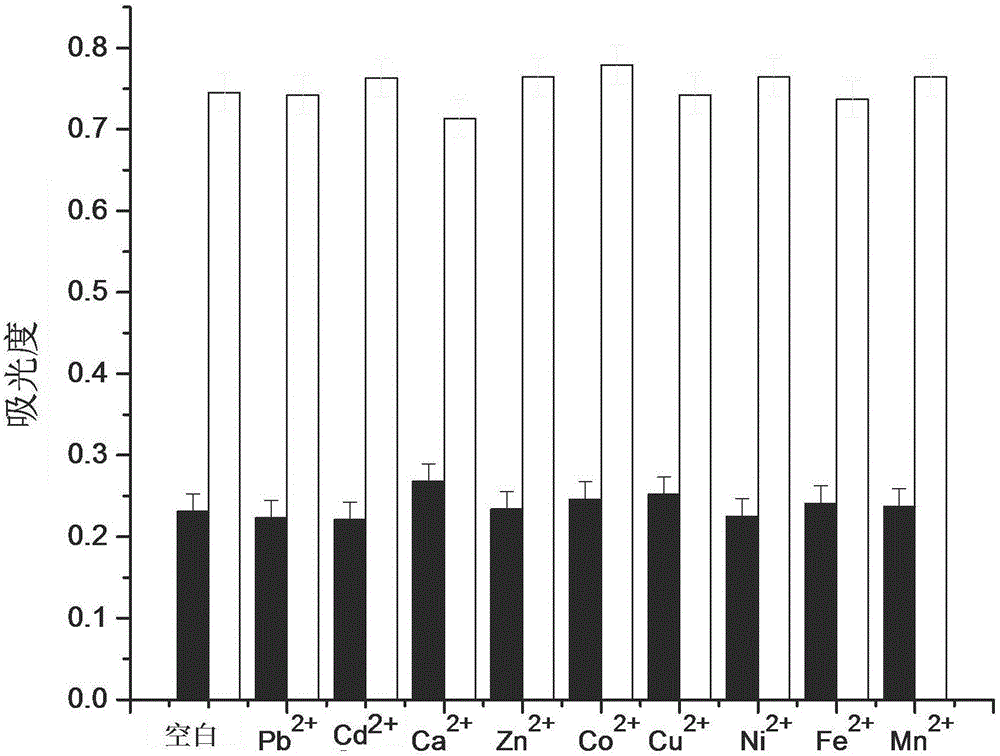
DNA colorimetric logic gate construction method based on metal ion regulation and control of exonuclease III shearing action
The invention discloses a DNA colorimetric logic gate construction method based on metal ion regulation and control of exonuclease III shearing action and belongs to the technical field of molecular computer. Double-stranded DNA containing T-T or C-C mismatched base cannot be sheared by exonuclease III. When there exists Hg<2+> or Ag<+>, 3' end completely matched double-stranded DNA formed by action of T-Hg<2+>-T or C-Ag<+>-C can be sheared by exonuclease III, and released single-stranded DNA hybridizes with a DNA signal probe 1 or DNA signal probe 2, thus leading to formation or disintegration of a G-quadruplex structure. Hereby, Hg<2+> and Ag<+> are used as input signals, and logic operation is carried out through the DNA signal probe so as to construct multiple DNA colorimetric logic gates.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Biosensor for detecting adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
InactiveCN108107028AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityFluorescence/phosphorescenceAtp contentExonuclease III
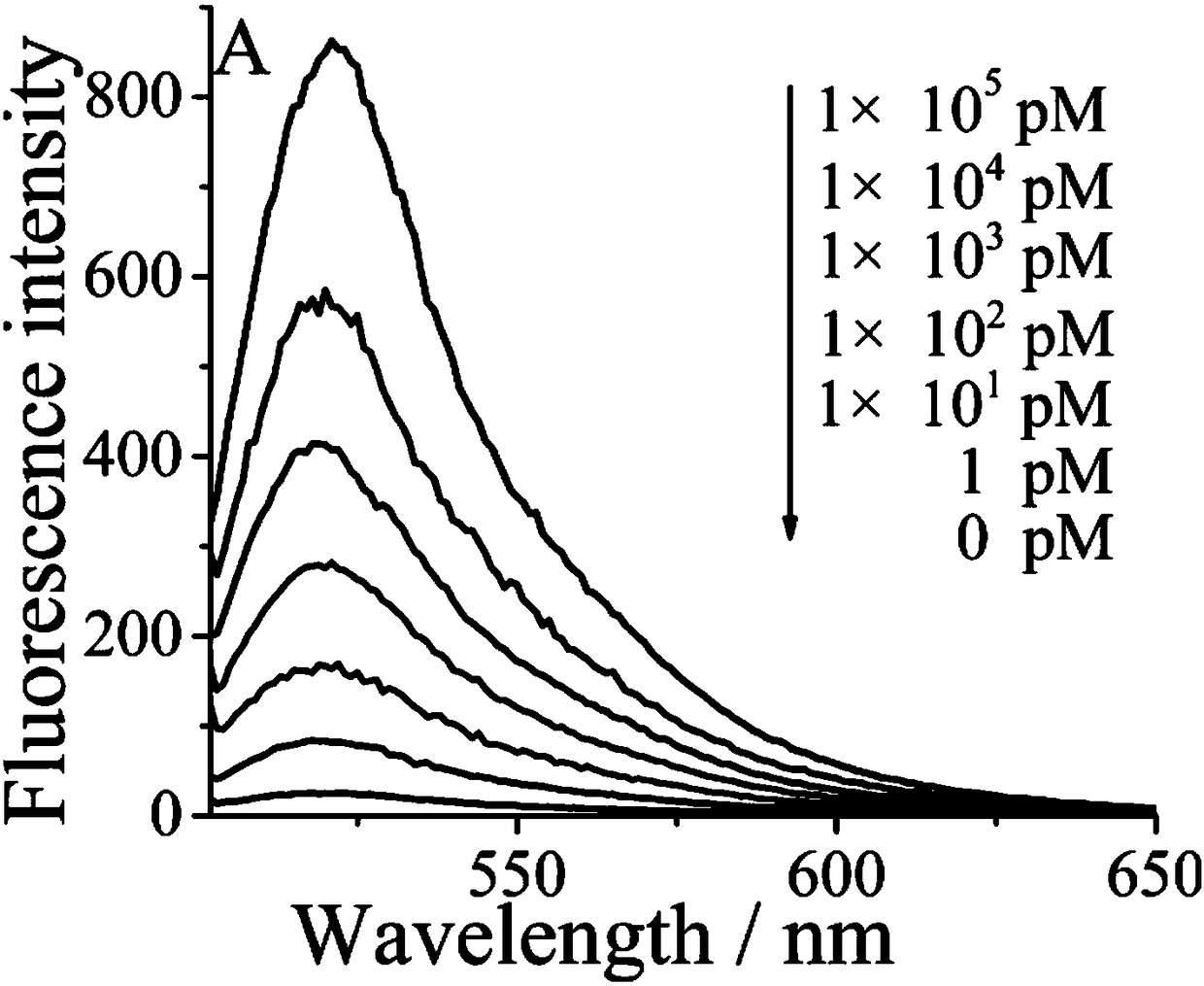
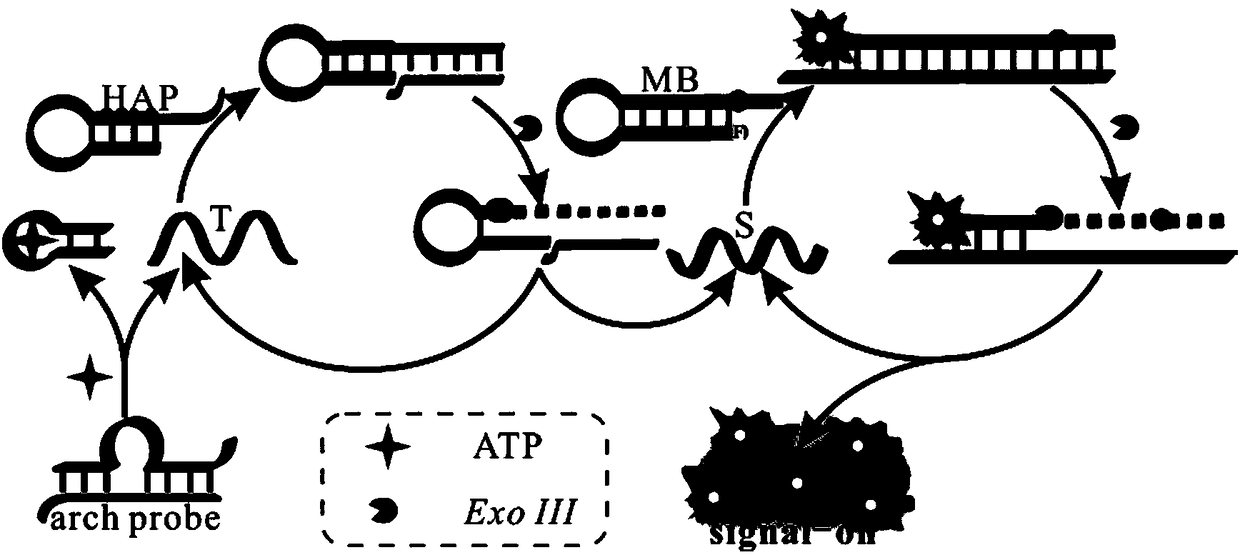
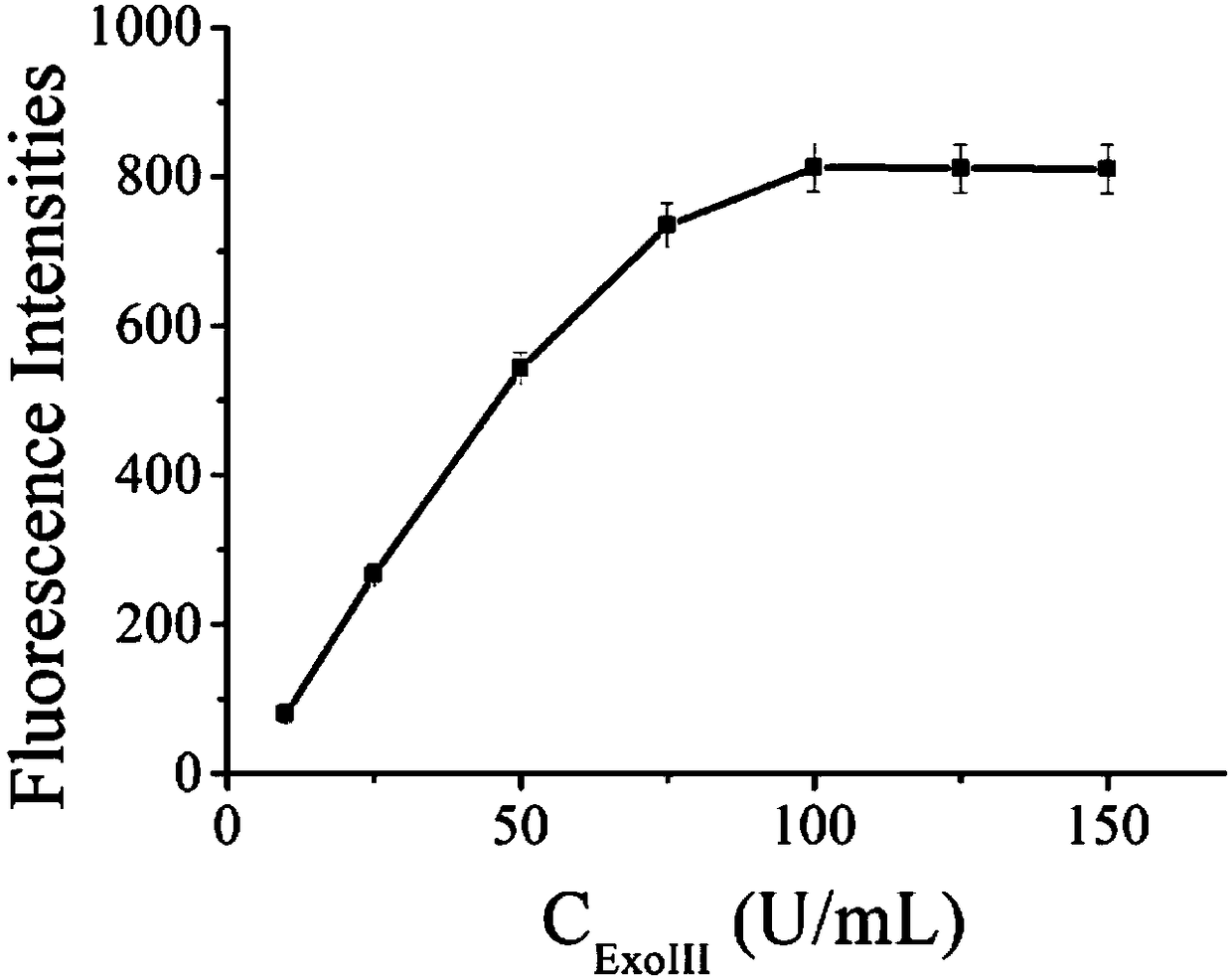
The invention provides a biosensor for detecting adenosine triphosphate (ATP). The biosensor comprises exonuclease III, a triggering chain, an ATP exonuclease, a hairpin probe and a molecular beacon,wherein the ATP content in a solution can be detected through fluorescence; the excitation wavelength of the fluorescence is 486nm; the emission wavelength is 518nm; the detection ranges is 500-650nm.The biosensor is high in specificity, high in sensitivity, mild in reaction conditions, and high in repeatability; the detection method is simple and convenient to operate; the detection period is short; the main detection process is performed in homogeneous phase, so that the reaction speed is increased, and the complexity of operation is reduced.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
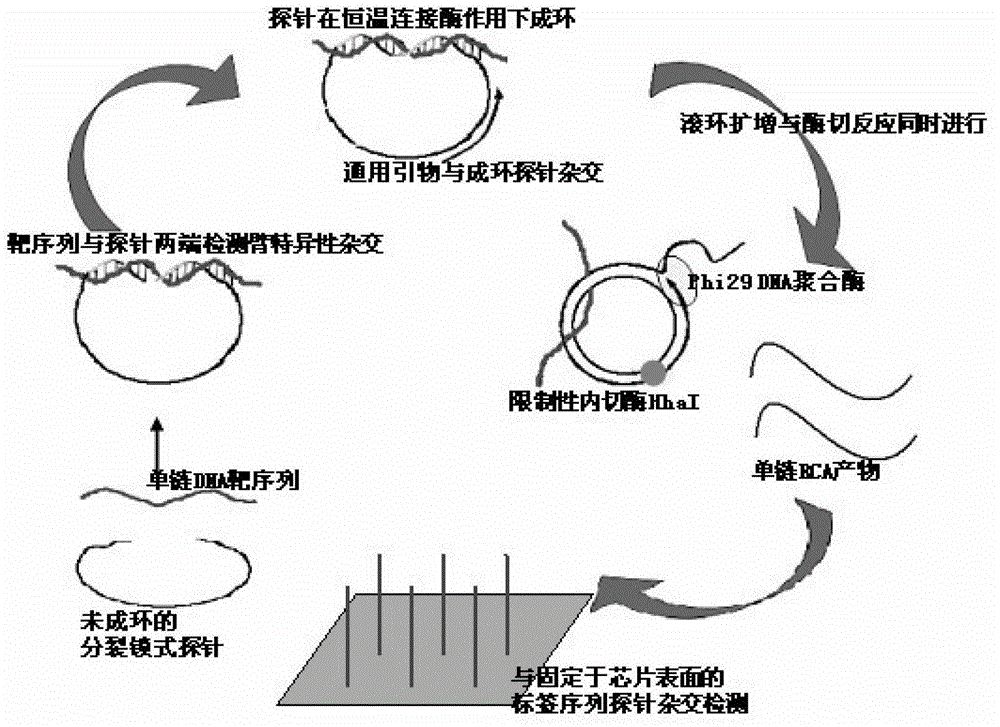
Multi-RCA (rolling circle amplification) method based on split padlock probes
InactiveCN102719550AEasy to operateStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementPolymerase LExonuclease I
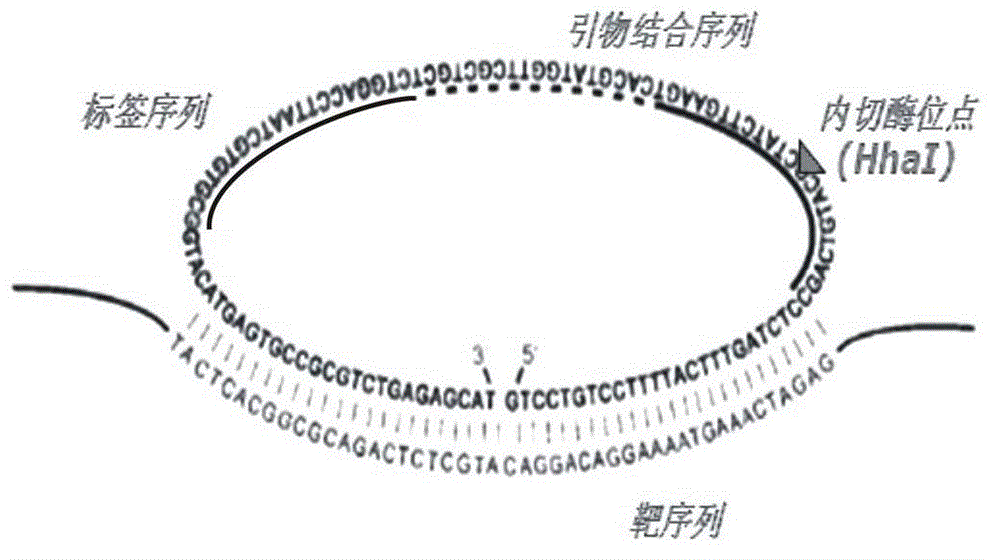
The invention discloses a multi-RCA (rolling circle amplification) method based on split padlock probes. Each novel split padlock probe is about 90bp in length and comprises four parts, namely a detection arm, a universal primer area, an HhaI endonuclease site and a tag sequence area, wherein an amplification system is composed of a connection system and an RCA system. The concrete detection method comprises the steps of: firstly, carrying out coupled reaction, mixing a target sequence DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) segment and four split padlock probes of which the final concentration is 1mol / L, hybridizing for 15 minutes after boiling and degenerating, adding T4DNA ligase and T4DNA ligase buffer solution, supplying 10 muL of reaction system; carrying out exonuclease I and exonuclease III exterior contact for 45 minutes at 37 DEG C, preparing an annular template and then carrying out RCA reaction; mixing, boiling and degenerating 10 muL of connection product and universal primer, respectively adding dNTP, phi29DNA polymerase, HhaI restriction enzyme and buffer solution to form 20 muL of reaction system, stewing for 60 minutes at 37 DEG C; finally detecting single-chain DNA product of RCA with a specific tag sequence, thus obtaining a corresponding test conclusion according to the result.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA
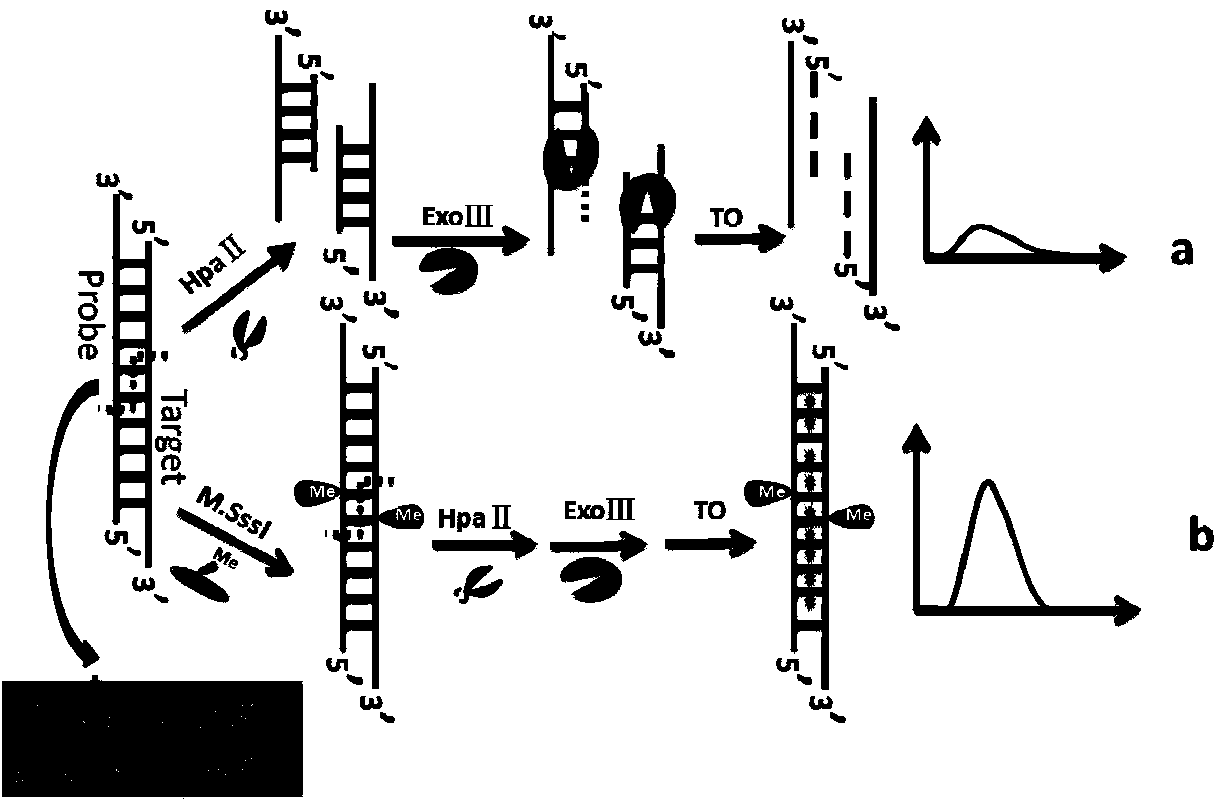
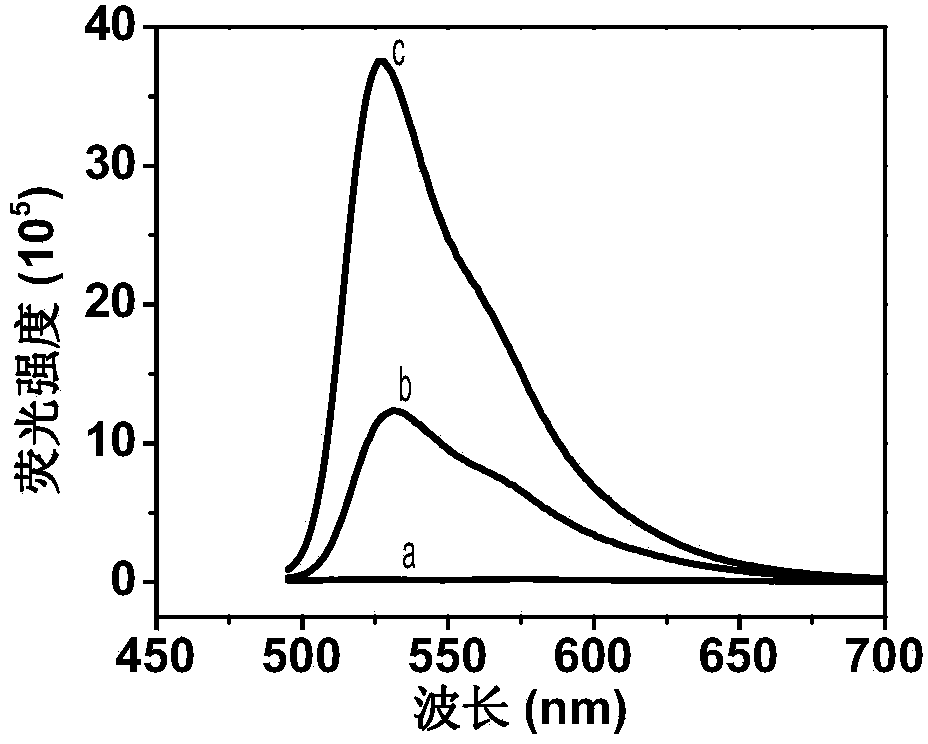
Method for detecting activity of DNA methylase and DNA methyltranseferase by unlabeled fluorescent detection based on restriction endonuclease and exonuclease III
InactiveCN103993083ALow costAvoid accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementSignalling moleculesSingle strand dna
The invention discloses a method for detecting the activity of DNA methylase and DNA methyltranseferase based on restriction endonuclease Hpa pi and exonuclease III. An unlabeled DNA probe is prepared and the sequence of the probe comprises a cleavage site of the restriction endonuclease and a methylated CpG site. The purpose of detecting the activity of the methylase and methyltranseferase is reached by steps of hybridizing the unlabeled DNA probe with the target DNA, carrying out methylation treatment by the methylase, carrying out the specific cleavage of the restriction endonuclease Hpa pi and enabling exonuclease III having the activity of 3'->5' exonuclease to act on the double-stranded DNA and then adding fluorescence signal molecules thiazole orange which having different signals to single-stranded DNA and double-stranded DNA. According to the method, since no complex material or labeling of DNA probes need to be prepared, the defects of high detection cost, cumbersome operations and poor reproducibility caused by the preparation of the material and labeling of DNA probes are avoided. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of low cost and high sensitivity and is fast and simple.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Quantitative amplification with a labeled probe and 3' to 5' exonuclease activity
This invention provides methods and kits for performing a quantitative amplification reaction. The method employs a polymerase enzyme and an enzyme having a 3′ to 5′ exonuclease activity that cleaves the 3′ oligonucleotide of the probe.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
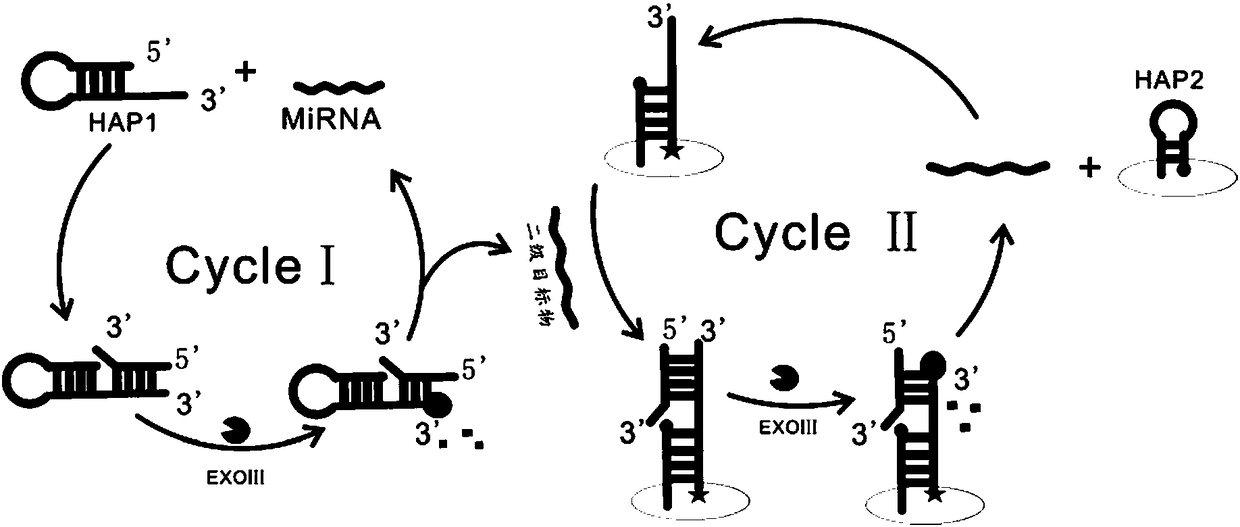
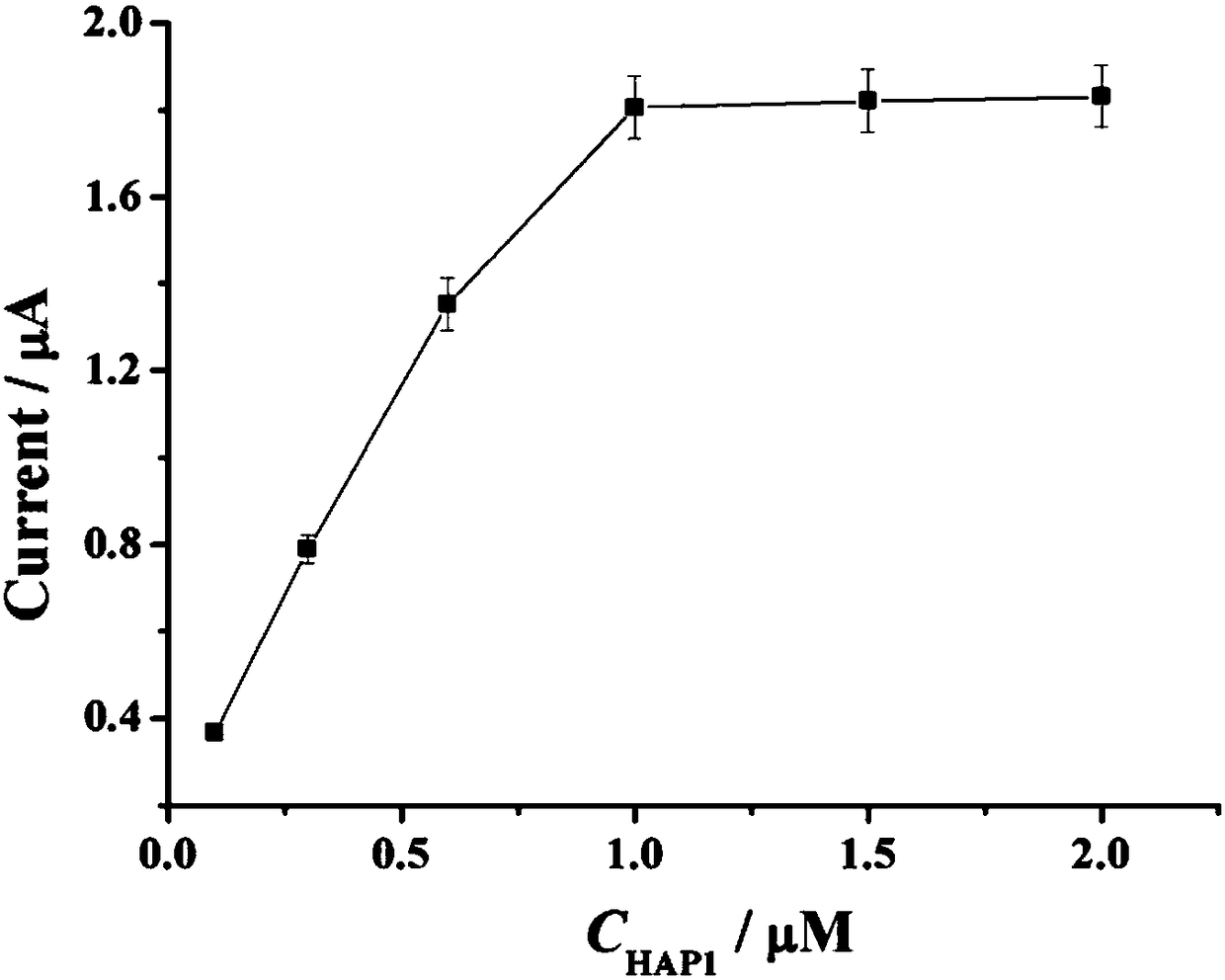
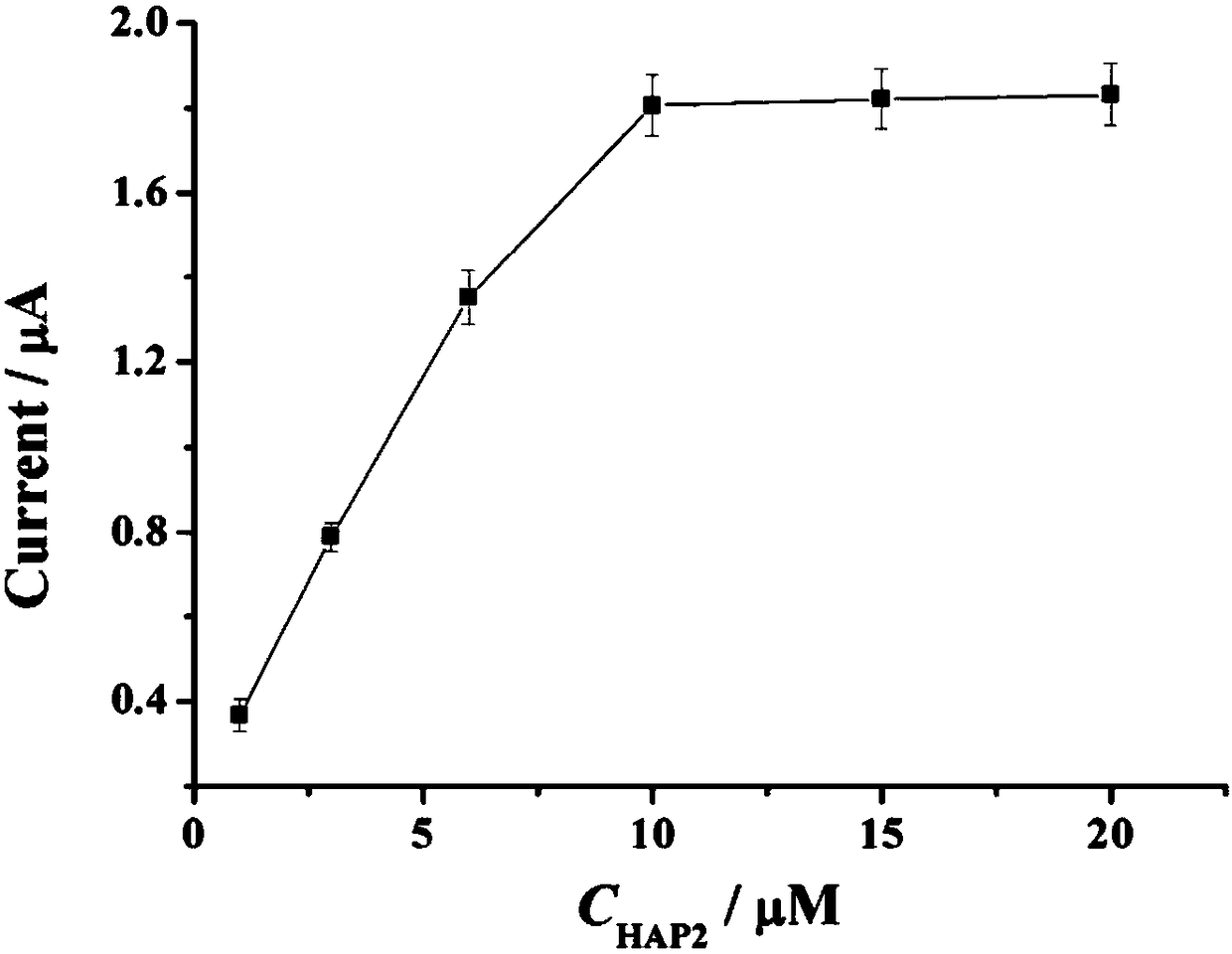
Electrochemical biosensor for detecting miRNA-122
InactiveCN108169311AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMaterial electrochemical variablesElectrochemical biosensorExonuclease III
The invention provides an electrochemical biosensor for detecting miRNA-122. The electrochemical biosensor comprises HAP1 (hairpin probe 1), ExoIII enzyme (exonuclease III), a gold electrode and a HAP2 (hairpin probe 2)-auxiliary probe modifying the surface of the gold electrode. The electrochemical biosensor has the advantages of good specificity, high sensitivity, mild reaction conditions, fastreaction speed, use of the simple gold electrode, small size, carrying easiness, reusability, simple preparation processes, stable performances, good electrode repeatability and feasibility of detection of miRNA-122 in human tissues and biosensor industrialization.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
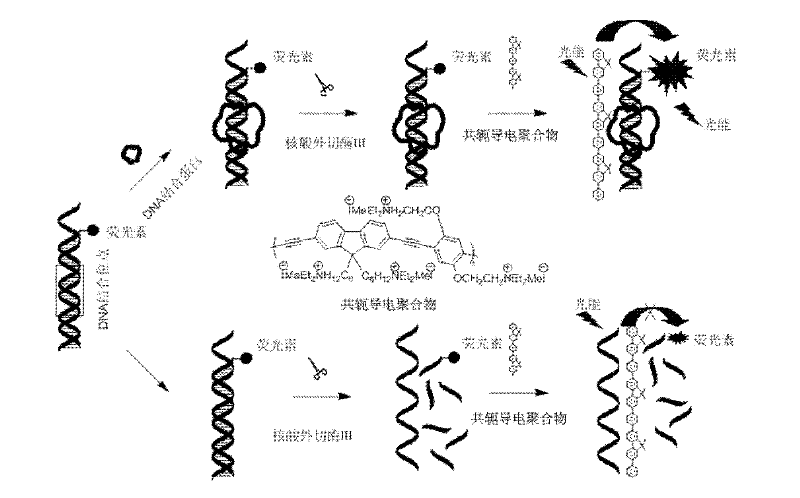
Fluorescence detection method for detecting desoxyribonucleic acid binding protein
InactiveCN102384978AShorten detection timeHigh selectivityBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceProtein targetNucleic Acid Probes
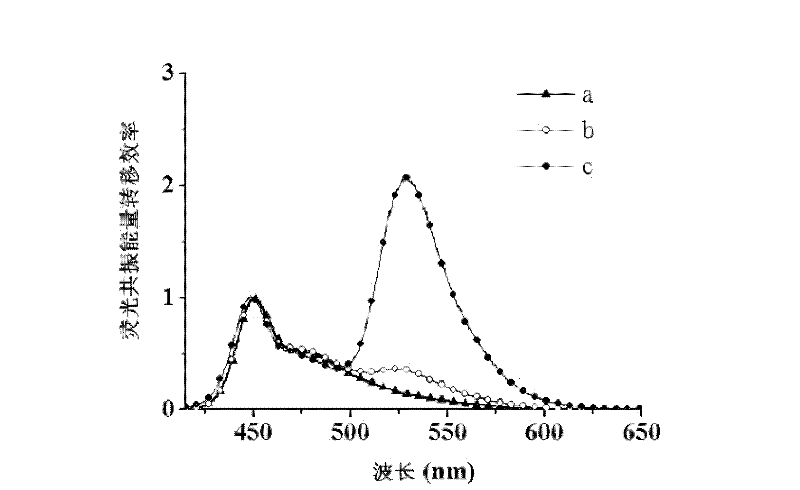
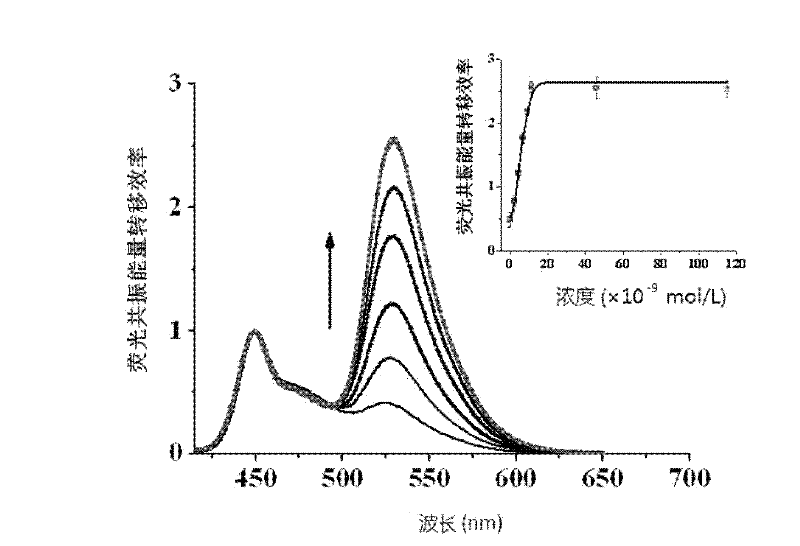
Provided is a fluorescence detection method for detecting desoxyribonucleic acid binding protein. The method utilizes double-strand nucleic acid containing protein binding locus and marked by fluorescein as a probe, the probe is bound with target protein to form a nucleic acid probe / desoxyribonucleic acid binding protein composite which provides protection space for the nucleic acid probe, so that the nucleic acid probe can be prevented from being hydrolyzed by nuclease, the nucleic acid probe can be bound with cationic water-soluble conjugated polymer through a static reaction, the distance between the fluorescein and the polymer is small, and high-efficient fluorescence resonance energy transfer can be generated. Based on the water-soluble conjugated polymer and exonuclease III, the method includes the following steps: a, preparing the double-strand desoxyribonucleic acid fluorescence probe capable of binding protein with specificity; b, binding the double-strand desoxyribonucleic acid fluorescence probe with the desoxyribonucleic acid binding protein; c, enzyme restriction can be conducted on the composite through exonuclease III; and d, adding the water-soluble conjugated polymer into the reaction system for fluorescent detection.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
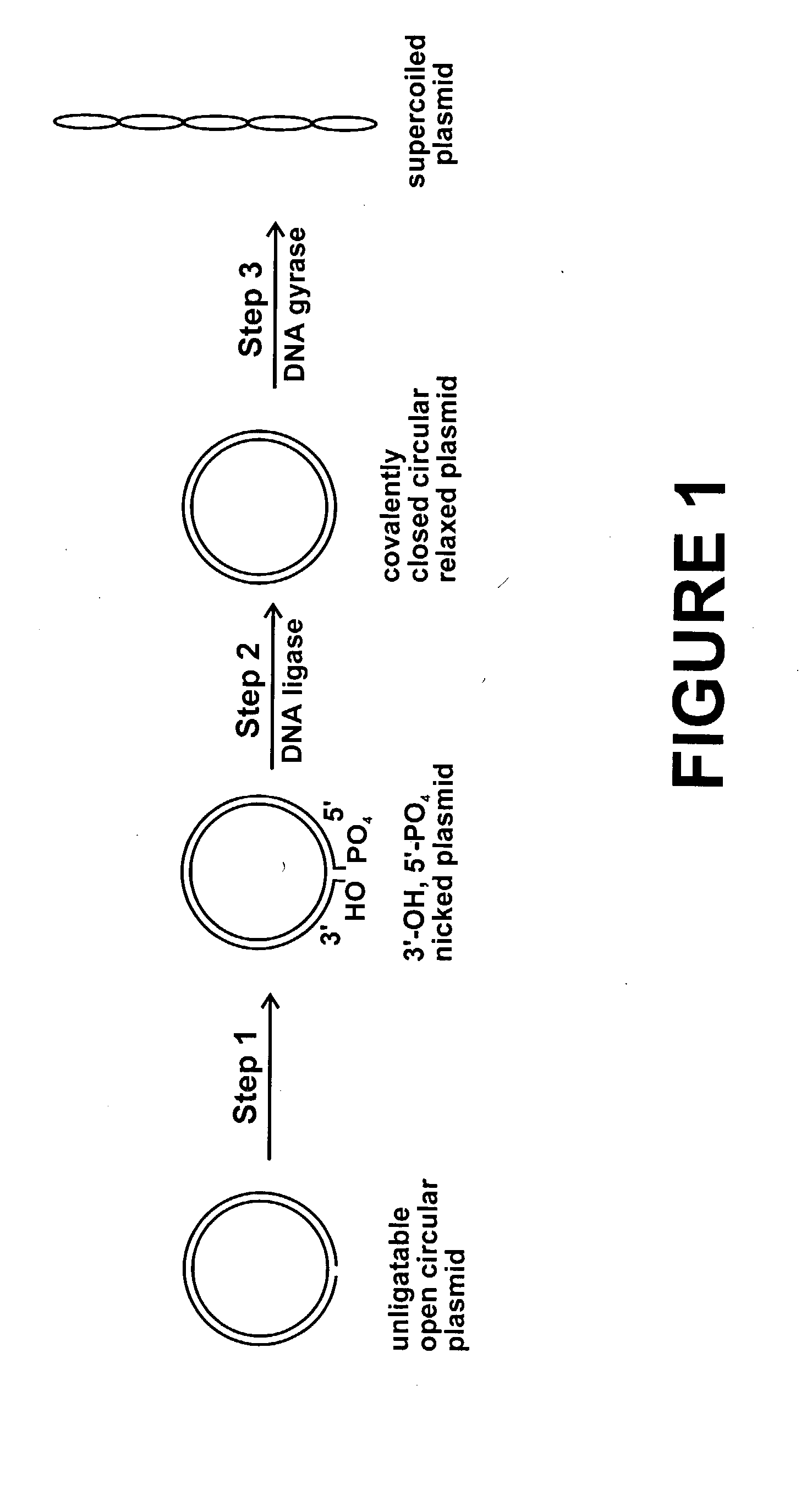
Method for plasmid preparation by conversion of open circular plasmid
InactiveUS20040191871A1Increase percentageFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionNucleotidePhosphoric acid
In accordance with the invention, there is provided a method for preparing plasmid from host cells which contain the plasmid, comprising the steps: (a) preparing a cleared lysate of the host cells, wherein the cleared lysate comprises unligatable open circular plasmid, wherein the open circular plasmid is not 3'-hydroxyl, 5-phosphate nicked plasmid; (b) incubating the unligatable open circular plasmid with one or more enzymes in the presence of their appropriate nucleotide cofactors, whereby the unligatable open circular plasmid is converted to 3'-hydroxyl, 5'-phosphate nicked plasmid; (c) incubating the 3'-hydroxyl, 5'-phosphate nicked plasmid with DNA ligase in the presence of DNA ligase nucleotide cofactor, whereby 3'-hydroxyl, 5'-phosphate nicked plasmid is converted to relaxed covalently closed circular plasmid; and (d) incubating the relaxed covalently closed circular plasmid with DNA gyrase in the presence of DNA gyrase nucleotide cofactor, whereby relaxed covalently closed circular plasmid is converted to negatively supercoiled plasmid. Preferably, the enzymatic steps (b), (c), and (d) are performed in a single step using an enzyme mixture comprising DNA polymerase, DNA ligase, and DNA gyrase. Preferably, the mixture further comprises a 3' terminus deblocking enzyme, such as exonuclease III or 3'-phosphatase. Preferably, the mixture further comprises one or more regenerating enzymes and a high energy phosphate donor, whereby the nucleotide by-products of the nucleotide cofactors generated by DNA ligase and DNA gyrase are converted to back to nucleotide cofactor. Preferably, the enzyme mixture further comprises one or more exonucleases, such as ATP dependent exonuclease, whereby linear chromosomal DNA is selectively degraded.
Owner:HYMAN EDWARD DAVID
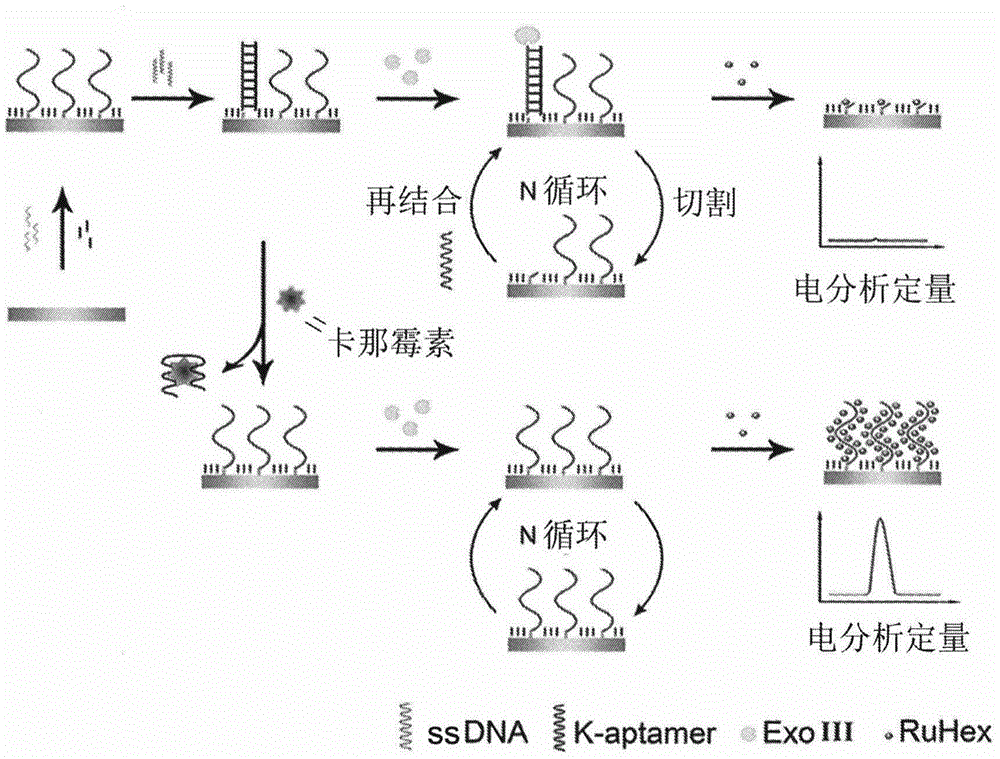
Method for detecting residual kanamycin
InactiveCN105651850ASensitive detectionRealize detectionMaterial electrochemical variablesKanamycinEnzyme digestion
The invention discloses a method for detecting residual kanamycin and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of analysis chemistry, wherein the detection method is based on aptamer initiated cyclic enzyme digestion of exonuclease III (Exo III). According the method, mercapto self-assembly is utilized, single stranded DNA (ssDNA) that is complementary with kanamycin aptamer (K-aptamer) is grafted on the surface of a gold electrode, then a little amount of K-aptamer is added, and the K-aptamer is matched with ssDNA to form a little amount of double stranded DNA (dsDNA). Then Exo III is added, the ssDNA in dsDNA can be specifically digested by Exo III, thus the residual aptamers are released, the released aptamers can combine with ssDNA to form dsDNA, another enzyme digestion is triggered then, and after several circulations, the modified ssDNA is completely digested by enzymes. Kanamycin exists in the system, through the combination between kanamycin and aptamers, the circulation enzyme digestion is inhibited, thus ssDNA is preserved, and the amount of preserved ssDNA is related with the concentration of kanamycin. An electro-analysis method is used to absorb electrical signal molecules namely hexaammine ruthenium (RuHeX) through static electricity absorption so as to quantitatively detect residual kanamycin; and the method has high sensitivity and can sensitively detect residual kanamycin in milk.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Double-circulation cascade signal amplification DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) combination probe composition on basis of exonuclease III assistance, method for preparing double-circulation cascade signal amplification DNA combination probe composition and application thereof
ActiveCN106191042AHigh sensitivityImprove featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationCyclic processReal time analysis
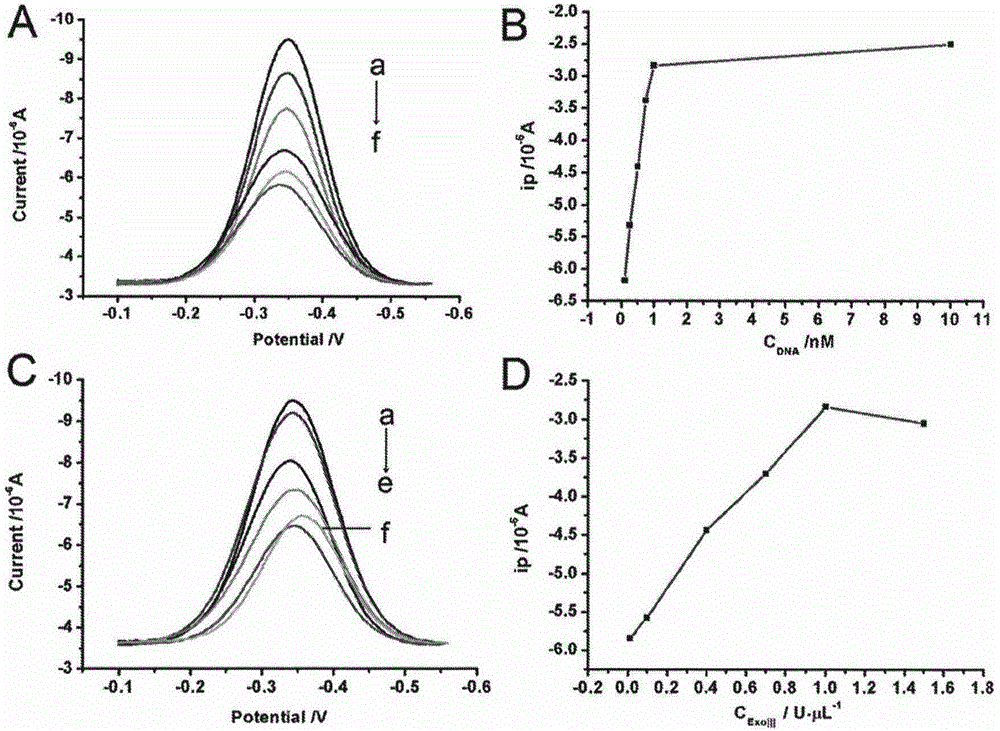
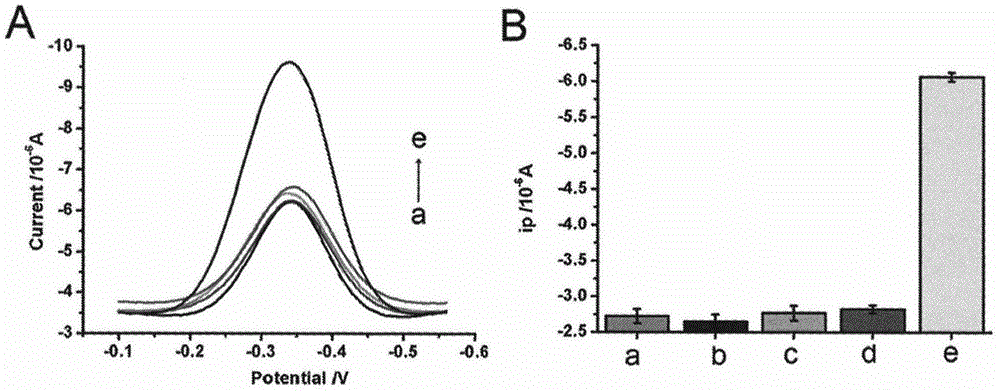
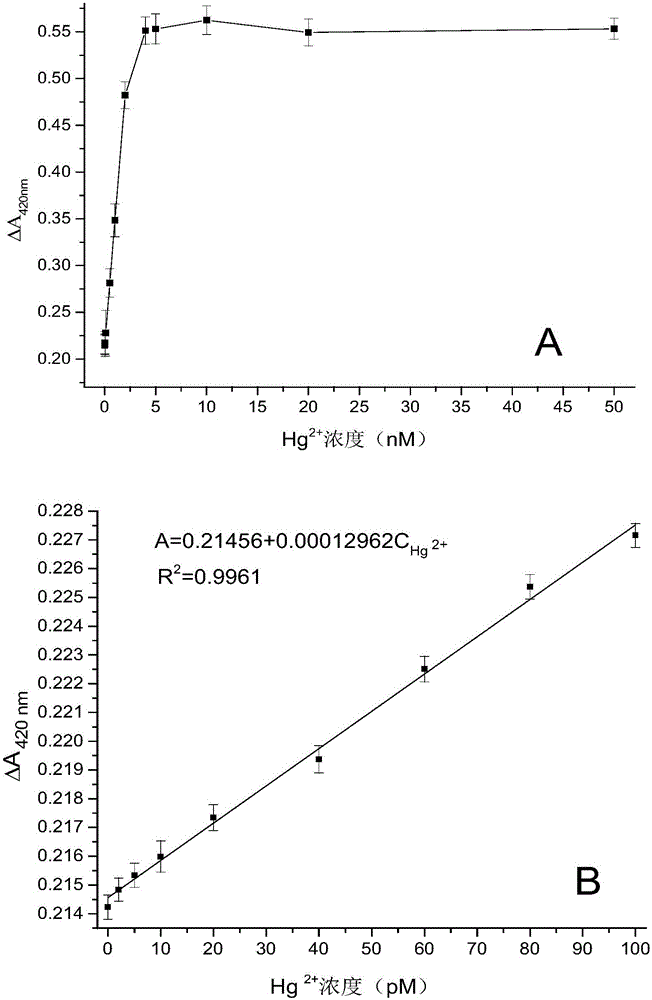
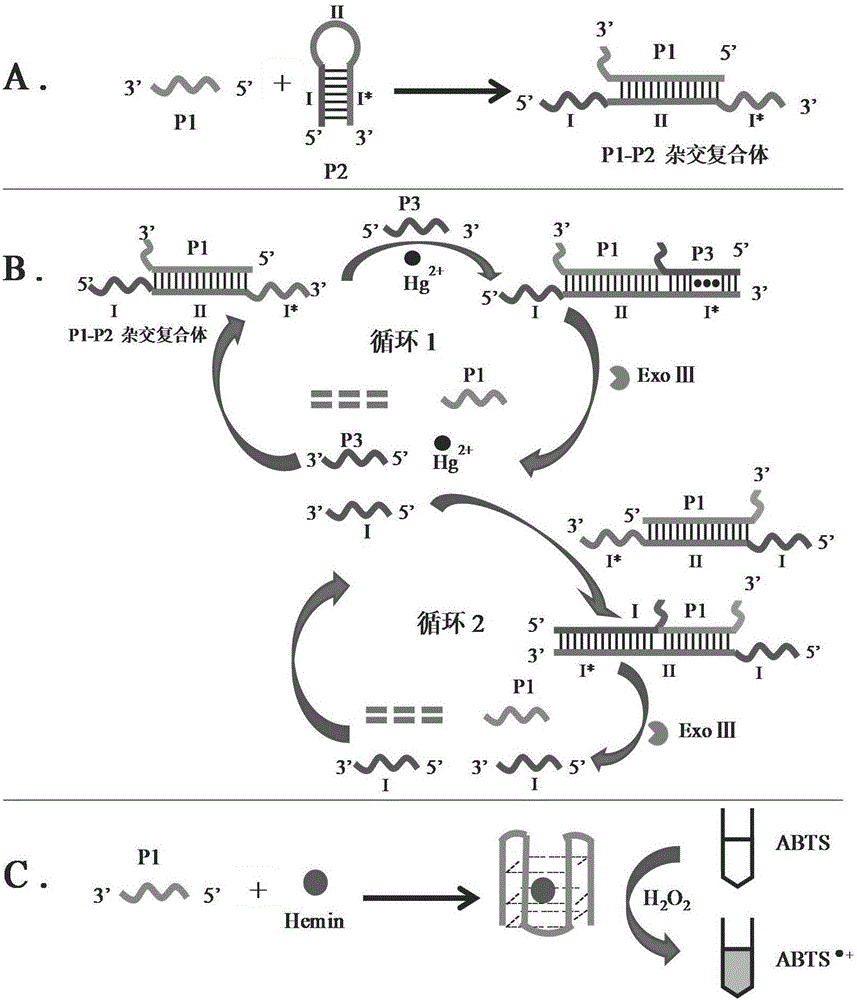
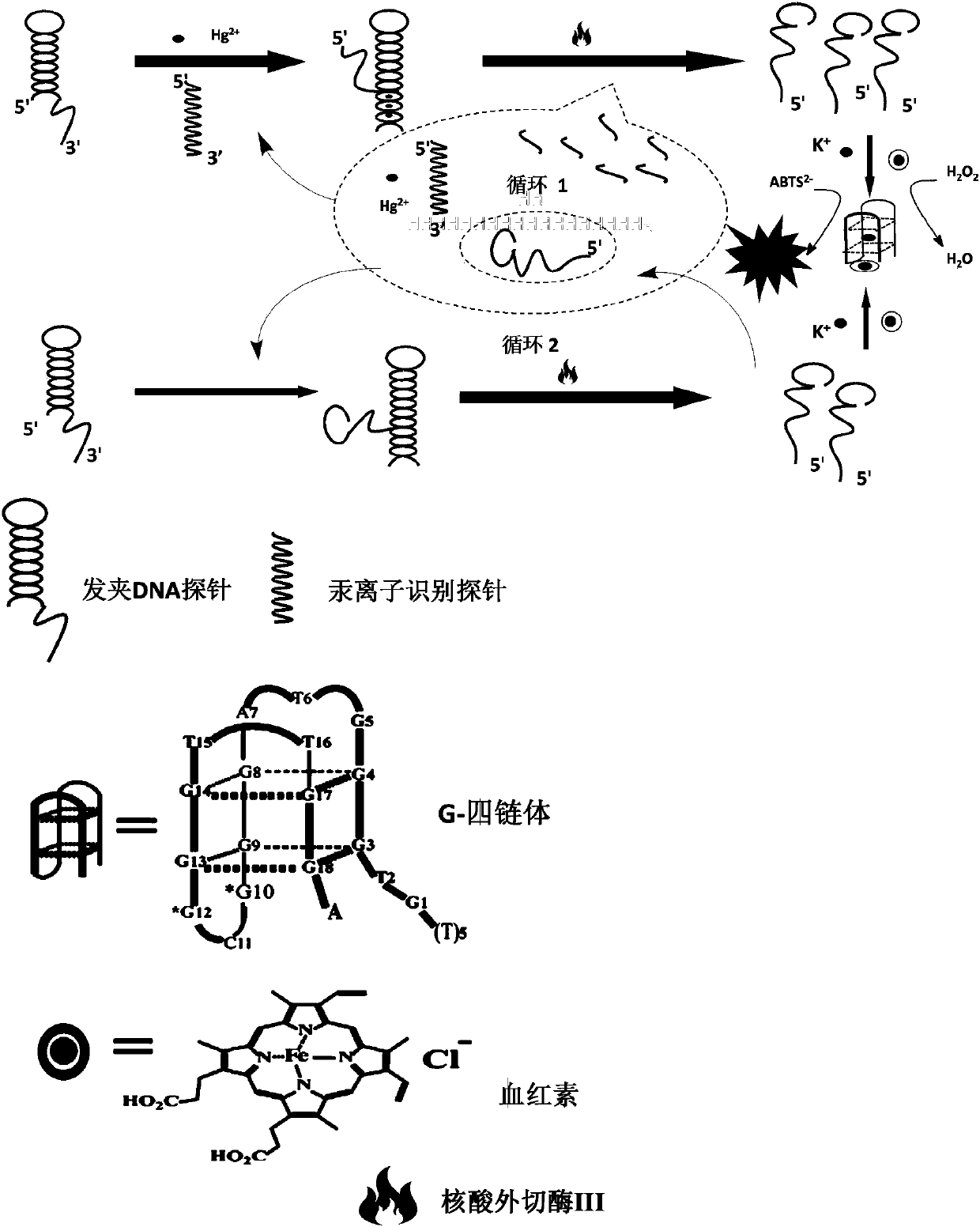
The invention discloses a double-circulation cascade signal amplification DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) combination probe composition on the basis of exonuclease III assistance. The double-circulation cascade signal amplification DNA combination probe composition comprises a triggering DNA probe, a hairpin DNA probe, a mercury ion recognition probe and exonuclease III. The triggering DNA probe contains sequences formed by G-quadruplex; a 3' end and a 5' end of the hairpin DNA probe are complementary to each other to form a stem-shaped zone, and sequences of an annular zone are complementary to the triggering DNA probe. A large quantity of G-quadruplex DNA probes can be generated in two spontaneous circulation procedures after a small quantity of Hg2+ is triggered, and are bound with heme to generate G-quadruplex-heme DNA enzymes, ABTS-H2O2 reaction can be catalyzed, and light green ABTS+ which can be visually observed or can be measured by the aid of spectrophotometry processes can be generated; a method for preparing the double-circulation cascade signal amplification DNA combination probe composition is extremely high in sensitivity and specificity, high in detection speed, easy to implement and suitable to be developed to obtain environmental monitoring field real-time analysis technologies; the double-circulation cascade signal amplification DNA combination probe composition is particularly suitable for environments where diversified heavy metal ions are simultaneously available and is applicable to Hg ion monitoring environments when diversified metal pollutants are available.
Owner:HUNAN INSTITUTE OF ENGINEERING
Application and seamless cloning method of DNA exonuclease
PendingCN107760706AImprove digestion efficiencyFlexible site selectionVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliHomologous sequence
The invention provides application of DNA exonuclease to DNA recombinant seamless cloning and provides a kit capable of being used for DNA recombinant seamless cloning. The DNA exonuclease is T5 exonuclease, T7 exonuclease, exonuclease III or Lambda exonuclease or a mixture thereof. The invention further provides a seamless cloning method applying the DNA exonuclease, which comprises the followingsteps: linearizing a vector through a PCR method or restriction endonuclease digestion; introducing homologous sequences that are respectively homologous to the two ends of the vector at the two endsof a target gene fragment through PCR to obtain an amplified target gene fragment; after the treated target fragment and the treated linearized vector are mixed, adding the DNA exonuclease and a reaction solution for temperature bath to obtain a vector and fragment mixture; converting an echerichia coli receptive cell by using the obtained vector and fragment mixture. The application and the method provided by the invention have the following advantages that the site selection can be flexibly performed, and the gene cloning can be performed in any position of the vector; the vector construction can be quickly, simply and conveniently completed within 10 minutes; meanwhile, the cloning is accurate and efficient.
Owner:NOVOPROTEIN SCI INC
Detection of transcription factor protein by double chain RNA molecule with special labeling fixed to micro-plate coated by exonuclease III
InactiveCN1721547ALimit commercializationHigh Throughput Analysis CapabilitiesMicrobiological testing/measurementRegulation of gene expressionTissue extracts
Transcription factor is one important protein for gene regulation, is center of gene expression regulating passage and network, is important target of functional genome and protein block research and important target site of transcription treatment and medicine research. The present invention proposes exonuclease III digesting double stranded nucleic acid molecule coated in microporous plate and containing special marker to detect transcription factor protein. The process of analyzing transcription factor expression and activation level includes the following steps: preparing nucleic acid; fixing the nucleic acid molecules to the pores of the microporous plate; incubation of cell or tissue extract containing transcription factor in the plate; incubation of exonuclease III reaction liquid in the plate; incubation of specific conjugate with special marker on nucleic acid on the plate; detecting and analyzing the specific conjugate to obtain the expression and activation level.
Owner:王进科 +1
Mercury ion detection probe group based on exonuclease III, kit and mercury ion detection method
ActiveCN107586827AAchieve ultra-high sensitivity detectionAchieving Sensitive DetectionMicrobiological testing/measurementExonuclease IIIUrine sample
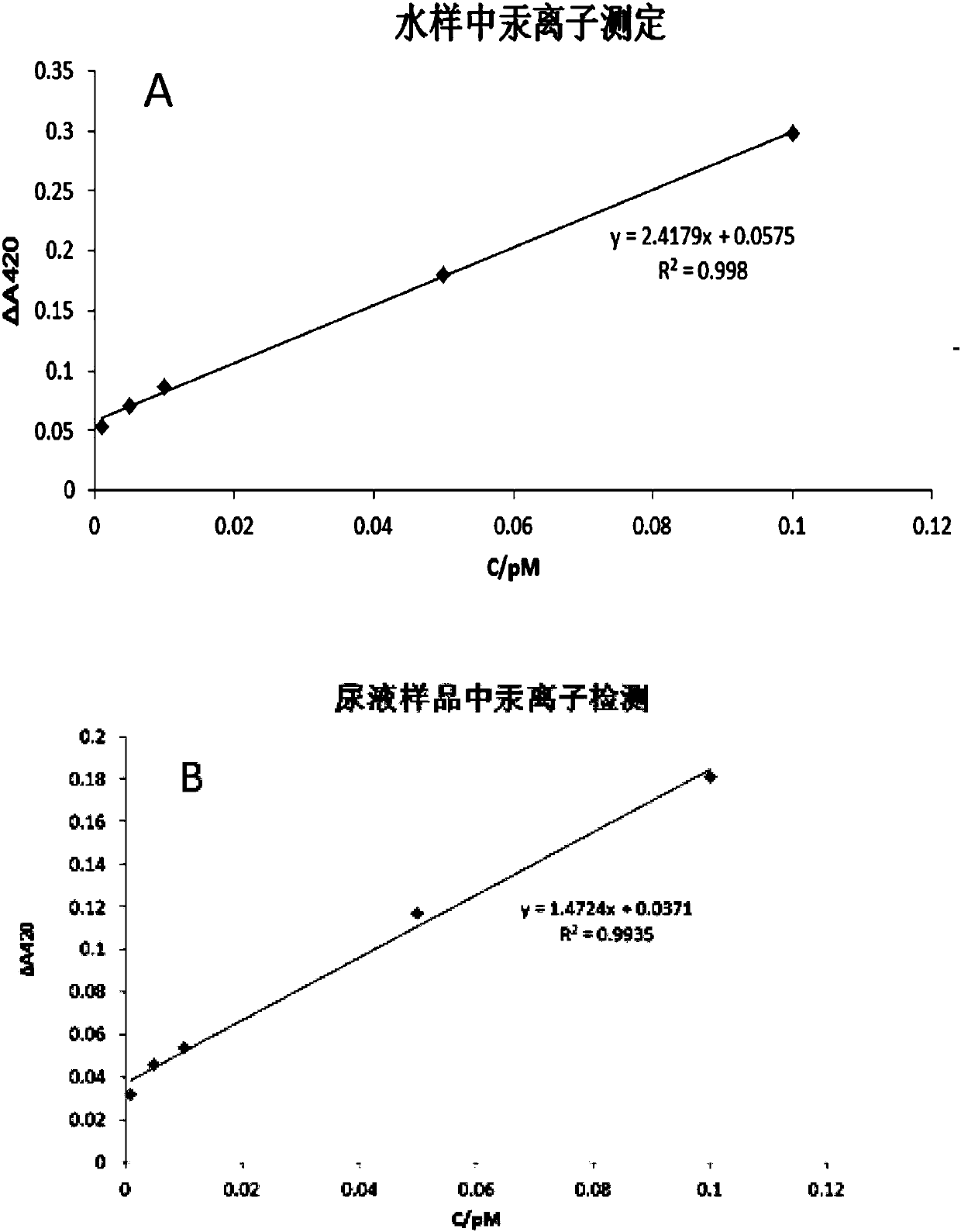
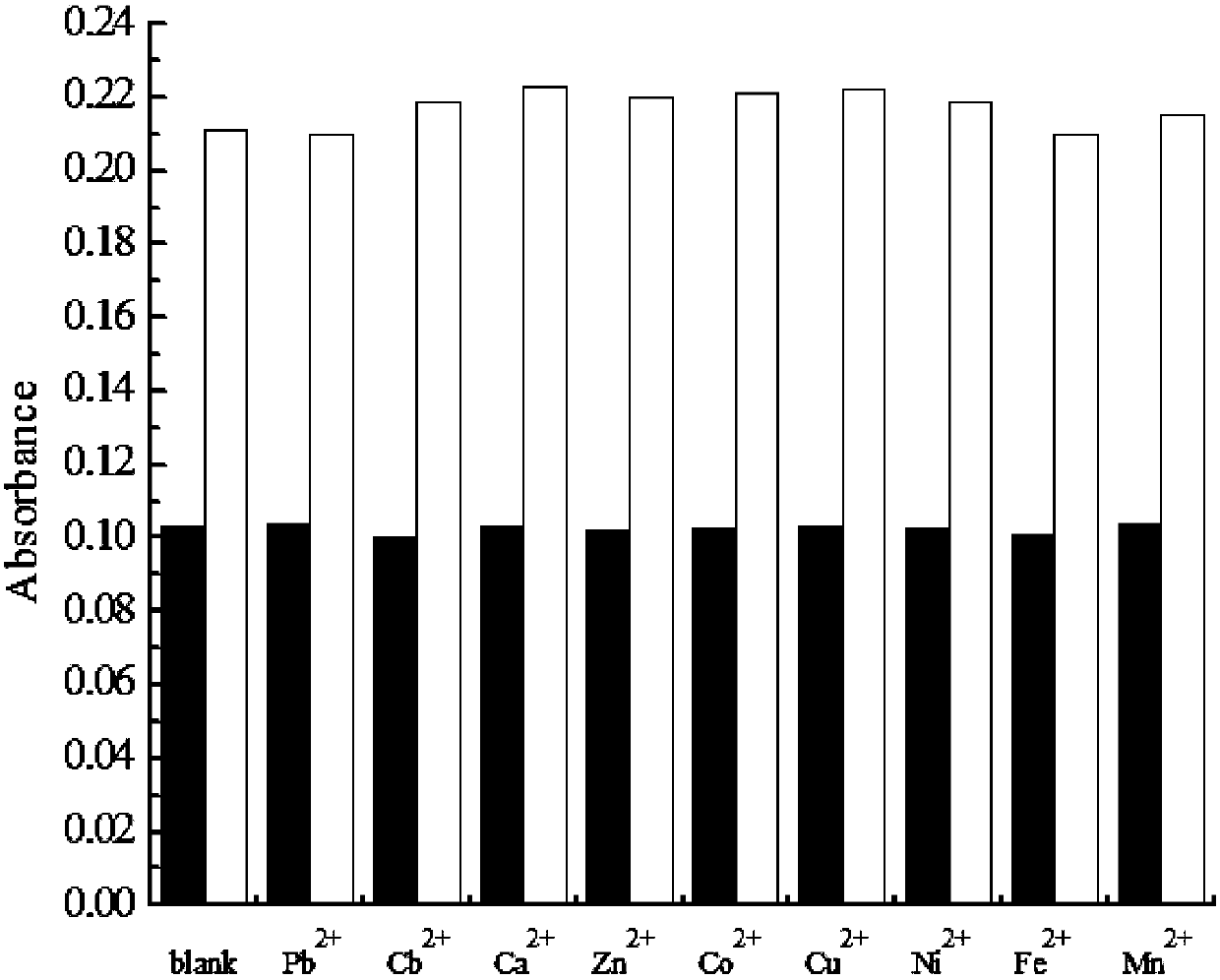
The invention relates to a mercury ion detection probe group based on exonuclease III, a kit and a mercury ion detection method and belongs to the technical field of heavy metal detection. The mercuryion detection probe group based on the exonuclease III, provided by the invention, comprises a hairpin DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) probe and a mercury ion recognition probe. The probe group and the kit, provided by the invention, can realize ultrahigh-sensitivity detection of mercury ions in a water body sample and a urine sample, have strong specificity and high stability and are not influencedby other metal ions.
Owner:HUNAN INSTITUTE OF ENGINEERING
Novel exonuclease-III-based mercury ion detection method
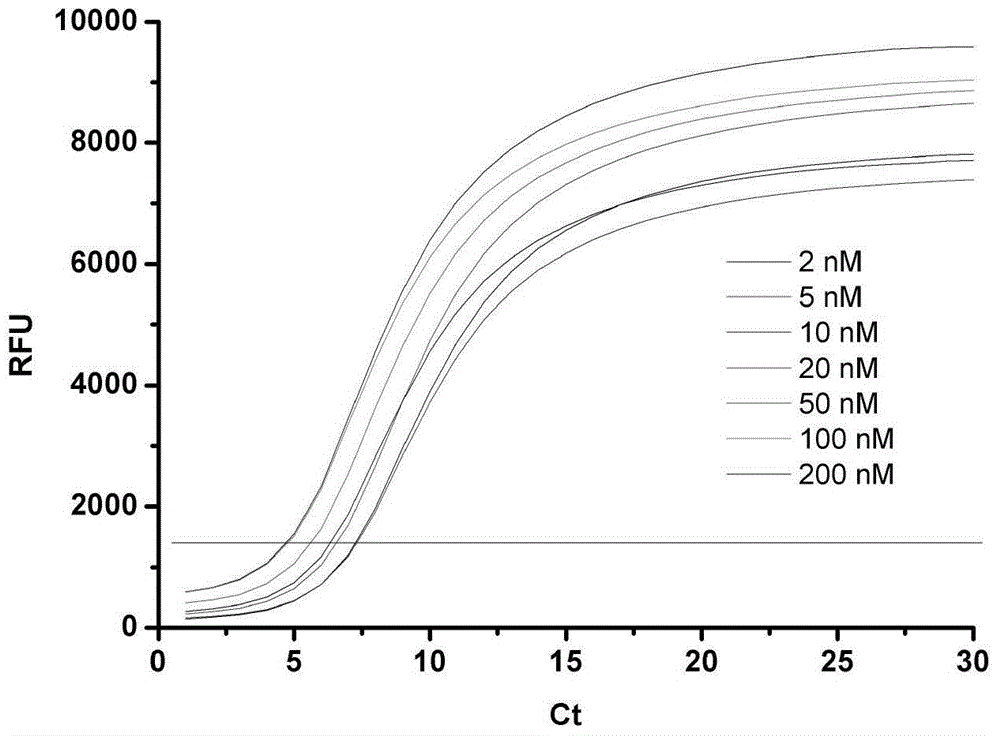
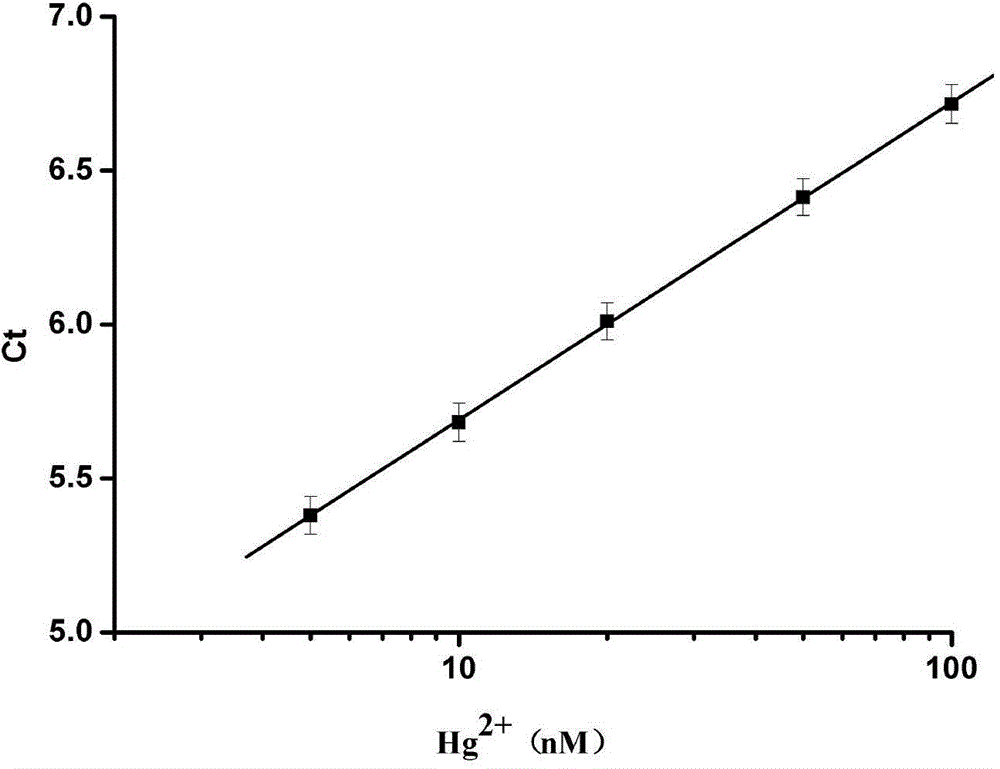
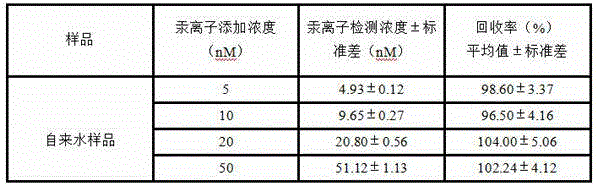
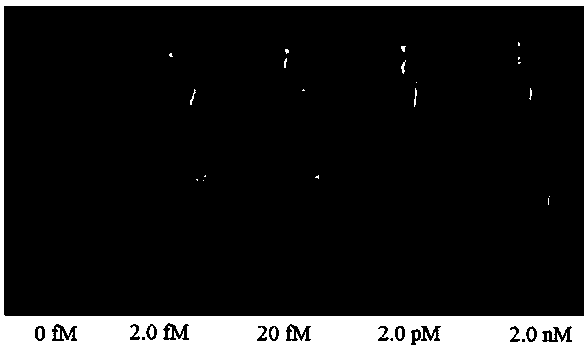
The invention relates to a novel exonuclease-III-based mercury ion detection method which comprises the following steps: (1) mixing two DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) segments, which can specifically recognize mercury ions and contain rich T bases, with a sample to be detected so that the two DNA segments are combined into a 3'-terminal closed double-chain DNA under the action of Hg<2+> in the sample to be detected; (2) carrying out enzyme digestion on the double-chain DNA by using exonuclease III; (3) carrying out fluorescent quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification on the rest DNA segments which are not subjected to enzyme digestion; and (4) determining the Hg<2+> concentration according to the fluorescent detection result. The invention designs a mercury ion biosensor which is used for implementing simple quick high-sensitivity detection on the mercury ions in water.
Owner:CHANGSHU INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Visual colorimetric sensor for detecting mercury ions
ActiveCN107941797ASimple and fast operationLow costMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorEnzyme digestionEnvironment water
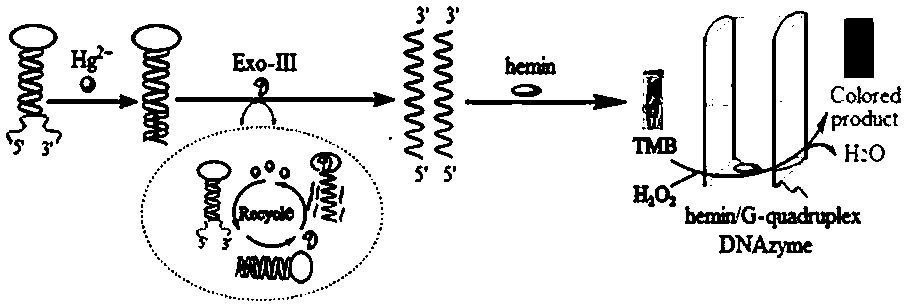
The invention provides a visual colorimetric sensor for detecting mercury ions. An H-DNA (Hinge-Deoxyribonucleic Acid) with a special hairpin structure is designed; in the presence of the mercury ions, a 3' end and a 5' end of the H-DNA are complementary and paired through a T-Hg<2+>-T structure, so that a stem part of the H-DNA is completely complementary and exonuclease III is triggered to shearthe stem part, and then more and more single-stranded DNAs containing rich guanine are generated; released Hg<2+> also reacts with the H-DNA to trigger enzyme digestion reaction; the cycle is carriedout so that the H-DNA is continuously sheared and more and more single-stranded DNAs containing G are generated; in the presence of hematin chloride, a DNA catalyzing enzyme is formed, and 3,3',5,5'-tetramethylbenzidine is catalyzed to react with H2O2, so that a blue product is generated and the mercury ions are visibly detected. The method provided by the invention is simple to operate, low in cost and short in time, can be used for rapidly and visibly detecting the content of the mercury ions in an environment water sample and is hopefully applied to detection of mercury in the environmentwater sample.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Fluorescent biosensor for detecting triphosadenine and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109470673ARealize highly sensitive detectionLow detection limitFluorescence/phosphorescenceExonuclease IExonuclease III
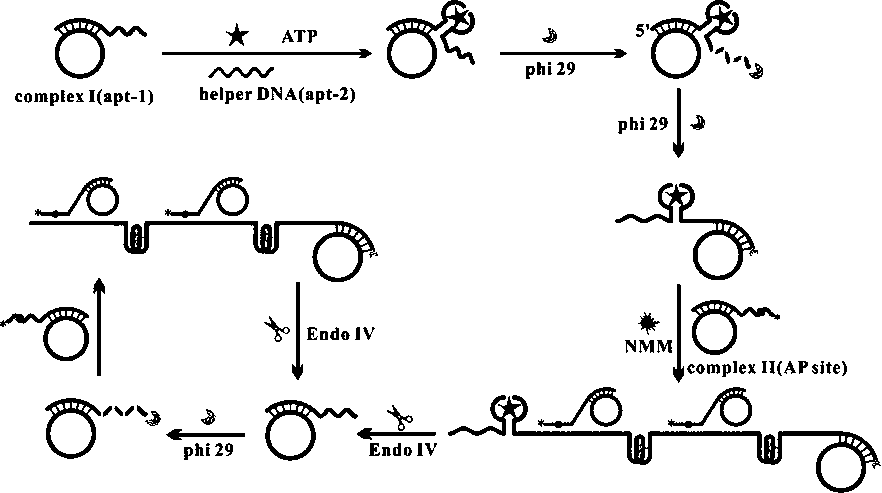
The invention relates to the technical field of biosensors, in particular to a fluorescent biosensor for detecting triphosadenine based on rolling circle amplification and incision enzyme feedback amplification. The biosensor comprises two aptamer DNA sequences, a linear padlock probe, a connecting probe, an AP probe, a T4 DNA ligase buffer solution, exonuclease I, exonuclease III, a PBS buffer solution, dNTP, phi29 DNA polymerase and endonuclease IV. A preparation method of the fluorescent biosensor comprises the following steps: (1) constructing an annular template to prepare a compound probe; and (2) combining a compound probe with an incision enzyme and a target object to achieve signal amplification. The probe can be used for achieving detection of high specificity and ultra-sensitivity. The fluorescent biosensor is mild in reaction, fast to detect and good in repeatability.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Method for separating antibiotic peptide and separated antibiotic peptide
InactiveCN1557960AEfficient separationHigh antibacterial activityFermentationHybrid peptidesEscherichia coliLiquid medium
The invention relates to a method of isolating antibacterial peptides and the isolated peptides thereof. The method comprises: constructing a fusion DNA sequence of yeast alpha mating factor leader sequence and a random peptide, inserting the sequence into a saccharomyces cerevisiae vector which contains an inducible promotor, digesting the unlinked linear DNA with exonuclease III and mungbean sprout nuclease, electrotransforming the yeast vector after purification, culturing the transformant 24h and covering the transformant with the upper medium which contains E. coli K12D31, and detecting the bacterial inhibition ring and the bacterial inhibition rate after inducing the expression by liquid medium, selecting the positive clones and amplifying by PCR, and determining the sequence. The method of the present invention can be used easily and effectively to isolate antibacterial oligopeptides and polypeptides and can be used as an alternative way to find antibiotics.
Owner:刘秋云 +1
Exonuclease III/I protection analysis based fluorescent biosensor method for detecting single nucleotide polymorphism
InactiveCN101705292AReduce dosageRapid automation implementationMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceDiseasePrenatal diagnosis
The invention discloses an exonuclease protection analysis based fluorescent biosensor method for detecting single nucleotide polymorphism, which comprises allele-specific extension of micromolecule modified single nucleotide, interaction between an oligonucleotide DNA strand primer with micromolecules after extension and binding protein, protection analysis of the exonuclease III / I and fluorescent quantitative detection of a hairpin type oligonucleotide DNA probe primer subjected to end protection based on double-strand indicating dye. The method adopts allele-specific extension of the primer to combine the micromolecule modified single nucleotide at 3' end of a specific primer and then combine the specificity of the binding protein of the micromolecule to protect the primer from being degraded by the exonuclease III / I, and detects single nucleotide polymorphism genotyping through fluorescence of the complex of the protected oligonucleotide DNA primer and double-strand inserting dye. The method features simple and convenient operation, economy, fast speed, sensitivity and strong specificity and is expected to provide a universal technology platform for screening and prenatal diagnosis of the population suffering from gene mutation related genetic diseases.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Fluorescence detection kit based on aptamer
ActiveCN107870242AEasy to prepareEasy to storeBiological material analysisBiological testingAptamerWater source
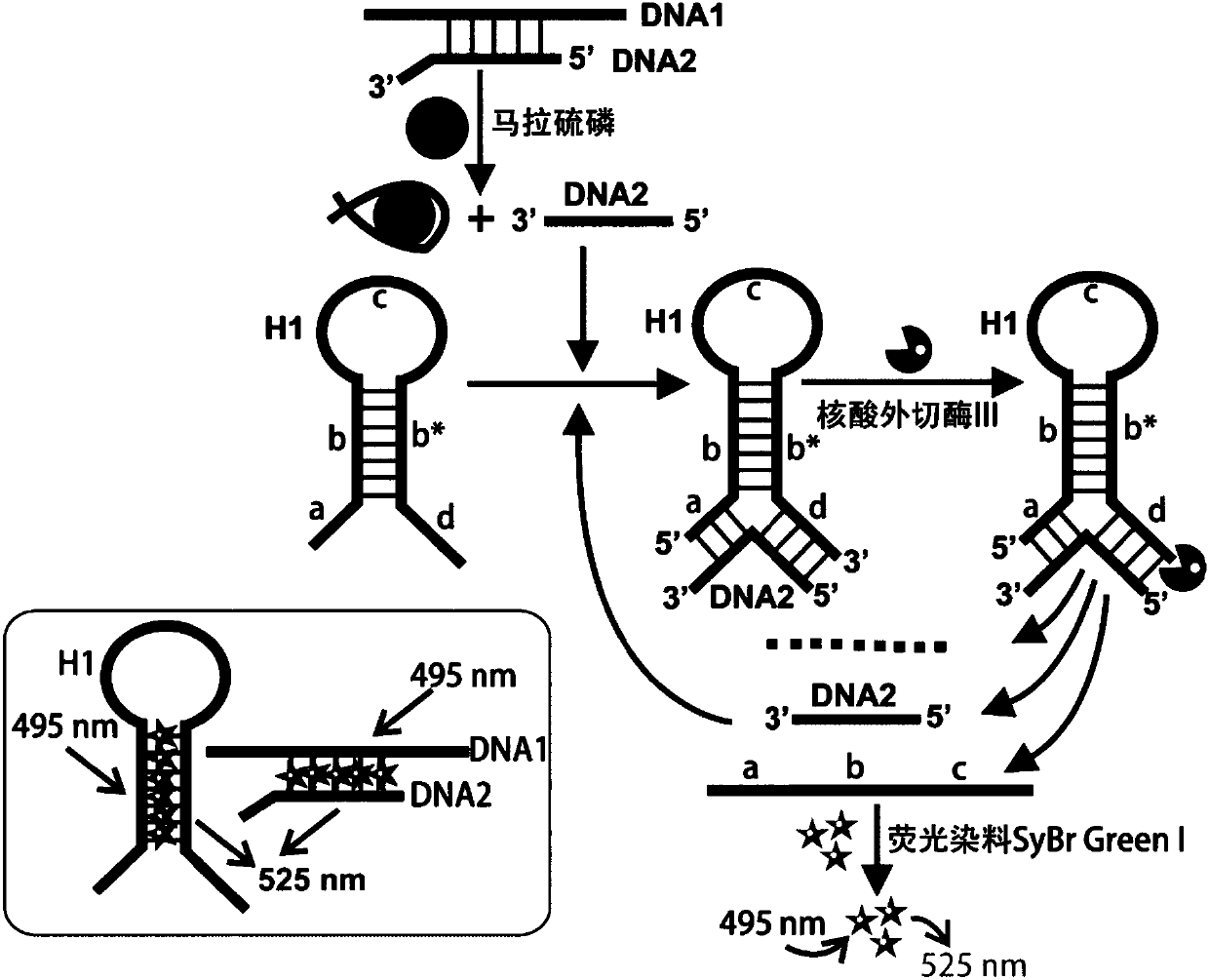
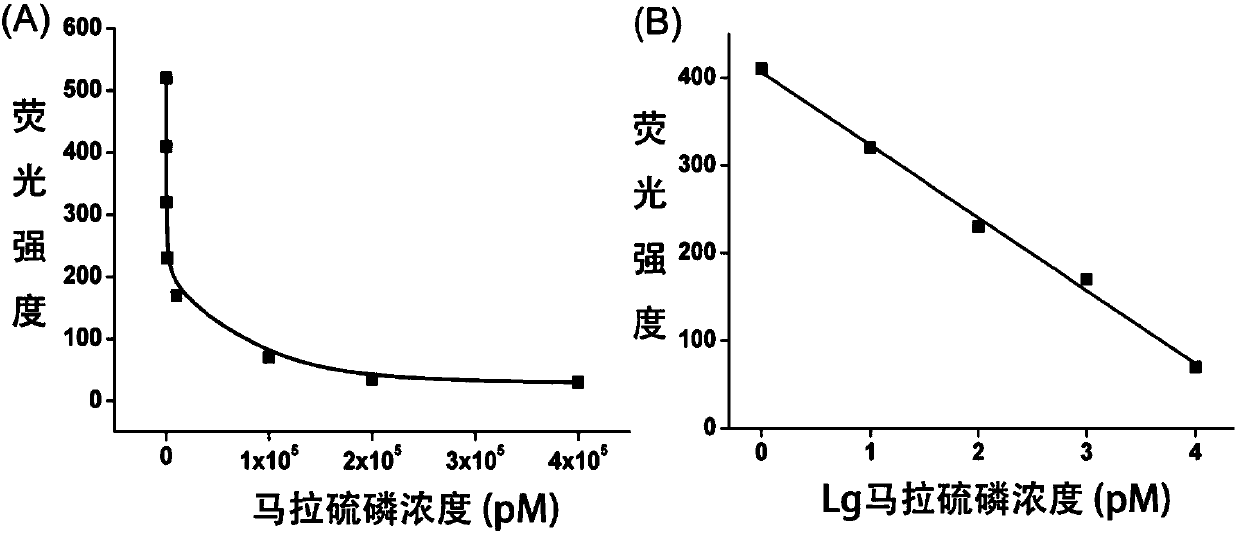
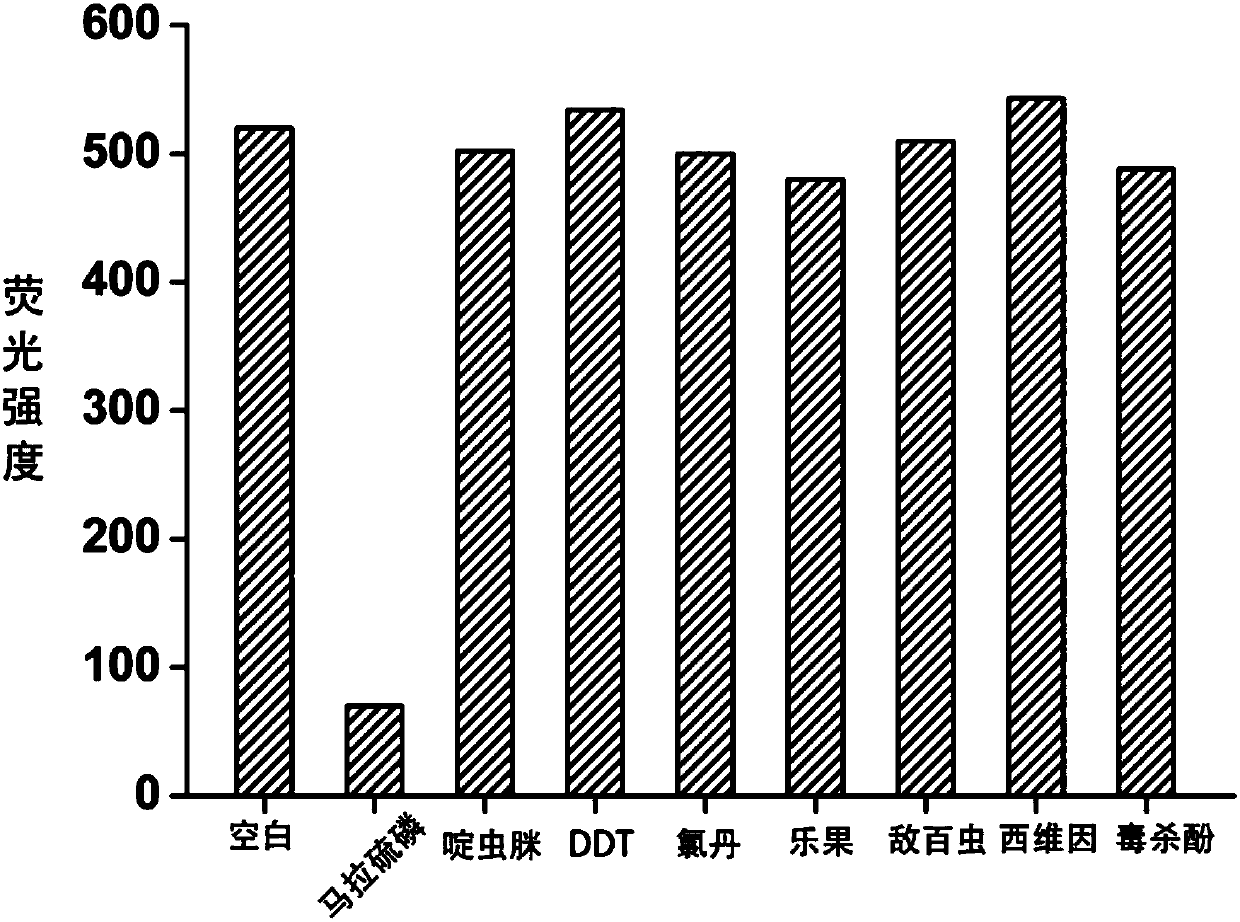
The invention discloses a fluorescence detection kit based on an aptamer. The fluorescence detection kit comprises exonuclease III, a reaction buffer solution, DNA1, DNA2 and stem-loop structure nucleic acid H1. The aptamer is used for specific recognition of a molecular recognition element, a 3' double-chain nucleic acid structure with a flush end is obtained, and circular signal amplification isperformed after exonuclease III is added, so that a large amount of double-chain DNA become single-chain DNA; after fluorescent dye is added, the content of to-be-detected molecules is detected by distinguishing fluorescence intensity change. The linear range for malathion detection is 10 pM to 100 nM, and the limit of detection is 5 pM; meanwhile, the detection system has good specificity and the detection results cannot be interfered by other common analogues. No separation and purification processes are required in the detection process, the kit can be used for detection after simple mixing, has the advantages of being simple to operate, low in cost, rapid in response and the like and can be used for rapid and high-sensitivity detection of pesticide residues in food, water sources, soil and other samples.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF ECO ENVIRONMENT & SOIL SCI
Positive feedback amplification electrochemical sensor based on exonuclease (Exo) III
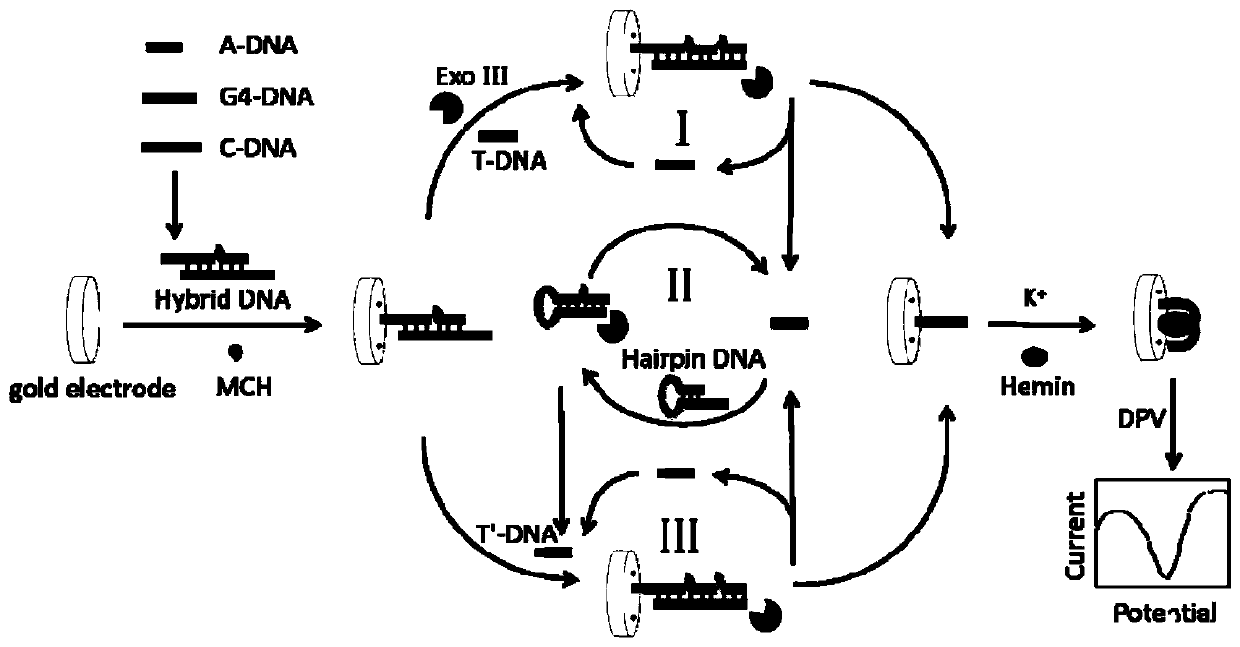
ActiveCN109738503AHigh selectivityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial electrochemical variablesExonuclease IC-DNA
The invention discloses a positive feedback amplification electrochemical sensor based on exonuclease (Exo) III. The positive feedback amplification electrochemical sensor comprises a gold electrode and Hybrid DNA fixed to the gold electrode; the Hybrid DNA sequentially comprises a sulfur-hydrogen bond, a double-stranded DNA structure and a single-stranded DNA structure from the 5' end to the 3' end; the double-stranded DNA structure is prepared from C-DNA and A-DNA as well as G4-DNA which are hybridized; the basic group sequence of the single-stranded DNA structure is complementary with the basic group sequence of T-DNA; and the Hybrid DNA is fixed to the gold electrode through an S-Au key. Through Hairpin DNA and the Hybrid DNA which are ingeniously designed, and target object circular amplification based on the Exo III, a positive feedback amplification strategy combining a homogeneous phase reaction with a heterogeneous phase reaction is achieved; and the strategy shows ultra-highsensitivity, the detection limit is as low as 0.12 aM T-DNA, and high selectivity for the T-DNA and other base group mismatch DNA is achieved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) methylation detection kit and application method thereof
InactiveCN108018336AHigh sensitivityHigh detection sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA methylationPotassium
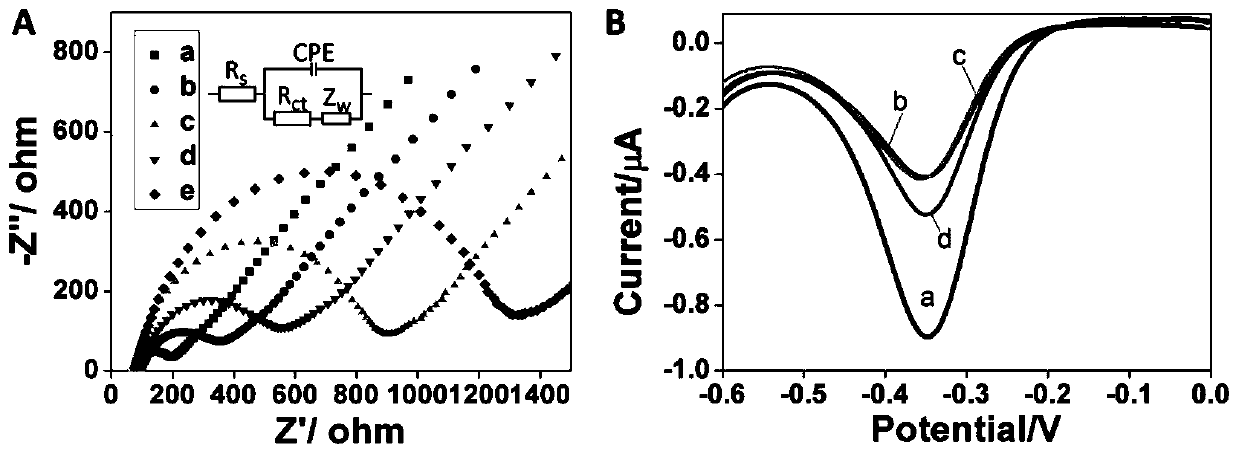
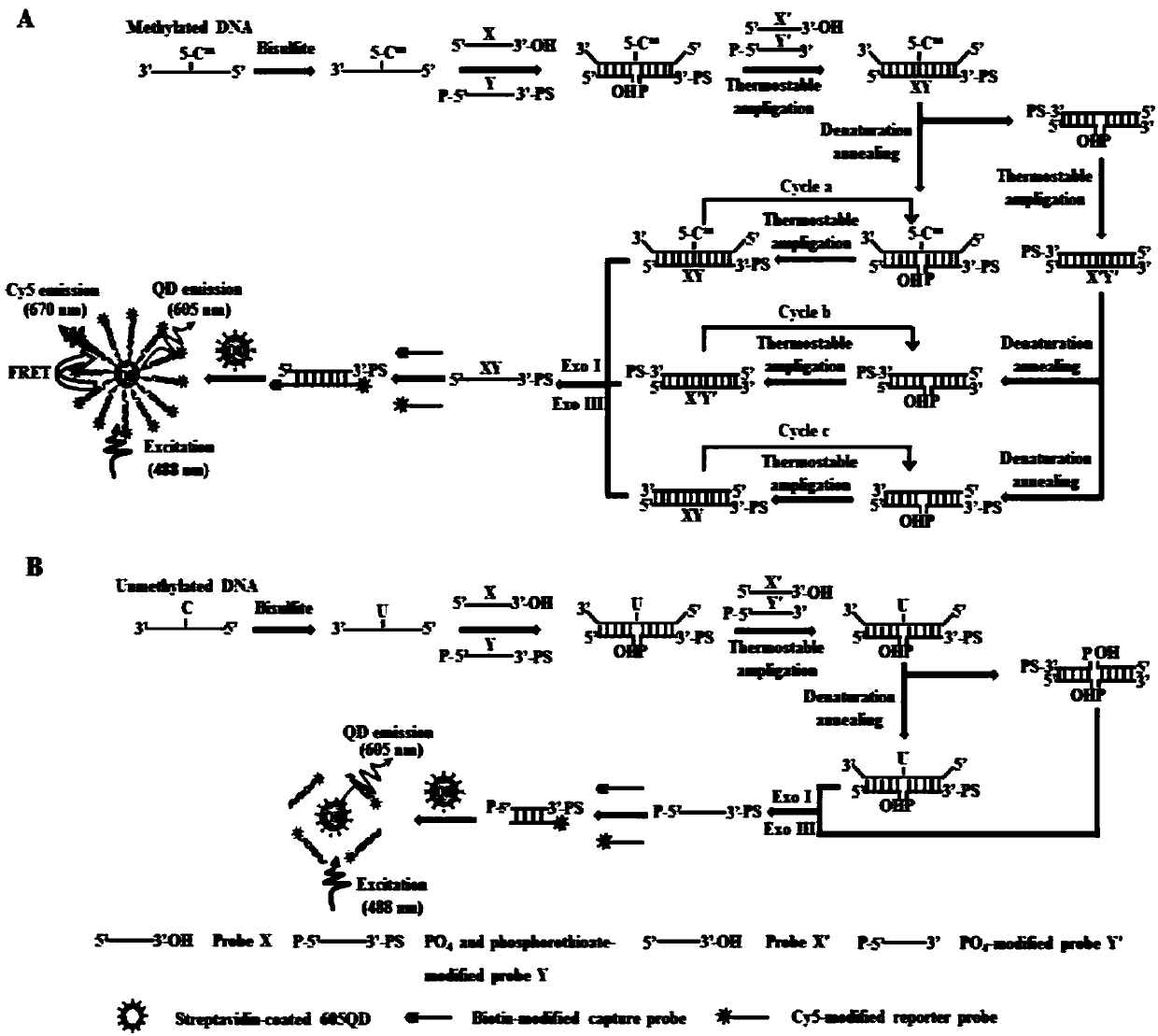
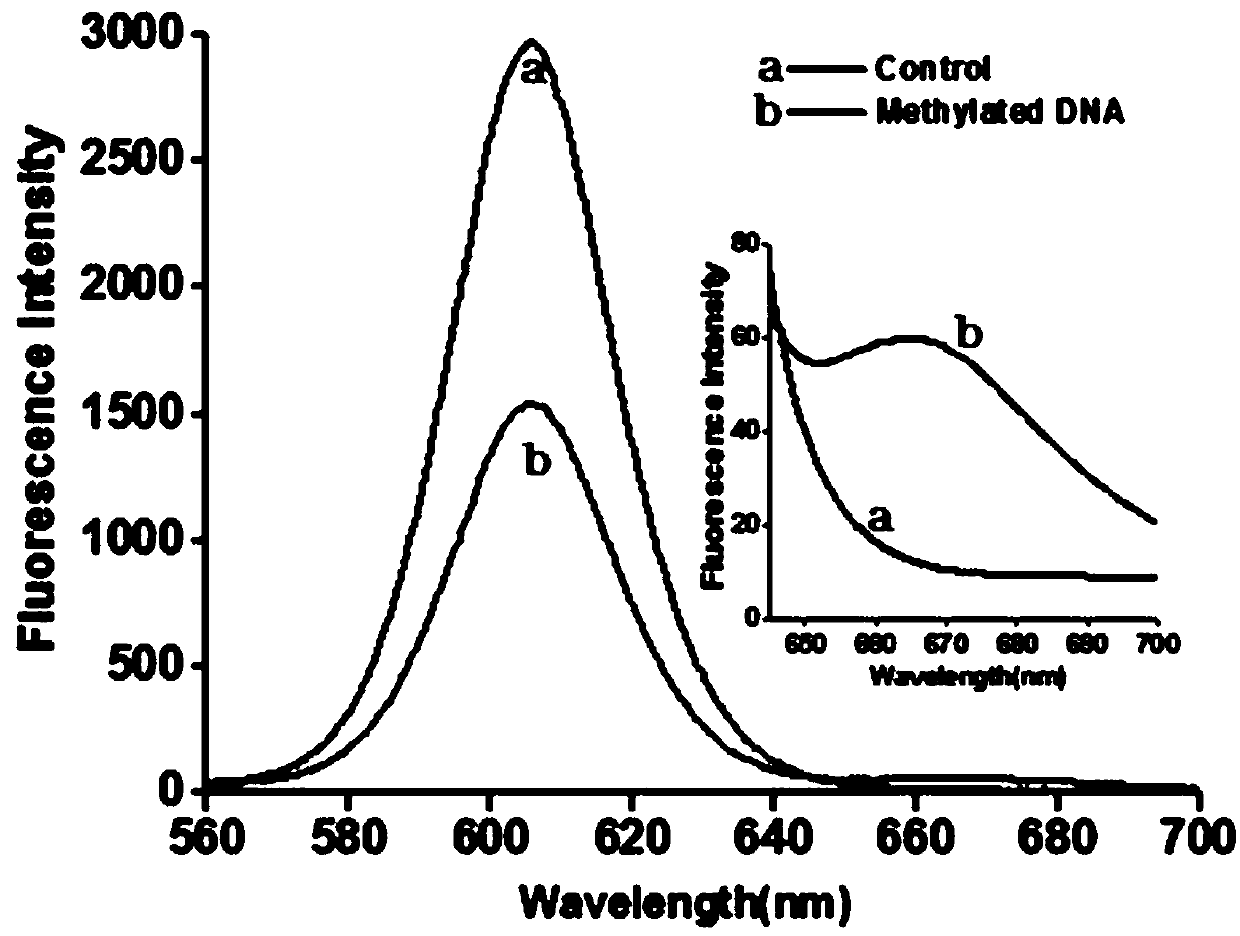
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological analysis and in particular relates to a DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) methylation detection kit and an application method thereof. The kit is prepared from sodium bisulfite, hydroquinone, a desalting column, 0.3mol / L sodium hydroxide, ammonium acetate, ethanol, triaminomethane hydrochloride, potassium chloride, magnesium chloride, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, polyethylene glycol octylphenol ether, a probe X, a probe Y, a probe X', a probe Y', exonuclease I, exonuclease III, 10*NEBuffer I, ammonium sulfate, a Cy5-labeled reporter probe, a biotin-labeled capturing probe, thermal stabilization ligase and a 605 quantum point. The kit provided by the invention has the advantages of high sensitivity, strong high specificity and simple operation and DNA methylation detection can be carried out on cytosine / guanine dinucleotide (CpG) and non-cytosine / guanine dinucleotide (CpG) sites.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
Electrochemical sensor for detecting telomerase activity and detection method thereof
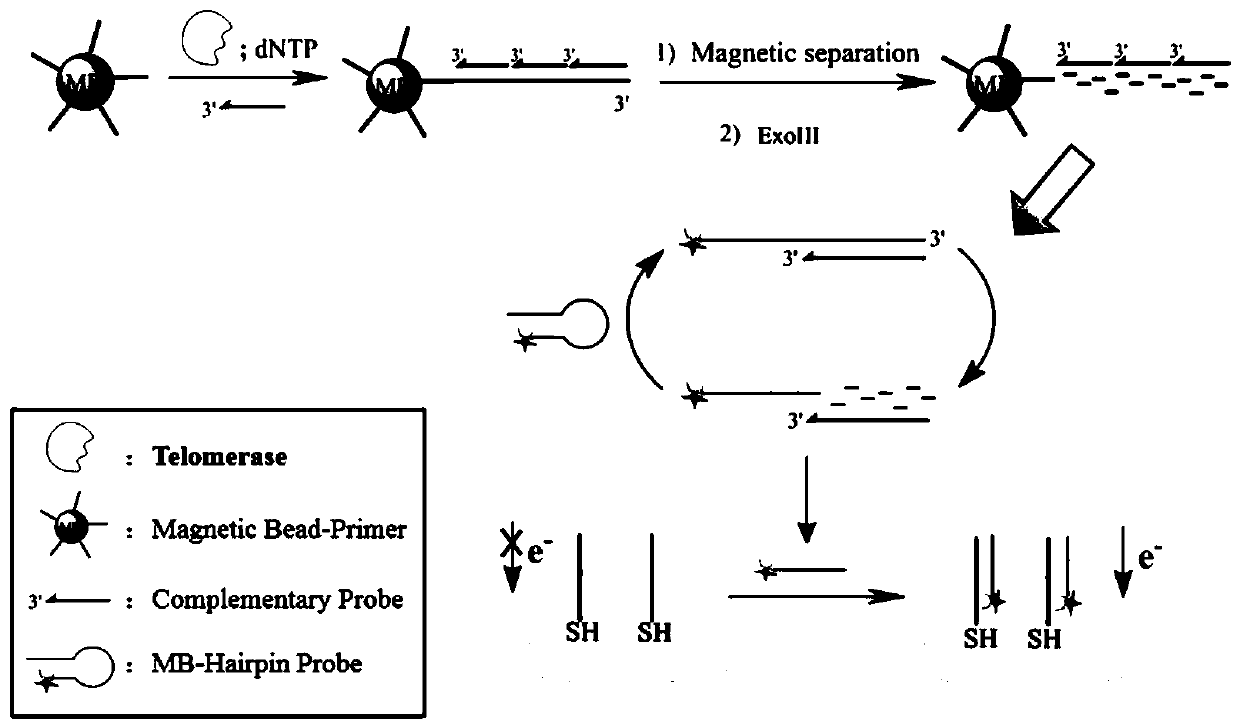
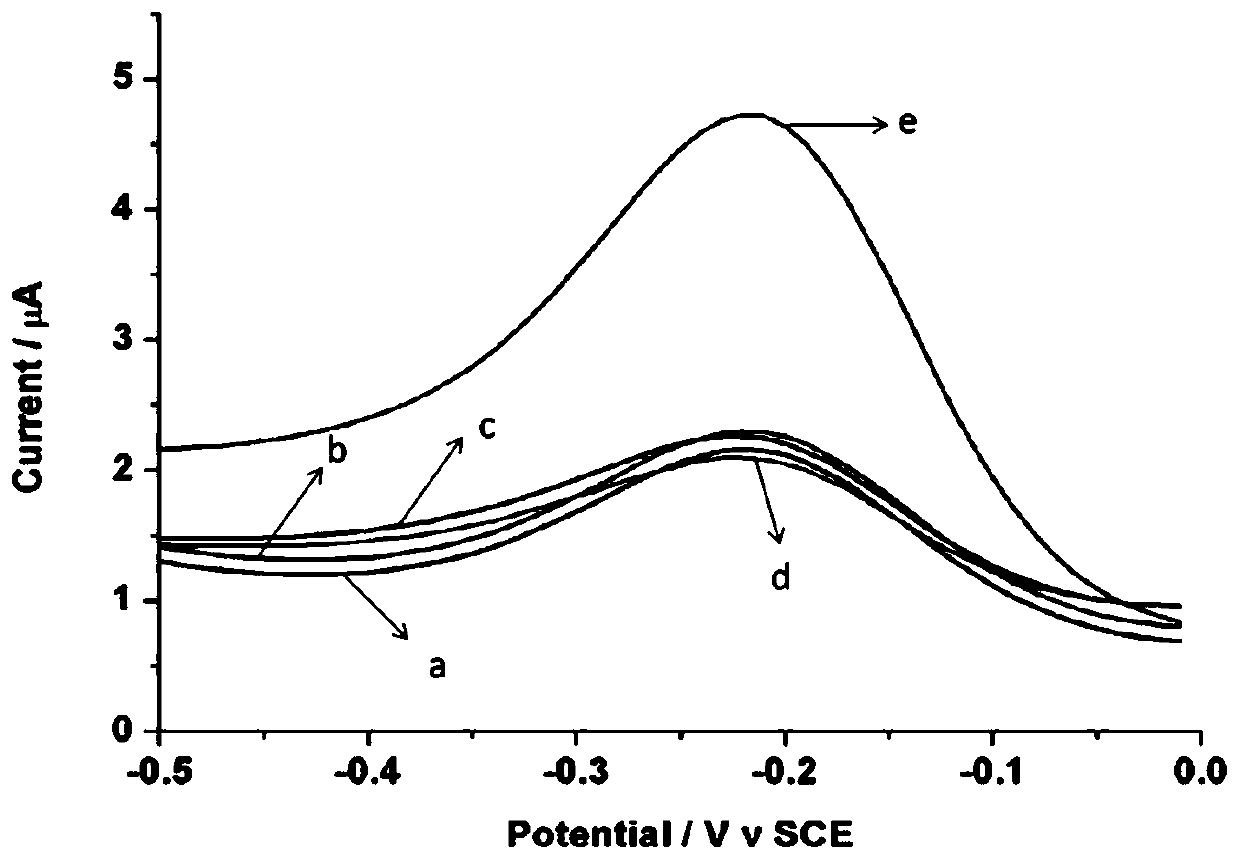
ActiveCN110243905AAvoid steric hindranceIncrease contactMaterial electrochemical variablesTelomeraseMagnetic bead
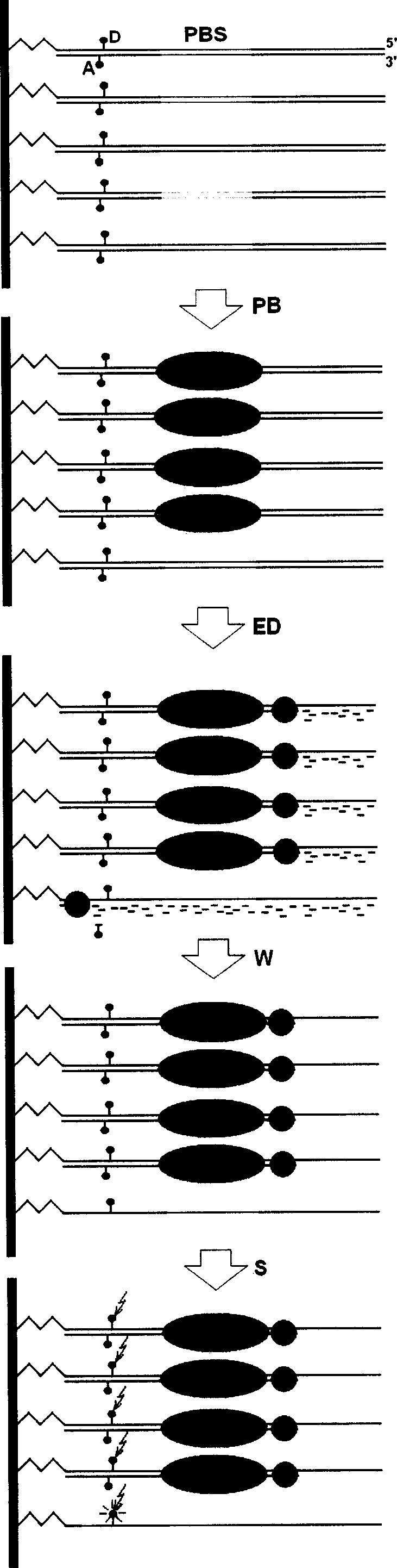
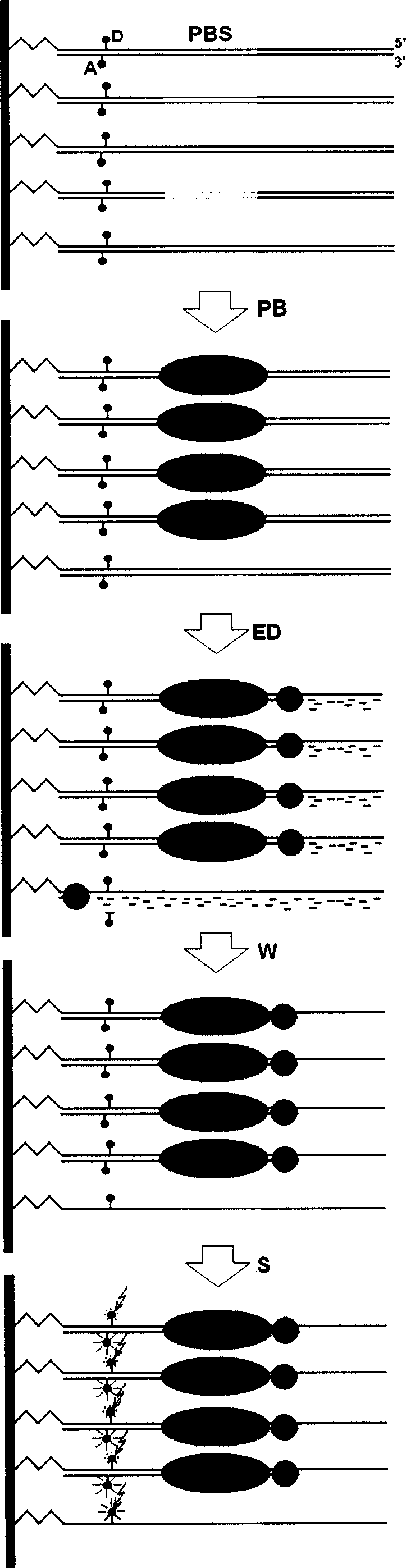
The invention provides an electrochemical sensor for detecting telomerase activity and a detection method thereof which are constructed based on functionalized nanometer magnetic beads and an exonuclease III-assisted amplification strategy, and the detection of the telomerase activity of the tumor cells is realized. In the invention, complementary probes can be hybridized with an extended telomerase primer repeated sequence, a hybrid is separated by the magnetic beads, a telomerase primer repeated sequence chain is identified and degraded by exonuclease III, a plurality of methylene blue marked hairpin DNA probes can be hybridized and opened by the released complementary probes, after the secondary degradation of the exonuclease III, the complementary probes can enter the next cycle of hybridization with an MB-marked hairpin-like structure, and the MB-marked probe is combined with a capture probe on the surface of a gold electrode, so that a peak current value which is in direct proportion to the telomerase activity is generated. According to the electrochemical sensor and the detection method thereof, the telomerase activity can be detected at a single-cell level.
Owner:THE SECOND HOSPITAL OF NANJING +1
Target protein-induced deoxyribonuclease (DNase) cycle generation-based homogeneous immunoassay method
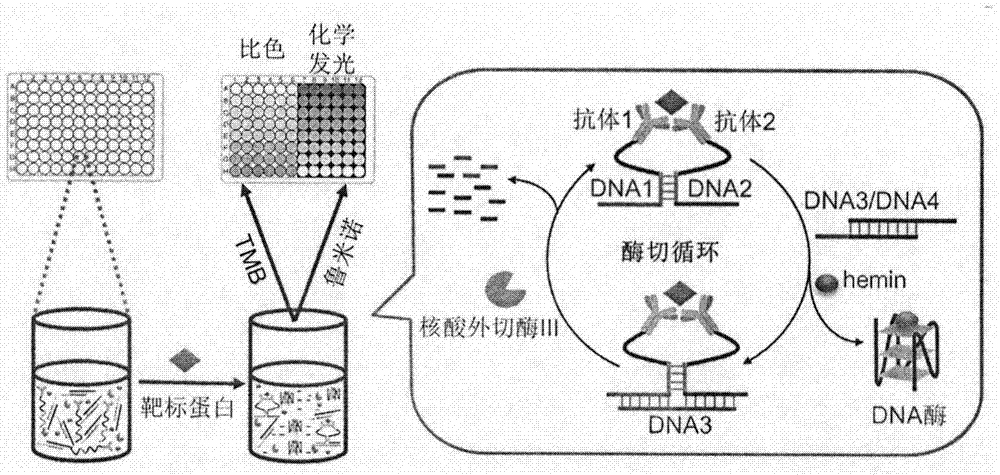
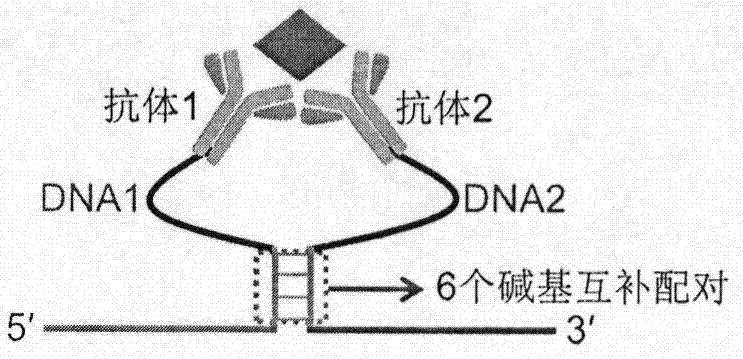
ActiveCN106980022AA New Simple Homogeneous Immunoassay MethodEasy to operateBiological testingAgainst vector-borne diseasesProtein targetHemin
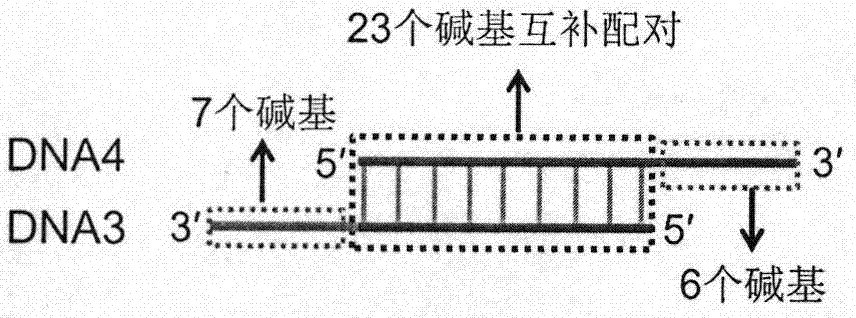
The invention relates to a target protein-induced deoxyribonuclease (DNase) cycle generation-based homogeneous immunoassay method. A detection solution of the immunoassay method is prepared from an antibody 1-DNA1 conjugate, an antibody 2-DNA2 conjugate, hemin, exonuclease III and DNA3 / DNA 4 double-stranded DNA. When a target protein exists, the target protein can be immunologically recognized by the antibody 1-DNA1 conjugate and the antibody 2-DNA2 conjugate at the same time; based on an ortho effect, a complex is formed by hybridizing DNA1 and DNA2 and then has a chain substitution reaction with DNA3 on the double-stranded DNA, so that DNA4 rich in a G4 sequence is released and combines with the hemin so as to form G-quadruple chain / hemin DNase; in addition, the DNA3 reacting with the DNA1 and the DNA2 can be recognized and cut by the exonuclease III, so that the DNA1 and the DNA2 can undergo a chain substitution reaction with another DNA3, and another DNA4 is accordingly released to produce DNase; therefore, if repeating in this way, a large amount of DNase can be produced. The DNase can catalyze the color development of tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) and the luminescence of luminol, and can be used for carrying out sensitive quantitative analysis on the target protein by means of color comparisons and chemiluminiscence. The immunoassay method is simple to operate, rapid, sensitive and high in universality, and has a certain clinical application value.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Exonuclease III digesting FRET-dsDNA microarray chip for detecting transcription factor protein
InactiveCN1733934ASolve application problemsEnable high-throughput detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingProtein detectionFluorescence
Disclosed is a transcription factor protein detection method through exonuclease III digestion FRET-dsDNA micro array chips, wherein the expression and activation levels of the transcription factor are analyzed through the following steps: (1) preparing FRET-dsDNA micro array chips, (2) reacting the transcription factor with FRET-dsDNA micro array chips, (2) reacting the exonuclease III with FRET-dsDNA micro array chips, (1) proceeding detection and analysis to the FRET-dsDNA micro array chips.
Owner:王进科 +1
Method for flexibly detecting DNA through exonuclease III assisted multiple circulation amplification
InactiveCN109706224ASimple designLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseConjugated protein
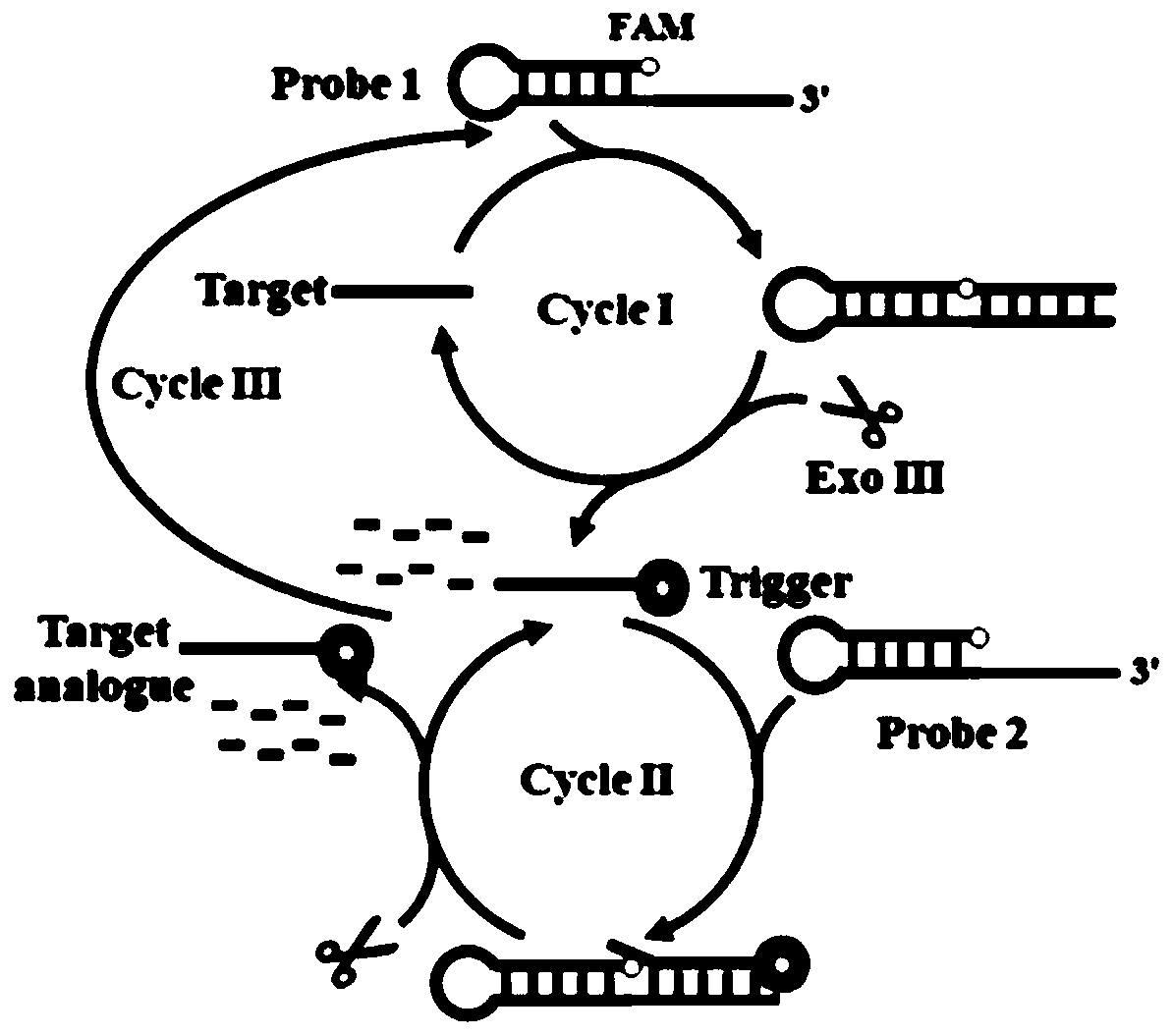
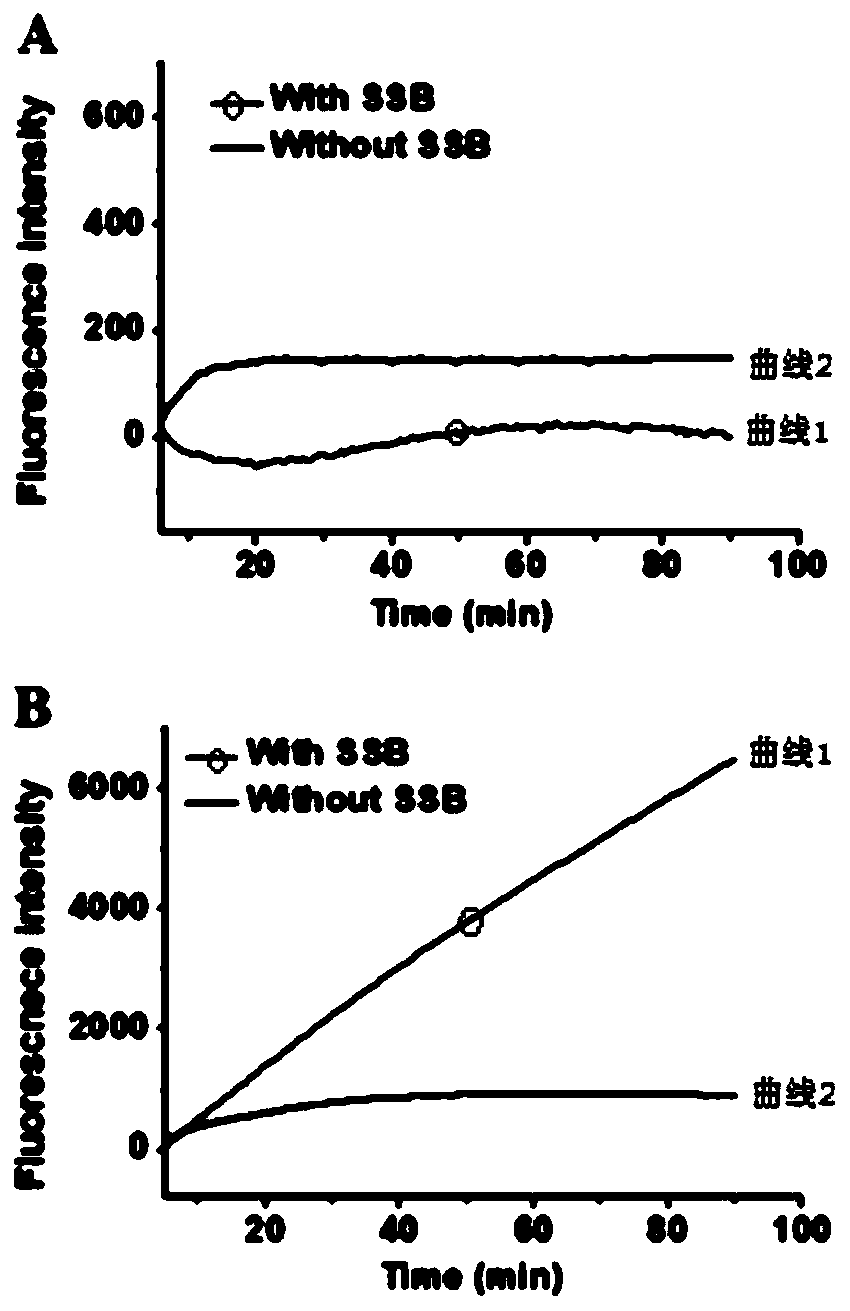
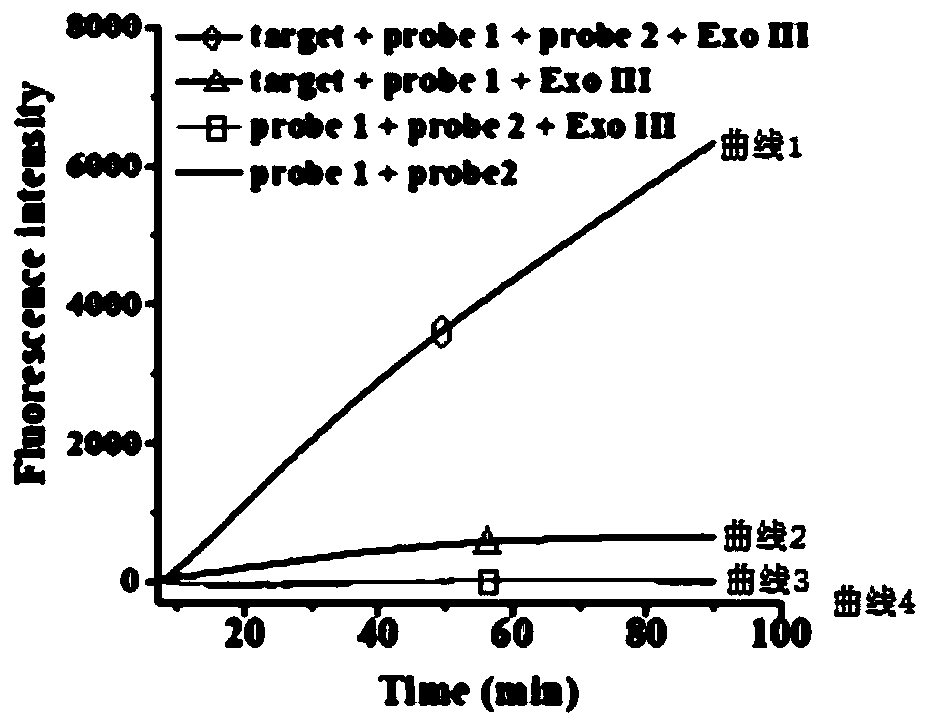
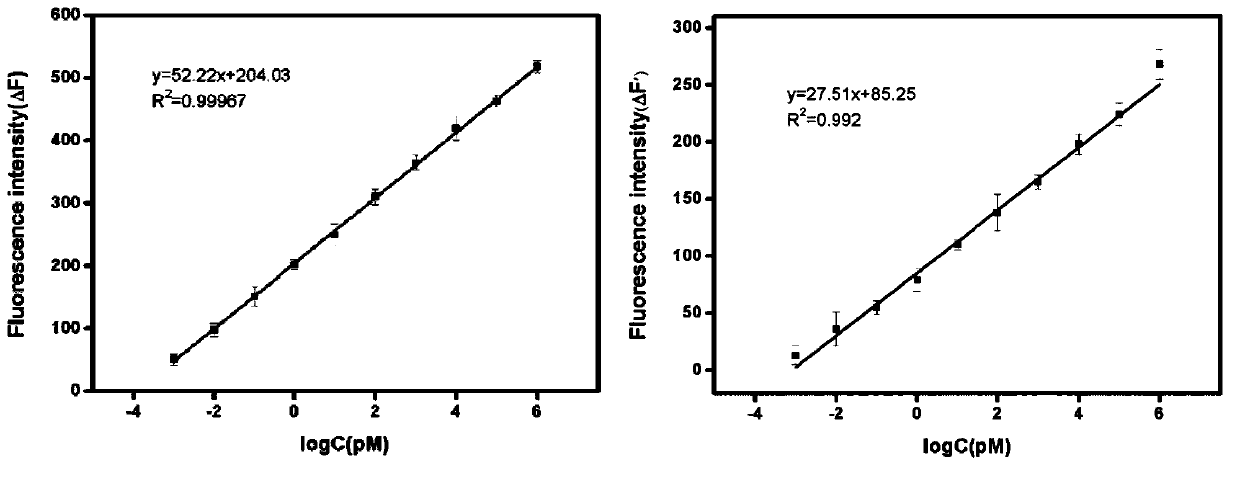
The invention specifically relates to a method for flexibly detecting DNA through exonuclease III assisted multiple circulation amplification. According to the technical scheme, through combination ofsingle-stranded DNA conjugated protein (SSB) with a barrette probe, the non-specific digestion of exonuclease III (Exo III) is effectively avoided, so that a background signal nearly zero is produced. The existence of a target DNA causes exonuclease III (Exo III) assisted multiple circulation amplification, the sensitivity is high, the detection limit is 3mol / litre, excellent selectivity is achieved, single alkali base mismatch can be recognized, and the method has tremendous potential in the respects of disease diagnosis and biomedical science research.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
Fluorescent biosensor based on nucleic acid recognition induction and application thereof
InactiveCN110951831AHigh strengthPlay the role of signal amplificationMicrobiological testing/measurementNanoparticleExonuclease I
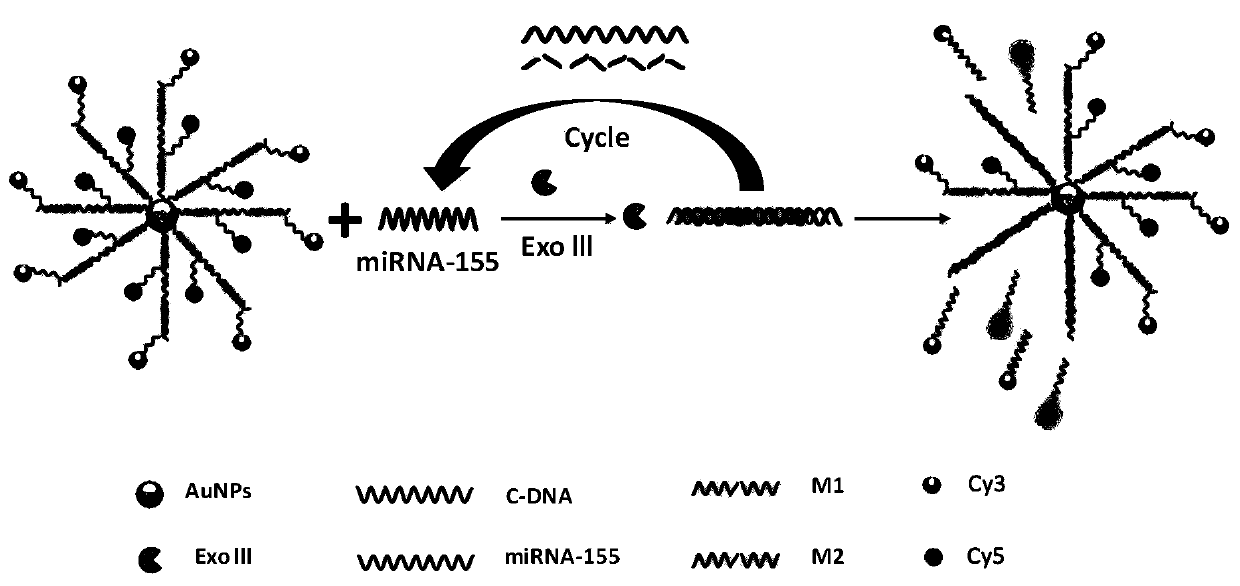
The invention provides a fluorescent biosensor based on nucleic acid recognition induction and an application thereof. The fluorescent biosensor is composed of gold nanoparticles, a recognition sequence and n signal probes, the recognition sequence is single-stranded DNA, the surfaces of the gold nanoparticles are connected with one ends of a plurality of recognition sequences; the signal probe issingle-stranded DNA of which one end is connected with a fluorophore; and the fluorophores of the signal probes are different. The single-stranded DNA sequence of the signal probe is composed of a first DNA sequence and a second DNA sequence. The fluorophore is connected with a second DNA sequence; each recognition sequence connected with the gold nanoparticles is hybridized with the first DNA sequence of the n signal probes; the recognition sequence is complementary with the miRNA-155, and after the recognition sequence is hybridized with the miRNA-155, the 3'end of the recognition sequenceis changed into a blunt end which can be recognized and hydrolyzed by the exonuclease III, and the n signal probes are all unlinked with the recognition sequence; wherein n is a natural number greaterthan 1.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
Detection system of nucleic acid and detection method and application thereof
ActiveCN108251507AExcellent fluorescence quenching performanceDistinguish mutationsMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceExonuclease III
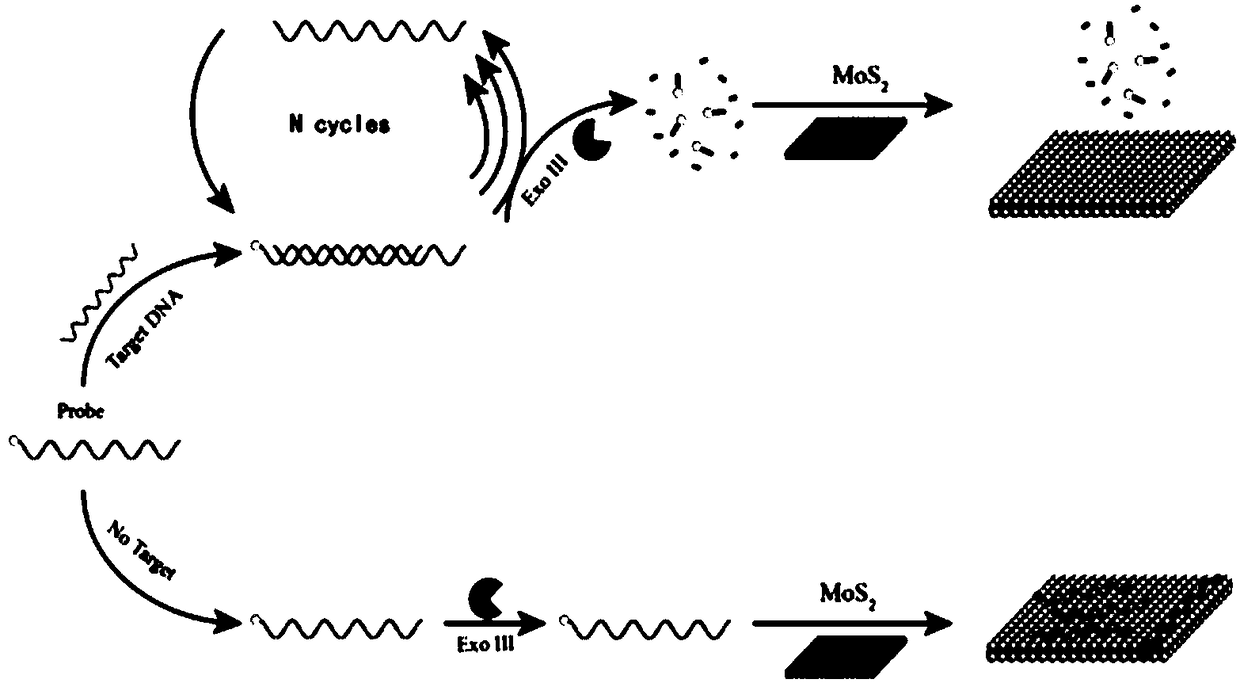
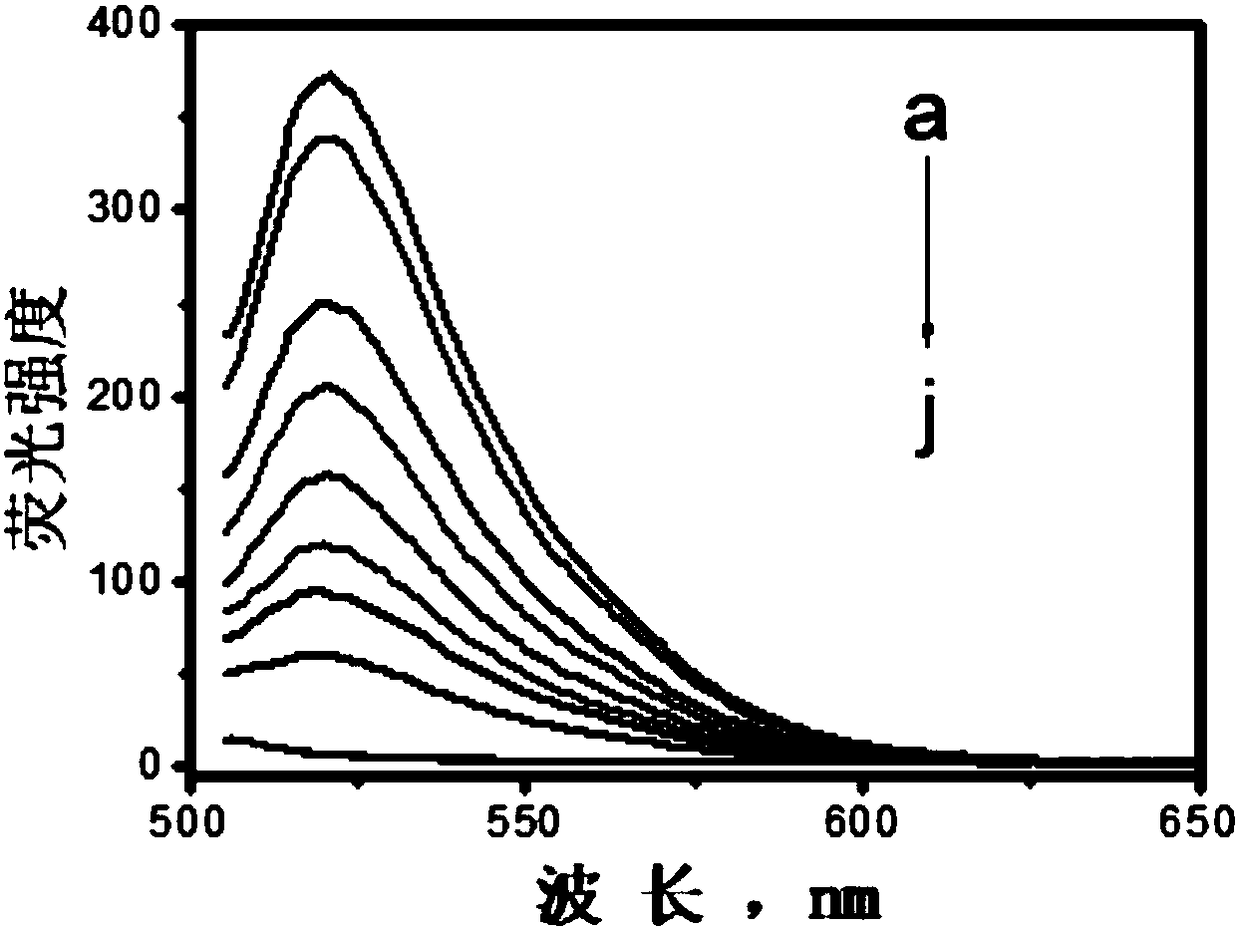
The invention provides a detection system of nucleic acid and a detection method and application thereof. The detection system comprises 30-50U of exonuclease III, fluorescence probe and 60-80 micrograms / mL of monolayer molybdenum disulfide nano-sheet with diameter of 0.5-2 microns and thickness of 0.5-2nm; by applying the monolayer molybdenum disulfide nano-sheet to the fluorescence detection system of exonuclease III, the cyclic amplification function of the exonuclease III and the quenching function of the molybdenum disulfide nano-sheet are played to the greatest extent by optimizing a reaction condition and procedures for the specific nucleotide sequence; various steps are in synergistic interaction, the sensitivity and the specificity of the detection system are improved, the operation is simple and convenient, concise and efficient, and extensive in application prospect.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MEASUREMENT & TESTING TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com