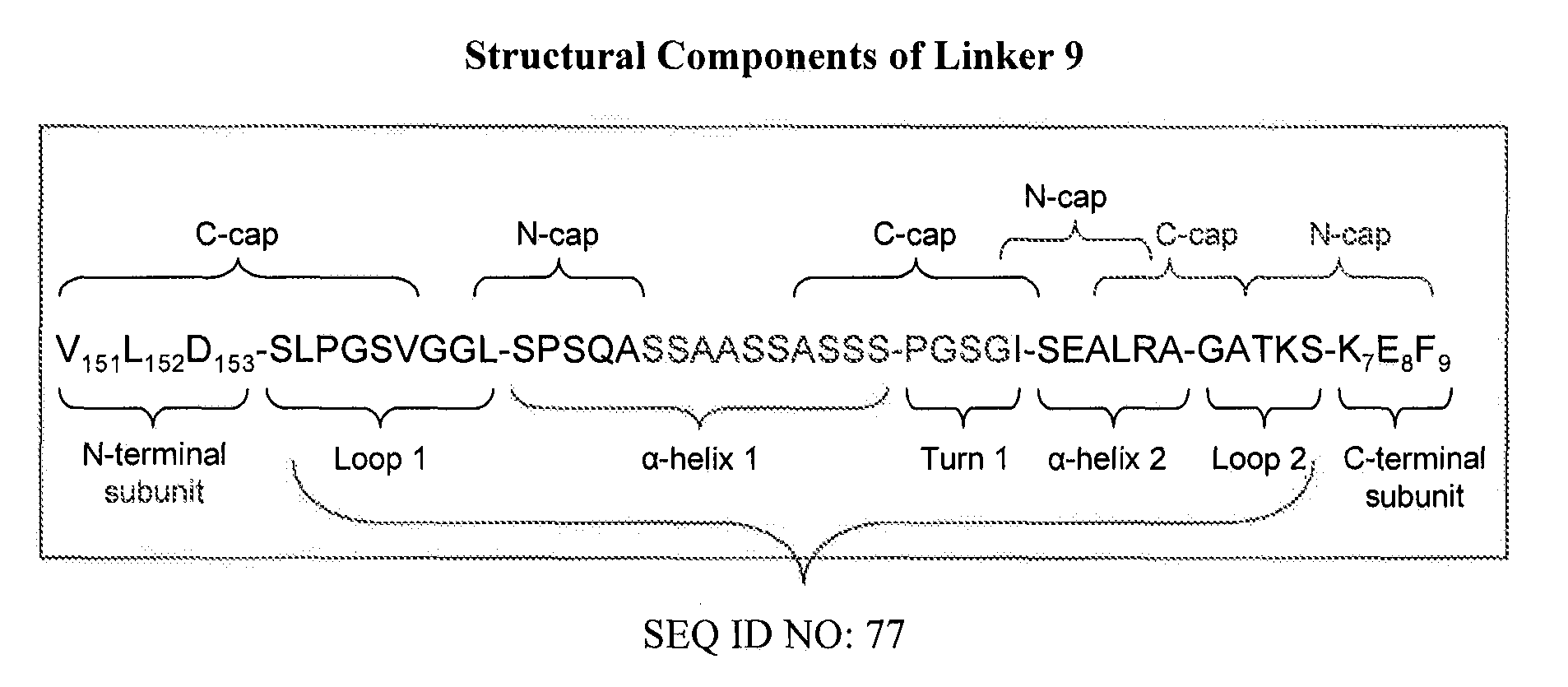
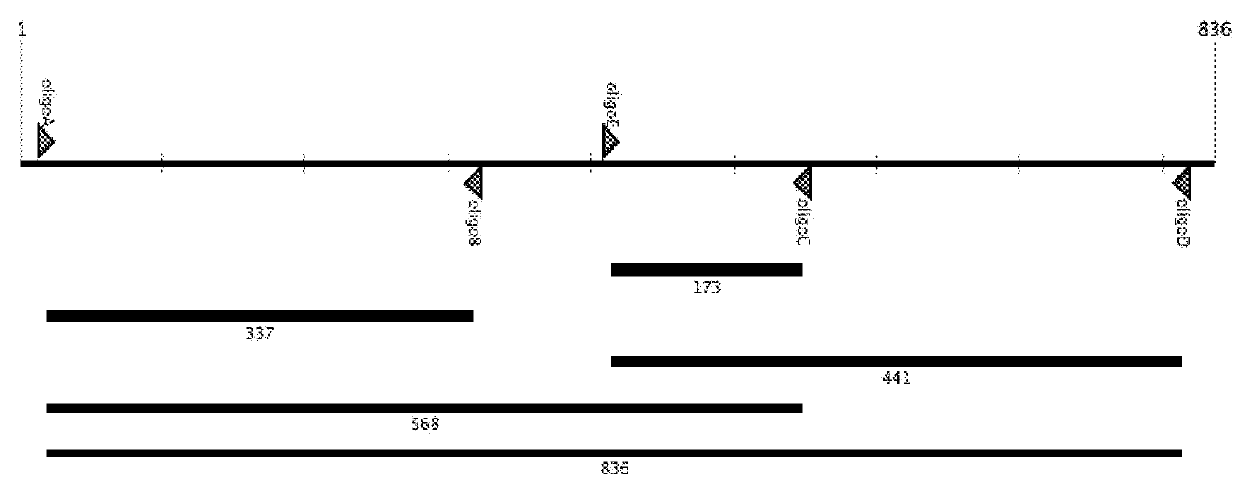
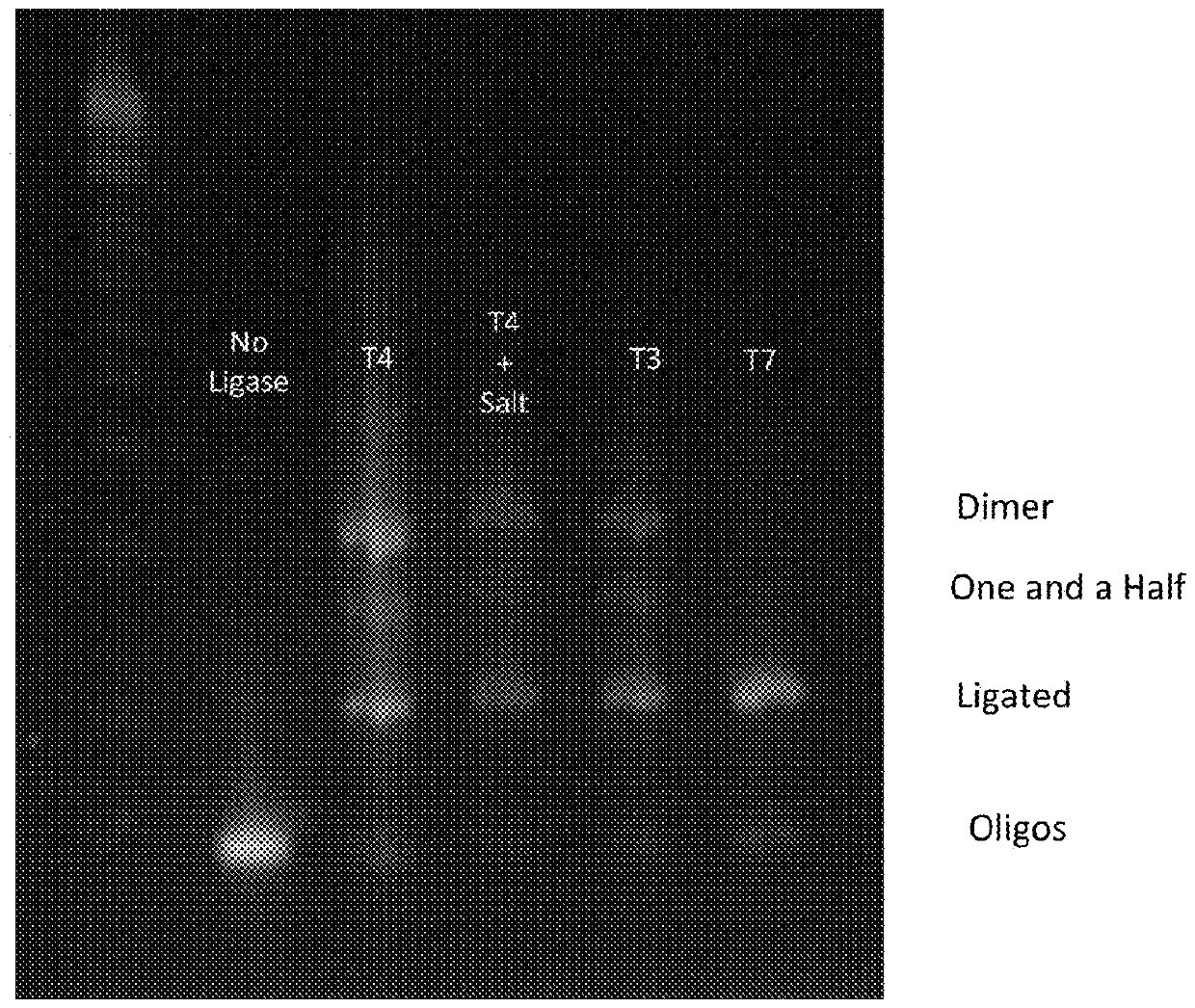
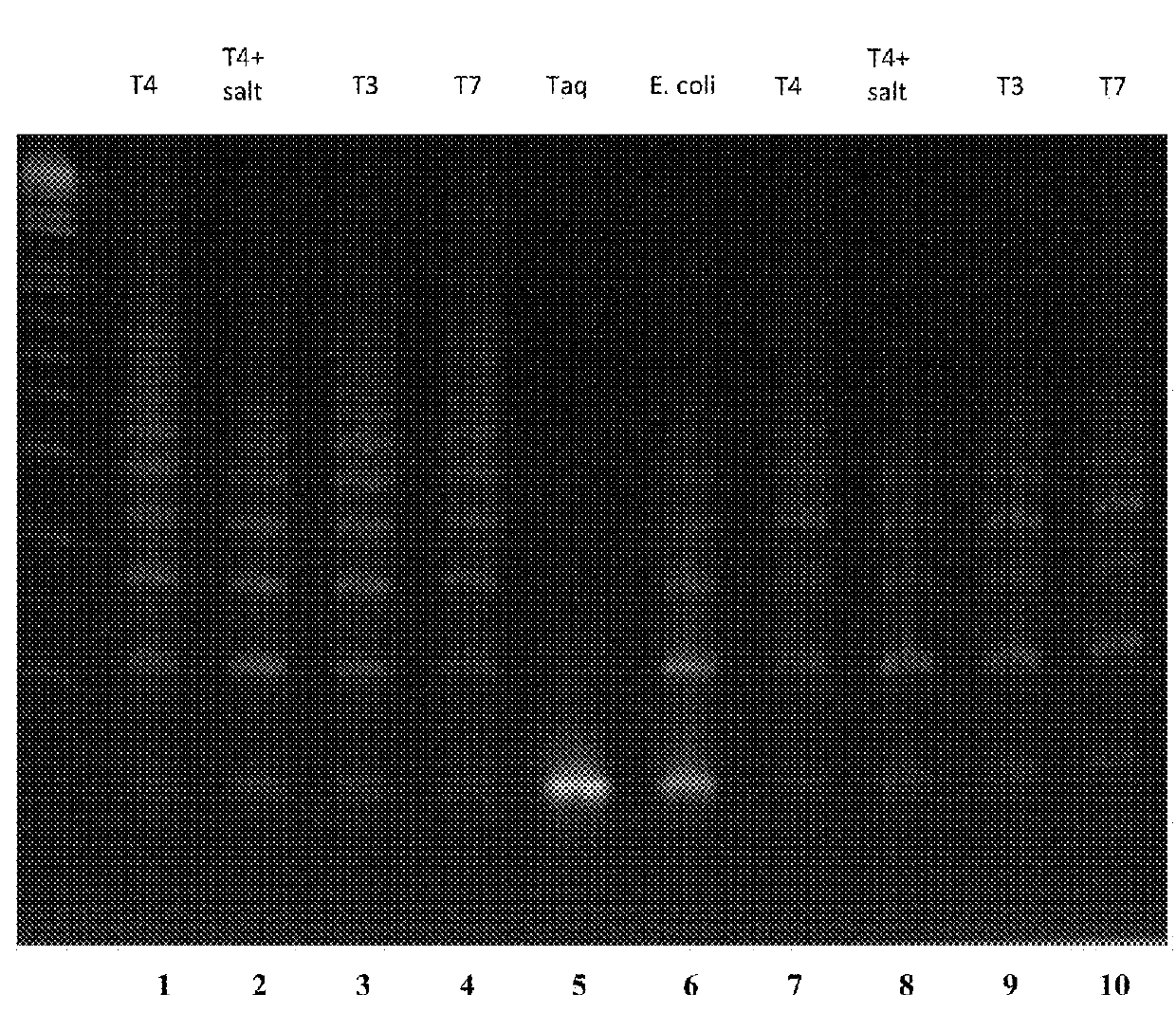
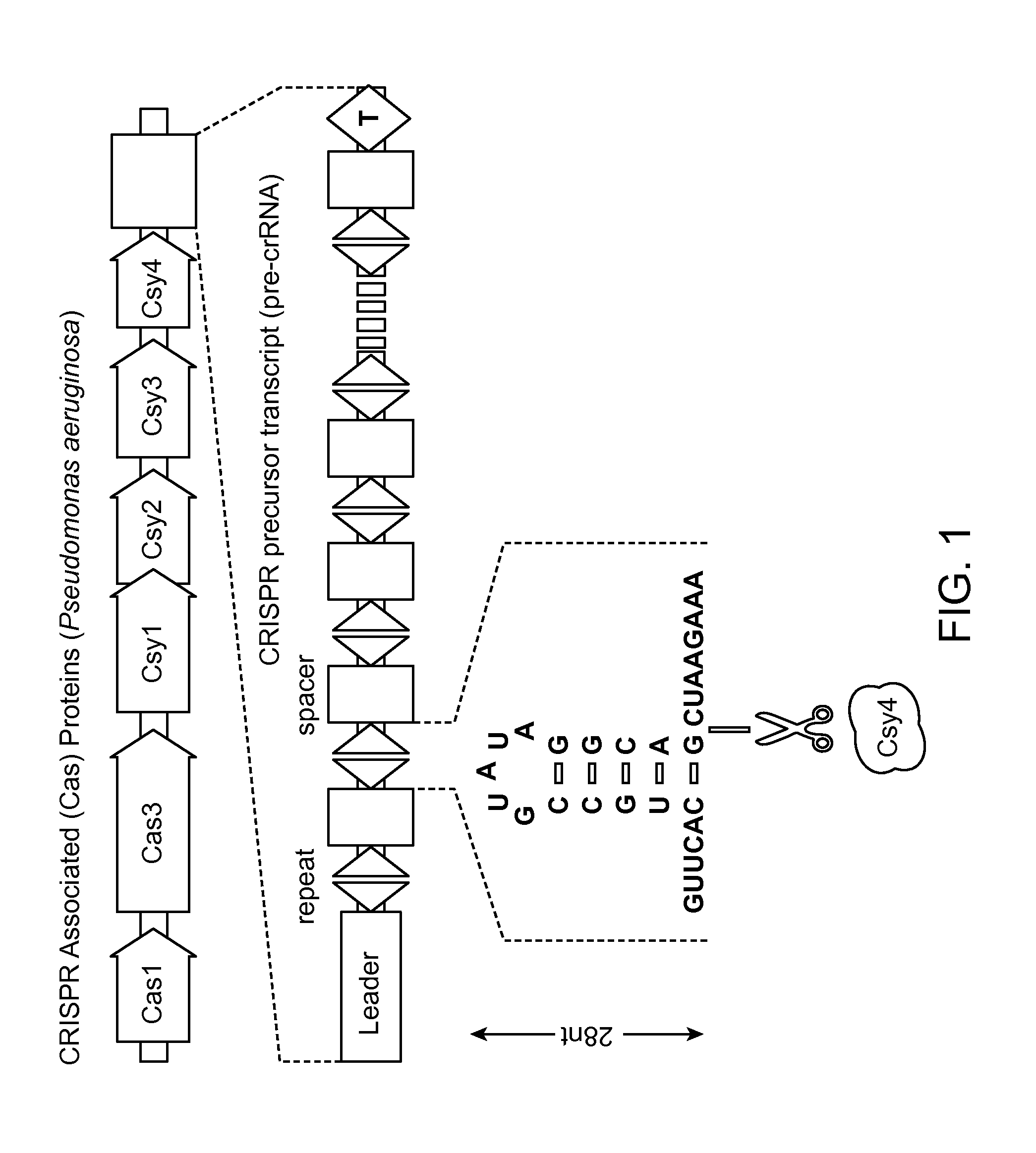
Patents
Literature
586 results about "Recognition sequence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A recognition sequence is a DNA sequence to which a structural motif of a DNA-binding domain exhibits binding specificity. Recognition sequences are palindromes. The transcription factor Sp1 for example, binds the sequences 5'-(G/T)GGGCGG(G/A)(G/A)(C/T)-3', where (G/T) indicates that the domain will bind a guanine or thymine at this position.
Rationally-designed single-chain meganucleases with non-palindromic recognition sequences
Disclosed are rationally-designed, non-naturally-occurring meganucleases in which a pair of enzyme subunits having specificity for different recognition sequence half-sites are joined into a single polypeptide to form a functional heterodimer with a non-palindromic recognition sequence. The invention also relates to methods of producing such meganucleases, and methods of producing recombinant nucleic acids and organisms using such meganucleases.
Owner:PRECISION BIOSCI
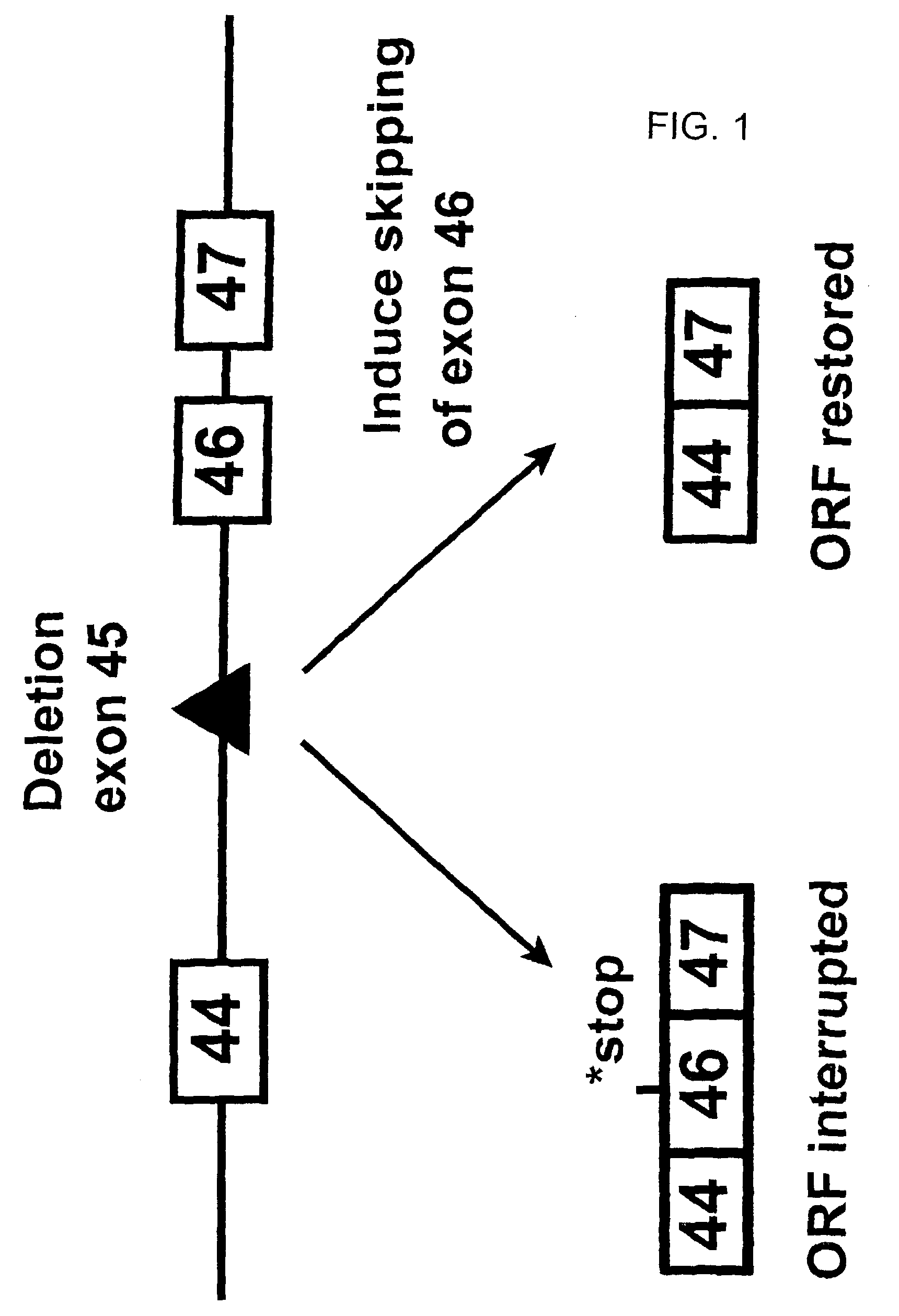
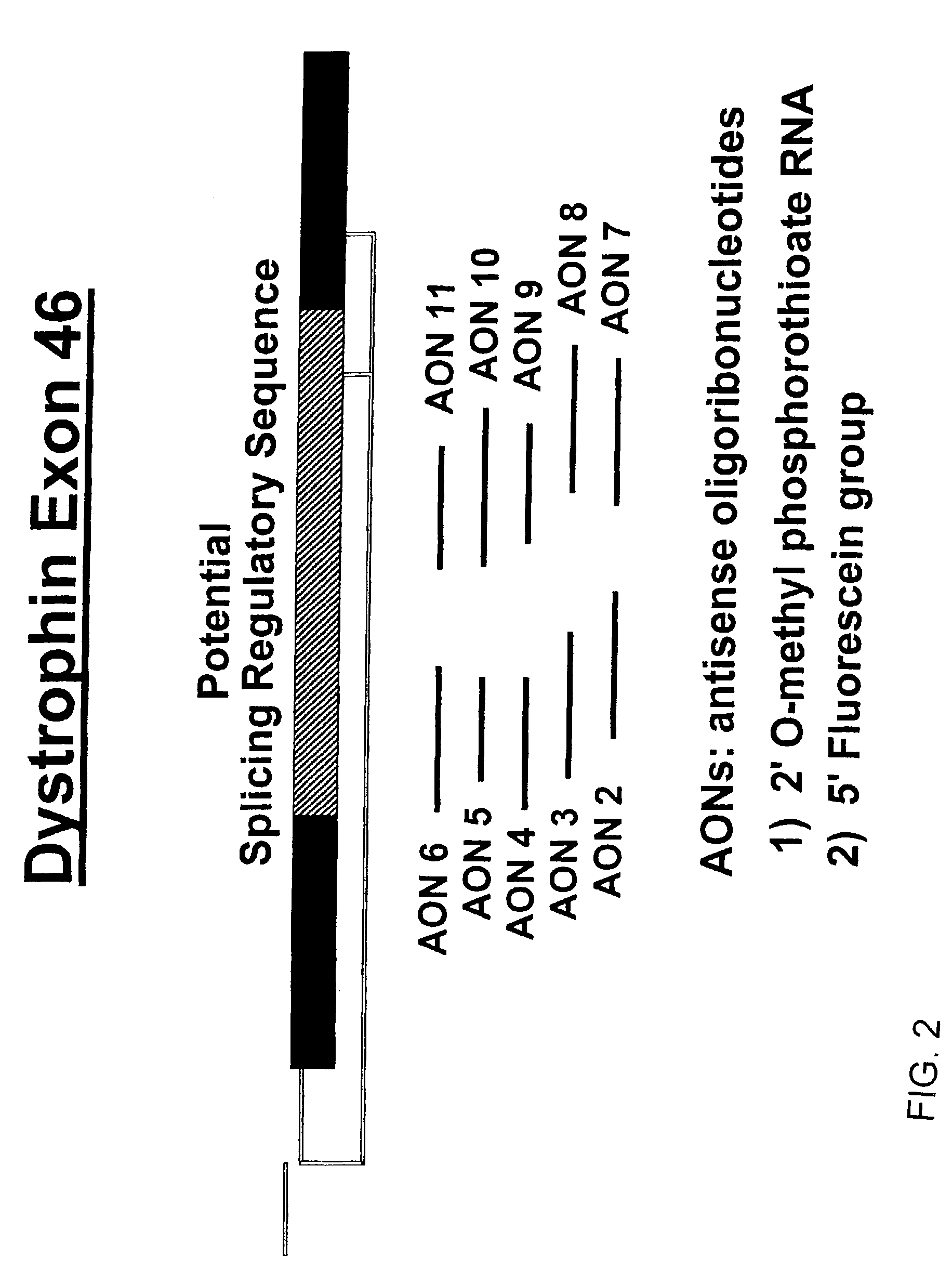
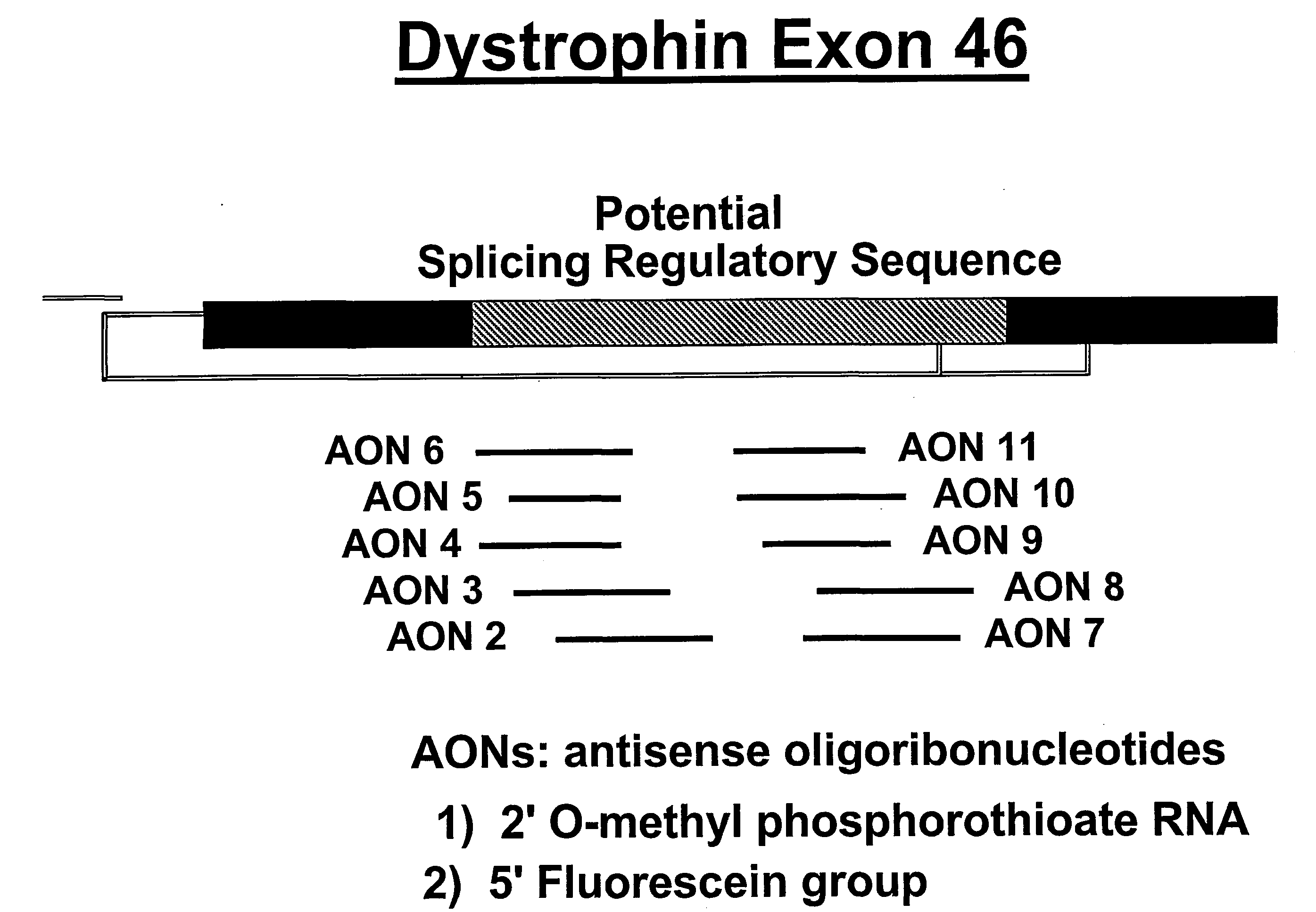
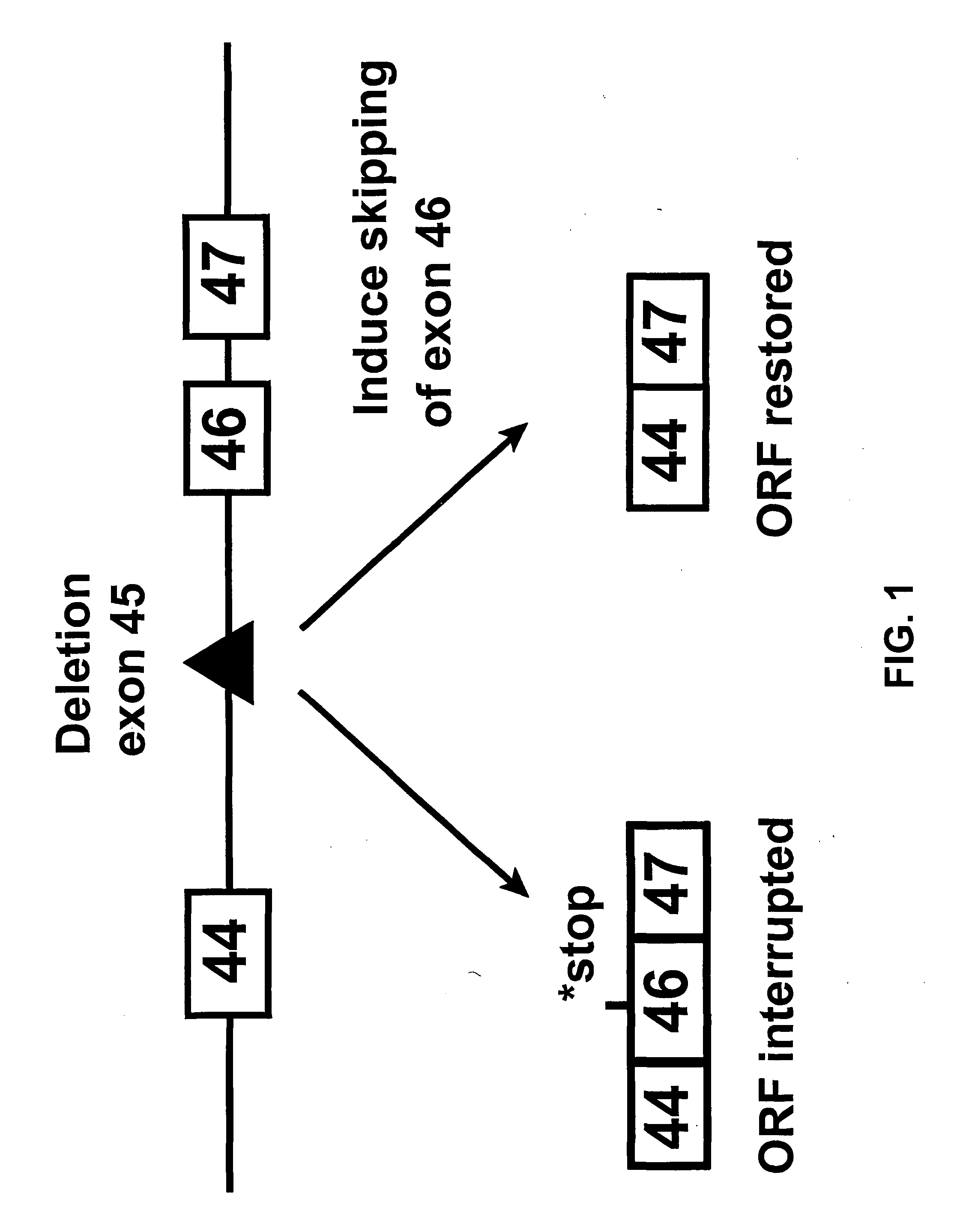
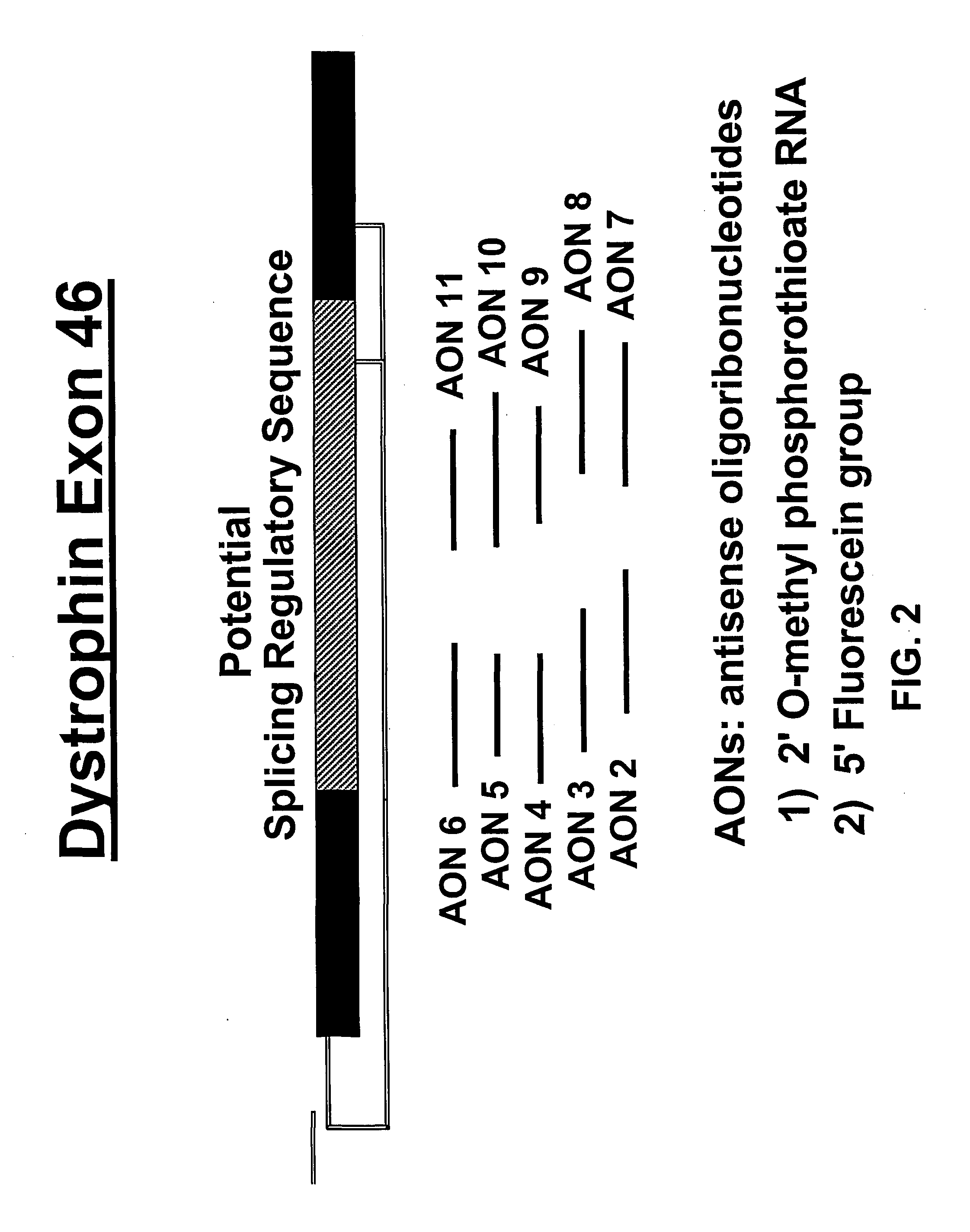
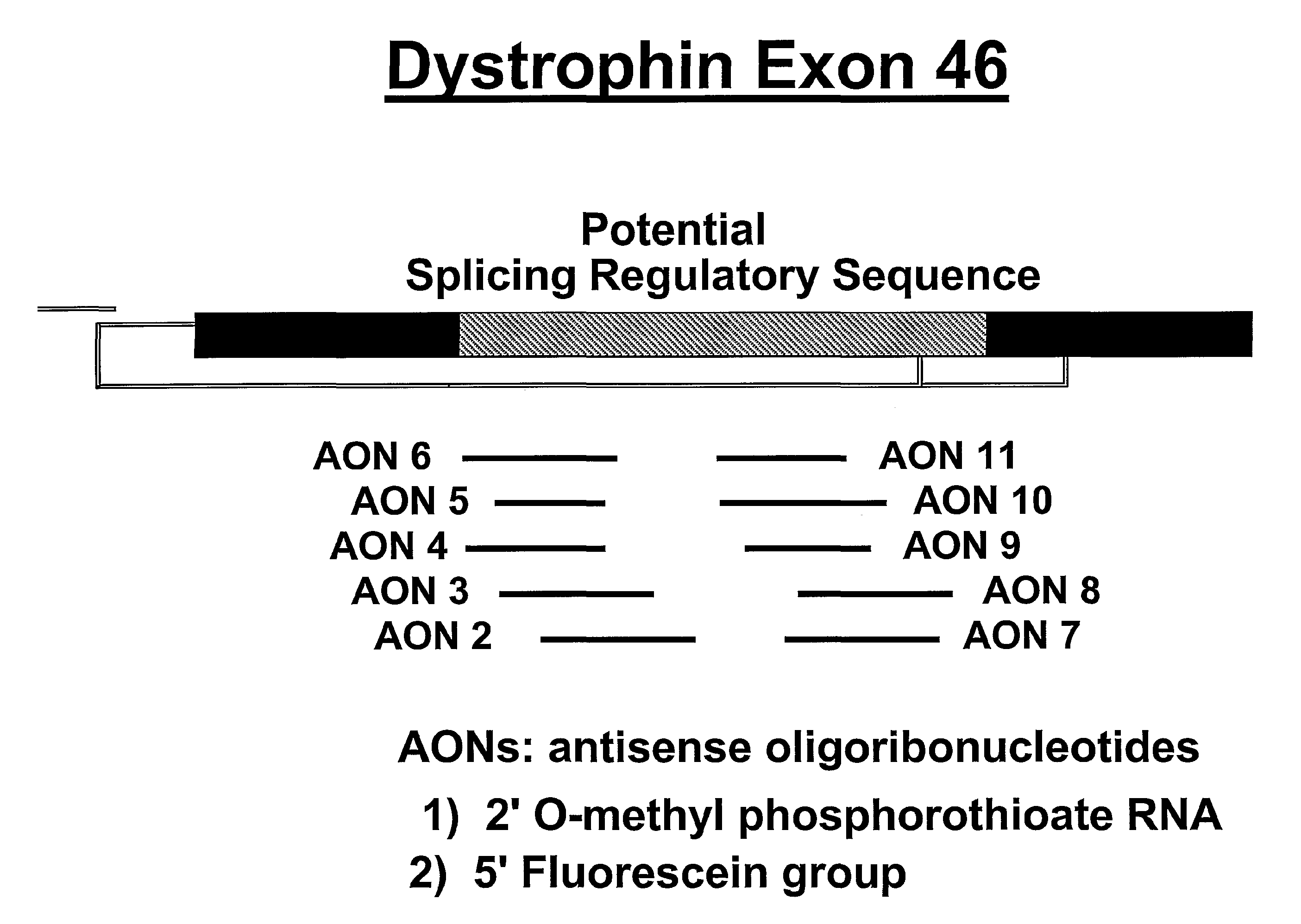
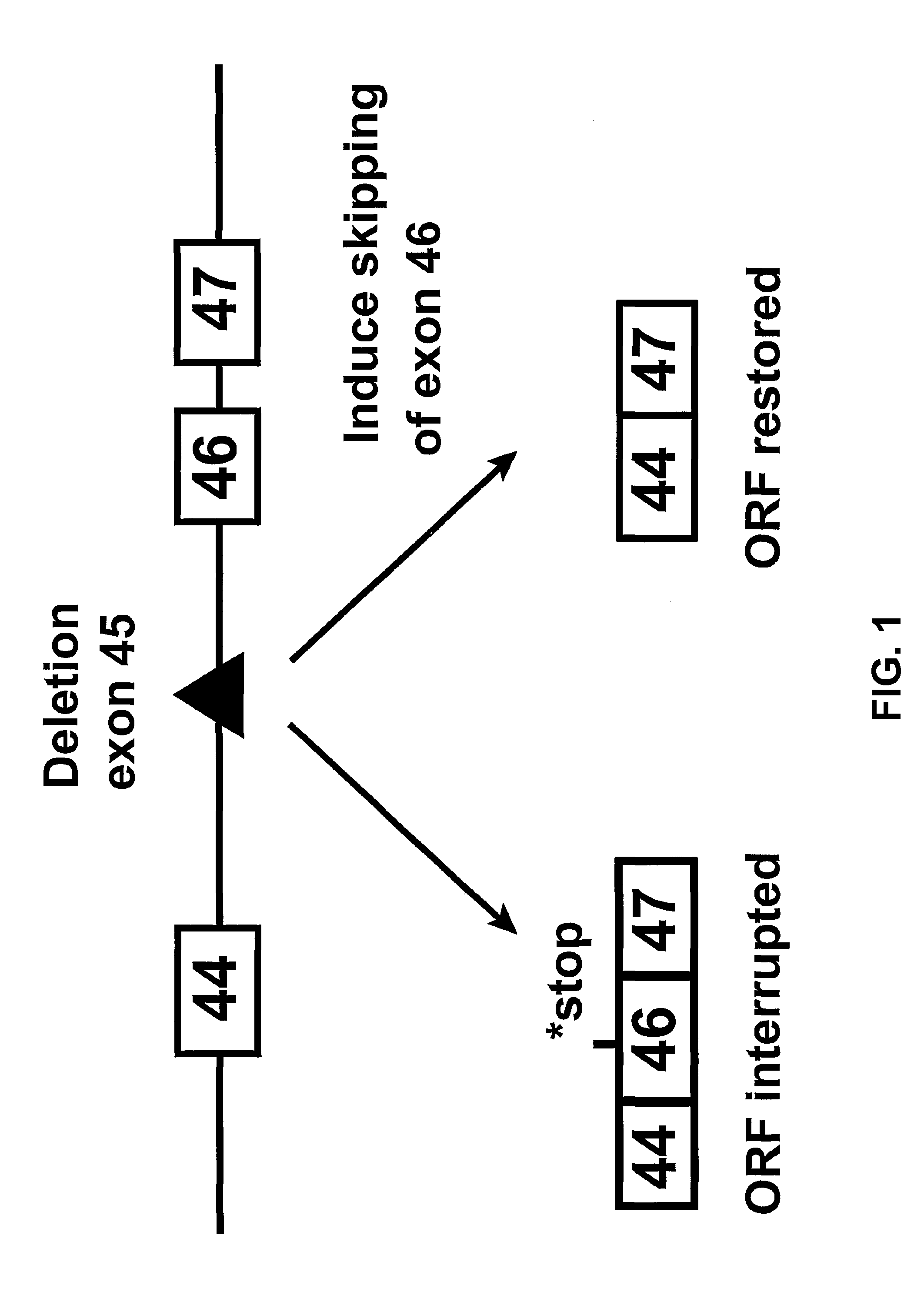
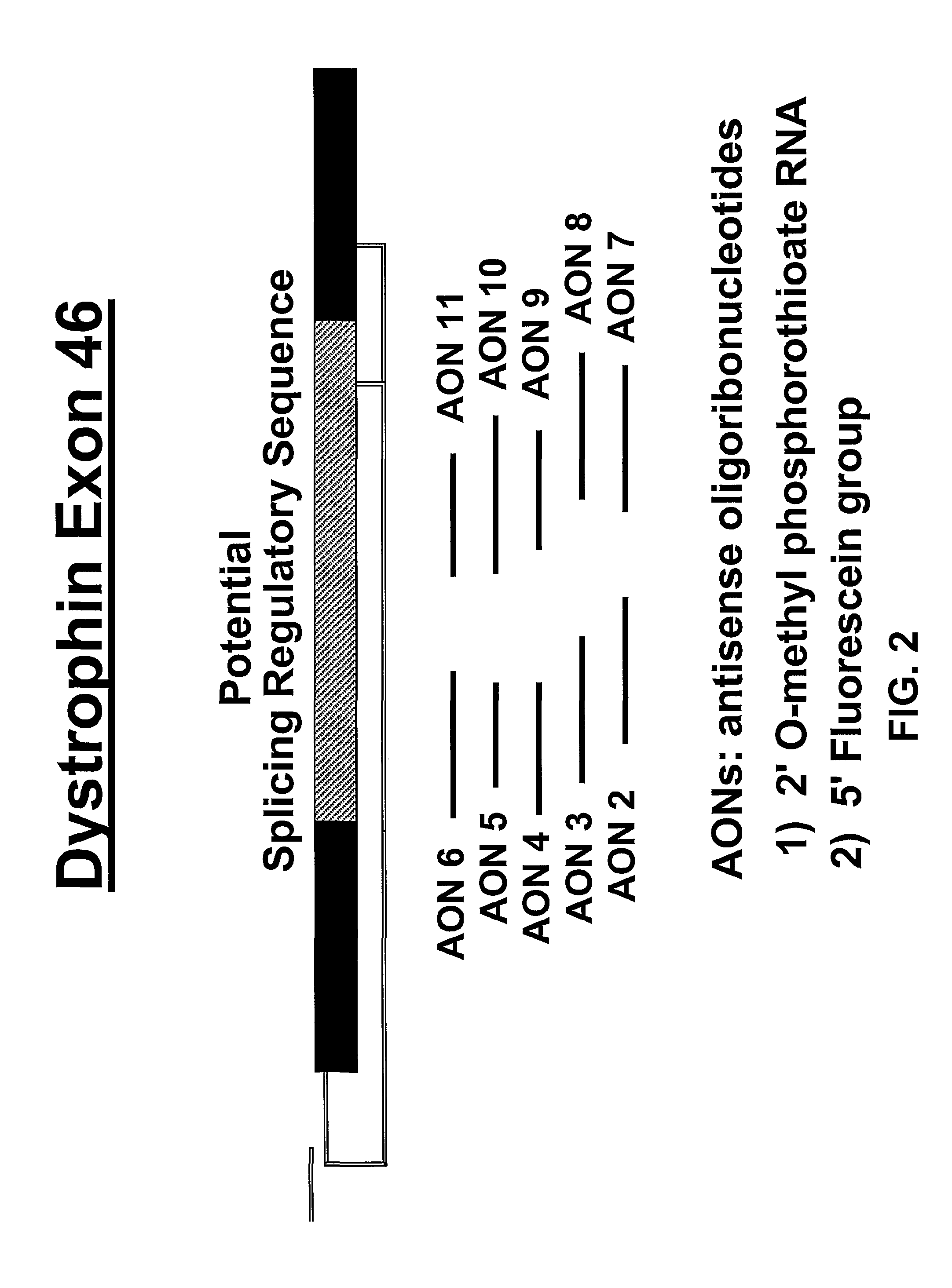
Induction of exon skipping in eukaryotic cells
InactiveUS7973015B2Efficiently maskedPotential for manipulationOrganic active ingredientsSplicing alterationPrecursor mRNARecognition sequence
The present invention provides a method for at least in part decreasing the production of an aberrant protein in a cell, the cell comprising pre-mRNA comprising exons coding for the protein, by inducing so-called exon skipping in the cell. Exon-skipping results in mature MRNA that does not contain the skipped exon, which leads to an altered product of the exon codes for amino acids. Exon skipping is performed by providing a cell with an agent capable of specifically inhibiting an exon inclusion signal, for instance, an exon recognition sequence, of the exon. The exon inclusion signal can be interfered with by a nucleic acid comprising complementarity to a part of the exon. The nucleic acid, which is also herewith provided, can be used for the preparation of a medicament, for instance, for the treatment of an inherited disease.
Owner:LEIDEN ACADEMISCH ZIEKENHUIS
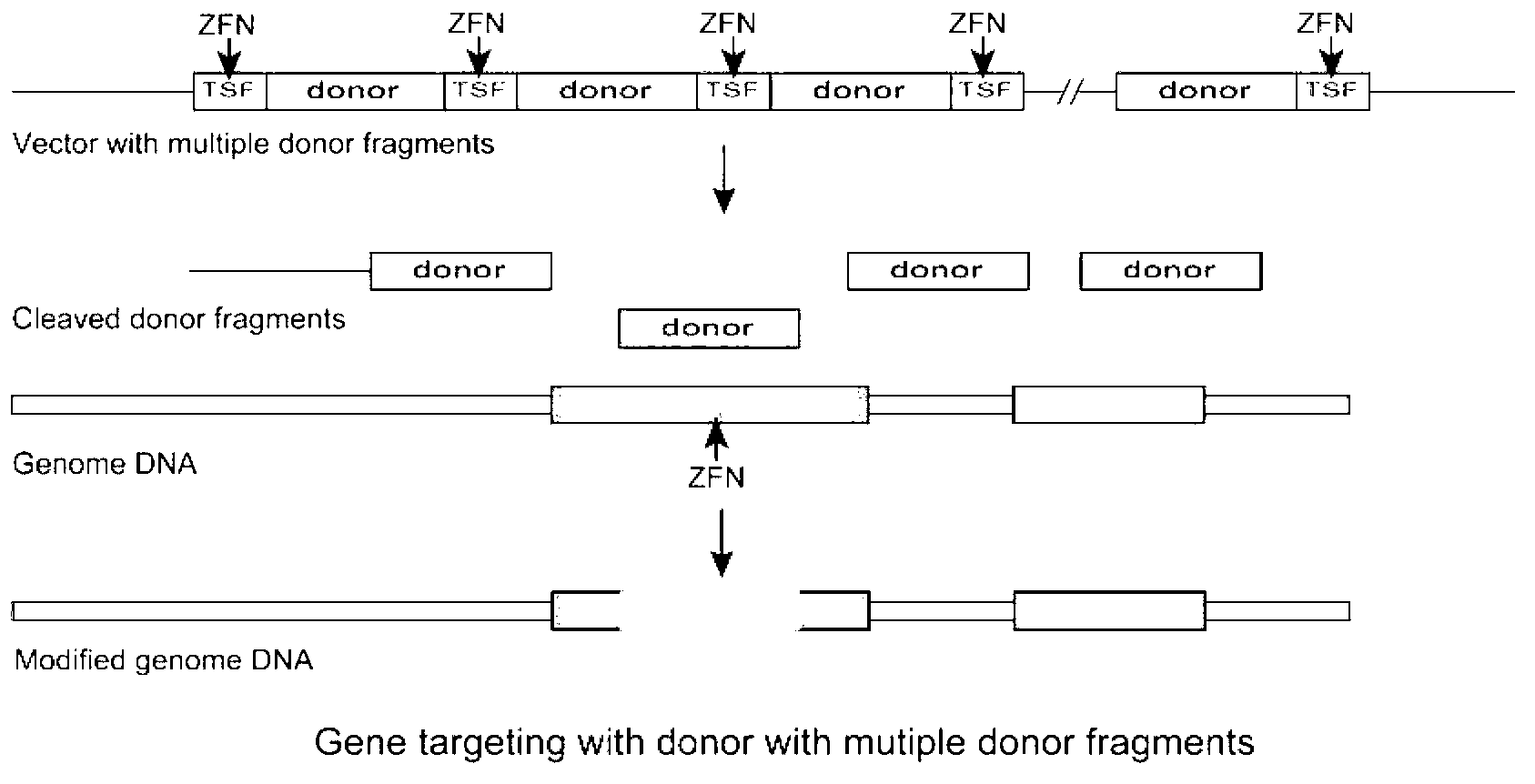
Gene targeting system
InactiveCN103224947AImprove the level ofHigh target shooting efficiencyVector-based foreign material introductionGene targetsZinc finger nuclease
The invention relates to a gene targeting system, which comprises two parts such as a site-specific cleavage nuclease expression vector and a targeting vector, wherein the targeting vector contains 2-10 donor DNA fragments, 5' ends and 3' ends of every donor DNA fragment are respectively inserted into recognition sequences of the site-specific cleavage nuclease, the donor DNA comprises an upstream homologous arm, a downstream homologous arm and an exogenous DNA sequence positioned between the upstream homologous arm and the downstream homologous arm, and the site-specific cleavage nuclease expression vector is any one selected from an expression vector carrying zinc finger nuclease, a transcription activator-like effector nuclease expression vector, and a RNA-mediated nuclease RNA:Cas9 expression vector.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
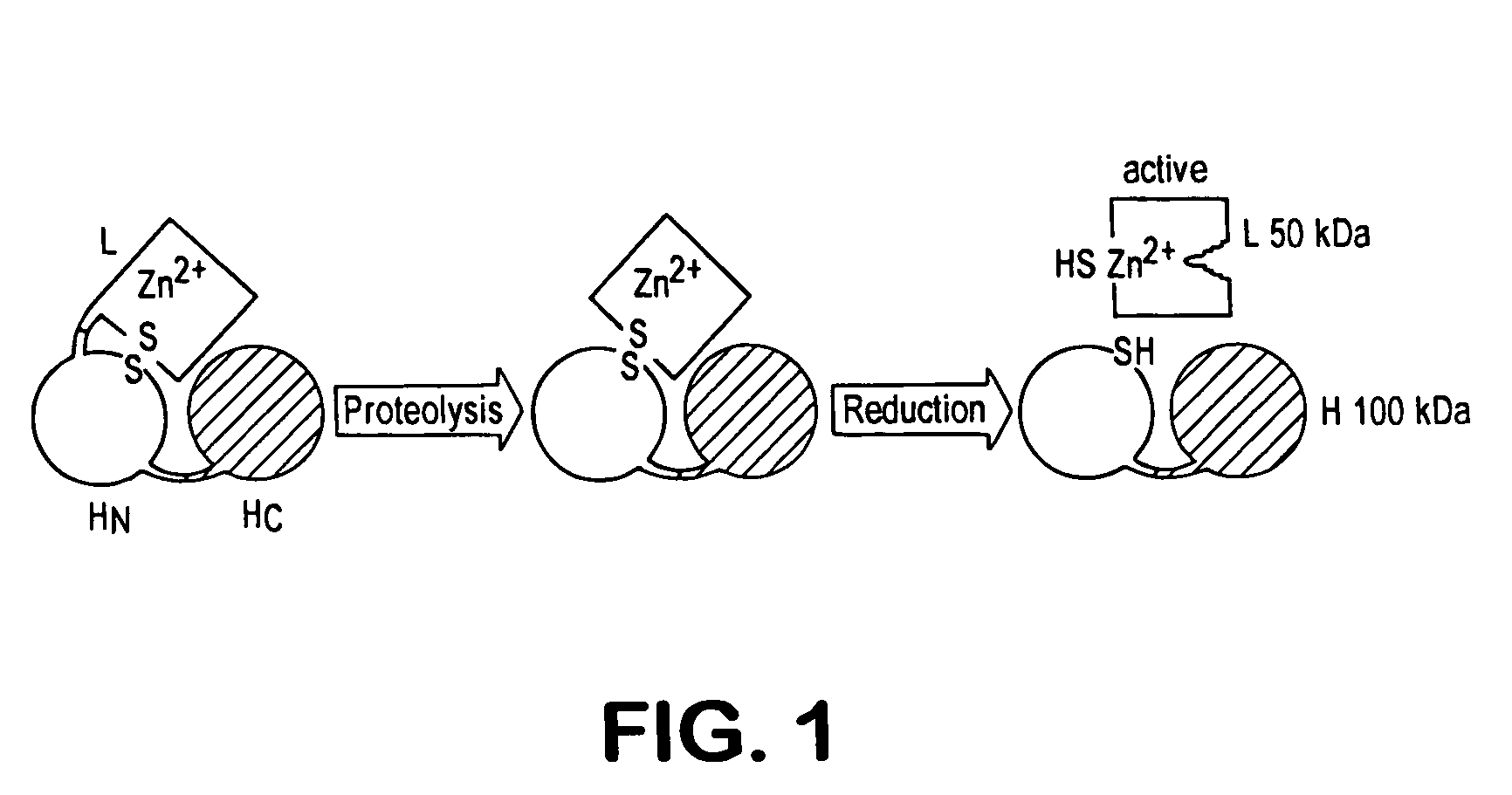
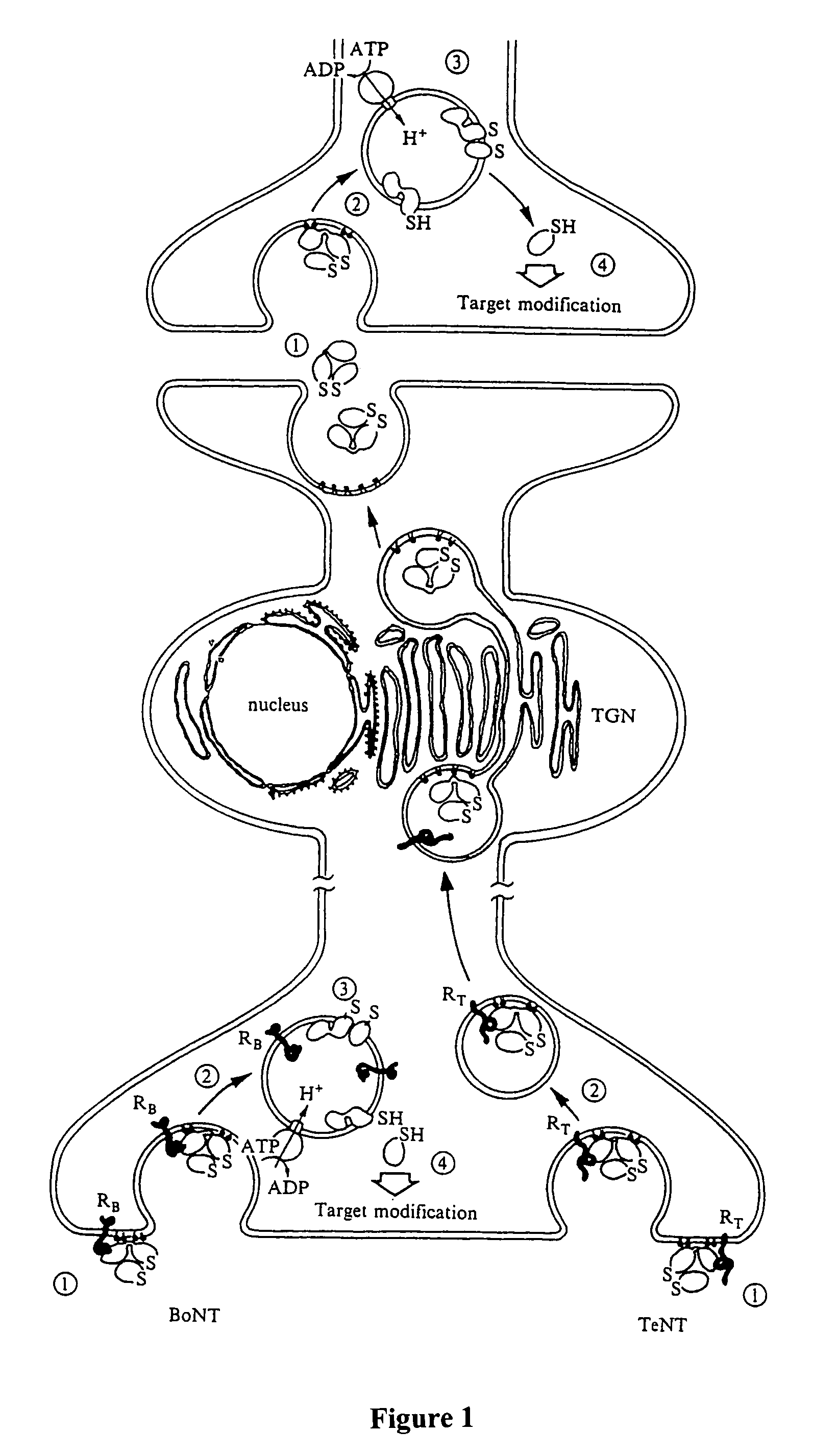
Fret protease assays for botulinum serotype A/E toxins
InactiveUS7208285B2Used to determineDecreased acceptor fluorescence intensityBacteriaSugar derivativesFluorophoreReceptor for activated C kinase 1
The present invention provides clostridial toxin substrates useful in assaying for the protease activity of any clostridial toxin, including botulinum toxins of all serotypes as well as tetanus toxins. A clostridial toxin substrate of the invention contains a donor fluorophore; an acceptor having an absorbance spectrum overlapping the emission spectrum of the donor fluorophore; and a clostridial toxin recognition sequence that includes a cleavage site, where the cleavage site intervenes between the donor fluorophore and the acceptor and where, under the appropriate conditions, resonance energy transfer is exhibited between the donor fluorophore and the acceptor.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Compositions and Methods For High Fidelity Assembly of Nucleic Acids
InactiveUS20130059296A1Nucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzymatic digestionPolymerase L
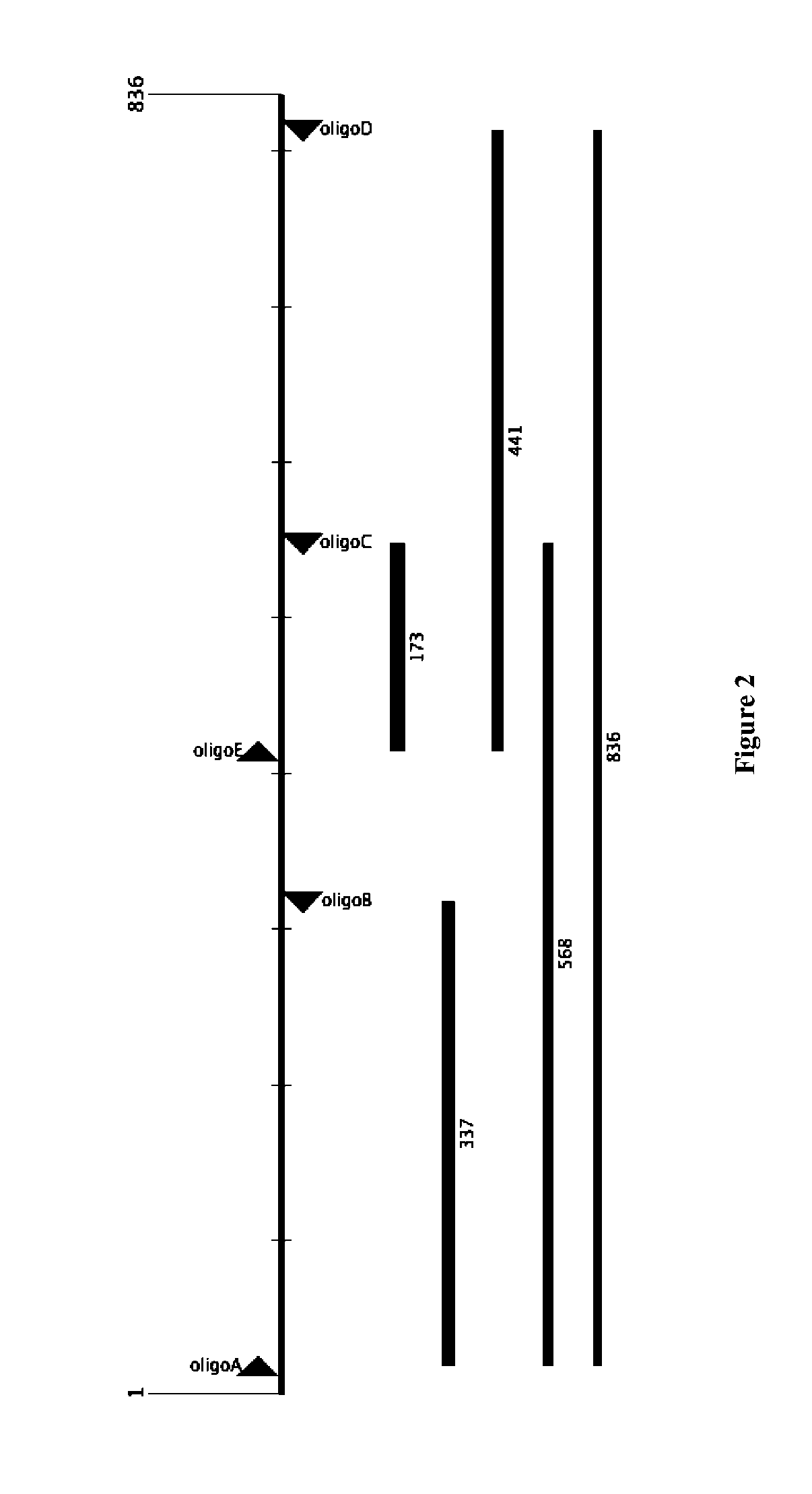
Aspects of the invention relate to methods, compositions and algorithms for designing and producing a target nucleic acid. The method can include: (1) providing a plurality of blunt-end double-stranded nucleic acid fragments having a restriction enzyme recognition sequence at both ends thereof; (2) producing via enzymatic digestion a plurality of cohesive-end double-stranded nucleic acid fragments each having two different and non-complementary overhangs; (3) ligating the plurality of cohesive-end double-stranded nucleic acid fragments with a ligase; and (4) forming a linear arrangement of the plurality of cohesive-end double-stranded nucleic acid fragments, wherein the unique arrangement comprises the target nucleic acid. In certain embodiments, the plurality of blunt-end double-stranded nucleic acid fragments can be provided by: releasing a plurality of oligonucleotides synthesized on a solid support; and synthesizing complementary strands of the plurality of oligonucleotides using a polymerase based reaction.
Owner:GEN9
Methods and Compositions for Controlling Gene Expression by RNA Processing
The present disclosure provides nucleic acids encoding an RNA recognition sequence positioned proximal to an insertion site for the insertion of a sequence of interest; and host cells genetically modified with the nucleic acids. The present disclosure also provides methods of modifying the activity of a target RNA, and kits and compositions for carrying out the methods.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Regulation analysis by cis reactivity, RACR
ActiveUS20070020669A1Facilitates high throughput analysisHigh throughput analysisSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPresent methodInteractor
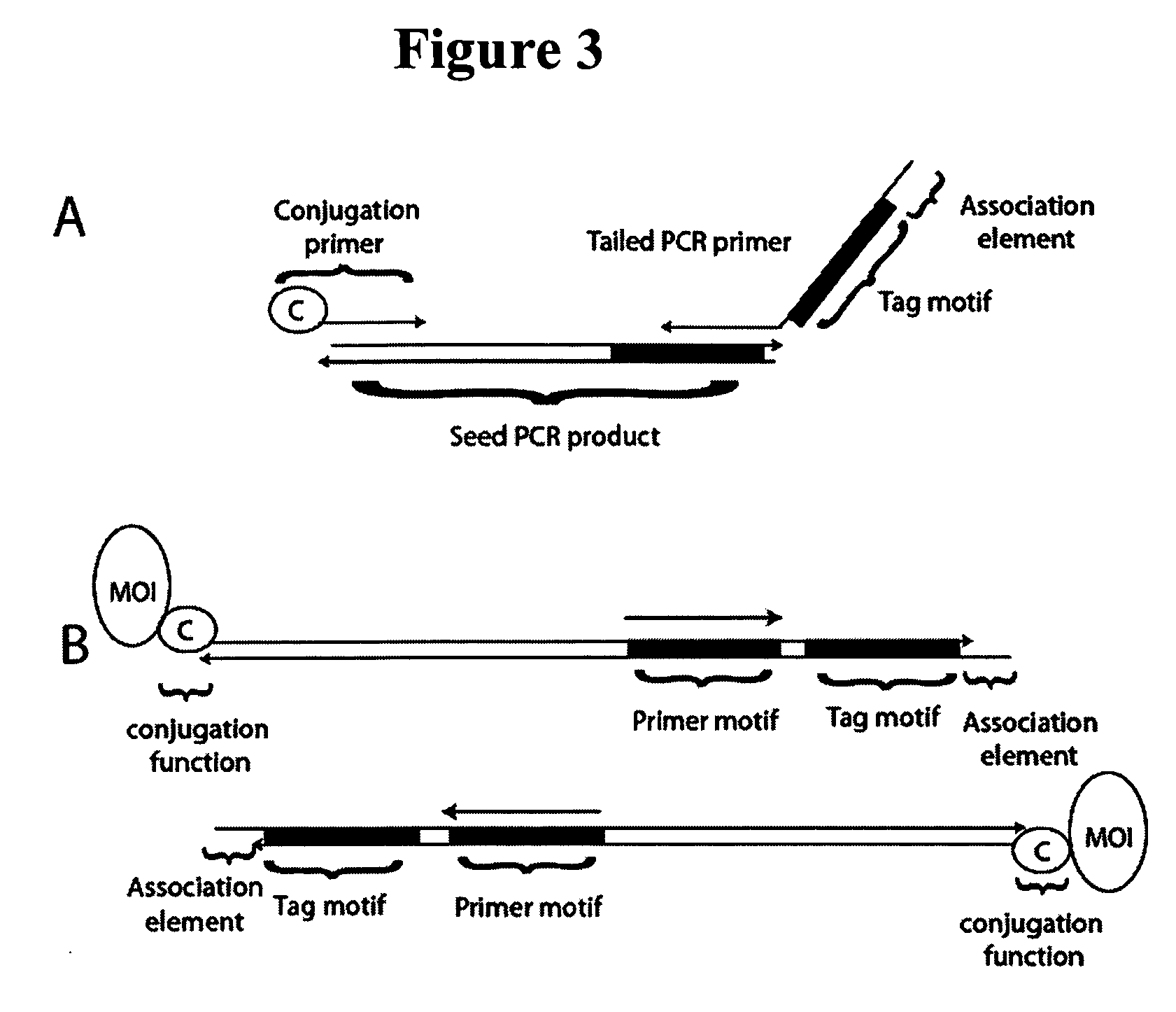
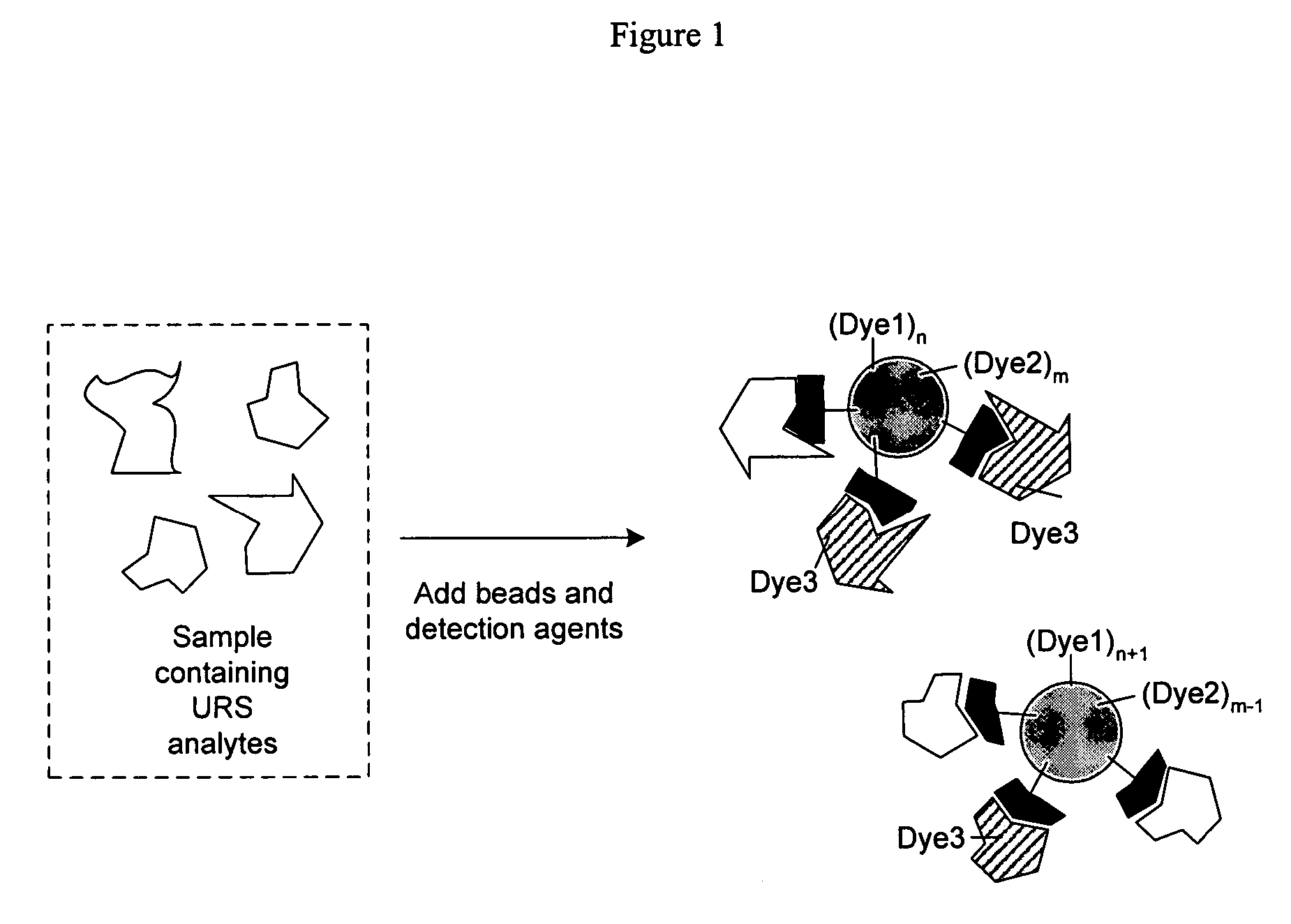
Methods of detecting affinity interactions between at least two molecules of interest are provided. The method comprises: a. forming a plurality of interactors by coupling each molecule of interest with at least one nucleic acid moiety comprising an identification sequence element and at an association element; b. promoting an association between at least two nucleic acid moieties from different interactors to form a plurality of unique associated oligonucleotides, wherein each nucleic acid moiety may form more than one unique associated oligonucleotide, and wherein each unique associated oligonucleotide comprises at least two identification sequence elements derived from the at least two nucleic acid moieties; c. selecting the plurality of unique associated oligonucleotides; and d. subjecting the selected associated oligonucleotides to an analysis that permits detection of the at least two identification sequence elements. Similar methods directed to detecting functional interactions, libraries of interactors employable in the present methods, and kits comprising those libraries are also provided.
Owner:OLINK PROTEOMICS AB
Proteome epitope tags and methods of use thereof in protein modification analysis
InactiveUS20060014212A1High clinical application valueReliable detectionLibrary screeningNanoinformaticsEpitopePost translational
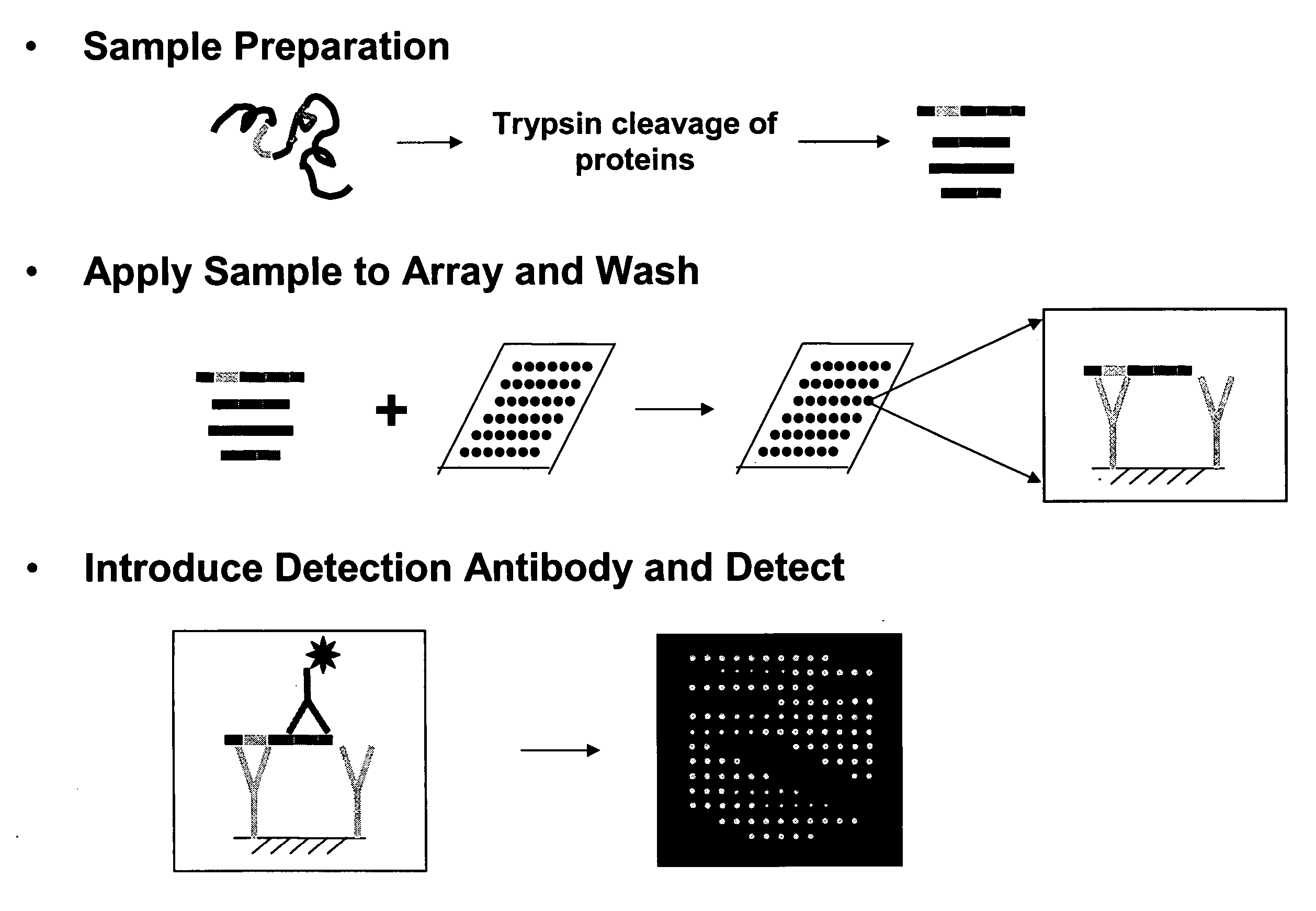
Disclosed are reagents and methods for reliably detecting the presence and measuring the amount of proteins, including proteins with various post-translational modifications (phosphorylation, glycosylation, methylation, acetylation, etc.) in a sample by the use of one or more capture agents that recognize and interact with recognition sequences uniquely characteristic of a protein or a set of proteins (Proteome Epitope Tags, or PETs) in the sample. Arrays comprising these capture agents or PETs are also provided.
Owner:EPITOME BIOSYST
Induction of exon skipping in eukaryotic cells
InactiveUS20090228998A1Efficiently maskedPotential for manipulationOrganic active ingredientsSplicing alterationPrecursor mRNARecognition sequence
The present invention provides a method for at least in part decreasing the production of an aberrant protein in a cell, the cell comprising pre-mRNA comprising exons coding for the protein, by inducing so-called exon skipping in the cell. Exon-skipping results in mature mRNA that does not contain the skipped exon, which leads to an altered product of the exon codes for amino acids. Exon skipping is performed by providing a cell with an agent capable of specifically inhibiting an exon inclusion signal, for instance, an exon recognition sequence, of the exon. The exon inclusion signal can be interfered with by a nucleic acid comprising complementarity to a part of the exon. The nucleic acid, which is also herewith provided, can be used for the preparation of a medicament, for instance, for the treatment of an inherited disease.
Owner:ACADEMISCH ZIEKENHUIS BIJ DE UNIV VAN AMSTERDAM ACADEMISCH MEDISCH CENT
Induction of exon skipping in eukaryotic cells
InactiveUS20080209581A1Reduce productionReduce amountOrganic active ingredientsSplicing alterationPrecursor mRNARecognition sequence
Described is a method for at least in part decreasing the production of an aberrant protein in a cell, the cell comprising pre-mRNA comprising exons coding for the protein, by inducing so-called exon skipping in the cell. Exon-skipping results in mature mRNA that does not contain the skipped exon, which leads to an altered product of the exon codes for amino acids. Exon skipping is performed by providing a cell with an agent capable of specifically inhibiting an exon inclusion signal, for instance, an exon recognition sequence, of the exon. The exon inclusion signal can be interfered with by a nucleic acid comprising complementarity to a part of the exon. The nucleic acid, which is also herewith provided, can be used for the preparation of a medicament, for instance, for the treatment of an inherited disease.
Owner:ACADEMISCH ZIEKENHUIS BIJ DE UNIV VAN AMSTERDAM ACADEMISCH MEDISCH CENT
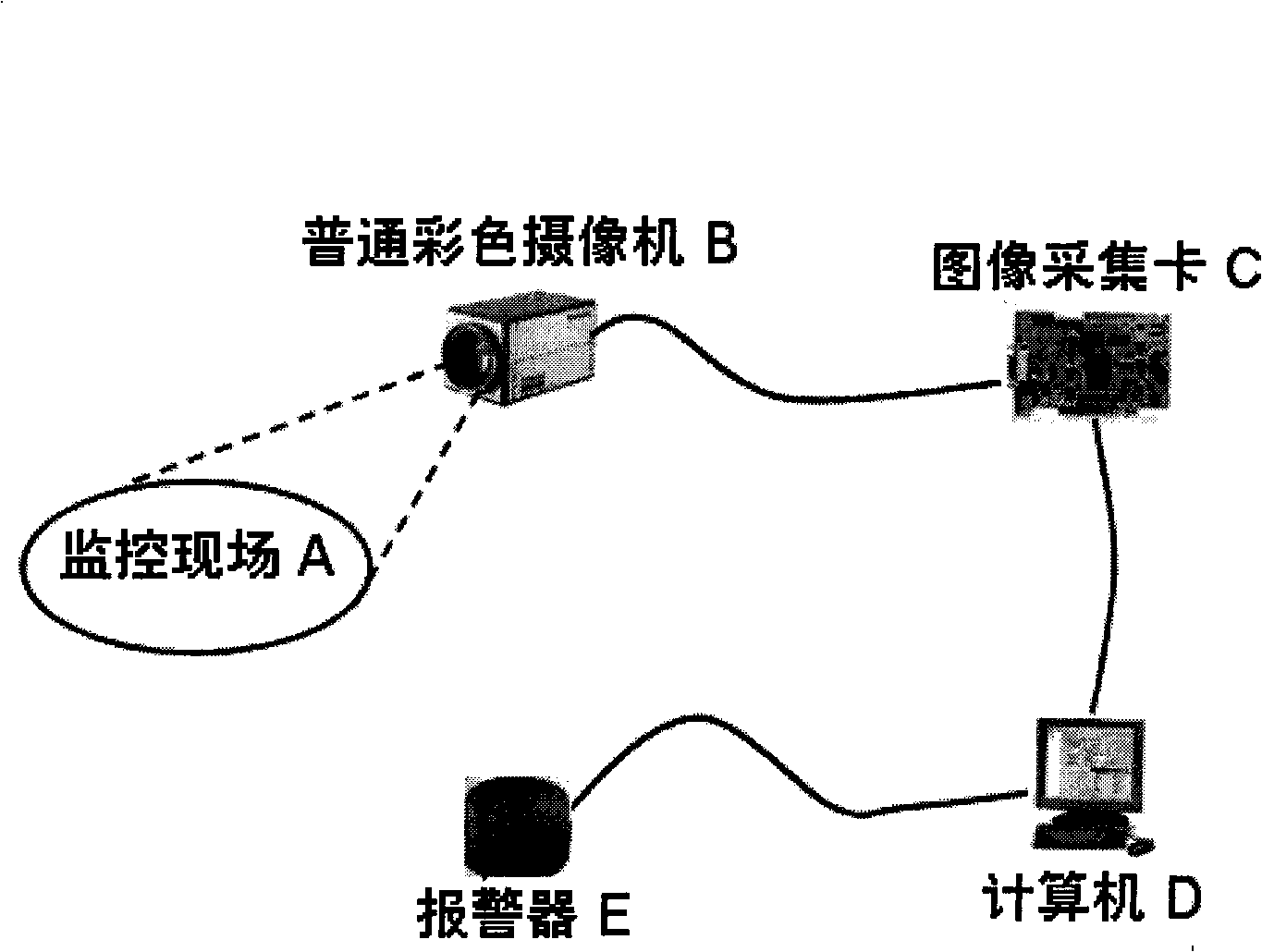
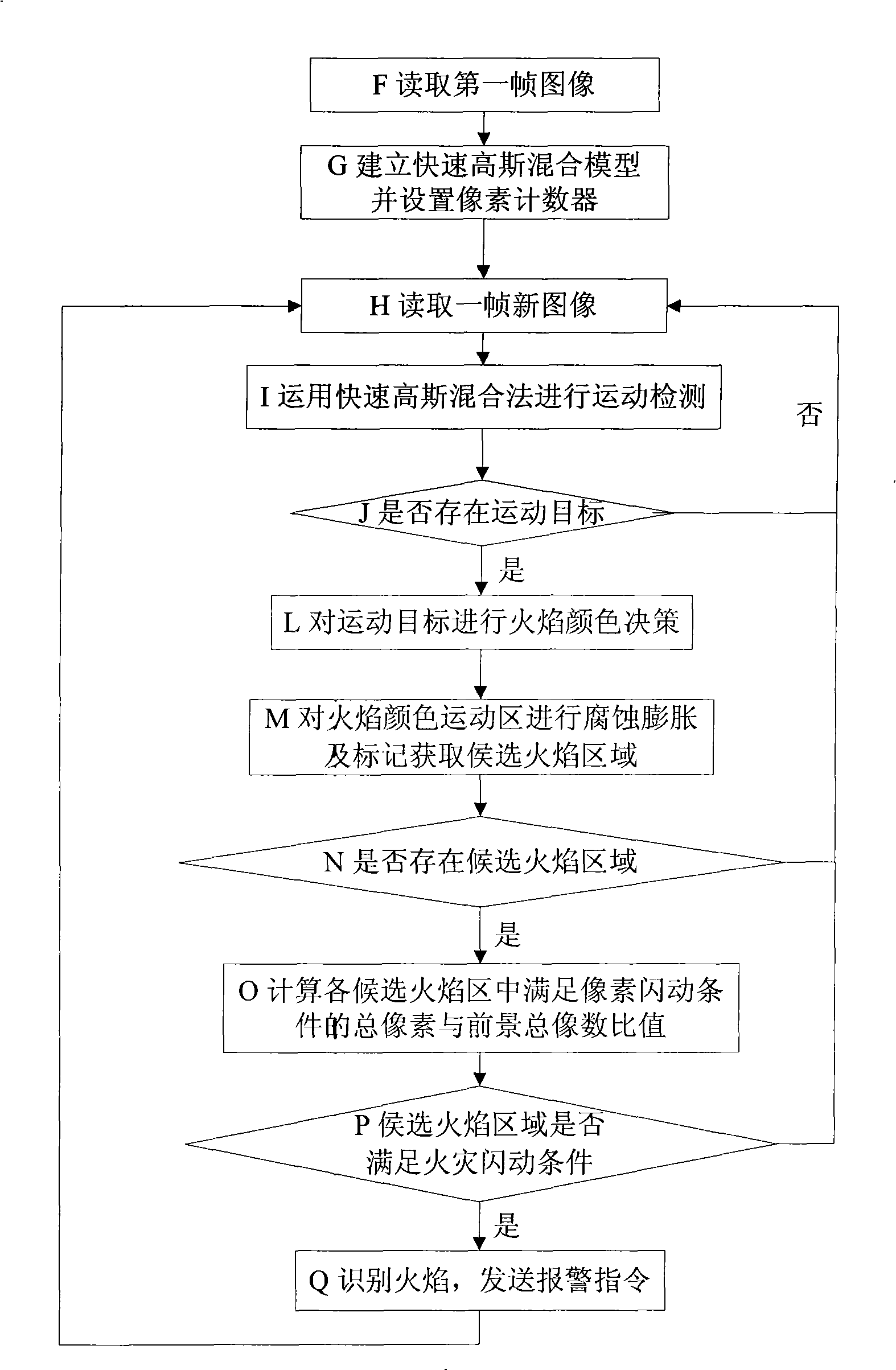
Rapid video flame detection method based on multi-characteristic fusion
InactiveCN101493980AProcessing speedSimplified update methodImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionMonitoring siteFlame detection
The invention discloses a video flame-detecting method based on multi-features fusion, which is characterized in that: a fast Gaussian hybrid model is established and a pixel counter is arranged when a computer reads a first frame image a monitoring site captured by a colored camera; when the computer reads new images of a second frame and the following frames, a fast Gaussian hybrid method is firstly used for carrying out motion detection so as to extract a moving object and then a flame color decision is carried out to the moving object to obtain an alternative flame area; and finally, flicker analysis is carried out on the alternative flame area so as to identify a real flame object. The video flame-detecting method carries out modeling to flame color characteristics, motion characteristics and flickering characteristics in flame areas; various flame detection interfering resources are gradually and rapidly eliminated in accordance with the recognition sequence of motion, color and flickering. The test results show that the method has relatively strong robustness; in addition, based on an AMD 2.04GHz processor, the processing speed can reach 22 frames per second for video images with pixels of 320 multiplied by 240.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
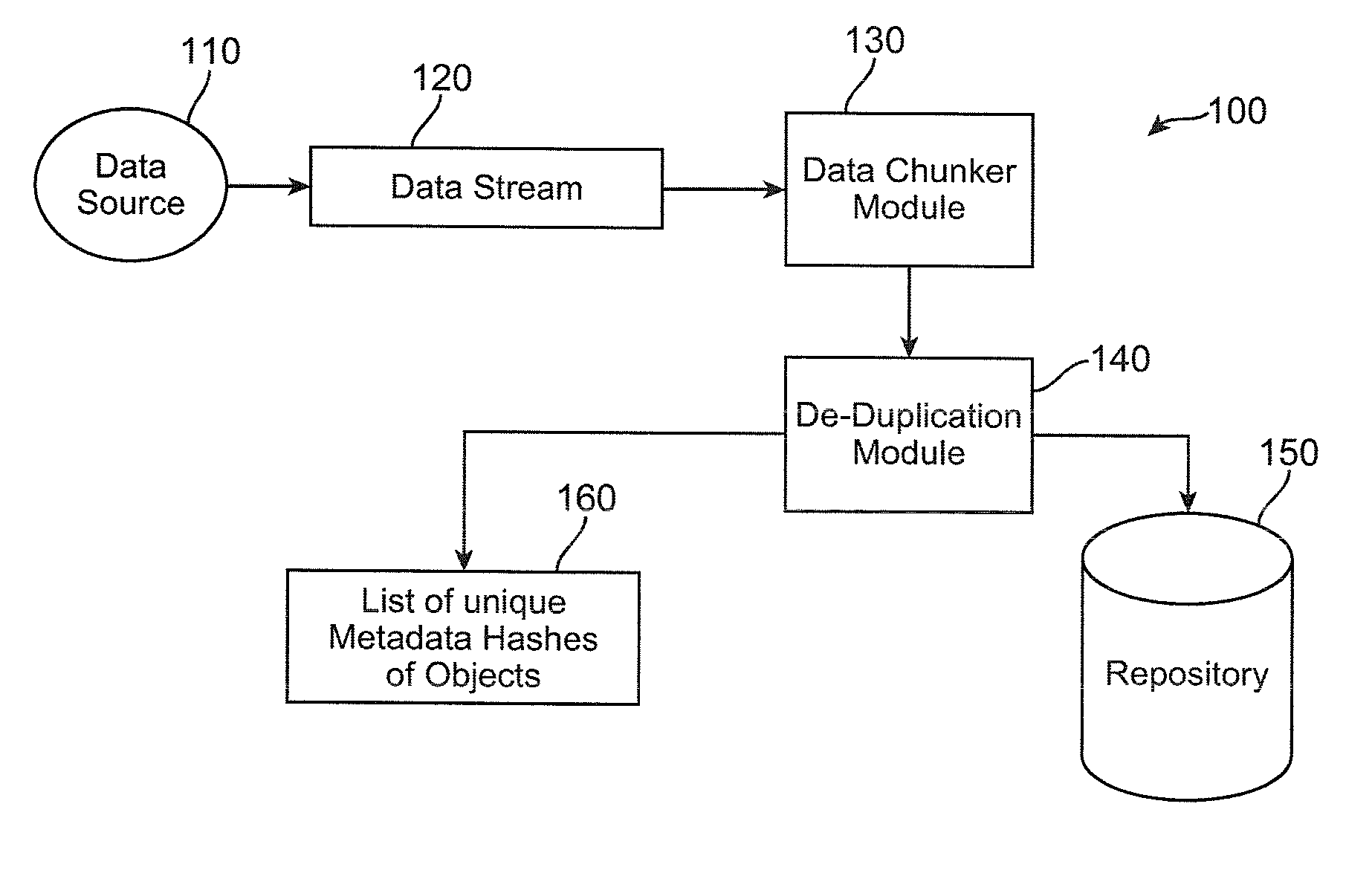
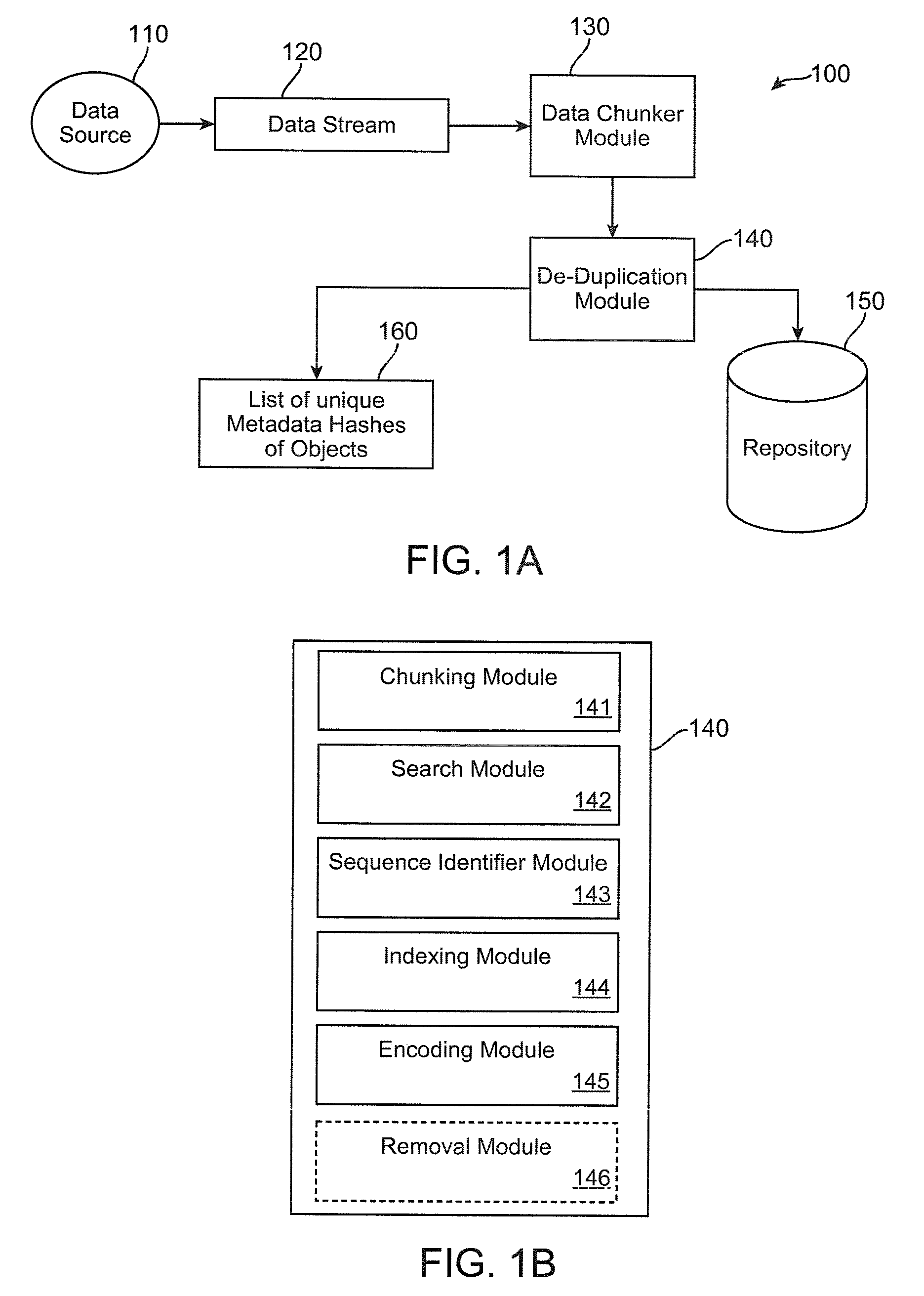
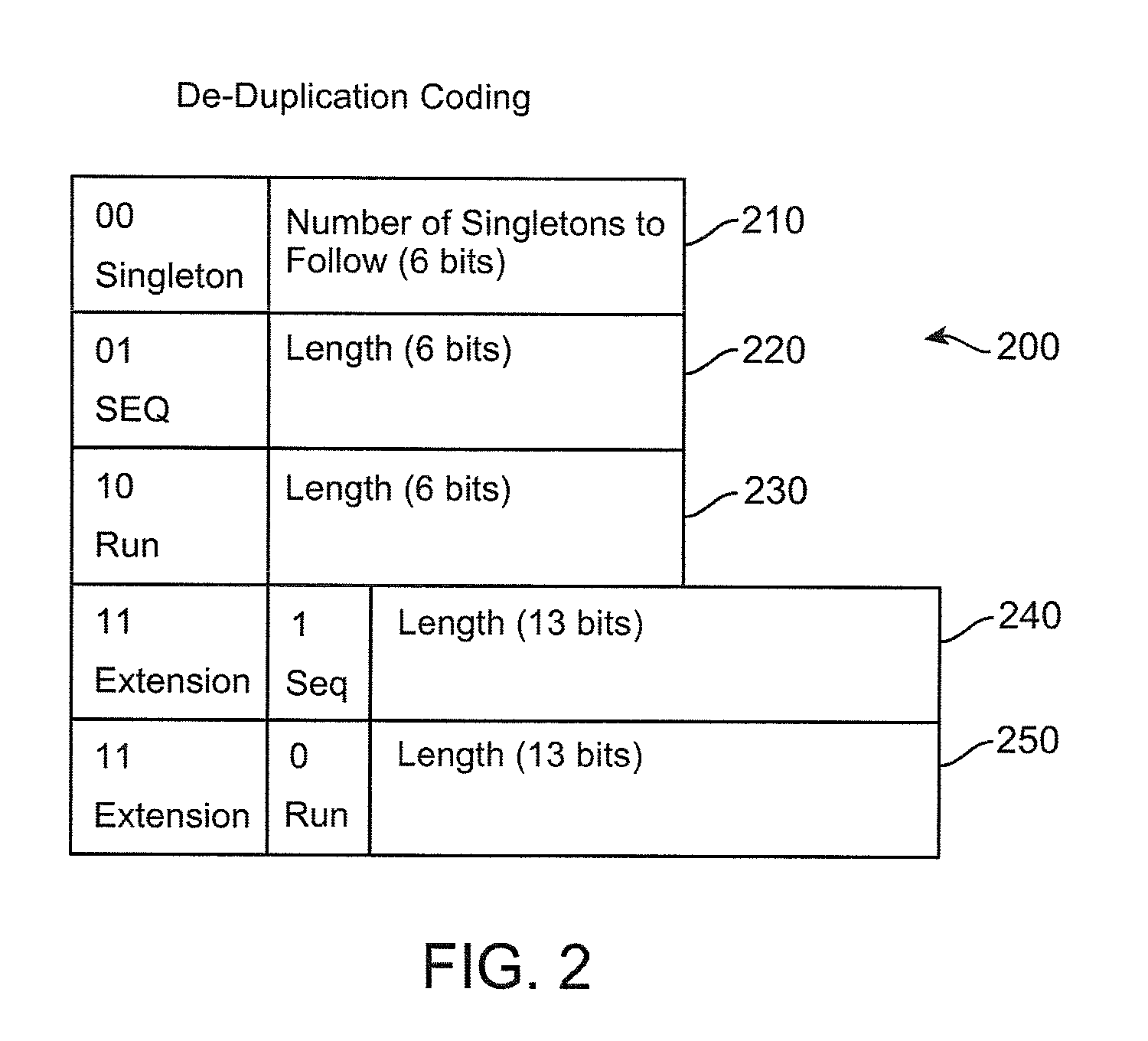
Method and apparatus to minimize metadata in de-duplication
ActiveUS20090300321A1Reduce recognitionAvoiding repeated stored identificationMemory systemsMicro-instruction address formationRecognition sequenceComputer science
Owner:IBM CORP
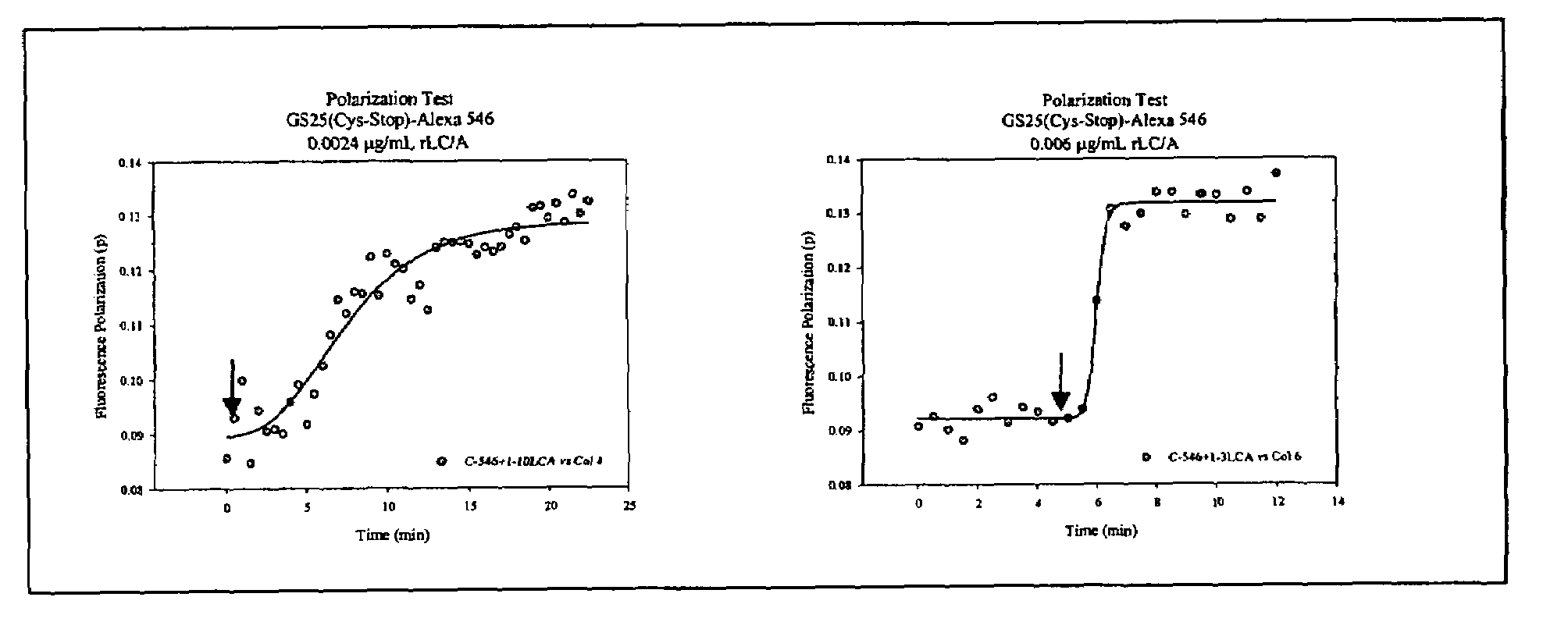
Fluorescence polarization assays for determining clostridial toxin activity
The present invention provides a method of determining the presence or activity of a clostridial toxin by (a) treating with a sample, under conditions suitable for clostridial toxin protease activity, a clostridial toxin substrate which includes a fluorophore; a bulking group; and a clostridial toxin recognition sequence containing a cleavage site that intervenes between the fluorophore and the bulking group; (b) exciting the fluorophore with plane polarized light; and (c) determining fluorescence polarization of the treated substrate relative to a control substrate, where a change in fluorescence polarization of the treated substrate as compared to fluorescence polarization of the control substrate is indicative of the presence or activity of the clostridial toxin.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
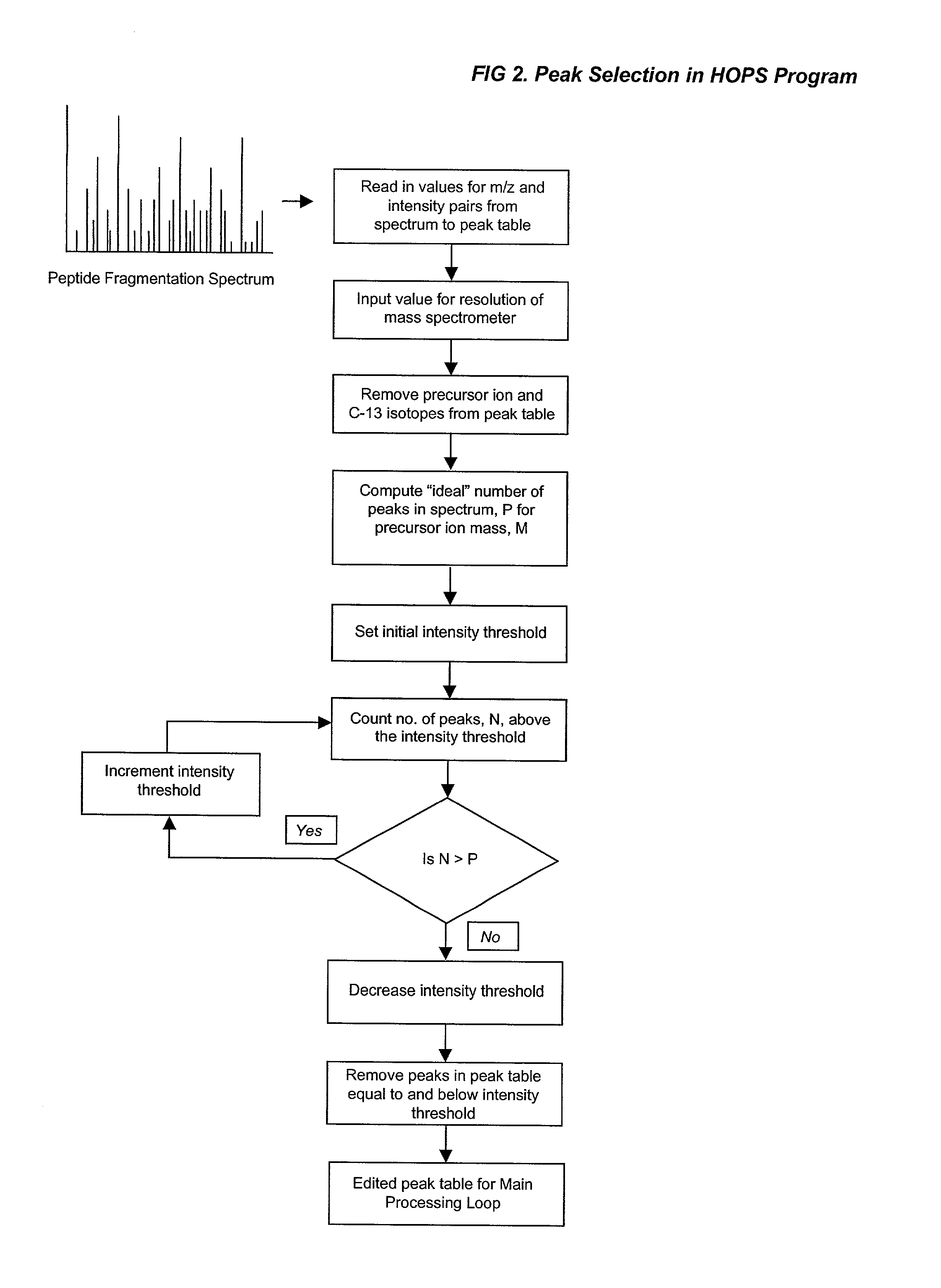
Automated identification of peptides
InactiveUS20020102610A1Quick identificationCharacter and pattern recognitionBiological testingPresent methodPost translational
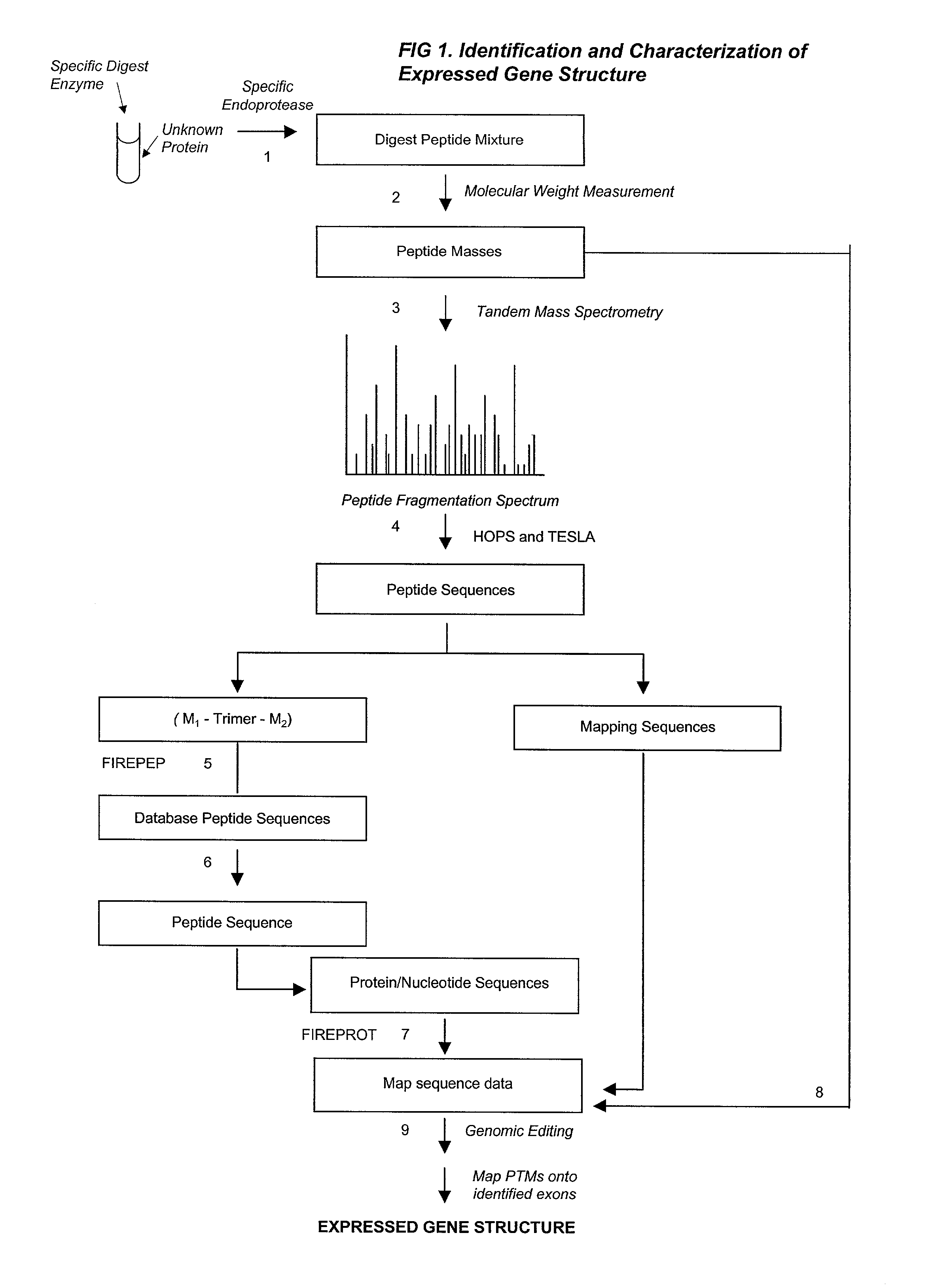
A fully automated, user-independent method is described for computer-mediated interpretation of data derived by mass spectrometry of an experimental peptide to identify and characterize a corresponding peptide sequence in a peptide database. The method identifies the corresponding sequence if it is present in the database, without the need for a skilled observer to choose from amongst a list of possible matches. By using an automated back-read process, the present method can uniquely identify a corresponding peptide sequence in a database based on a single matching peptide sequence. The method also permits mapping of mass spectral data to sequences in peptide or nucleotide databases for unambiguous identification of exons; determining a correct reading frame; identifying artefacts and errors in sequences; identifying mutations and polymorphisms; identifying post-translational modifications; and identifying exon-intron boundaries.
Owner:OXFORD GLYCOSCI UK
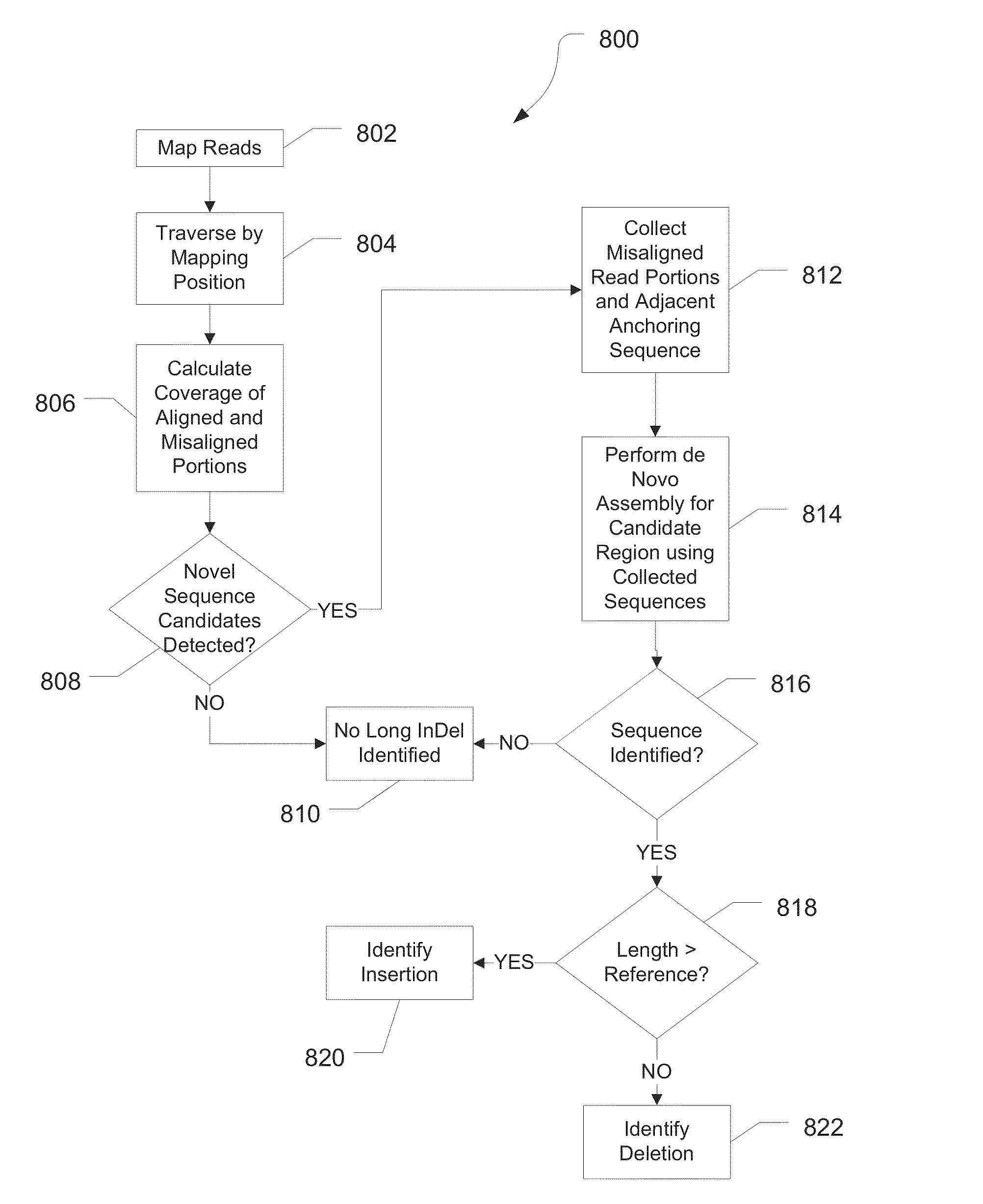
Systems and methods for identifying sequence variation
InactiveUS20130345066A1Microbiological testing/measurementAnalogue computers for chemical processesRecognition sequenceContext specific
Systems and method for determining variants can receive mapped reads, align flow space information to a flow space representation of a corresponding portion of the reference. Reads spanning a position with a potential variant can be evaluated in a context specific manner. A list of probable variants can be provided.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
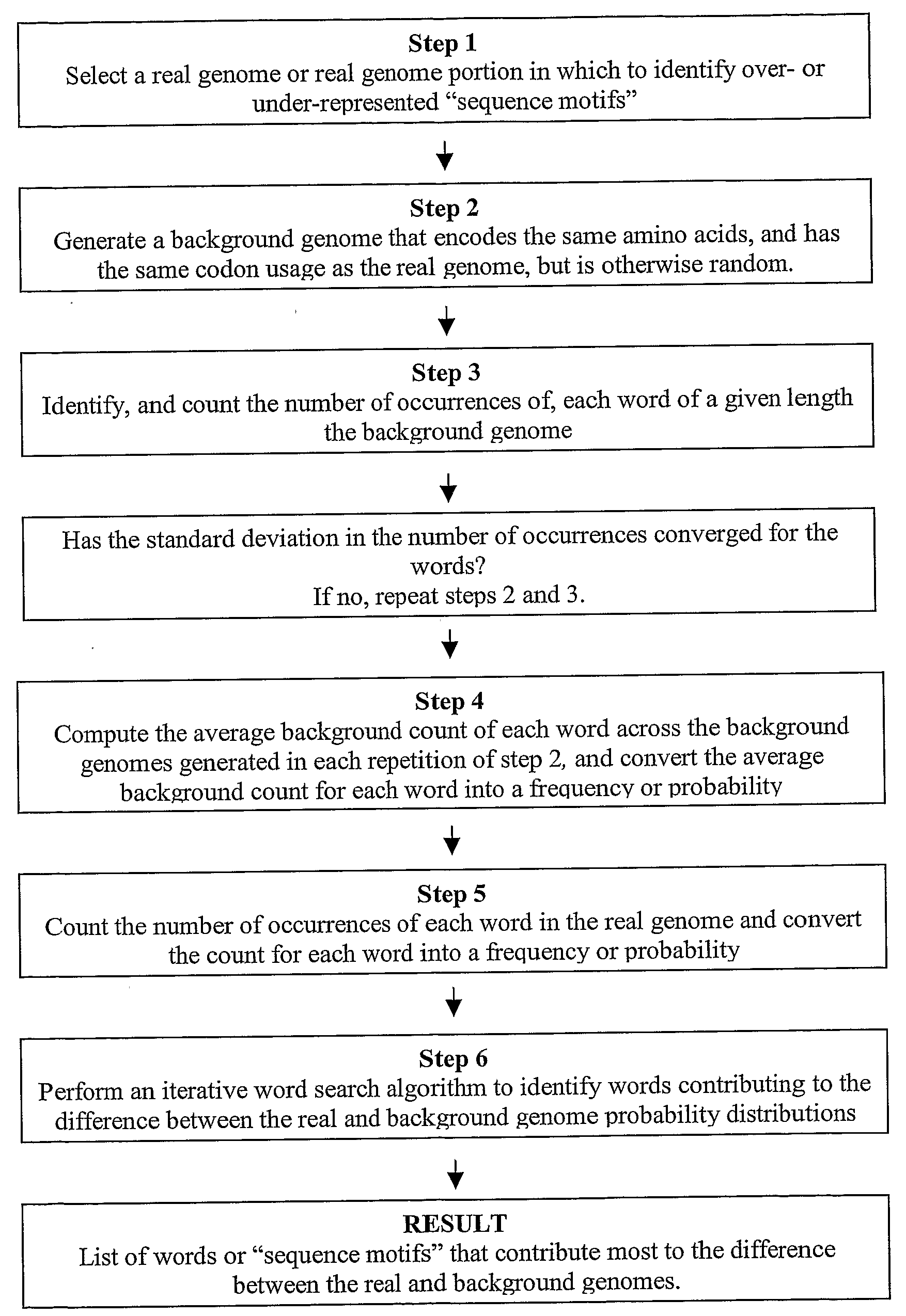
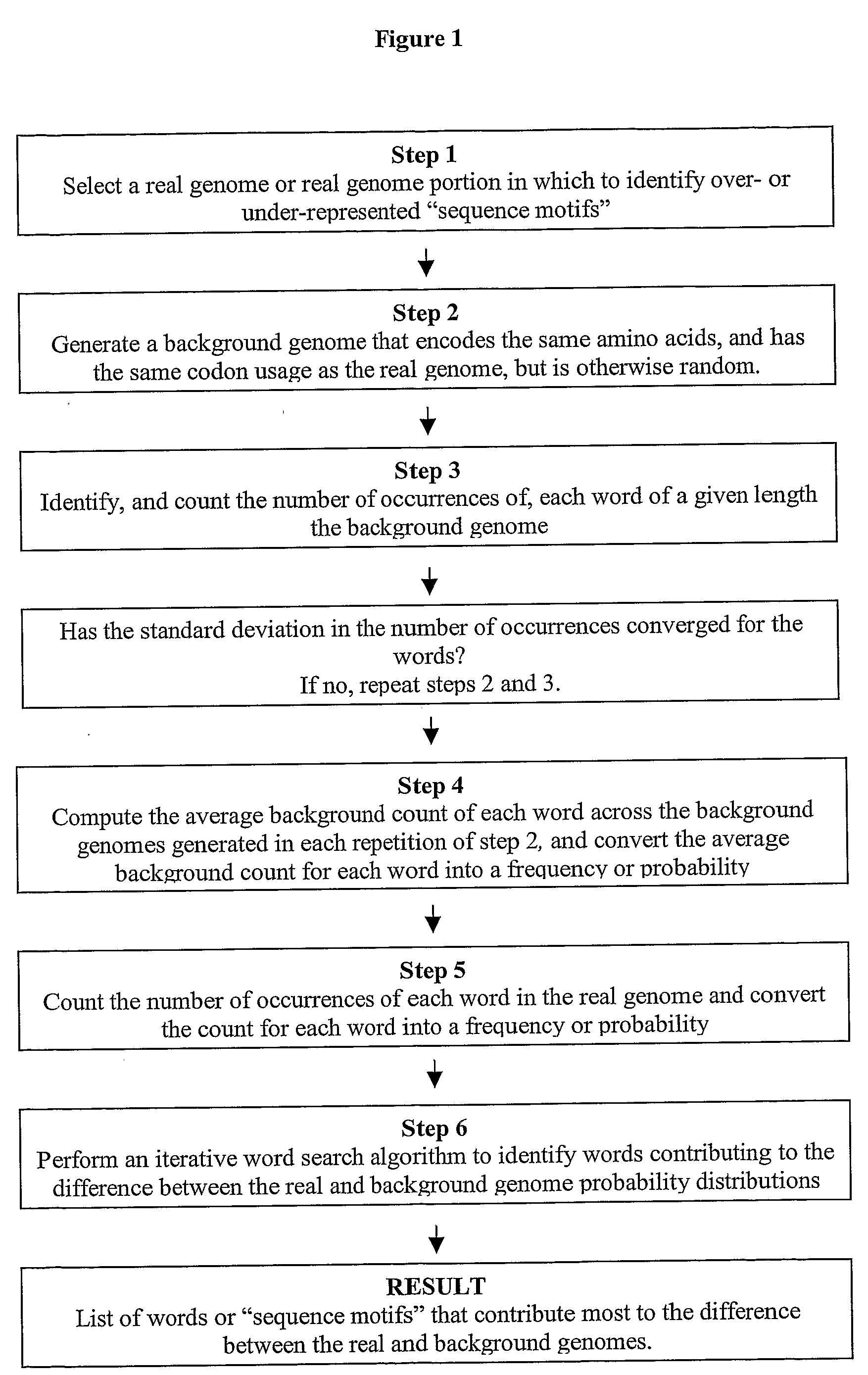
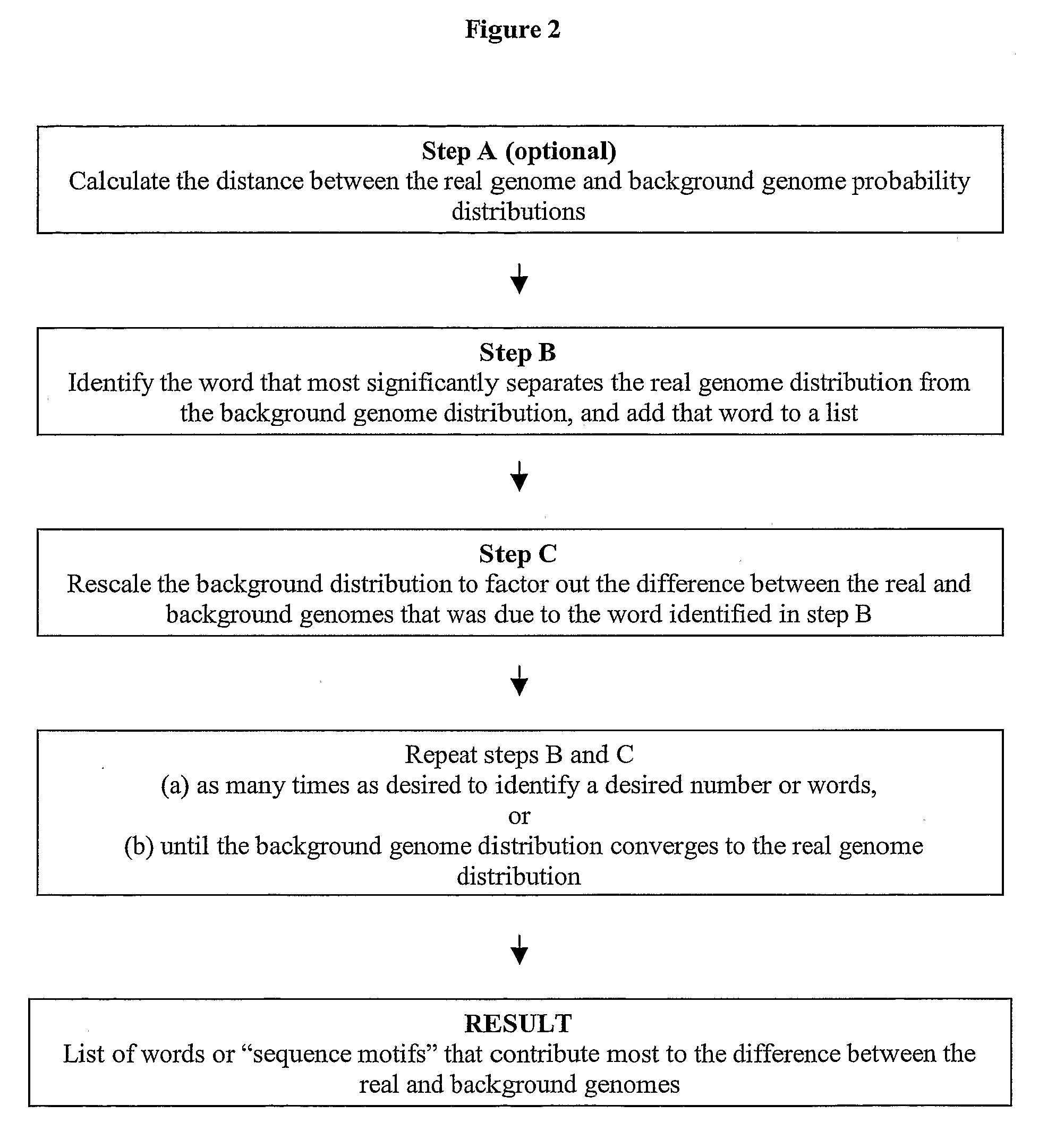
Methods for identifying sequence motifs, and applications thereof
InactiveUS20090208955A1Reduce in quantityIncrease the number ofMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsBinding siteInstability
The present invention relates to methods and algorithms that can be used to identify sequence motifs that are either under- or over-represented in a given nucleotide sequence as compared to the frequency of those sequences that would be expected to occur by chance, or that are either under- or over-represented as compared to the frequency of those sequences that occur in other nucleotide sequences, and to methods of scoring sequences based on the occurrence of these sequence motifs. Such sequence motifs may be biologically significant, for example they may constitute transcription factor binding sites, mRNA stability / instability signals, epigenetic signals, and the like. The methods of the invention can also be used, inter alia, to classify sequences or organisms in terms of their phylogenetic relationships, or to identify the likely host of a pathogenic organism. The methods of the present invention can also be used to optimize expression of proteins.
Owner:INST FOR ADVANCED STUDY
Methods for ligation and uses thereof
ActiveUS20110321183A1Effective limitFacilitate N-terminal ligationHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsAcyl groupRecognition sequence
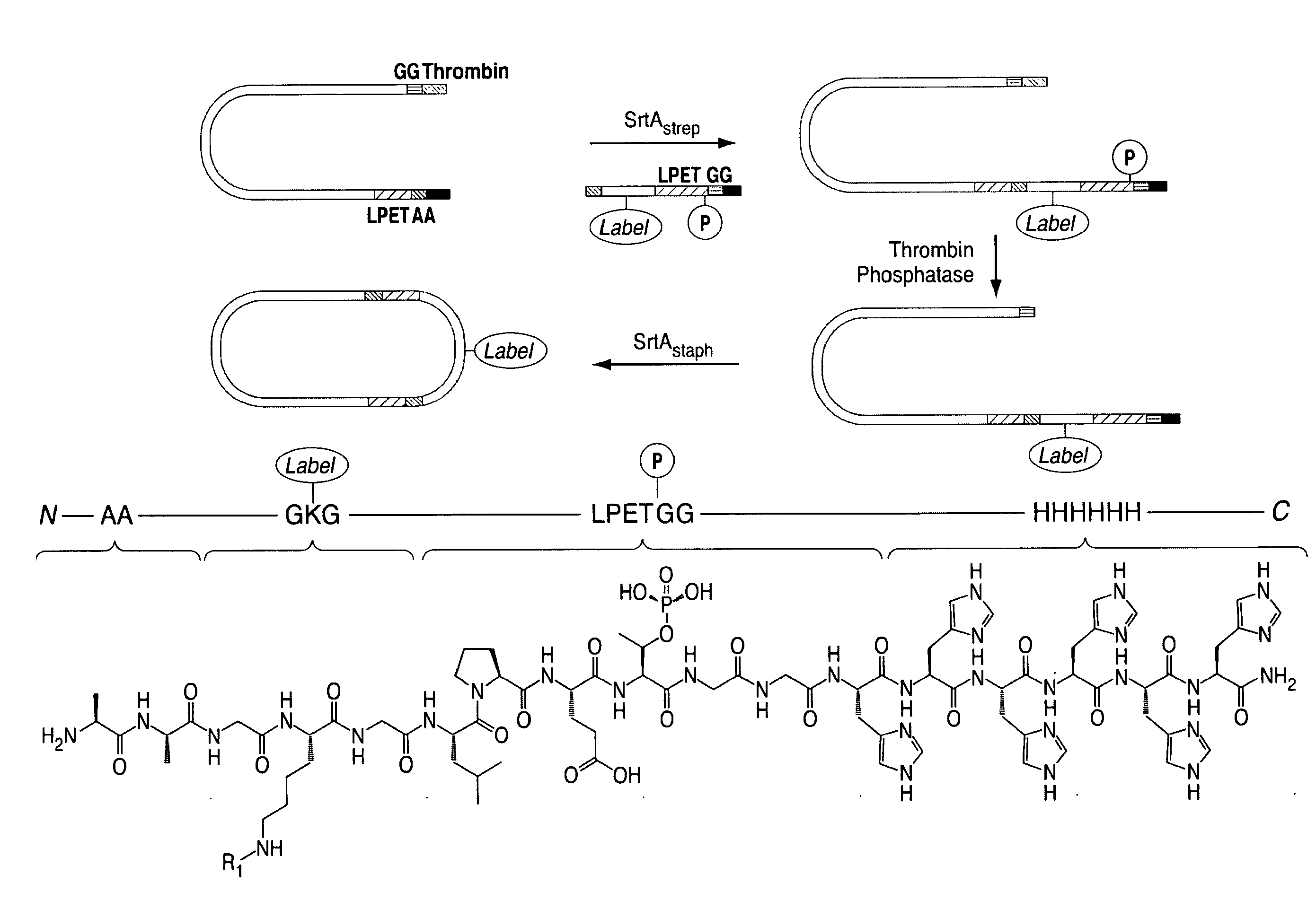
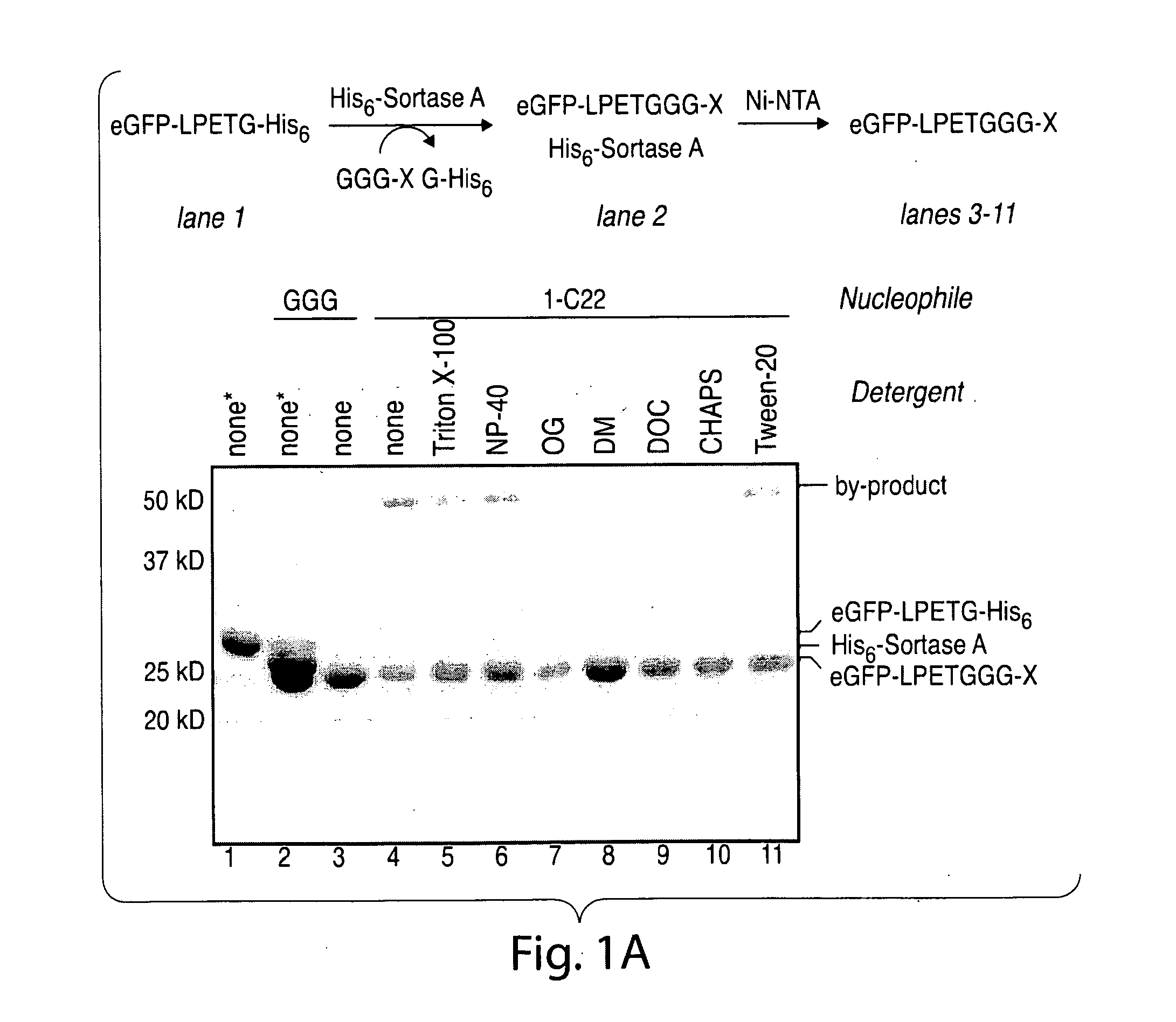
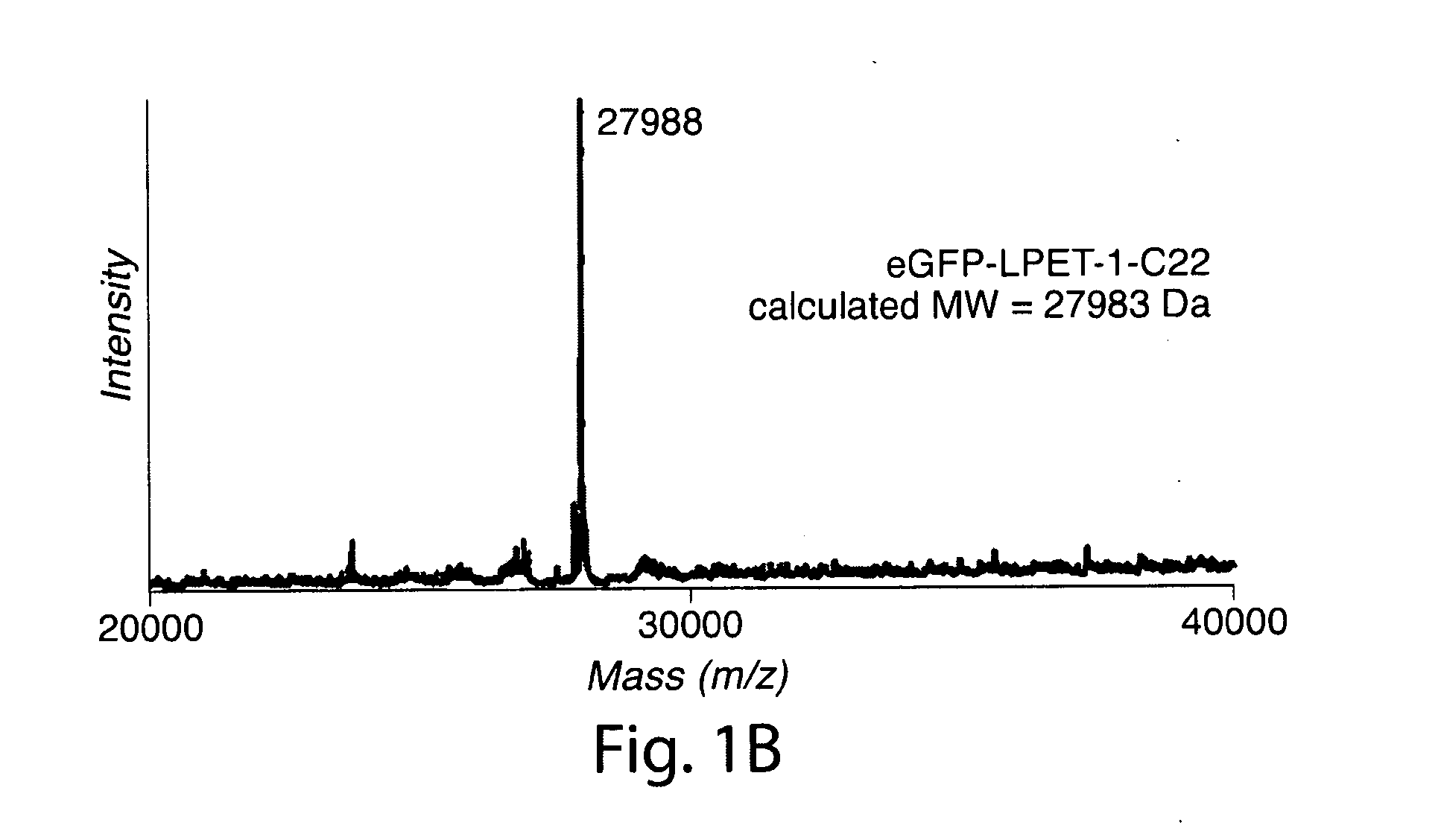
The present invention relates to methods for ligation. The invention provides novel reagents and methods for ligating an acyl donor compound with an acyl acceptor compound. Provided acyl donor compounds comprise a transamidase recognition sequence that allows ligation with a nucleophilic acyl acceptor in the presence of transamidase. The invention further provides kits comprising acyl donor compounds and optionally comprising other reagents for ligation.
Owner:WHITEHEAD INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES
Systems and methods for identifying sequence variation
Systems and method for determining variants can receive mapped reads, and call variants. In embodiments, flow space information for the reads can be aligned to a flow space representation of a corresponding portion of the reference. Reads spanning a position with a potential variant can be grouped and a score can be calculated for the variant. Based on the scores, a list of probable variants can be provided. In various embodiments, low frequency variants can be identified where multiple potential variants are present at a position.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Compositions and Methods for High Fidelity Assembly of Nucleic Acids
InactiveUS20150203839A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationEnzymatic digestionPolymerase L
Aspects of the invention relate to methods, compositions and algorithms for designing and producing a target nucleic acid. The method can include: (1) providing a plurality of blunt-end double-stranded nucleic acid fragments having a restriction enzyme recognition sequence at both ends thereof; (2) producing via enzymatic digestion a plurality of cohesive-end double-stranded nucleic acid fragments each having two different and non-complementary overhangs; (3) ligating the plurality of cohesive-end double-stranded nucleic acid fragments with a ligase; and (4) forming a linear arrangement of the plurality of cohesive-end double-stranded nucleic acid fragments, wherein the unique arrangement comprises the target nucleic acid. In certain embodiments, the plurality of blunt-end double-stranded nucleic acid fragments can be provided by: releasing a plurality of oligonucleotides synthesized on a solid support; and synthesizing complementary strands of the plurality of oligonucleotides using a polymerase based reaction.
Owner:GEN9
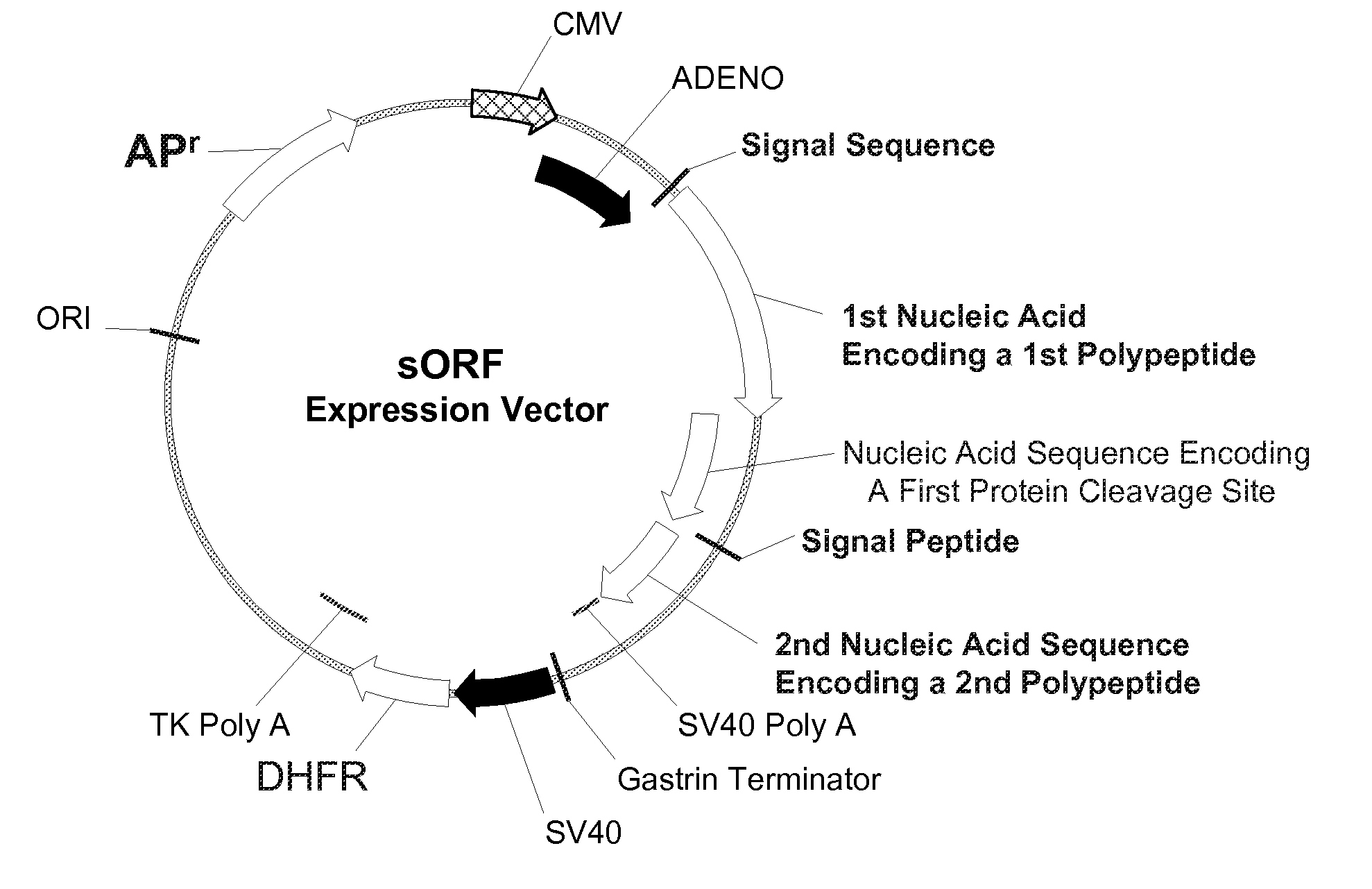
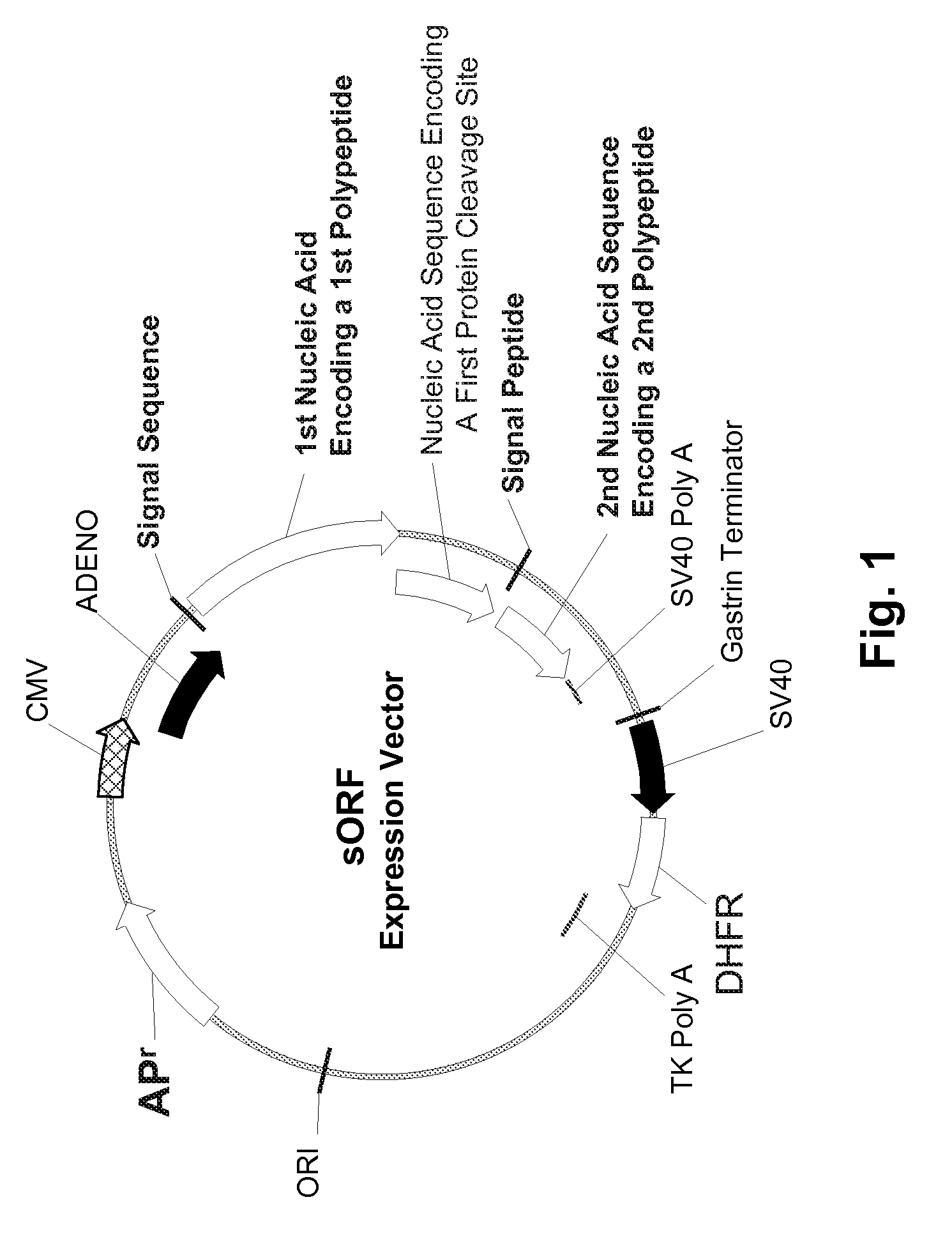
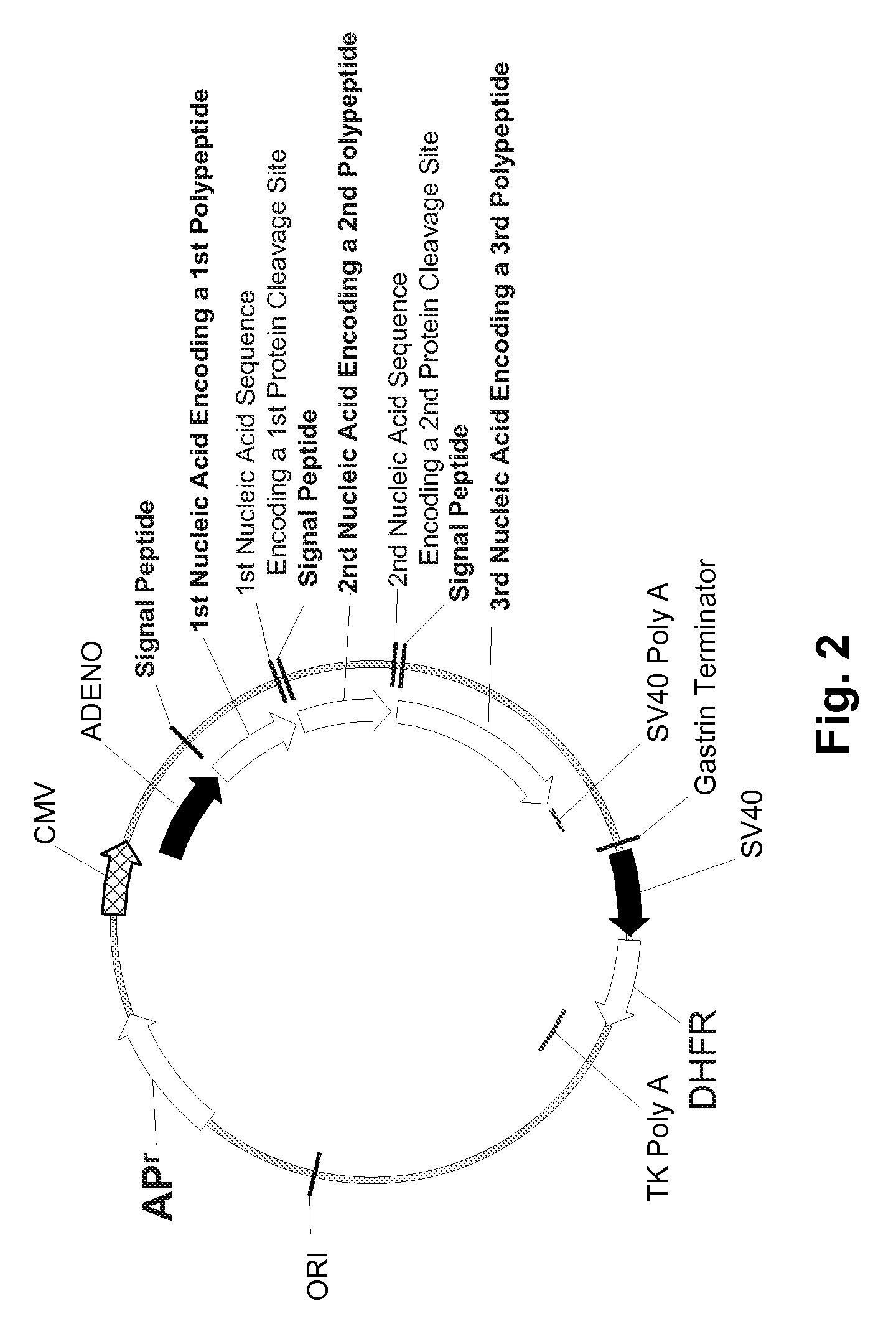
Multiple Gene Expression including sORF Constructs and Methods with Polyproteins, Pro-Proteins, and Proteolysis
InactiveUS20070065912A1Efficient expressionImprove economyFungiFusion with post-translational modification motifOpen reading frameADAMTS Proteins
Disclosed are useful constructs and methods for the expression of proteins using primary translation products that are processed within a recombinant host cell. Constructs comprising a single open reading frame (sORF) are described for protein expression including expression of multiple polypeptides. A primary translation product (a pro-protein or a polyprotein) contains polypeptides such as inteins or hedgehog family auto-processing domains, or variants thereof, inserted in frame between multiple protein subunits of interest. The primary product can also contain cleavage sequences such as other proteolytic cleavage or protease recognition sites, or signal peptides which contain recognition sequences for signal peptidases, separating at least two of the multiple protein subunits. The sequences of the inserted auto-processing polypeptides or cleavage sites can be manipulated to enhance the efficiency of expression of the separate multiple protein subunits. Also disclosed are independent aspects of conducting efficient expression, secretion, and / or multimeric assembly of proteins such as immunoglobulins. Where the polyprotein contains immunoglobulin heavy and light chain segments or fragments capable of antigen recognition, in an embodiment a selectable stoichiometric ratio is at least two copies of a light chain segment per heavy chain segment, with the result that the production of properly folded and assembled functional antibody is made. Modified signal peptides, including such from immunoglobulin light chains, are described.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
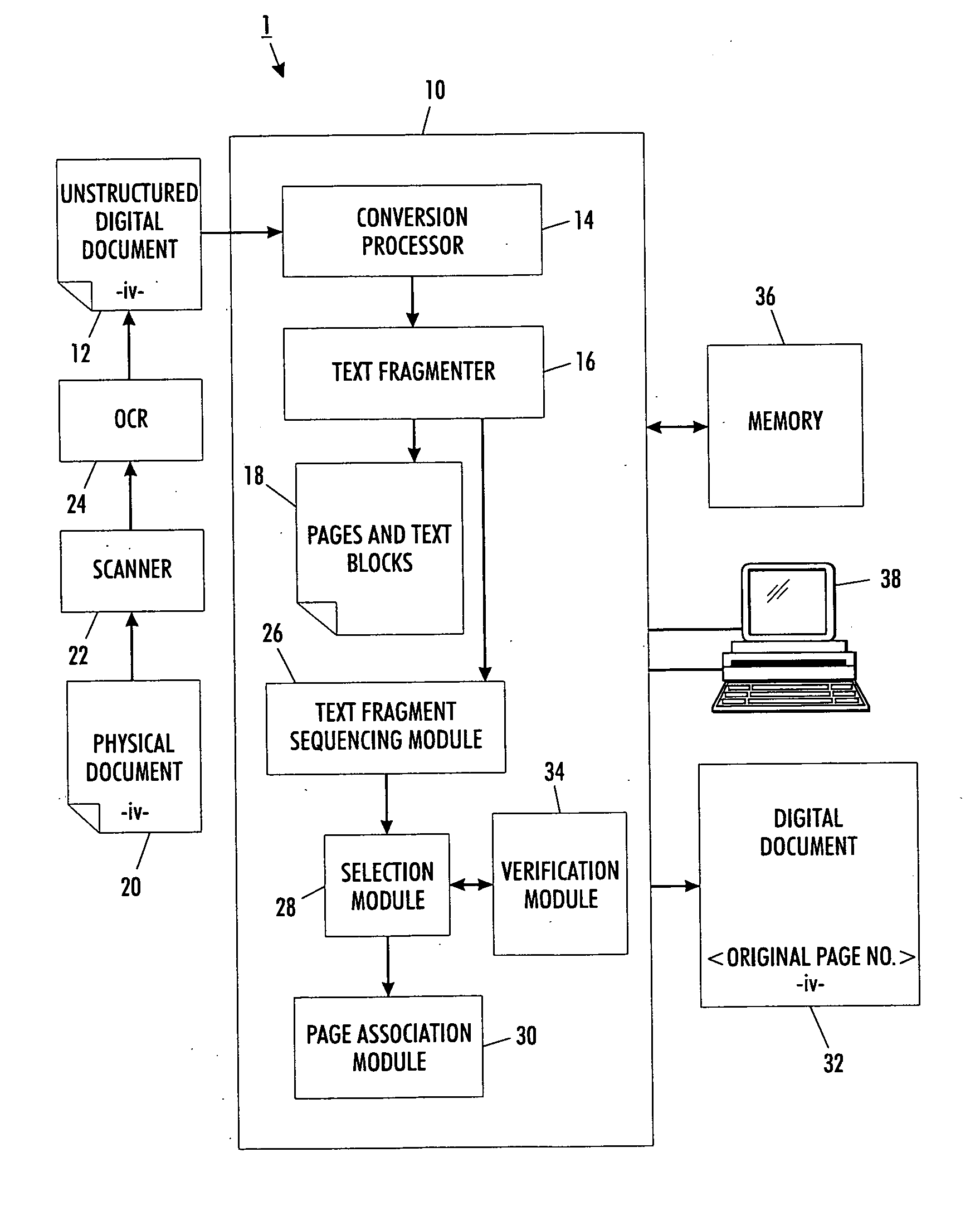
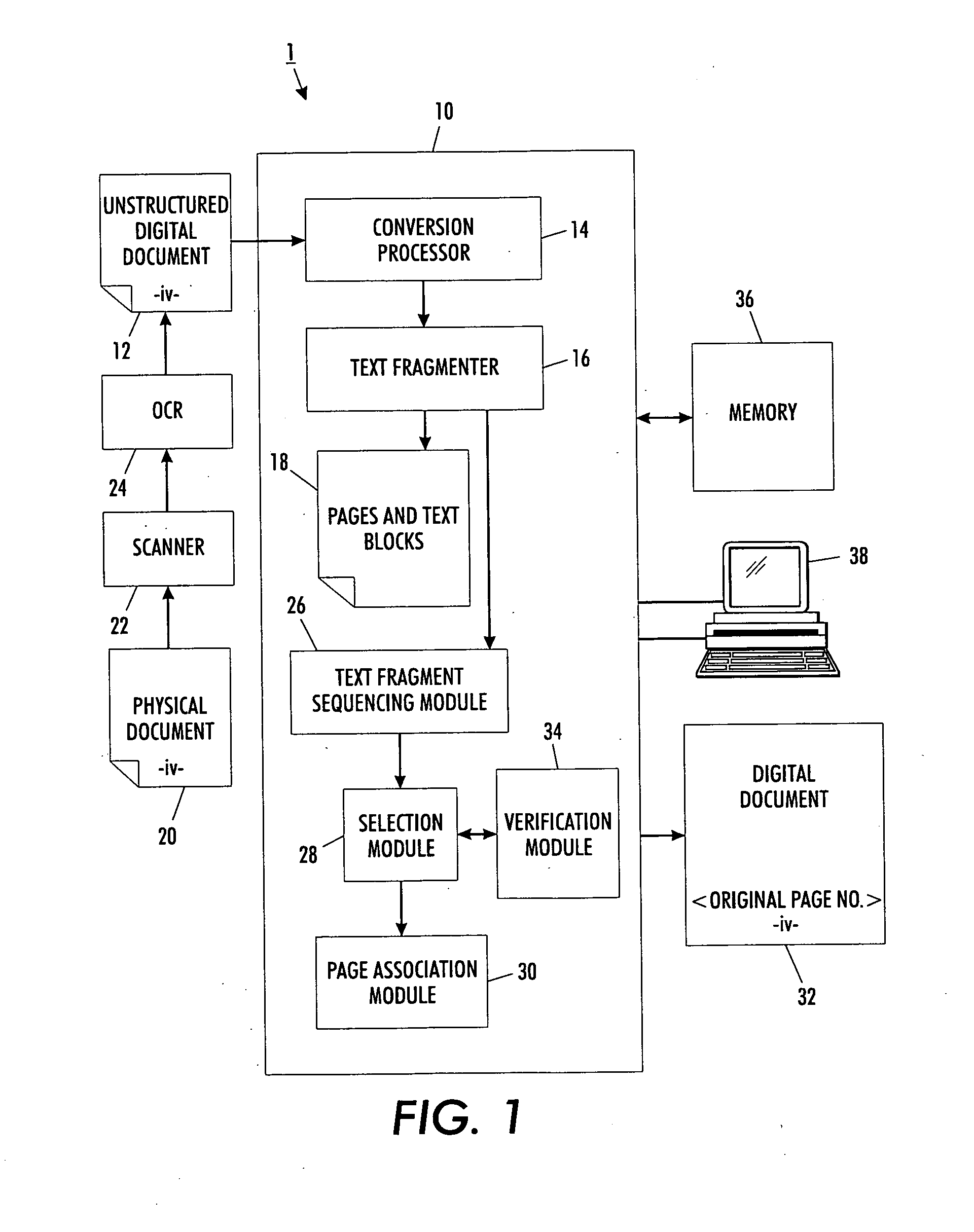
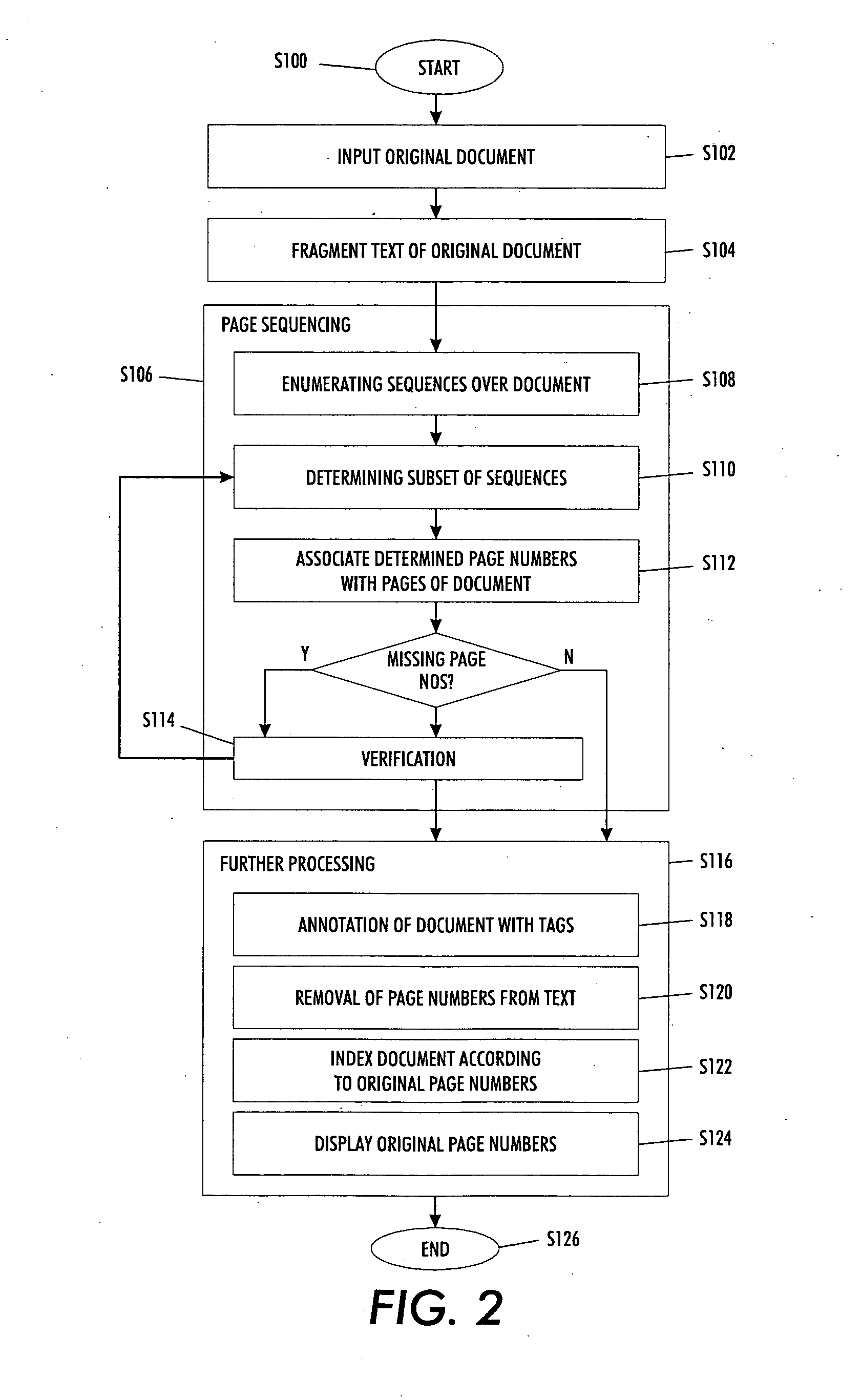
Versatile page number detector
InactiveUS20080114757A1Digital data information retrievalCharacter and pattern recognitionRecognition sequenceDocument preparation
A method for detection of page numbers in a document includes identifying a plurality of text fragments associated with a plurality of pages of a document. From the identified text fragments, at least one sequence is identified. Each identified sequence includes a plurality of terms. Each term of the sequence is derived from a text fragment selected from the plurality text fragments. The terms of an identified sequence comply with at least one predefined numbering scheme which defines a form and an incremental state of the terms in a sequence. A subset of the identified sequences which cover at least some of the pages of the document is computed. Terms of at least some of the subset of the identified sequences are construed as page numbers of pages of the document. Additional page numbers may be identified by considering one or more features of the terms in the subset of identified sequences.
Owner:XEROX CORP
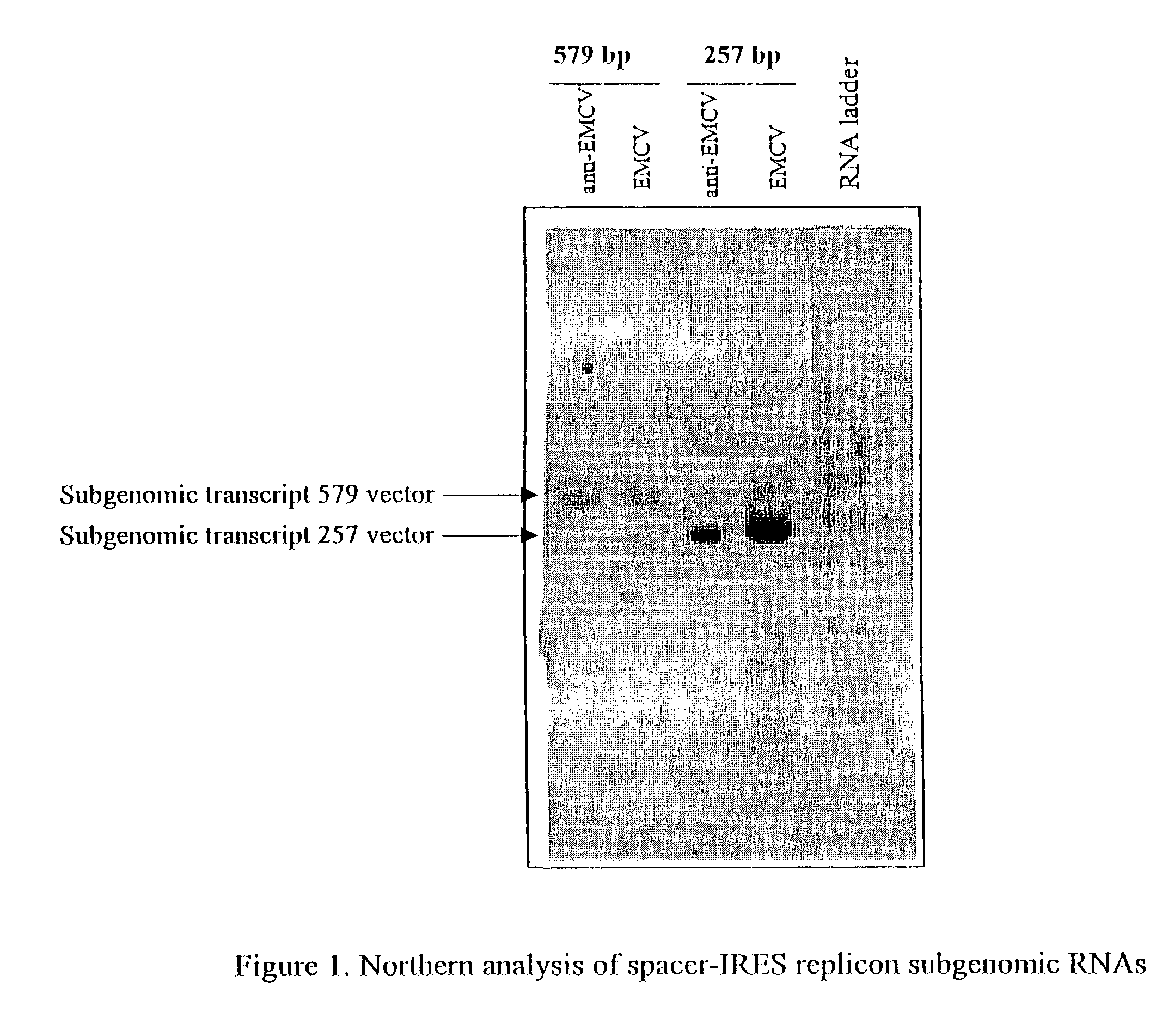
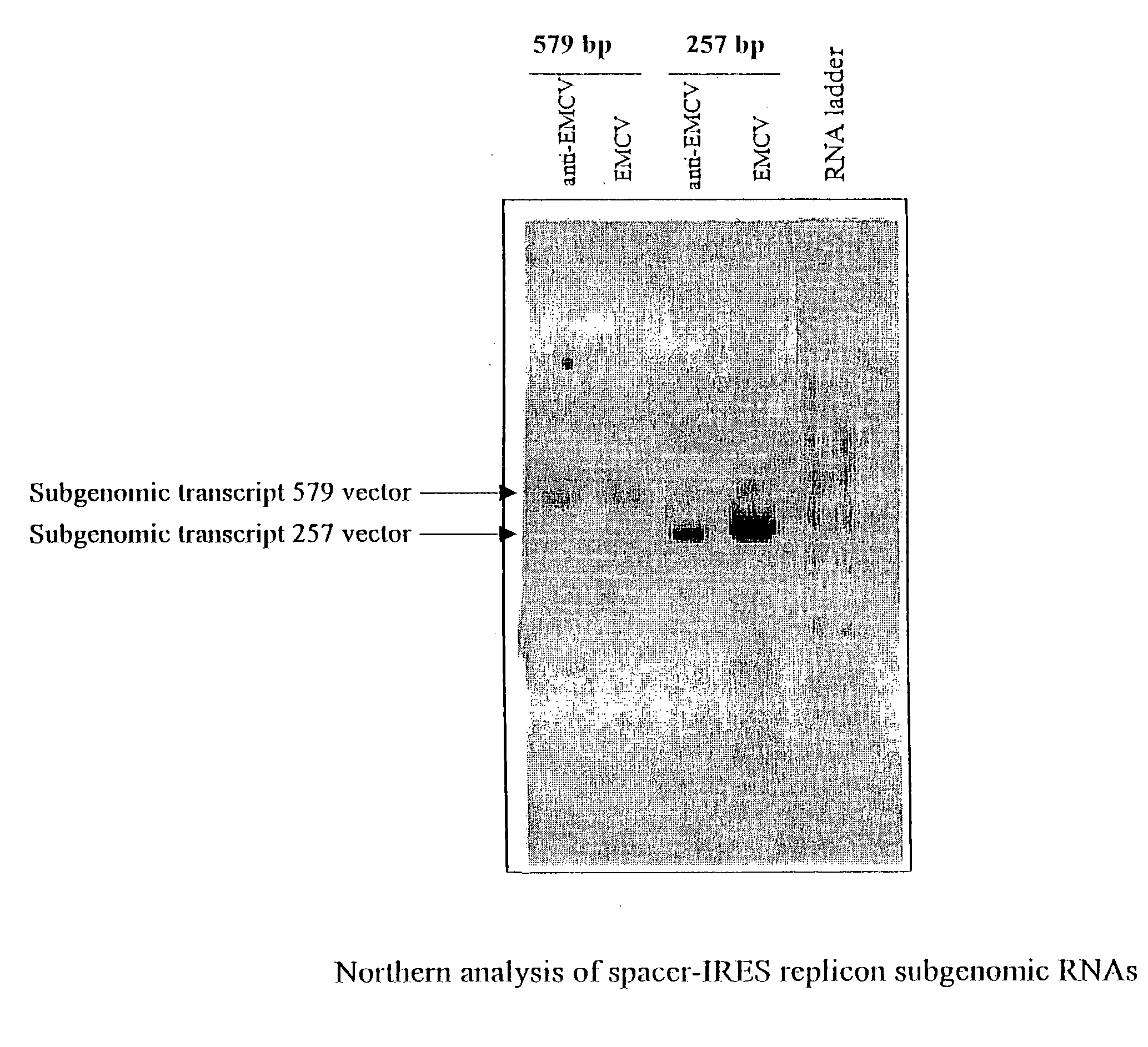
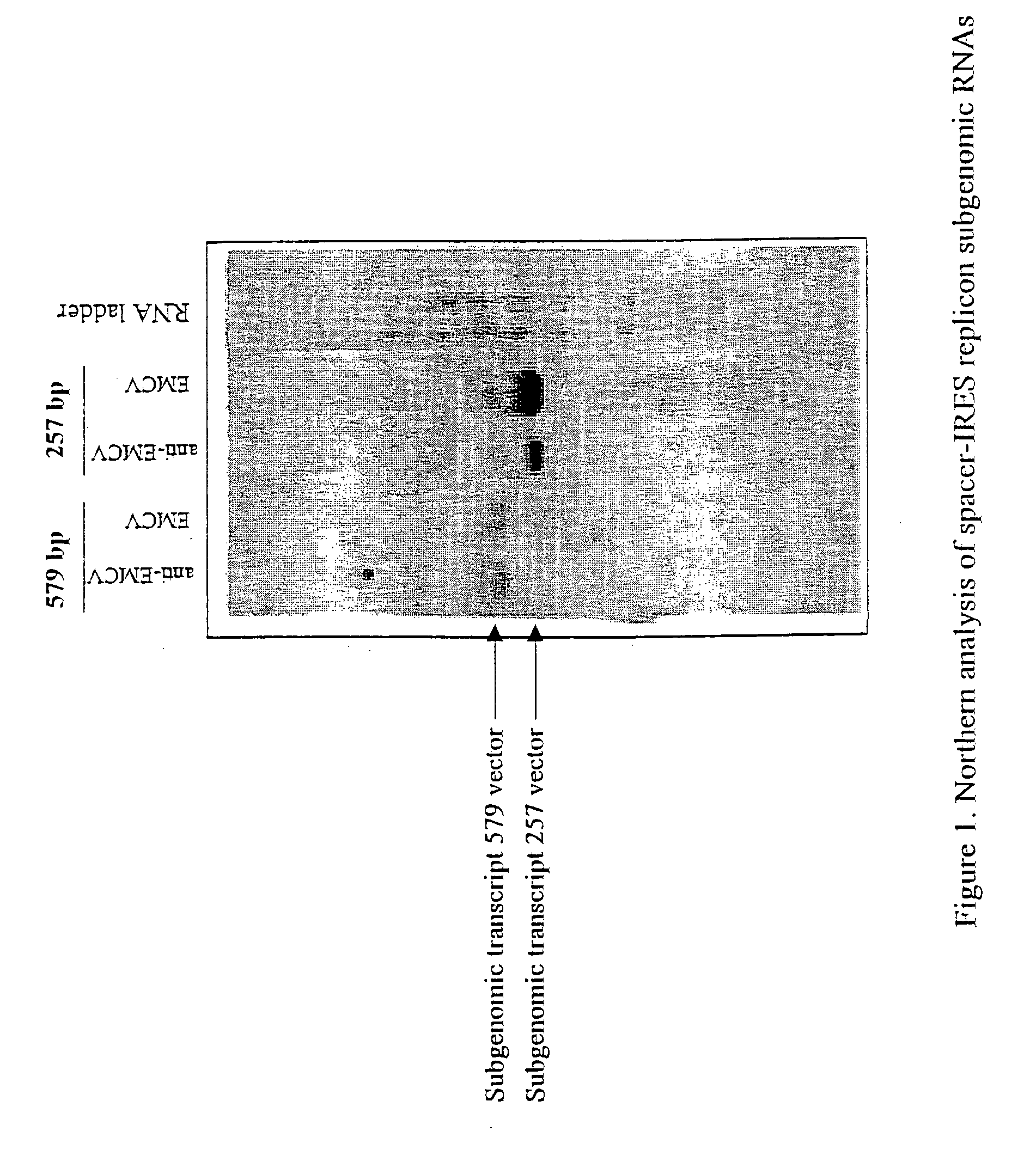
Alphavirus replicons and helper constructs
Owner:ALPHAVAX INC
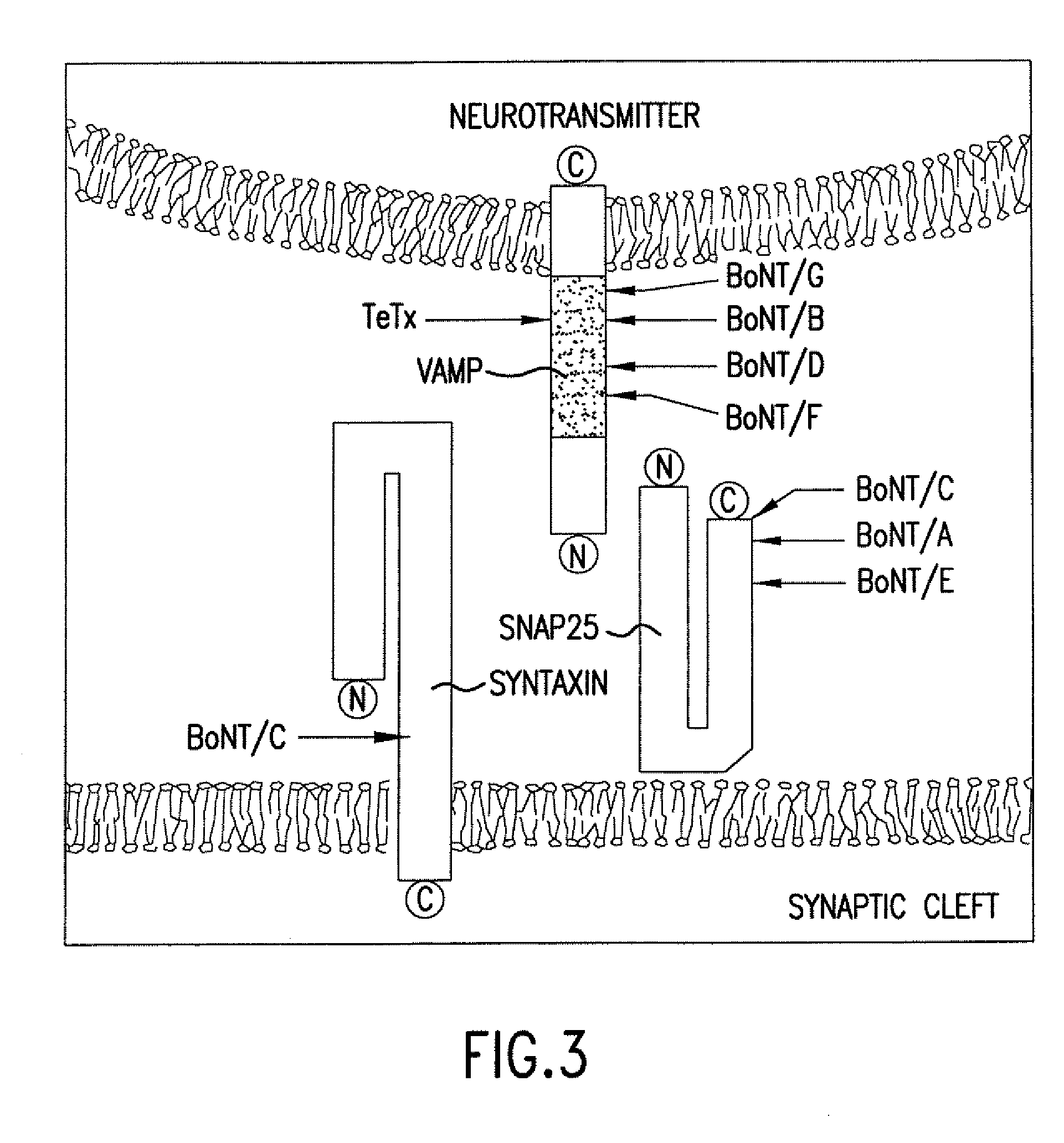
GFP-SNAP25 fluorescence release assay for botulinum neurotoxin protease activity
The present invention provides a nucleic acid molecule which contains a nucleotide sequence encoding a SNAP-25 substrate which includes (i) a green fluorescent protein; (ii) a first partner of an affinity couple; and (iii) a portion of SNAP-25 that includes a BoNT / A, BoNT / C1 or BoNT / E recognition sequence containing a cleavage site, where the cleavage site intervenes between the green fluorescent protein and the first partner of the affinity couple. Further provided herein is a nucleic acid molecule which contains a nucleotide sequence encoding a tagged toxin substrate which includes (i) a fluorescent protein; (ii) a first partner of an affinity couple; and (iii) a clostridial toxin recognition sequence containing a cleavage site, where the cleavage site intervenes between the fluorescent protein and the first partner of the affinity couple.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Cell-based fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) assays for clostridial toxins
InactiveUS20070122858A1Decreased acceptor fluorescence intensityHigh fluorescence intensityAntibacterial agentsBacteriaClostridial toxinEnergy transfer
The present invention provides a method of determining clostridial toxin activity by (a) contacting with a sample a cell containing a clostridial toxin substrate that includes a donor fluorophore; an acceptor having an absorbance spectrum overlapping the emission spectrum of the donor fluorophore; and a clostridial toxin recognition sequence containing a cleavage site that intervenes between the donor fluorophore and the acceptor, where resonance energy transfer is exhibited between the donor fluorophore and the acceptor under the appropriate conditions; (b) exciting the donor fluorophore; and (c) determining resonance energy transfer of the contacted cell relative to a control cell, where a difference in resonance energy transfer of the contacted cell as compared to the control cell is indicative of clostridial toxin activity.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
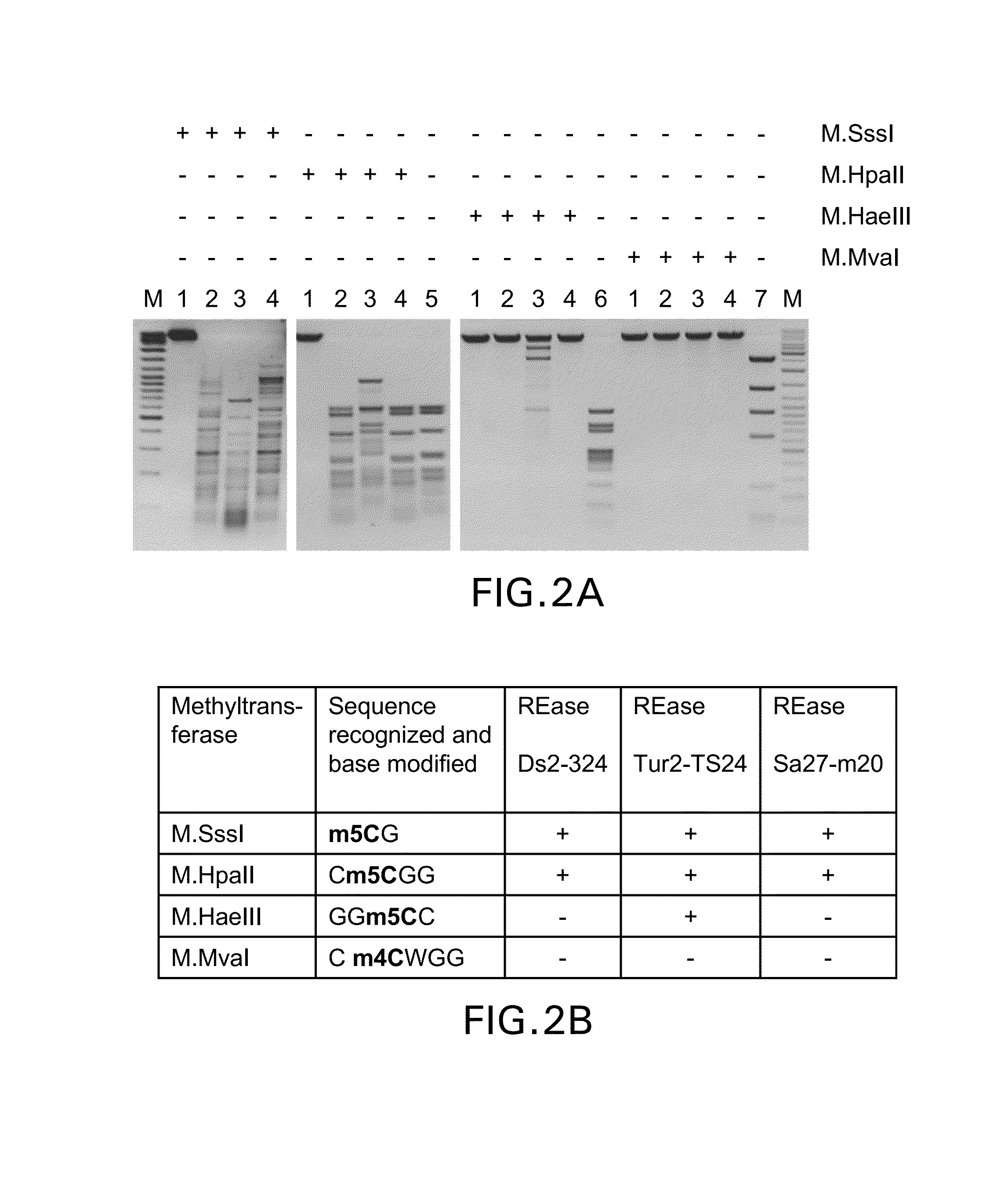
Restriction endonucleases and their applications
Provided is a methylation-specific restriction endonuclease for a DNA duplex substrate, which endonuclease recognizes in a strand of the duplex a 2 to 6 nucleotide recognition sequence comprising a 5-methylcytosine, and cleaves each strand of the duplex at a fixed position outside the recognition sequence.
Owner:THERMO FISHER SCI BALTICS UAB
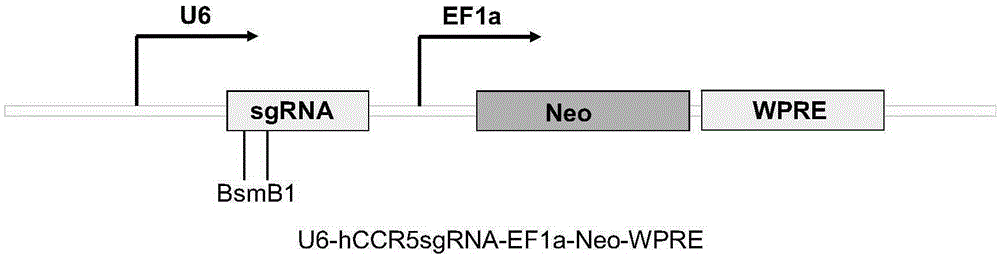
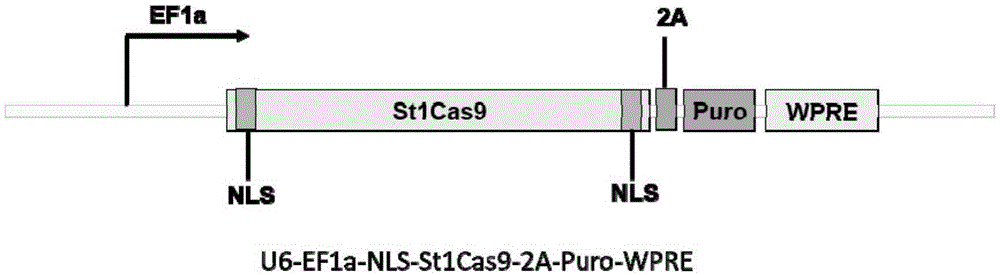
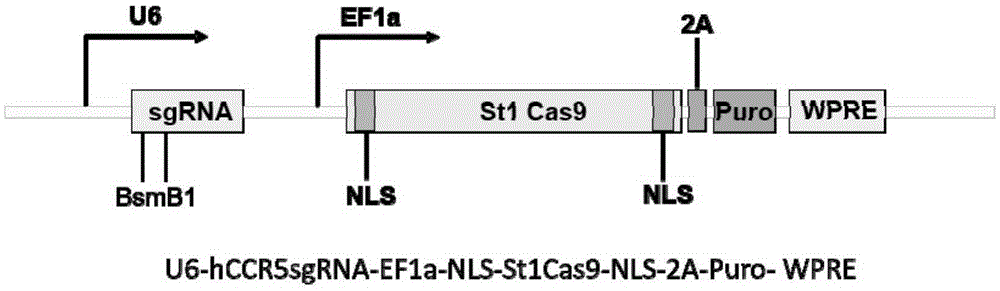
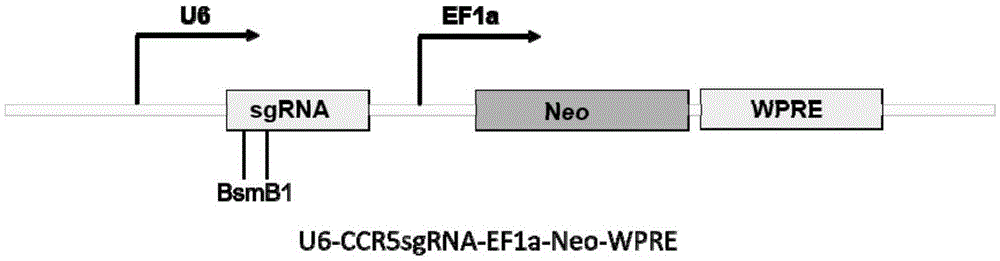
Human CCR5 gene target sequence recognized by streptococcus thermophilus CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat)-Cas9 (CRISPR-associated protein 9) system, sgRNA (single guide ribonucleic acid) and application
InactiveCN105331607AAchieve preventionAchieve therapeutic effectGenetic material ingredientsAntiviralsGene targetsA-DNA
Owner:张竞方
Alphavirus replicons and helper constructs
The present invention provides a recombinant nucleic acid comprising: a first nucleic acid sequence encoding a 5′ alphavirus replication recognition sequence; at least one second nucleic acid sequence encoding an alphavirus nonstructural protein; at least one alphavirus subgenomic promoter; at least one IRES element; at least one heterologous nucleic acid; and a third nucleic acid encoding a 3′ alphavirus replication recognition sequence. Further provided are methods of making alphavirus particles comprising a recombinant nucleic acid of this invention and methods of using the compositions of this invention. Also provided is a recombinant helper nucleic acid comprising: a first nucleic acid sequence encoding a 5′ alphavirus replication recognition sequence; an alphavirus subgenomic promoter; an IRES element; a second nucleic acid encoding an alphavirus structural protein; and a third nucleic acid encoding a 3′ alphavirus replication recognition sequence.
Owner:ALPHAVAX INC
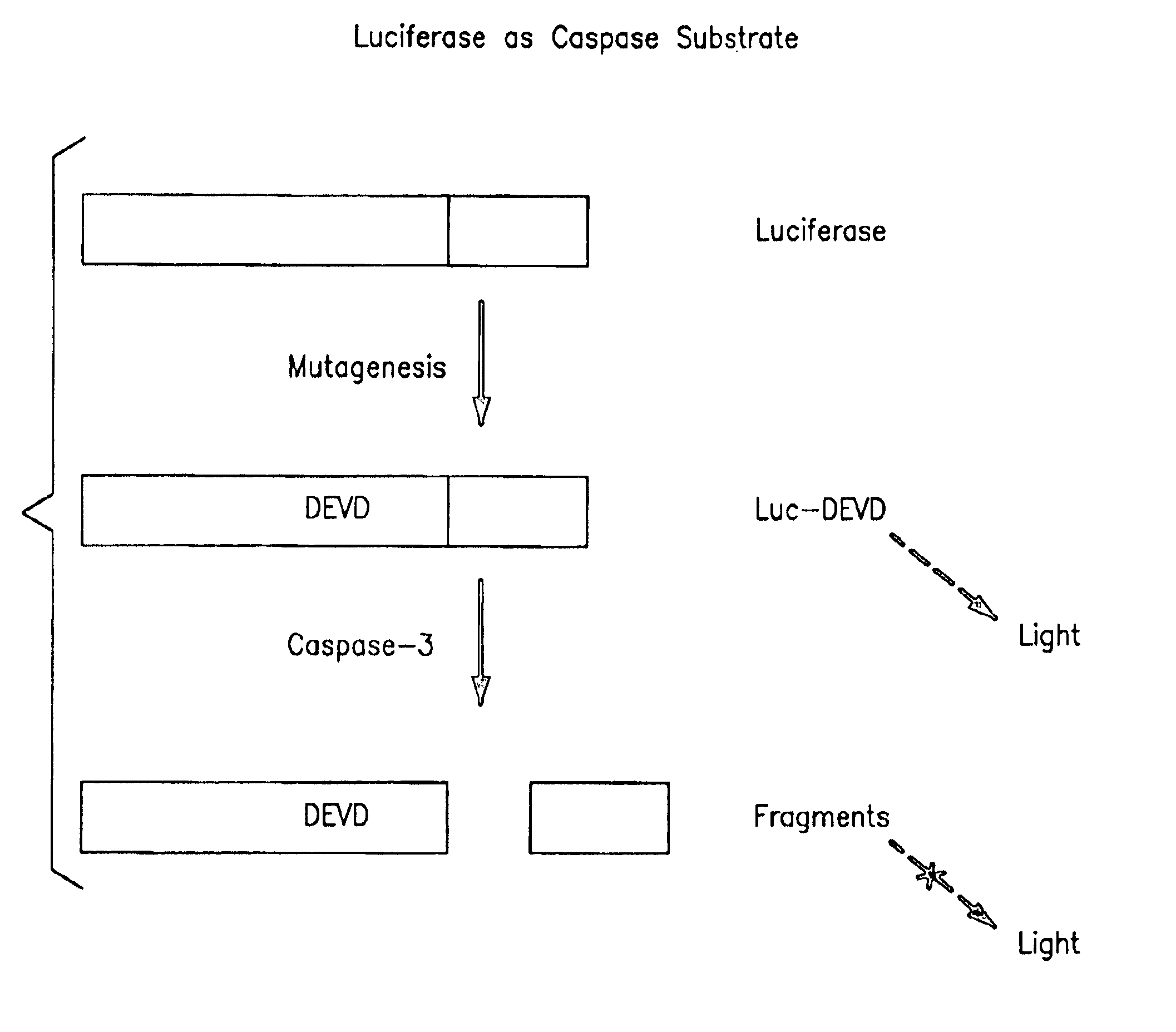
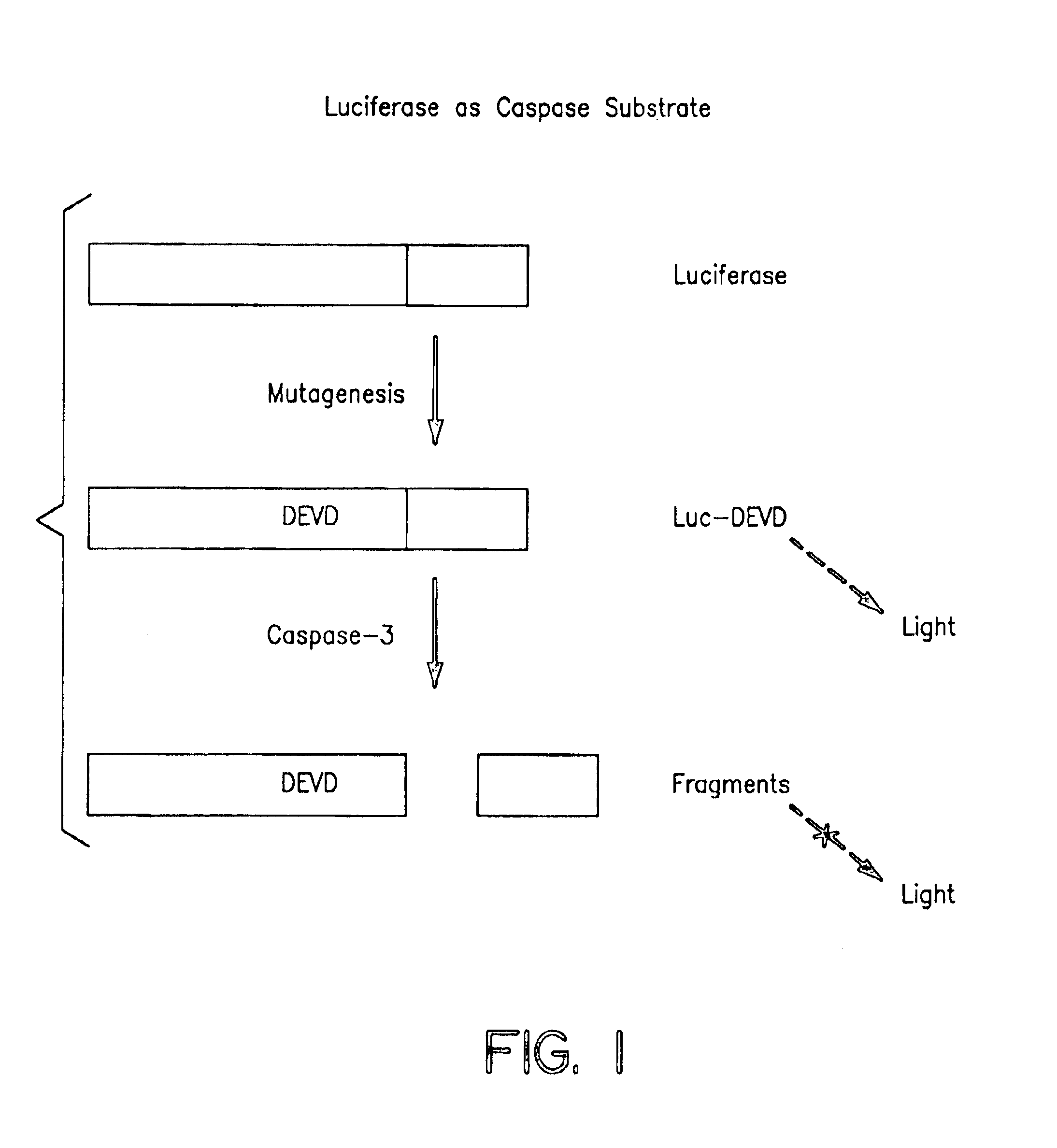
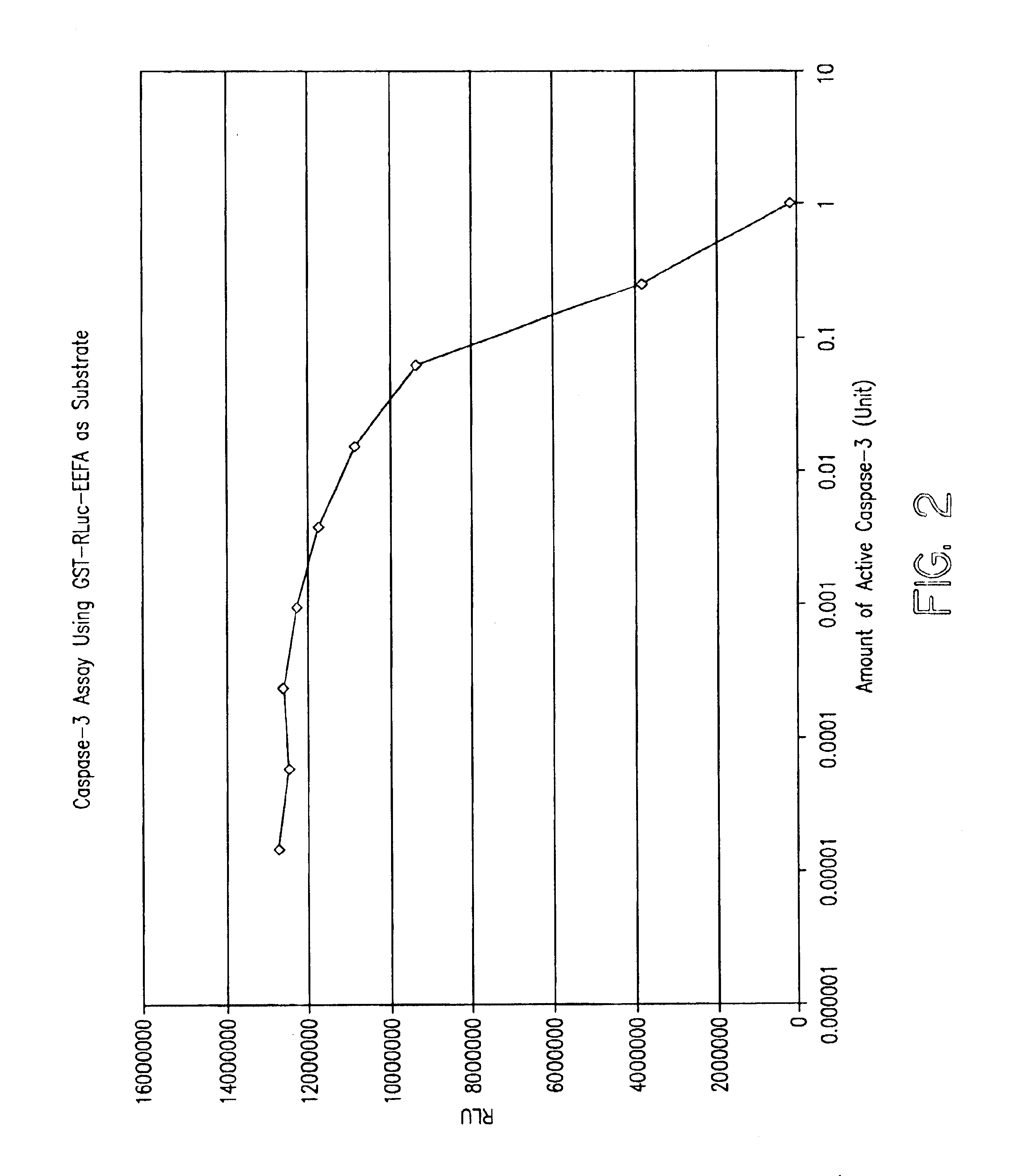
Protease specific cleavable luciferases and methods of use thereof
Provided are methods and compositions useful in detecting protease activity in a sample, as well as methods of identifying agents that modulate protease activity. The methods and compositions provide a modified luciferase polynucleotide sequence and a luciferase polypeptide containing protease recognition sequences, wherein cleavage of the recognition sequence by a protease inhibits luciferase activity. Further provided are methods and compositions for detecting and modulating caspase activity and apoptosis.
Owner:MILLIPORE CORP
Lanthanide-based substrates and methods for determining clostridial toxin activity
InactiveUS20060063221A1Microbiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against bacteriaEnergy transferClostridial toxin
The present invention provides a clostridial toxin substrate that contains (a) a lanthanide donor complex; (b) an acceptor having an absorbance spectrum overlapping the emission spectrum of the lanthanide donor complex; and (c) a clostridial toxin recognition sequence containing a cleavage site that intervenes between the lanthanide donor complex and the acceptor, where, under the appropriate conditions, resonance energy transfer is exhibited between the lanthanide donor complex and the acceptor.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
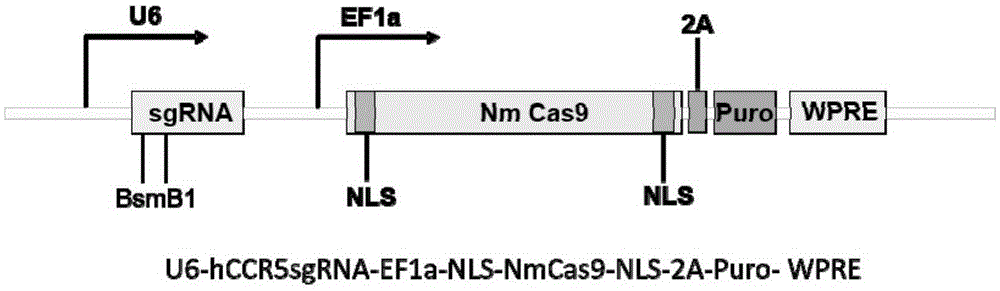
Human CCR5 gene target sequence identified by neisseria meningitidis CRISPR-Cas9 system, sgRNA and application of target sequence and sgRNA
InactiveCN105331609AAchieve preventionAchieve therapeutic effectOrganic active ingredientsHydrolasesGene targetsHIV receptor
The invention belongs to the field of gene engineering and discloses a target sequence identified by a CRISPR-Cas9 system from neisseria meningitidis. The target sequence is as shown in the nth-24th sites of optional one of SEQ ID No. 1-20, and n=1-9. The invention further discloses sgRNA and coding DNA molecules thereof, the sequence of the sgRNA is 5'-identificiation sequence-sequence recruiting Cas9 protein-3', and the DNA sequence corresponding to the identification sequence is identical with the target sequence. The invention also discloses the CRISPR-Cas9 system which comprises the Cas9 protein, the sgRNA and / or a coding sequence carrying the Cas9 protein and a vector of the coding sequence of the sgRNA. The invention also discloses application of the CRISPR-Cas9 system to editing of CCR5 genes and preparation of medicine for HIV infection. By the CRISPR-Cas9 system, the CCR5 genes can be edited, and cells cannot be infected by HIV.
Owner:张竞方
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com