Induction of exon skipping in eukaryotic cells
a technology of exon skipping and eukaryotic cells, which is applied in the field of gene therapy, can solve the problems of insufficient accuracy and interference with the splicing process, and achieve the effects of reducing the amount of aberrant protein, efficient multiplication and spread, and reducing the production of aberrant protein
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
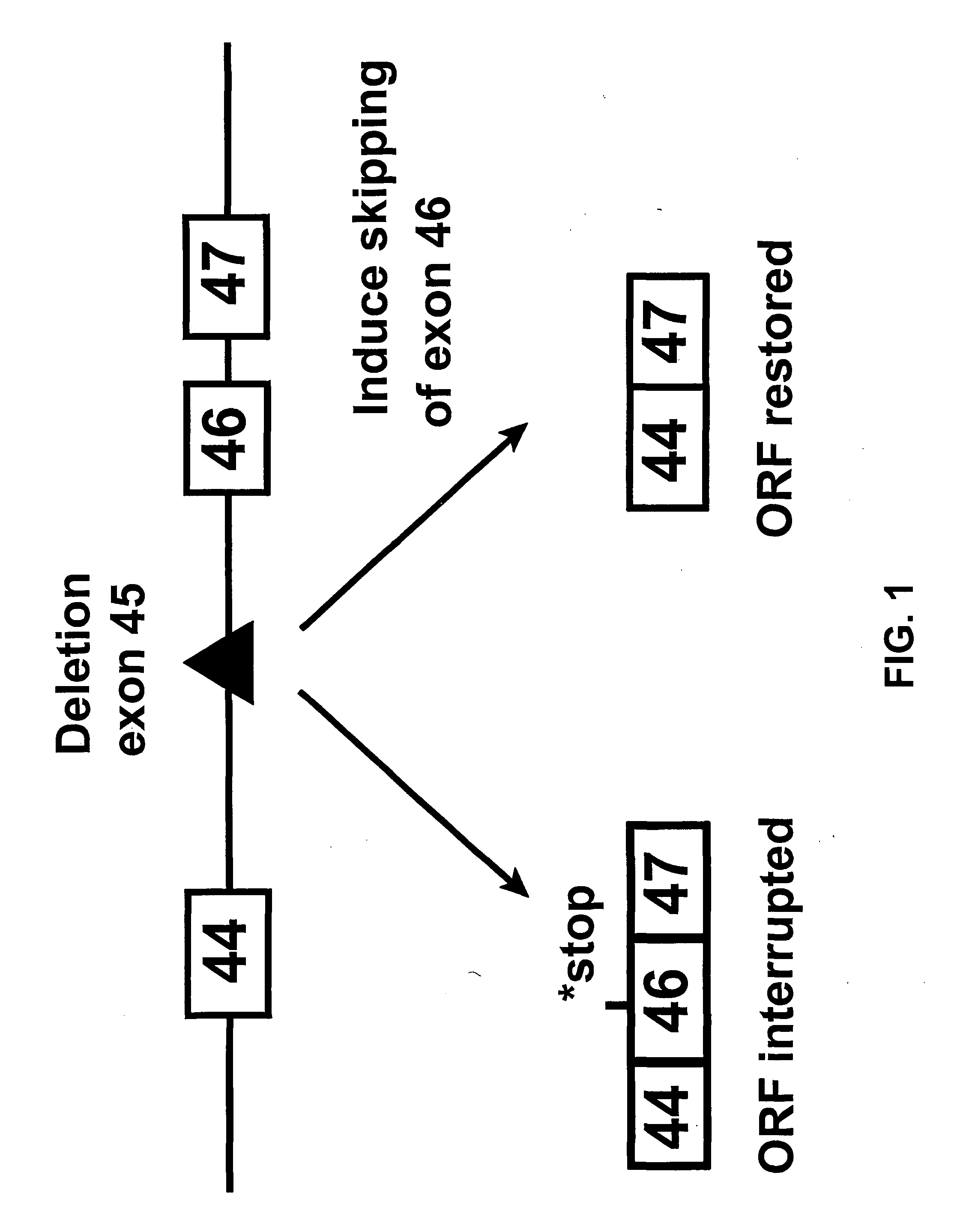
[0044]Since exon 45 is one of the most frequently deleted exons in DMD, we initially aimed at inducing the specific skipping of exon 46 (FIG. 1). This would produce the shorter, largely functional dystrophin found in BMD patients carrying a deletion of exons 45 and 46. The system was initially set up for modulation of dystrophin pre-mRNA splicing of the mouse dystrophin gene. We later aimed for the human dystrophin gene with the intention to restore the translational reading frame and dystrophin synthesis in muscle cells from DMD patients affected by a deletion of exon 45.
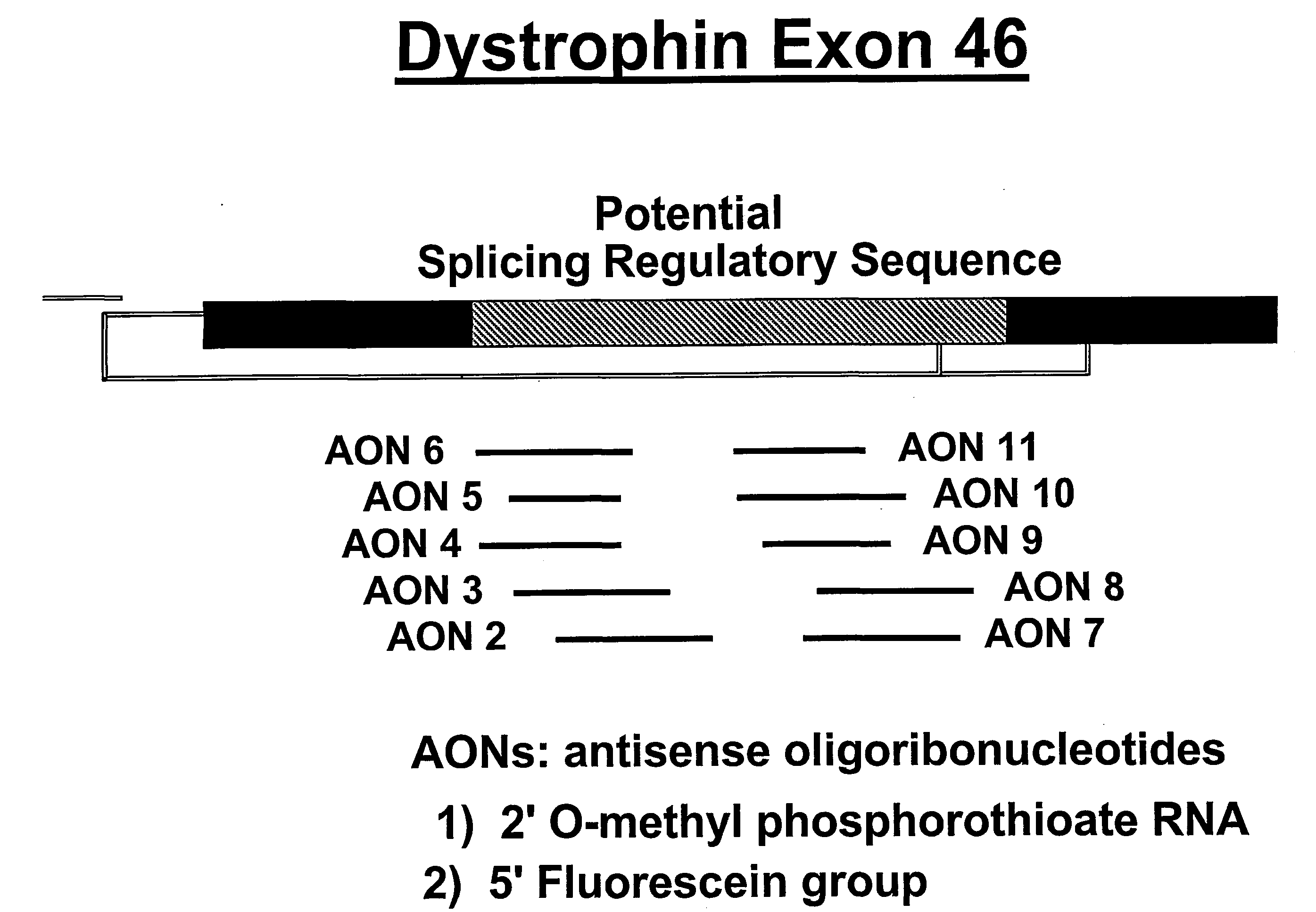
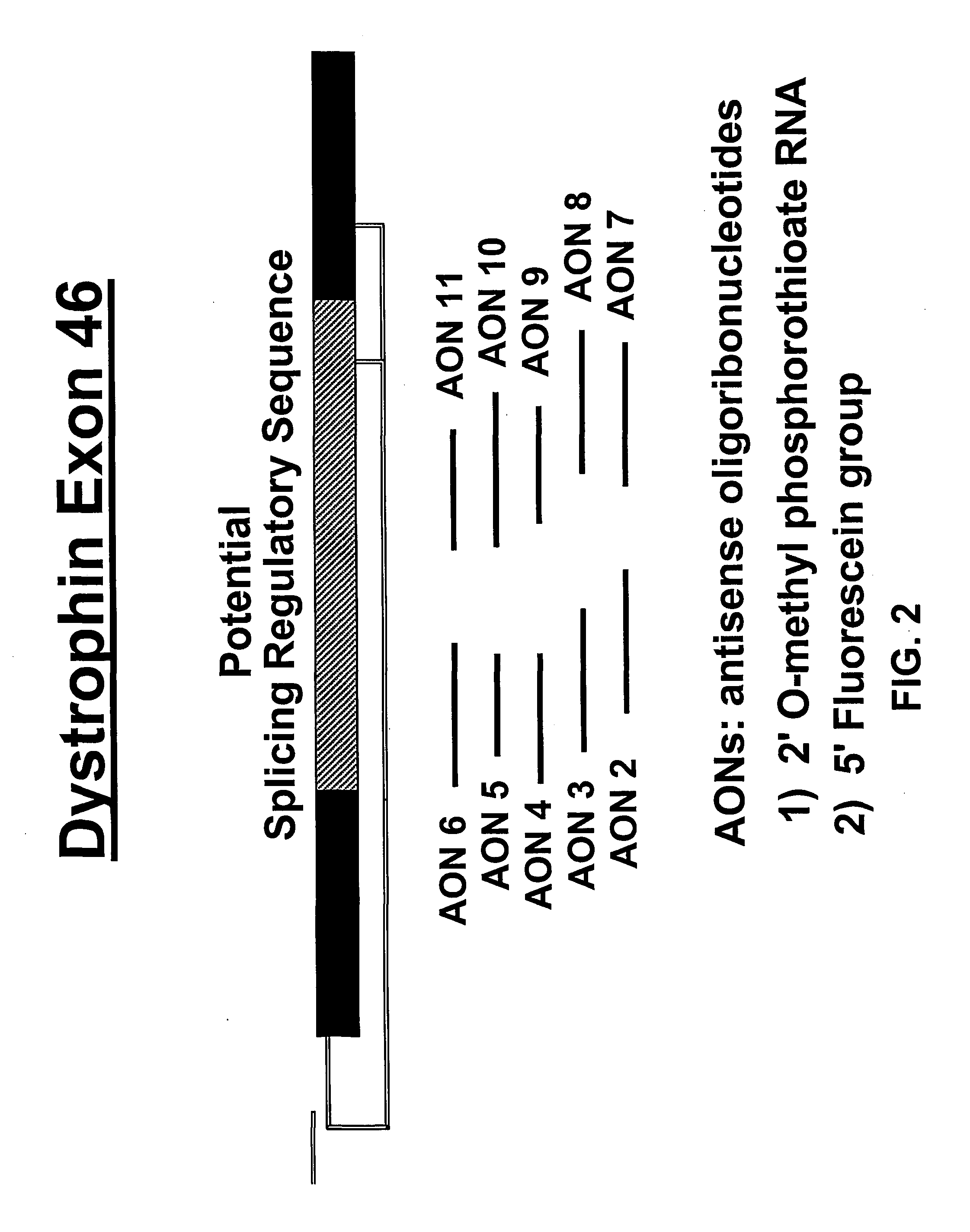
Design of mAONs and hAONs
[0045]A series of mouse- and human-specific AONs (mAONs and hAONs) was designed, directed at an internal part of exon 46 that contains a stretch of purine-rich sequences and is hypothesized to have a putative regulatory role in the splicing process of exon 46 (FIG. 2). For the initial screening of the AONs in the gel mobility shift assays (see below), we used non-modified DNA-oligonucleotid...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| binding affinity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| nucleic acid | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| nucleic acid sequence | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com