Patents
Literature
72results about How to "Efficiently masked" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
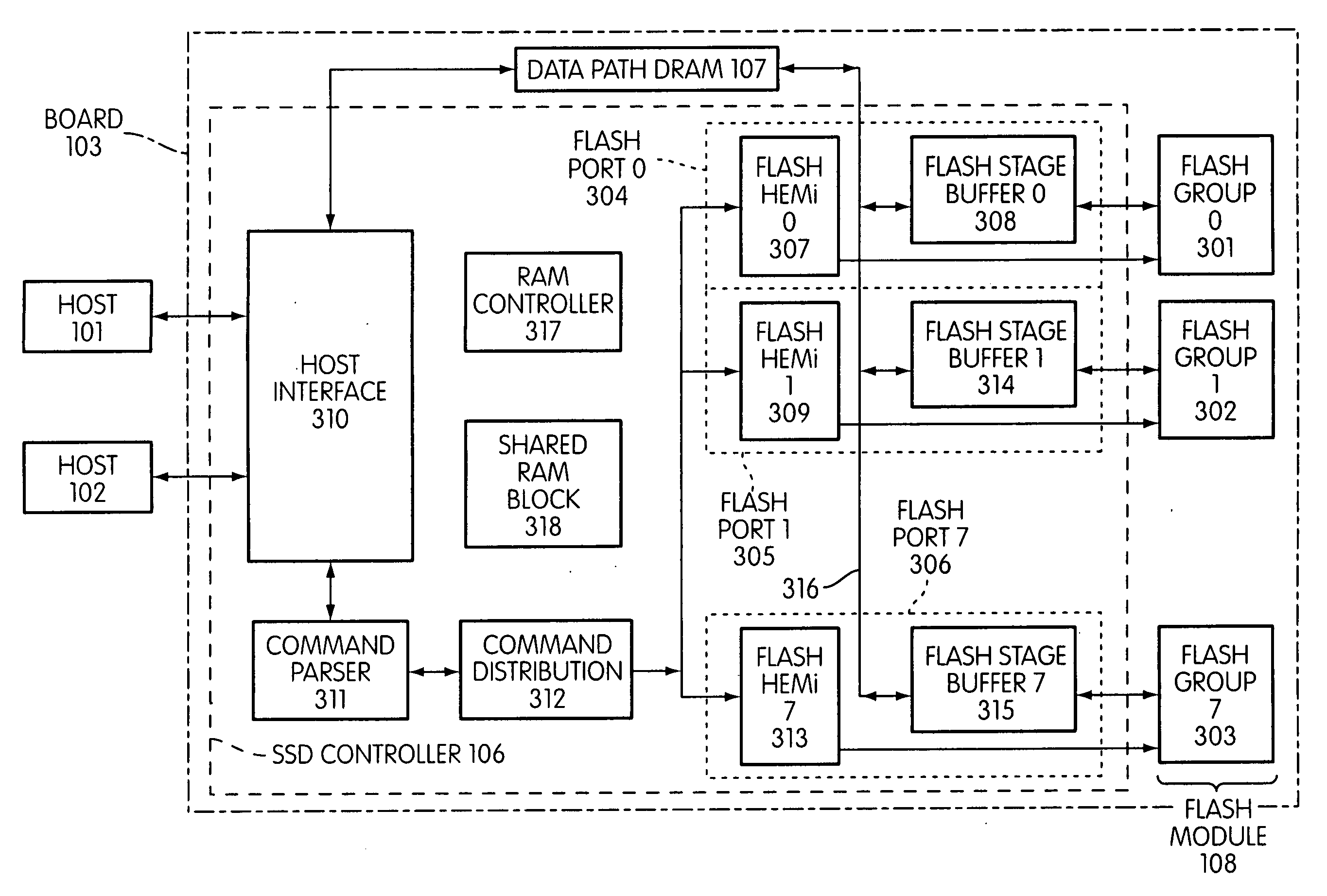
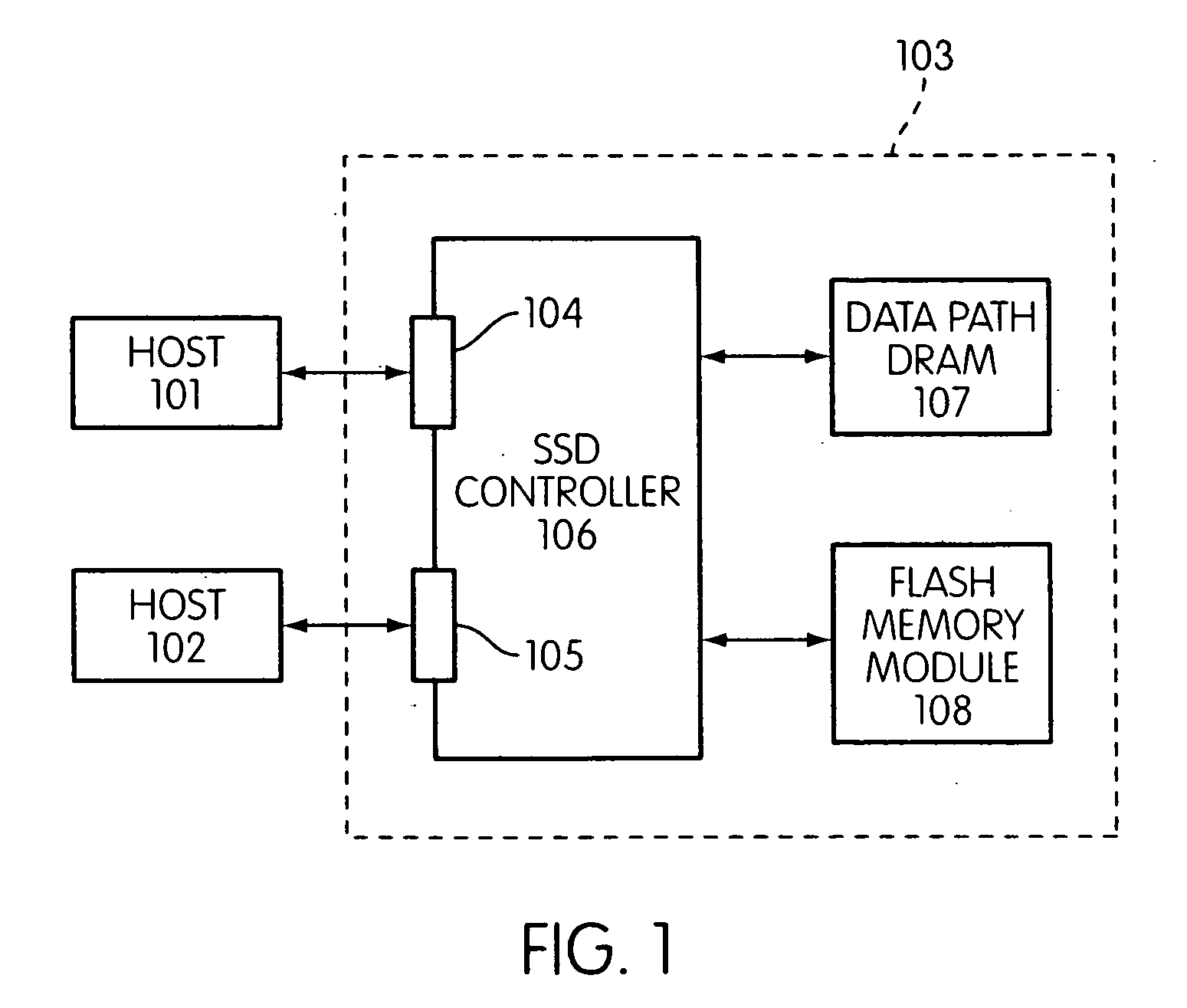
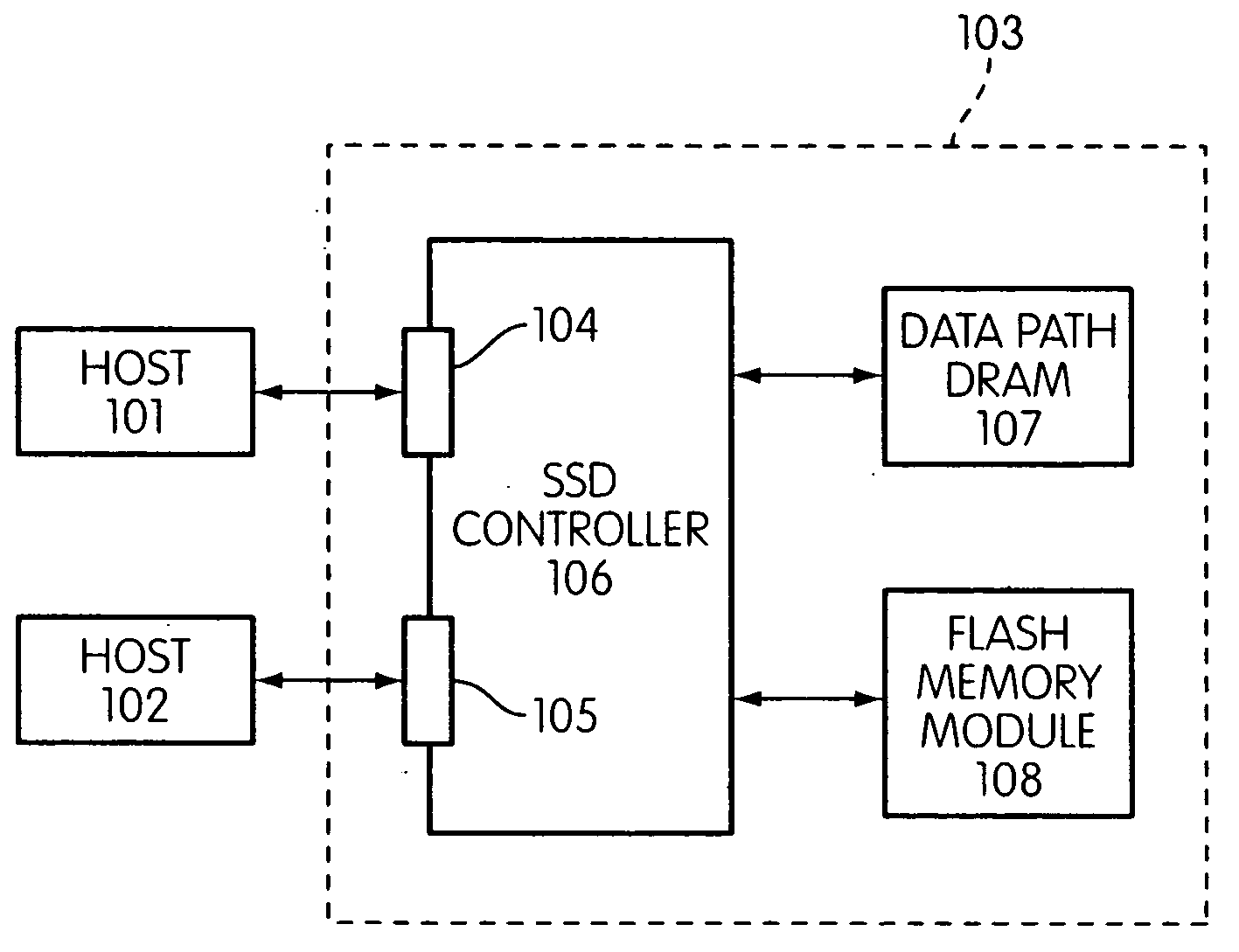
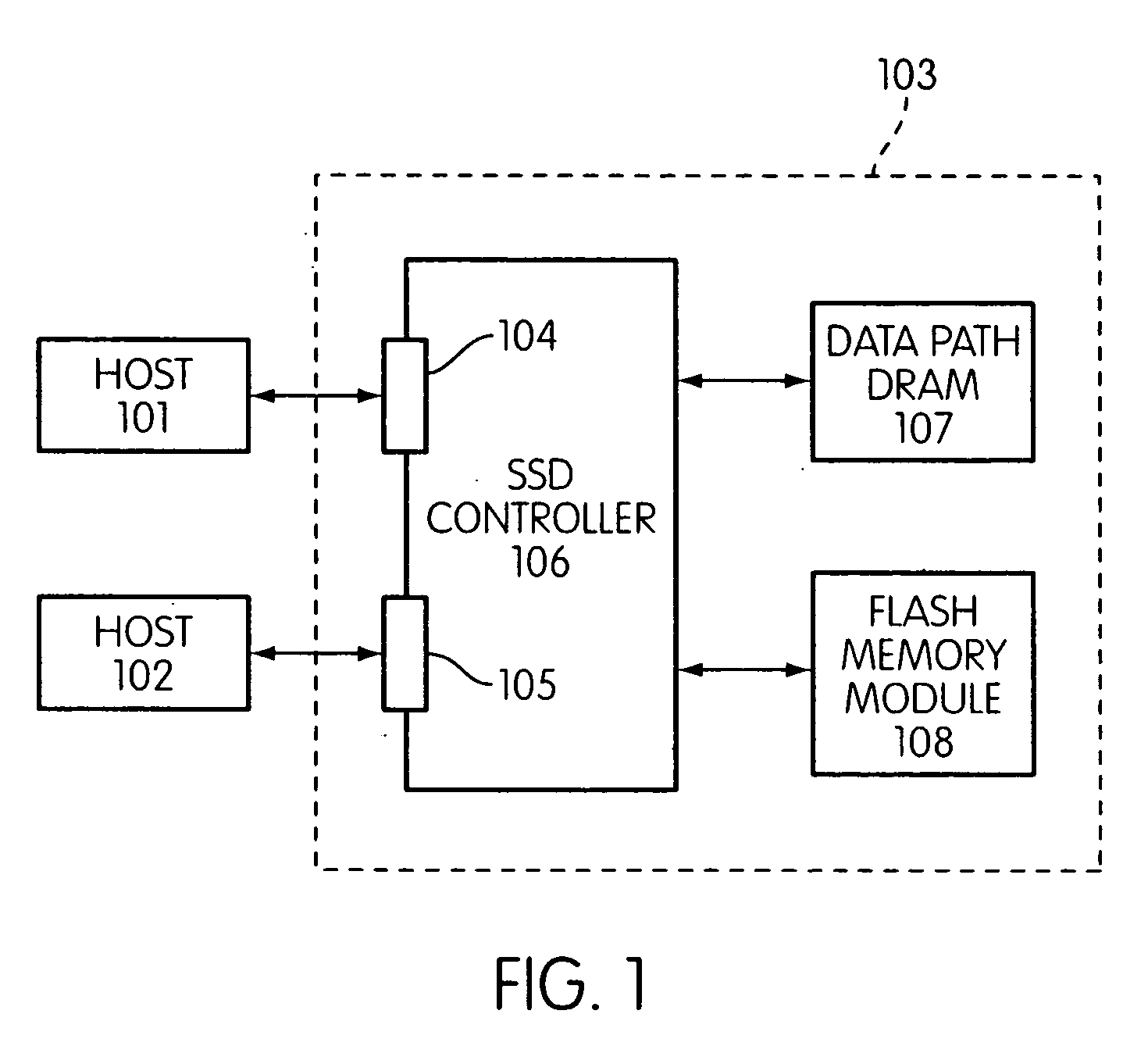
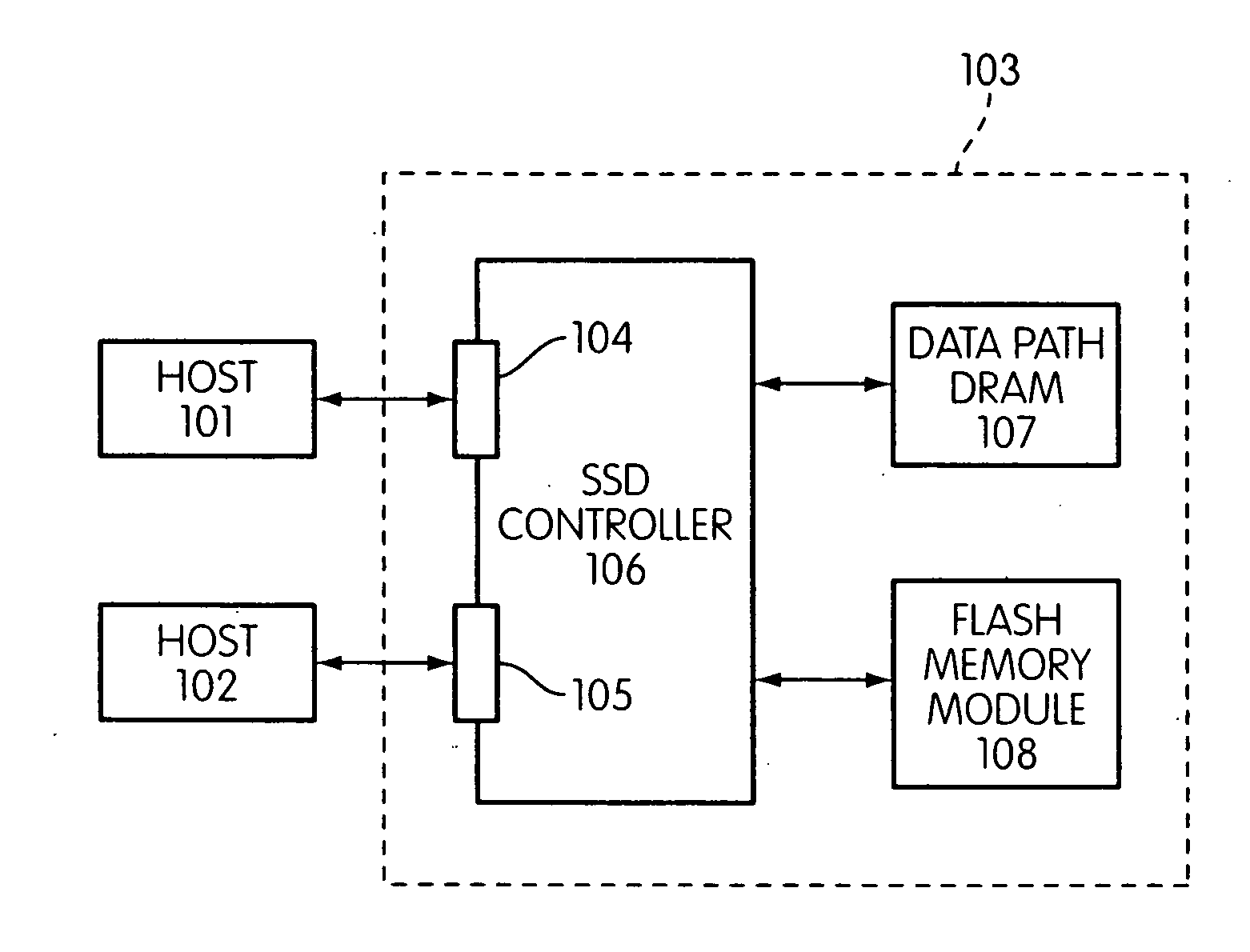
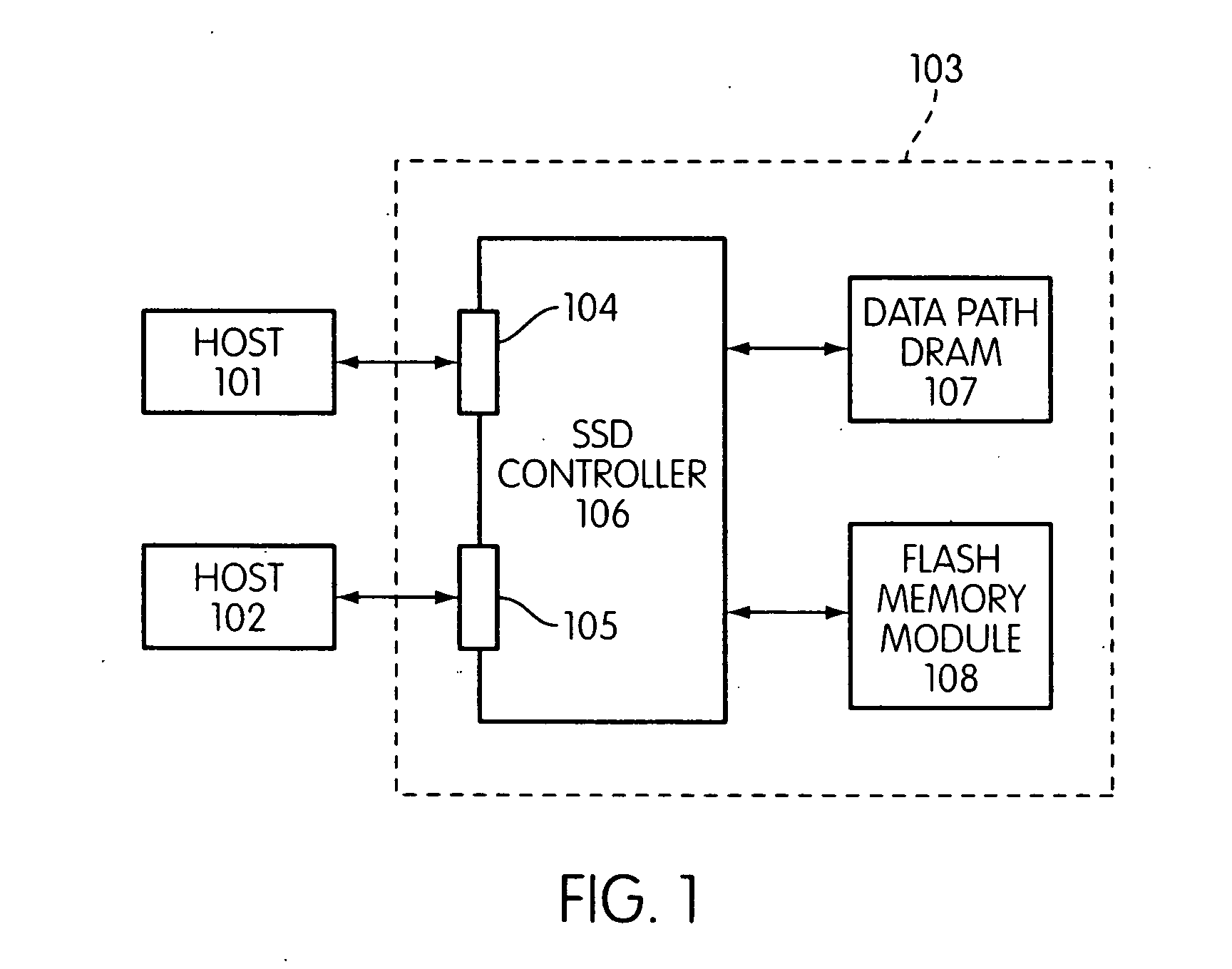
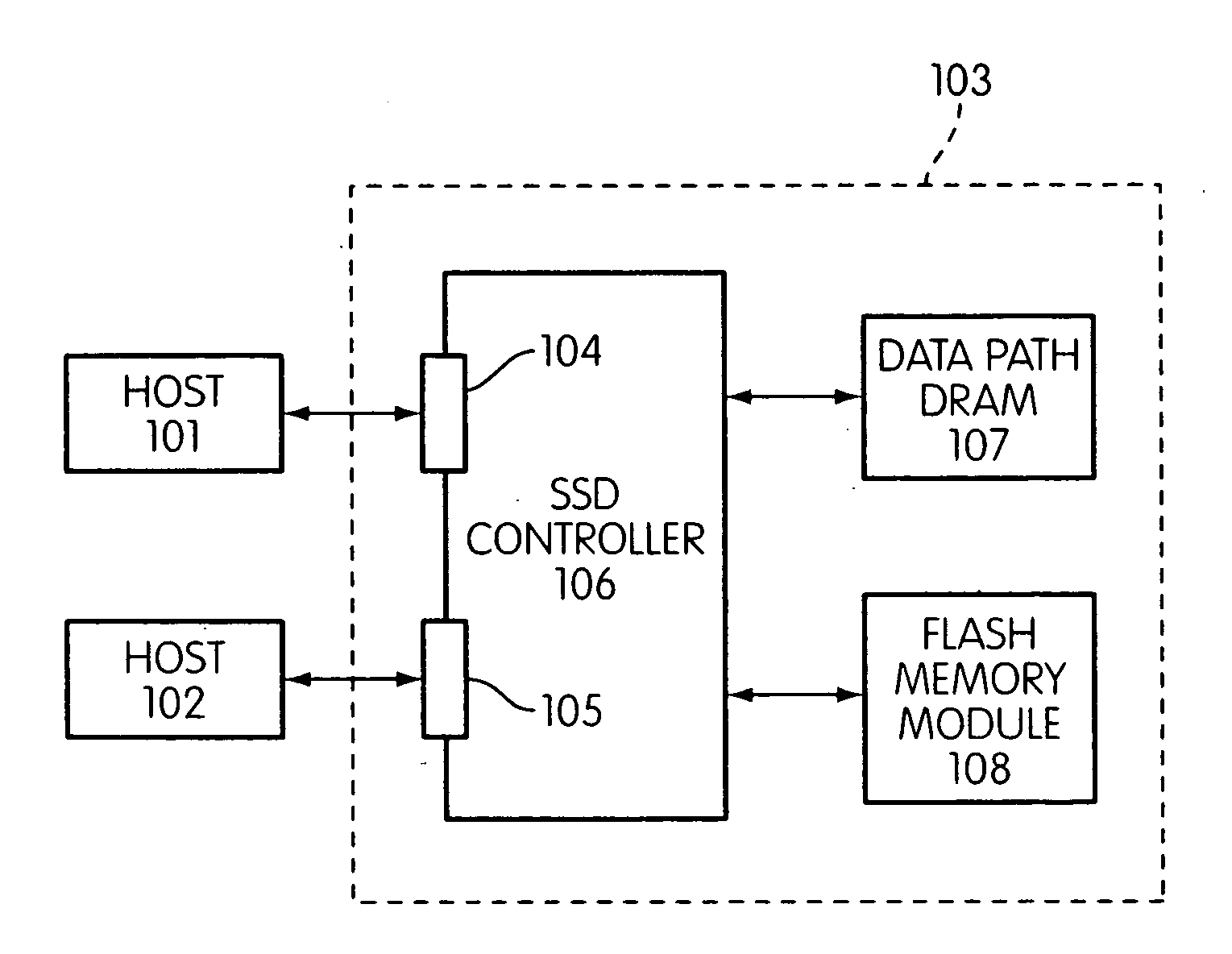
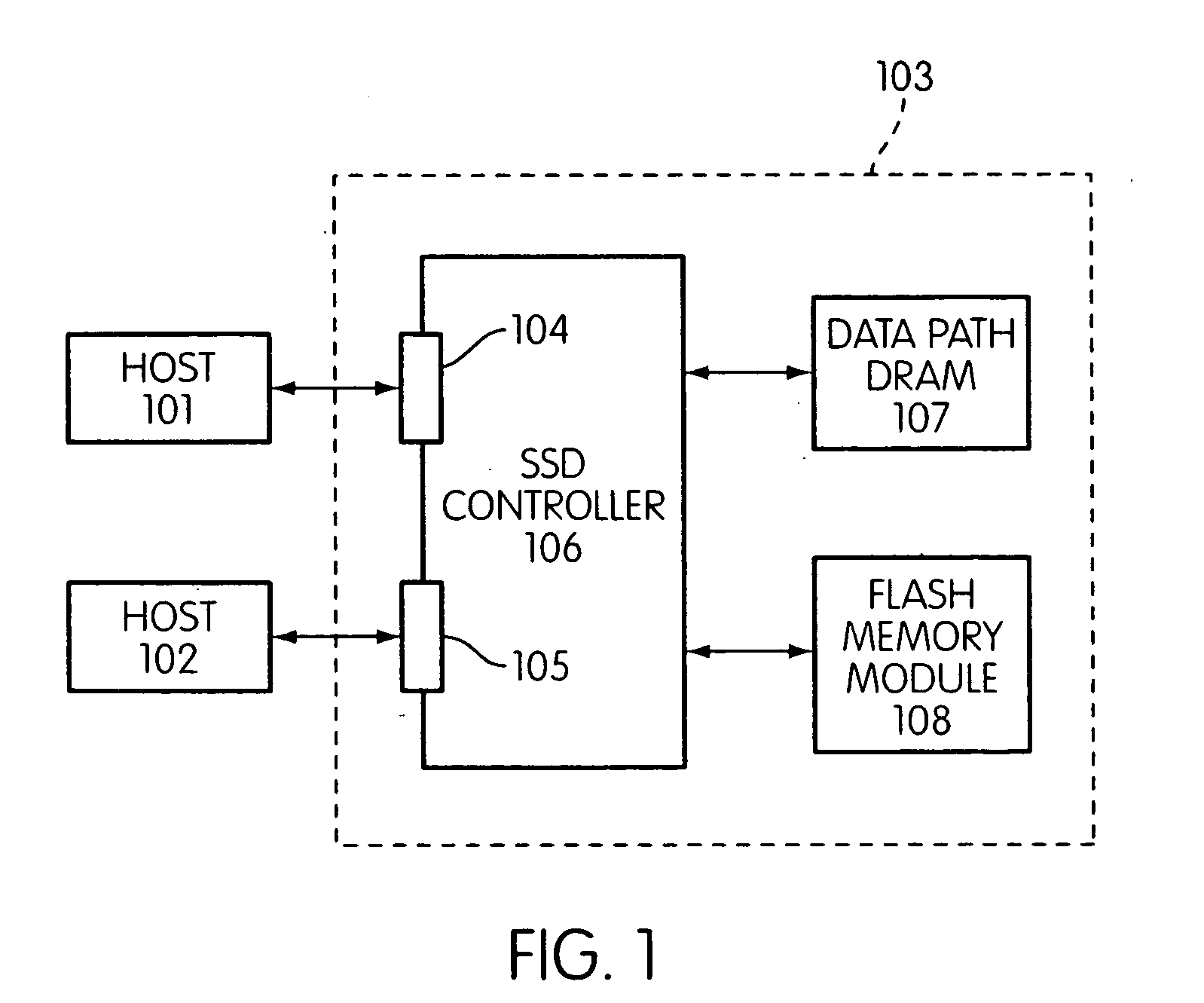
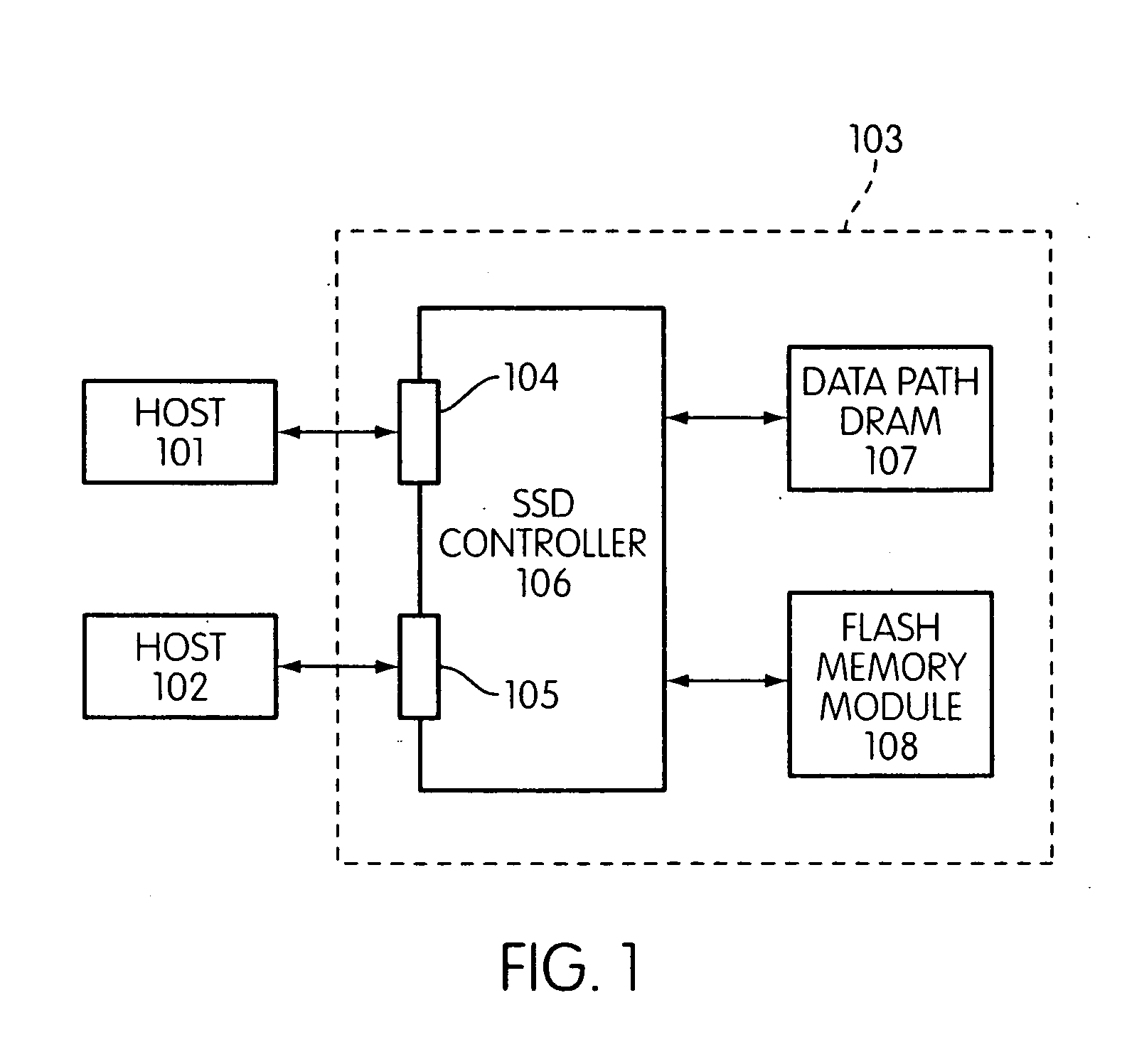
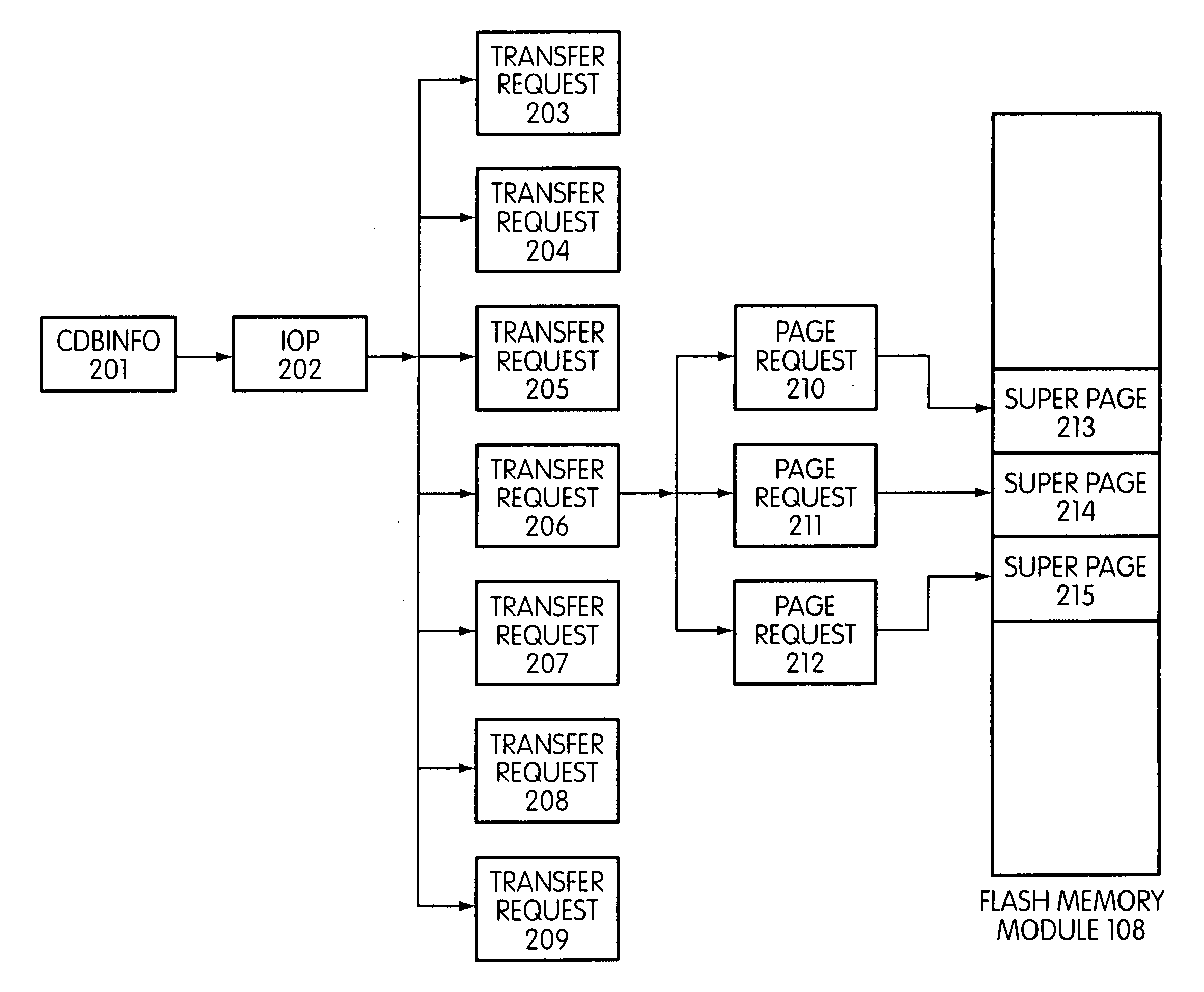
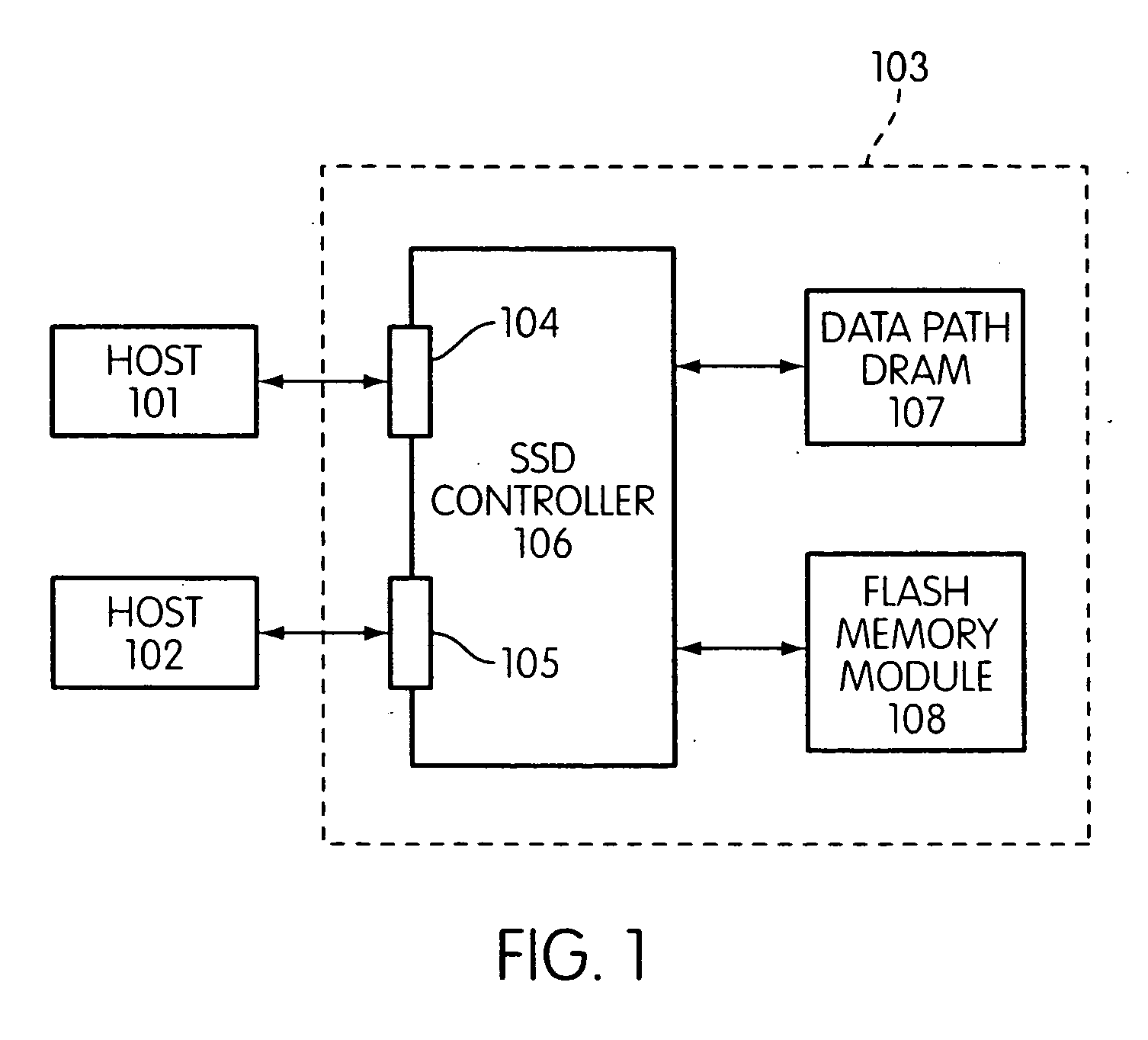
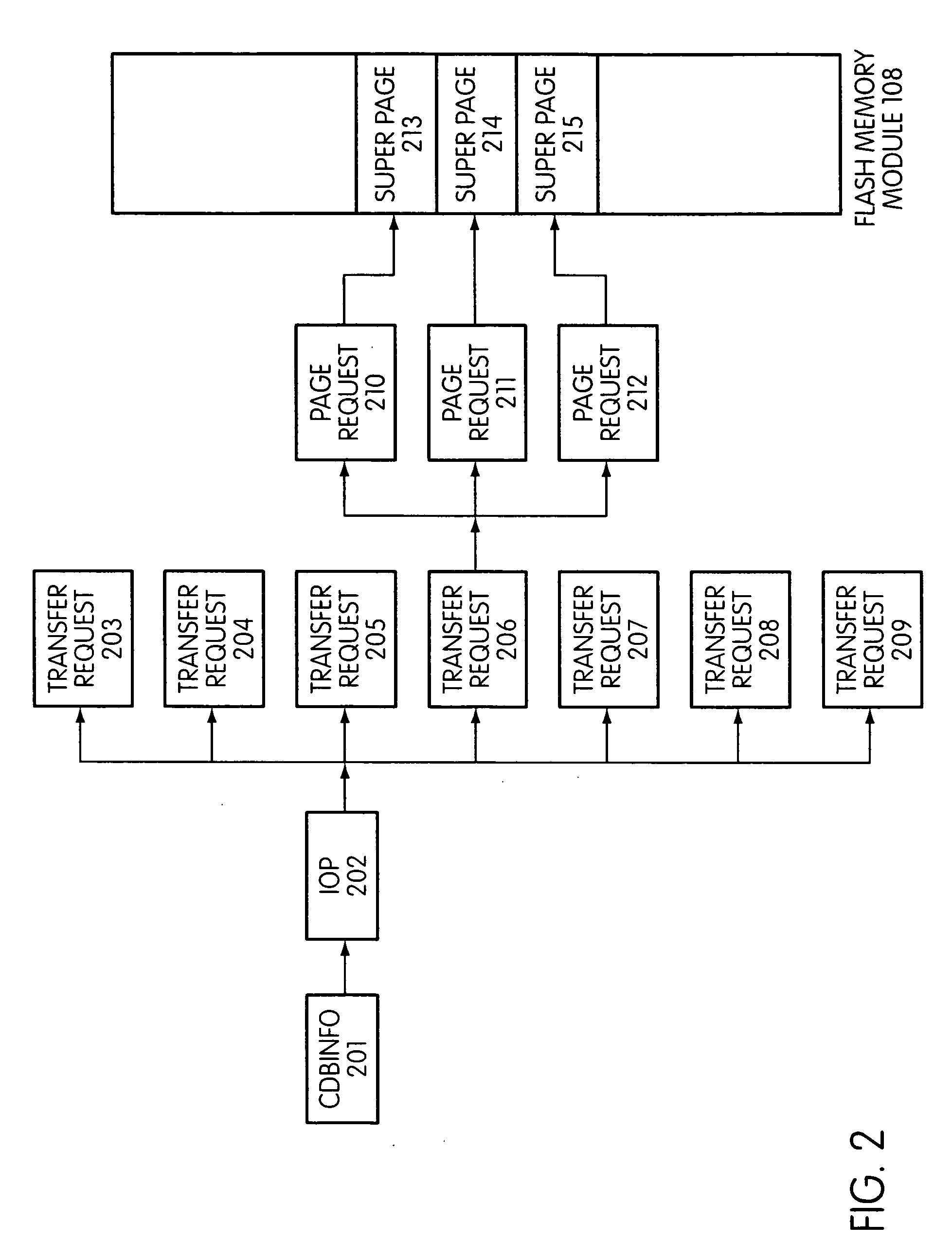
Storage controller for flash memory including a crossbar switch connecting a plurality of processors with a plurality of internal memories
ActiveUS20090172308A1Affect performance of systemMaximize useMemory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesController designCrossbar switch
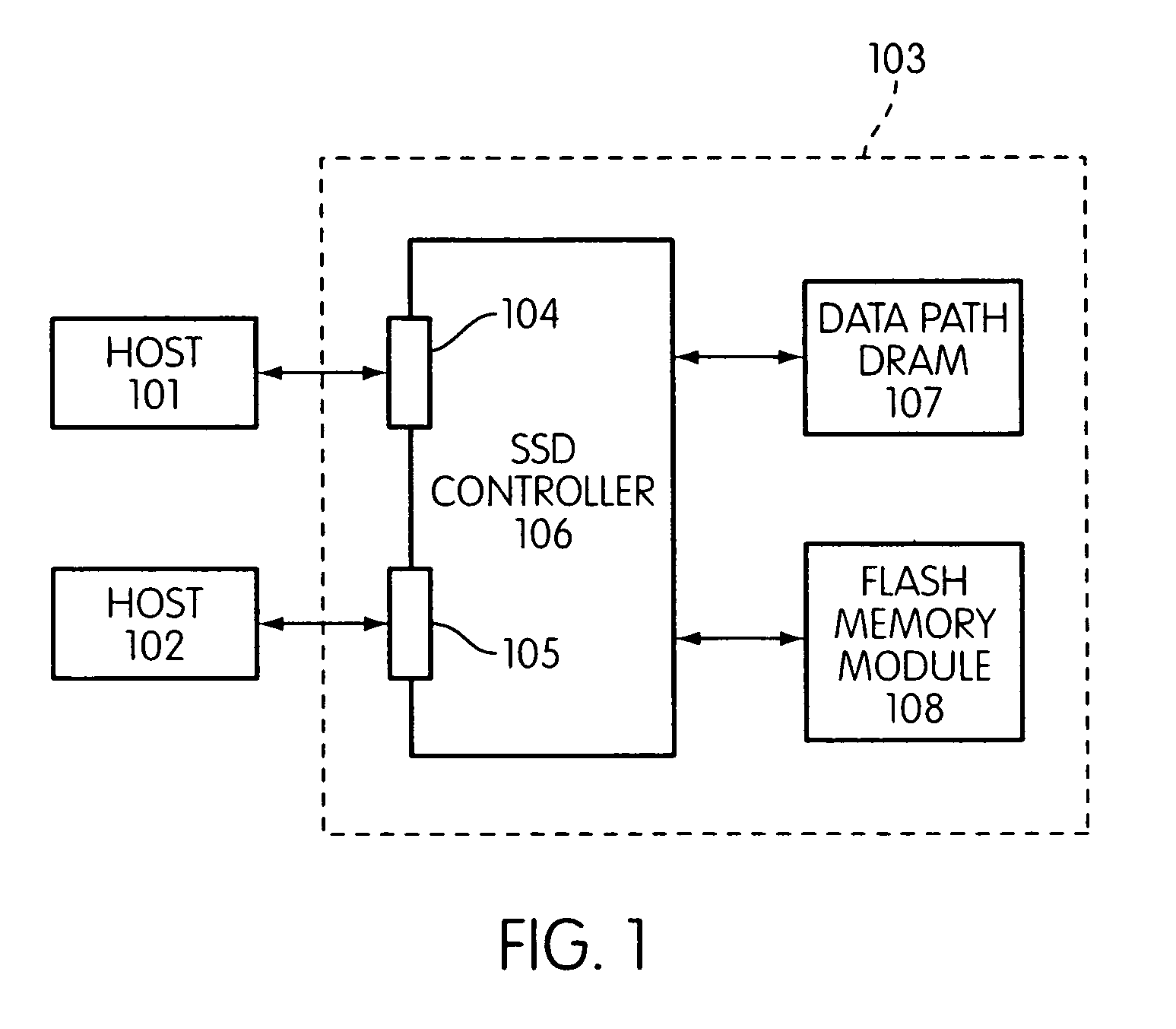
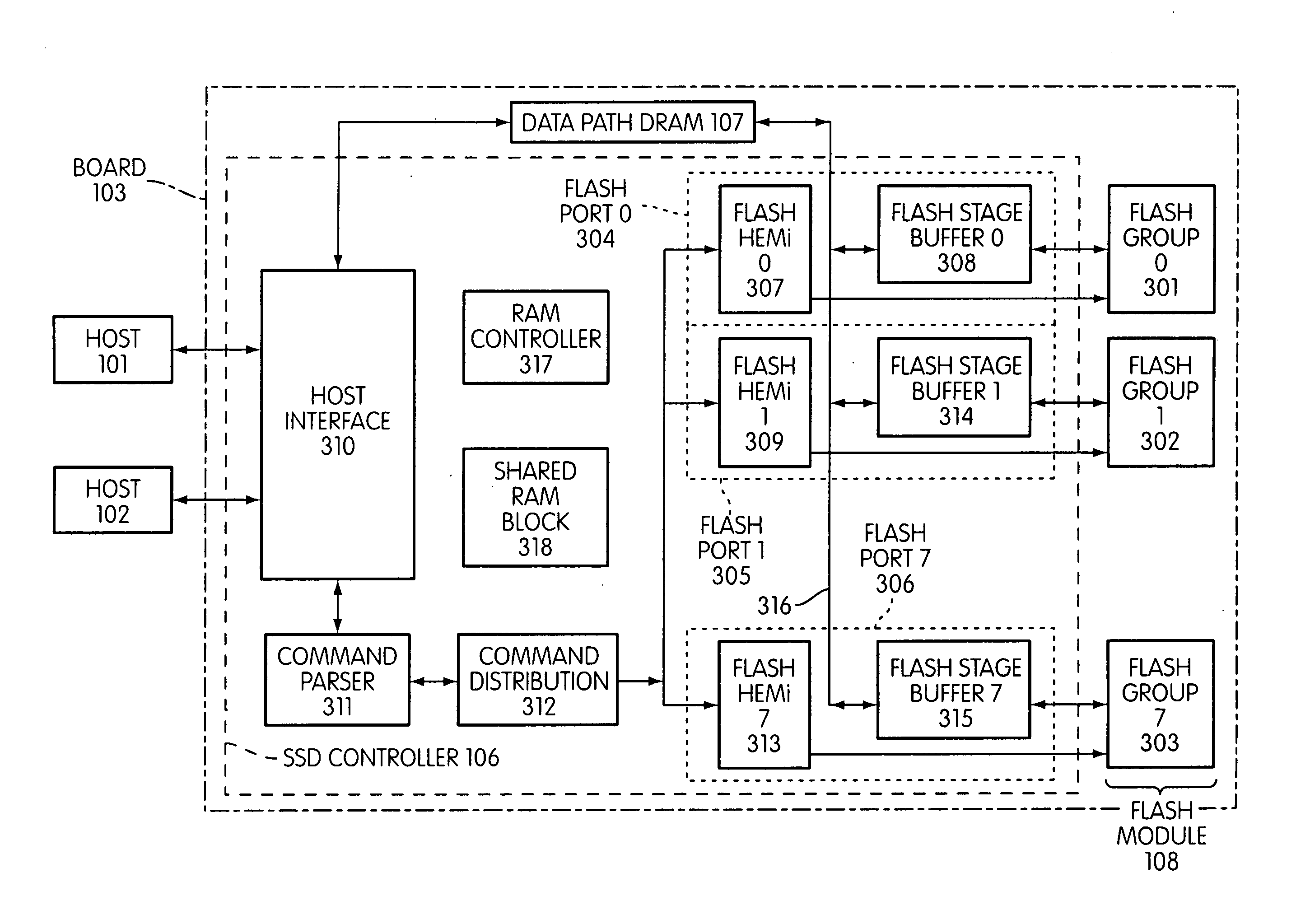
A controller designed for use with a flash memory storage module, including a crossbar switch designed to connect a plurality of internal processors with various internal resources, including a plurality of internal memories. The memories contain work lists for the processors. In one embodiment, the processors communicate by using the crossbar switch to place tasks on the work lists of other processors.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Metadata rebuild in a flash memory controller following a loss of power
ActiveUS20090172262A1Maximize useImprove performanceMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationFlash memory controllerMemory controller
A method of rebuilding metadata in a flash memory controller following a loss of power. The method includes reading logical address information associated with an area of flash memory, and using time stamp information to determine if data stored in the flash memory area is valid.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Flash memory controller garbage collection operations performed independently in multiple flash memory groups
ActiveUS20090172258A1Affect performanceMaximize useMemory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesWaste collectionFlash memory controller
A flash memory controller connected to multiple flash memory groups performs independent garbage collection operations in each group. For each group, the controller independently determines the amount of free space and performs garbage collection operations if the amount falls below a threshold.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Patrol function used in flash storage controller to detect data errors
ActiveUS20090172499A1Affect performance of systemMaximize useMemory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesData errorFlash memory
A patrol function performed in a storage controller connected to a flash memory storage module. The function causes selected areas of the flash storage to be read for purposes of detecting and correcting errors.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
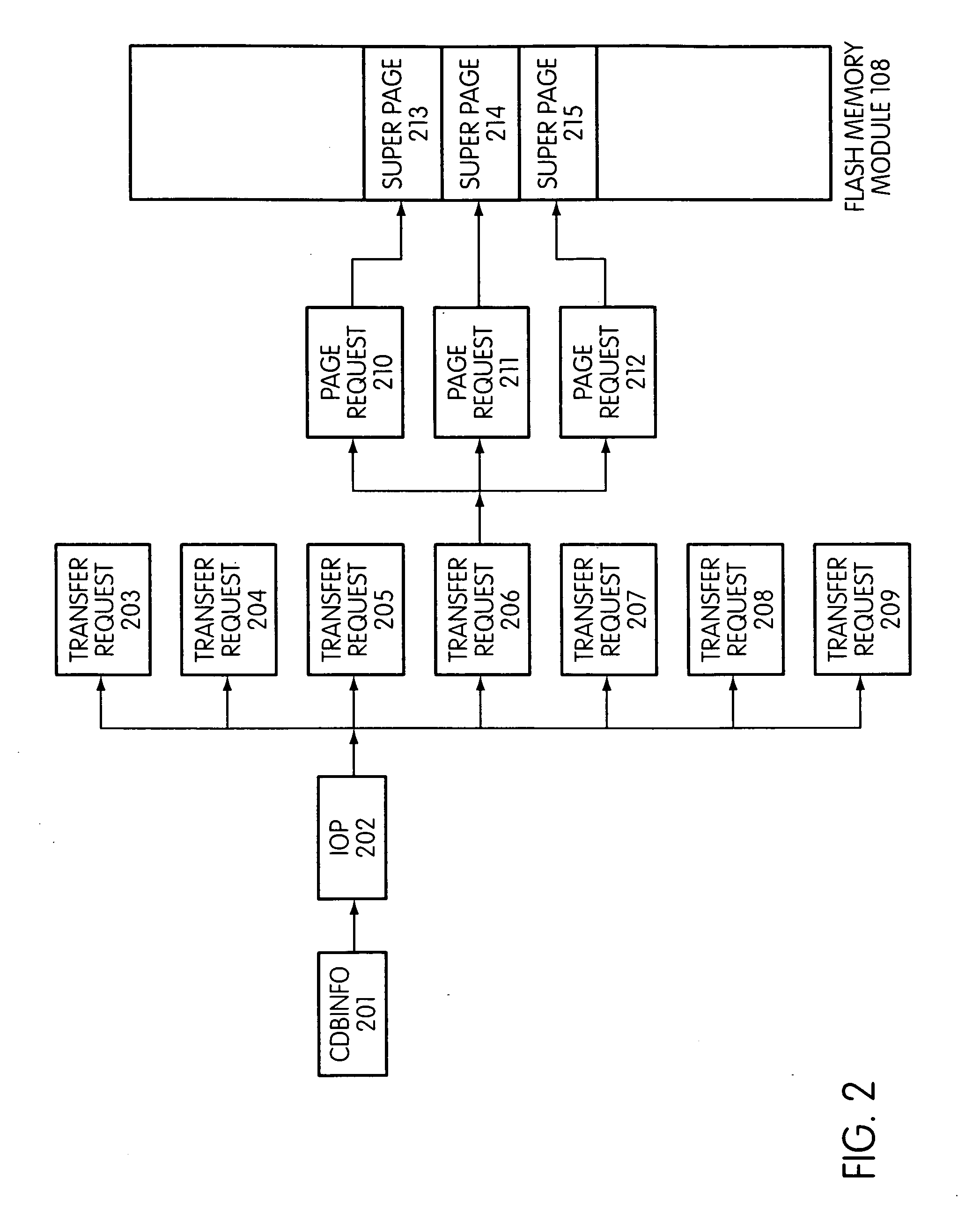
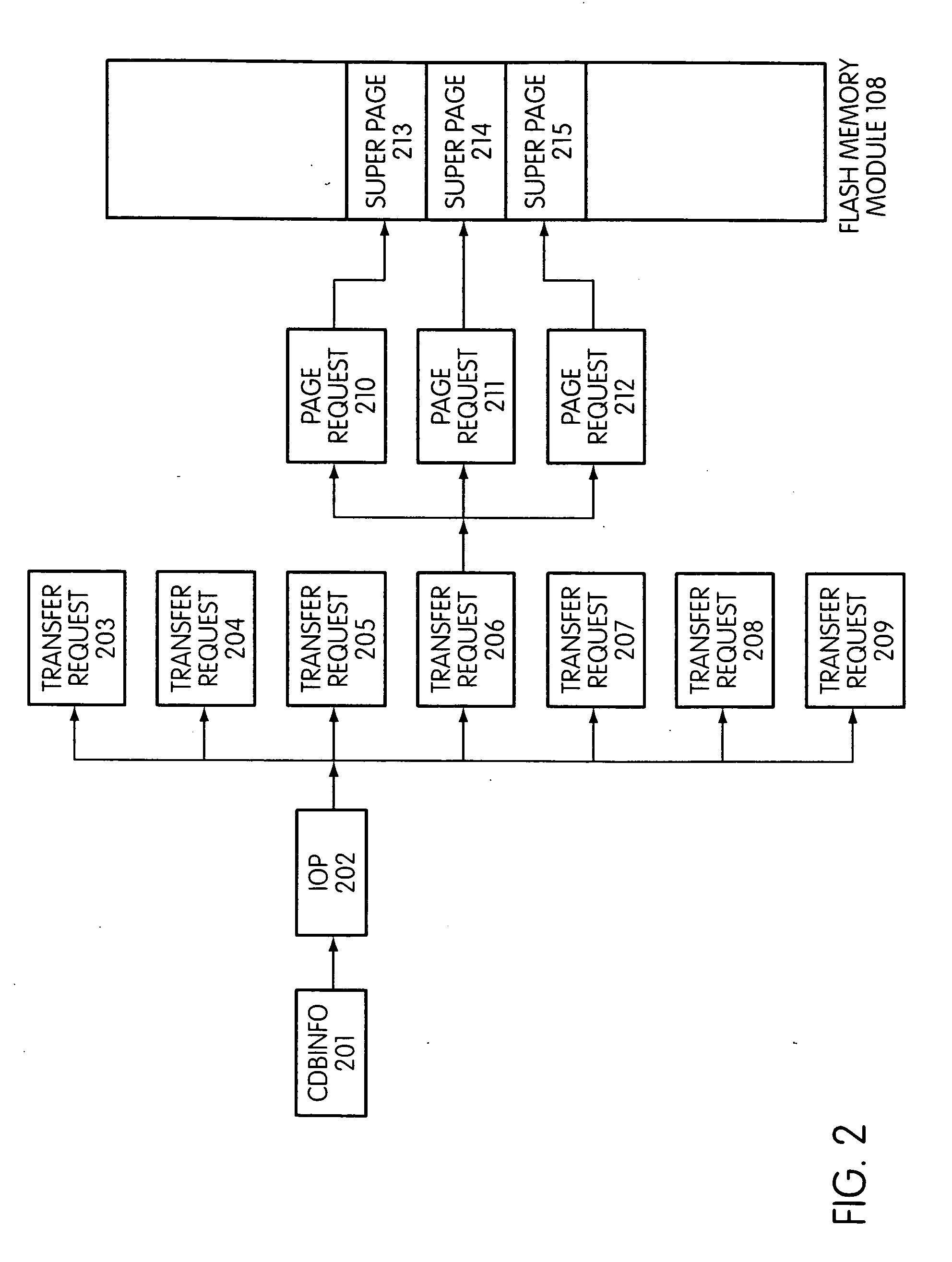
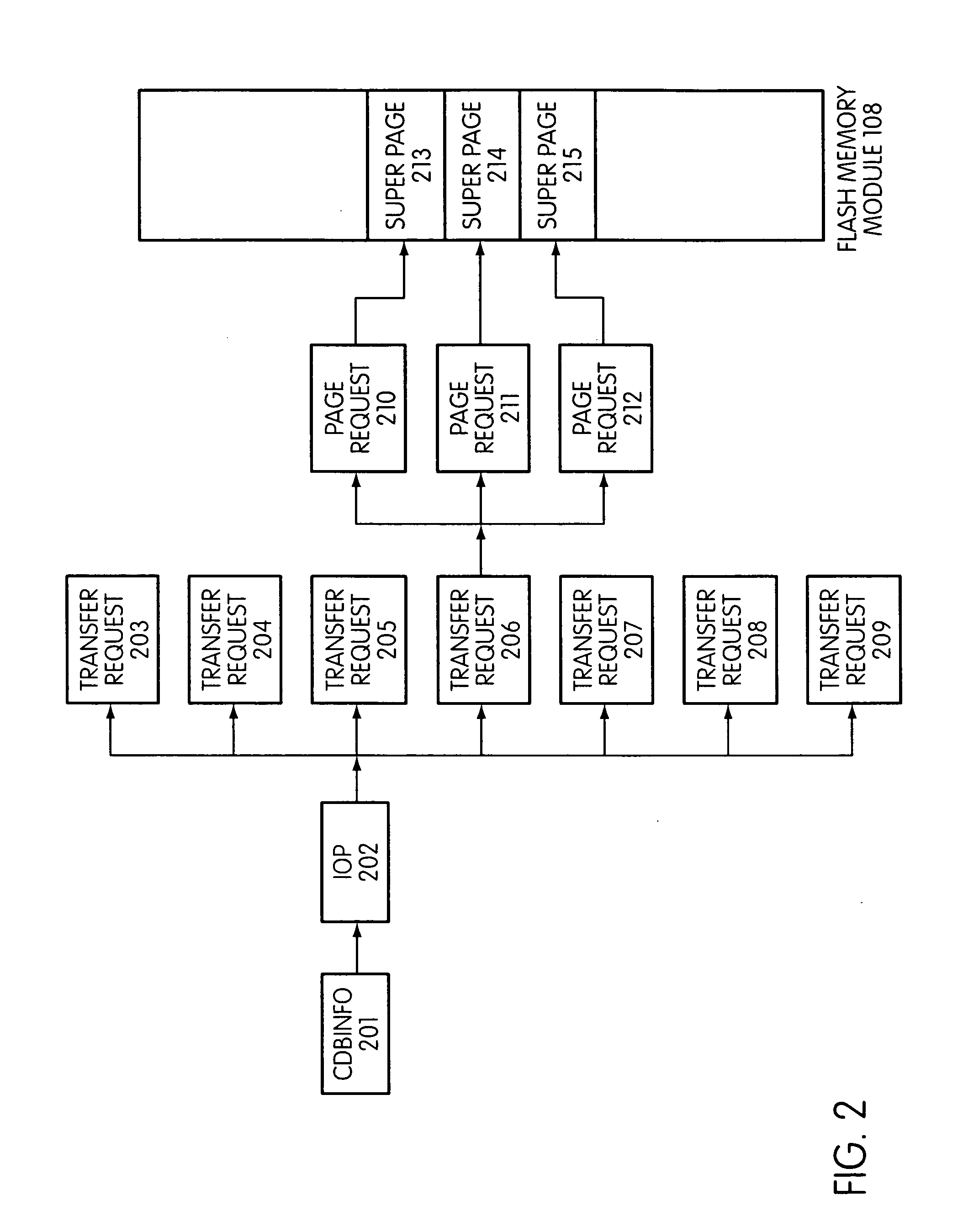
System and method for performing host initiated mass storage commands using a hierarchy of data structures
ActiveUS7934052B2Maximize useImprove performanceMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationFlash memory controllerParallel processing
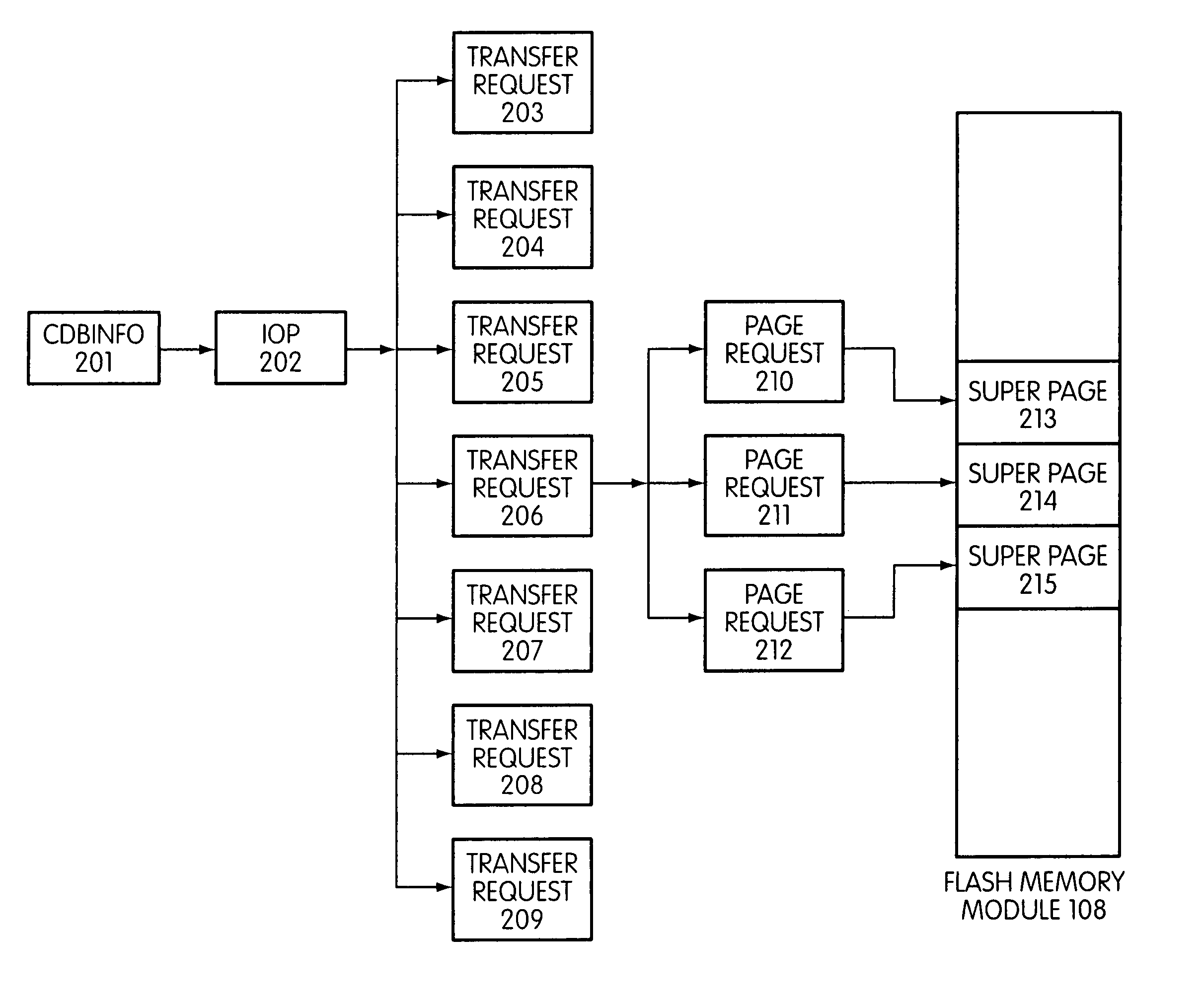
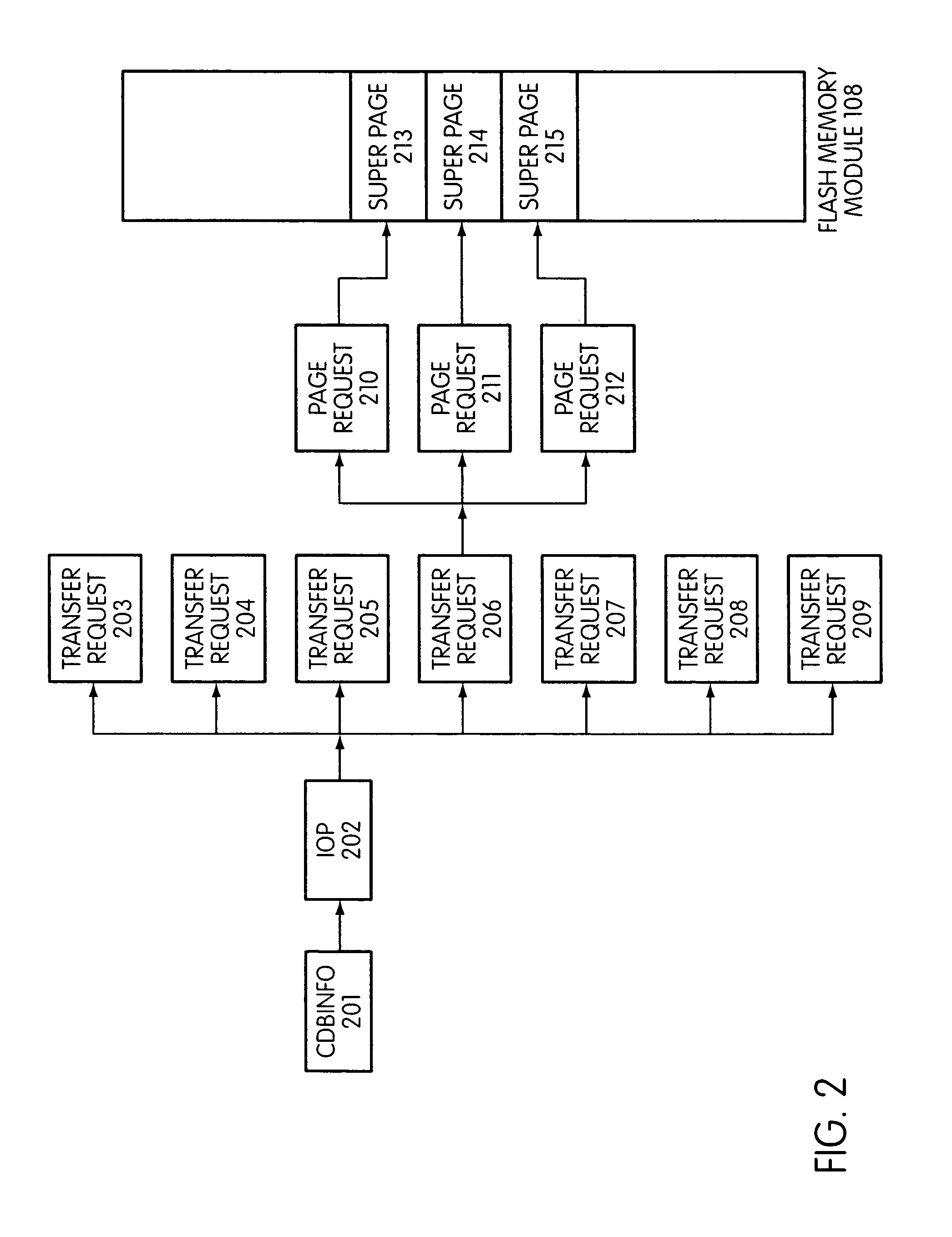
Disclosed is a mass storage system and method for breaking a host command into a hierarchy of data structures. Different types of data structures are designed to handle different phases of tasks required by the host command, and multiple data structures may be used to handle portions of the host command in parallel, thereby allowing increased performance. The disclosed embodiments include a flash memory controller designed to allow a high degree of pipelining and parallelism.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Flash memory controller and system including data pipelines incorporating multiple buffers
ActiveUS20090172260A1Increase performanceMaximize useMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationFlash memory controllerFlash memory
A storage controller connected to a flash memory storage module, the controller and module including multiple sets of buffers. The buffers are part of one or more pipelines through which data is moved between the storage module and one or more hosts.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
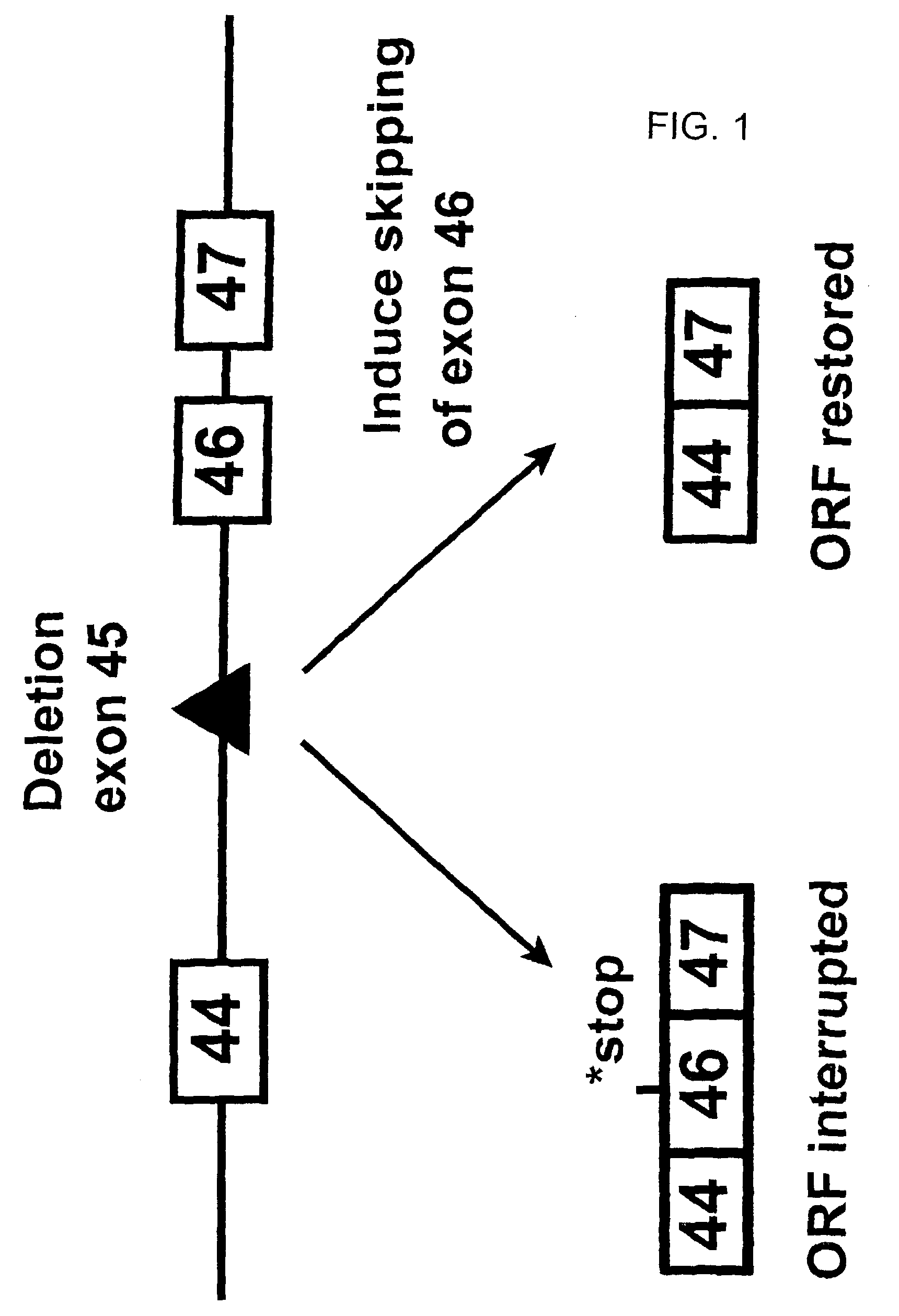
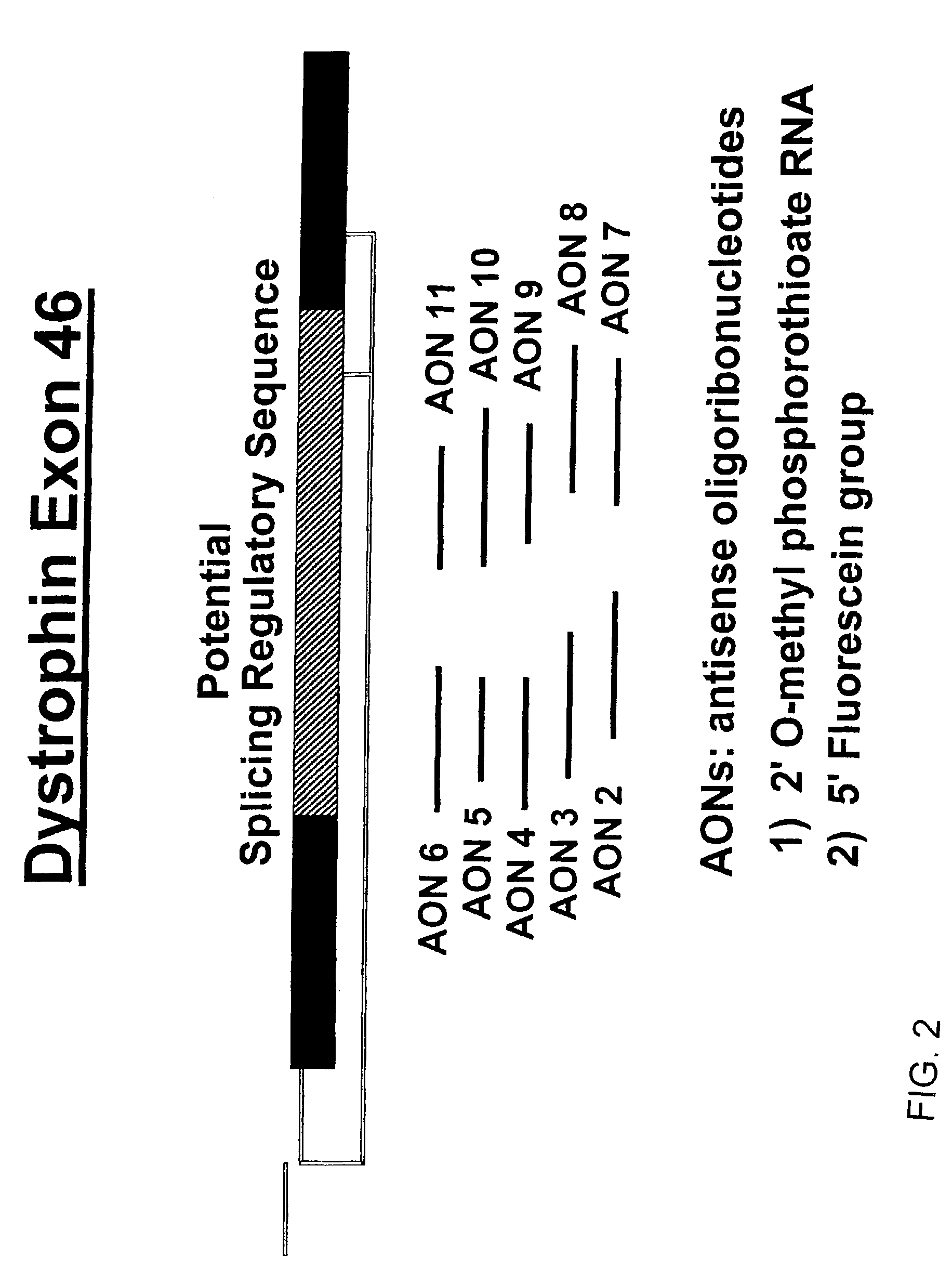
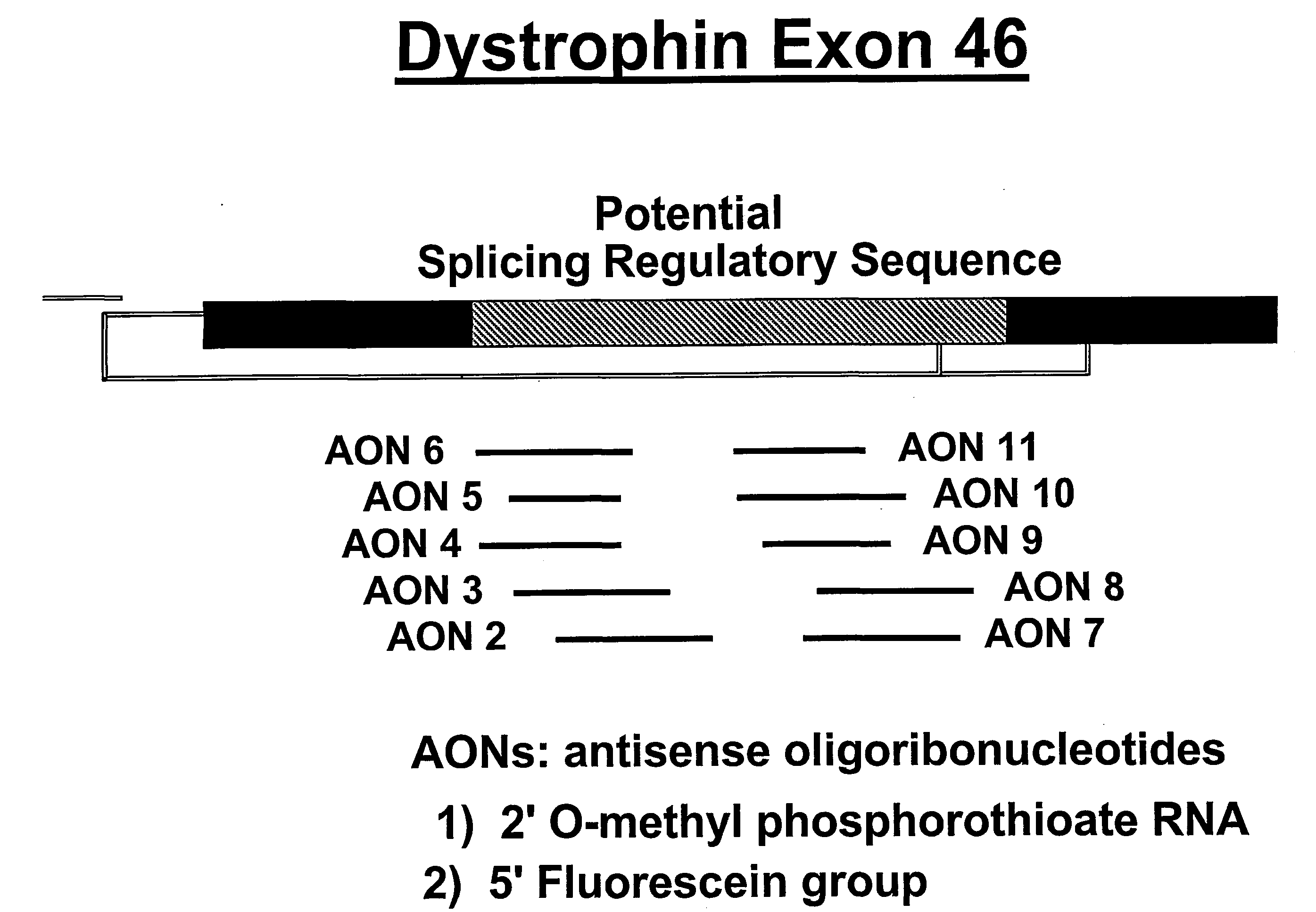
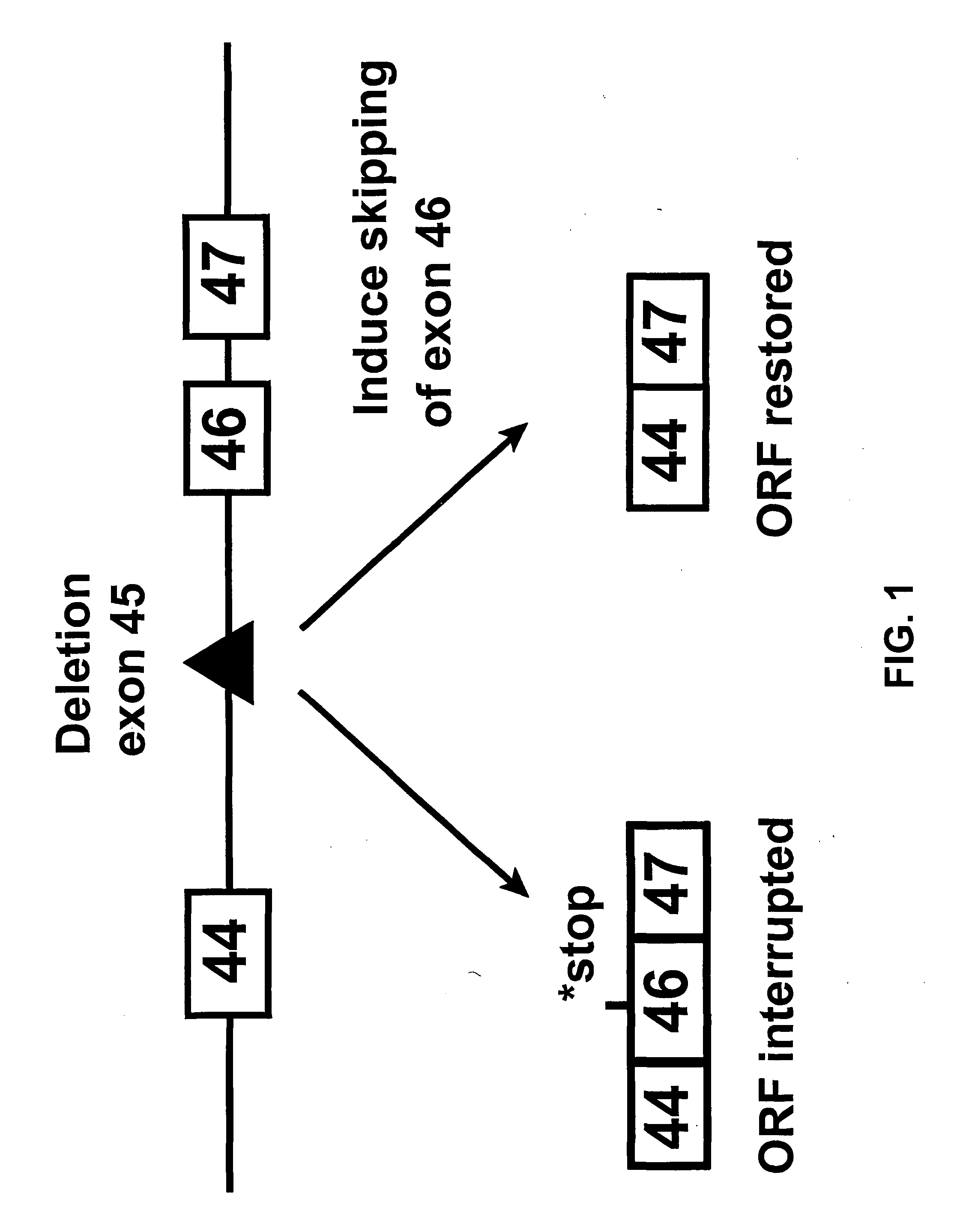
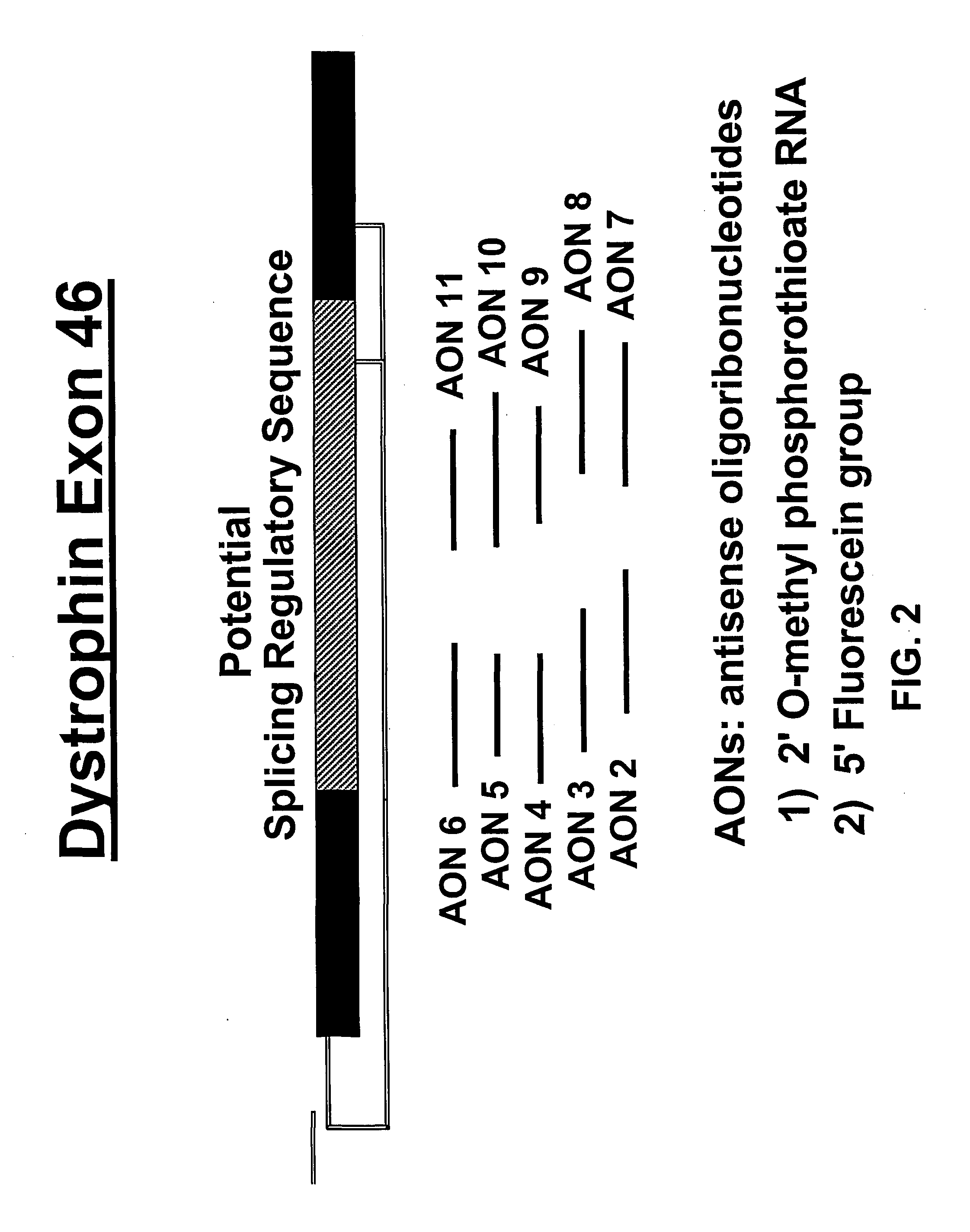
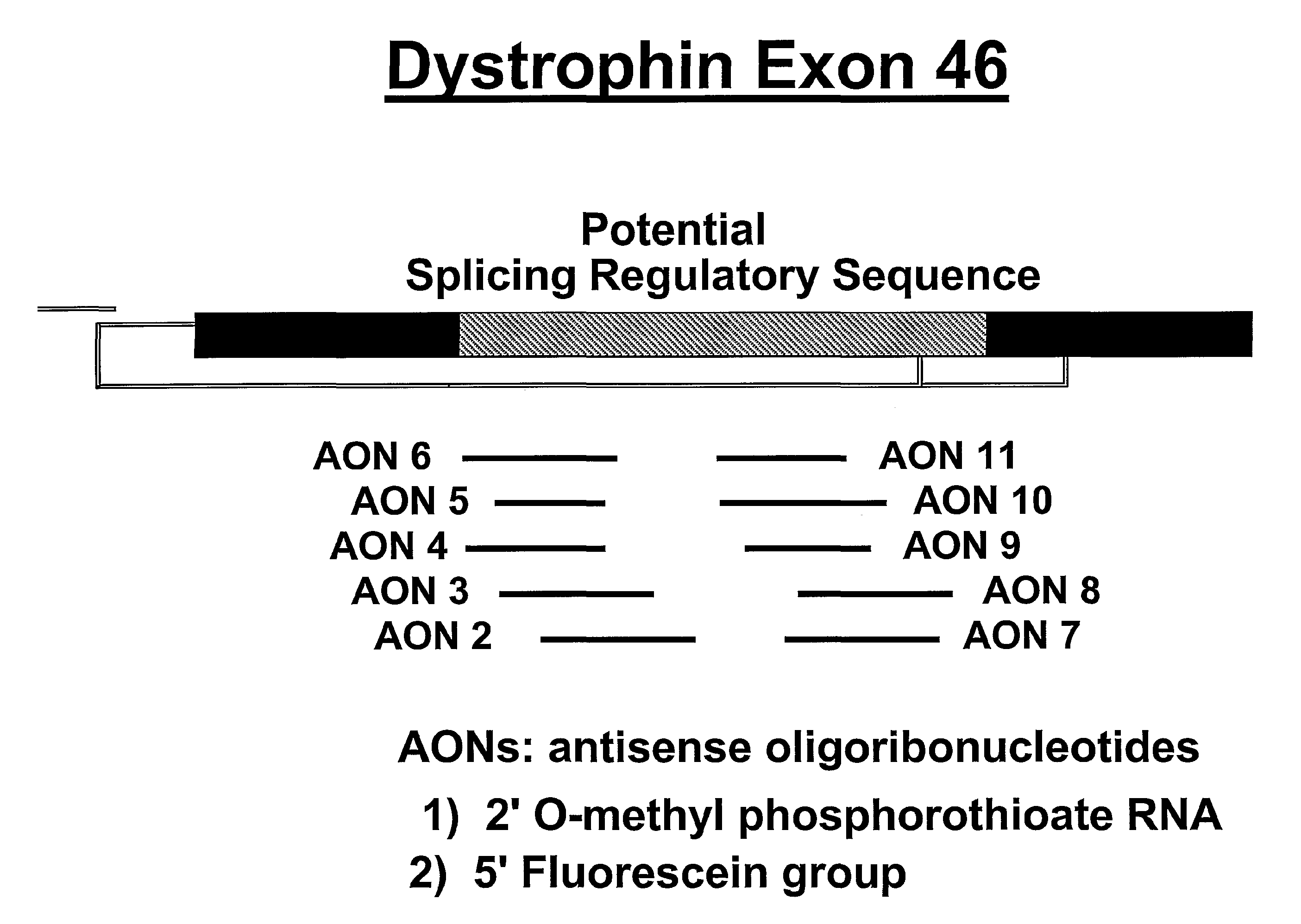
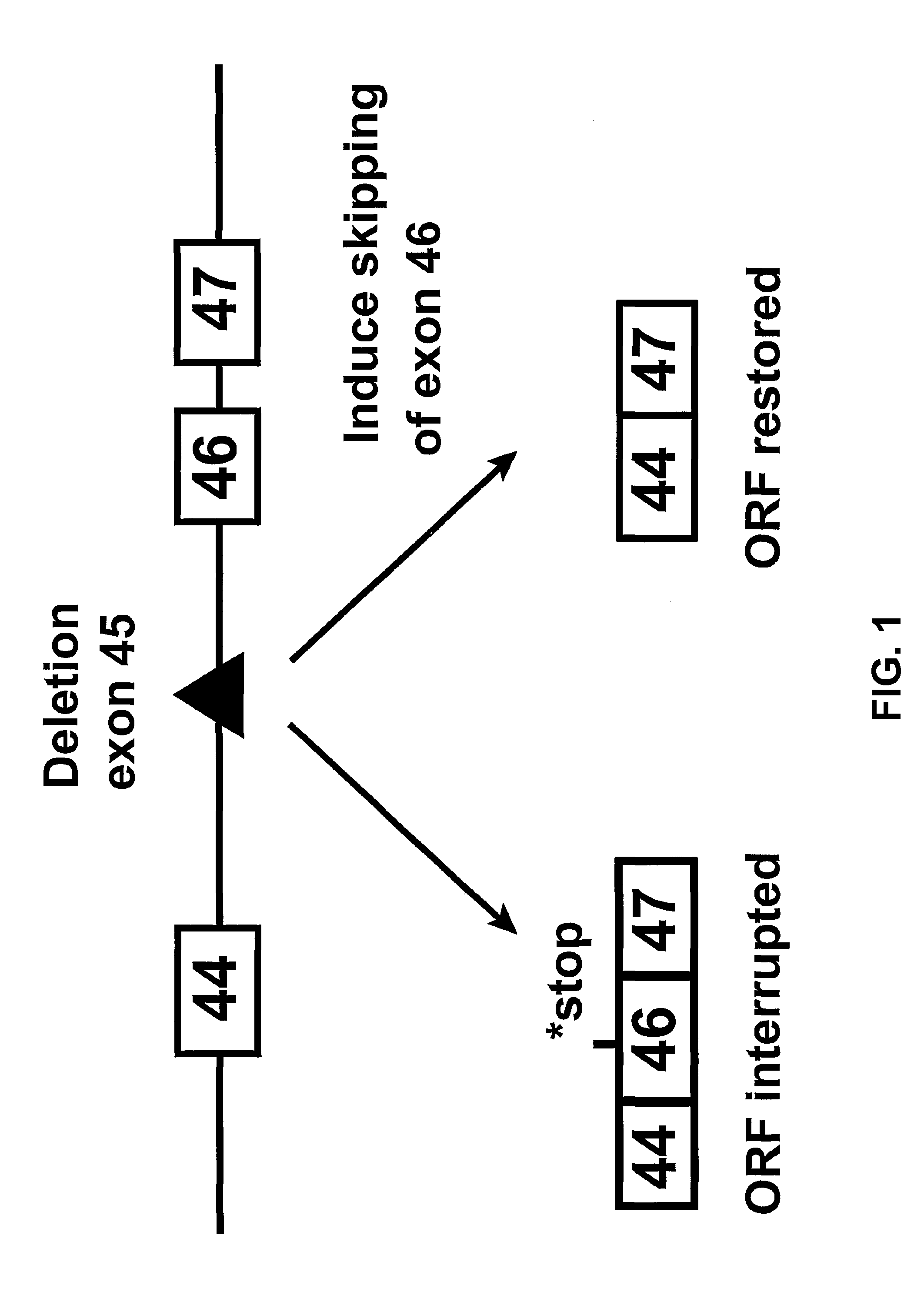
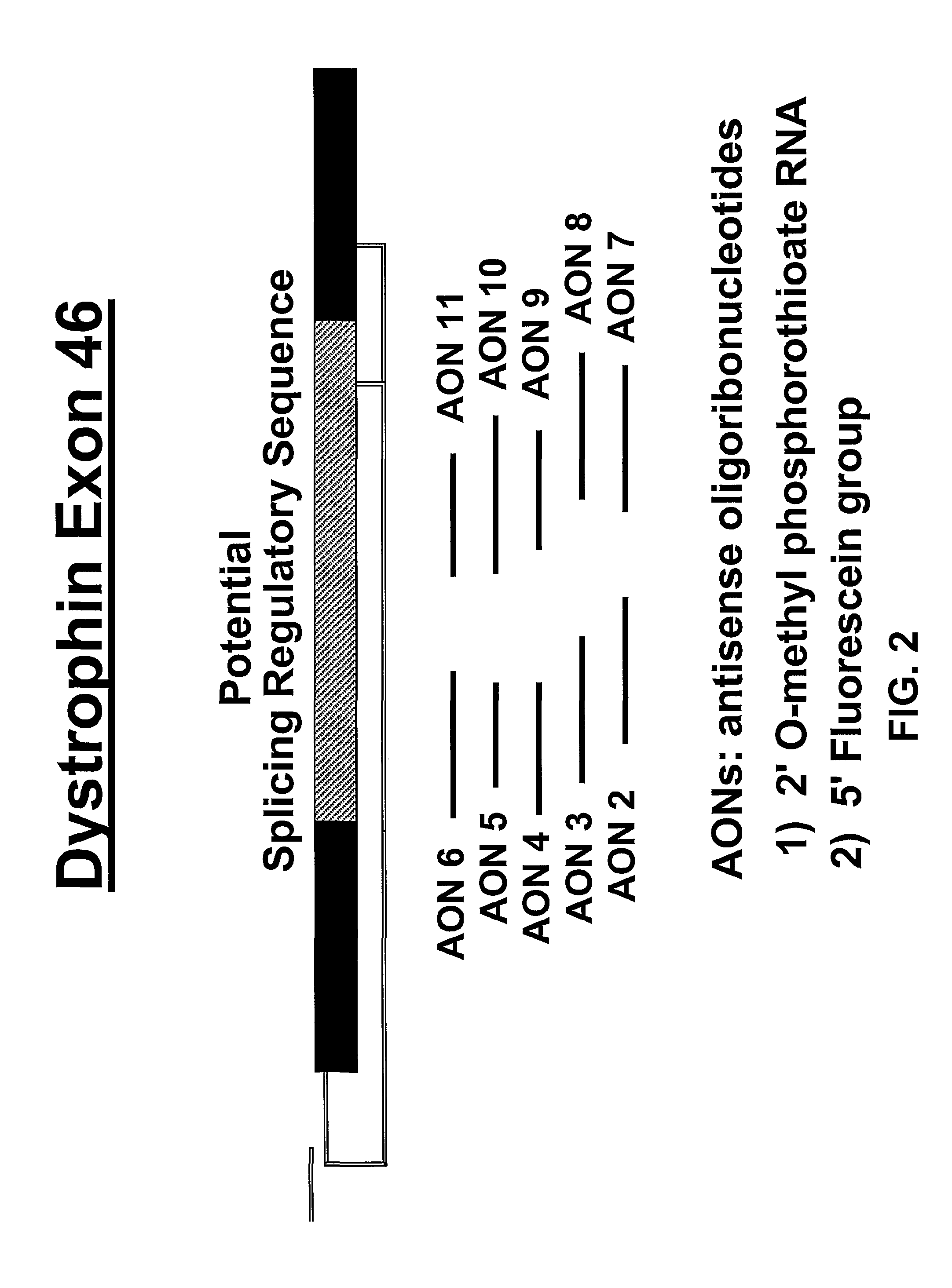
Induction of exon skipping in eukaryotic cells
InactiveUS7973015B2Efficiently maskedPotential for manipulationOrganic active ingredientsSplicing alterationPrecursor mRNARecognition sequence
The present invention provides a method for at least in part decreasing the production of an aberrant protein in a cell, the cell comprising pre-mRNA comprising exons coding for the protein, by inducing so-called exon skipping in the cell. Exon-skipping results in mature MRNA that does not contain the skipped exon, which leads to an altered product of the exon codes for amino acids. Exon skipping is performed by providing a cell with an agent capable of specifically inhibiting an exon inclusion signal, for instance, an exon recognition sequence, of the exon. The exon inclusion signal can be interfered with by a nucleic acid comprising complementarity to a part of the exon. The nucleic acid, which is also herewith provided, can be used for the preparation of a medicament, for instance, for the treatment of an inherited disease.
Owner:LEIDEN ACADEMISCH ZIEKENHUIS
Induction of exon skipping in eukaryotic cells
InactiveUS20090228998A1Efficiently maskedPotential for manipulationOrganic active ingredientsSplicing alterationPrecursor mRNARecognition sequence
The present invention provides a method for at least in part decreasing the production of an aberrant protein in a cell, the cell comprising pre-mRNA comprising exons coding for the protein, by inducing so-called exon skipping in the cell. Exon-skipping results in mature mRNA that does not contain the skipped exon, which leads to an altered product of the exon codes for amino acids. Exon skipping is performed by providing a cell with an agent capable of specifically inhibiting an exon inclusion signal, for instance, an exon recognition sequence, of the exon. The exon inclusion signal can be interfered with by a nucleic acid comprising complementarity to a part of the exon. The nucleic acid, which is also herewith provided, can be used for the preparation of a medicament, for instance, for the treatment of an inherited disease.
Owner:ACADEMISCH ZIEKENHUIS BIJ DE UNIV VAN AMSTERDAM ACADEMISCH MEDISCH CENT
Induction of exon skipping in eukaryotic cells
InactiveUS20080209581A1Reduce productionReduce amountOrganic active ingredientsSplicing alterationPrecursor mRNARecognition sequence
Described is a method for at least in part decreasing the production of an aberrant protein in a cell, the cell comprising pre-mRNA comprising exons coding for the protein, by inducing so-called exon skipping in the cell. Exon-skipping results in mature mRNA that does not contain the skipped exon, which leads to an altered product of the exon codes for amino acids. Exon skipping is performed by providing a cell with an agent capable of specifically inhibiting an exon inclusion signal, for instance, an exon recognition sequence, of the exon. The exon inclusion signal can be interfered with by a nucleic acid comprising complementarity to a part of the exon. The nucleic acid, which is also herewith provided, can be used for the preparation of a medicament, for instance, for the treatment of an inherited disease.
Owner:ACADEMISCH ZIEKENHUIS BIJ DE UNIV VAN AMSTERDAM ACADEMISCH MEDISCH CENT
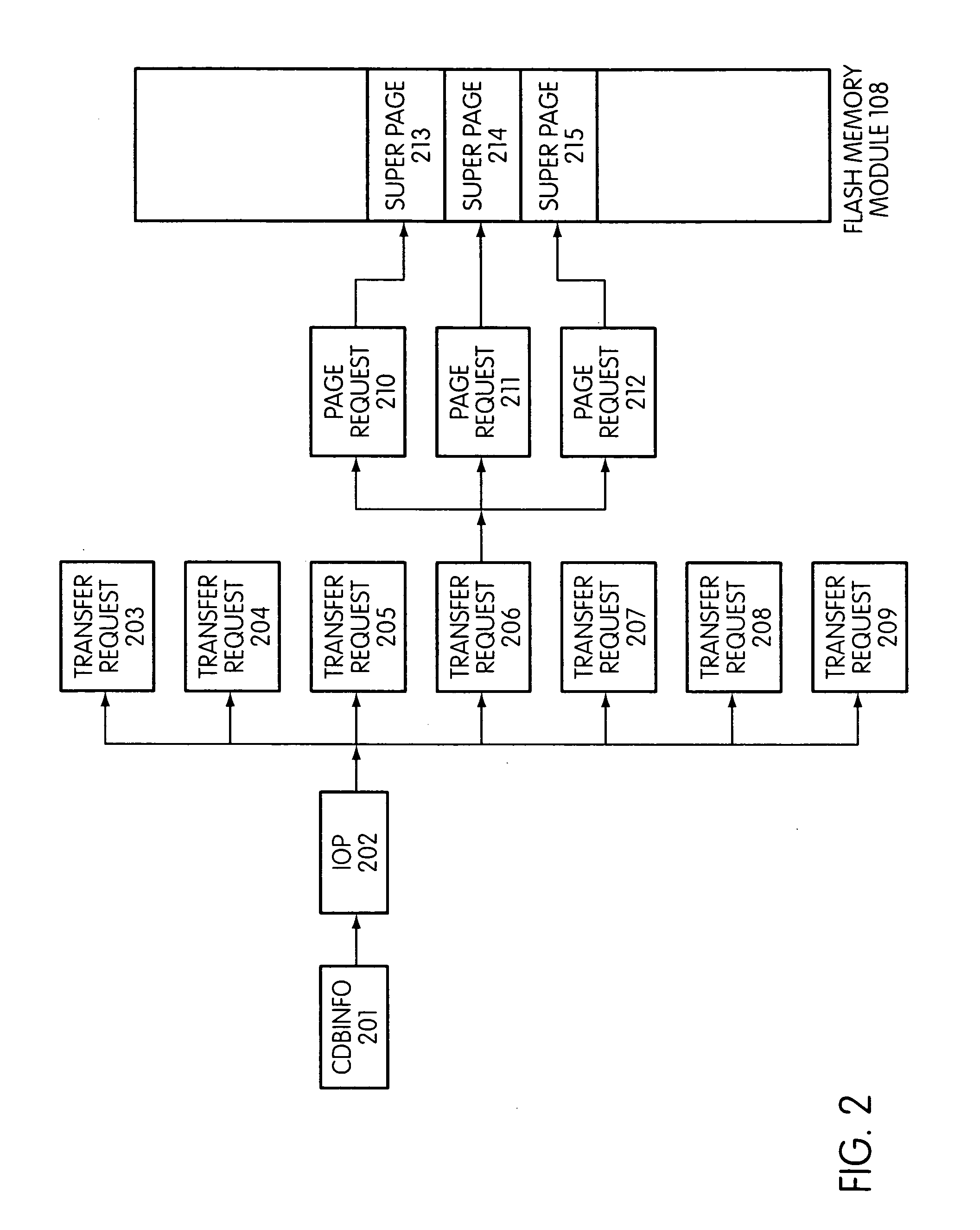
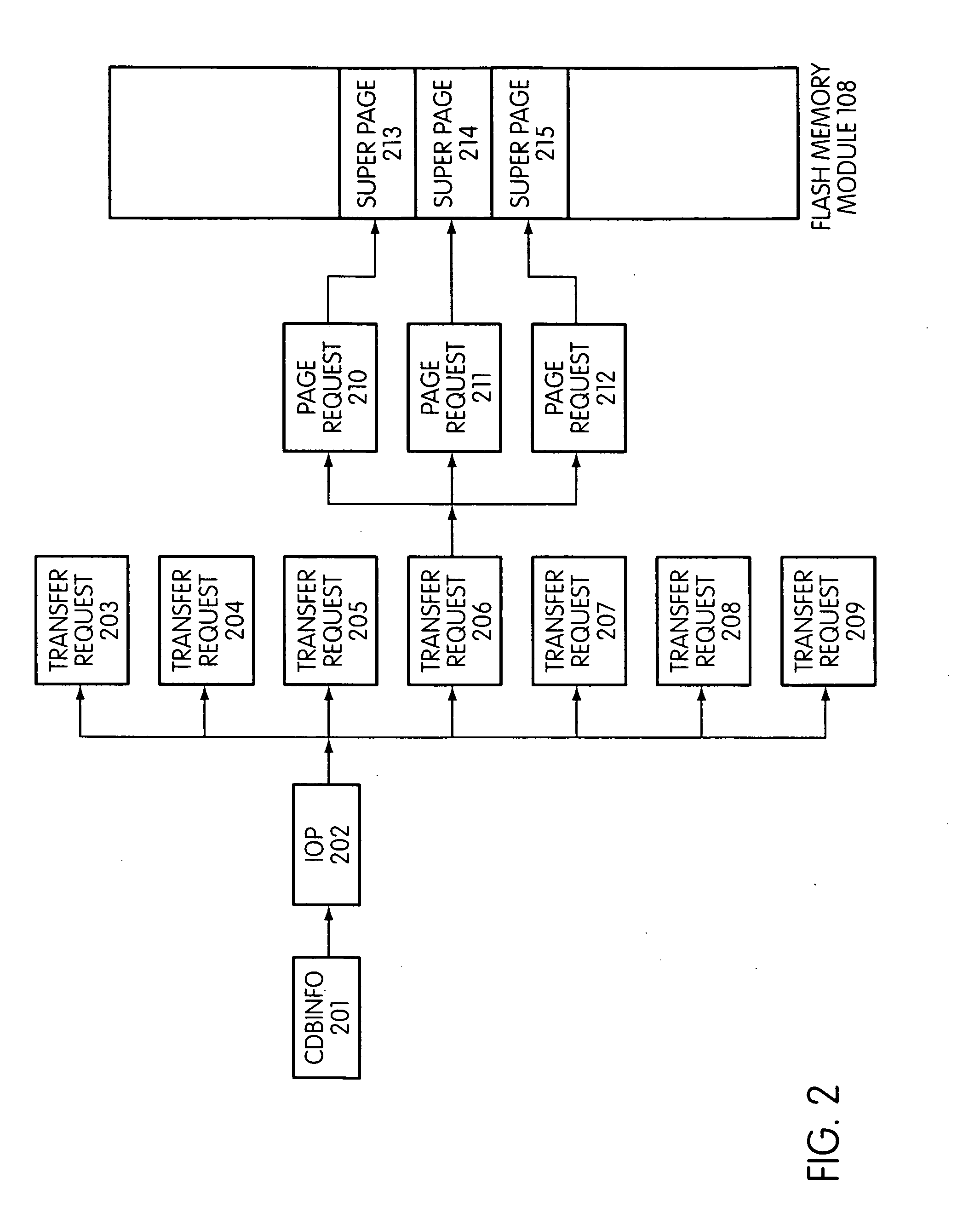
Flash storage controller execute loop
ActiveUS20090172263A1Maximize useImprove performanceMemory architecture accessing/allocationInput/output to record carriersArray data structureControl store
In a storage controller connected to a flash memory module, an execute loop used to carry out tasks related to reading or writing data from the module. The loop includes reading a data structure from a queue and carrying out a task specified by the data structure, unless resources required by the task are not available, in which event the loop moves on to another data structure stored in another queue. Data structures bypassed by the loop are periodically revisited, until all tasks required are completed. Data structures store state information that is updated when tasks are completed.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Rapid acting and long acting insulin combination formulations
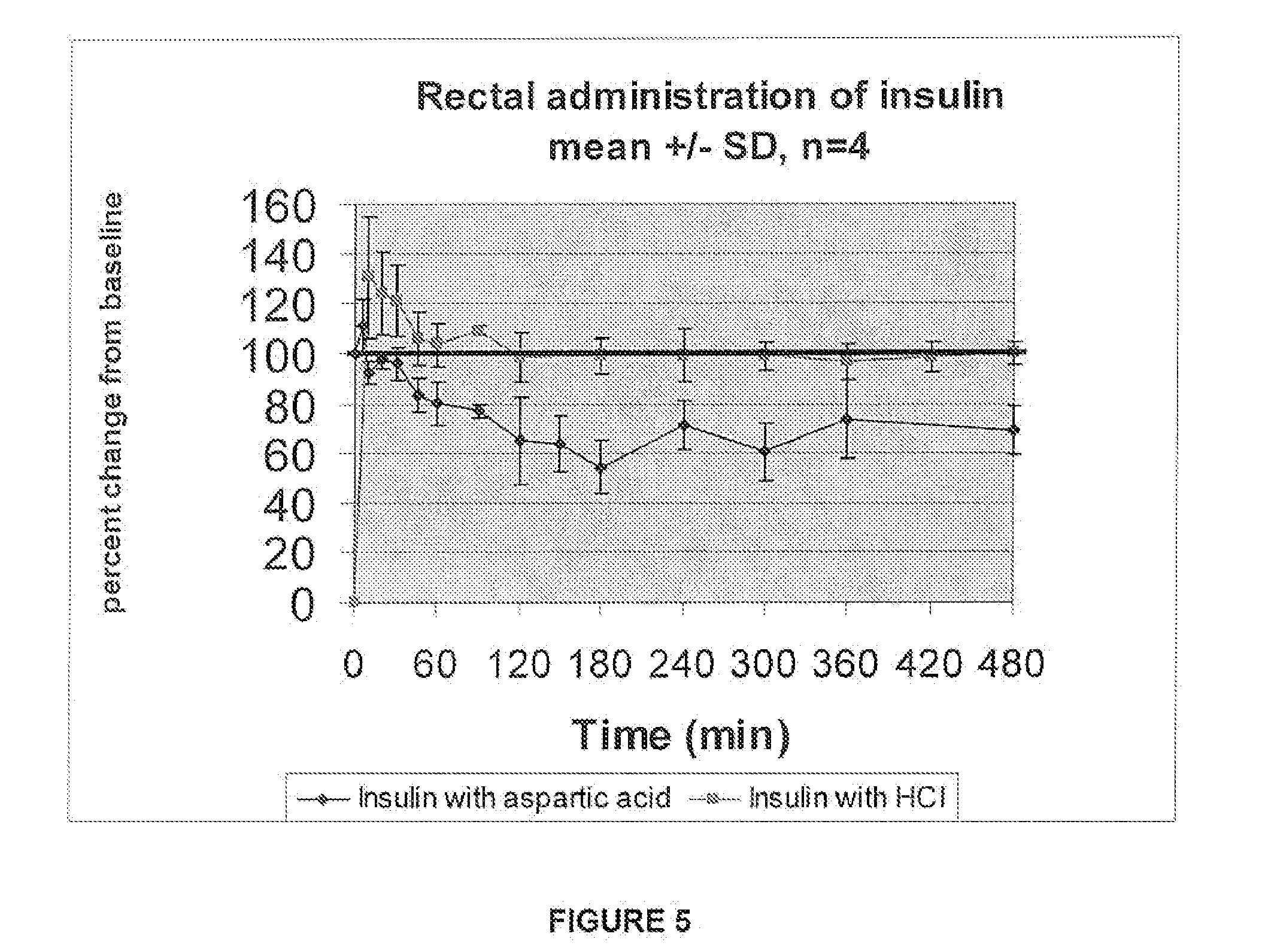
ActiveUS20080039368A1Increase speedReduce the amount of solutionPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderBefore BreakfastIntensive insulinotherapy
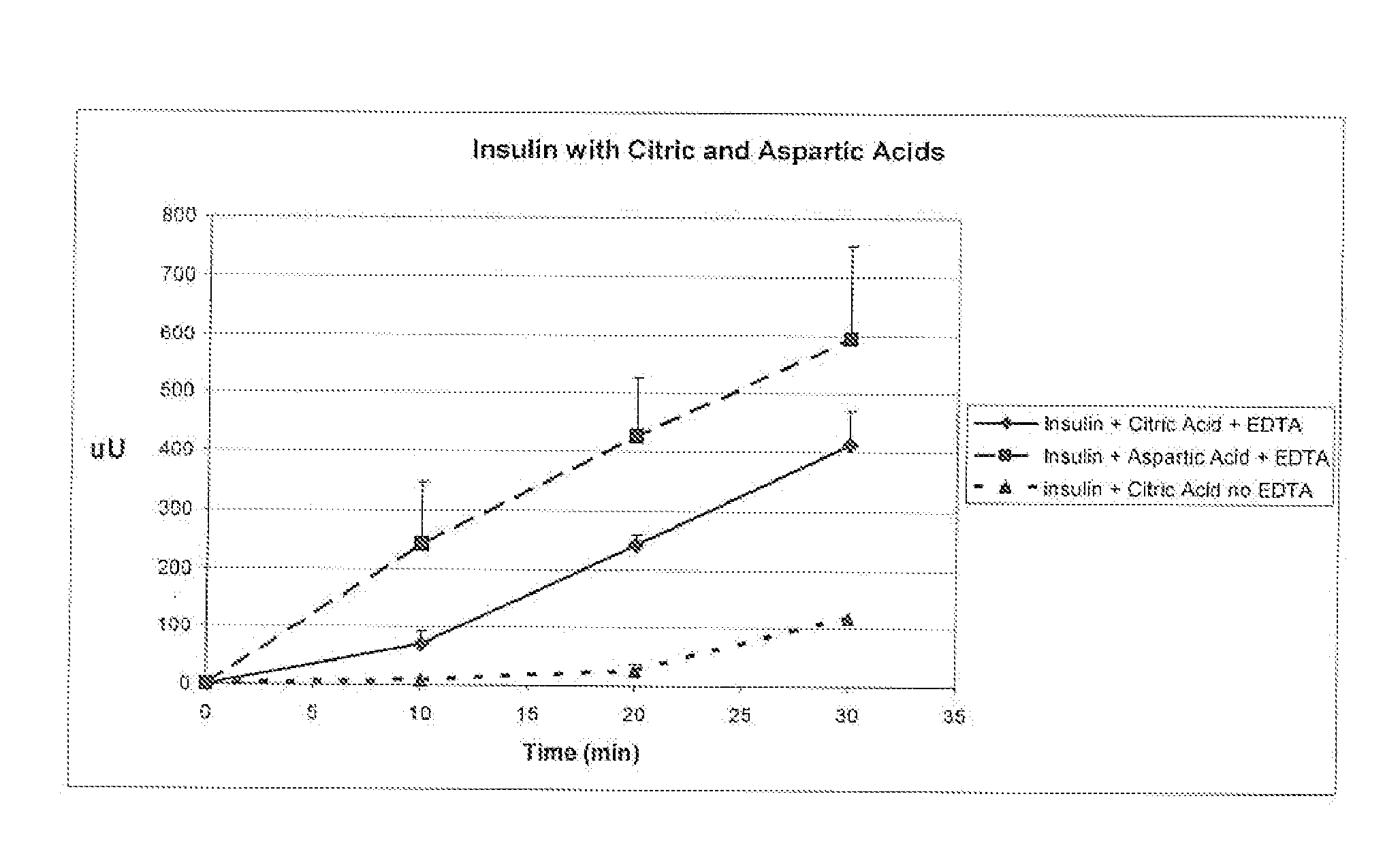
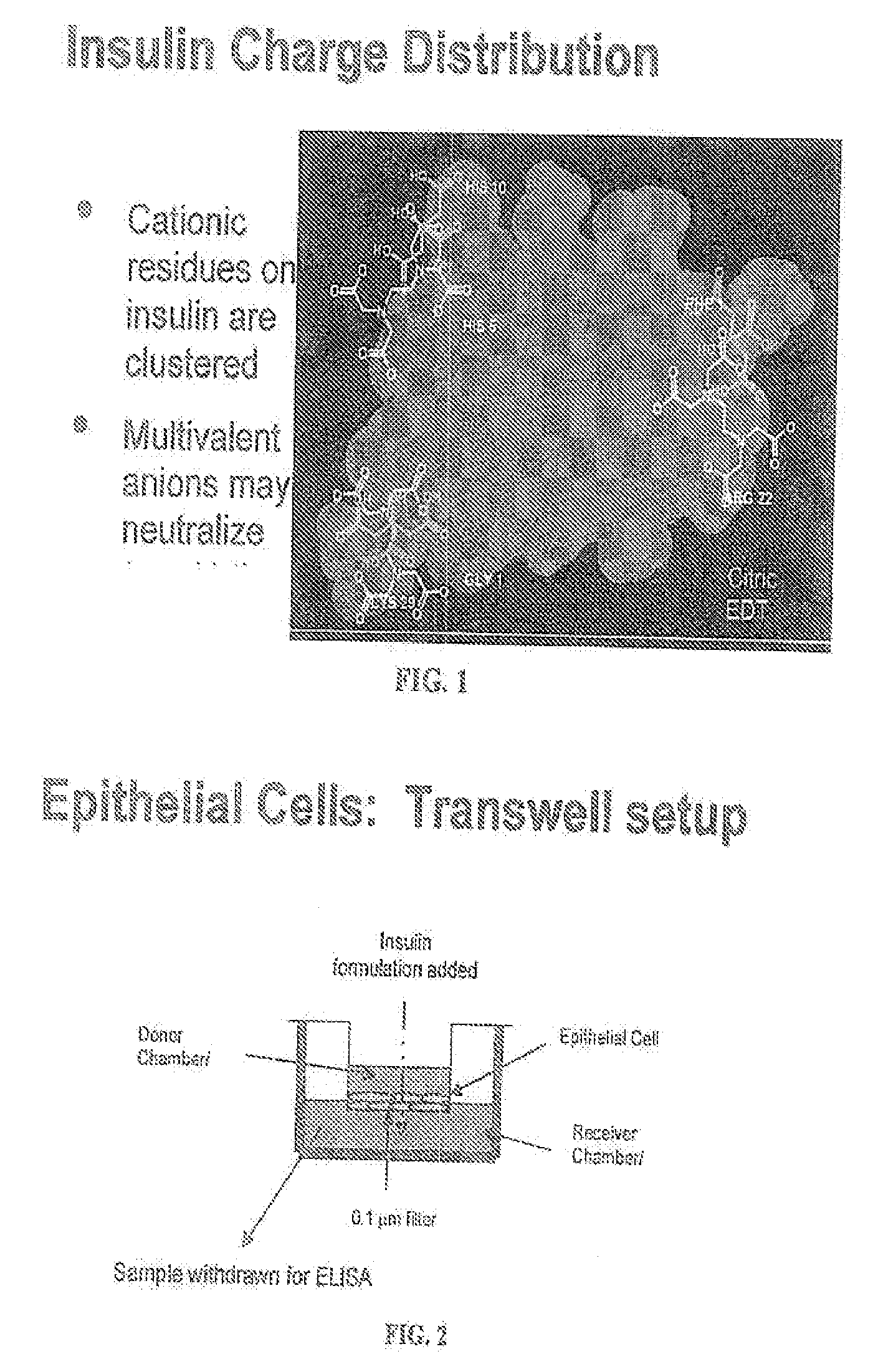
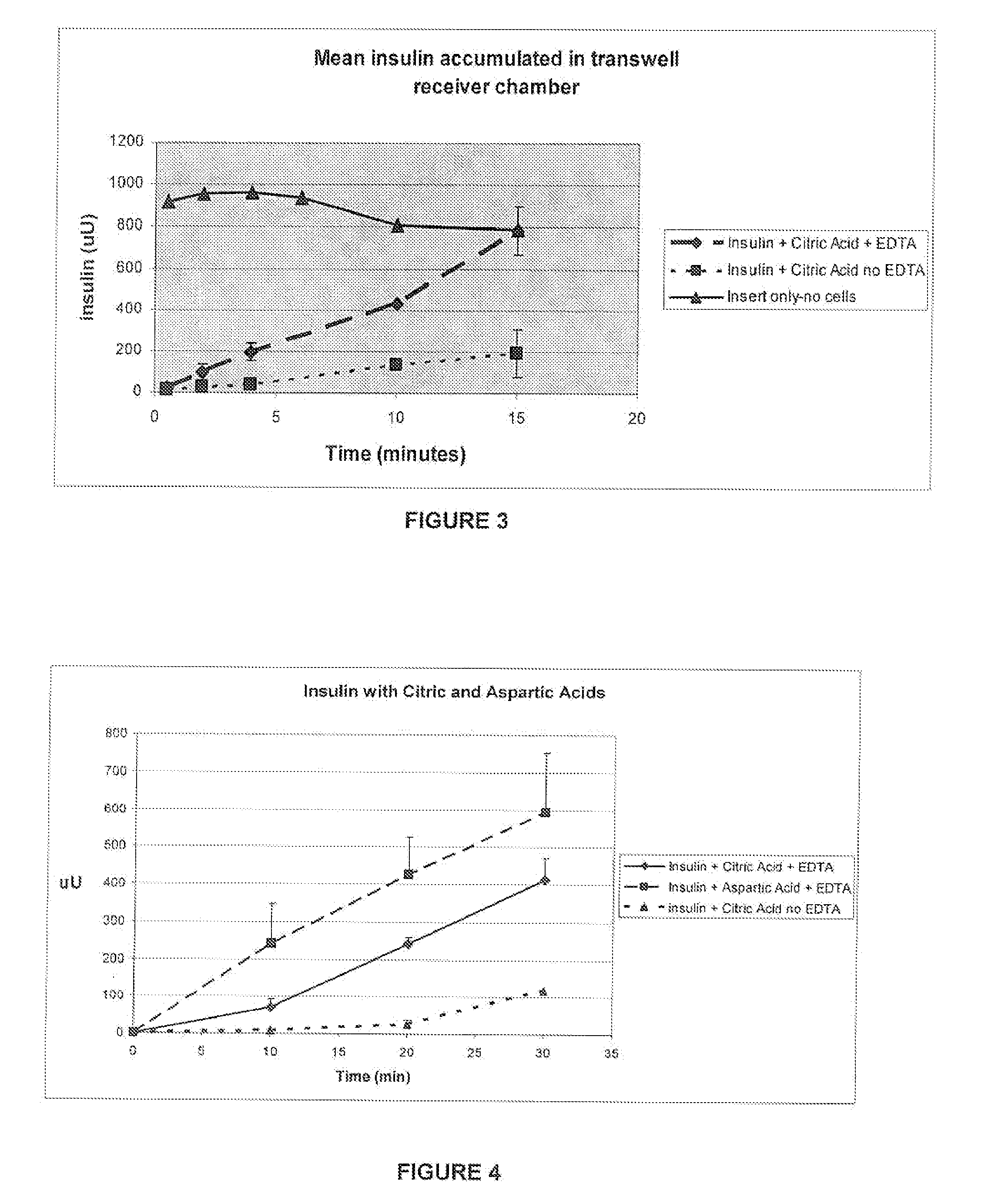
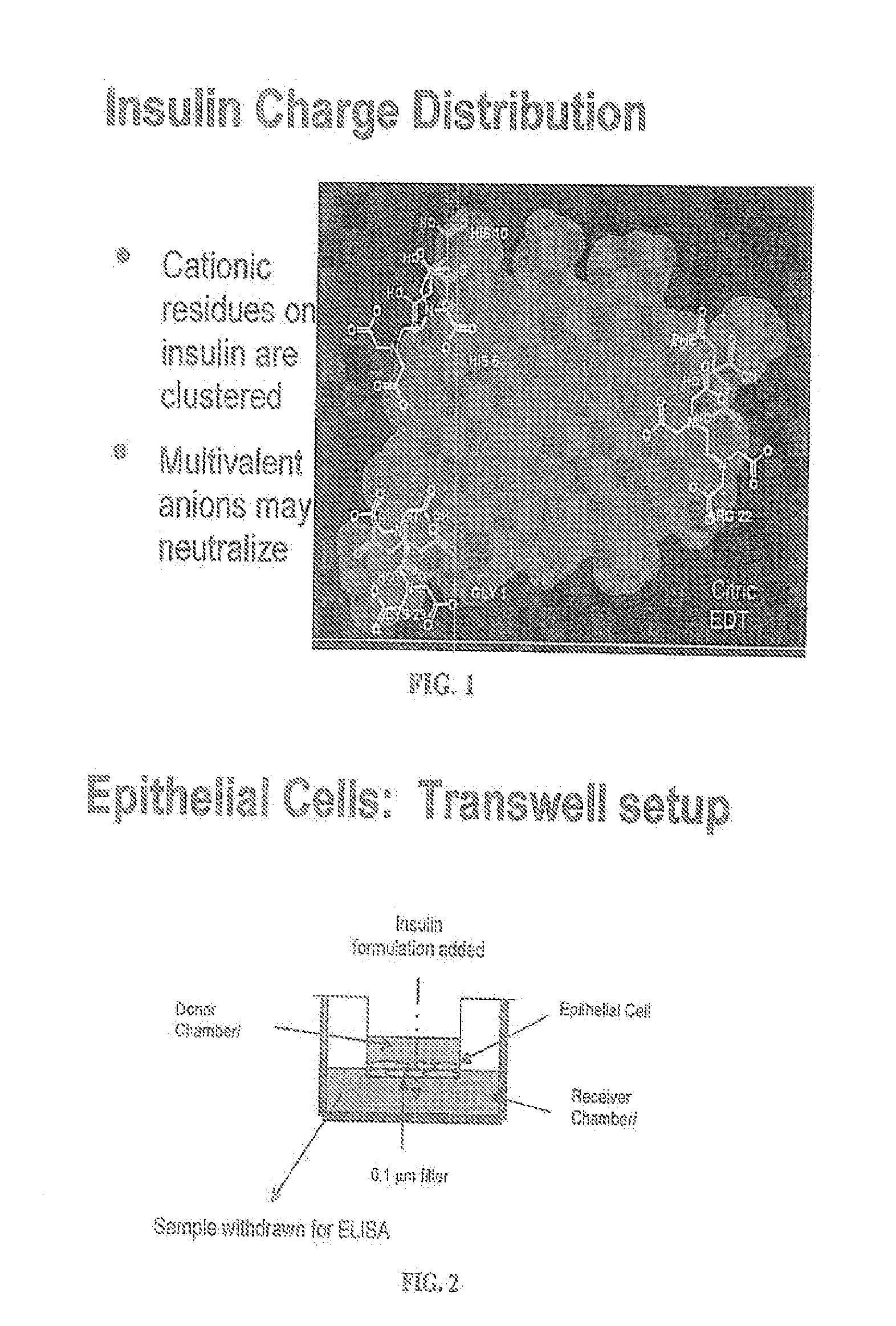
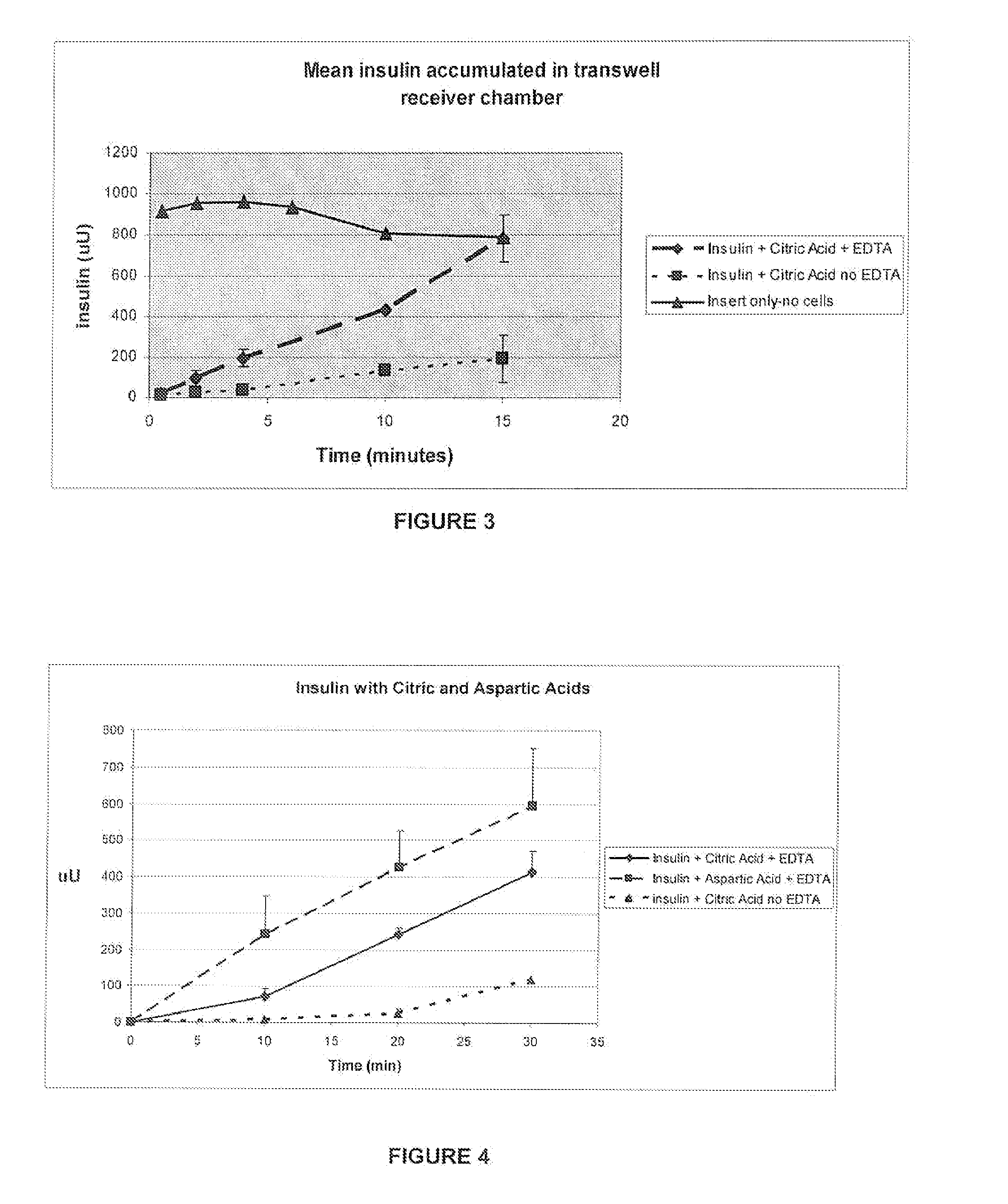
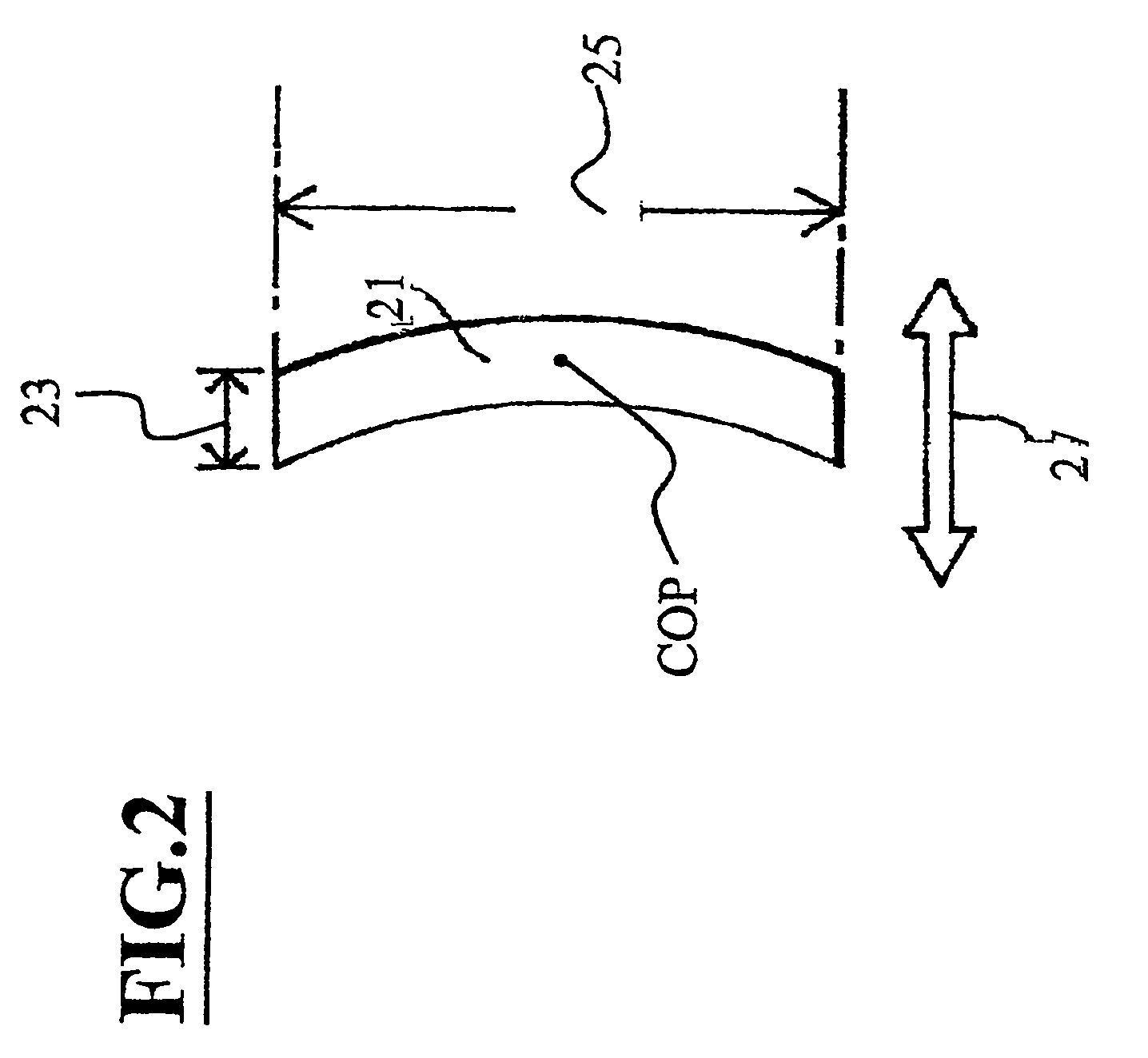
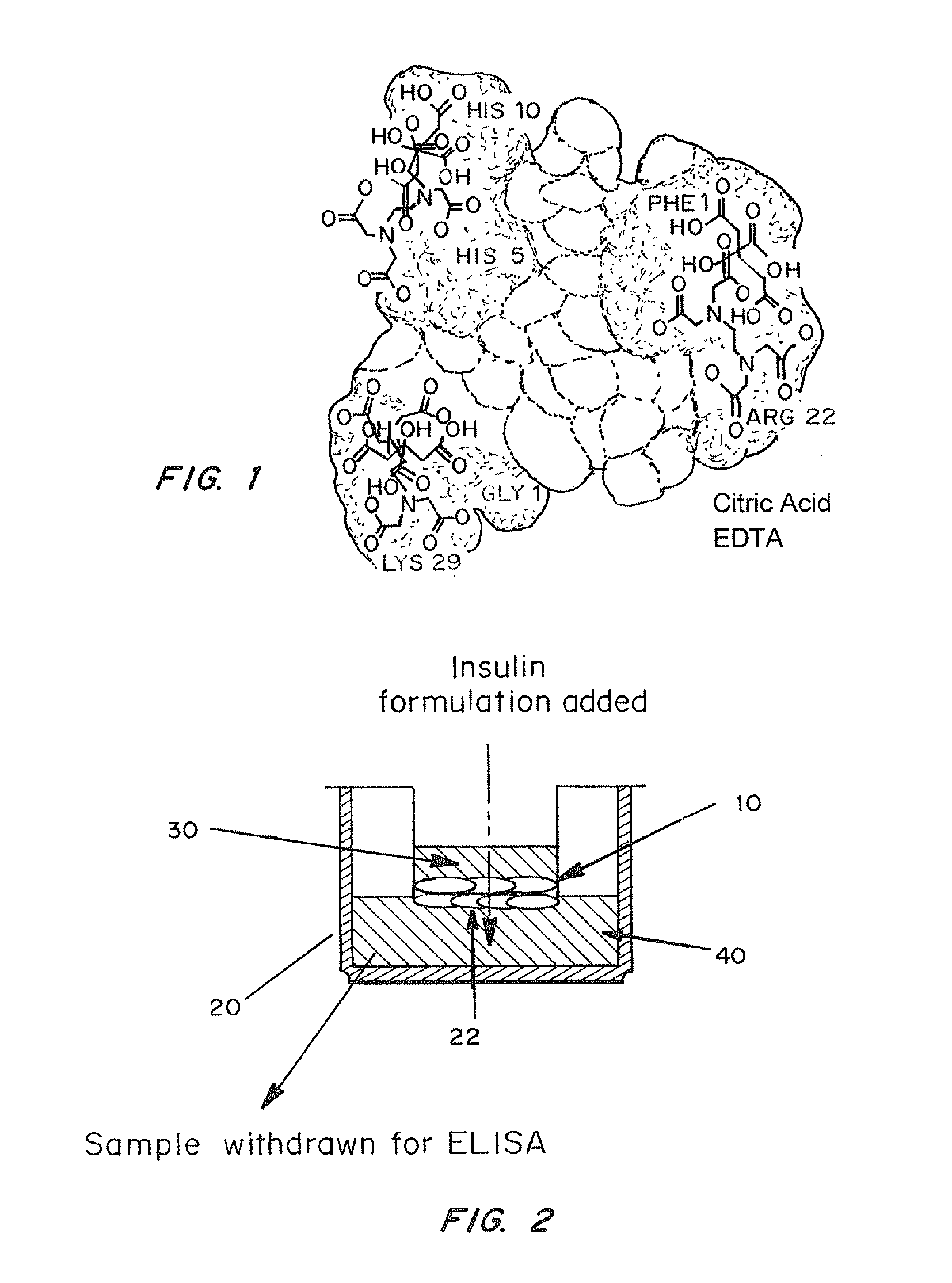
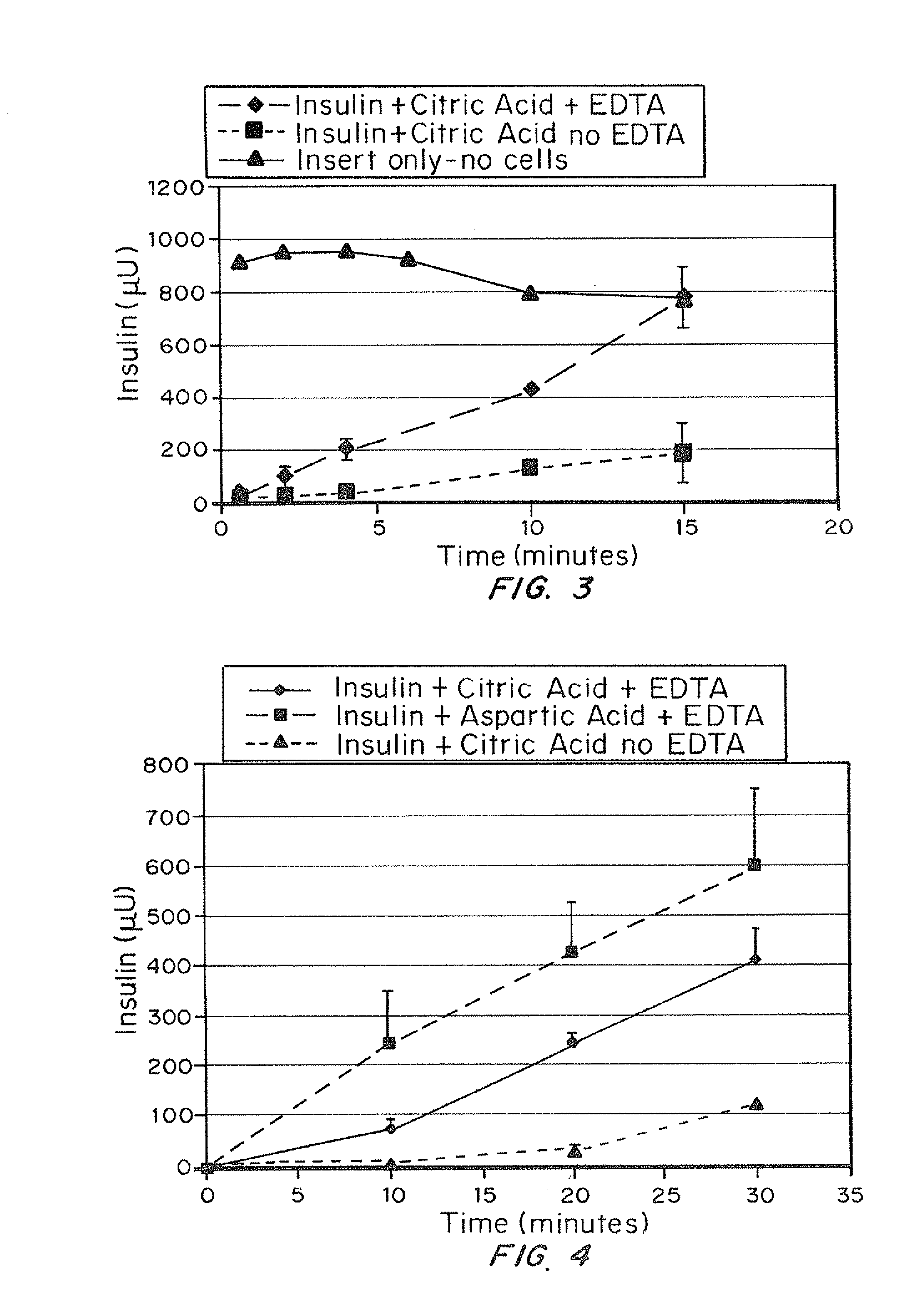
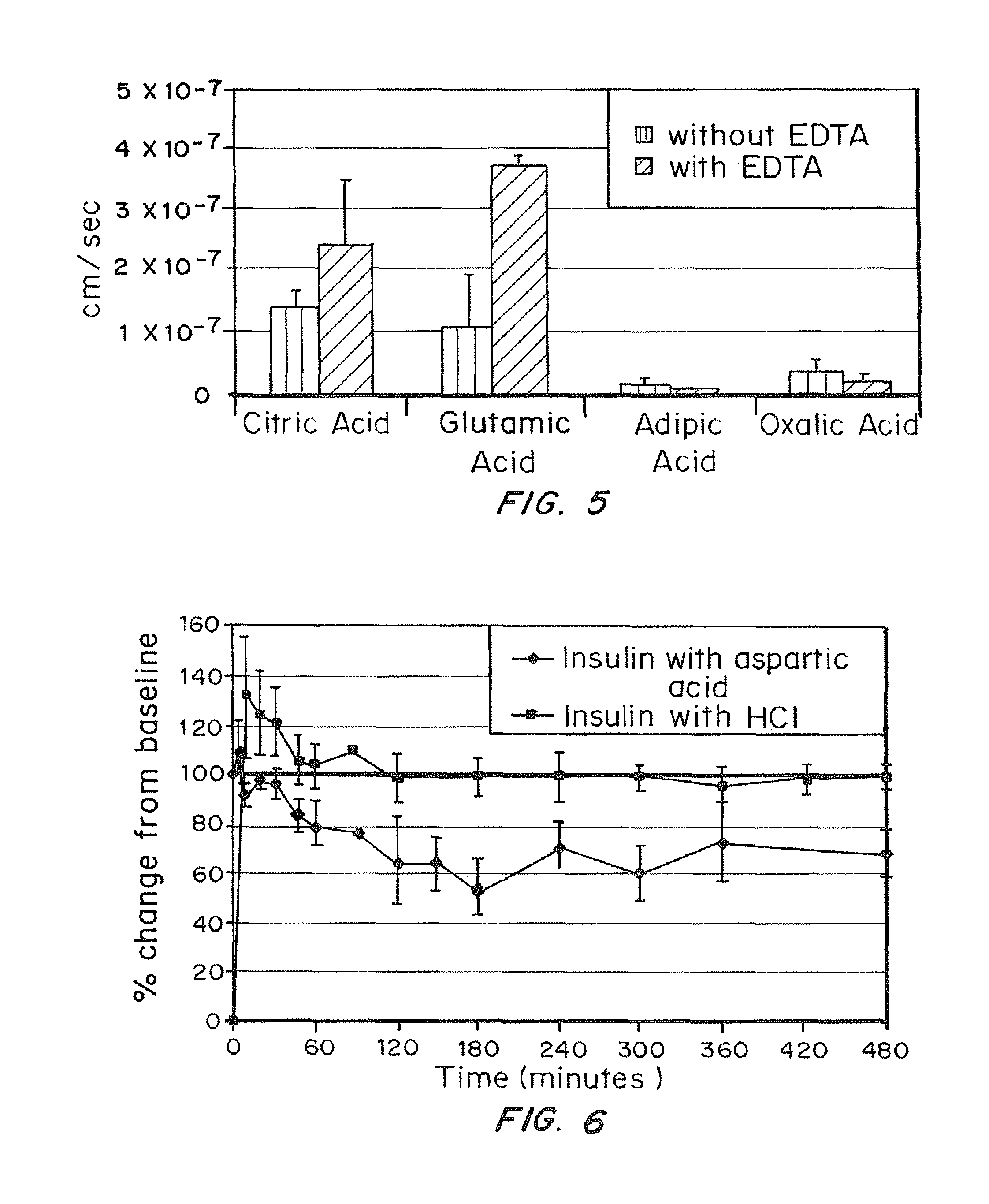
A combined rapid acting-long acting insulin formulation has been developed wherein the pH of the rapid acting insulin is adjusted so that the long acting glargine remains soluble when they are mixed together. In the preferred embodiment, this injectable basal bolus insulin is administered before breakfast, provides adequate bolus insulin levels to cover the meal, does not produce hypoglycemia after the meal and provides adequate basal insulin for 24 hours. Lunch and dinner can be covered by two bolus injections of a fast acting, or a rapid acting or a very rapid acting insulin. As a result, a patient using intensive insulin therapy should only inject three, rather than four, times a day. Experiments have been performed to demonstrate, the importance of the addition of specific acids to hexameric insulin to enhance speed and amount of absorption and preserve bioactivity following dissociation into the monomeric form by addition of a chelator such as EDTA. As shown by the examples, the preferred acids are aspartic, maleic, succinic, glutamic and citric acid. These are added in addition to a chelator, preferably ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA). The results show that the citric acid formulation was more effective at dropping the blood glucose rapidly than the identical rapid acting formulation prepared with HCl in swine. Charge masking by the polyacid appears to be responsible for rapid insulin absorption. EDTA was not effective when used with adipic acid, oxalic acid or HCl at hastening the absorption of insulin. These results confirm the results seen in clinical subjects and patients with diabetes treated with the rapid acting insulin in combination with citric acid and EDTA.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
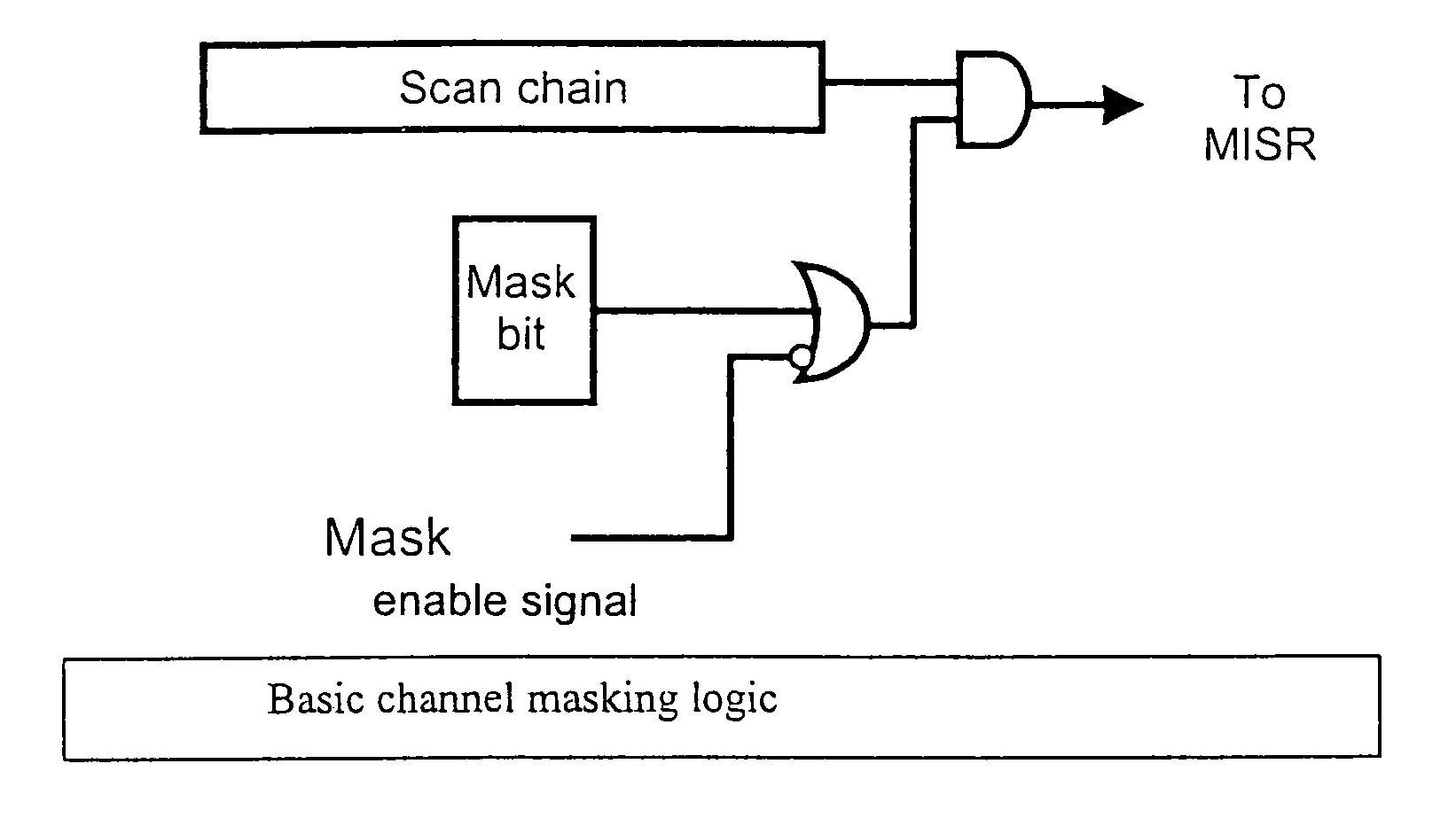
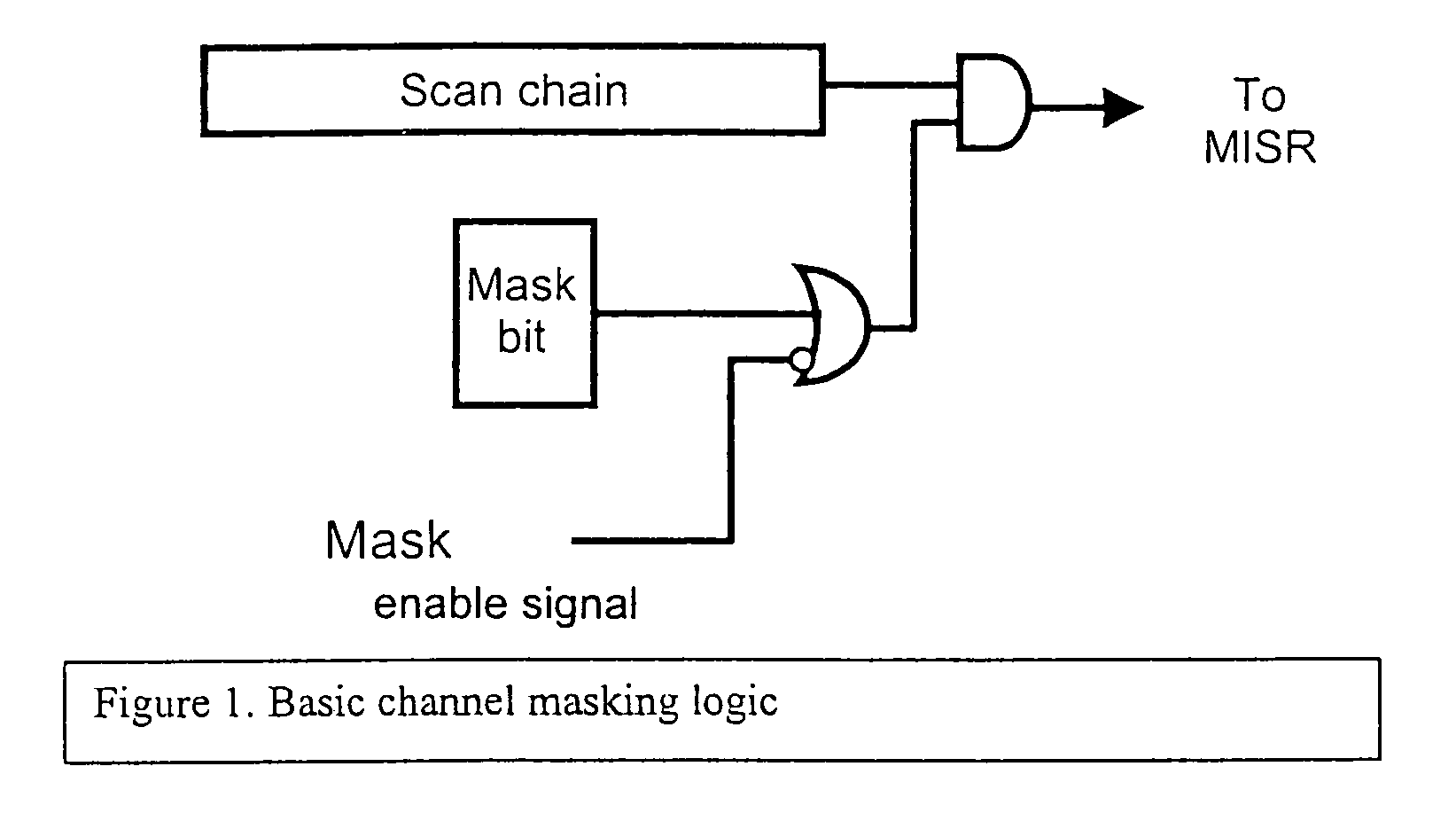
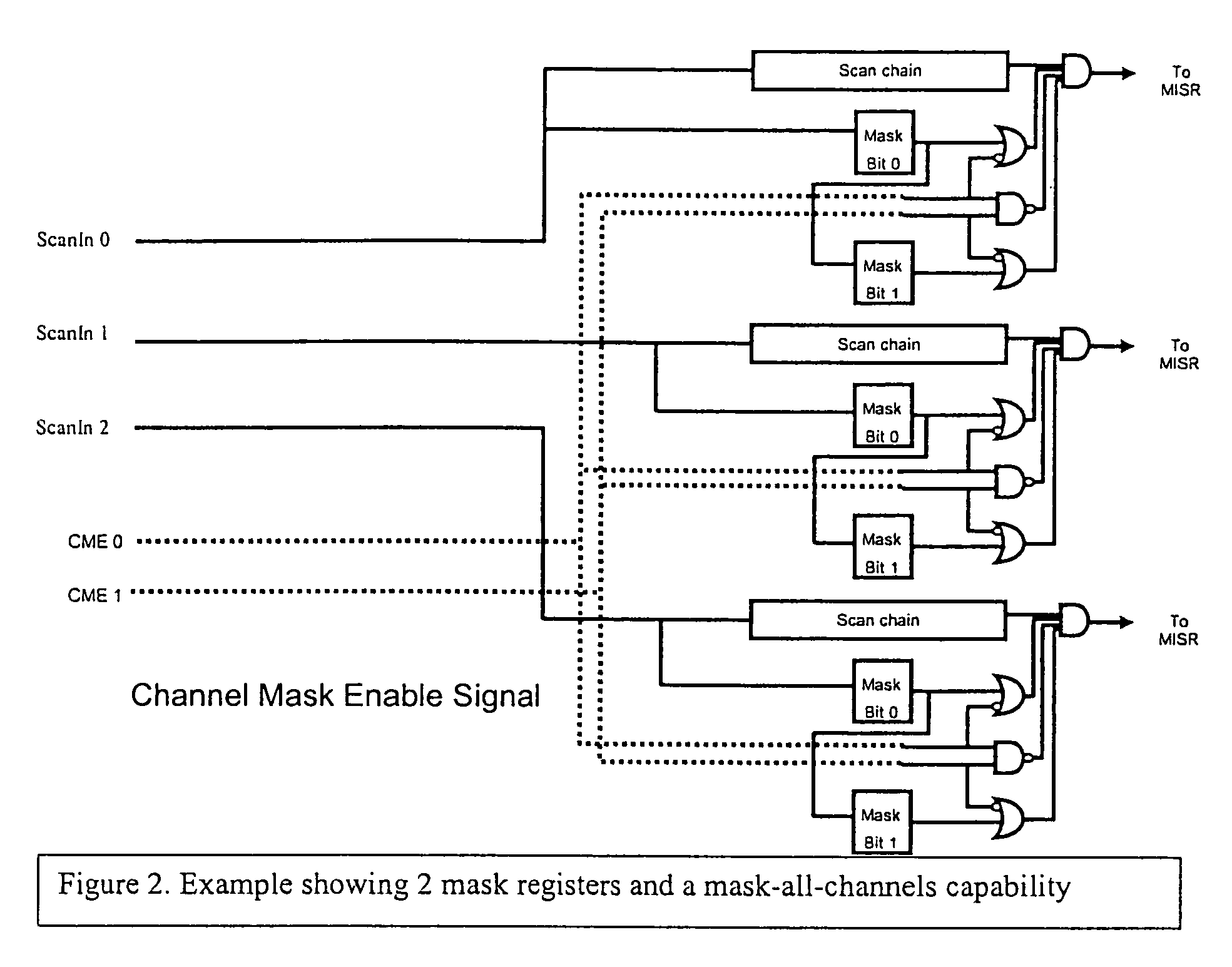
Channel masking during integrated circuit testing
During testing of an integrated circuit (IC), a channel masking capability is used for masking out unknown or unpredictable (X) values from being compressed into a signature register. The approach provides flexibility to allow for masking of unknown values, while avoiding many of the problems caused by over-masking of known values. The circuitry added to the design to allow for masking is reasonably small, and provides an effective way of masking unknown values during the testing process.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
Method and system for coating tubular medical devices
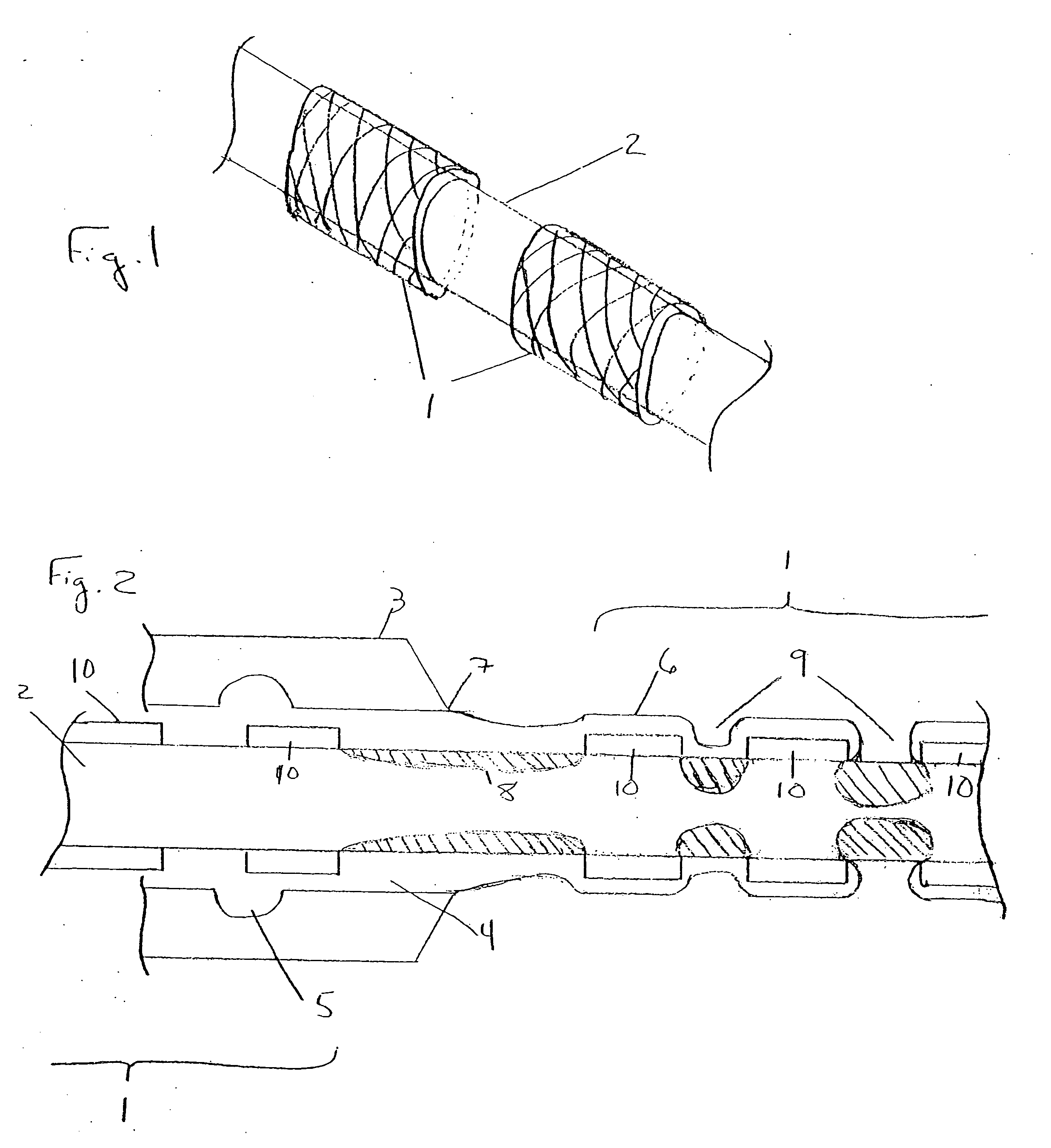
InactiveUS20050147734A1Reduce the overall diameterPreventing “webbing” or “bridgingStentsPharmaceutical containersHigh volume manufacturingInsertion stent
A system and method for application of therapeutic and protective coatings to multiple tubular medical devices in a high volume production process. One or more tubular medical devices, such as stents, are placed on a coating-absorbent core, and coating is applied to the device(s), for example, as when the device-carrying core is passed through an extrusion coating machine to apply the coating in a uniform manner. Once coated, the medical device(s) may be quickly and efficiently removed from the core by causing the core diameter to decrease, such as by applying elongating tension to the core to cause the core diameter to radially contract, thereby allowing the coated device(s) to be simultaneously freed from the core. Improved coating uniformity, increased coated device removal ease and minimized bridging of openings in the tubular medical device may be obtained with a core that absorbs excess coating.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Rapid Acting and Long Acting Insulin Combination Formulations
InactiveUS20080039365A1Promote absorptionAct quicklyBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsBefore BreakfastIntensive insulinotherapy
A combined rapid acting-long acting insulin formulation has been developed wherein the pH of the rapid acting insulin is decreased so that the long acting glargine remains soluble when they are mixed together. In the preferred embodiment, this injectable basal bolus insulin is administered before breakfast, provides adequate bolus insulin levels to cover the meal, does not produce hypoglycemia after the meal and provides adequate basal insulin for 24 hours. Lunch and dinner can be covered by two bolus injections of a fast acting, or a rapid acting or a very rapid acting insulin. As a result, a patient using intensive insulin therapy should only inject three, rather than four, times a day. Experiments have been performed to demonstrate the importance of the addition of specific acids to hexameric insulin to enhance speed and amount of absorption and preserve bioactivity following dissociation into the monomeric form by addition of a chelator such as EDTA. As shown by the examples, the preferred acids are aspartic, glutamic and citric acid. These are added in addition to a chelator, preferably ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA). The results show that the citric acid formulation was more effective at dropping the blood glucose rapidly than the identical rapid acting formulation prepared with HCl in swine. Charge masking by the polyacid appears to be responsible for rapid insulin absorption. EDTA was not effective when used with adipic acid, oxalic acid or HCl at hastening the absorption of insulin. These results confirm the results seen in clinical subjects and patients with diabetes treated with the rapid acting insulin in combination with citric acid and EDTA.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
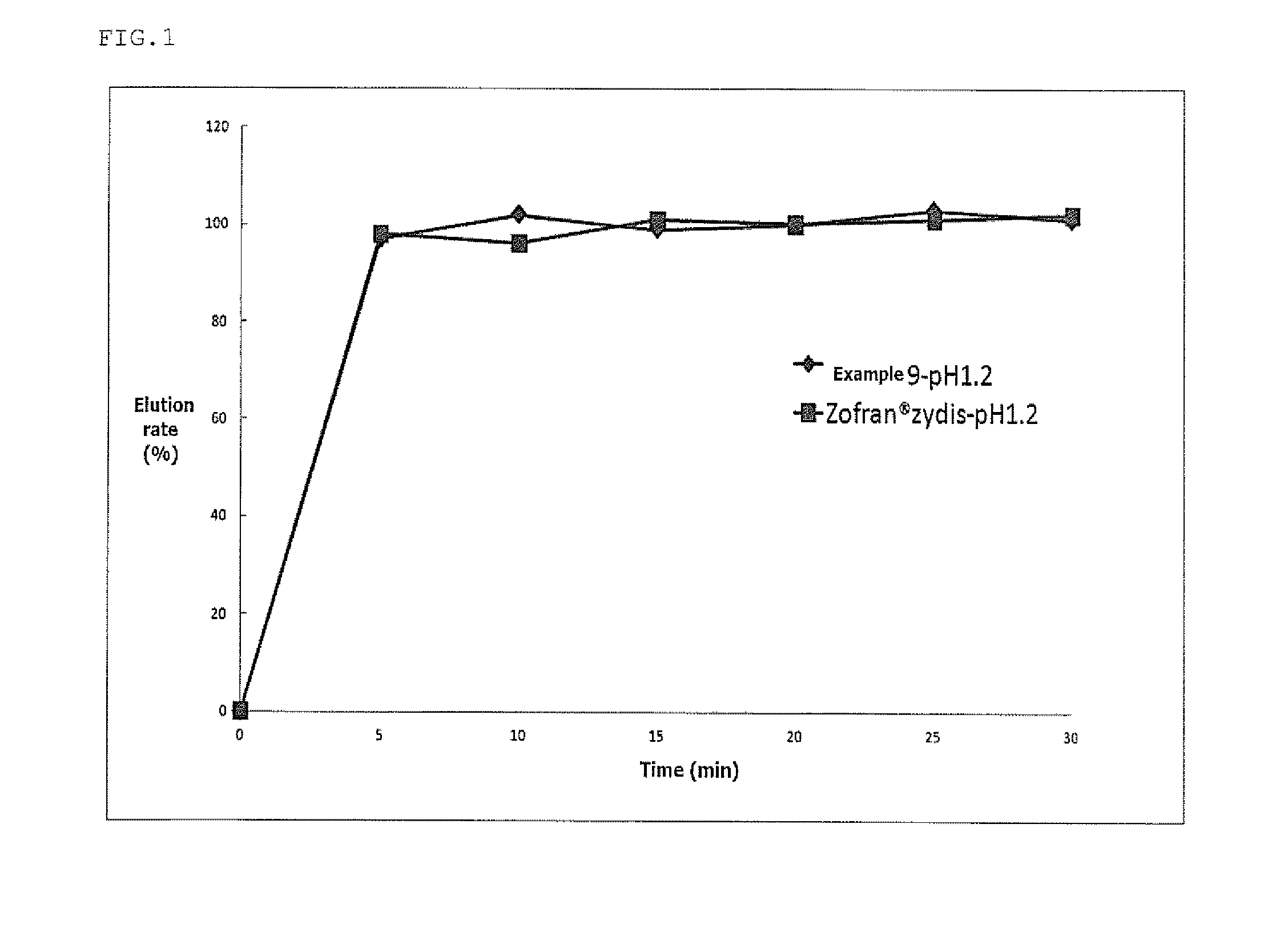
Compressible-Coated Pharmaceutical Compositions and Tablets and Methods of Manufacture
InactiveUS20110129530A1Improving tableting propertyImprove propertiesBiocideNervous disorderControlled releaseOrally disintegrating tablet
There is provided a method for preparing a pharmaceutical composition comprising compressible coated, taste-masked and / or controlled-release coated drug-containing particles, rapidly-dispersing microgranules comprising a disintegrant and a sugar alcohol, a saccharide, or a mixture thereof, and other optional, pharmaceutically acceptable excipients wherein the orally disintegrating tablet (ODT) or rapidly dispersing tablet (RDT) composition having acceptable tableting, organoleptic, and pharmacokinetic properties.
Owner:ADARE PHARM INC
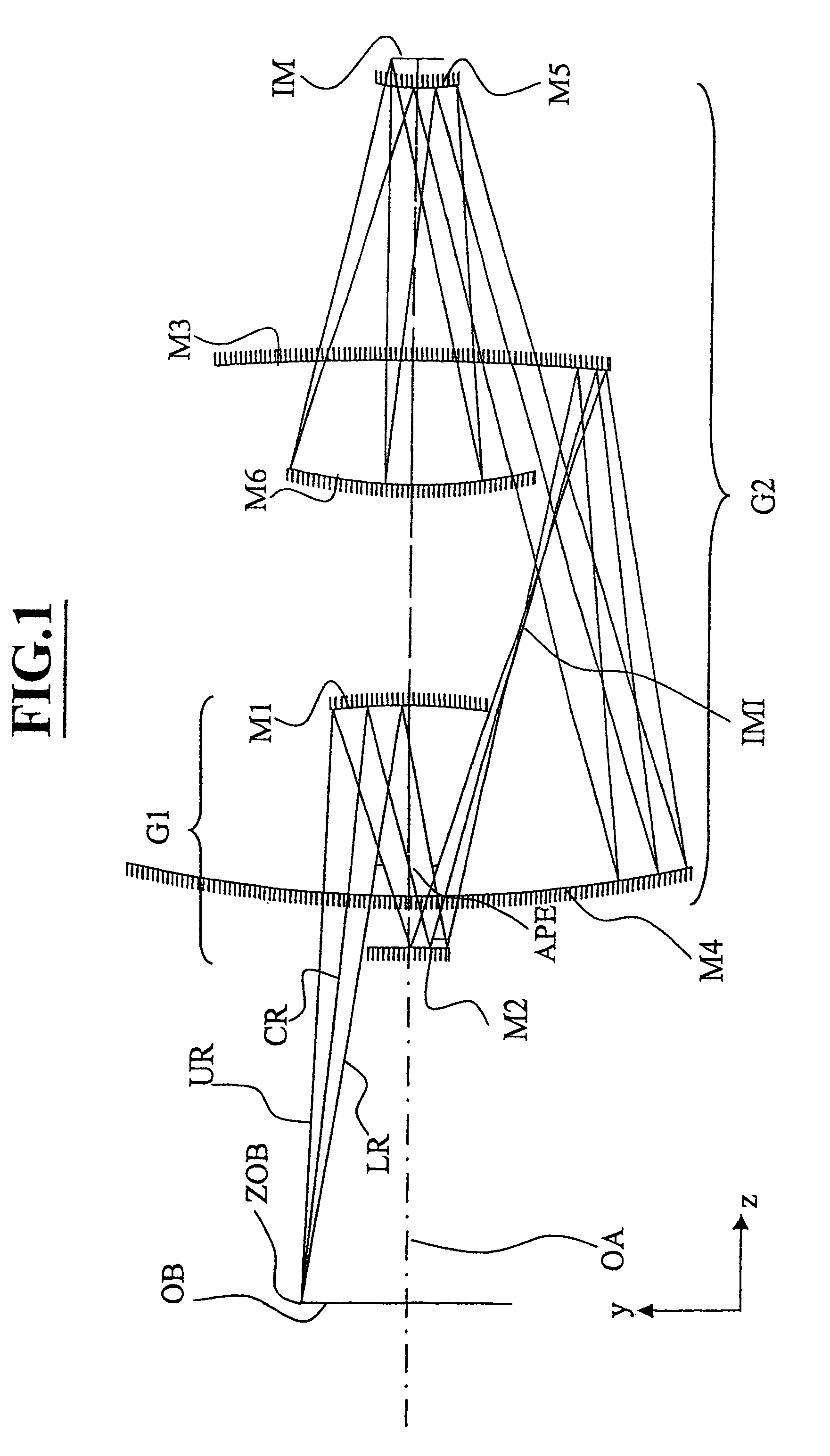
Microlithography reduction objective and projection exposure apparatus
InactiveUS6902283B2Efficiently maskedThe implementation process is simpleMirrorsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusImage planePhysics
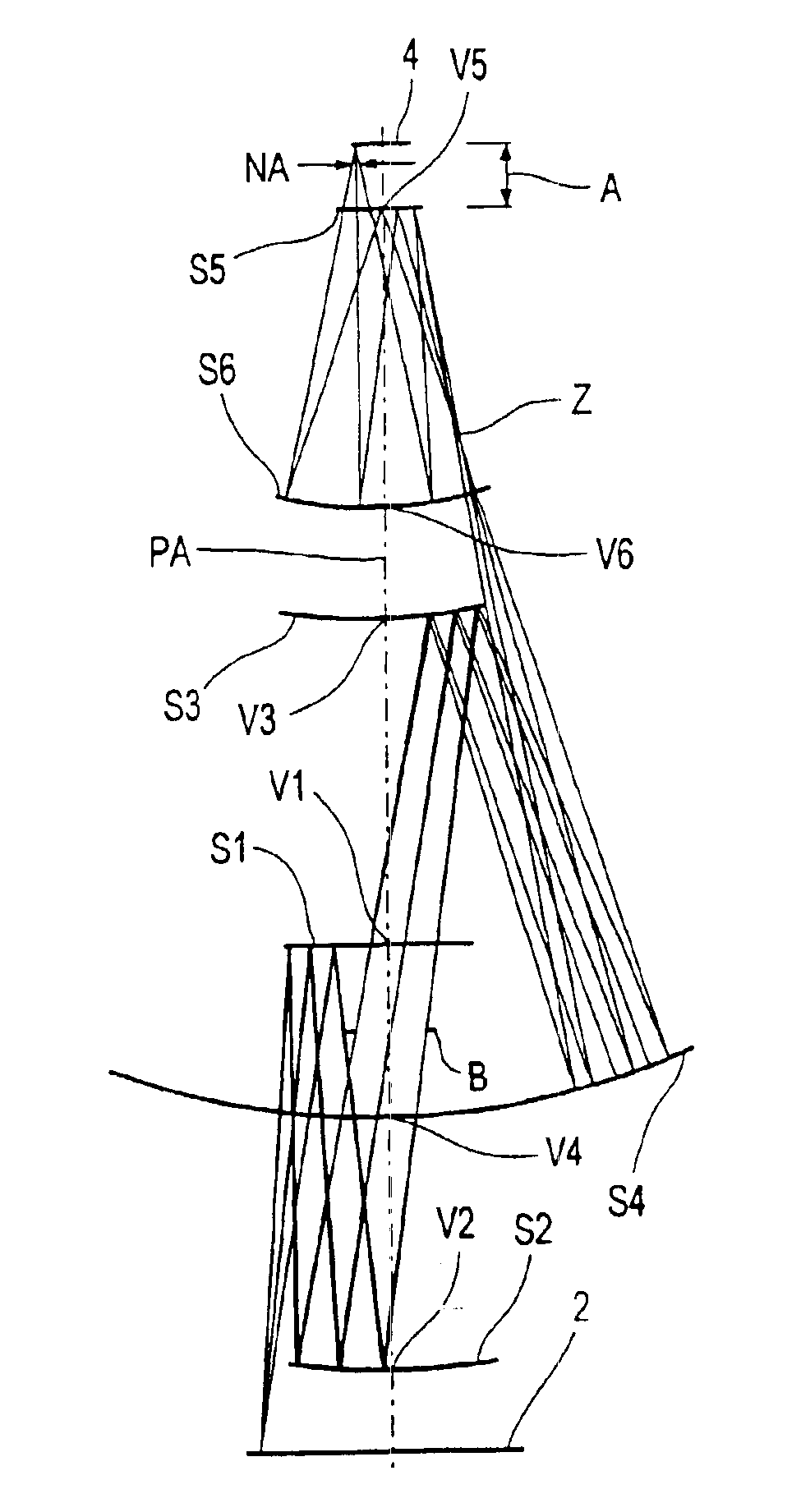
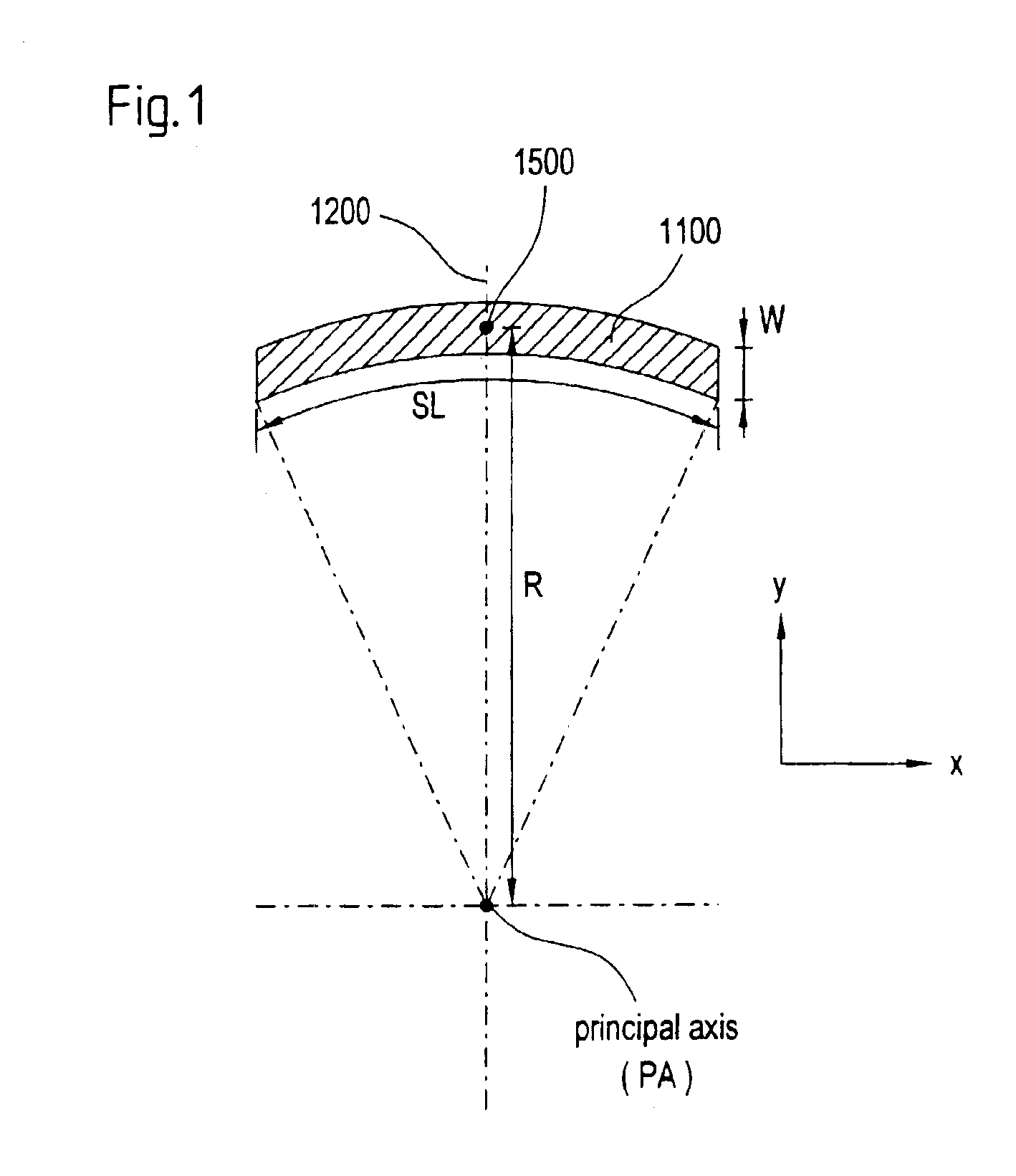
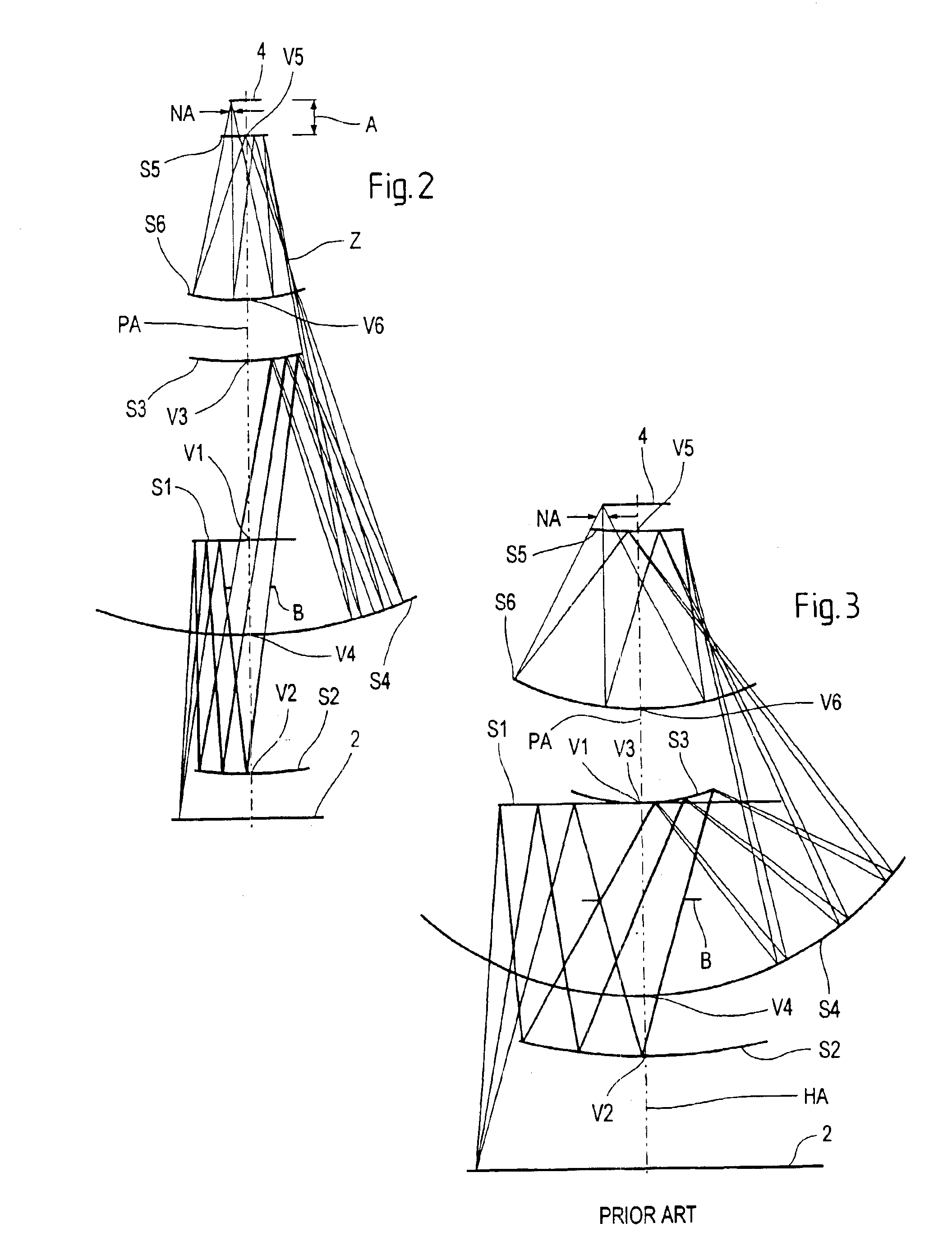
A projection objective formed from six mirrors arranged in a light path between an object plane and an image plane is provided. The projection objective, in some examples, is characterized by having a physical distance between the vertexes of adjacent mirrors that is large enough to allow for the six mirrors to have sufficient thickness and stability properties to prevent surface deformations due to high layer tensions. In some embodiments, mirror thickness are such that surface deformations are prevented with mirrors having layer tensions lower than 350 MPa. Mirror surfaces may comprise multilayer systems of Mo / Be or Mo / Si layer pairs. In some examples, the physical distance between a vertex of the third mirror and a vertex of the sixth mirror (S3S6) satisfies the following relationship: 0.3×(a used diameter of the third mirror S3+a used diameter of the sixth mirror S6)<S3S6. In some examples, a ratio of a physical distance between a vertex of the first mirror and a vertex of the third mirror (S1S3) to a physical distance between the vertex of the first mirror and a vertex of the second mirror (S1S2) is within the range of: 0.5<S1S3 / S1S2<2. In some examples, the physical mirror surfaces of the mirrors have a rotational symmetry with respect to a principal axis (PA). In some examples, all physical mirror surfaces are aspherical. In some examples, at most five physical mirror surfaces are aspherical. Other examples are provided, along with microlithography projection exposure apparatuses and processes for producing a microelectronic device.
Owner:CARL ZEISS STIFTUNG
Projection system for EUV lithography
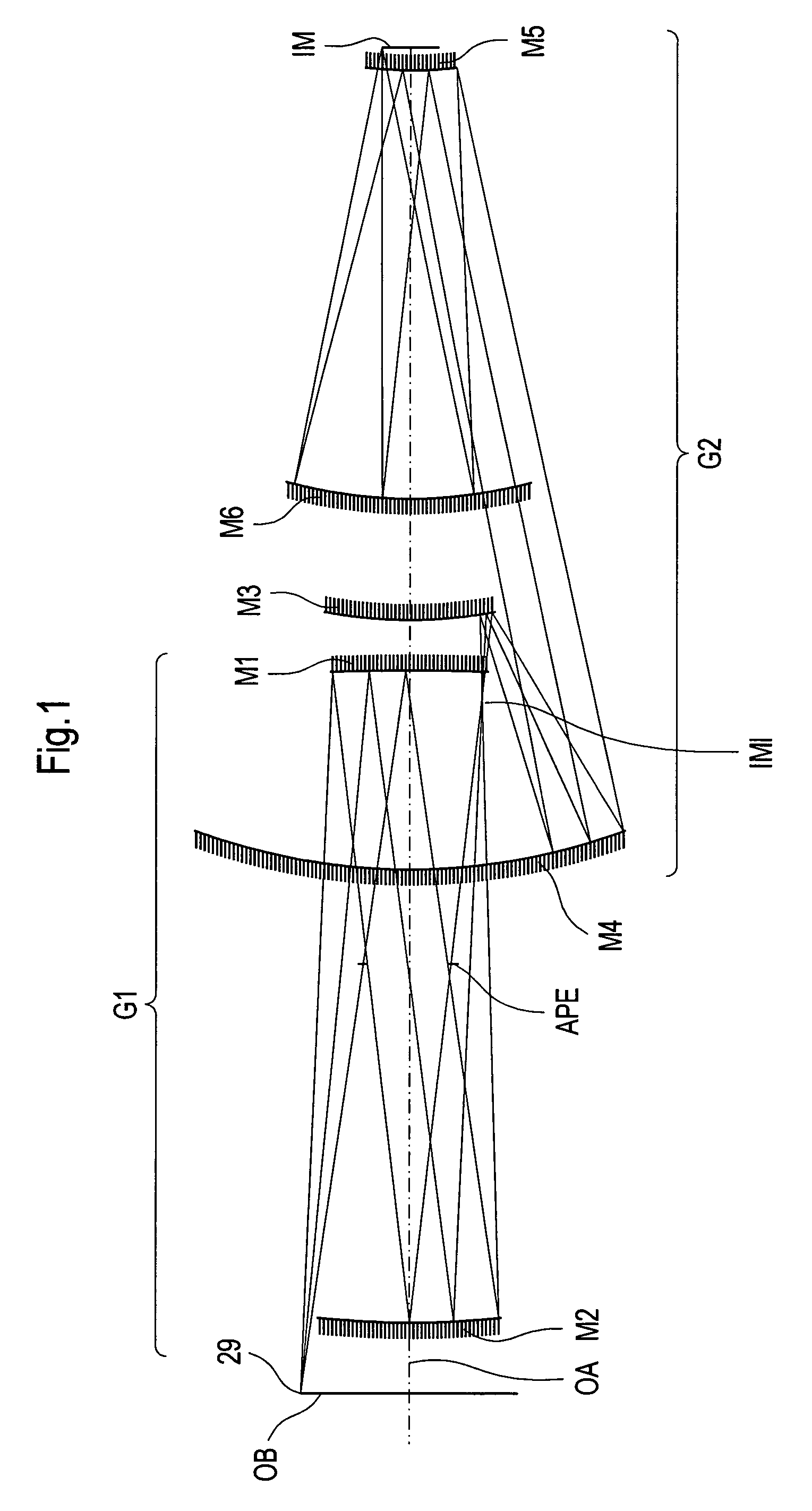
InactiveUS6985210B2Preventing Image Quality DeteriorationEasy mounting and adjustingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusIntermediate imageOptical axis
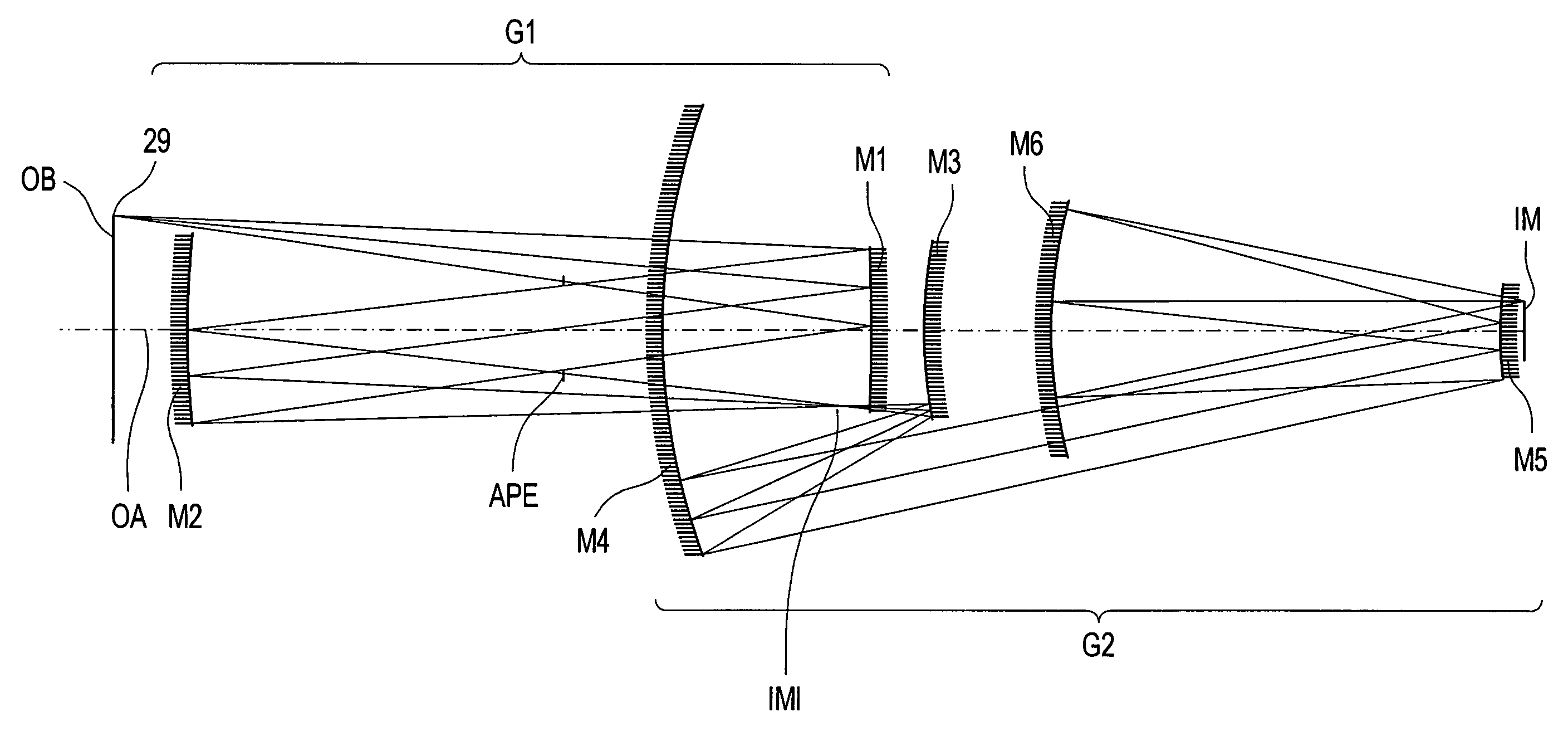
An EUV optical projection system includes at least six reflecting surfaces for imaging an object (OB) on an image (IM). The system is preferably configured to form an intermediate image (IMI) along an optical path from the object (OB) to the image (IM) between a secondary mirror (M2) and a tertiary mirror (M3), such that a primary mirror (M1) and the secondary mirror (M2) form a first optical group (G1) and the tertiary mirror (M3), a fourth mirror (M4), a fifth mirror (M5) and a sixth mirror (M6) form a second optical group (G2). The system also preferably includes an aperture stop (APE) located along the optical path from the object (OB) to the image (IM) between the primary mirror (M1) and the secondary mirror (M2). The secondary mirror (M2) is preferably concave, and the tertiary mirror (M3) is preferably convex. Each of the six reflecting surfaces preferably receives a chief ray (CR) from a central field point at an incidence angle of less than substantially 15°. The system preferably has a numerical aperture greater than 0.18 at the image (IM). The system is preferably configured such that a chief ray (CR) converges toward the optical axis (OA) while propagating between the secondary mirror (M2) and the tertiary mirror (M3).
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
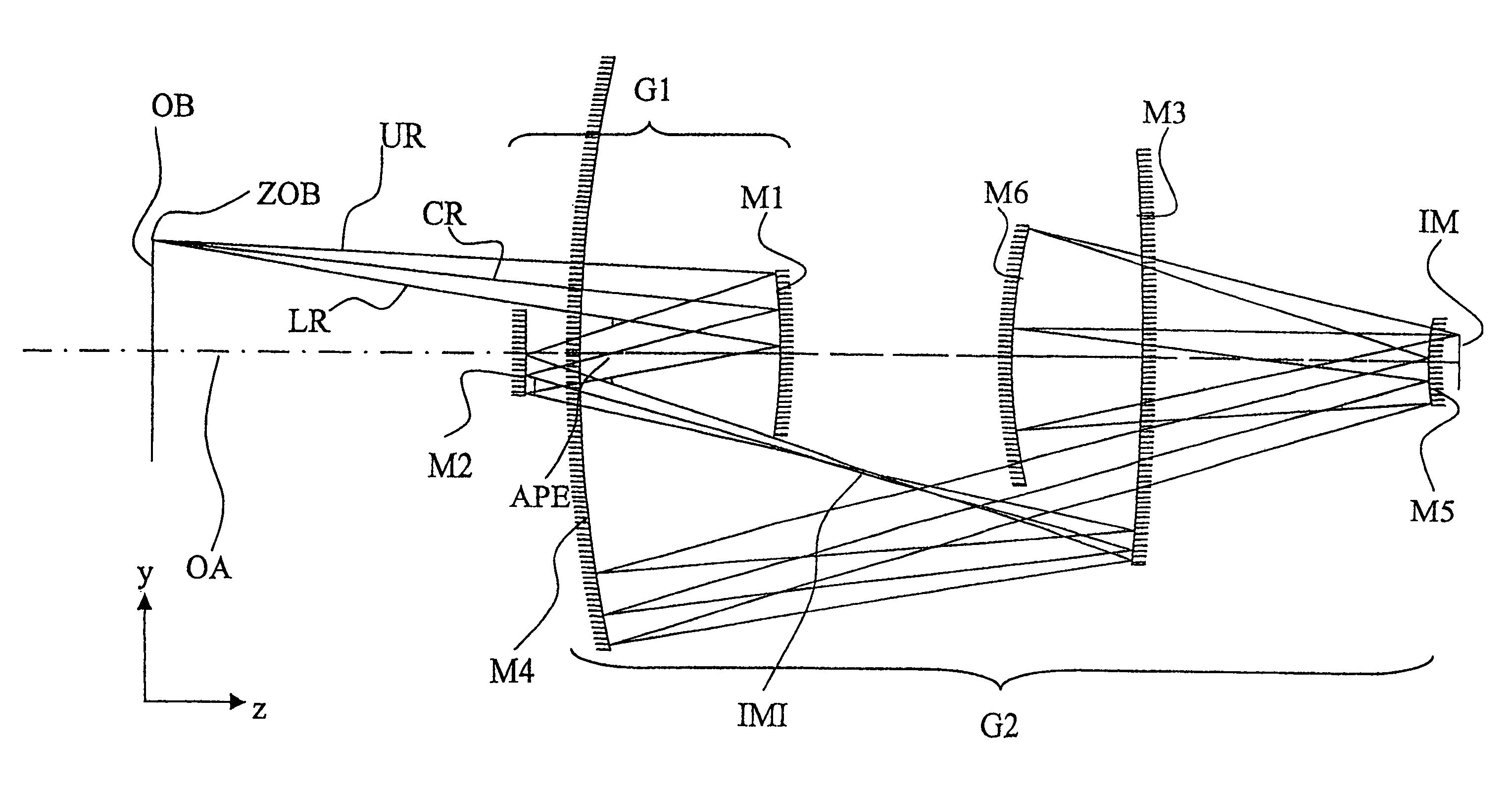
Projection system for EUV lithography
InactiveUS7151592B2Preventing Image Quality DeteriorationEasy mounting and adjustingMirrorsMicroscopesLithographic artistIntermediate image
An EUV optical projection system includes at least six mirrors (M1, M2, M3, M4, M5, M6) for imaging an object (OB) to an image (IM). At least one mirror pair is preferably configured as an at least phase compensating mirror pair. The system is preferably configured to form an intermediate image (IMI) along an optical path from the object (OB) to the image (IM) between a second mirror (M2) and a third mirror (M3), such that a first mirror (M1) and the second mirror (M2) form a first optical group (G1) and the third mirror (M3), a fourth mirror (M4), a fifth mirror (M5) and a sixth mirror (M6) form a second optical group (G1). The system also preferably includes an aperture stop (APE) located along the optical path from the object (OB) to the image (IM) between the first mirror (M1) and the second mirror (M2). The second mirror (M2) is preferably convex, and the third mirror (M3) is preferably concave. The system preferably forms an image (IM) with a numerical aperture greater than 0.18.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Laser Weldable Label and Shaped Composite Article Therewith
InactiveUS20080317979A1Improve adhesionEfficiently maskedStampsSynthetic resin layered productsAdhesiveOptical transmittance
The laser-transmissive welding label of the present invention is a resin label which comprises at least a resin layer and is affixable to a resin shaped article by a laser welding, wherein the resin layer has a light-scattering property, and the transmittance of the resin layer relative to a laser beam having an oscillation wavelength within the range of 740 to 1100 nm is not less than 20%, and the total light transmittance of the resin layer relative to a visible light (in accordance with ASTM D1003) is not more than 50%. The resin layer may comprise a thermoplastic resin which may have a compatibility with a resin for the resin shaped article. The label may be able to mask the resin shaped article, or may be colored with a coloring agent. A shaped composite article (e.g., a toner cartridge) may be formed by bonding the label to the resin shaped article with use of the laser welding. The present invention provides the resin label which is affixable to the resin shaped article in an easy and simple way, without an adhesive.
Owner:DAICEL POLYMER LTD +1
Rapid acting and long acting insulin combination formulations
ActiveUS8084420B2Short durationImprove blood sugar controlPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderBefore BreakfastInsulin injection
An injectable formulation containing a rapid acting insulin and a long acting insulin has been developed. The pH of the rapid acting insulin is adjusted so that the long acting insulin, remains soluble when they are mixed together. Preferably, the formulation is administered before breakfast, provides adequate bolus insulin levels to cover the meal and basal insulin for up to 24 hours, and does not produce hypoglycemia after the meal. Lunch and dinner can be covered by two bolus injections of a fast, rapid, or very rapid acting insulin. Alternatively, by adjusting the ratio of rapid to long acting insulin, the long acting insulin may be shortened to a 12 hour formulation, and re-administered to the patient at dinner time, providing a safe and effective basal insulin level until morning. As a result, a patient using intensive insulin therapy should only inject three times a day.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Character string processing method, apparatus, and program
InactiveUS20070157123A1Efficiently maskedShort timeNatural language data processingSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmString analysis
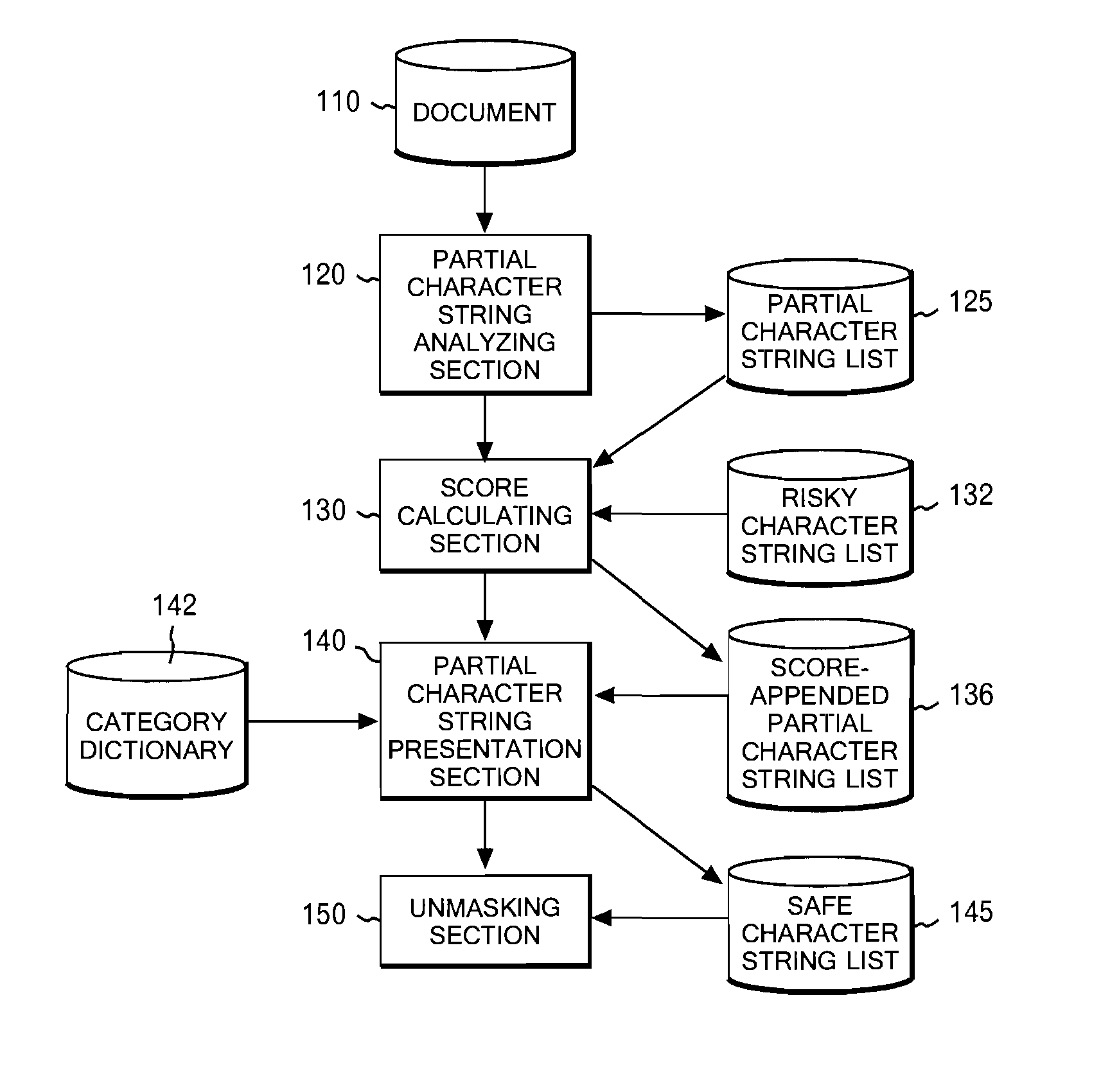
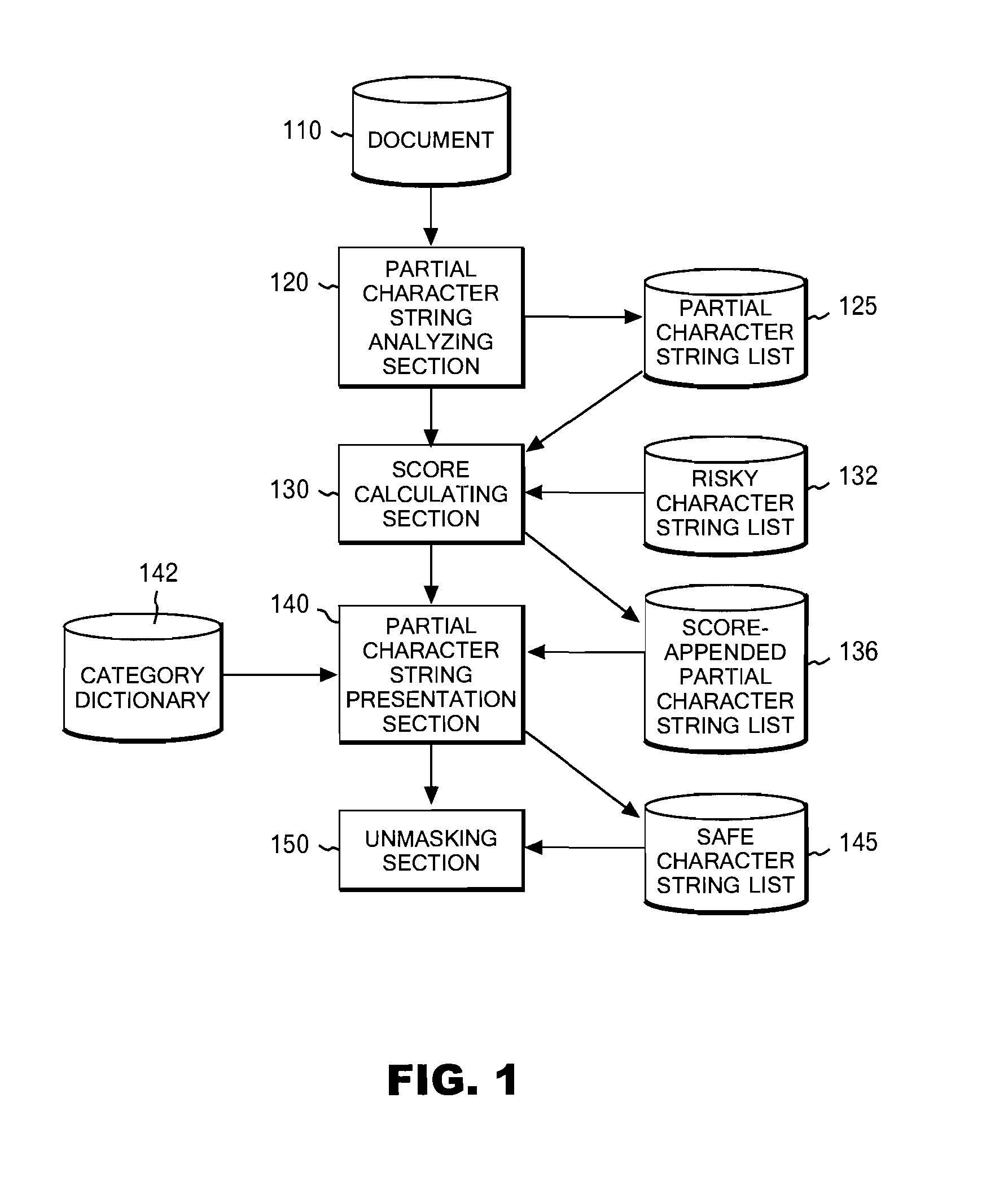
In order to solve the above problem, disclosed as a first aspect is a method including the steps of analyzing a character string in a document into partial character strings; calculating, with respect to each of the partial character strings, a score incorporating appearance frequency of the partial character string; presenting the partial character strings and the scores to a user; determining which ones of the partial character strings have been selected by the user; storing the selected partial character strings as a safe partial character string list; and replacing, with predetermined replacement character strings, the partial character strings excluding the partial character strings existing in the safe partial character string list.
Owner:IBM CORP
Salt replacing composition, process for its preparation and food systems containing such composition
InactiveUS20080199595A1Reduce sodiumIncrease PotassiumMilk preparationFood preparationPotassiumAmino acid
A salt replacing composition for replacing sodium chloride in food contains a major amount of potassium chloride, ammonium chloride and at least one of an amino acid and a salt of an amino acid. A reduced sodium chloride composition contains the salt replacing composition and sodium chloride. A food containing the salt replacing composition and a process for making the salt replacing composition.
Owner:MCCORMICK & CO INC
Perfume compositions and methods to mask amine malodors
InactiveUS6979667B1Easy to cleanMasking malodorAnionic surface-active compoundsDetergent solventsSolventSURFACTANT BLEND
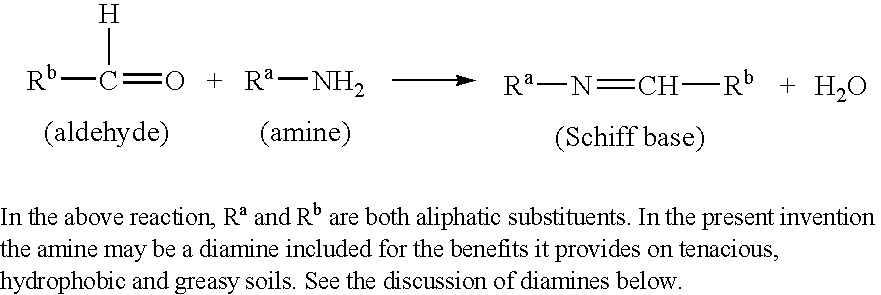
Disclosed are detergent compositions, particularly for manual dishwashing which, by incorporating a combination of anionic surfactants, solvents and certain selected perfume compositions that do not have the maladors associated with certain nitrogenous ingredients such as amines. Also disclosed are the perfume compositions themselves, characterised by 30% to 100% of an odor neutralizer capable of forming a Schiff base when reacted with an amine, said compositions having a pH of from 8.5 to 12.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Tooth whitening compositions and methods for using the same
InactiveUS20060104922A1Maximizing whitening resultEffectively conceals tooth discoloration within a short period of timeCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsTooth discolorationTooth whitening
A tooth whitening system that effectively conceals tooth discoloration within a short period of time. The system includes a single, spectrally pure, substantially violet dye and a carrier for applying the dye to teeth.
Owner:COMPWHITE
Chromatographic materials for the separation of unsaturated molecules
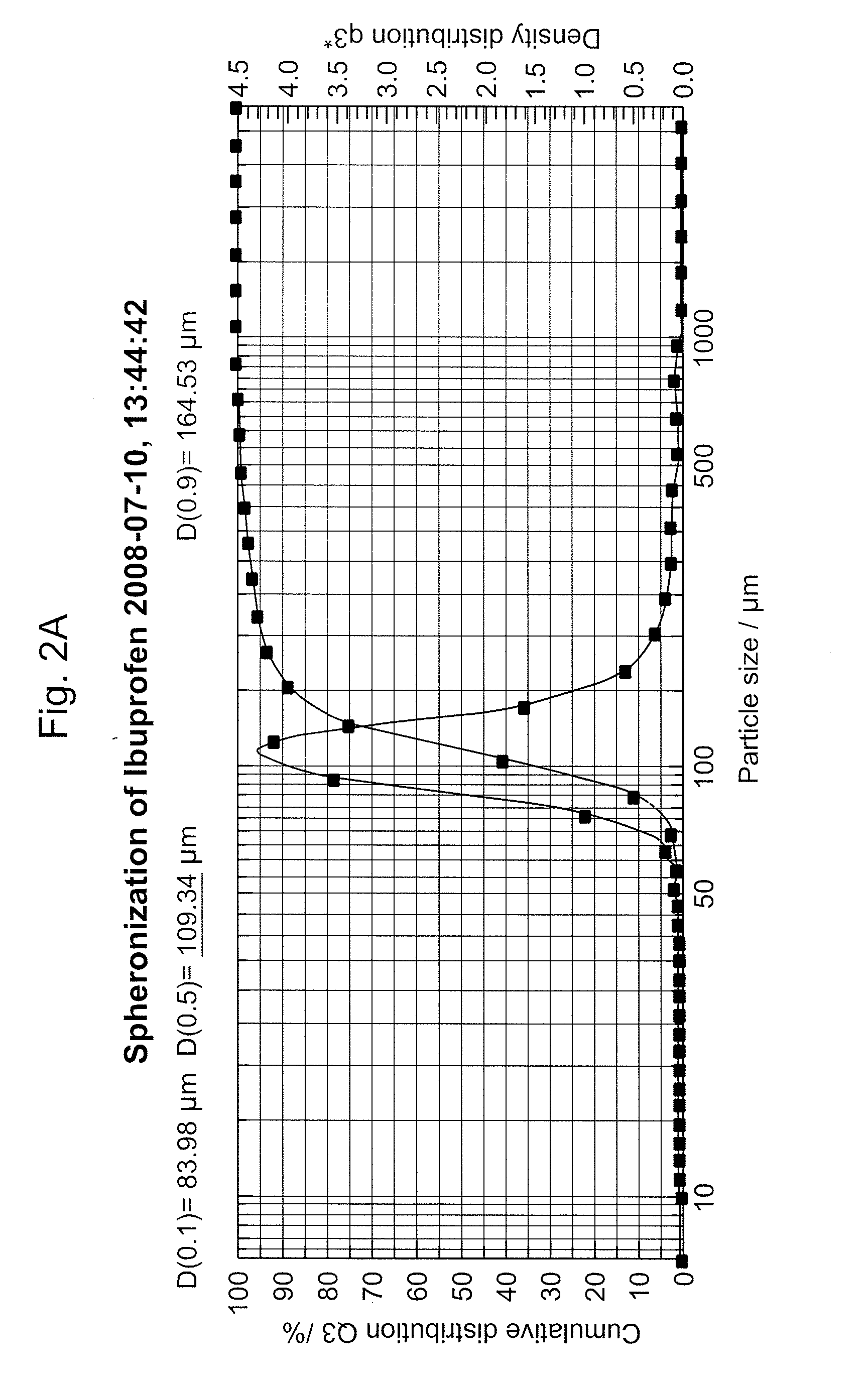
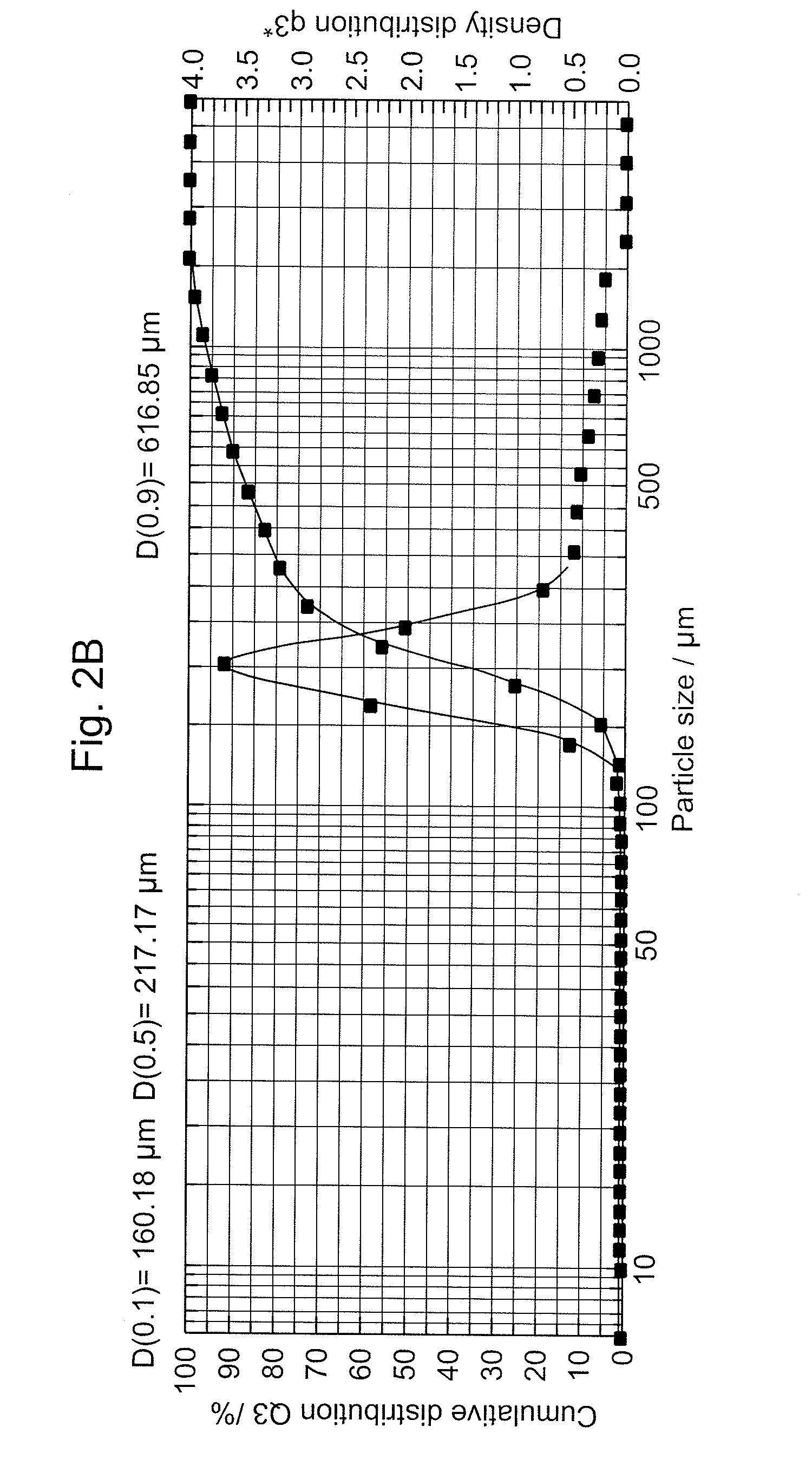
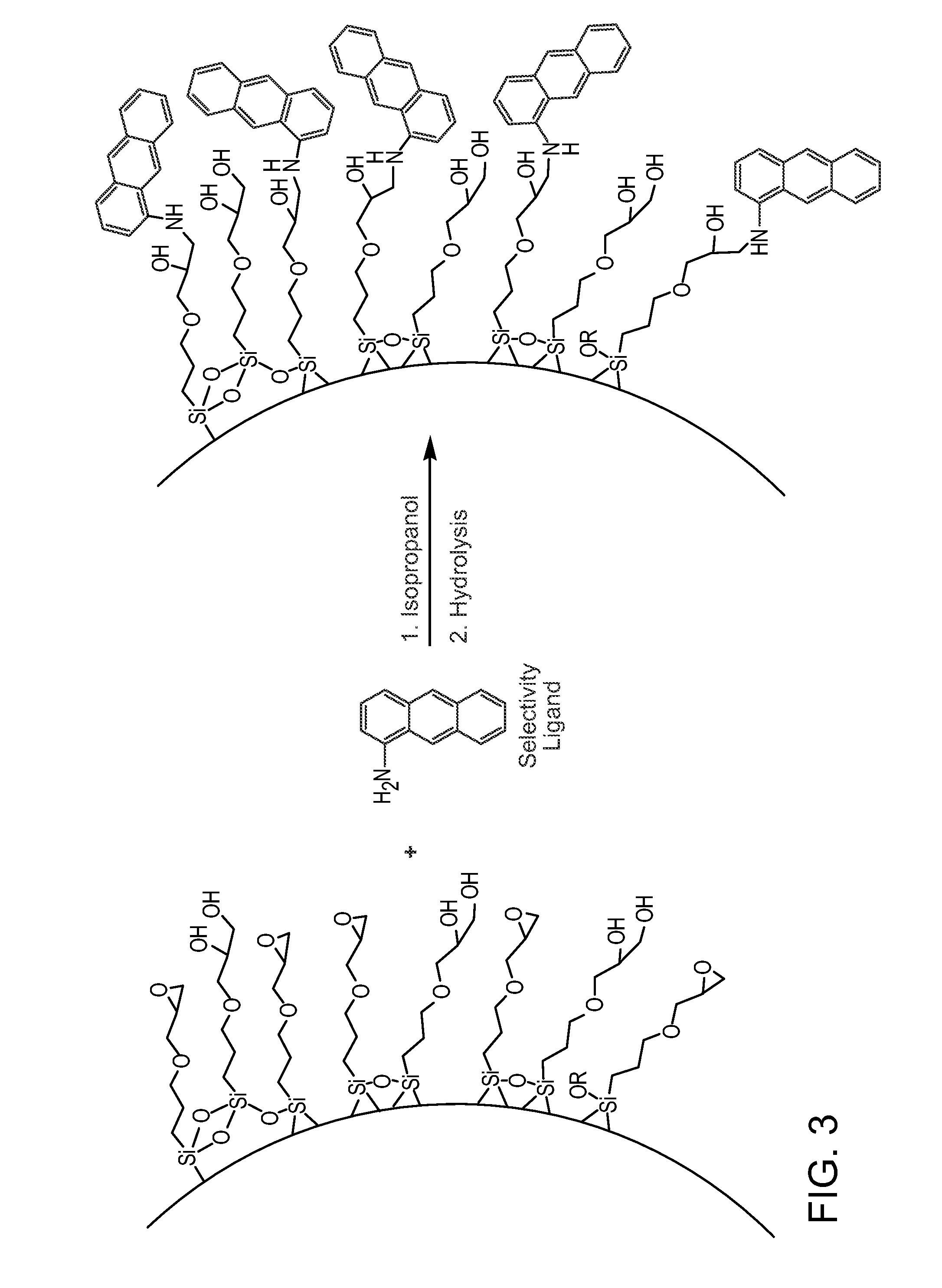
ActiveUS20140319057A1Superior retention , peak capacity and peak shapeImprove peak capacity and tailingIon-exchange process apparatusSilicon organic compoundsChemistryStationary phase
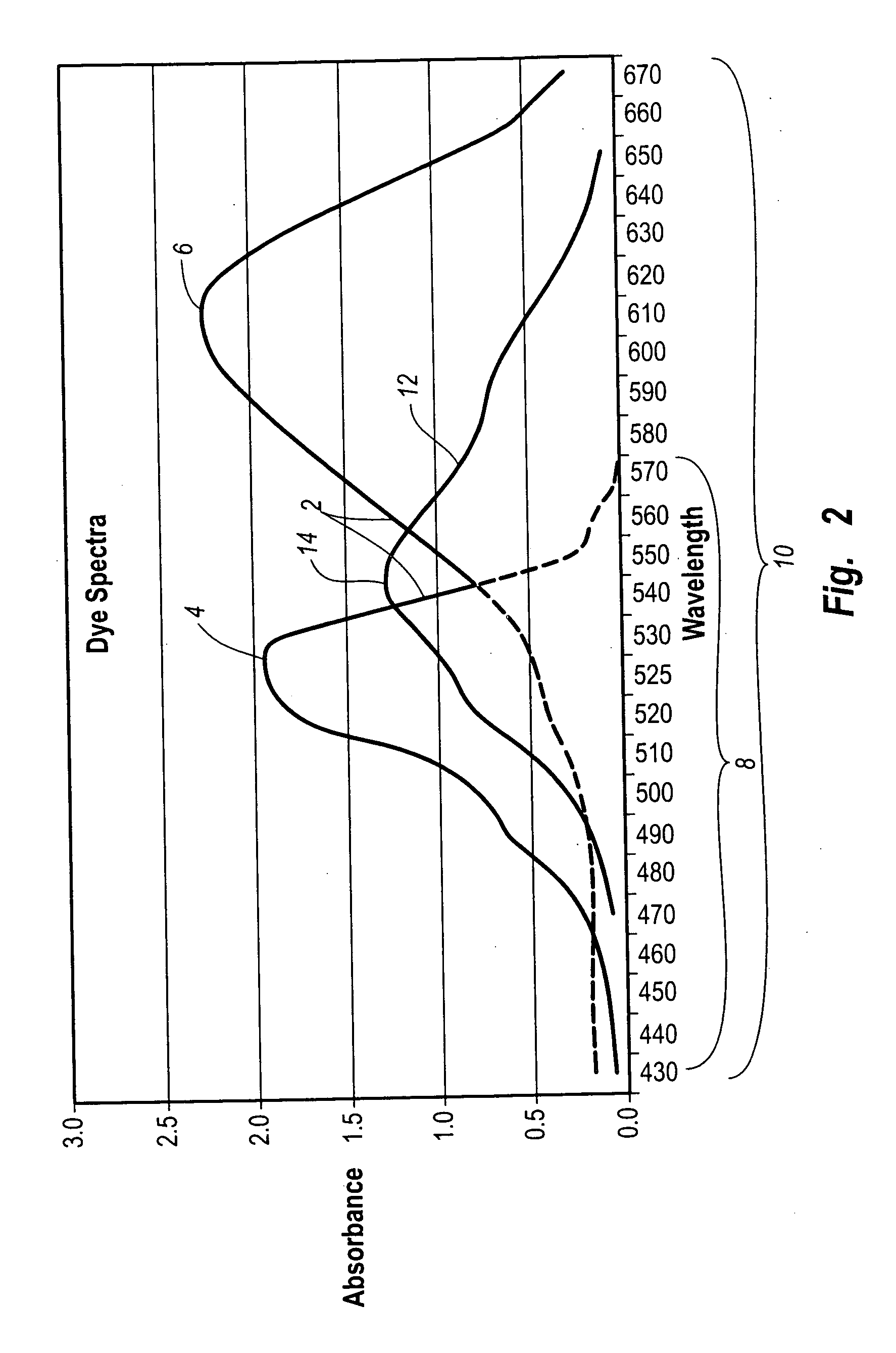
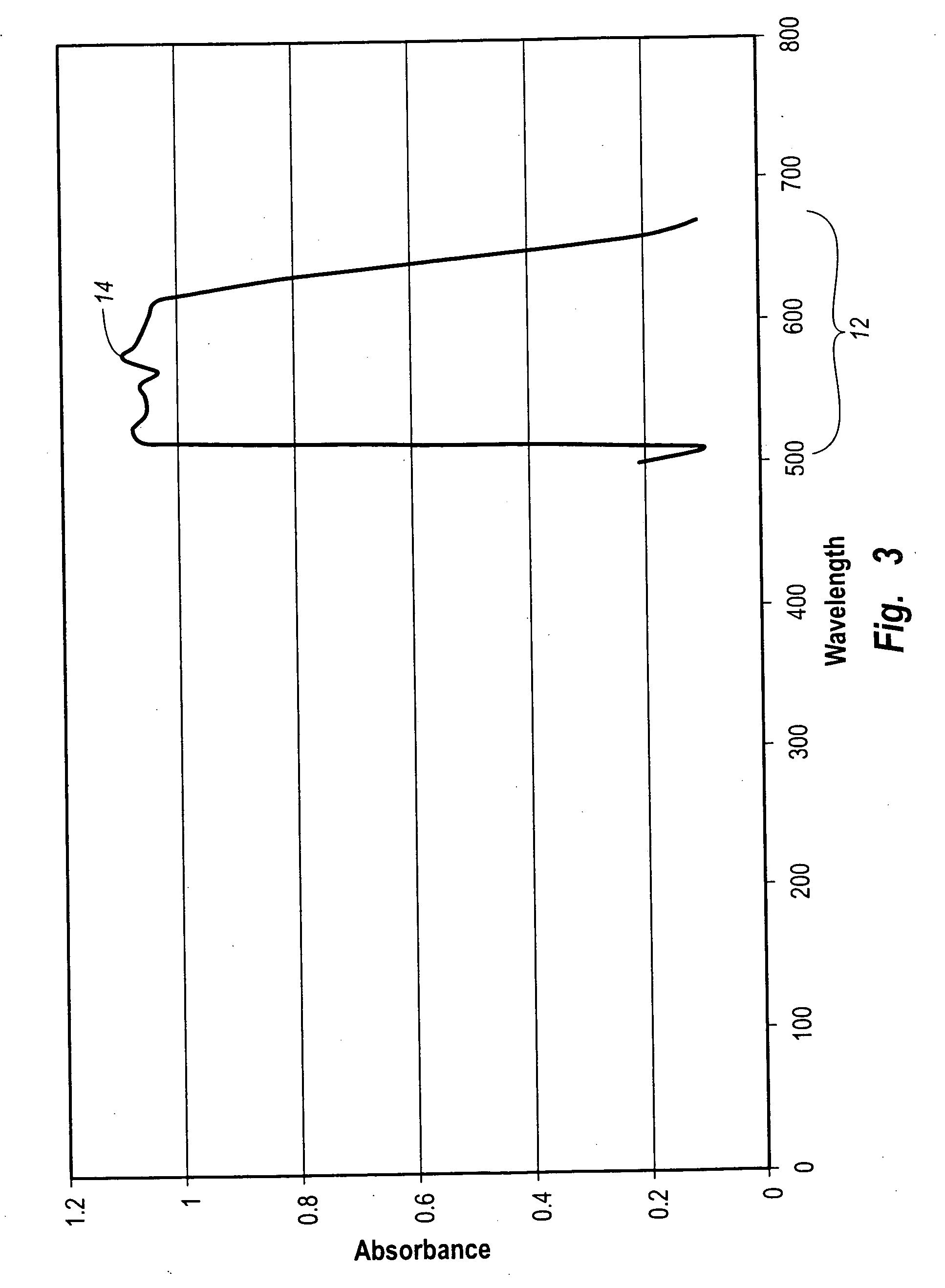
The present disclosure relates to a method of separating a compound of interest, particularly unsaturated compound(s) of interest, from a mixture. The compound is separated using a column having a chromatographic stationary phase material for various different modes of chromatography containing a first substituent and a second substituent. The first substituent minimizes compound retention variation over time under chromatographic conditions. The second substituent chromatographically and selectively retains the compound by incorporating one or more aromatic, polyaromatic, heterocyclic aromatic, or polyheterocyclic aromatic hydrocarbon groups, each group being optionally substituted with an aliphatic group.
Owner:WATERS TECH CORP
Bispectral multilayer photodiode detector and method for manufacturing such a detector
ActiveUS20120068225A1Avoids pinch-offCurrent is limitedSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantElectrical conductor
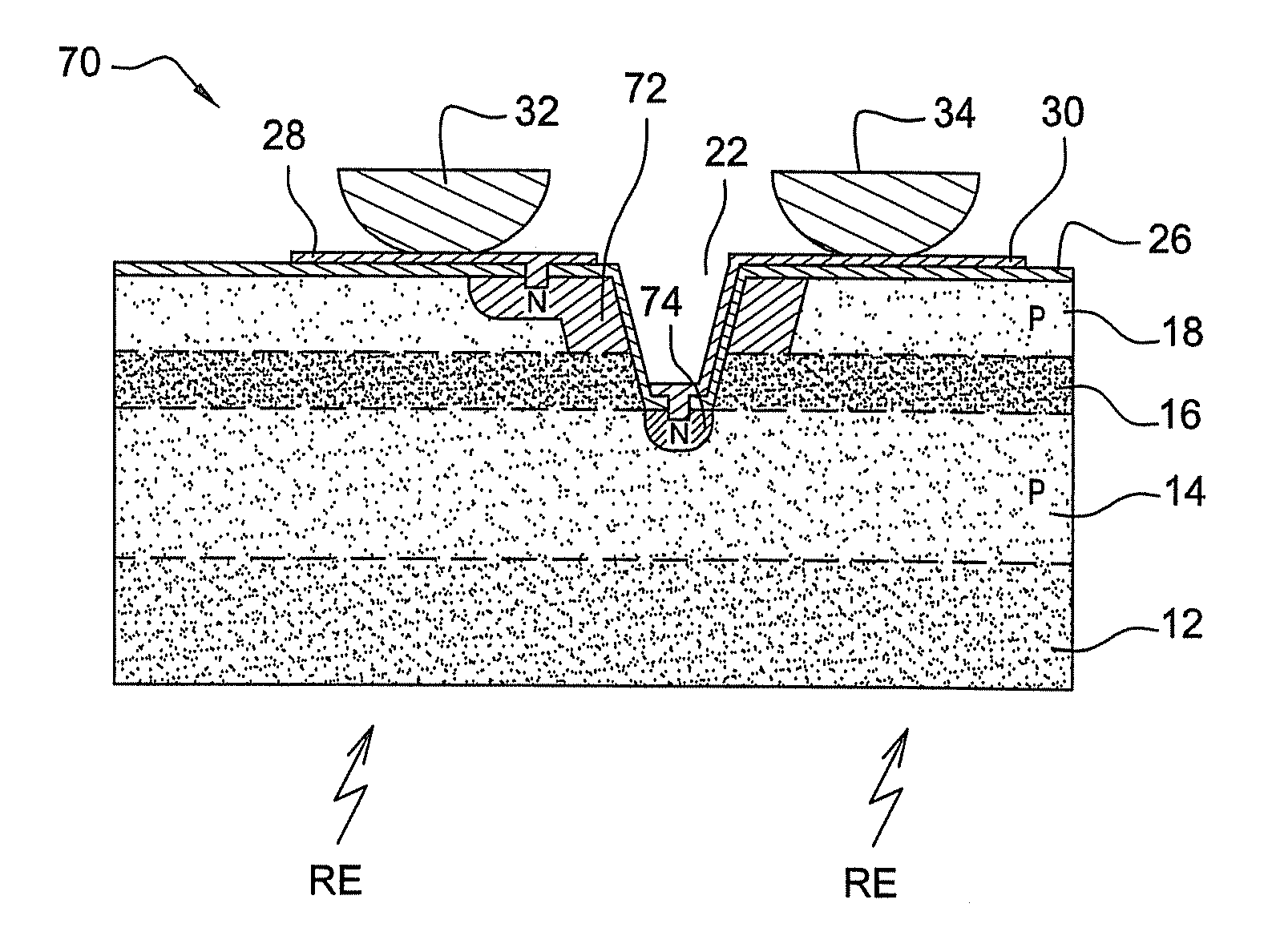
A bispectral detector comprising upper and lower semiconductor layers of a first conductivity type in order to absorb a first and a second electromagnetic spectrum, separated by an intermediate layer that forms a barrier; semiconductor zones of a second conductivity type implanted in upper layer and lower layer and each implanted at least partially in the bottom of an opening that passes through upper layer and intermediate layer; and conductor elements connected to semiconductor zones. At least that part of each opening that passes through upper layer is separated from the latter by a semiconductor cap layer: whereof the concentration of dopants of the second conductivity type is greater than 1017 cm−3; and whereof the thickness is chosen as a function of said concentration so that it exceeds the minority carrier diffusion length in the cap layer.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
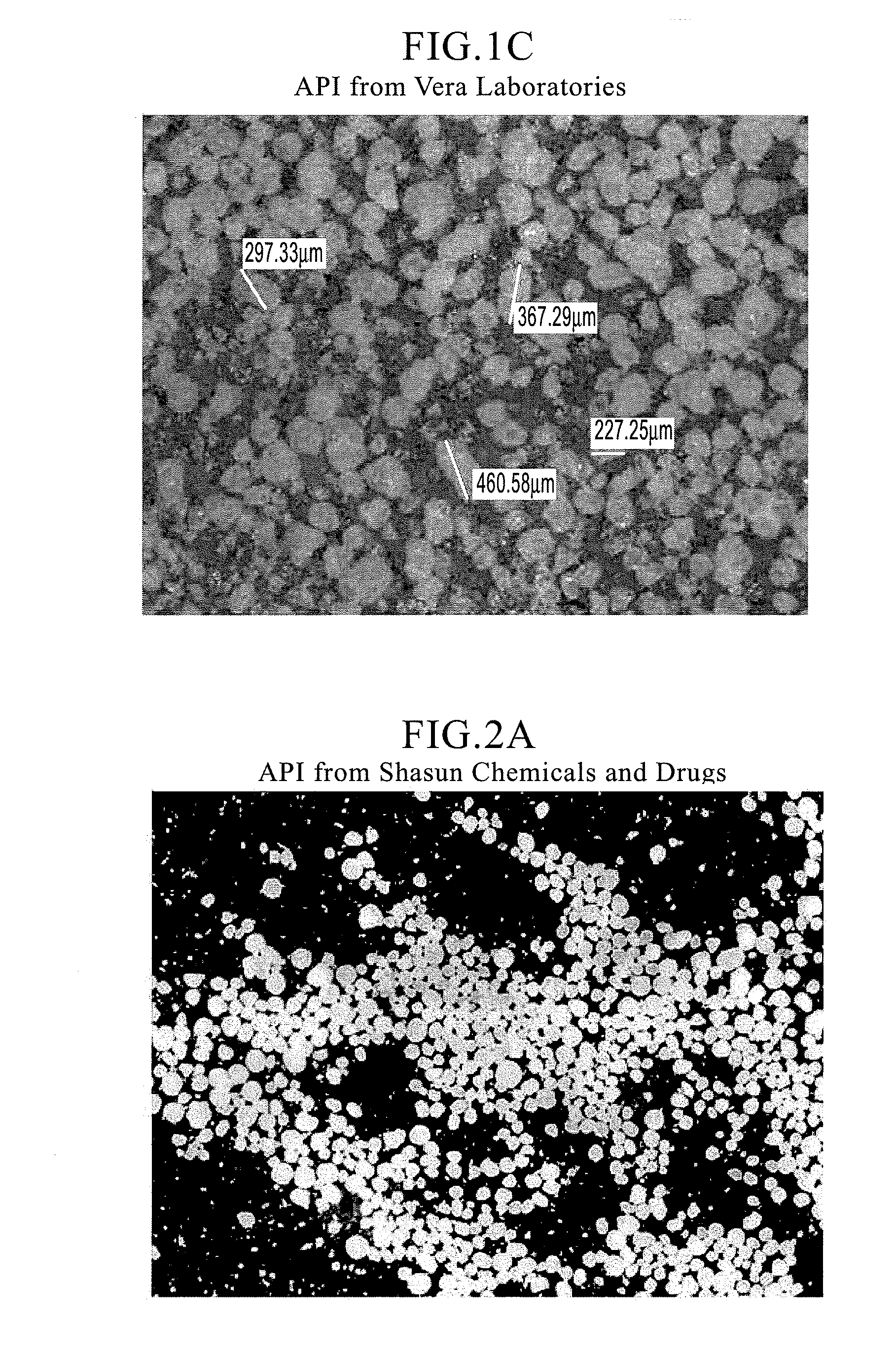
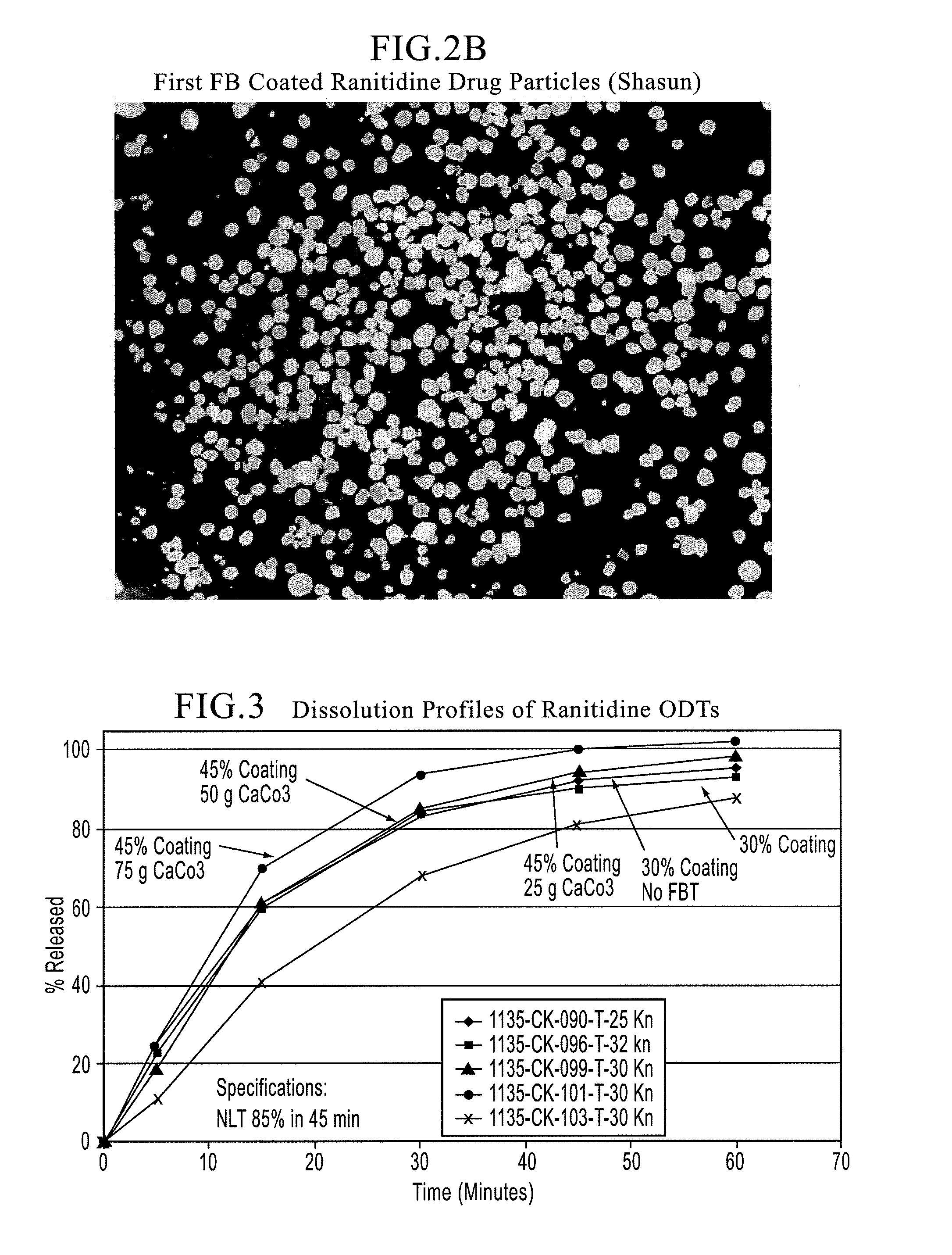
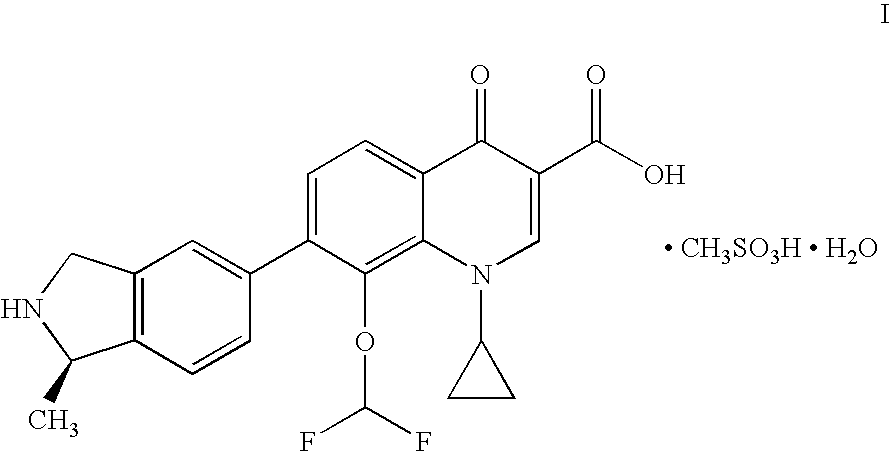
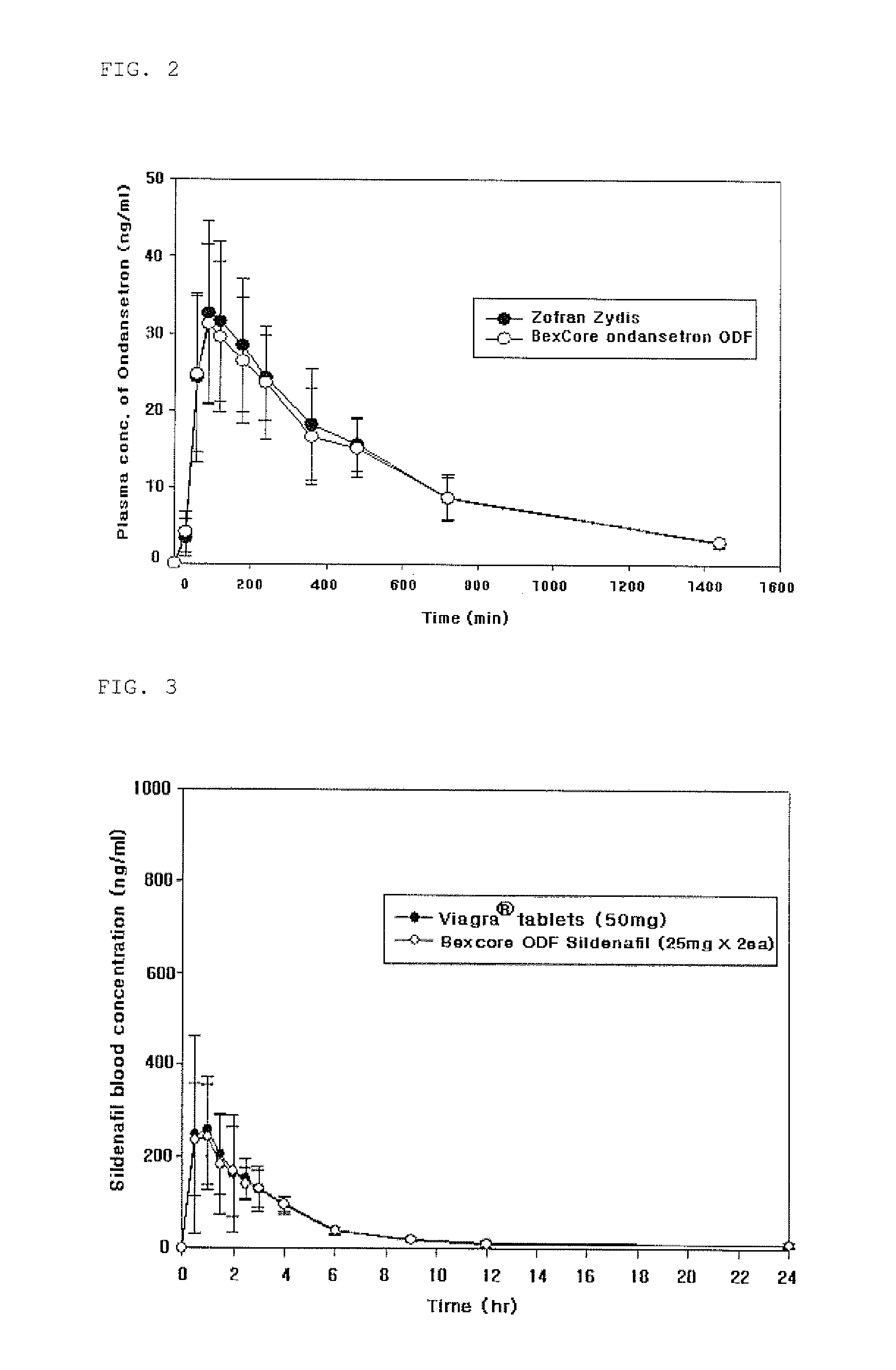
Orally disintegrating tablet compositions of ranitidine and methods of manufacture
InactiveUS20090202630A1Effectively tasteEffectively taste/aftertasteBiocideDigestive systemDrugDisease
The present invention is directed to pharmaceutical compositions comprising taste-masked microcapsules comprising ranitidine, orally disintegrating tablets comprising such compositions, and methods of making the pharmaceutical compositions and dosage forms of the present invention. The present invention is also directed to methods of administering the pharmaceutical compositions and orally disintegrating tablets to treat or prevent gastrointestinal disorders.
Owner:VENKATESH GOPI +3
Palatable oral suspension and method
InactiveUS7175856B2Reduce and minimize solubilityReduces and masks bitter tasteAntibacterial agentsBiocideOral suspensionsSolubility
A drug formulation in the form of a dry powder is provided which when mixed with water forms a palatable oral suspension substantially free of bitter taste, the dry powder being formed of a drug, preferably des-quinolone, which in solution has a bitter taste, and a pH modifying agent which is preferably an alkaline material such as L-arginine, where upon mixing the dry-powder in water causes the drug to have reduced solubility or precipitate in-situ to form a palatable oral suspension essentially free of bitter taste.An oral suspension, methods for making same and a method for masking the bitter taste of drugs employing one or more pH modifying agents are also provided.
Owner:TOYAMA CHEM CO LTD
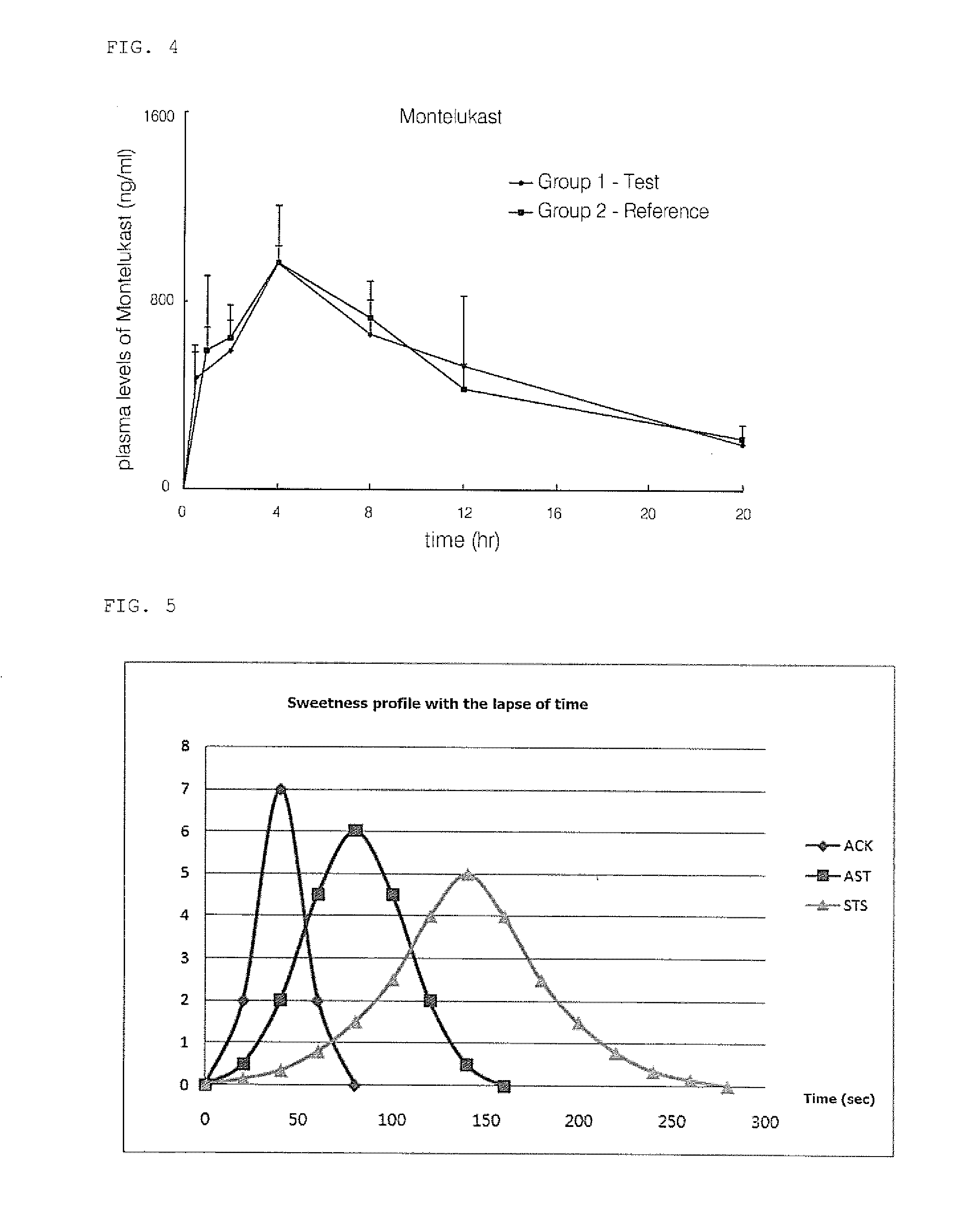
Quickly soluble oral film dosage containing steviosides as a unpleasant taste masking agent
InactiveUS20120156229A1Excellent effect of masking nasty tasteLow costDigestive systemSnake antigen ingredientsMasking agentDrug
Disclosed is a quickly soluble oral film dosage for masking a nasty taste, in particular, a quickly soluble oral film dosage comprising a stevioside based sweetener and a high potency sweetener in a ratio by weight (w / w) of 1:3 to 3:1, which may efficiently mask a bitter or nasty taste of a medicine and may be quickly dissolved in a mouth without water, thereby improving an aftertaste thereof thus enhancing dosage acceptability of a patient.
Owner:CHA BIOTECH
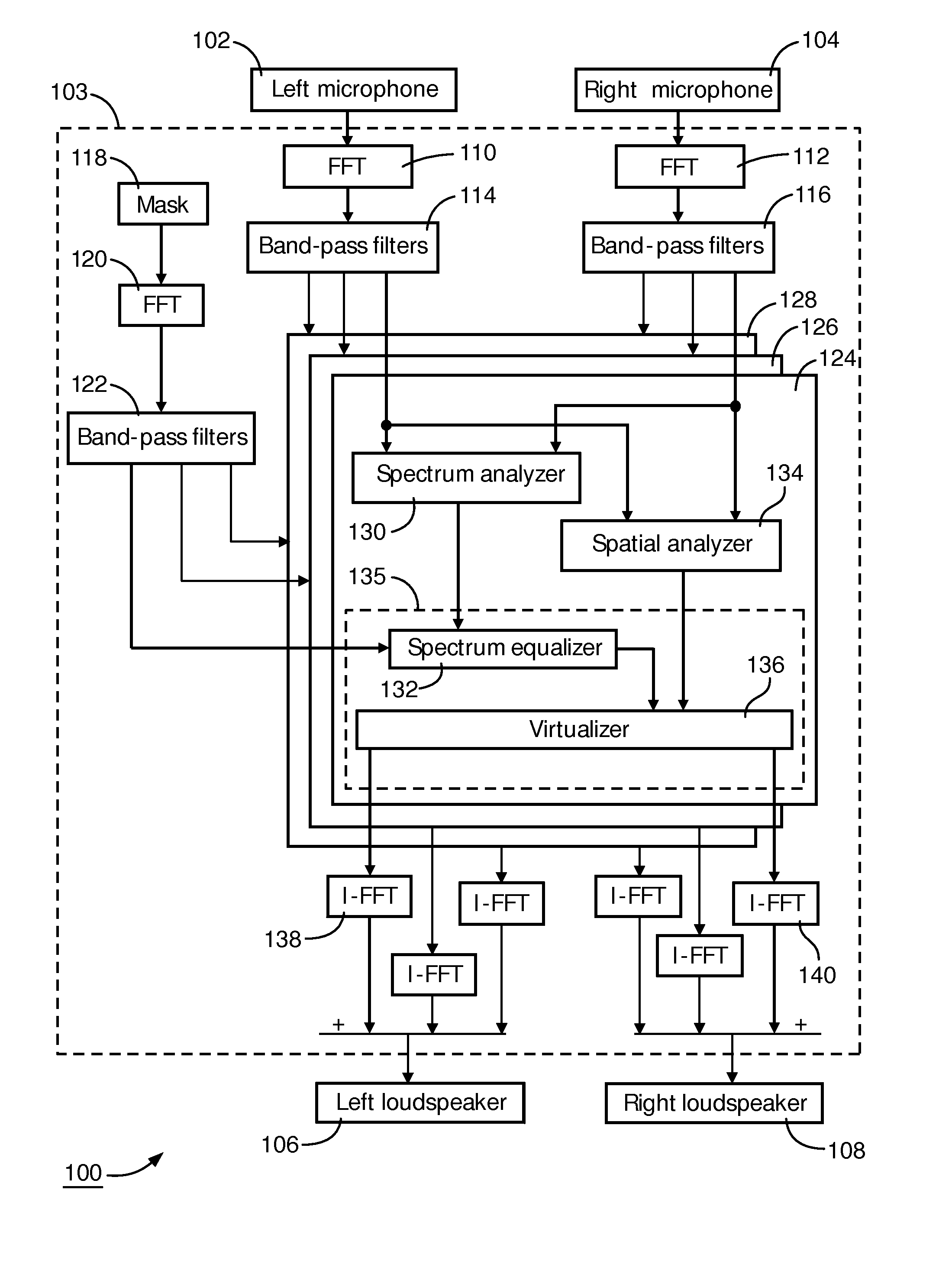
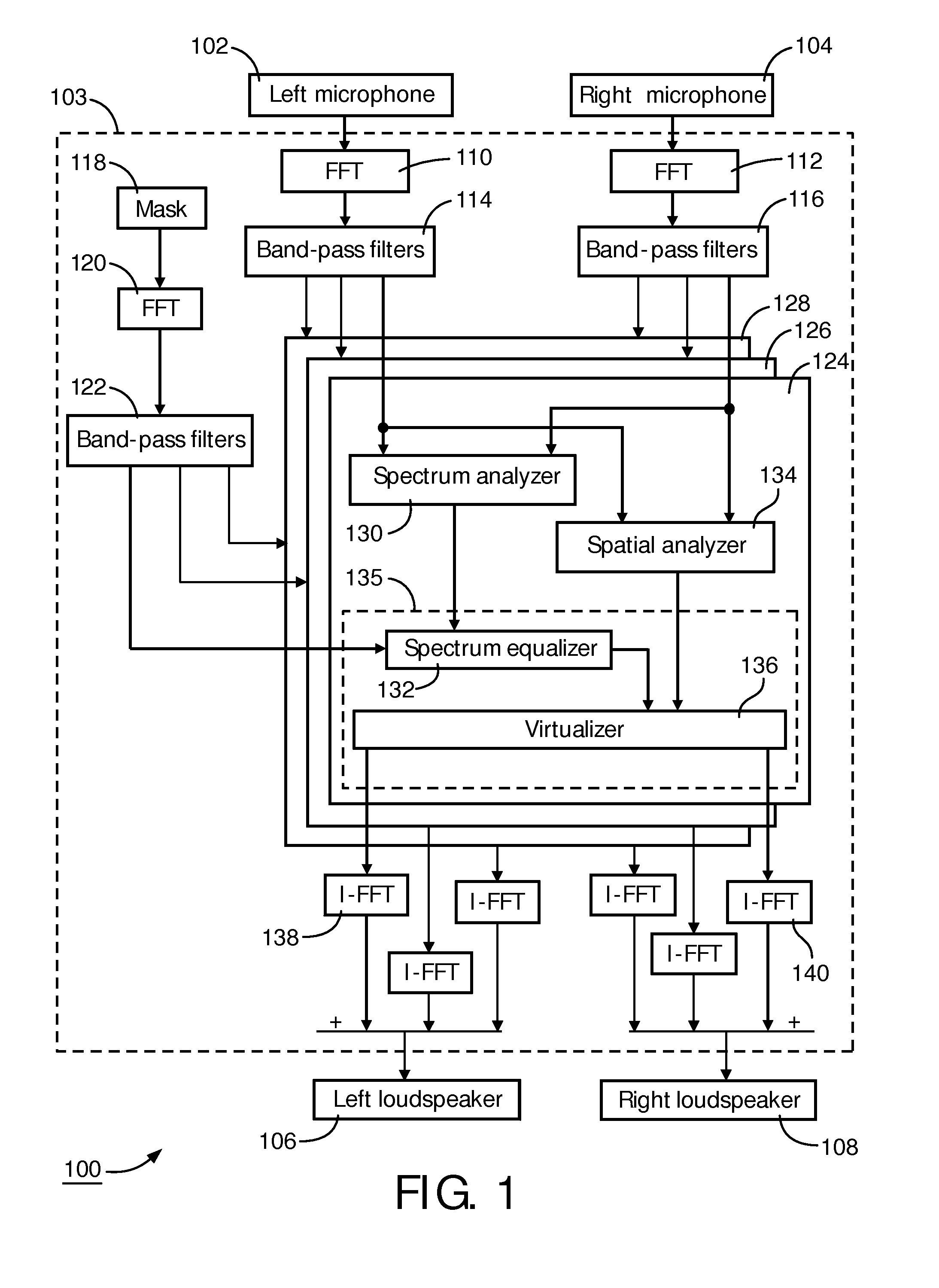
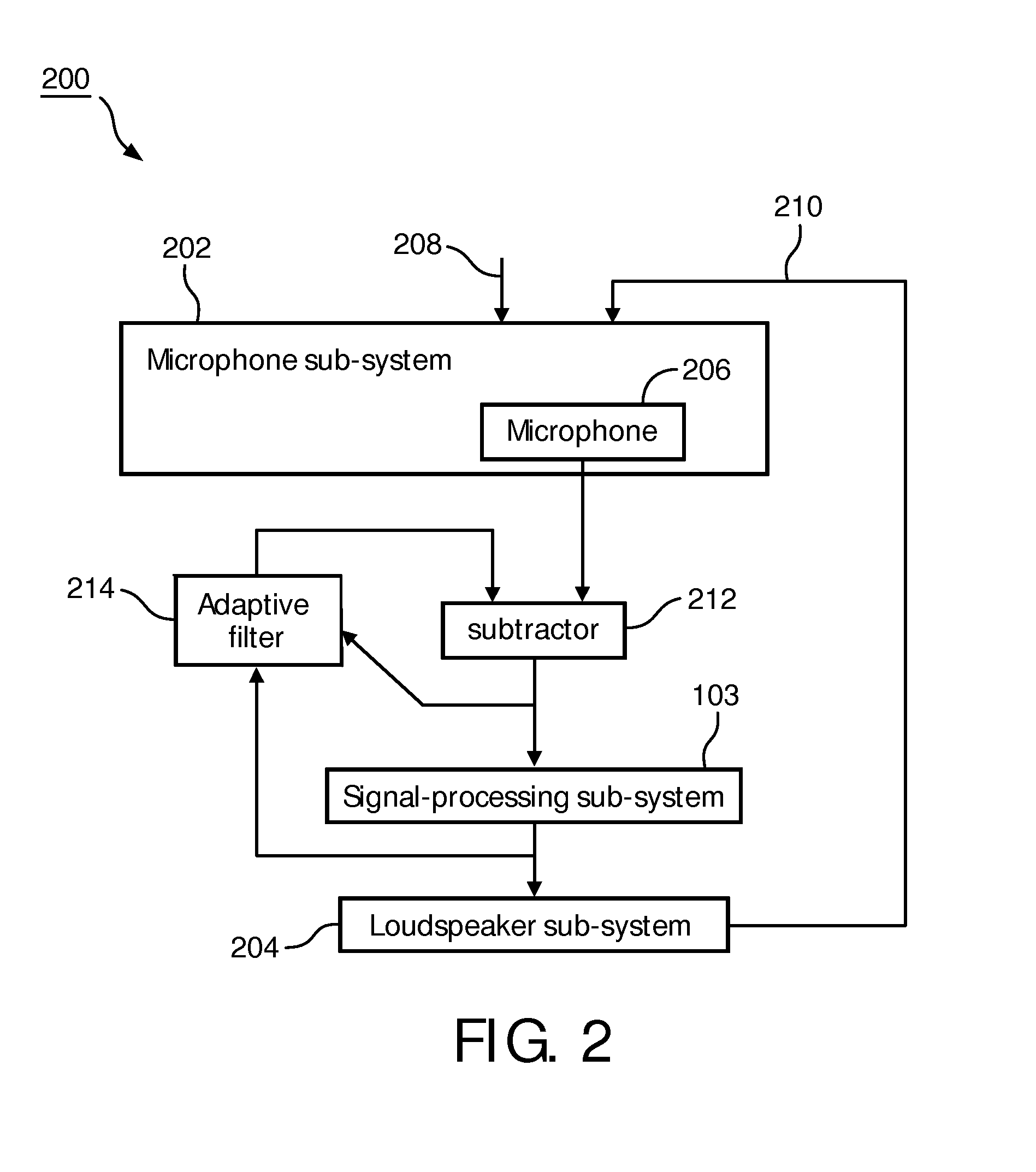
Directional sound masking
ActiveUS20150194144A1Limit brain capacityEasy to identifyCommunication jammingTransducer acoustic reaction preventionMicrophoneSpectrum analyzer
The invention relates to a system for masking a sound incident on a person. The system comprises a microphone sub-system for capturing the sound. The system further comprises a spectrum-analyzer for determining a power attribute of the sound captured by the multiple microphone sub-system, and a spatial analyzer for determining a directional attribute of the captured sound representative of a direction of incidence on the person. The system further comprises a generator sub-system for generating a masking sound under combined control of the power attribute and the spatial attribute, for masking the incident sound.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com