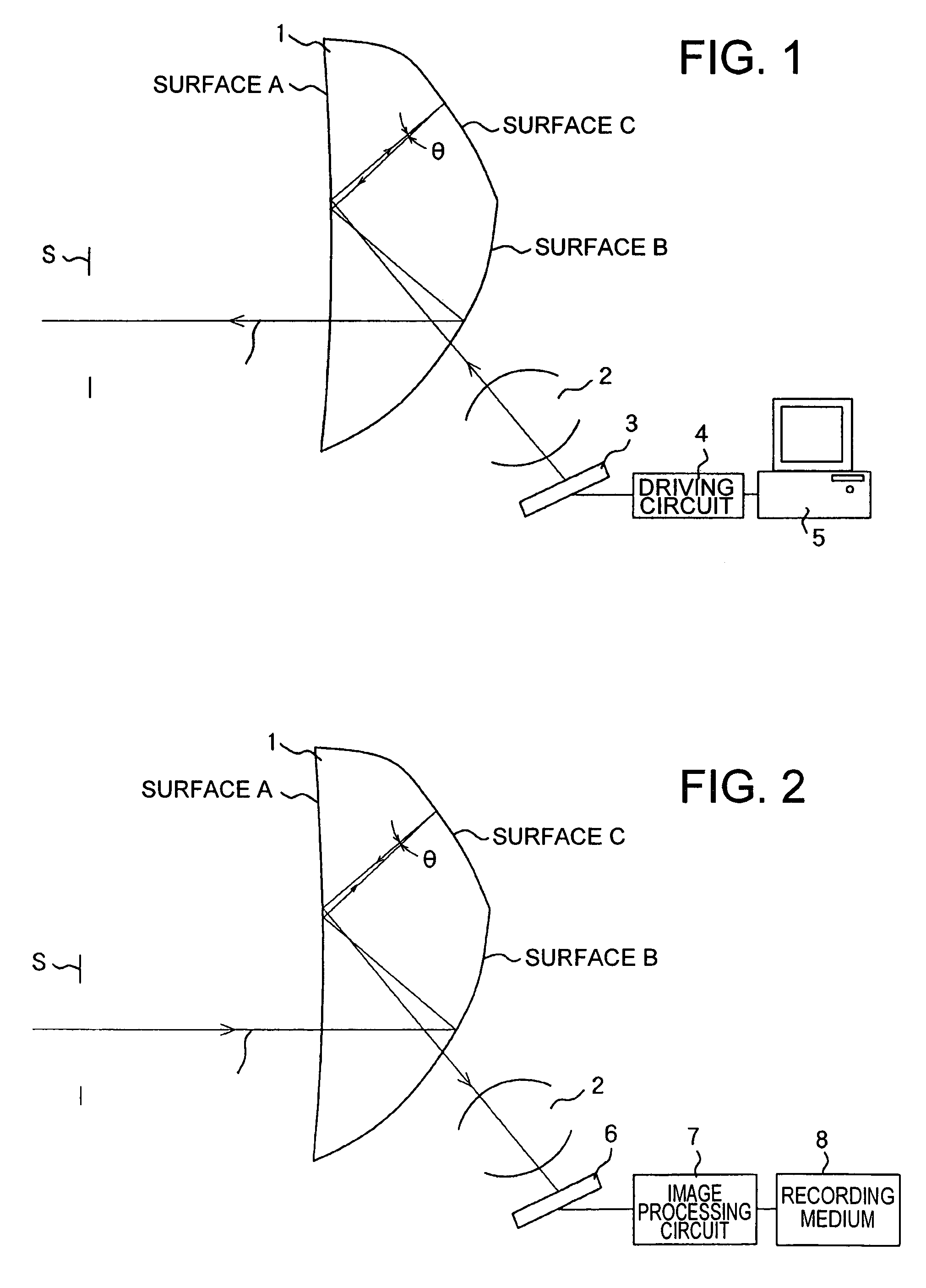
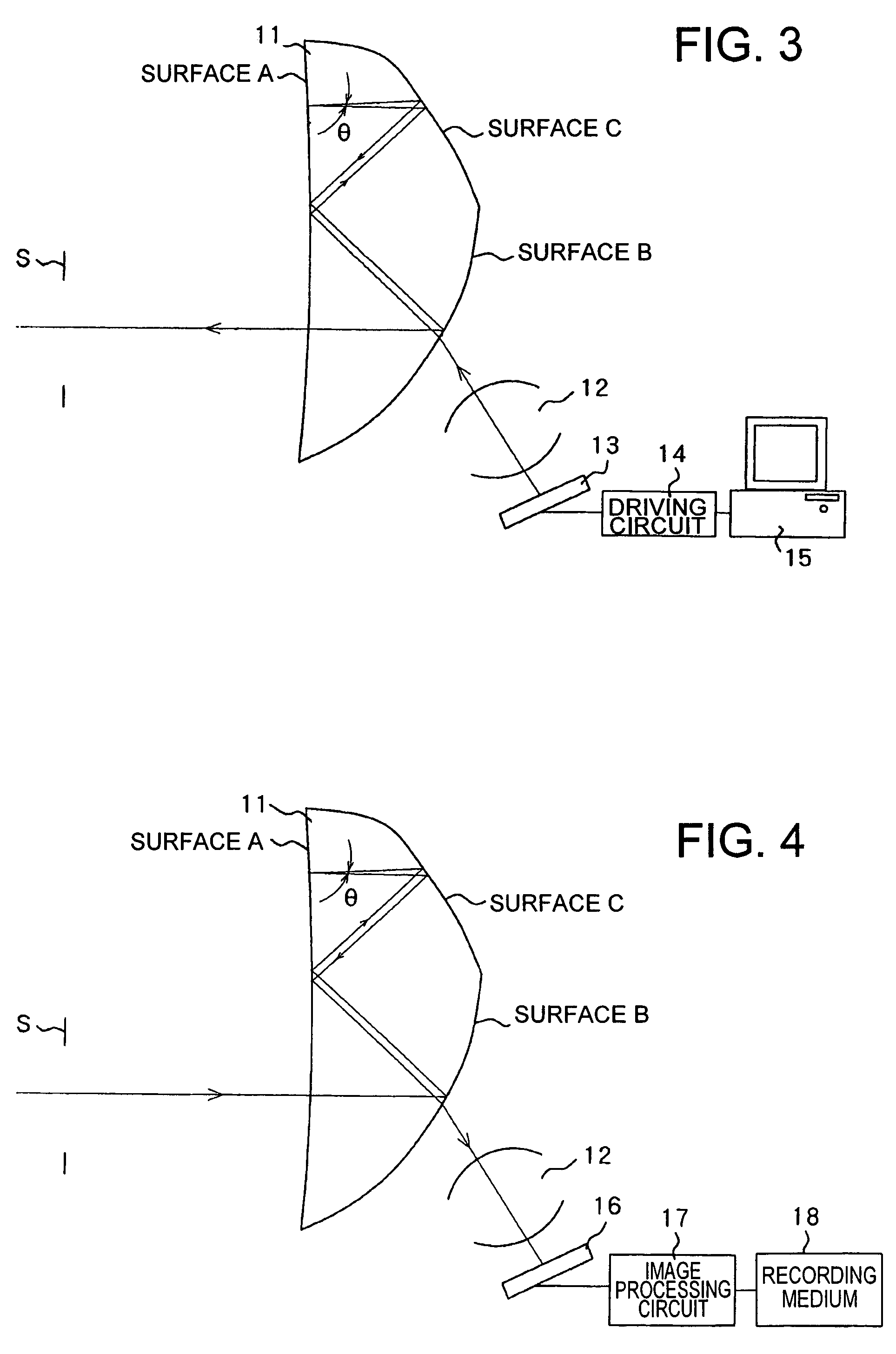
Patents
Literature
90 results about "Central field" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
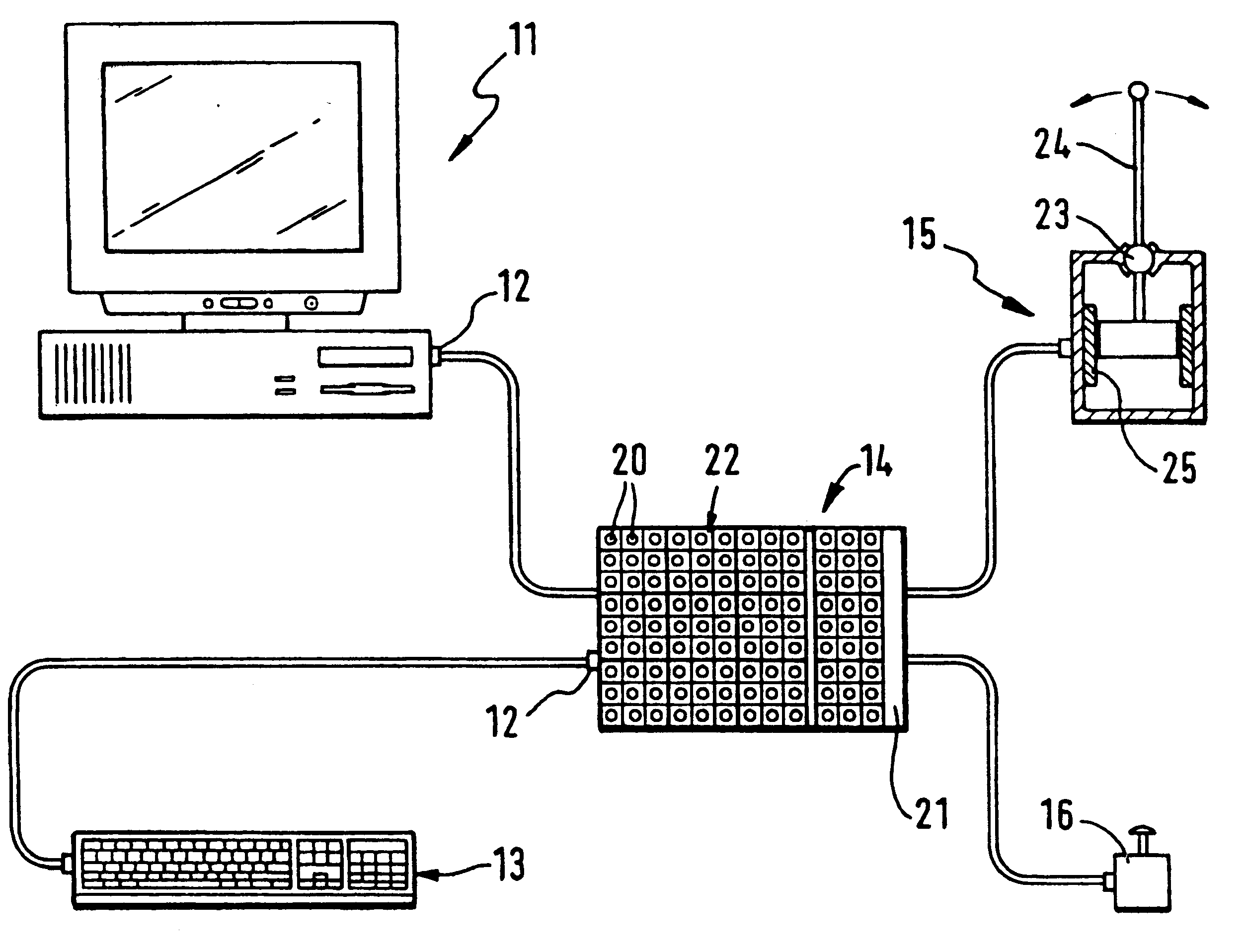
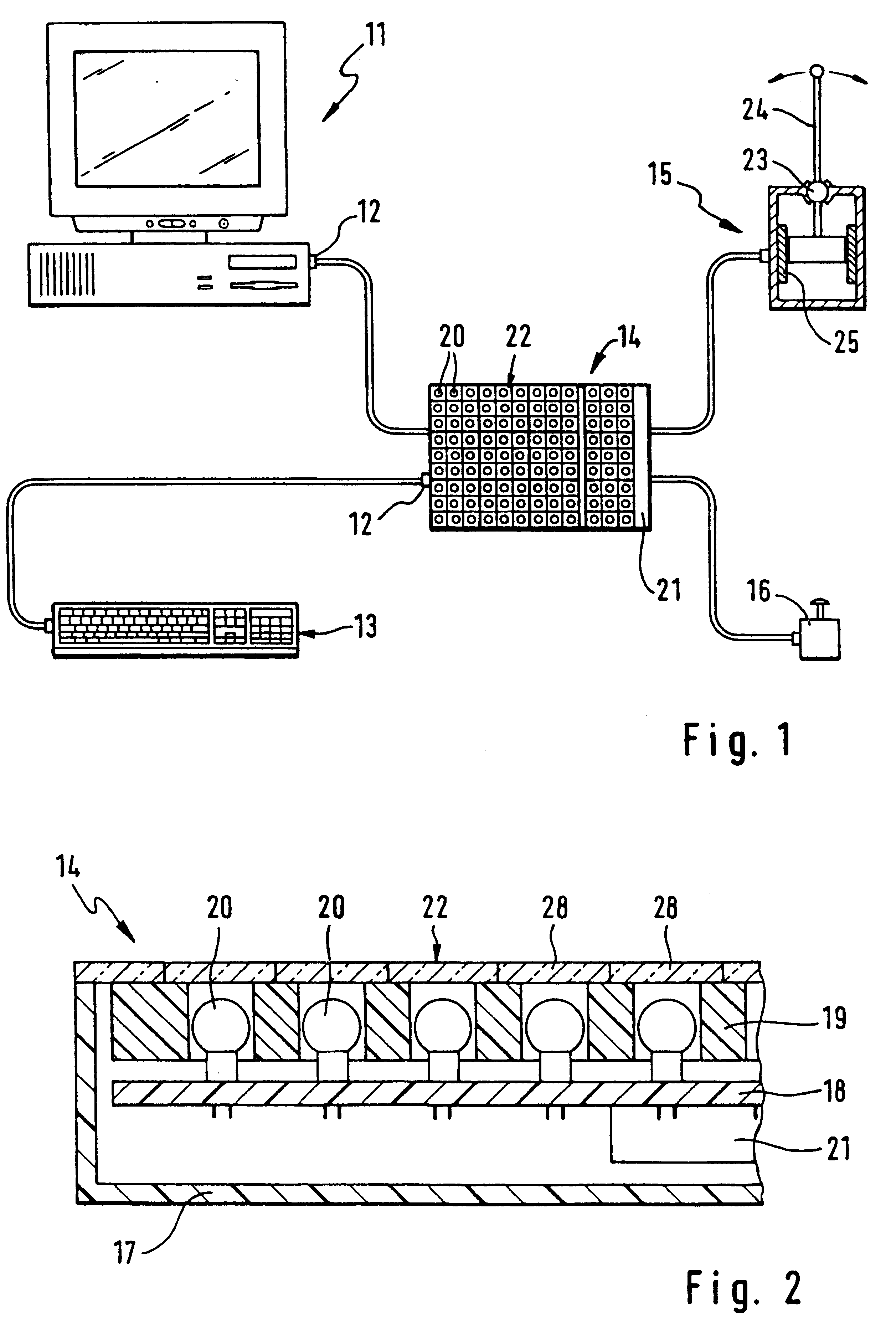
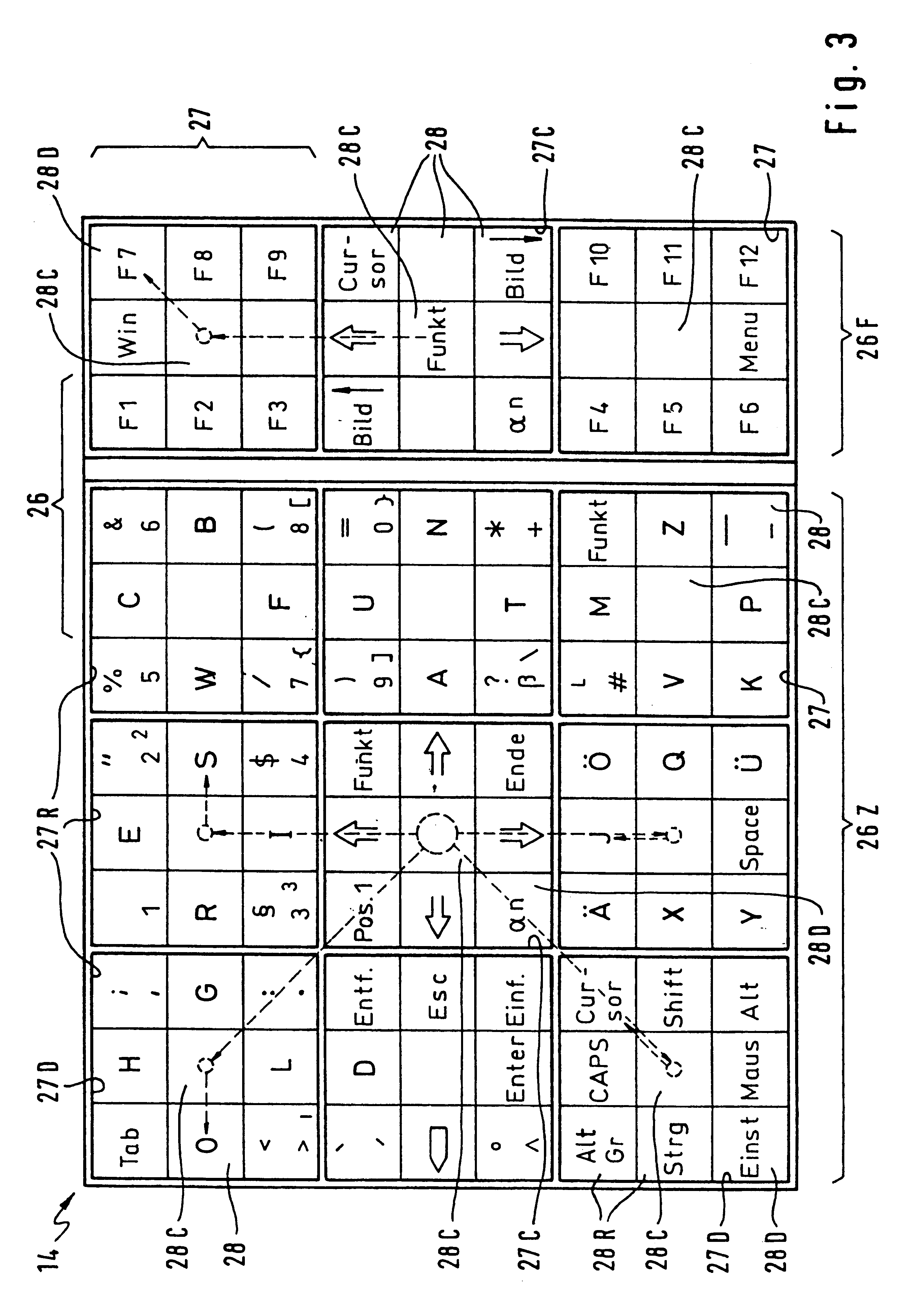
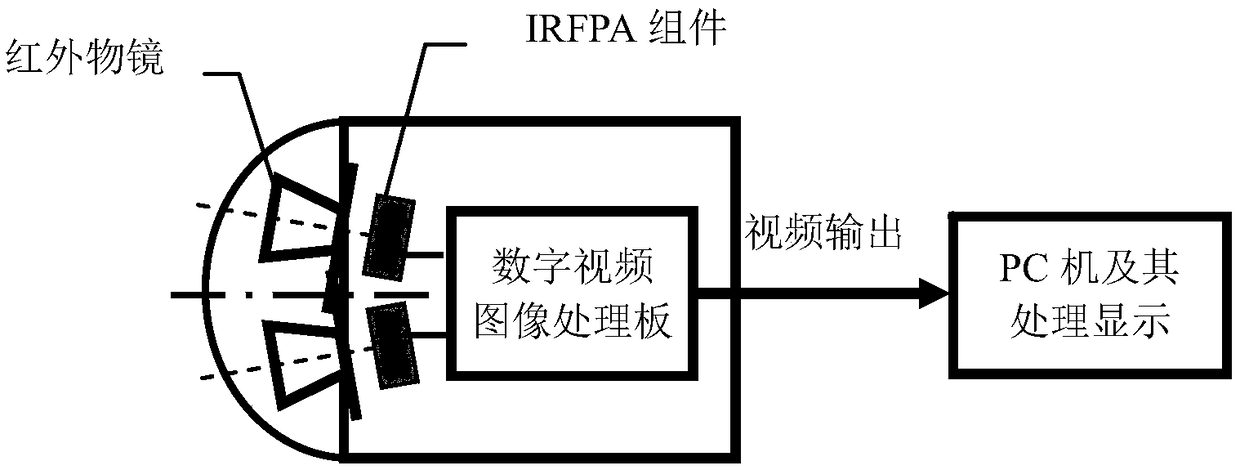
Method for transferring characters especially to a computer and an input device which functions according to this method
InactiveUS6580414B1Easy to operateAddressing slow performanceInput/output for user-computer interactionElectronic switchingJoystickPersonal computer
A personal computer for a handicapped person includes an input panel that is subdivided into a group of fields, with one of the fields designated as a central field for the group. Each field is, in turn, subdivided into nine elements (spaces) comprised of a neutral central element surrounded by eight output elements. Each of those eight output elements has an output character representing a respective output signal. A mark (cursor) is moved across the panel by a control stick that is manipulated by a user. The cursor is always initially located at the center element of the central field. In order to move the cursor to a desired output element, the user: (a) identifies the field in which the desired output character is located, (b) moves the cursor in a first direction to the central element of that identified field, and (c) moves the cursor by one space directly to the desired output element in a second direction oriented either orthogonally or diagonally to the first direction.
Owner:WERGEN GERHARD +1
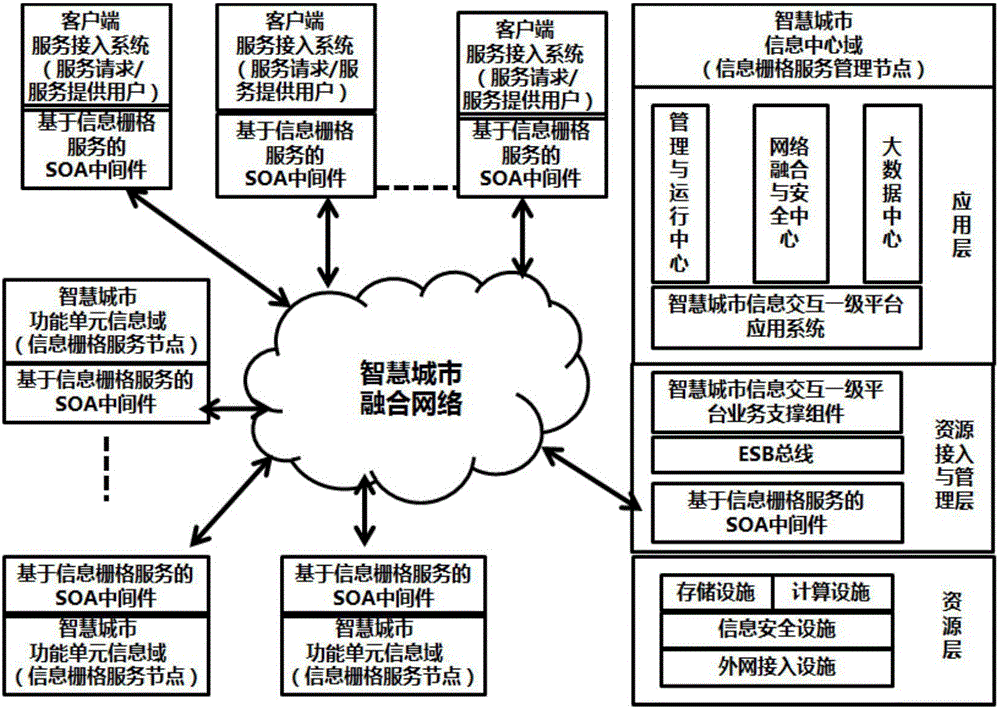
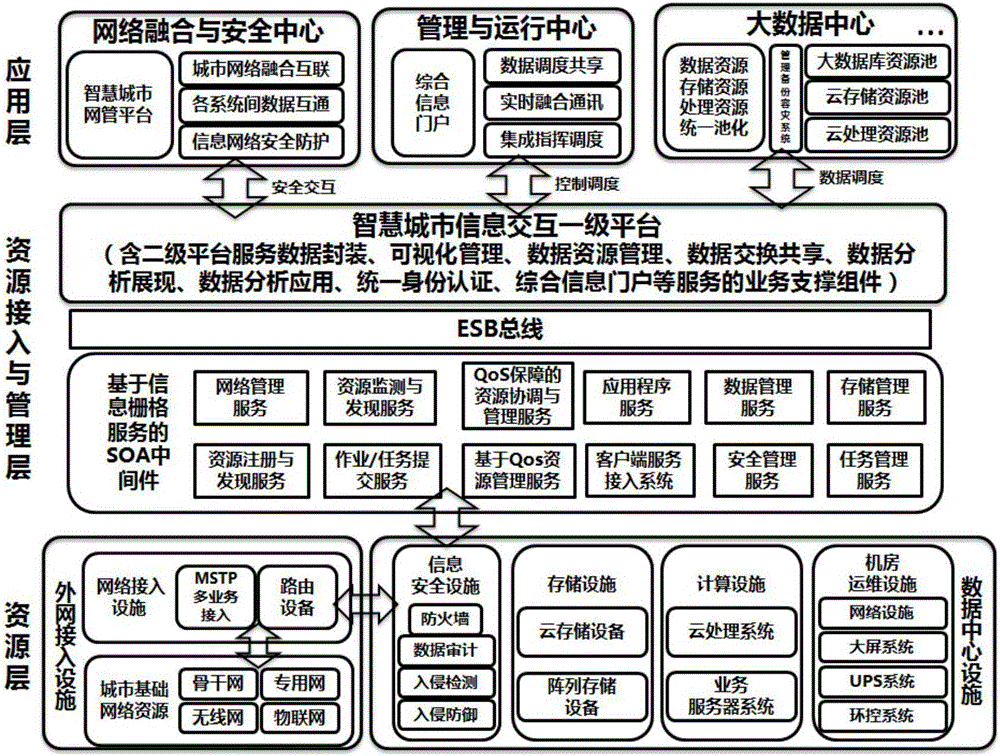
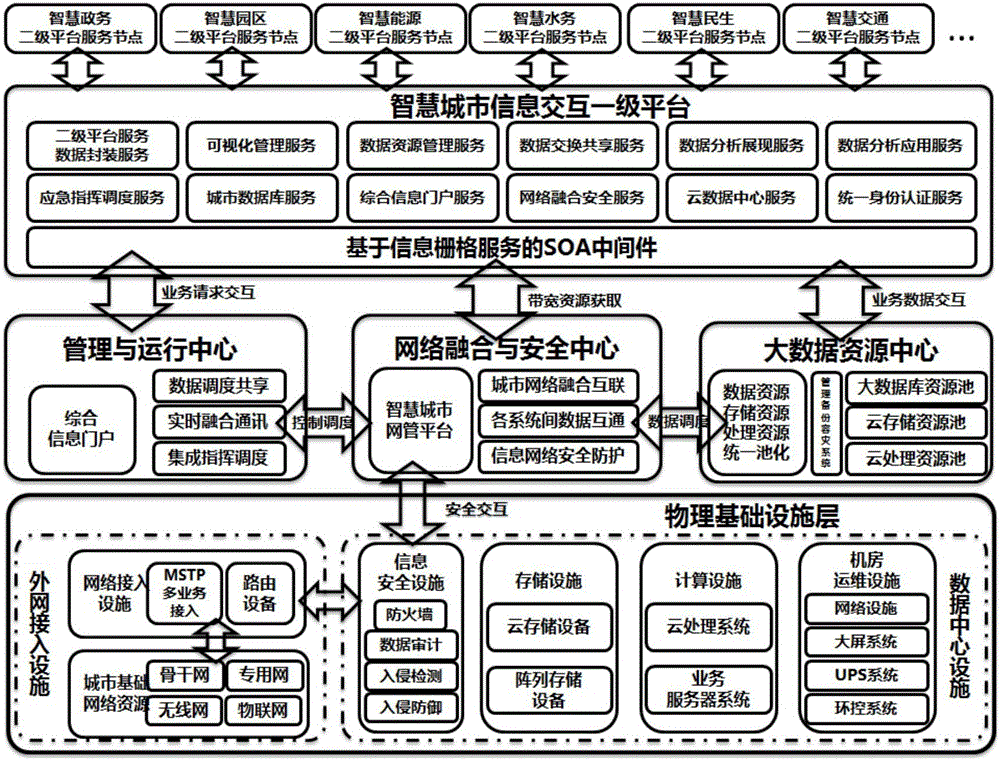
Smart city service configuration based on information grid service
InactiveCN105931168AInterconnectionImprove interoperabilityData processing applicationsTransmissionInterconnectionSmart city
The invention discloses a smart city service configuration based on the information grid service, and the configuration comprises a smart city information central field, a smart city fusion network, at least one smart city function unit information field, and at least one client service access system. The smart city information central field is an information grid service management node, and the smart city function unit information fields are the information grid service nodes. The smart city information central field, the smart city function unit information fields and the client service access system are respectively connected to the smart city fusion network through the locally set SOA middleware based on information grid service. The configuration solves a problem of the resource integration among all function units in a smart city information construction through the technology of information grid service, so as to truly achieve the purposes of network interconnection, information intercommunication, data sharing and function cooperation. The configuration is high in access rate, is high in stability, can meet the requirements of smart mutual operation, and can be widely used in the field of smart city.
Owner:广州葵翼信息科技有限公司
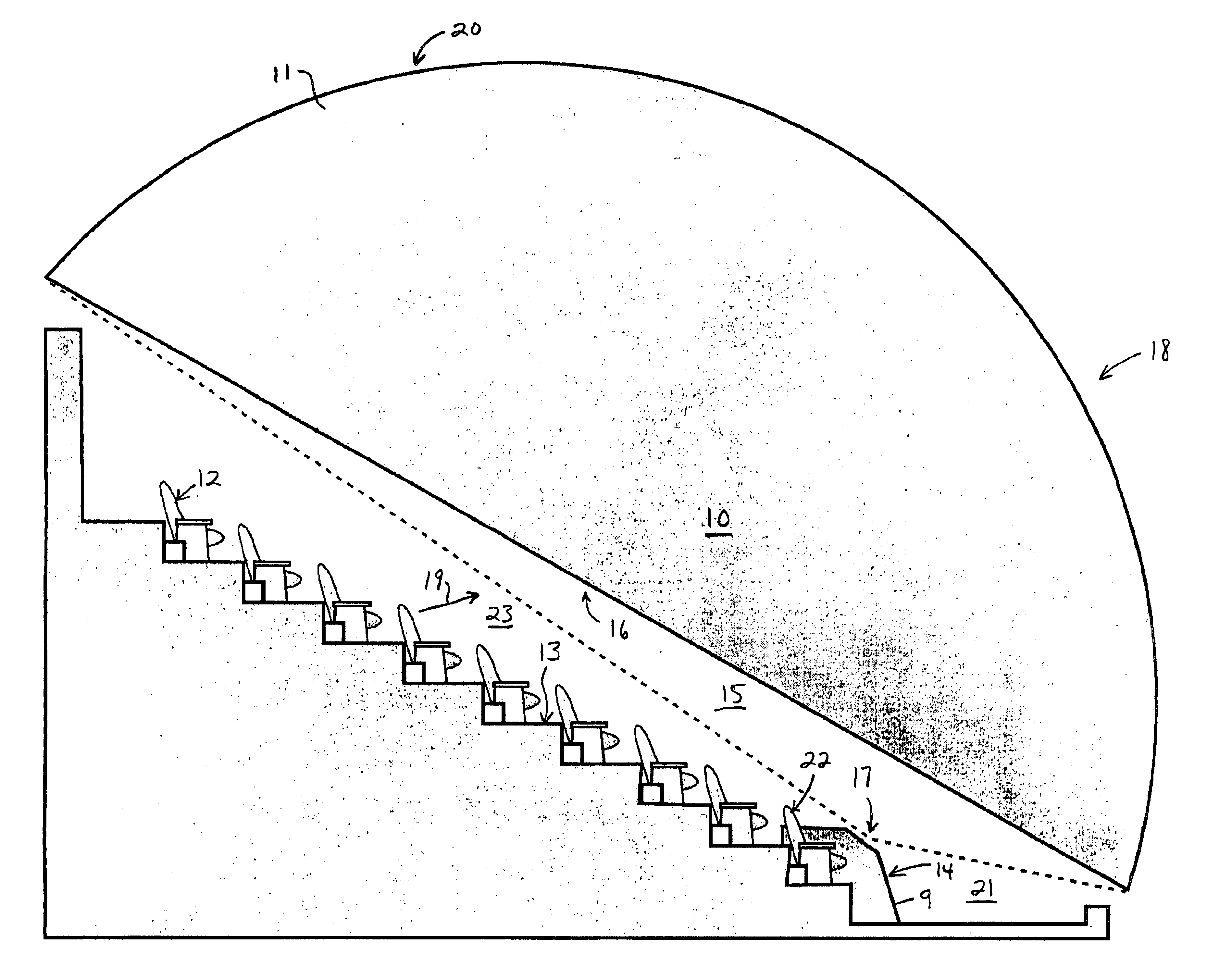
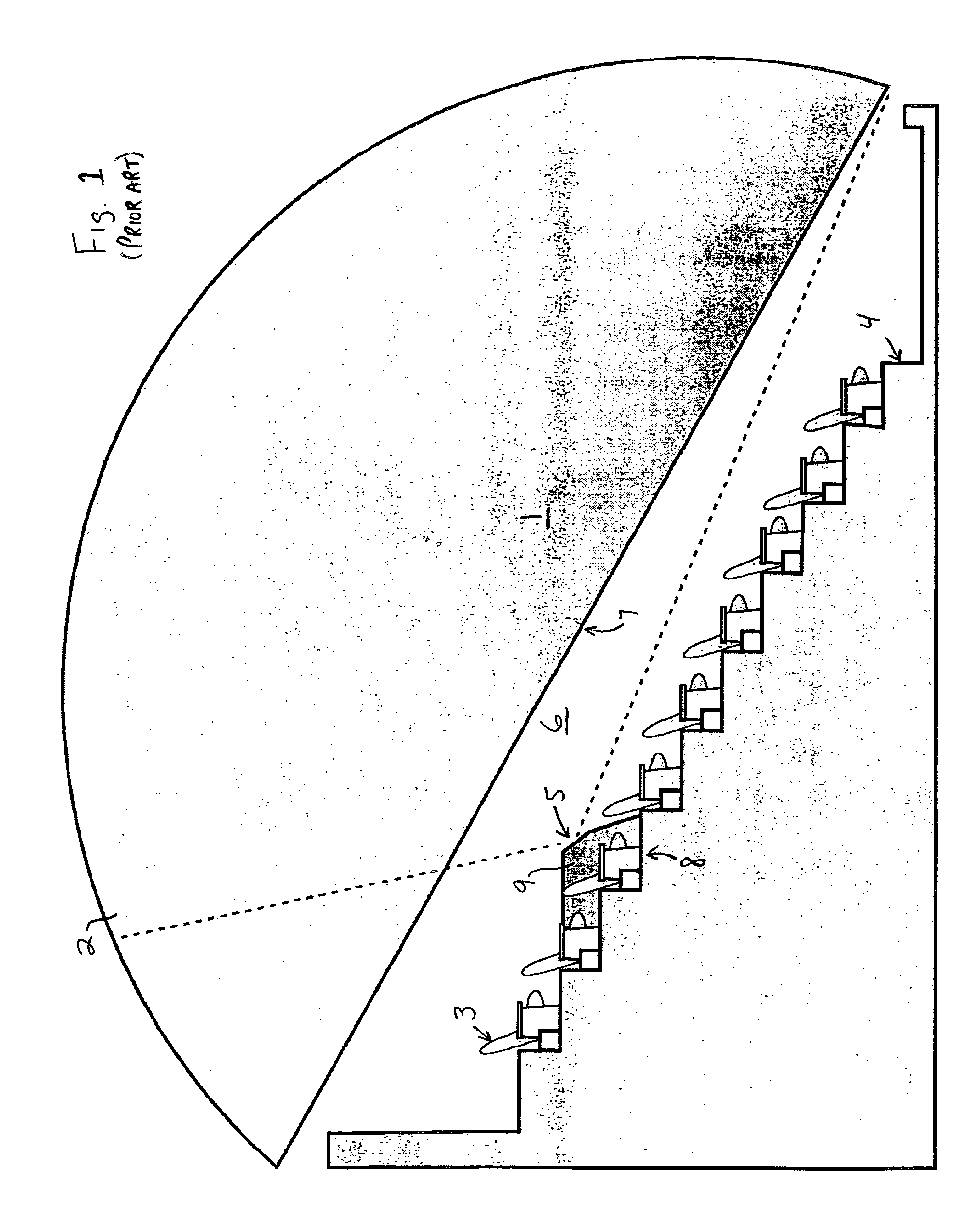
Foveated display system
InactiveUS6909543B2Improve imaging resolutionImprove image contrastProjectorsTelevision systemsImage resolutionImage contrast
An improved theater geometry which is capable of providing improved image resolution and improved image contrast over prior systems is achieved with a unique projection geometry and image re-mapping technique. The projected image is provided with a continuously variable image resolution and brightness over the surface of a preferably dome-shaped screen which is to receive the image, concentrating the resolution and the brightness of the image within the central field-of-view of viewers that are unidirectionally seated in the theater, and sacrificing resolution and brightness toward the outside edges of the viewers' field-of-view. The result is a more efficient use of available projector resolution and brightness, an increase in the number of quality seats available in the theater, and an enhanced image contrast due to reductions in the light which is scattering from image elements to the rear of the screen.
Owner:SPITZ
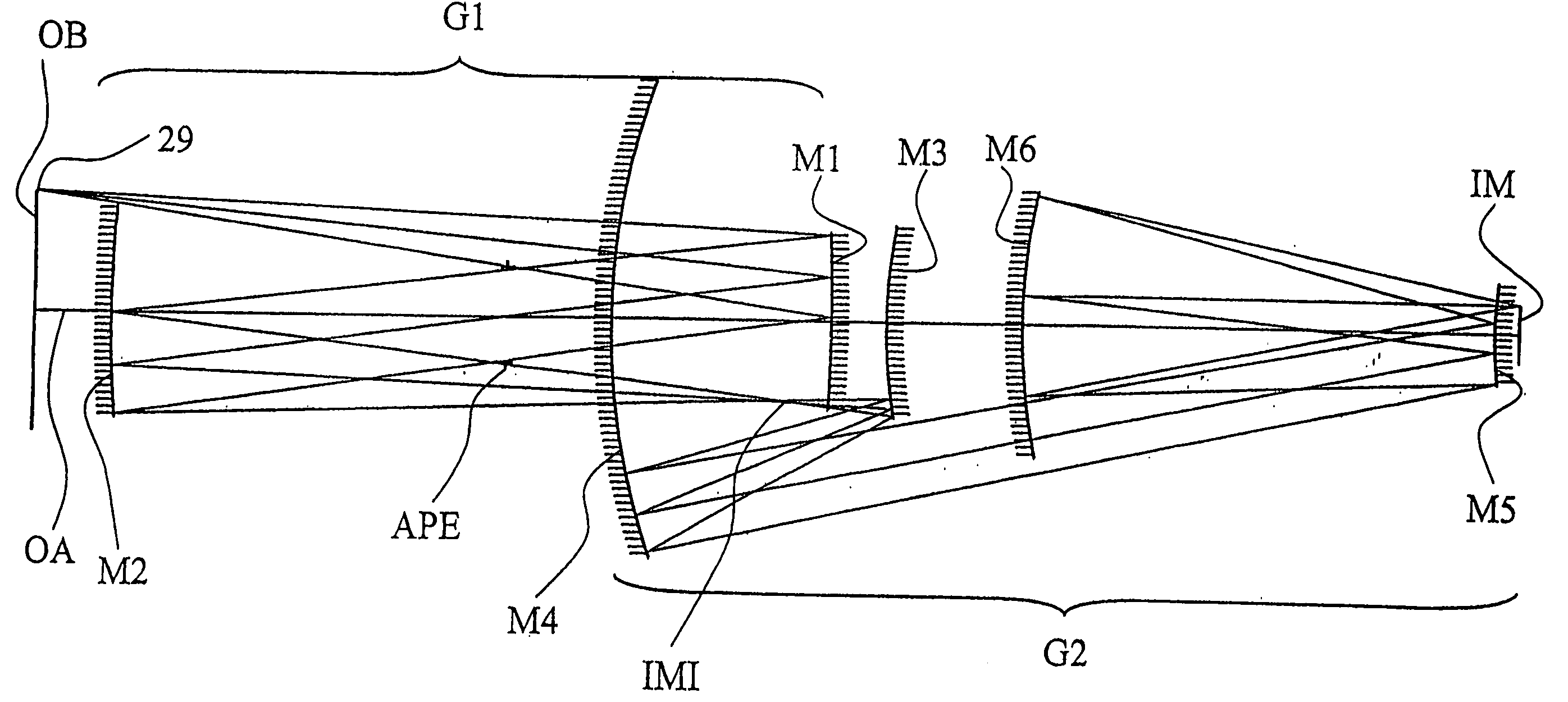
Projection system for EUV lithography
InactiveUS6985210B2Preventing Image Quality DeteriorationEasy mounting and adjustingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusIntermediate imageOptical axis
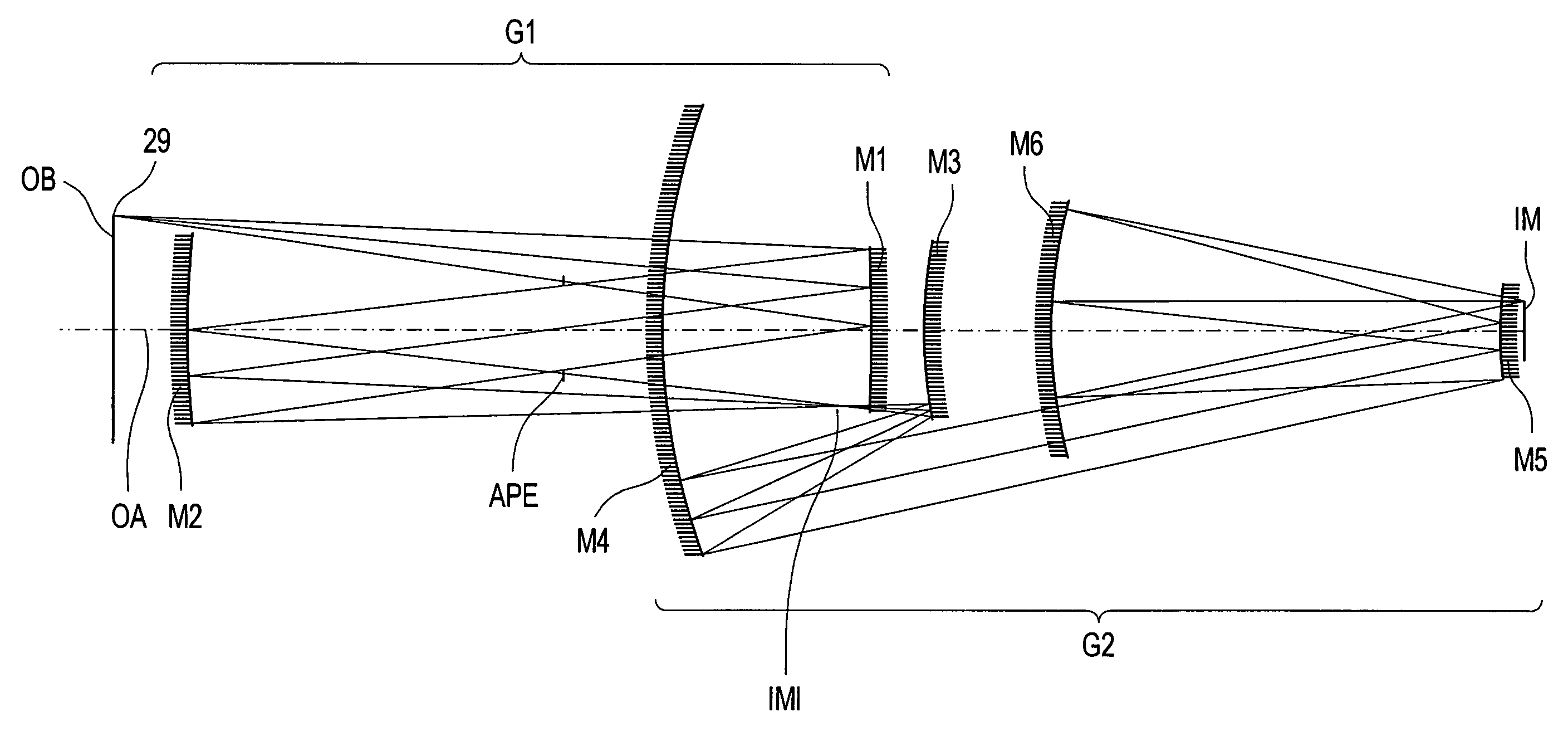
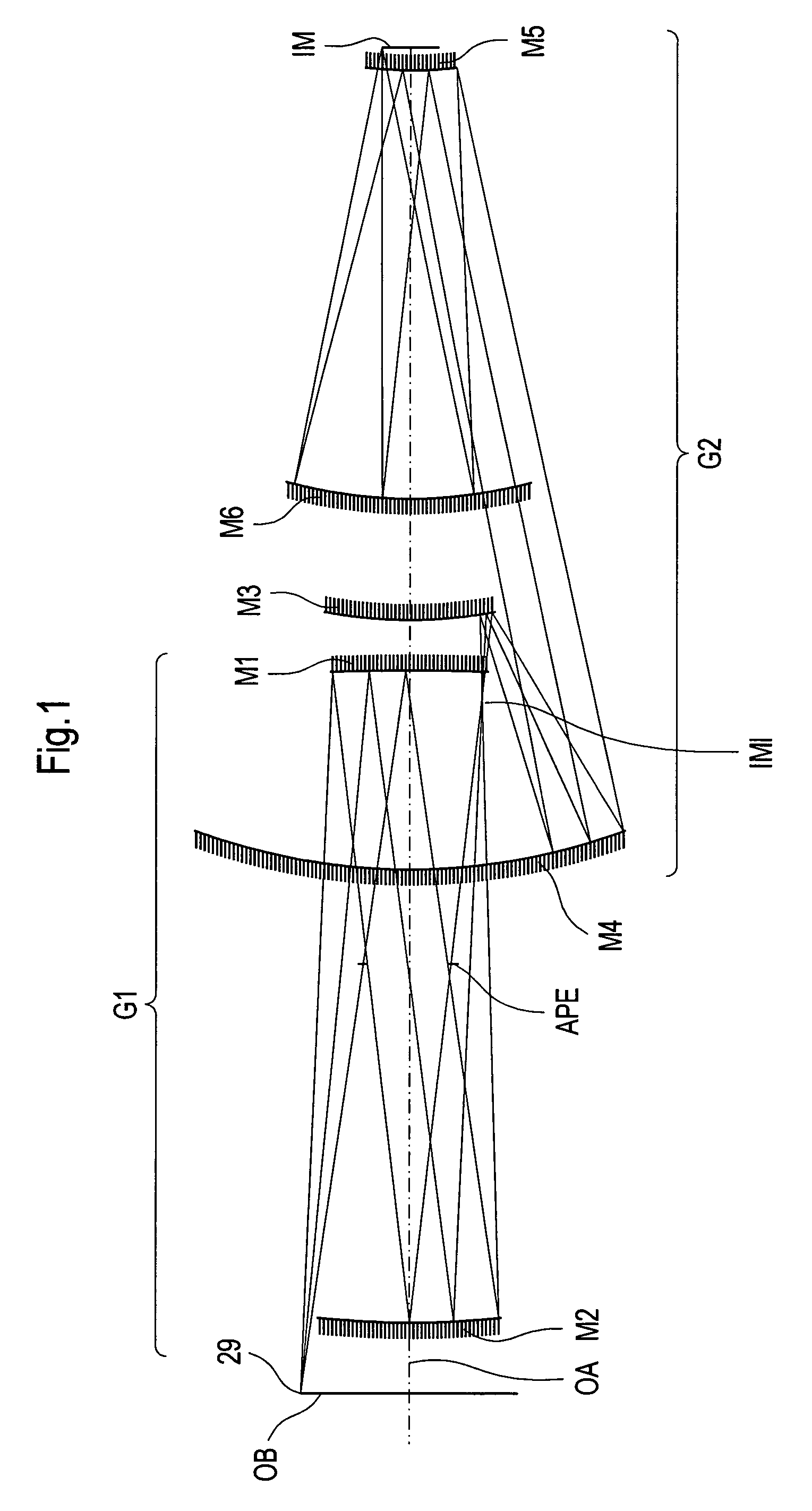
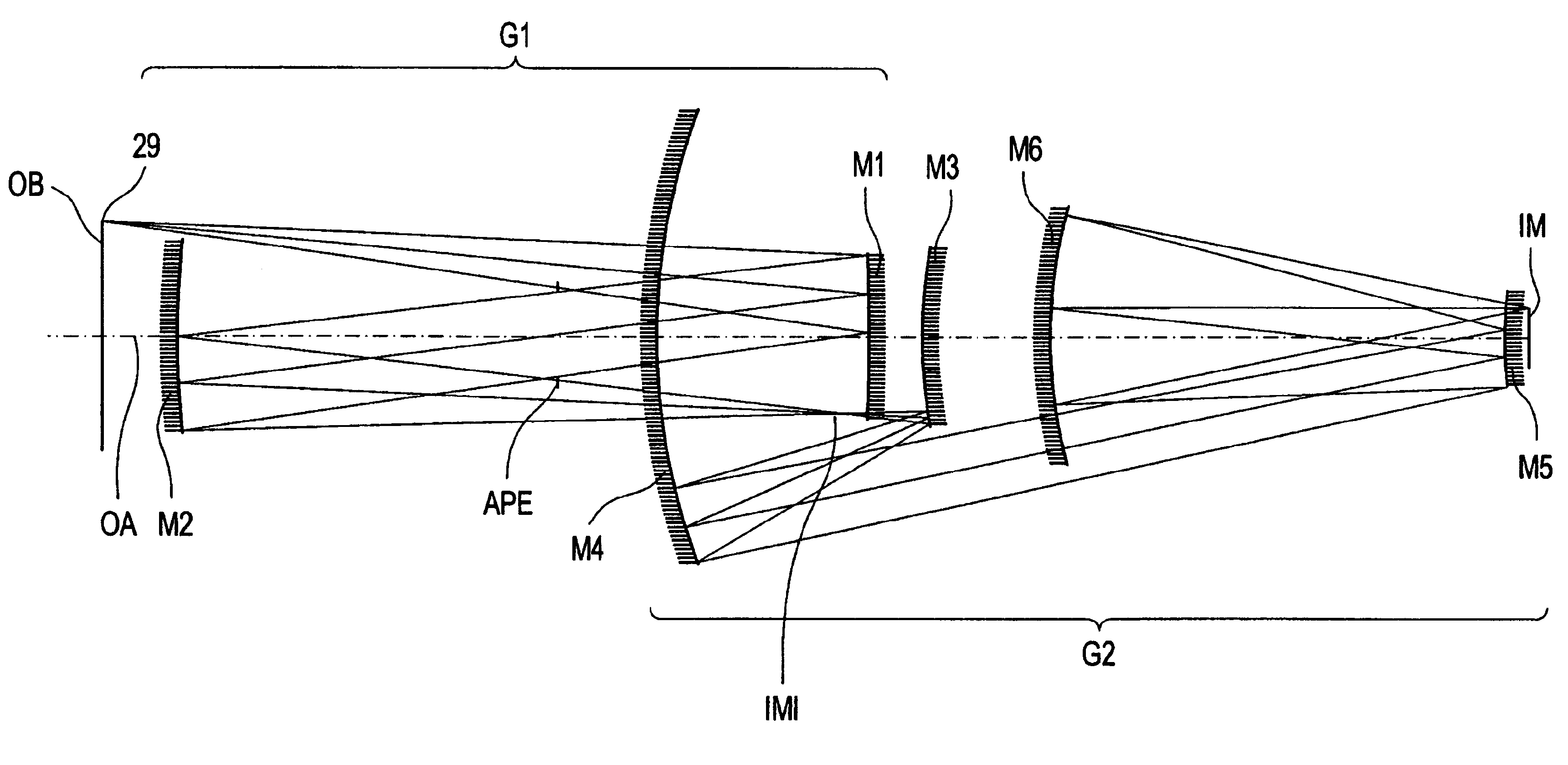
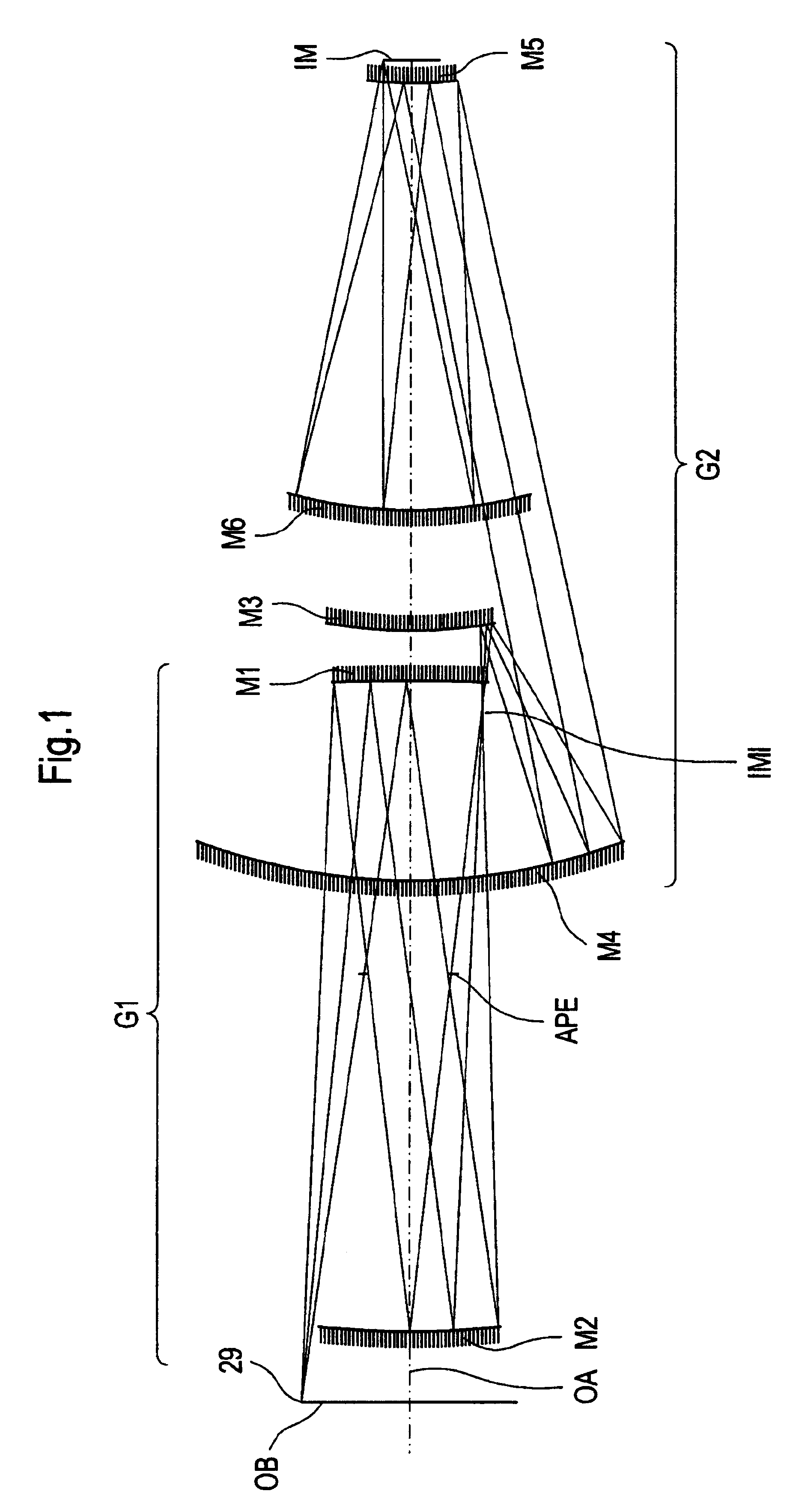
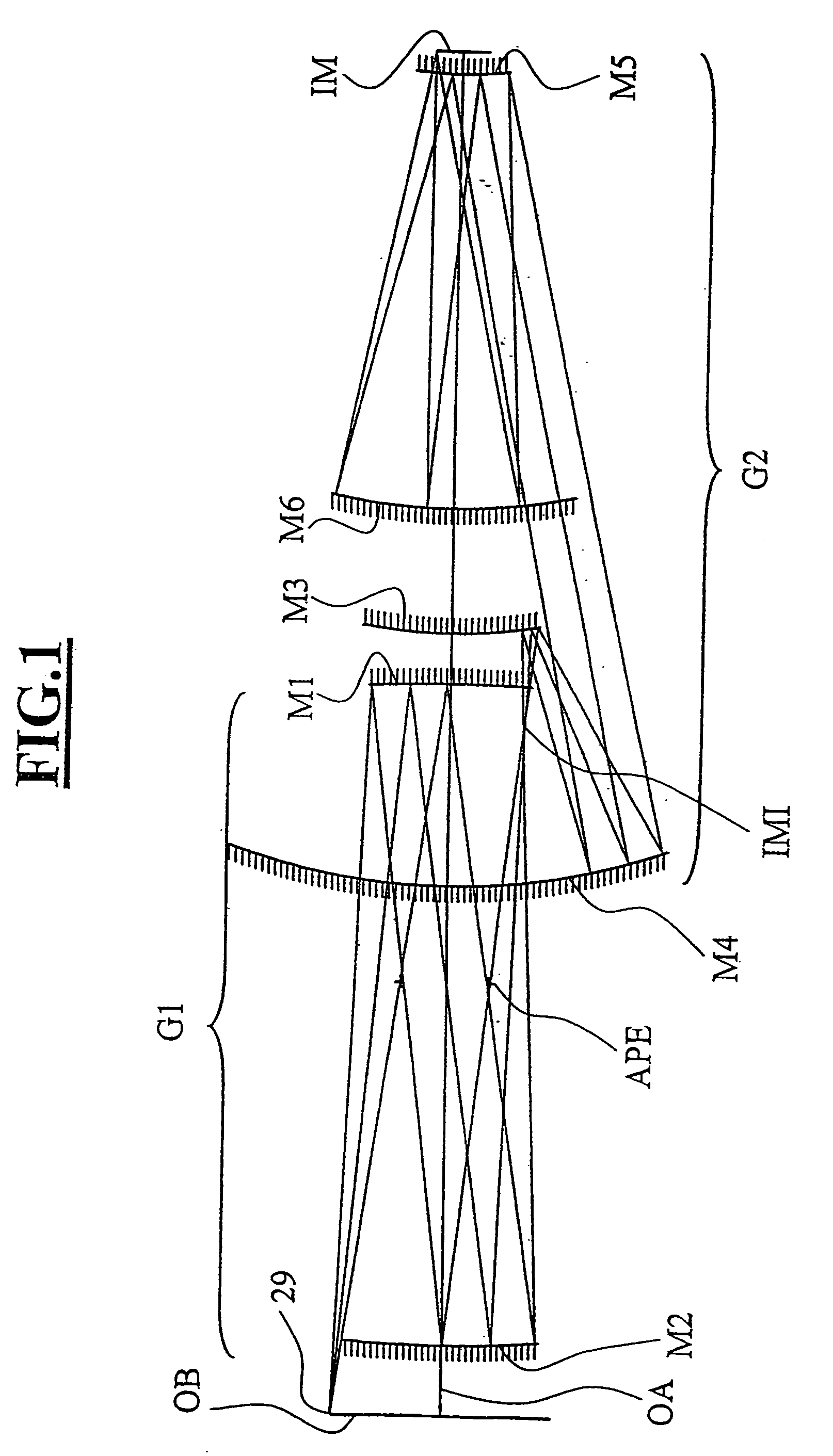
An EUV optical projection system includes at least six reflecting surfaces for imaging an object (OB) on an image (IM). The system is preferably configured to form an intermediate image (IMI) along an optical path from the object (OB) to the image (IM) between a secondary mirror (M2) and a tertiary mirror (M3), such that a primary mirror (M1) and the secondary mirror (M2) form a first optical group (G1) and the tertiary mirror (M3), a fourth mirror (M4), a fifth mirror (M5) and a sixth mirror (M6) form a second optical group (G2). The system also preferably includes an aperture stop (APE) located along the optical path from the object (OB) to the image (IM) between the primary mirror (M1) and the secondary mirror (M2). The secondary mirror (M2) is preferably concave, and the tertiary mirror (M3) is preferably convex. Each of the six reflecting surfaces preferably receives a chief ray (CR) from a central field point at an incidence angle of less than substantially 15°. The system preferably has a numerical aperture greater than 0.18 at the image (IM). The system is preferably configured such that a chief ray (CR) converges toward the optical axis (OA) while propagating between the secondary mirror (M2) and the tertiary mirror (M3).
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
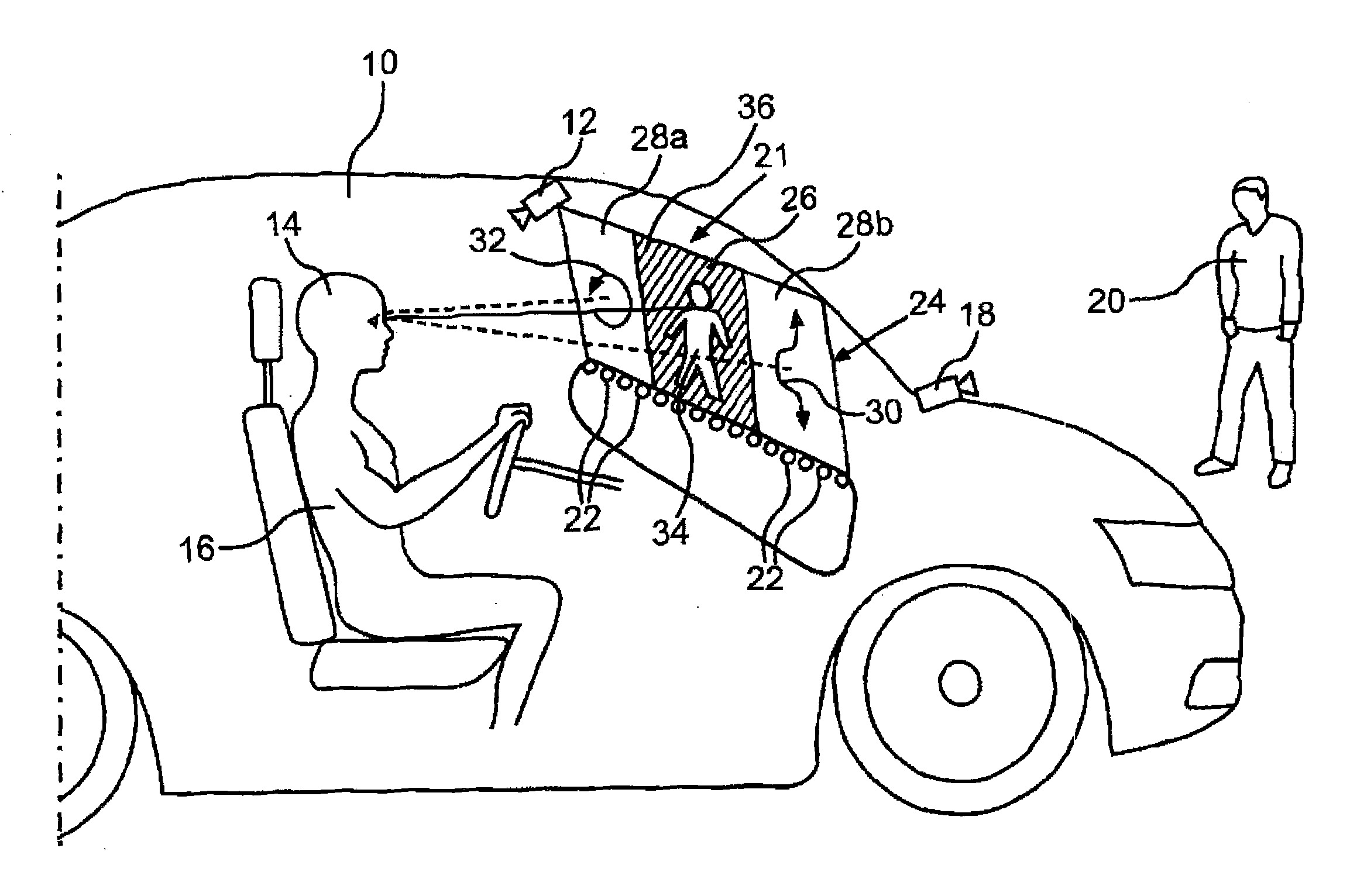
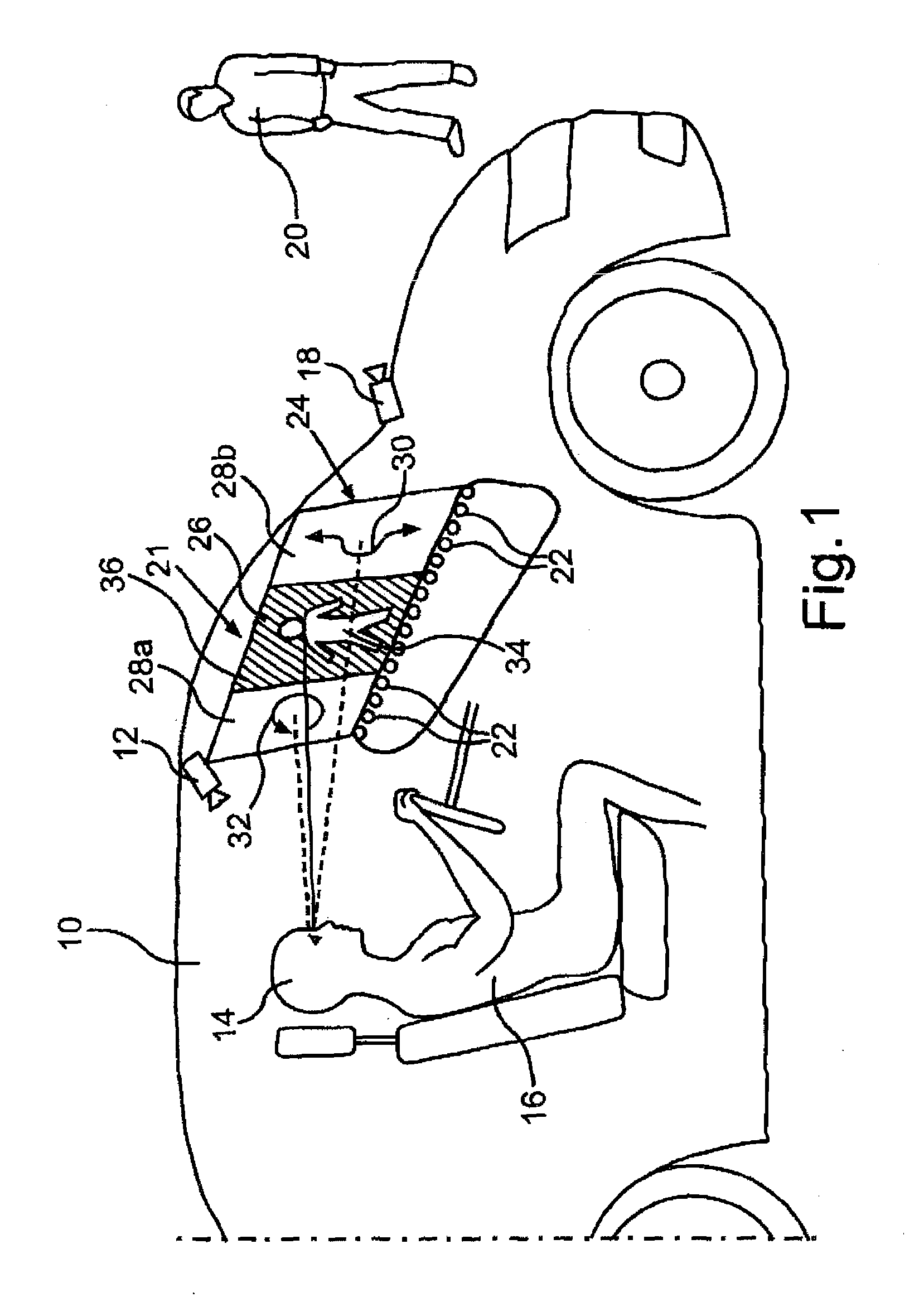
Method for providing a representation in a motor vehicle depending on a viewing direction of a vehicle operator
ActiveUS20130235200A1Stable supportColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsTemporal changeMotorized vehicle
The physiological characteristics of the eye are particularly well taken into account in a motor vehicle by selecting a representation at a representation site from at least two types of representations depending on whether the respective representation site is located in a central field of view of the vehicle operator or is located in a peripheral field of view of the vehicle operator. Preferably, intensive colors and strong color contrasts are selected in the central field of view of the vehicle operator, whereas representations that change over time are selected in the peripheral field of view.
Owner:AUDI AG
Gamma radiation breast imaging apparatus
ActiveUS20140093035A1Enhance the imageAvoid noiseRadiation/particle handlingPatient positioning for diagnosticsVolumetric imagingField of view
A gamma radiation breast imaging apparatus, comprising an object positioning device, defining an imaging space and having as an intended insertion direction of the breast to be imaged, and a gamma camera positioned to image a volume in said imaging space. The gamma camera comprises a collimator with a first plurality of focused pinholes, the individual fields of view of the first pinholes defining a common central field of view having a geometrical centre. The apparatus also has a gamma sensitive detector to receive images from the collimator. The first pinholes are provided non-symmetrically with respect to a first plane through said geometrical centre that is perpendicular to the collimator and parallel to said intended insertion direction. Hereby, more angular information about the scanned volume can be obtained for the same detector size, in particular when combined with a similar opposite camera.
Owner:MILABS BV
Plenoptic imaging device equipped with an enhanced optical system
ActiveUS20180067237A1Improve qualityReduced and without optical aberrationTelevision system detailsImage analysisOptical axisMicro lens array
A plenoptic imaging device is described including a micro-lens array placed between a main lens and a photosensor. The micro-lens array has a plurality of micro-lenses each configured to project a micro-image onto the photosensor, the main lens covering a central field-of-view of the scene according to capture axis. The plenoptic imaging device includes multi-faceted optical means structure having at least two facets and placed in a plane adjacent to the aperture diaphragm plane and centered on the main optical axis, each facet being configured to angularly rotated the capture axis with respect to the main optical axis so as to capture a rotated field-of-view from the central field-of-view, and so that the captured rotated field-of-views form an expanded field-of-view covering the central field-of-view.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL CE PATENT HLDG
Projection system for EUV lithography
InactiveUSRE42118E1Efficiently maskedThe implementation process is simpleSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusIntermediate imageOptical axis
An EUV optical projection system includes at least six reflecting surfaces for imaging an object (OB) on an image (IM). The system is preferably configured to form an intermediate image (IMI) along an optical path from the object (OB) to the image (IM) between a secondary mirror (M2) and a tertiary mirror (M3), such that a primary mirror (M1) and the secondary mirror (M2) form a first optical group (G1) and the tertiary mirror (M3), a fourth mirror (M4), a fifth mirror (M5) and a sixth mirror (M6) form a second optical group (G2). The system also preferably includes an aperture stop (APE) located along the optical path from the object (OB) to the image (IM) between the primary mirror (M1) and the secondary mirror (M2). The secondary mirror (M2) is preferably concave, and the tertiary mirror (M3) is preferably convex. Each of the six reflecting surfaces preferably receives a chief ray (CR) from a central field point at an incidence angle of less than substantially 15°. The system preferably has a numerical aperture greater than 0.18 at the image (IM). The system is preferably configured such that a chief ray (CR) converges toward the optical axis (OA) while propagating between the secondary mirror (M2) and the tertiary mirror (M3).
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
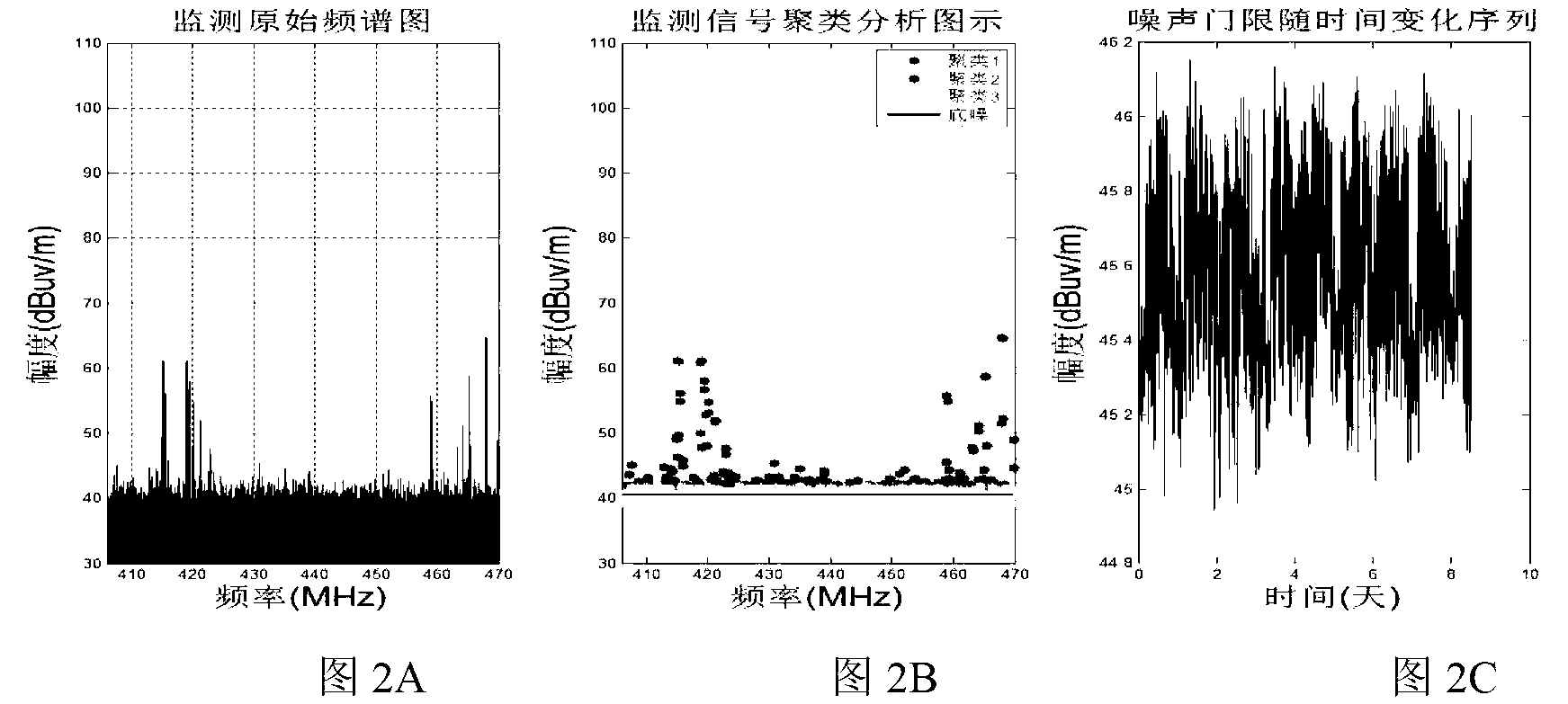
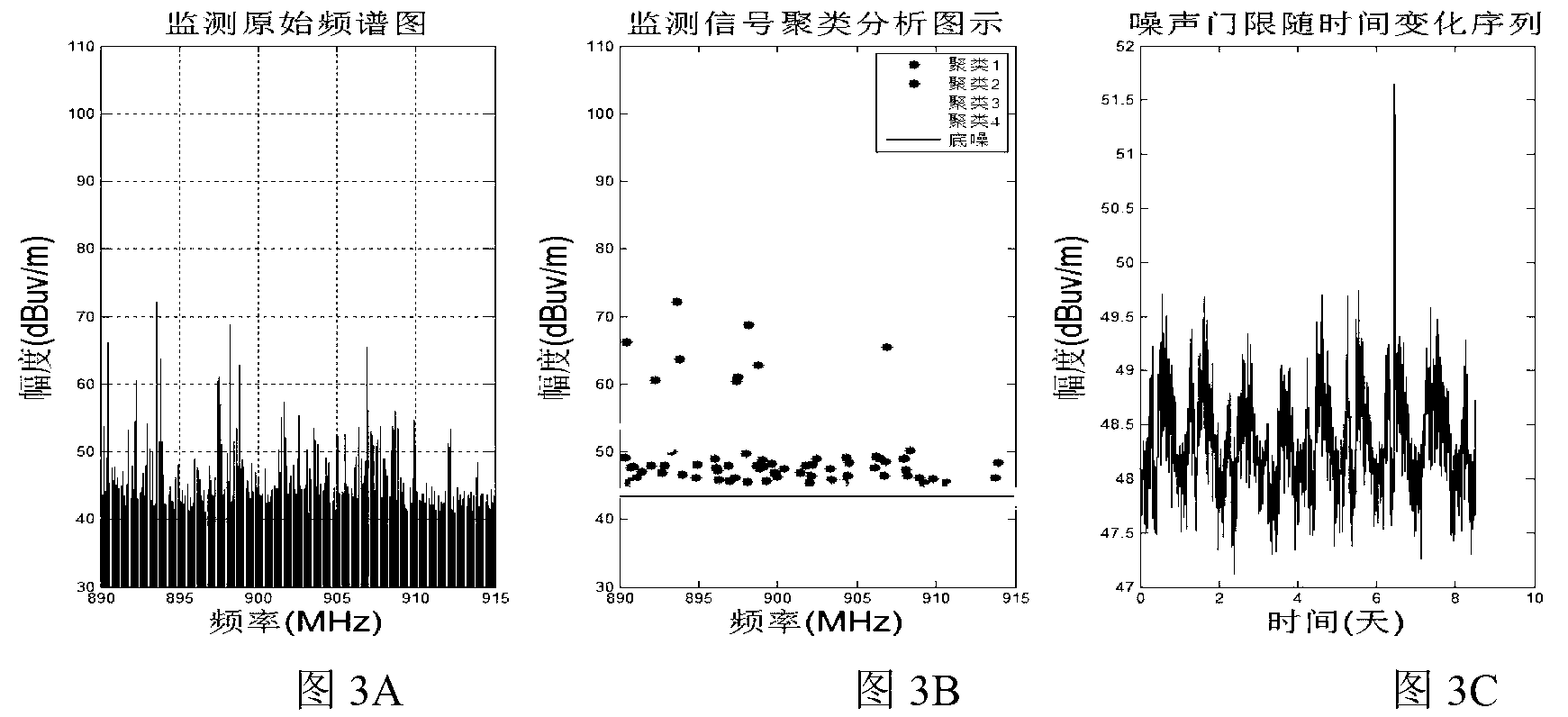
Electromagnetic background noise extraction method based on hierarchy-clustering algorithm
ActiveCN103267905AImprove scienceHigh degree of automationNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementCluster algorithmPattern recognition
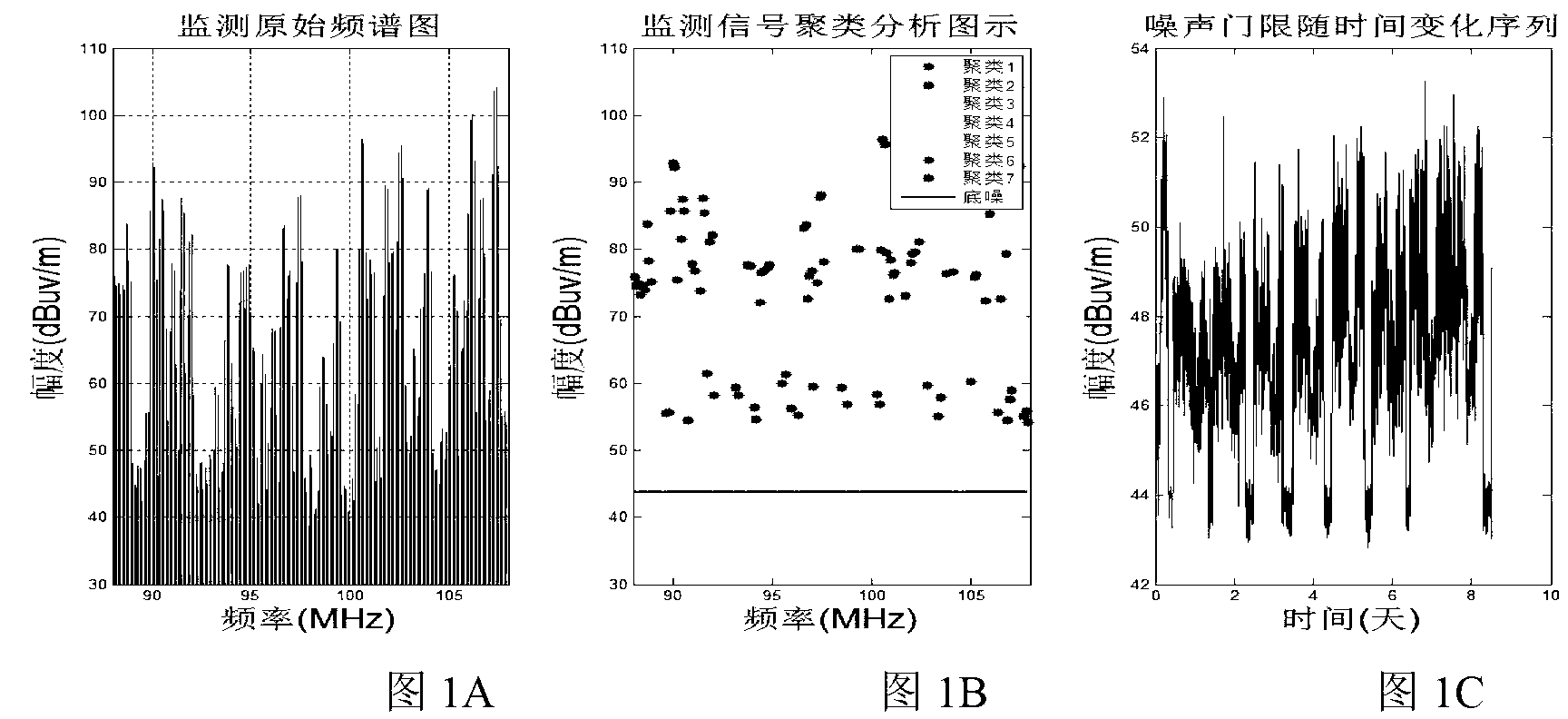
The invention discloses an electromagnetic background noise extraction method based on a hierarchy-clustering algorithm and relates to the technical field of radio management. The extraction method includes the steps of firstly establishing a spectrum-field intensity data set obtained through frequency spectrum monitoring and scanning, secondly carrying out data subset division and filed intensity hierarchy on the spectrum-field intensity data set so as to obtain central field intensity values of each cluster, thirdly, sequencing the central field intensity values of the clusters to obtain electromagnetic background noise sample values, and finally forming an electromagnetic background noise sample sequence and obtaining electromagnetic background noise levels in unit time. The electromagnetic background noise extraction method based on the hierarchy-clustering algorithm improves scientificity and automation degrees of electromagnetic background noise measurement, effectively overcomes the defect that an estimated noise value is lower than a real value due to the fact that actual wireless system emission factors are not considered in noise curves given by the ITU-RP.372 method, changes the mode that free frequency point field intensity is selected manually as noise sample values in the ITU-RP.372 method, and improves accuracy of electromagnetic background noise computation.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Spunbond facing and faced insulation assembly
A faced building insulation assembly includes a first facing forming a first major surface of the assembly with a central field portion having one or more spunbond continuous polymeric filament mat layers. Preferably, the facing is fungi growth resistant and has a selected water vapor permeance rating as applied to an insulation layer of the assembly. The facing may also include one or more polymeric film layers, a fungi growth inhibiting agent, a pesticide, and / or a heat activated bonding agent that bonds the facing to the insulation layer of the assembly. The insulation assembly may also include a second facing forming a second major surface of the assembly that has a water vapor permeance rating equal to or differing from the first facing.
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
Brushless three-phase synchronous generator having enhanced rotor field system
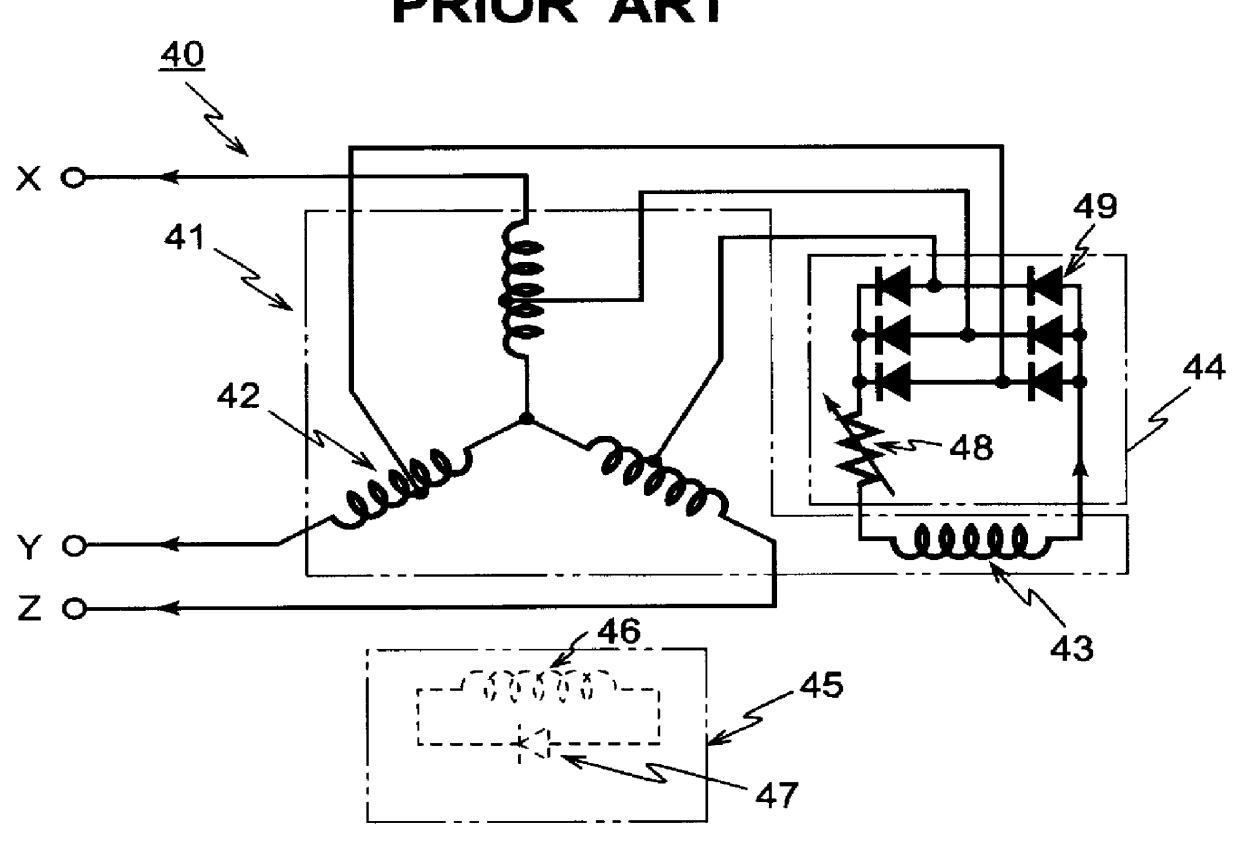
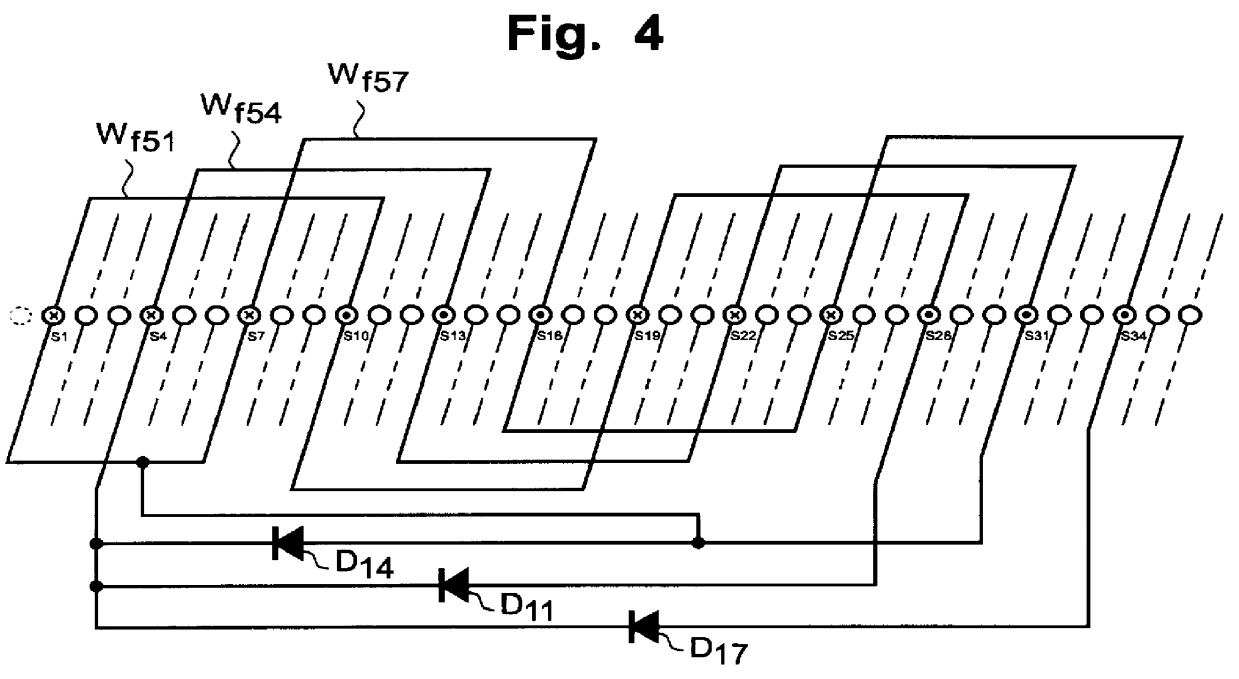
A brushless three-phase synchronous generator includes a stator having primary generating windings and stator excitation windings whose number of poles is odd-number times the number of poles of the primary generating windings. The generator further includes a cylindrical rotor on which a plurality of field windings are wound in a full-pitch concentrated winding form. The plurality of field windings are respectively short-circuited by the corresponding diodes. A plurality of field windings in which voltages of the same phase are induced based on the odd-order spatial higher harmonic magnetic fields are connected in parallel and further connected in parallel to the central field windings which effectively produce primary field magnetic fluxes. A circulating rectifier element is connected in parallel to the central field windings. Improvement in the waveforms of the primary magnetic fields can be achieved and self-excitation in the case where the single-phase loads are connected can be prevented from occurring while magnetic coupling of the rotor field windings to the spatial higher harmonic components of the armature reaction magnetic fields is effectively maintained well.
Owner:SATAKE CORP
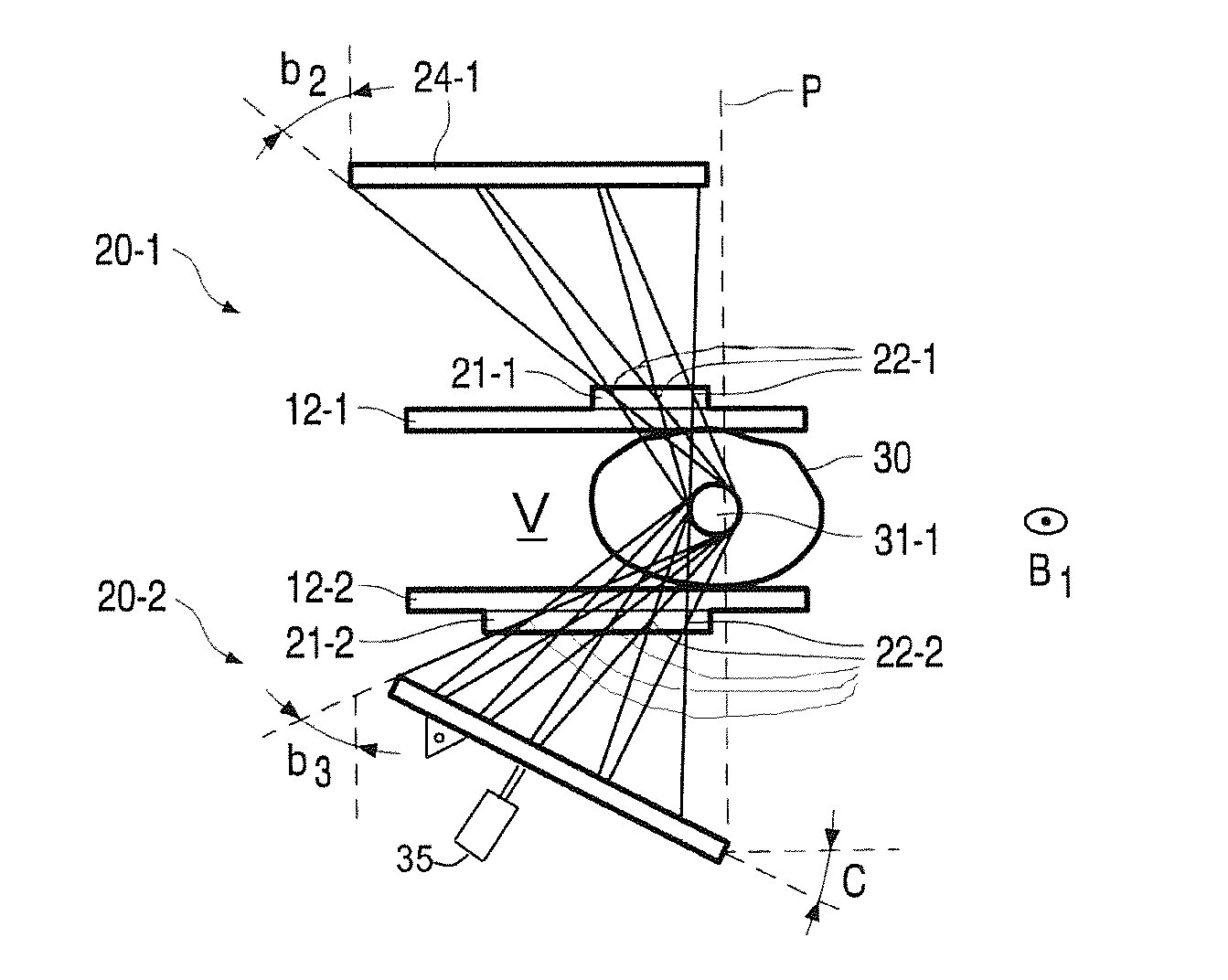
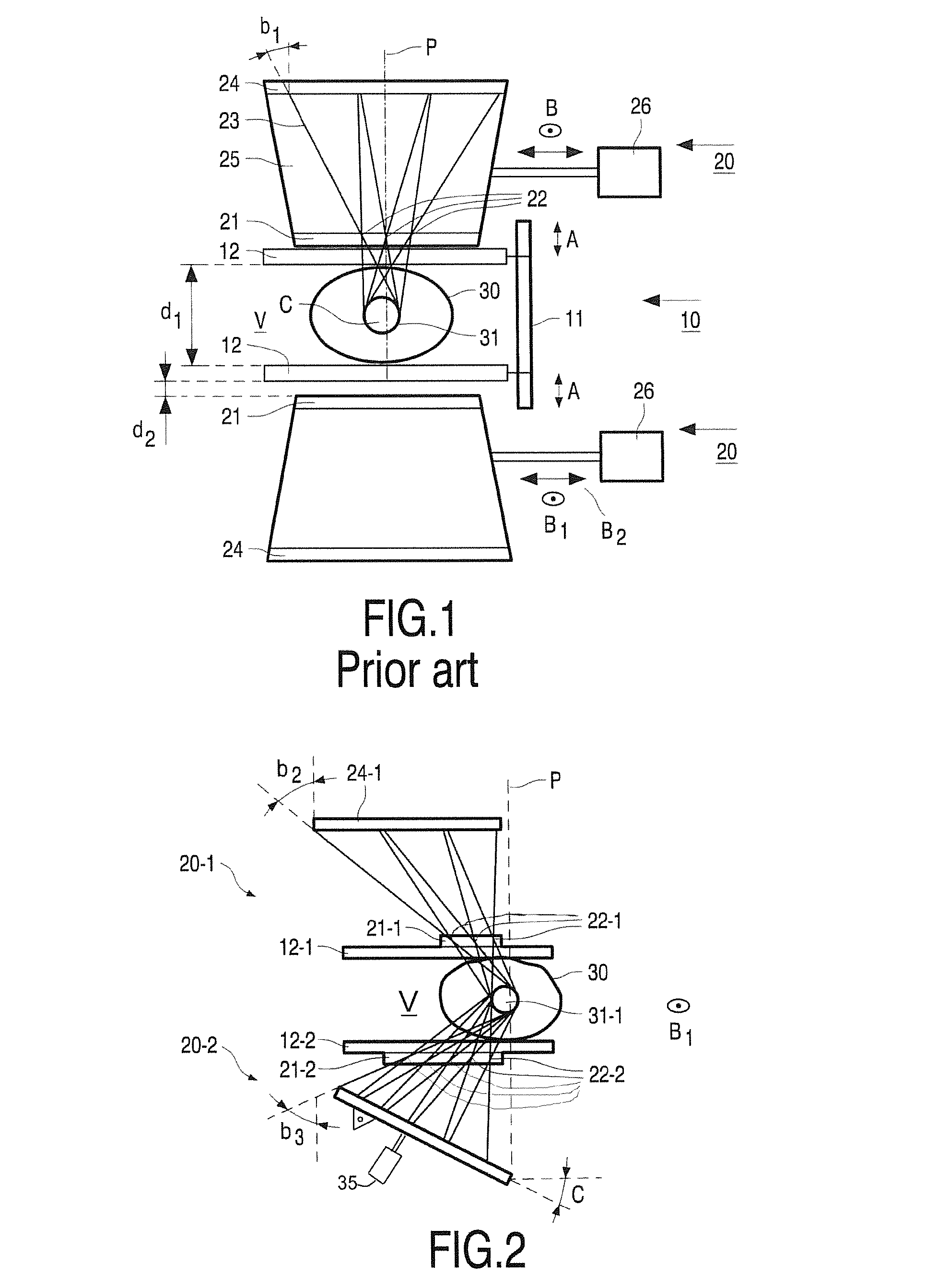
Image observing apparatus
An image observing apparatus has two light sources, a scanning mirror upon which light beams from the two light sources are incident in common, and two optical systems. The two optical systems respectively lead the light beams emitted from the two light sources and scanned by the scanning mirror to the right and left eyes of an observer. The light beams emitted respectively from the two light sources are scanned by the scanning mirror and form two-dimensional images for the right and left eyes on predetermined surfaces. Central field angle principal rays emitted respectively from the two light sources and reflected by the scanning mirror, exist on the same plane. Then, an angle made by the scanning mirror and by a surface vertical to the central field angle principal rays emerging from the two optical systems, is set so as to fall within a predetermined range.
Owner:CANON KK
Optical system, display optical system and image-taking optical system
InactiveUS7210803B2Easy to reachImprove aberrationTelevision system detailsMirrorsOptical surfaceHigh magnification
An optical system is disclosed with which higher magnification can be easily achieved and aberrations can be favorably corrected, yet is compact. The optical system includes a plurality of optical surfaces including a first surface which has at least a reflective action, a second surface reflecting the light rays reflected by the first surface back toward the first surface, and a diffractive optical surface. The first surface reflects a central field-angle principal ray, which comes from the second surface and is again incident on the first surface, to the opposite side of the previous reflection with respect to a normal at a hit point of the central field-angle principal ray on the first surface.
Owner:CANON KK
Magnetic rotary encoder
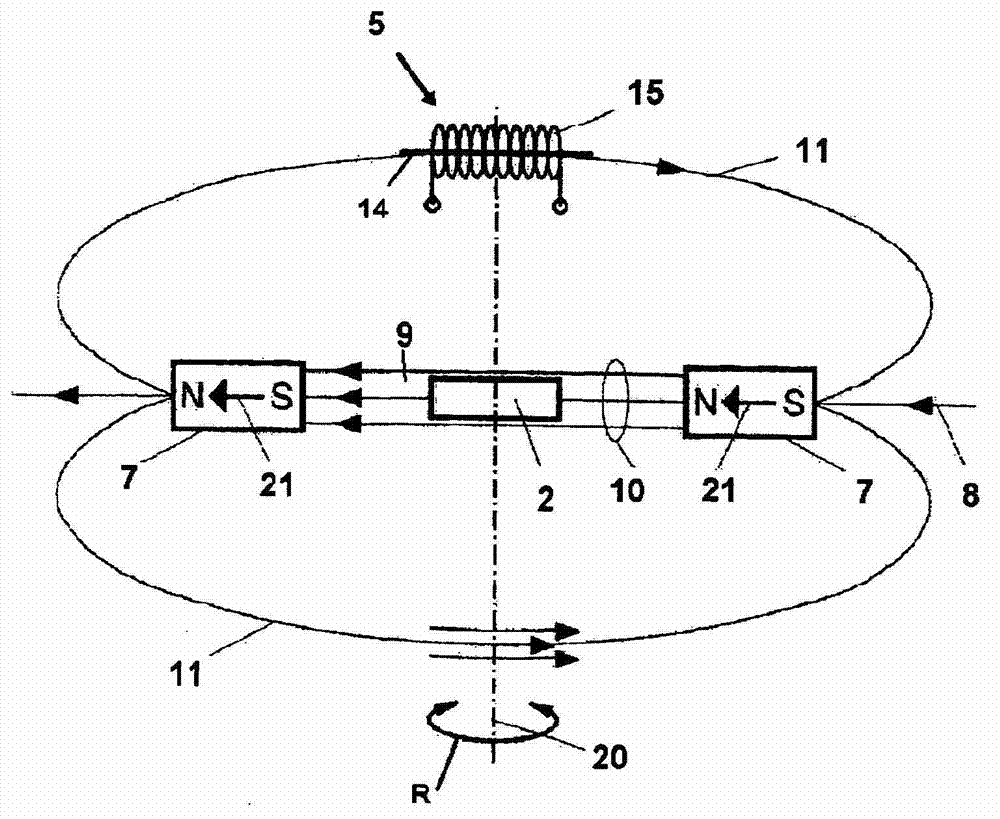
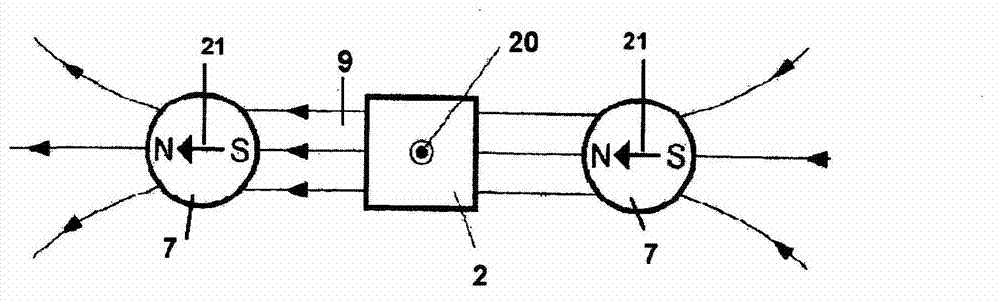
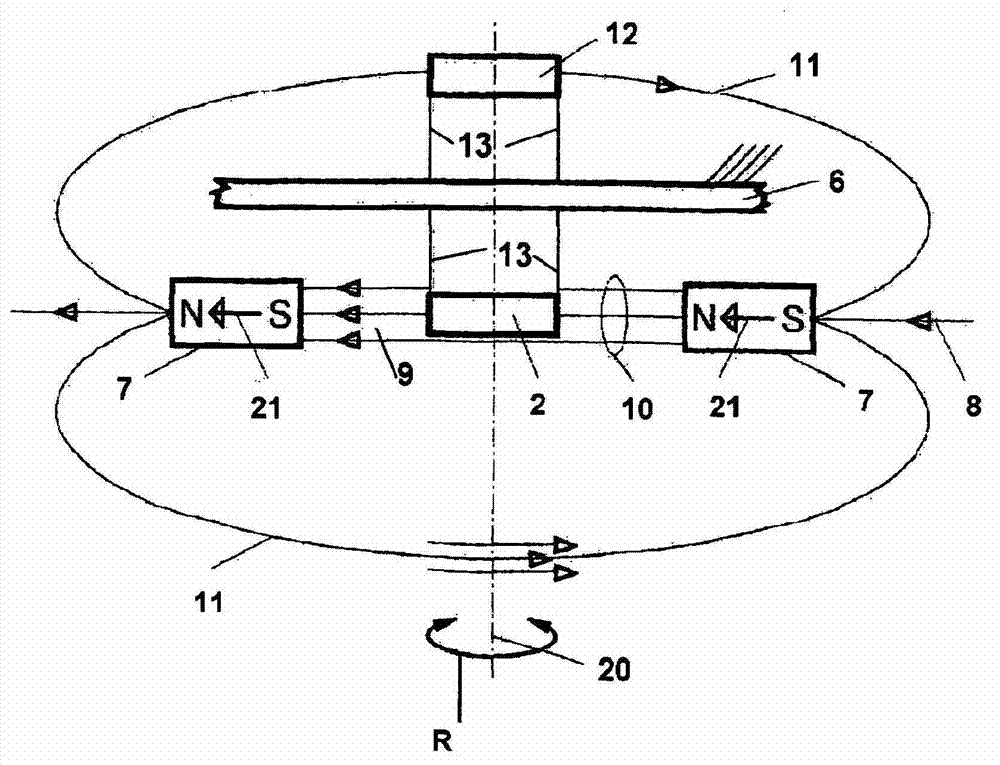
The invention relates to a magnetic rotary encoder, comprising for fine resolution of the angle of rotation of a shaft (1) an exciter unit which images the rotation to be monitored and rotates about an axis of rotation (20), a stationary fine resolution sensor unit (2) for fine resolution of each resolution and an electronic processing unit. Said rotary encoder is characterised in that the exciter unit comprises two first permanent magnets (7, 7), which are disposed symmetrically with respect to the axis of rotation with mutual spacing so that the magnetisation vectors (21, 21) thereof extending through the respective centre of gravity extend in the same direction relative to the common field lines and form a central field space (9) which directly connects the permanent magnets, and that at least the fine resolution sensor unit is disposed in such a way that it can use the field (10) of the central field space for measurement.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Spunbond facing and faced insulation assembly
A faced building insulation assembly includes a first facing forming a first major surface of the assembly with a central field portion having one or more spunbond continuous polymeric filament mat layers. Preferably, the facing is fungi growth resistant and has a selected water vapor permeance rating as applied to an insulation layer of the assembly. The facing may also include one or more polymeric film layers, a fungi growth inhibiting agent, a pesticide, and / or a heat activated bonding agent that bonds the facing to the insulation layer of the assembly. The insulation assembly may also include a second facing forming a second major surface of the assembly that has a water vapor permeance rating equal to or differing from the first facing.
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
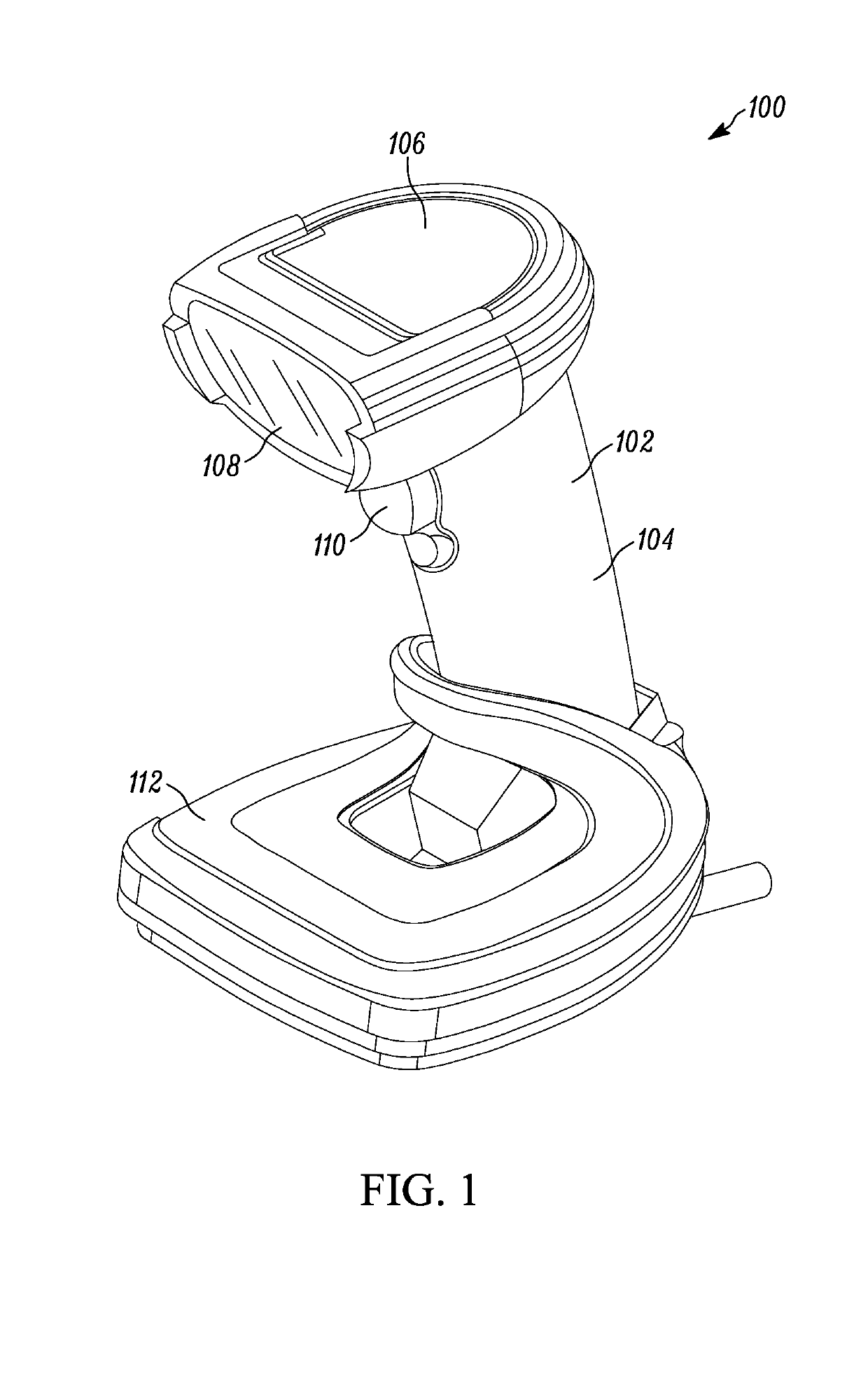
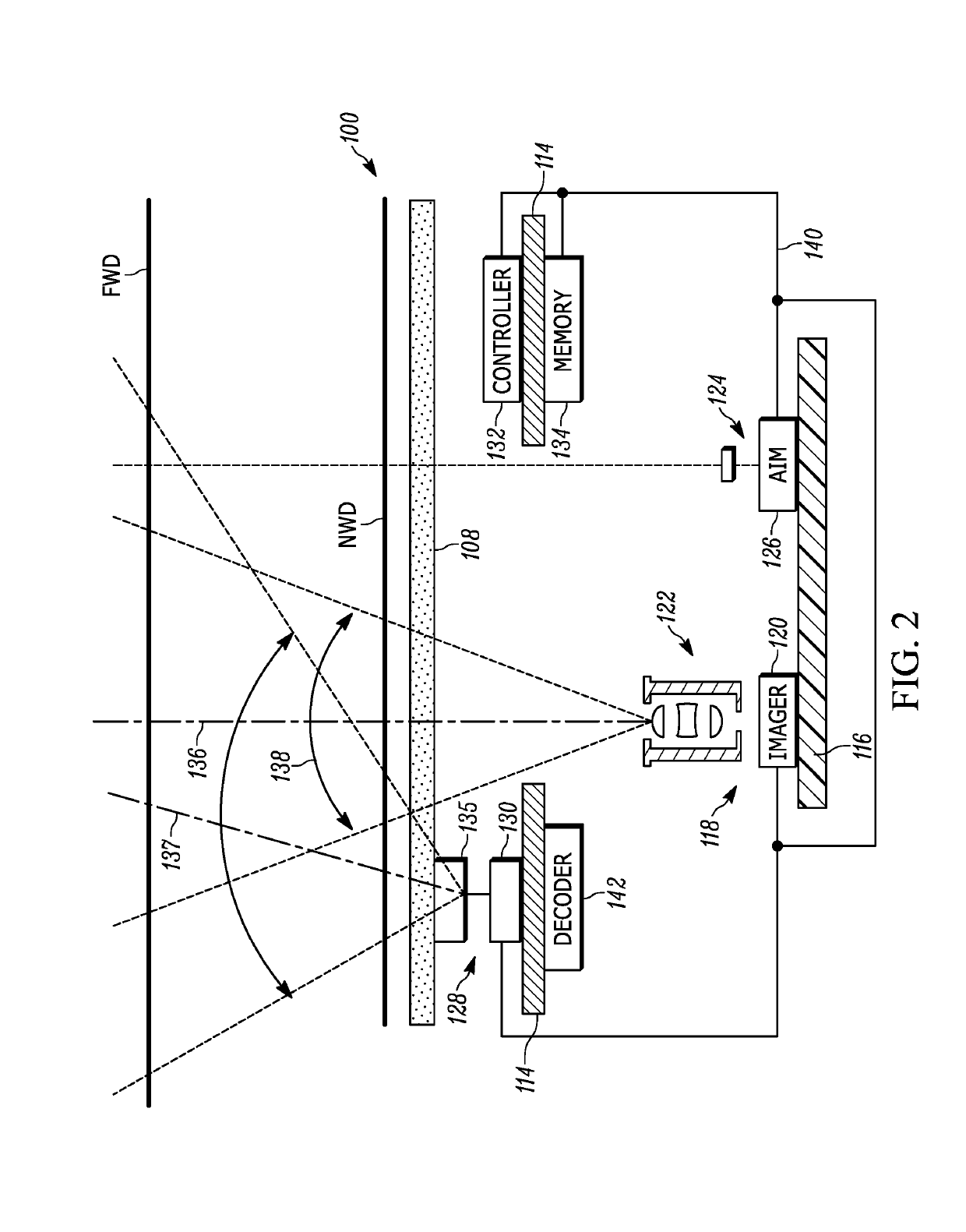
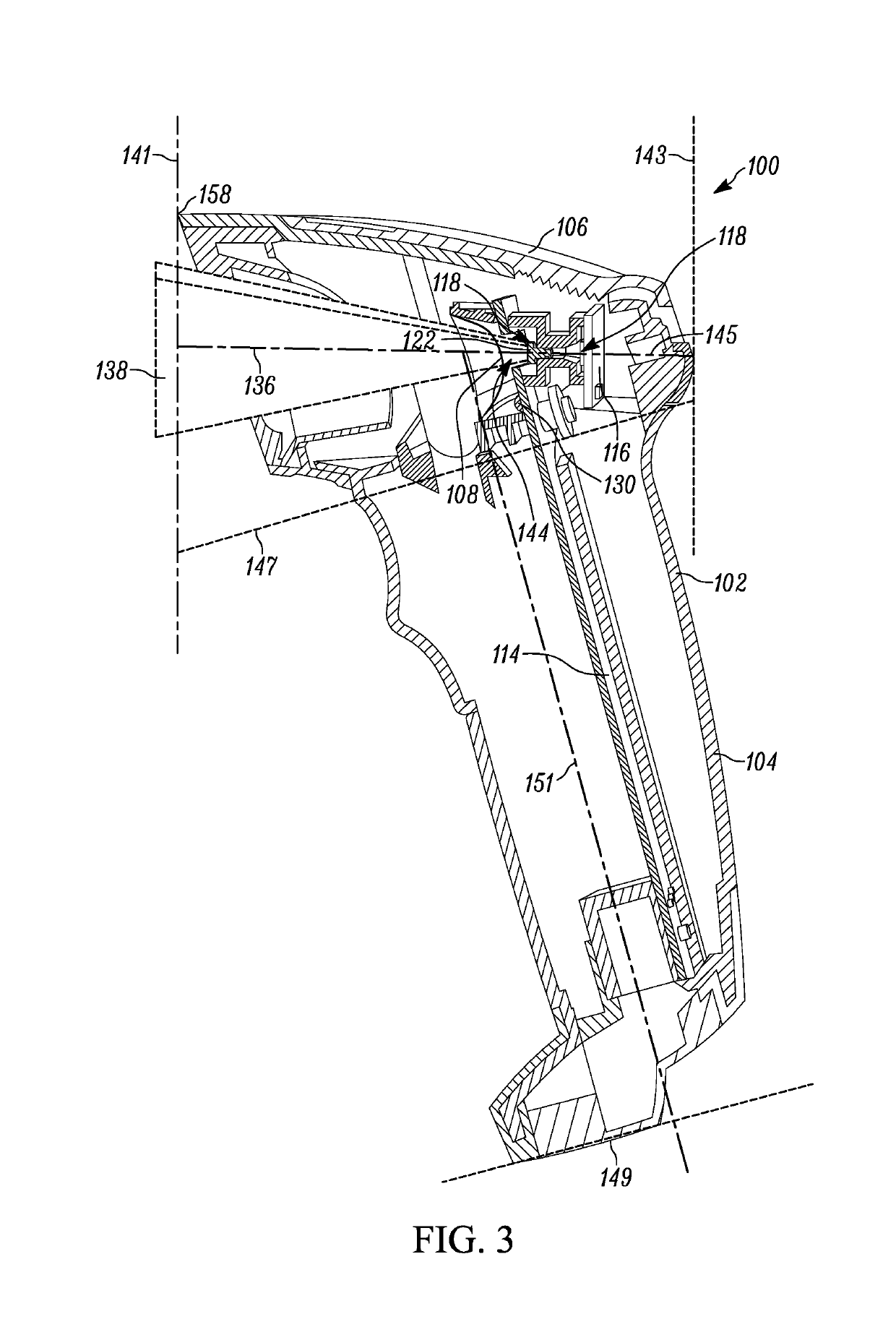
Handheld symbol reader with optical element to redirect central illumination axis
An apparatus and assembly for redirecting the central illumination axis of an illumination assembly towards the central field of view (FOV) axis of an imaging assembly using an optical element that provides an optical magnification of less than 1.5×, where the central illumination axis at the point of the illumination assembly is non-parallel to the central FOV axis.
Owner:ZEBRA TECH CORP
Optical receiving device capable of controlling optical efficiency in subdivision field
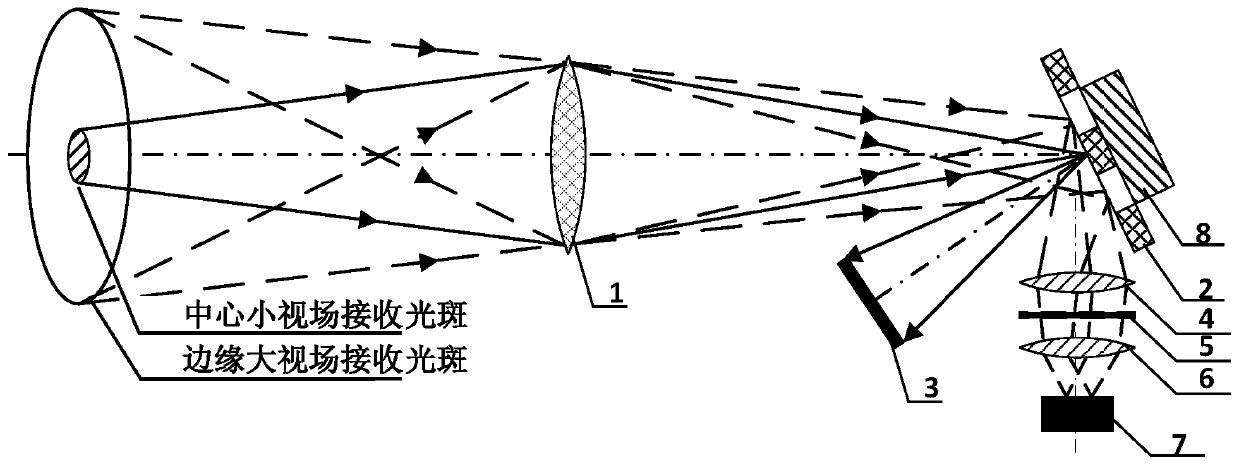
ActiveCN110441754AChange in optical efficiencyChange the attenuation ratioWave based measurement systemsICT adaptationUltrasound attenuationRadar systems
An optical receiving device capable of controlling optical efficiency in a subdivision field. The optical receiving device comprises a receiving main lens, a DMD, a light absorbing body, a collimatinglens, a narrow band optical filter, a focusing lens, a detector, and a DMD driving control module. The optical receiving device can attenuate strong receiving light in a central small field and ensure weaker receiving light in a marginal large field to be received by the high sensitivity detector, thereby effectively overcoming the problem of signal saturation in he central field when laser radarmeasures a strong scattering medium. On the basis of ensuring the optical efficiency of the received light in the marginal large field, the optical receiving device achieves attenuation to the received light in the central small field, so as to effectively improve dynamic detection range of a laser radar system in strong scattering media such as water and fog.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
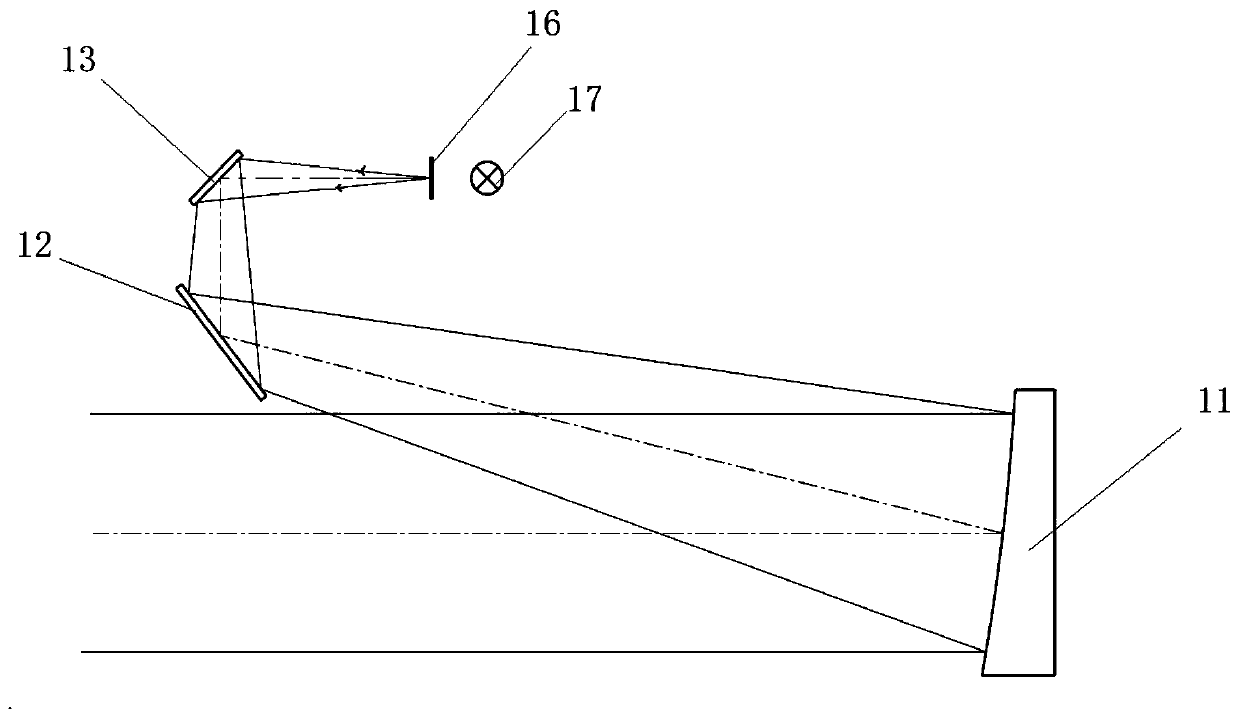
Ultra-wide field-of-view off-axis three-reflector optical imaging system
The invention discloses an ultra-wide field-of-view off-axis three-reflector optical imaging system which comprises a main reflector with positive focal power, a second reflector with negative focal power, and a third reflector with positive focal power. The reflecting surface of the main reflector is a spherical surface. The reflecting surfaces of the secondary mirror and the third reflector are flat spherical secondary curved surfaces. The curvature radii of top points of the three reflectors approximately satisfy a flat image field condition. The main reflector generates a real image of a far scene between the main reflector and the second reflector. The second reflector and the third reflector perform relay imaging of the real image on an image plane. An aperture diaphragm is placed on the front focal plane of the third reflector, thereby realizing an image-side telecentric optical path. The main reflector inclines along an X-axis relative to incident main light of a central field-of-view. The second reflector is coaxial with the third reflector. After the main light of the central field-of-view in a meridian plane is reflected by the main reflector, an included angle is formed between the reflected main light and the common symmetric axis of the second reflector and the third reflector. The ultra-wide field-of-view off-axis three-reflector optical imaging system has advantages of ultra-wide field-of-view, intermediate relative aperture, wide working wave band, no image-side telecentric barrier, small object-side distortion, high imaging quality, etc. The ultra-wide field-of-view off-axis three-reflector optical imaging system is suitable for earth imaging observation field of a spatial camera, an imaging spectrometer, etc.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Method for filling isolation plough groove
ActiveCN101197305AWon't hurtIncreasing the thicknessSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical conductorHigh density
The invention relates to an isolation groove filling method which comprises the following steps that: a semiconductor substrate is provided; the surface of the substrate is provided with an isolation groove; at least a high-density plasma chemical vapor deposition technique and at least an etching technique are performed; insulating substance is deposited on the groove till the groove is filled in; the high-density plasma chemical vapor deposition technique with a first sputtering yield is continued to perform; a covering layer is deposited on the surface of the insulating substance; the high-density plasma chemical vapor deposition technique with a second sputtering yield is performed; another covering layer is also deposited on the surface of the covering layer; the second sputtering yield is greater than the first sputtering yield. The isolation groove filling method of the invention can increase the thickness of the insulating layer on the fringe field of a wafer after the wafer with large dimension is filled in the isolation groove, thereby improving the consistency and flatness of the insulating layer thickness of the central field and the fringe field of the wafer.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP +1
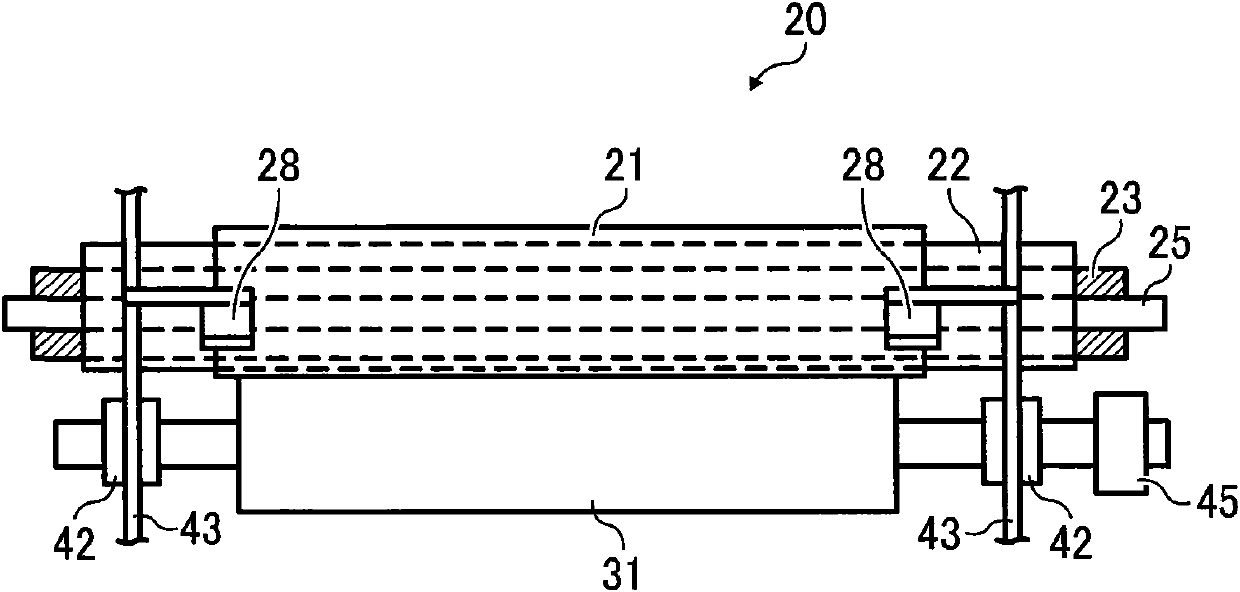
Fixing device and image forming device
InactiveCN101995802AEasy to moveAvoid deformationElectrographic process apparatusImage formationEngineering
The invention provides a fixing device and an image forming device for stabilizing the mobility of a fixing component and inhibiting the deformation of the fixing component close to outlet of a recording medium, wherein a nip portion is formed between the fixing component and a pressing component. By utilizing the method, the scraping plate (28) is in close sliding contact with two end parts of afixing belt (21) in width direction so as to prevent the fixing belt (21) from moving relative to the width direction, stabilize the movement of the fixing belt (21) and reduce the leakage of a lubricant between the fixing belt (21) and a retaining component (22). Furthermore, according to the rigidity of the fixing belt (21) in width direction, the scraping plate (28) is in sliding contact with an obviously deformed portion in circumferential surface of the fixing belt (21), that is, the portion in sliding contact with the scraping plate (28) can inhibit interspace and deformation in whole width direction, even if in the central field of a recording medium passage in width direction.
Owner:RICOH KK
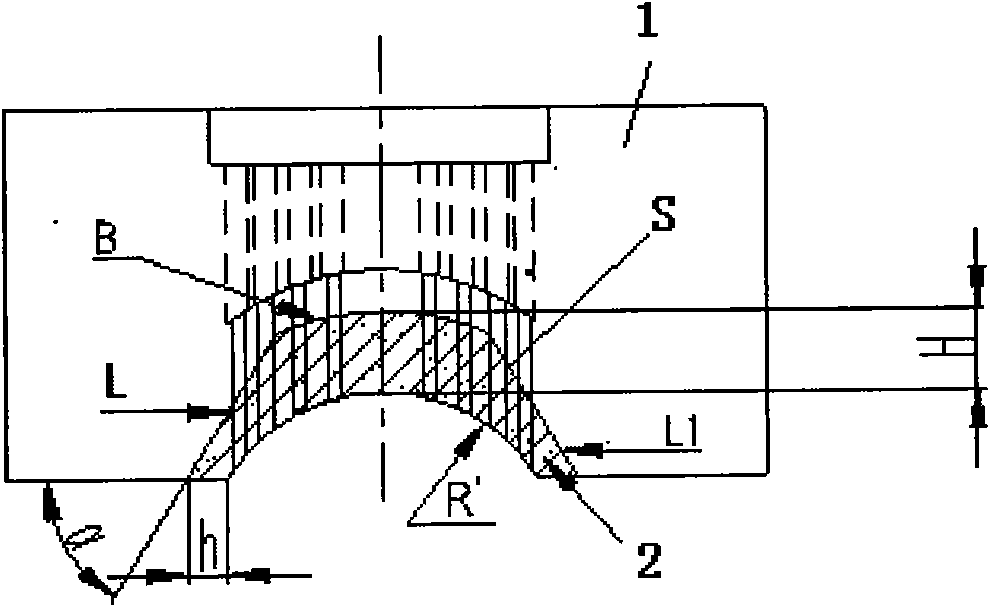
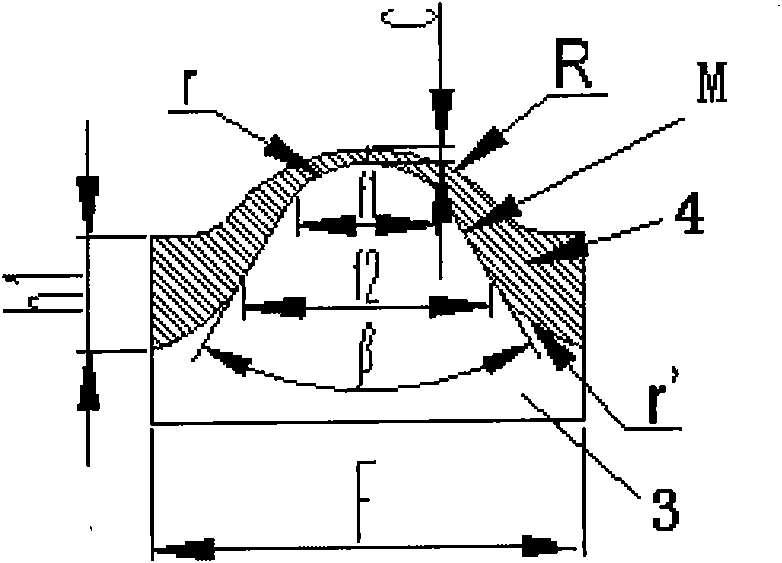
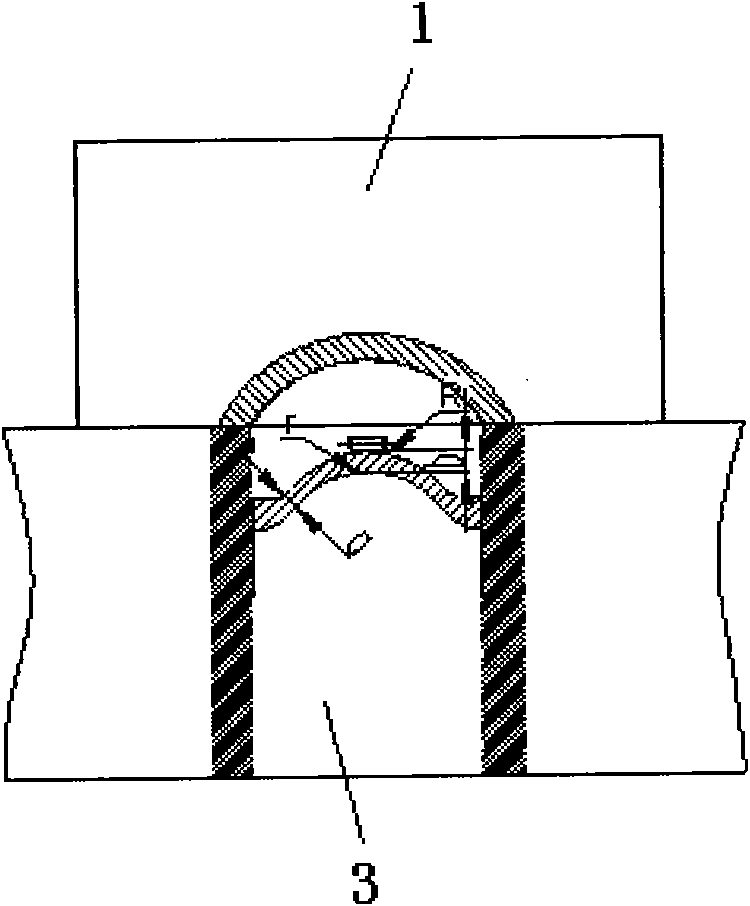
Magnetic circuit structure of high-central-field magnetic shoe mould
ActiveCN101934551AHigh center fieldHigh and high surface magnetismCeramic shaping apparatusElectric machineryEngineering
The invention relates to a magnetic circuit structure of a high-central-field magnetic shoe mould, which comprises an upper punch head and a lower punch head, wherein the upper punch head and the lower punch head are made of magnetic-conducting materials, a magnetic-conducting material layer is respectively embedded between the molding surfaces of the upper punch head and the lower punch head and a basal body to form a magnetic-flux refracting surface, and the shape of the magnetic non-conducting material embedded layer of the upper punch head is formed from a line segment L and a line segment L1 at both sides and a line segment B at the top end, wherein the line segment L and the line segment L1are straight line segments, the line segment B is an arc line segment or a straight line segment, an included angle alpha is 50-72 degrees, the embedded shape of the lower punch head is formed from an arc line at the top end, straight lines at both sides and an arc line at the bottom side, and an included angle beta=2(90 degrees-alpha)+0-11). In the invention, the upper punch head and the lower punch head, made of the magnetic-conducting materials, are respectively embedded into the magnetic non-conducting material layer with the finely designed shape to form the more effective magnetic-flux refracting surface, thereby realizing that magnetic particles are subjected to the action of a more ideal polymerization magnetic field to carry out more appropriate orientation when a blank body is molded, realizing the high central field and the high middle-position surface magnet of a magnetic shoe and generating an active contribution to effectively improving the mechanical characteristic of a motor.
Owner:安徽金寨将军磁业有限公司
Multi-aperture variable spatial resolution bionic thermal imaging method and device
InactiveCN108965678AQuick detectionTelevision system detailsSensing radiation from moving bodiesHigh resolution imagingBase function
The invention discloses a multi-aperture variable spatial resolution bionic thermal imaging method and device. The multi-aperture variable spatial resolution bionic thermal imaging method and device in the invention can eliminate the contradiction between large field-of-view search and high-resolution imaging, realize target space information acquisition and rapid detection of moving targets, andincrease the target detection / recognition capability. The multi-aperture variable spatial resolution bionic thermal imaging method and device in the invention utilizes a plurality of sets of single-aperture infrared imaging detector components with fixed tilt angles to image the target, partial overlap of the field of view is formed, and the field of view is divided into multiple sub-fields; the more the overlapped detectors are, the higher the resolution of the region is; a visual mode of large field-of-view search and central field-of-view resolution similar to the human eyes is constructedthrough large field-of-view splicing and high resolution image processing so as to achieve the basic functions of multi-aperture variable spatial resolution bionic thermal imaging and alleviate the contradiction between the field of view and the high resolution; and a multi-view stereo vision with divergent visual axis is formed by using the overlapped field formed by the sub-aperture, so that target space positioning and rapid detection of the moving target can be realized.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Projection system for EUV lithography
InactiveUS20060050258A1Preventing Image Quality DeteriorationEasy mounting and adjustingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusIntermediate imageOptical axis
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
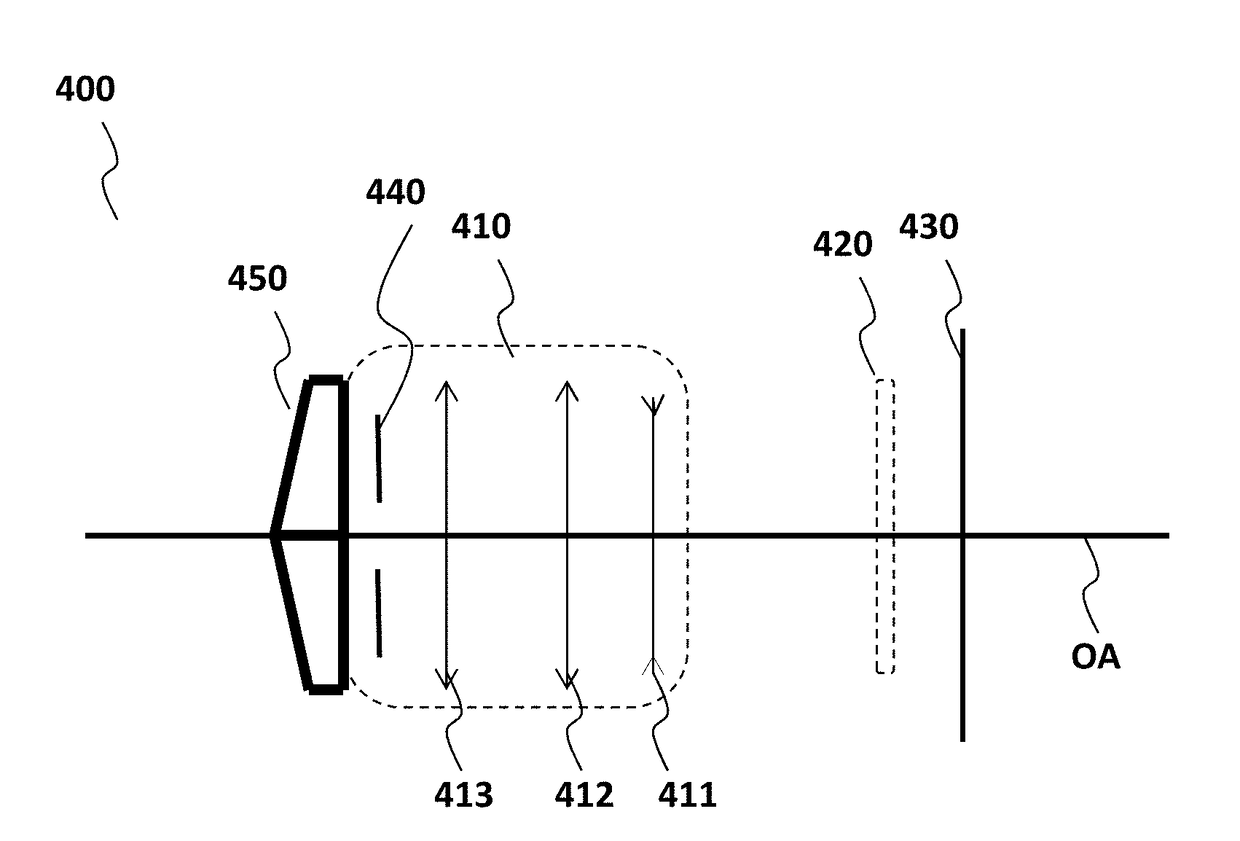
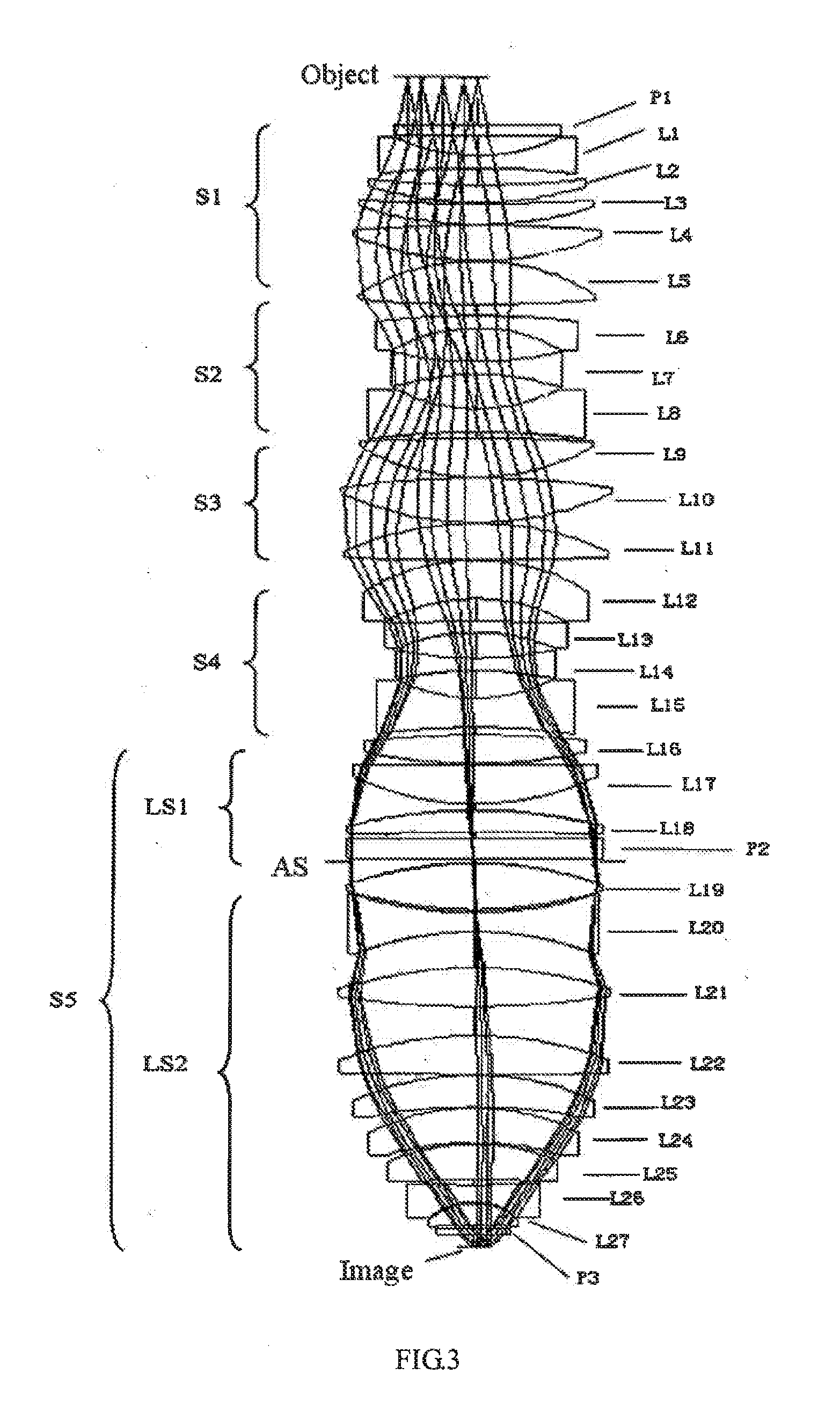
Projection objective lens system
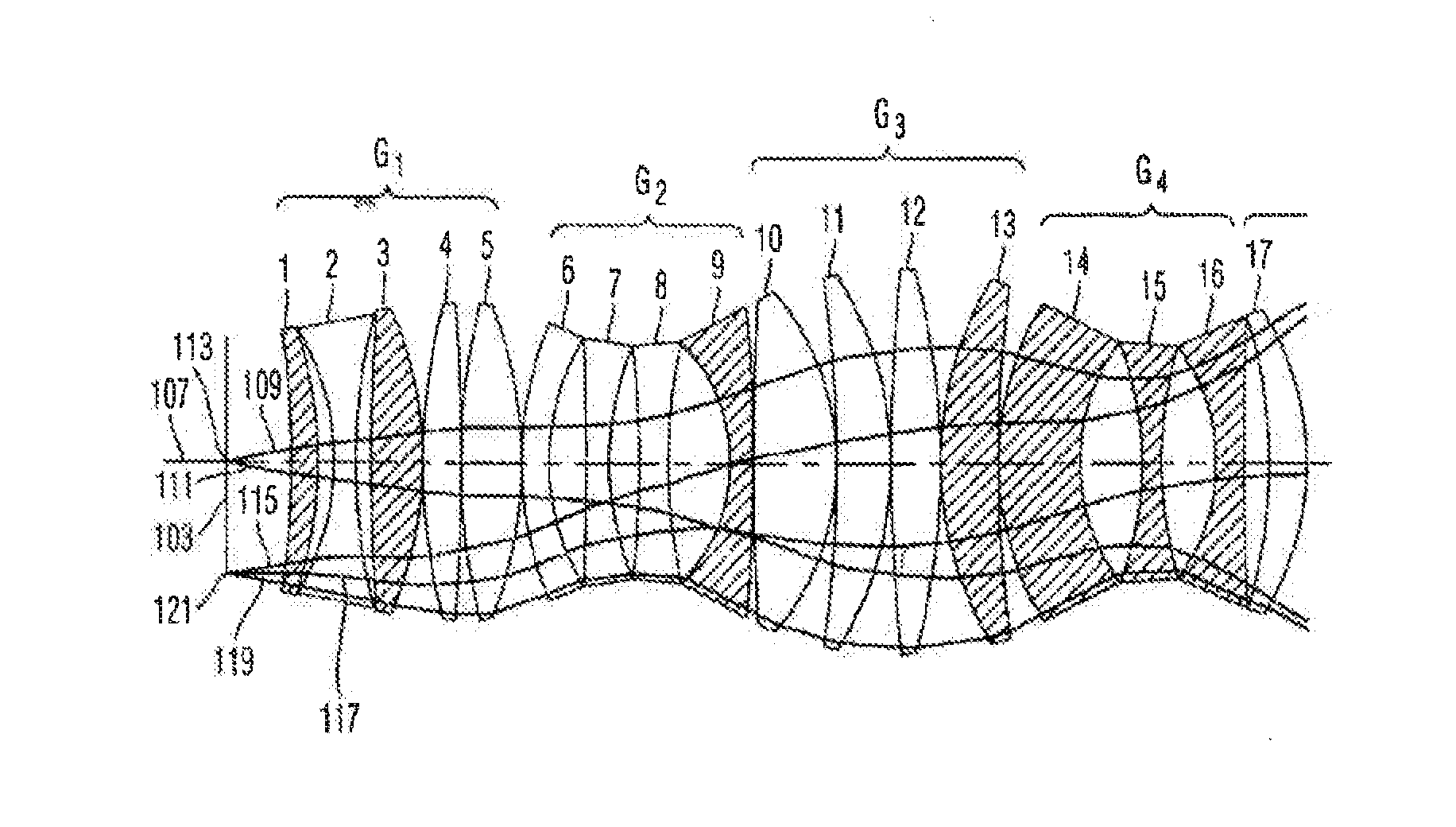
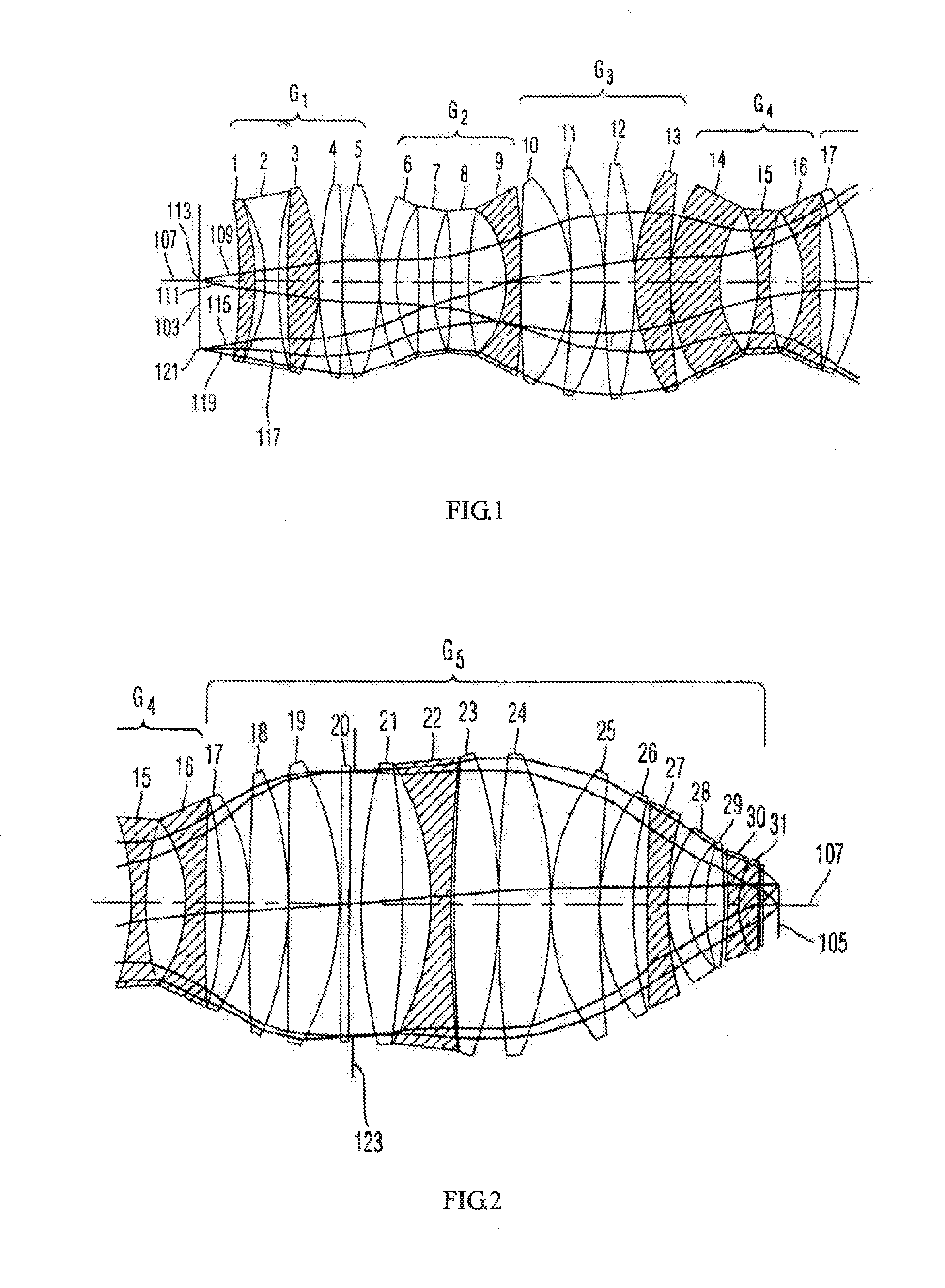
ActiveUS20130250434A1Avoid of reduced imaging qualityPhotomechanical apparatusLensLight beamImage plane
A projection objective lens system includes from an object plane to an image plane: a first lens group (S1) with a positive refractive power; a second lens group (S2) with a negative refractive power; a third lens group (S3) with a positive refractive power; a fourth lens group (S4) with a negative refractive power; and a fifth lens group (S5) with a positive refractive power being divided into two sub-lens groups. An aperture stop (AS) is provided between the two sub-lens groups. The following conditions are met: 0.12<|L / f|<0.4, and ΔR / R<1%, wherein, f is an effective focal length of the system, L is a distance between the object and image planes, ΔR represents a difference between radii at the aperture stop of a marginal field beam bundle and a central field beam bundle, and R represents a radius at the aperture stop of a central field beam bundle.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICRO ELECTRONICS EQUIP (GRP) CO LTD
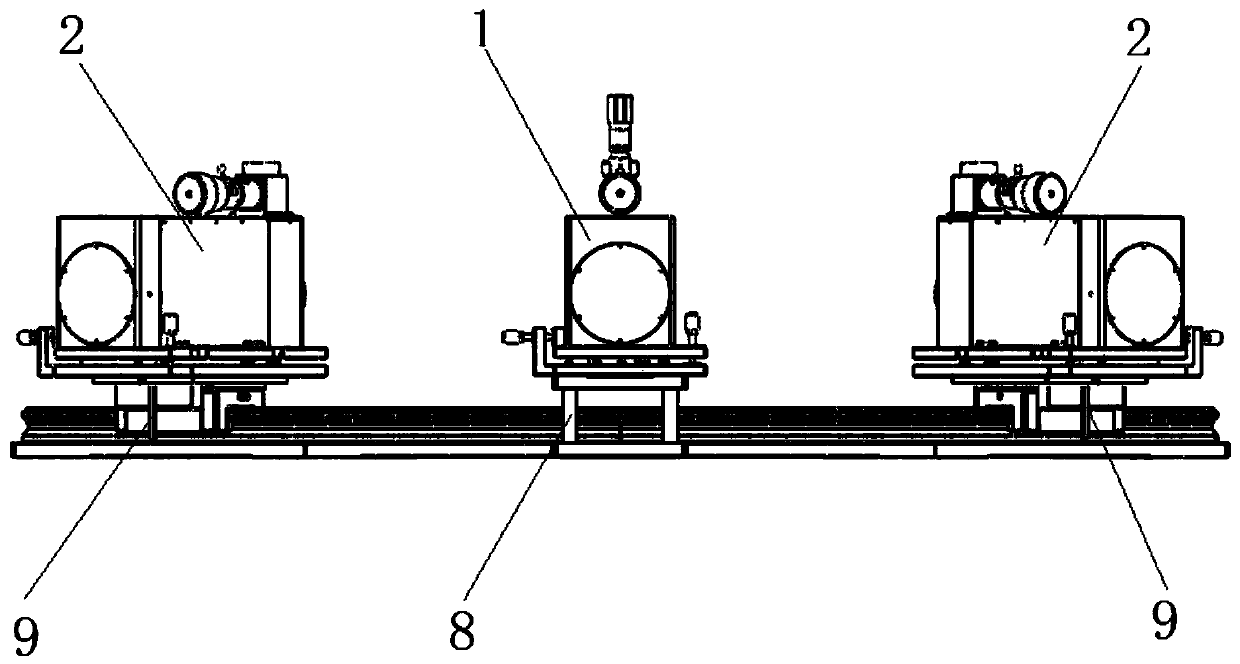
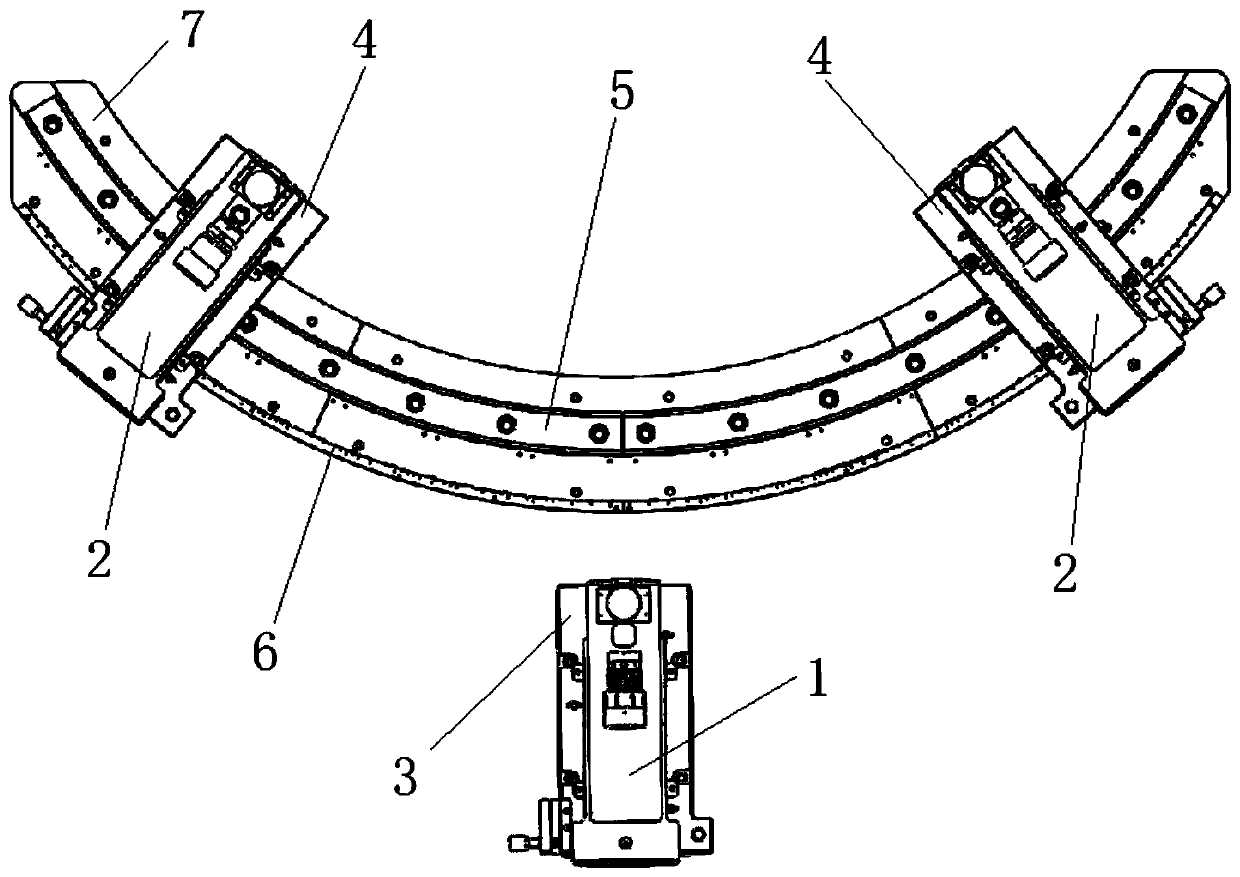
Large field-of-view optical system detecting device and detecting method
PendingCN109781392AEasy to detectEasy to assembleTesting optical propertiesOptical axisImaging quality
The invention provides a large field-of-view optical system detecting device and detecting method, thereby solving problems that the existing detecting device can only detect the imaging quality of the central field of view of the optical system and thus the detection range is limited and the accuracy is low. The detecting device comprises a circular arc guide rail, a self-collimating collimator and at least one collimator. The self-collimating collimator is disposed outside the circular arc guide rail; and a first two-dimensional adjustment platform is disposed at the bottom of the self-collimating collimator. The at least one collimator is arranged on the circular arc guide rail in a sliding manner by a second two-dimensional adjustment platform; and the range of the field of view can beadjusted based on needs to carry out detection of the large field of view. The optical axes of parallel beams emitted by the self-collimating collimator and the at least one collimator are located onthe same horizontal plane and are intersected at the circle center of the circular arc guide rail. Therefore, the detection of the imaging quality of the large field of view of the optical system isrealized; and the operation becomes simple and the detection precision is high.
Owner:西安科佳光电科技有限公司
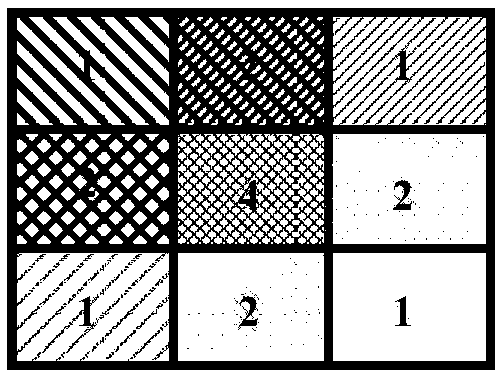
Field diaphragm assembly for spectrometer adjustment test
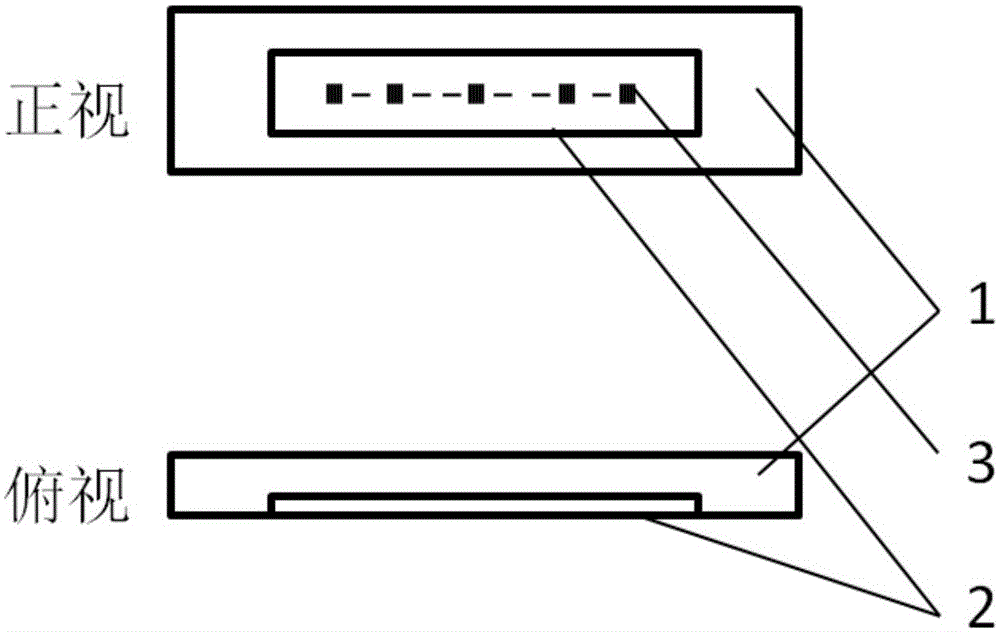
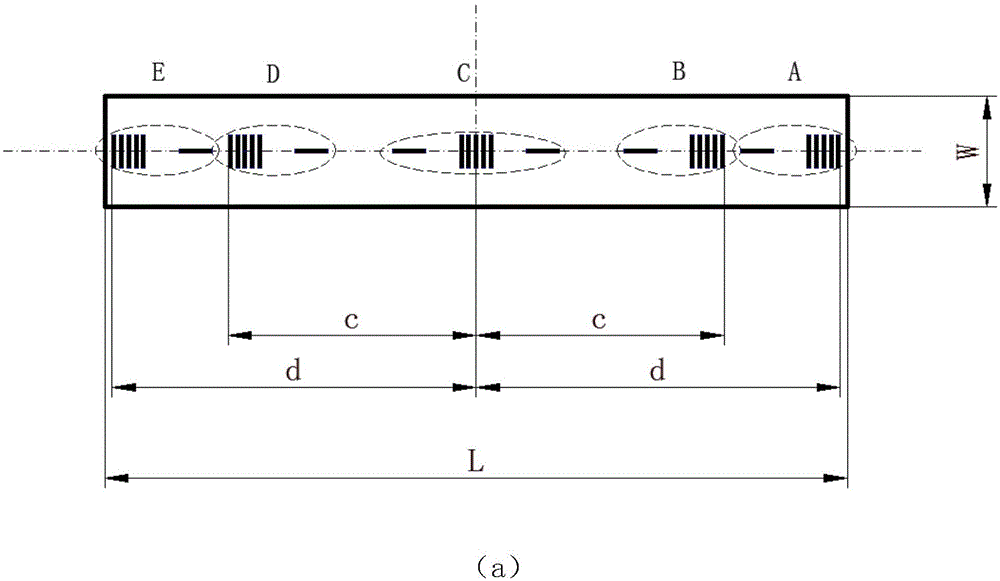
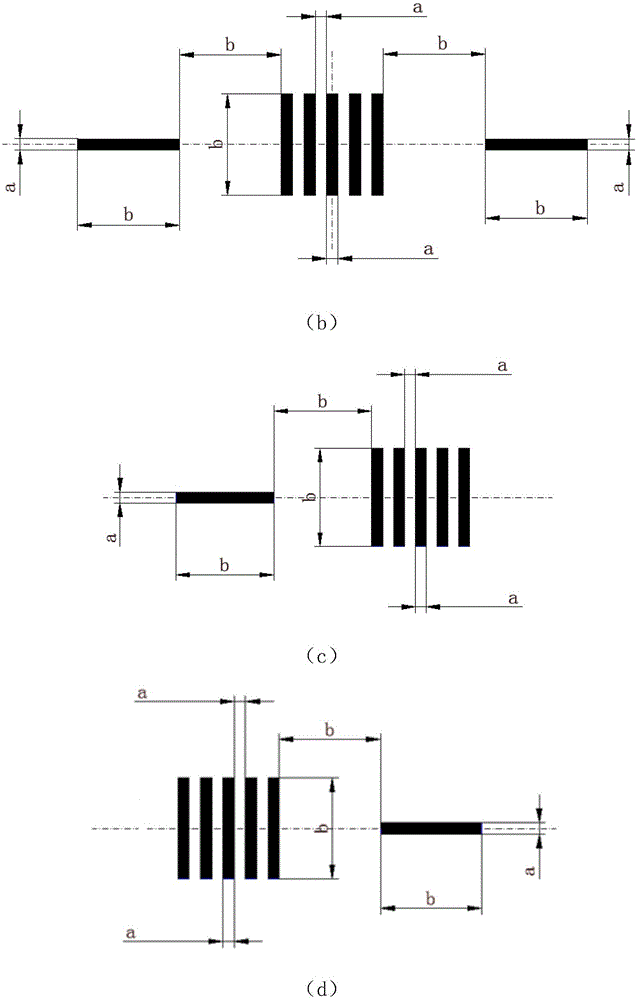
ActiveCN105157831ATest Space Imaging QualityEasy to observeRadiation pyrometrySpectrometry/spectrophotometry/monochromatorsGratingImaging quality
The invention discloses a field diaphragm assembly for spectrometer adjustment test, which comprises a diaphragm seat and a diaphragm substrate. One surface of the diaphragm substrate has a two-dimensional pattern; the two-dimensional pattern is a group of regularly-distributed light and shade stripes in a central field, a middle field and an edge field. When a mercury lamp light source is combined to light the field diaphragm, six-dimensional adjustment of a detector in relative to the field diaphragm can be carried out at the same time, rotation disorder of a grating in relative to the field diaphragm can be detected, and grating adjustment is carried out. When a complex color light source is combined to light the field diaphragm, the spatial imaging quality of the central field, the middle field and the edge field of the spectrometer can be tested. According to the field diaphragm assembly with the two-dimensional pattern, the problems that states of a spectral dimension and a spatial dimension on a detector array can not be observed conveniently during the traditional single-slit field diaphragm photoelectric joint adjusting process can be solved, and the adjustment efficiency and the adjusting precision can be effectively improved.
Owner:上海济物光电技术有限公司
A large field of view mid-wave infrared optical athermalization system
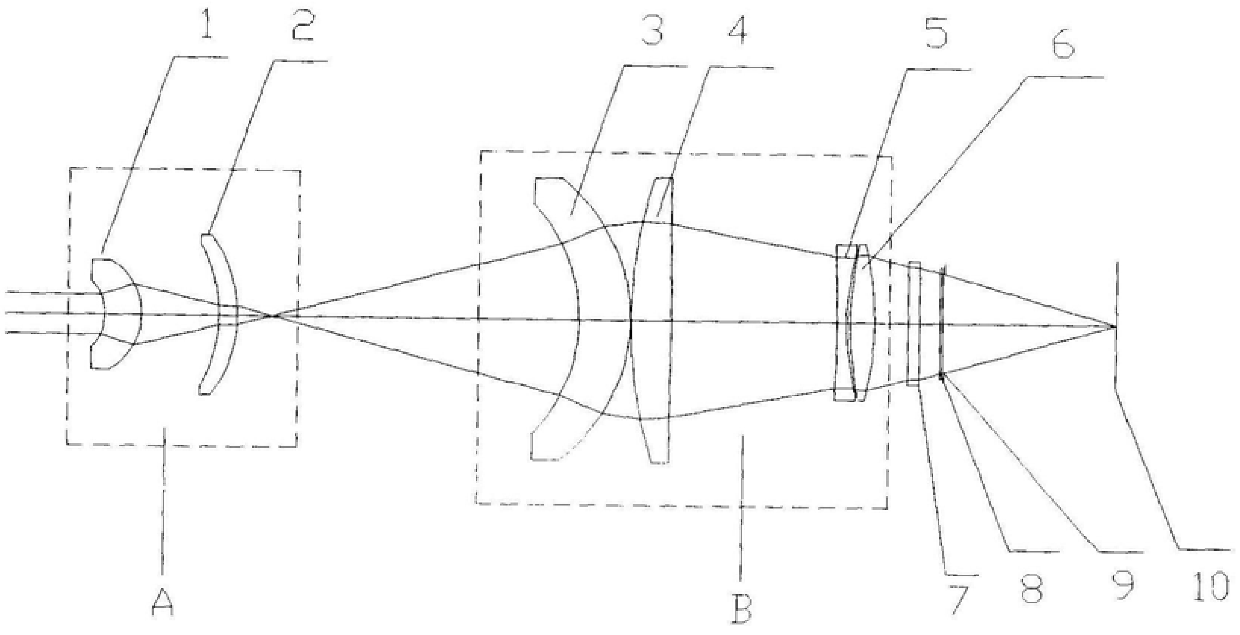
InactiveCN106342269BEliminate thermal differenceSmall distortionOptical elementsImaging qualityDistortion
The present invention is a medium-wave infrared optical athermalization system with a large field of view, which includes a primary imaging objective lens A, a secondary imaging objective lens B, a detector protection light window, a detector filter and a cold diaphragm, and is characterized in that: a primary imaging Objective lens A is composed of lens I and lens II, and adopts a convex-convex lens configuration. The focal length of primary imaging objective lens A is 11.65mm, and both lens I and lens II are convex lenses; secondary imaging objective lens B is composed of lens III, lens IV, lens V, Lens VI is composed of a convex-convex lens layout. The focal length of the secondary imaging objective lens B is 30.07mm. Both lens III and lens IV are convex lenses. The focal length of lens III and lens IV is 29.67mm. Lens V(5) is Concave lens, lens VI (6) is a convex lens; the focal length of lens V and lens VI is 73.74mm; the distance between primary imaging objective lens A and secondary imaging objective lens B is 51.02mm. The effect of the technical solution of the present invention is: 1. In a wide temperature range (-40 ℃~+60 ℃), the imaging quality of the optical system is higher, the center field of view, the MTF value at 20lp / mm is not less than 0.55, and the edge field of view, The MTF value at 20lp / mm is not less than 0.55; 2. The distortion of the large field of view is small, and the distortion of the full field of view is less than 5%.
Owner:LUOYANG INST OF ELECTRO OPTICAL EQUIP OF AVIC
Recursive ontology-based systems engineering
ActiveUS20160026441A1Quality improvementSemantic analysisModel driven codeDevelopment teamKnowledge representation and reasoning
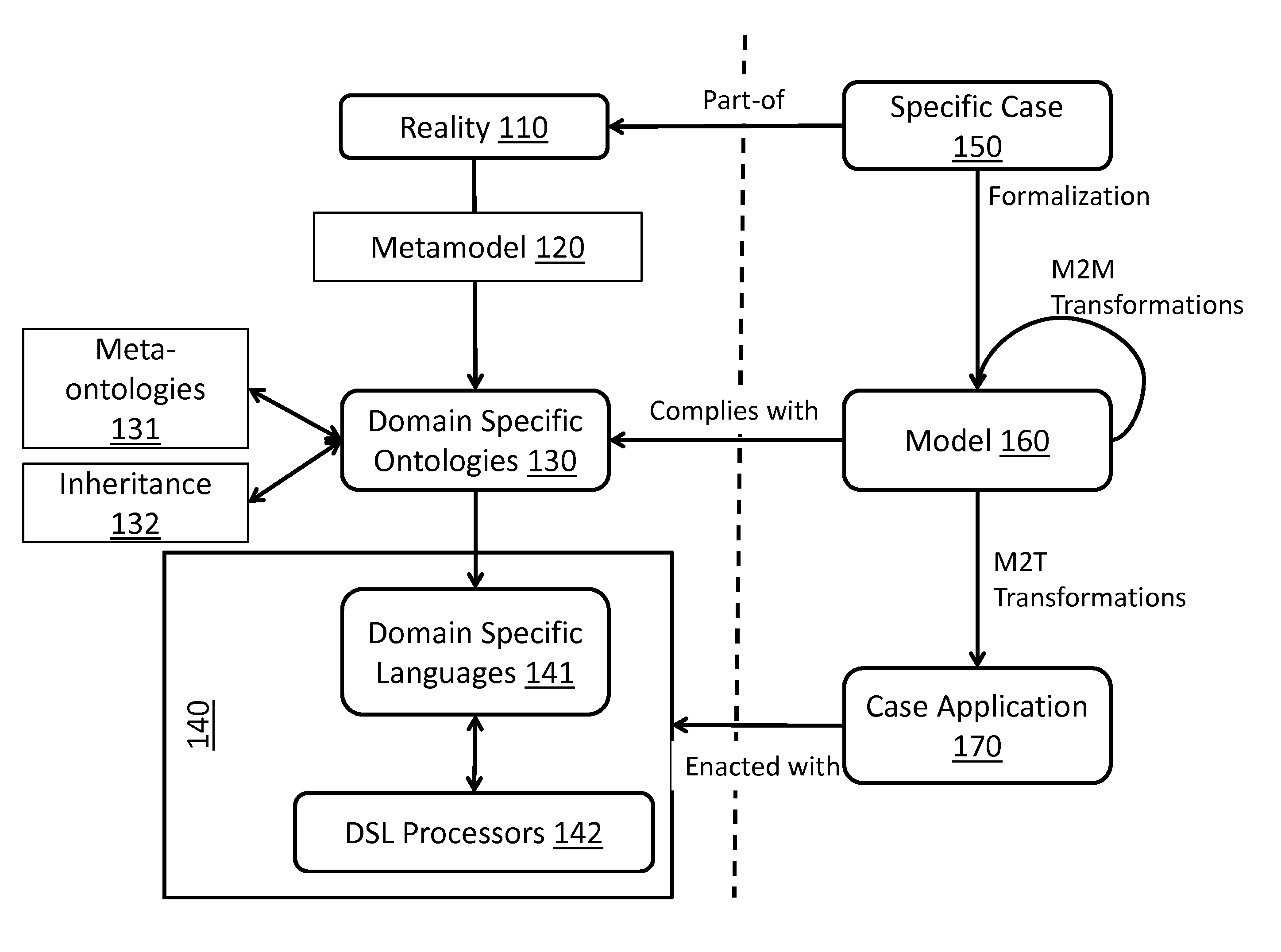
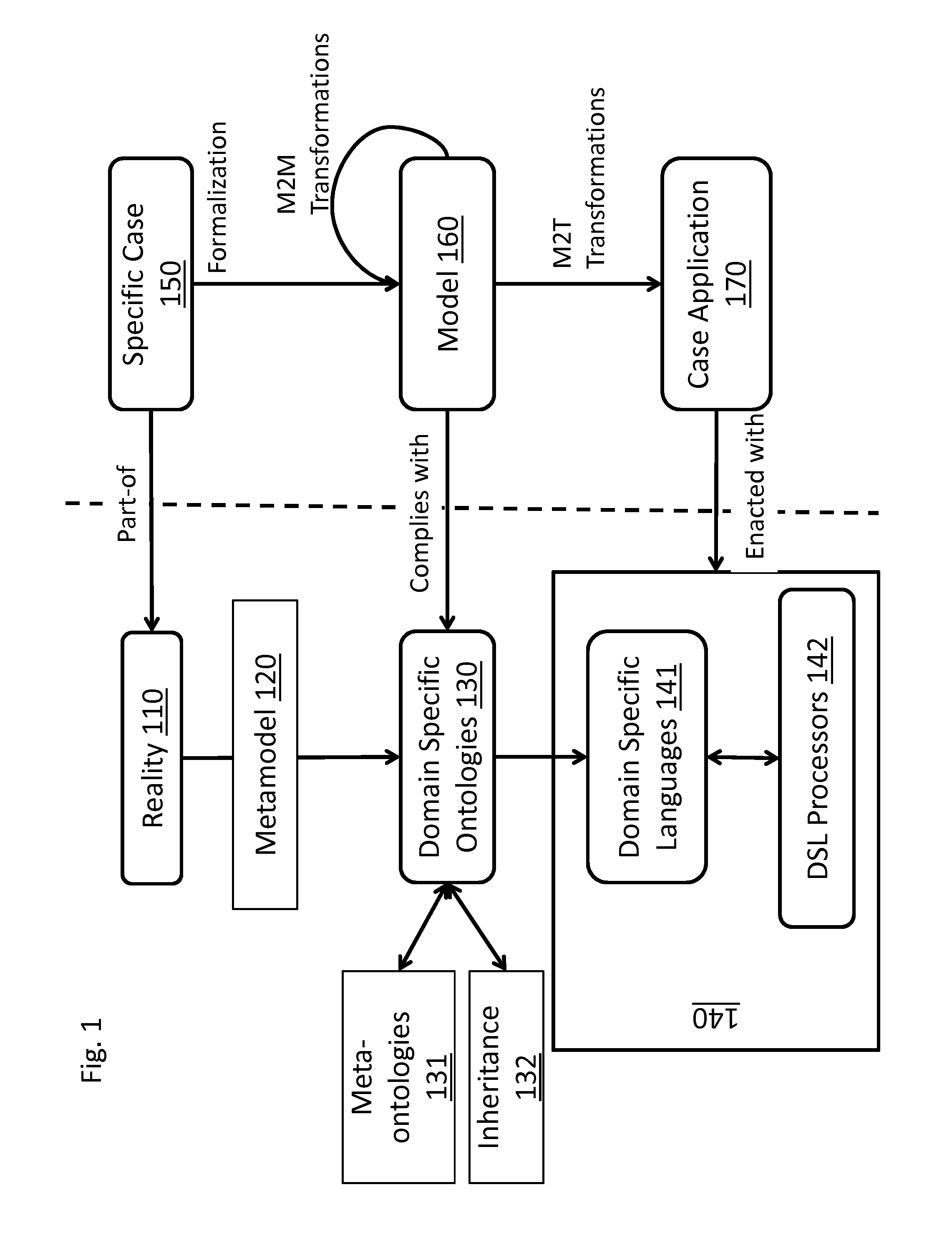
The present disclosure proposes a new model engineering method and system that permits the creation of application systems without the need of program development. The system allows organizations to search for high performance development teams and methods, and develop high quality solutions. The present disclosure covers the three central areas of systems engineering: (1) a method for creating models which represent reality in a standardized way; (2) a procedure for transforming models into computable artifacts, that is, computer systems that behave as specified in the model; and (3) a collaborative method based in knowledge representations.
Owner:DIEZ ALFONSO
Moisture removing system and method for structural roofs
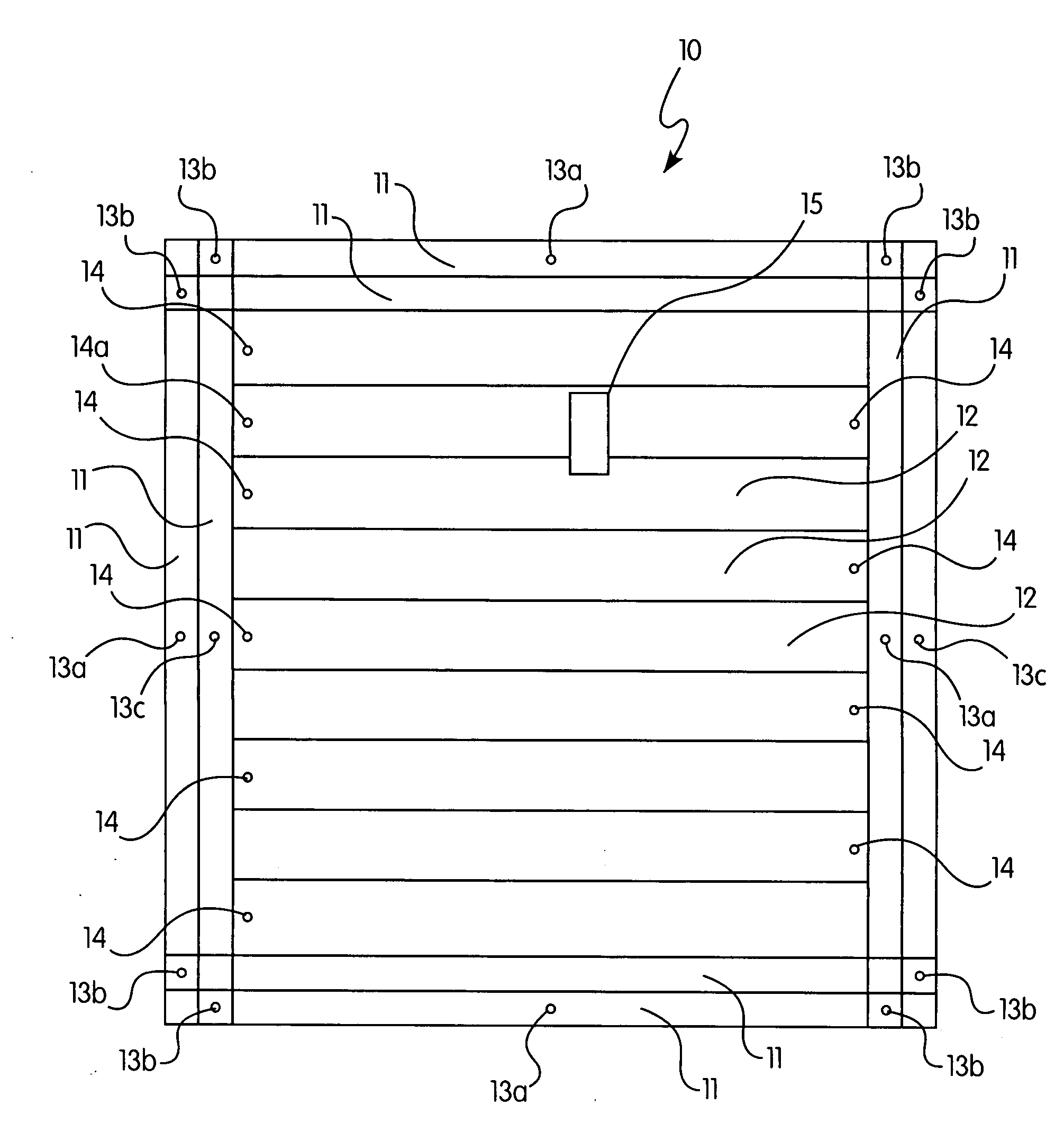
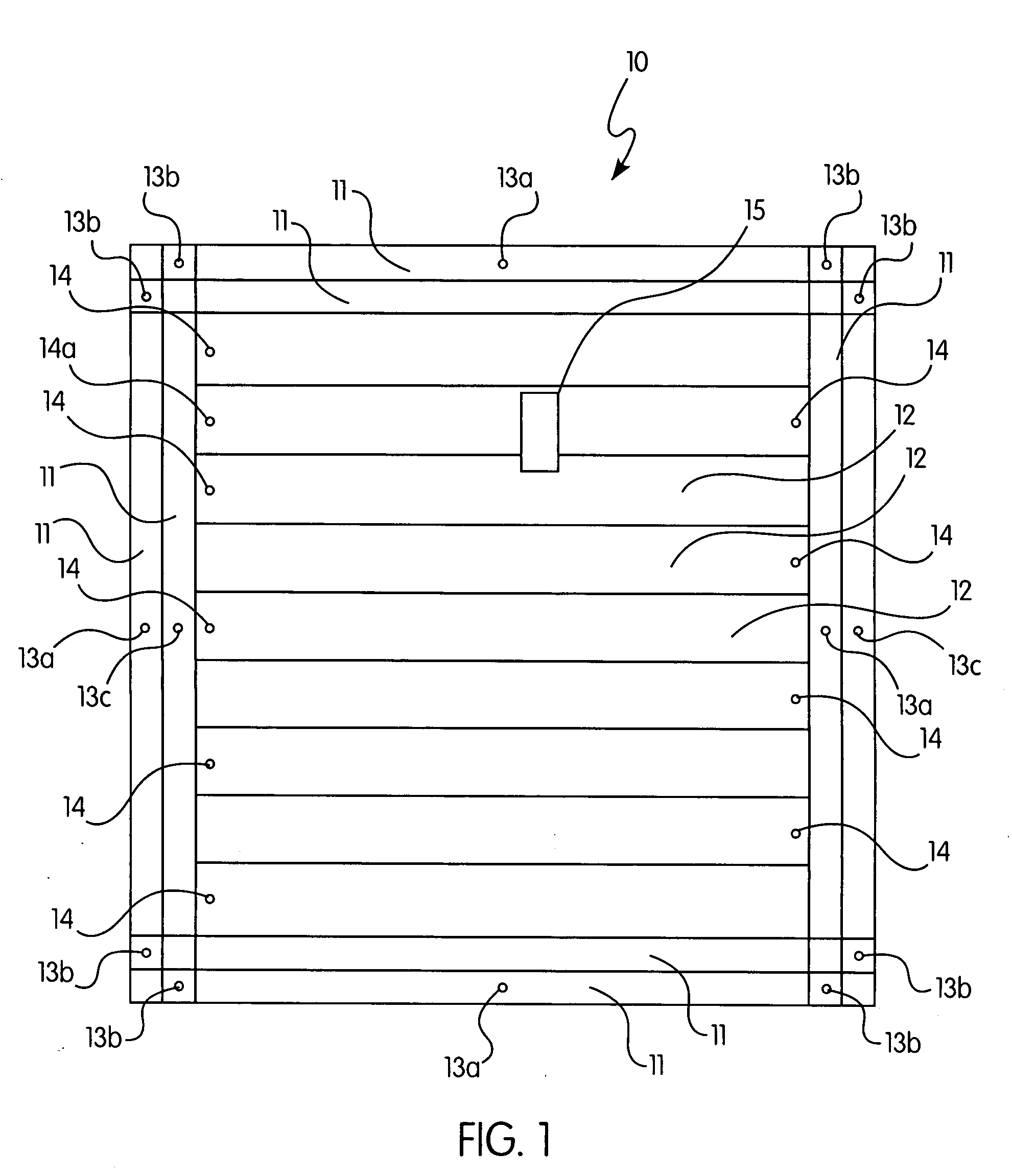
InactiveUS20090229204A1Improved and moisture-resistant systemEfficient designConstruction materialRoof covering using flexible materialsEngineeringMoisture
An improved system for removing moisture from a roof envelope made from low permeability membrane sheets that includes: a plurality of elongate membrane sheets positioned and attached, in adjacent rows, over a central region of the roof, to form central channels, with each channel having at least one one-way roof vent positioned near one end of that channel, and a perimeter attachment means. The perimeter attachment means is selected from: (a) a plurality of elongate membrane sheets that are position and attached to form at least one perimeter channel at each perimeter side of the roof; (b) at least on perimeter channel positioned and fastened along the perimeter sides of the roof parallel to the central region channels and fasteners bisecting the central field channels along all other perimeter sides of the roof; (c) fasteners or other attachment means bisecting the central region channels parallel to perimeter sides parallel to said central region channels and fasteners or other attachment means bisecting the central region channels perpendicular to the remaining perimeter sides of the roof; and (d) a fully adhered perimeter.
Owner:KASSEM GARY M
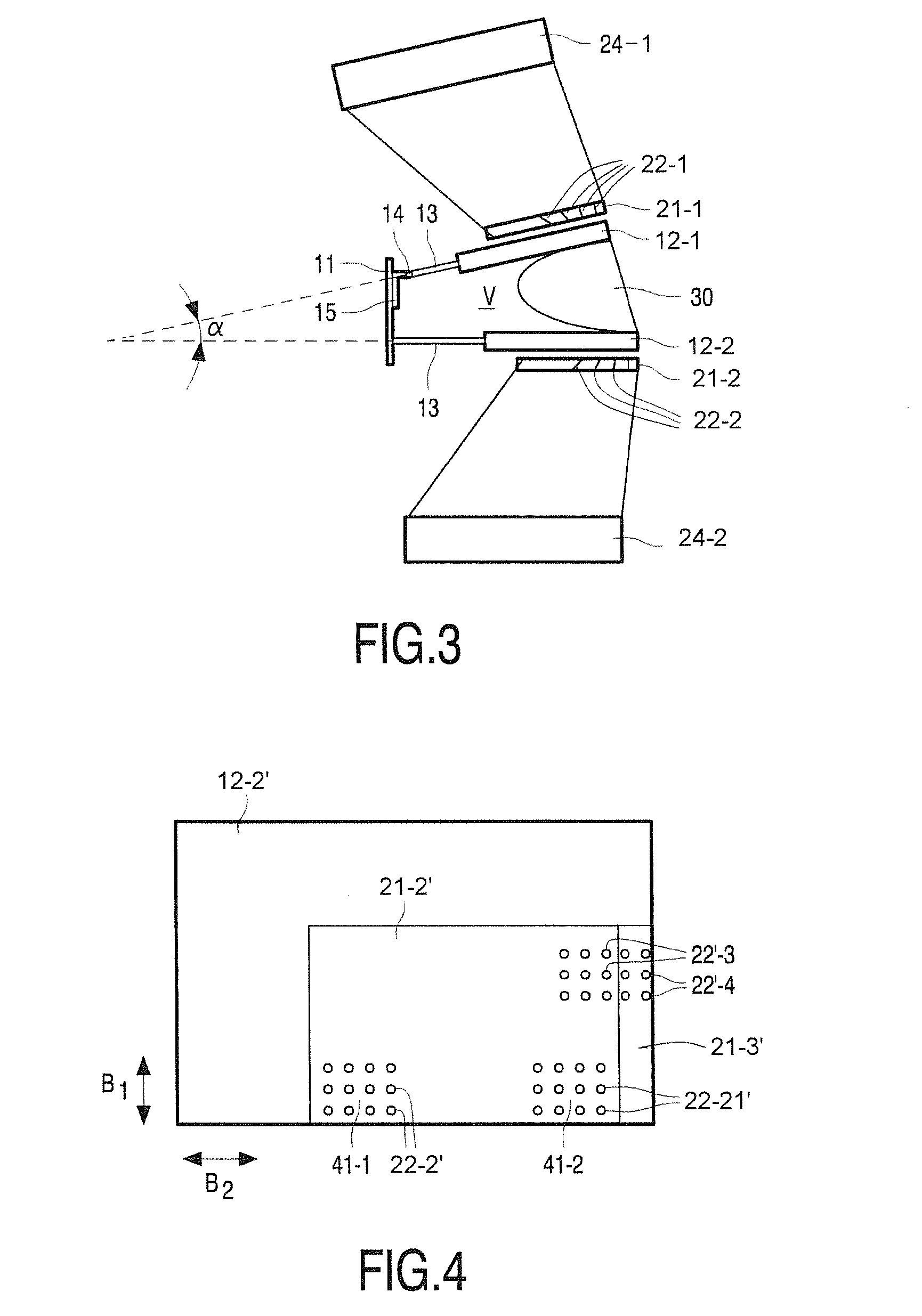
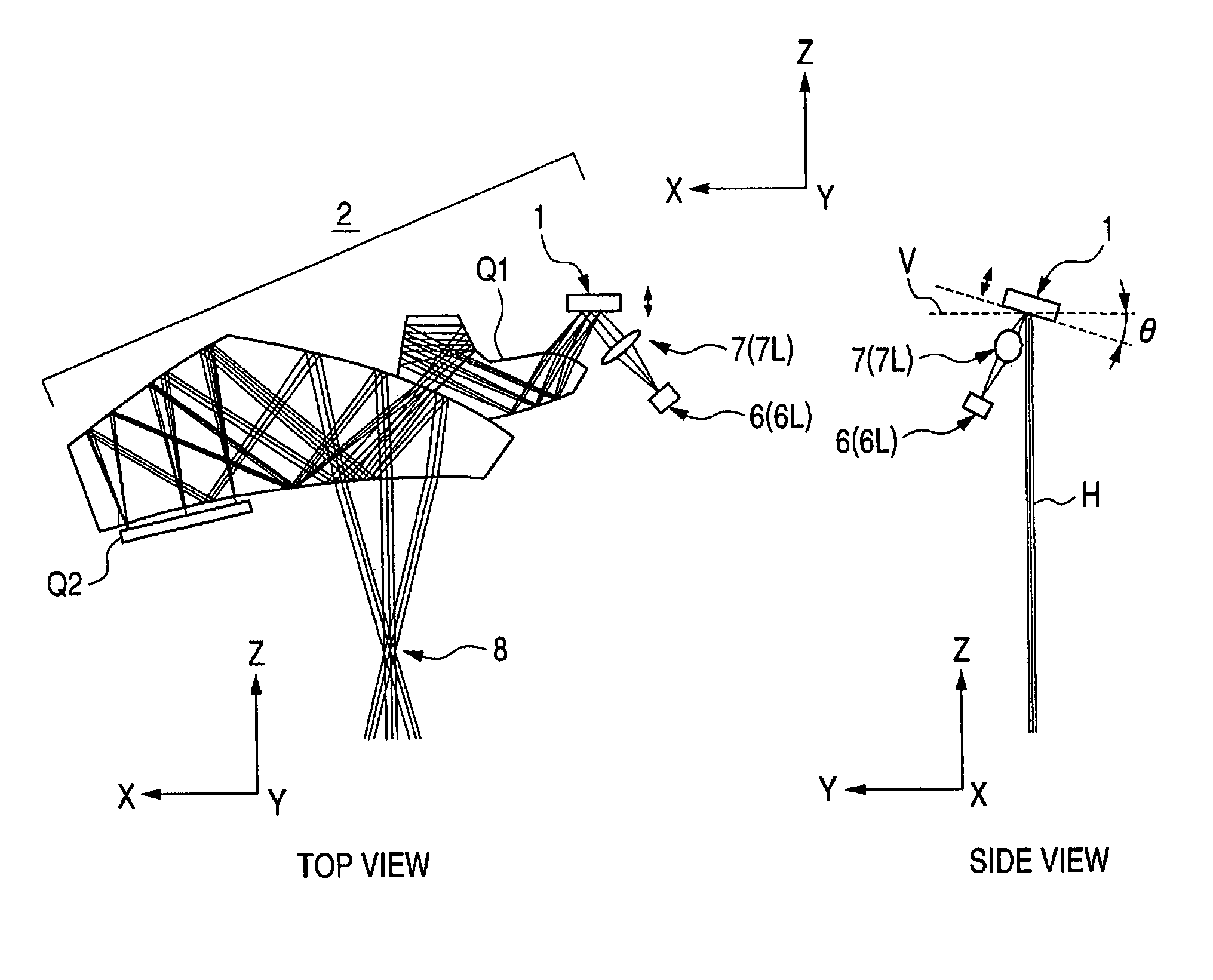
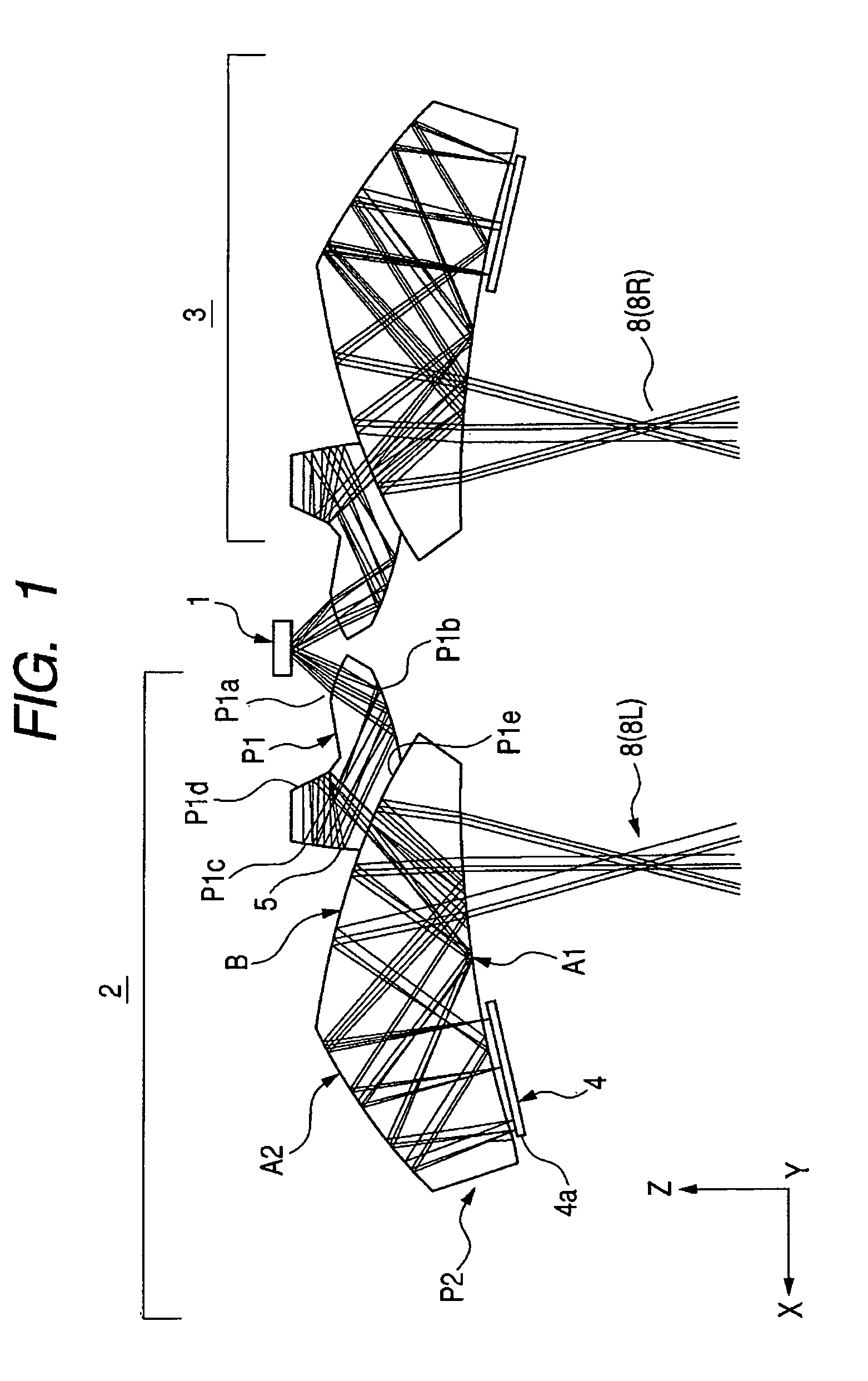
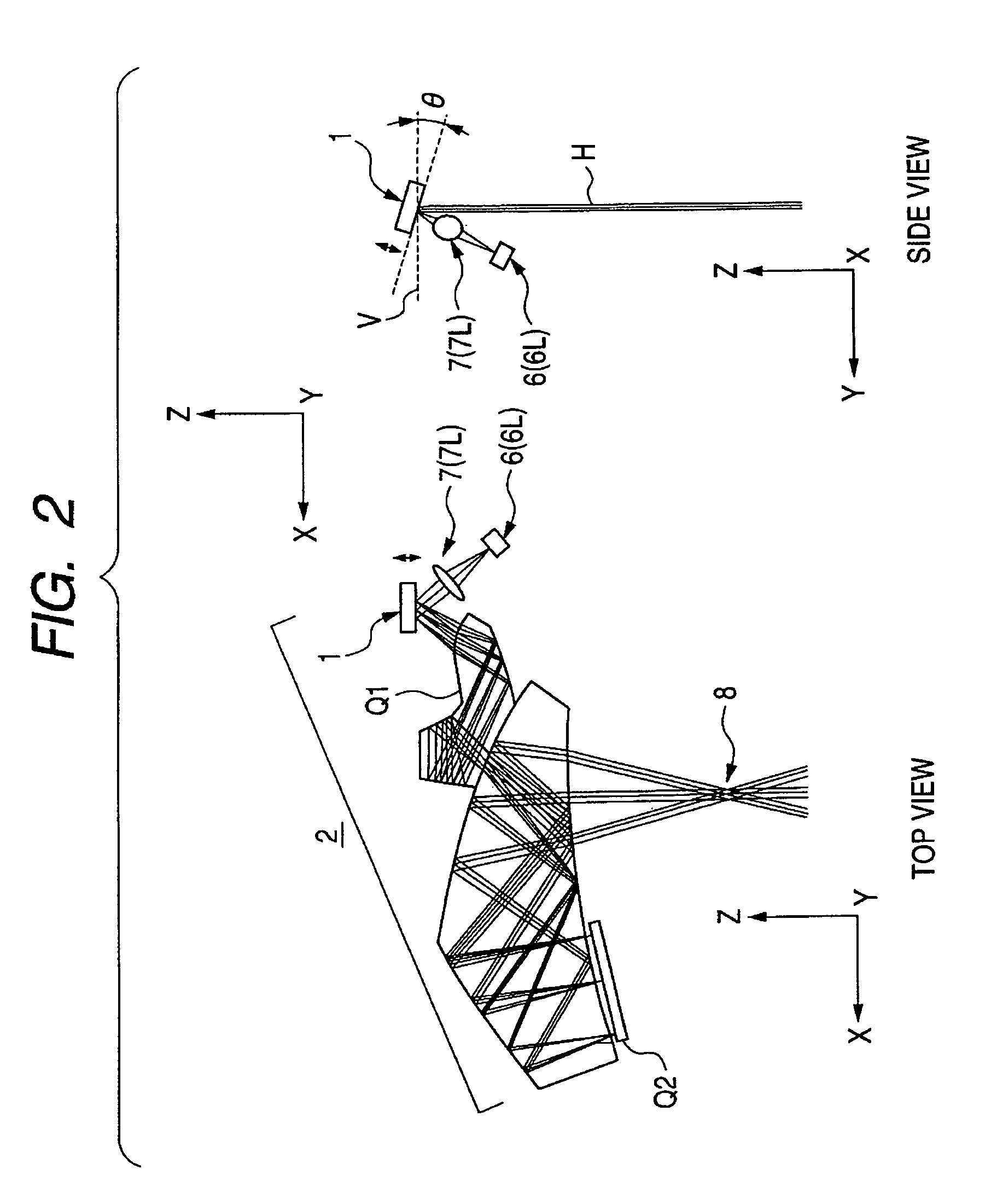
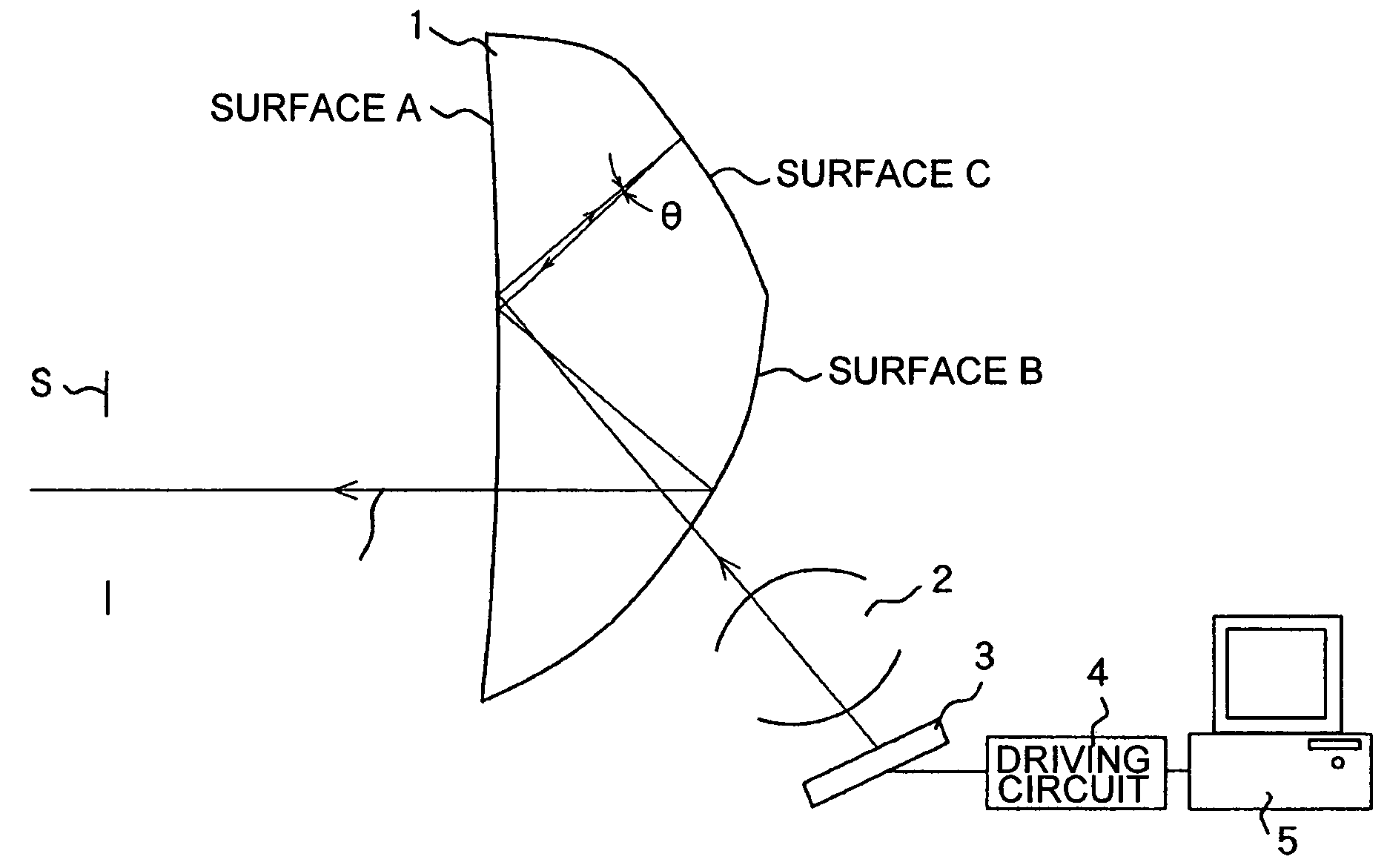
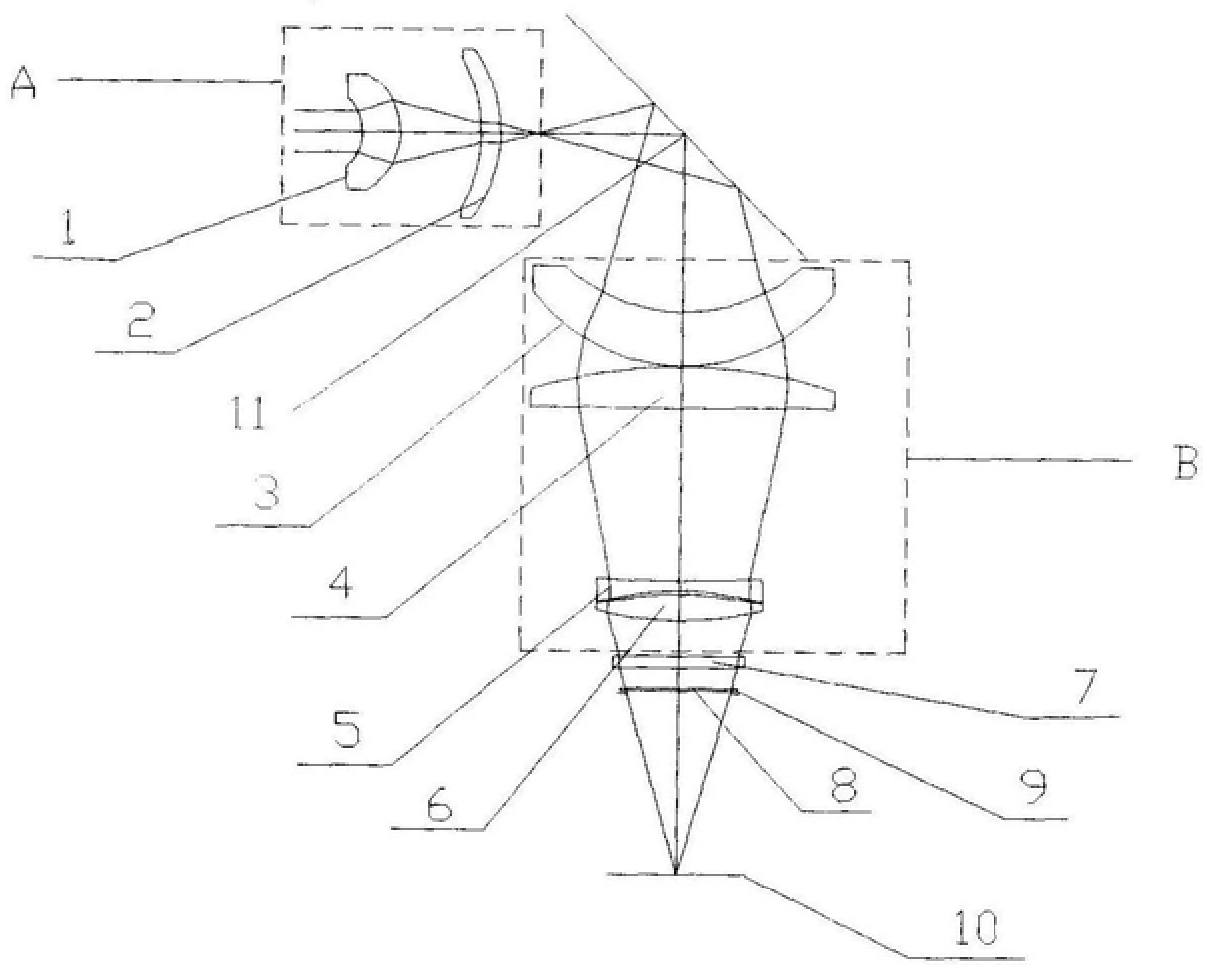
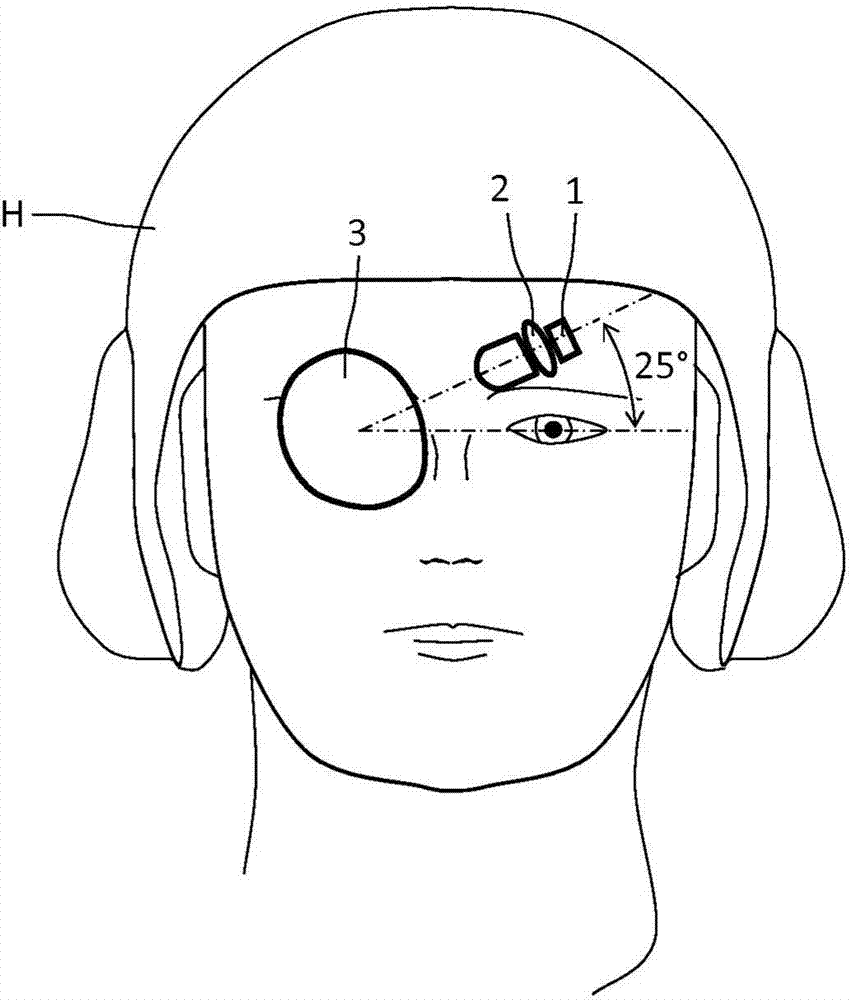
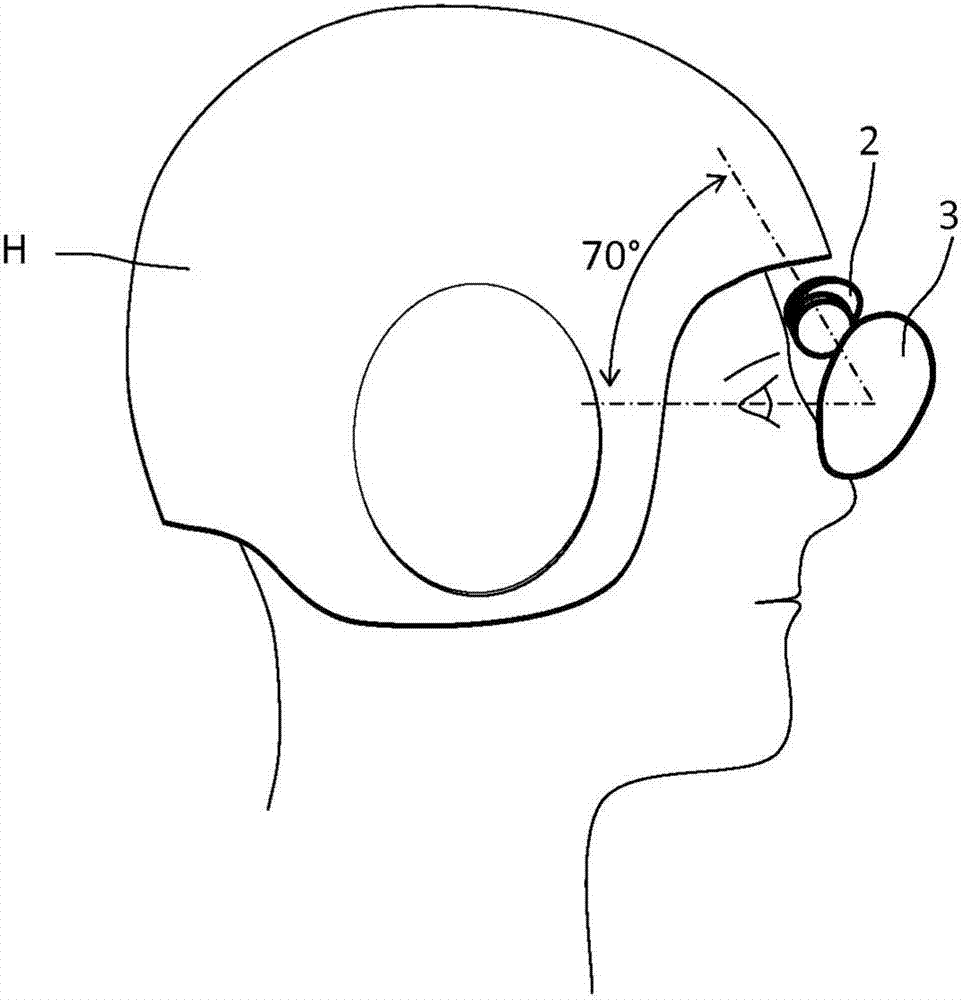
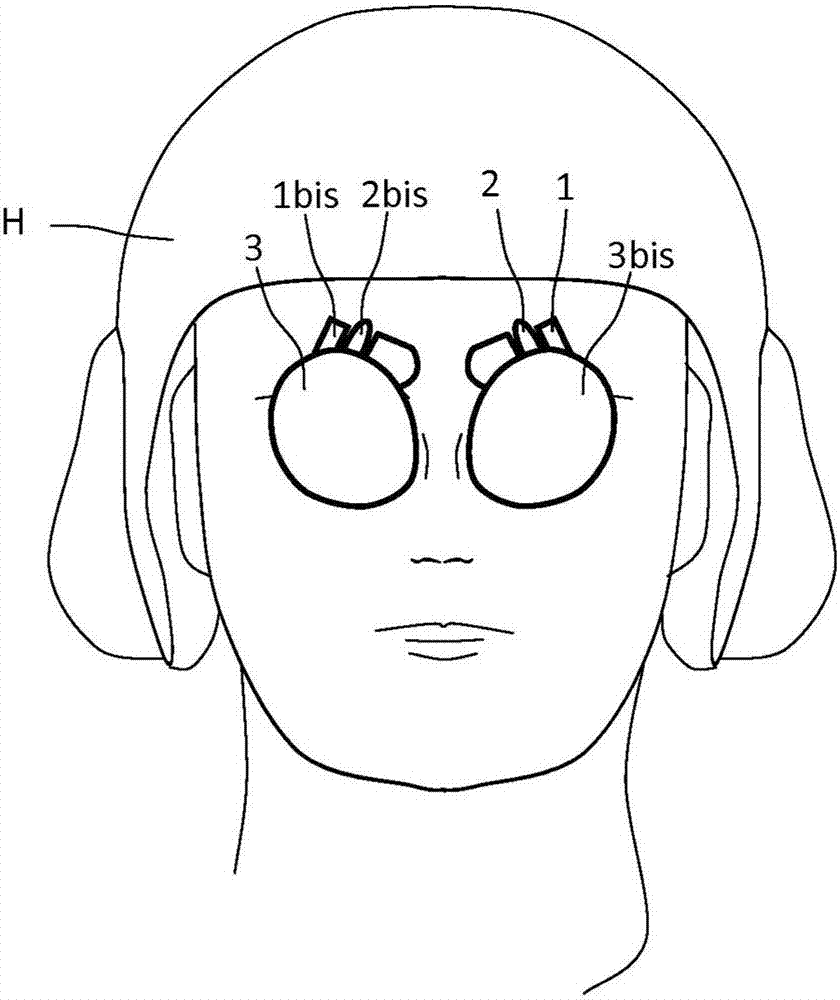
Head-borne viewing system comprising crossed optics
Owner:THALES SA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com