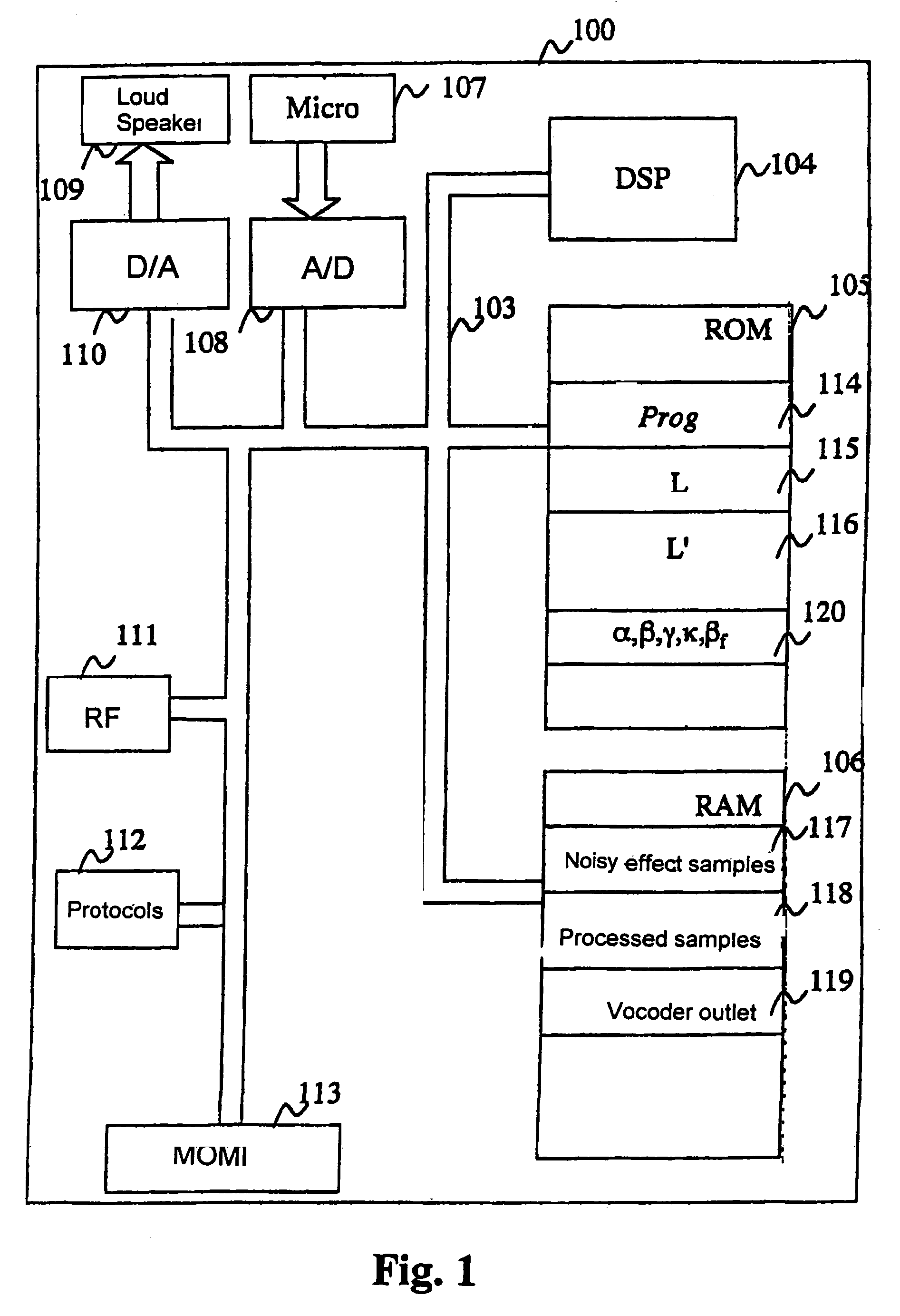
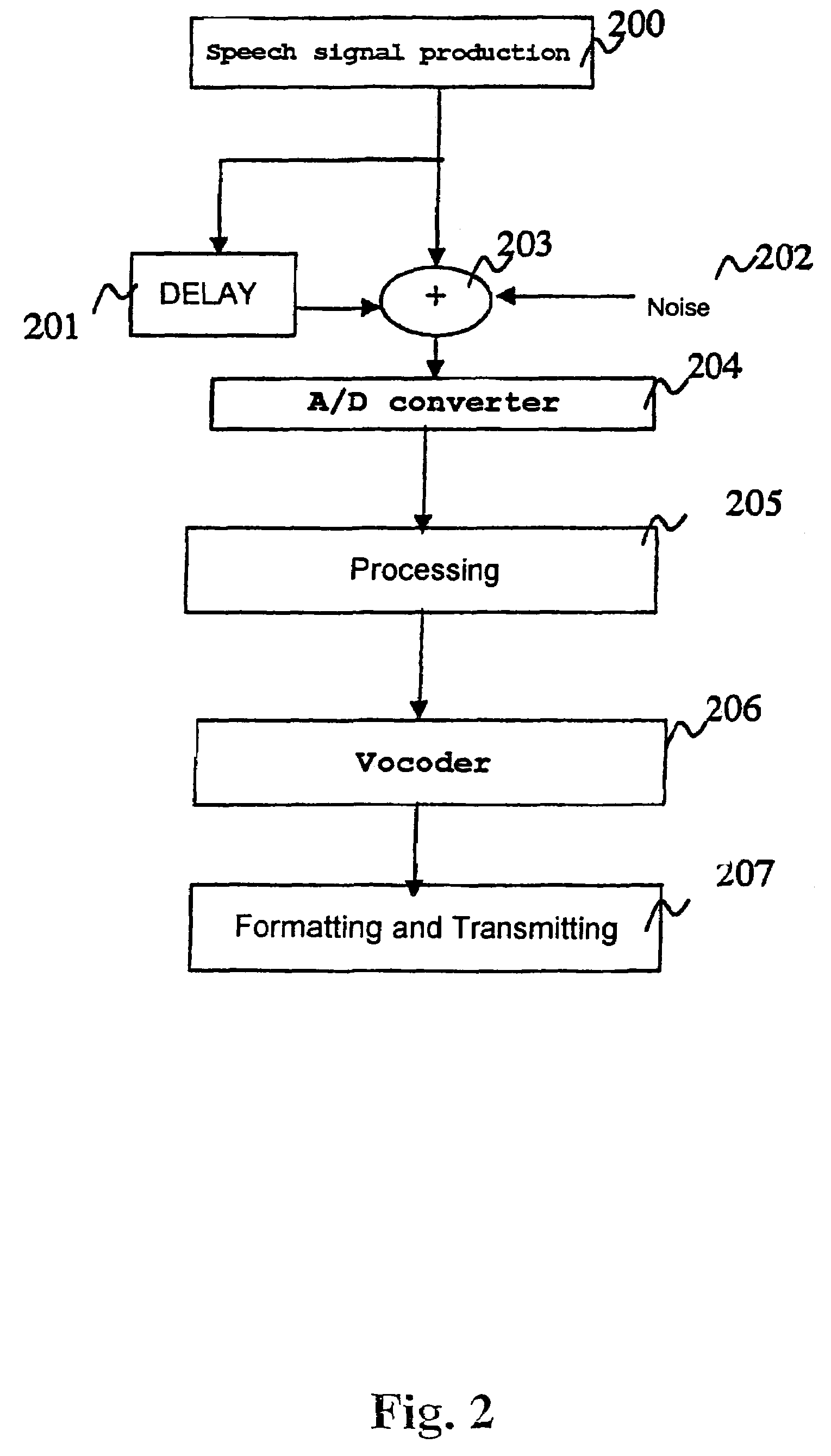
Patents
Literature
906 results about "Sample sequence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
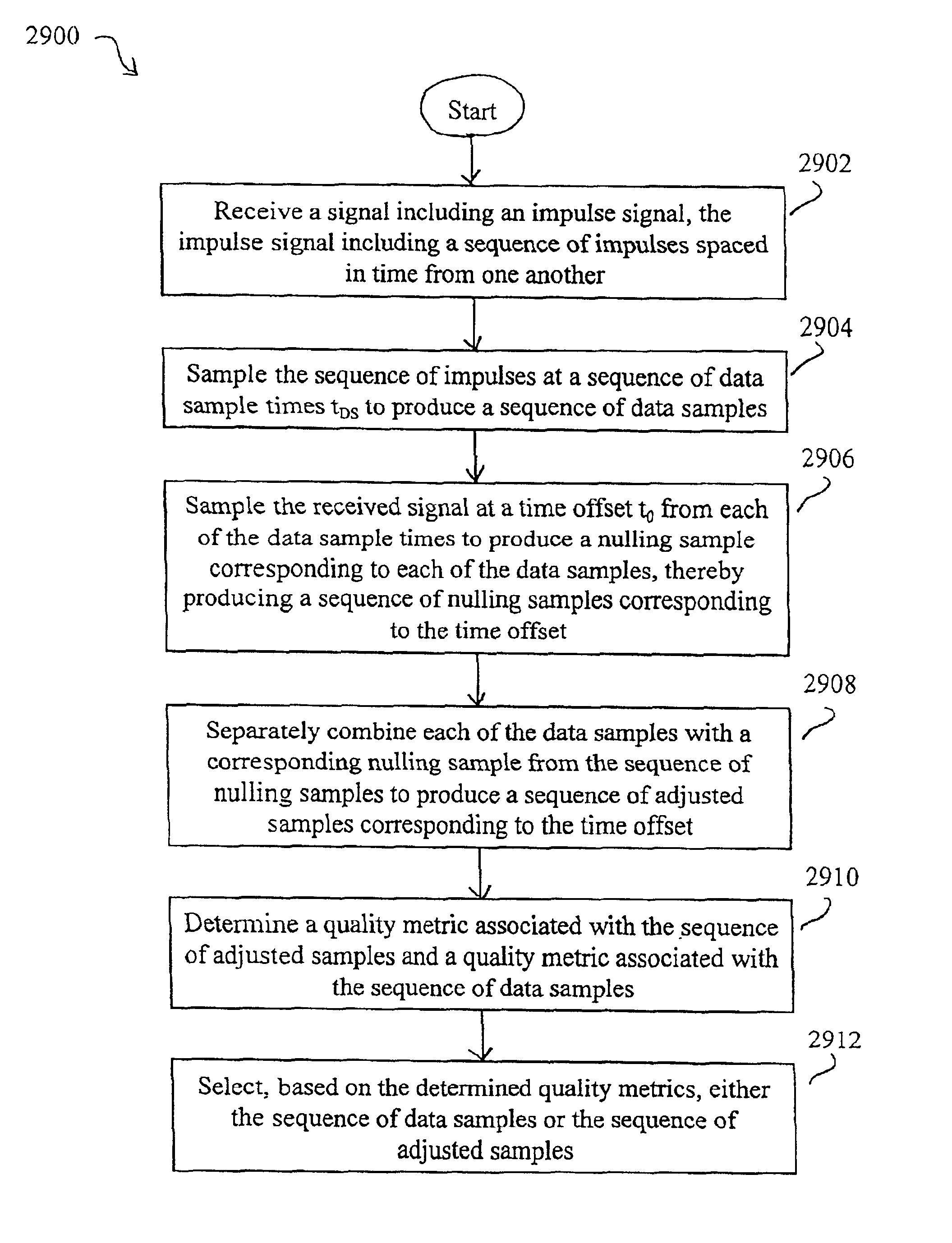
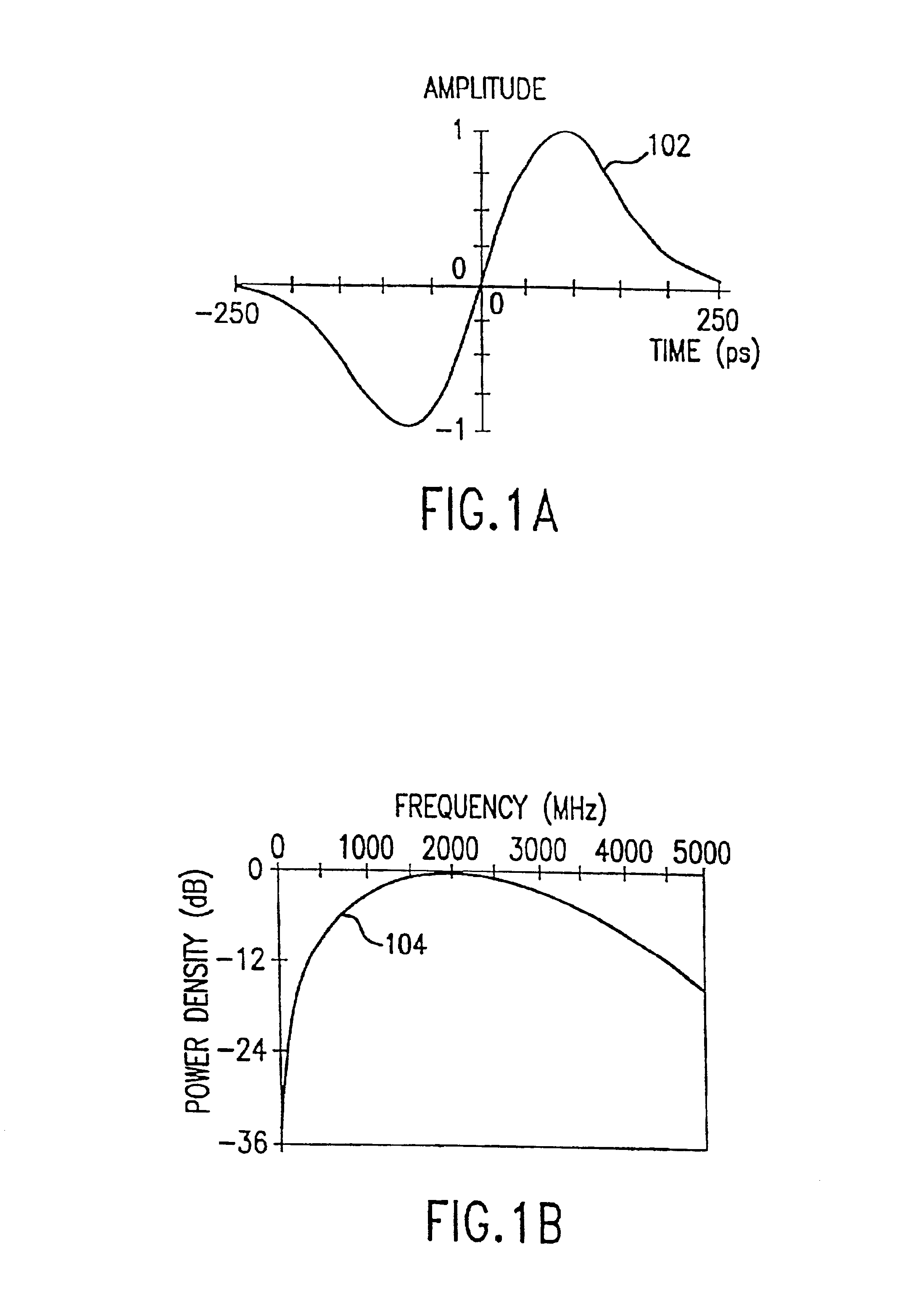
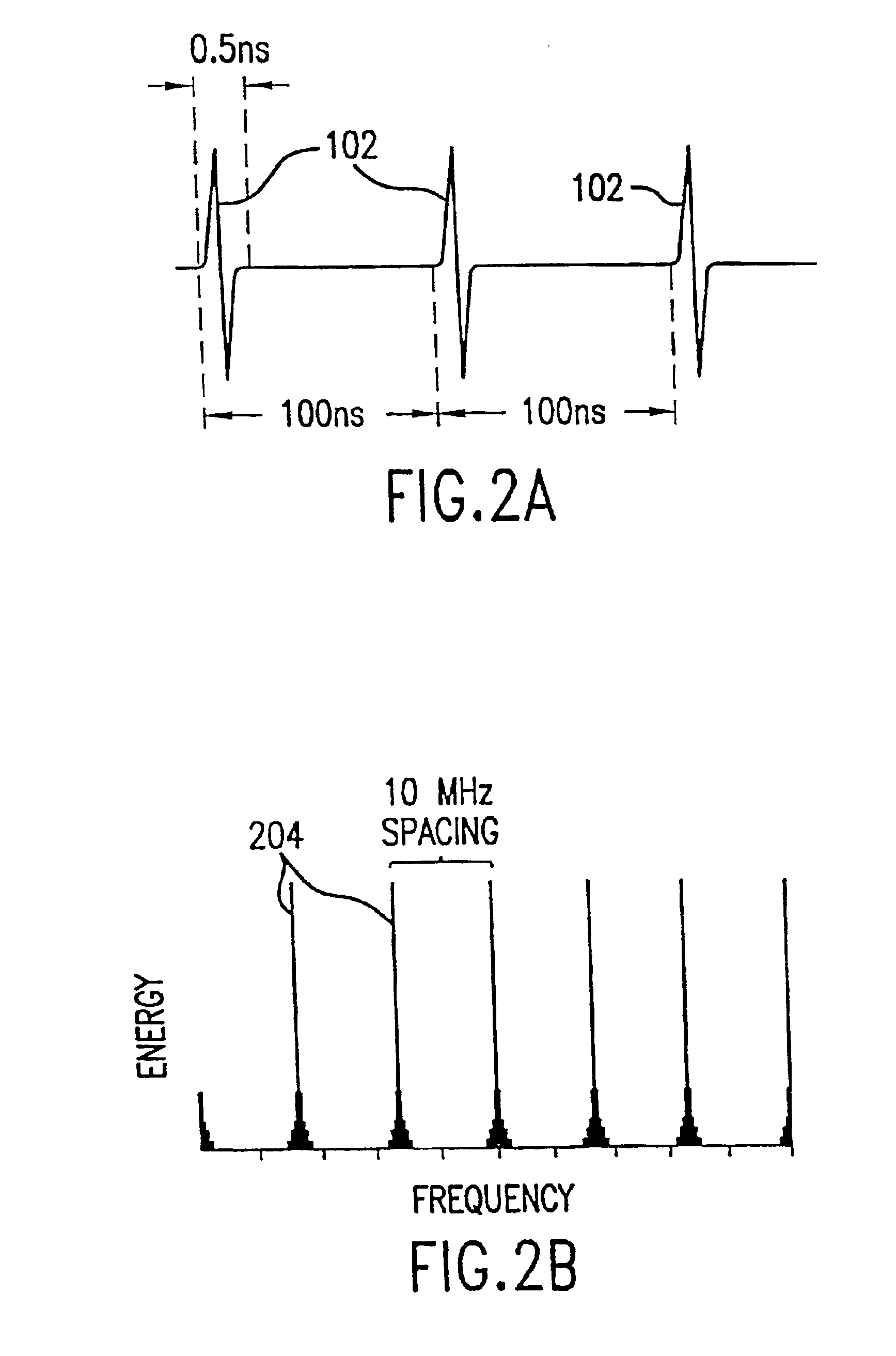
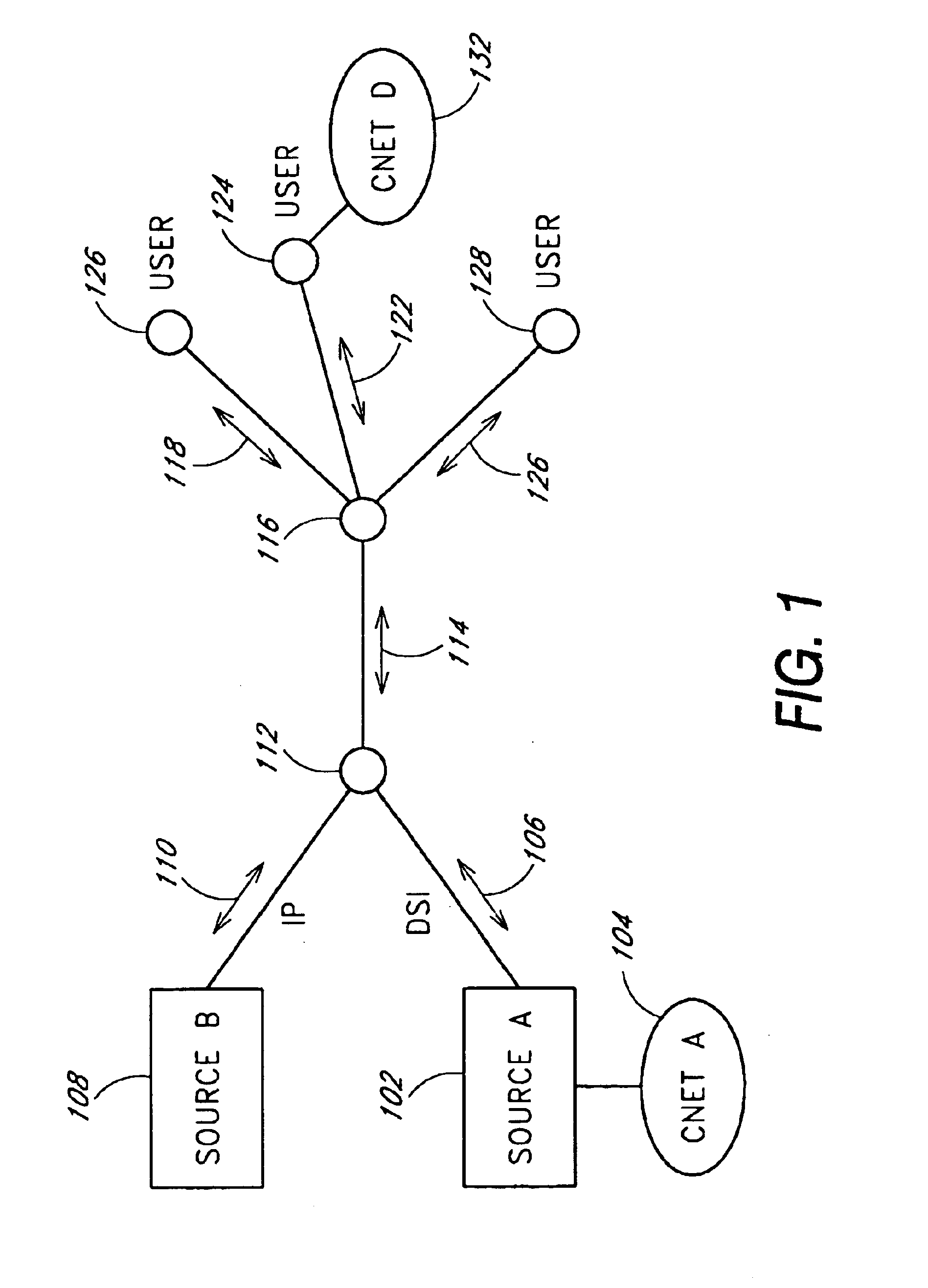
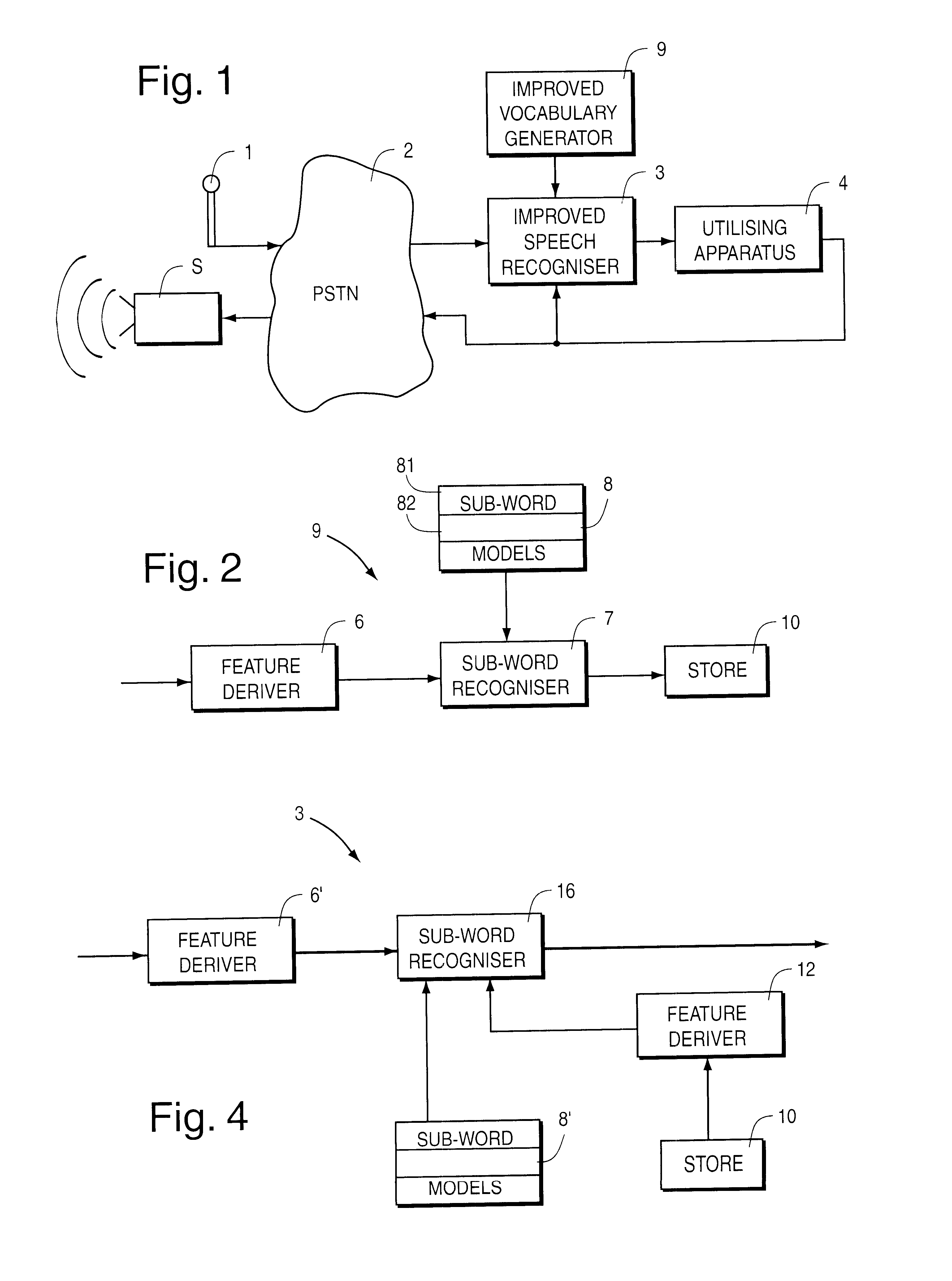
Method and system for reducing potential interference in an impulse radio
InactiveUS6914949B2Reduce distractionsReduce broadband noiseError preventionTransmission systemsInterference ratioRadio reception
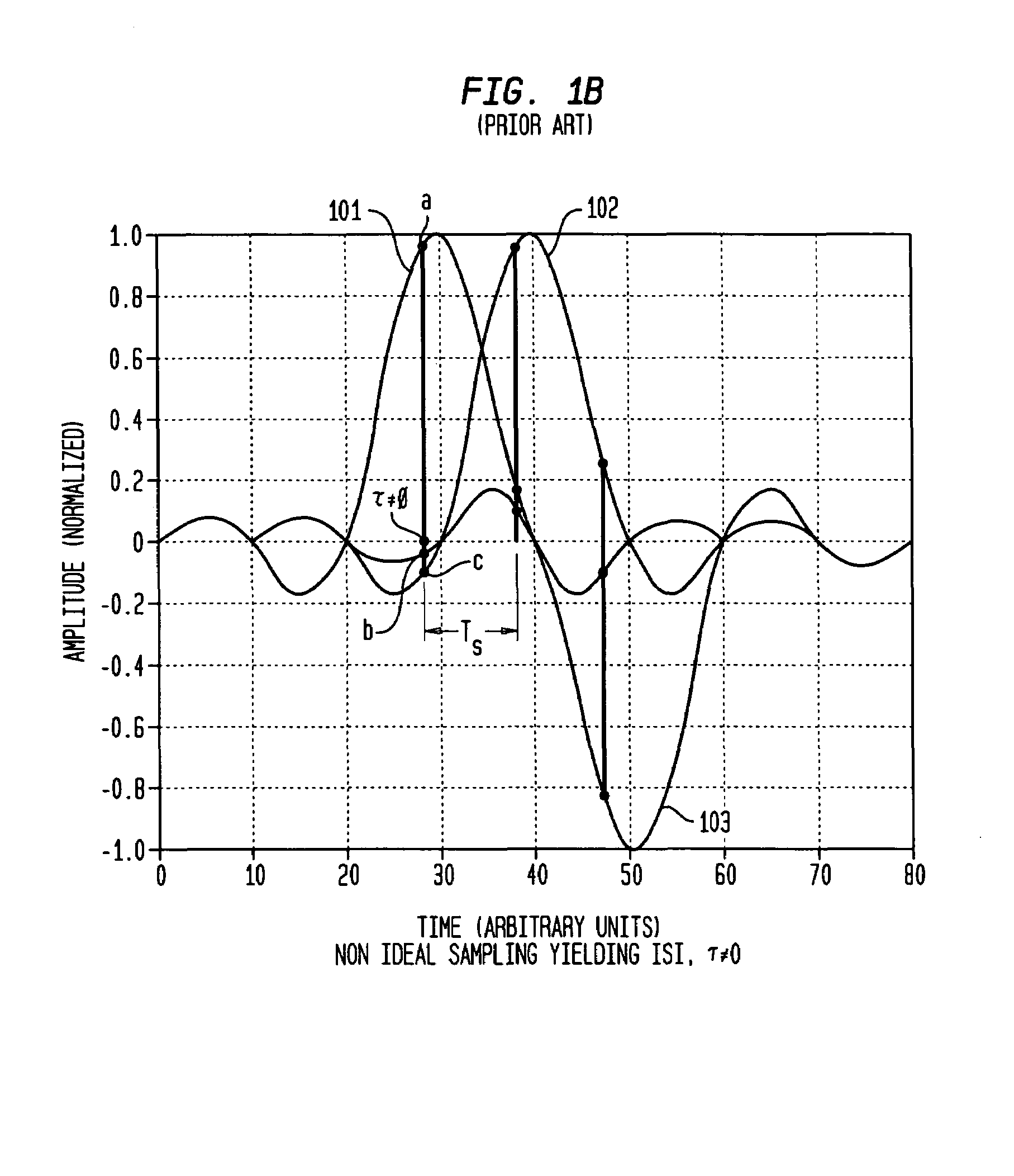
Potential interference is reduced in an impulse radio. A signal including an impulse signal and potential interference is received by the impulse radio. The impulse signal includes a sequence of impulses. The sequence of impulses of the received signal is sampled at a sequence of data sample times to produce a sequence of data samples. The received signal is also sampled at a plurality of time offsets from each of the data sample times to produce a plurality of nulling samples corresponding to each of the data samples. A separate sequence of nulling samples for each of the time offsets is thereby produced. Each of the data samples is then separately combined with a corresponding nulling sample from each of the separate sequences of nulling samples to produce a separate sequence of adjusted samples corresponding to each of the time offsets. A separate quality metric, representative of a signal-to-interference level, is then determined for each of the separate sequences of adjusted samples. A preferred sequence of samples is selected for further signal processing based on the determined quality metrics. Alternatively or additionally, one of the plurality of time offsets is selected as the preferred time offset based on the determined quality metrics.
Owner:ALEREON
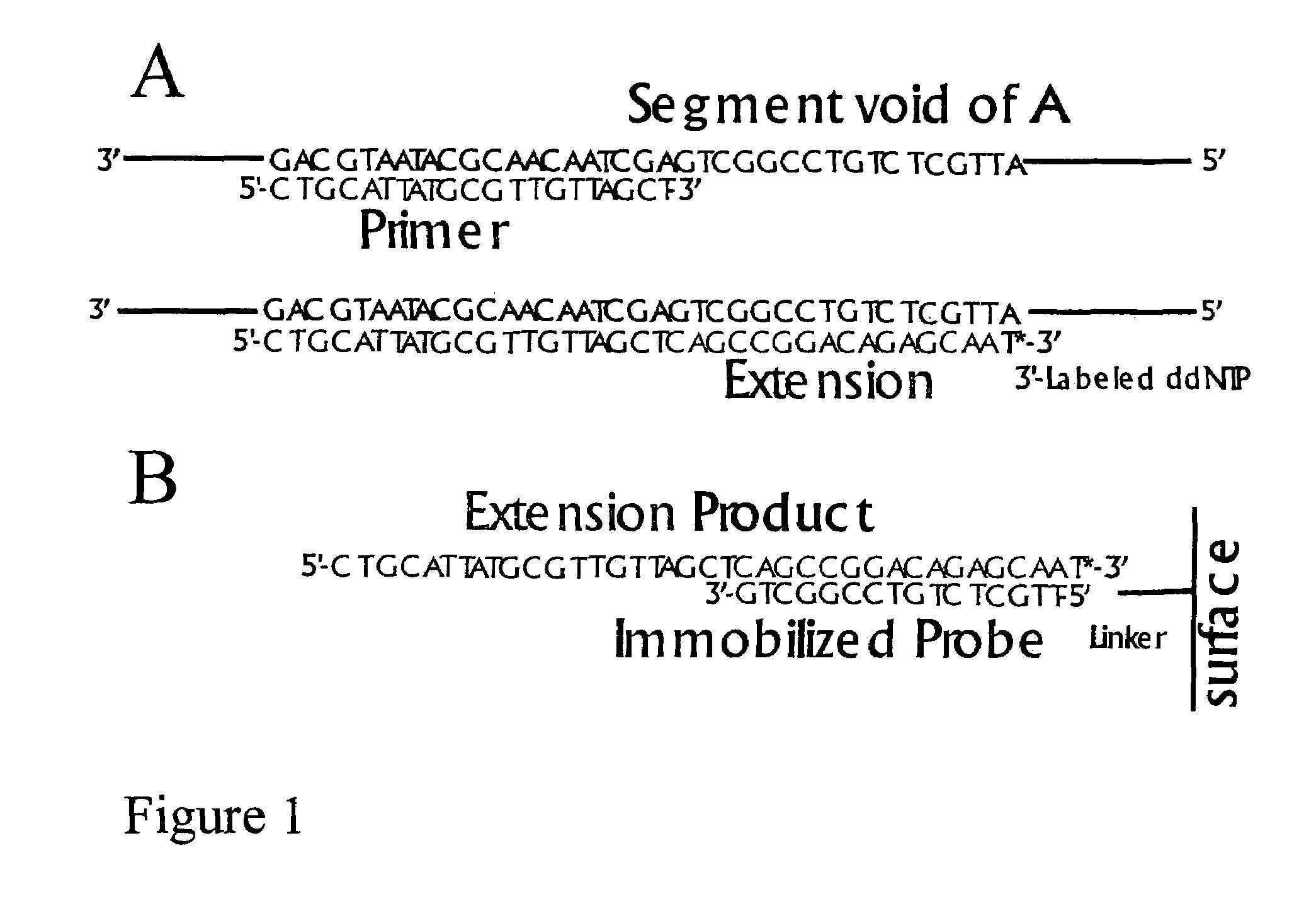
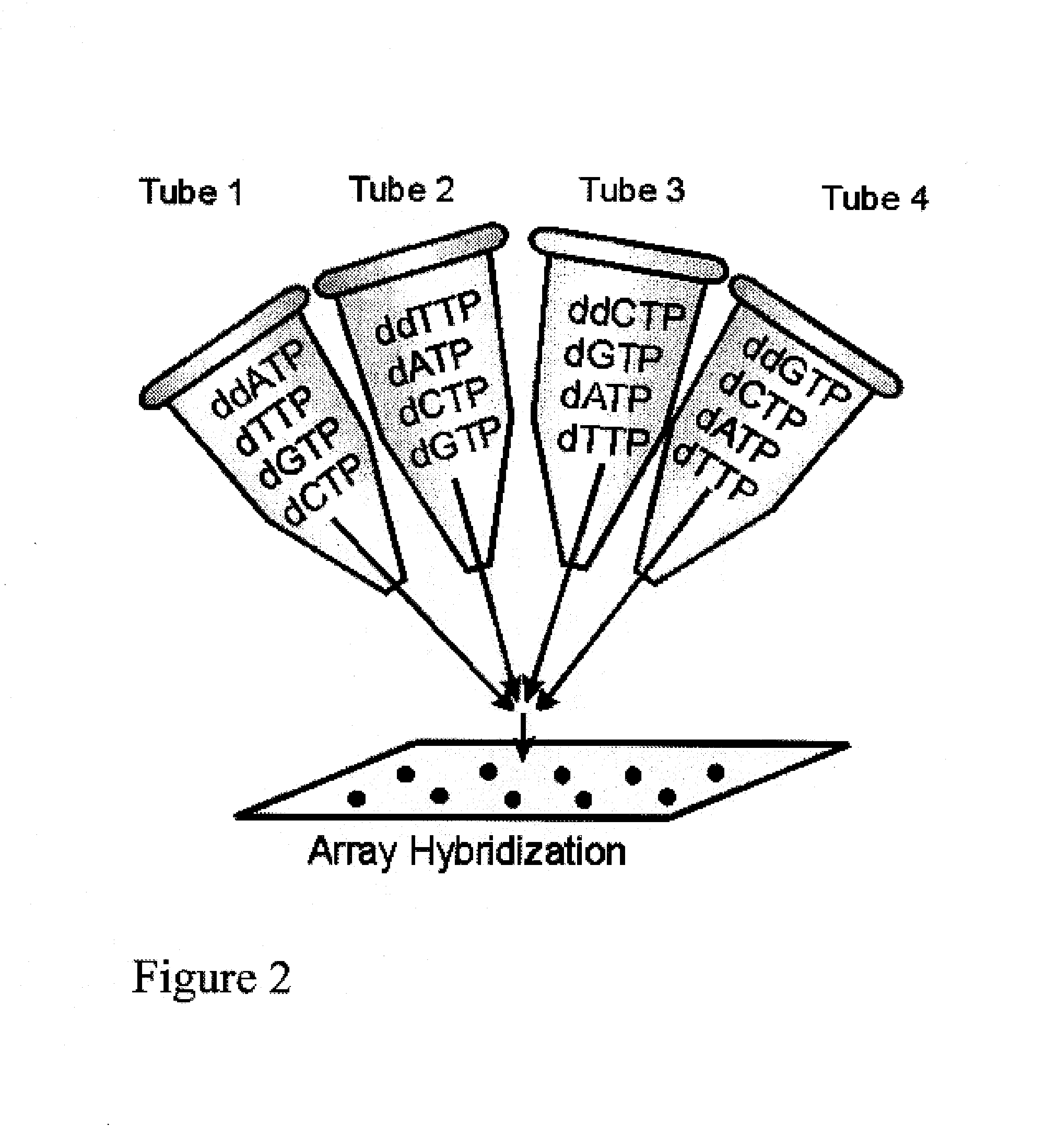
DNA sequence detection by limited primer extension
A novel limited primer extension reaction improves detection sensitivity and specificity in a variety of hybridization platforms. In the invention, a sequence of target DNA that lacks one of the four types of nucleic acid bases for a span of eight or more adjacent nucleotide positions is selected for use. This sequence is referred to as the extension complement sequence, or ECS. A primer with a sequence that is complementary to the target sequence that is immediately downstream (to the 3′ side) of this ECS is used to initiate an extension reaction. Extension occurs using a DNA polymerase and standard deoxynucleoside triphosphates for three of the four types of nucleic acid bases. The fourth base, which is complementary to the base missing in the ECS, is either absent or present only in the form of a dideoxynucleoside triphosphate, which does not support further extension. In either case, the extension reaction does not proceed past the first occurrence in the template of the base that is missing in the ECS. This results in a primer extension product with fixed length determined by the length of the ECS. The process can be repeated using a thermal-stable polymerase in a thermal-cycled reaction that results in a linear amplification of the targeted sequence. The resulting limited primer extension products serve as ideal hybridization analytes for determination of sample sequence content using microarrays.
Owner:ATOM SCI
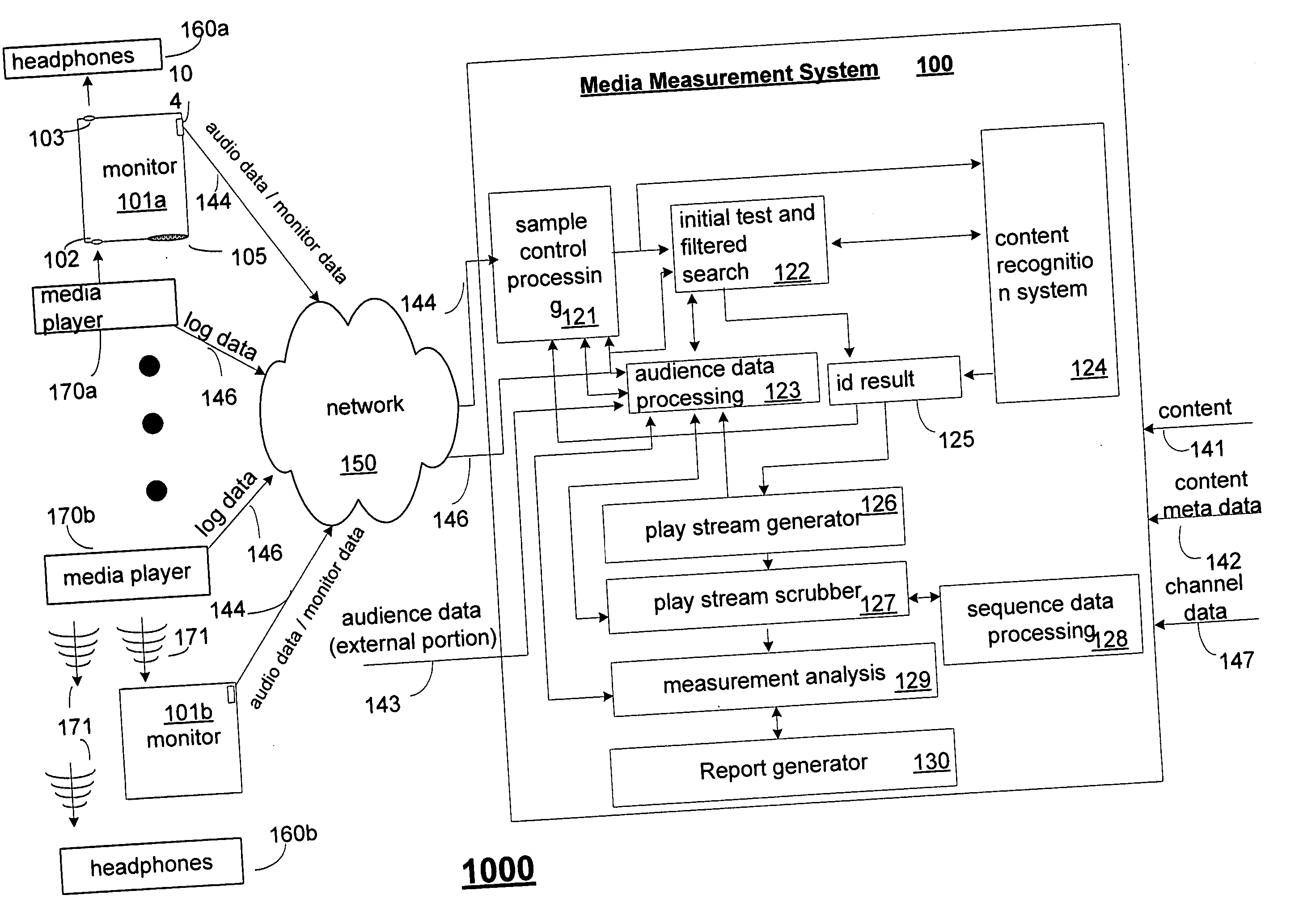
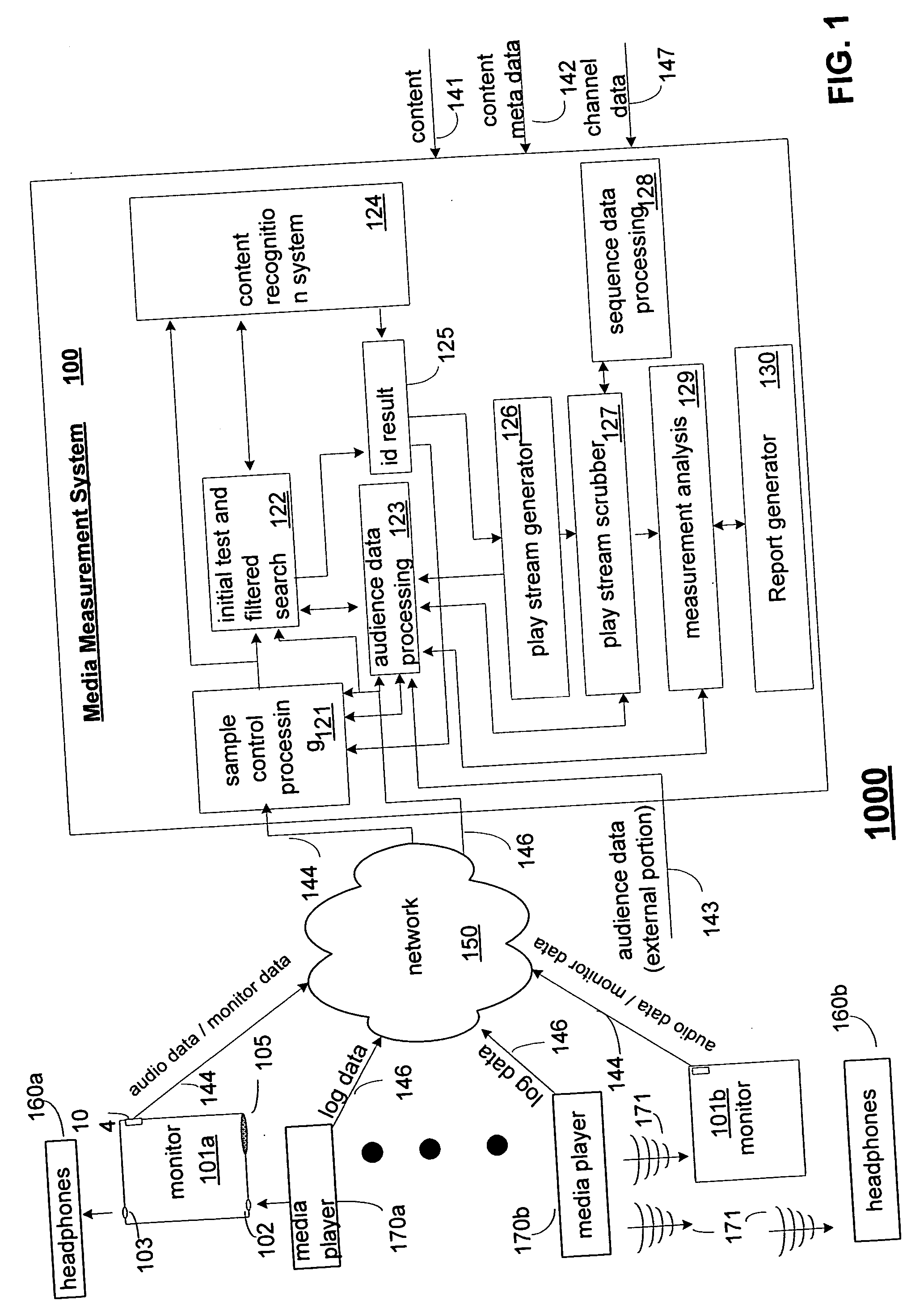
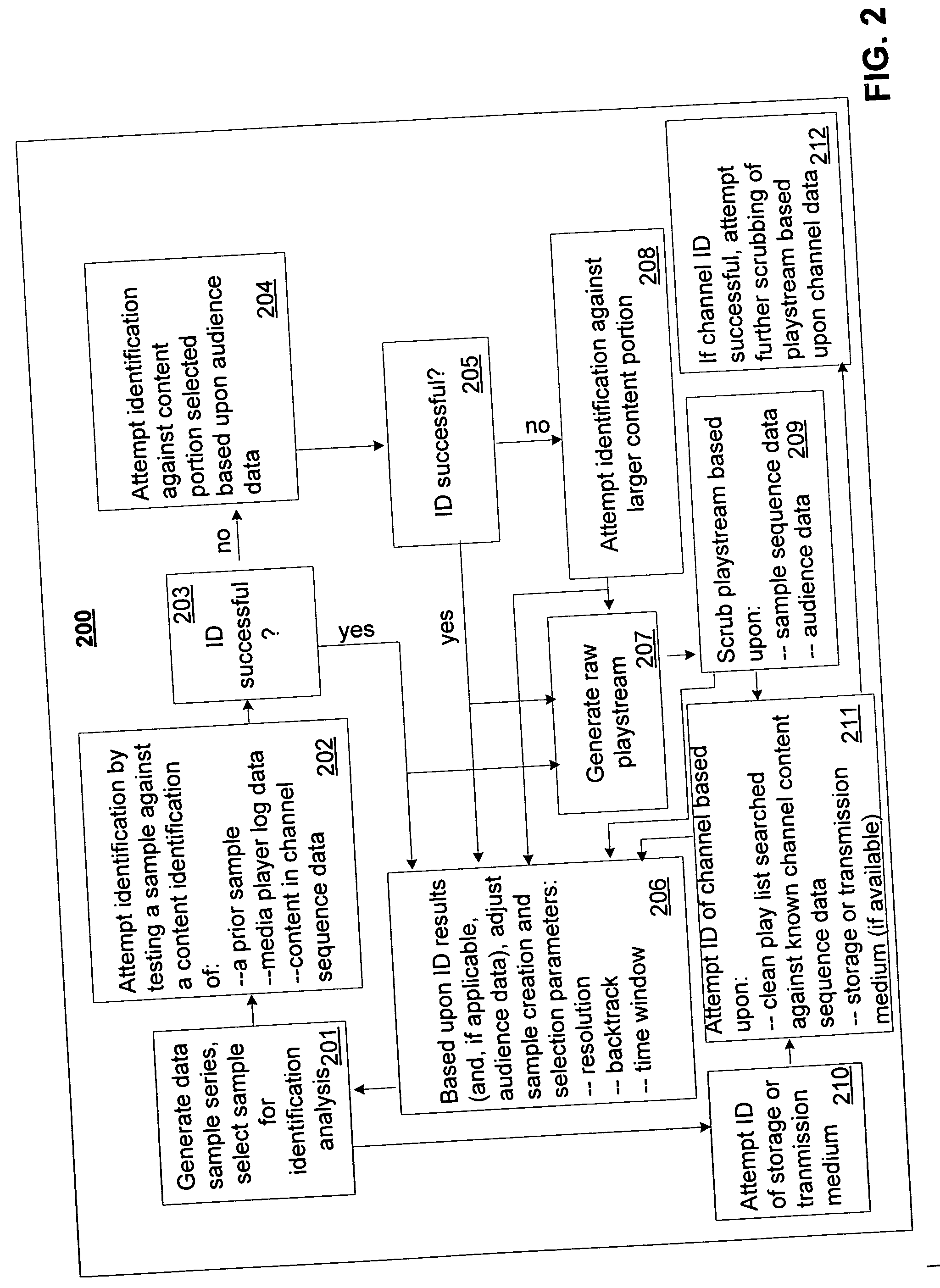
Media usage monitoring and measurement system and method
InactiveUS20050267750A1Easy to identifyEnhance content identificationBroadcast information monitoringBroadcast characteristics identification/recognitionComputer networkSample sequence
Media monitoring and measurement systems and methods are disclosed. Some embodiments of the present invention provide a media measurement system and method that utilizes audience data to enhance content identifications. Some embodiments analyze media player log data to enhance content identification. Other embodiments of the present invention analyze sample sequence data to enhance content identifications. Other embodiments analyze sequence data to enhance content identification and / or to establish channel identification. Yet other embodiments provide a system and method in which sample construction and selection parameters are adjusted based upon identification results. Yet other embodiments provide a method in which play-altering activity of an audience member is deduced from content offset values of identifications corresponding to captured samples. Yet other embodiments provide a monitoring and measurement system in which a media monitoring device is adapted to receive a wireless or non-wireless audio signal from a media player, the audio signal also being received wirelessly by headphones of a user of the monitoring device.
Owner:ANONYMOUS MEDIA RES
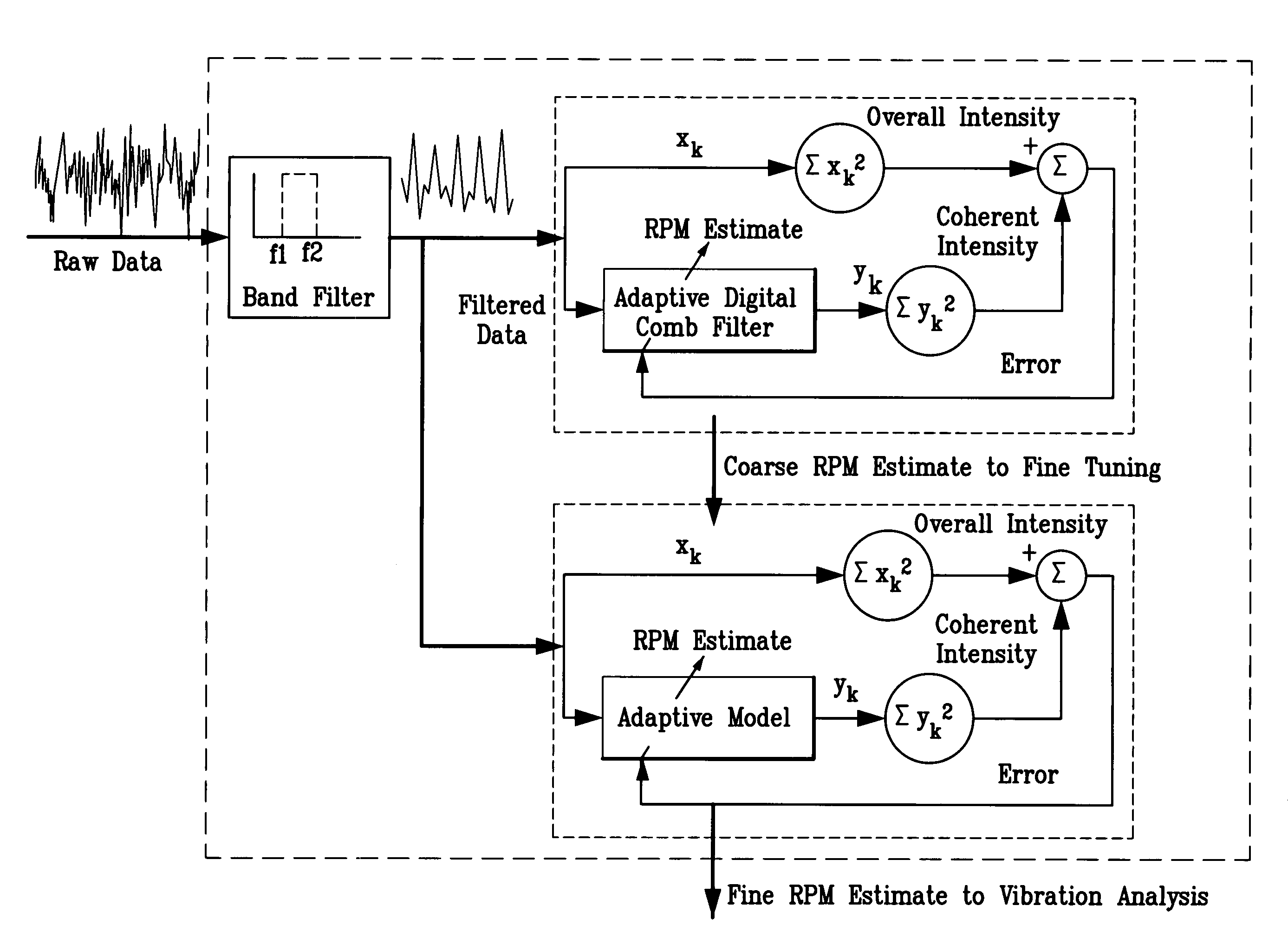
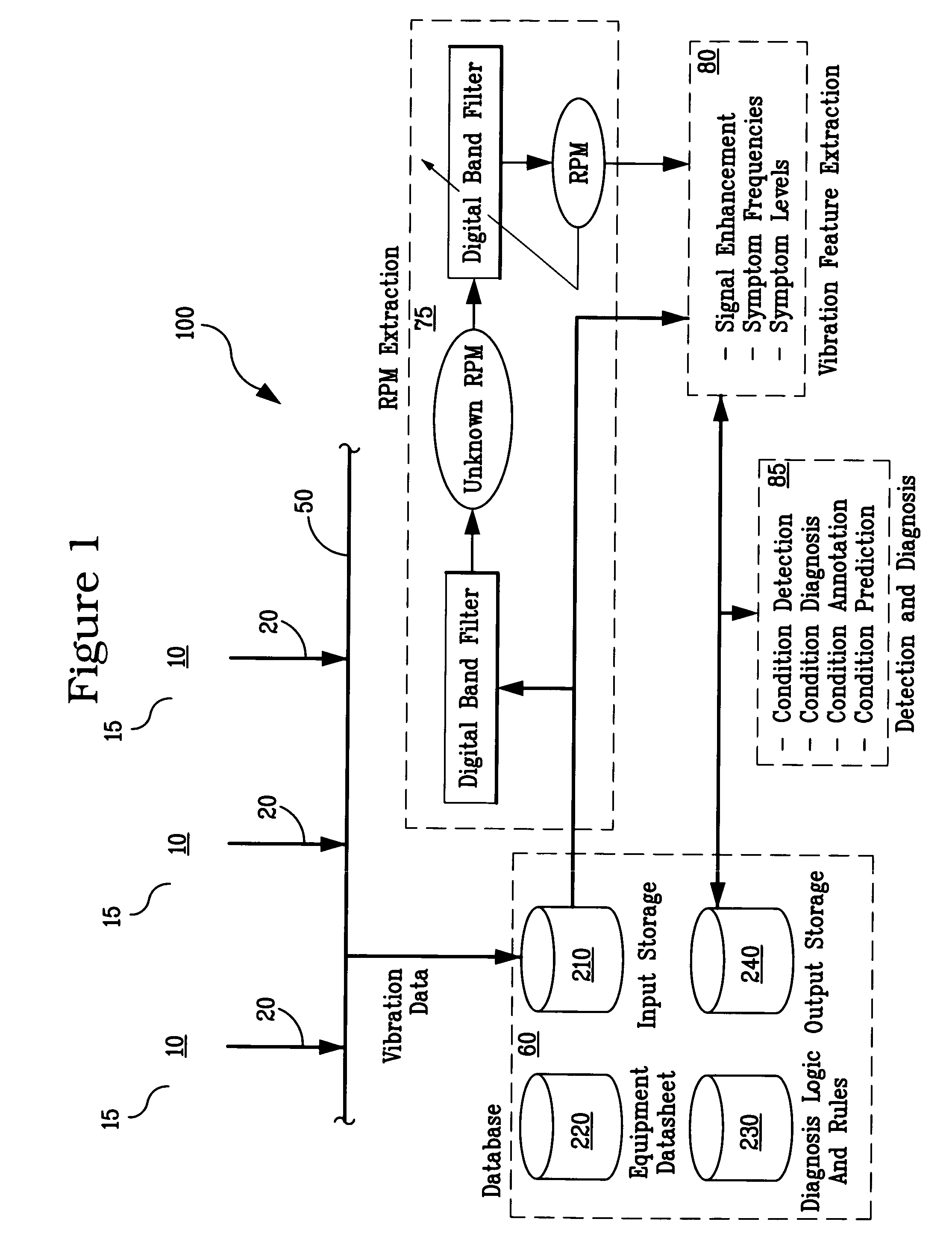
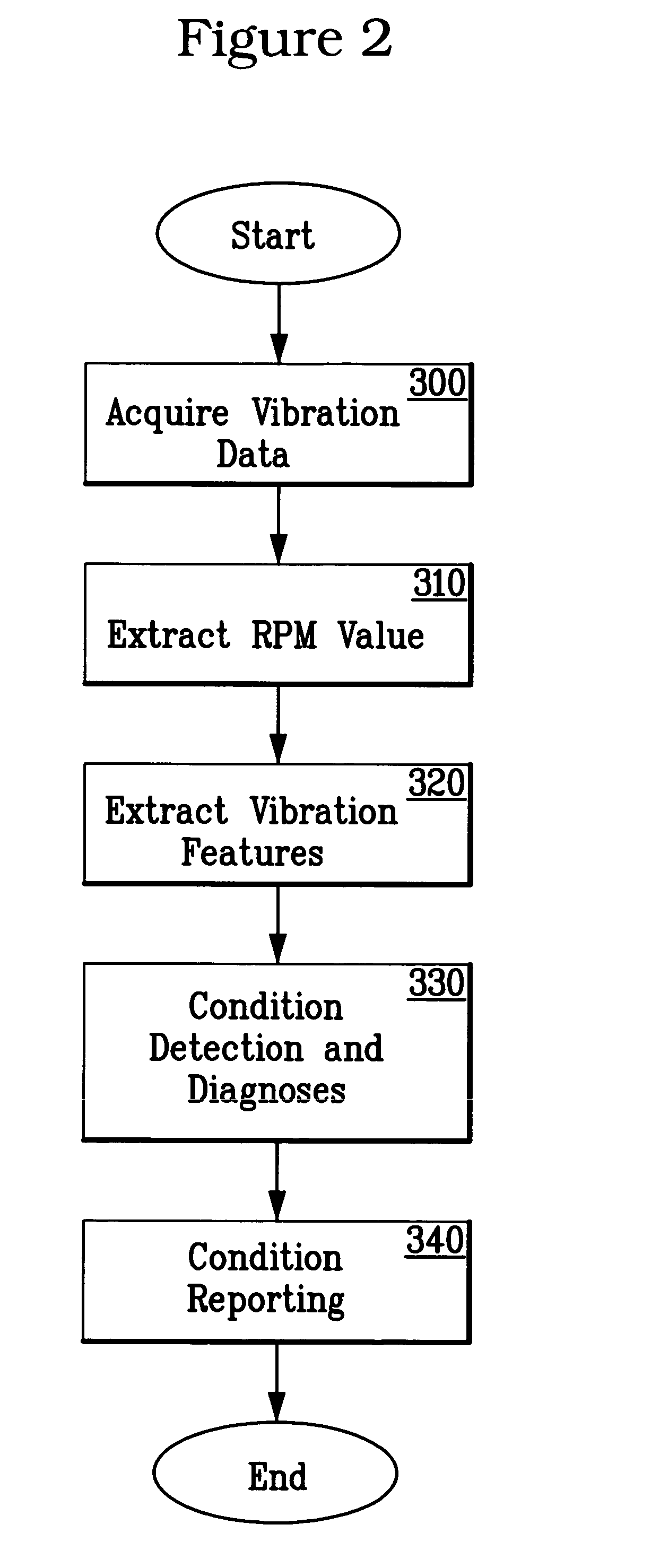
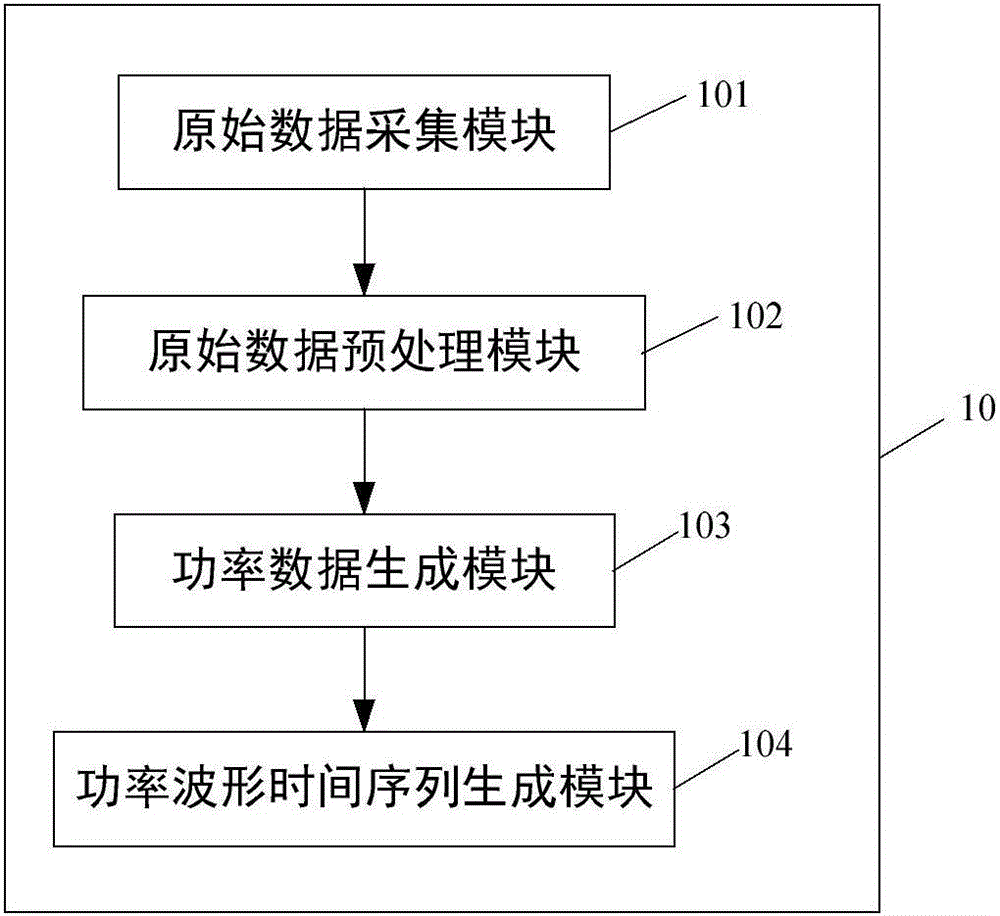
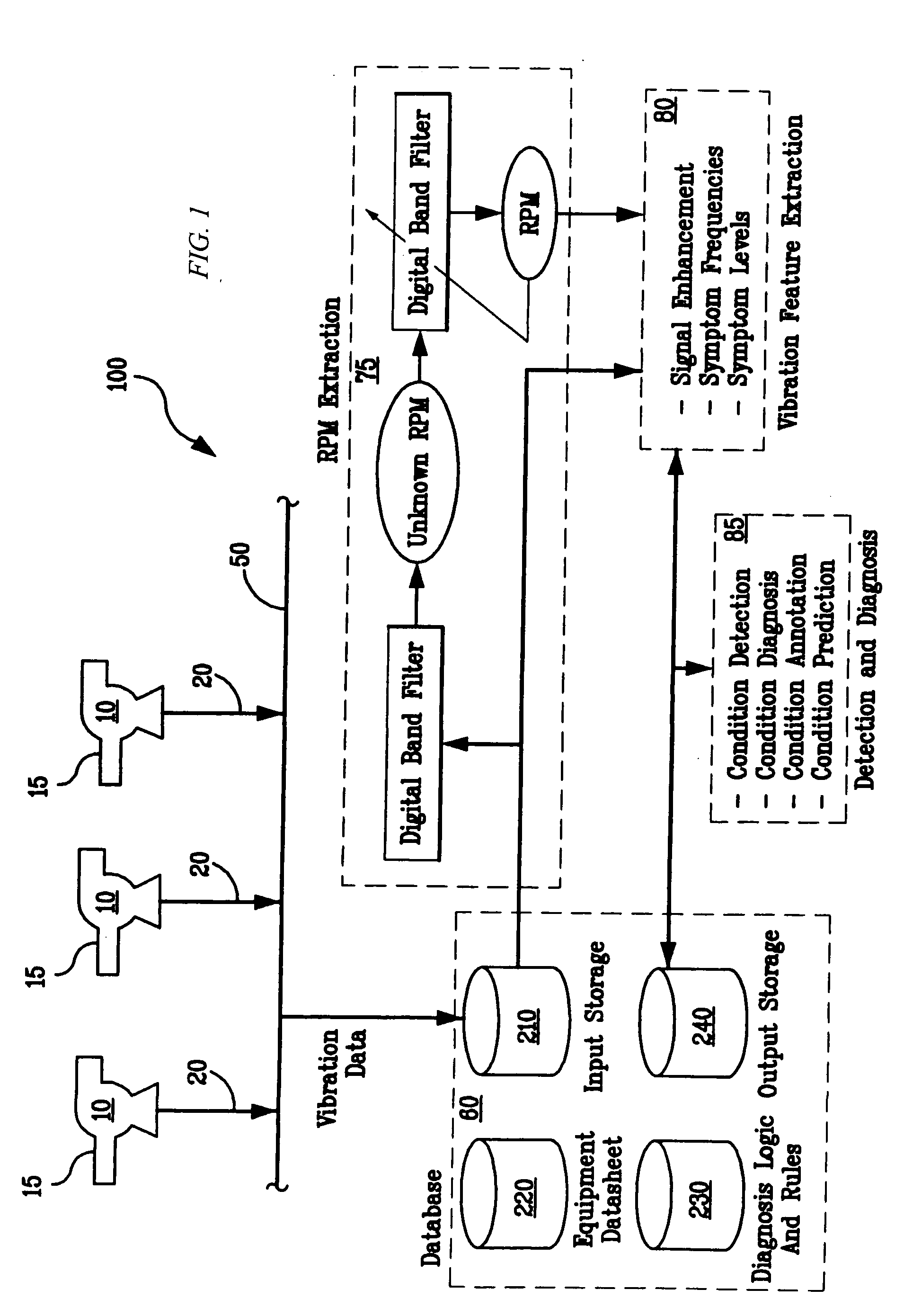
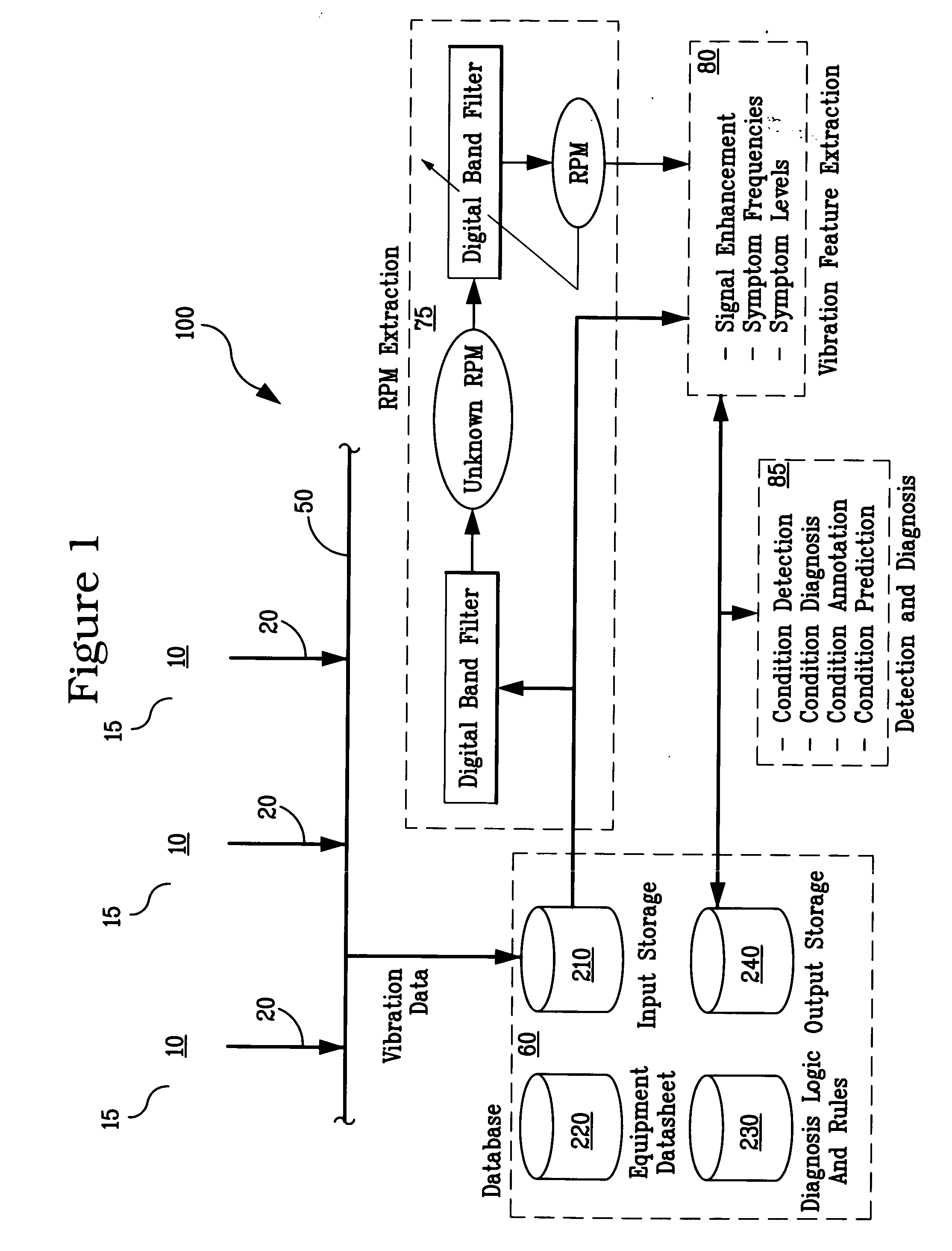
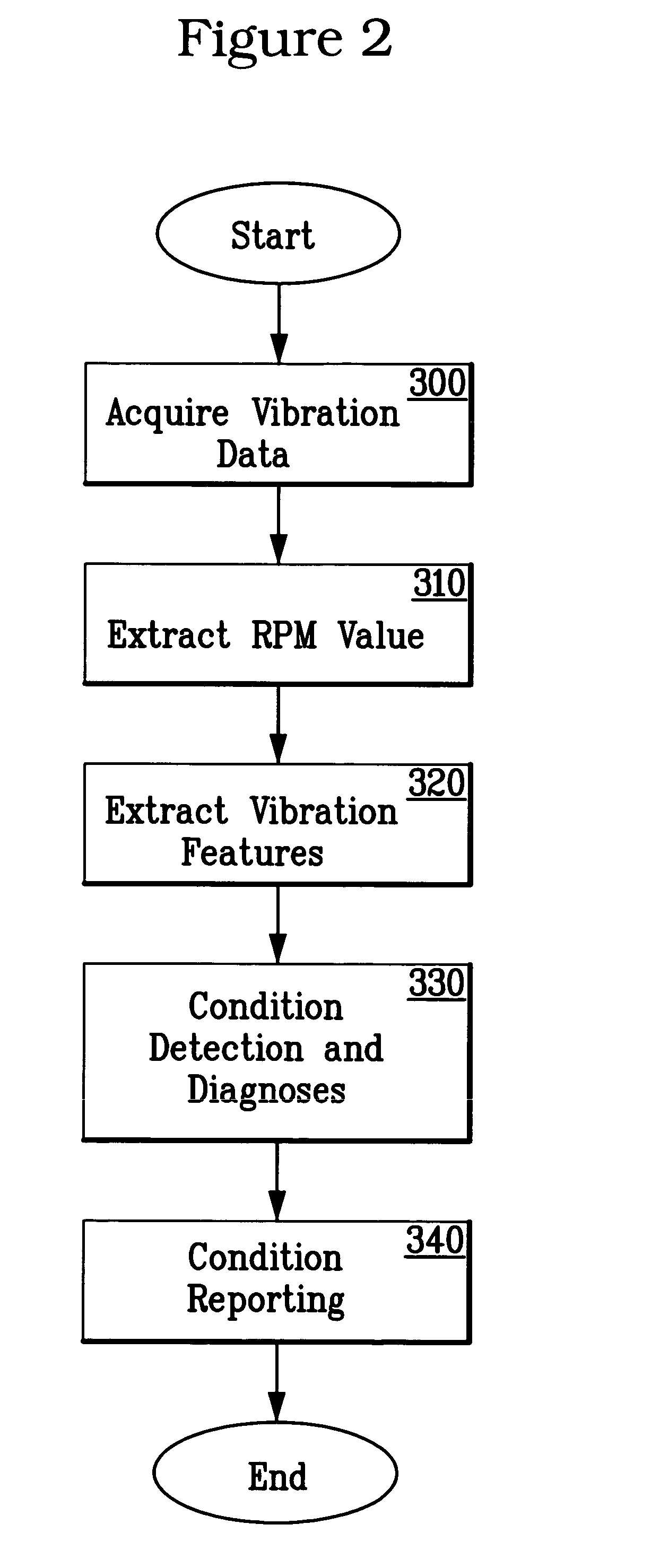
System and methodology for vibration analysis and condition monitoring
InactiveUS7133801B2Accurate speedImplemented quickly and inexpensivelyDigital computer detailsDevices using electric/magnetic meansTransducerSample sequence
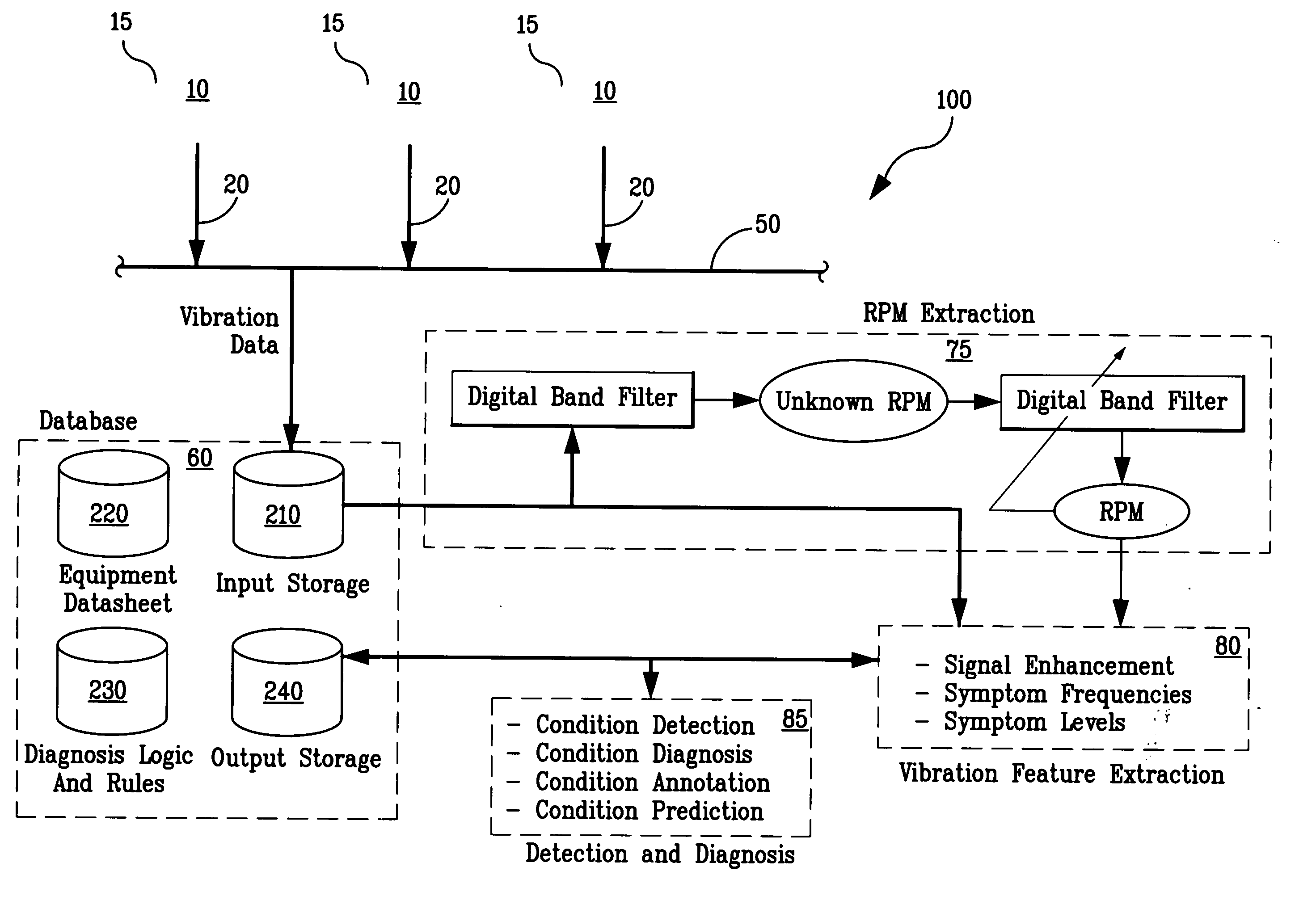
A system and methodology for continuous condition monitoring of rotating equipment. Employ adaptive signal processing techniques to determine the RPM of a rotating machine from time-based vibration data. RPM is determined based upon the input of a digitized time-based sample sequence of vibration data acquired directly from a vibration transducer for on-line real-time measurement of the machine RPM. Once RPM is determined, online vibration analysis for a given RPM or set of RPMs may be performed. The present invention extracts characteristic vibration features from vibration data and uses these extracted values to provide condition detection and diagnoses of machine faults.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
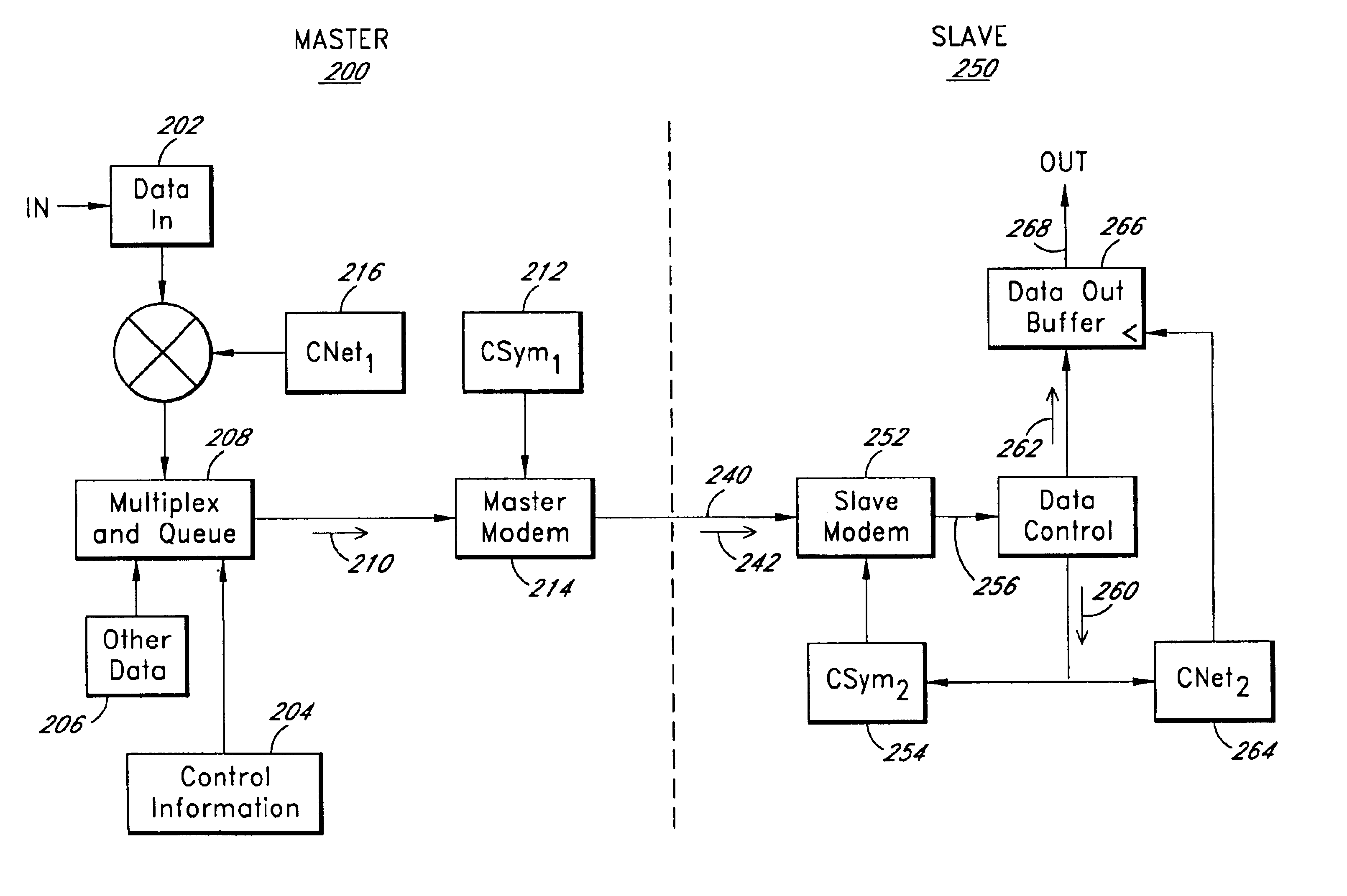
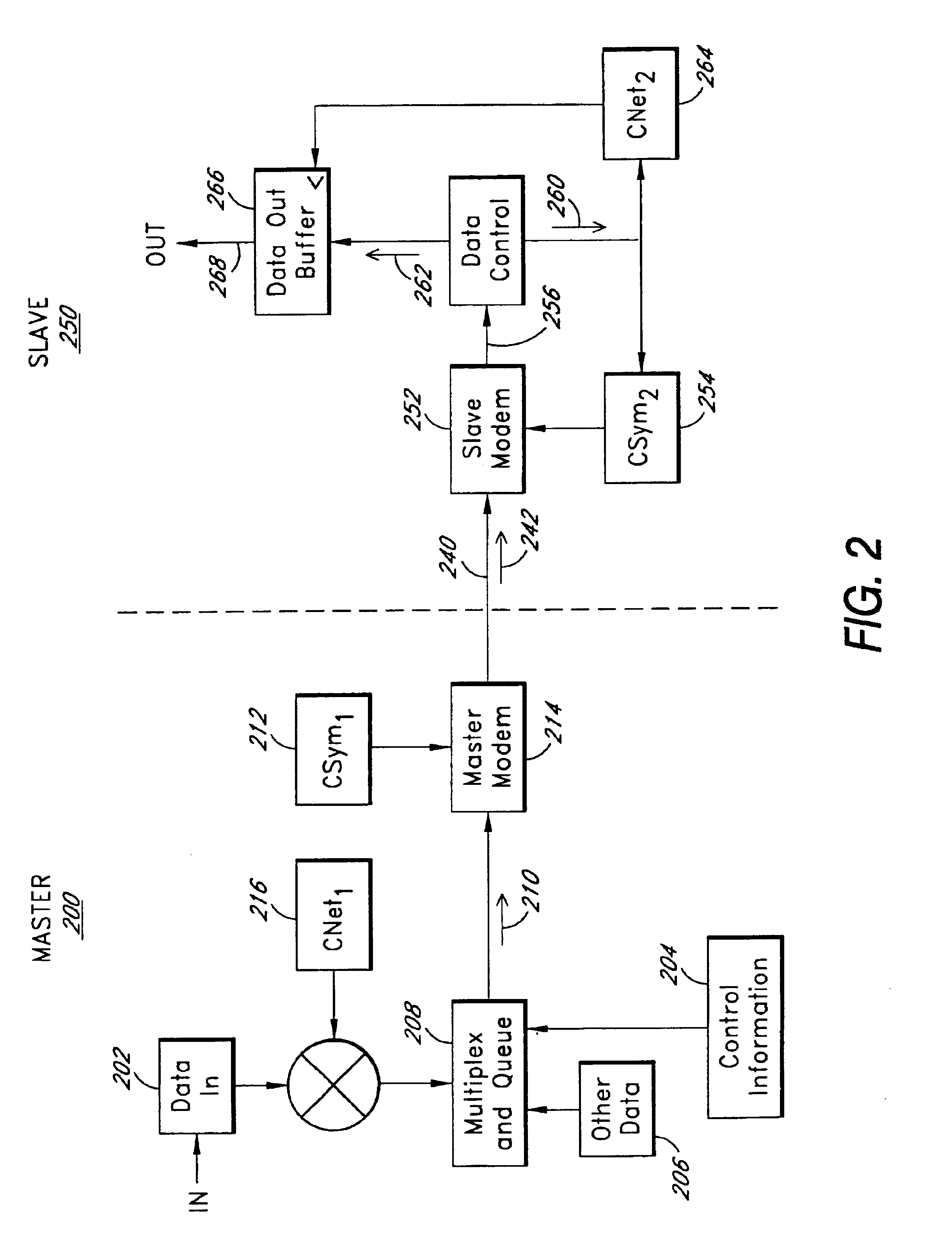
Synchronizing clocks across a communication link
InactiveUS6944188B2Accurate and fast data transferSynchronization is simpleSynchronisation arrangementNetwork traffic/resource managementTelecommunications linkImage resolution
Apparatus, system and method for synchronizing one or more clocks across a communication link. A slave clock may be synchronized to a master clock by means of a synchronization signal sent from the master to the slave clock side of the link. The synchronization signal may be an expected signal pattern sent at intervals expected by the slave side. The slave clock may correlate received signals with a representation of the expected synchronization signal to produce a correlation sample sequence at a first sample rate which is related as n times the slave clock rate. The synchronization signal receipt time indicated by the correlation sample sequence may be refined by interpolating the correlation sample sequence around a best correlation sample to locate a best interpolation at an interpolation resolution smaller than the sample resolution. The best interpolation may in turn be further refined by estimating between interpolator outputs adjacent to the best interpolation output. The synchronization signal receipt time thus determined is compared to the expected time based upon the slave clock, which is adjusted until the times match. After initialization, all slave clock errors are preferably accumulated to prevent long-term slip between the slave and master clocks. Formerly independent master and slave clocks synchronized across the communication link constitute a noncommon clock which may be compared on each side of the link to secondary independent clocks, and the secondary independent clocks may then be separately synchronized by adjusting one to have the same difference from its local noncommon clock as the secondary clock on the other side of the link has from its local noncommon clock.
Owner:WI LAN INC
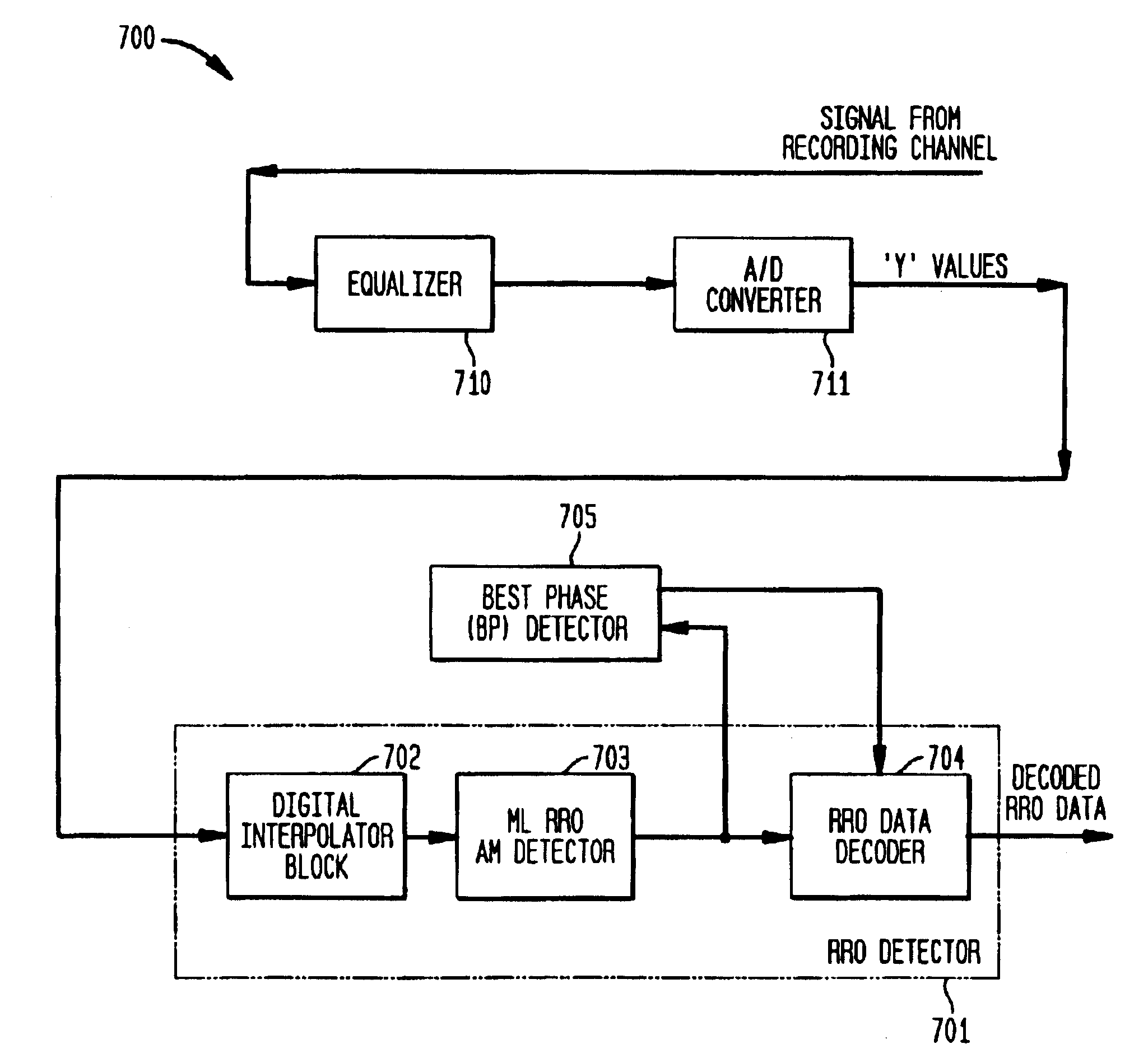
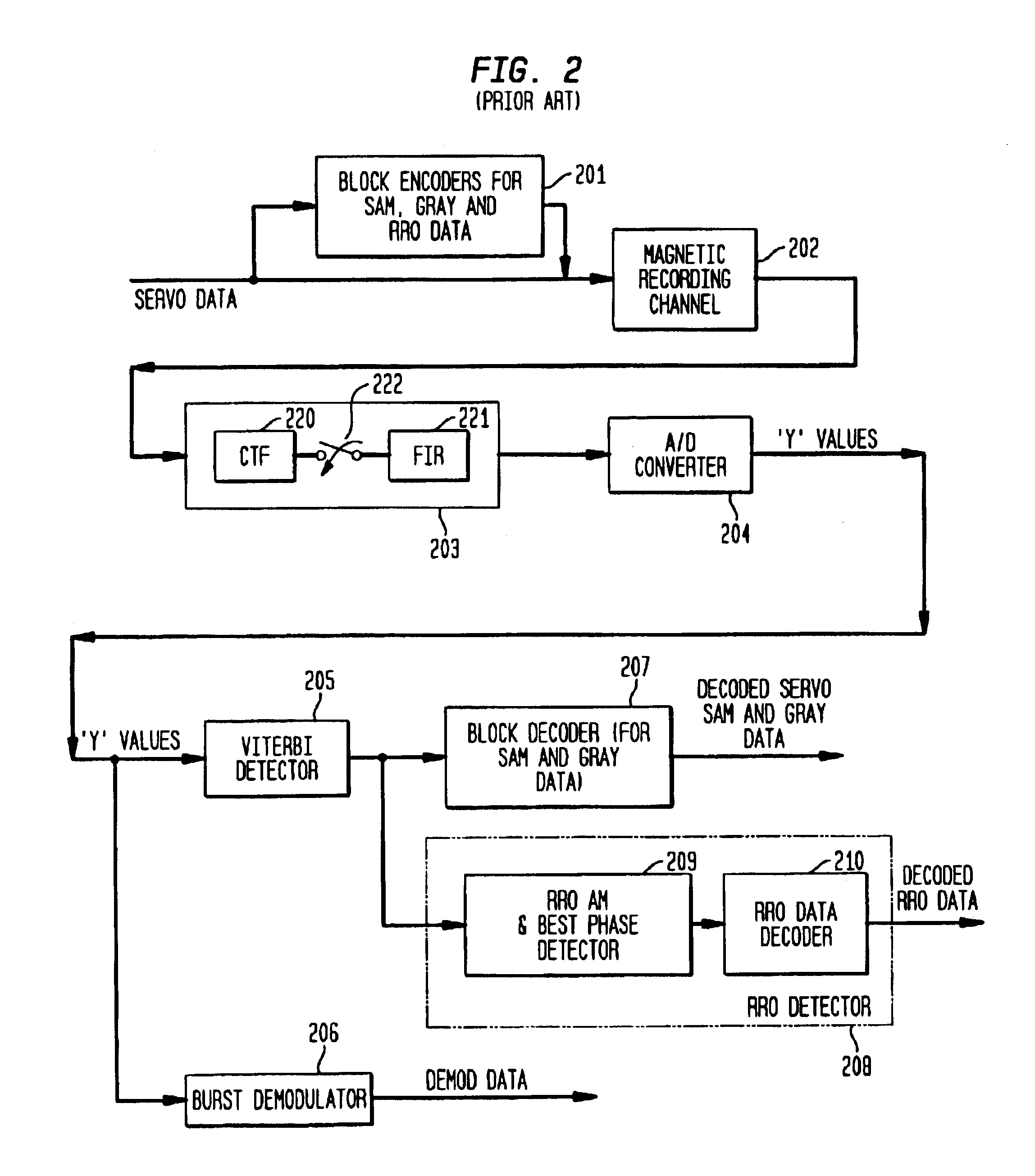
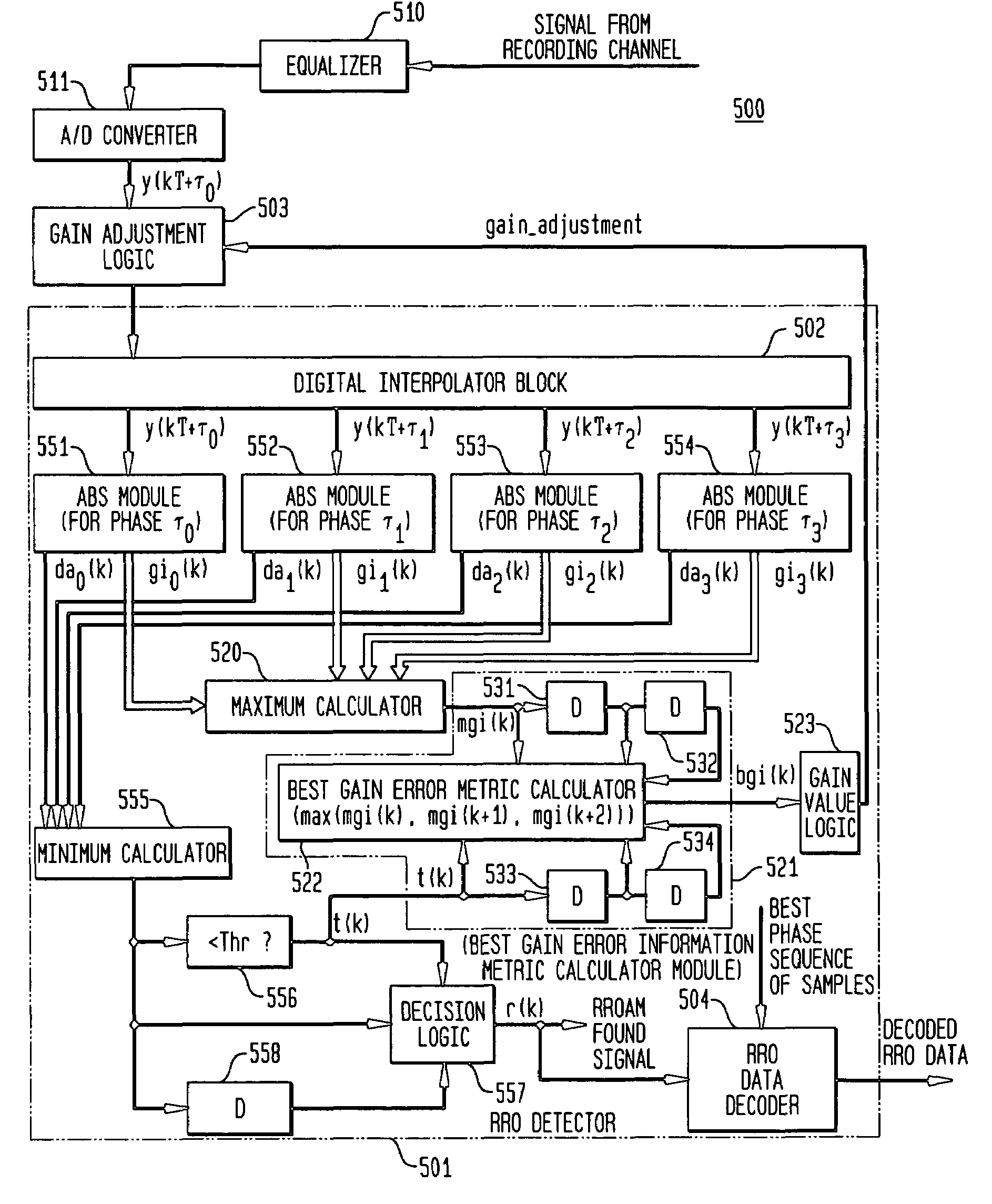
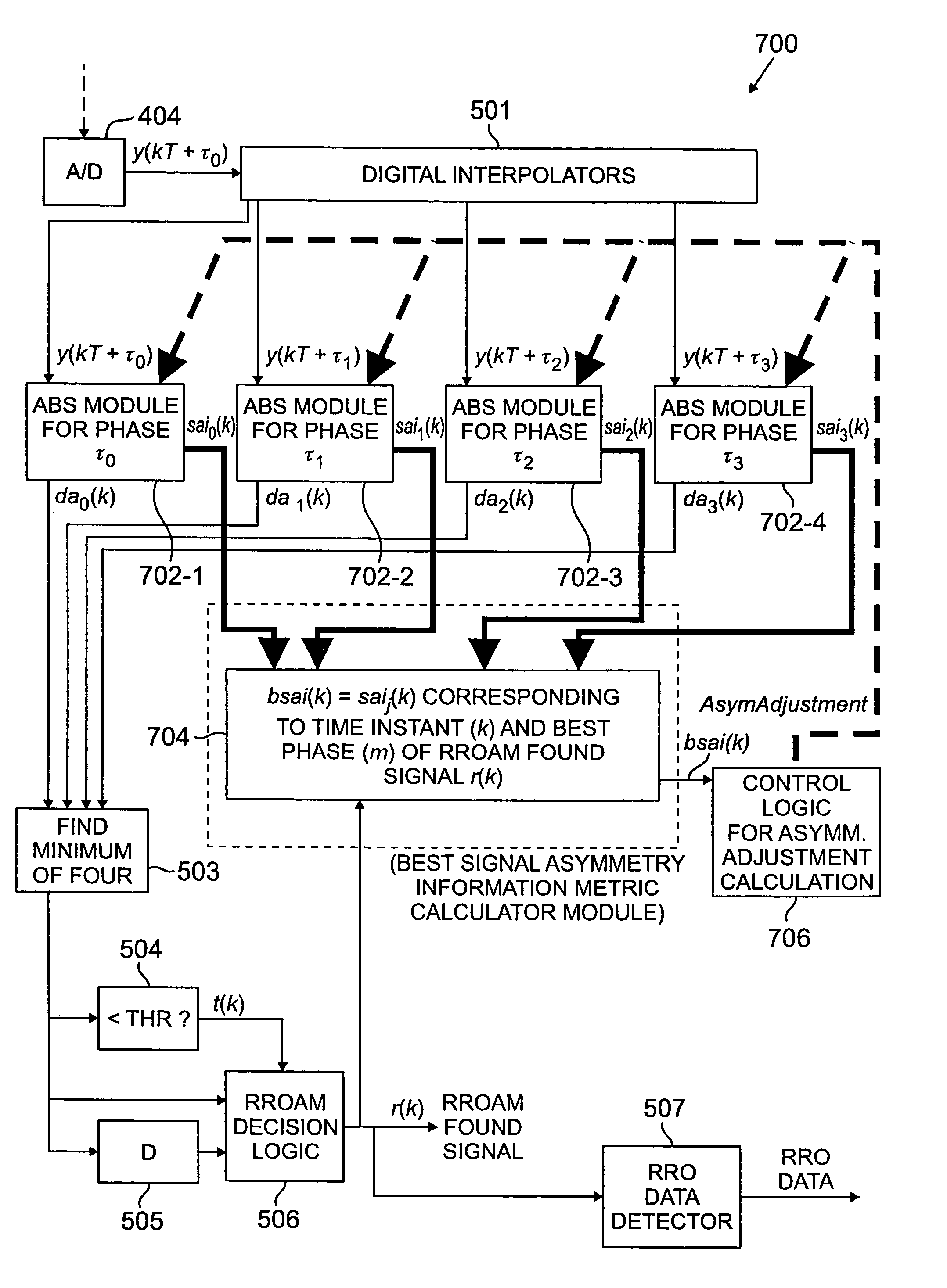
Maximum likelihood detection of asynchronous servo data employing interpolation
ActiveUS6912099B2Modification of read/write signalsSynchronisation error detectionSample sequenceMaximum likelihood detection
A repeatable run-out (RRO) detector employs one or more digital interpolators to interpolate asynchronous sample values representing an RRO address mark (AM) and RRO data, an asynchronous maximum-likelihood (AML) detector to detect the RRO AM, and a RRO data decoder to decode the RRO data. The AML detector employs an AML algorithm, such as a Viterbi algorithm, to detect the series of peaks of the RRO AM based on detection of the entire sequence of observed peaks. AML detection selects one of either the asynchronous or interpolated sample sequences that are closest in distance to the ideal RRO AM sample sequence. Once the RRO AM is detected, the AML detector provides a RRO AM found signal as well as the selected one of the sample sequences having the best phase for detecting and decoding the RRO data.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Client-based web server application verification and testing system
InactiveUS20060117055A1Improve automationFacilitates rapid generationDigital data processing detailsError detection/correctionWeb siteWeb service
A client-based web server application verification and testing system that requires no technical training, yet provides effective and efficient automated testing. The invention facilitates the rapid generation of test cases for a web site, and the automated execution of those test cases via distributed computing. The transitions through a web site are mapped onto a tree control to exploit user familiarity with a dual pane graphical interface and the drag / drop operation on tree controls. The tree is populated primarily by an autonomous spider exploring the site. Complex sequences requiring form inputs are added by recording sample sequences and then allowing the user to prune from all possible permutations of those samples. The export and import of form input data to a spreadsheet provides additional flexibility. Both the exploration and validation tasks may be distributed to a network of computers.
Owner:DOYLE JOHN
Detection of recorded data employing interpolation with gain compensation
ActiveUS7002767B2Modification of read/write signalsDriving/moving recording headsSample sequenceComputer science
A repeatable run-out (RRO) detector employs one or more digital interpolators to interpolate asynchronous sample values representing an RRO address mark (AM) and RRO data, and an asynchronous maximum-likelihood (AML) detector to detect the RRO AM. The AML detector selects one of either the asynchronous or interpolated sample sequences that are closest in distance to the ideal RRO AM sample sequence. In addition, a gain value is generated for each of the asynchronous and interpolated sample sequences. Once the RRO AM is detected, the AML detector provides a RRO AM found signal. Gain estimate values for either the selected asynchronous or selected interpolated sample sequences corresponding to the RRO AM found signal are averaged over a predefined number of detection events to generate a best gain error metric (BGEM). The BGEM is employed to adjust the gain of the asynchronous sample sequence.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
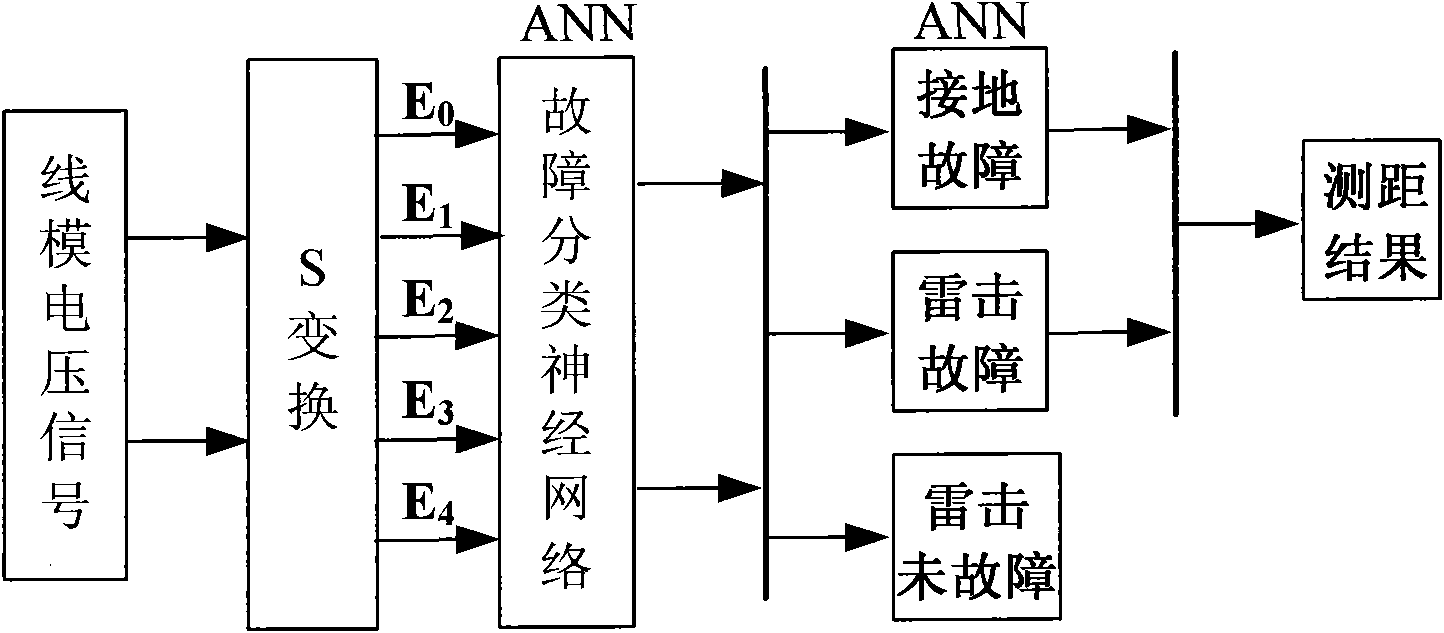
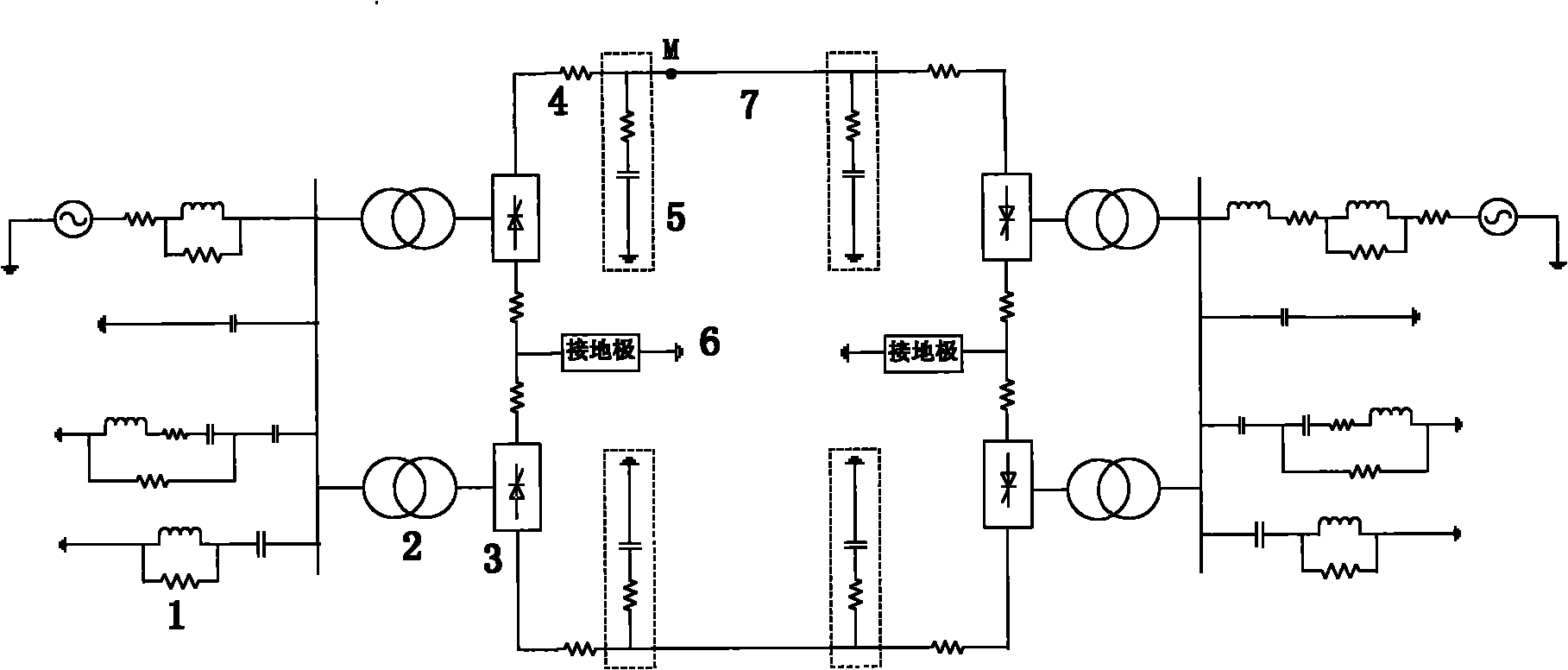
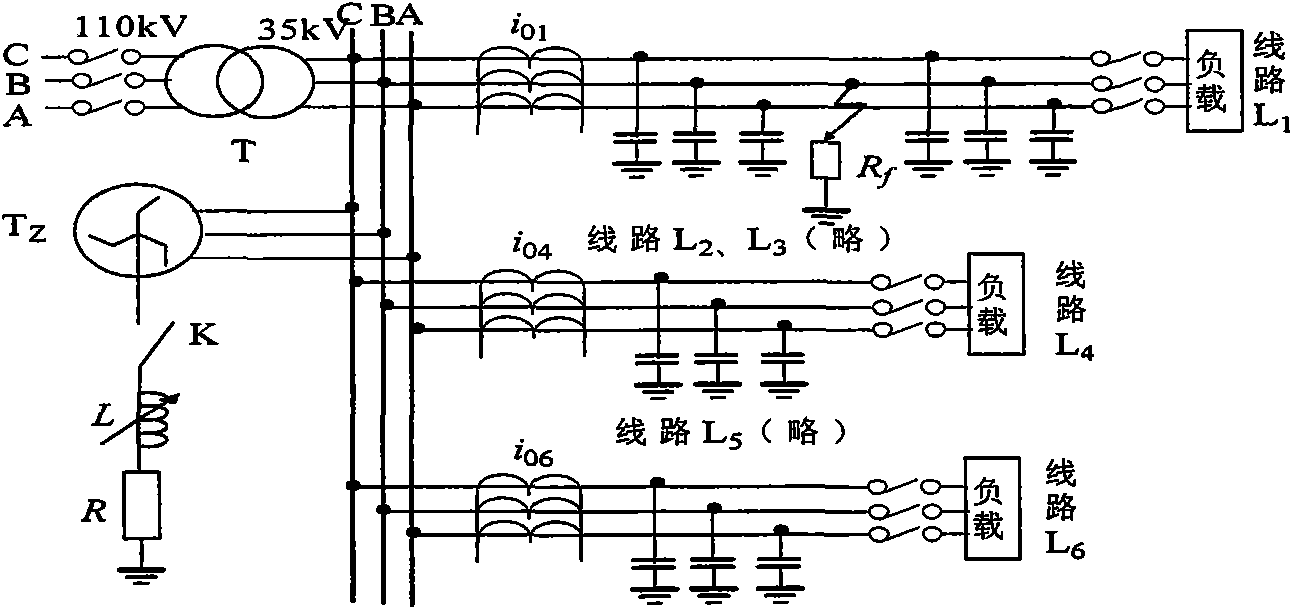
Intelligent fault classification and location method for ultra-high voltage direct current transmission line
ActiveCN101975910ALower requirementPracticalFault locationNeural learning methodsUltra high voltageElectric power system
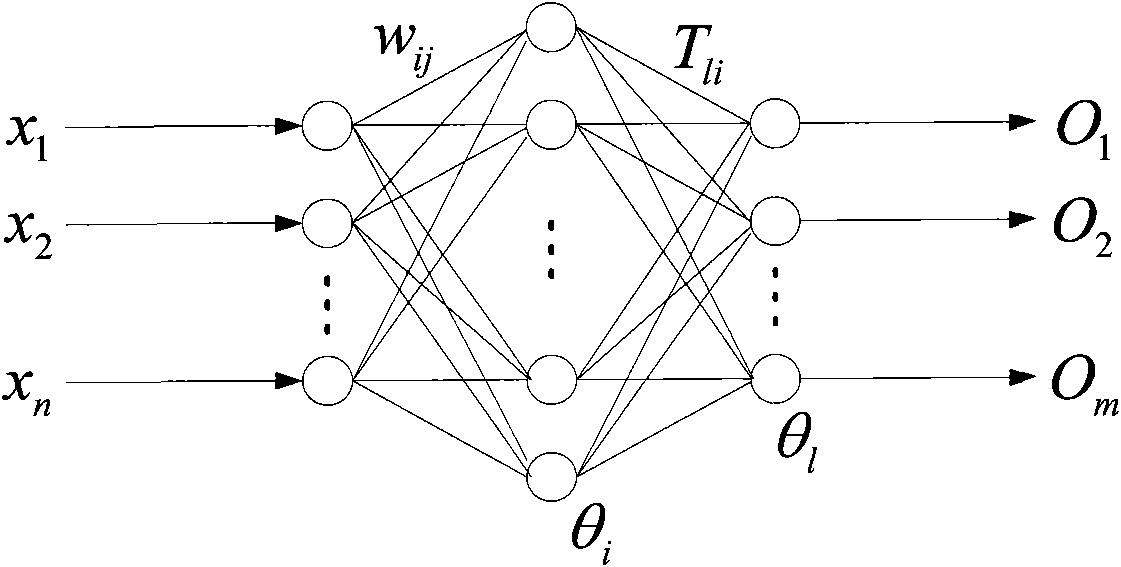
The invention discloses an intelligent fault classification and location method for an ultra-high voltage direct current transmission line, and belongs to the technical field of relay protection of power systems. The method comprises the following steps of: classifying fault data by using a neural network by adopting a layered and distributed neural network model; distinguishing fault types; sending the classified data into different neural networks respectively for performing fault location; when the direct current transmission line has a fault and a sampling frequency is 10 kHz, selecting a discrete line mode voltage signal which has the sampling sequence length of 100 after the fault and performing S-transform, wherein a transform result is a complex time-frequency matrix of 51*100; solving the modulus of each element in the complex matrix to obtain transient energy distribution of the line mode voltage at all frequencies; selecting first five energy spectrums as sample properties; selecting a transfer function and a learning rule; setting proper neural network parameters for constructing a BP network model; and performing fault classification and fault location. A large number of simulation results show that the method has a good effect.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
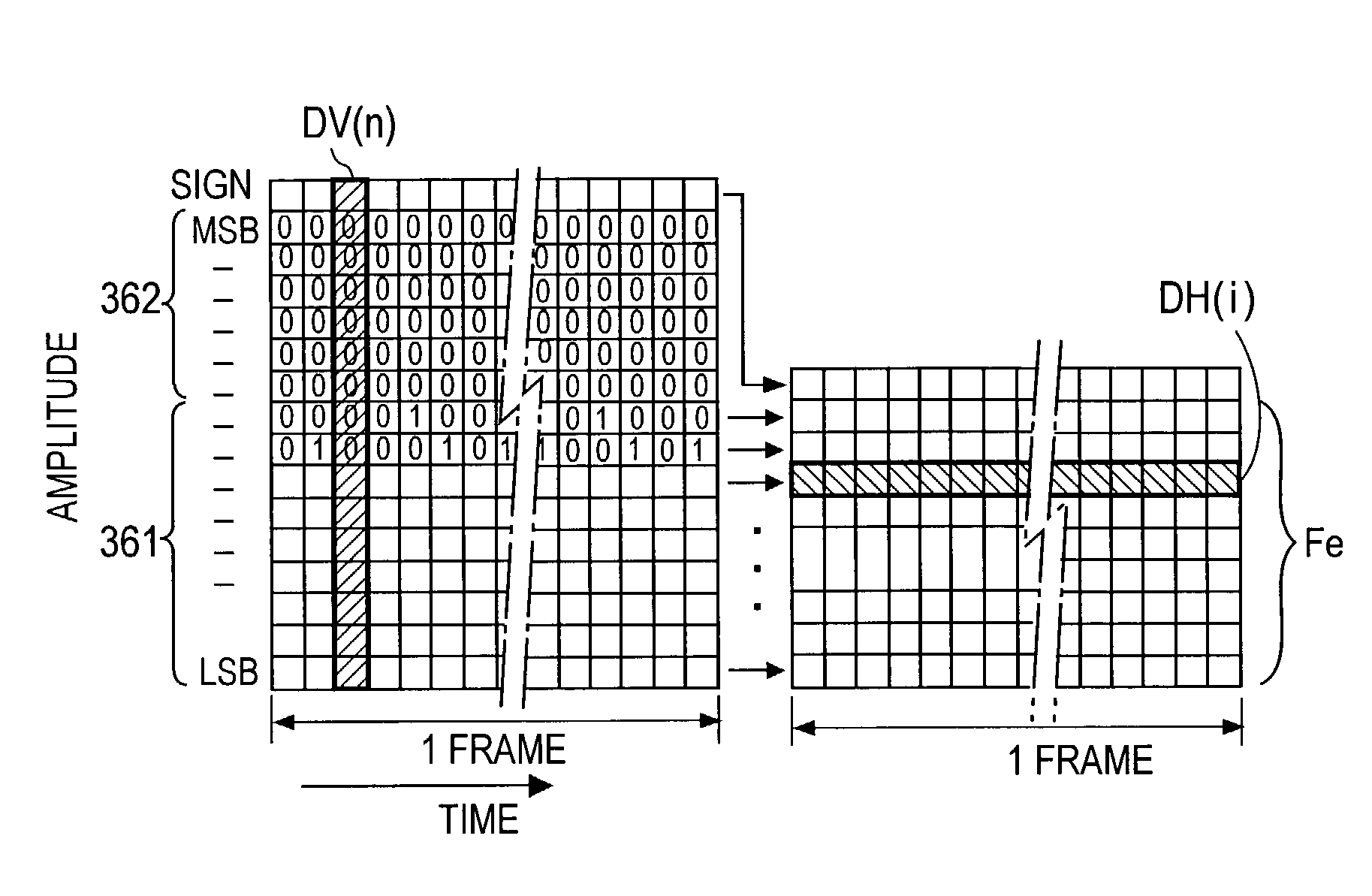
Digital signal coding and decoding methods and apparatuses and programs therefor
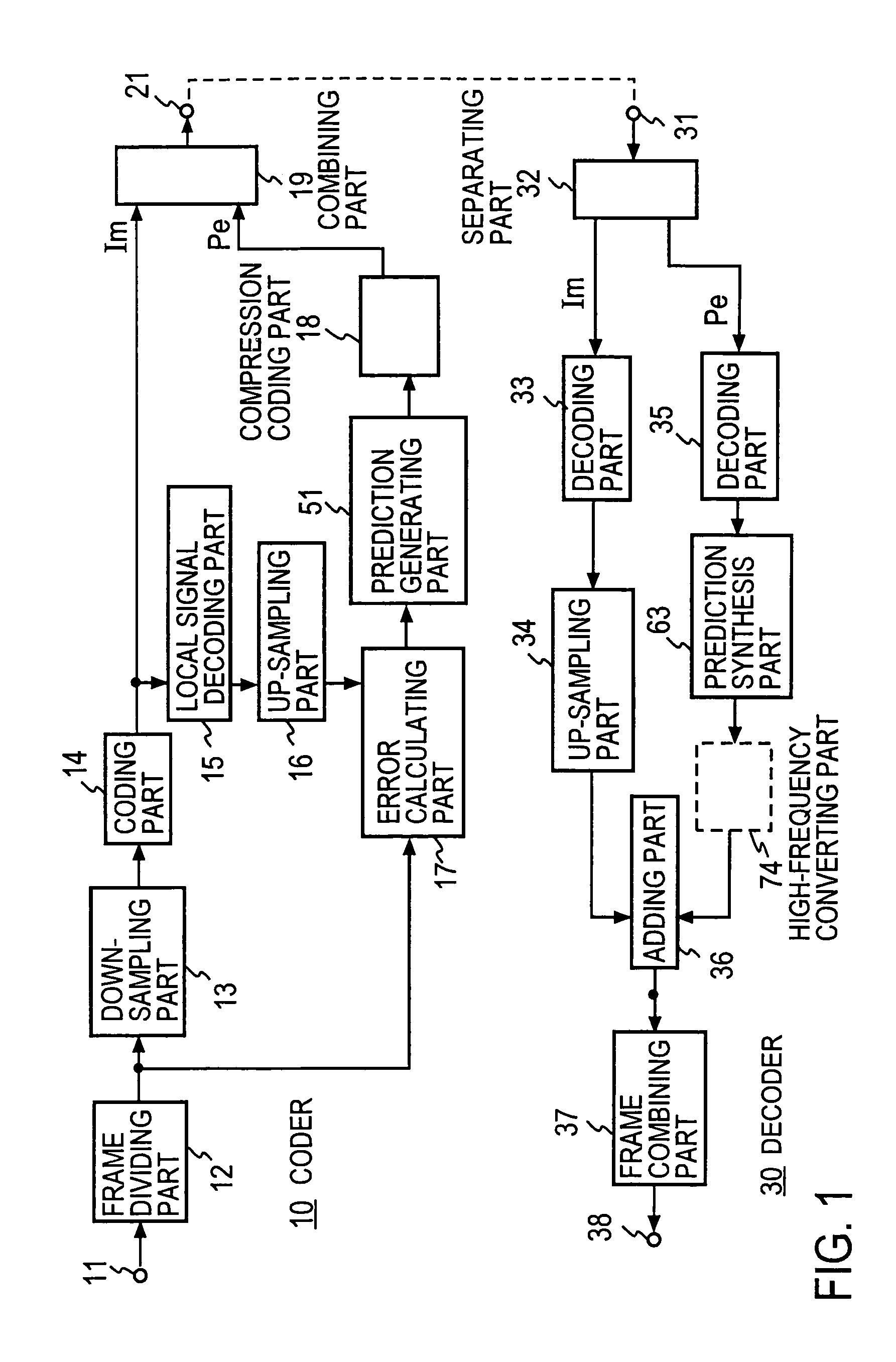
ActiveUS7200561B2Reduce the amount of informationSpeech analysisCode conversionDecoding methodsFrequency spectrum
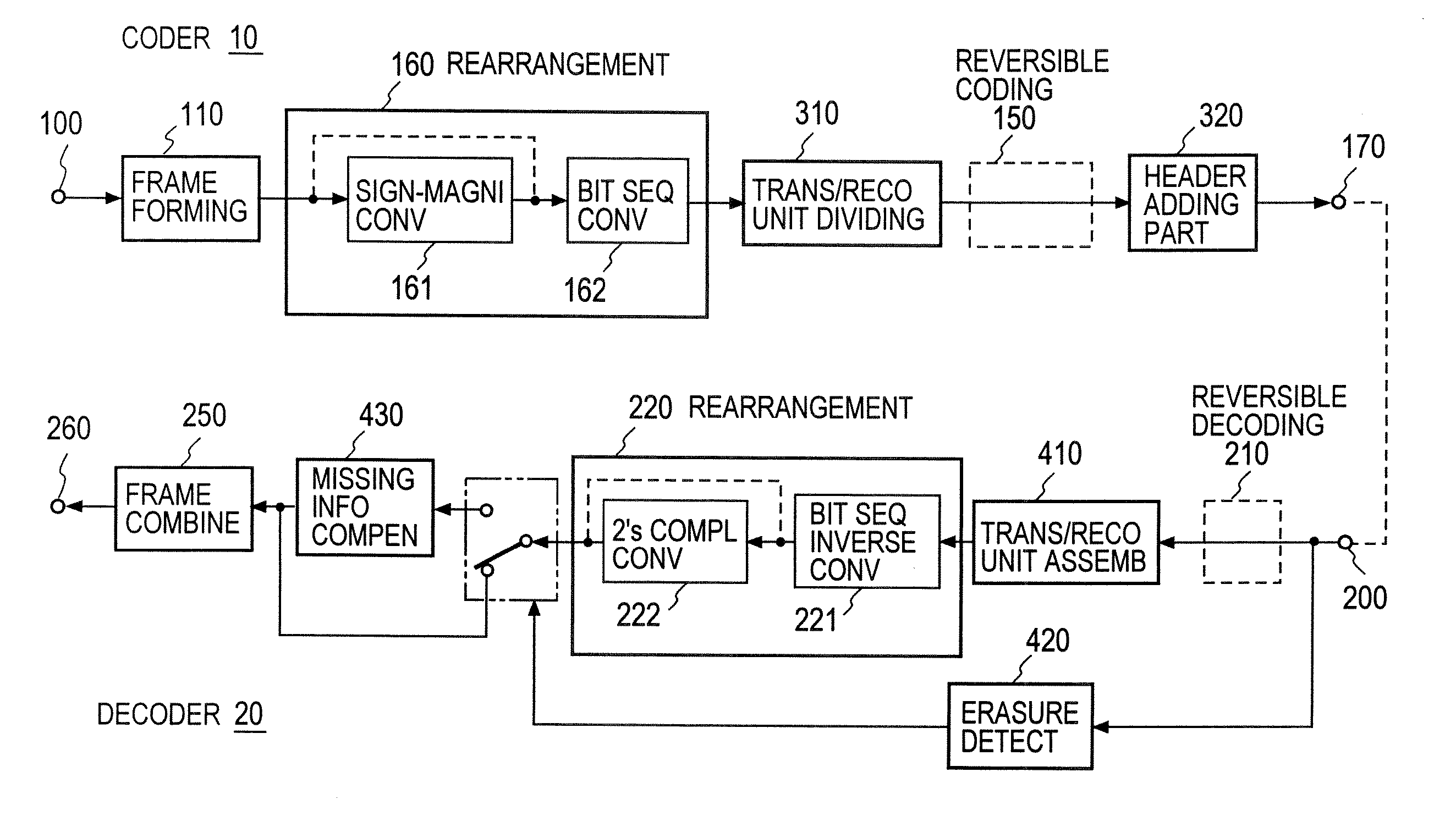
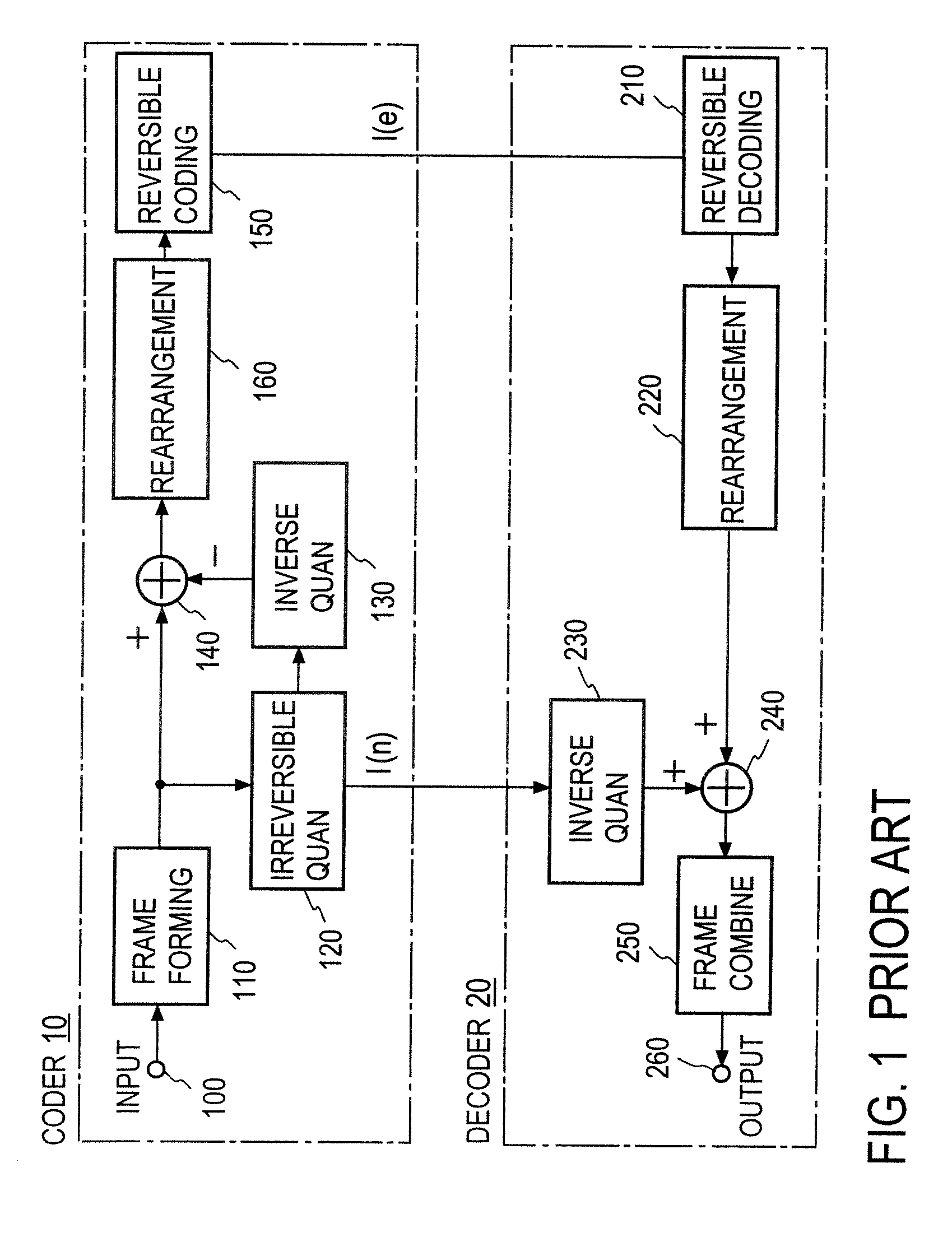
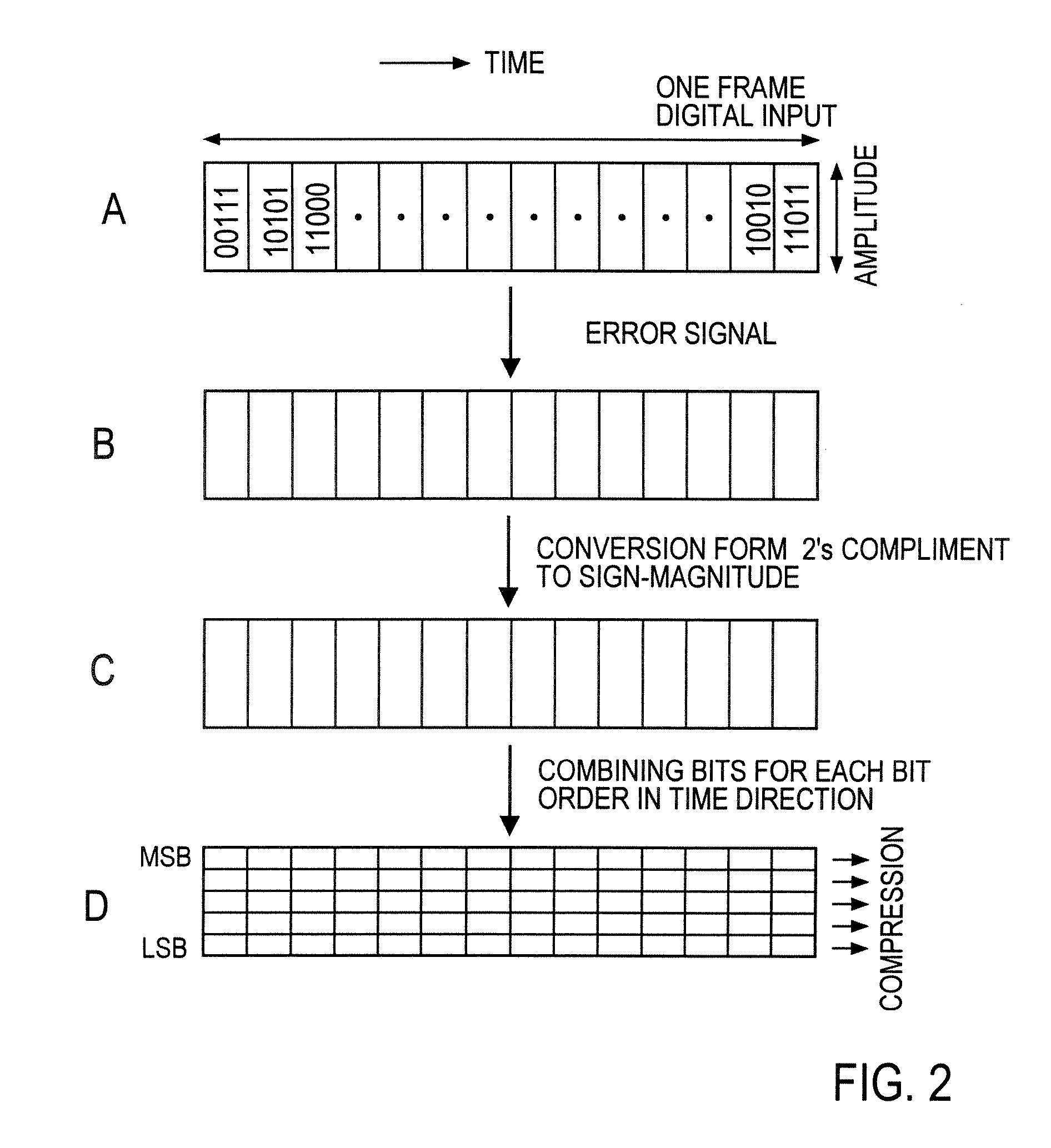
At the coder side, bits of samples of each frame of an input digital signal are concatenated every digit common to the samples across each frame to generate equi-order bit sequences, which are output as packets. At the decoding side, the input equi-order sequences are arranged inversely to their arrangement at the coder side to reconstruct sample sequences. When a packet dropout occurs, a missing information compensating part 430 correct the reconstructed sample sequences in a manner to reduce an error between the spectral envelope of the reconstructed sample sequence concerned and a known spectral envelope.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
Digital signal processing method, processor thereof, program thereof, and recording medium containing the program
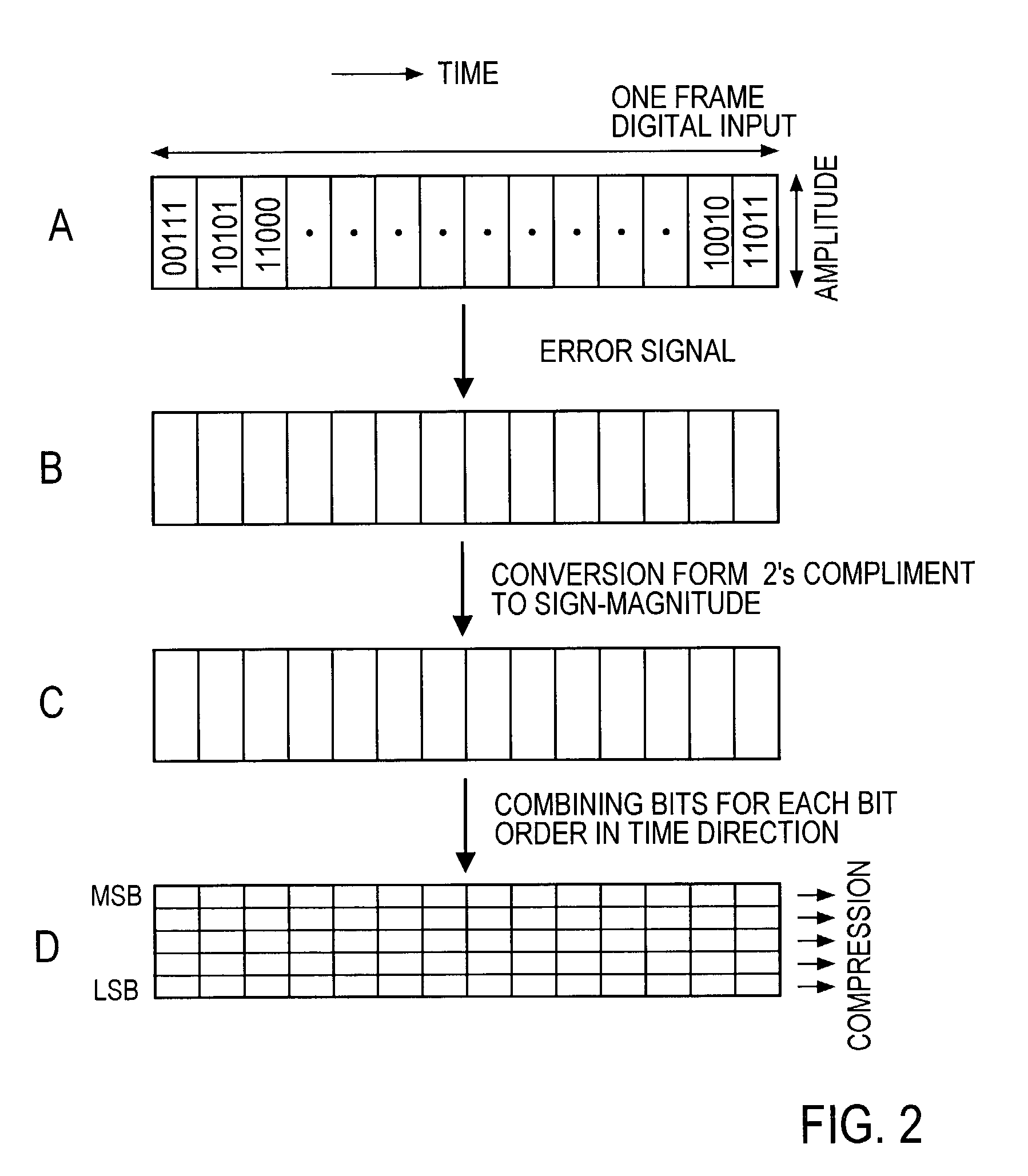
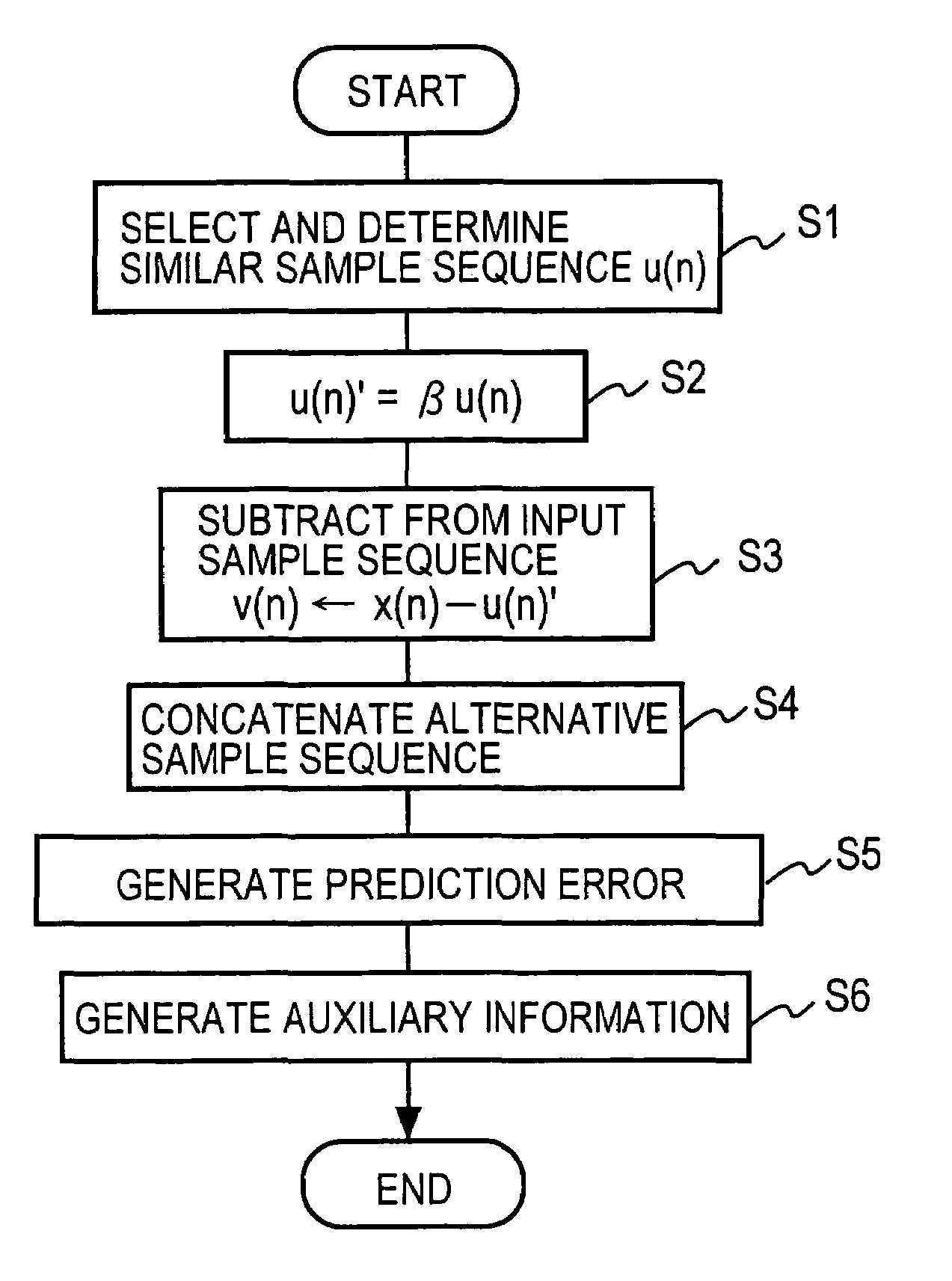
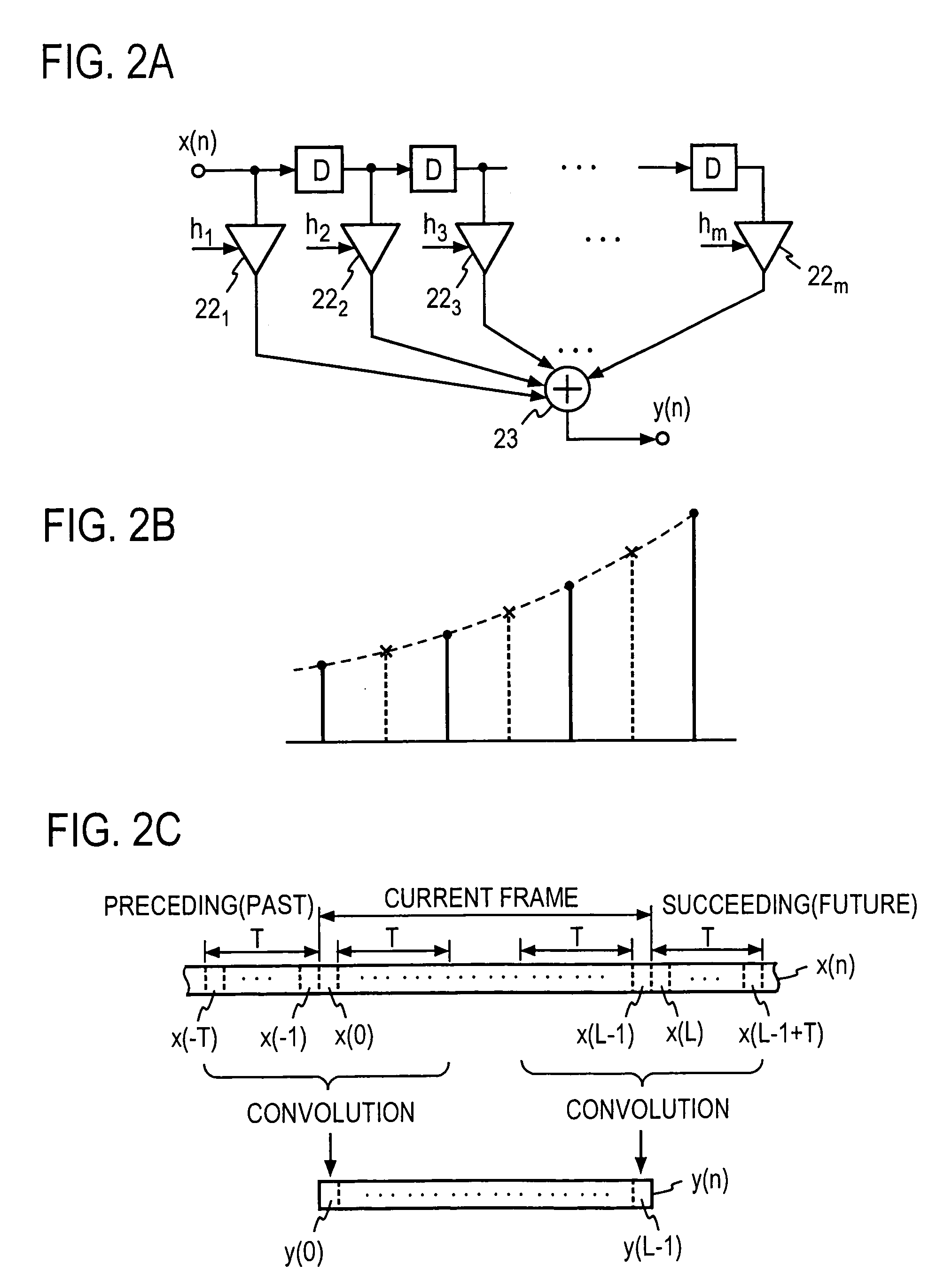
InactiveUS7145484B2Suppress discontinuityQuality improvementElectric signal transmission systemsSpeech analysisPattern recognitionDigital signal processing
A sample sequence ΔS similar to a first or last sample sequence of the current frame is extracted from its samples SFC and concatenated, as an alternative sample sequence AS, to each of the front and back of the current frame, and the current frame with the alternative sample sequence concatenated thereto is subjected to filtering or prediction coding to obtain processing result SOU of the current frame. In the case of prediction coding, auxiliary information, which indicates which part of the current frame was used as the alternative sample sequence, is also output. By this, filtering, autoregressive prediction coding and decoding, which require processing extending over preceding and succeeding frames as in an interpolation filter, can be concluded in the current frame with substantially no degradation of the continuity and coding efficient of the reconstructed signal.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
Method and apparatus for maximum likelihood detection of data employing interpolation with compensation of signal asymmetry
ActiveUS7180693B2Modification of read/write signalsDriving/moving recording headsSample sequenceMaximum likelihood detection
A method and apparatus are disclosed for detecting data, such as a sample sequence read from a recording channel. Interpolation techniques are employed to generate one or more interpolated sample sequences from the data. Each interpolated sample sequence has a different corresponding phase relative to the data. A distance measure is generated between a portion of each interpolated sample sequence and an ideal sample sequence. The ideal sample sequence corresponds to peaks in the data. According to one aspect of the invention, a signal asymmetry measure is computed for the portion of each sample sequence and is used to adjust an ideal sample sequence.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and apparatus for identifying, classifying, or quantifying DNA sequences in a sample without sequencing
InactiveUS6418382B2Rapid and economical and quantitative and precise determination and classificationSufficient discrimination and resolutionData processing applicationsMicrobiological testing/measurementSample sequenceSingle sequence
This invention provides methods by which biologically derived DNA sequences in a mixed sample or in an arrayed single sequence clone can be determined and classified without sequencing. The methods make use of information on the presence of carefully chosen target subsequences, typically of length from 4 to 8 base pairs, and preferably the length between target subsequences in a sample DNA sequence together with DNA sequence databases containing lists of sequences likely to be present in the sample to determine a sample sequence. The preferred method uses restriction endonucleases to recognize target subsequences and cut the sample sequence. Then carefully chosen recognition moieties are ligated to the cut fragments, the fragments amplified, and the experimental observation made. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is the preferred method of amplification. Another embodiment of the invention uses information on the presence or absence of carefully chosen target subsequences in a single sequence clone together with DNA sequence databases to determine the clone sequence. Computer implemented methods are provided to analyze the experimental results and to determine the sample sequences in question and to carefully choose target subsequences in order that experiments yield a maximum amount of information.
Owner:CURAGEN CORP
Blind cost criterion timing recovery
Symbol timing recovery employs a blind cost criterion from the Bussgang class of functions, and its stochastic gradient, to generate a timing phase error used to adjust sampling of received symbols. For one implementation, the estimate is derived in accordance with the Constant Modulus (CM) criterion and its gradient via the CM algorithm (CMA), and the estimate is calculated from a sequence of samples. This estimate is then used to adjust the period and phase of the sample sequence toward the period and phase of the transmitted symbols, driving the timing phase error to zero. The values used may be either i) samples themselves, ii) processed (e.g., interpolated) samples, or iii) equalized and processed samples. In addition, timing phase error estimates for other cost criteria, including the least mean squares algorithm, may be generated. These timing phase error estimates are selected either alone or in combination for deriving the timing phase error used to adjust the period and phase of the sample sequence.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
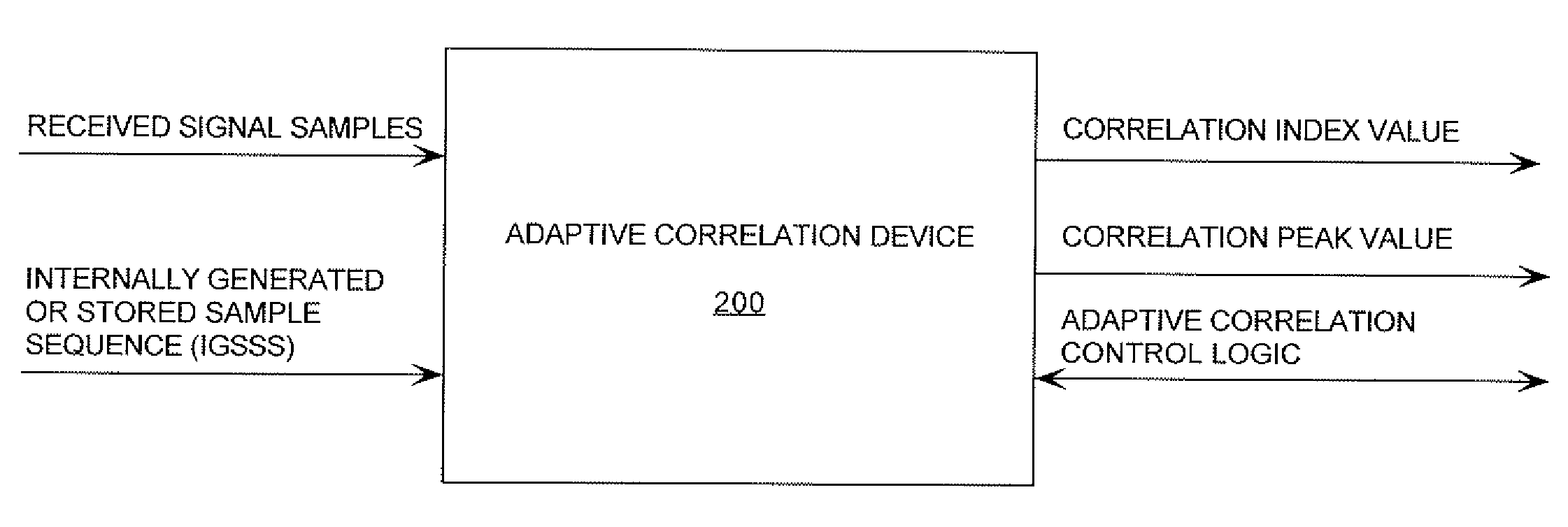
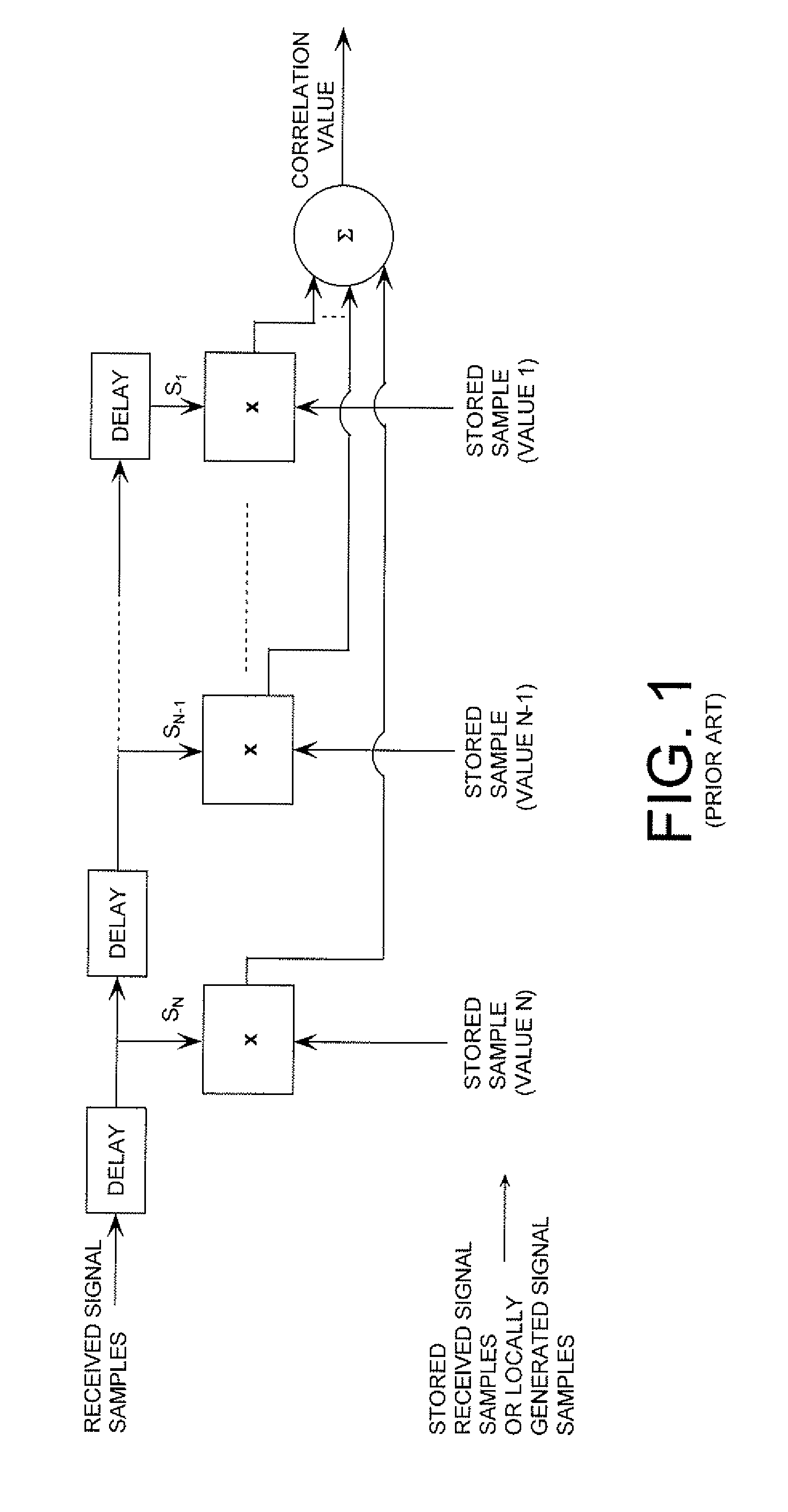
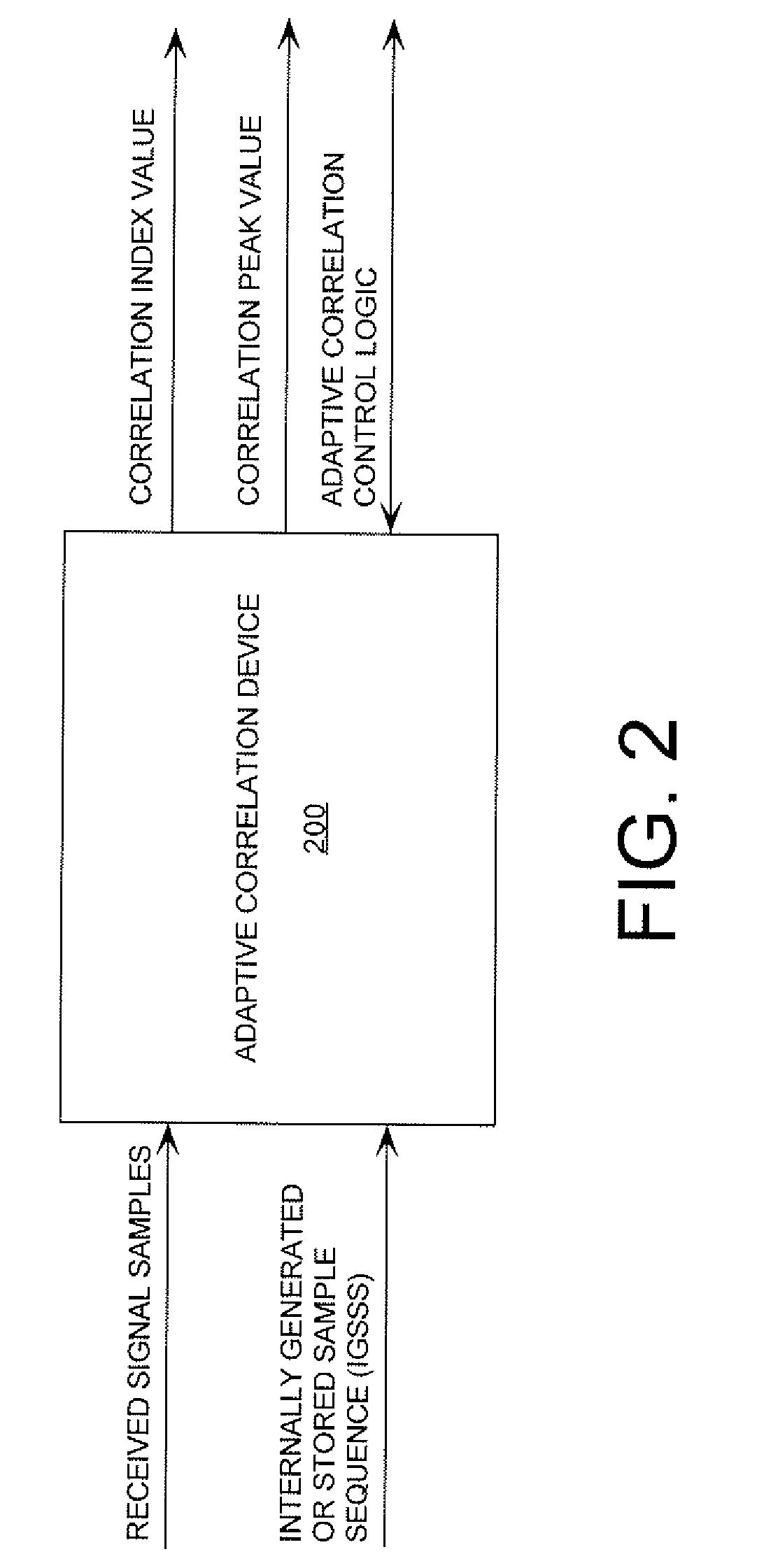
Adaptive correlation
ActiveUS20090296860A1Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsAmplitude demodulationImage resolutionSample sequence
A method is provided for correlating samples of a received signal and samples of an internally generated / stored sample sequence (“IGSSS”). The method involves performing a first iteration of a first-resolution correlation state. The first-resolution correlation state involves: selecting a first N sets of samples from the received signal; selecting a first set of samples from the IGSSS; and concurrently comparing each of the N sets of samples with the first set of samples to determine if a correlation exists between the same. If it is determined that a correlation does not exist between one of the N sets of samples and the first set of samples, then a second iteration of the first-resolution correlation state is performed. If it is determined that a correlation exists between one of the N sets of samples and the first set of samples, then a first iteration of a second-resolution correlation state is performed.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
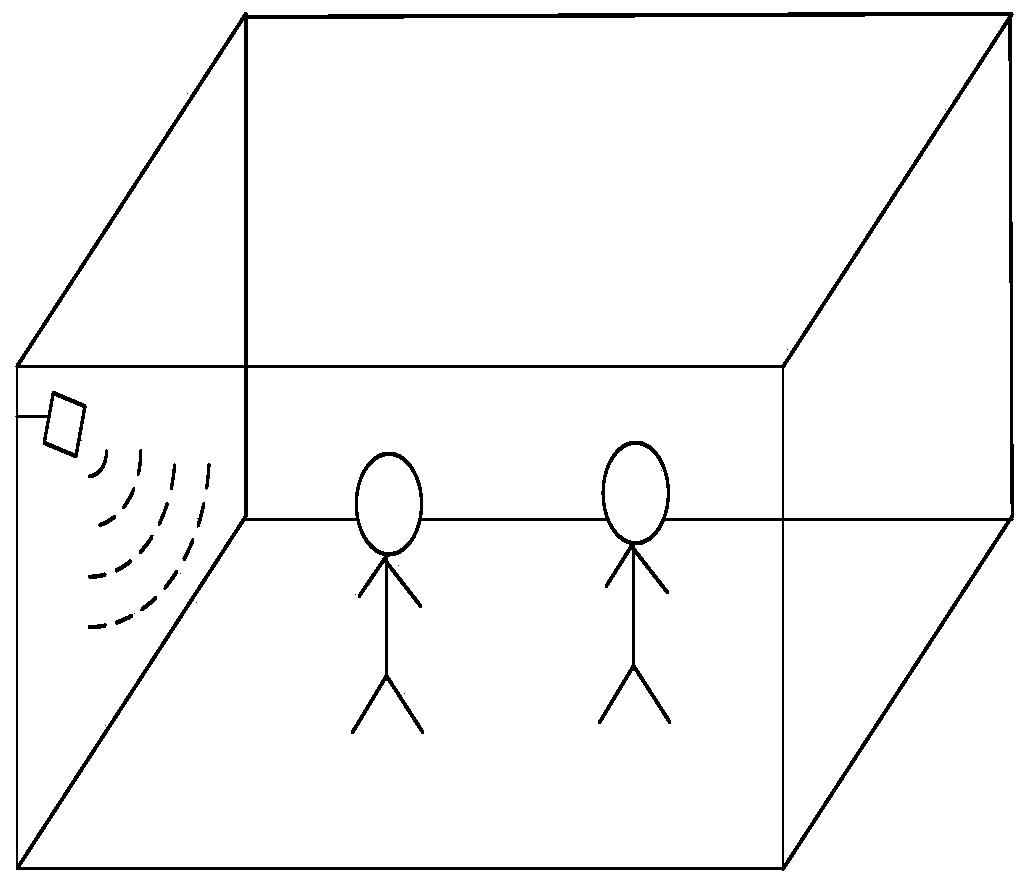
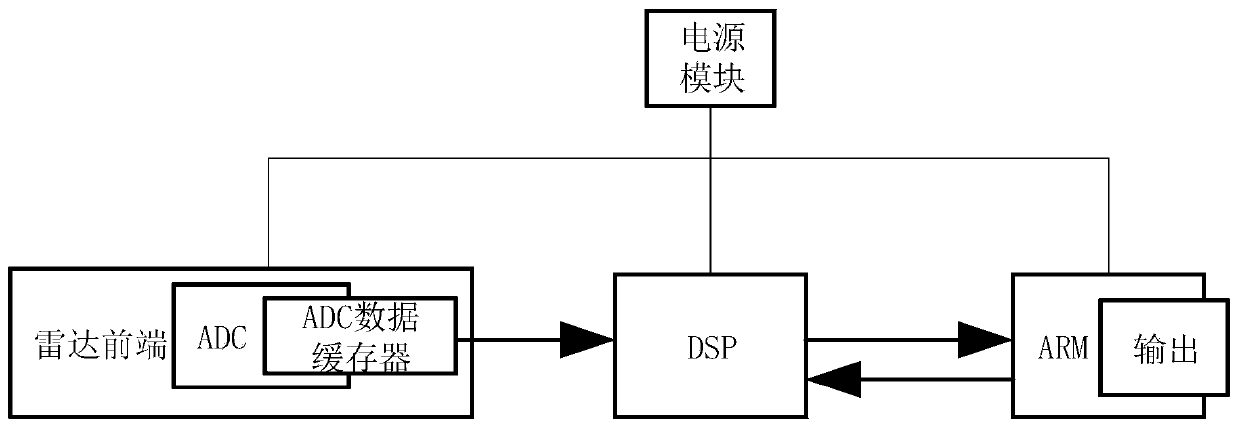
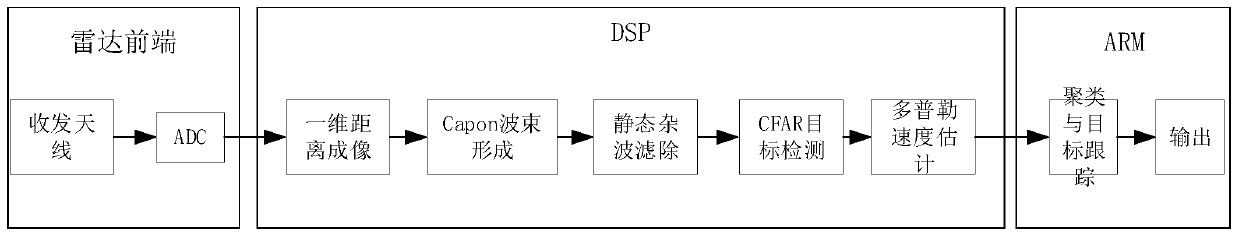
Personnel detection and counting system based on millimeter wave radar
ActiveCN110118966AEasy to detectAchieve countRadio wave reradiation/reflectionDigital signal processingData set
The invention provides a personnel detection and counting system based on a millimeter wave radar, wherein the millimeter wave radar is installed at a set position of a monitoring area, the millimeterwave radar transmits millimeter wave band radio frequency signals to the monitoring area through a multi-transmitting and multi-receiving antenna of the millimeter wave radar and receives echo signals at the same time, the echo signals are subjected to frequency mixing with the transmitted signals and then subjected to down-conversion to obtain beat intermediate frequency signals, and the beat intermediate frequency signals are sampled to obtain an echo sampling sequence. A digital signal processor reads the echo sampling sequence and performs signal processing to obtain a detected point cloud data set. An ARM processor reads the point cloud data set, meanwhile, Kalman filtering tracking is carried out on the point cloud data, continuous observation of states and the number of a pluralityof human body moving targets is achieved, the positions and the number of people in the monitoring area are obtained, and the number of people in the monitoring area is counted. The personnel detection and counting system based on the millimeter wave radar can track at least 20 targets simultaneously, provide the position and speed information of the targets, effectively judge the state of the targets and give early warning in time.
Owner:长沙莫之比智能科技有限公司
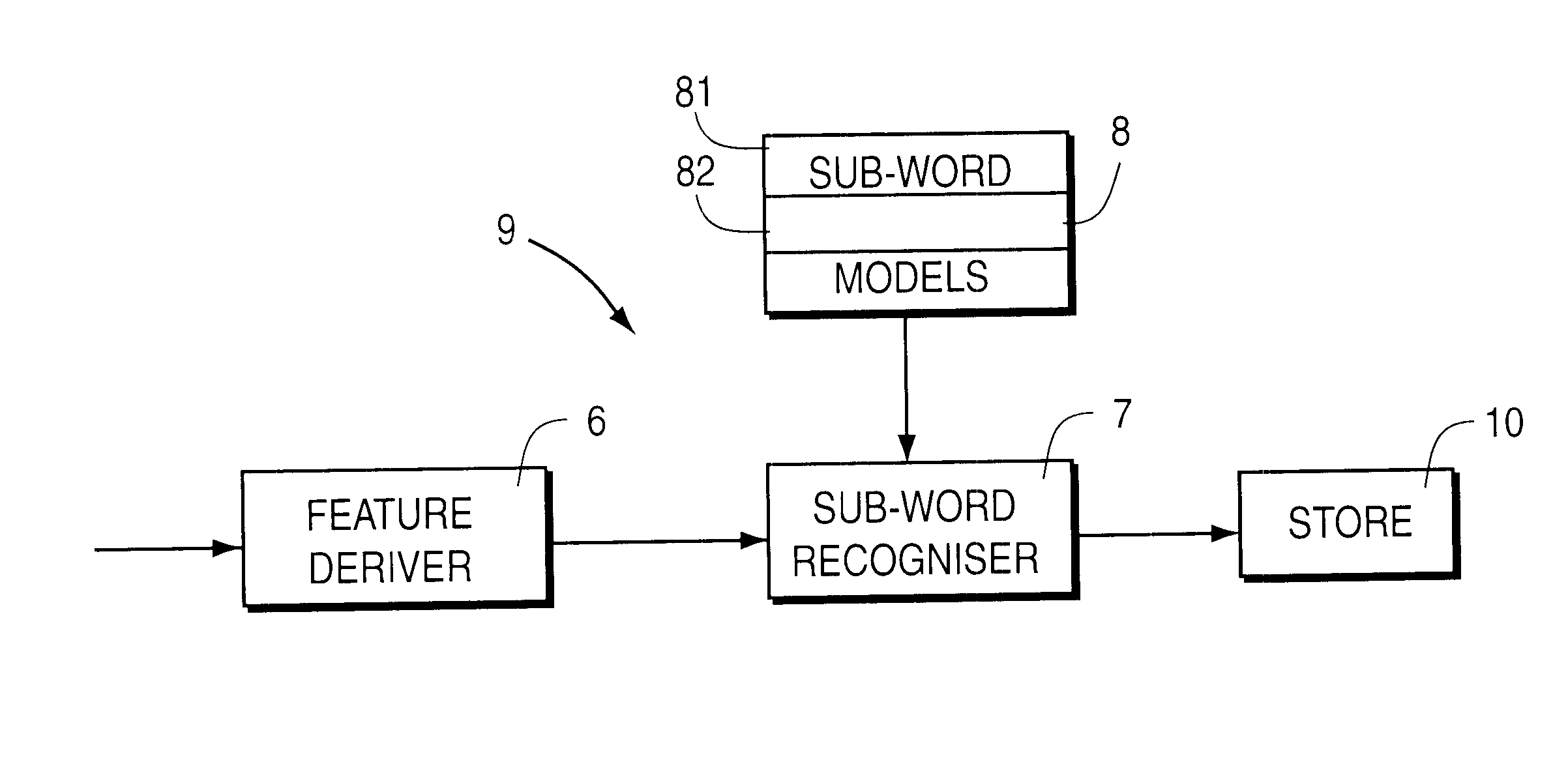
System and method for generating a phonetic baseform for a word and using the generated baseform for speech recognition
Out-of-vocabulary word models for a speech recognizer vocabulary are generated by forming phonemic transcriptions (phonetic baseforms) of user's utterances in terms of existing reference phonemes by using a speech recognition algorithm to match input sub-word feature sample sequences to suitably-constrained allowable sequences of existing reference phoneme features. The resultant new-vocabulary-word phonetic baseform models are stored for subsequent speech recognition using the same recognition algorithm.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
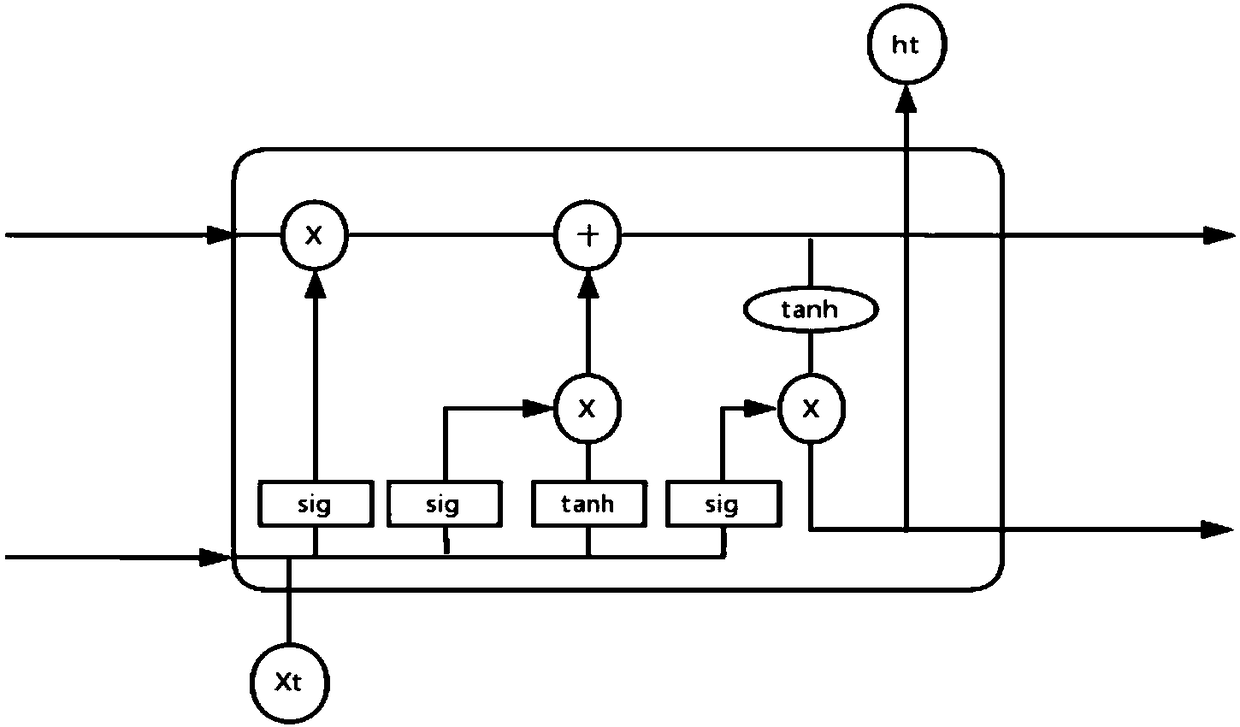
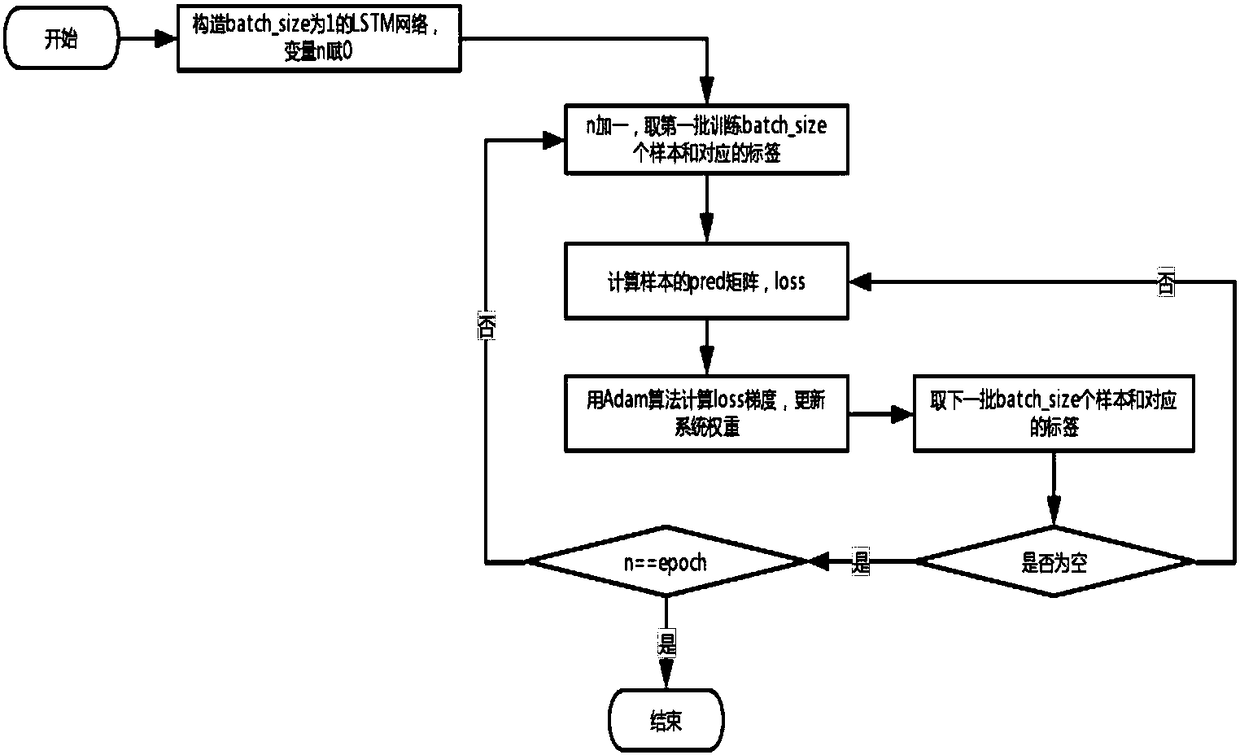
Cloud data center load prediction method based on LSTM (Long Short-Term Memory)
InactiveCN108170529AGood conditionImprove learning efficiencyResource allocationCharacter and pattern recognitionNerve networkEstimation methods
The invention discloses a cloud data center load prediction method based on LSTM (Long Short-Term Memory), and aims to solve the problem that optimal utilization can not be obtained by the limited calculation resources of a cloud data center. The method comprises the following steps that: taking the mass historical records of the cloud data center as a basis to manufacture a training sample and atesting sample; in addition, constructing a neural network connected by LSTM units; continuously inputting training samples on batch to obtain an output value. A neural network optimization algorithmadopts a new adaptation moment estimation method, parameters in each unit are continuously updated through iterative training, and global optimum is realized after training is finished, only the testing sample needs to be input into the network to obtain the next prediction value of a sample sequence; and if an input sequence is continuously updated by the prediction value, a prediction value sequence in one future period of time can be obtained.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Apparatus for encoding and decoding
InactiveUS20100027625A1Less effortEfficient codingColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionSample sequenceArtificial intelligence
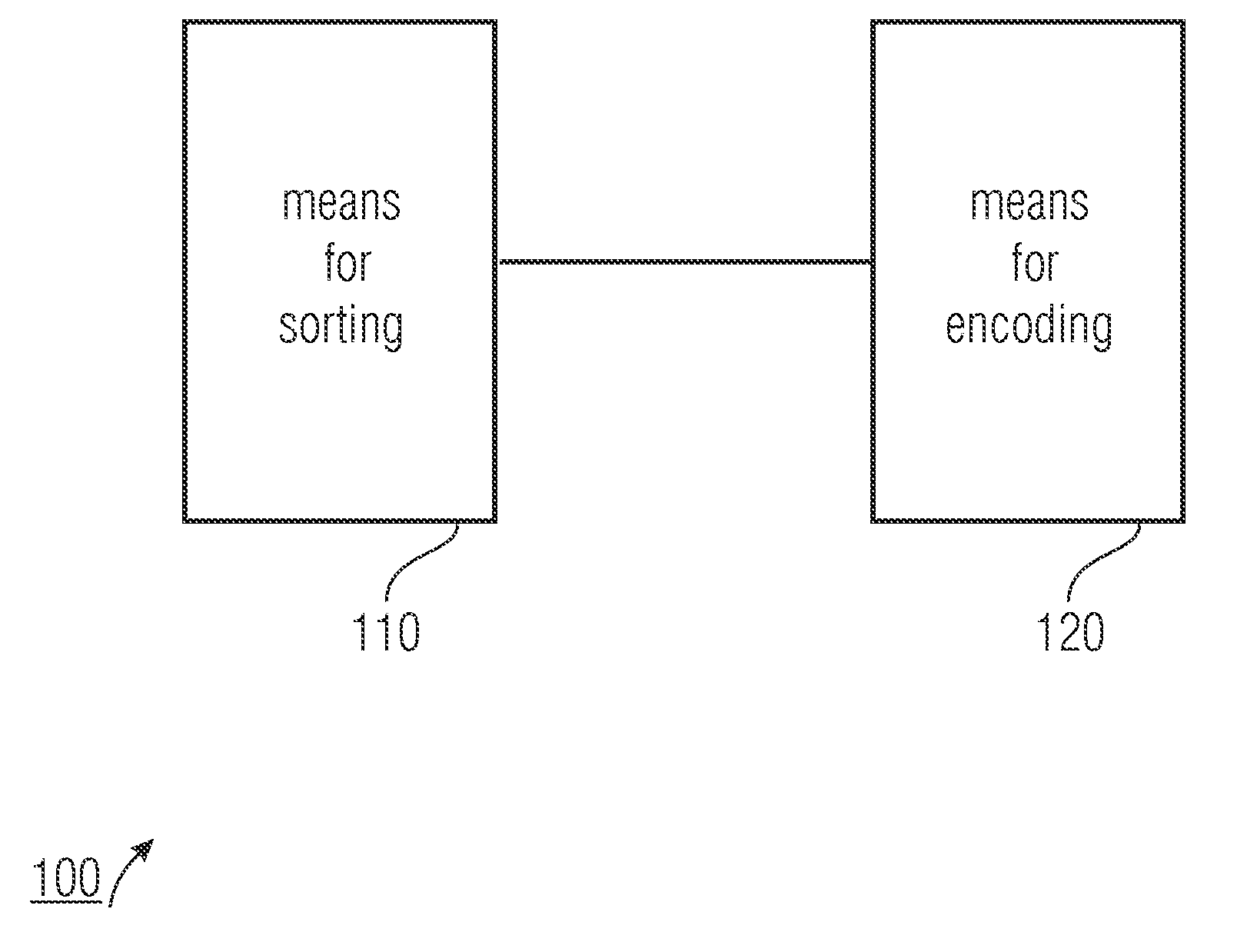
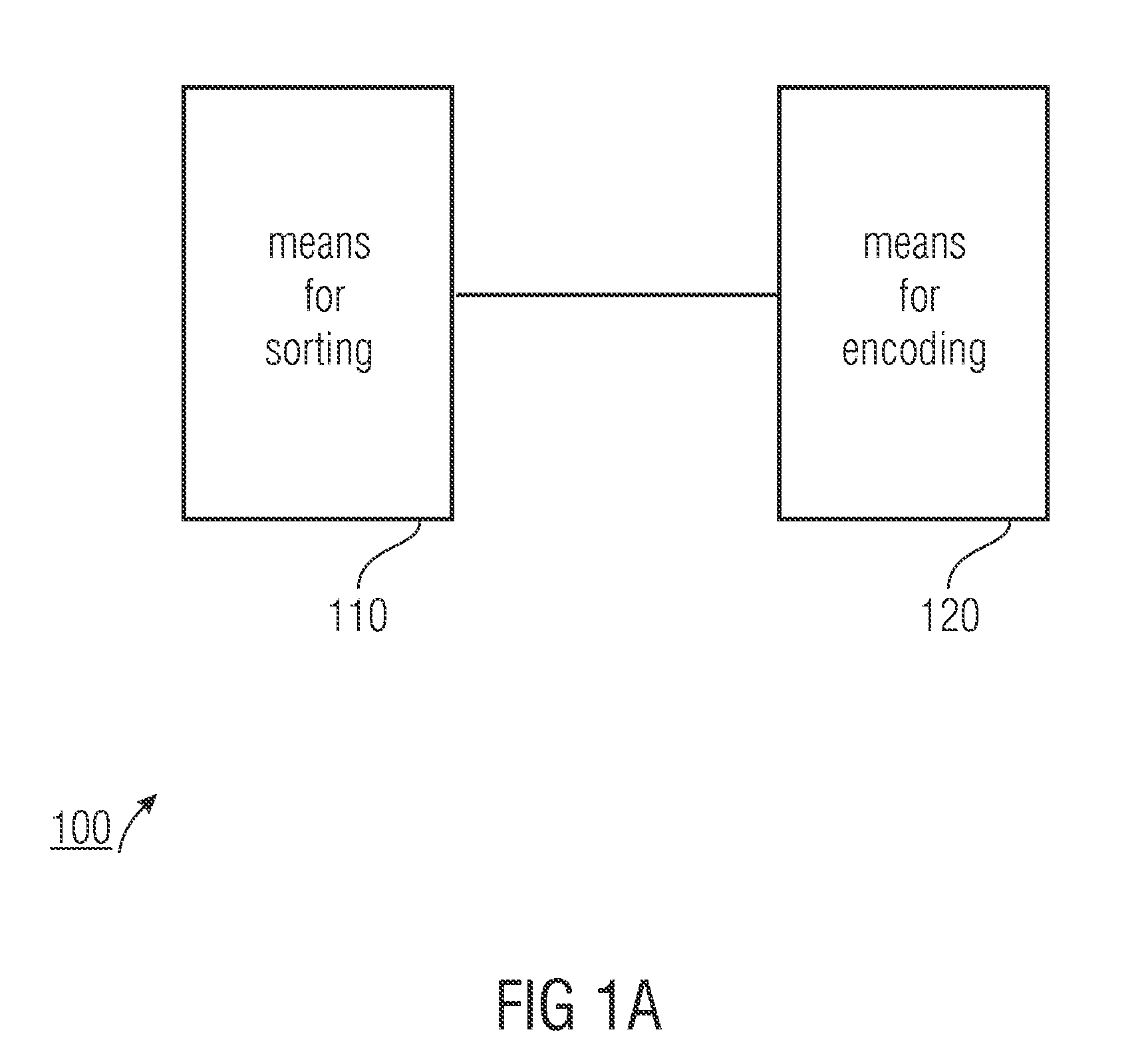
An apparatus for encoding a sequence of samples of an audio signal, with each sample within the sequence having an original position, includes a sorter for sorting the samples depending on their sizes, in order to obtain a sorted sequence of samples, with each sample having a sorting position within the sorted sequence. Furthermore, the apparatus has an encoder for encoding the sorted samples and information on a relation between the original and sorting positions of the samples.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Device and method for processing an audio signal
InactiveUS7295968B2Easy to implementSimple processDigital computer detailsSpeech recognitionSample sequenceAudio signal flow
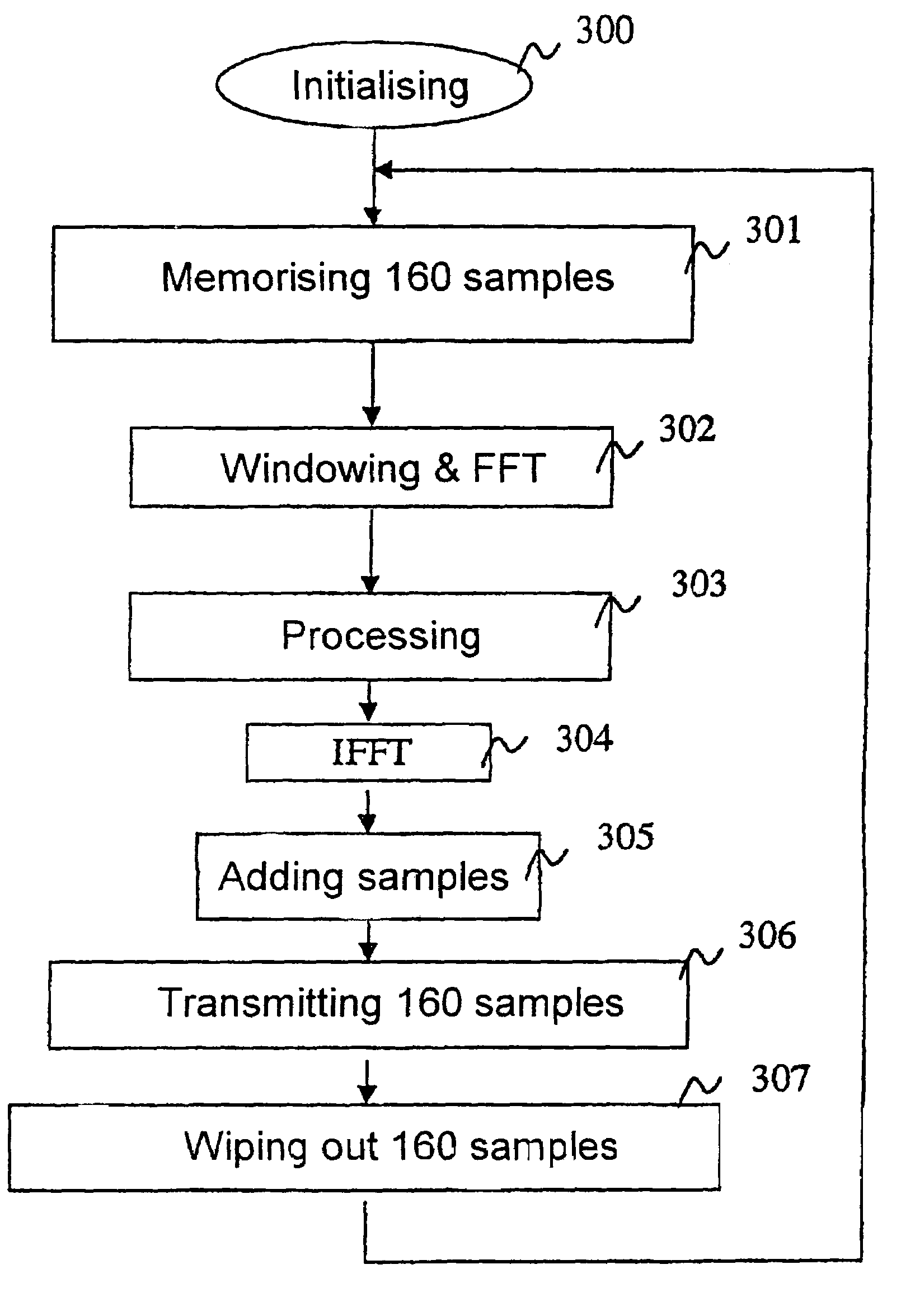
The invention concerns audio signal processing, comprising: a first processing of an audio source signal, using at least a mathematical transform applied on first sequences of samples obtained by applying first segmentation windows on the audio source signal; and a second audio processing applied on second sequences of samples obtained by applying second segmentation windows on the signal delivered by the first step; the two successive first windows and / or the two successive second windows overlapping, the overlaps being such that the segmentations are synchronous.
Owner:WAVECOM SA
Method and system for identifying transient process of non-intrusive load
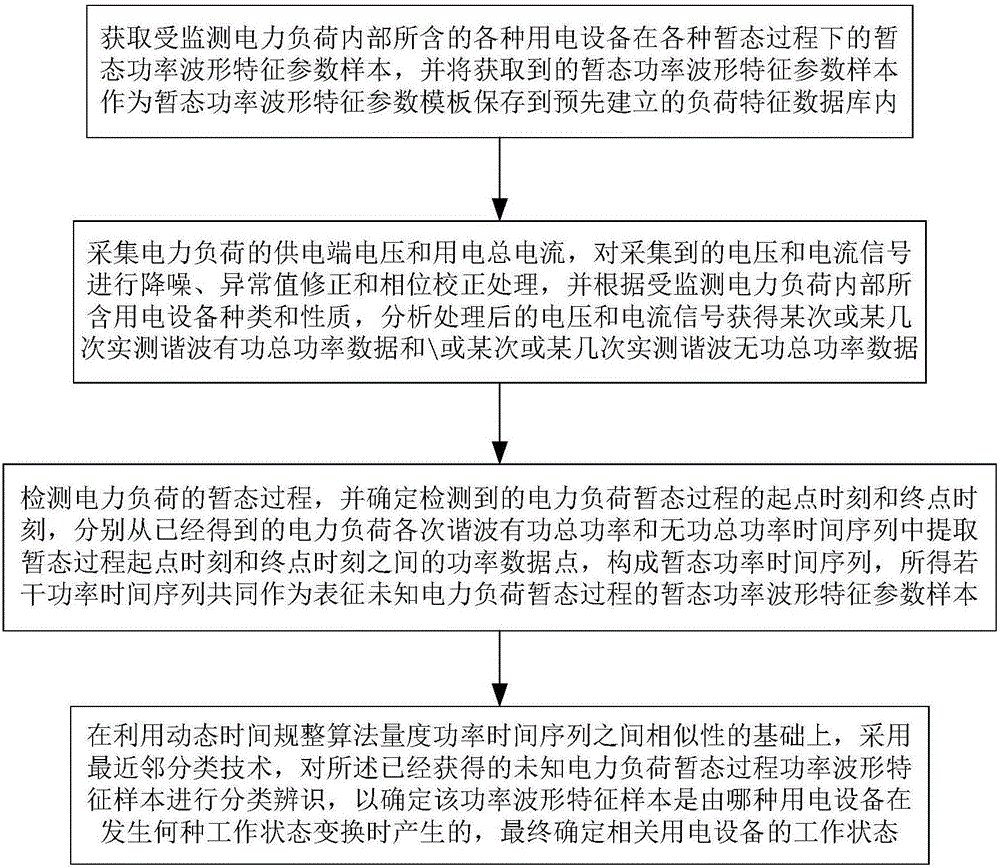
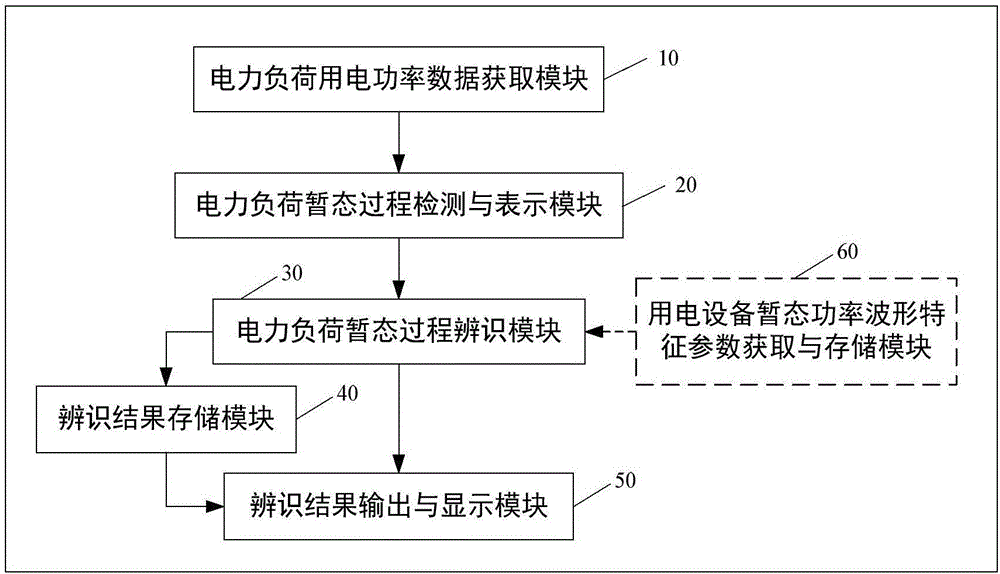
ActiveCN106786534AAdaptableImprove accuracyAc network circuit arrangementsNear neighborSample sequence
The invention belongs to the field of load power use monitoring and energy management, and particularly relates to a method and system for identifying transient process of a non-intrusive load. The method comprises the following steps: by virtue of transient power waveform characteristics of multiple types, measuring similarity of a transient power waveform characteristic parameter sample sequence of an unfixed length and a template sequence by using a dynamic time warping algorithm within a time domain, on the basis, establishing a load transient process classification identification scheme based on a nearest neighbor classification strategy, and confirming power use equipment with the load transient process, thereby achieving artificial working state identification on the non-intrusive type power use equipment. The method and the system have the beneficial effects that accuracy and robustness of power load transient process identification can be improved, the cost of a monitoring system can be effectively controlled, and the practicability of the monitoring system can be effectively improved, therefore, practical popularization of an NILM (Non-Intrusive Load monitoring) technique can be greatly improved.
Owner:TIANJIN TRANSENERGY TECH
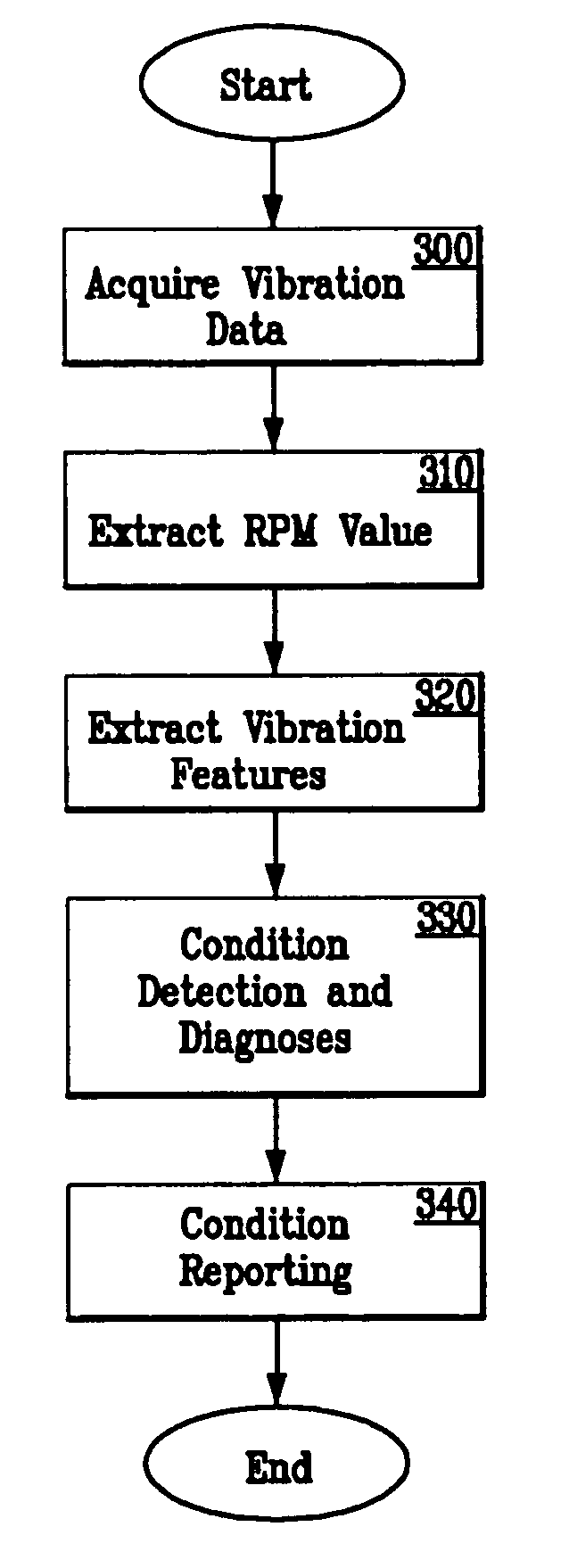
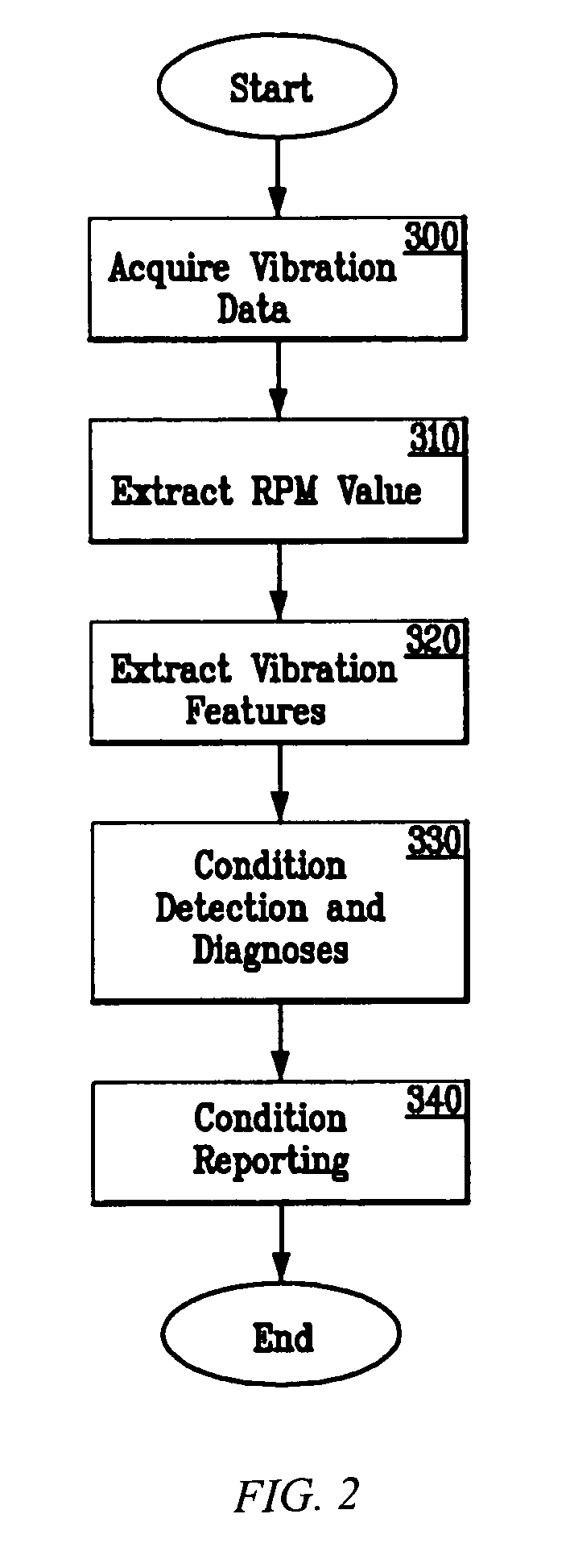
System and methodology for vibration analysis and conditon monitoring
InactiveUS20070032966A1Implemented quickly and inexpensivelyAccurate speedTesting/monitoring control systemsDigital computer detailsTransducerSample sequence
A system and methodology for continuous condition monitoring of rotating equipment employ adaptive signal processing techniques to determine the RPM of a rotating machine from the time-based vibration data. RPM is determined based upon the input of a digitized time-based sample sequence of vibration data acquired directly from a vibration transducer for on-line real-time measurement of the machine RPM. Once RPM is determined, online vibration analysis for a given RPM or set of RPMs may be performed. The present invention extracts characteristic vibration features from vibration data and uses these extracted values to provide condition detection and diagnoses of machine faults.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL RES & ENG LAW DEPT
Digital signal coding and decoding methods and apparatuses and programs therefor
InactiveUS20070083362A1Reduce the amount of informationSpeech analysisCode conversionDecoding methodsSample sequence
At the coder side, bits of samples of each frame of an input digital signal are concatenated every digit common to the samples across each frame to generate equi-order bit sequences, which are output as packets. At the decoding side, the input equi-order sequences are arranged inversely to their arrangement at the coder side to reconstruct sample sequences. When a packet dropout occurs, a missing information compensating part 430 correct the reconstructed sample sequences in a manner to reduce an error between the spectral envelope of the reconstructed sample sequence concerned and a known spectral envelope.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
System and methodology for vibration analysis and condition monitoring
InactiveUS20050209814A1Accurate speedImplemented quickly and inexpensivelyDigital computer detailsDevices using electric/magnetic meansTransducerSample sequence
A system and methodology for the continuous condition monitoring of rotating equipment. The present invention comprises a method that employs adaptive signal processing techniques to determine the RPM of a rotating machine from the time-based vibration data. According to a preferred embodiment of the present invention, RPM is determined based upon the input of a digitized time-based sample sequence of vibration data acquired directly from a vibration transducer mounted on the machine for on-line real-time measurement of the machine RPM. Alternatively, the input to the “virtual RPM sensor” could come from a database or file where the sample sequences of the vibration signal are stored for off-line measurement of the machine RPM. Once RPM is determined, online vibration analysis for a given RPM or set of RPMs may be performed. The present invention extracts characteristic vibration features from vibration data and uses these extracted values to provide condition detection and diagnoses of machine faults.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
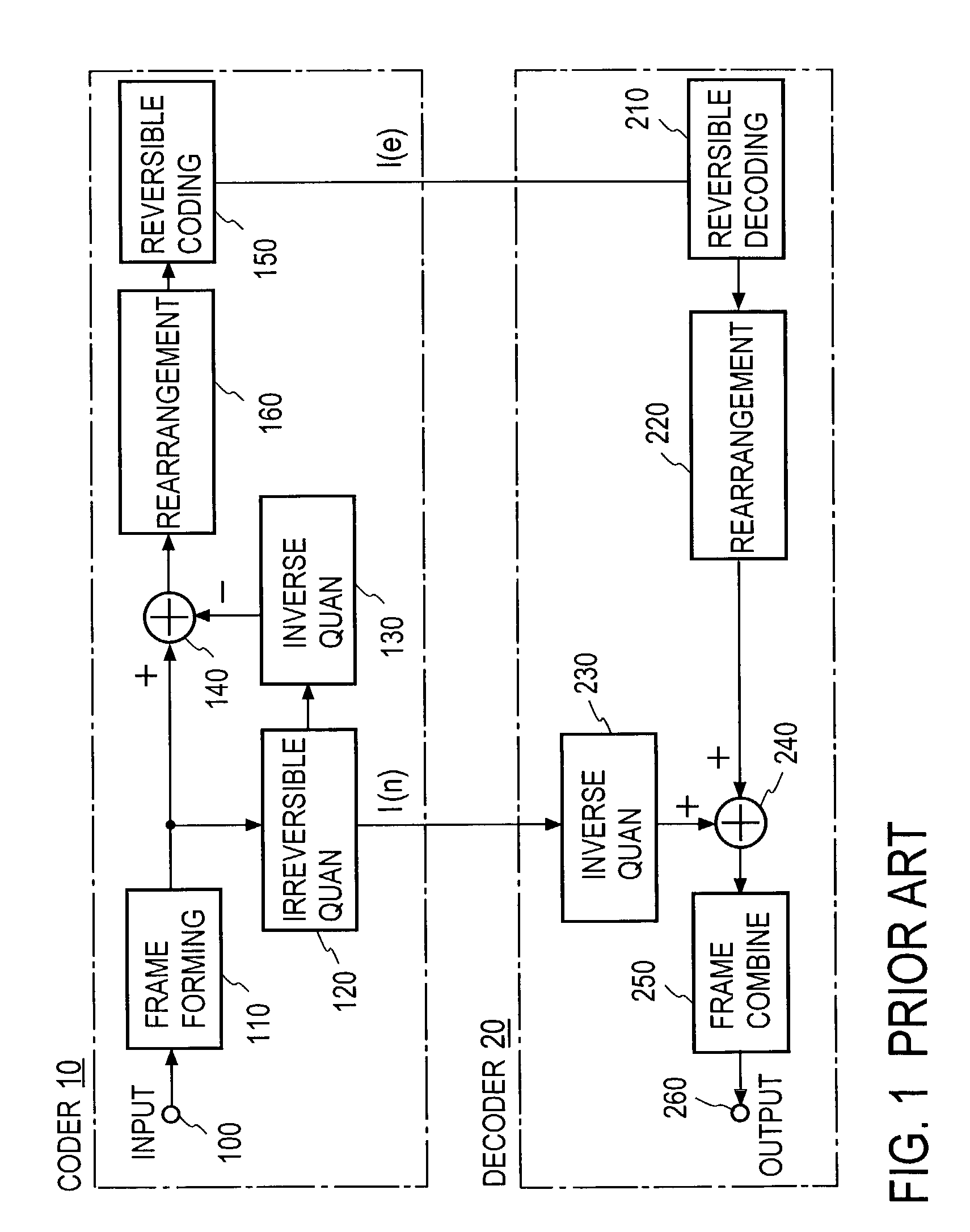
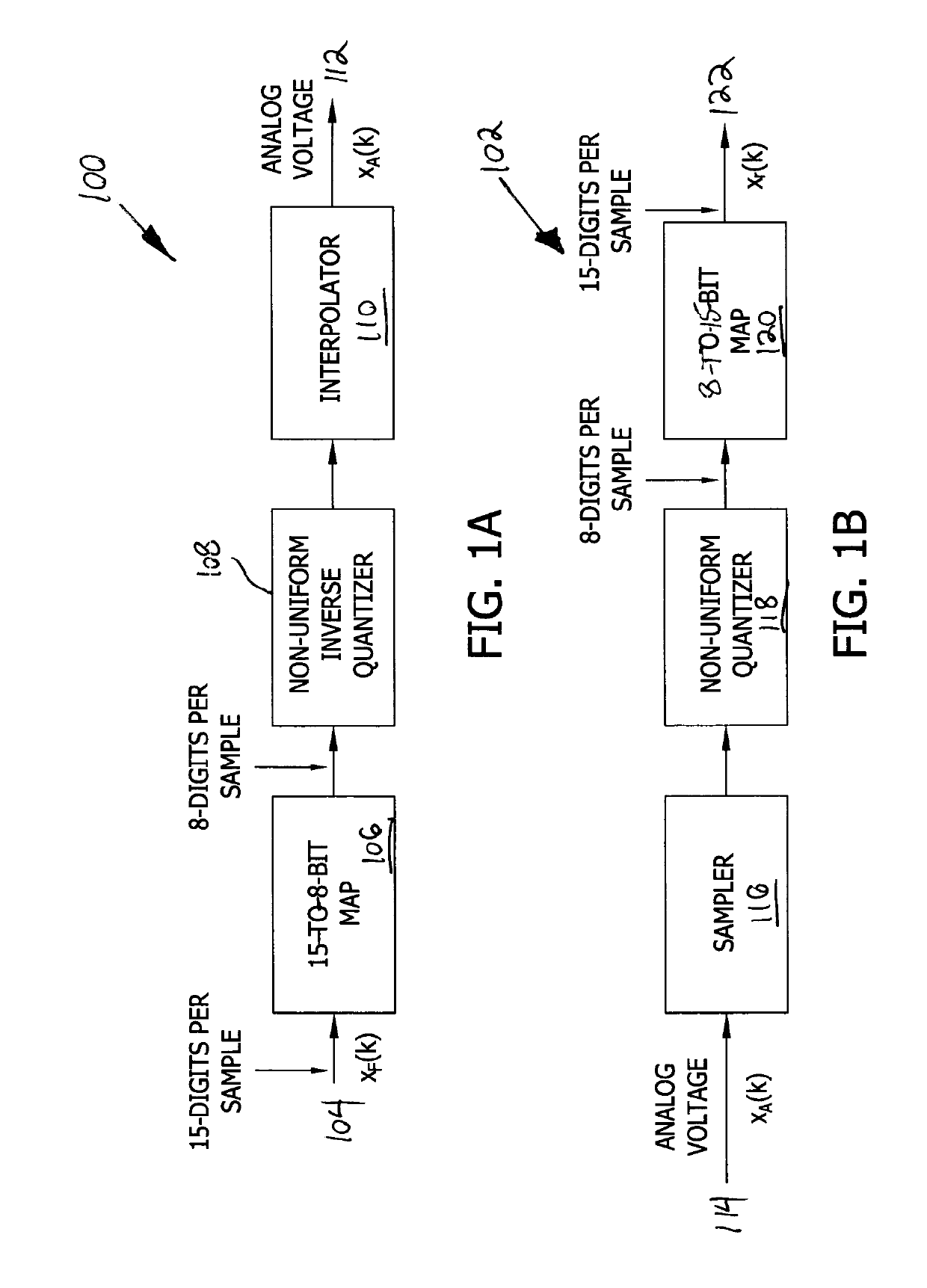
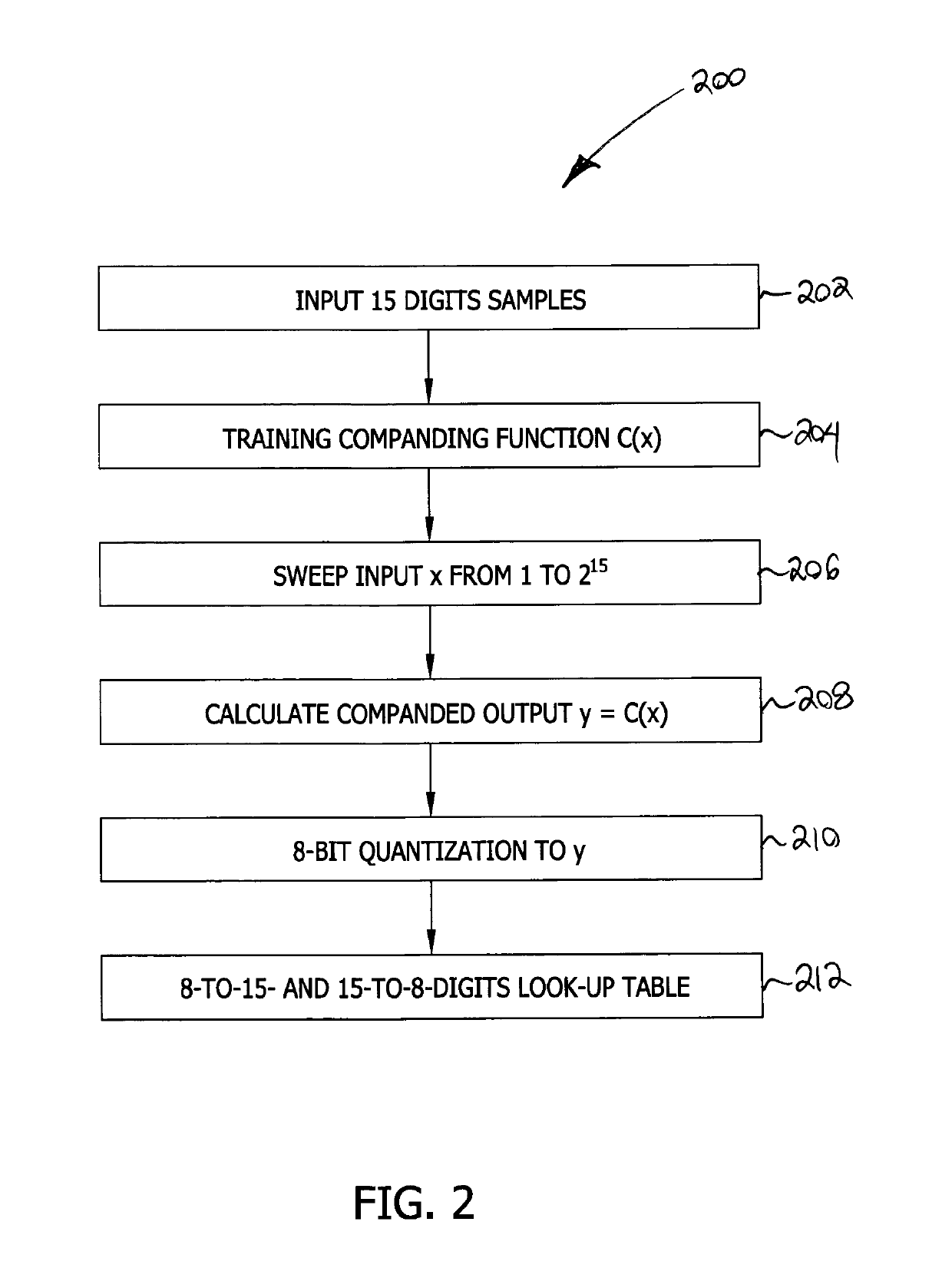
System and methods for data compression and nonuniform quantizers
ActiveUS20190110084A1Reconfigurable analogue/digital convertersOptical mode multiplex systemsOptical linkData compression
An optical network includes a transmitting portion configured to (i) encode an input digitized sequence of data samples into a quantized sequence of data samples having a first number of digits per sample, (ii) map the quantized sequence of data samples into a compressed sequence of data samples having a second number of digits per sample, the second number being lower than the first number, and (iii) modulate the compressed sequence of data samples and transmit the modulated sequence over a digital optical link. The optical network further includes a receiving portion configured to (i) receive and demodulate the modulated sequence from the digital optical link, (ii) map the demodulated sequence from the second number of digits per sample into a decompressed sequence having the first number of digits per sample, and (iii) decode the decompressed sequence.
Owner:CABLE TELEVISION LAB
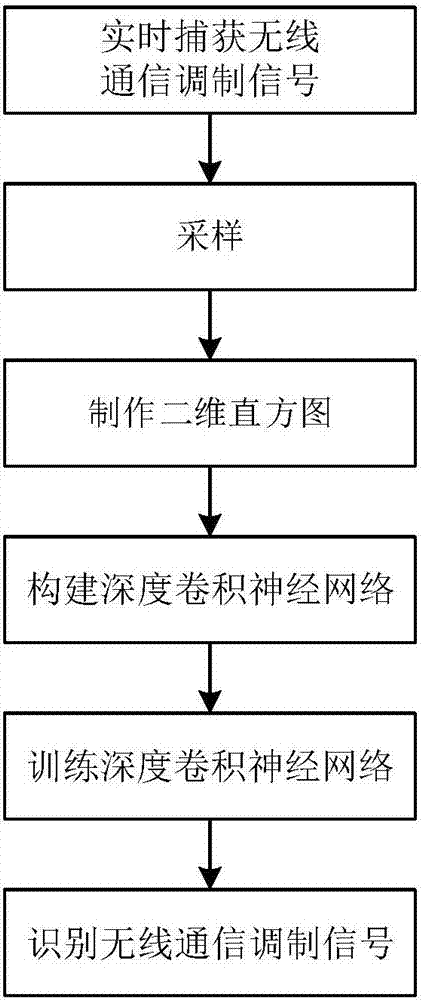
Wireless communication modulating signal identification method based on deep learning
InactiveCN107547460AImprove versatilityImprove recognition accuracyModulated-carrier systemsFeature extractionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention discloses a wireless communication modulating signal identification method based on deep learning for mainly solving the problem that the identification effect depends too much on manualmodulating signal feature extraction in the prior art and improving the drawbacks of low identification accuracy in the case of low signal to noise ratio in the prior art. The method comprises the following steps: sampling captured to-be-identified modulating signals; performing normalization on a sampling sequence obtained by sampling, and drawing a two-dimensional histogram of the modulating signals according to the normalized sampling sequence; constructing a deep convolutional neural network; training the deep convolutional neural network by using training examples; and identifying wireless communication modulating signals by using the trained deep convolutional neural network. By adoption of the wireless communication modulating signal identification method disclosed by the invention, the identification effect of the modulating signals does not depend on the manual feature selection and extraction, and very high identification accuracy is also ensured in the case of low signal tonoise ratio.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Radial basis function (RBF) neural network parameter self-optimizing-based multi-step prediction method for water quality
InactiveCN102737288AImprove the performance of multi-step forecastingEfficient intelligent automatic early warningBiological neural network modelsForecastingSample waterSample sequence
The invention discloses a radial basis function (RBF) neural network parameter self-optimizing-based multi-step prediction method for water quality. The method comprises the following steps of: first storing the data of each monitoring station into a database of a local server by using the remote transmission of an online water quality monitoring instrument; then performing normalization processing on a water quality sample sequence, calculating an autocorrelation coefficient to determine an input variable of an RBF neural network, and converting sample data into a standard dynamic sequence data format trained and predicted by the RBF neutral network; next searching for and determining an optimal value of a spreading coefficient spread of the RBF neural network by utilizing a differential evolution algorithm and taking a relative standard error as a target function to obtain an optimal prediction model; and finally sampling water quality data in real time, performing multi-step prediction by using the obtained optimal prediction model and adopting a single-point iteration method, and evaluating a water quality prediction result to realize an early warning function. The water quality can be intelligently warned.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Fault line selection method of distribution network based on empirical mode decomposition (EMD)
ActiveCN102129010AShort data lengthLow hardware requirementsFault locationElectrical resistance and conductancePower flow
The invention relates to a fault line selection method of a distribution network based on empirical mode decomposition (EMD), belonging to the technical field of the relay protection of a power system. The fault line selection method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of: solving a zero-sequence current by utilizing the Clarke transformation theory according to the three-phase current of each line when the distribution network fails and a protection element starts, wherein the three-phase current of each line is measured at the protection mounting part; selecting a discrete zero-sequence current signal with the sampling sequence length of 100 dots, and carrying out EMD (Empirical Mode Decomposition) on the discrete zero-sequence current signal so as to acquire m IMF (Intrinsic Mode Function) components; respectively solving the absolute values of the m IMF components of the zero-sequence current of each line to acquire m absolute values of IMFt (i); and then, summing the m absolute values of IMFt (i) of the zero-sequence current of each line to acquire EMD energy Ei, wherein the line with the maximum Ei value is a fault line. By adopting the sampling frequency of 10 kHz and the time window of 10 ms, the fault line selection method provided by the invention needs data shorter in length, has the advantages of low hardware requirements, easiness in technological implementation, stronger tolerance to transition resistance and stronger practicability and is free from interference influences.
Owner:CHUXIONG POWER SUPPLY BUREAU OF YUNNAN POWER GRID CO LTD
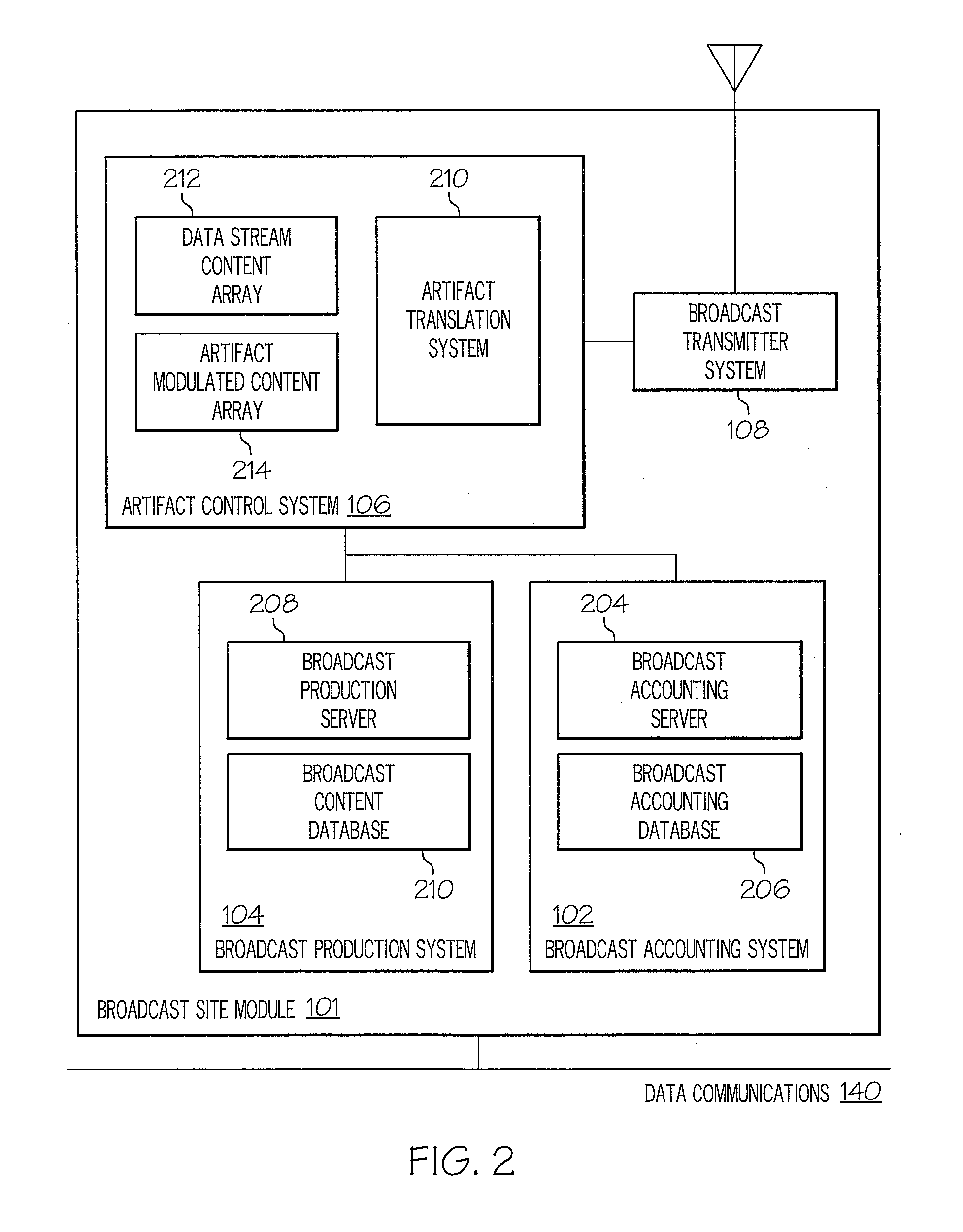
Method, system and program product for broadcast advertising and other broadcast content performance verification utilizing digital artifacts
ActiveUS20070220544A1Simple methodTelevision system detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsDigital dataTelevision receivers
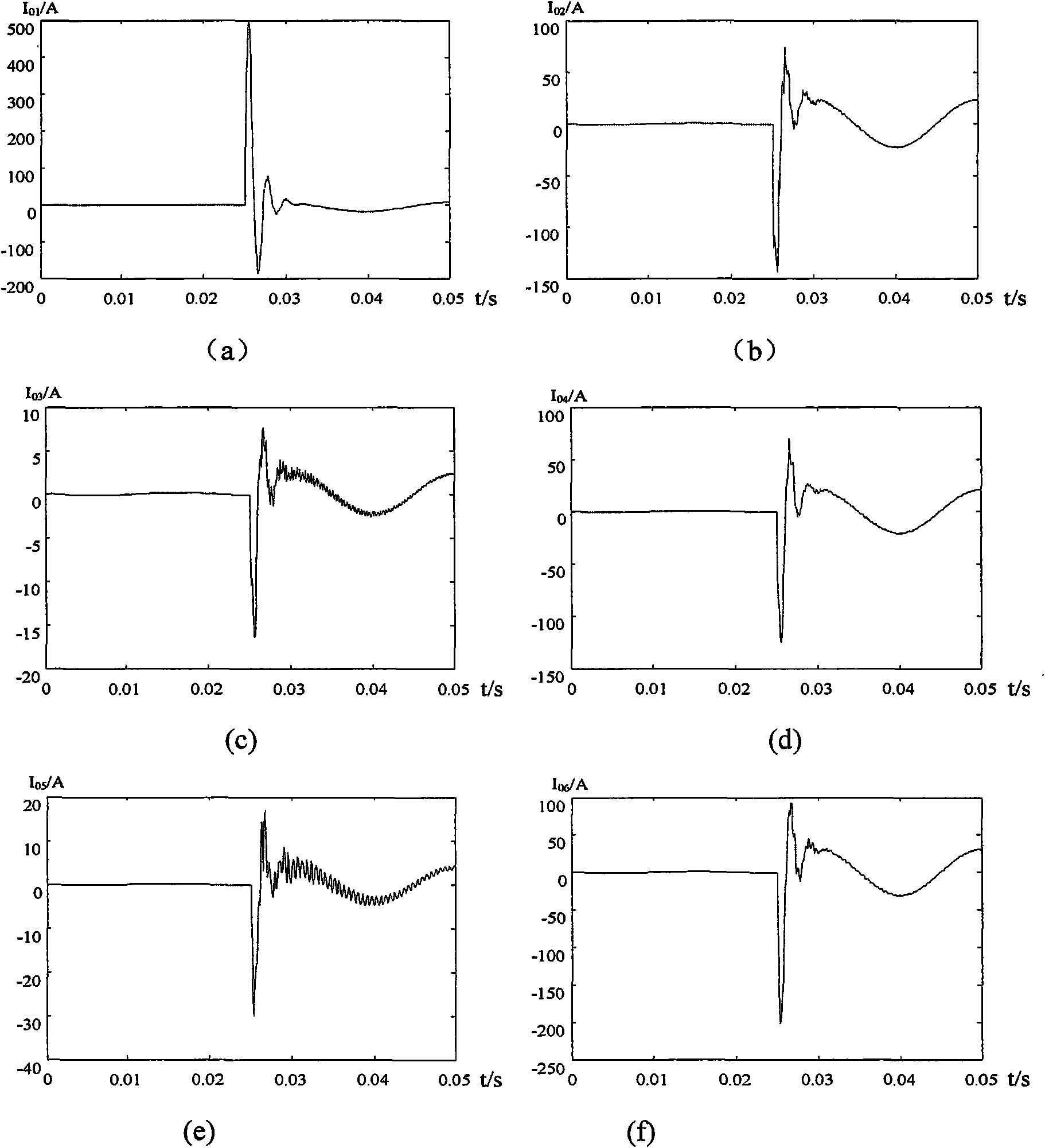
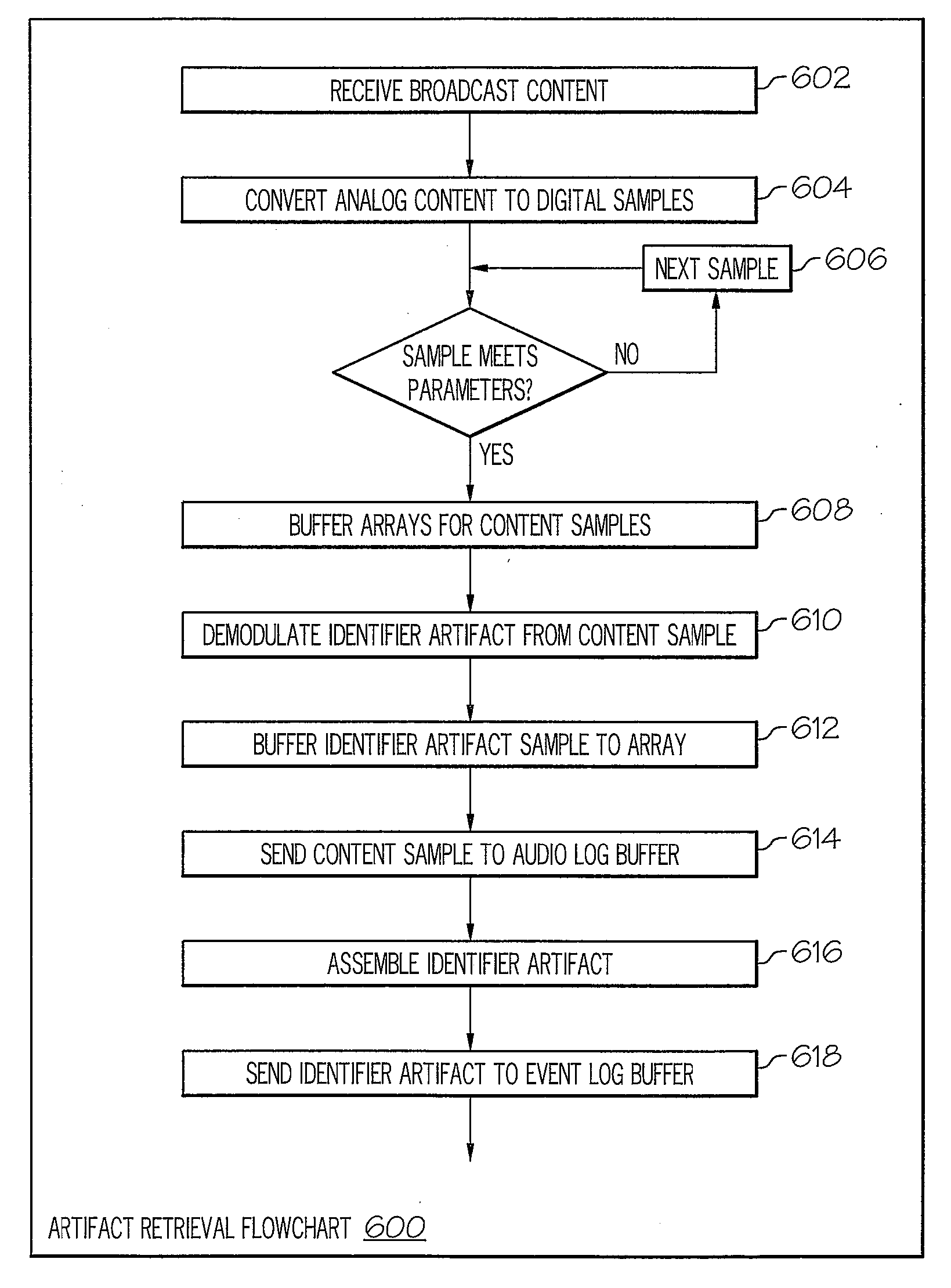
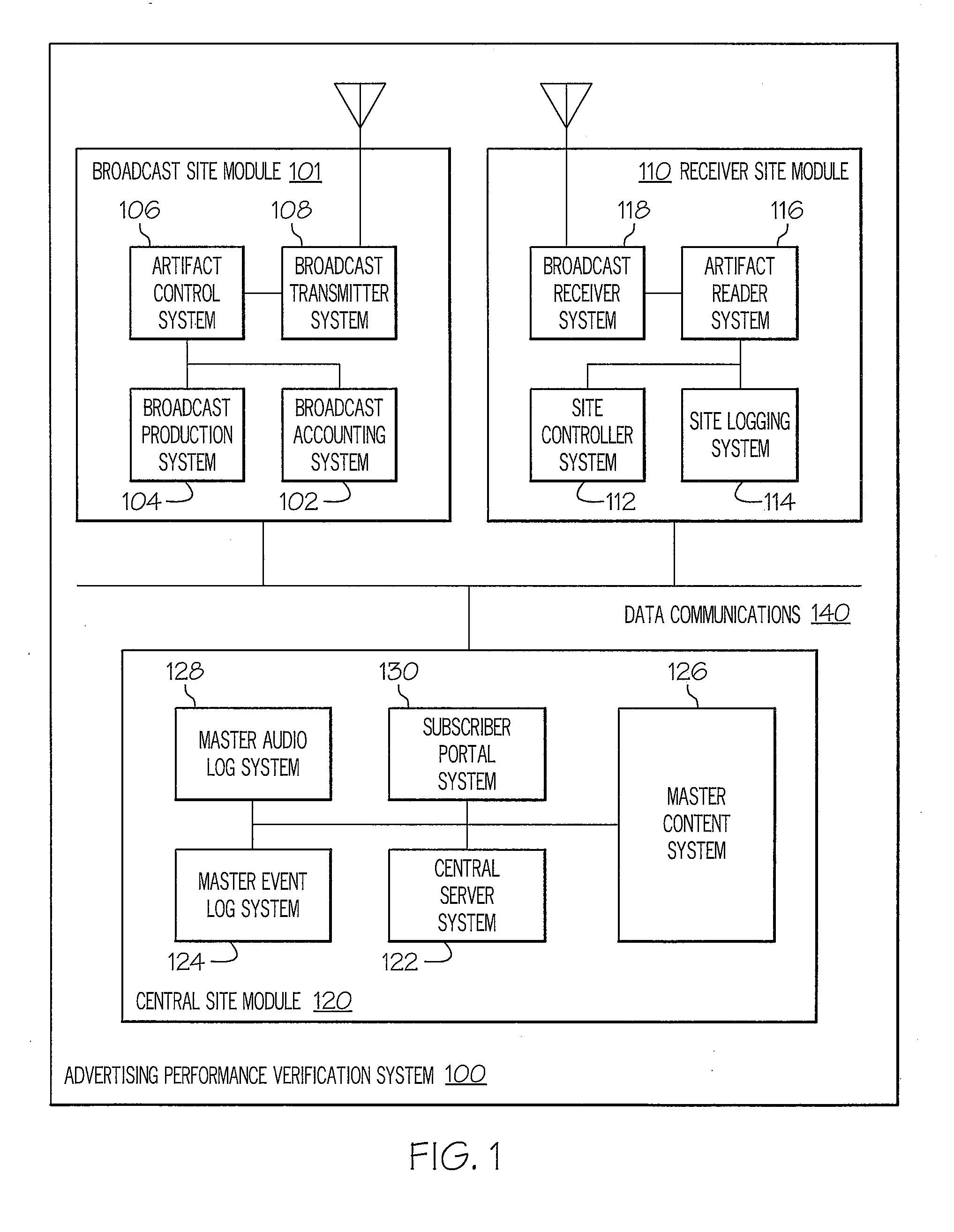
A verification system that injects a inaudible identification code into a broadcast advertisement immediately prior to its radio frequency transmission is disclosed. An amplitude modulated sample sequence called a “digital artifact” containing, for example, a date and time code, is generated and inserted into the audio or video or composite audio and video data stream called a content “carrier.” The combined data signal is converted from a digital stream to an analog signal and processed by standard broadcast transmission and transmitted in the radio frequency spectrum in the conventional manner. A radio frequency spectrum radio or television receiver receives the broadcast signal and converts to a digital data stream. A decoder processes the transmitted content carrier and extracts the digital artifact from the data stream. The derived information is evaluated, quantified, and transmitted to a central control point where it is compared with original reference and identification data.
Owner:GULA CONSULTING LLC
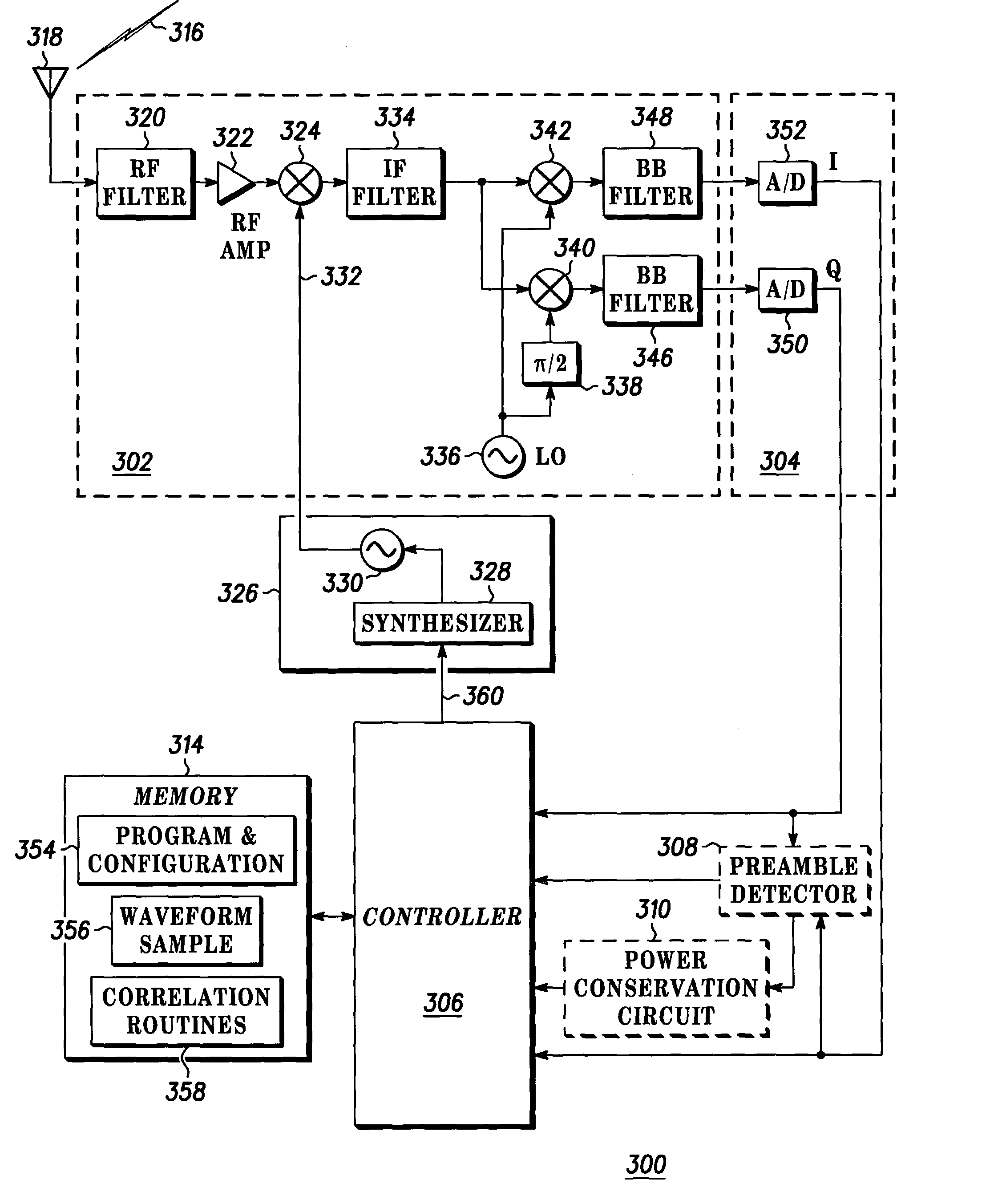
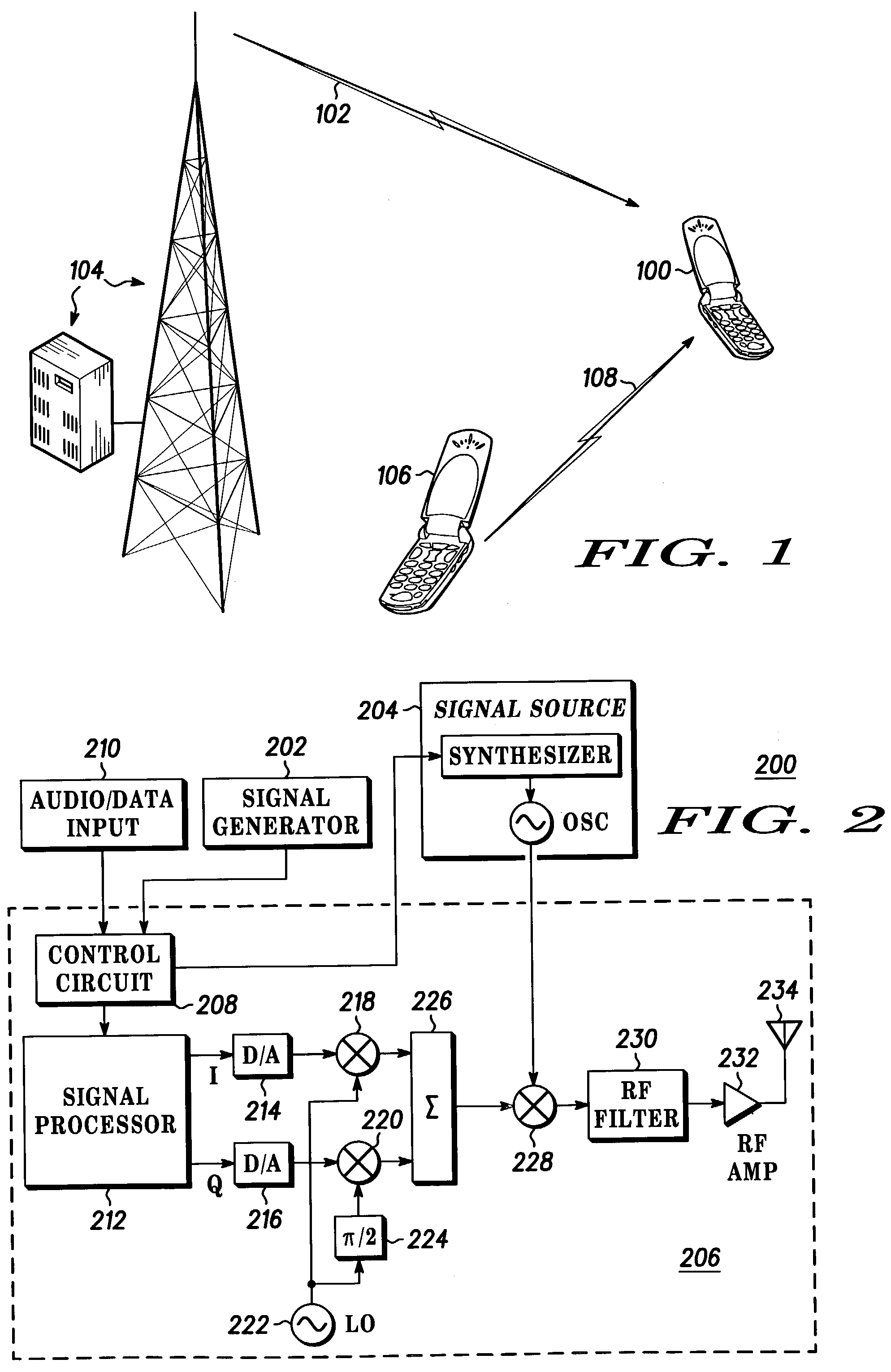
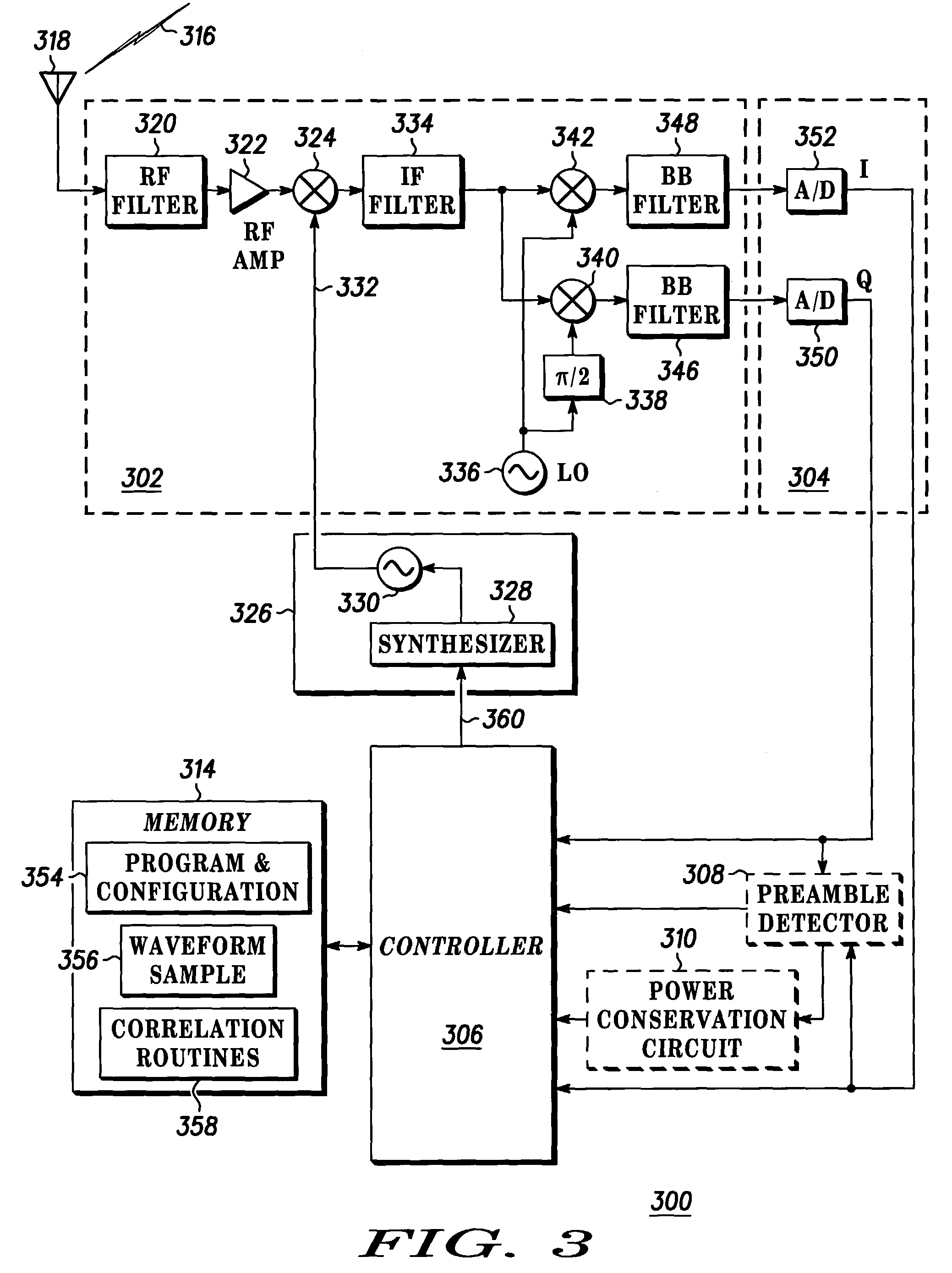
Method and wireless device employing a preamble to initiate communications
InactiveUS7106814B2Improve appreciationInvention is limitedPower managementCarrier regulationPower modeSample sequence
A wireless receiver 300 and corresponding method to detect a message identifier or preamble that has been generated and provided by a transmitter 200 uses FFTs to estimate frequency and time offset. The wireless receiver 300 scans, asynchronously and sequentially during a wakeup time, a plurality of predetermined frequencies for the message identifier or specialized preamble. A plurality of received sample sequences are collected, one received sample sequence collected at each of the plurality of predetermined frequencies. A correlation between data corresponding to the preamble and data corresponding to a received sample sequence is compared to a threshold value to determine when the preamble has been detected. The wireless receiver 300 is wakened from a low power mode when the preamble is detected.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com