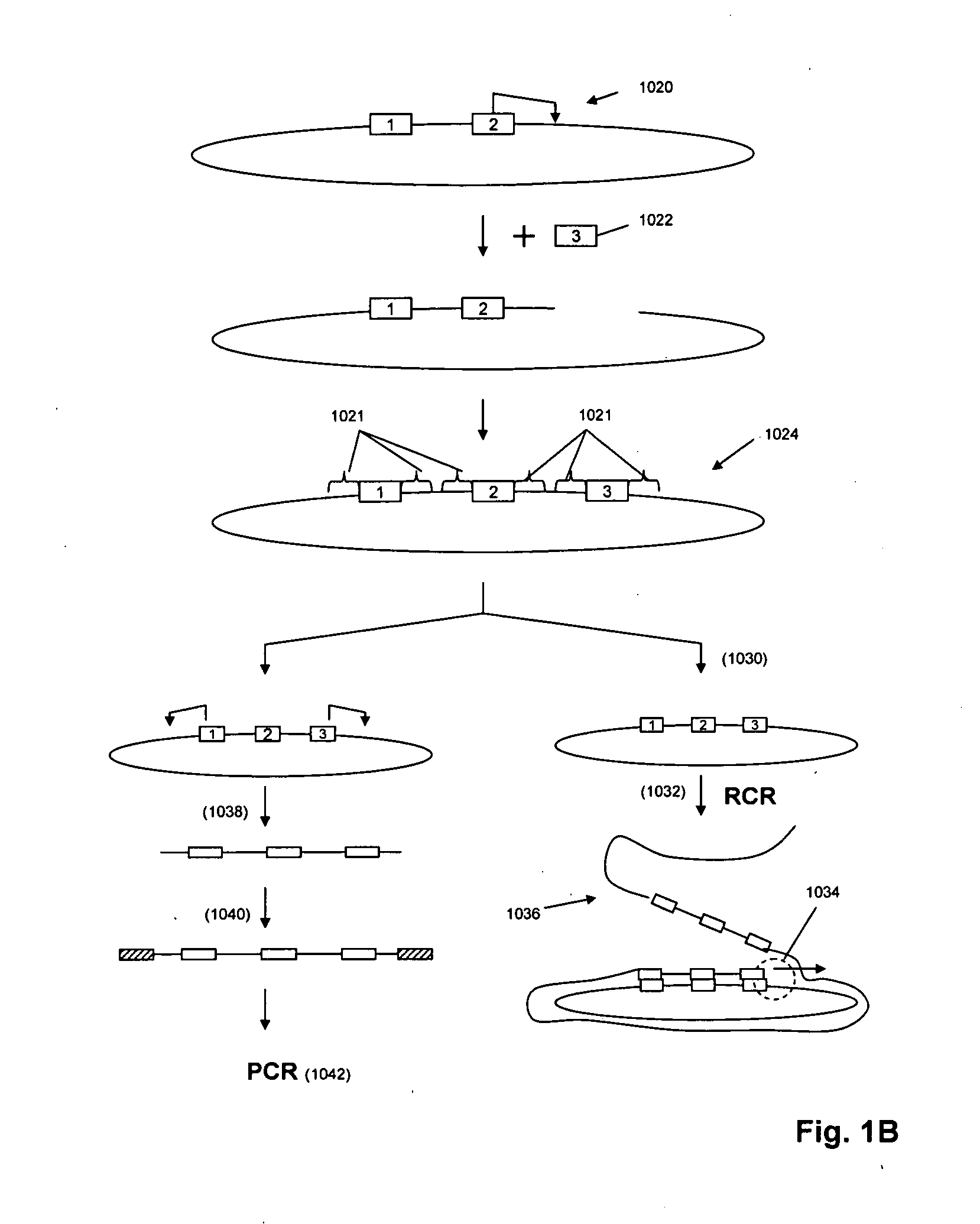
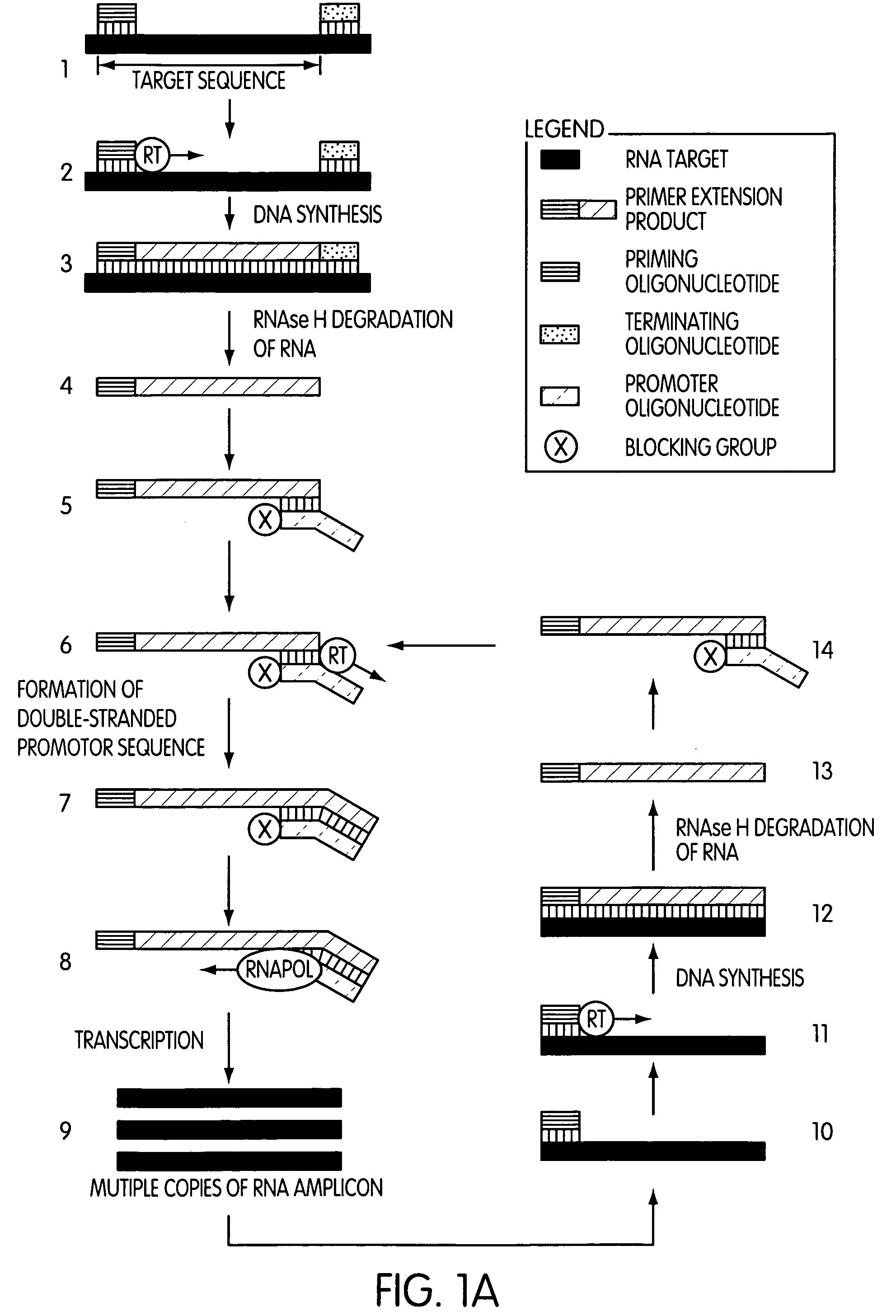
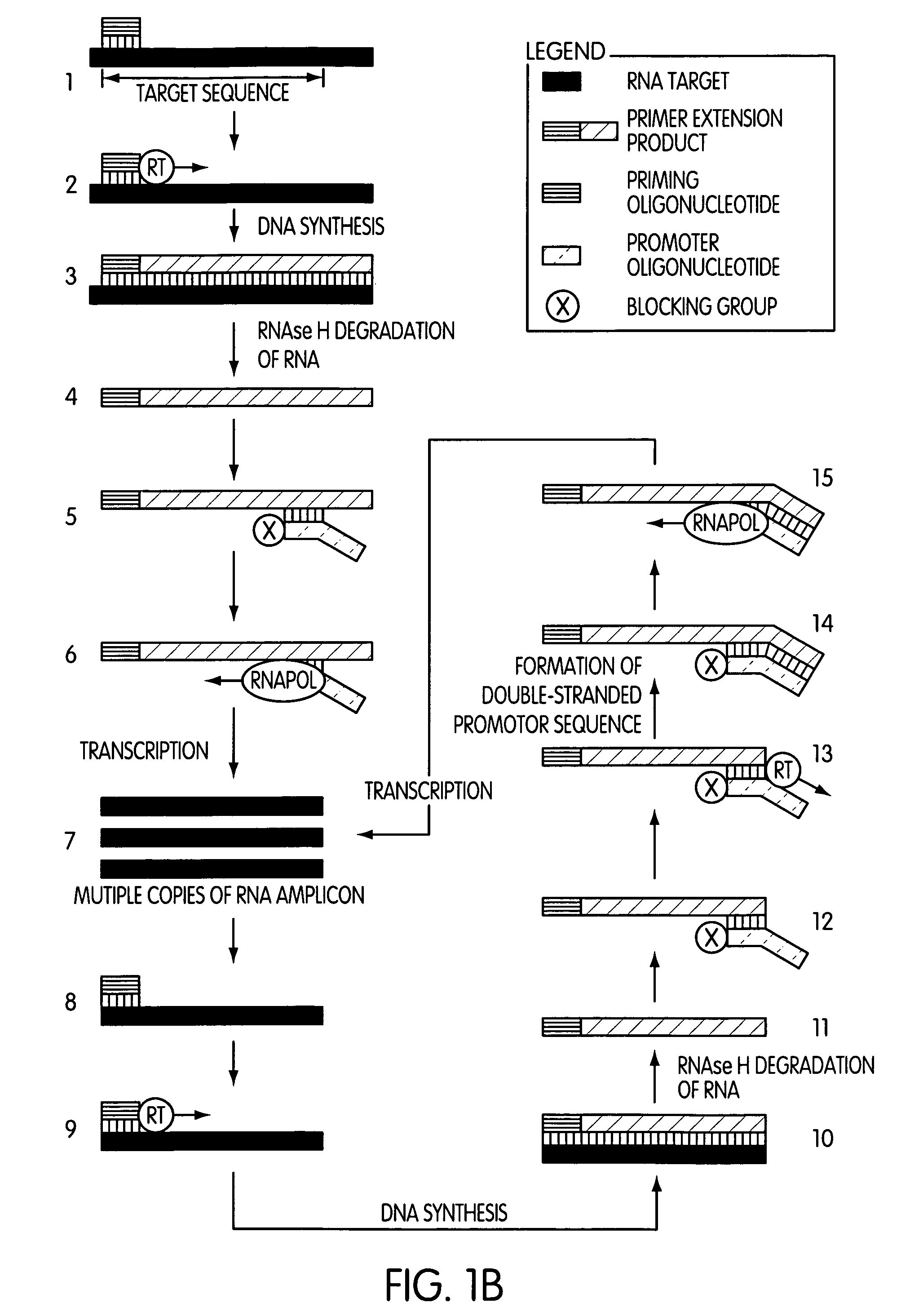
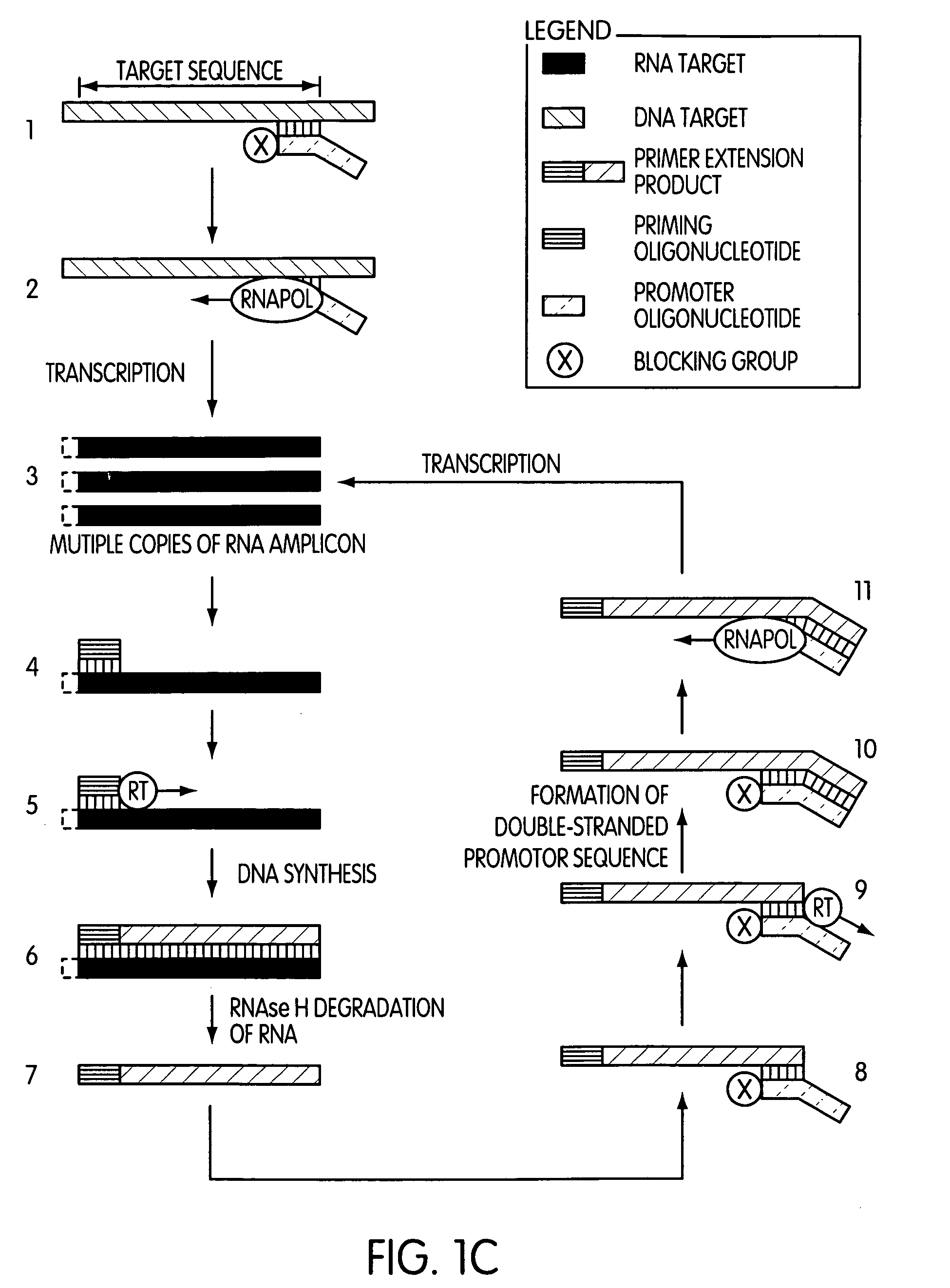
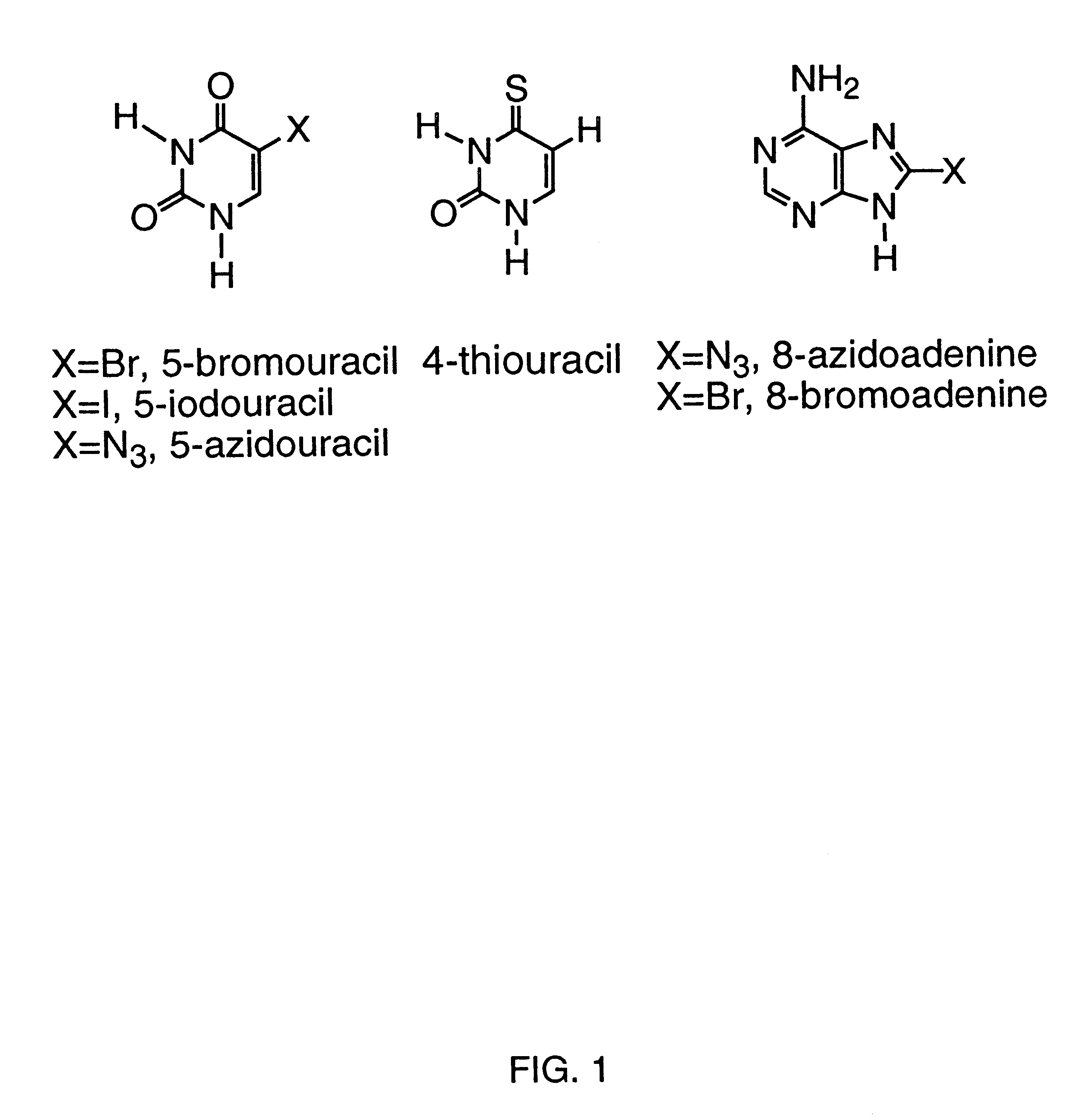
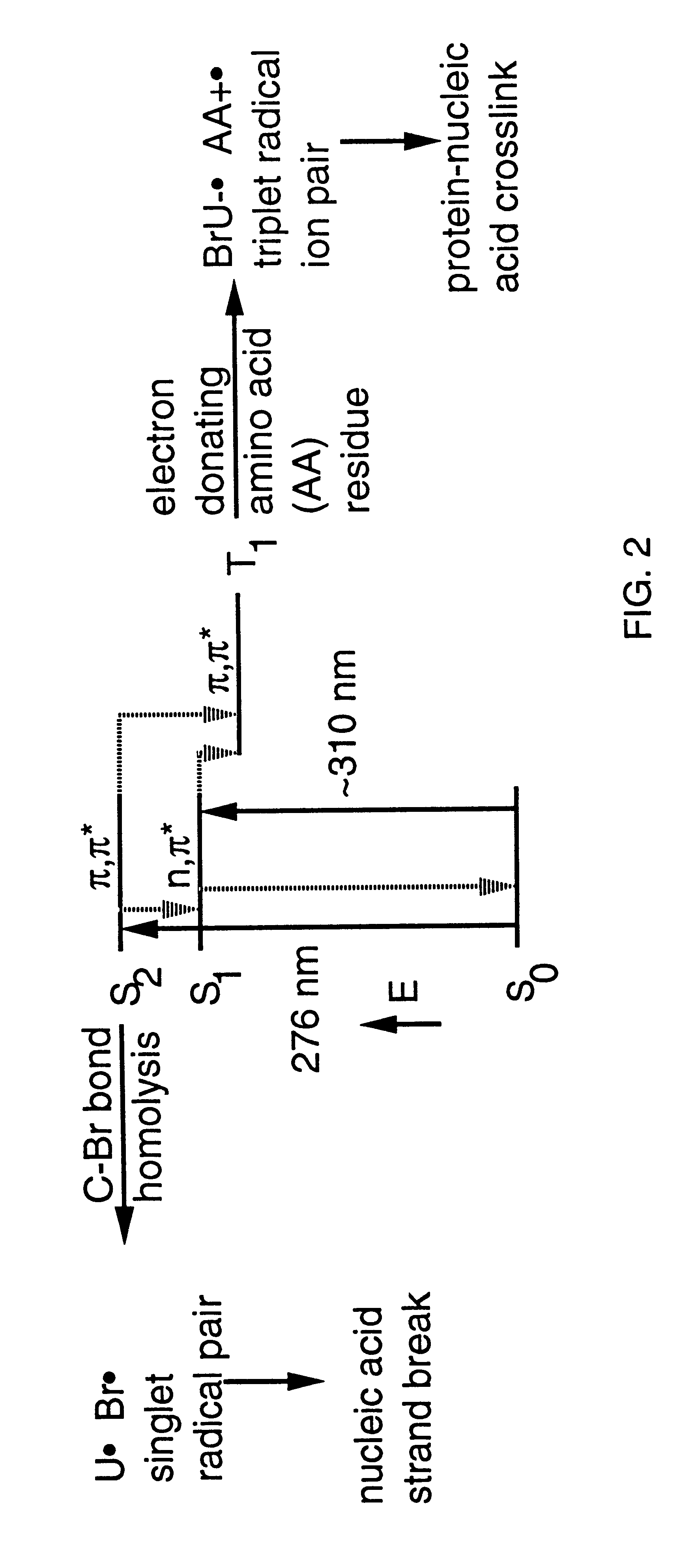
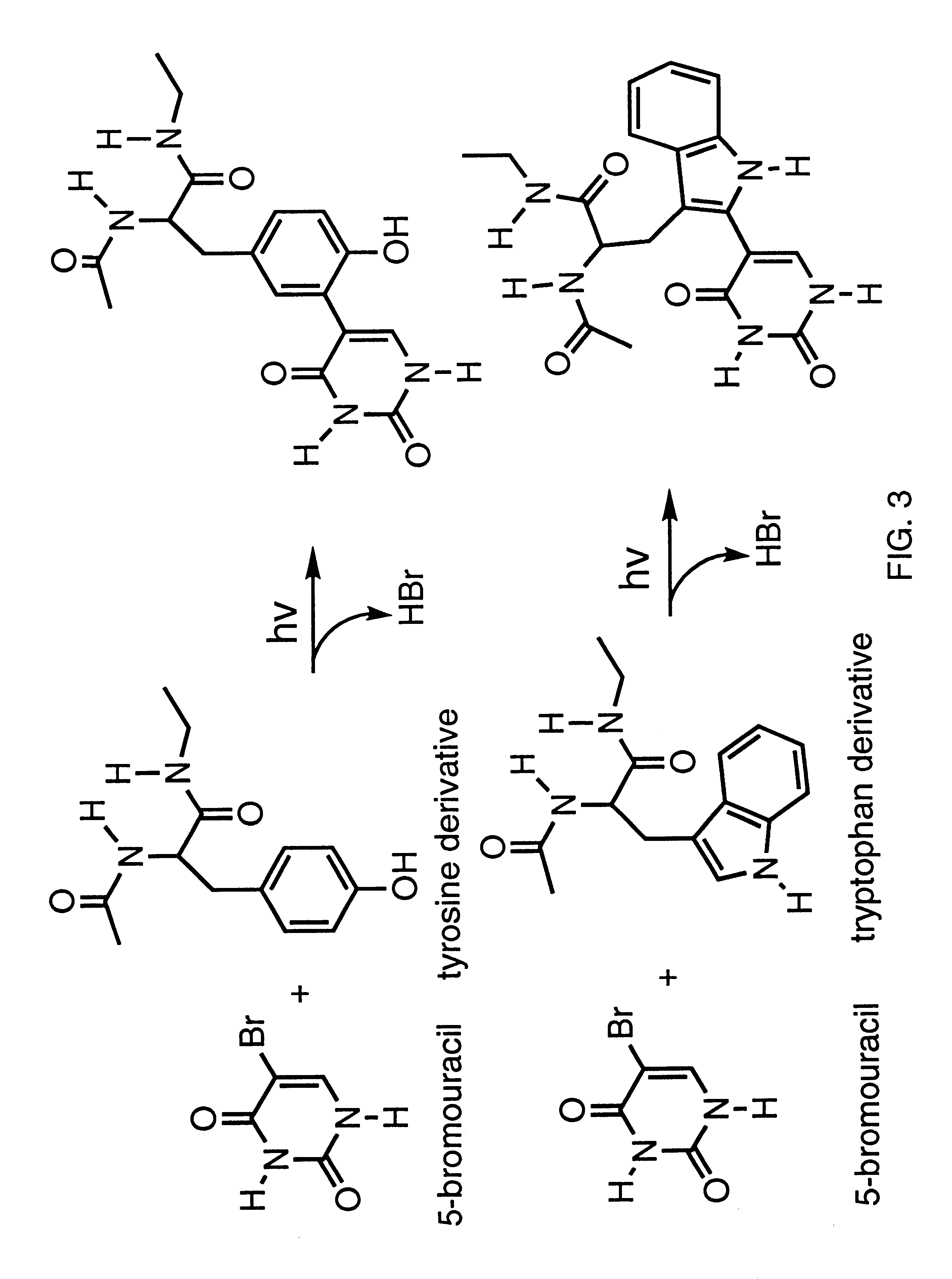
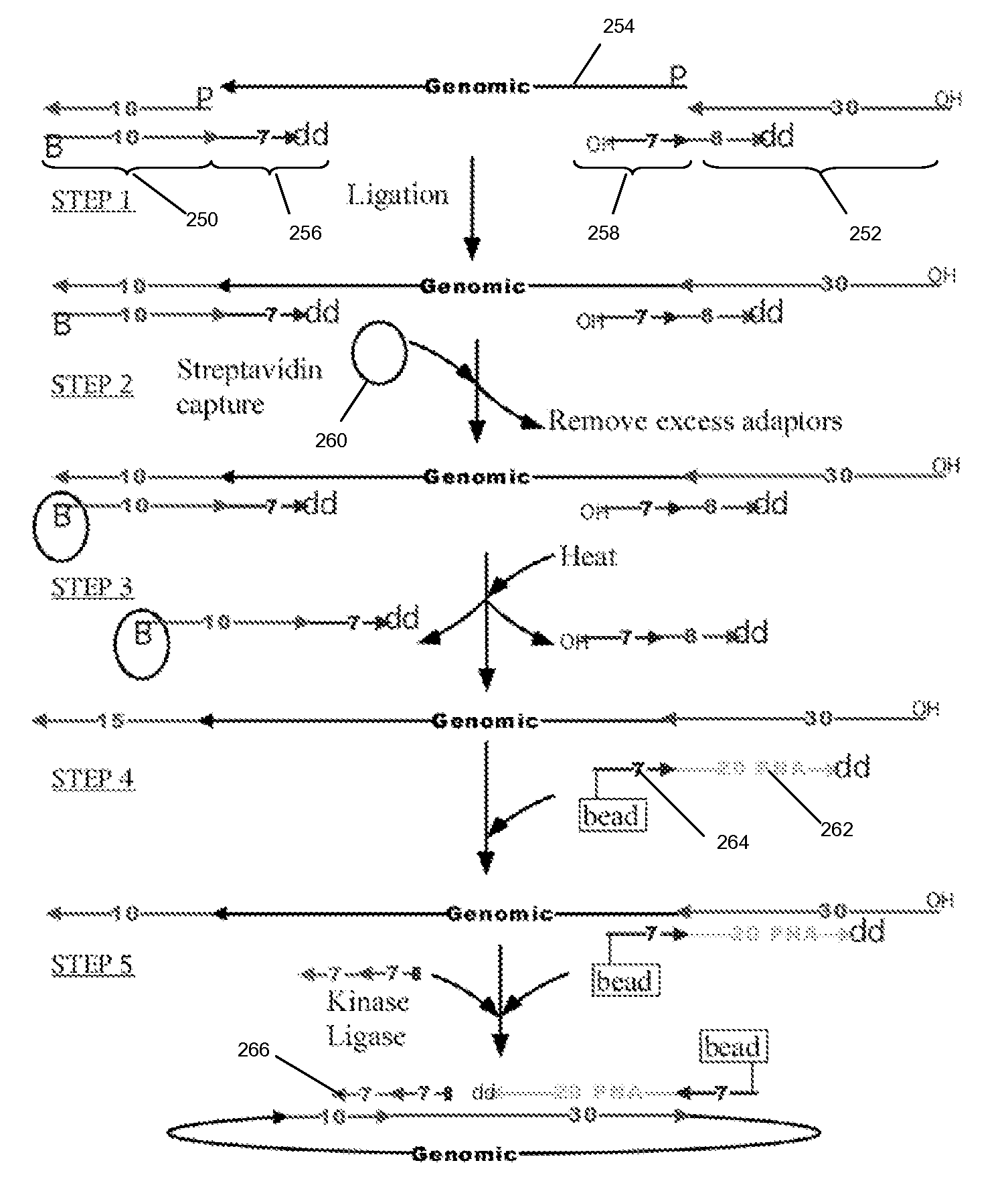
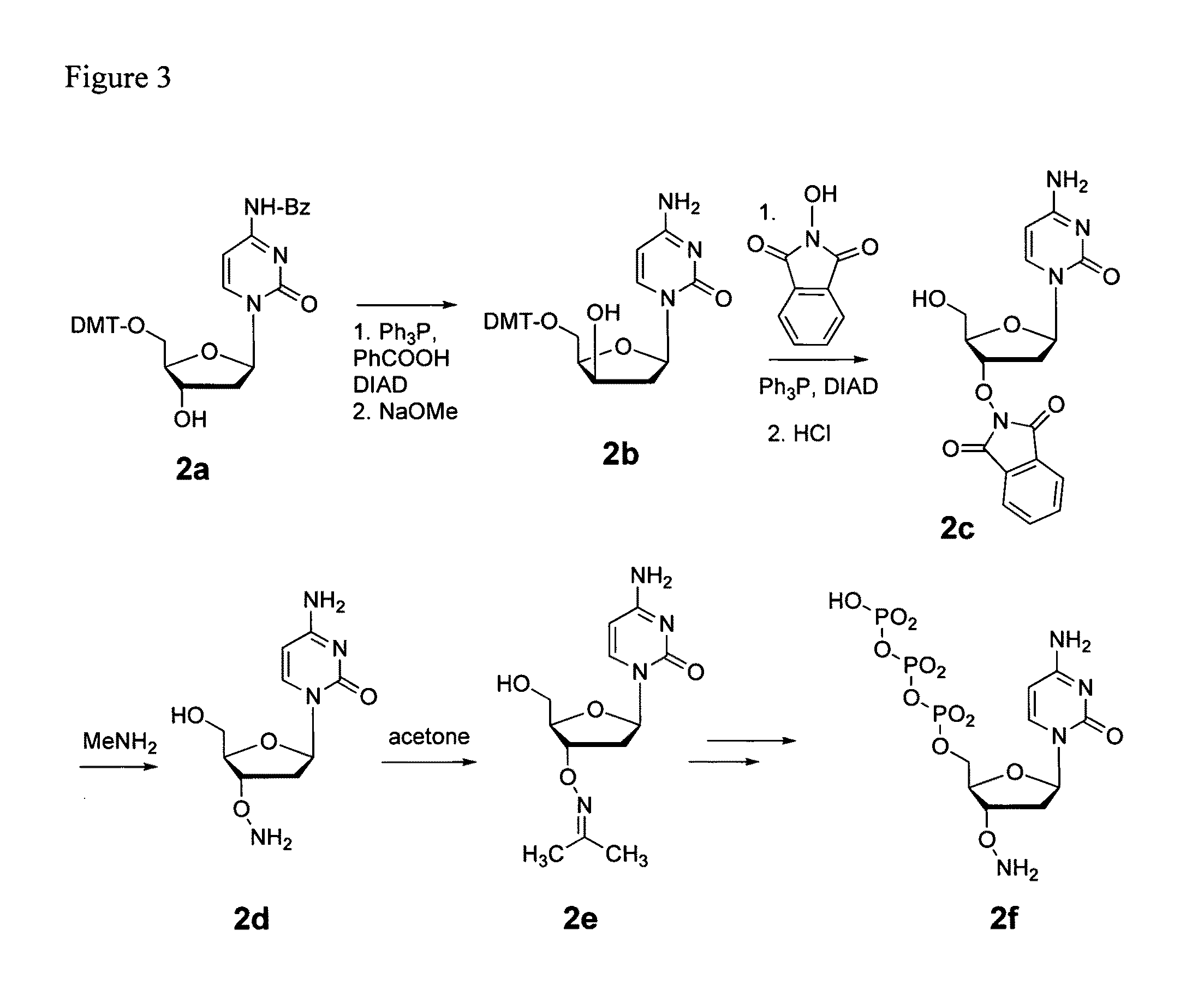
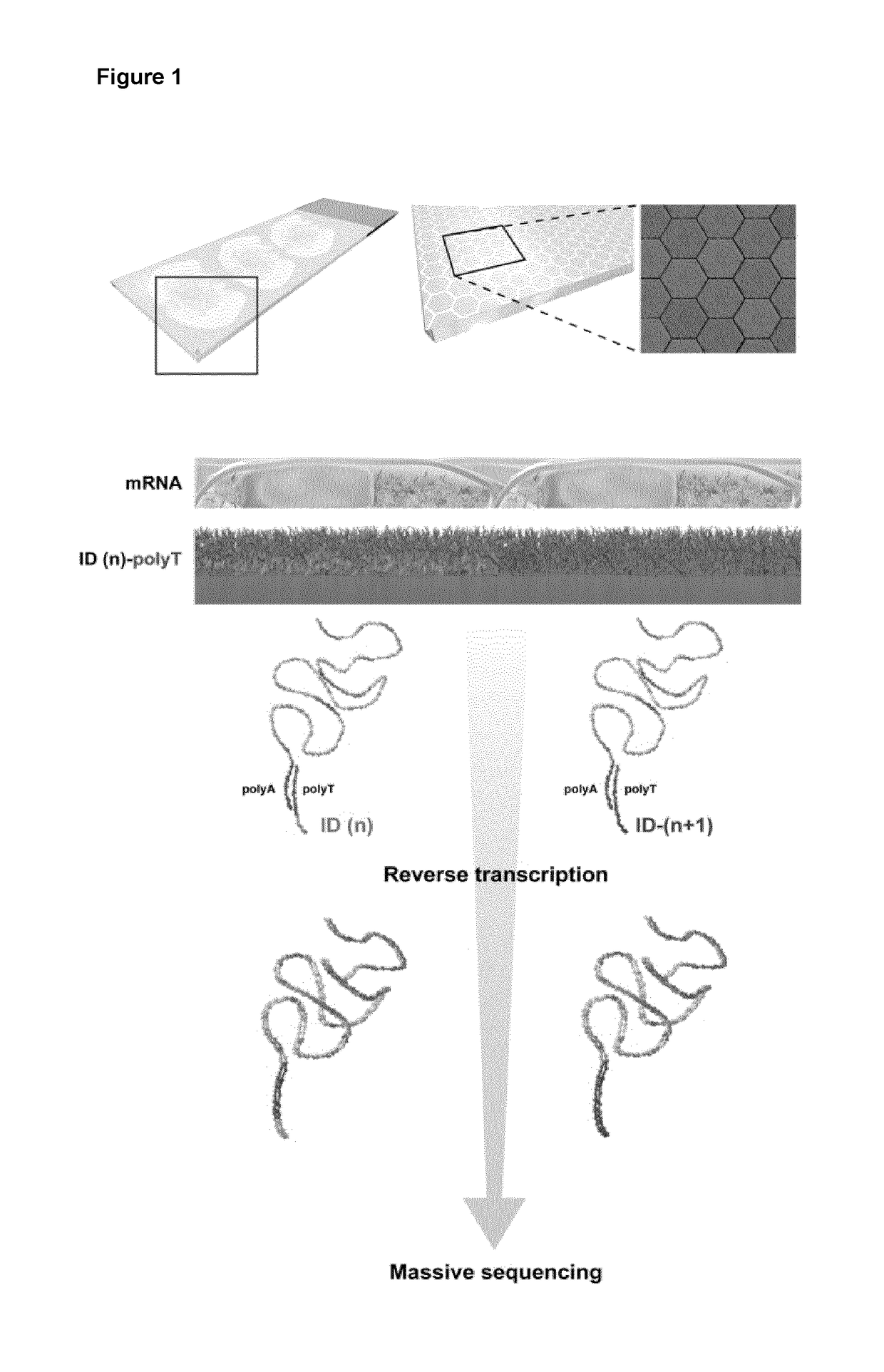
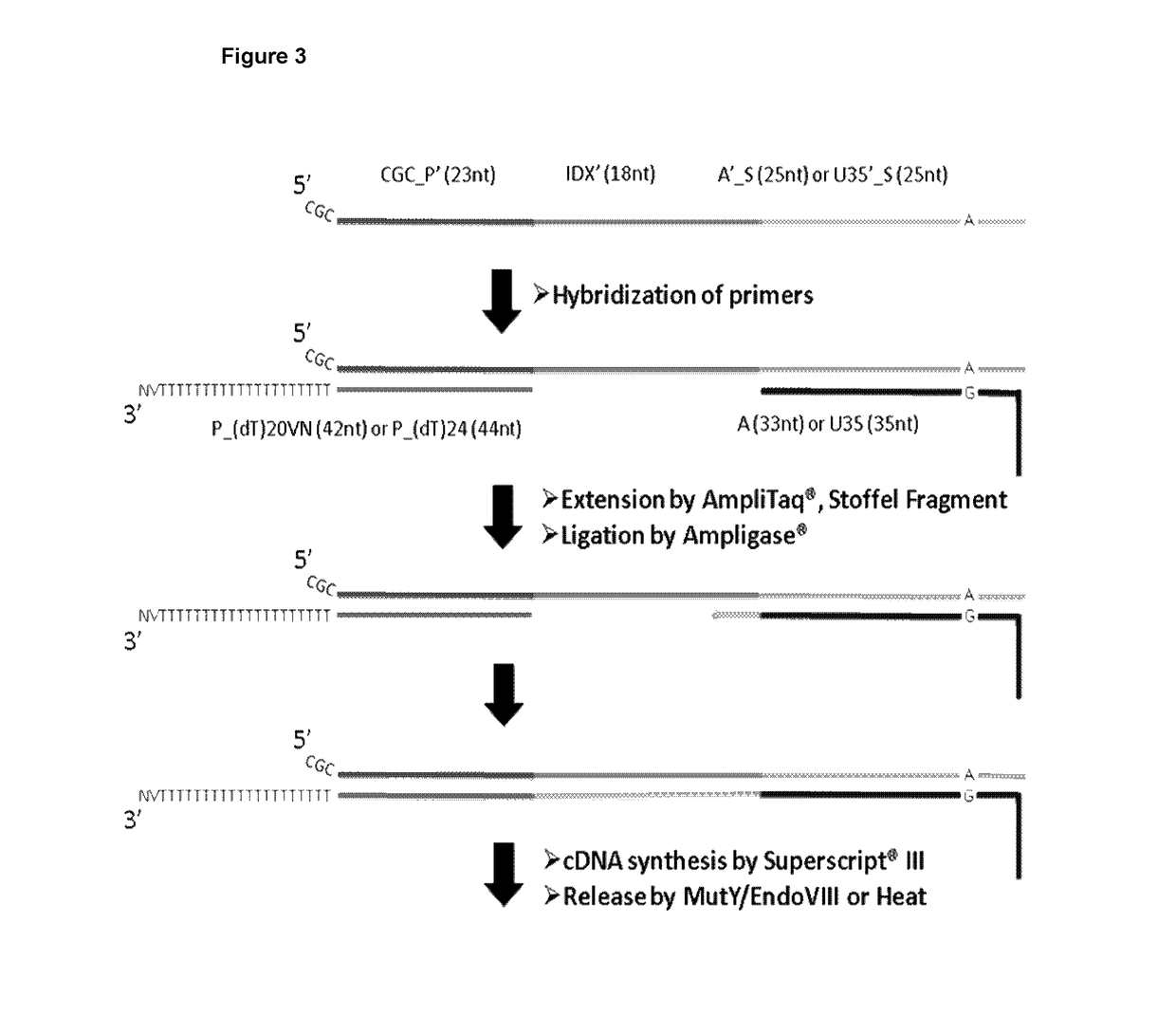
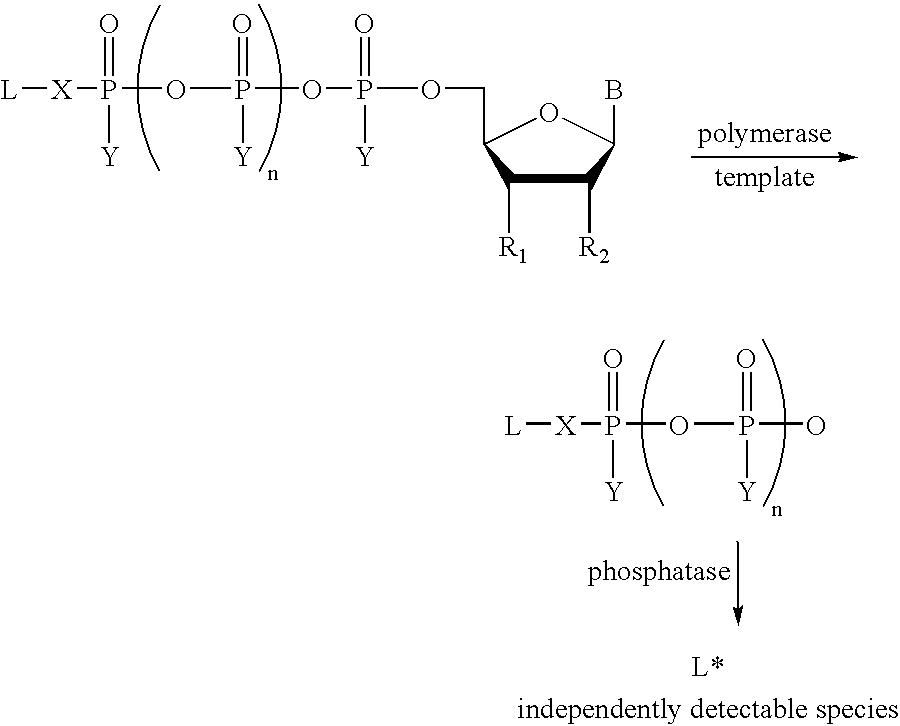Patents
Literature
481 results about "Primer extension" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
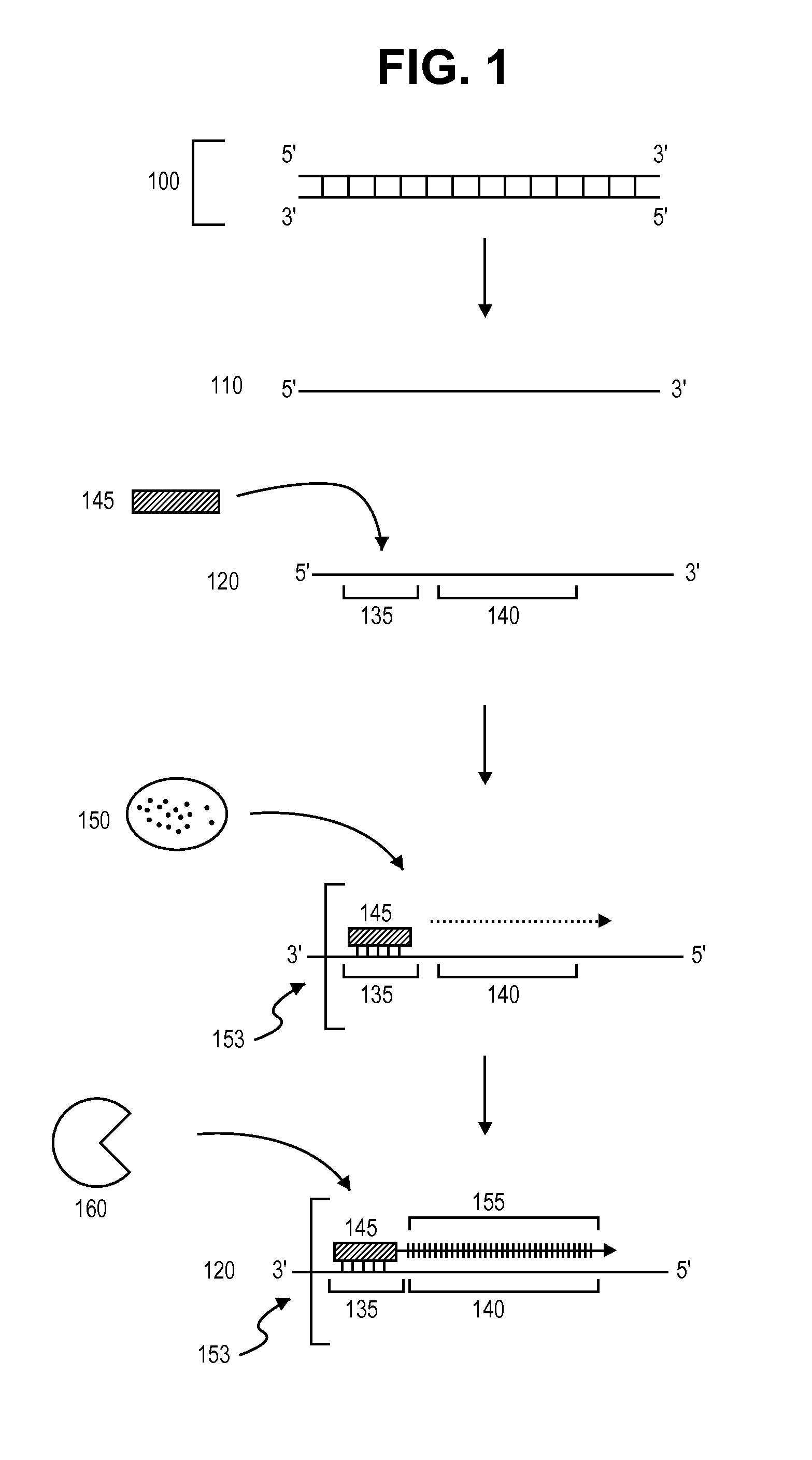
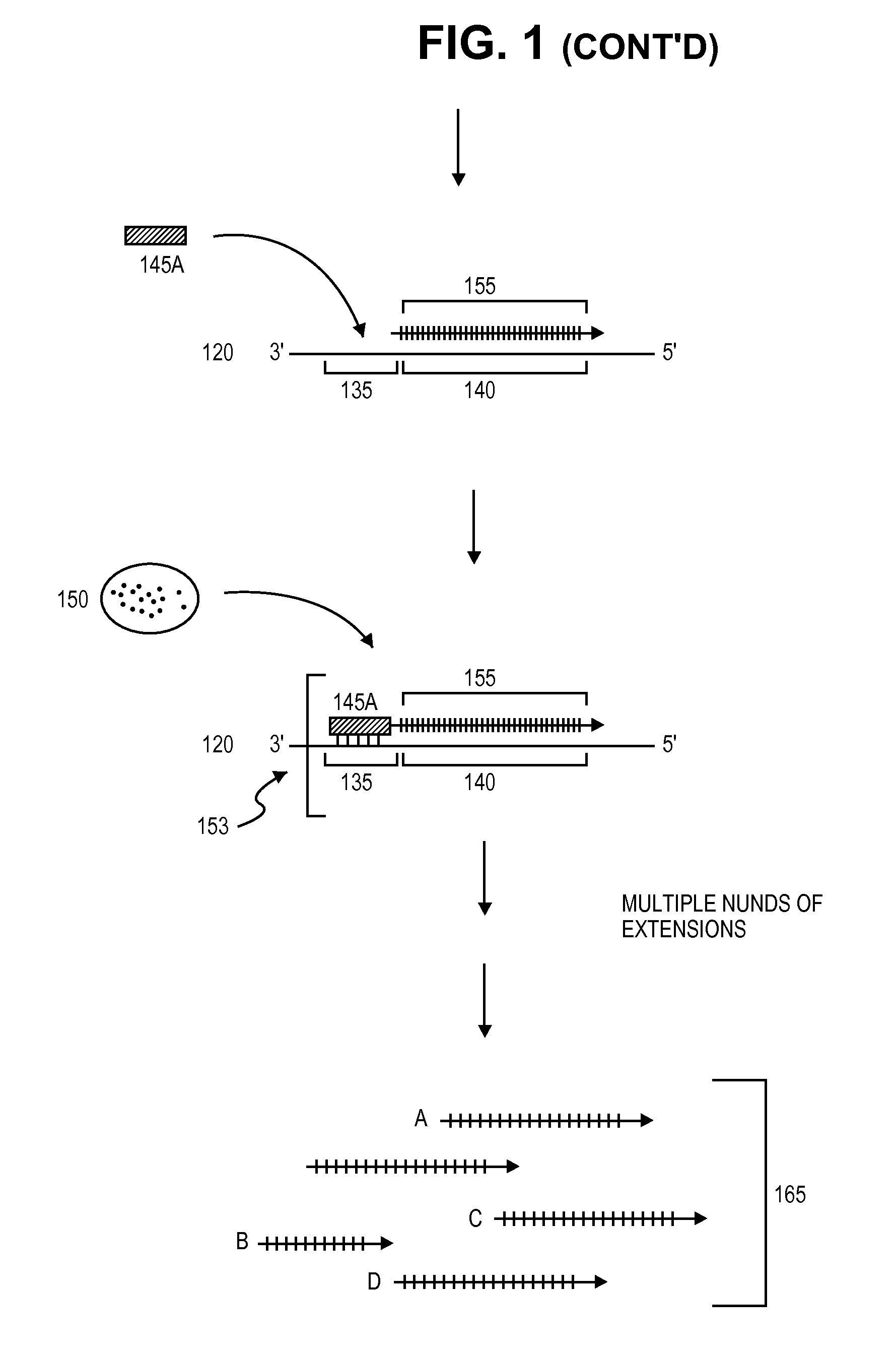
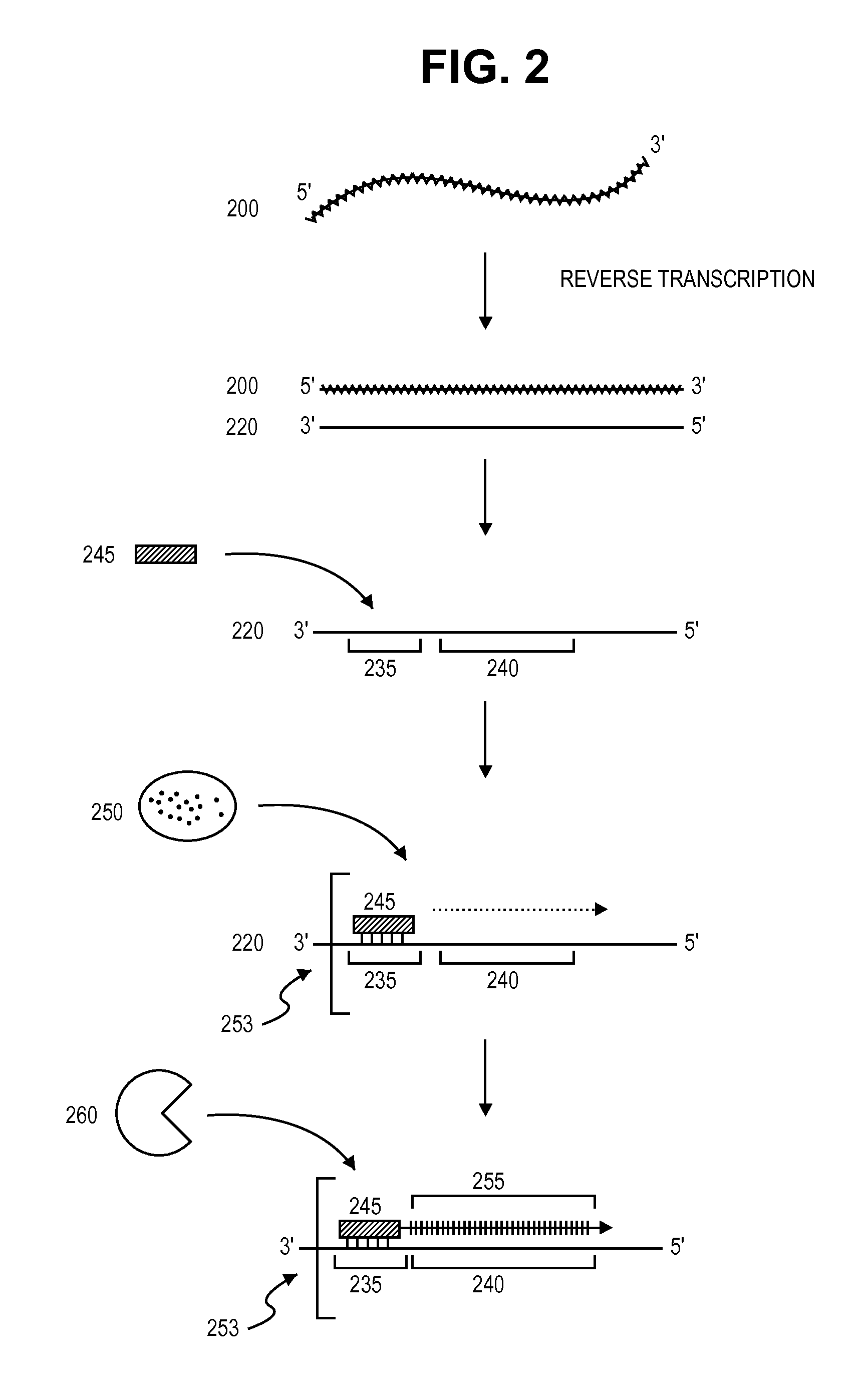
Primer extension is a technique whereby the 5' ends of RNA can be mapped - that is, they can be sequenced and properly identified. Primer extension can be used to determine the start site of transcription (the end site cannot be determined by this method) by which its sequence is known. This technique requires a radiolabelled primer (usually 20 - 50 nucleotides in length) which is complementary to a region near the 3' end of the mRNA. The primer is allowed to anneal to the RNA and reverse transcriptase is used to synthesize cDNA from the RNA until it reaches the 5' end of the RNA. By denaturing the hybrid and using the extended primer cDNA as a marker on an electrophoretic gel, it is possible to determine the transcriptional start site. It is usually done so by comparing its location on the gel with the DNA sequence (e.g. Sanger sequencing), preferably by using the same primer on the DNA template strand. The exact nucleotide by which the transcription starts at can be pinpointed by matching the labelled extended primer with the marker nucleotide, who are both sharing the same migration distance on the gel.
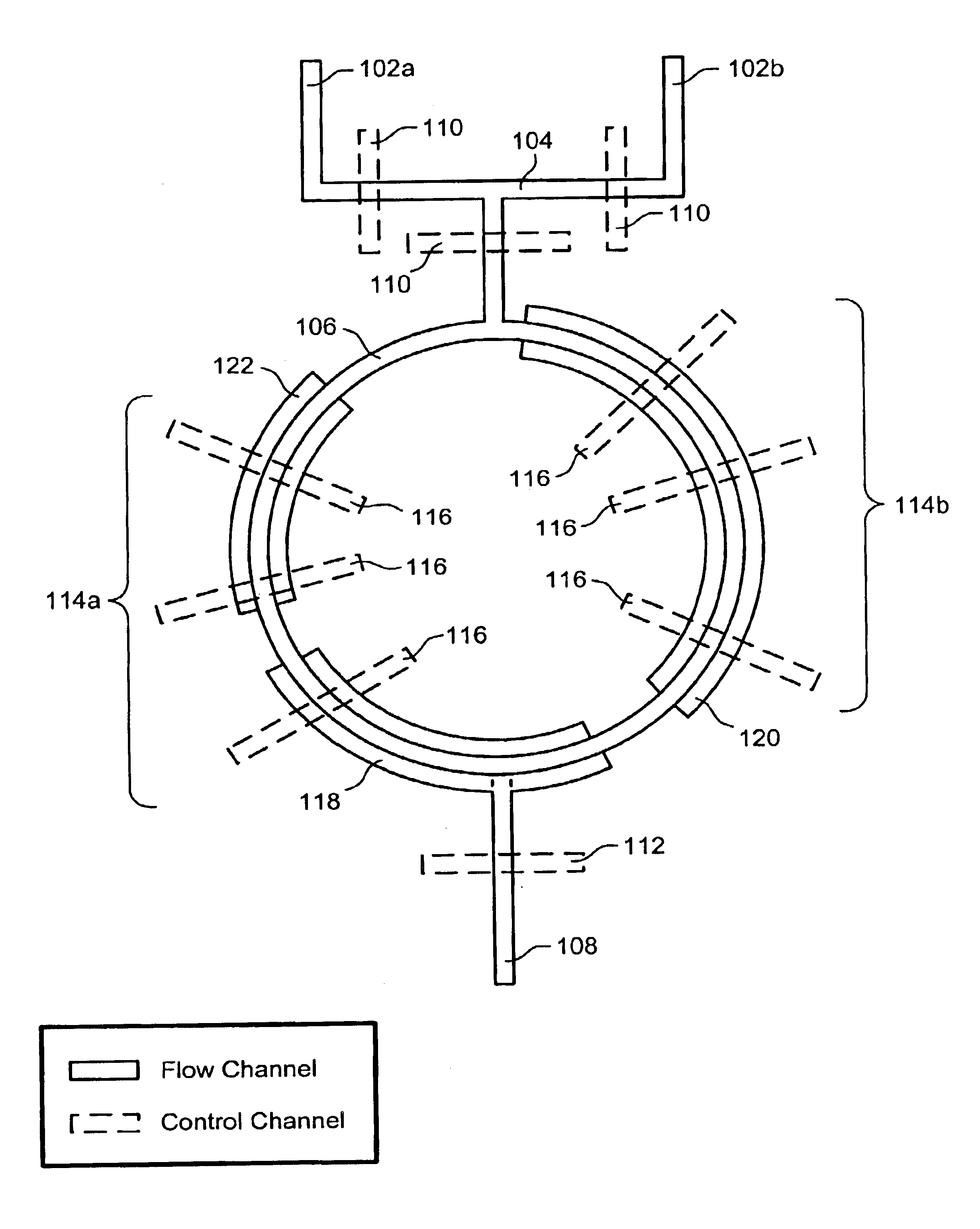
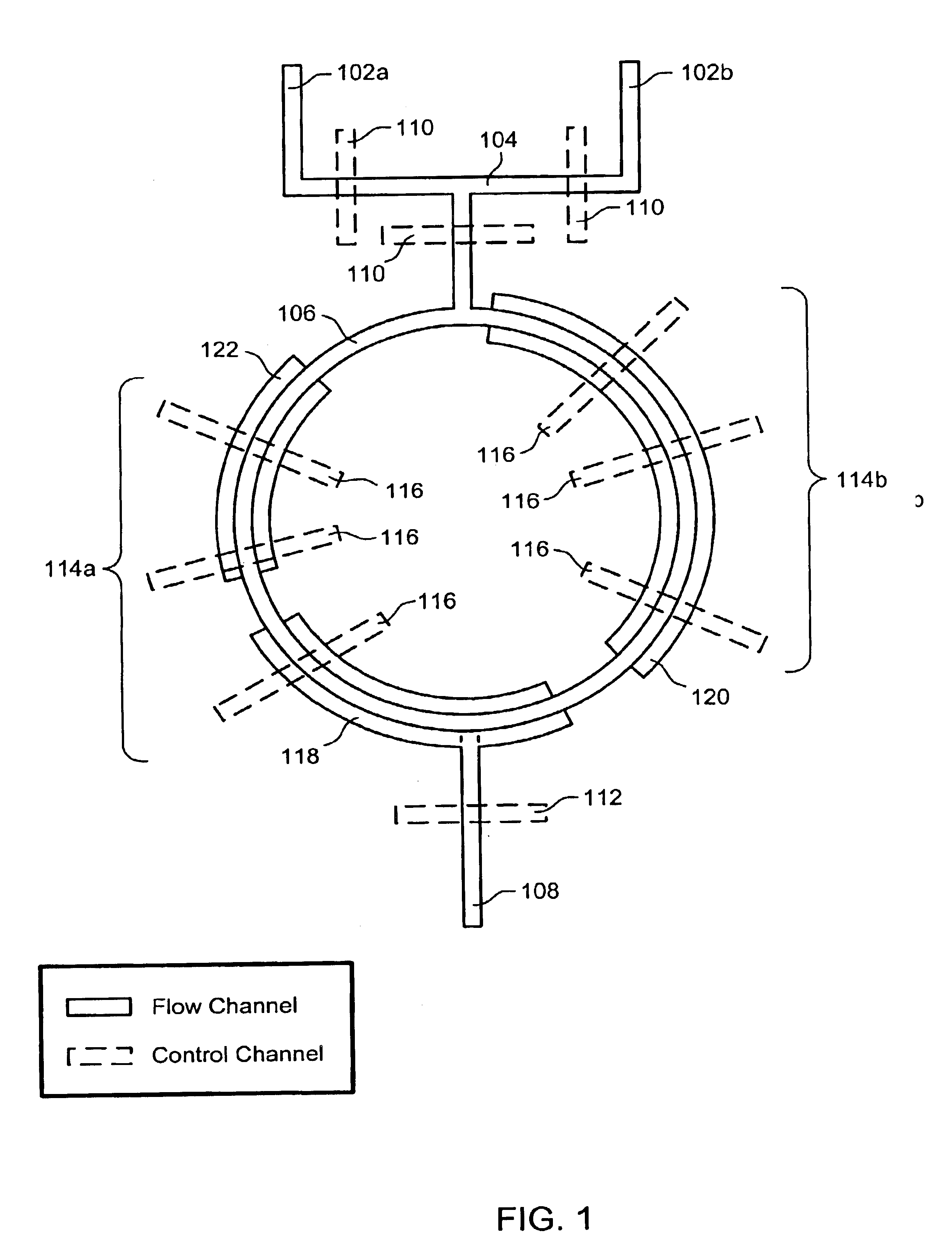
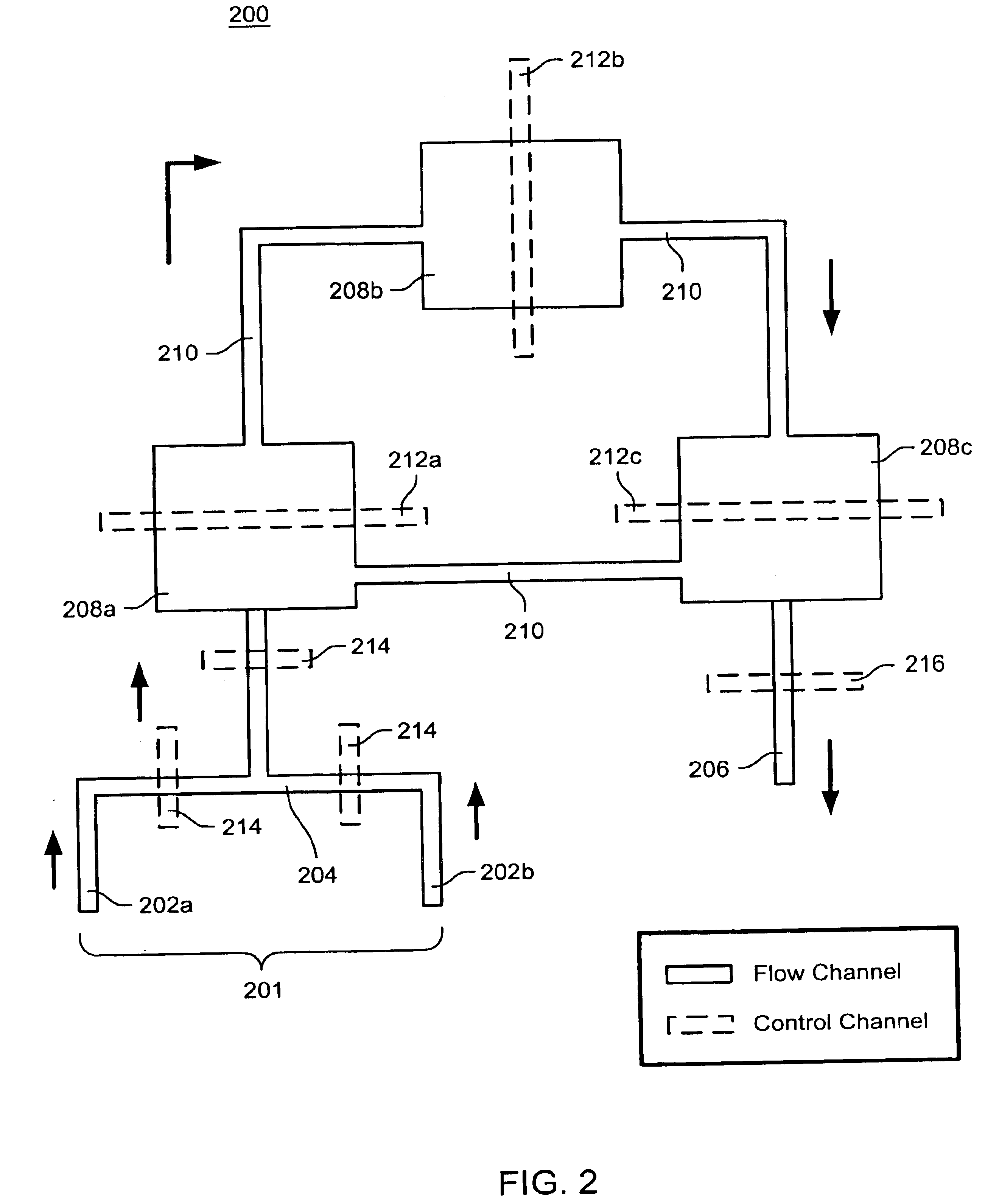
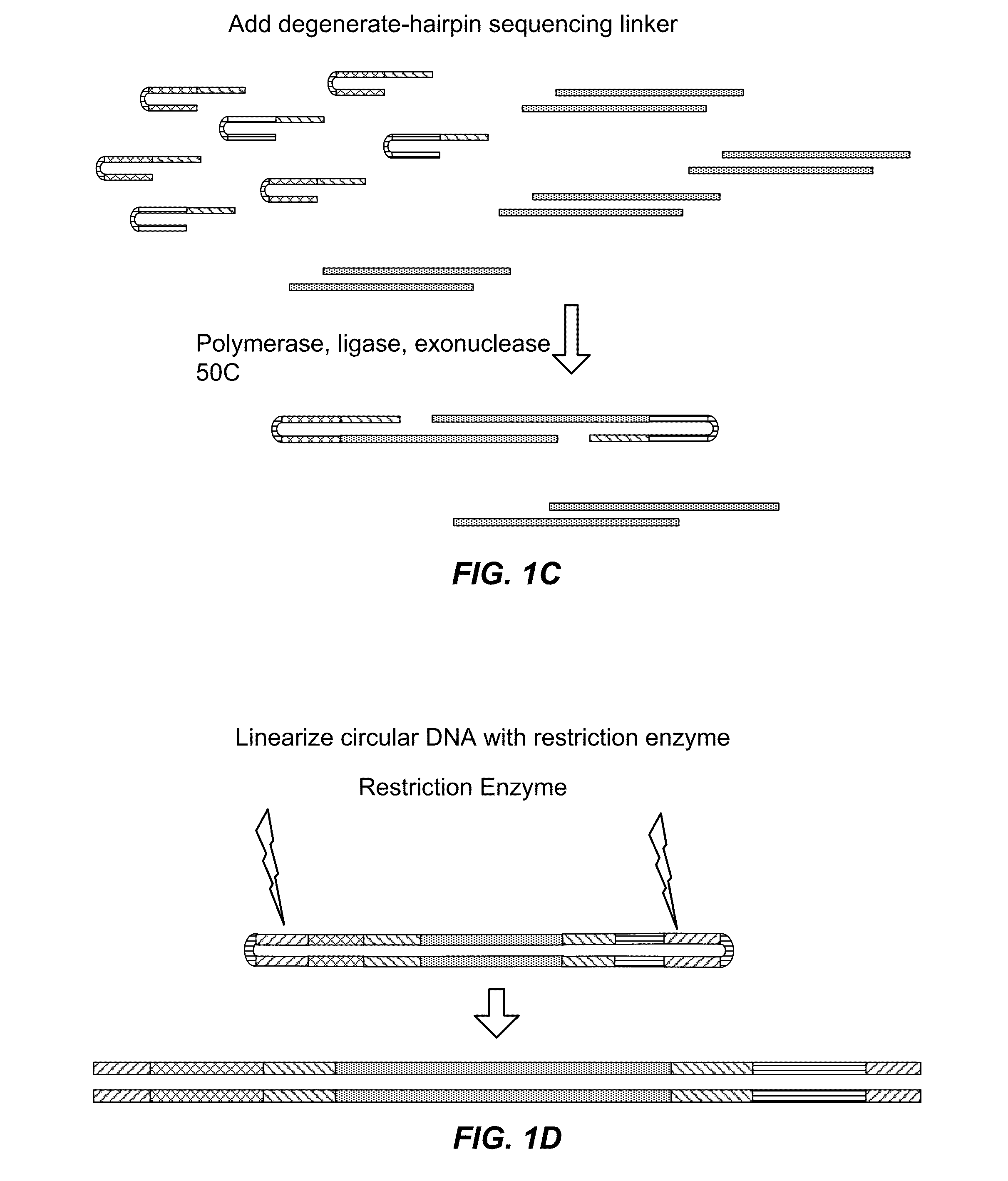
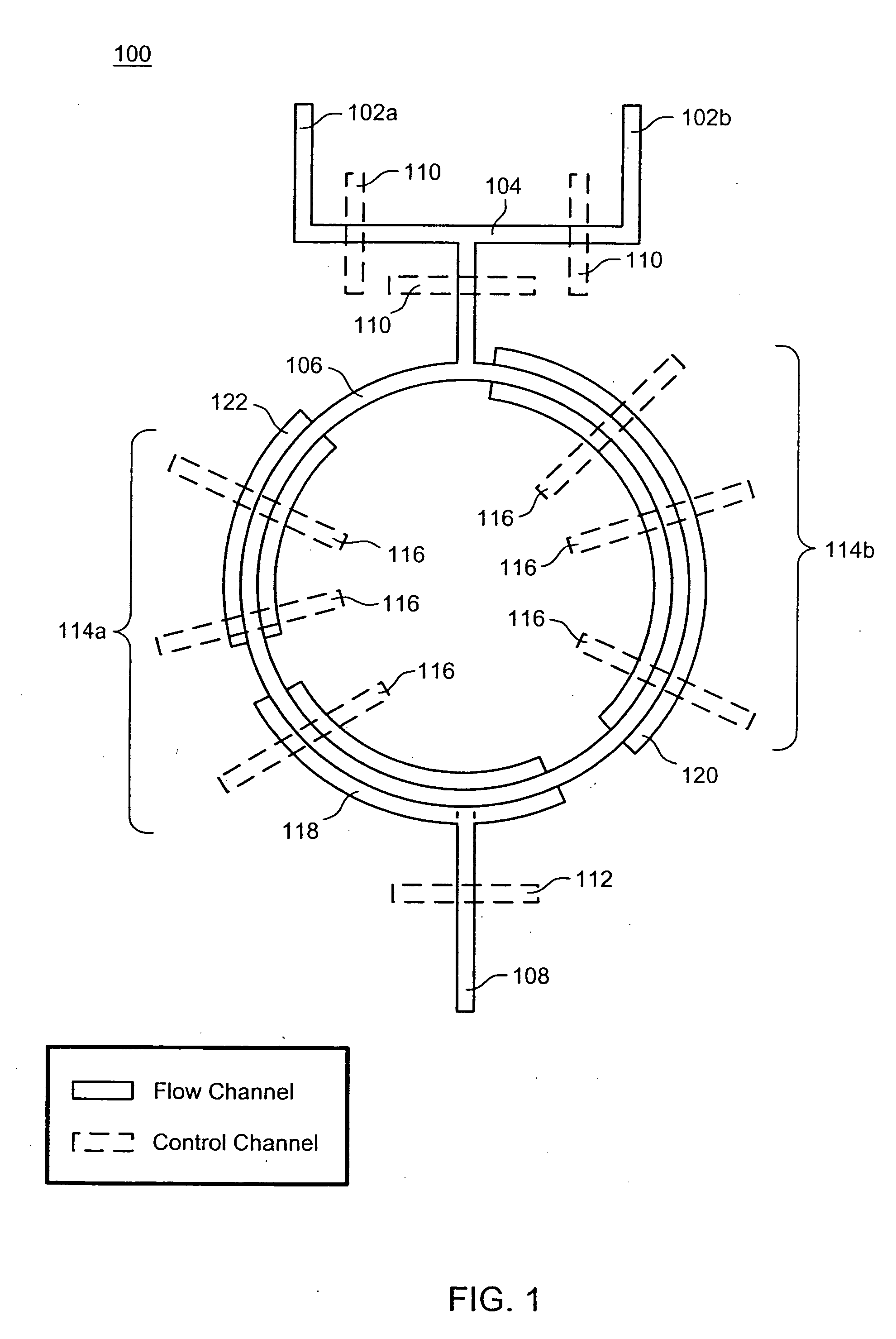
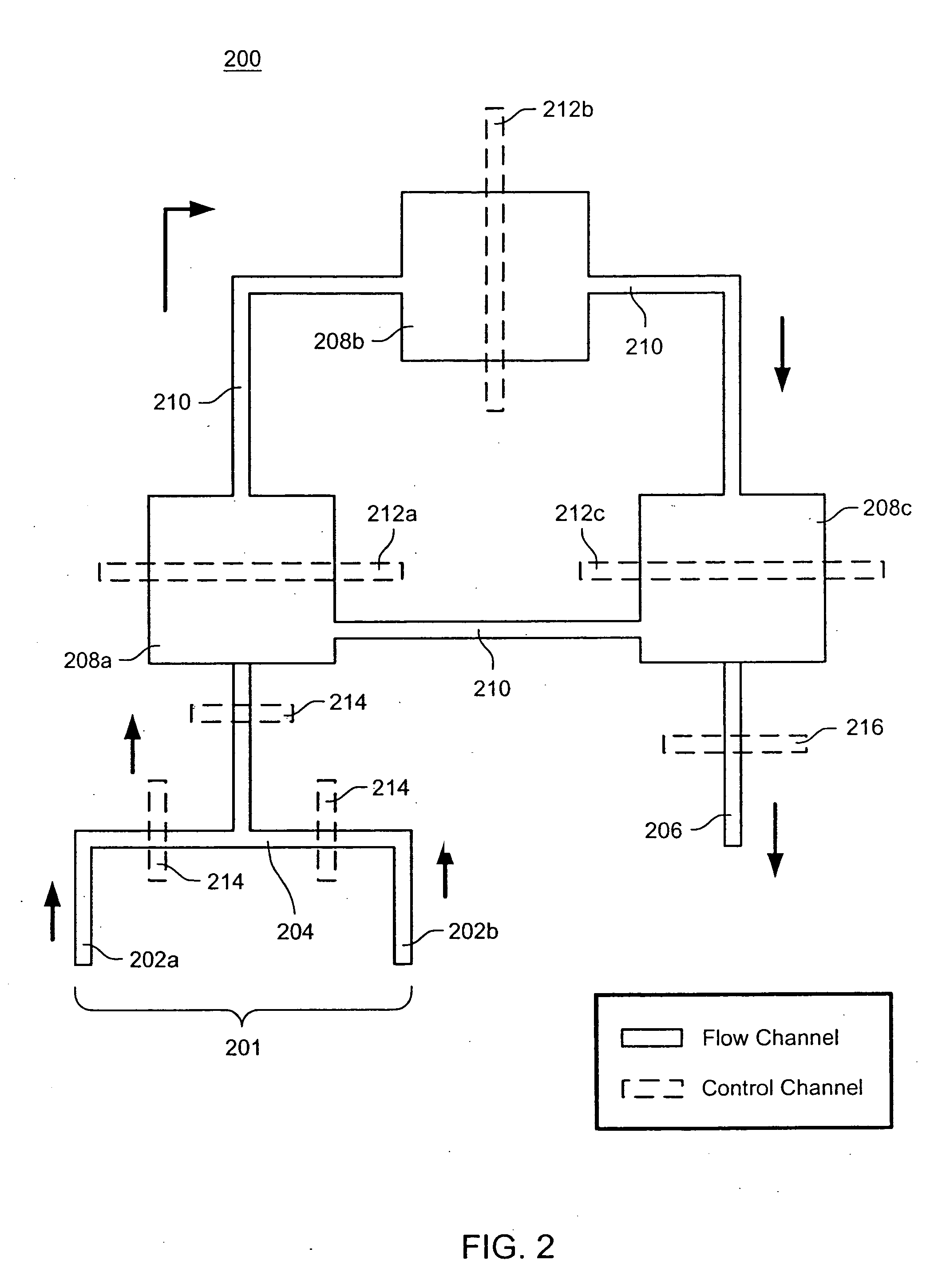
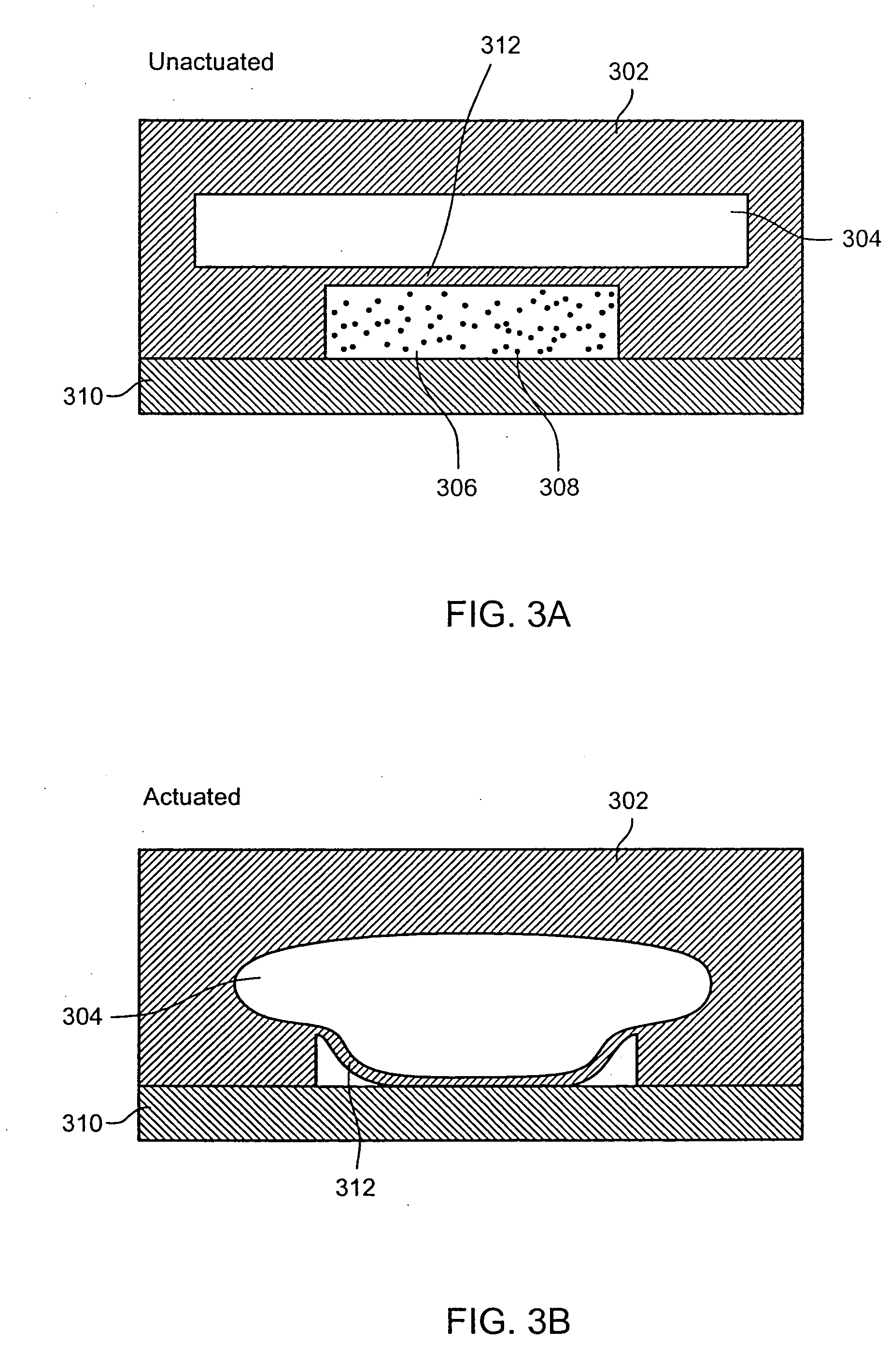
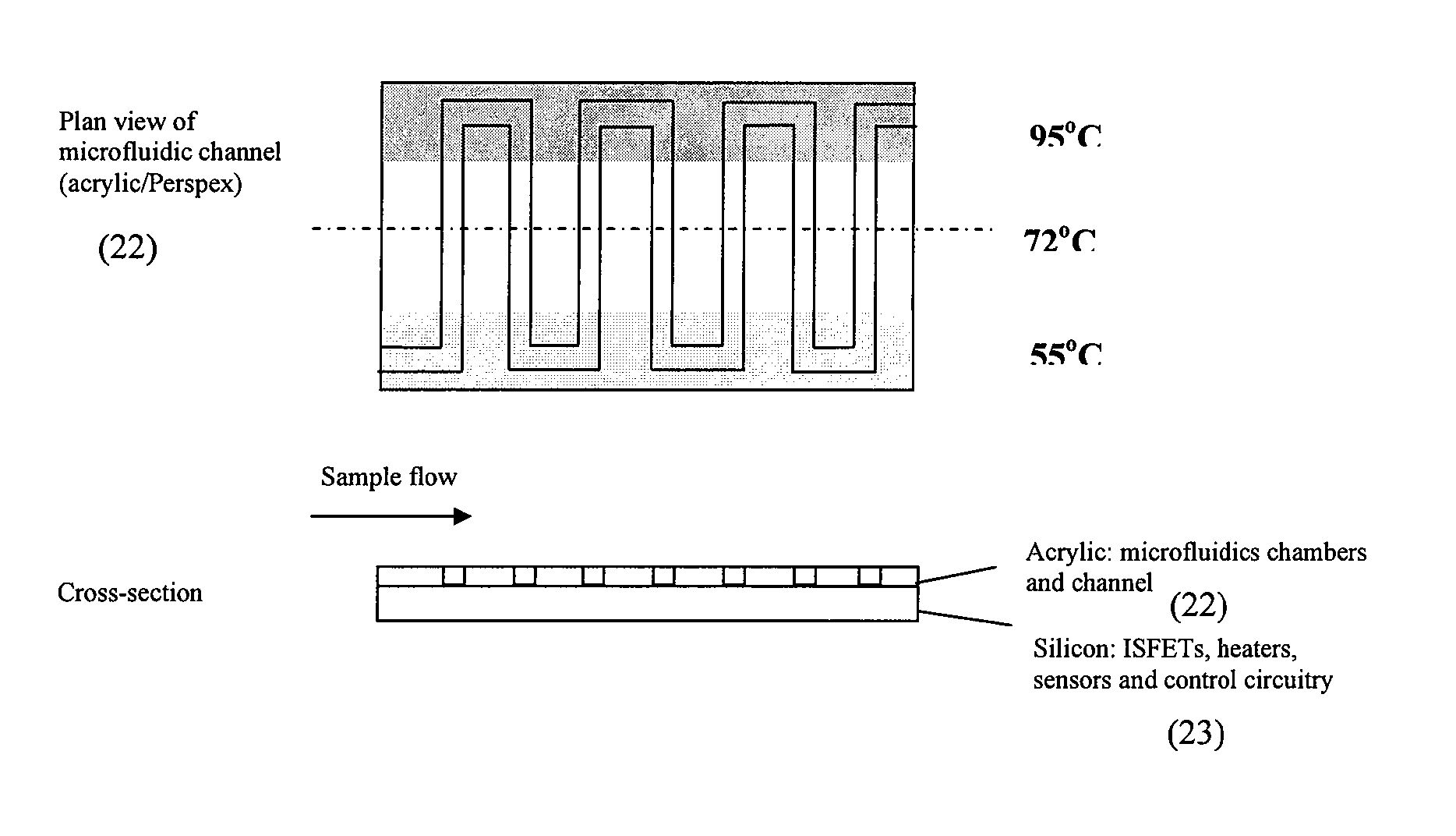
Nucleic acid amplification utilizing microfluidic devices
InactiveUS6960437B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRegulation temperatureEngineering
The present invention provides microfluidic devices and methods using the same in various types of thermal cycling reactions. Certaom devices include a rotary microfluidic channel and a plurality of temperature regions at different locations along the rotary microfluidic channel at which temperature is regulated. Solution can be repeatedly passed through the temperature regions such that the solution is exposed to different temperatures. Other microfluidic devices include an array of reaction chambers formed by intersecting vertical and horizontal flow channels, with the ability to regulate temperature at the reaction chambers. The microfluidic devices can be used to conduct a number of different analyses, including various primer extension reactions and nucleic acid amplification reactions.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
High throughput genome sequencing on DNA arrays
ActiveUS20090005252A1Simple processMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationRe sequencingNucleotide
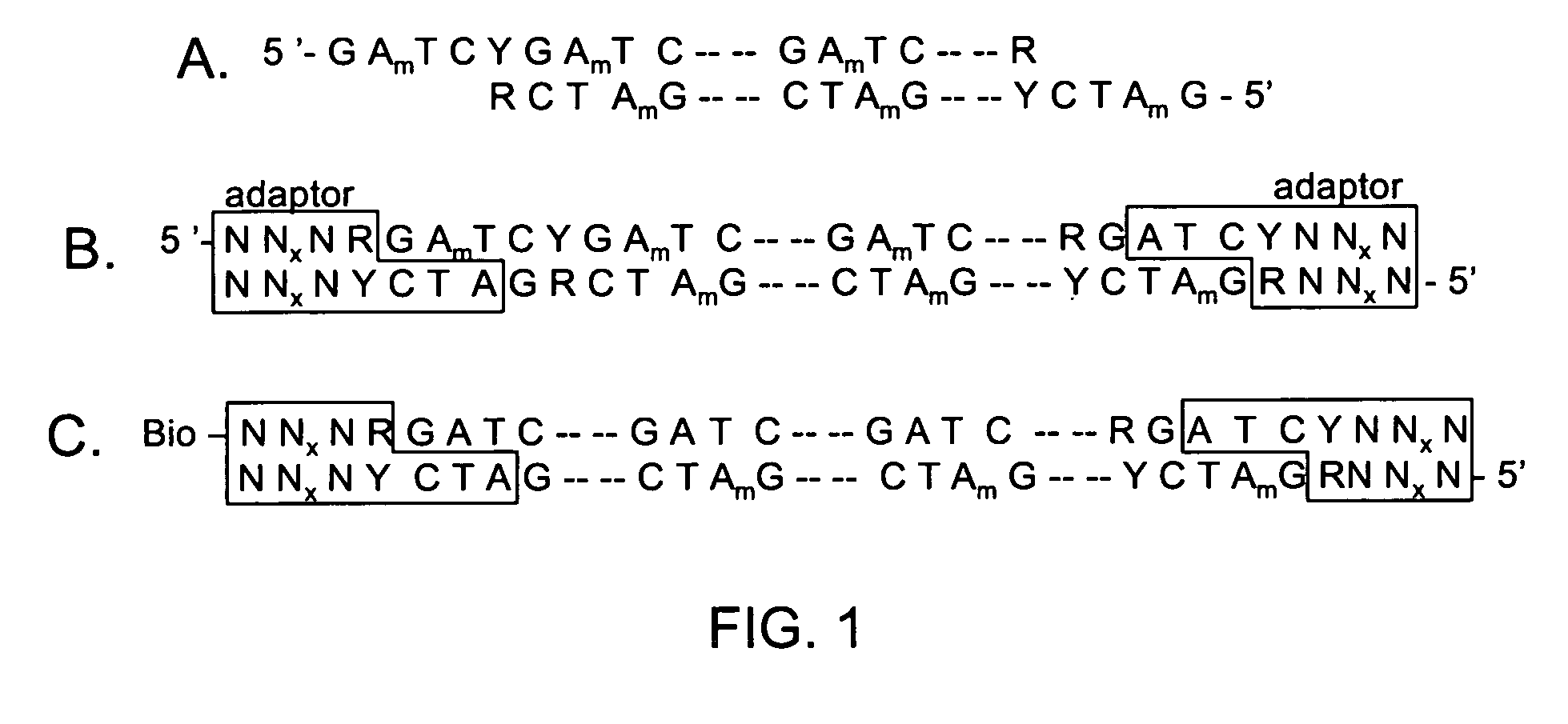
The present invention is directed to methods and compositions for acquiring nucleotide sequence information of target sequences using adaptors interspersed in target polynucleotides. The sequence information can be new, e.g. sequencing unknown nucleic acids, re-sequencing, or genotyping. The invention preferably includes methods for inserting a plurality of adaptors at spaced locations within a target polynucleotide or a fragment of a polynucleotide. Such adaptors may serve as platforms for interrogating adjacent sequences using various sequencing chemistries, such as those that identify nucleotides by primer extension, probe ligation, and the like. Encompassed in the invention are methods and compositions for the insertion of known adaptor sequences into target sequences, such that there is an interruption of contiguous target sequence with the adaptors. By sequencing both “upstream” and “downstream” of the adaptors, identification of entire target sequences may be accomplished.
Owner:COMPLETE GENOMICS INC
High throughput genome sequencing on DNA arrays
ActiveUS20090011943A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningRe sequencingNucleotide sequencing
The present invention is directed to methods and compositions for acquiring nucleotide sequence information of target sequences using adaptors interspersed in target polynucleotides. The sequence information can be new, e.g. sequencing unknown nucleic acids, re-sequencing, or genotyping. The invention preferably includes methods for inserting a plurality of adaptors at spaced locations within a target polynucleotide or a fragment of a polynucleotide. Such adaptors may serve as platforms for interrogating adjacent sequences using various sequencing chemistries, such as those that identify nucleotides by primer extension, probe ligation, and the like. Encompassed in the invention are methods and compositions for the insertion of known adaptor sequences into target sequences, such that there is an interruption of contiguous target sequence with the adaptors. By sequencing both “upstream” and “downstream” of the adaptors, identification of entire target sequences may be accomplished.
Owner:COMPLETE GENOMICS INC
Single-primer nucleic acid amplification methods
ActiveUS7374885B2Reduce appearanceHigh levelMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationNucleotideNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention is directed to novel methods of synthesizing multiple copies of a target nucleic acid sequence which are autocatalytic (i.e., able to cycle automatically without the need to modify reaction conditions such as temperature, pH, or ionic strength and using the product of one cycle in the next one). In particular, the present invention discloses a method of nucleic acid amplification which is robust and efficient, while reducing the appearance of side-products. The method uses only one primer, the “priming oligonucleotide,” a promoter oligonucleotide modified to prevent polymerase extension from its 3′-terminus and, optionally, a means for terminating a primer extension reaction, to amplify RNA or DNA molecules in vitro, while reducing or substantially eliminating the formation of side-products. The method of the present invention minimizes or substantially eliminates the emergence of side-products, thus providing a high level of specificity. Furthermore, the appearance of side-products can complicate the analysis of the amplification reaction by various molecular detection techniques. The present invention minimizes or substantially eliminates this problem, thus providing an enhanced level of sensitivity.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
Nucleic acid encoding reactions
ActiveUS20130005585A1Avoid substantial annealingNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideBarcode
Described herein are methods useful for incorporating one or more adaptors and / or nucleotide tag(s) and / or barcode nucleotide sequence(s) one, or typically more, target nucleotide sequences. In particular embodiments, nucleic acid fragments having adaptors, e.g., suitable for use in high-throughput DNA sequencing are generated. In other embodiments, information about a reaction mixture is encoded into a reaction product. Also described herein are methods and kits useful for amplifying one or more target nucleic acids in preparation for applications such as bidirectional nucleic acid sequencing. In particular embodiments, methods of the invention entail additionally carrying out bidirectional DNA sequencing. Also described herein are methods for encoding and detecting and / or quantifying alleles by primer extension.
Owner:FLUIDIGM CORP
Nucleic acid amplification using microfluidic devices
InactiveUS20050221373A1Facilitate amplification reactionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusRegulation temperatureEngineering
The present invention provides microfluidic devices and methods using the same in various types of thermal cycling reactions. Certaom devices include a rotary microfluidic channel and a plurality of temperature regions at different locations along the rotary microfluidic channel at which temperature is regulated. Solution can be repeatedly passed through the temperature regions such that the solution is exposed to different temperatures. Other microfluidic devices include an array of reaction chambers formed by intersecting vertical and horizontal flow channels, with the ability to regulate temperature at the reaction chambers. The microfluidic devices can be used to conduct a number of different analyses, including various primer extension reactions and nucleic acid amplification reactions.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Kits for amplifying and detecting nucleic acid sequences, including a probe
InactiveUS6040166AStrong specificityReduce manpowerNanotechSequential/parallel process reactionsOligonucleotide primersNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention is directed to a process for amplifying any target nucleic acid sequence contained in a nucleic acid or mixture thereof using a thermostable enzyme. The process comprises treating separate complementary strands of the nucleic acid with a molar excess of two oligonucleotide primers, extending the primers with a thermostable enzyme to form complementary primer extension products which act as templates for synthesizing the desired nucleic acid sequence, and detecting the sequence so amplified. The steps of the reaction can be repeated as often as desired and involve temperature cycling to effect hybridization, promotion of activity of the enzyme, and denaturation of the hybrids formed.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment: photoselection of nucleic acid ligands and solution selex
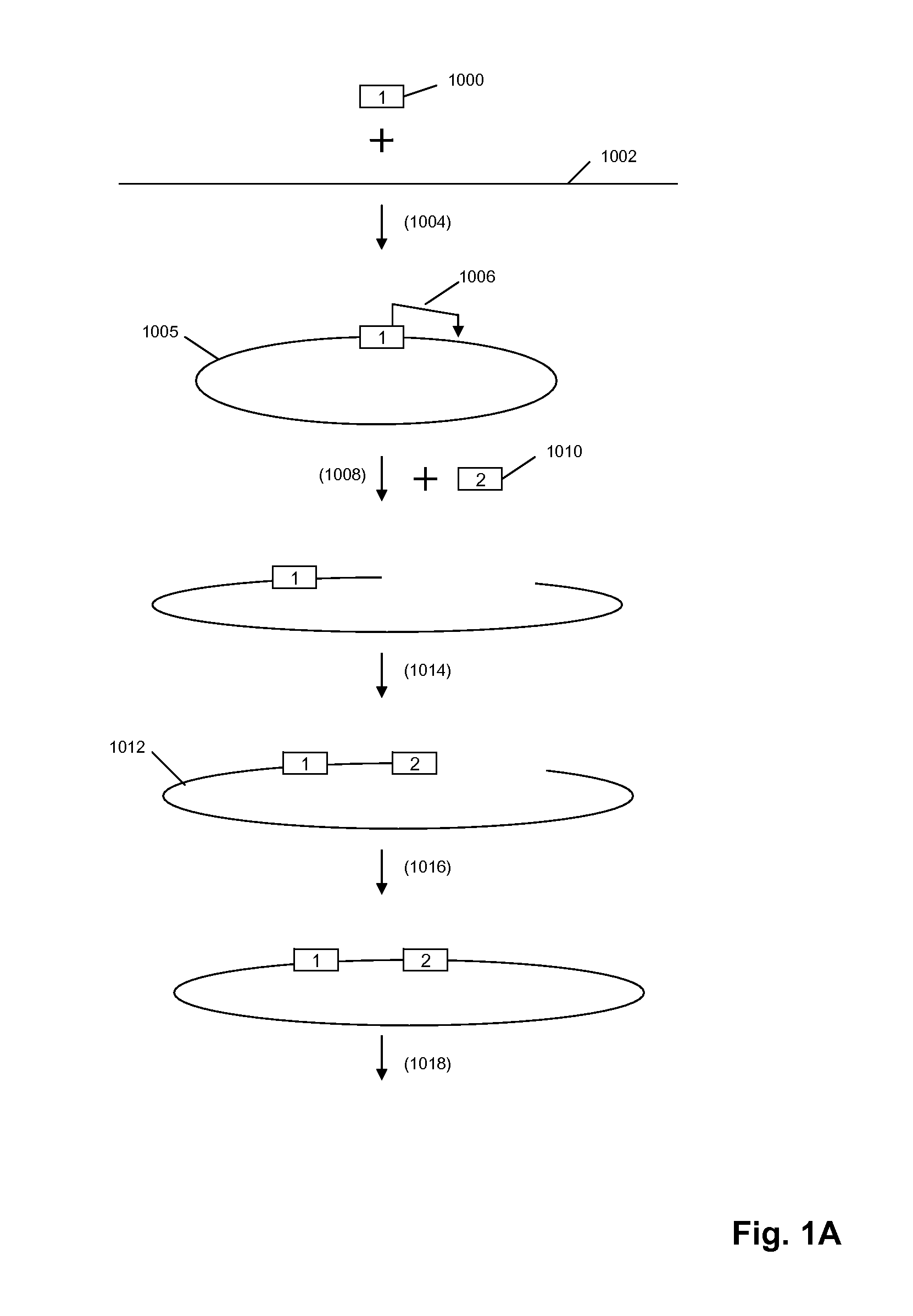
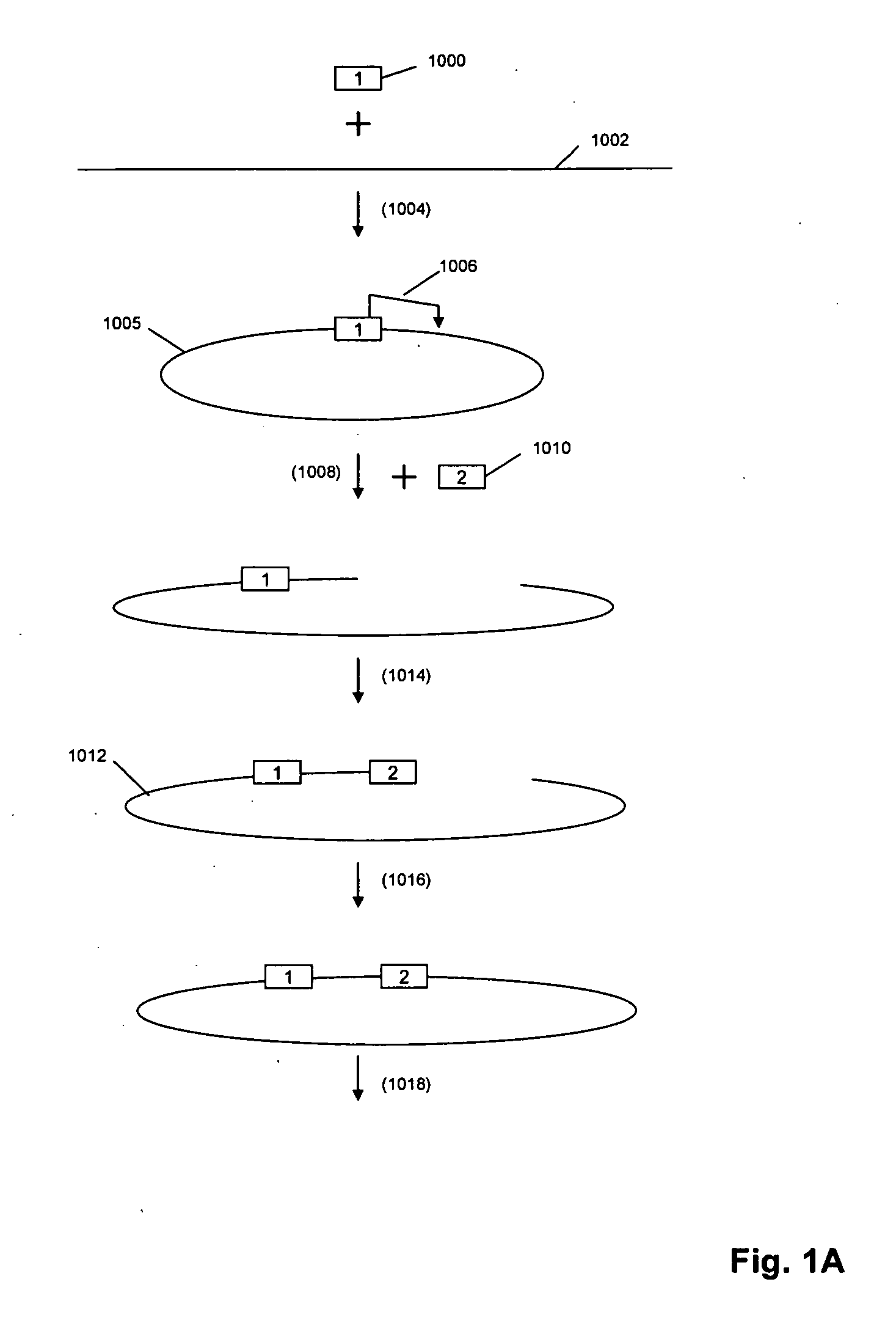
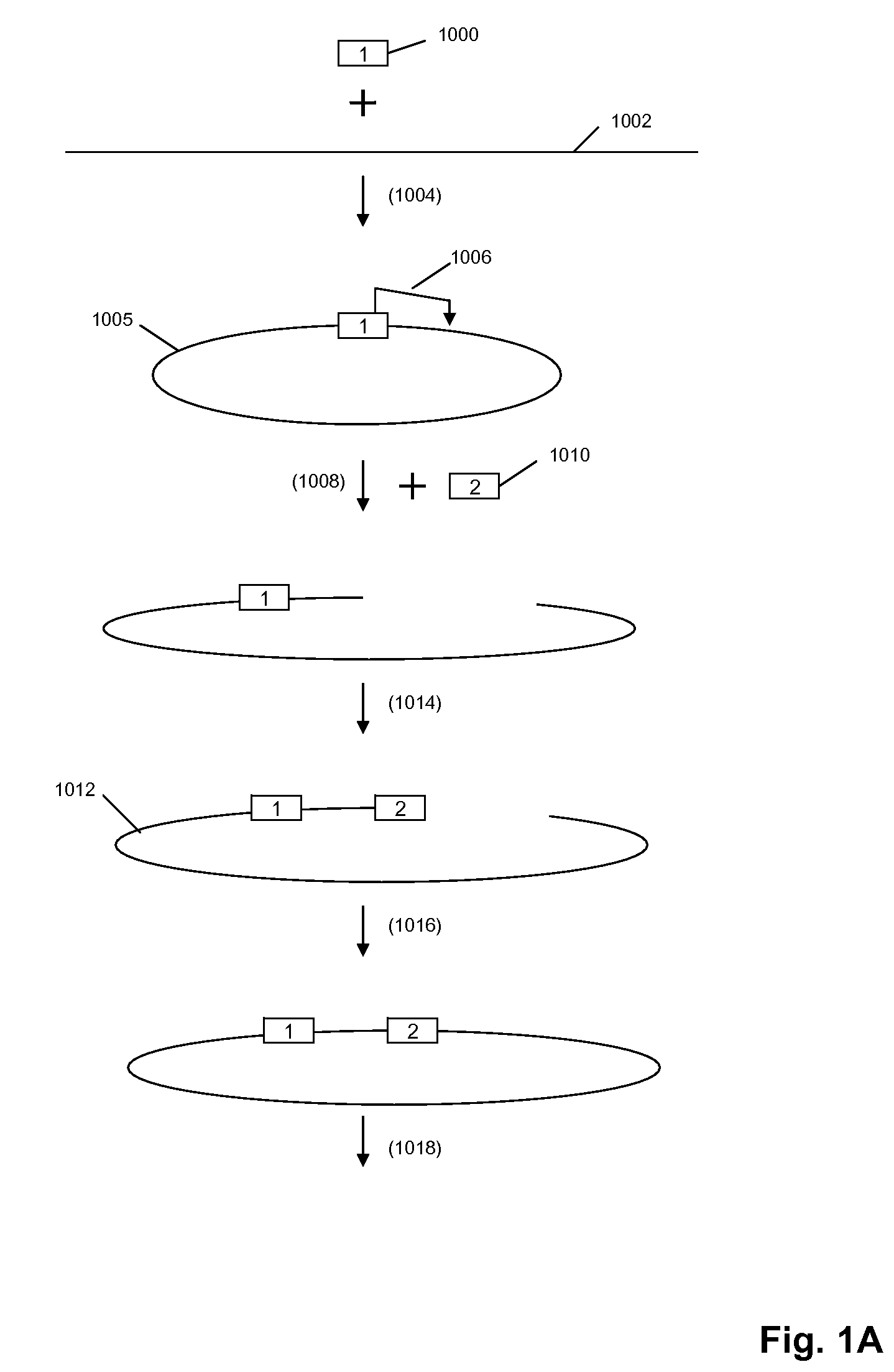
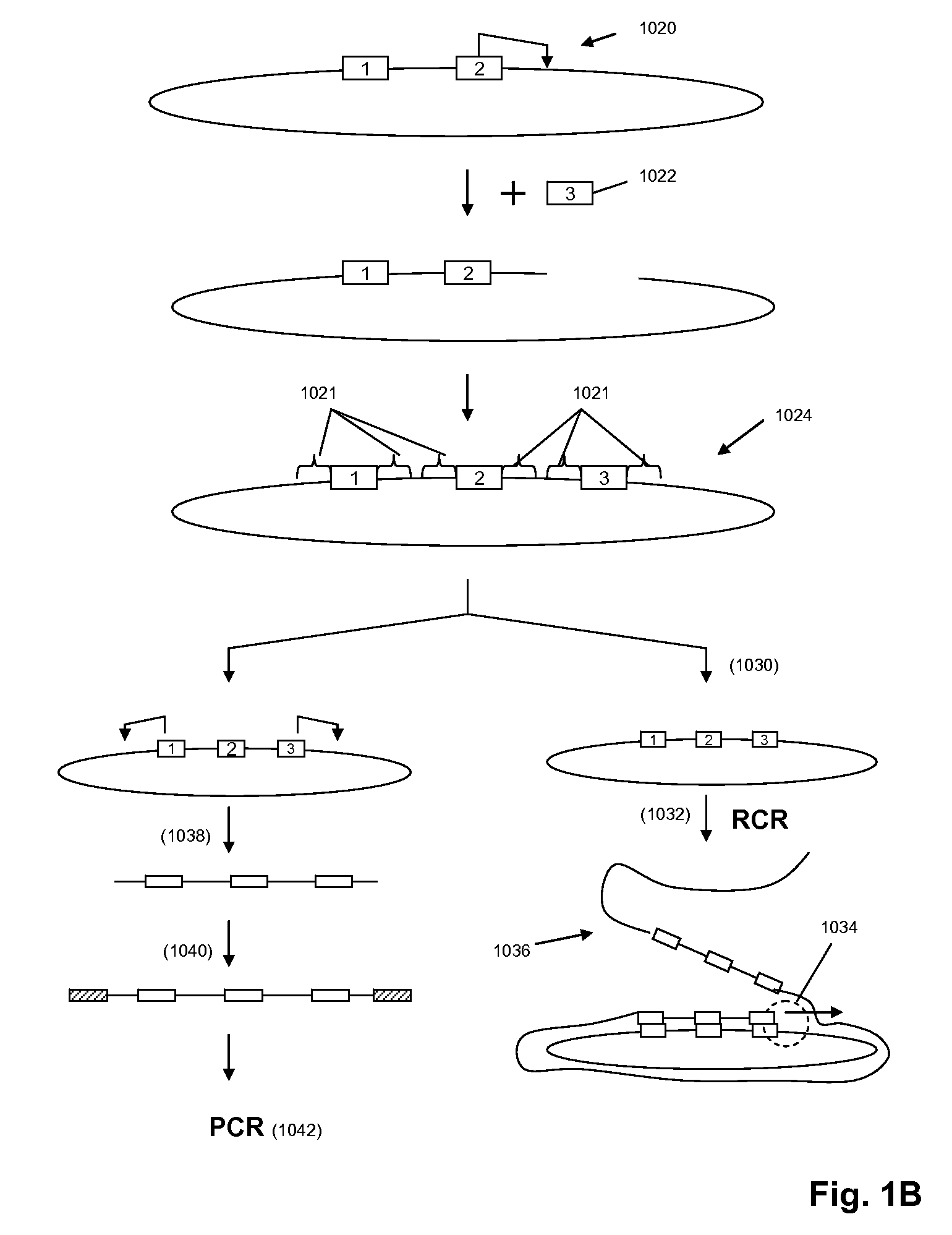
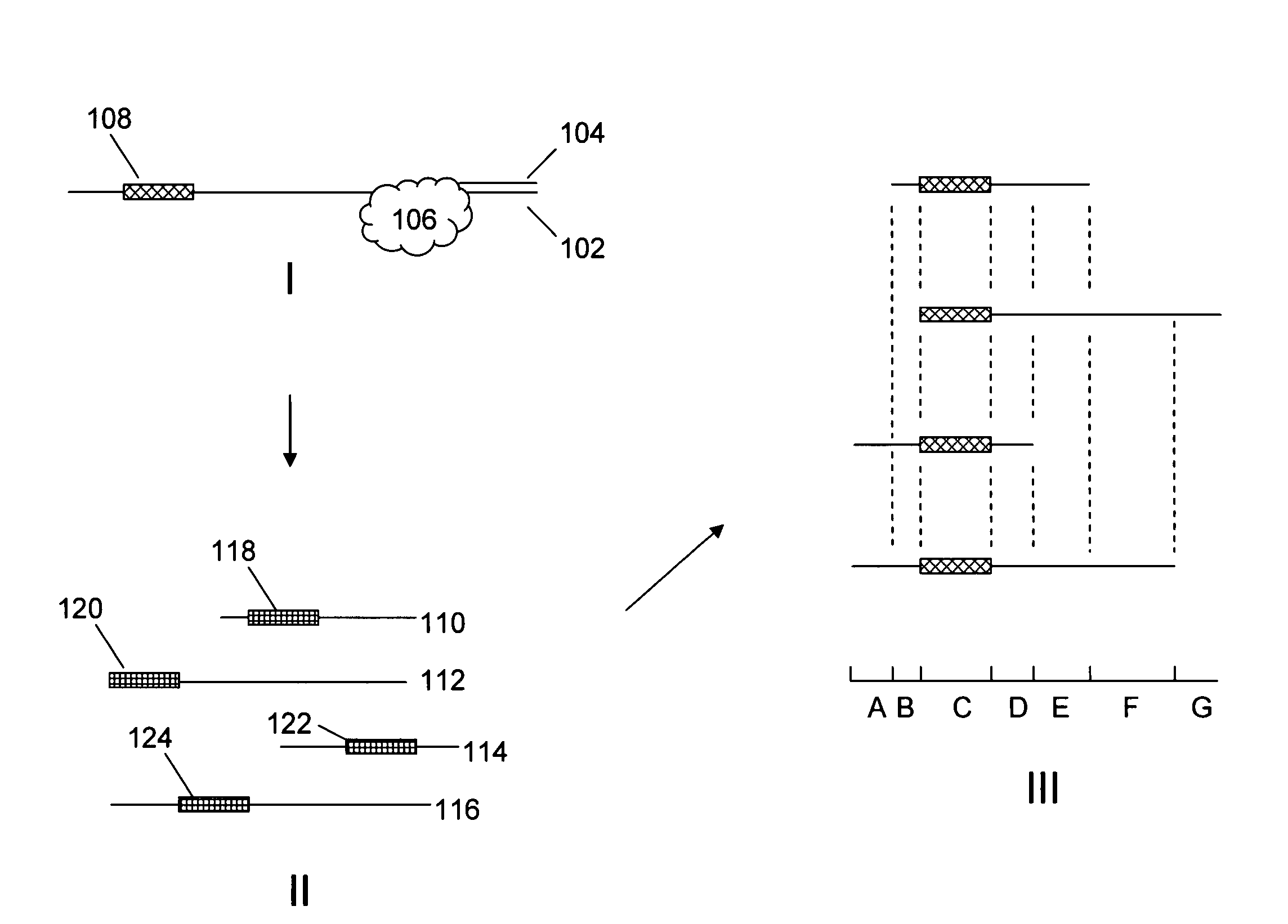
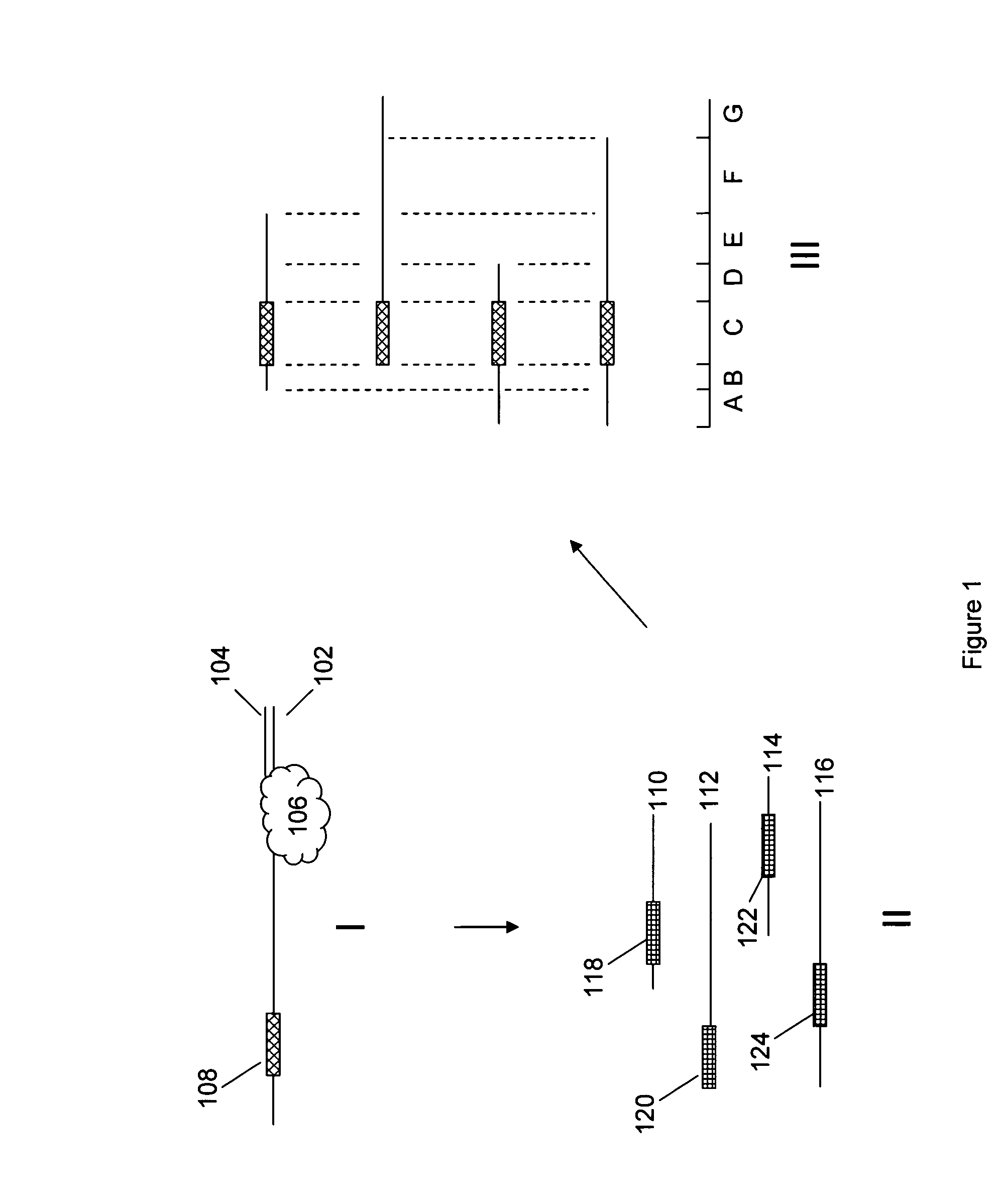
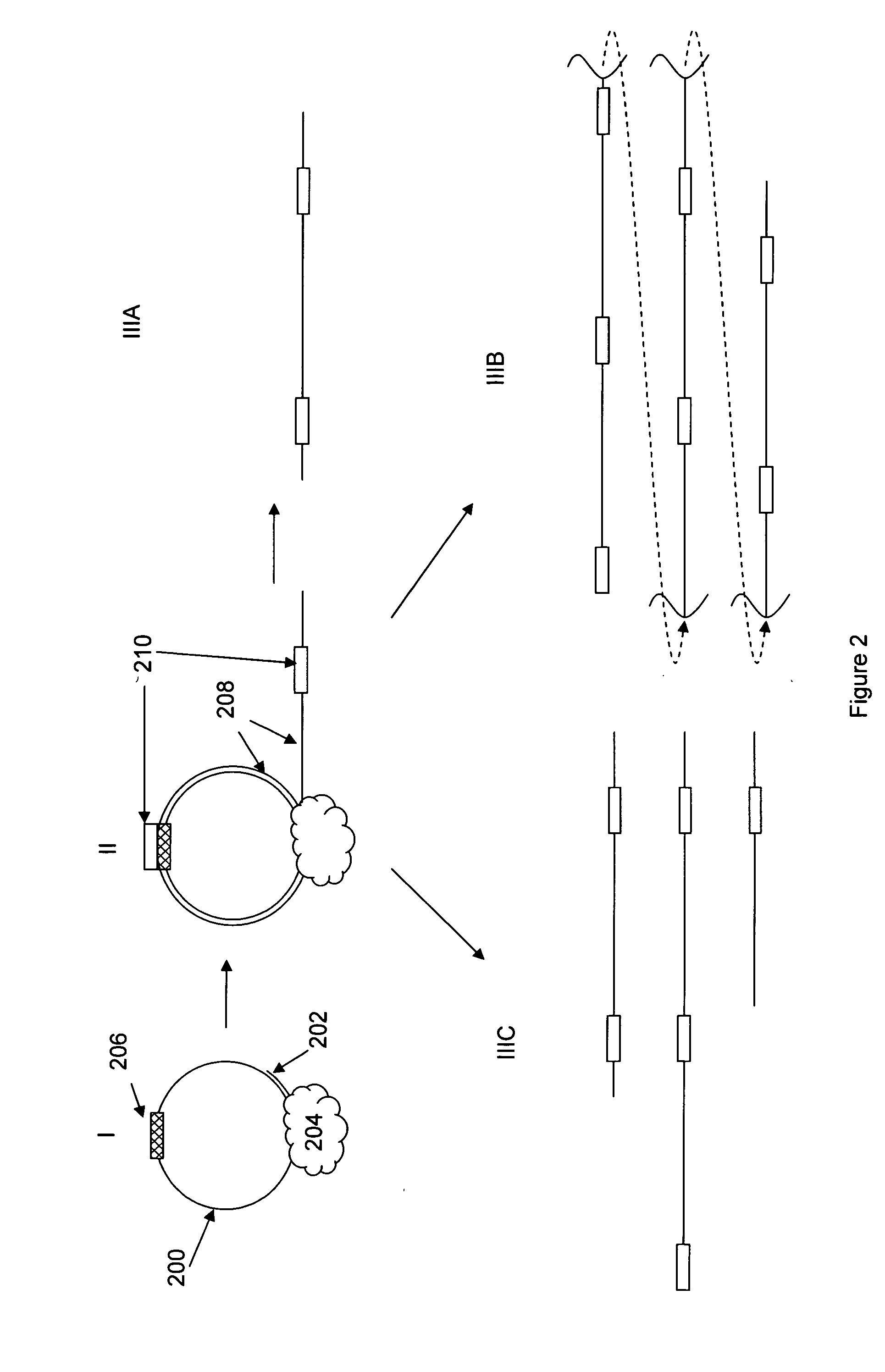
A method for identifying nucleic acid ligands to target molecules using the SELEX procedure wherein the candidate nucleic acids contain photoreactive groups and nucleic acid ligands identified thereby are claimed. The complexes of increased affinity nucleic acids and target molecules formed in the procedure are crosslinked by irradiation to facilitate separation from unbound nucleic acids. In other methods partitioning of high and low affinity nucleic acids is facilitated by primer extension steps as shown in the figure in which chain termination nucleotides, digestion resistant nucleotides or nucleotides that allow retention of the cDNA product on an affinity matrix are differentially incorporated into the cDNA products of either the high or low affinity nucleic acids and the cDNA products are treated accordingly to amplification, enzymatic or chemical digestion or by contact with an affinity matrix.
Owner:SOMALOGIC INC
High throughput genome sequencing on DNA arrays
The present invention is directed to methods and compositions for acquiring nucleotide sequence information of target sequences using adaptors interspersed in target polynucleotides. The sequence information can be new, e.g. sequencing unknown nucleic acids, re-sequencing, or genotyping. The invention preferably includes methods for inserting a plurality of adaptors at spaced locations within a target polynucleotide or a fragment of a polynucleotide. Such adaptors may serve as platforms for interrogating adjacent sequences using various sequencing chemistries, such as those that identify nucleotides by primer extension, probe ligation, and the like. Encompassed in the invention are methods and compositions for the insertion of known adaptor sequences into target sequences, such that there is an interruption of contiguous target sequence with the adaptors. By sequencing both “upstream” and “downstream” of the adaptors, identification of entire target sequences may be accomplished.
Owner:COMPLETE GENOMICS INC
Molecular redundant sequencing
ActiveUS20090029385A1Improve accuracySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPolymerase LNucleic acid sequencing
Methods, systems and compositions where a target nucleic acid includes a registration sequence disposed therein for identification of the number or relative position of determined sequence from the template sequence. Particularly preferred aspects include a registration sequence in a circular template nucleic acid sequence which is, in turn, used in sequence by incorporation processes that rely upon template dependent, polymerase mediated primer extension in the identification of the sequence of the template.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Methods and compositions for isolating nucleic acid sequence variants
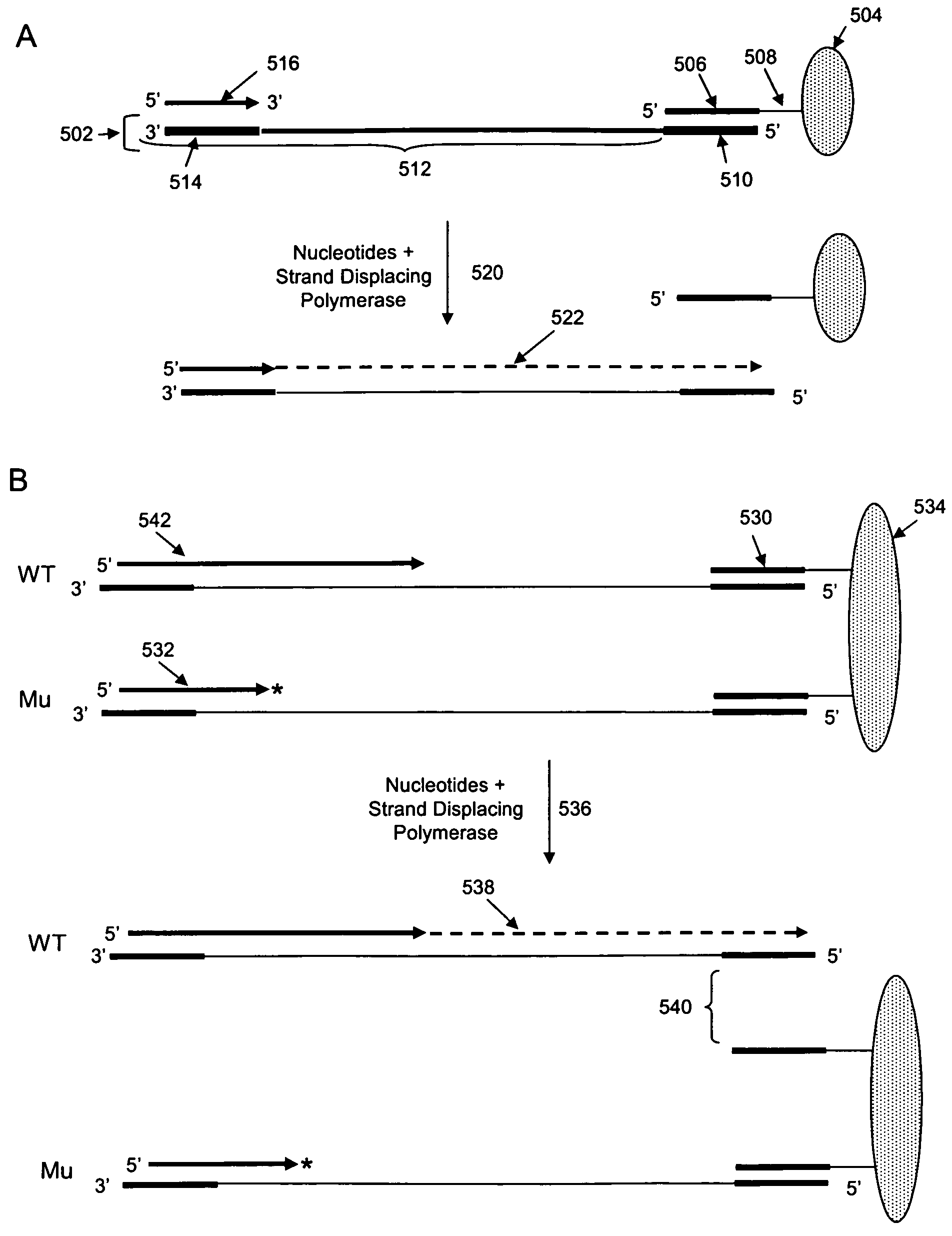
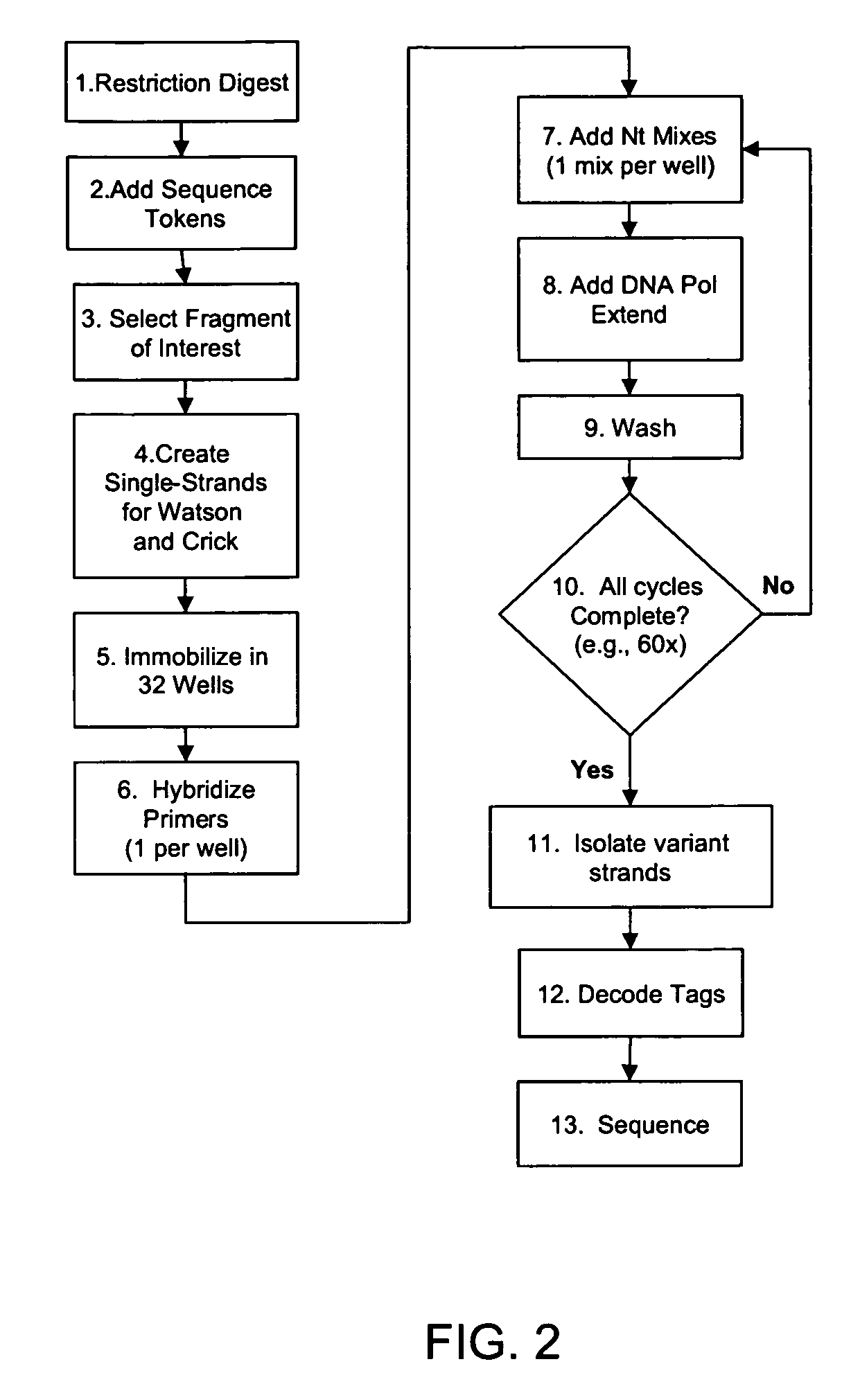
The invention is drawn to isolating sequence variants of a genetic locus of interest using a modified iterative primer extension method. The nucleic acids analyzed are generally single stranded and have a reference sequence which is used as a basis for performing iterative single nucleotide extension reactions from a hybridized polymerization primer. The iterative polymerization reactions are configured such that polymerization of the strand will continue if the sequence of the nucleic acid being analyzed matches the reference sequence, whereas polymerization will be terminated if the nucleic acid being analyzed does not match the reference sequence. Nucleic acid strands that have mutations can be isolated using a variety of methods and sequenced to determine the precise identity of the mutation / polymorphism. By performing the method on both strands of the nucleic acid being analyzed, virtually all possible mutations can be identified.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
New sequencing method for sequencing rna molecules
InactiveUS20060166203A1Reduce decreaseMicrobiological testing/measurementReverse transcriptaseNucleotide
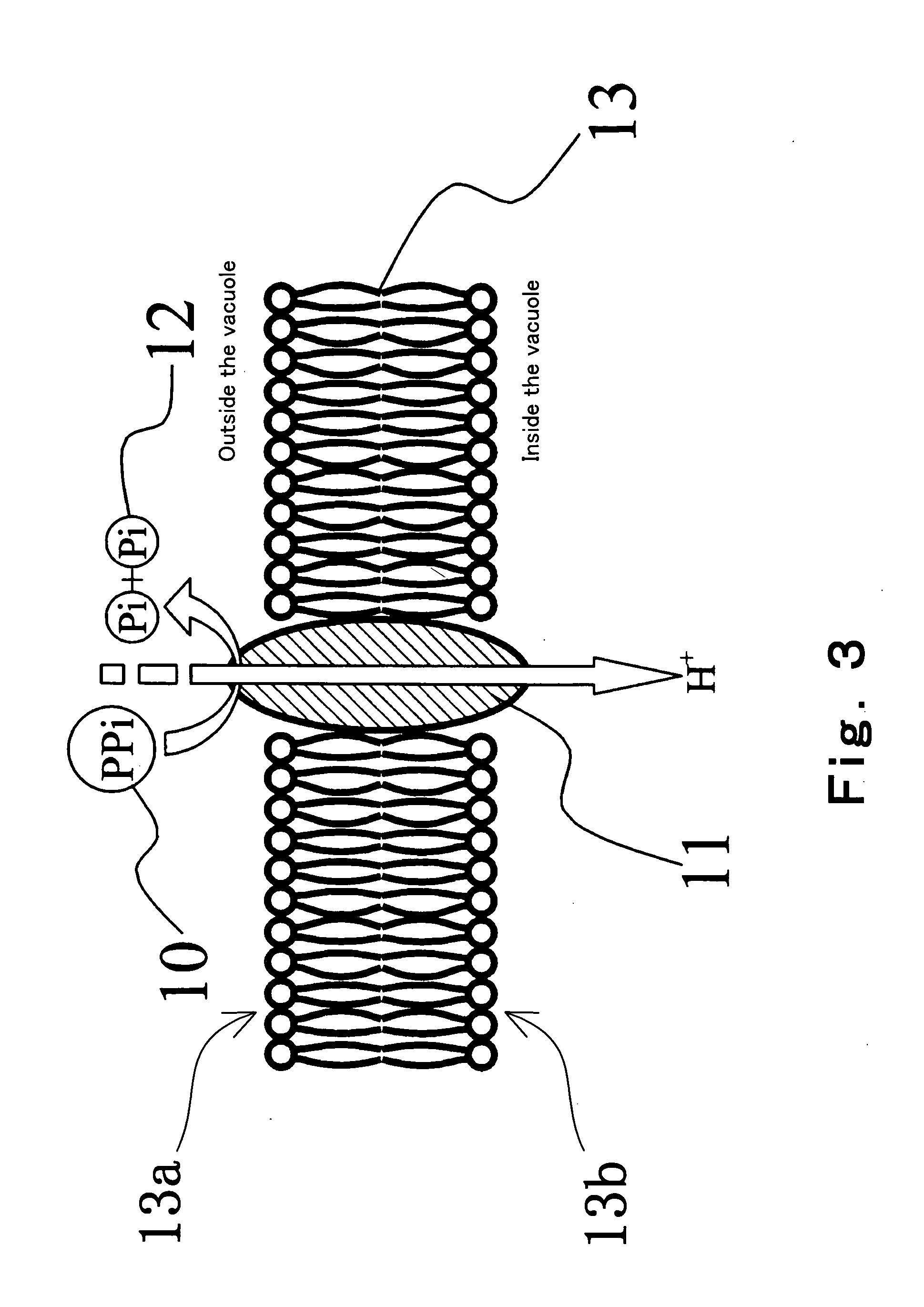
The present invention provides a method for determination of the identity of at least one nucleotide in a RNA-molecule comprising the steps of: (i) providing the RNA-molecule, an oligonucleotide primer binding to a predetermined position of the RNA molecule, a reverse transcriptase, deoxynucleotides and other necessary reagents, in a reaction vessel; (ii) performing a primer extension reaction, whereby the oligonucleotide primer is extended on the RNA-molecule through incorporation of at least one deoxynucleotide by the action of a reverse transcriptase, resulting in the release of a PPi molecule only upon incorporation of a deoxynucleotide; and (iii) detecting the presence or absence of incorporation, thereby indicating the nucleotide identity of the RNA molecule in the relevant position. In a preferred embodiment, the sequencing of the invention is coupled to the Pyrosequencing™ reaction. A variant of the method employs incorporation of modified nucleotides, with an optionally cleavable linker arm to which is attached a label.
Owner:TOOKE NIGEL
Sensing apparatus and method
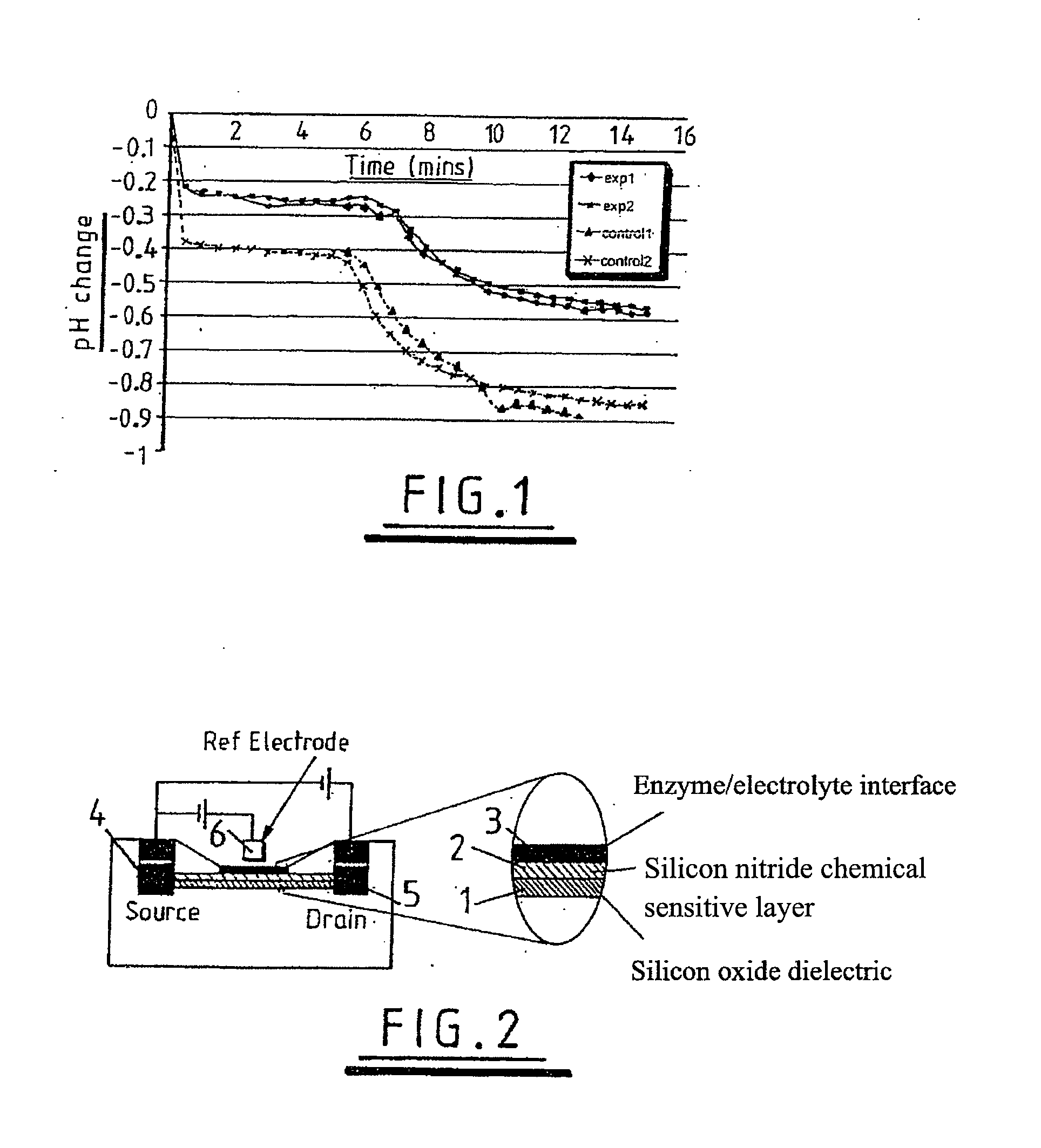
InactiveUS20080032295A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsChemical physicsProton
Use of a pH sensor comprising an ion-sensitive field effect transistor (ISFET) to perform real time detection / quantification of nucleic acid amplification, e.g. polymerase chain reaction (PCR) nucleic acid amplification, based on detection of protons released during the primer extension phase.
Owner:DNAE GRP HLDG
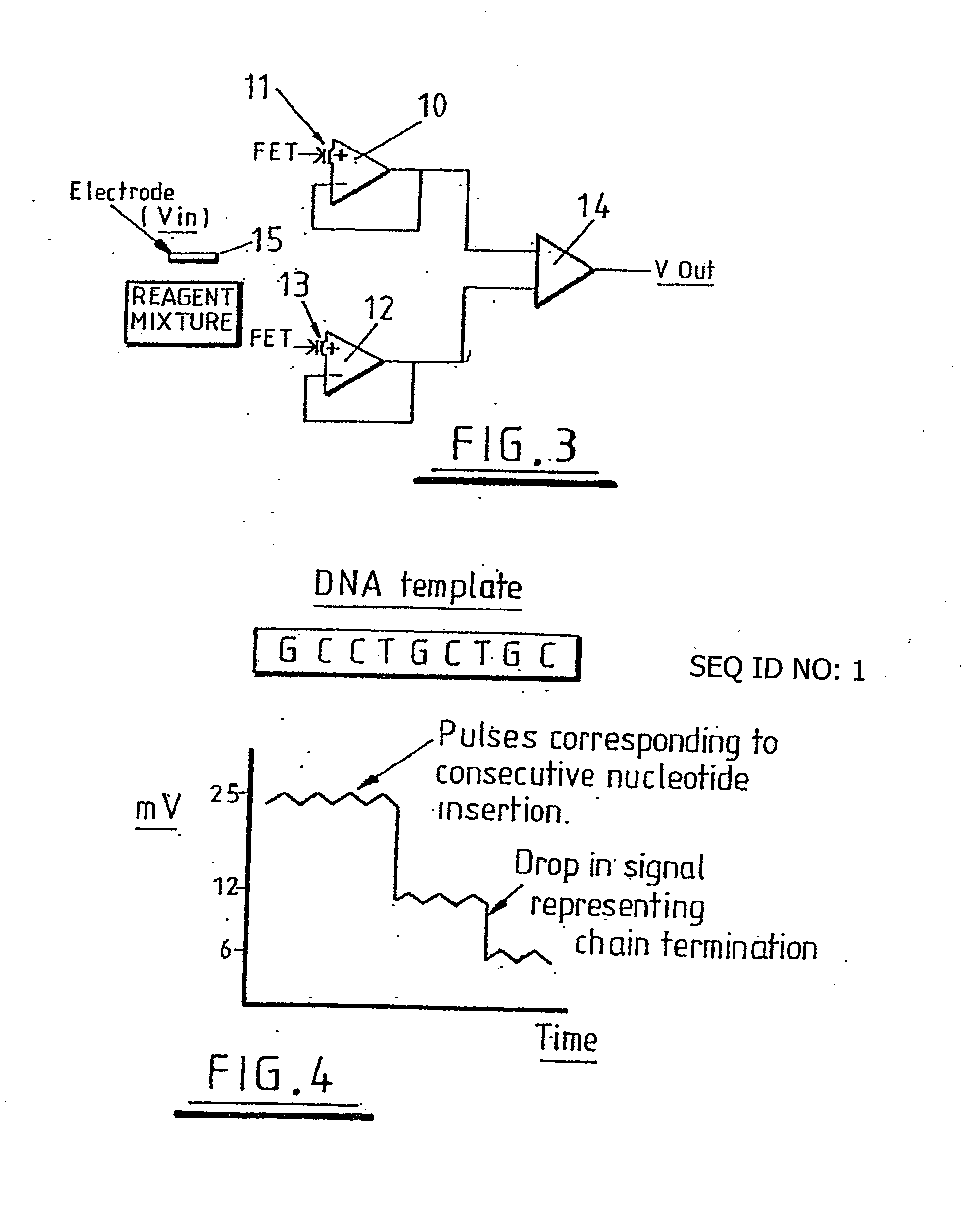
Method of detecting primer extension reaction, method of discriminating base type, device for discriminating base type, device for detecting pyrophosphate, method of detecting nucleic acid and tip for introducing sample solution
InactiveUS20050032075A1Decrease of H+ concentrationImprove concentrationMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisBase JNucleotide
Convenient techniques for discriminating the base type in a base sequence of a nucleic acid are provided. The technique includes the step (a) of preparing a sample solution containing a nucleic acid, a primer having a base sequence that includes a complementary binding region which complementarily binds to the nucleic acid, and a nucleotide; the step (b) of allowing the sample solution to stand under a condition to cause an extension reaction of the primer, and producing pyrophosphate when the extension reaction is caused; the step (c) of bringing the sample solution into contact with the front face of a H+ hardly permeable membrane having H+-pyrophosphatase, which penetrates from front to back of the membrane, of which active site that hydrolyzes pyrophosphate being exposed to the front face; the step (d) of measuring the H+ concentration of at least either one of the solution at the front face side of the H+ hardly permeable membrane or the solution at the back face side of the H+ hardly permeable membrane, in a state where the H+-pyrophosphatase is immersed in the solution; the step (e) of detecting the extension reaction on the basis of the result of measurement in the step (d) ; and the step (f) of discriminating the base type in the base sequence of the nucleic acid on the basis of the result of detection in the step (e).
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
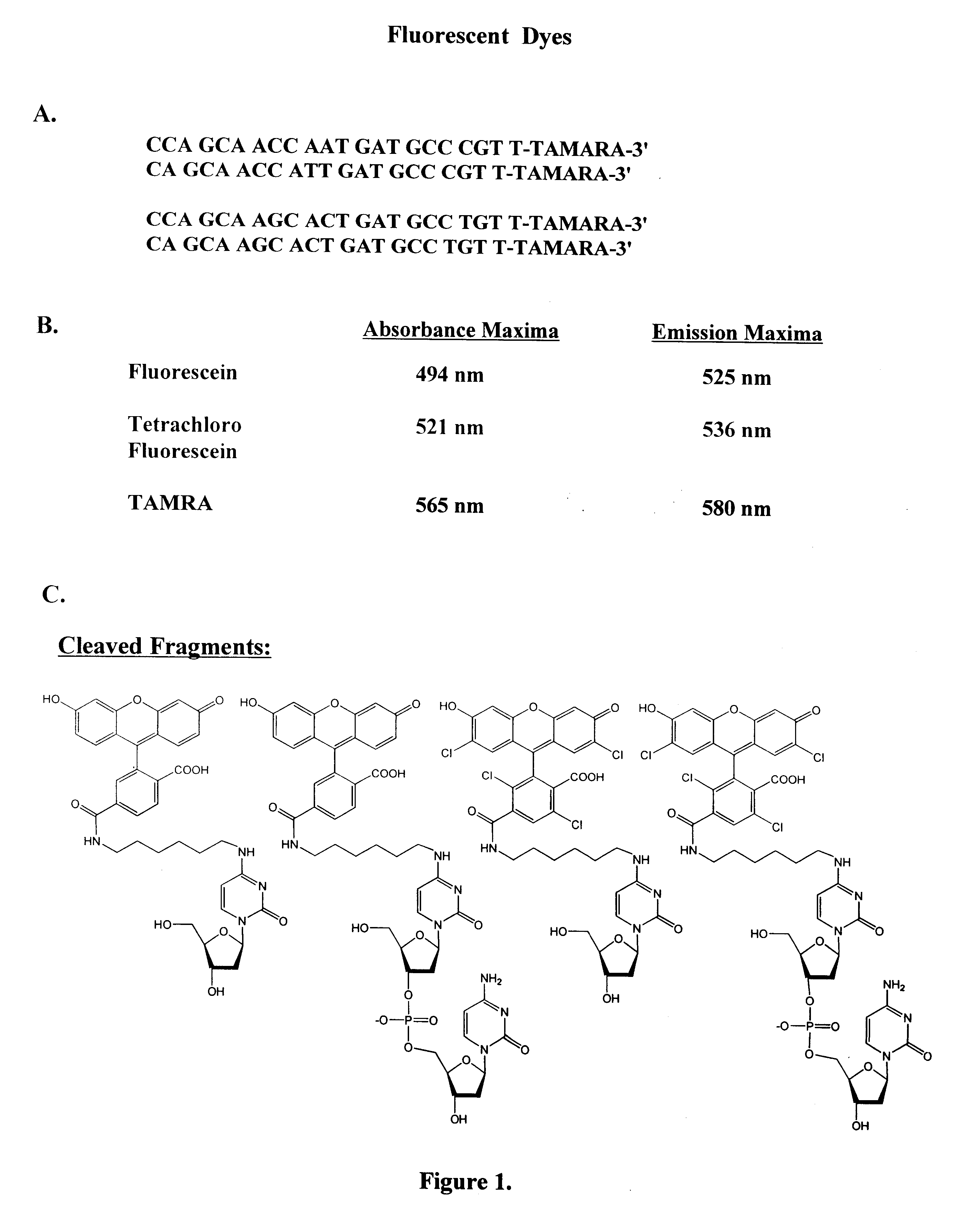
Single nucleotide detection using degradation of a fluorescent sequence
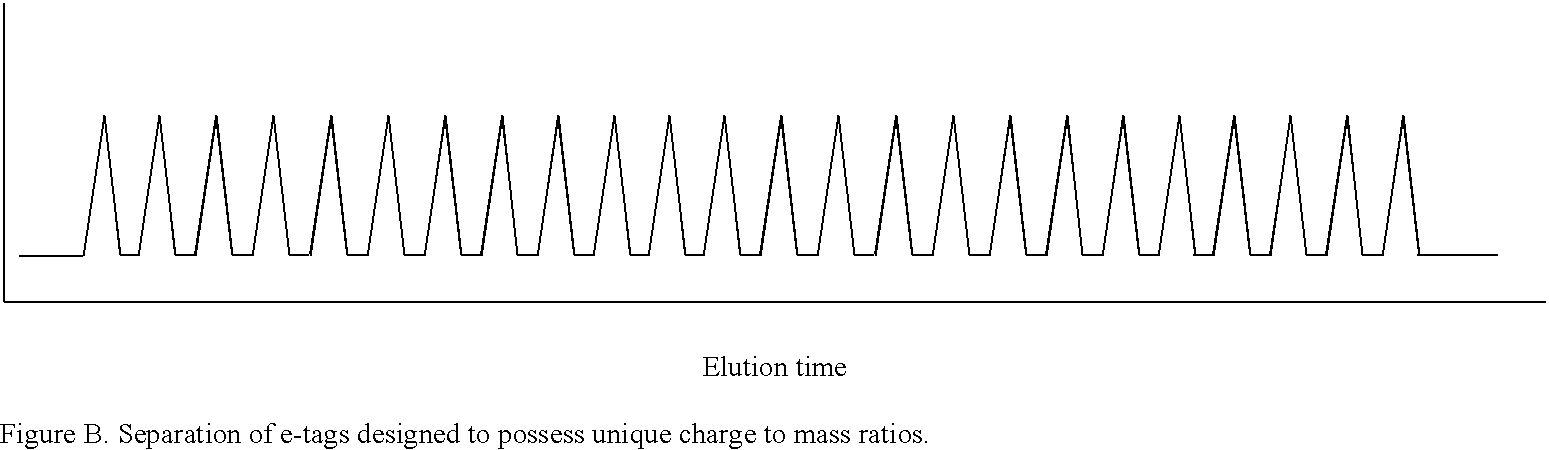
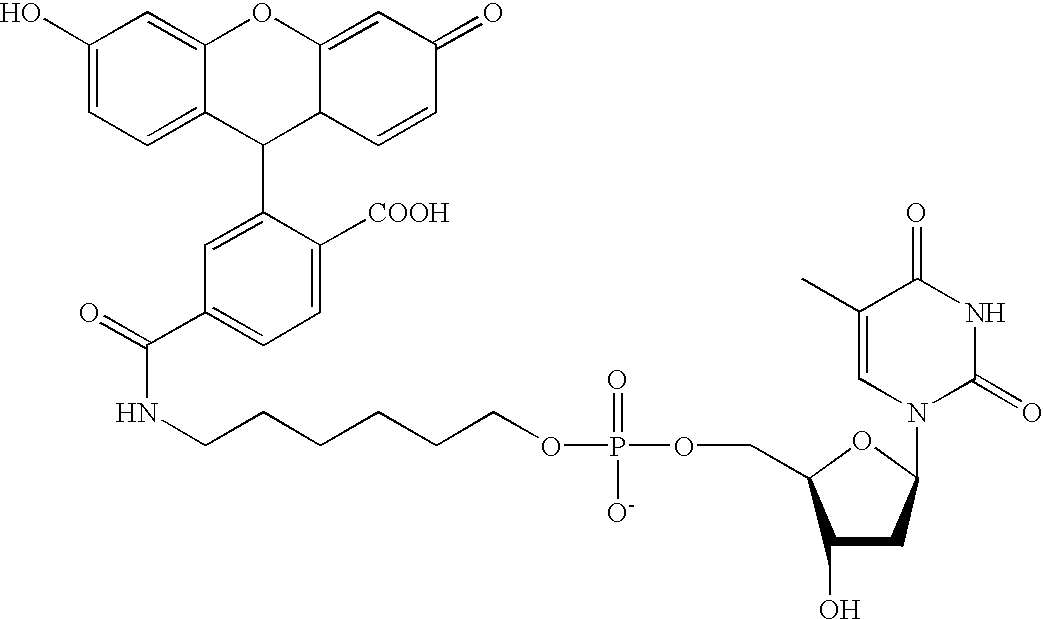
Methods and compositions are provided for detecting single nucleotide polymorphisms using a pair of oligonucleotides, a primer and a snp detection sequence, where the snp detection sequence hybridizes to the target DNA downstream from the primer and in the direction of primer extension. The snp detection sequence is characterized by having a nucleotide complementary to the snp and adjacent nucleotide complementary to adjacent nucleotides in the target and an electophoretic tag bonded to the 5'-nucleotide. The pair of oligonucleotides is combined with the target DNA under primer extension conditions, where the polymerase has 5'-3' exonuclease activity. When the snp is present, the electophoretic tag is released from the snp detection sequence, and can be detected by electrophoresis as indicative of the presence of the snp in the target DNA.
Owner:MONOGRAM BIOSCIENCES
Genome walking by selective amplification of nick-translate DNA library and amplification from complex mixtures of templates
Improved methods and reagents for chromosome walking of nucleic acid are discussed herein. A library of amplifiable nick translation molecules is generated, and a chromosome walk is initiated from a known sequence in the nucleic acid by producing at least one nick translate molecule, sequencing part of the nick translate molecule, and producing a second nick translate molecule by initiating the primer extension from the region of the obtained sequence of the prior nick translate molecule.
Owner:TAKARA BIO USA INC
Reagents for reversibly terminating primer extension
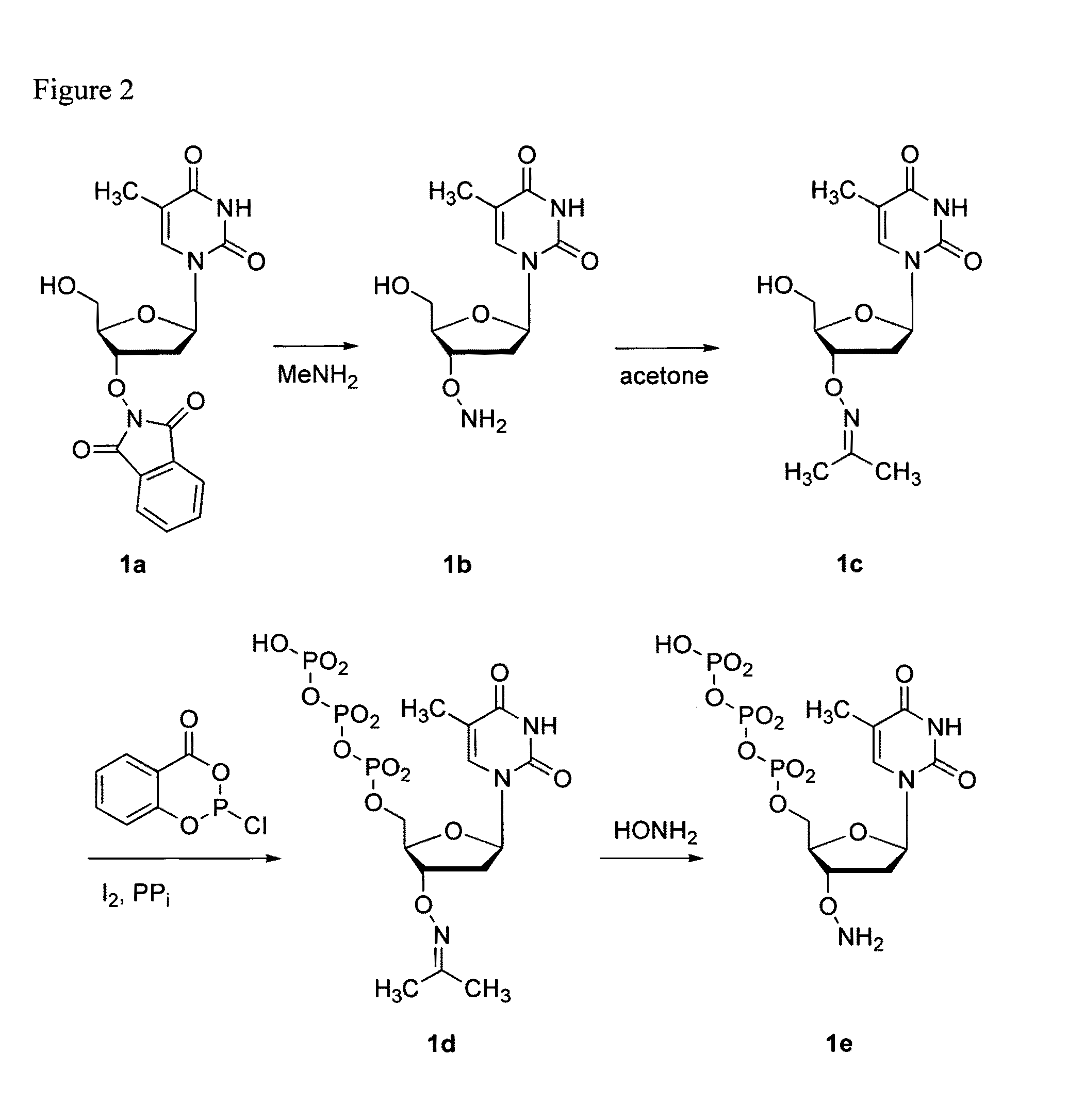
Processes are disclosed that use 3′-reversibly terminated nucleoside triphosphates to analyze DNA for purposes other than sequencing using cyclic reversible termination. These processes are based on the unexpected ability of terminal transferase to accept these triphosphates as substrates, the unexpected ability of polymerases to add reversibly and irreversibly terminated triphosphates in competition with each other, the development of cleavage conditions to remove the terminating group rapidly, in high yield, and without substantial damage to the terminated oligonucleotide product, and the ability of reversibly terminated primer extension products to capture groups. The presently preferred embodiments of the disclosed processes use a triphosphate having its 3′-OH group blocked as a 3′-ONH2 group, which can be removed in buffered NaNO2 and use variants of Taq DNA polymerase, including one that has a replacement (L616A).
Owner:BENNER STEVEN ALBERT +3
Method and product for localized or spatial detection of nucleic acid in a tissue sample
ActiveUS10030261B2High resolutionMultiplicity of analysesMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationTissue sampleBiology
The present invention relates to methods and products for the localized or spatial detection of nucleic acid in a tissue sample and in particular to a method for localized detection of nucleic acid in a tissue sample comprising: (a) providing an array comprising a substrate on which multiple species of capture probes are directly or indirectly immobilized such that each species occupies a distinct position on the array and is oriented to have a free 3′ end to enable said probe to function as a primer for a primer extension or ligation reaction, wherein each species of said capture probe comprises a nucleic acid molecule with 5′ to 3′: (i) a positional domain that corresponds to the position of the capture probe on the array, and (ii) a capture domain; (b) contacting said array with a tissue sample such that the position of a capture probe on the array may be correlated with a position in the tissue sample and allowing nucleic acid of the tissue sample to hybridize to the capture domain in said capture probes; (c) generating DNA molecules from the captured nucleic acid molecules using said capture probes as extension or ligation primers, wherein said extended or ligated DNA molecules are tagged by virtue of the positional domain; (d) optionally generating a complementary strand of said tagged DNA and / or optionally amplifying said tagged DNA; (e) releasing at least part of the tagged DNA molecules and / or their complements or amplicons from the surface of the array, wherein said part includes the positional domain or a complement thereof; and (f) directly or indirectly analyzing the sequence of the released DNA molecules.
Owner:10X GENOMICS SWEDEN AB
Method of producing a DNA library using positional amplification
InactiveUS20060068394A1Microbiological testing/measurementOrganic chemistry methodsCDNA libraryPentamer
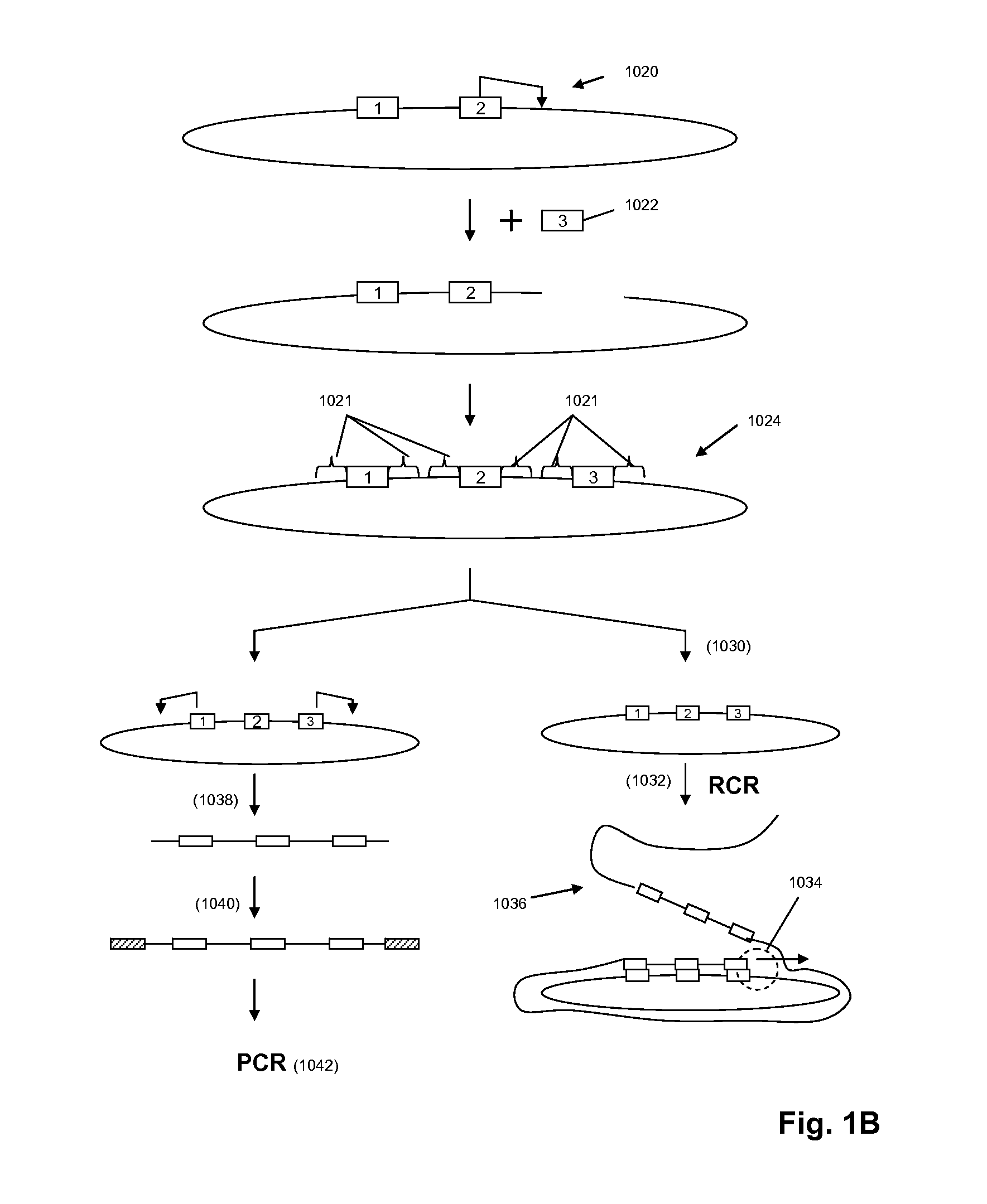
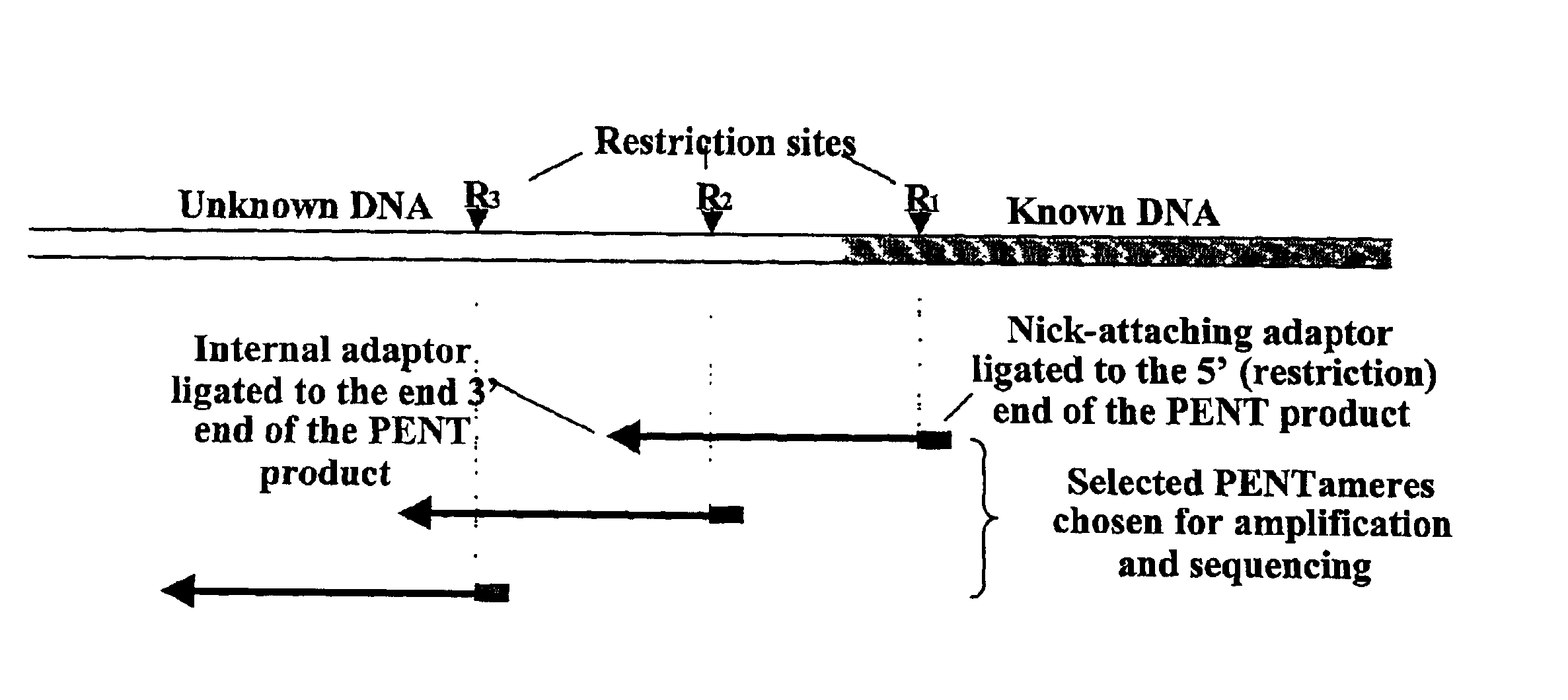
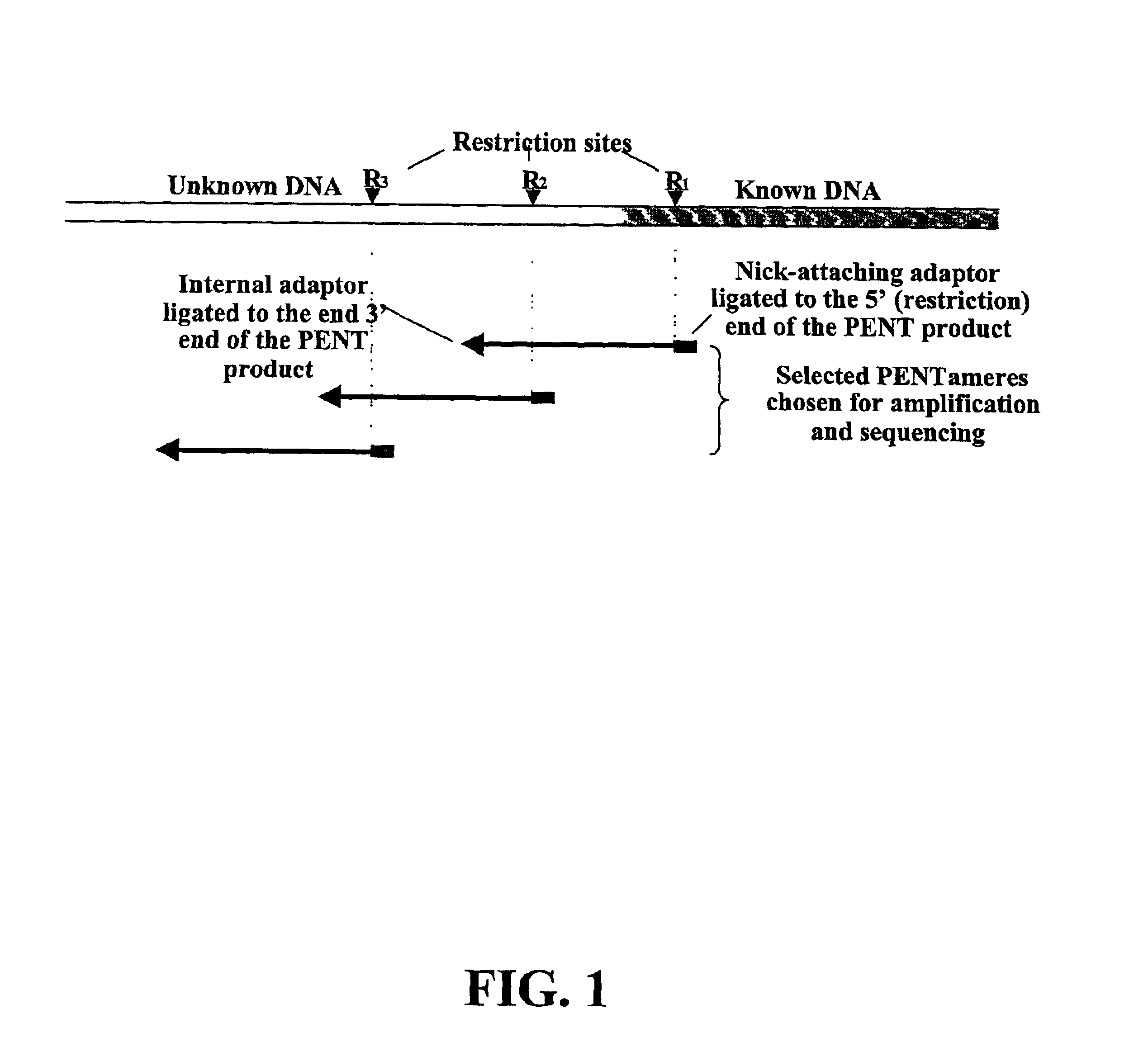
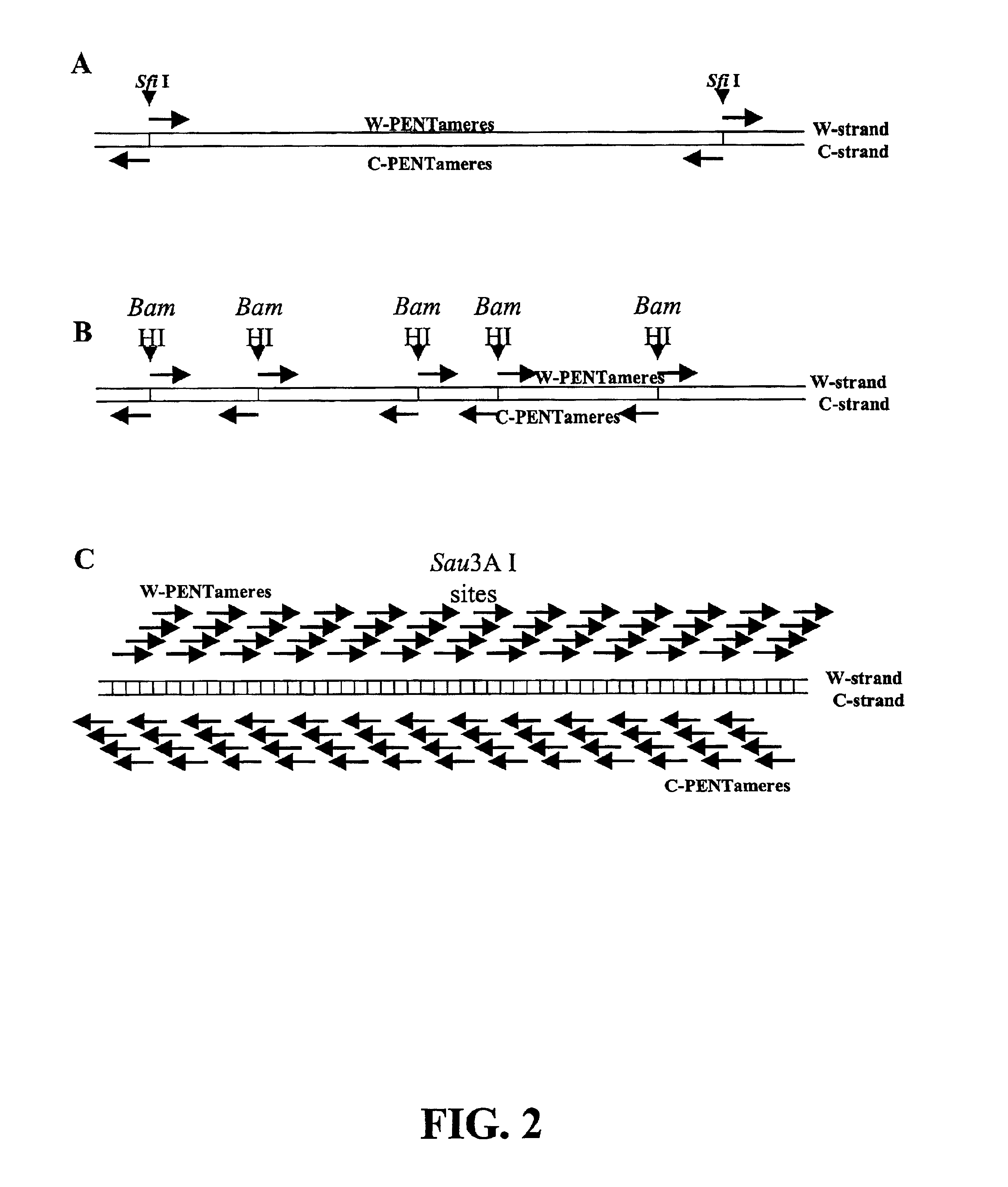
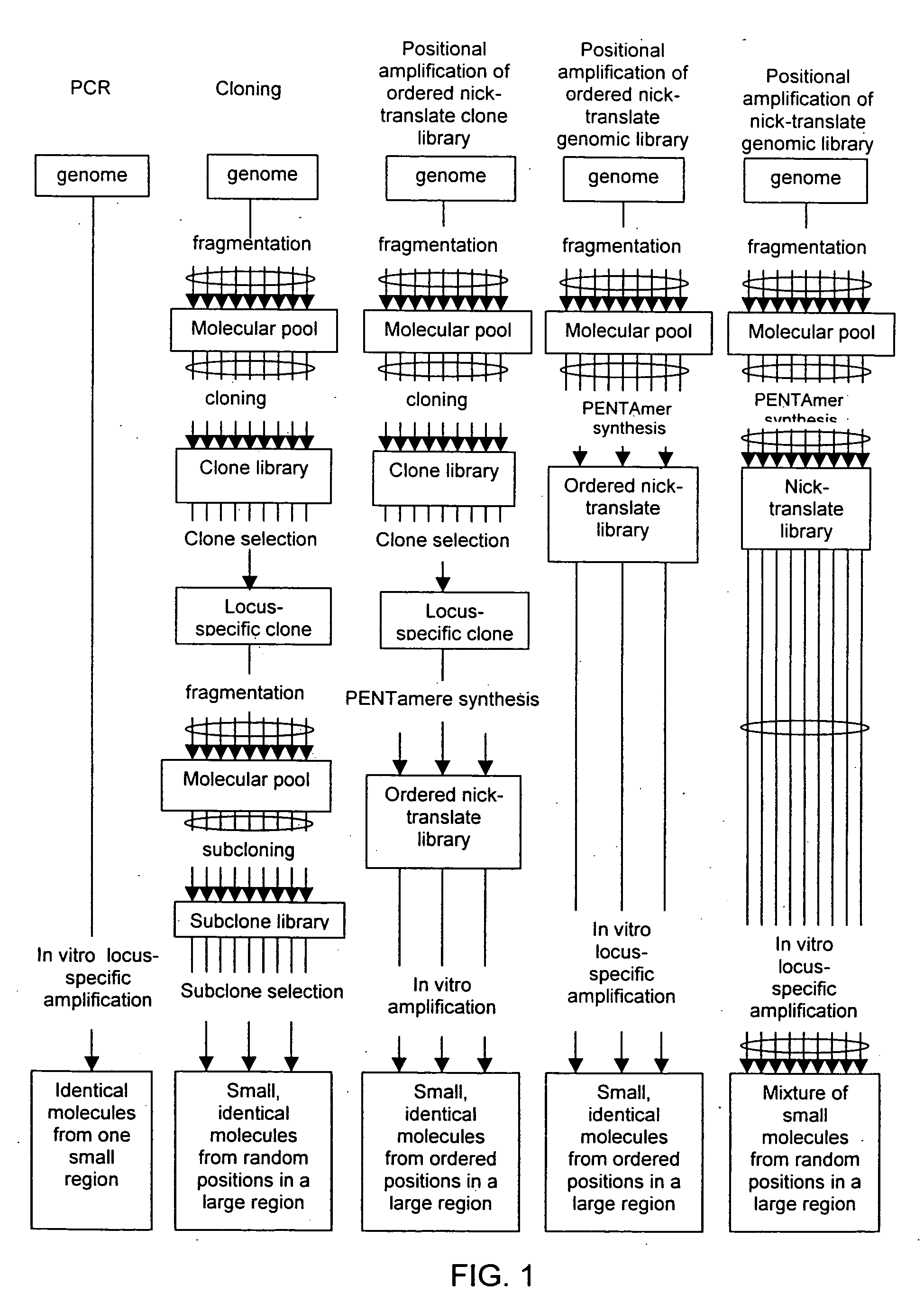
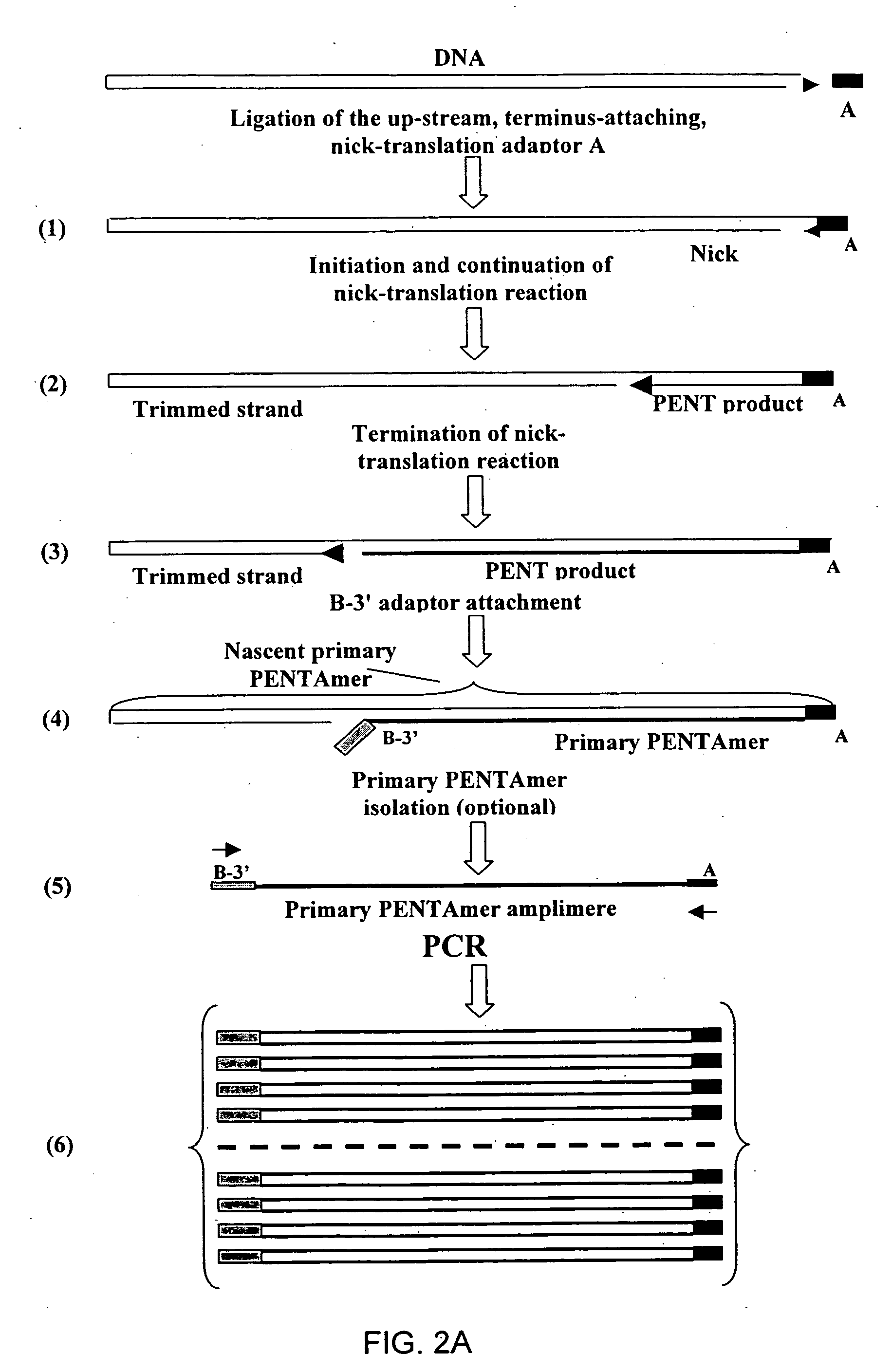
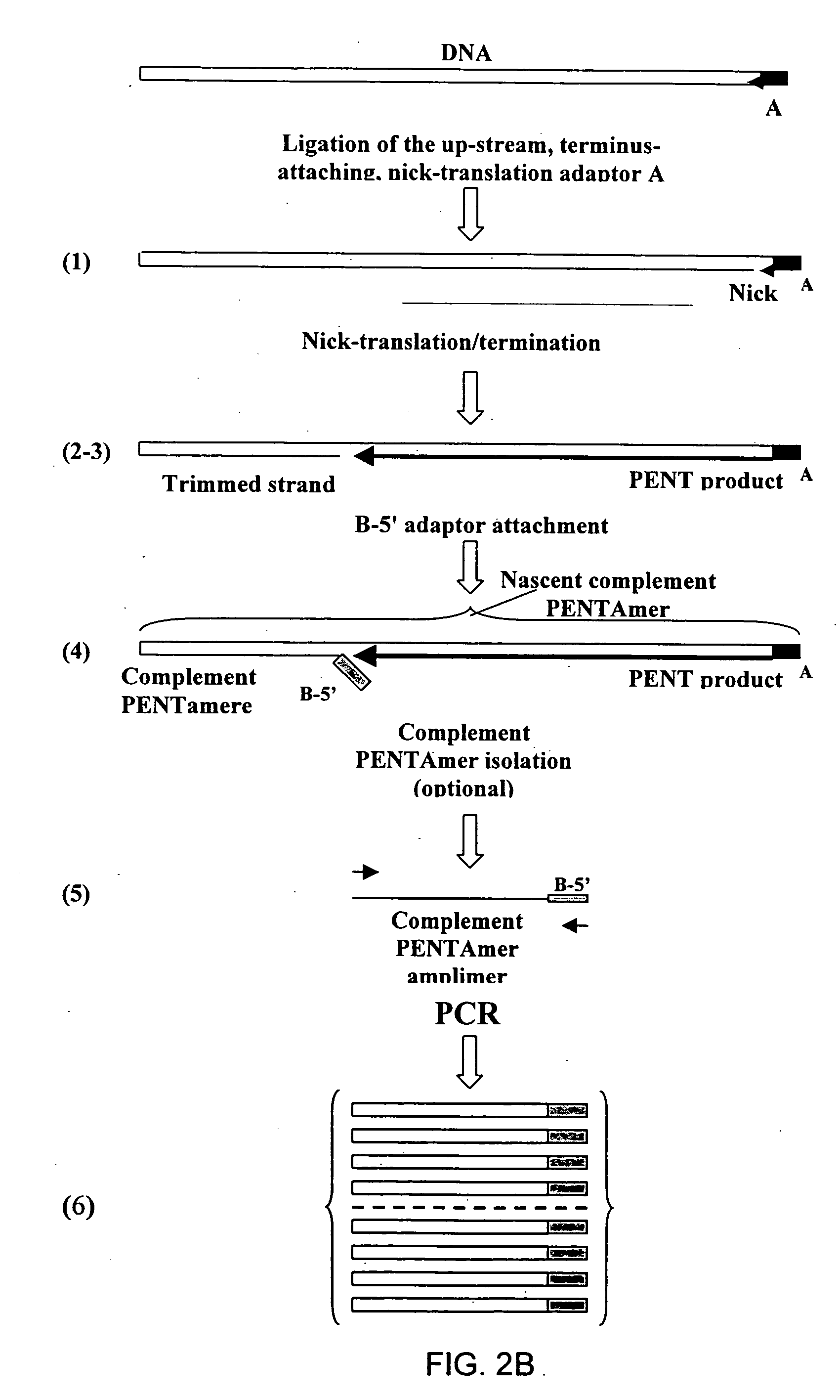
The disclosed invention relates to general and specific methods to use the Primer Extension / Nick Translation (PENT) reaction to create an amplifiable DNA strand, called a PENTAmer. A PENTAmers can be made for the purpose of amplifying a controlled length of DNA located at a controlled position within a DNA molecule, a process referred to as Positional Amplification by Nick Translation (PANT). In contrast to PCR, which amplifies DNA between two specific sequences, PANT can amplify DNA between two specific positions. PENTAmers can be created to amplify-very large regions of DNA (up to 500,000 bp) as random mixtures (unordered positional libraries), or as molecules sorted according to position (ordered positional libraries). PANT is fast and economical, because PENTAmer preparation can be multiplexed. A single PENTAmer preparation can include very complex mixtures of DNA such as hundreds of large-insert clones, complete genomes, or cDNA libraries. Subsequent PCR amplification of the preparation using a single specific primer can positionally amplify contiguous regions along a specific clone, along a specific genomic region, or along a specific expressed sequence.
Owner:LANGMORE JOHN +1
DNA polymerases and related methods
ActiveUS20090148891A1Improved nucleic acid extension rateIncrease chanceBacteriaSugar derivativesPolymerase LDNA polymerase
Disclosed are mutant DNA polymerases having improved extension rates relative to a corresponding, unmodified polymerase. The mutant polymerases are useful in a variety of disclosed primer extension methods. Also disclosed are related compositions, including recombinant nucleic acids, vectors, and host cells, which are useful, e.g., for production of the mutant DNA polymerases.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
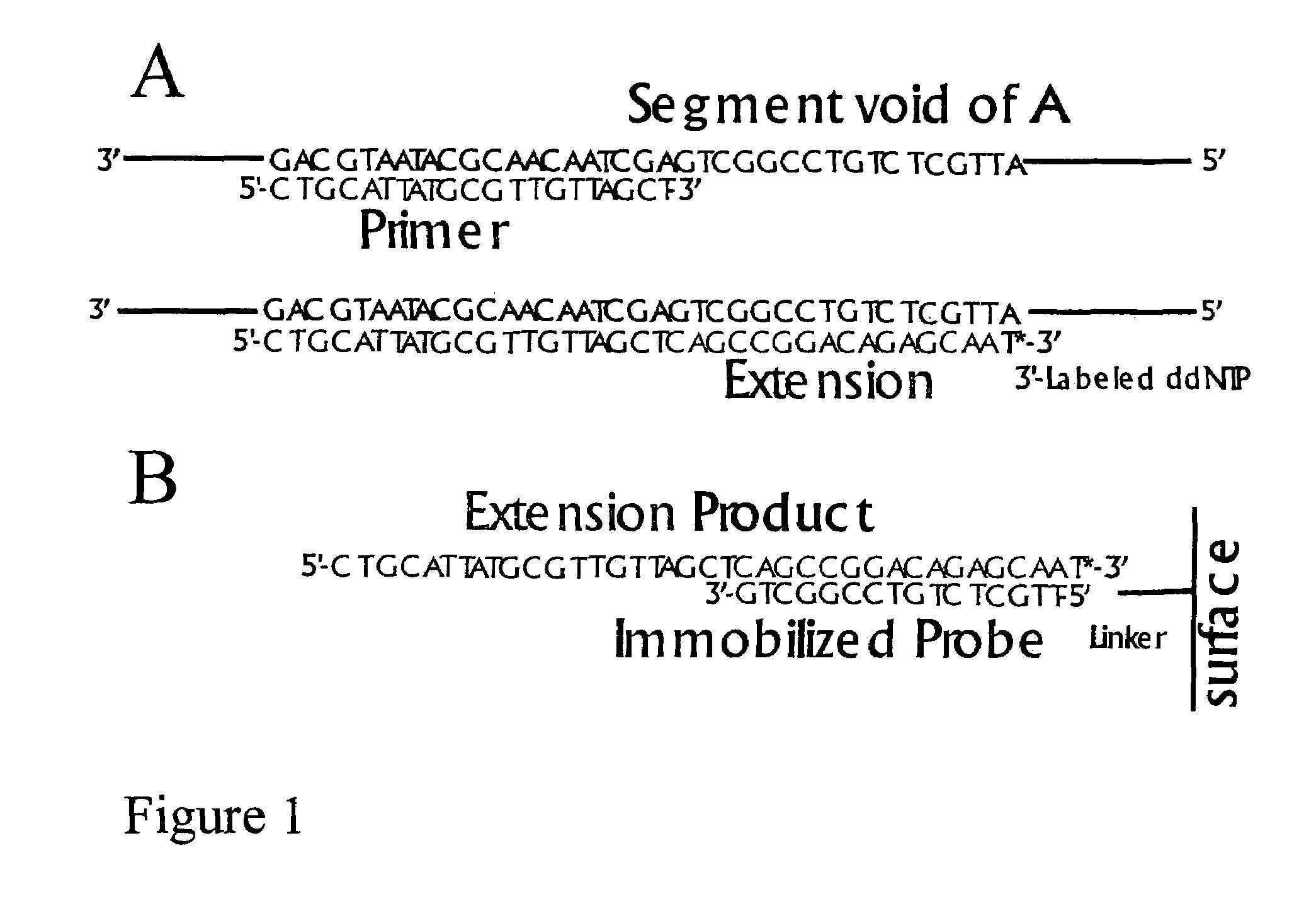
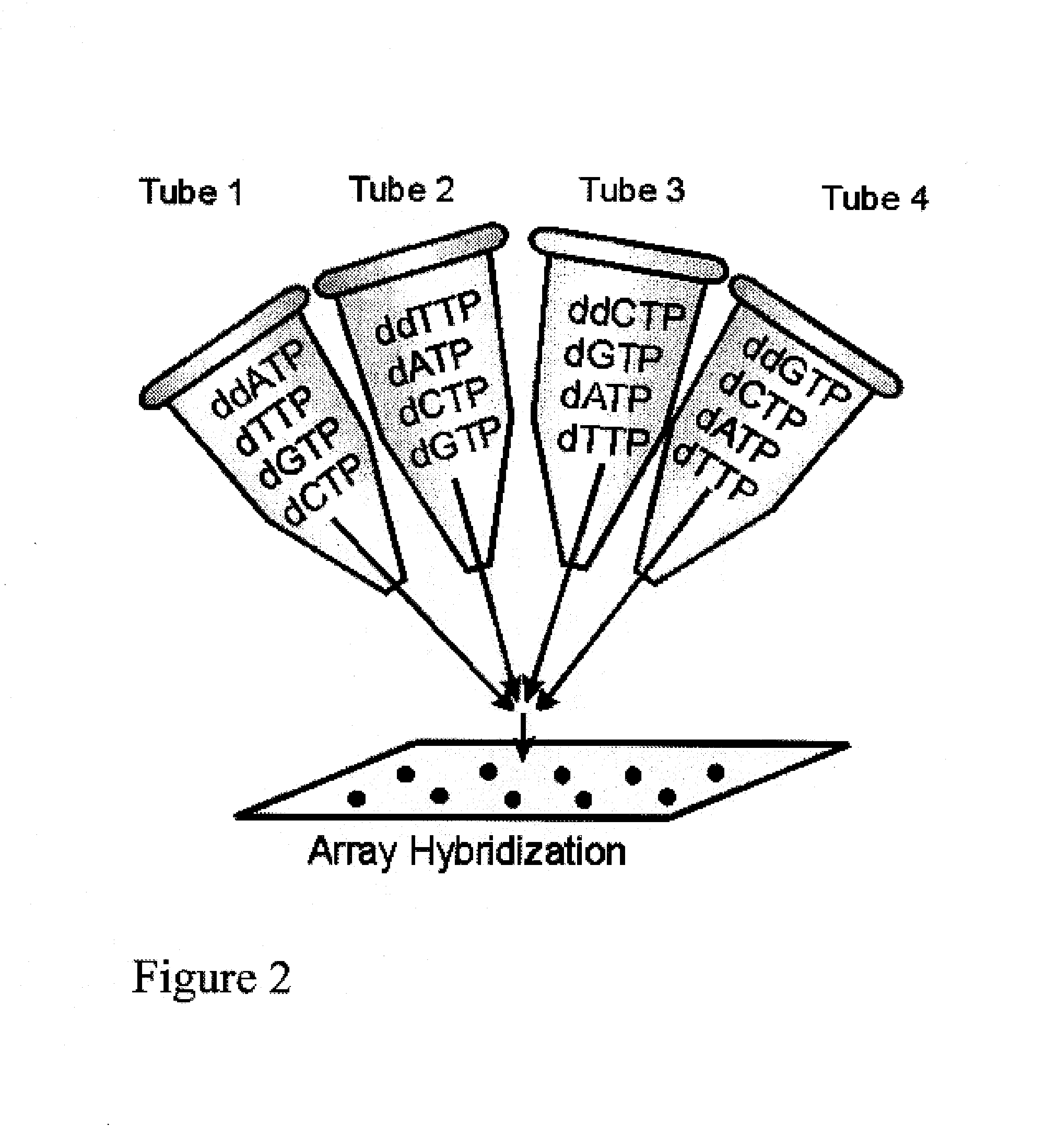
DNA sequence detection by limited primer extension
A novel limited primer extension reaction improves detection sensitivity and specificity in a variety of hybridization platforms. In the invention, a sequence of target DNA that lacks one of the four types of nucleic acid bases for a span of eight or more adjacent nucleotide positions is selected for use. This sequence is referred to as the extension complement sequence, or ECS. A primer with a sequence that is complementary to the target sequence that is immediately downstream (to the 3′ side) of this ECS is used to initiate an extension reaction. Extension occurs using a DNA polymerase and standard deoxynucleoside triphosphates for three of the four types of nucleic acid bases. The fourth base, which is complementary to the base missing in the ECS, is either absent or present only in the form of a dideoxynucleoside triphosphate, which does not support further extension. In either case, the extension reaction does not proceed past the first occurrence in the template of the base that is missing in the ECS. This results in a primer extension product with fixed length determined by the length of the ECS. The process can be repeated using a thermal-stable polymerase in a thermal-cycled reaction that results in a linear amplification of the targeted sequence. The resulting limited primer extension products serve as ideal hybridization analytes for determination of sample sequence content using microarrays.
Owner:ATOM SCI
Nano-PCR: methods and devices for nucleic acid amplification and detection
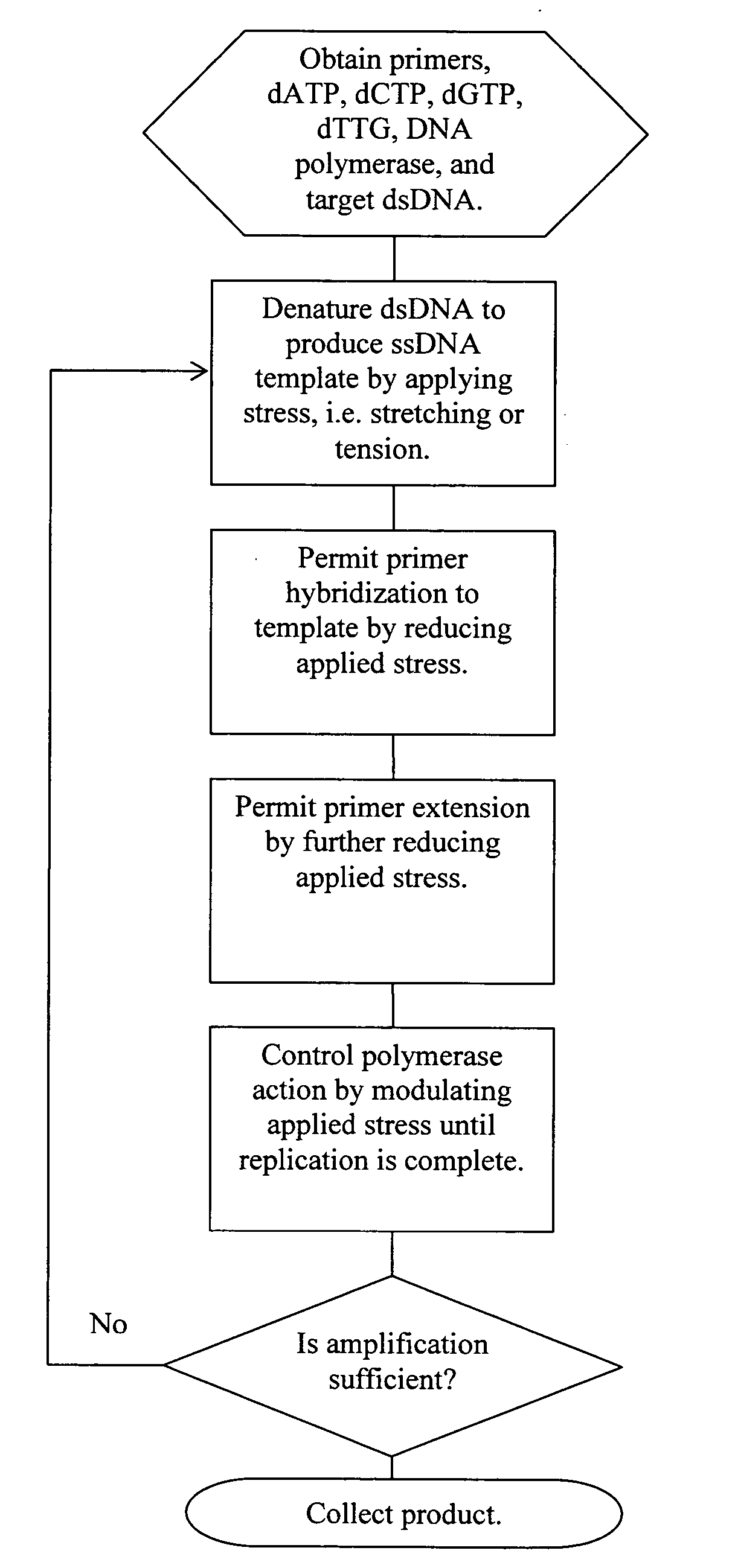
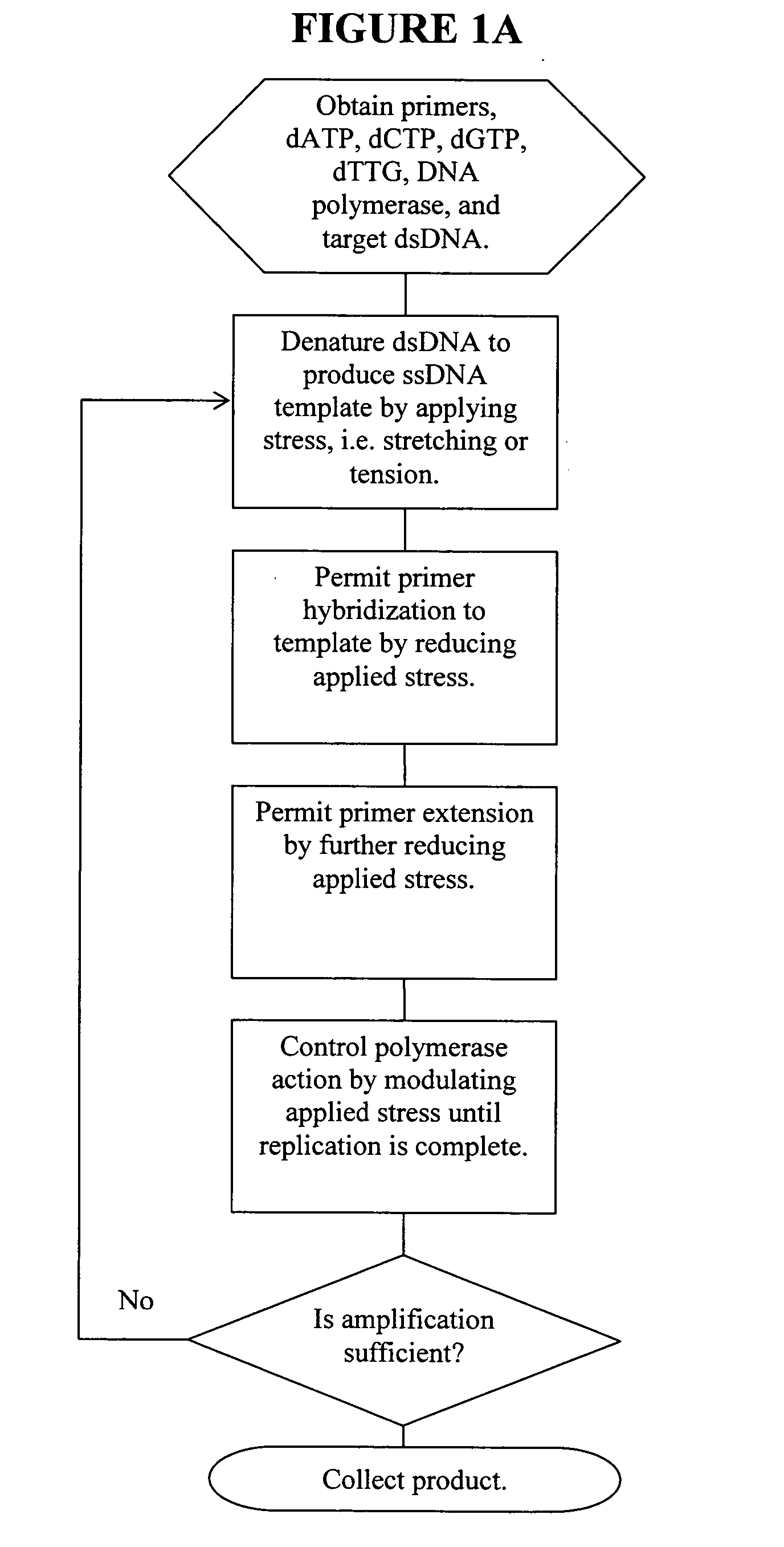
ActiveUS20060019274A1Significant improvementMaterial nanotechnologyHeating or cooling apparatusNucleic acid sequencingPcr method
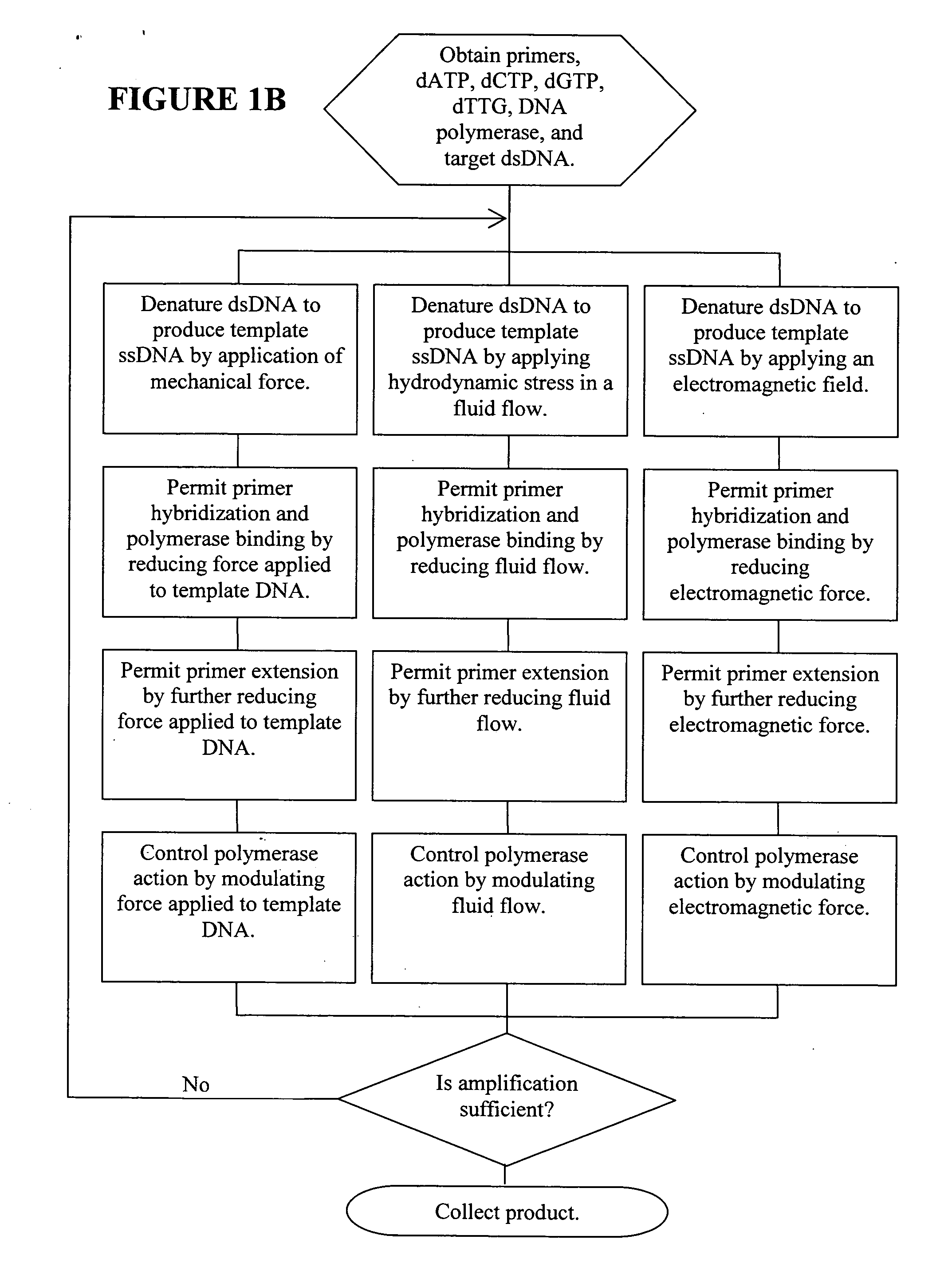
Methods, devices, and compositions are described that provide for amplification of nucleic acid sequences without reliance upon temperature cycling, thus freeing the methods from conventional benchtop thermal cycling devices. Denaturation of double stranded nucleic acids, primer annealing, and precision control over primer extension by polymerase can be accomplished by applying stress to a nucleic acid. These methods can provide one ore more benefits over conventional PCR methods including: precision control over the PCR process; generally improved fidelity; improved accuracy over problematic sequences such as GC-rich or tandem repeat regions; greater sequence length; increased reaction yield; reduced experimental time; greater efficiency; lower cost; greater portability; and, robustness to various environmental parameters, such as temperature, pH, and ionic strengths.
Owner:NANOBIOSYM INC
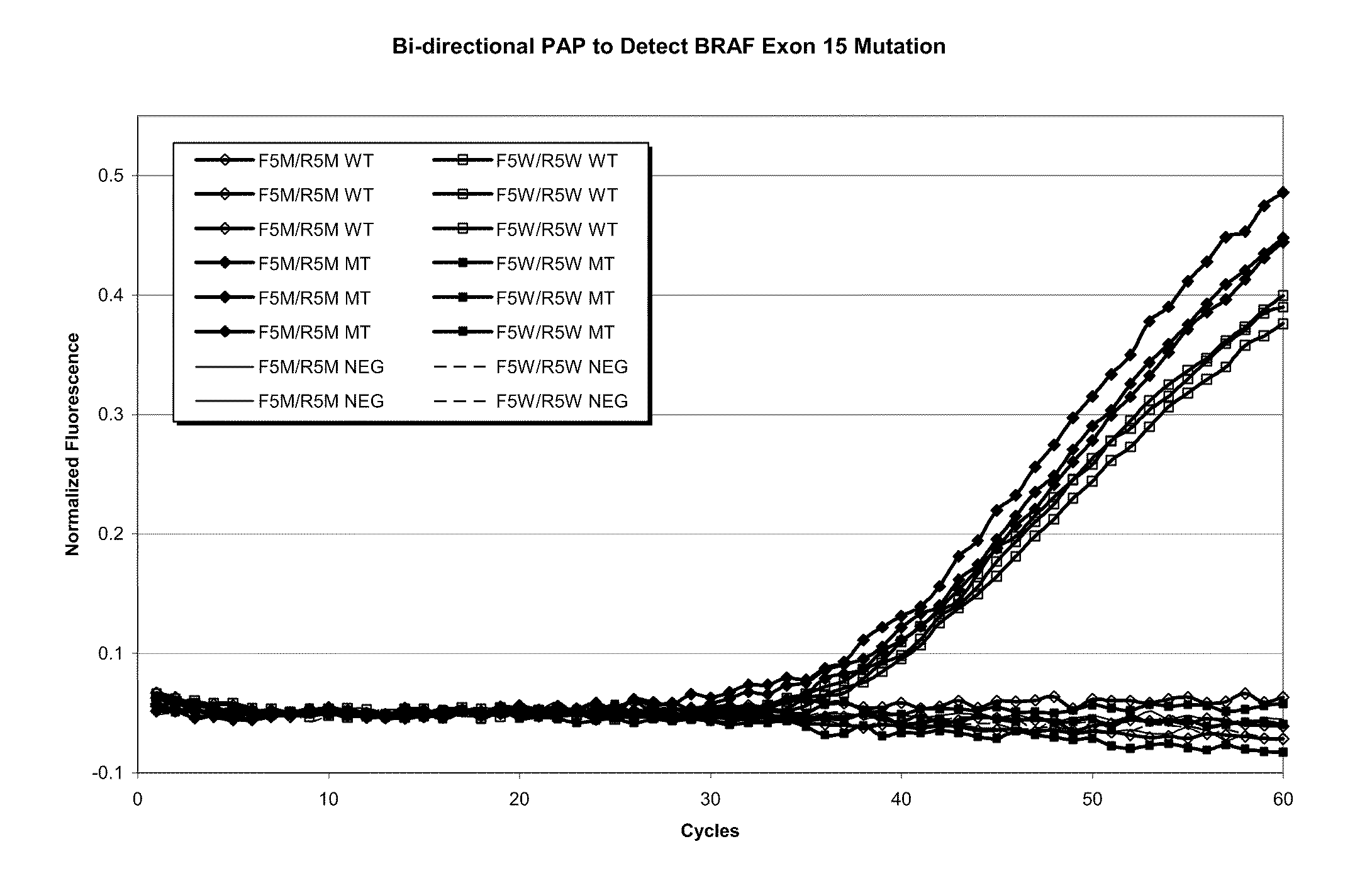
Allele specific primer extension
InactiveUS20040048301A1Rapid rise in fluorescenceEnhanced signalSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPhosphateNucleotide
A method of characterizing a nucleic acid sample is provided that includes the steps of: (a) conducting a DNA polymerase reaction that includes the reaction of a template, an allele specific primer, at least one terminal phosphate-labeled nucleotide, DNA polymerase, and optionally an enzyme having 3'->5' exonuclease activity when the primer is non-hydrolyzable, which reaction results in the production of labeled polyphosphate; (b) permitting the labeled polyphosphate to react with a phosphatase to produce a detectable species; (c) detecting the detectable species; and (d) characterizing the nucleic acid sample based on such detection.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
Single-stranded polynucleotide amplification methods
The present invention provides amplification methods for producing a population of single stranded polynucleotides from a target polynucleotide, comprising (a) extending an RNA primer in a complex comprising (i) a DNA template comprising a sequence that is complementary to the target polynucleotide, and (ii) the RNA primer, wherein the RNA primer is hybridized to the DNA template, and (b) cleaving the RNA primer with an enzyme that cleaves RNA from an RNA / DNA hybrid such that another RNA primer hybridizes to the DNA template and repeats primer extension by strand displacement.
Owner:ELIM BIOPHARMLS
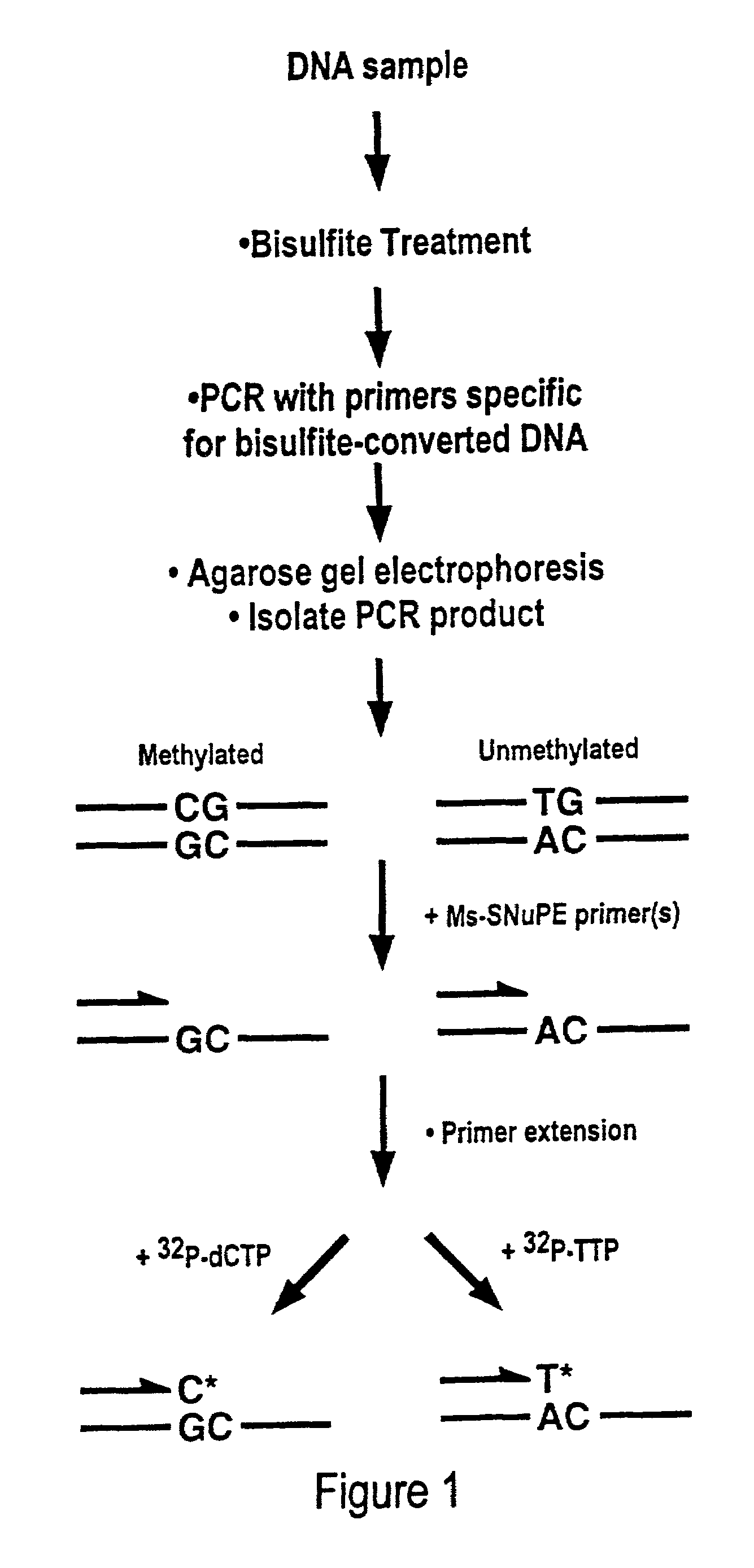
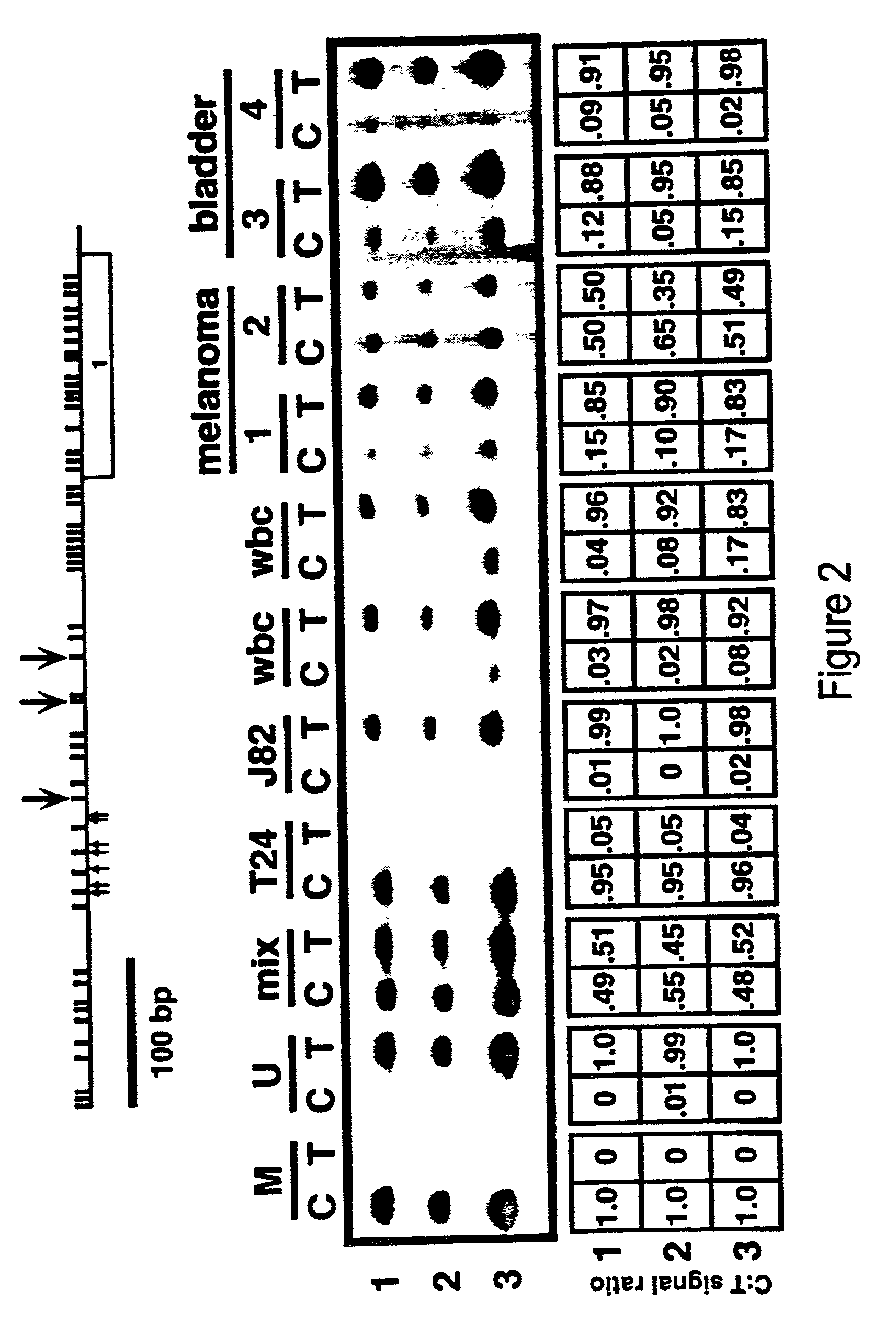
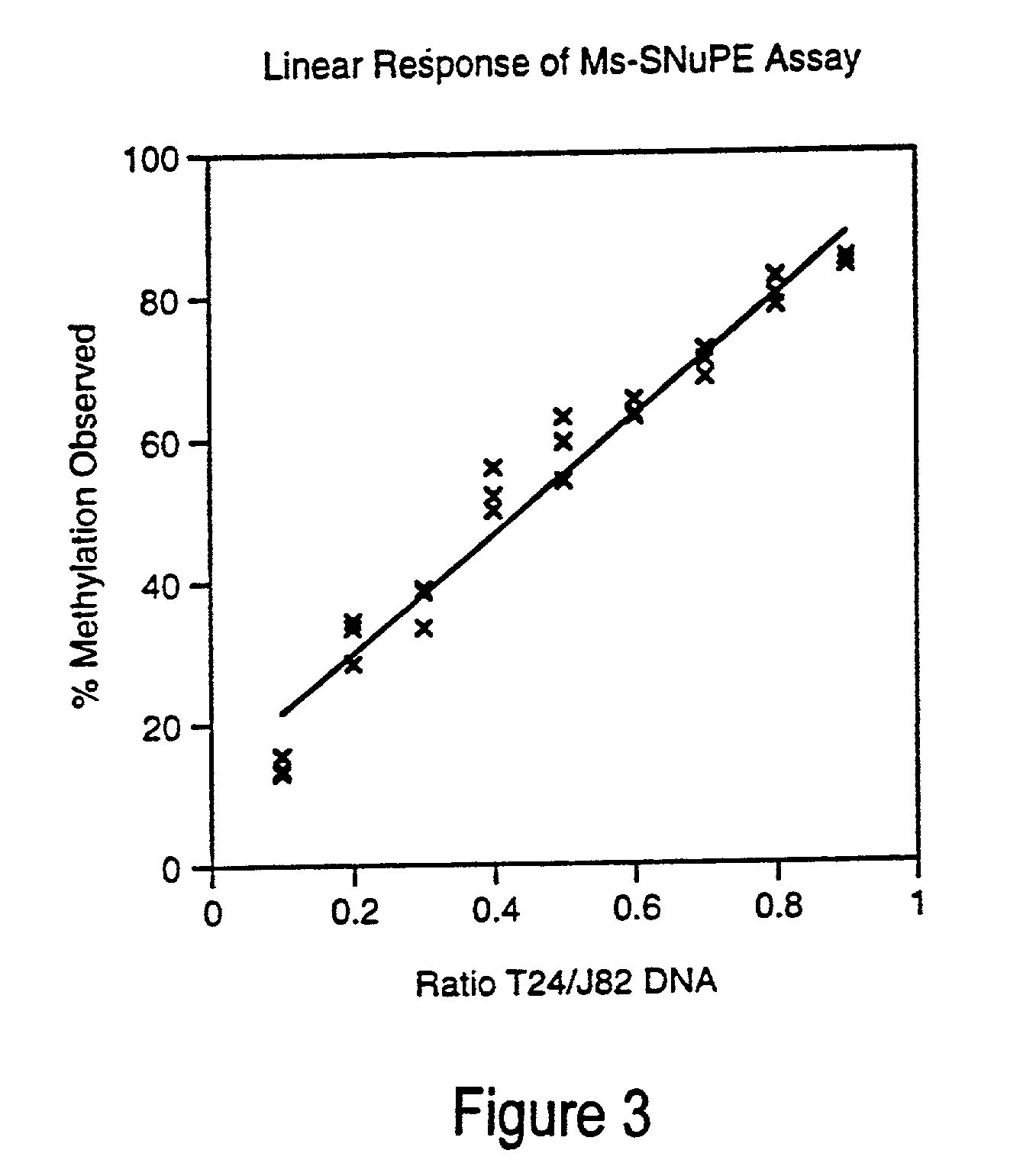
Cancer diagnostic method based upon DNA methylation differences
There is disclosed a cancer diagnostic method based upon DNA methylation differences at specific CpG sites. Specifically, the inventive method provides for a bisulfite treatment of DNA, followed by methylation-sensitive single nucleotide primer extension (Ms-SNuPE), for determination of strand-specific methylation status at cytosine residues.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
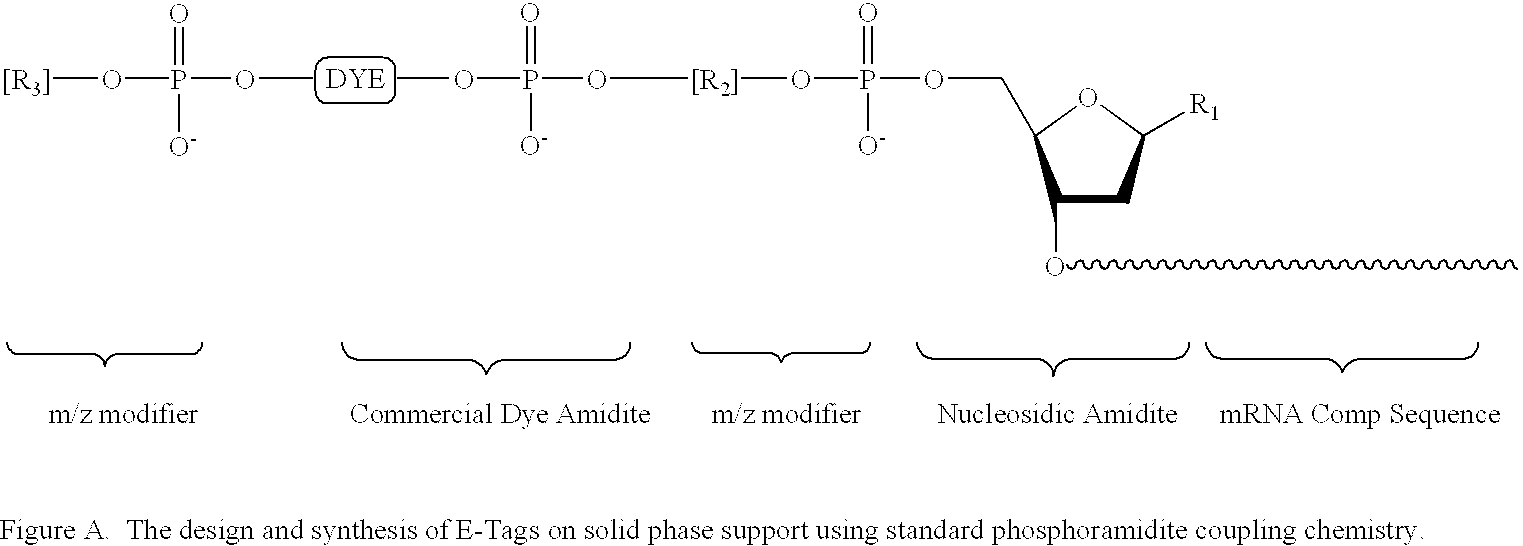
Quantification of nucleic acids and proteins using oligonucleotide mass tags
InactiveUS20090305237A1Efficient amplificationReadily and easily be resolvedMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic Acid ProbesSingle strand
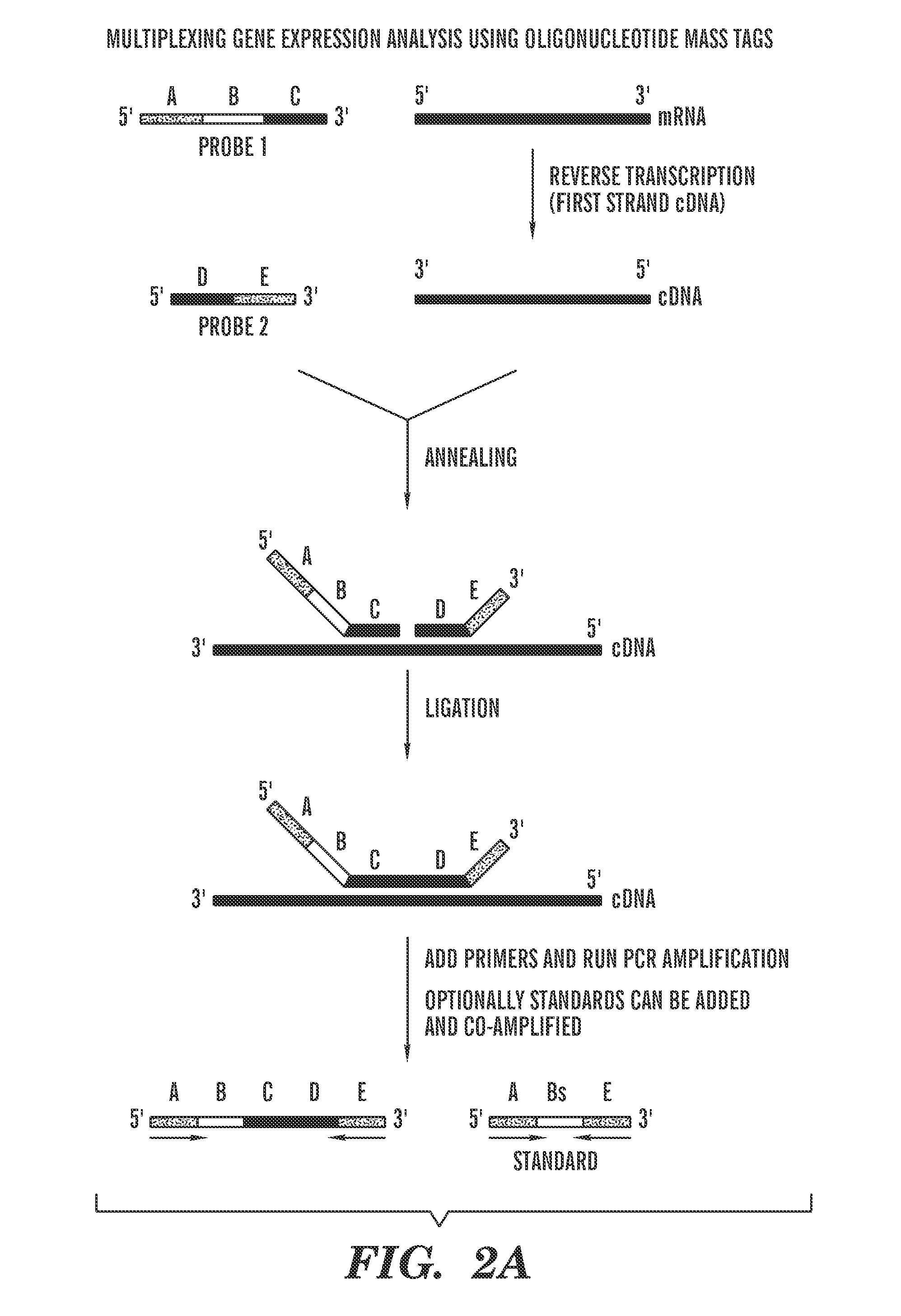
The invention provides a method for detecting and quantifying the amount of target molecules, such as nucleic acids or proteins in a sample. The target molecules are first recognized and bounded by target-specific probes, generally nucleic acids or proteins that bind specifically to the targets, each of which is labeled with a short single-stranded nucleic acid probe, either DNA or RNA, with distinct molecular weight. This label is called an oligonucleotide mass tag. One or several standard oligonucleotide sequences can be designed with similar sequence but distinct molecular weight to those oligonucleotide mass tags. Then the oligonucleotide mass tags associated with bounded probes and the standard sequences are co-amplified using a pair of common primers. The presence and / or amount of each oligonucleotide mass tag, which corresponds to the amount of corresponding target molecule, is determined by a primer extension reaction and quantification of the primer extension product.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
Kits for amplifying and detecting nucleic acid sequences
InactiveUS6514736B1Strong specificityReduce manpowerNanotechSequential/parallel process reactionsOligonucleotide primersNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention is directed to a process for amplifying any target nucleic acid sequence contained in a nucleic acid or mixture thereof using a thermostable enzyme. The process comprises treating separate complementary strands of the nucleic acid with a molar excess of two oligonucleotide primers, extending the primers with a thermostable enzyme to form complementary primer extension products which act as templates for synthesizing the desired nucleic acid sequence, and detecting the sequence so amplified. The steps of the reaction can be repeated as often as desired and involve temperature cycling to effect hybridization, promotion of activity of the enzyme, and denaturation of the hybrids formed.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Methods of RNA amplification in the presence of DNA
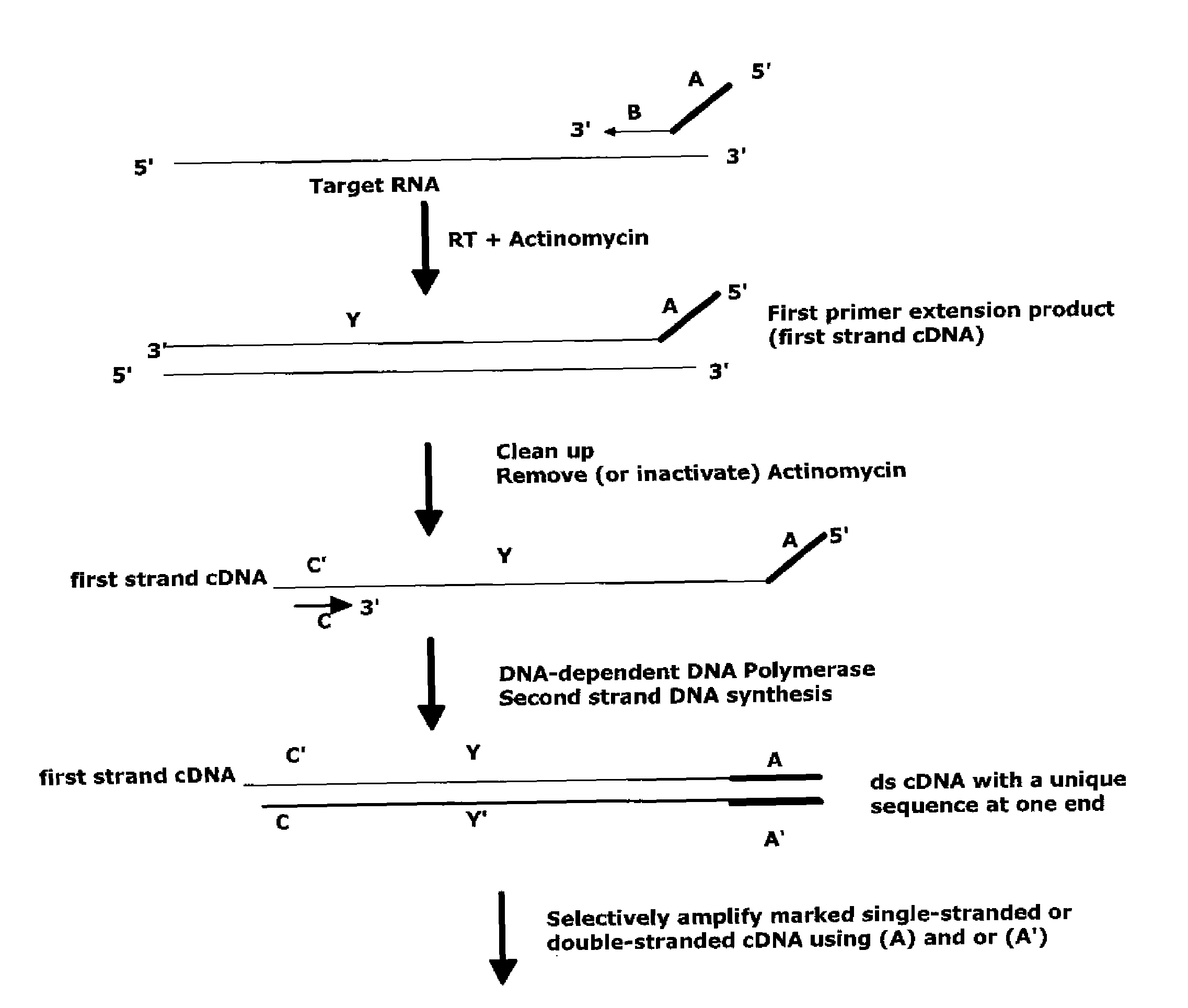
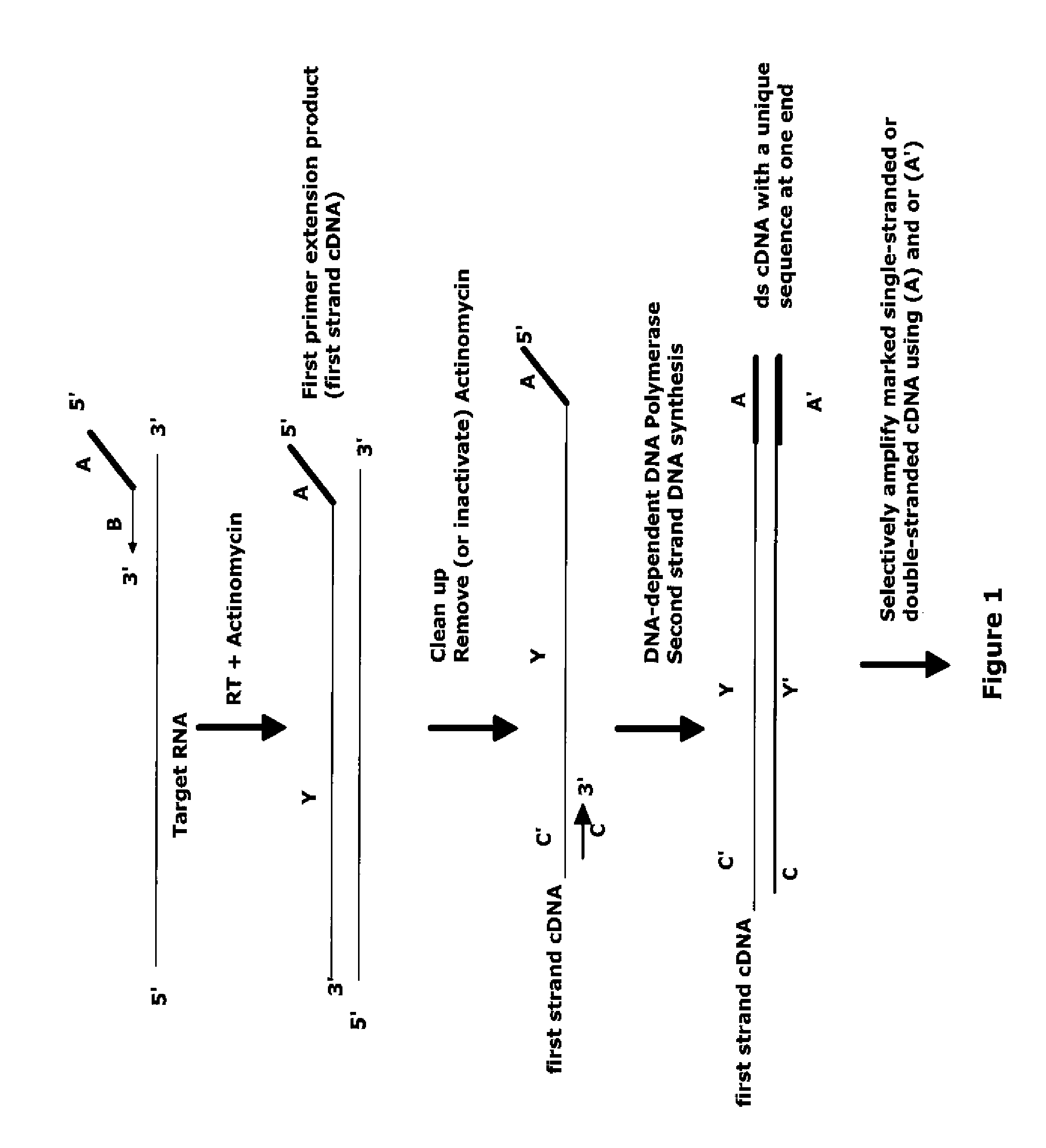
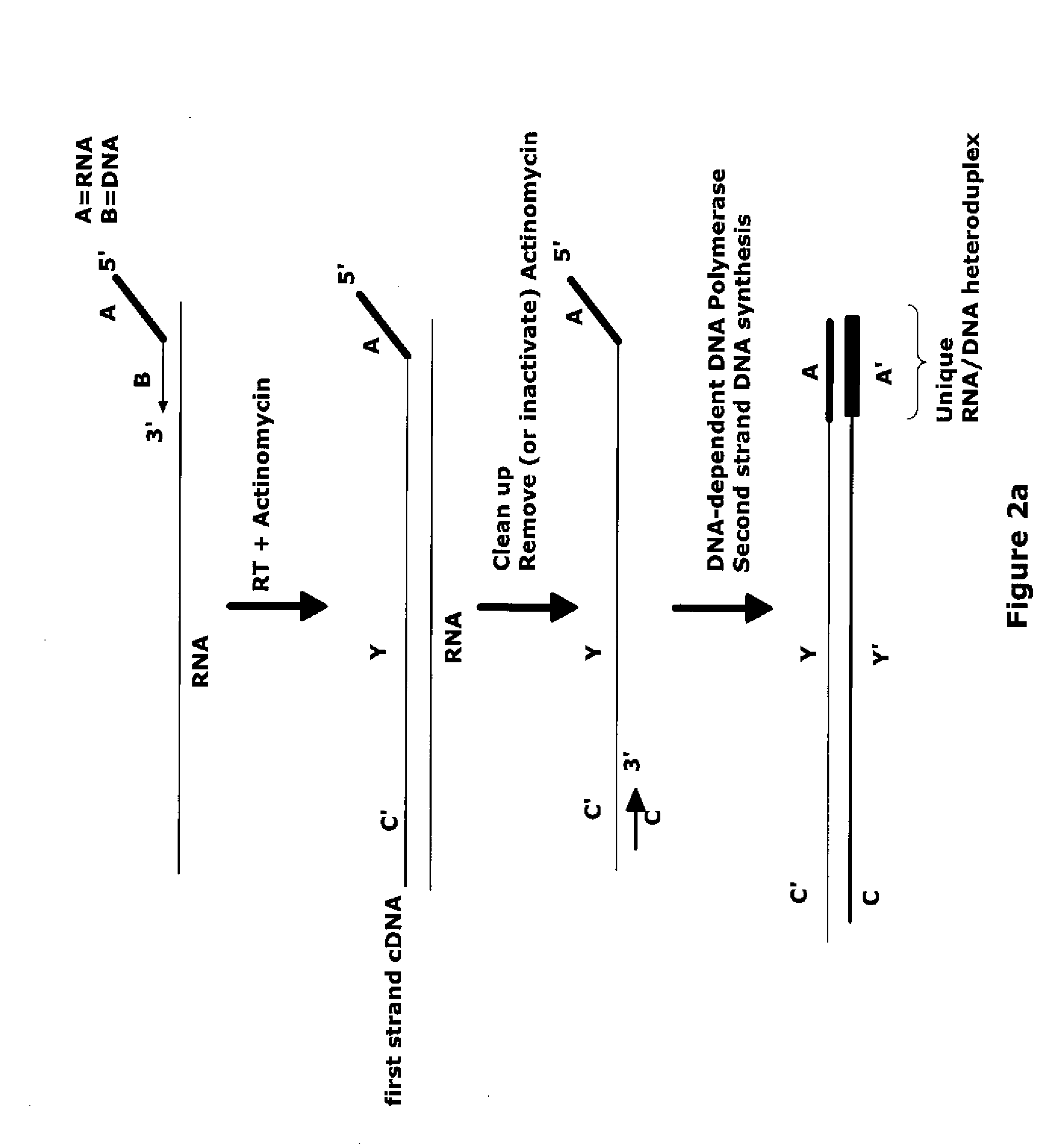
The invention provides methods for amplification of RNA. The methods are particularly suitable for specifically amplifying RNA in the presence of DNA. The methods involve producing a marked first primer extension product from a target RNA in the presence of a DNA-dependent DNA polymerase inhibitor, which prevents replication of DNA by the reverse transcriptase enzyme. The marked nucleic acid products are subsequently selectively amplified in the presence on non-marked nucleic acids. The methods are useful for production and analysis of polynucleotide sequences complementary to an RNA sequence. The methods are useful for preparation of nucleic acid libraries and substrates for analysis of gene expression of cells in biological samples. The invention also provides compositions and kits for practicing the amplification methods, as well as methods which use the amplification products.
Owner:NUGEN TECH
Nucleic acid detection using degradation of a tagged sequence
Methods and compositions are provided for detecting target molecules, e.g. DNA sequences, particularly single nucleotide polymorphisms, using a pair of nucleotide sequences, a primer and a snp detection sequence, where the snp detection sequence binds downstream from the primer to the target DNA in the direction of primer extension, or ligands and receptors. The methods employ e-tags comprising a mobility-identifying region joined to a detectable label and a target-binding region. The result of the binding of the target-binding region to the target is to have a bond cleaved in the starting material with the production of a detectable product with a different mobility from the starting material, where the different e-tags can be separated and detected.
Owner:MONOGRAM BIOSCIENCES
Mutation analysis using mass spectrometry
InactiveUS6503710B2Rapid and economic sample preparationAccurate massSamplingSugar derivativesChemical treatmentFree form
The invention presents a method for examining genetic material (deoxyribonucleic acid, DNA) to detect the presence of pre-known mutations, especially single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP), using mass spectrometry with ionization by matrix-assisted laser desorption (MALDI). The invention uses nucleoside triphosphates with modified sites for the method of primer extension in a duplicating, enzymatic reaction and at least partially removal of primers from the extension product, in combination with product neutralization by chemical treatment of the modified sites, so that the resulting DNA products can be, by using special matrix materials, preferredly ionized in an adduct-free form over other constituents in the reaction solution without any further cleaning. The method is particularly suitable for simultaneous identification of several mutations by multiplexing.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com