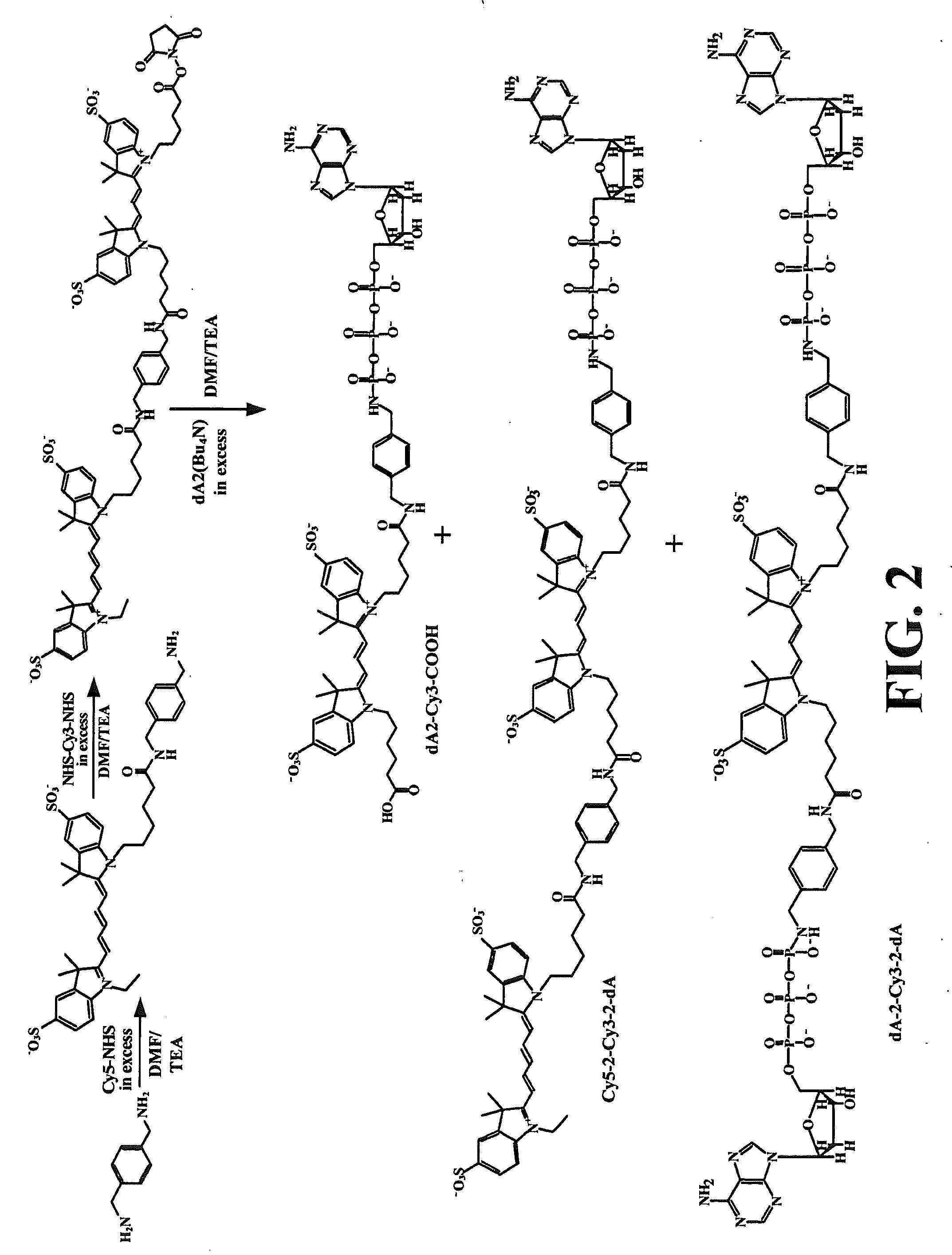
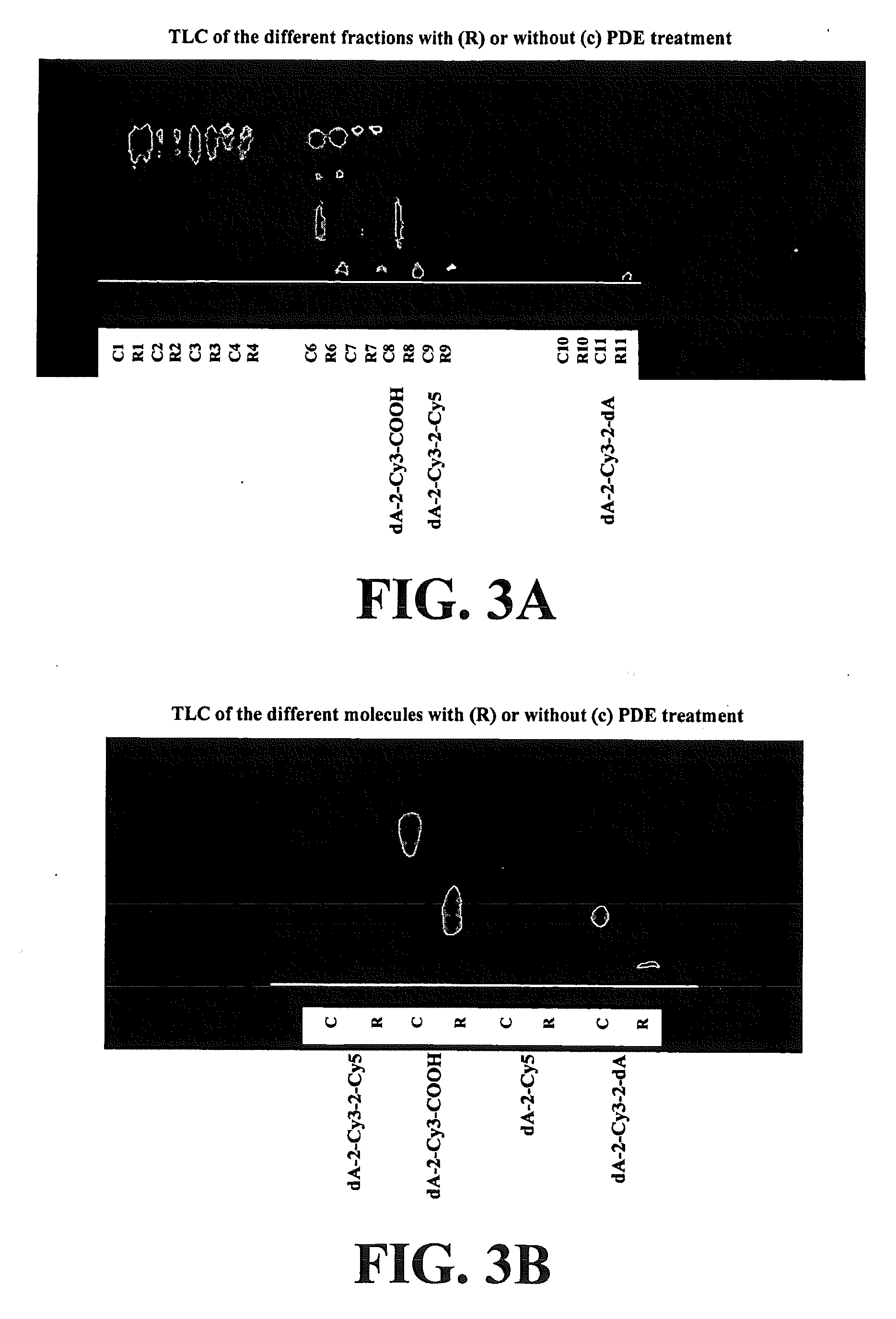
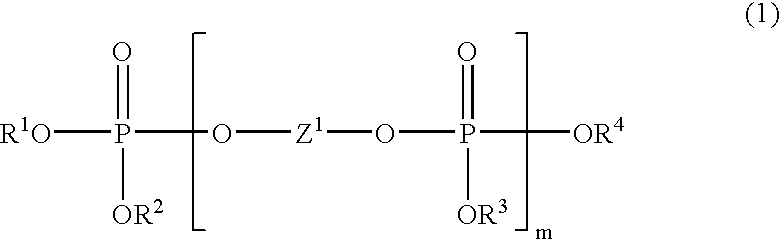
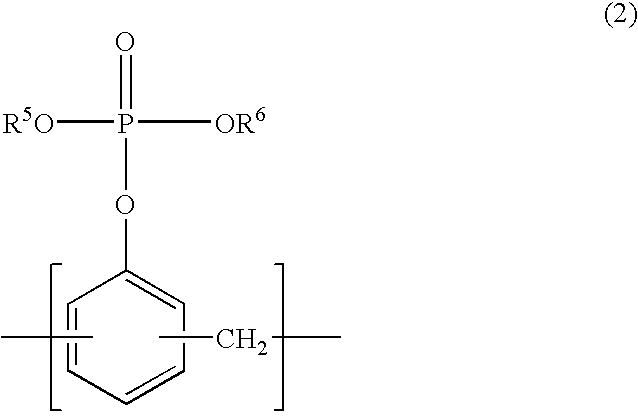
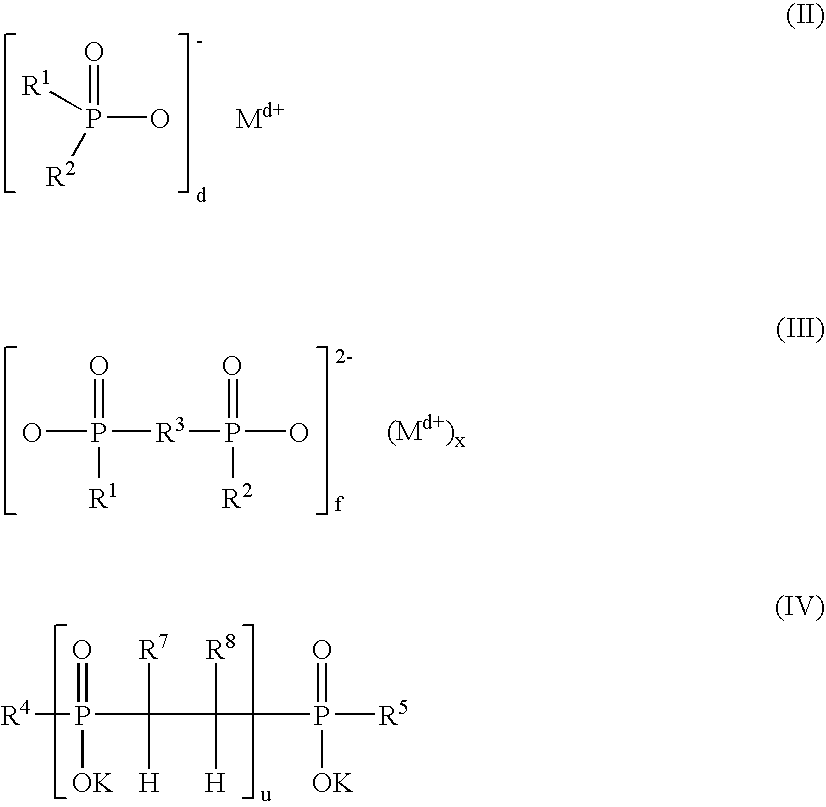
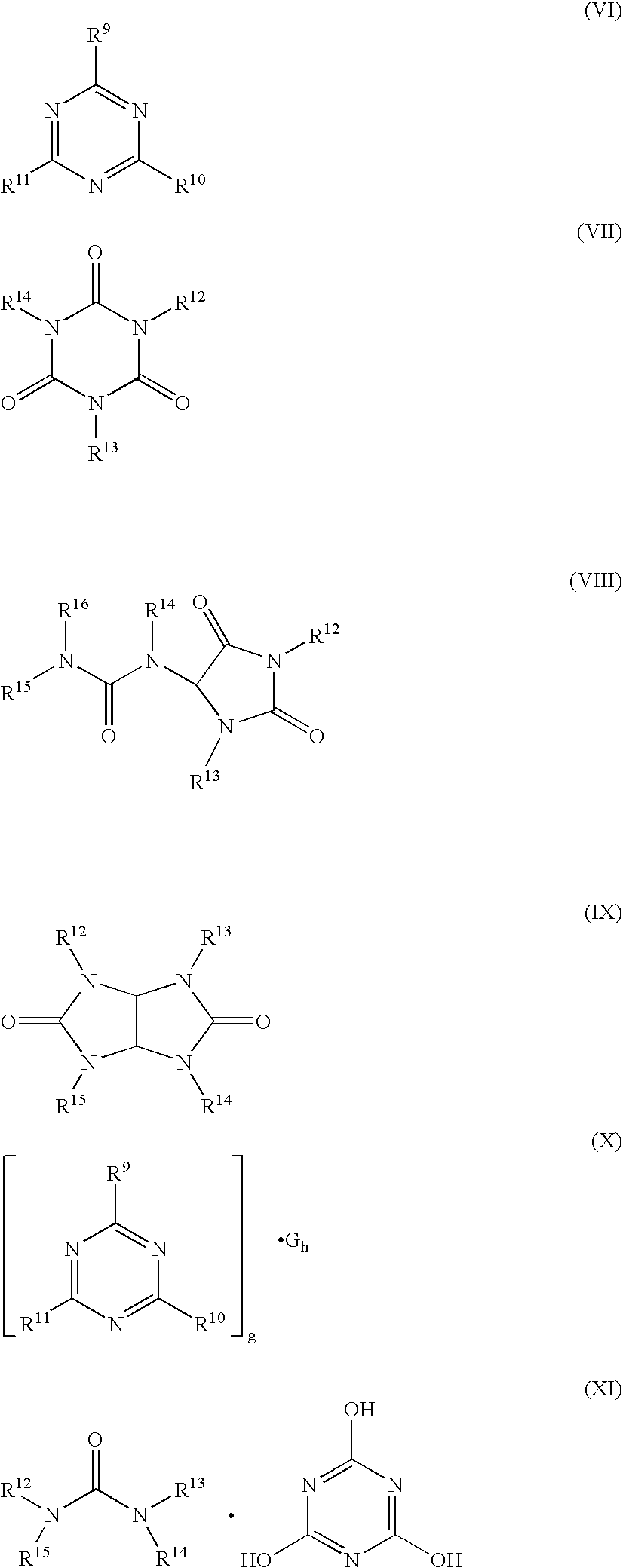
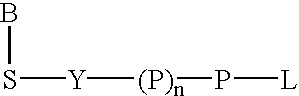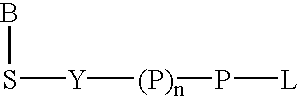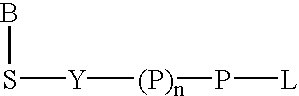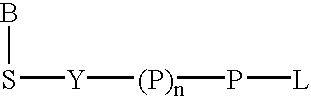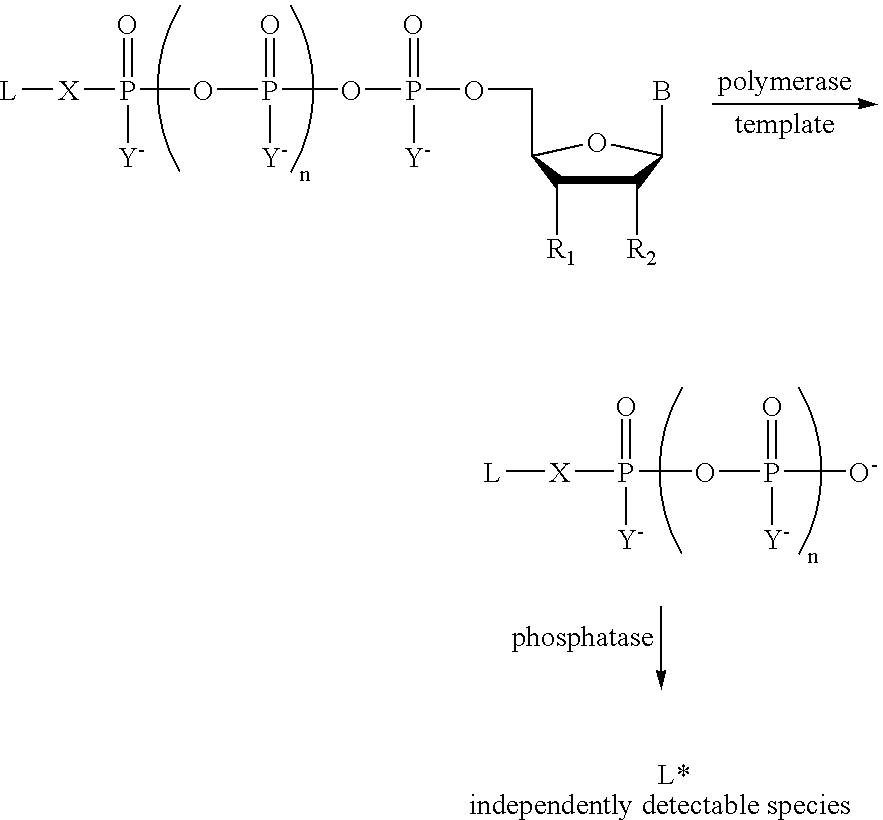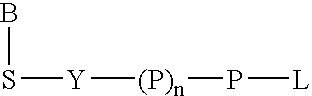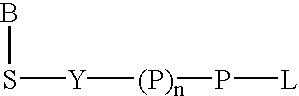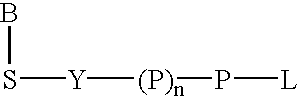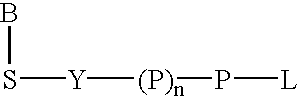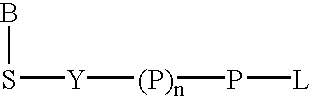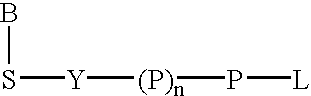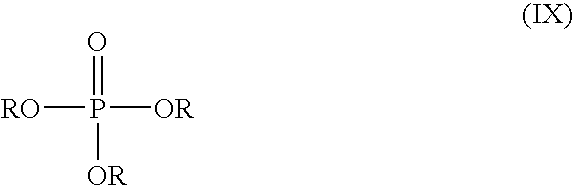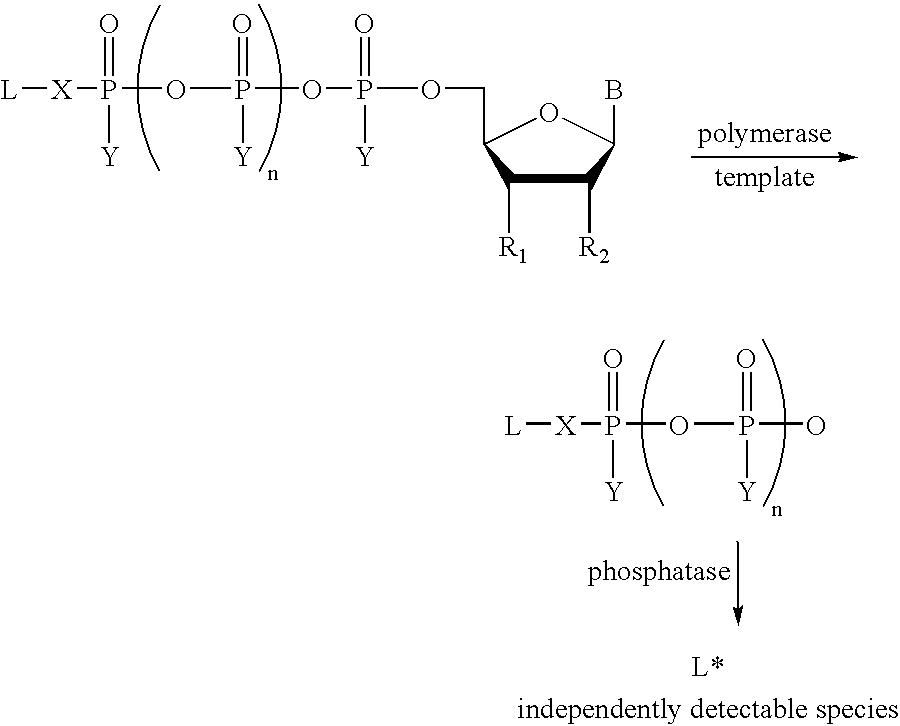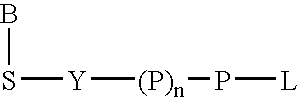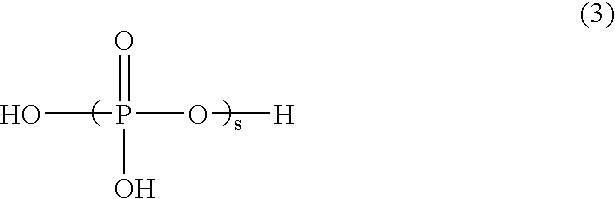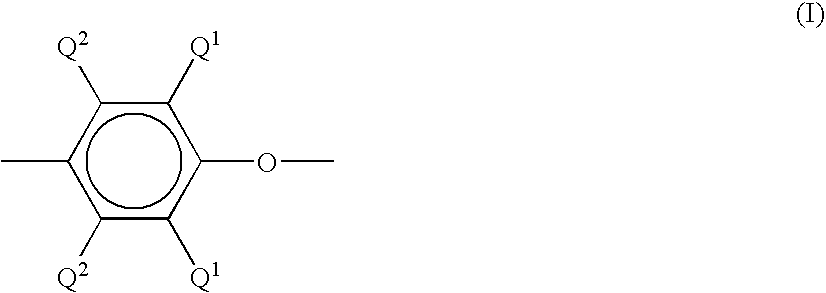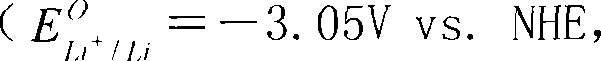Patents
Literature
2427 results about "Polyphosphate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Polyphosphates are salts or esters of polymeric oxyanions formed from tetrahedral PO₄ (phosphate) structural units linked together by sharing oxygen atoms. Polyphosphates can adopt linear or a cyclic ring structures. In biology, the polyphosphate esters ADP and ATP are involved in energy storage. A variety of polyphosphates find application in mineral sequestration in municipal waters, generally being present at 1 to 5 ppm. GTP, CTP, and UTP are also nucleotides important in the protein synthesis, lipid synthesis, and carbohydrate metabolism, respectively.
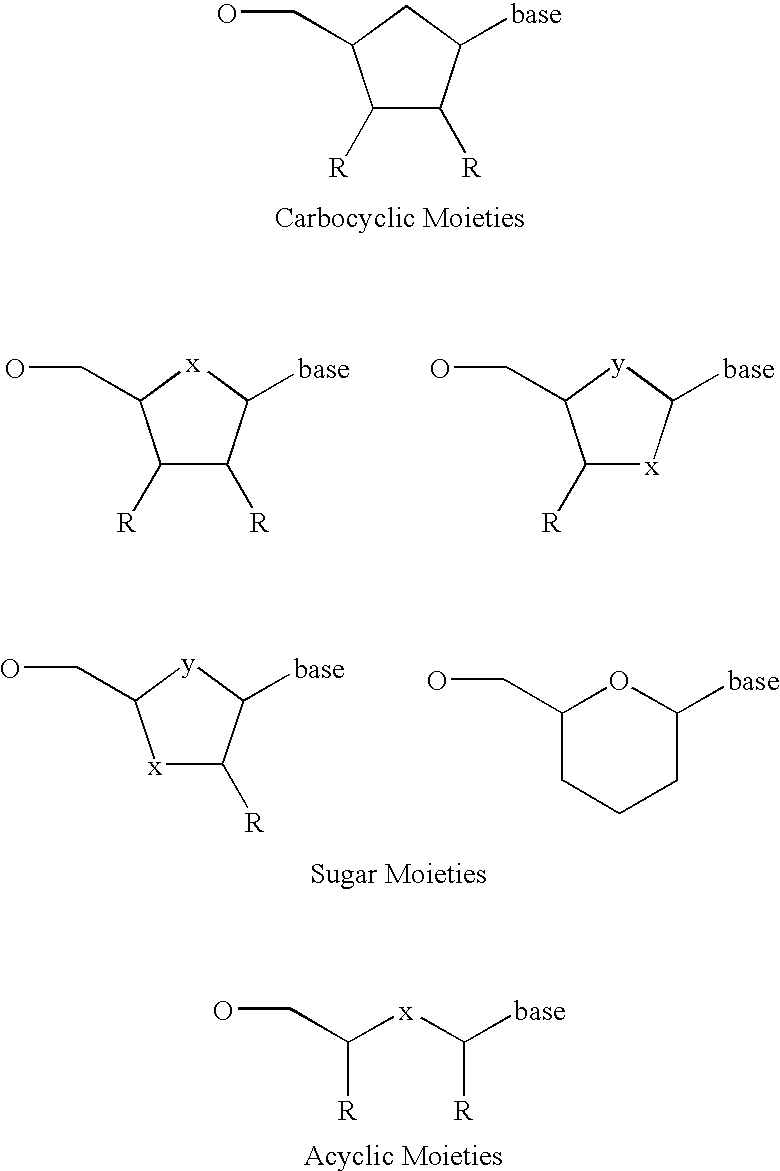
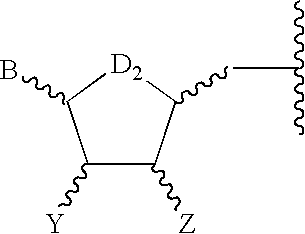
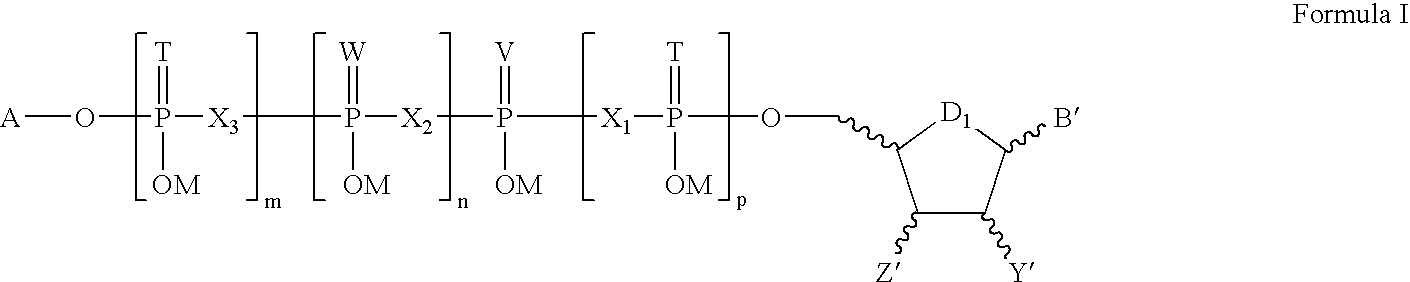
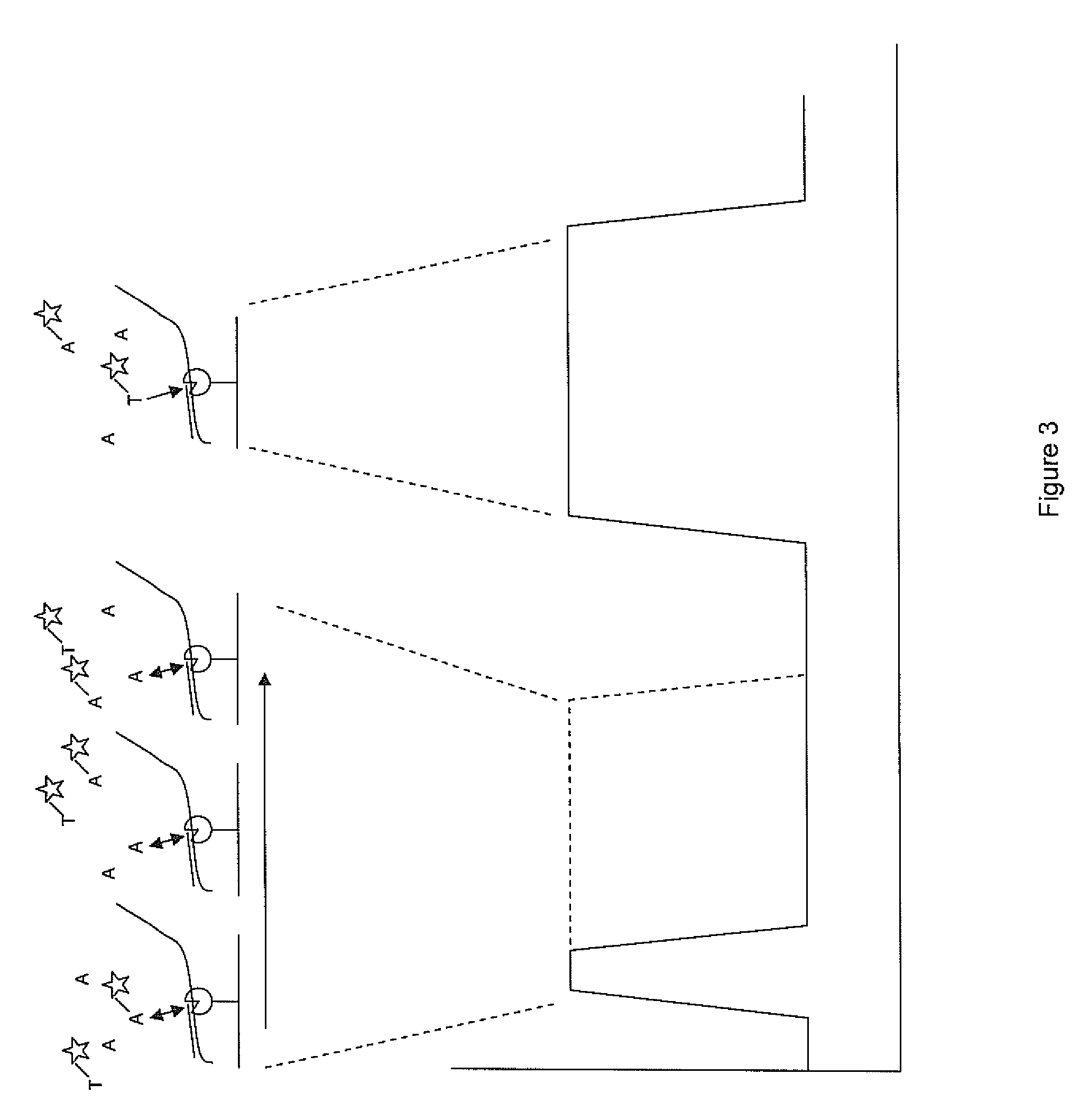
Labeled nucleoside polyphosphates
InactiveUS7041812B2Sugar derivativesMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorNucleic acid detectionFluorescence
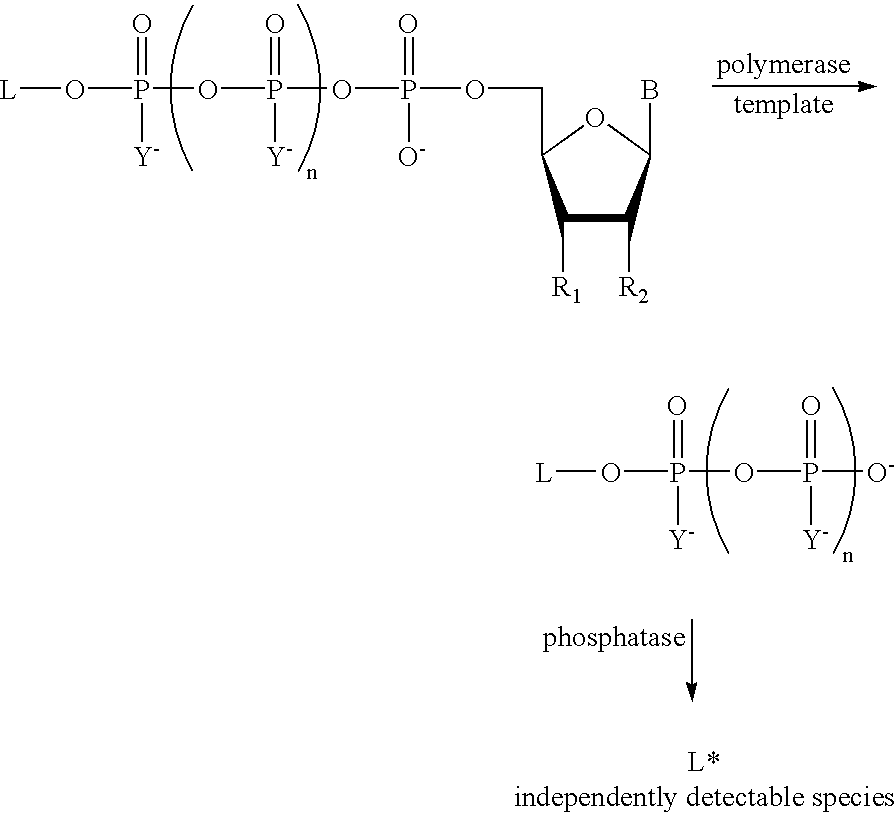
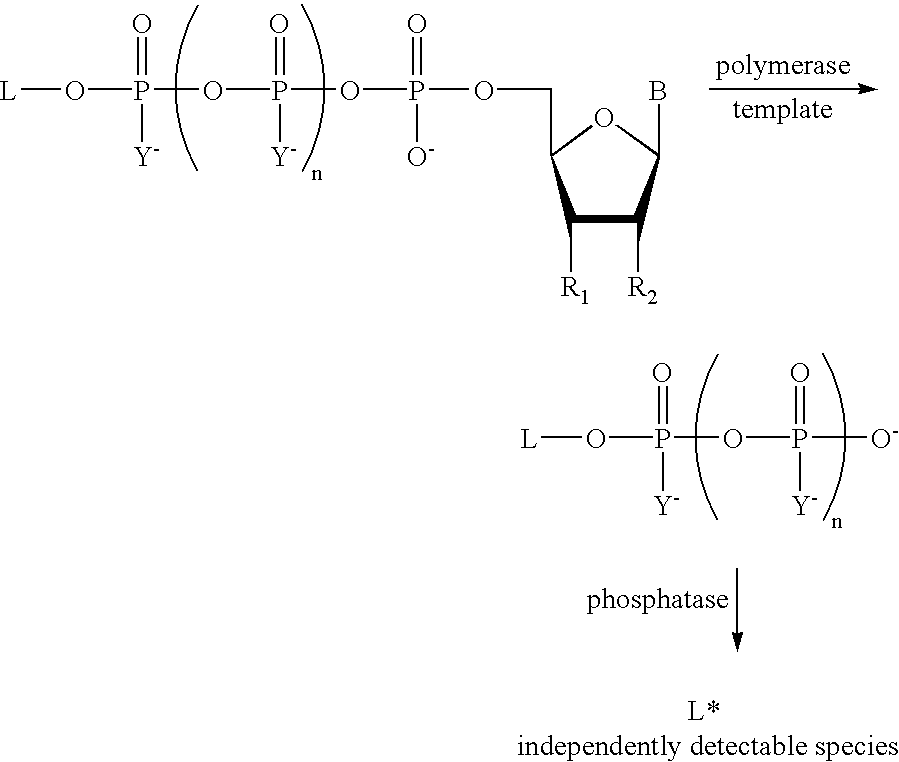
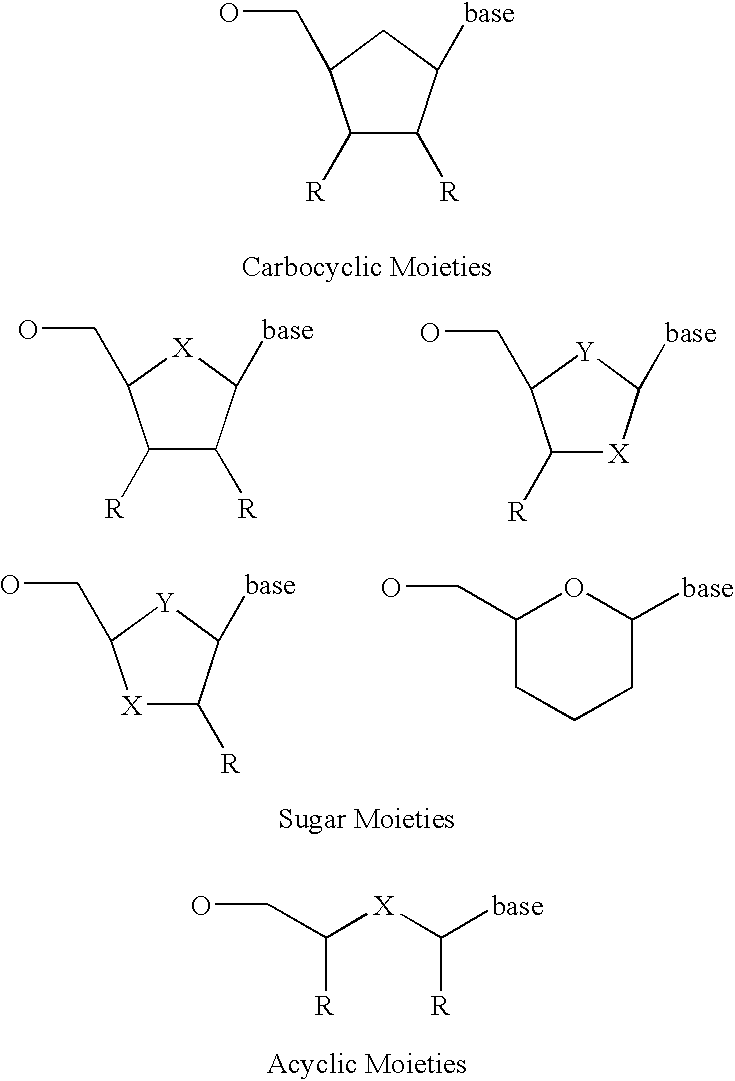
The present invention describes new compositions of matter in the form of labeled nucleoside polyphosphates with four or more phosphates. In addition compositions of nucleoside polyphosphates with four or more phosphates that are substrates for nucleic acid polymerases with enhanced substrate properties and methods of using these nucleoside polyphosphates for nucleic acid detection, characterization and quantification are described. The compositions provided by this invention include nucleoside polyphosphate, dideoxynucleoside polyphosphate, or deoxynucleoside polyphosphate analogues which have colorimetric, chemiluminescent, or fluorescent moieties, mass tags or an electrochemical tags attached to the terminal-phosphate. When a nucleic acid polymerase uses this analogue as a substrate, an enzyme-activatable label would be present on the inorganic polyphosphate by-product of phosphoryl transfer. Removal of the polyphosphate product of phosphoryl transfer via phosphate or polyphosphate transferring enzyme leads to a detectable change in the label attached thereon. When the polymerase assay is performed in the presence of a phosphatase, there is provided a convenient method for real-time monitoring of DNA or RNA synthesis and detection of a target nucleic acid.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
Single nucleotide amplification and detection by polymerase
A method of characterizing a nucleic acid sample is provided that includes the steps of: (a) conducting a DNA polymerase reaction that includes the reaction of a template, a non-hydrolyzable primer, at least one terminal phosphate-labeled nucleotide, DNA polymerase, and an enzyme having 3′→5′ exonuclease activity which reaction results in the production of labeled polyphosphate; (b) permitting the labeled polyphosphate to react with a phosphatase to produce a detectable species characteristic of the sample; (c) detecting the detectable species; and (d) characterizing the nucleic acid sample based on the detection.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
Flame retardant resin compositions
This invention relates to flame retardants for polyester and polyamide compositions, and specifically relates to compositions containing (1) about 30 to about 70 weight percent of a polyester or a synthetic, aliphatic polyamide and synthetic aliphatic, aromatic polyamide copolymers or a mixture thereof; (2) about 15 to about 40 weight percent of glass or mineral reinforcing agent; and (3) a flame retardant of (a) about 5 to about 45 weight percent of melamine polyphosphate; (b) about 15 to about 30 weight percent of melamine polyphosphate and up to about 10 weight percent of a charring catalyst; (c) about 15 to about 30 weight percent of melamine polyphosphate, up to about 10 weight percent of a charring catalyst and up to about 10 weight percent of a char former, wherein all percents by weight are based on the total weight of (1)+(2)+(3) only.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Analyte detection
A method of characterizing an analyte sample is provided that includes the steps of: (a) anchoring the analyte to a nucleic acid template of known sequence; (b) conducting a DNA polymerase reaction that includes the reaction of a template, a non-hydrolyzable primer, at least one terminal phosphate-labeled nucleotide, DNA polymerase, and an enzyme having 3'->5' exonuclease activity which reaction results in the production of labeled polyphosphate; (c) permitting the labeled polyphosphate to react with a phosphatase to produce a detectable species characteristic of the sample; (d) detecting the detectable species. The method may include the step of characterizing the nucleic acid sample based on the detection. Also provided are methods of analyzing multiple analytes in a sample, and kits for characterizing analyte samples.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
Methods of cementing high temperature wells and cement compositions therefor
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Labeled nucleoside polyphosphates
InactiveUS20030124576A1Sugar derivativesMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorNucleic acid detectionFluorescence
The present invention describes new compositions of matter in the form of labeled nucleoside polyphosphates with four or more phosphates. In addition compositions of nucleoside polyphosphates with four or more phosphates that are substrates for nucleic acid polymerases with enhanced substrate properties and methods of using these nucleoside polyphosphates for nucleic acid detection, charcterization and quantification are described. The compositions provided by this invention include nucleoside polyphosphate, dideoxynucleoside polyphosphate, or deoxynucleoside polyphosphate analogues which have calorimetric, chemiluminescent, or fluorescent moieties, mass tags or an electrochemical tags attached to the terminal-phosphate. When a nucleic acid polymerase uses this analogue as a substrate, an enzyme-activatable label would be present on the inorganic polyphosphate by-product of phosphoryl transfer. Cleavage of the polyphosphate product of phosphoryl transfer via phosphatase leads to a detectable change in the label attached thereon. When the polymerase assay is performed in the presence of a phosphatase, there is provided a convenient method for real-time monitoring of DNA or RNA synthesis and detection of a target nucleic acid.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
Terminal-phosphate-labeled nucleotides and methods of use
The present invention describes methods of detecting a nucleic acid in a sample, based on the use of terminal-phosphate-labeled nucleotides as substrates for nucleic acid polymerases. The methods provided by this invention utilize a nucleoside polyphosphate, dideoxynucleoside polyphosphate, or deoxynucleoside polyphosphate analogue which has a colorimetric dye, chemiluminescent, or fluorescent moiety, a mass tag or an electrochemical tag attached to the terminal-phosphate. When a nucleic acid polymerase uses this analogue as a substrate, an enzyme-activatable label would be present on the inorganic polyphosphate by-product of phosphoryl transfer. Cleavage of the polyphosphate product of phosphoryl transfer via phosphatase leads to a detectable change in the label attached thereon. When the polymerase assay is performed in the presence of a phosphatase, there is provided a convenient method for real-time monitoring of DNA or RNA synthesis and detection of a target nucleic acid.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
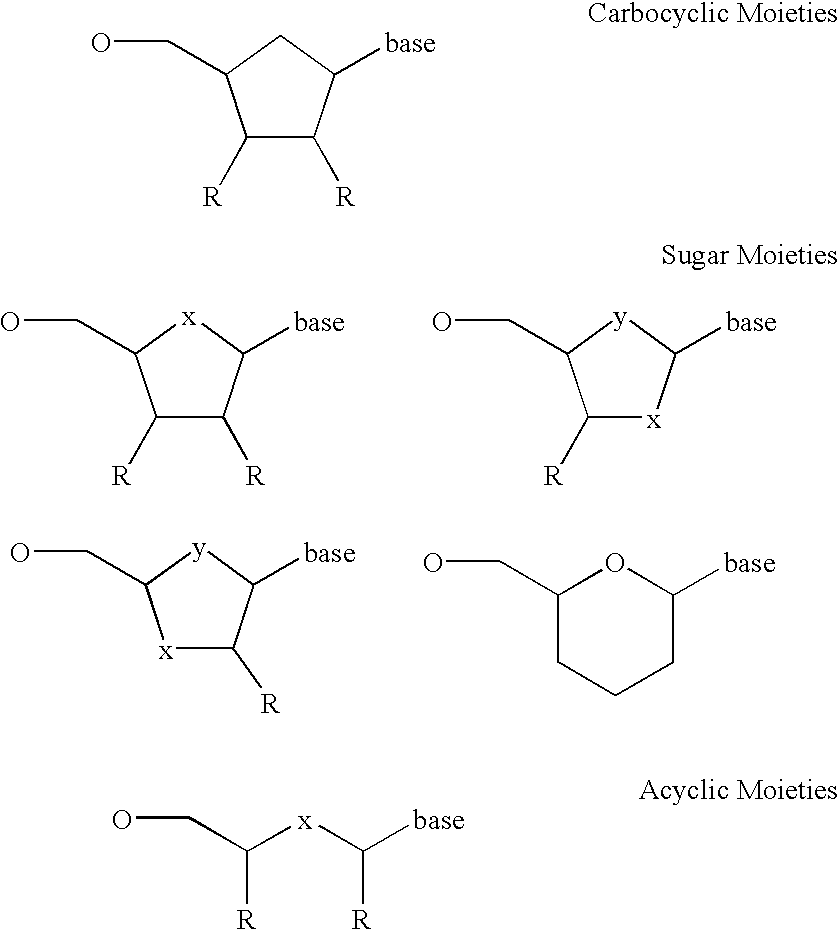
Water-Absorbing Polysaccharide and Method for Producing the Same
InactiveUS20080009616A1Drying processImprove retentionSugar derivativesBaby linensPolyphosphatePhosphoric acid
The present invention relates to a process for producing a water-absorbent polysaccharide including the process steps of bringing into contact an uncrosslinked polysaccharide with a polyphosphate or a polyphosphoric acid as crosslinking agent in the presence of water to form a polysaccharide gel and crosslinking the polysaccharide gel. The invention further relates to a water-absorbent polysaccharide obtainable by this process, a water-absorbent polysaccharide, a composite, a process for producing a composite, a composite produced by this process, the use of the water-absorbent polysaccharides or of the composites as well as the use of polyphosphates.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Terminal-phosphate-labeled nucleotides and methods of use
The present invention relates to improved methods of detecting a target using a labeled substrate or substrate analog. The methods comprise reacting the substrate or substrate analog in an enzyme-catalyzed reaction which produces a labeled moiety with independently detectable signal only when such substrate or substrate analog reacts. The present invention, in particular, describes methods of detecting a nucleic acid in a sample, based on the use of terminal-phosphate-labeled nucleotides as substrates for nucleic acid polymerases. The methods provided by this invention utilize a nucleoside polyphosphate, dideoxynucleoside polyphosphate, or deoxynucleoside polyphosphate analogue which has a colorimetric dye, chemiluminescent, or fluorescent moiety, a mass tag or an electrochemical tag attached to the terminal-phosphate. When a nucleic acid polymerase uses this analogue as a substrate, an enzyme-activatable label would be present on the inorganic polyphosphate by-product of phosphoryl transfer. Cleavage of the polyphosphate product of phosphoryl transfer via phosphatase leads to a detectable change in the label attached thereon. When the polymerase assay is performed in the presence of a phosphatase, there is provided a convenient method for real-time monitoring of DNA or RNA synthesis and detection of a target nucleic acid.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
Flame retardant thermoplastic composition and articles comprising the same
A flame retardant thermoplastic composition comprises: a poly(arylene ether); an impact modifier; a polyolefin; a phosphoric acid salt selected from the group consisting of melamine phosphate, melamine pyrophosphate, melamine orthophosphate, diammonium phosphate, monoammonium phosphate, phosphoric acid amide, melamine polyphosphate, ammonium polyphosphate, polyphosphoric acid amide, and combinations of two or more of the foregoing; a metal hydroxide; and an organic phosphate wherein the amount of phosphoric acid salt by weight is greater than or equal to the amount of organic phosphate by weight. The flame retardant composition is may be used in the production of electrical wires.
Owner:SHPP GLOBAL TECH BV
Allele specific primer extension
InactiveUS20040048301A1Rapid rise in fluorescenceEnhanced signalSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPhosphateNucleotide
A method of characterizing a nucleic acid sample is provided that includes the steps of: (a) conducting a DNA polymerase reaction that includes the reaction of a template, an allele specific primer, at least one terminal phosphate-labeled nucleotide, DNA polymerase, and optionally an enzyme having 3'->5' exonuclease activity when the primer is non-hydrolyzable, which reaction results in the production of labeled polyphosphate; (b) permitting the labeled polyphosphate to react with a phosphatase to produce a detectable species; (c) detecting the detectable species; and (d) characterizing the nucleic acid sample based on such detection.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
Process aid for preparing a flowable slurry
A process for preparing a flowable slurry comprising mixing 25-70 wt. % water; an alkaline material selected from the group consisting of chlorosilicon manufacturing byproducts, direct process residue gels, cement kiln dust, and mixtures thereof; and a process aid selected from the group consisting of sucrose, raffinose, lignin, methylglucopyranoside, lactose, fructose, sodium polyphosphate, trehalose and mixtures thereof to form a flowable slurry. This slurry is especially useful in the manufacture of cement.
Owner:DOW CORNING CORP
Cis reactive oxygen quenchers integrated into linkers
The present invention provides methods and compositions for performing illuminated reactions, particularly sequencing reactions, while mitigating and / or preventing photodamage to reactants that can result from prolonged illumination. In particular, the invention provides methods and compositions for incorporating photoprotective agents into conjugates comprising reporter molecules and nucleoside polyphosphates.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Flame-retardant resin composition
A flame-retardant resin composition comprises 10 to 300 parts by weight of a flame retardant (B) and 1 to 200 parts by weight of an inorganic filler (C) (a glass fiber and / or a glass flake), relative to 100 parts by weight of a base resin (A). The flame retardant (B) comprises a polyphenylene oxide-series resin and / or a polyphenylene sulfide-series resin (B1), a phosphoric ester (B2), and a nitrogen-containing cyclic compound (B3) (for example, a polyphosphate of an amino group-containing triazine compound). The inorganic filler (C) has been treated with a surface-treatment agent or sizing agent containing a novolak epoxy resin. Such a resin composition is useful for obtaining a shaped article which has been inhibited from dripping and to which flame retardancy is highly imparted.
Owner:POLYPLASTICS CO LTD
Composition and method for inhibiting platelet aggregation
The present invention provides novel compounds of dinucleotide polyphosphates and the method of preventing or treating diseases or conditions associated with platelet aggregation. The method comprises administering systemically to a patient a pharmaceutical comprising a purinergic P2τ receptor antagonist, in an amount effective to elevate its extracellular concentration to bind to P2τ receptors and inhibit P2τ receptor-mediated platelet aggregation. Methods of systemic administration include injection by intravenous, intramuscular, intrasternal and intravitreal routes, infusion, transdermal administration, oral administration, rectal administration and intra-operative instillation.
Owner:INSPIRE PHARMA +1
Compositions and methods for use in analytical reactions
ActiveUS8252911B2Rate of reactionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisPolyphosphate
Compositions, methods, substrates and systems for use in analysis of single molecule reactions and particularly single molecule nucleic acid sequence analysis. Compositions that include non-reactive, distinguishable or undetectable competitive substrates for the reaction system of interest are provided, as well as their use in systems and substrates for such applications, such compounds typically preferably polyphosphate chains or analogous structures.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Tooth whitening compositions and delivery systems therefor
InactiveUS20060024244A1Sufficient amountCosmetic preparationsContainers for annular articlesPolyphosphateSilicon dioxide
Stain-removing oral compositions, such as gum compositions are herein provided. The compositions include an orally acceptable carrier and a stain-removing anionic surfactant. The surfactant includes a fatty acid salt having at least one hydroxyl functionality. The fatty acid salt may be a salt of ricinoleic acid, and may be combined with a chelating agent and / or an abrasive. The chelating agent may be a polyphosphate and the abrasive may be a silica abrasive.
Owner:INTERCONTINENTAL GREAT BRANDS LLC
Aluminum phosphate or polyphosphate particles for use as pigments in paints and method of making same
InactiveUS20060045831A1PhosphatesPeroxides/peroxyhydrates/peroxyacids/superoxides/ozonidesAluminium sulfateOrganic acid
An aluminum phosphate or polyphosphate-based pigment product is made by a process comprising contacting phosphoric acid with aluminum sulfate and an alkaline solution to produce an aluminum phosphate based product; and optionally calcining the aluminum phosphate based product at an elevated temperature, wherein the process is substantially free of an organic acid. The aluminum phosphate or polyphosphate-based pigment is amorphous. The amorphous aluminum phosphate or polyphosphate characterized by a bulk density of less than 2.30 grams per cubic centimeter and a phosphorus to aluminum mole ratio of greater than 0.8. The composition is useful in paints and as a substitute for titanium dioxide.
Owner:BUNGE AMORPHIC SOLUTIONS +1
Flame retardant thermoplastic composition and articles comprising the same
ActiveUS20070261878A1Decreasing and eliminating plate-outDecreasing and eliminating and migrationPlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsDyeing processElectrical conductorPolyolefin
A flame retardant thermoplastic composition comprising a poly(arylene ether), a block copolymer, a liquid polyolefin, and a flame retardant additive composition. The flame retardant additive composition comprises a metal hydroxide, an organic phosphate, and a phosphoric acid salt selected from the group consisting of melamine phosphate, melamine pyrophosphate, melamine orthophosphate, melem polyphosphate, melam polyphosphate, diammonium phosphate, monoammonium phosphate, phosphoric acid amide, melamine polyphosphate, ammonium polyphosphate, polyphosphoric acid amide, and combinations of two or more of the foregoing. The block copolymer comprises a block that is a controlled distribution copolymer having terminal regions that are rich in alkylene units and a center region that is rich in aryl alkylene units. The flame retardant composition may be used in the production of covered conductors.
Owner:SHPP GLOBAL TECH BV
Methods for preparing modified biomolecules, modified biomolecules and methods for using same
InactiveUS20090186343A1Low backgroundIncrease the number ofSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotidePolyphosphate
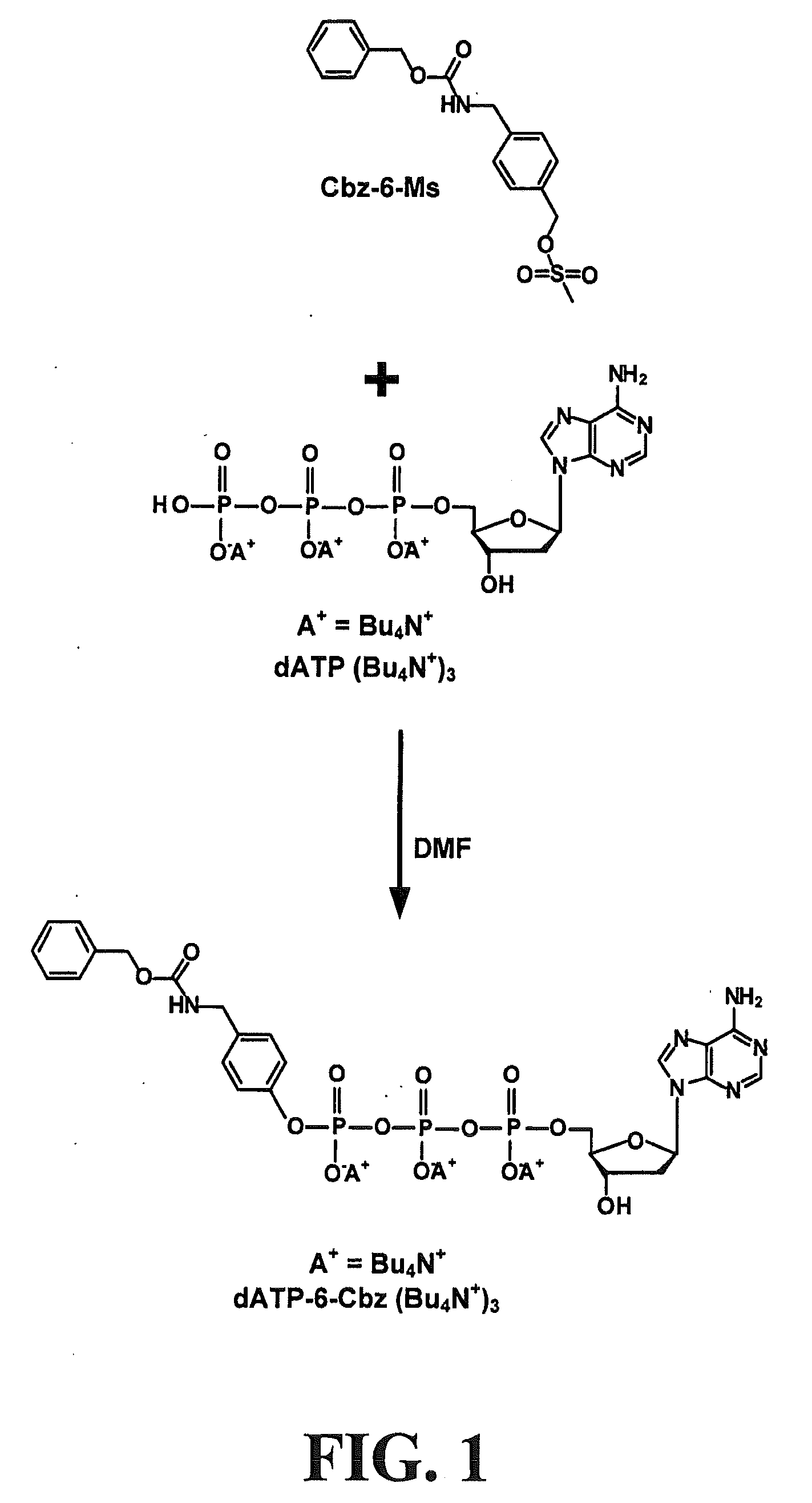
A novel and efficient single pot synthetic schemes are disclosed for preparing modified nucleotides, nucleotide analogs, nucleotide polyphosphates, and nucleotide polyphosphate analogs. The novel method is used to prepare nucleotides, nucleotide analogs, nucleotide polyphosphates, and nucleotide polyphosphate analogs having non-persistent or persistent and non-persistent modifications. Novel biomolecular reactions are also disclosed using the novel modified biomolecules disclosed herein.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Skin care compositions
InactiveUS6063406AImprove permeabilityFacilitate propertyBiocideInorganic phosphorous active ingredientsCross-linkSodium bicarbonate
Owner:CHEMCRAFT +1
Flame-retardant resin composition
InactiveUS20050004292A1Improve flame retardant performanceSpecial tyresPolyesterPhosphoric Acid Esters
A flame-retardant resin composition comprises (A) abase resin; (B) a flame retardant comprising (B1) at least one aromatic resin selected from a pblyphenylene oxide-series resin and a polyphenylene sulfide-series resin, (B2) a phosphoric ester, and (B3) a nitrogen-containing cyclic compound; and (C) a styrenic resin having a melt flow rate of not more than 8 g / 10 minutes. The base resin may be a polyester-series resin. The styrenic resin (C) may be a styrenic resin having a melt flow rate of 0.1 g / 10 minutes to not more than 5 g / 10 minutes. The phosphoric ester (B2) may be a condensed phosphoric ester, and the nitrogen-containing cyclic compound (B3) may be a polyphosphate of an amino group-containing triazine compound, a polyphosphoric acid amide, or others. The present invention provides a flame-retardant resin composition which has been flame-retarded without using a halogen-containing flame retardant.
Owner:POLYPLASTICS CO LTD
Flame Retardant Poly(Arylene Ether)/Polyamide Composition
A composition comprises a compatibilized poly(arylene ether) / polyamide blend, an optional electrically conductive filler, a phosphinate, and flame retardant augment selected from the group consisting of melamine polyphosphate, zinc borate, low melting glass, talc, and combinations of two or more of the foregoing flame retardant augments.
Owner:SABIC INNOVATIVE PLASTICS IP BV
Expanding fire retardant composition without halide for polyolefine
The fire retardant composition consists of pentaerythritol phosphate 18-54 wt%, melamine polyphosphate 40-80 wt%, stearic acid or zinc stearate 0.1-5 wt%, coupling agent 0.1-5 wt% and stuffing 0.1-5 wt%. It is used as fire retardant for polypropylene powder or grains, and when the addition amount is 28 wt% fireproof level of UL94V-0 is reached; and is also used as fire retardant for polyethylene,and when the addition amount is 30 wt% fireproof level of UL94V-0 is reached.
Owner:BALING PETRO CHEM CO LTD SINOPEC
Oral Stannous Compositions
ActiveUS20090136432A1High activityLow levelCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsPhosphateDivalent metal ions
The present invention relates to an aqueous oral composition comprising:a) from 0.2% to 3% divalent metal ions comprising:i. from 0.1% to 1.5% of zinc ions;ii. from 0.1% to 2% of tin (II) ions; andb) a source of fluoride ions;c) a silica dental abrasive;d) one or more chelants having a MW of less than 1000 and capable of forming water-soluble complexes with the zinc ions, wherein the chelants comprise less than 0.2% linear polyphosphates having a chain length of four or more;e) an orally acceptable carrier comprising at least 20% total water;wherein the pH of the composition is from 5 to 6.5, the molar ratio of the chelants to the divalent metal ions is at least 0.70:1 and at least 80% by weight of the total zinc ions are solubilised within the composition.The composition of the invention has been found to give improved antimicrobial activity from the zinc / stannous combination without significant taste, staining or stability problems, compared to compositions having lower levels of chelants.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Surface treating method for magnesium lithium alloy
InactiveCN101245485AGood effectImprove corrosion resistanceAnodisationMicro arc oxidationPlasma electrolytic oxidation
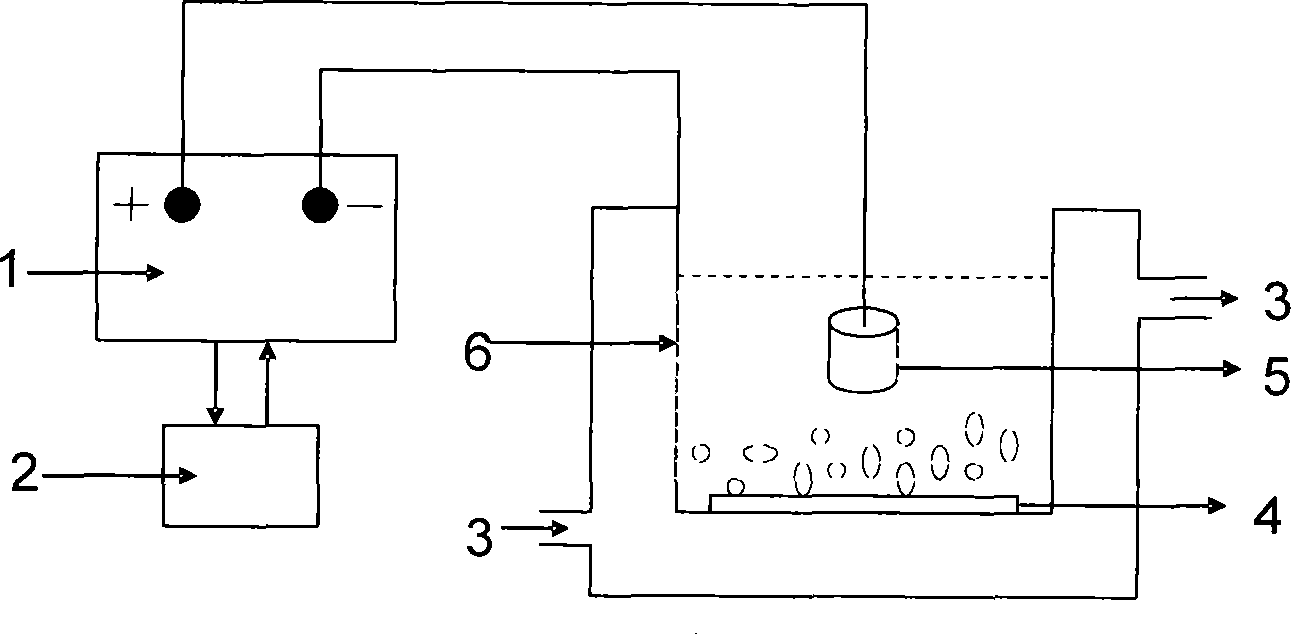
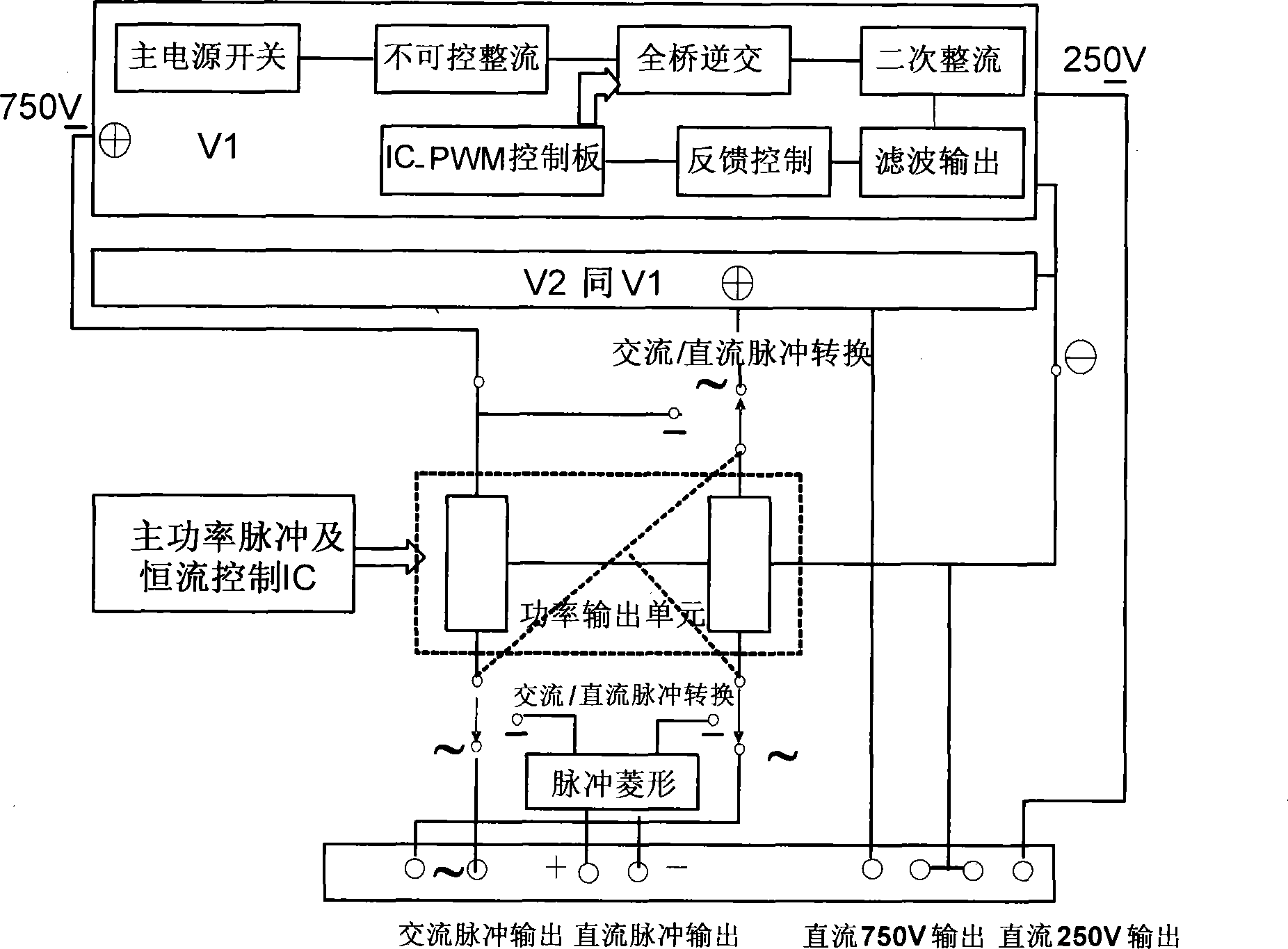
The invention provides a method for processing the surface of magnesium-lithium alloy. The technique of micro-arc oxidation is successfully applied to processing the surface of the magnesium-lithium alloy. Direct current / DC pulse / alternating current pulse multiplex power supply is used and the magnesium-lithium alloy with different lithium contents in a compound electrolyte system of sodium polyphosphate, sodium silicate, calgon and sodium hydroxide is carried out by micro-arc oxidation for 2-120min. A ceramic oxide film of 10-100Mum with a rigidity higher than 200Hv is formed in situ on the surface of the magnesium-lithium alloy, thus remarkably improving corrosion resistant property compared with an alloy matrix, solving the problem known at home and abroad concerning processing the surface of the magnesium-lithium alloy and broadening the application in the fields of aviation, aerospace, car, electronic, etc.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Preparation of aluminum phosphate or polyphosphate particles
InactiveUS20080038556A1High mixingHigh shear stress performanceMaterial nanotechnologyPigmenting treatmentSodium aluminatePolyphosphate
A process for the preparation of amorphous aluminum phosphate or polyphosphate-based pigment by reacting aluminum phosphate and sodium aluminate is provided. The amorphous aluminum phosphate or polyphosphate is characterized by a skeletal density of less than 2.50 grams per cubic centimeter and a phosphorus to aluminum mole ratio of greater than 0.8. In one embodiment, the composition is useful in paints as a substitute for titanium dioxide.
Owner:BUNGE AMORPHIC SOLUTIONS +1
Nucleic acid amplification with terminal-phosphate labeled nucleotides
ActiveUS7125671B2Reduce generationMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationNucleotideFluorescence
The present invention relates generally to the use of terminal-phosphate-labeled nucleotides having three or more phosphates as substrates for nucleic acid polymerases and their use in DNA amplification. The labels employed are chemiluminescent, fluorescent, electrochemical and chromogenic moieties as well as mass tags and include those that are directly detectable, detectable after enzyme activation or feed into other processes to generate a different signal. The signal generated from the attached dyes may also be used to quantify the amount of amplification. Further provided are stabilizers that enhance the stability of terminal-phosphate labeled nucleoside polyphosphates in aqueous solutions and are useful for reducing non-enzymatic hydrolysis of these nucleotides, hence decrease background.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
Polyurethane/Polyolefin Blends with Improved Strain and Scratch Whitening Performance
ActiveUS20130081853A1Improve performanceGood strainPlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsInsulated cablesPolyolefinPhosphate
A composition, preferably a halogen-free, flame retardant composition, comprising in weight percent based on the weight of the composition:A. 1 to 90% TPU polymer,B. 1 to 90% polyolefin polymer, preferably a polar polyolefin polymer,C. 1 to 60% phosphorus-based, intumescent flame retardant,D. 0.5 to 25% liquid phosphate modifier, e.g., bis-phenol-A-polyphosphate, andE. Optional additives and / or fillers.The compositions exhibit excellent strain and scratch whitening performance in combination with excellent burn performance, good flexibility and tensile properties, and good fabrication extrusion characteristics including improved surface smoothness.
Owner:UNION CARBIDE CORP
Flame retardant composition
A flame retardant additive composition comprising a phosphoric acid salt selected from the group consisting of melamine phosphate, melamine pyrophosphate, melamine orthophosphate, ammonium phosphate, ammonium phosphate amide, phosphoric acid amide, melamine polyphosphate, ammonium polyphosphate, ammonium polyphosphate amide, polyphosphoric acid amide and combinations of two or more of the foregoing; a metal hydroxide; and an organic phosphate. The flame retardant additive is useful in a wide range of thermoplastic compositions.
Owner:SABIC INNOVATIVE PLASTICS IP BV
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com