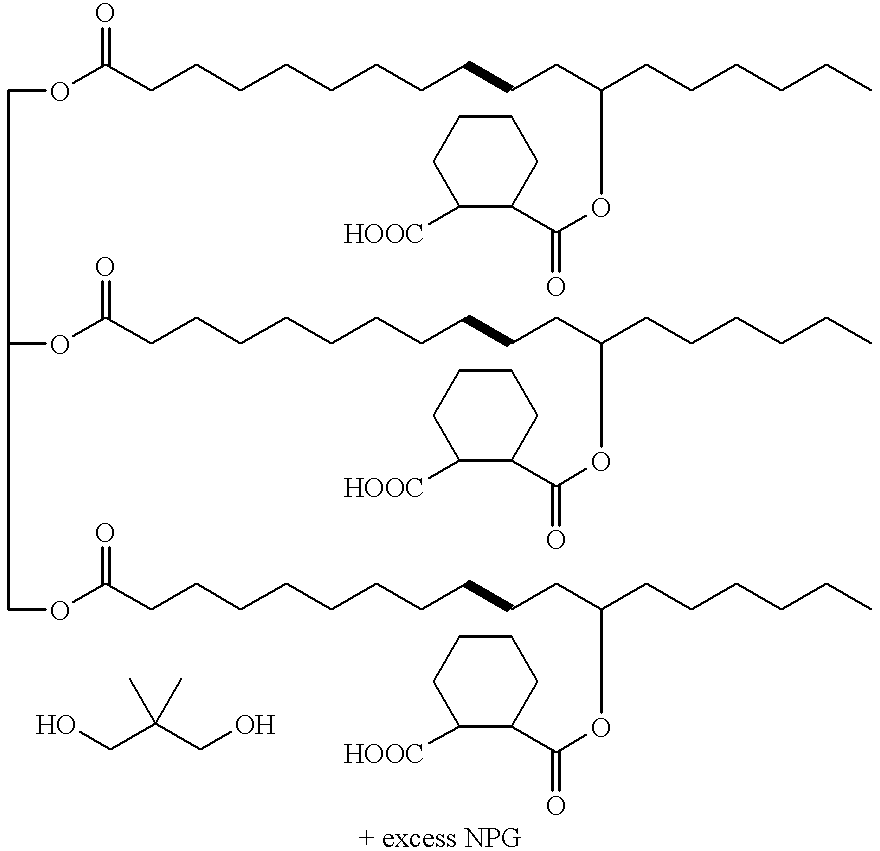
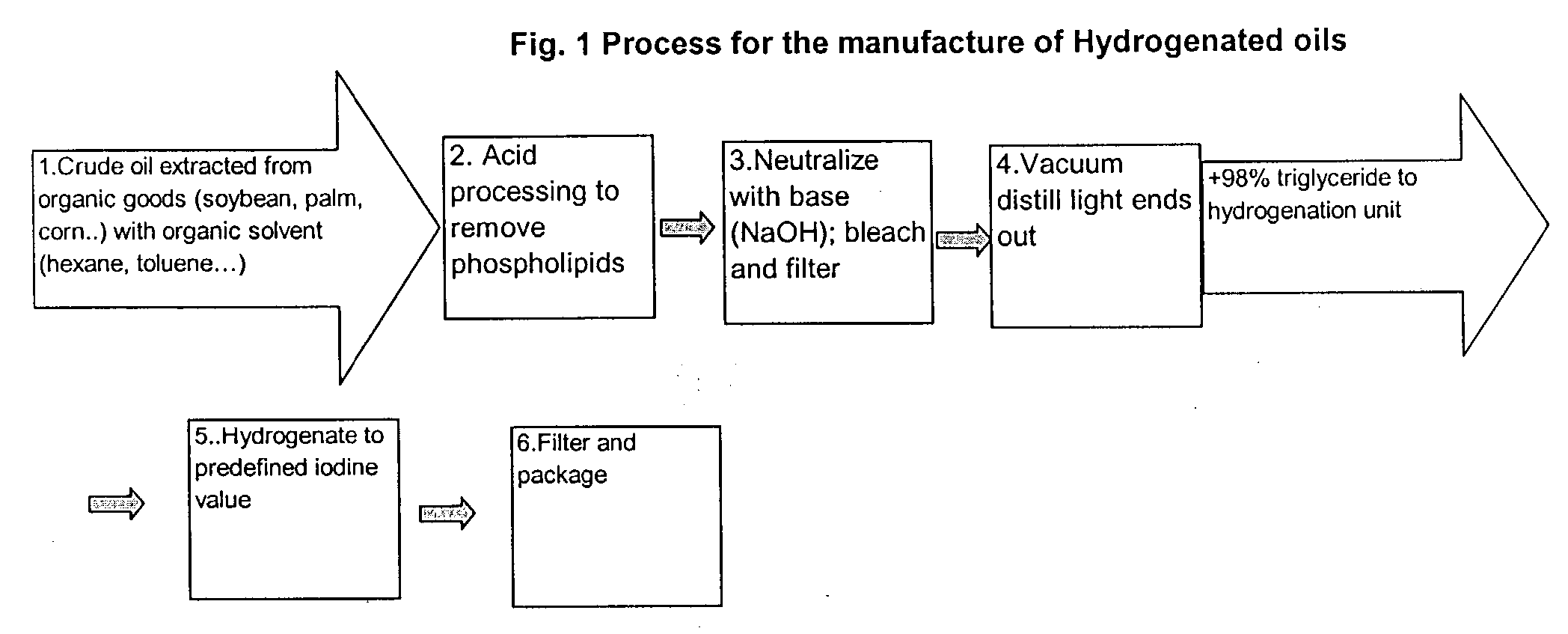
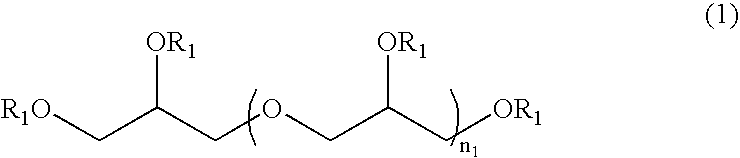
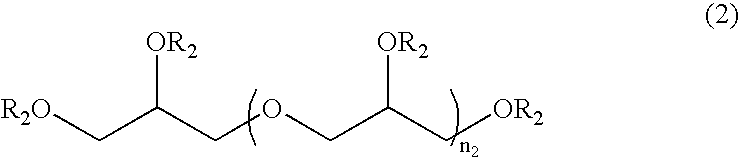
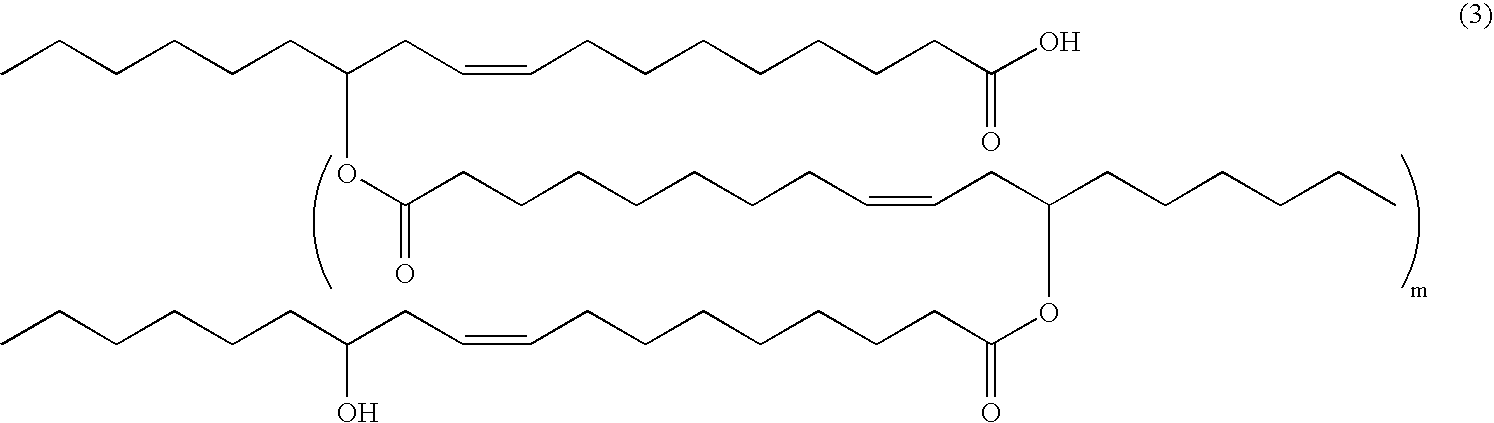
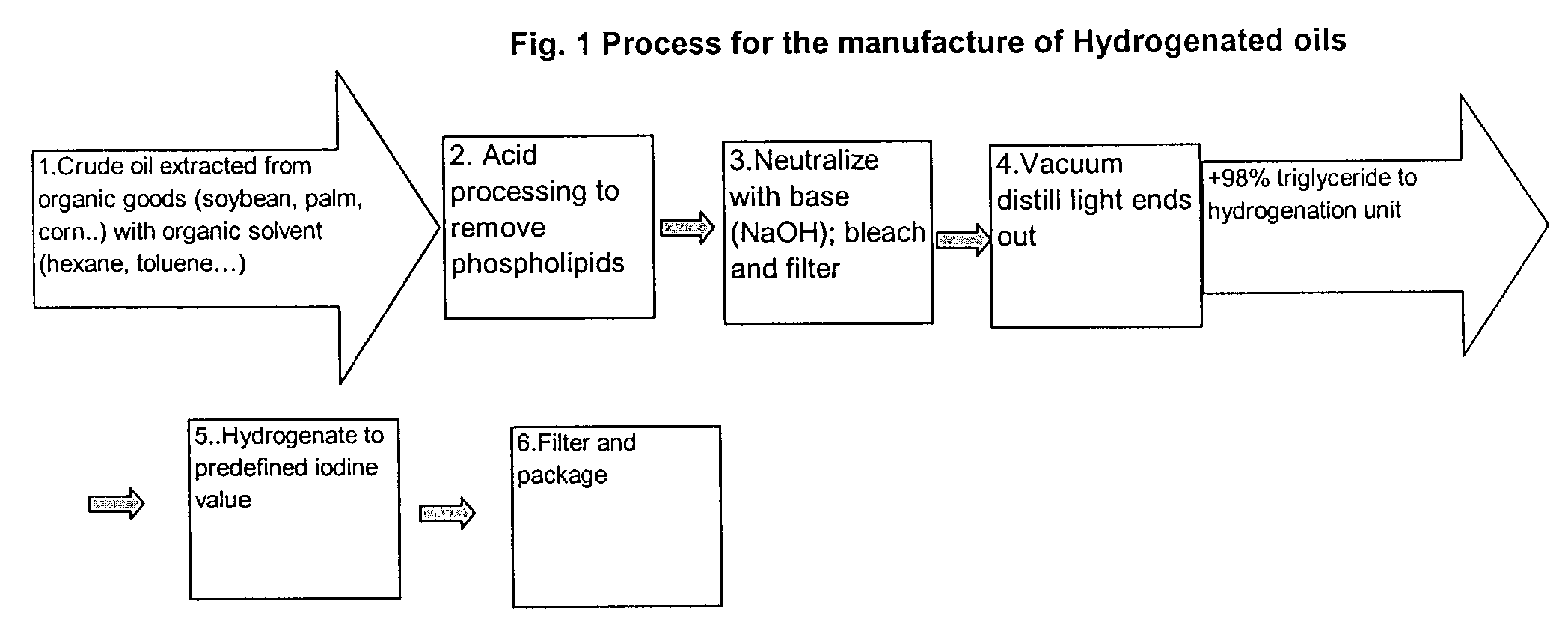
Patents
Literature
531 results about "Ricinoleic acid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
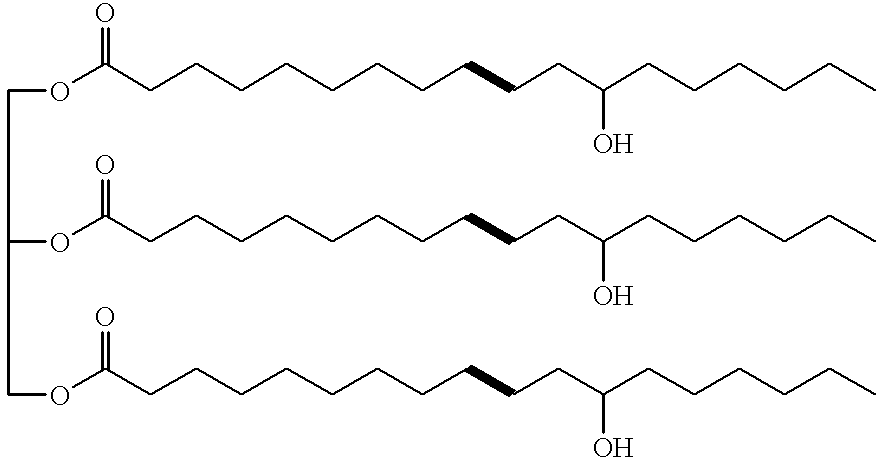
Ricinoleic acid, formally called 12-hydroxy-9-cis-octadecenoic acid is a fatty acid. It is an unsaturated omega-9 fatty acid and a hydroxy acid. It is a major component of the seed oil obtained from mature Castor plant (Ricinus communis L., Euphorbiaceae) seeds or in sclerotium of ergot (Claviceps purpurea Tul., Clavicipitaceae). About 90% of the fatty acid content in castor oil is the triglyceride formed from ricinoleic acid.
Elastomeric material compositions obtained from castor oil and epoxidized soybean oil
Elastomers are formed from castor oil and / or ricinoleic acid estolides and a polyester formed from an epoxidized vegetable oil such as ESO and a polycarboxylic acid such as sebacic acid, optionally in the presence of a peroxide initiator, or include crosslinked reaction products derived from ricinoleic acid or castor oil estolides, epoxy group-containing compounds such as epoxy resins and / or epoxidized vegetable oil, epoxy hardeners such as polyamine and polycarboxylic acid hardeners, thermally activated free radical initiators such as peroxides, and optionally but preferably include fillers such as limestone or wood flour. The elastomers can be prepared using a two-step, solvent-less procedure at elevated or ambient temperatures. These predominantly “all-natural” elastomers have physical properties comparable to conventional petroleum-based elastomers and composites and exhibit good flexibility, resiliency, abrasion resistance and inertness to hydrolysis. The resulting elastomers display good mechanical strength and resiliency, are resistant to abrasion and hydrolysis, and can be processed into sheet materials, which makes them attractive as floor covering components.
Owner:AFI LICENSING +1
Tooth whitening compositions and delivery systems therefor
InactiveUS20060024244A1Sufficient amountCosmetic preparationsContainers for annular articlesPolyphosphateSilicon dioxide
Stain-removing oral compositions, such as gum compositions are herein provided. The compositions include an orally acceptable carrier and a stain-removing anionic surfactant. The surfactant includes a fatty acid salt having at least one hydroxyl functionality. The fatty acid salt may be a salt of ricinoleic acid, and may be combined with a chelating agent and / or an abrasive. The chelating agent may be a polyphosphate and the abrasive may be a silica abrasive.
Owner:INTERCONTINENTAL GREAT BRANDS LLC
Glass fiber reinforced polypropylene composite material with low odor and preparation method thereof
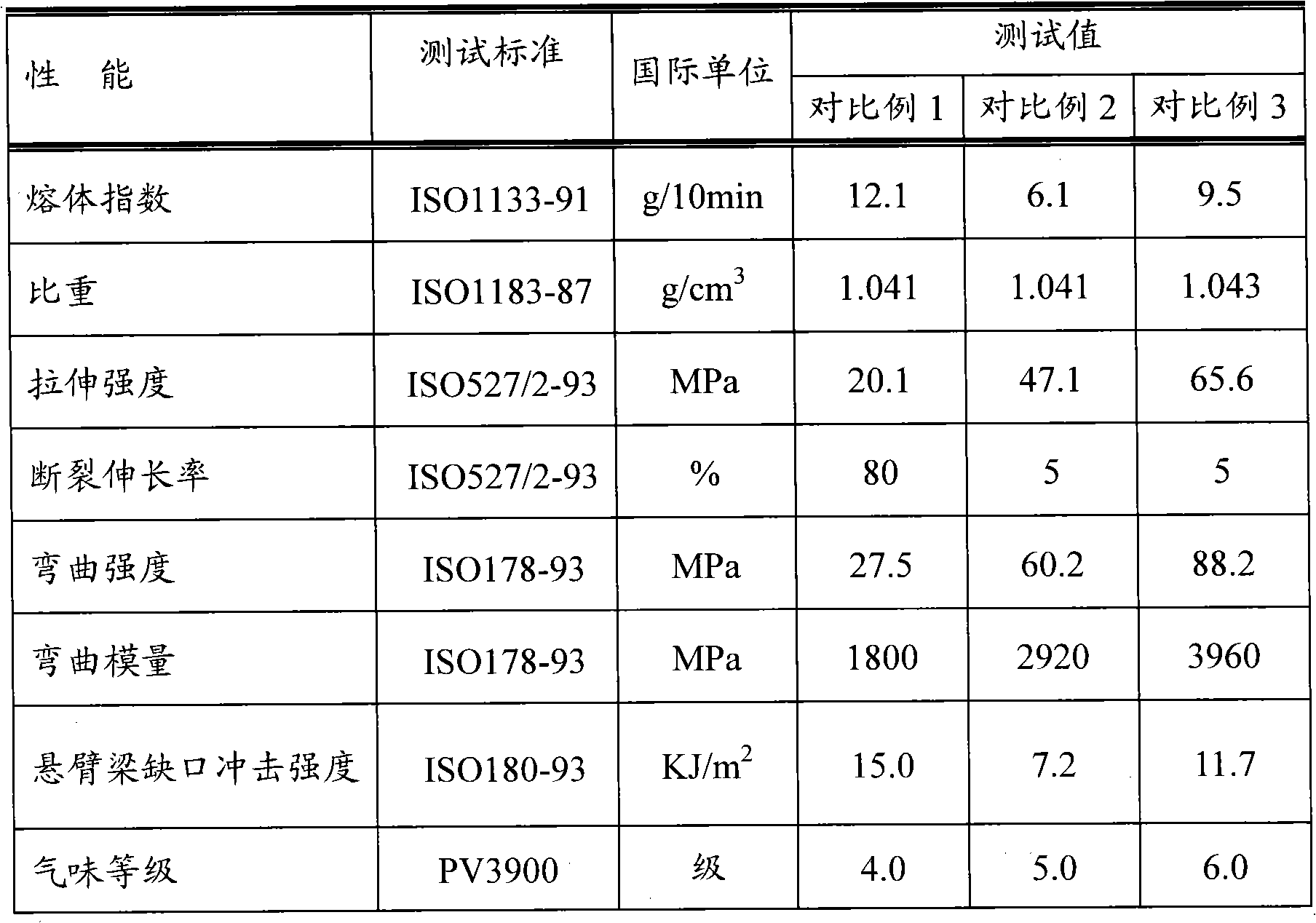
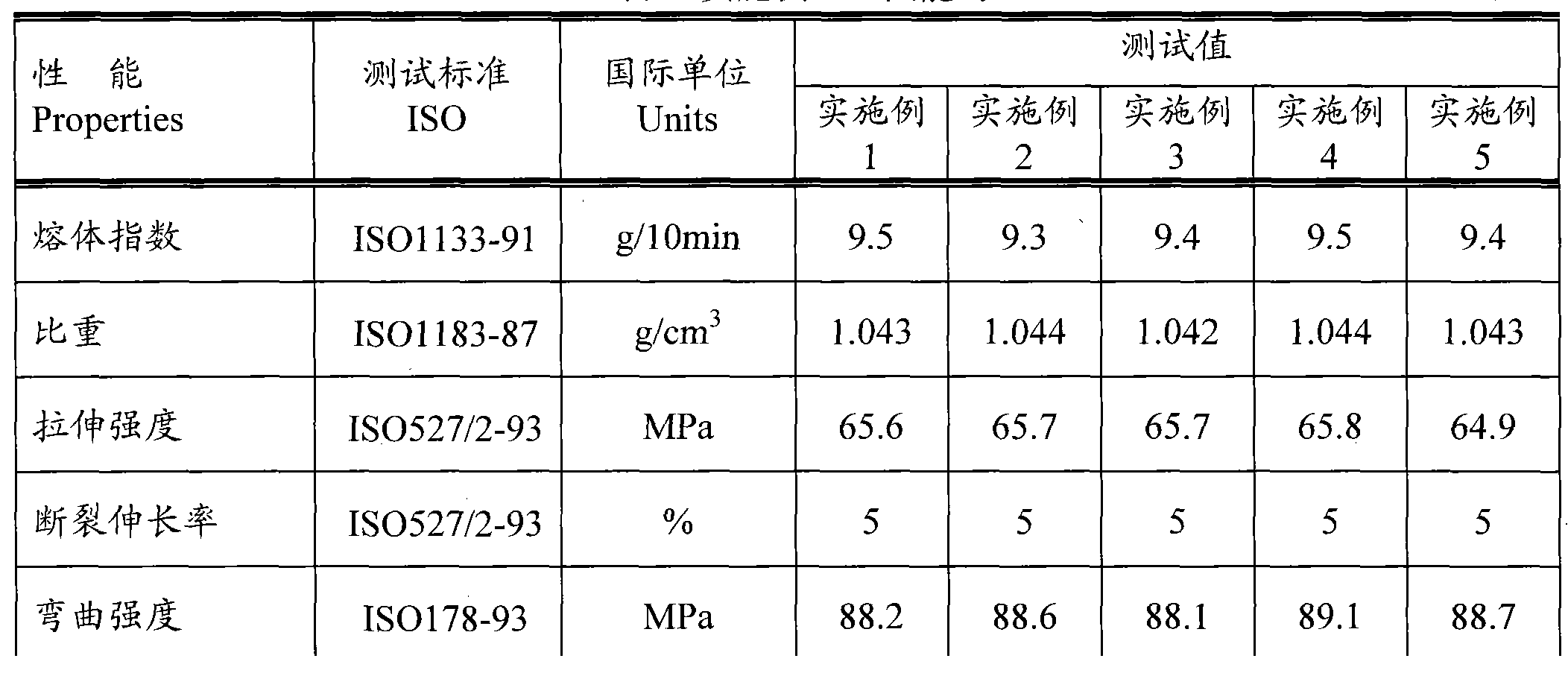
The invention discloses a glass fiber reinforced polypropylene composite material with low odor and a preparation method thereof. The glass fiber reinforced polypropylene composite material comprises the following components: 32-91% of polypropylene resin, 5-50% of glass fiber, 2-8% of compatilizer, 1-6% of odor inhibitor and 1-4% of other auxiliary agent. The reinforced polypropylene material with low odor is prepared by fusing, extruding and granulating the components through a double screw extruder under the temperature control condition of 220-240 DEG C. The odor inhibitor comprises 30-50% of ricinoleic acid zinc, 20-40% of metal oxide and 10-30% of a clay mineral system. The odor of the glass fiber reinforced polypropylene composite material can be inhibited through combining a physical method and a chemical method. The glass fiber reinforced polypropylene composite material prepared by the method has excellent odor performance; the odor level can be reduced below level 3; the physical property of the glass fiber reinforced polypropylene composite material per se is not influenced after the odor inhibitor is added; and the application field of the glass fiber reinforced polypropylene material in vehicle interior trim parts and a part of home appliance parts can be widened.
Owner:CHENGDU KINGFA SCI & TECH ADVANCED MATERIALS CO LTD +3
Elastomeric material compositions obtained from castor oil and epoxidized soybean oil
Elastomers are formed from castor oil and / or ricinoleic acid estolides and a polyester formed from an epoxidized vegetable oil such as ESO and a polycarboxylic acid such as sebacic acid, optionally in the presence of a peroxide initiator, or include crosslinked reaction products derived from ricinoleic acid or castor oil estolides, epoxy group-containing compounds such as epoxy resins and / or epoxidized vegetable oil, epoxy hardeners such as polyamine and polycarboxylic acid hardeners, thermally activated free radical initiators such as peroxides, and optionally but preferably include fillers such as limestone or wood flour. The elastomers can be prepared using a two-step, solvent-less procedure at elevated or ambient temperatures. These predominantly "all-natural" elastomers have physical properties comparable to conventional petroleum-based elastomers and composites and exhibit good flexibility, resiliency, abrasion resistance and inertness to hydrolysis. The resulting elastomers display good mechanical strength and resiliency, are resistant to abrasion and hydrolysis, and can be processed into sheet materials, which makes them attractive as floor covering components.
Owner:AFI LICENSING +1
Polyhydroxyl-compositions derived from castor oil with enhanced reactivity suitable for polyurethane-synthesis
InactiveUS6897283B2Improve hydrophobicityImprove responsePolyureas/polyurethane adhesivesPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsPolyesterPolyol
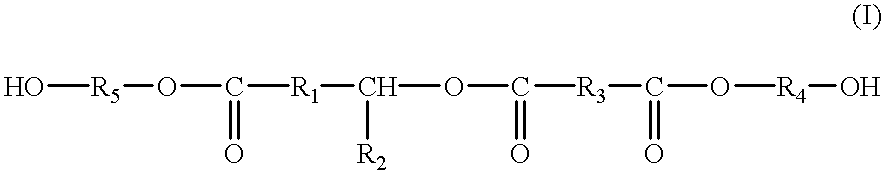
A reactive polyester polyol is described that is obtainable by half ester formation starting from at least one dicarboxylic anhydride and at least one hydroxyl group carrying, saturated or unsaturated fatty acid and / or a respective ester, in particular castor oil and / or ricinoleic acid, as well as final esterification by at least one polyol.
Owner:SIKA SCHWEIZ AG
Novel wax emulsion coating applications
Waxes prepared from hydrogenated plant oils, such as castor, palm, and soybean, are used to prepare water based emulsions. The inventive waxes, obtained from naturally derived, renewable resources, were emulsified under anionic, cationic and nonionic conditions, producing emulsions having a solids content up to about 45% solids. When used to coat fibrous cellulosic articles, such as paperboard, the emulsions' performance was similar to emulsions containing petroleum-derived waxes. The inventive waxes have a low iodine value (between 2-5), and melting points between approximately 120-200 degrees F. (Mettler Drop Point). These waxes comprise a triglyceride whose fatty acids are predominantly stearic acid or ricinoleic acid. The inventive waxes are used as an alternative to petroleum-derived, or expensive naturally-occurring waxes in the manufacture of emulsions used in coatings, polishes, adhesives, paper products, paperboard and other manufacturing operations.
Owner:MARCUS OIL & CHEM
Method and composition for neutralizing odors
InactiveUS20060228250A1Effective directional deliveryEliminate the problemFire rescueDeodrantsAir cycleNuclear chemistry
The present invention includes a composition, system and method for odor neutralization of an air circulation system or an enclosed area. The present invention includes a deodorizing composition for odor neutralization consisting essentially of from about 0.1% to about 2%, by weight of ethoxylated alkyphenol, from about 5% to about 20%, by weight of triethylene glycol, from about 25% to about 40%, by weight of ethanol, from about 1% to about 5%, by weight of ricinoleic acid, from about 3% to about 15%, by weight of water and citric acid.
Owner:RID ODOR ENTERPRISES
Method for stabilizing reduced coenzyme Q10
ActiveUS20070104701A1Stable storageIncrease residual ratioPeptide/protein ingredientsCapsule deliveryGlycerolCompound (substance)
The present invention has its object to provide a method for stabilizing reduced coenzyme Q10, which is usable as foods, functional nutritive foods, specific health foods, nutritional supplements, nutrients, animal drugs, drinks, feeds, cosmetics, medicines, remedies, preventive drugs and the like. Reduced coenzyme Q10, which is readily oxidized in the air, is stabilized by causing ascorbic acid or a related compound thereof to coexist with a polyglycerol fatty acid ester with a polymerization degree of glycerol being not lower than 3 and / or a condensed ricinoleic acid polyglyceride in a mixture of the reduced coenzyme Q10 and an oil and fat.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Wax emulsion coating applications
Owner:MARCUS OIL & CHEM
Deodorizing composition and method of forming thereof
An odor absorbing composition is provided comprising zinc salt of ricinoleic acid, a solubility promoter including sodium iminodisuccinate, water and optionally, other ingredients such as perfumes and antifungal agents or bactericides. The zinc ricinoleate can be completely solubilized in water, yet the solution will exhibit low foaming and friability. In addition, the end product may be in the form of a sprayable liquid, a thick liquid capable of clinging to a vertical surface, a gel or solid tablet, a powder, or any other form. The present invention further relates to a method for forming an odor absorbing composition comprising zinc salt of ricinoleate acid, sodium iminodisuccinate and water.
Owner:ZORBX
Suppression of carcinoma using high purity conjugated linoleic acid (CLA)
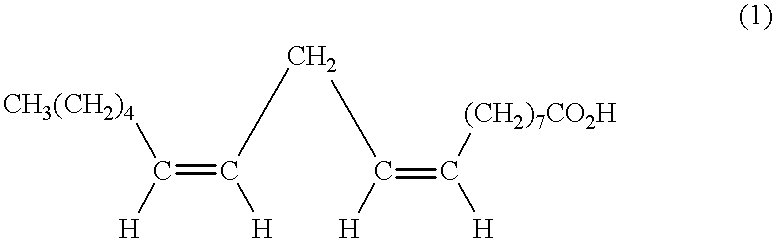
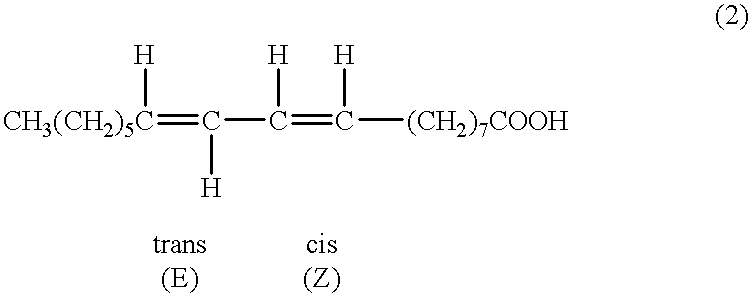
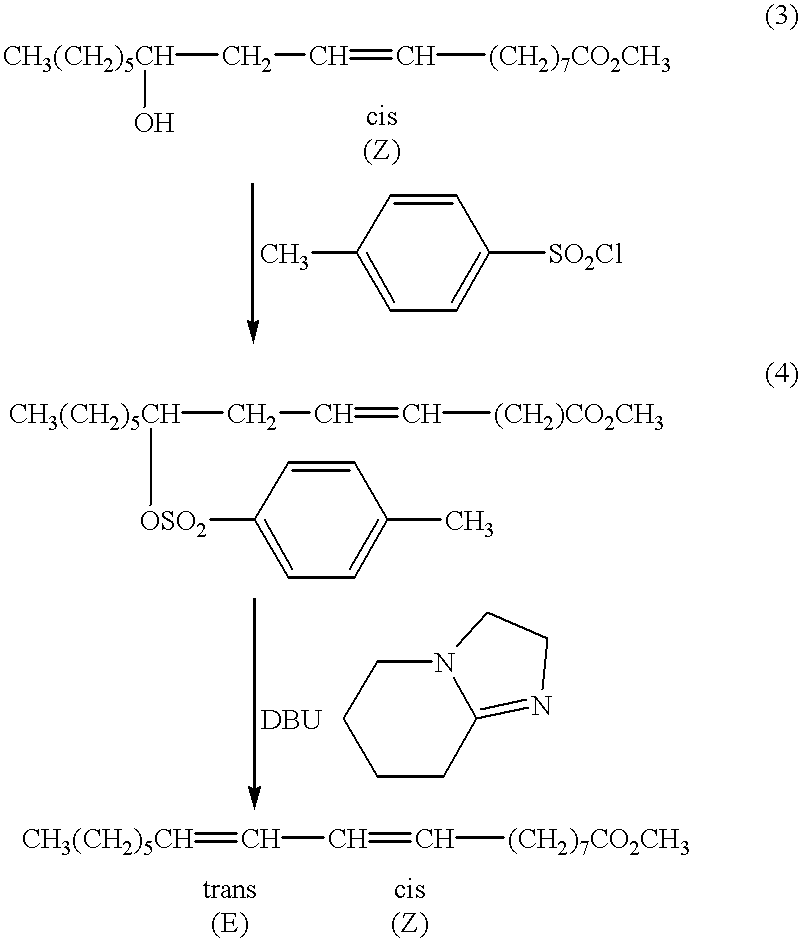
A method for the treatment of carcinoma in a human is disclosed, including administering to a human a therapeutically effective amount of 9-cis, 11-trans octadecadienoic acid formed by reacting an ester of ricinoleic acid with a tosyl chloride or a mesyl chloride to form a tosylate or mesylate of an ester of ricinoleic acid, and reacting the tosylate or mesylate of an ester of ricinoleic acid with diazabicyclo-undecene. The method includes administering to a human a purified conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) produced by a novel synthesis process for producing 9-cis, 11-trans octadecadienoic acid at room temperature in high yield including providing a tosylate or mesylate of a methyl ester of ricinoleic acid and providing a purified 9-cis, 11-trans octadecadienoic acid formed when the tosylate or mesylate reacts with diazabicyclo-undecene.
Owner:MATREYA
Castor oil-based hydrophilic chain extender as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107556452AIncrease added valueReduce environmental problemsSulfide preparationEmulsionRenewable resource
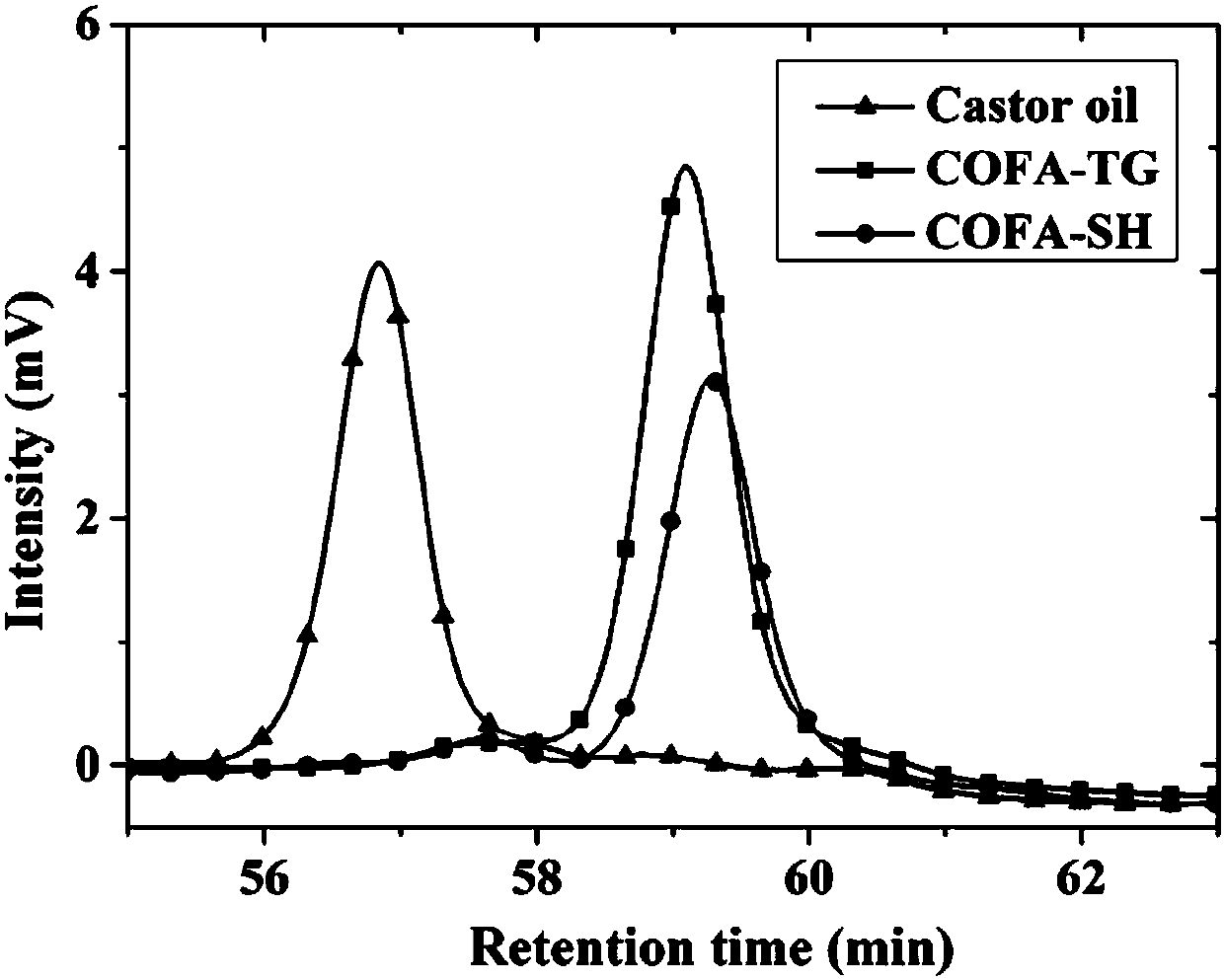
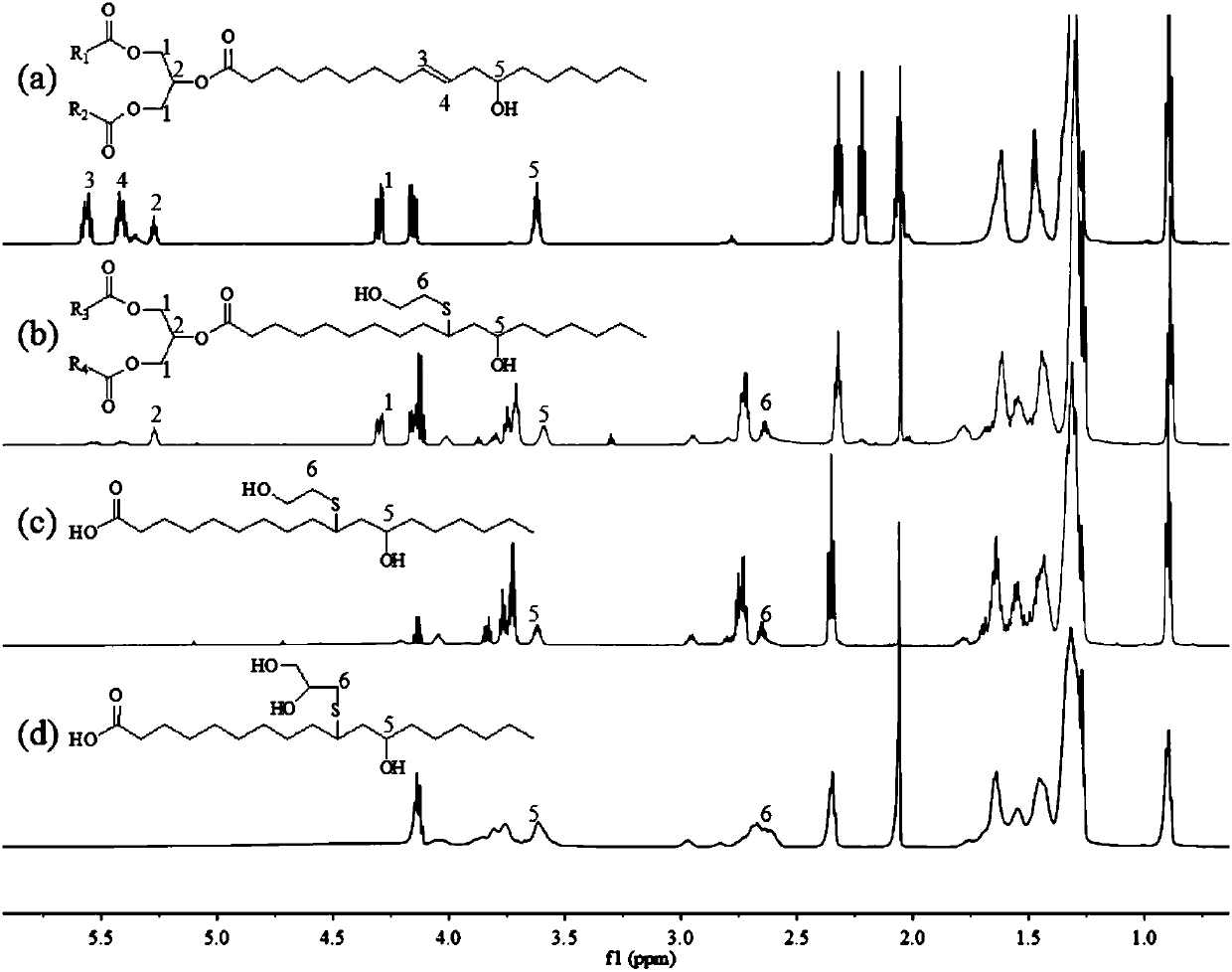
The invention discloses a castor oil-based hydrophilic chain extender as well as a preparation method and application thereof. According to the castor oil-based hydrophilic chain extender, starting from castor oil, one of the renewable resources, a hydroxyl group is introduced by mercapto group-ene light click reaction to obtain an intermediate, and then a carboxyl group is generated through hydrolysis reaction of an ester group (or ricinoleic acid is generated through ester hydrolysis reaction of castor oil first, and then the hydroxyl group is introduced by mercapto group-ene light click reaction), the hydrophilic chain extender containing at least two hydroxyl groups and a carboxyl group is prepared, and the hydrophilic chain extender is applied to preparation of anionic aqueous polyurethane emulsion. According to the castor oil-based hydrophilic chain extender as well as the preparation method and the application thereof, the castor oil is applied to hydrophilic chain extender rawmaterials, has positive reference value for broadening application and increasing added value of natural fat products and also plays a positive role in reducing or replacing an environment problem caused by the use of petroleum non-renewable resources. The castor oil-based hydrophilic chain extender prepared by the invention is liquid at normal temperature, a contact area with other raw materialsduring a reaction is larger, the mixing is more uniform and the reaction speed is higher.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
High recycle content polyester polyols
ActiveUS20160053050A1Nice appearanceDesirable functionalityPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsParticulatesPolyester
Polyester polyols made from thermoplastic polyesters are disclosed. The polyols are reaction products of a thermoplastic polyester, a glycol, and a hydrophobe selected from ricinoleic acid, ethoxylated castor oil, saturated or unsaturated C9-C18 dicarboxylic acids, tung oil, soybean oil, sunflower oil, cardanol-based products, recycled cooking oil, isostearyl alcohol, hydroxy-functional materials derived from epoxidized, ozonized, or hydroformylated fatty esters or fatty acids, and mixtures thereof. In one process, the polyols are made by reacting the thermoplastic polyester with a glycol to give a digested intermediate, which is then reacted with the hydrophobe. In another process, the thermoplastic polyester, glycol, and hydrophobe are combined and reacted in a single step. These hydrophobes facilitate the production from recycled thermoplastics of polyols that have good transparency and little or no particulate settling or phase separation. High-recycle-content polyols having desirable properties and attributes for formulating polyurethane products, including aqueous polyurethane dispersions, can be made. The polyols provide a sustainable alternative to bio- or petrochemical-based polyols.
Owner:RESINATE MATERIALS GRP
Demoulding agent used for precast concrete component and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104403768AExtended storage timeDoes not affect the surfaceLubricant compositionPalmitoleic acidPrecast concrete
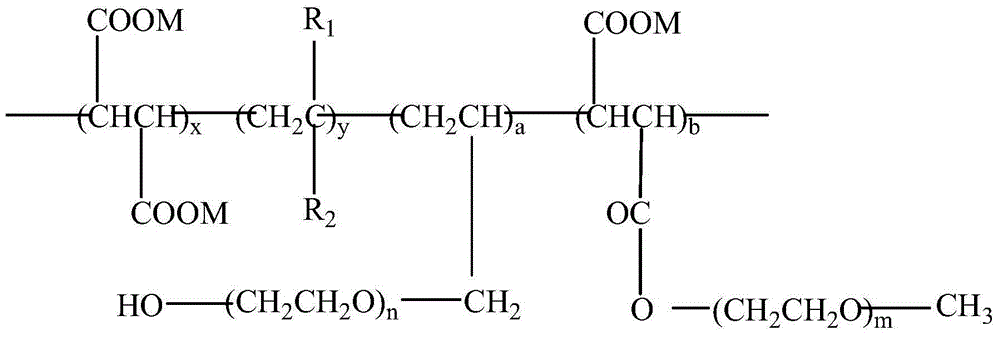
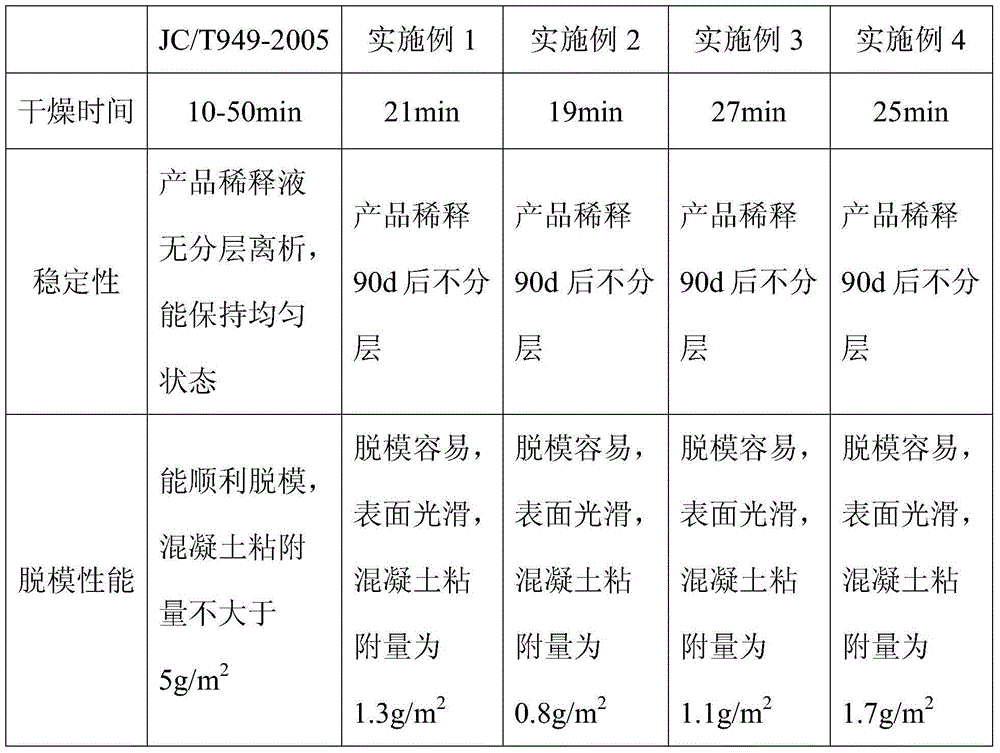
The invention discloses a demoulding agent used for precast concrete components. The demoulding agent includes following raw materials, by weight, 10-30 parts of an unsaturated fatty acid, 5-20 parts of an oily density adjusting agent and an aqueous density adjusting agent, 1-5 parts of an oily emulsifier, 1-5 parts of an aqueous emulsifier, 0.1-4 parts of an emulsification additive, 0.1-2 parts of a defoaming agent, 0.1-2 parts of an anti-rust agent, 1-5 parts of a settling-resistant and thickening thixotropic agent and 40-65 parts of water. The unsaturated fatty acid is oleinic acid, palmitoleic acid or ricinoleic acid. The emulsification additive has a structure formula represented as follows, wherein R1 is H or CH3, R2 is CONH2, CH2SO3Na or COOM, the x, the y, the a and the b are linking numbers of a copolymer repetitive unit and are ranged from 1 to 10, the m and the n are addition mole average numbers and are ranged from 10-50, wherein M is a hydrogen atom, a monovalent metal ion, an amino group or an organic ammonium group. The demoulding agent is low in cost, is free of generation of oil contamination, is long in storage time, is not liable to decay, deteriorate and layer, and is free of influence on surface and internal quality of concrete.
Owner:KZJ NEW MATERIALS GROUP CO LTD +1
Process for changing phenolic nitrate effluent into useful material by extracting, evaporating, crystallizing and coupling
InactiveCN101654305ASolve bottlenecksSolve the miscibility problemEvaporationSolution crystallizationPhenolSodium sulfate
The invention discloses a process for changing phenolic nitrate effluent into useful material by extracting, evaporating, crystallizing and coupling, belonging to the field of changing waste water into useful materials. The process comprises the steps of pre-treating waste water, extracting phenol, performing triple effect evaporation and recycling sodium sulfate. Phenol is extracted with ricinoleic acid and is recycled, so the industrial usage of the phenol is decreased. The oil-water mutual solving problem is efficiently solved by utilizing the salting-out effect of the sodium sulfate highlycontained in the waste water. By adopting triple effect evaporation of counter-current operation under a basic condition, the phenol is efficiently prevented from secondarily returning into air, so the phenol contained in the treated waste water is less than 0.5mg / l and can be used as the scouring water for preparing process or can be directly discharged. The by-product sodium sulfate solid is efficiently recycled and the purity of the sodium sulfate is above 99.9%. The produced sodium sulfate makes up for the steam consumption during the evaporation process. Furthermore, the process has theadvantages of low treating cost, economic benefit and obvious environmental benefit.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Preparations with deodorizing action comprising the zinc salt of ricinoleic acid and at least one amino functional amine acid
ActiveUS7226584B2Good water solubilityImprove solubilityCosmetic preparationsOrganic detergent compounding agentsOrganic acidSolubility
Preparations with deodorizing action are provided. The preparations include the zinc salt of ricinoleic acid; amino-functional amino acids; solubility promoters; organic and / or inorganic acids; and, optionally, water.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Polymeric formulations for drug delivery
Poly(ester-anhydrides) or polyesters formed from ricinoleic acid and natural fatty diacids and their method of preparation and its use for delivering bioactive agents including small drug molecules, peptides and proteins, DNA and DNA complexes with cationic lipids or polymers or nano and microparticles loaded with bioactive agents are disclosed herein. The drug delivery compositions are administered to a patient in a liquid form, increase in viscosity in vivo to form a drug depot or implant, and are able to release the incorporated bioactive agent for weeks. In the preferred embodiment, the drug delivery formulations are administered by injection. In one embodiment, the compositions are suitable for local or regional delivery of drugs to diseased sites, such as treating solid tumors and bone infections. In a preferred embodiment, the drug delivery compositions are suitable for site-specific chemotherapy for the treatment of solid tumors including: squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) of the head and neck, prostate cancer, and sarcomas for intratumoral injection or insertion.
Owner:EFRAT BIOPOLYMERS LTD
Diesel anti-wear agent
InactiveCN102965174AImprove the lubrication effectChange the problem of cloggingLiquid carbonaceous fuelsFuel additivesRefluxMonoglyceride
The invention discloses a diesel anti-wear agent. The diesel anti-wear agent is prepared by taking ricinoleic acid, propanetriol and solvent oil as raw materials. A preparation method of the diesel anti-wear agent disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: (1) preparing ricinoleic acid monoglyceride: firstly adding the ricinoleic acid and the propanetriol into a reaction kettle, further adding the solvent oil, adding a catalyst for performing esterification reaction, stirring, increasing the temperature to 160-180 DEG C, removing water for 5-6h under a reflux state, washing a generated material with the water for removing the acidic catalyst after the end of the esterification reaction, and finally performing decompression distillation to dehydrate the material so as to get the ricinoleic acid monoglyceride; and (2) compounding: firstly adding ricinoleic acid into the reaction kettle, increasing the temperature to 100-110 DEG C, keeping for 1h, removing the water, then cooling to below 50 DEG C, adding ricinoleic acid monoglyceride, and uniformly stirring to get the diesel anti-wear agent. The diesel anti-wear agent disclosed by the invention has the advantages of reducing the emission of harmful substances, protecting an environment and greatly improving the lubricating performance of diesel.
Owner:江苏汉光实业股份有限公司
Botanical pesticide for vegetable root knot nematodes
InactiveCN102613212AEfficient killingInhibition is effectiveBiocideNematocidesAdditive ingredientBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The invention discloses a botanical pesticide for vegetable root knot nematodes, which comprises, by weight, tea saponin 30-35 parts, nicotine 16-20 parts, ricinoleic acid 20-30 parts and brucine12-18 parts. The botanical pesticide uses the tea saponin as a main active ingredient and uses the nicotine, the ricinoleic acid and the brucine1 as auxiliary ingredients and can effectively kill and restrain target nematodes.
Owner:袁为祥
Benzothiazole ionic liquid and preparation method as well as application thereof
ActiveCN105461654AHigh activityHigh catalytic efficiencyOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsOrganic synthesisPhosphoric acid
The invention discloses benzothiazole ionic liquid and a preparation method as well as application thereof. The preparation method of the benzothiazole ionic liquid comprises the steps of reacting benzothiazole and acid containing target anions, with equal molar weight, under a low temperature condition, and preparing corresponding benzothiazole salt ionic liquid, wherein the acid containing the target anions is one of sulfuric acid, phosphoric acid, perchloric acid and nitric acid. The benzothiazole ionic liquid can serve as a mild, special and efficient catalyst of a specific organic synthesis reaction, and is convenient to recover and reuse circularly and capable of effectively alleviating corrosion to equipment, and the production cost is lowered. In a ricinoleic acid dihydric alcohol ether ester preparation process, by adopting the benzothiazole salt ionic liquid as the catalyst, the catalytic efficiency is high, the catalyst and a product are easy to separate, the synthetic product is high in purity, the posttreatment is simple, the generation of a great amount of wastewater due to catalyst treatment is avoided, and the environmental pollution is reduced.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV +1
Disposable medical supplies from hydrolytically biodegradable plastics
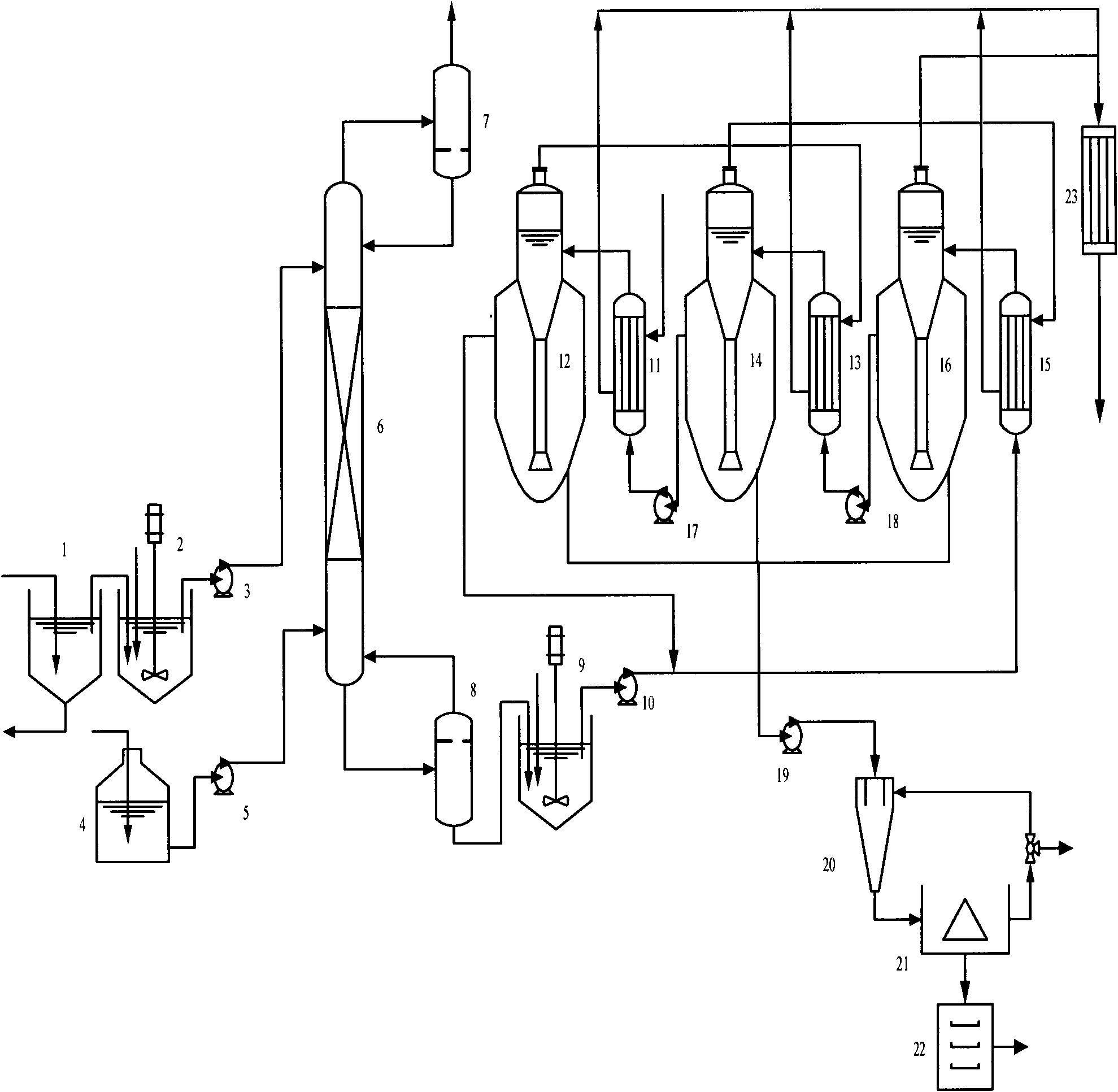
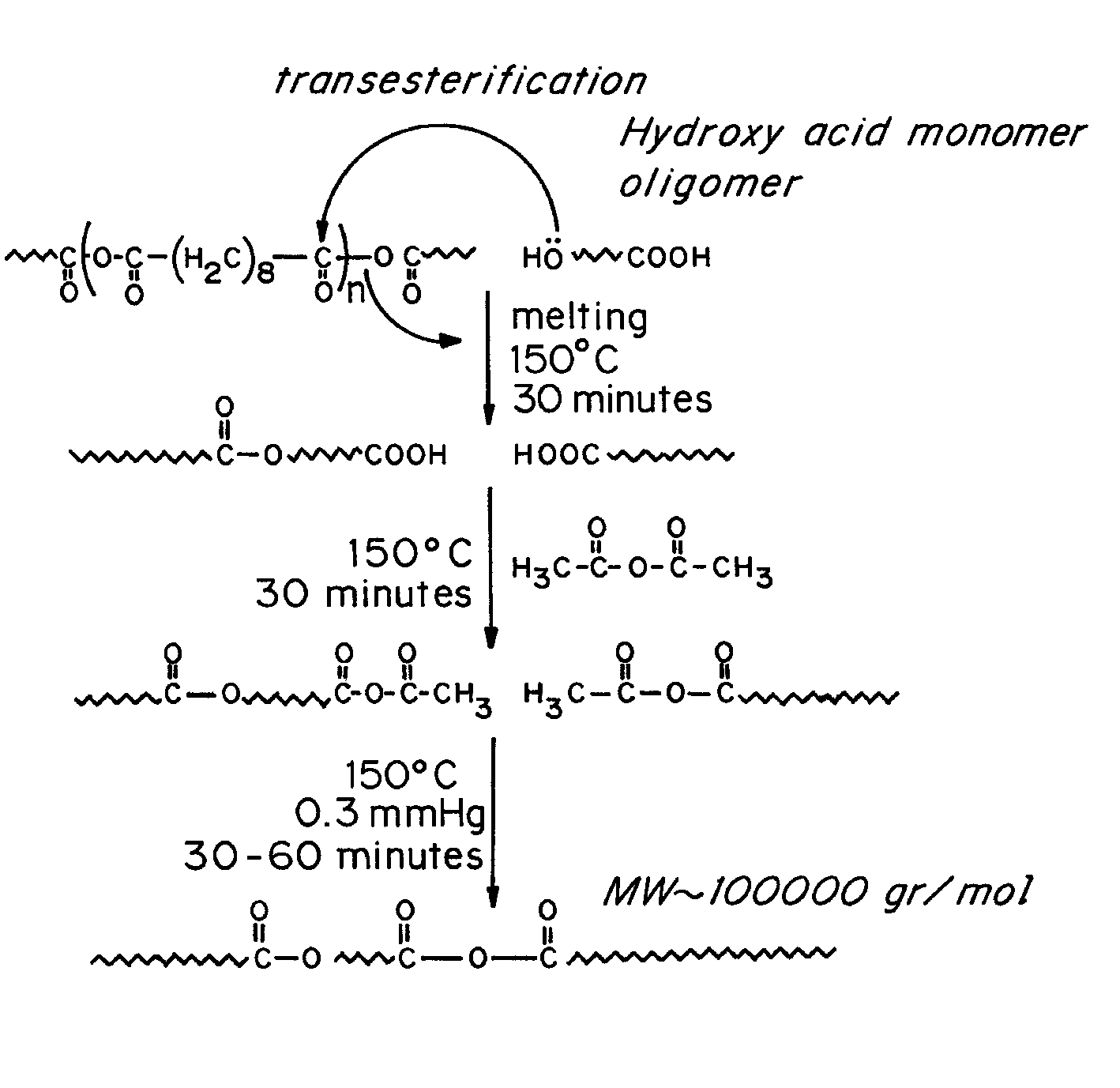
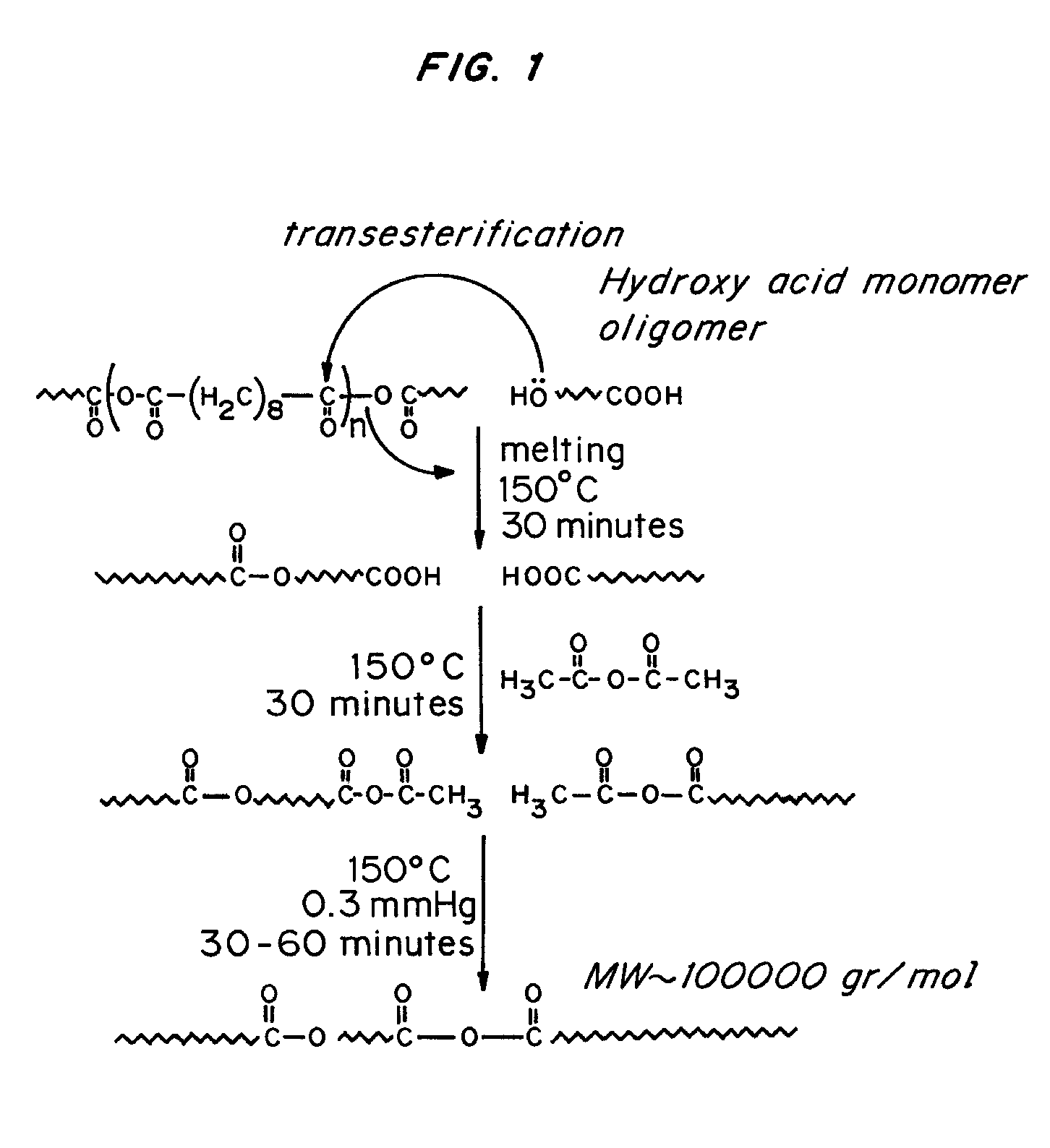
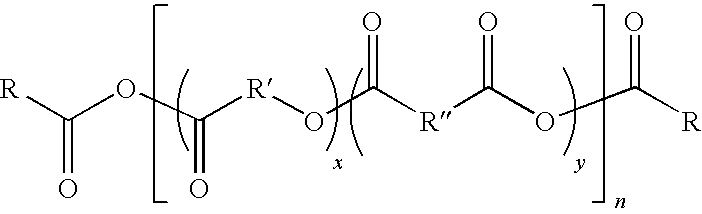
InactiveUS8143368B2Improve compatibilityReduce the possibilityEngine sealsSynthetic resin layered productsPolyesterFatty acid
Hydrolytically degradable polymers in the form of biodegradable disposable medical devices for use in medicine and laboratories such as syringes, test tubes, catheters, tubing, trays, medical fabrics, and gloves are described. The devices are formed in whole or in part of a hydrolytically degradable polymer. In the preferred embodiment, the devices or structural components thereof degrade in a period of weeks to months, preferably within a year and more preferably within six months of exposure to aqueous solutions. Conventional hydrolytically degradable polymers may be utilized or these may be modified to increase mechanical or processing characteristics, for example, using a polyfunctional branching agent and / or a chain extending agent. In one embodiment, the hydrolytically degradable polymer is a member of a new class of polyesters comprising an aliphatic dicarboxylic acid, an aliphatic diol and optionally, one or more bifunctional fatty acids such as ricinoleic acid and / or castor oil. The devices are prepared using standard techniques, such as by injection molding, extrusion or melt spinning. The devices can be formed entirely of the degradable polymer, or they can be coated with a polymer coating in order to increase the compatibility of and reduce the possibility for interaction between the surface of the device and liquids that may come in contact with the device, or they may include core or other internal structural member formed of either the biodegradable or non-biodegradable material.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Tooth whitening compositions and delivery systems therefor
Stain-removing oral compositions, such as gum compositions are herein provided. The compositions include an orally acceptable carrier and a stain-removing anionic surfactant. The surfactant includes a fatty acid salt having at least one hydroxyl functionality. The fatty acid salt may be a salt of ricinoleic acid, and may be combined with a chelating agent and / or an abrasive. The chelating agent may be a polyphosphate and the abrasive may be a silica abrasive.
Owner:INTERCONTINENTAL GREAT BRANDS LLC
Water-based metal cutting fluid suitable for soft water
InactiveCN103045335ASpeed up foam releaseImprove stabilityLubricant compositionWater basedSoft water
The invention discloses a water-based metal cutting fluid suitable for soft water. The water-based metal cutting fluid comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 20-45% of base oil, 5-15% of modified polymerized ricinoleic acid, 0.5-5% of non-ionic surfactant, 5-15% of anionic surfactant, 5-15% of synthetic ester, 1-6% of coupling agent, 1-5% of additive and water in balancing amount. According to the invention, as the special molecular structure of the modified polymerized ricinoleic acid is skillfully utilized in the formula of the cutting fluid, the bubble releasing speed of the cutting fluid in the soft water is effectively increased, and the stability and lubricating property of the cutting fluid are greatly improved.
Owner:QUAKER CHEM CHINA
Thermoplastic powder coating
InactiveCN103740181AReduce surface temperatureEasy to usePolyurea/polyurethane coatingsPowdery paintsAluminateCooling effect
The invention discloses a thermoplastic powder coating. The thermoplastic powder coating is composed of following raw materials in parts by weight: 90-94 parts of polyethylene E309, 6-10 parts of thermoplastic polyurethane elastomer, 1-2 parts of perfluor-butyl potassium sulphonate, 0.2-0.4 part of tetramethyl thiuram disulfide, 0.4-1 part of N,N-diethyl aniline, 1-2 parts of ricinoleic acid, 1-2 parts of 1-ethoxyl-2-oleic imidazoline, 0.5-1 part of distearoyl isopropoxy aluminate, 2-4 parts of guar gum, 10-14 parts of epoxy soybean oil and 15-20 parts of modified fillers. The powder coating provided by the invention is particularly suitable for heat radiation coating of an LED (Light Emitting Diode) lamp and is convenient to use; the surface temperatures of a heat radiation cup, an aluminum substrate, a lamp cover and the like of the LED lamp so that the cooling effect is realized.
Owner:WUHU BAOYI AMUSEMENT EQUIP
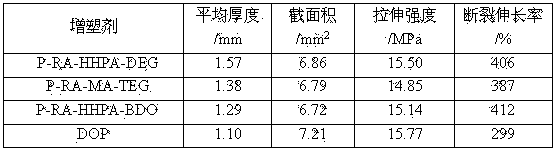
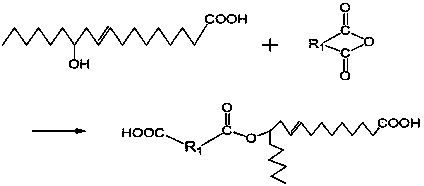
Method for preparing caster oil-based polyester serving as PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) plasticizer
The invention discloses a method for preparing caster oil-based polyester serving as a PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) plasticizer, belonging to the technical field of chemical synthesis. The method comprises the following steps: preparing caster oil-based dicarboxylic acid by reacting a down-stream product, namely, ricinoleic acid of low-price bio-based raw caster oil, dihydric anhydride and dihydric alcohol serving as raw materials in two steps: preparing caster oil-based dicarboxylic acid by using ricinoleic acid and dihydric anhydride, and carrying out a polyesterification reaction on the caster oil-based dicarboxylic acid and the dihydric alcohol in the coexistence of a catalyst and a water-carrying agent; and distilling under reduced pressure to obtain the caster oil-based polyester PVC plasticizer. A PVC plastic test piece is prepared by treating the caster oil-based polyester PVC plasticizer, PVC resin and a thermal stabilizer according to a certain formula through a solvent film casting method. The test piece is soft, and is equivalent to a PVC plastic piece plasticized by dioctyl phthalate (DOP) in the transparency under the same condition. The raw material is caster oil-based, recyclable, low in price and independent of petroleum, a preparation process is simple, and three wastes are not produced. The product is non-toxic, environment-friendly, resistant to migration, and superior in plasticizing performance, and has a good application prospect.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for Making Tire with Black Sidewall and Tire Made by the Method
The present invention is directed to a method for maintaining the black sidewall appearance of a tire, comprising the step of fabricating the tire with a rubber sidewall compound comprising 100 parts by weight of at least one diene based rubber; from 10 to 70 parts by weight, per 100 parts by weight of diene based rubber (phr) of a rubber process oil selected from the group consisting of aromatic, paraffinic, naphthenic, vegetable oils other than castor oil, and low PCA oils including MES, TDAE, SRAE and heavy naphthenic oils; and from 0.5 to 3 parts by weight, per 100 parts by weight of diene based rubber (phr) of a triglyceride derived from fatty acids comprising at least 80 percent by weight of at least one of ricinoleic acid and 12-hydroxy stearic acid.
Owner:JUNG MANFRED JOSEF +6
High-strength printed circuit board conductive silver paste and preparing method thereof
ActiveCN103985431ALow melting pointImprove thermal conductivityNon-conductive material with dispersed conductive materialCable/conductor manufacturePrinted circuit boardDimethyl benzene
High-strength printed circuit board conductive silver paste is composed of, by weight, 6-8 parts of nanoscale spherical silver powder, 6-8 parts of nanoscale sheet-shaped silver powder, 30-40 parts of micron-order spherical silver powder, 30-40 parts of micron-order sheet-shaped silver powder, 4-6 parts of ethylene glycol, 1-2 parts of ricinoleic acid, 0.5-1 part of ole-monoethanolamine, 8-10 parts of glass powder, 0.2-0.3 part of polyethylene wax, 4-7 parts of butyl alcohol, 4-6 parts of acetone, 3-5 parts of menthol, 0.3-0.6 part of triethanolamine, 5-8 parts of xylene and 4-6 parts of calcium sulfate whiskers. According to the high-strength printed circuit board conductive silver paste, the silver powder with different grain diameters and different shapes is matched so that the good conductivity can be achieved; the glass powder is used, so that the fusion point is low, the thermal expansivity is low, and the performance of a circuit is stable; the calcium sulfate whiskers are added, so that the strength of the circuit is high and the circuit is resistant to abrasion, not prone to breakage and durable.
Owner:CHIZHOU HUASHUO ELECTRONICS TECH
Environmentally friendly cutting fluid containing graphene and preparation method therefor
InactiveCN103710123AImprove the lubrication effectImprove anti-wear performanceLubricant compositionSolventMonomer
Provided is a environmentally friendly cutting fluid containing graphene. The cutting fluid is prepared from the following raw materials, by weight, 2-3 parts of graphene, 1-2 parts of silane coupling agent KH-550, 3-4 parts of vinyl acetate, 4-5 parts of dibutyl phosphate, 10-12 parts of drainage oil, 13-15 parts of propylene glycol, 2-3 parts of zirconium fluoride, 3-4 parts of ricinoleic acid, 1-2 parts of polyoxyethylene octylphenol ether, 1-2 parts of sodium butylnaphthalenesulfonate, 6-8 parts of auxiliary agents and 200 parts of water. Through application of graphene and zirconium fluoride, the lubricating property and abrasion resistance of the cutting fluid are enhanced greatly, and the service life of the cutting fluid is prolonged. Through application of drainage oil, the lubricating property is raised, and the cutting fluid is beneficial for environmental protection. Through application of surfactants, high-molecular monomers, solvents and coupling agents, the cutting fluid is advantaged by stable emulsification and no sedimentation.
Owner:MAANSHAN HENGYI MACHINERY MFG
Finishing process of quilt cover fabric
InactiveCN104452286AImprove wrinkle resistanceImprove antibacterial propertiesFibre treatmentWrinkle skinSodium sulfate
The invention discloses a finishing process of a quilt cover fabric. The finishing process comprises the following steps of (1) adding 1.1 parts by mass of chitosan, 1.4 parts by mass of calcium hydrogen carbonate and 2.6 parts by mass of dodecyl trimethyl ammonium chloride to 14.7 parts by mass of deionized water, and uniformly stirring; (2) then sequentially adding 2.5 parts by mass of magnesium chloride and 1.3 parts by mass of ricinoleic acid butyl ester sodium sulfate, and continuously stirring till sufficient and uniform mixing is achieved to prepare finishing liquid; and (3) carrying out dipping treatment on the quilt cover fabric in the finishing liquid, and drying at constant temperature. The quilt cover fabric finished by adopting the finishing process of the quilt cover fabric has the advantages of washing resistance and excellent wrinkle-resistant property and anti-bacterial property.
Owner:CHANGSHU HUABO WOOLEN TEXTILE
Organic nitrogen molybdenum fullerene lubricant and preparing method thereof
ActiveCN105018186AImprove the lubrication effectImprove wear resistanceAdditivesSolubilityAntioxidant
The invention discloses organic nitrogen molybdenum fullerene lubricant and a preparing method thereof. The lubricant is prepared through polarity modification fullerene C60, succinamide and sulfur-and-phosphorus-free organic molybdenum, wherein the weight ratio of the polarity modification fullerene C60 to the succinamide to the sulfur-and-phosphorus-free organic molybdenum is 1 to 5-8 to 30-35. The polarity modification fullerene C60 is prepared through fullerene C60, concentrated nitric acid, concentrated hydrochloric acid and ricinoleic acid in a reacted mode. The additive is the organic nitrogen molybdenum fullerene lubricant, serves as friction improving agent, antiwear agent and antioxidant of lubricating oil and particularly serves as friction improving agent, antiwear agent and antioxidant of lubricating oil for internal combustion engines, and the oil saving effect is remarkable; as sulfur, phosphorus and chlorine are free, the additive further has the advantages that energy is saved, and the environment is protected; the production method is simple, cost is low, the oil solubility is good, and productivity is high.
Owner:华亿金卫(杭州)能源有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com