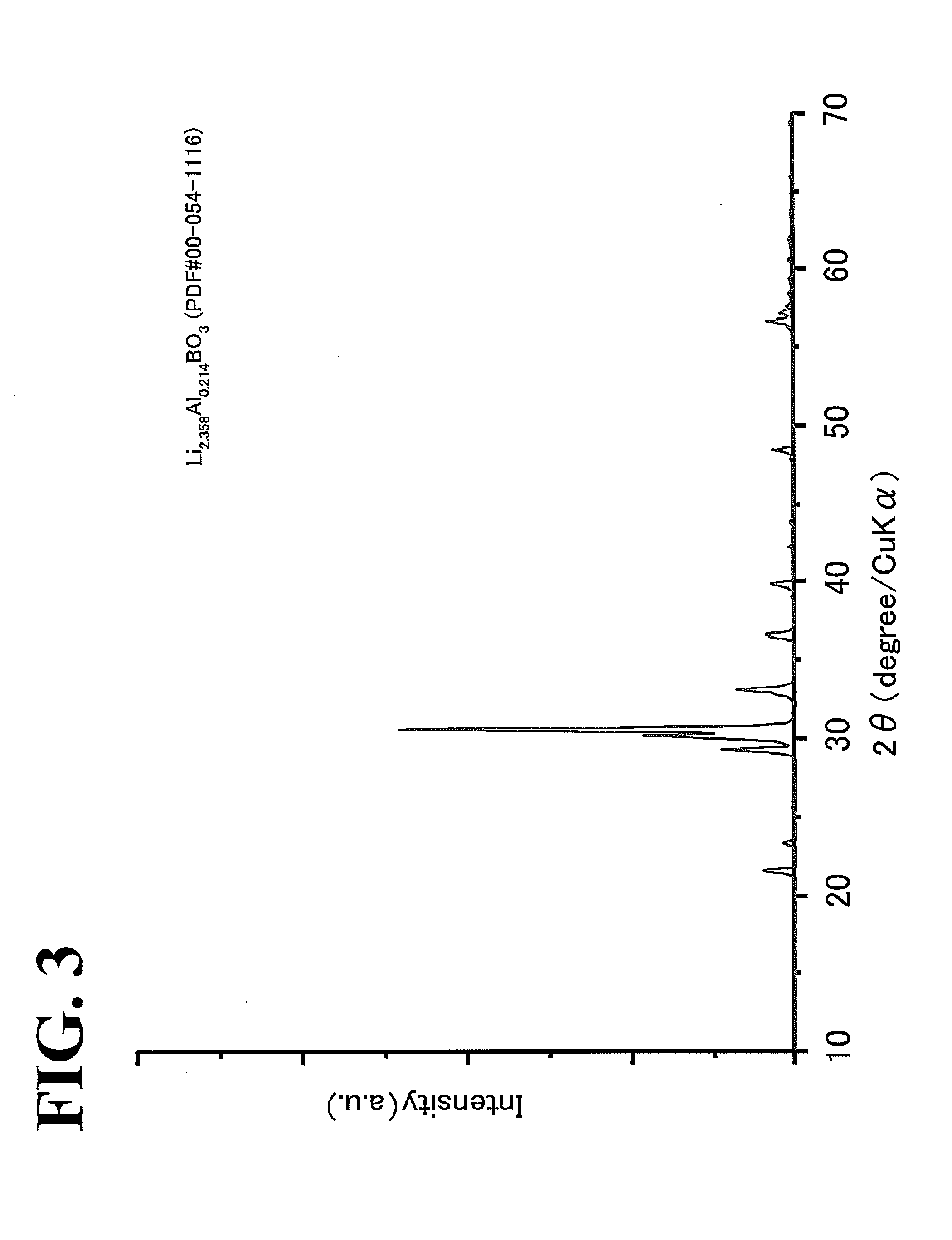
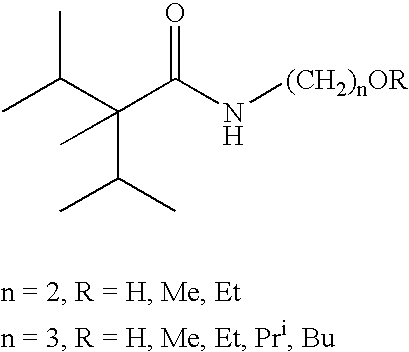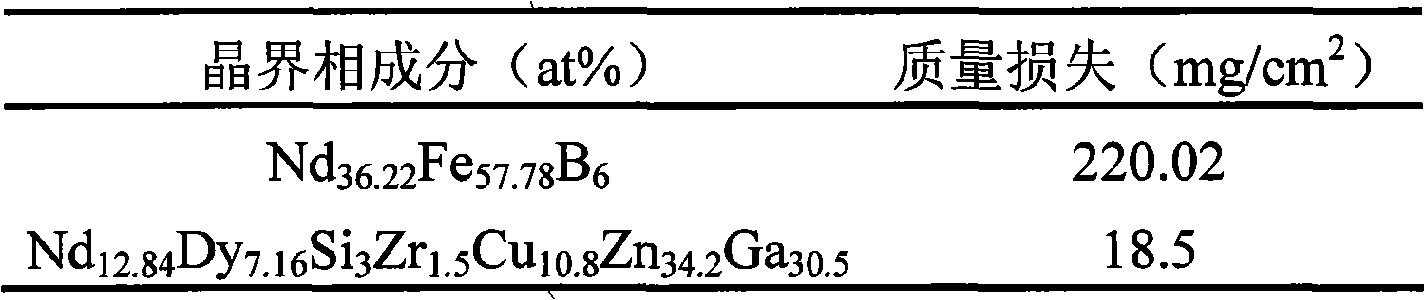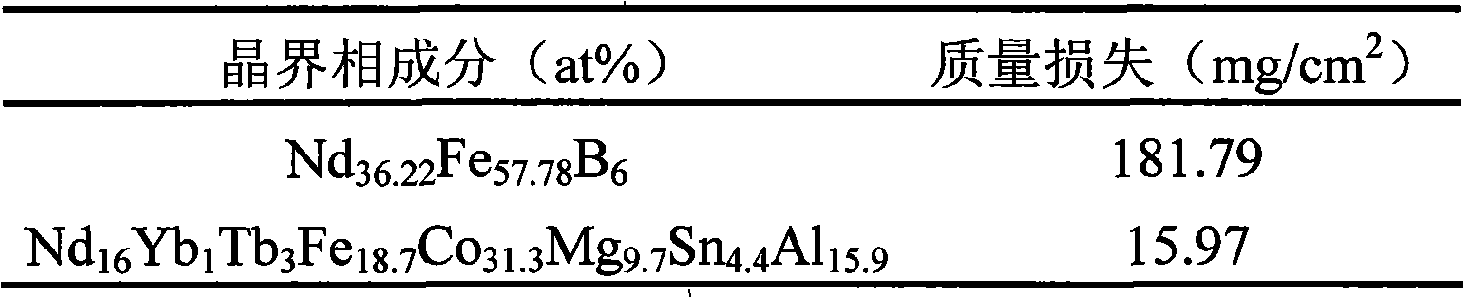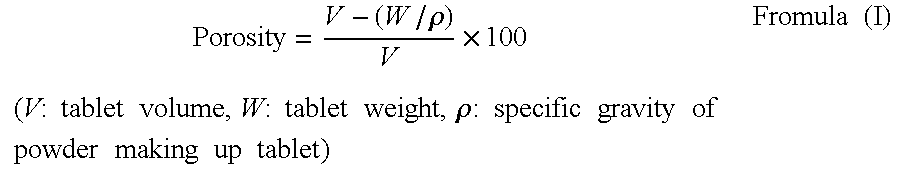Patents
Literature
6093results about How to "Low melting point" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
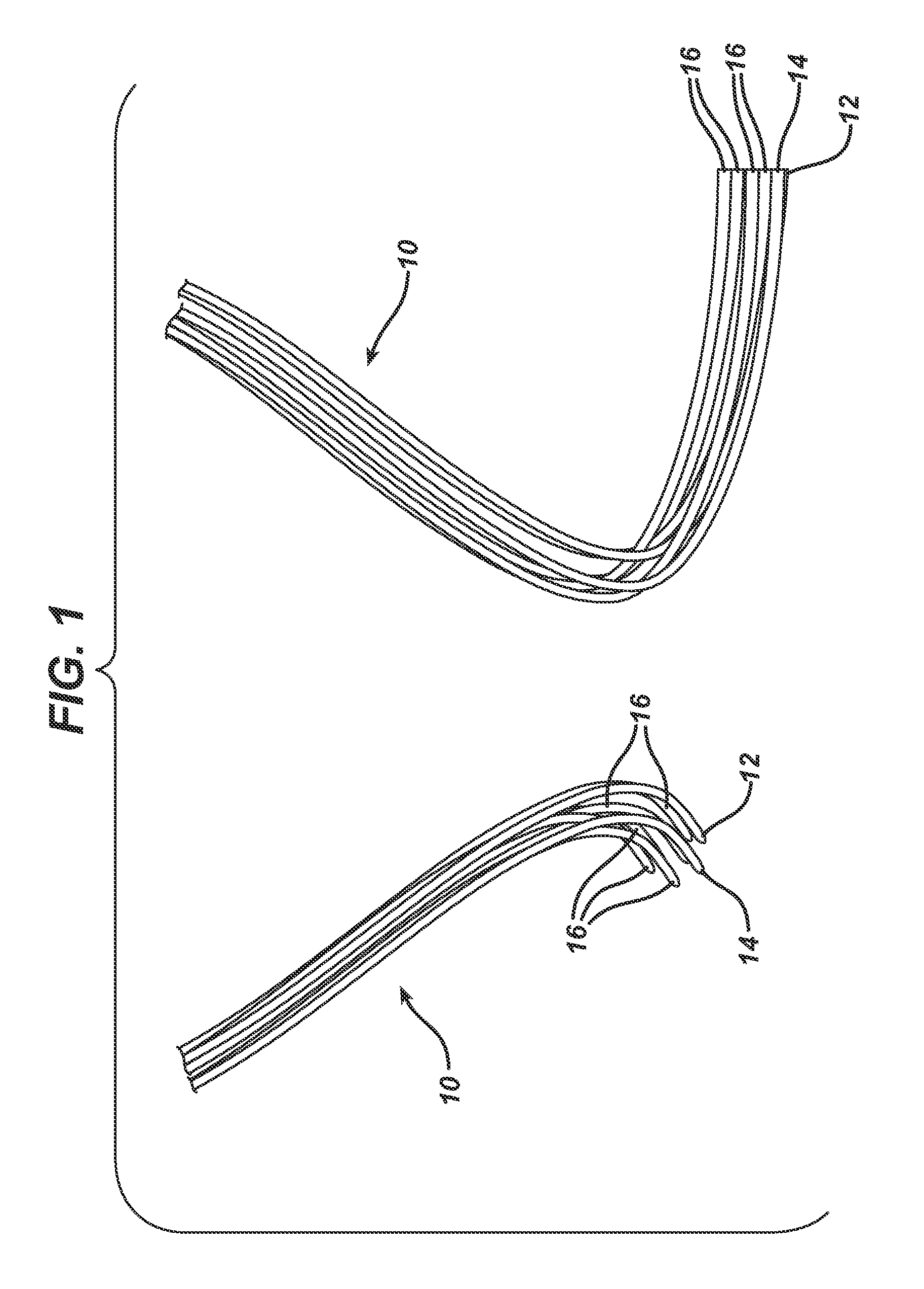
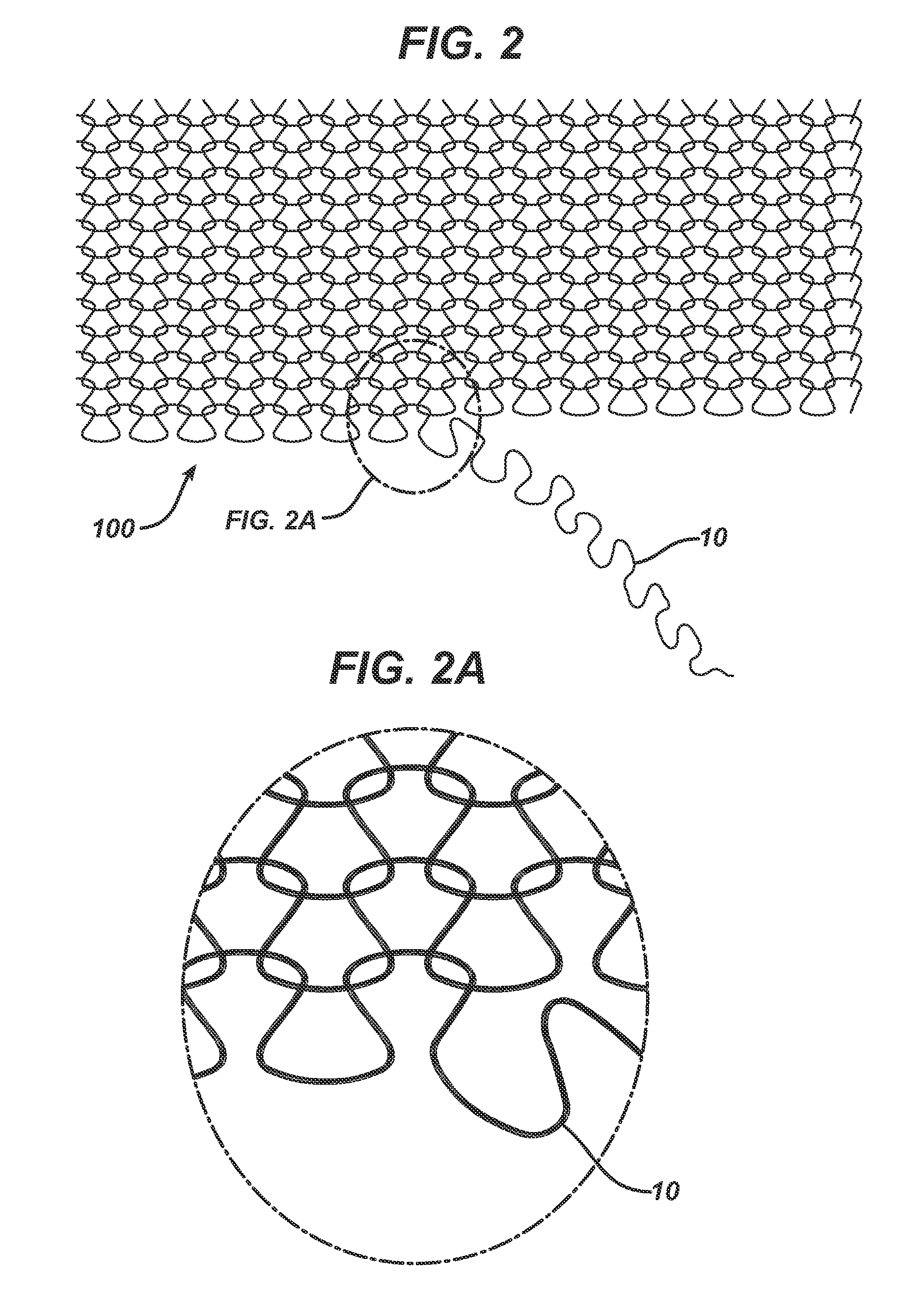
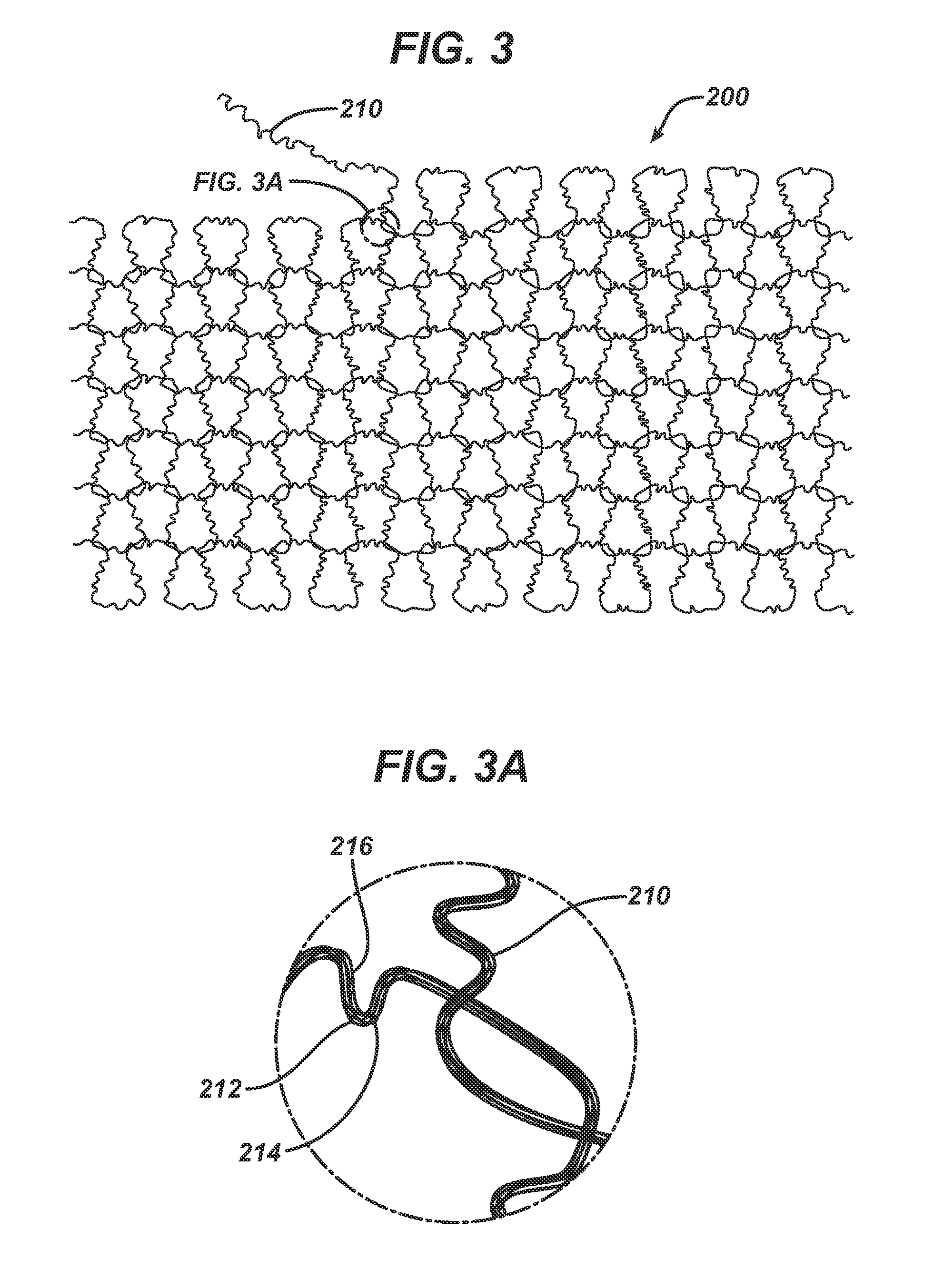
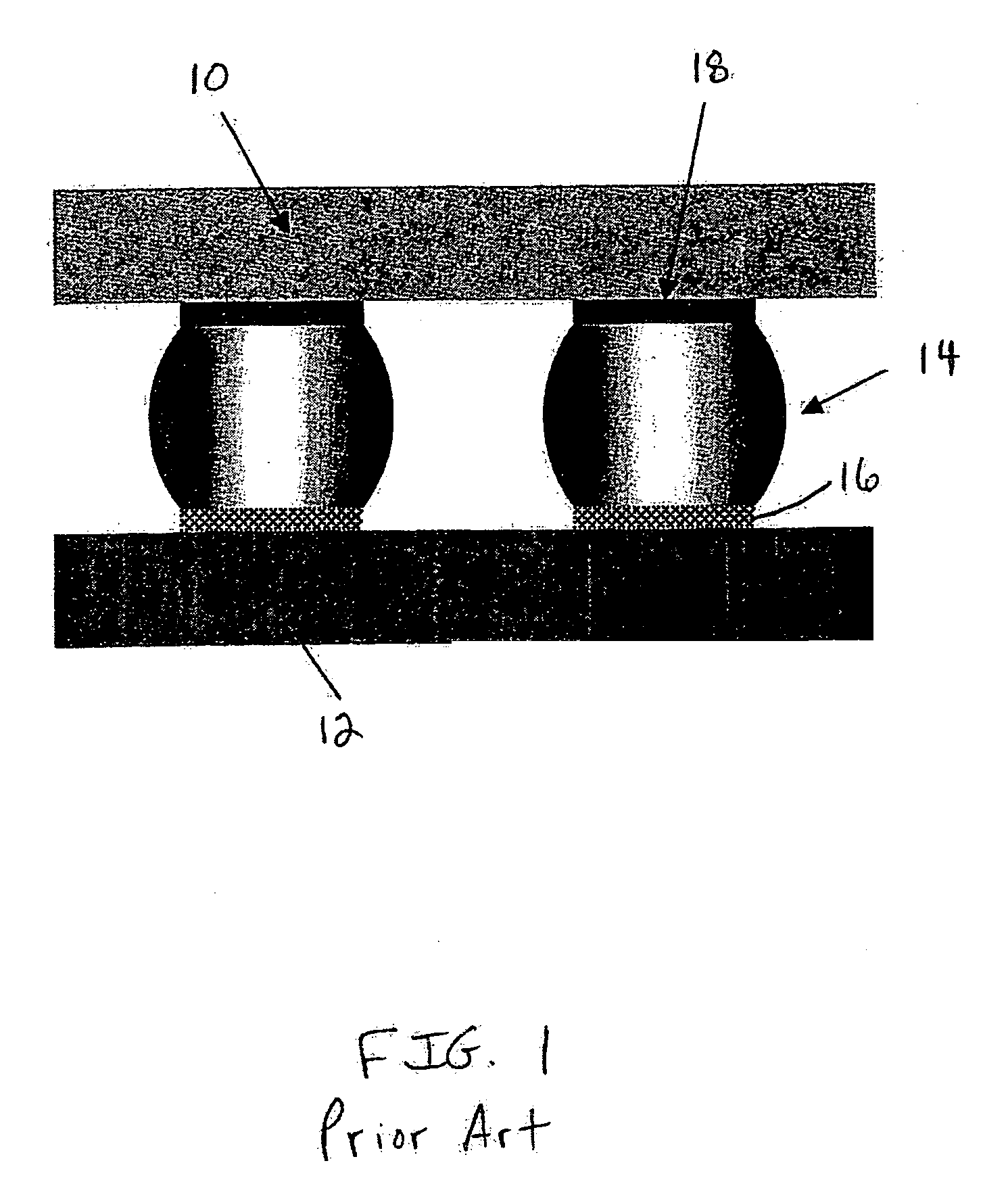
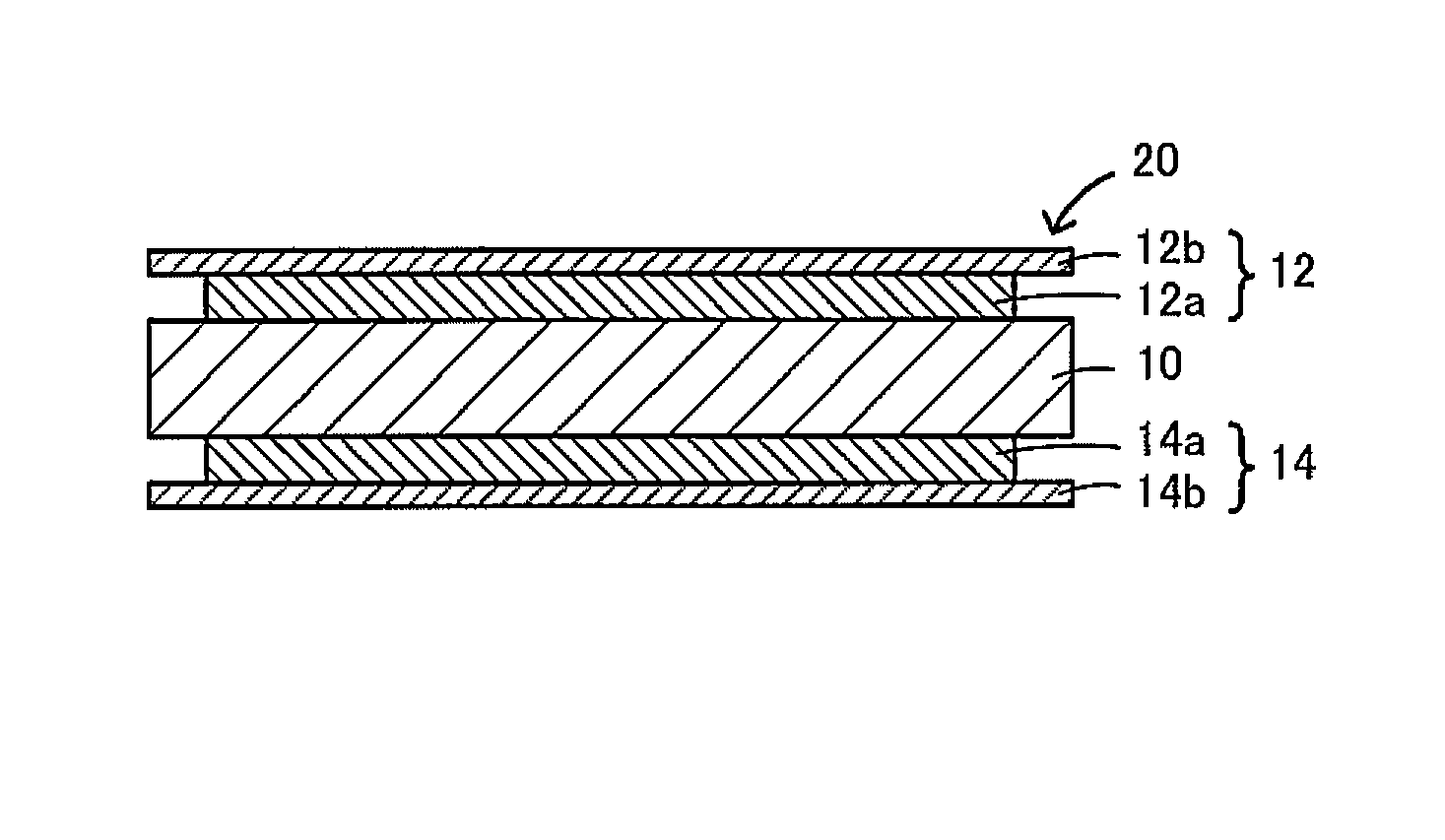
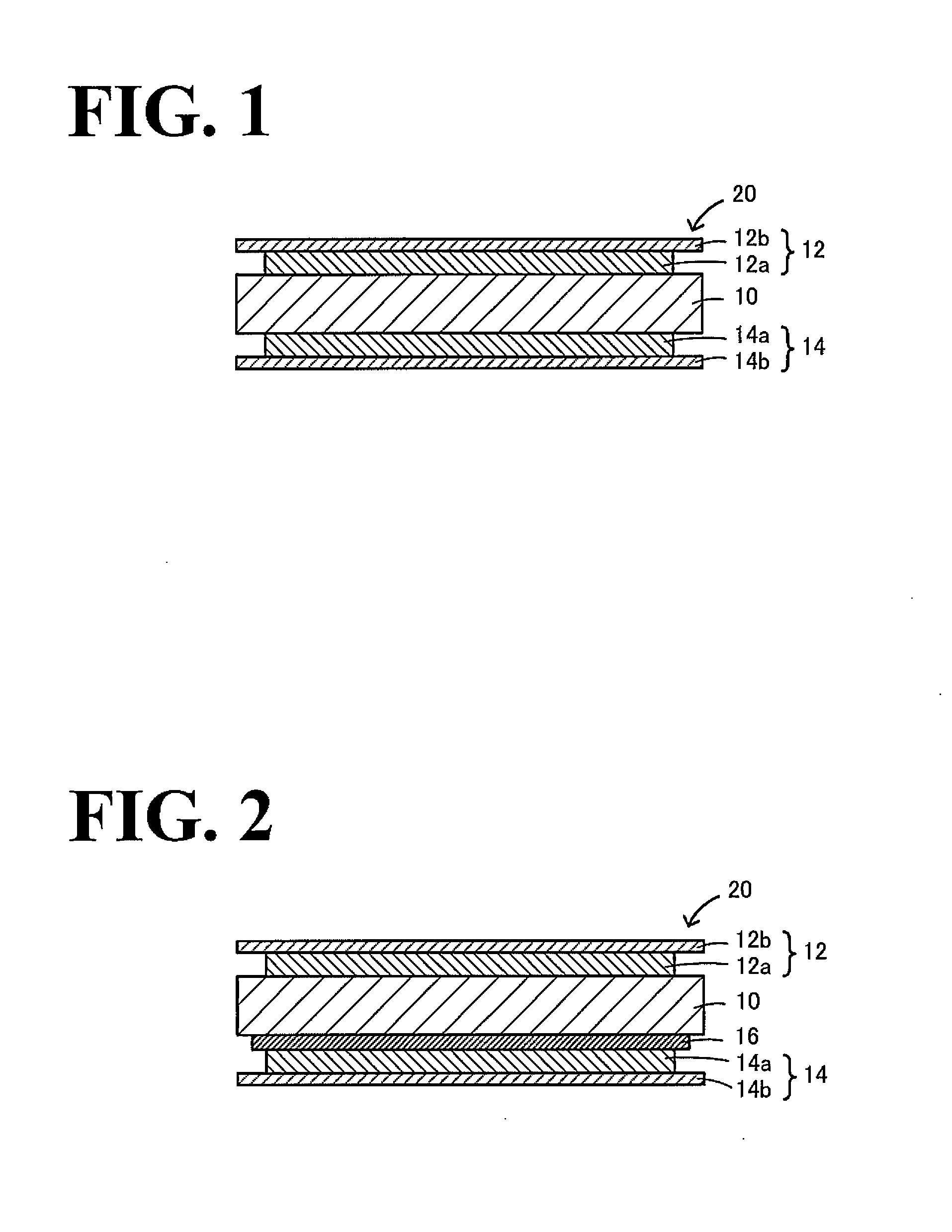
Method of forming an implantable device
ActiveUS9352071B2Greater and beneficial tissue ingrowthLow melting pointWeft knittingMedical devicesImplanted devicePliability
Owner:ETHICON INC
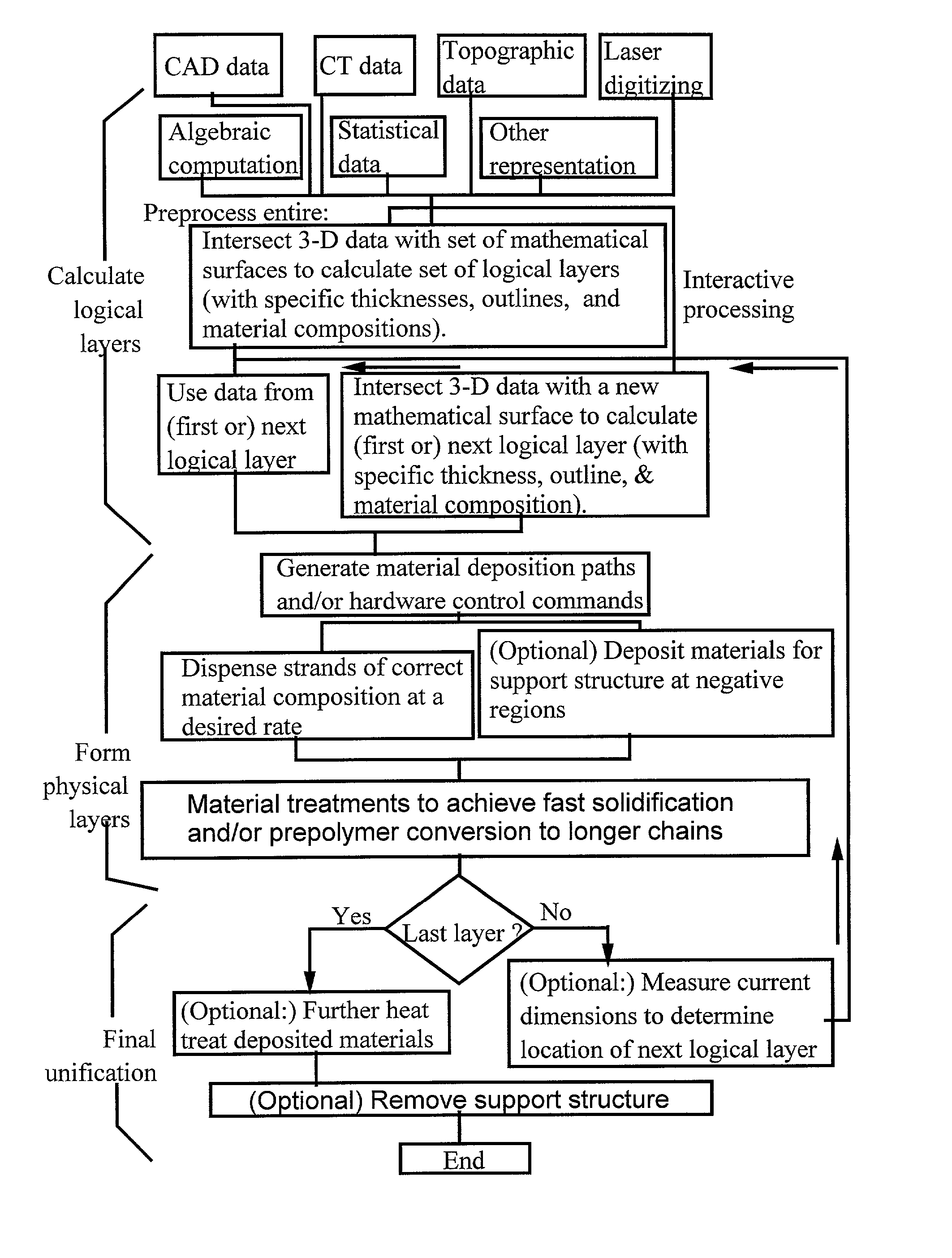
Freeform fabrication method using extrusion of non-cross-linking reactive prepolymers
InactiveUS20020113331A1Fast formingDifficult to prepareProgramme controlComputer controlCross-linkThermoplastic
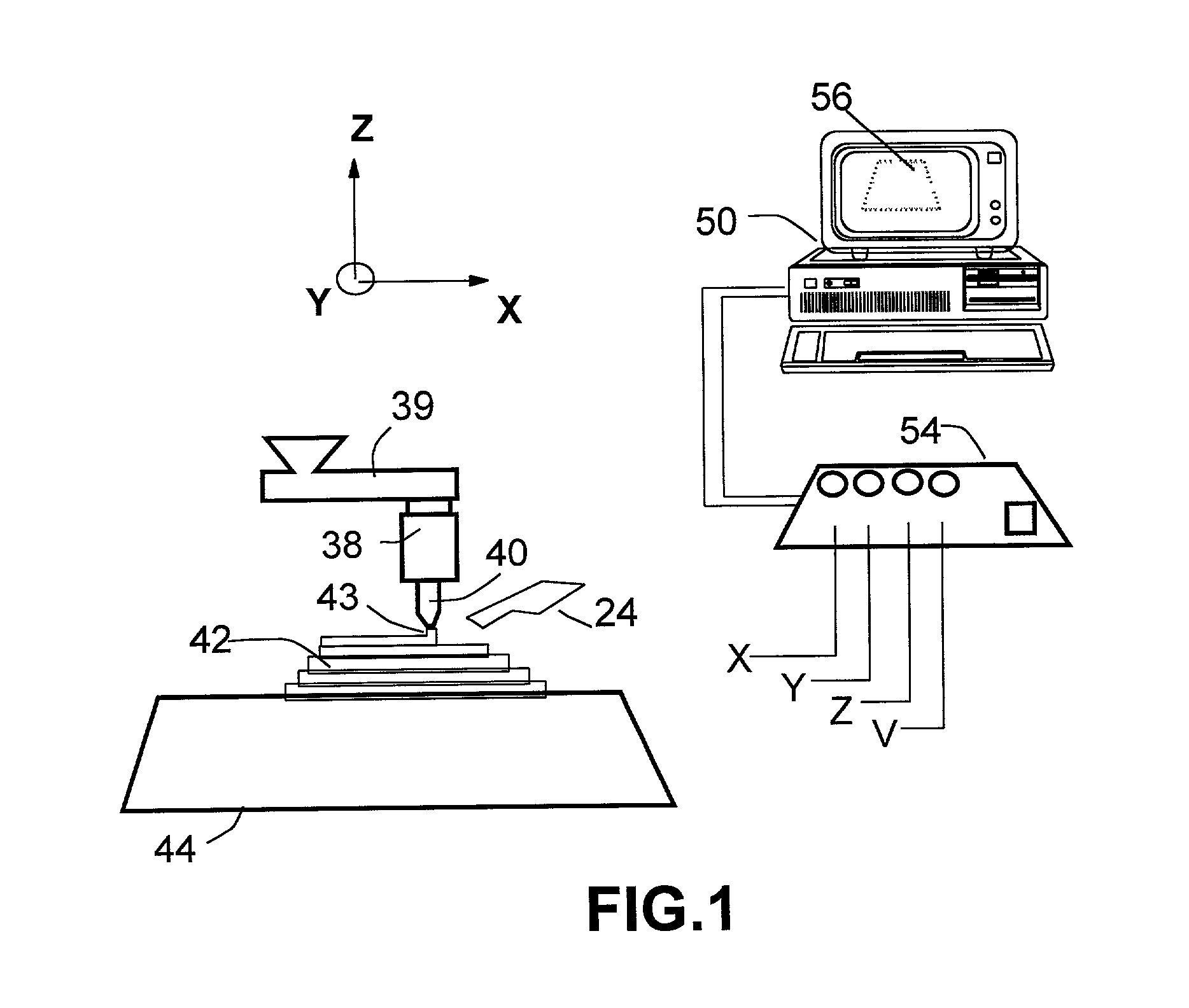
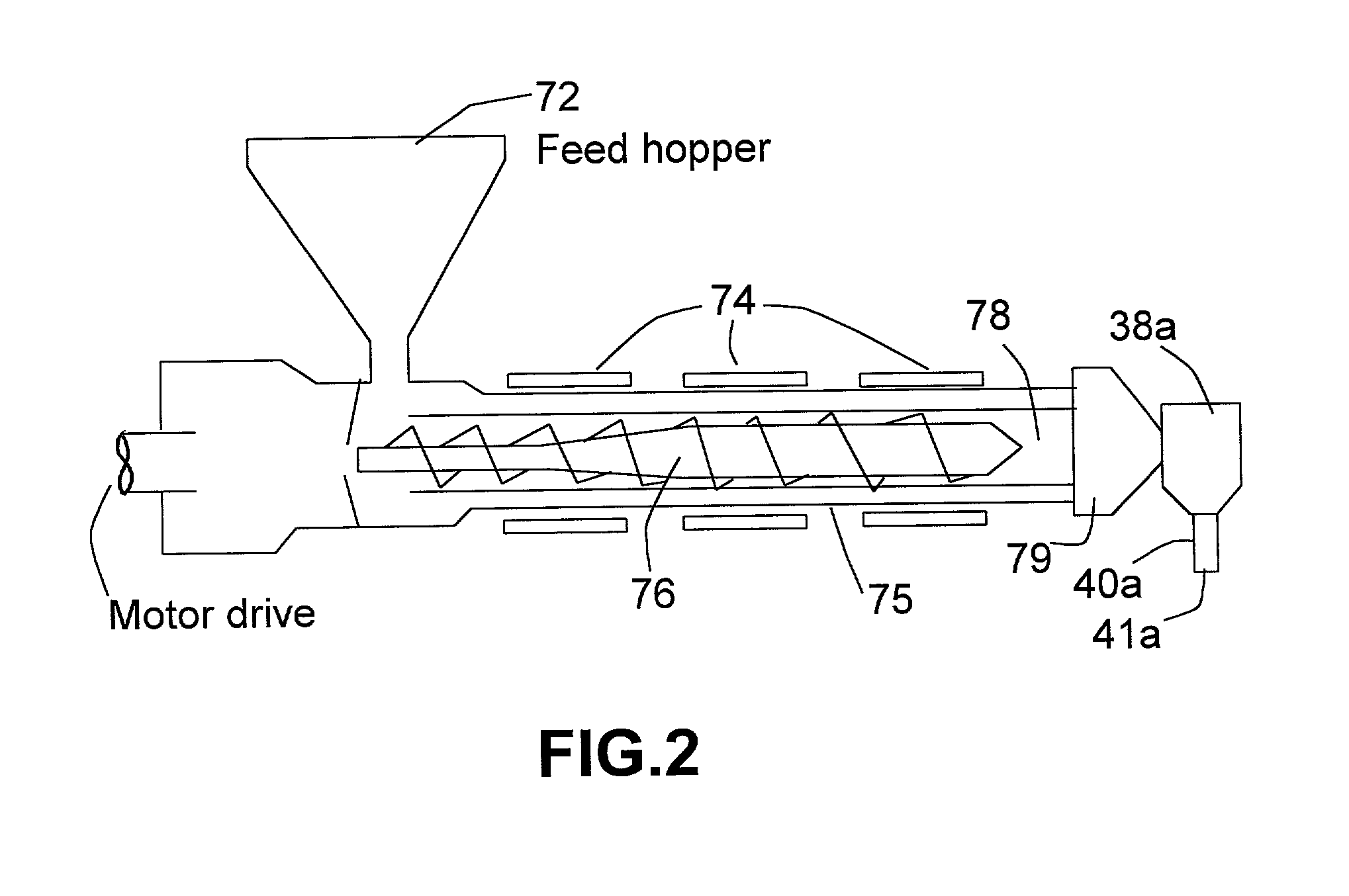
An extrusion-based freeform fabrication method for making a three-dimensional object from a design created on a computer, including (a) providing a support member; (b) operating a dispensing head having at least one dispensing nozzle with a discharge orifice for dispensing continuous strands of a material composition in a fluent state at a first temperature onto the support member, the material composition including a reactive prepolymer with a melting point above 23° C. and the first temperature being greater than the prepolymer melting point; (c) operating material treatment devices for causing the dispensed strands of material composition to rapidly achieve a rigid state in which the material composition is substantially solidified to build up the 3-D object, the material treatment devices also working to convert the reactive prepolymer to a higher molecular weight thermoplastic resin; and (d) operating control devices for generating control signals in response to coordinates of the object design to control the movement of the dispensing nozzle relative to the support member and for controlling the strand dispensing of the material composition to construct the 3-D object.
Owner:ZHANG TAN +3
Precursor compositions for the deposition of electrically conductive features
InactiveUS6951666B2Reduce settlementGood dispersionRadiation applicationsConductive materialElectrically conductiveCopper metal
A precursor composition for the deposition and formation of an electrical feature such as a conductive feature. The precursor composition advantageously has a viscosity of at least about 1000 centipoise and can be deposited by screen printing. The precursor composition also has a low conversion temperature, enabling the deposition and conversion to an electrical feature on low temperature substrates. A particularly preferred precursor composition includes silver and / or copper metal for the formation of highly conductive features.
Owner:CABOT CORP
Compounds with physiological cooling effect
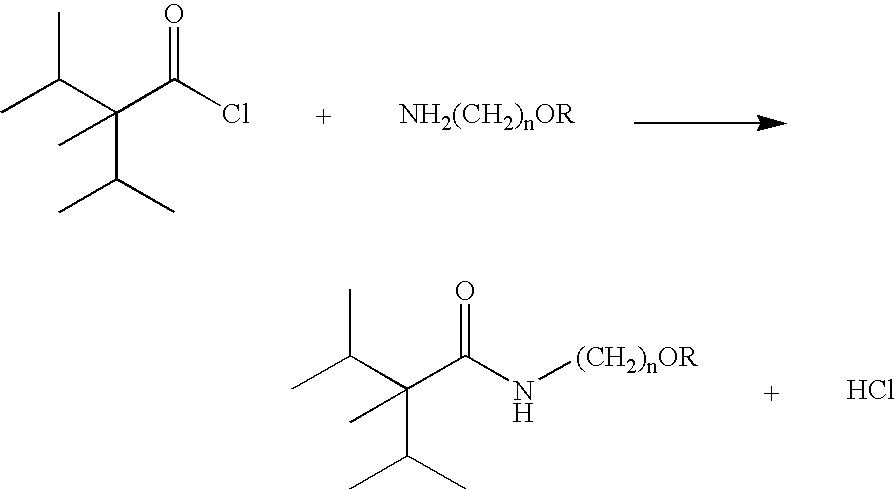
Novel compounds of 2,3-dimethyl-2-isopropylbutyric acid were claimed in this patent to possess pronounced cooling effect on the skin and on the mucous membranes of the body. These compounds also possess good taste quality and low melting points with no malodor. The preparations and some illustrative application of these compounds are also disclosed.
Owner:QAROMA
Earth-boring bits
ActiveUS20050247491A1Low melting pointLowered melting point of the binder facilitates proper infiltration of the massDrill bitsCutting machinesBorideNiobium
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for forming a bit body for an earth-boring bit. The bit body may comprise hard particles, wherein the hard particles comprise at least one carbide, nitride, boride, and oxide and solid solutions thereof, and a binder binding together the hard particles. The binder may comprise at least one metal selected from cobalt, nickel, and iron, and, optionally, at least one melting point reducing constituent selected from a transition metal carbide in the range of 30 to 60 weight percent, boron up to 10 weight percent, silicon up to 20 weight percent, chromium up to 20 weight percent, and manganese up to 25 weight percent, wherein the weight percentages are based on the total weight of the binder. In addition, the hard particles may comprise at least one of (i) cast carbide (WC+W2C) particles, (ii) transition metal carbide particles selected from the carbides of titanium, chromium, vanadium, zirconium, hafnium, tantalum, molybdenum, niobium, and tungsten, and (iii) sintered cemented carbide particles.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC +1
Chemically toughened glasses
InactiveUS6518211B1Promote meltingNot affecting strain pointGlass/slag layered productsThin material handlingToughened glass
A glass composition capable of being chemically strengthened by ion-exchange within 100 hours to provide a glass with a surface compressive stress of greater then 400 MPa and an ion-exchange depth greater then 200 microns comprising: SiO2 58% to 70% (by weight), Al2O3 5% to 15%, Na2O 12% to 18%, K2O 0.1% to 5%, MgO 4% to 10%, CaO 0% to 1% with the provisos that the total of the Al2O3 and MgO is in excess of 13%, the total of the amounts of Al2O3 plus MgO divided by the amount of K2O is at least 3 and that the sum of the amounts of Na2O, K2O and MgO is at least 22%.
Owner:GKN AEROSPACE SERVICES LTD
Saline soluble inorganic fibres
InactiveUS7153796B2Improve fiber qualityMinimise reduction is solubilityInorganic material artificial filamentsHeat proofingFiberThermal insulation
Thermal insulation is provided for use in applications requiring continuous resistance to temperatures of 1260° C. without reaction with alumino-silicate firebricks, the insulation comprises fibers having a composition in wt %65%<SiO2<86%MgO<10%14%<CaO<28%Al2O3<2%ZrO2<3%B2O3<5%P2O5<5%72%<SiO2+ZrO2+B2O3+5*P2O5 95%<SiO2+CaO+MgO+Al2O3+ZrO2+B2O3+P2O5 Addition of elements selected from the group Sc, La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb, Lu, Y or mixtures thereof improves fiber quality and the strength of blankets made from the fibers.
Owner:THE MORGAN CRUCIBLE CO PLC
Inhibitor nucleic acids
InactiveUS20050256071A1Low melting pointQuality improvementOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderAptamerHalf-life
The present invention provides methods and compositions for attenuating expression of a target gene in vivo. In general, the method includes administering RNAi constructs (such as small-interfering RNAs (i.e., siRNAs) that are targeted to particular mRNA sequences, or nucleic acid material that can produce siRNAs in a cell), in an amount sufficient to attenuate expression of a target gene by an RNA interference mechanism. In particular, the RNAi constructs may include one or more modifications to improve serum stability, cellular uptake and / or to avoid non-specific effect. In certain embodiments, the RNAi constructs contain an aptamer portion. The aptamer may bind to human serum albumin to improve serum half life. The aptamer may also bind to a cell surface protein that improves uptake of the construct.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Tools and methods for forming conductive bumps on microelectronic elements
InactiveUS20060183270A1Easy to wetGood adhesionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingContact padEngineering
A method of making a microelectronic assembly includes providing a microelectronic element having a front face and contact pads accessible at the front face, providing a dispensing tool containing a molten metal and having a discharge port for dispensing the molten metal, and aligning the discharge port of the dispensing tool with one of the contact pads of the microelectronic element. A mass of the molten metal is dispensed through the discharge port and onto the one of the contact pads of the microelectronic element; and ultrasonic waves are applied to the mass of molten metal during the dispensing step for facilitating wetting of the mass of molten metal with the one of the contact pads of the microelectronic element.
Owner:TESSERA INC
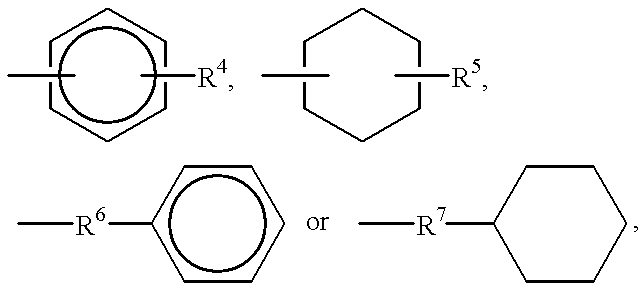
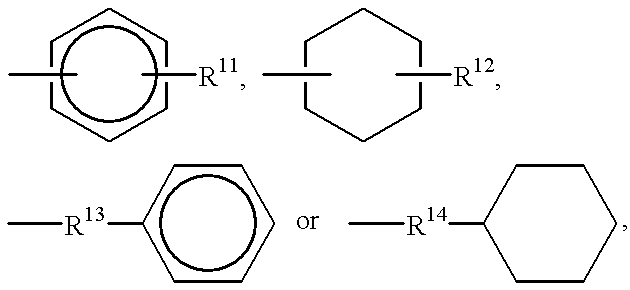
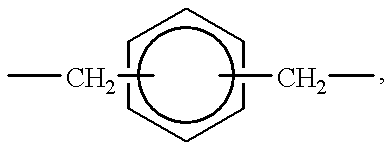
Crystalline polypropylene resin composition and amide compounds
InactiveUS6235823B1Low melting pointLess force for deformation under heatingOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationPolypropylenePolymer chemistry
Disclosed are a crystalline polypropylene resin composition comprising a crystalline polyproplylene resin and a beta-nucleating agent, and a method of increasing the proportion of beta-form crystals in a crystalline polypropylene resin molding comprising molding the composition, the beta-nucleating agent being a diamide compound.
Owner:NEW JAPAN CHEM CO
Glass-to-metal feedthrough seals having improved durability particularly under AC or DC bias
A hermetic implantable medical device (IMD) is provided with a single or multi-pin arrangement including selected glass to metal seals for a feedthrough including a ceramic disk member coupled to the sealing glass surface in potential contact with body fluids. By judicious selection of component materials (ferrule, seal insulator and pin) provides for either compression or match seals for electrical feedthroughs (having a single or multi-pin array) provide corrosion resistance and biocompatibility required in IMDs. The resultant feedthrough configuration accommodates one pin within a single ferrule or at least two pins in a single ferrule having a pin surrounded by insulator material (e.g., alumina ceramic, zirconia ceramic, zirconia silicate ceramic, mullite, each having higher melting points than the sealing glass distributed around the pin within the ferrule, or feldspar porcelain materials or alumino-silicate glasses having a lower melting point than the sealing glass) distributed around the pin within the ferrule.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Soybean wax candles
InactiveUS6599334B1Increase profitWithout and crackingSolid fuelsCapillary burnersVegetable oilAlpha-olefin
A solid fuel candle which is highly adapted for use both in a container and also as a free-standing candle includes at least 85 percent hydrogenated soybean oil, approximately 0 to 4 percent synthetic wax composition, approximately 0 to 4 percent of a second hydrogenated vegetable or petroleum oil, approximately 0 to 10 percent fragrance or scent, and approximately 0 to 3 percent dye. The hydrogenated vegetable oil most preferably has an iodine value of approximately 50 and a melting point of approximately 125 degrees Fahrenheit, with a free fatty acid content of less than one-tenth of one percent. The synthetic wax composition is most preferably formed from alpha olefin monomers and oligomers under free radical conditions at relatively low pressures to yield a highly branched polymer wax having congealing and melting points lower than the starting alpha olefin material and a higher molecular weight.
Owner:ANDERSON JILL M
Resistance spot welding of steel to pre-coated aluminum
ActiveUS20140360986A1Low melting pointImprove the immunityWelding/soldering/cutting articlesResistance welding apparatusTitanium zirconiumConversion coating
Resistance spot welding of a steel workpiece to an aluminum or an aluminum alloy workpiece can be facilitated by replacing the refractory aluminum oxide-based layer(s) on at least the faying surface of the aluminum or aluminum alloy workpiece with a protective coating that is more conducive to the spot welding process. The protective coating may be a metallic coating or a metal oxide conversion coating. In a preferred embodiment, the protective coating is a coating of zinc, tin, or an oxide of titanium, zirconium, chromium, or silicon.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Activated organic coatings on a fiber substrate
InactiveUS6517906B1Easy and less-expensive to manufactureImprove versatilityOther chemical processesFibre typesFiberDecomposition
A composite contains substrate fibers, and an activated organic coating, on the substrate fibers. The activated organic coating is formed at a low temperature, making possible the use of substrate fibers have a softening or decomposition temperature of at most 500° C.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Semiconductor device with joint structure having lead-free solder layer over nickel layer
InactiveUS6879041B2Low melting pointImpact resistancePrinted circuit assemblingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDevice materialSulfur
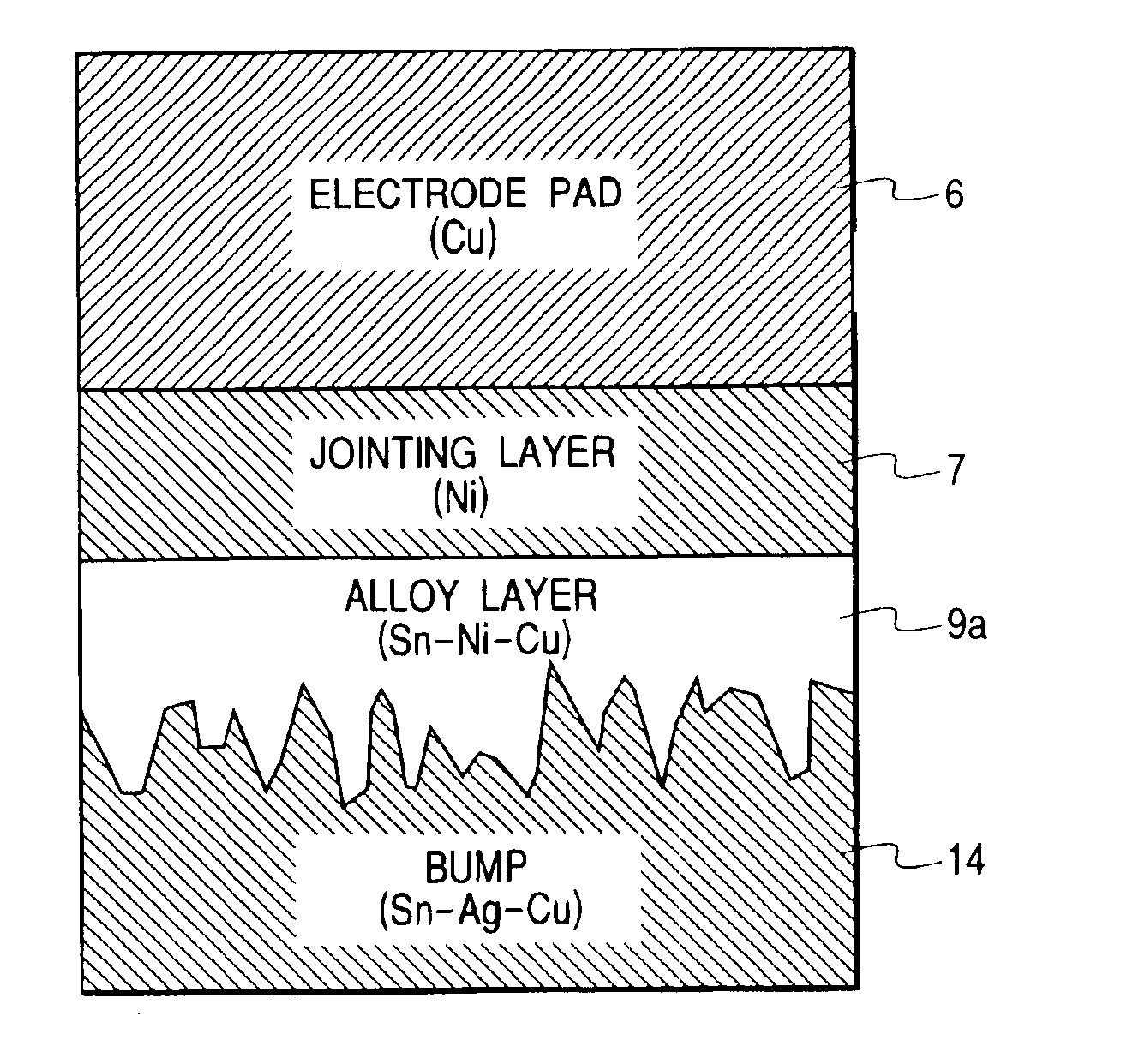
The impact strength resistance of a solder joint portion of a semiconductor device is improved. The semiconductor device has a joint structure wherein a jointing layer which does not contain sulfur substantially is arranged between an underlying conductive layer and a lead-free solder layer and further between the jointing layer and the lead-free solder layer is formed an alloy layer comprising elements of these layers.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
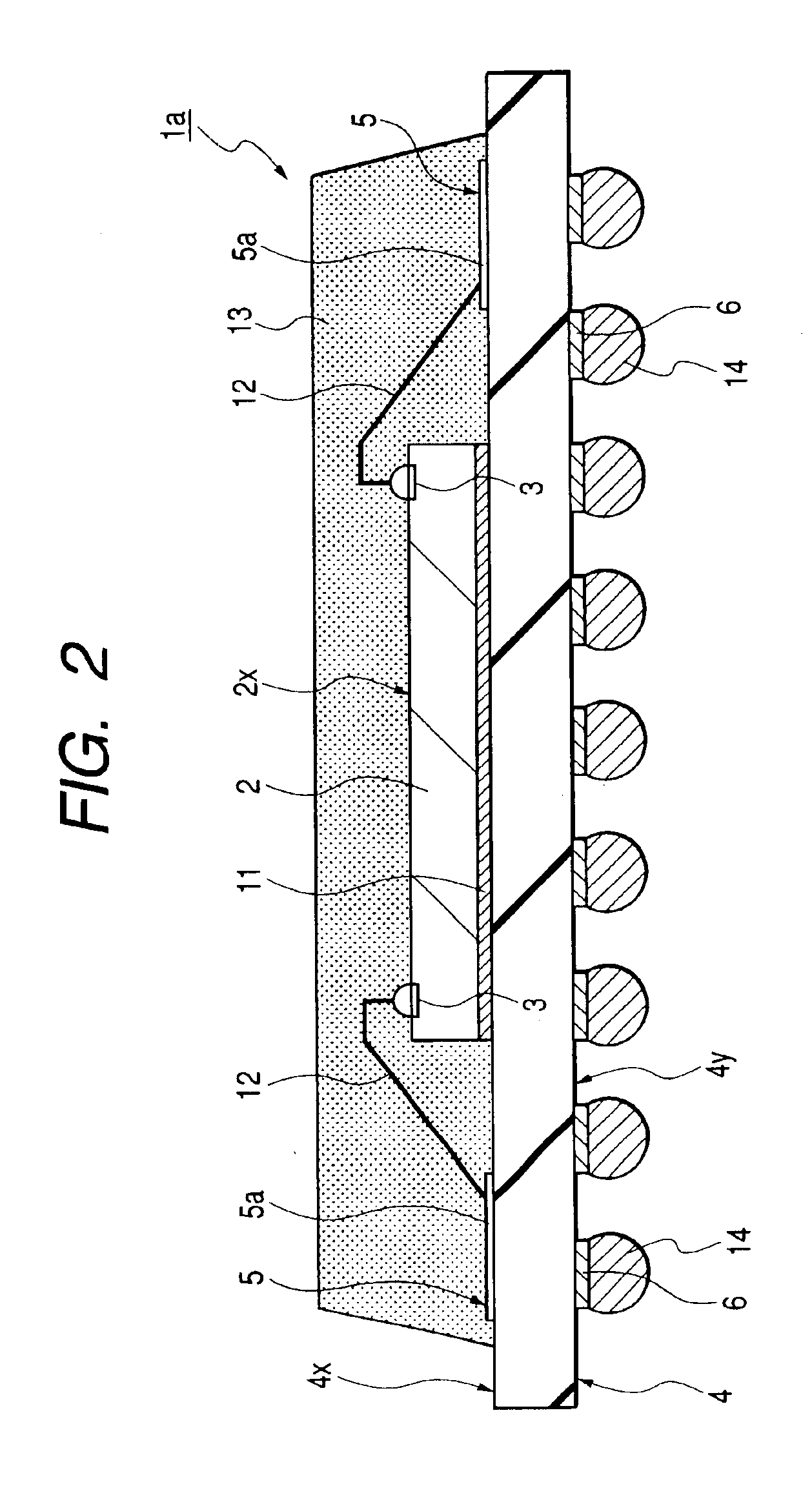
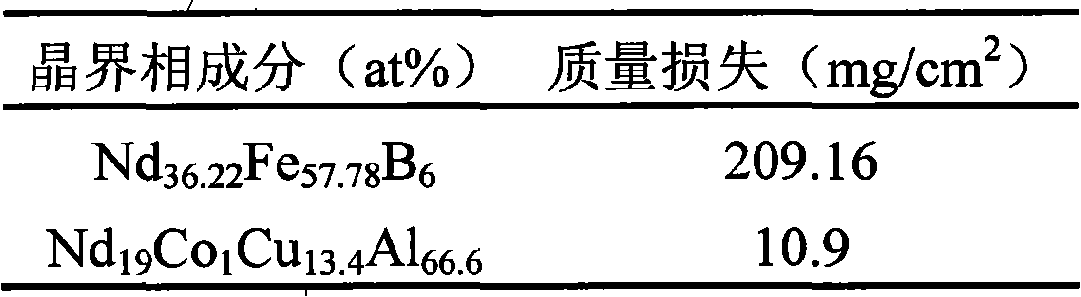
Grain boundary phase-reconstructed high-corrosion resistance Sintered NdFeB magnet and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101320609ALow melting pointGuaranteed MagneticInorganic material magnetismInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureElectrode potentialPowder mixture
The invention discloses a sintered Nd-Fe-B magnet with high corrosion resistance and the grain boundary reconstruction and a preparation method thereof. The composition of the invention is that: NdeFe100-e-f-gBfMg, wherein, e is greater than or equal to 6 and equal to or less than 24, f is greater than or equal to 5. 6 and equal to or less than 7, g is greater than or equal to 0.03 and equal to or less than 8, M is one or some of elements Dy, Tb, Pr, Sm, Yb, La, Co, Ni, Cr, Nb, Ta, Zr, Si, Ti, Mo, W, V, Ca, Mg, Cu, Al, Zn, Ga, Bi, Sn and In; The method is that: main phrase alloy and reconstructed grain boundary phase alloy are respectively pulverized and mixed uniformly; the powder mixture is pressed to a mould in the magnetic field, and fabricated into a sintering magnet in a high vacuum sintering furnace. By the reconstruction of the grain boundary phase composition, the invention can obtain the grain boundary phase alloy with low melting point and high electrode potential, decrease the potential difference between the main phase and the grain boundary phase on the basis of ensuring the magnetic properties, promote the intrinsic corrosion resistance of magnet, and has the advantages of simple process, low cost and being suitable for the batch production. Therefore, by combining the grain boundary reconstruction and double alloy method, the sintered Nd-Fe-B magnet with high intrinsic corrosion resistance can be prepared.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
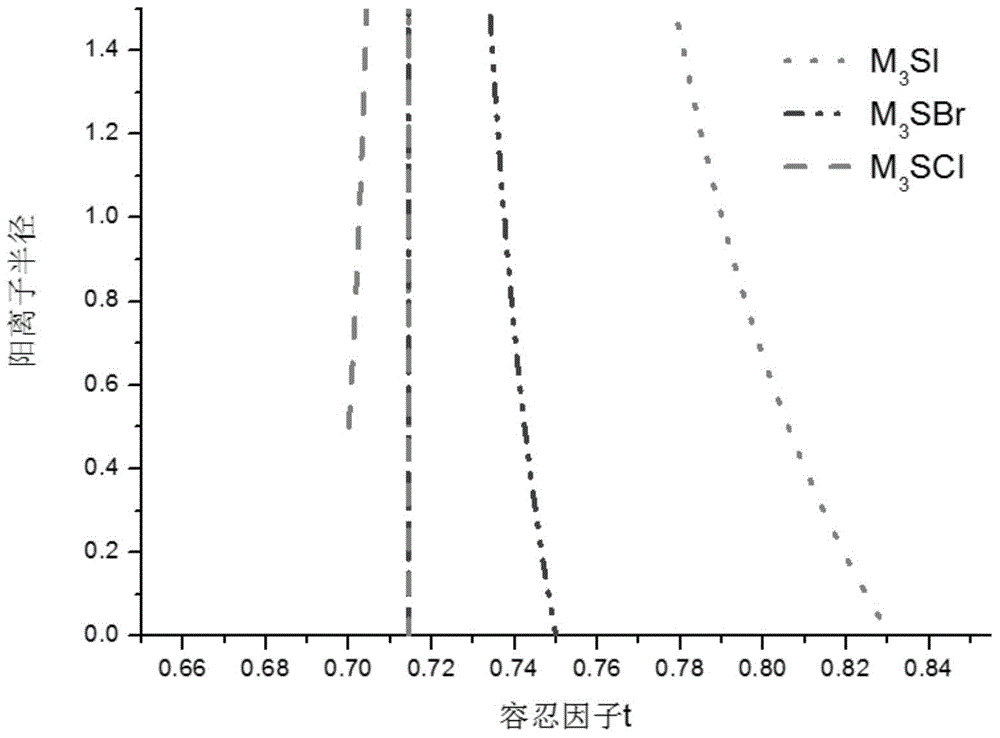
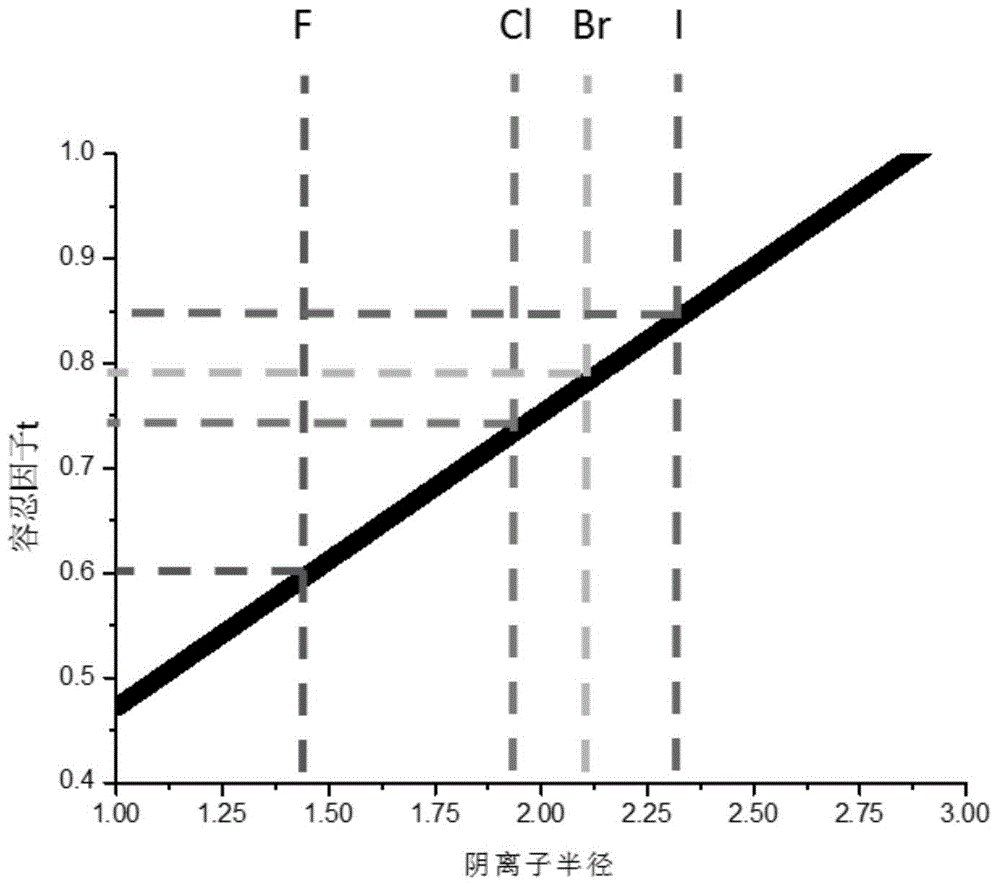
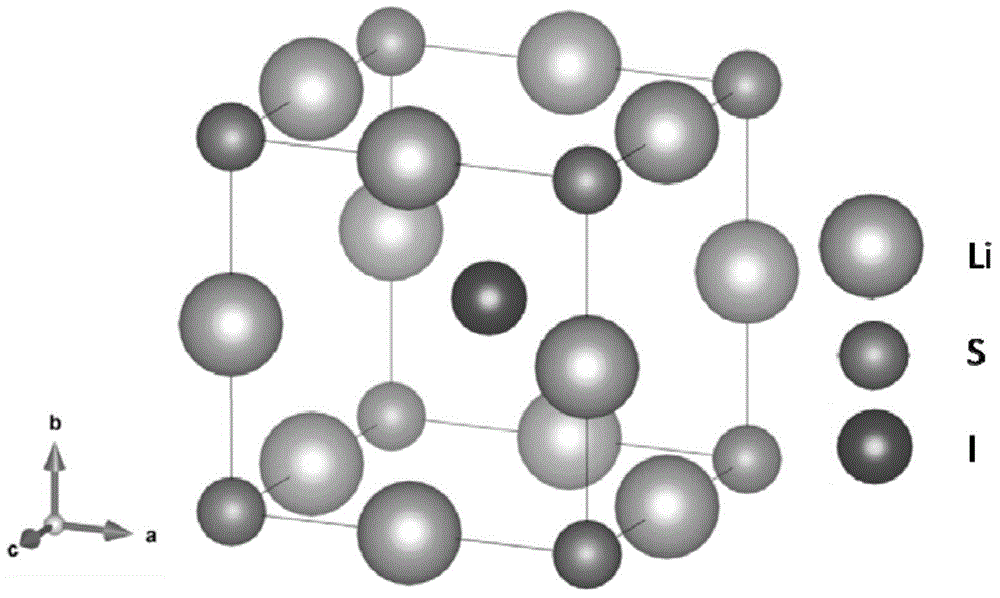
Lithium-enriched anti-perovskite sulfides, solid electrolyte material containing lithium-enriched anti-perovskite sulfides and application of solid electrolyte material
ActiveCN104466239AIncrease the carrier concentrationIncrease charge and discharge rateSecondary cellsElectrolytesWorking temperatureOperating temperature range
The invention discloses lithium-enriched anti-perovskite sulfides and a solid electrolyte material. The general formula of the lithium-enriched anti-perovskite sulfides is (LimMn)3-xS1-y(XaYb)1-z, wherein m is more than 0 and less than or equal to 1, n is more than or equal to 0 and less than to 0.5, (m+n) is less than or equal to 1, a is more than 0 and less than or equal to 1, b is more than or equal to 0 and less than 1, (a+b) is less than or equal to 1, x is more than or equal to 0 and less than or equal to 0.5, y is more than or equal to 0 and less than or equal to 0.5, z is more than or equal to 0 and less than or equal to 0.5 and x=2y+z; M is H, Na, K, Rb, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Y, La, Ti, Zr, Zn, B, Al, Ga, In, C, Si, Ge, P, S or Se; and X is Fe, Cl, Br or I, and Y is a negative ion. The solid electrolyte material has high ion conductivity and thermal stability and a wide working temperature range, and can be applied to lithium ion batteries, rechargeable metal lithium batteries, lithium liquid flow batteries or lithium ion capacitors.
Owner:BEIJING WELION NEW ENERGY TECH CO LTD
Cover assembly for a concealed sprinkler head
A concealed sprinkler head is mounted above the ceiling of a fire protected zone. The sprinkler head includes a housing within which a valve and other operative parts are contained. A decorative cover plate is secured to the housing to conceal the sprinkler head within the ceiling so that none of the operative parts is visible. The cover assembly includes a thin metallic cover plate made of a heat conductive material such as copper, and a metallic skirt including a cylindrical wall threaded on the housing, an annular flange extending outwardly from one end of the cylindrical wall, and a plurality of tabs extending downwardly from the flange. A plurality of heat insulative elements are disposed between the tabs and the cover plate. A metallic layer is attached to the lower surface of each of the insulative elements. A layer of fusible material is disposed between the metallic layer and the cover plate to secure each of the insulative elements to the cover plate through the metallic layer.
Owner:SENJU SPRINKLER
Photovoltaic element and fabrication method thereof
A photovoltaic element is obtained which allows use of a low-melting solder and can suppress reduction in reliability and output thereof due to mechanical stress or water intrusion.The photovoltaic element has a photoelectric conversion layer and a collector electrode provided on at least one surface of the photoelectric conversion layer. Characteristically, a collector electrode covering layer for covering a surface of the collector electrode is provided and a tab electrode for electrical connection to an exterior electrode is provided on a top surface of the collector electrode through the collector electrode covering layer. A portion of the collector electrode covering layer that lies between the tab electrode and collector electrode comprises a solder layer and another portion of the collector electrode covering layer that covers a lateral surface of the collector electrode comprises a thermosetting resin layer.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
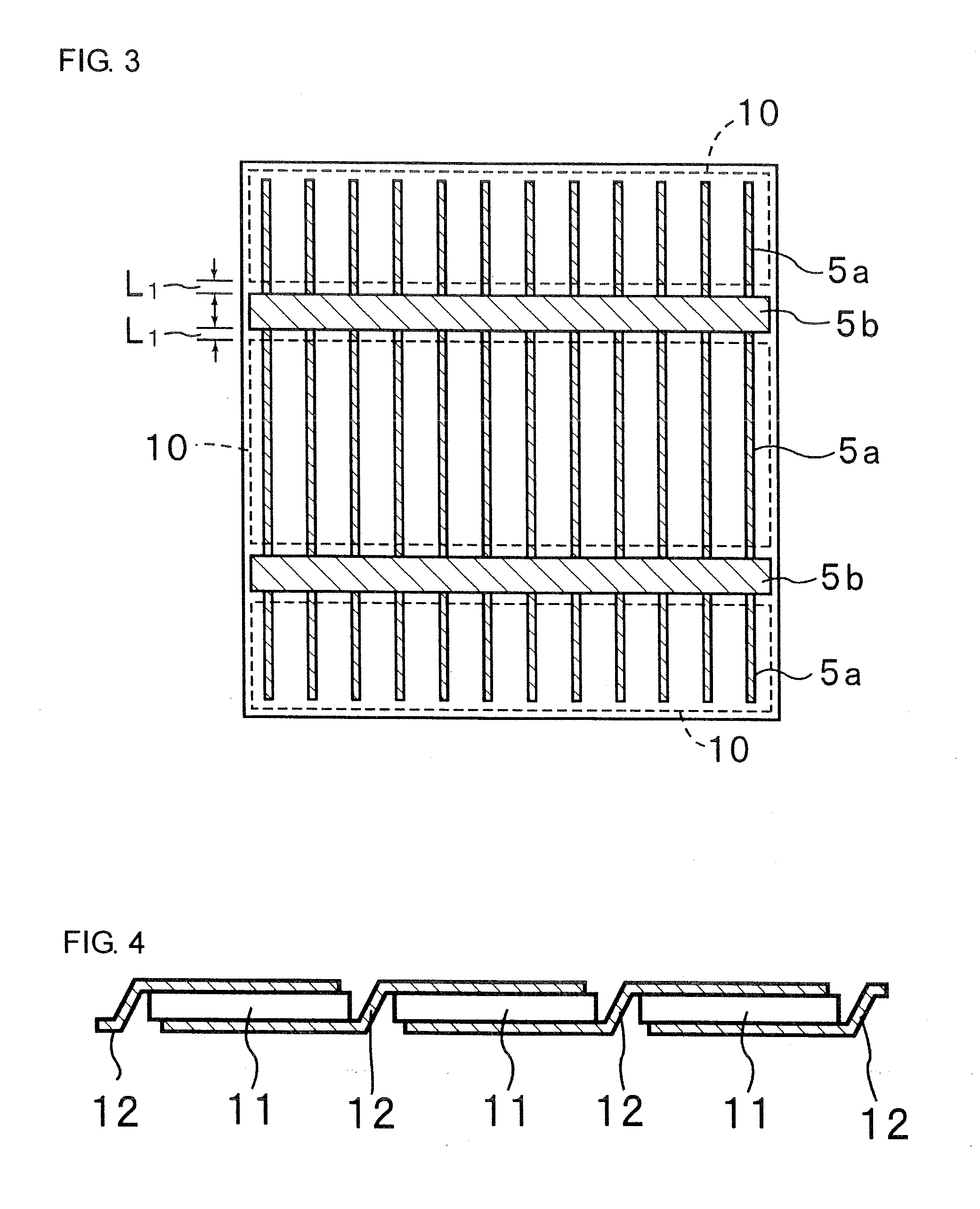
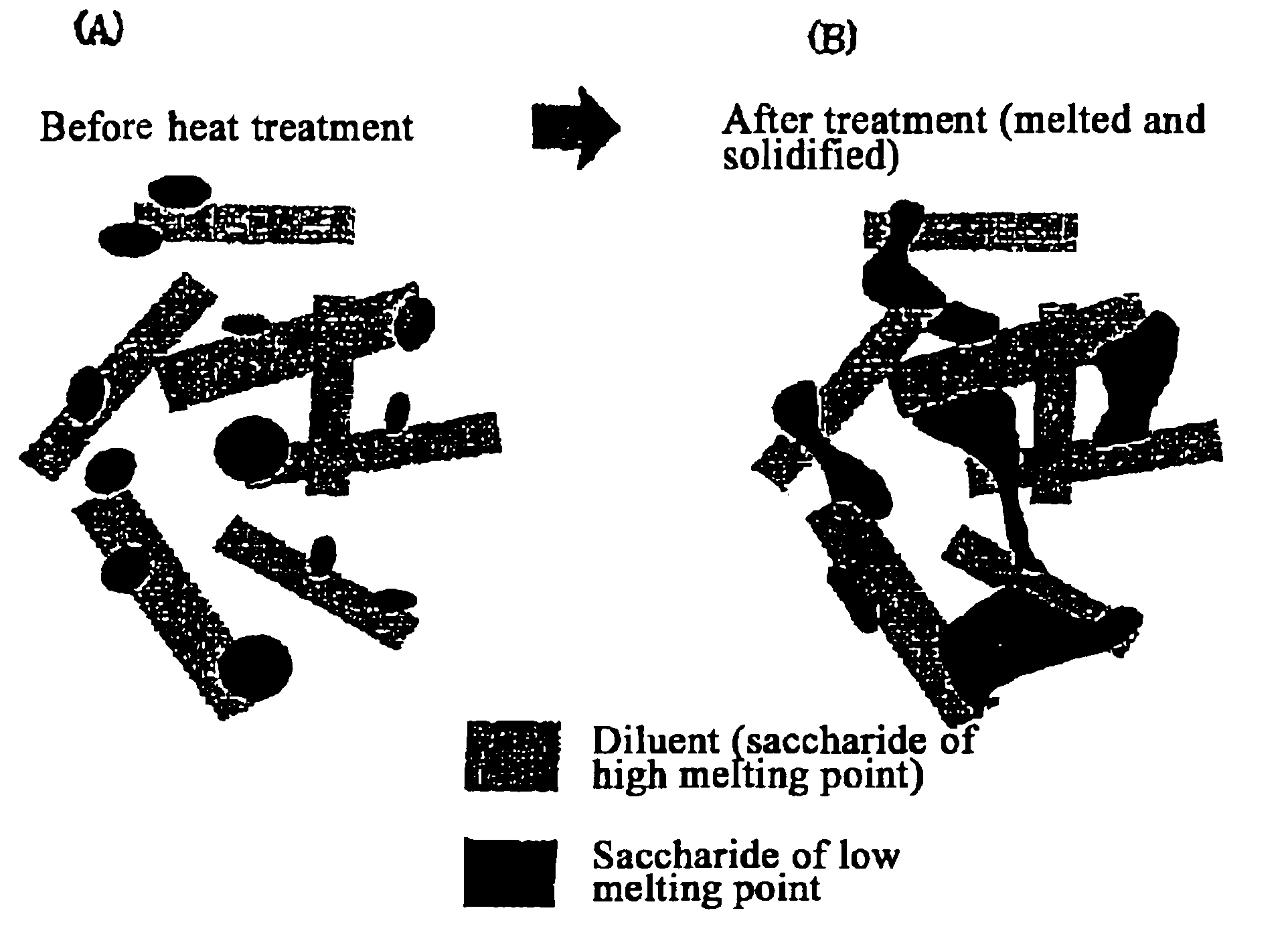
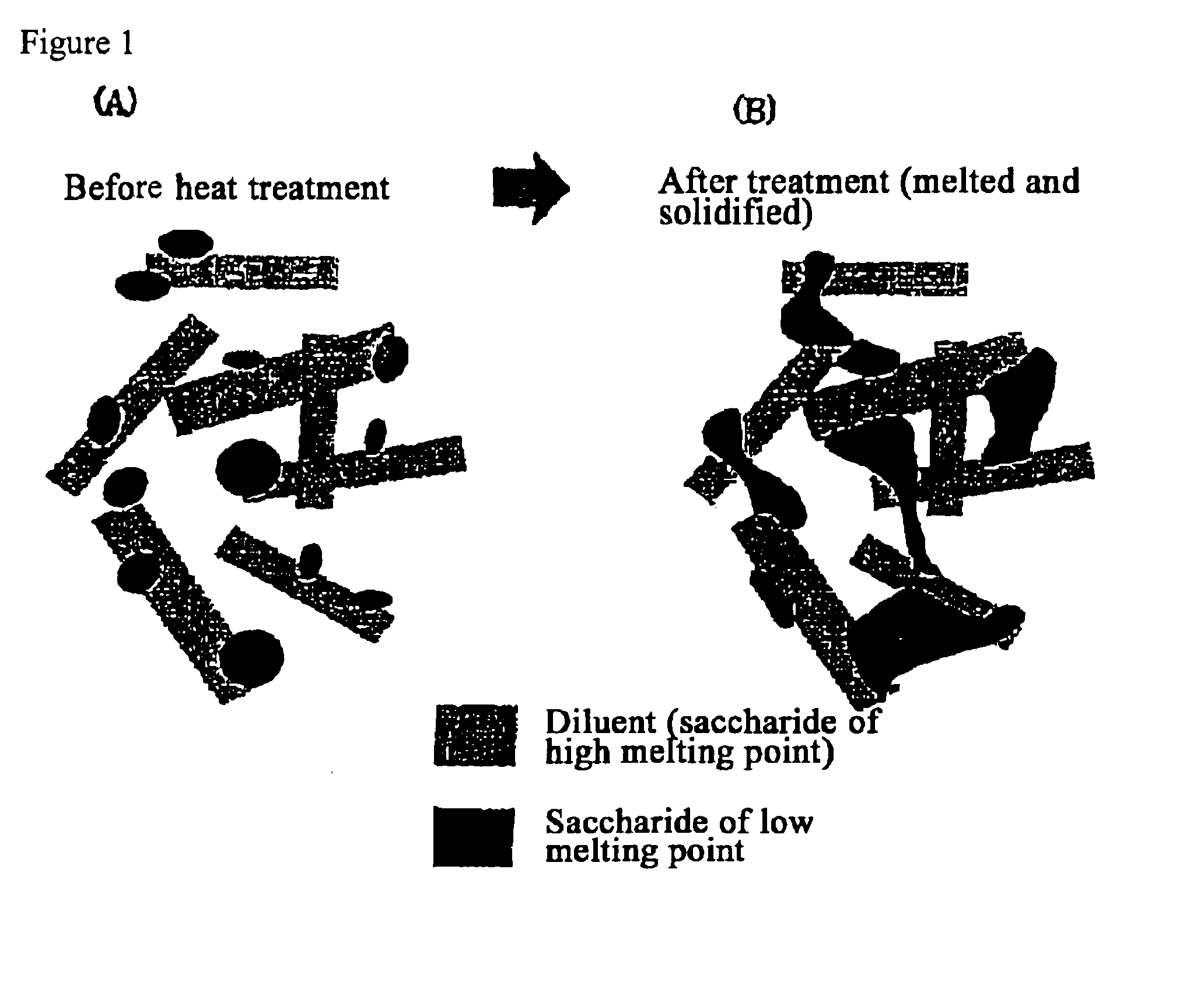
Quick-disintegrating tablet in buccal cavity and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS6872405B2Improves friabilityHigh strengthPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsDrageesPharmaceutical SubstancesOrganic chemistry
The present invention relates to a quick-disintegrating tablet in the buccal cavity comprising a drug, a diluent, and a saccharide with a relatively lower melting point than the drug and the diluent, which is obtained by uniformly mixing the saccharide with a low melting point in the tablet so that a bridge will be formed between said drug and / or said diluent particles by the product of melting and then solidification of this saccharide with a low melting point. Moreover, the present invention relates to a method of manufacturing a quick-disintegrating tablet in the buccal cavity comprising a drug, a diluent and a saccharide with a relatively lower melting point than the drug and the diluent, which comprises (a) the process whereby tablet starting materials including a drug, a diluent, and a saccharide with a relatively lower melting point than the drug and the diluent are molded under the low pressure necessary for retaining the shape of a tablet, (b) the process whereby the molded product obtained in process (a) is heated to at least the temperature at which this saccharide with a low melting point will melt, and (c) the process whereby the molded product obtained in process (b) is cooled to at least the temperature at which the molten saccharide with a low melting point solidifies. The present invention presents a quick-disintegrating tablet in the buccal cavity that can be used for practical purposes in that it has almost the same properties as conventional oral pharmaceutical tablets, that is, it has sufficient tablet strength that it can be used with automatic unit dosing machines, and it is produced by conventional tableting machines, and a manufacturing method thereof. Moreover, the present invention presents a quick-disintegrating tablet in the buccal cavity which, in comparison to conventional quick-disintegrating tablets in the buccal cavity, has increased tablet strength and an improved friability without prolonging the disintegration time in the buccal cavity, and a manufacturing method thereof.
Owner:ASTELLAS PHARMA INC
Monocrystal-like lithium battery ternary cathode material and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a monocrystal-like lithium battery ternary cathode material and a preparation method thereof. The chemical formula of the cathode material is LiNi(1-x-y-z)CoxMnyMzO2, wherein x is larger than 0 and smaller than or equal to 0.65, y is larger than 0 and smaller than or equal to 0.3, z is larger than or equal to 0 and smaller than or equal to 0.05, and M is one or more of Mg, Ca, Ti, Zn, Cr, Fe, Zr, Co, Cu and Ru. The preparation method of the cathode material comprises the following steps of 1 precursor synthesizing; 2 material mixing, wherein a fluxing agent is added in the material mixing process; 3 sintering and the like. According to the method, the melting point of the material is lowered by adding the fluxing agent, therefore, precursors and lithium salts are in a molten environment, dispersion of metal ions is accelerated, and crystal grains start to grow and development at low temperature, break limitation of precursor aggregates after growing to a certain degree to be dispersed into monocrystal grains and finally grow into the cathode material with the monocrystal morphology; the sintering frequency and the sintering time in the existing monocrystal material synthesizing process are decreased, and then the production cost is reduced.
Owner:HENAN KELONG NEW ENERGY CO LTD
Laser-cladded composite wear-resisting layer on surfaces of copper and copper alloys and preparation method
InactiveCN102041503ADense tissueReduce energy consumptionMetallic material coating processesCobalt based alloyCopper alloy
The invention relates to a laser-cladded composite wear-resisting layer on the surfaces of copper and copper alloys and a preparation method. The composite wearing layer is a multi-layered laser cladding layer comprising at least two or more than two layers, wherein the coating connected with a substrate is the first layer, which is also called as a transition layer and is a copper-based alloy prepared from the following components in percentage by weight: 20.0-30.0 percent of Cu, 6.0-8.0 percent of Al, 0.3-0.6 percent of Si, 1.7-2.4 percent of Zr and the balance of Ni; and the rest layer is a cobalt-based alloy prepared from the following components in percentage by weight: 1.0-1.5 percent of C, 25-30 percent of Cr, 2-4 percent of Fe, 10-15 percent of W, 0.8-1.2 percent of Si, 3-4 percent of B, 8-12 percent of Ti, 10-12 percent of Ni and the balance of Co. The composite wear-resisting layer provided by the invention has compact tissues without cracks or pores and forms favorable metallurgy combination with the surfaces of copper and copper alloys. The preparation method provided by the invention can be used for accurately controlling the thickness of the composite wear-resisting layer and automatically controlling the whole process, and has the advantages of low energy consumption, no pollution, high efficiency and low cost.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Use of non-spreading silicone surfactants in agrochemical compositions
InactiveUS6734141B2Improve performanceReduce decreaseBiocideAnimal repellantsHydrogenChemical composition
This invention provides for, inter alia, a method for increasing the rainfastness of an agrochemical composition without increasing its spreading properties, which comprises adding to said agrochemical composition an effective amount of one or more silicone surfactants of the formulawhereinn is 1 to 3,R is an alkyl radical with 1 to 6 carbon atoms,R' is a radical of the structurewhereinm is 2 to 6,R'' is independantly methyl, ethyl or phenyl,Z is hydrogen, an alkyl radical with 1 to 4 carbon atoms, or an acyl radical with 2 to 6 carbon atoms,y is 6 to 30,z is 0 to 10,with the proviso that the ratio y / z is 1 or greater, and that the total number of alkylene oxide groups n*(y+z) in the siloxane polymer (I) is at least 12.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
All-solid-state lithium secondary battery and method for producing the same
ActiveUS20140162113A1Increase energy densityLow melting pointElectrode thermal treatmentFinal product manufactureAll solid stateClose contact
An all-solid-state lithium secondary battery includes a positive electrode; a negative electrode; and a solid electrolyte arranged between the positive and negative electrodes, to conduct lithium ions. In the all-solid-state lithium secondary battery, a mixed layer is in close contact with a surface of the solid electrolyte adjacent to the positive electrode, the mixed layer containing the positive-electrode active material and (Lix(1−α), Mxα / β)γ+(B1−y, Ay)z+O2−δ (wherein in the formula, M and A each represent at least one or more elements selected from C, Al, Si, Ga, Ge, In, and Sn, α satisfies 0≦α<1, β represents the valence of M, γ represents the average valence of (Li+x(1−α), Mα), y satisfies 0≦y<1, z represents the average valence of (B1−y, Ay) and x, α, β, γ, z, and γ satisfy the relational expression (x(1−α)+xα / β)γ+z=2δ) serving as a matrix.
Owner:TOYOTA CENT RES & DEV LAB INC
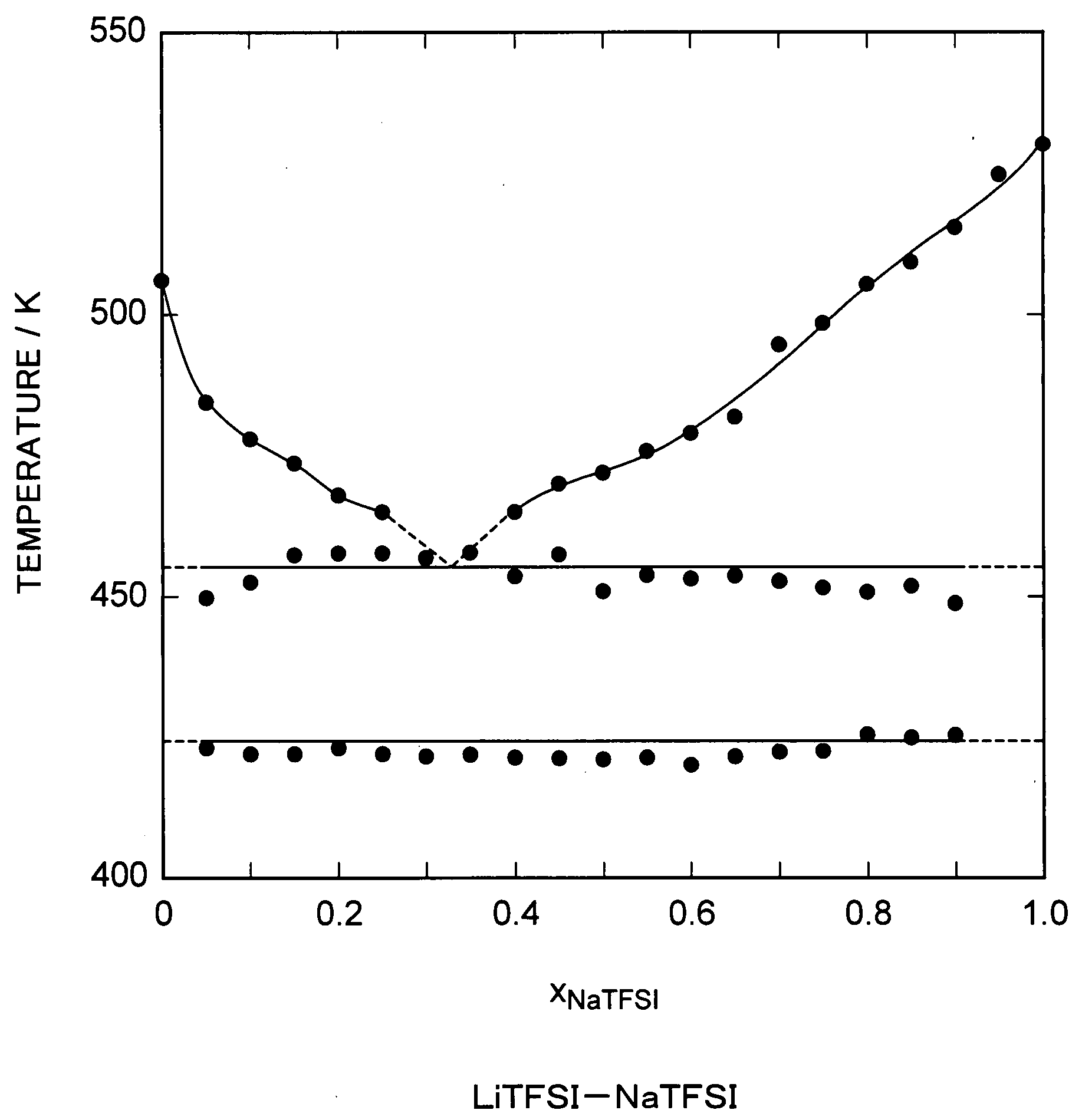
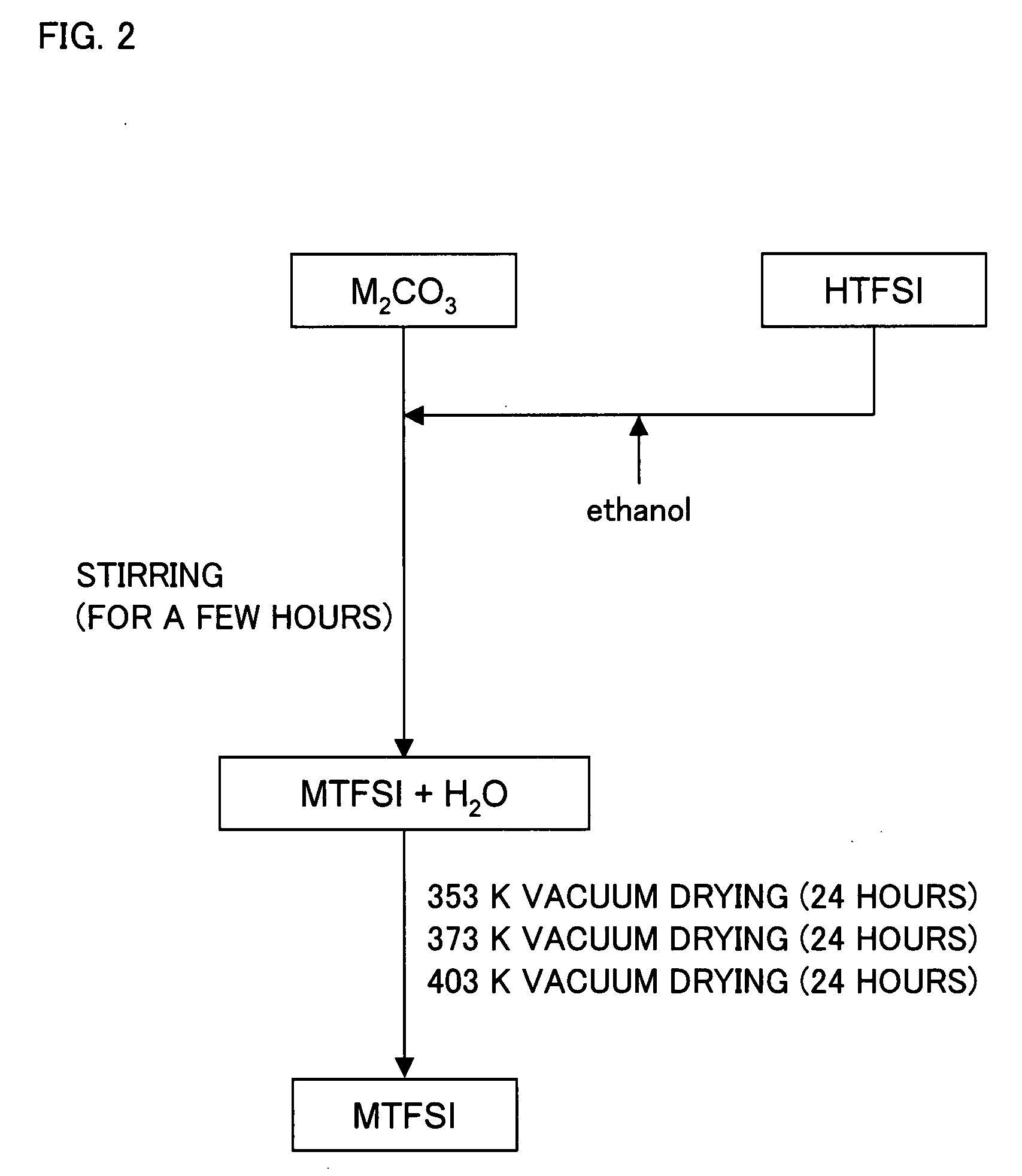
Molten Salt Composition and Use Thereof
ActiveUS20090212743A1High surface finishUniform platingNon-metal conductorsBatteries circuit arrangementsImideMolten salt
A molten salt composition is disclosed containing two or more types of molten salt MTFSI whose anion is an imide anion TFSI and whose cation is an alkali metal M exhibits a lower electrolyte melting point and a wider operating temperature range than a simple salt does. This brings about various advantages such as a wider range of materials that are chosen for use in batteries and the like.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Device for supplying inhalation gas to and removing exhalation gas from a patient
InactiveUS6634360B1Easy to transportThe equipment is easy to operateTracheal tubesSurgeryTracheal tubeLarynx
An integrated tracheal tube / suction ventilation and co-committal secretion removal device having first and second coaxially arranged conduits where the first interior conduit forms a lumen to deliver gas, and a circumferentially arranged second conduit lumen is structurally adapted to serve as an integral suction lumen for removal of both expiratory gases and secretions. The distal end outlets of both lumens terminate between the device's fixing member and its distal end. The two lumen outlets are arranged such that relative to each other and the device the first interior pipe conduit forming lumen's outlet is located at the distal end and the second pipe conduit lumen's outlet is located at or near the distal side of the fixing member. This selection of relative positioning facilitates optimal deliver of breathing gas to a user in conjunction with removal of expiratory gases and secretions. The device is sized for location of the fixing member to its distal end from a patient's carina to a patient's larynx.
Owner:ALORO MEDICAL
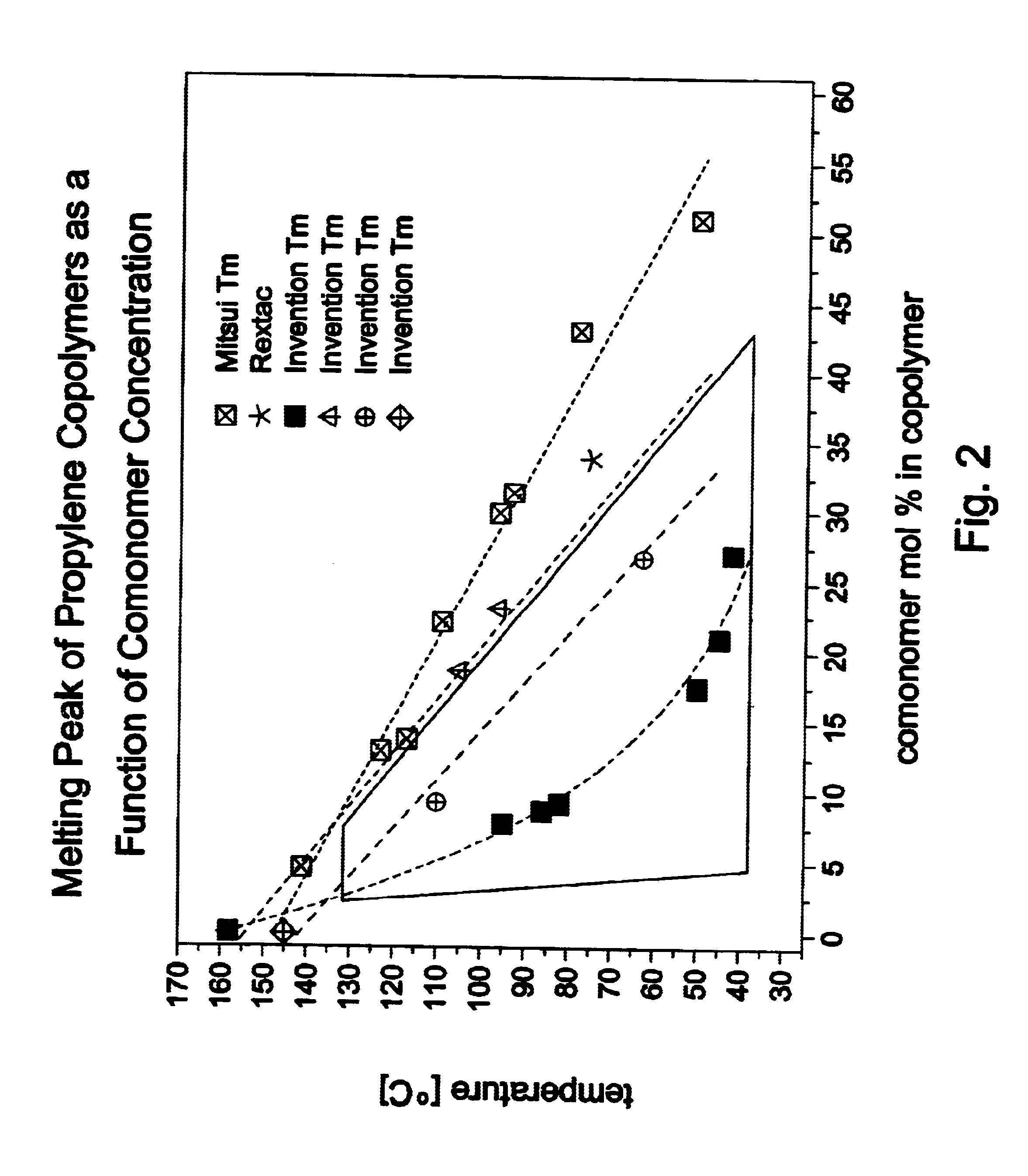
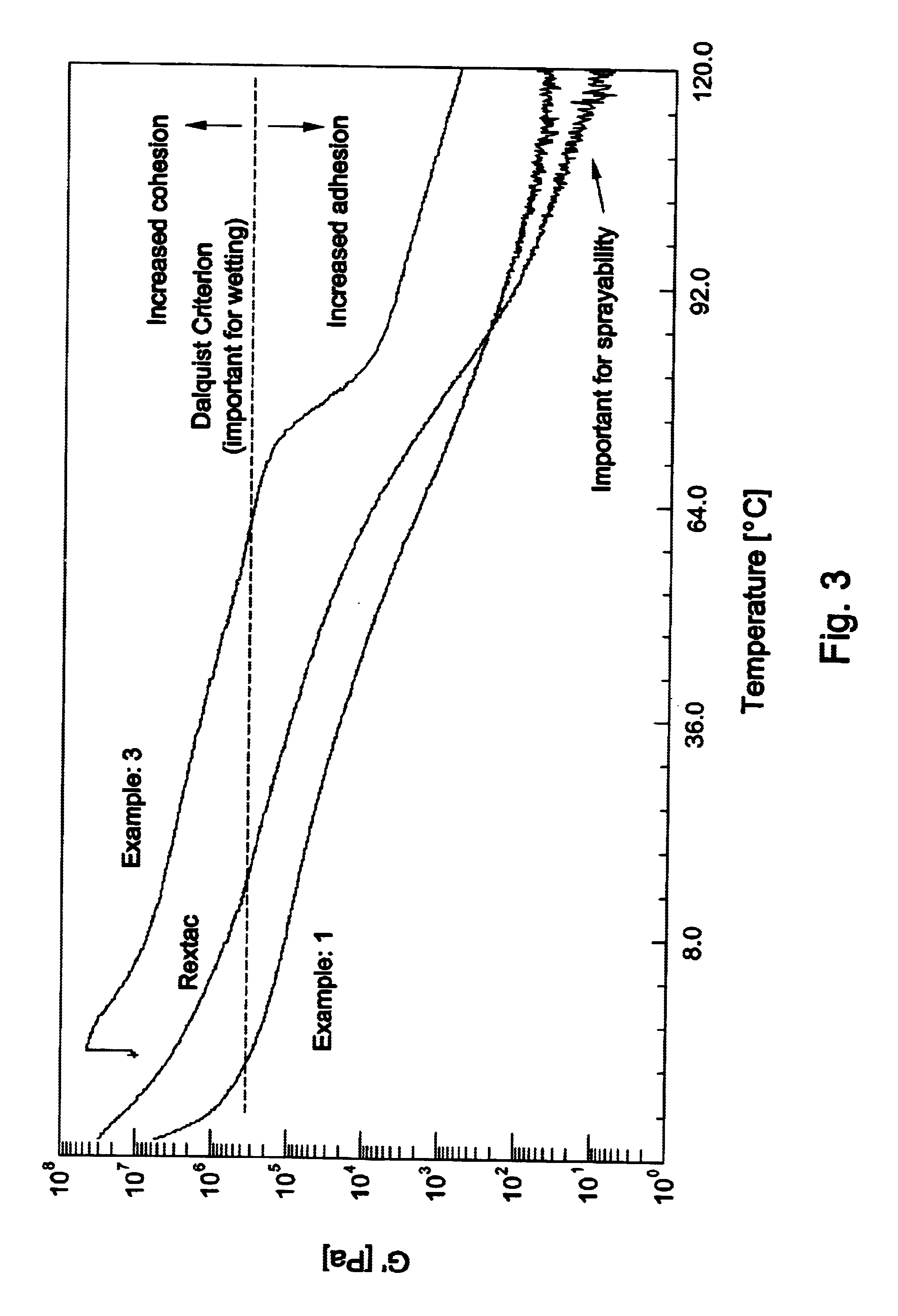
Adhesive alpha-olefin inter-polymers
The invention relates to novel adhesive alpha-olefin inter-polymers which are largely amorphous and have a rheological behavior that makes them suitable for adhesive use, both without and with minimized amounts of tackifying resins. Specifically, the invention poly-alpha olefin inter-polymer may be composed of A) from 60 to 94 mol % of units derived from one alpha mono-olefin having from 3 to 6 carbon atoms and B) from 6 to 40 mol % of units derived from one or more other mono-olefins having from 4 to 10 carbon atoms and at least one carbon atom more than A); and C) optionally from 0 to 10 mol % of units derived from another copolymerizable unsaturated hydrocarbon, different from A) and B); the diad distribution of component A in the polymer as determined by <13>C NMR as described herein showing a ratio of experimentally determined diad distribution over the calculated Bernoullian diad distribution of less than 1.07; and the storage modulus G' of said polymer, determined upon cooling as described herein, intersecting a value of 3.10<5 >Pa at a temperature of less than 85° C. The invention also describes polymerization processes suitable for the manufacture of these adhesive alpha-olefin inter-polymers.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Preparation method of ceramizing fire-resistant silicon rubber
ActiveCN105694471AImprove flame retardant performanceWill not affect other performanceHalogenCombustion
The invention relates to a preparation method of ceramizing fire-resistant silicon rubber. The rubber comprises the following components in parts by weight: 100 parts of methyl vinyl silicon rubber, 20-50 parts of white carbon black, 2-10 parts of hydroxyl silicone oil, 1-5 parts of a coupling agent, 25-100 parts of ceramizing powder, 2-5 parts of a heat stabilizer, 10-40 parts of a fire retardant, and 1-2 parts of a vulcanizer. The preparation method includes the following steps: adding the methyl vinyl silicon rubber in a kneading machine; then adding the white carbon black and the hydroxyl silicone oil; mixing for 30 minutes at the temperature of 80 DEG C; then adding the coupling agent, the ceramizing powder, the heat stabilizer and the fire retardant; mixing for 1-1.5 hours; raising the temperature to be 100 DEG C and keeping high vacuum for 30 minutes; and after cooling to room temperature, adding the vulcanizer on an open mixing machine for mixing to obtain the ceramizing fire-resistant silicon rubber. The rubber has good mechanical property and electrical property at normal temperature, does not contain halogen, is smokeless and non-toxic during combustion, can be extinguished quickly and forms a ceramizing shell to guarantee integrity of the inside.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Carbonaceous composite heat spreader and associated methods
InactiveUS20050189647A1Low melting pointSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesGraphiteMetal
A carbonaceous composite heat spreader includes a plurality of diamond grits present in an amount greater than about 50% by volume of the heat spreader and a metal matrix holding the diamond grits in a consolidated mass. The metal matrix contains at least about 50% aluminum by volume. The heat spreader can include a quantity of graphite, with the plurality of diamond grits being in substantially intimate contact with the graphite and with the metal matrix holding the graphite and the diamond grits in a consolidated mass. The quantity of graphite can include at least two distinct layers of graphite and the diamond grits can be arranged in a layer disposed between the layers of graphite.
Owner:SUNG CHIEN MIN
Powdery alloy processing material in site by movable laser smelt-coating process
A movable field processing alloy powder material for the laser melting is to reinforce the nickel-base alloy using the below elements: Cr, W, Mo, Al, Ti, Co; also it can be added with the Co, C, N, Nb, Cu, B, Si and the minim rare-earth metal which can be the Ce, Y and the Hf. The invention has the high hardness, the strength and the low melting point, high wearing resistance. It has improved the cracking resistance, moldability, the stability and the uniformity of the laser melting layer. So it can repair the high temperature alloy, the carbon steel, the structural steel and the stainless steel by the laser melting.
Owner:SHENYANG DALU LASER TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com