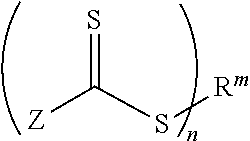
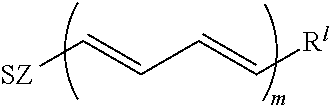
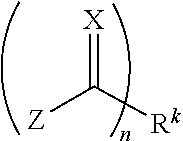Patents
Literature
220 results about "Melting layer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
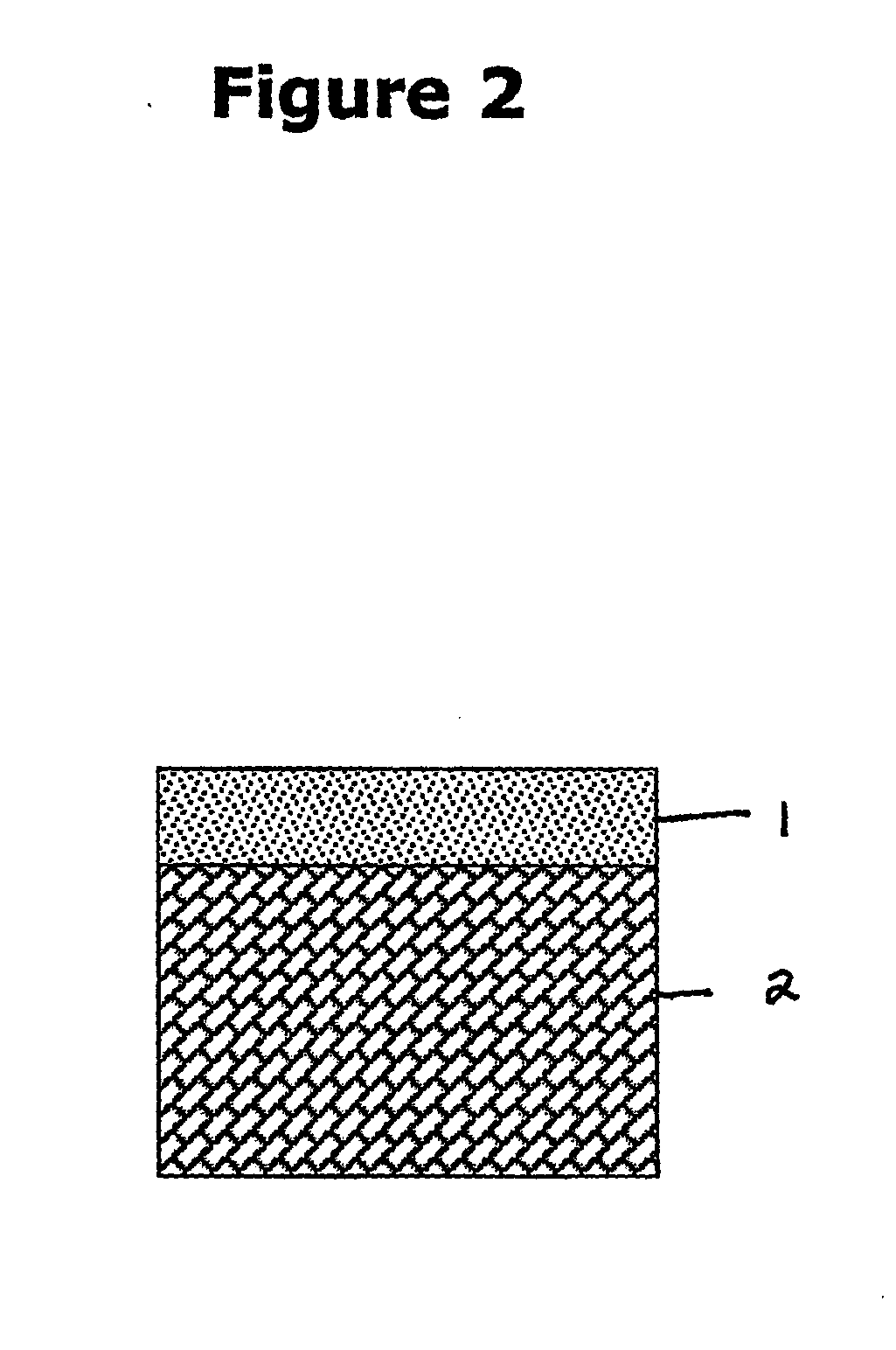
Melting layer. The altitude interval throughout which ice-phase precipitation melts as it descends. The top of the melting layer is the melting level. The melting layer may be several hundred meters deep, reflecting the time it takes for all the hydrometeors to undergo the transition from solid to liquid phase.
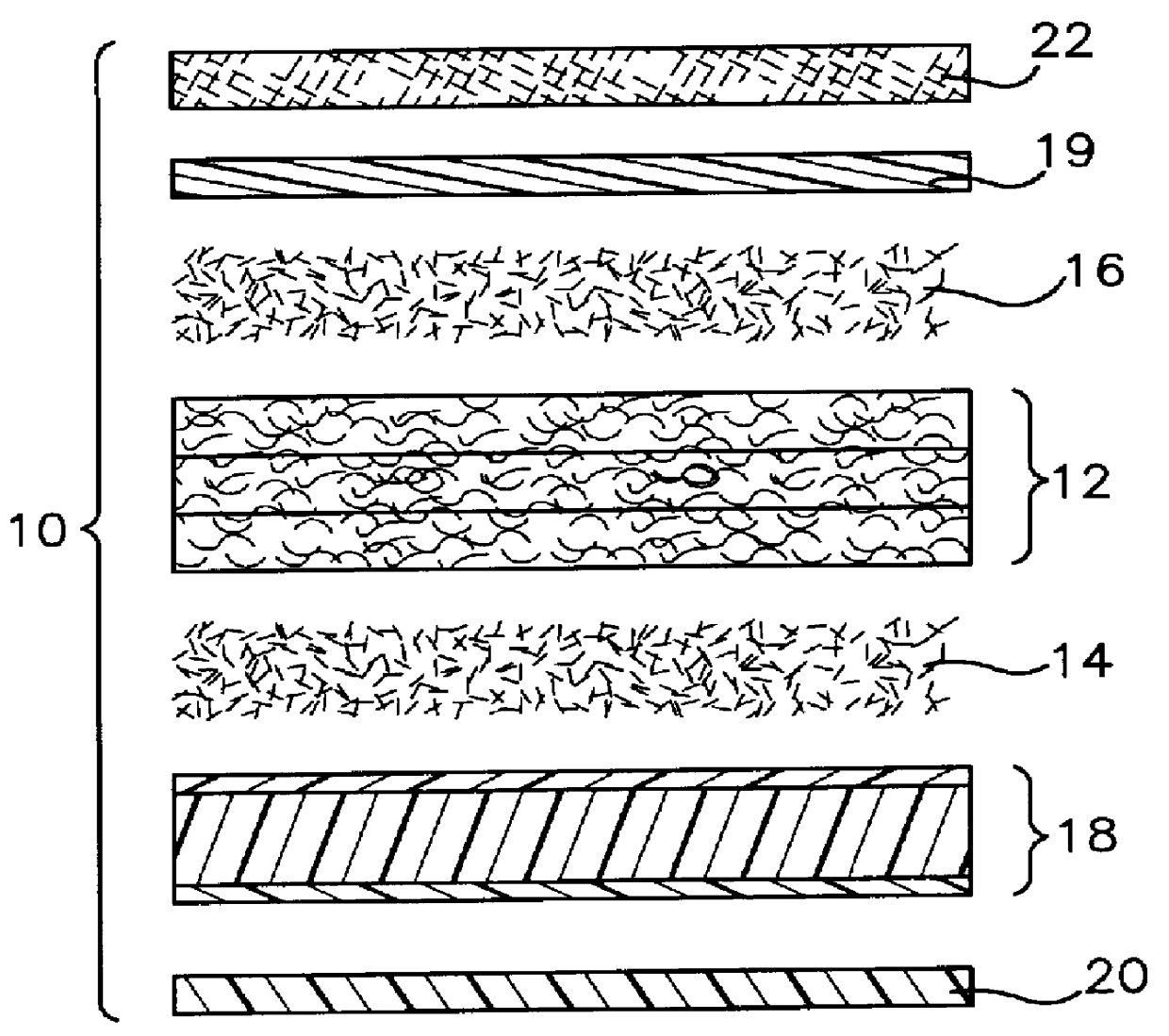
Composite panels
A composite panel consisting of outer skins and an inner core consisting of a foamed polymer, wherein the structure or properties of the inner core are anisotropic. The composite panel can be made by applying external heat and pressure to melt a skin of thermoplastic composite and an initial thickness of a thermoplastic core which has anisotropic properties causing the skin and core to fuse together followed by cooling the fused structure. The composite panel can be made by applying external heat and pressure to melt layers of a thermoplastic adhesive positioned between the outer skins and an inner core consisting of a foamed polymer, wherein the structure or properties of the inner core are anisotropic, so that the skins are bonded to the core by the melted layers of the thermoplastic adhesive followed by cooling the bonded structure.
Owner:EDWARDS CHRISTOPHER M
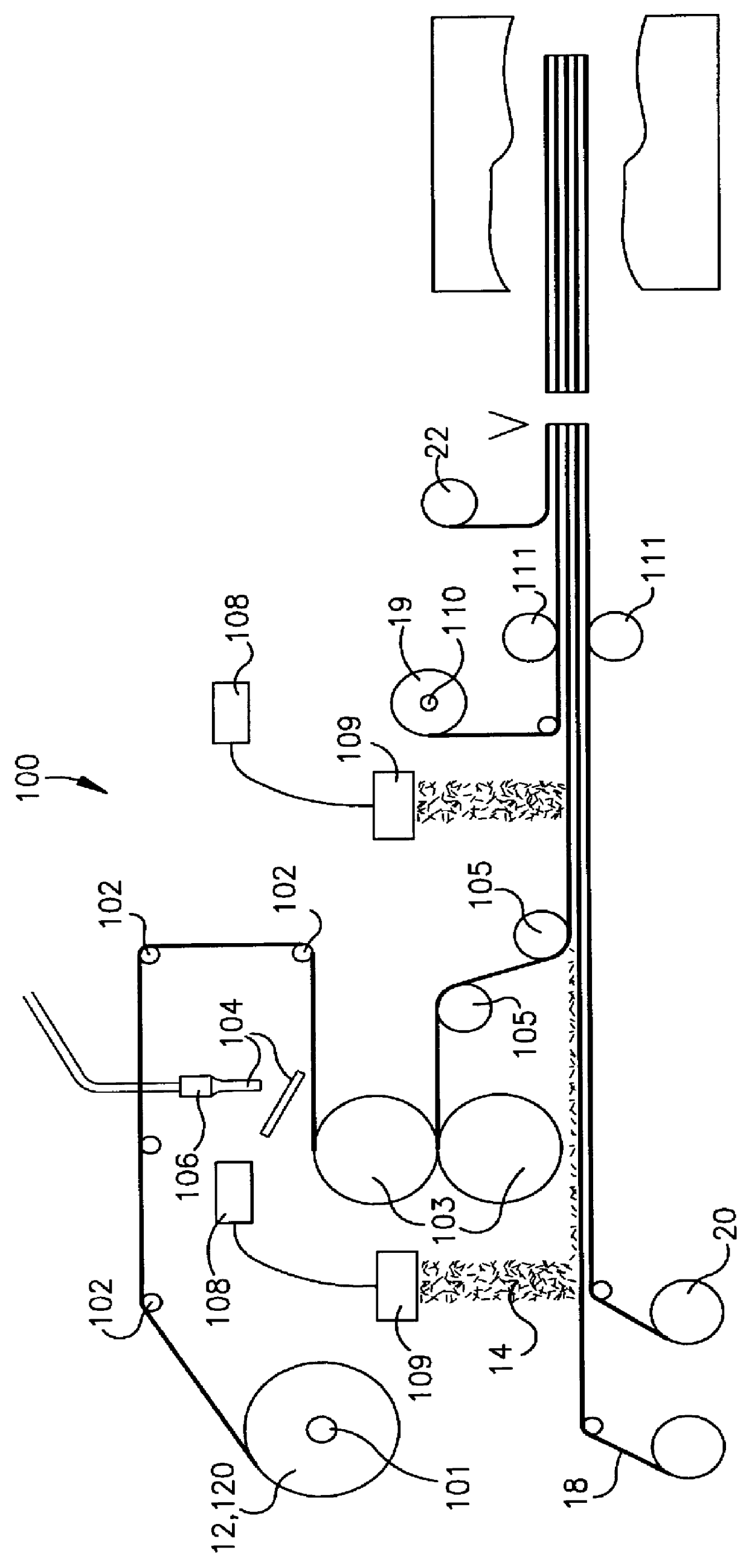
Laminated structures with multiple denier polyester core fibers, randomly oriented reinforcement fibers, and methods of manufacture
InactiveUS6156682AEnhanced sound absorption and structural propertySynthetic resin layered productsLaminationFiberPolyester
A laminated panel-type structure particularly suited for vehicle interior applications such as headliners and door panels has a multiple denier polyester fiber core and randomly oriented structural reinforcing fibers. The laminated structure has superior sound attenuation properties resulting from a core of intertwined polyester fibers of differing deniers, with preferably relatively larger denier fibers on exterior areas of the core and some bicomponent fibers, short non-woven reinforcing fiber strands which are randomly attached and intertwined with the core on opposing major sides of the core, an impervious polymer film with a low melt layer which retains the reinforcing fibers against one side of the core and is attached to a scrim layer, and a polymer web on an opposite side of the core which retains the reinforcing fiber strands on the opposing major side of the core and to which a cover stock is applied. The invention further includes a method of manufacturing the laminated structure wherein the various layers are sequentially unfurled from spools, passed through nip rollers at points of various subcombinations of materials and layers, the reinforcing fiber strands are randomly distributed on to the carrying layers from hoppers or directly from a fiber chopping device, and the completed laminated structure is cut and molded.
Owner:SK AUTOMOTIVE S DE R L DE
Electrostatic chuck member
InactiveUS20090080136A1Avoid damageAvoid layeringSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrostatic holding devicesSurface roughnessSpray coating
An electrostatic chuck member comprises an electrode layer and an electric insulating layer, wherein a spray coating layer of an oxide of a Group 3A element in the Periodic Table is formed as an outermost layer of the member and a surface of the spray coating layer is rendered into a densified re-melting layer having an average surface roughness (Ra) Of 0.8-3.0 μm.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD +1
Specialized substrates for use in sequential lateral solidification processing
InactiveUS6582827B1Polycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh conductivitySilicon
Substrates having modified effective thermal conductivity for use in the sequential lateral solidification process are disclosed. In one arrangement, a substrate includes a glass base layer, a low conductivity layer formed adjacent to a surface of the base layer, a high conductivity layer formed adjacent to the low conductivity layer, a silicon compound layer formed adjacent to the high conductivity layer, and a silicon layer formed on the silicon compound layer. In an alternative arrangement, the substrate includes an internal subsurface melting layer which will act as a heat reservoir during subsequent sequential lateral solidification processing.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Powdery alloy processing material in site by movable laser smelt-coating process
A movable field processing alloy powder material for the laser melting is to reinforce the nickel-base alloy using the below elements: Cr, W, Mo, Al, Ti, Co; also it can be added with the Co, C, N, Nb, Cu, B, Si and the minim rare-earth metal which can be the Ce, Y and the Hf. The invention has the high hardness, the strength and the low melting point, high wearing resistance. It has improved the cracking resistance, moldability, the stability and the uniformity of the laser melting layer. So it can repair the high temperature alloy, the carbon steel, the structural steel and the stainless steel by the laser melting.
Owner:SHENYANG DALU LASER TECH
Copolyamide powder and its preparation, use of copolyamide powder in a shaping process and mouldings produced from this copolyamide powder
ActiveUS20090236775A1Low viscosityHigh dimensional accuracyAdditive manufacturing apparatusElectric discharge heatingLaurolactamPolyamide
A task often encountered in very recent times is the rapid provision of prototypes. Particularly suitable processes are those based on pulverulent materials and in which the desired structures are produced layer-by-layer through selective melting and solidification. The invention provides the constitution, production and use of a copolyamide powder which was produced using the following monomer units: a) laurolactam or ω-aminoundecanoic acid, and also b) dodecanedioic acid, and either c) decanediamine or dodecanediamine, in shaping processes, and also to mouldings produced through a layer-by-layer process which selectively melts regions of a powder layer, using this specific powder. Once the regions previously melted layer-by-layer have been cooled and solidified, the moulding can be removed from the powder bed. The mouldless layer-by-layer processes for the production of components using the copolyamide powder result in simplified and more reliable conduct of the process and better recyclability.
Owner:EVONIK OPERATIONS GMBH
Method of heat treatment and heat treatment apparatus
InactiveUS20060249073A1No longer performedEfficient productionPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsSeed crystalEquipment use
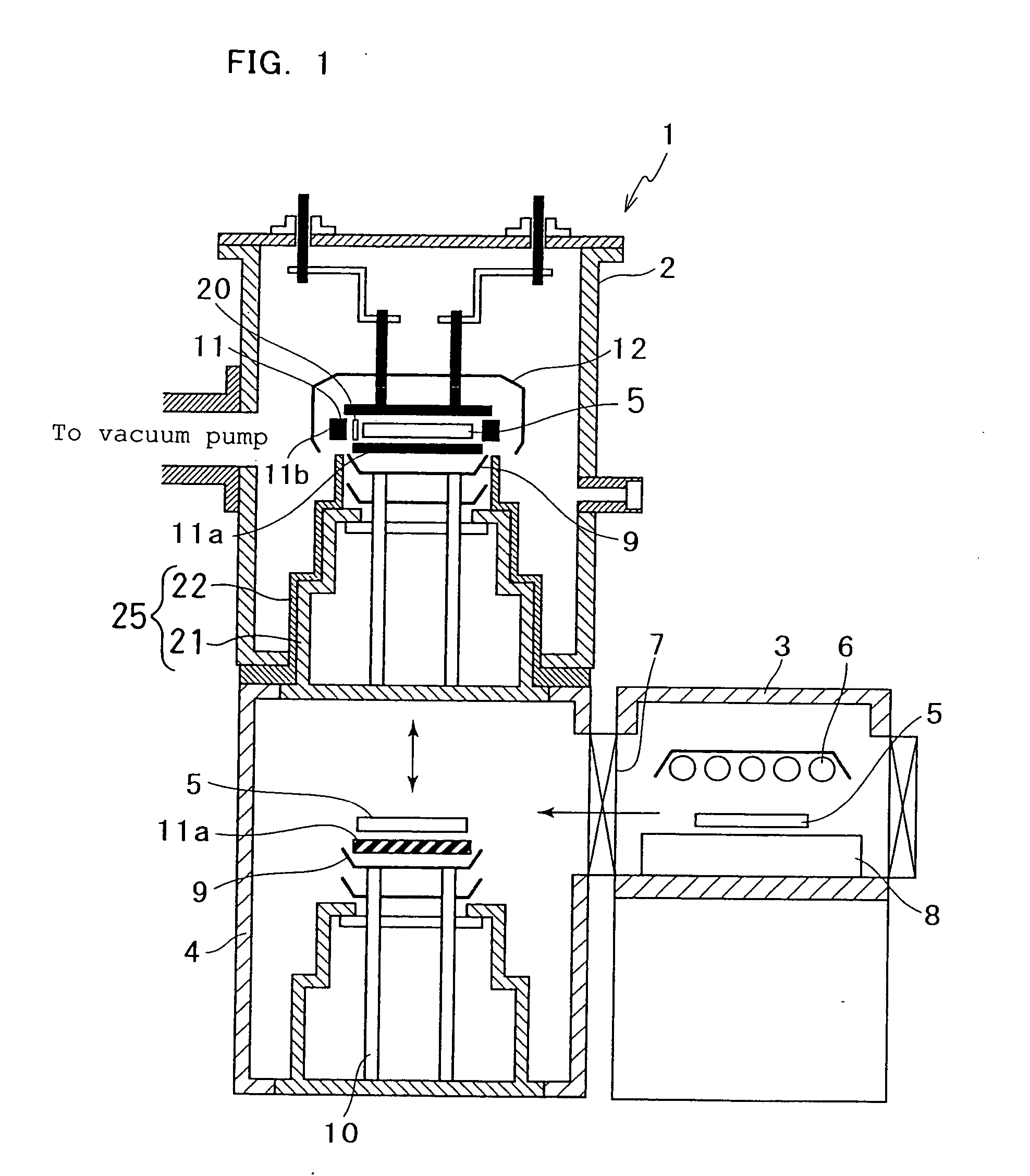
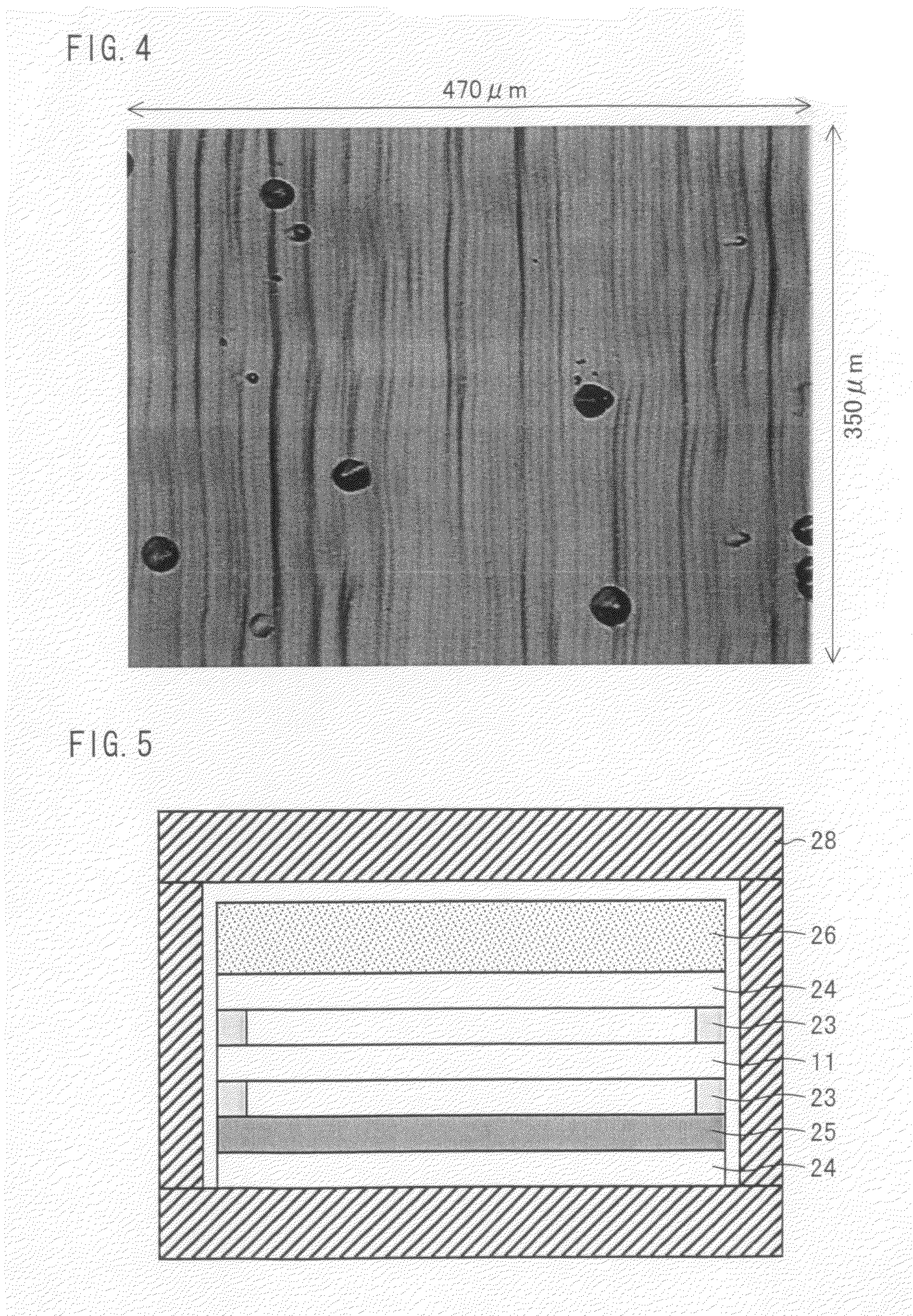
The present invention is a method suitable for heat treatment, or a heat treatment method for growing single crystal silicon carbide by a liquid phase epitaxial method, wherein a monocrystal silicon carbide substrate as a seed crystal and a polycrystal silicon carbide substrate are piled up, placed inside a closed container, and subjected to high-temperature heat treatment, by which very thin metallic silicon melt layer is interposed between the monocrystal silicon carbide substrate and the polycrystal silicon carbide substrate during heat treatment, and single crystal silicon carbide is liquid-phase epitaxially grown on the monocrystal silicon carbide substrate. The closed container is in advance heated to a temperature exceeding approximately 800° C. in an preheating chamber kept at a pressure of approximately 10−5 Pa or lower, the closed container is reduced in pressure to approximately 10−5 Pa or lower, and the container is transported and placed in the heat chamber, which is in advance heated to a prescribed temperature in a range from approximately 1400° C. to 2300° C., in a vacuum at a pressure of approximately 10−2 Pa or lower or in an inert gas atmosphere at a prescribed reduced pressure, by which the monocrystal silicon carbide substrate and the polycrystal silicon carbide substrate are heated in a short time to a prescribed temperature in a range from approximately 1400° C. to 2300° C. to produce single crystal silicon carbide which is free of fine grain boundaries and approximately 1 / cm2 or lower in density of micropipe defects on the surface. Further, the present invention is heat treatment equipment used in carrying out the heat treatment method.
Owner:THE NEW IND RES ORG
Sic epitaxial substrate and method for producing the same
InactiveUS20100119849A1High film thicknessReduce in quantityPolycrystalline material growthBy zone-melting liquidsSingle crystalOptoelectronics
In one embodiment of the present invention, a monocrystal SiC epitaxial substrate is produced which includes a monocrystal SiC substrate; a buffer layer made of a first SiC epitaxial film formed on the monocrystal SiC substrate; and an active layer made of a second SiC epitaxial film formed on the buffer layer. The buffer layer is grown by heat-treating a set of the monocrystal SiC substrate, a carbon source plate, and a metal Si melt layer having a predetermined thickness and interposed between the monocrystal SiC substrate and the metal Si melt layer, so as to epitaxially grow monocrystal SiC on the monocrystal SiC substrate. The active layer is grown by epitaxially growing monocrystal SiC on the buffer layer by vapor phase growth method. This allows for production of a monocrystal SiC epitaxial substrate including a high-quality monocrystal SiC active layer being low in defects.
Owner:RES INST OF INNOVATIVE TECH FOR THE EARTH +1
Differential melt-electrospinning jet head
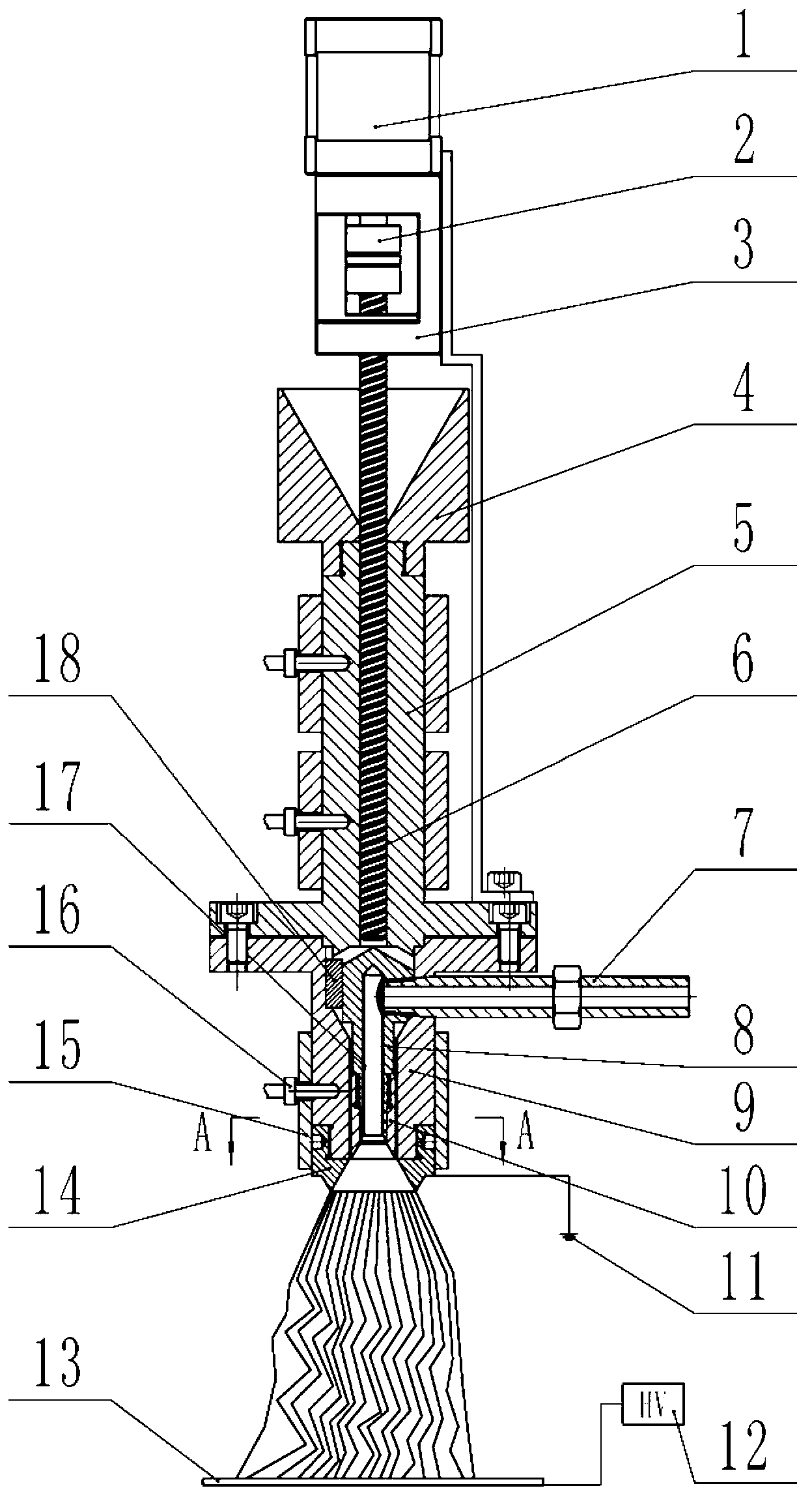
The invention discloses a differential metl-electrospinning jet head and belongs to the field of electrostatic spinning. The differential metl-electrospinning jet head mainly comprises a hopper, a charging barrel, a jet head body, an internal cone-shaped jet head, an airflow channel air inlet pipe, an airflow channel standpipe, an airflow channel insulating layer, a jet head inner body, a button, a jackscrew, a heating device, a temperature sensor, a screw rod, a coupler, a servomotor, a motor support, a grounding electrode, a receiving electrode plate and a high-voltage electrostatic generator. The differential metl-electrospinning jet head adopts a center-feeding and side-air-intake manner, ensures uniform melt circumferential distribution through the adjustment of the jackscrew, adopts the inner cone-shaped jet head, and can spin dozens of filaments through a single jet head, thereby achieving high spinning efficiency; and by the aid of hot air, the melt layer on the inner cone surface can be blown thinner, the filaments can be drawn, and a heat insulation role can be played on the environmental temperature to slow down cooling of the filaments and prolong the filament drawing time. Therefore, the spun filaments are thinner. The differential metl-electrospinning jet head has the advantages of simple structure, capability of spinning thin fibers and high spinning efficiency.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Method of sealing a free edge of a composite material
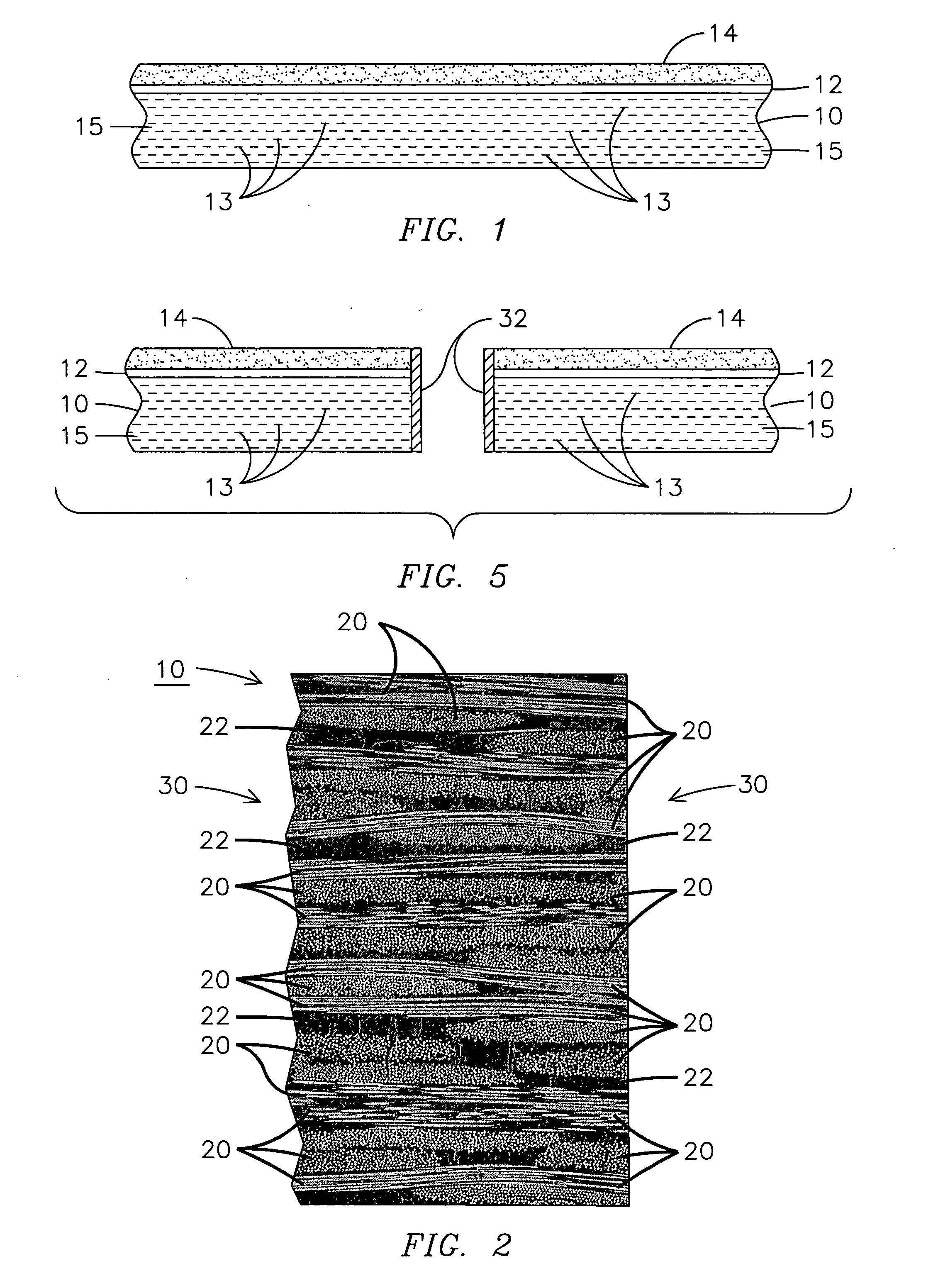
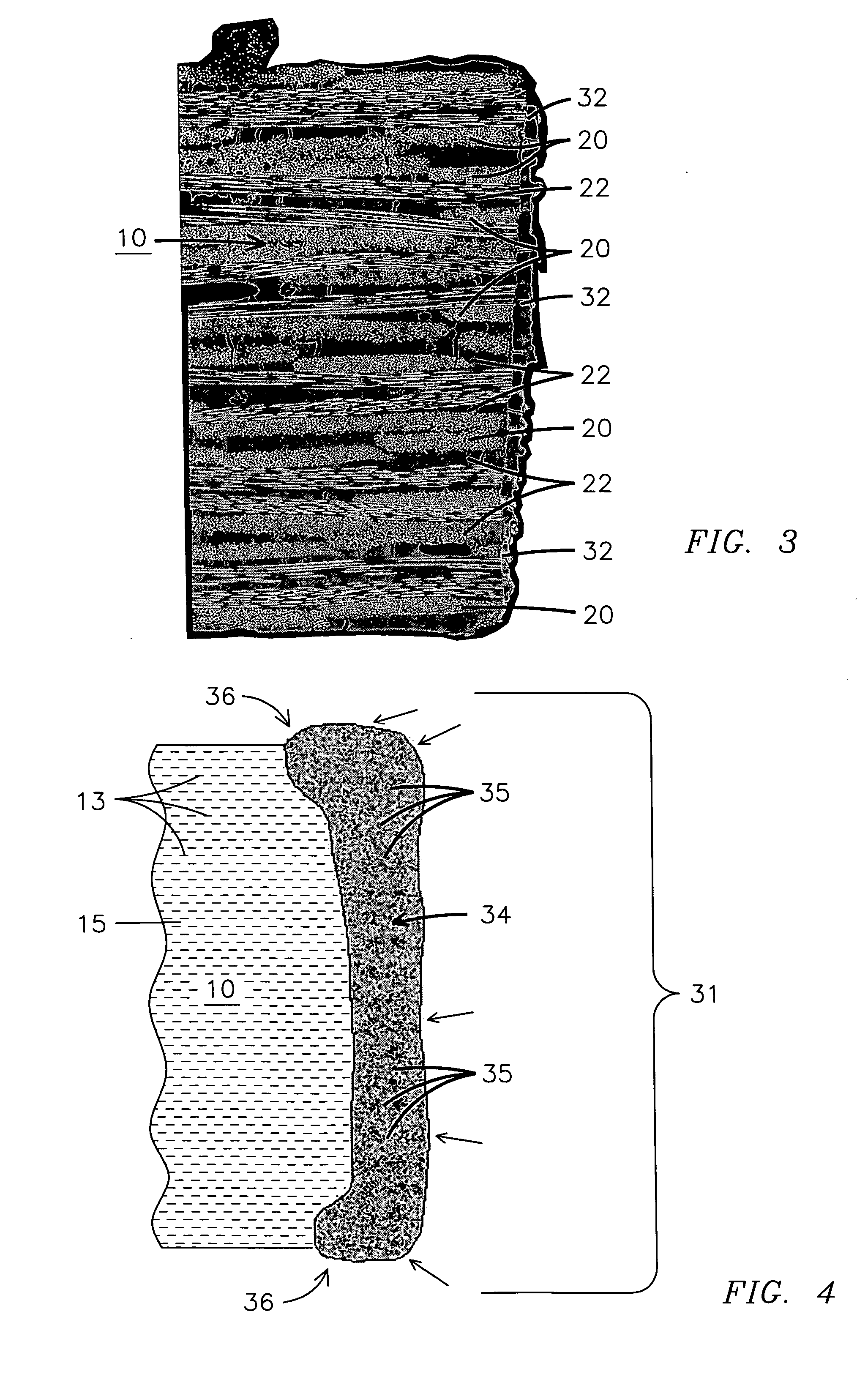
A method of coating an edge surface (30) of an anisotropic ceramic matrix composite material (10) for use in a high temperature environment is disclosed where the edge surface (30) has exposed reinforced fiber layers (20). A laser beam may be used to melt a portion of the ceramic matrix composite material (10) on the edge surface (30) forming a melt layer. The melt layer is retained proximate the edge surface and the laser beam is controlled to form an isotropic protective coating (32, 34) on a portion of the edge surface (30). A method may be used to form a component for use in a high temperature environment that includes directing a laser beam toward a ceramic matrix composite material (10), controlling the laser beam to melt a portion of the ceramic matrix composite material (10) and forming a homogeneous protective coating (32, 34) from a melt layer that exerts compression on at least a portion of the ceramic matrix composite material (10) when the melt layer is cooled. A powder material (35) may be added to a surface of the ceramic matrix composite material (10) selected to melt with the ceramic matrix composite material (10) to improve the wear resistance or hardness of the isotropic protective coating (32, 34).
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
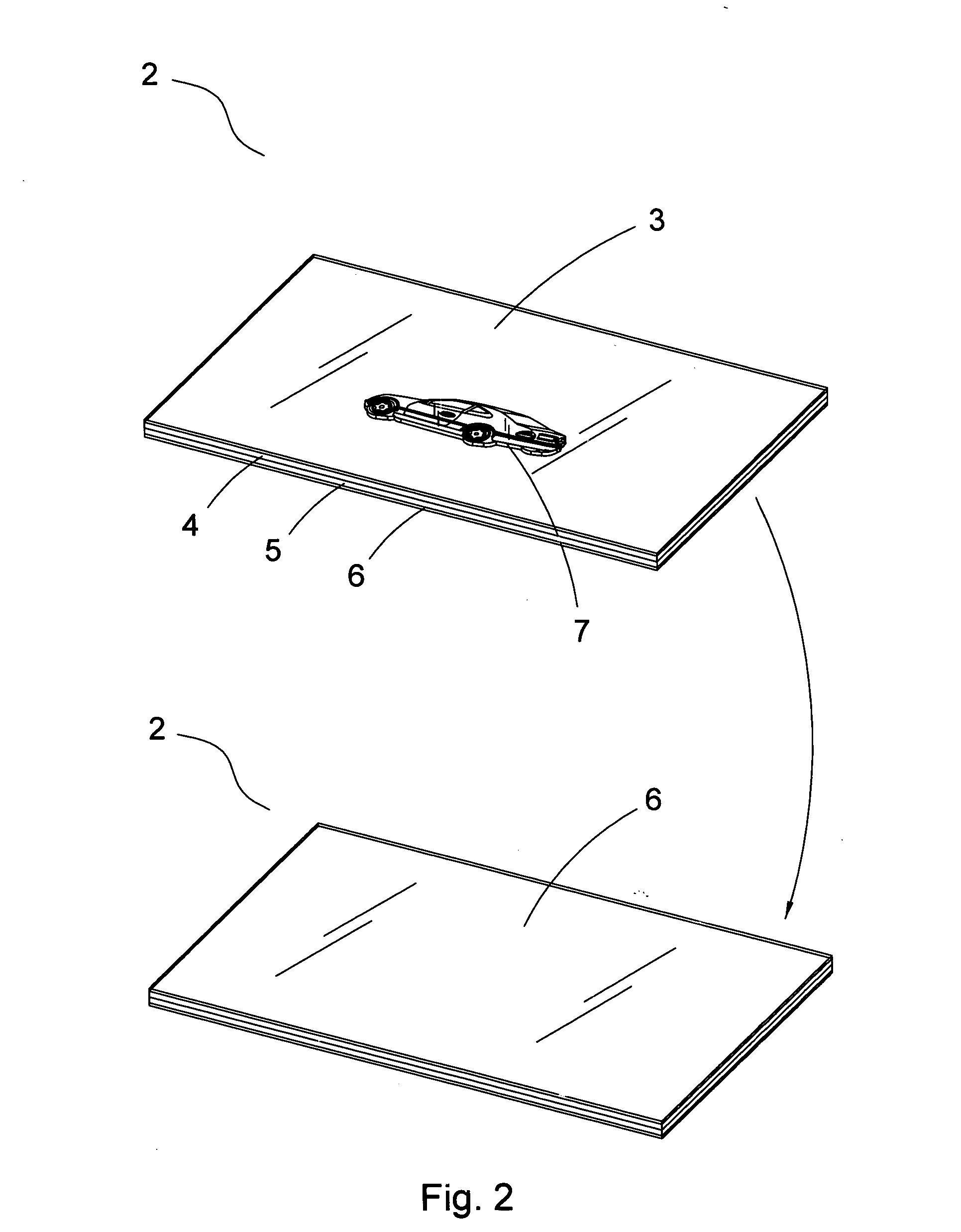
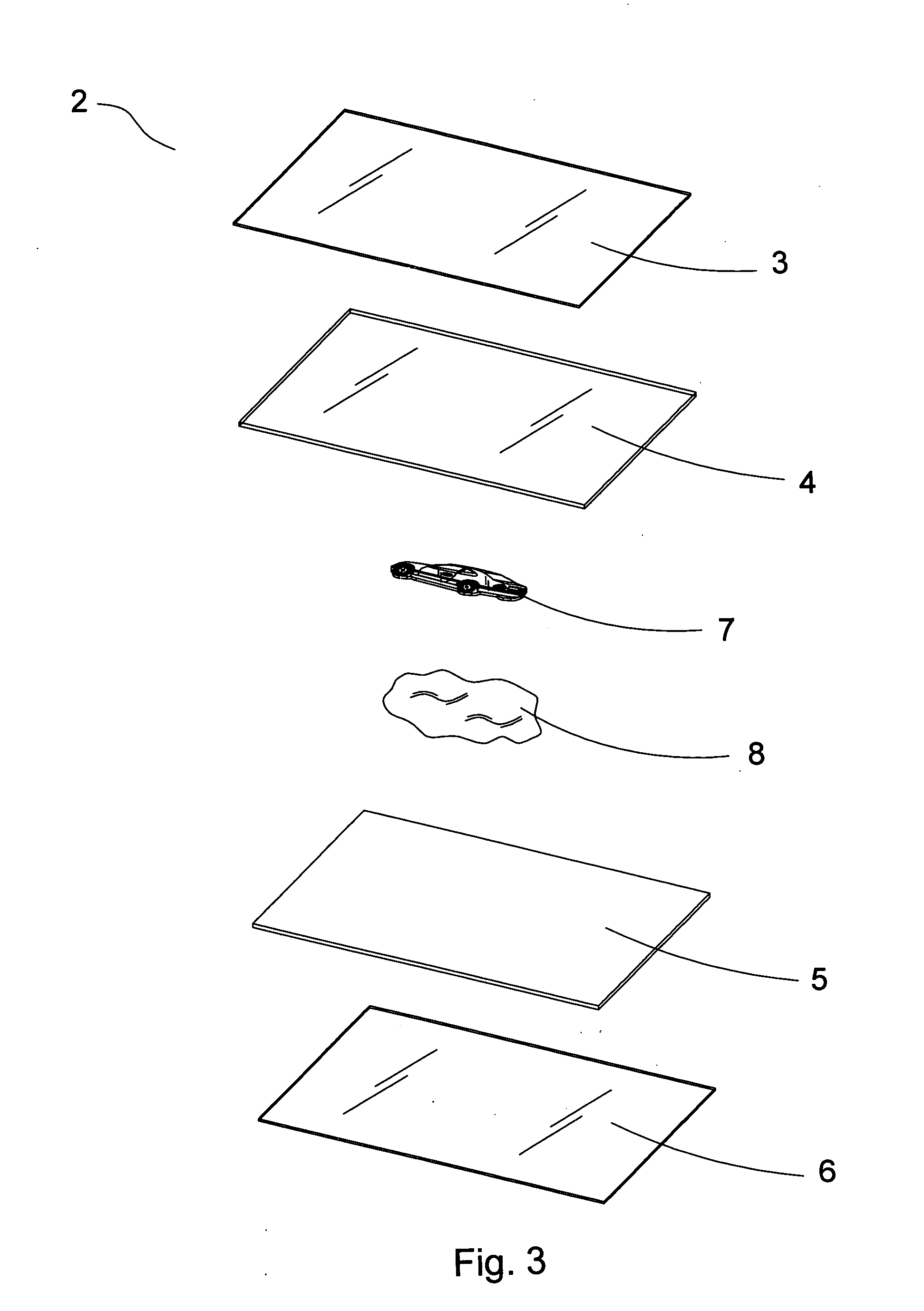
Card with a picture-contained mirror surface layer
InactiveUS20070020443A1Decorative surface effectsDuplicating/marking methodsSurface layerEngineering
A card with a picture-contained mirror surface layer comprises an upper covering layer; an upper middle layer installed below the upper covering layer; a lower middle layer installed below the upper middle layer; a lower covering layer installed below the lower middle layer; and a picture-contained mirror surface layer installed at a position between the upper covering layer and the upper middle layer or between the upper middle layer and the lower middle layer, or the picture-contained mirror surface layer is installed between the lower middle layer and the lower covering layer. Or the combination of the different layers is performed by mechanically melting the layers and then combining the melting layers. The picture-contained mirror surface layer is made from compound material or metals. The picture is selected from textures, numbers, figures, or the combinations of above items. The different layers have present different light effect.
Owner:TAIWAN NAME PLATE
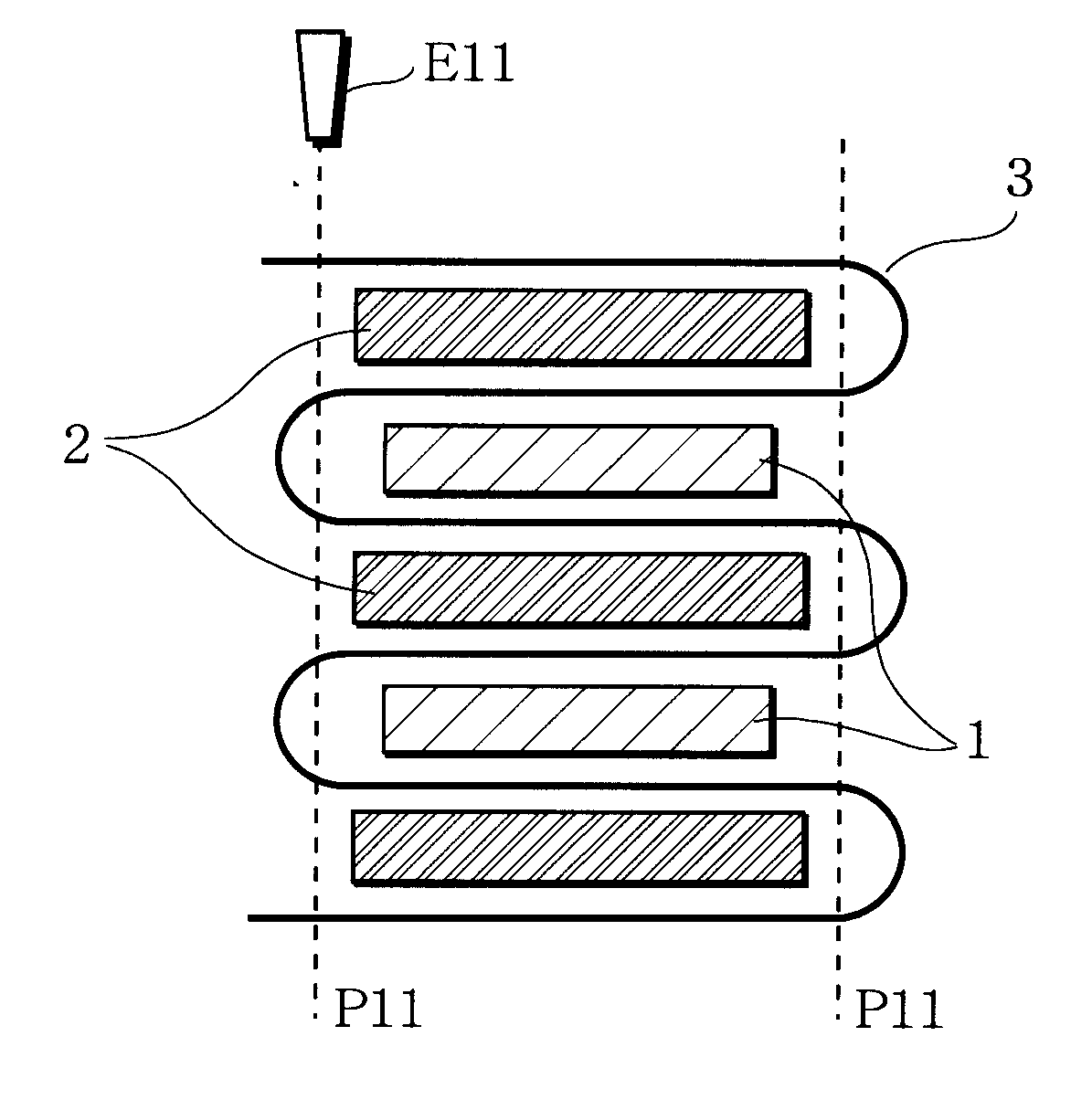
Stack type battery
InactiveUS20110244304A1Raise security concernsCell seperators/membranes/diaphragms/spacersCell electrodesElectrical batteryHeat resistance
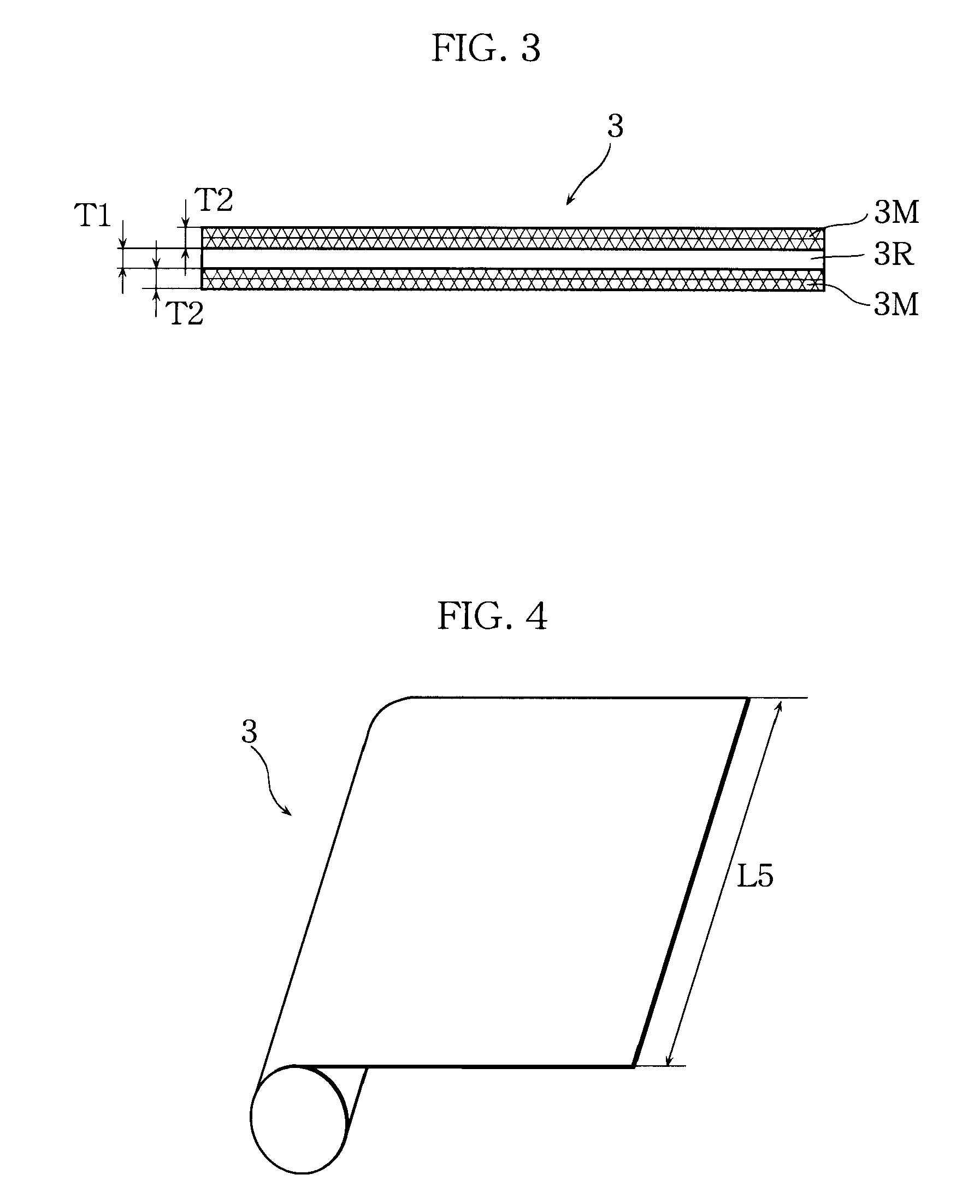
A stack type battery has a plurality of positive electrode plates (1), a plurality of negative electrode plates (2), and a separator (3) interposed therebetween. The positive electrode plates (1) and the negative electrode plates (2) are alternately stacked one on the other. The separator (3) has a heat-resistant layer (3R) having heat resistance and heat-melting layers (3M), each of the heat-melting layers (3M) having a shutdown function and a melting point lower than the melting point of the heat-resistant layer (3R) and disposed over the entire surface of each of both sides of the heat-resistant layer (3R). The heat-melting layers (3M) of the separator (3) are fixed to each other by thermal welding.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Device for manufacturing nano laminated composite material
The invention relates to a device for manufacturing a nano laminated composite material, which comprises a plastifying device, a converging device, a laminated composite generator and a molding device which are sequentially connected in series front and back, wherein the laminated composite generator is used for averagely dividing n layers of polymer melts extruded by the converging device into m equal parts along the width direction; when each equal part of melt continues to forwards flow in the laminated composite generator, the melt is rotated for 90 degrees and broadened by m times so as to mutually converge with an adjacent melt layer into a laminated structure at an outlet end; then an identical laminated composite generator is connected in series to obtain an n*m*m structure; and if k identical laminated composite generators are connected in series, a multi-layer structure composite material with n*mk layers can be obtained. In the invention, the laminated composite generators rotating for 90 degrees after melt segmentation are adopted, thus the segmentation quantity is large, the quantity of serial units can be reduced, and the melt is easy to maintain a symmetrical structure in a flow broadening and thinning process, so that the layer thickness precision is easy to guarantee, and a nano laminated composite multi-layer product can be obtained.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Polymer powder for producing three-dimensional objects
InactiveUS20140121327A1Improve stabilityLow viscosityAdditive manufacturing apparatusAdditive manufacturing with solidsPowder mixtureMetallurgy
The invention relates to the use of a powder made of a polymer, which of two or more components with functionalities suitable for Diels-Alder reactions, or of a powder mixture (dry blend) made of powders respectively of at least one of the reactive components, where these together enter into the Diels-Alder reaction with one another and are capable of a retro-Diels-Alder reaction, in a rapid-prototyping process.The invention further relates to moldings produced with use of said polymer powder through a layer-by-layer shaping process in which regions of a powder layer are melted selectively. The molding here can be removed from the powder bed after cooling and hardening of the regions previously melted layer-by-layer.
Owner:EVONIK OPERATIONS GMBH
Laminated structures with multiple denier polyester core fibers, randomly oriented reinforcement fibers, and methods of manufacture
InactiveUS20010000162A1Enhanced sound absorption and structural propertyAdhesive processesWood working apparatusUltrasound attenuationFiber
A laminated panel-type structure particularly suited for vehicle interior applications such as headliners and door panels has a multiple denier polyester fiber core and randomly oriented structural reinforcing fibers. The laminated structure has superior sound attenuation properties resulting from a core of intertwined polyester fibers of differing deniers, with preferably relatively larger denier fibers on exterior areas of the core and some bicomponent fibers, short non-woven reinforcing fiber strands which are randomly attached and intertwined with the core on opposing major sides of the core, an impervious polymer film with a low melt layer which retains the reinforcing fibers against one side of the core and is attached to a scrim layer, and a polymer web on an opposite side of the core which retains the reinforcing fiber strands on the opposing major side of the core and to which a cover stock is applied. The invention further includes a method of manufacturing the laminated structure wherein the various layers are sequentially unfurled from spools, passed through nip rollers at points of various subcombinations of materials and layers, the reinforcing fiber strands are randomly distributed on to the carrying layers from hoppers or directly from a fiber chopping device, and the completed laminated structure is cut and molded.
Owner:SK AUTOMOTIVE S DE R L DE
Reactive dye printing process
InactiveUS6840614B2Prevent premature and undesired reactionAbove the melting point of the waxRecording apparatusInk ribbonsDisperse dyeCellulose
A formulation and method of printing an ink or meltable ink layer having reactive dyes or mixtures of reactive dyes and disperse dyes as colorants. The ink or ink melt layer also includes an alkaline substance, a binder, and optionally, a heat-activated printing additive. Permanently bonded color images are provided by the reaction between the reactive dye and the final substrate, which may be any cellulosic, protein, or polyamide fiber material, or mixtures with polyester. Reaction occurs upon heat activation of the printed ink image.
Owner:SAWGRASS SYST INC
Aluminum thermal self-propagating-injection depth reduction based method for preparing metal titanium
ActiveCN104131178AShort processReduce energy consumptionIncreasing energy efficiencyRoom temperatureMedium frequency
An aluminum thermal self-propagating-injection depth reduction based method for preparing metal titanium belongs to the technical field of metal titanium smelting. The method is as below: using an aluminum thermal self-propagating reduction process to reduce rutile or high titanium slag to obtain a high temperature melt; then conducting insulation smelting separation on the high temperature melt in a medium frequency induction furnace to form a slag layer with alumina as an upper layer and a titanium melt layer as a lower layer; injecting CaF2-CaO pre-melted slag to the alumina based slag layer in a bottom blowing way; washing slag and refining; then injecting a high temperature calcium magnesium steam or a high-temperature steam to the high temperature titanium metal melt layer through inert carrier gas carrying in a bottom blowing mode, and conducting eccentric mechanical stirring and depth reduction refining; and finally, cooling the high temperature melt to room temperature to remove the upper metal smelting slag, so as to obtain the metal titanium. The method of the invention can realize low cost and short process preparation of metal titanium, and the prepared metal titanium has oxygen removed completely. The method has the advantages of short process, low energy consumption and simple operation, etc.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
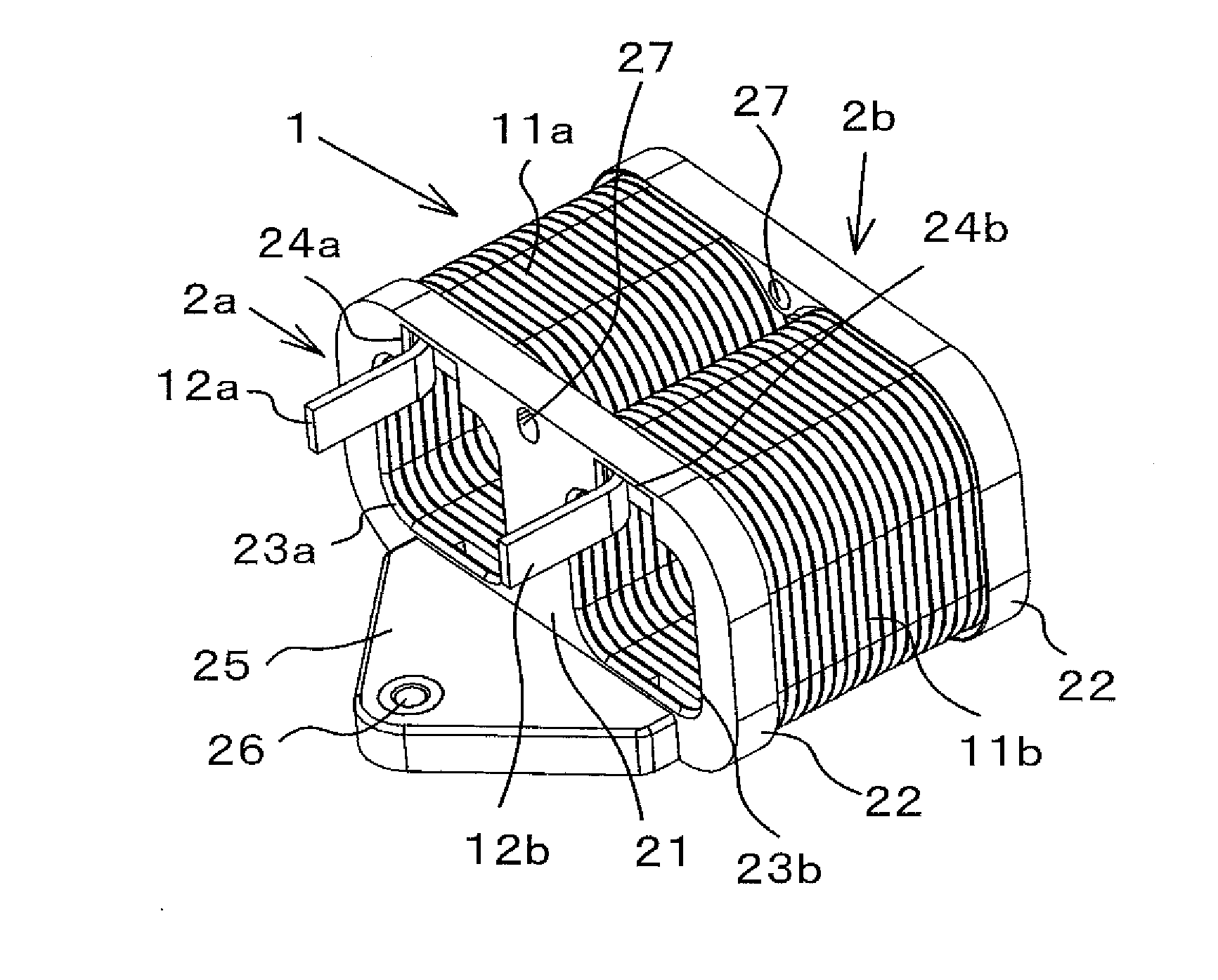
Coil and manufacturing method for same, and reactor
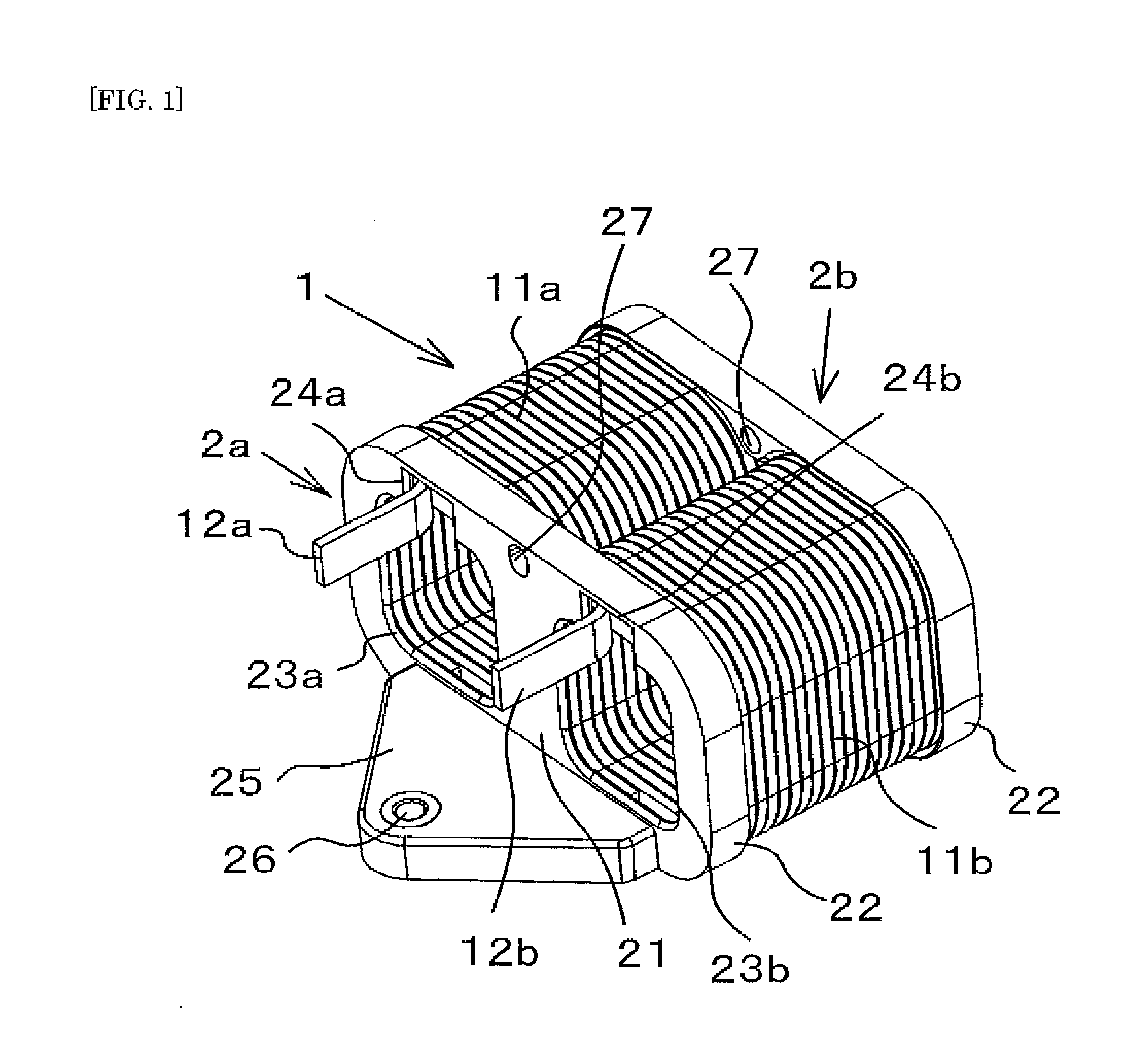
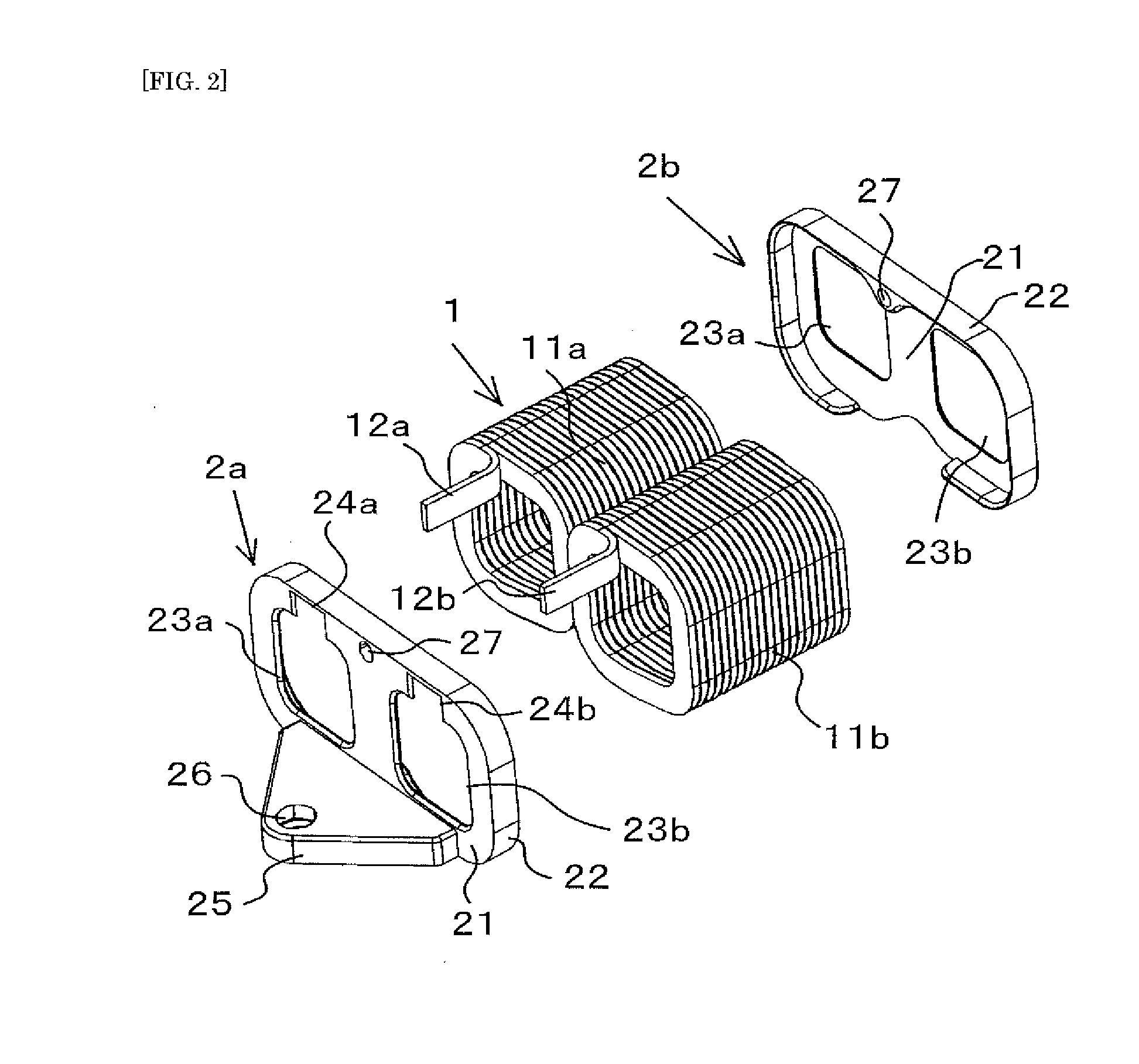
ActiveUS20150162119A1Avoid easy removalReduce the number of stepsTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsElectric component structural associationEngineeringMelting layer
A coil includes a coil unit provided with a wire and a self-melting layer formed on surfaces of the wire, and a resin member affixed to the wire. The wire is adhered and affixed to the resin member by the self-melting layer.
Owner:TAMURA KK
Composite film structure for manufacturing pouches using rotary thermic sealing
A sealant layer for use in a composite film structure, which includes at least one non-melting layer, the structure being for manufacturing pouches for containing flowable material utilizing high speed vertical form, fill and seal processes with rotary thermic sealing, the sealant layer comprising from about 70 to about 90% by weight of a single-site catalyst C4-C10 ethylene alpha-olefin polymer having a density in the range of from 0.890 to about 0.912 gm / cc and a melt index in the range of from about 0.2 to about 2.0 dg / cc, and from about 10 to about 30% by weight of one or more of the following: a linear low density polyethylene selected from single-site catalyst and multi-site catalyst polymers, the polyethylenes having a density in the range of from about 0.916 to about 0.930 gm / cc, a high pressure low density polyethylene and processing additives.
Owner:DUPONT CA
Device and method for removing re-melting layers on inner walls of air film holes of blades
InactiveCN102335789AImprove cooling effectExtended service lifeElectrolysis componentsElectrochemical machining apparatusTemperature controlControl system
The invention provides a device and method for removing re-melting layers on inner walls of air film holes of blades. In the invention, the re-melting layers on the inner walls of the air film holes of the blades are uniformly removed by adopting an electrolyte-plasma machining technology. The device is characterized by comprising a direct-current (DC) power supply, a control system, a temperature control system, a filter system and a hydraulic system. The invention has the beneficial effects that the inner walls of the air film holes of the blades are processed with high-pressure internal flushing electrolyte in a non-immersion manner so as to effectively remove the re-melting layers of micro-holes; the device and method provided by the invention are convenient for implementation, achieve the effects of uniform allowance, no re-melting layer residue and high dimensional precision, have high operating efficiency improved by dozens of times as compared with an abrasive flow method, greatly enhance the air film cooling effect and prolong the service life of the blades.
Owner:SHENYANG LIMING AERO-ENGINE GROUP CORPORATION
Preparation method of rear-earth magnesium alloy product
The invention relates to a preparation method of a rear-earth magnesium alloy product. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: placing dehydrated rear-earth chlorate in a melting electrolysis device; adding dehydrated magnesium chloride, potassium chloride and titanium dichloride for dispersing, mixing and carrying out melting electrolysis, so that rear-earth magnesium intermediate alloy is generated by co-electrodeposition of rear-earth ion and magnesium ion at a negative electrode; burdening and mixing the rear-earth magnesium intermediate alloy and the metal magnesium in a smelting device, wherein a molar ratio of the rear-earth metal to the magnesium is (0.1-1.0):100; heating up the rear-earth magnesium alloy mixture for melting, immersing the smelting agent inside the melt and stirring, increasing the temperature to 780 DEG C and stewing for 20 minutes for dividing the melt into an upper layer, a middle layer and a lower layer, wherein the middle melt layer is used as the rear-earth magnesium alloy melt; casting after pre-cooling, cooling and forming, and carrying out surface treatment after carrying out mechanical processing and thermal processing, so that a compact proactive film layer is covered on the surface of the rear-earth magnesium alloy product. The preparation method of the rear-earth magnesium alloy product is high in preparation efficiency, safe and reliable in process, environment-friendly and low in energy consumption.
Owner:YANGZHOU FENG MING METAL PROD
Reactive dye printing process
InactiveUS6961076B2Prevent premature and undesired reactionAbove the melting point of the waxRecording apparatusInk ribbonsDisperse dyeCellulose
A formulation and method of printing an ink or meltable ink layer having reactive dyes or mixtures of reactive dyes and disperse dyes as colorants. The ink or ink melt layer also includes an alkaline substance, a binder, and optionally, a heat-activated printing additive. Permanently bonded color images are provided by the reaction between the reactive dye and the final substrate, which may be any cellulosic, protein, or polyamide fiber material, or mixtures with polyester. Reaction occurs upon heat activation of the printed ink image.
Owner:WAGNER BARBARA +1
Plasma arc melting enrichment method and plasma arc melting enrichment device for recycling metal elements of platinum group
InactiveCN102649999AHigh recovery rateFast smelting reductionProcess efficiency improvementSolid carbonMelting tank
The invention relates to a method and a device for recycling metal elements, in particular to a plasma arc melting enrichment method and a plasma arc melting enrichment device for recycling metal elements of a platinum group. The method comprises the steps of: mixing and grinding substances containing metal elements of the platinum group, ferric oxide, solid carbon reducer and fluxing agent in a dry method to be placed into a powder spraying tank, utilizing inert gases and / or reducing gases as carrier gases to convey materials in a suspension way so as to pass through an axial central hole of a graphite electrode of a plasma arc melting furnace adopting a close negative-pressure melting way, directly sending the materials into plasma arc to be reduced and melted and to enter a melting pool, utilizing iron collecting agent to collect and carry the elements of the platinum group so as to pass through a melted slag layer to enter a valuable iron melting layer, discharging glass-status melting slag and valuable iron out of a furnace body after standing, carrying out water quenching and granulating on the melting slag discharged from the furnace body, selecting the valuable iron particles or fine grains of the valuable iron to enter a wet metallurgic procedure together with the discharged valuable iron melting body, and continuously separating and purifying the metal elements of the platinum group.
Owner:HOOTECH
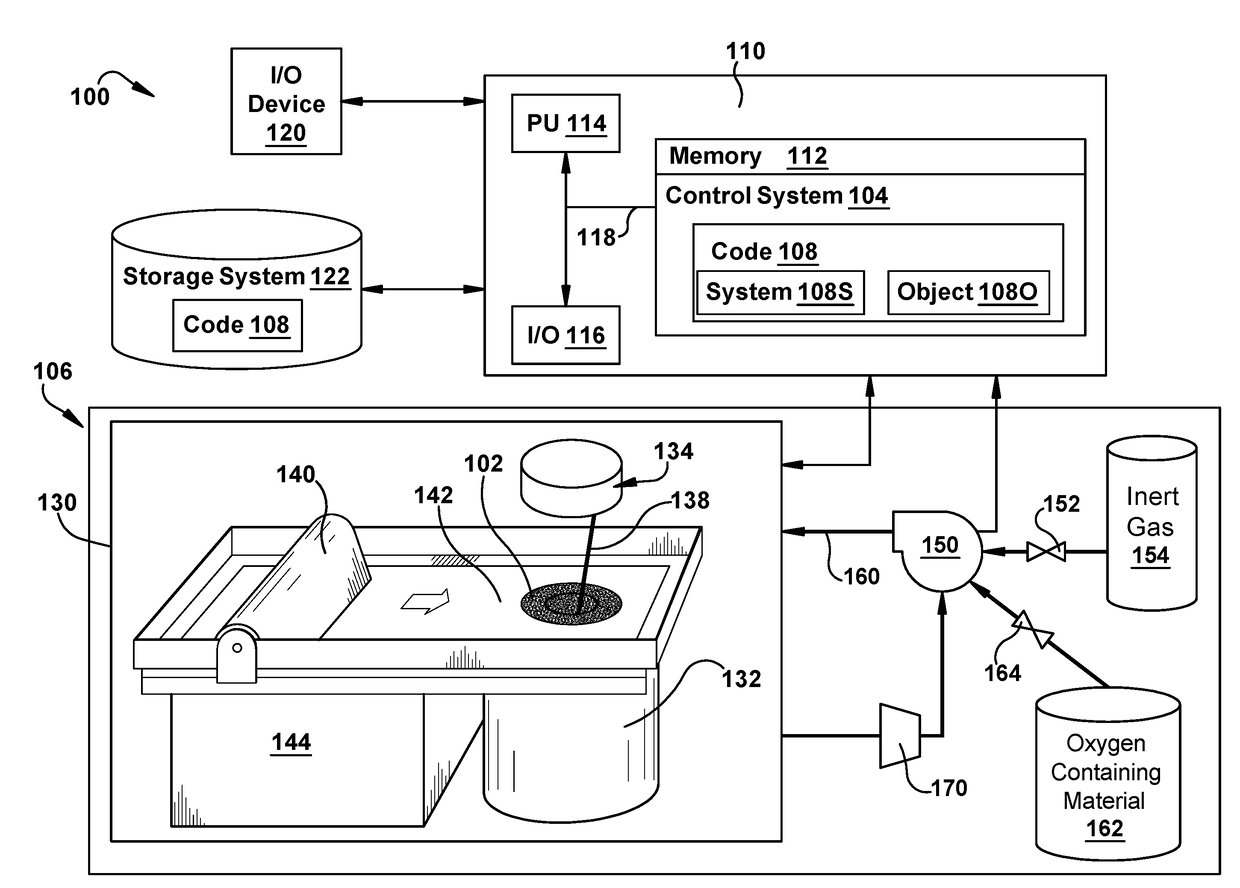
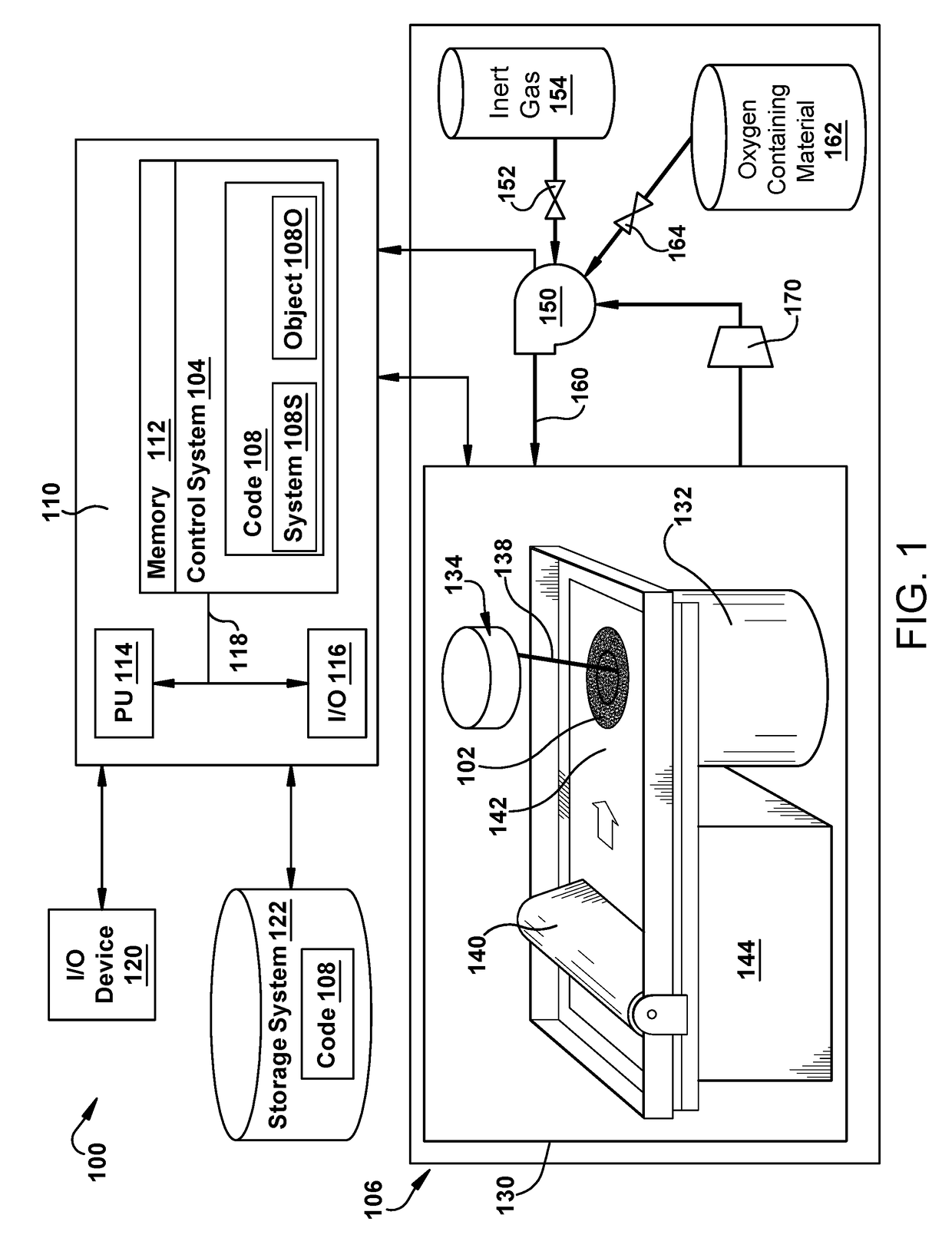
Metal additive manufacturing using gas mixture including oxygen
ActiveUS20170182598A1Additive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyControl systemOxygen
A metal powder additive manufacturing system and method are disclosed that use increased trace amounts of oxygen to improve physical attributes of an object. The system may include: a processing chamber; a metal powder bed within the processing chamber; a melting element configured to sequentially melt layers of metal powder on the metal powder bed to generate an object; and a control system configured to control a flow of a gas mixture within the processing chamber from a source of inert gas and a source of an oxygen containing material, the gas mixture including the inert gas and oxygen from the oxygen containing material.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Preparation method and device of in situ aluminum matrix composite
The invention relates to an aluminum matrix composite, in particular to a preparation method and device of an in situ aluminum matrix composite. The preparation method of the in situ aluminum matrix composite is characterized by comprising the steps that firstly, under the protection of gas, reactants are involved into melt layer by layer for a full contact reaction by means of electromagnetic stirring and interface reverse shear stirring formed by a graphite rotor; then the graphite rotor is placed into the reacting melt for continuous reverse stirring; and finally, casting molding is conducted at a normal casting temperature. The preparation method has the characteristics that composite reinforcement bodies are high in reacting generation efficiency and even in distribution; and the composite is stable in performance; the preparation method is easy to achieve; and industrial application is facilitated.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
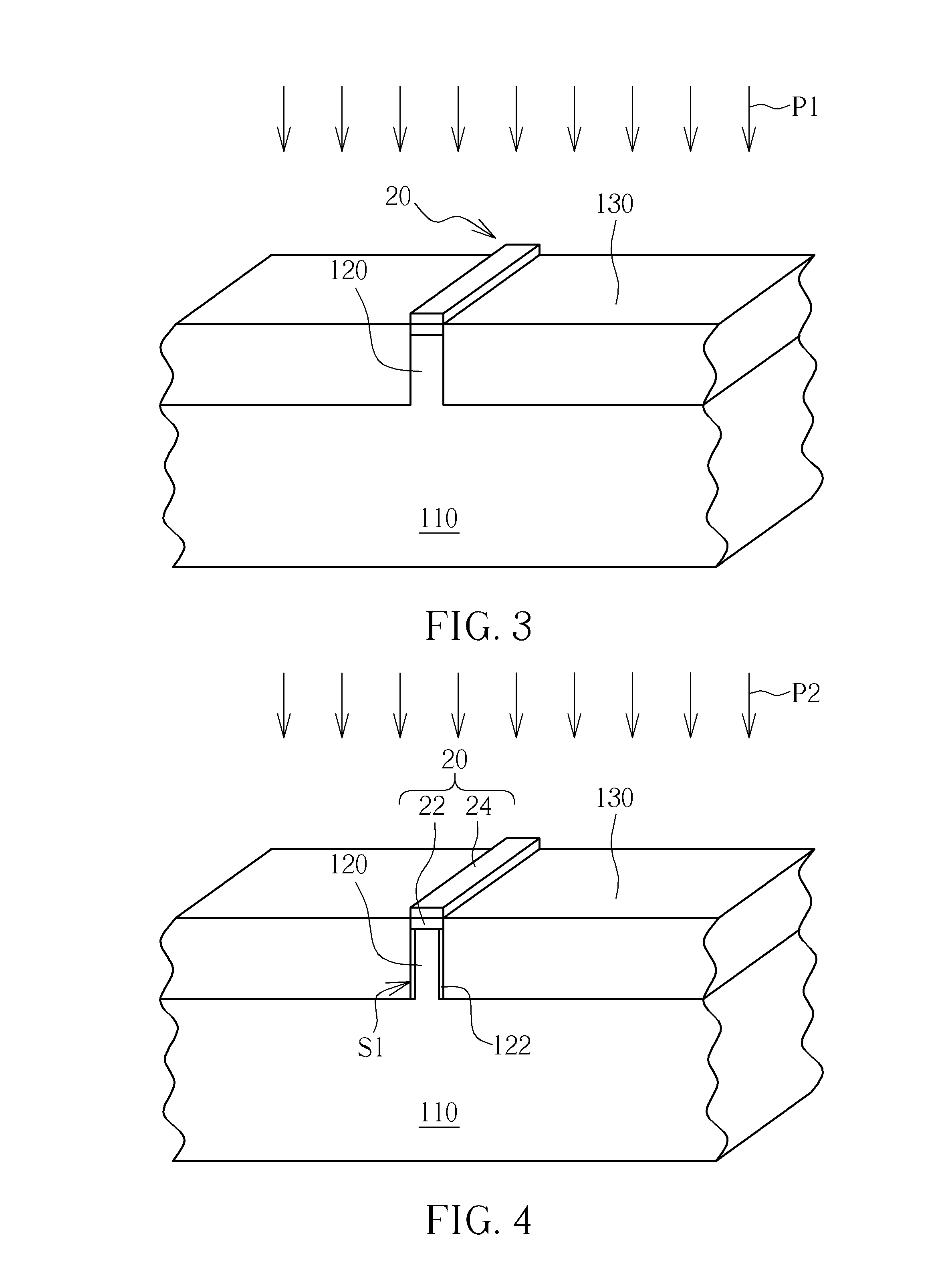
Semiconductor process
ActiveUS20130078818A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesThermal treatmentSemiconductor
A semiconductor process includes the following steps. A substrate is provided. At least a fin-shaped structure is formed on the substrate and an oxide layer is formed on the substrate without the fin-shaped structure forming thereon. A thermal treatment process is performed to form a melting layer on at least a part of the sidewall of the fin-shaped structure.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
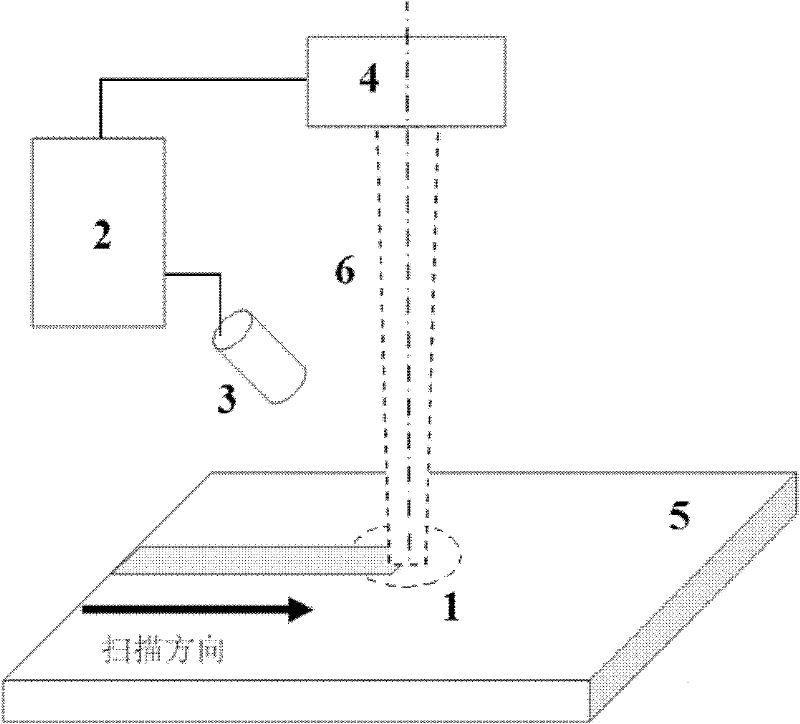
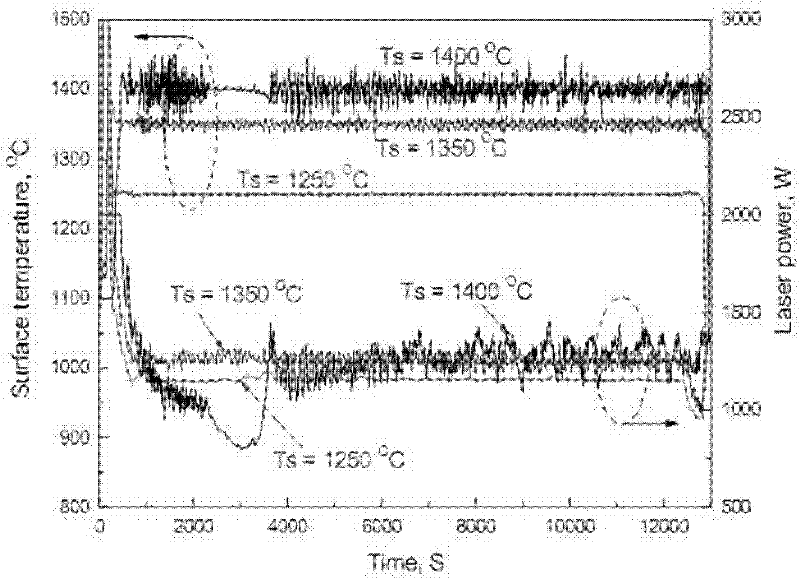
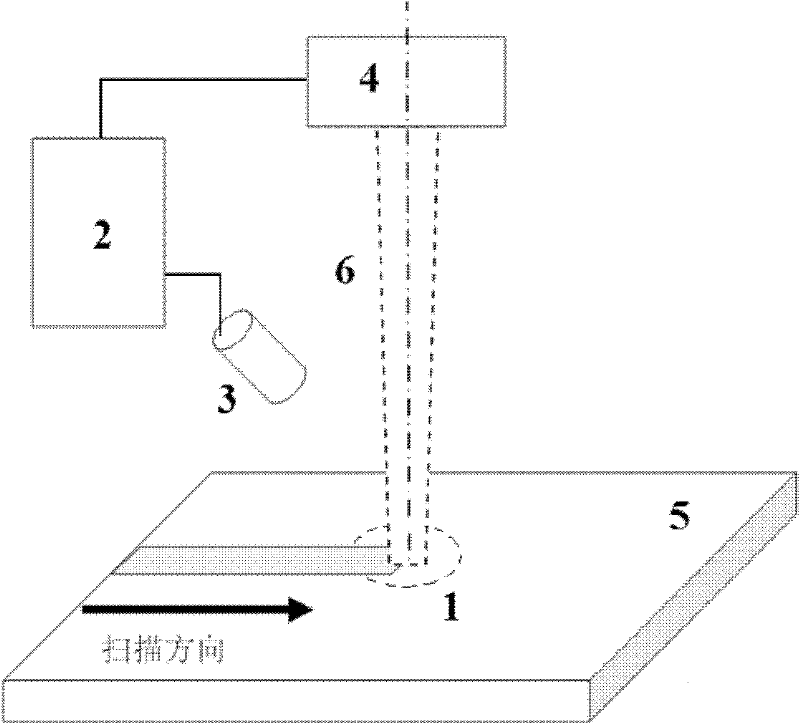
Depth uniformity control method for laser surface quenching hardening layer and device thereof
A depth uniformity control method for a laser surface quenching hardening layer and a device thereof belongs to the technical field of material surface treatment. A charge coupled device (CCD) camera is enhanced by infrared to shoot temperature field images of a heating area in a quenching process, actual heating peak temperature can be obtained by analyzing the temperature field images, and laser power is fed back and controlled by closed loop control to adjust the actual peak temperature to heating peak temperature preset before quenching laser surface. When the preset heating peak temperature and the moving speed of laser is fixed values, uniformity of the depth of the hardening layer on the metal surface can be achieved. The depth uniformity control method enables temperature along the thickness direction to exceed phase transformation points to reach an austenite state and be quickly cooled to lead depth areas of a martensite layer to be matched at every point on the metal surface. Furthermore, the depth of the hardening layer is easy to control in laser surface quenching, a melting layer or an overheating layer is prevented from appearing on the metal surface, and the non-uniformity problem of the thickness of the hardening layer in the scanning direction caused by different cold and hot states is greatly resolved.
Owner:上海岳乾激光科技有限公司
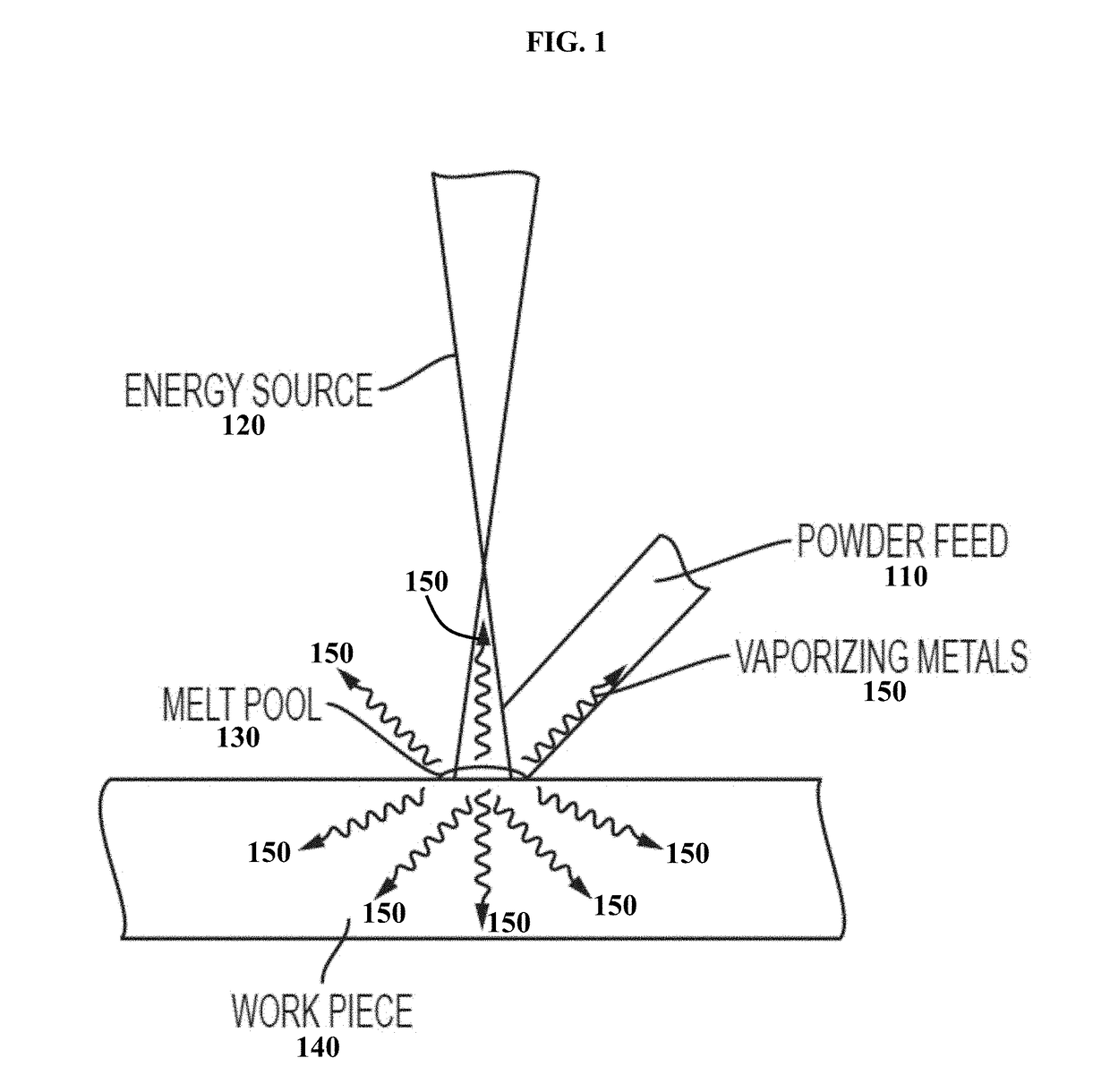
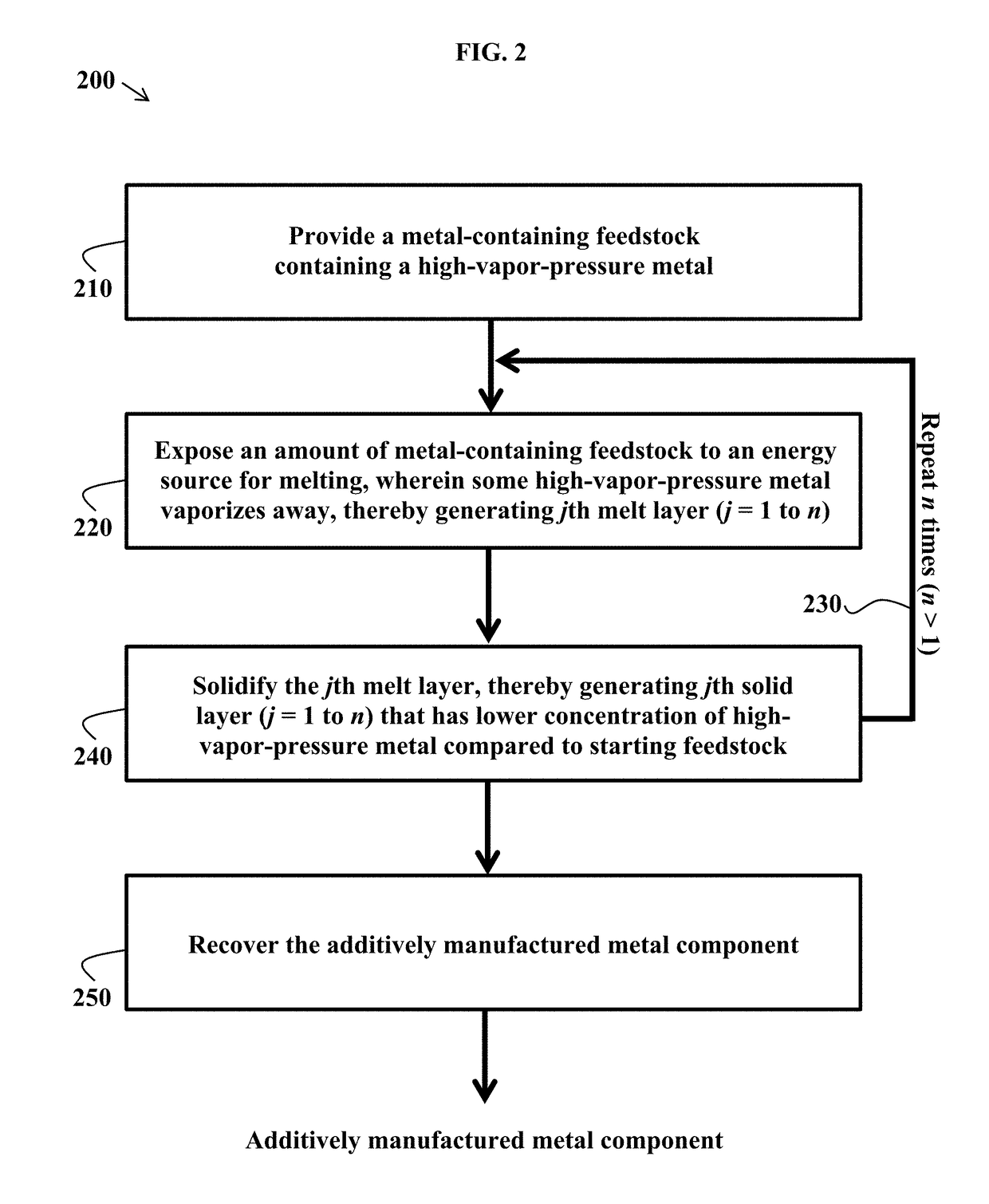
Feedstocks for additive manufacturing, and methods of using the same
InactiveUS20190040503A1Increase concentrationAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyHigh concentrationMetallurgy
Some variations provide a method of making an additively manufactured metal component, comprising: providing a feedstock that includes a high-vapor-pressure metal; exposing a first amount of the feedstock to an energy source for melting; and solidifying the melt layer, thereby generating a solid layer of an additively manufactured metal component. The metal-containing feedstock is enriched with a higher concentration of the high-vapor-pressure metal compared to its concentration in the additively manufactured metal component. The high-vapor-pressure metal may be selected from Mg, Zn, Li, Al, Cd, Hg, K, Na, Rb, Cs, Mn, Be, Ca, Sr, or Ba, for example. Additively manufactured metal components are provided. Metal-containing feedstocks for additive manufacturing are also disclosed, wherein concentration of at least one high-vapor-pressure metal in the feedstock is selected based on a desired concentration of the high-vapor-pressure metal in an additively manufactured metal component derived from the metal-containing feedstock. Various feedstock compositions are disclosed.
Owner:HRL LAB
Method for producing single crystal silicon carbide
InactiveUS20090038538A1Easy to useReduce conductivityPolycrystalline material growthLiquid-phase epitaxial-layer growthMicrometerCarbide
Single crystal SiC, having no fine grain boundaries, a micropipe defect density of 1 / cm2 or less and a crystal terrace of 10 micrometer or more is obtained by a high-temperature liquid phase growth method using a very thin Si melt layer. The method does not require temperature difference control between the growing crystal surface and a raw material supply polycrystal and preparation of a doped single crystal SiC is possible.
Owner:KWANSEI GAKUIN EDUCATIONAL FOUND
Static suppressor with overcurrent protection functions, and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN103943291AExcellent over-current and over-voltage protectionImprove reliabilityCurrent responsive resistorsResistor manufactureSuppressorCopper
The invention discloses a static suppressor with overcurrent protection functions, and a manufacturing method thereof. The manufacturing method comprises following steps: (1) a ceramic substrate is selected; (2) a front side electrode and a back side electrode are formed via printing on the upper surface and the lower surface of the ceramic substrate respectively, and are dried; (3) an upper surface electrode is formed via printing on the upper surface and the lower surface, or one selected from the upper surface and the lower surface of the ceramic substrate, and is dried; (4) the electrodes above are subjected to sintering; (5) insulating layers are formed via respective printing on the surface electrodes; (6) the insulating layers are subjected to sintering; (7) the surface electrodes and the insulating layers are subjected to cutting so as to form gaps; (8) printing of pressure sensitive material layers is performed so as to fill the gaps, and solidification is realized; (9) printing of a first protection layer is carried out, and solidification is realized; (10) melt layers are formed; (11) printing of a second protection is carried out, and solidification is realized; (12) first cutting is carried out; (13) side surface internal electrodes are formed; (14) second cutting is carried out; (15) copper internal electrodes are formed; and (16) nickel coatings and tin coatings are formed via electroplating so as to obtain the static suppressor with overcurrent protection functions.
Owner:NANJING SART SCI & TECH DEV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com