Patents
Literature
3865results about "Additive manufacturing with solids" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
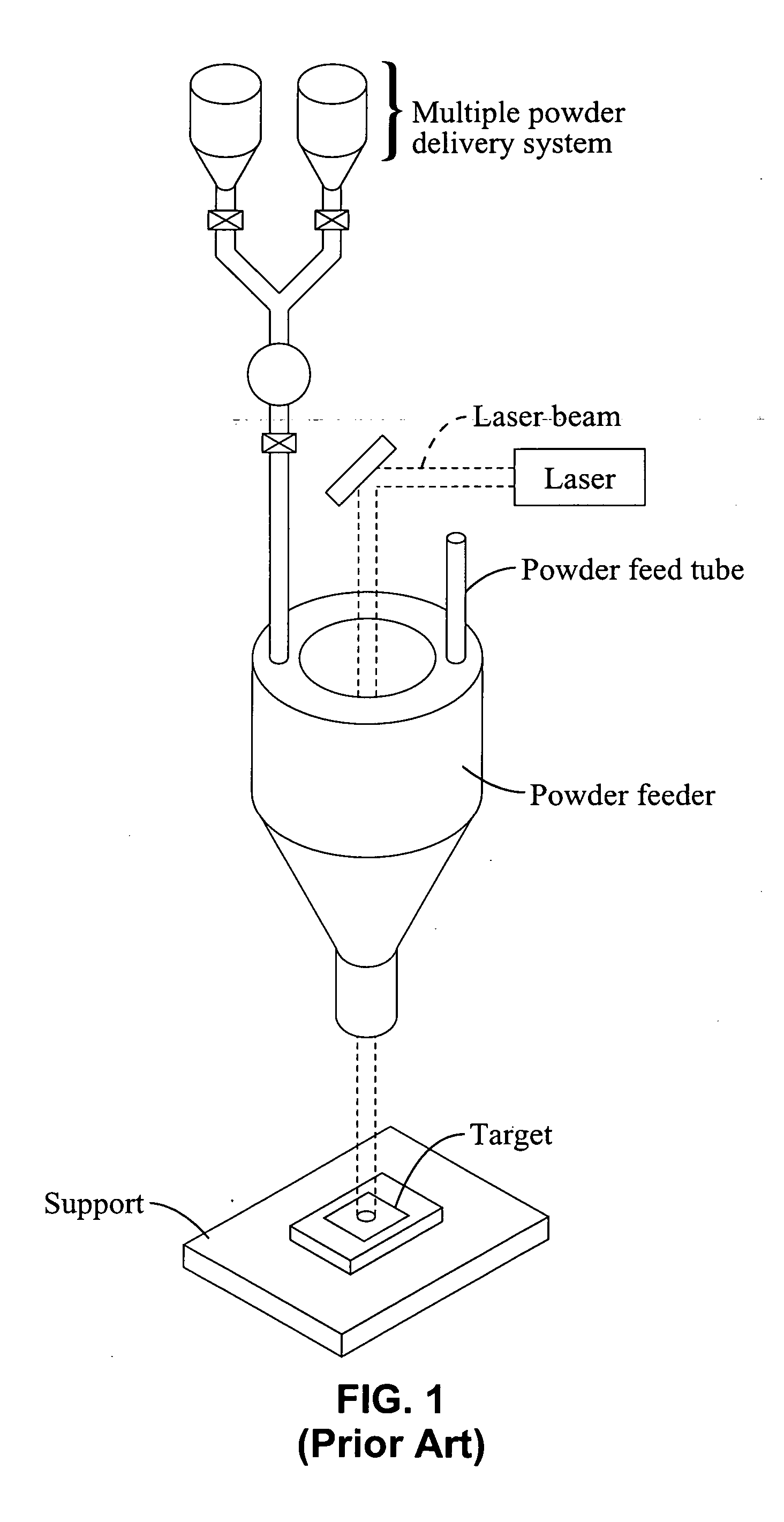
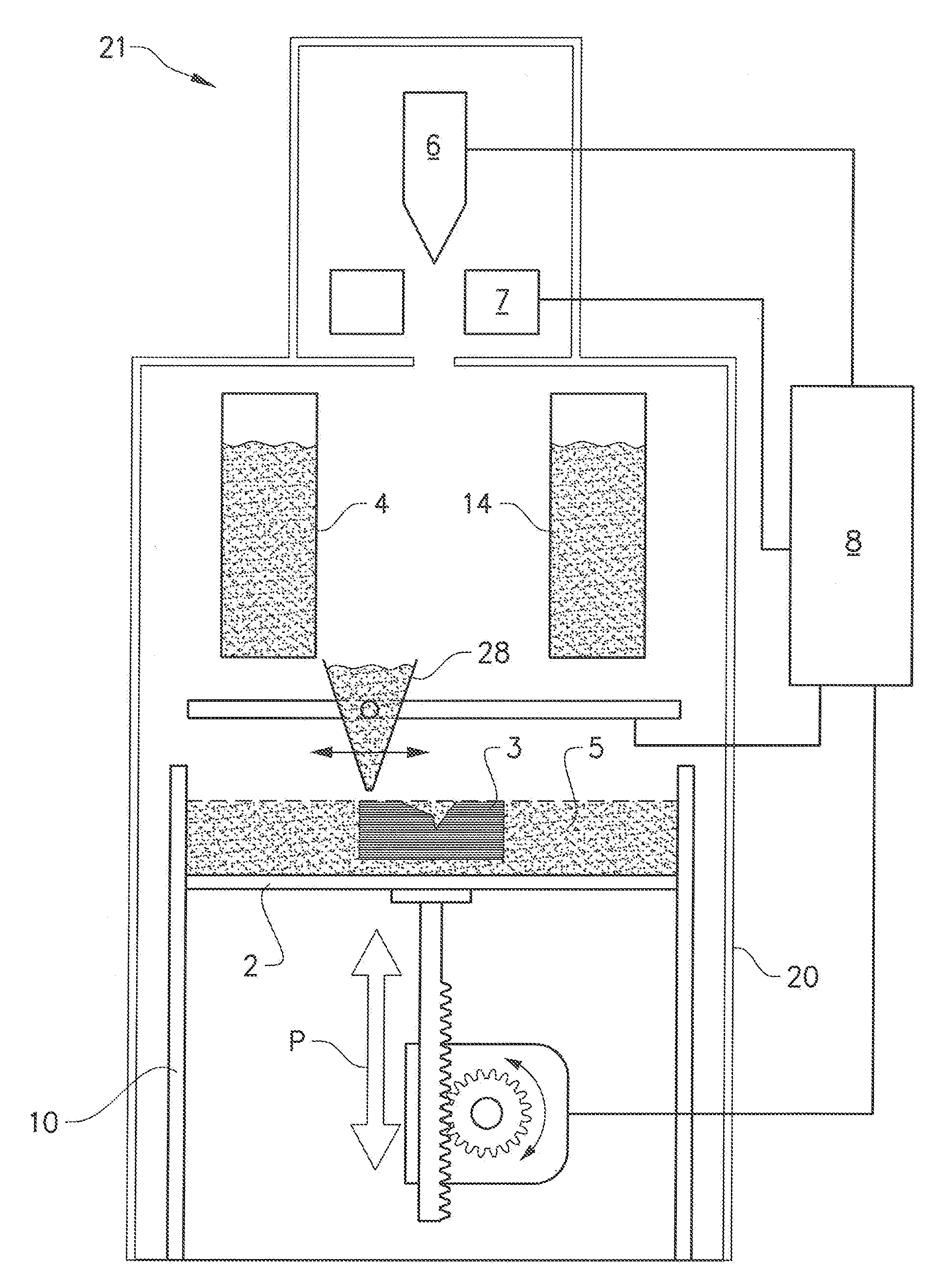
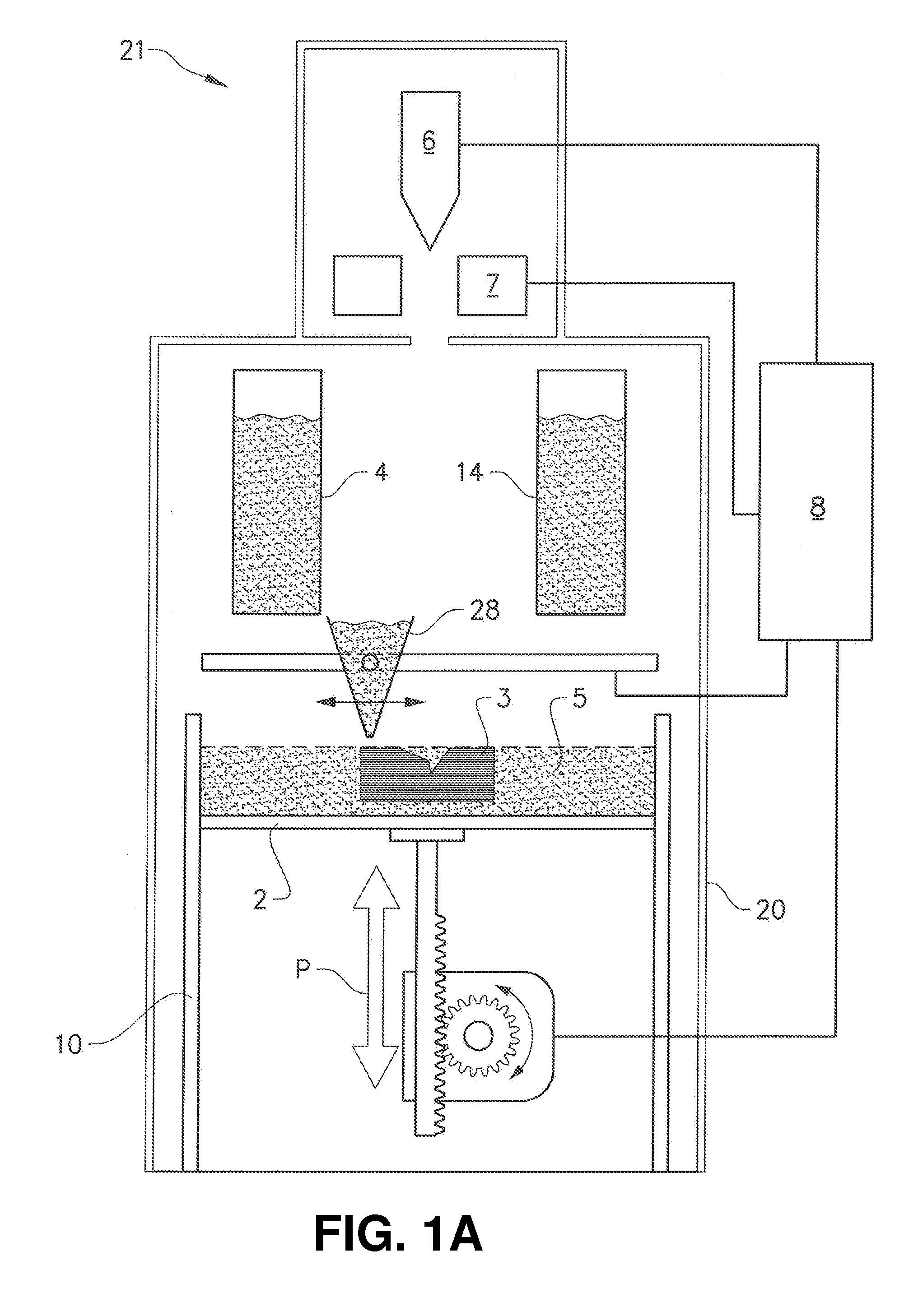
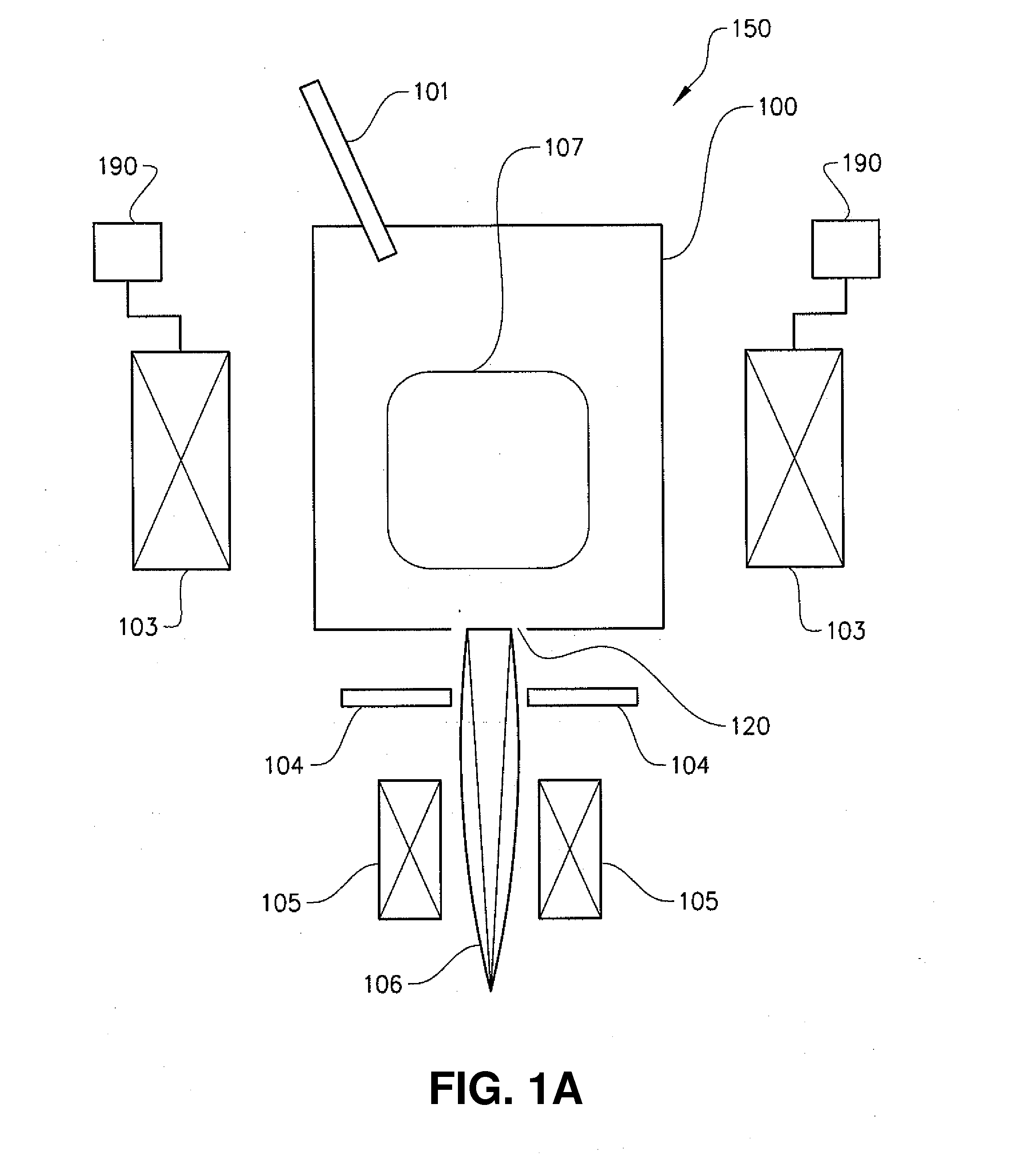
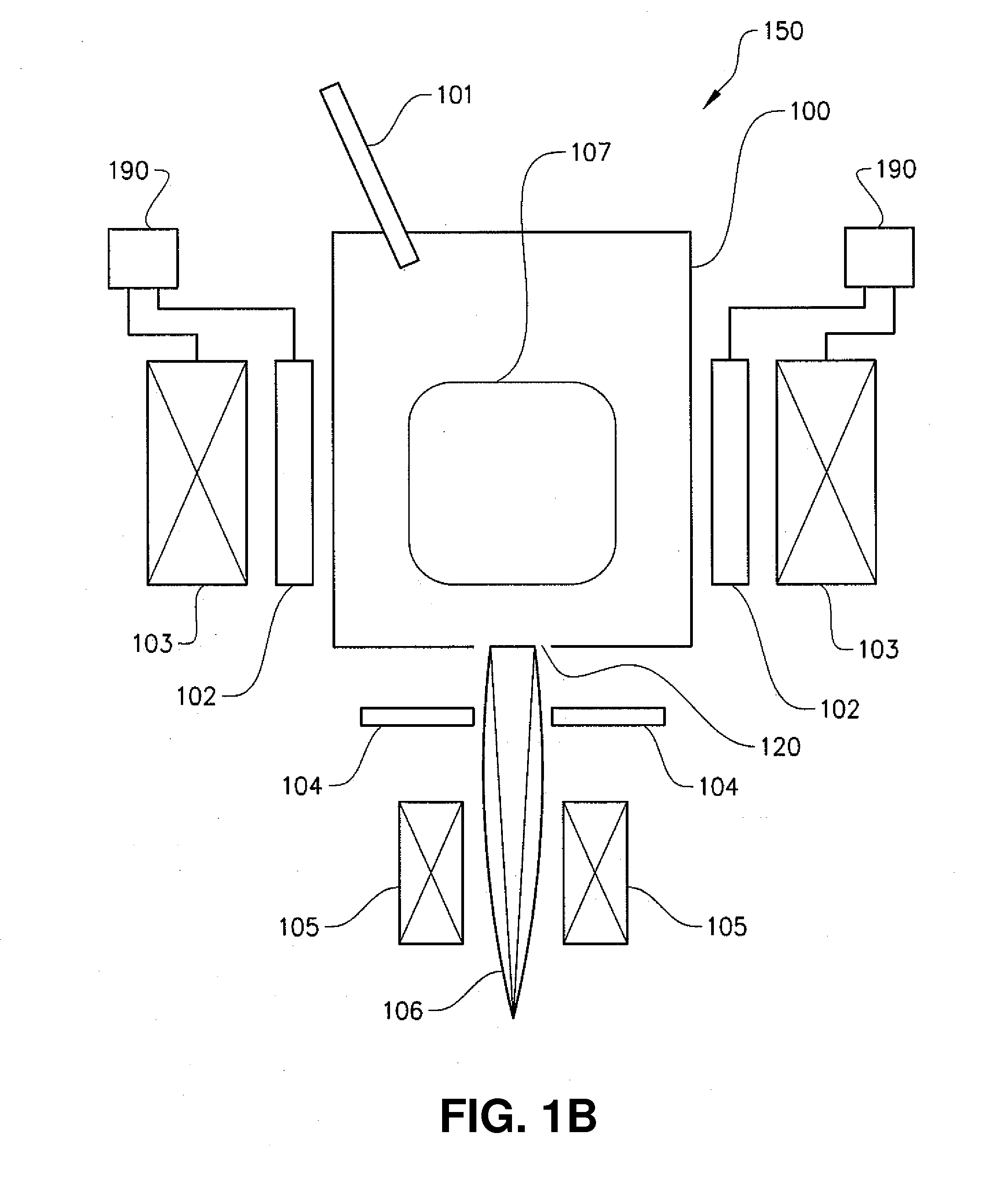
3D printing using spiral buildup
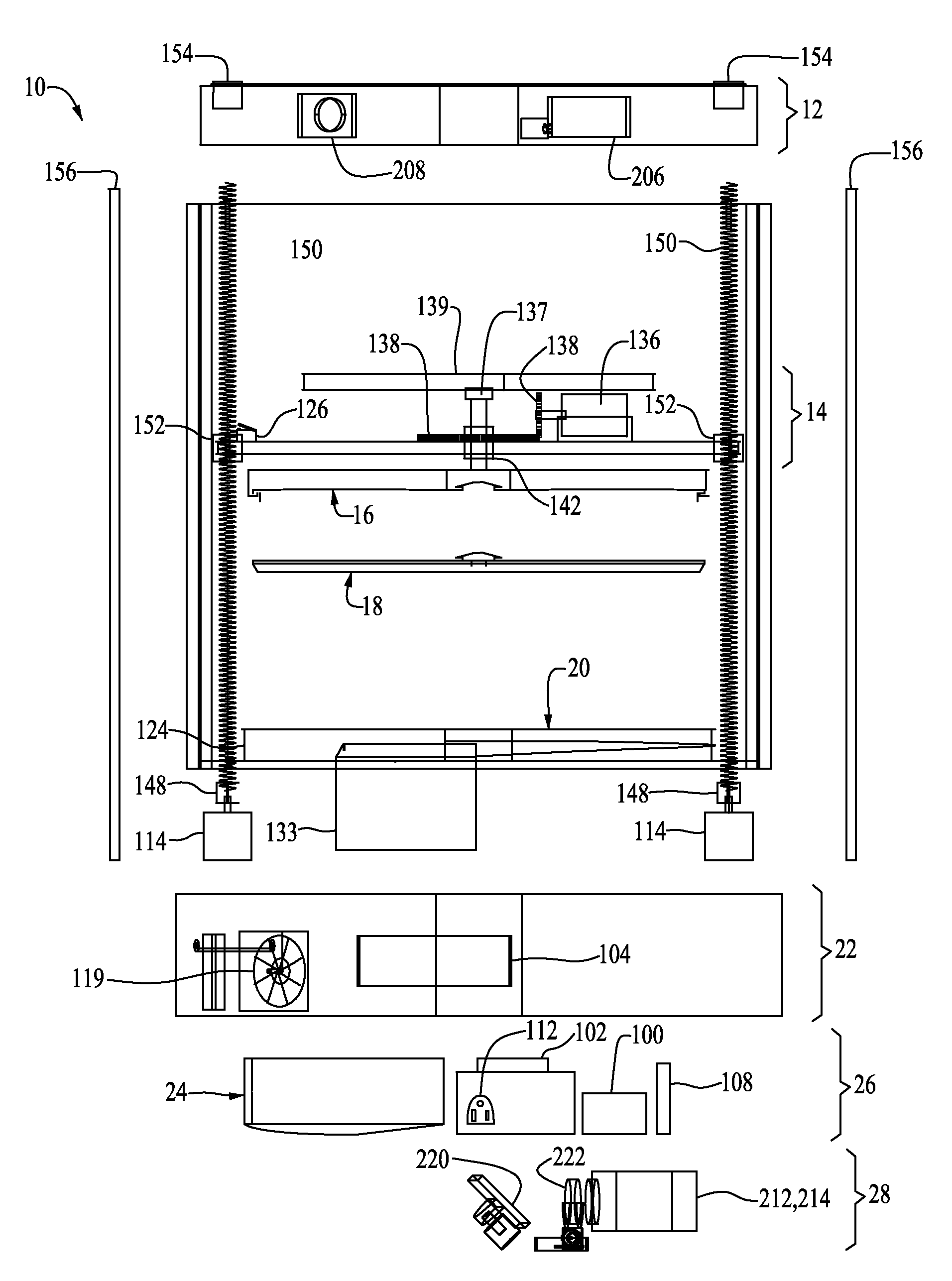
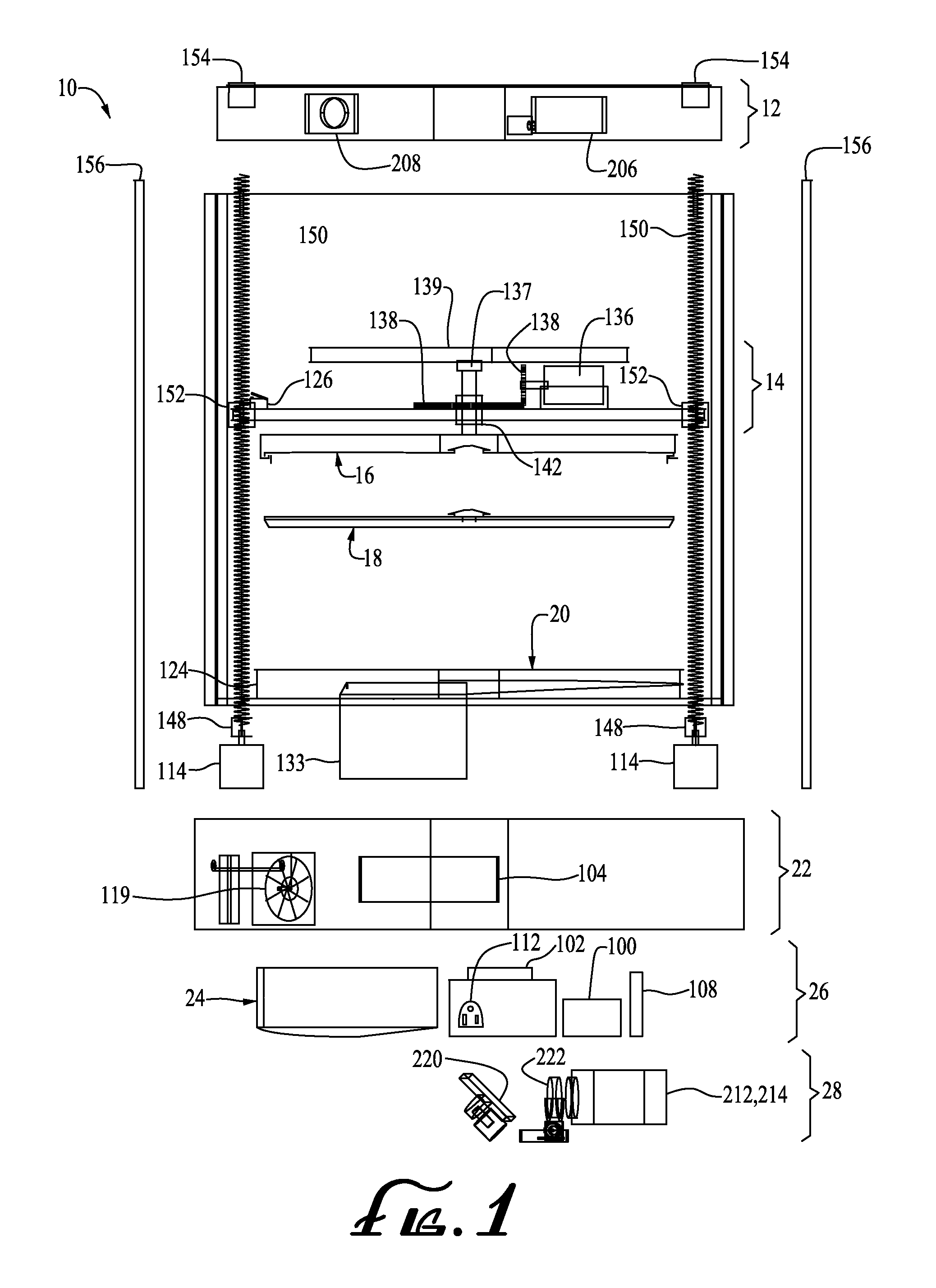
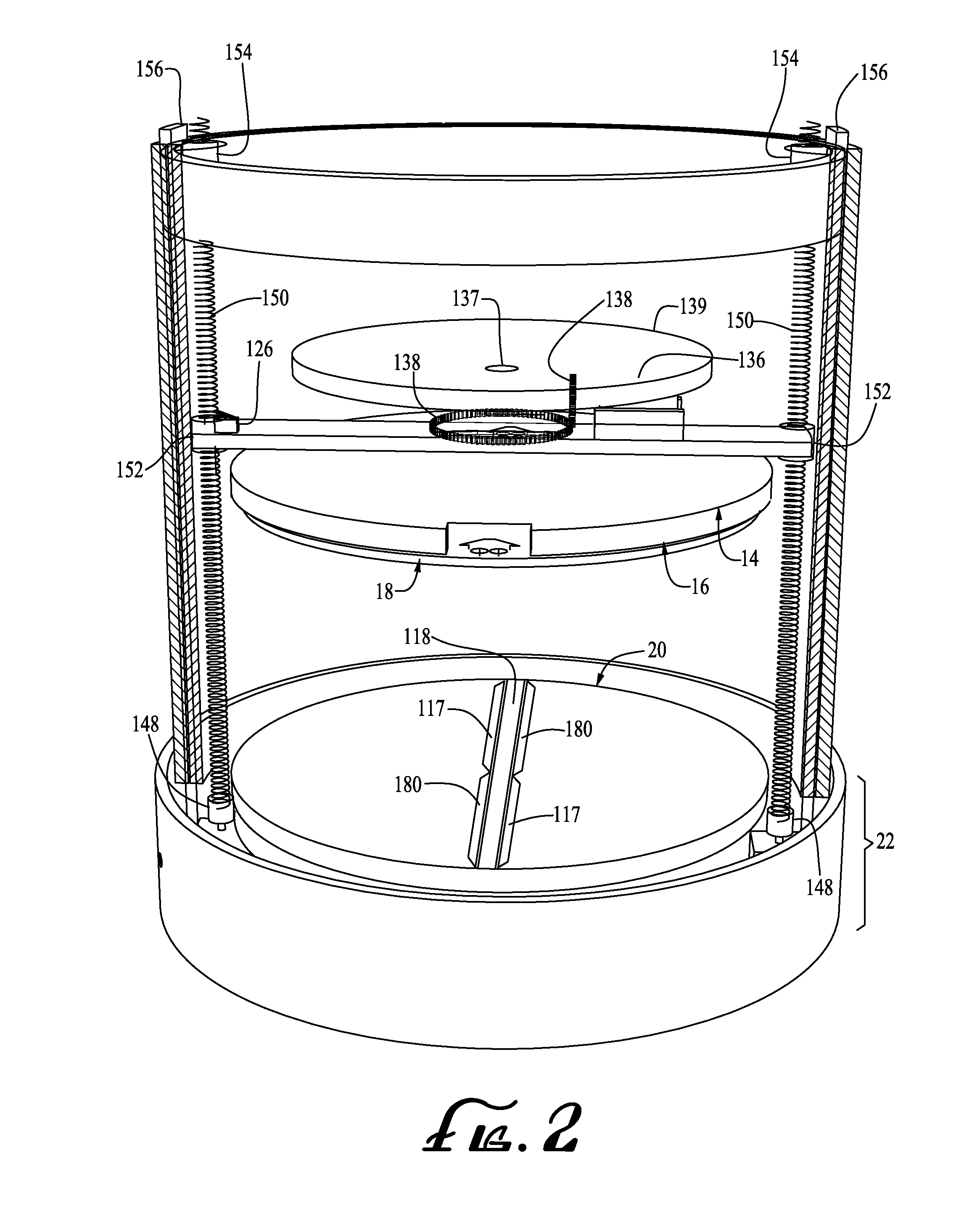
ActiveUS20140265034A1High and accurate level of detailShort timeManufacturing platforms/substratesManufacturing driving meansSingle CenterPhotopolymer
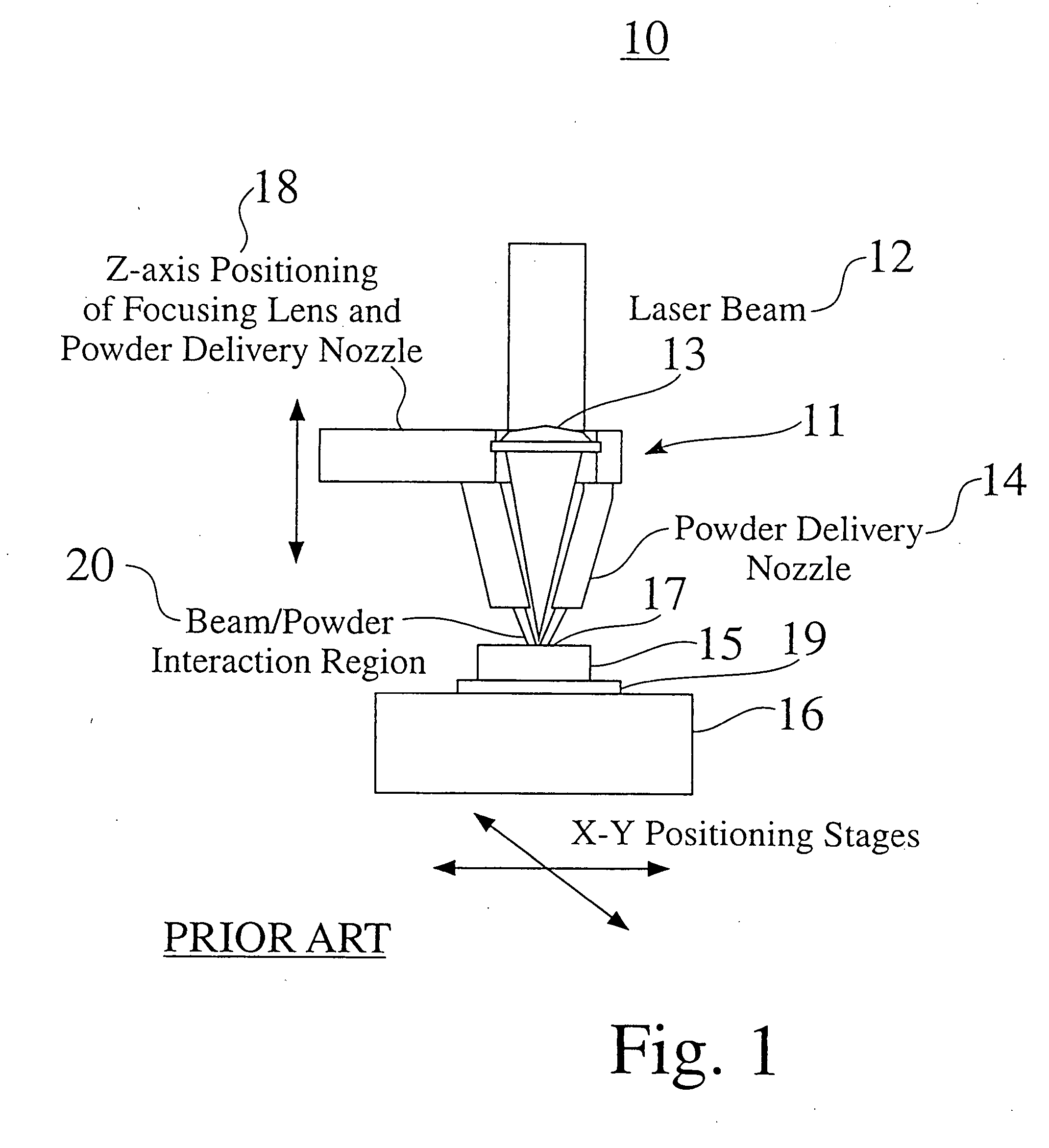
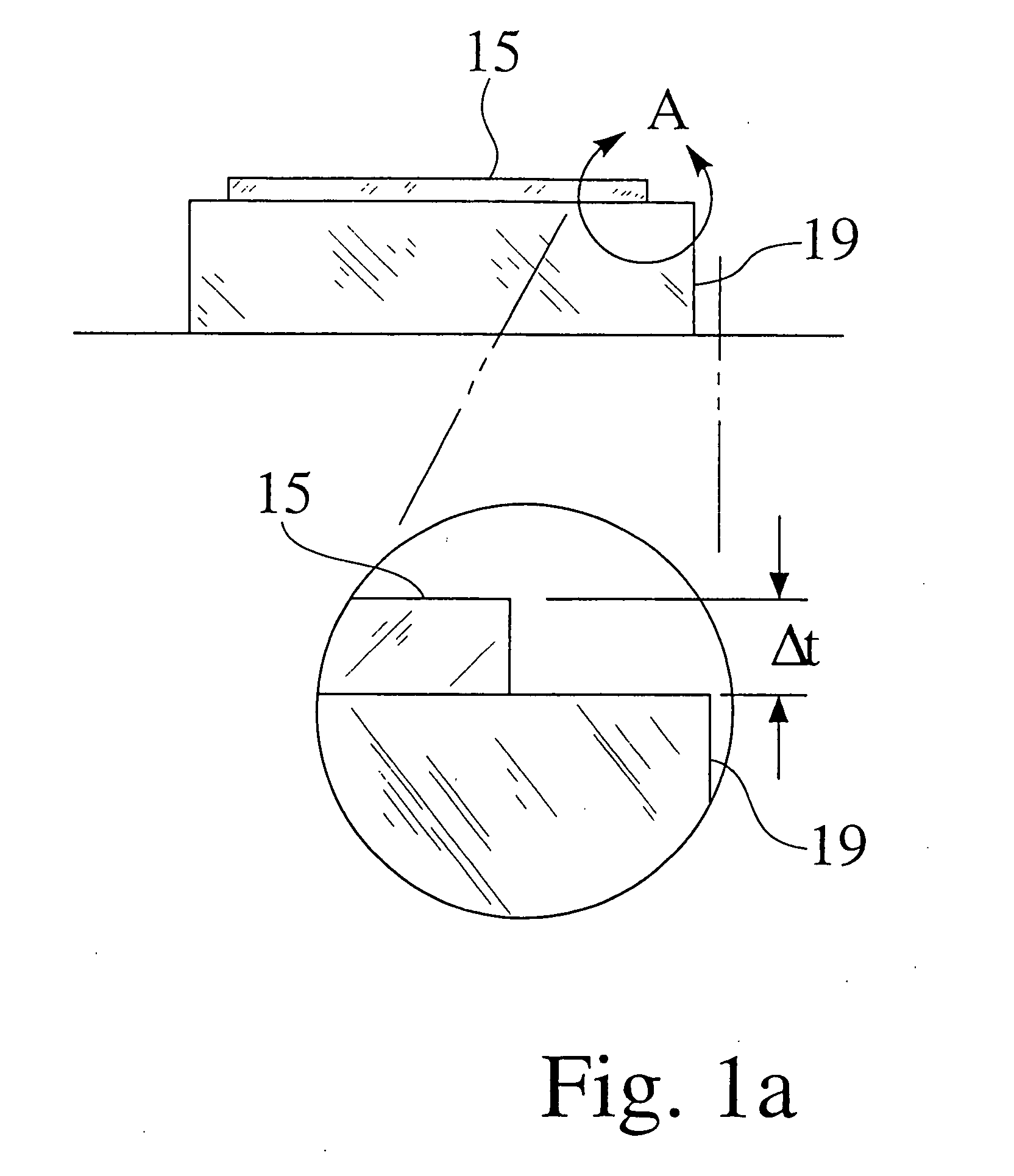
Methods, devices and systems for efficient 3D printing that address conventional inefficiencies while utilizing a single compact device are set forth. Some embodiments utilize a circular-shaped build area revolving symmetrically around a single center point utilizing a continuous helical printing process. In one embodiment a liquid photopolymer for solidification is deposited on a build platform to form the physical object The Build platform is continuously rotated and simultaneously raised in a gradual programmed manner. Focused from below the platform produces a single continuous “layer” of material deposited and bonded in a helical fashion.
Owner:ORANGE MAKER
Solid free-form fabrication methods for the production of dental restorations
InactiveUS20050023710A1Improve bindingImpression capsCeramic shaping apparatusPolymer scienceFree form
Solid free form fabrication techniques can be utilized indirectly to manufacture substrates, dies, models, near-net shapes, shells, and wax-ups that are then used in the manufacture of dental articles. Digital light processing is the most preferred indirect method for the production of substrates. After the substrates are produced, various coating or deposition techniques such as gel casting, slip casting, slurry casting, pressure infiltration, dipping, colloidal spray deposition or electrophoretic deposition are used to manufacture the dental article.
Owner:IVOCLAR VIVADENT AG
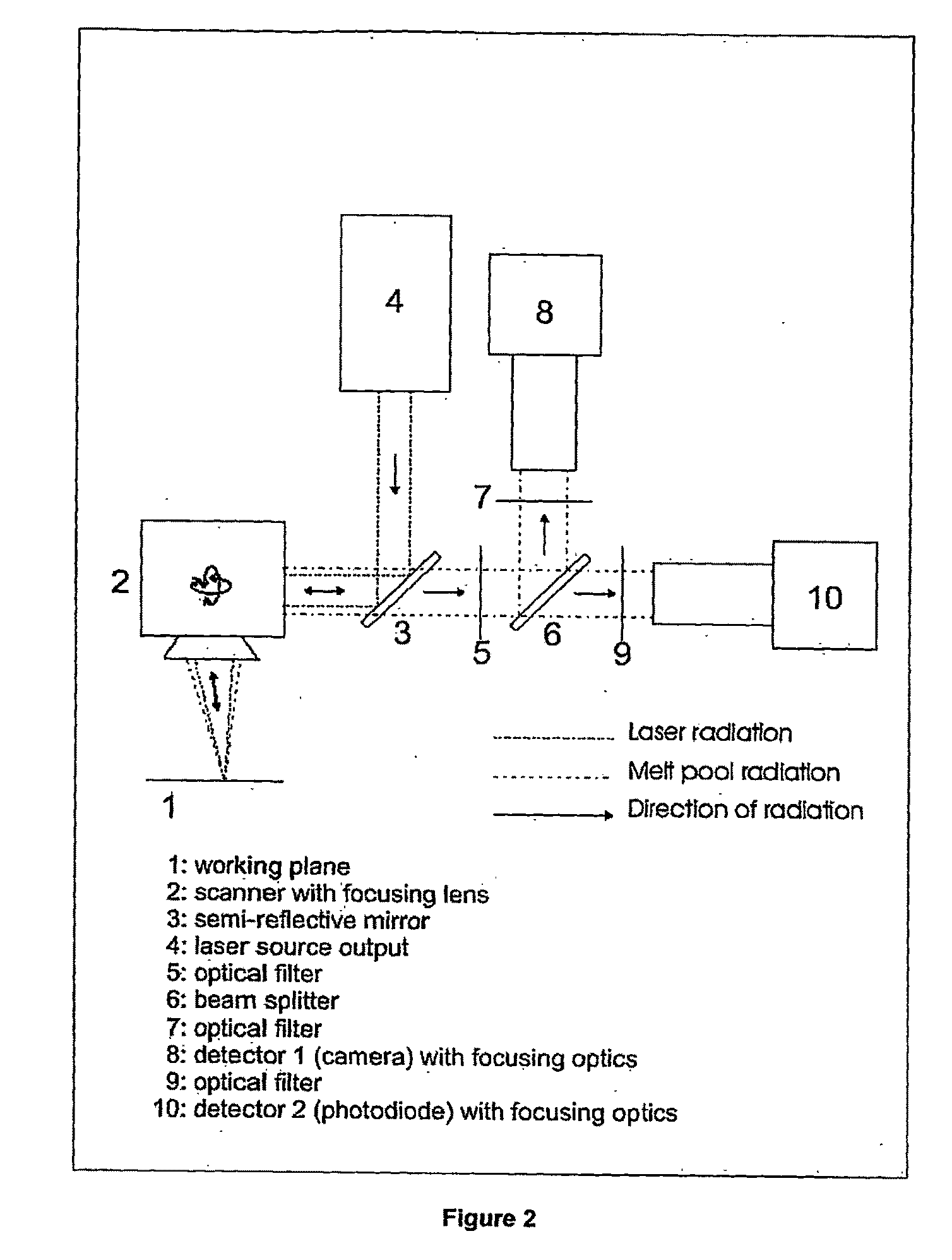
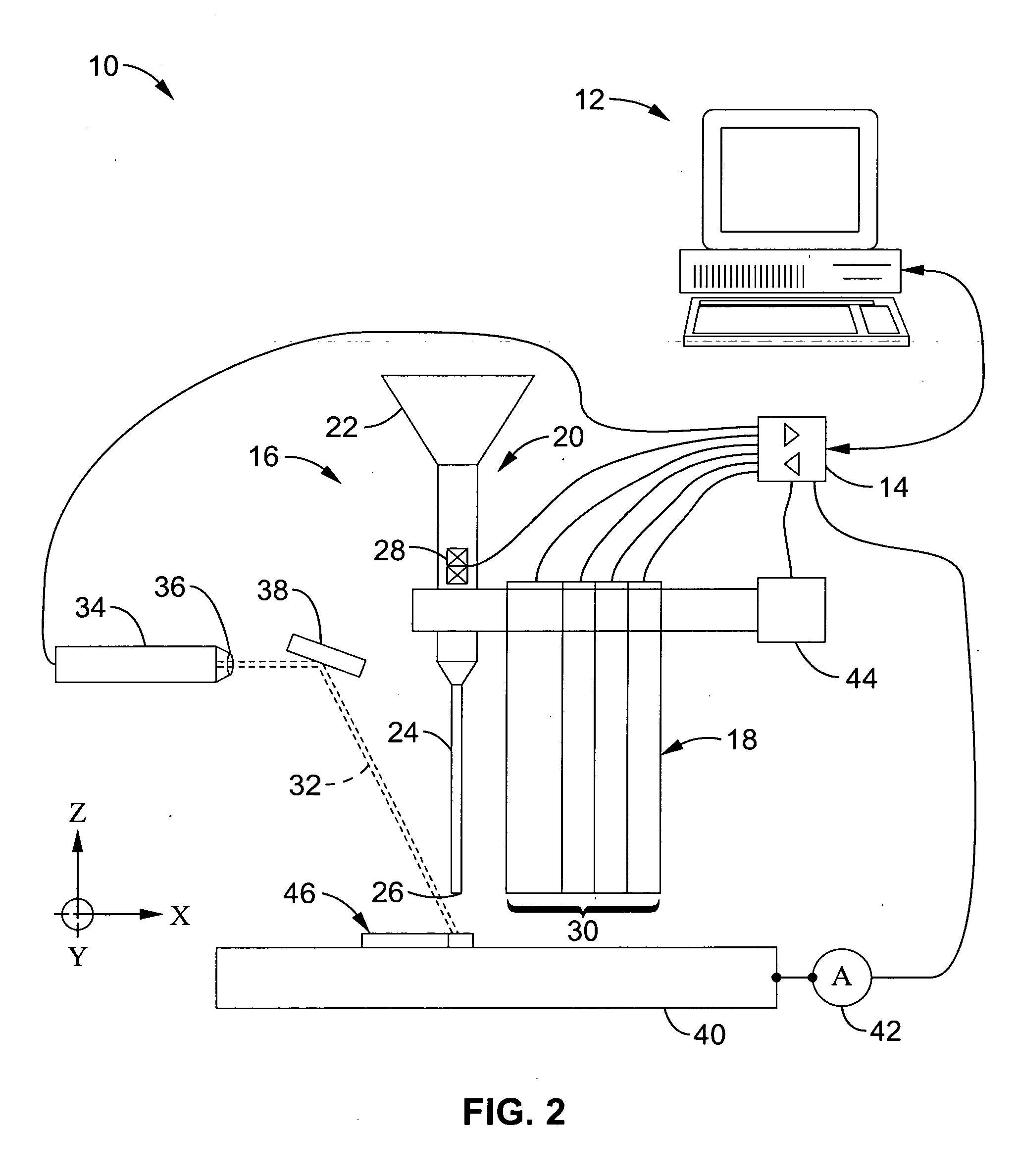
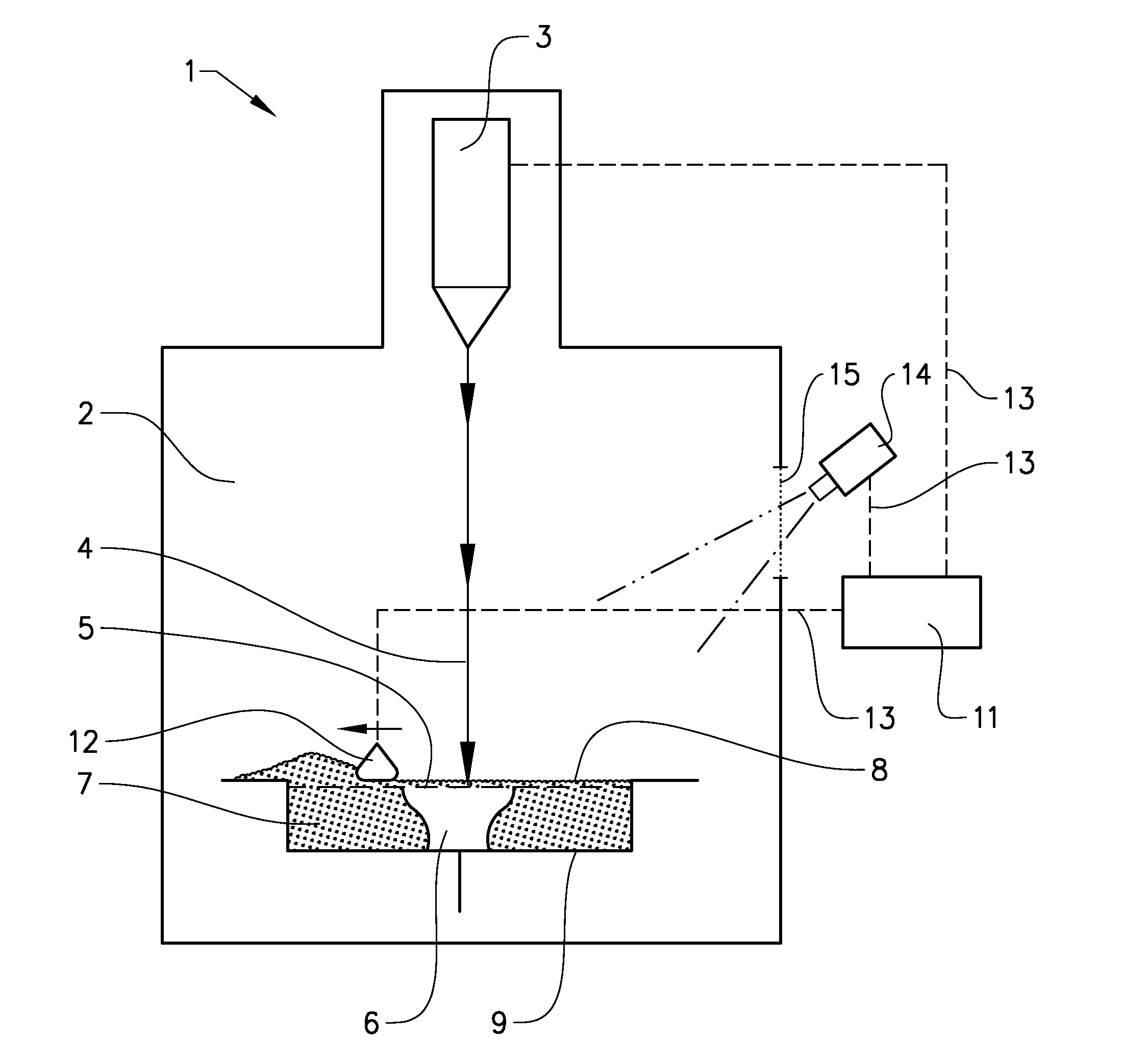
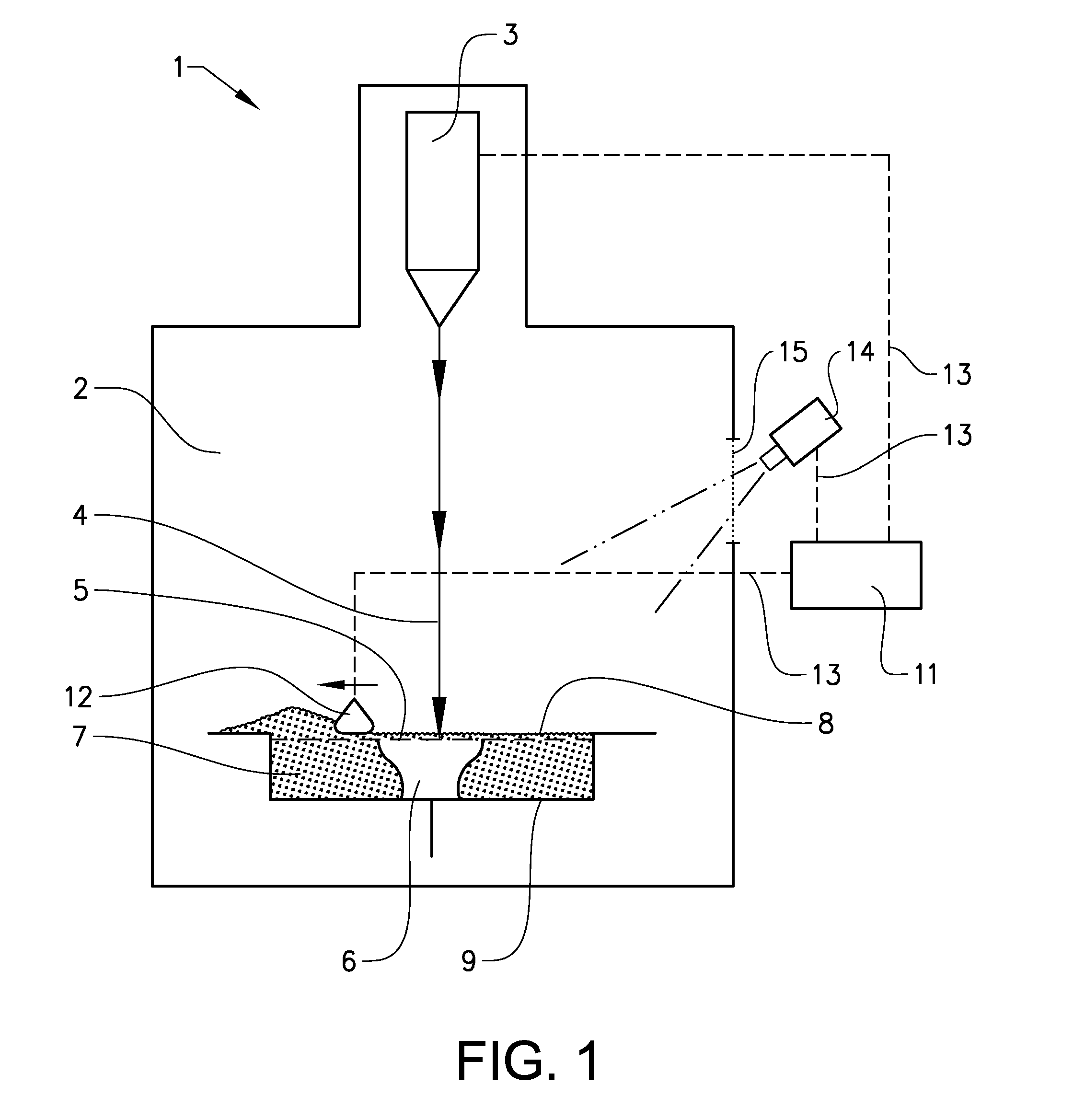
Procedure and apparatus for in-situ monitoring and feedback control of selective laser powder processing
InactiveUS20090206065A1Quality improvementReduce spectral distortionAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyControl systemFeedback controller
The present invention relates to a method and a device to monitor and control the Selective Laser Powder Processing. A Selective Laser Powder Processing device comprising a feedback controller to improve the stability of the Selective Laser Powder Processing process is presented. A signal reflecting a geometric quantity of the melt zone is used in the feedback controller to adjust the scanning parameters (e.g. laser power, laser spot size, scanning velocity, . . . ) of the laser beam (4) in order to maintain the geometric quantity of the melt zone at a constant level. The signal reflecting the geometric quantity of the melt zone can also be displayed in order to monitor the Selective Laser Powder Processing process. The present invention allows for the production of three-dimensional objects from powder material and improves the state of the art by compensating variations of the border conditions (e.g. local heat conduction rate) by a feedback control system based on a geometric quantity of the melt zone resulting in e.g. a lower amount of dross material when overhang planes are scanned.
Owner:KRUTH JEAN PIERRE +1
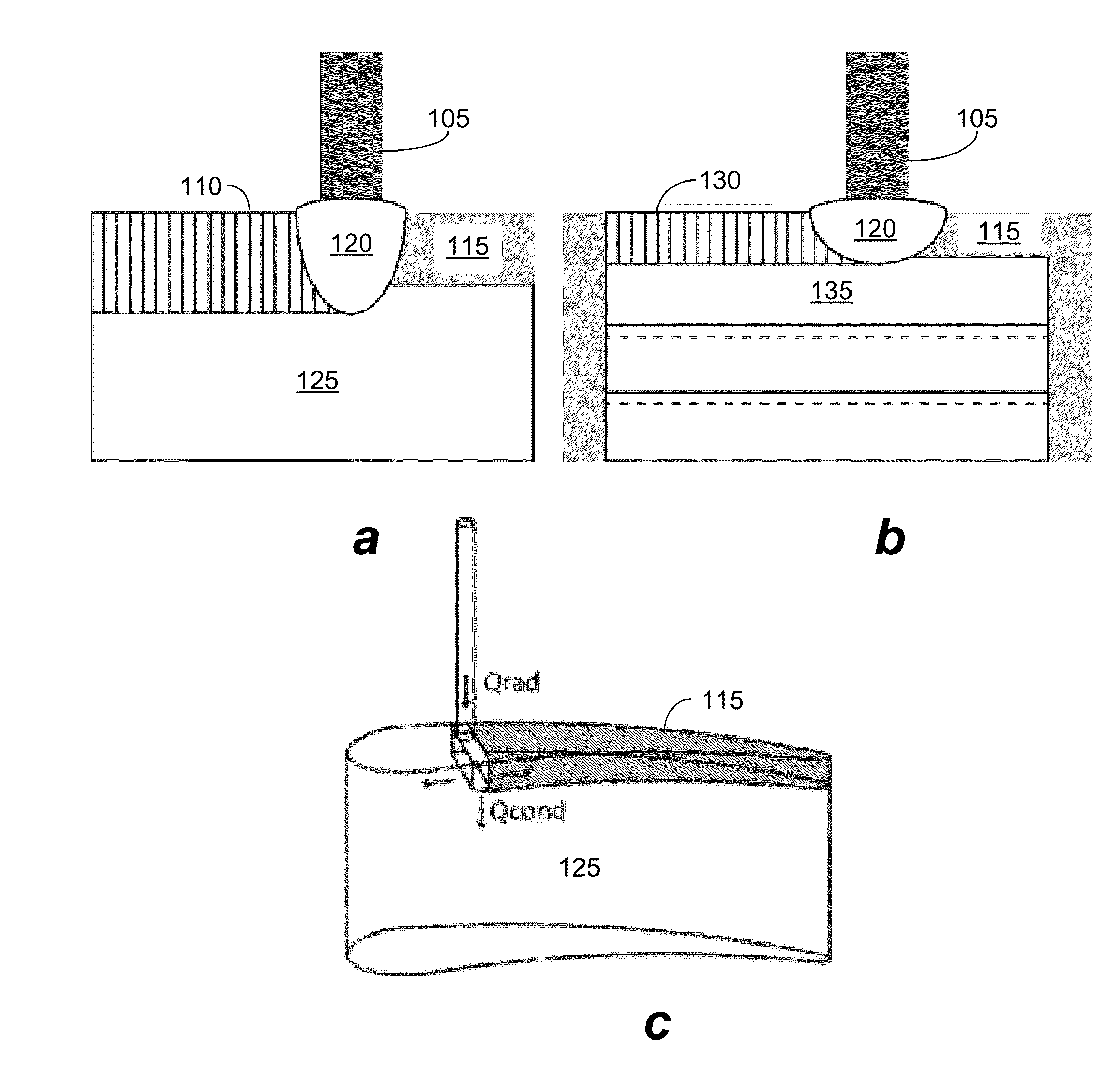
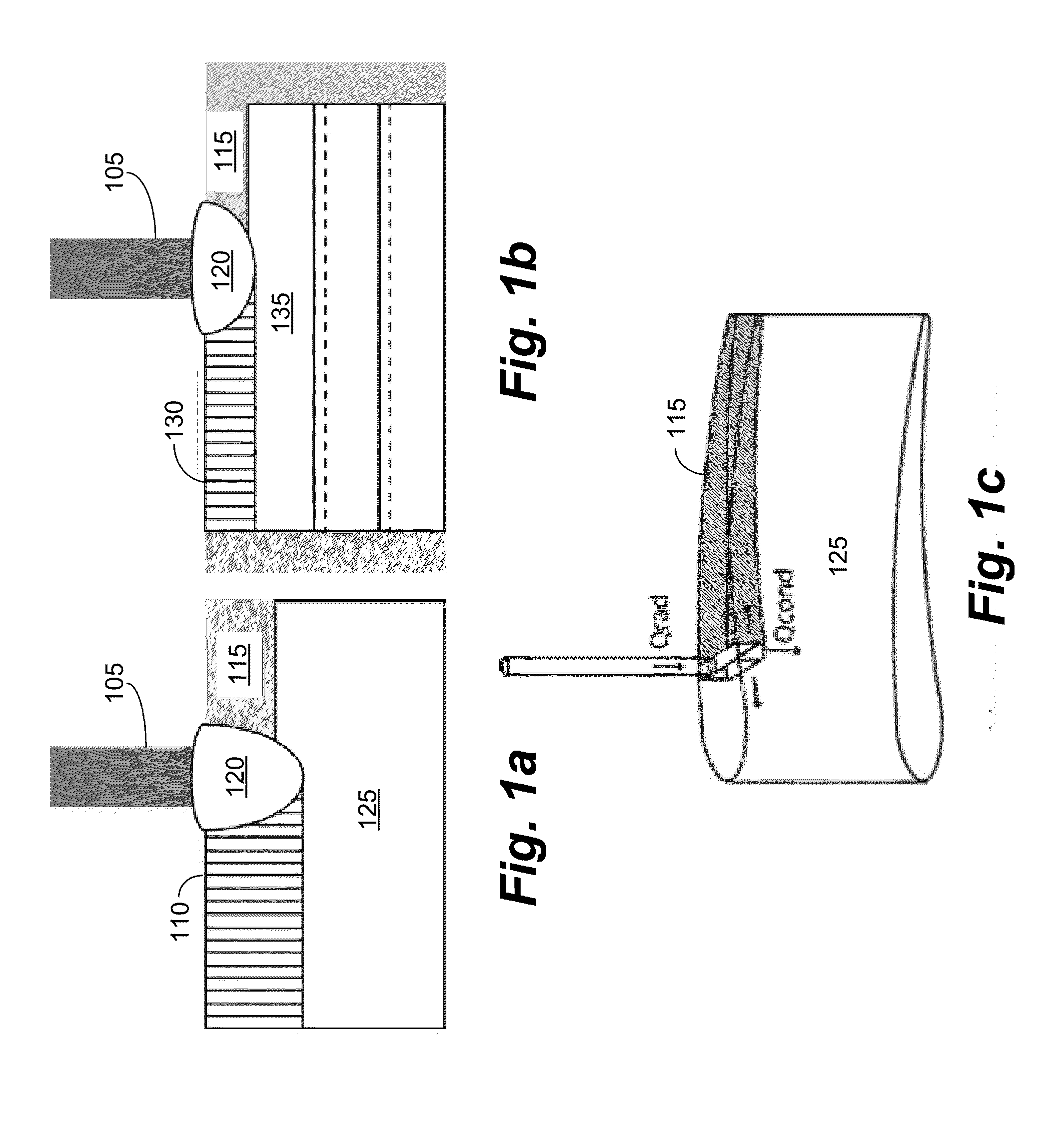
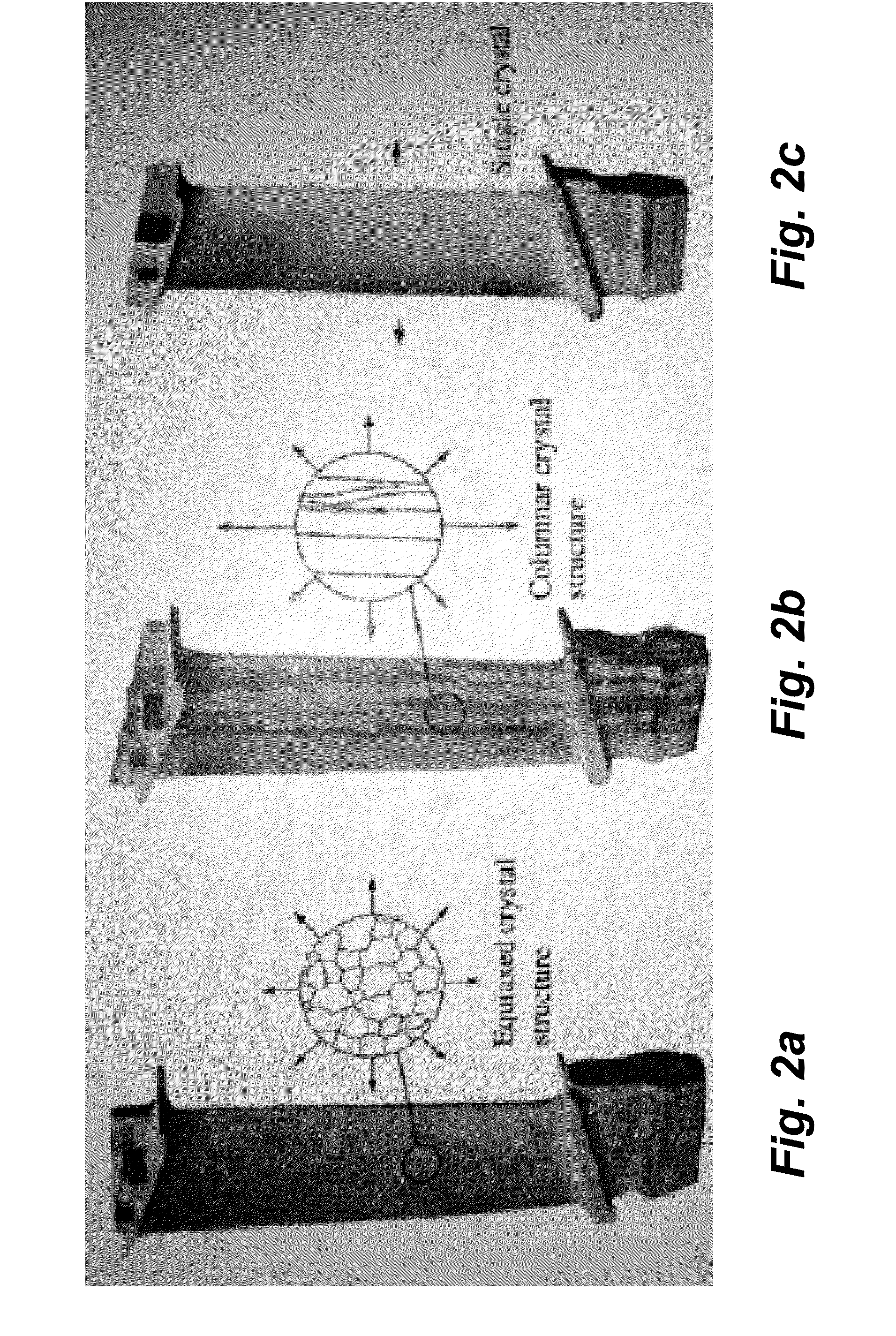
Systems and methods for additive manufacturing and repair of metal components
Scanning Laser Epitaxy (SLE) is a layer-by-layer additive manufacturing process that allows for the fabrication of three-dimensional objects with specified microstructure through the controlled melting and re-solidification of a metal powders placed atop a base substrate. SLE can be used to repair single crystal (SX) turbine airfoils, for example, as well as the manufacture functionally graded turbine components. The SLE process is capable of creating equiaxed, directionally solidified, and SX structures. Real-time feedback control schemes based upon an offline model can be used both to create specified defect free microstructures and to improve the repeatability of the process. Control schemes can be used based upon temperature data feedback provided at high frame rate by a thermal imaging camera as well as a melt-pool viewing video microscope. A real-time control scheme can deliver the capability of creating engine ready net shape turbine components from raw powder material.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Method for producing a three-dimensional object
InactiveUS6042774AShorten production timeAdditive manufacturing apparatus3D object support structuresIrradiationMaterials science
A method of producing an object by successive solidification of layers of a powder material is disclosed. The method provides a preformed base plate having a metal plate with a solidified layer of a powder material formed thereon. Then, successive layers of said powder material are applied and solidified on the solidified layer of the base plate to form the object. In further detail, the method for produces a three-dimensional by providing a support and a preformed base plate having an upper surface for supporting the object. The base plate is removably attached to the support. Means are provided for adjusting the elevation of said upper surface. A layer of the powder material is applied to the upper surface of the base plate. The powder material is solidified at points corresponding to a cross-section of the object by irradiation with electromagnetic or particle radiation. Then, the applying and solidifying steps are repeated for completing the object.
Owner:EOS ELECTRO OPTICAL SYST
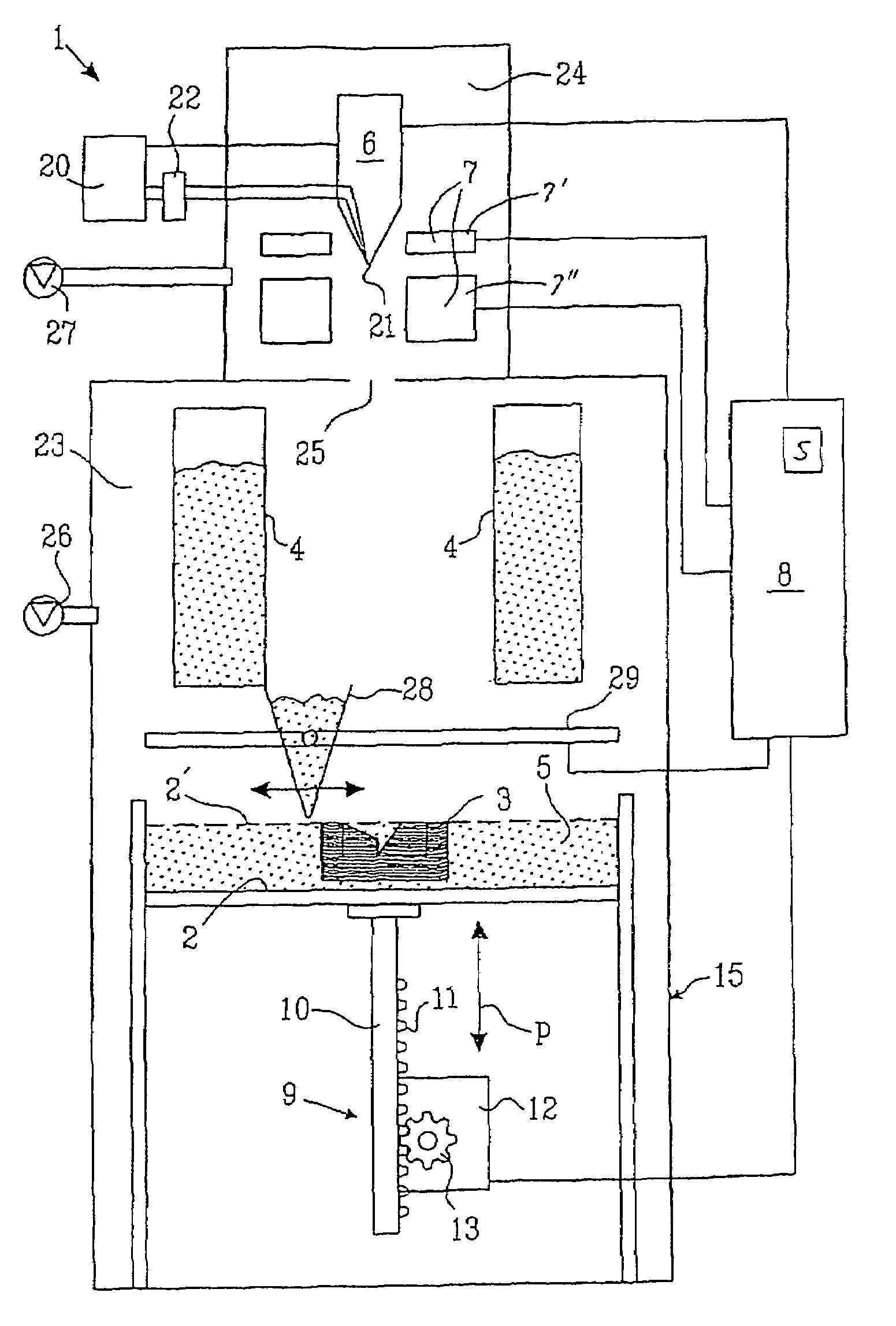
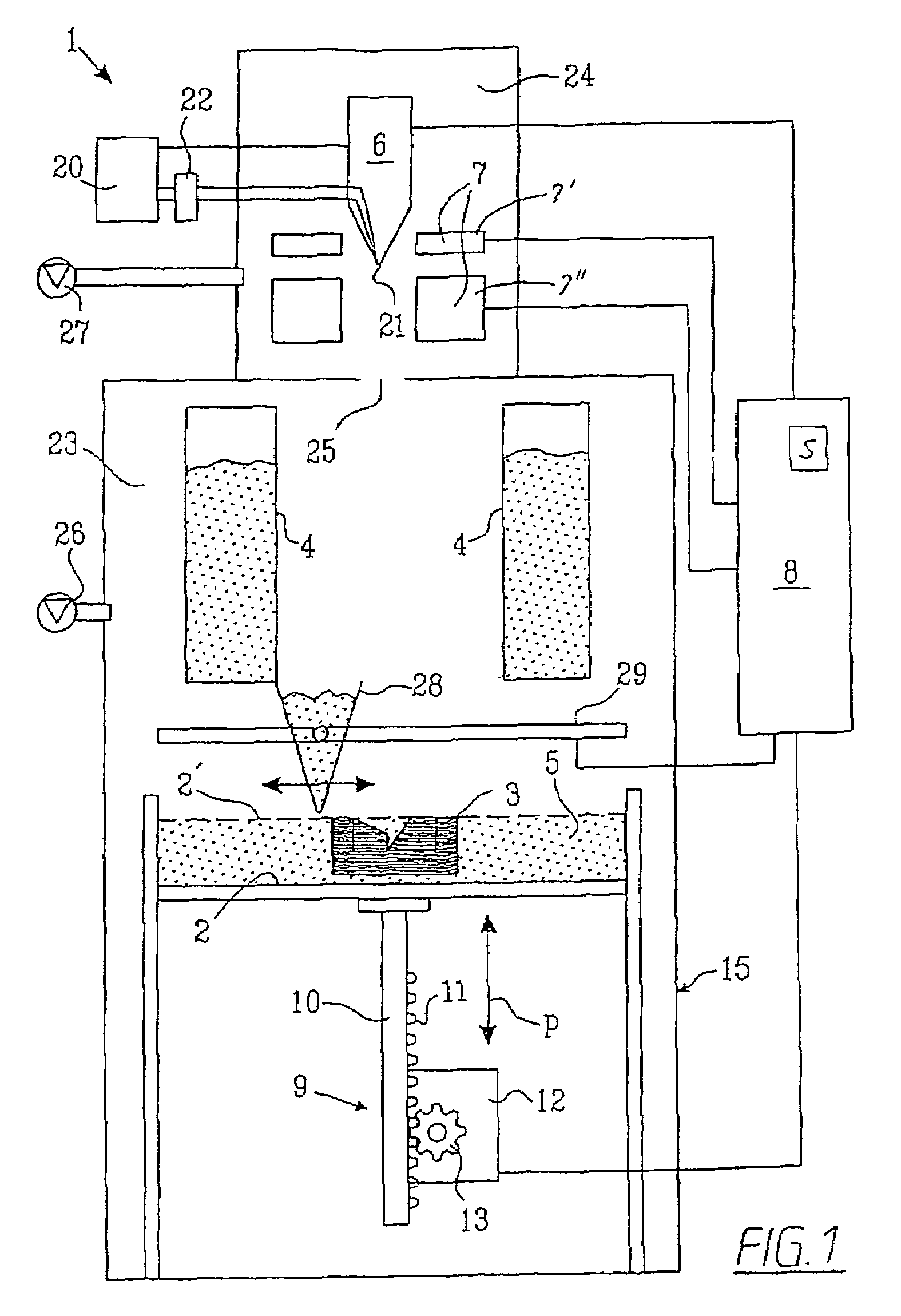
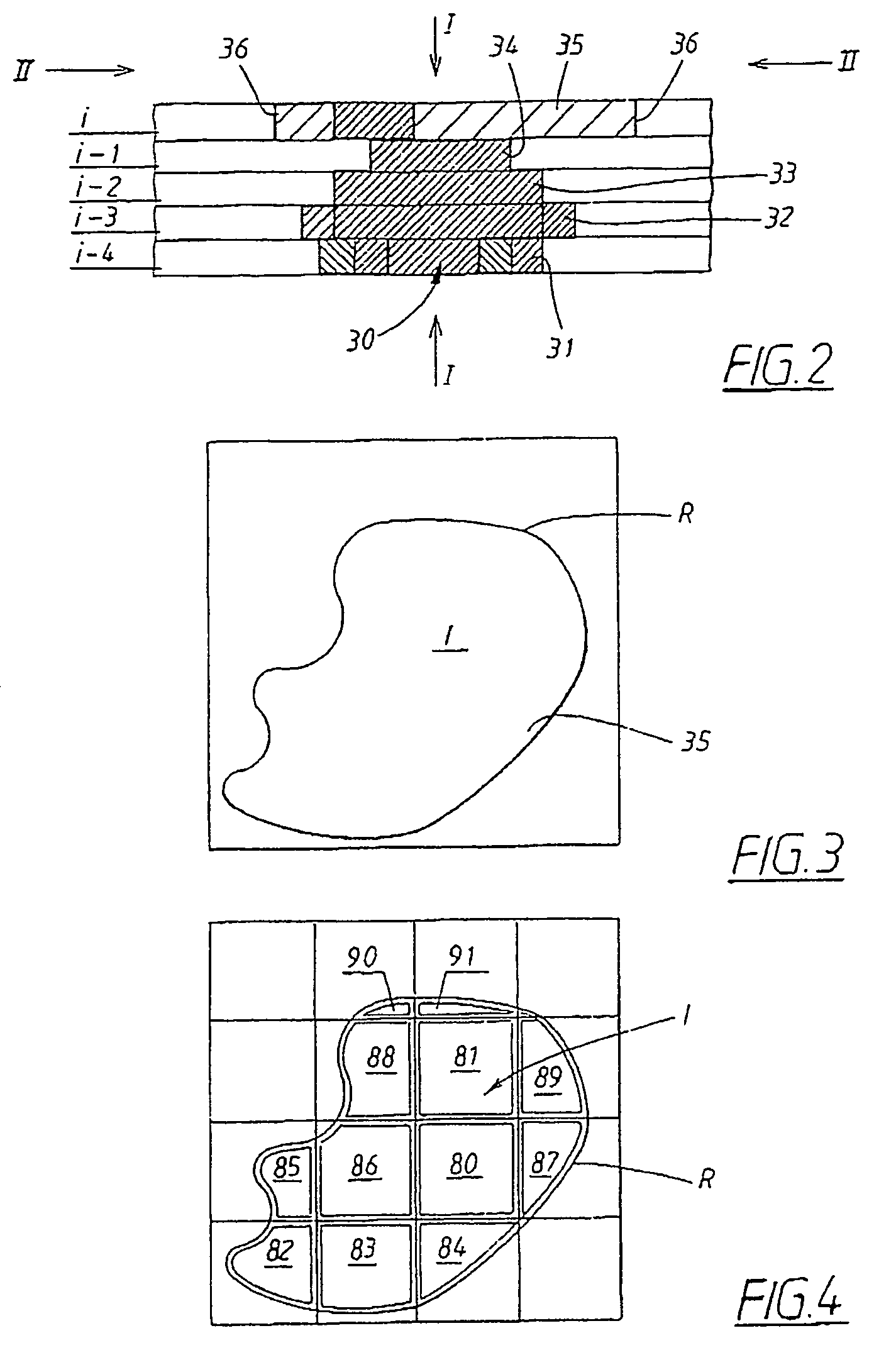
Method and device for manufacturing three-dimensional bodies
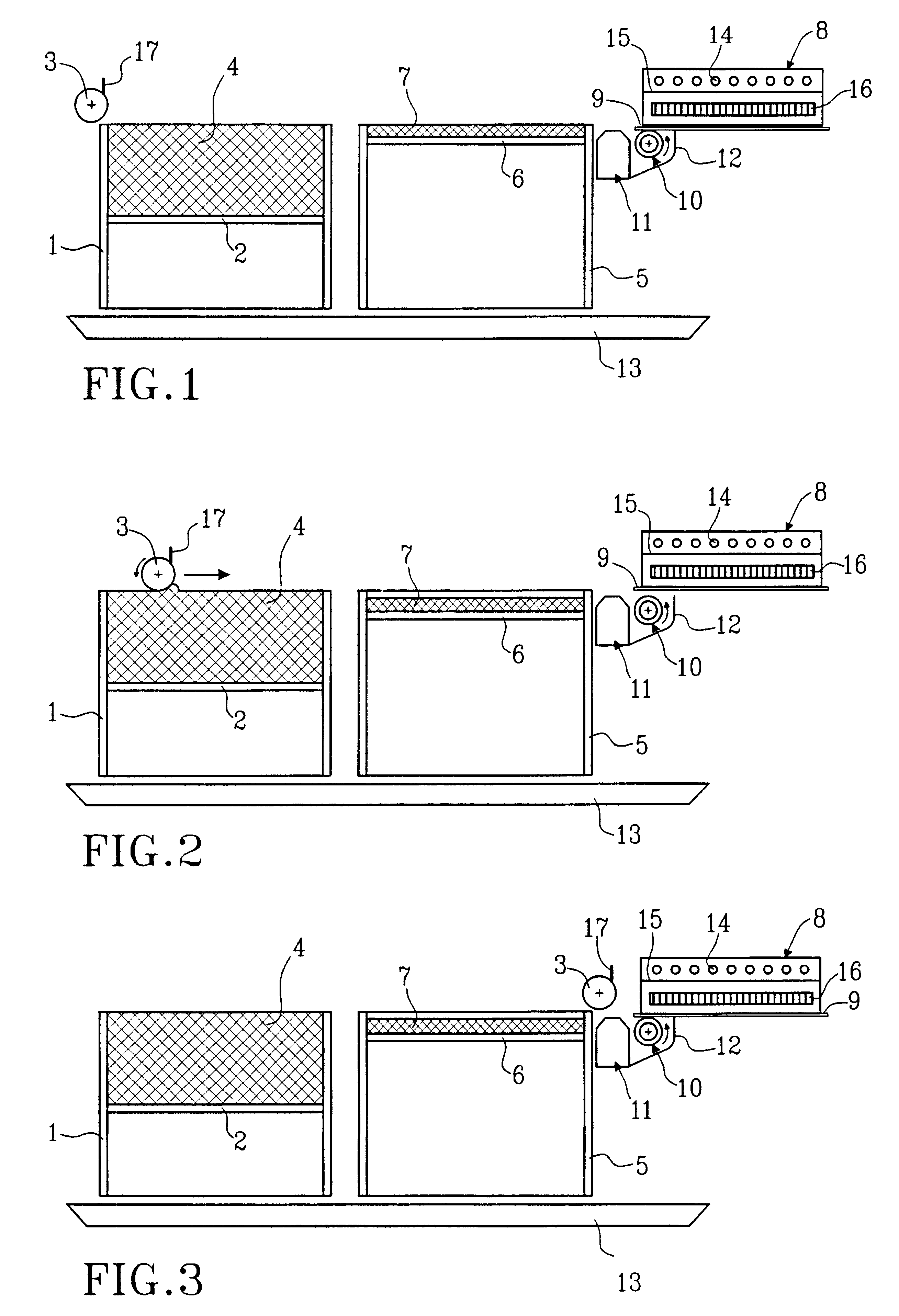
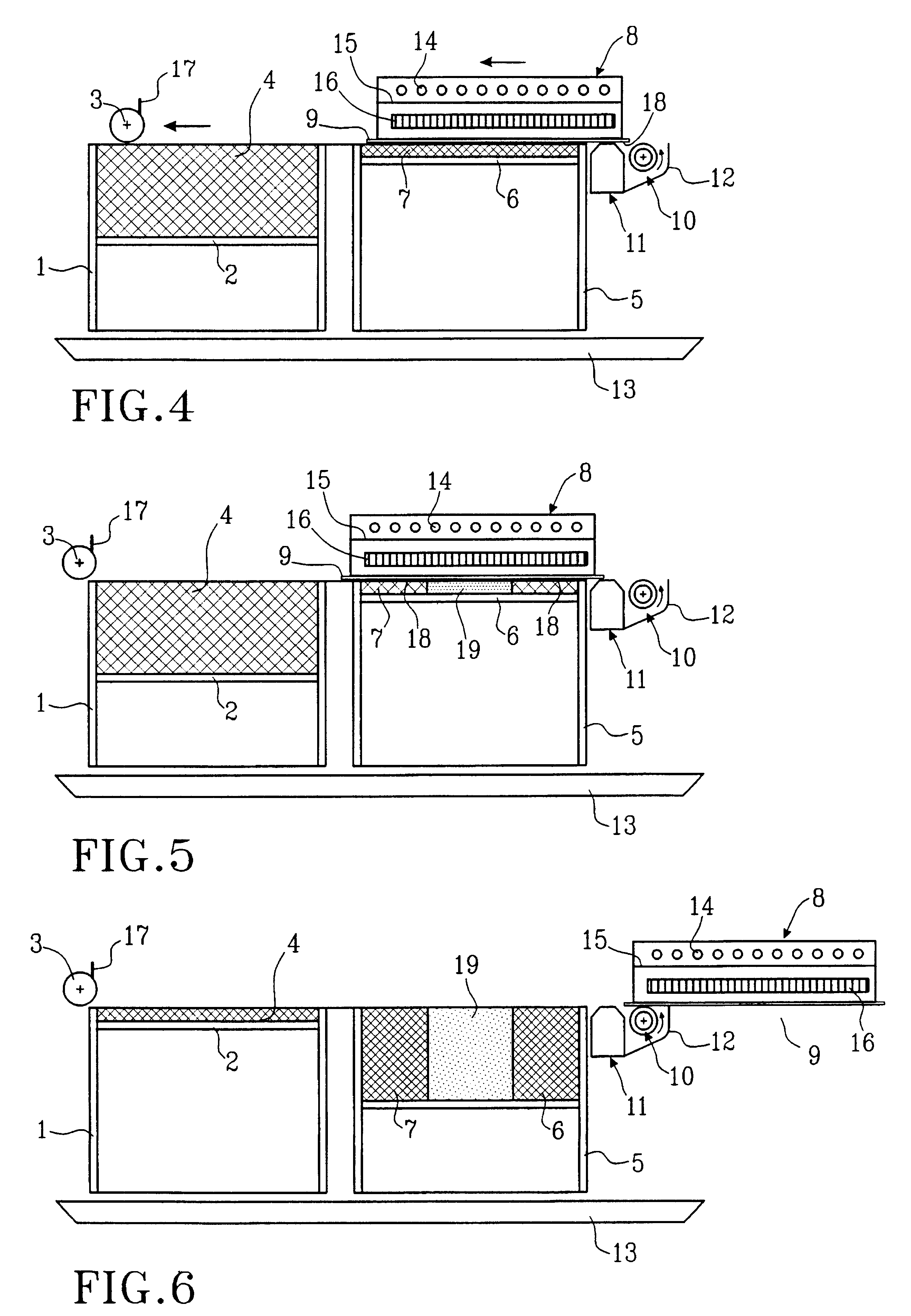
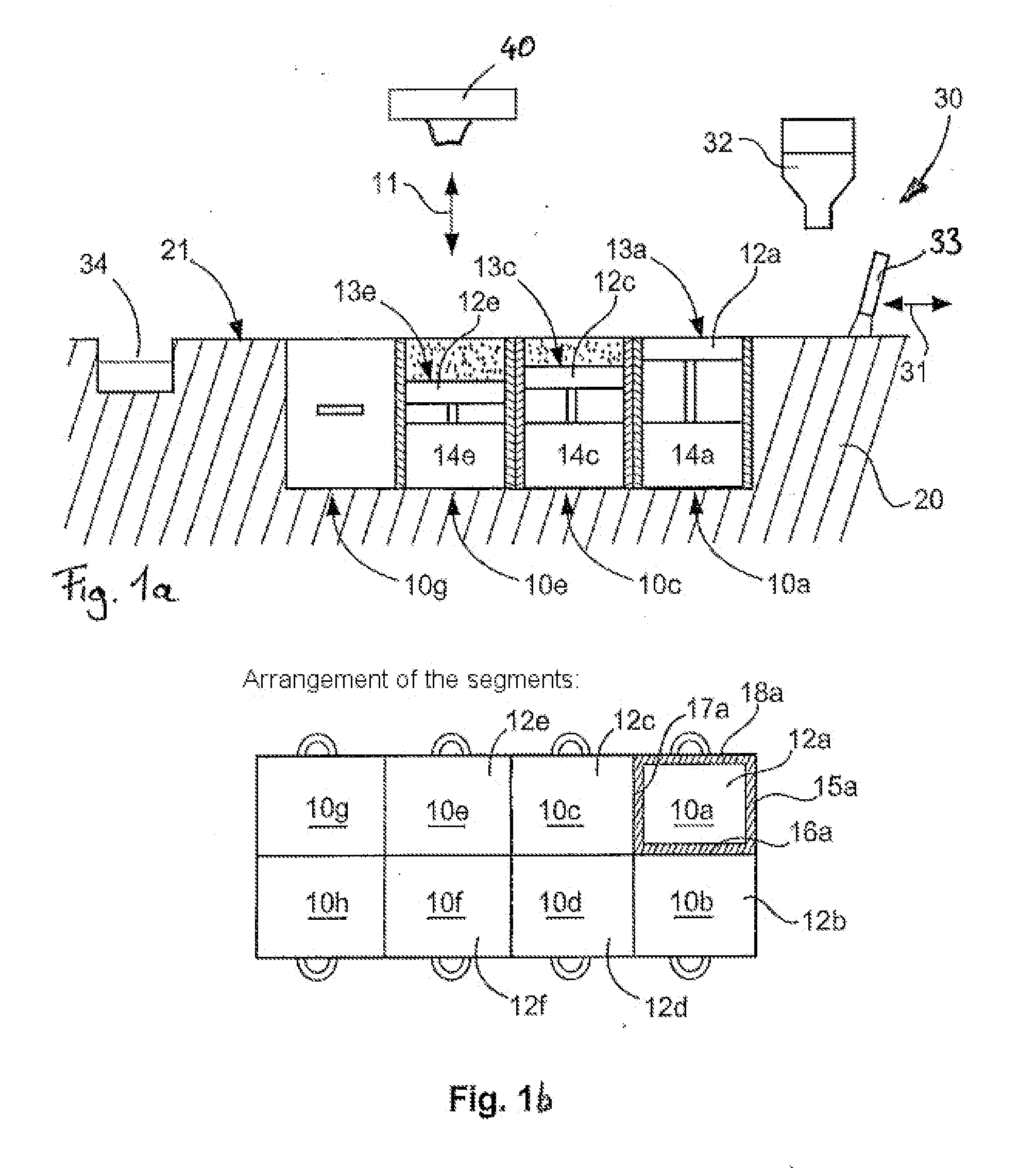
A method for producing three-dimensional bodies of a large number of mutually connected layers of a particle-shaped material such as a powder, and where the information of the appearance of each layer is achieved from a computer's CAD-unit or similar. An essentially even particle layer (7) of building material is applied on a support base (6) and on a masking device (9) is arranged a masking pattern in accordance with the information from the CAD-unit, which masking device is led over said particle layer and close to it. A radiation producer (8) is arranged or is led over the masking device (9), whereby the particles which are not covered by the masking pattern are exposed for radiation and thereby are attached to each other. The masking pattern is removed from the masking device and new sequences in accordance with the above are carried through until the three-dimensional body (19) is produced.
Owner:SPEED PART RP
Additive manufacturing apparatus and method
ActiveUS20160236279A1Sufficient reflectivityAdditive manufacturing apparatusSpectrum investigationManufactured apparatusFeedback control
This invention concerns a laser solidification apparatus for building objects by layerwise solidification of powder material. The apparatus including a build chamber containing a build platform, a device for depositing layers of powder material on to the build platform, an optical unit for directing a laser beam to selectively solidify areas of each powder layer and a spectrometer for detecting characteristic radiation emitted by plasma formed during solidification of the powder by the laser beam. The invention also relates to a spectrometer for detecting characteristic radiation generated by interaction of the metal with the or a further laser beam. The spectra recorded using the spectrometer may be used for feedback control during the solidification process.
Owner:RENISHAW PLC
Orthopedic implant and method of making metal articles
The present application is directed to an orthopedic implant. More specifically, the orthopedic implant is suitable for arthroplasty procedures where optimized multifunctional behavior of the implant is desired. In some embodiments the implant is suitable for the replacement of a spinal disc. In one embodiment, the present application is directed to an orthopedic implant including a first plate a second plate and a flexible support. The flexible support may have a single connection to the first plate and a single connection to the second plate and may vary in cross section. The first plate, the second plate and the flexible support may be unitarily formed. This application is also directed to methods of producing metal articles having microstructure for improved mechanical properties. Such methods may be suitable for the production of medical devices. In one embodiment, the method includes directing a stream including a particulate material in a pattern corresponding to at least a portion of a structure of an orthopedic implant and fusing at least a portion of the particulate material with a laser.
Owner:DEPUY ACROMED INC
Method and apparatus for additive manufacturing
ActiveUS20140348691A1Large build volumeSacrificing qualityAdditive manufacturing apparatusAuxillary shaping apparatusBeam sourceEngineering
A method for forming a three-dimensional article through successive fusion of parts of a powder bed, which parts corresponds to successive cross sections of the three-dimensional article, said method comprising the steps of: providing a model of said three dimensional article, providing a first powder layer on a work table, directing a first energy beam from a first energy beam source over said work table causing said first powder layer to fuse in first selected locations according to said model to form a first cross section of said three-dimensional article, directing a second energy beam from a second energy beam source over said work table causing said first powder layer to fuse in second selected locations according to said model to form the first cross section of said three-dimensional article, wherein said first and second locations of said first powder layer are at least partially overlapping each other.
Owner:ARCAM AB
Direct write and freeform fabrication apparatus and method
InactiveUS20050288813A1Improved part accuracyImprove accuracyAdditive manufacturing apparatusCeramic shaping apparatusTarget surfaceChemical reaction
A direct write or freeform fabrication apparatus and process for making a device or a three-dimensional object. By way of example the method comprises: (a) providing a target surface on an object-supporting platform; (b) operating a material deposition sub-system comprising a liquid deposition device for dispensing at least a liquid composition and a solid powder-dispensing device for dispensing solid powder particles to selected locations on the target surface; (c) operating a directed energy source for supplying energy to the dispensed liquid composition and the dispensed powder particles to induce a chemical reaction or physical transition thereof at the selected locations; and (d) moving the deposition sub-system and the object-supporting platform relative to one another in a plane defined by first and second directions to form the dispensed liquid composition and the dispensed powder particles into the device or object. An apparatus is also provided for carrying out this process.
Owner:NORTH DAKOTA STATE UNIVERSITY
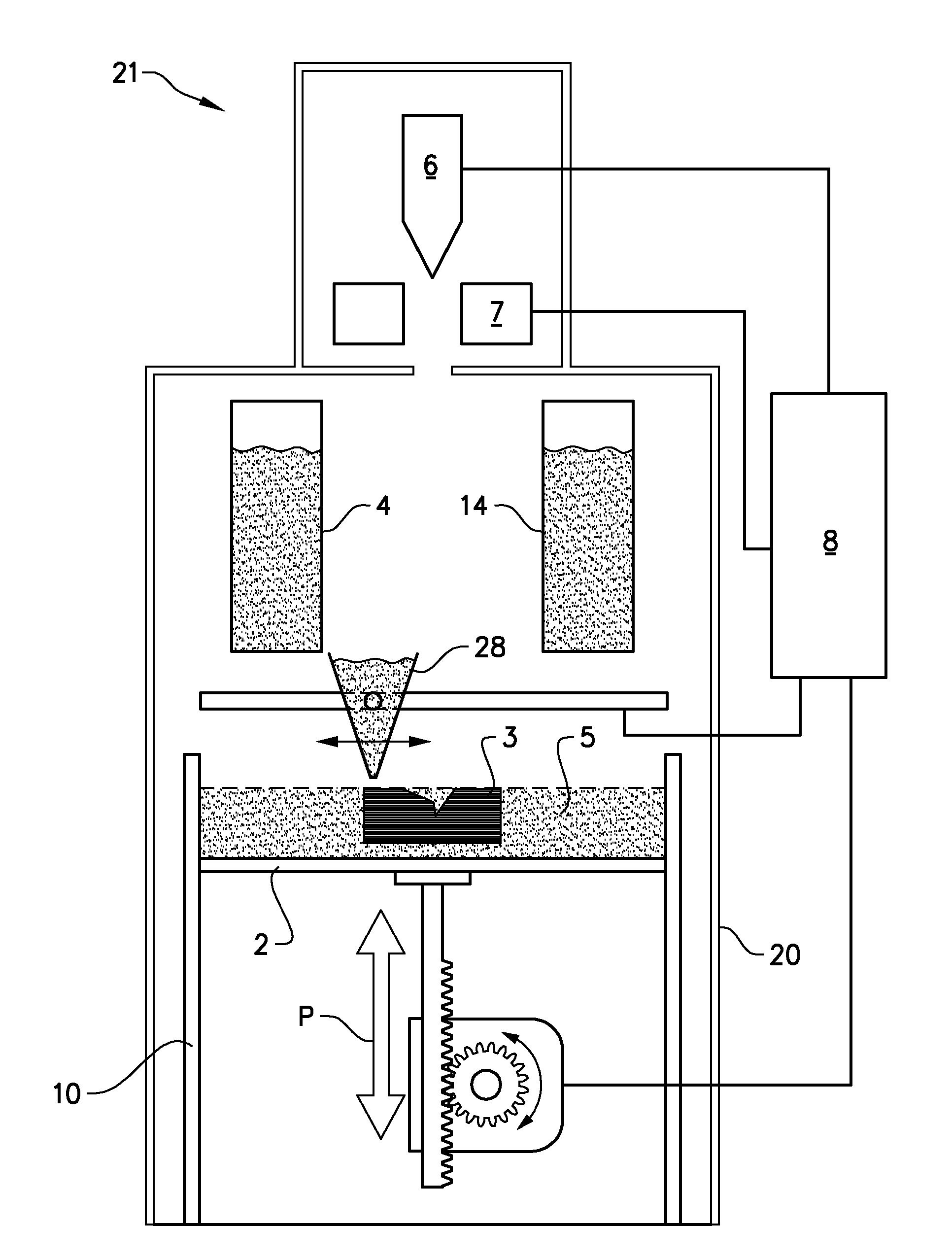
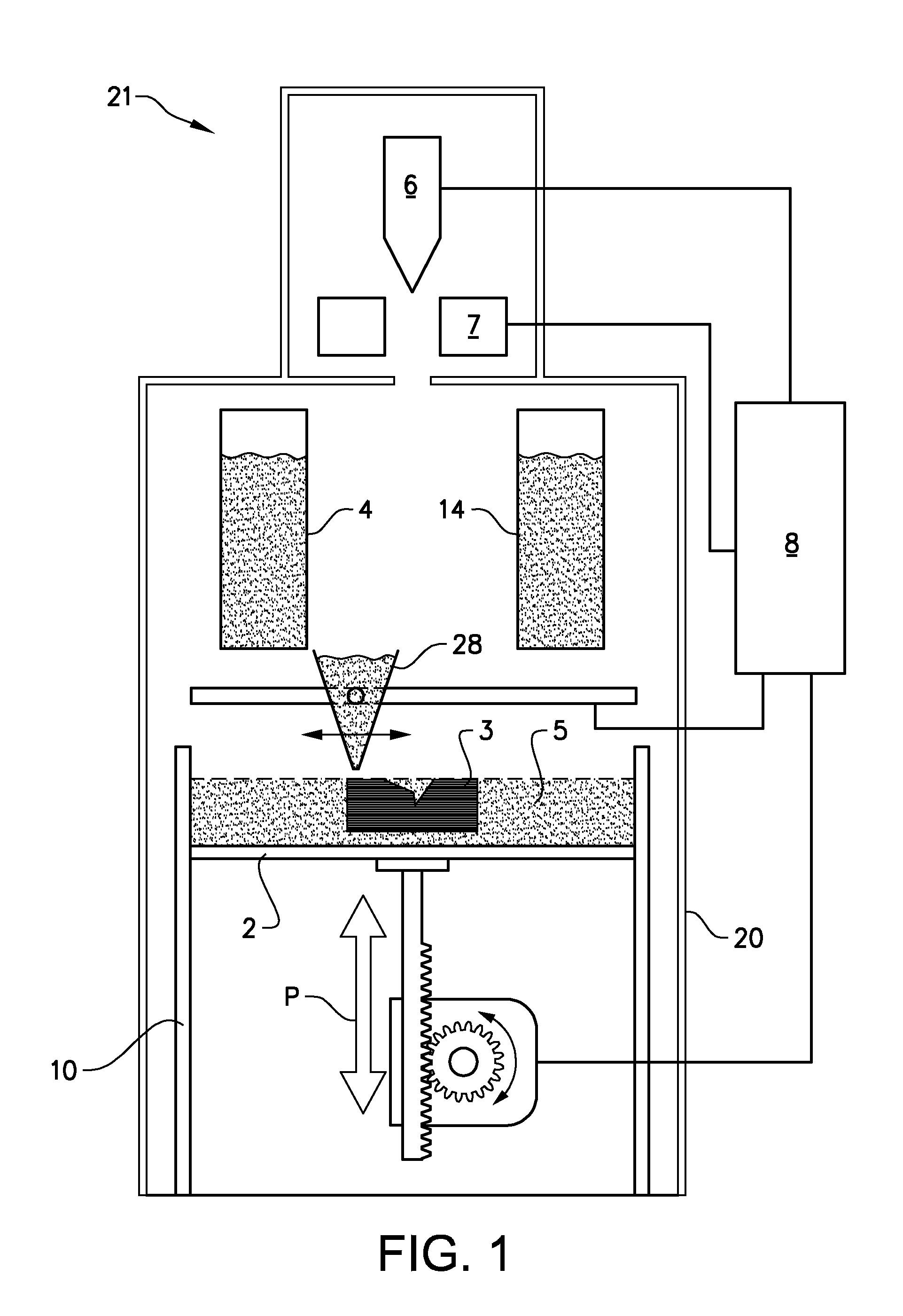
Arrangement and method for producing a three-dimensional product
Arrangement for producing a three-dimensional product, which arrangement comprises a work table on which said three-dimensional product is to be built up, a powder dispenser which is arranged so as to distribute a thin layer of powder on the work table for forming a powder bed, a radiation gun for delivering energy to the powder, fusing together of the powder then taking place, means for guiding the beam emitted by the radiation gun over said powder bed for forming a cross section of said three-dimensional product by fusing together parts of said powder bed, and a control computer in which information about successive cross sections of the three-dimensional product is stored, which cross sections build up the three-dimensional product, where the control computer is intended to control said means for guiding the radiation gun over the powder bed according to an operating scheme forming a cross section of said three-dimensional body, said three-dimensional product being formed by successive fusing together of successively formed cross sections from by the powder dispenser, and method for producing three-dimensional product using such an arrangement.
Owner:ARCAM AB
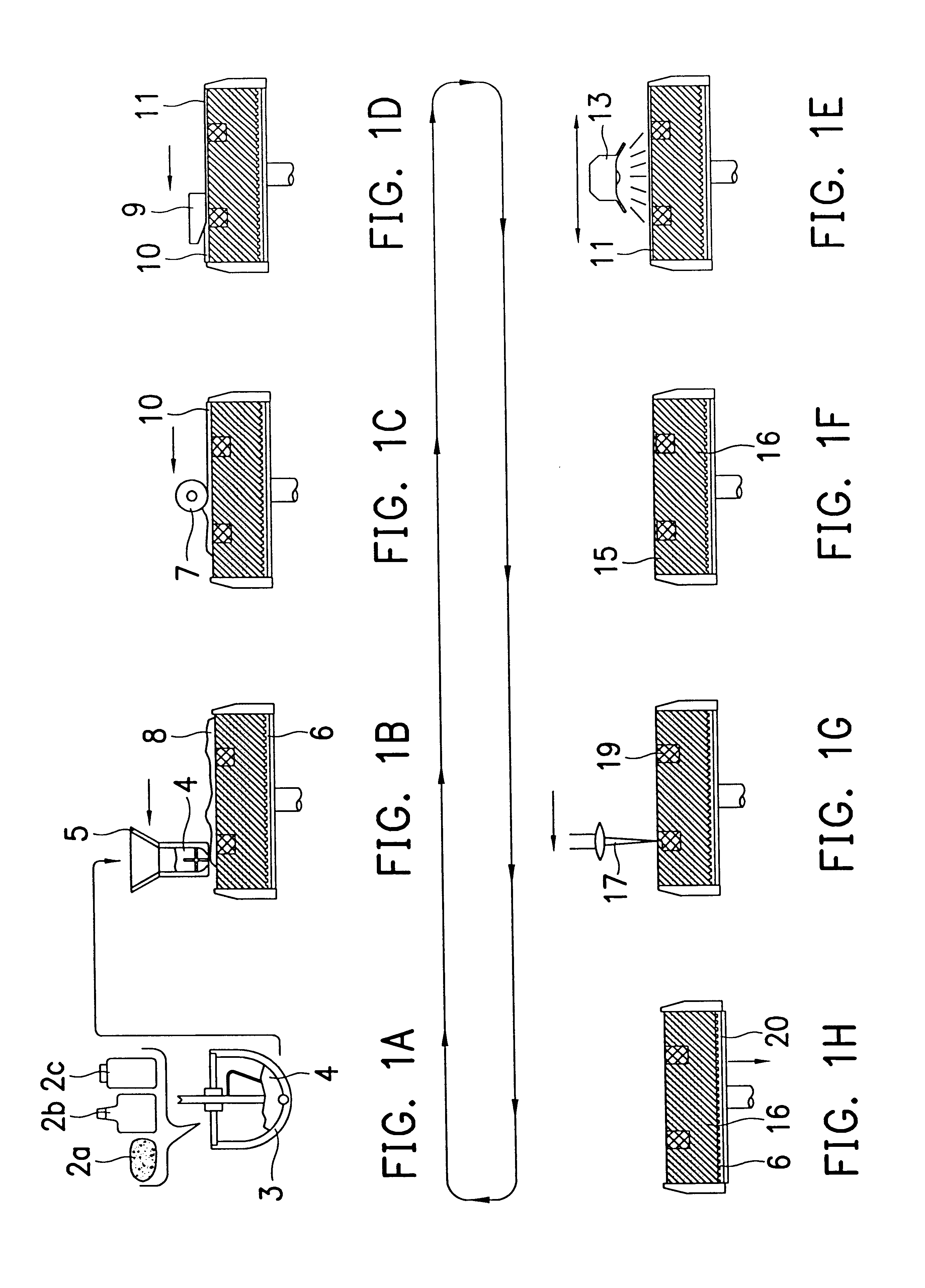
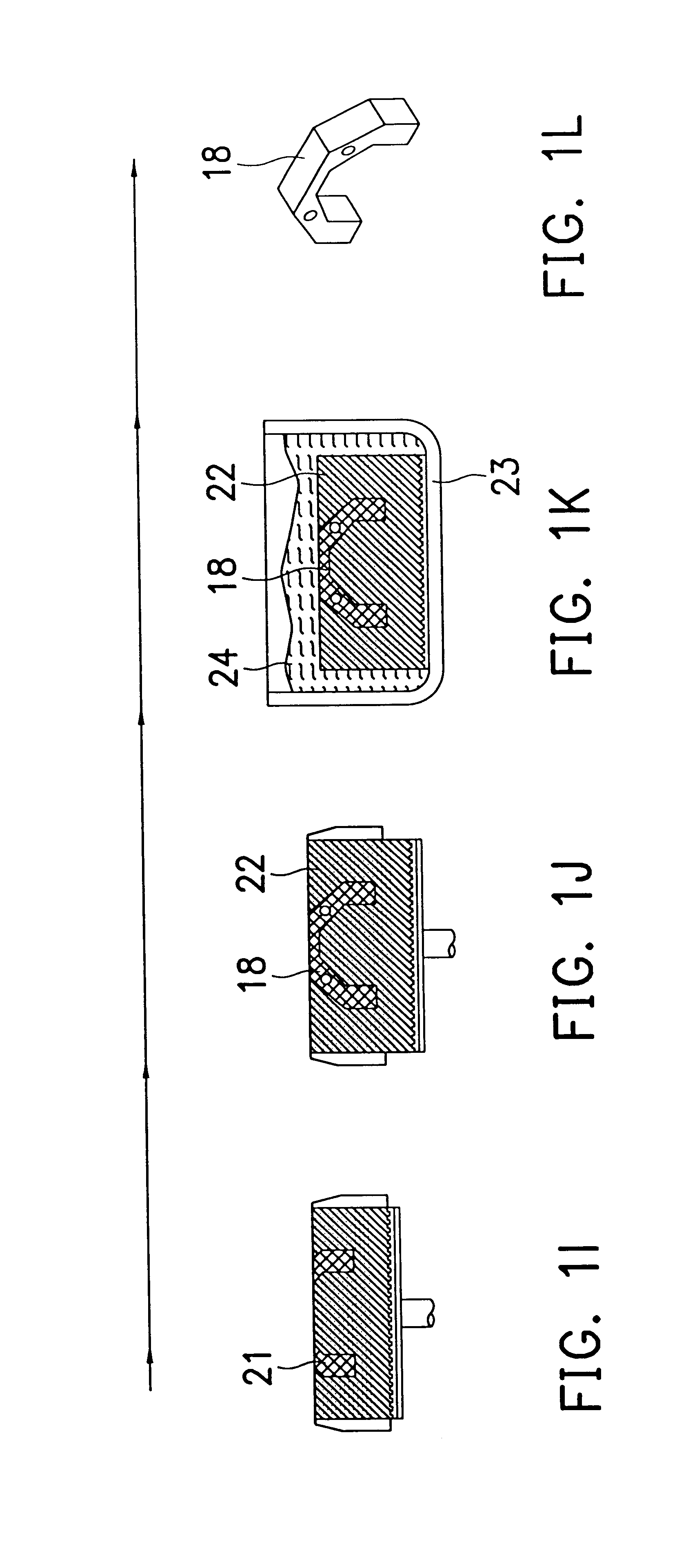
Method for rapid forming of a ceramic work piece
InactiveUS6217816B1Rapid productionPrevent dislocationAdditive manufacturing apparatusFeeding arrangmentsHeat fusionLaser beams
An inorganic binder and a dissolving agent are put into ceramic powder. They are mixed to form a plastic green mixture. Then the said mixture is formed into a thin green layer. Preferably, this thin green layer will be preheated and dried such that the thin green layer will be hardened due to the bonding effect of the inorganic binder. A portion of the thin green layer exposed under a directed high-energy beam is sintered, preferably by a laser beam, to cause ceramic molecules to bond together locally due to heat fusion. By controlling the scanning path of the high-energy beam, a two-dimensional thin cross section of the ceramic part in arbitrary form can be produced. A second thin ceramic layer can be built onto the first thin ceramic layer and bonded to it by the same method. After multiple repetitions of this procedure a three dimensional ceramic part can be fabricated layer upon layer. The green portion, which is not scanned by the high-energy beam, will be removed with suitable method. A ceramic part can be rapidly produced in this way.
Owner:NAT SCI COUNCIL
Method and apparatus for additive manufacturing
ActiveUS20140314964A1Improve conductivityReduce probabilityVacuum evaporation coatingPretreated surfacesMetallurgyElectron
Various embodiments provide a method and apparatus for forming a three-dimensional article through successive fusion of parts of at least one layer of a powder bed provided on a work table in an additive manufacturing machine, which parts corresponds to successive cross sections of the three-dimensional article. The method comprises the steps of: applying a layer of predetermined thickness of powder particles on the work table, applying a coating on at least a portion of the powder particles, which coating is at least partially covering the powder particles, and fusing the powder particles on the work table with an electron beam.
Owner:ARCAM AB
Device for the generative manufacturing of three-dimensional components
ActiveUS20130108726A1Efficient and cost-effective operationEfficiently formedManufacturing platforms/substratesConfectioneryEngineeringMonochrome
The invention relates to a device for producing products having individual geometries, comprising a substrate carrier device, a material application device for applying material, preferably above the substrate carrier device, which material application device can be moved relative to the substrate carrier device, and a control device which is coupled to the material application device for signaling. According to the invention, the material application device is coupled to an input interface for signaling and for selection of a first or a second application mode, the control device and the application device being designed such as to produce, in the first application mode, a three-dimensional product on the surface of a substrate plate by way of an additive production method, said substrate plate being connected to the substrate carrier device. According to the additive production method, a curable material is applied in consecutive layers, one or more predetermined regions are selectively cured after or during each application of a layer, the predetermined regions being bonded to one or more regions of the underlying layer. The predetermined region(s) is / are predetermined by a cross-section geometry of the product in the respective layer and is / are stored in the control device, and the curable material is applied in a plurality of consecutive layers to produce the three-dimensional product. The control device and the application device are further designed such that in the second mode of application one or more colors are applied to predetermined regions of a print substrate material connected to the substrate carrier device to produce a monochrome or polychrome print.
Owner:BEGO MEDICAL
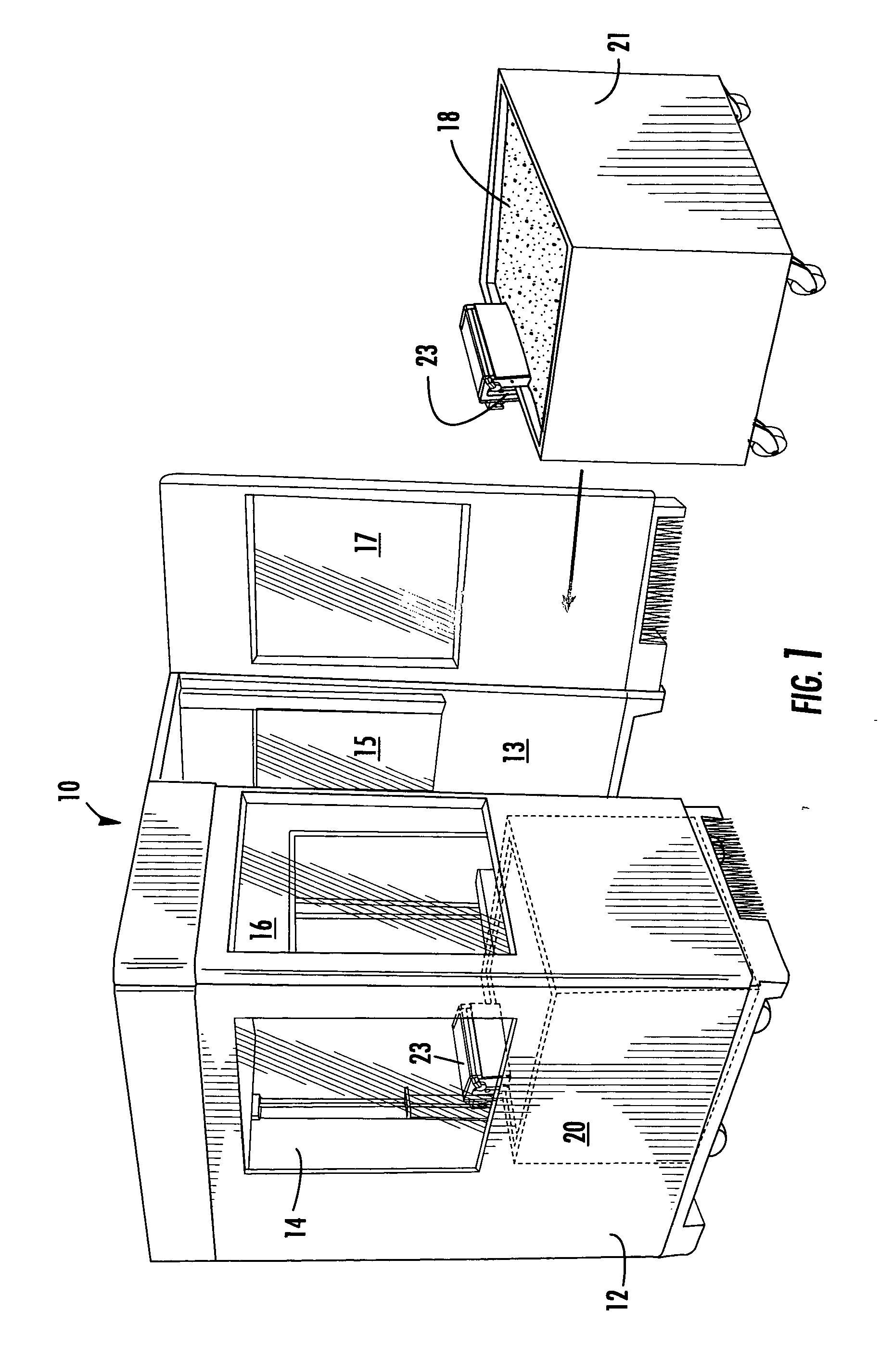
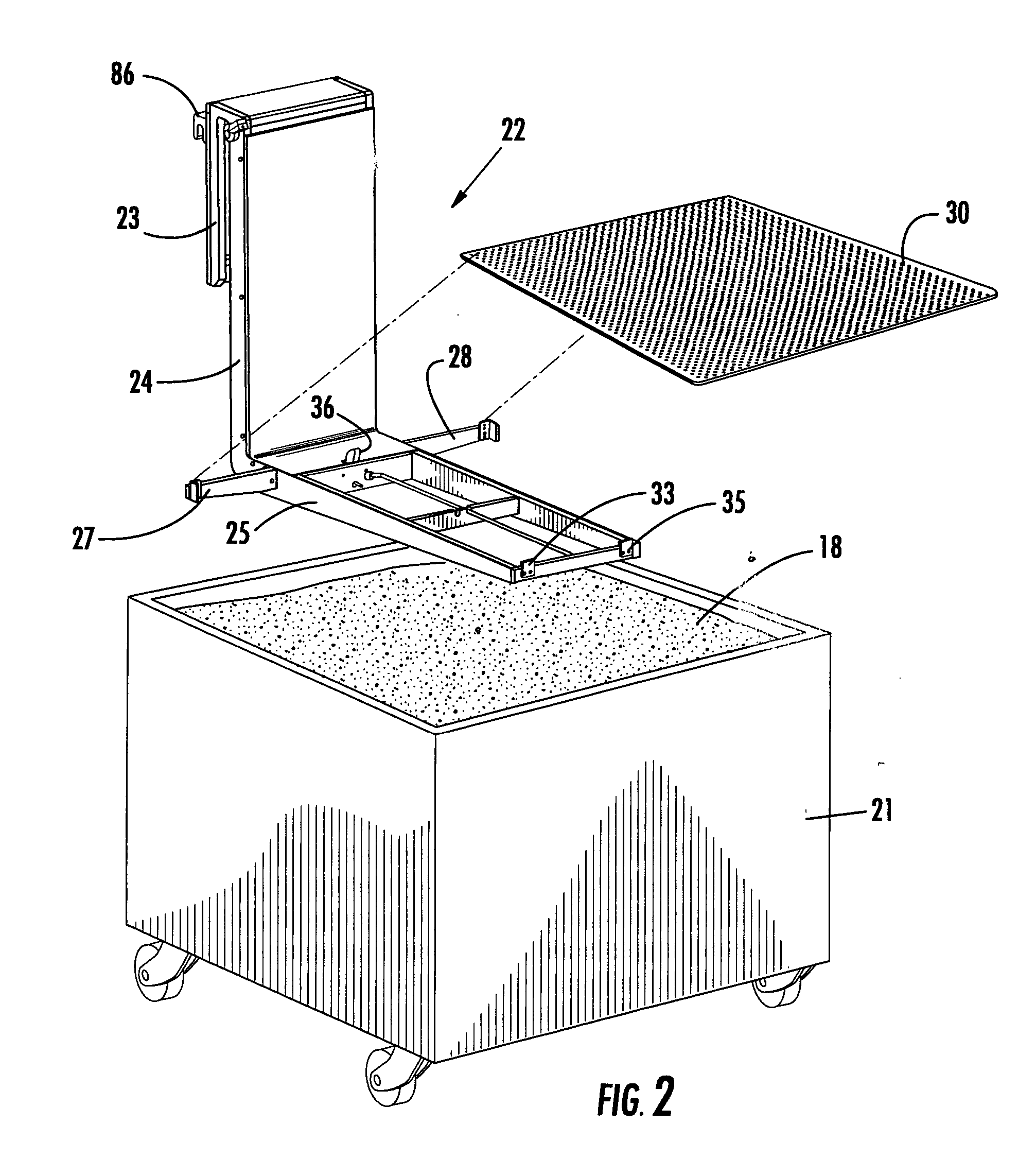
Device and arrangement for producing a three-dimensional object
InactiveUS20040026807A1Reduced form requirementsSmall sizeConfectioneryWood working apparatusThin layerRunning time
A device for manufacturing a three-dimensional product, which device comprises a work table on which said three-dimensional product is to be built, a powder dispenser which is arranged to lay down a thin layer of powder on the work table for the formation of a powder bed, a ray gun for giving off energy to the powder whereby fusion of the powder takes place, members for controlling of the beam released by the ray gun across said powder bed for the formation of a cross section of said three-dimensional product through fusion of parts of said powder bed, and a controlling computer in which information about successive cross sections of the three-dimensional product is stored, which cross sections build the three-dimensional product, the controlling computer intended to control said members for guiding the ray gun across the powder bed according to a running schedule forming a cross section of said three-dimensional body, whereby said three-dimensional product is formed by successive fusion of successively formed cross sections from powder layers successively laid down by the powder dispenser.
Owner:ARCAM AB
Three-dimensional design and manufacturing systems
ActiveUS20140156053A1Use directlyMinimize amount of processingAdditive manufacturing apparatusData processing applications3d print3d design
A method of authenticating the printing of a three-dimensional (3D) article at a 3D printer according to a 3D print file describing a three-dimensional design is described. The method comprises: receiving an authentication request from a 3D print server that is associated with the 3D printer, the request comprising a unique design identifier associated with a 3D design file and a unique 3D printer identifier associated with a 3D printer, the received unique 3D design identifier being related to the received 3D printer ter identifier in accordance with a first relationship; using at least one of the received unique identifiers to access a verifying 3D design identifier and a verifying 3D printer identifier, the verifying identifiers being related to each other in accordance with a second relationship; comparing the first and second relationships between the received and verifying identifiers; generating an authentication signal if the first relationship corresponds with the second relationship; obtaining a decryption key associated with the received identifiers in response to the authentication signal; and transferring the decryption key to the 3D print server to authenticate and enable the printing of the 3D article on the 3D printer.
Owner:DNA AM LTD
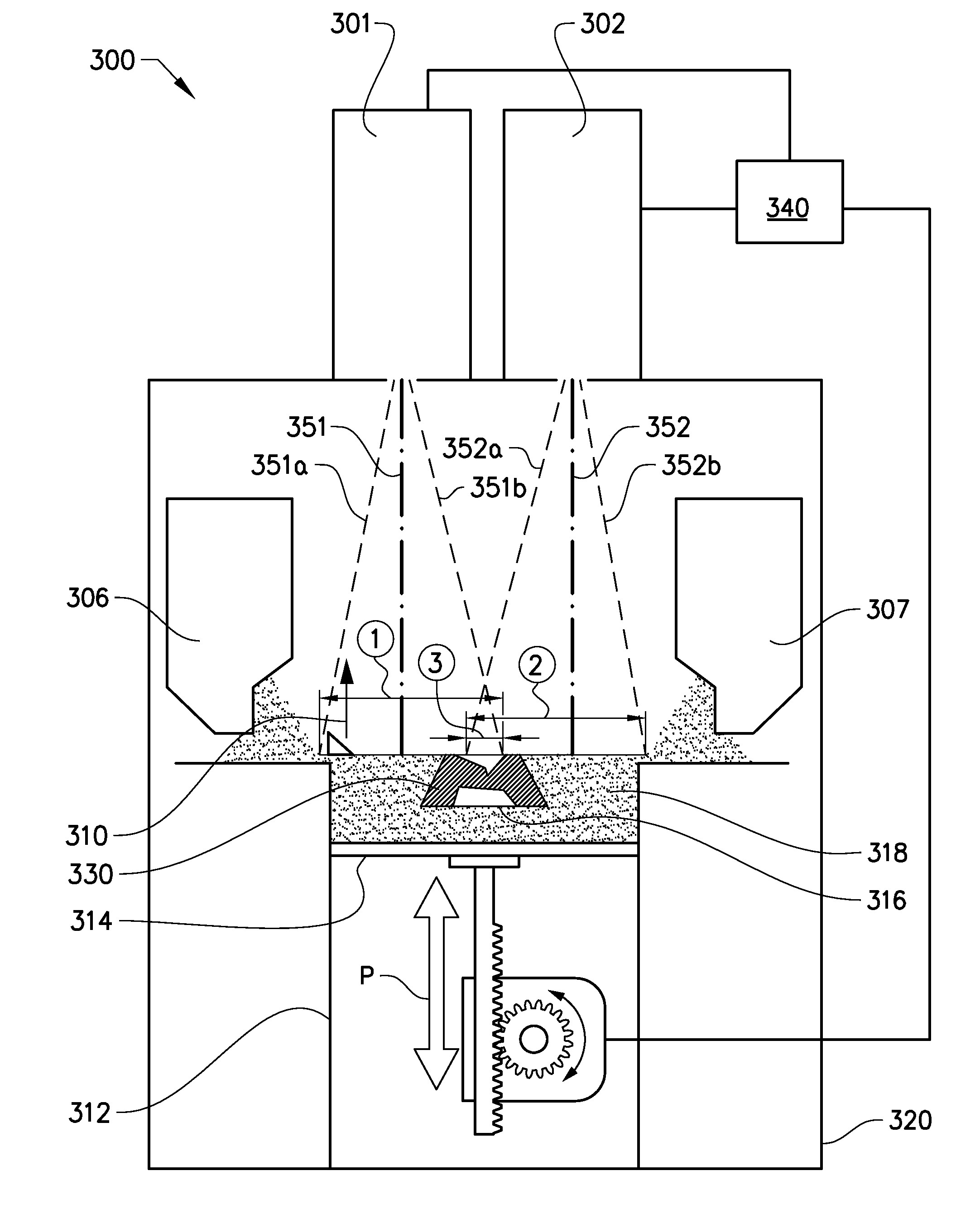
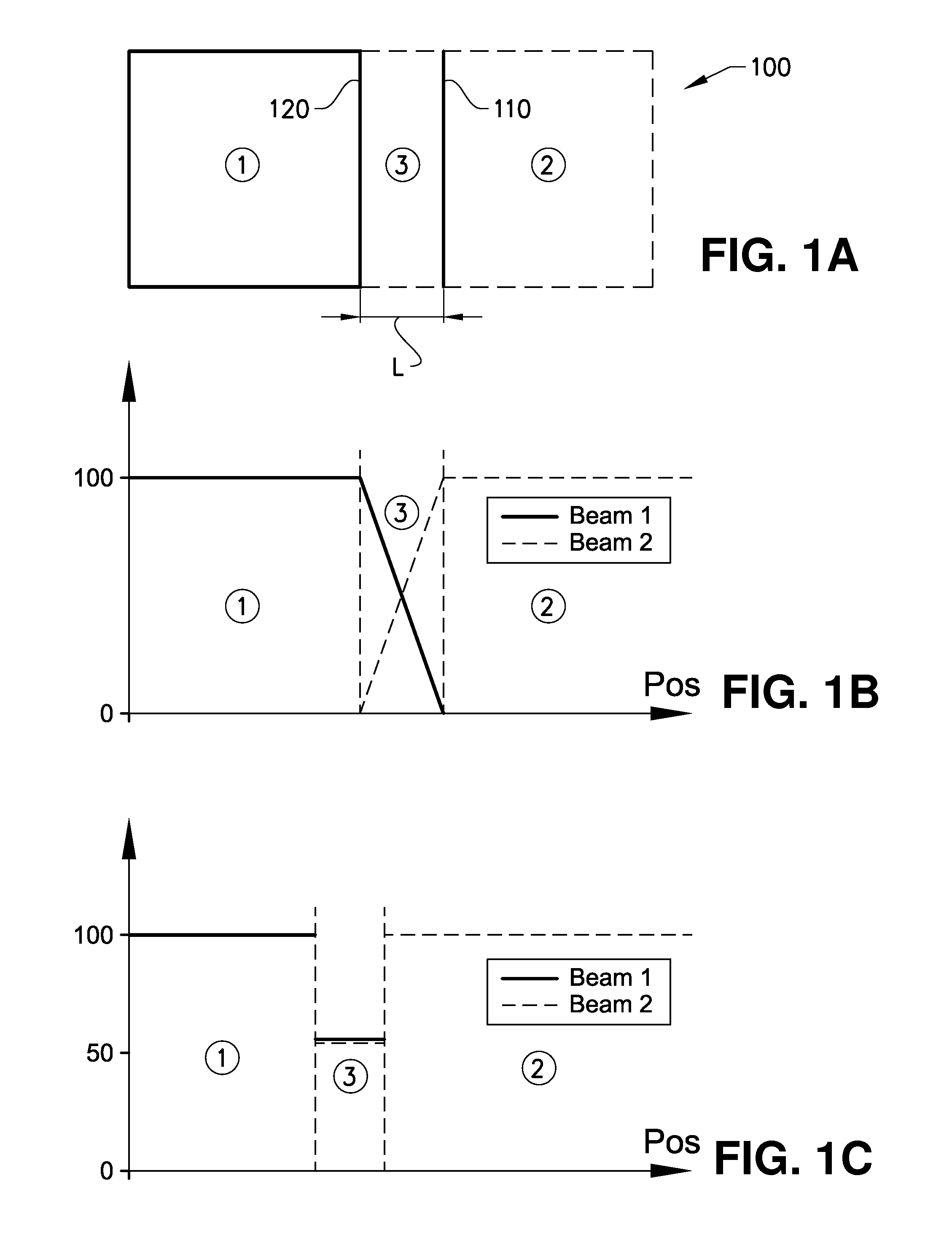
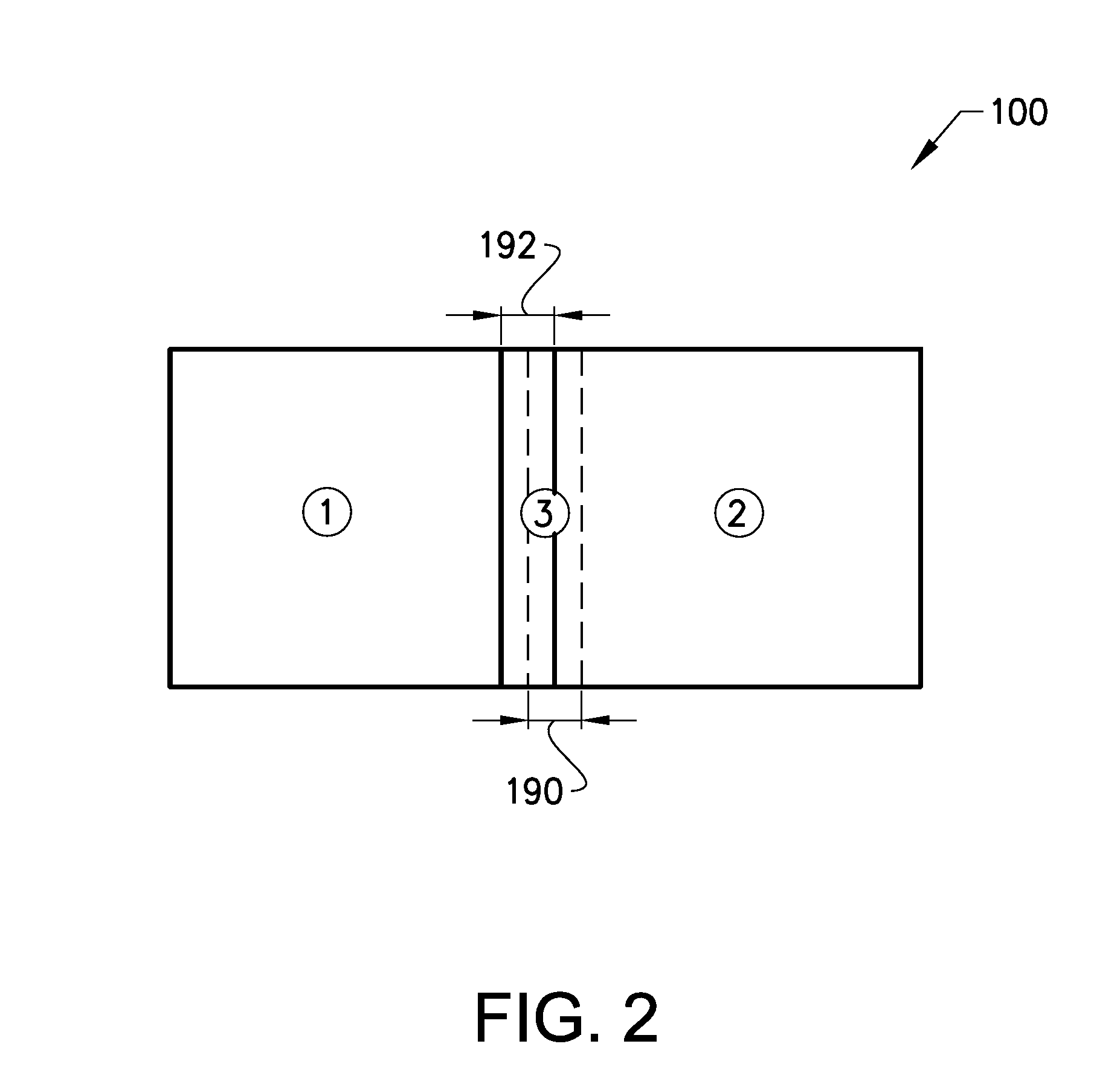
Multiple beam additive manufacturing
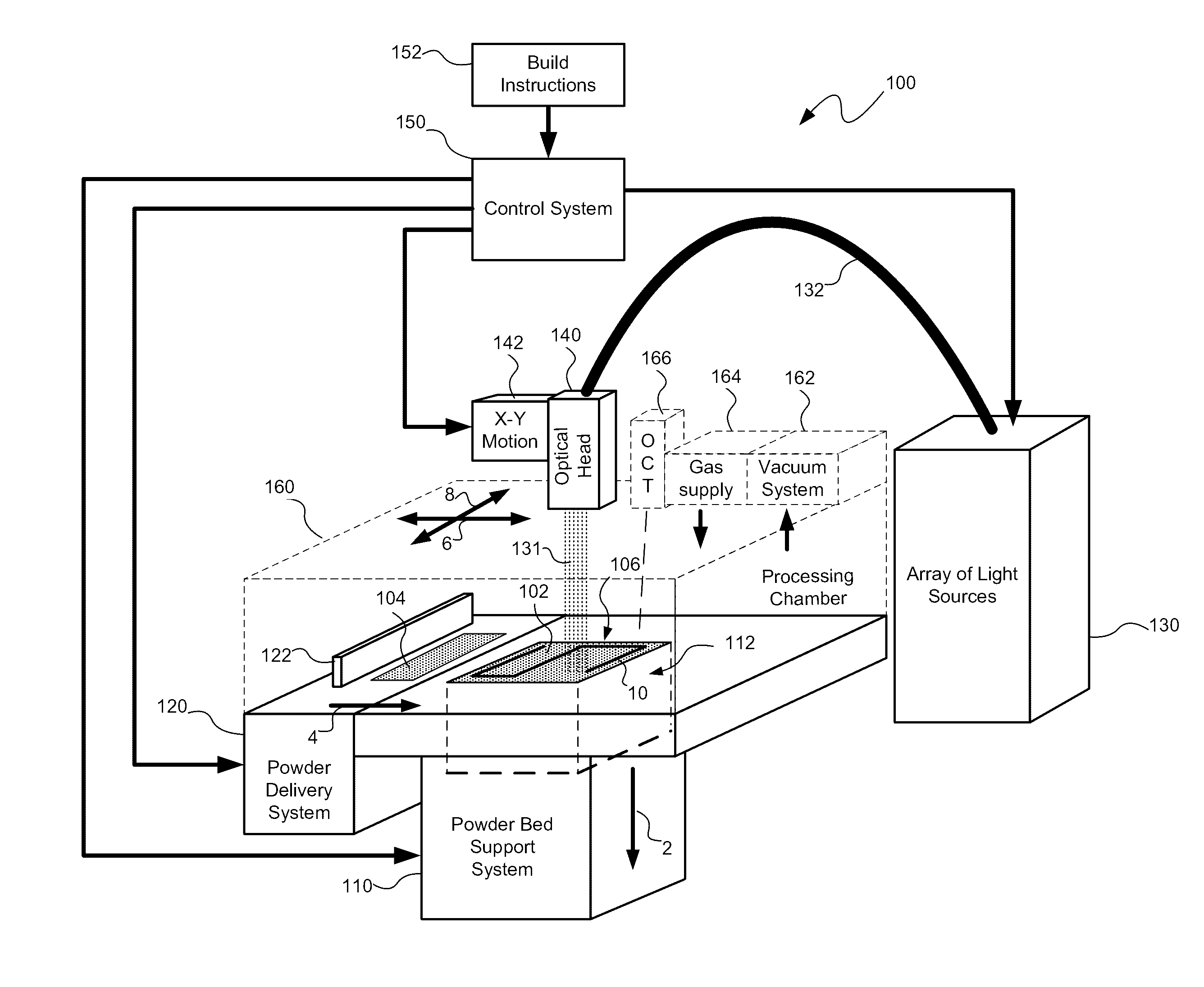
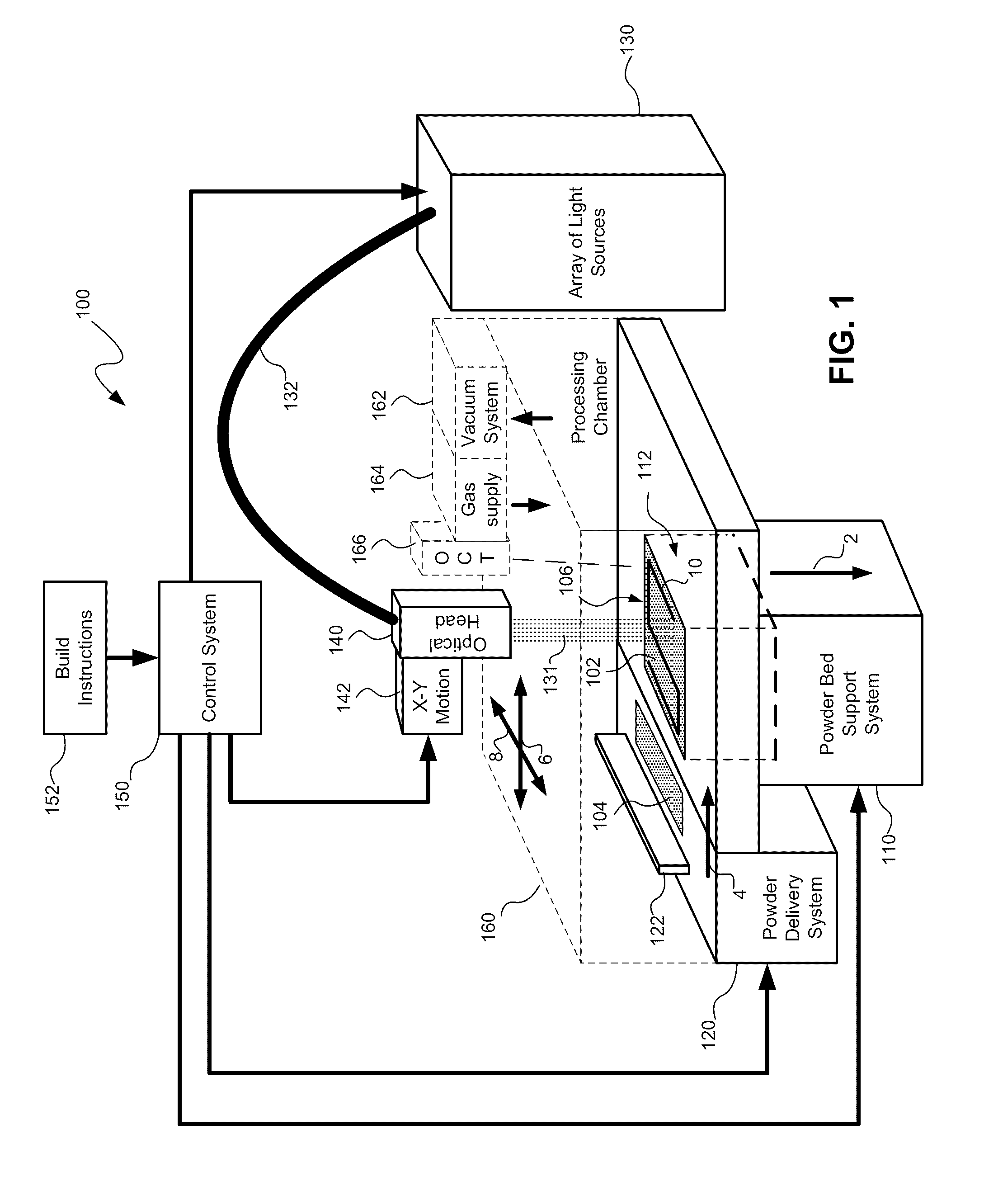
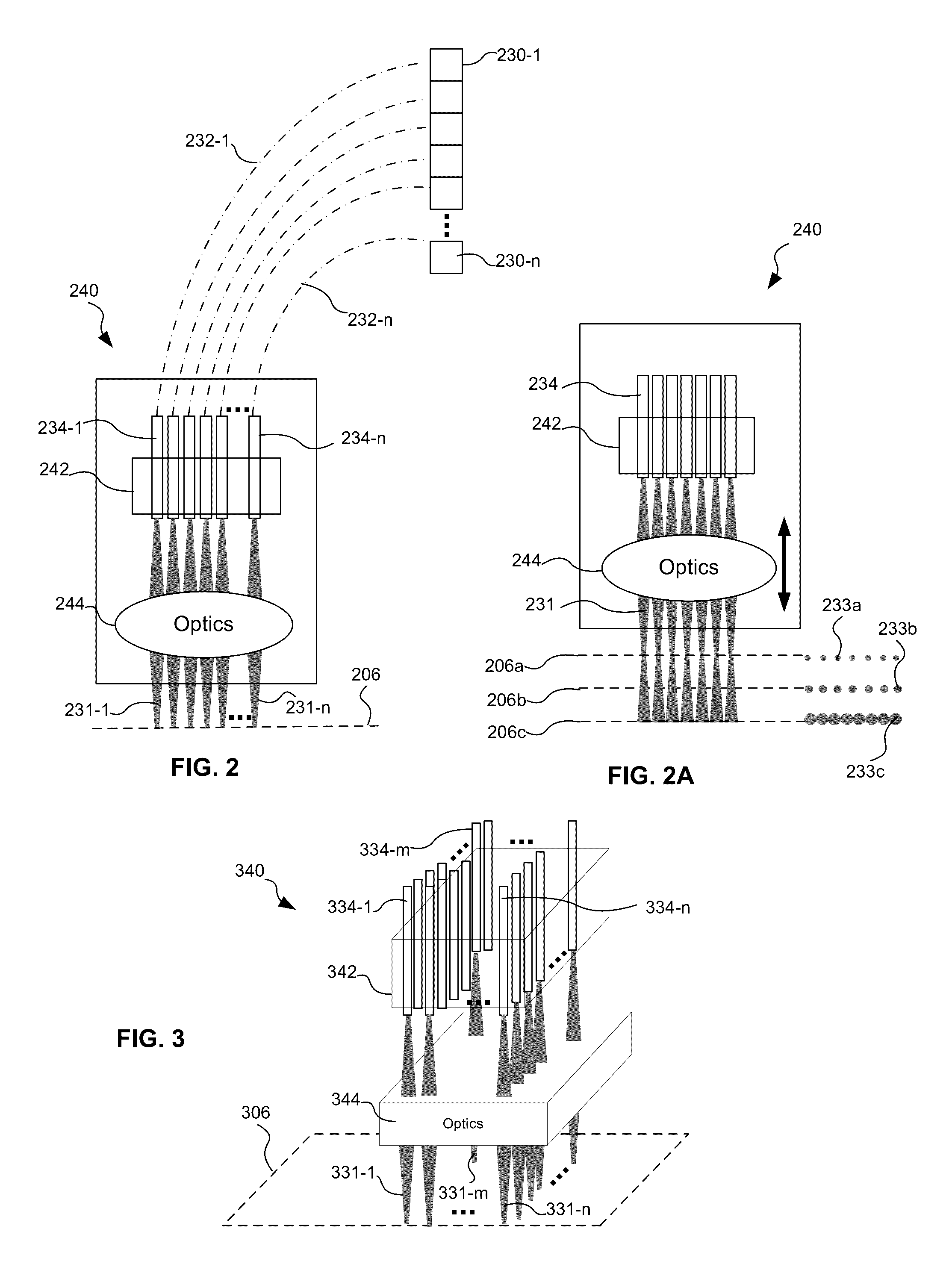
Systems and methods for multiple beam additive manufacturing use multiple beams of light (e.g., laser light) to expose layers of powder material in selected regions until the powder material fuses to form voxels, which form build layers of a three-dimensional structure. The light may be generated from selected light sources and coupled into an array of optical fibers having output ends arranged in an optical head in at least one line such that multiple beams are sequentially directed by the optical head to the same powder region providing multiple beam sequential exposures (e.g., with pre-heating, melting and controlled cool down) to fuse the powder region. The multiple sequential beams may be moved using various techniques (e.g., by moving the optical head) and according to various scan patterns such that a plurality of fused regions form each build layer.
Owner:IPG PHOTONICS CORP
Device and arrangement for producing a three-dimensional object
InactiveUS7537722B2Reduce biasReduce riskAdditive manufacturing apparatusAuxillary shaping apparatusThin layerRunning time
A device for manufacturing a three-dimensional product, which device comprises a work table on which said three-dimensional product is to be built, a powder dispenser which is arranged to lay down a thin layer of powder on the work table for the formation of a powder bed, a ray gun for giving off energy to the powder whereby fusion of the powder takes place, members for controlling of the beam released by the ray gun across said powder bed for the formation of a cross section of said three-dimensional product through fusion of parts of said powder bed, and a controlling computer in which information about successive cross sections of the three-dimensional product is stored, which cross sections build the three-dimensional product, the controlling computer intended to control said members for guiding the ray gun across the powder bed according to a running schedule forming a cross section of said three-dimensional body, whereby said three-dimensional product is formed by successive fusion of successively formed cross sections from powder layers successively laid down by the powder dispenser.
Owner:ARCAM AB
Three dimensional structure producing device and producing method
An apparatus for making a three-dimensional object includes a powdery layer-forming unit for forming a powdery layer on a table and an optical beam-irradiating unit for irradiating an optical beam on a predetermined region of the powdery layer to sinter the predetermined region. The optical beam-irradiating unit is disposed at a position spaced from immediately above an optical beam-irradiating range to obliquely irradiate the optical beam on the powdery layer. Because fumes generated by irradiating and heating the powdery layer with the optical beam rise towards a position immediately above them, the optical beam is irradiated from the position spaced from immediately above the optical beam-irradiating range, thereby reducing a cloud of the optical beam-irradiating unit that may be caused by the fumes.
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
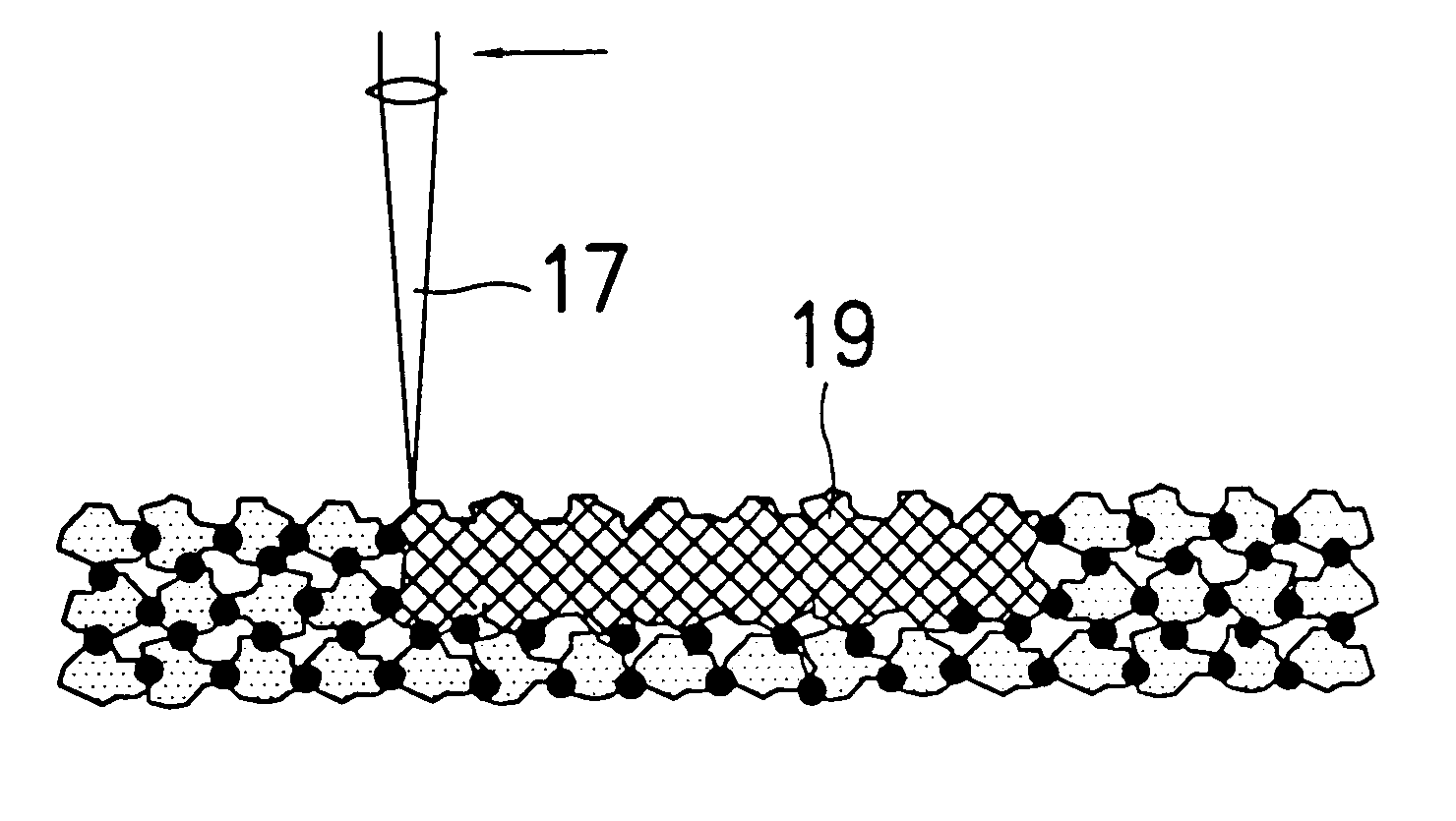
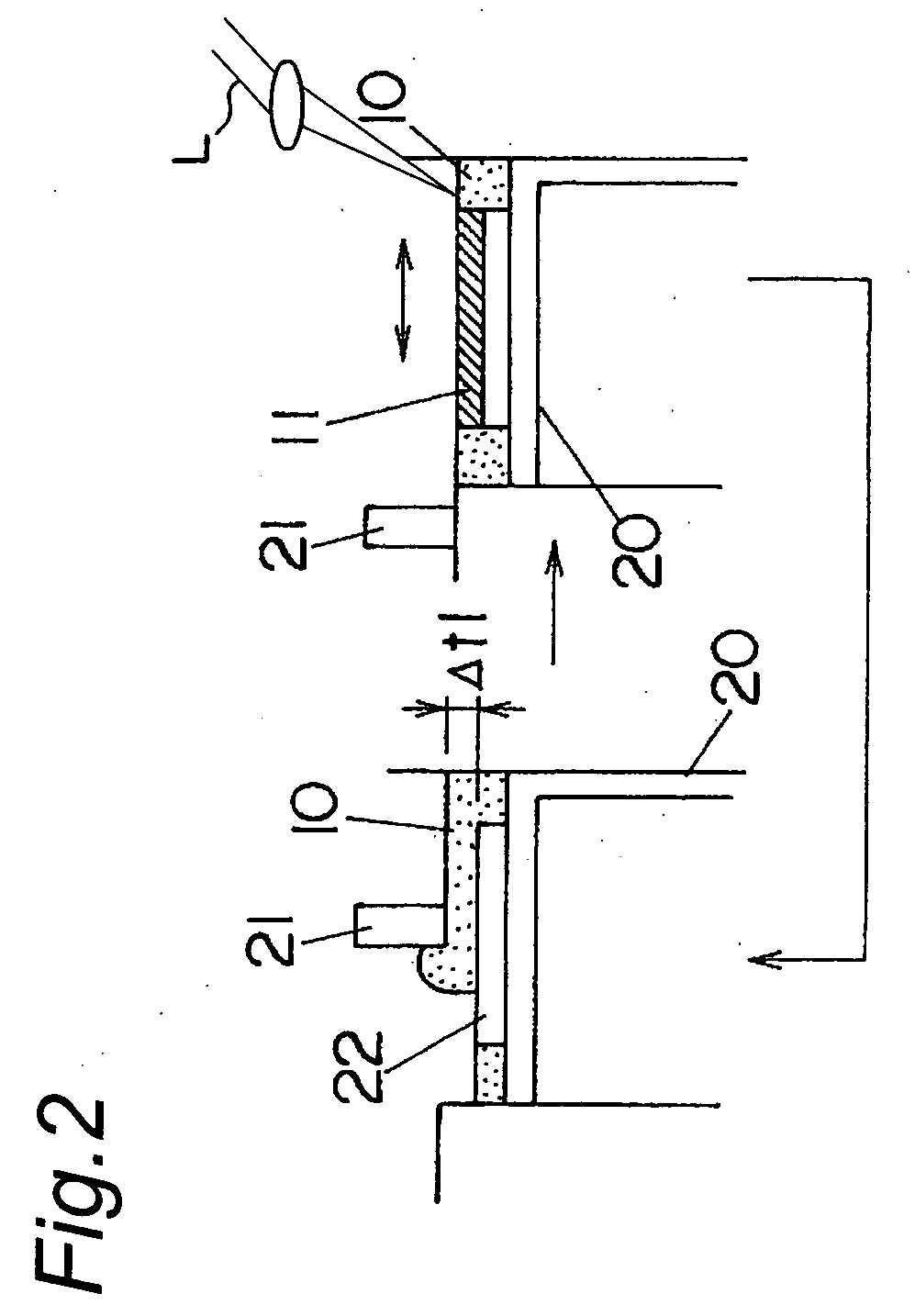
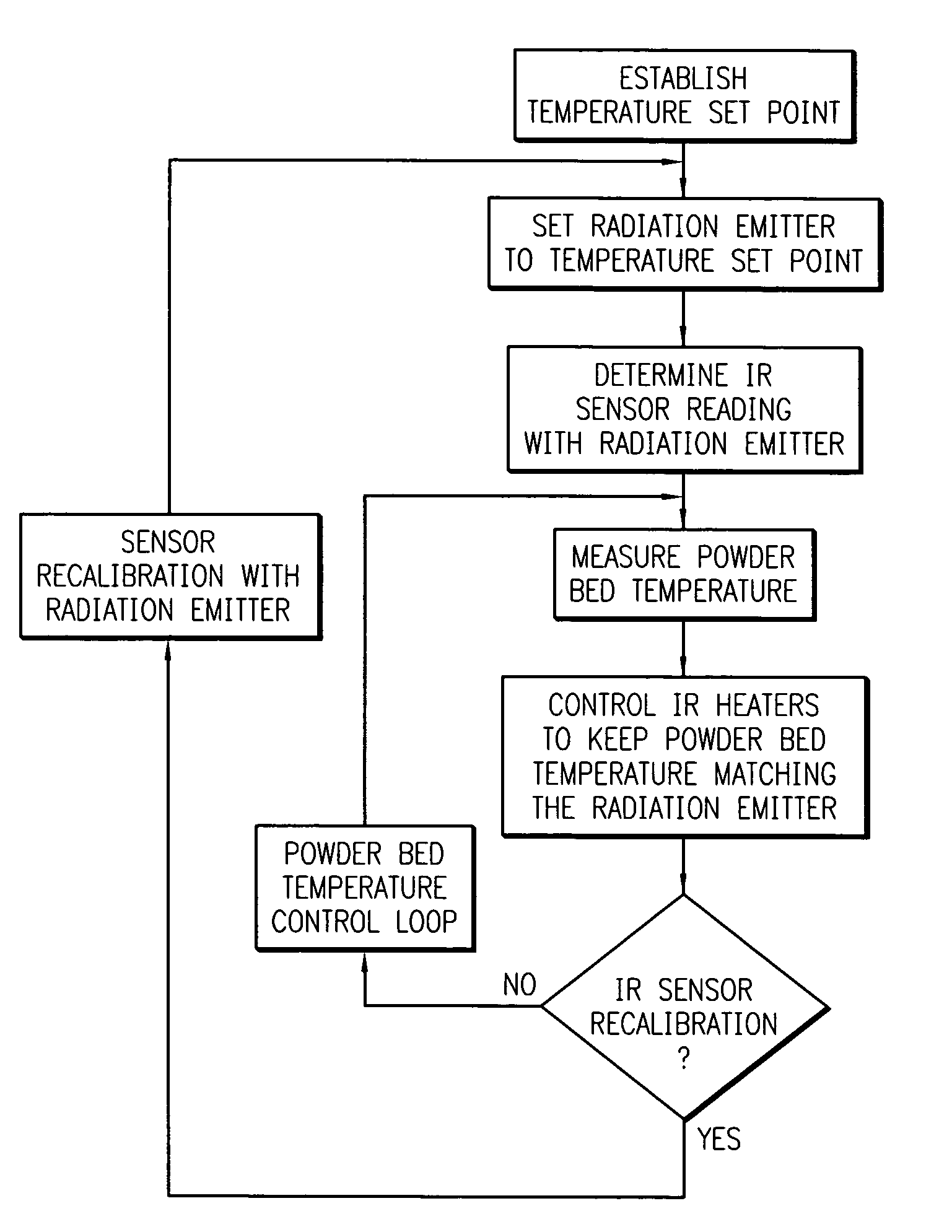
Continuous calibration of a non-contact thermal sensor for laser sintering
ActiveUS6930278B1Accurate monitoringHighly consistent mechanical propertyAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyAcousticsLaser
An apparatus and a method of using the apparatus wherein a radiation emitter is positioned adjacent a sensor apparatus within a process chamber in a laser sinter system that emits radiation to the sensor apparatus and a calibration apparatus receives readings from the sensor apparatus to compare temperature sensings received from the sensor apparatus with set emission signals from the radiation emitter to adjust the temperature sensings to calibrate the sensor apparatus during the forming of a three-dimensional article. The calibration is done repeatedly during the build process of the three-dimensional article.
Owner:3D SYST INC
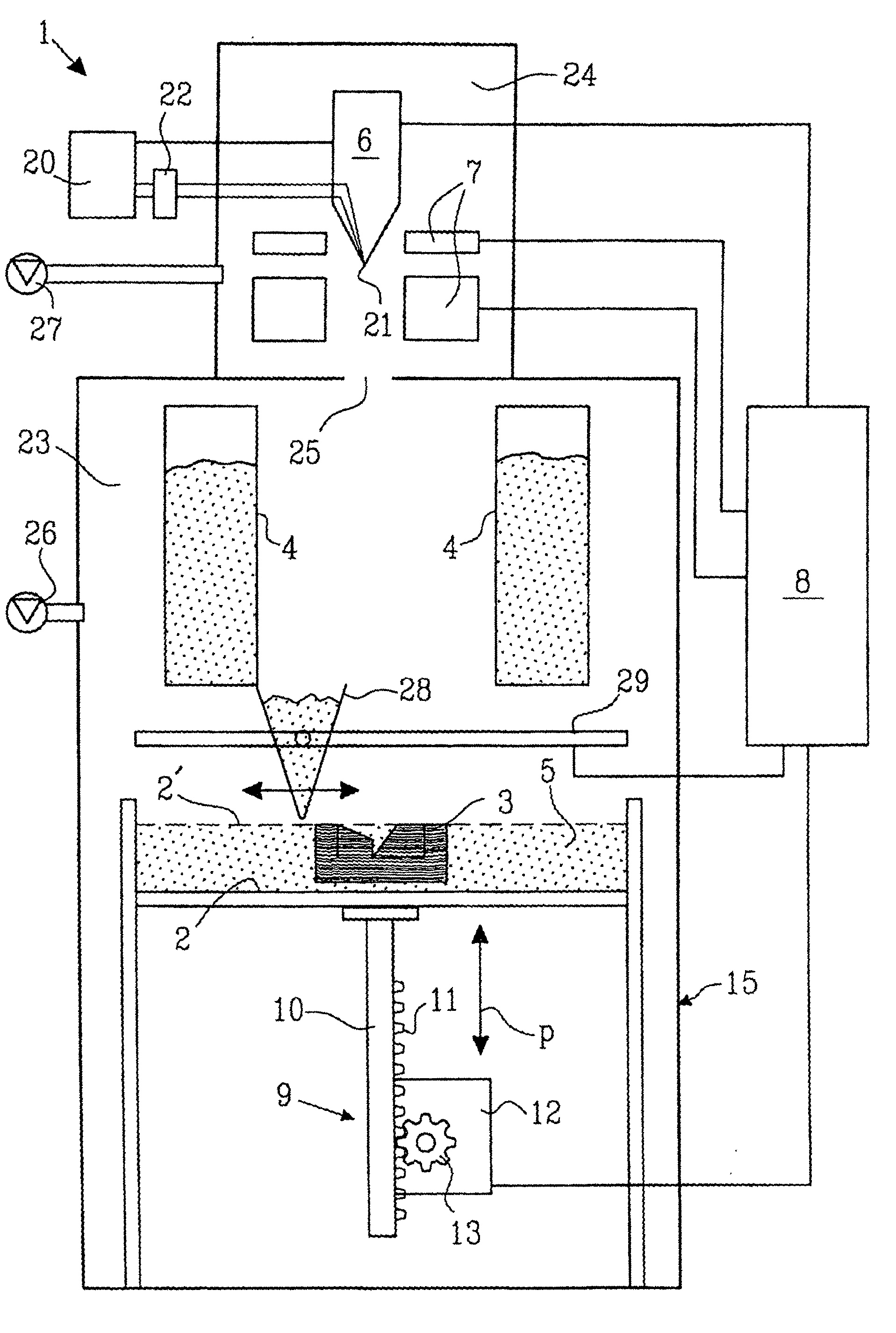
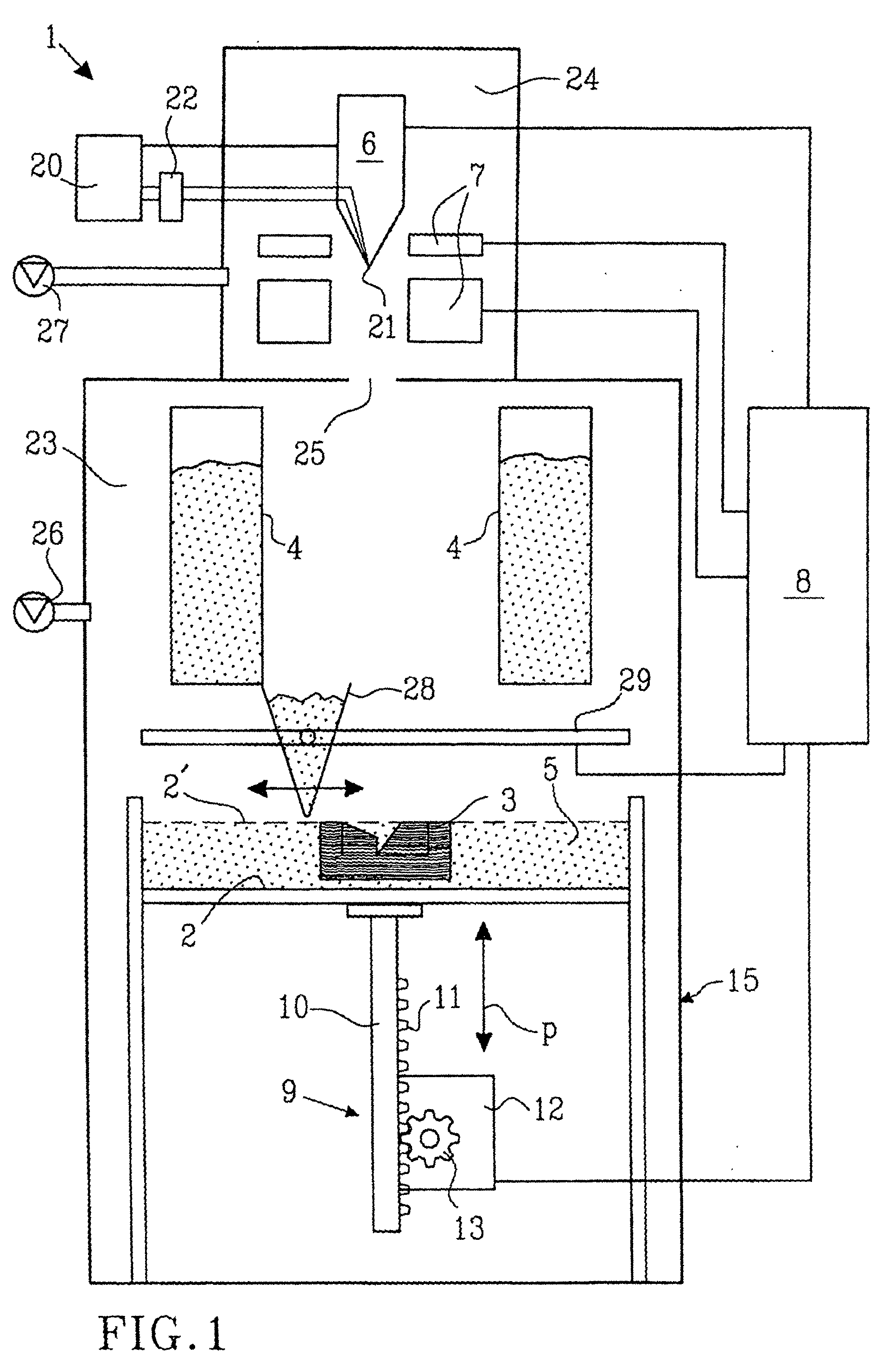
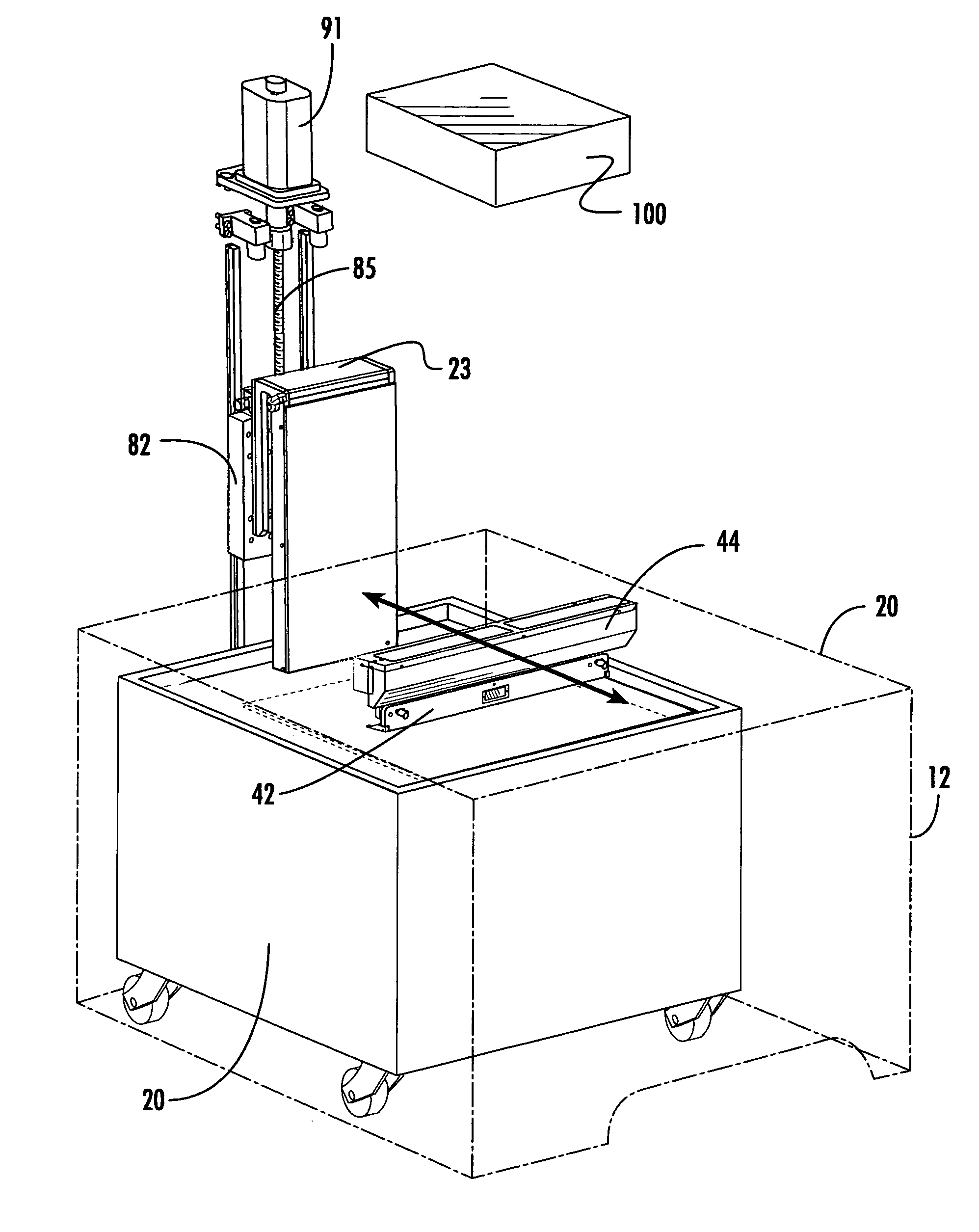
Rapid prototyping and manufacturing system and method
ActiveUS20070074659A1Simplify obtaining precisionFast preparationConfectioneryPretreated surfacesEngineeringRapid prototyping
A stereolithography apparatus having a resin vat with resupply containers in one-way flow communication and a leveling container in two-way flow communication, an automatic offload cart to remove and replace build support platforms, an elevator assembly for supporting and releasably retaining a build platform removably attached to the stereolithography apparatus frame such that elevator forks supporting the build platform can be released into the vat and removed from the stereolithography apparatus with the vat, and a recoater assembly and recoater blade for mapping the resin surface in the vat and applying a fresh coating of resin to a cross-section being built in the vat.
Owner:3D SYST INC
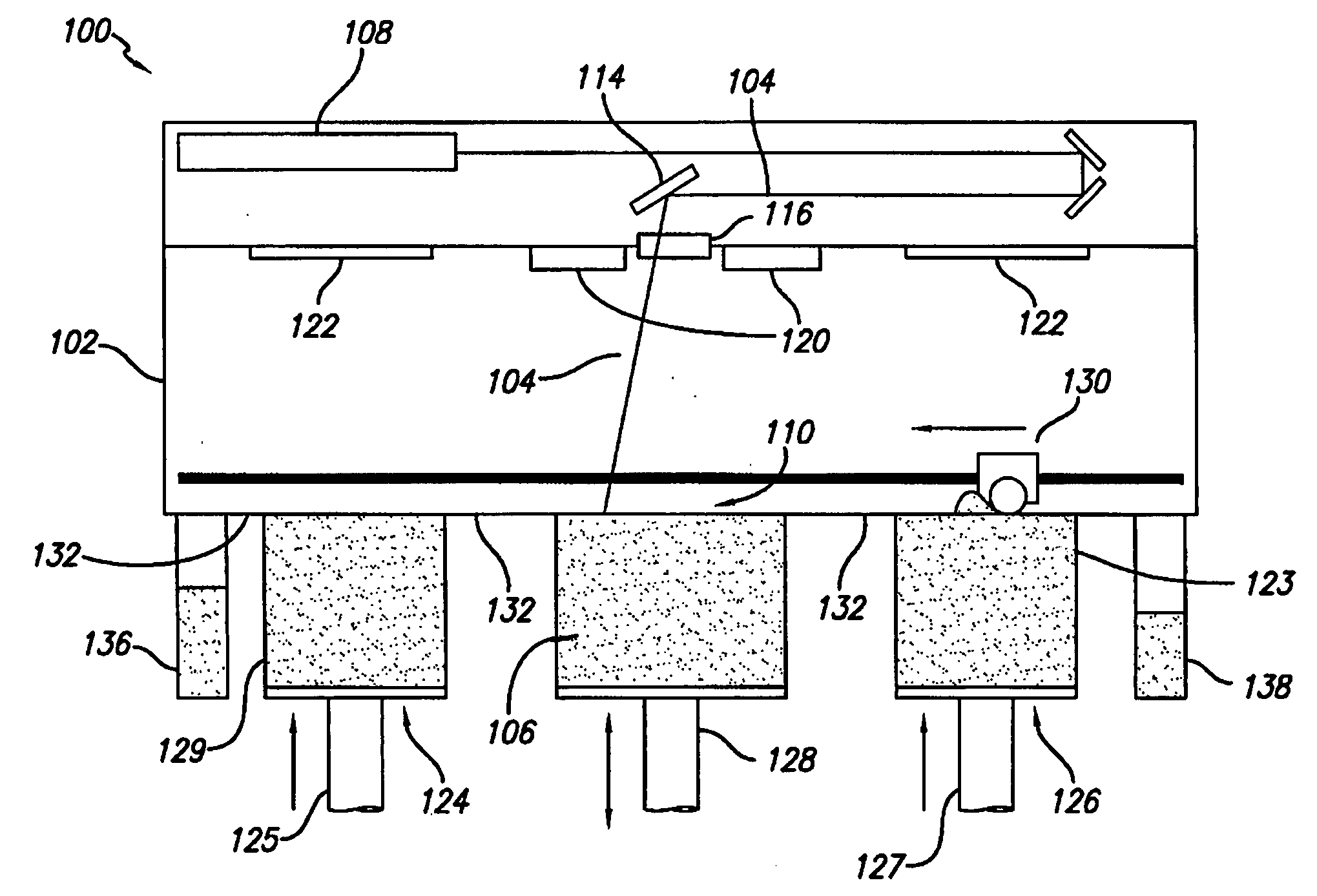
Controlled cooling methods and apparatus for laser sintering part-cake
ActiveUS20060118532A1Effectively transferring heat awayEfficient heatingAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyMetallurgyLaser
The invention is a method for controllably cooling at least a portion of a part-cake from a laser sintering system to minimize cool down time, maximize throughput, and minimize thermal gradients within the part-cake. The method generally comprises forming one or more thermal transfer channels within the part-cake. The thermal transfer channels can include ducts and cooling fins in the part-cake surrounding the formed part. The method can further comprise removing unfused powder from the ducts and introducing cooling media into the ducts. The invention also includes a part-cake having thermal transfer channels formed therein and a laser sintering apparatus comprising a part-cake containing cylinder having permanent fittings therein for receiving terminal portions of thermal transfer channels formed in the part-cake.
Owner:3D SYST INC
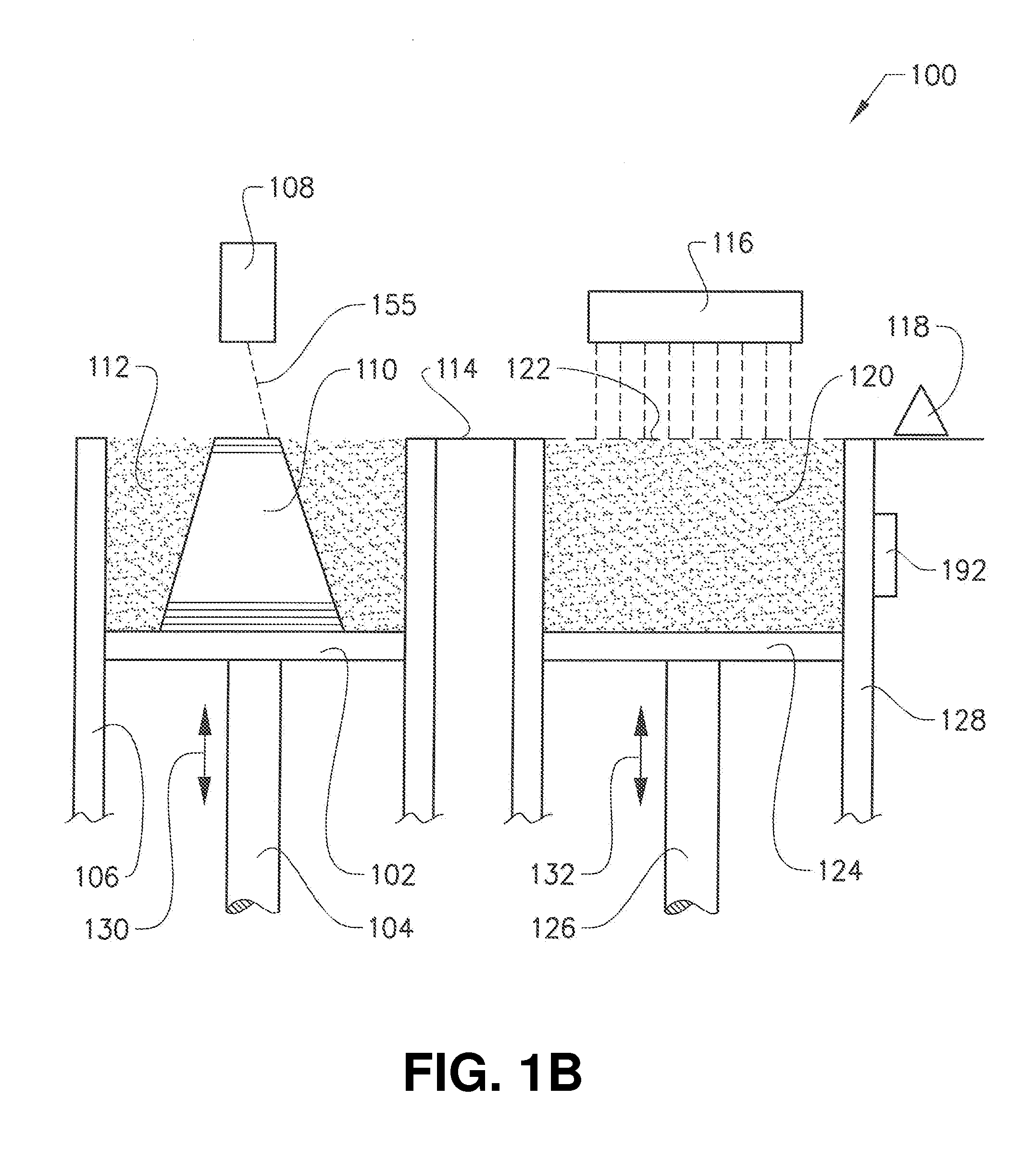
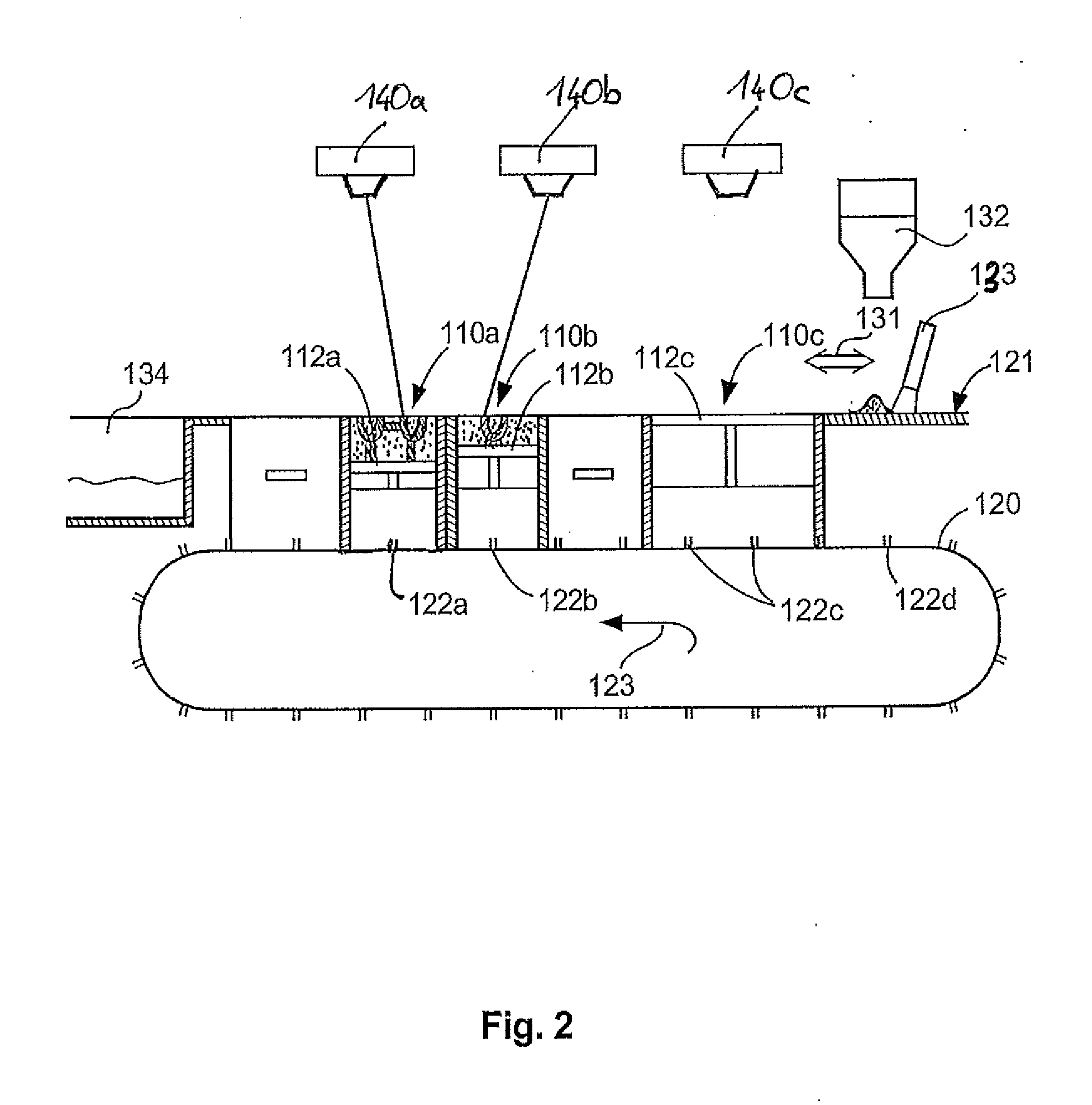
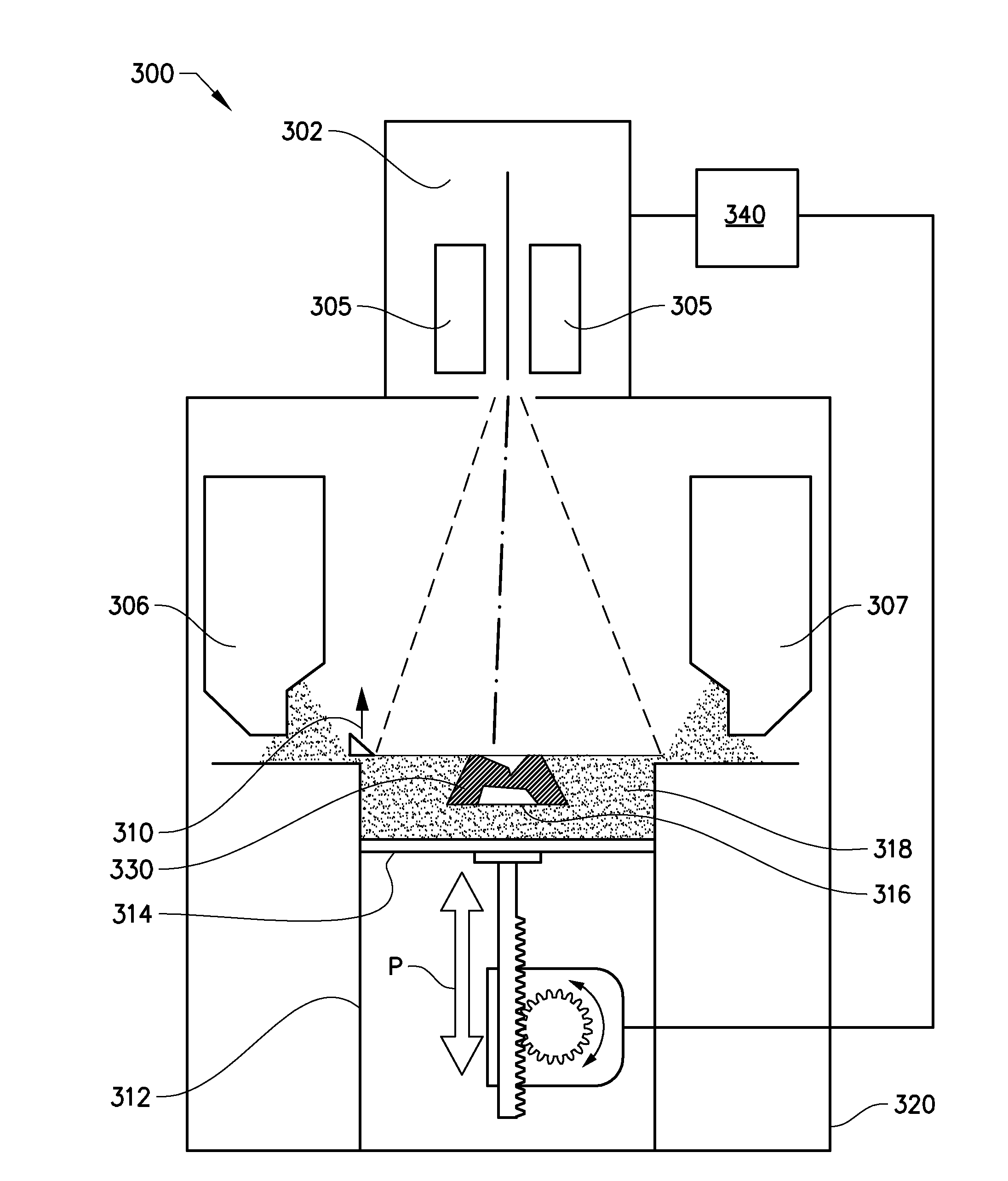
Powder distribution in additive manufacturing of three-dimensional articles
ActiveUS20150071809A1Additive manufacturing apparatusTransportation and packagingMetallurgyAdditive layer manufacturing
The present invention relates to a method for forming a three-dimensional article through successive fusion of parts of at least one layer of a powder bed provided on a work table. Said method comprising the steps of: providing at least a first and second powder tank, providing a first type of powder in said first powder tank having a first particle size distribution, providing a second type of powder in said second powder tank having a second particle size distribution, providing a first sub-layer of said first type of powder on said work table, providing a second sub-layer of said second type of powder on top of said first layer of said first type of powder, fusing said first and second sub-layers simultaneously with a high energy beam from a high energy beam source for forming a first cross section of said three-dimensional article.
Owner:ARCAM AB
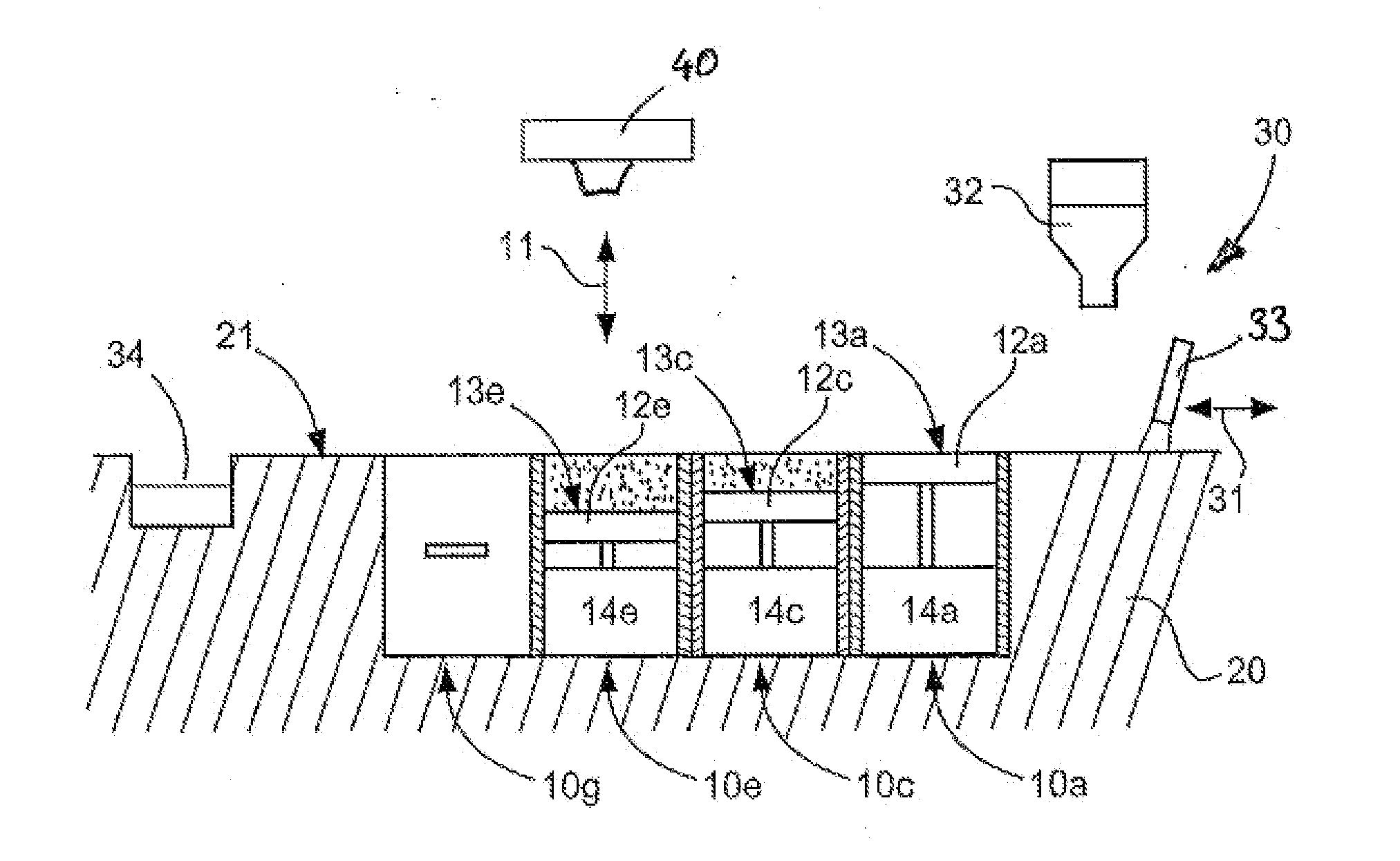
Method of, and apparatus for, applying flowable material across a surface
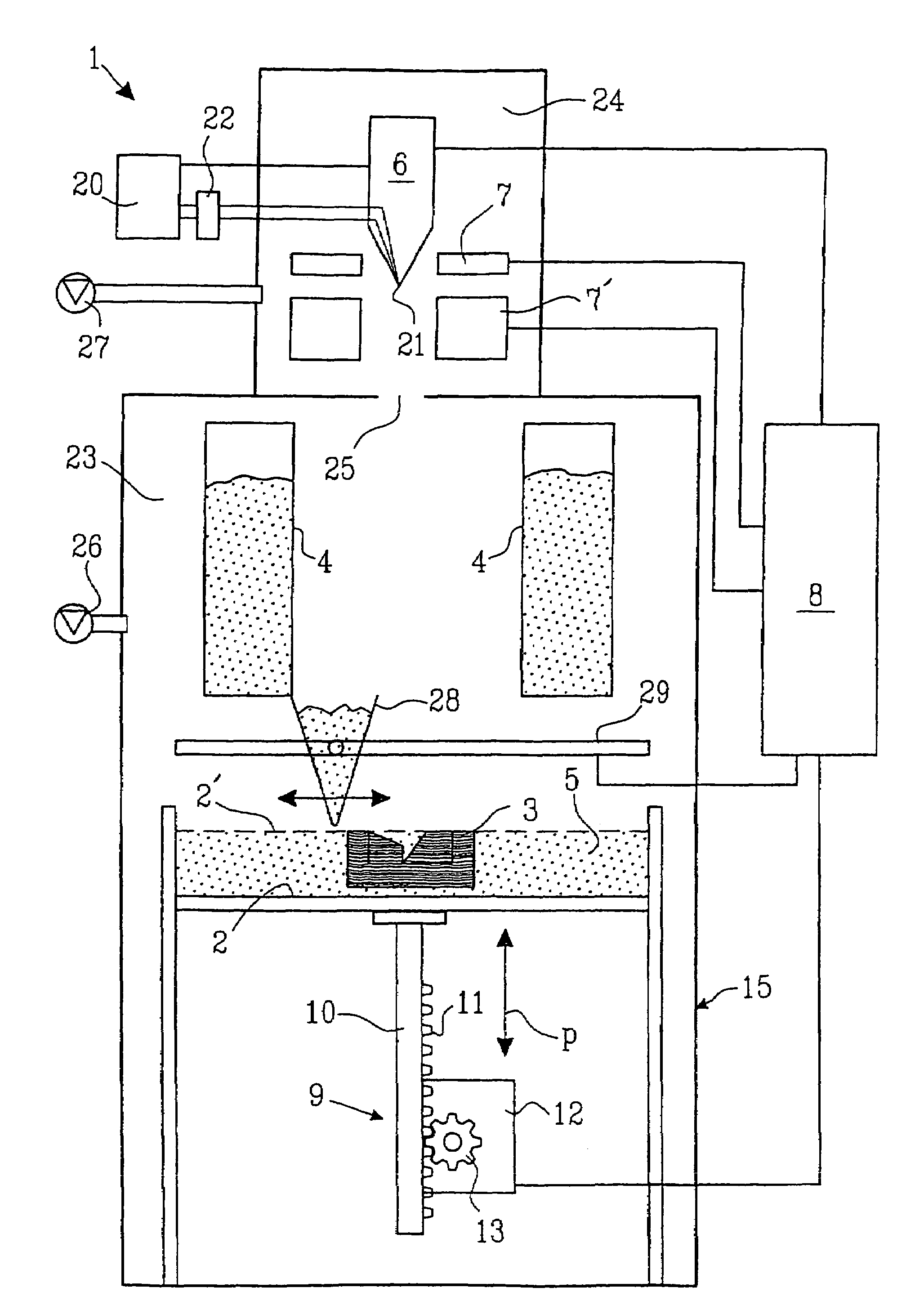
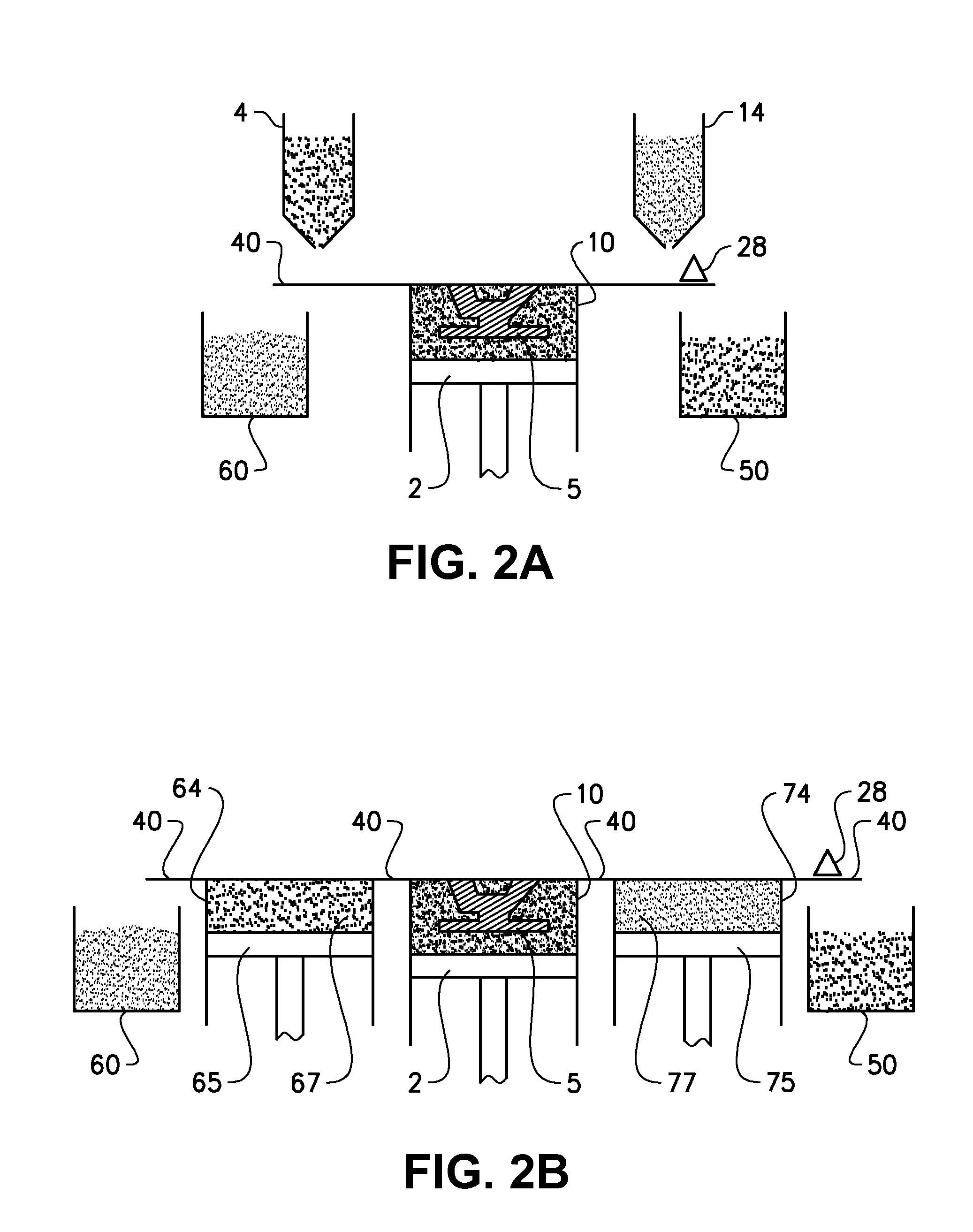
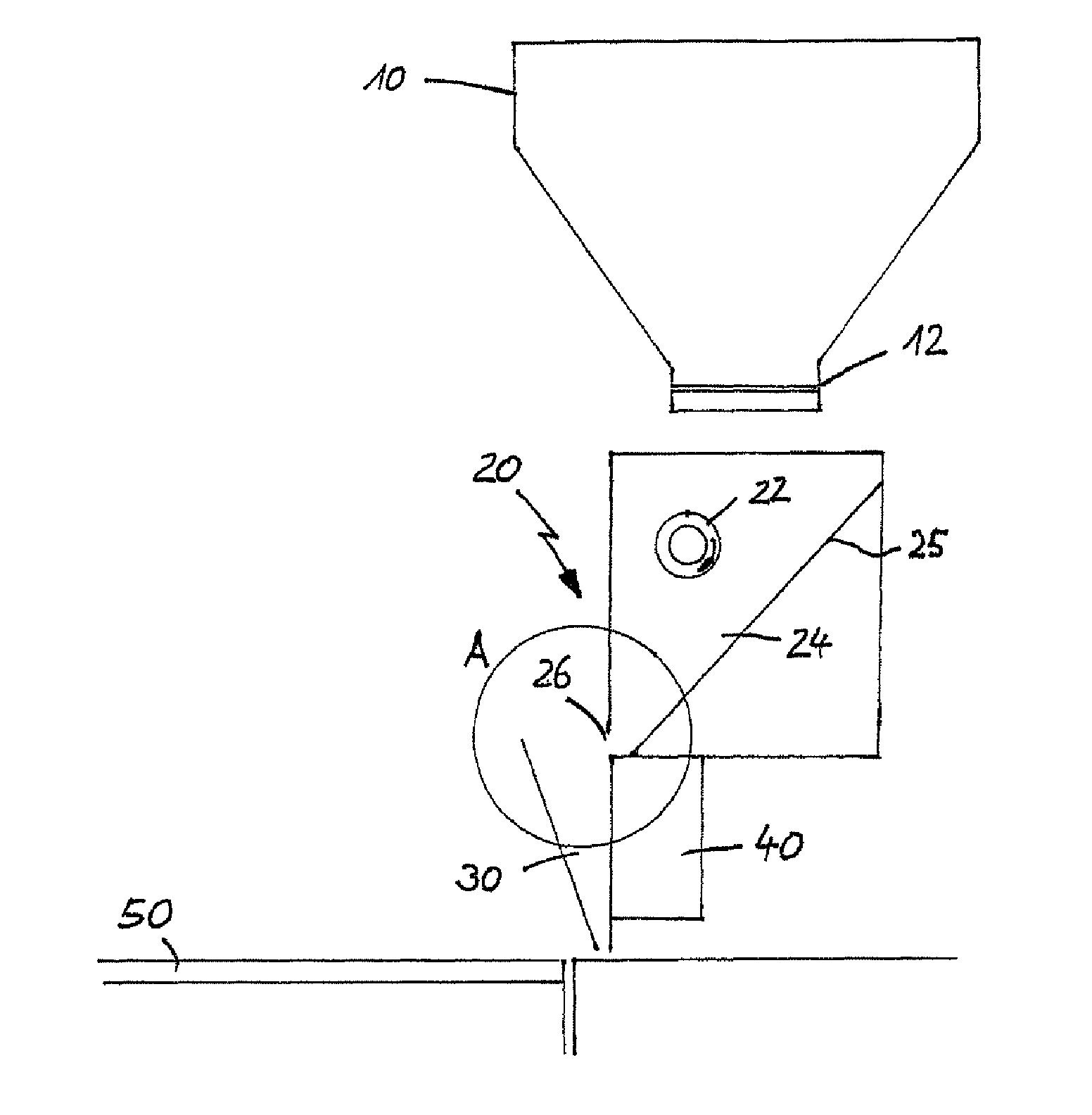
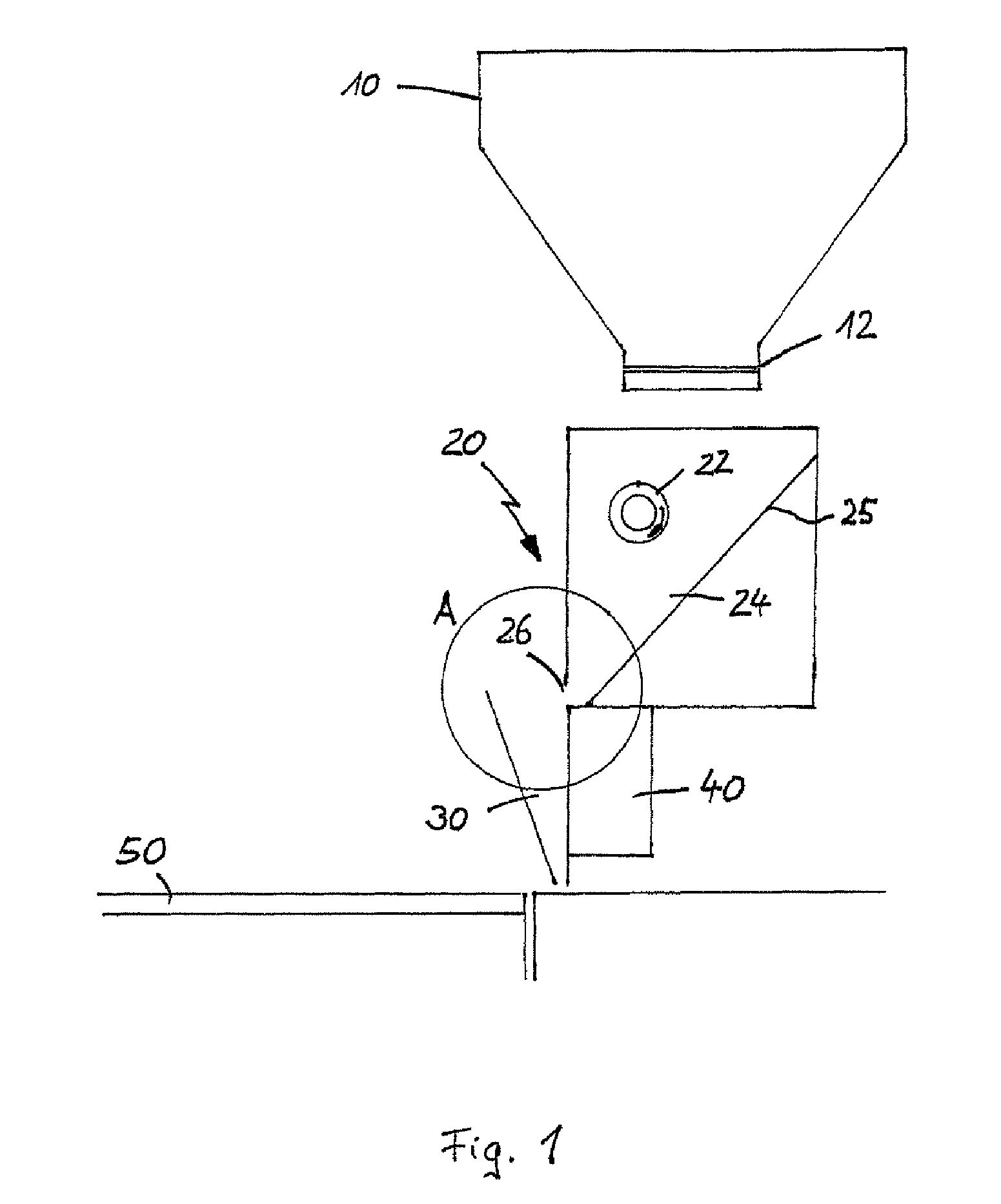
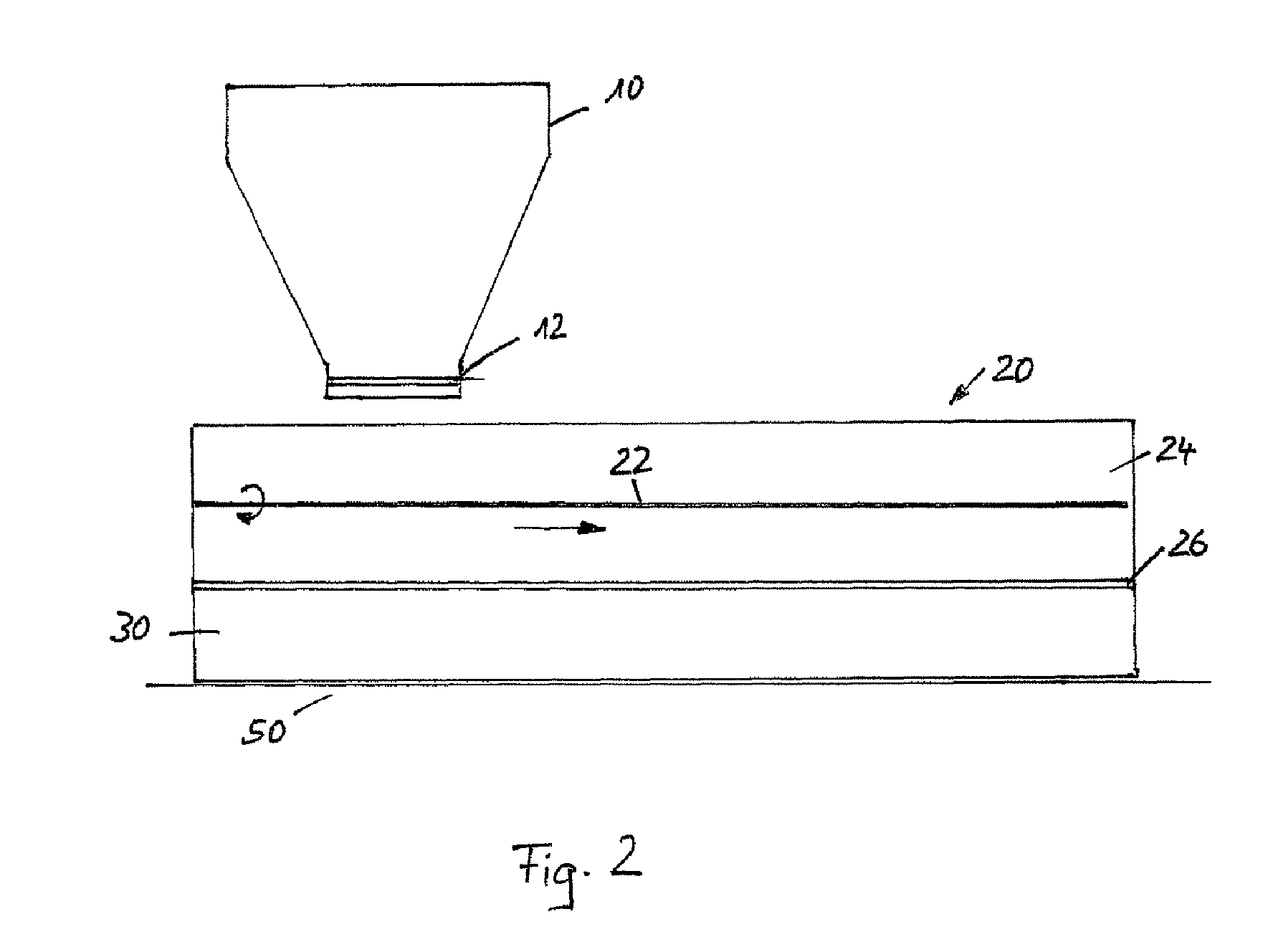
ActiveUS7799253B2Reduce volume of containerReduce in quantityAdditive manufacturing apparatusLiquid surface applicatorsFirst FillEngineering
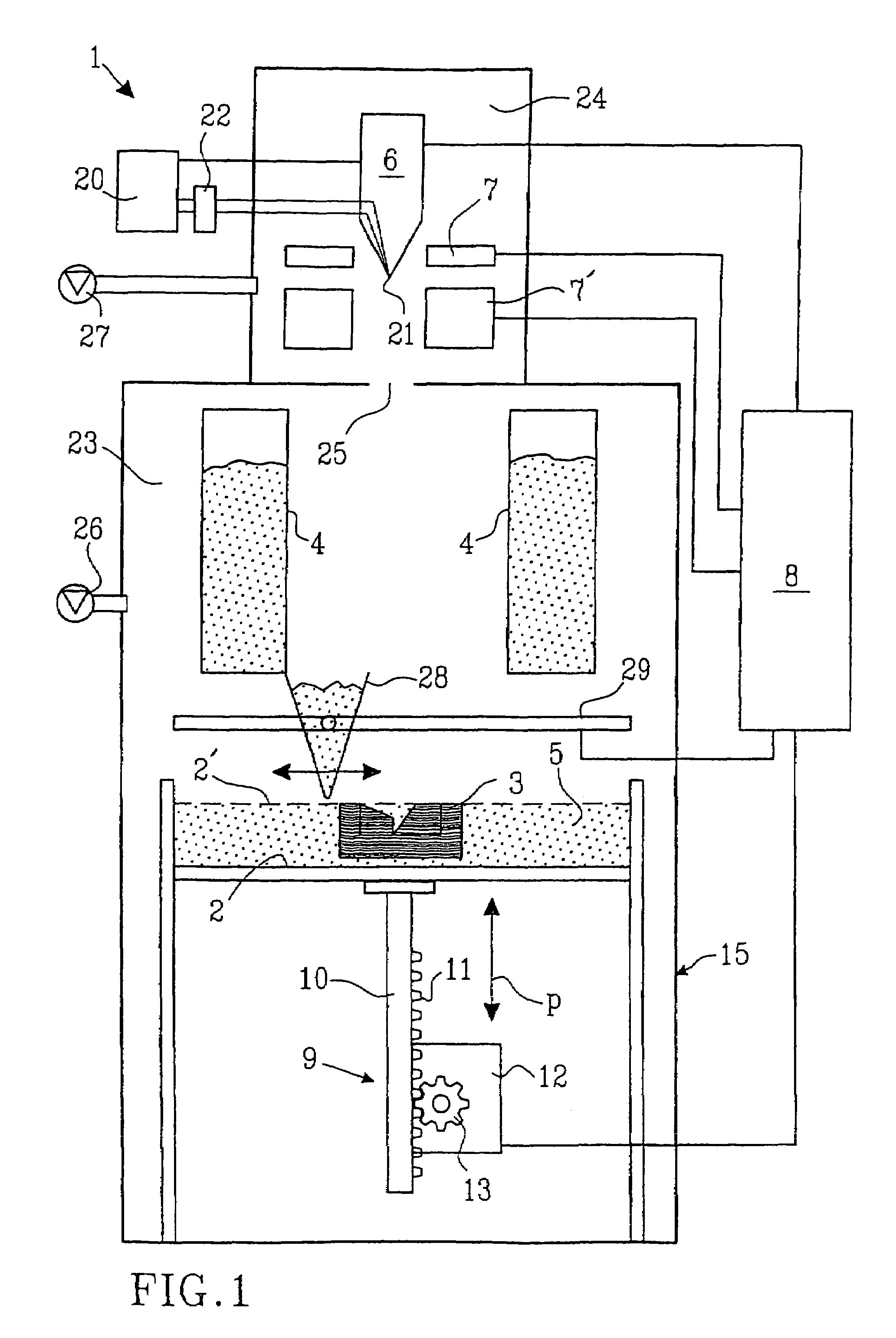
The invention relates to a method and a device for applying for a flowable material, especially a particulate material, in individual superimposed layers across a support (50), the flowable material being first filled from a stationary feed station (10) into a storage container (24) of an application device. In the application device (30), which travels back and forth across the support, the flowable material is distributed inside the storage container across the entire length of the device and is then metered through a slot into a metering shaft in such a manner that the filling level in the metering shaft remains constant during application of the flowable material from the metering shaft onto the support.
Owner:EXONE
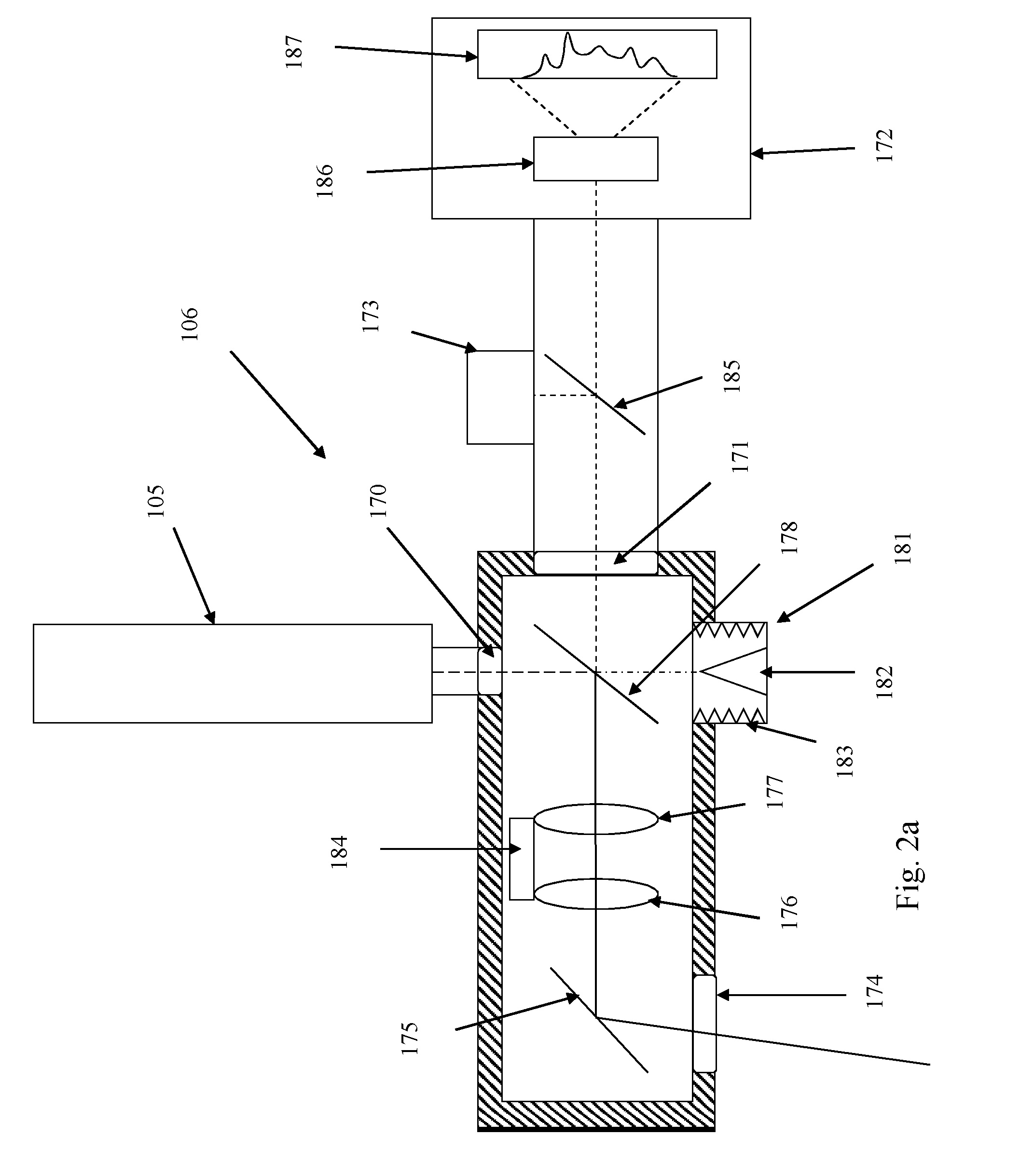
System and method for controlling the size of the molten pool in laser-based additive manufacturing
InactiveUS6995334B1High geometric accuracyEasy to controlAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyMelting tankLaser Nozzle
According to one embodiment of the invention, a method for controlling the size of the molten pool in a laser based additive manufacturing process includes coaxially aligning an imaging device with a laser nozzle and imaging a molten pool, created by a laser, on a substrate with the imaging device. The method further includes comparing at least one characteristic of the molten pool with a respective characteristic of a target molten pool, and adjusting, in substantially real-time, a laser power of the laser based on the comparison in order to correlate the characteristic of the molten pool with the respective characteristic of the target molten pool.
Owner:SOUTHERN METHODIST UNIVERSITY
Method and apparatus for generating electron beams
InactiveUS20130300286A1Quick controlEasy to controlAdditive manufacturing apparatusElectrode and associated part arrangementsPlasma electronElectron source
Various embodiments of the present invention relate to a plasma electron source apparatus. The apparatus comprises a cathode discharge chamber in which a plasma is generated, an exit hole provided in said cathode discharge chamber from which electrons from the plasma are extracted by an accelerating field provided between said cathode discharge chamber and an anode, at least one plasma confinement device, and a switching mechanism for switching the at least one plasma confinement device between a first value allowing for electron extraction from the plasma and a second value prohibiting electron extraction from the plasma. Associated methods are also provided.
Owner:ARCAM AB
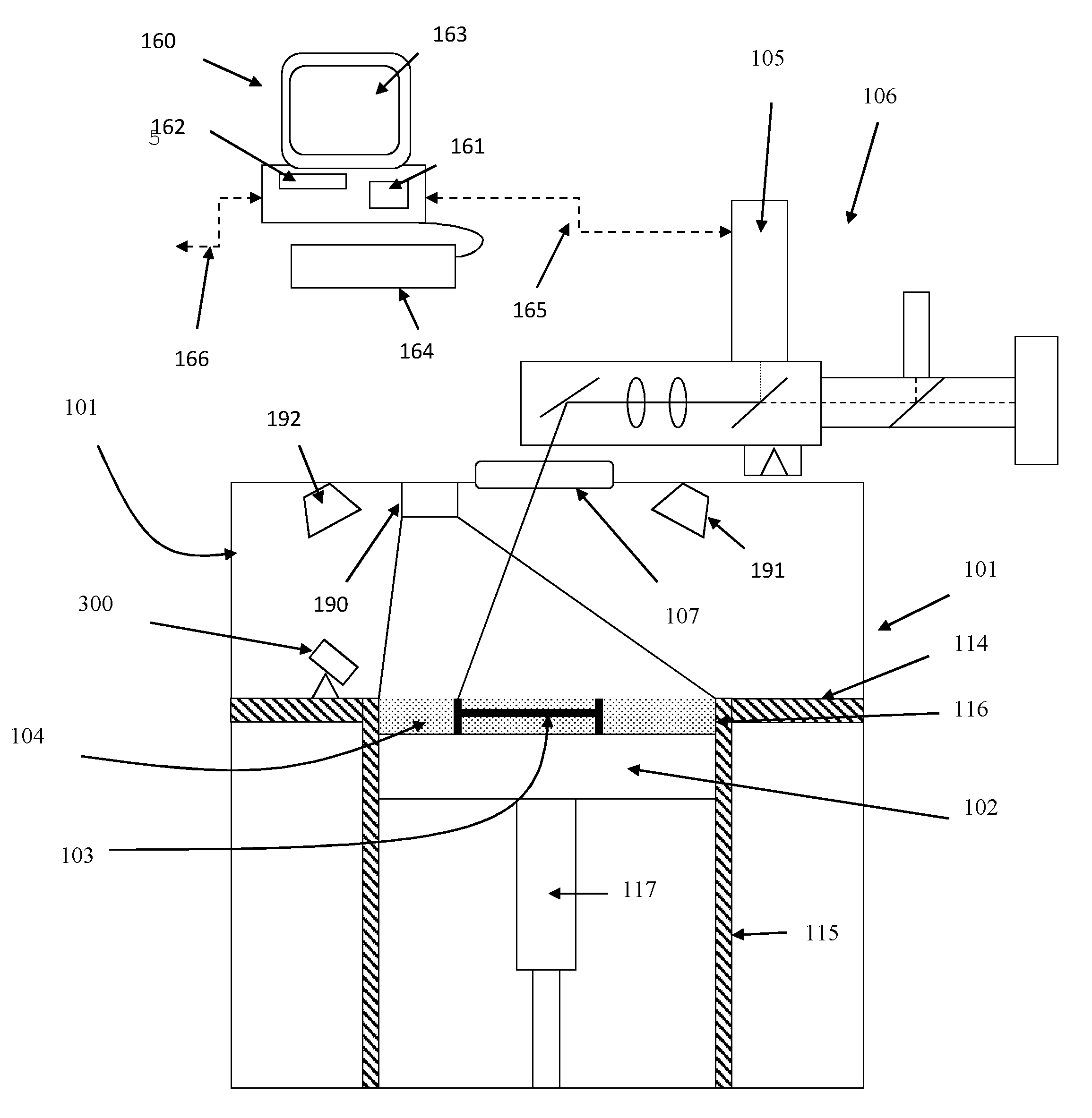
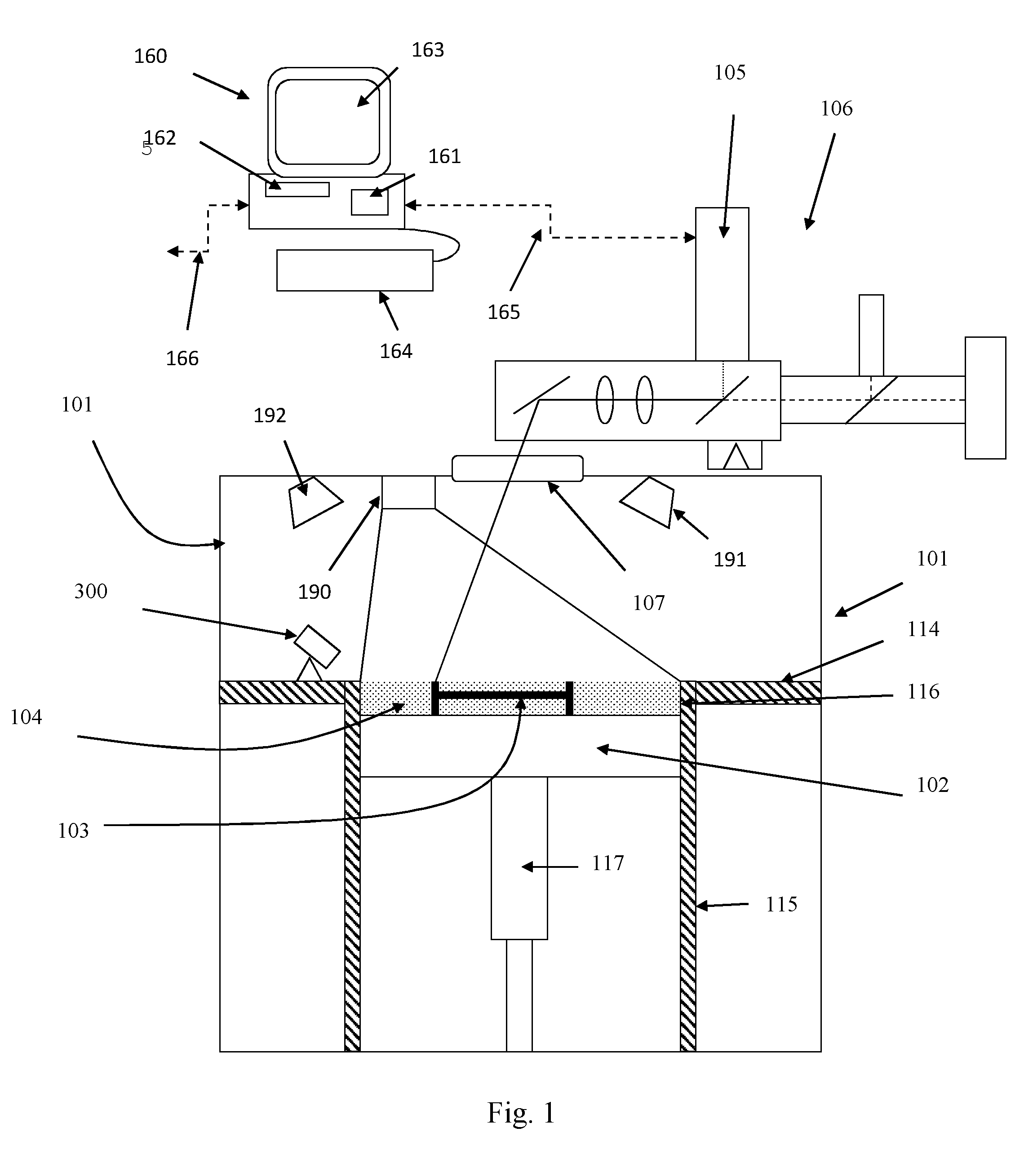
Method and apparatus for producing three-dimensional objects
ActiveUS20120100031A1Equally distributedAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyHigh energy beamMaterials science
Owner:ARCAM AB
Powder feeder for material deposition systems
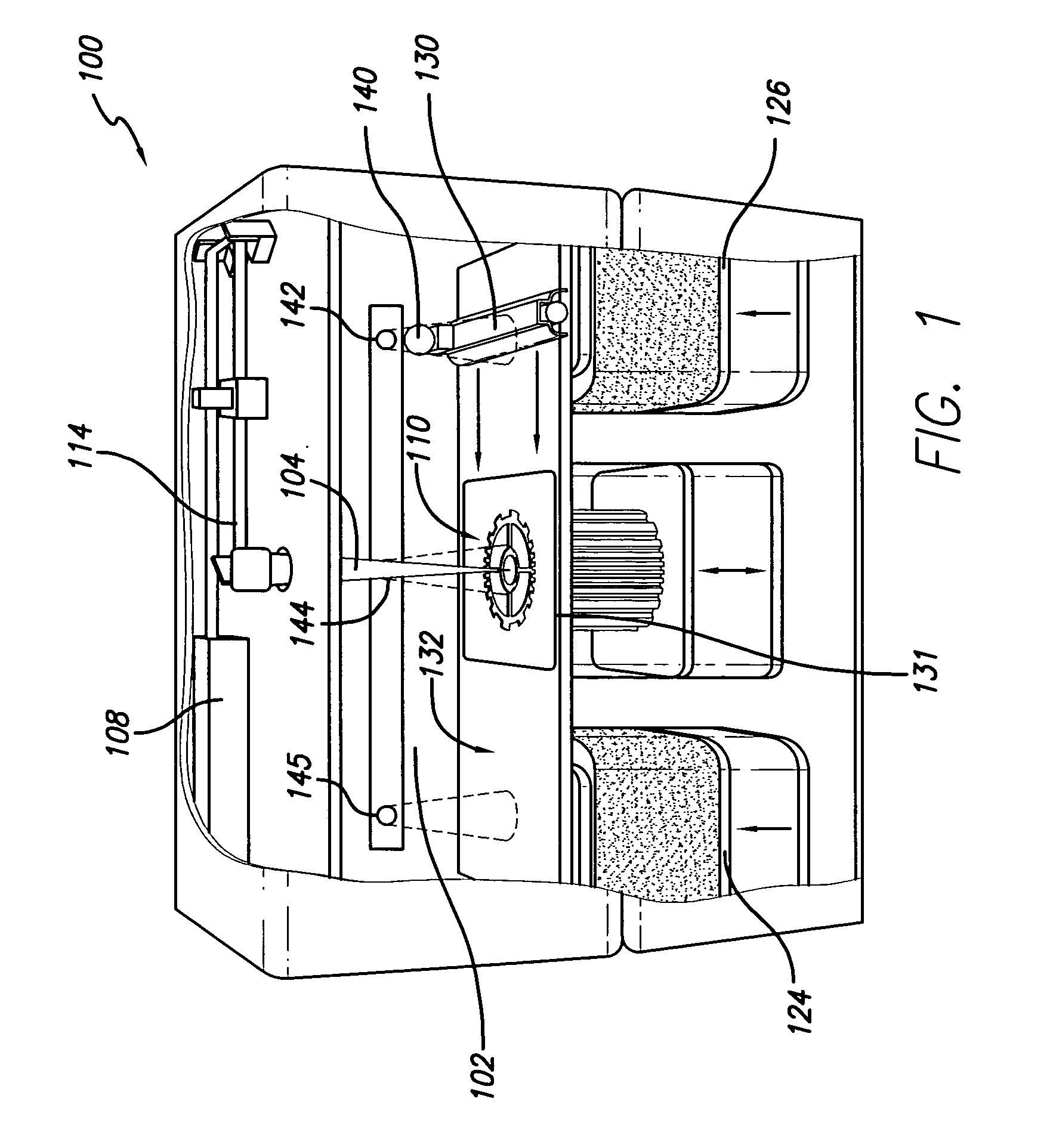
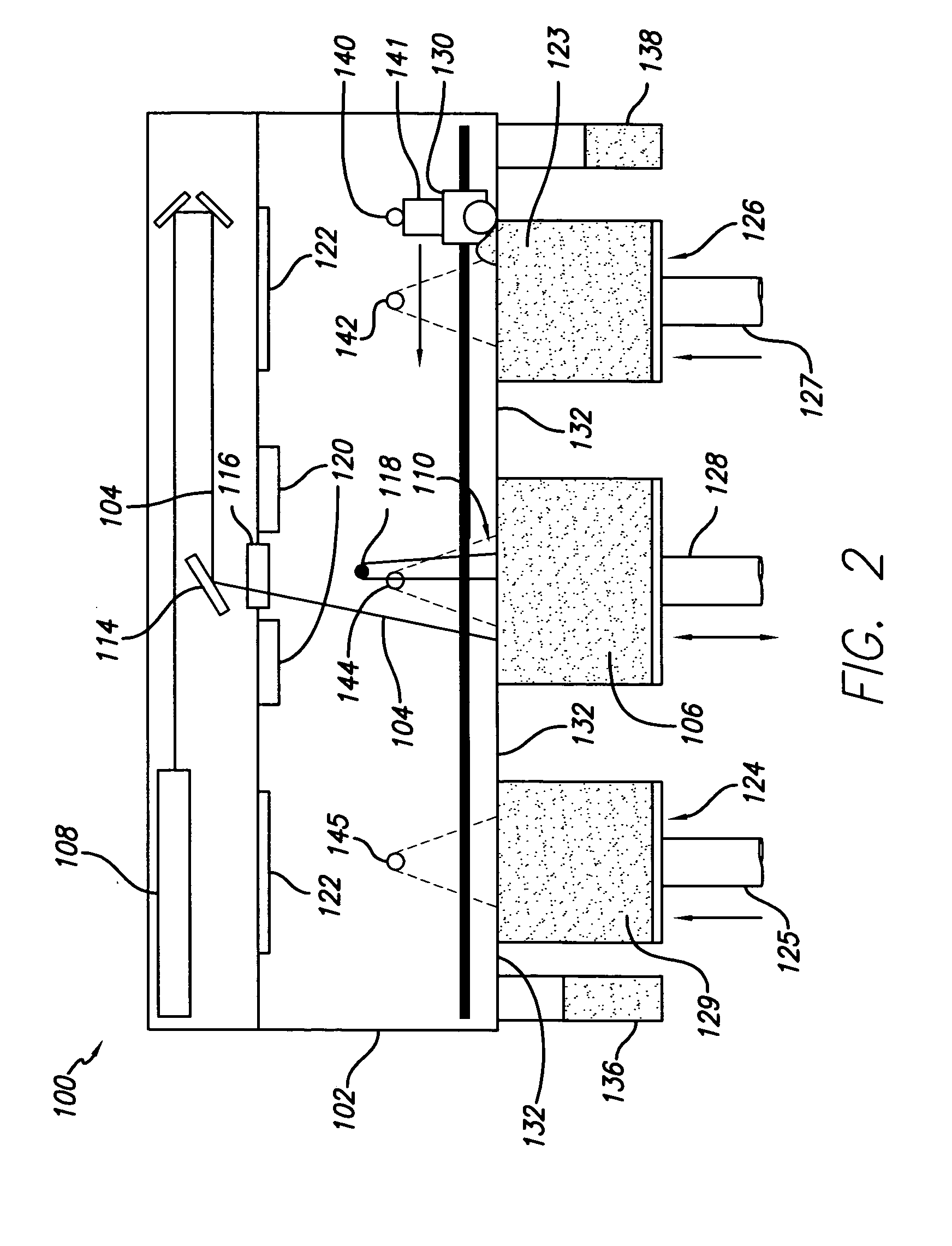
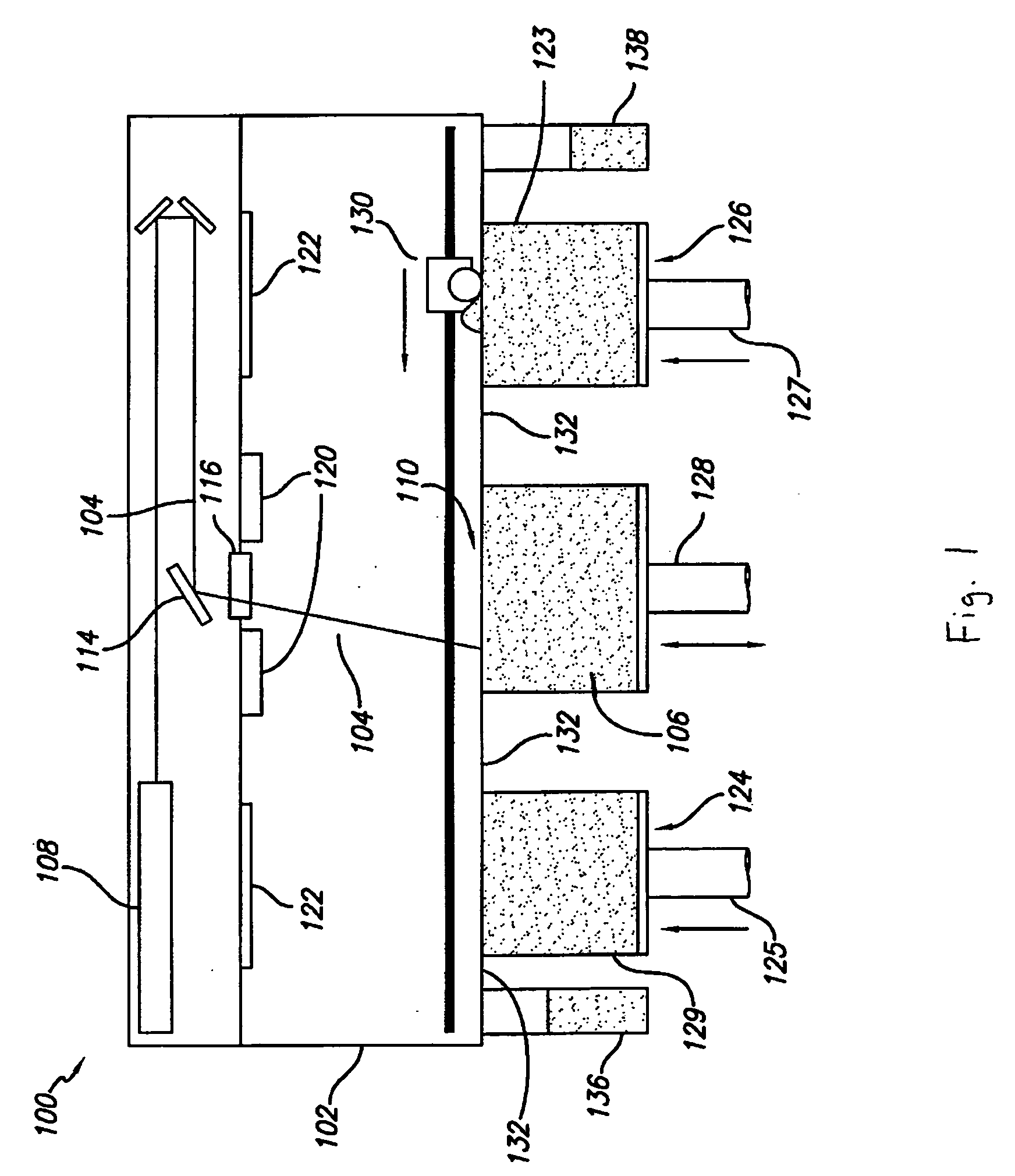
InactiveUS20050133527A1Small sizeEliminate warpingPower operated devices3D object support structuresSolid componentCoolant flow
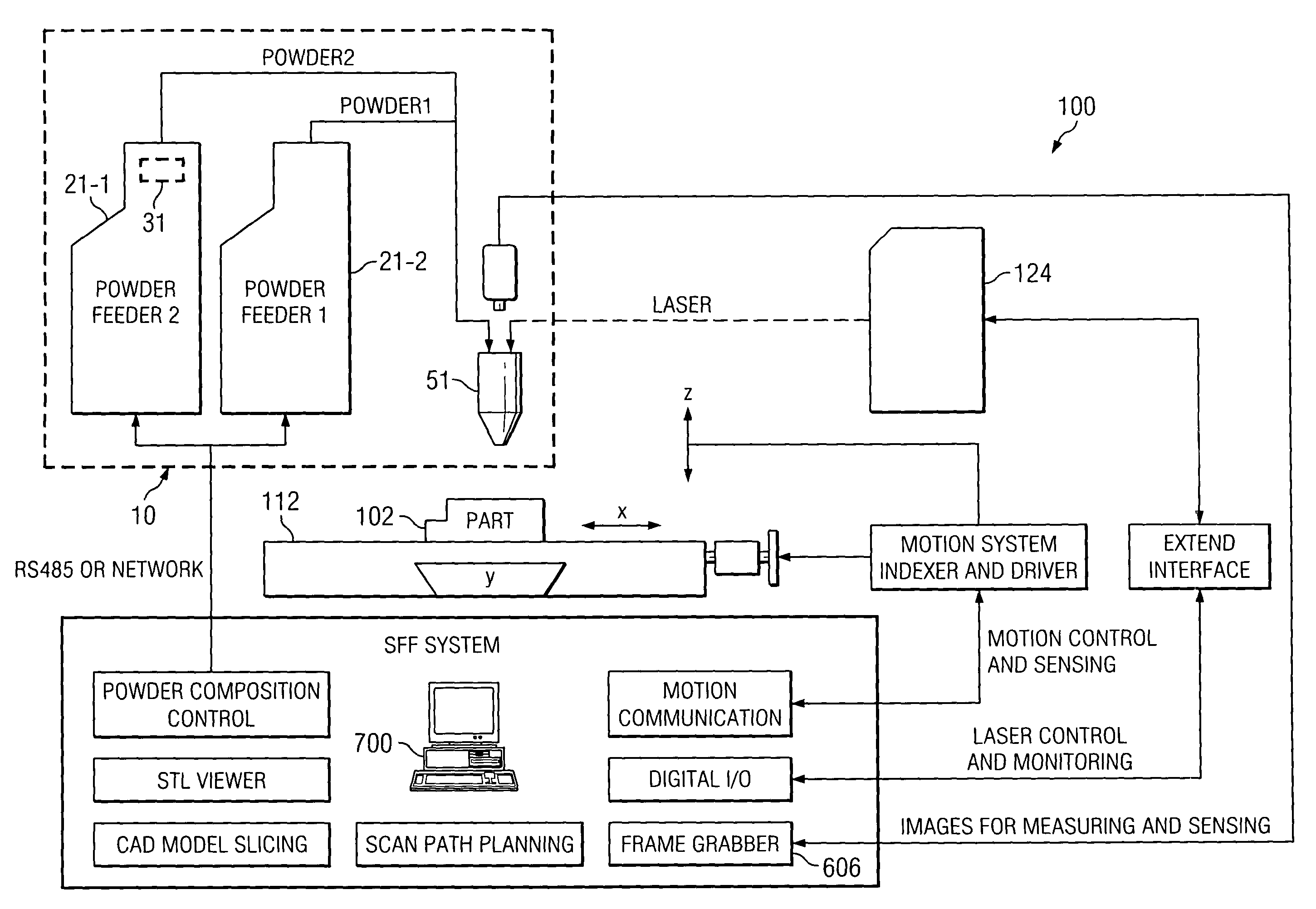
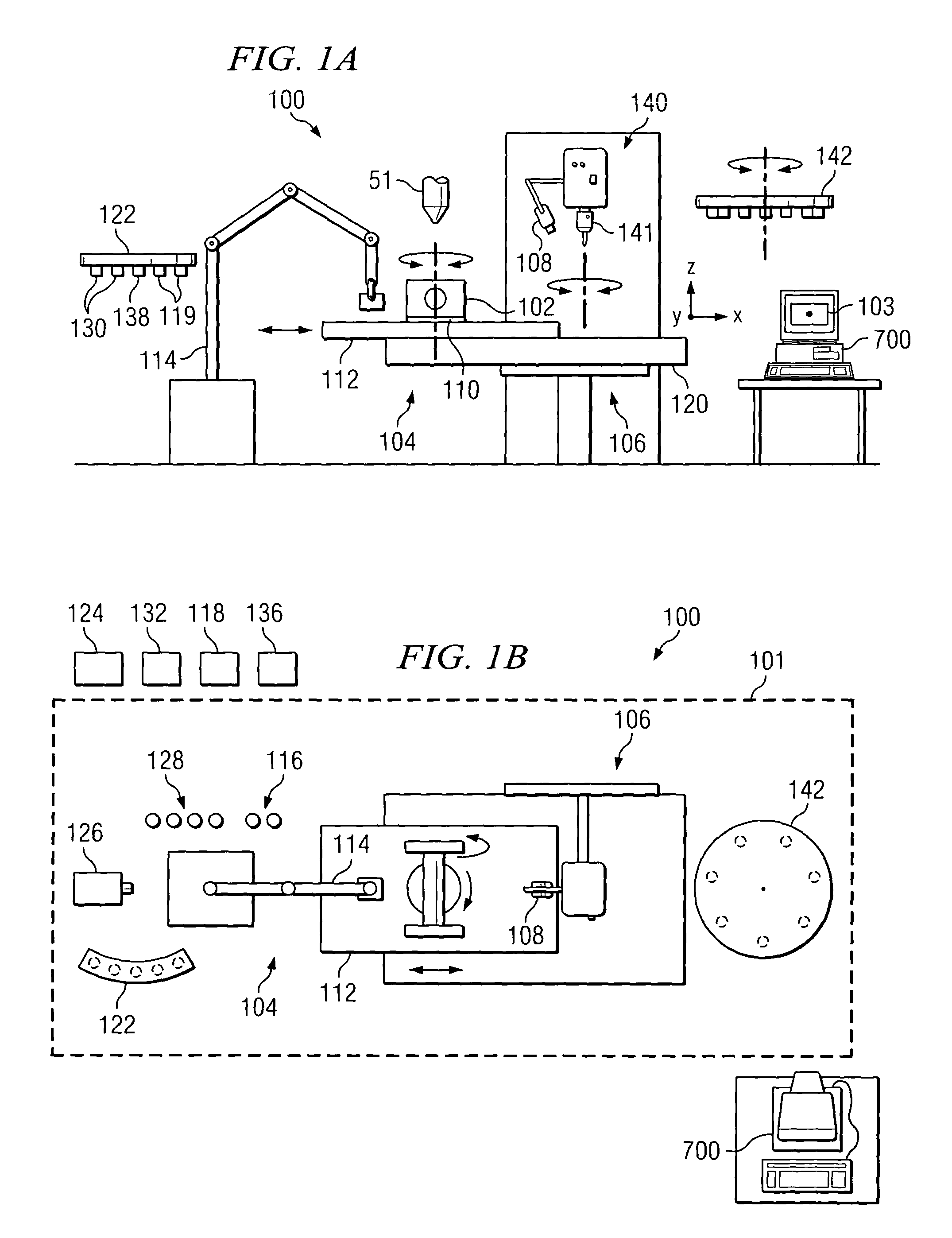
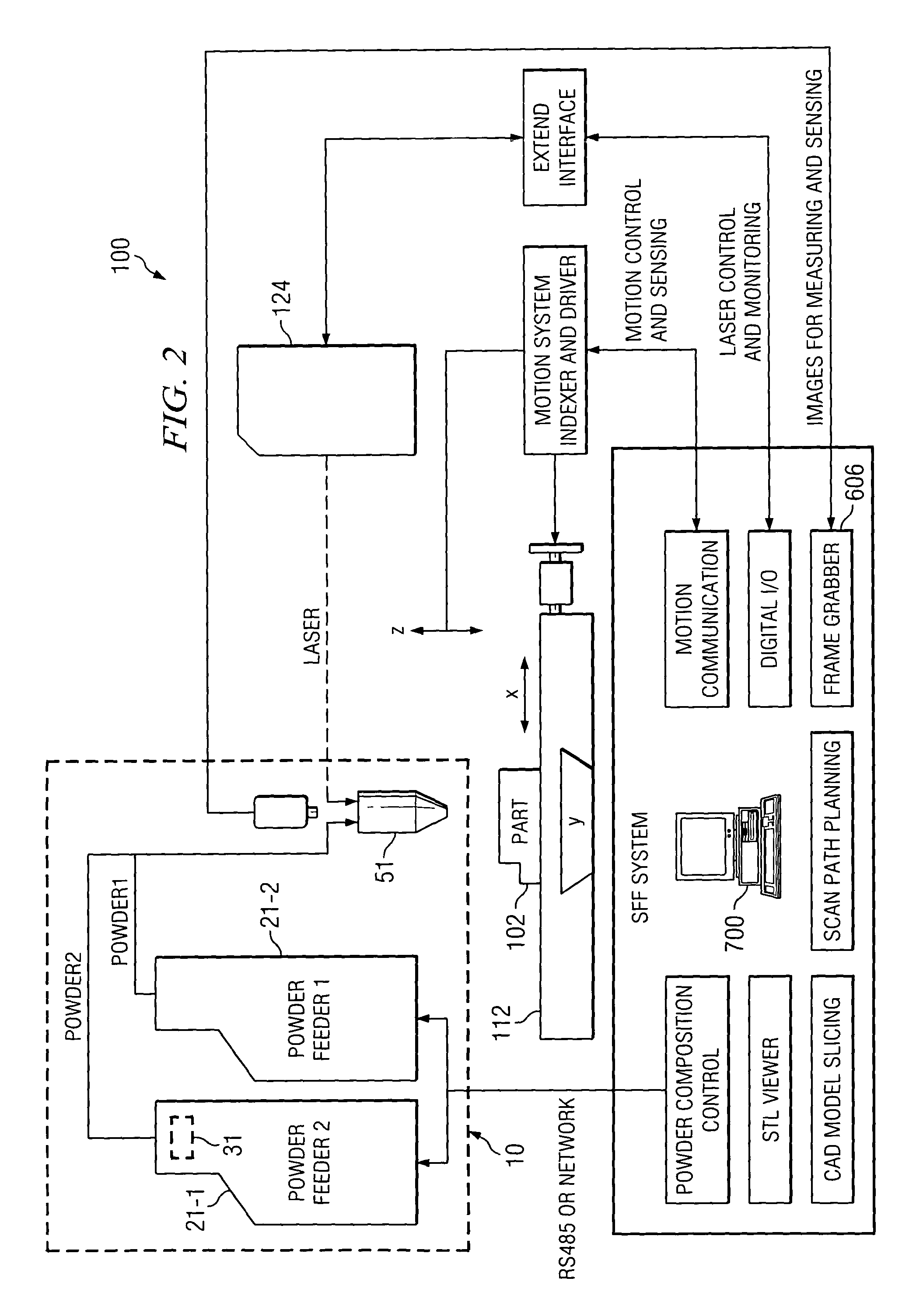
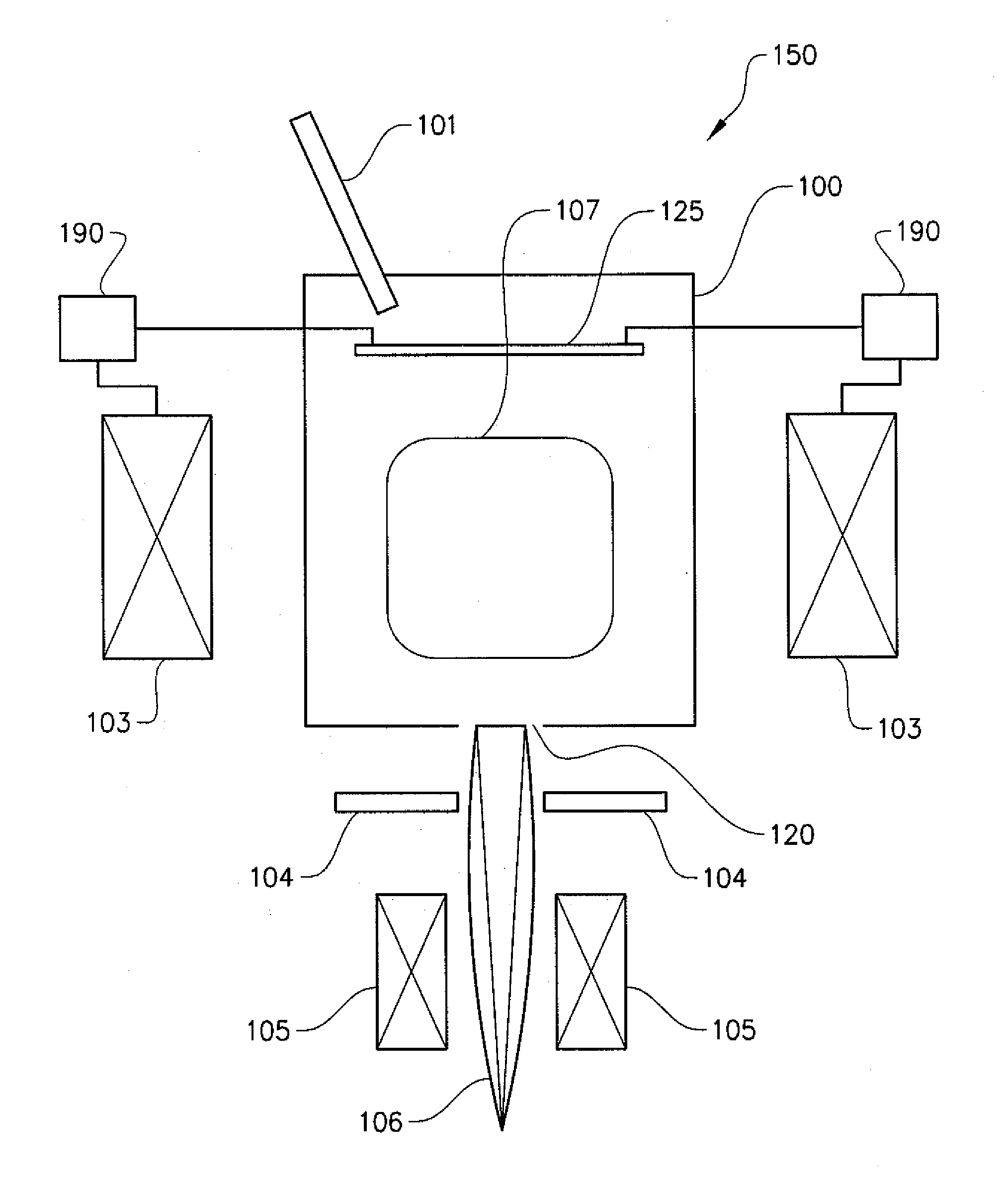
A method and apparatus for embedding features and controlling material composition in a three-dimensional structure (130) is disclosed. The invention enables the control of material characteristics, within a structure (130) made from a plurality of materials, directly from computer renderings of solid models of the components. The method uses stereolithography and solid model computer file formats to control a multi-axis head (480) in a directed material deposition process (123). Material feedstock (126, 127) is deposited onto a pre-heated substrate (19). Depositions (15) in a layer-by-layer pattern, defined by solid models (141, 146), create a three-dimensional article having complex geometric details. Thermal management of finished solid articles (250-302), not available through conventional processing techniques, is enabled by embedded voids (152) and / or composite materials (126, 127), which include dissimilar metals (210, 216). Finished articles control pressure drop and produce uniform coolant flow and pressure characteristics. High-efficiency heat transfer is engineered within a solid structure by incorporating other solid materials with diverse indexes. Embedding multi-material structures (132, 134) within a normally solid component (141) produces articles with diverse mechanical properties. Laser and powder delivery systems (420, 170) are integrated in a multi-axis deposition head (480) having a focused particle beam (502) to reduce material waste.
Owner:OPTOMEC DESIGN CO
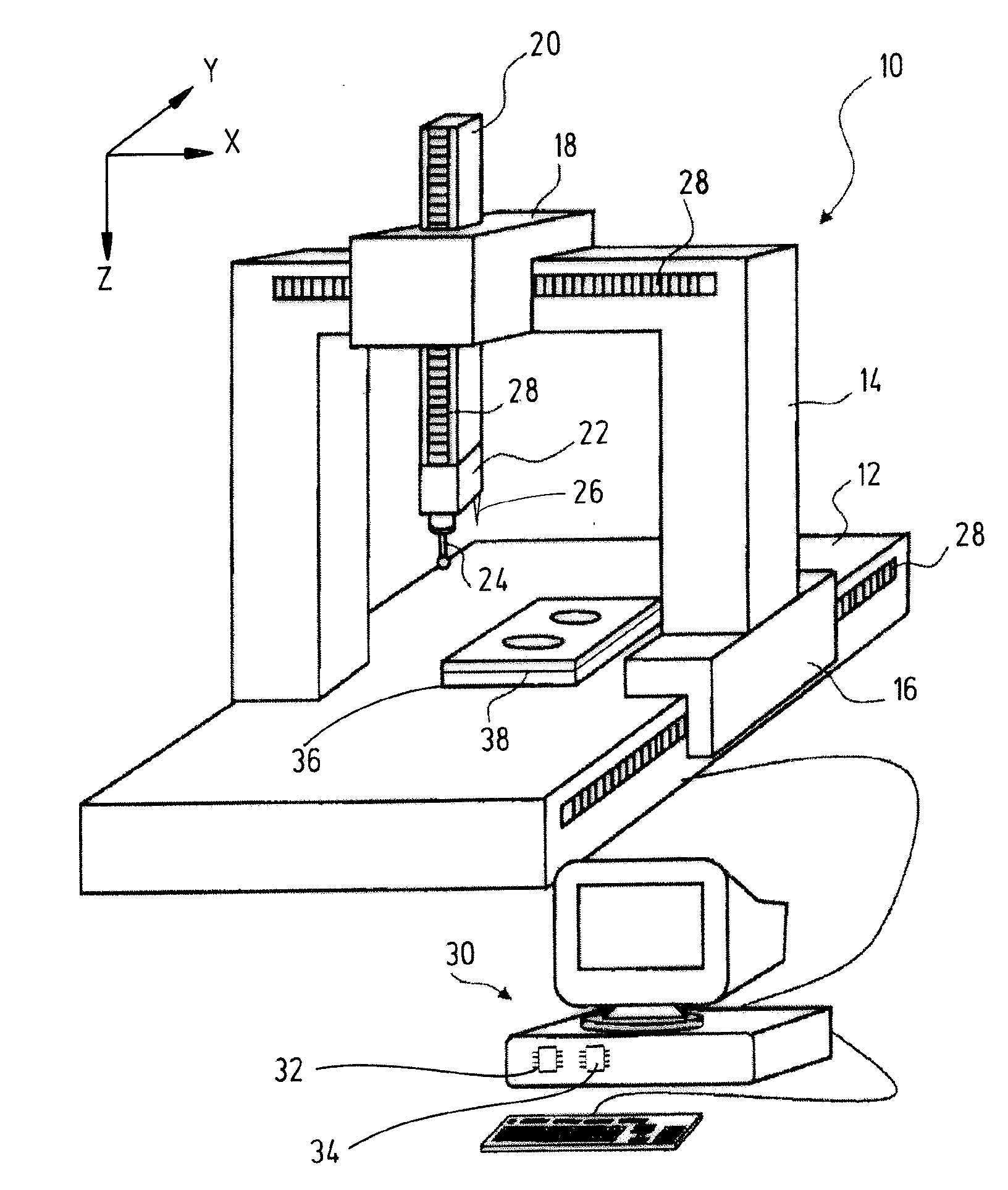
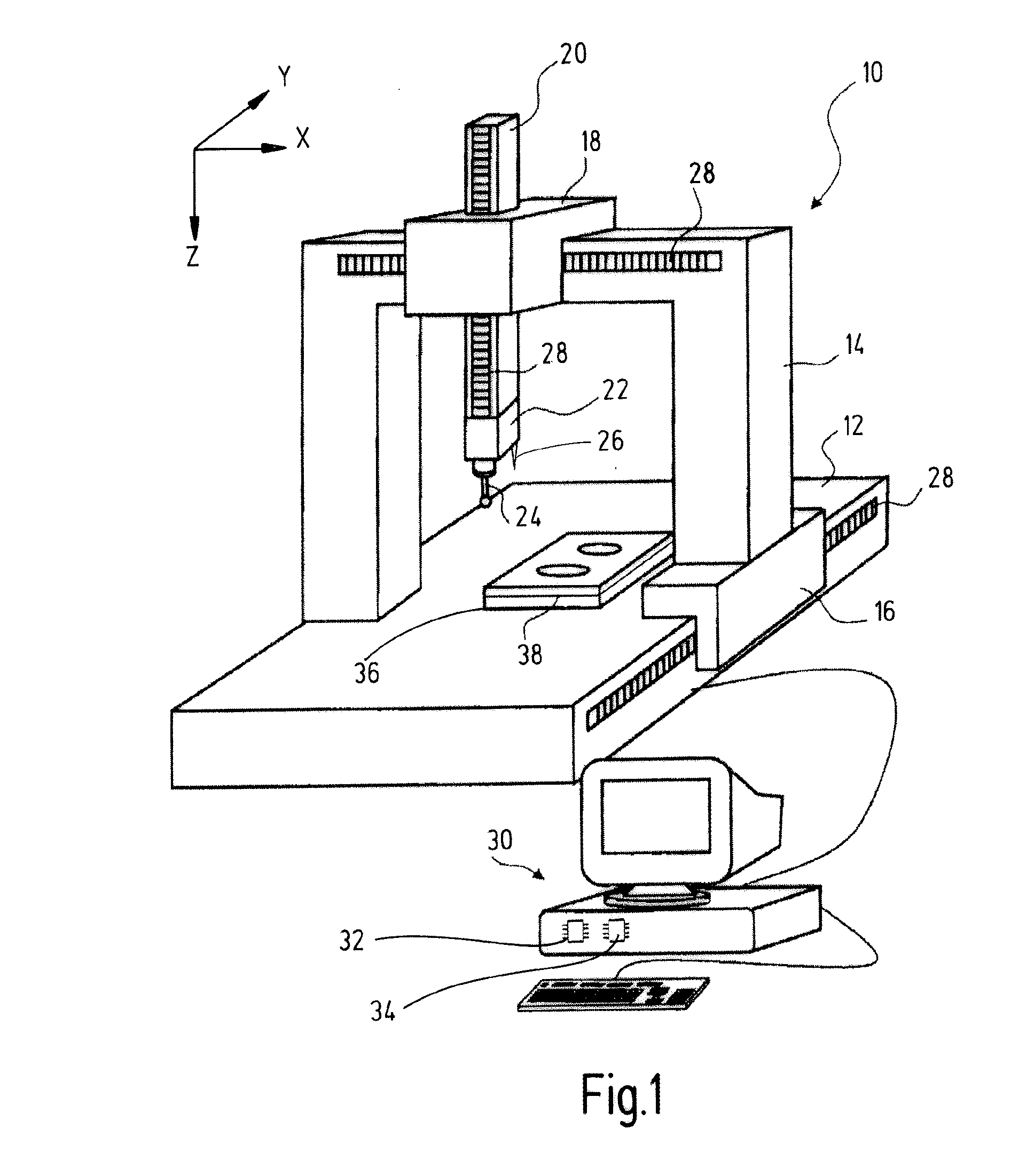
Method and arrangement for producing a workpiece by using additive manufacturing techniques
ActiveUS20150061170A1Cost-efficient productionAdditive manufacturing apparatusAuxillary shaping apparatusManufacturing technologyProcess measurement
A method and an arrangement for producing a workpiece using additive manufacturing techniques involve in-process measurement in order to determine individual characteristics of one or more workpiece layers. In particular, dimensional and / or geometrical characteristics of a workpiece layer are measured before the next workpiece layer is produced. Advantageously, the measurement results are fed back into the production process in order to increase accuracy and precision of the production process.
Owner:CARL ZEISS IND MESSTECHN GMBH +1
Method for fusing a workpiece
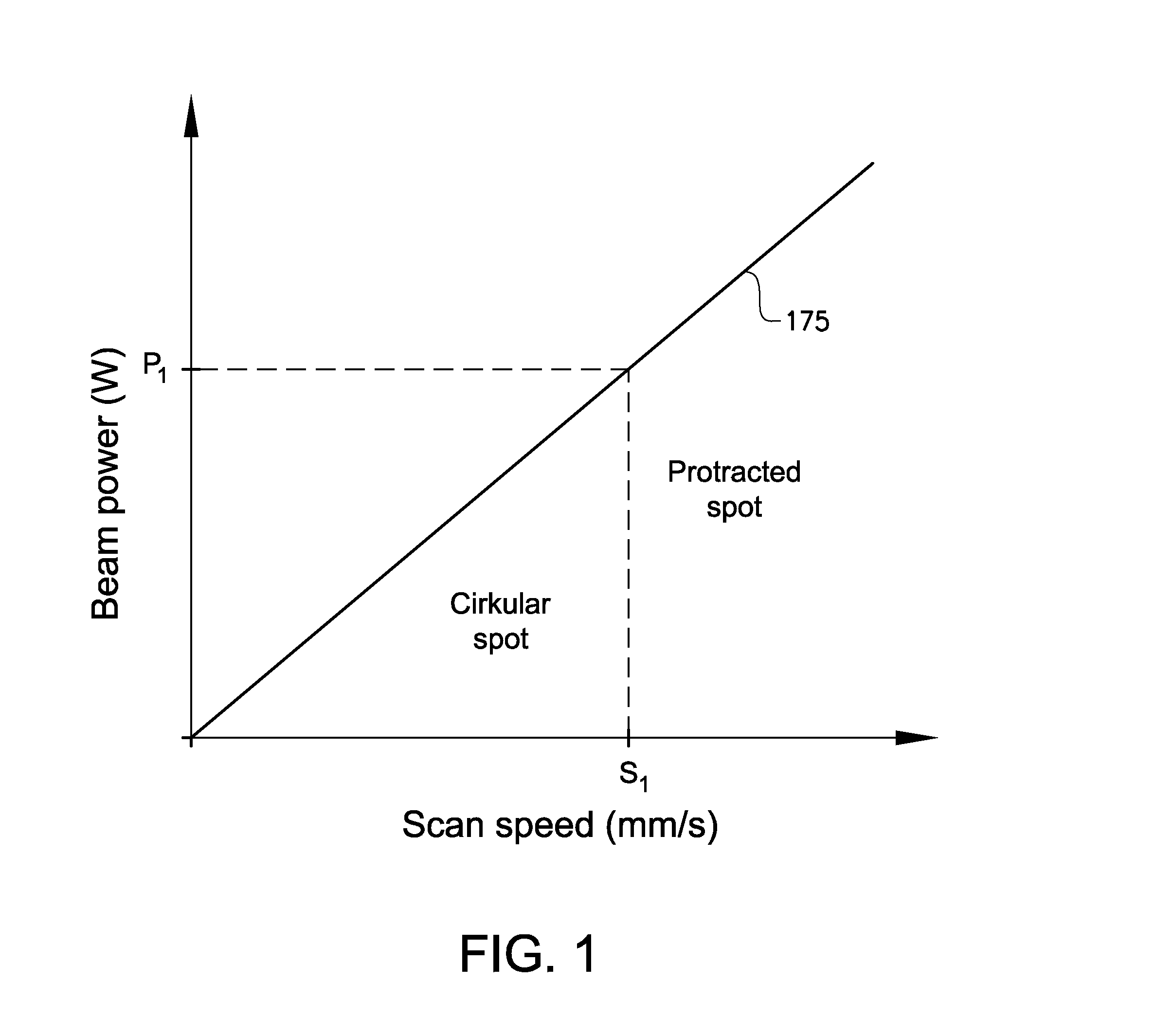
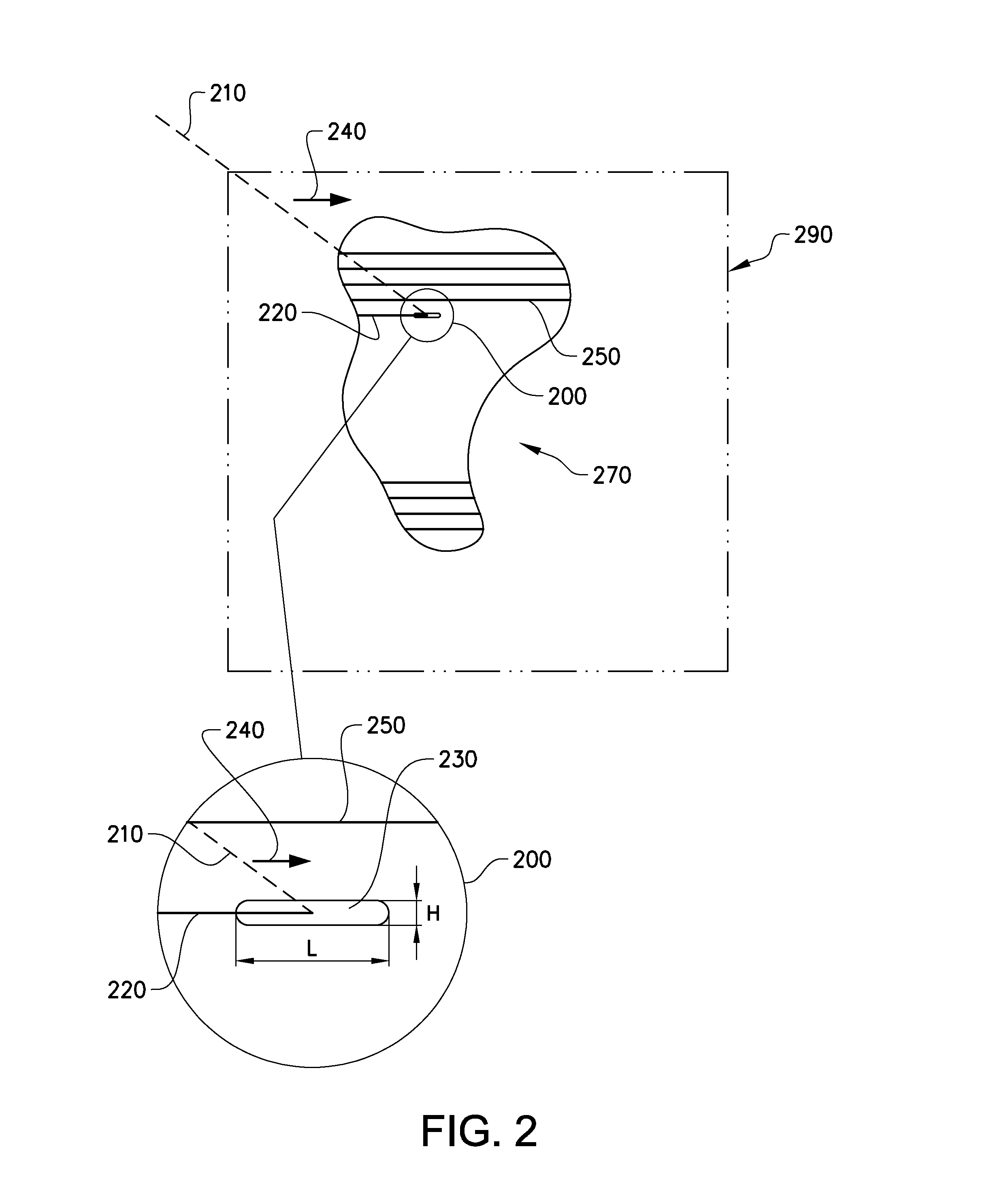
InactiveUS20150283613A1Increase powerSolve the slow scanning speedAdditive manufacturing apparatusAuxillary shaping apparatusEngineeringHigh energy beam
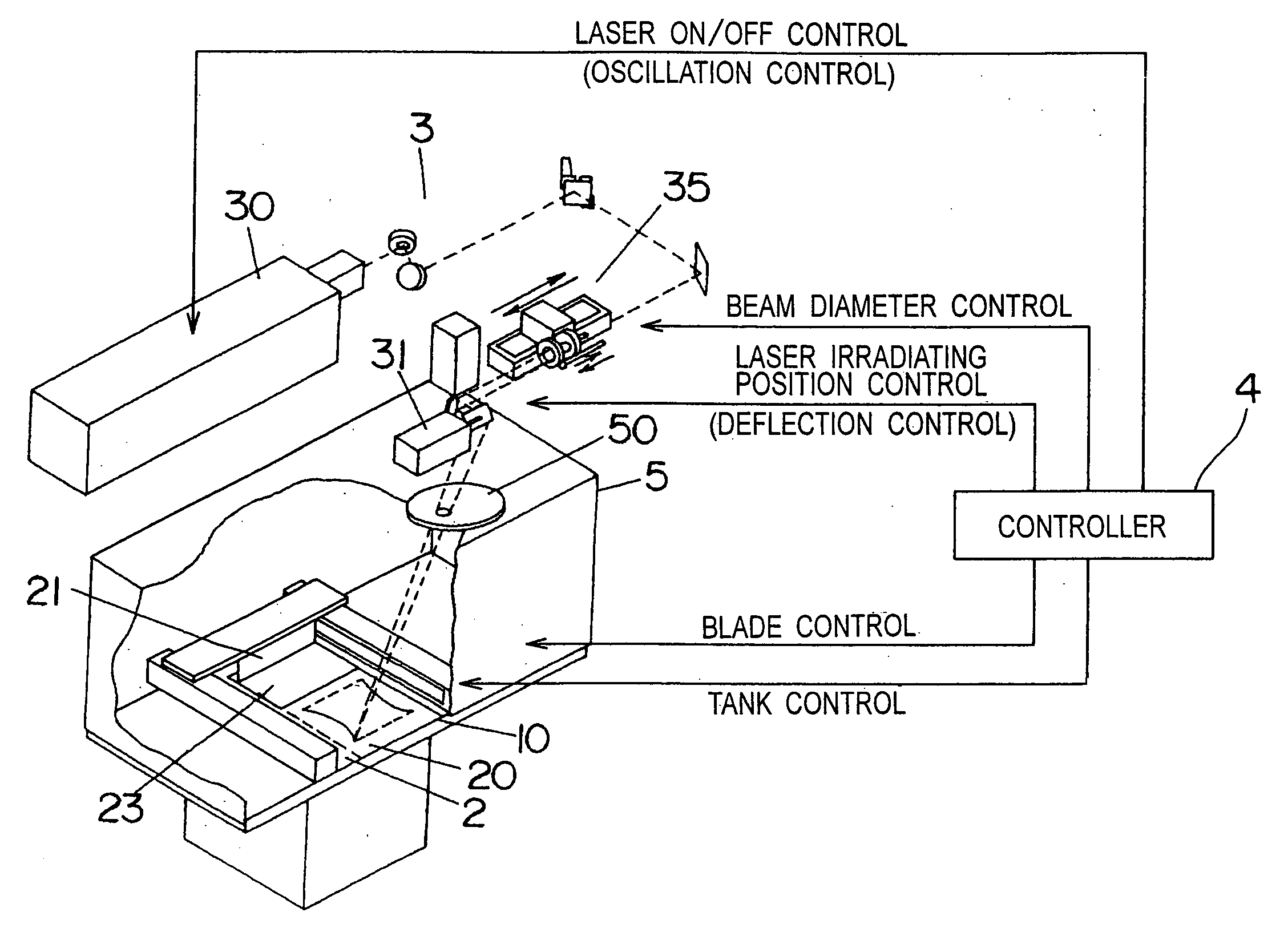
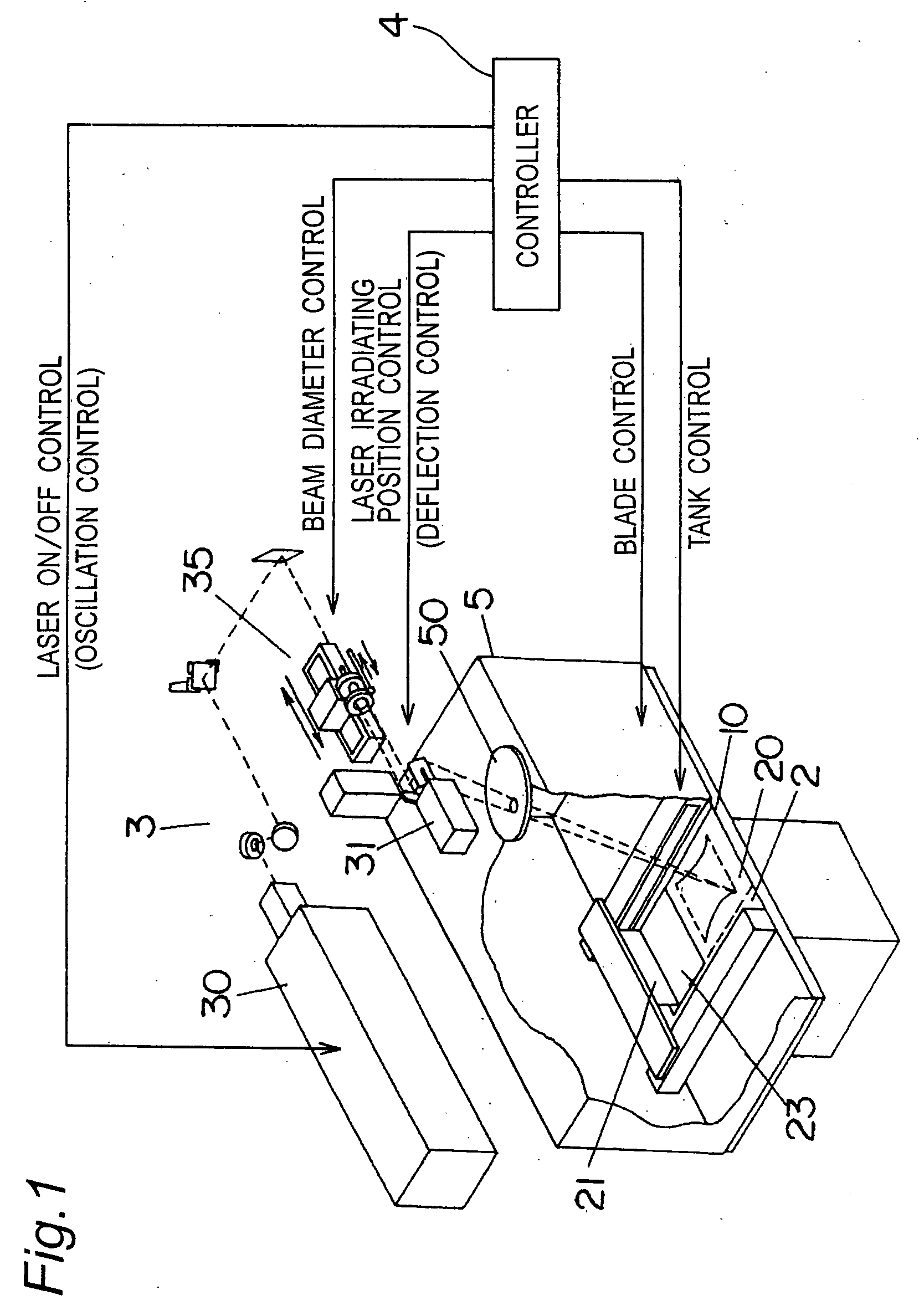
Various embodiments of the present invention relate to a method for welding a workpiece comprising the steps of: making a first weld at a first position on said workpiece with a high energy beam, deflecting the high energy beam with at least one deflection lens for making a second weld at a second position on said workpiece, focusing the high energy beam on said workpiece with at least one focusing lens, shaping the high energy beam on said workpiece with at least one astigmatism lens so that the shape of the high energy beam on said workpiece is longer in a direction parallel to a deflection direction of said high energy beam than in a direction perpendicular to said deflection direction of said high energy beam. The invention is also related to the use of an astigmatism lens and to a method for forming a three dimensional article.
Owner:ARCAM AB
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com