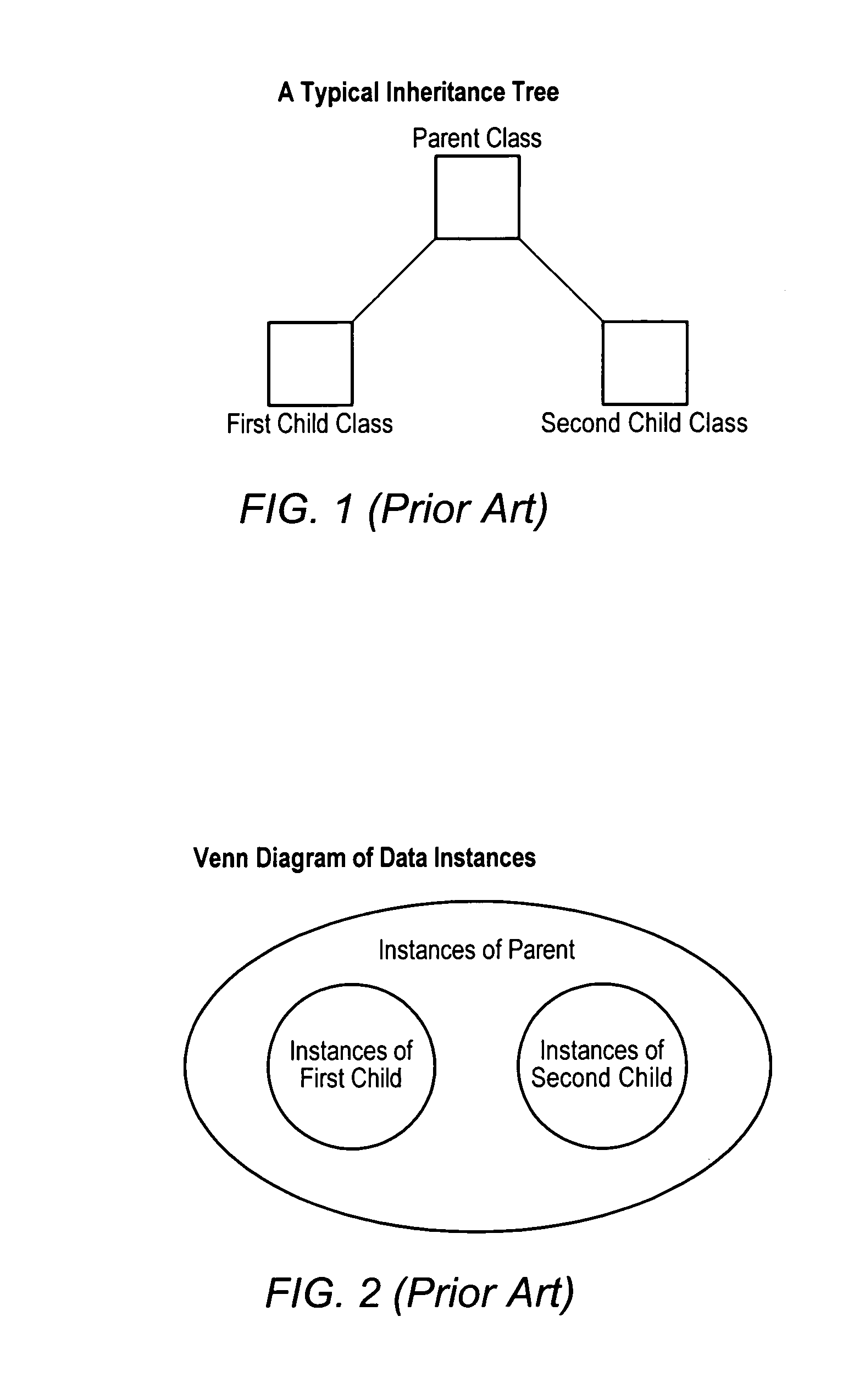
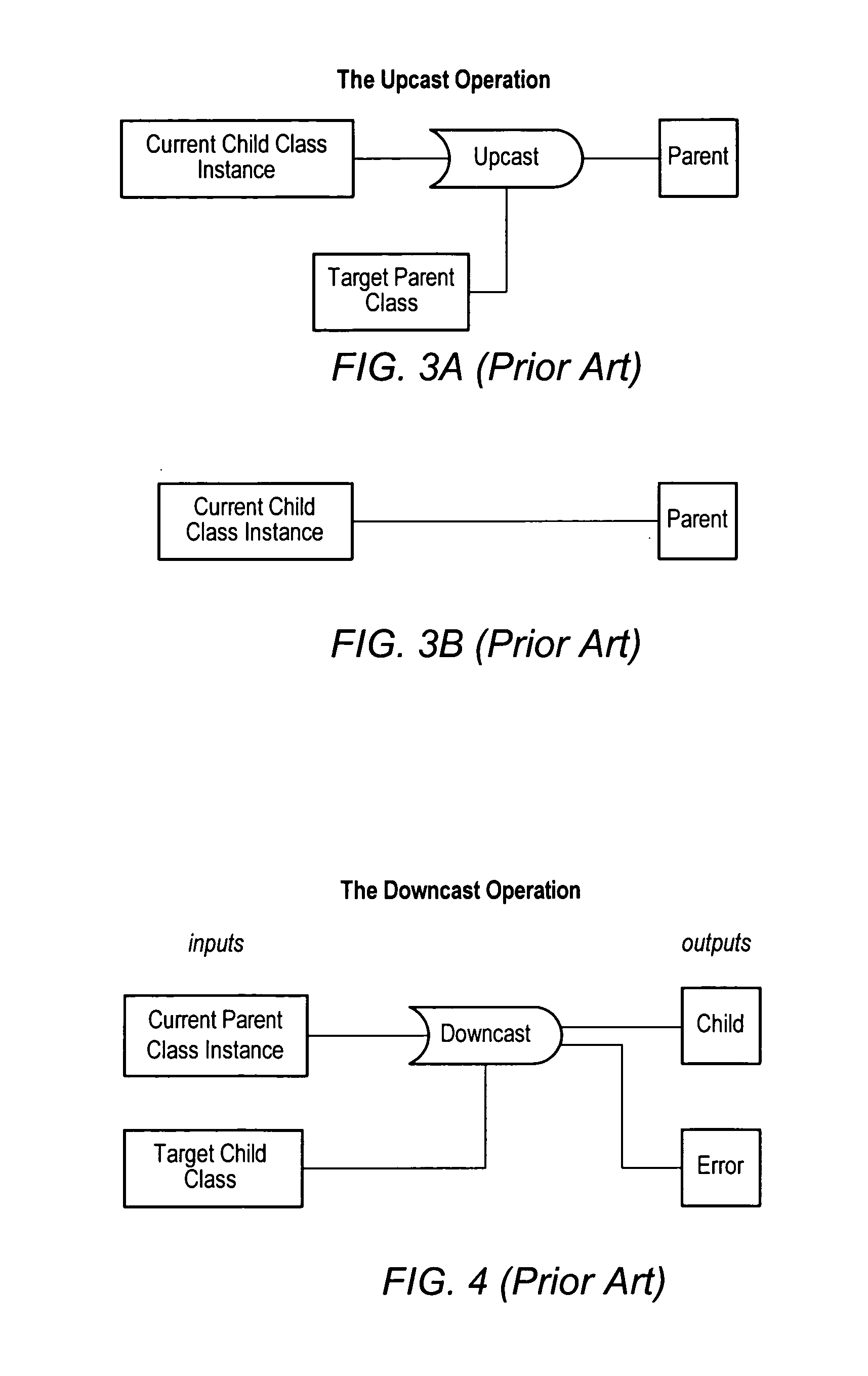
Patents
Literature
25442 results about "Casting" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Casting is a manufacturing process in which a liquid material is usually poured into a mold, which contains a hollow cavity of the desired shape, and then allowed to solidify. The solidified part is also known as a casting, which is ejected or broken out of the mold to complete the process. Casting materials are usually metals or various time setting materials that cure after mixing two or more components together; examples are epoxy, concrete, plaster and clay. Casting is most often used for making complex shapes that would be otherwise difficult or uneconomical to make by other methods. Heavy equipment like machine tool beds, ships' propellers, etc. can be cast easily in the required size, rather than fabricating by joining several small pieces.
Solid free-form fabrication methods for the production of dental restorations
InactiveUS20050023710A1Improve bindingImpression capsCeramic shaping apparatusPolymer scienceFree form
Solid free form fabrication techniques can be utilized indirectly to manufacture substrates, dies, models, near-net shapes, shells, and wax-ups that are then used in the manufacture of dental articles. Digital light processing is the most preferred indirect method for the production of substrates. After the substrates are produced, various coating or deposition techniques such as gel casting, slip casting, slurry casting, pressure infiltration, dipping, colloidal spray deposition or electrophoretic deposition are used to manufacture the dental article.
Owner:IVOCLAR VIVADENT AG
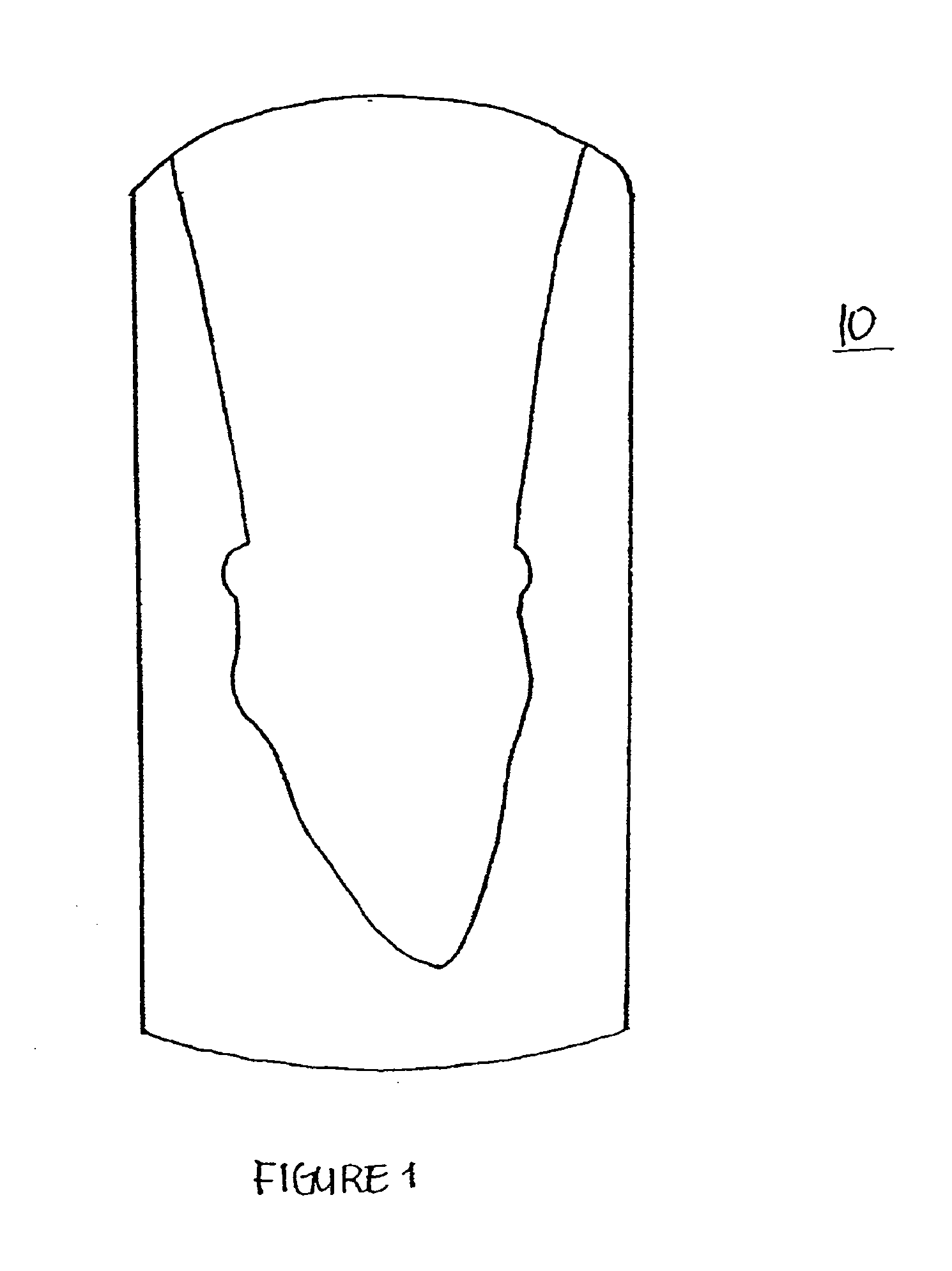
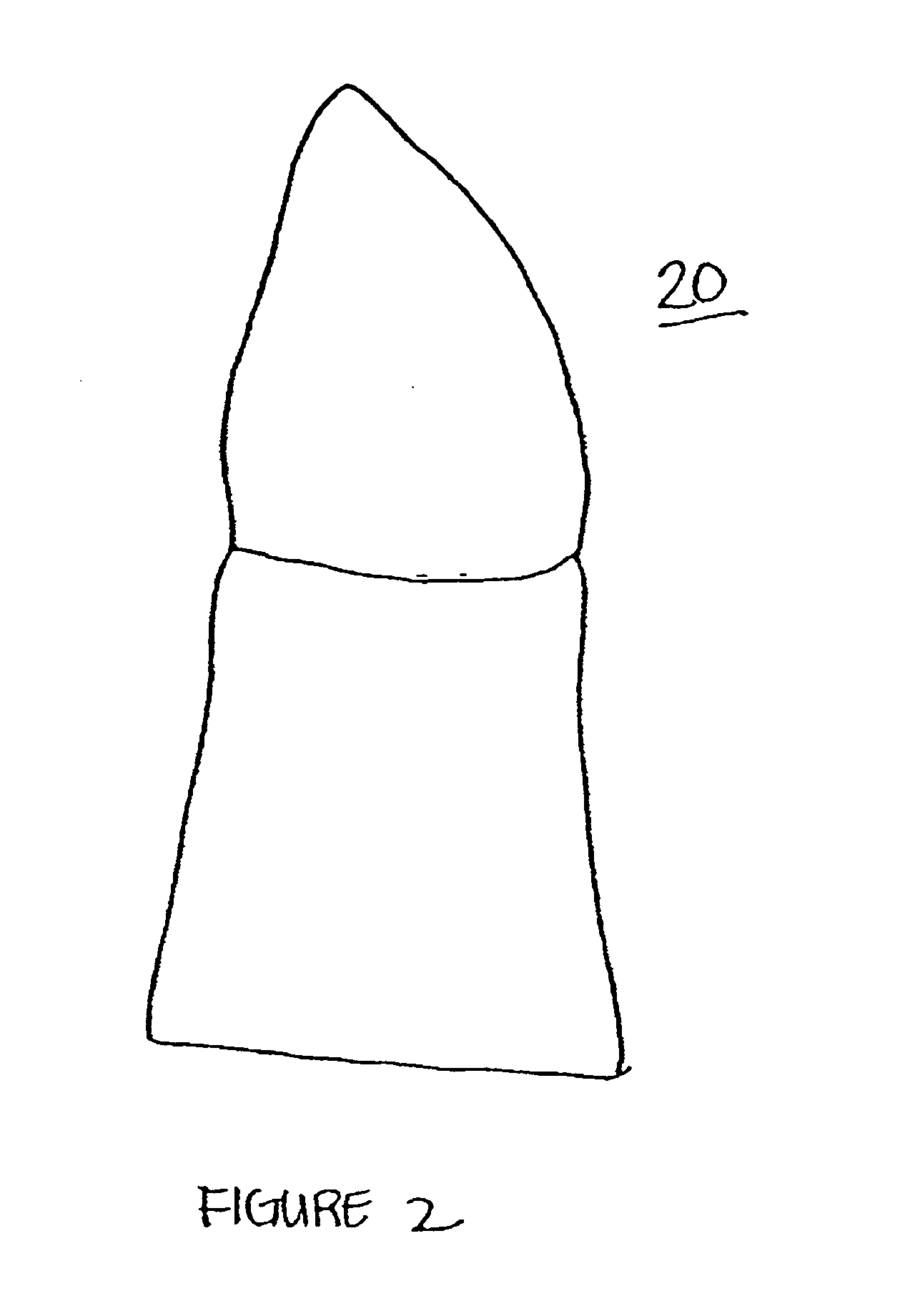
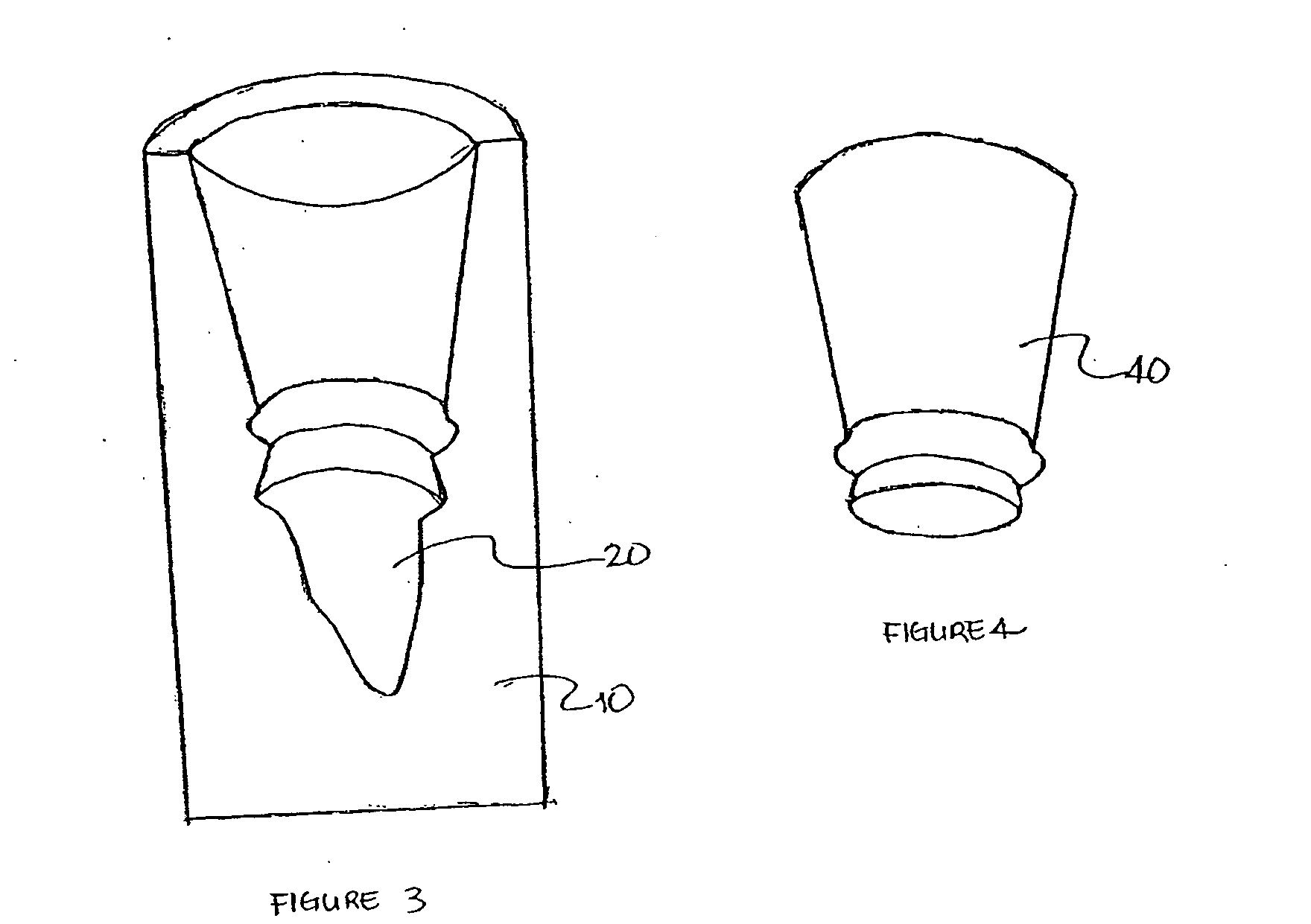
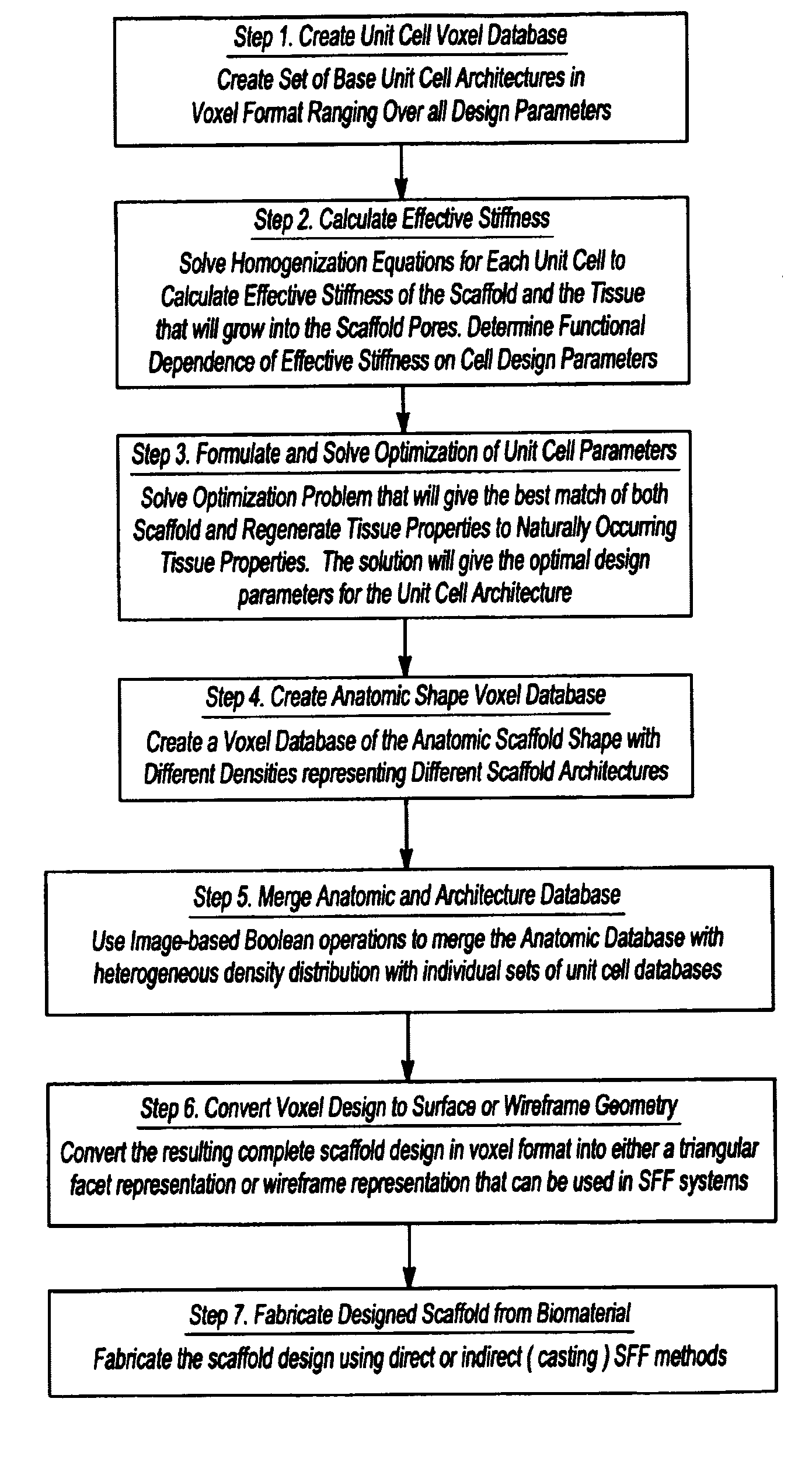
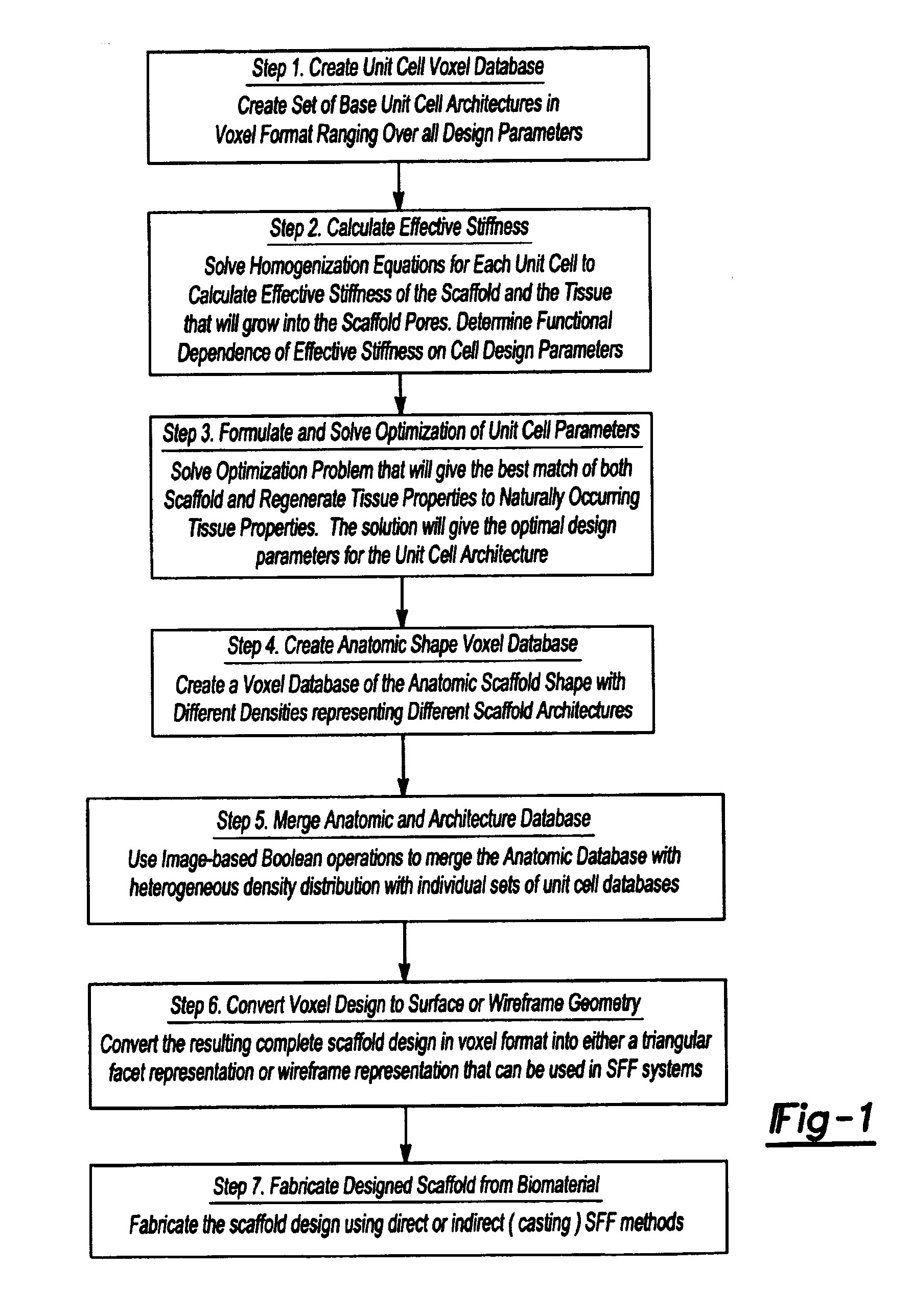
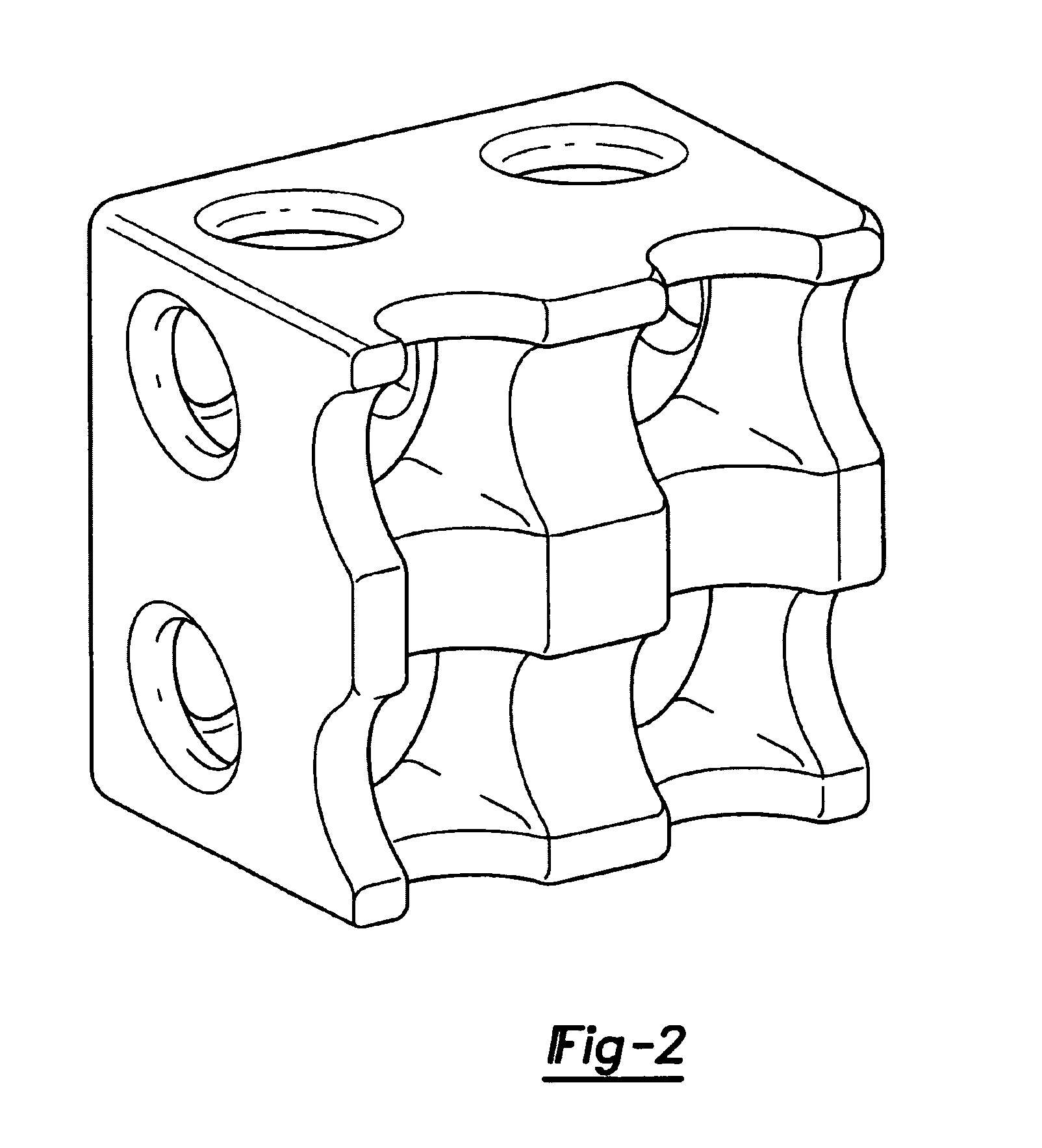
Design methodology for tissue engineering scaffolds and biomaterial implants
A design methodology is provided for creating biomaterial scaffolds optimized for in vivo function with any 3D anatomic shape. The method creates all designs using voxel based design techniques. It also provides for optimization of implant and scaffold microstructure to best match functional and biofactor delivery (including cells, genes and proteins) requirements. The voxel based design techniques readily allow combination of any scaffold or implant microstructure database with any complex 3D anatomic shape created by CT or MRI scanners. These designs can be readily converted to formats for layered manufacturing or casting.
Owner:HOLLISTER SCOTT J +2
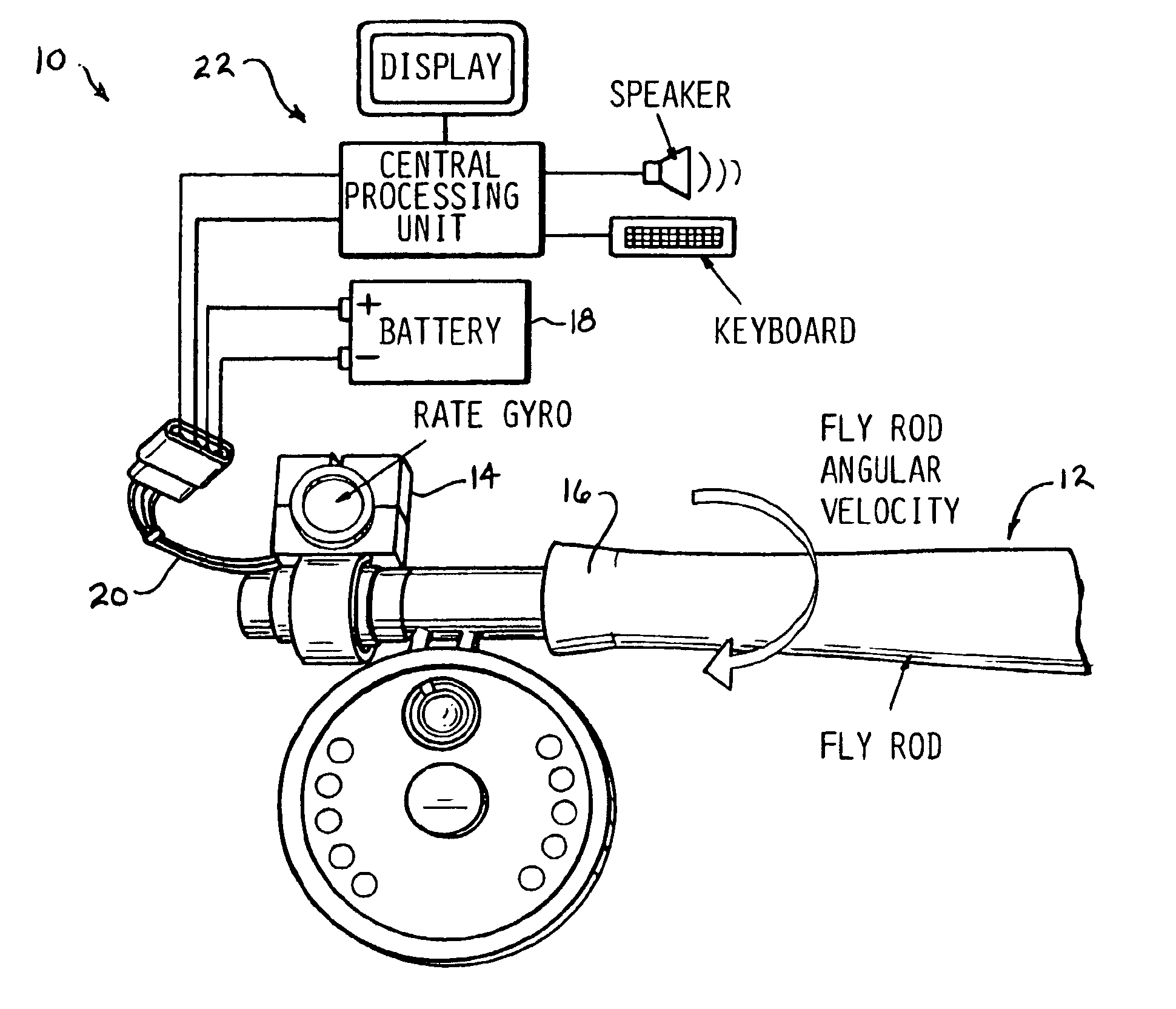
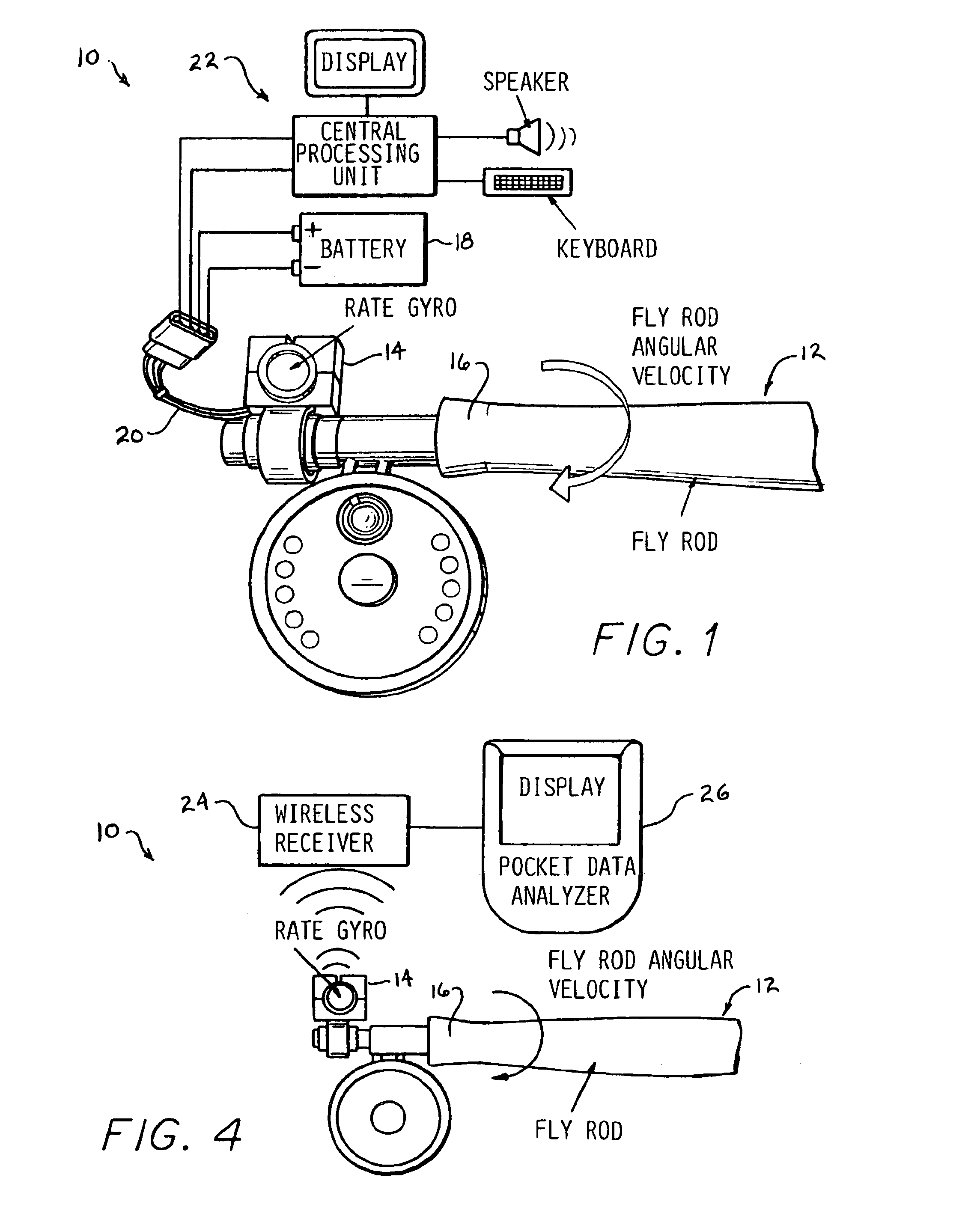
Electronic measurement of the motion of a moving body of sports equipment
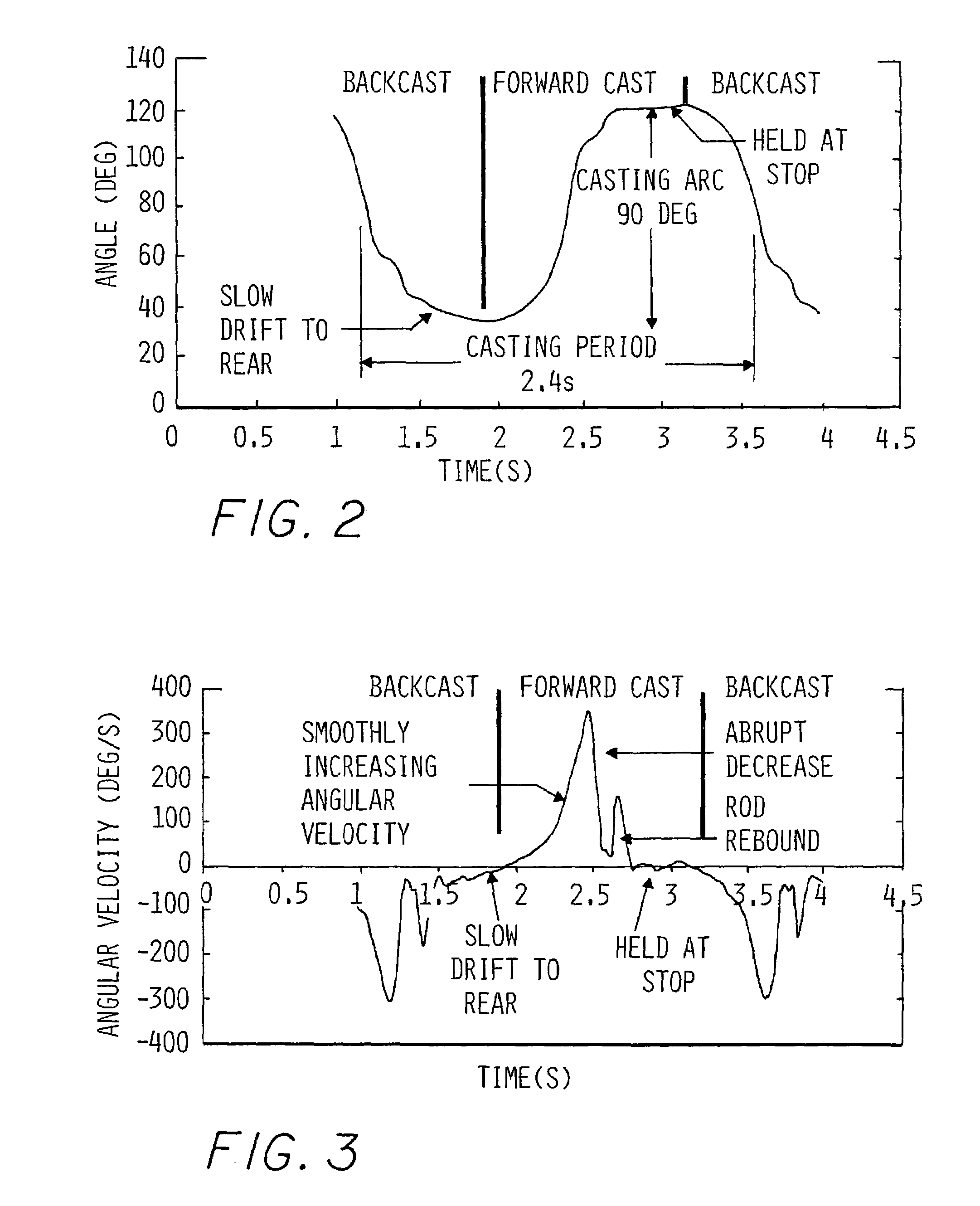
An application of rate gyros and accelerometers allows electronic measurement of the motion of a rigid or semi-rigid body, such as a body associated with sporting equipment including a fly rod during casting, a baseball bat, a tennis racquet or a golf club during swinging. For instance, data can be collected by one gyro according to the present invention is extremely useful in analyzing the motion of a fly rod during fly casting instruction, and can also be used during the research, development and design phases of fly casting equipment including fly rods and fly lines. Similarly, data collected by three gyros and three accelerometers is extremely useful in analyzing the three dimensional motion of other sporting equipment such as baseball bats, tennis racquets and golf clubs. This data can be used to support instruction as well as design of the sporting equipment.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Method for casting composite ingot
ActiveUS20050011630A1Easy to controlImprove corrosion resistanceThin material handlingIngotMaterials science
A method and apparatus are described for the casting of a composite metal ingot comprising at least two separately formed layers of one or more alloys. An open ended annular mould has a feed end and an exit end and divider wall for dividing the feed end into at least two separate feed chambers, where each feed chamber is adjacent at least one other feed chamber. For each pair of adjacent feed chambers a first alloy stream is fed through one of the pair of feed chambers into the mould and a second alloy stream is fed through another of the feed chambers. A self-supporting surface is generated on the surface of the first alloy stream and the second alloy stream is contacted with the first stream such that the upper surface of the second alloy stream is maintained at a position such that it first contacts the self-supporting surface where the self-supporting surface temperature is between the liquidus and solidus temperatures of the first alloy or it first contacts the self-supporting surface where the self-supporting surface temperature is below the solidus temperatures of the first alloy but the interface between the two alloys is then reheated to between the liquidus and solidus temperatures, whereby the two alloy streams are joined as two layers. The joined alloy layers are then cooled to form a composite ingot. This composite ingot has a substantially continuous metallurgical bond between alloy layers with dispersed particles of one or more intermetallic compositions of the first alloy in a region of the second alloy adjacent the interface.
Owner:NOVELIS INC
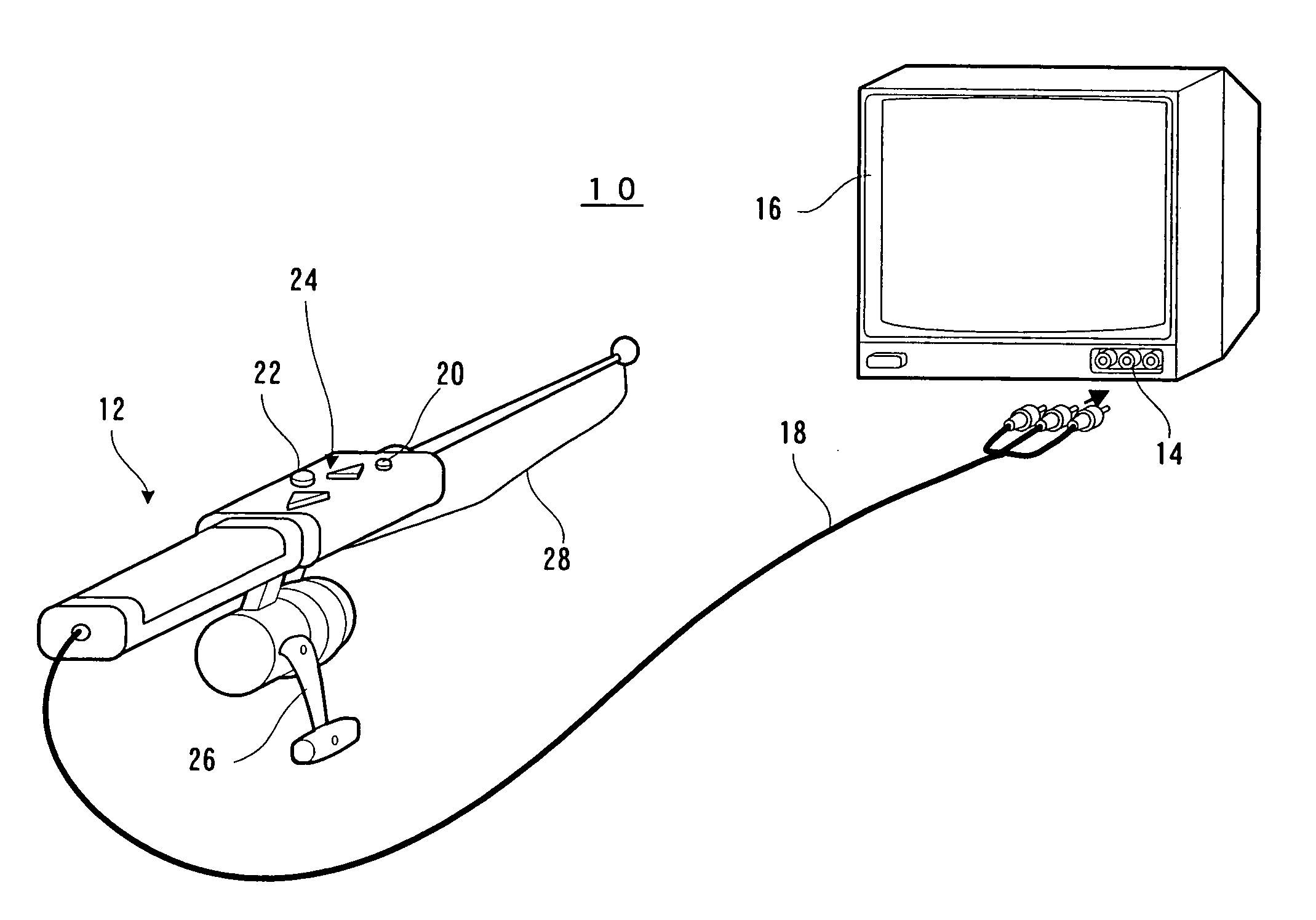
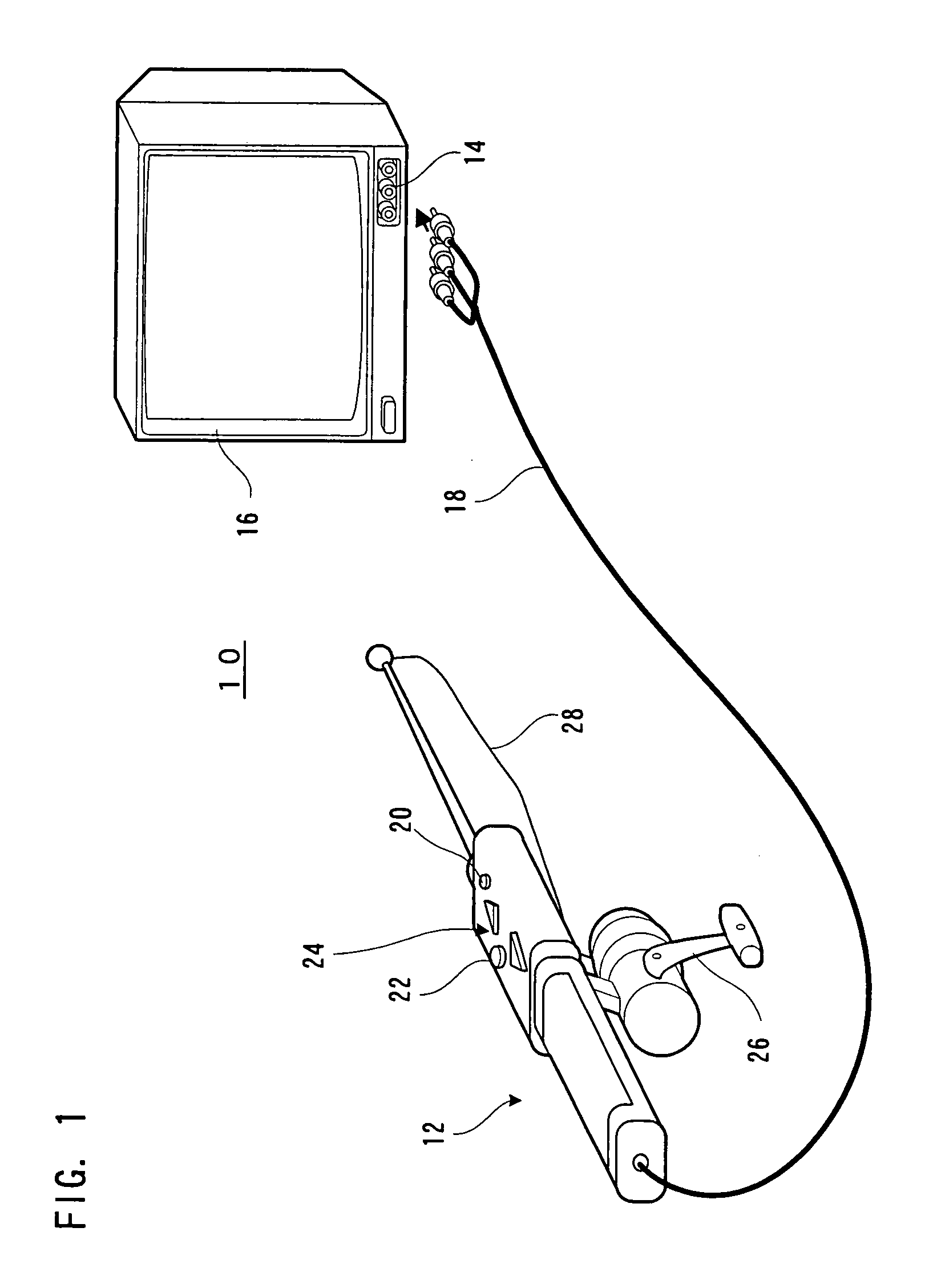
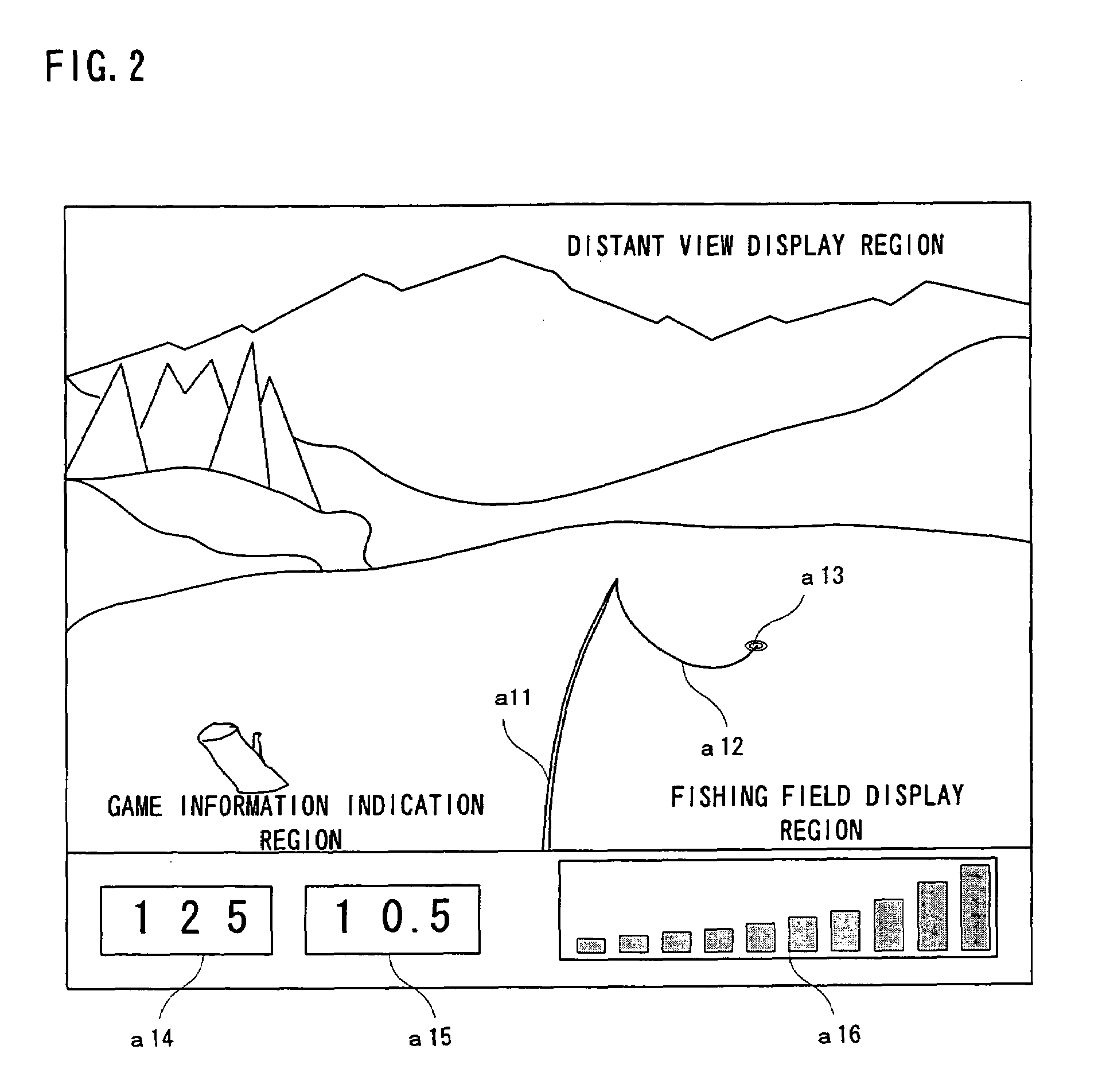
Fishing game device
InactiveUS6929543B1Realistic sensationEasy to enjoyVideo gamesSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringFishing
A fishing game apparatus (10) has a casting rod (12) connected to a television monitor (16). The casting rod (12) is built therein with a game processor and an acceleration sensor. During casting, an acceleration signal is inputted from the acceleration sensor to the game processor. The game processor calculates a corresponding casting distance and displays, on a game screen of the monitor (16), a splashdown point according to a distance calculated. By providing a light gun in the casting rod (12), the game processor can recognize a direction of casting and move the rod in that direction on the game screen.
Owner:SHINSEDAI KK
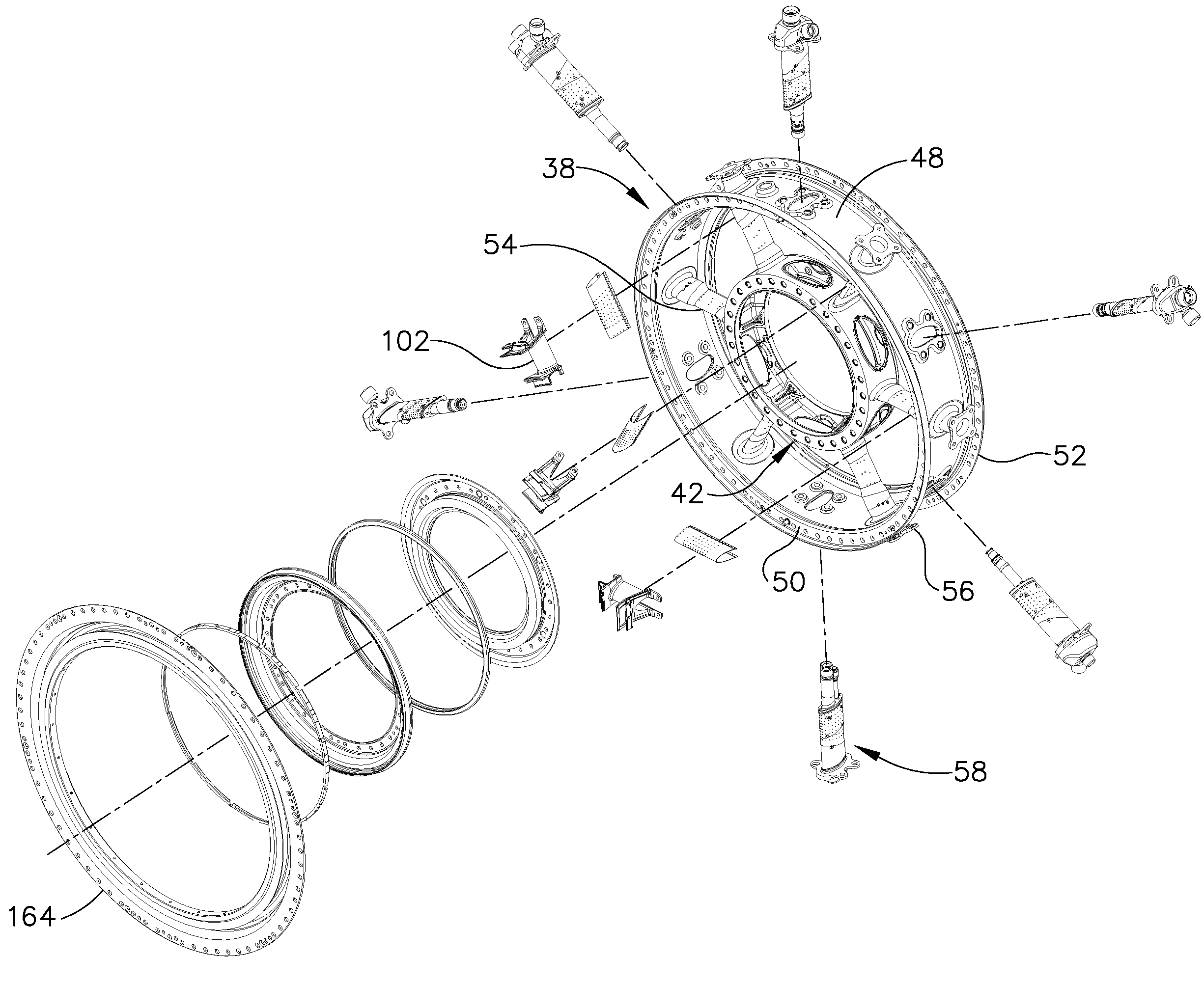
Turbine frame assembly and method for a gas turbine engine
A turbine frame assembly for a gas turbine engine includes: (a) a turbine frame including: (i) an outer ring; (ii) a hub; (ii) a plurality of struts extending between the hub and the outer ring; (b) a two-piece strut fairing surrounding each of the struts, including: (i) an inner band; (ii) an outer band; and (iii) an airfoil-shaped vane extending between the inner and outer bands; (d) a plurality of nozzle segments disposed between the outer ring and the hub, each nozzle segment being an integral metallic casting including: (i) an arcuate outer band; (ii) an arcuate inner band; and (ii) an airfoil-shaped vane.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Golf club head structure
A golf club head structure includes a body portion, a hitting plate portion, and a club body combining portion. The body portion has a first junction surface forming a first hook angle therewith. The hitting plate portion has a hitting surface and a second junction surface with a buffer region spaced there-between. The second junction surface forms a second hook angle with the hitting plate portion, and butts against and attaches to the first junction surface on the same plane. The club body combining portion is provided for combining a club body. Therefore, a joint structure with a junction portion as a plane, capable of not being located on the surface of the club head and spaced by a buffer region with the hitting surface, is formed, which is applicable for solving the combination problem of the junction surface on the same plane that the casting is deformed.
Owner:ADVANCED INT MULTITECH CO LTD
Dental restorations using nanocrystalline materials and methods of manufacture
Dental articles are produced using relatively low sintering temperatures to achieve high density dental articles exhibiting strengths equal to and greater than about 700 MPa. Ceramic powders comprised of nanoparticulate crystallites are used to manufacture dental articles. The ceramic powders may include sintering agents, binders and other similar additives to aid in the processing of the ceramic powder into a dental article. The ceramic powders may be processed into dental articles using various methods including, but not limited to, injection molding, gel-casting, slip casting, or electroforming, hand, cad / camming and other various rapid prototyping methods. The ceramic powder may be formed into a suspension, pellet, feedstock material or a pre-sintered blank prior to forming into the dental article.
Owner:IVOCLAR VIVADENT AG
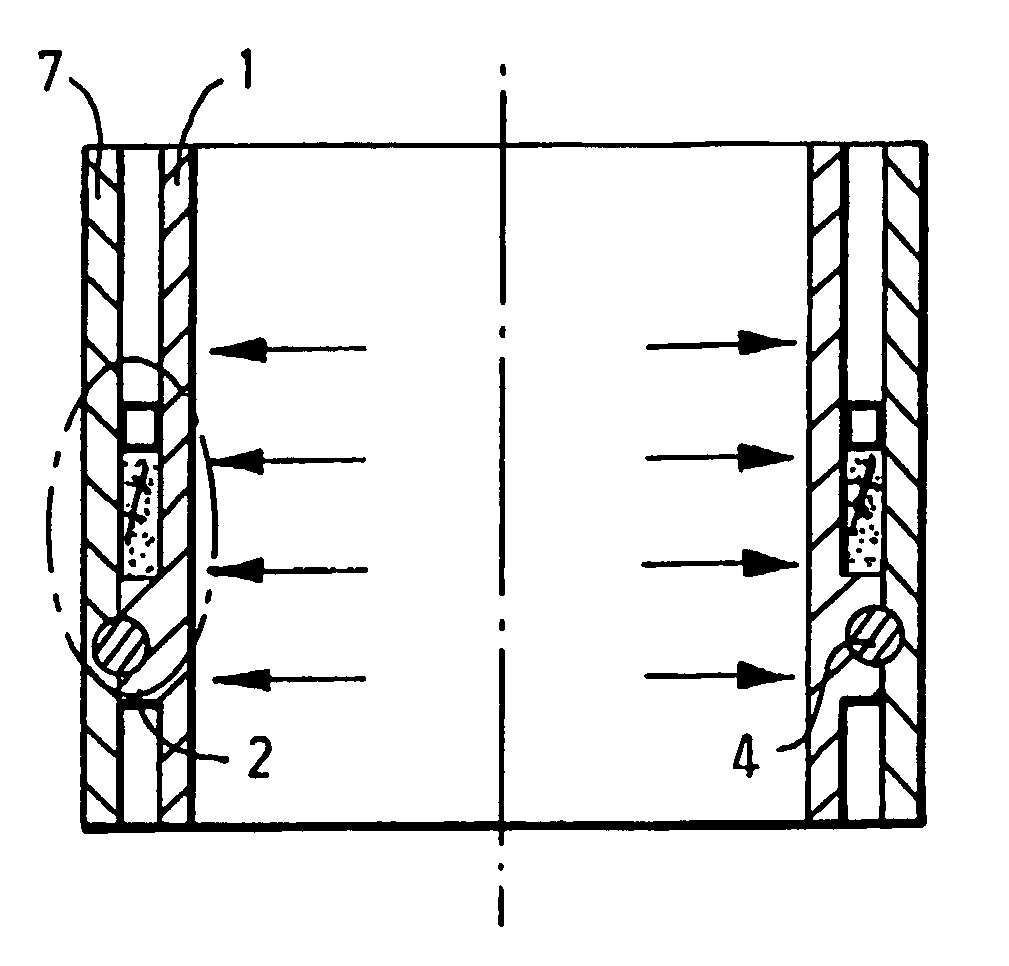
In-situ casting of well equipment
A method is provided of in-situ casting well equipment wherein a metal is used which expands upon solidification. A body of such metal is placed in a cavity in a well. Before or after placing the metal in the cavity in the well, the body is brought at a temperature above the melting point of the metal. The metal of the body in the cavity is solidified by cooling it down to below the melting point of the metal.
Owner:SHELL USA INC
Aluminum alloy lead with lanthanon yttric and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101587757AImprove conductivityHigh strengthSingle bars/rods/wires/strips conductorsMetal/alloy conductorsRare earthTime effect
The invention discloses an aluminum alloy lead with lanthanon yttric and preparation method thereof. The specific component and weight percentage of the invention are Si0.5%-0.7%, Mg0.6%-0.9%, Fe 0.1%-0.2%, Y 0.2%-0.8%, Al residue. The preparation method is following: preparing the elements according to the alloy design to prepare aluminum alloy wire material via melting, casting, homogenization, extrusion and wire drawing, preparing the cables via winding to obtain the aluminum alloy lead with great intensity and conduction via the electric field time effect heat treatment. The aluminum alloy lead with high intensity of the invention adds the lanthanon yttric to purify the melting body and reduce the silicon quantity in the alloy further enhance the conductive rate of the melting on the one hand; on another hand to thin the crystal grain and enhance intensity of the alloy wire; the generatrix intending intensity is 260MPa and the conductive rate can achieve 57% IACS.
Owner:HUNAN XIANGNENG ELECTRIC WORKS
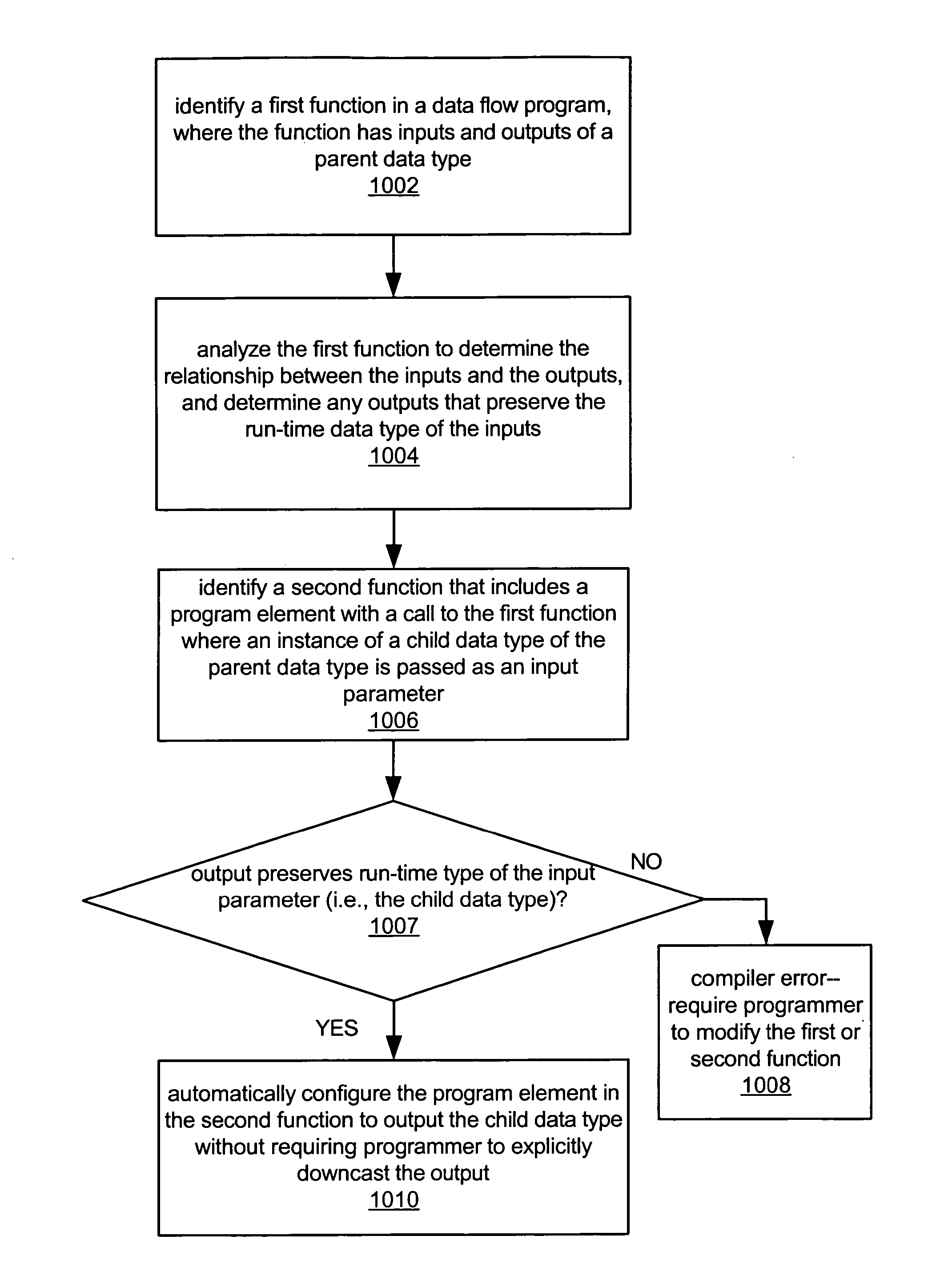
Type propagation for automatic casting of output types in a data flow program
ActiveUS20060117302A1Specific program execution arrangementsMemory systemsData streamAuto-configuration
System and method for implicit downcasting at compile time in a data flow program. A first data flow function in an object-oriented dataflow program is identified, where the first function includes an input of a parent data type and an output of the parent data type. The first function is analyzed to determine if the output preserves the run-time data type of the input. A second dataflow function in the object-oriented data flow program is identified, where the second function includes a program element that calls the first function, passing an input parameter of a child data type of the parent data type as input. If the analysis determines that an output parameter returned by the output of the first function will always be of the child data type, the program element is automatically configured at compile time to always downcast the output parameter from the parent data type to the child data type at run-time.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
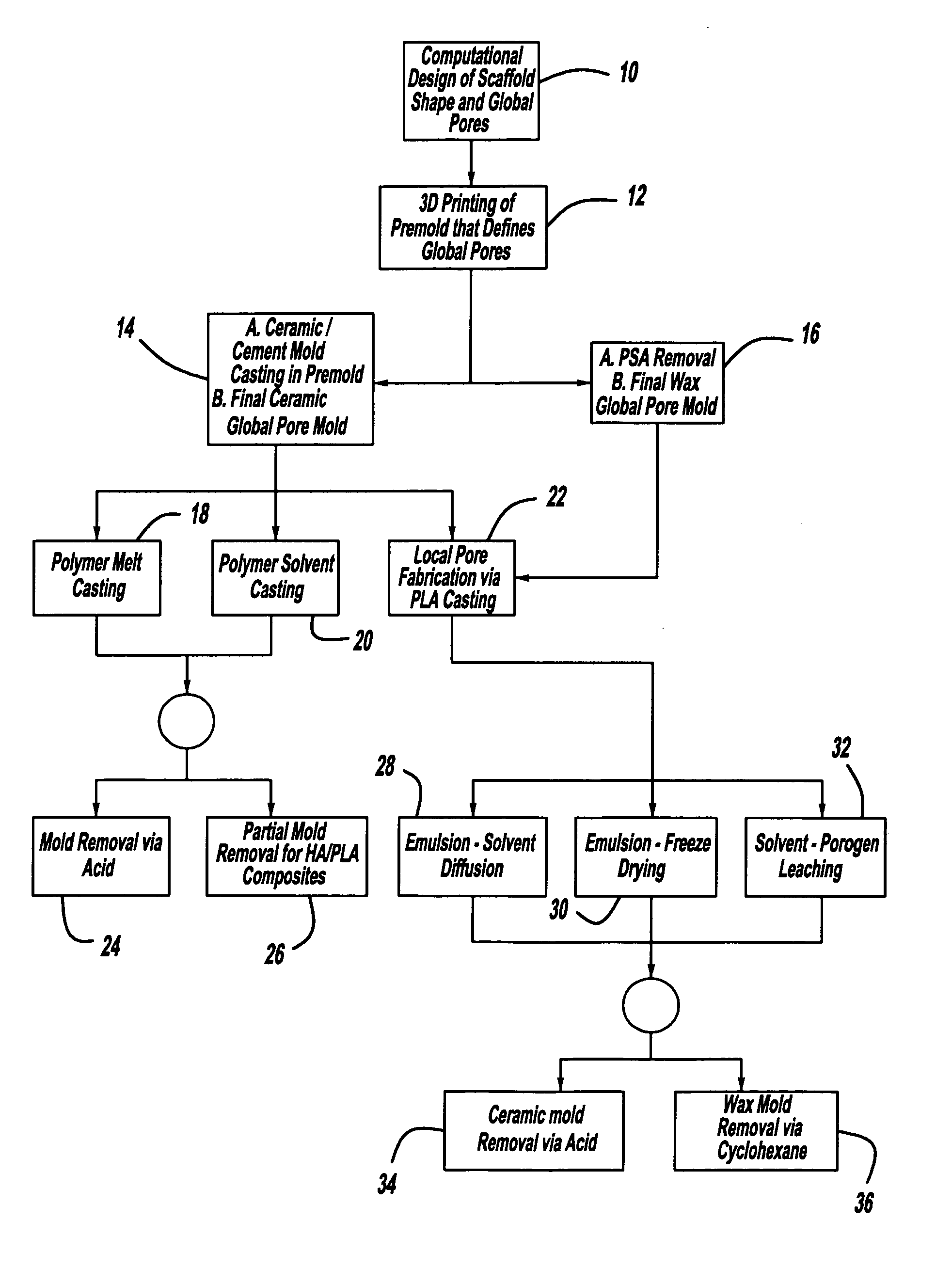
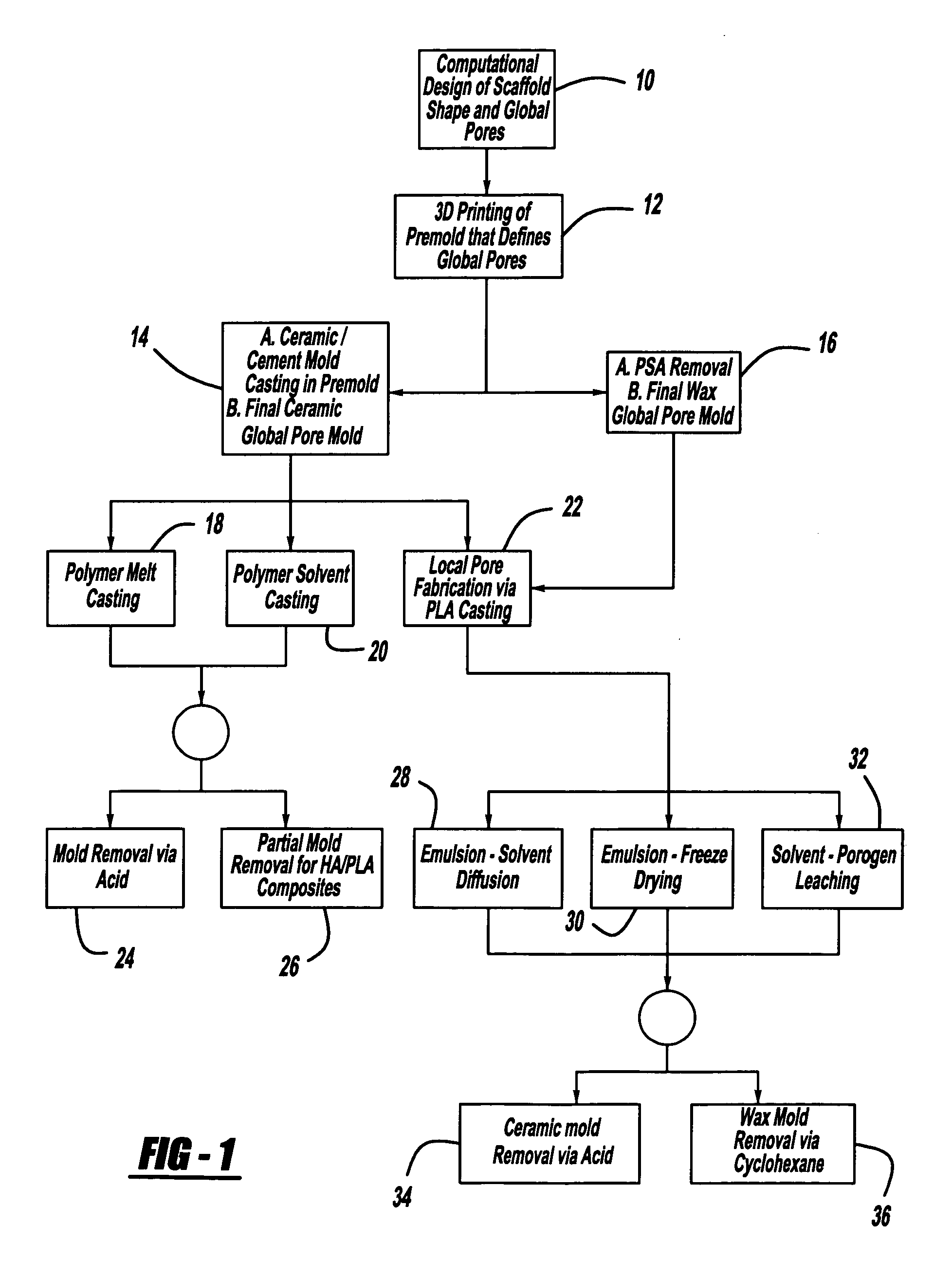
Controlled local/global and micro/macro-porous 3D plastic, polymer and ceramic/cement composite scaffold fabrication and applications thereof
InactiveUS7087200B2Easy to controlImprove interconnectivityMouldsJoint implantsManufacturing technologyFree form
An indirect solid free form scaffold manufacturing technique is provided. More particularly, the present invention provides a set of molds, casting methods, mold removals, and surface modification techniques that are compatible with image-based design methods and with solvent, melt, and slurry casting of polymers and ceramics.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Dental instrument
InactiveUS6322362B1Comfortable gripReduce fatigueDental toolsTooth cleaningDental instrumentsCore component
An apparatus for a dental instrument and specifically for a dental curette. The dental instrument comprises a handle having a first end and a second end. The handle has a substantially elongate form, and is molded from a composite of nonmetallic components. The handle also includes a first tip and a second tip that are received into the first end and the second end of the handle, respectively. The first tip and the second tip include metal tools, preferably formed from a stainless steel. The handle includes a core component comprising of a substantially rigid material, and a grip component comprising of a substantially elastic material. Selected thermosetting or thermoplastic polymeric casting resins, which are autoclaveable and chemclaveable, provide the desired tactile and structural qualities for the core component and the grip component.
Owner:HOLMS ALLAN G
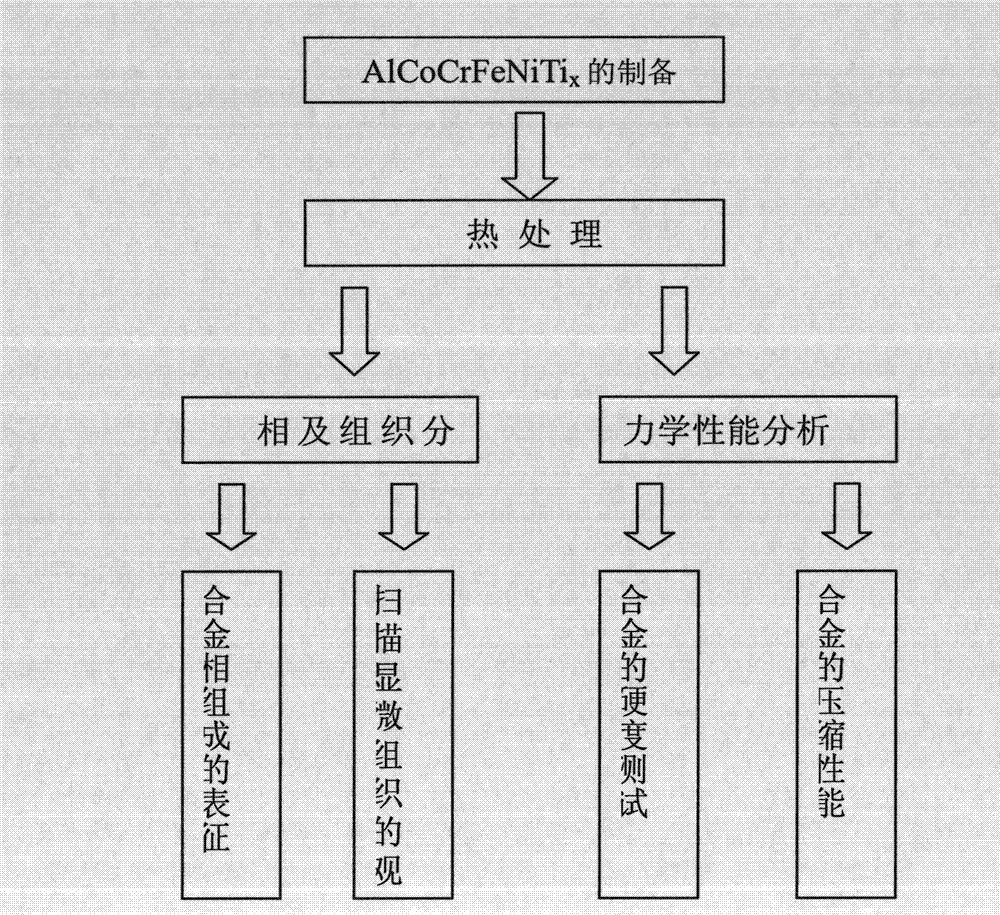
AlCoCrFeNiTix high-entropy alloy material and method for preparing same
The invention relates to a high-entropy alloy material and a method for preparing the same. The component of the high-entropy alloy material is AlCoCrFeNiTix, wherein x represents a molar ratio, and the value range is between 0.1-0.4. The method for preparing the material comprises: preparing raw materials, adopting the alloy smelting raw materials including Al, Co, Cr, Fe, Ni and Ti, and accurately weighing and proportioning according to the molar ratio; then, purifying oxide on a metal surface; putting the prepared raw materials into a tank in a water-cooling copper-formed mold smelting pool, vacuumizing, filling argon, controlling smelting current to be at about 250 ampere and smelting time for 30-60 seconds, turning an alloy block after alloys are fully mixed, putting an alloy ingot into a tank of a water-cooling copper-formed mold, regulating the smelting current, opening a suction casting air suction valve after the alloys are uniformly smelted, utilizing the negative pressure in a pump for suction casting, and taking out the alloy ingot after an alloy mould is cooled. Compared with the conventional crystalline state alloy, the high-entropy alloy material has relative high thermal stability, hardness, yield strength, breaking tenacity, plastic deformation and work hardening capacity.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
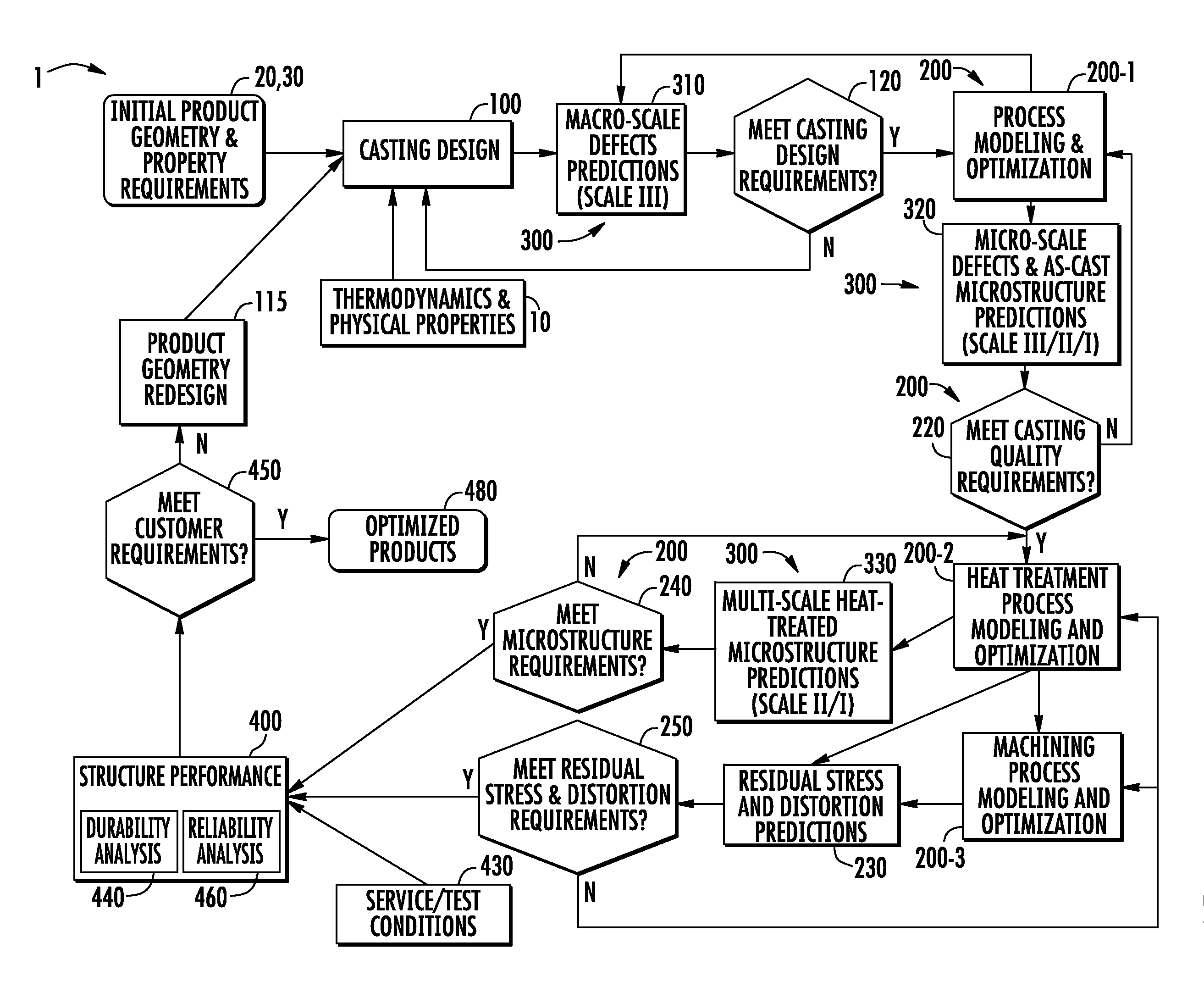
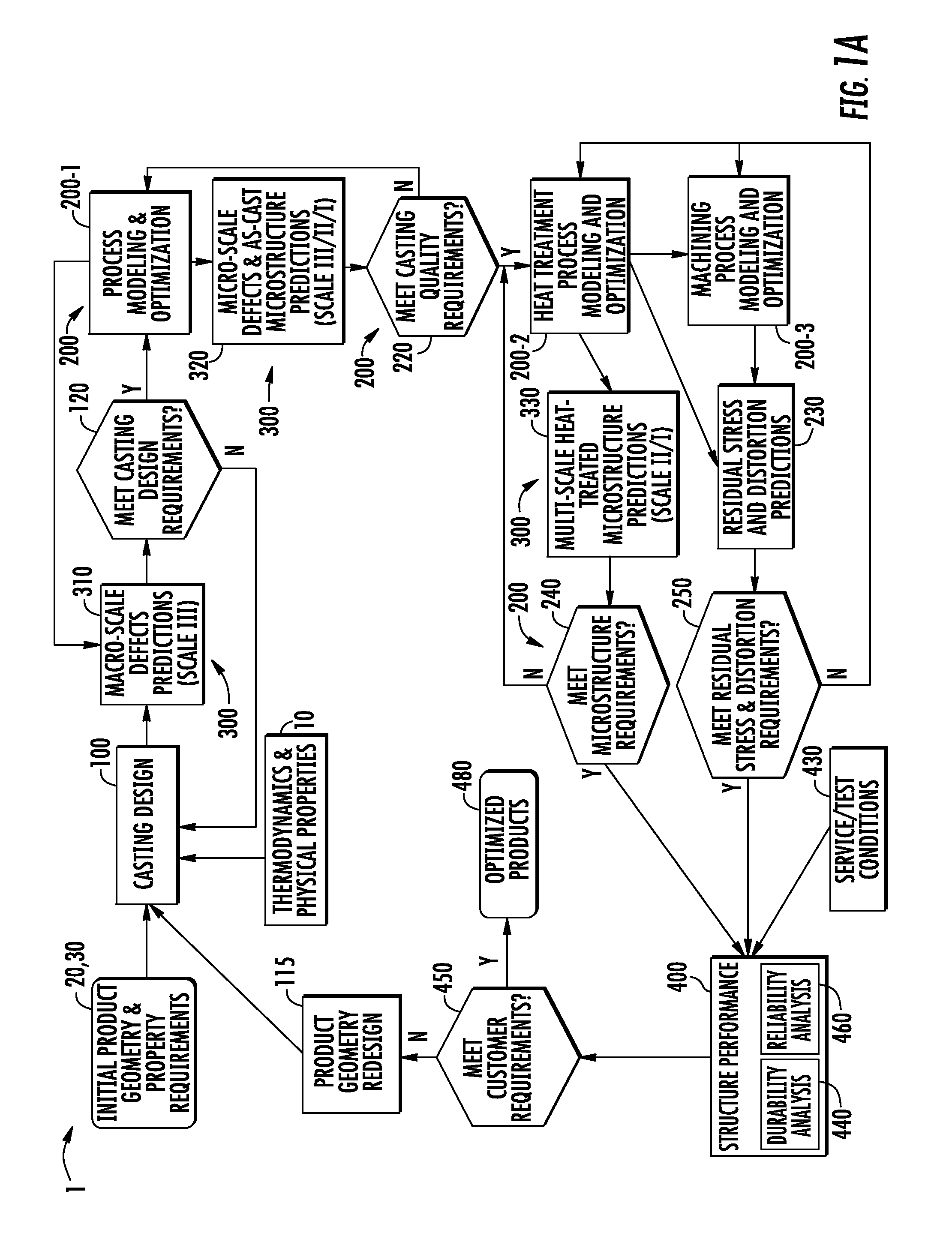
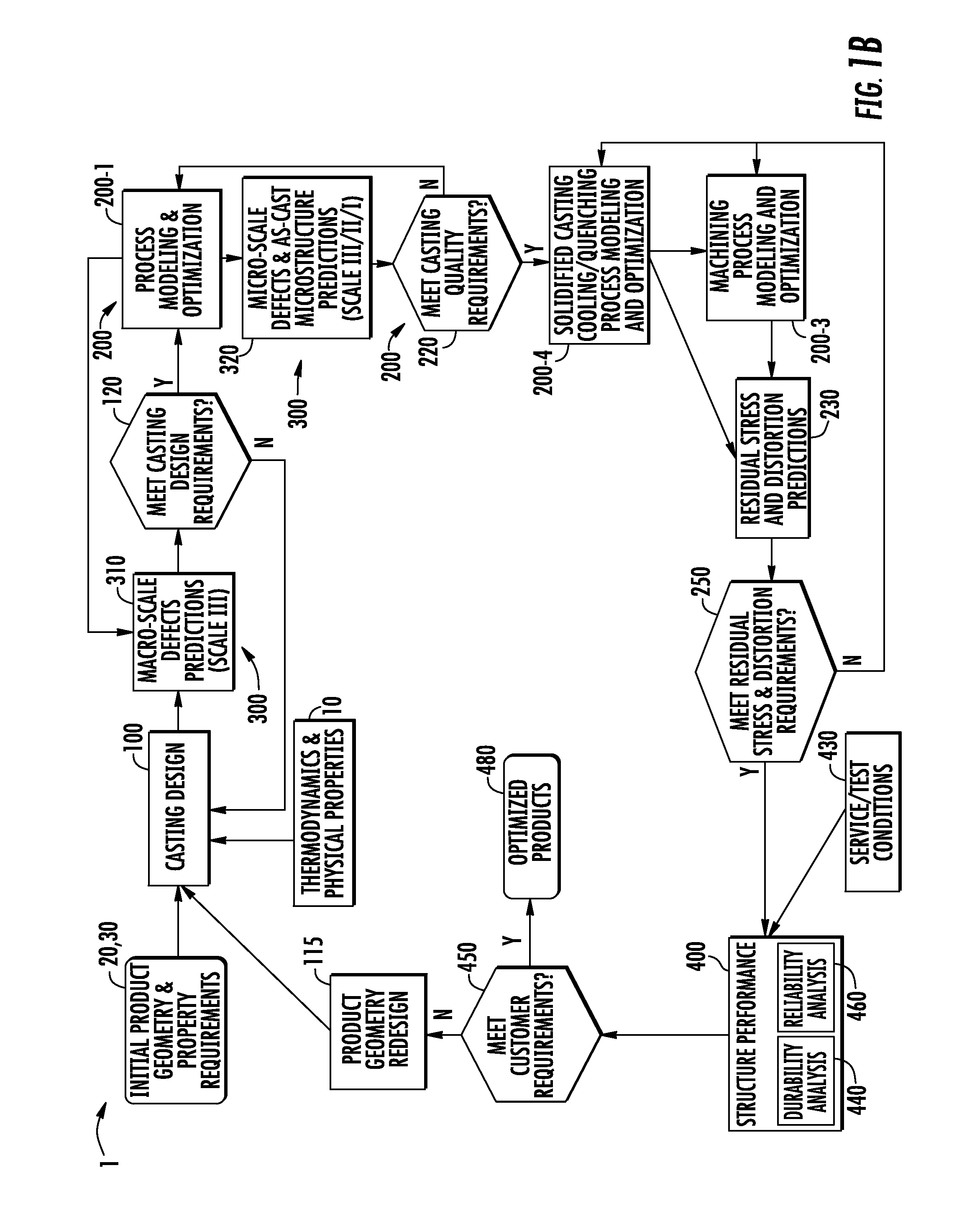
Systems and methods for computationally developing manufacturable and durable cast components
A method and system for optimizing a simulated casting of a light weight alloy component. The simulation includes passing component design data through various computational modules relating to casting designs, process modeling and optimization, material microstructure and defects and product performance. Variations in microstructure and defects across various very small size scales are extended to increasingly larger scales to permit structural performance calculations of the cast component to take such non-uniformities into consideration. At least some of the modules employ an expert system-based approach to achieve the optimized results. The results can be compared to end user needs to determine if redesign of the part geometry or manufacturing process is needed.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Method, machine-readable medium and computer concerning the manufacture of dental prostheses
InactiveUS20080153069A1Easy and inexpensive to manufactureEasy and inexpensiveTooth crownsTeeth cappingMaterials scienceDental prosthesis
The invention relates to a method by which a mold for casting, such as metal casting, of dental prostheses is prepared, with the step of: preparing the mold on the basis of mold model data with a CAM / CAD method. Furthermore, the invention relates to a method for the determination of a shape of a mold for casting, such as metal casting, of dental prostheses with the step of: creating mold model data describing the shape of the mold.
Owner:INSTITUT STRAUMANN AG
Silicon Casting Apparatus and Method of Producing Silicon Ingot
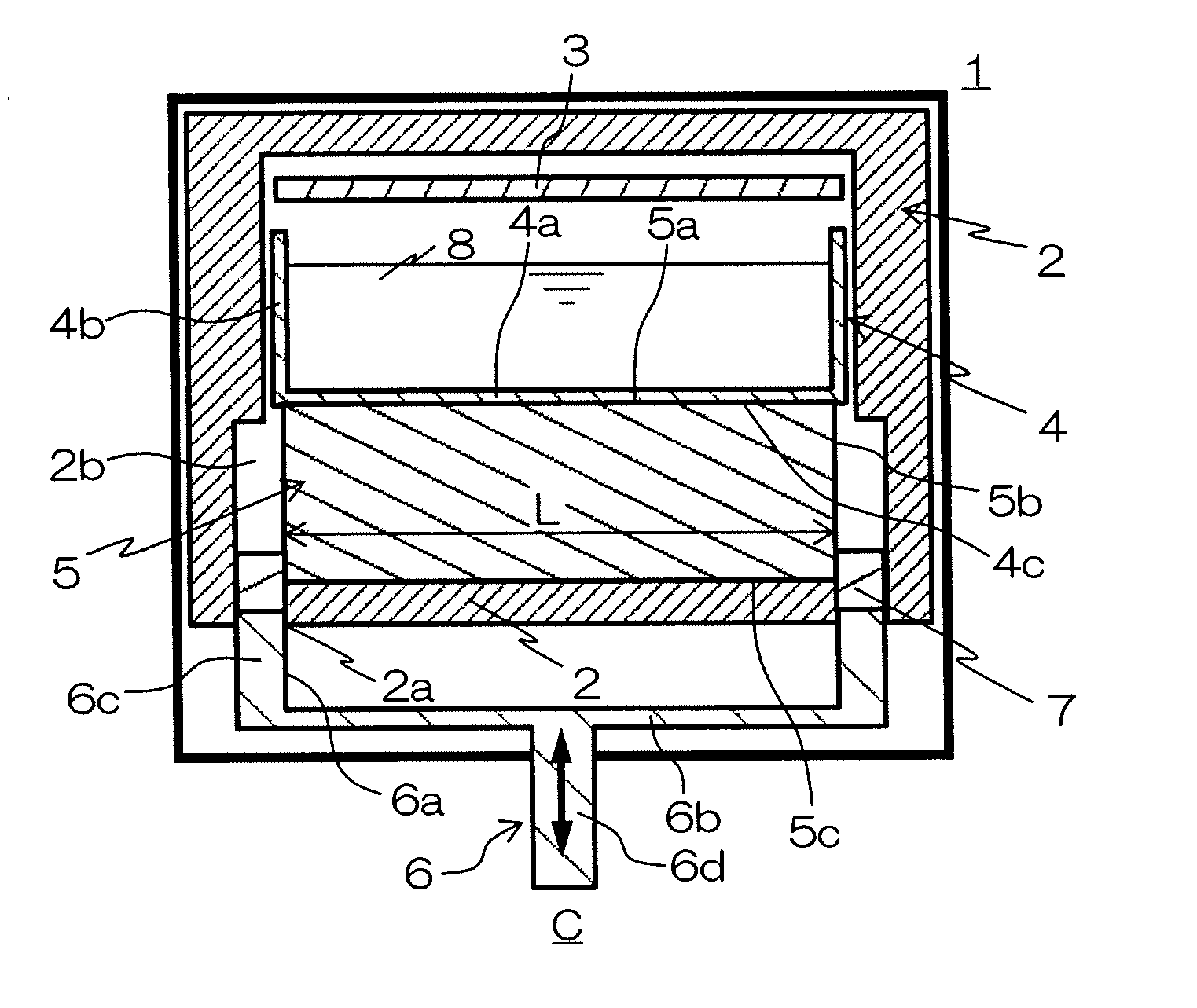
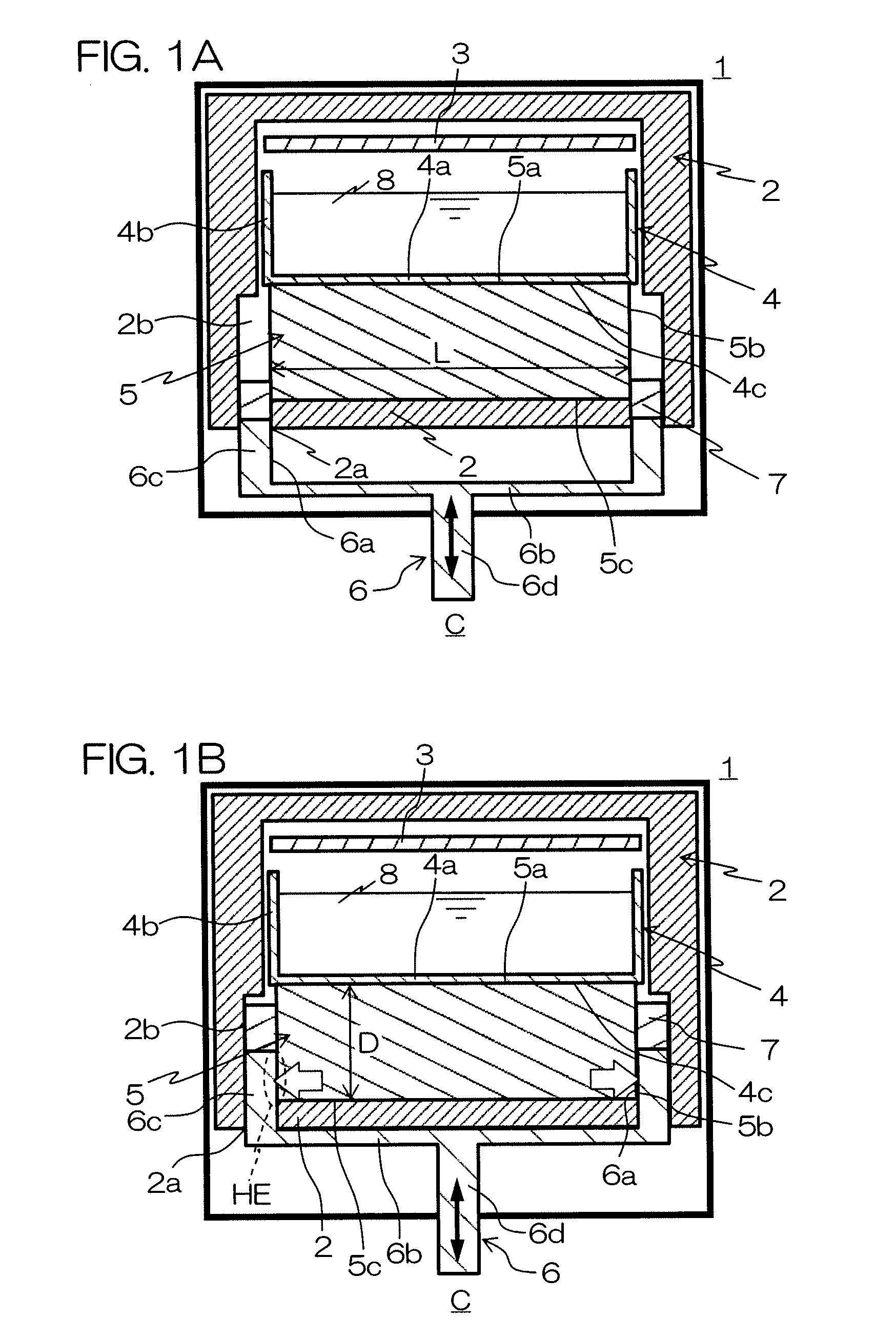
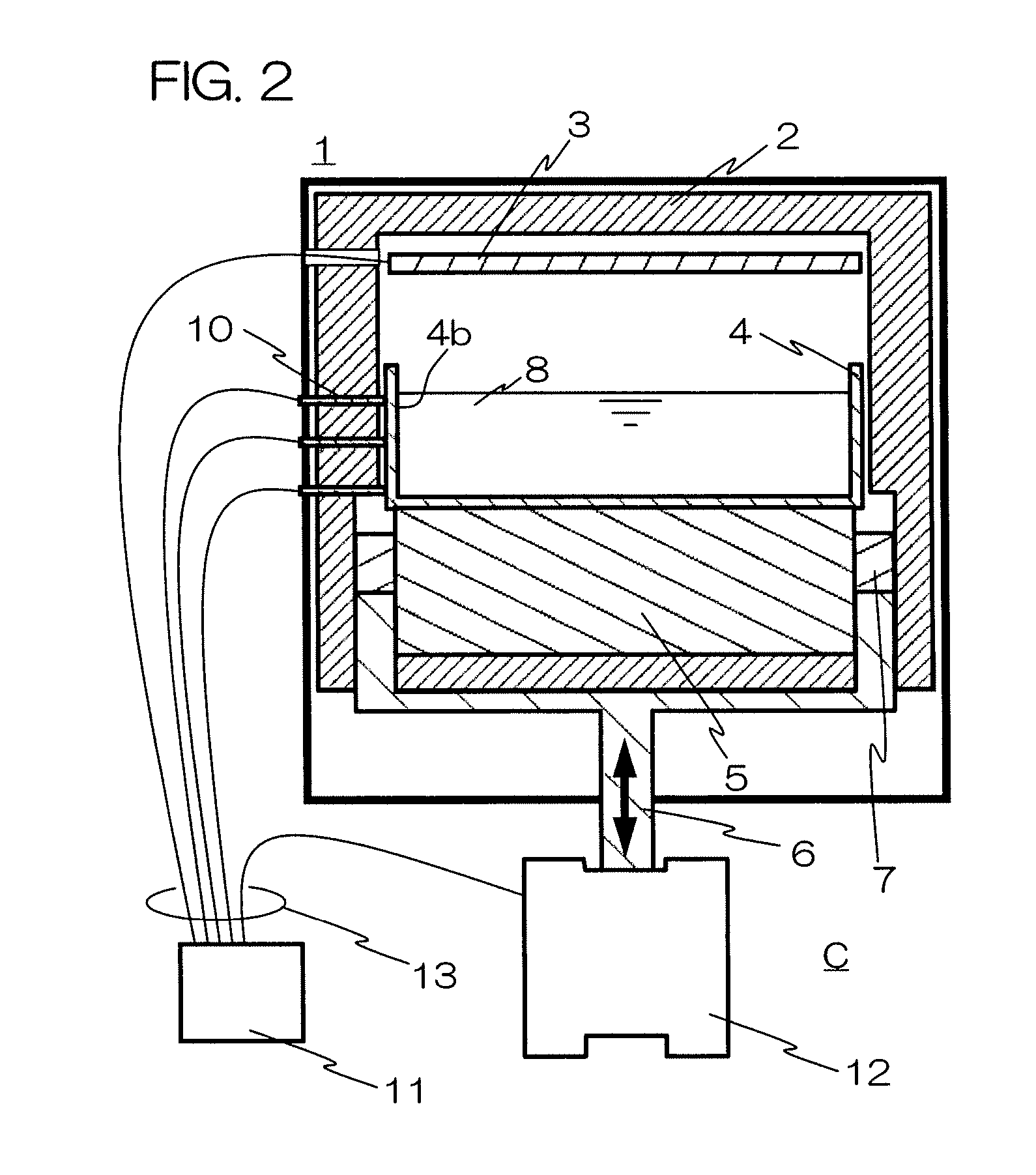
InactiveUS20070227189A1Good reproducibilityLow costFinal product manufactureGlass drawing apparatusIngotTemperature gradient
A silicon casting apparatus for producing polycrystal silicon ingot by heating a silicon melt (8) held in a mold (4) from above by a heater (3) and cooling it from below while changing the heat exchange area of a heat exchange region (HE), defined between a pedestal (5) having the mold (4) placed thereon and a bottom cooling member (6), in such a manner as to keep pace with the rise of the solid-liquid interface of the silicon melt (8), thereby causing unidirectional solidification upward along the mold (4); and a method of producing polycrystal silicon ingot using such apparatus. According to this production method, the temperature gradient given to the silicon melt (8) can be maintained at constant by adjusting the heat exchange area, so that polycrystal silicon ingot having good characteristics can be produced with good reproducibility.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Substrate for electronic device and electronic device
ActiveUS20120168206A1Good heat dissipationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted electric component incorporationCarbon nanotubeOptoelectronics
A substrate includes a plurality of through electrodes. The through electrode has a nanocomposite structure including a nm-sized carbon nanotube and is a casting formed by using a via formed in the substrate as a mold.
Owner:NAPRA
Cellulose Ester Compositions Having Low Bifringence and Films Made Therefrom
The present invention relates to cellulose esters having low hydroxyl content for use in optical applications, such as liquid crystal display (LCD) films. Films made with low hydroxyl levels and a given ratio of non-acetyl ester to hydroxyl level have been found to have low intrinsic birefringence. Therefore, these films can be cast, molded, or otherwise oriented without an appreciable birefringence or optical distortion (i.e. retardation). Such features make these films useful in polarizer, protective, and compensator films as well as molded optical parts, such as lenses. Furthermore, it has also been found that resins of the present invention can also be made to have “+C plate” behavior either by melt or solvent based processing, a characteristic which is not typical of cellulose esters. Such +C behavior allows films to be produced having unique compensatory behavior. Other embodiments of the invention relate to methods melt casting films while minimizing birefringence formation.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Automotive vehicle cast frame components
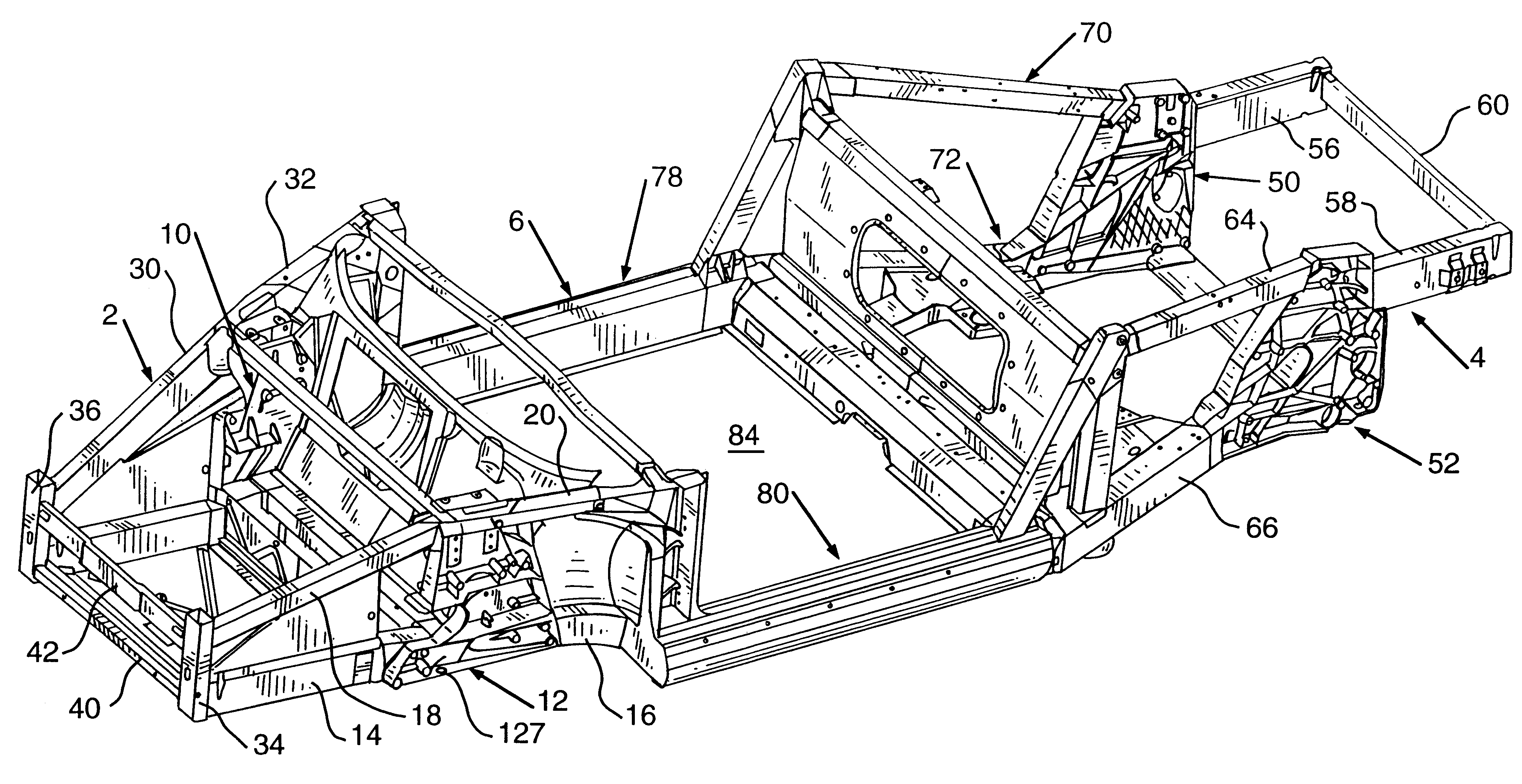
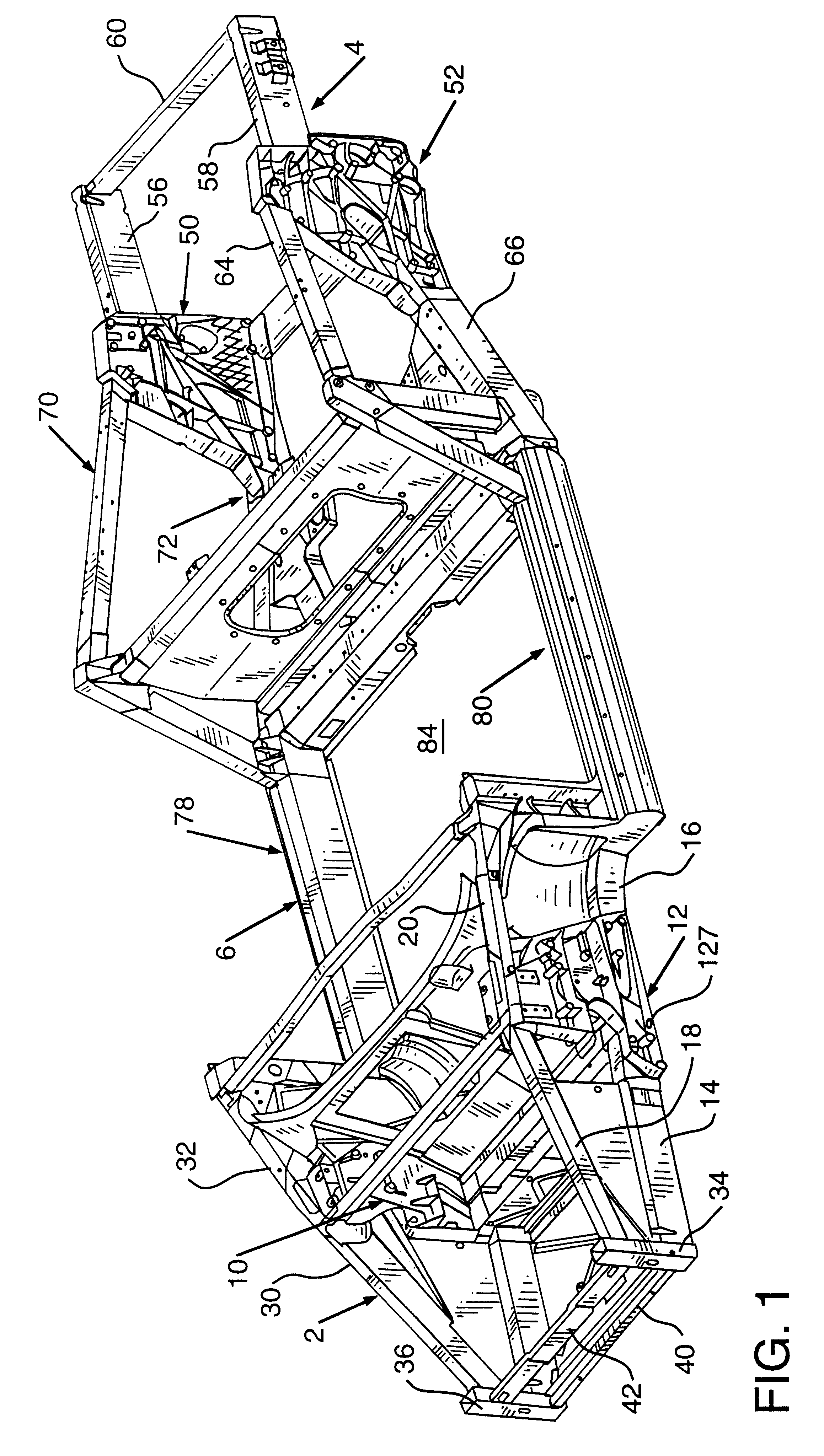
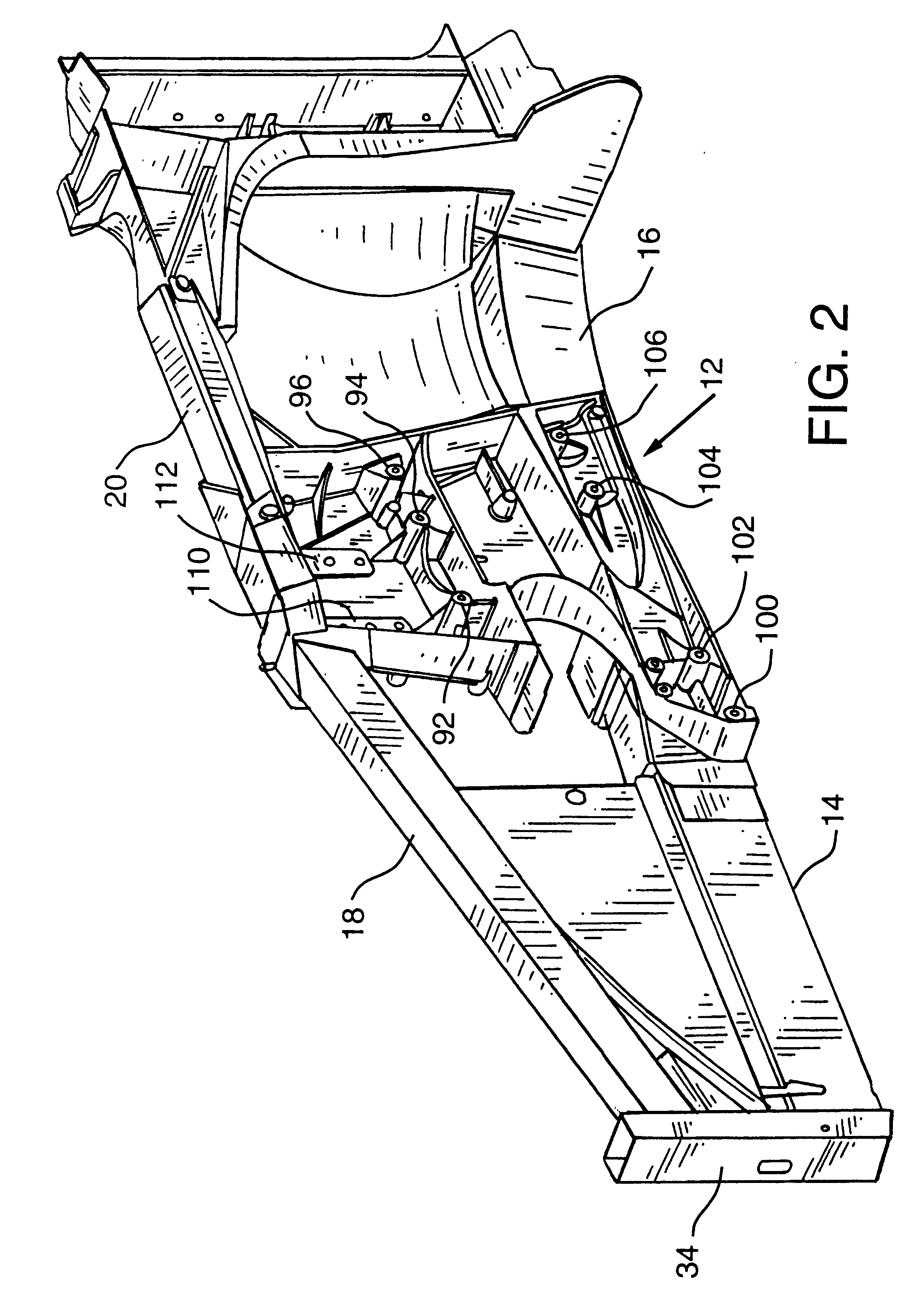
InactiveUS6193273B1Reduce frame assembly time of frameEasy to useVehicle body-frame connectionsUnderstructuresMobile vehicleVehicle frame
An automotive vehicle frame has a front frame portion, a rear frame portion and an intermediate frame portion connecting the front frame portion and the rear frame portion. The front frame portion has a pair of relatively spaced front strut towers and the rear frame portion has a pair of relatively spaced rear strut towers. Each of the front strut towers and each of the rear strut towers may have a plurality of frame components connected thereto. Portions of the vehicle suspension system may be secured to the front strut towers and the rear strut towers. The strut towers may have vehicle shock absorbers secured thereto. Numerous other vehicle components may be secured to the strut towers. The strut towers are unitary metal castings.
Owner:ARCONIC INC
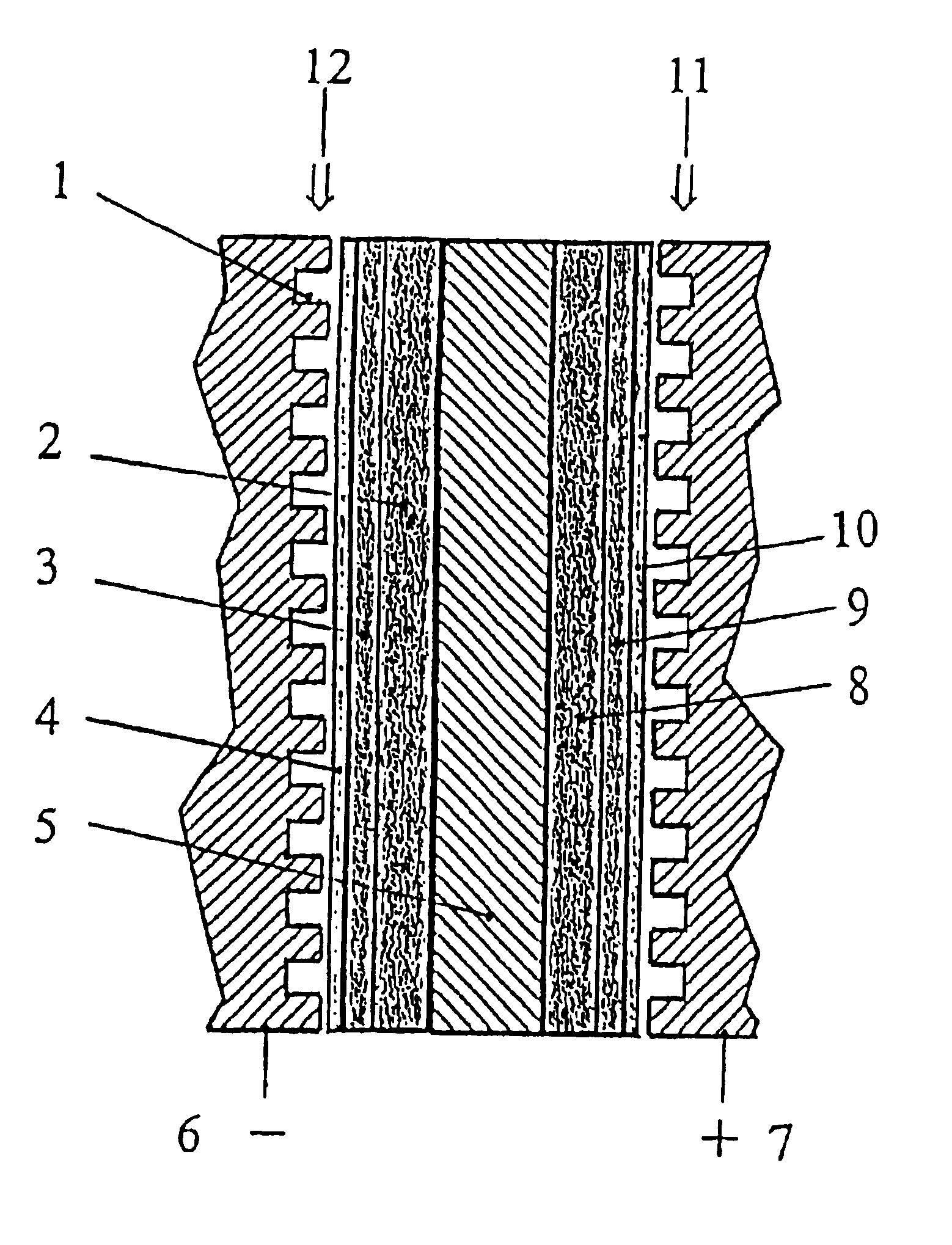
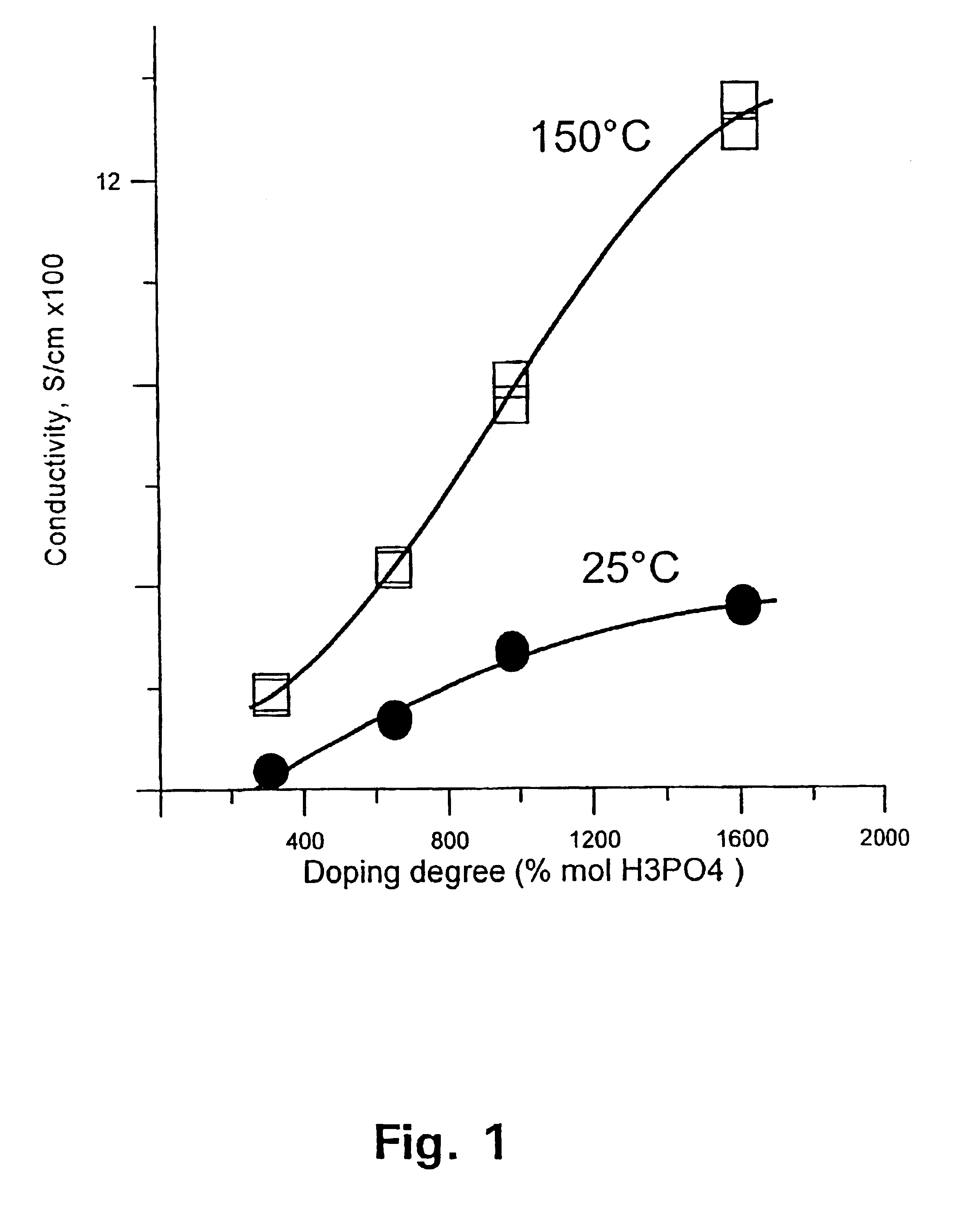
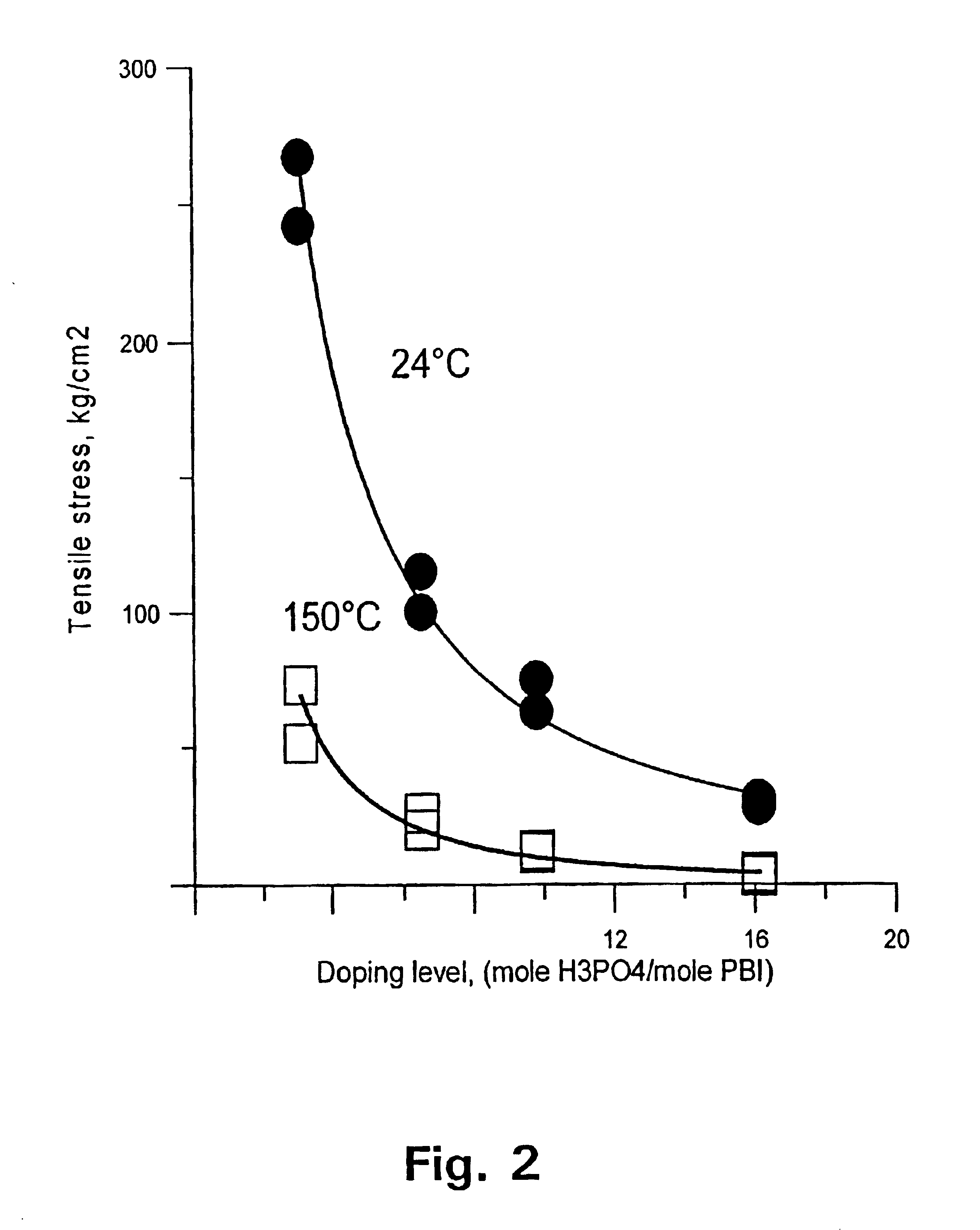
Polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells
InactiveUS6946211B1Improve performanceImprove toleranceSolid electrolytesPrimary cellsThermoplasticGas diffusion electrode
A method for preparing polybenzimidazole or polybenzimidazole blend membranes and fabricating gas diffusion electrodes and membrane-electrode assemblies is provided for a high temperature polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell. Blend polymer electrolyte membranes based on PBI and various thermoplastc polymers for high temperature polymer electrolyte fuel cells have also been developed. Miscible blends are used for solution casting of polymer membranes (solid electrolytes). High conductivity and enhanced mechanical strength were obtained for the blend polymer solid electrolytes. With the thermally resistant polymer, e.g., polybenzimidazole or a mixture of polybenzimidazole and other thermoplastics as binder, the carbon-supported noble metal catalyst is tape-cast onto a hydrophobic supporting substrate. When doped with an acid mixture, electrodes are assembled with an acid doped solid electrolyte membrane by hot-press. The fuel cell can operate at temperatures up to at least 200° C. with hydrogen-rich fuel containing high ratios of carbon monoxide such as 3 vol % carbon monoxide or more, compared to the carbon monoxide tolerance of 10-20 ppm level for Nafion®-based polymer electrolyte fuel cells.
Owner:DANISH POWER SYST
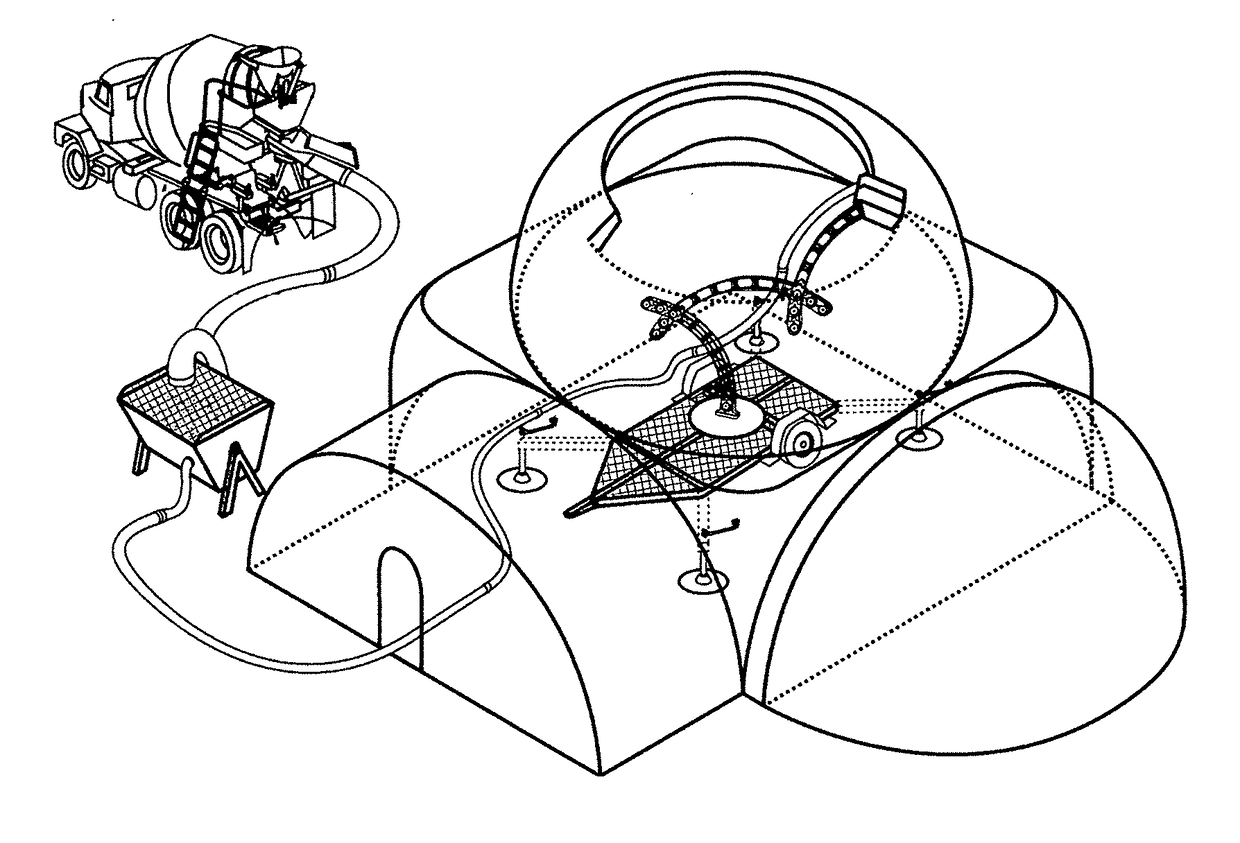
Method of reinforced cementitious constrauction by high speed extrusion printing and apparatus for using same
ActiveUS20180071949A1Low costAdditive manufacturing apparatusConstruction materialReinforced concreteBrick
The present invention relates to methods and apparatuses for an automated reinforced concrete construction system for onsite slip-form molding and casting a variety of cementitious mixes in a cast in place leave in place externally moldable flexible reinforced containment sleeve providing a wide variety of interchangeable full-scale molding configurations simultaneously optimizing a wide variety of cementitious mix curing characteristics, further having optional internal reinforcement net(s), for layer wise interlocking additive printed brick deposition providing improved slip-form mold casting of a wide variety of reinforced concrete structures; the present invention further includes a variety of operating platforms suitable for on and offsite construction as disclosed herein.
Owner:ARMATRON SYST LLC
Cellulose acylate film and method for producing same
InactiveUS20050150426A1Change unevennessVisibility changeNatural resin coatingsPolarising elementsCelluloseVisibility
Disclosed is a cellulose acylate film produced according to a melt casting process and having an Re unevenness of from 0 to 10%. When built in a liquid-crystal display device, the film significantly solves the problem of display unevenness and humidity-dependent visibility change.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
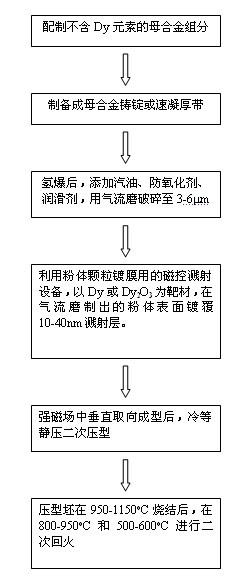
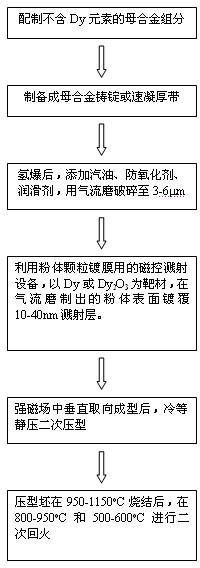
A preparation method of high-performance sintered NdFeB with low dysprosium content
The invention discloses a method for preparing sintered NdFeB with low dysprosium (Dy) content and high performance; the method comprises the following steps of: sputtering and plating the Dy element on the surface of jet mill powder by using the powder plate technology based on magnetron sputtering on the basis of preparing NdFeB powder, and then sufficiently dispersing the Dy element to micron-sized NdFeB crystal particles by dispersing the Dy element at high temperature in the sintering and tempering process, thereby achieving the effect of improving magnetic performance of the sintered NdFeB. Compared with the introduction of the Dy element in the proportioning process of the prior art, the method disclosed by the invention has the advantages: the low dysprosium content and high performance is limited in the nano-size by adopting the physical gas-phase deposition, the consumption quantity of the Dy element during the production process is controlled effectively and the preparationof sintered NdFeB with low dysprosium content and high performance is realized. Compared with the sintered NdFeB of the same components prepared by the traditional casting and powder metallurgy process, both the intrinsic coercivity and the maximum magnetic energy product of the sintered NdFeB rare-earth permanent magnetic material obtained according to the invention are improved obviously; compared with the sintered NdFeB with the same performance prepared by the traditional casting and powder metallurgy process, the dosage of the dysprosium element is reduced remarkably. The method can be widely applicable to producing and manufacturing sintered NdFeB with high performance.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Uniform films for rapid dissolve dosage form incorporating taste-masking compositions
ActiveUS20080044454A1Evenly distributedMinimize incorporationPowder deliveryInorganic non-active ingredientsControl releaseOral medication
The present invention relates to rapid dissolve thin film drug delivery compositions for the oral administration of active components. The active components are provided as taste-masked or controlled-release coated particles uniformly distributed throughout the film composition. The compositions may be formed by wet casting methods, where the film is cast and controllably dried, or alternatively by an extrusion method.
Owner:AQUESTIVE THERAPEUTICS INC
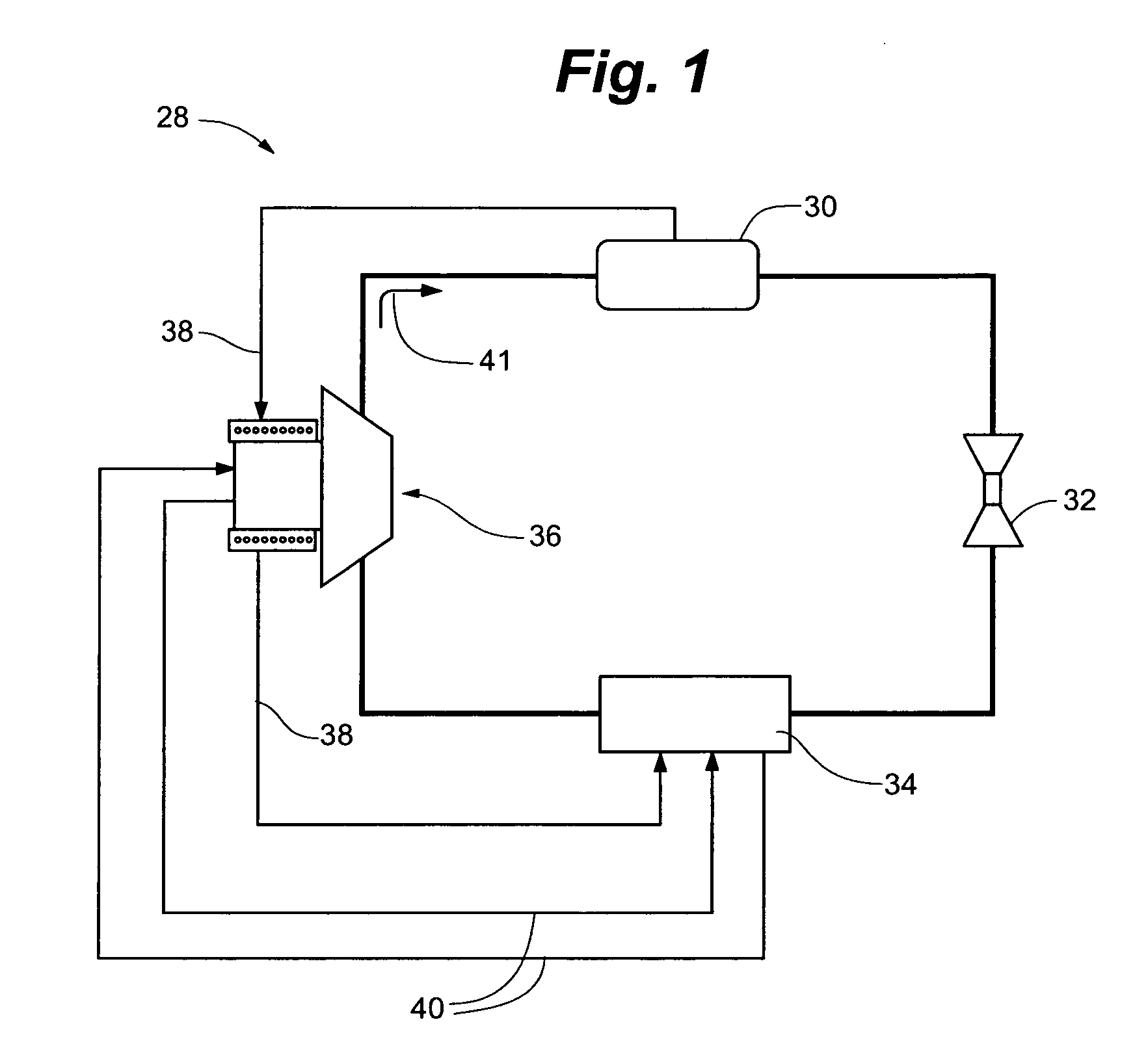
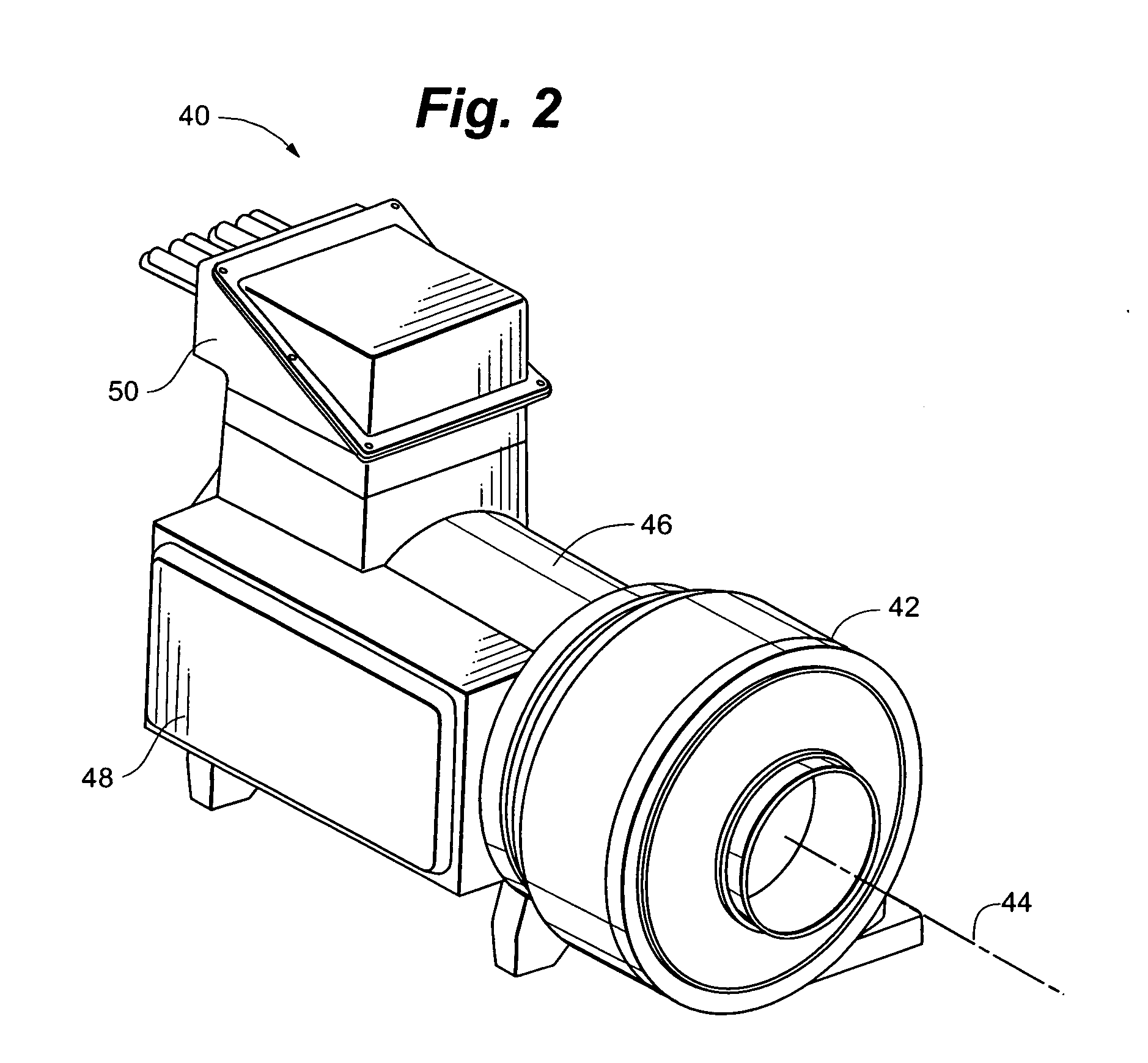
High capacity chiller compressor
ActiveUS20080115527A1Improve efficiencyIncrease power outputWind motor controlEfficient regulation technologiesMagnetic bearingEngineering
A high efficiency, low maintenance single stage or multi-stage centrifugal compressor assembly for large cooling installations. The assembly is highly efficient by virtue of a variable frequency drive (VFD) that drives a permanent magnet motor and matches compressor speed with compressor load, a direct drive impeller that eliminates gearing losses, and magnetic bearings that reduce frictional losses. The back-emf produced by the motor provides an intermediate power source for the magnetic bearings in the event of a loss of electrical power. A cooling system provides direct cooling of the rotor with gas refrigerant, and cooling of the stator with liquid refrigerant. Modular construction allows the compressor to be retrofit with upgrades. An inlet guide vane system operates without need for oil lubrication. The use of light metal castings and elimination of gearing reduces the weight to one-third or less of comparably powered conventional units.
Owner:DAIKIN IND LTD
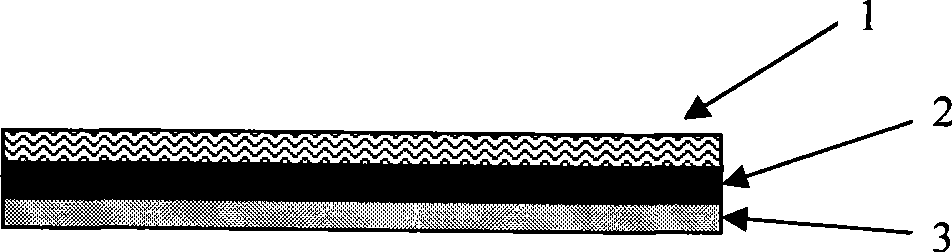
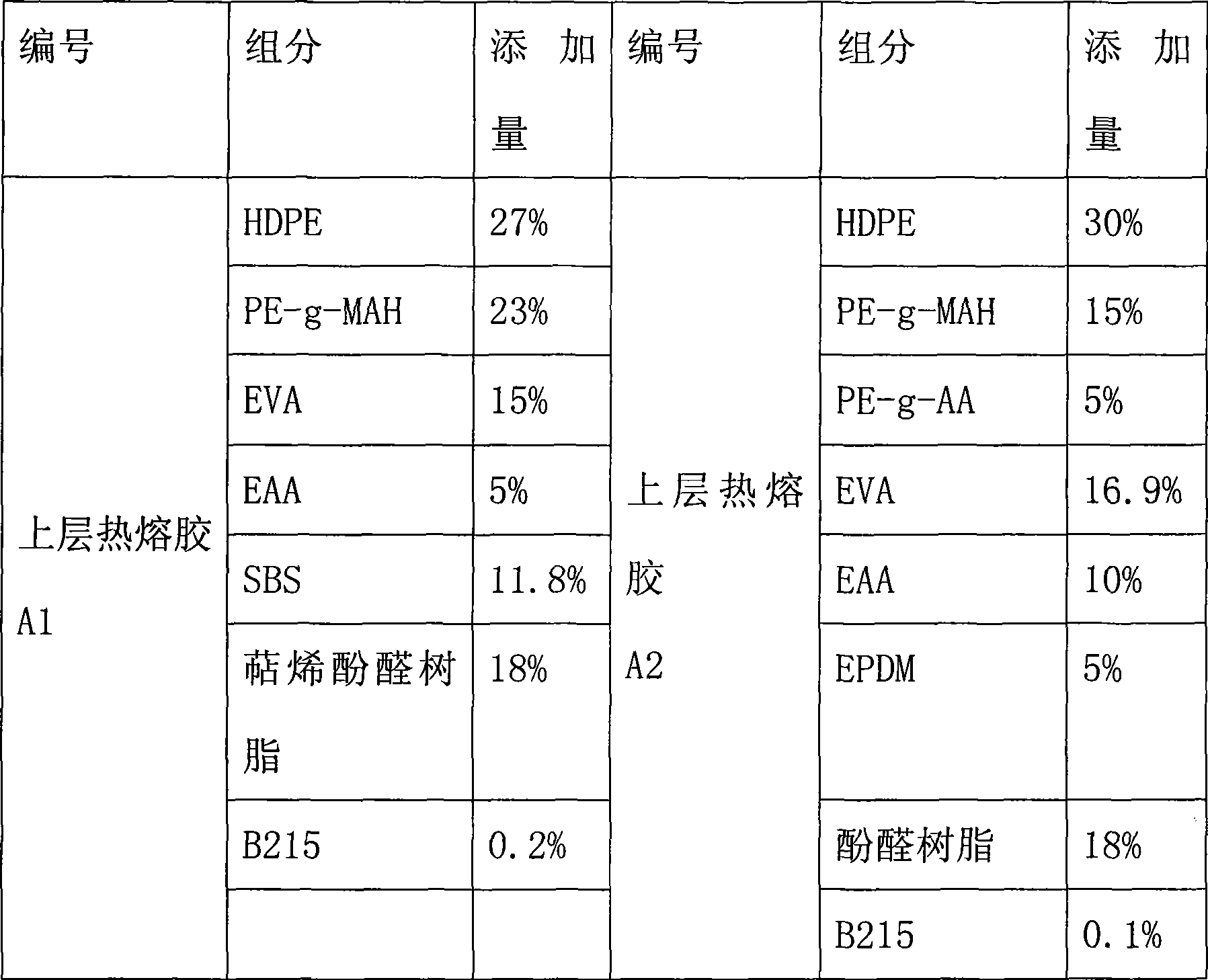
Double-layer composite hot melt adhesive film for bonding metal and plastic
The invention discloses a double-layer composite hot melt adhesive film adhering metal and plastic, which is formed by compounding an upper adhesive film layer and a lower adhesive film layer, wherein the lower adhesive film layer is attached to a piece of release paper, the thickness of the composite adhesive film is 0.05 to 0.20 millimeter, the upper adhesive film layer is a hot melt adhesive layer adhered with the metal, the thickness of the upper adhesive film layer is 30 to 60 percent of the thickness of the composite film, the lower adhesive film layer is a hot melt adhesive layer adhered with the plastic, the thickness of the lower adhesive film layer is 40 to 70 percent of the thickness of the composite film, and the lower adhesive film layer is attached to a piece of glassine release paper. The double-layer composite hot melt adhesive film directly compounds two modified hot melt adhesives with different adhesive properties, is adhered with the release paper to prevent rolling from adhering and the adhesive film from being damaged, reduces application of a middle isolating layer, reduces the thickness of the composite adhesive film, and is prepared by once casting through coextrusion casting equipment or twice casting through common coextrusion casting equipment. The double-layer composite hot melt adhesive film can be used for composite adhesion of metallic materials such as aluminum, stainless steel and the like and plastic such as ABS, PVC, PET and the like, is particularly suitable for mutual adhesion between sheets, plates and films of the metal and the plastic, and has simple and convenient operation and no pollution.
Owner:GUANGZHOU LUSHAN NEW MATERIALS
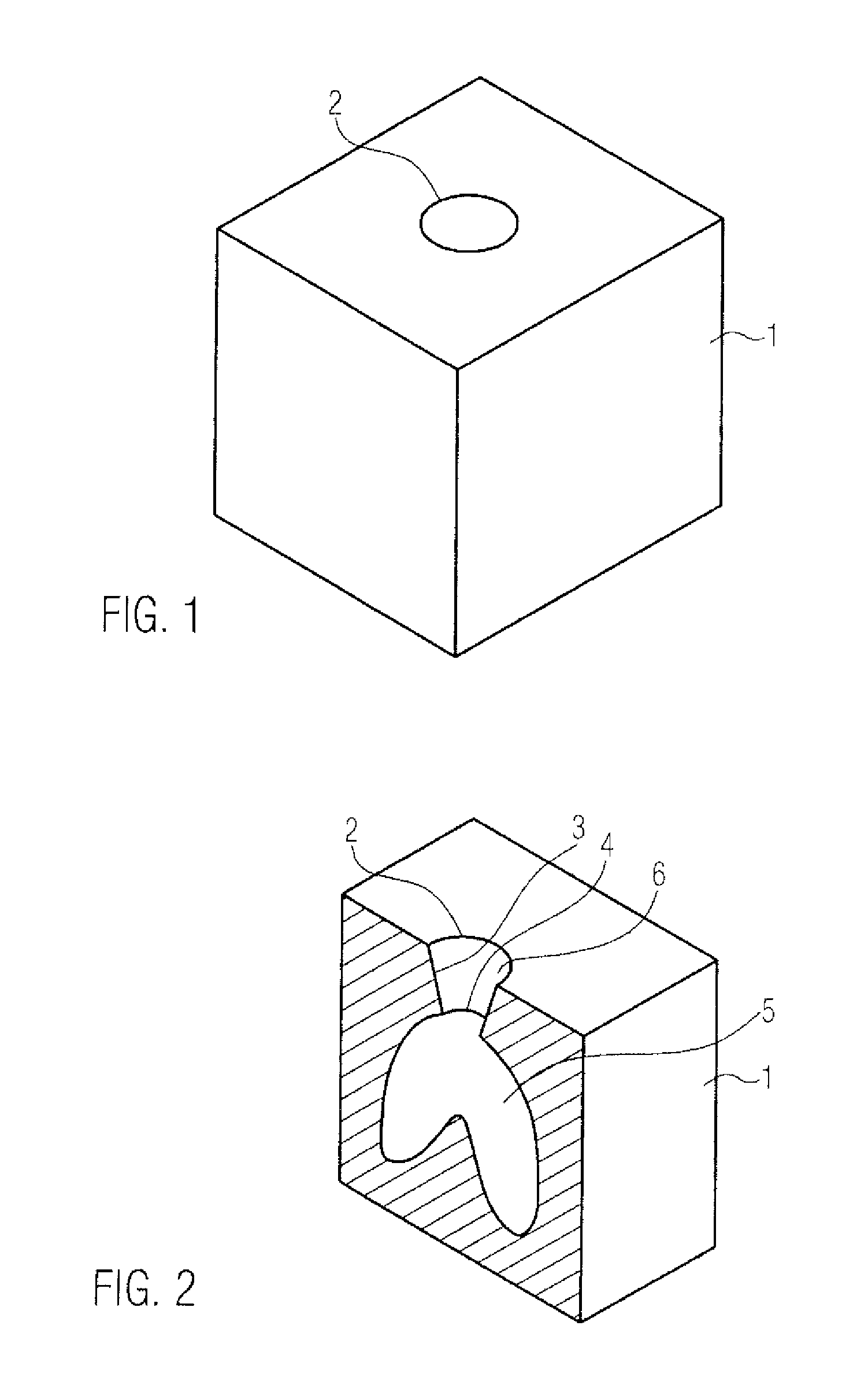
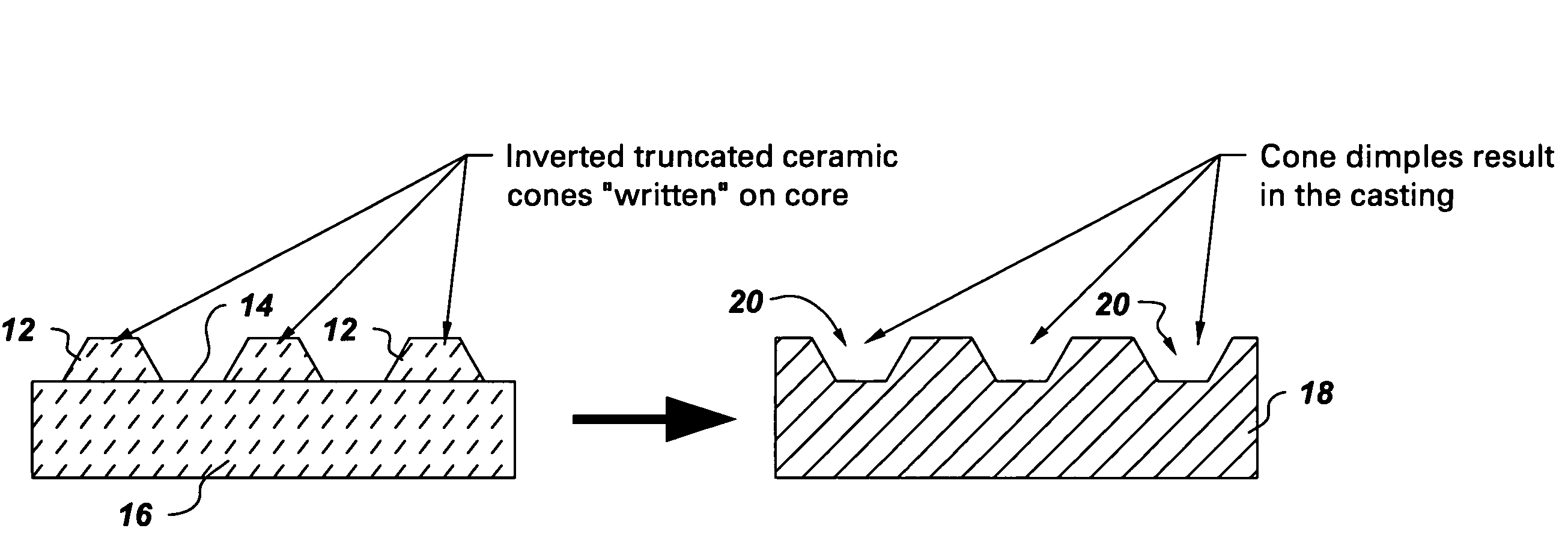
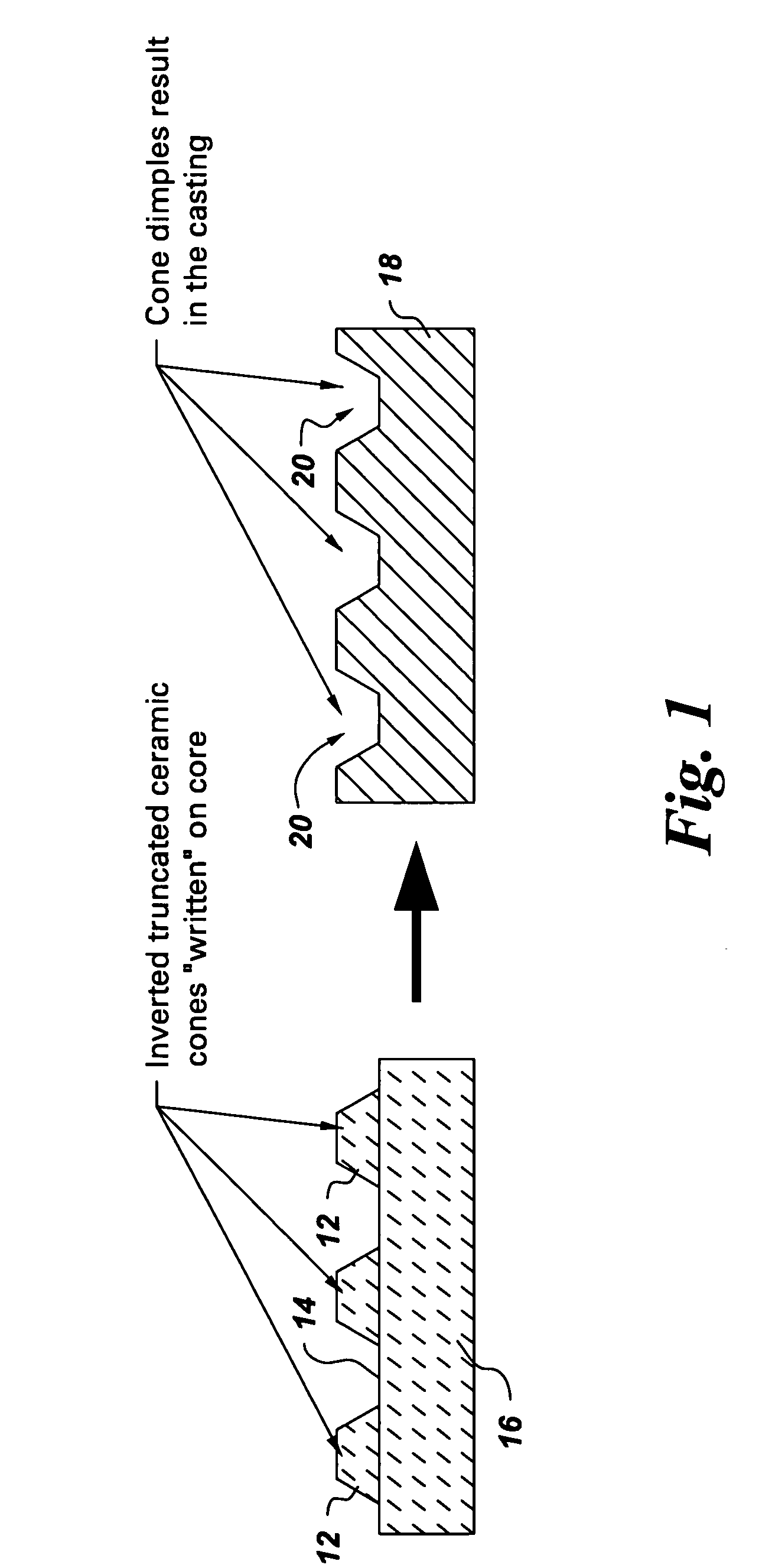
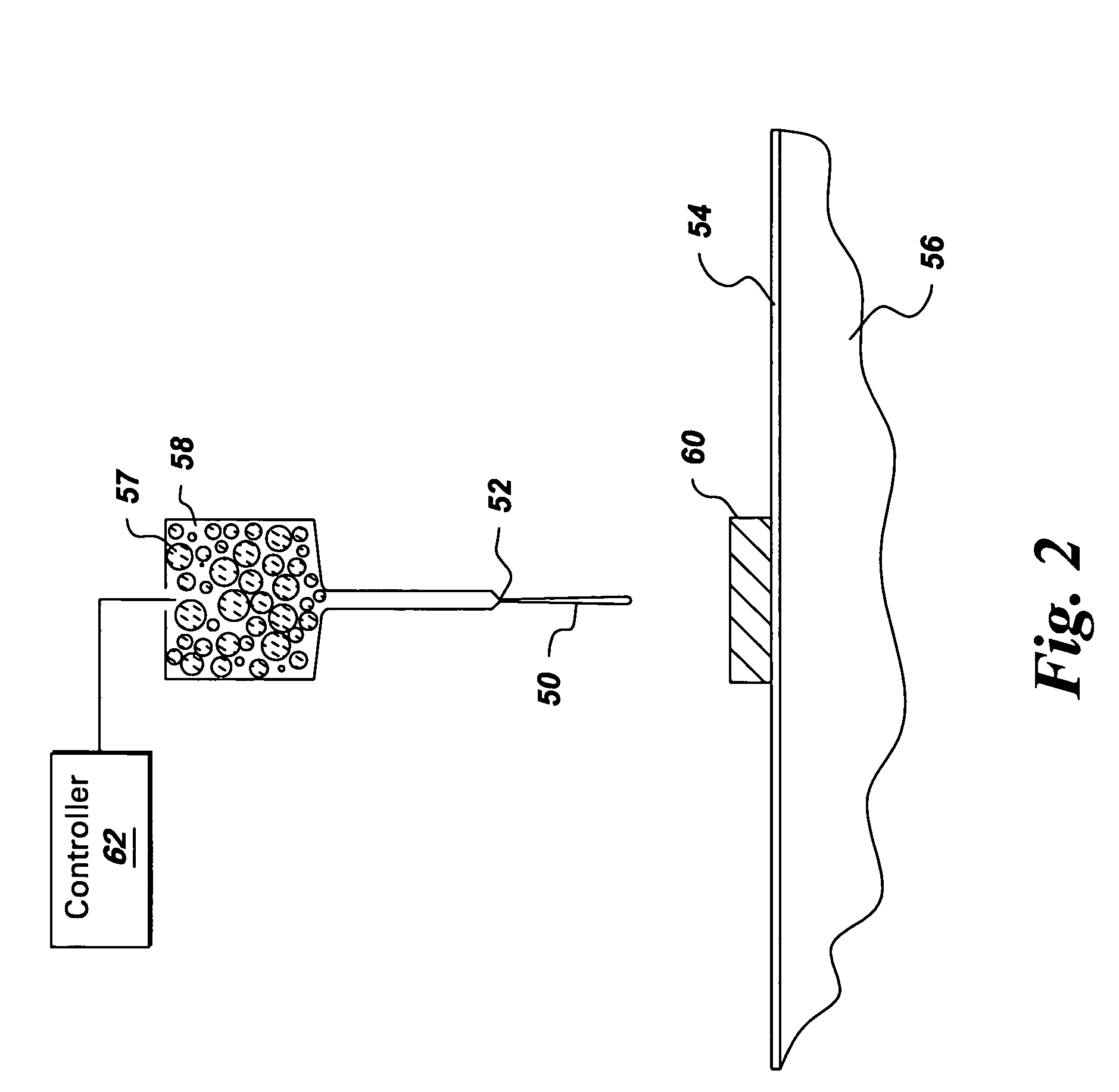
Method of forming concavities in the surface of a metal component, and related processes and articles
ActiveUS7302990B2Forming accuratelyAdditive manufacturing apparatusMolten spray coatingHeat treatedMetal
A method of forming at least one concavity of a selected size and shape within a surface of an internal passageway of a metallic component comprises: depositing a ceramic-based material by a direct-write technique onto a ceramic core which is suitable for forming the internal passageway during a casting process to form the metallic component, wherein the ceramic-based material is deposited as a positive feature; heat-treating the deposited ceramic-based material; forming the metallic component by a casting process in which the ceramic core is incorporated into the casting, in a position selected as a desired position for the internal passageway; and then removing the ceramic core from the metal component after the casting process is complete, thereby forming the internal passageway, with the concavity contained within the surface of the passageway, said concavity formed by removal of the positive feature of the ceramic-based material.
Owner:GE INFRASTRUCTURE TECH INT LLC
Castable aluminum alloy
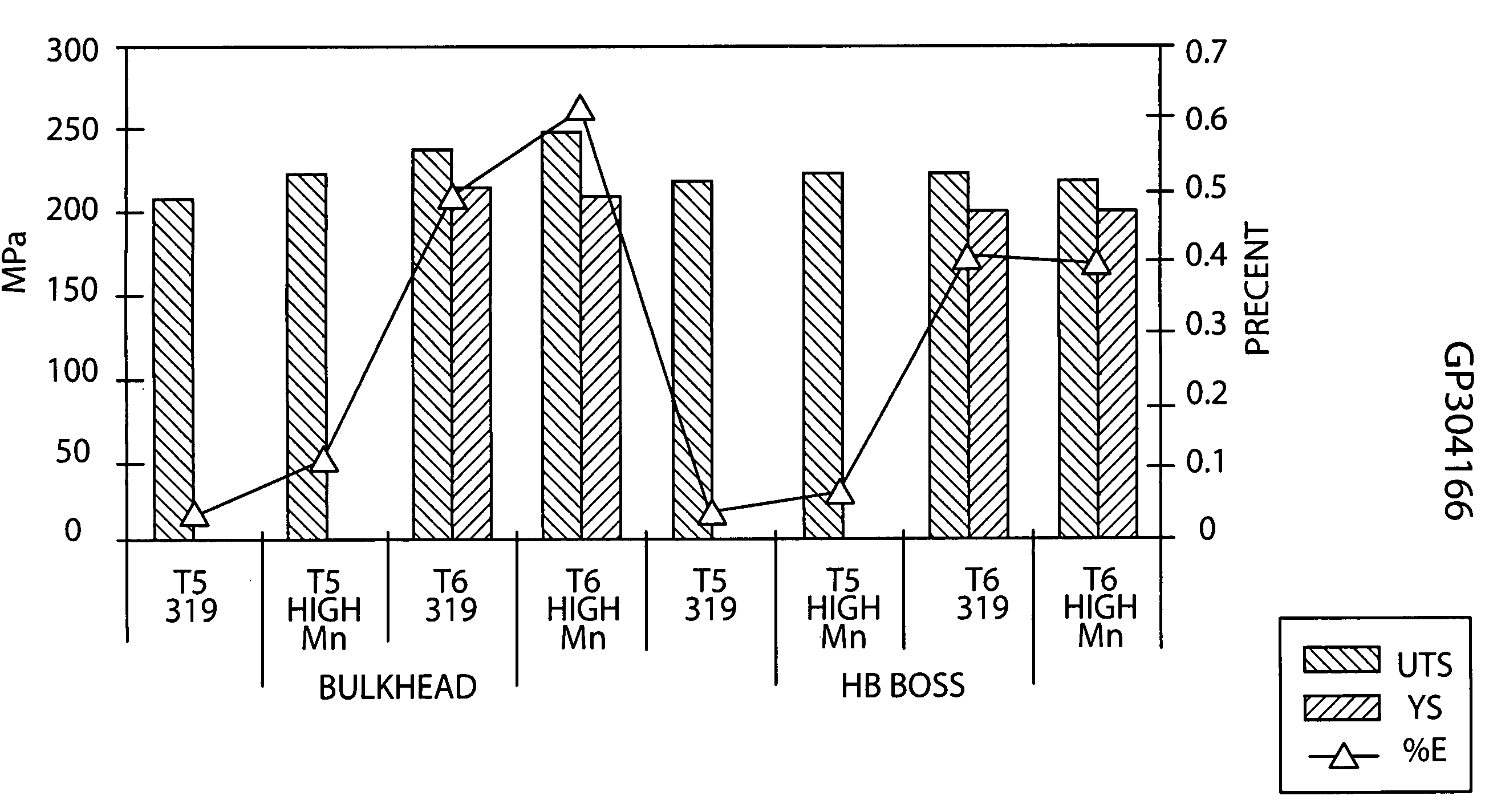
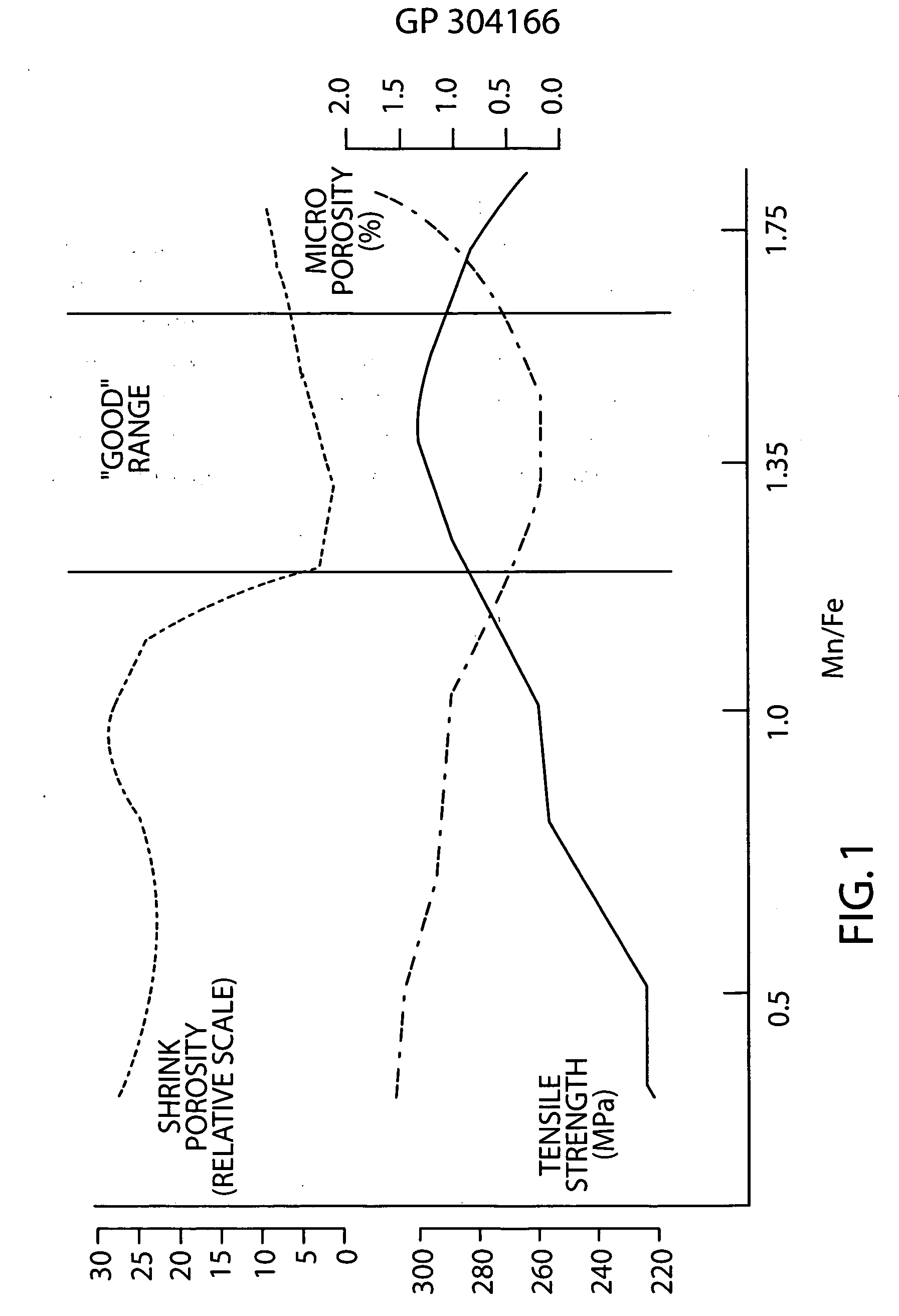
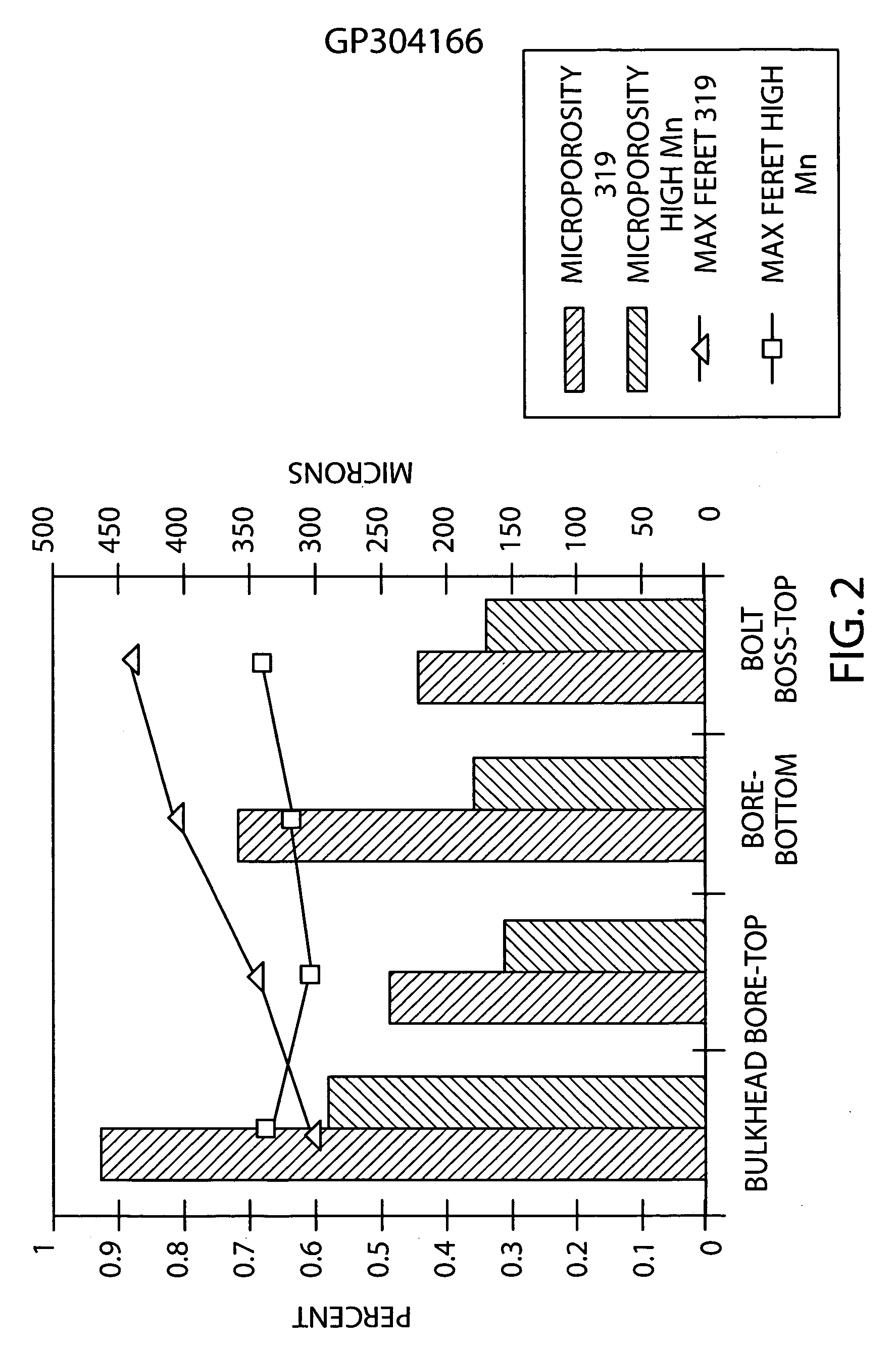
A castable aluminum alloy includes, in weight %, 0 to about 19% Si, 0 to about 5.0% Cu, 0 to about 1.5% Mg, up to about 3.0% Zn, up to about 2.0% Ni, up to about 0.3% Ti, greater than 0 to about 1.5 weight % Fe, about 0.2% to about 3.0% Mn, wherein a weight ratio of Mn / Fe is 0.6 or greater when Fe is less than 0.4 weight % and the weight ratio of Mn / Fe is 1.0 or greater when Fe is equal to or greater than 0.4 weight % to reduce porosity and increase tensile strength of a casting made from the alloy.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com