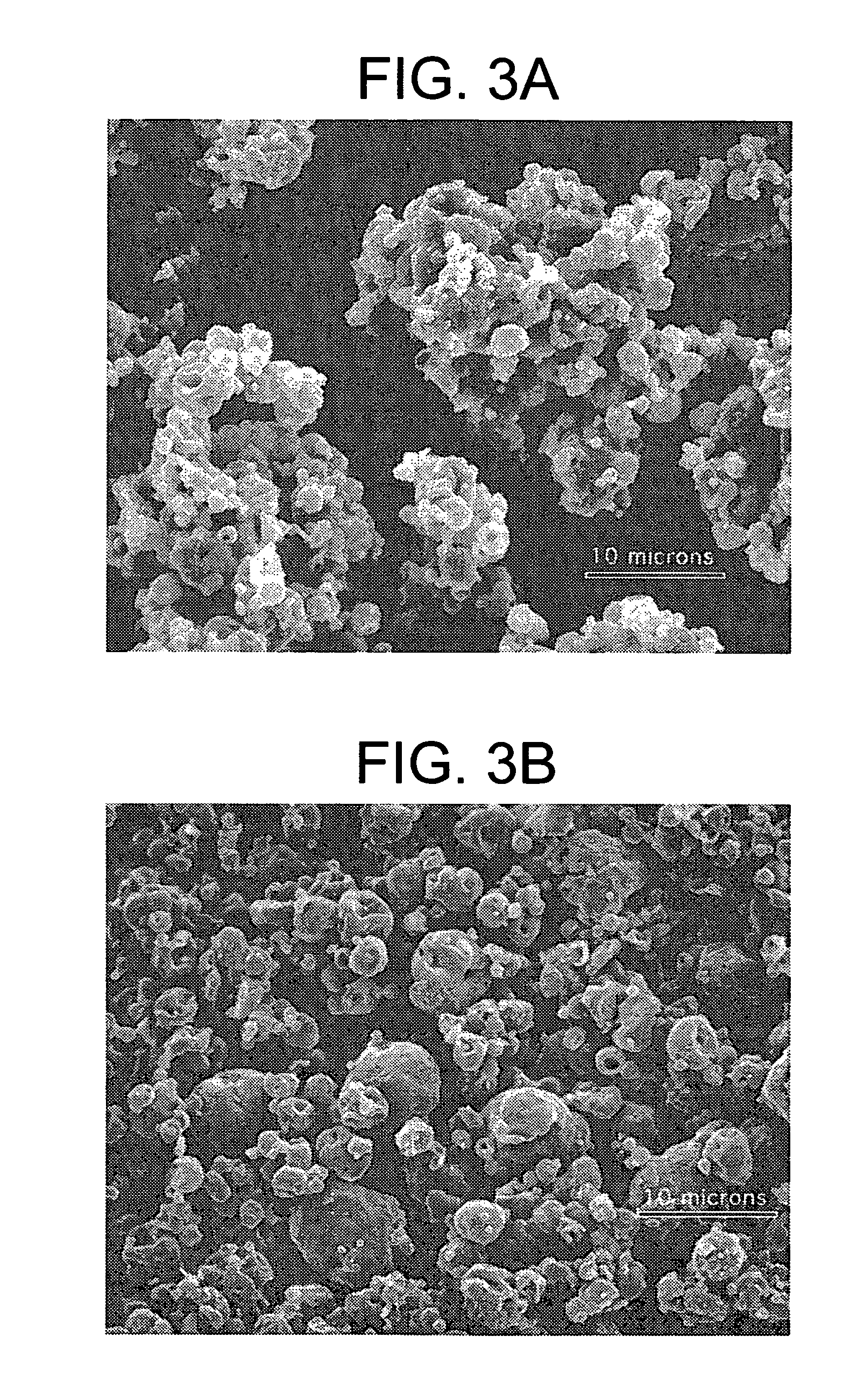
Patents
Literature
685 results about "Jet mill" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
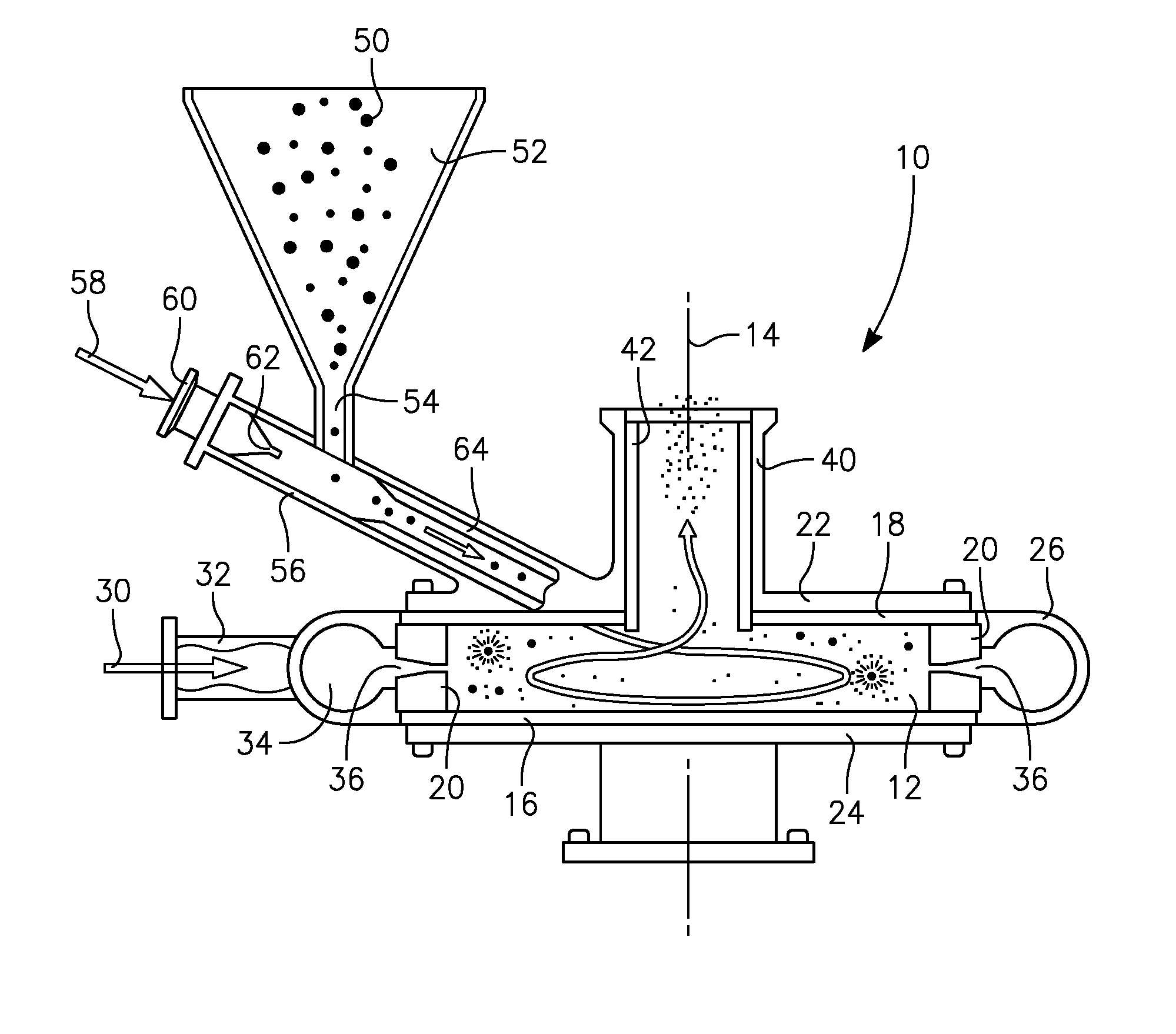
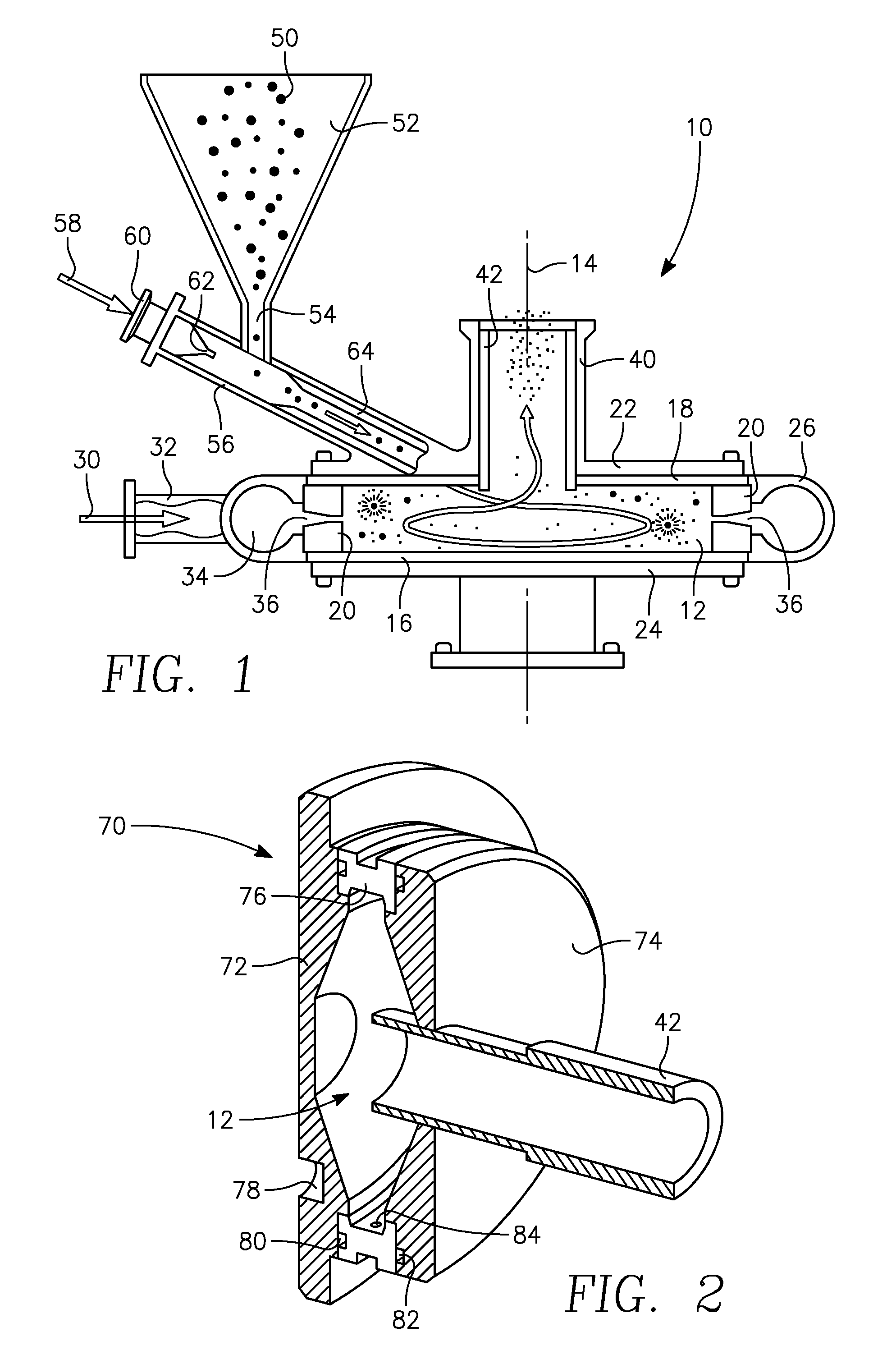
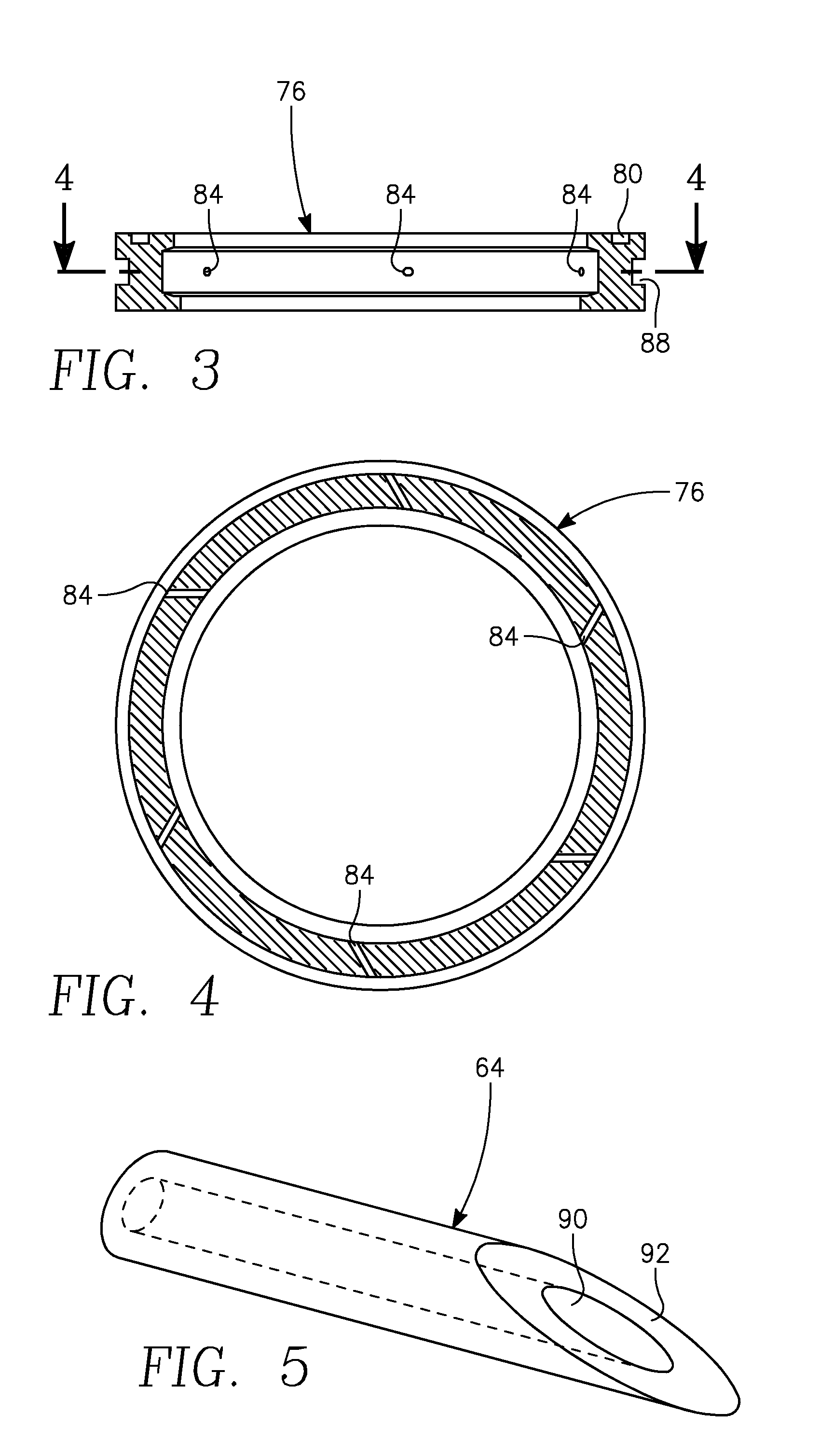
A jet mill grinds materials by using a high speed jet of compressed air or inert gas to impact particles into each other. Jet mills can be designed to output particles below a certain size, while continue milling particles above that size, resulting in a narrow size distribution of the resulting product. Particles leaving the mill can be separated from the gas stream by cyclonic separation.
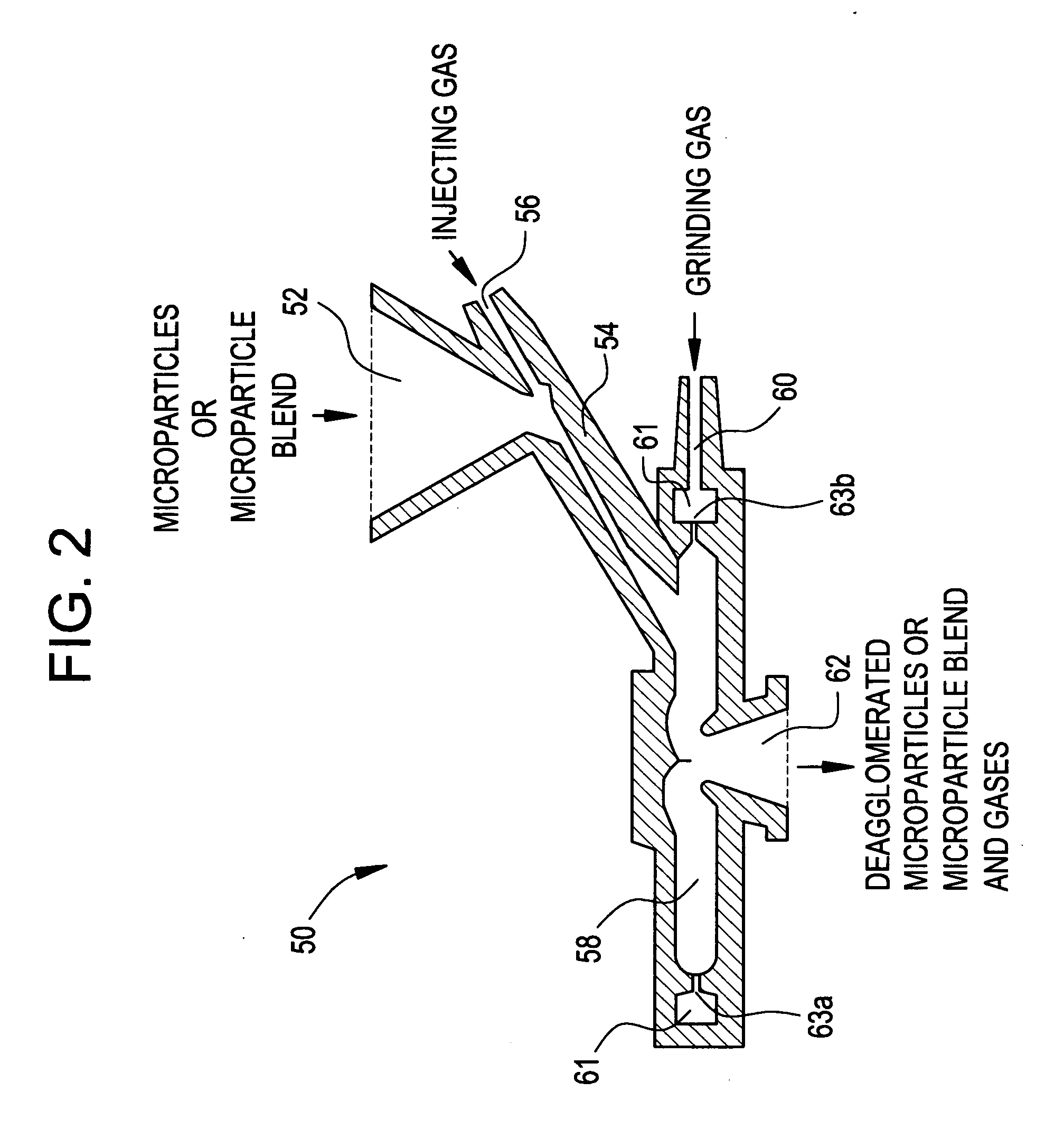
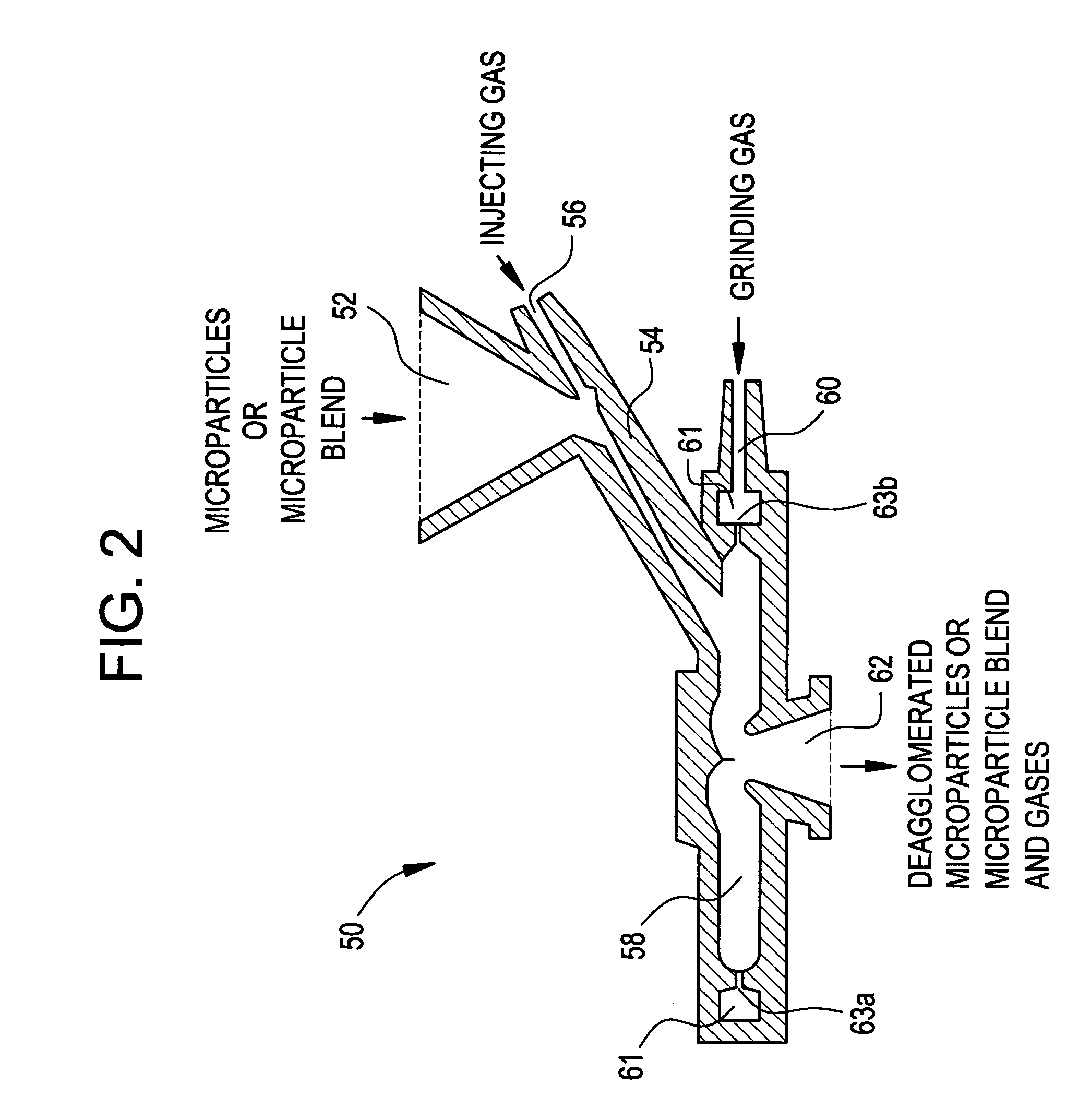
Methods for making pharmaceutical formulations comprising microparticles with improved dispersibility, suspendability or wettability
InactiveUS20050079138A1Good dispersibilityImproved suspendabilityPowder deliveryGranulation by liquid drop formationPowder mixtureMicroparticle
Methods are provided for making a dry powder blend pharmaceutical formulation, comprising the steps of: (a) providing microparticles which comprise a pharmaceutical agent; (b) blending the microparticles with at least one excipient in the form of particles to form a powder blend; and (c) jet milling the powder blend to form a dry powder blend pharmaceutical formulation having improved dispersibility, suspendability, or wettability as compared to the microparticles of step (a) or the powder blend of step (b). The method can further include dispersing the dry powder blend pharmaceutical formulation in a liquid pharmaceutically acceptable vehicle to make an formulation suitable for injection. Alternatively, the method can further include processing the dry powder blend pharmaceutical formulation into a solid oral dosage form. In one embodiment, the microparticles of step (a) are formed by a solvent precipitation or crystallization process.
Owner:ACUSPHERE INC
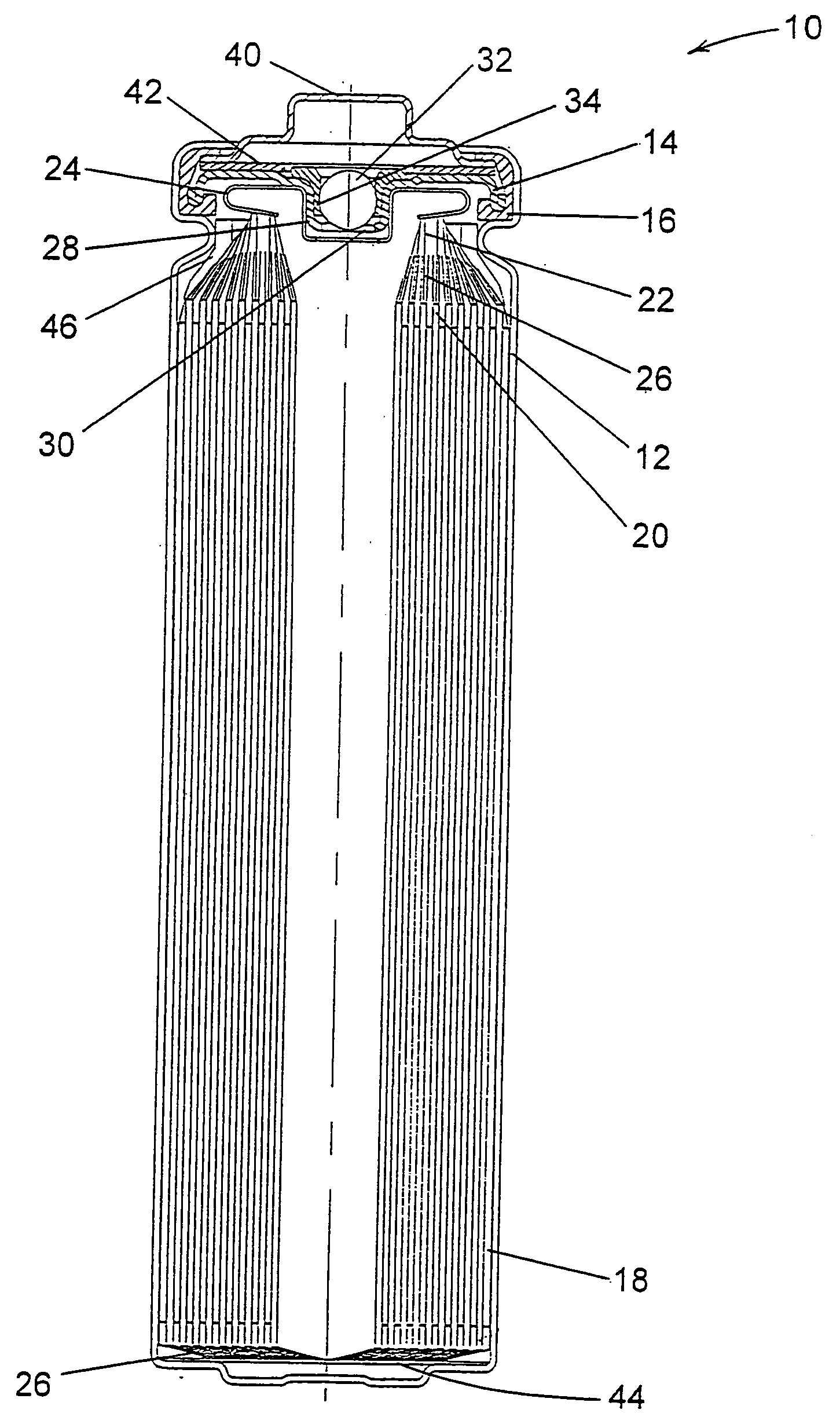
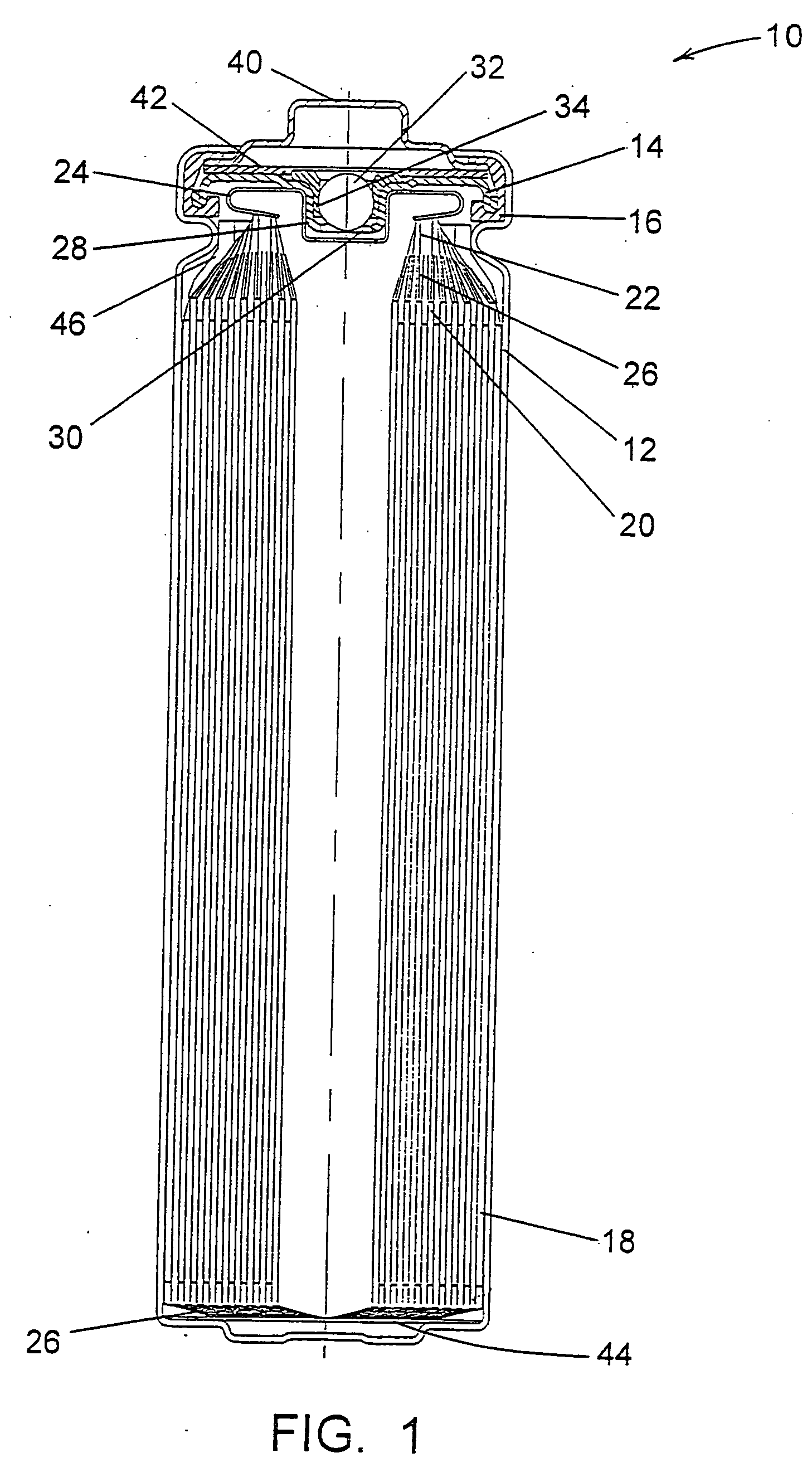
High discharge capacity lithium battery
InactiveUS20050233214A1Improve discharge performanceIncrease energy densityFinal product manufactureOrganic electrolyte cellsHigh rateIron disulfide
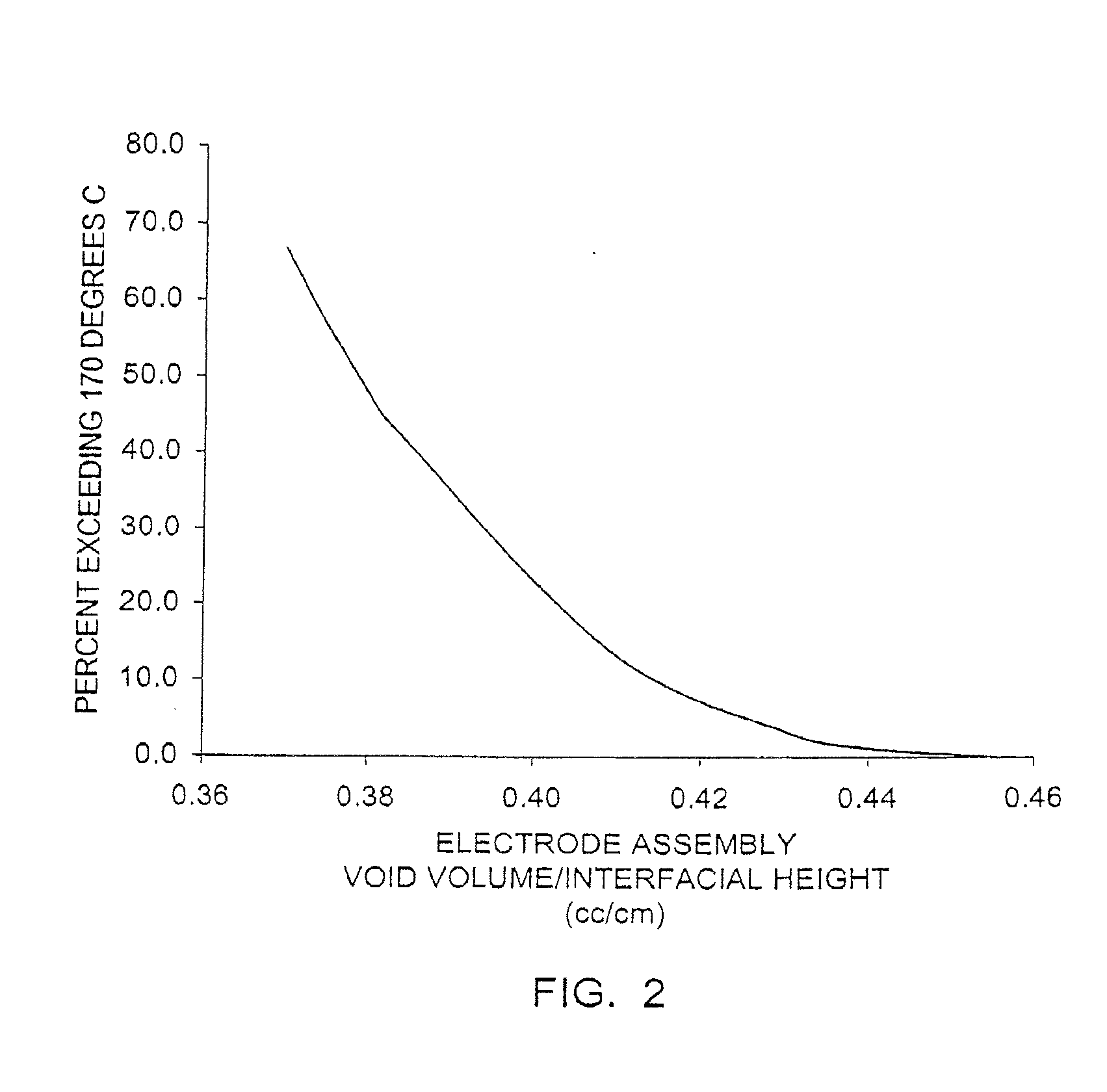
A lithium / iron disulfide electrochemical battery cell with a high discharge capacity. The cell has a lithium negative electrode, an iron disulfide positive electrode and a nonaqueous electrolyte. The iron disulfide of the positive electrode has a controlled average particle size range which allows the electrochemical cells to exhibit desired properties in both low and high rate applications. In various embodiments, the iron disulfide particles are wet milled, preferably utilizing a media mill or milled utilizing a non-mechanical mill such as a jet mill, which reduces the iron disulfide particles to a desired average particle size range for incorporation into the positive electrode.
Owner:EVEREADY BATTERY CO INC
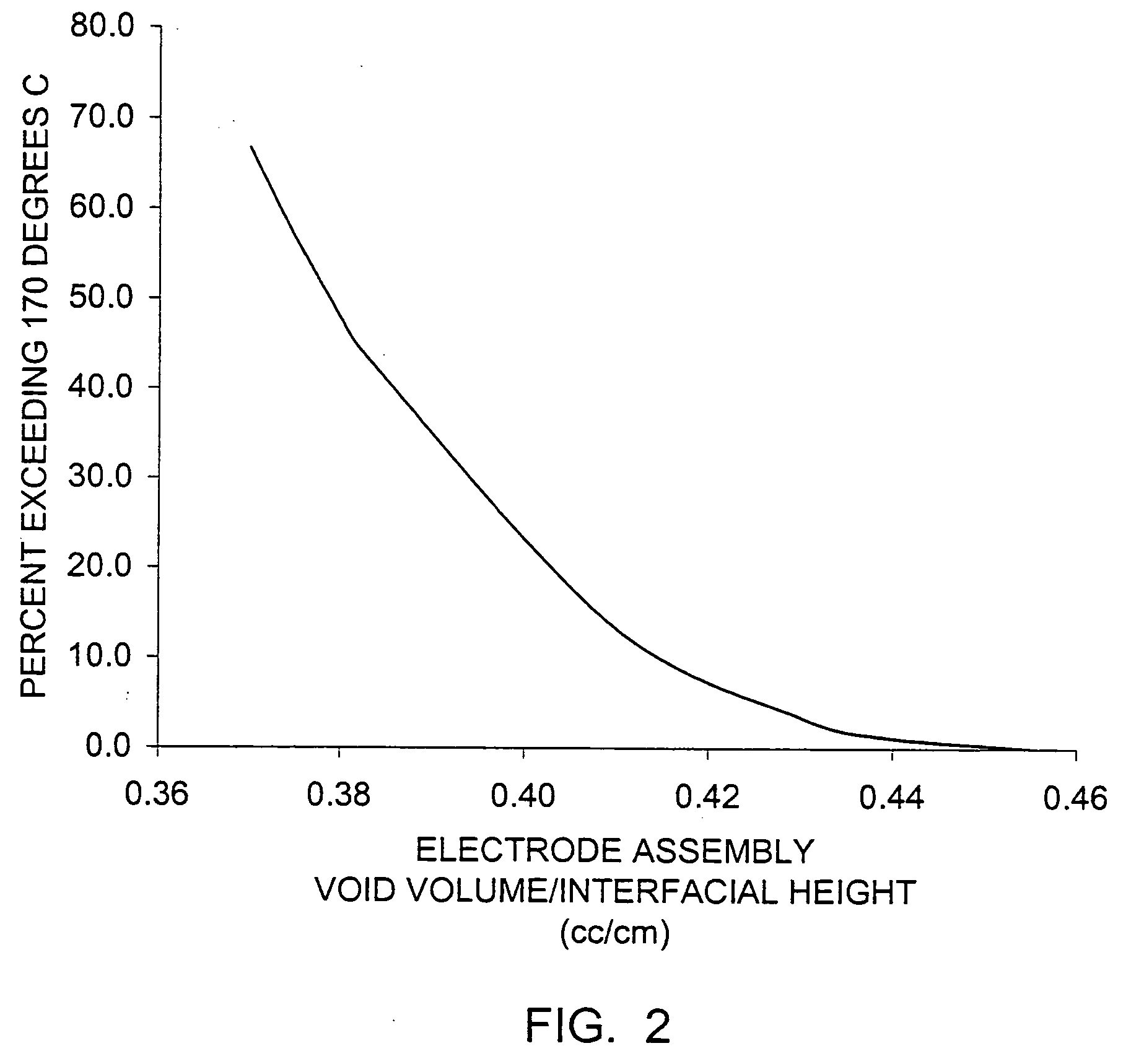
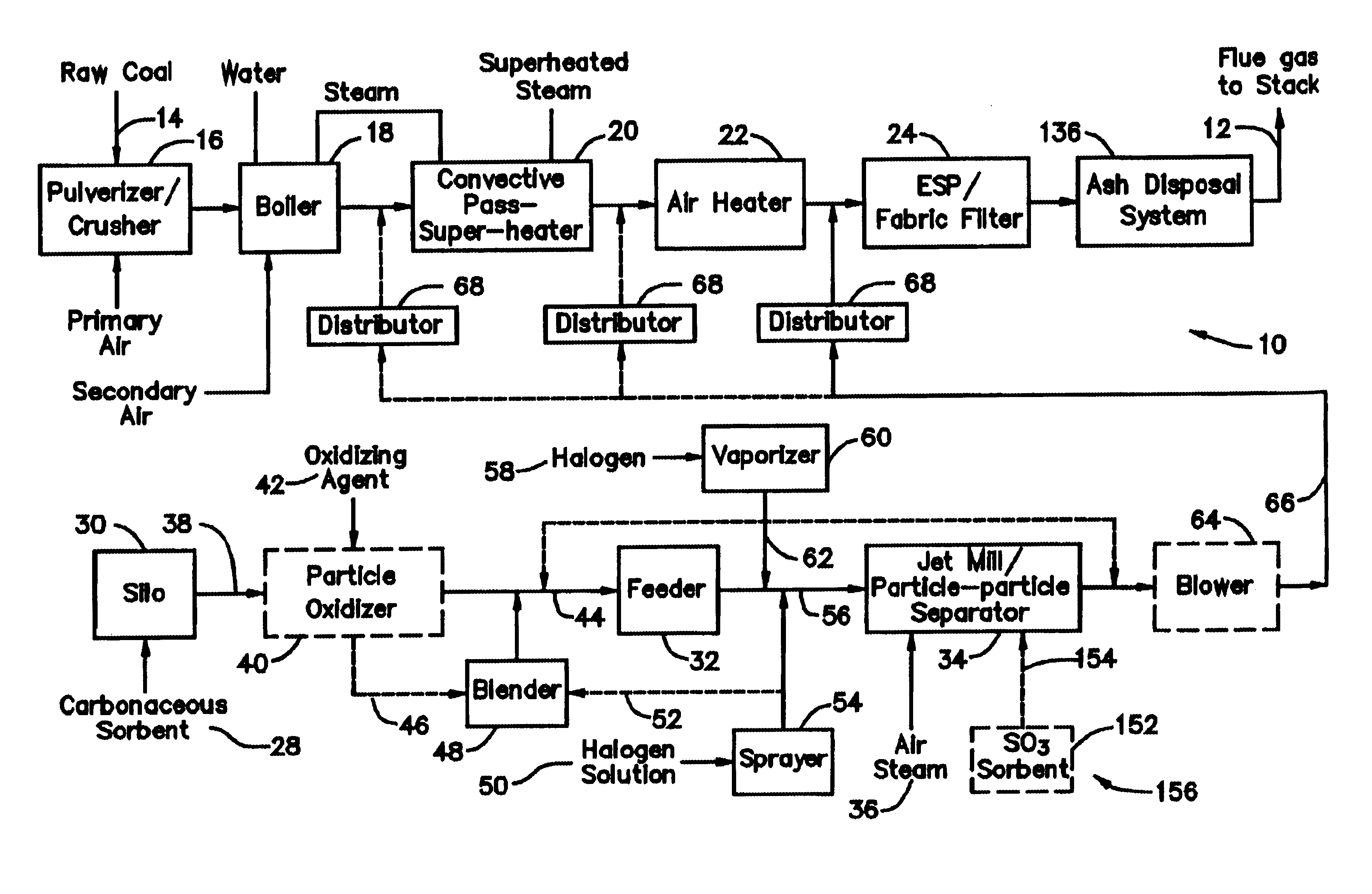
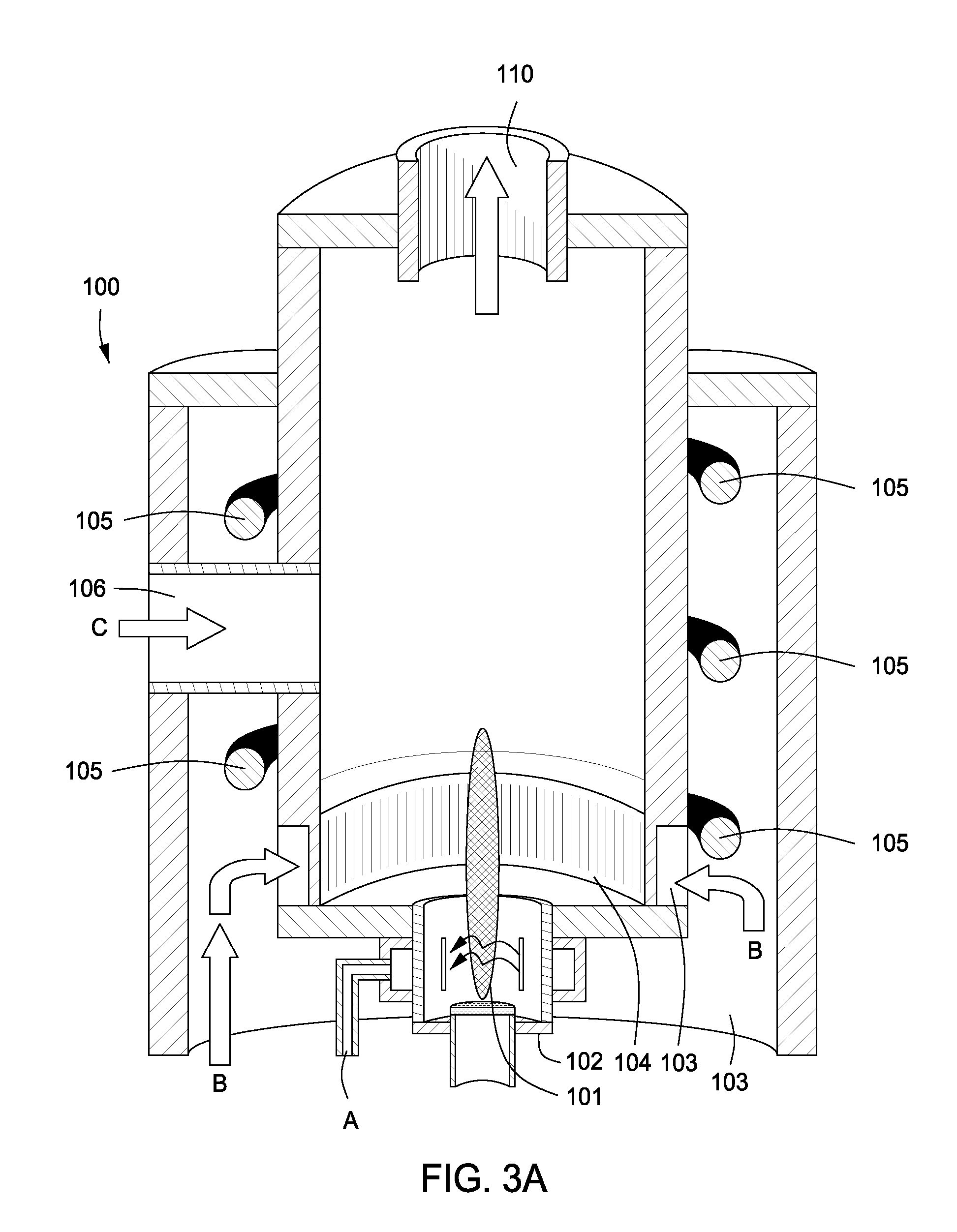
Control of mercury emissions from solid fuel combustion
InactiveUS6848374B2Remove pollutantsEasy to captureCombination devicesGas treatmentSorbentSolid fuel
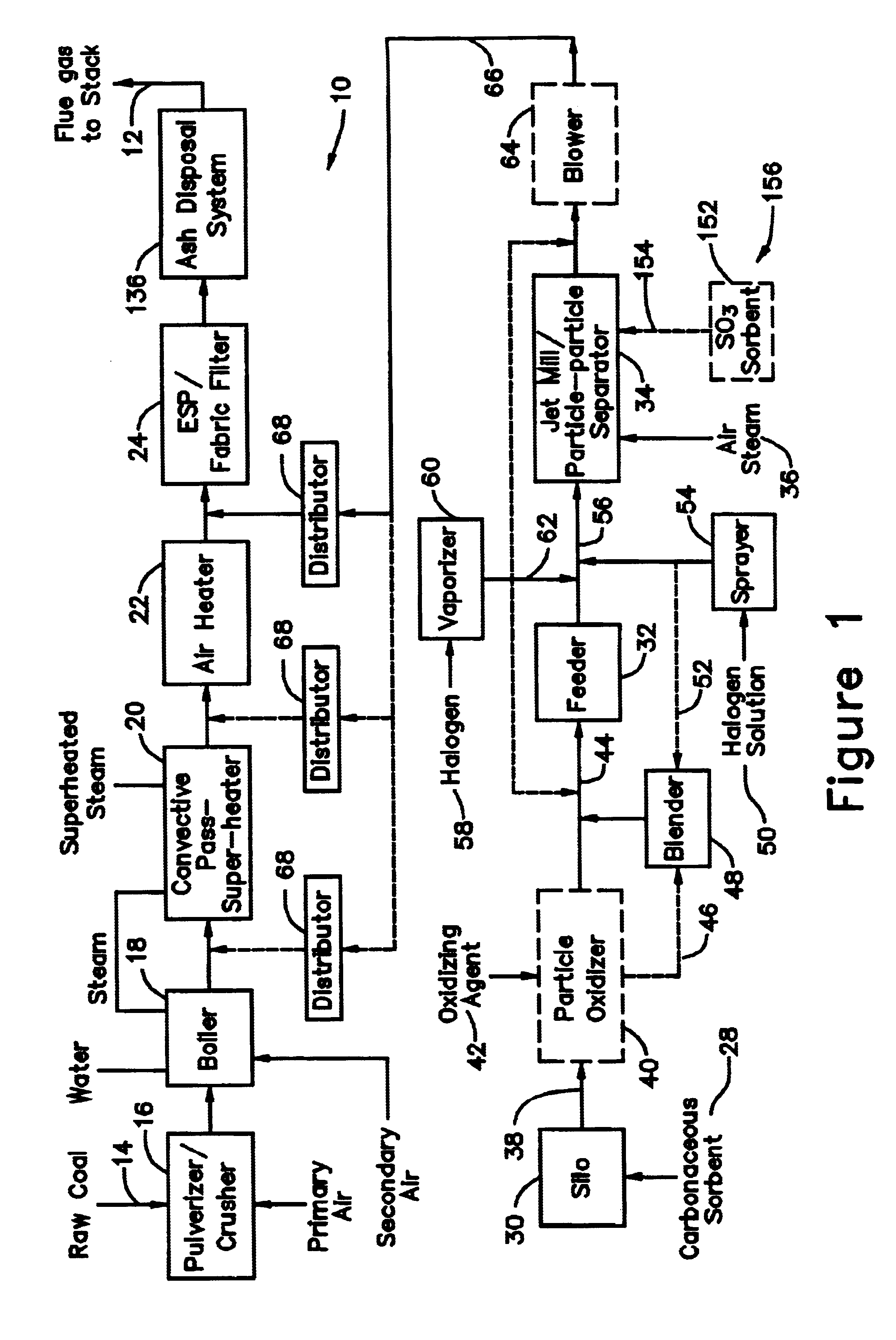
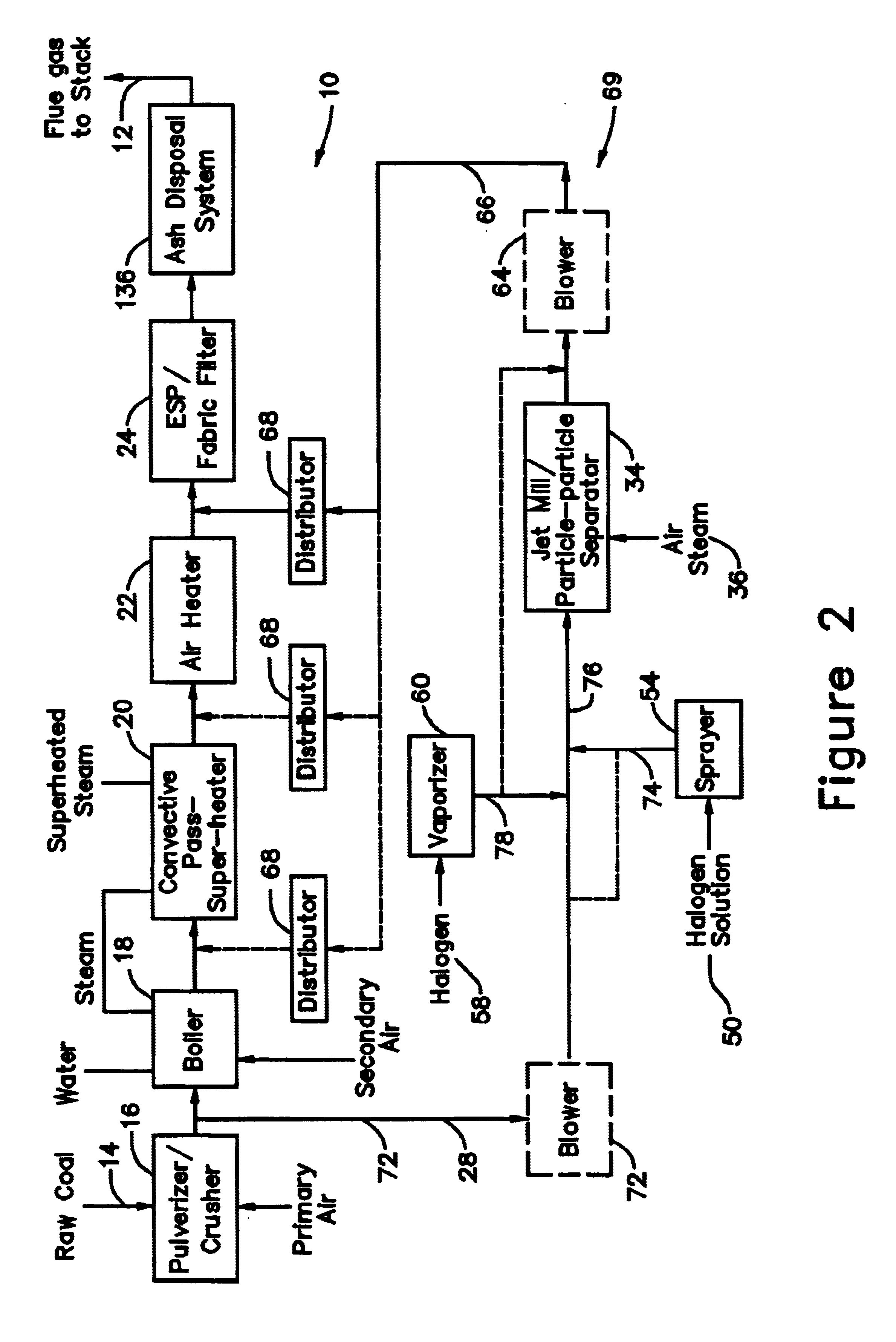
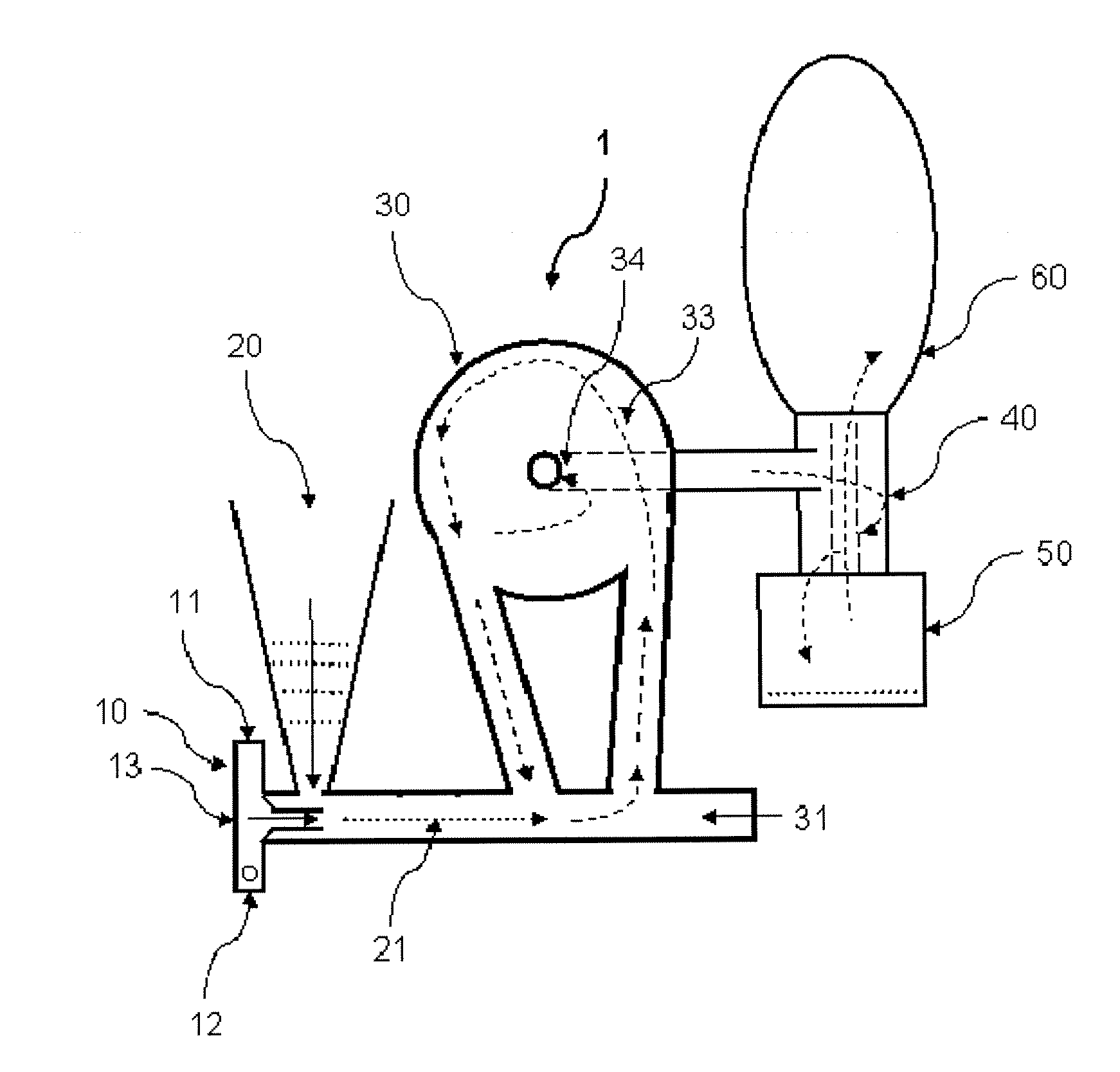
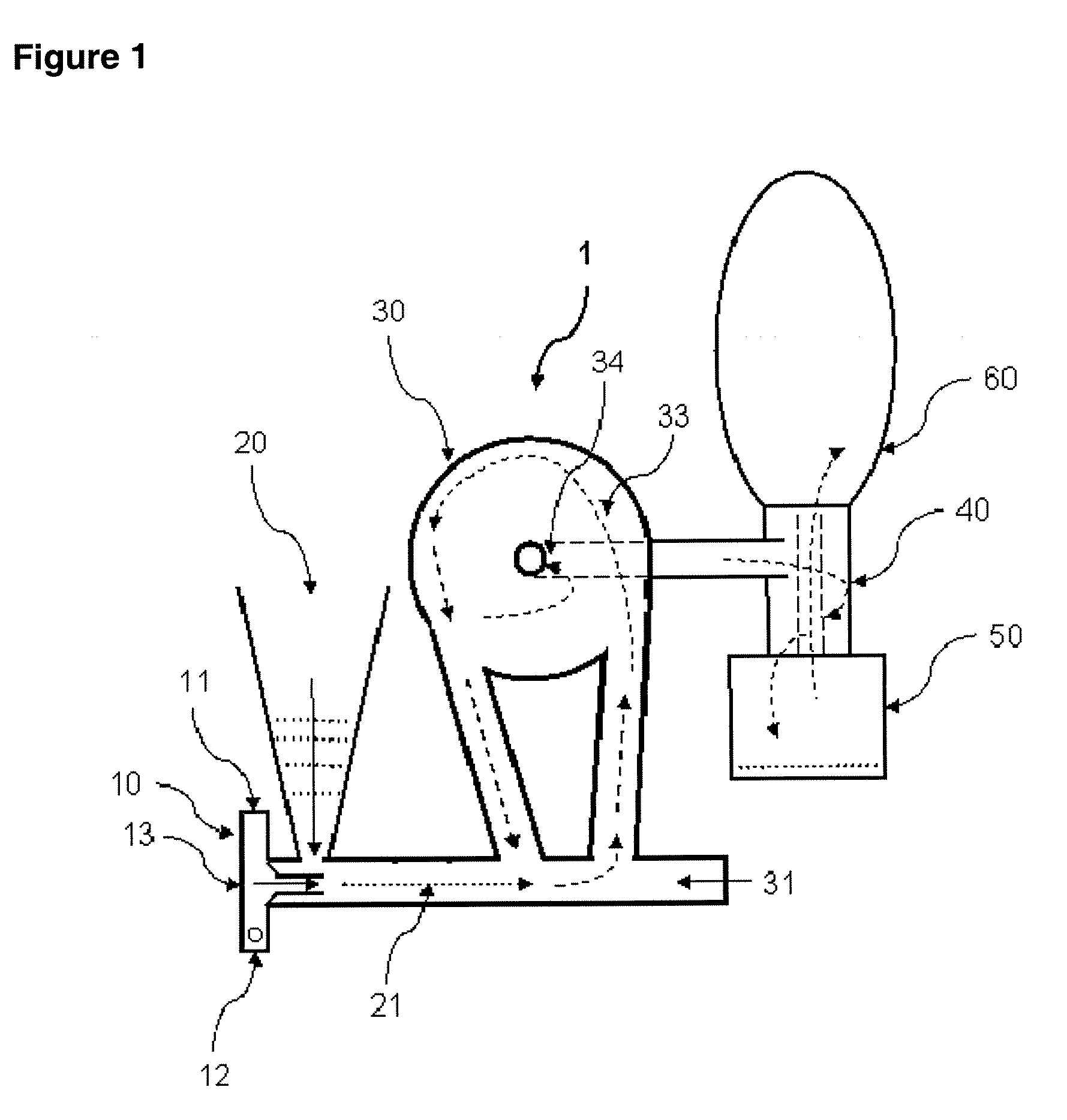
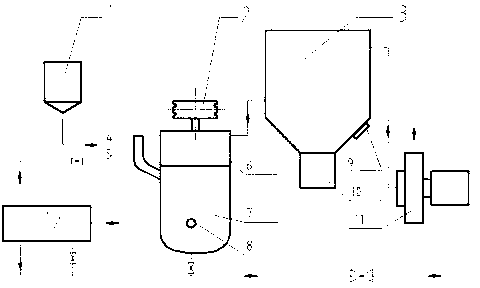
A system 26 for removing elemental mercury or mercury compounds handles carbonaceous sorbent 28 of a starter batch stored in a silo 30 in an agglomerated state. The sorbent 28 is fed by a feeder 32 to a separation device 34, which comminutes (if necessary) and de-agglomerates the sorbent particles 28 to their primary size distribution. This device 34 may be a particle-particle separator or a jet mill, where compressed air or high-pressure steam is the energy source. The de-agglomerated sorbent 28 of a contact batch created from the starter batch is conveyed by an airsteam for injection at a contact location 66 in a flue gas duct whereat carbonaceous sorbent of the contact batch adsorbs mercury from the flue gas.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC TECH GMBH
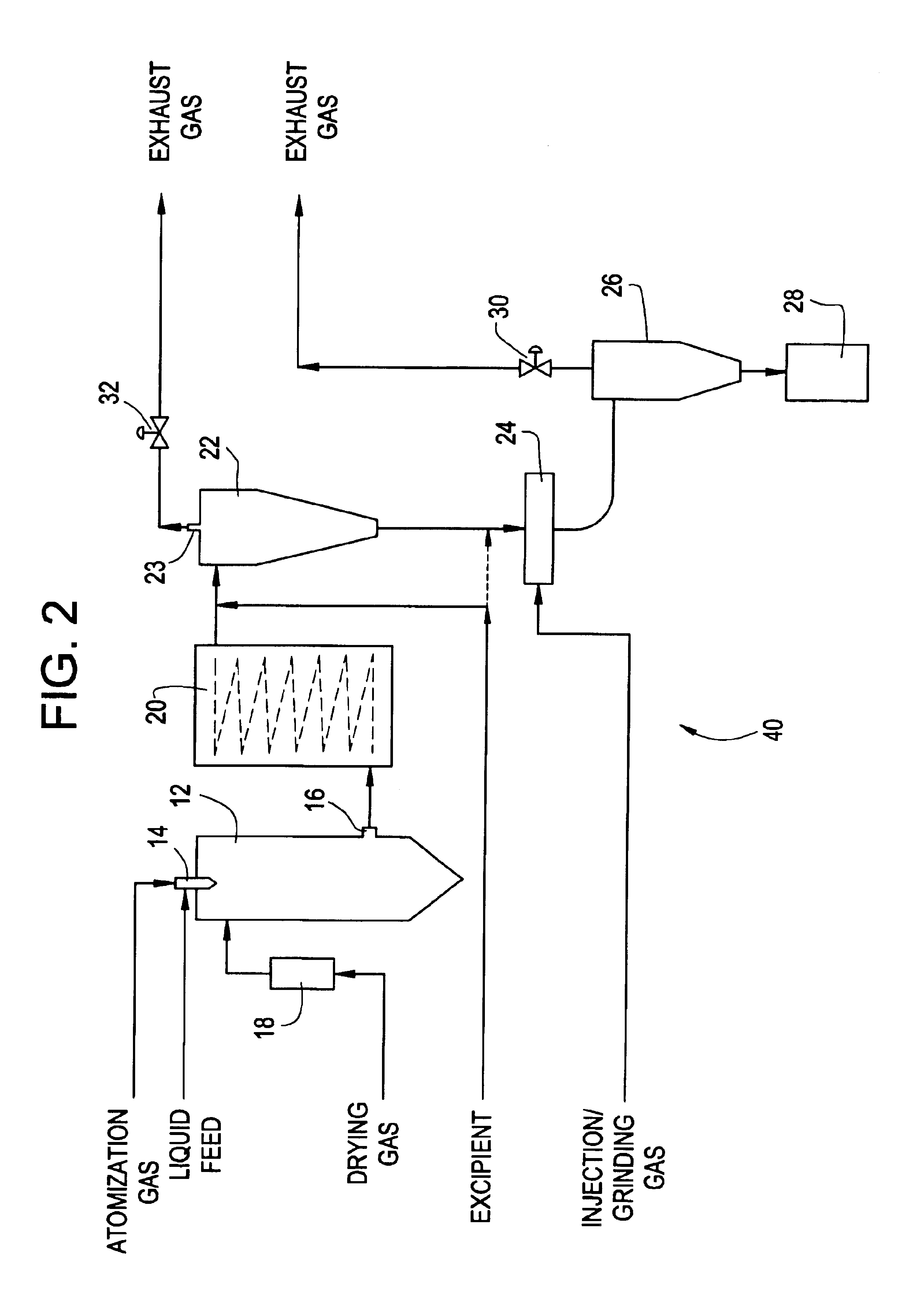
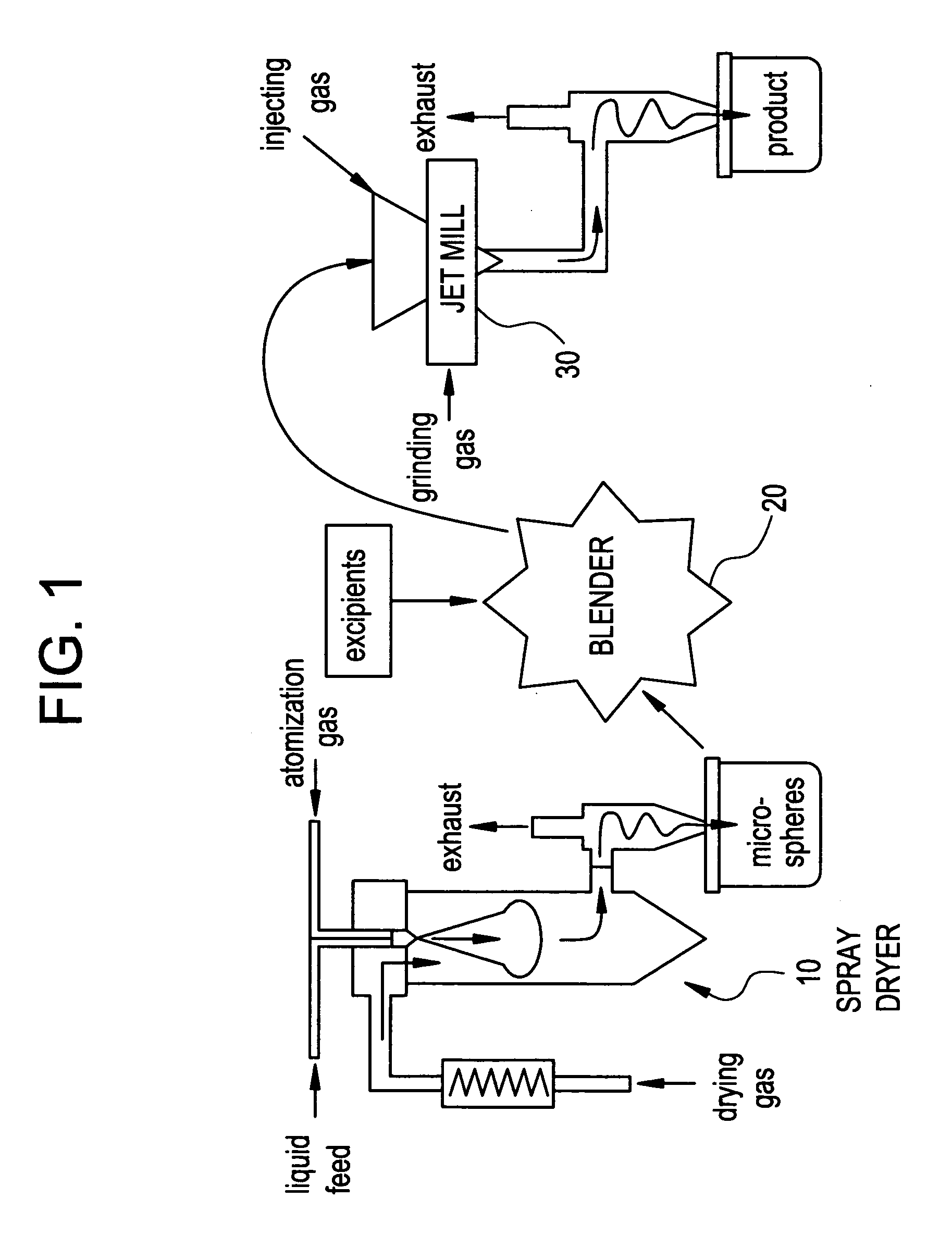
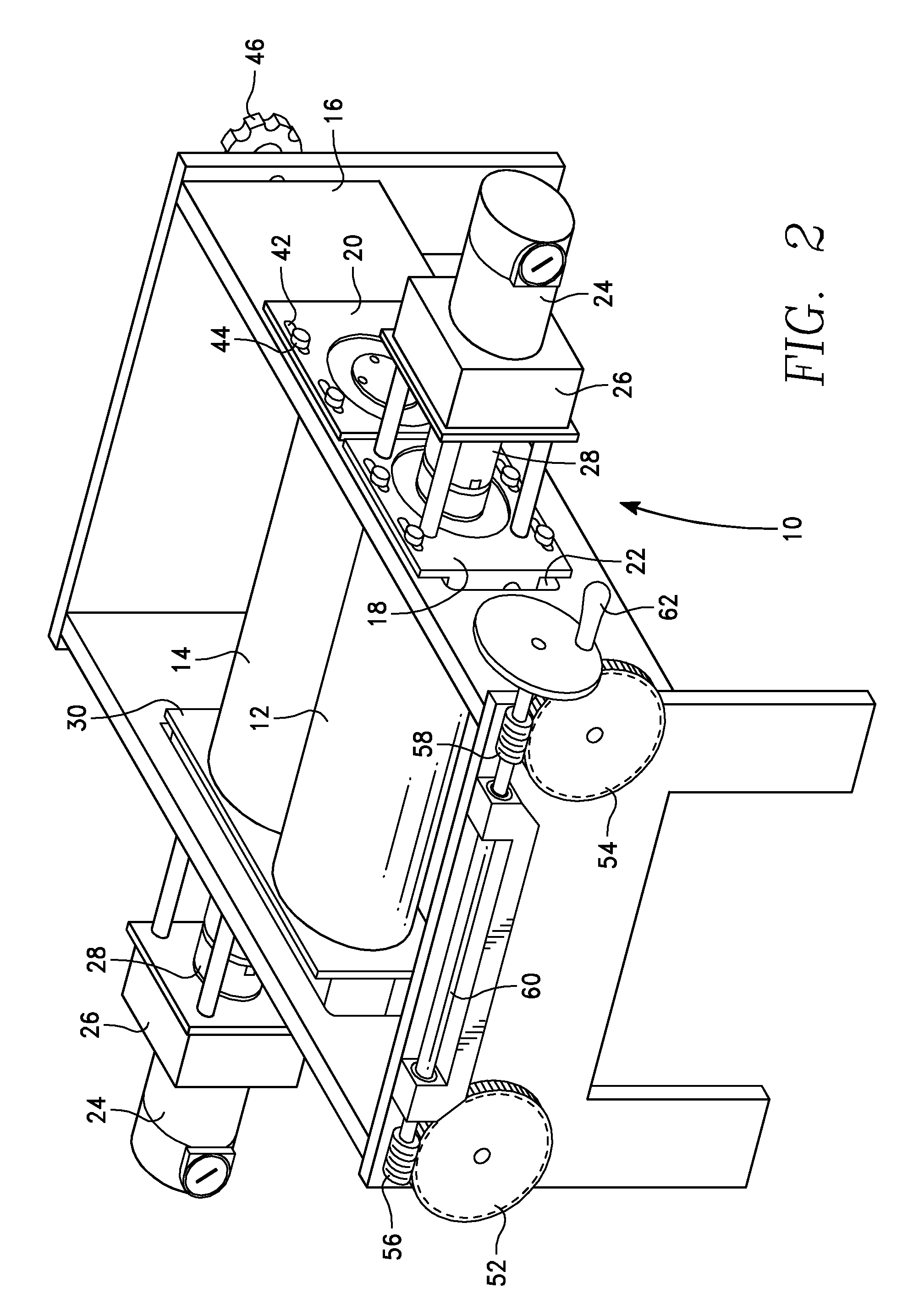
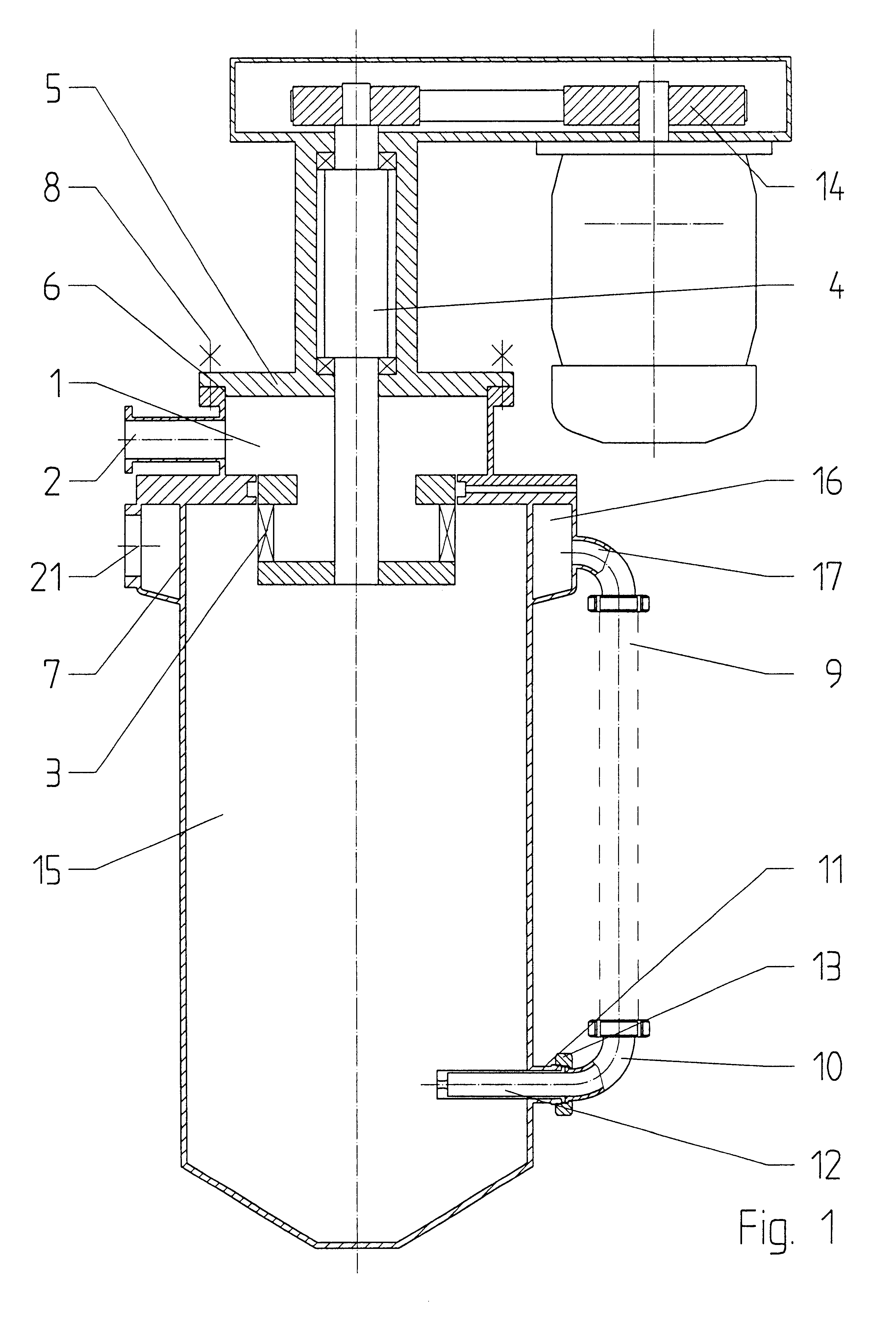
Methods and apparatus for making particles using spray dryer and in-line jet mill
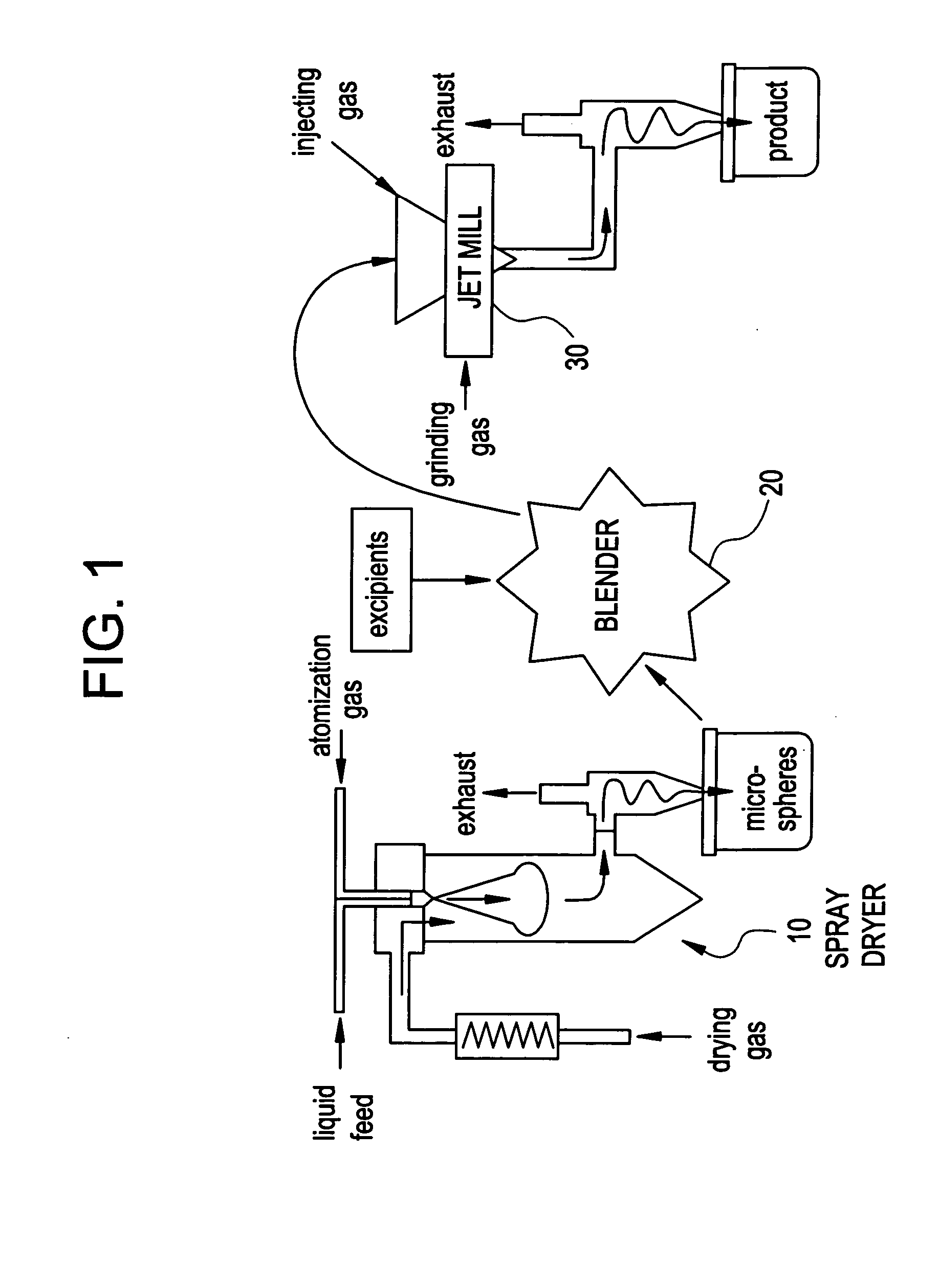
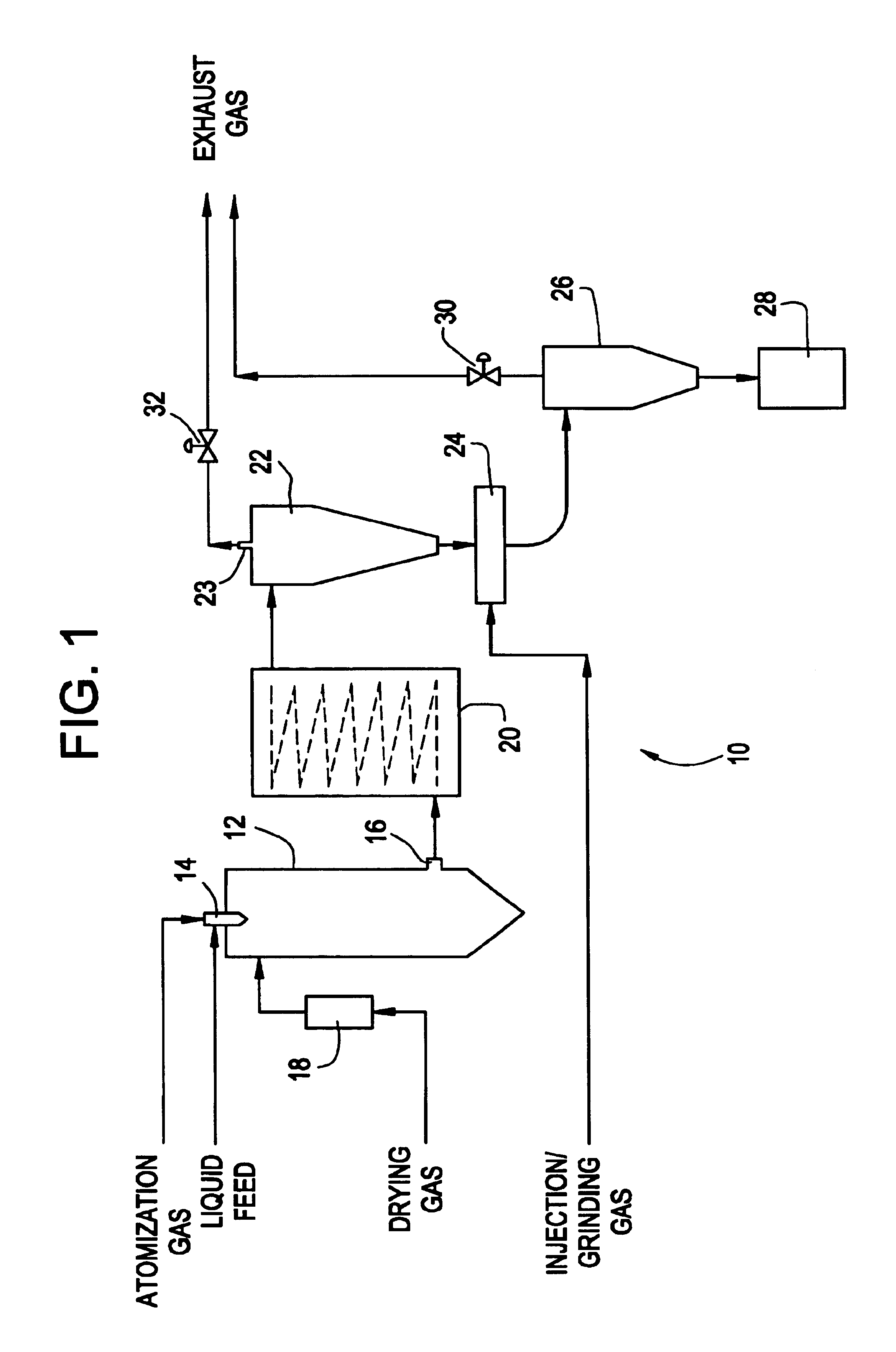
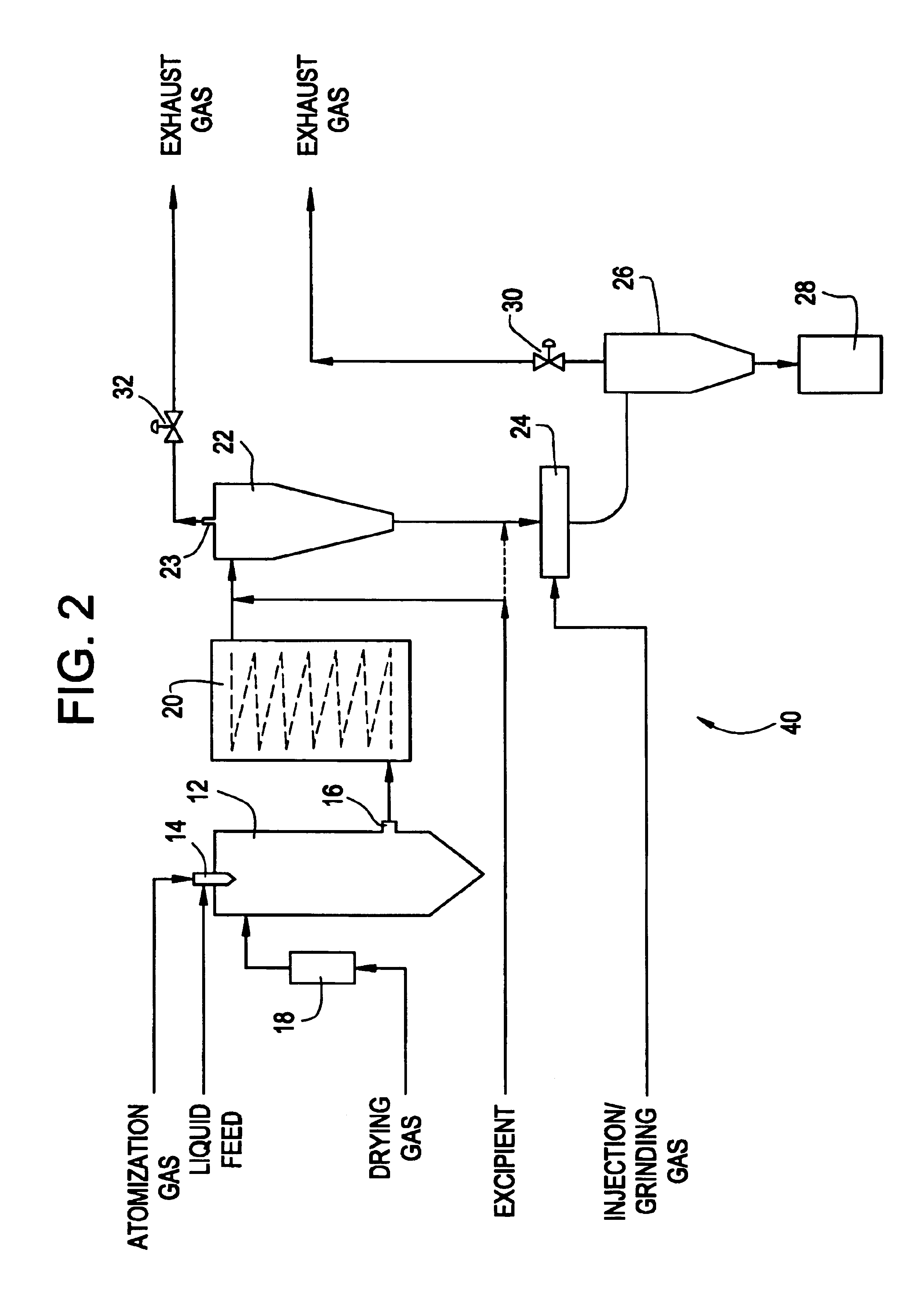
InactiveUS6918991B2Reduce processing timeDrying solid materials with heatGranulation by liquid drop formationPolymer scienceEmulsion
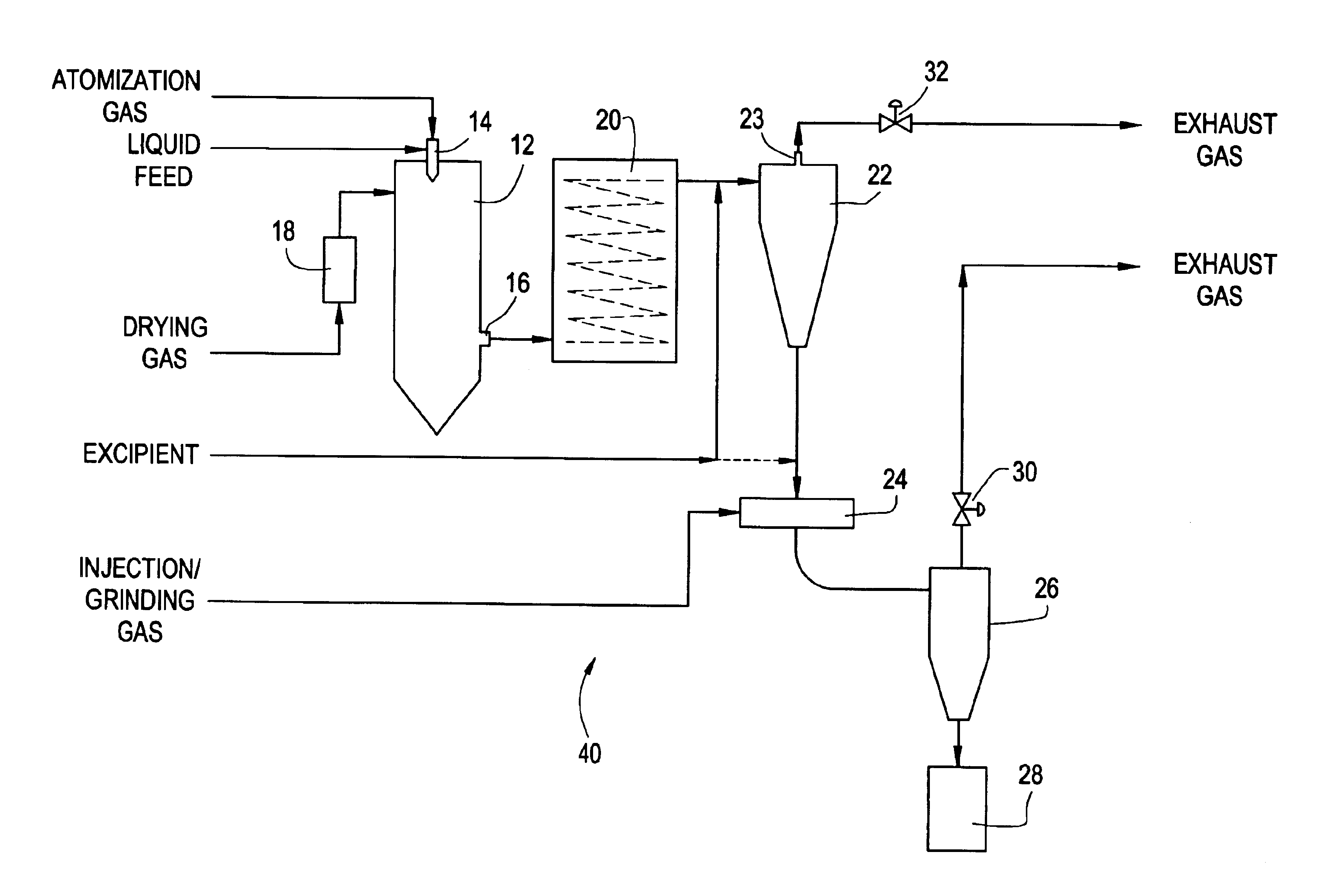
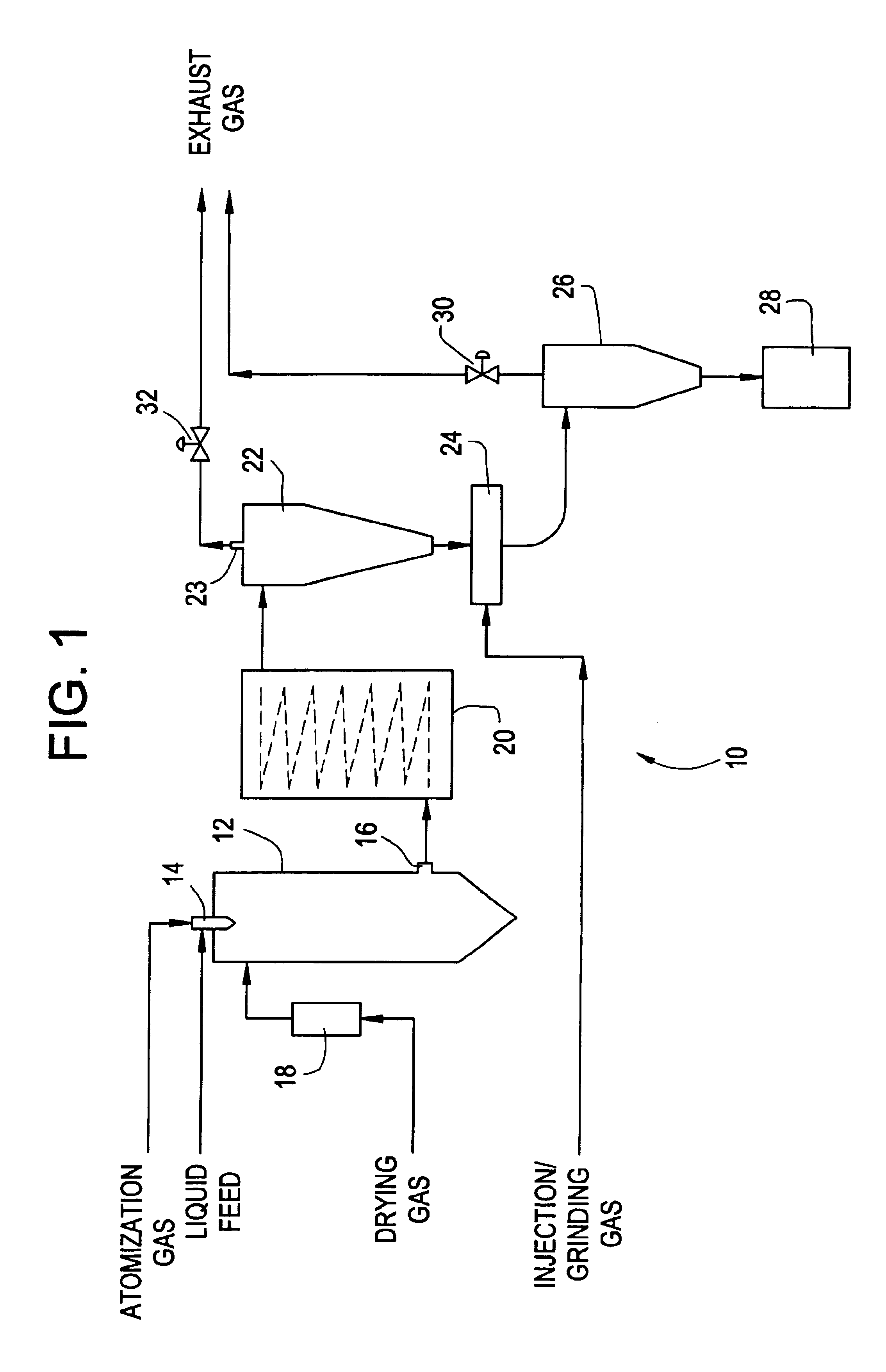
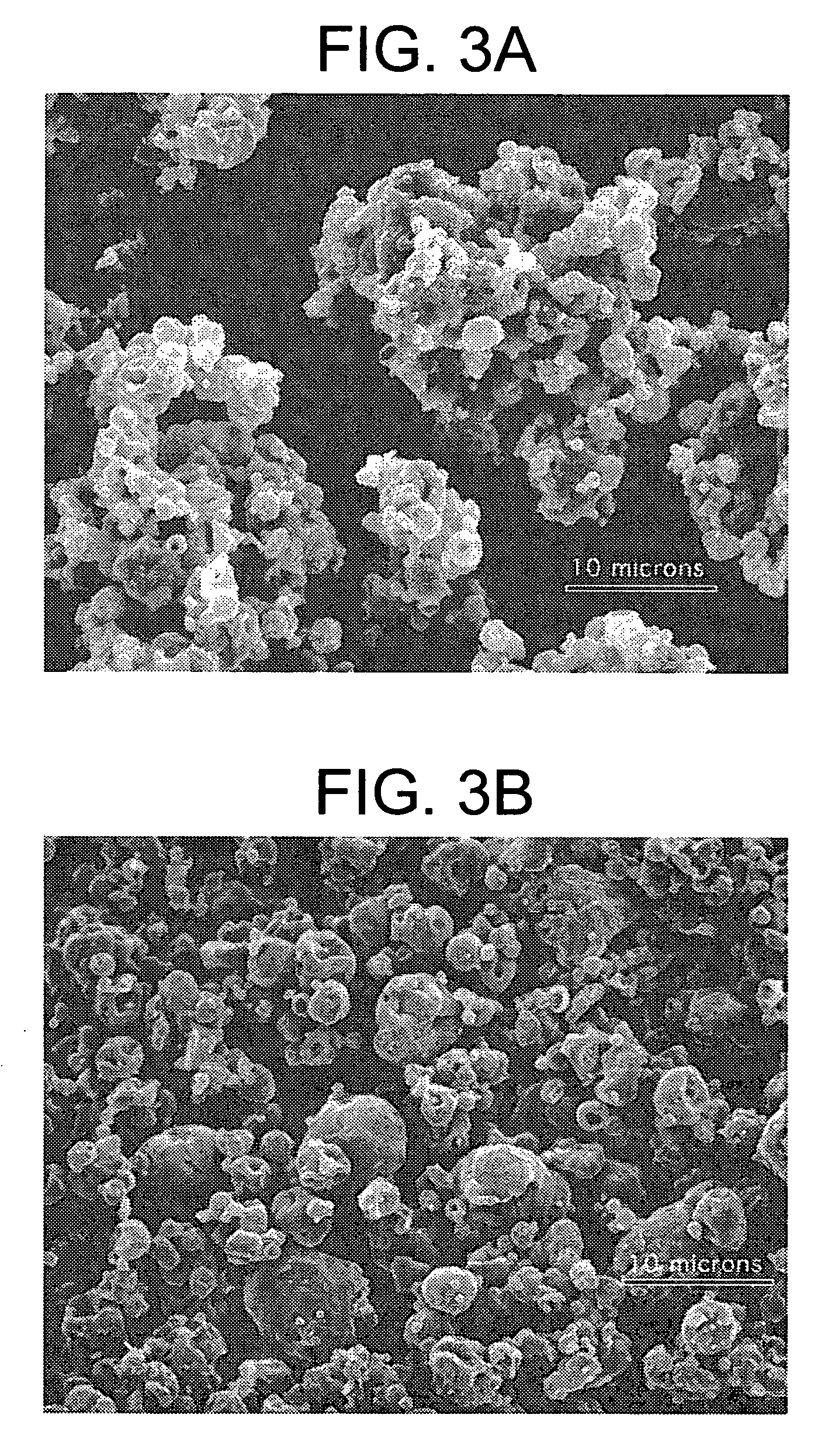
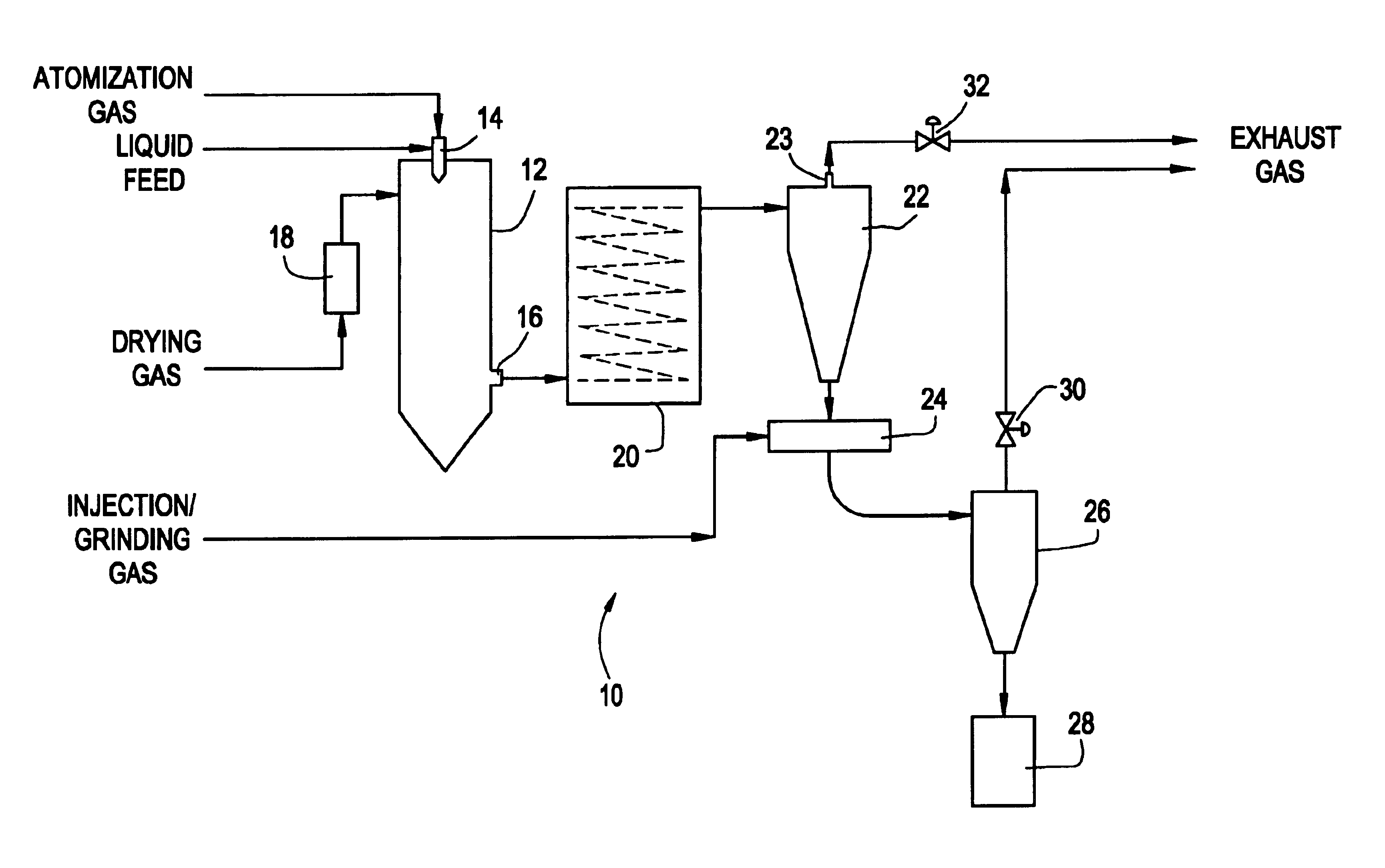
Methods and apparatus are provided for making particles comprising: (a) spraying an emulsion, solution, or suspension, which comprises a solvent and a bulk material (e.g., a pharmaceutical agent), through an atomizer and into a primary drying chamber, having a drying gas flowing therethrough, to form droplets comprising the solvent and bulk material dispersed in the drying gas; (b) evaporating, in the primary drying chamber, at least a portion of the solvent into the drying gas to solidify the droplets and form particles dispersed in drying gas; and (c) flowing the particles and at least a portion of the drying gas through a jet mill to deagglomerate or grind the particles. By coupling spray drying with “in-line” jet milling, a single step process is created from two separate unit operations, and an additional collection step is advantageously eliminated. The one-step, in-line process has further advantages in time and cost of processing.
Owner:ACUSPHERE INC
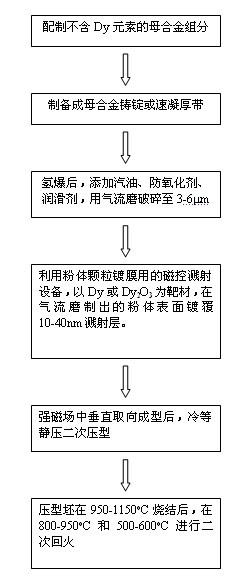
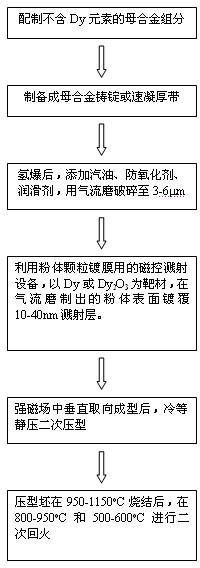
A preparation method of high-performance sintered NdFeB with low dysprosium content
The invention discloses a method for preparing sintered NdFeB with low dysprosium (Dy) content and high performance; the method comprises the following steps of: sputtering and plating the Dy element on the surface of jet mill powder by using the powder plate technology based on magnetron sputtering on the basis of preparing NdFeB powder, and then sufficiently dispersing the Dy element to micron-sized NdFeB crystal particles by dispersing the Dy element at high temperature in the sintering and tempering process, thereby achieving the effect of improving magnetic performance of the sintered NdFeB. Compared with the introduction of the Dy element in the proportioning process of the prior art, the method disclosed by the invention has the advantages: the low dysprosium content and high performance is limited in the nano-size by adopting the physical gas-phase deposition, the consumption quantity of the Dy element during the production process is controlled effectively and the preparationof sintered NdFeB with low dysprosium content and high performance is realized. Compared with the sintered NdFeB of the same components prepared by the traditional casting and powder metallurgy process, both the intrinsic coercivity and the maximum magnetic energy product of the sintered NdFeB rare-earth permanent magnetic material obtained according to the invention are improved obviously; compared with the sintered NdFeB with the same performance prepared by the traditional casting and powder metallurgy process, the dosage of the dysprosium element is reduced remarkably. The method can be widely applicable to producing and manufacturing sintered NdFeB with high performance.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
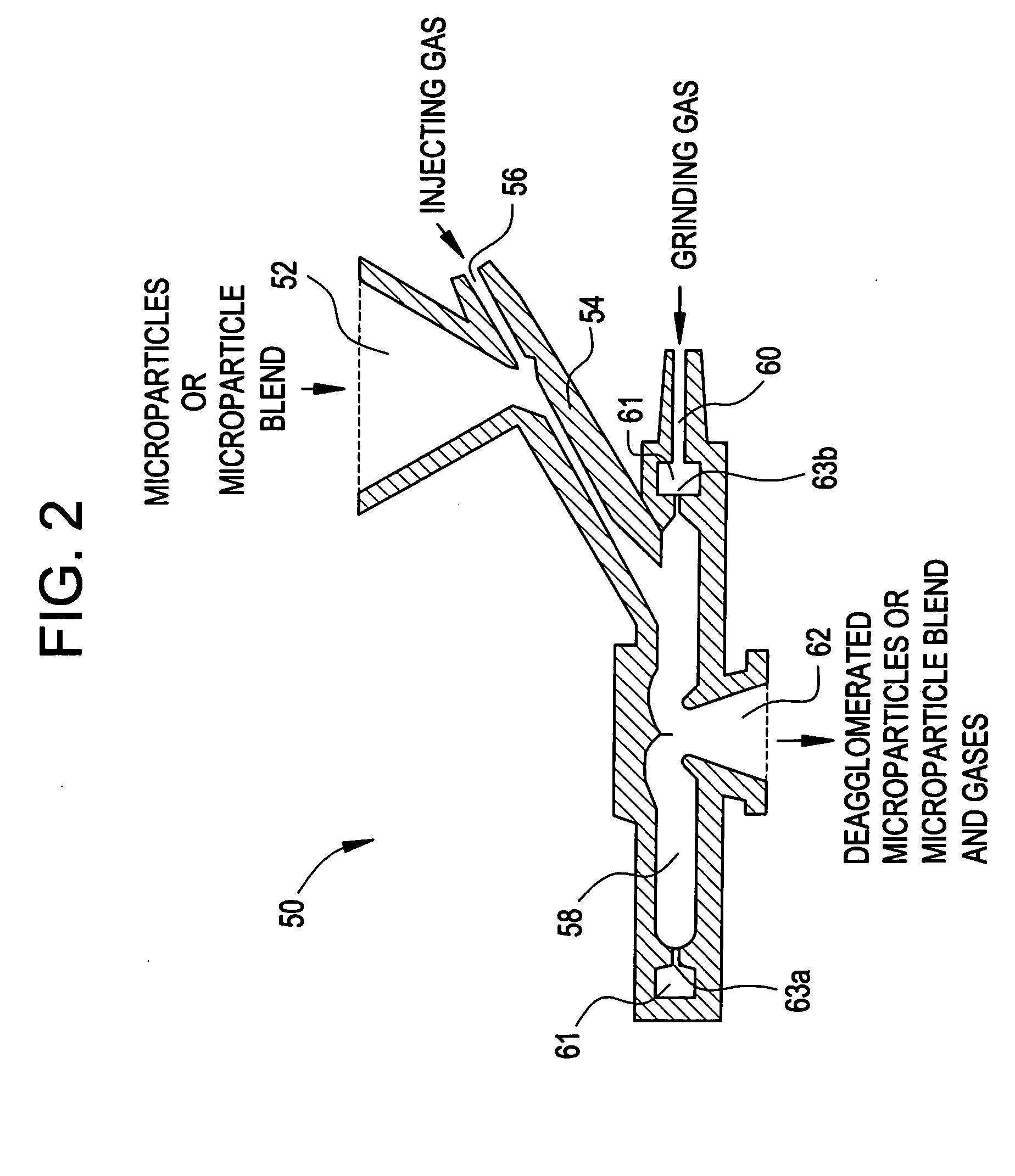
Methods for making pharmaceutical formulations comprising deagglomerated microparticles
InactiveUS20060093678A1High crystallinityReduce contentPowder deliveryGranulation by liquid drop formationMicroparticleVolume average
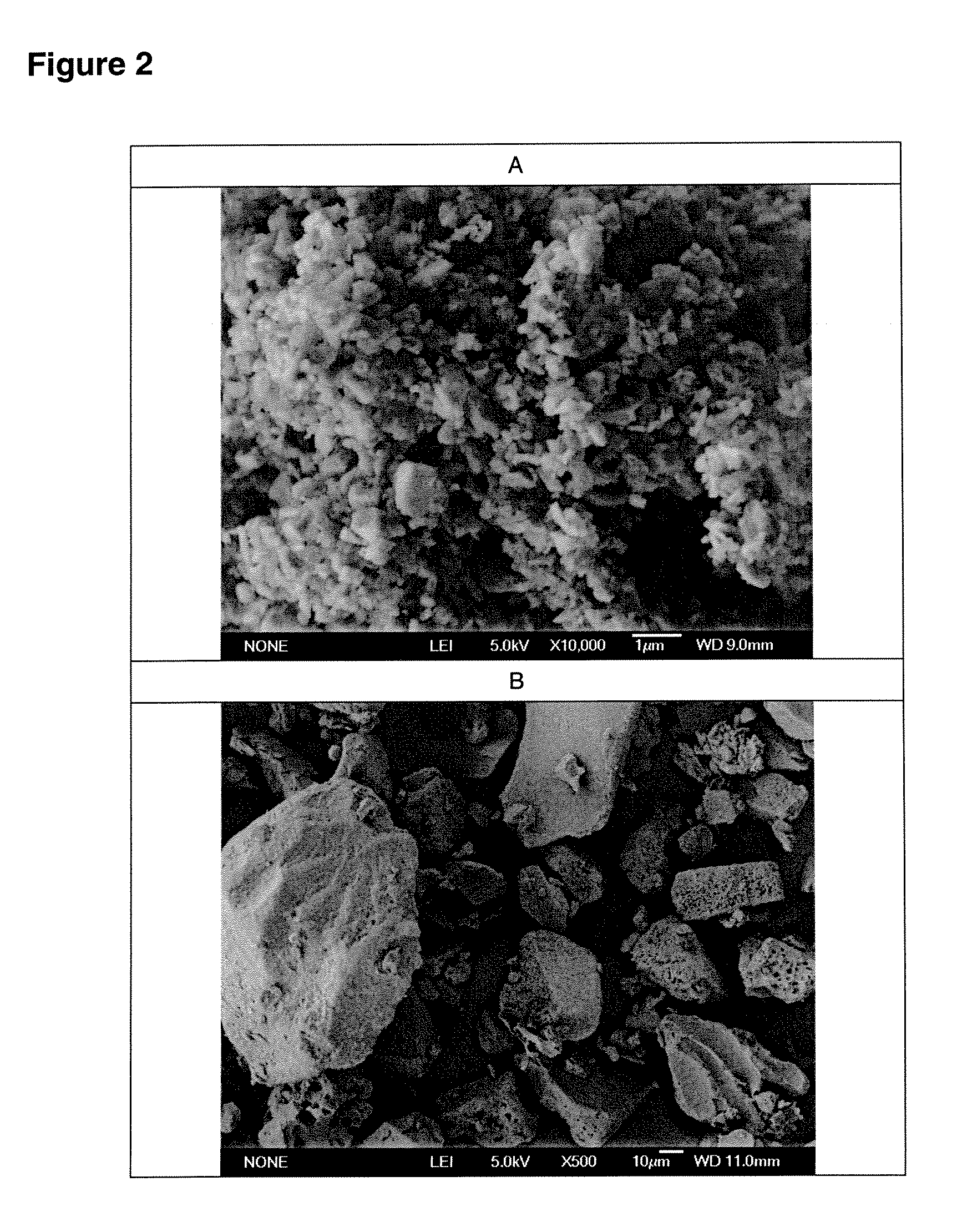
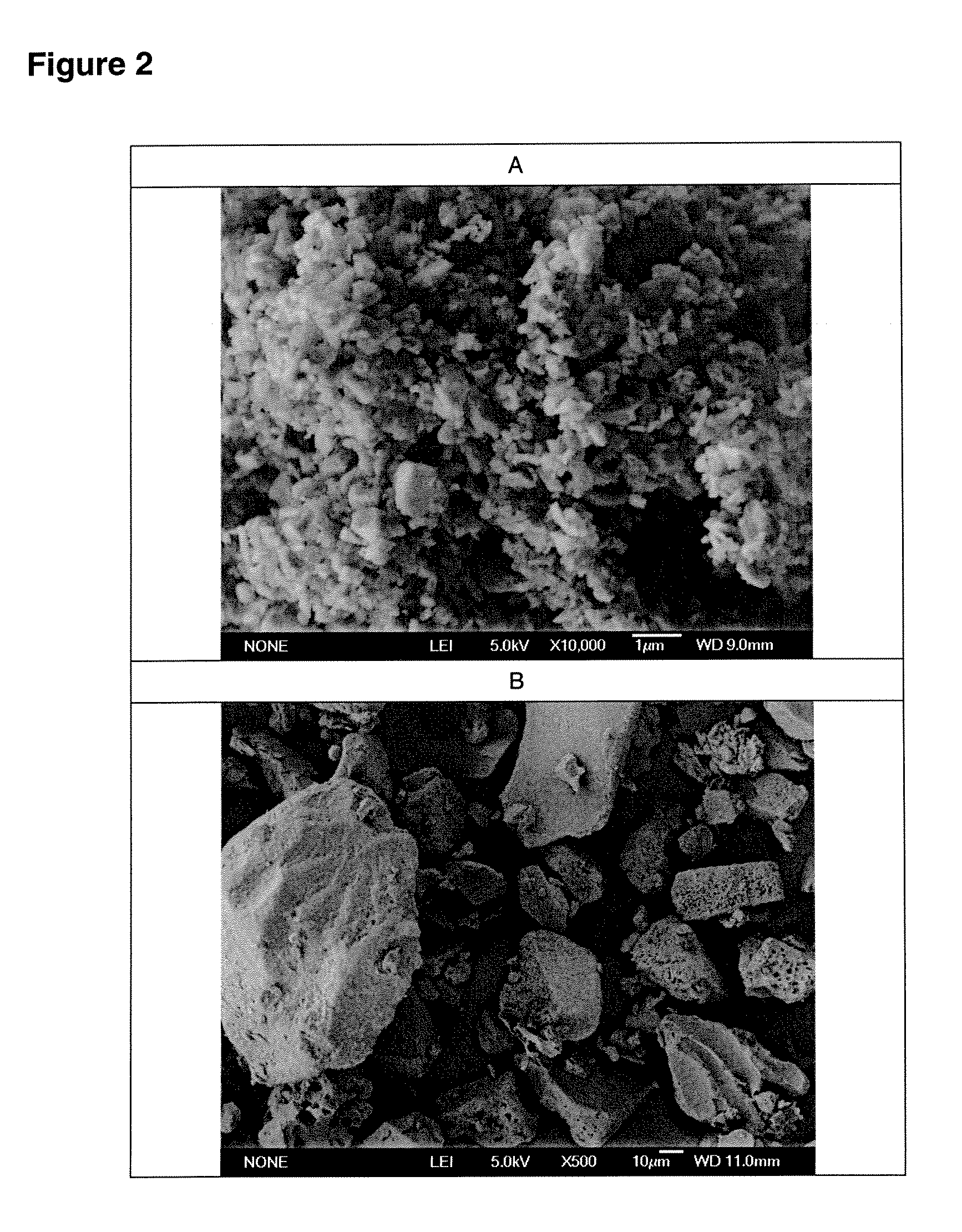
Methods are provided for making a dry powder blend pharmaceutical formulation comprising (i) forming microparticles which comprise a pharmaceutical agent; (ii) providing at least one excipient in the form of particles having a volume average diameter that is greater than the volume average diameter of the microparticles; (iii) blending the microparticles with the excipient to form a powder blend; and (iv) jet milling the powder blend to deagglomerate at least a portion of any of the microparticles which have agglomerated, while substantially maintaining the size and morphology of the individual microparticles. Jet milling advantageously can eliminate the need for more complicated wet deagglomeration processes, can lower residual moisture and solvent levels in the microparticles (which leads to better stability and handling properties for dry powder formulations), and can improve wettability, suspendability, and content uniformity of dry powder blend formulations.
Owner:CHICKERING DONALD E III +6
Methods and apparatus for making particles using spray dryer and in-line jet mill
InactiveUS6921458B2Reduce processing timeDrying solid materials with heatGranulation by liquid drop formationPolymer scienceEmulsion
Methods and apparatus are provided for making particles comprising: (a) spraying an emulsion, solution, or suspension, which comprises a solvent and a bulk material (e.g., a pharmaceutical agent), through an atomizer and into a primary drying chamber, having a drying gas flowing therethrough, to form droplets comprising the solvent and bulk material dispersed in the drying gas; (b) evaporating, in the primary drying chamber, at least a portion of the solvent into the drying gas to solidify the droplets and form particles dispersed in drying gas; and (c) flowing the particles and at least a portion of the drying gas through a jet mill to deagglomerate or grind the particles. By coupling spray drying with “in-line” jet milling, a single step process is created from two separate unit operations, and an additional collection step is advantageously eliminated. The one-step, in-line process has further advantages in time and cost of processing.
Owner:ACUSPHERE INC
Process for milling and preparing powders and compositions produced thereby
ActiveUS20080029625A1Low costImprovement in particle size reduction efficiencyPowder deliveryGrain treatmentsDrug carrierProduct gas
A method of milling a powder comprising introducing a gas stream containing a cryogenic liquid and a drug carrier gas into a jet mill, and milling a powder with the jet mill in one or more milling passes. A product produced by the method. A milling apparatus comprising a cryogenic gas input system, a powder feeder, a main jet-mill, and at least one output port for collecting the powder.
Owner:NANOSHIFT LLC
High Discharge Capacity Lithium Battery
ActiveUS20120021266A1Improve discharge performanceIncrease energy densityCell seperators/membranes/diaphragms/spacersCell electrodesHigh rateIron disulfide
A lithium / iron disulfide electrochemical battery cell with a high discharge capacity. The cell has a lithium negative electrode, an iron disulfide positive electrode and a nonaqueous electrolyte. The iron disulfide of the positive electrode has a controlled average particle size range which allows the electrochemical cells to exhibit desired properties in both low and high rate applications. In various embodiments, the iron disulfide particles are wet milled, preferably utilizing a media mill or milled utilizing a non-mechanical mill such as a jet mill, which reduces the iron disulfide particles to a desired average particle size range for incorporation into the positive electrode.
Owner:ENERGIZER BRANDS
Jet Mill Producing Fine Silicon Powder
A method of jet milling silicon powder in which silicon pellets are fed into a jet mill producing a gas vortex in which the pellets are entrained and pulverized by collisions with each other or walls of the milling chamber. The chamber walls are advantageously formed of high-purity silicon as are other parts contacting the unground pellets or ground powder. The pellets and chamber parts may be formed of electronic grade silicon but polycrystalline silicon may be used for chamber parts. Additionally, the particle feed tube in which the particles are entrained in a gas flow and the vortex finder operating as the outlet at the center of the vortex may be formed of silicon. The milling and feed gas may be nitrogen supplied from a liquid-nitrogen tank lined with stainless steel. The feed pellets may be formed by chemical vapor deposition.
Owner:INTEGRATED PHOTOVOLTAICS
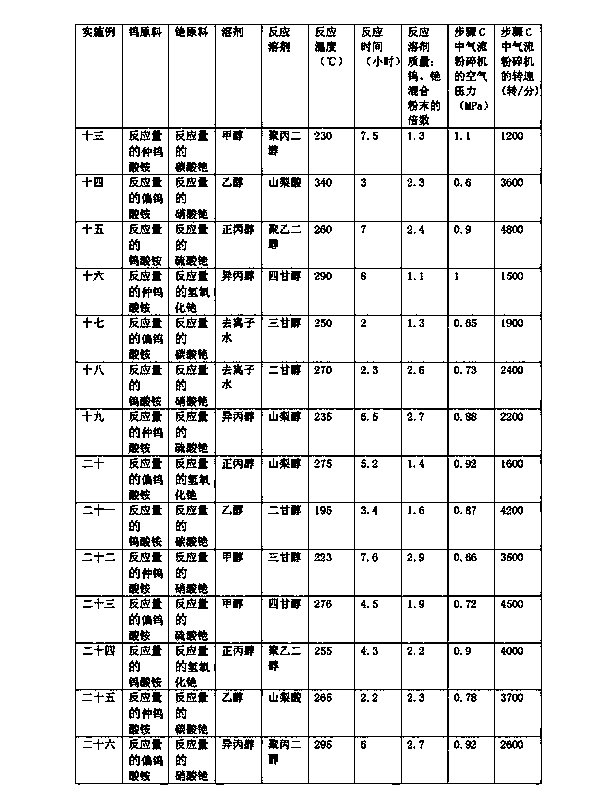
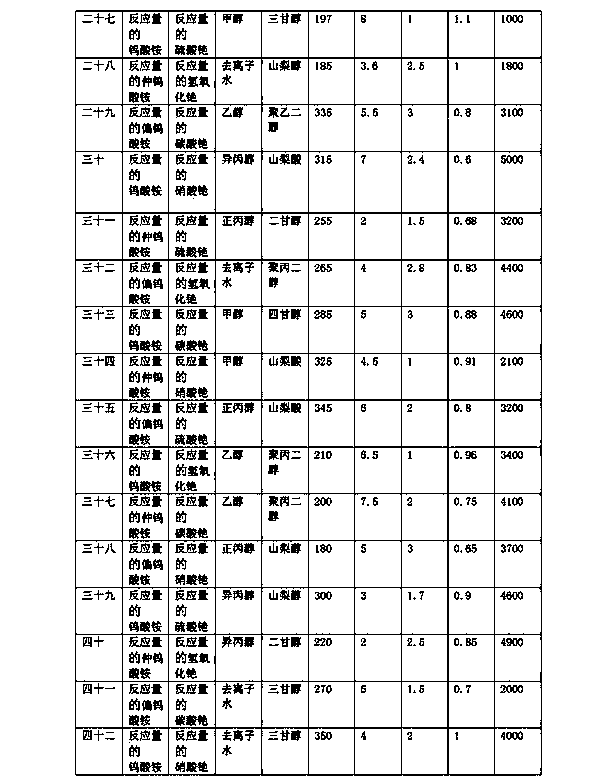
Preparation method of cesium tungstate nanopowder
ActiveCN104192910ALow degree of reunionIncrease productivityMaterial nanotechnologyTungsten compoundsTungstatePhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a preparation method of cesium tungstate nanopowder. The preparation method comprises the following steps of A, dissolving reacting doses of tungsten raw materials and cesium carbonate raw materials into a solvent, drying the solution to obtain particles, and further smashing the obtained particles to obtain tungsten and cesium mixed powder; B, placing the tungsten and cesium mixed powder into a sealed reaction kettle with a stirring function, adding a reaction solvent in the sealed reaction kettle, and reacting at the temperature of 180-350 DEG C for 2-8h while stirring, wherein the mass of the reaction solvent is 1-3 times as mush as that of the tungsten and cesium mixed powder; and C, separating the reaction product obtained in the step B, washing by using deionized water or ethanol, then, drying, and milling by using a jet mill to obtain a target product, namely the cesium tungstate nanopowder. The cesium tungstate nanopowder prepared by using the preparation method is low in agglomeration degree; and the preparation method is high in production efficiency and low in cost.
Owner:宁波今心新材料科技有限公司
Doping and milling of granular silicon
Doped silicon particles, including powder suitable for plasma spraying semiconductor devices, is formed by liquid doping applied to larger particles, which are then milled to a smaller size. Doped or undoped silicon may be milled by a roller mill including silicon rollers and advantageously having feed and collection systems formed of silicon and operated in a nitrogen ambient. A two-stage system includes sieving the rolled product for further size reduction in a jet mill.
Owner:INTEGRATED PHOTOVOLTAICS
Preparation method of high-purity micro-fine low-oxygen titanium powder
The invention provides a preparation method of high-purity micro-fine low-oxygen titanium powder, which belongs to the technical field of powder preparation in the powder metallurgy process. The preparation method is characterized by combining hydrogenation and dehydrogenation with a jet milling process, firstly carrying out hydrogenation treatment on a titanium sponge to prepare titanium hydride powder, then utilizing a jet mill to break the titanium hydride, then carrying out vacuum dehydrogenation, and finally utilizing the jet mill to carry out breaking gradation and vacuum package and obtaining a titanium powder product. Compared with the traditional ball milling process, the jet milling process causes no pollution, and iron impurities caused by collision of steel balls in the ball milling process can be avoided; due to jet milling and high-vacuum dehydrogenation treatment, the content of oxygen can be controlled to be lowest, and the powder taking and packaging operations are respectively carried out in a glove box, so that the powder and the air are isolated in the whole process, and further, the prepared high-purity micro-fine low-oxygen titanium powder is prepared.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Method for producing phosphorus building gypsum by phosphorous gypsum
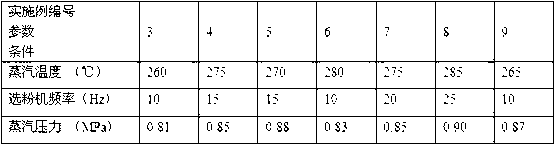
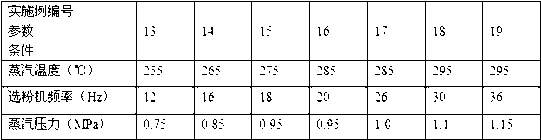
The invention discloses a method for producing phosphorus building gypsum by phosphorous gypsum. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of drying industrial residual phosphorous gypsum by a pneumatic drier to a state that water content is smaller than 5%; sending the dried phosphorous gypsum to a steam jet mill, grinding the industrial residual phosphorous gypsum by the steam jet mill and dewatering, collecting the grinded phosphorous gypsum by a dust collector and cooling the phosphorous gypsum to obtain the phosphorus building gypsum, wherein the power medium of the steam jet mill is superheated steam; a frequency of a powder concentrator is 10 Hz-40 Hz; the temperature of the superheated steam is 250 DEG C-300 DEG C; and a pressure of the superheated steam is 0.7 MPa-1.2 MPa. In the method, the industrial residual phosphorous gypsum is used as a raw material; the superheated steam generated by industrial waste heat is used as a power for the steam jet mill to prepare the phosphorus building gypsum. The method has the characteristics of wide available raw materials, simple production equipment, high yield, low cost, large-scale production, etc. The prepared phosphorus building gypsum can be used for preparing building functional mortar and producing gypsum boards and building blocks, and has strong practicality.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Jet mill producing fine silicon powder
Owner:INTEGRATED PHOTOVOLTAICS
Preparation method of carbon nano-tube/epoxy resin composite material
InactiveCN101054461AIncreased Surface Functionalization EfficiencyLower surface energyEpoxyChemical reaction
The invention discloses a producing method for carbon nano tube / epoxide resin compound material, including steps of: processing the native carbon in the flowing bed jet mill, carboxylation, introducing polyatomic alicyclic amine with a flexibility structure on the carbon nano tube surface. The carbon nano tube / epoxide resin compound material is produced by mixing the epoxide resin and carbon nano tube by hot melt method, high speed stirring, ultrasonic treatment, then adding aromatic amine for solidification moulding. The advantages of the invention is that grafting polyatomic alicyclic amine on the carbon nano tube surface improves the surface function efficiency of the carbon nano tube, reduces the surface energy of the carbon nano tube, decreases the self-aggregation of the carbon nano tube, promotes both affinity and achieves organic connection of the carbon nano tube and epoxide resin by resin chemical reaction. The invention has a simple craft, a qualified mechanical property of obtained compound material, and an ulterior industry application convenient for the carbon nano tube.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
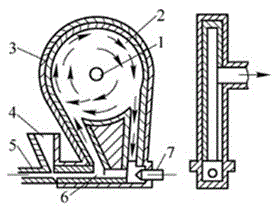
Separator mill
Owner:HOSOKAWA ALPINE AG
Methods for making pharmaceutical formulations comprising deagglomerated microparticles
InactiveUS20060093677A1High crystallinityReduce contentPowder deliveryGranulation by liquid drop formationMicroparticleVolume average
Methods are provided for making a dry powder blend pharmaceutical formulation comprising (i) forming microparticles which comprise a pharmaceutical agent; (ii) providing at least one excipient in the form of particles having a volume average diameter that is greater than the volume average diameter of the microparticles; (iii) blending the microparticles with the excipient to form a powder blend; and (iv) jet milling the powder blend to deagglomerate at least a portion of any of the microparticles which have agglomerated, while substantially maintaining the size and morphology of the individual microparticles. Jet milling advantageously can eliminate the need for more complicated wet deagglomeration processes, can lower residual moisture and solvent levels in the microparticles (which leads to better stability and handling properties for dry powder formulations), and can improve wettability, suspendability, and content uniformity of dry powder blend formulations.
Owner:CHICKERING DONALD E III +6
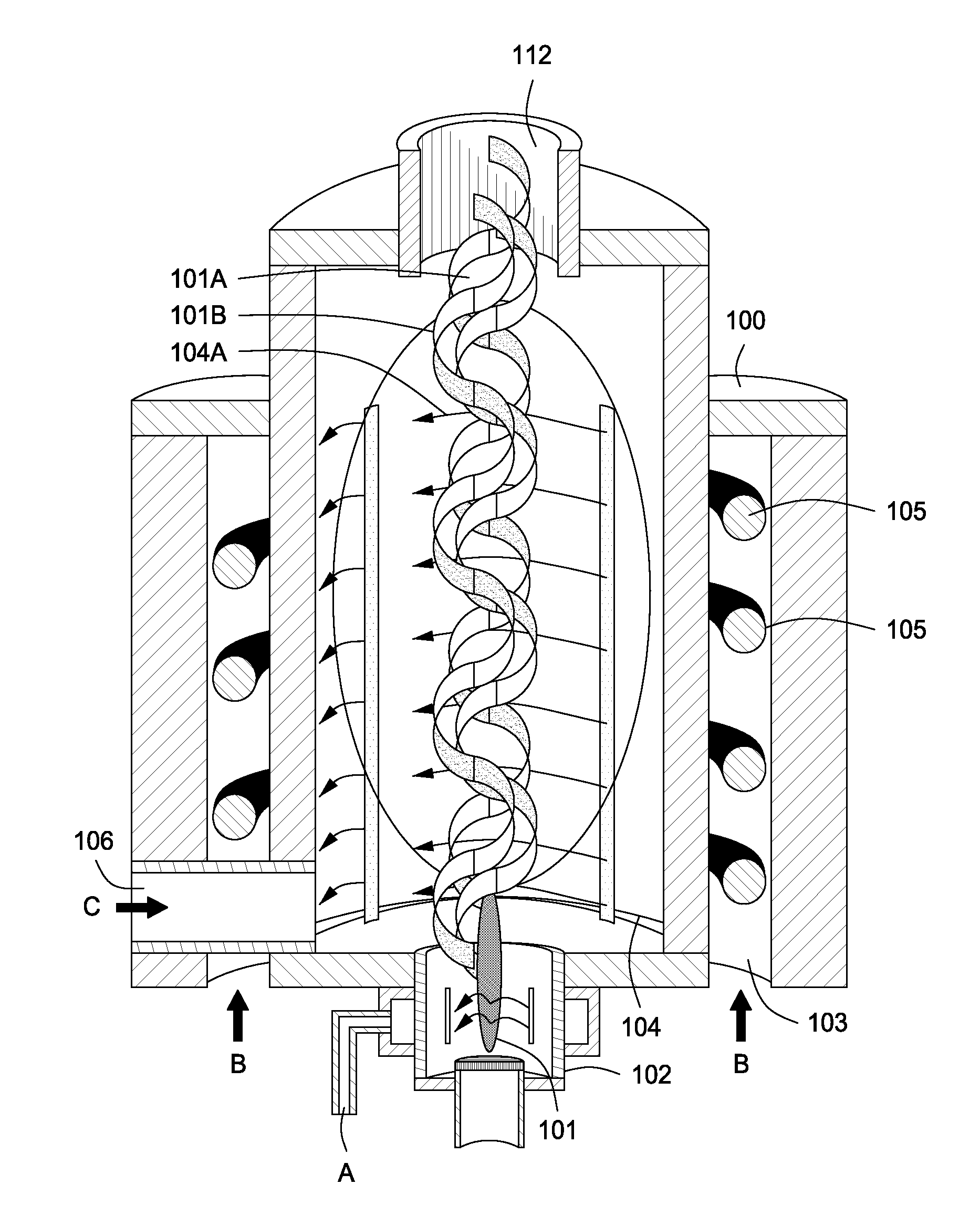
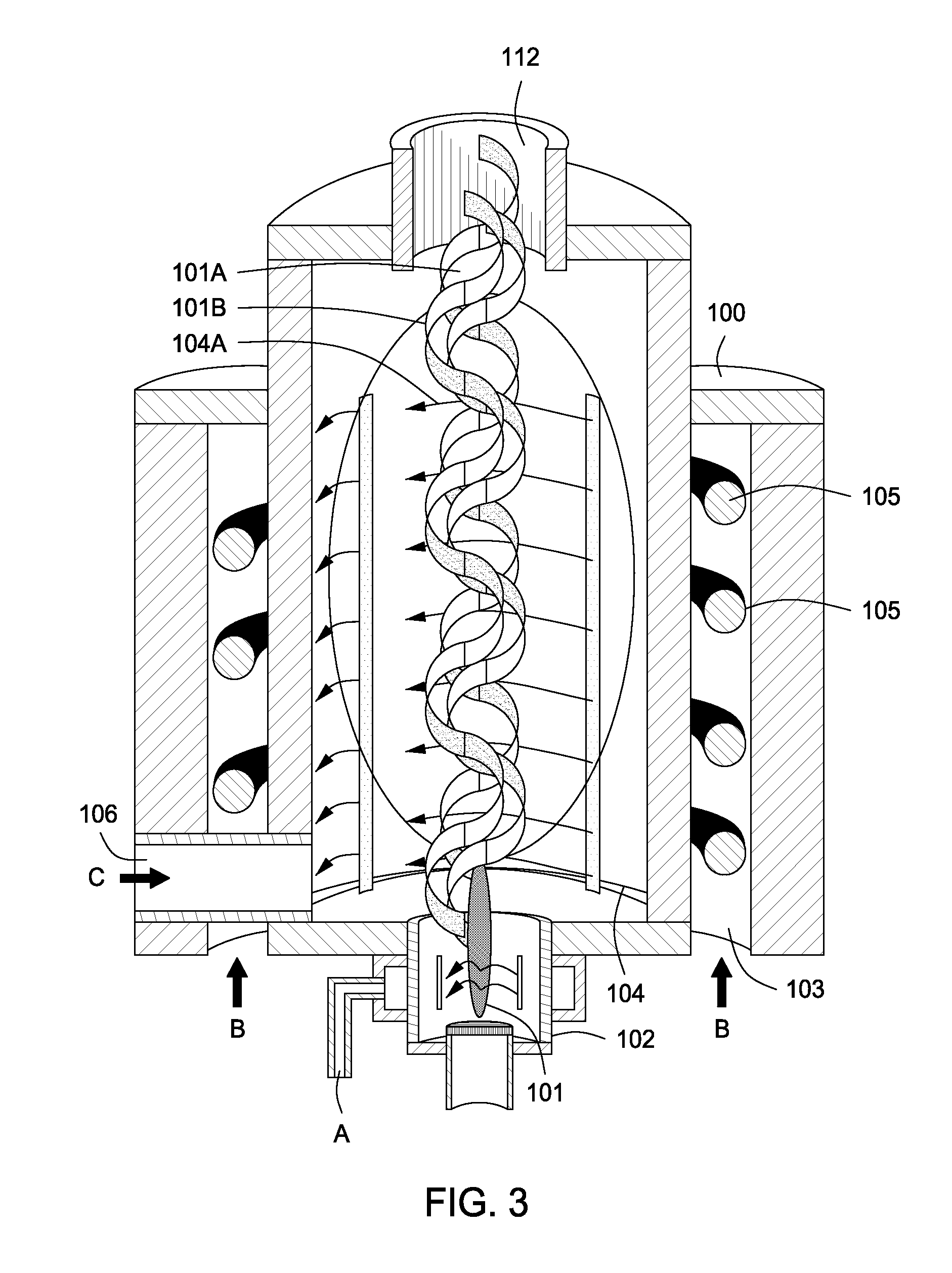
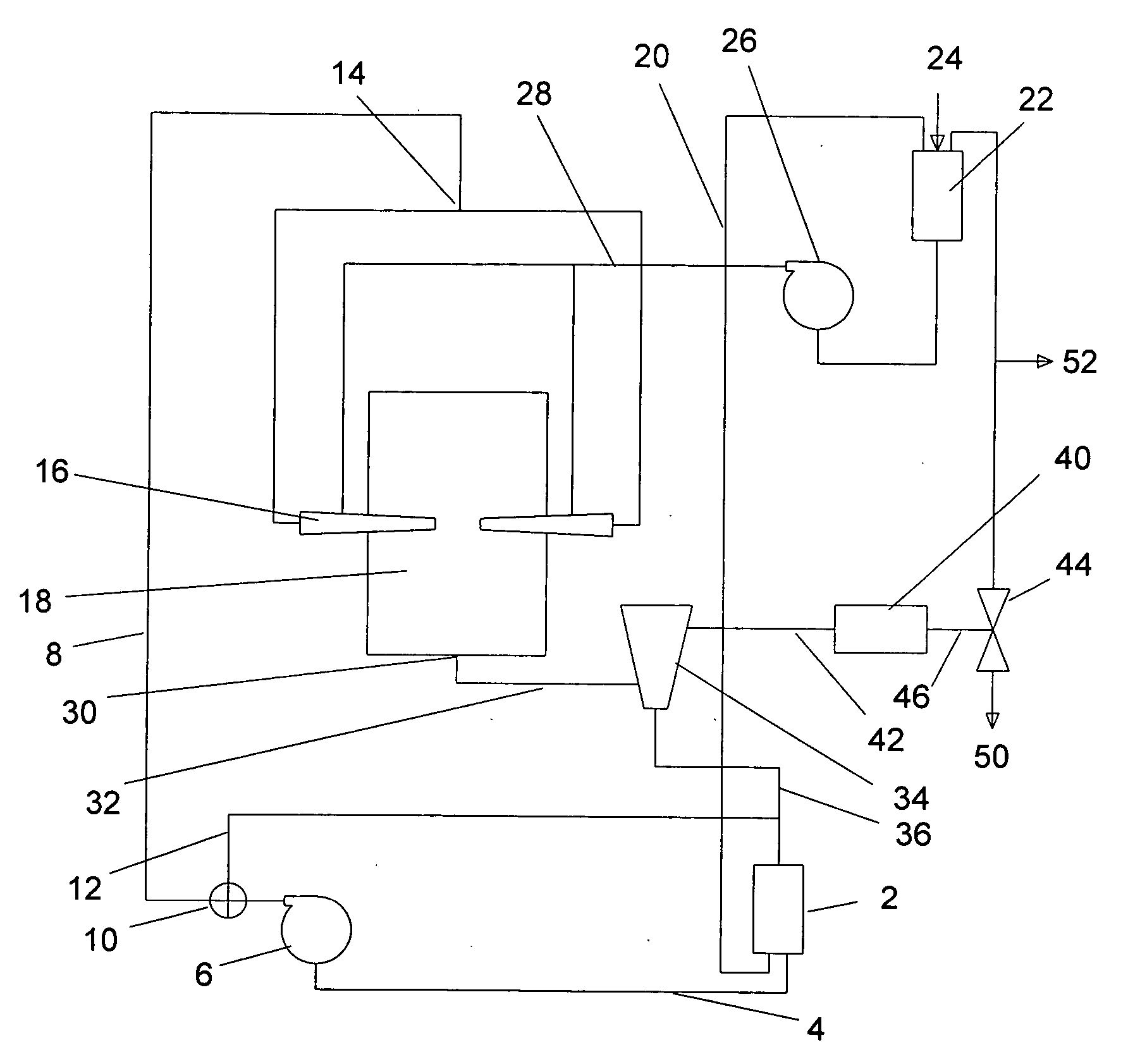
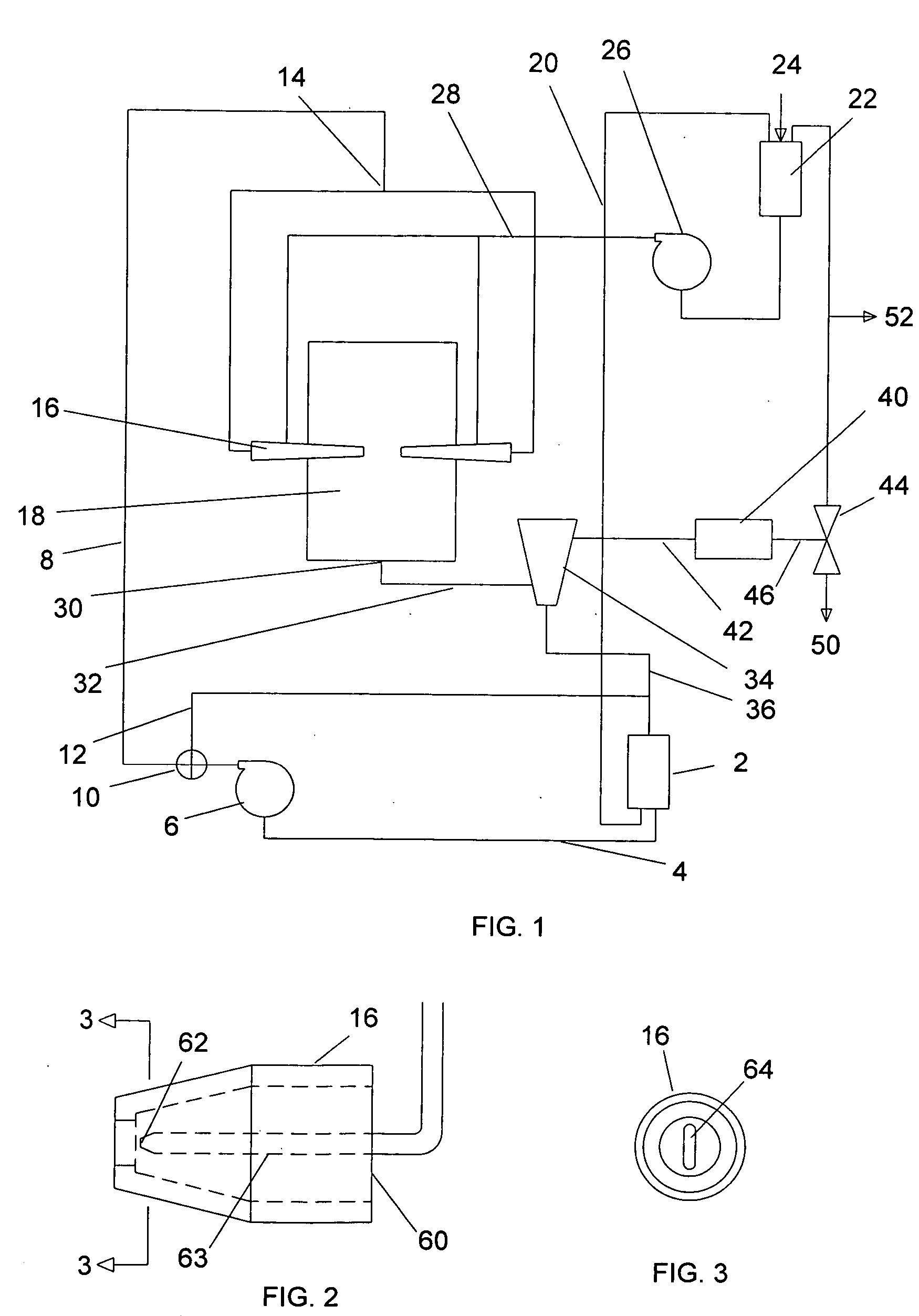
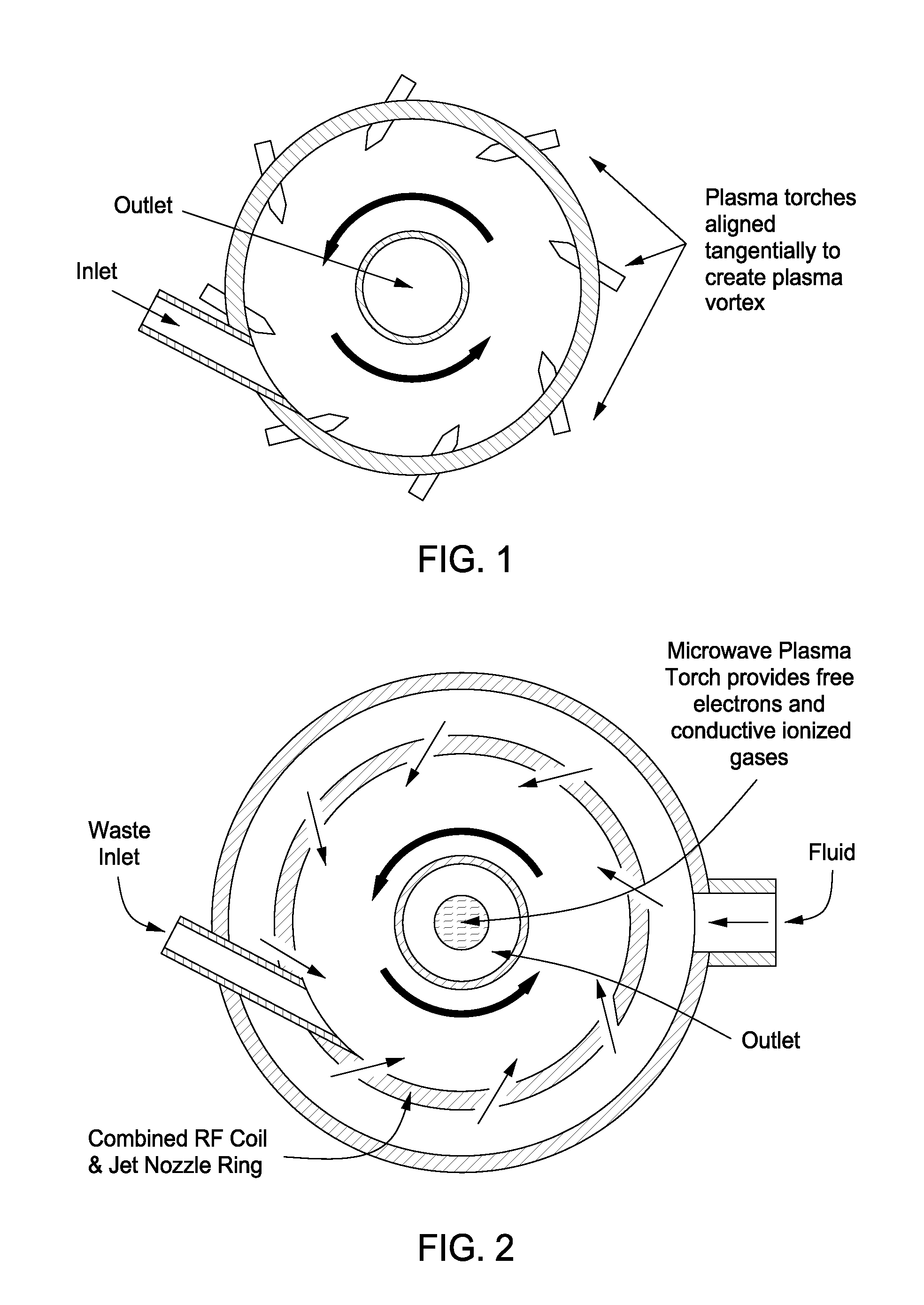
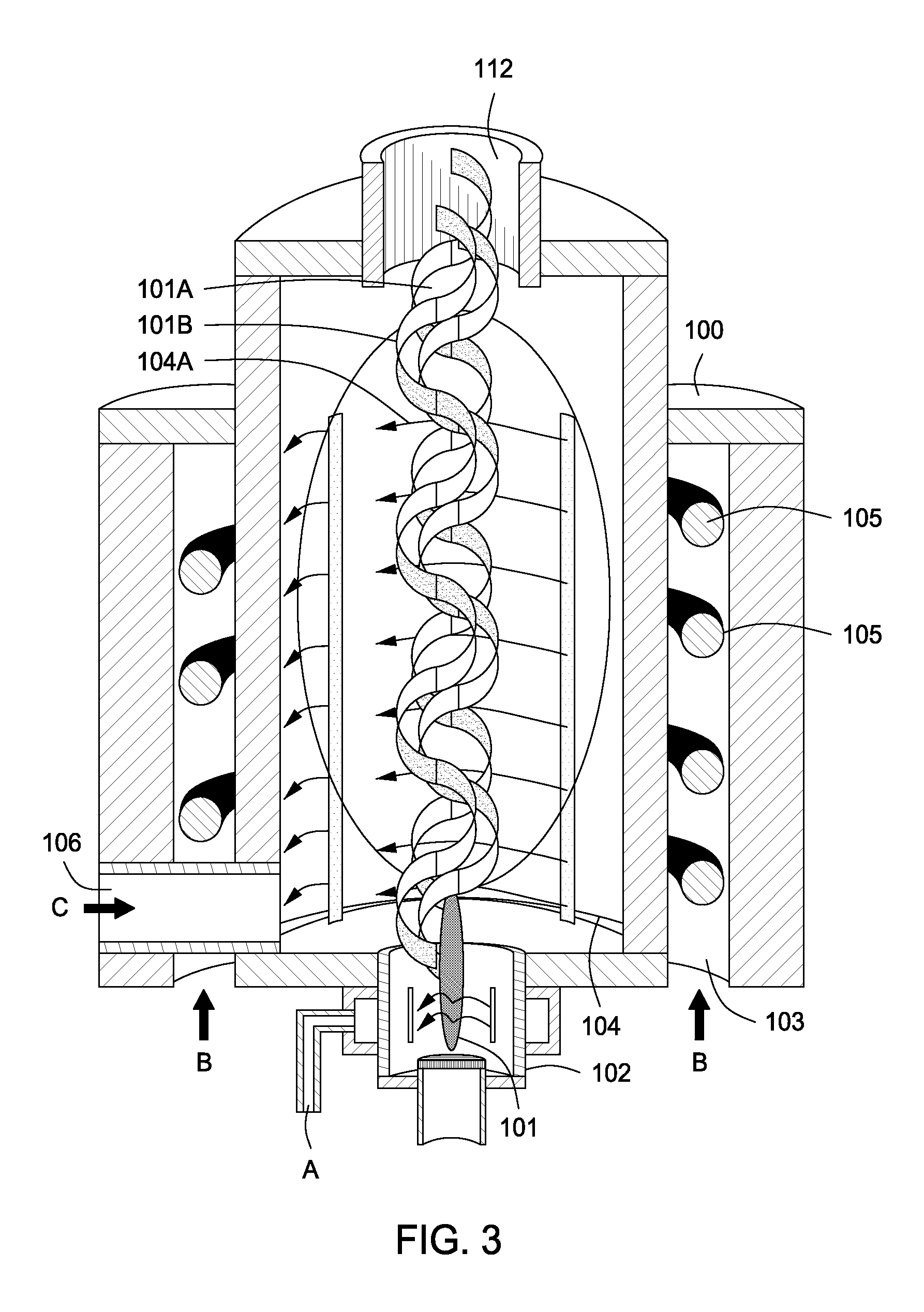
Plasma whirl reactor apparatus and methods of use
InactiveUS20100044483A1Calcium/strontium/barium carbonatesAluminium compoundsSingle processAngular momentum
An apparatus for synergistically combining a plasma with a comminution means such as a fluid kinetic energy mill (jet mill), preferably in a single reactor and / or in a single process step is provided by the present invention. Within the apparatus of the invention potential energy is converted into kinetic energy and subsequently into angular momentum by means of wave energy, for comminuting, reacting and separation of feed materials. Methods of use of the apparatus in the practice of various processes are also provided by the present invention.
Owner:FORET PLASMA LABS
Magnesium hydroxide flame retardant and flame retardant polymer for cables
ActiveCN101712875AEasy to changeEasy to replacePlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsInsulated cablesPolyolefinCrack resistance
The invention relates to improvements of a magnesium hydroxide flame retardant and a flame retardant polymer for cables. Natural magnesium hydroxide with the Mg(OH)2 content being not smaller than 96wt percent is adopted, and micro powder with a mean grain size of 0.5-1 micrometer is obtained through physical ultrafine grinding and grading; then 0.8-3wt percent of coupling agent is added, and an obtained mixture is stirred at a high speed, sufficiently mixed and then subjected to secondary surface processing by high-pressure airflows in a jet mill so as to obtain the magnesium hydroxide flameretardant with good smoothness and basically no aggregates; and the magnesium hydroxide flame retardant can smoothly flow like vegetable seeds under pushing by external forces. A polyolefin flame retardant polymer for cables is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 100 parts of polyolefin, 100-150 parts of submicron scale magnesium hydroxide, 2-10 parts of oxosilane, 0.2-1 part of antioxygen, 1-10 parts of processing aid and 0-6 parts of functional aid. The flame retardant polymer for cables has the following parameters: the oxygen index (OI) is up to 36-42, the tensile strength is not smaller than 10Mpa, the breaking elongation rate is not smaller than 200 percent, and the volume resistivity is not smaller than 10*1,015. The cracking resistance of the flame retardant polymer for cables is good, and the flame retardant polymer for cables cannot crack within one hour at a temperature of 130 DEG C and exceed the standard of the JB10707-2007 low-smoke non-halogen flame-retardant cable material. The flame retardant polymer for cables has good extrusion manufacturability and wide extrusion temperature range and can be effectively extruded at a temperature of 165-190 DEG C. The extrusion torque is small and reduced by 30 percent, thus the flame retardant polymer for cables can be smoothly extruded out by original equipment without a special screw rod.
Owner:无锡市英普立阻燃材料有限公司
Sintered neodymium iron boron waste remoulding method
ActiveCN102719725ANo abnormal coarse crystal phenomenonEasy to operateInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic materialsMetallurgyBulky waste
The invention discloses a sintered neodymium iron boron waste remoulding method. The sintered neodymium iron boron waste remoulding method comprises the steps of: a), crushing neodymium iron boron bulky waste into powder smaller than 40 meshes, putting the powder into a jet mill, and pulverizing, wherein the rotation speed of the jet mill speed is set at 800-1000rpm, the interior of the jet mill is protected by nitrogen gas, and the oxygen content is controlled at 2ppm; b), filling the powder finely ground by the jet mill into a material barrel protected by the nitrogen gas, adding 1-2ml of gasoline and 0.2-1ml of an oxidation preventer into each kilogram of the powder, and putting the material barrel into a mixer for stirring and mixing; and c) moulding the mixed powder, and sintering into a neodymium iron boron magnet. The neodymium iron boron magnet prepared by the method has normal cross-section crystallization; abnormal coarse-grained phenomenon does not appear; the performance of the neodymium iron boron magnet is consistent with that before the neodymium iron boron magnet is processed; and a normal material flow can be adopted. The sintered neodymium iron boron waste remoulding method is easy and convenient to operate and convenient and direct to process; and by the sintered neodymium iron boron waste remoulding method, waste of resources can be reduced and cost can be saved.
Owner:NINGBO KETIAN MAGNET +1
Hydraulic opposed jet mill
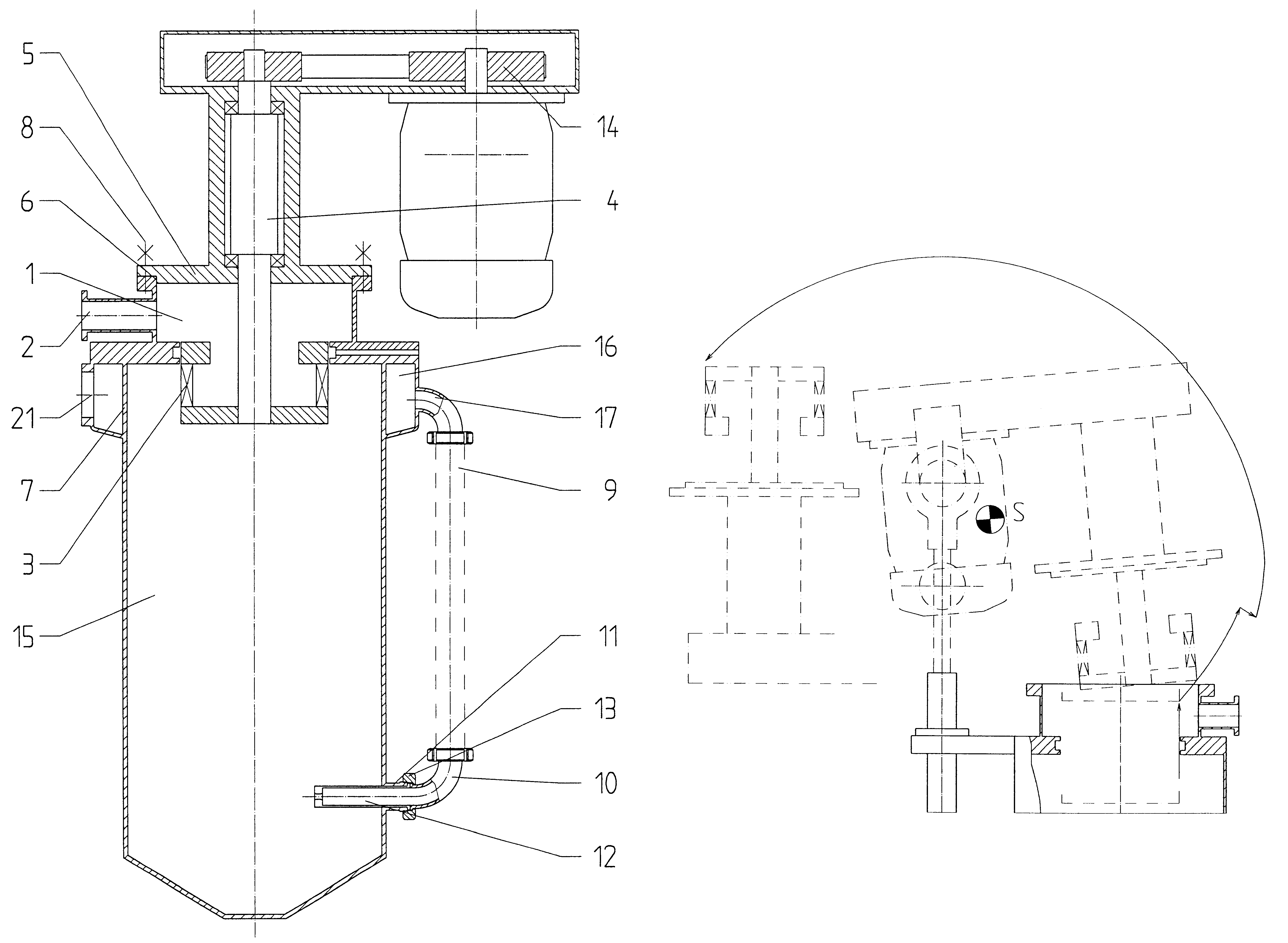
InactiveUS20060032953A1Increase water speedHigh speedGas current separationGrain millingWater flowMineral particles
Embodiments of an hydraulic opposed jet mill are disclosed which may be used to crush various minerals, including mica, or other materials to sub-micron size. At least one positive displacement pump forces an incompressible liquid, such as water, through a pair of opposed jets such that the two streams of water collide between the jets. A slurry of an incompressible liquid, such as water, and the mineral to be crushed is introduced into the jets at a point near the outlet end of the jets. The entrained mineral particles are forced out of the jets with great energy which causes multiple collisions and pulverization. In a second embodiment of the instant invention the slurry strikes an impingement plate rather than an opposed slurry stream.
Owner:KRUSE GEORGE
Apparatus for Treating a Substance with Wave Energy from Plasma and an Electrical Arc
InactiveUS20120020844A1Water/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsEngineeringMechanical engineering
An apparatus for synergistically combining a plasma with a comminution means such as a fluid kinetic energy mill (jet mill), preferably in a single reactor and / or in a single process step is provided by the present invention. Within the apparatus of the invention potential energy is converted into kinetic energy and subsequently into angular momentum by means of wave energy, for comminuting, reacting and separation of feed materials. Apparatuss of use of the apparatus in the practice of various processes are also provided by the present invention.
Owner:FORET PLASMA LABS
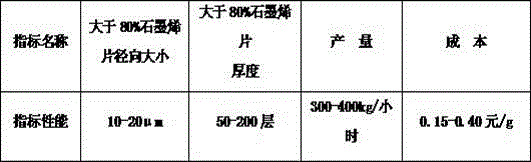
Method for preparing graphene micro-sheets by using counter-jet jet mill
The invention relates to the field of graphene materials, particularly relates to preparation methods for graphene micro-sheets and particularly relates to a method for preparing the graphene micro-sheets by using a counter-jet jet mill. According to the method, the graphene sheets are obtained through enabling melted ferric chloride and potassium chloride to enter an interlayer of graphite, enabling the powder materials to be in collision through high-speed airflow in the counter-jet jet mill by using the characteristic of brittleness of ferric chloride and potassium chloride crystal grains and the characteristics of good fluidity and difficulty in agglomeration of talcum powder, delaminating the graphite and the talcum powder by generated impact force, shearing force and frictional force, carrying out further separation by a grading room, refluxing unqualified powder material to a crushing chamber, and yielding delaminated graphite and talcum powder as well as gas together. The continuous and large-scale production of the graphene micro-sheets, which are uniform in layer number dispersion and good in fluidity and are not prone to agglomeration, is achieved, the yield is high, the cost is low, no pollution is caused, and the layer thickness meets the requirements of use in the fields of rubber reinforcing, plastic reinforcing, coating material anticorrosion, lubrication and sewage treatment, so that the promotion of the large-scale application of graphene is facilitated.
Owner:CHENDU NEW KELI CHEM SCI CO LTD
Preparation method of beche-de-mer capsules
The present invention relates to a preparing method of a sea cucumber capsule, , comprising the following processes: cleaning the raw material, namely fresh see cucumbers, Rubbing, placing in a sealed container; heating for 1min to 20h at 70-130 DEG C; freezing and drying the gelled sea cucumbers till the water content is less than 10%; roughly grinding the dried sea cucumbers to obtain sea cucumber powder with a fineness of 10-300 meshes; superfine milling with fluid jet mill to obtain 100-3,000 meshes superfine powder; nano-grinding the sea cucumber superfine powder through fluid milling with high-energy ball mill pulverizer to obtain 10-1,000nm powder, filling into capsules. The residue of the nano-powder prepared by gelling after enzymolysis is only 3.7% of the raw materials, while residue of the nano-powder prepared without gelling after enzymolysis si 53.9% of the raw materials. Test prove that the absorption and utilization of proteins are greatly improved after the sea cucumbers are gelled.
Owner:DALIAN HAIYANTANG BIOLOGY
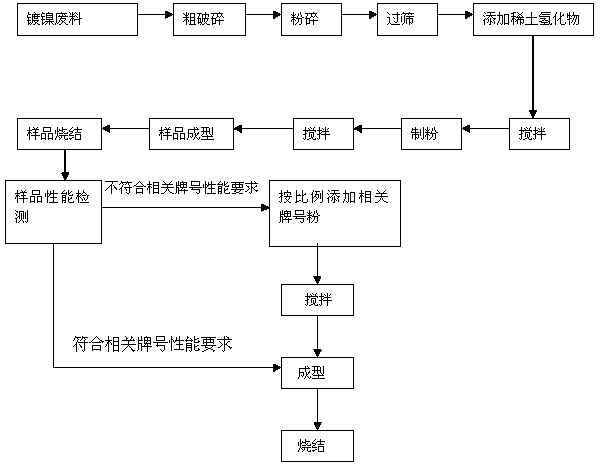
Method for recycling nickel-plated sintered NdFeB waste
ActiveCN103426579AIncrease profitSimple processInorganic material magnetismEarth materialsWaste material
The invention provides a method for recycling nickel-plated sintered NdFeB waste. The method includes the steps that a material is smashed into powder with the grain size below 3mm, the powder is sieved in a sealed nitrogen tank to remove most of flaky things of a nickel-plated layer, rare earth hydride is added in the sieved powder, the mixture is stirred evenly, the powder is made into 3-5-micrometer fine powder through a jet mill, the appropriate powder is taken to be formed in a compression mode, a sample is sintered to perform performance test, 0-60% by weight of powder of a related trade mark is added according to sample testing results and product performance requirements, the mixture is stirred evenly, and the qualified powder is formed in a compression mode and sintered into NdFeB magnets. For recycling of the nickel-plated sintered NdFeB waste, nickel-plated sintered NdFeB waste does not need to be roasted or remelted, sieving is performed after the smashing process, the rare earth hydride is added for powder manufacturing, the sample is trial-manufactured firstly to test the performance of the powder, a certain amount of powder of the related trade mark is added according to the performance requirements of products to be manufactured, and various sintered NdFeB products meeting the different performance requirements can be manufactured. The technological process is simple, the utilization rate of the NdFeB material and the utilization rate of the rear earth material are improved, and energy conservation and environment protection are also facilitated.
Owner:宁波科田磁业股份有限公司 +1
High discharge capacity lithium battery
A lithium / iron disulfide electrochemical battery cell with a high discharge capacity. The cell has a lithium negative electrode, an iron disulfide positive electrode and a nonaqueous electrolyte. The iron disulfide of the positive electrode has a controlled average particle size range which allows the electrochemical cells to exhibit desired properties in both low and high rate applications. In various embodiments, the iron disulfide particles are wet milled, preferably utilizing a media mill or milled utilizing a non-mechanical mill such as a jet mill, which reduces the iron disulfide particles to a desired average particle size range for incorporation into the positive electrode.
Owner:ENERGIZER BRANDS
Process for milling and preparing powders and compositions produced thereby
A method of milling a powder comprising introducing a gas stream containing a cryogenic liquid and a drug carrier gas into a jet mill, and milling a powder with the jet mill in one or more milling passes. A product produced by the method. A milling apparatus comprising a cryogenic gas input system, a powder feeder, a main jet-mill, and at least one output port for collecting the powder.
Owner:NANOSHIFT LLC
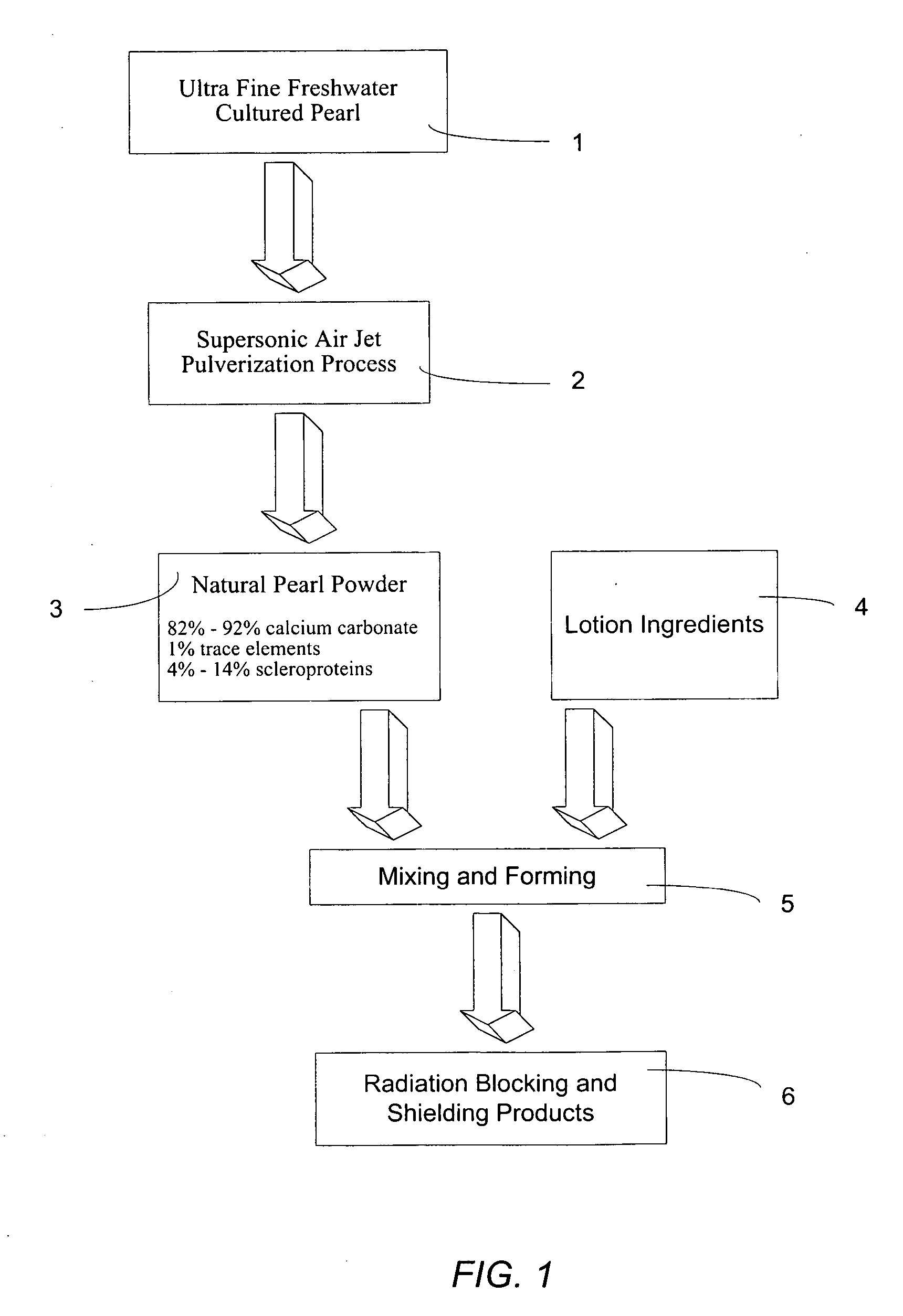
Nano pearl cream
InactiveUS20050226830A1Superior radiation blockingGood shielding protectionBiocideCosmetic preparationsCultured pearlPurified water
A topical application comprises cultured pearl powder of particle size ranging between 0.4 μm and 1 μm ground by an ultrasonic gas jet mill, and purified water suspending the cultured pearl powder.
Owner:FANG HARVARD
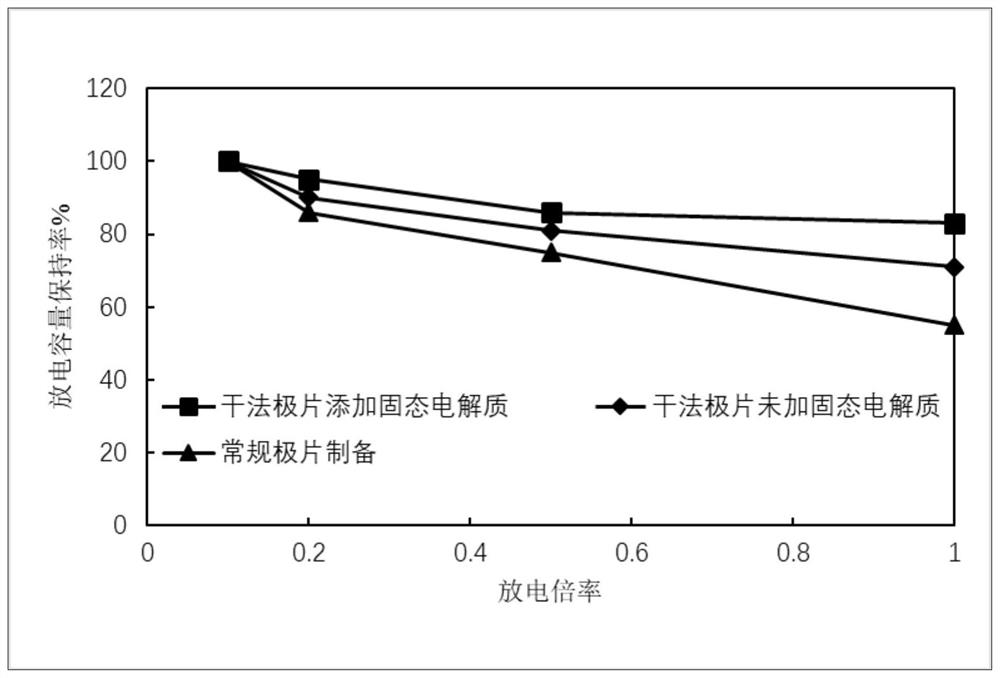
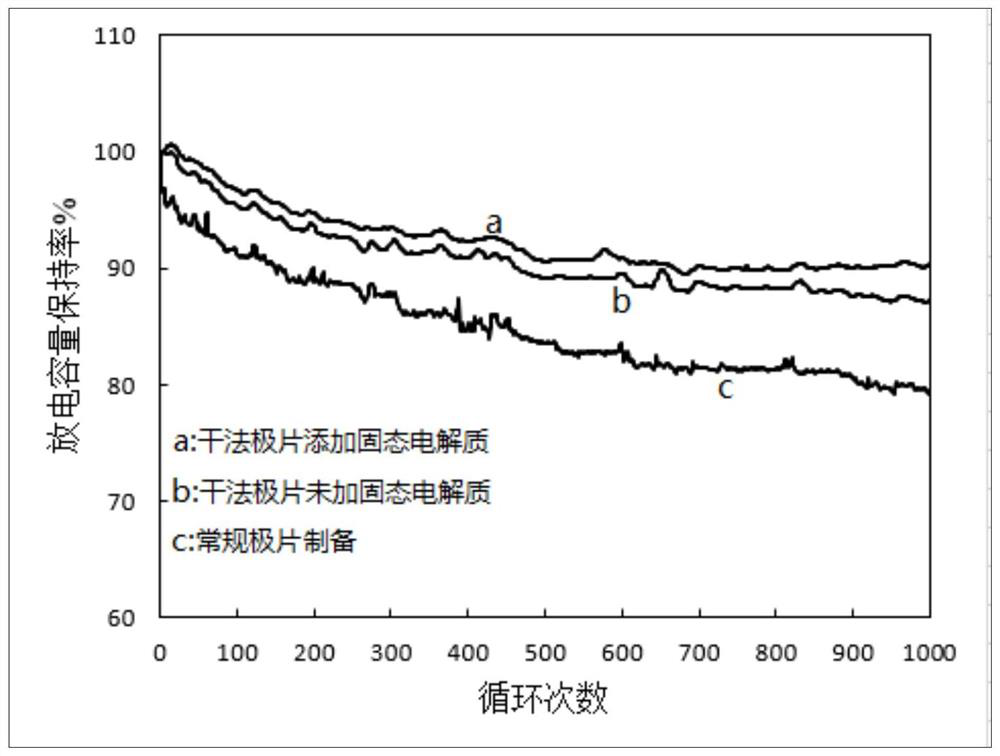
Dry method for preparing lithium battery positive and negative plates
ActiveCN112420986AReduce circulationReduced service lifeElectrode rolling/calenderingFinal product manufactureSolid state electrolyteElectrolytic agent
The invention discloses a method for preparing positive and negative plates of a lithium battery by a dry method, and the method comprises the following steps: mixing an active substance, a conductiveagent, a binder and solid electrolyte powder according to a certain proportion and a certain sequence in a solvent-free manner, uniformly mixing by using a stirrer, and performing mechanical mixing by using a jet mill; extruding the uniform dry powder into continuous sheets by using a screw extruder, and finally rolling the continuous sheets on a current collector at high temperature for multipletimes to form the dry electrode. The invention solves the problems of high cost, difficult recovery and heavy pollution of the solvent used in the existing lithium battery production; meanwhile, thesolid electrolyte powder is added into the positive electrode and the negative electrode, so that the polarization of the battery can be reduced, the battery impedance is reduced, the battery performance is improved, electrolyte is reduced or even not added, and the safety problem caused by using organic electrolyte by the lithium battery is solved.
Owner:NANJING BOCHI NEW ENERGY CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com