Patents
Literature
17452results about "Inductances/transformers/magnets manufacture" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
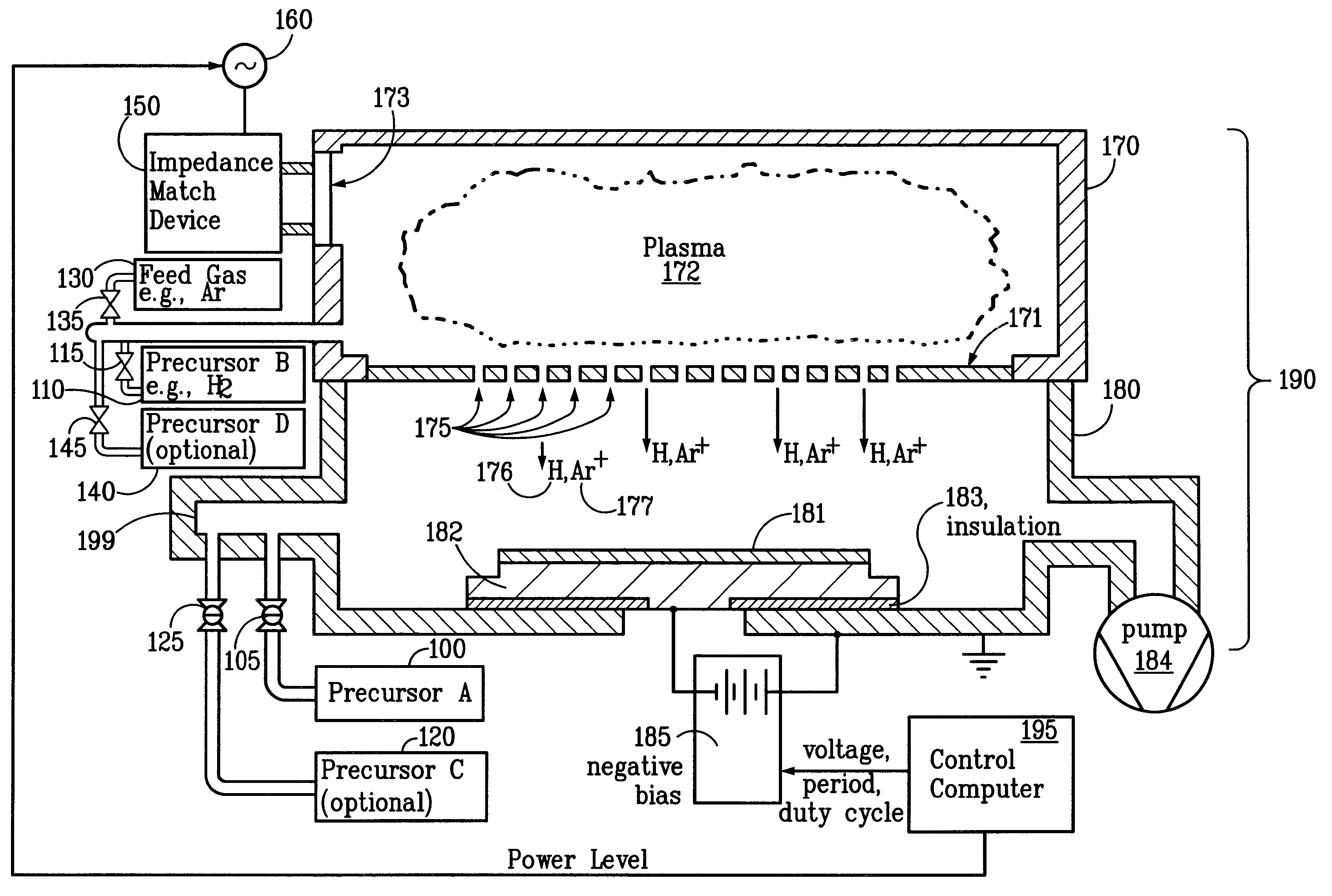
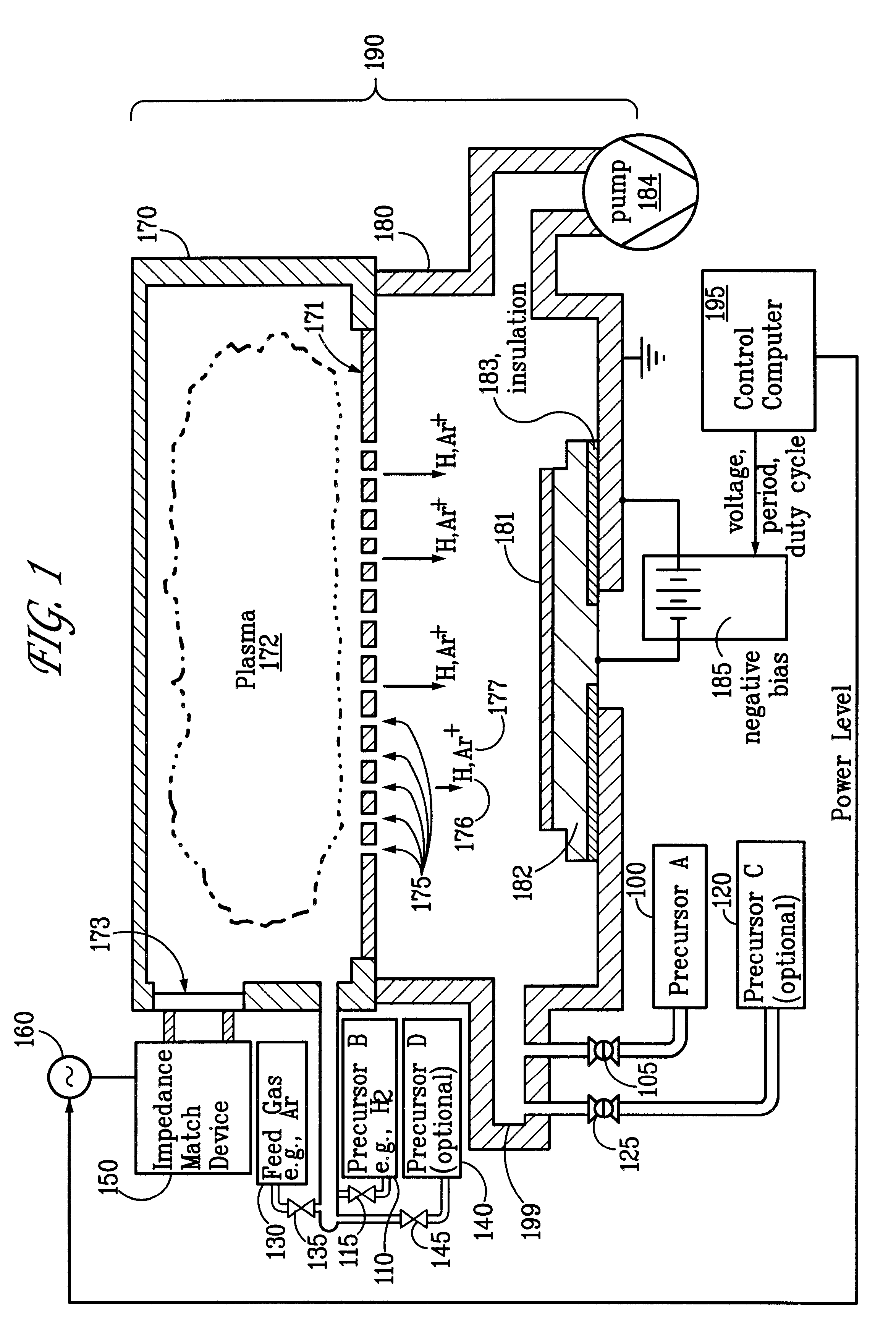
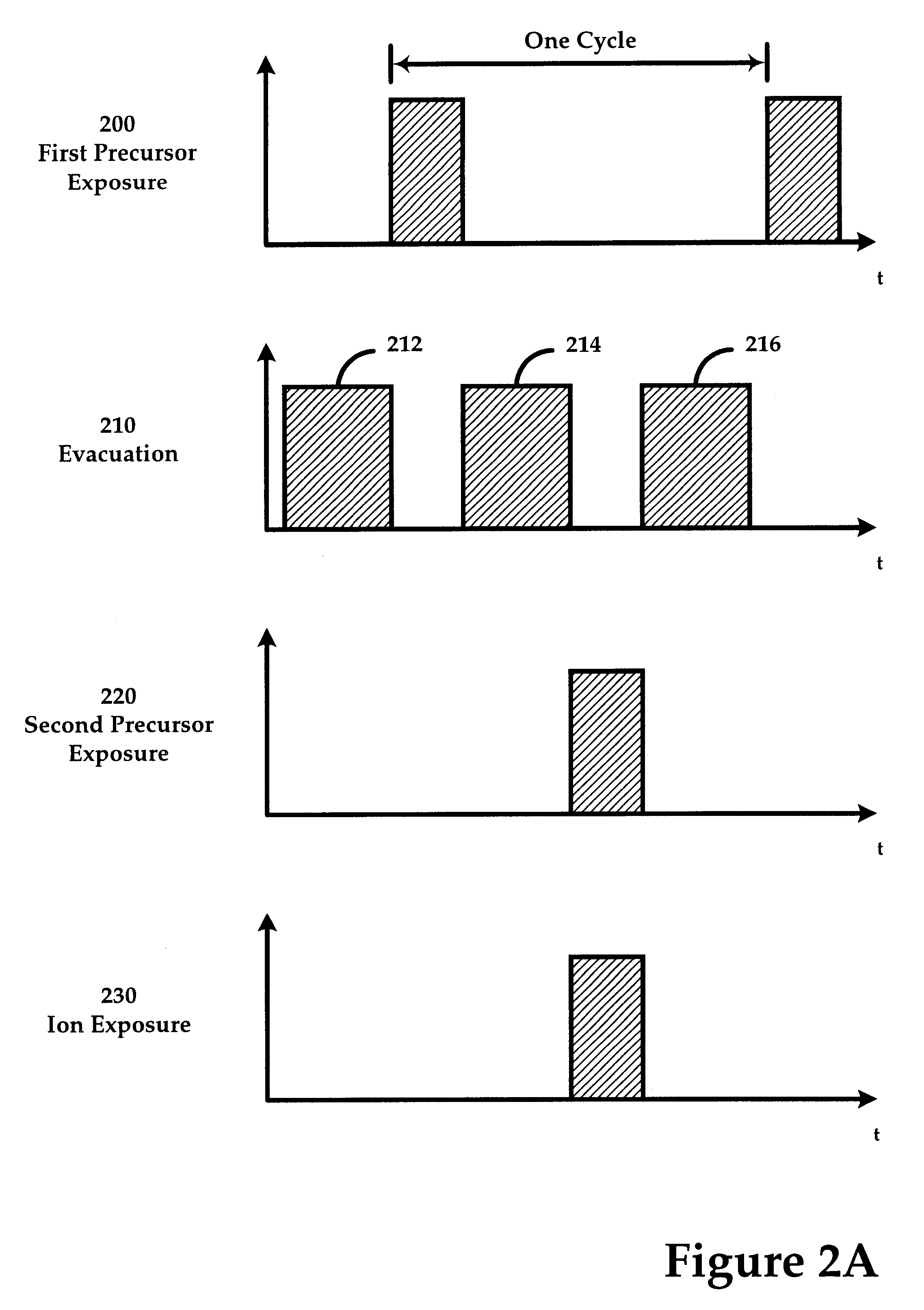
Sequential method for depositing a film by modulated ion-induced atomic layer deposition (MII-ALD)
InactiveUS6428859B1Faster efficient meanSimple methodVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingSequential methodHigh density
The present invention relates to an enhanced sequential atomic layer deposition (ALD) technique suitable for deposition of barrier layers, adhesion layers, seed layers, low dielectric constant (low-k) films, high dielectric constant (high-k) films, and other conductive, semi-conductive, and non-conductive films. This is accomplished by 1) providing a non-thermal or non-pyrolytic means of triggering the deposition reaction; 2) providing a means of depositing a purer film of higher density at lower temperatures; and, 3) providing a faster and more efficient means of modulating the deposition sequence and hence the overall process rate resulting in an improved deposition method. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract that will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
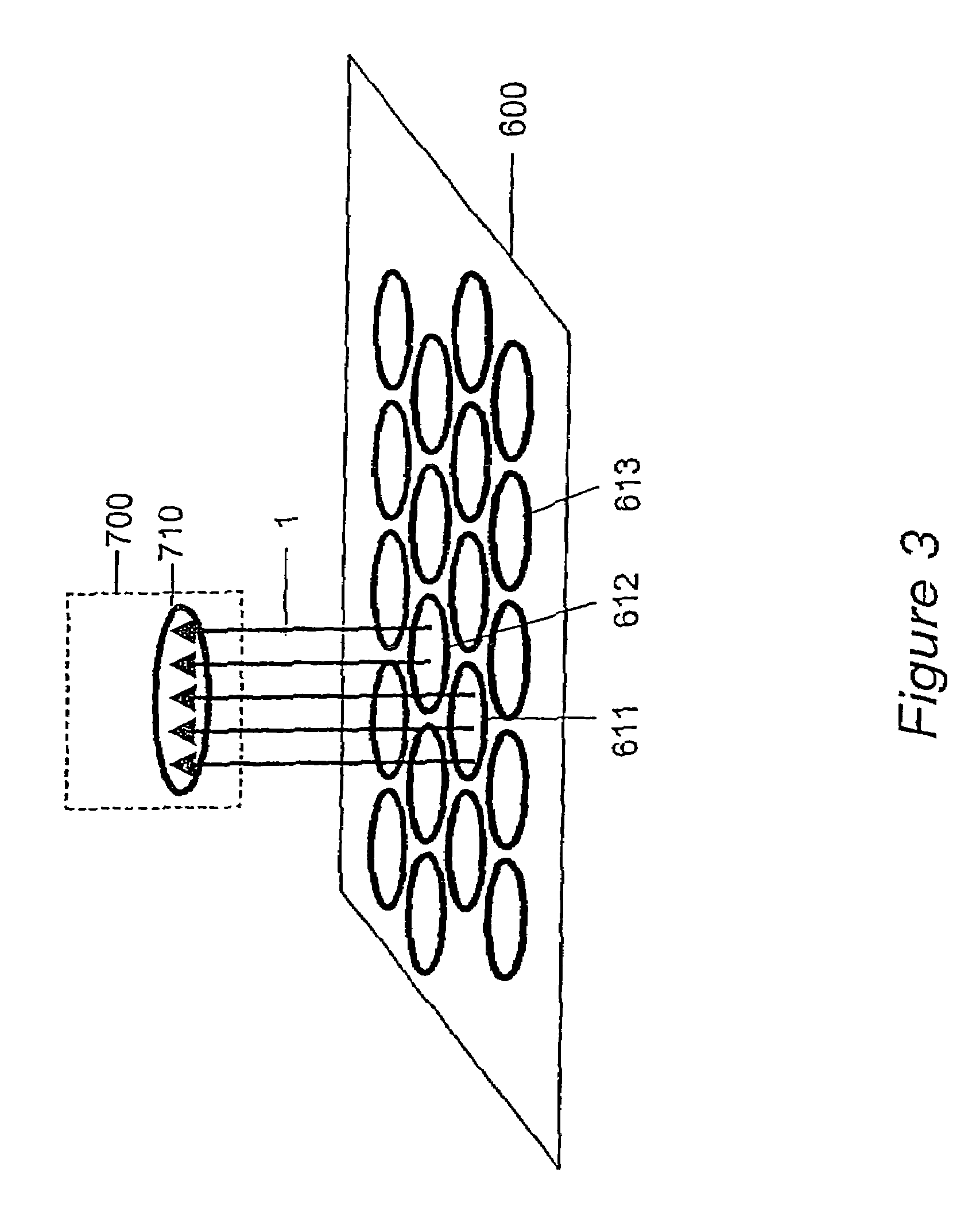
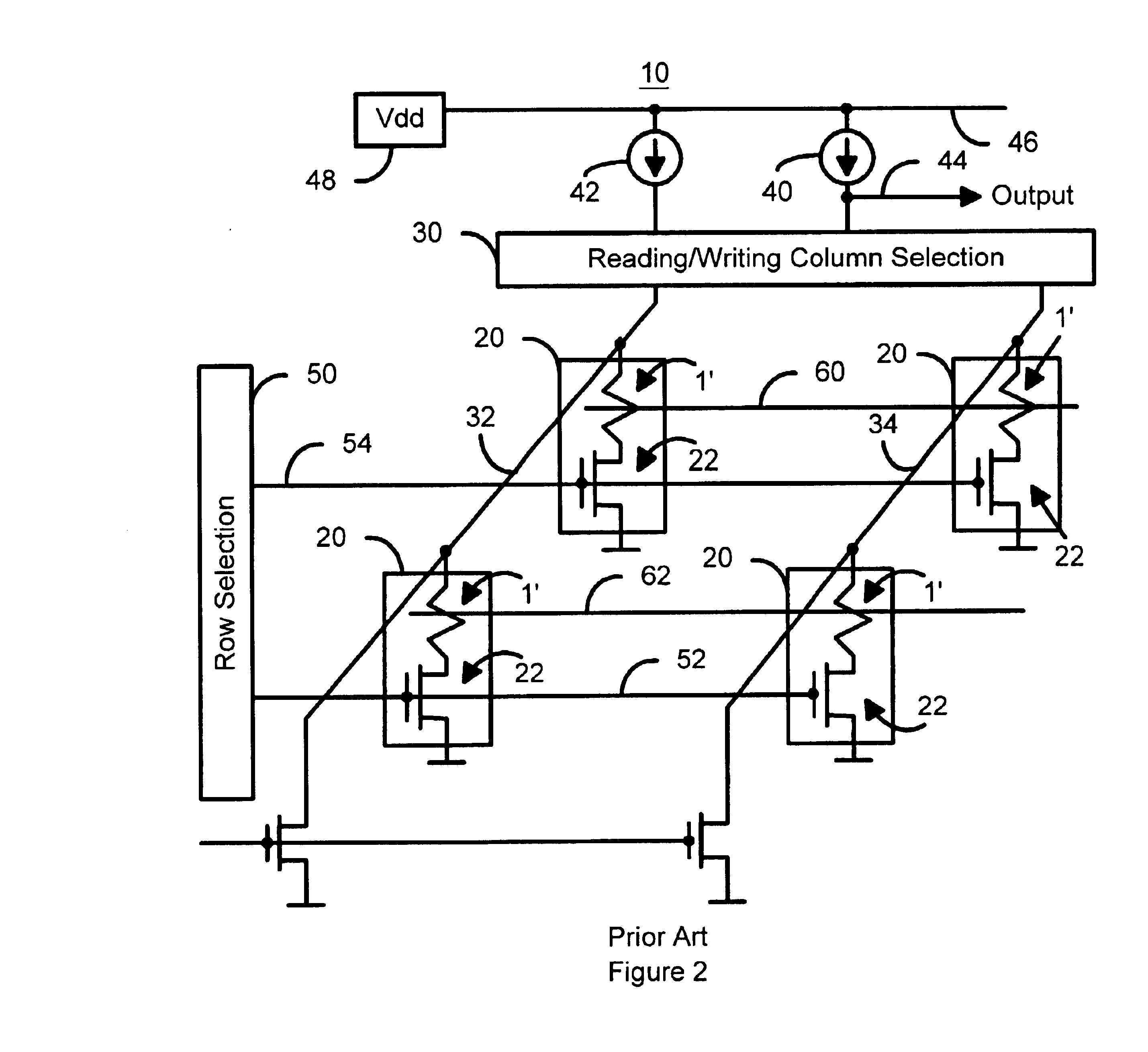
Contact-less power transfer
A system and method for transferring power does not require direct electrical conductive contacts. There is provided a primary unit having a power supply and a substantially laminar surface having at least one conductor that generates an electromagnetic field when a current flows therethrough and having an active area defined within a perimeter of the surface, the at least one conductor being arranged such that electromagnetic field lines generated by the at least one conductor are substantially parallel to the plane of the surface within the active area; and at least one secondary device including at least one conductor that may be wound about a core; wherein the active area has a perimeter large enough to surround the conductor or core of the at least one secondary device in any orientation thereof substantially parallel to the surface of the primary unit in the active area, such that when the at least one secondary device is placed on or in proximity to the active area in a predetermined orientation, the electromagnetic field induces a current in the at least one conductor of the at least one secondary device.
Owner:PHILIPS IP VENTURES BV
Portable contact-less power transfer devices and rechargeable batteries
InactiveUS7248017B2Maximise currentMaximise voltageTransformersTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsElectric power transmissionElectrical conductor
There is disclosed a system and method for transferring power without requiring direct electrical conductive contacts. There is provided a primary unit having a power supply and a substantially laminar charging surface having at least one conductor that generates an electromagnetic field when a current flows therethrough and having an charging area defined within a perimeter of the surface, the at least one conductor being arranged such that electromagnetic field lines generated by the at least one conductor are substantially parallel to the plane of the surface or at least subtend an angle of 45° or less to the surface within the charging area; and at least one secondary device including at least one conductor that may be wound about a core. Because the electromagnetic field is spread over the charging area and is generally parallel or near-parallel thereto, coupling with flat secondary devices such as mobile telephones and the like is significantly improved in various orientations thereof.
Owner:PHILIPS IP VENTURES BV
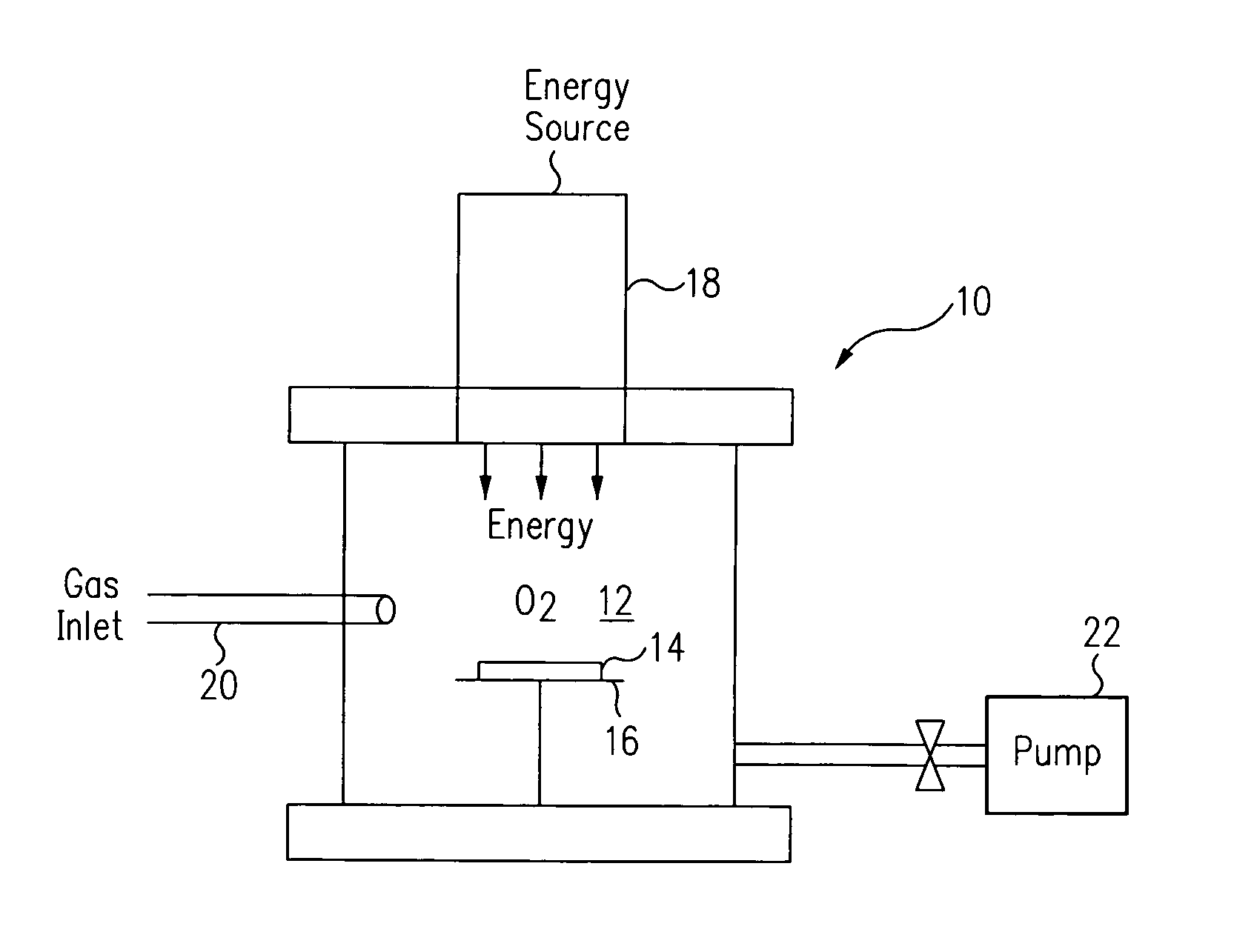
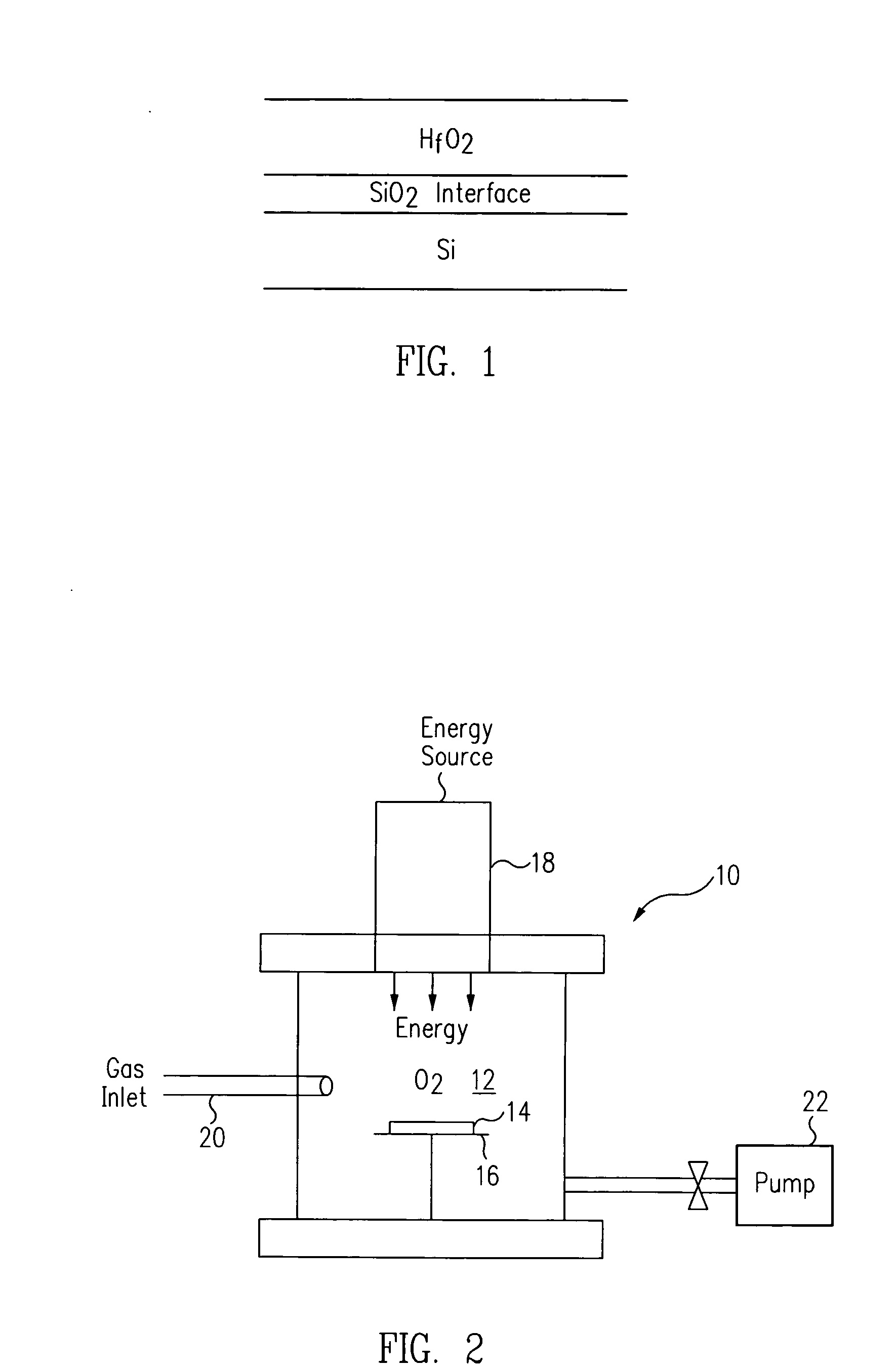
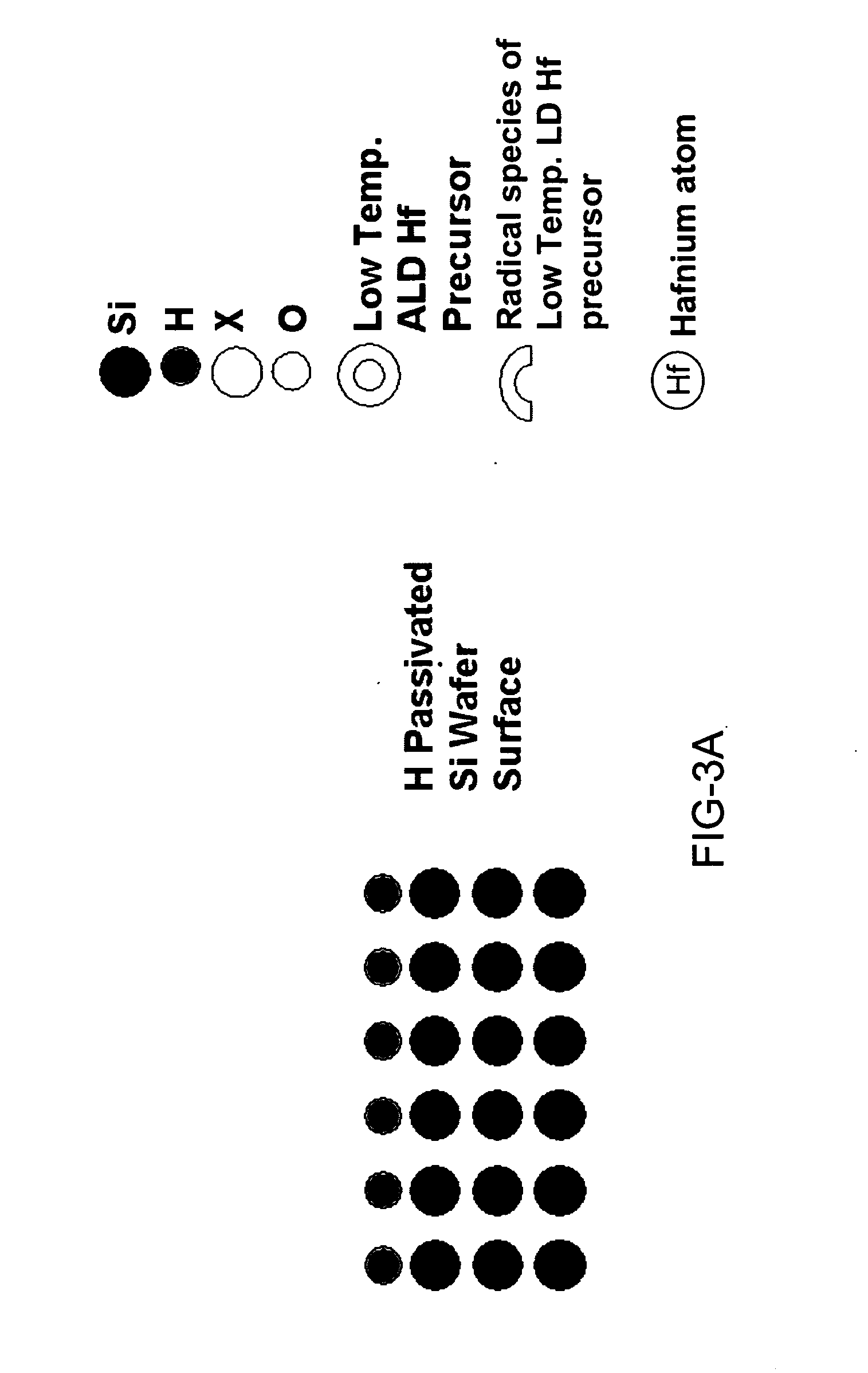
Method for energy-assisted atomic layer deposition and removal
InactiveUS20050175789A1High energyGood initiativeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPretreated surfacesProduct gasElectromagnetic radiation
A method for energy-assisted atomic layer deposition and removal of a dielectric film are provided. In one embodiment a substrate is placed into a reaction chamber and a gaseous precursor is introduced into the reaction chamber. Energy is provide by a pulse of electromagnetic radiation which forms radical species of the gaseous precursor. The radical species react with the surface of the substrate to form a radical terminated surface on the substrate. The reaction chamber is purged and a second gaseous precursor is introduced. A second electromagnetic radiation pulse is initiated and forms second radical species. The second radical species of the second gas react with the surface to form a film on the substrate. Alternately, the gaseous species can be chosen to produce radicals that result in the removal of material from the surface of the substrate.
Owner:HELMS JR AUBREY L +3
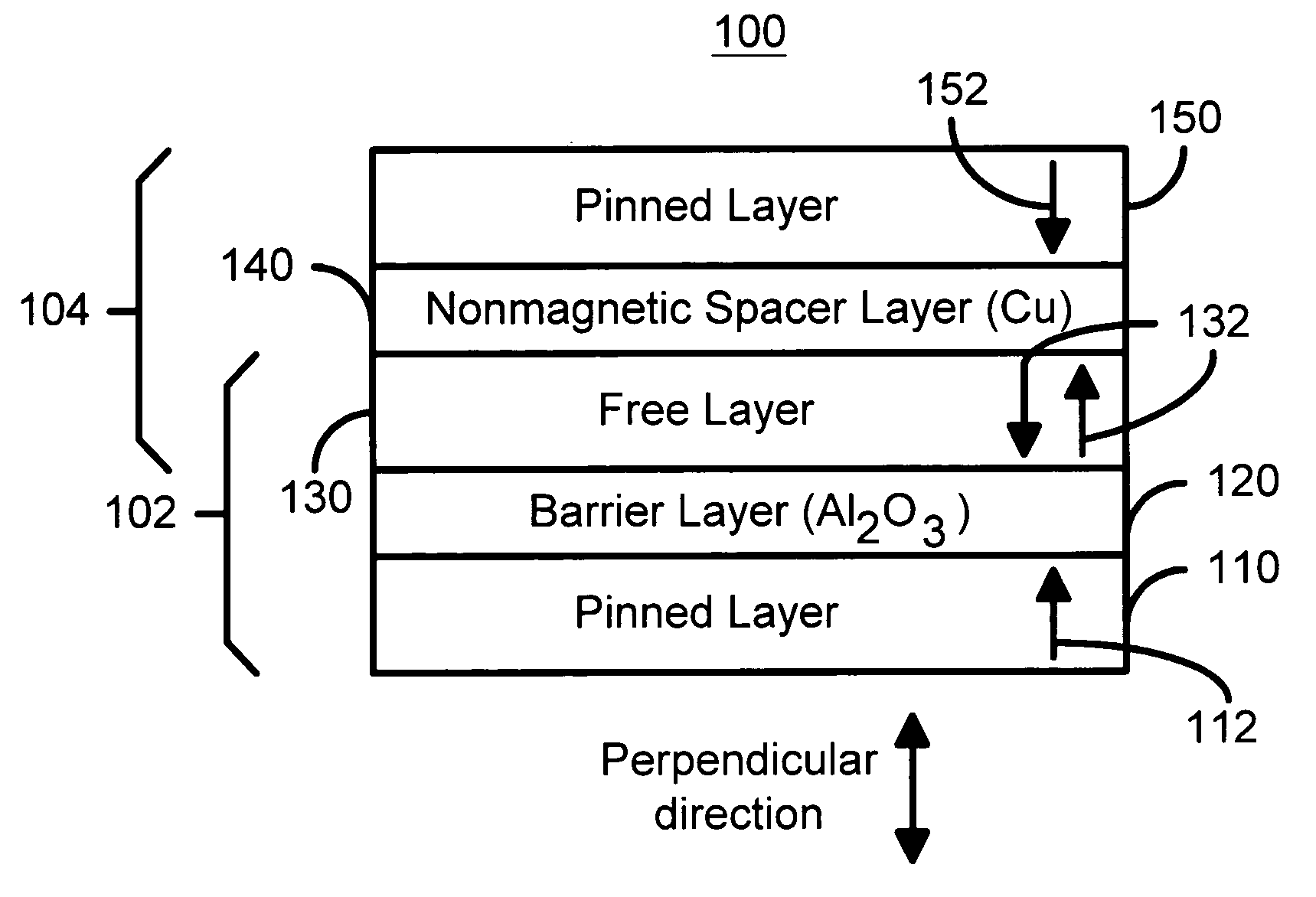
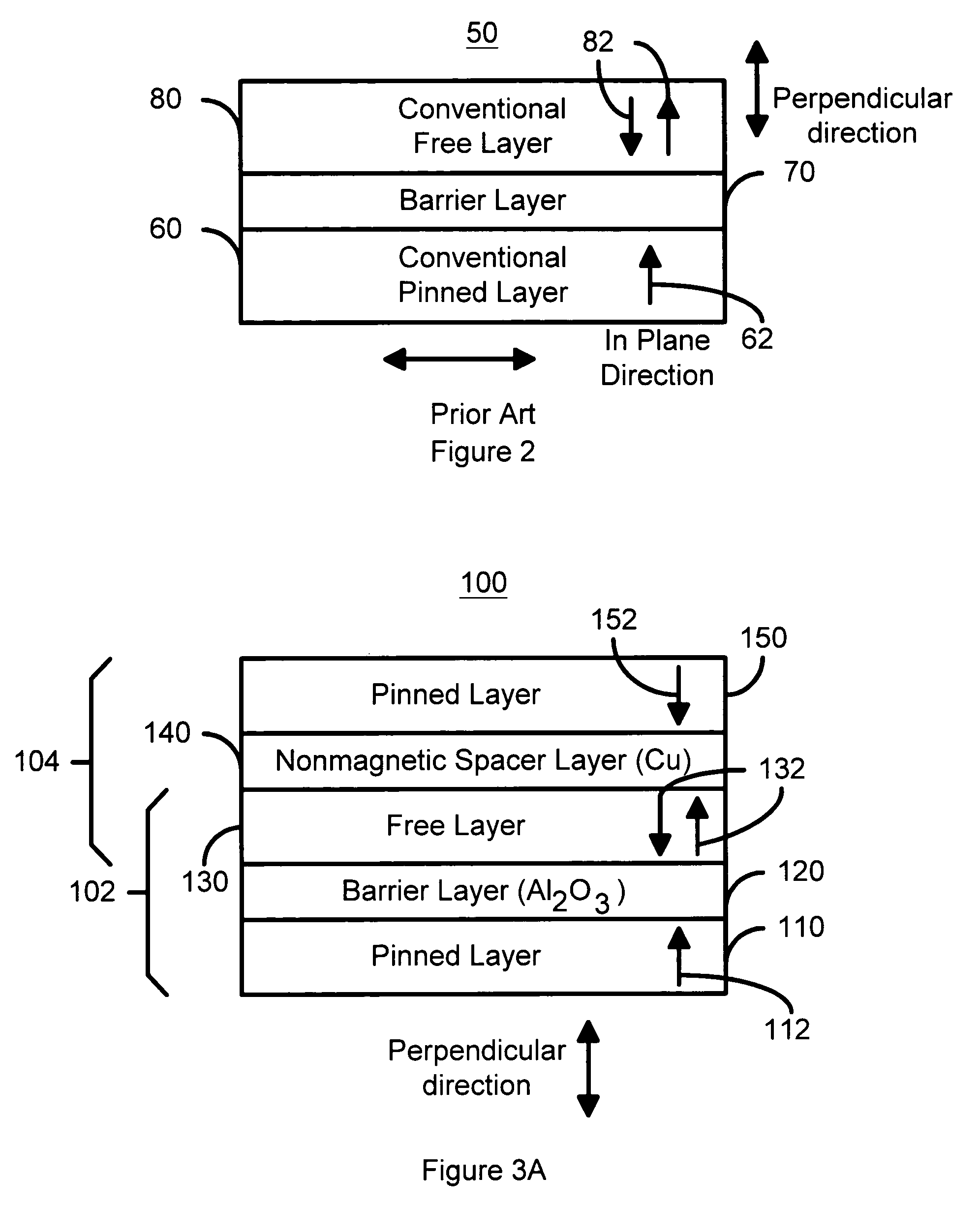
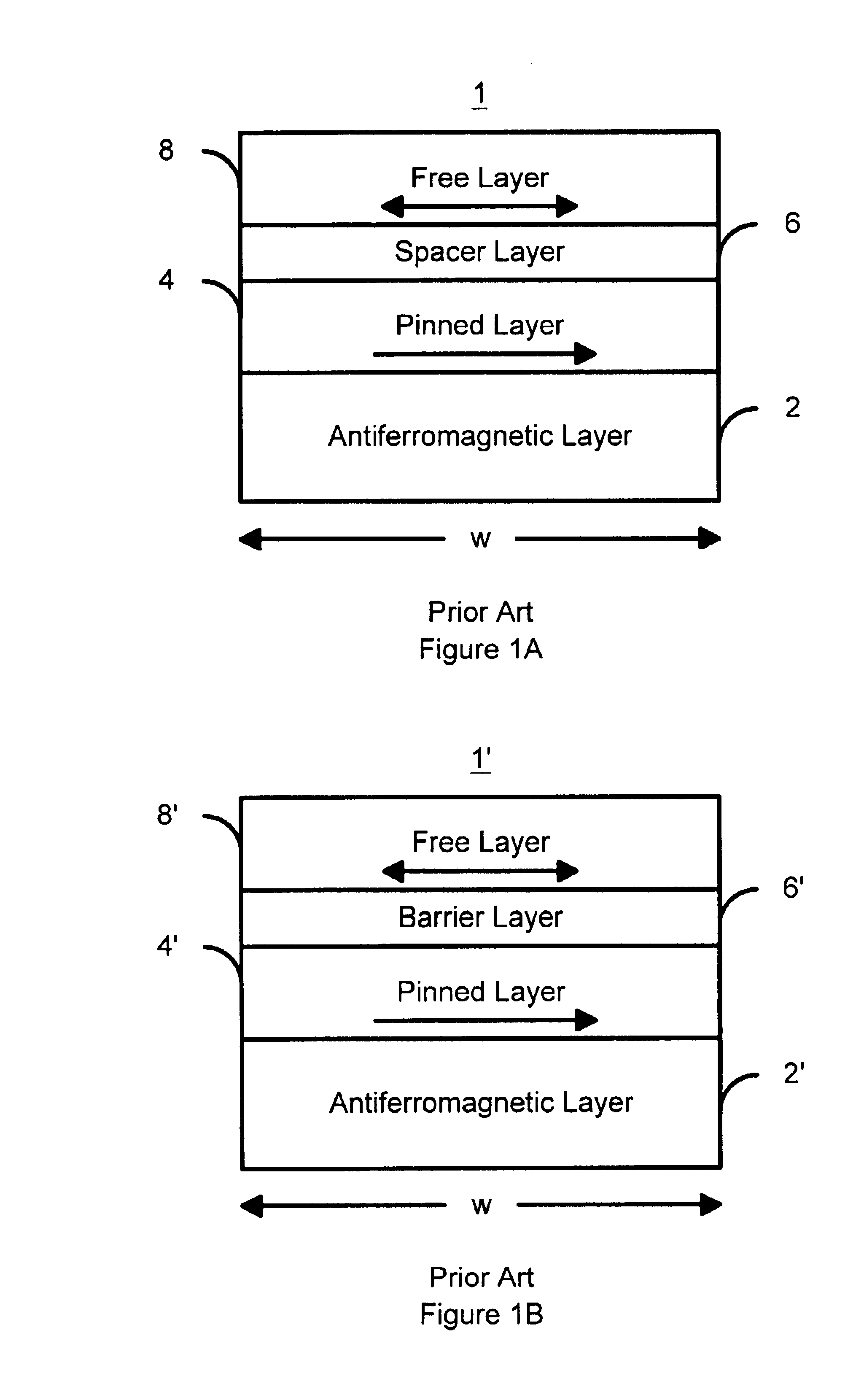
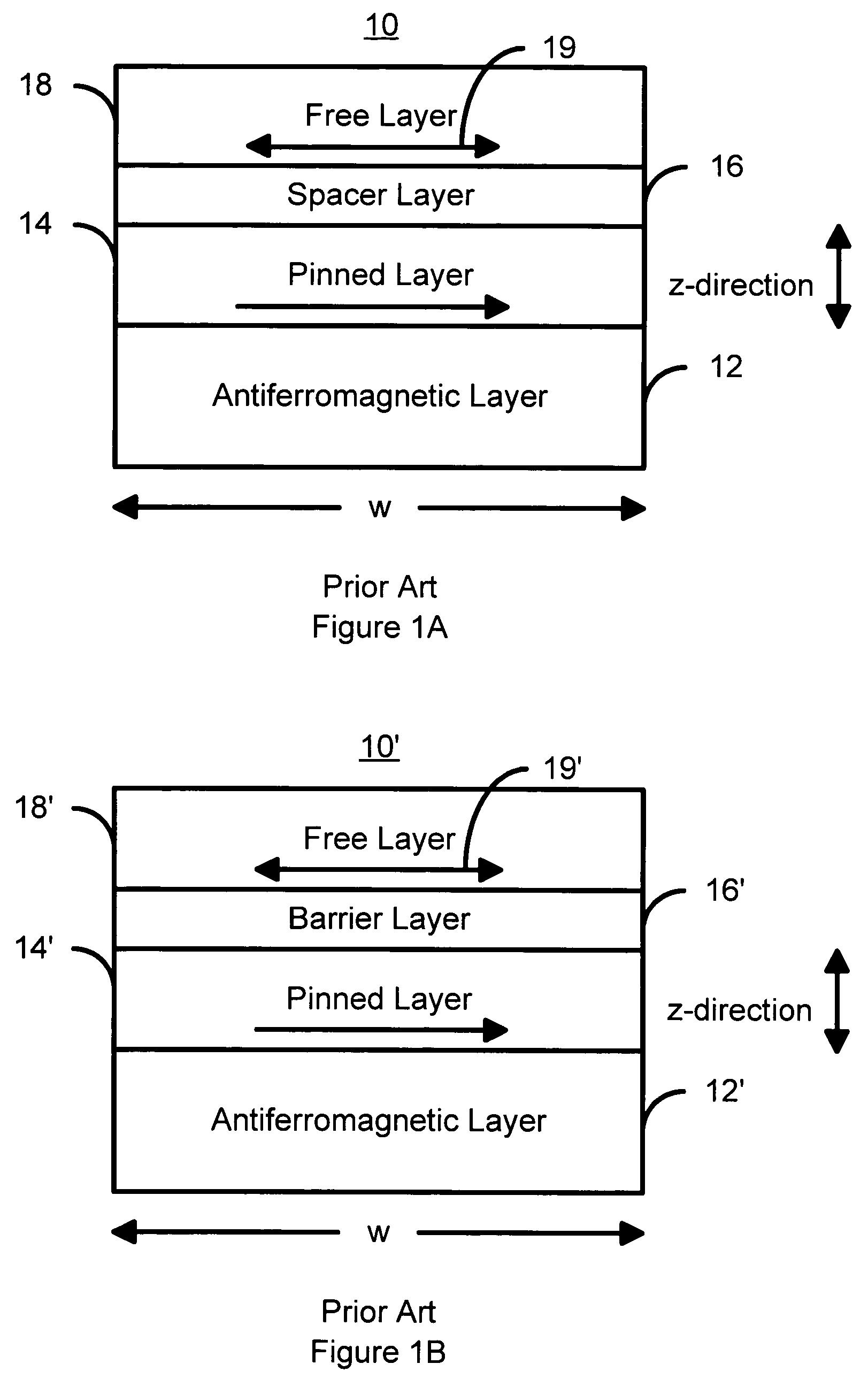
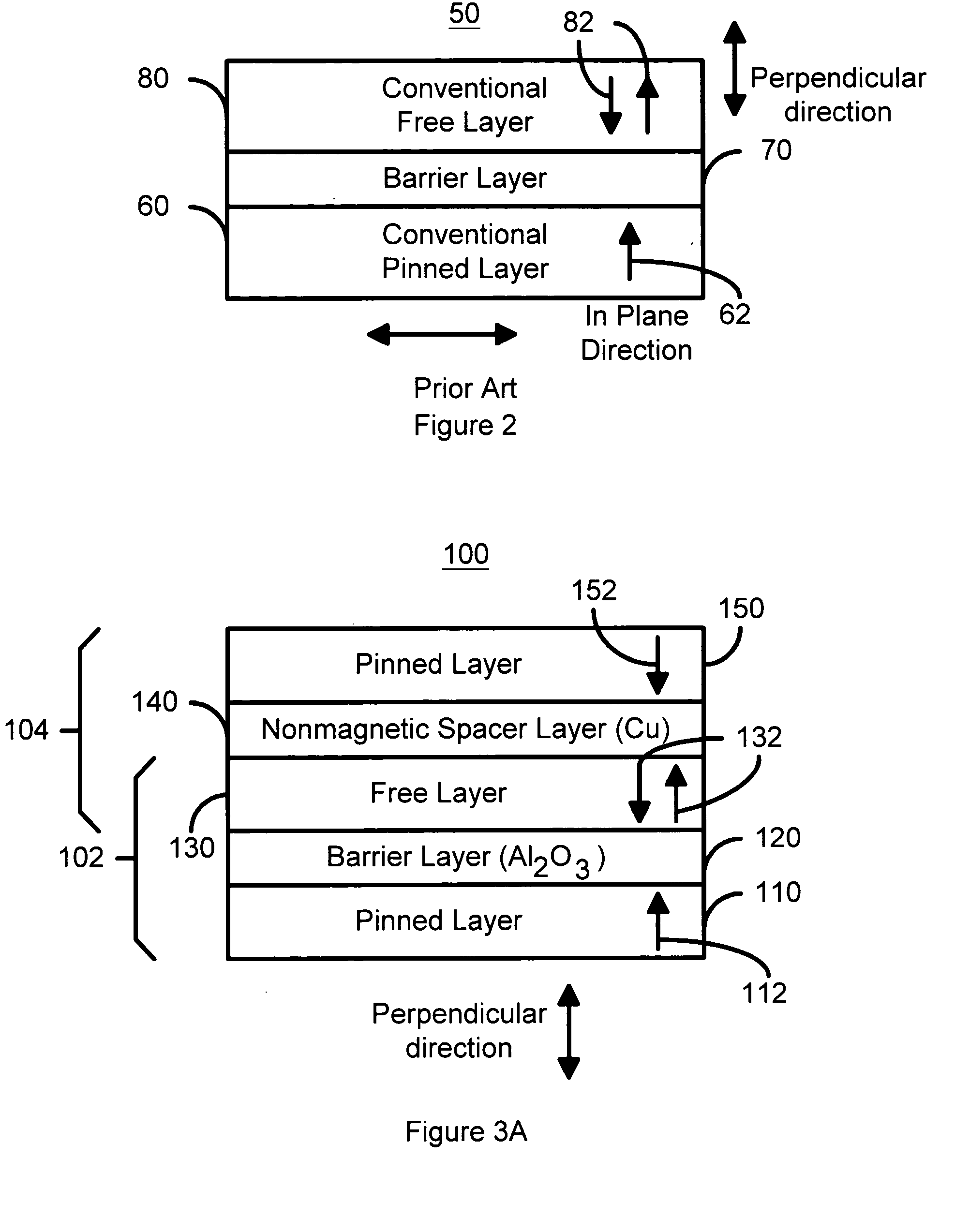
Perpendicular magnetization magnetic element utilizing spin transfer
ActiveUS6967863B2Reduce currentNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsPerpendicular magnetizationMagnetic memory
A method and system for providing a magnetic element that can be used in a magnetic memory is disclosed. The method and system include providing a first pinned layer, a barrier layer, a free layer, a conductive nonmagnetic spacer layer, and a second pinned layer. Each pinned layer has a pinned layer easy axis. At least a portion of the pinned layer easy axis is in a perpendicular direction. The barrier layer resides between the first pinned layer and the free layer. The spacer layer is between the free layer and the second pinned layer. The free layer has a free layer easy axis, at least a portion of which is in the perpendicular direction. The magnetic element is also configured to allow the free layer to be switched due to spin transfer effect when a write current is passed through the magnetic element. Because of the perpendicular magnetization(s), the writing current for spin transfer may be significantly reduced.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
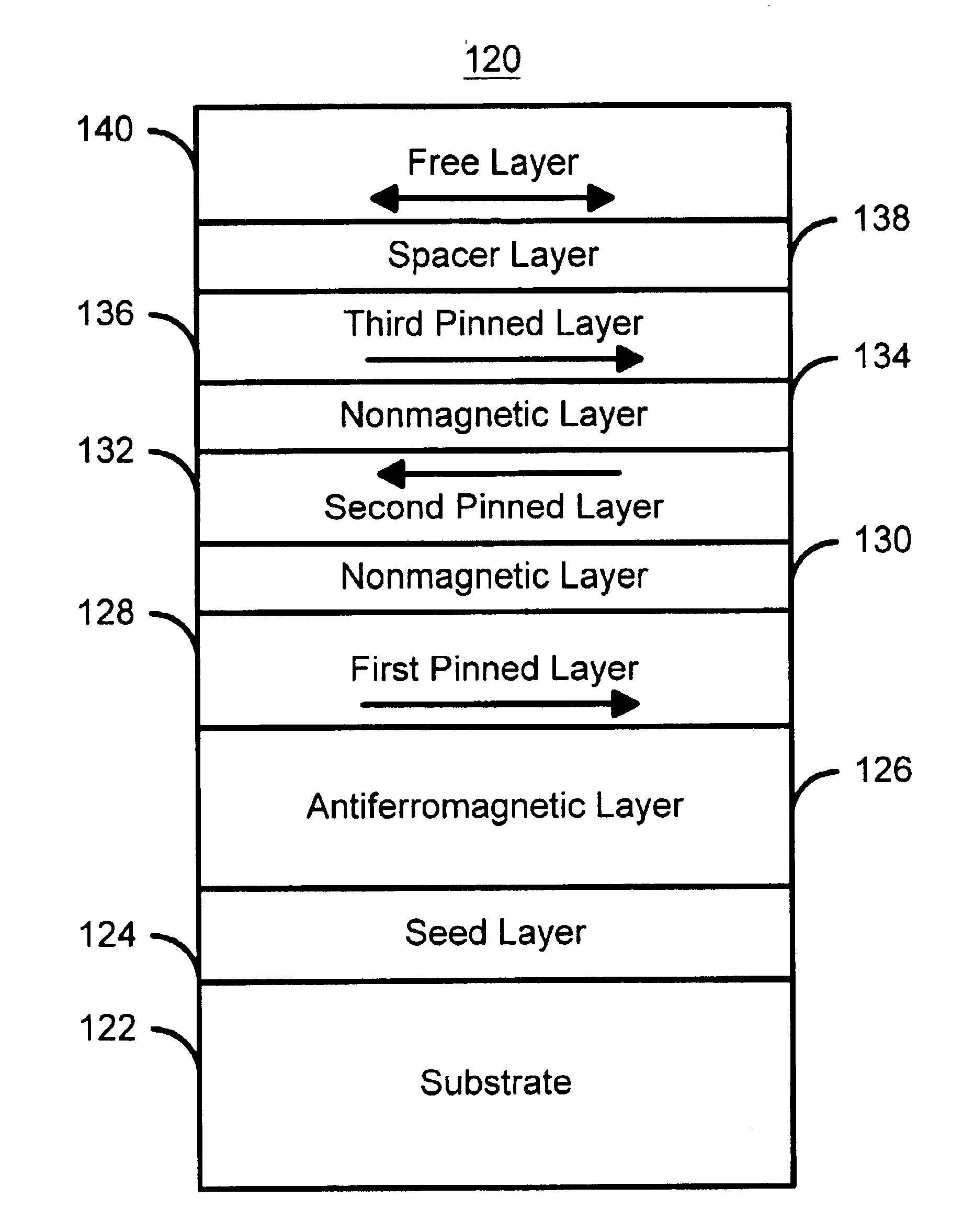
Thermally stable magnetic elements utilizing spin transfer and an MRAM device using the magnetic element
InactiveUS6838740B2Improve performanceImprove thermal stabilityTransistorNanomagnetismAntiferromagnetic couplingMagnetic memory
A method and system for providing a magnetic element capable of being written using spin-transfer effect while being thermally stable and a magnetic memory using the magnetic element are disclosed. The magnetic element includes a first, second and third pinned layers, first and second nonmagnetic layers, a free layer and a nonmagnetic spacer layers. The first, second and third pinned layers are ferromagnetic and have first, second and third magnetizations pinned in first, second and third directions. The first and second nonmagnetic layers include first and second diffusion barriers, respectively. The first and second nonmagnetic layers are between the first and second pinned layers and the second and third pinned layers, respectively. The first and second pinned layers and the second and third pinned layers are antiferromagnetically coupled. The nonmagnetic spacer layer is conductive and resides between the free layer and the third pinned layer. In addition, performance can be further improved by doping Co containing ferromagnetic layers with Cr and / or Pt.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
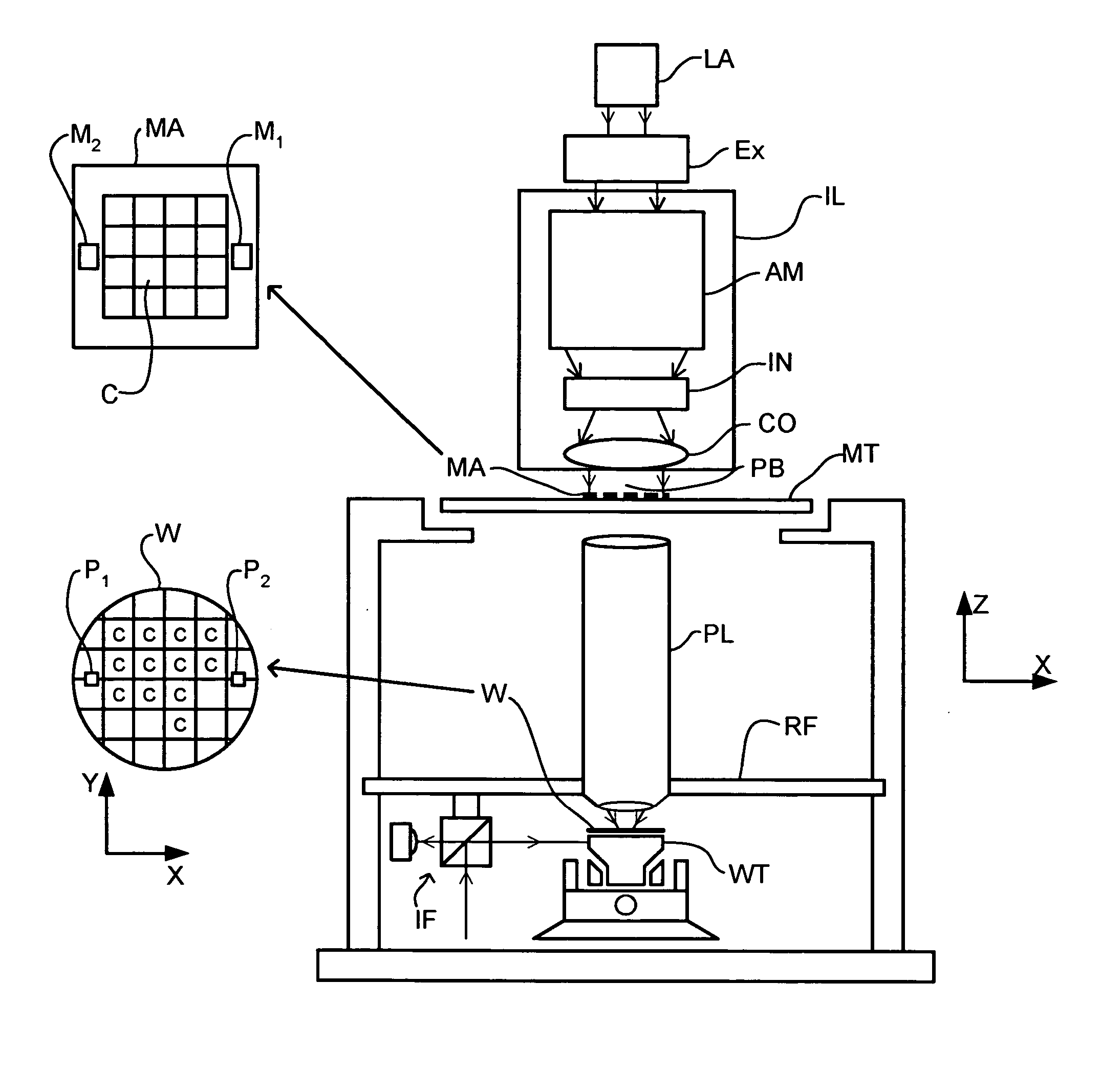
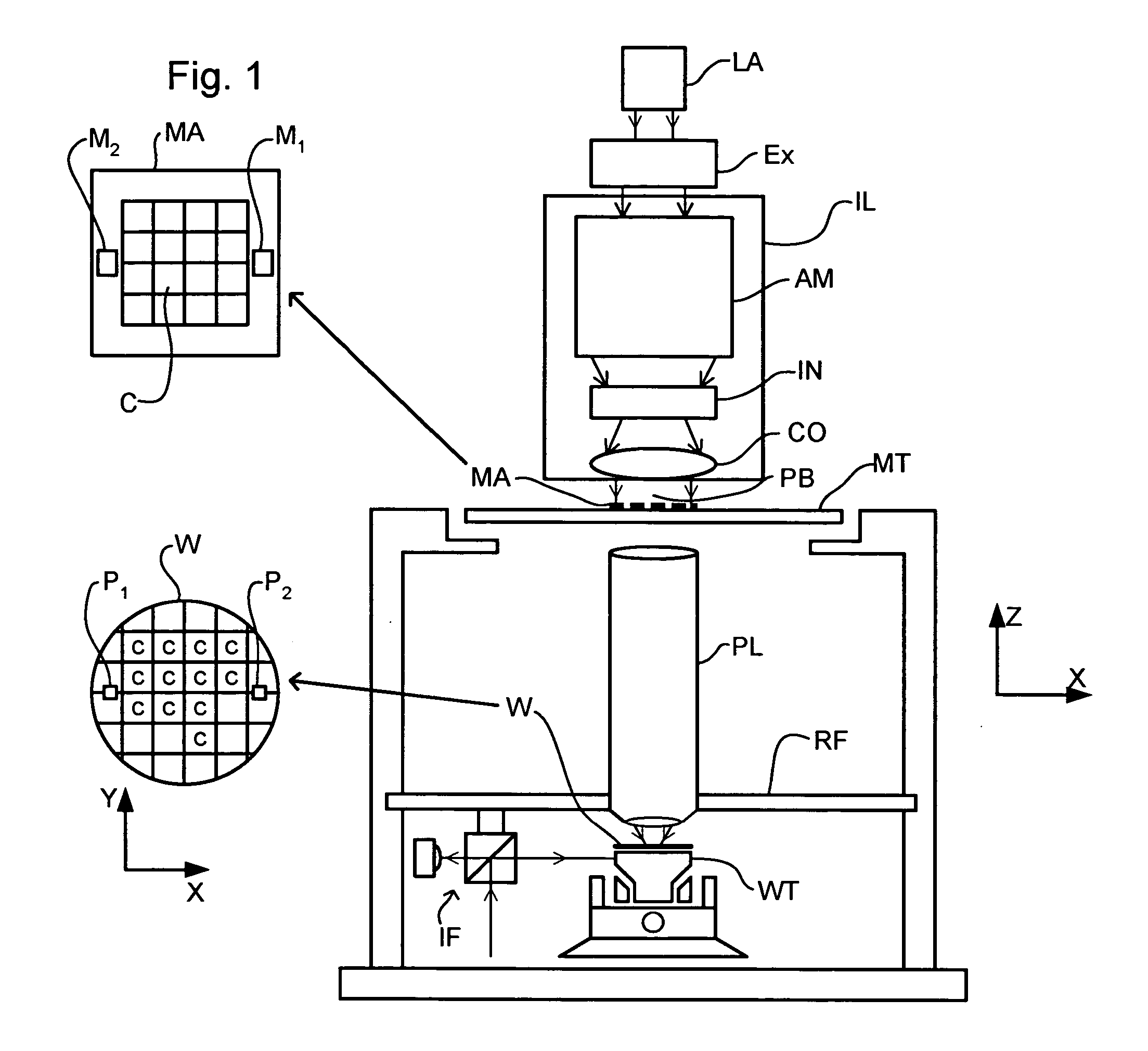
Lithographic apparatus and device manufacturing method
InactiveUS20050048220A1ConstantAvoid pollutionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPretreated surfacesEngineeringImmersion lithography
In an immersion lithography apparatus, the immersion liquid is supplied from a tank via a flow restrictor. The liquid held in the tank is maintained at a substantially constant height above the flow restrictor to ensure a constant flow of liquid.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Ferromagnetic powder for dust core
InactiveUS7498080B2Increase resistanceTotal current dropLiquid surface applicatorsInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureElectrical resistance and conductanceEddy current
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD
Roll to roll nanoimprint lithography
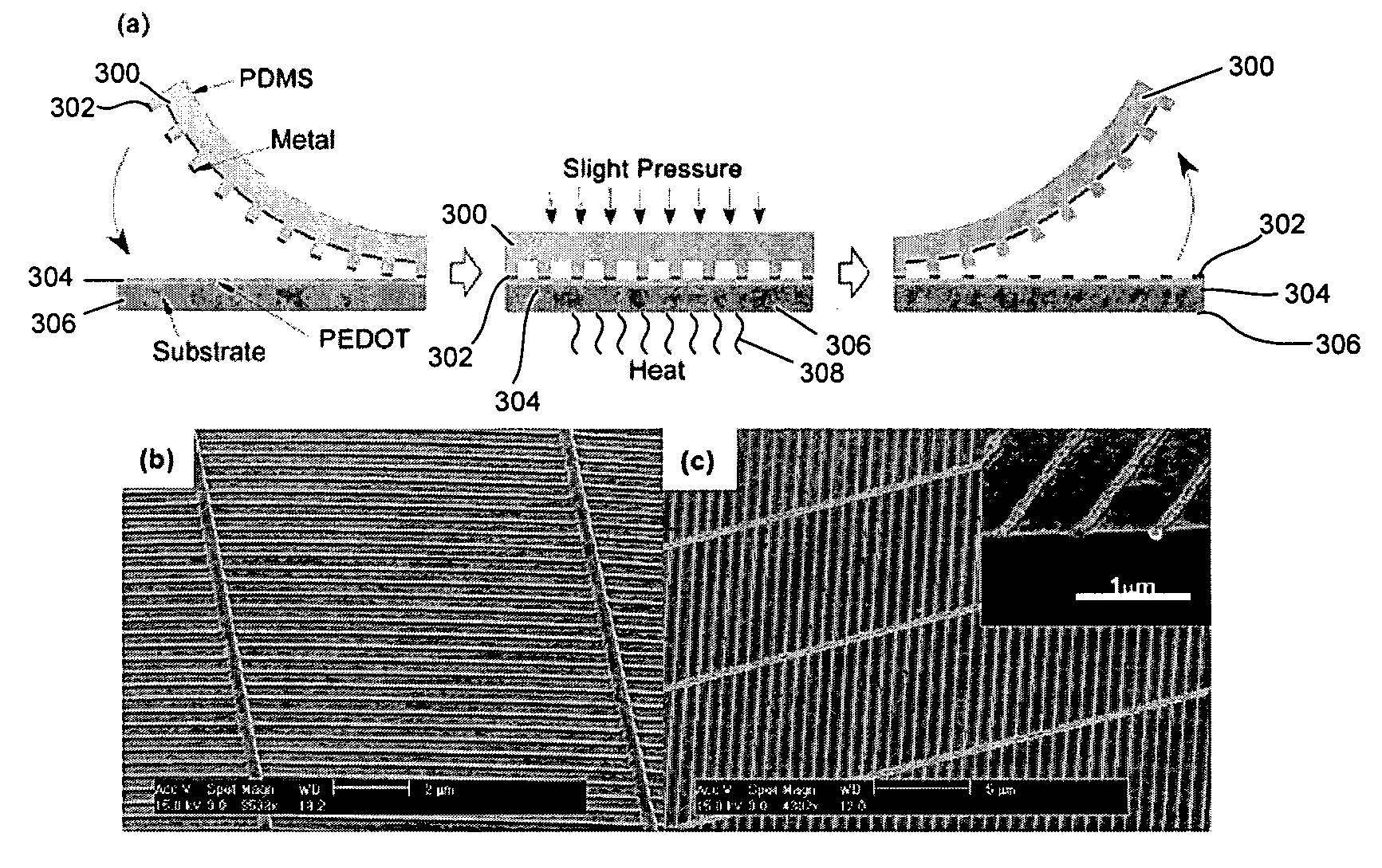
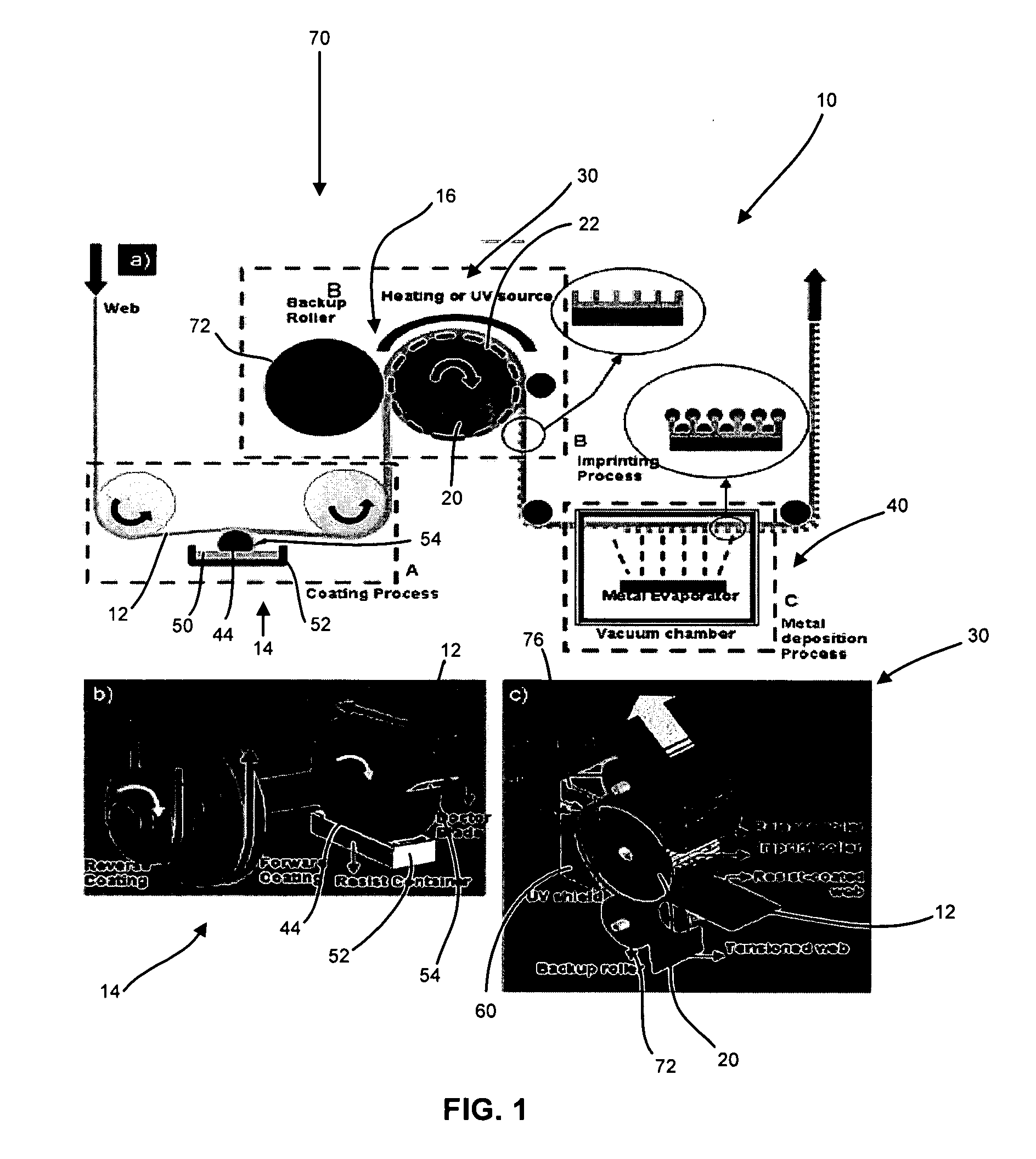
Apparatus and methods for a nano-patterning process to fabricate nanostructures. A roller type mold is used to continuously imprint nanostructures onto a flexible web or a rigid substrate. The process includes a coating and an imprinting module, which rotate the web synchronously. Liquid resist materials are used for imprinting and the patterns are set by thermal or UV curing. The process is used to produce bilayer metal wire-grid polarizers, organic solar cells, and organic light emitting diodes.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
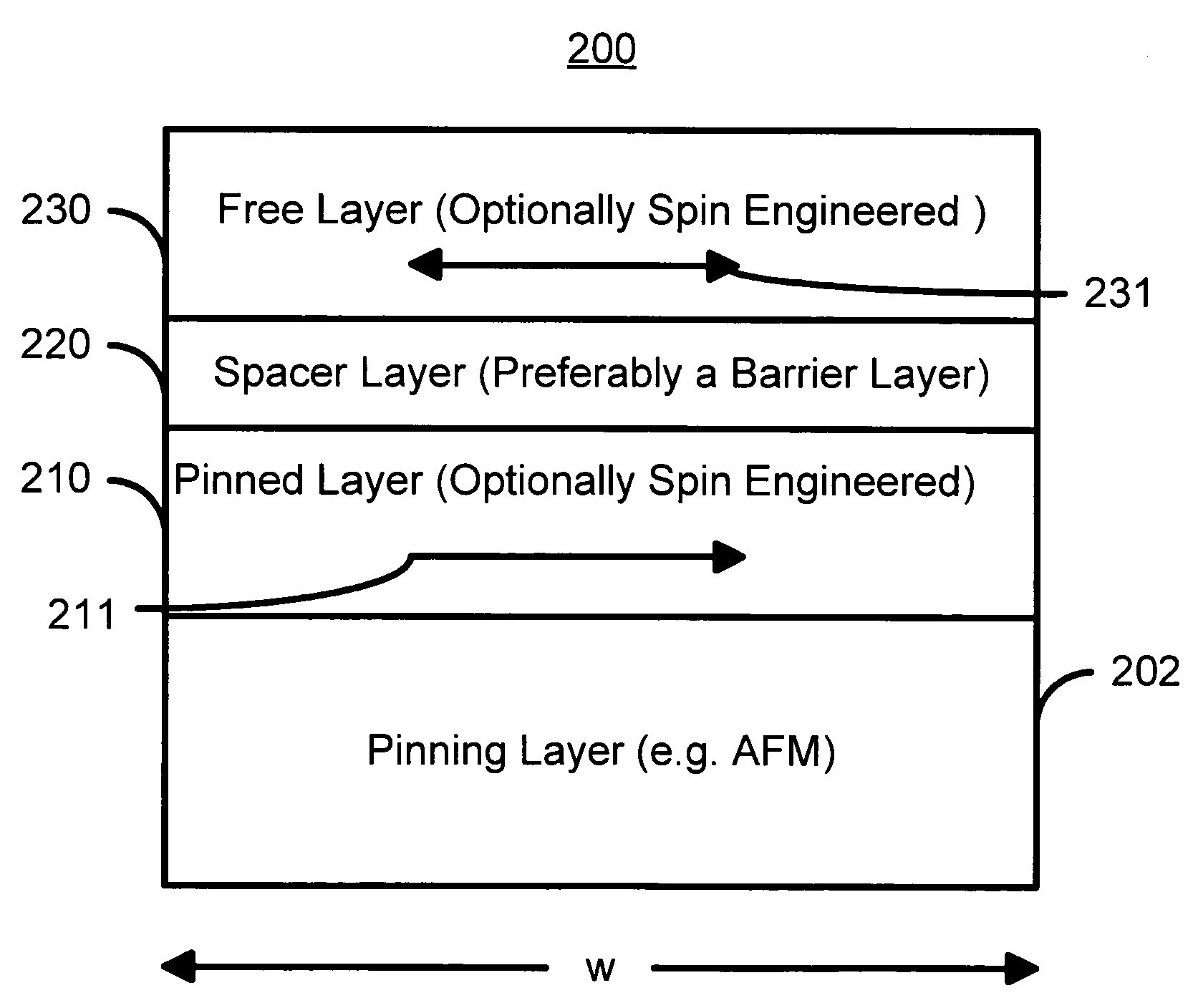
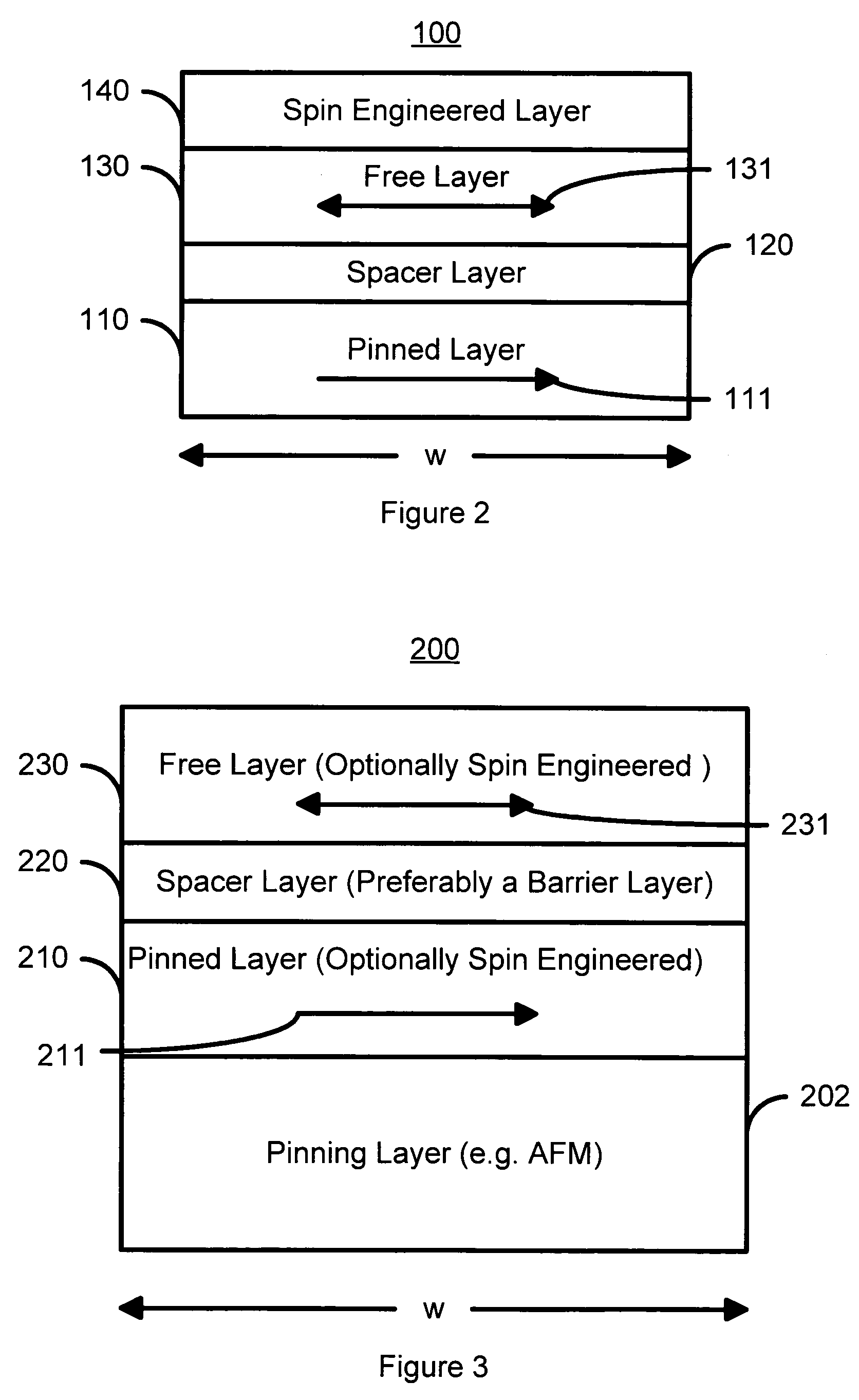
Magnetic elements with spin engineered insertion layers and MRAM devices using the magnetic elements
ActiveUS7369427B2Lower average currentReduce consumptionNanomagnetismGalvano-magnetic material selectionSpinsSpin transfer
A method and system include providing a pinned layer, a free layer, and a spacer layer between the pinned and free layers. The spacer layer is nonmagnetic. The magnetic element is configured to allow the free layer to be switched due to spin transfer when a write current is passed through the magnetic element. In one aspect, the method and system include providing a spin engineered layer adjacent to the free layer. The spin engineered layer is configured to more strongly scatter majority electrons than minority electrons. In another aspect, at least one of the pinned, free, and spacer layers is a spin engineered layer having an internal spin engineered layer configured to more strongly scatter majority electrons than minority electrons. In this aspect, the magnetic element may include another pinned layer and a barrier layer between the free and pinned layers.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
Thermal controlling method, magnetic field generator and MRI apparatus
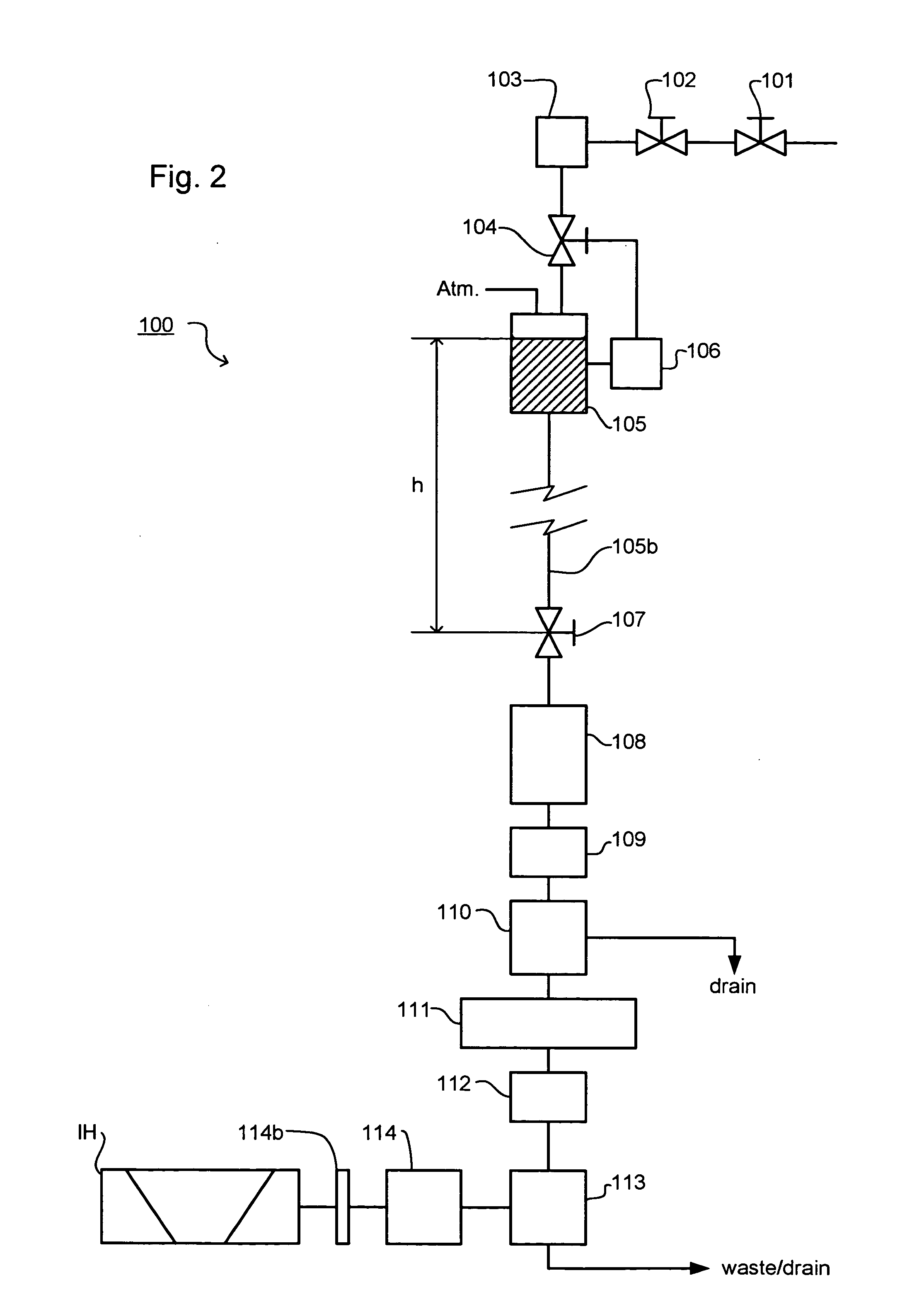
InactiveUS20080048656A1Permanent magnetsInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic polesRoom temperature
With a view toward implementing a thermal controlling method for making reversible a temperature characteristic of a magnetic field generator using permanent magnets small in Hcj, a magnetic field generator whose temperature characteristic is reversible, using permanent magnets small in Hcj, and an MRI apparatus provided with such a magnetic field generator, there is provided a method for controlling the temperature of a magnetic field generator having a pair of disc-shaped permanent magnets whose magnetic poles opposite in polarity to each other are opposed to each other with spacing defined therebetween, and a yoke that forms return passes for magnetic fluxes of the permanent magnets, comprising the steps of raising the temperature from room temperature to a temperature higher than the room temperature, maintaining the temperature higher than the room temperature, and lowering the temperature from the temperature higher than the room temperature to the room temperature, whereby the temperature characteristics of the permanent magnets are made reversible.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
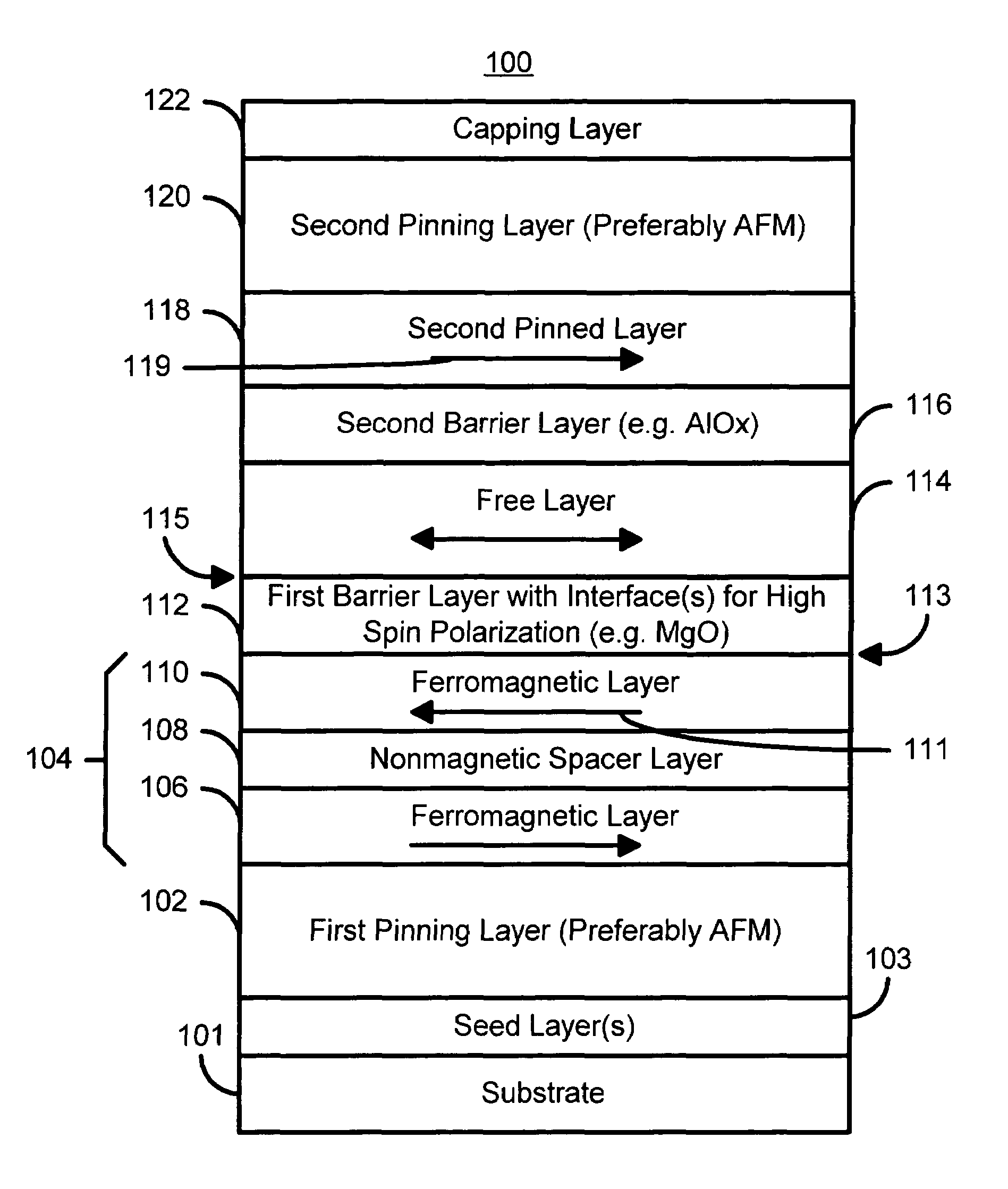
MTJ elements with high spin polarization layers configured for spin-transfer switching and spintronics devices using the magnetic elements
ActiveUS20060141640A1Write currentEnhanced signalNanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSpin transferSpin polarization
A method and system for providing a magnetic element are disclosed. The method and system include providing first and second pinned layers, a free layer, and first and second barrier layers between the first and second pinned layers, respectively, and the free layer. The first barrier layer is preferably crystalline MgO, which is insulating, and configured to allow tunneling through the first barrier layer. Furthermore, the first barrier layer has an interface with another layer, such as the free layer or the first pinned layer. The interface has a structure that provides a high spin polarization of at least fifty percent and preferably over eighty percent. The second barrier layer is insulating and configured to allow tunneling through the second barrier layer. The magnetic element is configured to allow the free layer to be switched due to spin transfer when a write current is passed through the magnetic element.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
MTJ elements with high spin polarization layers configured for spin-transfer switching and spintronics devices using the magnetic elements
ActiveUS7241631B2Write currentEnhanced signalNanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSpin transferSpin polarization
A method and system for providing a magnetic element are disclosed. The method and system include providing first and second pinned layers, a free layer, and first and second barrier layers between the first and second pinned layers, respectively, and the free layer. The first barrier layer is preferably crystalline MgO, which is insulating, and configured to allow tunneling through the first barrier layer. Furthermore, the first barrier layer has an interface with another layer, such as the free layer or the first pinned layer. The interface has a structure that provides a high spin polarization of at least fifty percent and preferably over eighty percent. The second barrier layer is insulating and configured to allow tunneling through the second barrier layer. The magnetic element is configured to allow the free layer to be switched due to spin transfer when a write current is passed through the magnetic element.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
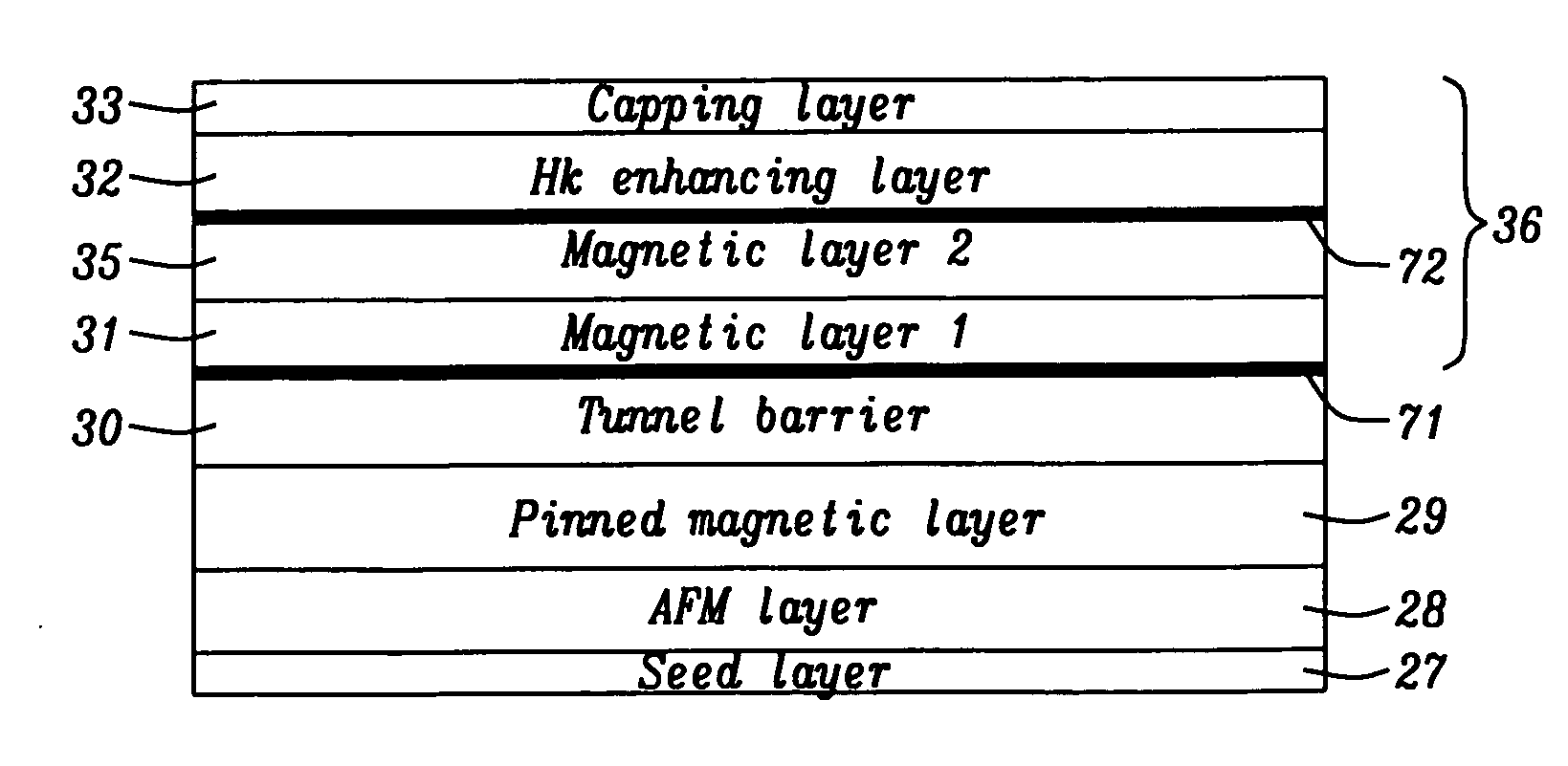
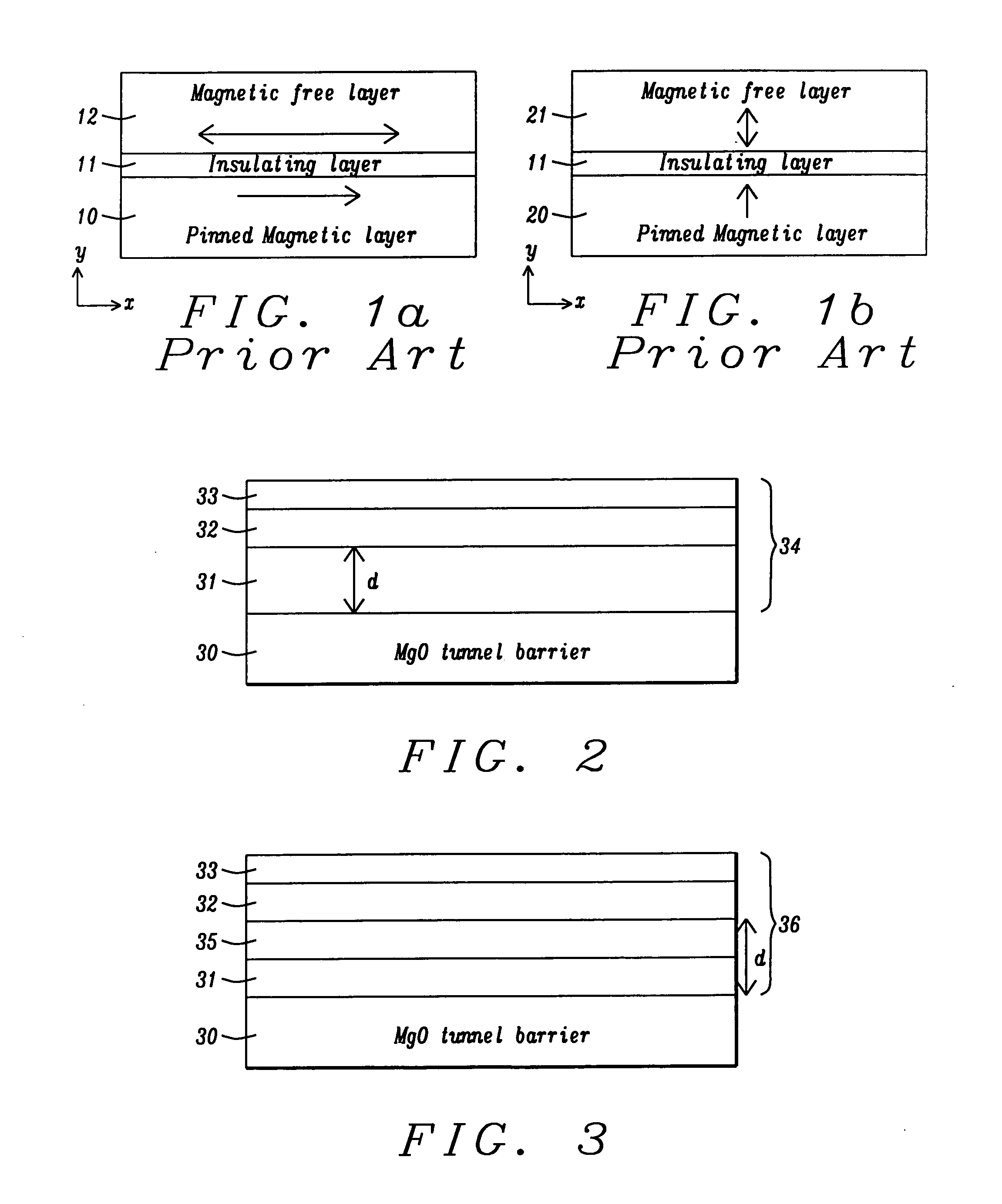
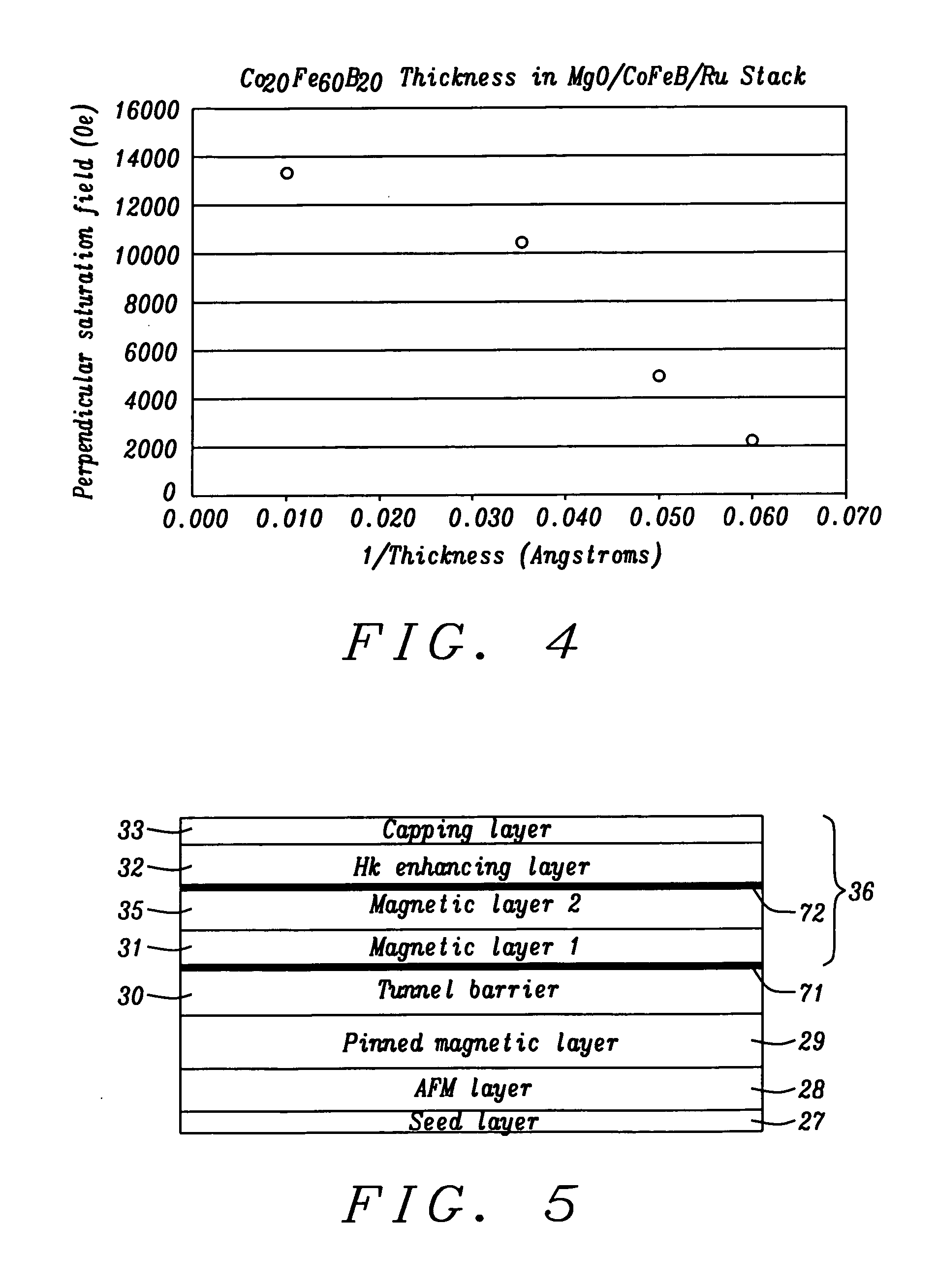
Magnetic element with improved out-of-plane anisotropy for spintronic applications
ActiveUS20120205758A1Without degrading thermal stability and MR ratioEnhanced interfacial perpendicular anisotropyMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsGalvano-magnetic material selectionPerpendicular anisotropyAlloy
A magnetic element is disclosed wherein first and second interfaces of a free layer with a Hk enhancing layer and tunnel barrier, respectively, produce enhanced surface perpendicular anisotropy to lower switching current or increase thermal stability in a magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ). In a MTJ with a bottom spin valve configuration where the Hk enhancing layer is an oxide, the capping layer contacting the Hk enhancing layer is selected to have a free energy of oxide formation substantially greater than that of the oxide. The free layer may be a single layer or composite comprised of an Fe rich alloy such as Co20Fe60B20. With a thin free layer, the interfacial perpendicular anisotropy may dominate the shape anisotropy to generate a magnetization perpendicular to the planes of the layers. The magnetic element may be part of a spintronic device or serve as a propagation medium in a domain wall motion device.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
System and method for inductively transferring ac power and self alignment between a vehicle and a recharging station
InactiveUS20110204845A1Reducing induced noiseImprove efficiencyBatteries circuit arrangementsCharging stationsElectrical batteryTransformer
A method and apparatus for hands free inductive charging of batteries for an electric vehicle is characterized by the use of a transformer having a primary coil connected with a charging station and a secondary coil connected with a vehicle. More particularly, the when the vehicle is parked adjacent to the charging station, the primary coil is displaced via a self alignment mechanism to position the primary coil adjacent to the secondary coil to maximize the inductive transfer of charging current to the secondary coil. The self alignment mechanism preferably utilizes feedback signals from the secondary coil to automatically displace the primary coil in three directions to position the primary coil for maximum efficiency of the transformer.
Owner:PLUGLESS POWER INC
High performance MTJ element for STT-RAM and method for making the same
ActiveUS20090027810A1Low angular dispersionEasy to operateNanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSpin angular momentum of lightDamping factor
We describe the structure and method of forming a STT-MTJ MRAM cell that utilizes transfer of spin angular momentum as a mechanism for changing the magnetic moment direction of a free layer. The device includes an IrMn pinning layer, a SyAP pinned layer, a naturally oxidized, crystalline MgO tunneling barrier layer that is formed on an Ar-ion plasma smoothed surface of the pinned layer and, in one embodiment, a free layer that comprises an amorphous layer of Co60Fe20B20. of approximately 20 angstroms thickness formed between two crystalline layers of Fe of 3 and 6 angstroms thickness respectively. The free layer is characterized by a low Gilbert damping factor and by very strong polarizing action on conduction electrons. The resulting cell has a low critical current, a high dR / R and a plurality of such cells will exhibit a low variation of both resistance and pinned layer magnetization angular dispersion.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
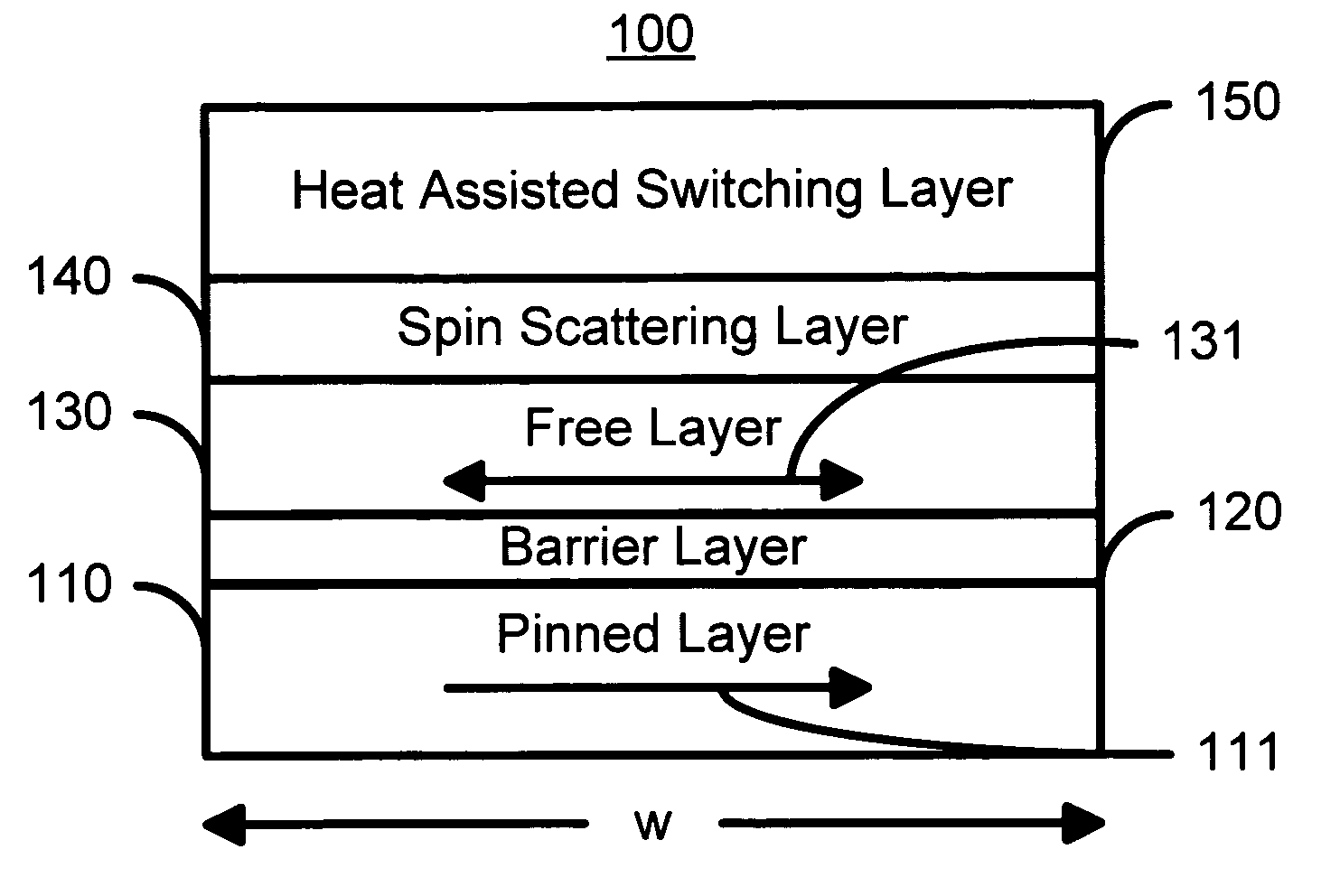
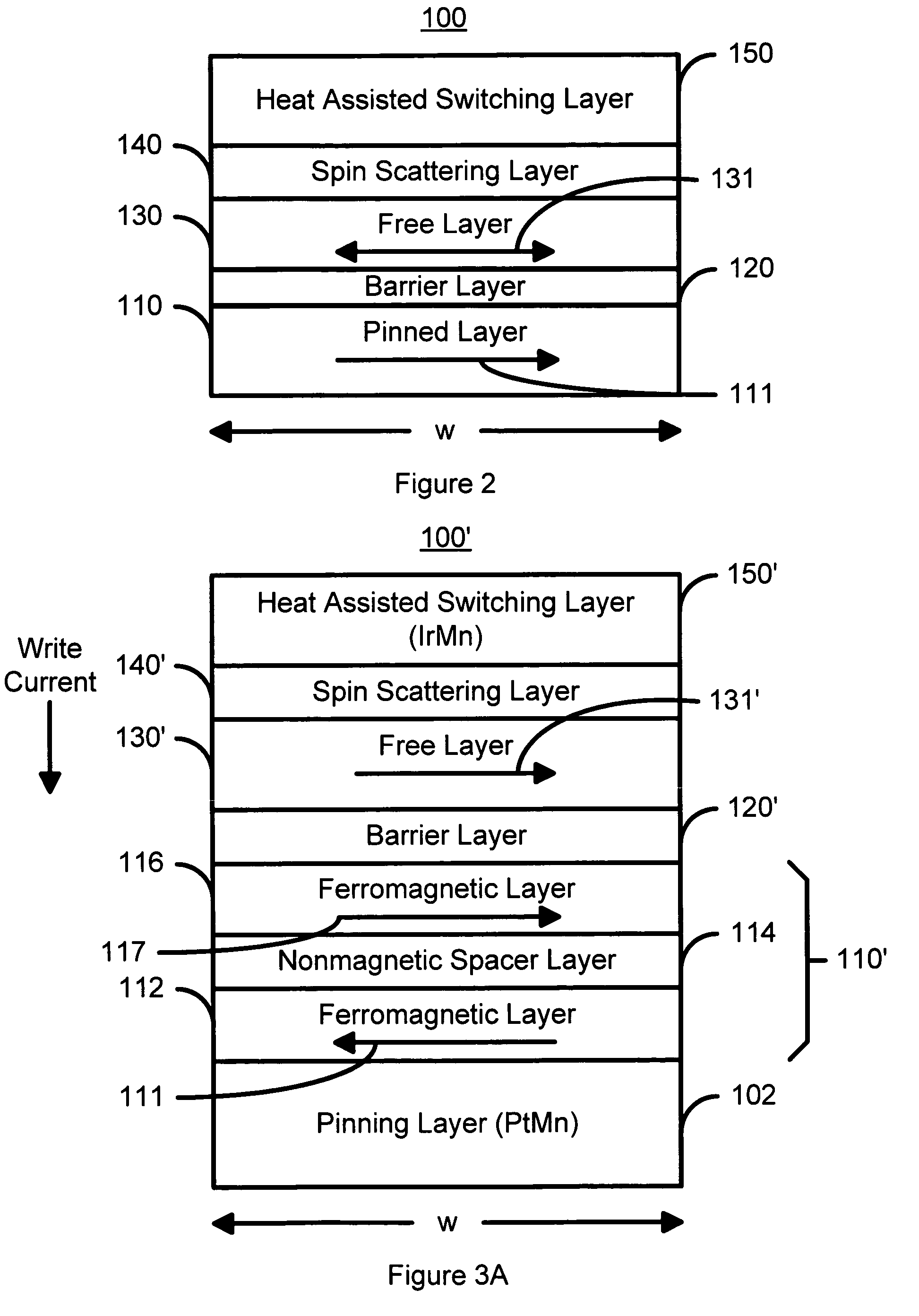
Spin scattering and heat assisted switching of a magnetic element
ActiveUS7126202B2Improve thermal stabilityStrong scatteringNanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSpinsThermal stability
A method and system for providing a magnetic element is disclosed. The magnetic element include providing a pinned layer, a spacer layer, and a free layer. The method and system also include providing a heat assisted switching layer and a spin scattering layer between the free layer and the heat assisted switching layer. The spin scattering layer is configured to more strongly scatter majority electrons than minority electrons. The heat assisted switching layer is for improving a thermal stability of the free layer when the free layer is not being switched. Moreover, the magnetic element is configured to allow the free layer to be switched due to spin transfer when a write current is passed through the magnetic element.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
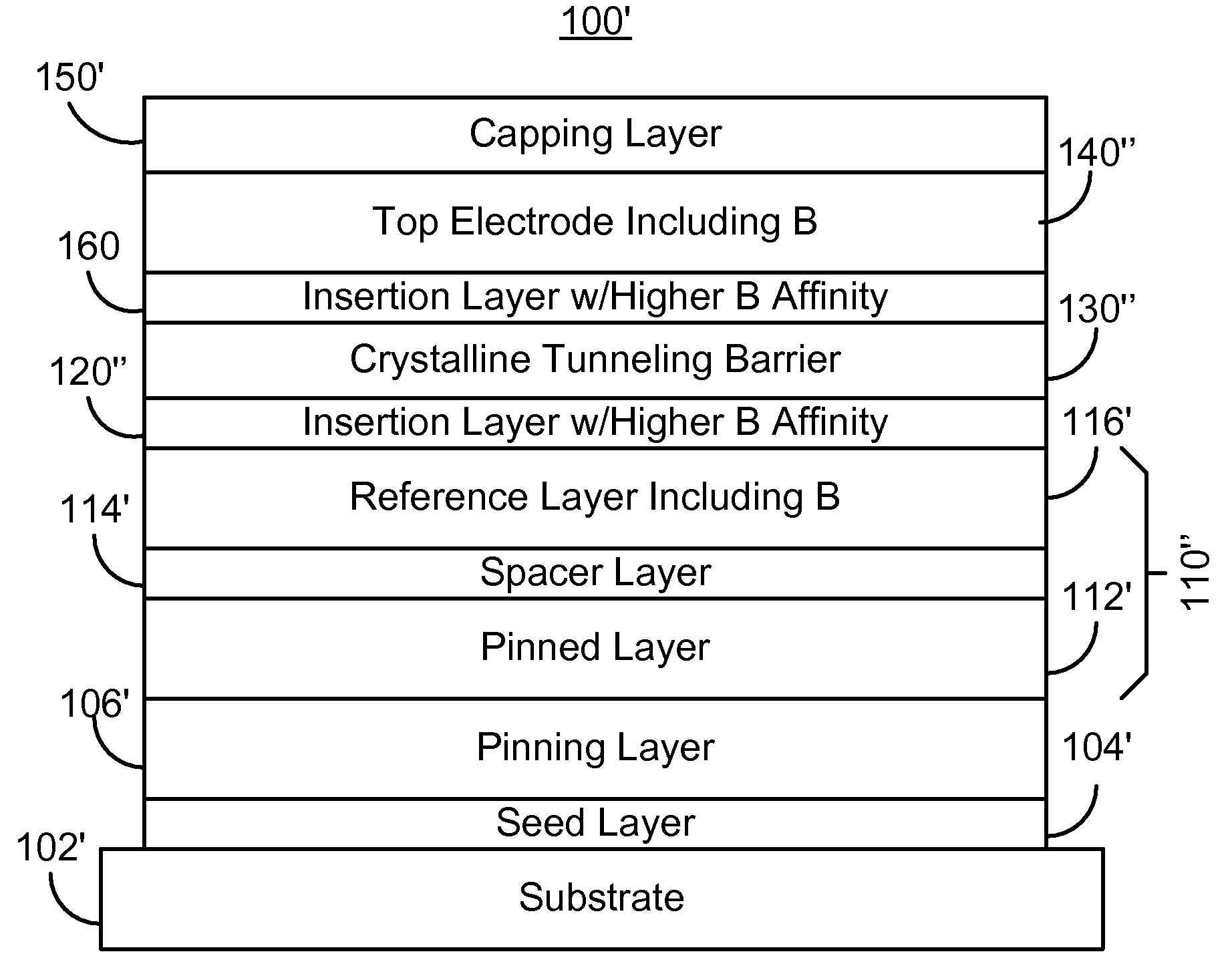
Method and system for providing a magnetoresistive structure
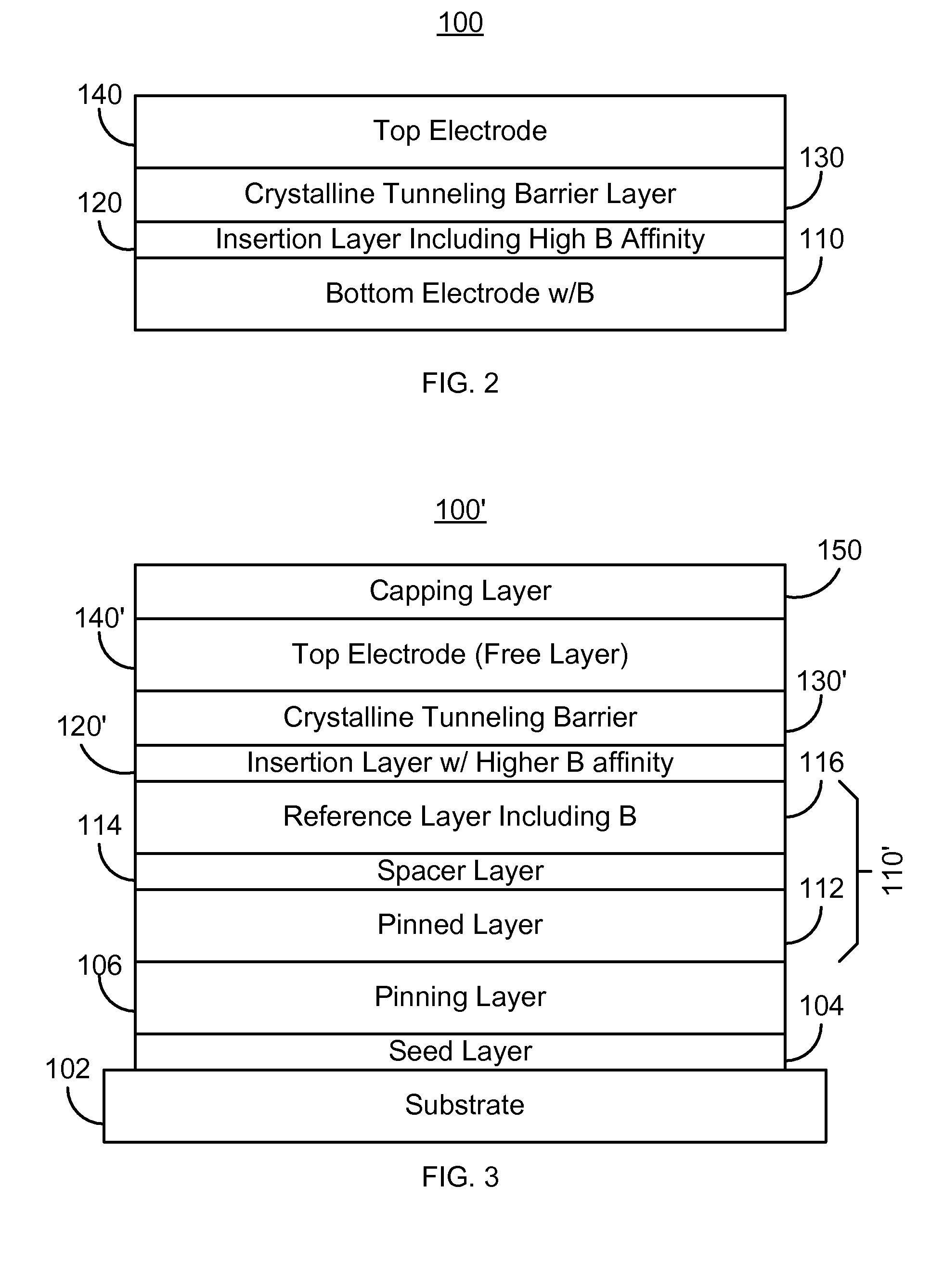
A method and system for providing a magnetoresistive structure are described. The magnetoresistive structure includes a first electrode, an insertion layer, a crystalline tunneling barrier layer, and a second electrode. The first electrode includes at least a first magnetic material and boron. The crystalline tunneling barrier layer includes at least one constituent. The insertion layer has a first boron affinity. The at least one constituent of the crystalline tunneling barrier layer has at least a second boron affinity that is less than the first boron affinity. The second electrode includes at least a second magnetic material.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
MTJ incorporating CoFe/Ni multilayer film with perpendicular magnetic anisotropy for MRAM application
ActiveUS20110096443A1Minimize impinging ion energyMaximize PMA propertyMagnetic measurementsVacuum evaporation coatingSpin transferSpin valve
A MTJ for a spintronic device is disclosed and includes a thin composite seed layer made of at least Ta and a metal layer having fcc(111) or hcp(001) texture as in Ta / Ti / Cu to enhance perpendicular magnetic anisotropy (PMA) in an overlying laminated layer with a (CoFe / Ni)X, (Co / NiFe)X, (Co / NiCo)X, (CoFe / NiFe)X, or (CoFe / NiCo)X composition where x is from 5 to 30. In one embodiment, a CPP-TMR spin valve has one or both of a laminated free layer and laminated reference layer with the aforementioned compositions. The MTJ includes an interfacial layer made of CoFeB, CoFeB / CoFe, or CoFe / CoFeB between each laminated structure and the tunnel barrier. The laminated layers are deposited by a low power and high Ar pressure process to avoid damaging interfaces between adjoining layers. Annealing occurs at 220° C. to 400° C. A laminated layer with high PMA may also be included in one or more layers of a spin transfer oscillator.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
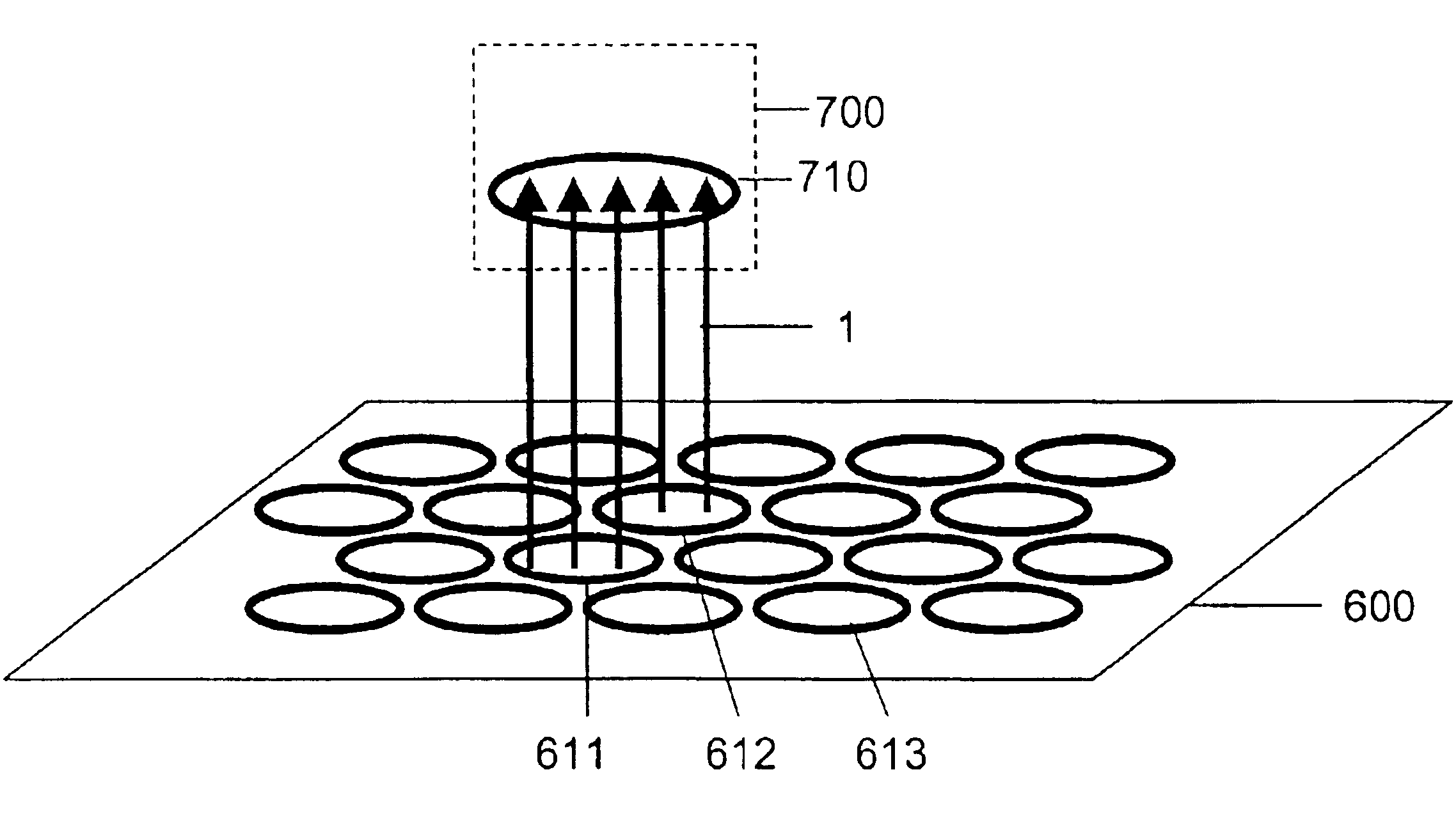
Method for Fabricating a Long-Range Ordered Periodic Array of Nano-Features, and Articles Comprising Same
A long range, periodically ordered array of discrete nano-features (10), such as nano-islands, nano-particles, nano-wires, non-tubes, nano-pores, nano-composition-variations, and nano-device-components, are fabricated by propagation of a self-assembling array or nucleation and growth of periodically aligned nano-features. The propagation may be induced by a laterally or circularly moving heat source, a stationary heat source arranged at an edge of the material to be patterned (12), or a series of sequentially activated heaters or electrodes. Advantageously, the long-range periodic array of nano-features (10) may be utilized as a nano-mask or nano-implant master pattern for nano-fabrication of other nano-structures. In addition, the inventive long-range, periodically ordered arrays of nano-features are useful in a variety of nanoscale applications such as addressable memories or logic devices, ultra-high-density magnetic recording media, magnetic sensors, photonic devices, quantum computing devices, quantum luminescent devices, and efficient catalytic devices.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
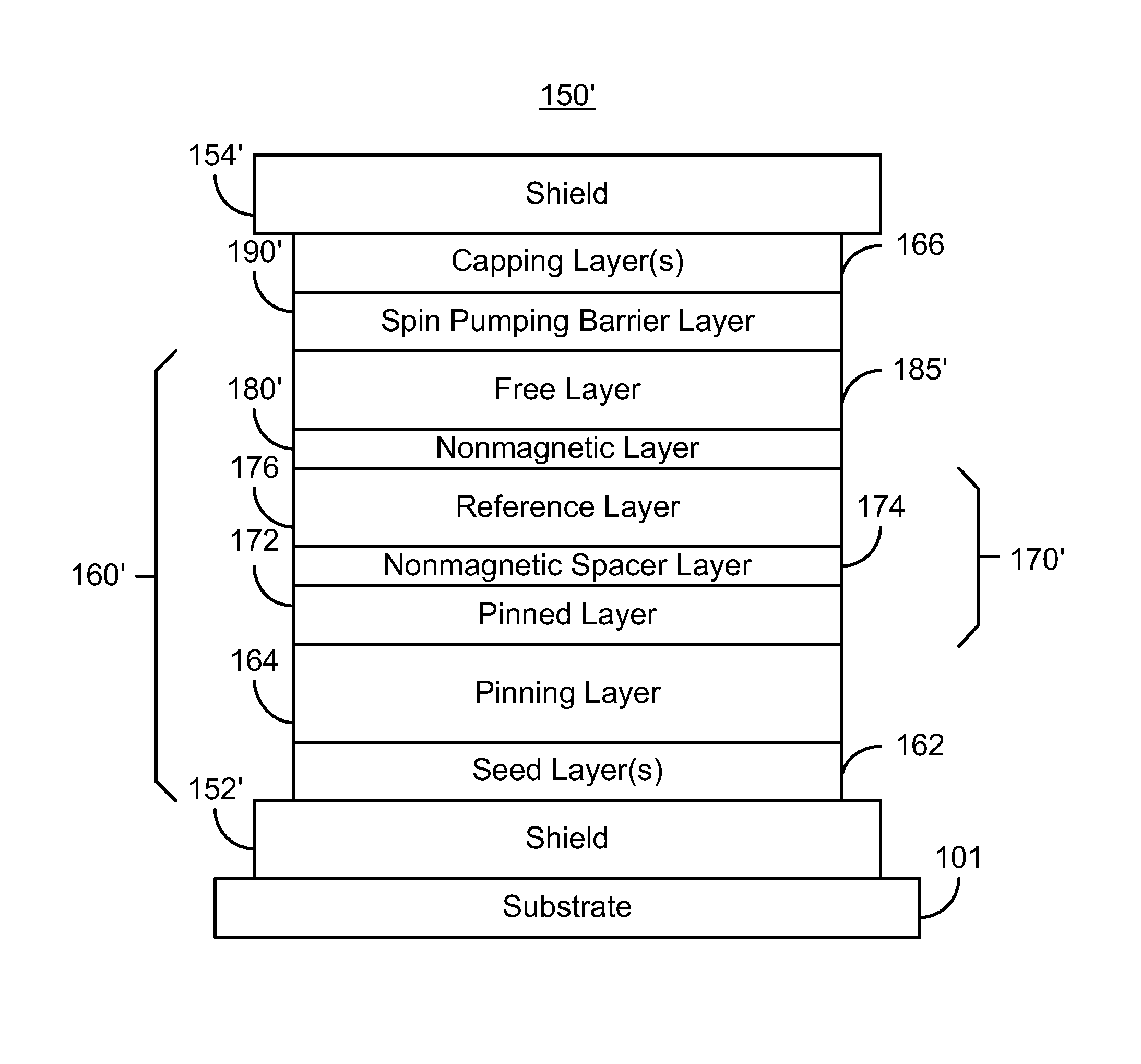
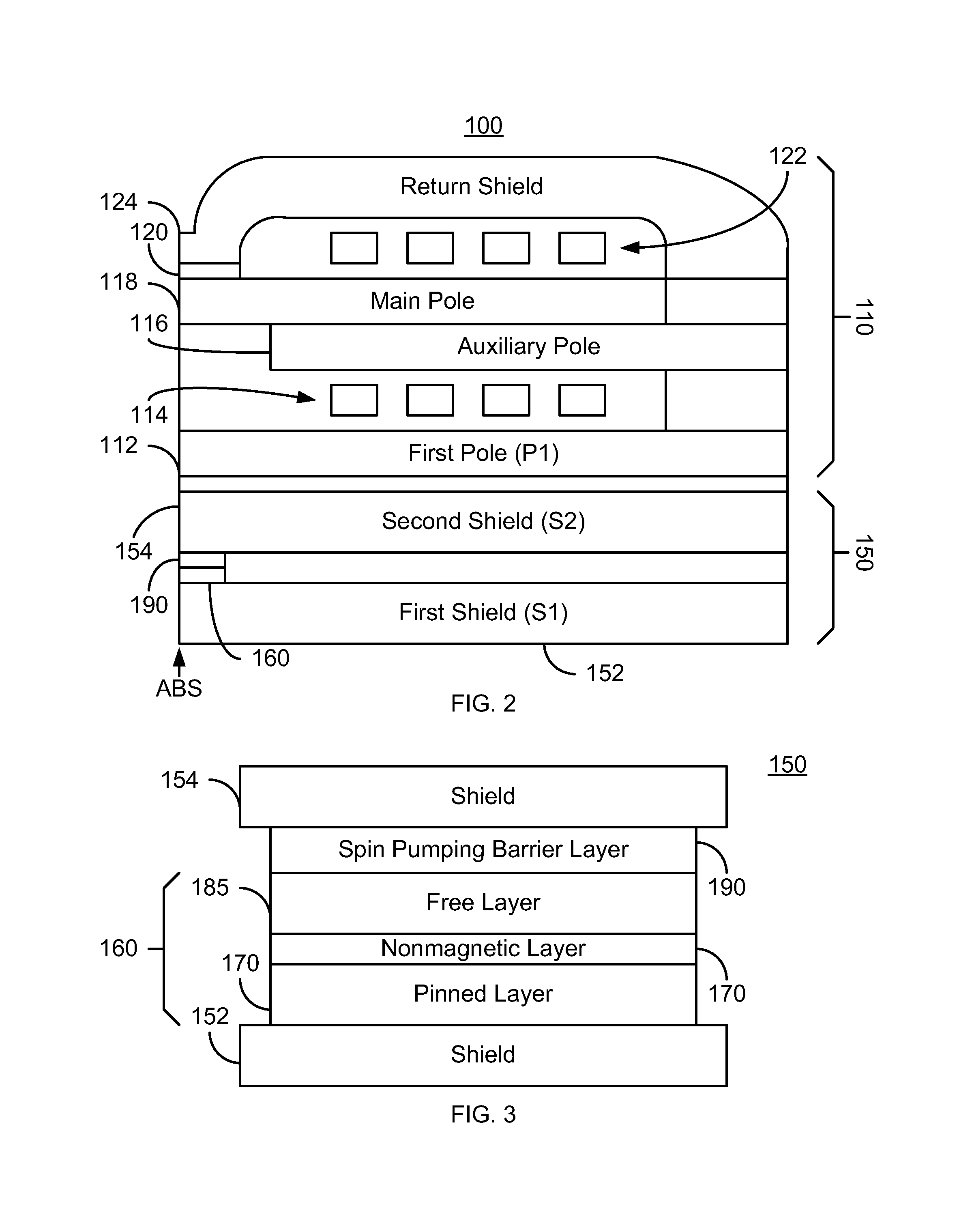
Method and system for providing a magnetic read transducer having an improved signal to noise ratio
ActiveUS8493695B1Magnetic measurementsMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Transducer
A method and system for providing a magnetic read transducer is described. The magnetic read transducer includes a magnetoresistive sensor a shield, and a spin pumping barrier layer. The magnetoresistive sensor includes a pinned layer, a spacer layer, and a free layer. The spacer layer is nonmagnetic and resides between the pinned layer and the free layer. The free layer is between the pinned layer and the shield. The spin pumping barrier layer is between the shield and the free layer.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Method for providing a magnetic recording transducer
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Perpendicular magnetization magnetic element utilizing spin transfer
ActiveUS20050185455A1Reduce currentNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsPerpendicular magnetizationMagnetic memory
A method and system for providing a magnetic element that can be used in a magnetic memory is disclosed. The method and system include providing a first pinned layer, a barrier layer, a free layer, a conductive nonmagnetic spacer layer, and a second pinned layer. Each pinned layer has a pinned layer easy axis. At least a portion of the pinned layer easy axis is in a perpendicular direction. The barrier layer resides between the first pinned layer and the free layer. The spacer layer is between the free layer and the second pinned layer. The free layer has a free layer easy axis, at least a portion of which is in the perpendicular direction. The magnetic element is also configured to allow the free layer to be switched due to spin transfer effect when a write current is passed through the magnetic element. Because of the perpendicular magnetization(s), the writing current for spin transfer may be significantly reduced.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
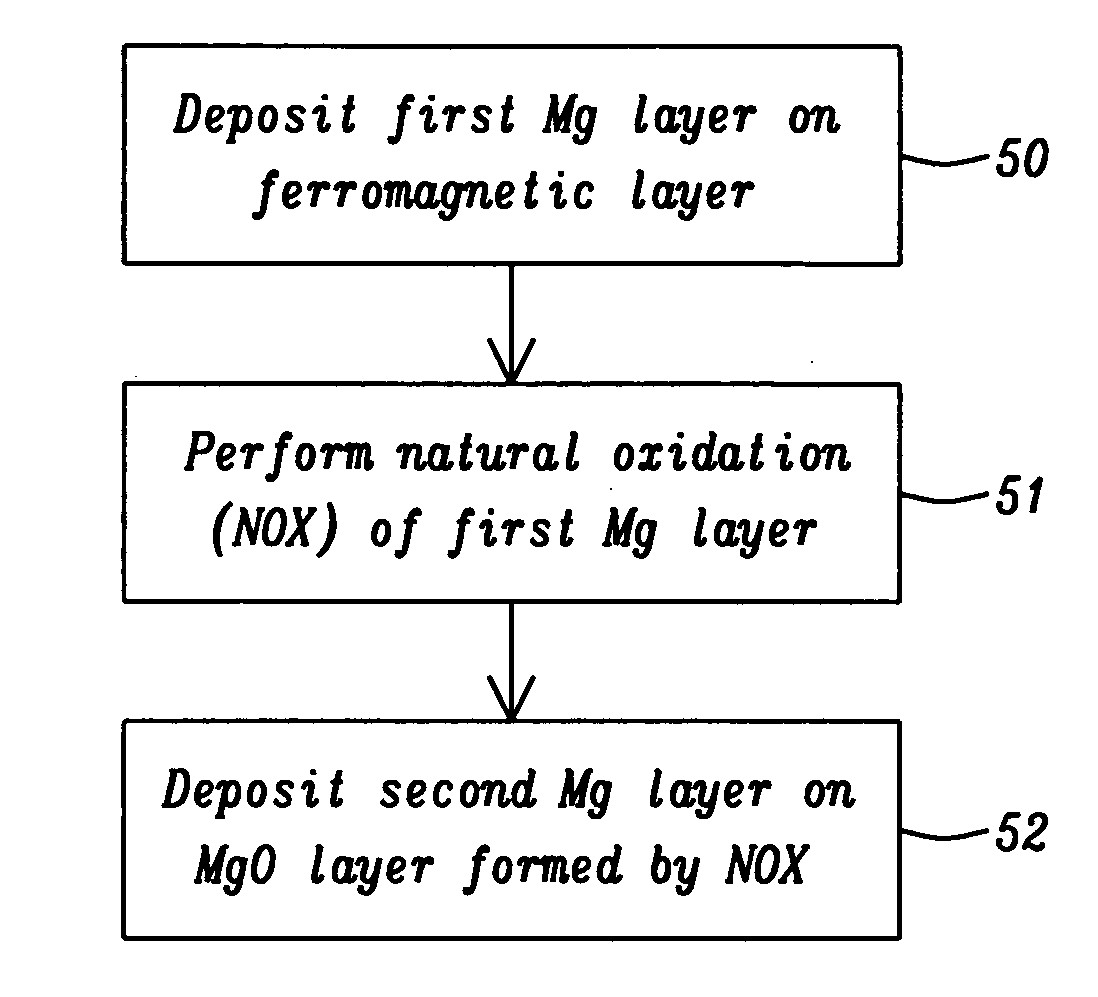
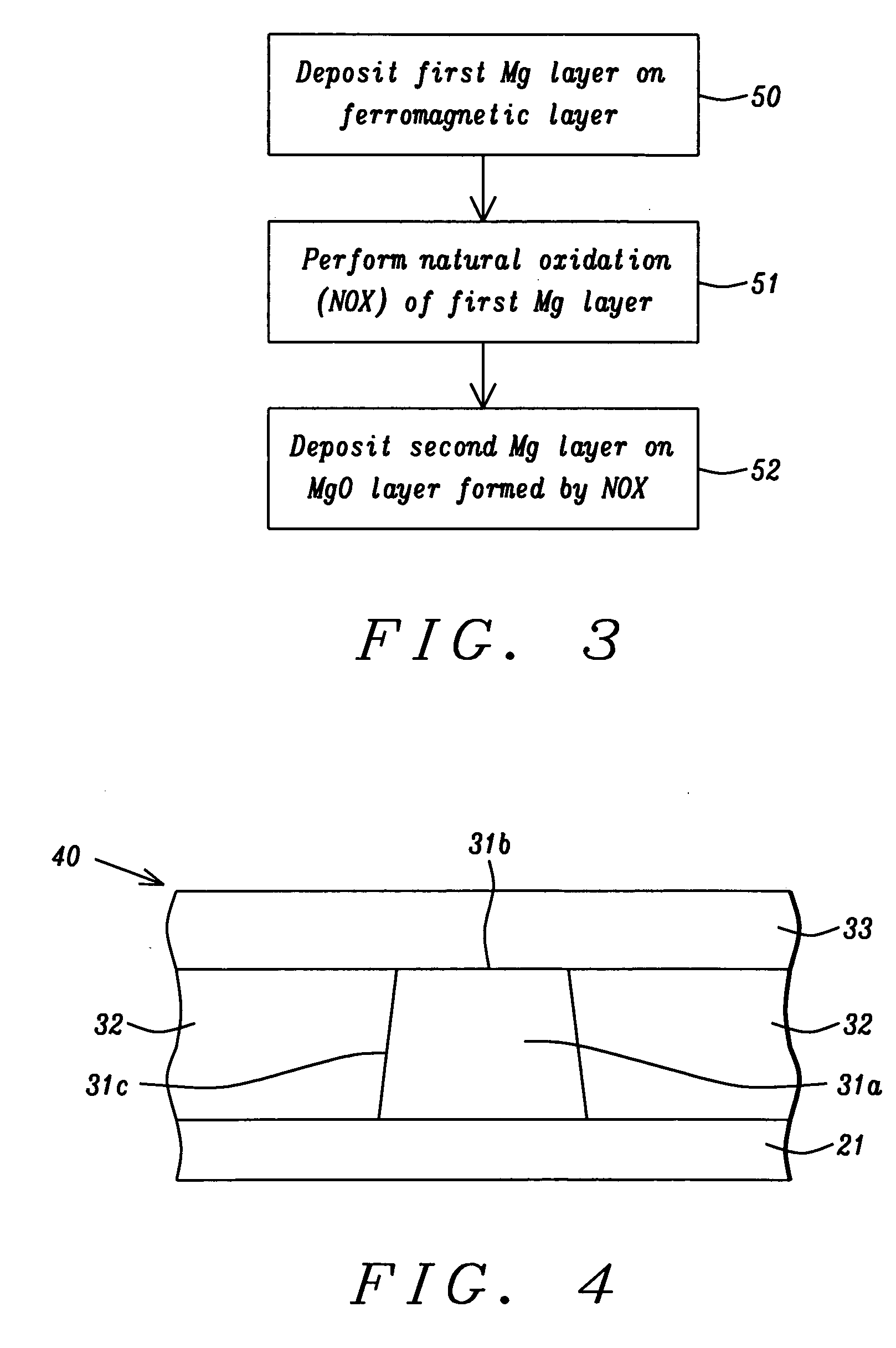
Low resistance tunneling magnetoresistive sensor with natural oxidized double MgO barrier
ActiveUS20070111332A1Improve uniformityHigh MR ratioNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsSpin valveMaterials science
A high performance TMR sensor is fabricated by incorporating a tunnel barrier having a Mg / MgO / Mg configuration. The 4 to 14 Angstroms thick lower Mg layer and 2 to 8 Angstroms thick upper Mg layer are deposited by a DC sputtering method while the MgO layer is formed by a NOX process involving oxygen pressure from 0.1 mTorr to 1 Torr for 15 to 300 seconds. NOX time and pressure may be varied to achieve a MR ratio of at least 34% and a RA value of 2.1 ohm-um2. The NOX process provides a more uniform MgO layer than sputtering methods. The second Mg layer is employed to prevent oxidation of an adjacent ferromagnetic layer. In a bottom spin valve configuration, a Ta / Ru seed layer, IrMn AFM layer, CoFe / Ru / CoFeB pinned layer, Mg / MgO / Mg barrier, CoFe / NiFe free layer, and a cap layer are sequentially formed on a bottom shield in a read head.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
Method and apparatus for controlling magnetostriction in a spin valve sensor
A method and system for providing a magnetic element are described. The method and system include providing a pinned layer, fabricating a metallic spacer layer and oxidizing a portion of the spacer layer in an environment including at least oxygen and a gas inert with respect to the spacer layer to provide an oxide layer. The method and system also include creating a free layer. The oxide layer is between a remaining metallic portion of the spacer layer and the free layer. In one aspect, the system includes a chamber and a gas diffusion apparatus within the chamber. The gas diffusion apparatus includes a plurality of nozzles and defines a plane. The gas exits each of the plurality of nozzles in a cone having an apex angle. The nozzles are directed at a nozzle tilt angle of at least half of the apex angle from the plane and the spacer layer.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Tunable embedded inductor devices
ActiveUS7884697B2Transformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureCouplingDielectric substrate
The invention provides tunable embedded high frequency inductor devices. The inductor device comprises a dielectric substrate. A first conductive line is disposed on a first surface of the dielectric substrate. A second conductive line is disposed on a second surface of the dielectric substrate. An interconnection is disposed perforating the dielectric substrate and connecting the first conductive line with the second conductive line. A coupling region is defined between the first and the second conductive lines. A conductive plug connecting the first conductive line and the second line is disposed in the coupling region. Alternatively, an opening is disposed in the first and second conductive lines to tune inductance of the inductor.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Methods for coating a metal substrate and related coated substrates
ActiveUS7749368B2Volume/mass flow measurementFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsElectrogalvanizationMetallic substrate
Owner:PPG IND OHIO INC
Installation
An installation for the non-contact transfer of energy includes at least one primary conductor system and a pick-up, including at least one secondary winding inductively coupled to the primary conductor system, the secondary winding including at least one flat ribbon cable, which has at least two electrical conductors extending in parallel, that are held at a distance from each other and are insulated with respect to each other, the secondary winding being made up of part windings, which in each case are formed from one of the electrical conductors, each of the part windings, together with an associated capacitance, forming a series resonant circuit, whose resonant frequency corresponds substantially to the medium frequency of the primary current.
Owner:SEW-EURODRIVE GMBH & CO KG
Extended E Matrix Integrated Magnetics (MIM) Core
InactiveUS20080024259A1Easy and less-expensive to fabricateLow profileAc-dc conversion without reversalTransformers/inductances magnetic coresMechanical engineeringMagnetic core
Owner:MYPAQ HLDG LTD
Method for fabricating a thin film inductor
InactiveUS6040226AClose toleranceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesLithographic artistEngineering
A method is provided for the manufacture of precision electronic components such as resistors, inductors, and capacitors on a polymer or ceramic surface. The electronic components can be deposited and trimmed to precise or matched values without having precise depositions of all of the pre-patterned materials. Thin film electronic components are deposited on a surface, parameter values are measured or estimated, a correction offset file is generated, and the components are trimmed using adaptive lithography to a very close tolerance. A computer program can be used to enable the adjustment of electronic components by techniques such as changing the physical length of an inductor coil or resistor lead, or by changing a capacitor plate area.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Popular searches
Vehicle route interaction devices Route devices for controlling vehicles Radiation electrical energy Energy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processes Ion implantation coating Special surfaces Chemical vapor deposition coating Plasma technique Secondary cells charging/discharging Electric power
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com