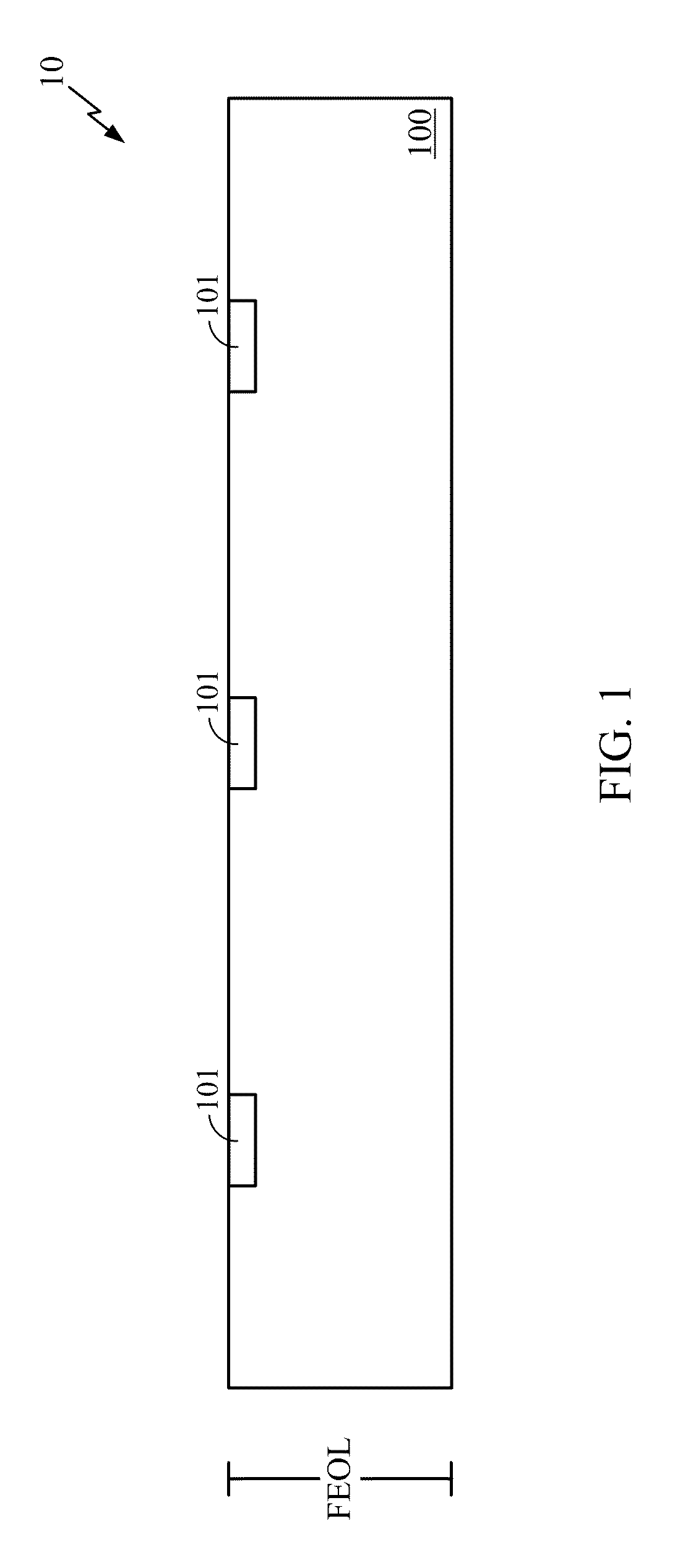
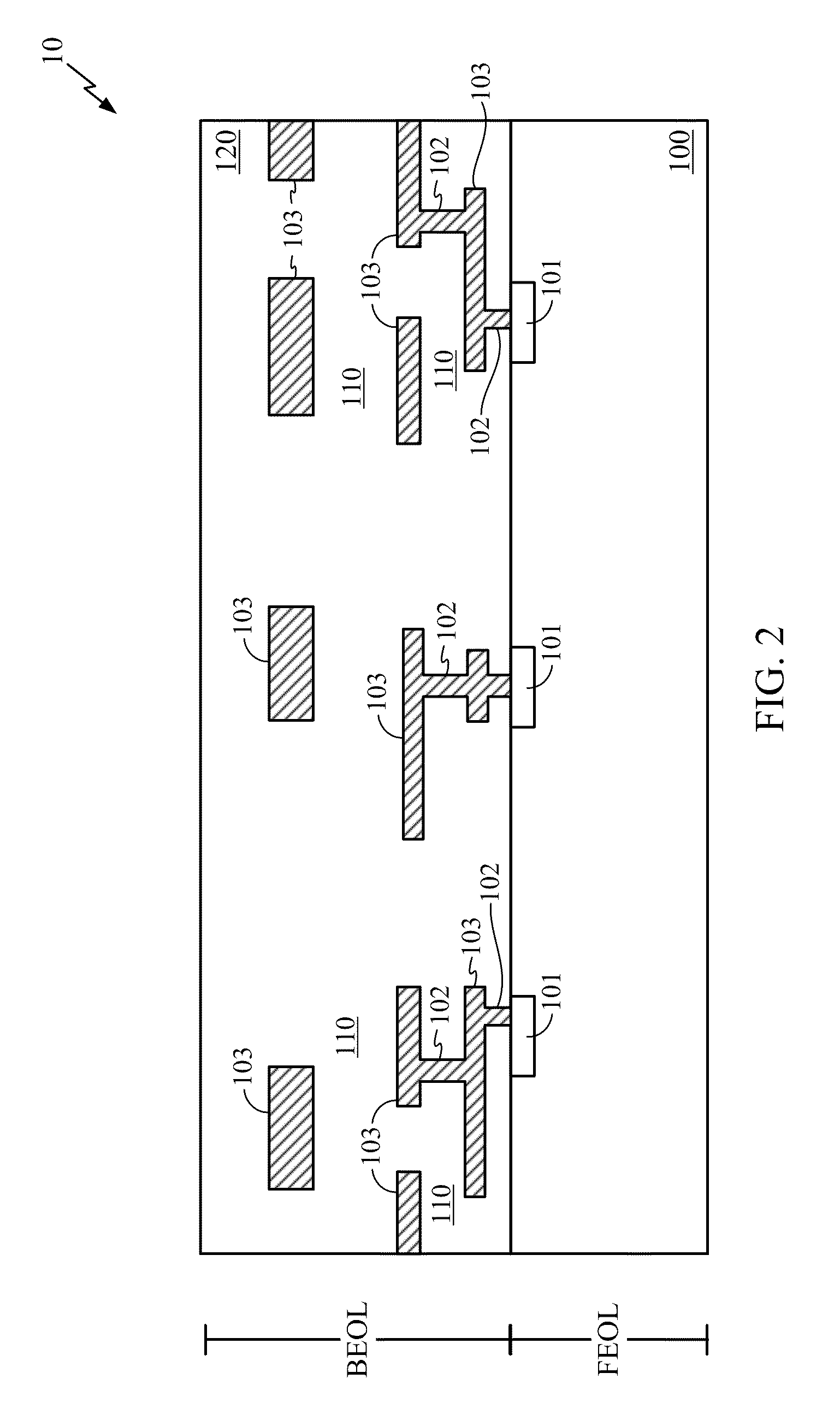
Patents
Literature
9327 results about "Dielectric substrate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
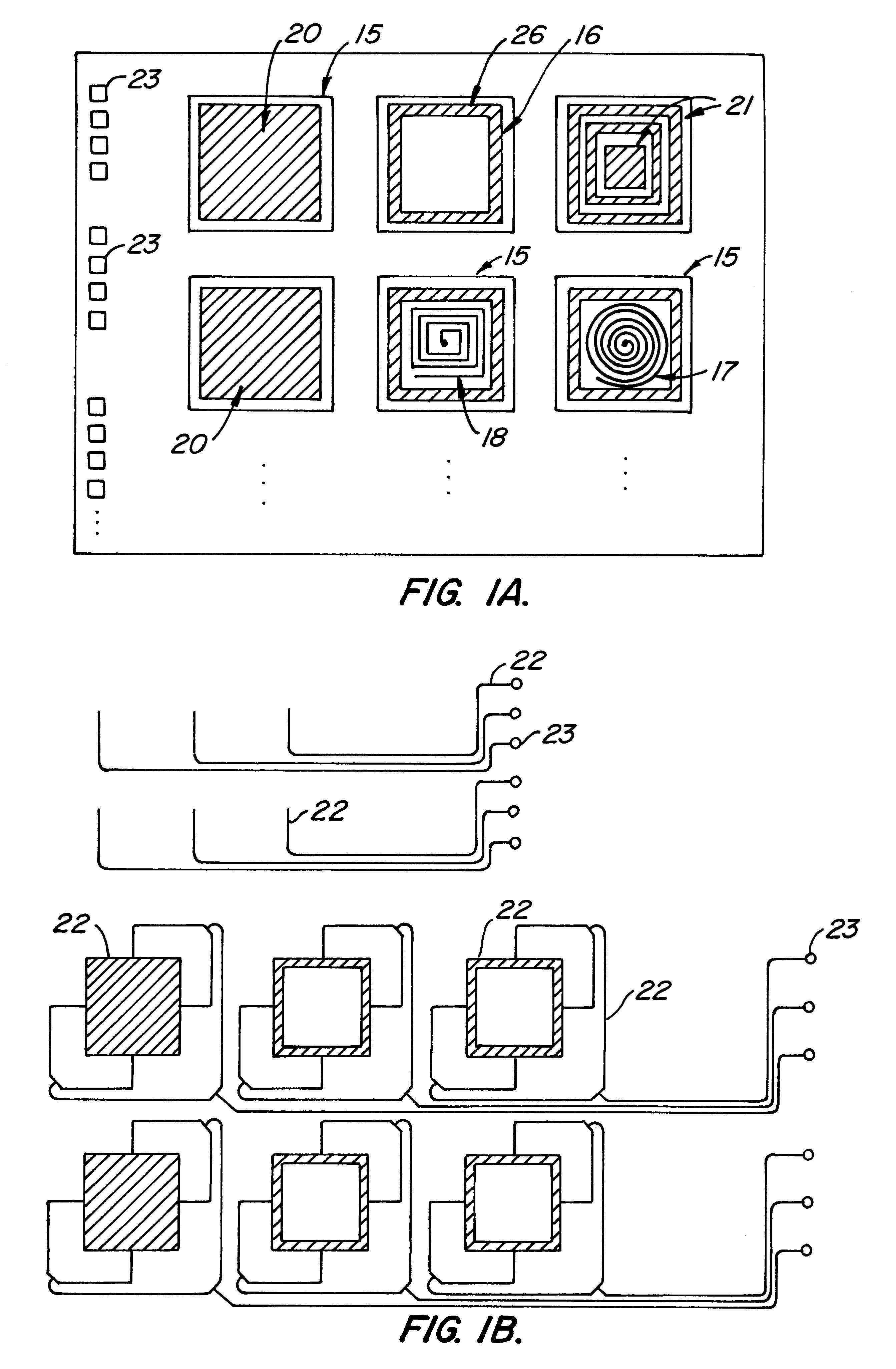
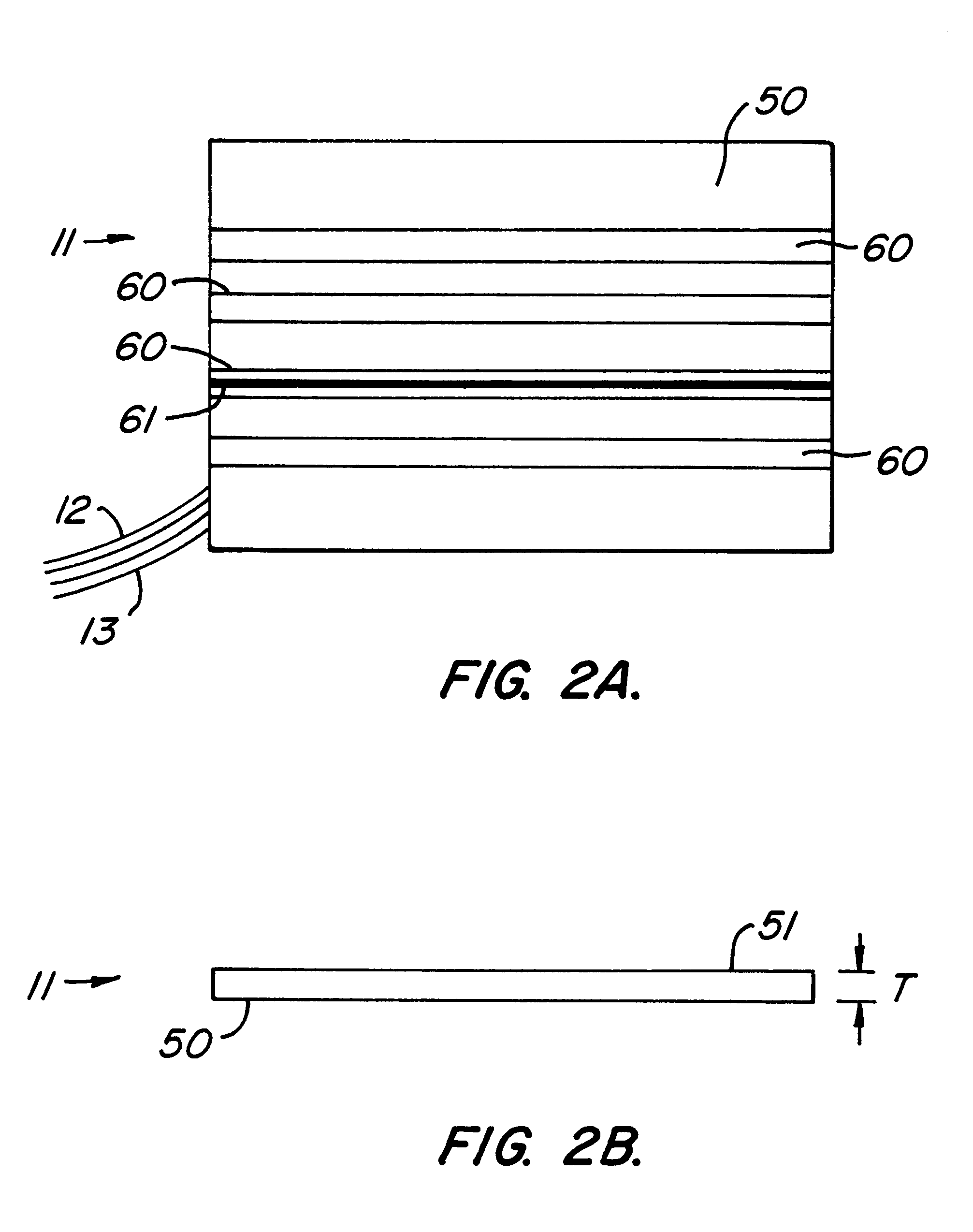
The dielectric material is used as PCB for fabricating the RF circuit layout as per design of various RF/microwave systems. The dielectric substrate selection plays very vital role in size reduction and impedance matching.
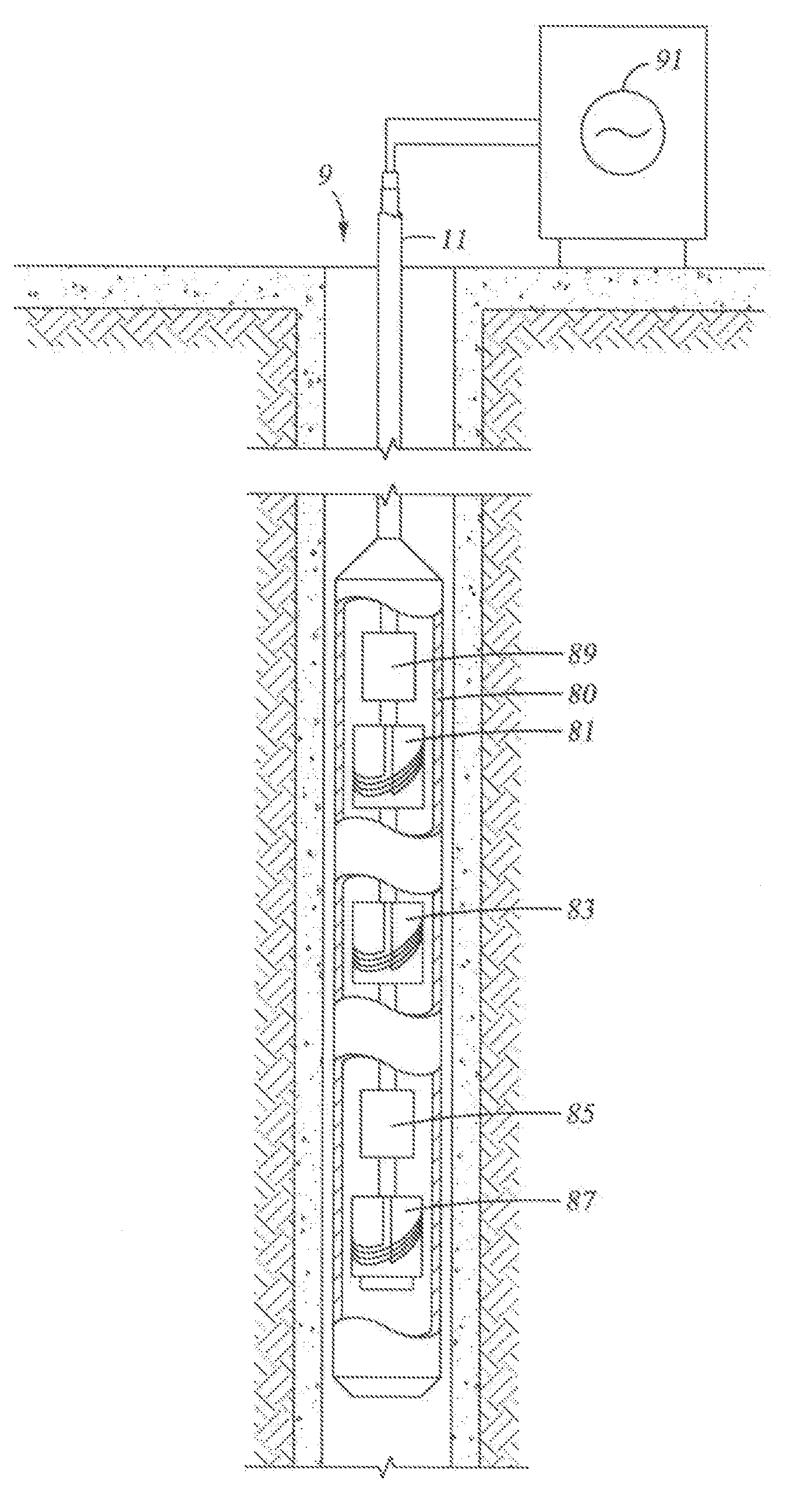
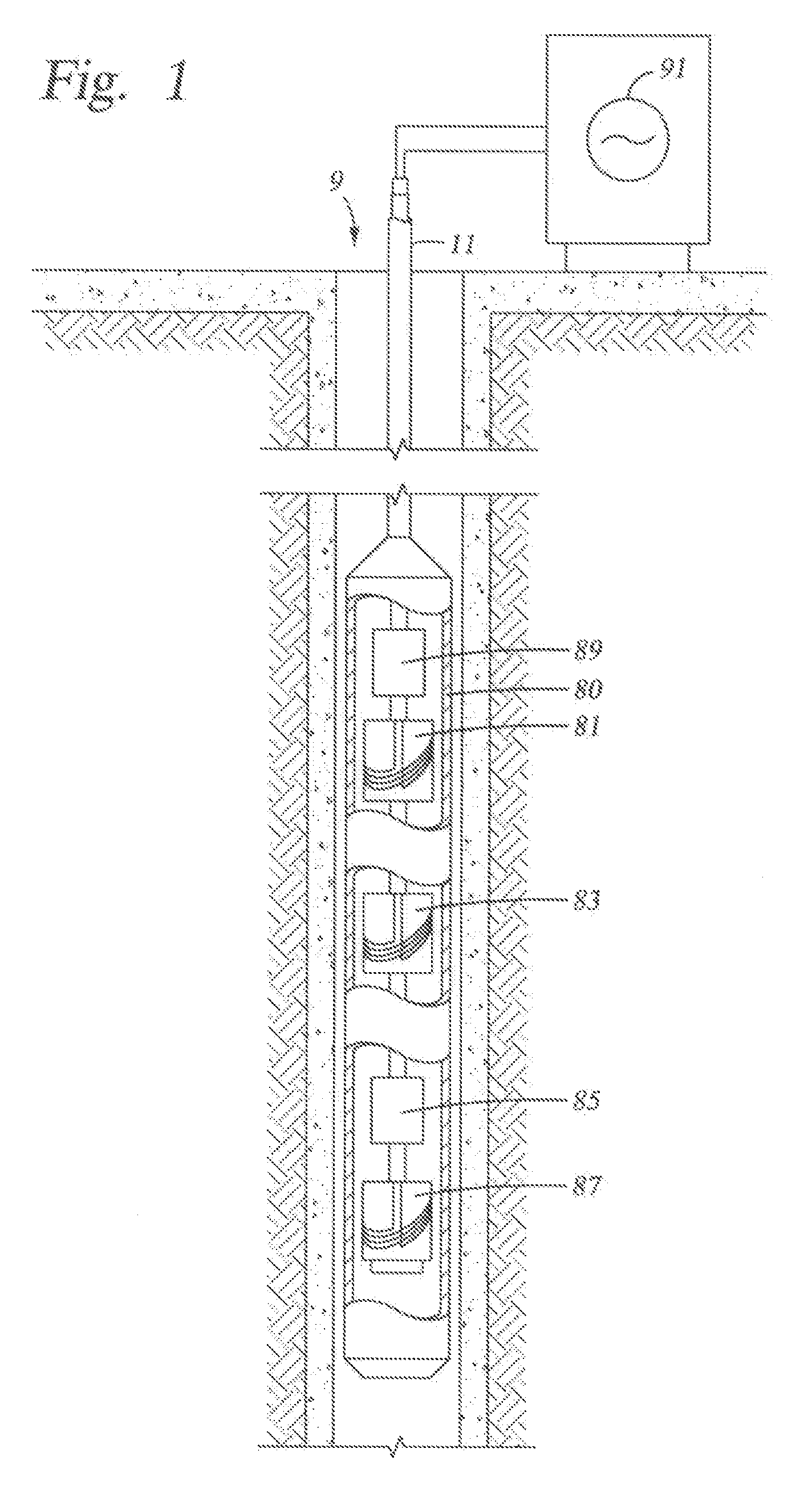
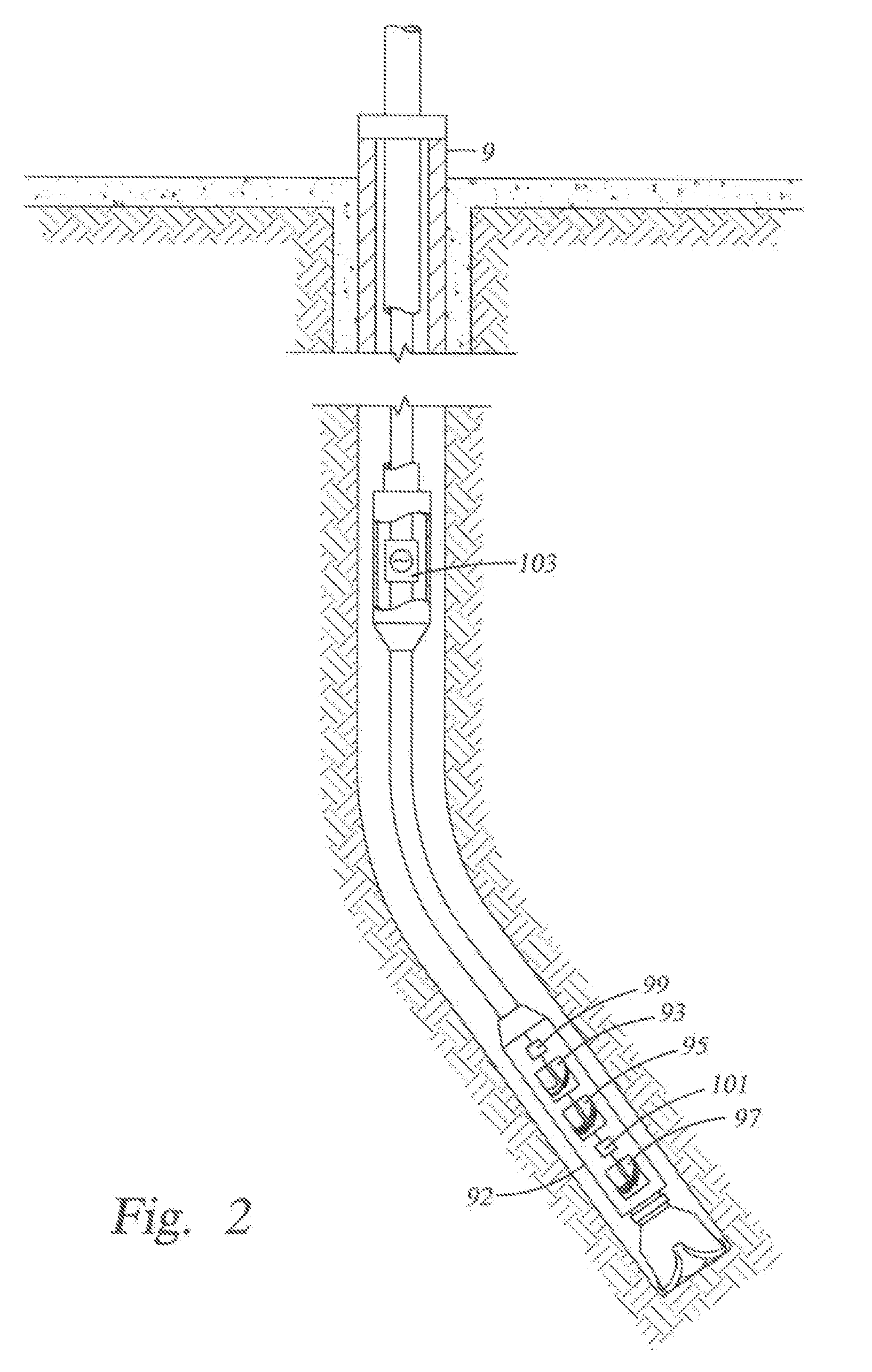
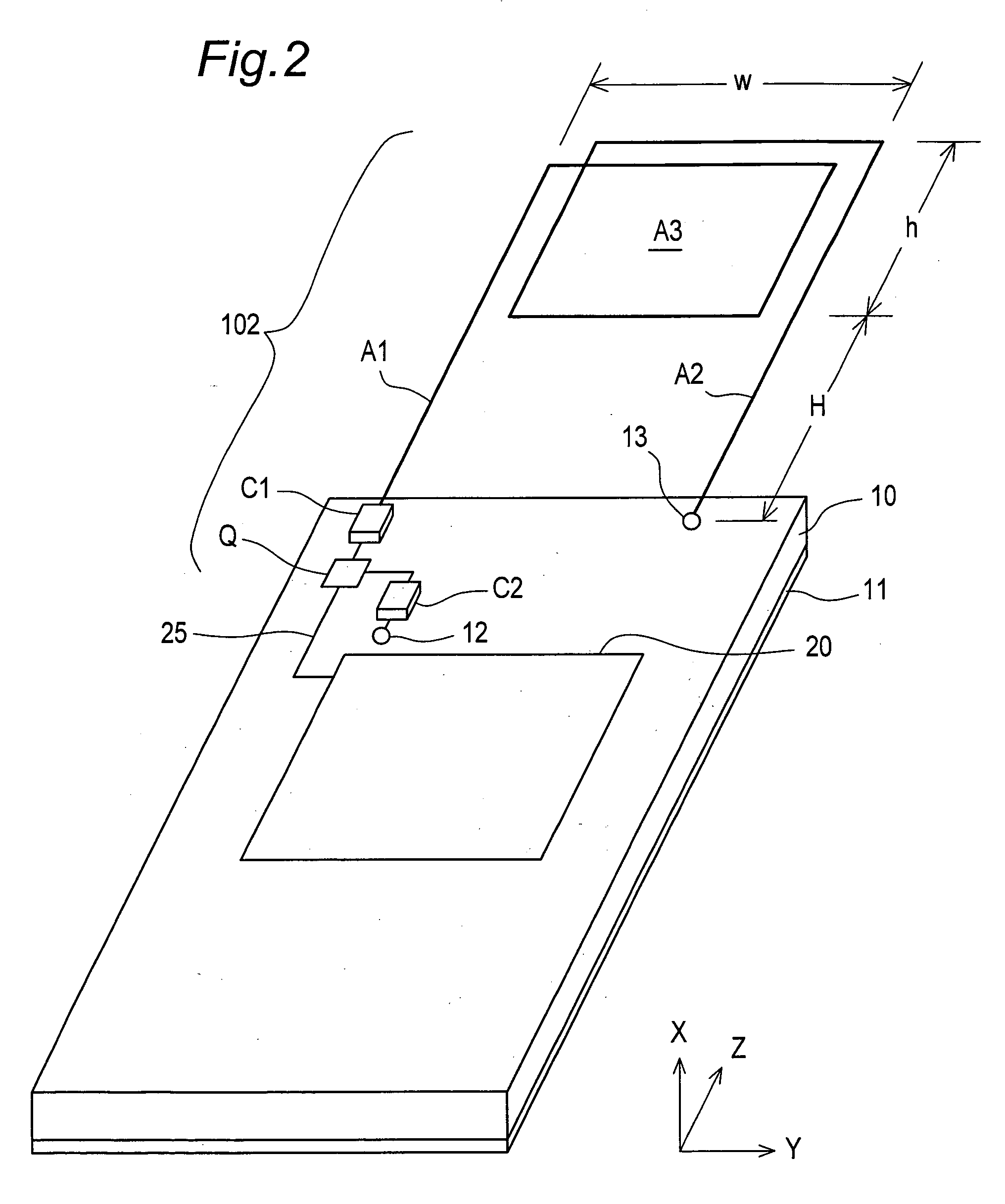
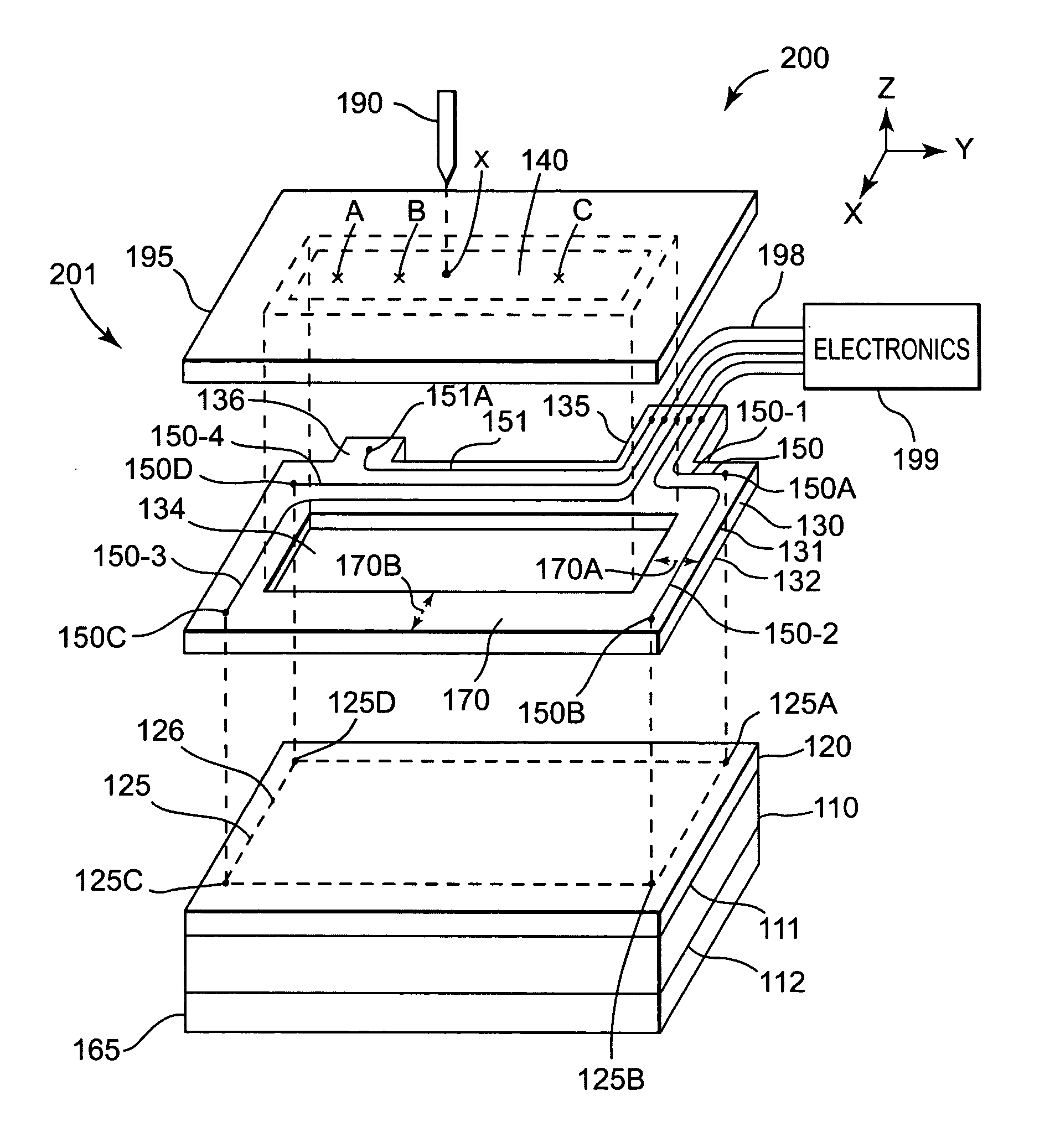
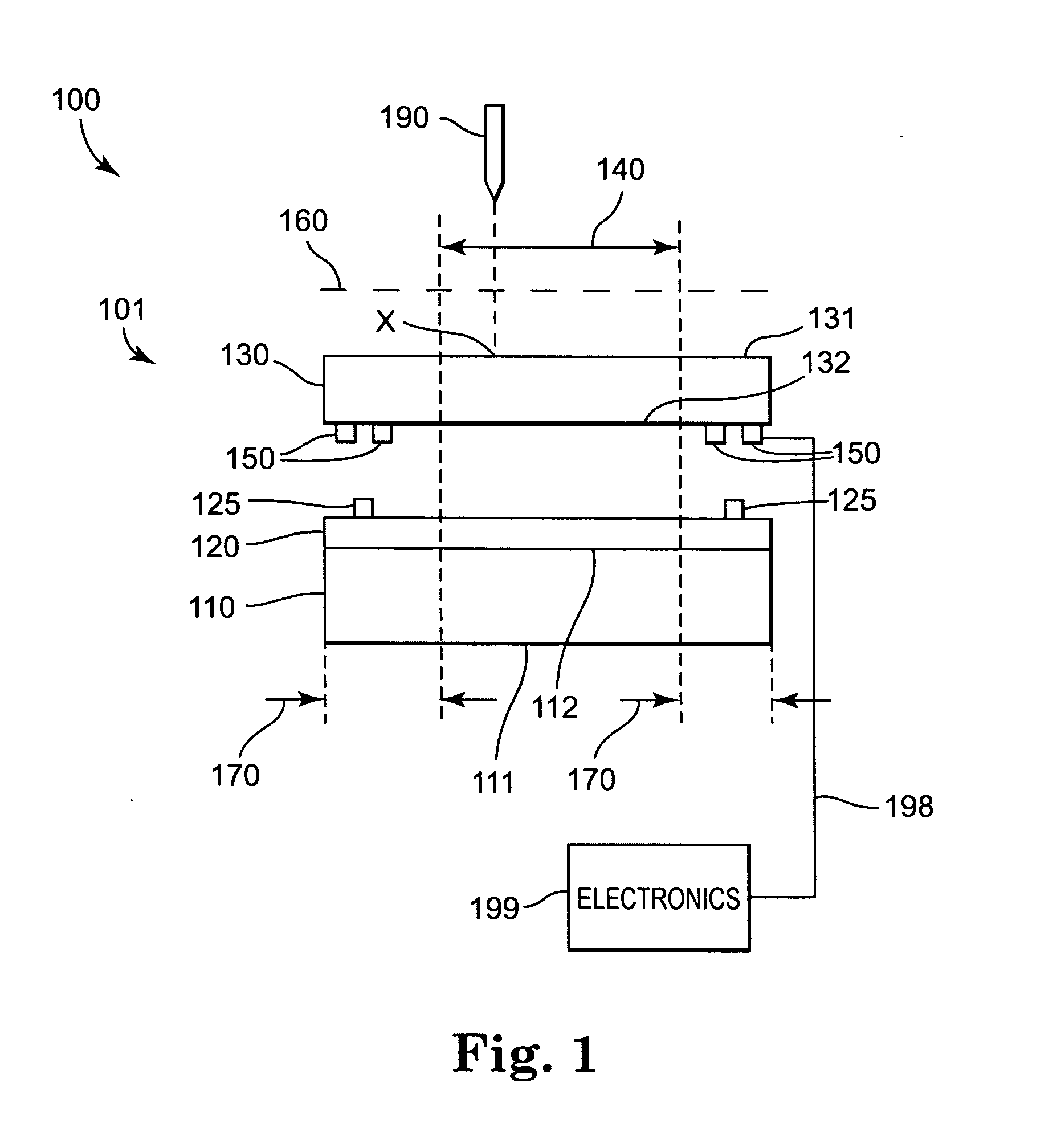
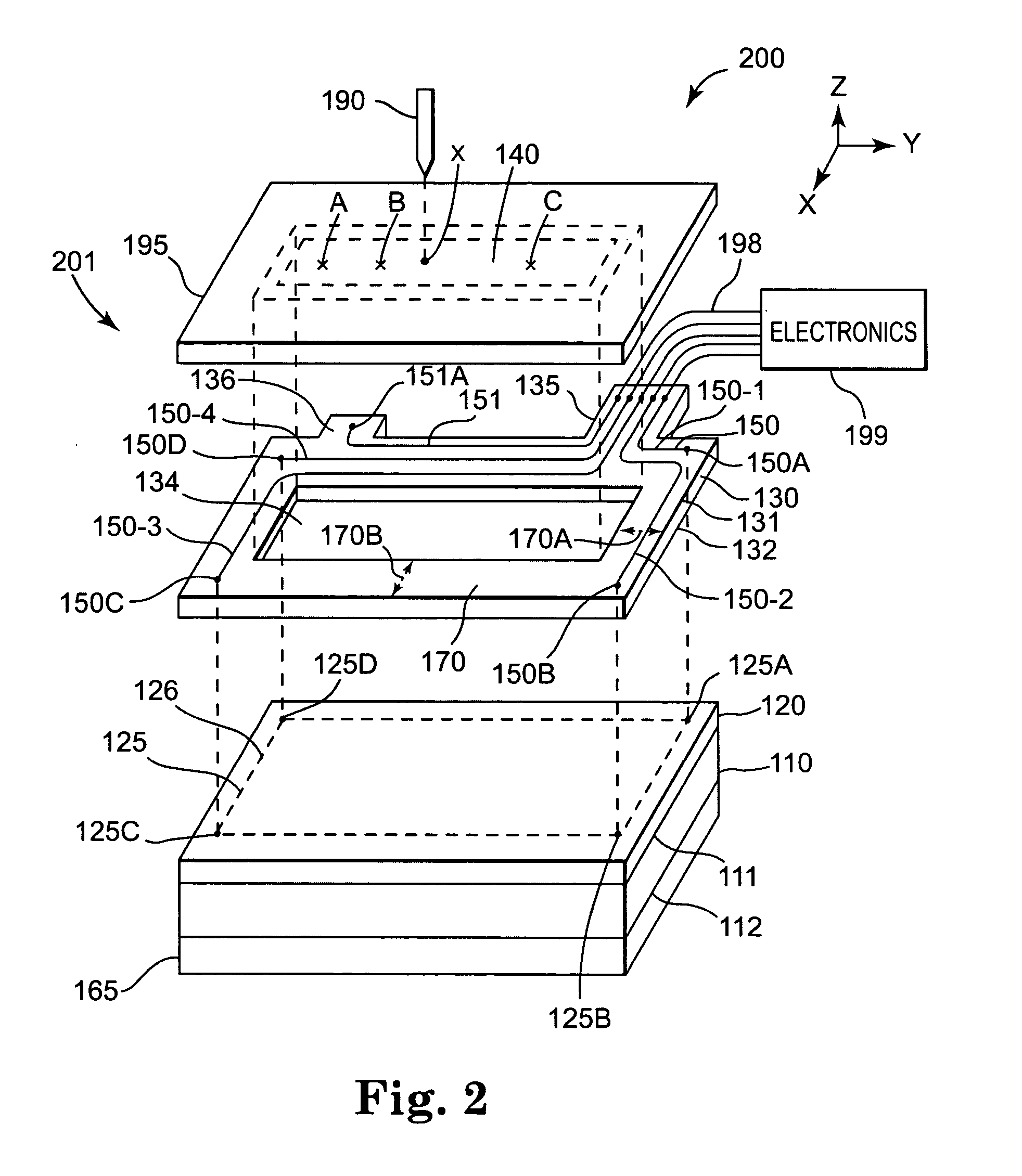
Flexible Circuit for Downhole Antenna
ActiveUS20080030415A1Antenna supports/mountingsRadiating elements structural formsElectrical conductorFlexible circuits
An antenna for an electromagnetic tool having a longitudinal axis and a core. The antenna includes a flexible dielectric substrate flexibly conformed about the core and an electrical conductor disposed on the dielectric substrate. The electrical conductor is disposed on the substrate such that the antenna has a dipole moment having any desired direction relative to the longitudinal axis of the tool.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Forming radio frequency integrated circuits
Method of forming a radio frequency integrated circuit (RFIC) is provided. The RFIC comprises one or more electronic devices formed in a semiconductor substrate and one or more passive devices on a dielectric substrate, arranged in a stacking manner. Electrical shield structure is formed in between to shield electronic devices in the semiconductor substrate from the passive devices in the dielectric substrate. Vertical through-silicon-vias (TSVs) are formed to provide electrical connections between the passive devices in the dielectric substrate and the electronic devices in the semiconductor substrate.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Millimeter-wave quasi-optical integrated dielectric lens antenna and array thereof
InactiveCN101662076AWith quasi-optical Gaussian beam radiation characteristicsGuaranteed normal transmissionAntenna arraysDielectric resonator antennaDielectric substrate
The invention relates to the technical field of radar, in particular to a millimeter-wave quasi-optical integrated dielectric lens antenna and an array thereof. The array consists of a microstrip integrated antenna, a dielectric lens, an objective lens, an array base, a reflecting mirror, a protective cover and a beam transfer switch; one end face of the dielectric lens is a hemisphere or an ellipsoid, while the other end face is a cylindrical section; the microstrip integrated antenna is generated by an dielectric substrate, the front surface of the dielectric substrate is closely adhered tothe cylindrical section of the dielectric lens and serves as a feed source, and the back surface is grounded; the hemispherical or ellipsoidal end face of the dielectric lens is an antenna radiating surface; the length of the cylindrical part of the dielectric lens can be changed; the antenna array is arranged into a linear array or an area array; the array base and the reflecting mirror have conical quasi-optical reflecting mirror surfaces; the focus of the objective lens of the linear array or the area array aligns with the central line of the dielectric lens; the protective cover is arranged outside; and the antenna array is controlled by the beam transfer switch. The antenna structure has strong shock resistance and dust prevention, and is suitable for millimeter-wave radars for planes, automobiles and ships, and receiving / emitting sensing of communication equipment.
Owner:阮树成
Apparatus for transitioning millimeter wave between dielectric waveguide and transmission line
InactiveUS20100253450A1Easy to provideLess timeOne-port networksResonatorsDielectric substrateMillimetre wave
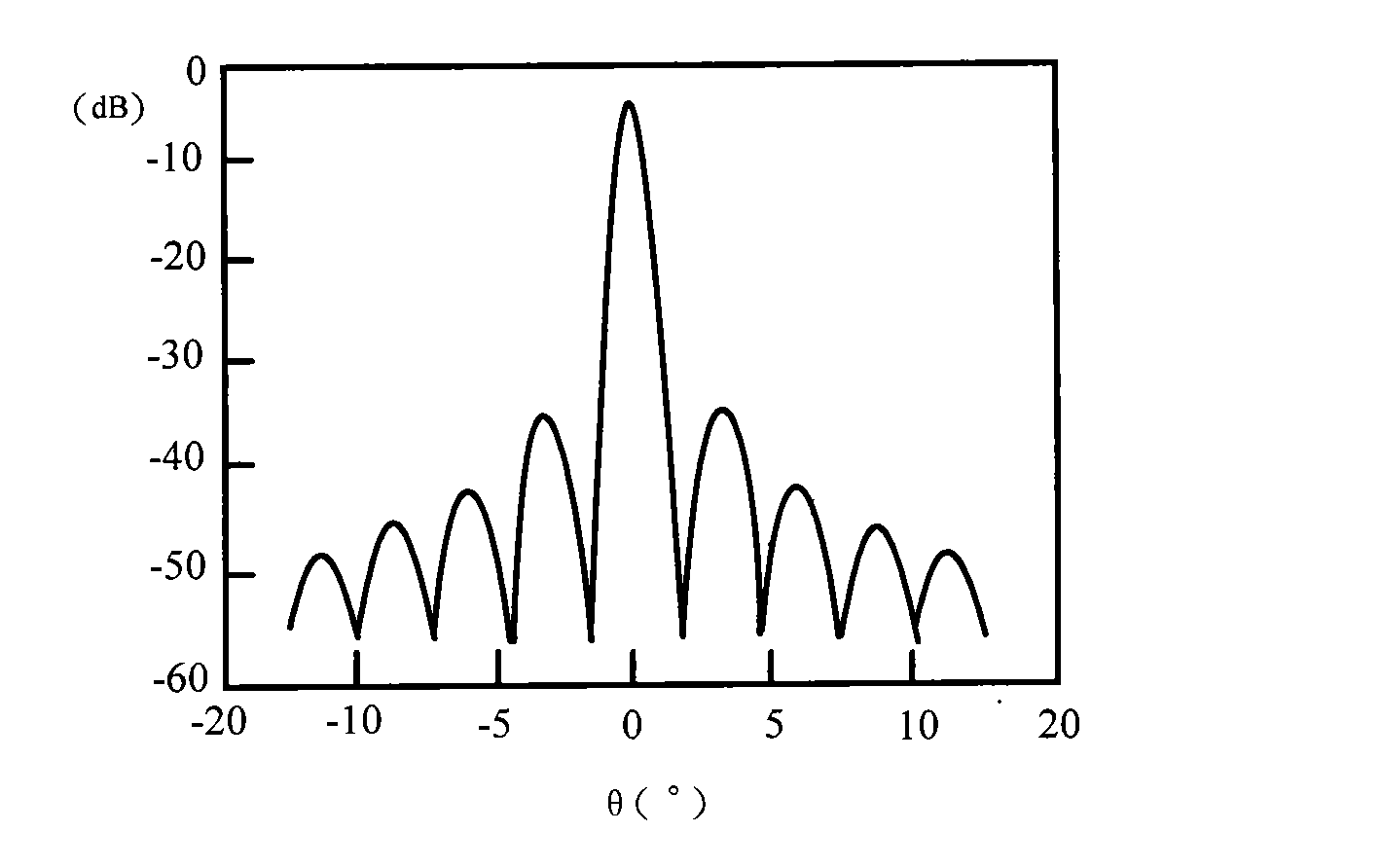
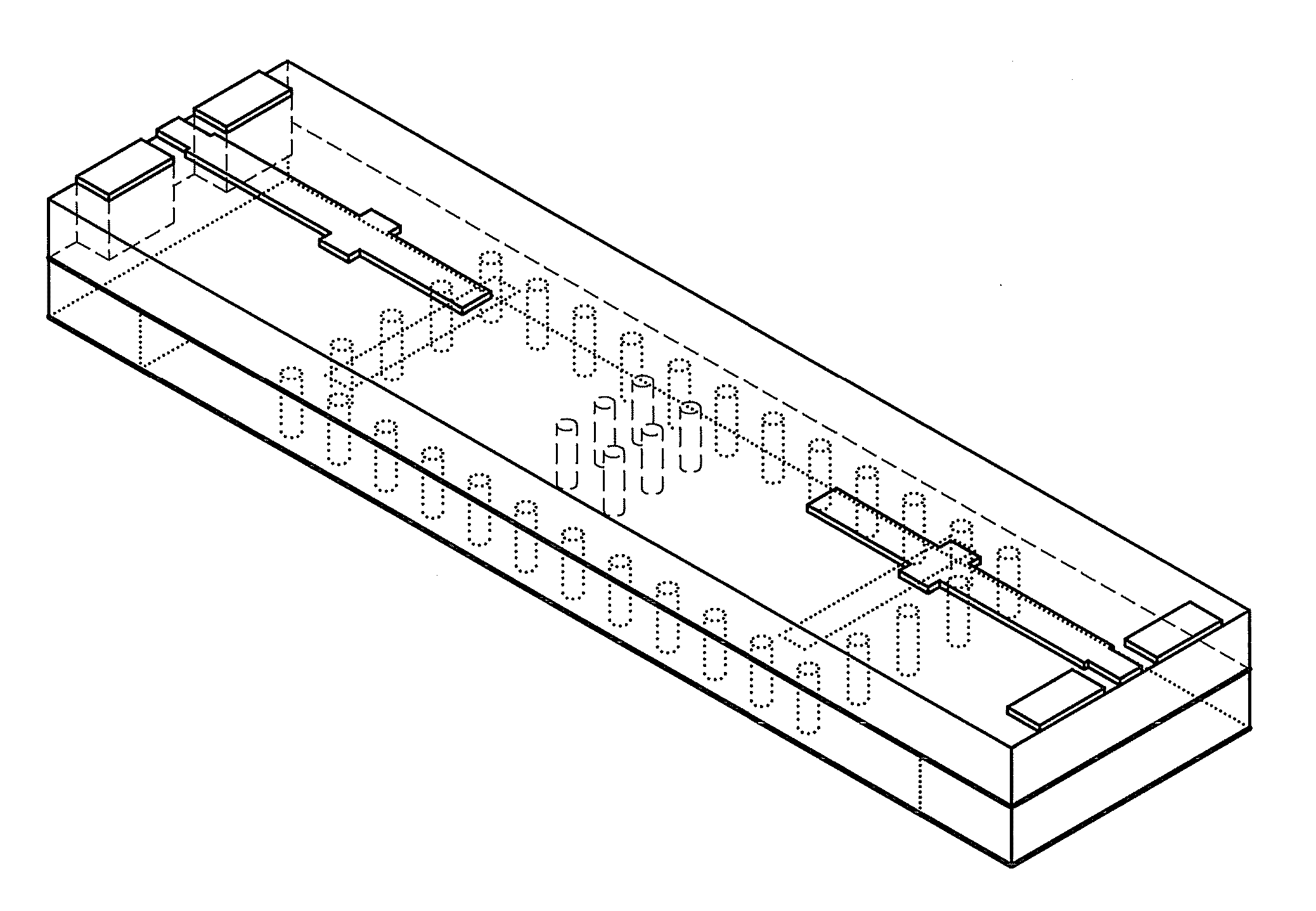
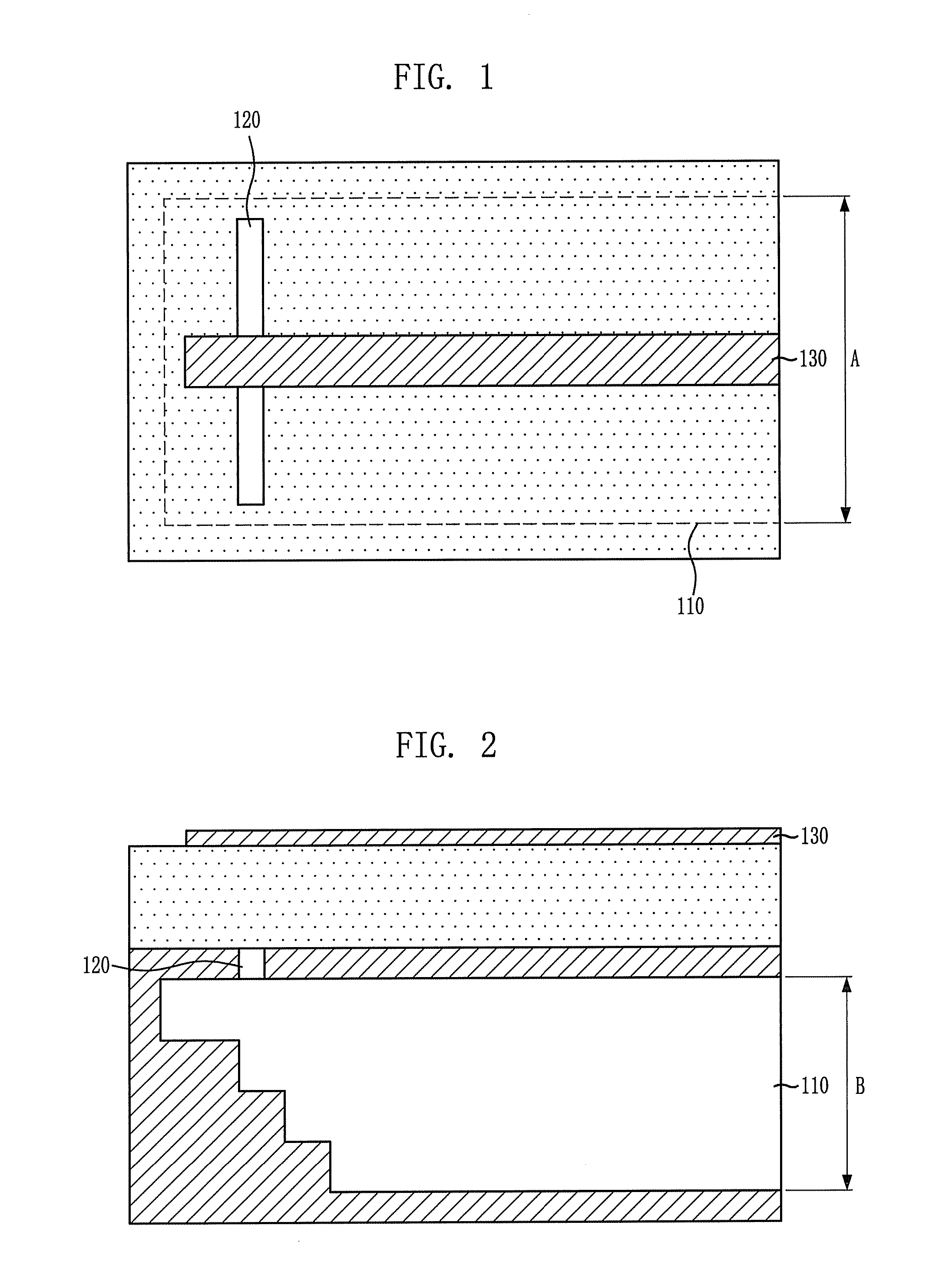
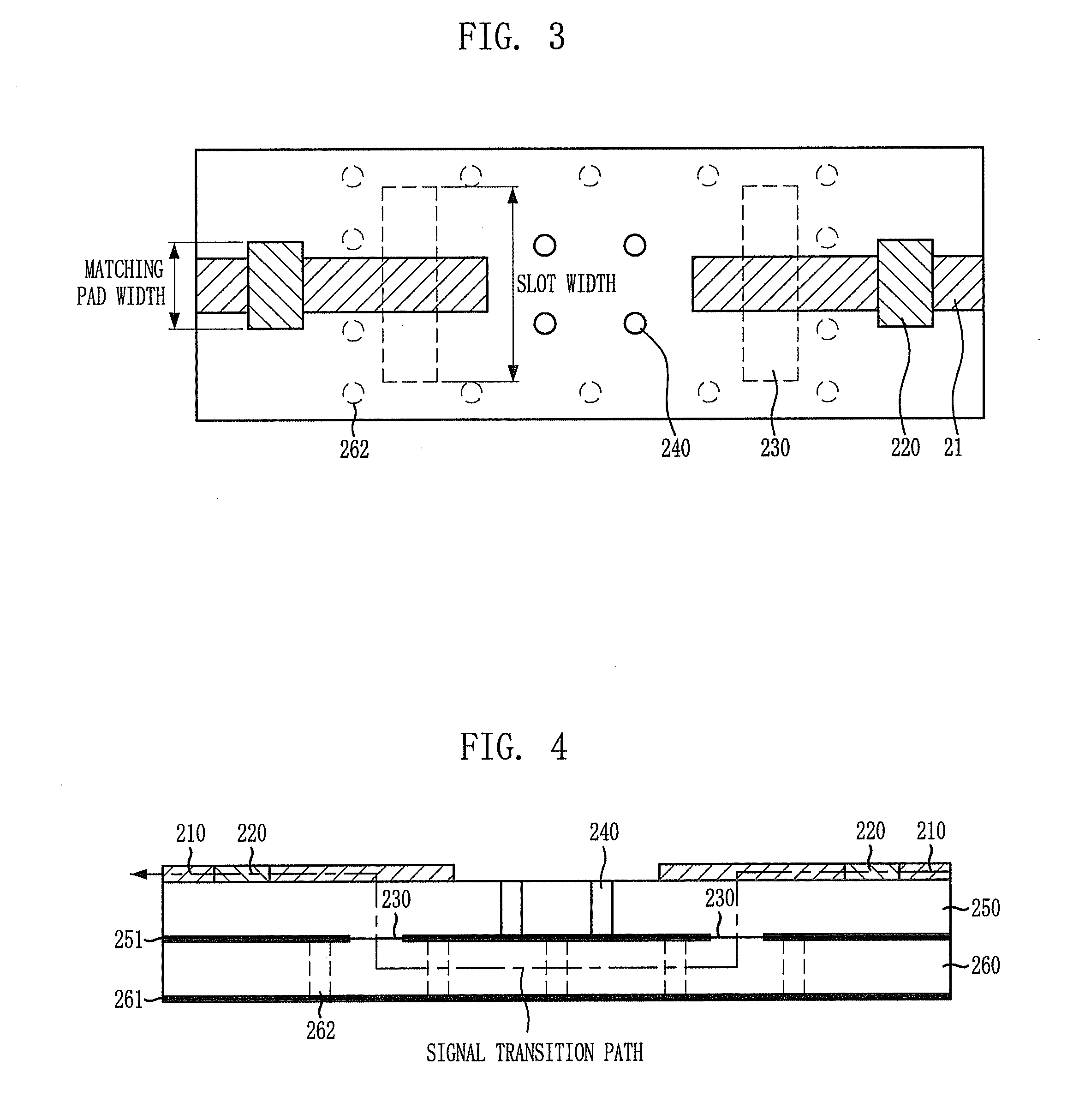
Provided is an apparatus for transitioning a millimeter wave between dielectric waveguide and transmission line using a millimeter wave transition structure formed by the dielectric waveguide, the transmission line, and a slot to transition a signal with lower losses. The apparatus includes: transmission lines disposed respectively at input and output terminals on an uppermost dielectric substrate in a signal transition direction and adapted to transition a signal; a dielectric waveguide formed by a via array disposed between top and bottom ground surfaces of a lowermost dielectric substrate in the signal transition direction as a signal transition path; and slots disposed at a signal transition path of an upper ground surface of each dielectric substrate to connect the transmission lines to the dielectric waveguide so as to transition a signal from the transmission line of the input terminal to the transmission line of the output terminal through the dielectric waveguide.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Self-aligned contact etch with high sensitivity to nitride shoulder
InactiveUS20060051968A1Reliable controlHigh selectivityElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMedium densityDielectric substrate
A method and apparatus are provided for etching semiconductor and dielectric substrates through the use of plasmas based on mixtures of a first gas having the formula CaFb, and a second gas having the formula CxHyFz, wherein a / b≧⅔, and wherein x / z≧½. The mixtures may be used in low or medium density plasmas sustained in a magnetically enhanced reactive ion chamber to provide a process that exhibits excellent corner layer selectivity, photo resist selectivity, under layer selectivity, and profile and bottom CD control. The percentages of the first and second gas may be varied during etching to provide a plasma that etches undoped oxide films or to provide an etch stop on such films.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Microwave garment for heating and/or monitoring tissue
InactiveUS6330479B1Reduce manufacturing costImproved patient comfortElectrotherapyMicrowave therapyDielectric substrateEngineering
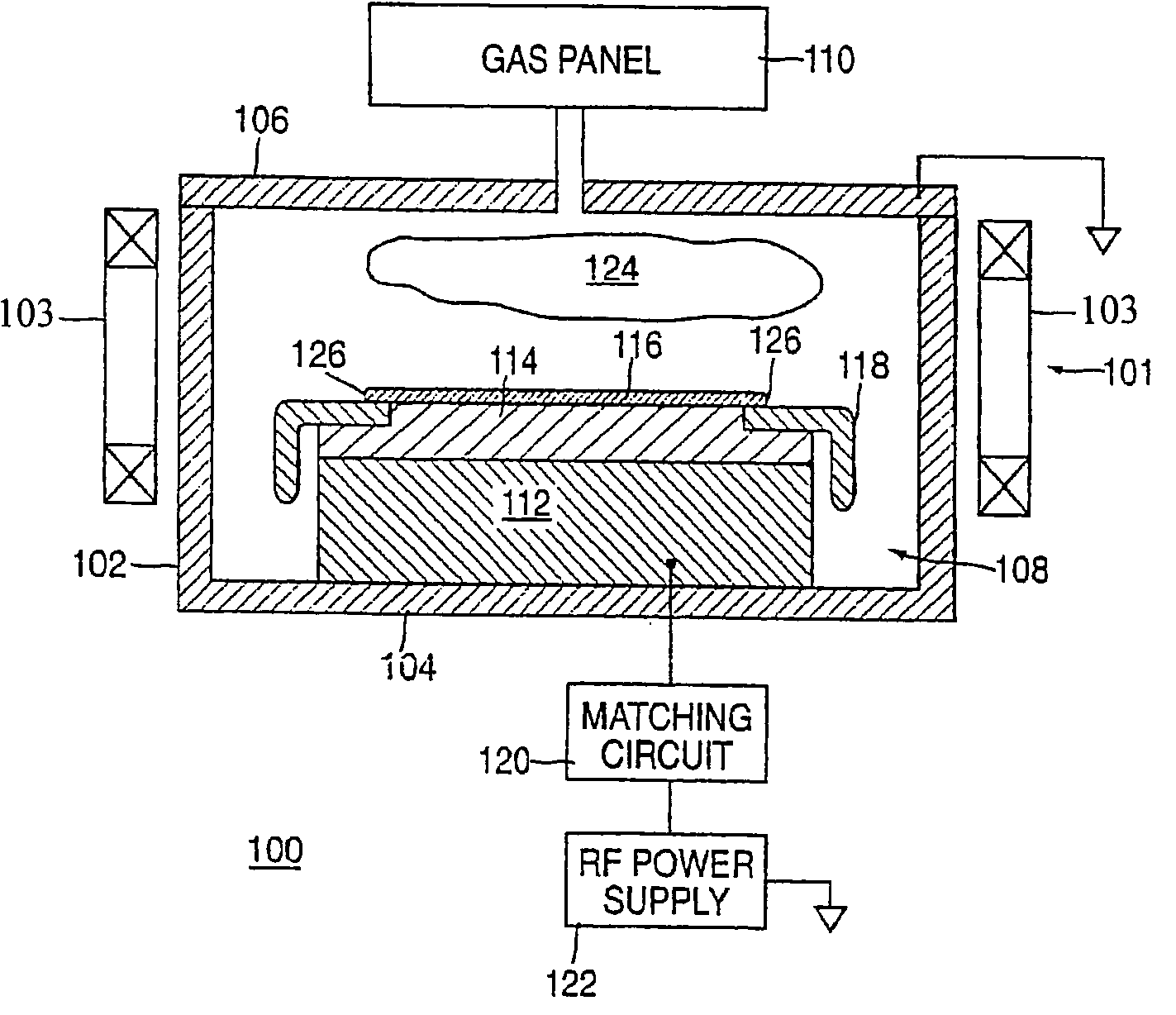
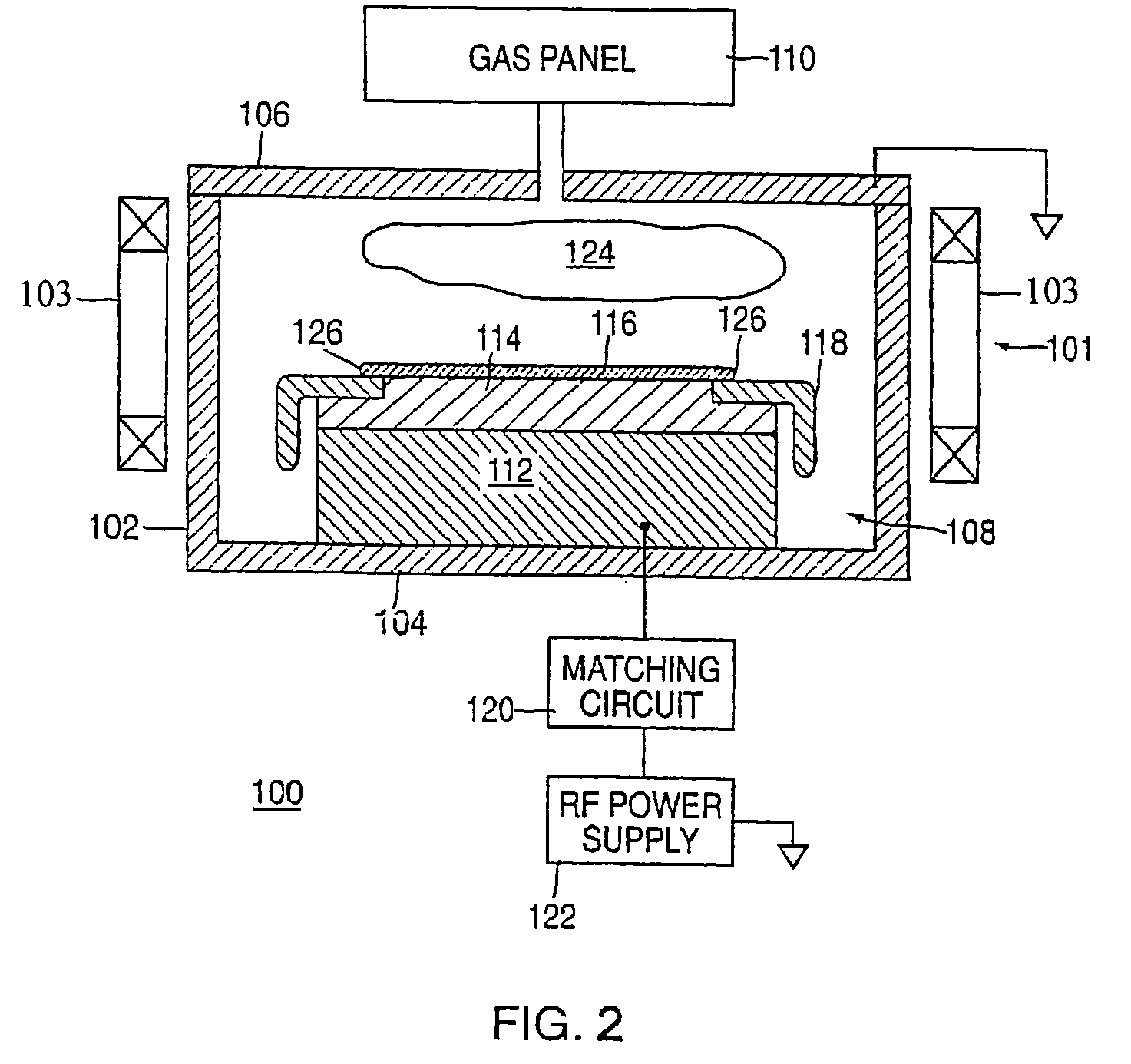
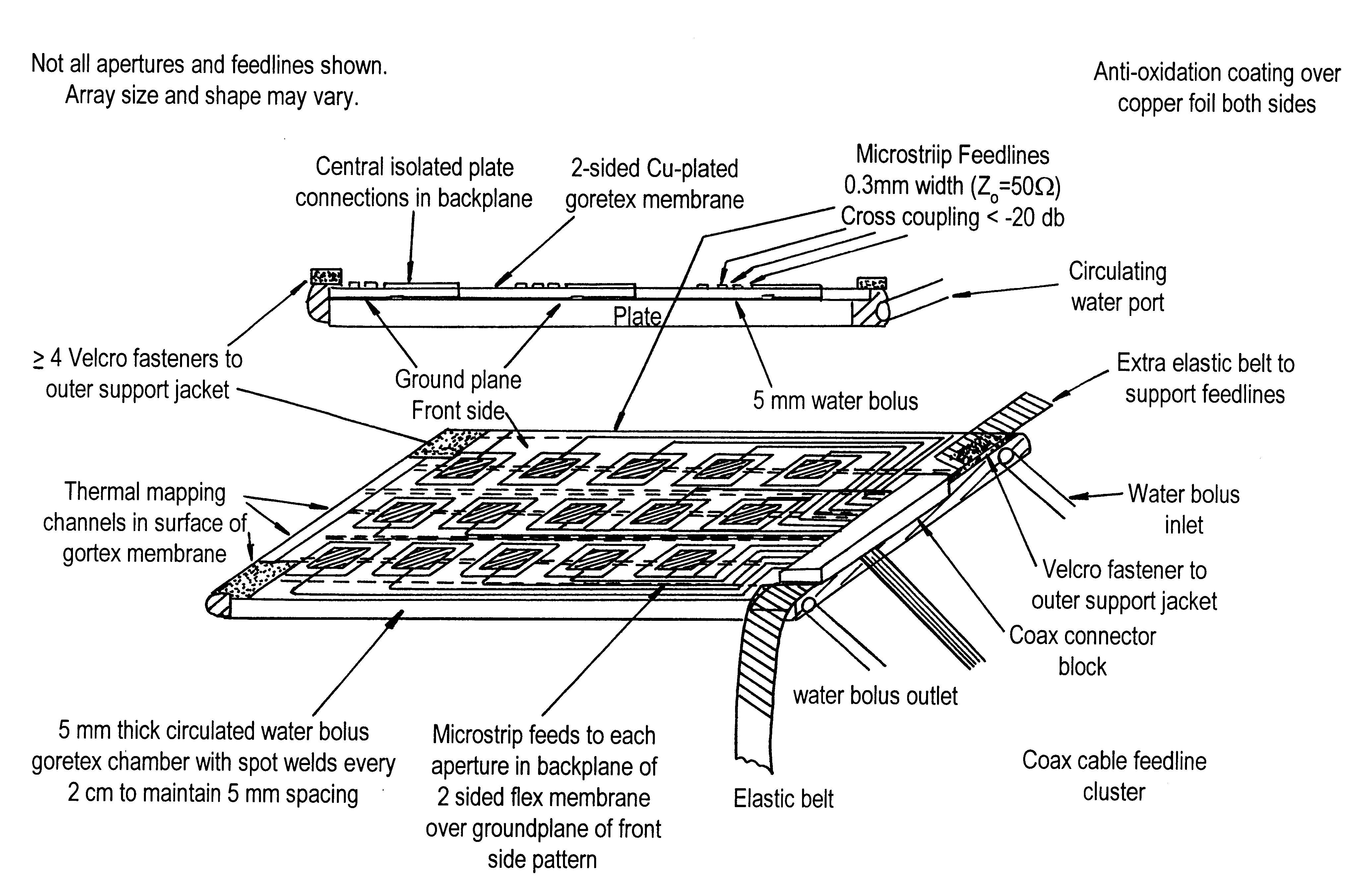
A flexible microwave applicator and method of use thereof. The applicator includes a flexible, dielectric-containing compartment (e.g. temperature regulated water or oil) having a variable contour, tissue-engaging surface and an opposite non-tissue-engaging surface and an antenna array adjacent to a non-tissue-engaging surface. The antenna array includes at least one flexible printed circuit board having a front metal surface, a dielectric substrate, a back metal surface, a connection structure for connecting the antenna array to at least one external microwave device, at least one dual concentric conductor aperture on the front surface, and at least one microstrip feedline in communication with the dual concentric conductor aperture and the connection structure. The microwave applicator also includes flexible attachment material for placement over the antenna array and dielectric compartment to allow the microwave applicator to be attached to a subject like a garment which closely conforms to the anatomy portion to be heated. The flexible attachment material may be configured such that the microwave applicator is configured as an appropriately-shaped type of garment, for example, a vest, jacket, cap, hood, blanket, custom shaped conformal wrap, sleeve, or as a pair of shorts.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
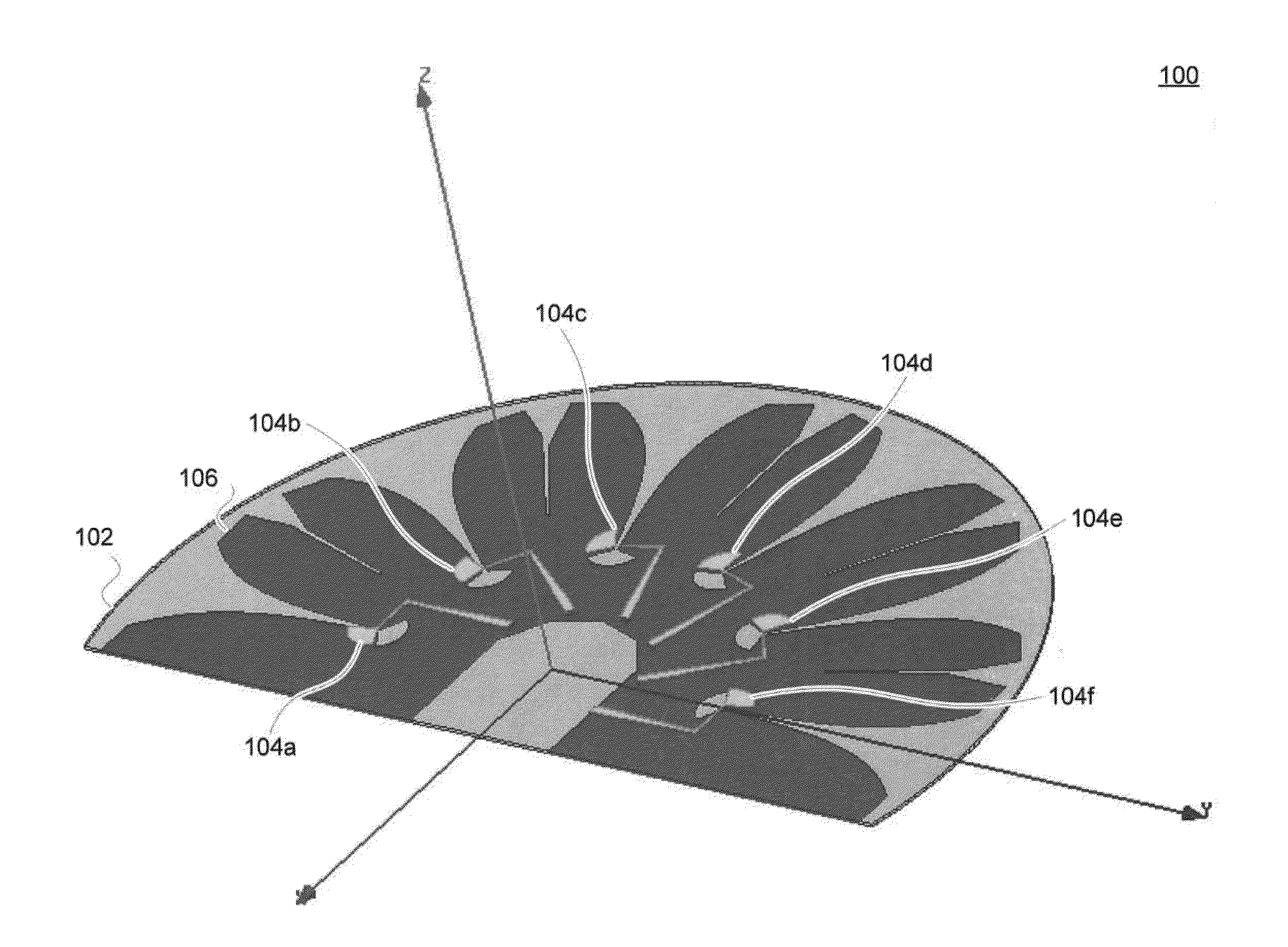
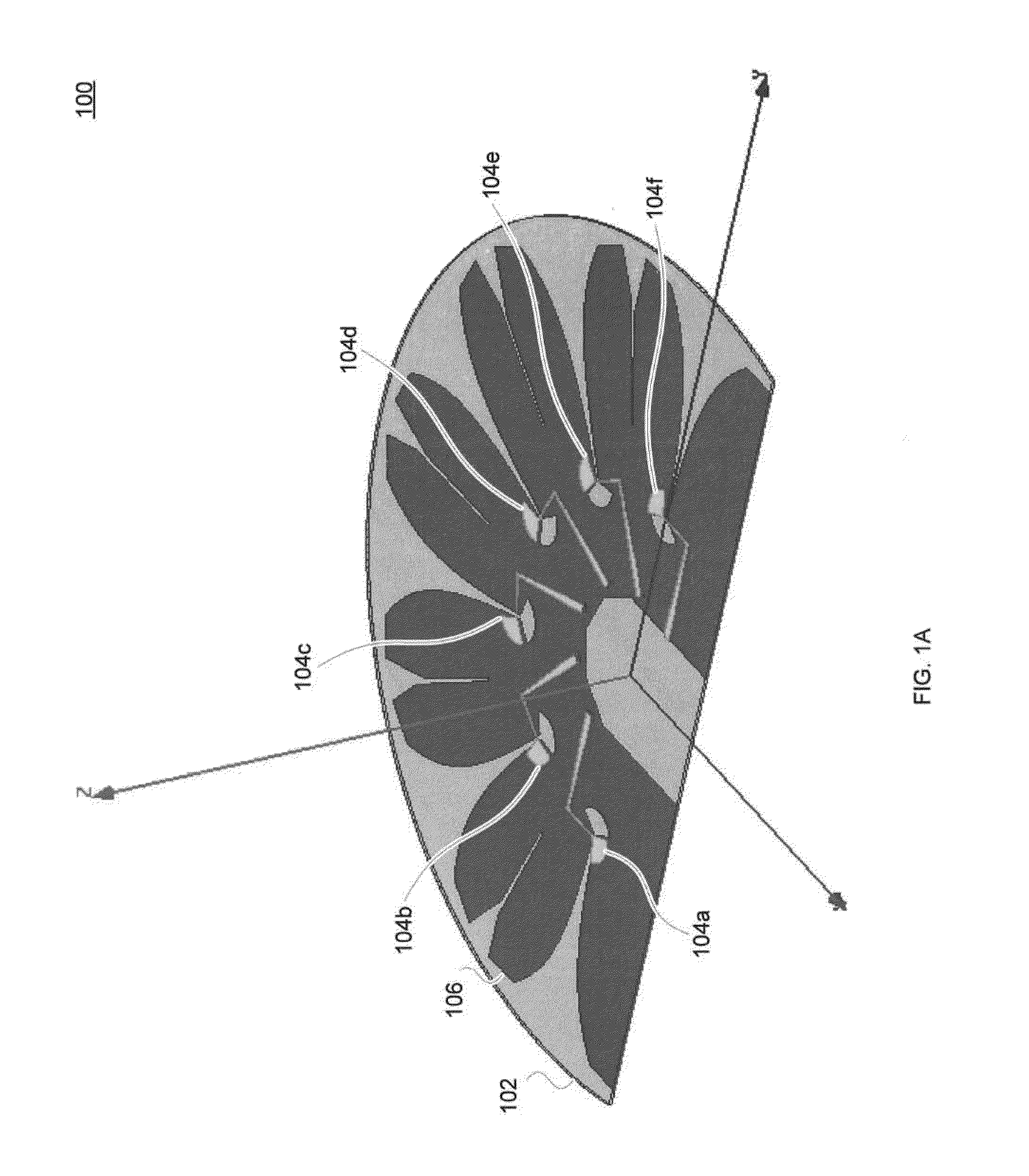
Antennas
InactiveUS20150009089A1Radiating element housingsIndividually energised antenna arraysDielectric substrateConductive materials
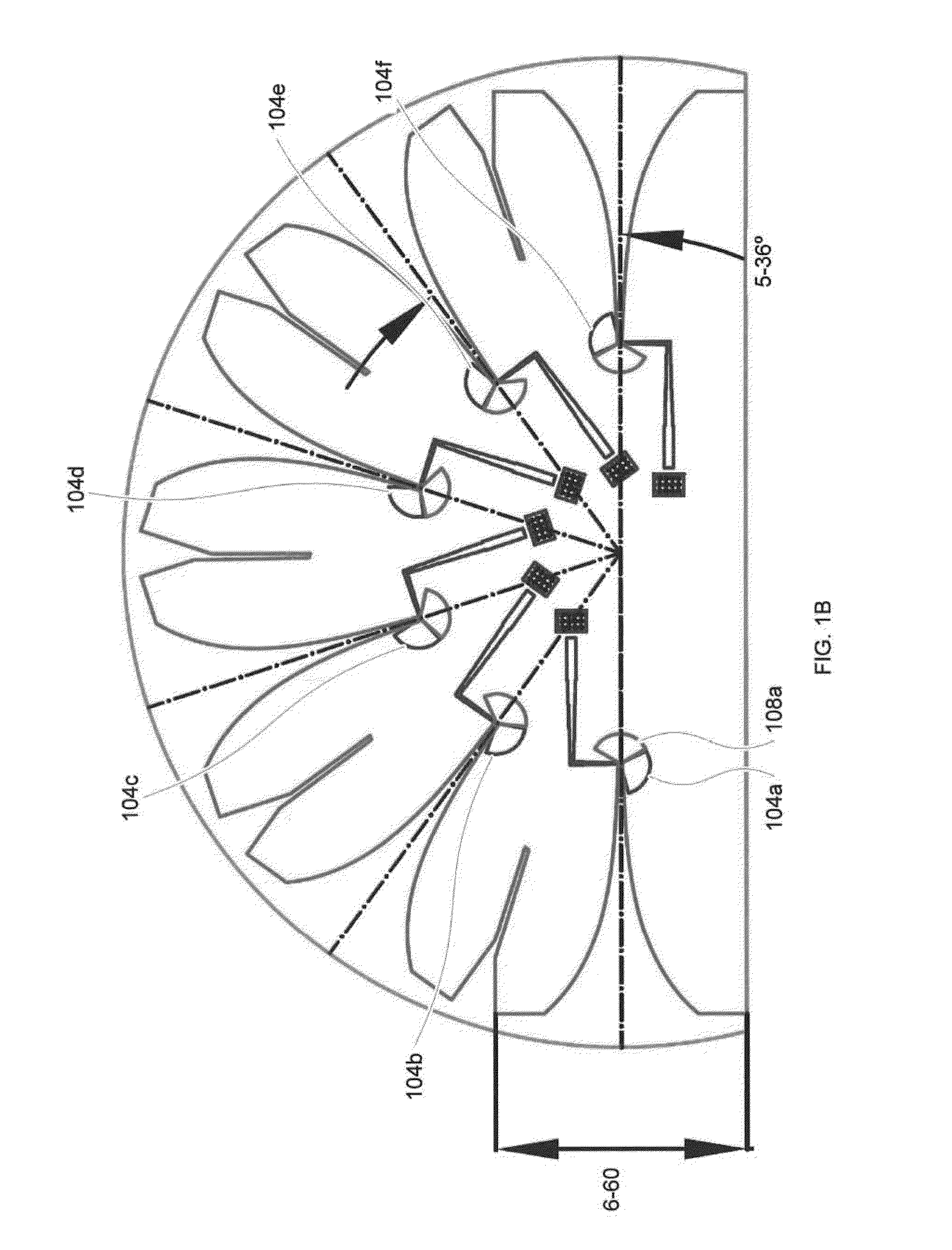
One aspect of the invention provides an antenna including: a dielectric substrate and a plurality of antenna elements positioned on a surface of the dielectric substrate. Each antenna element includes: a sector-shaped sheet of conductive material and a conductive feed line coupled to the sector-shape sheet of conductive material. Another aspect of the invention provides an antenna including: a dielectric substrate, a plurality of antenna elements positioned on a surface of the dielectric substrate at substantially uniform angular intervals along an arc, and a ground layer mounted to an opposite side of the dielectric substrate from the plurality of antenna elements. Each antenna element includes: a sector-shaped sheet of conductive material having a central angle between about 90° and about 180° and a conductive feed line coupled to the sector-shape sheet of conductive material.
Owner:L COM
Substrate embedded horn antenna having selection capability of vertical and horizontal radiation pattern
Substrate embedded horn antenna includes a dielectric, metal patterns, metal vias and a ground plate. The metal patterns are embedded by being stacked in dielectric. Metal patterns are hollow rectangle types or hollow circle types. Metal vias connect layers of metal patterns by being embedded between layers of metal patterns. Ground plate is formed in an upper side of dielectric. Metal patterns form waveguide structure by being stacked in radial shape. Waveguide structure propagates electromagnetic wave by focusing electromagnetic wave. Embedded horn antenna capable of selectively using vertical radiation and horizontal radiation may be implemented using the via and metal pattern in dielectric substrate. Embedded horn antenna may be implemented in small size with high gain. Vertical embedded horn antenna and horizontal embedded horn antenna may be implemented in a substrate. Method of manufacturing embedded horn antenna capable of selectively using vertical radiation and horizontal radiation may be provided.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Protable radio terminal testing apparatus using single self-complementary antenna
InactiveUS6839032B2Simple structureEasy to operateTransmitters monitoringPower managementCouplingImpedance transformer
Owner:ANRITSU CORP
Compact antenna
ActiveUS20080180333A1Improve antenna performanceReducing antennas reflection coefficientSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsCouplingDielectric substrate
An antenna, including a planar dielectric substrate and a conductive ground plane formed on the substrate. A conductive monopole is formed on the substrate and has an end point located in proximity to a feed region of the ground plane. A conductive coupling element is formed on the substrate and is coupled to the ground plane at a coupling region of the ground plane. The coupling element is folded around the monopole.
Owner:GALTRONICS USA INC
MRI Compatible Implanted Electronic Medical Device
An implantable electronic medical device is compatible with a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scanner. The device has a housing with exterior walls, each formed by a dielectric substrate with electrically conductive layers on interior and exterior surfaces. A series of slots divide each layer into segments. Segmenting the layers provides high impedance to eddy currents produced by fields of the MRI scanner, while capacitive coupling of the segments provides radio frequency shielding for components inside the housing. Electrical leads extending from the housing have a pair of coaxially arranged conductors and traps that attenuate currents induced in the conductors by the fields of the MRI scanner.
Owner:KENERGY INC
Antenna apparatus utilizing minute loop antenna and radio communication apparatus using the same antenna apparatus
ActiveUS7250910B2Antenna supports/mountingsElongated active element feedDielectric substrateAntenna element
An antenna apparatus includes a minute loop antenna and at least one antenna element. The minute loop antenna is provided to be electromagnetically close to a dielectric substrate including a grounding conductor, has a predetermined number N of turns and a predetermined minute length, operates as a magnetic ideal dipole when a predetermined metal plate is located closely to the antenna apparatus, and operates as a current antenna when the metal plate is located apart from the antenna apparatus. The antenna element is connected to the minute loop antenna, and operates as a current antenna. In the antenna apparatus, one end of the antenna apparatus is connected to a feeding point, and another end of the antenna apparatus is connected to the grounding conductor of the dielectric substrate.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
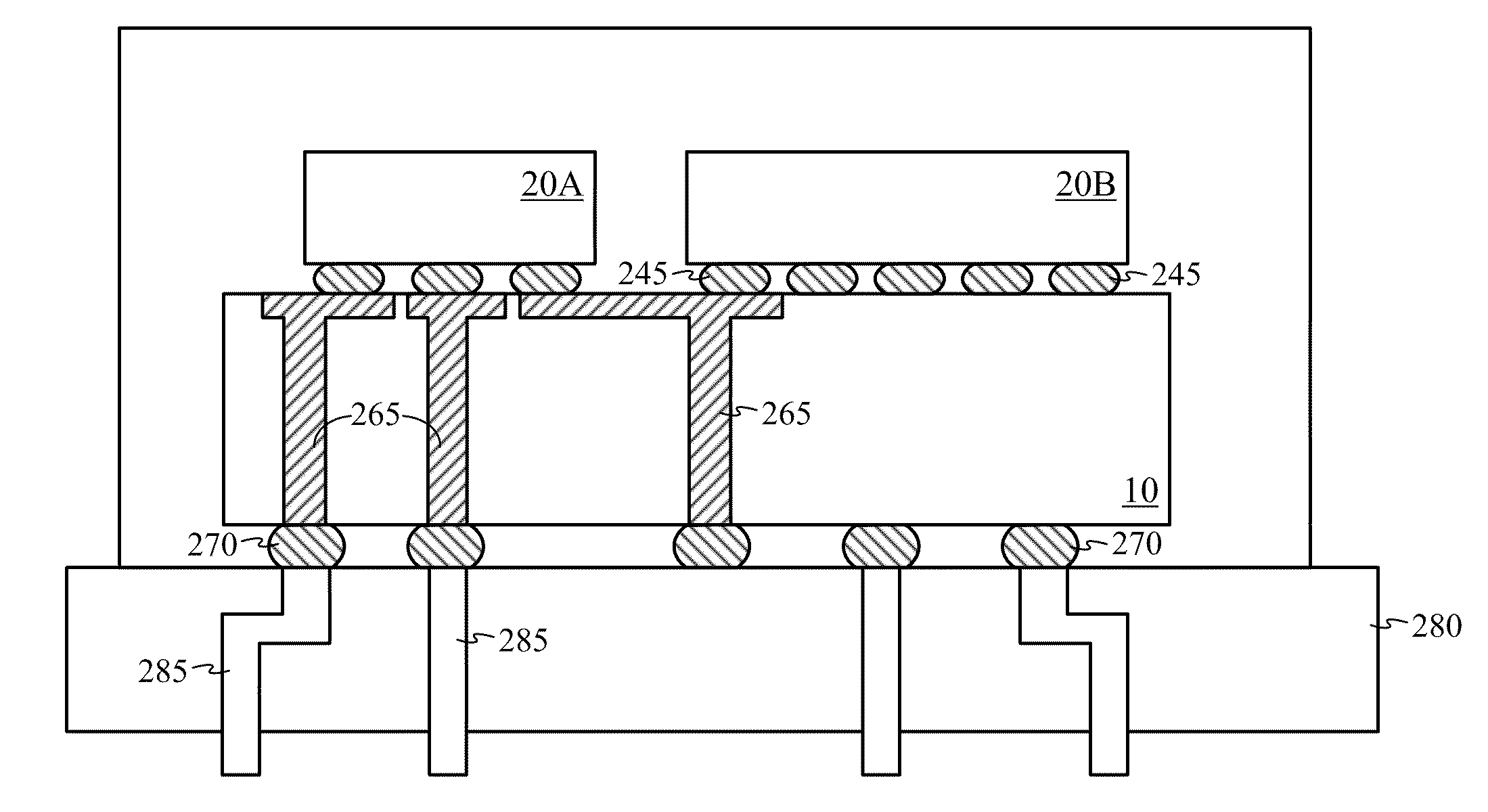
Compositions and structures for chemical mechanical polishing of FeRAM capacitors and method of fabricating FeRAM capacitors using same
InactiveUS6346741B1Easy to manufactureBig advantageOther chemical processesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLead zirconate titanateBarium strontium titanate
An integrated circuit structures formed by chemical mechanical polishing (CMP) process, which comprises a conductive pathway recessed in a dielectric substrate, wherein the conductive pathway comprises conductive transmission lines encapsulated in a transmission-enhancement material, and wherein the conductive pathway is filled sequentially by a first layer of the transmission-enhancement material followed by the conductive transmission line; a second layer of transmission-enhancement material encapsulating the conductive transmission line and contacting the first layer of the transmission-enhancement material, wherein the transmission-enhancement material is selected from the group consisting of high magnetic permeability material and high permittivity material. Such integrated circuit structure may comprise a device structure selected from the group consisting of capacitors, inductors, and resistors. Preferably, the transmission-enhancement material comprises MgMn ferrites, MgMnAl ferrites, barium strontium titanate, lead zirconium titanate, titanium oxide, tantalum oxide, etc.
Owner:GULA CONSULTING LLC
Resonator system
ActiveUS7193418B2Improve efficiencySmall angleMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionElectricityResonance
Owner:BRUKER SWITZERLAND AG
Multi-layered wiring board for slot coupling a transmission line to a waveguide
InactiveUS6870438B1Small signal lossSmall reflectionOne-port networksSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectrical conductorDielectric substrate
A wiring board includes a dielectric substrate, a signal transmission line formed on one surface of the dielectric substrate, a grounded layer formed on the other surface of the dielectric substrate, and a connection portion for connecting portion for connecting the signal transmission line to a waveguide, the connection portion being formed on the grounded layer. The grounded layer has a slot at a position opposed to an end of the signal transmission line. The connection portion includes a first dielectric portion disposed to cover the slot of the ground layer, a second dielectric portion laminated on the first dielectric portion, and a patch conductor provided at a position opposed to said slot on an interface between the first dielectric portion and the second dielectric portion. The wiring board enables the signals to be efficiently transmitted from the signal transmission line to the waveguide with a small loss and a small reflection.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Substrate Integrated Waveguide Antenna Array
InactiveUS20090066597A1Reduce the overall heightMeet cutting requirementsLinear waveguide fed arraysWaveguidesMobile antennasDielectric substrate
A substrate integrated waveguide (SIW) slot full-array antenna fabricated employing printed circuit board technology. The SIW slot full-array antenna using either single or multi-layer structures greatly reduces the overall height and physical steering requirements of a mobile antenna when compared to a conventional metallic waveguide slot array antenna. The SIW slot full-array antenna is fabricated using a low-loss dielectric substrate with top and bottom metal plating. An array of radiating cross-slots is etched in to the top plating to produce circular polarization at a selected tilt-angle. Lines of spaced-apart, metal-lined vias form the sidewalls of the waveguides and feeding network. In multi-layer structures, the adjoining layers are coupled by transverse slots at the interface of the two layers.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
Millimeter-wave quasi-optical integrated dielectric lens antenna and array thereof
InactiveCN101662076BWith quasi-optical Gaussian beam radiation characteristicsGuaranteed normal transmissionAntenna arraysDielectric substrateIntegrated antenna
The invention relates to the technical field of radar, in particular to a millimeter-wave quasi-optical integrated dielectric lens antenna and an array thereof. The array consists of a microstrip integrated antenna, a dielectric lens, an objective lens, an array base, a reflecting mirror, a protective cover and a beam transfer switch; one end face of the dielectric lens is a hemisphere or an ellipsoid, while the other end face is a cylindrical section; the microstrip integrated antenna is generated by an dielectric substrate, the front surface of the dielectric substrate is closely adhered tothe cylindrical section of the dielectric lens and serves as a feed source, and the back surface is grounded; the hemispherical or ellipsoidal end face of the dielectric lens is an antenna radiating surface; the length of the cylindrical part of the dielectric lens can be changed; the antenna array is arranged into a linear array or an area array; the array base and the reflecting mirror have conical quasi-optical reflecting mirror surfaces; the focus of the objective lens of the linear array or the area array aligns with the central line of the dielectric lens; the protective cover is arranged outside; and the antenna array is controlled by the beam transfer switch. The antenna structure has strong shock resistance and dust prevention, and is suitable for millimeter-wave radars for planes, automobiles and ships, and receiving / emitting sensing of communication equipment.
Owner:阮树成
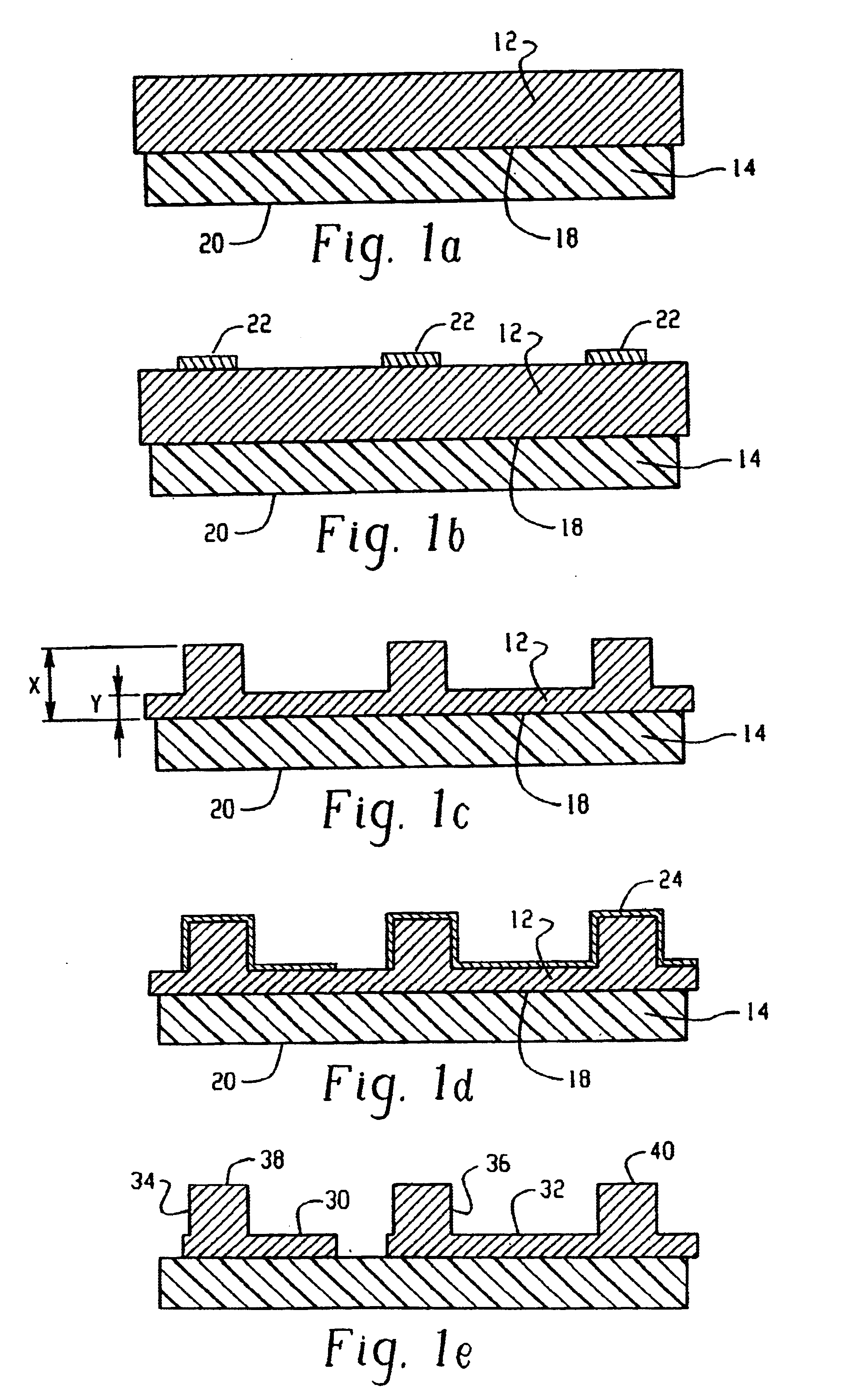
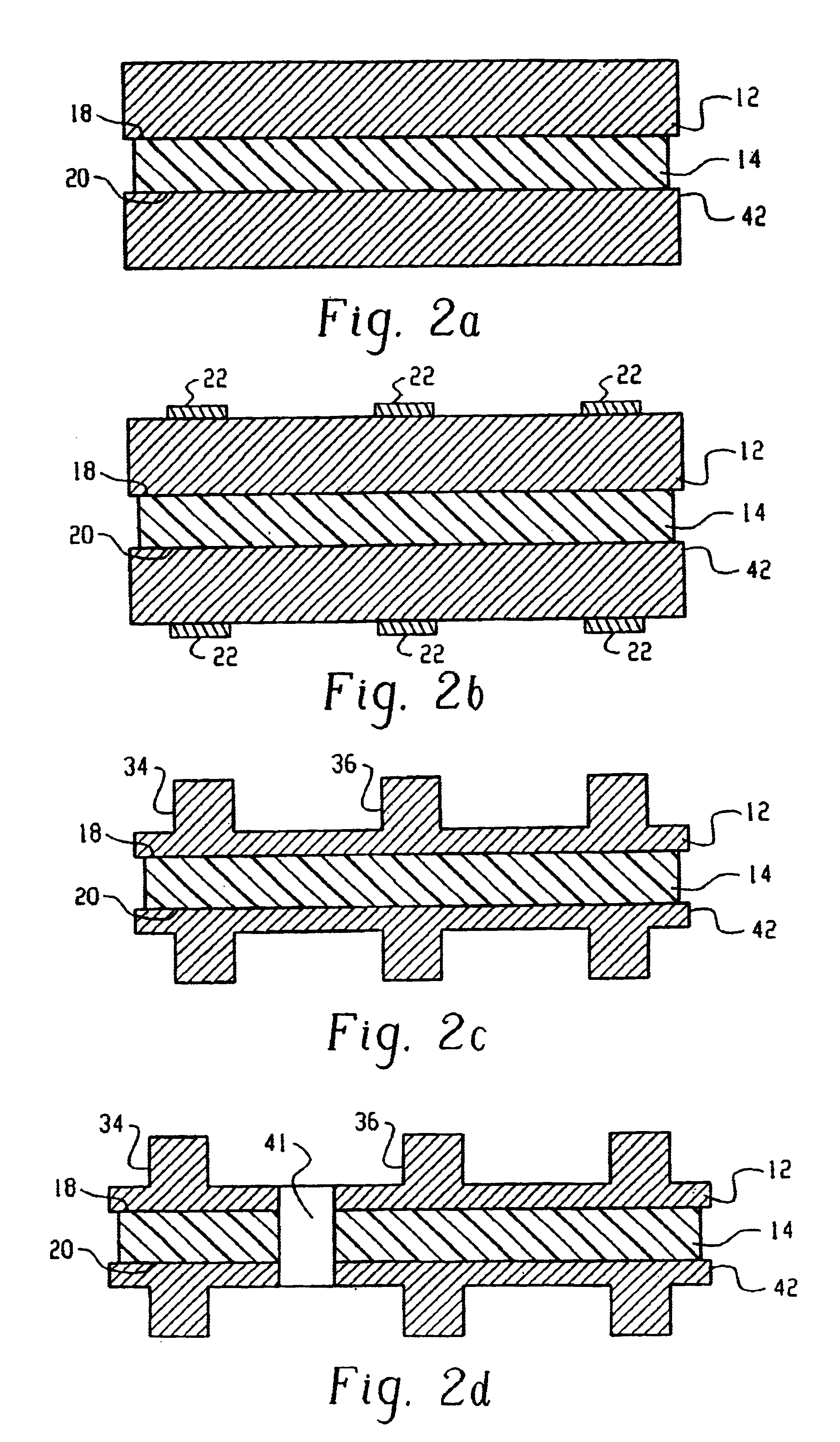
Manufacturing methods for printed circuit boards
InactiveUS6902869B2Improve rigidityEasy to handleLine/current collector detailsWave amplification devicesDielectric substratePhotoresist
A method of forming a plurality of solid conductive bumps for interconnecting two conductive layers of a circuit board with substantially coplanar upper surfaces. The method comprises the steps of applying a continuous homogenous metal layer onto a dielectric substrate, applying a first photoresist and exposing and developing said first photoresist to define a pattern of conductive bumps; etching the metal layer exposed by said development to form said plurality of conductive bumps; removing said first photoresist; applying a second photoresist onto the metal layer; exposing and developing said second photoresist to define a pattern of conductive bumps and circuit lines; etching the metal layer exposed by said development to form a pattern of circuit lines in said metal layer; and removing said second photoresist. The methods of the present invention also provides for fabricating a multilayer circuit board and a metallic border for providing rigidity to a panel.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
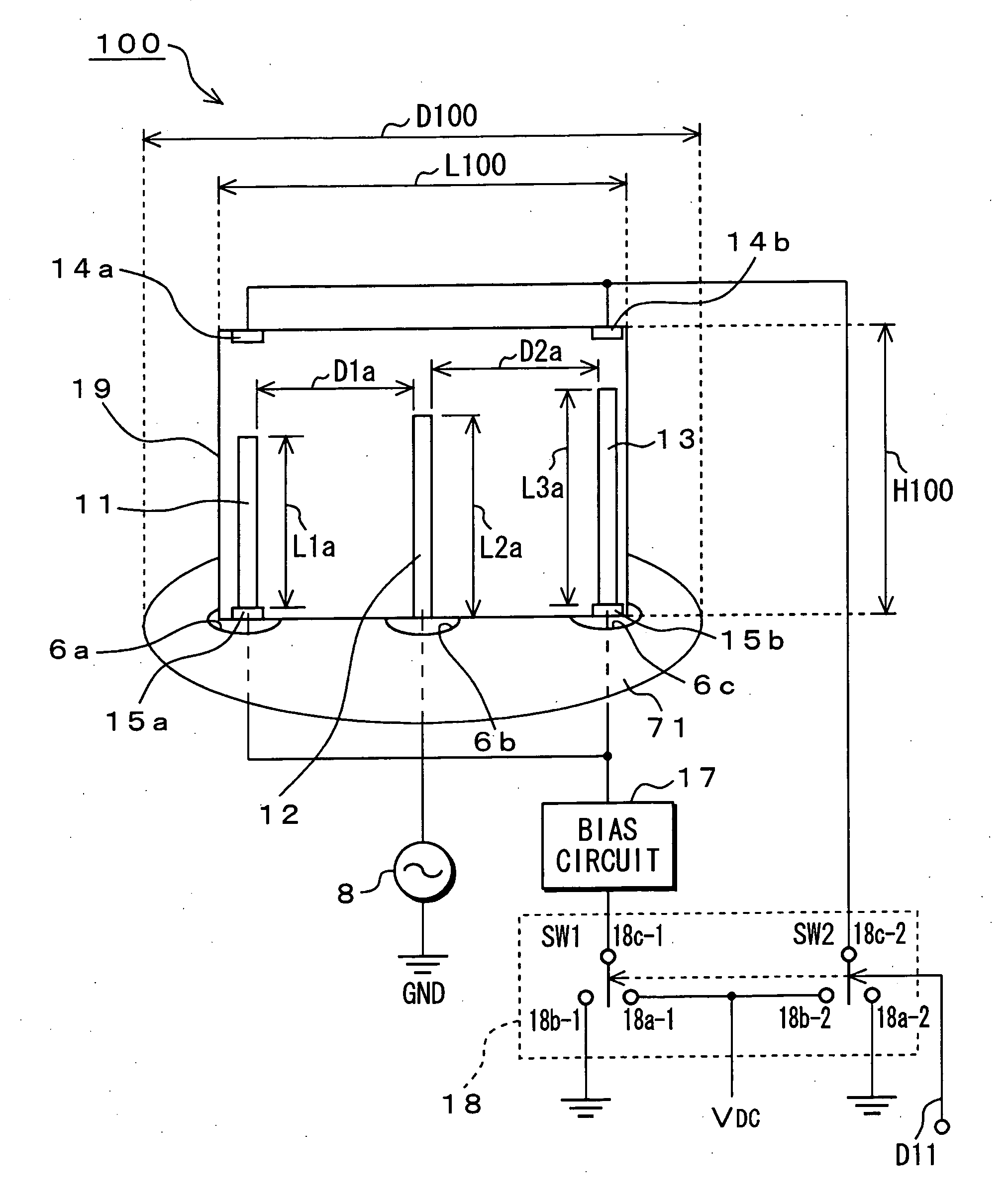
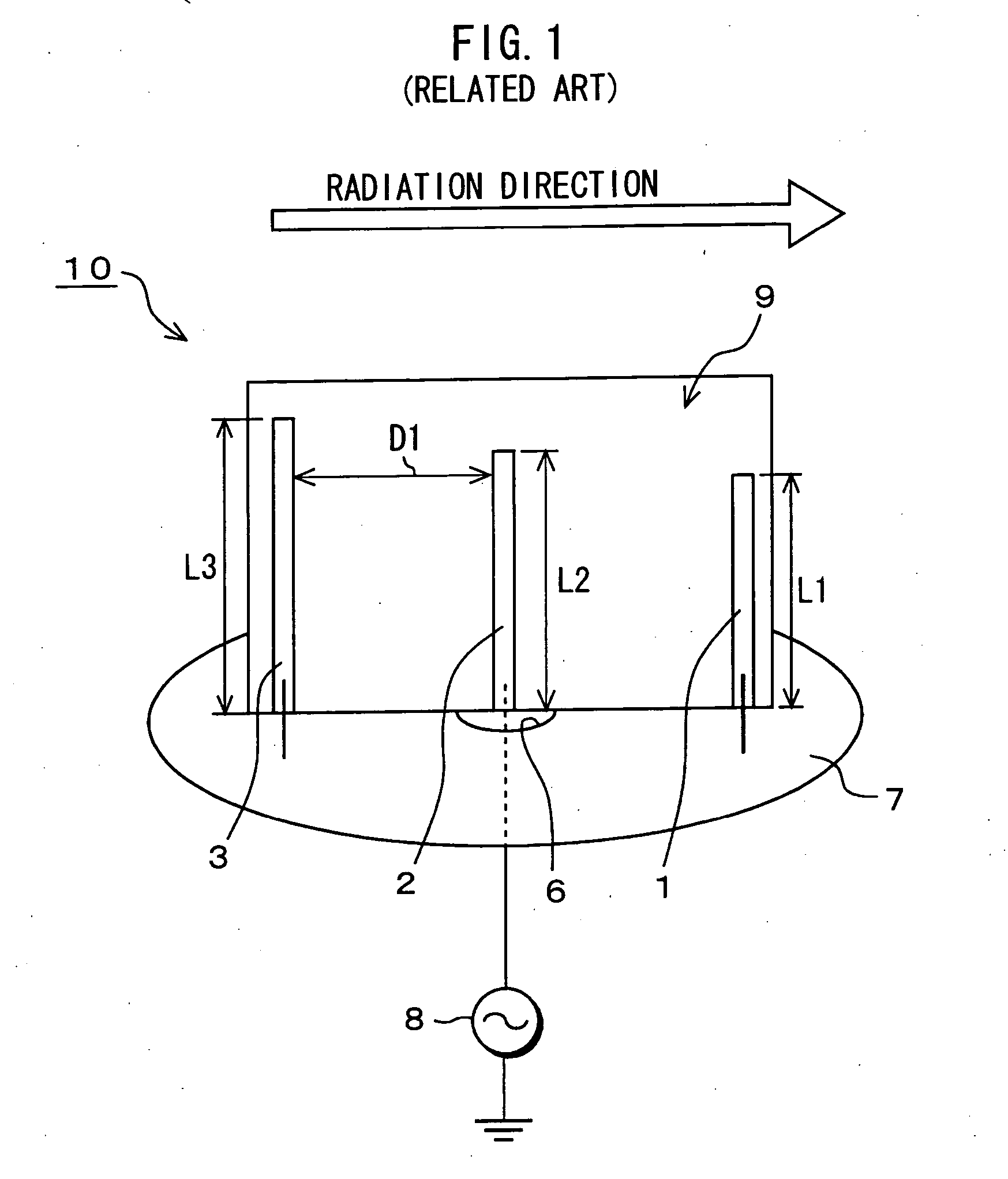
Antenna device, wireless communication apparatus using the same, and control method of controlling wireless communication apparatus
An antenna device has semi-conductive antenna bodies each having a predetermined length, which are positioned on a dielectric substrate, and control electrodes that are respectively connected with the semi-conductive antenna bodies. Direct-current biased voltage applied across each of the control electrodes is controlled to switch each of the antenna bodies between their insulation state and their conductive state.
Owner:SONY CORP
Mobile device and antenna structure
ActiveUS20140125528A1Antenna supports/mountingsAntenna equipments with additional functionsDielectric substrateMobile device
A mobile device includes a dielectric substrate, a metal layer, a metal housing, a nonconductive partition, at least one connection element, and a feeding element. The metal layer is disposed on the dielectric substrate, and includes an upper element and a main element, wherein a slot is formed between the upper element and the main element. The metal housing is substantially a hollow structure, and has a slit, wherein the slit is substantially aligned with the slot of the metal layer. The connection element couples the upper element of the metal layer to the metal housing. The feeding element is coupled to the upper element of the metal layer or coupled to the metal housing. An antenna structure is formed by the feeding element, the upper element of the metal layer, the connection element, and the metal housing.
Owner:HTC CORP
Tunable embedded inductor devices
ActiveUS7884697B2Transformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureCouplingDielectric substrate
The invention provides tunable embedded high frequency inductor devices. The inductor device comprises a dielectric substrate. A first conductive line is disposed on a first surface of the dielectric substrate. A second conductive line is disposed on a second surface of the dielectric substrate. An interconnection is disposed perforating the dielectric substrate and connecting the first conductive line with the second conductive line. A coupling region is defined between the first and the second conductive lines. A conductive plug connecting the first conductive line and the second line is disposed in the coupling region. Alternatively, an opening is disposed in the first and second conductive lines to tune inductance of the inductor.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Internal antennas for mobile communication devices
InactiveUS6466176B1Promote resultsImprove efficiencySimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsMulti bandElectrical conductor
A multi-band microwave antenna which is resonant and radiant at a high frequency band and at one or more lower frequency bands includes an electrically-conductive ground plane on one face of a dielectric substrate; an electrically conductive strip line on the opposite face of the dielectric substrate; a curved slot formed in the ground plane having a feed side electromagnetically coupled to the feed end of the strip line, and a load side electromagnetically coupled to the load end of the strip line, such that the slot is resonant and radiant at the high frequency band; and a further electrical conductor electrically connected to the ground plane to serve as a continuation thereof at the load side of the slot and electromagnetically coupled to the slot at the lower frequency bands such as to cause the slot to be resonant and radiant also at the lower frequency band or bands.
Owner:IN4TEL
Dual-band omnidirectional antenna for wireless local area network
InactiveUS6859176B2Easy to operateReduce manufacturing costSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsDual frequencyOmnidirectional antenna
The present invention relates to a dual-band omnidirectional antenna for wireless LANs. The antenna has a planar dielectric substrate, and first and second conductive patterns. The planar dielectric substrate has two parallel surfaces. The first conductive pattern is arranged on one surface of the substrate, and is provided with a first feeder line arranged on a longitudinal central line of the substrate and a plurality of radiating elements connected to the first feeder line and designed such that some of them operate in a high frequency band (4.9 to 5.85 GHz frequency band), and others thereof operate in a low frequency band (2.4 to 2.5 GHz frequency band). The second conductive pattern is arranged on the other surface of the substrate, and provided with a second feeder line arranged on a longitudinal central line of the substrate and a plurality of radiating elements connected to the second feeder line arid up-down symmetrically arranged with respect to the radiating elements on the first conductive pattern.
Owner:SUNWOO COMM +1
Chiral Metamaterials
InactiveUS20100141358A1Effective controlEnhance the imagePrinted circuit assemblingMultiple-port networksDielectric substrateLength wave
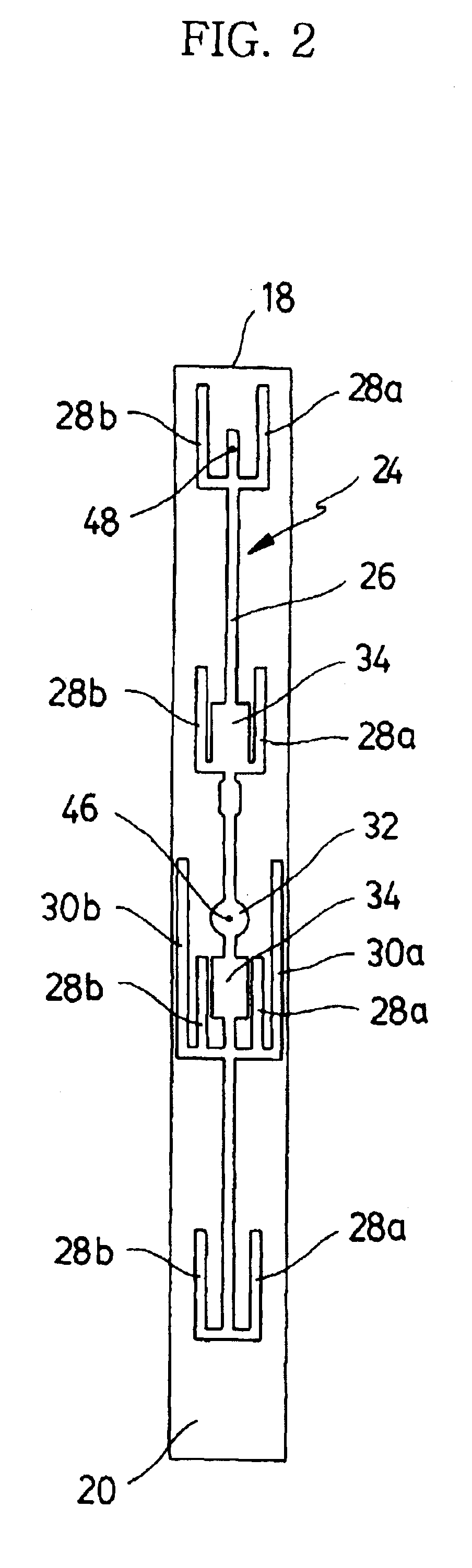
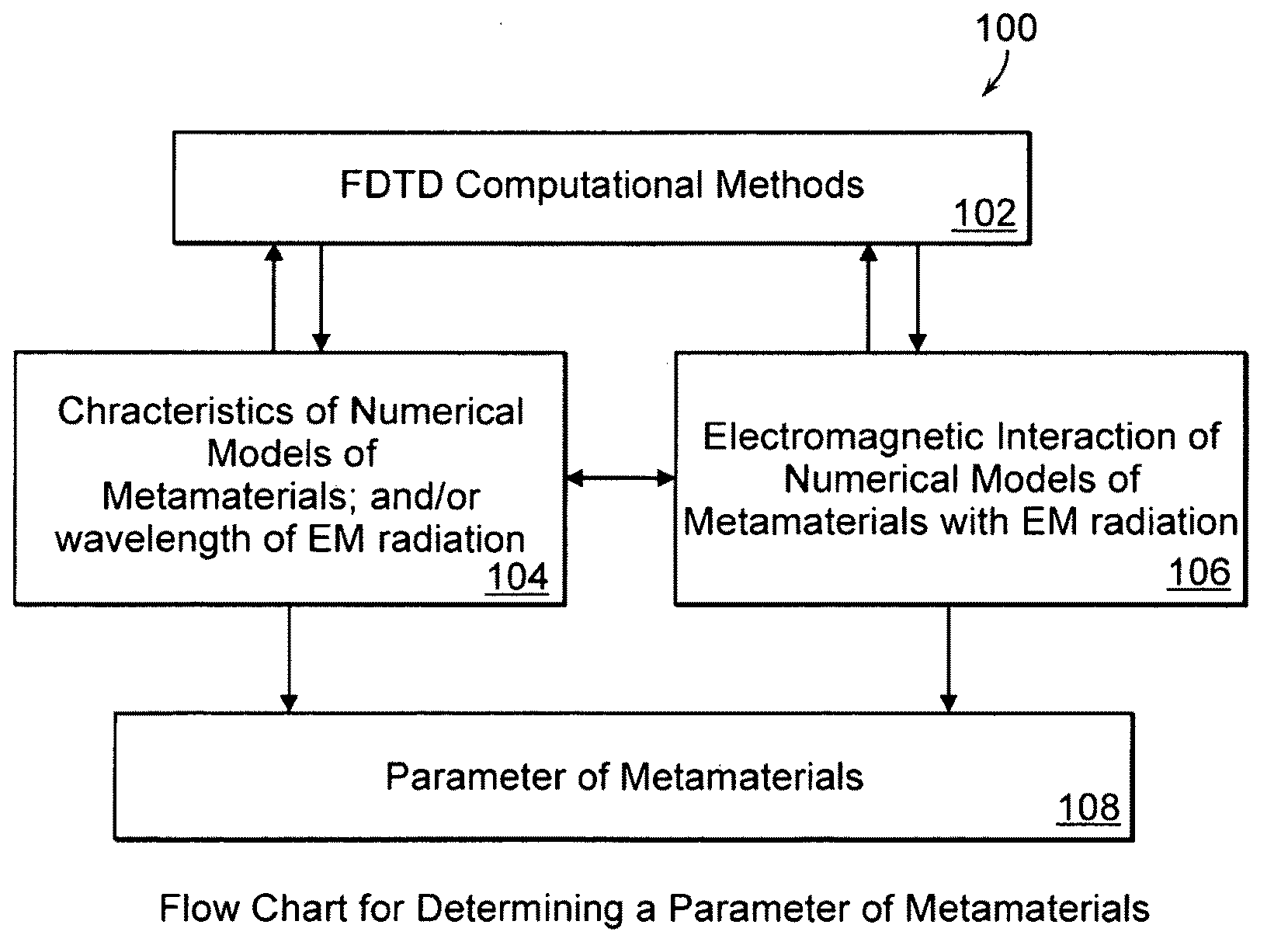
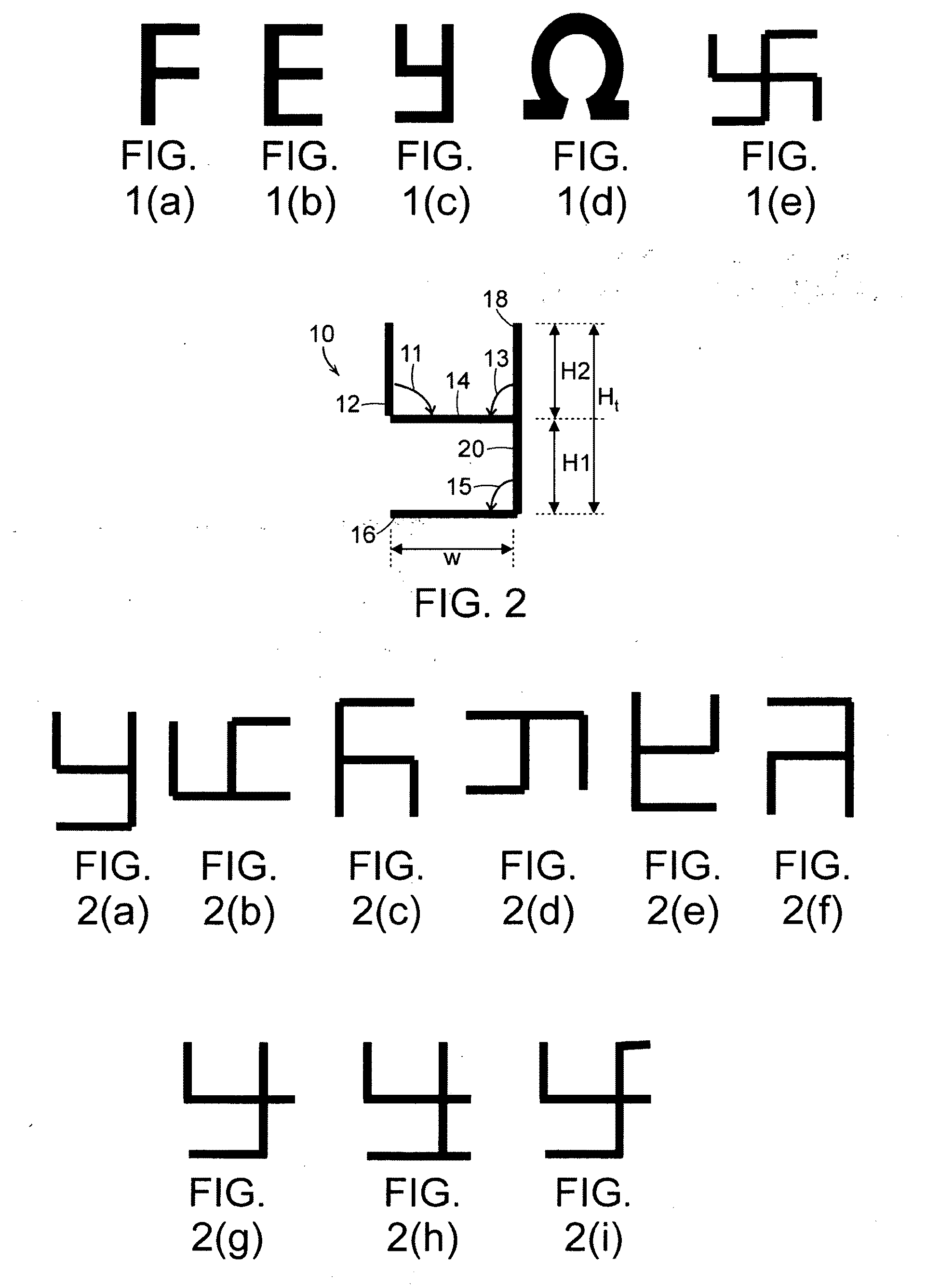
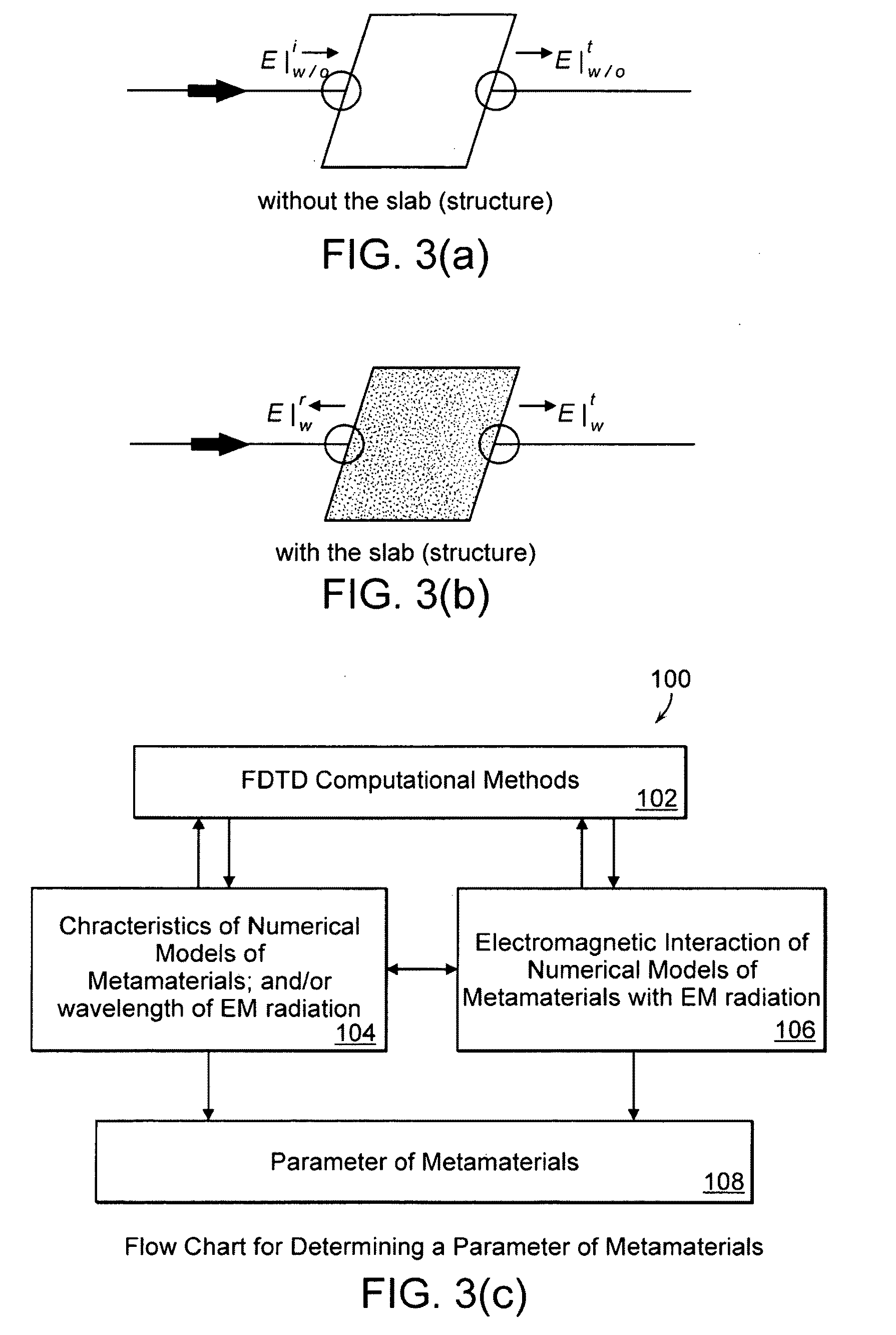
A metamaterial includes a dielectric substrate and an array of discrete resonators at the dielectric substrate, wherein each of the discrete resonators has a shape that is independently selected from: an F-type shape; an E-type shape; or a y-type shape. A parameter of a chiral metamaterial is determined and a chiral metamaterial having such a parameter is prepared by the use of a model of the chiral metamaterial. The metamaterial model includes an array of discrete resonators. In one embodiment, each of the discrete resonators has a shape that is independently selected from the group consisting of: an F-type shape; an E-type shape; and a y-type shape. To the metamaterial model, electromagnetic (EM) radiation, preferably plane-polarized EM radiation in a visible, ultraviolet or near-infrared region, having at least one wavelength that is larger than the largest dimension of at least resonator of the metamaterial model, is applied. Varying at least one characteristic of the metamaterial model and / or at least one wavelength of the applied EM radiation modulates EM interaction of the applied EM radiation with the metamaterial model, thereby determining a parameter of the chiral metamaterial. By the use of a model of the chiral metamaterial, a number of discrete resonators of a chiral metamaterial that are arrayed in a direction perpendicular to a propagation axis of EM radiation is also determined.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS LOWELL
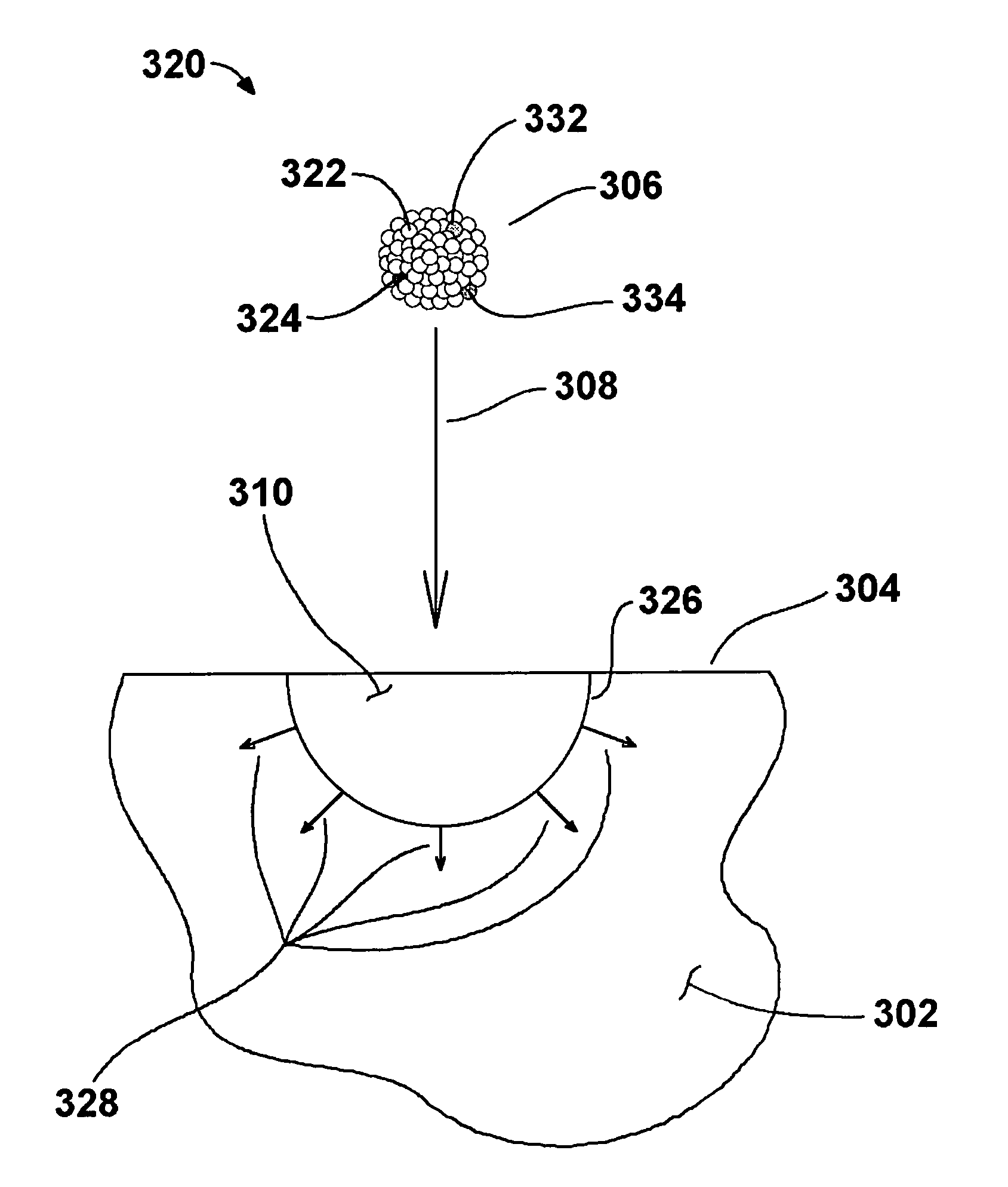
Methods of forming doped and un-doped strained semiconductor materials and semiconductor films by gas-cluster-ion-beam irradiation and materials and film products
ActiveUS7259036B2Electric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantSemiconductor materials
Methods and apparatus are described for irradiating one or more substrate surfaces with accelerated gas clusters including strain-inducing atoms for blanket and / or localized introduction of such atoms into semiconductor substrates, with additional, optional introduction of dopant atoms and / or C. Processes for forming semiconductor films infused into and / or deposited onto the surfaces of semiconductor and / or dielectric substrates are also described. Such films may be doped and / or strained as well.
Owner:EPION
Antenna device and communication apparatus using the same
InactiveUS6281848B1High strengthInhibition decreasedSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsDielectric substrateOptoelectronics
An antenna device comprising: a feeding radiation electrode and a non-feeding radiation electrode separately disposed on a surface of a dielectric substrate; a short circuit part of the feeding radiation electrode and a short circuit part of the non-feeding radiation electrode adjacently disposed to each other on one side surface of the dielectric substrate; and an open end of the feeding radiation electrode and an open end of the non-feeding radiation electrode disposed on mutually different surface sides of the dielectric substrate other than the surface on which said short circuit parts are disposed.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Capacitive liquid level indicator
A capacitive liquid level indicator having a capacitive sensor array superposed on each side of a dielectric substrate, wherein the sensor signal detection electronics are located immediately adjacent each capacitive sensor. These provisions result in high sensitivity of detection of submergence in the liquid, as well as essentially eliminating parasitic electric fields. The preferred capacitive sensors are interdigitated capacitors, and the preferred sensor signal detection circuit is an RC bridge and a comparator, wherein the comparator senses a voltage difference in the RC bridge between a sensor resistor and sensor capacitor of a first leg thereof and a reference resistor and reference capacitor of a second leg thereof. It is preferred for the capacitive liquid level indicator to be coated with a low dielectric conformal coating to thereby insulate the electronic components (inclusive of the capacitive sensors) thereof with respect to the liquid into which it is submerged. The sensitivity of the capacitive liquid level sensor according to the present invention is extremely high; as a result, a reference capacitive sensor is obviated, and there are no false indications of liquid due to any film of the liquid clinging to an exposed portion of the capacitive liquid level sensor.
Owner:GDM
Antenna apparatus utilizing minute loop antenna and radio communication apparatus using the same antenna apparatus
ActiveUS20060114159A1Antenna supports/mountingsElongated active element feedElectrical conductorDielectric substrate
An antenna apparatus includes a minute loop antenna and at least one antenna element. The minute loop antenna is provided to be electromagnetically close to a dielectric substrate including a grounding conductor, has a predetermined number N of turns and a predetermined minute length, operates as a magnetic ideal dipole when a predetermined metal plate is located closely to the antenna apparatus, and operates as a current antenna when the metal plate is located apart from the antenna apparatus. The antenna element is connected to the minute loop antenna, and operates as a current antenna. In the antenna apparatus, one end of the antenna apparatus is connected to a feeding point, and another end of the antenna apparatus is connected to the grounding conductor of the dielectric substrate.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Substrate integrated waveguide antenna array
InactiveUS7808439B2Reduce the overall heightMeet cutting requirementsLinear waveguide fed arraysWaveguidesMobile antennasDielectric substrate
A substrate integrated waveguide (SIW) slot full-array antenna fabricated employing printed circuit board technology. The SIW slot full-array antenna using either single or multi-layer structures greatly reduces the overall height and physical steering requirements of a mobile antenna when compared to a conventional metallic waveguide slot array antenna. The SIW slot full-array antenna is fabricated using a low-loss dielectric substrate with top and bottom metal plating. An array of radiating cross-slots is etched in to the top plating to produce circular polarization at a selected tilt-angle. Lines of spaced-apart, metal-lined vias form the sidewalls of the waveguides and feeding network. In multi-layer structures, the adjoining layers are coupled by transverse slots at the interface of the two layers.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
Wiring harness and touch sensor incorporating same
InactiveUS20050126831A1Transmission systemsCathode-ray tube indicatorsDielectric substrateAuxiliary electrode
A wiring harness and a touch sensor incorporating same are disclosed. The touch sensor includes a sensing electrode disposed in a touch sensitive area. The touch sensor further includes a plurality of auxiliary electrodes disposed on a self-supporting dielectric substrate in a border area. The auxiliary electrodes transmit a touch signal to electronics configured to use the touch signal to determine the touch location.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com