Patents
Literature
7796 results about "Millimetre wave" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
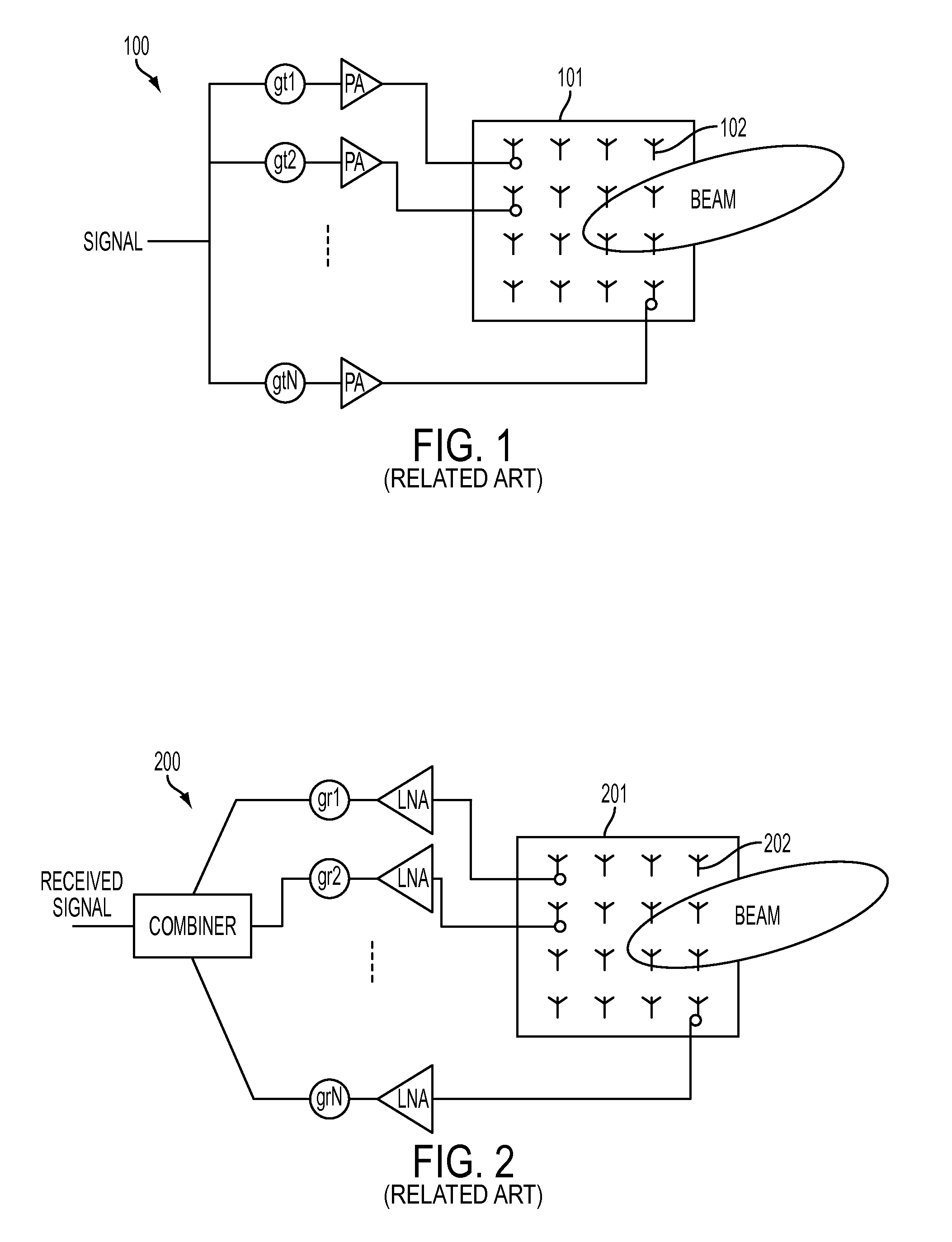
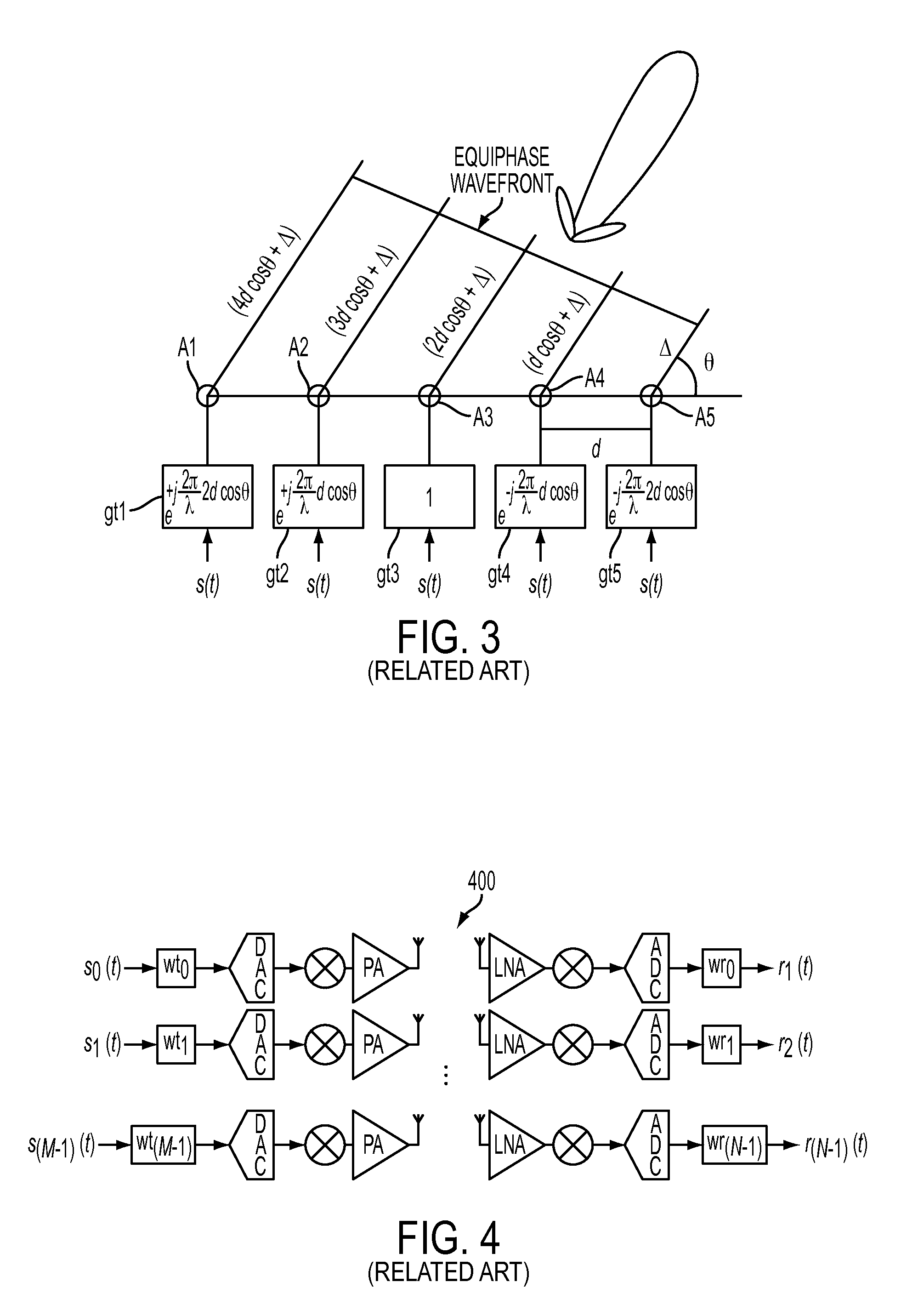
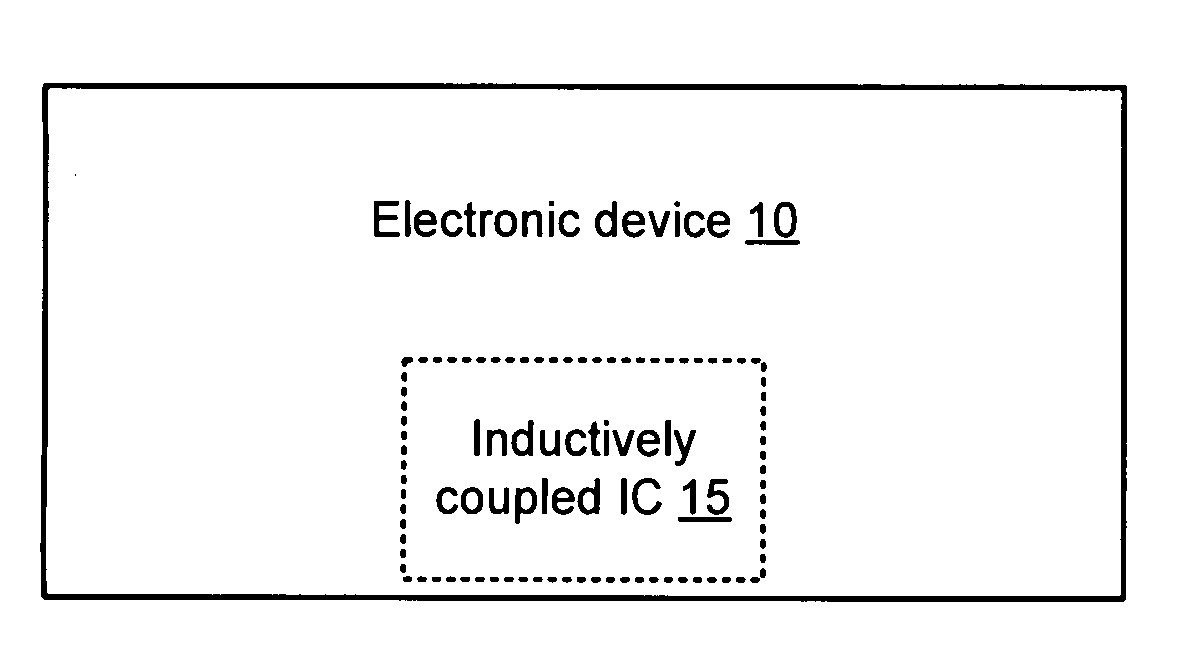
Millimeter wave is an undeveloped band of spectrum that can be used in a broad range of products and services like high speed, point-to-point wireless local area networks (WLANs) and broadband access. In telecommunications, millimeter wave is used for a variety of services on mobile and wireless networks, as it allows for higher data rates up to 10 Gbps.
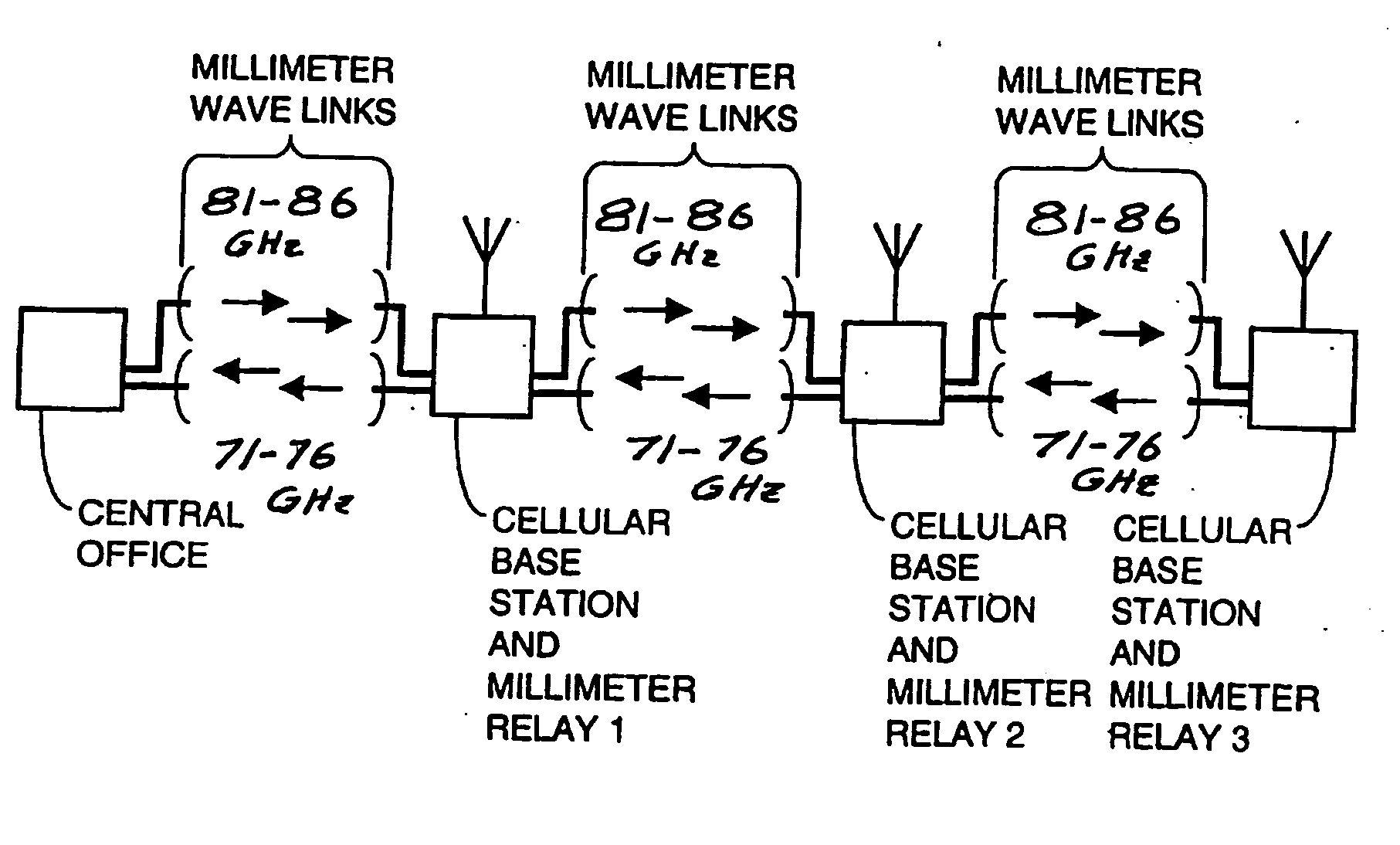
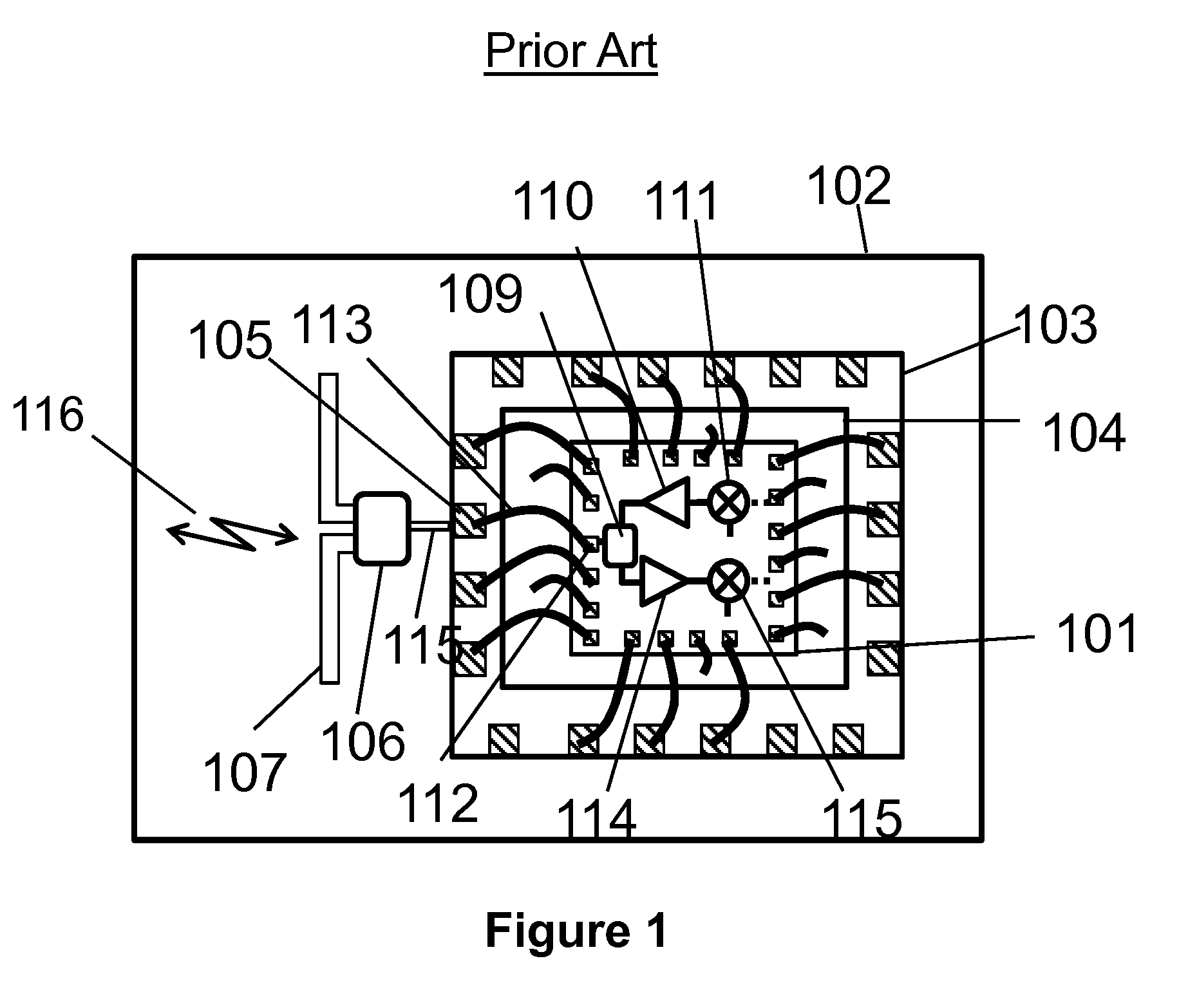
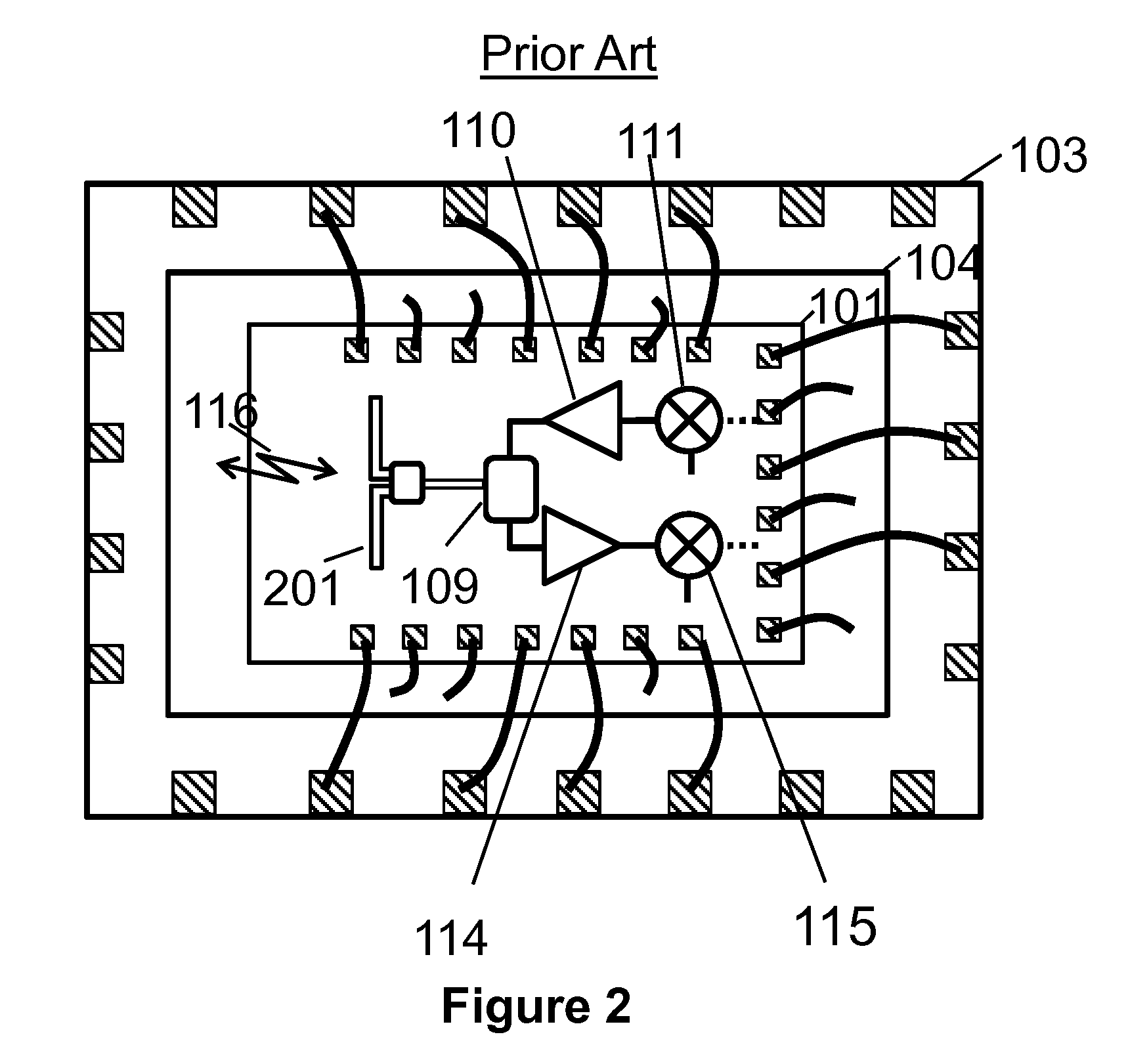
Cellular systems with distributed antennas
InactiveUS20090258652A1Efficient use ofIncrease data rateNetwork topologiesInformation formatWireless transceiverTransceiver
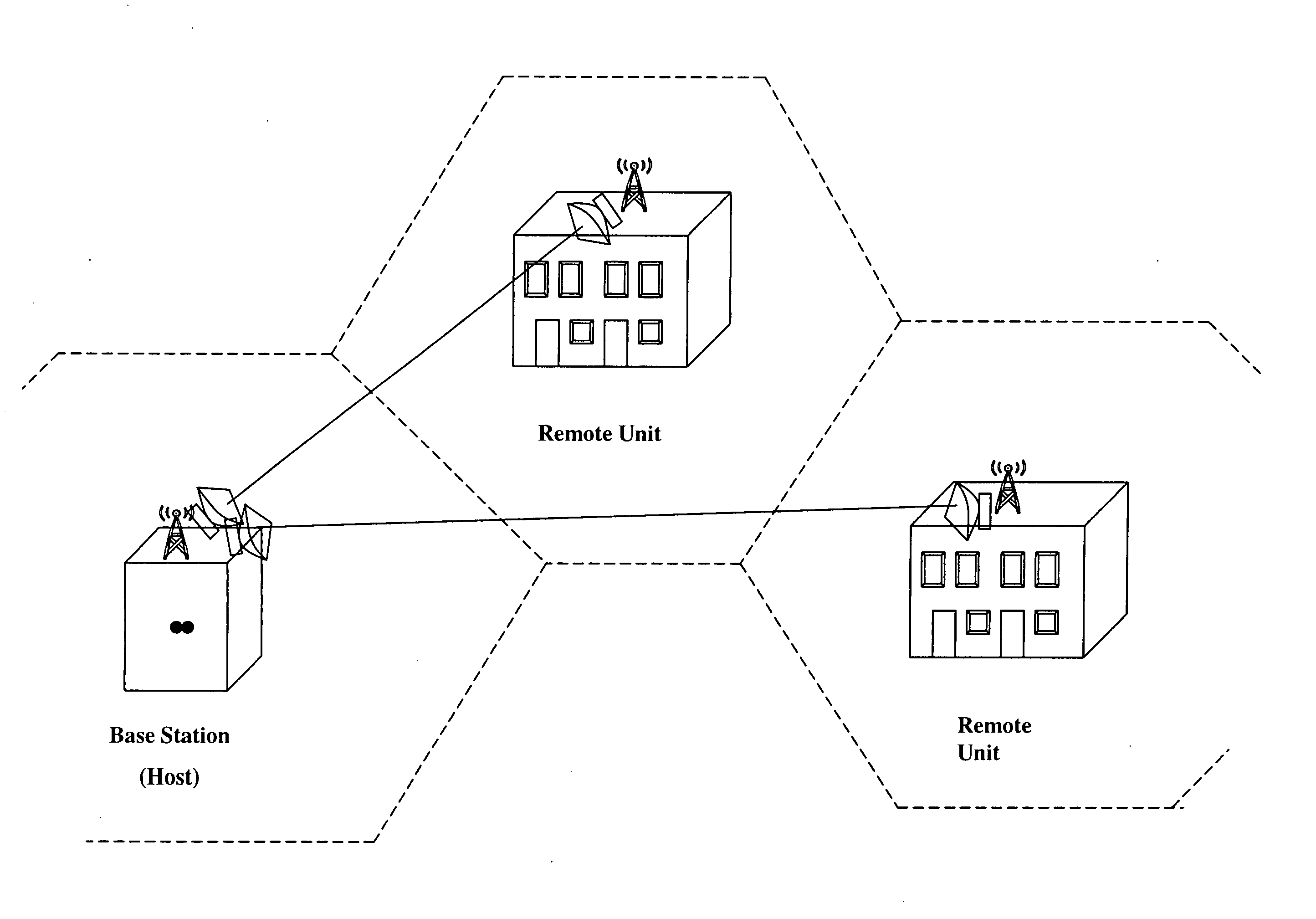
A communication system providing wireless communication among wireless users through a number of cellular base stations, each including at least transport management equipment and broadband equipment, at least one of which supports at least remote cellular station including RF equipment for communication with users of cellular devices. The system includes at lease one wireless narrow beam communication link operating at millimeter wave frequencies in excess of 60 GHz connecting a remote cellular station with a cellular base station equipped with broad band conversion electronic equipment and transport management equipment. In preferred embodiment the communication system includes a large number of remote cellular stations with each remote cellular station serving a separate communication cell. Each remote cellular station is equipped with a low frequency wireless transceiver for communicating with the wireless users within the cell at a radio frequency lower than 6 GHz and a narrow beam millimeter wave wireless transceiver operating at a millimeter wave frequency higher than 60 GHz for communicating with another millimeter wave transceiver at another remote cellular station or a millimeter wave transceiver at a base station.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
Apparatus and method for spatial division duplex (SDD) for millimeter wave communication system
ActiveUS20110243040A1Antenna arraysFrequency-division multiplex detailsMillimeter wave communication systemsMobile communication systems
An apparatus and method for full-duplex millimeter wave mobile wireless communication are provided. The apparatus includes a Spatial Division Duple (SDD) mobile communication system using millimeter waves, the SDD mobile communication system including a first wireless terminal having a first transmit antenna array having a plurality of first transmit antennas for transmitting a spatially beamformed first transmit beam, and a first receive antenna array having a plurality of first receive antennas for forming a spatially beamformed first receive beam and a second wireless terminal including a second transmit antenna array having a plurality of second transmit antennas for transmitting a spatially beamformed second transmit beam directed towards a receive beam of the first wireless terminal, and a second receive antenna array having a plurality of second receive antennas for forming a spatially beamformed second receive beam directed toward the transmit beam of the first terminal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
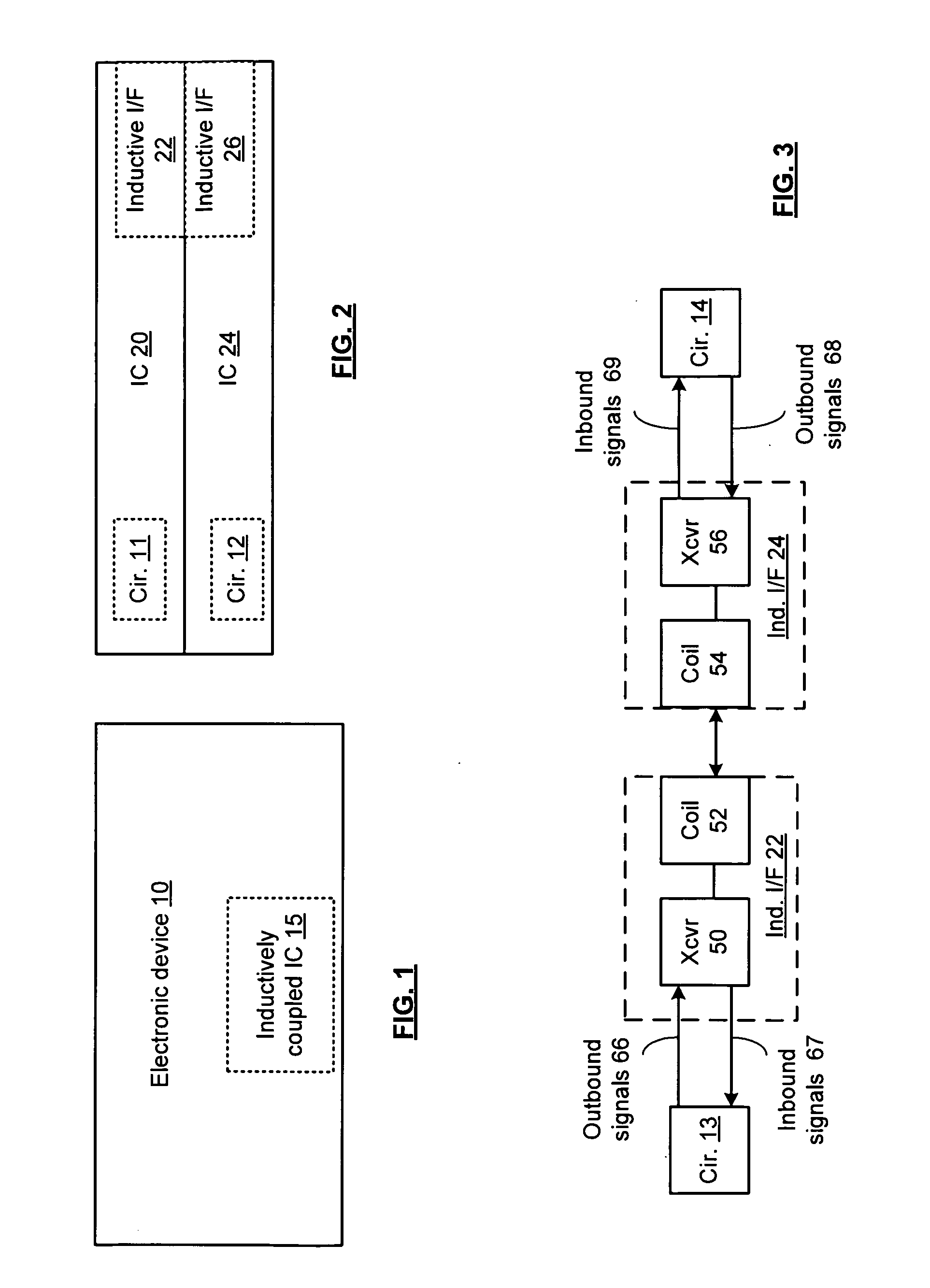
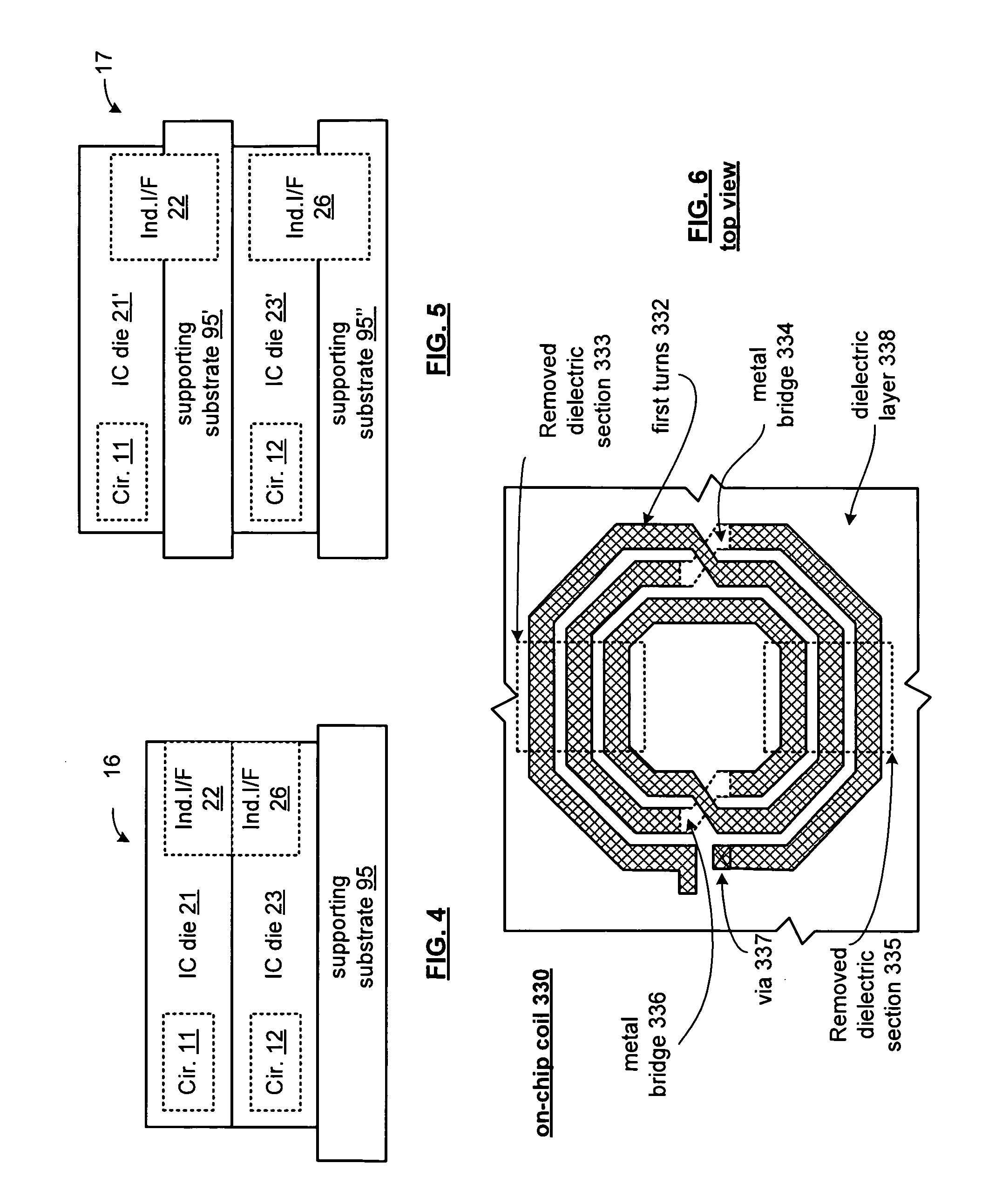
Integrated circuit with millimeter wave and inductive coupling and methods for use therewith
ActiveUS20090218407A1Near-field transmissionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringMillimetre wave
A circuit includes a plurality of integrated circuits or dies having corresponding circuits, the plurality of integrated circuits or dies include a first plurality of integrated circuits or dies having corresponding millimeter wave interfaces and a second plurality of integrated circuits or dies having corresponding inductive interfaces. The first plurality of integrated circuits or dies communicate first signals therebetween via the corresponding millimeter wave interfaces and the second plurality of integrated circuits or dies communicate second signals therebetween via the corresponding inductive interfaces.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
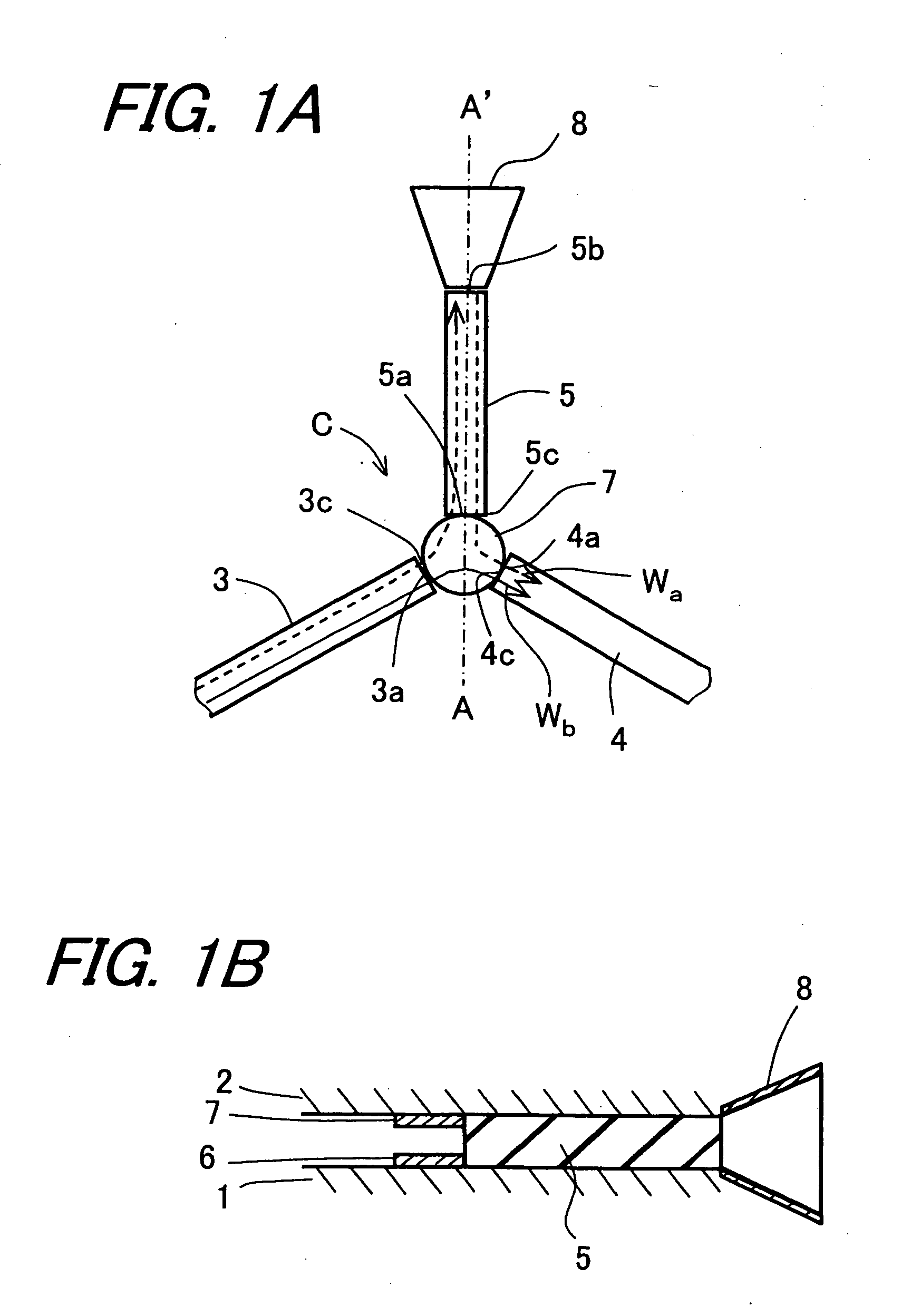
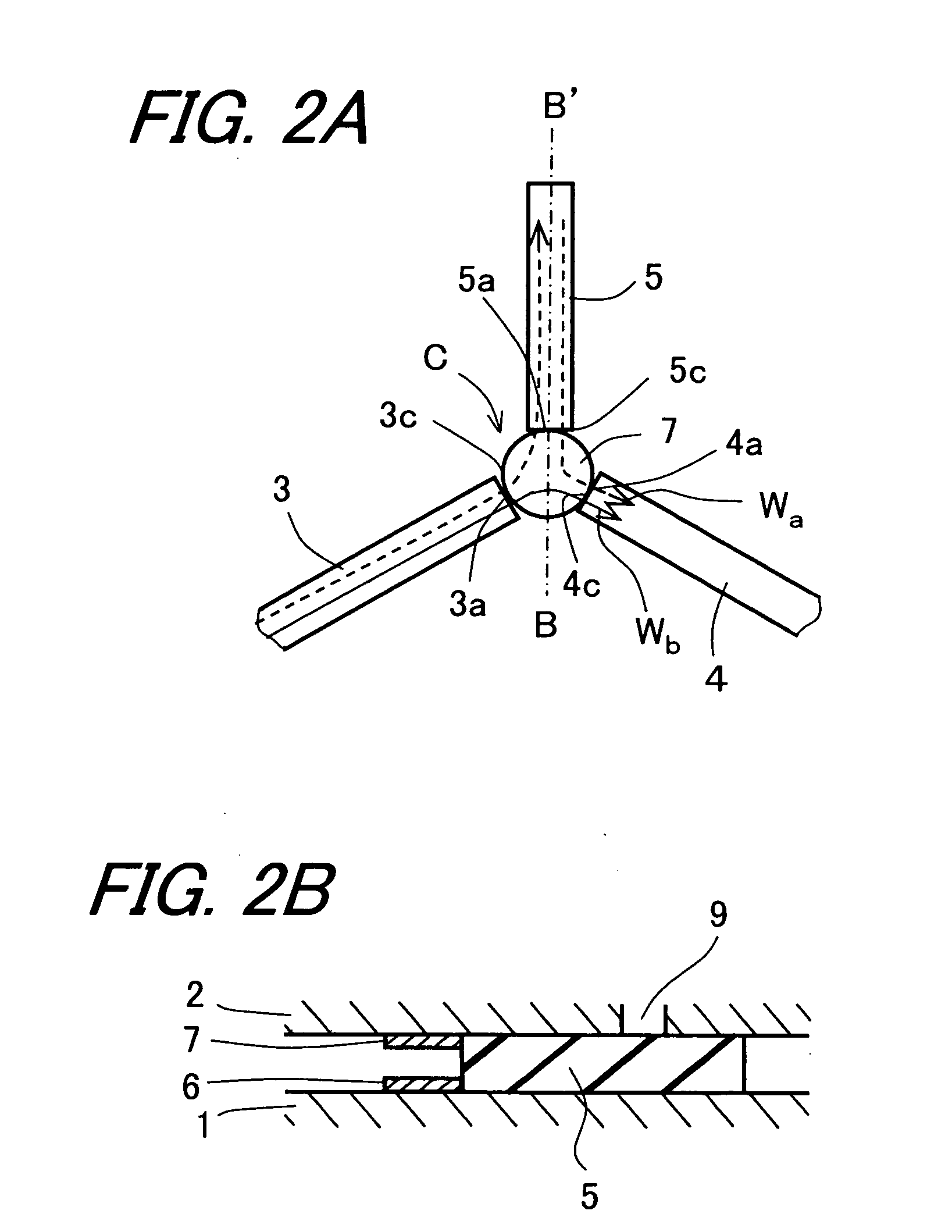
Transmitting/receiving antenna, isolator, high-frequency oscillator, and high-frequency transmitter-receiver using the same
InactiveUS20050190101A1Satisfactory characteristicOscillation stabilityWaveguide type devicesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionDielectricPhase difference
A millimeter-wave transmitter-receiver uses an NRD guide as a fundamental configuration and includes a millimeter-wave signal oscillator, a pulse modulator, a circulator, an antenna and a mixer. In the millimeter-wave transmitter-receiver, a line length of a third dielectric guide is set so that δ=±π in which δ is a phase difference at a center frequency between a portion of a transmission millimeter-wave signal, which is reflected via a third dielectric guide on the leading end portion of the third dielectric guide and returned to leak to a third connecting portion of the circulator, and another portion of the millimeter-wave signal, which leaks from a first connecting portion to the third connecting portion of the circulator. It is possible to reduce the change in the mixer output and enhance the millimeter-wave transmission / reception performance.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Communication device and communication method using millimeter-wave frequency band
InactiveUS20140073337A1Interference minimizationAntenna arraysNetwork planningComputer hardwareManagement unit
There are provided a communication device using a millimeter-wave frequency band and a communication method using the millimeter-wave frequency band. The communication device includes a beam scheduling unit configured to schedule uplink and downlink beams corresponding to movement of a terminal, a core network interface unit configured to transmit data provided from the beam scheduling unit to a core network, and to provide data received from the core network to the beam scheduling unit, a mobility management unit configured to configure an uplink and downlink beam set based on inter-beam interference information provided from the beam scheduling unit, and an inter-base station interface unit configured to exchange a control message with another base station under control of the mobility management unit. Therefore, it is possible to efficiently build a cellular network using the millimeter-wave frequency band.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Wireless communication system
InactiveUS20060111047A1Efficient use ofLow frequency wireless internet access bandwidth isNetwork topologiesRepeater circuitsTransceiverWireless transceiver
A communication system providing wireless communication among wireless users through a number of cellular base stations. The system includes a connecting station with a millimeter wave wireless transceiver in communication with a fiber optic or high-speed cable communication network. The transceiver is adapted to communicate at millimeter wave frequencies higher than 60 GHz with another millimeter wave transceiver at one of the cellular base stations. Each of the base stations serves a separate communication cell. Each base station is equipped with a low frequency wireless transceiver for communicating with the wireless users within the cell at a radio frequency lower than 6 GHz and a millimeter wave wireless transceiver operating at a millimeter wave frequency higher than 60 GHz for communicating with another millimeter wave transceiver at another base stations or a millimeter wave transceiver at said at the connecting station. The base stations also are equipped with data transfer means for transferring data communicated through the low frequency transceiver to the millimeter wave wireless transceiver and for transferring data communicated through the millimeter wave wireless transceiver to the low frequency wireless transceiver. In preferred embodiments the system a part of a telephone system, an Internet system or a computer network.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
Cellular systems with distributed antennas
InactiveUS8090379B2Efficient use ofLow frequency wireless internet access bandwidth isInformation formatNetwork topologiesWireless transceiverTransceiver
A communication system providing wireless communication among wireless users through a number of cellular base stations, each including at least transport management equipment and broadband equipment, at least one of which supports at least remote cellular station including RF equipment for communication with users of cellular devices. The system includes at lease one wireless narrow beam communication link operating at millimeter wave frequencies in excess of 60 GHz connecting a remote cellular station with a cellular base station equipped with broad band conversion electronic equipment and transport management equipment. In preferred embodiment the communication system includes a large number of remote cellular stations with each remote cellular station serving a separate communication cell. Each remote cellular station is equipped with a low frequency wireless transceiver for communicating with the wireless users within the cell at a radio frequency lower than 6 GHz and a narrow beam millimeter wave wireless transceiver operating at a millimeter wave frequency higher than 60 GHz for communicating with another millimeter wave transceiver at another remote cellular station or a millimeter wave transceiver at a base station.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
Apparatus for transitioning millimeter wave between dielectric waveguide and transmission line
InactiveUS20100253450A1Easy to provideLess timeOne-port networksResonatorsDielectric substrateMillimetre wave
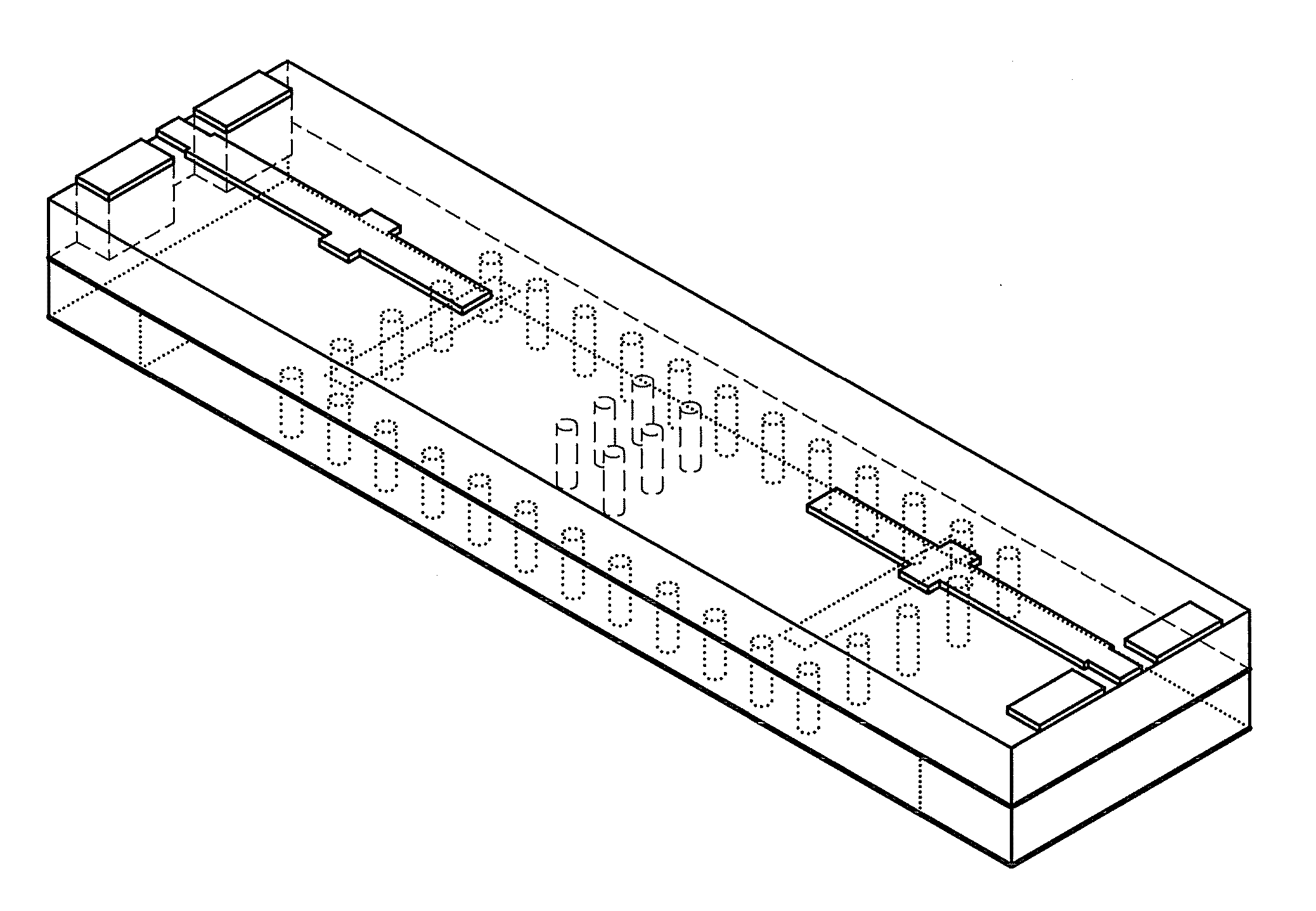
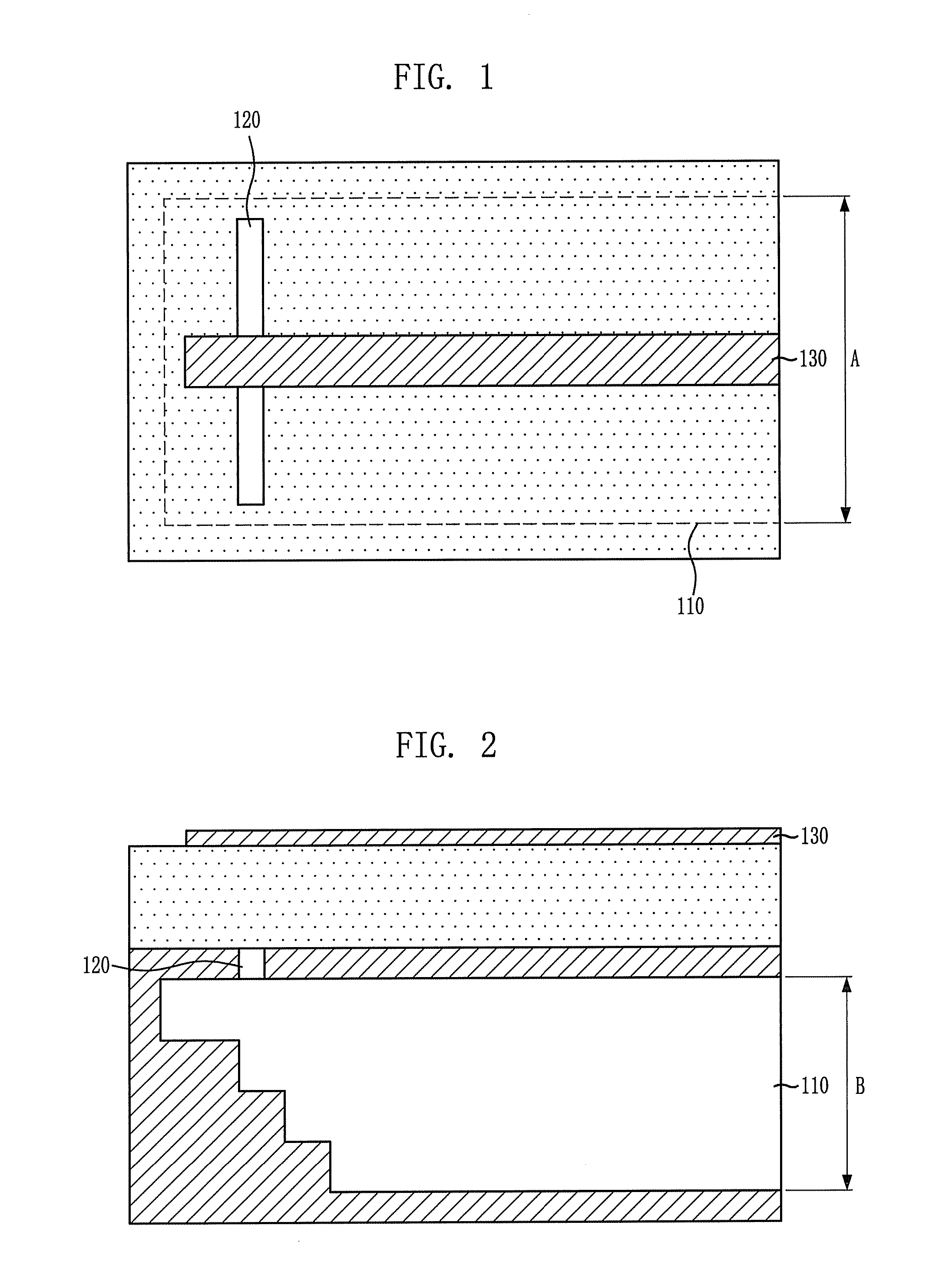
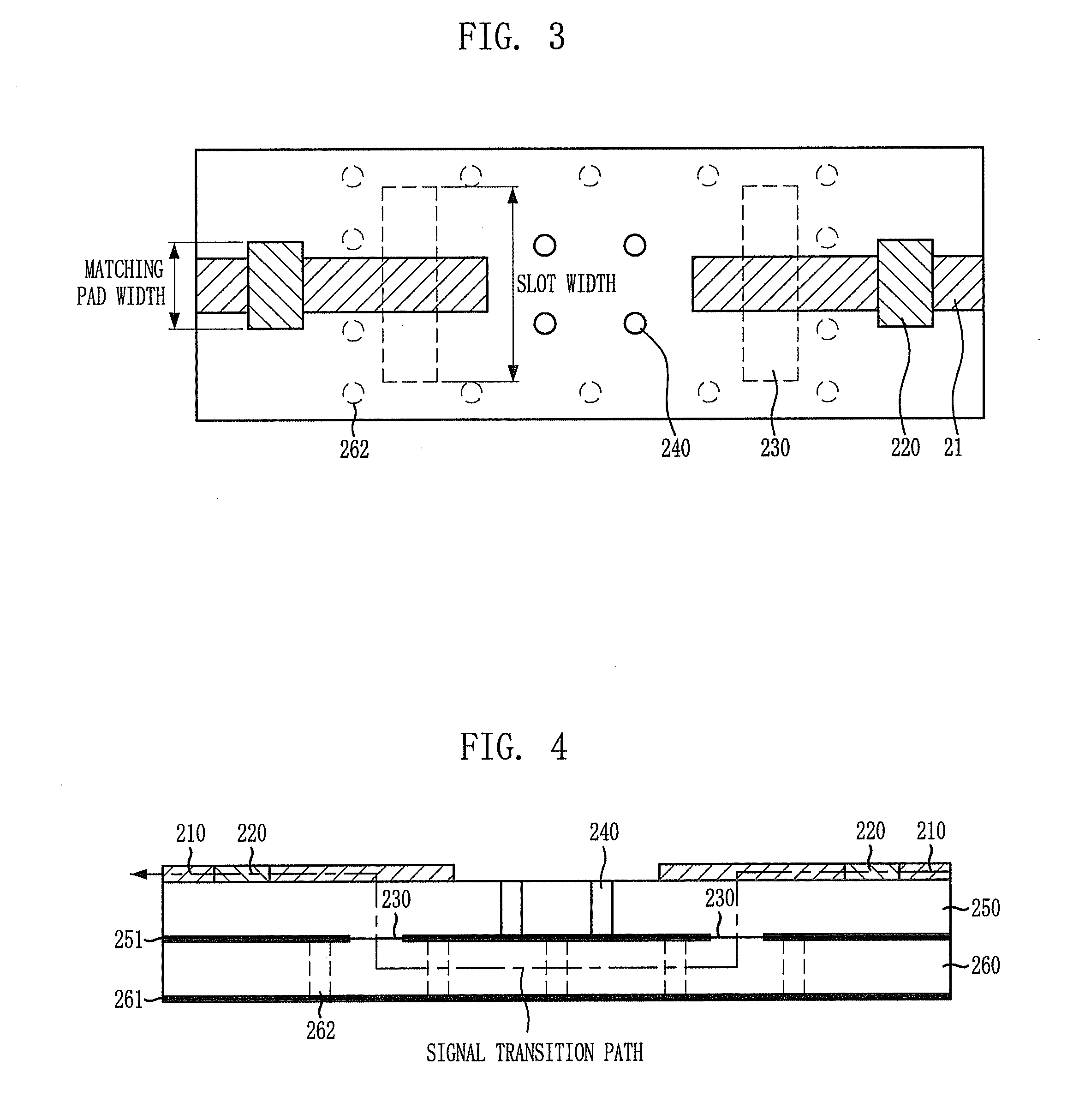
Provided is an apparatus for transitioning a millimeter wave between dielectric waveguide and transmission line using a millimeter wave transition structure formed by the dielectric waveguide, the transmission line, and a slot to transition a signal with lower losses. The apparatus includes: transmission lines disposed respectively at input and output terminals on an uppermost dielectric substrate in a signal transition direction and adapted to transition a signal; a dielectric waveguide formed by a via array disposed between top and bottom ground surfaces of a lowermost dielectric substrate in the signal transition direction as a signal transition path; and slots disposed at a signal transition path of an upper ground surface of each dielectric substrate to connect the transmission lines to the dielectric waveguide so as to transition a signal from the transmission line of the input terminal to the transmission line of the output terminal through the dielectric waveguide.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Low cost millimeter wave imager
InactiveUS7583074B1Low costUseful sensitivity levelMeasurement using dc-ac conversionMeasurement using ac-dc conversionLow noiseTunnel diode
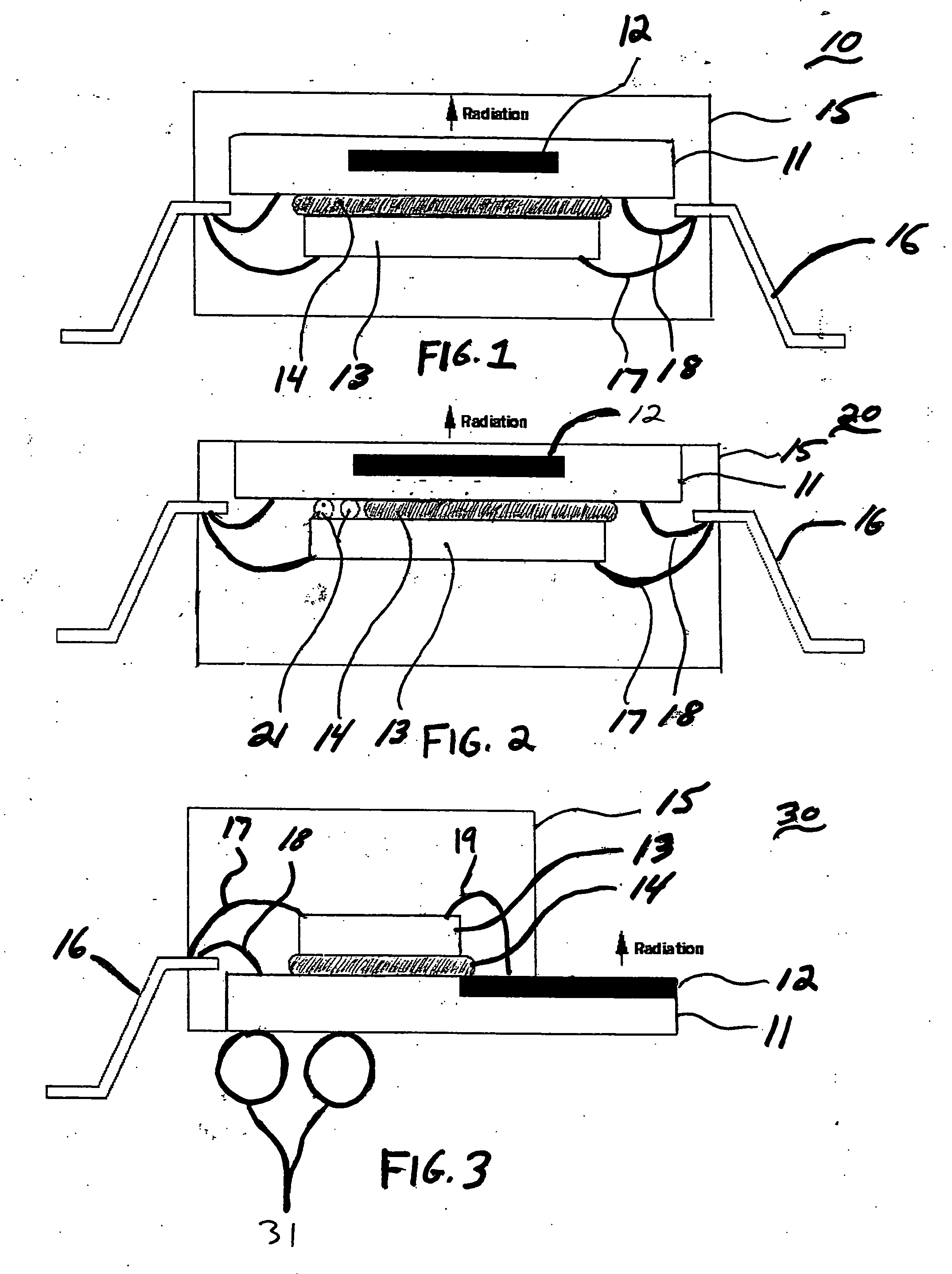
Low cost millimeter wave imagers using two-dimensional focal plane arrays based on backward tunneling diode (BTD) detectors. Two-dimensional focal arrays of BTD detectors are used as focal plane arrays in imagers. High responsivity of BTD detectors near zero bias results in low noise detectors that alleviate the need for expensive and heat generating low noise amplifiers or Dicke switches in the imager. BTD detectors are installed on a printed circuit board using flip chip packaging technology and horn antennas direct the waves toward the flip chip including the BTD detectors. The assembly of the horn antennas, flip chips, printed circuit board substrate, and interconnects together work as an imaging sensor. Corrugated surfaces of the components prevent re-radiation of the incident waves.
Owner:HRL LAB
Method and system for fabrication of integrated tunable/switchable passive microwave and millimeter wave modules
InactiveUS6876056B2Electrostatic/electro-adhesion relaysSolid-state devicesMetal interconnectMicrowave
An interconnect module and a method of manufacturing the same is described comprising: a substrate, an interconnect section formed on the substrate, and a variable passive device section formed on the substrate located laterally adjacent to the interconnect section. The interconnect section has at least two metal interconnect layers separated by a dielectric layer and the variable passive device has at least one moveable element. The moveable element is formed from a metal layer which is formed from the same material and at the same time as one of the two interconnect layers. The moveable element is formed on the dielectric layer and is released by local removal of the dielectric layer. Additional interconnect layers and intermediate dielectric layers may be added.
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW)
Mobile millimeter wave communication link
A point-to-point, wireless, millimeter wave communications link between two stations at least one of which is a mobile station. A millimeter wave transmitter system operating at frequencies higher than 57 GHz with a tracking antenna producing a beam having a half-power beam width of about 2 degrees or less and a millimeter wave receiver also with a tracking antenna having a half-power beam width of about 2 degrees or less. In preferred embodiments each mobile station has a global position system (GPS) and a radio transmitter and both tracking antennas are pointed utilizing GPS information from the mobile station or stations. The GPS information preferably is transmitted via a low frequency, low data rate radio. Each millimeter wave unit is capable of transmitting and / or receiving, through the atmosphere, digital information to / from the other station at rates in excess of 155 million bits per second during normal weather conditions. In preferred embodiments actually built and tested by Applicants digital information has been transmitted at rates of 1.25 gigabits per second. Preferred communication links described here are millimeter wave links operating at frequencies of 71-73 GHz and 74-76 GHz mounted on simple two-axis gimbals. Pointing information of the required accuracy is provided by GPS receivers and standard radio links which send the GPS calculated positions to the millimeter wave systems at the opposite end of the link. In these embodiments there is no need for any complicated closed loop pointing information derived from received signal intensity or phase. On moving platforms locally generated inertial attitude information is combined with the GPS positions to control pointing of the gimbaled transceivers.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
Out-of-band radio link protocol and network architecture for a wireless network composed of wireless terminals with millimetre wave frequency range radio units
ActiveUS20110053498A1Optimization rangeStable flowRadio relay systemsWireless communicationNetwork architectureDirectional antenna
The present invention relates to a wireless transmitter comprising a transmitter radio unit working a wireless transmitter comprising a transmitter radio unit working in the millimeter wave frequency band using a directional antenna and a bidirectional radio unit working in a frequency range different from said transmitter radio unit and using an omnidirectional antenna. The invention further relates to a wireless receiver and a wireless relay.
Owner:SONY CORP
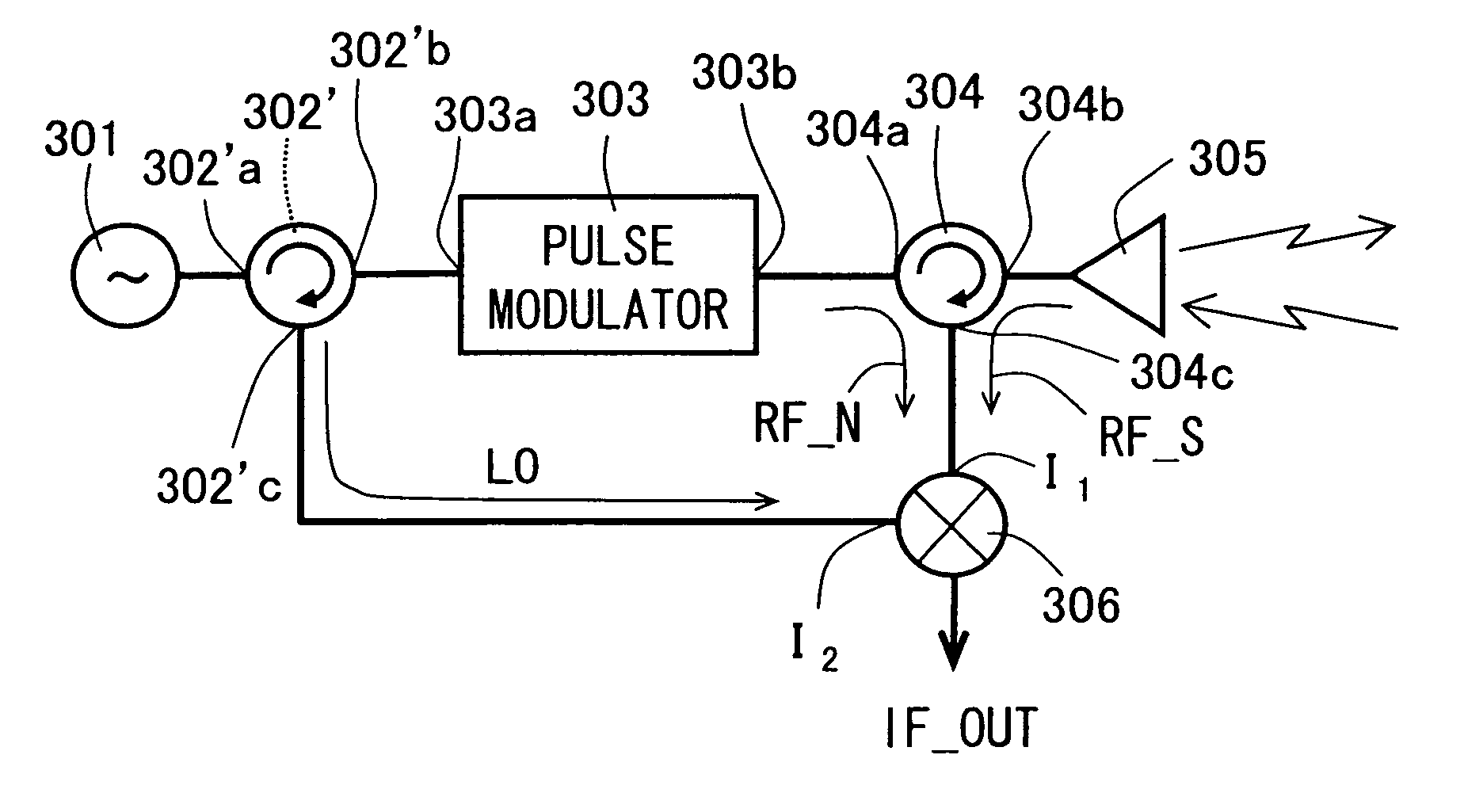
Millimeter wave pulsed radar system
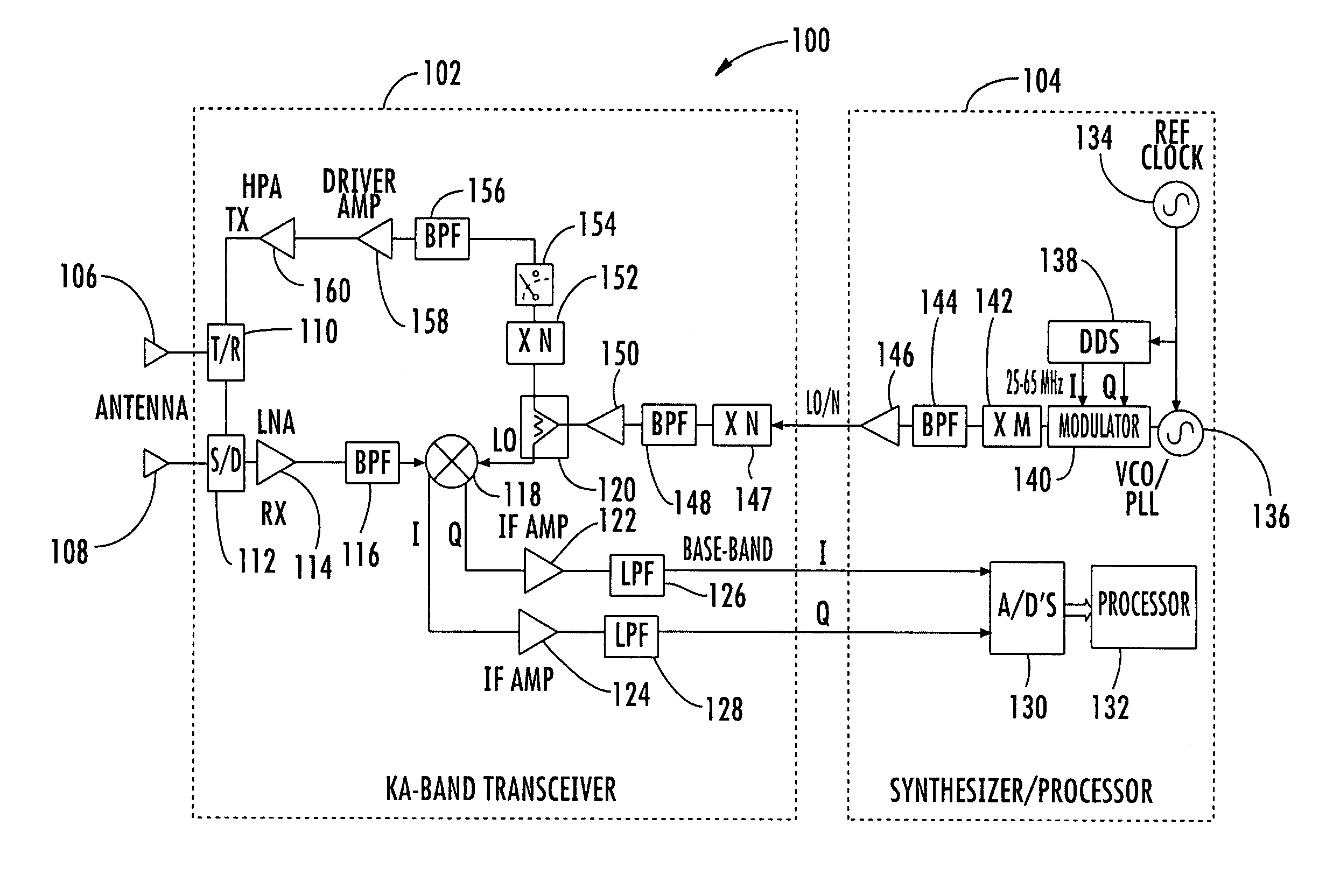
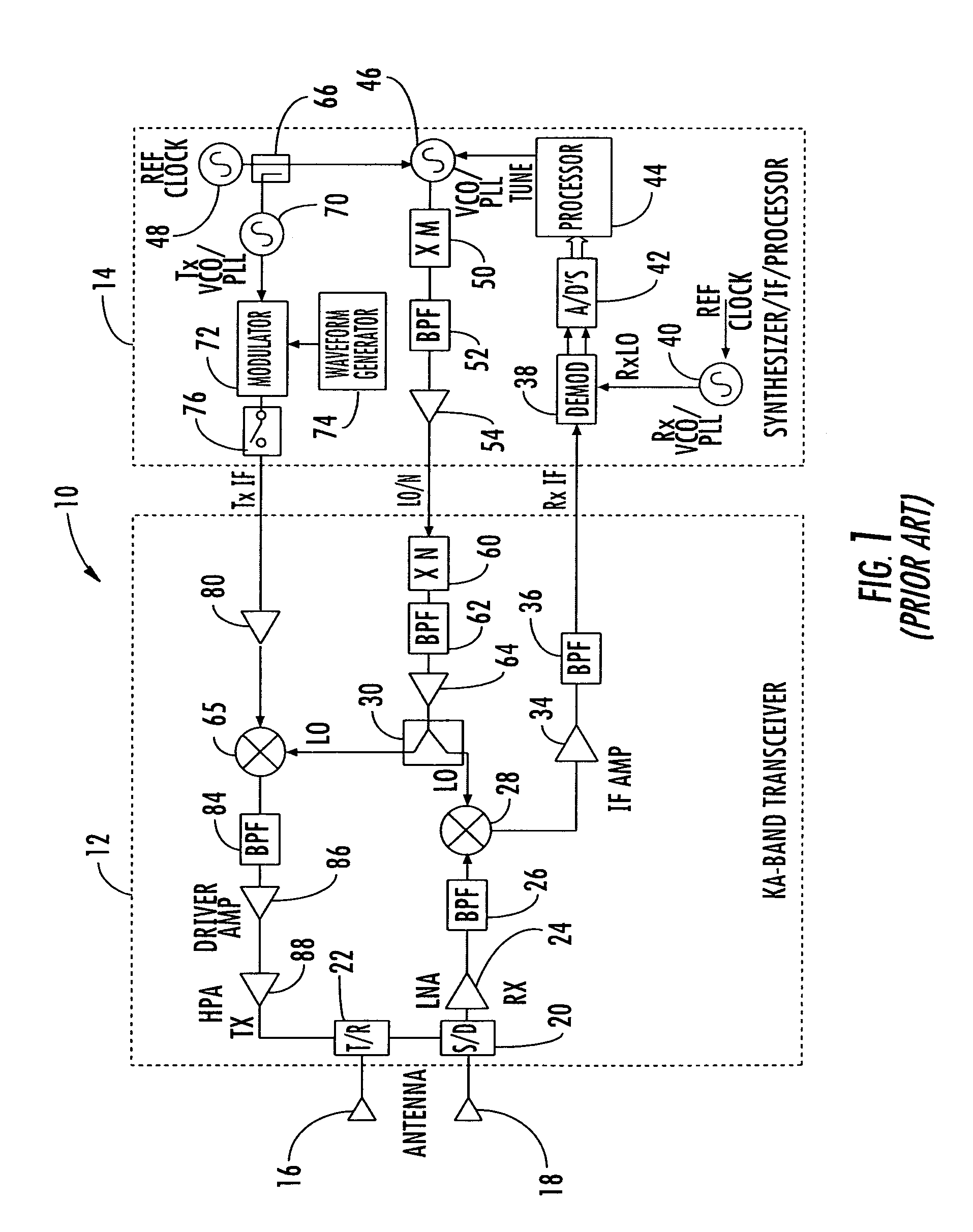
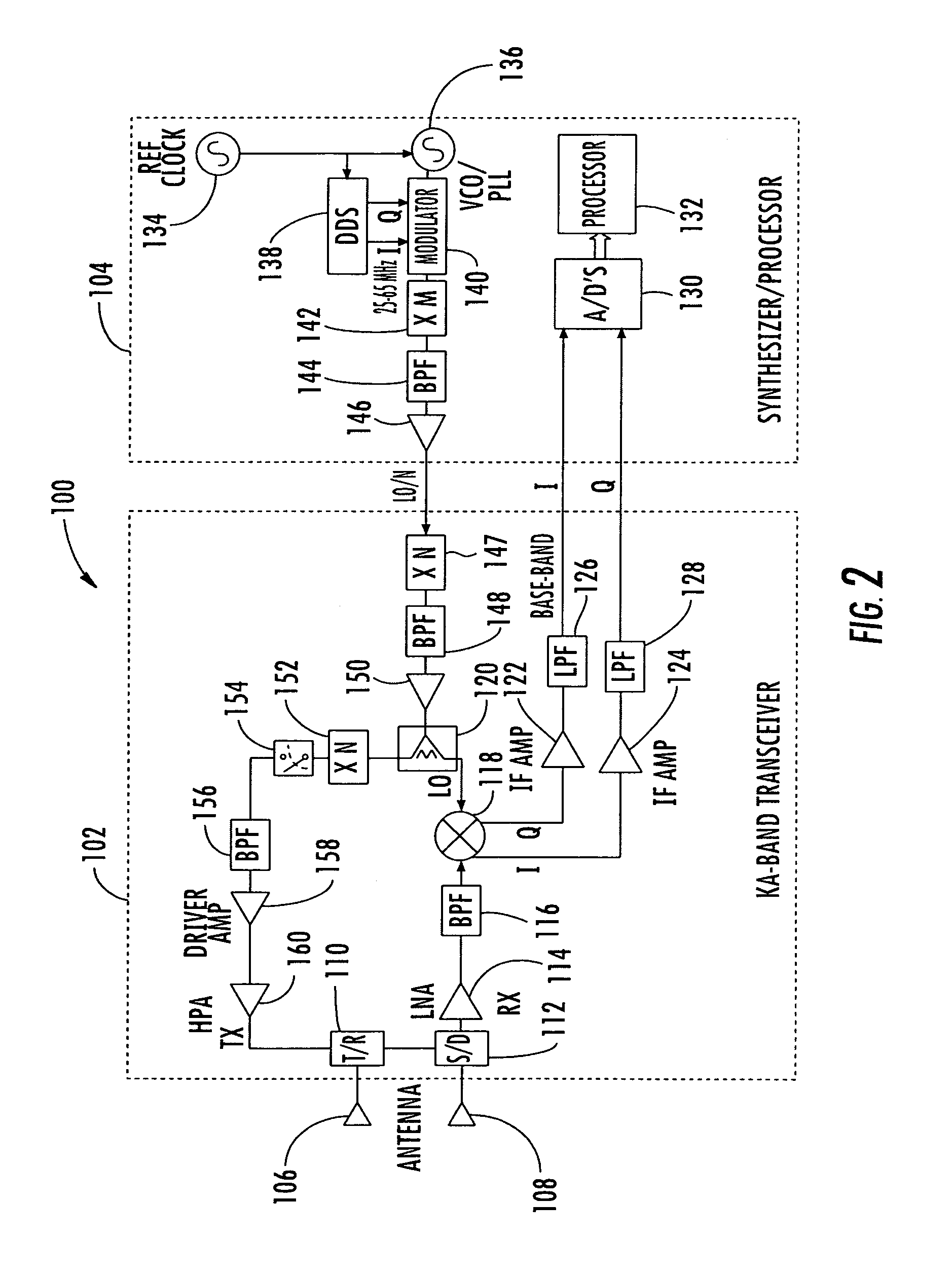
InactiveUS7002511B1Improve efficiencySimplified frequency synthesizer designRadio wave reradiation/reflectionQuadrature modulatorLocal oscillator signal
A millimeter wave pulsed radar system includes a radar synthesizer having a voltage controlled oscillator / phase locked loop (VCO / PLL) circuit, direct digital synthesizer (DDS) circuit and quadrature modulator circuit that are operative to generate an intermediate frequency local oscillator signal (IF / LO signal). A radar transceiver is operative with the radar synthesizer for receiving the IF / LO signal. A transmitter section has a frequency multiplier that multiplies the IF / LO signal up to a millimeter wave (MMW) radar signal and a receiver section and includes a direct conversion mixer that receives a MMW radar signal and the IF / LO signal to produce I / Q baseband signals that are later digitized and processed.
Owner:REVEAL IMAGING
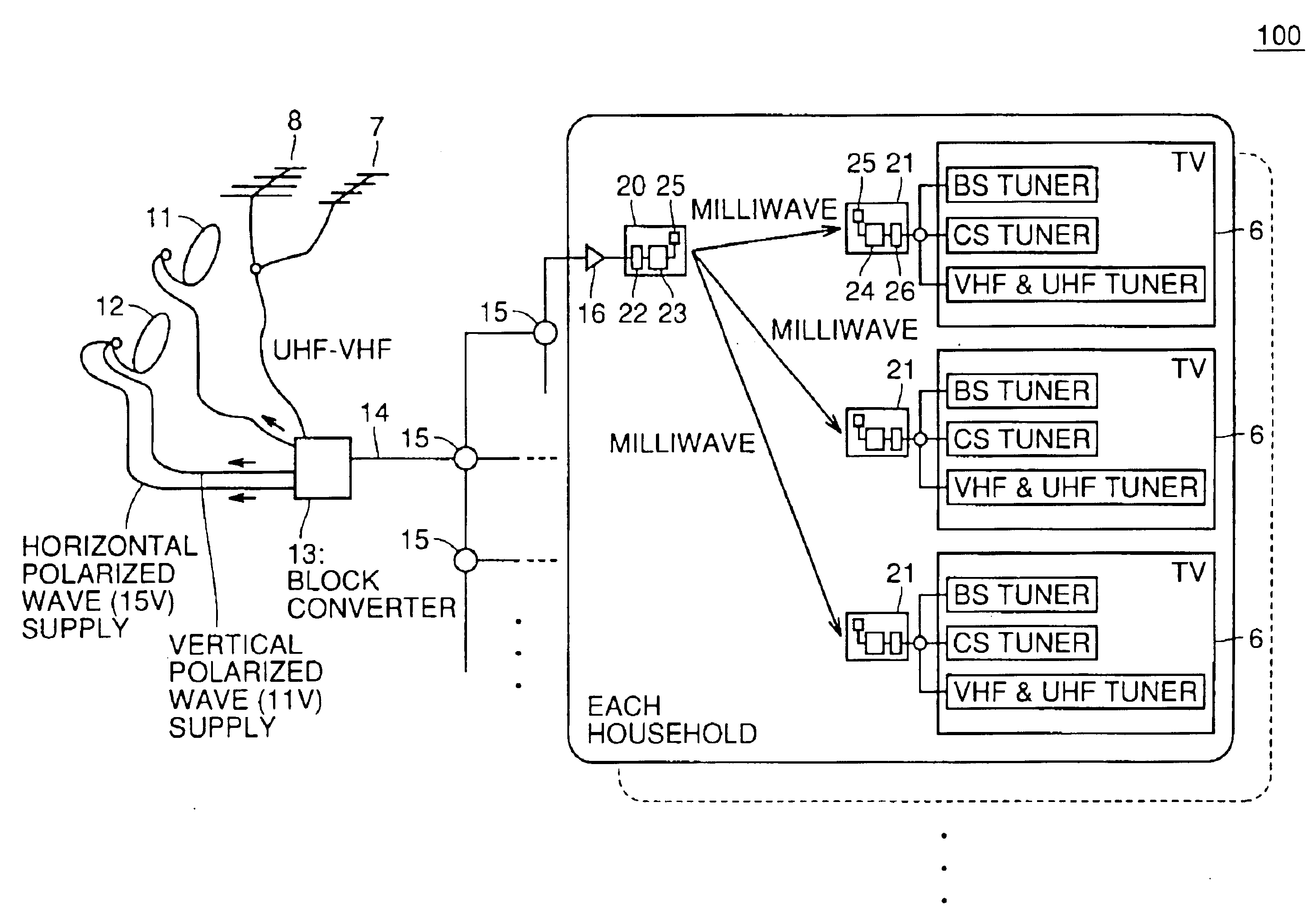
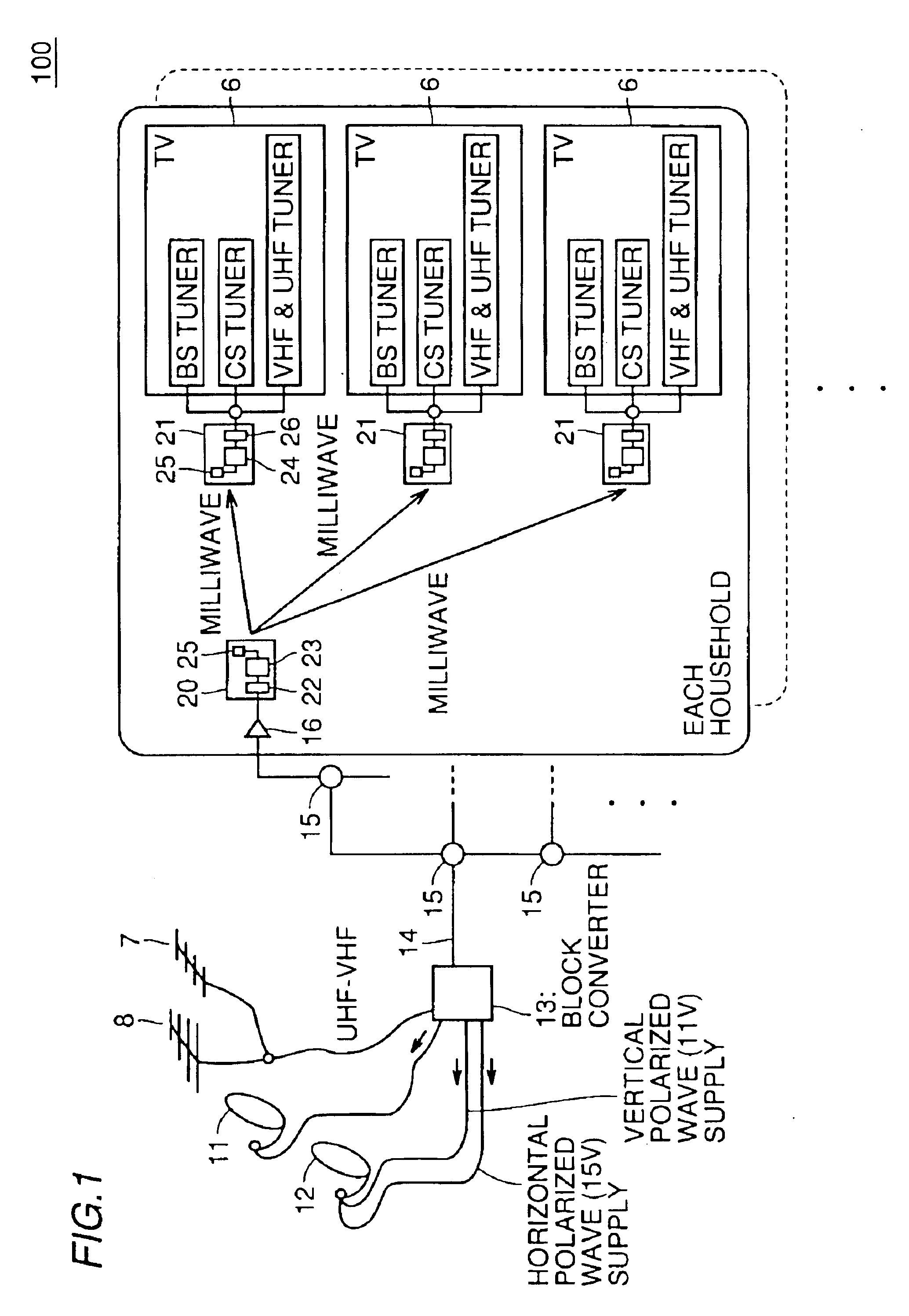
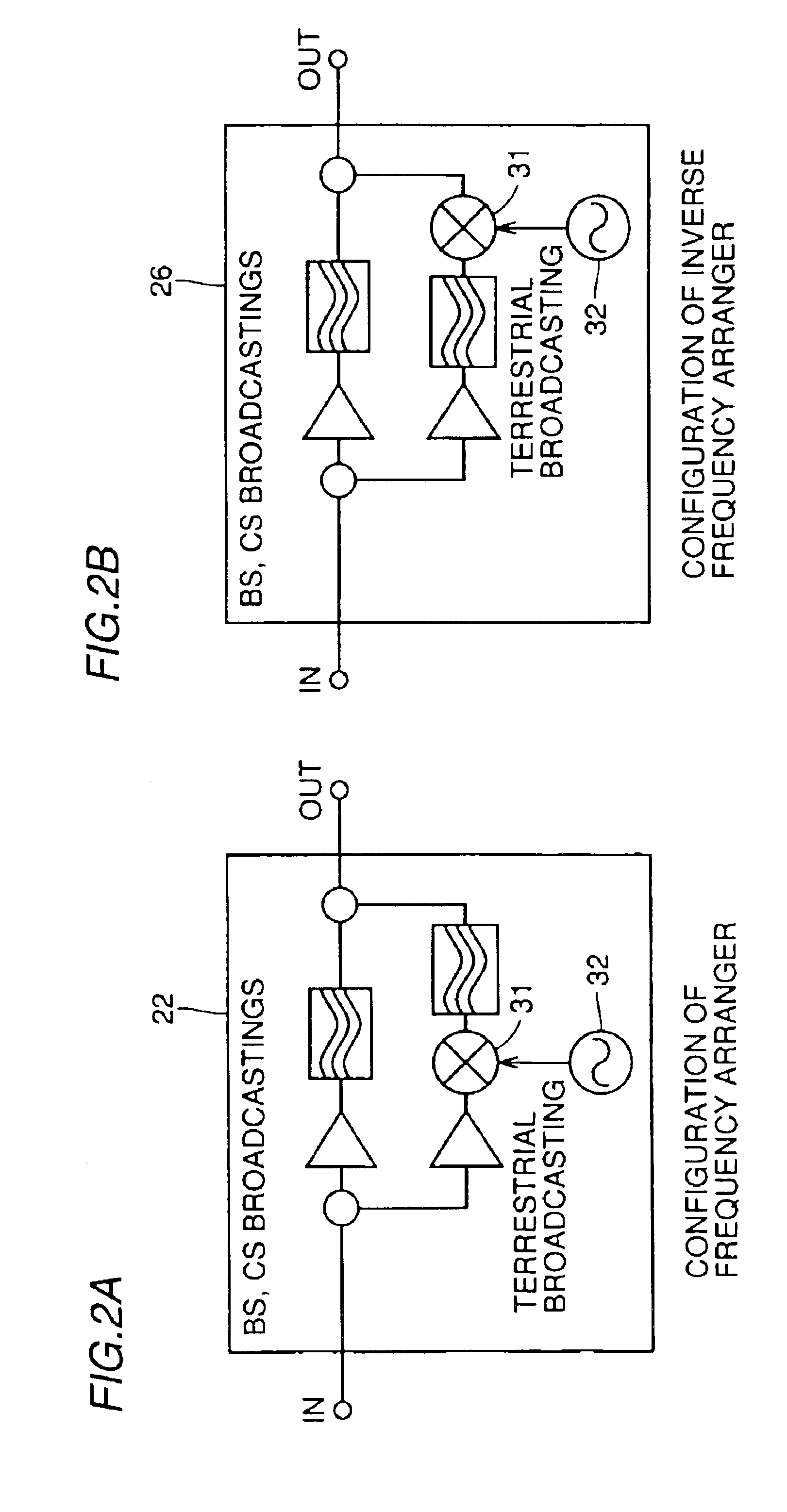
Milliwave transmitting device, milliwave receiving device and milliwave transmission and reception system capable of simplifying wiring of a receiving system of terrestrial broadcasting service and satellite broadcasting service
InactiveUS6915529B1Television system detailsSatellite broadcast receivingSatellite broadcastingMillimetre wave
In conventionally receiving satellite broadcasting (BS, CS) and terrestrial broadcasting (VHF, UHF) services, transmitting the services to a plurality of TV receivers in an individual house results in complicated wiring and a community house is also limited in the number of installed TV receivers due to previously setting a distributor and thus requires an additional distributor to be installed when a TV receiver is additionally installed. The milliwave receiving and transmitting system of the present invention allows a broadcast signal to be transmitted and received indoors via indoor, wireless milliwave transmission without using any indoor wiring.
Owner:SHARP KK
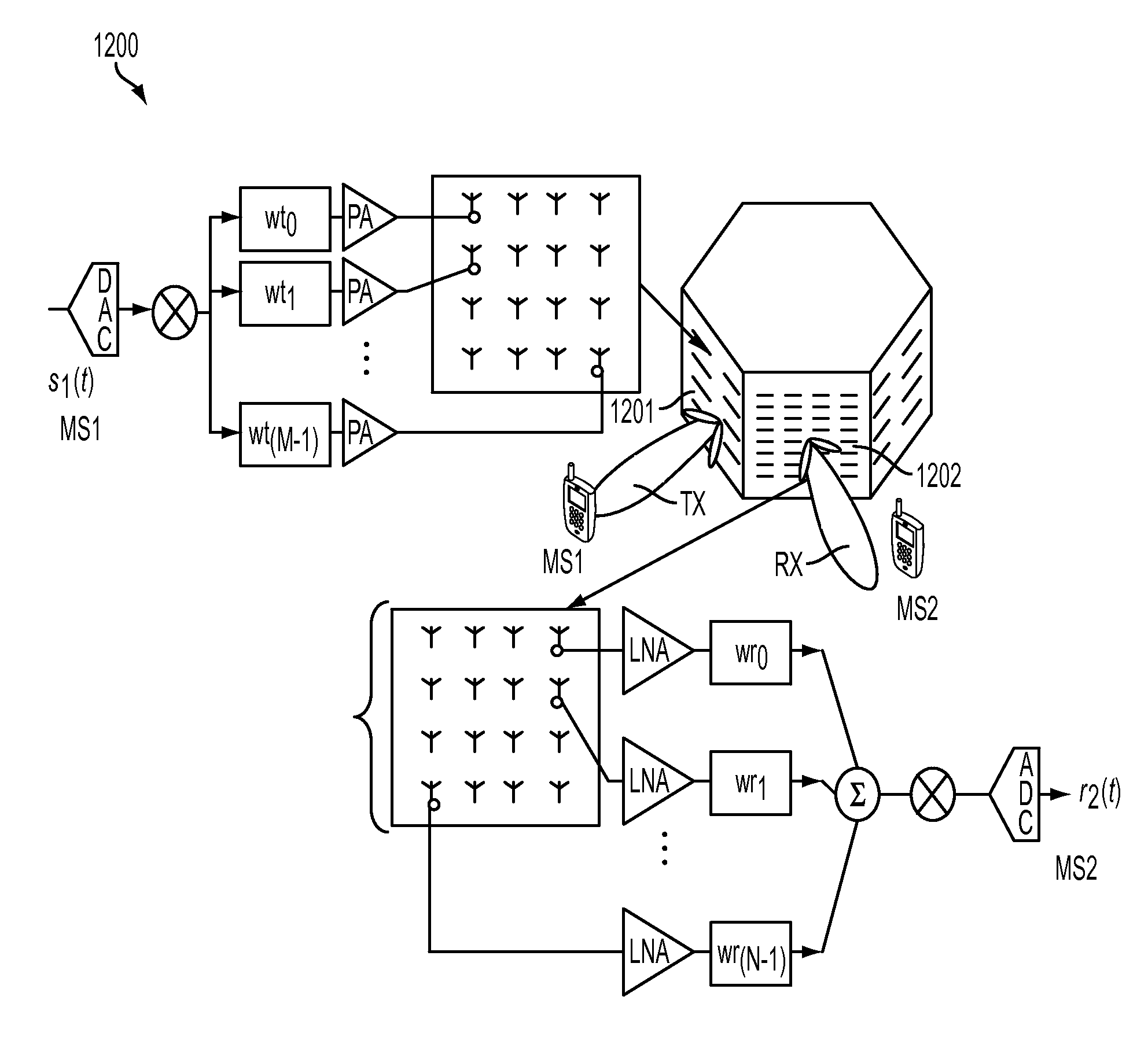
Mm-wave fully integrated phased array receiver and transmitter with on-chip antennas
ActiveUS20100231452A1Facilitate transmissionEasy to receiveWave based measurement systemsAntenna feed intermediatesMillimetre waveAntenna element
A phased array mm-wave device includes a substrate, a mm-wave transmitter integrated onto the substrate configured to transmit a mm-wave signal and / or a mm-wave receiver integrated onto the substrate and configured to receive a mm-wave signal. The mm-wave device also includes a phased array antenna system integrated onto the substrate and including two or more antenna elements. The phased array mm-wave device also includes one or more dielectric lenses. A distributed mm-wave distributed combining tree circuit includes at least two pairs of differential transconductors with regenerative degeneration and accepts at least two differential input signals. Two mm-wave loopback methods measure the phased array antenna patterns and the performance of an integrated receiver transmitter system.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Mmw contraband screening system
InactiveUS20050110672A1Geological detection using milimetre wavesMaterial analysis using microwave meansTemperature controlCheck point
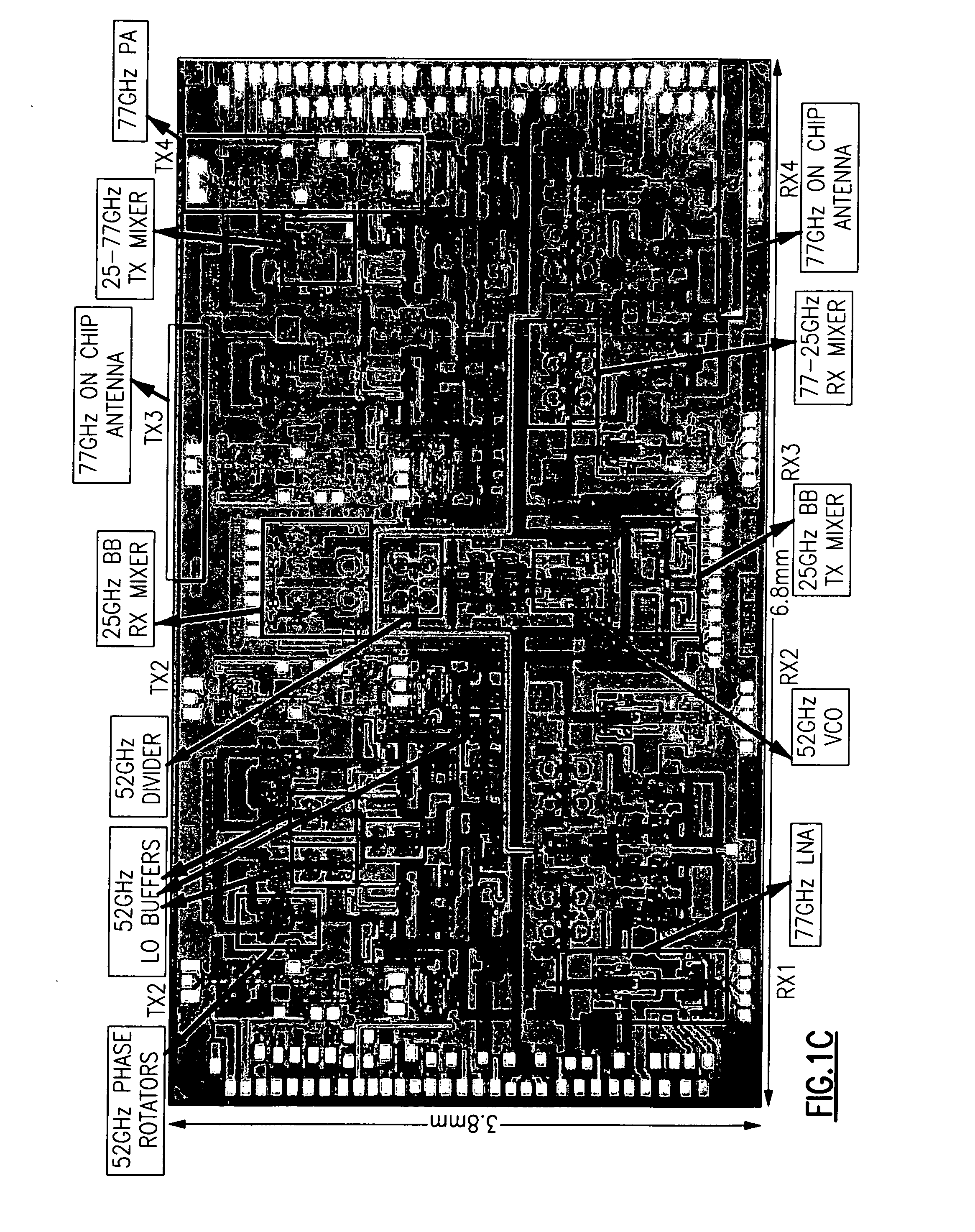
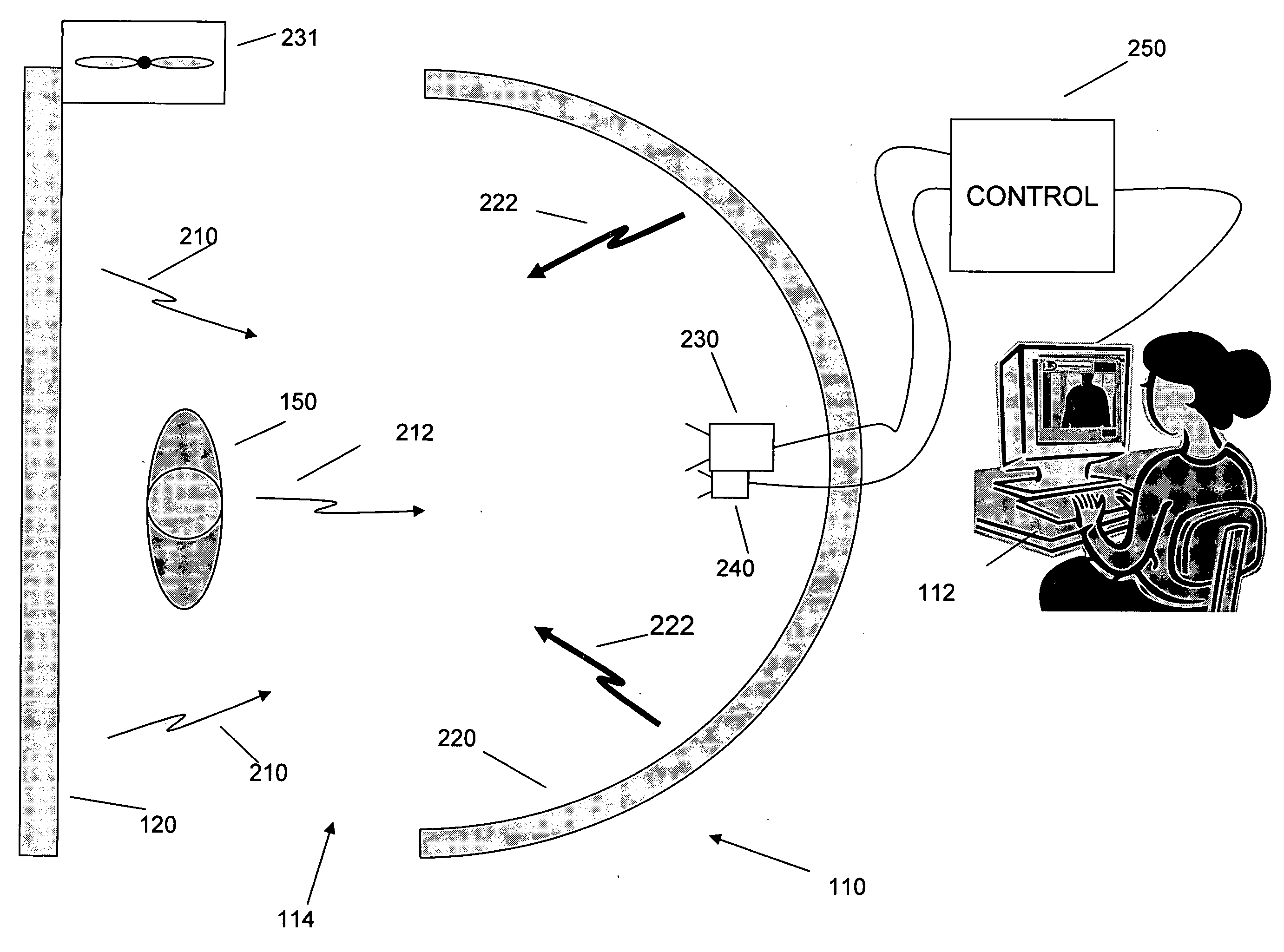
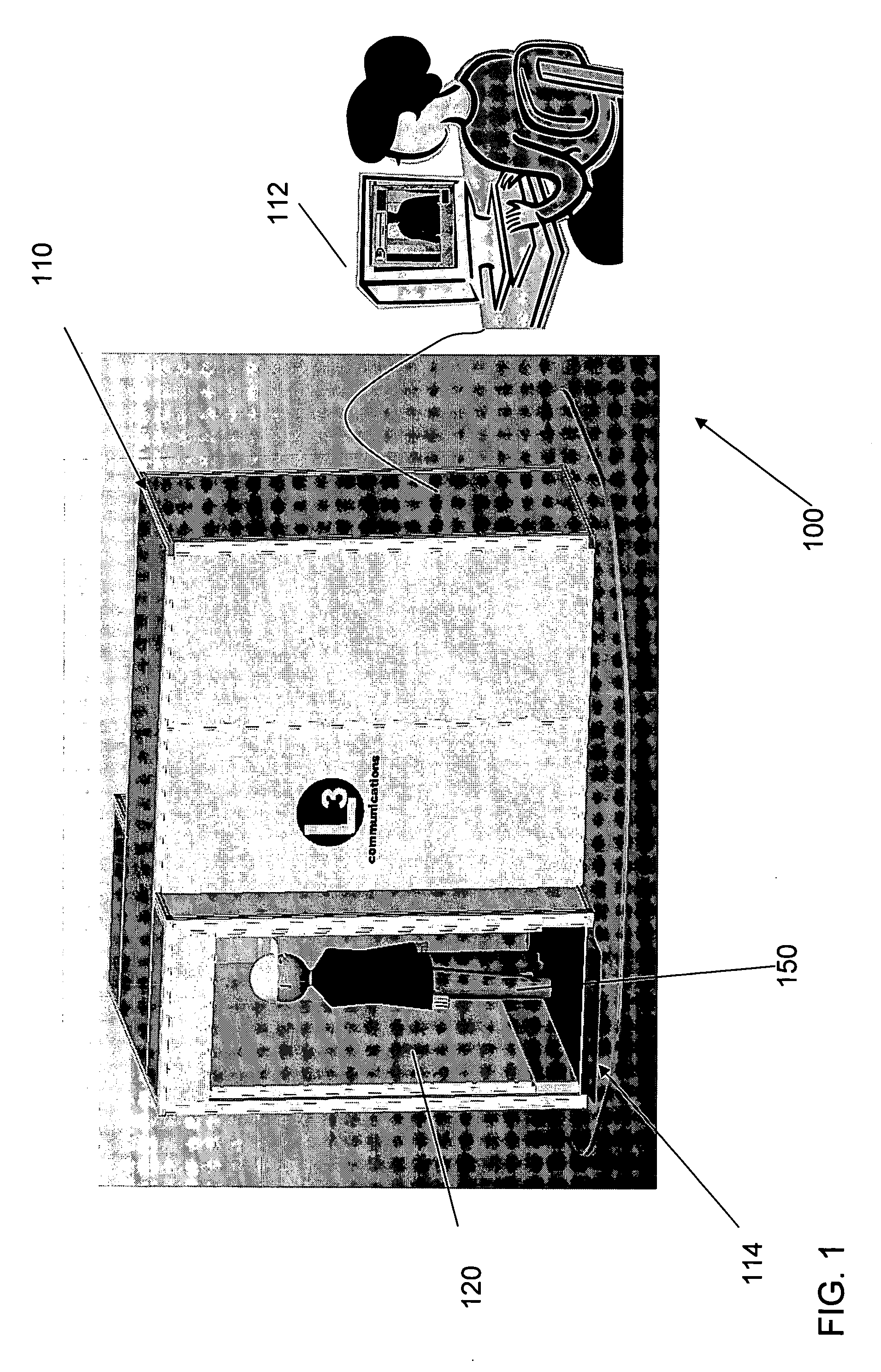
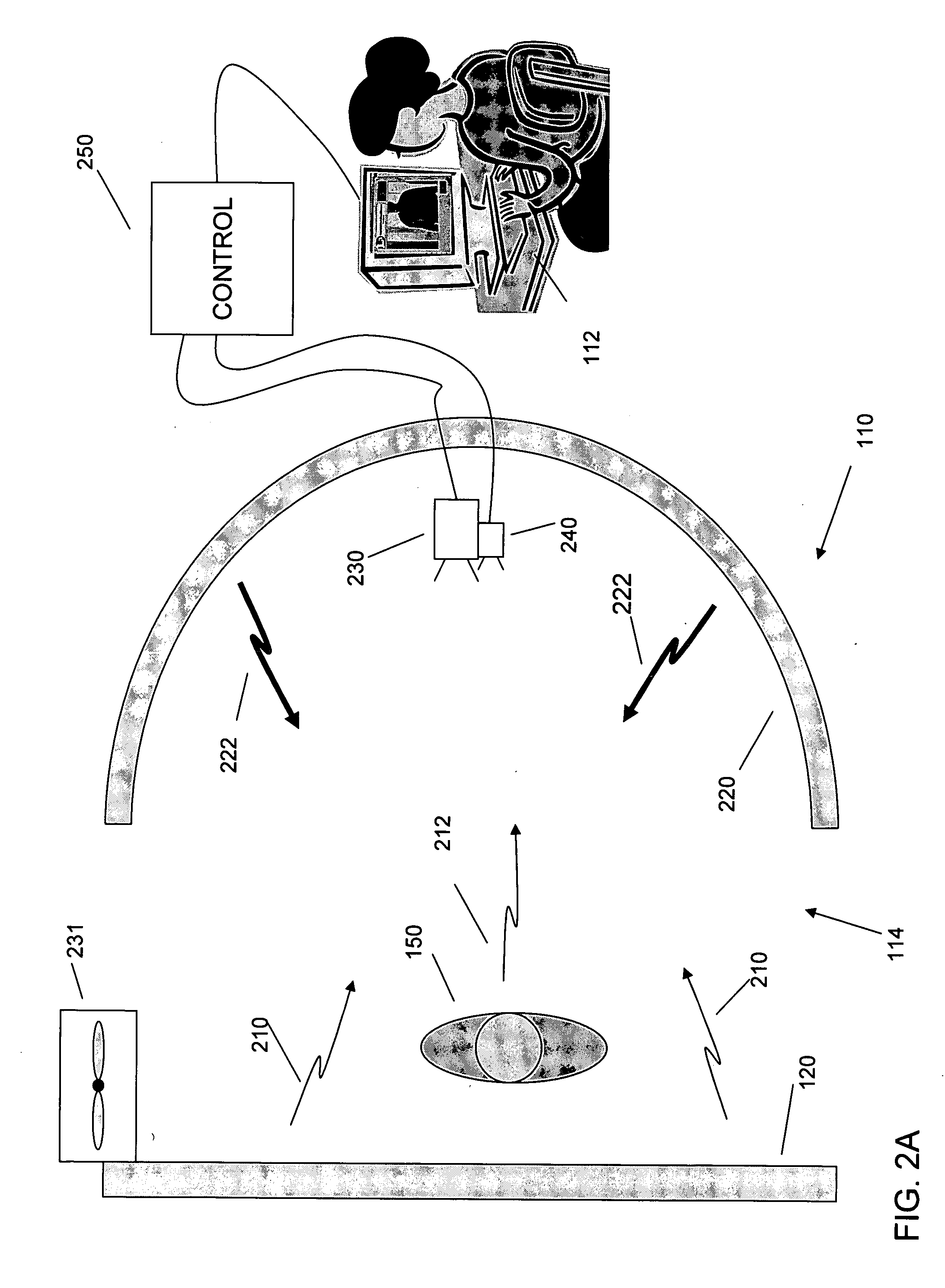
An inspection system that can detect contraband items concealed on, in or beneath an individual's clothing. The system employs mm wave radiation to detect contraband items. The system is described in connection with a check point security system that includes temperature controlled walls to enhance imaging of contraband items. Also, a mm wave camera is used in conjunction with a camera that forms visible images. To address privacy concerns of displaying images of people made with mm wave cameras that effectively “see through” clothes, the mm wave images are not displayed directly. Rather, computer processing produces indications of suspicious items from the underlying raw mm wave images. The indications of suspicious items are overlaid on the visible image.
Owner:L3 COMMUNICATIONS SECURITY & DETECTION SYSTEMS CORPORATION
Millimeter-wave signal transmission device
InactiveUS6952143B2Long distanceOvercome problemsMultiple-port networksOne-port networksTransducerWaveguide mode
A transition for transmitting a mm-wave signal from one plane to another, the transition comprising: (a) first and second transmission lines on parallel planes; (b) a third transmission line orthogonal to the first and second transmission lines, wherein either the first and second transmission lines are suitable for transmitting a TEM mode signal and the third transmission line is suitable for transmitting a waveguide mode signal, or the third transmission line is suitable for transmitting a TEM mode signal and the first and second transmission lines are suitable for transmitting a waveguide mode signal; and (c) first and second transducers, the first transducer coupled between the first and third transmission lines, the second transducer coupled between the second and third transmission lines, each of the transducers suitable for converting a TEM mode signal to a waveguide mode signal.
Owner:AUTOLIV ASP INC
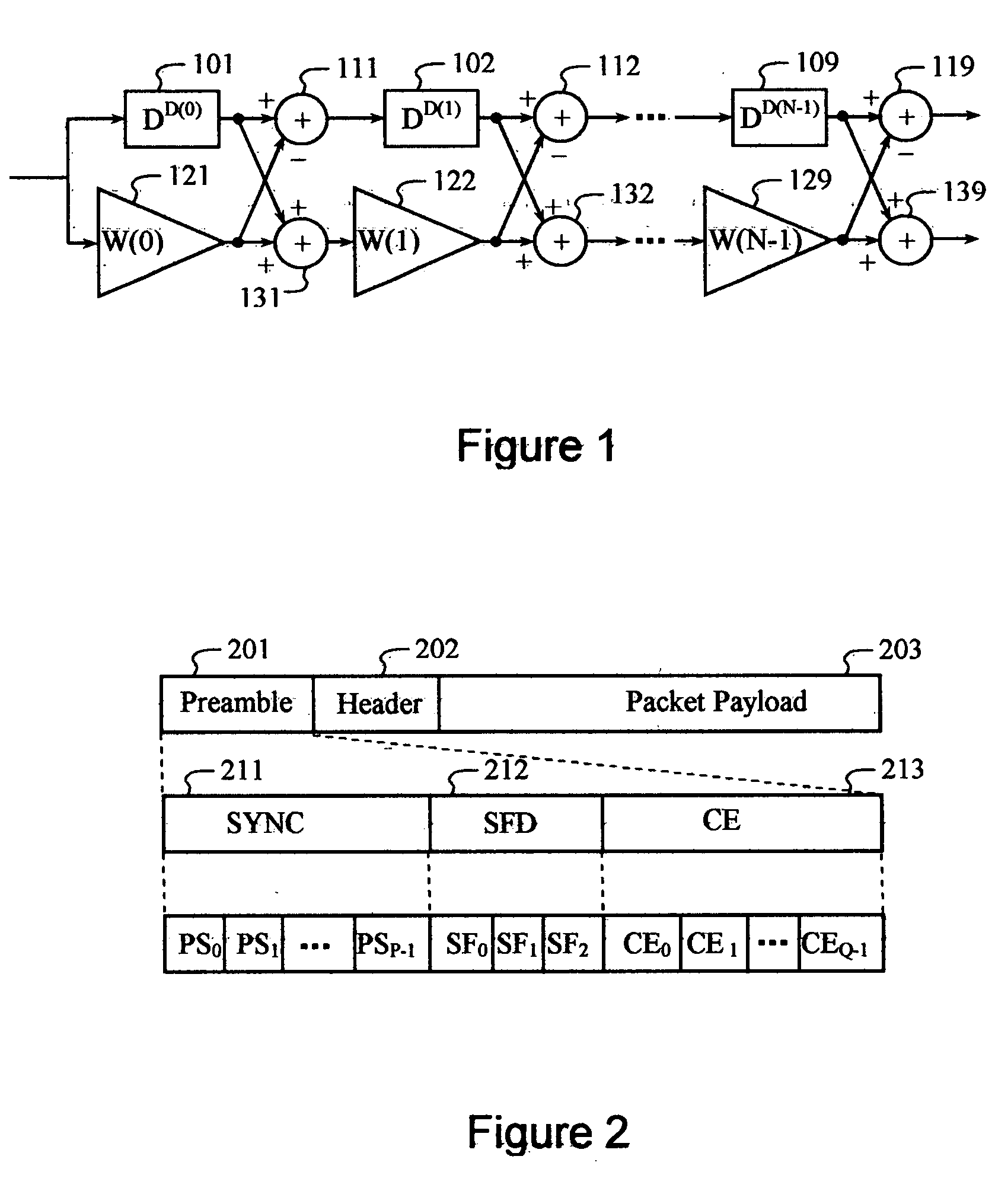
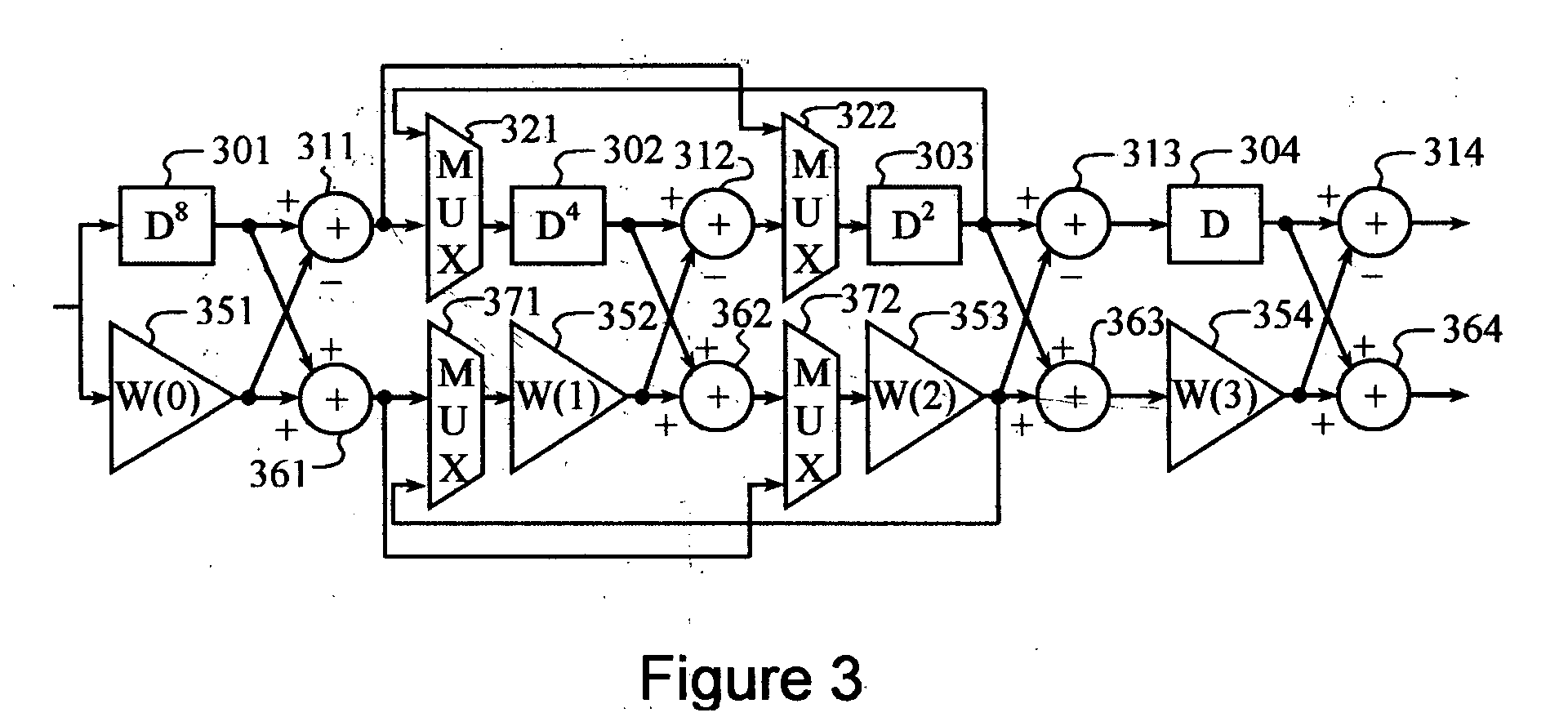
Frame format for millimeter-wave systems
ActiveUS20070168841A1Transmission path divisionCode conversionMillimeter wave communication systemsMultipath channels
A single frame format is employed by a millimeter wave communication system for single-carrier and OFDM signaling. A Golay-coded sequence in the start frame delimiter (SFD) field identifies the data transmission as single carrier or OFDM. Complementary Golay codes are employed in a channel estimation field to allow a perfect estimate of the multipath channel to be made. Marker codes generated from Golay codes are inserted periodically between slots for tracking and / or for reacquiring timing, frequency, and multipath channel estimates. The length of the marker codes may be adapted relative to the multipath delay spread.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
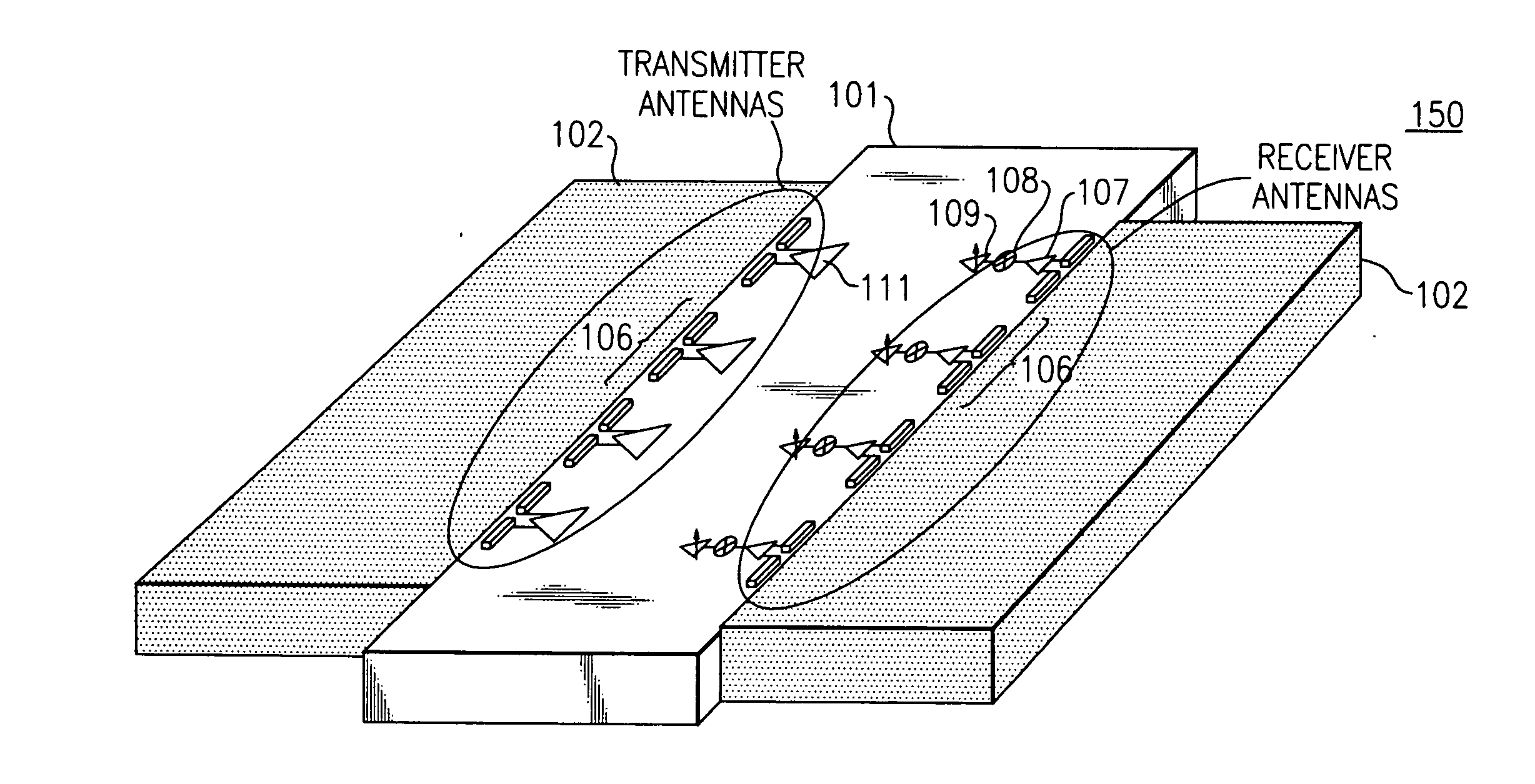
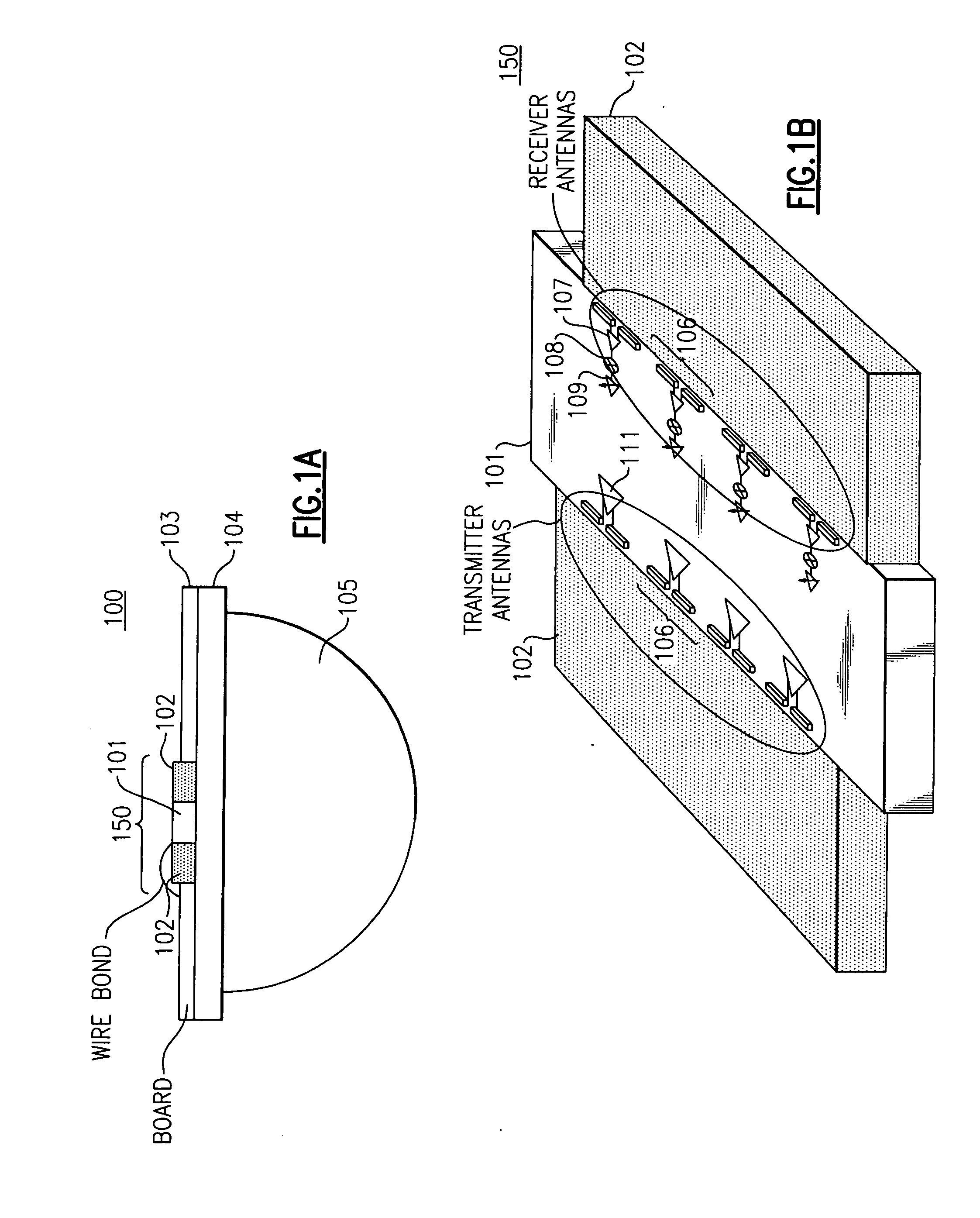
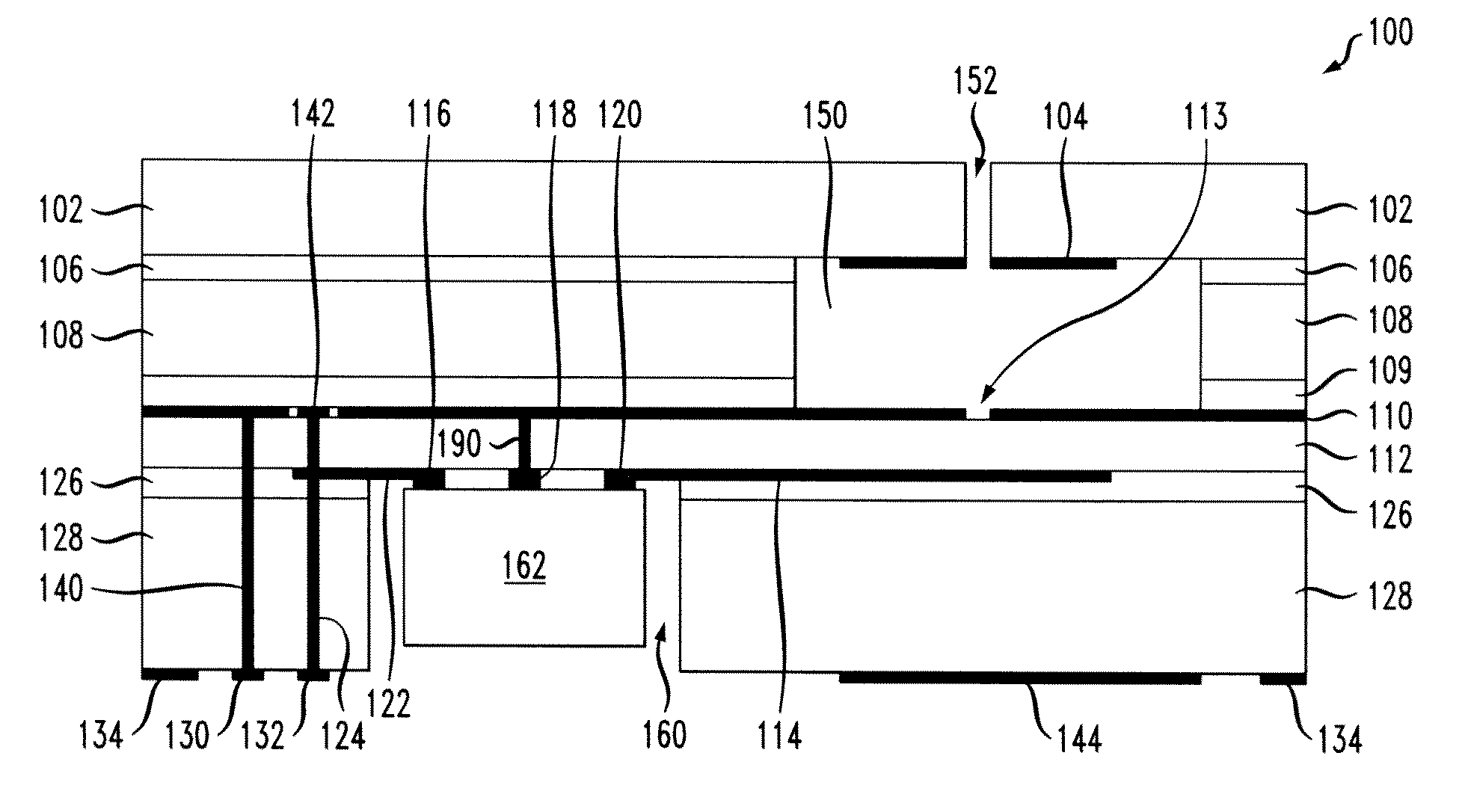
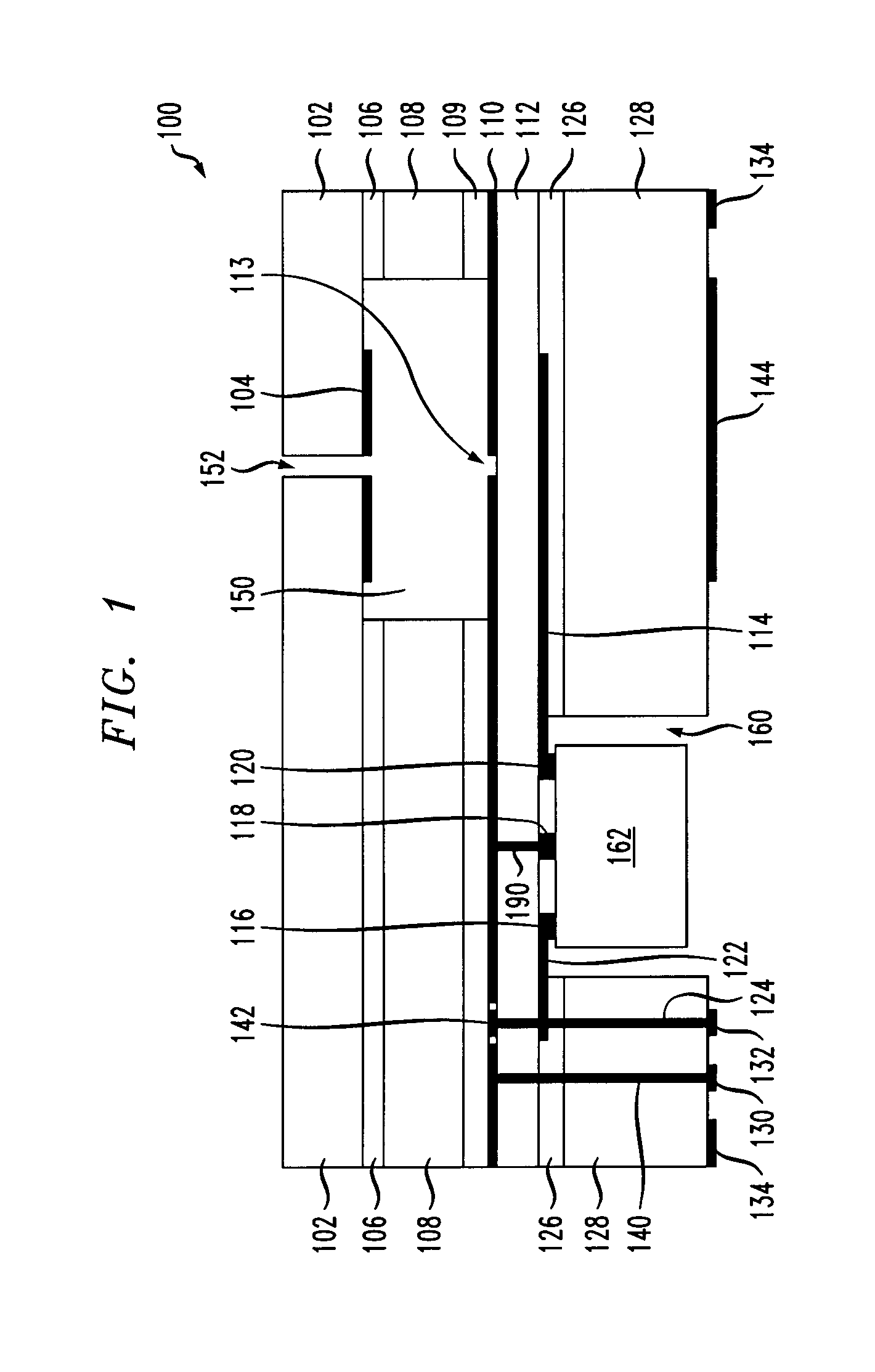
Apparatus and methods for packaging antennas with integrated circuit chips for millimeter wave applications
ActiveUS20070063056A1Highly-integratedSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesTransceiverCommunications system
Apparatus and methods are provided for integrally packaging antennas with semiconductor IC (integrated circuit) chips to provide highly-integrated and high-performance radio / wireless communications systems for millimeter wave applications including, e.g., voice communication, data communication and radar applications. For example, wireless communication modules are constructed with IC chips having receiver / transmitter / transceiver integrated circuits and planar antennas that are integrally constructed from BEOL (back end of line) metallization structures of the IC chip.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Microwave and millimeter wave circuit apparatus
InactiveUS6320543B1Easy to produceSmall sizeSimultaneous aerial operationsSolid-state devicesProduction rateReduced size
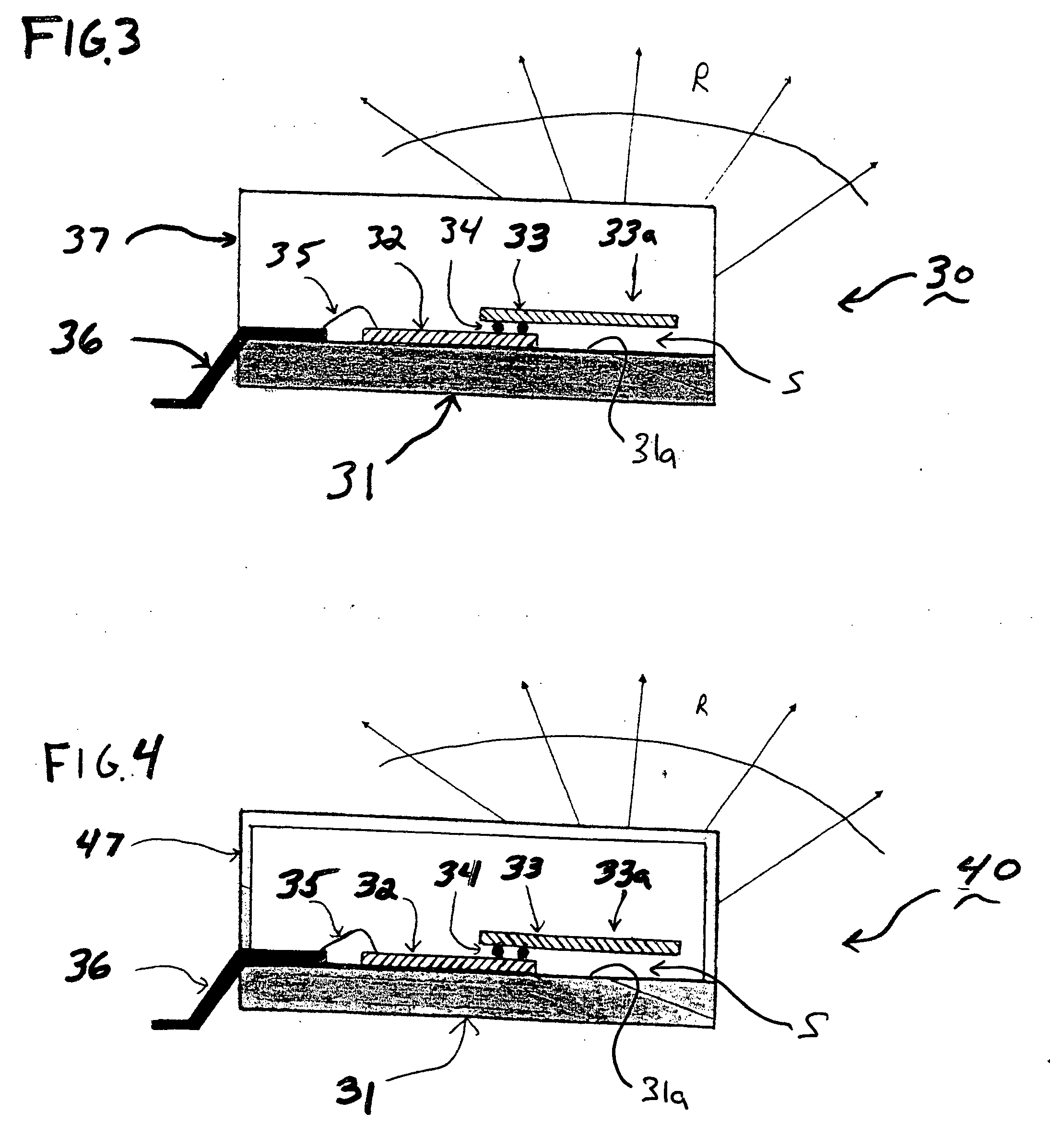
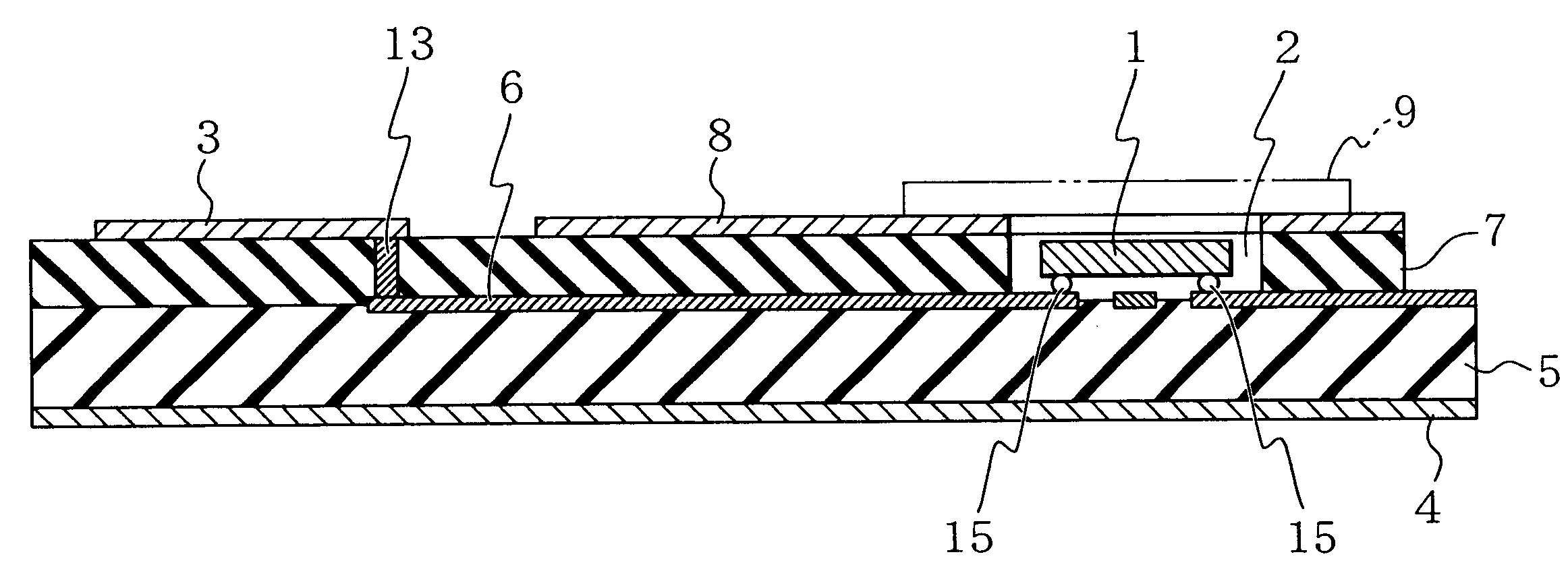
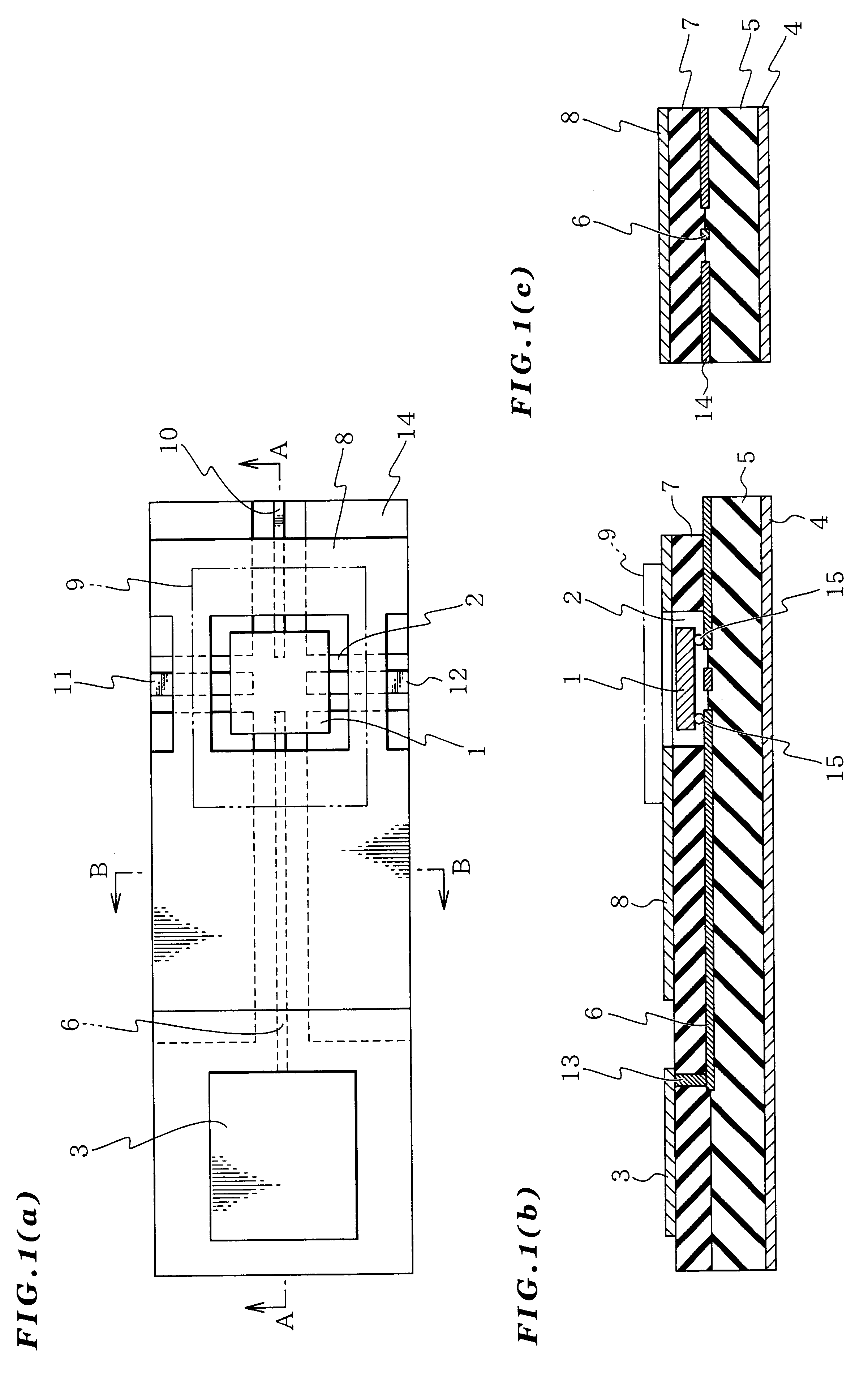
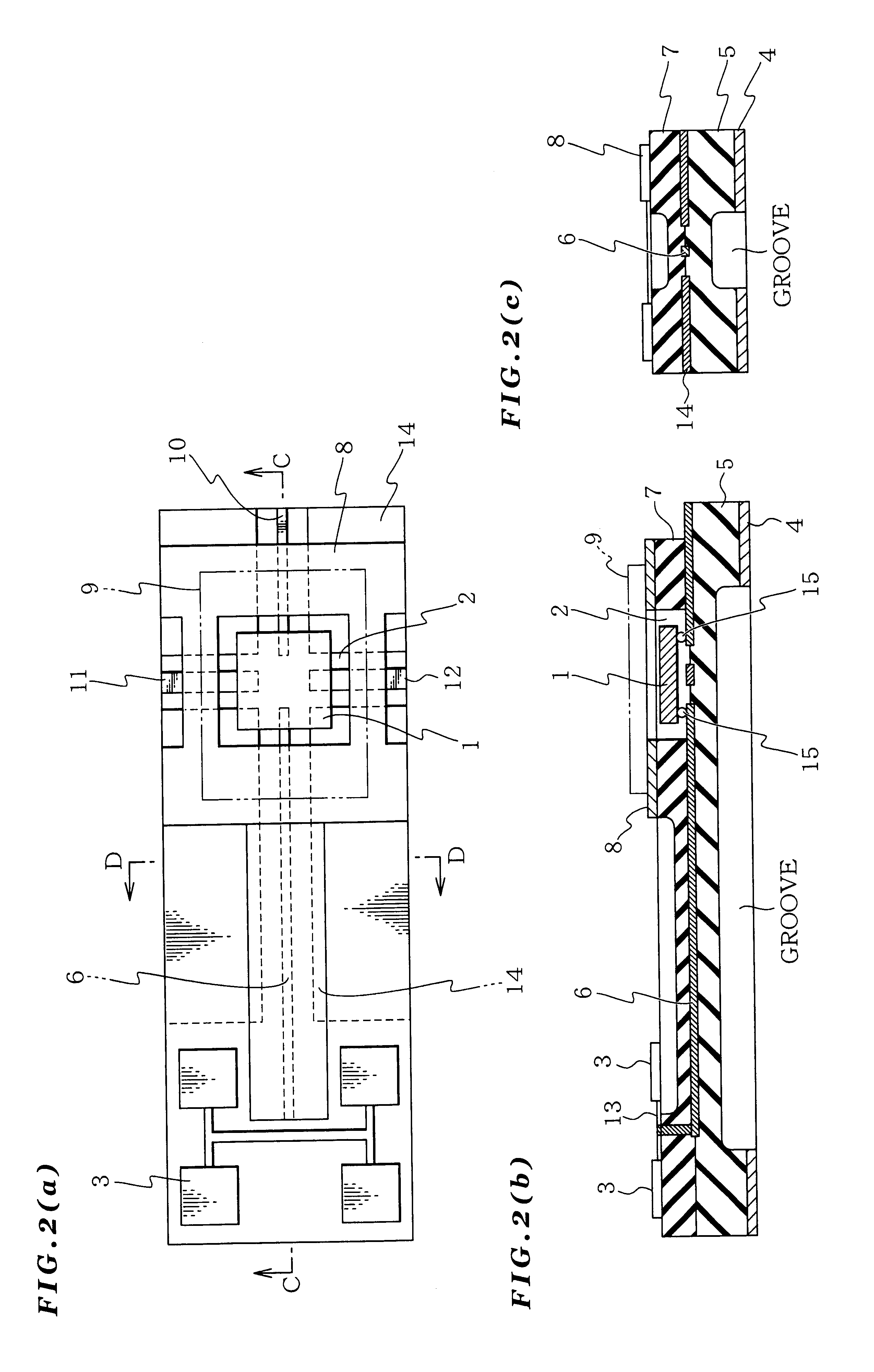
The present invention provides a microwave and millimeter wave circuit apparatus having a reduced size and which can be produced easily, improving productivity. The microwave and millimeter wave circuit apparatus includes: a grounding conductive layer 4 grounded; a first dielectric layer 5 formed on this grounding conductive layer 4; a signal line selectively formed on this first dielectric layer 5; a second dielectric layer 7 covering at least a portion of the signal line 6; a cavity 2 formed in this second dielectric layer 7 and extending to the signal line 6; a monolithic microwave integrated circuit 1 arranged in the cavity 2 and connected to the signal line 6; and an antenna connected to the signal line 6.
Owner:NEC CORP
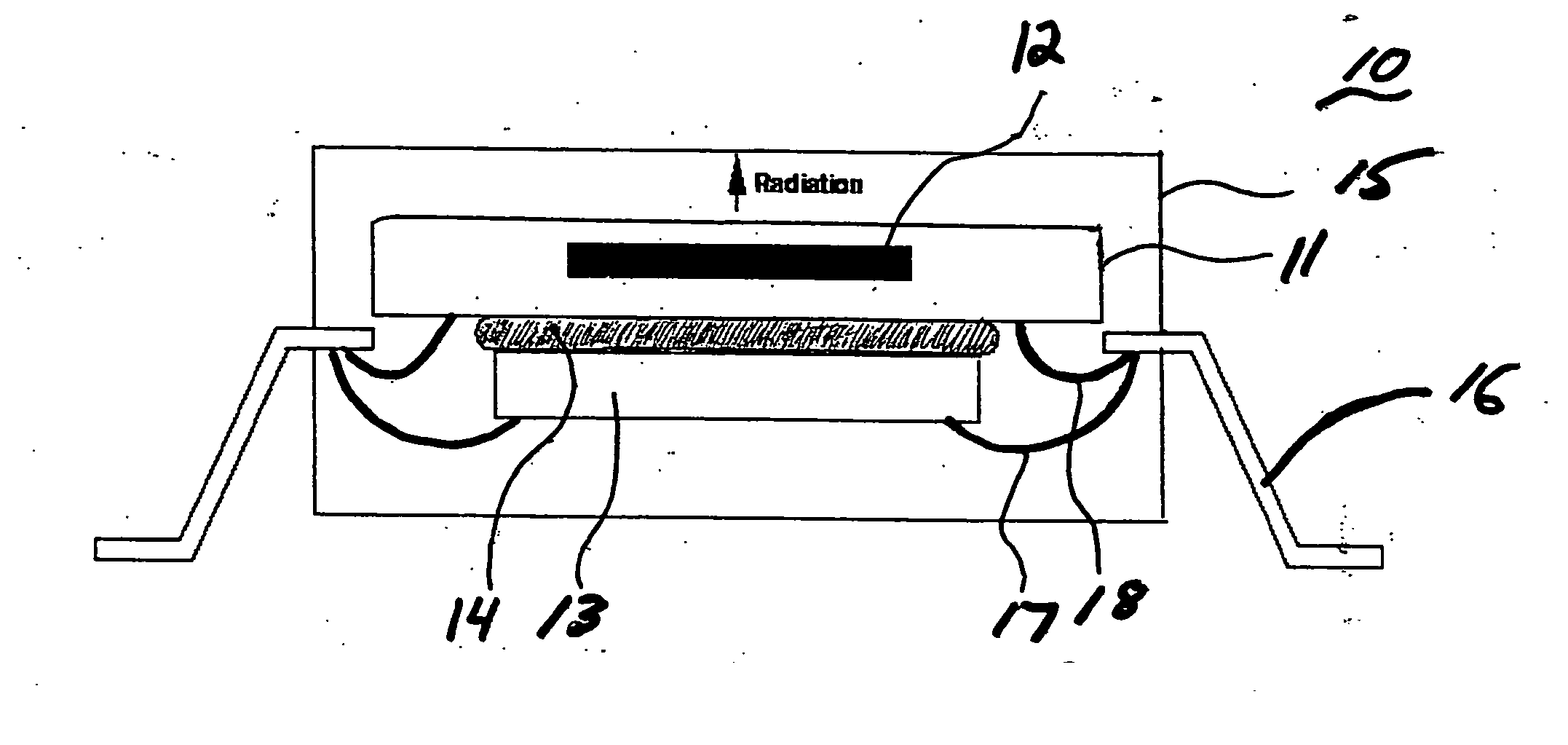
Architecture and method of coupling electromagnetic energy to thermal detectors
InactiveUS6329655B1Antenna supports/mountingsSolid-state devicesSensing applicationsElectromagnetic shielding
A radiation sensor. The inventive sensor has a two-level detector structure formed on a substrate in which a thermal detector element is suspended over the substrate as a microbridge structure. A receiver of electromagnetic radiation is provided on the same side of the substrate in a manner that efficiently couples the radiation field to the thermal detector element. The thermal detector element has a sandwich structure including a heater metal layer, a dielectric layer, and a thin film thermo-resistive material. The thermal detector element is suspended out of physical contact with the receiver. In one embodiment, the receiver is an antenna having a crossed bowtie configuration that efficiently couples the radiation field to the detector element. The inventive radiation sensors are especially useful for mm-wave and microwave sensing applications. The sensor can be used individually or in linear or two-dimensional arrays thereof. The invention also is directed to a method of fabricating such a radiation sensor.
Owner:HRL LAB +1
Antennas Using Chip-Package Interconnections for Millimeter-wave Wireless Communication
InactiveUS20100283700A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesInterconnectionIntegrated antenna
A compact millimeter-wave transmitter and receiver make use of interconnections within a chip-containing package for providing an integrated antenna. Due to shorter wavelength of millimeter-waves, these interconnections can be used as antennas for radiation of electromagnetic waves. A dielectric cover or lens is provided within the package to increase the antenna's directivity and to provide a mechanical shield for the chip.
Owner:ANOKIWAVE
Compact millimeter wave packages with integrated antennas
ActiveUS20100327068A1Simultaneous aerial operationsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringIntegrated antenna
A radio-frequency integrated circuit chip package has at least one integrated antenna. The package includes at least one generally planar ground plane formed with at least one slot therein. A first substrate structure has an outer surface and an inner surface. The at least one generally planar ground plane is formed on the outer surface of the first substrate structure. At least one feed line is spaced inwardly from the ground plane and parallel thereto. The at least one feed line has an inner surface and an outer surface and is a transmission line formed on the inner surface of the first substrate structure with the outer surface of the at least one feed line adjacent the inner surface of the first substrate structure. At least one radio frequency chip is coupled to the feed line and the ground plane. A second substrate structure, spaced inwardly from the feed line, defines a chip-receiving cavity. The chip is located in the chip-receiving cavity. The inner surface of the at least one feed line borders the chip-receiving cavity. An antenna patch may be provided. Planar phased array embodiments, assemblies with motherboards and heat sinks, and fabrication techniques are also disclosed.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC +1
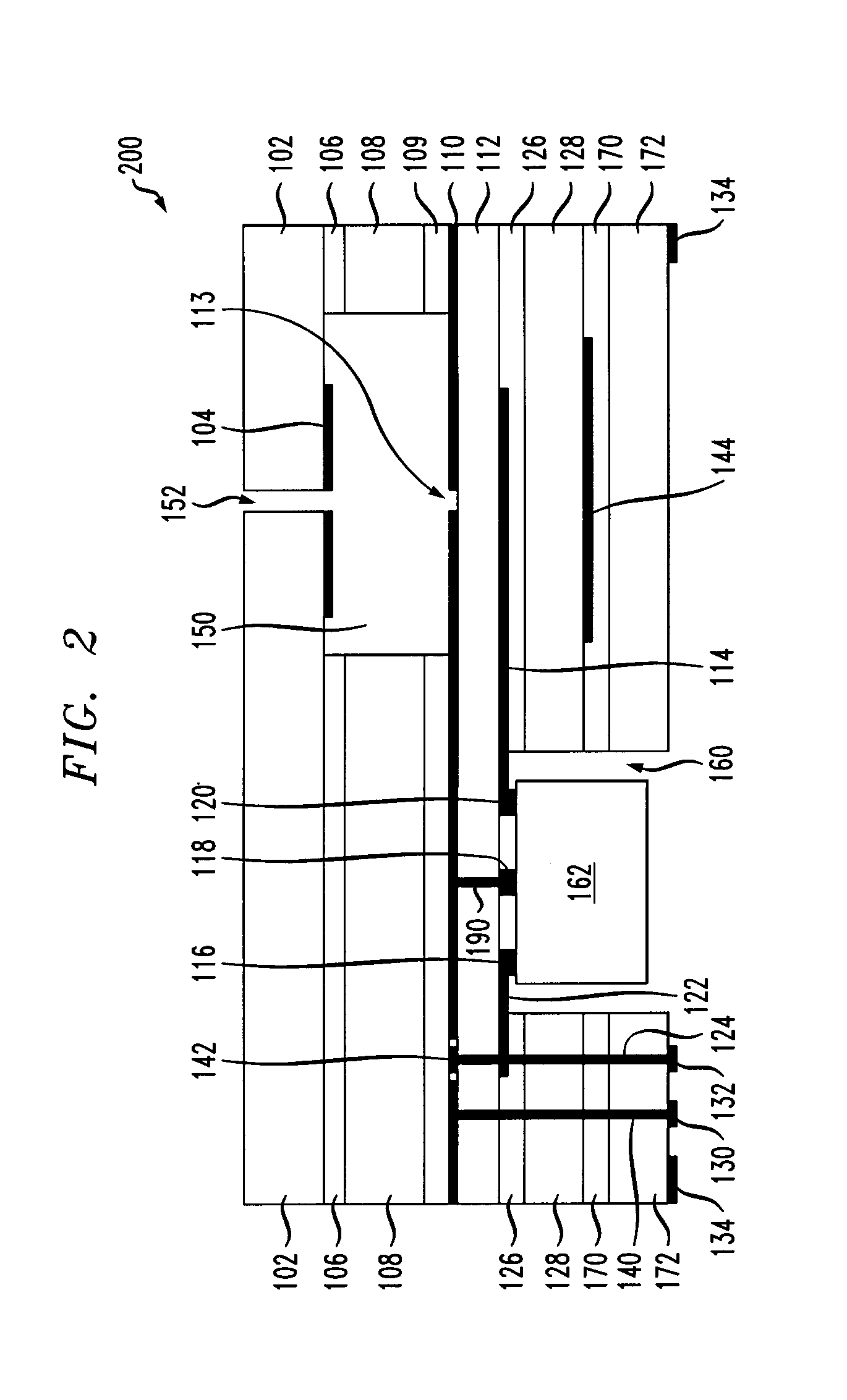
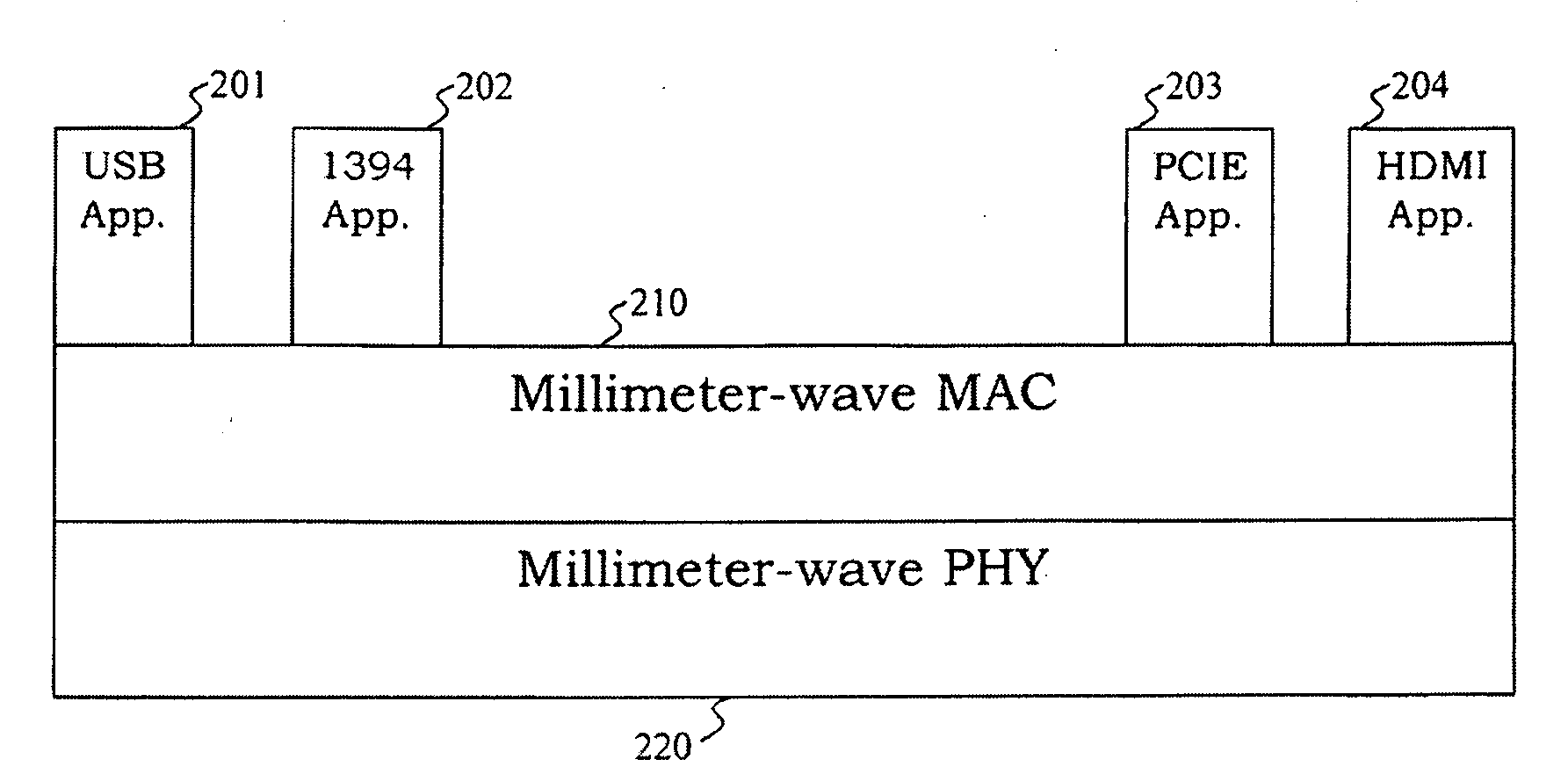
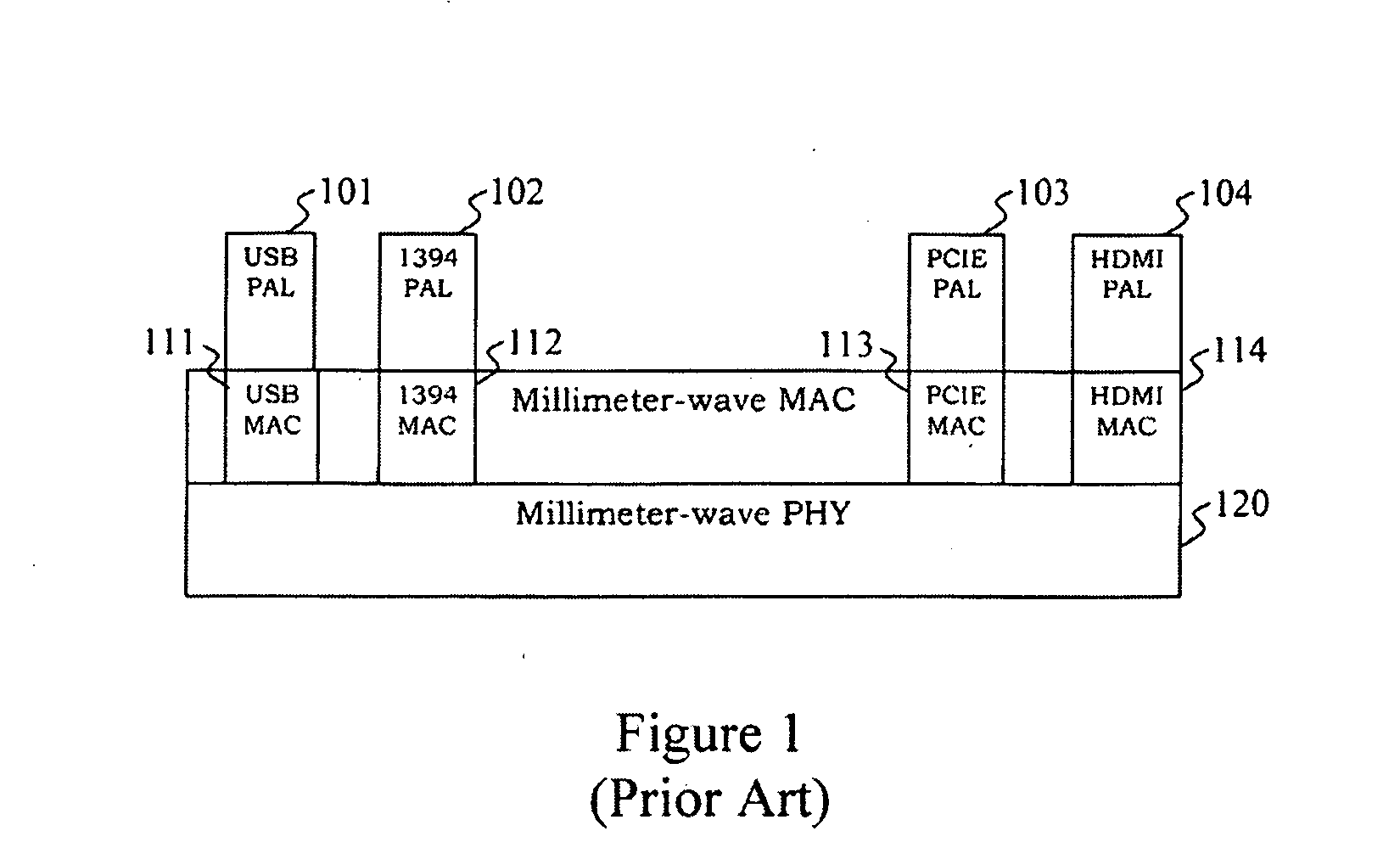
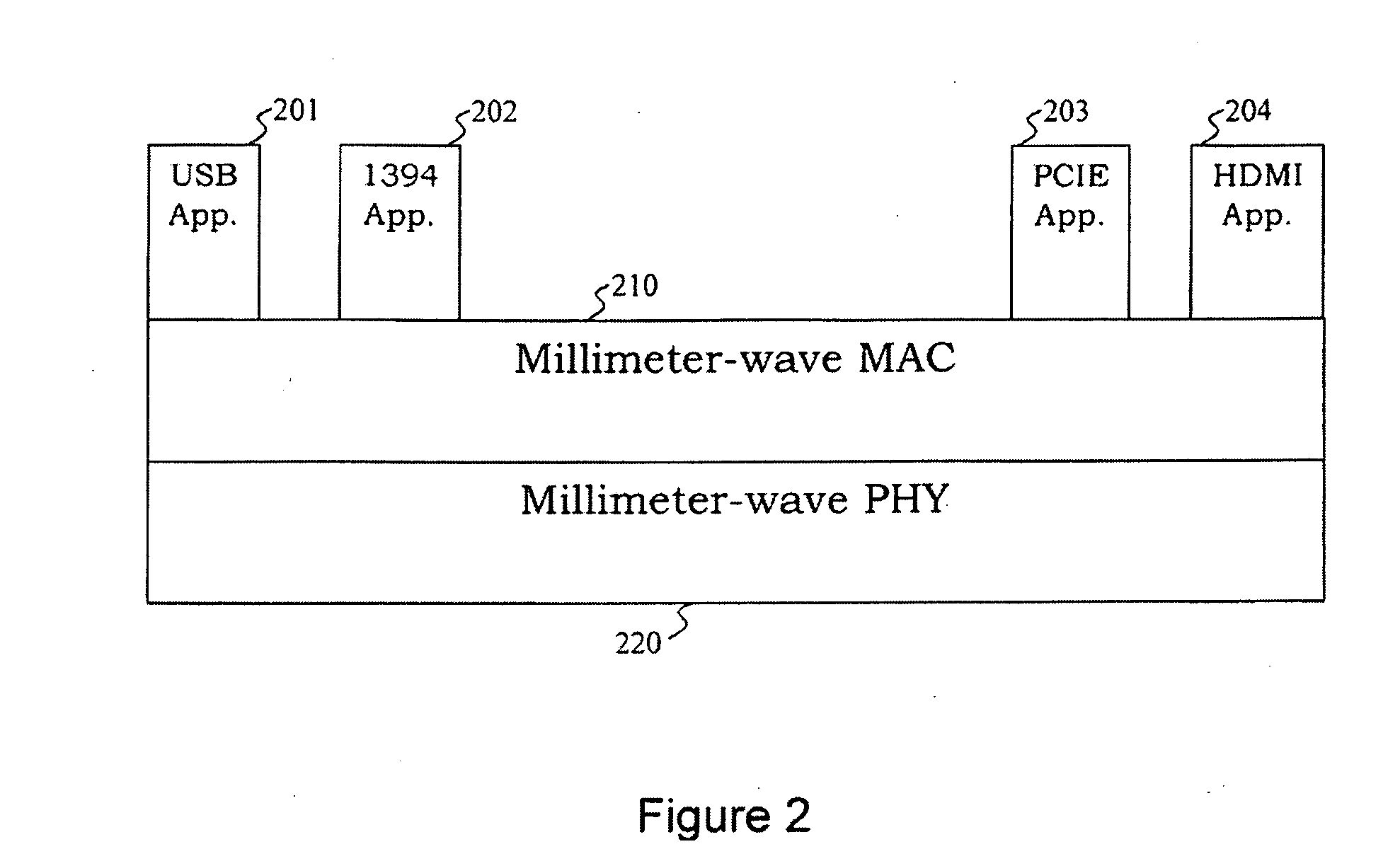
Millimeter-wave communications for peripheral devices
A wireless device couples an electronic device employing a wired-link protocol to, for example, a wireless personal area network (WPAN). The wireless device comprises a wired interface configured for coupling to the electronic device, a wired transceiver coupled to the wired interface, the at least one wired transceiver configured for functioning as a terminus of a wired link coupled to the electronic device, and a wireless transmitter or transceiver coupled to the wired transceiver and configured for functioning as a terminus of a wireless link in the WPAN. The wireless device may be configured for coupling a plurality of dissimilar wired devices together via a wireless link.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Imaging millimeter wave radar system
InactiveUS7019682B1Linear waveguide fed arraysRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFrequency spectrumDisplay device
An imaging millimeter wave radar system. The system includes a millimeter wave transmitter transmitting a frequency scanned millimeter beam that is narrow in the scanned direction and wide in a direction perpendicular to the scanned direction. The system includes a receive antenna and a Rotman type lens for forming a one-dimensional image in the perpendicular direction of targets in the antennas field of view based on millimeter wave radiation reflected from the targets. A computer creates a two dimensional image based on the scanning direction of the transmit beam of the transmit antenna and the one dimensional image from the receive antenna. Distance to the target is determined based on difference in frequency of the transmit signal and the receive signal. Thus, a three dimensional view of the systems field of view is determined by the system. This view can be displayed on a monitor using color to represent target distance. In a preferred embodiment the scanned direction is the vertical direction and the receive antenna forms a horizontal image from signals reflected from targets in the field of view. In this preferred embodiment the transmit antenna is a variable frequency millimeter wave single channel wave guide antenna operating in the 78 GHz to 81 Ghz spectral range to produce a scanning range of 10 degrees and a scanning rate of 60 Hz. The receive antenna is a multi-channel (176 channels) strip-line antenna also operating in the 78 GHz to 81 GHz spectral range, which with the Rotman lens, provides 192 horizontal pixel resolution.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
Forward-looking radar system
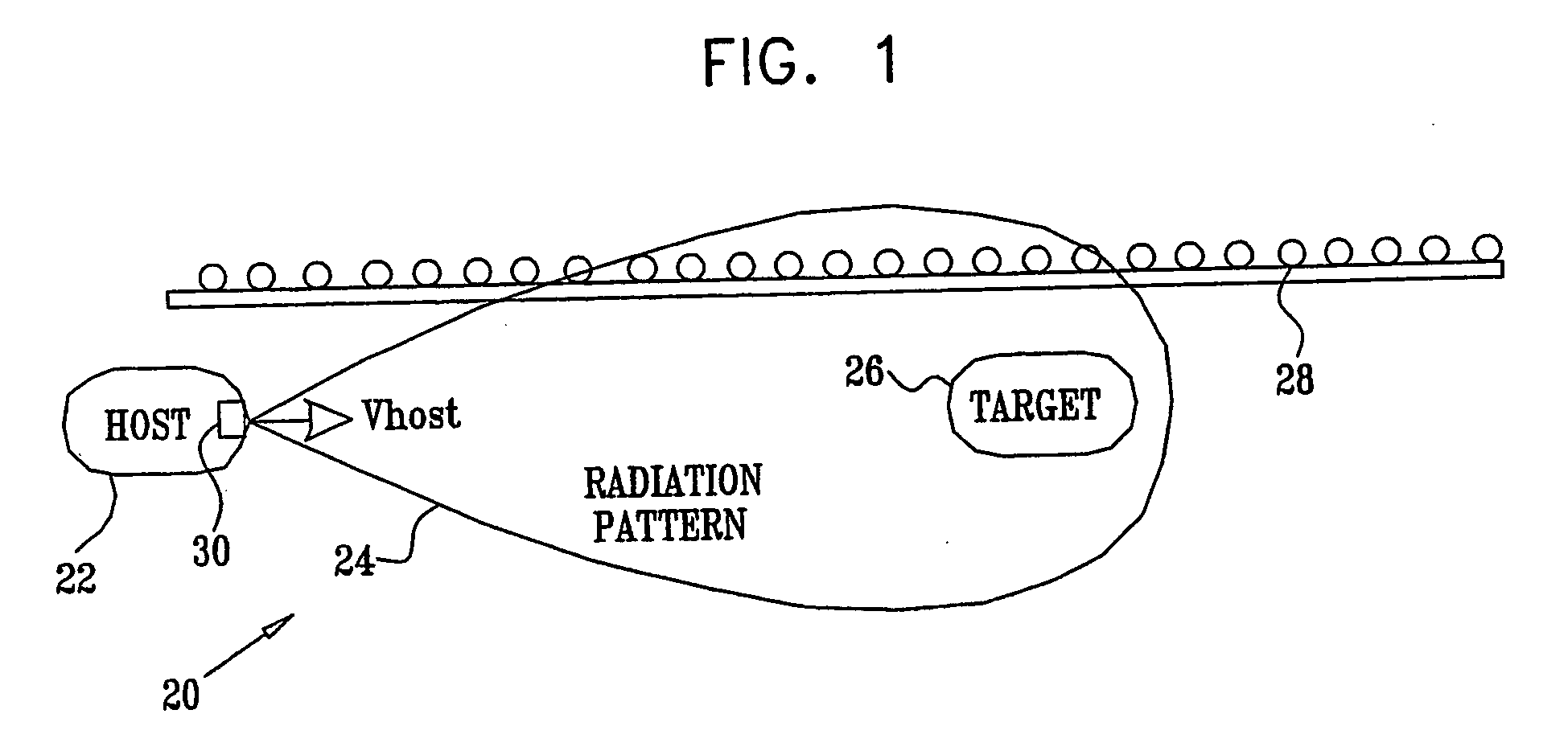
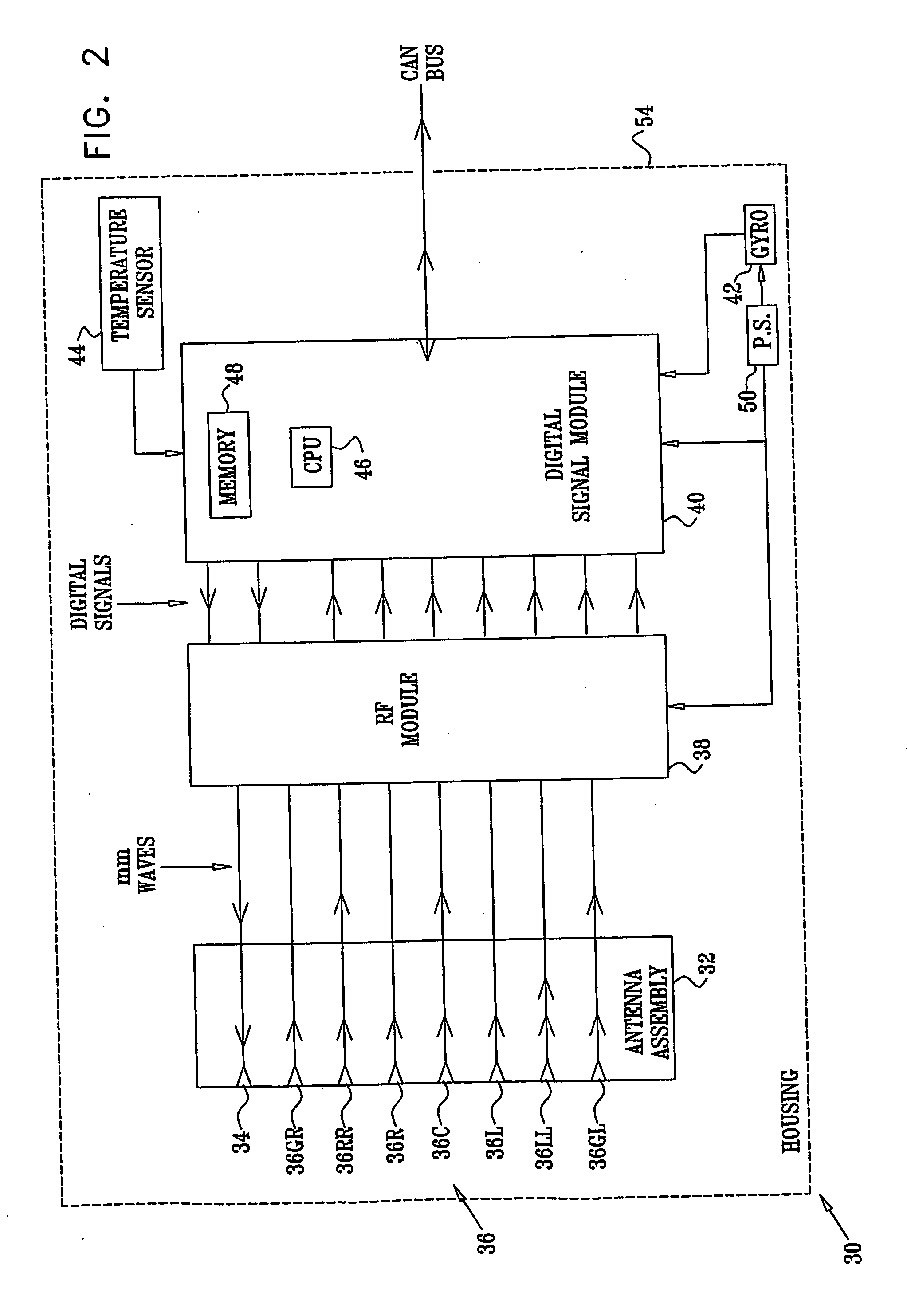
InactiveUS20050285773A1Improve discriminationPrecise maintenanceAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionElectricityRadar systems
An assembly for receiving and transmitting millimeter (mm) waves, including at least one mm wave reflector (84, 86, 88)and at least one mm transmission wave feed (72) configured in a transmission feed location (34) within the at least one mm wave reflector. The assembly also includes a plurality of receiving mm wave feeds (72) configured in respective receiving feed locations (36) within the at least one mm wave reflector; and a radio frequency (RF) module (38). The RF module is coupled to the at least one mm transmission wave feed and to the plurality of the receiving mm wave feeds, so as to drive the at least one mm transmission wave feed to transmit outgoing mm waves and to simultaneously receive incoming mm waves from all of the plurality of the receiving mm wave feeds.
Owner:GROENEVELD TRANSPORT EFFICIENCY
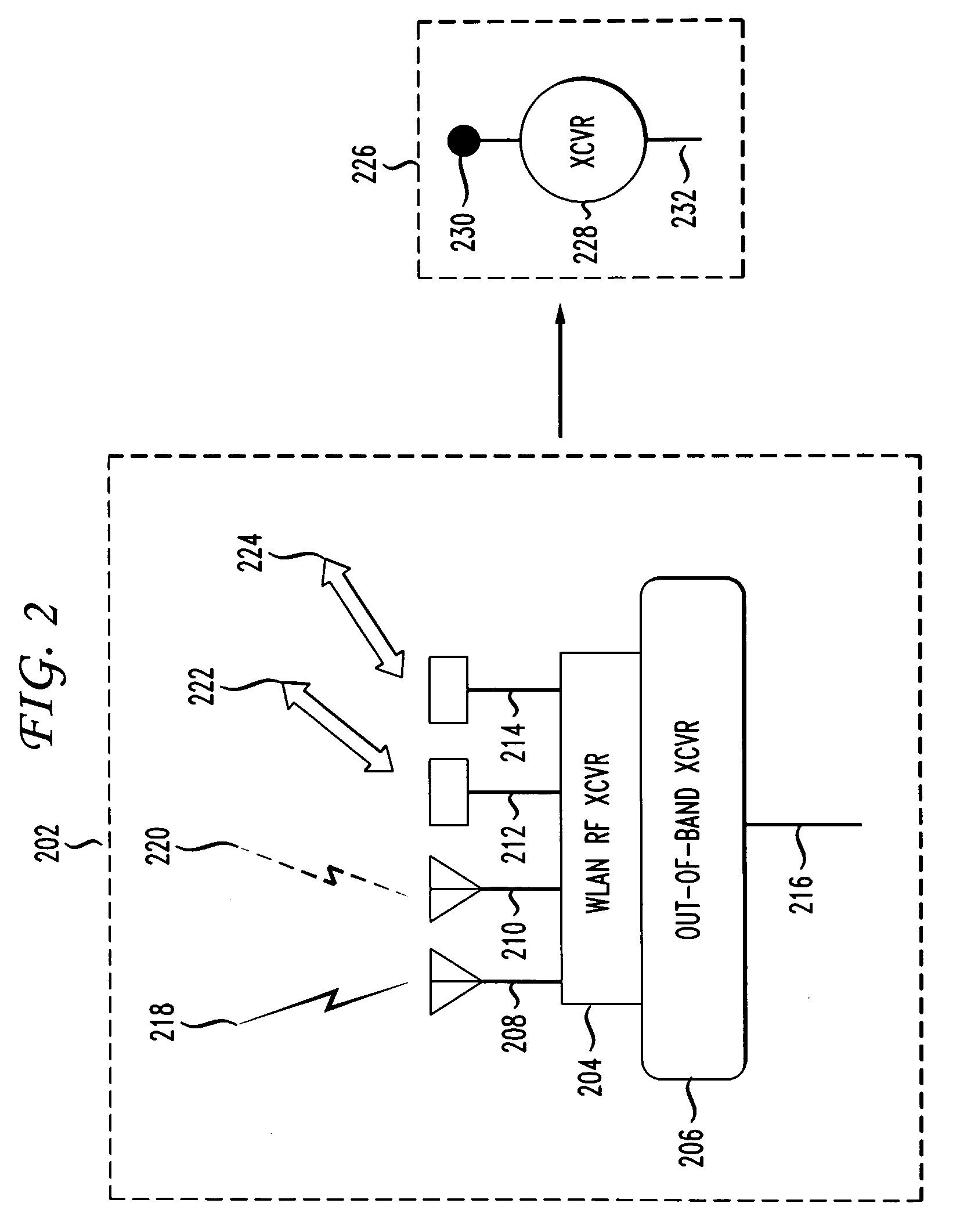
Method and apparatus for microwave and millimeter-wave imaging
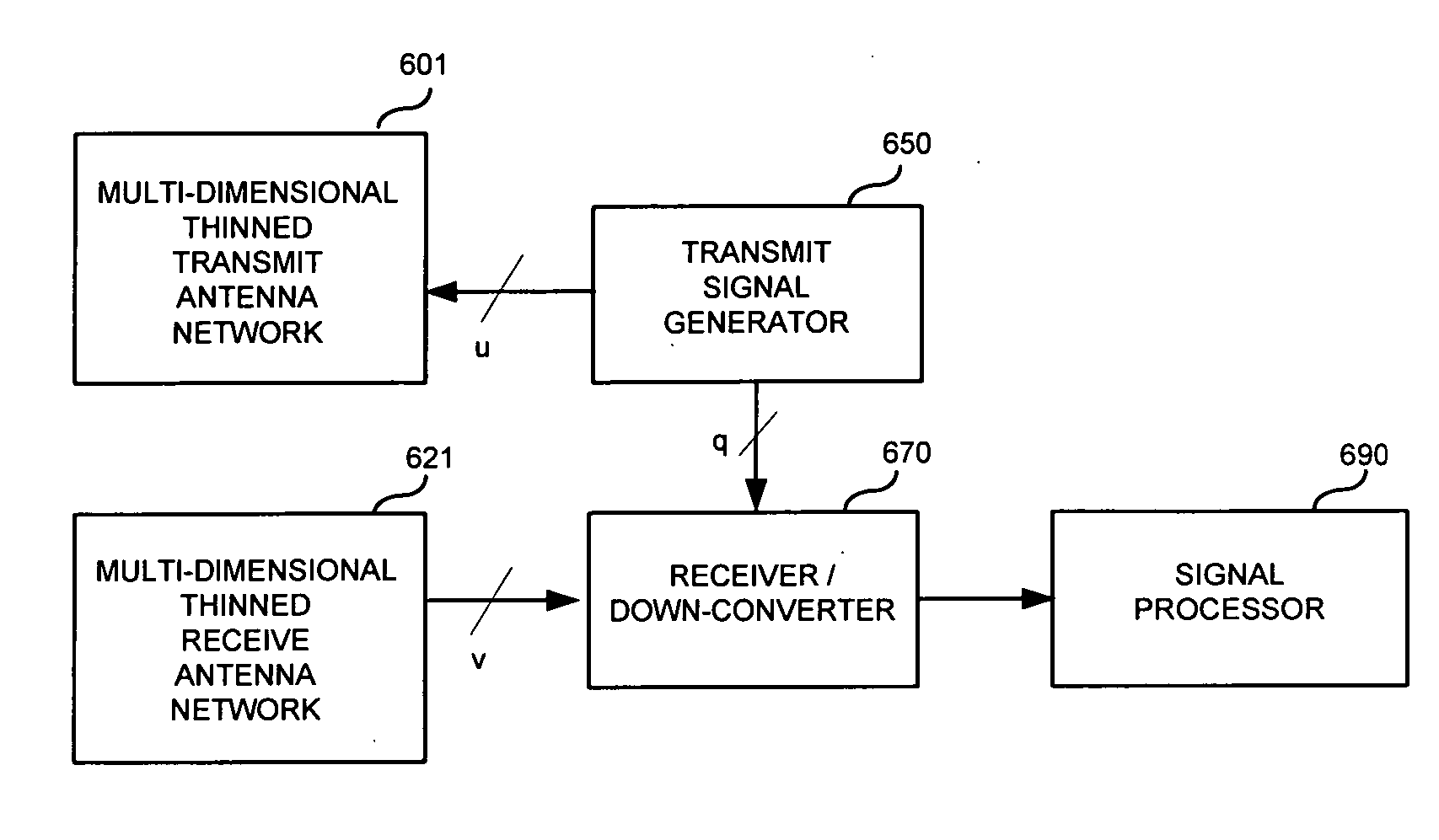
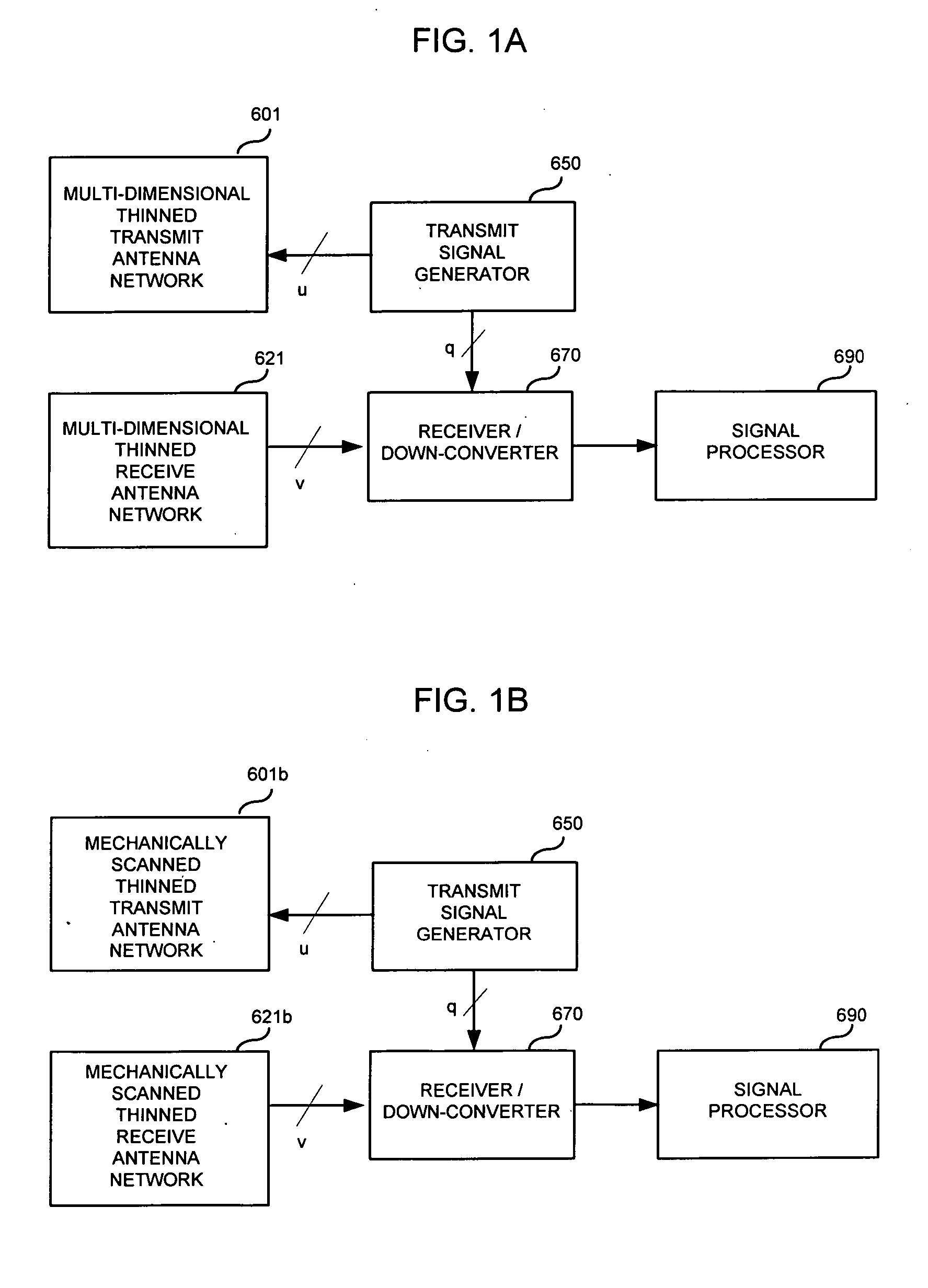
InactiveUS20080100510A1Differential interacting antenna combinationsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionEngineeringMillimetre wave
An antennae system for a detector. The antennae system includes a two-dimensional electro-magnetic transmitter array that has an x number of transmitter elements, and a two-dimensional electro-magnetic receiver array that has a y number of receiver elements. The two-dimensional electro-magnetic transmitter and receiver arrays have a spatial relationship such that at least one subset of the two-dimensional electro-magnetic transmitter and receiver arrays forms a regular array of spatial displacements of z pairwise combinations of transmitter and receiver elements, where z is greater than the sum of x and y.
Owner:BONTHRON ANDREW J +1
Macrocell Enabled MM-Wave Superspot for Mobility
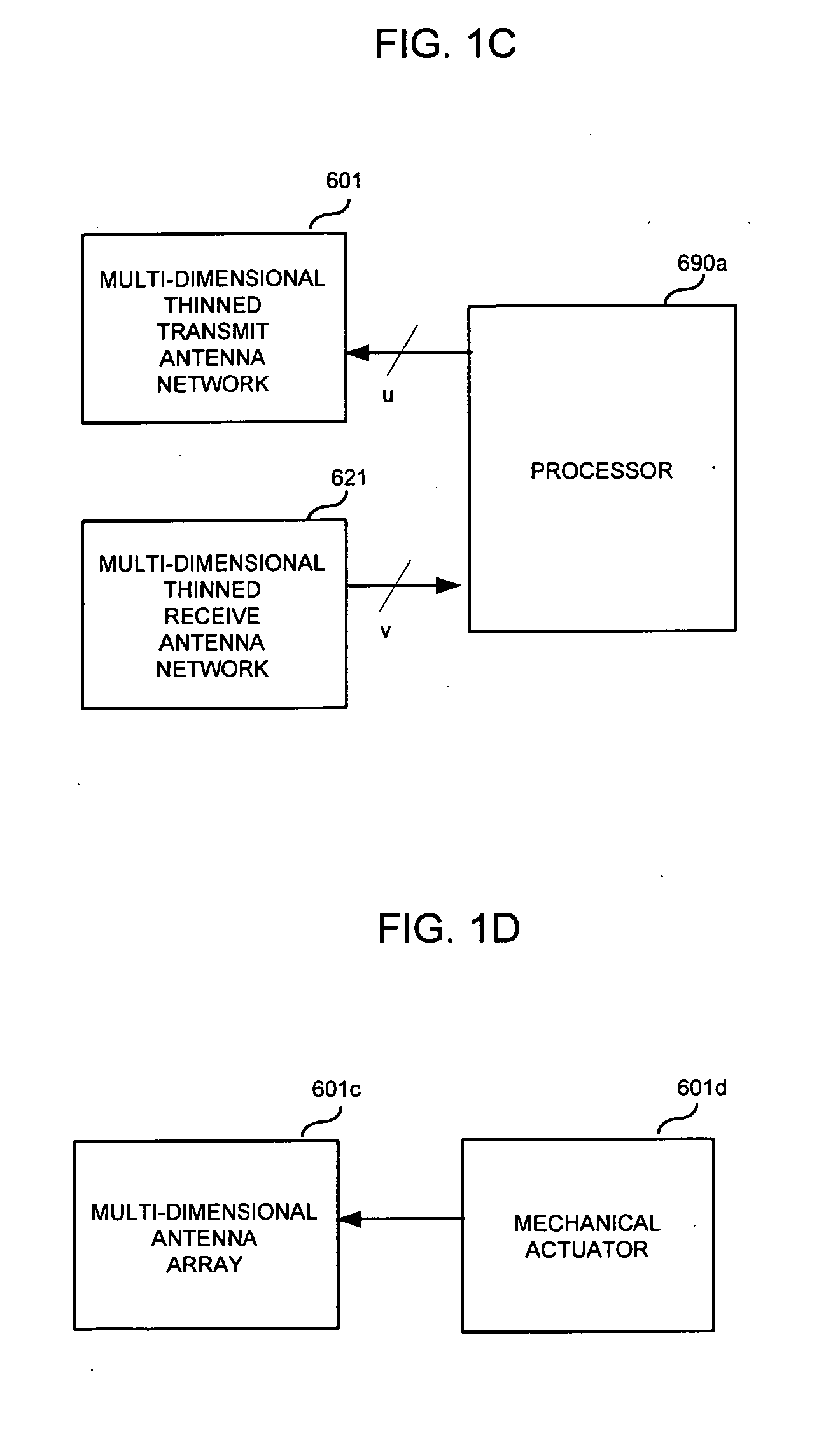
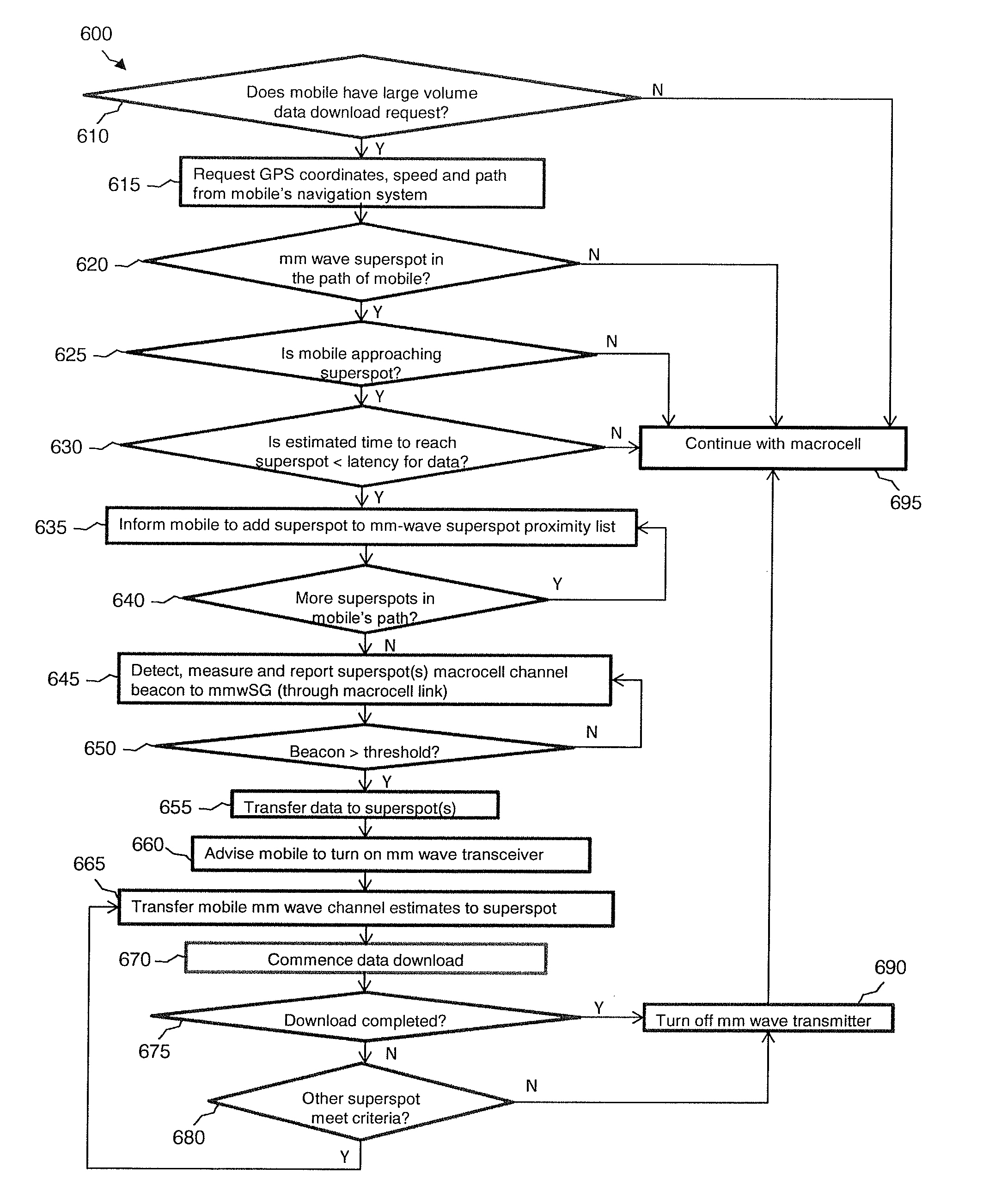
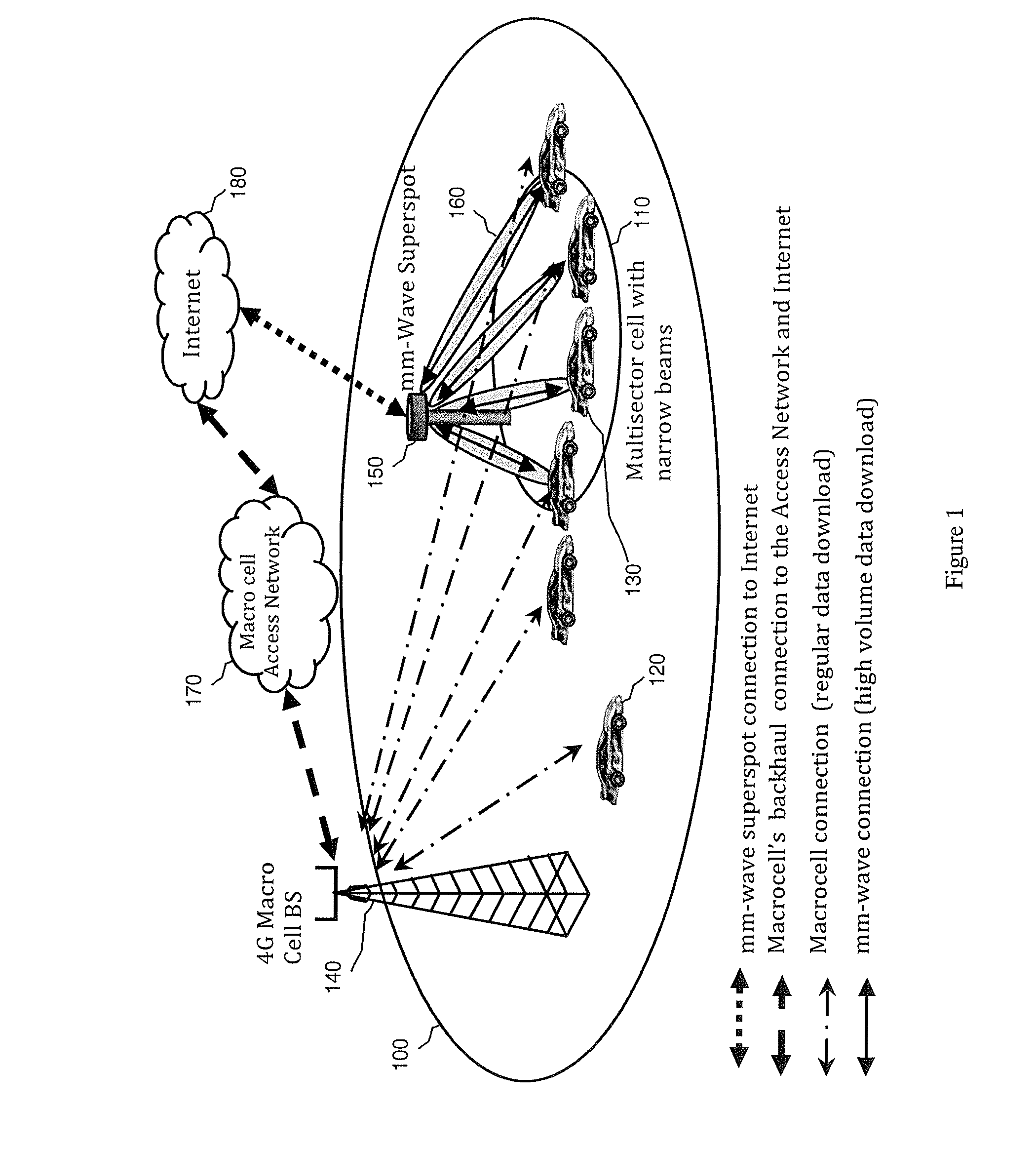
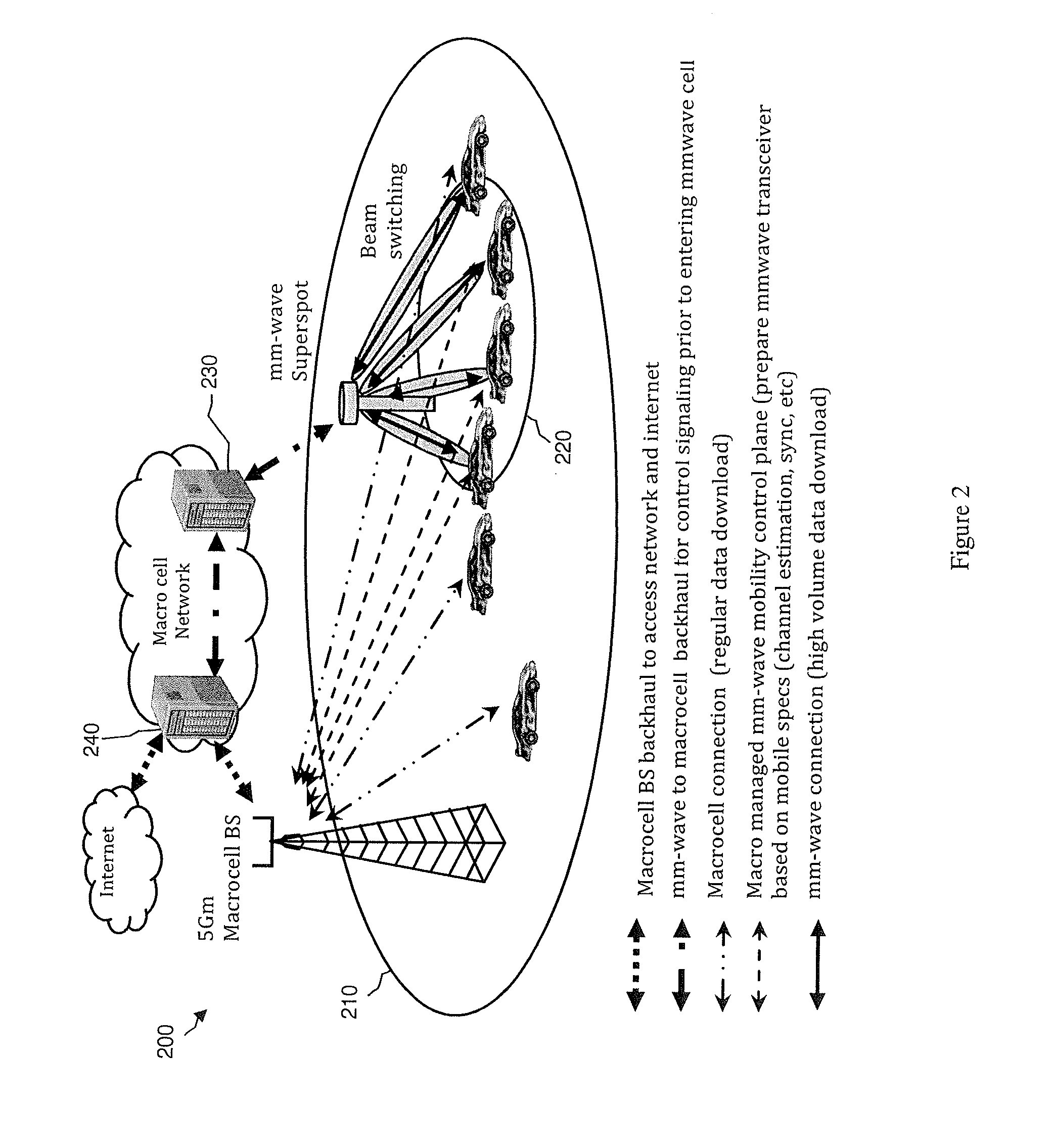
InactiveUS20150092676A1Increase speedInformation formatConnection managementSignal qualityMillimetre wave
A system and method may use mm-wave superspots to download high volumes of data to a moving or stationary mobile device traveling along a travel route that the moving mobile device is traveling. A macrocell in communication with the mobile device may predict the route that the mobile device is traveling, such as via GPS location, moving speed and direction, map information, etc. Alternatively, the route being taken may be determined by wireless communication, such as between the mobile device and a macrocell and / or superspot. The macrocell and / or superspot may determine whether (1) there are any mm-wave superspots along the predicted or known route that the mobile device is taking; (2) there is any data that is requested or remaining to download to the moving mobile device; and / or (3) the received signal quality, channel conditions, and / or macrocell traffic to the mobile device are favorable for superspot downloading.
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
Mesh free-space optical system for wireless local area network backhaul
InactiveUS20080304831A1Improve network reliabilityOptimize networkNetwork topologiesElectromagnetic transmissionCoaxial cableHigh density
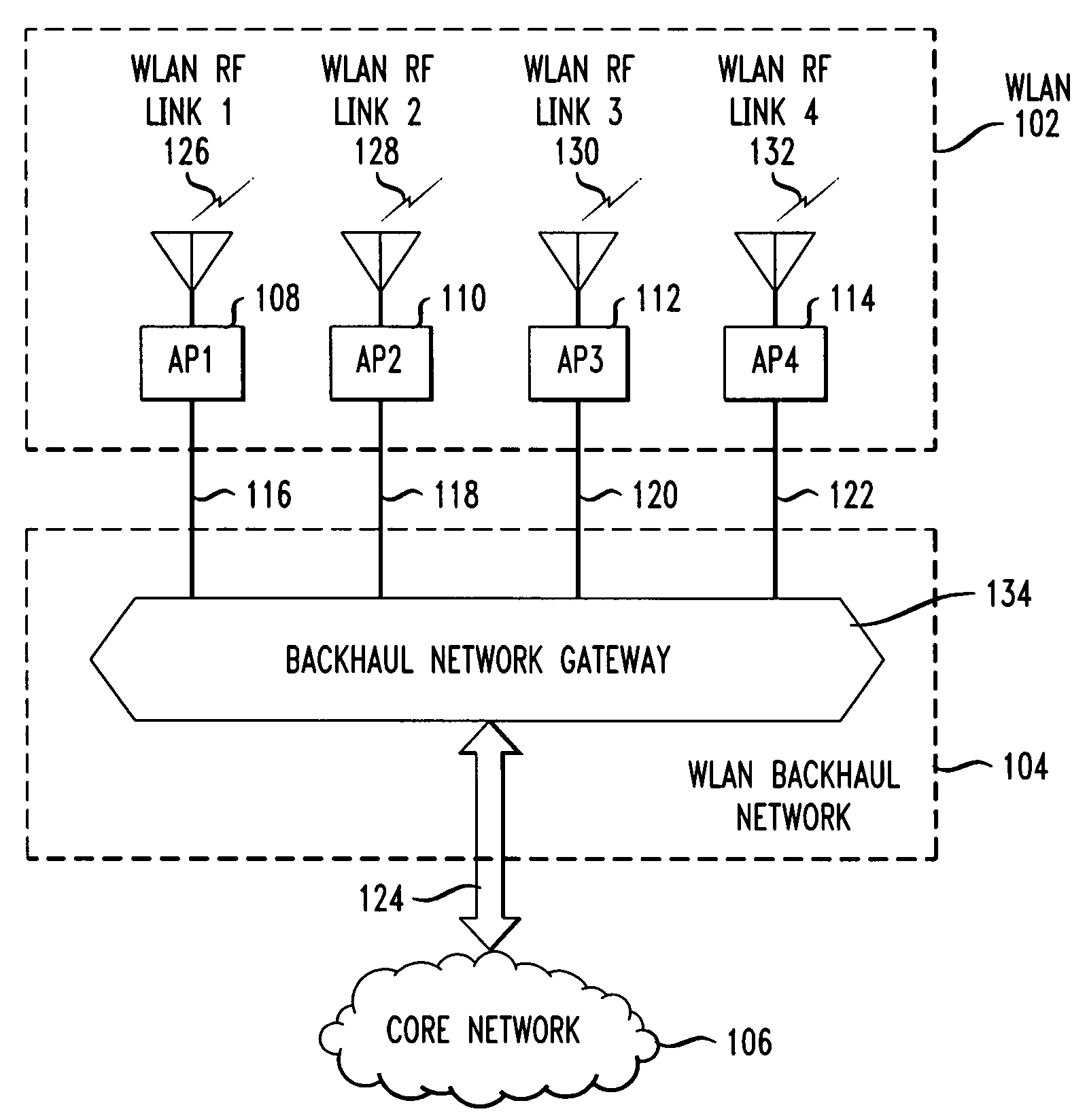
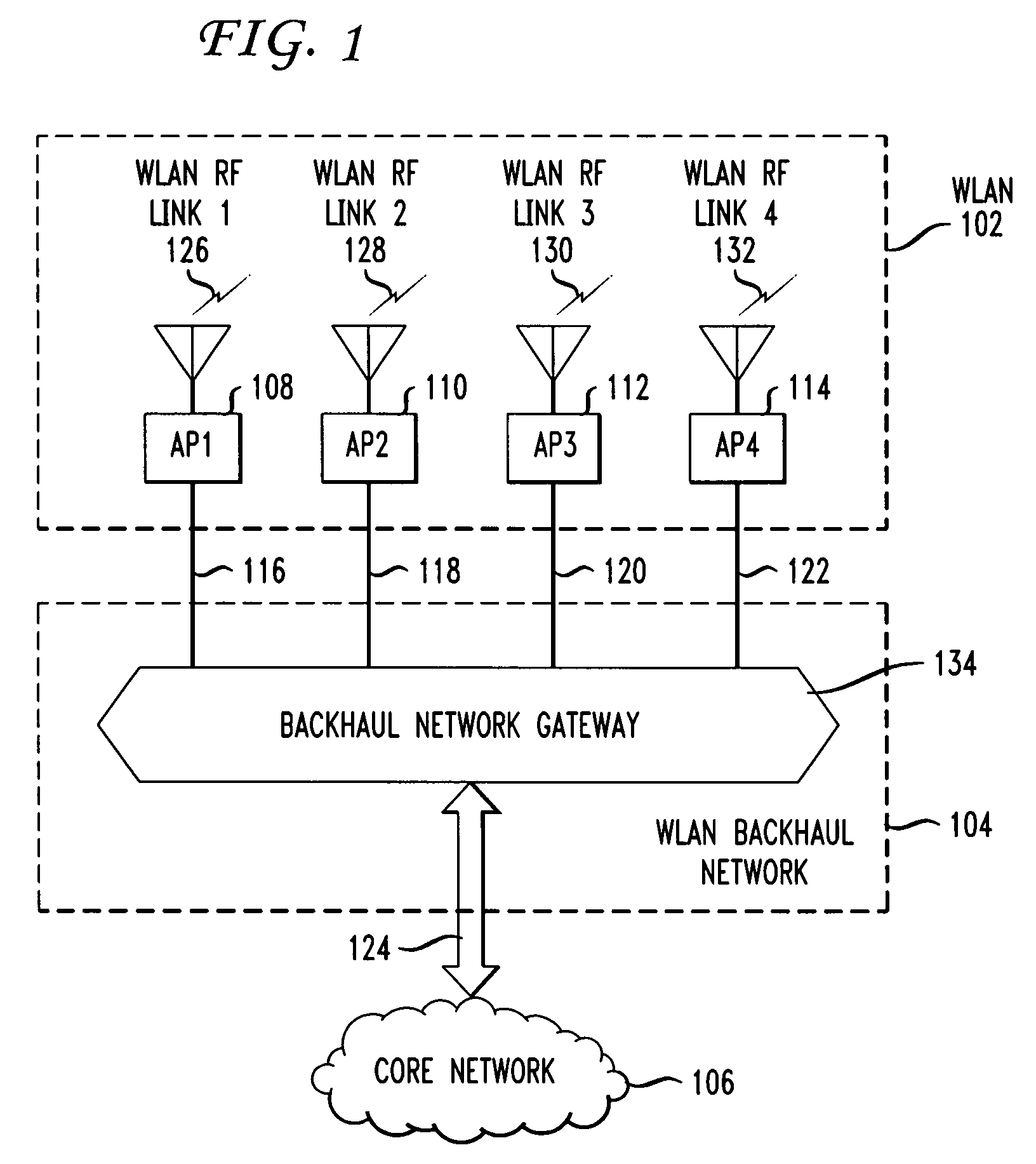
In wireless local area networks (WLANS) with a large number of access points, the provisioning and capacity of the WLAN backhaul network connecting the access points to a core network becomes a major issue in network design. Some network services call for access points to be deployed in high densities in a wide range of environments, including outdoor environments. Traditional backhaul networks using fixed media such as twisted pair cable, coax cable, or optical fiber, in many instances are not physically or economically viable. Disclosed are method and apparatus for connecting access points via a mesh network using free-space optical links. The free-space optical links may be supplemented with mm-wave links to increase reliability and capacity.
Owner:AT&T LABS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com