Patents
Literature
2125 results about "Twisted pair" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Twisted pair cabling is a type of wiring in which two conductors of a single circuit are twisted together for the purposes of improving electromagnetic compatibility. Compared to a single conductor or an untwisted balanced pair, a twisted pair reduces electromagnetic radiation from the pair and crosstalk between neighboring pairs and improves rejection of external electromagnetic interference. It was invented by Alexander Graham Bell.
Synchronous network for digital media streams
InactiveUS6611537B1Avoid collisionPulse modulation television signal transmissionTime-division multiplexData streamNetwork clock
A network adapter for a synchronous logical ring network operates on existing physical twisted-pair telephone topologies. Information propagates around the logical ring, reaching every device on each revolution around the network. Network devices are full-duplex, transmitting and receiving information on every clock cycle. Network devices arbitrate to be elected the network clock device. By synchronizing all network devices to a single reference clock, and providing fixed frames of information propagating around the network at consistent time intervals, the logical ring network ensures that information propagates from one device to another at consistent time intervals. The fixed-length frames are divided into two independent streams: a data stream for the distribution of real-time continuous digital media streams; and a system command stream for the distribution of system commands.
Owner:CENTILLIUM COMM
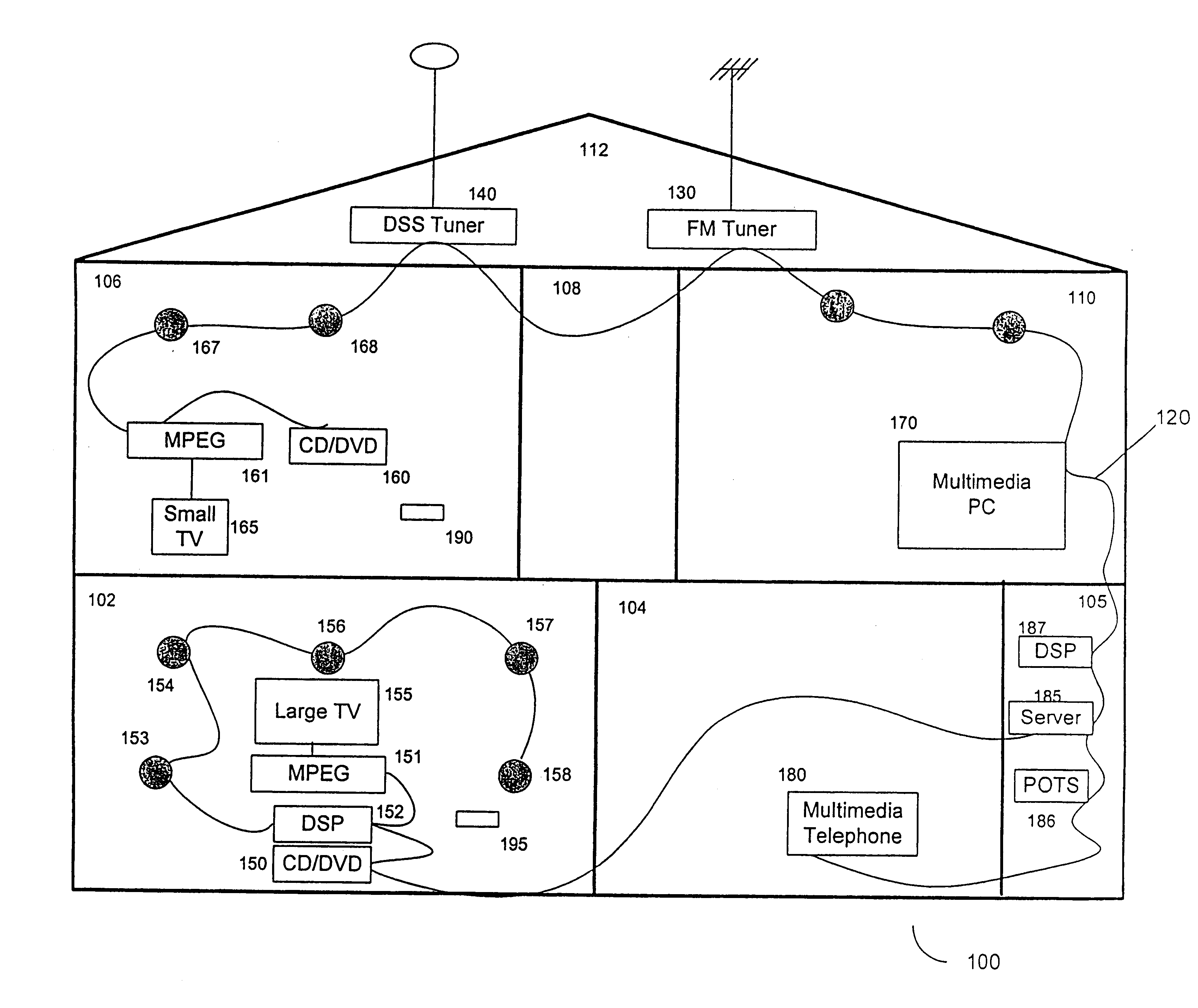
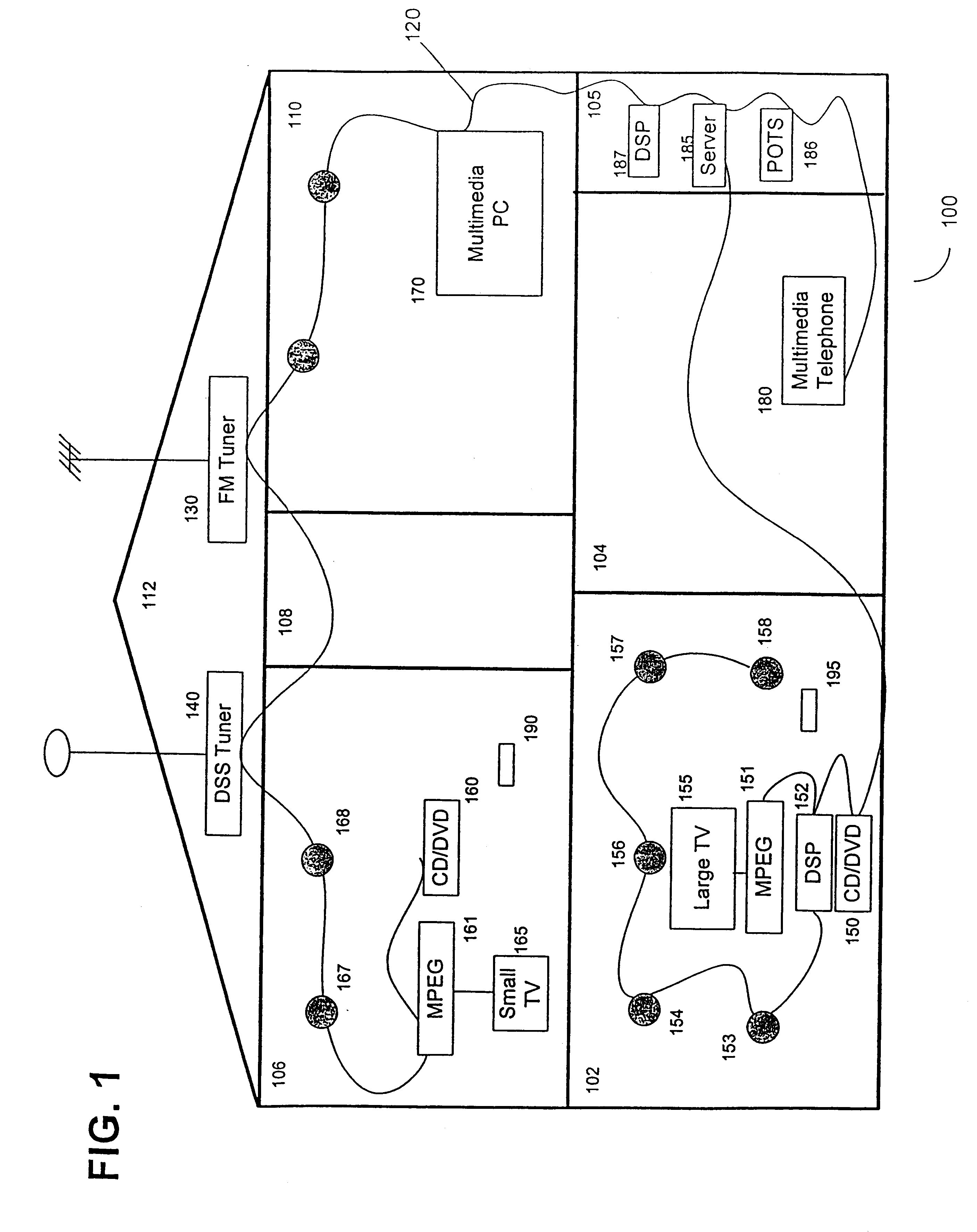
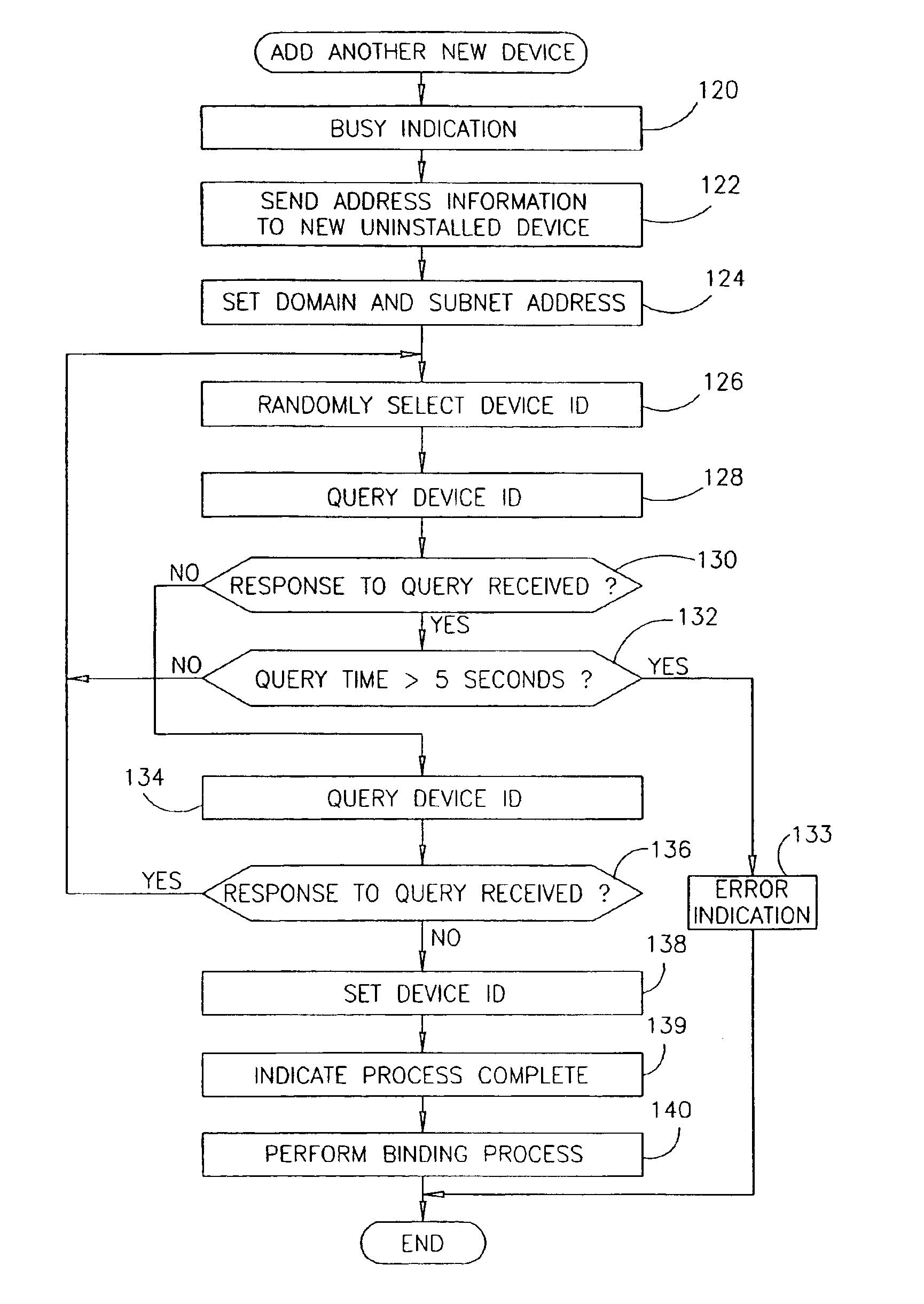
Method of adding a device to a network
InactiveUS6901439B1Low-cost implementationElectric light circuit arrangementMultiple digital computer combinationsHome environmentLonWorks
A method of adding a device to an existing or new electrical or electronic automation or multimedia network. The invention facilitates adding a device to the network that can communicate using various protocols such as LonWorks, CEBus, X-10, etc. over media such as AC power line, IR, RF, twisted pair, optical fiber, etc. The method is a mechanism for adding a device to a system that can be used by an ordinary user of network capable electrical devices. The method comprises the steps an installer would perform including the handshaking that needs to occur between devices to accomplish the binding process. A Functional Profile for LonWorks networks is given as an example. This includes a Home Device profile that employs an automated explicit type messaging for all devices intended for use in a home environment. The invention includes adding to the device an install button and a visual indicator for status such as an LED. Alternatively, existing buttons and LEDs on the device may be used for installed and binding purposes. Other methods of binding can be employed by the use of wired or wireless handheld tools, remote controls, etc. Other interfaces and user feedback can be used such as touch screen, personal computers, cellular phones, PDAs, etc which can offer simple ‘virtual’ binding by the press of an icon versus the physical button on the device. The binding can be performed locally or remotely such as via LAN, WAN, Internet, etc.
Owner:LEVITON MFG
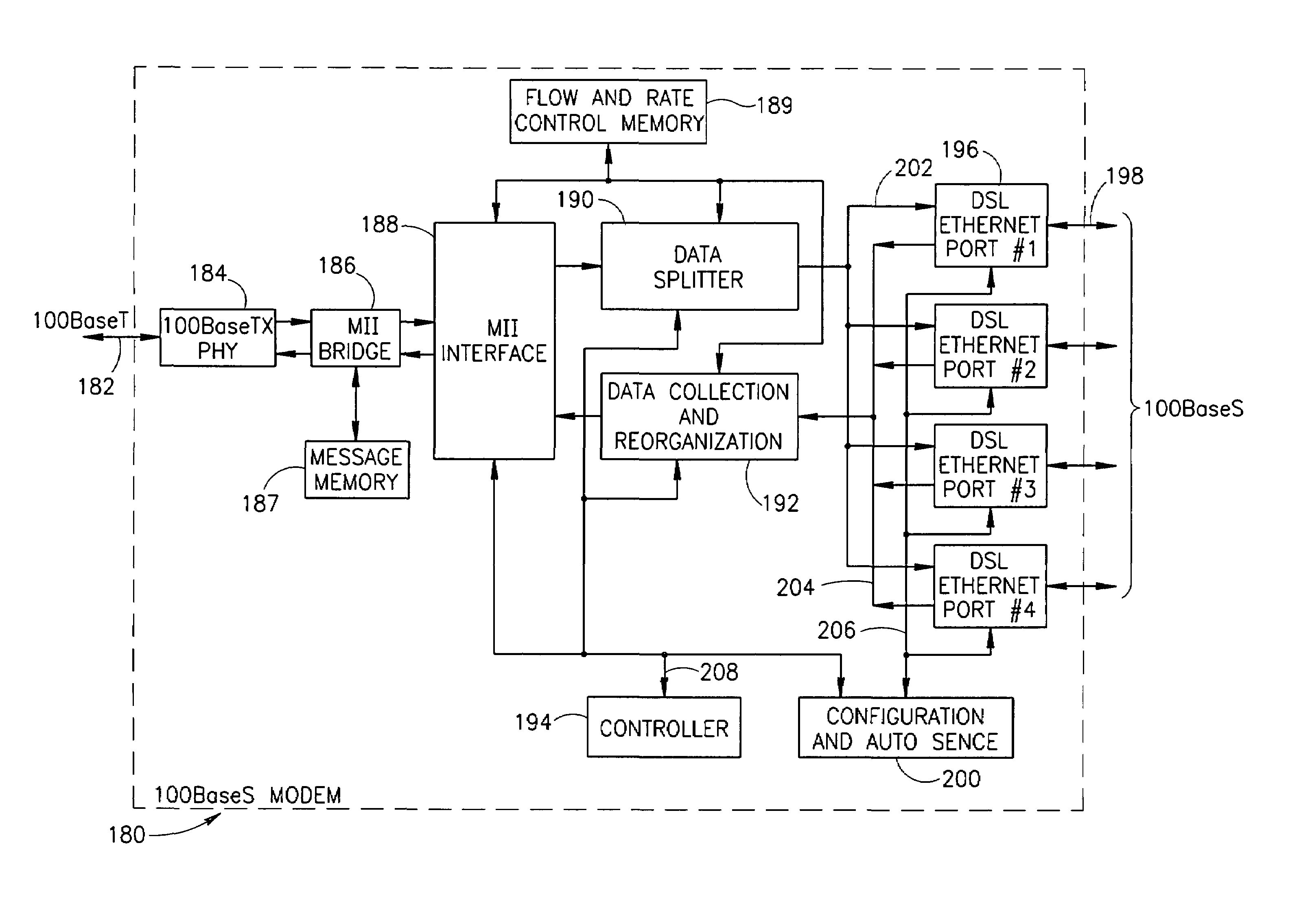
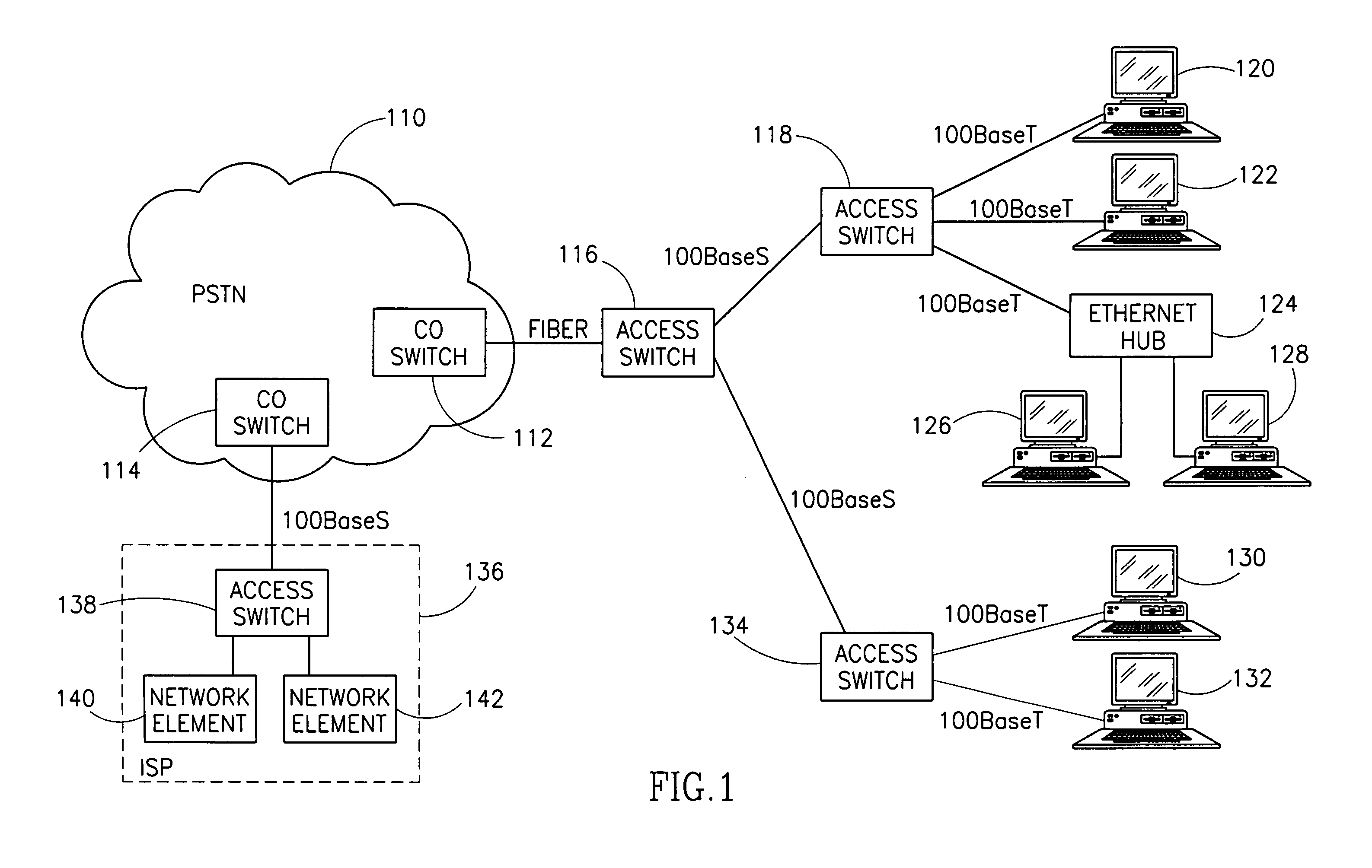
High data rate ethernet transport facility over digital subscriber lines
InactiveUS7054376B1Simple and cost-effectiveIncrease transfer speedMultiple-port networksError preventionTransport systemModem device
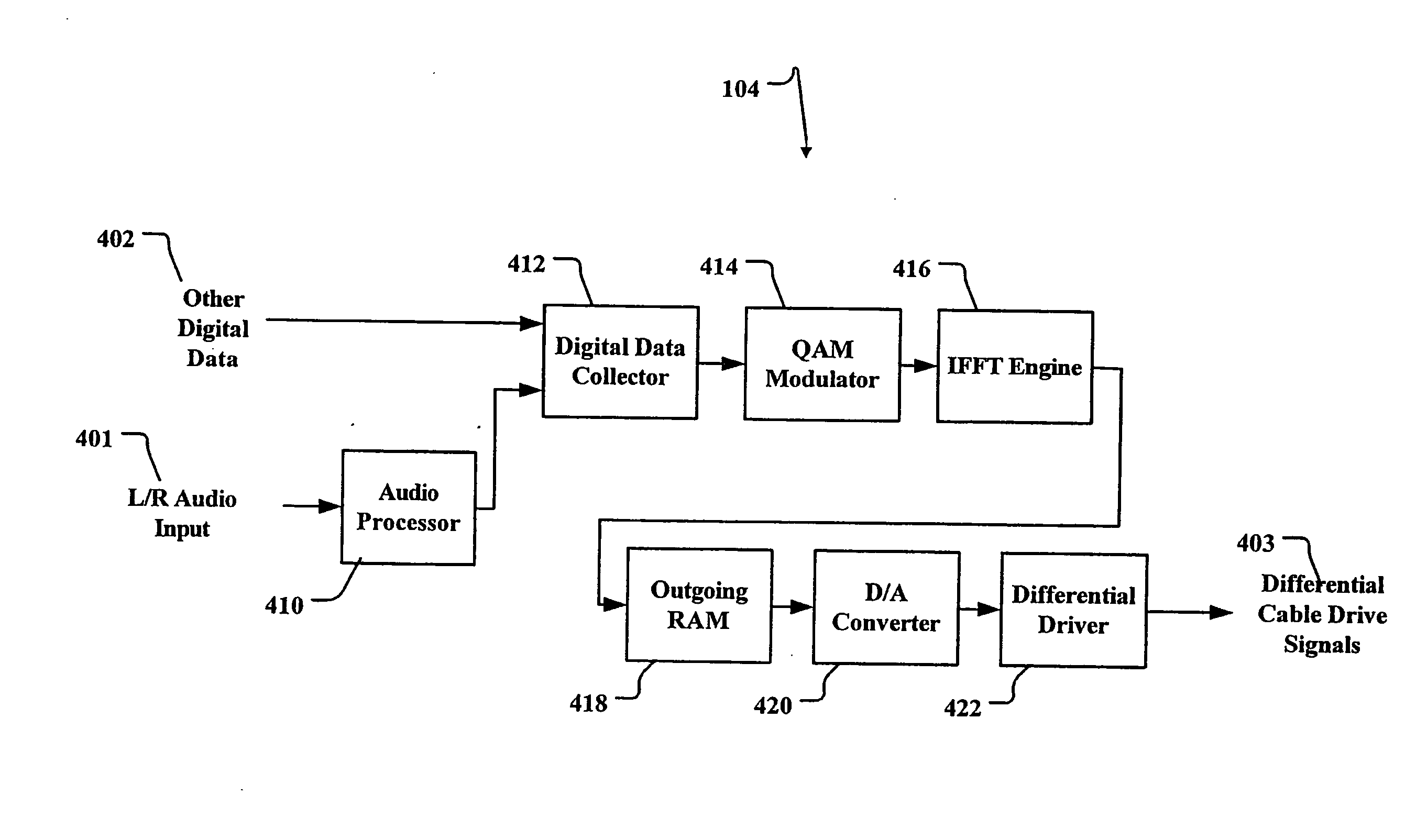
A facility transport system for transporting high speed Ethernet data over digital subscriber lines. The system, referred to as 100BaseS, is capable of transmitting 100 Mbps Ethernet over existing copper infrastructure up to distances of approximately 400 meters. The system achieves bit rates from 25 to 100 Mbps in increments of 25 Mbps with each 25 Mbps increment utilizing a separate copper wire pair. Each pair used provides a bidirectional 25 Mbps link with four copper wire pair connections providing 4×25 Mbps downstream channels and 4×25 Mbps upstream channels. The system utilizes framing circuitry to adapt the 100BaseT input data signal to up to four separate output signals. A DSL Ethernet Port card couples the modem to each twisted pair used. Each DSL Ethernet Port card comprises modem transmitter and receiver circuitry for sending and receiving 100BaseS signals onto twisted pair wires. The system utilizes QAM in combination with frequency division multiplexing (FDM) to separate downstream channels from upstream channels and to separate both the downstream and the upstream channels from POTS and ISDN signals.
Owner:LANTIQ BET GMBH & CO KG
Wiring and composite wiring
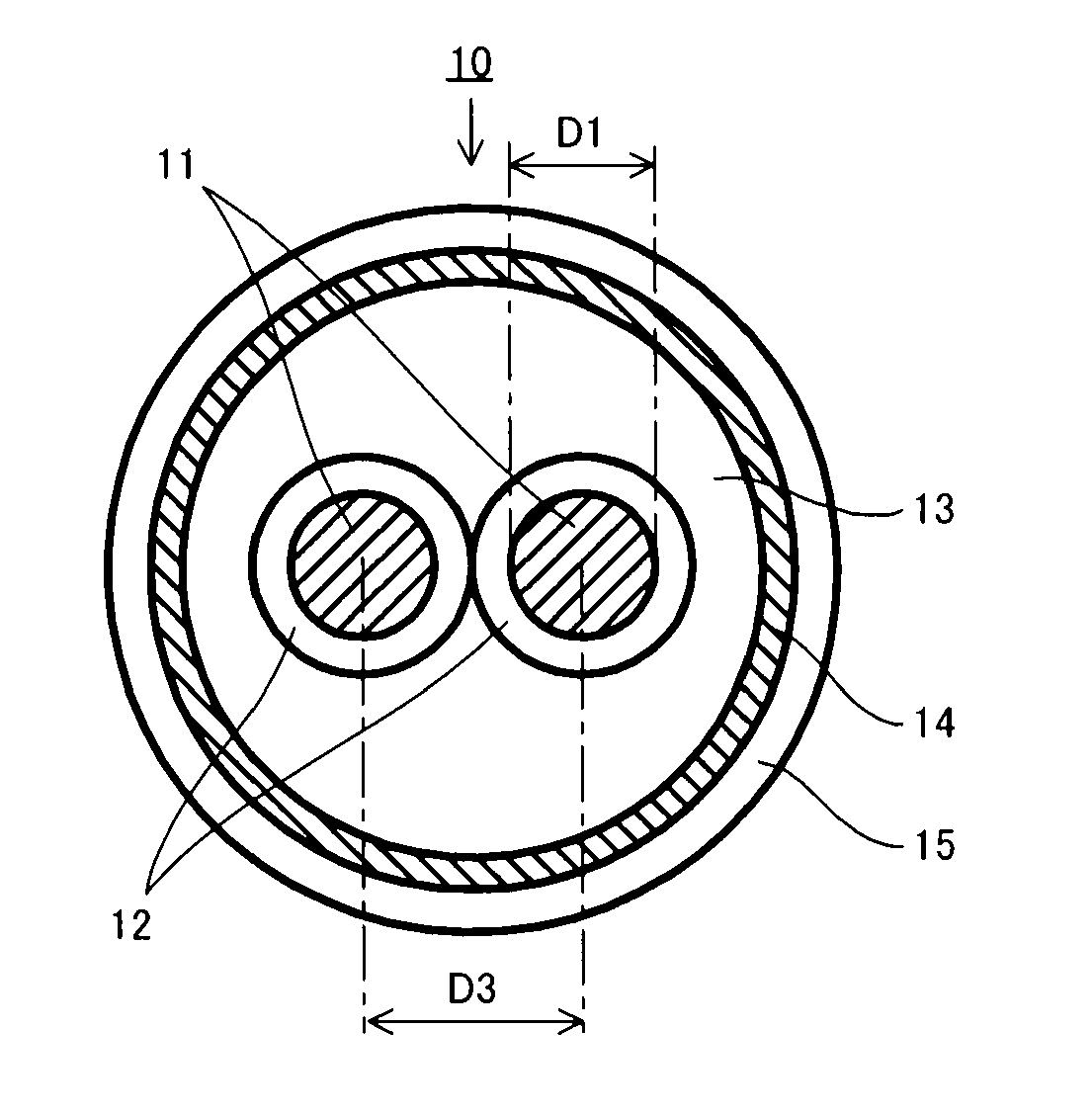
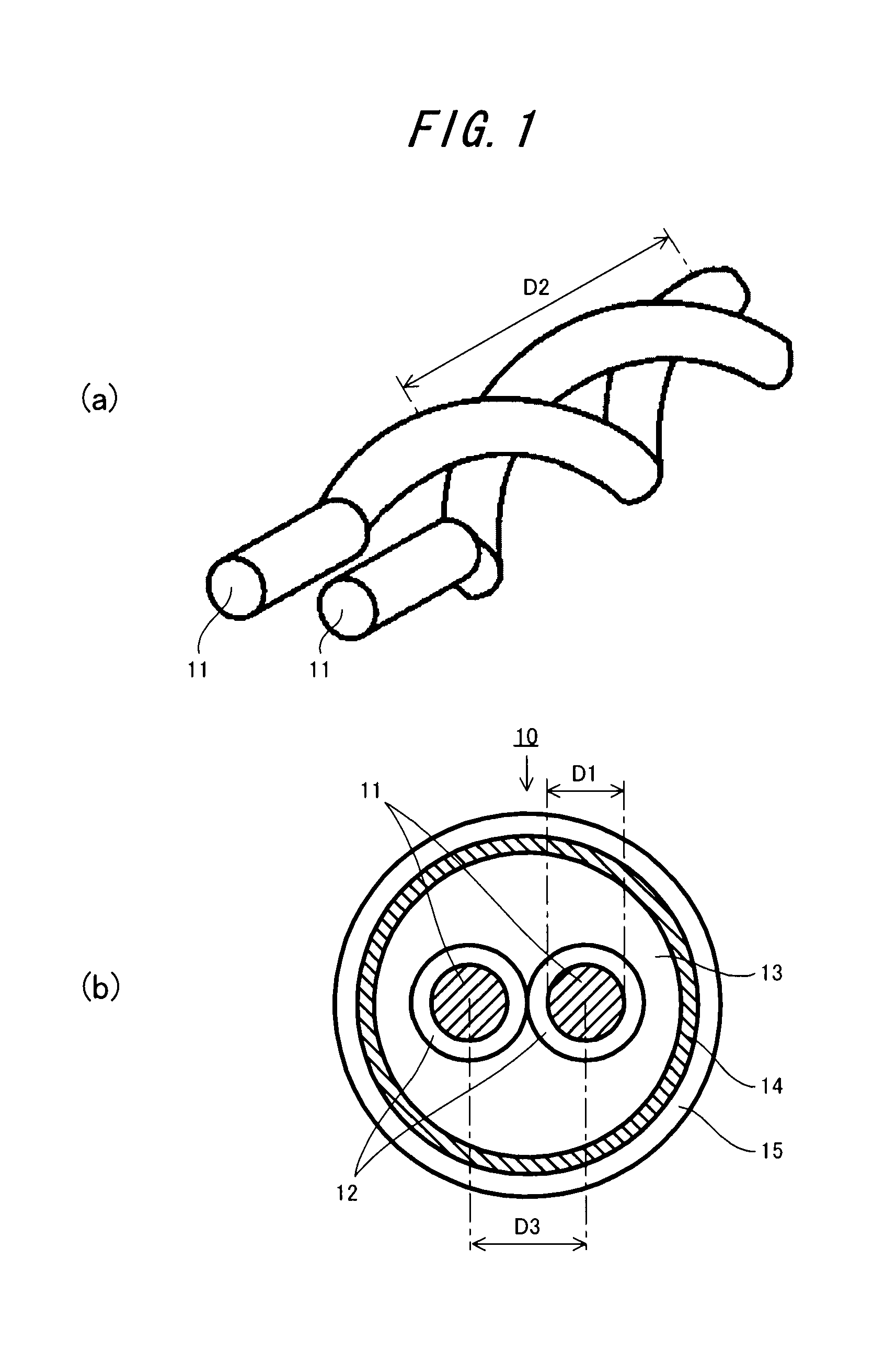
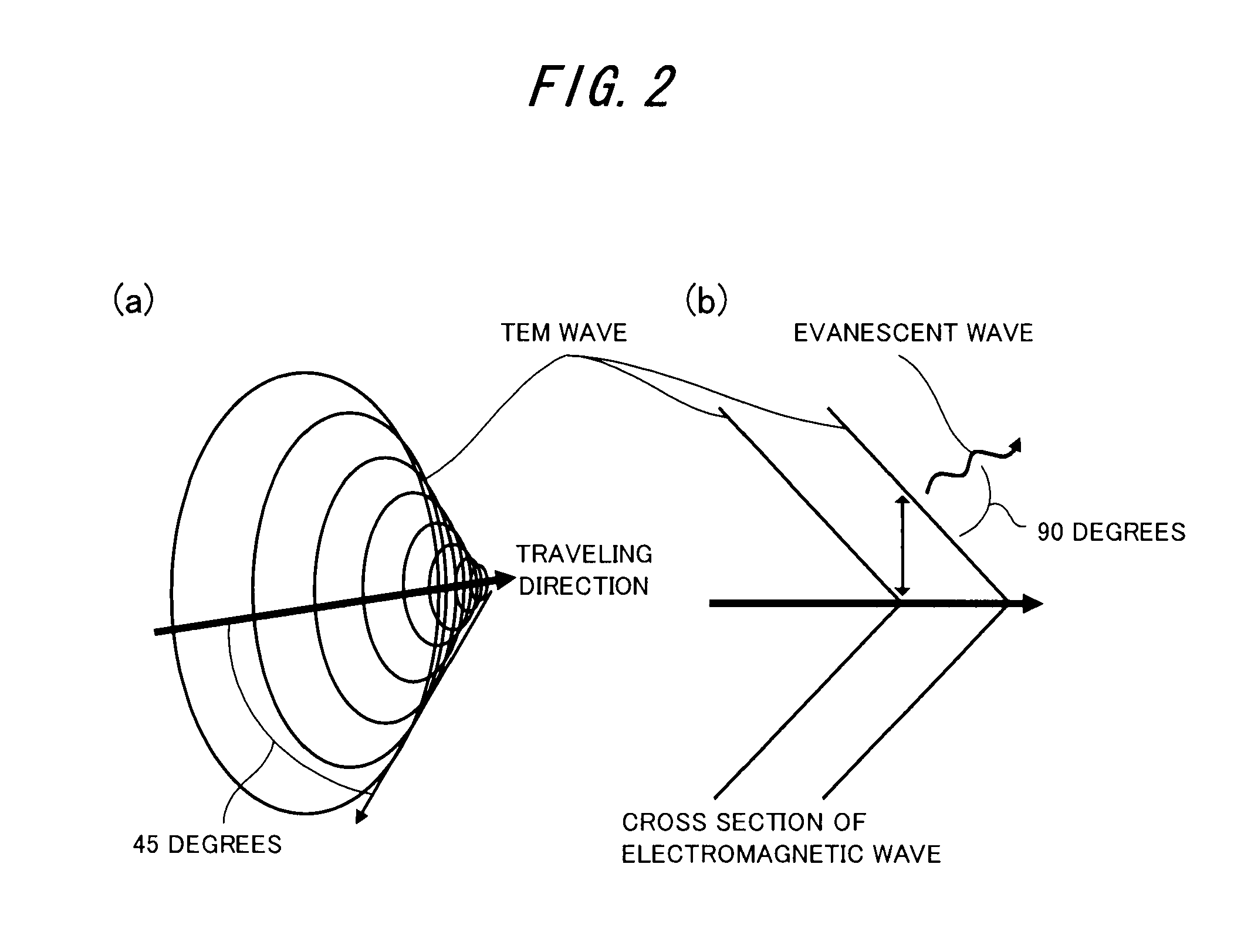
A wire (a twisted pair cable) that transmits a gigahertz band signal and that is provided with a pair of core wires that are twisted with each other, a first insulation coating material, a second insulation coating material, and a shield material that shields evanescent waves emitted from the pair of core wires. The pair of core wires have a twisting pitch, a diameter, and a spacing so that the wire has a characteristic impedance of 100 to 200Ω and the phases of the TEM (Transverse Electro-Magnetic) wave and the evanescent wave that are emitted from the pair of core wires are matched.
Owner:IBIDEN CO LTD +4
IP telephony transport
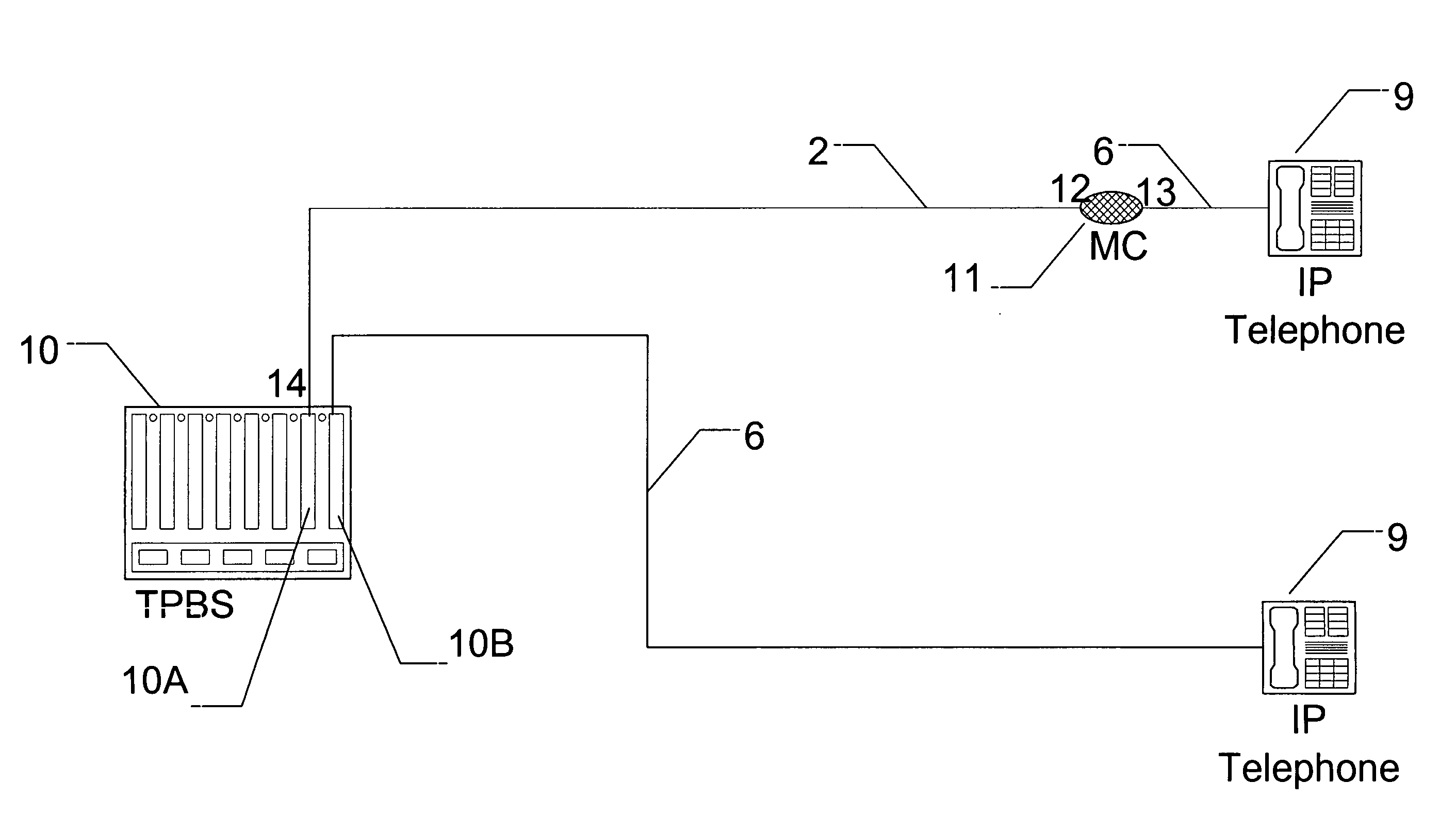
InactiveUS7408923B1Increase supplyEliminate needDigital data processing detailsData switching by path configurationElectric power transmissionEngineering
A system for simultaneously transporting internet protocol voice traffic and power to an internet protocol telephony transport using the existing twisted pair infrastructure of a traditional phone system. The system includes a twisted pair broadband switch. The twisted pair broadband switch connects on one end to an internet protocol telephone voice switch using Ethernet wiring and connects on another end to a media converter using a twisted pair wiring on the existing twisted pair infrastructure. The media converter condition the voice traffic between a twisted pair interface and an Ethernet interface to allow connection to an internet protocol telephone. Power is simultaneously transported with the voice traffic over the same twisted pair wiring of the existing twisted pair infrastructure.
Owner:KHAN MEHTAB +1
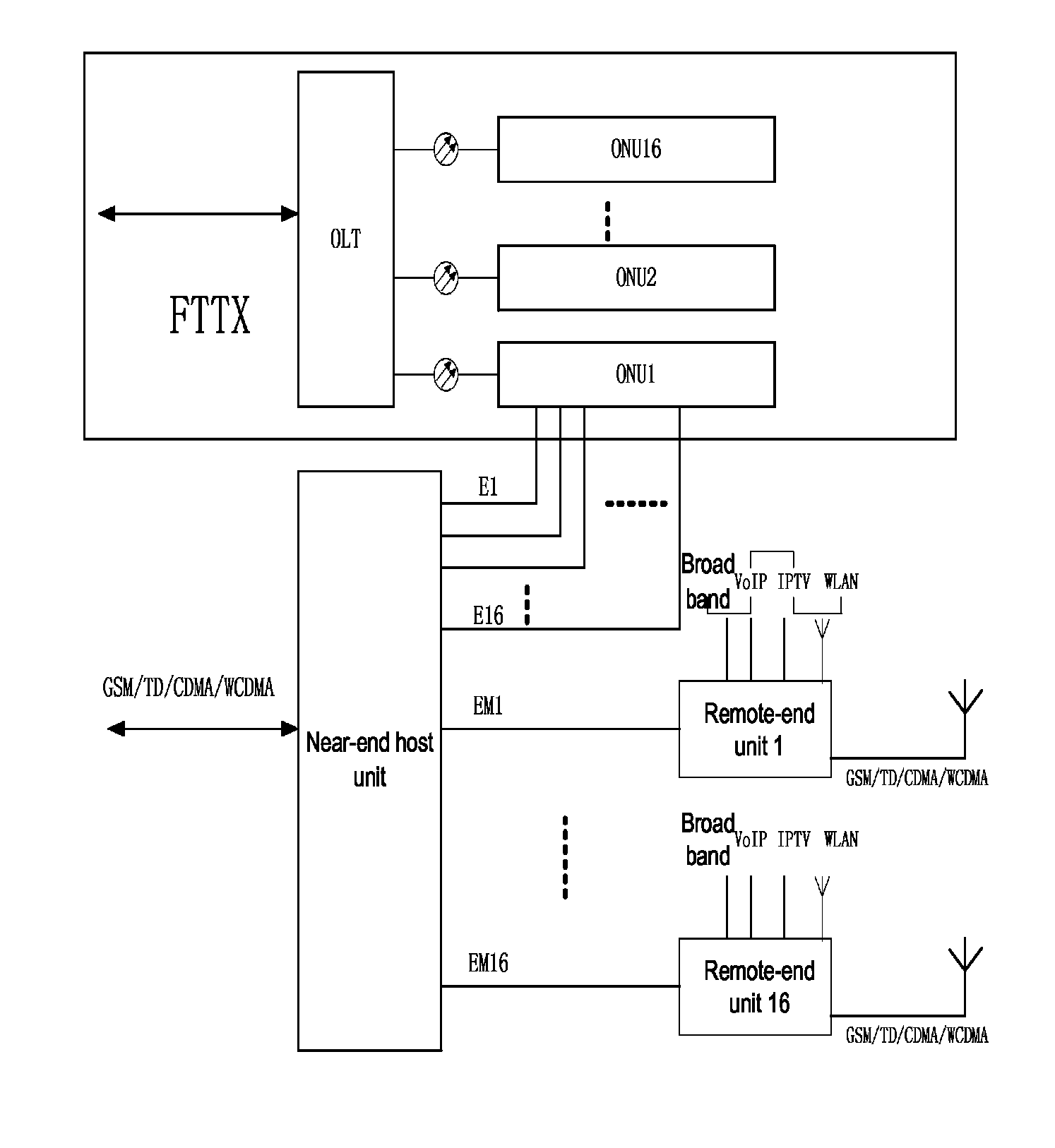
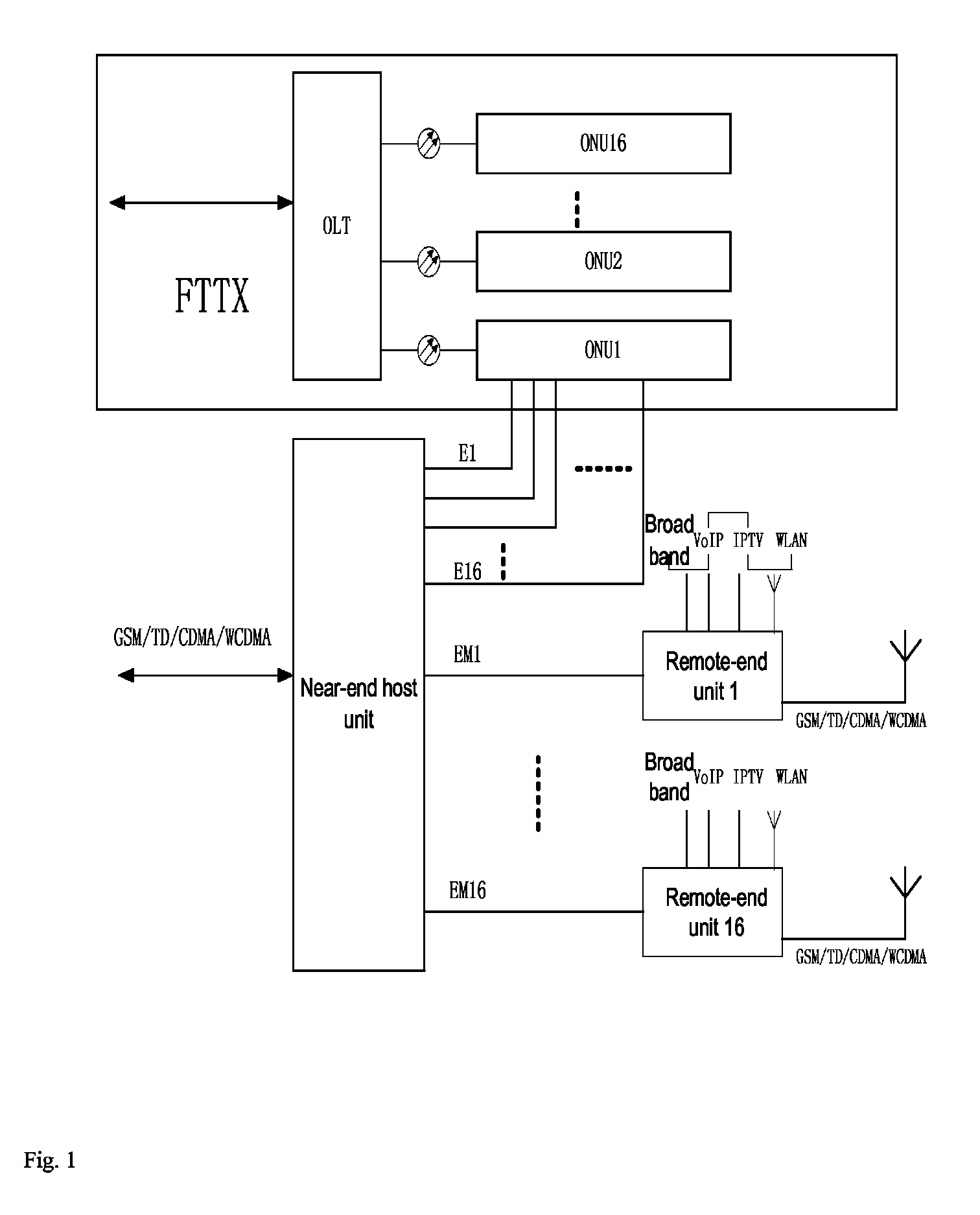
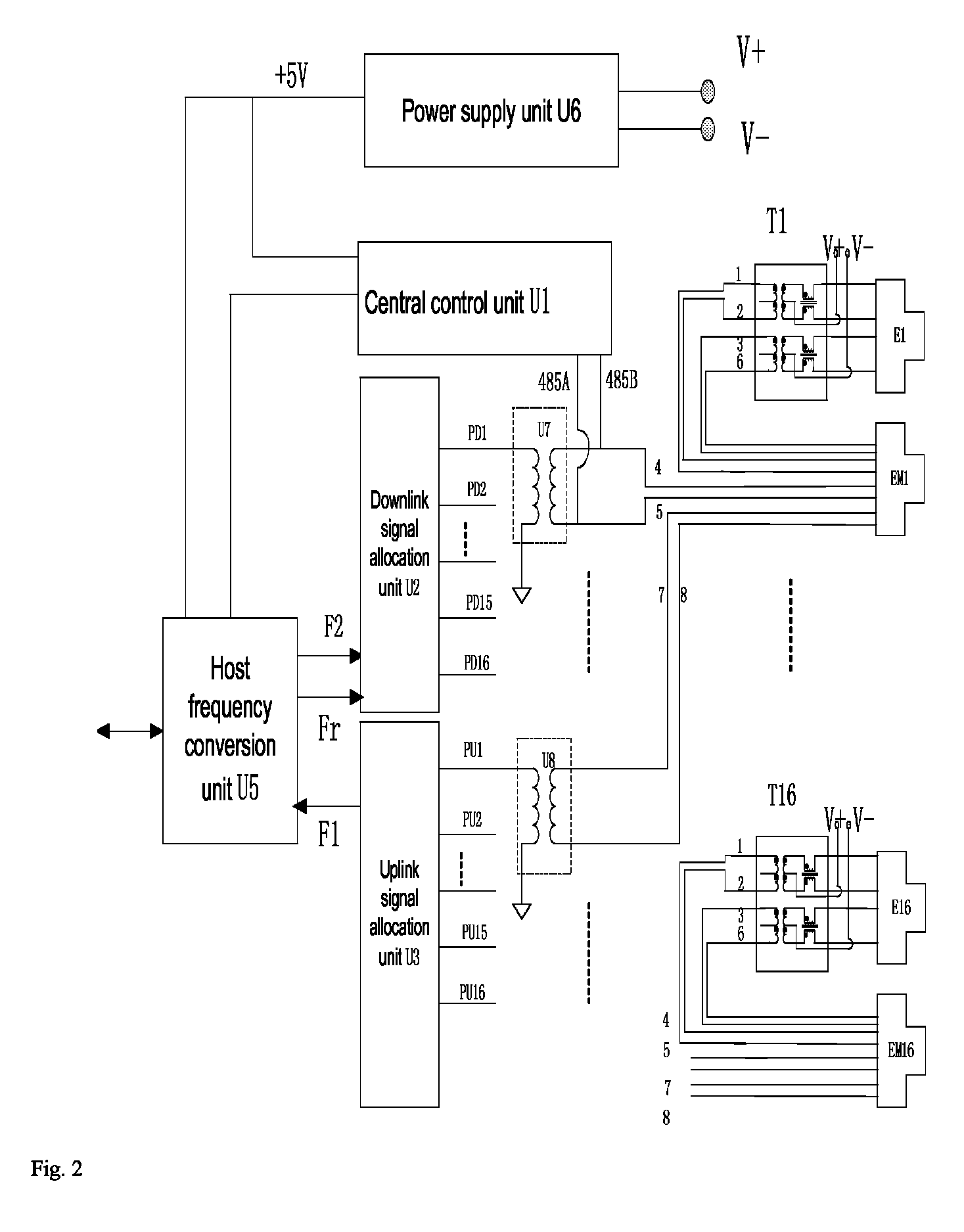
Access system and method for transmitting Ethernet signal and mobile communication signal
An access system and method for transmitting Ethernet signals and mobile communication signals. The system includes a near-end host unit and remote-end user units. Through the near-end host unit, the Ethernet signals and mobile communication signals can be combined. The near-end and remote-end host units are connected through four pairs of twisted pairs. The combined Ethernet and mobile communication signals are sent to a user terminal for providing broadband access service and wireless access service. Premises network resources can be used without re-laying category 5 cables, so the investment is less and it is quick and convenient to provide service. Furthermore there needs to be added only one host unit beside the optical network unit equipment, and replace the user terminal simultaneously. Power is not needed to be taken at the user's home. The placement position of the terminal is flexible without being limited by the power-taking positions.
Owner:CICT MOBILE COMM TECH CO LTD
Method and Apparatus for Providing Wireless Communications Within a Building
ActiveUS20100080203A1Avoid pollutionSubstation equipmentRadio transmissionPatch panelStructured cabling
A wireless distribution secured cabling system includes faceplates, each of which contains an antenna or other radiating element and an active amplifier, which serves as a bi-directional repeater for the wireless communication system. The system further includes a patch panel or distribution module which connects multiple cables, which may be either twisted pair or coaxial, to amplifier, acting as a power divider and / or an impedance matching device. An antenna, which may be mounted either outside of a building structure or inside the building structure, provides communications between the structured cabling system and a service provider base station.
Owner:OPTICAL CABLE CORPORATION
Method for providing high-speed data service and voice service
InactiveUS6970502B2Increase speedInterconnection arrangementsFrequency-division multiplexDigital subscriber lineTransport system
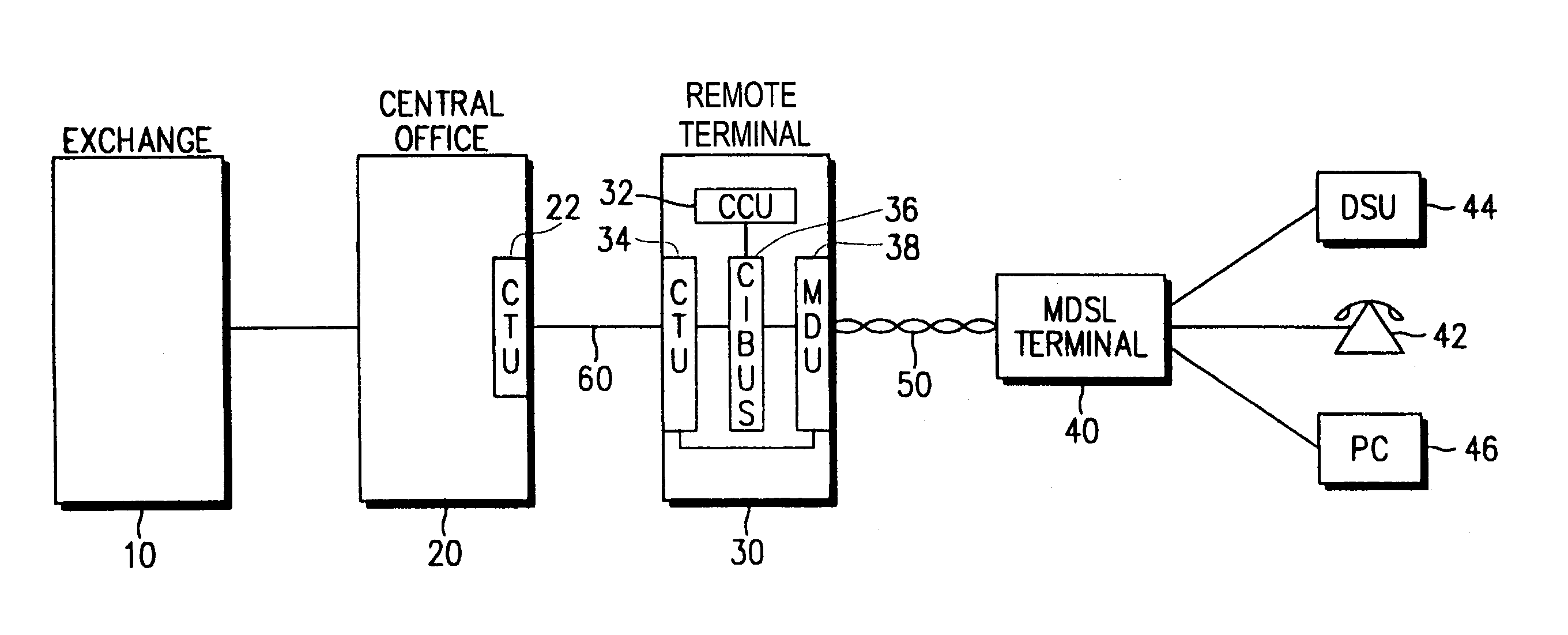
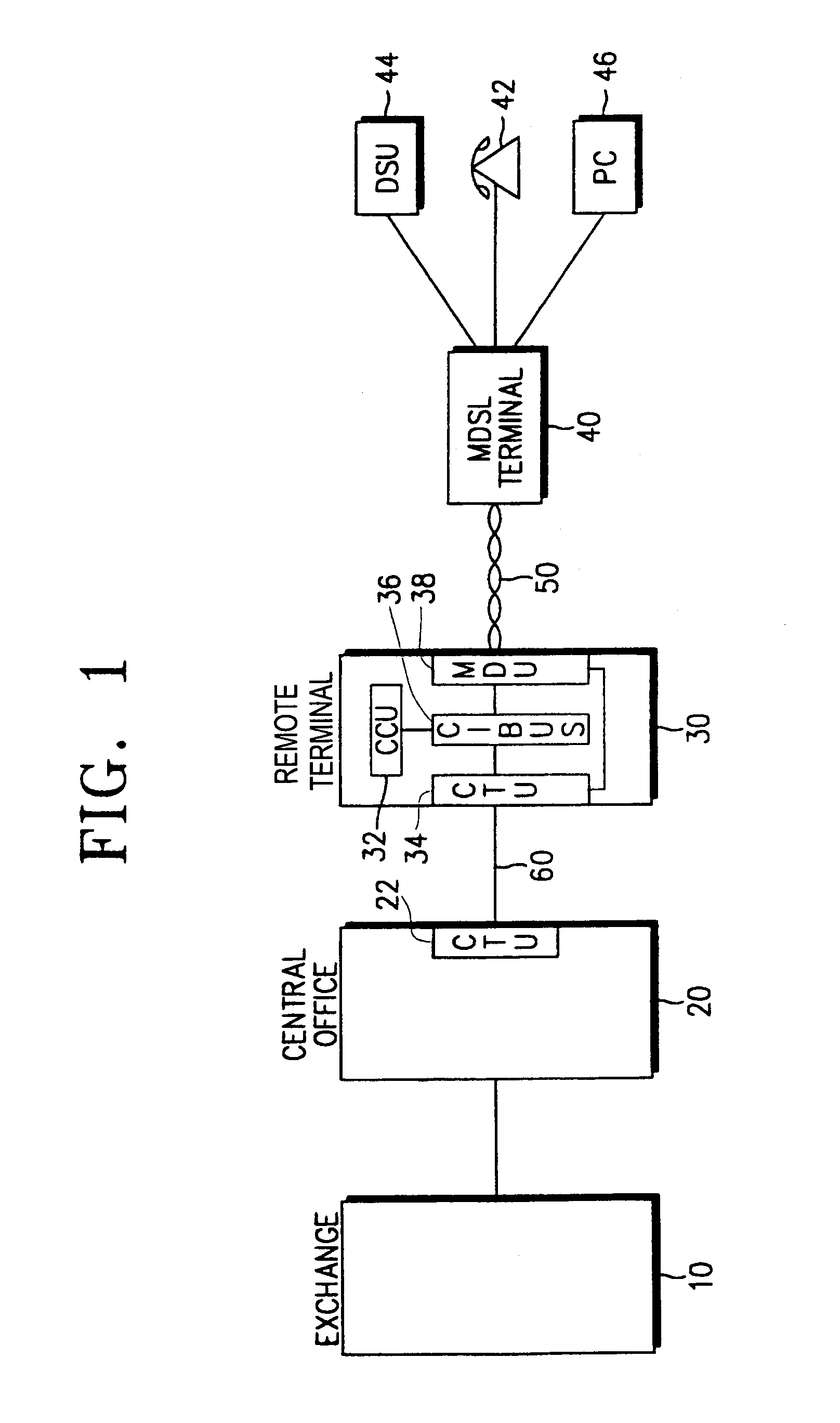
Providing a high-speed data service and voice service in a transmission system employing two binary, one quarternary (2B1Q) modulation / demodulation, using a high-speed data service remote terminal, a plurality of user data service and voice service terminals, and a multi-rate digital subscriber line (MDSL) terminal connected to the remote terminal through a twisted pair line, and to the user terminals. During downstream voice service, the remote terminal assembles and transmits an high bit rate digital subscriber line (HDSL) frame by including signaling signals for the voice service and signal processing mode information in a user-defined interval of the high bit rate digital subscriber line frame, to the multi-rate digital subscriber line terminal through the twisted pair line. During upstream voice service, the remote terminal receives the high bit rate digital subscriber line frame and transmits the signaling signals received to an exchange.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
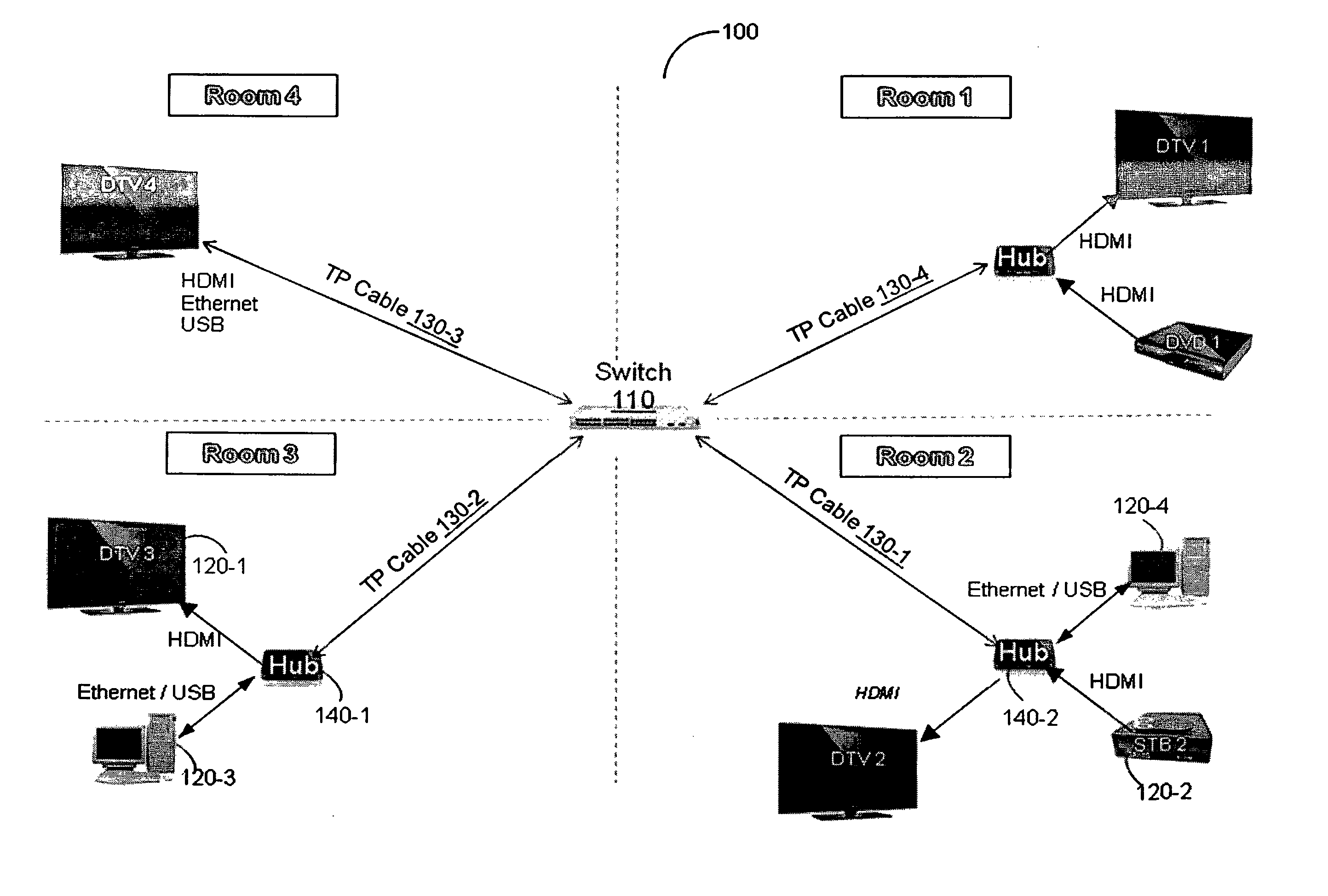
Home network architecture for delivering high-speed data services
InactiveUS9137485B2Closed circuit television systemsElectrical cable transmission adaptationNetwork architectureIBM Systems Network Architecture
A home multimedia network comprises a plurality of source nodes, wherein each of the source nodes includes an apparatus for concurrently transmitting and receiving high-speed data services; a plurality of sink nodes, wherein each of the sink nodes includes the apparatus for concurrently transmitting and receiving high-speed data services; a switch for connecting a first group of the plurality of source nodes located at one room to one or more sink nodes located at a different room than the first group of source nodes, the first group of source nodes and the one or more sink nodes are connected to the switch through a twisted-pair cable, the high-speed data services are concurrently transported over the twisted-pair cable, wherein the high-speed data services include at least uncompressed multimedia data, Ethernet data, and Universal Serial Bus data.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
Method of adding a device to a network
InactiveUS20060009861A1Low-cost implementationComputer controlSimulator controlLonWorksHome environment
A method of adding a device to an existing or new electrical or electronic automation or multimedia network. The invention facilitates adding a device to the network that can communicate using various protocols such as LonWorks, CEBus, X-10, etc. over media such as AC power line, IR, RF, twisted pair, optical fiber, etc. The method is a mechanism for adding a device to a system that can be used by an ordinary user of network capable electrical devices. The method comprises the steps an installer would perform including the handshaking that needs to occur between devices to accomplish the binding process. A Functional Profile for LonWorks networks is given as an example. This includes a Home Device profile that employs an automated explicit type messaging for all devices intended for use in a home environment. The invention includes adding to the device an install button and a visual indicator for status such as an LED. Alternatively, existing buttons and LEDs on the device may be used for installed and binding purposes. Other methods of binding can be employed by the use of wired or wireless handheld tools, remote controls, etc. Other interfaces and user feedback can be used such as touch screen, personal computers, cellular phones, PDAs, etc which can offer simple ‘virtual’ binding by the press of an icon versus the physical button on the device. The binding can be performed locally or remotely such as via LAN, WAN, Internet, etc.
Owner:LEVITON MFG
Discontinued cable shield system and method
ActiveUS20070037419A1Coupling protective earth/shielding arrangementsConnection contact member materialDifferential transmissionTwisted pair
Implementations of a discontinuous cable shield system and method include a shield having a multitude of separated shield segments dispersed along a length of a cable to reduce crosstalk between signals being transmitted on transmission lines, such as twisted wire pairs of a cable. The separated shield segments can serve as an incomplete, patch-worked, discontinuous, ‘granulated’ or otherwise perforated shield that can have effectiveness when applied as shielding for differential transmission lines such as with twisted wire pairs.
Owner:LEVITON MFG
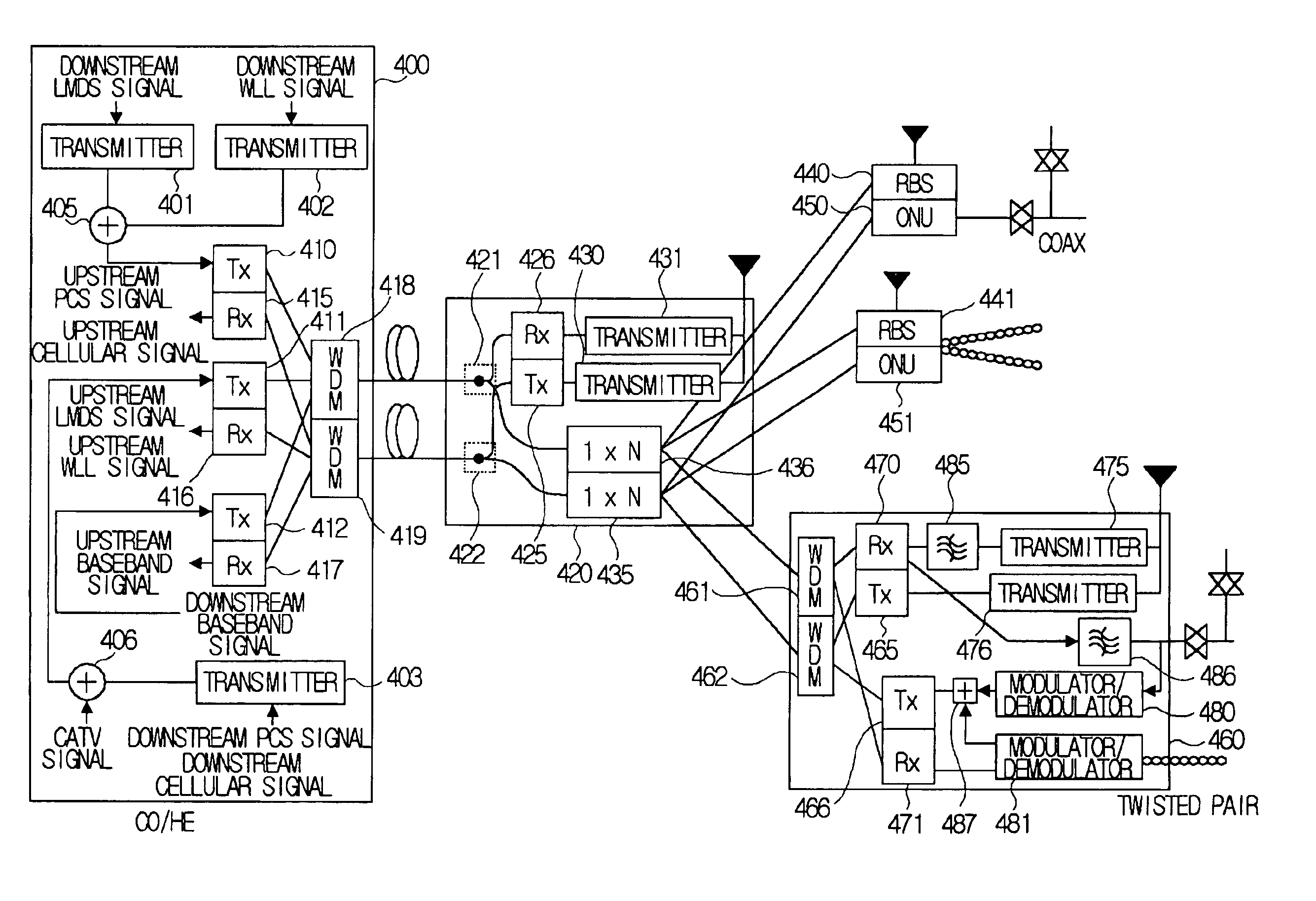
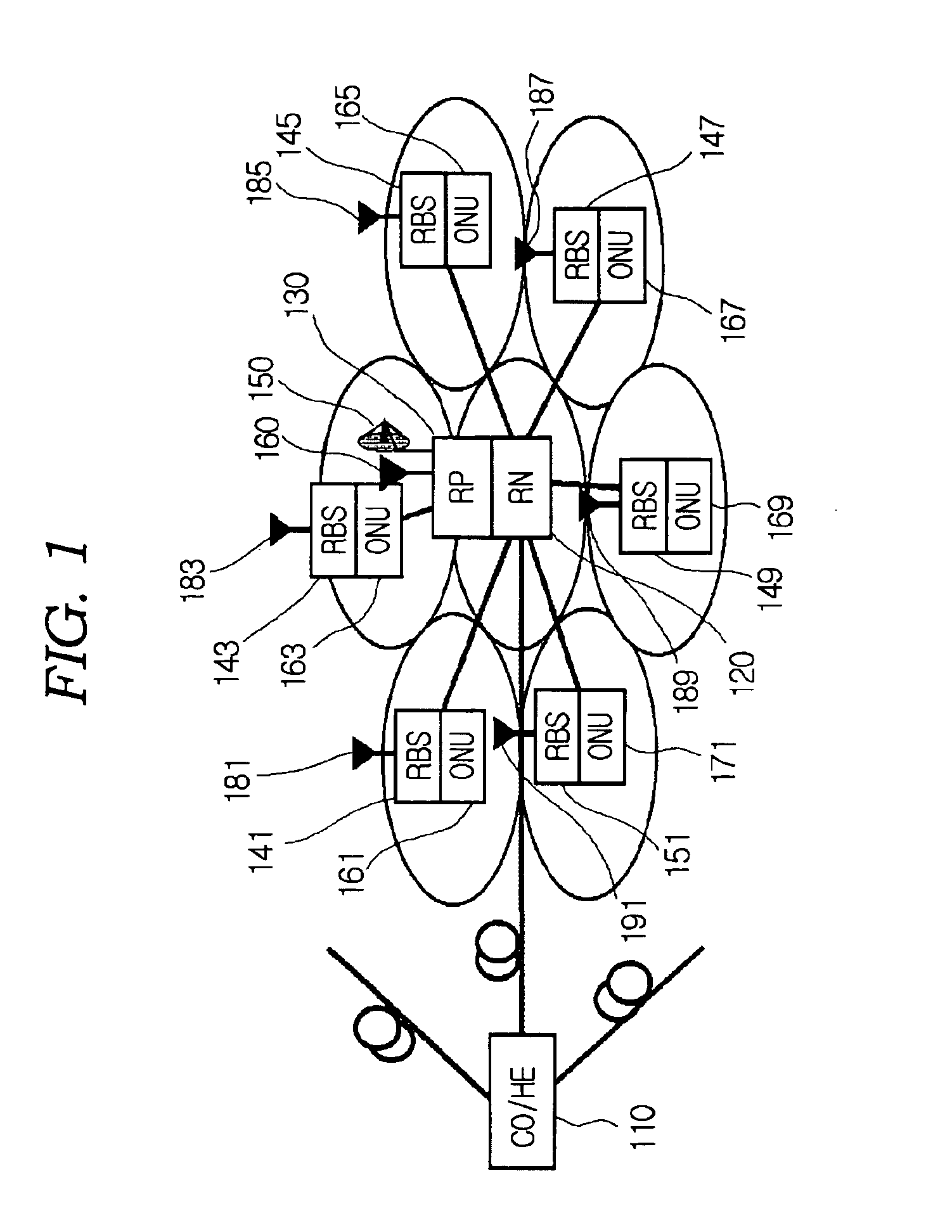
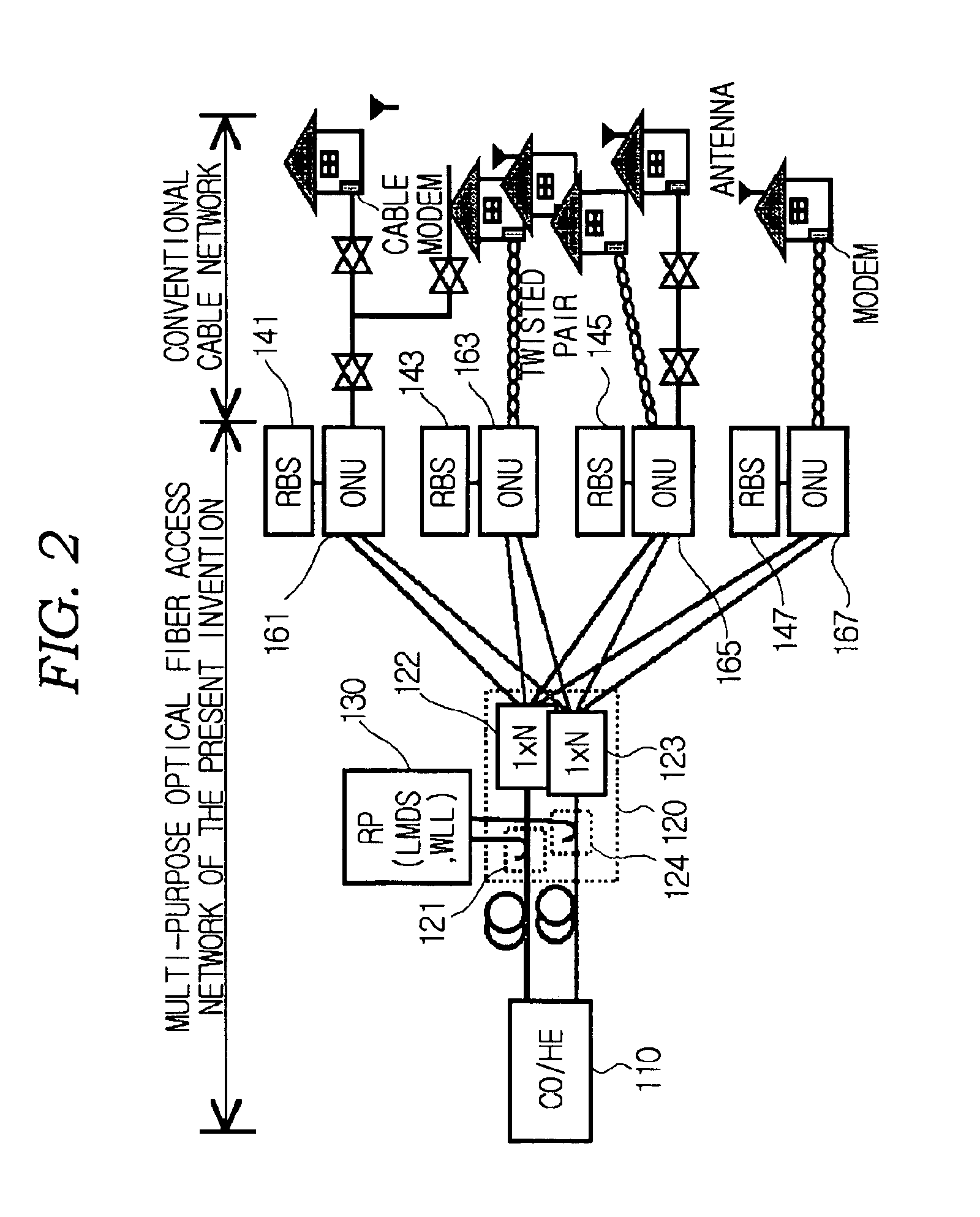
Multi-purpose optical fiber access network
InactiveUS6895185B1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsWireless communicationAccess networkCoaxial cable
The present invention relates to an optical fiber access network, and more particularly, to a multi-purpose optical fiber access network capable of accepting all services provided by hybrid wireline / wireless access network.According to the present invention, in an optical fiber access network of double star structure where a central office / headend and several optical network units are connected through a splitting / combining device, a multi-purpose optical fiber access network capable of accepting not only wired telephone service, wired CATV and wired data service but also various kinds of wireless services including LMDS, WLL, PCS and so forth, in which LMDS local wireless base station is located in a place adjacent to the splitting / combining device, WLL local wireless base station is located in a place adjacent to the splitting / combining device, optical network unit connects the conventional wired network composed of said optical fiber access network, twisted pair and coaxial cable, telephone service, data service and CATV service are provided through the optical network unit and PCS local wireless base station is located in a place adjacent to the optical network unit, is provided.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
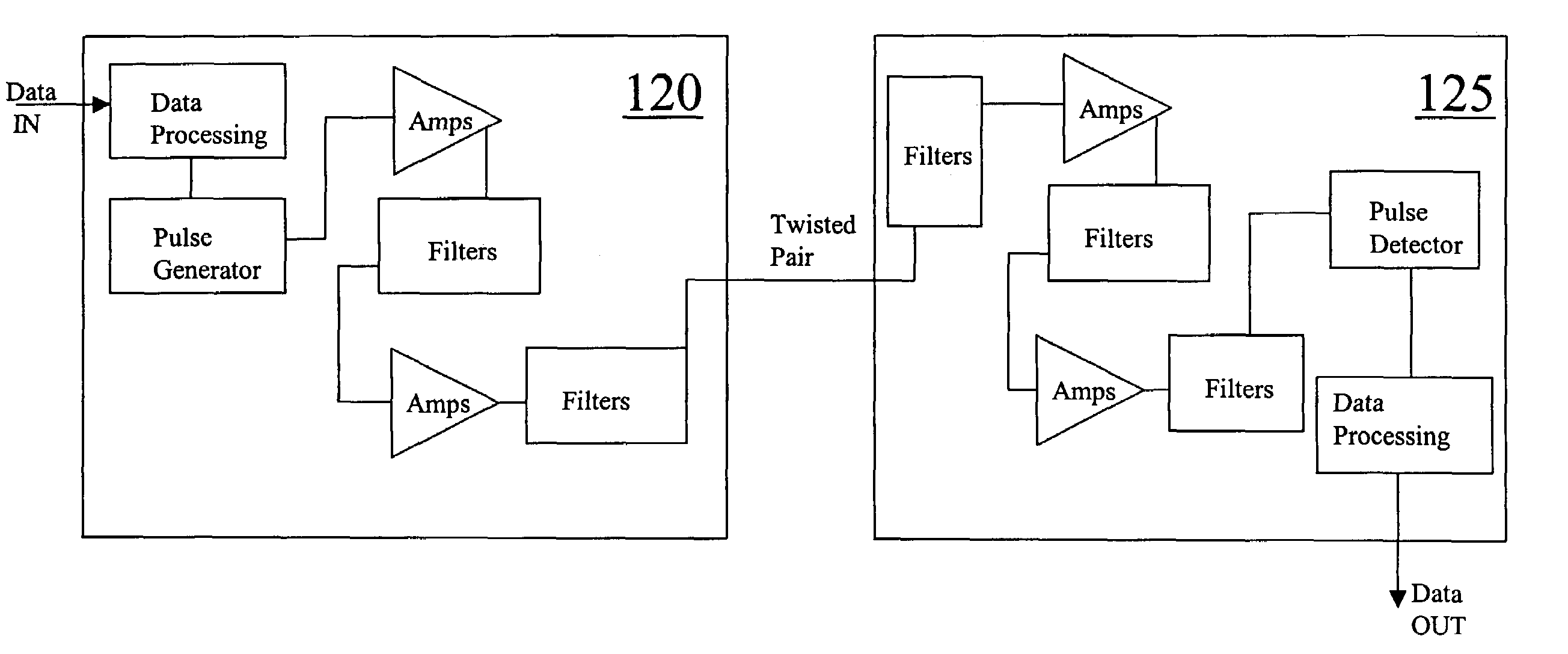
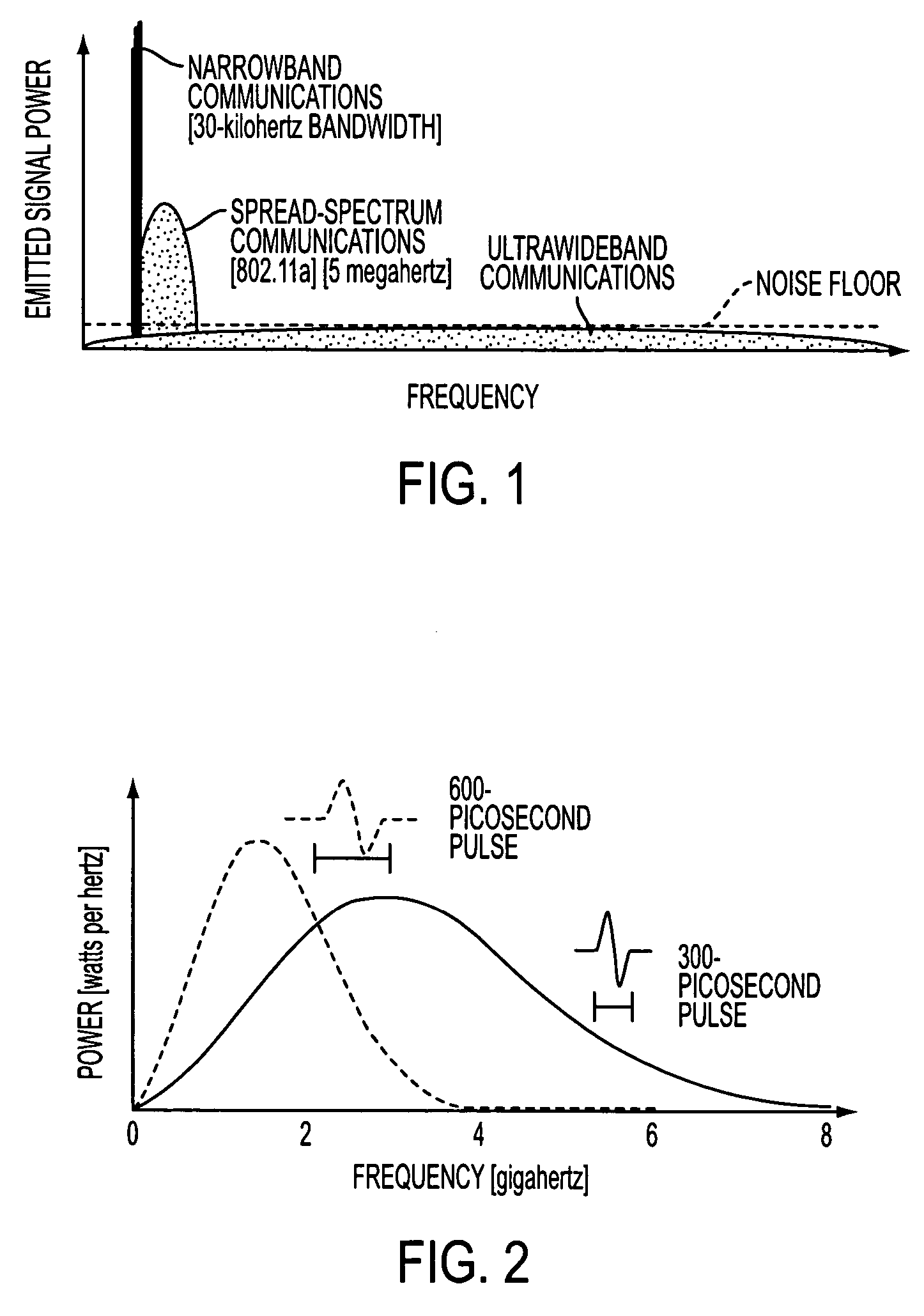
Ultra-wideband communication through twisted-pair wire media
InactiveUS7167525B2Transmission/receiving by adding signal to waveBroadband local area networksUltra-widebandBroadband pulse
Methods and apparatus that transmit ultra-wideband pulses through twisted-pair wire media are provided. One method includes transmitting an ultra-wideband pulse through the twisted-pair wire media at dissimilar time periods. Another method includes transmitting an ultra-wideband pulse through the twisted-pair wire media at dissimilar radio frequencies. Yet another method includes transmitting an ultra-wideband pulse through the twisted-pair wire media at dissimilar time periods and at dissimilar radio frequencies. This Abstract is provided for the sole purpose of complying with the Abstract requirement rules that allow a reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the disclosure contained herein. This Abstract is submitted with the explicit understanding that it will not be used to interpret or to limit the scope or the meaning of the claims.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES HLDG 73
Communications gateway and method of using the same
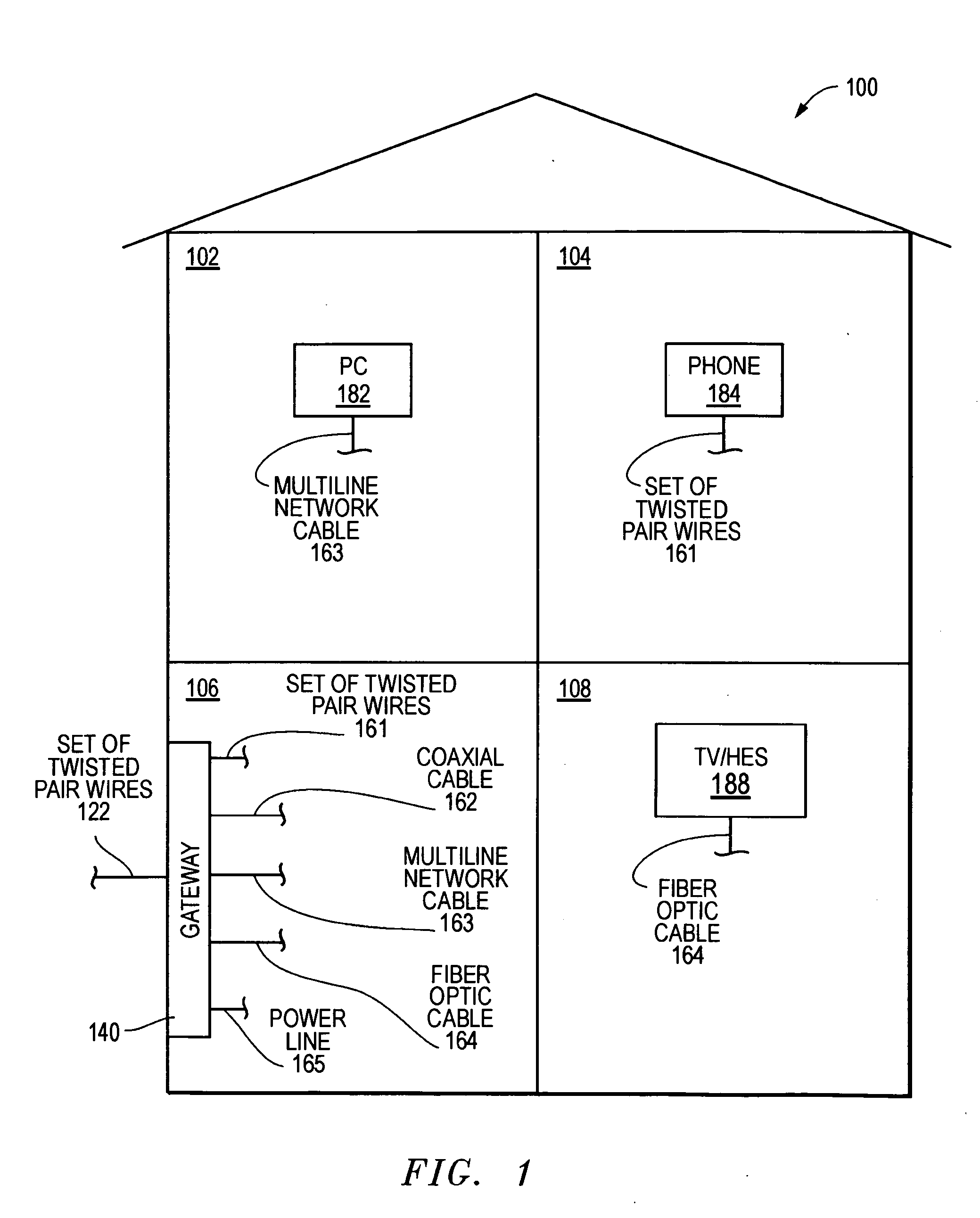
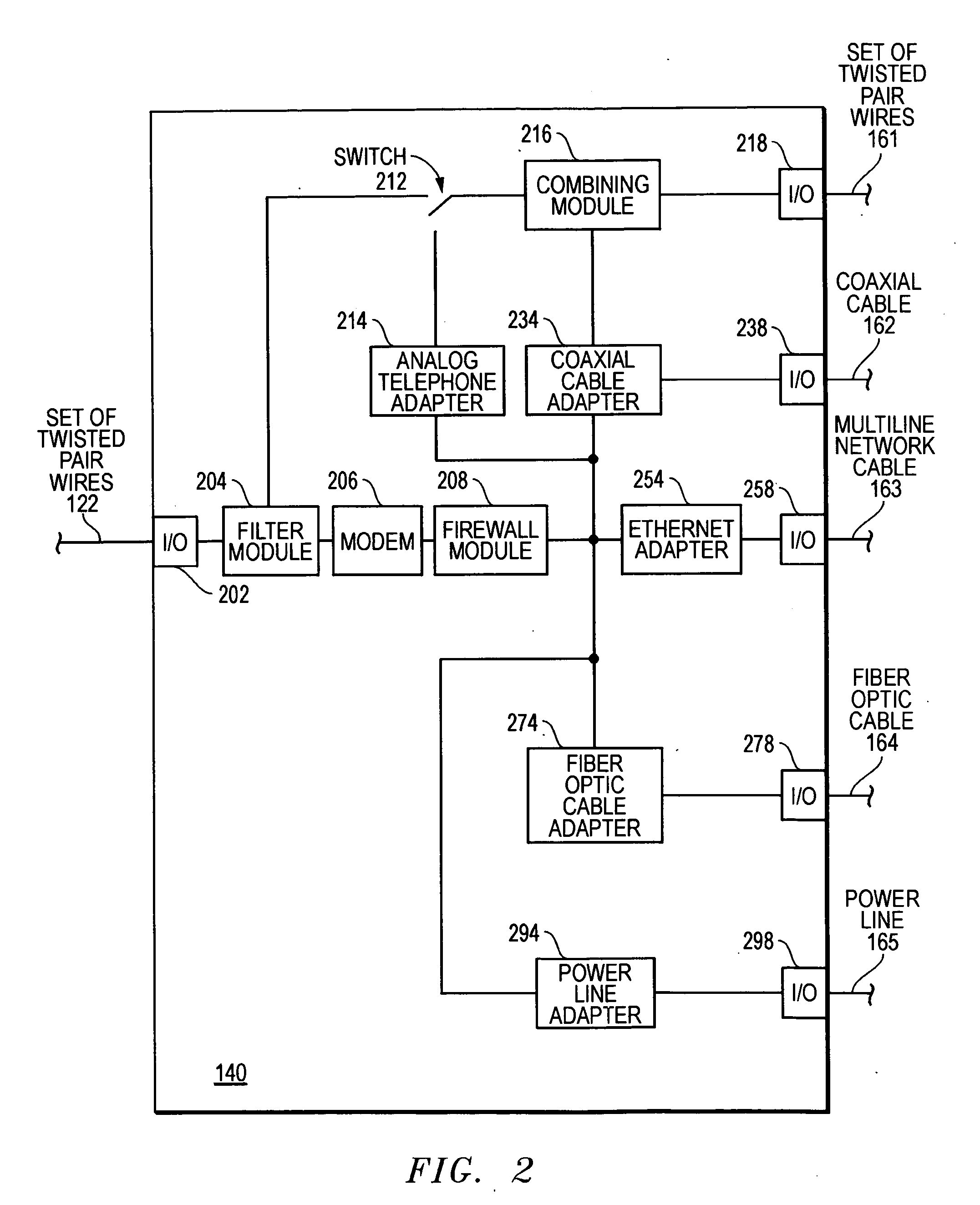
A communications gateway can be used to provide communications services from a communications service provide to electronic devices within a structure. Signals can be transmitted from the communications gateways to the electronic devices over a plurality of different types of wireline media. The communications gateway can allow communication services using a wireline medium (e.g., a set of twisted pair wires) to be transmitted within the structure by taking advantage of existing wireline media (e.g., CAT3 cable, coaxial cable, power lines, etc.).
Owner:SBC KNOWLEDGE VENTURES LP
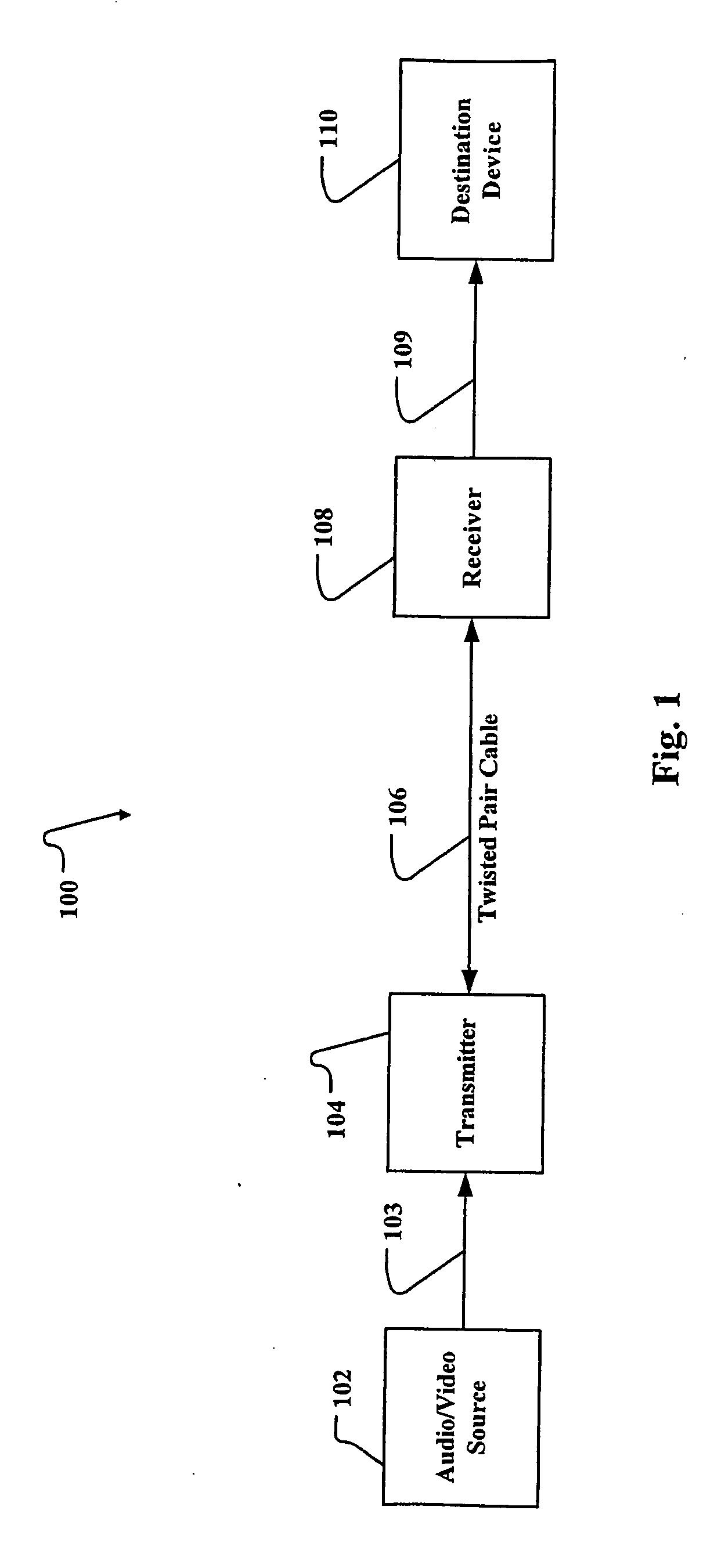
Method and apparatus for extending the transmission capability of twisted pair communication systems
InactiveUS20090059782A1Improve transmission performanceDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsCommunications systemClosed loop feedback
A closed loop feedback system is employed in a receiver to automatically compensate the communication signal from twisted pair cables for AC and DC losses. This is accomplished through the use of a reference pulse signal which is sent along with other digital information. At the receiver, the reference pulse signal is restored to its proper level through a Pulse Width Modulation (PWM)-controlled variable compensation amplifier circuit. The received reference signal is compared to a known reference value and the duty cycle of the PWM circuit is adjusted until the proper level reference signal is achieved. Thereafter, the digital signal is extracted. OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) with pilot tones are used to maximize payload while minimizing crosstalk effects. The pilot tones locate the OFDM symbols in time while supplying compensation information concerning the transmission medium.
Owner:RGB SYST INC
Active cable modem outside customer premises servicing multiple customer premises
InactiveUS7007296B2Affect numberAvoiding inefficiency of collisionTwo-way working systemsElectrical cable transmission adaptationDigital dataModem device
A signal distribution system to save on the cost of cable modems for cable TV headend operators who wish to deliver broadband digital data services, DSL, video-on-demand or POTS service over their HFC CATV delivery networks. All species within the genus have a shared cable modem and a filtration and combining circuit comprised of a plurality of diplexer filters or junction boxes or both which mix baseband packet data with analog CATV signals onto coax drop lines coupled to the various subscribers and connect POTS or DSL signals onto twisted pair portions of siamese cables. Various species have the cable modem feeding digital data or packets of DOCSIS or other data or digitized DSL signals sent over the HFC to the cable modem or digitized POTS signals send over the HFC to the cable modem to either a packet switch, a DSL concentrator, a voice-over-IP gateway or some combination of the above. This data is either delivered to each subscriber as LAN packets or analog POTS signals or DSL signals or some combination of the above using coaxial cable or siamese cable drop lines.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Communication cable
InactiveUS6300573B1Reduce the differenceIncrease spacingInsulated cablesPower cablesPolyolefinProximal point
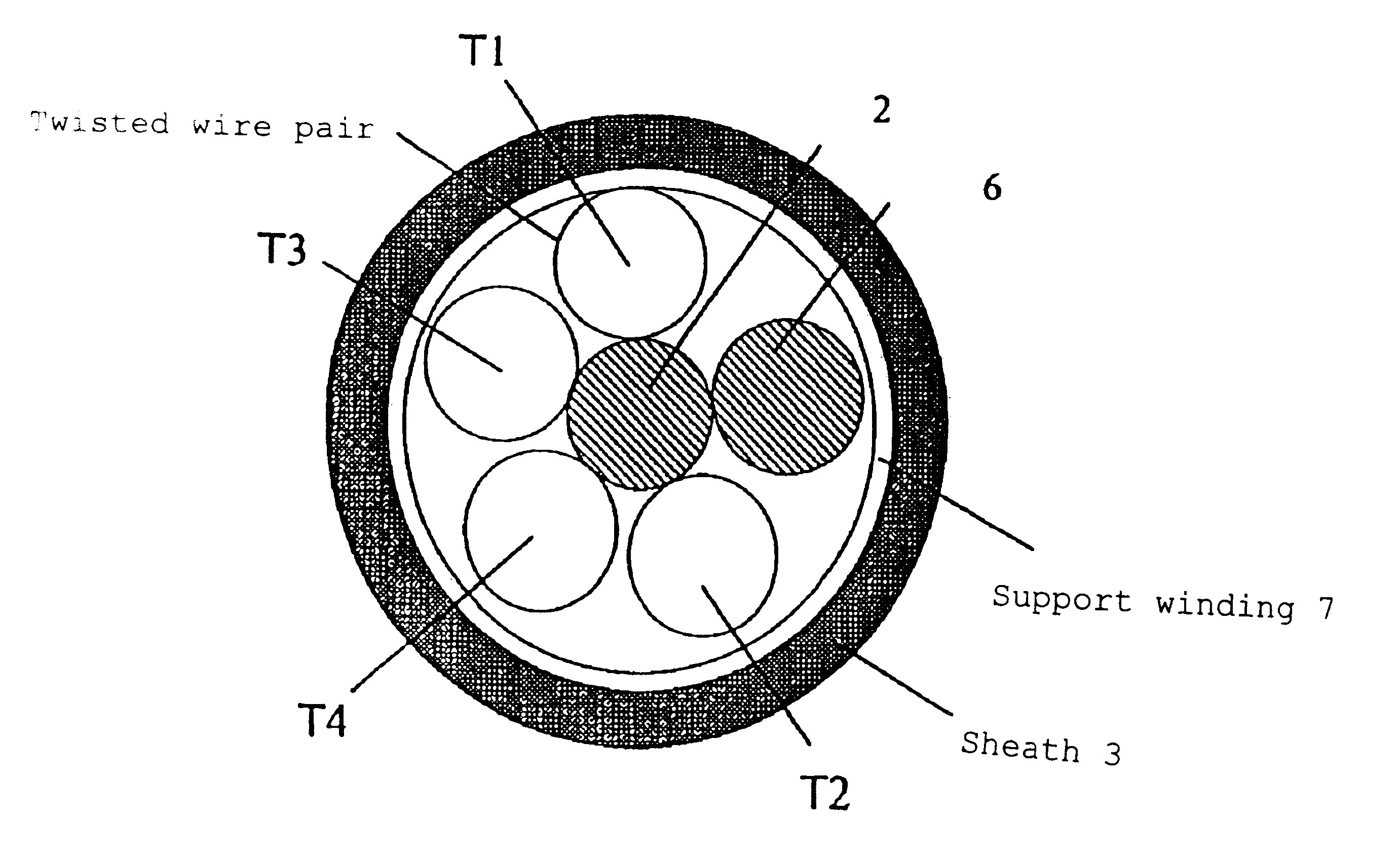
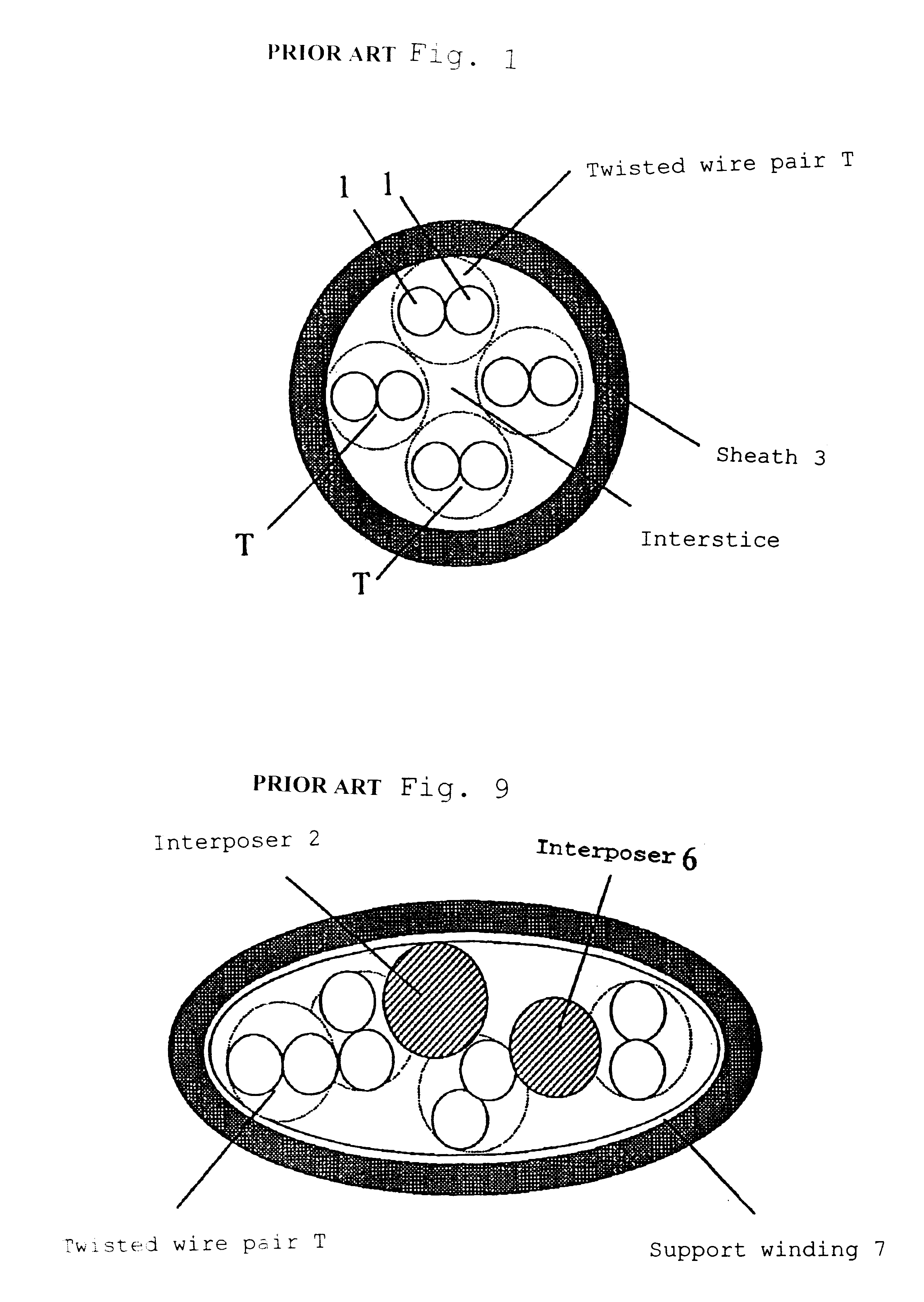
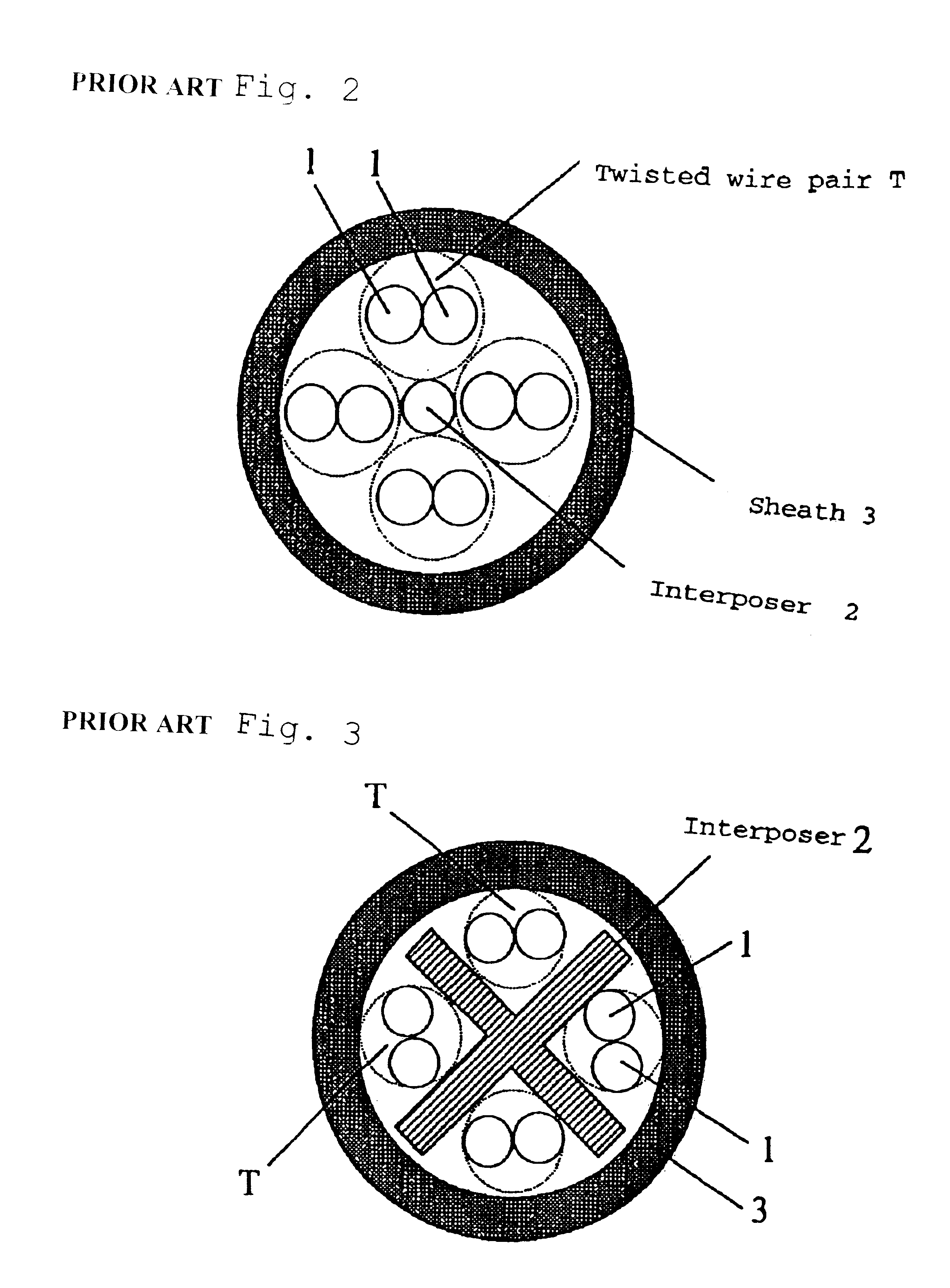
A communication cable is provided that satisfies the requirement of Cat.6 for near-end cross talk wherein the difference between the maximum and minimum values of delay time among the four twisted wire pairs constituting the cable is within 25 ns / 100 m. The communication cable is made by entwining four twisted wire pairs (T1), (T2), (T3), (T4) made by twisting pairs of insulated wires made by covering electrically conductive wires by polyolefin thermoplastic resin with each pair being twisted with a twist pitch different from the others (pitch: P1<P2<P3<P4) and the inter-pair interposer (6) made of polyolefin thermoplastic resin, while being entwined with each wire pair, around a central interposer (2) made of polyolefin thermoplastic resin having cross sectional area of S1. Cross sectional area S1 of the central interposer (2) satisfies the relationship of inequality S1>=[{4.1 d / (1+{square root over (2)})}.0.35]2xpi, while the inter-pair interposer (6) that is entwined with the twisted wire pairs is located at such a position as adjoins the twisted wire pair (T1) having the least pitch P1 and does not adjoin the twisted wire pair (T4) having the largest pitch P4.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
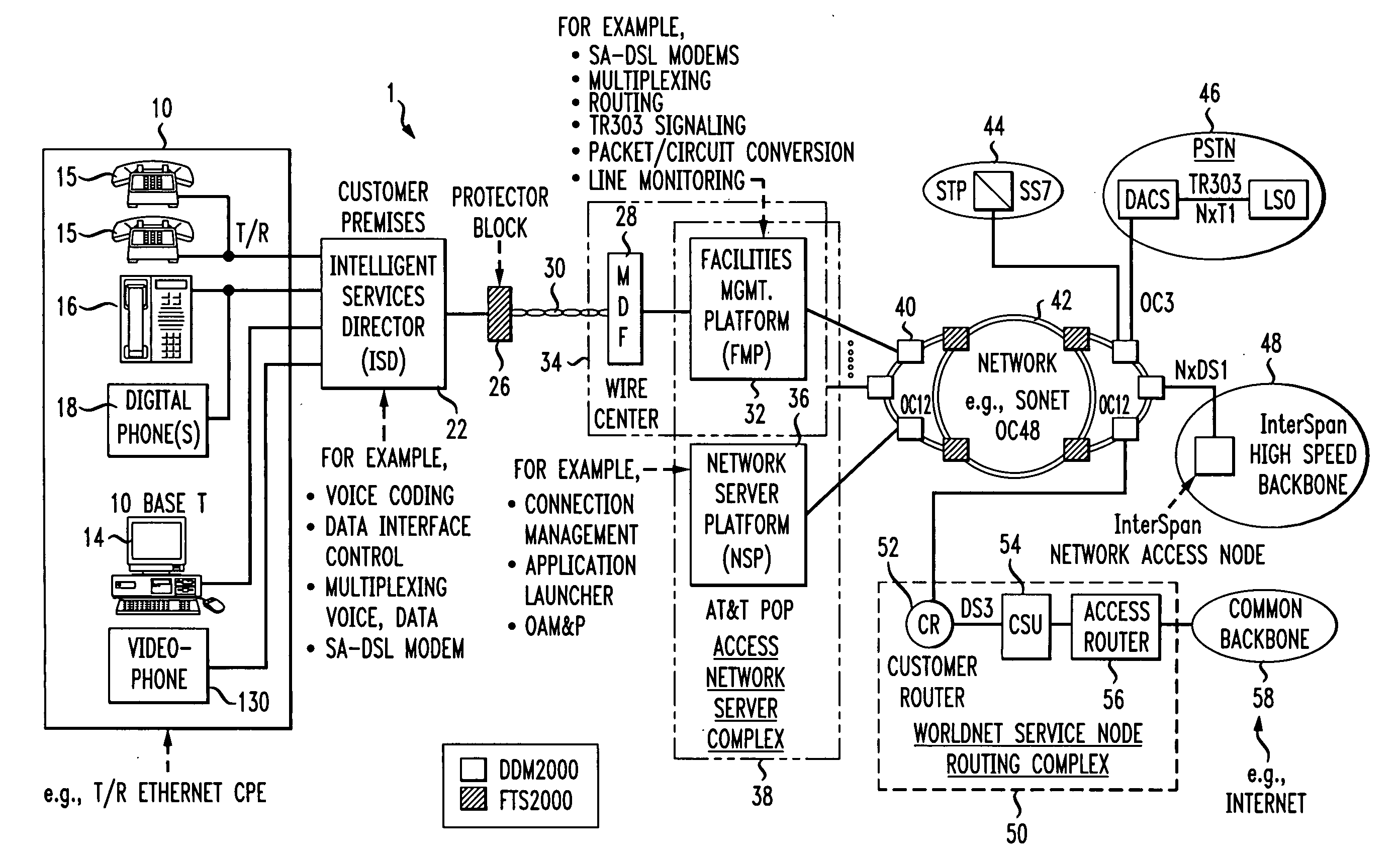
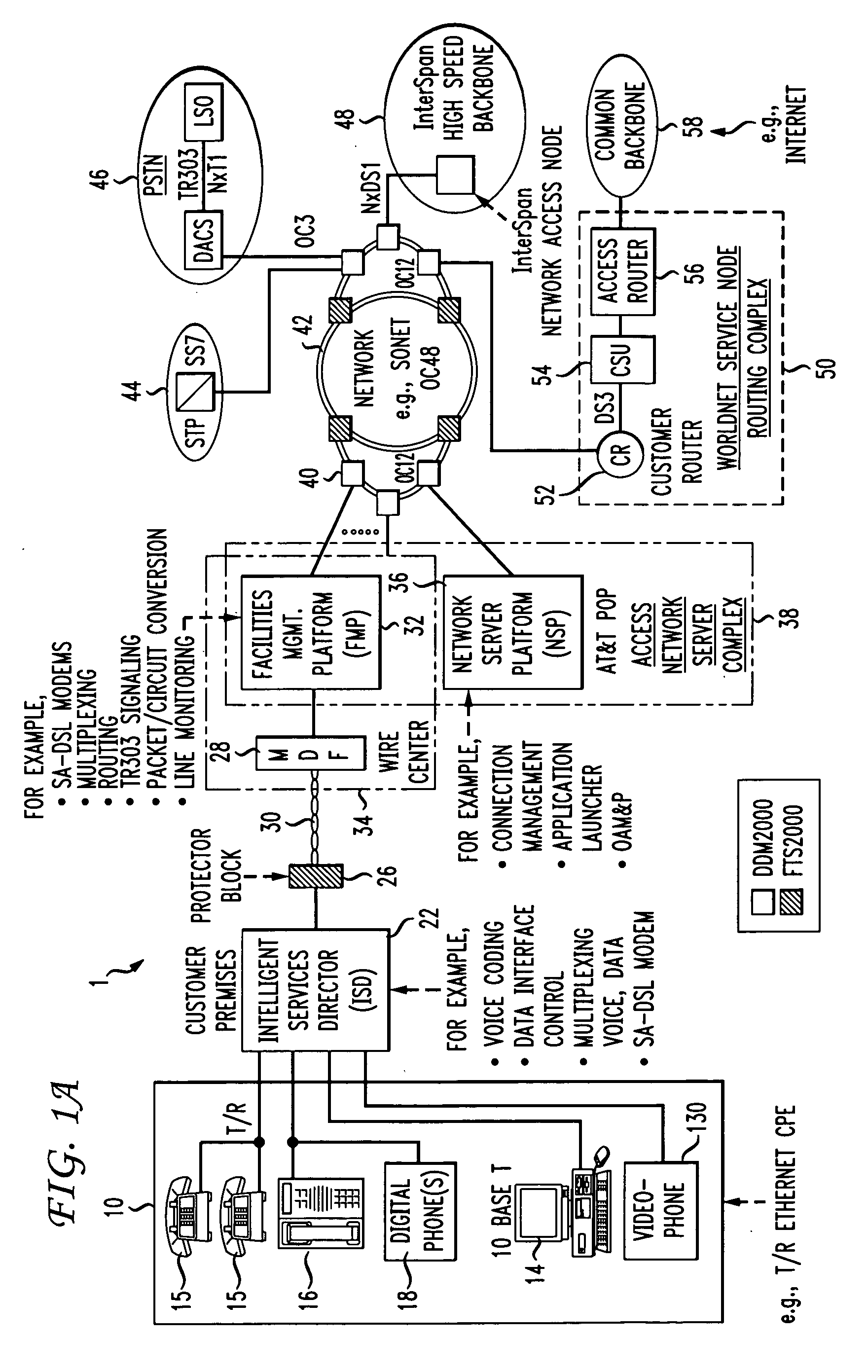
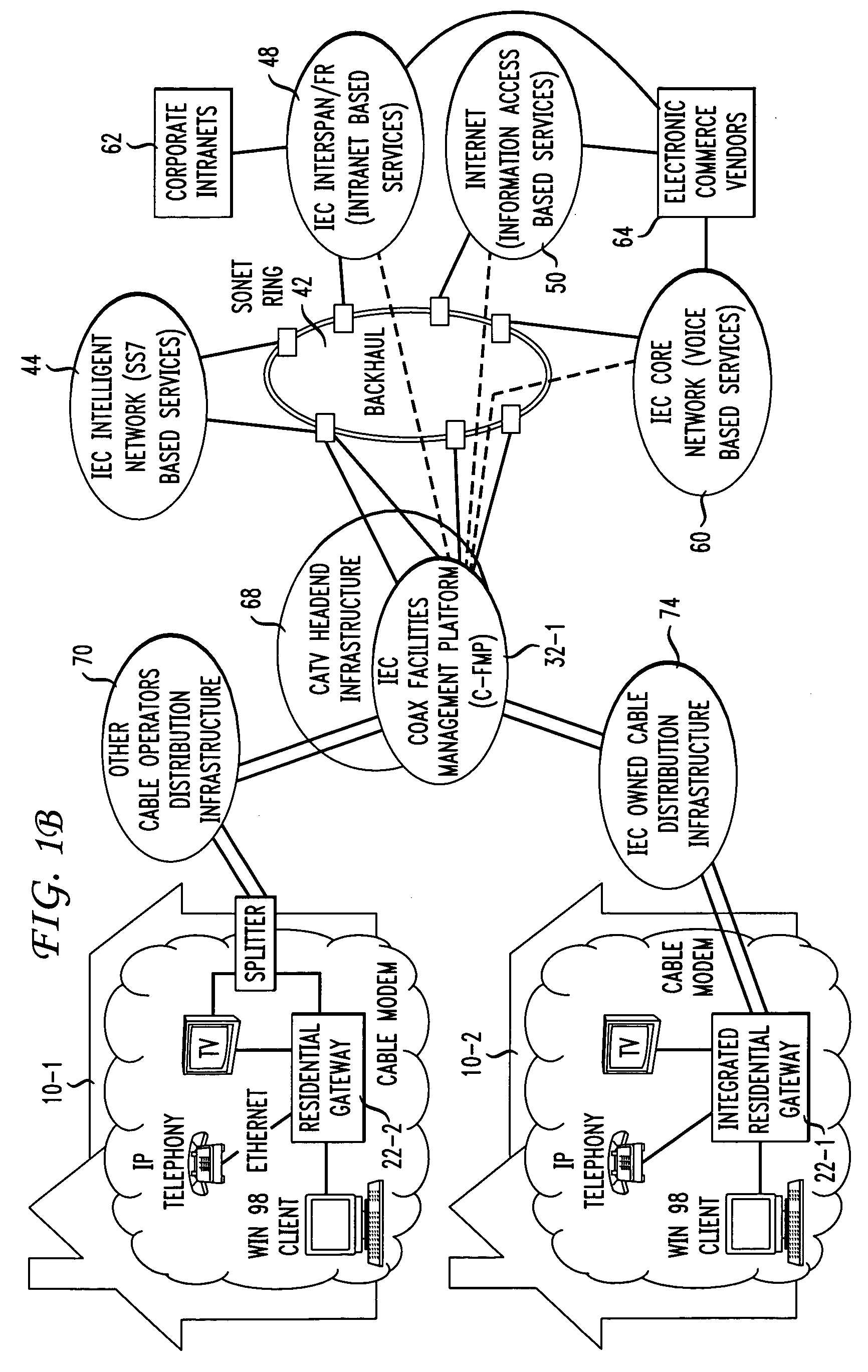
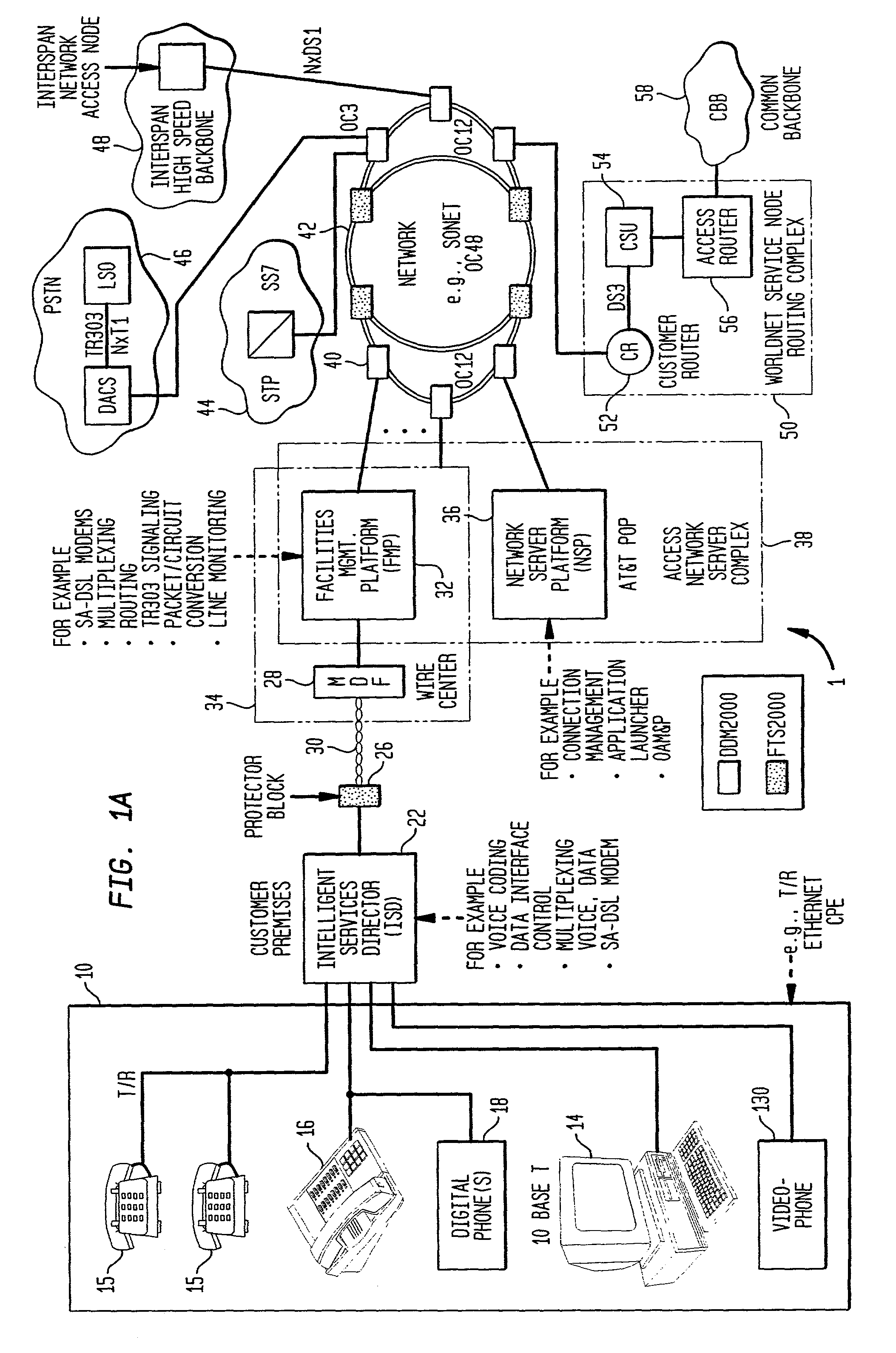
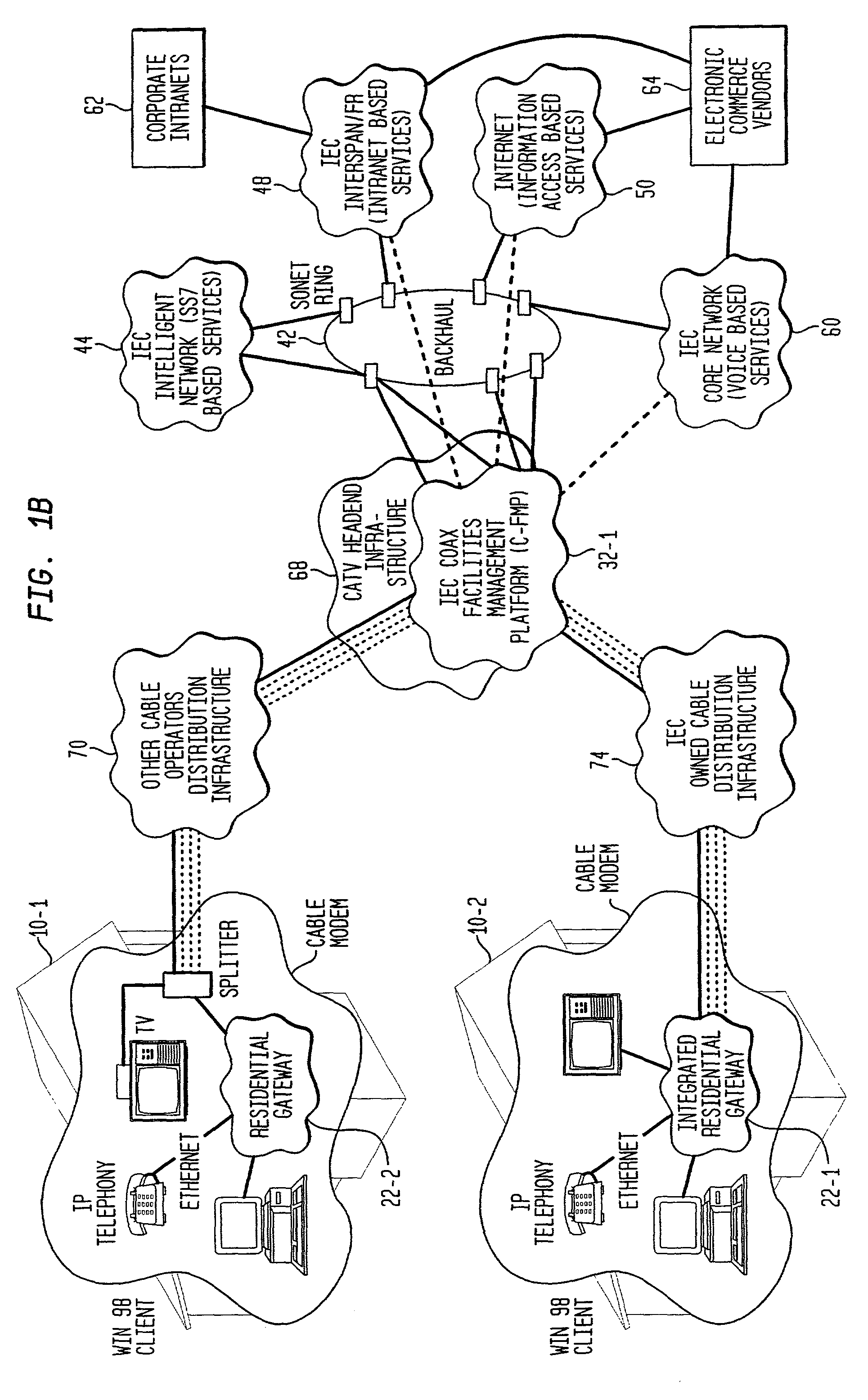
Facility management platform for a hybrid coaxial/twisted pair local loop network service architecture
InactiveUS20060159116A1High bandwidthImprove abilitiesSpecial service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsNetwork controlEngineering
The present invention provides a facility management platform to monitor and view the status of a plurality of individually addressable downstream devices including, but not limited to, addressable terminals, IRG's, settops, cable modems, taps, nodes, and / or hubs at a network control center. The FMP may display problems at these downstream devices, for example, power loss, and / or may automatically notify the appropriate companies and / or personnel to correct the problem.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
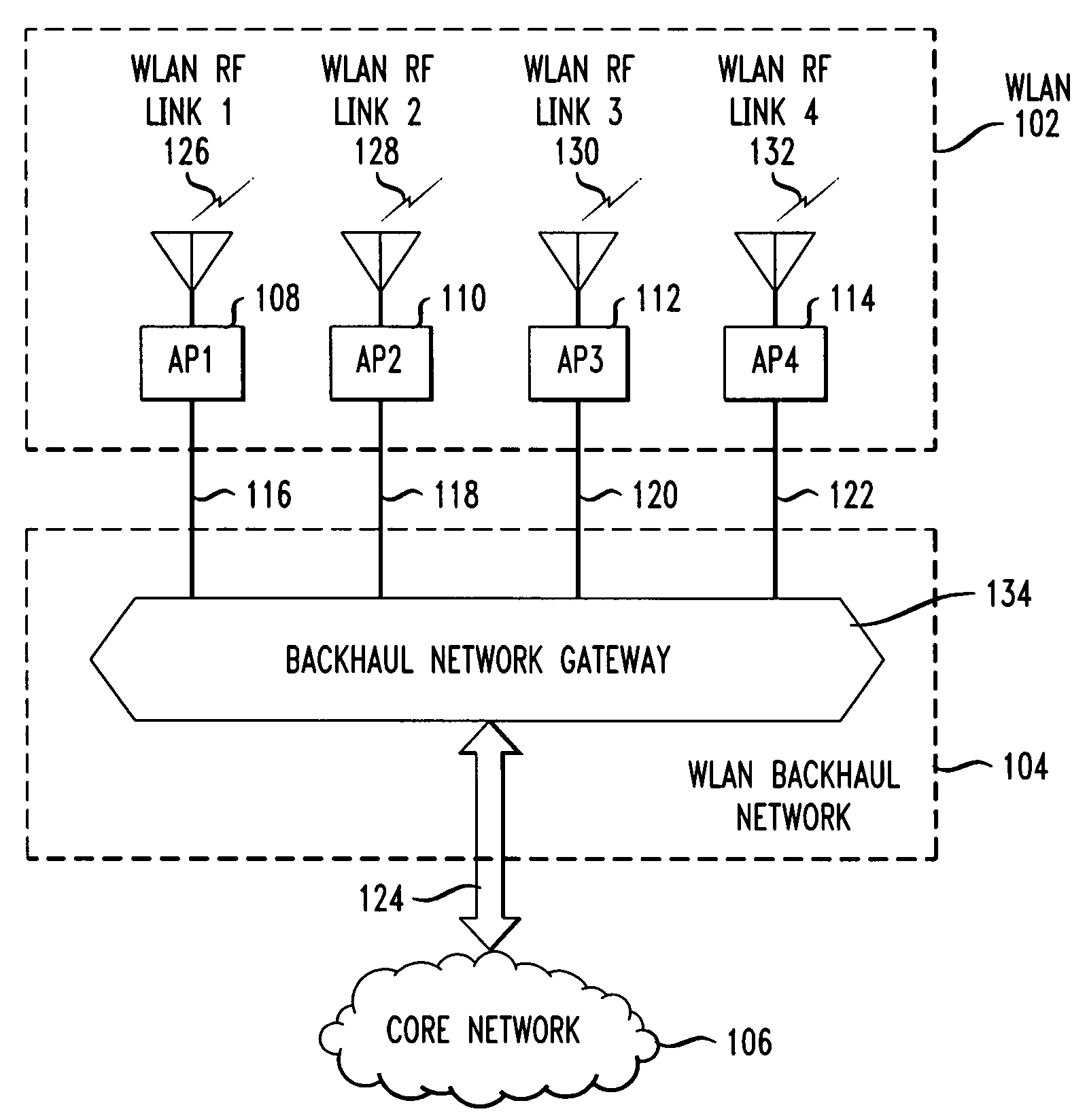
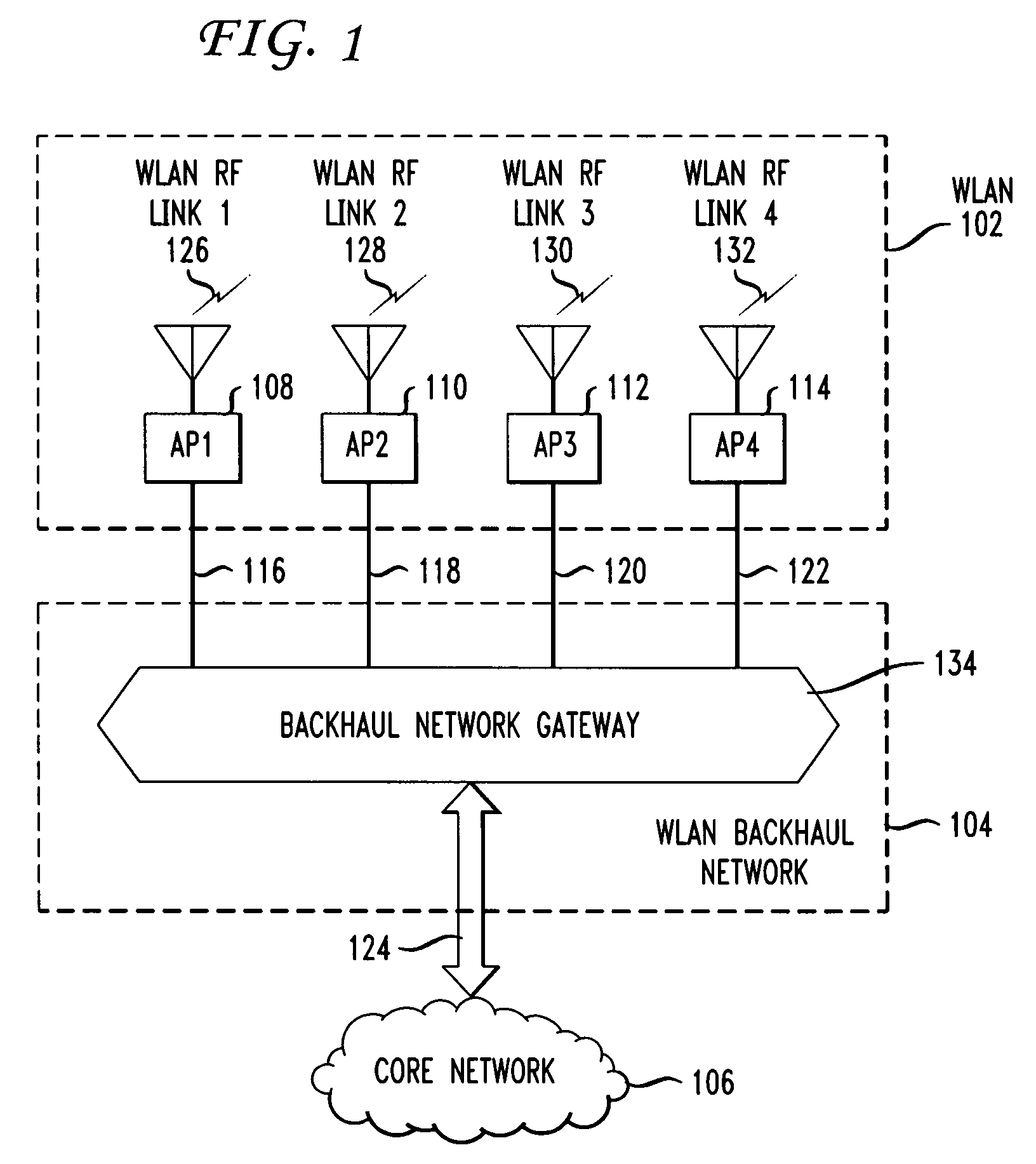
Mesh free-space optical system for wireless local area network backhaul
InactiveUS20080304831A1Improve network reliabilityOptimize networkNetwork topologiesElectromagnetic transmissionCoaxial cableHigh density
In wireless local area networks (WLANS) with a large number of access points, the provisioning and capacity of the WLAN backhaul network connecting the access points to a core network becomes a major issue in network design. Some network services call for access points to be deployed in high densities in a wide range of environments, including outdoor environments. Traditional backhaul networks using fixed media such as twisted pair cable, coax cable, or optical fiber, in many instances are not physically or economically viable. Disclosed are method and apparatus for connecting access points via a mesh network using free-space optical links. The free-space optical links may be supplemented with mm-wave links to increase reliability and capacity.
Owner:AT&T LABS
Multiple layer overlay modulation
ActiveUS8503546B1Improve spectral efficiencyTime-division multiplexSecret communicationFiberEngineering
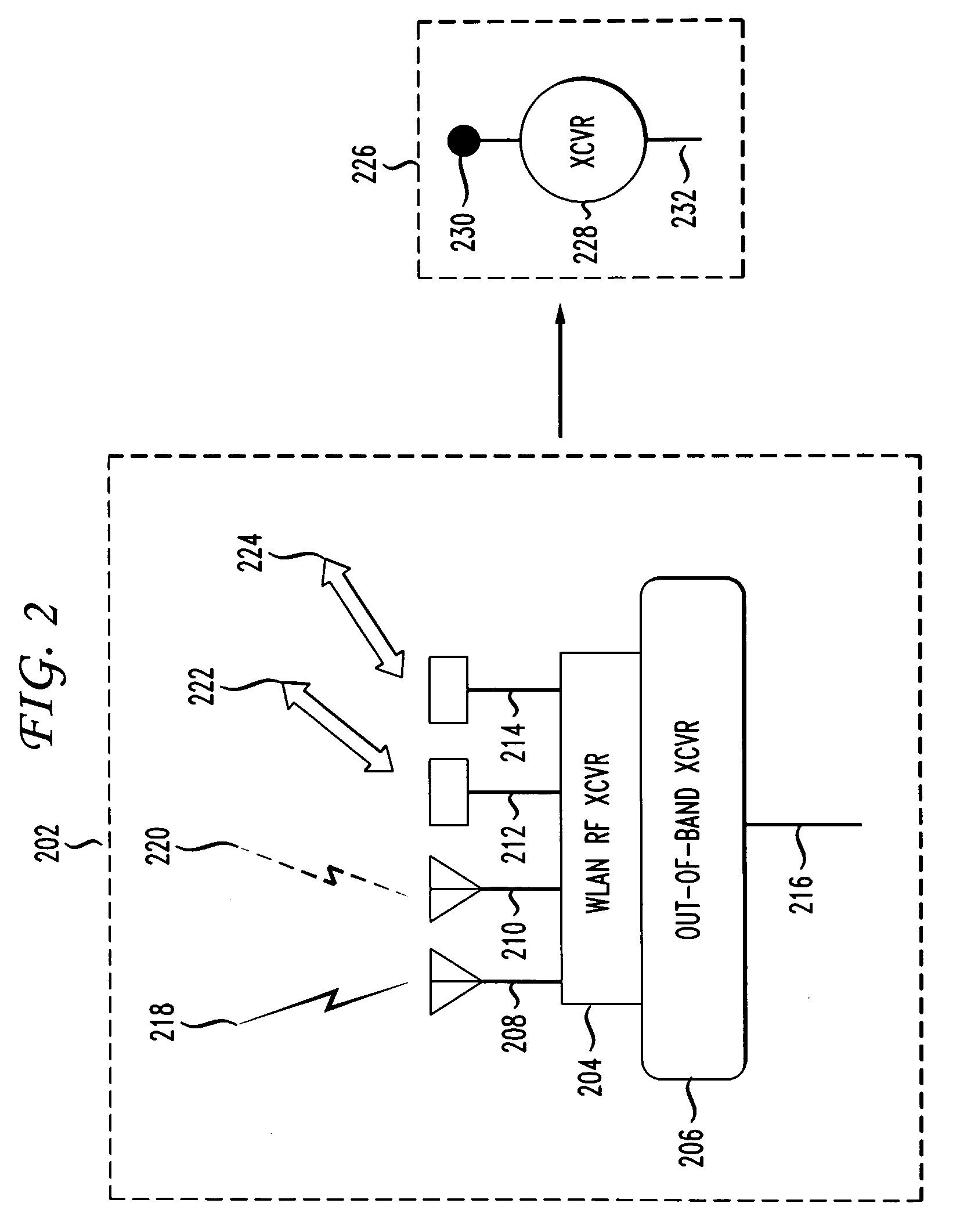
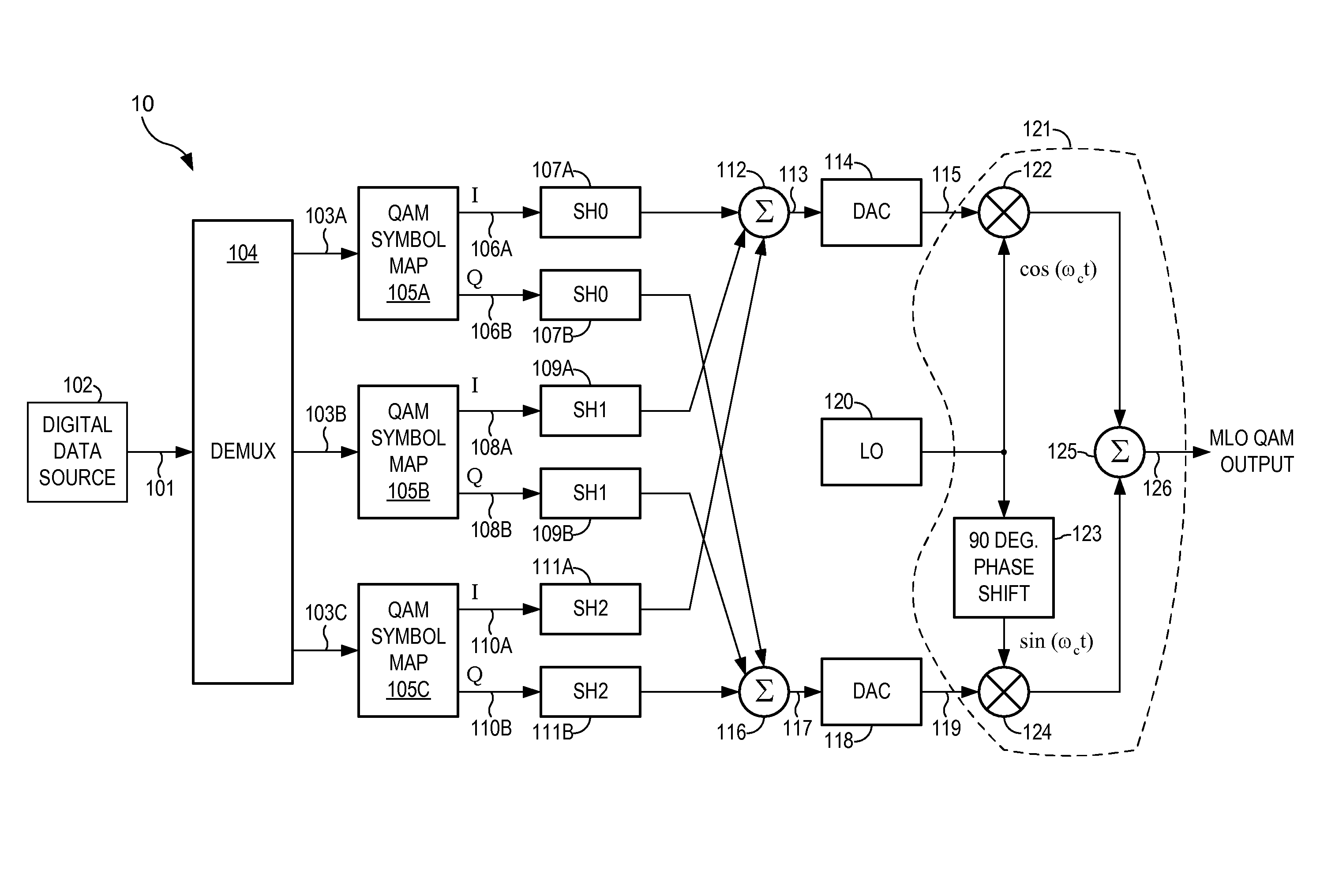
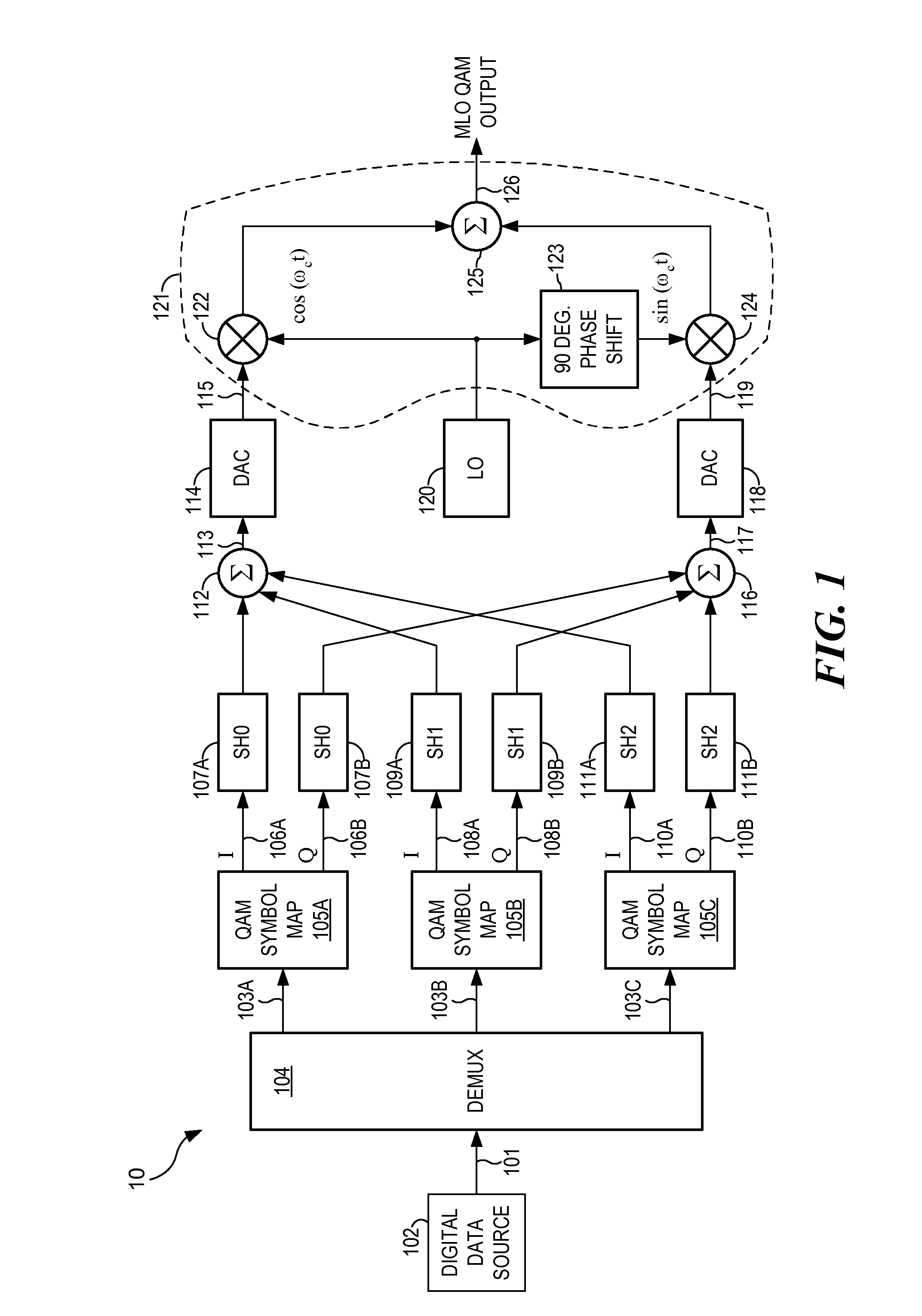
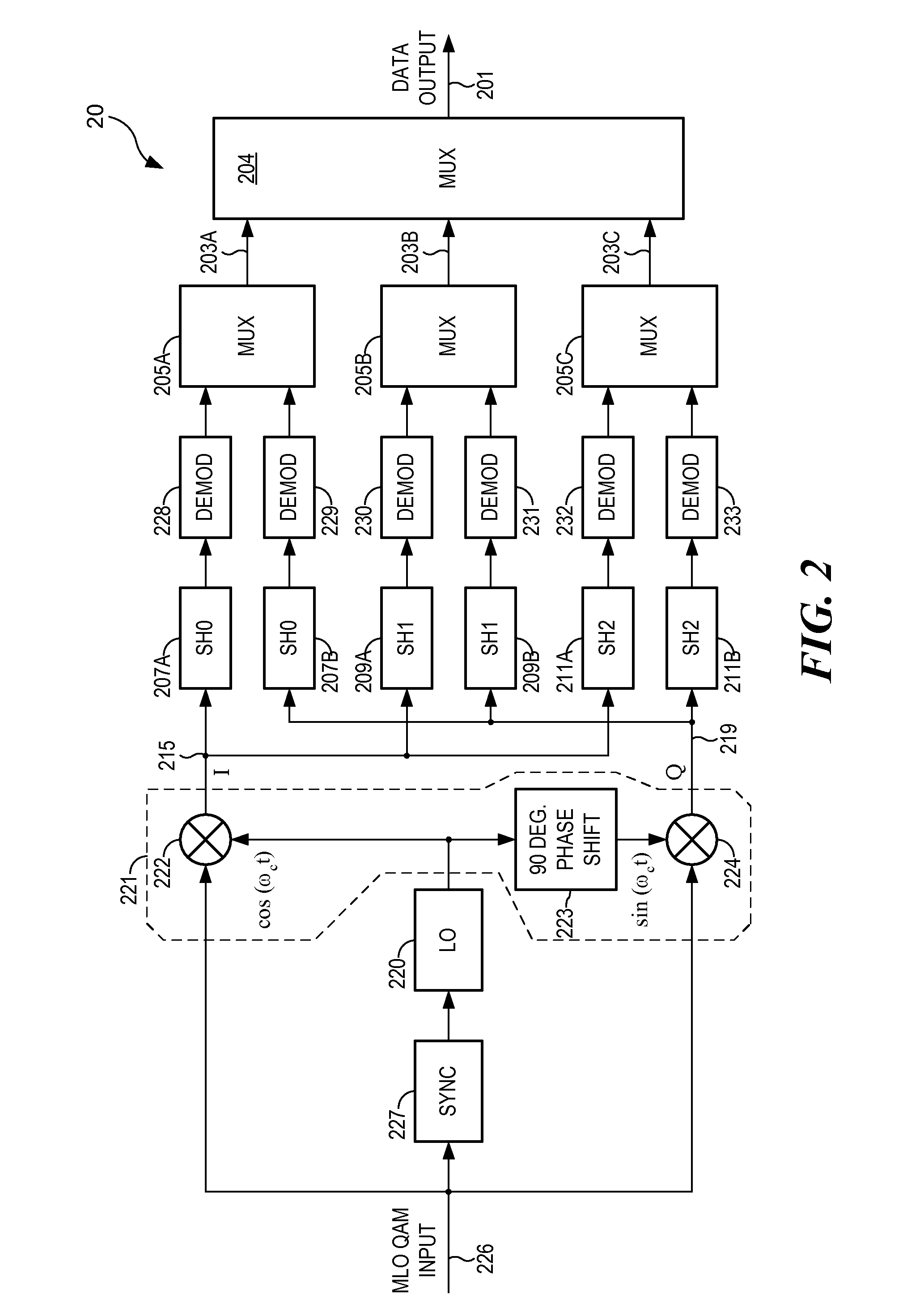
The present invention provides for a communication system and method that overlays signals which are simultaneously mutually orthogonal in both the time and frequency domains, thereby enhancing spectral efficiency. Whereas commonly used sinusoids provide only two mutually orthogonal functions (sine and cosine), certain polynomials provide multiple orthogonal functions, which are also finite in both time and frequency. Using multiple orders of the orthogonal functions allows overlaying signals within a symbol to generate a modulated signal carrying more information than with traditional QAM. Correlating a received signal with locally generated replicas of the orthogonal functions allows demodulation of the signal. This modulation is applicable to twisted pair, cable, fiber, satellite, broadcast and all types of wireless access. The method and system are compatible with many current and future multiple access systems, including EV-DO, UMB, WiMax, WCDMA (with or without MBMS / MIMO), HSPA Evolution, and LTE.
Owner:NXGEN PARTNERS IP
Data cable with cross-twist cabled core profile
Owner:BELDEN TECHNOLOGY INC
Facility management platform for a hybrid coaxial/twisted pair local loop network service architecture
InactiveUS7184428B1Improve abilitiesHigh bandwidthInterconnection arrangementsTime-division multiplexNetwork controlEngineering
The present invention provides a facility management platform to monitor and view the status of a plurality of individually addressable downstream devices including, but not limited to, addressable terminals, IRG's, settops, cable modems, taps, nodes, and / or hubs at a network control center. The FMP may display problems at these downstream devices, for example, power loss, and / or may automatically notify the appropriate companies and / or personnel to correct the problem.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
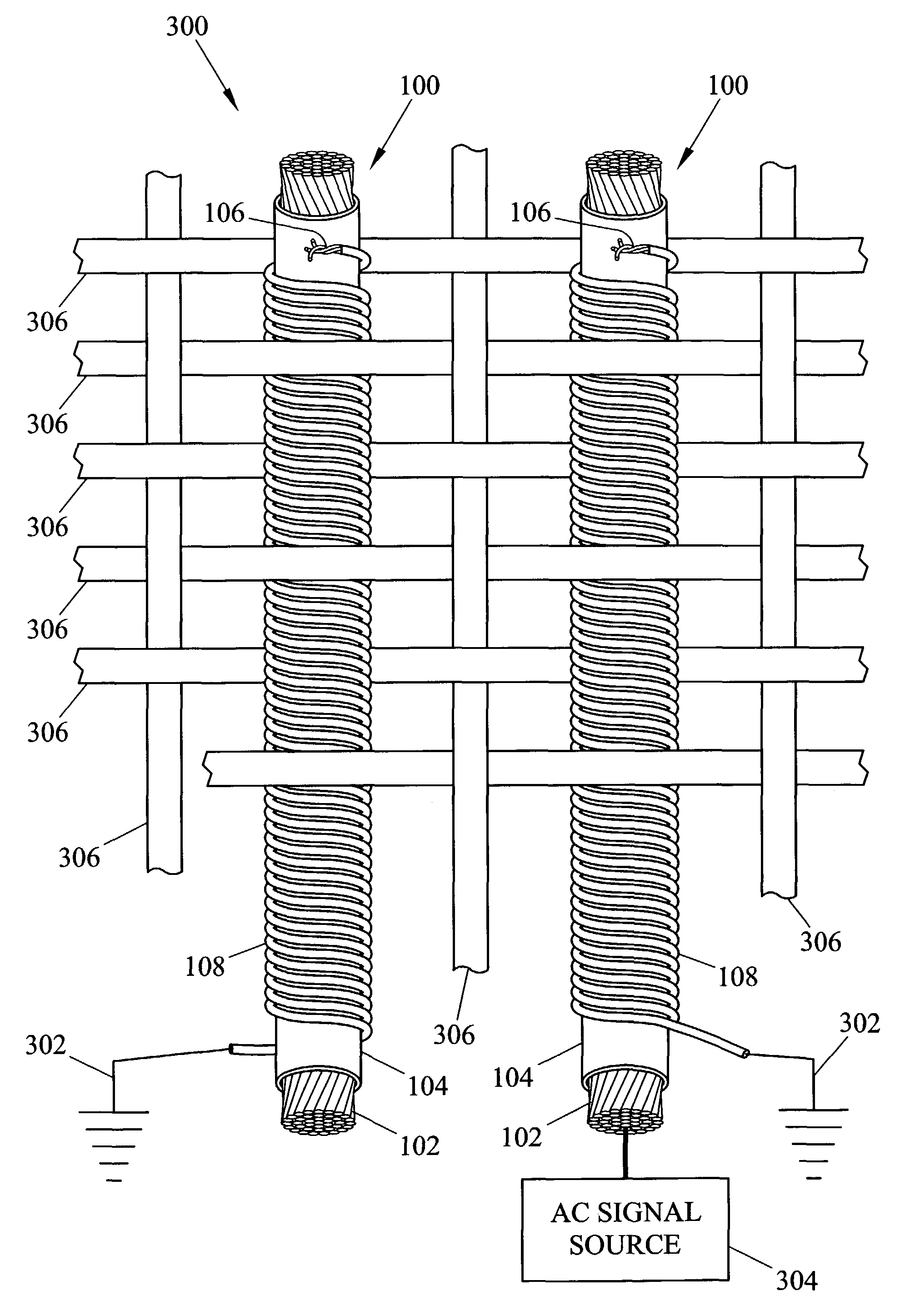
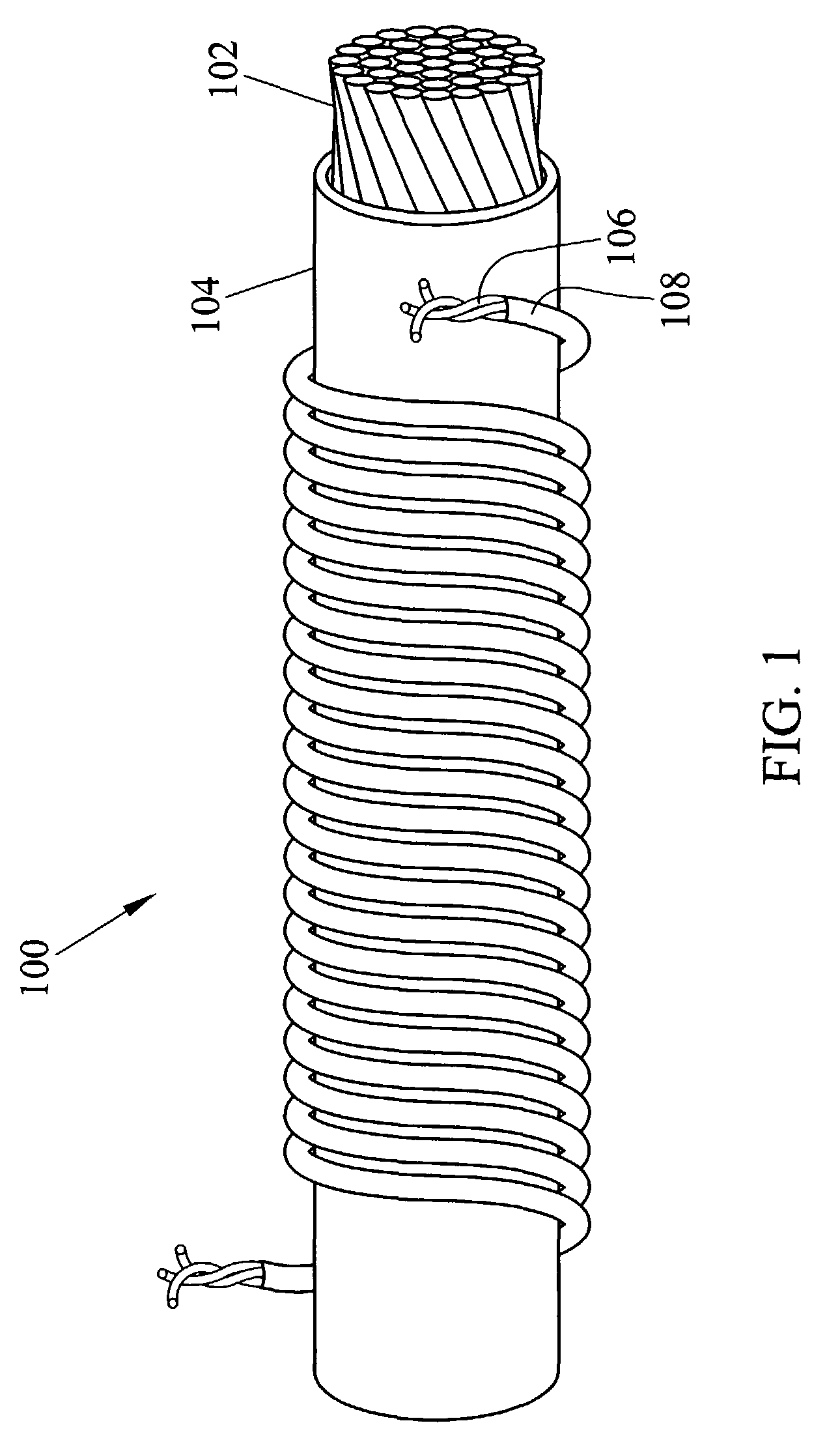
Fabric and yarn structures for improving signal integrity in fabric-based electrical circuits
InactiveUS7348285B2Reduce crosstalkImprove signal integrityAlcoholic beverage preparationPower cables with screens/conductive layersPower gridTwisted pair
Coaxial and twisted pair conductive yarn structures reduce signal crosstalk between adjacent lines in woven electrical networks. A coaxial conductive yarn structure includes an inner conductive yarn having a plurality of conductive strands twisted together. An outer conductive yarn is wrapped around the inner conductive yarn. An insulating layer separates the inner and outer yarns. A twisted pair conductive yarn structure includes first and second conductive yarns, each including a plurality of conductive strands being twisted together. The first and second conductive yarns are twisted together to form a helical structure. In a woven electrical network, at least one conductor of adjacent conductive yarn structures is connected to ground to reduce signal crosstalk. Coaxial and twisted pair yarn structures may also be formed simultaneously with weaving or knitting the threads that make up the structures into a fabric.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Surveillance Camera System
InactiveUS20080055409A1Easy to installEasy to upgradeTelevision system detailsColor television detailsComputer hardwareVideo transmission
A surveillance camera system capable of accepting any appropriate surveillance camera and video transmission option and is programmed to operate with a multitude of competitive communication protocols with minimal servicing required. The system can quickly convert and / or update the camera system to be able to transmit video data over coaxial cable, unshielded twisted-pair (UTP), fiber optics or IP. A conversion from UTP to IP can convert the camera assembly into a network server for TCP / IP communication enabling the camera to be controlled locally or from any location over the internet using any installed network video protocol. The camera assembly with the ability to quickly configure the communication video interface via switch selectable on-board communication protocols.
Owner:VICON INDS
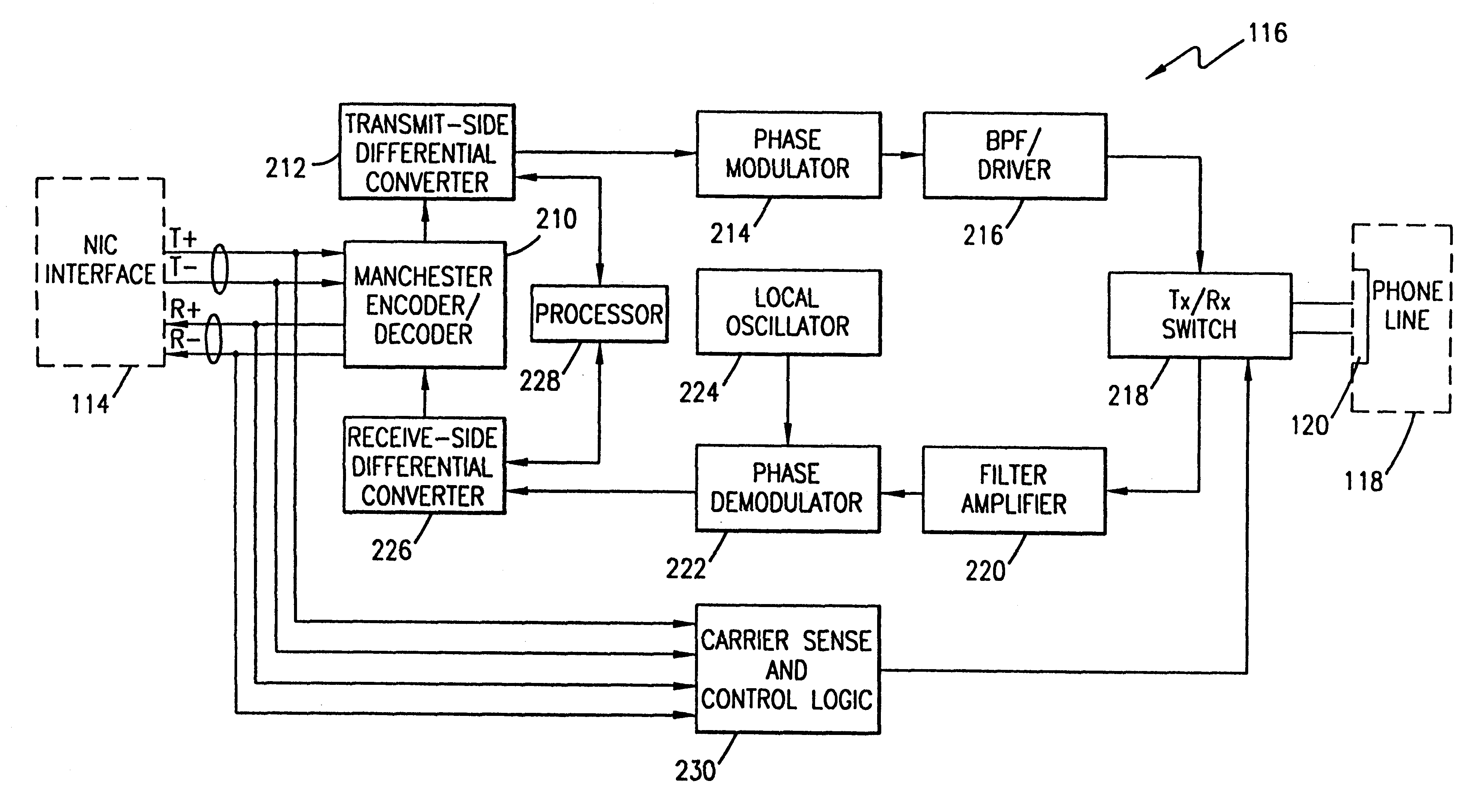
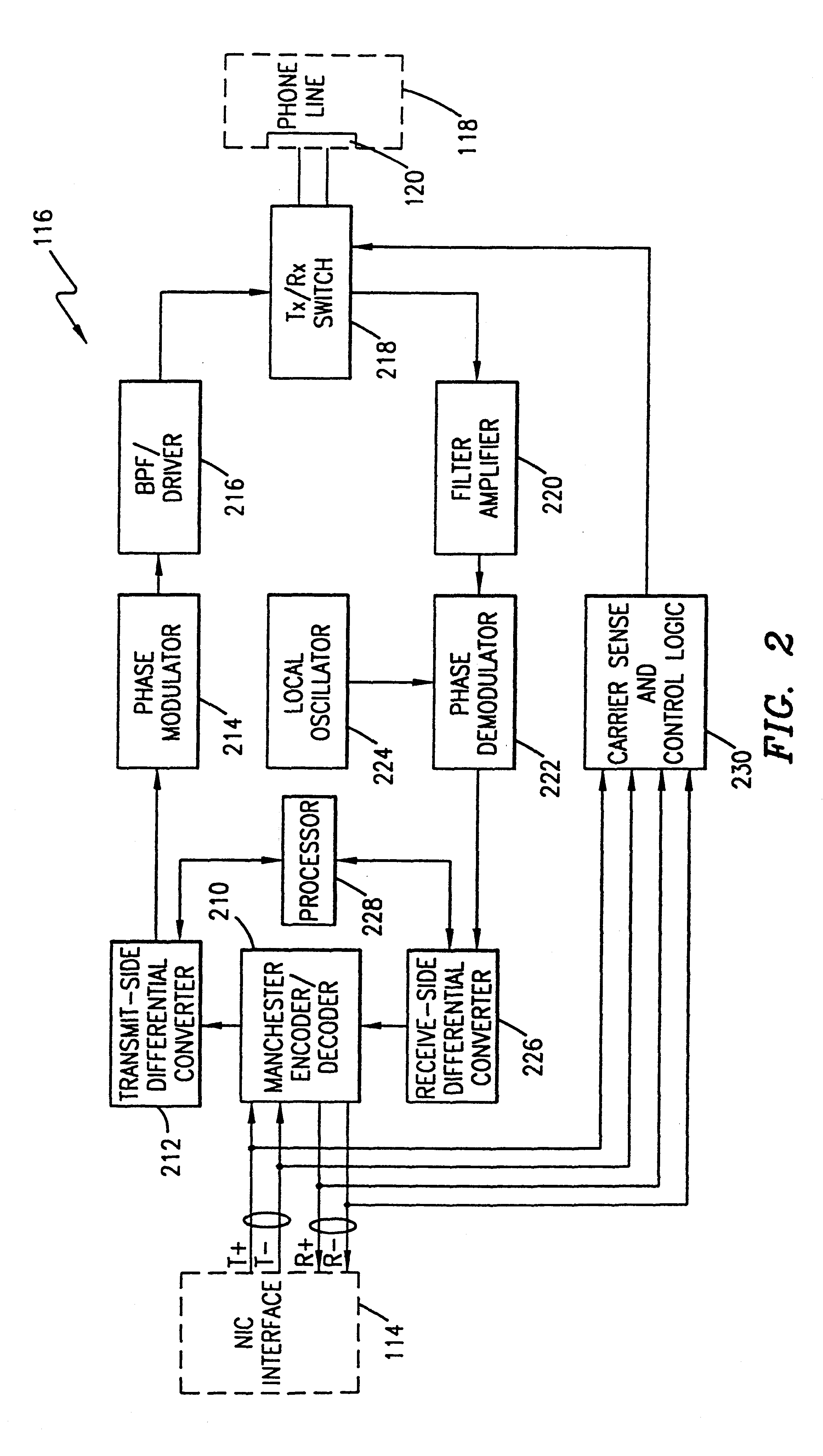
Ethernet to phase shift key converter
InactiveUS6556581B1Modulated-carrier systemsRepeater/relay circuitsBandpass filteringDifferential signaling
A device for seamlessly providing 10BASE-T compatible data communications over an ordinary single twisted-pair home phone line between multiple computers and / or peripherals is disclosed. Each component that is to communicate over a home phone line needs a 10BASE-T compatible network interface card (NIC) for interfacing with the device. A transmit / receive switch is used to switch the device between a transmit mode and a receive mode. When a signal is being transmitted from a component, a Manchester decoder converts the signals received from the NIC into a raw data stream. A differential converter converts the raw data signal received from the NIC to a differential signal. A modulator is used to modulate the signal to a RF signal using a PSK, QPSK, QAM, MCM or similar modulation schemes. A filter is used to limit the bandwidth of the modulated signal and a driver is used to amplify the signal to match the impedance of the phone line. When the device receives a signal over the phone line, the signal is filtered using a bandpass filter and then amplified. The signal is then demodulated using an appropriate demodulation scheme before being differentially encoded. A Manchester encoder encodes the received signal for compatible operation with a receiving NIC.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
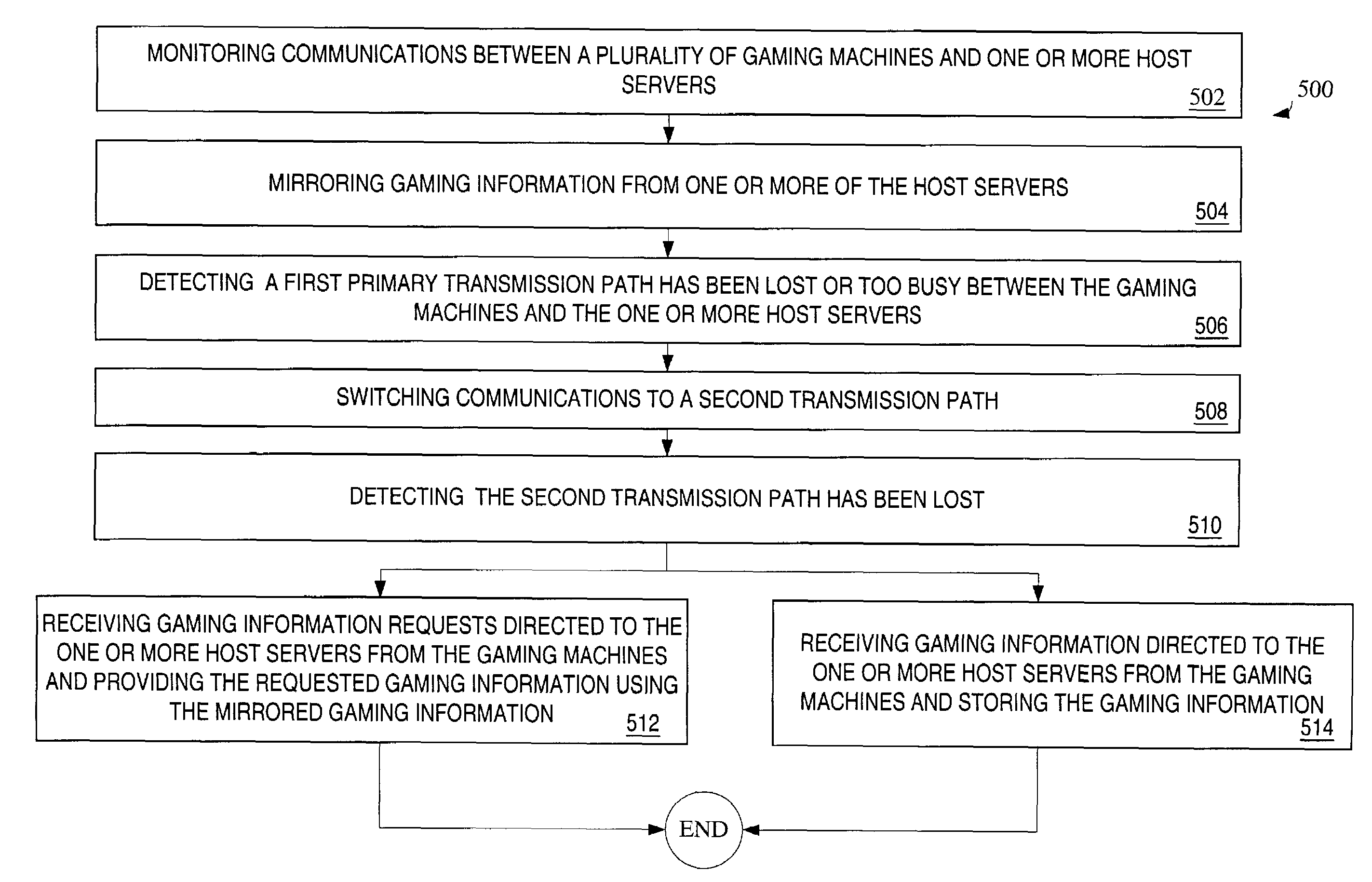
Redundant gaming network mediation
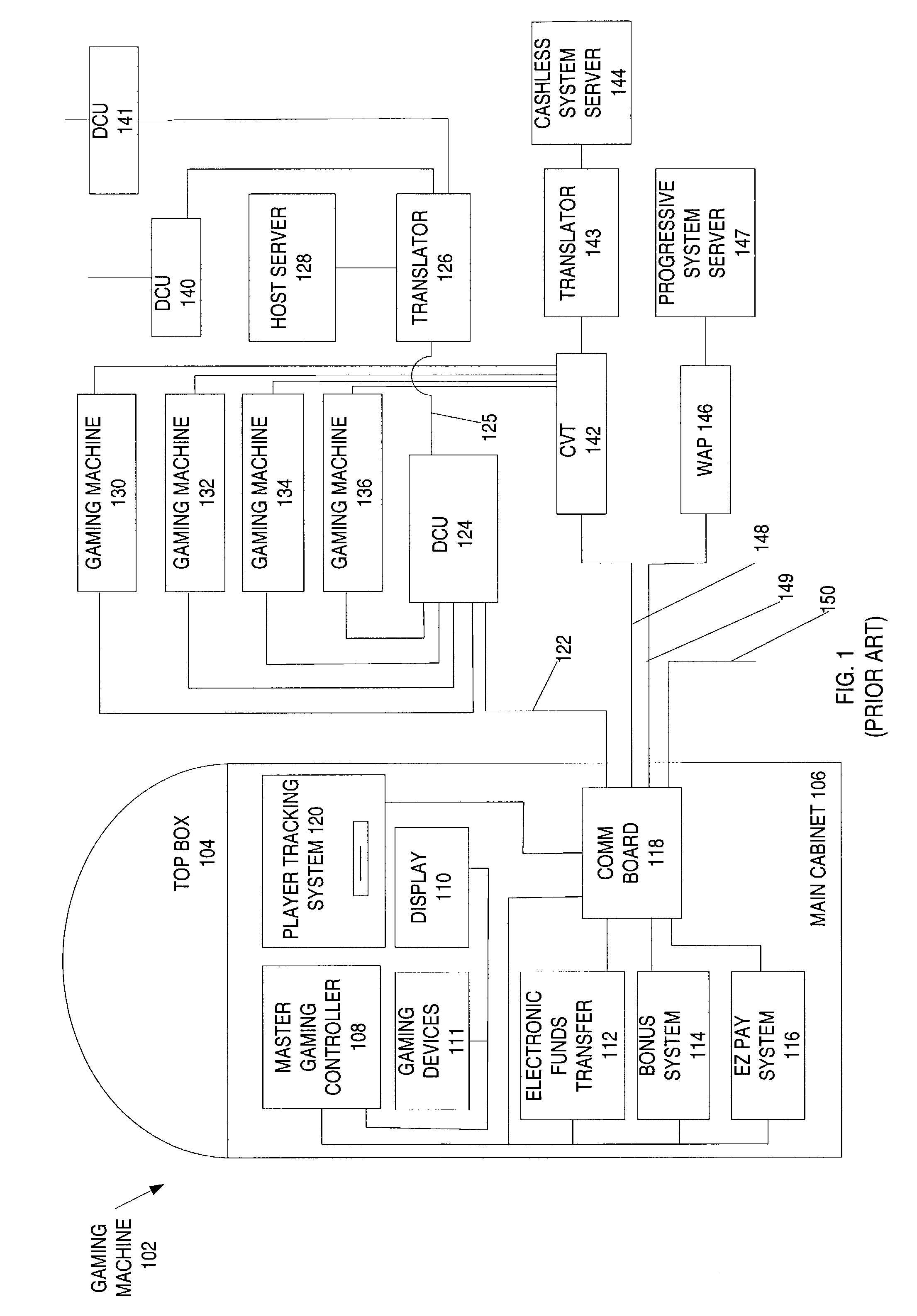
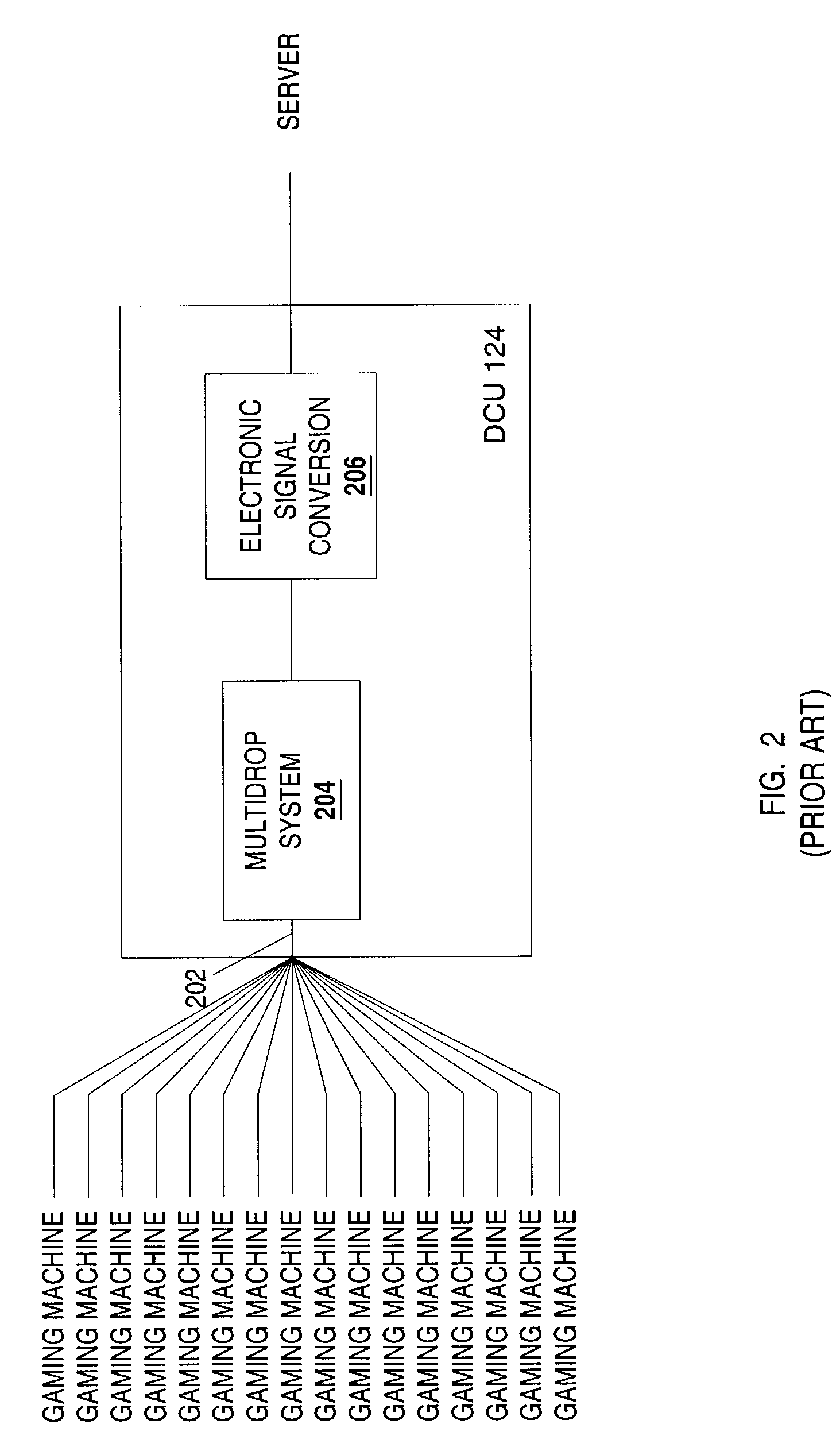
InactiveUS7455591B2Apparatus for meter-controlled dispensingVideo gamesWireless transmissionData store
A disclosed gaming communication network provides an enhanced DCU that provides redundant mediation between gaming machines on the gaming communication network and a host server. The enhanced DCU provides a first, primary transmission path and a second, redundant transmission path between the gaming machines and the host server. In the event one transmission path is disrupted, the other provides continuing transmissions between the gaming communication network and the host server. In the event both transmission paths are disrupted, the enhanced DCU functions as a local interim server and stores data received from the gaming machines on the gaming communication network until such time as the data can be transmitted to the host server. In some embodiments, the enhanced DCU acts as a local interim server to the gaming machines using data mirrored from the host server prior to transmission disruption. In some embodiments, the enhanced DCU functions as a download server and stores data received from the host server and asynchronously transmits the data to the gaming machines, so as to mitigate disruption of game play. In some embodiments, the enhanced DCU may also function as a local cache of information that is repeatedly accessed by the gaming machines on the gaming communication network so as to reduce the transmission load on the first and / or second transmission path. In some embodiments, the enhanced DCU provides different network input connection ports to enable utilization of the enhanced DCU with different network formats, such as fiber optic cable, twisted pair cable, or wireless transmission media.
Owner:IGT
Communication system architecture, exchange having a plurality of broadband modems and method of supporting broadband operation on a one to one basis
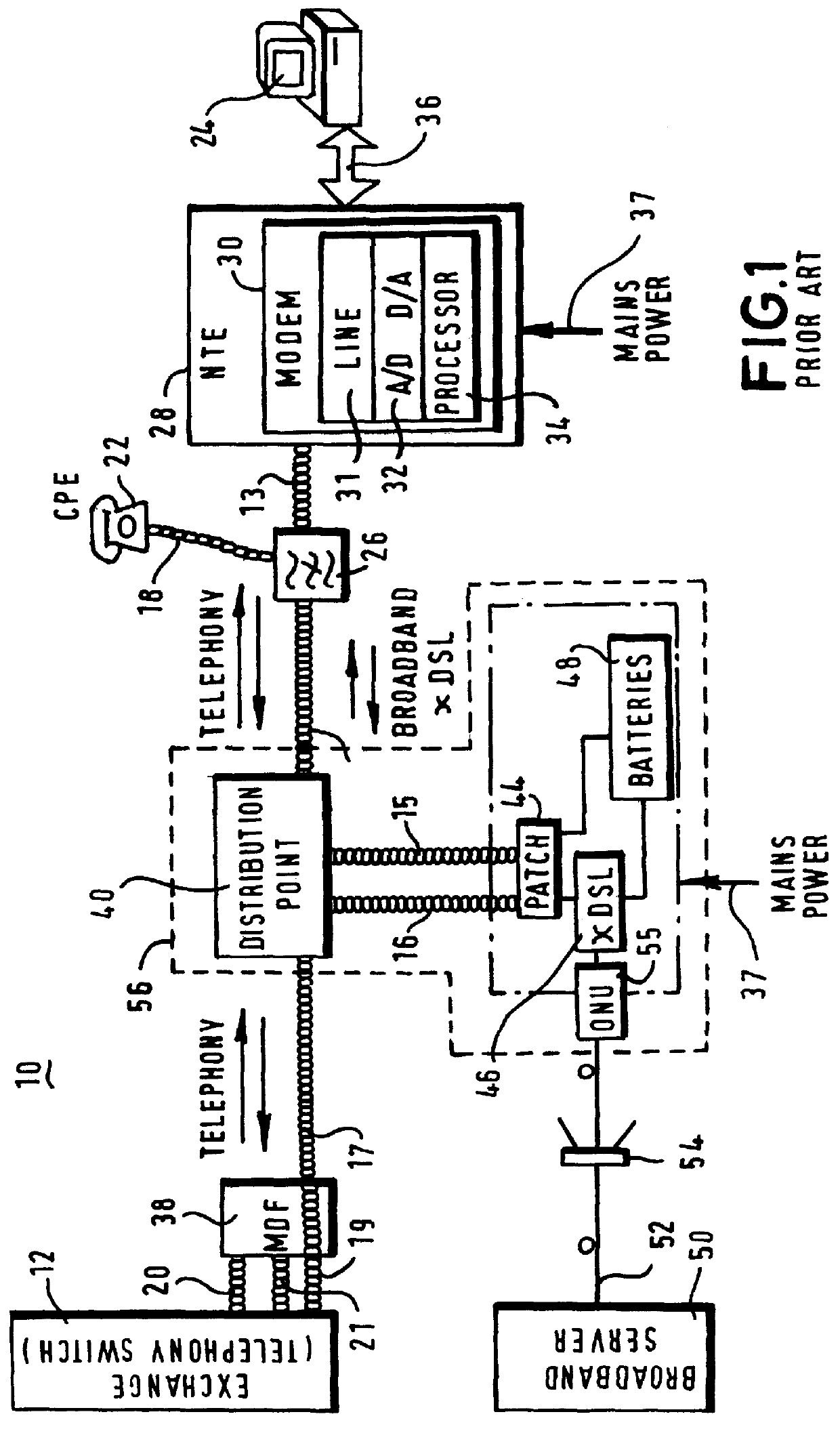
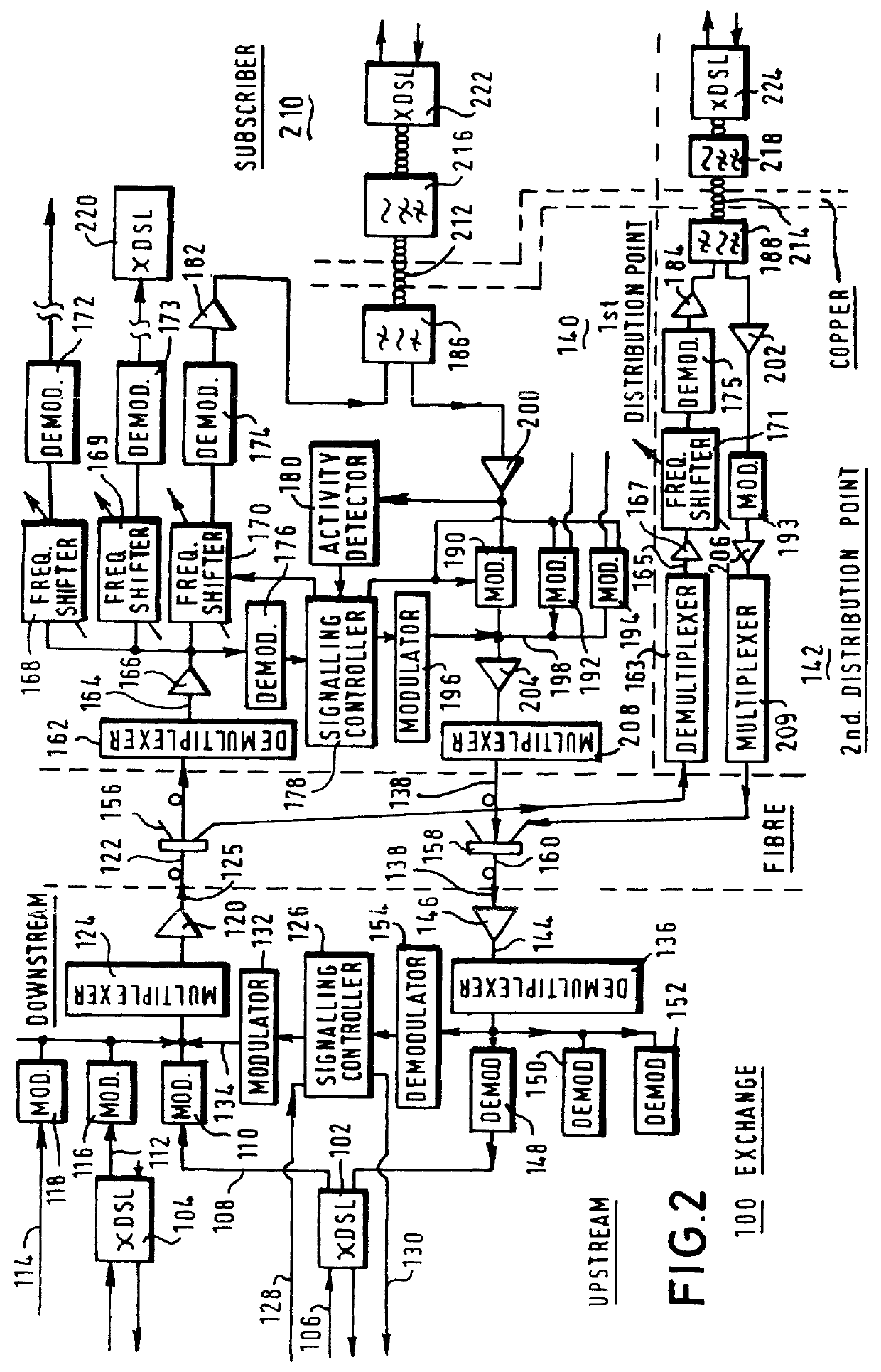
InactiveUS6148006AMinimize the numberSaving in each cost-per-customer connectionTelephonic communicationFrequency-division multiplexModem deviceTelecommunications network
To reduce the complexity, size and power dissipation associated with the deployment of xDSL-type modems in distribution points (140-142) of a telecommunications network, a transparent concentrating optical transmission scheme is interposed between an exchange (100) and a subscriber terminal (210). Specifically, xDSL-type modems (102-104 and 220-224) are employed both within the exchange (100) and, nominally each subscriber terminal (210) of the telecommunication system, while an optical fiber supports the transmission of frequency division multiplexed broadband signals sent between the exchange (100) and the distribution points (140-142). Twisted-pairs then couple respective broadband signals received and demultiplexed at the distribution points (140-142) to appropriately addressed subscriber terminals (210), while upstream transmissions are subjected to a complementary process from the xDSL modems (220-224) in the subscriber terminals (210) to the xDSL modems (220-224) in the exchange (100).
Owner:NORTEL NETWORKS LTD
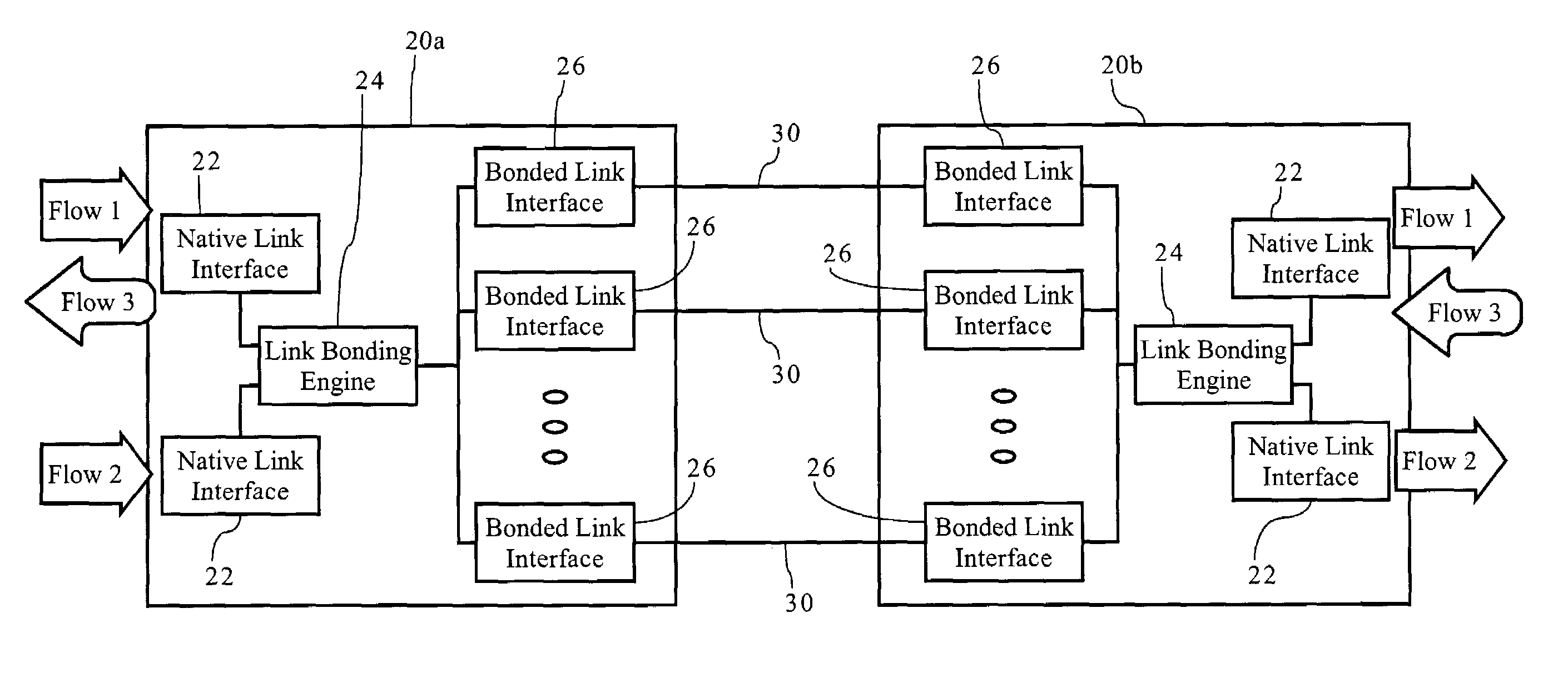
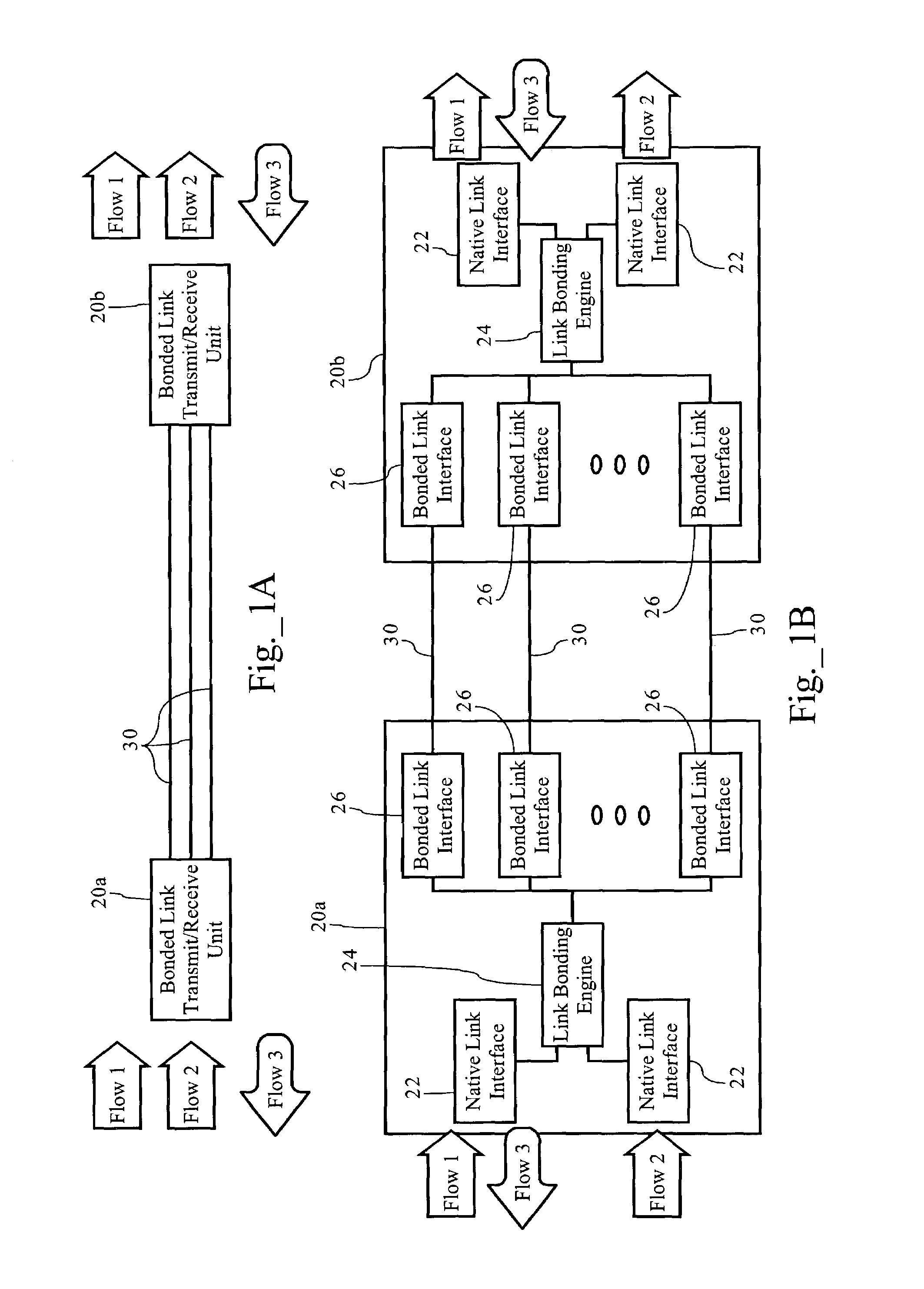
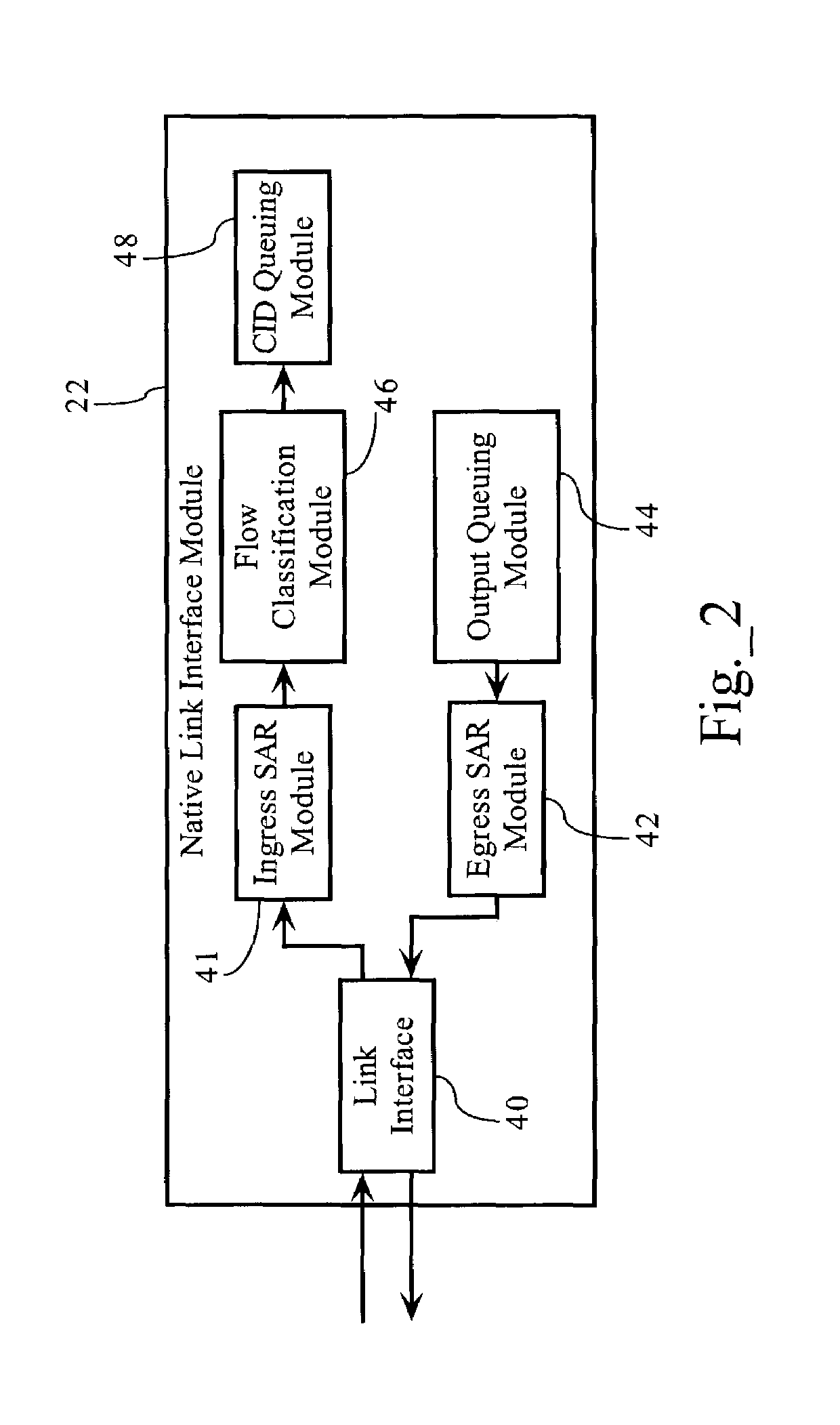
Methods, apparatuses and systems facilitating data transmission across bonded communications paths
InactiveUS7006500B1Improve data transfer efficiencyLow latency requirementEnergy efficient ICTTelephonic communicationRe sequencingData stream
Methods, apparatuses and systems facilitating the aggregation or bonding of communications paths into a higher-bandwidth, logical communications path. Embodiments of the present invention can be applied to bond different physical links (e.g., xDSL over twisted pairs), different channels on the same physical line, or even different channels or frequencies in a wireless communications network. The present invention further provides methods, apparatuses and systems facilitating the re-sequencing of data flows transmitted across bonded communications paths. In one embodiment, the re-sequencing methodology of the present invention adapts to the transmission delays (both absolute and relative) across the bonded communications path.
Owner:KLAMATH NETWORKS
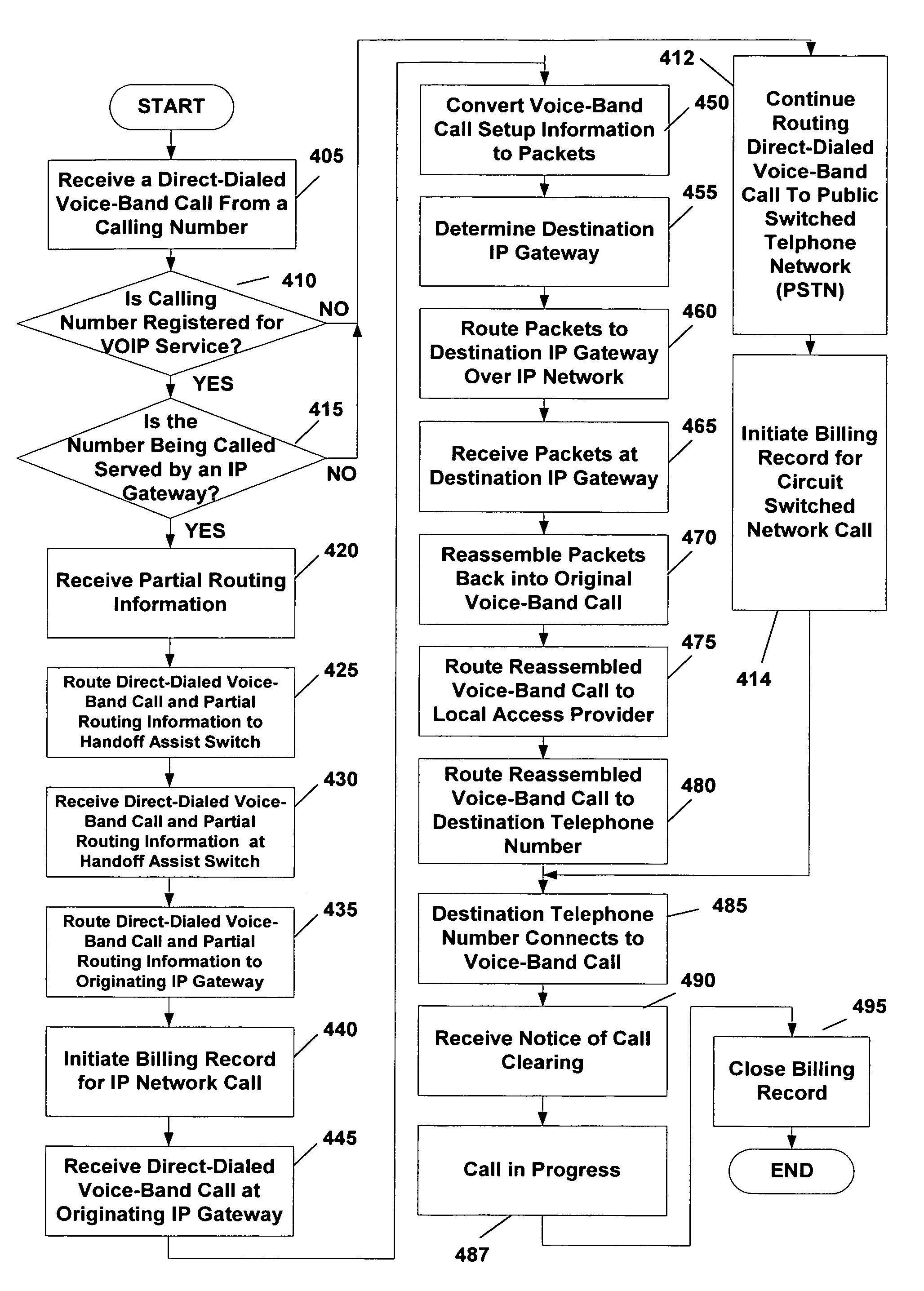
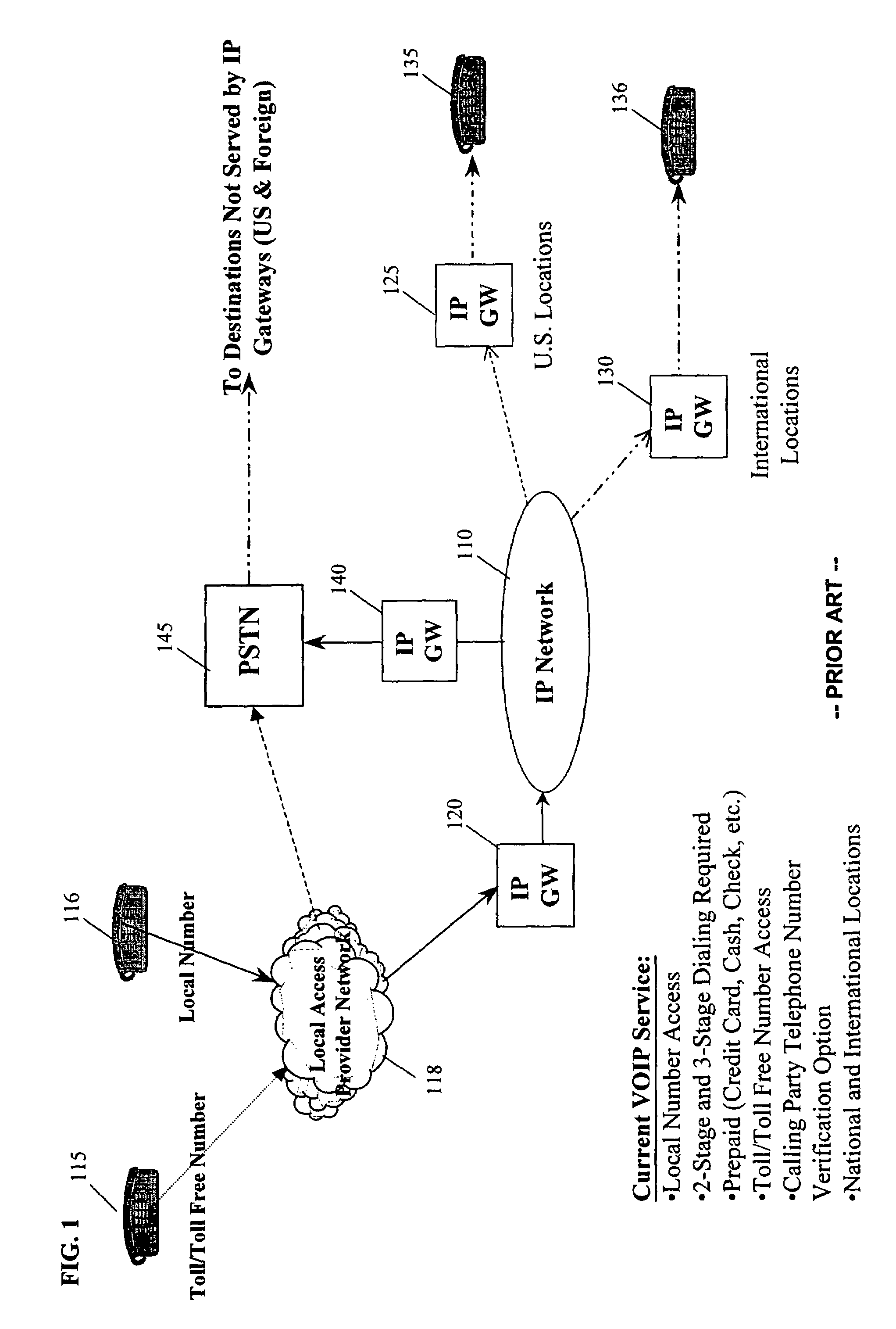
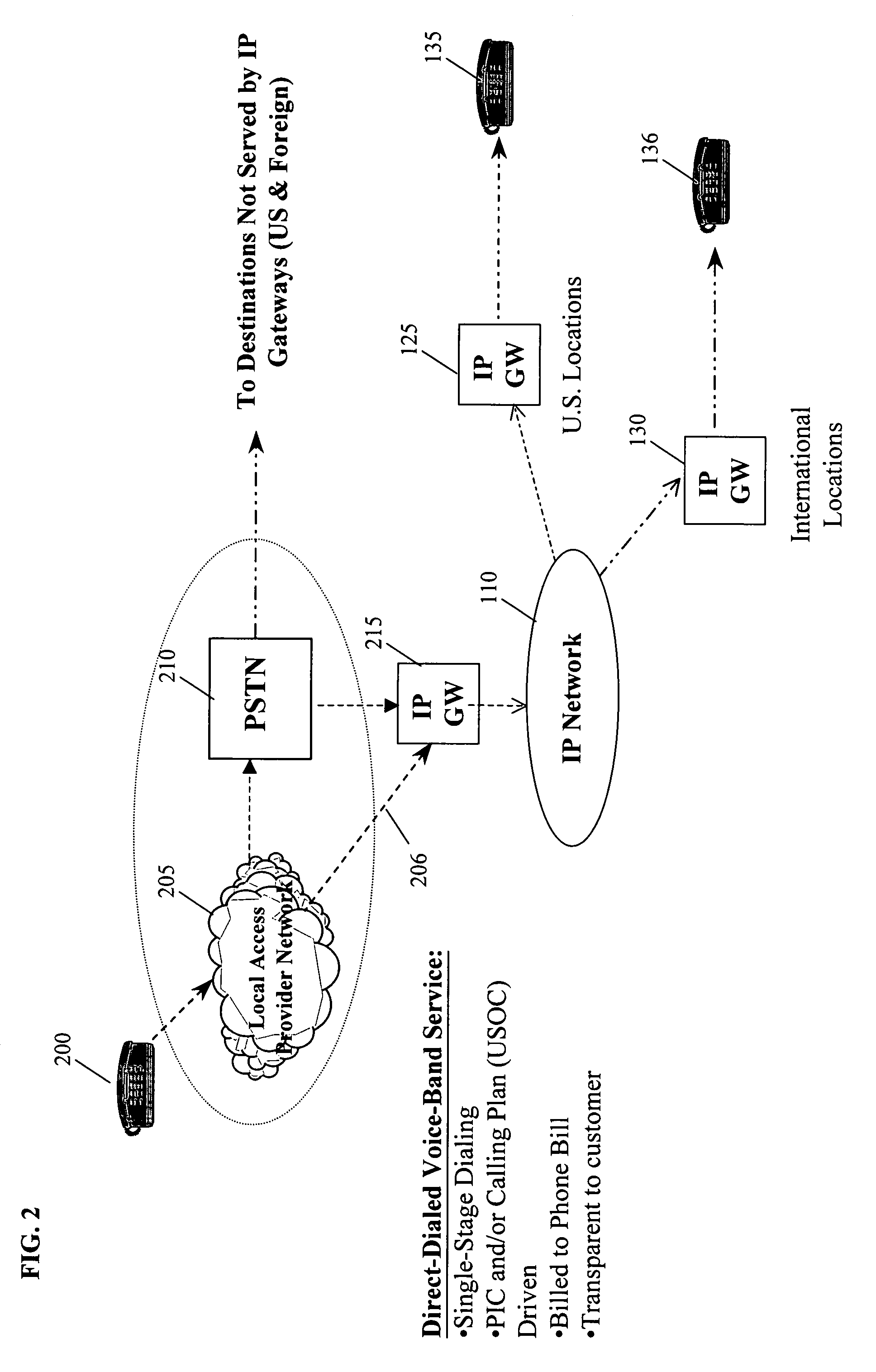
Method and system for customer selected direct dialed voice-over-internet protocol (VOIP)
A Voice-over-Internet protocol (VOIP) communications network system that enables direct-dialed (single-stage) access to the Internet Protocol (IP) network from the circuit-switched network. Specifically, the VOIP network system includes a VOIP service implemented on a communications system which, after a customer number has been registered for the service, automatically recognizes calls from the registered customer's telephone number and determines if the call can be routed as a VOIP call over the IP network. In embodiments of the present invention, the customer can register for the VOIP service by selecting both a provider (PIC) and a calling plan or by only selecting a provider. The system can be implemented to handle intra-state, inter-state and international voice-band calls (for example, regular telephone calls, facsimile transmissions and modem initiated calls) using standard circuit-switched telephone lines, cable, twisted pair, digital subscriber line (DSL) and wireless.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Local area network cabling arrangement with randomized variation
ActiveUS6875928B1Improved internalImproved alien crosstalk performanceInsulated cablesPower cablesArea networkEngineering
A cabling media includes a plurality of twisted wire pairs housed inside a jacket. Each of the twisted wire pairs has a respective twist length, defined as a distance wherein the wires of the twisted wire pair twist about each other one complete revolution. At least one of the respective twist lengths purposefully varies along a length of the cabling media. In one embodiment, the cabling media includes four twisted wire pairs, with each twisted wire pair having its twist length purposefully varying along the length of the cabling media. Further, the twisted wire pairs may have a core strand length, defined as a distance wherein the twisted wire pairs twist about each other one complete revolution. In a further embodiment, the core strand length is purposefully varied along the length of the cabling media. The cabling media can be designed to meet the requirements of CAT 5, CAT 5e or CAT 6 cabling, and demonstrates low alien and internal crosstalk characteristics even at data bit rates of 10 Gbit / sec.
Owner:COMMSCOPE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com