Patents
Literature
465 results about "Conductive yarn" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
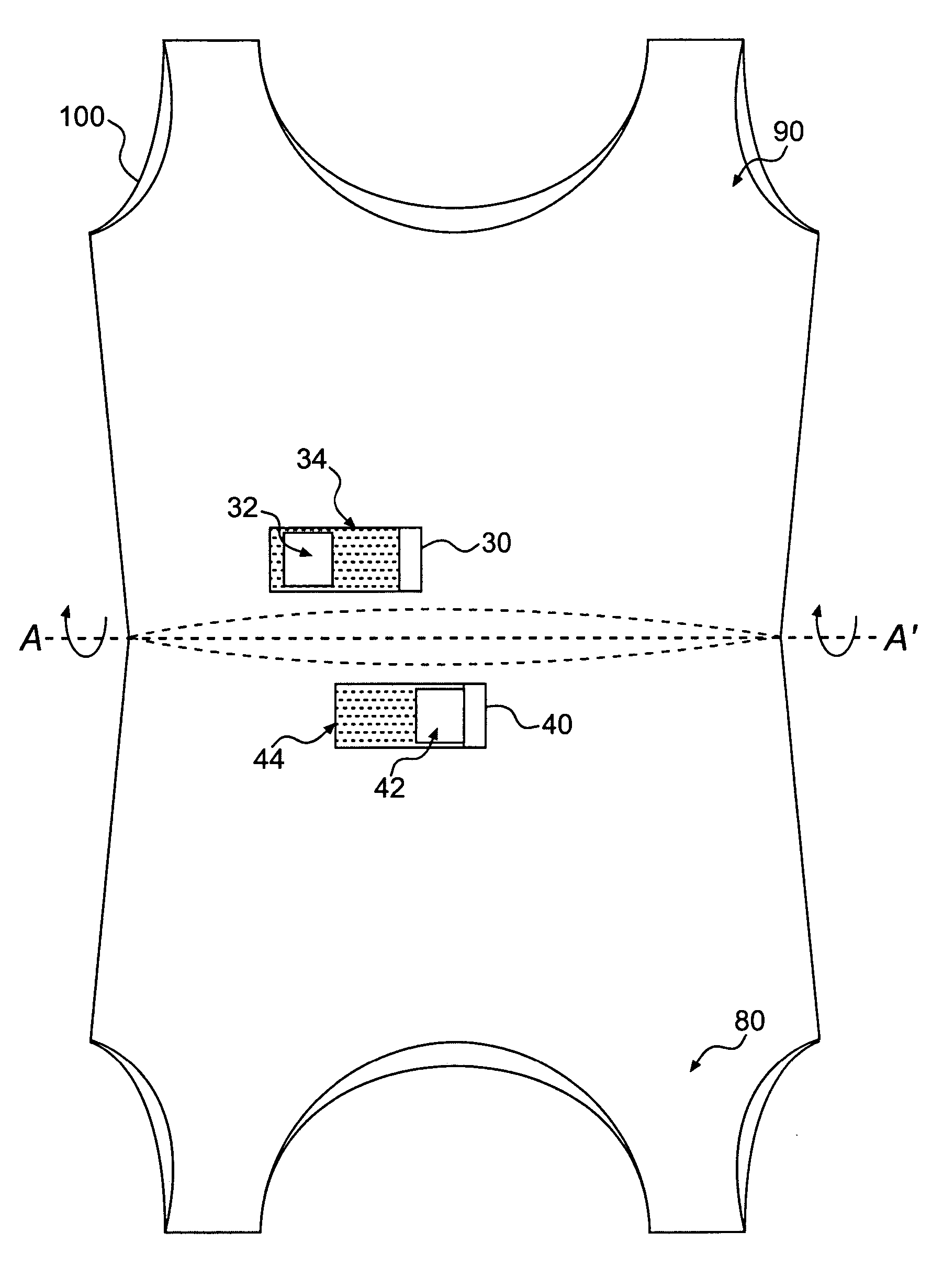
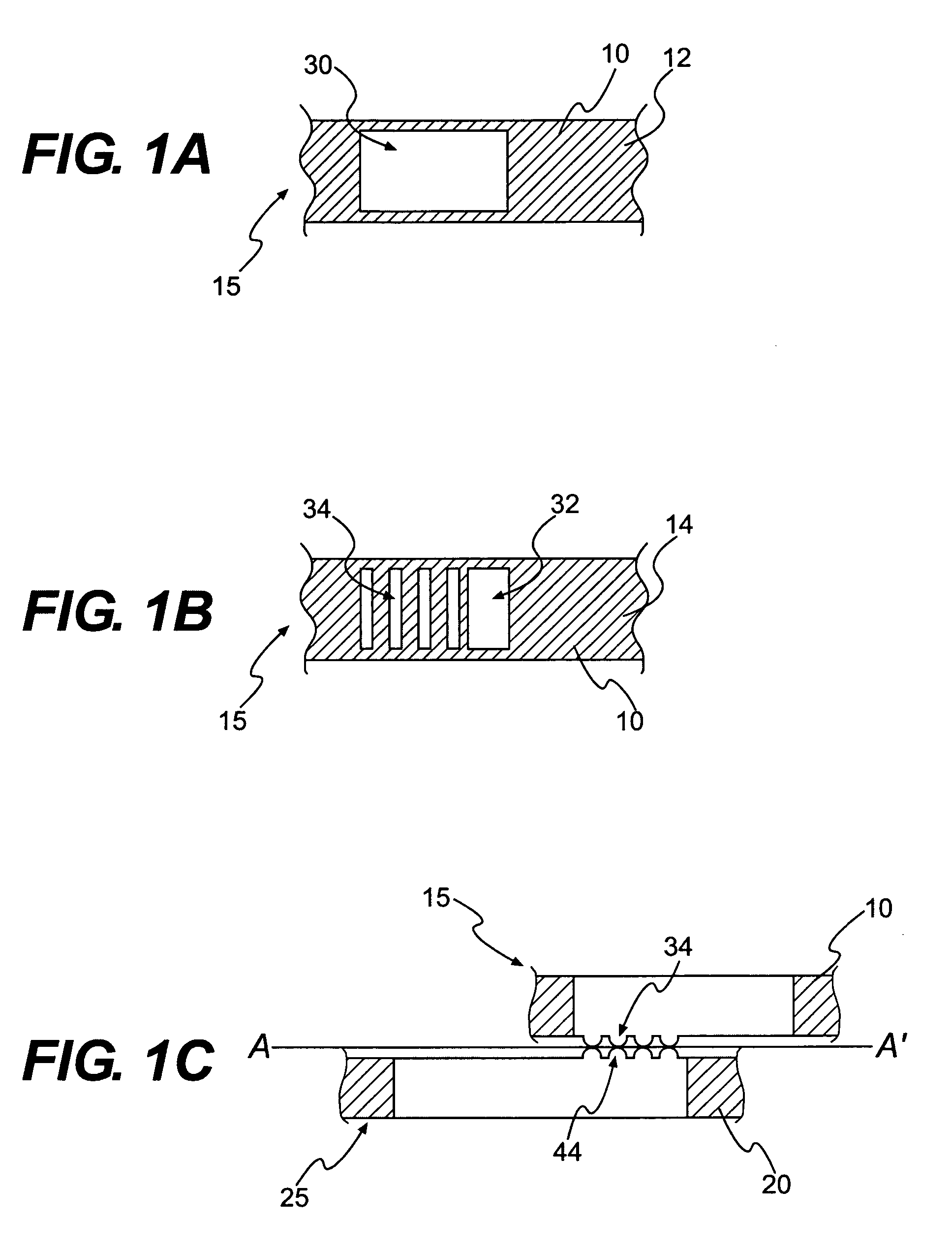
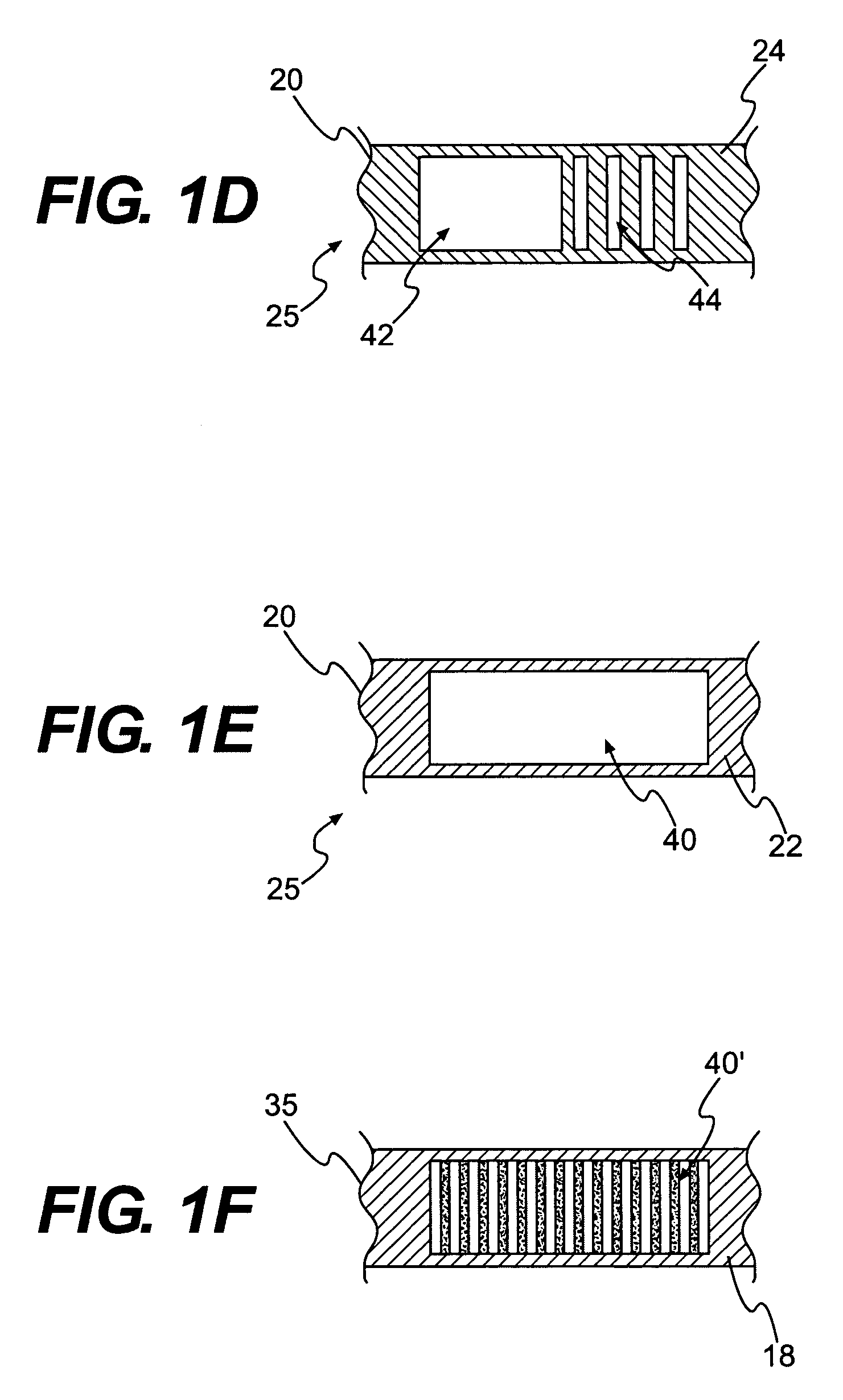
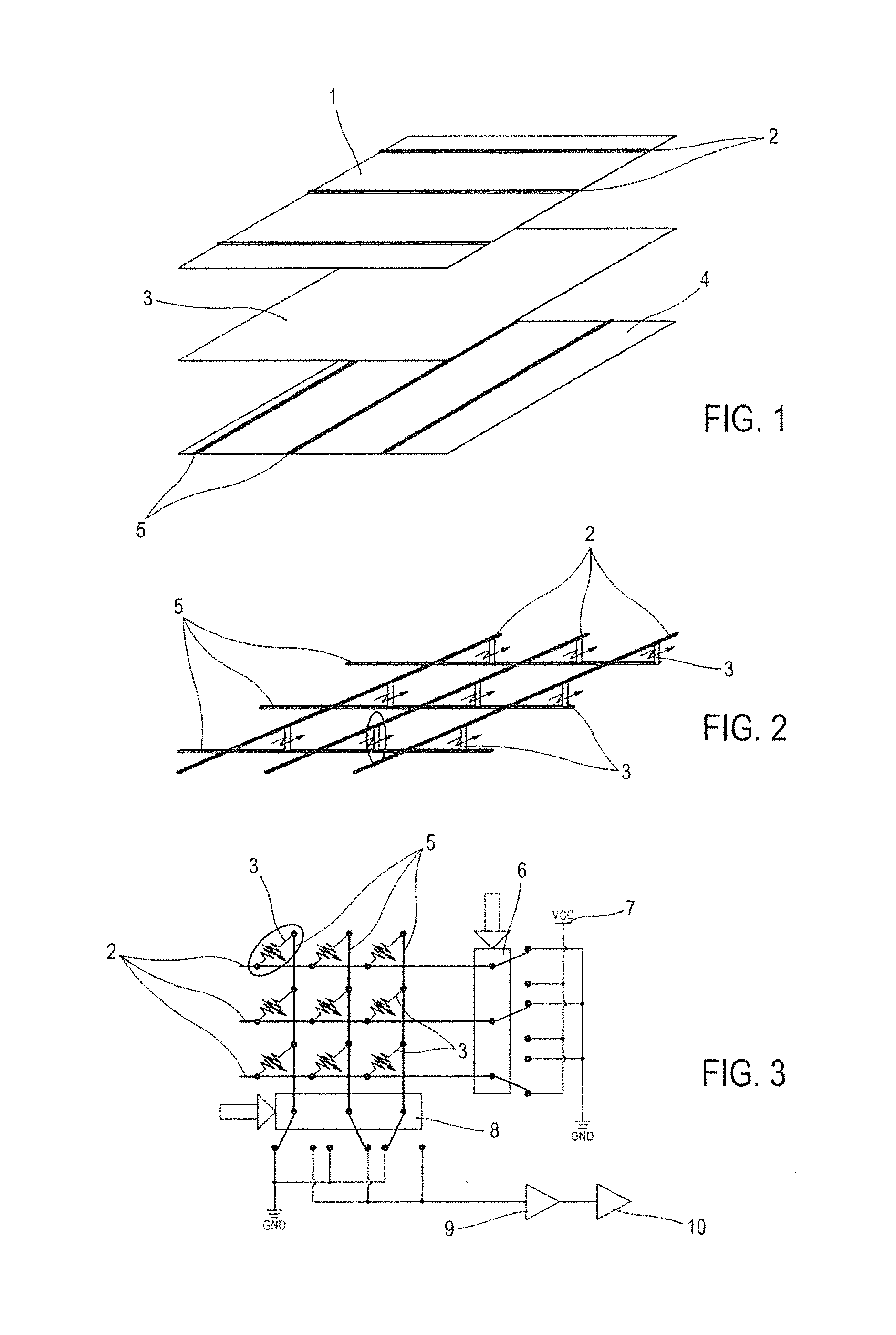
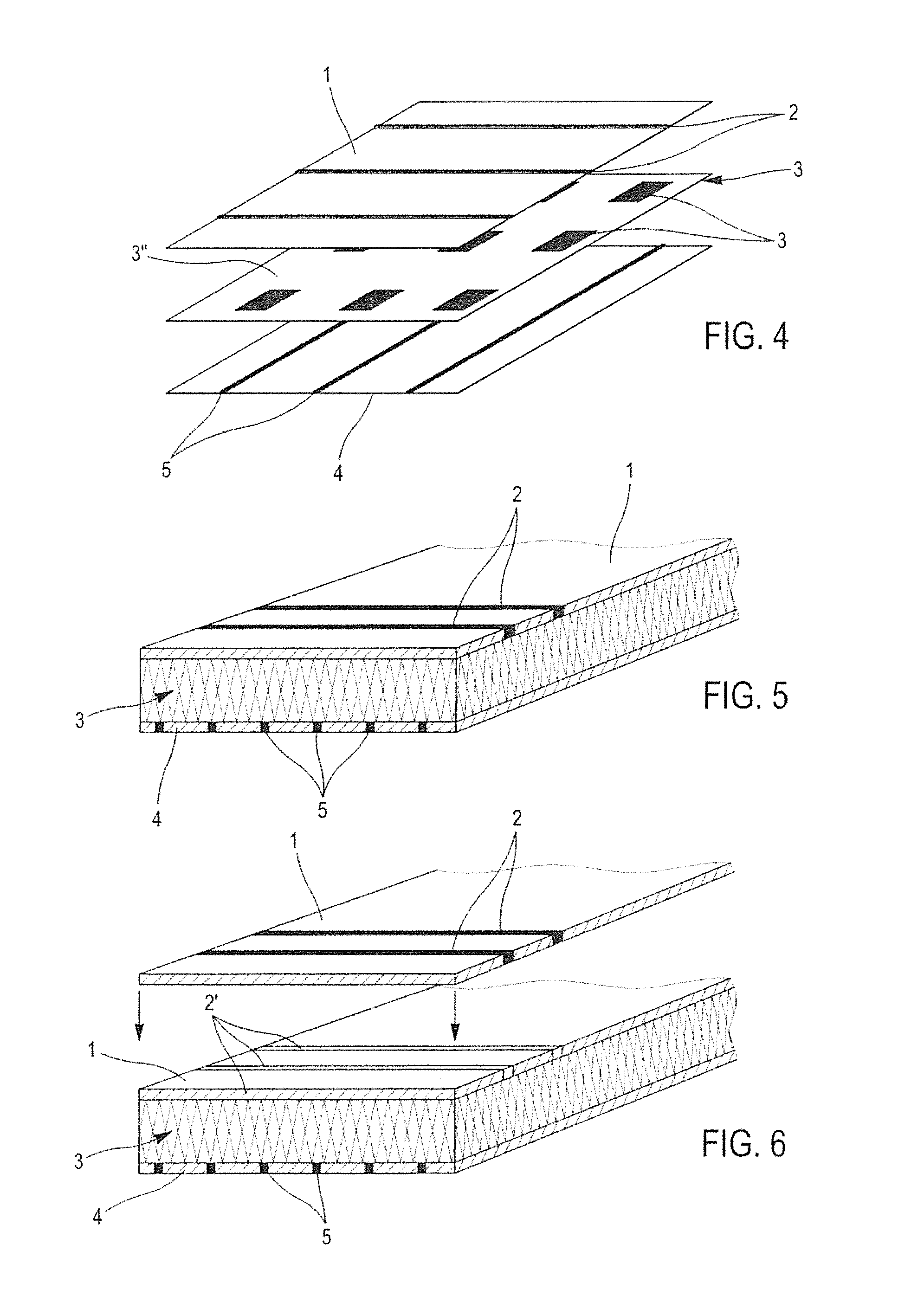
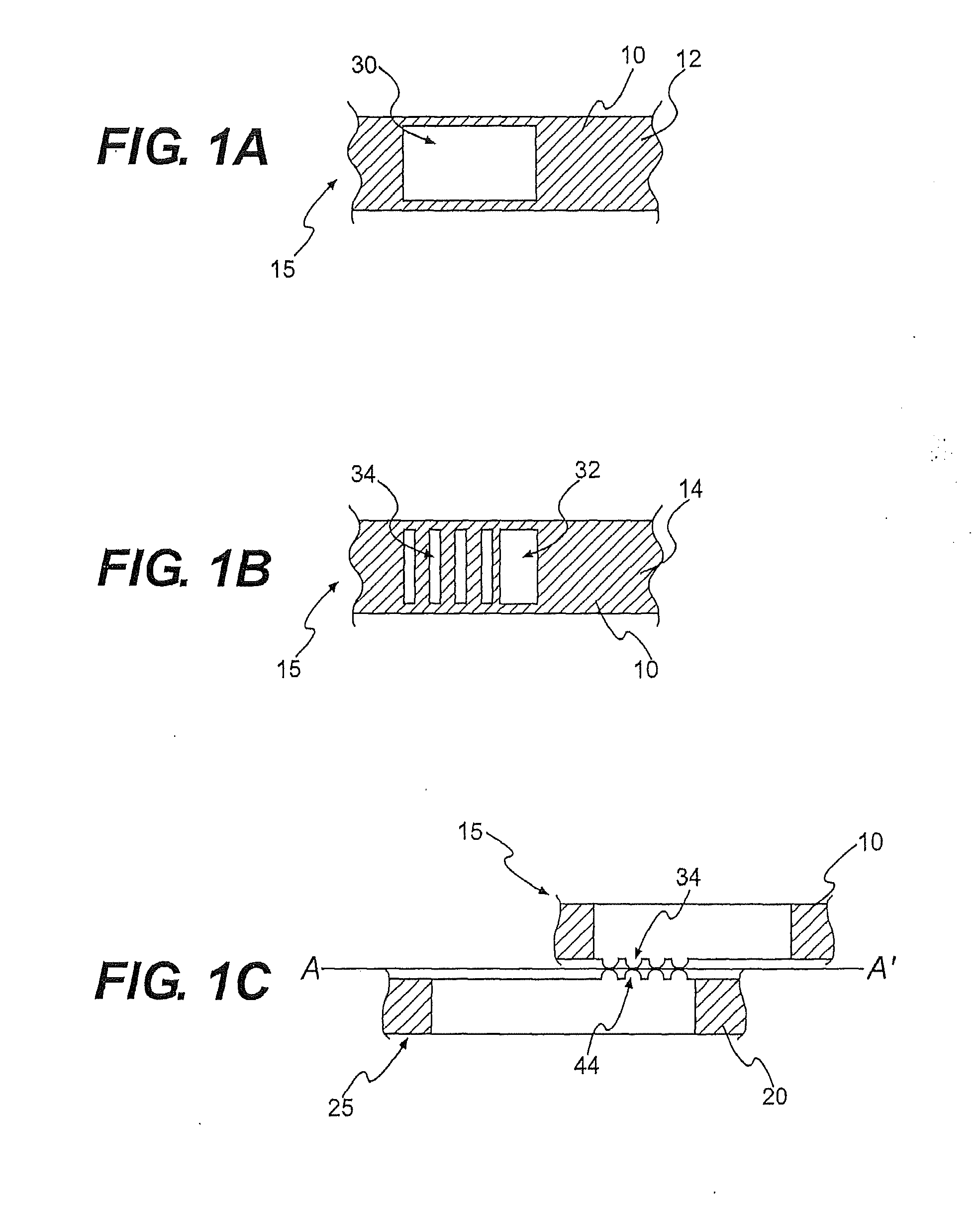
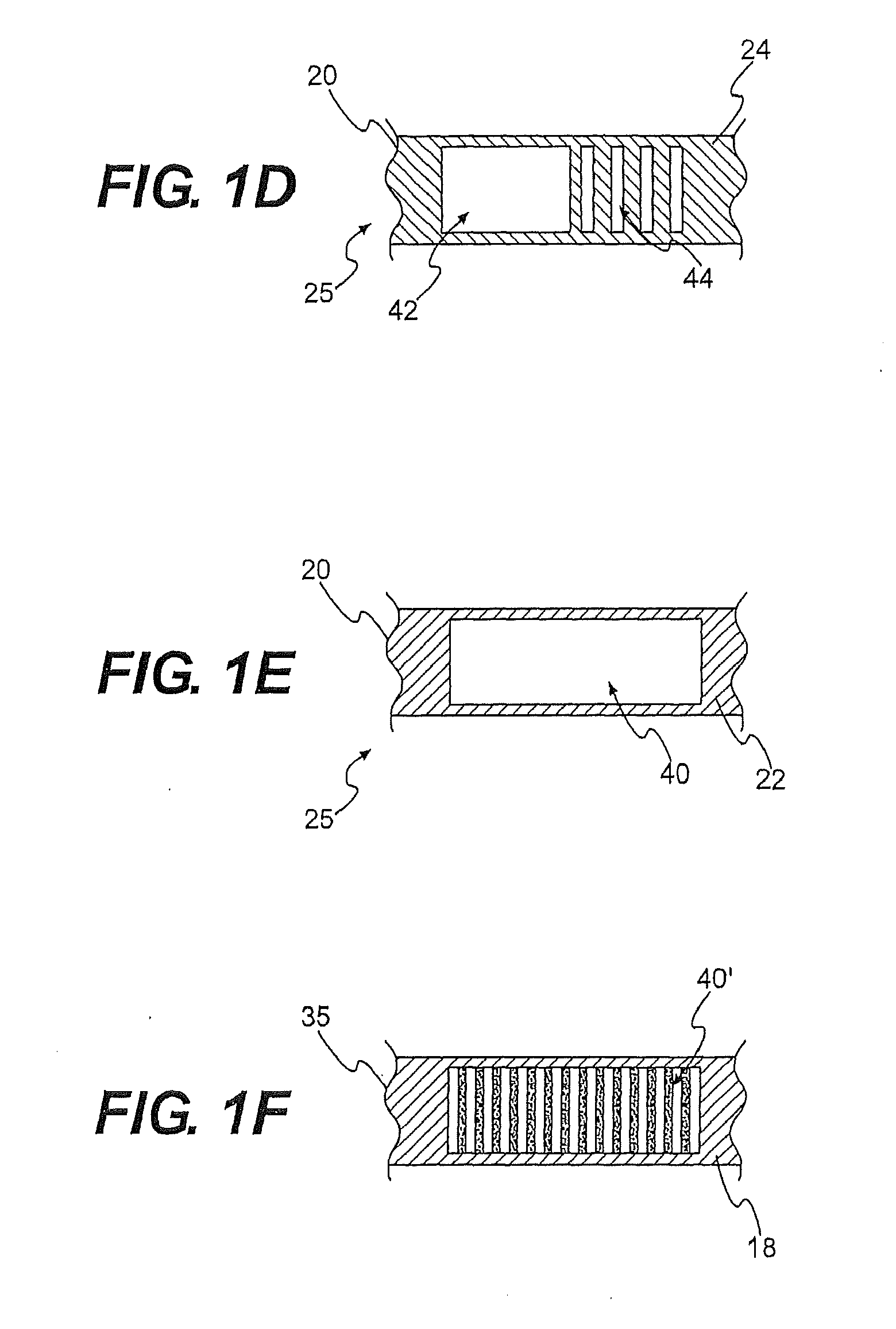
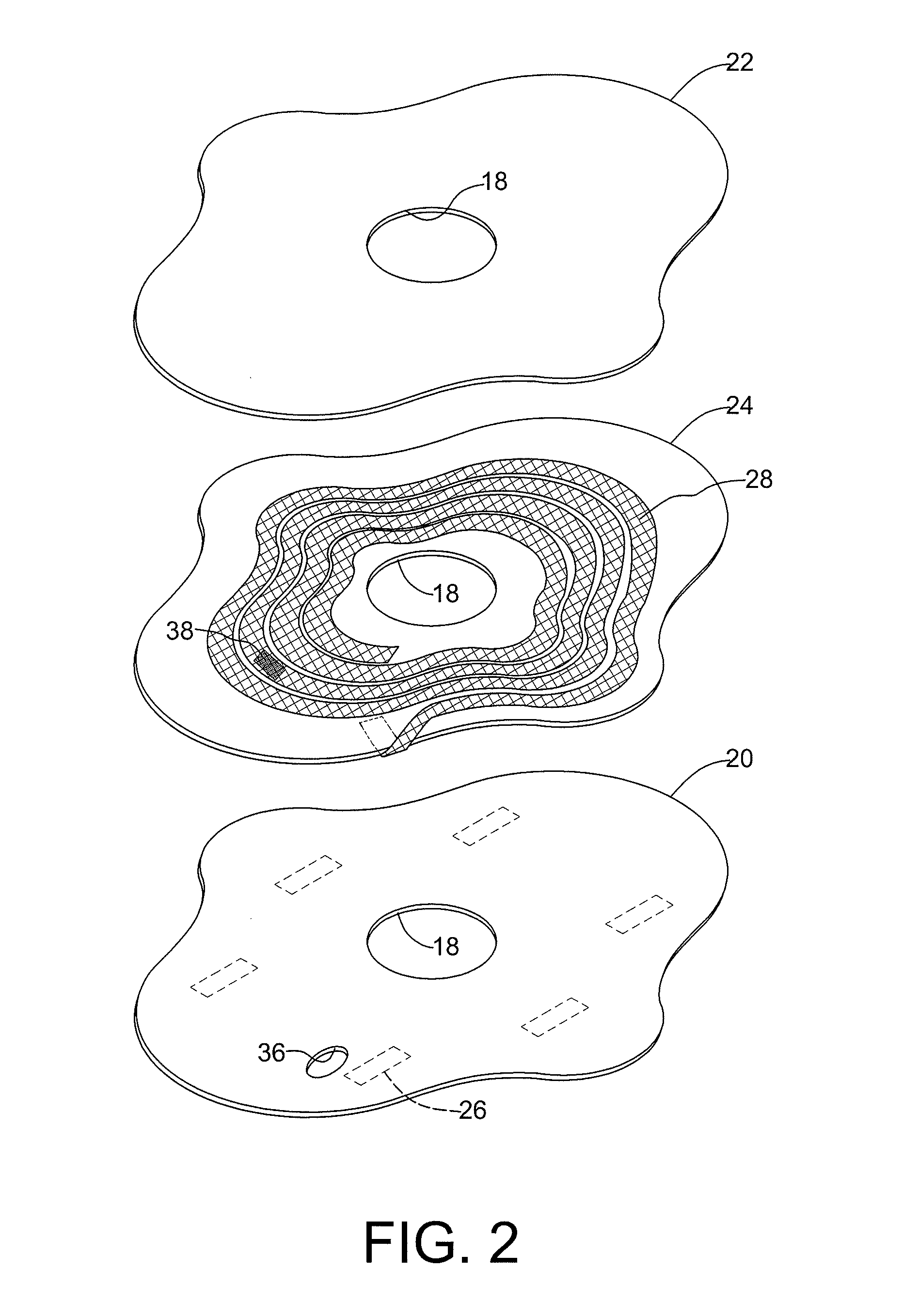
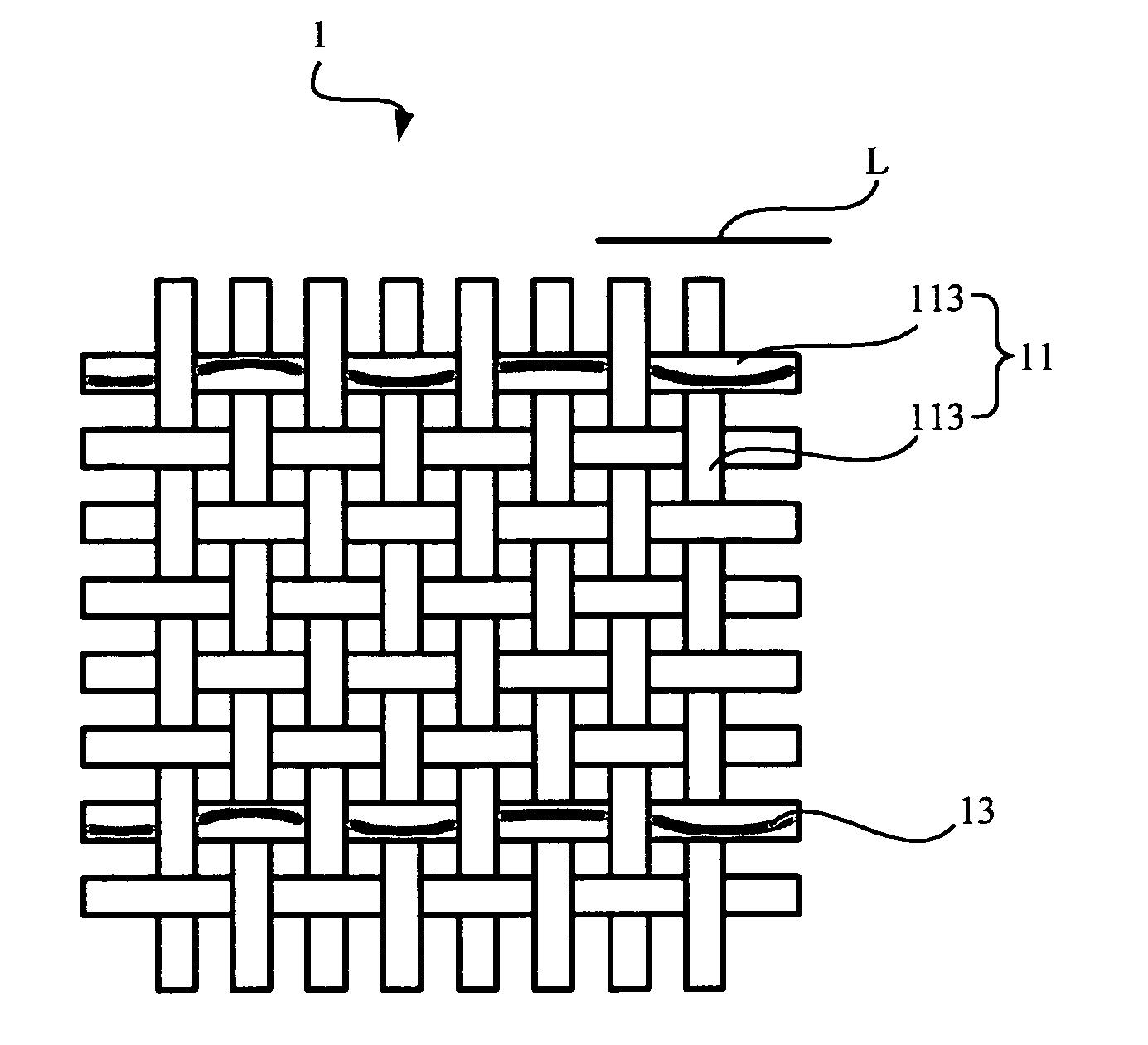
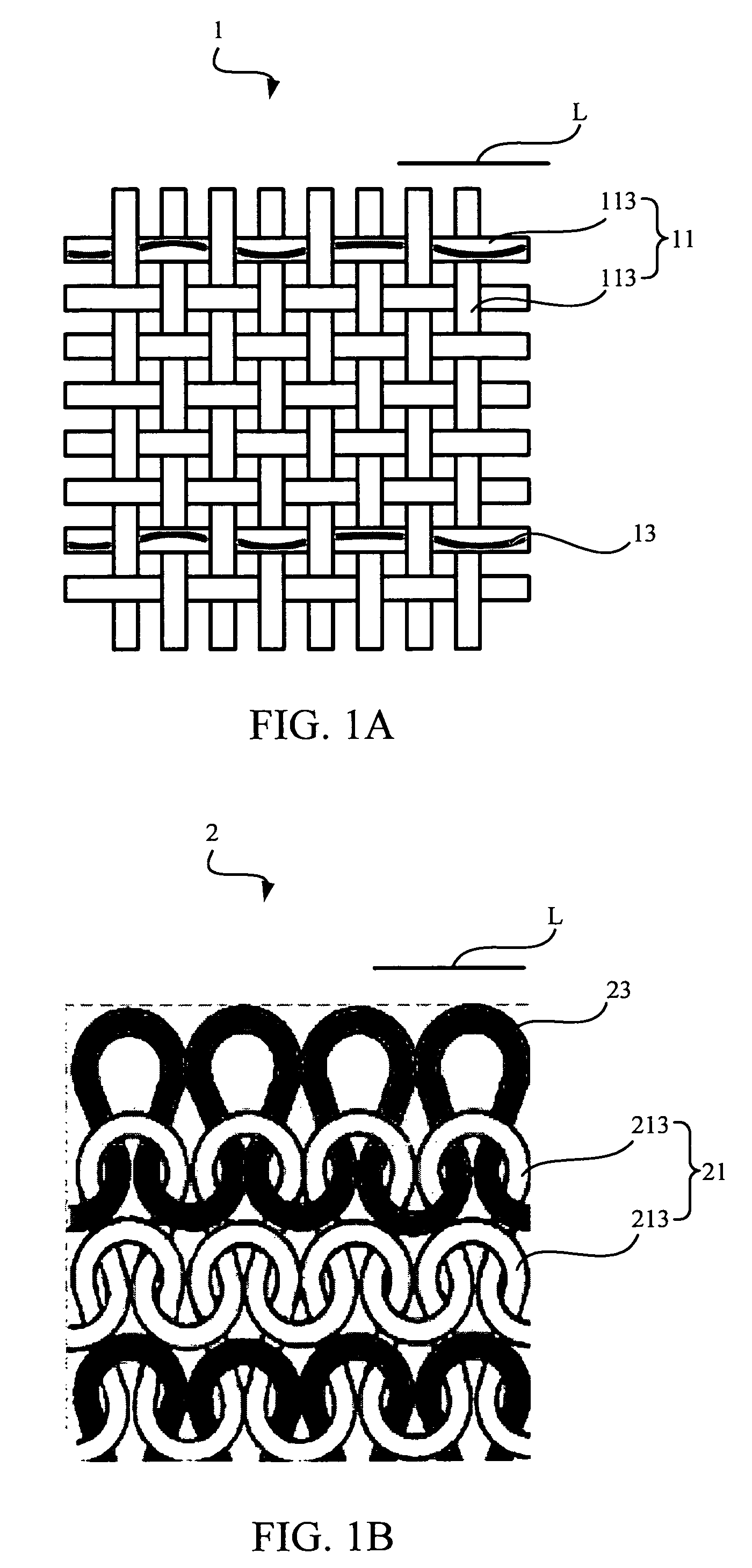
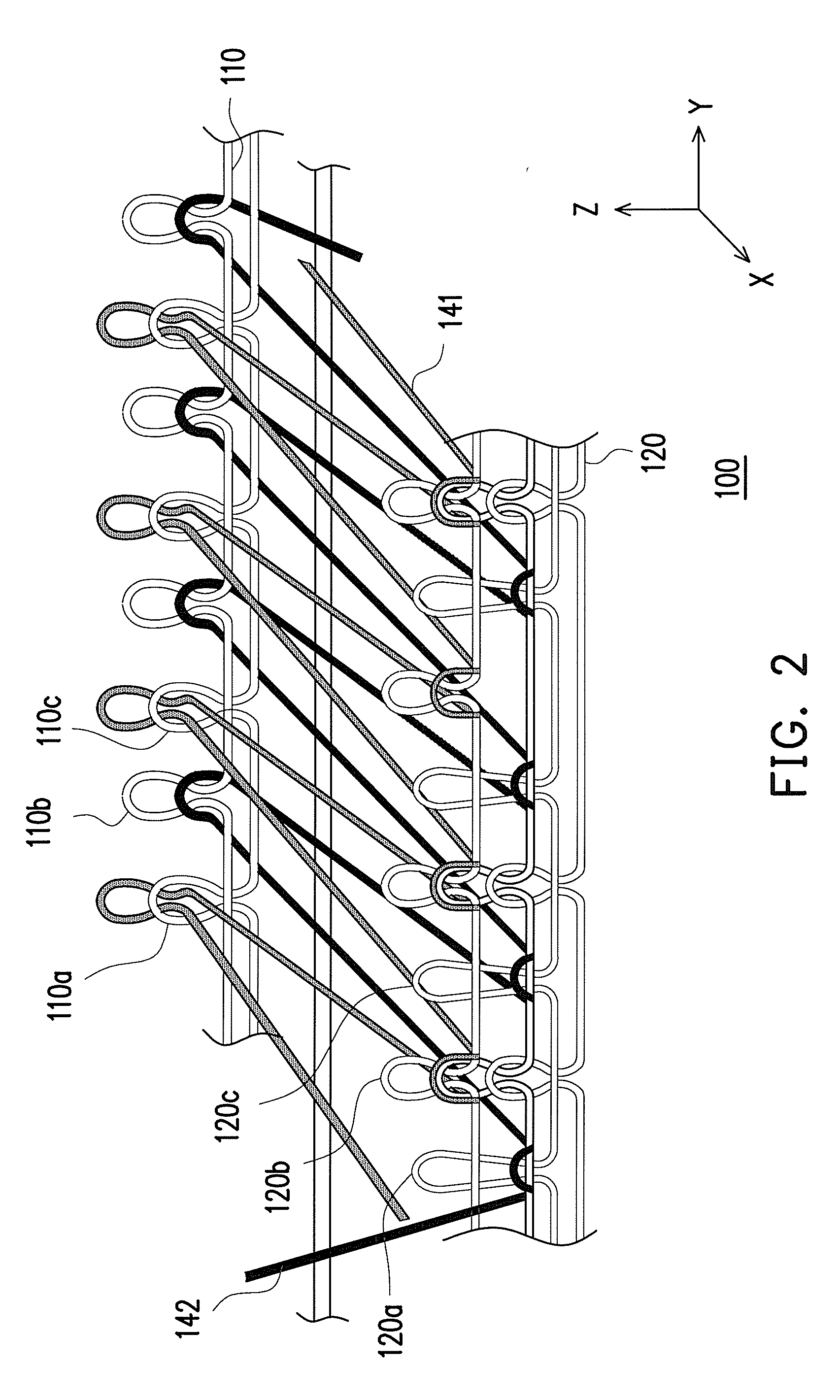
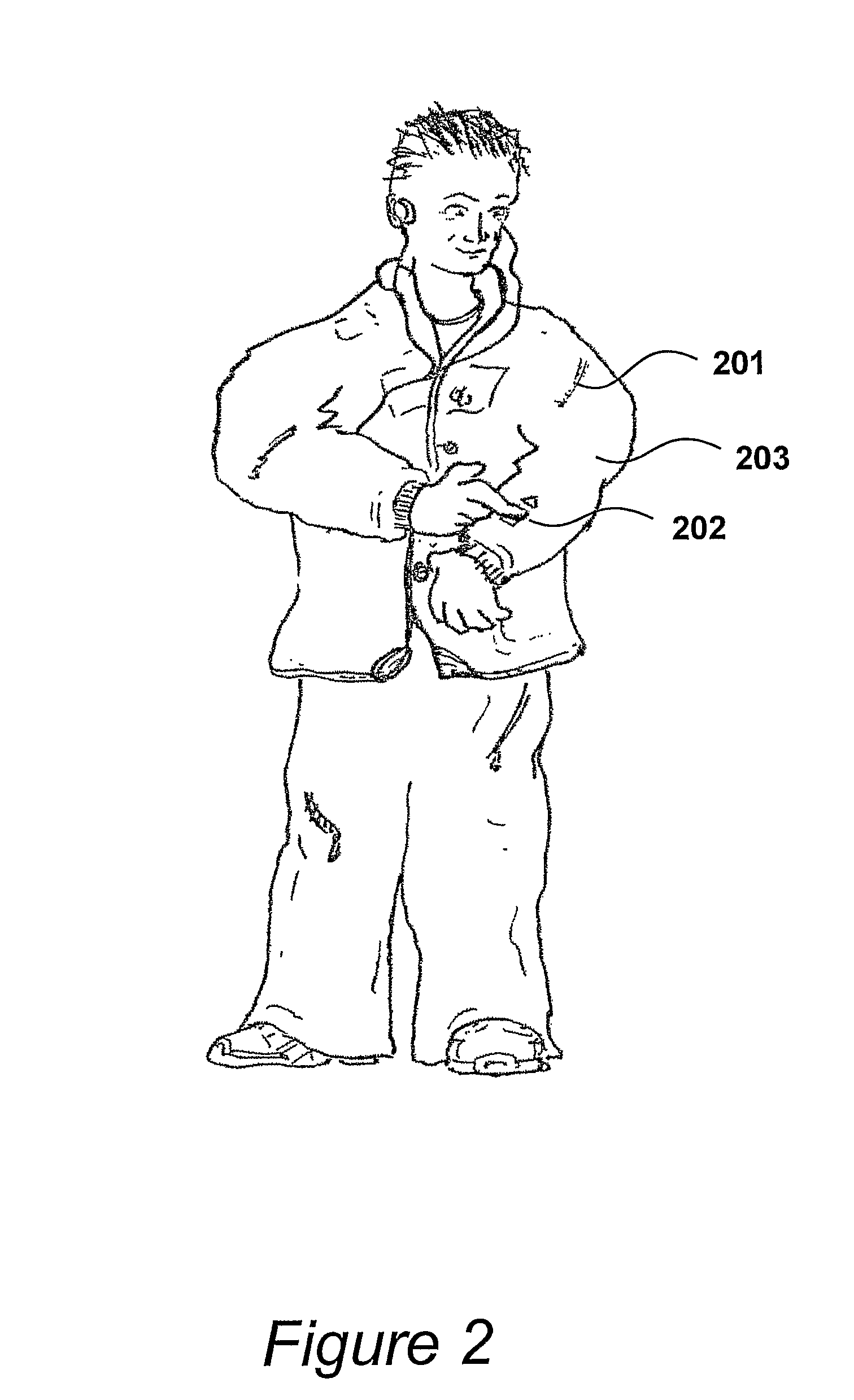
Textile-based electrode
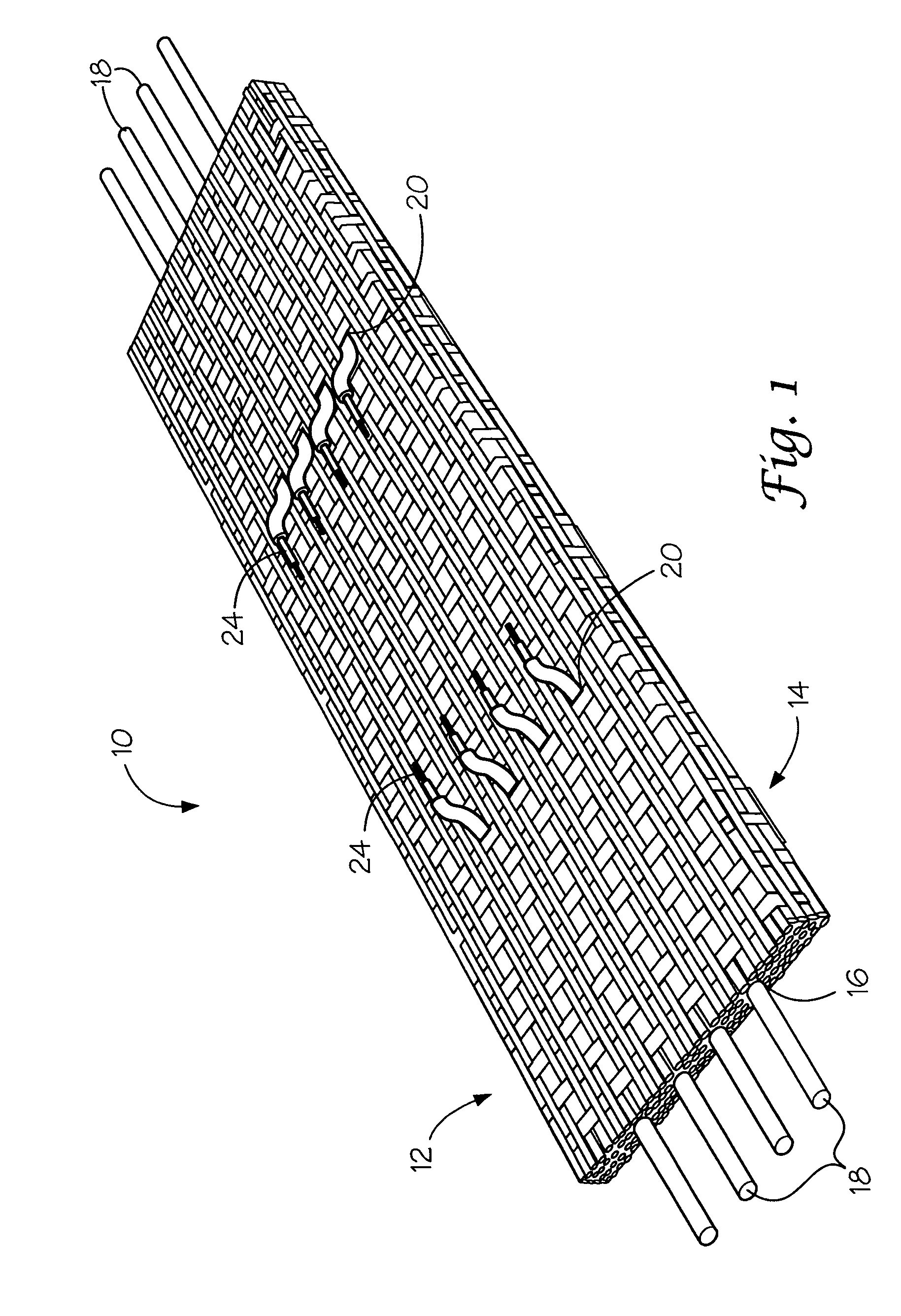
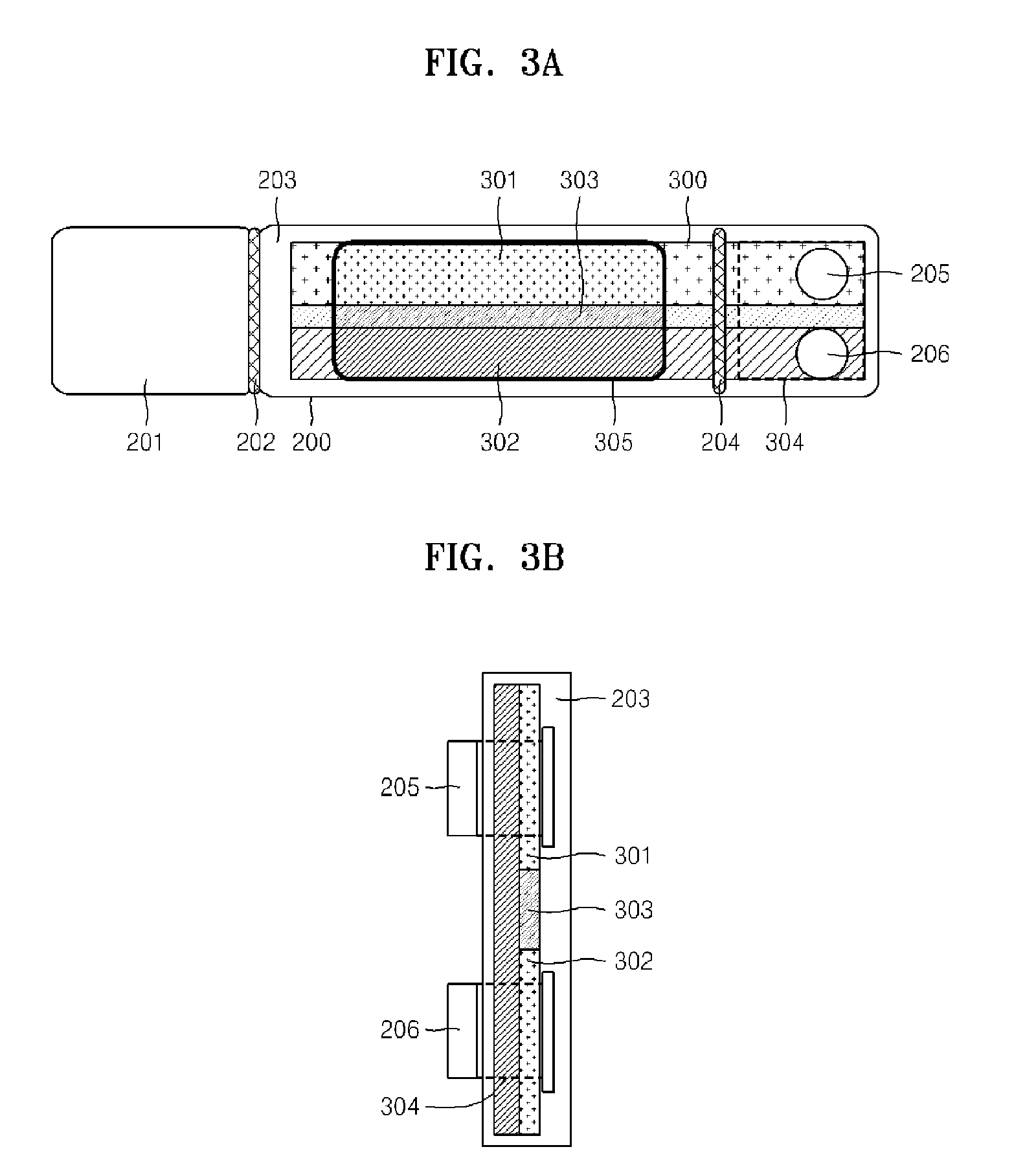
Textile-based electrodes include a fabric portion having stretch-recovery non-conductive yarns and an electrically conductive region having stretch-recovery electrically conductive yarn filaments. The electrodes can further include float yarns and can be configured in a textured or ribbed construction. When incorporated into a garment, the electrodes can be used to monitor biophysical characteristics, such as the garment wearer's heart rate.
Owner:ADIDAS +1
Fabric and yarn structures for improving signal integrity in fabric-based electrical circuits
InactiveUS7348285B2Reduce crosstalkImprove signal integrityAlcoholic beverage preparationPower cables with screens/conductive layersPower gridTwisted pair
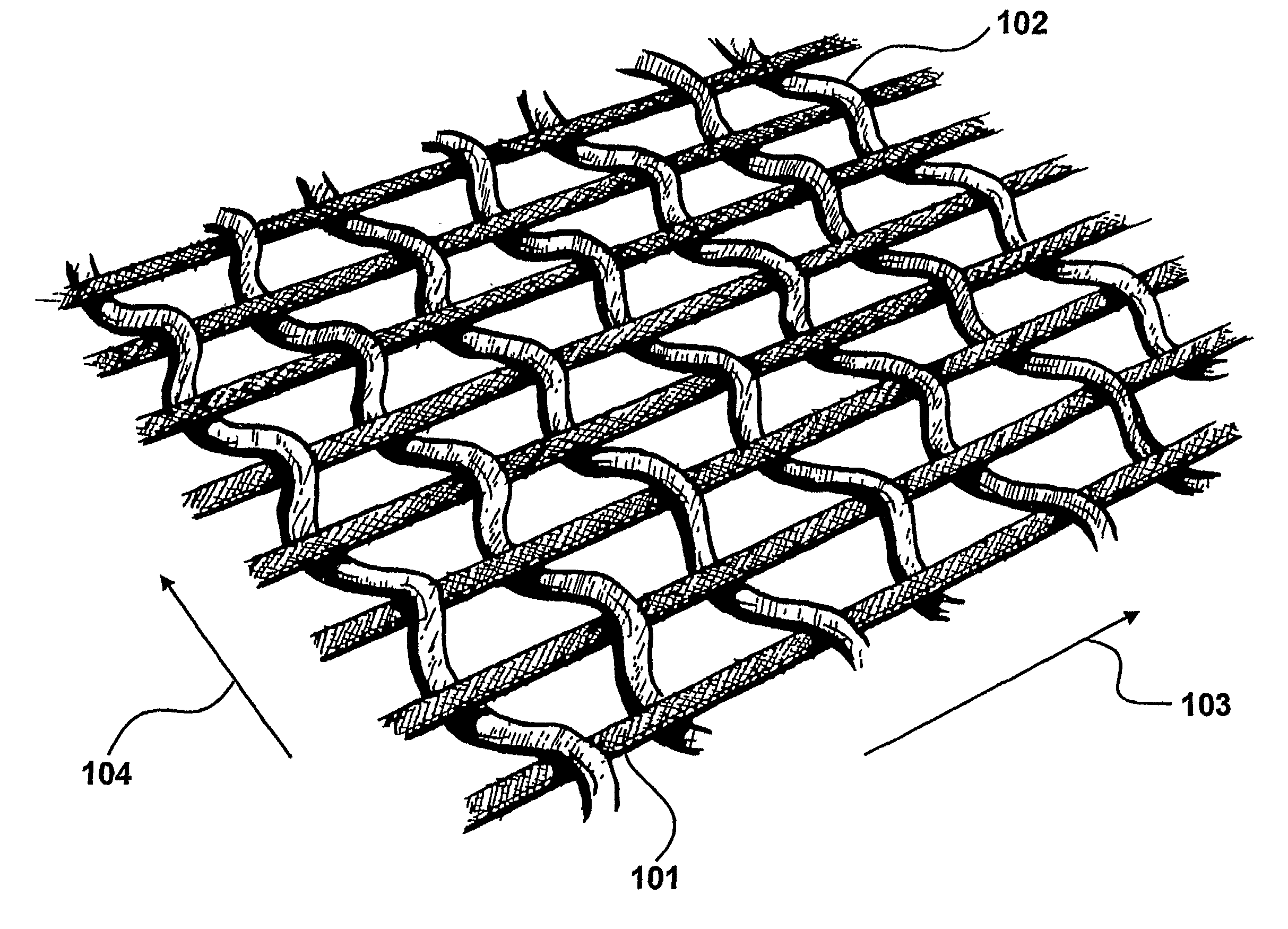
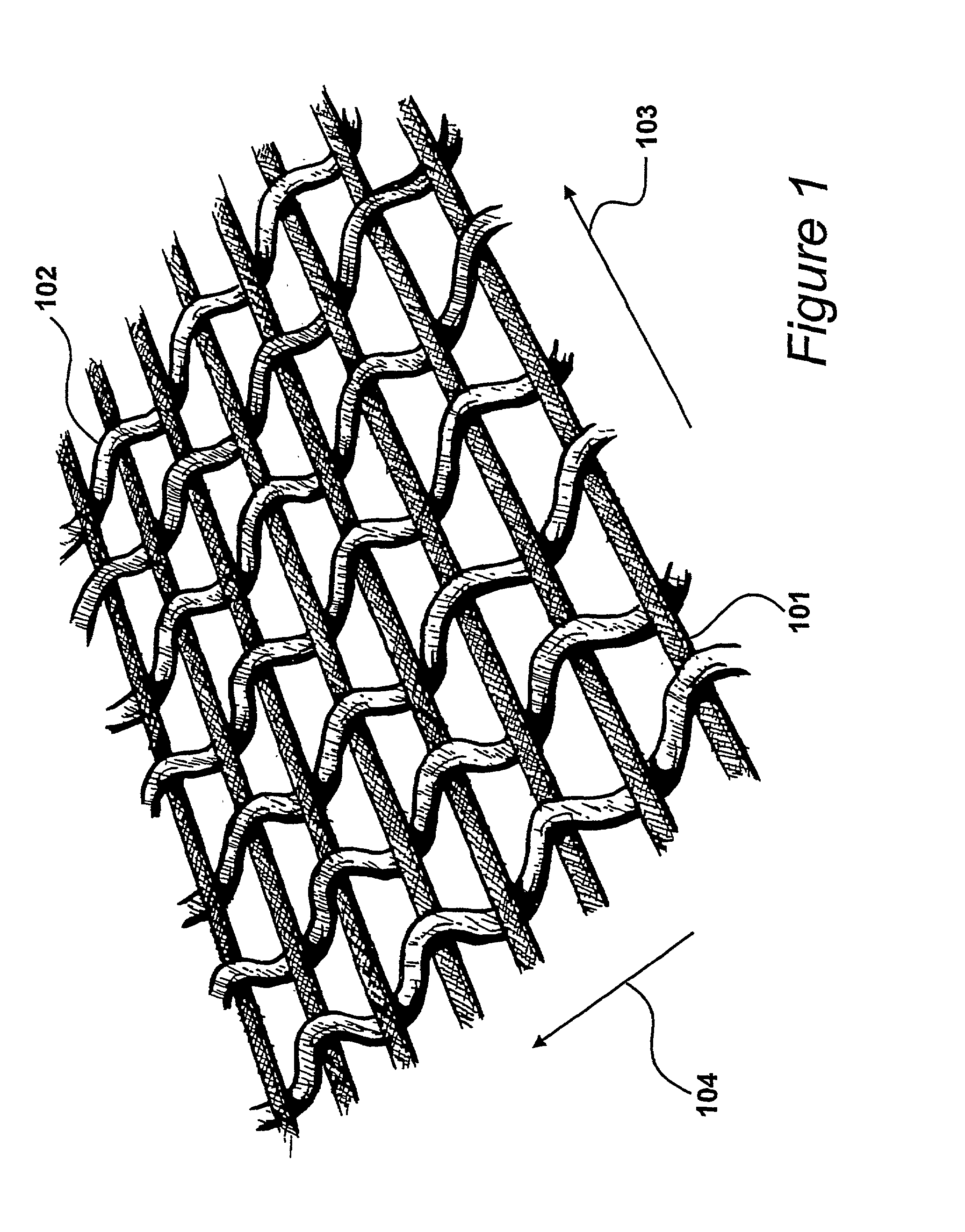
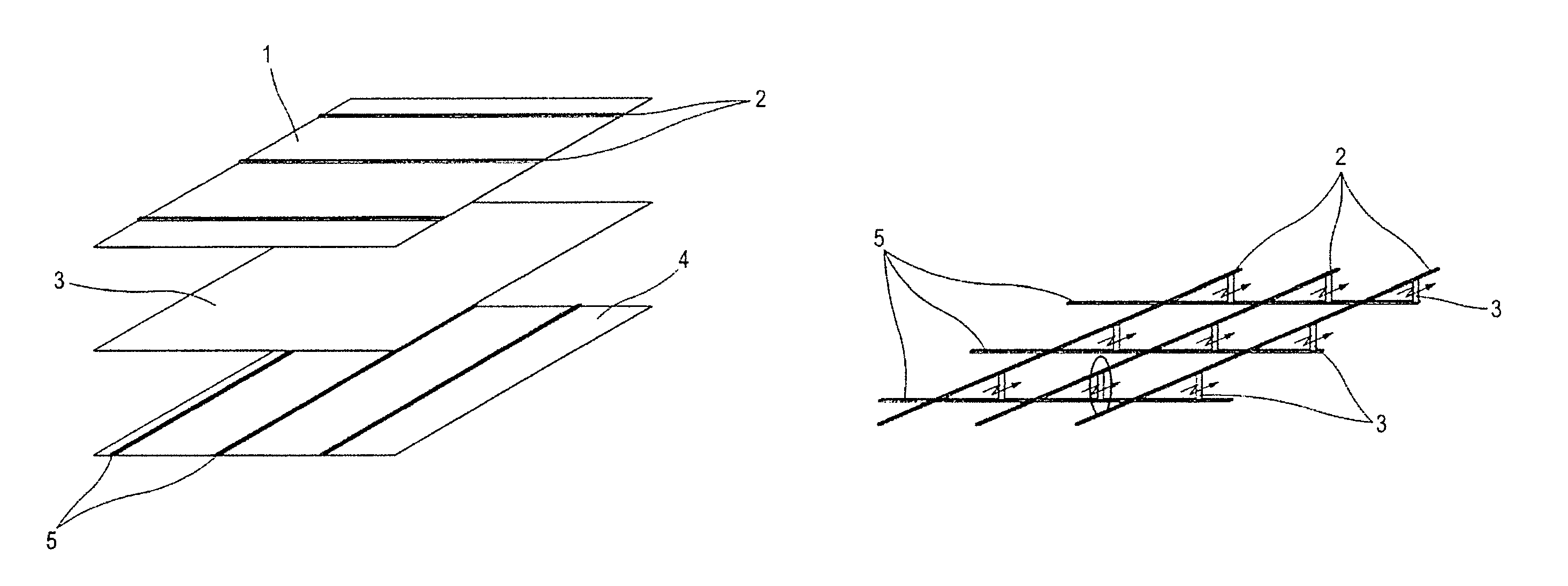
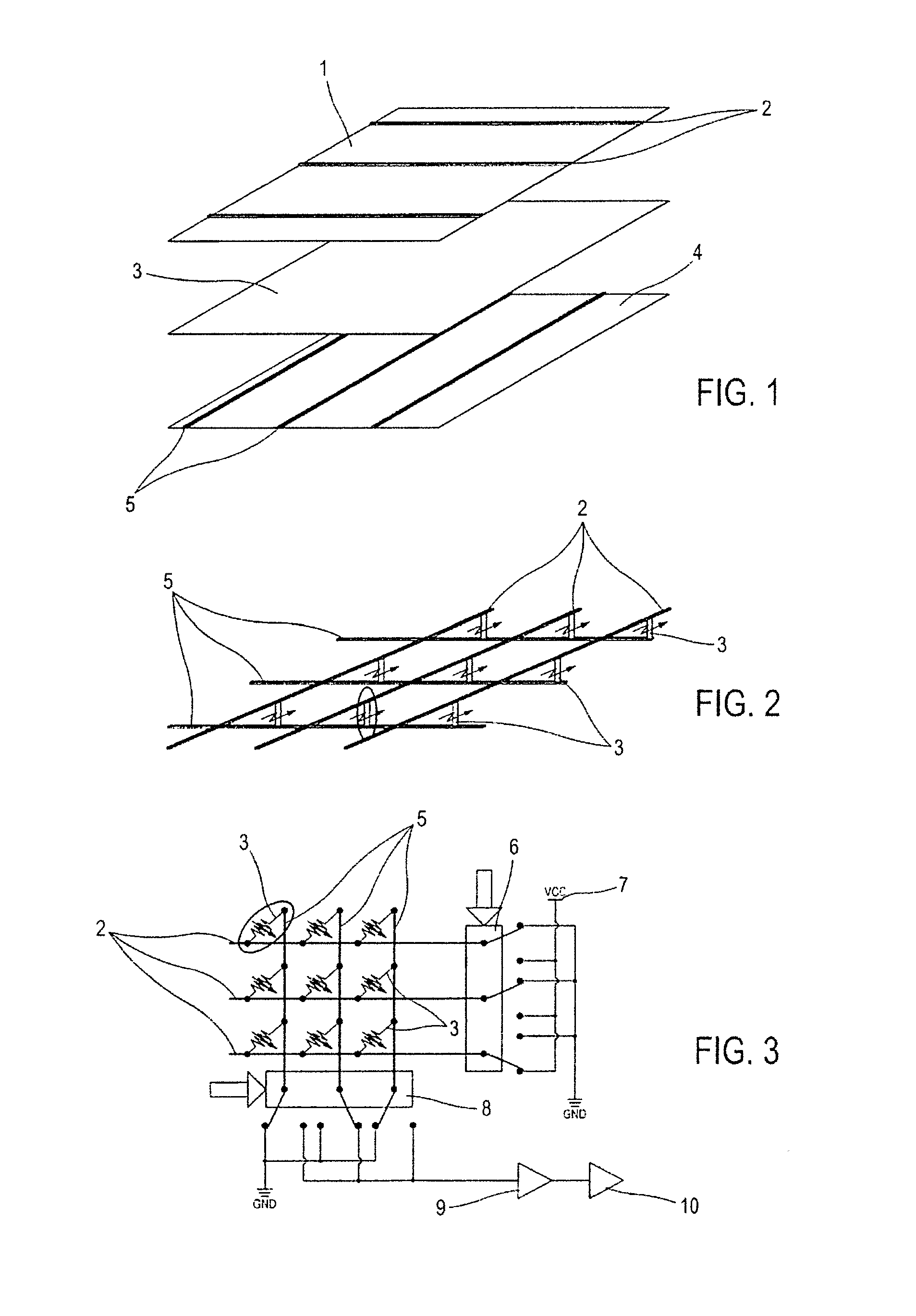
Coaxial and twisted pair conductive yarn structures reduce signal crosstalk between adjacent lines in woven electrical networks. A coaxial conductive yarn structure includes an inner conductive yarn having a plurality of conductive strands twisted together. An outer conductive yarn is wrapped around the inner conductive yarn. An insulating layer separates the inner and outer yarns. A twisted pair conductive yarn structure includes first and second conductive yarns, each including a plurality of conductive strands being twisted together. The first and second conductive yarns are twisted together to form a helical structure. In a woven electrical network, at least one conductor of adjacent conductive yarn structures is connected to ground to reduce signal crosstalk. Coaxial and twisted pair yarn structures may also be formed simultaneously with weaving or knitting the threads that make up the structures into a fabric.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Method for producing an electrically conductive yarn, the electrically conductive yarn and use of the electrically conductive yarn
InactiveUS6032450ACounteracts brittlenessImprove adhesionInorganic material artificial filamentsContinuous wound-up machinesTextile fiberYarn
A method for producing an electrically conductive compound yarn. An electrically conductive monofilament metal thread is spun into a compound yarn together with textile fibers. A compound yarn of this type is particularly suitable for producing woven and knit materials.
Owner:SPOERRY 1866 AG
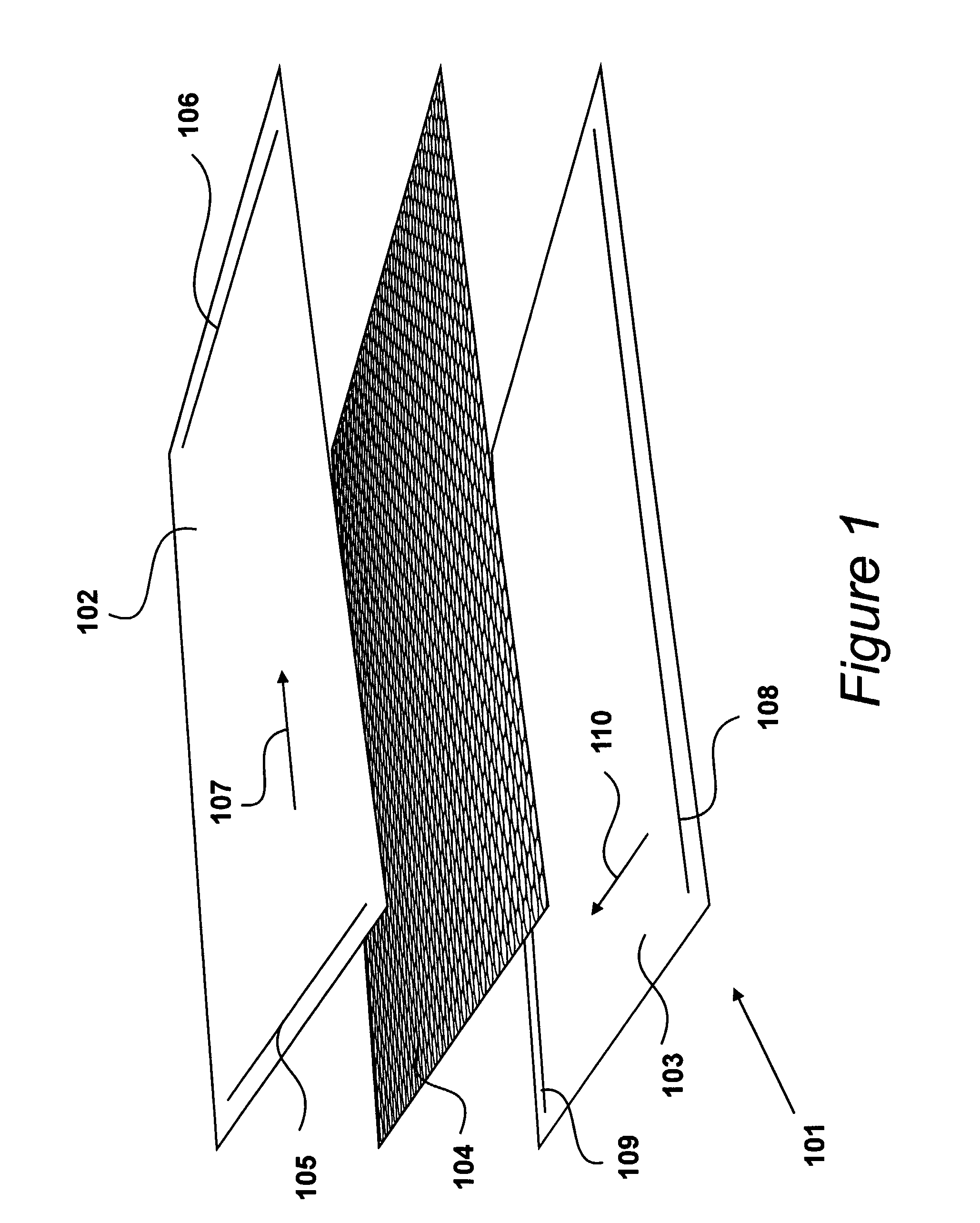
Device for Measuring Pressure from a Flexible, Pliable, and/or Extensible Object Made from a Textile Material Comprising a Measurement Device
ActiveUS20140150573A1Simple designLow costForce measurement using piezo-resistive materialsMulti-ply fabricsFiberElectrical resistance and conductance
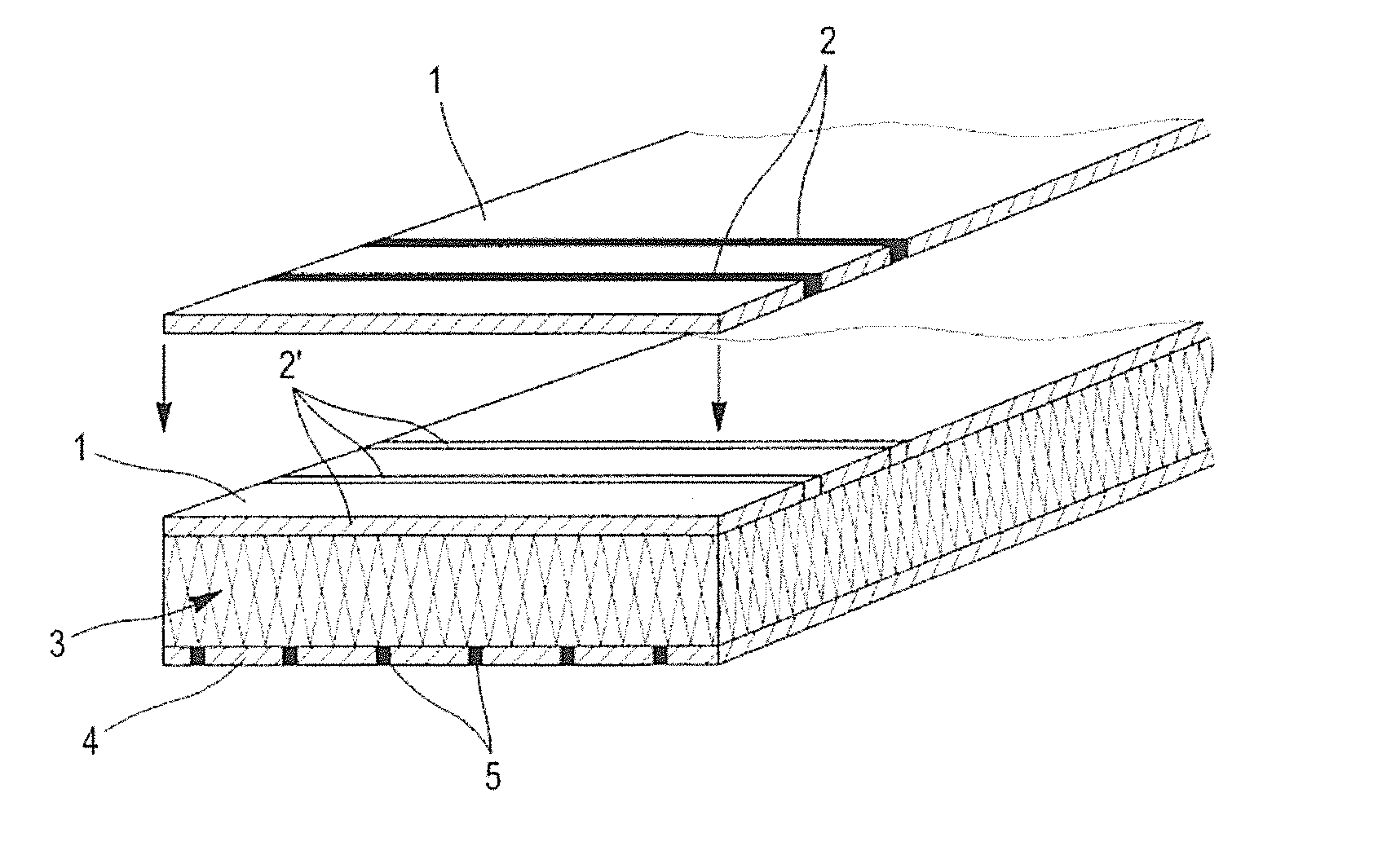
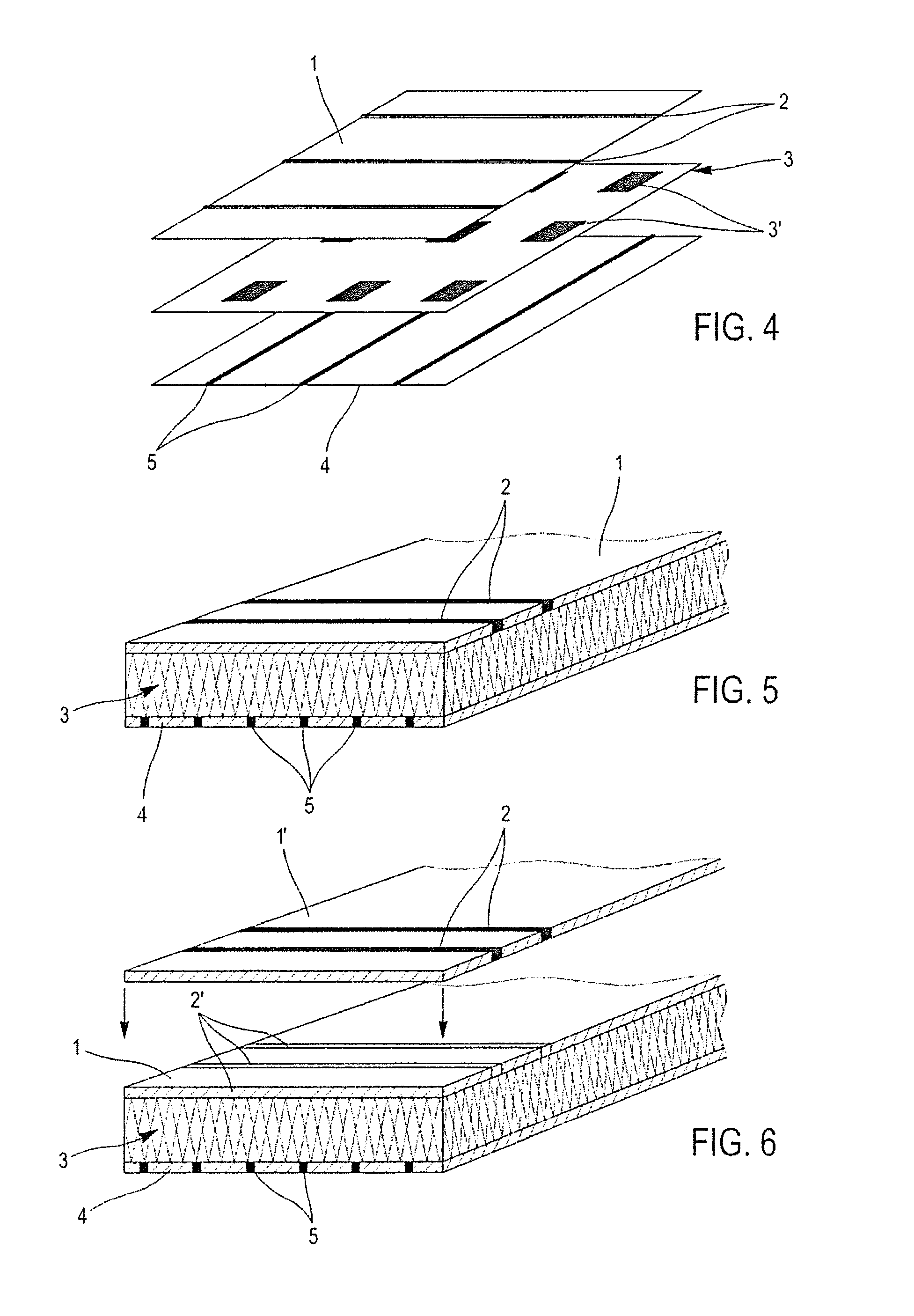
A device and method for measuring the pressure exerted at different points of a flexible, pliable and / or extensible fabric capable of being worn as a garment, lapel, or the like, which provides three stacked layers including a first insulating layer comprising an arrangement of insulating fibers and at least one row of at least one conductive yarn in contact with a first surface of a piezoresistive layer of fibers of a piezoresistive material, and a second insulating layer comprising an arrangement of insulating fibers, including at least one row of at least one conductive yarn, in contact with a second surface of the piezoresistive layer, and an electronic circuit capable of measuring the electric resistance variation when a pressure is exerted on the fabric, the pressure being a function of the resistance variation.
Owner:TEXISENSE
Elastic fabric with sinusoidally disposed wires
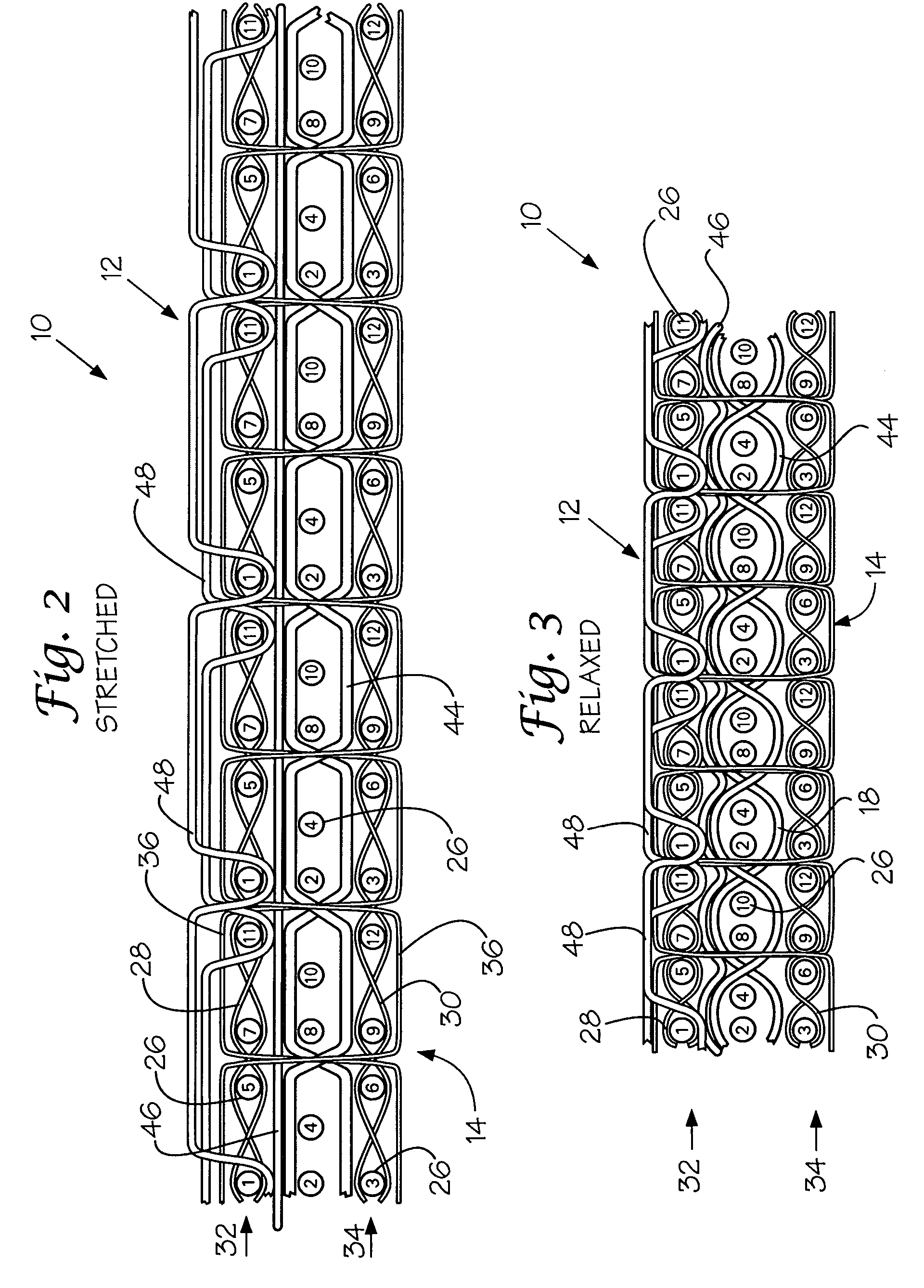
ActiveUS7191803B2Conductive stabilityShorten the lengthCircuit bendability/stretchabilityGarmentsEngineeringBody movement
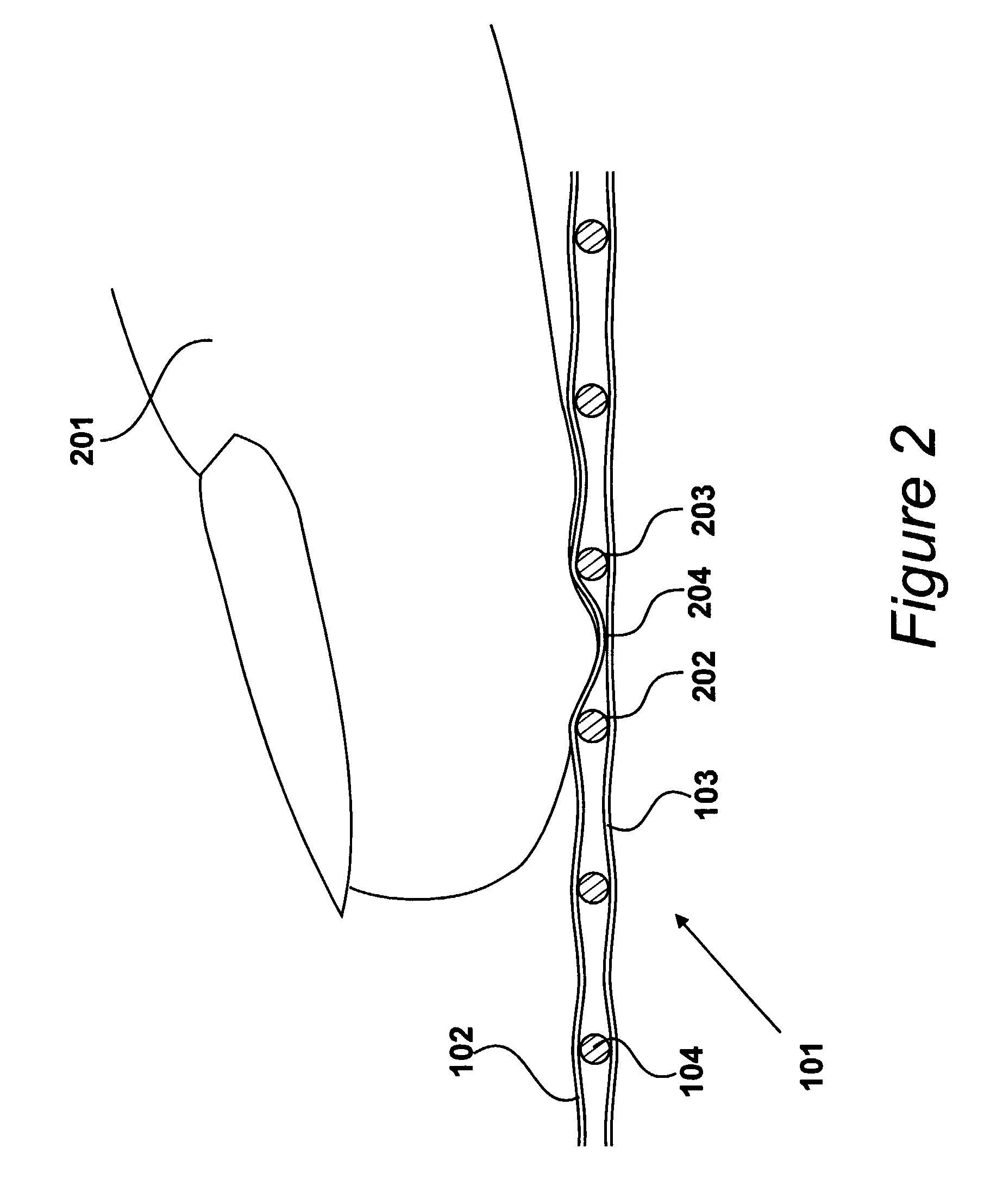
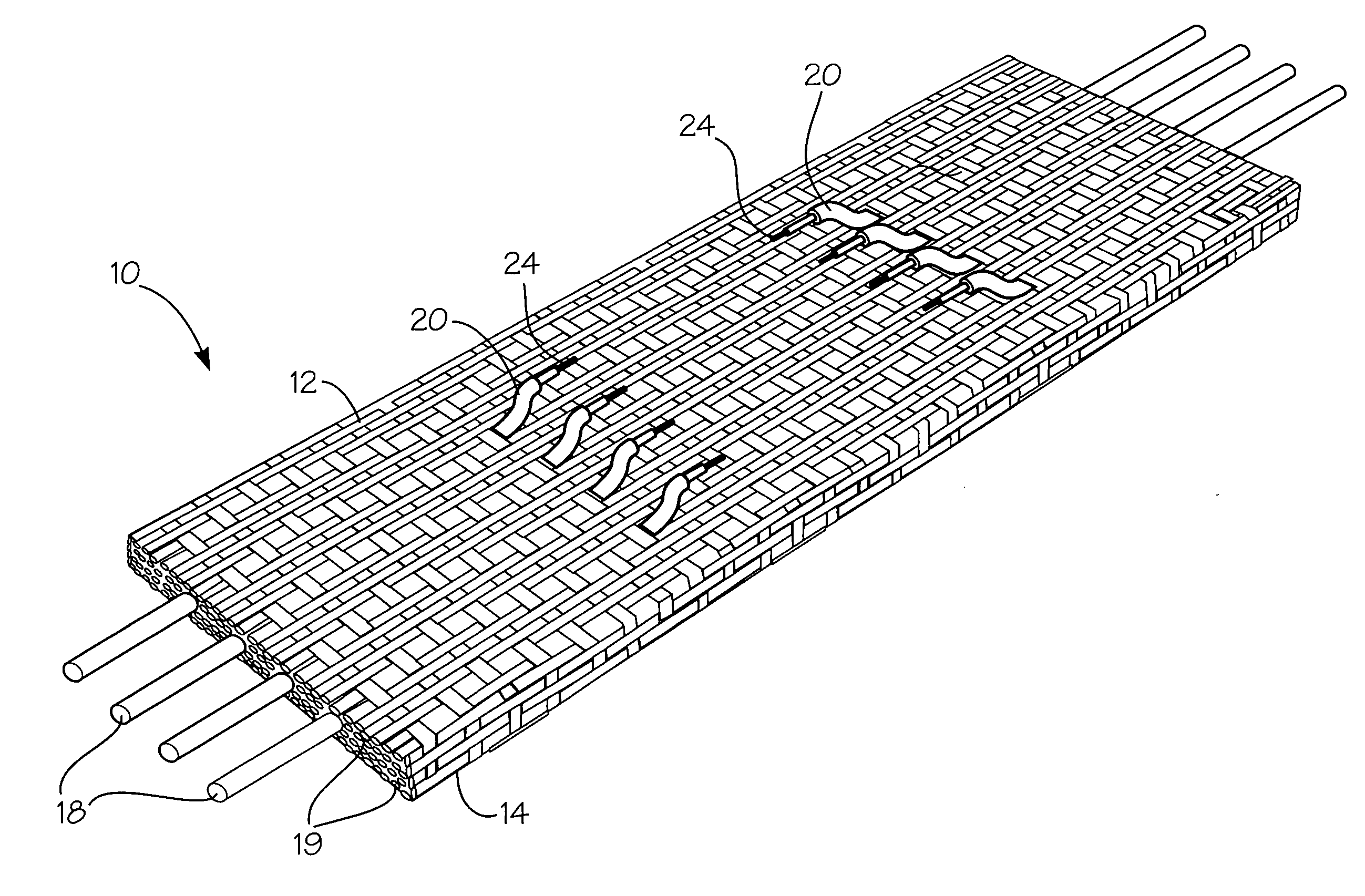
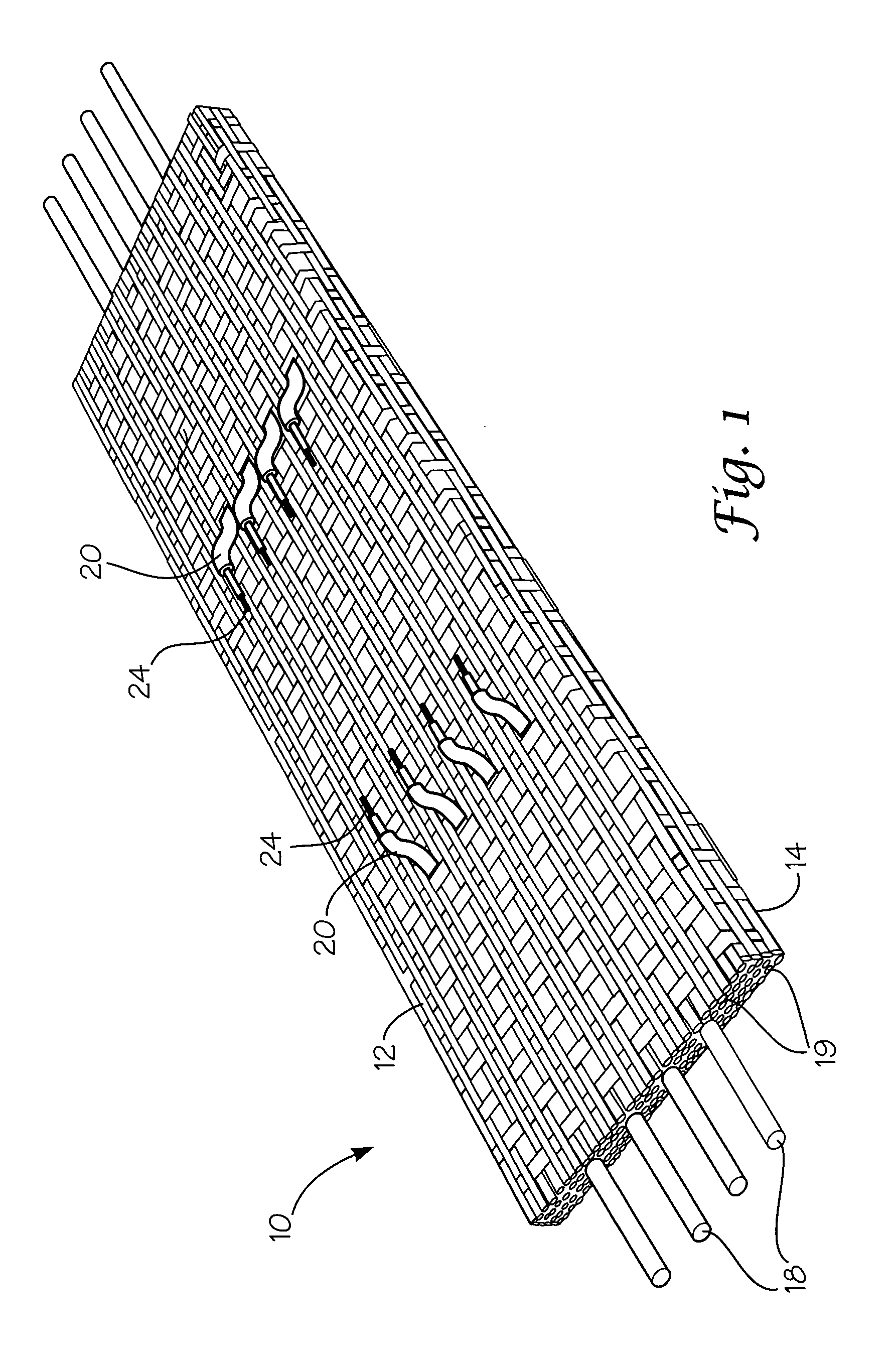
A fabric for use with a system for monitoring prescribed body functions comprising an elastic fabric, adapted to be carried by a torso, which is stretchable in its longitudinal direction so as to expand and contract in response to body movement and size. The carrier includes at least one conductive and inelastic yarn arranged longitudinally of and located between upper and lower surfaces. The conductive yarn is arranged in sinusoidal configurations longitudinally of the fabric. The conductive yarn forms a breakout through one of the outer surfaces, at selected locations along the length of the fabric, forming opposed exposed ends above the surface. A monitoring unit, which includes a connector and a sensor, is secured with the one surface at the breakout with the connector being united with the exposed ends of the conductive yarn. The fabric acts to maintain the monitoring unit in a desired stationary position allowing the sensor to sense signals emitted from the torso and transmit these senses signals.
Owner:WOVEN ELECTRONICS
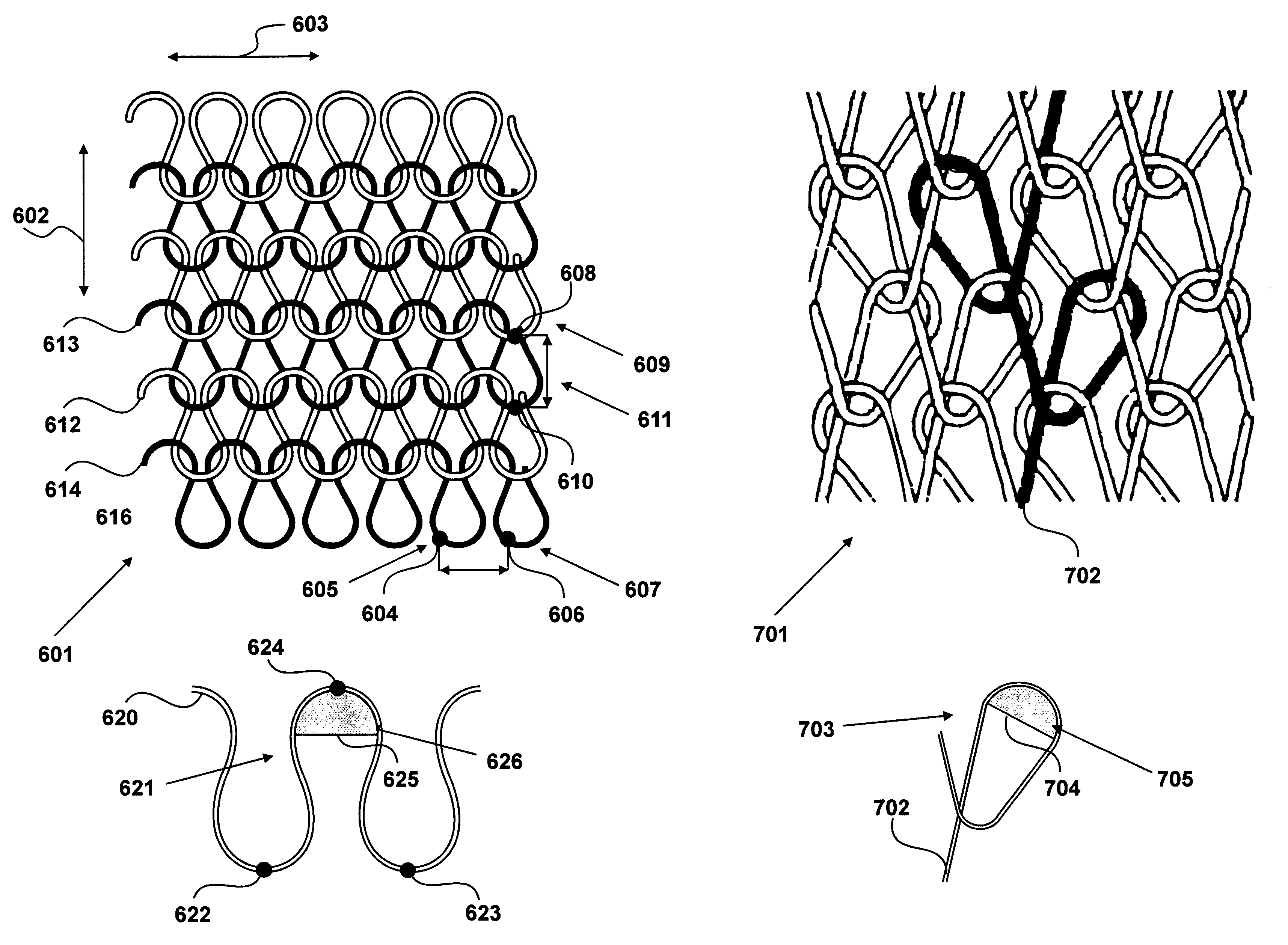
Knitted sensor
A sensor having a three layer construction comprising a first knitted conductive textile plane, a second conductive textile plane and an intermediate separating plane penetrable by the first knitted conductive textile plane to allow the first conductive textile plane and the second conductive textile plane to make electrical contact under a mechanical interaction. The intermediate separating plane defines structural endpoints from which the first knitted conductive textile plane deforms towards the second conductive textile plane under a mechanical interaction. The first knitted conductive textile plane has conductive yarn knitted to form a repeating pattern of stitches each comprising a stitch looping portion SLP having a looping portion footprint LPF. Within the sensor, there is at least one of a plurality of described dimensional relationships between stitches of the first knitted conductive textile plane and structural endpoints of the intermediate separating plane.
Owner:WEARABLE TECH LTD
Detector constructed from electrically conducting fabric
InactiveUS7161084B2Ornamental textile articlesStraight-bar knitting machinesConductive yarnElectrically conductive
The present invention relates to a detector constructed from electrically conducting fabric and configured to present a varying electrical characteristic in response to a mechanical interaction. The detector comprises a first conducting layer (401) which is displaced from a second conducting layer (402) such that conduction between the layers results when the layers are mechanically forced together. In addition, the first of the layers has a plurality of lengths of conductive yarn and a plurality of lengths of non-conductive yarn machined therein, such that at least one length of conductive yarn is electrically isolated from another of the lengths of conductive yarn and the conducting yarns in the first of the layers are electrically grouped to define a plurality of identifiable rows. Each identifiable row has a respective electrical conductor; and define specific regions of the detector.
Owner:WEARABLE TECH LTD
Conductive yarn and production method thereof
InactiveCN103820909AAdjustable resistanceHas bactericidal propertiesYarnNanowireCarbon nanomaterials
The invention relates to a conductive yarn, made by wrapping a yarn with a metal nano-wire and carbon nanomaterial, and a production method thereof. The method includes: soaking a yarn in metal nano-wire solution and evaporating and drying, or repeating the step, to obtain the metal nano-wire wrapped conductive yarn; or soaking the metal nano-wire wrapped yarn in carbon nanomaterial solution and evaporating and drying, or repeating the step several times, to obtain the conductive yarn wrapped with the metal nano-wire and the carbon nanomaterial material; or soaking a yarn in metal nano-wire and carbon nanomaterial mixed solution and evaporating and drying, or repeating the step several times, to obtain the conductive yarn wrapped with the carbon nanomaterial and the metal nano-wire. The production method is very simple, easy for industrialized production and applicable to production of textile electronic devise, and has very promising application prospect.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Fabrics and rust proof clothes excellent in conductivity and antistatic property
InactiveUS6432850B1Improve conductivityMaintain good propertiesGarmentsWoven fabricsEngineeringConductive yarn
There are provided fabrics excellent in electrical conductane and antistatic property as well as dust proof clothes using the same. Conductive yarn comprising synthetic filament yarn as the core covered with conductive bicomponent fibers is used as conductive yarn used in the warps and / or wefts at intervals.
Owner:SEIREN CO LTD
Textile-based electrodes incorporating graduated patterns
ActiveUS20110259638A1Lessen needle wear needle needleReduce needle breakageElectrocardiographyWeft knittingBiophysical profileEngineering
Textile-based electrodes incorporating graduated patterns include a fabric portion having non-conductive yarns and an electrically conductive region having electrically conductive yarn filaments. The electrodes can further include float yarns and can be configured in a textured or ribbed construction. When incorporated into a garment, the electrodes can be used to monitor biophysical characteristics, such as the garment wearer's heart rate.
Owner:ADIDAS
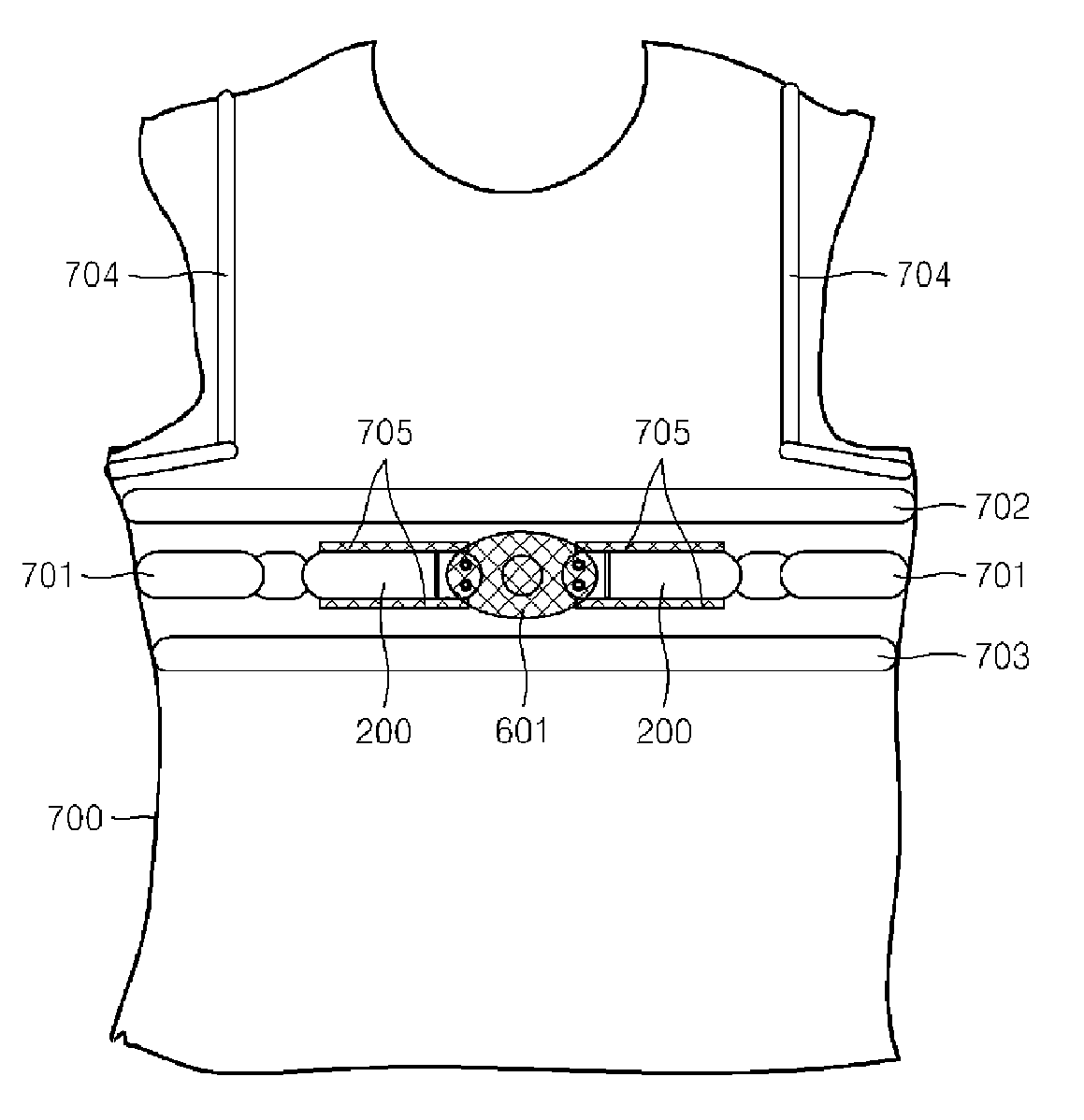
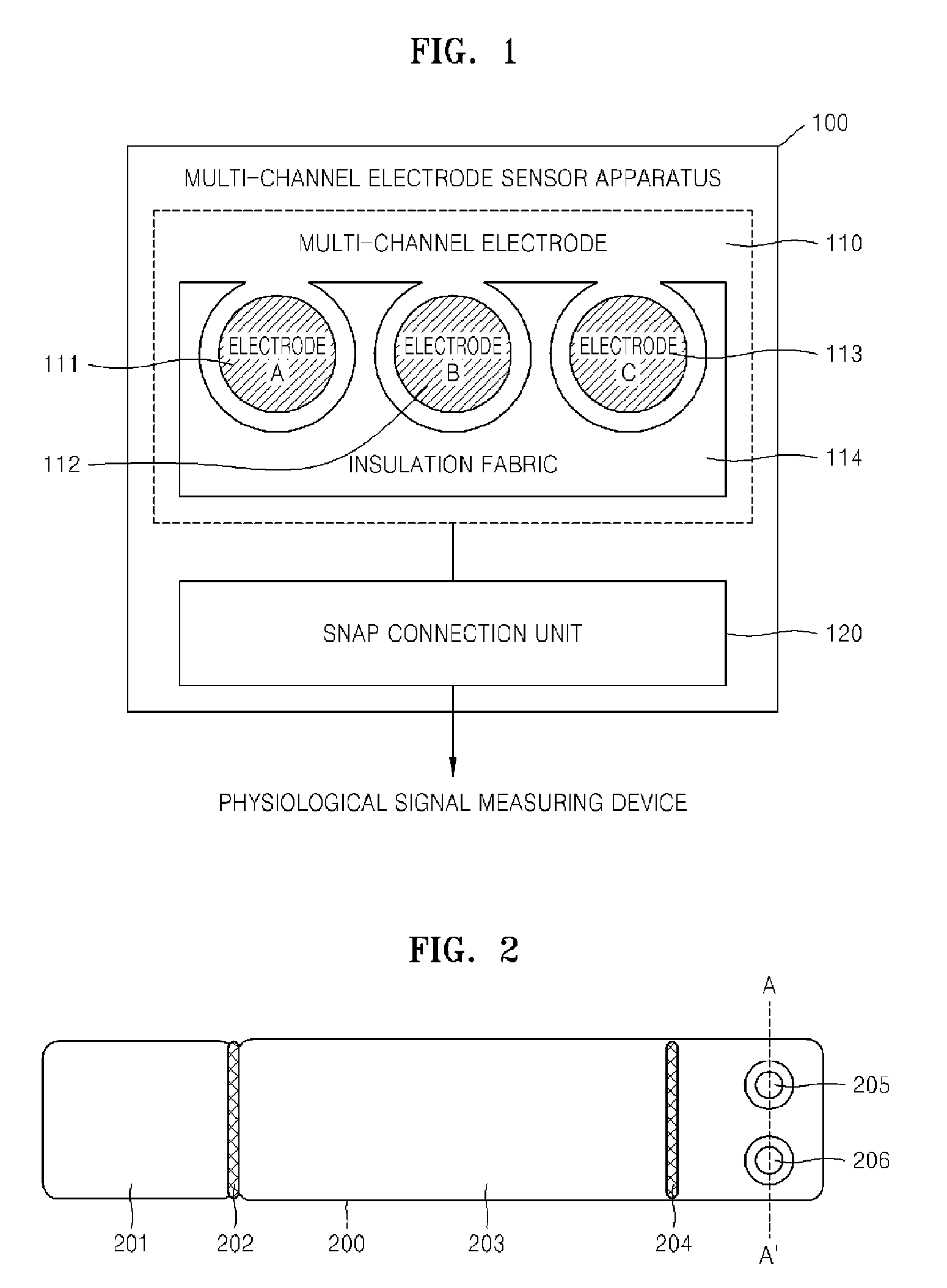
Multi-channel electrode sensor apparatus for simultaneously measuring a plurality of physiological signals
InactiveUS20100191090A1Accurate measurementPrevent movementDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMeasurement devicePotential difference
A multi-channel electrode sensor apparatus for measuring a plurality of physiological signals is provided. The multi-channel electrode sensor apparatus includes a multi-channel electrode having a plurality of electrodes that are weaved using respective conductive yarns to measure potential differences of a plurality of physiological signals and an insulation fabric that is weaved using a non-conductive yarn to insulate the electrodes from each other and a snap connection unit that connects the multi-channel electrode to a measuring device to transmit the physiological signals to the measuring device.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Elastic fabric with sinusoidally disposed wires
A fabric for use with a system for monitoring prescribed body functions comprising an elastic fabric, adapted to be carried by a torso, which is stretchable in its longitudinal direction so as to expand and contract in response to body movement and size. The carrier includes at least one conductive and inelastic yarn arranged longitudinally of and located between upper and lower surfaces. The conductive yarn is arranged in sinusoidal configurations longitudinally of the fabric. The conductive yarn breaks through one of the outer surfaces at a selected breakout along the length of the fabric. The conductive yarn is cut to present at least one exposed end above the one outer surface. A monitoring unit, which includes a connector and a sensor, is secured with the one outer surface of the fabric at the breakout with the connector being united with the at least one exposed end of the conductive yarn. The fabric acts to maintain the monitoring unit in a desired stationary position with the body allowing the sensor to sense signals emitted from the torso and transmit these senses signals through the conductive yarns.
Owner:WOVEN ELECTRONICS
Fabric and yarn structures for improving signal integrity in fabric-based electrical circuits
InactiveUS20080287022A1Reduce crosstalkImprove the immunityJacquardsLeno shedding mechanismPower gridTwisted pair
Coaxial and twisted pair conductive yarn structures reduce signal crosstalk between adjacent lines in woven electrical networks. A coaxial conductive yarn structure includes an inner conductive yarn having a plurality of conductive strands twisted together. An outer conductive yarn is wrapped around the inner conductive yarn. An insulating layer separates the inner and outer yarns. A twisted pair conductive yarn structure includes first and second conductive yarns, each including a plurality of conductive strands being twisted together. The first and second conductive yarns are twisted together to form a helical structure. In a woven electrical network, at least one conductor of adjacent conductive yarn structures is connected to ground to reduce signal crosstalk. Coaxial and twisted pair yarn structures may also be formed simultaneously with weaving or knitting the threads that make up the structures into a fabric.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Pressure-sensitive conductive yarn and biological information-measuring garment
InactiveCN101728005ASingle bars/rods/wires/strips conductorsDiagnostic recording/measuringElectrical resistance and conductanceFiber
An object of the present invention is to provide a pressure-sensitive conductive yarn capable of detecting different biological information simultaneously when used as an electrode. A pressure-sensitive conductive yarn comprising a core yarn formed of an elastic yarn around which a winding yarn having conductivity is wound, wherein the winding yarn is a mixed yarn of a conductive fiber and a nonconductive fiber to cause variations in its electrical resistance with elongation or contraction. The invention also provides a biological information-measuring garment.
Owner:THE RITSUMEIKAN TRUST +1
Heating Pad System For Orthopedic Braces And The Like
InactiveUS20090020521A1Easy to transportTransfer of heatHeating element shapesTherapeutic coolingEngineeringOrthopedic braces
A heating pad system comprises a pad formed of layers of flexible material, a heating element applied to or embedded within a layer of the pad and including conductive yarn, a temperature sensor associated with the pad to generate a temperature signal indicative of a temperature of the pad, and a battery-powered control module removably connected to the heating element and the temperature sensor. The control module is operable to supply current to the heating element to generate heat, wherein the current supplied to the heating element is regulated in response to the temperature signal from the temperature sensor to maintain the pad at a substantially constant temperature. The pad layers, heating element, and temperature sensor are machine-washable as a unit. The pad may be worn under an orthopedic or athletic brace.
Owner:ACCUMED TECH
Textile-based electrode
Two garments with textile based electrodes are disclosed. First, a wrist band for use with a cardiac patient remote monitoring system includes two fabric layers with integral textile-based electrodes. The textile based electrodes include a fabric portion having stretch-recovery non-conductive yarns and an electrically conductive region having stretch-recovery electrically conductive yarn filaments. The skin contacting surface of the band includes a conductive region formed as a continuous ring or stripe. A connector links the conductive region to a lead to a device. Second, an infant garment includes textile based electrodes at the torso region and optionally at other regions in order to monitor the infant's biophysical characteristics as the garment is worn.
Owner:ADIDAS
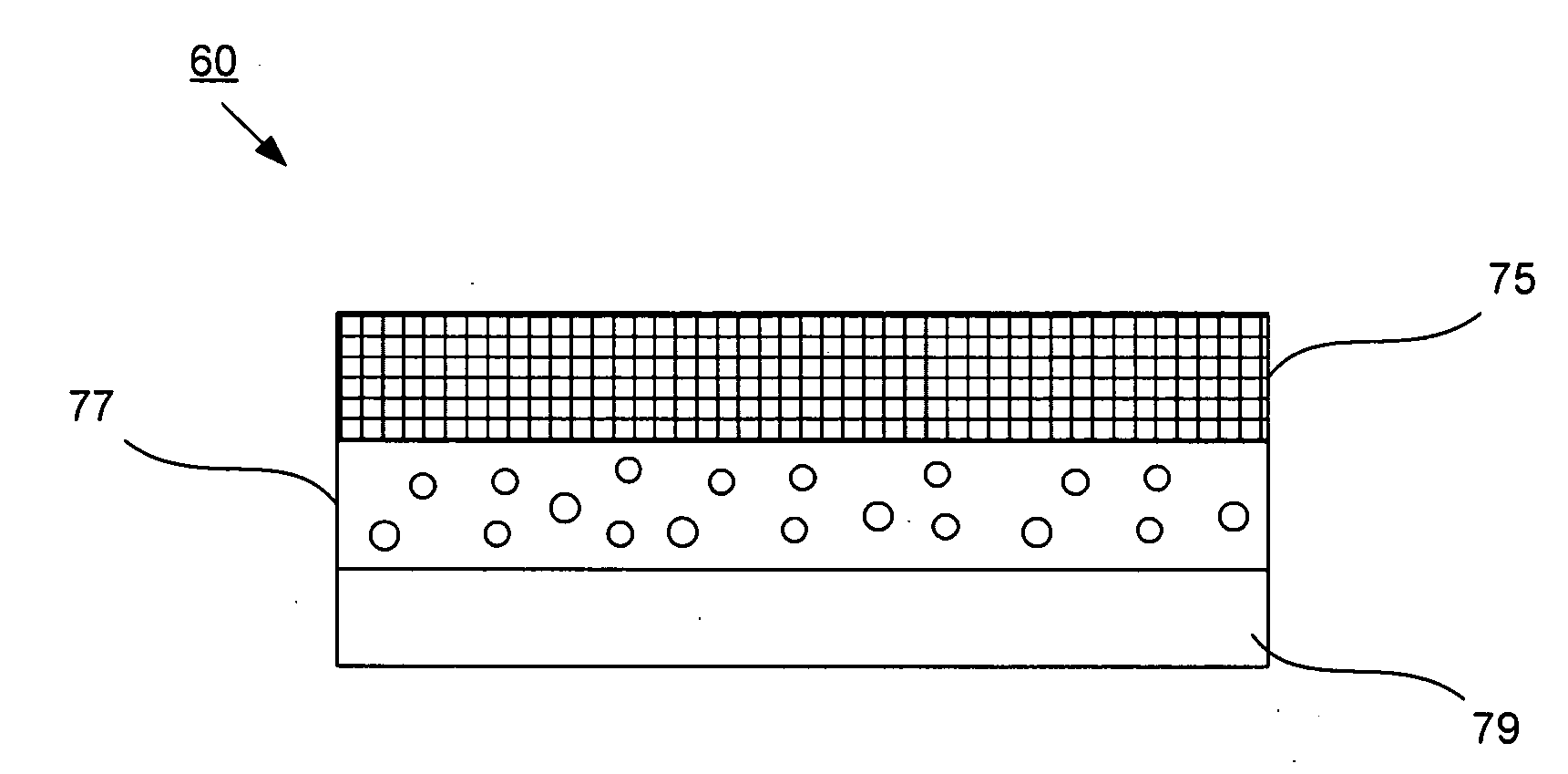
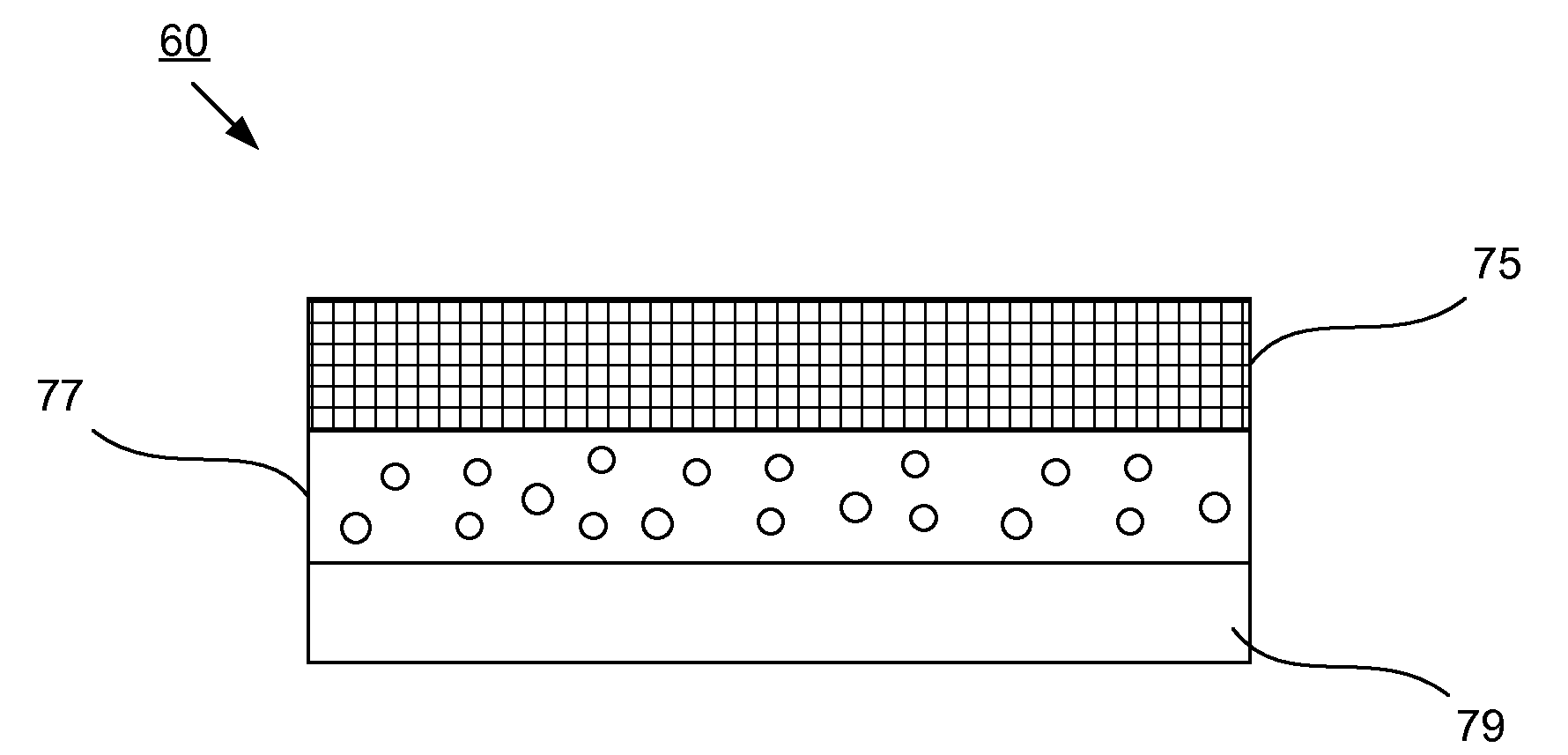
Conductive yarn and cloth containing the same
InactiveUS20110047957A1High energy consumptionEnergy lossCurtain accessoriesBed linenFiberElectricity
A conductive yarn and a cloth containing the same are revealed. A plurality of fibers is wound with a heating element in a spiral form so as to form a yarn with electrical conductivity and flexibility. The conductive yarn is used as a thread in a first direction while regular yarns with conductive metal wires arranged at the two sides thereof are used as threads in a second direction. Thus the threads are woven into a cloth that generates heat while being conducted with electricity. Thereby the cloth can be made into mattress, curtains, textile wall coverings, oversleeves, knee braces, waist supports, foot pads, seat cushions, and carpets etc so as to replace various heating equipment.
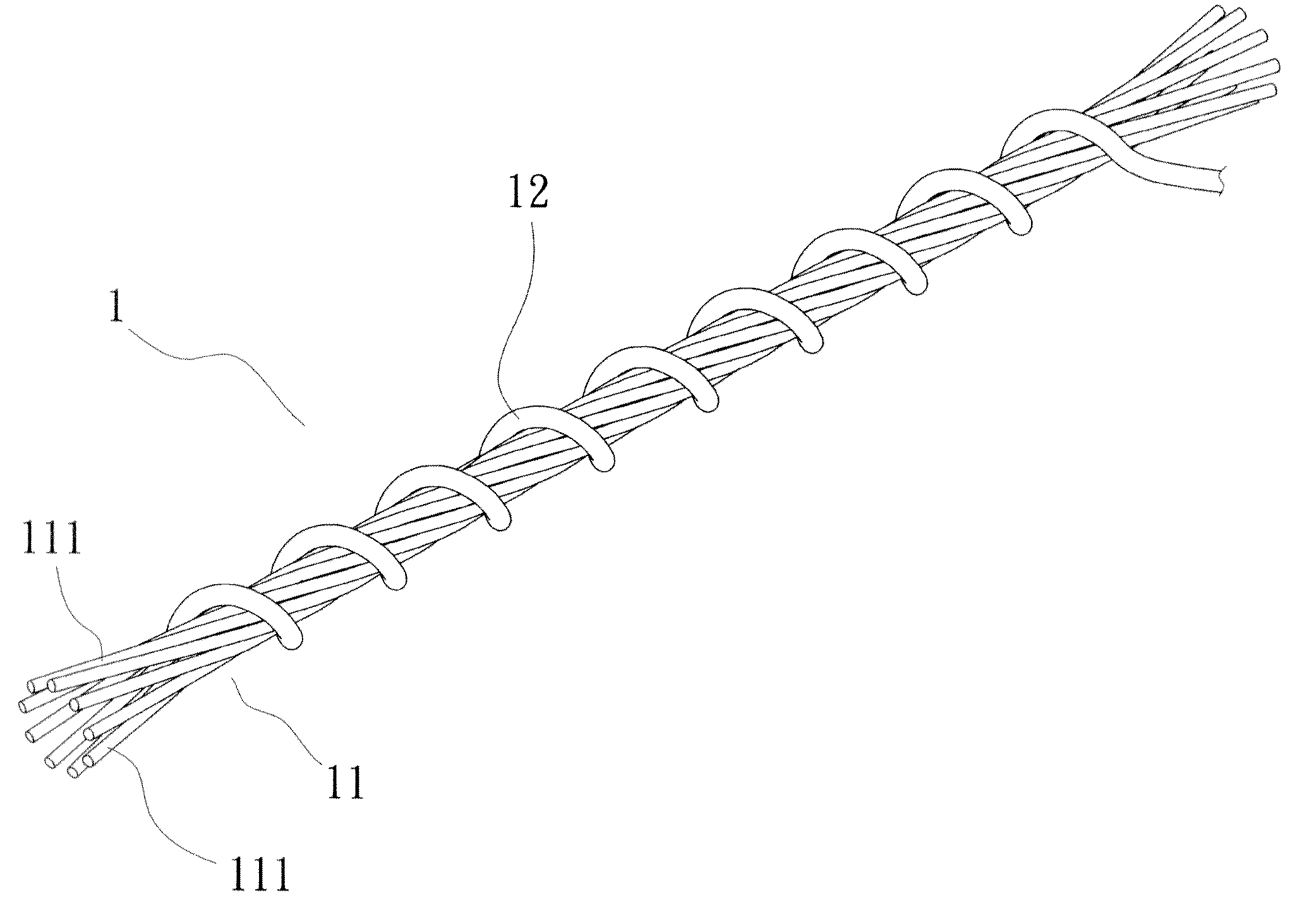
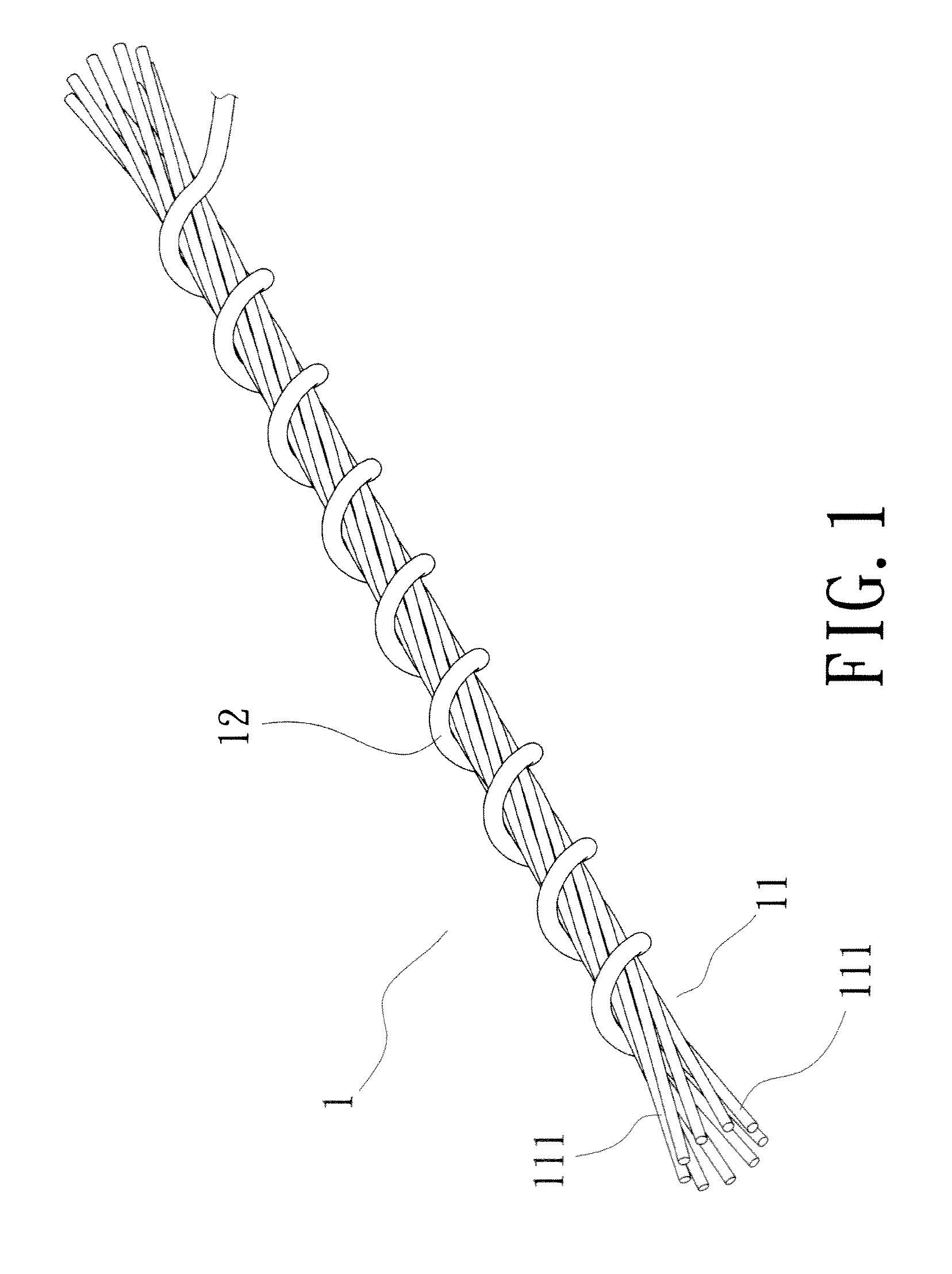
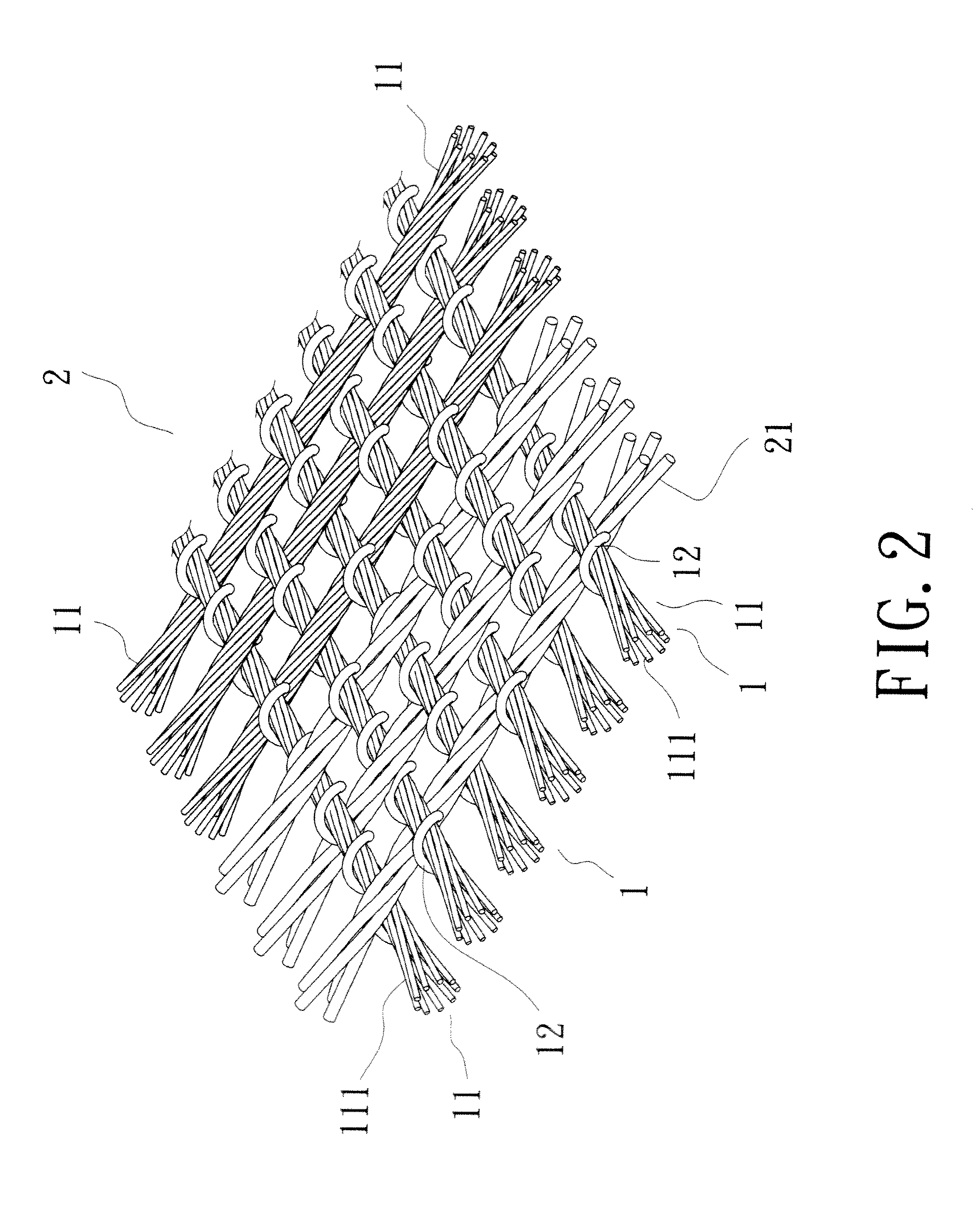
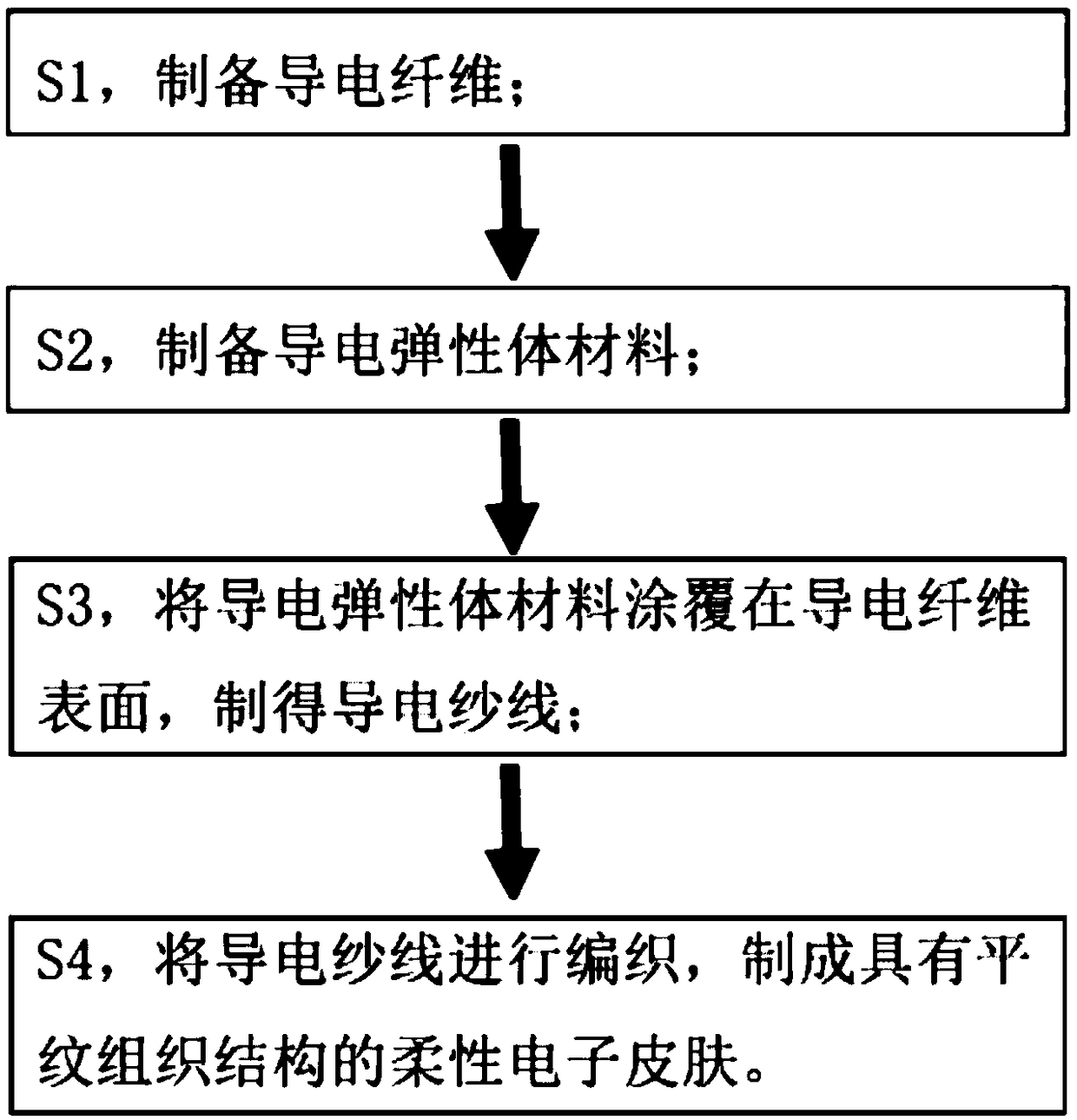
Flexible electronic skin capable of sensing pressure and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109307565AInhibit sheddingPrevent looseningForce measurement using piezo-resistive materialsAnimal fibresFiberElastomer
The invention provides a flexible electronic skin capable of sensing pressure and a preparation method thereof, relates to the technology field of flexible sensors. The flexible electronic skin is interwoven by a plurality of conductive yarns and forms a fabric structure. The conductive yarn comprises a conductive fiber as an inner core and a conductive elastomer material coated on the surface ofthe conductive fiber. The flexible electronic skin uses the conductive fiber as an electrode material and the conductive elastomer material layer as a sensitive material layer, and uses contact resistance change of warp and weft interlacing points of the conductive yarns as a signal for sensing pressure. The invention also provides a preparation method of the flexible electronic skin capable of sensing pressure. The prepared flexible electronic skin has good stability and high sensitivity, and does not need to introduce an external electrode, and can be directly woven into a textile, or used for mechanical sensing of the surface of a robot arm and a human prosthetic.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
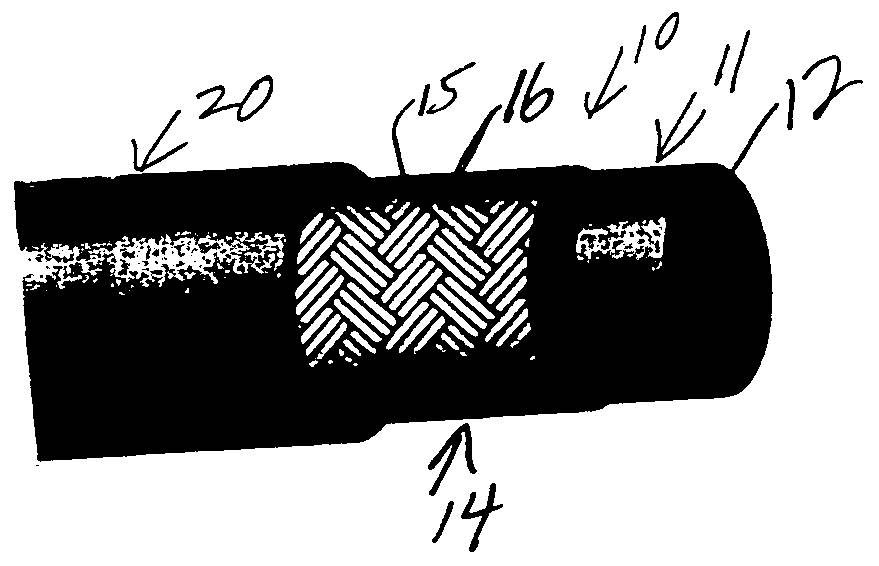
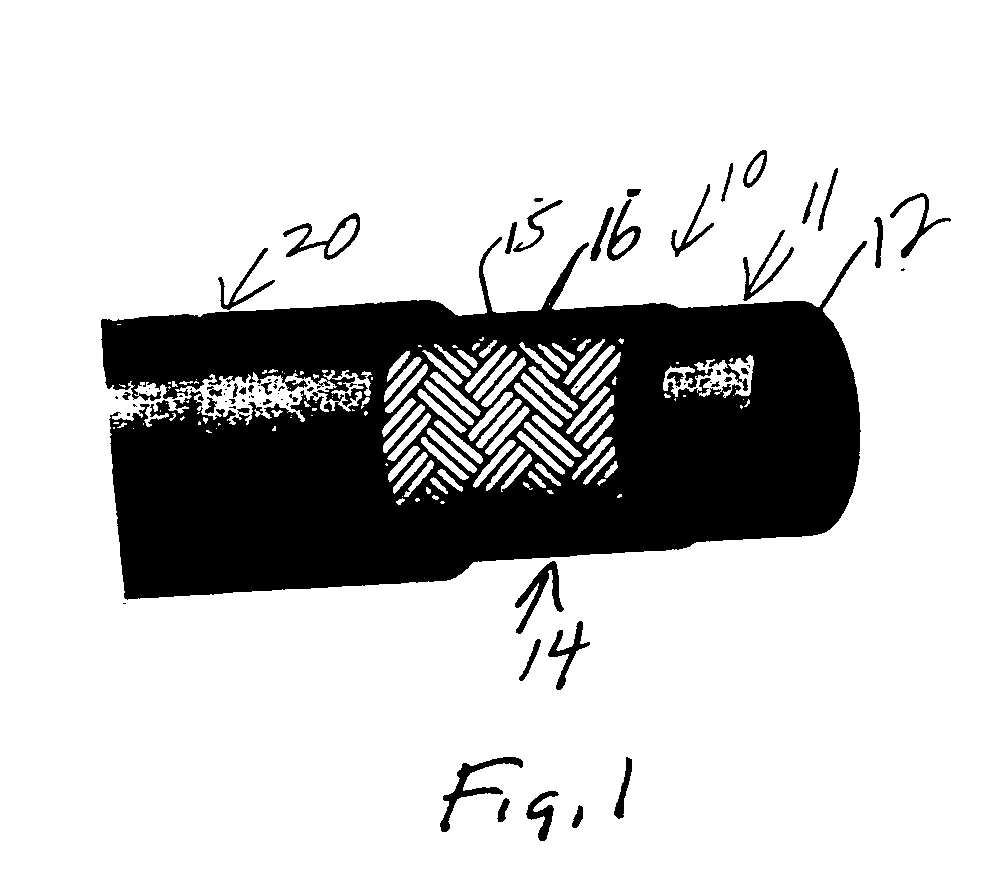
High pressure flexible hose
InactiveUS6978805B2High tensile strengthUniform diameterFlexible pipesRigid pipesTextile fiberMetal fiber
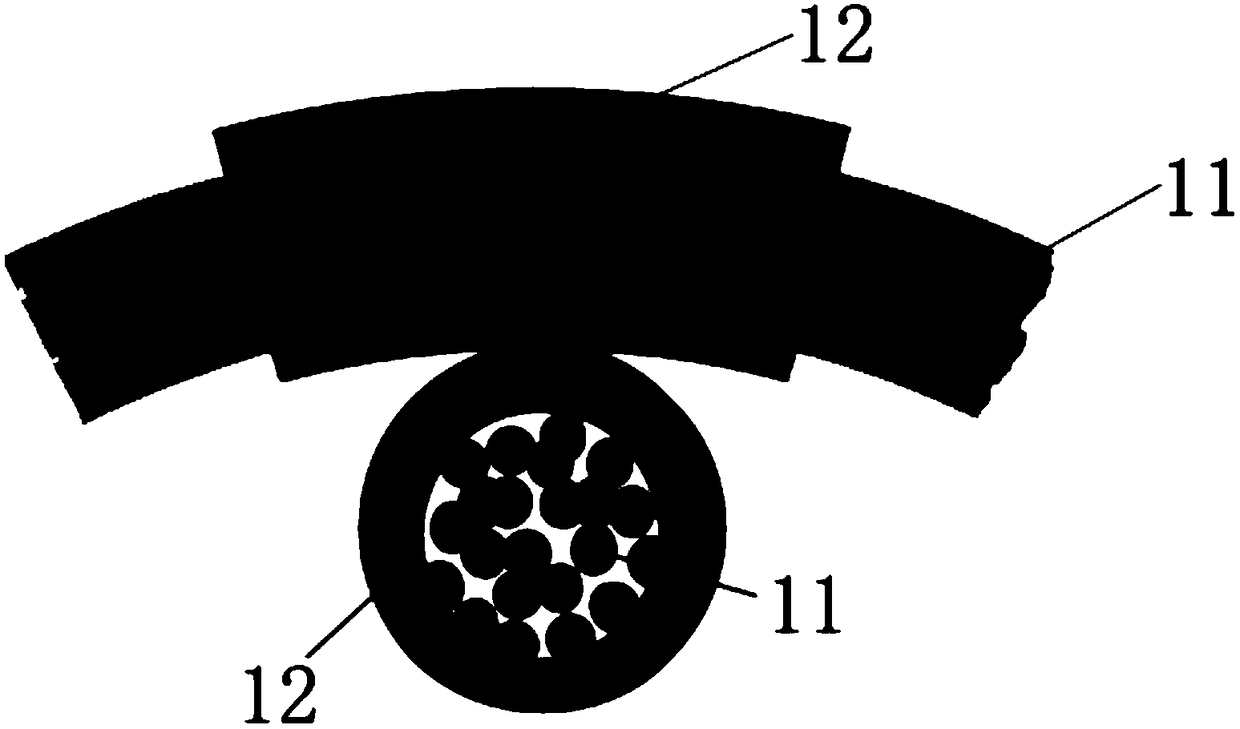
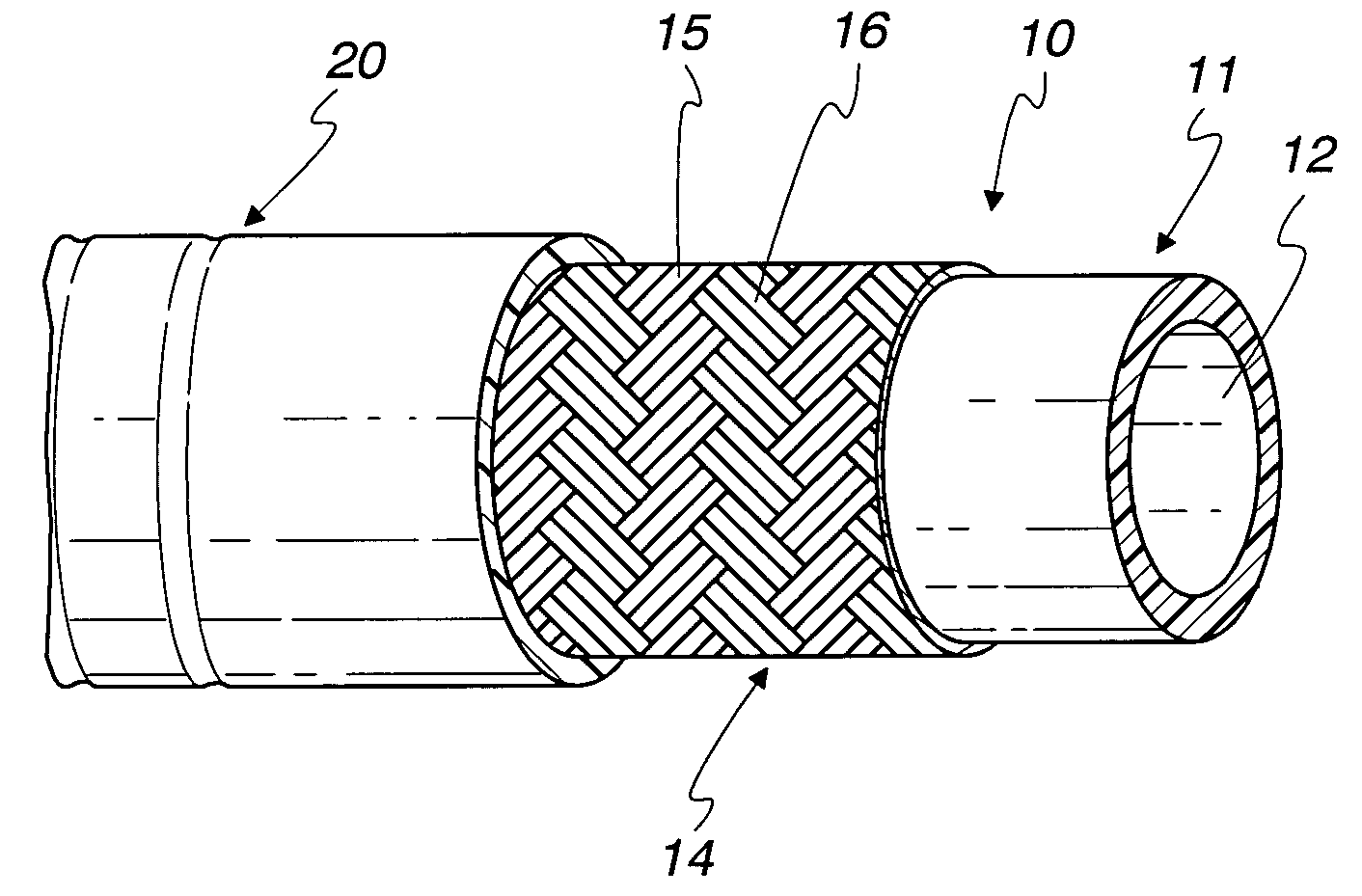
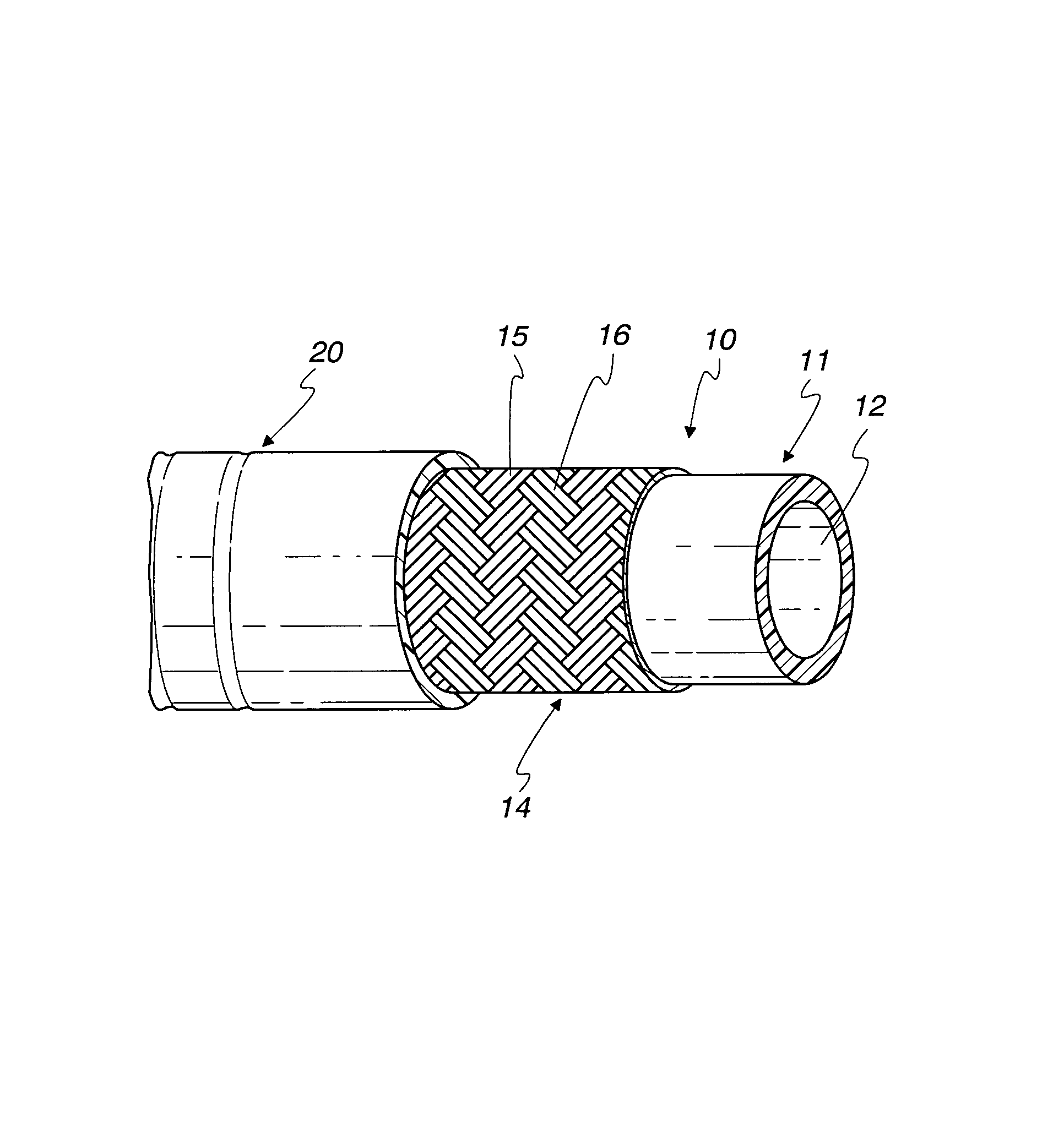
A flexible, thermoplastic hose for high pressure and high velocity flow is provided with a flexible braided reinforcement layer with a static drain therein for conducting static electricity towards a ground. This is achieved by having at least one textile fiber yarn with conductive fibers therein braided with non-conducting textile yarns to form the braided reinforcement layer. The preferred conducting fiber yarn is formed with metal fibers as well as plastic fibers. A method of manufacture of the hose comprises providing electrical conducting yarns and non-conducting yarns in a braiding machine and braiding them about a tube having a hollow bore through which fluid flows. An abrasion resistant outer cover layer of polyurethane is extruded over the braided layer having the drain therein. For higher pressure applications, a second braided reinforcement layer may also be provided over the inner braided layer having the electrically conductive yarns. Several conductive yarns may be used to have spaced electrically conductive yarns, e.g., at 3:00, 6:00, 9:00 and 12:00 in a circular cross-section through the hose.
Owner:DYNAFLEX
Fabric-based strain gauge
ActiveUS7750790B2Good flexibilityForce measurementDiagnostic recording/measuringEngineeringStrain gauge
The invention provides a strain gauge which includes a fabric base and at least one conductive yarn. In addition, the fabric base is weaved with a plurality of non-conductive yarns, and the fabric base thereon defines a sensing direction. Moreover, each of the conductive yarn is gimped by a textile process with one of the non-conductive yarns and is woven through the fabric base along the sensing direction. Furthermore, the at least one conductive yarn is capable of being applied by an electric power; when an external force acts on the fabric base, the geometrical property of the at least one conductive yarn alters so that a change of an electric property associated with the applied electric power is sensed to indicate an elongation of said strain gauge applied by the external force along the sensing direction.
Owner:YANG CHANG MING
Resistance-type pressure distribution fabric sensor
InactiveCN107144379AFlexible and convenient designStable structureForce measurement using piezo-electric devicesEngineeringConductive yarn
The present invention relates to a resistance-type pressure distribution fabric sensor. The resistance-type pressure distribution fabric sensor comprises an upper electrode layer, a conductive layer and a lower electrode layer which are laminated orderly from top to bottom, the upper and lower electrode layers are both fabrics formed by knitting the conductive yarns and the non conductive yarns into the stripes of different widths, wherein the stripes formed by the conductive yarns form the electrodes, the stripes formed by the non-conductive yarns form the electrode isolation belts, and the two types of stripes are arranged at intervals. The resistance-type pressure distribution fabric sensor of the present invention can sense the applied pressures and the pressure applying positions, and does not depend on the printed and coated conductive films on the surfaces of the fabrics.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
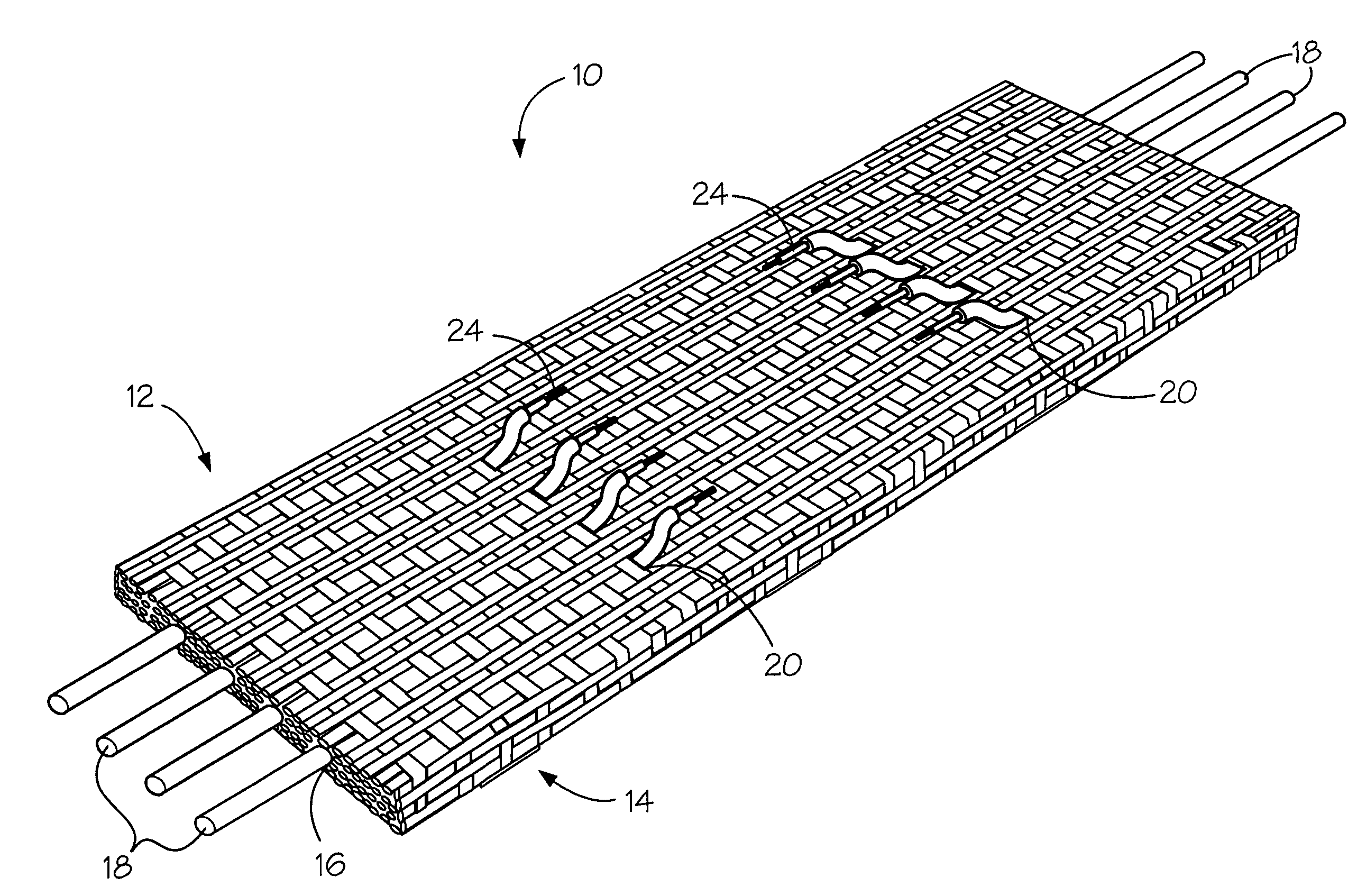
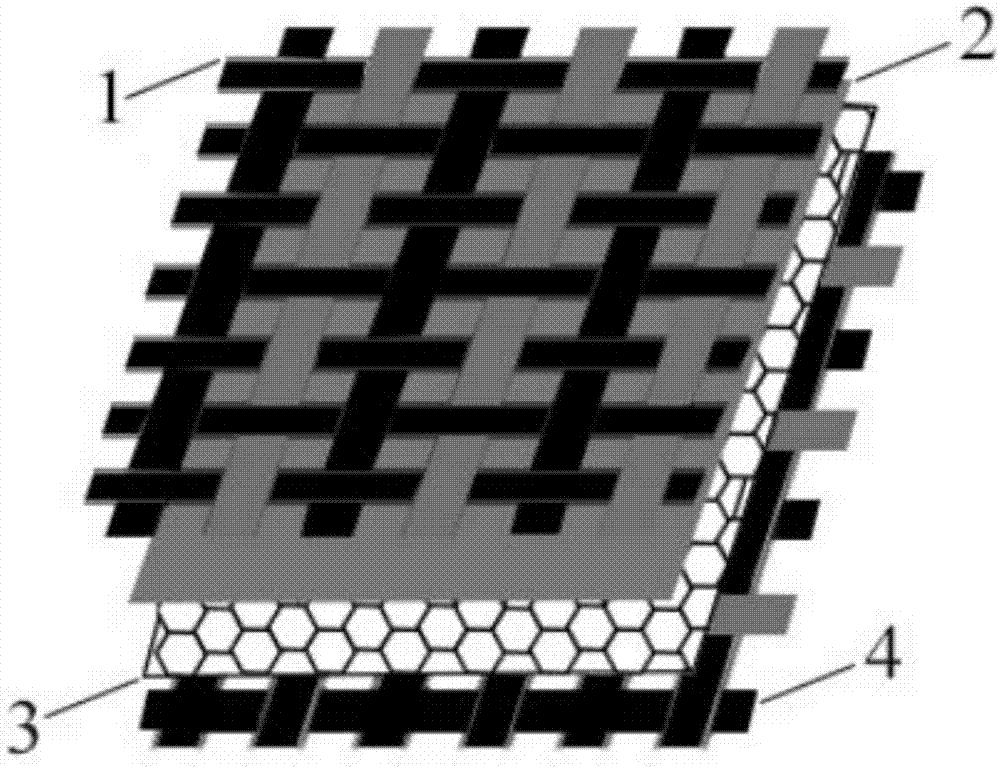
Integrally-woven three-layer heating textile
InactiveUS20100154918A1Shorten production timeSimple processWeft knittingMulti-ply fabricsEngineeringConductive yarn
An integrally-woven three-layer heating textile is provided. The integrally-woven three-layer heating textile includes a heat-isolated fabric layer, a thermal function fabric layer, a plurality of conductive yams and a plurality of connecting yarns. The conductive yarn is distributed between the heat-isolated fabric layer and the thermal function fabric layer. The connecting yam interlaces the heat-isolated fabric layer and the thermal function fabric layer so that the conductive yam is sandwiched between the heat-isolated fabric layer and the thermal function fabric layer.
Owner:TAIWAN TEXTILE RESEARCH INSTITUTE
High pressure flexible hose
InactiveUS20050051226A1Uniform diameterHigh tensile strengthFlexible pipesRigid pipesTextile fiberMetal fiber
A flexible, thermoplastic hose for high pressure and high velocity flow is provided with a flexible braided reinforcement layer with a static drain therein for conducting static electricity towards a ground. This is achieved by having at least one textile fiber yarn with conductive fibers therein braided with non-conducting textile yarns to form the braided reinforcement layer. The preferred conducting fiber yarn is formed with metal fibers as well as plastic fibers. A method of manufacture of the hose comprises providing electrical conducting yarns and non-conducting yarns in a braiding machine and braiding them about a tube having a hollow bore through which fluid flows. An abrasion resistant outer cover layer of polyurethane is extruded over the braided layer having the drain therein. For higher pressure applications, a second braided reinforcement layer may also be provided over the inner braided layer having the electrically conductive yarns. Several conductive yarns may be used to have spaced electrically conductive yarns, e.g., at 3:00, 6:00, 9:00 and 12:00 in a circular cross-section through the hose.
Owner:DYNAFLEX
Carbon heating clothes and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101396176AHeating up fastTastelessOhmic-resistance heatingGarment beltsSmart polymerEngineering
The invention relates to a garment and a preparation method thereof, in particular to a carbon heating garment taking carbon conductive yarns as a heating element and a preparation method thereof. The outside of the rear piece of the carbon heating garment is provided with a pocket which is positioned near the lumbar vertebrae of a human body; and the pocket is provided with a carbon heating sheet sewn and packed by nano bamboo charcoal knitted fabric, connecting wires and intelligent polymer lithium battery pack; the carbon heating sheet is connected with the anode and the cathode of the lithium battery pack by the connecting wires; and the carbon heating sheet is compounded by pressing and rolling carbon conductive fabric with an environment friendly polyurethane thin film or vinyl acetate thin film. The garment has the advantages of fast heating and temperature rise, no odor, no pollution and good effect, and the garment is an ideal warm garment with heat supply function.
Owner:SHANGHAI ZHONGDA TECHNOLOGY DEVELOPMENT CO LTD +1
Woven manually operable input device
InactiveUS8373079B2Inexpensive trackContact surface shape/structureWave amplification devicesControl signalEngineering
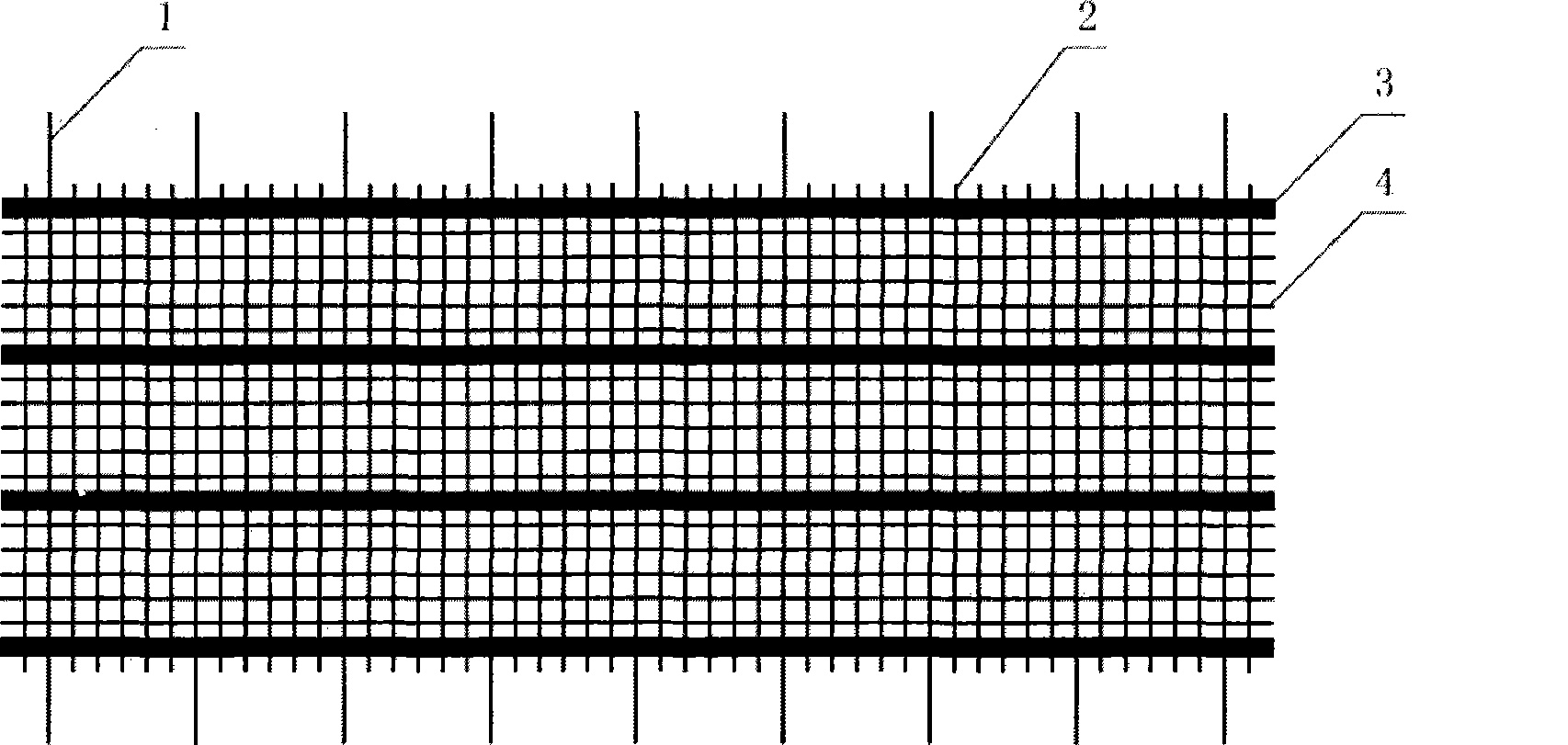
A manually operable sensor for providing control signals to an electronic device. A fabric has a length substantially longer than its width with insulating yarns and electrically conductive yarns included therein, such that the conductive yarns define three conductive tracks running the length of the fabric. The conductive tracks are configured to interface with an electronic device at a first end and, at a second end, an active region of the fabric forms part of a sensor assembly that is receptive to a manually applied pressure. The sensor comprises first and second conductive regions to which a first and a second conductive track are connected respectively, to apply an electric potential to each conductive region. A conductive path is formed between a connected conductive track and the third conductive track of said active region when manual pressure is applied to one of the conductive regions.
Owner:WEARABLE TECH LTD
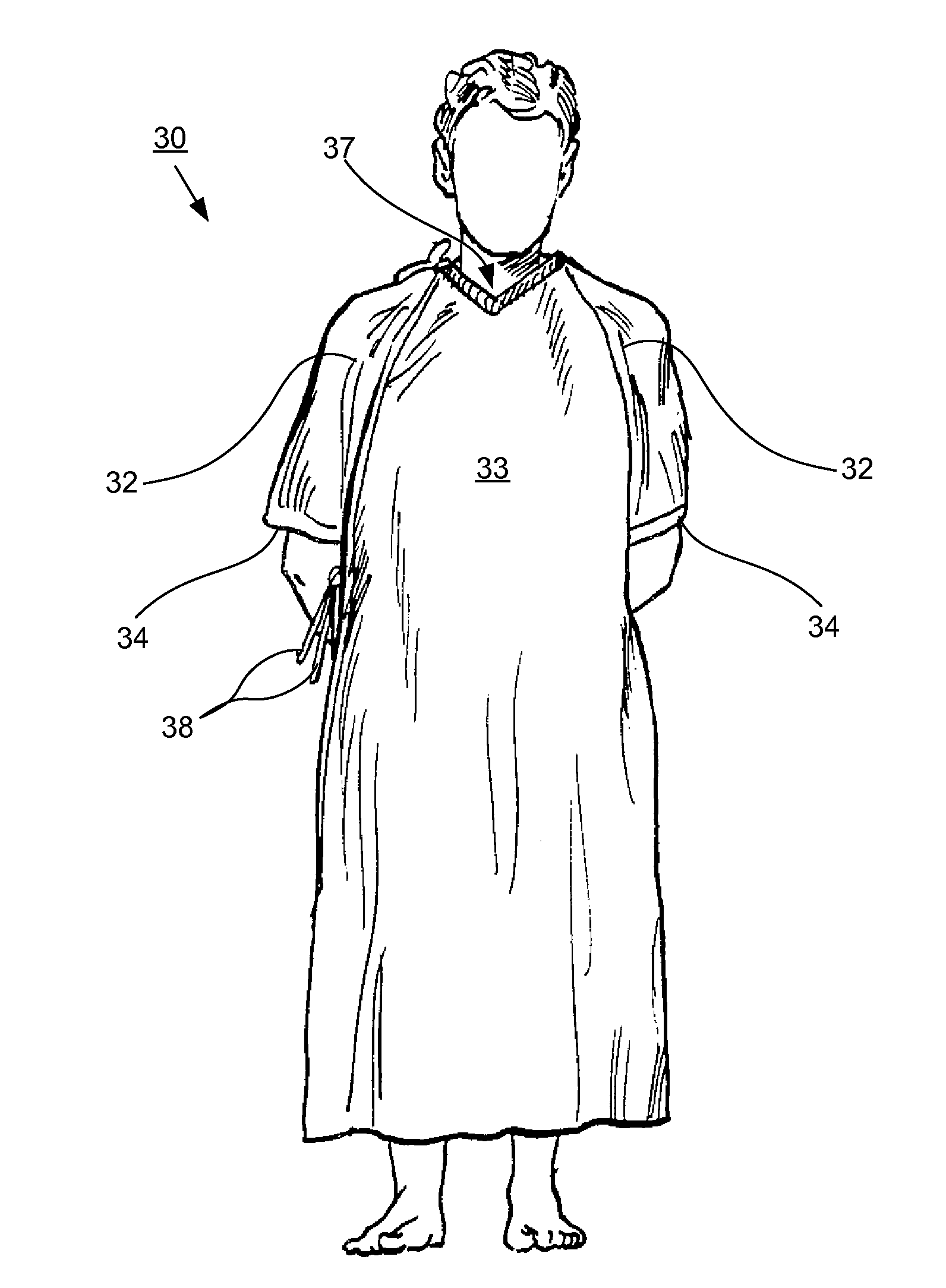
Synthetic woven patient gown for preventing and reducing skin wounds
InactiveUS20100050316A1More stain resistantDries more quicklyBiocideSewing apparatusInjury mouthEngineering
A patient gown comprised of therapeutic fabric for the prevention and treatment of skin wounds, and pressure wounds in particular, which includes a woven fabric having warp yarns and filling yarns woven to provide a smooth fabric surface. One of the warp or filling yarns is at least about 40% by weight of the fabric of continuous filament nylon, and the other of the warp or filling yarns is from about 0% to about 60% by weight of the fabric of continuous filament polyester or nylon having non-round filament cross sections. The fabric includes a conductive yarn at about 1% to about 2% by weight to control static dissipation, and an antimicrobial substance is topically applied or inherently available in the fabric. A method of using the patient gown to prevent and treat skin wounds, and pressure wounds in particular, is also disclosed.
Owner:PRECISION FABRICS GROUP
Electro-conductive fibers with carbon nanotubes adhered thereto, electro-conductive yarn, fibers structural object, and production processes thereof
ActiveUS20110151254A1Improve conductivityMinimizes change (or increase) in massLayered productsFibre typesElectrical resistance and conductanceCarbon nanotube
Electro-conductive fibers comprise synthetic fibers and an electro-conductive layer containing carbon nanotubes and covering a surface of the synthetic fibers, and the coverage of the electro-conductive layer relative to the whole surface of the synthetic fibers is not less than 60% (particularly not less than 90%). The electric resistance value of the electro-conductive fibers ranges from 1×10−2 to 1×1010 Ω / cm, and the standard deviation of the logarithm of the electric resistance value is less than 1.0. The thickness of the electro-conductive layer ranges from 0.1 to 5 μm, and the ratio of the carbon nanotubes may be 0.1 to 50 parts by mass relative to 100 parts by mass of the synthetic fibers. The electro-conductive layer may further contain a binder. The electro-conductive fibers may be produced by immersing the synthetic fibers in a dispersion with vibrating the synthetic fibers to form the electro-conductive layer adhered to the surface of the synthetic fibers. The electro-conductive fibers have the carbon nanotubes homogeneously and firmly adhered to an almost whole of a surface thereof and have an electro-conductivity and a softness.
Owner:CHAKYU DYEING +2
Underpad for preventing and reducing skin wounds
InactiveUS20090312684A1More stain resistantDries more quicklyBiocideNon-adhesive dressingsPolyesterBiomedical engineering
An underpad including a top fabric layer constructed of a therapeutic fabric for the prevention and treatment of skin wounds, and pressure wounds in particular, is disclosed. The underpad also includes an absorbent middle layer and liquid impermeable bottom layer. The therapeutic fabric includes warp yarns and filling yarns woven to provide a smooth fabric surface. One of the warp or filling yarns is at least about 40% by weight of the therapeutic fabric of continuous filament nylon, and the other of the warp or filling yarns is from about 0% to about 60% by weight of the therapeutic fabric of continuous filament polyester or nylon having non-round filament cross sections. The therapeutic fabric includes a conductive yarn at about 1% to about 2% by weight to control static dissipation, and an antimicrobial substance is topically applied or inherently available in the therapeutic fabric. A method of preventing and treating skin wounds, and pressure wounds in particular, is also disclosed.
Owner:PRECISION FABRICS GROUP
Fabrics for preventing and reducing skin wounds
InactiveUS20090308404A1More stain resistantDries more quicklyBiocideNon-adhesive dressingsEngineeringConductive yarn
A fabric for the prevention and treatment of skin wounds, and pressure wounds in particular, which includes a woven fabric having warp yarns and filling yarns woven to provide a smooth fabric surface. One of the warp or filling yarns is at least about 40% by weight of the fabric of continuous filament nylon, and the other of the warp or filling yarns is from about 0% to about 60% by weight of the fabric of continuous filament polyester or nylon having non-round filament cross sections. The fabric includes a conductive yarn at about 0% to about 2% by weight to control static dissipation, and an antimicrobial substance is topically applied or inherently available in the fabric. The fabric can be used in bedding, including underpads, and patient gowns. Methods of preventing and treating skin wounds, and pressure wounds in particular, are also disclosed.
Owner:PRECISION FABRICS GROUP
Device for measuring pressure from a flexible, pliable, and/or extensible object made from a textile material comprising a measurement device
ActiveUS9448127B2Simple designLow costForce measurement using piezo-resistive materialsMulti-ply fabricsElectrical resistance and conductanceFiber
A device and method for measuring the pressure exerted at different points of a flexible, pliable and / or extensible fabric capable of being worn as a garment, lapel, or the like, which provides three stacked layers including a first insulating layer comprising an arrangement of insulating fibers and at least one row of at least one conductive yarn in contact with a first surface of a piezoresistive layer of fibers of a piezoresistive material, and a second insulating layer comprising an arrangement of insulating fibers, including at least one row of at least one conductive yarn, in contact with a second surface of the piezoresistive layer, and an electronic circuit capable of measuring the electric resistance variation when a pressure is exerted on the fabric, the pressure being a function of the resistance variation.
Owner:TEXISENSE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com