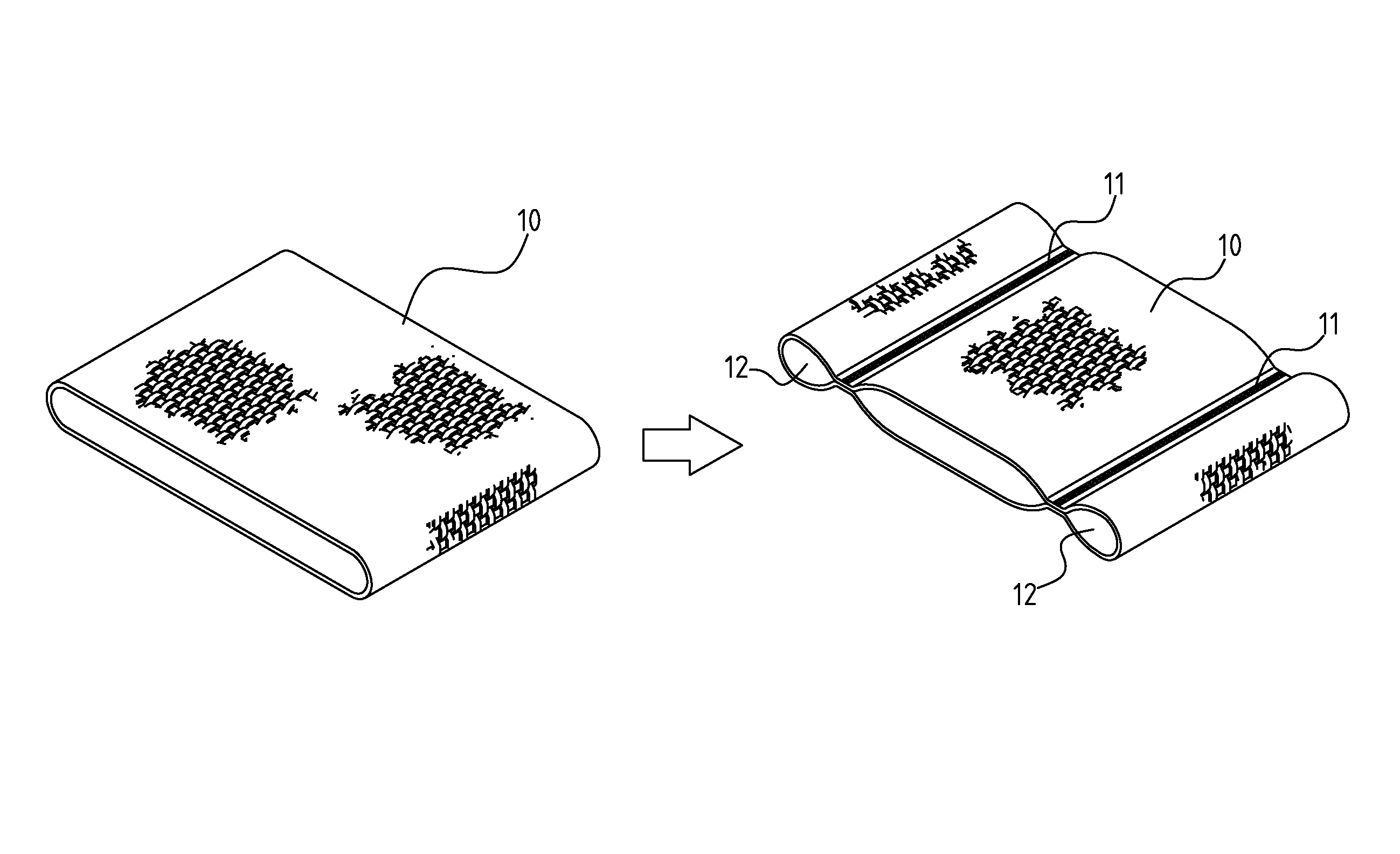
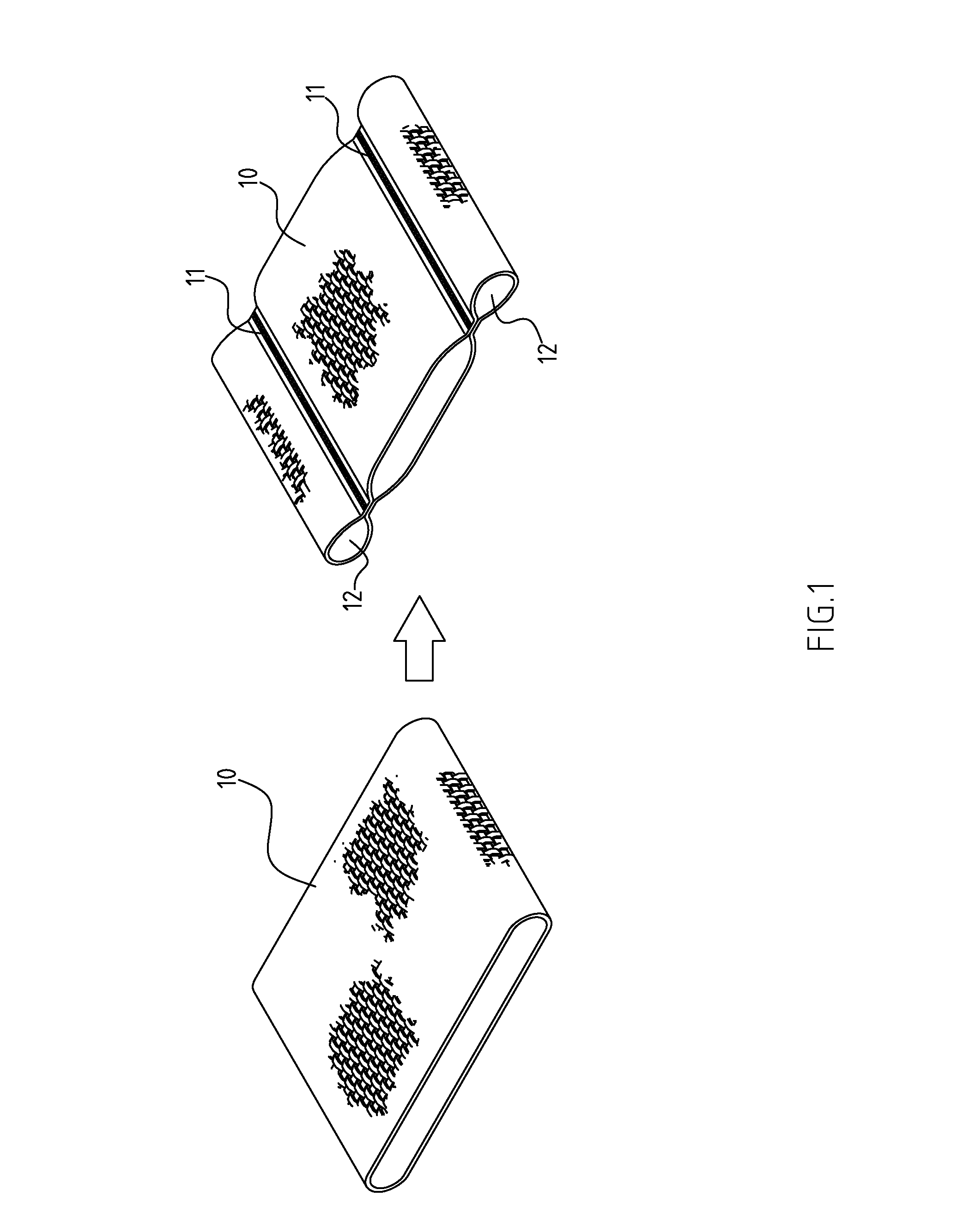
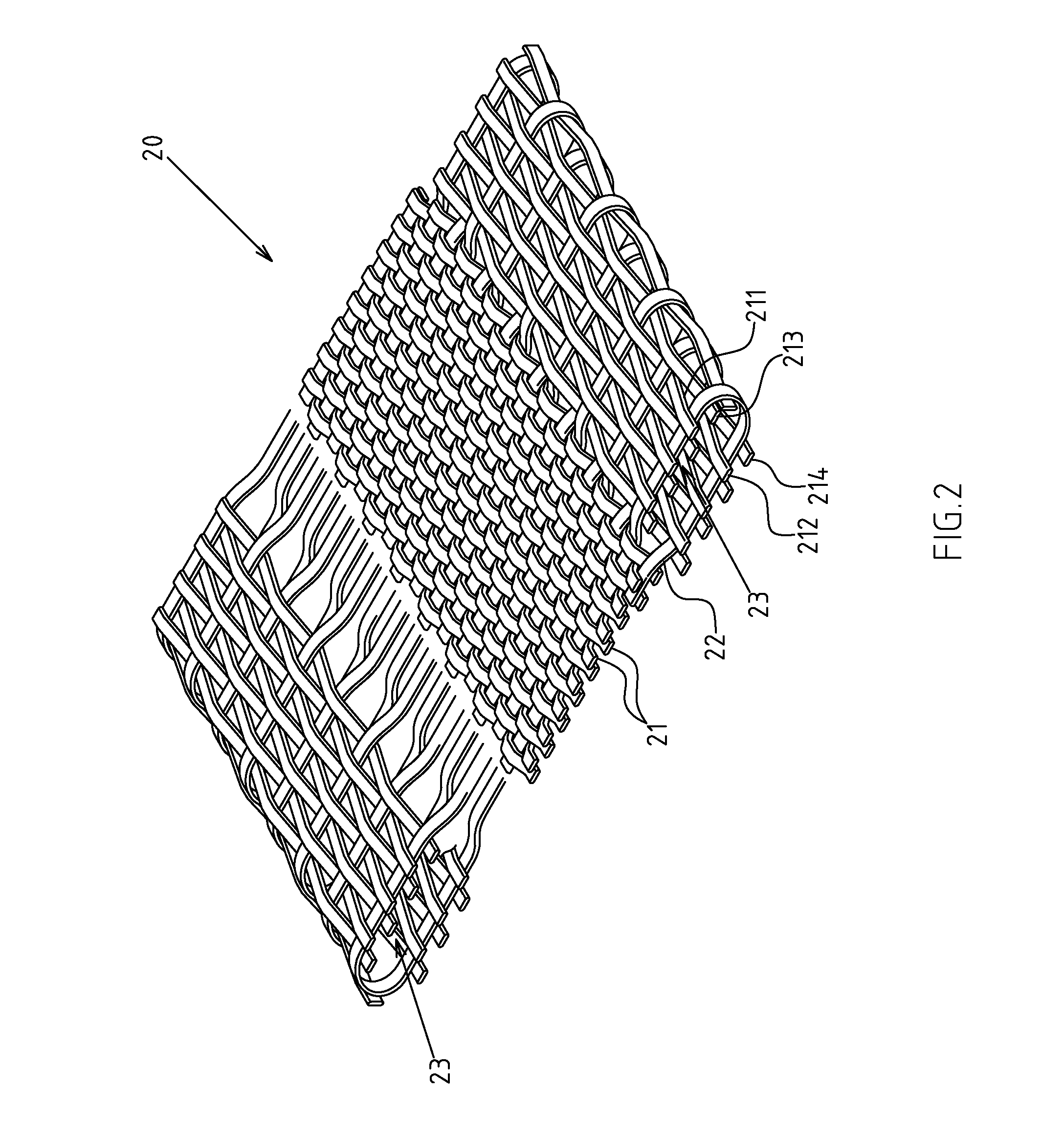
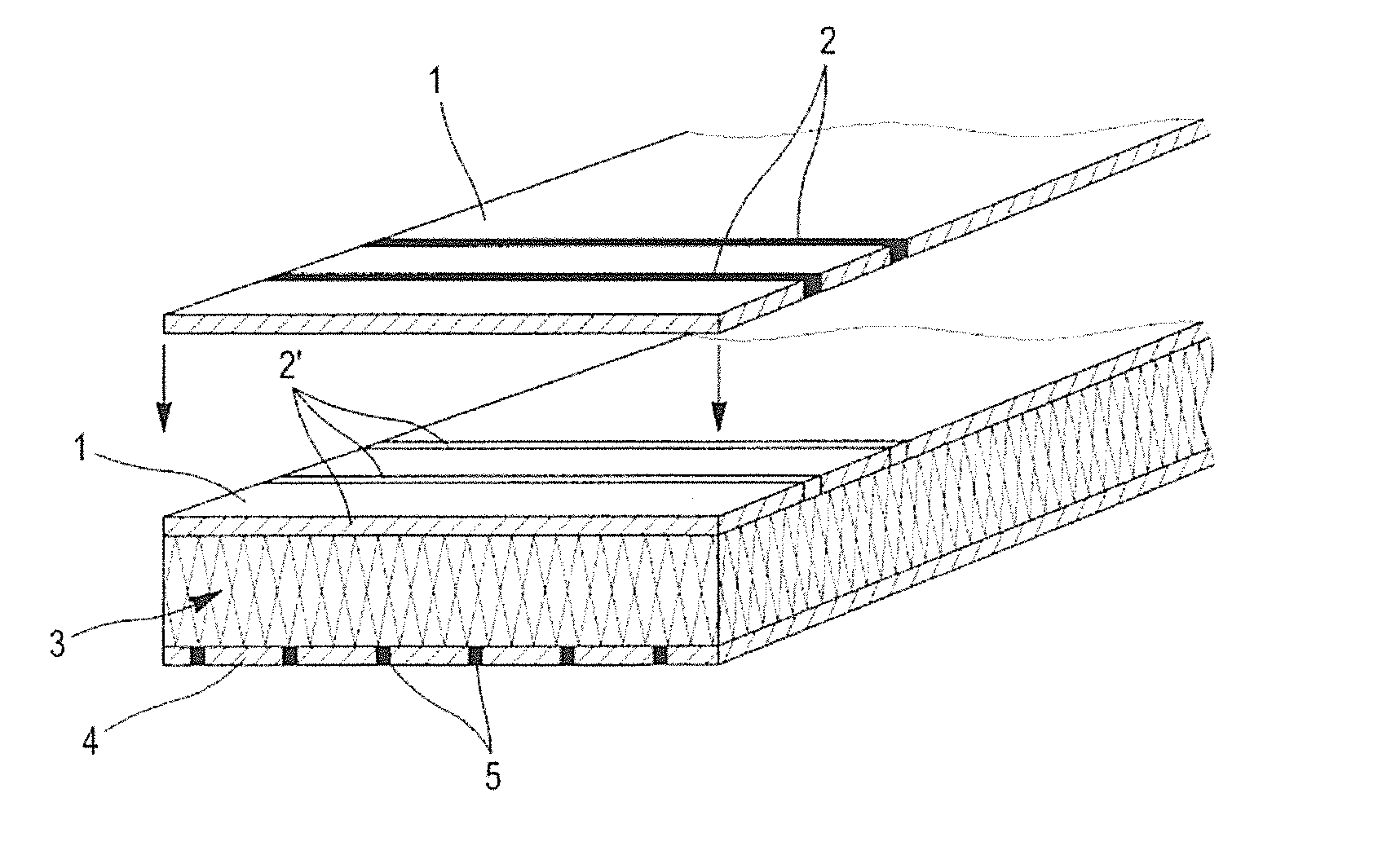
Patents
Literature
2111results about "Multi-ply fabrics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
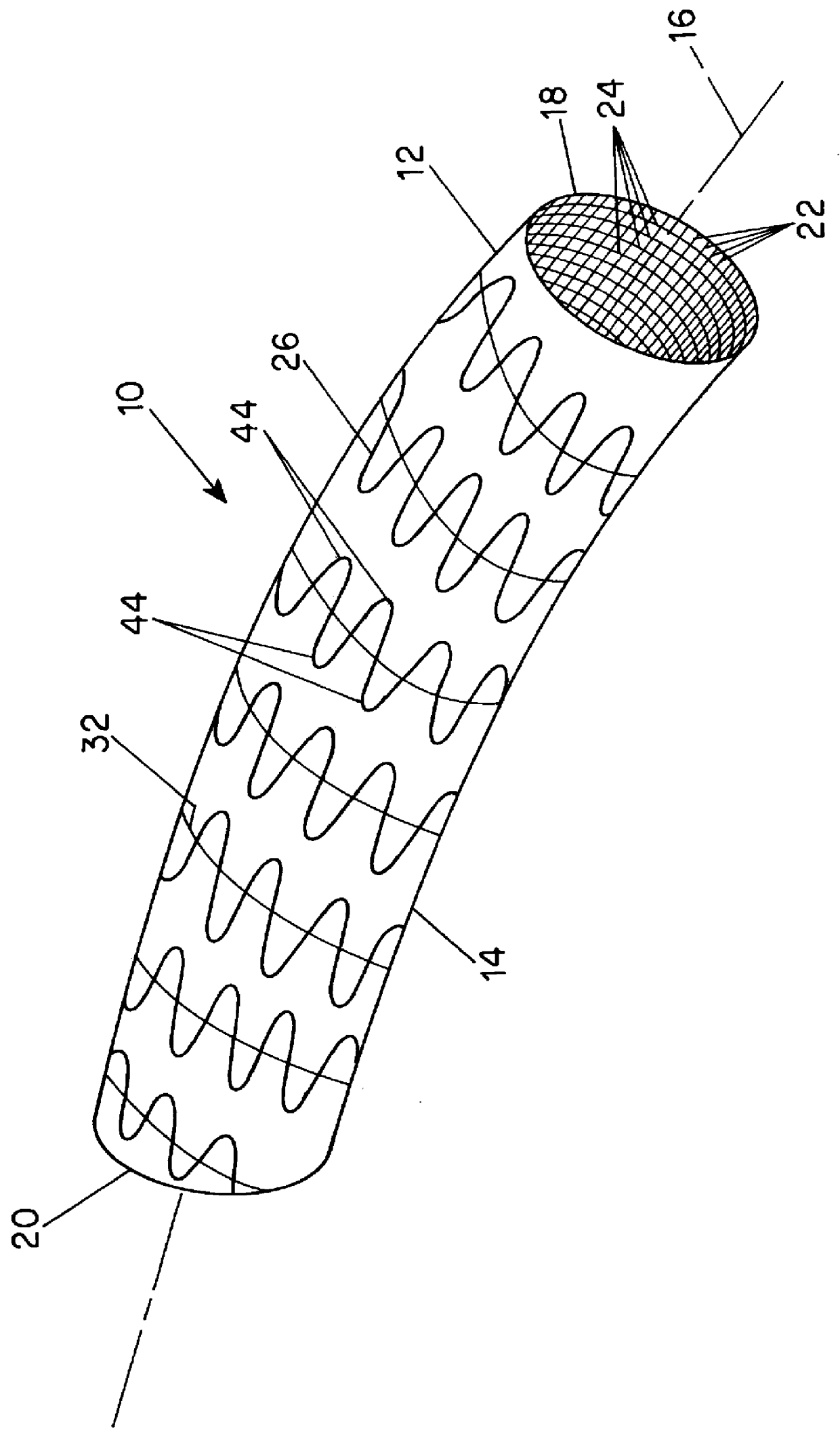
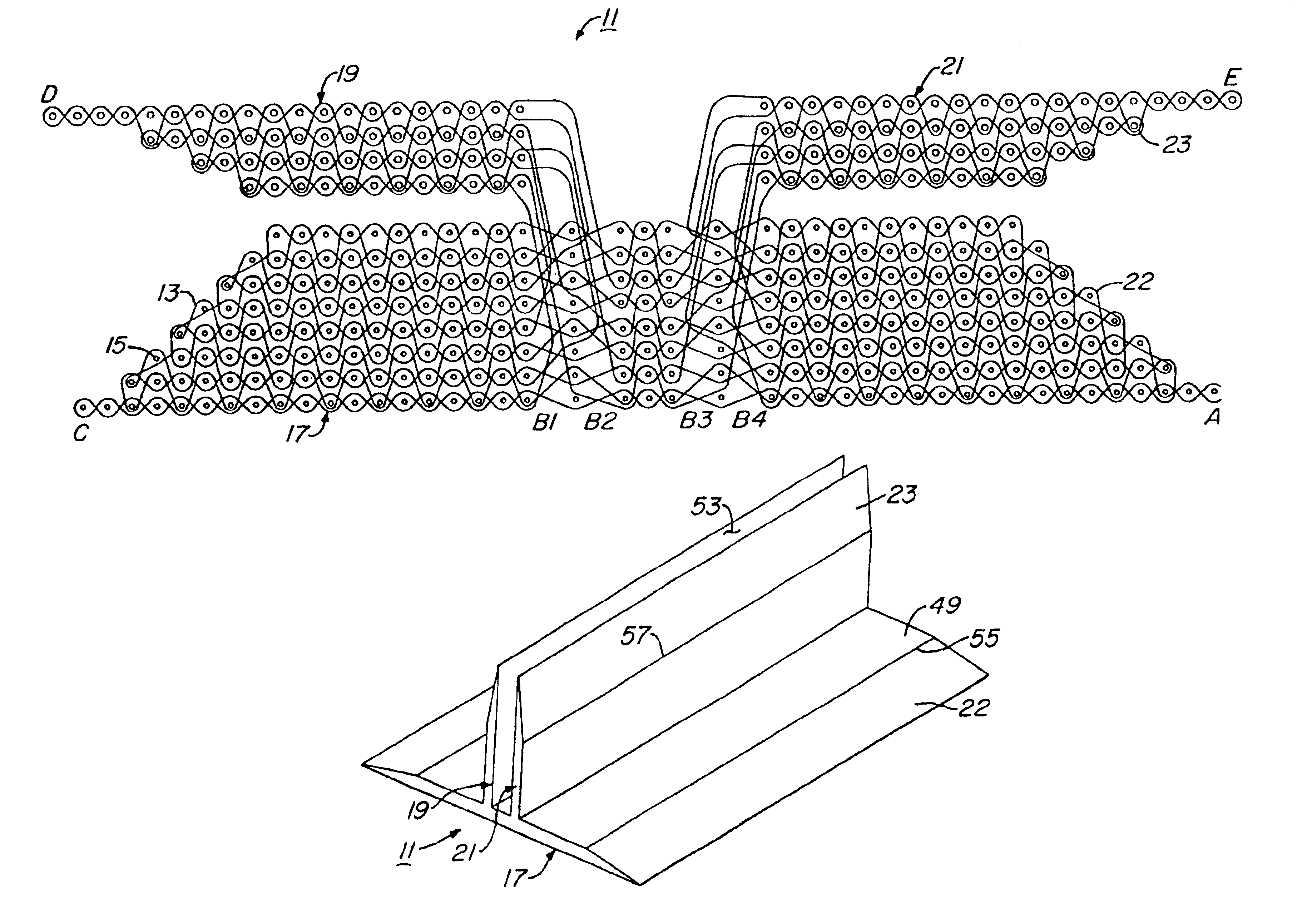
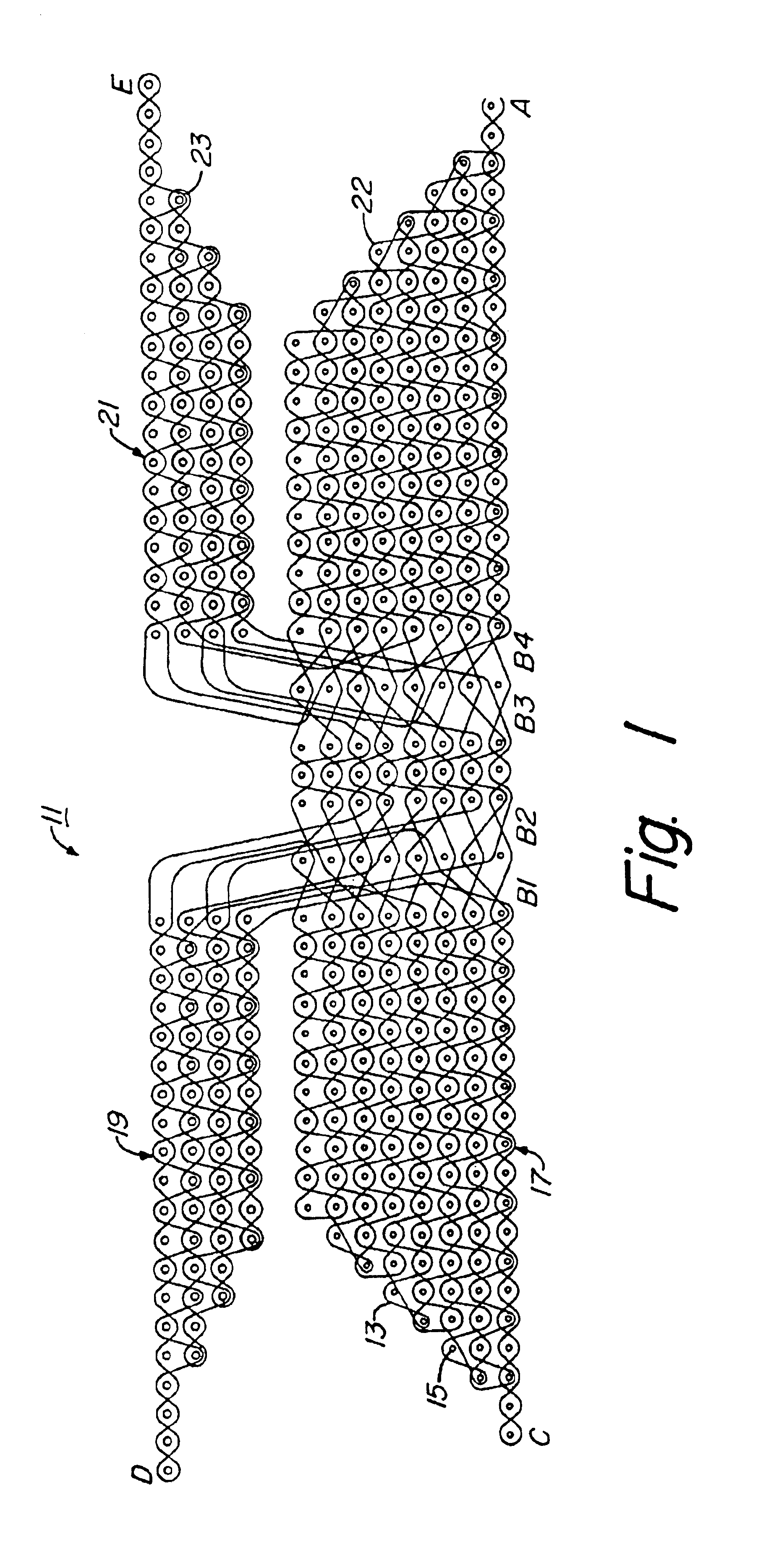
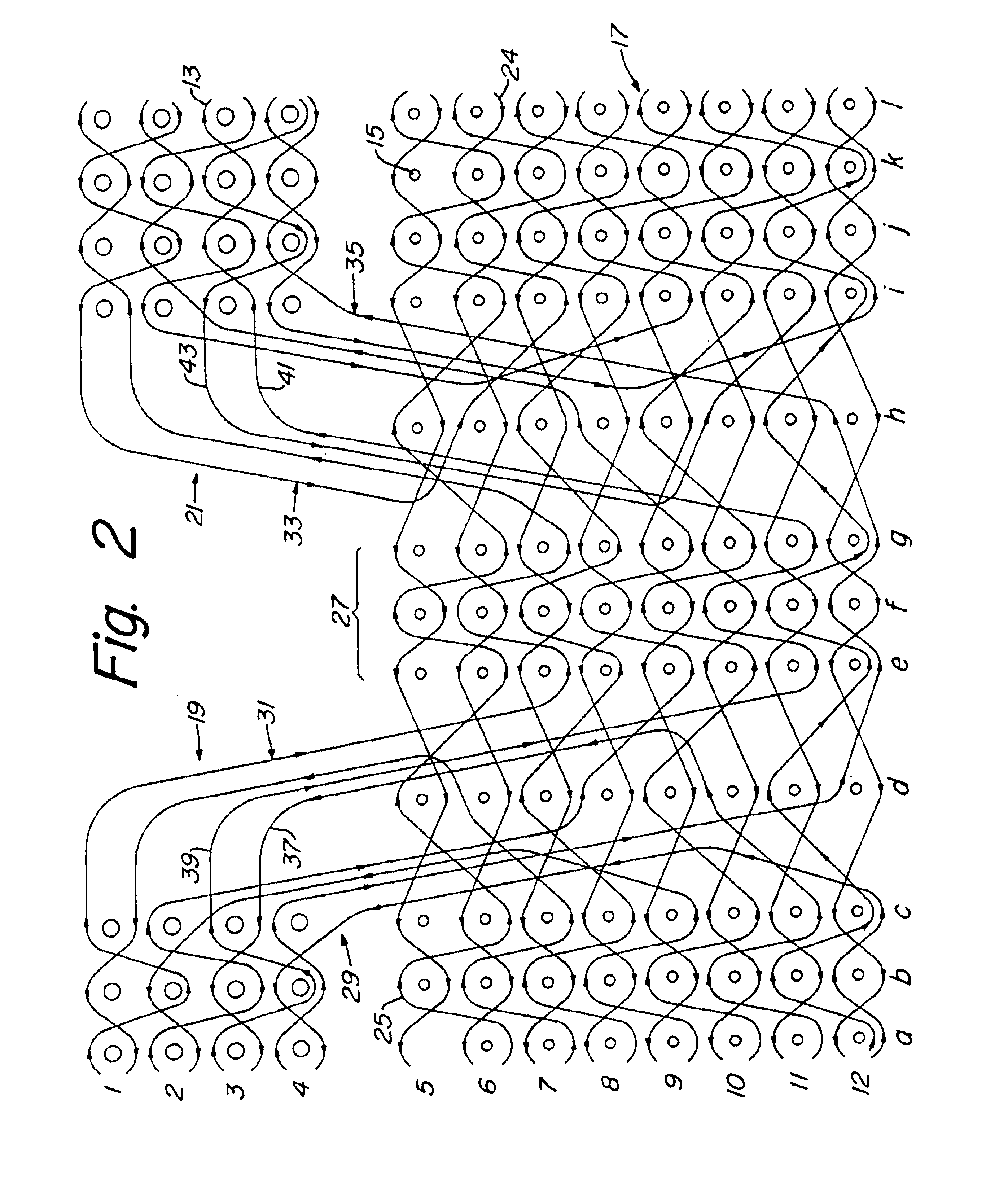
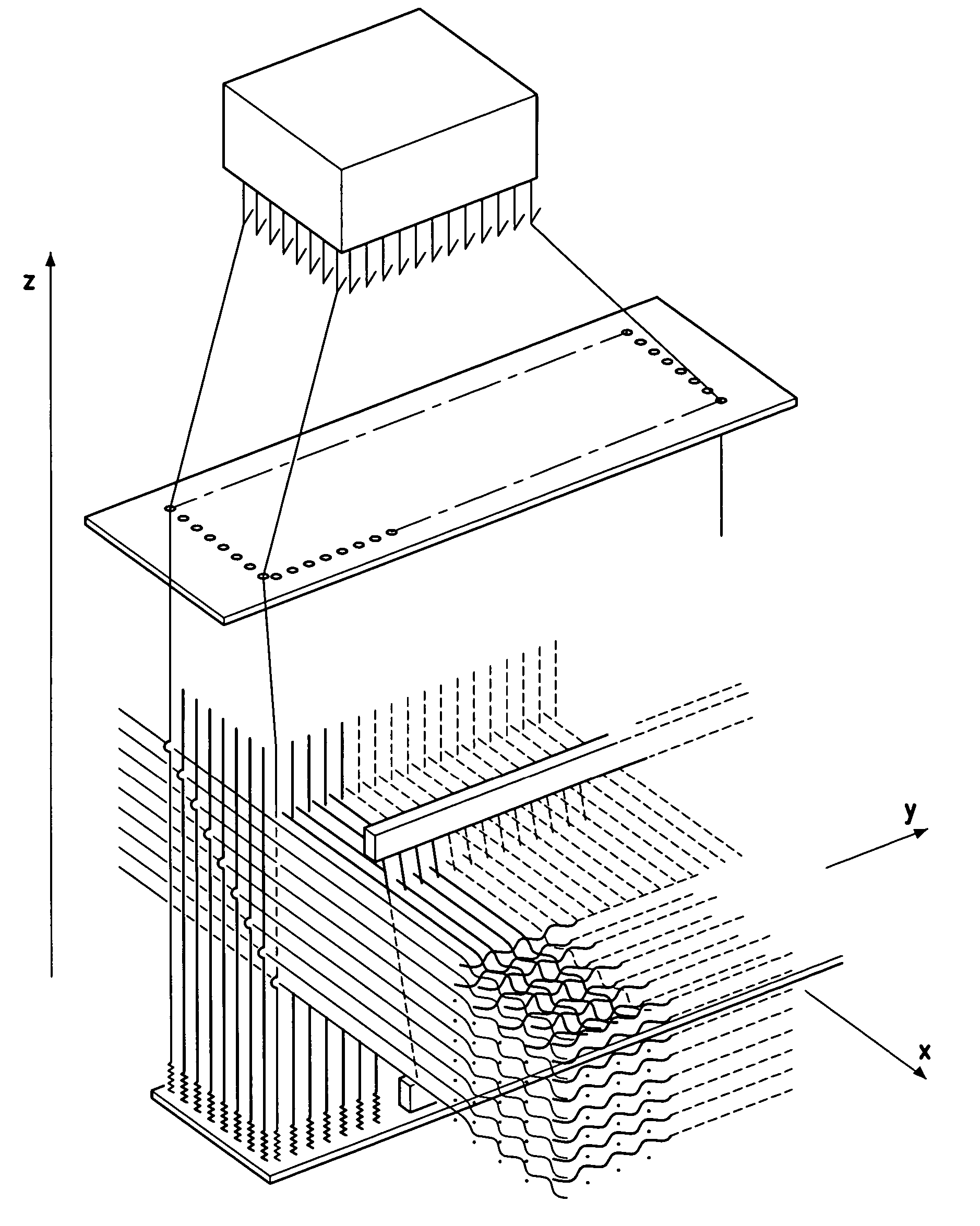
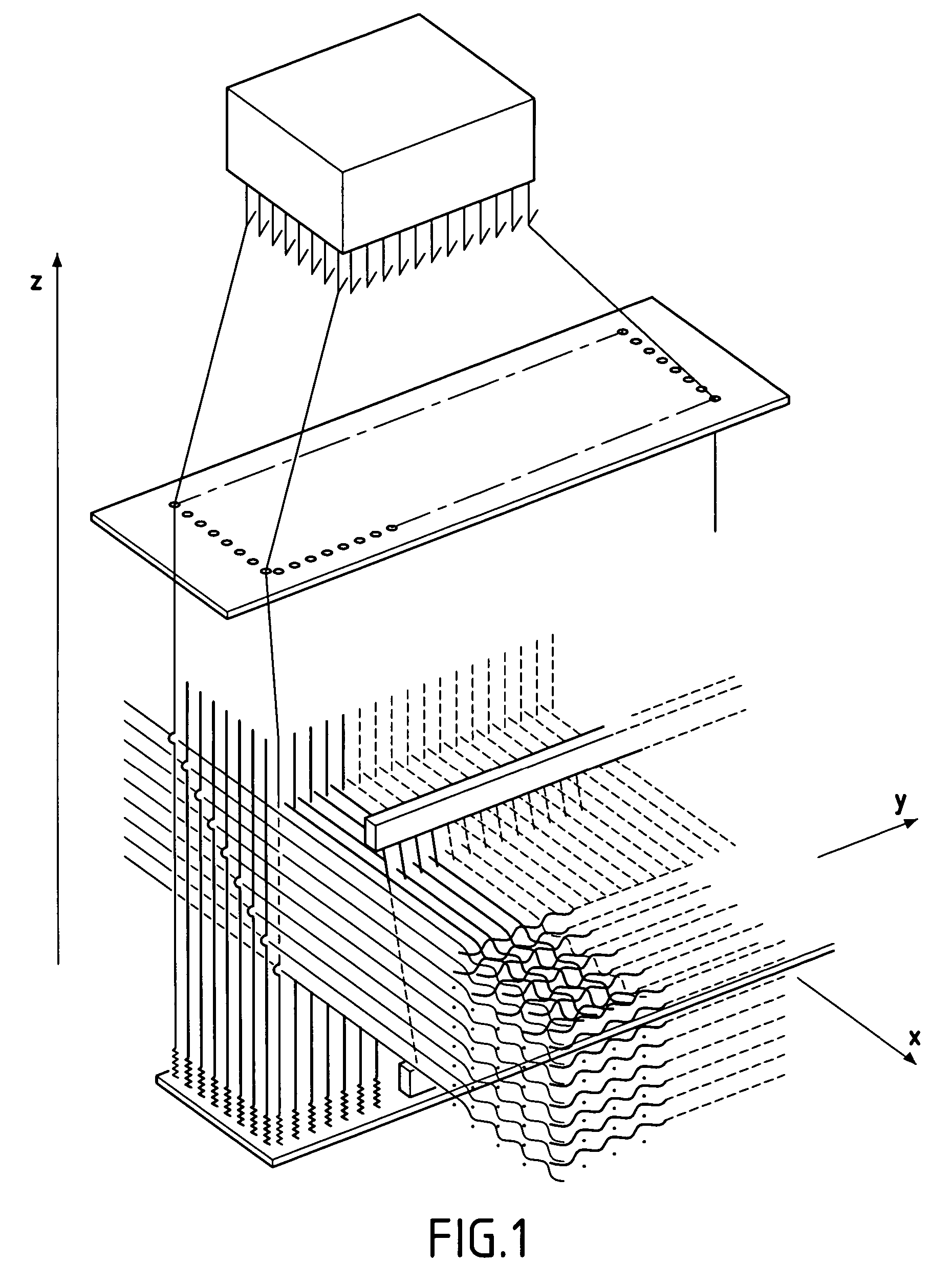
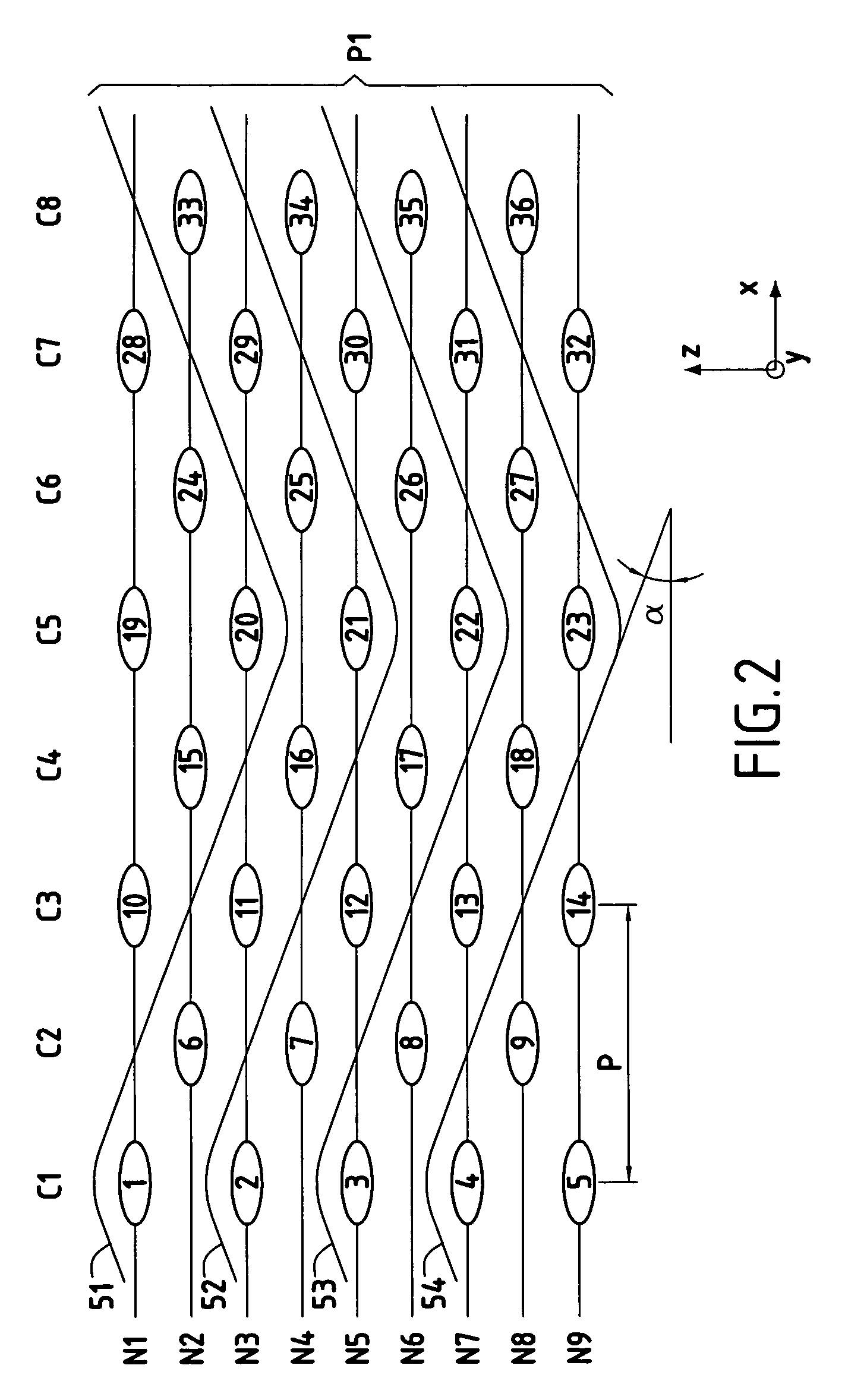
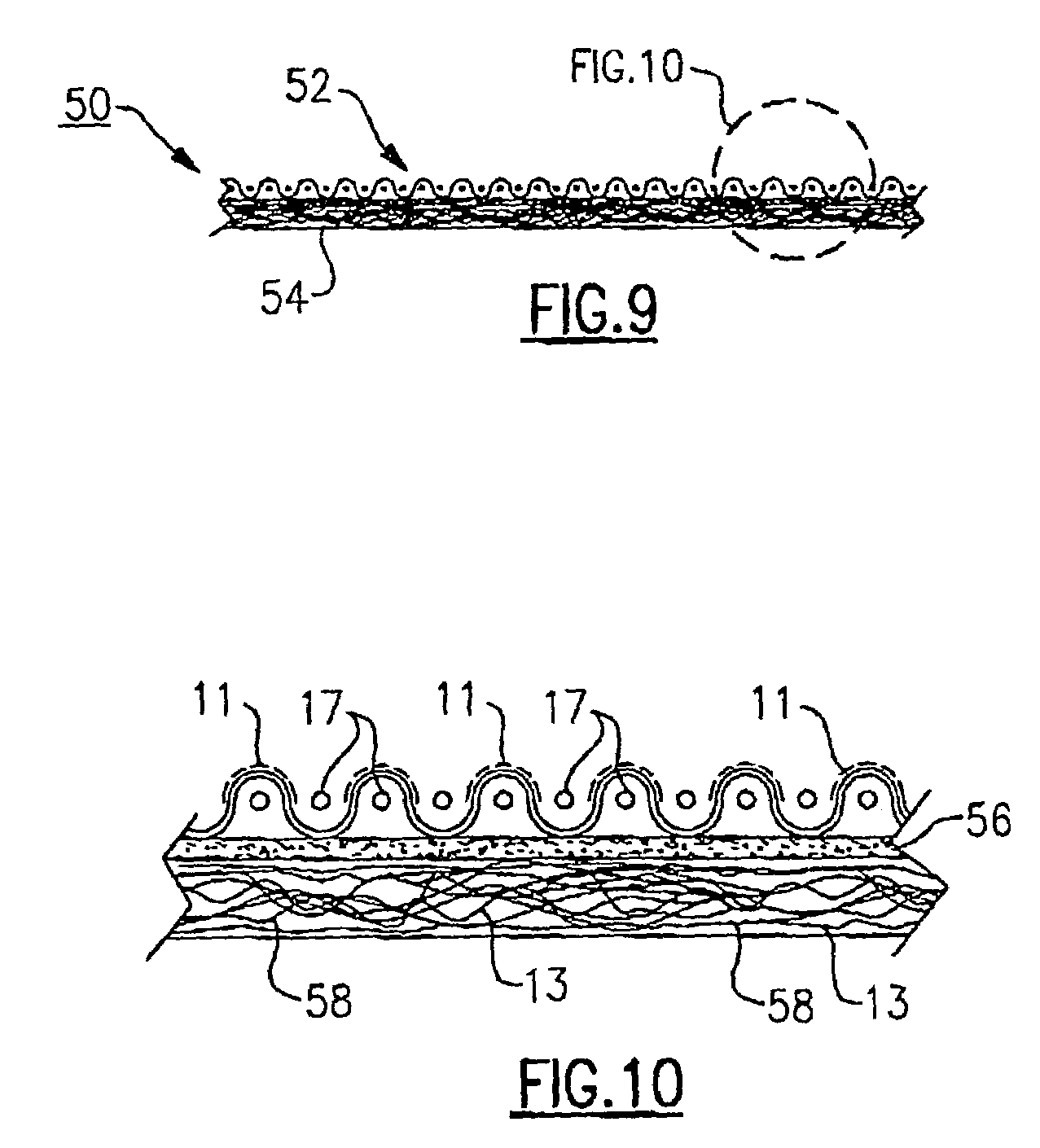
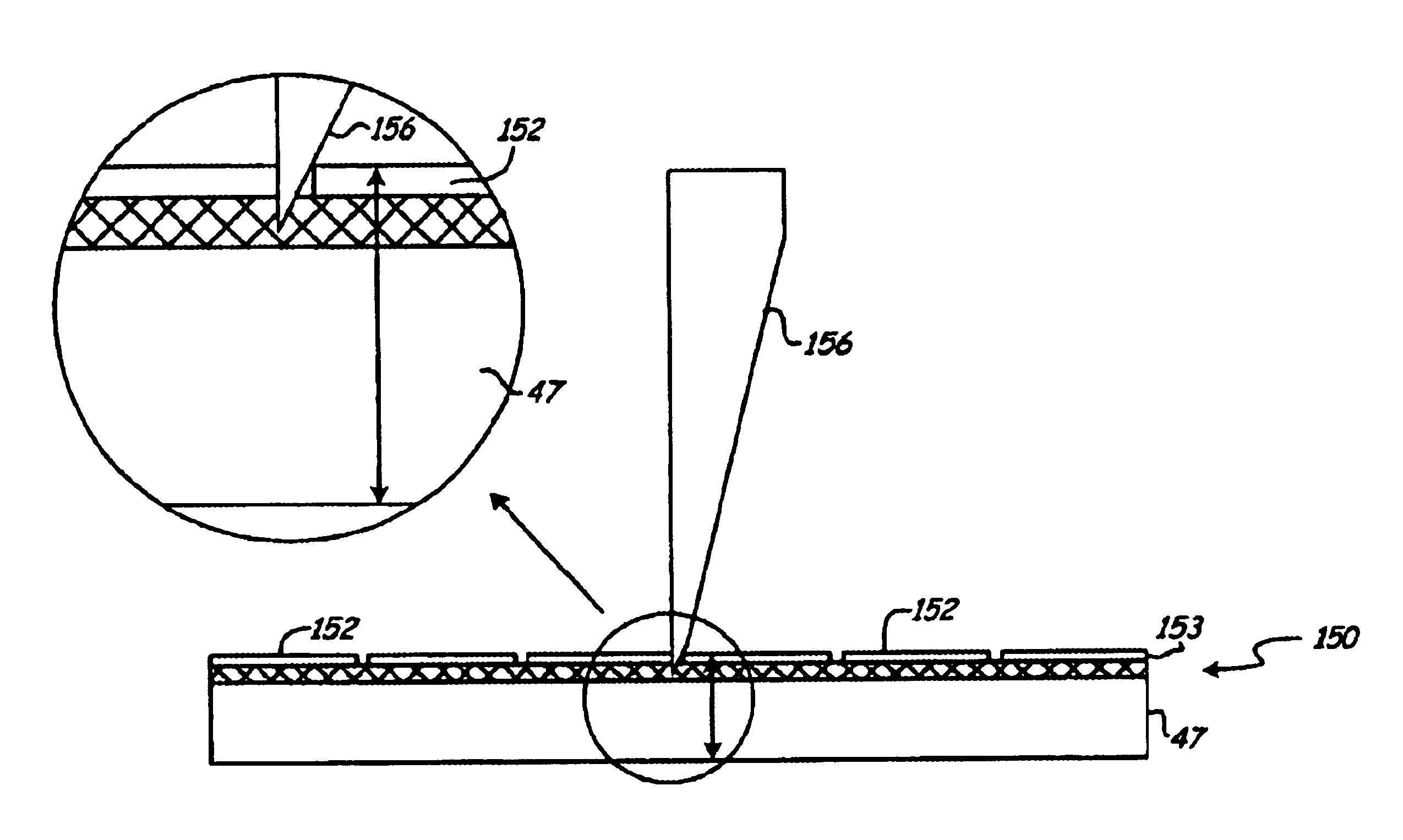
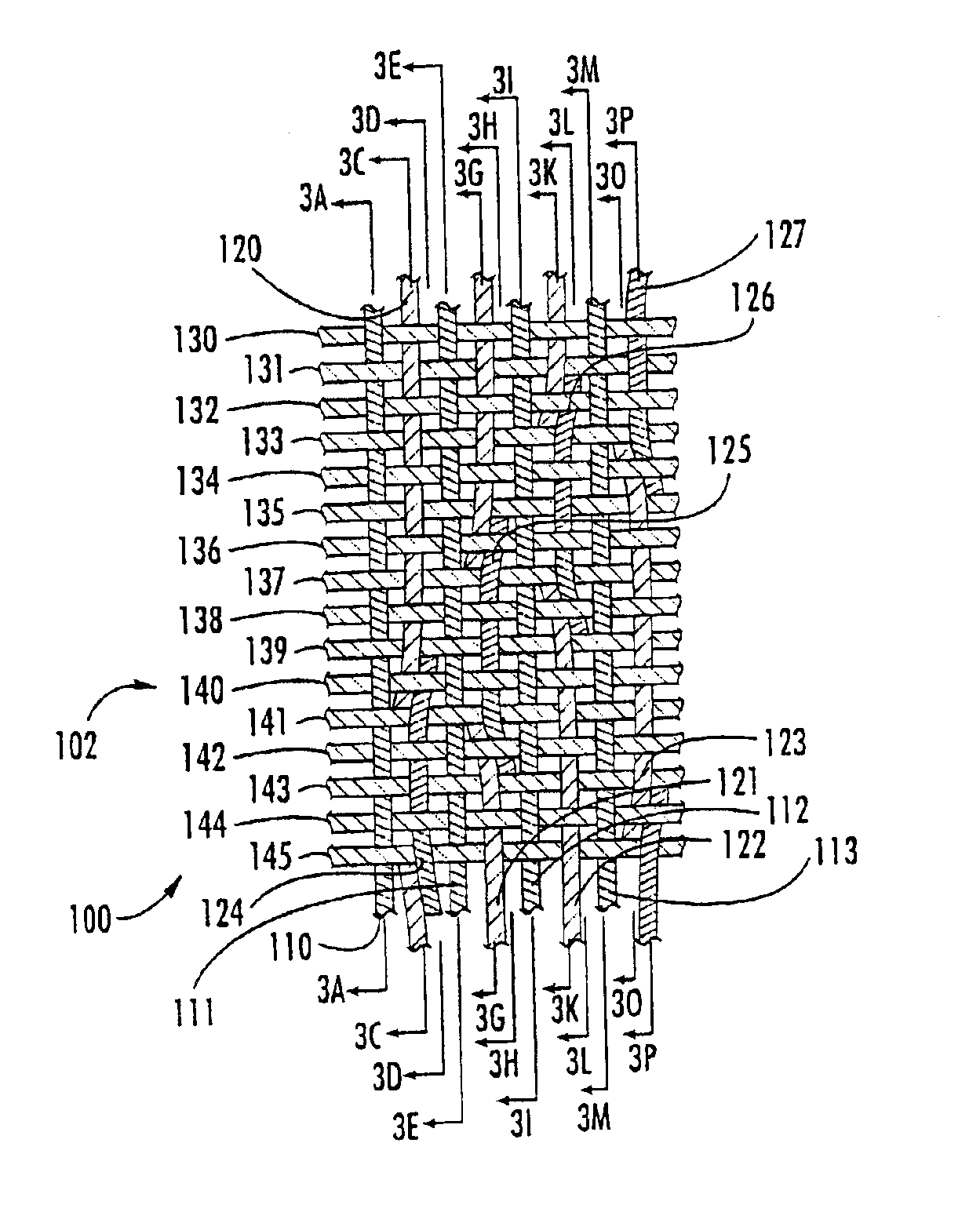
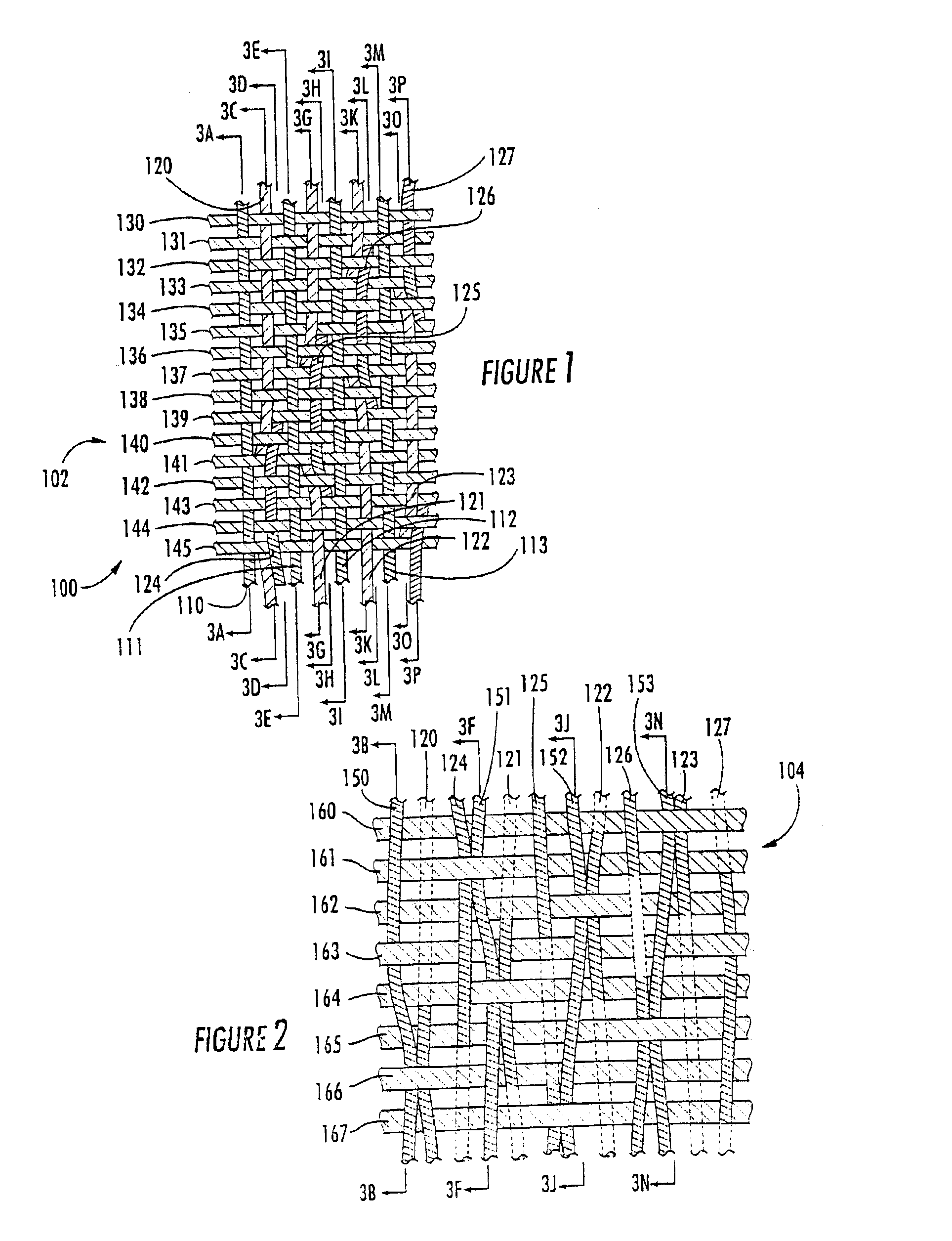
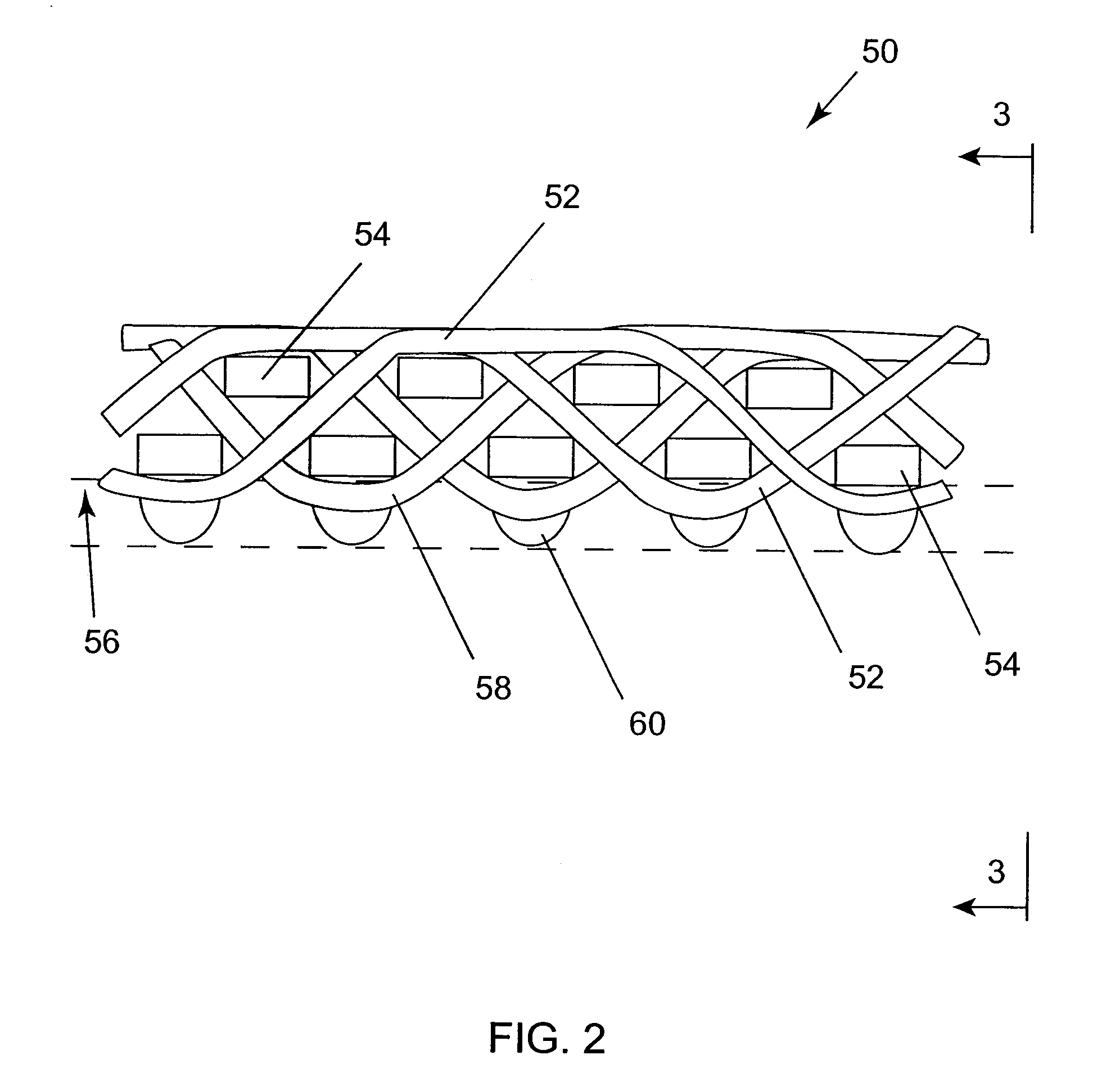
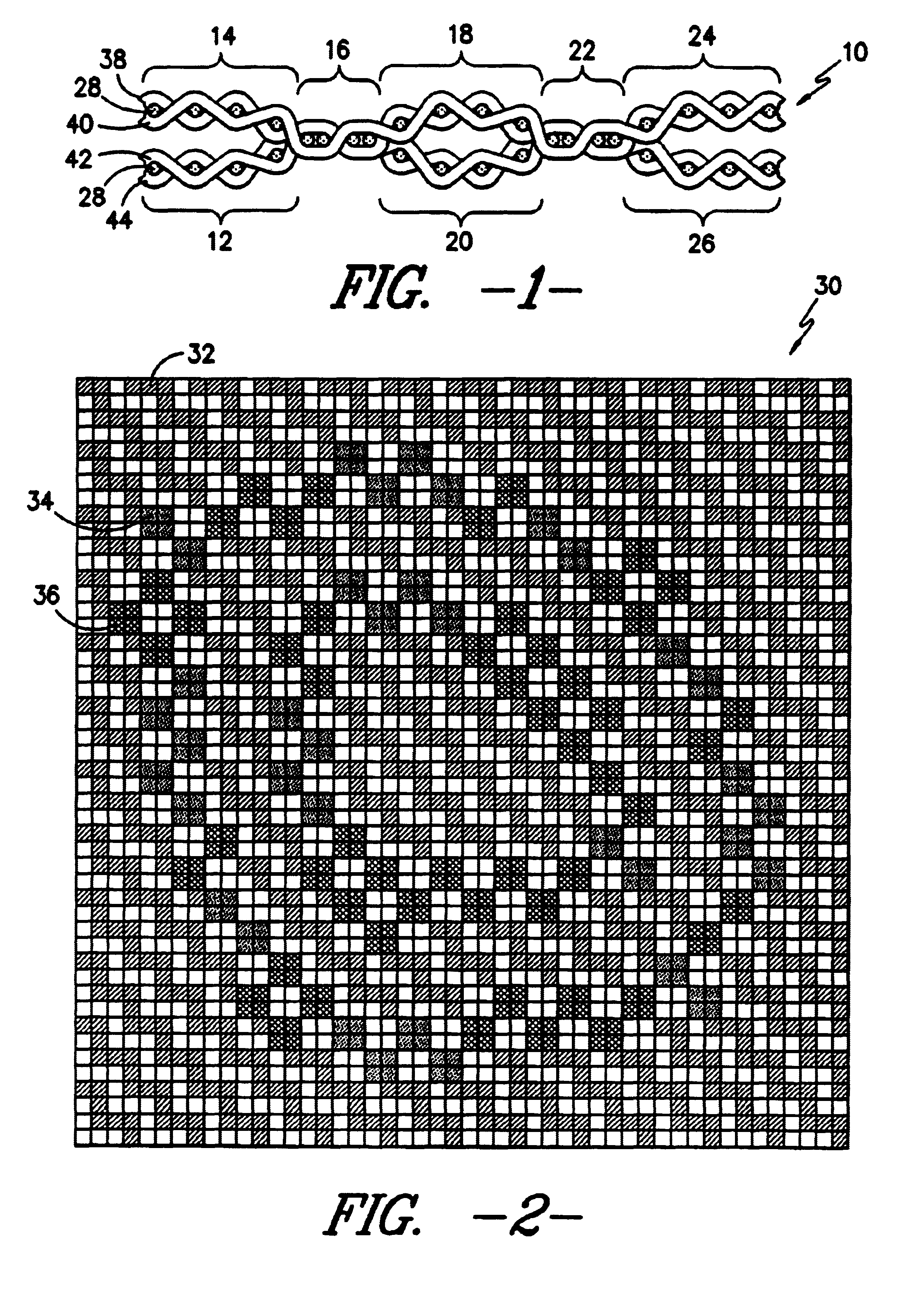
Woven stent/graft structure
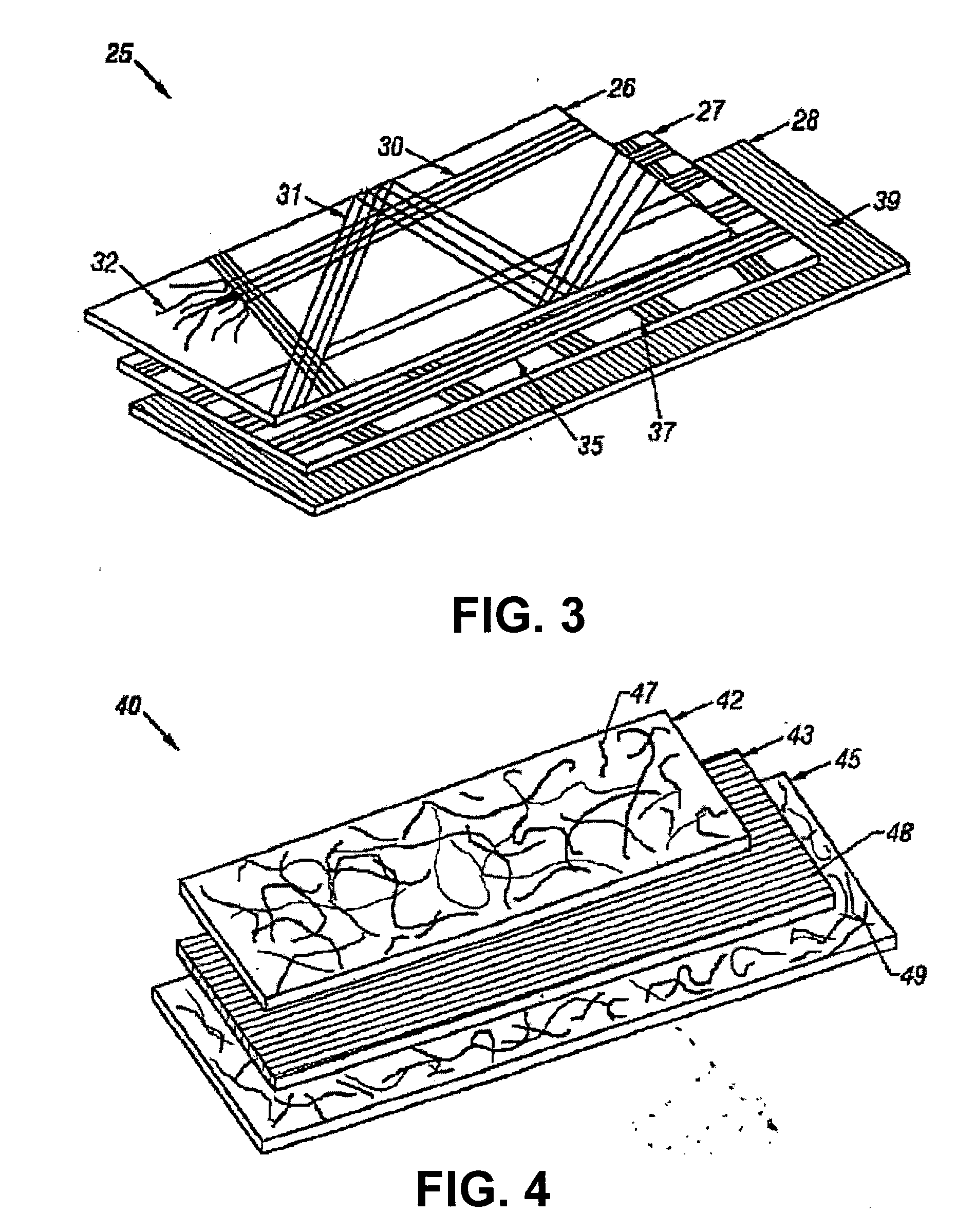
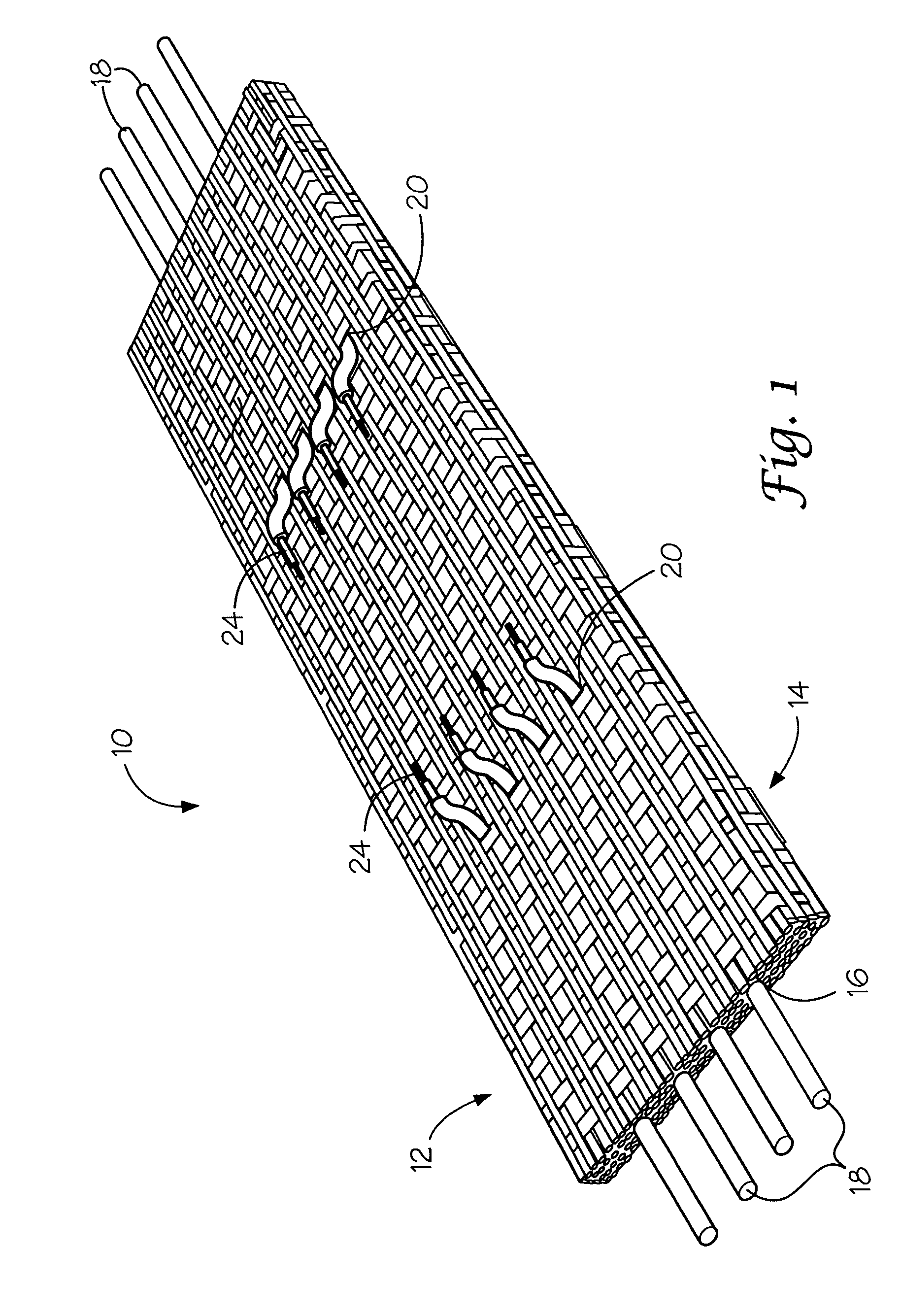
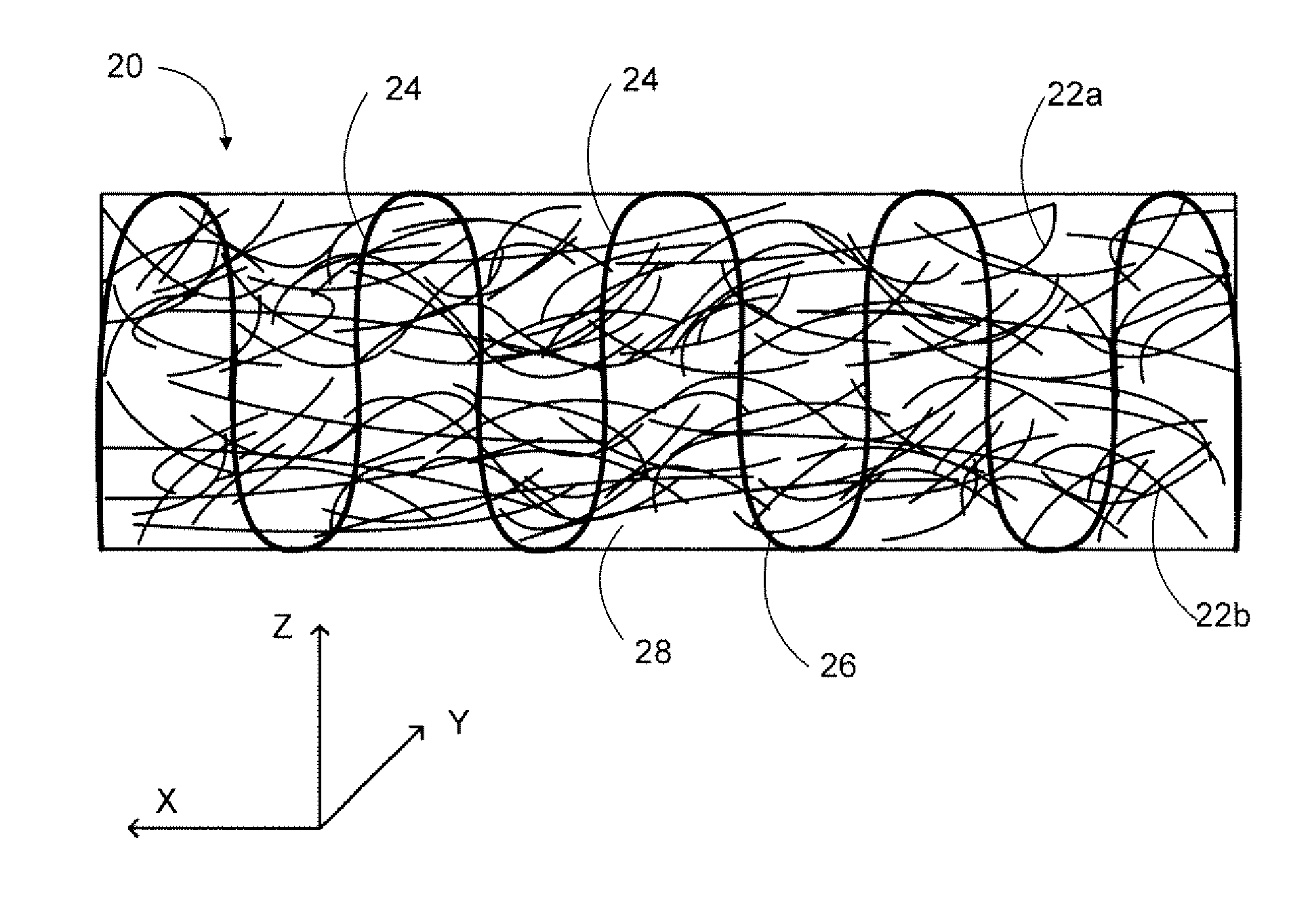
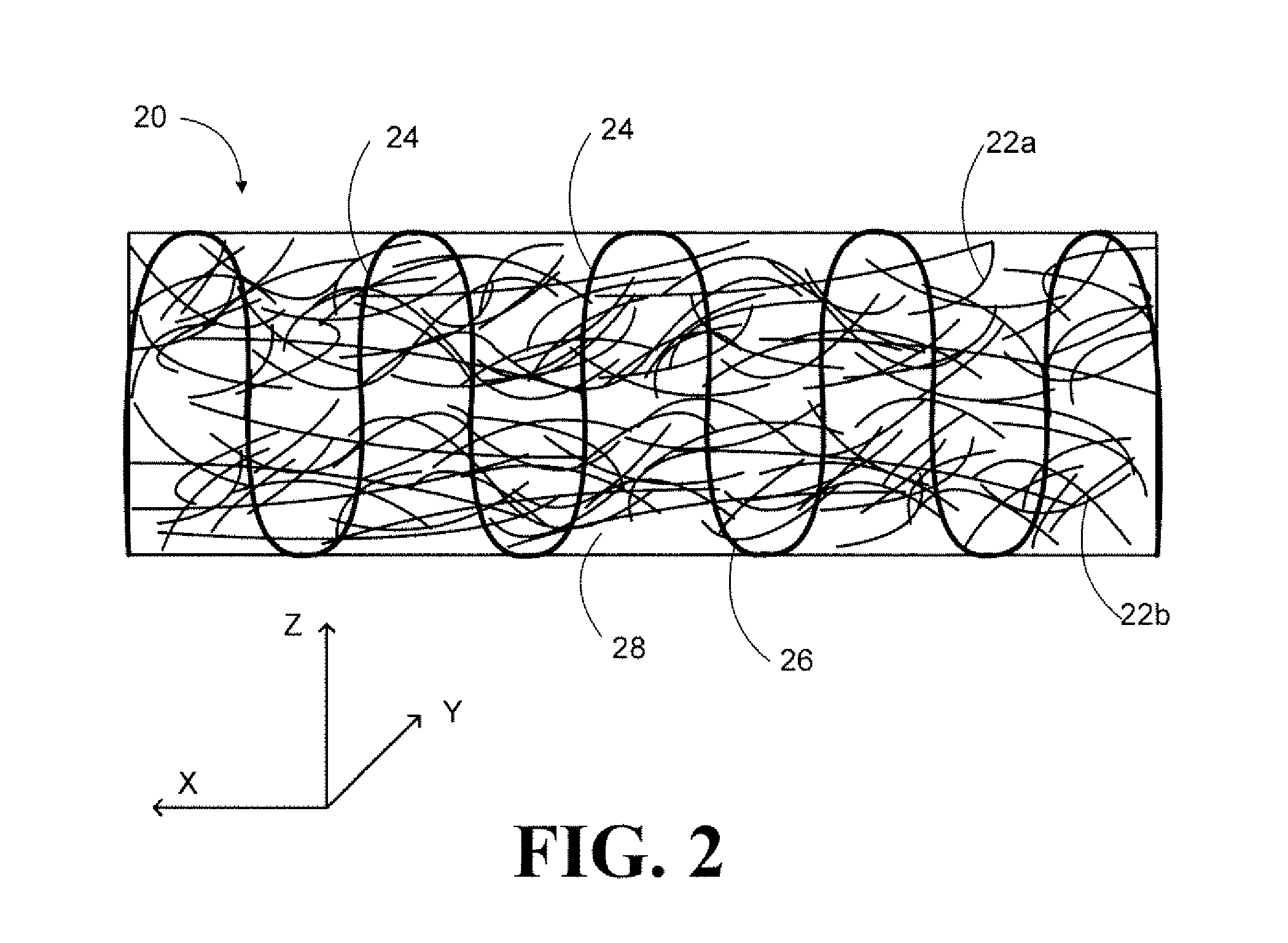
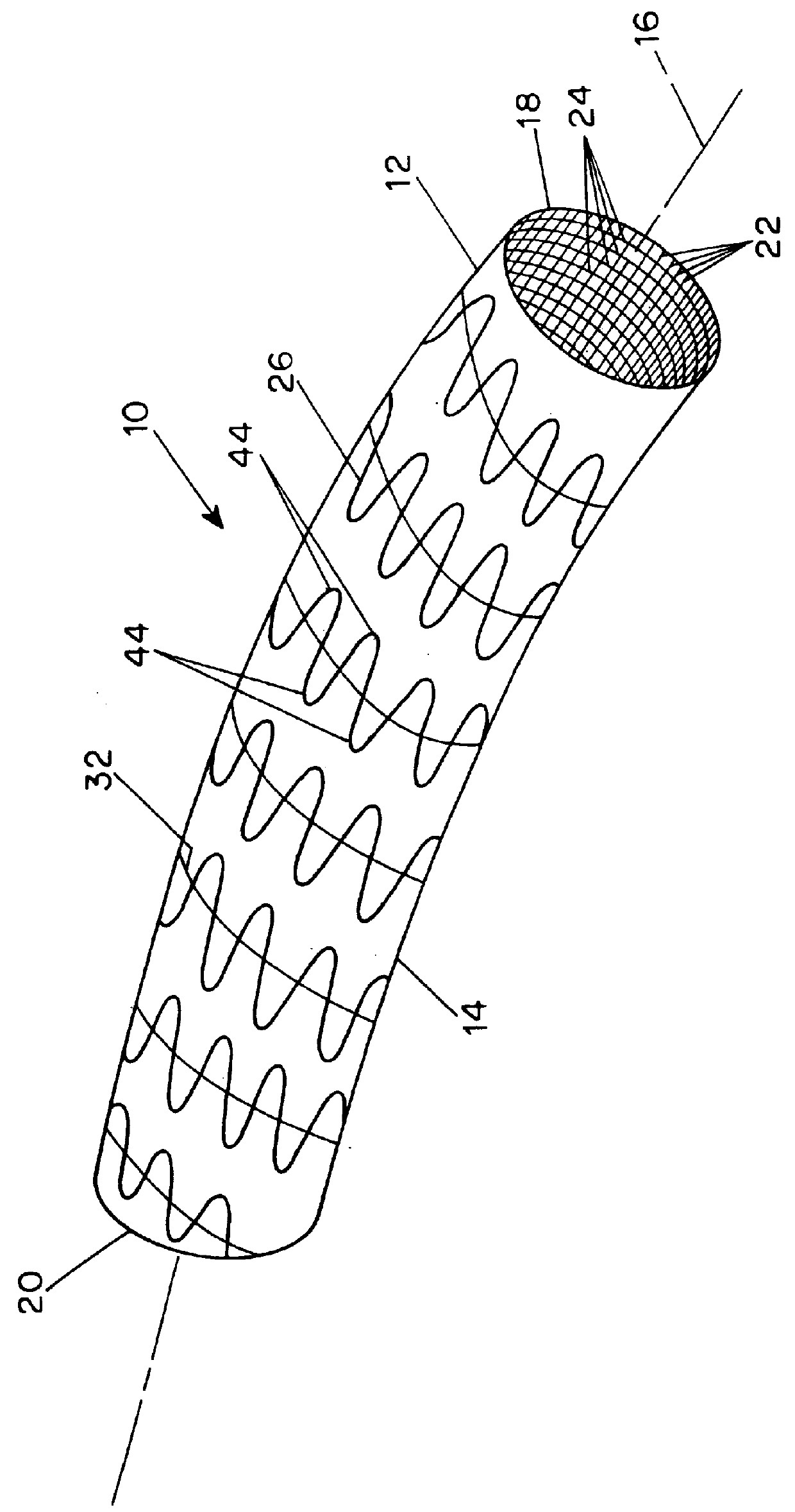
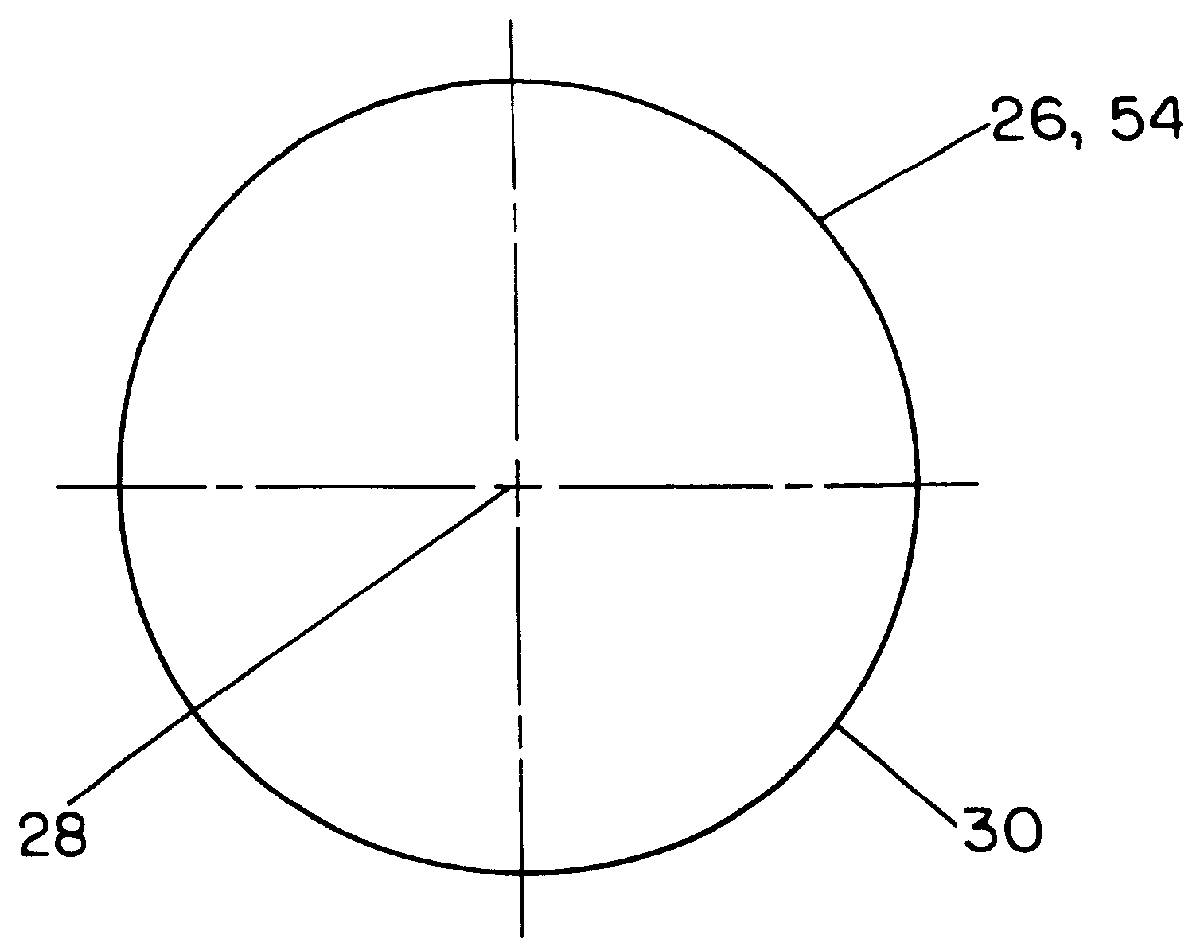
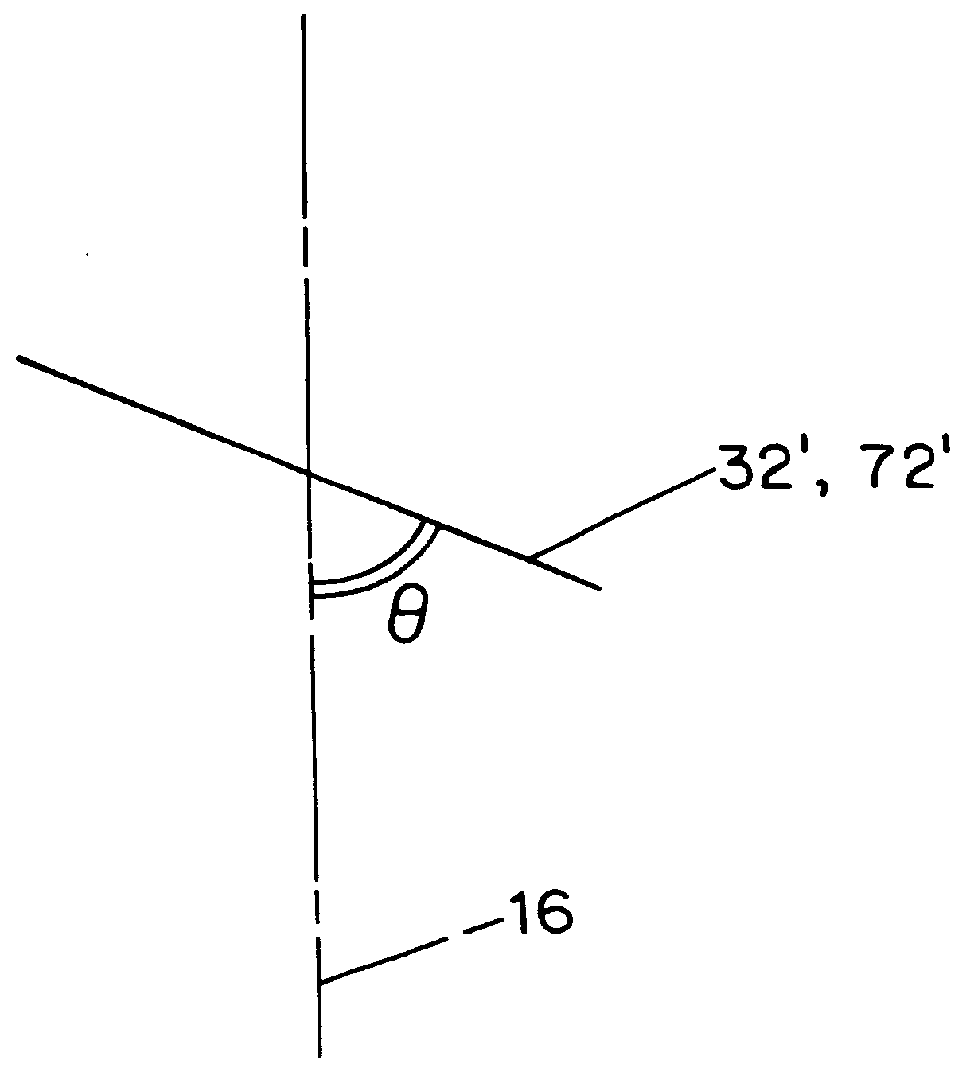
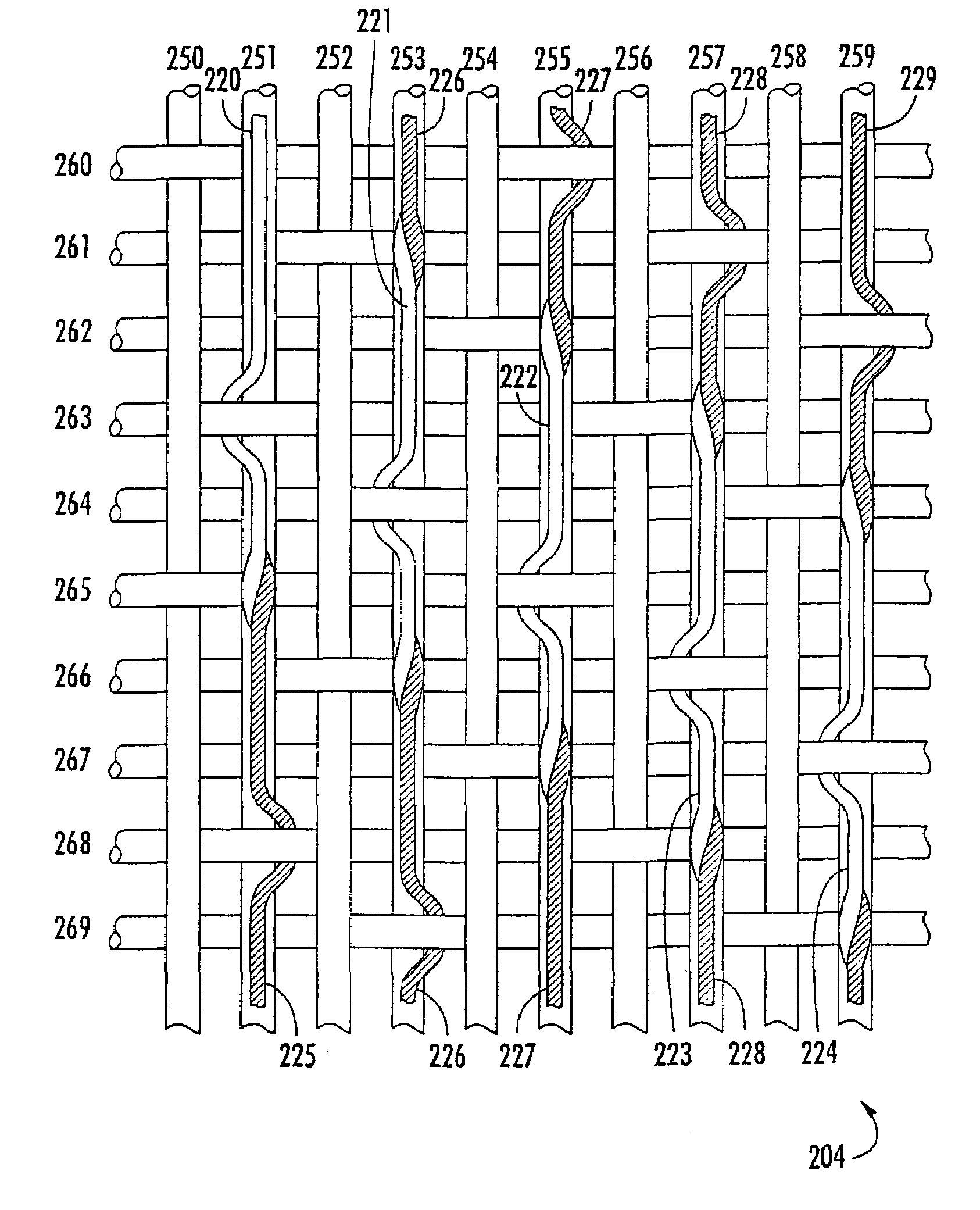
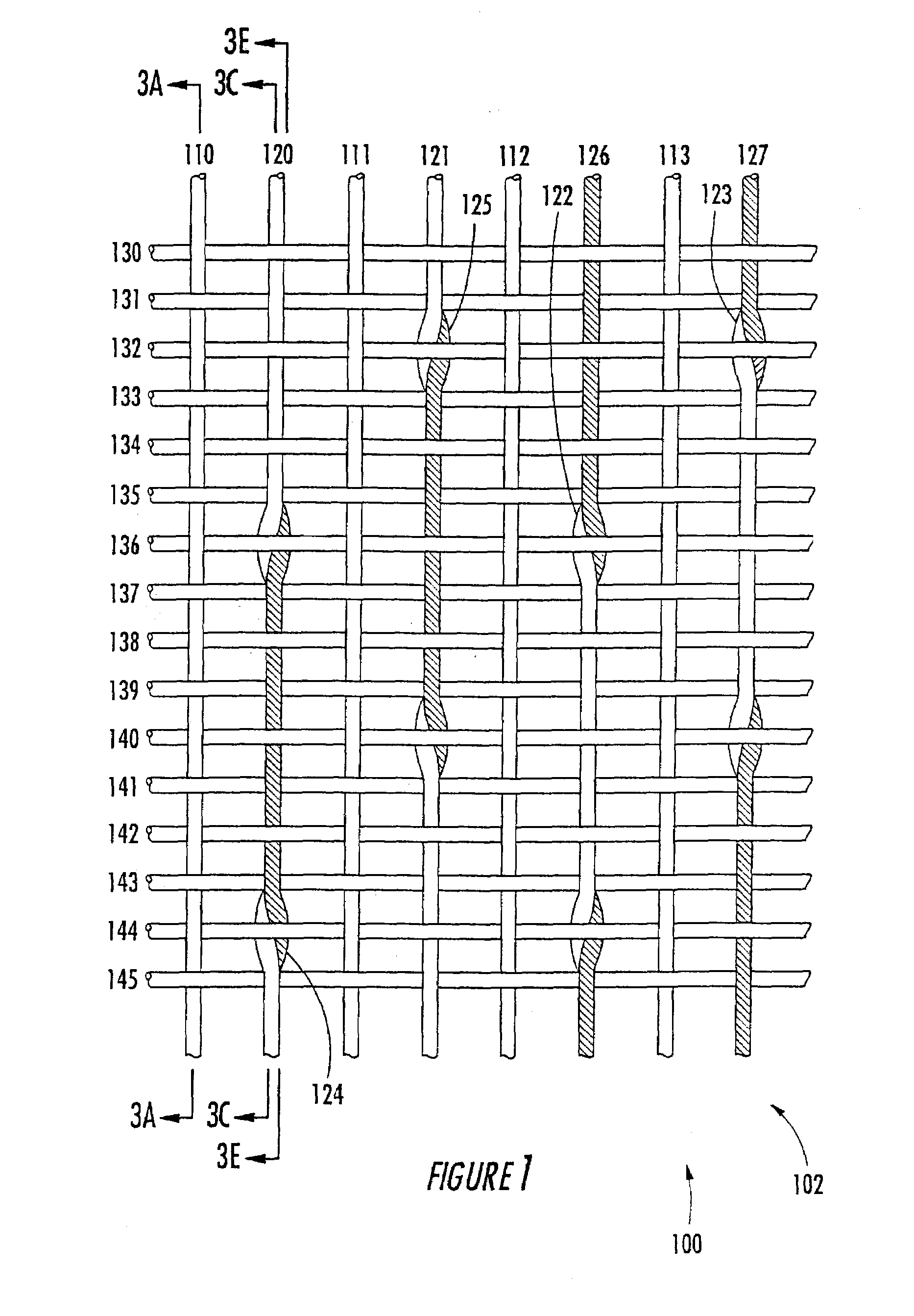
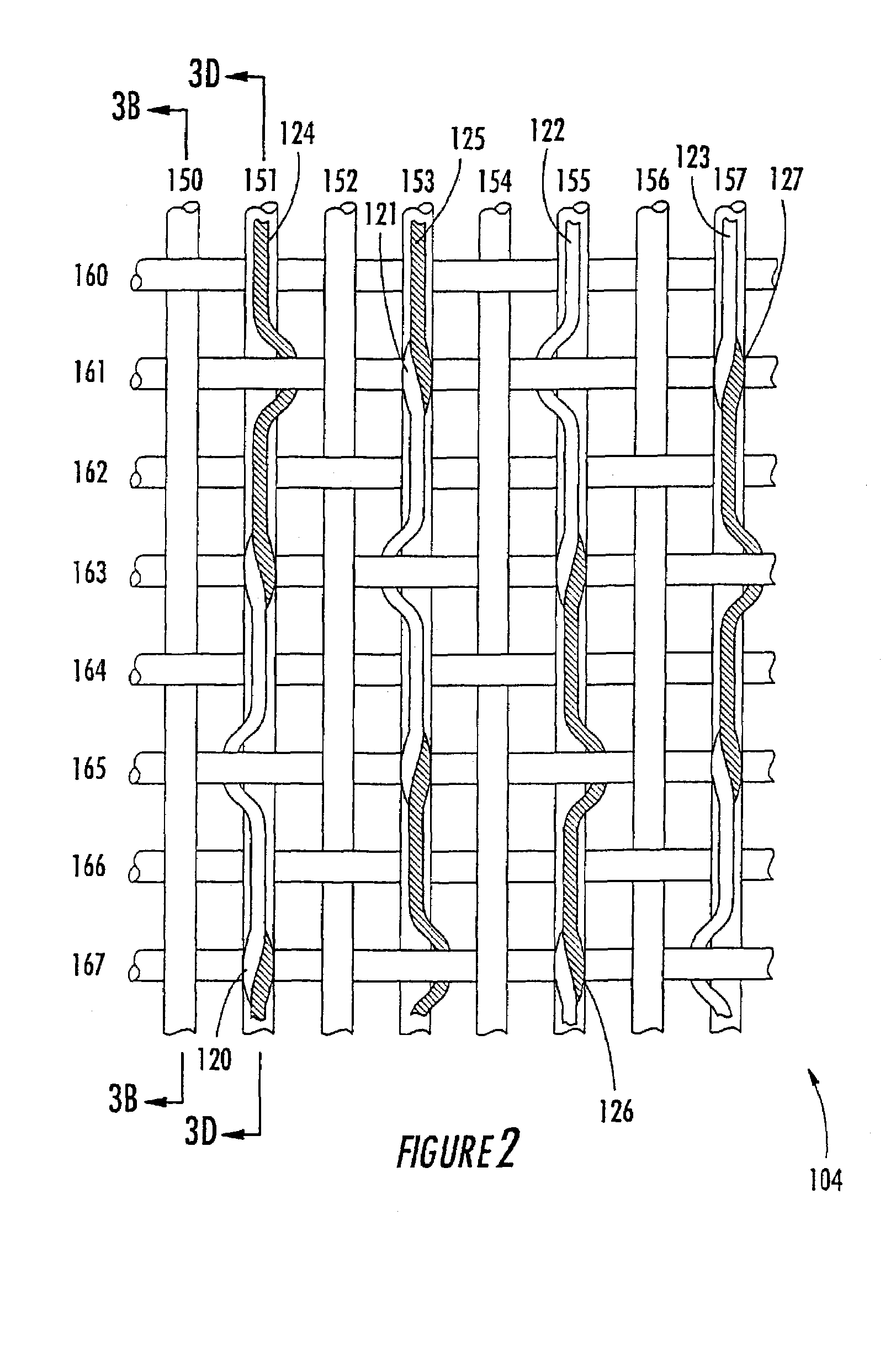
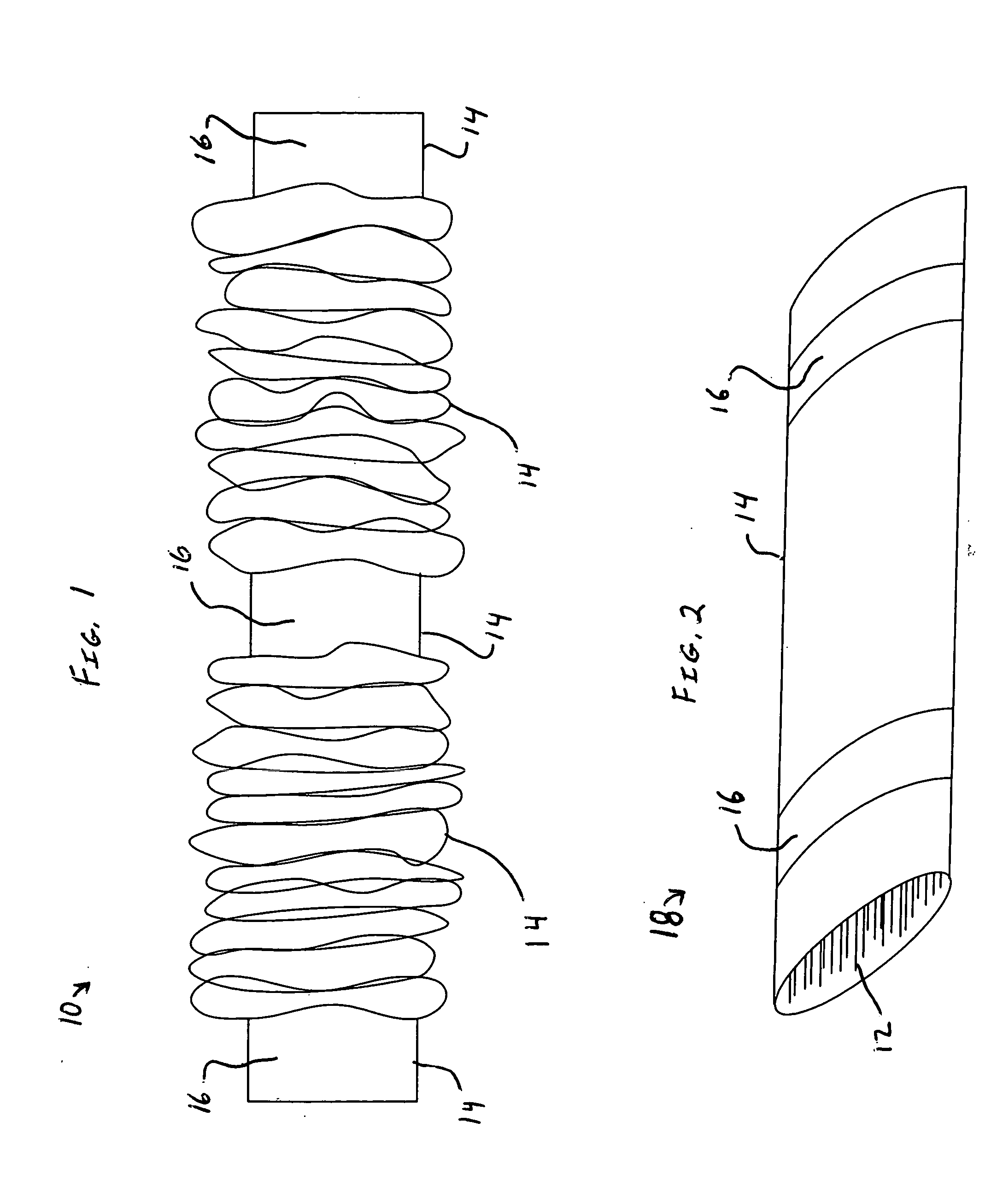
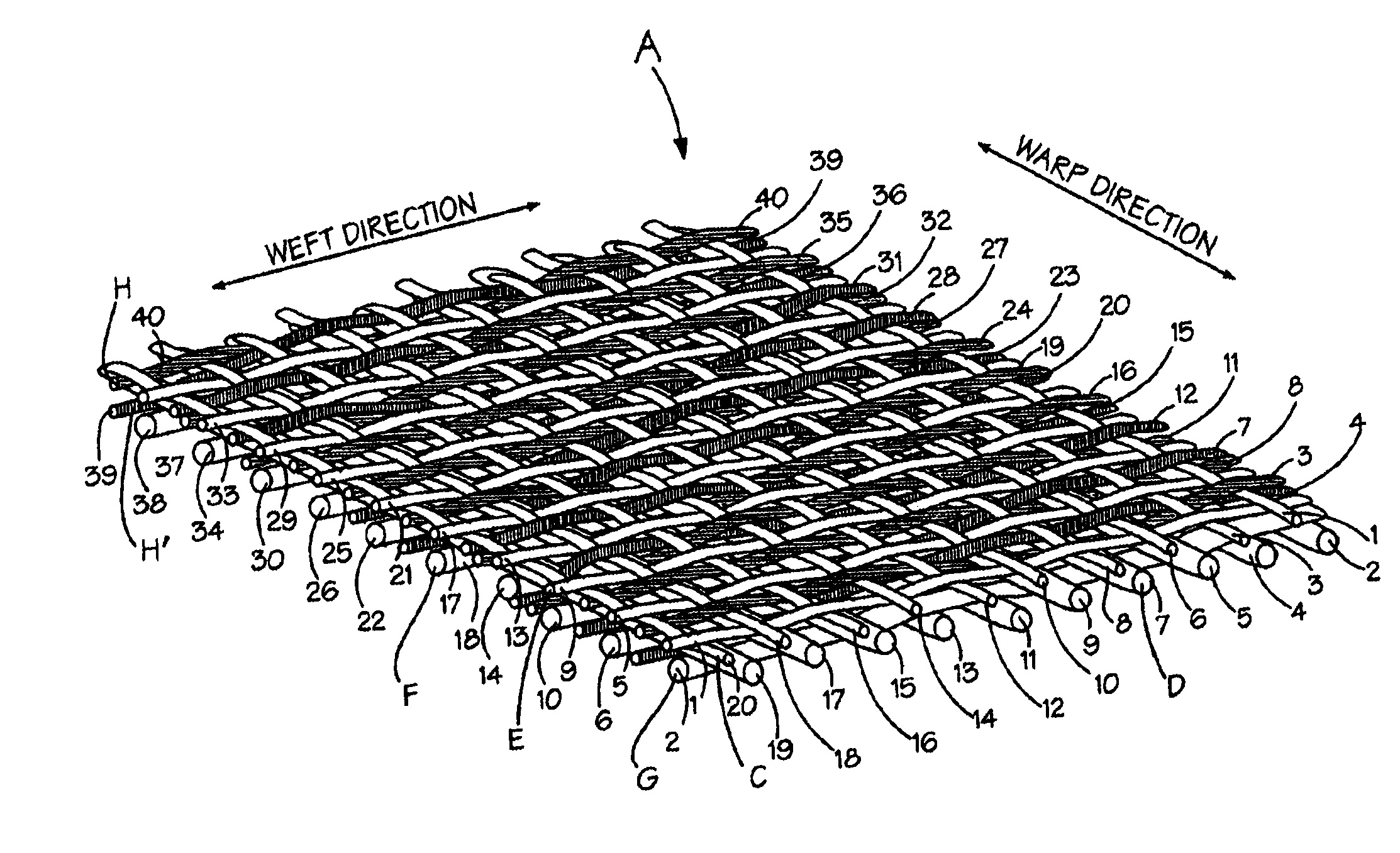
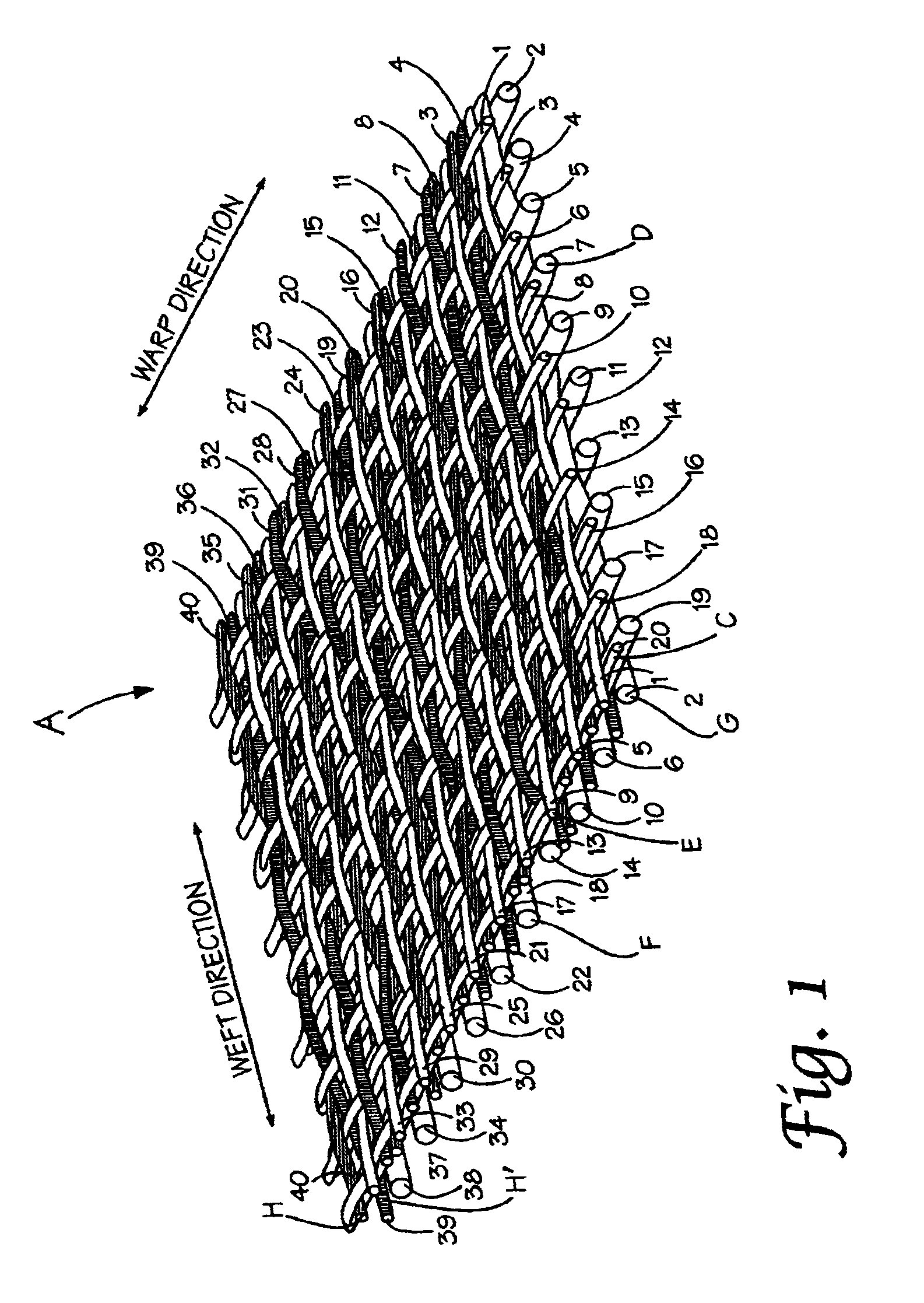
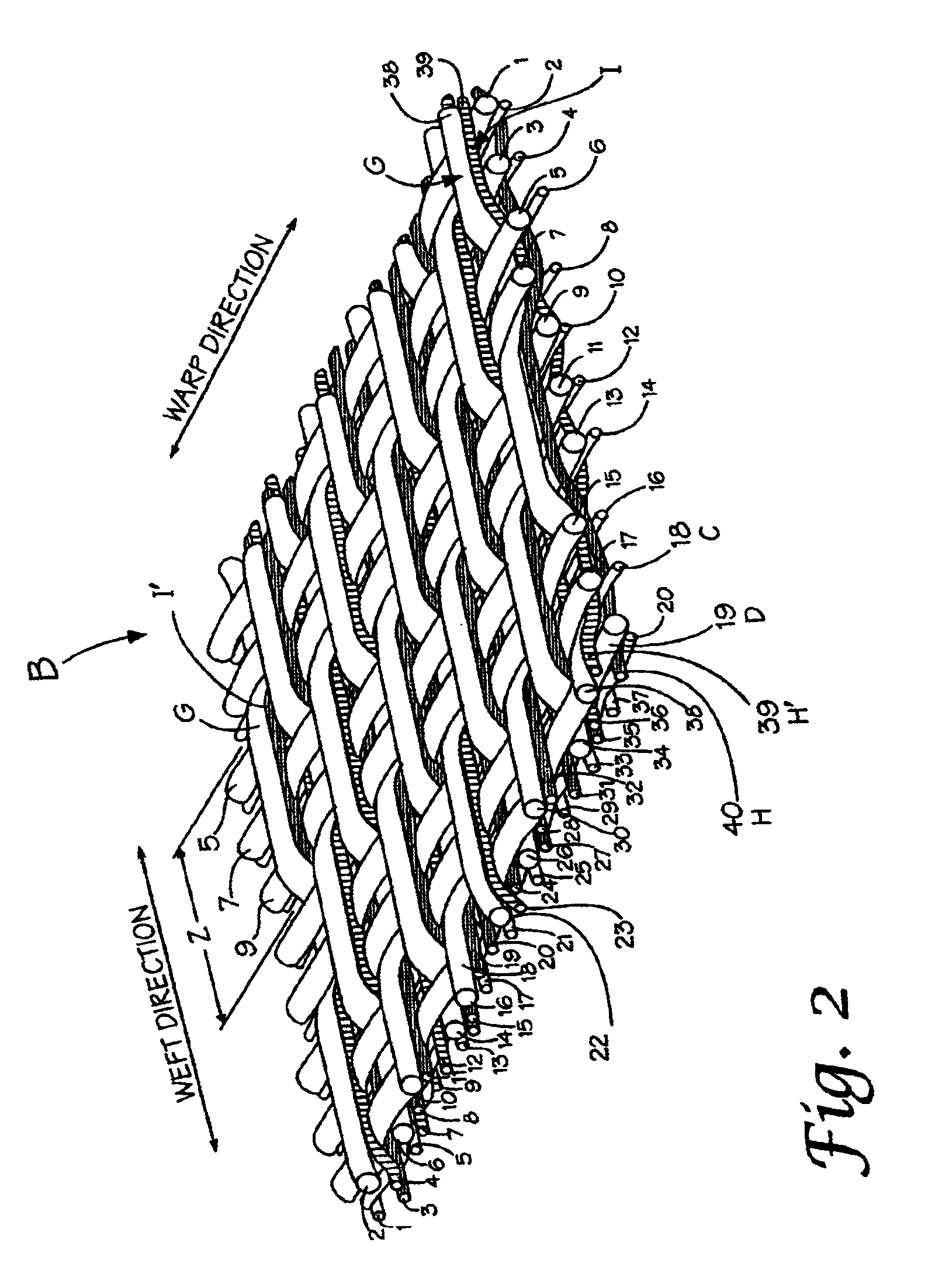
A combined stent / graft structure for repair of a body tube in a living body. The structure includes a textile graft adapted to enhance fluid integrity of the body tube and a stent expandable between a first position permitting easy insertion of the stent into the body tube and a second position wherein the stent presses securely against the inside surface of the body tube. The stent includes a first elongate wire-shaped stent member with both a stent member global axis and a stent member local axis, and is integrally secured to the graft by at least one graft yarn of which the graft is formed. Substantial portions of the first stent member global axis form a non-orthogonal angle with the graft main portion axis when projected into a plane containing the graft main portion axis. A woven textile is also part of the invention as is a method of manufacturing such a woven textile, which can be used to produce stent / graft structures according to the invention.
Owner:SECANT MEDICAL
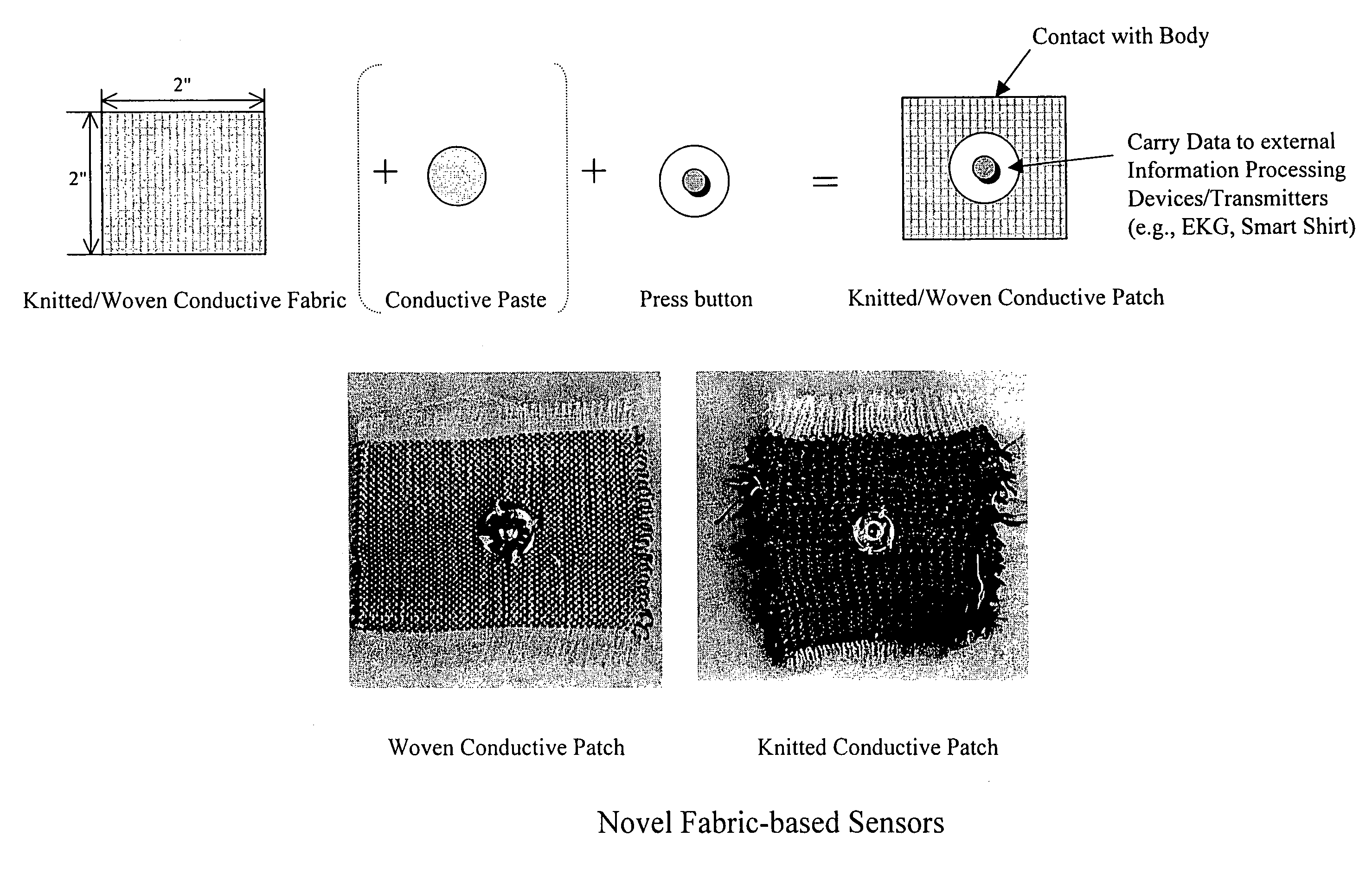
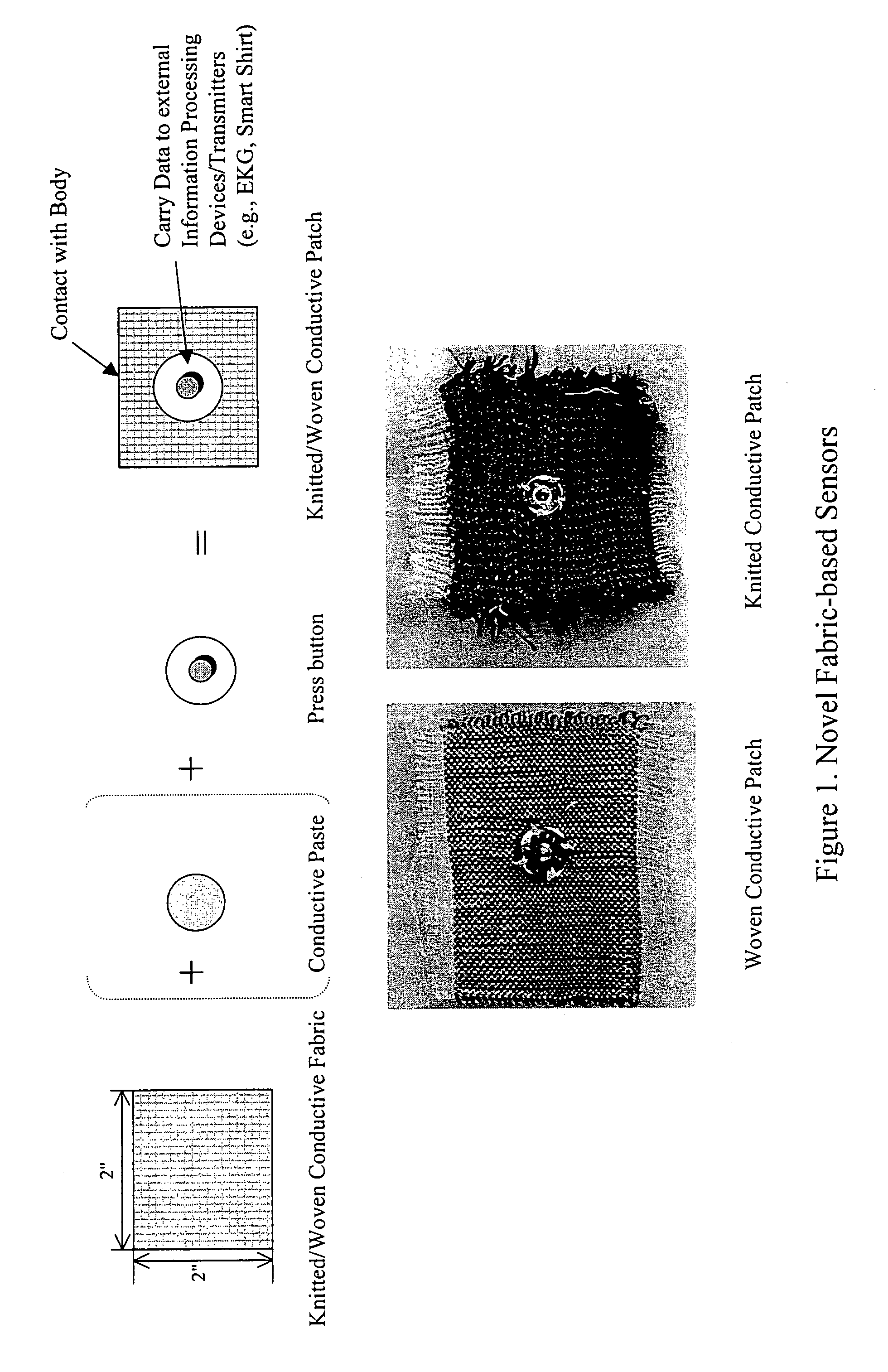
Fabric-based sensor for monitoring vital signs
The present invention comprises a fabric-based sensor for monitoring vital signs or other electrical impulses of a subject. The sensor is woven or knitted from conductive fibers and, when in contact with the body, receives signals from the wearer and transmits them to a processing or monitoring device through a data-output terminal. The sensor may be integrated into the fabric of a garment or used independently as a conductive patch. Additionally, the sensor may provide bi-directional communication by both monitoring electrical impulses and sending them.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Carbon nanotube fabrics
The present invention provides fabrics that have unique chemical, electrical, and thermal properties. The fabrics comprise layers of yarns woven together wherein the yarns further comprise carbon nanotube fibers. These carbon nanotube fibers may be either single-walled or multi-walled carbon nanotubes. The use of carbon nanotube fibers allows the fabrics to insulate, semi-conduct or super-conduct electrical charges. Additionally, the thermal properties of carbon nanotubes allow thermal energy to flow efficiently between the fabric and a heat sink or source. Additional yarns of materials other than carbon nanotubes can be integrated or woven into the fabric to provide other unique properties for the fabric. These fabrics can be layered to form unique garments or structures.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
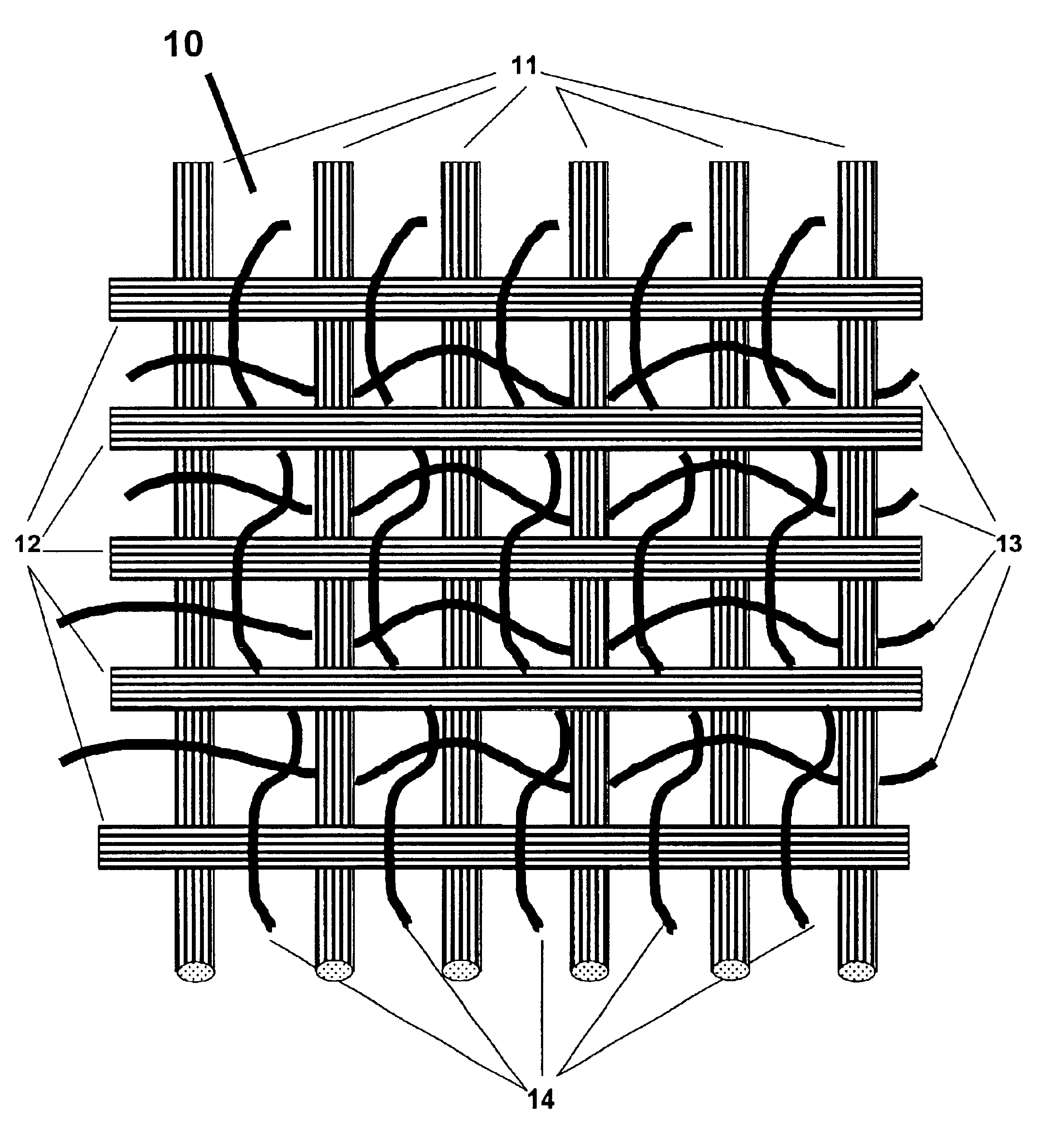
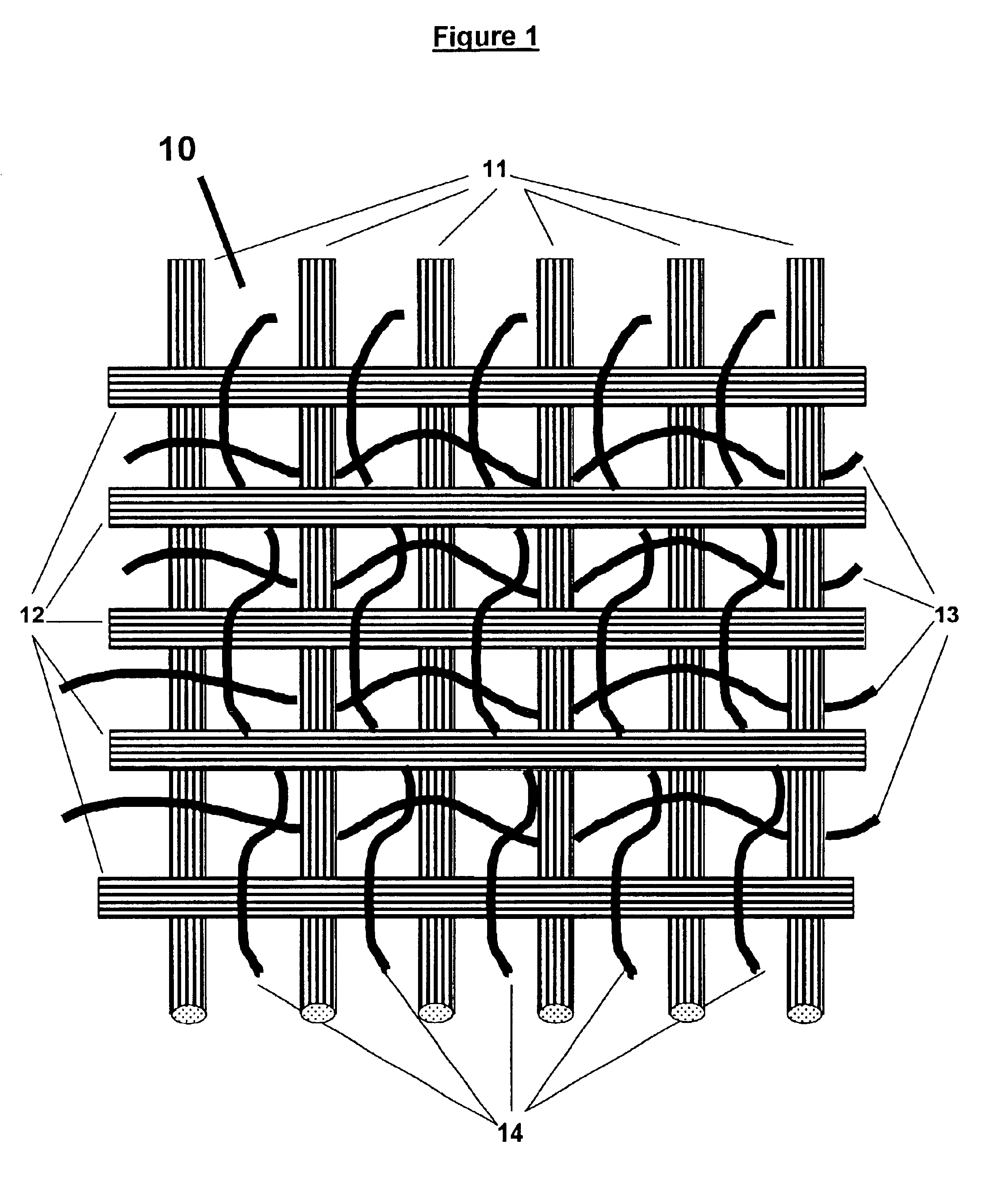
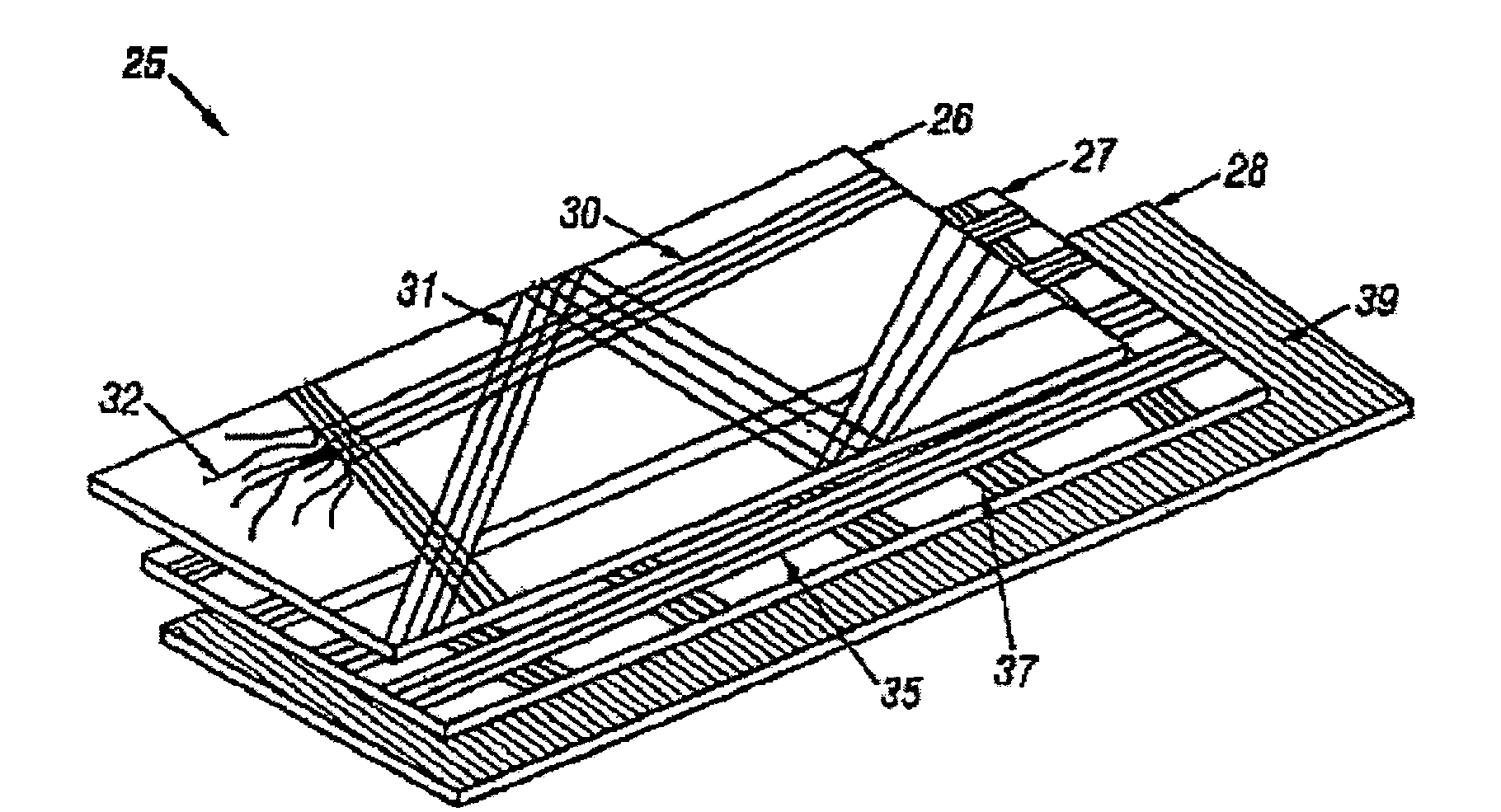
Bi-directional and multi-axial fabrics and fabric composites
InactiveUS6841492B2Increase resistanceImprove effectivenessOrnamental textile articlesProtective fabricsYarnEngineering
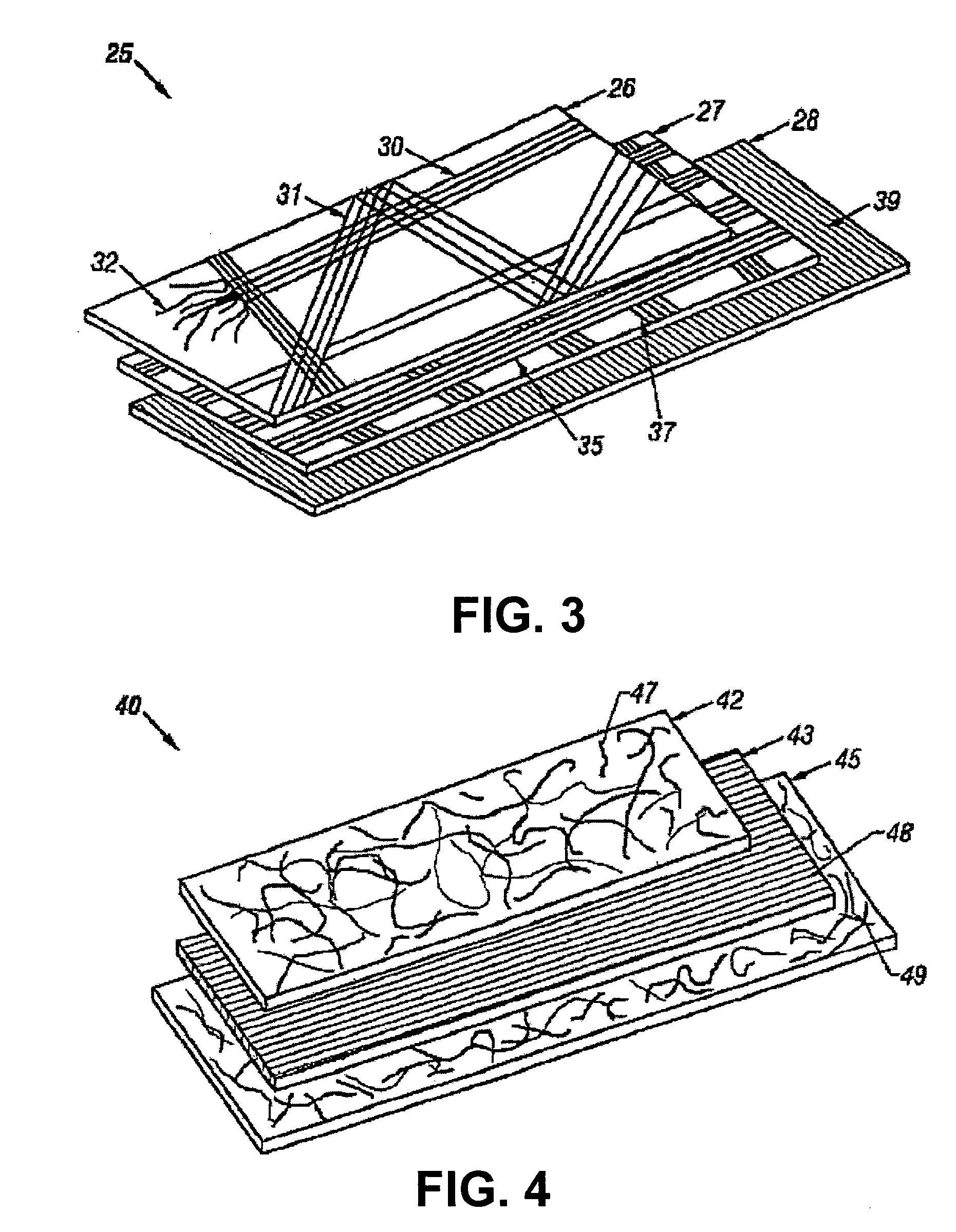
Bi-directional and multi-axial fabrics, fabric composites, ballistically resistant assemblies thereof, and the methods by which they are made. The fabrics are comprised of sets of strong, substantially parallel, unidirectional yarns lying in parallel planes, one above the other, with the direction of the yarns in a given plane rotated at an angle to the direction of the yarns in adjacent planes; and one or more sets of yarns having lower strength and higher elongation interleaved with the strong yarns. The fabrics of the invention provide superior ballistic effectiveness compared to ordinary woven and knitted fabrics but retain the ease of manufacture on conventional looms and knitting machines.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Full-fashioned weaving process for production of a woven garment with intelligence capability
A full-fashioned weaving process for the production of a woven garment which can accommodate and include holes, such as armholes. The garment is made of only one single integrated fabric and has no discontinuities or seams. Additionally, the garment can include intelligence capability, such as the ability to monitor one or more body vital signs, or garment penetration, or both, by including a selected sensing component or components in the weave of the garment.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
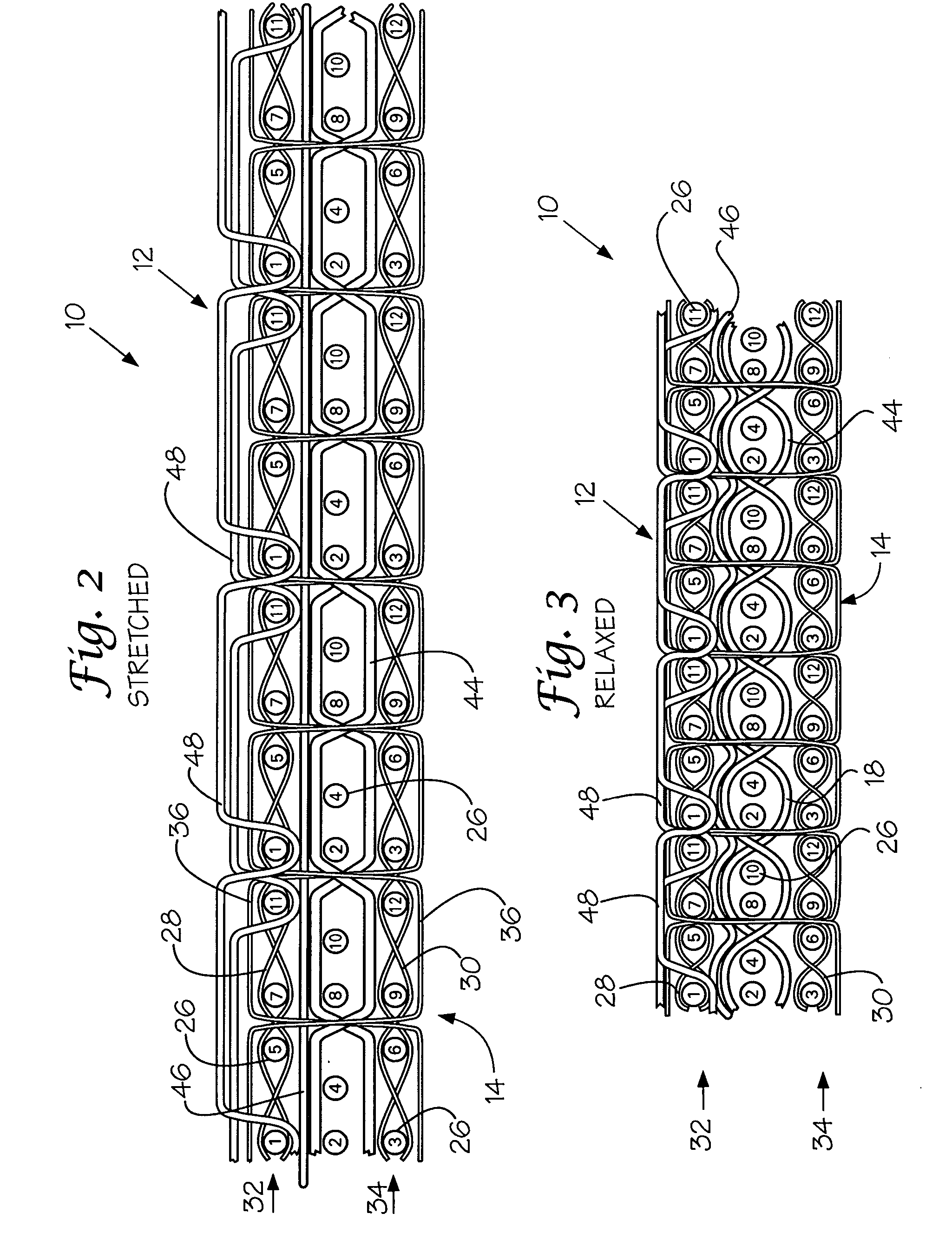
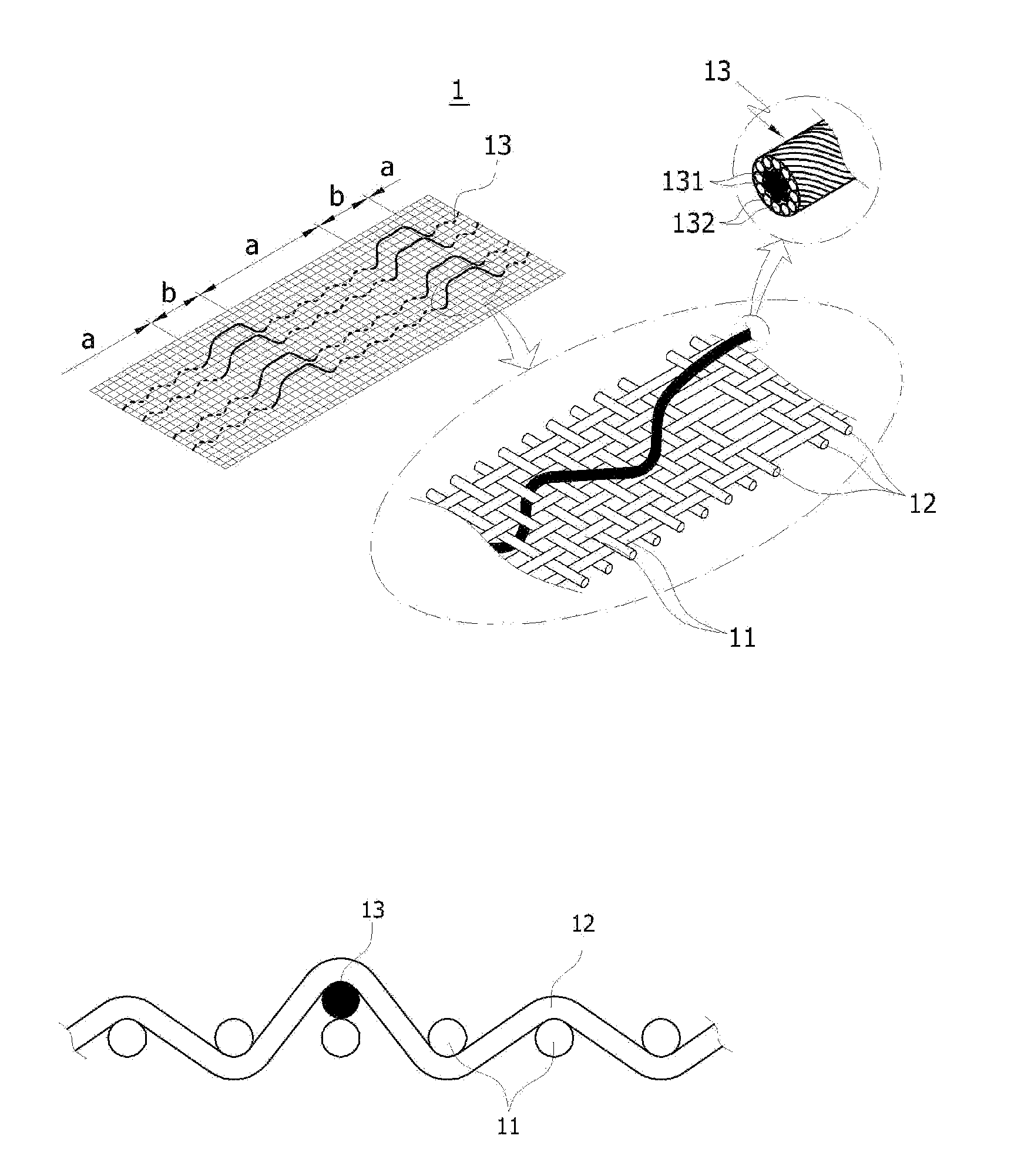
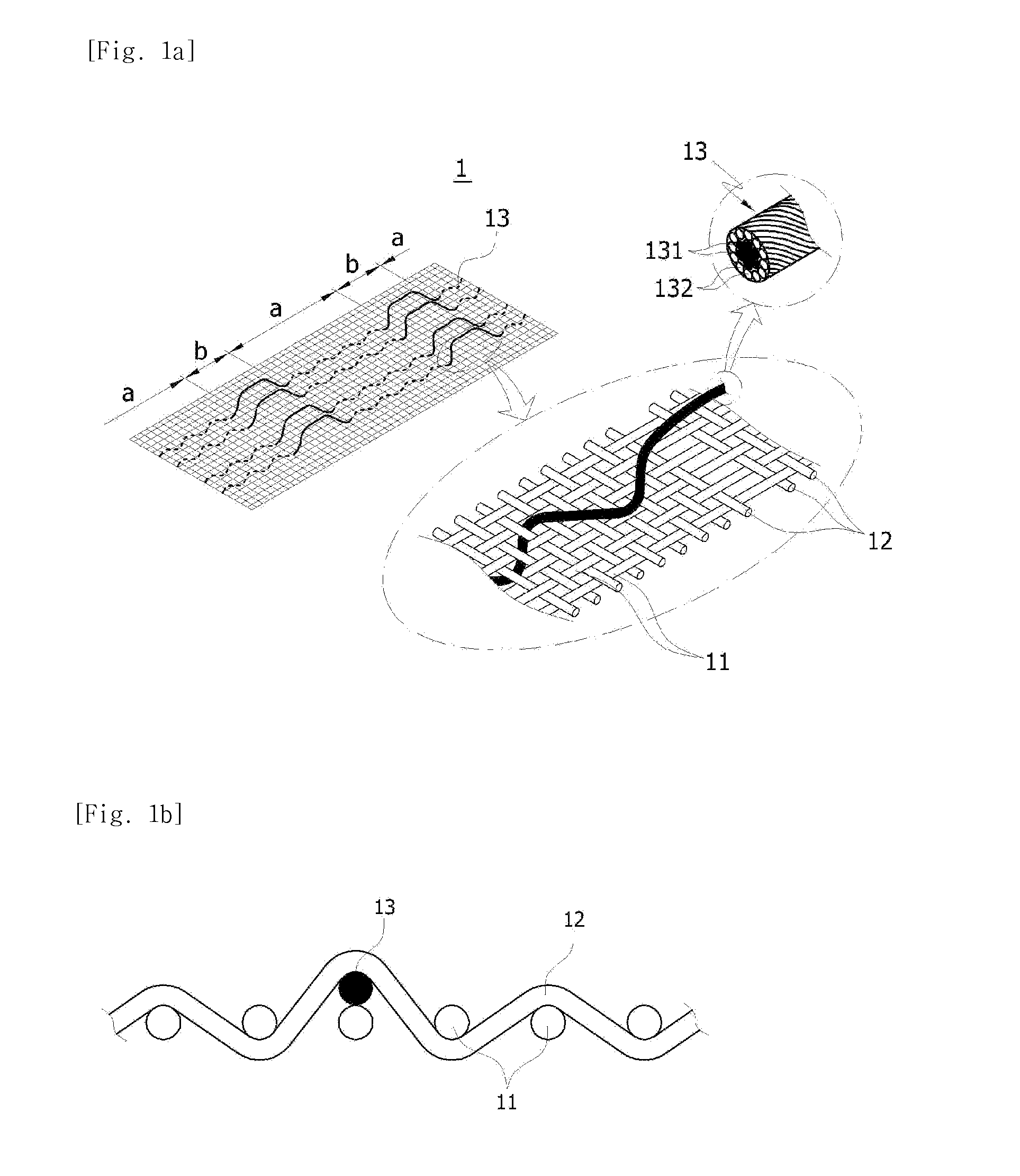
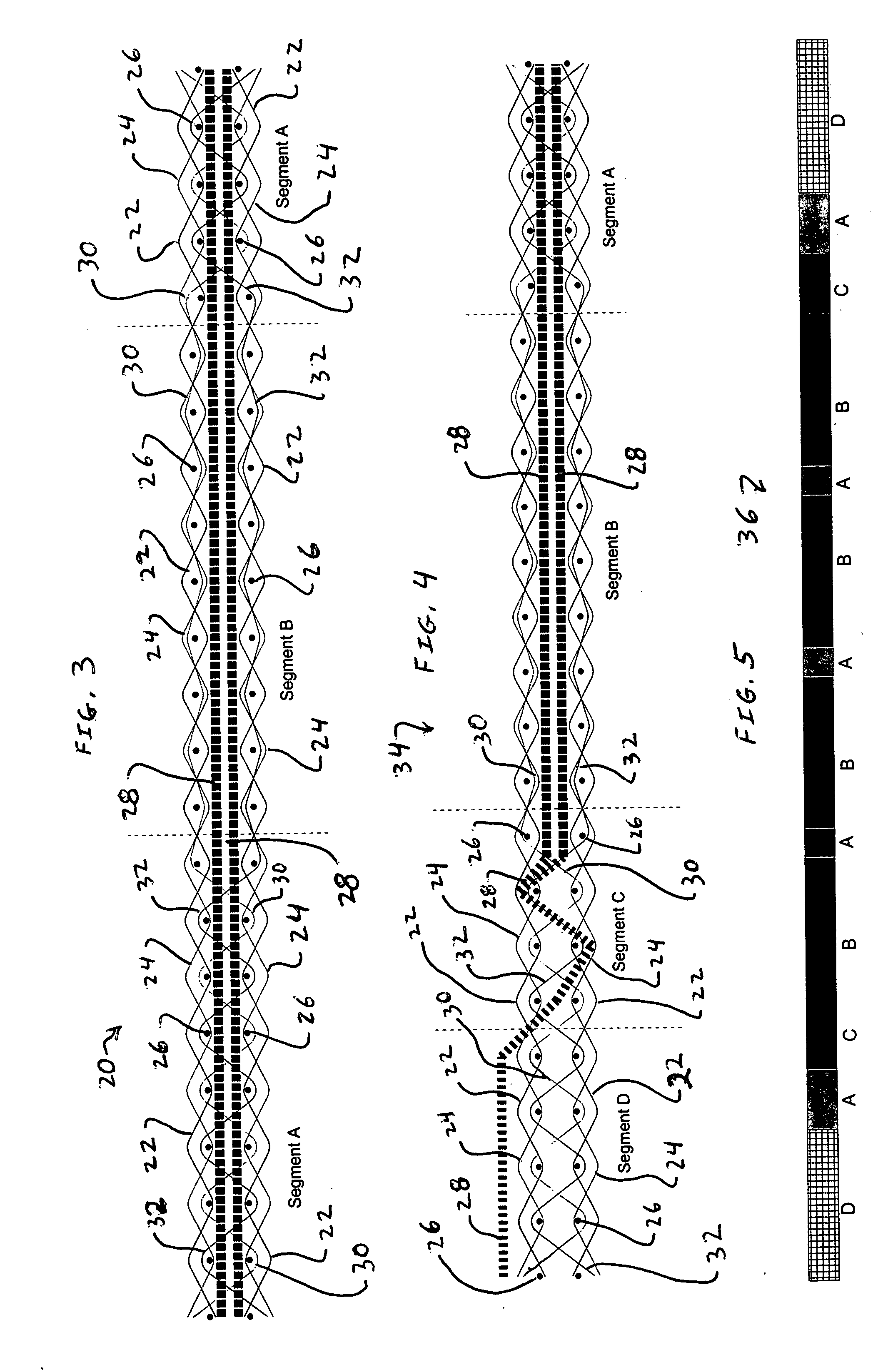
Elastic fabric with sinusoidally disposed wires
ActiveUS20060124193A1Reducing fabric lengthConductive stabilityCircuit bendability/stretchabilityGarmentsYarnEngineering
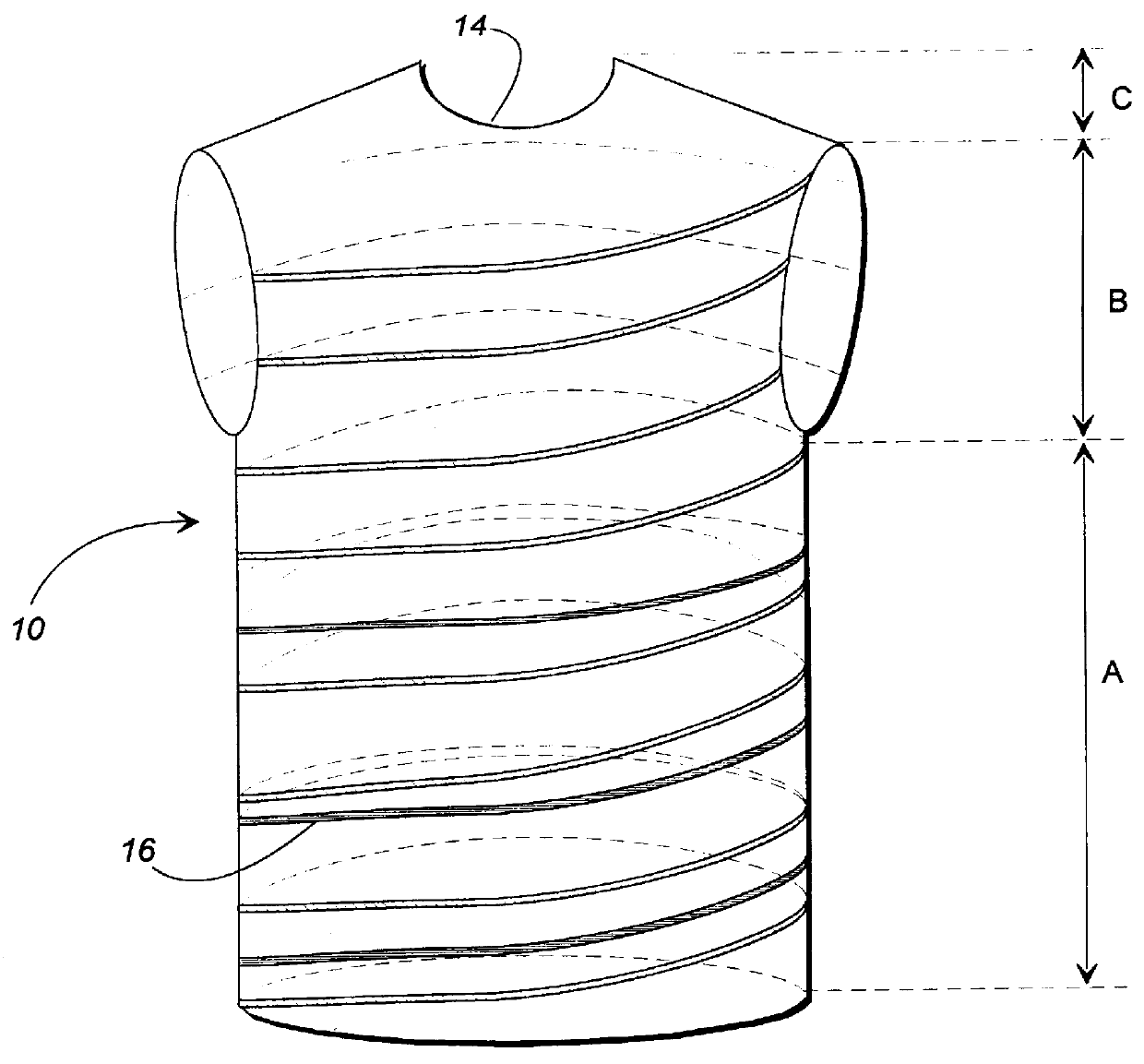
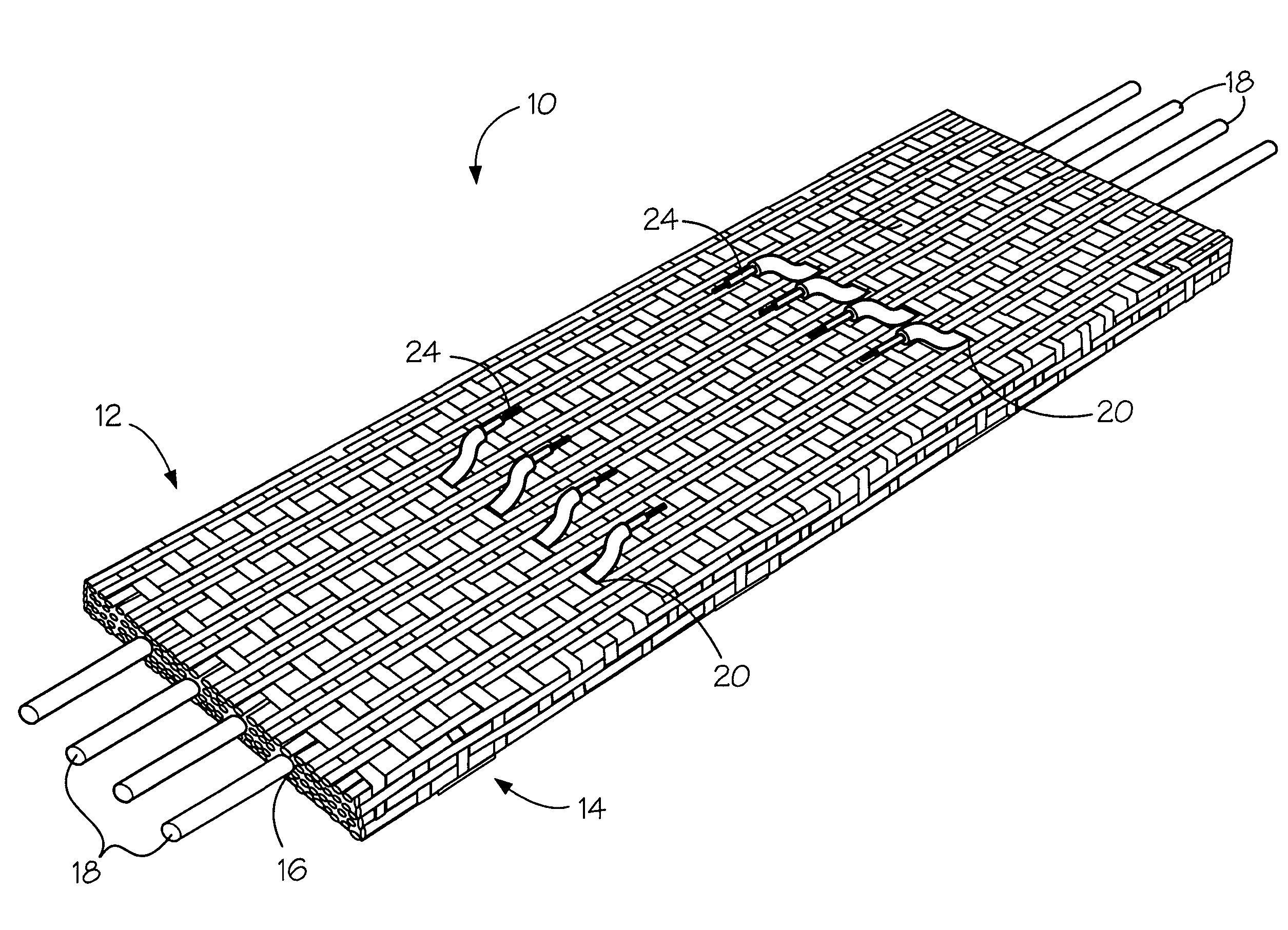
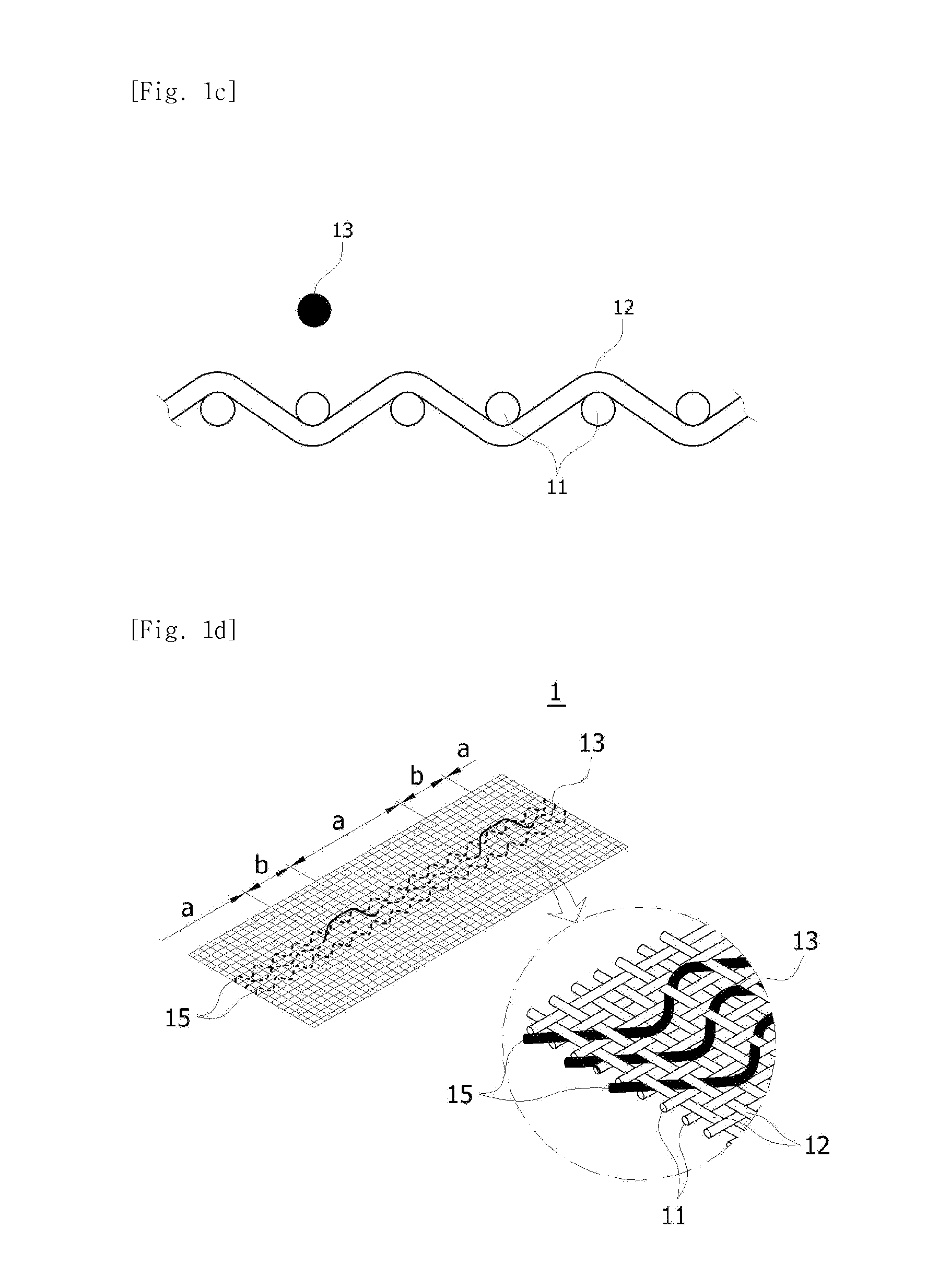
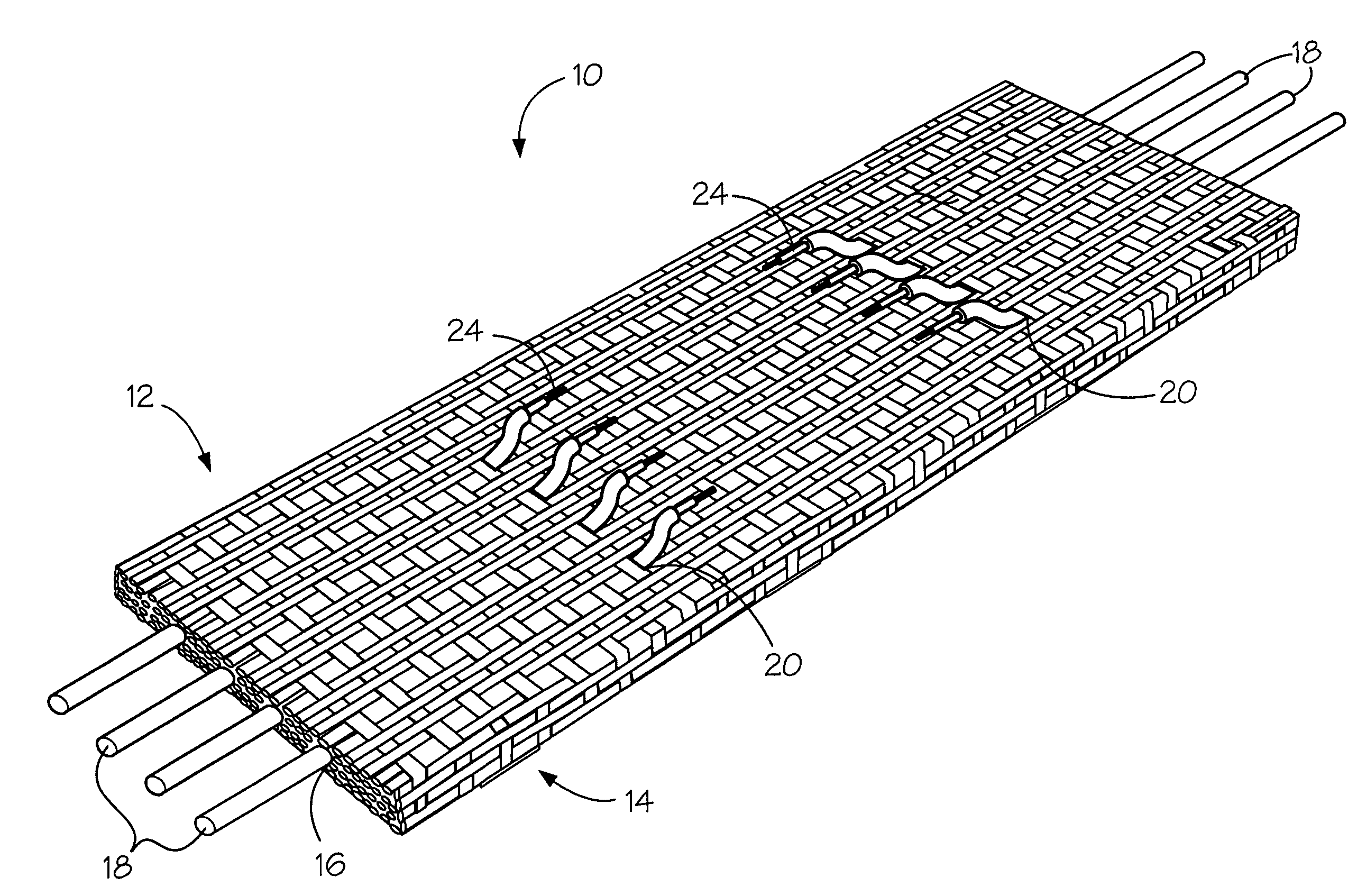
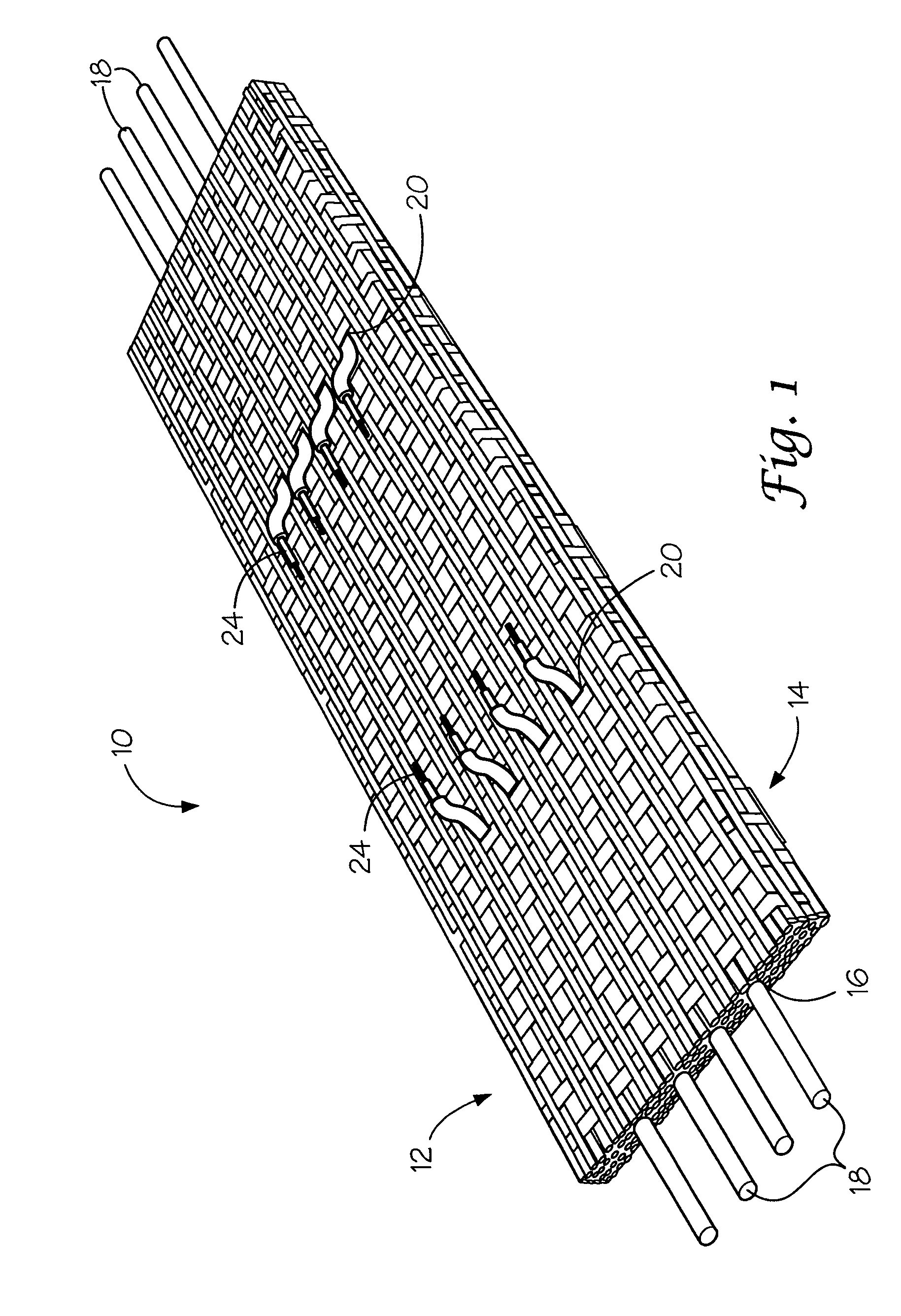
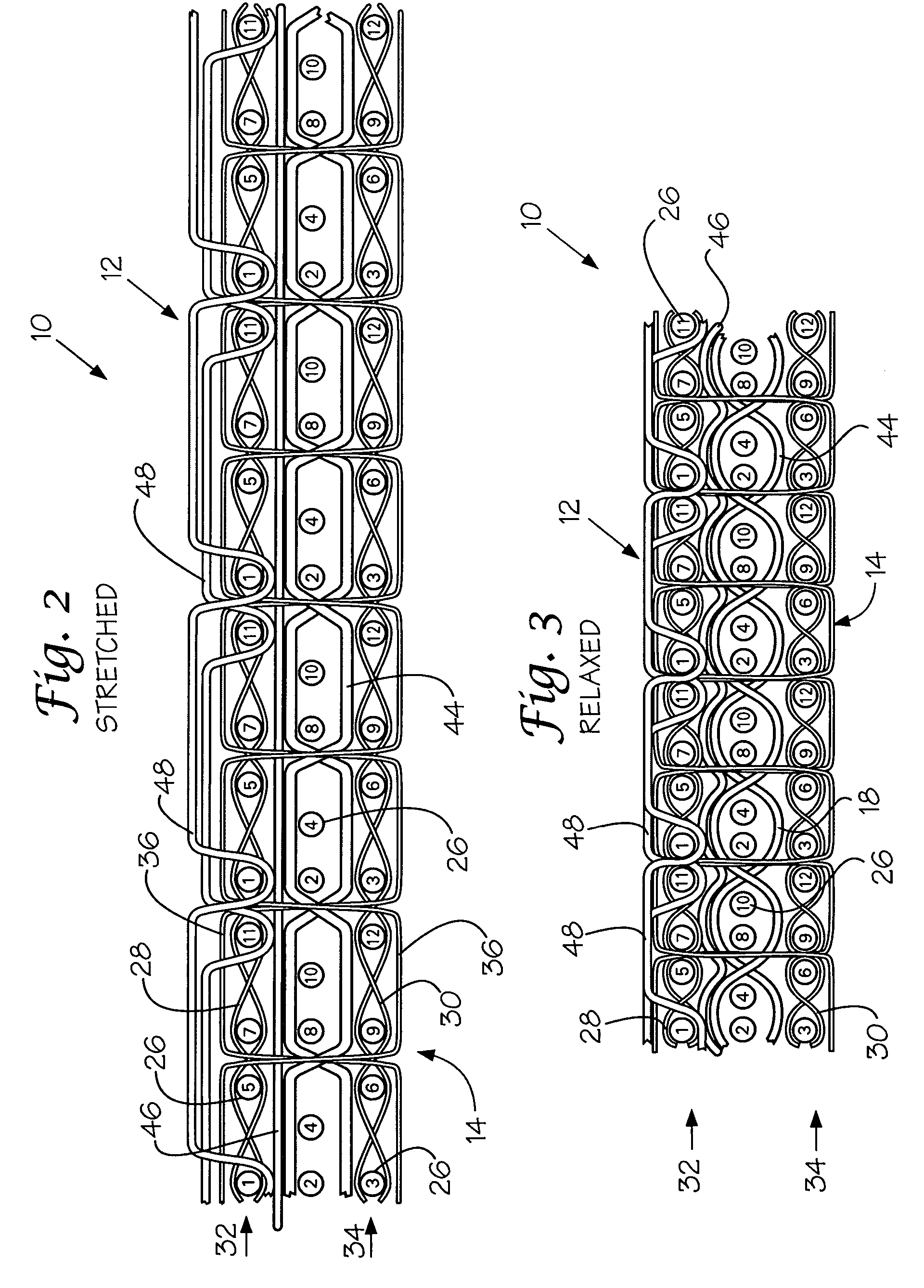
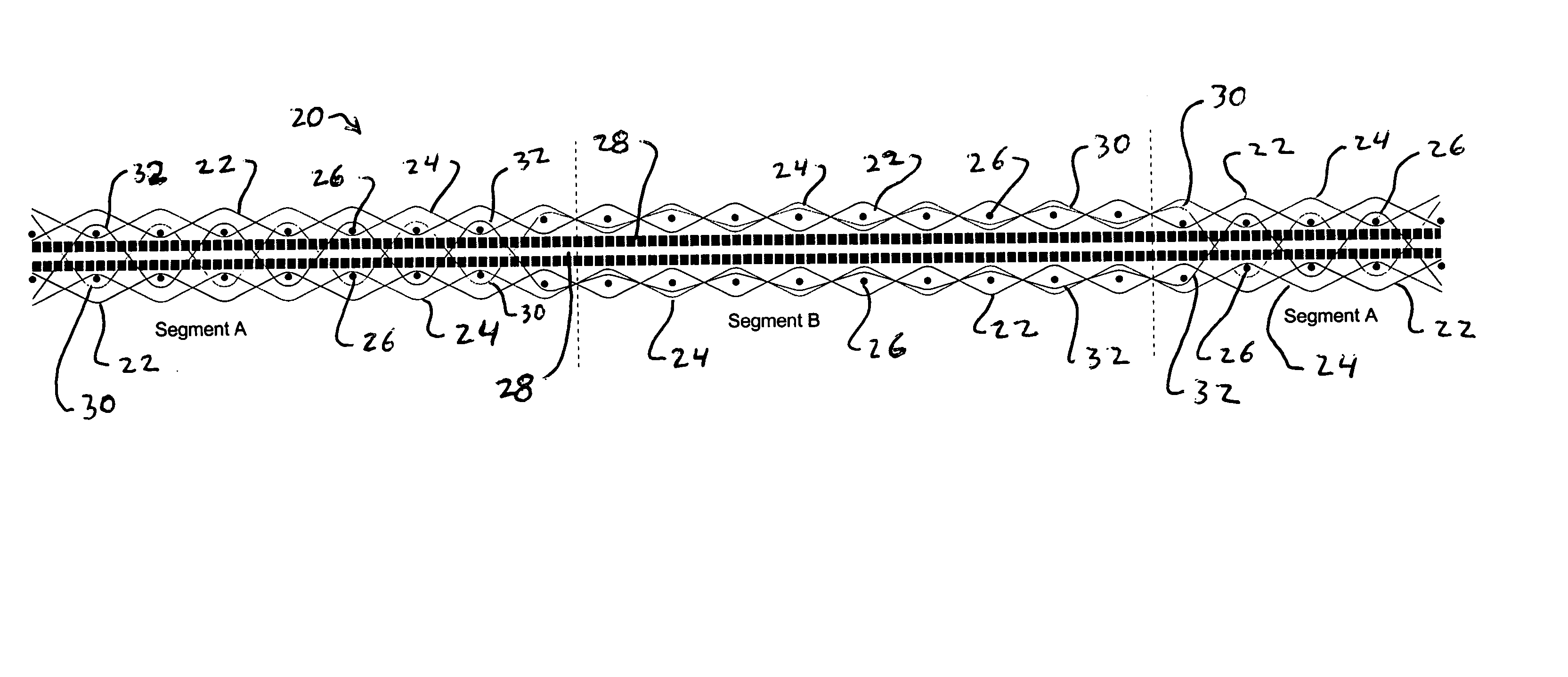
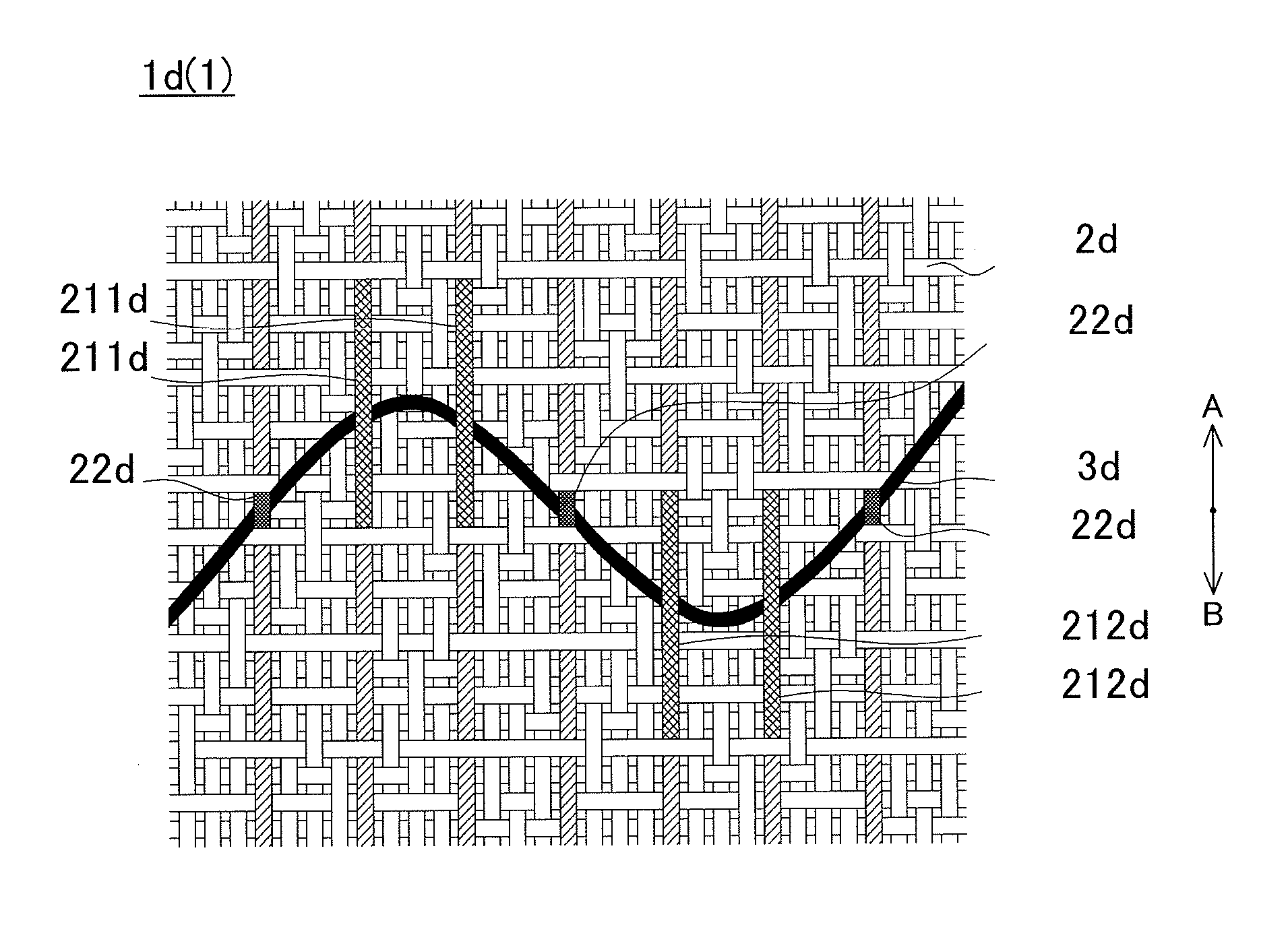
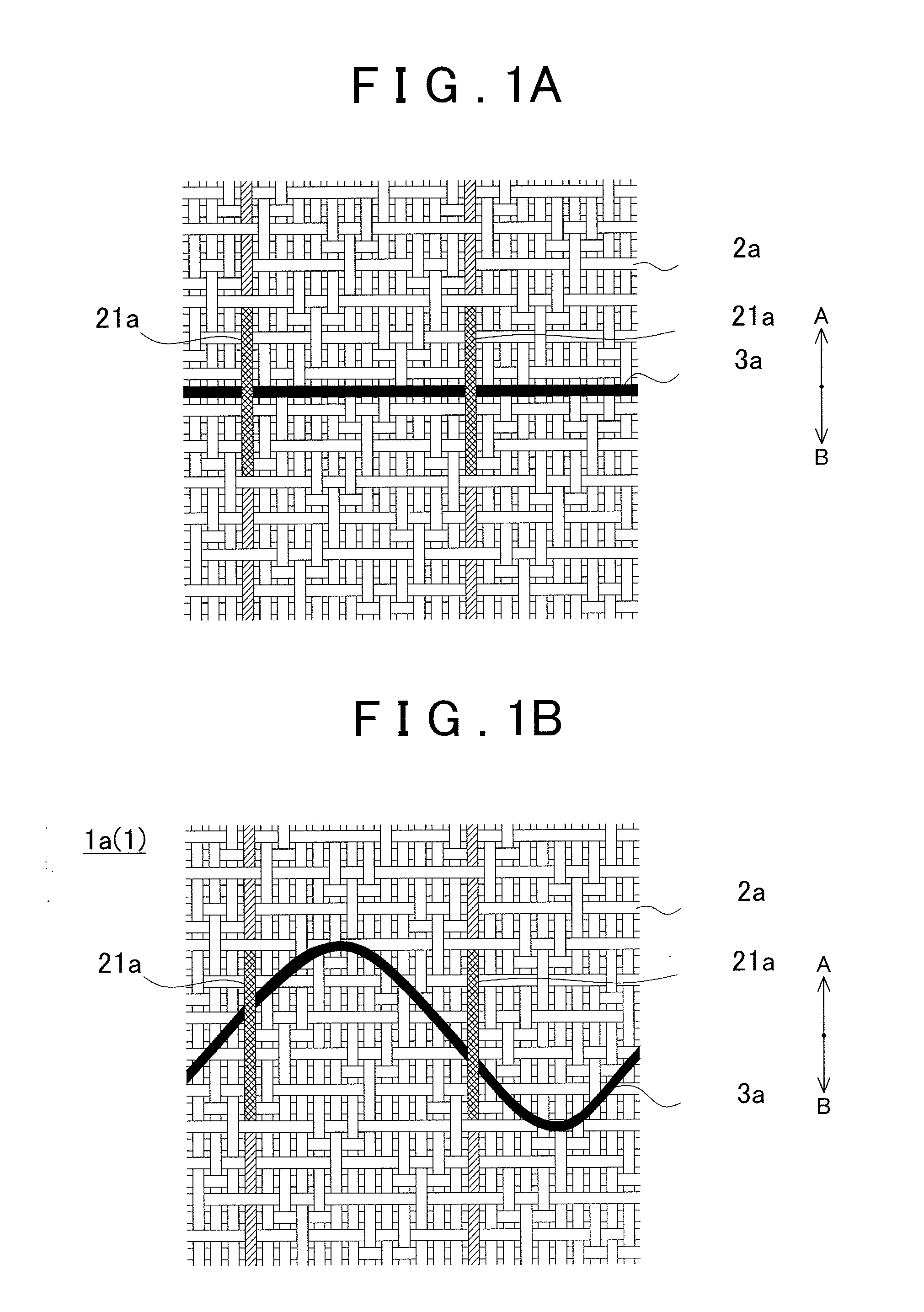
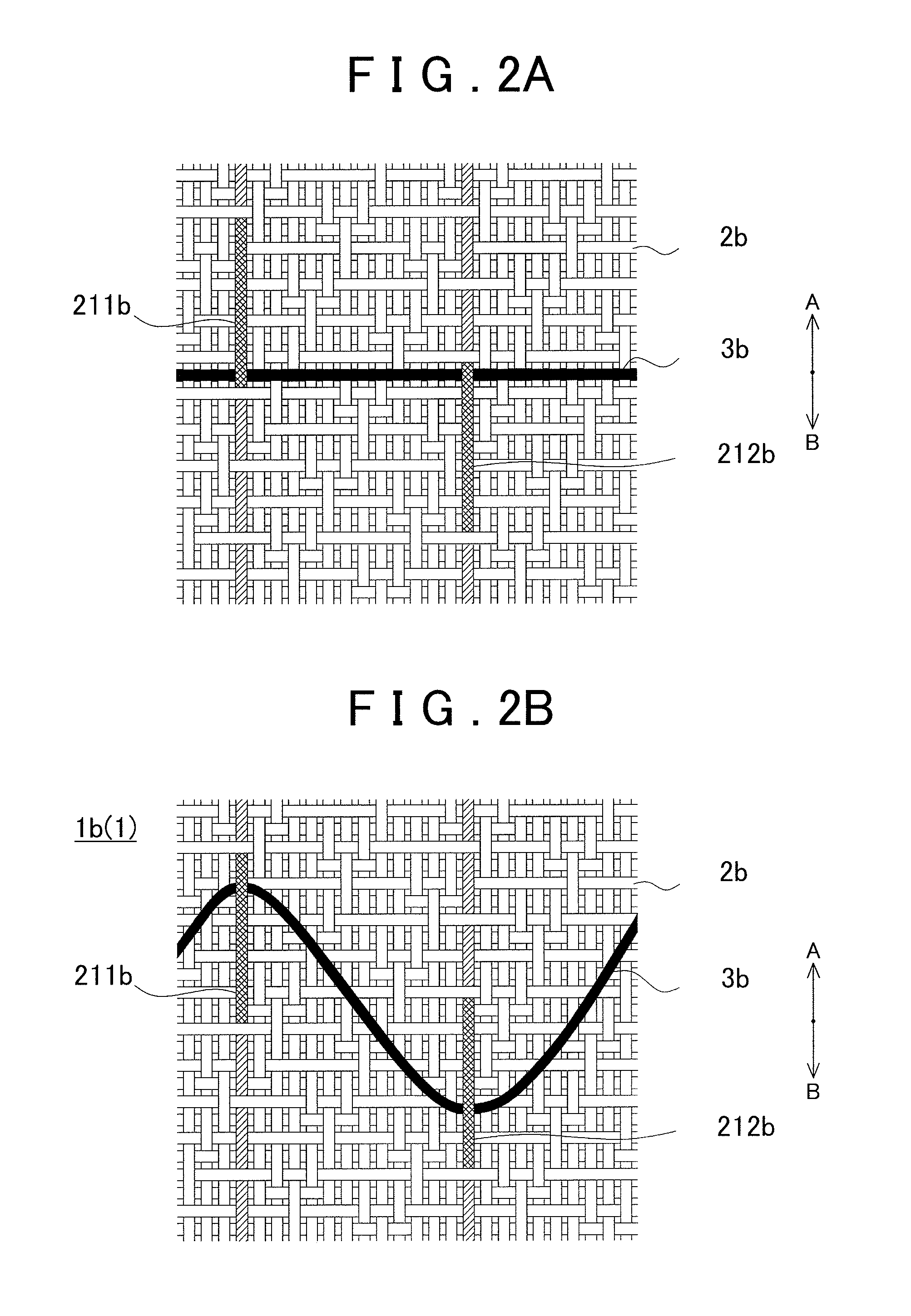
A fabric for use with a system for monitoring prescribed body functions comprising an elastic fabric, adapted to be carried by a torso, which is stretchable in its longitudinal direction so as to expand and contract in response to body movement and size. The carrier includes at least one conductive and inelastic yarn arranged longitudinally of and located between upper and lower surfaces. The conductive yarn is arranged in sinusoidal configurations longitudinally of the fabric. The conductive yarn forms a breakout through one of the outer surfaces, at selected locations along the length of the fabric, forming opposed exposed ends above the surface. A monitoring unit, which includes a connector and a sensor, is secured with the one surface at the breakout with the connector being united with the exposed ends of the conductive yarn. The fabric acts to maintain the monitoring unit in a desired stationary position allowing the sensor to sense signals emitted from the torso and transmit these senses signals.
Owner:WOVEN ELECTRONICS
Carbon nanotube fabrics
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
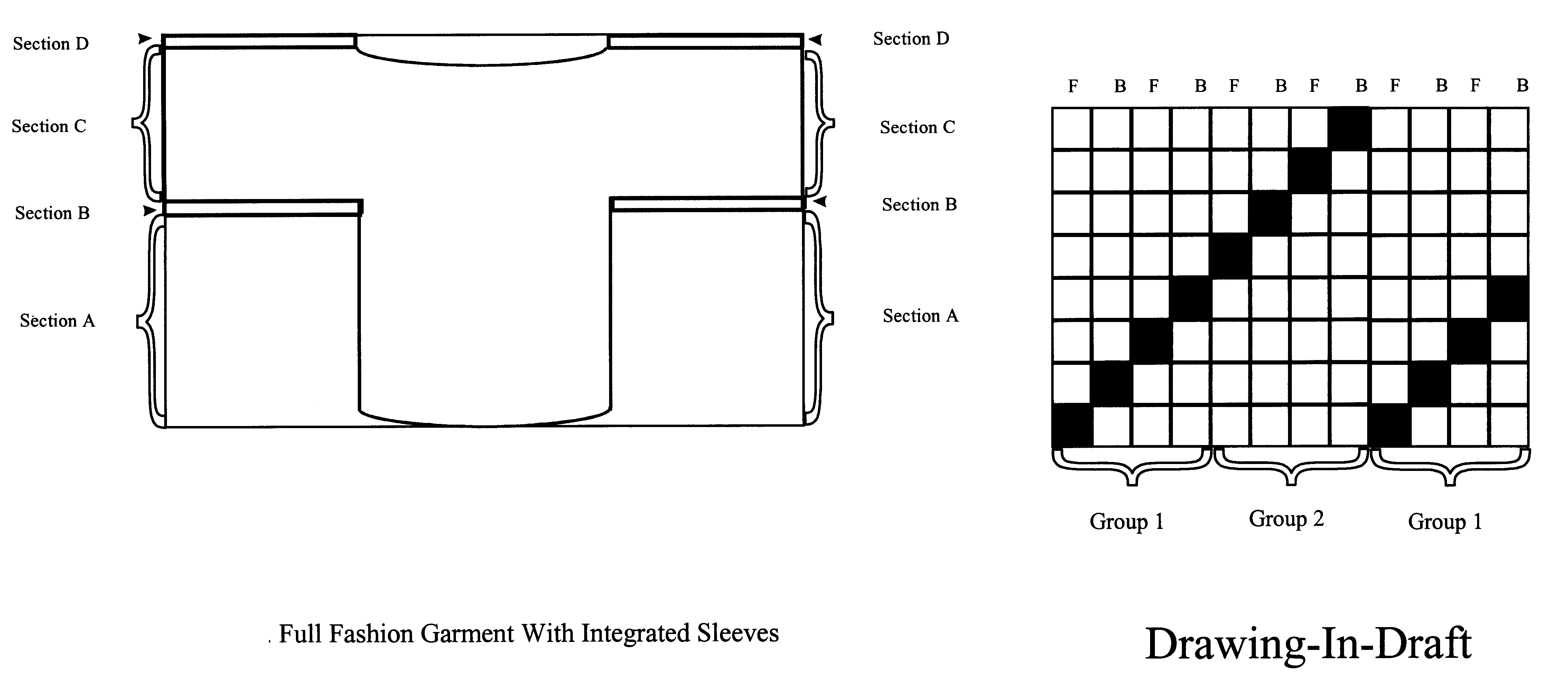
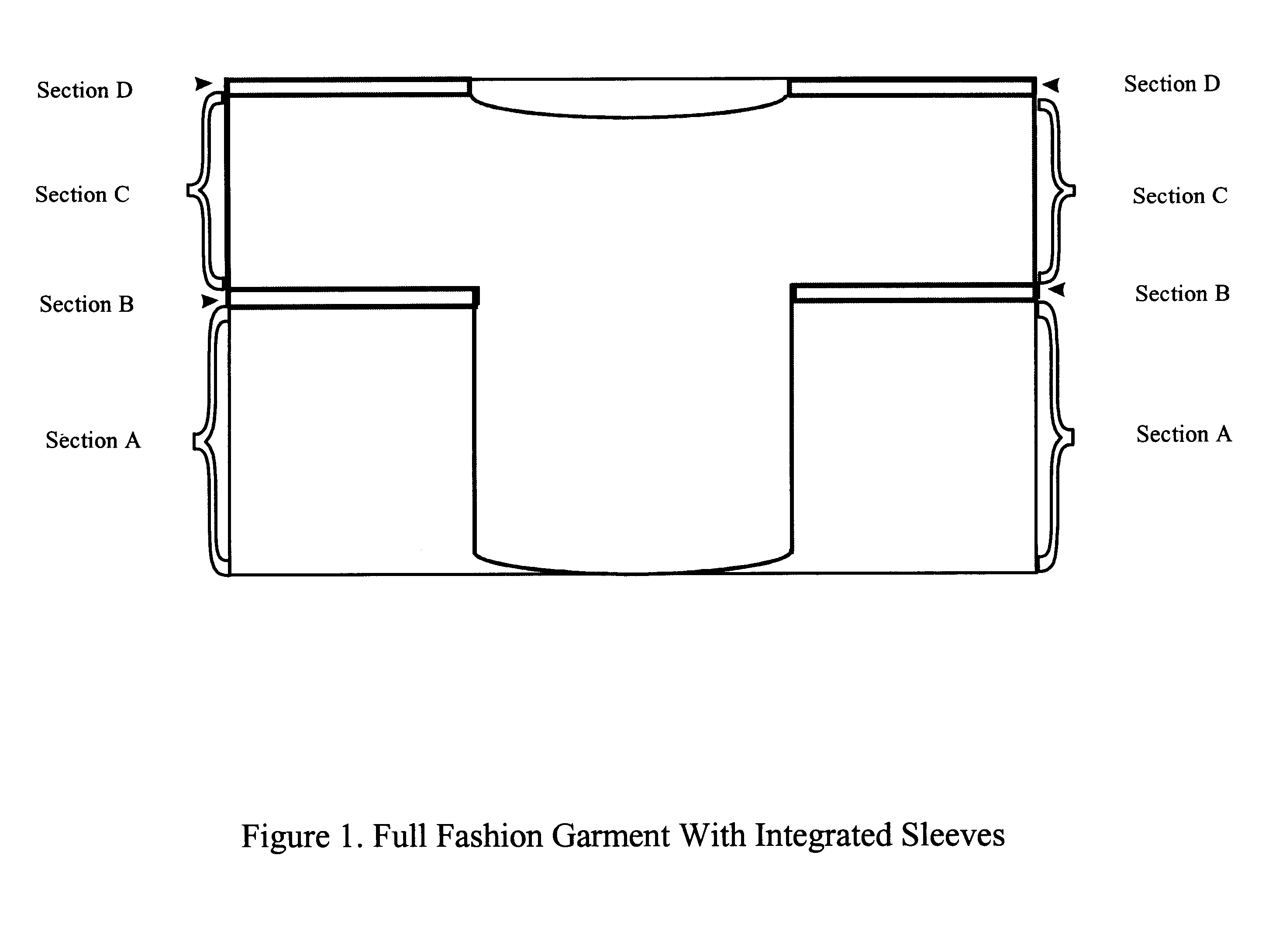
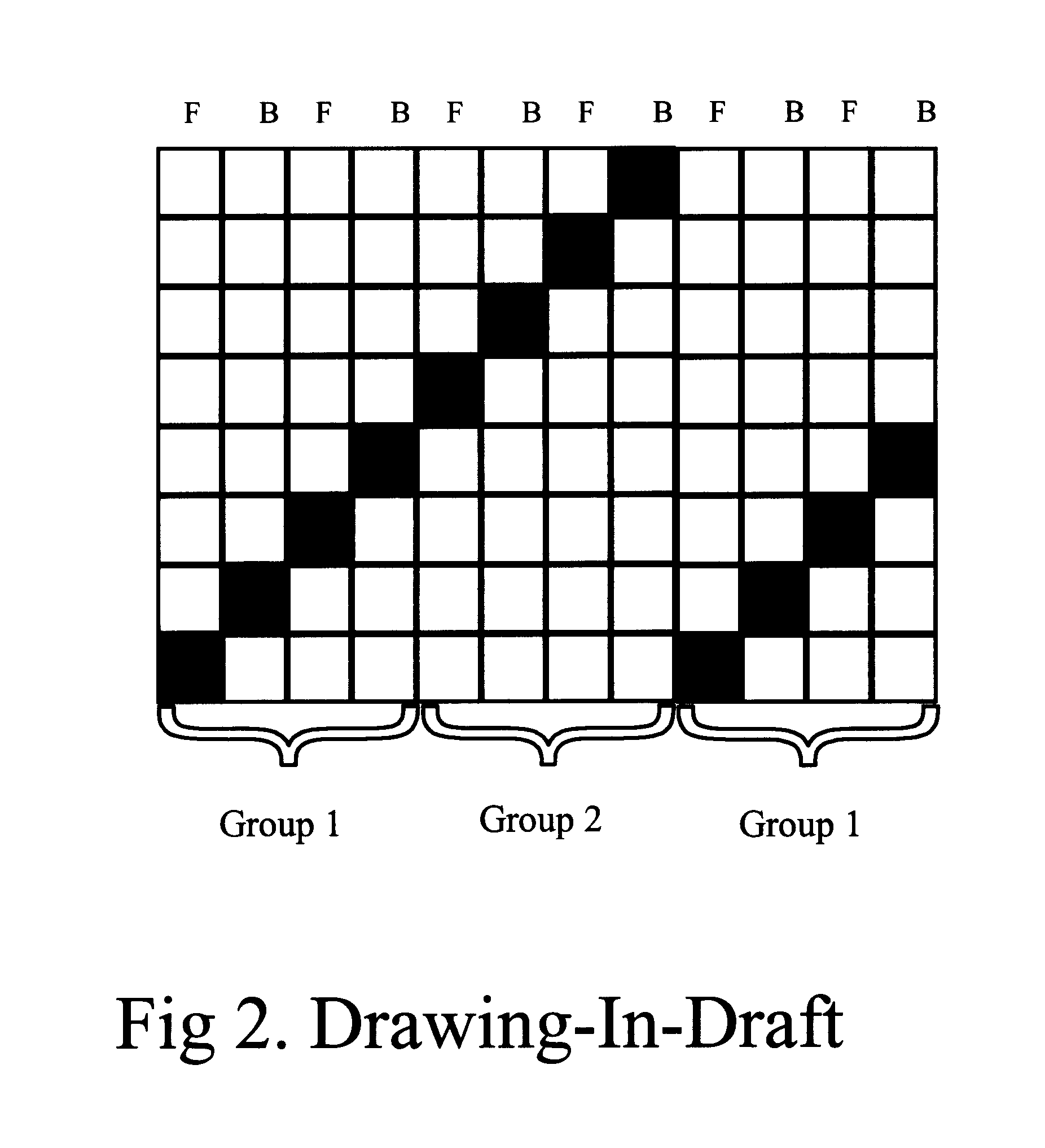
Full-fashioned garment with sleeves having intelligence capability
The invention comprises a full-fashioned weaving process for the production of a woven garment which can accommodate and include sleeves. The garment is made of only one, single integrated fabric and has no discontinuities or seams. Additionally, the garment can include intelligence capability, such as the ability to monitor one or more body vital signs, or garment penetration, or both, by including a selected sensing component or components in the weave of the garment.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Woven preform for structural joints
A preform for structural joints has a three-dimensional weave architecture with fill fibers woven to provide layer-to-layer interlocking of layers of warp fiber as well as interlocking of fibers within each layer. At least two legs extend from a base, the base and legs each having at least two layers of warp fibers. The legs are connected at a symmetrical, distributed-column intersection, with an odd number of columns of warp fibers being located being the legs. The outer ends of the base and legs preferably have tapers formed from terminating layers of warp fibers in a stepped pattern. Tracer fibers that include a colored strand and an x-ray opaque strand are woven into the preform at selected locations as a warp fiber. The tracer fibers allow for identification of a selected location or a selected portion of the preform through visual inspection or by x-ray image.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Turbomachine blade, in particular a fan blade, and its method of manufacture
Owner:SN DETUDE & DE CONSTR DE MOTEURS DAVIATION S N E C M A
Moisture management system
InactiveUS7169720B2Efficient evaporationReduce capacityOrnamental textile articlesInsolesEngineeringWater repellent
Owner:ETCHELLS MARC D +2
Supple penetration resistant fabric and method of making
InactiveUS6962739B1High fabric strengthStrong materialGlovesSynthetic resin layered productsBiomedical engineeringMedical treatment
Owner:HIGHER DIMENSION MATERIALS INC (US)
Shaping method and structure of woven fabric with a groove
InactiveUS7484539B1Low efficiencyIncrease costMulti-ply fabricsOpen work fabricsMechanical engineeringWoven fabric
A shaping method for a woven fabric having a hollow looped portion includes the steps of laying top longitudinals and bottom longitudinals in a pattern corresponding to a shape and size of the hollow looped portions, forming top warps and bottom warps in a generally planar pattern, flat weaving a weft through and between the top warps and the bottom warps such that the top warps reside above the weft and said bottom warps reside below the weft, passing the weft between the top longitudinals and the bottom longitudinals in the hollow looped portion such that the top longitudinals reside above the weft and the bottom longitudinals reside below the weft.
Owner:CHING SHI IND
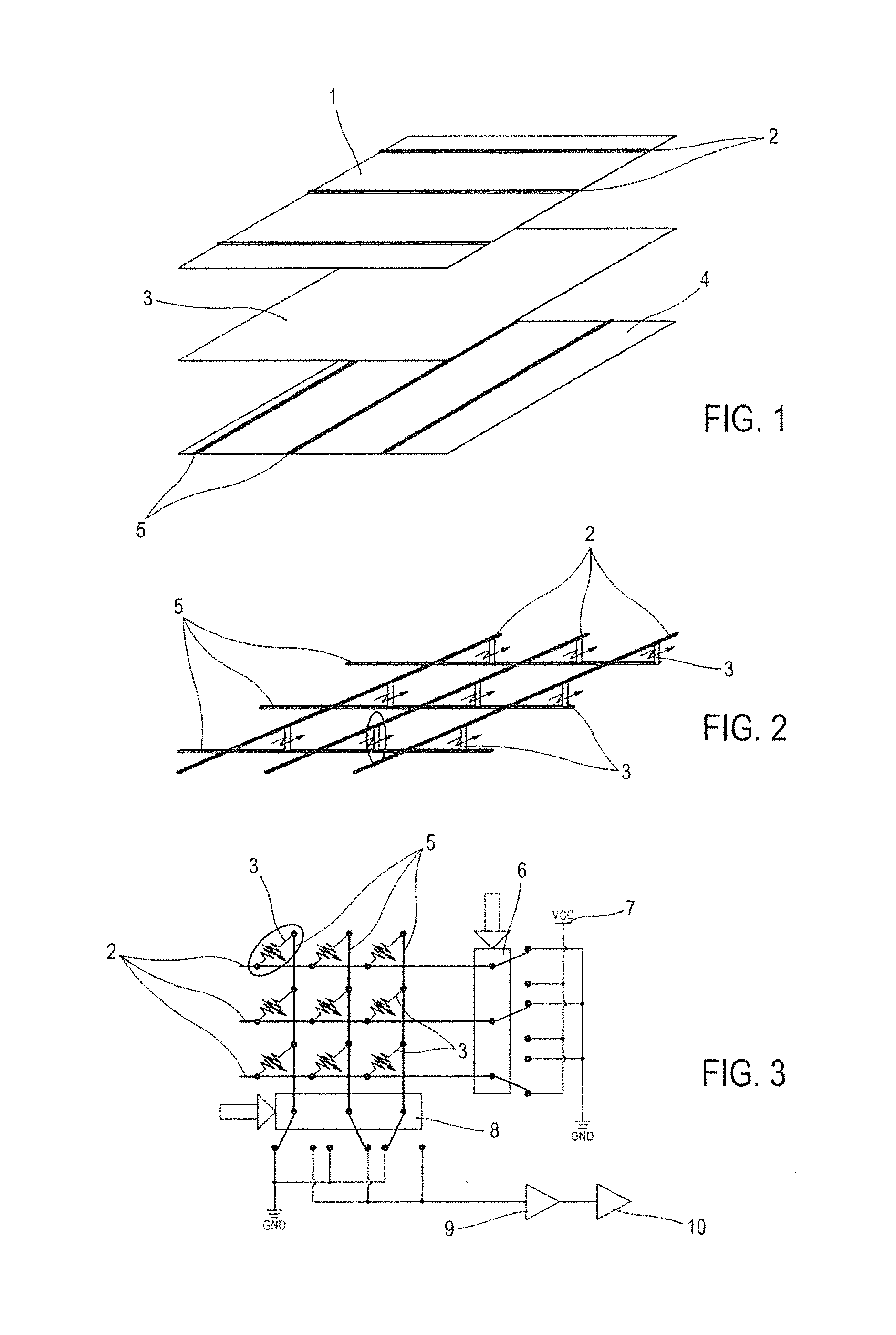
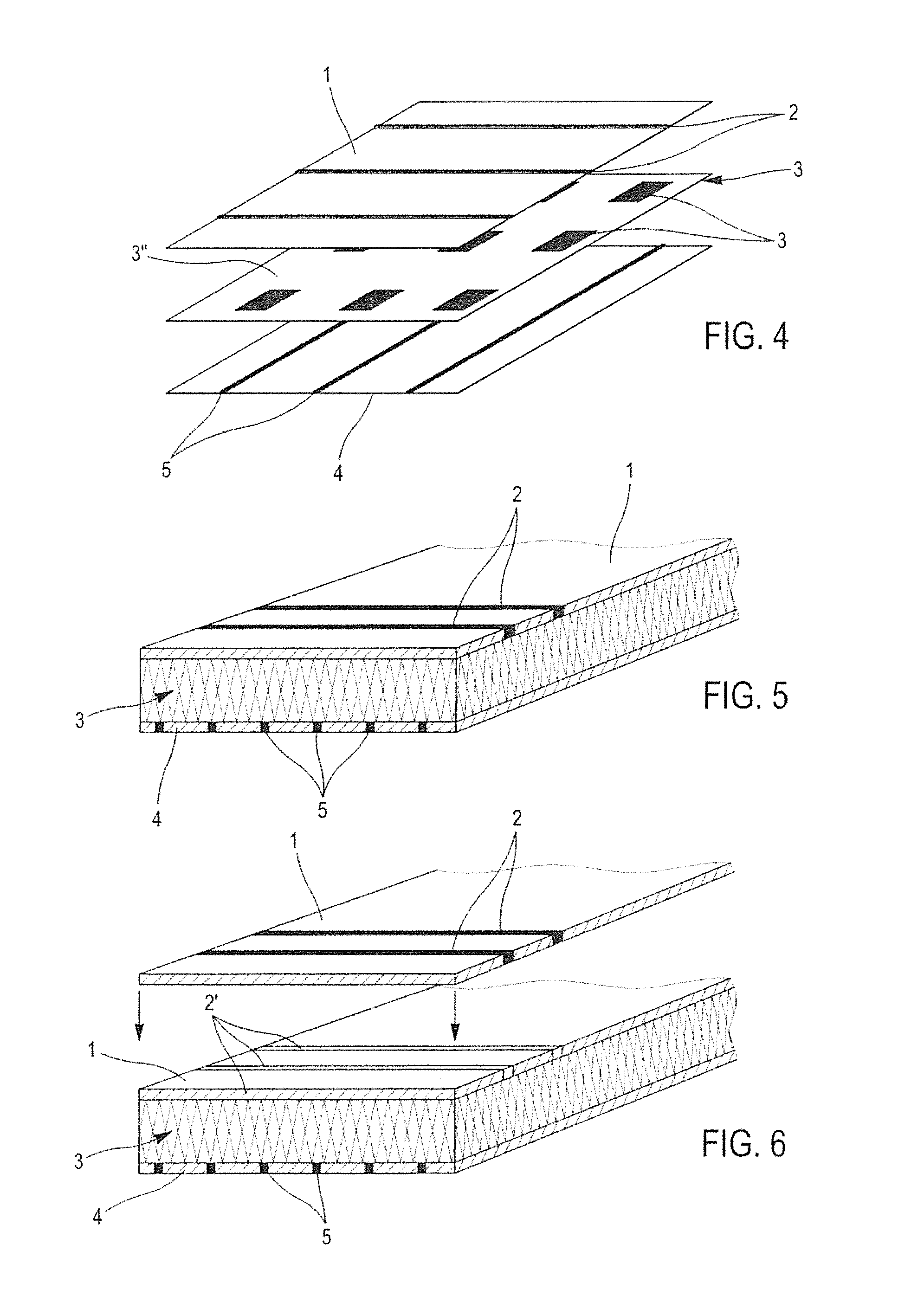
Device for Measuring Pressure from a Flexible, Pliable, and/or Extensible Object Made from a Textile Material Comprising a Measurement Device
ActiveUS20140150573A1Simple designLow costForce measurement using piezo-resistive materialsMulti-ply fabricsFiberElectrical resistance and conductance
A device and method for measuring the pressure exerted at different points of a flexible, pliable and / or extensible fabric capable of being worn as a garment, lapel, or the like, which provides three stacked layers including a first insulating layer comprising an arrangement of insulating fibers and at least one row of at least one conductive yarn in contact with a first surface of a piezoresistive layer of fibers of a piezoresistive material, and a second insulating layer comprising an arrangement of insulating fibers, including at least one row of at least one conductive yarn, in contact with a second surface of the piezoresistive layer, and an electronic circuit capable of measuring the electric resistance variation when a pressure is exerted on the fabric, the pressure being a function of the resistance variation.
Owner:TEXISENSE
Multidirectionally Reinforced Shape Woven Preforms for Composite Structures
ActiveUS20090202763A1High strengthReadily conformsLoomsPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementFiberNacelle
The present invention relates to multidirectionally reinforced fiber preforms that conform easily to complex curvatures, such as, composite turbine fan cases, jet engine containment rings, aircraft fuselage frames, aircraft window frames, and flanged rings for attaching nacelles to aircraft engines. The present invention provides multidirectionally reinforced shape woven preforms with improved strength for composite structures that are axisymmetric as well as non-axisymmetric in nature. The invention is a preform used to reinforce a composite structure which includes a contour woven fabric portion, bi-axially braided, tri-axially braided or bias fabric portion, and / or a polar woven fabric portion, and a method of making thereof. The preform may optionally include a three-dimensionally woven portion. The combination of different forms of fabrics allows the preform to be produced without cutting and darting of the individual plies. Eliminating these cuts and darts improves the strength and performance of the resulting structure.
Owner:ALBANY ENGINEERED COMPOSITES
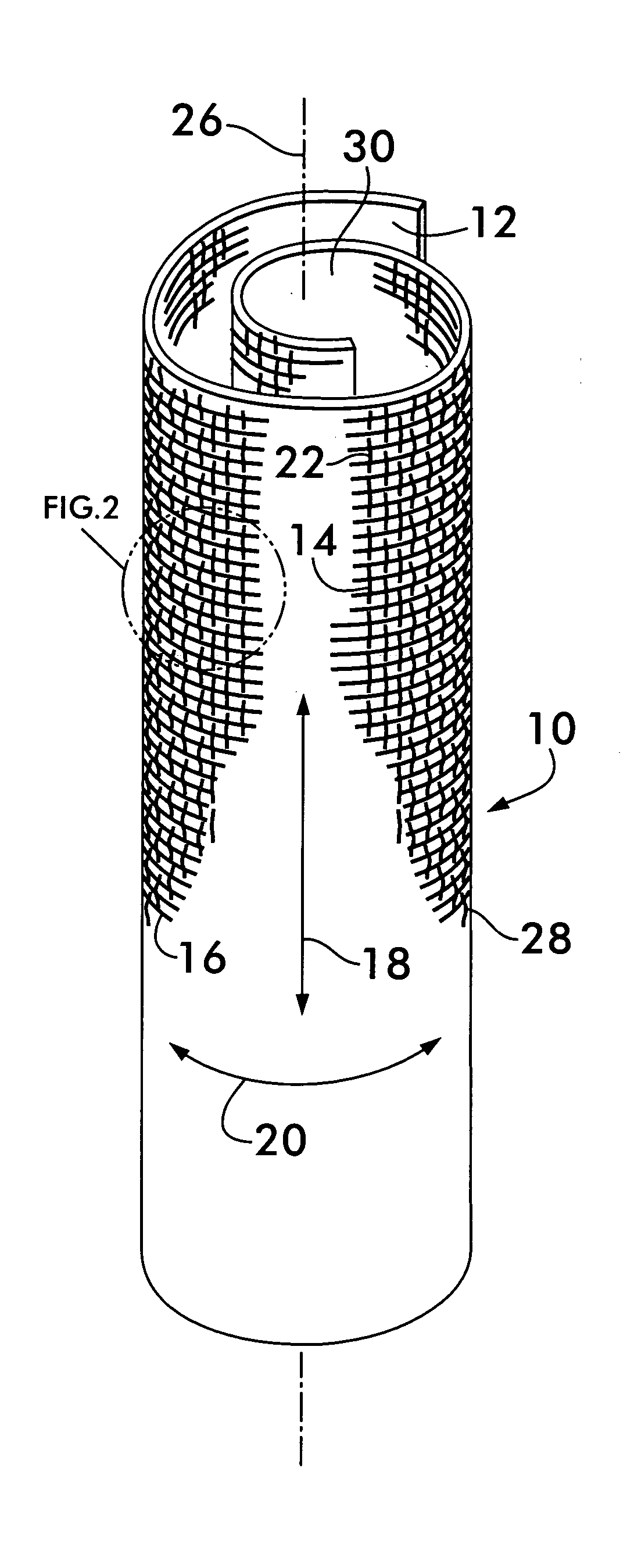
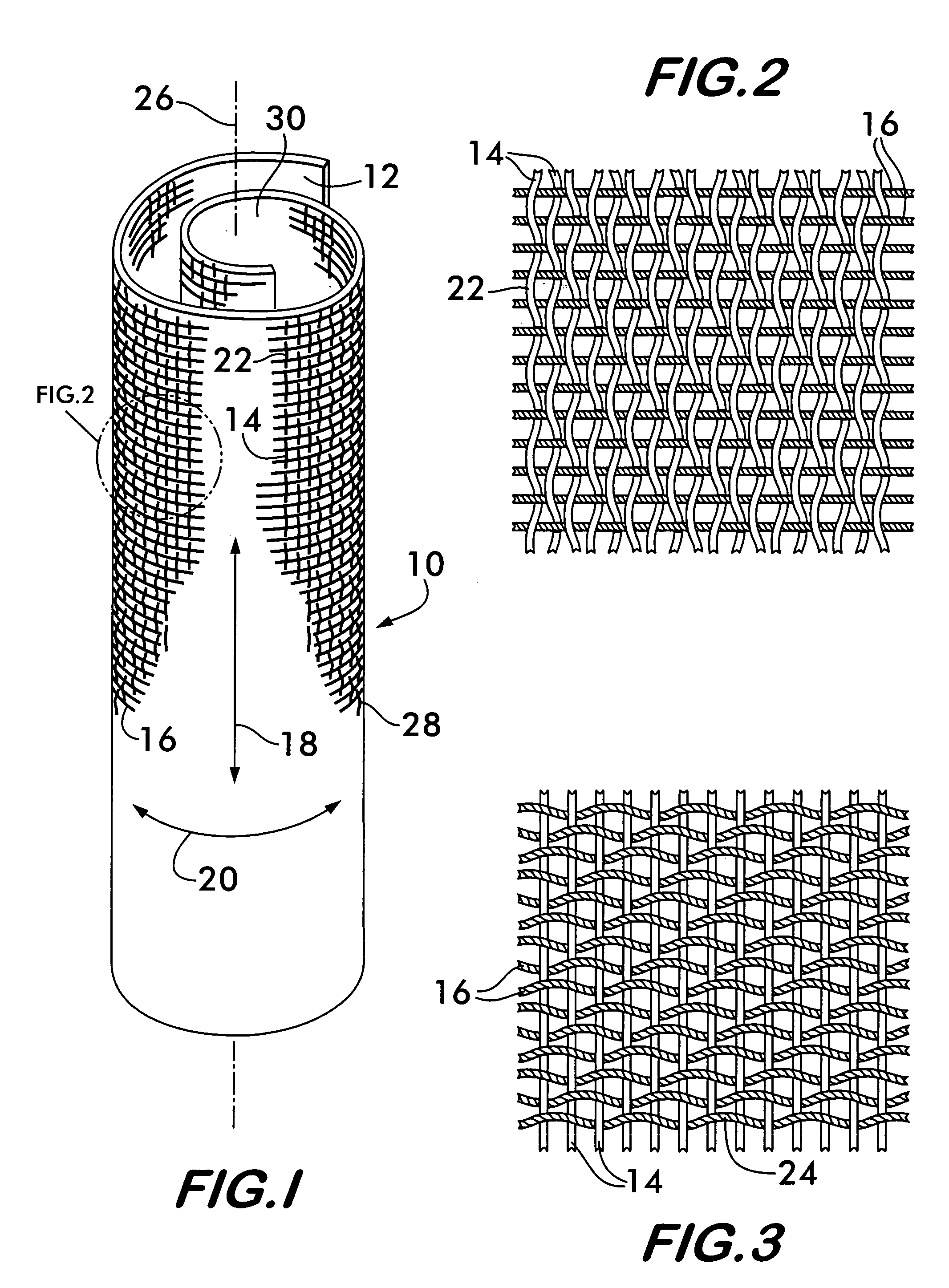
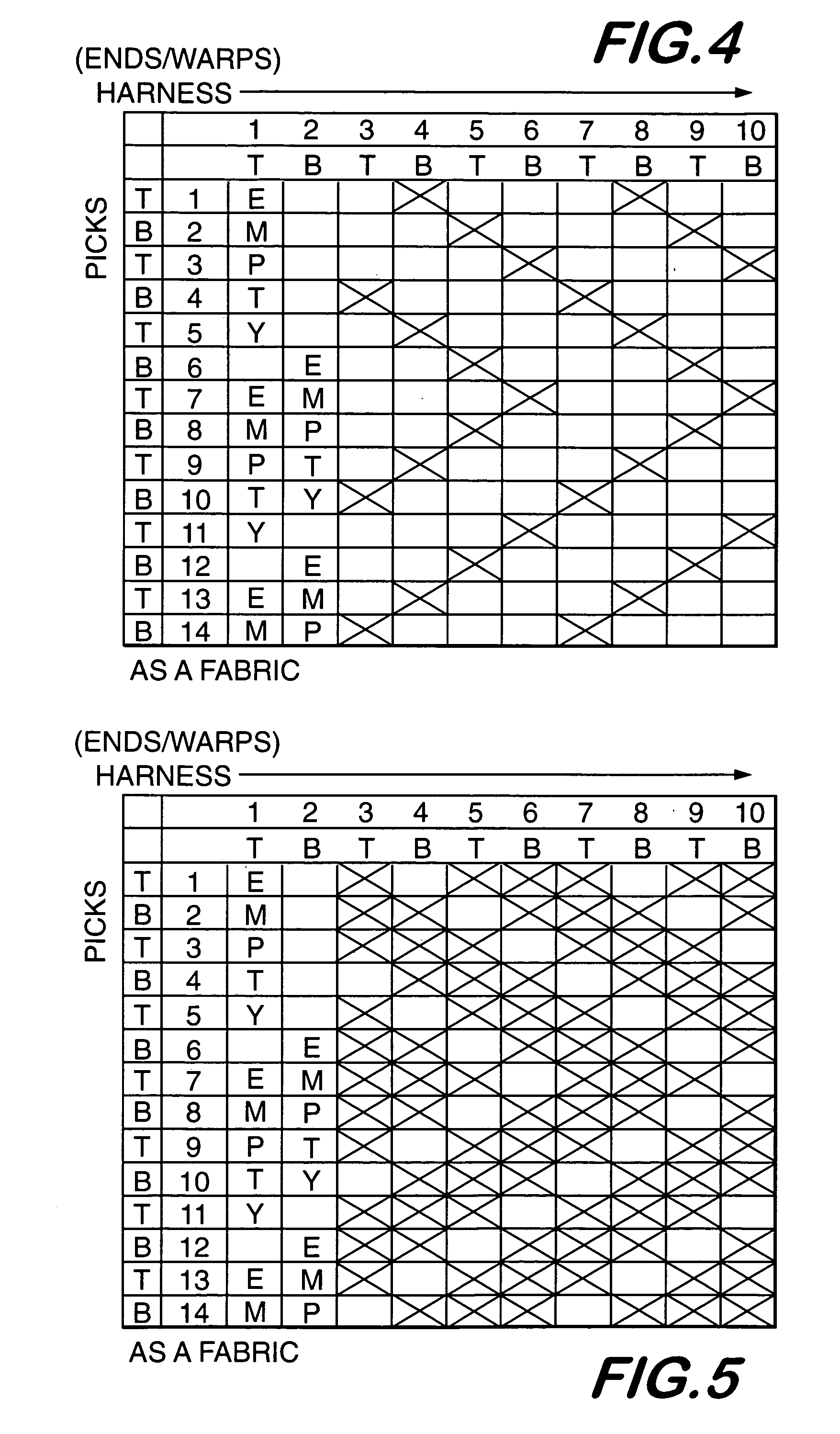
Non-kinking self-wrapping woven sleeve and method of construction thereof
ActiveUS20120037263A1Increase flexibilityRaise countElectrical apparatusLoomsUltimate tensile strengthWeft yarn
A wrappable textile sleeve and method of construction thereof is provided. The textile sleeve includes an elongate wall extending along a longitudinal axis between opposite ends with lengthwise extending edges extending along the longitudinal axis between the opposite ends. The wall is woven from lengthwise extending warp yarns and circumferentially extending weft yarns with at least some of the weft yarns being heat-set to impart a self curling bias on the wall to bring the edges into overlapping relation with one another. Further, the weft yarns form a plurality of discrete annular bands that extend circumferentially about the longitudinal axis with adjacent bands having different picks-per-inch from one another to provide the sleeve with enhance regions of flexibility, self-curling bias and hoop strength.
Owner:FEDERAL MOGUL POWERTAIN LLC
Composite material and method for increasing z-axis thermal conductivity of composite sheet material
InactiveUS20100021682A1Increases Z-axis thermal conductivityHand sewingLayered productsGlass fiberCarbon fibers
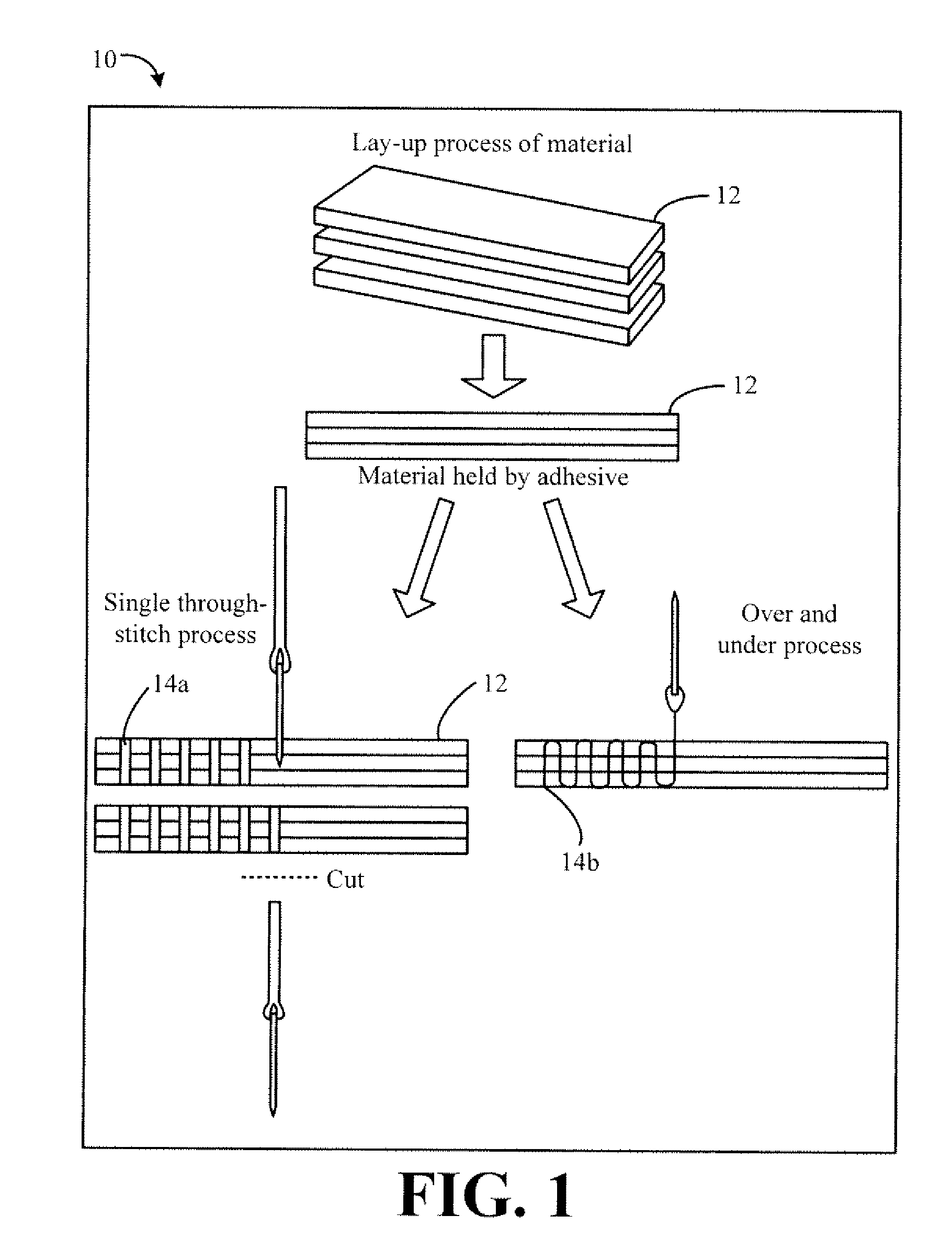
Methods are provided for making a composite material that includes (a) providing at least one sheet which includes woven or non-woven glass fibers, carbon fibers, aramid fibers, or nanoscale fibers; and (b) stitching a plurality of stitches of a thermally conductive fiber through the at least one sheet in a Z-axis direction to form paths of higher conductivity through the sheet of material to increase its thermal conductivity in the Z-axis.
Owner:FLORIDA STATE UNIV RES FOUND INC
Electrically conductive fabric and manufacturing method and apparatus thereof
InactiveUS20130102217A1Improve workabilityIncrease productivityLoomsWarp knittingComputer moduleEngineering
The present invention discloses to relates to an electrically conductive fabric, and a manufacturing method and an apparatus thereof, and more specifically to an electrically conductive fabric, and a manufacturing method and an apparatus thereof, wherein part of electrically conductive wire woven together into fabric is selectively exposed to the outside of the fabric to perform the tying of electrically conductive wires and the connection of various elements and modules quickly and conveniently, so that workability and productivity can be improved.
Owner:SILVERAY CO LTD
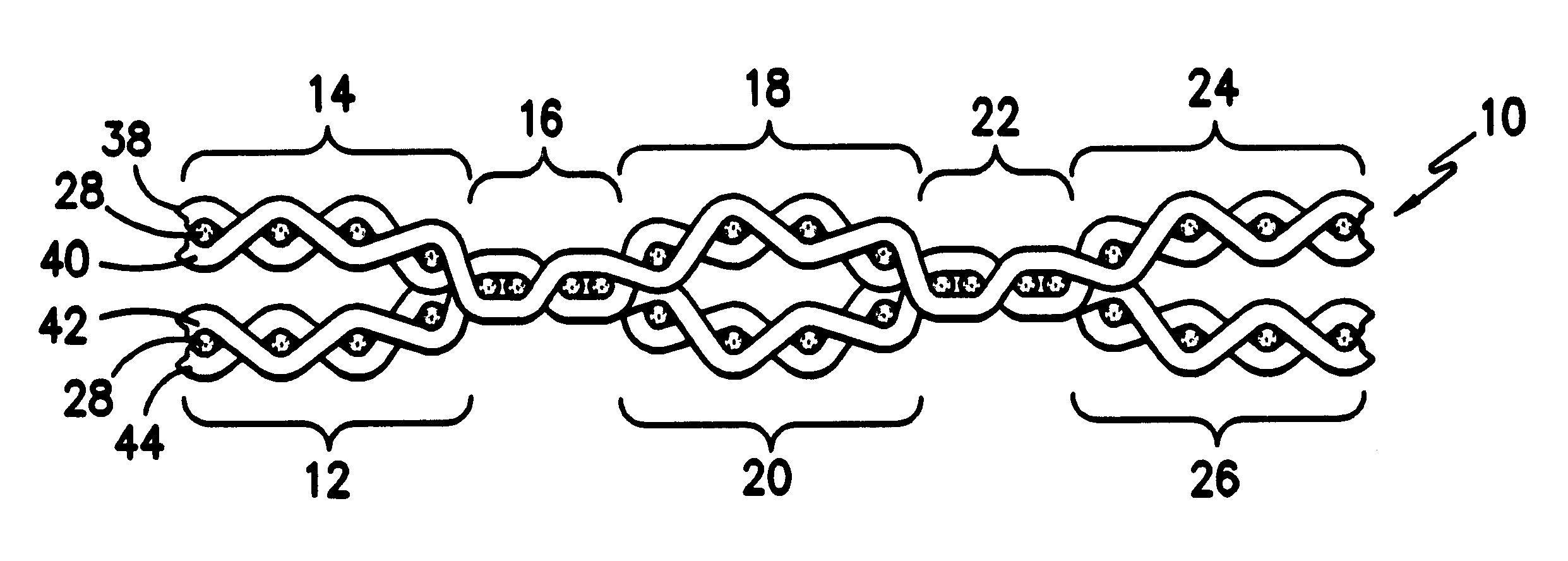
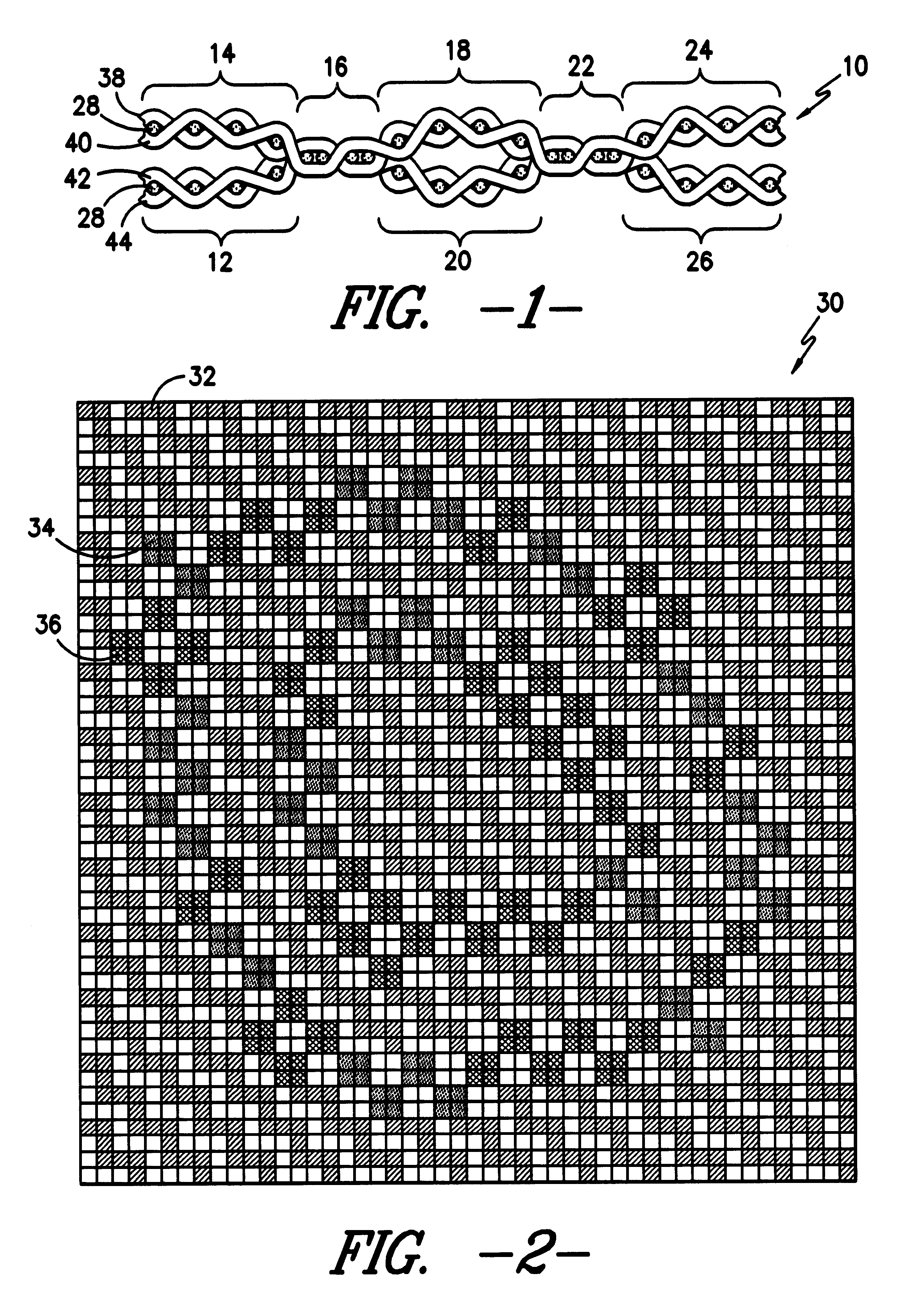
Elastic fabric with sinusoidally disposed wires
ActiveUS7191803B2Conductive stabilityShorten the lengthCircuit bendability/stretchabilityGarmentsEngineeringBody movement
A fabric for use with a system for monitoring prescribed body functions comprising an elastic fabric, adapted to be carried by a torso, which is stretchable in its longitudinal direction so as to expand and contract in response to body movement and size. The carrier includes at least one conductive and inelastic yarn arranged longitudinally of and located between upper and lower surfaces. The conductive yarn is arranged in sinusoidal configurations longitudinally of the fabric. The conductive yarn forms a breakout through one of the outer surfaces, at selected locations along the length of the fabric, forming opposed exposed ends above the surface. A monitoring unit, which includes a connector and a sensor, is secured with the one surface at the breakout with the connector being united with the exposed ends of the conductive yarn. The fabric acts to maintain the monitoring unit in a desired stationary position allowing the sensor to sense signals emitted from the torso and transmit these senses signals.
Owner:WOVEN ELECTRONICS
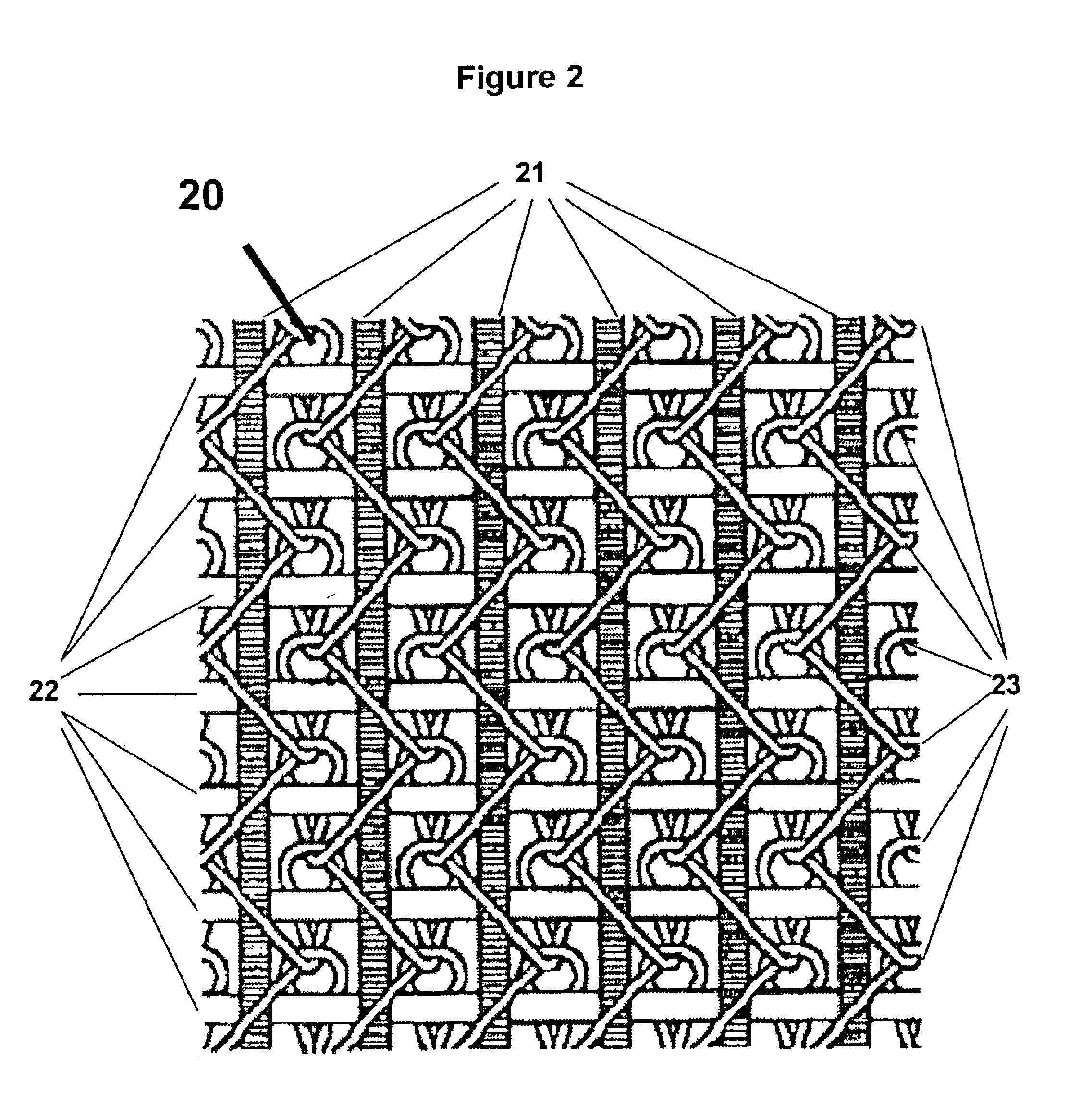
Machine direction yarn stitched triple layer papermaker's forming fabrics
InactiveUS6896009B2Excellent characteristicsImprove permeabilityPaper/cardboardMachine wet endYarnEngineering
Triple layer papermaker's forming fabrics having a set of top MD yarns that are interwoven exclusively with a set of top CMD yarns to form at least part of a top fabric layer and a set of bottom MD yarns that are interwoven exclusively with a set of bottom CMD yarns to form at least part of a bottom fabric layer are provided. These fabrics further include a set of stitching MD yarn pairs. The stitching MD yarns that comprise each such pair weave in both the top fabric layer and the bottom fabric layer such that at locations where the first yarn in the pair weaves in the top fabric layer the second yarn in the pair drops down into the bottom fabric layer. In embodiments of the present invention, each stitching MD yarn may also be woven so as to form side-by-side machine direction knuckles on the bottom surface of the bottom fabric layer with a bottom MD yarn. In other embodiments of the invention, at least some of the top CMD yarns that the stitching MD yarns of the stitching MD yarn pairs pass over immediately before dropping down into the bottom fabric layer have a larger diameter and / or a higher modulus than the remainder of the top CMD yarns.
Owner:WEAVEXX
Method of fabrication of a dryer fabric and a dryer fabric with backside venting for improved sheet stability
InactiveUS7005043B2Reduce decreaseSimpler and less-costly to manufacture and seamNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperYarnPolymer resin
A method of manufacturing and a papermaker's or industrial fabric, such as a dryer fabric for the dryer section of a paper machine, includes the application of a polymeric resin material onto preselected locations on the backside of a base substrate using a piezojet array which deposits the polymeric resin material in droplets having an average diameter of 10μ (10 microns) or more to build up discrete, discontinuous deposits of the polymeric resin material having a height of about 0.5 mm at the preselected locations. The preselected locations may be the knuckles formed by the interweaving of the yarns making up the fabric. The purpose of the deposits is to separate the backside of the dryer fabric from a surface, such as that of a dryer cylinder or turning roll, to enable air trapped between the dryer fabric and the surface to escape in lengthwise and crosswise directions parallel to the surface, instead of being forced through the fabric, possibly causing “drop off”. The polymeric resin material is set by means appropriate to its composition, and, optionally, and, if necessary, may be abraded to provide the deposits with a uniform height above the surface plane of the base substrate.
Owner:ALBANY INT CORP
Low permeability airbag cushions having film coatings of extremely low thickness
InactiveUS6698458B1Beneficial and long-term low permeabilityExcellent long-term storage stabilityLeno shedding mechanismPreformed elementsNeopreneEngineering
Coated inflatable fabrics, more particularly airbags to which very low add-on amounts of coating have been applied, are provided which exhibit extremely low air permeability. The inventive inflatable fabrics are primarily for use in automotive restraint cushions that require low permeability characteristics (such as side curtain airbags). Traditionally, heavy, and thus expensive, coatings of compounds such as neoprene, silicones and the like, have been utilized to provide such required low permeability. The inventive fabric utilizes an inexpensive, very thin coating to provide such necessarily low permeability levels. Thus, the inventive coated inflatable airbag comprises a film laminated on at least a portion of the target fabric surface wherein the film possesses a tensile strength of at least 2,000 and an elongation at break of at least 180%. The film provides a low permeability airbag cushion exhibiting a leak-down time of at least 5 seconds wherein the film is present on the surface in an amount of at most 3.0 ounces per square yard of the fabric.
Owner:MILLIKEN & CO
Warp-stitched multilayer papermaker's fabrics
InactiveUS7059357B2Easy to drainImprove joint strengthCellulosic pulp after-treatmentNon-fibrous pulp additionWeft yarnWarp knitting
A warp-stitched multilayer papermaker's fabric has a set of bottom warp yarns, a set of bottom weft yarns, a set of top weft yarns and a set of warp stitching yarn pairs. The bottom warp yarns are interwoven with the bottom weft yarns. The stitching warp yarns interweave with both the bottom weft yarns and the top weft yarns, and are woven such that at locations where the first of the stitching warp yarns in a pair weaves in the top fabric layer, the second stitching warp yarn in the pair drops below the top fabric layer to interweave with one or more bottom weft yarns to bind the top fabric layer and the bottom fabric layer together. The first stitching warp yarn of the stitching warp yarn pair may weave on a first side of one of the bottom warp yarns while the second stitching warp yarn of each stitching yarn pair may weave on the other side of that bottom warp yarn. Each stitching yarn pair may be substantially stacked above a bottom warp yarn. The fabric may further include a set of top warp yarns that interweave with the top weft yarns in the top fabric layer. The set of top warp yarns may be woven from a first warp beam, the set of bottom warp yarns may be woven from a second warp beam and the set of stitching warp yarns may be woven from a third warp beam.
Owner:WEAVEXX
Shock absorbing lanyards
InactiveUS20050189169A1Shorten the lengthStop fallingSafety beltsMountaineeringAbsorbed energyHigh intensity
A shock absorbing lanyard is a one-piece webbing. The shock absorbing lanyard has a tubular-shaped high strength outer sheath and a high elongation member inside of the outer sheath. The outer sheath and the high elongation member are secured together at spaced apart connection locations and the high elongation member is generally not secured to the outer sheath between the connection locations. Heat treatment shrinks the length of the high elongation member. The outer sheath does not substantially shrink from the heat treatment relative to the high elongation member and gathers together in an accordion-like arrangement. A tensile load applied to the lanyard stretches the high elongation member and unfolds the gathered outer sheath. The high strength outer sheath supports the tensile load when completely unfolded while the high elongation member absorbs energy as it stretches or elongates.
Owner:YKK CORP OF AMERICA
Low permeability airbag cushions having film coatings of extremely low thickness
InactiveUS6429155B1High leak-down timeReduce penetrationEnvelopes/bags making machineryPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementEngineeringNeoprene
Coated inflatable fabrics, more particularly airbags to which very low add-on amounts of coating have been applied, are provided which exhibit extremely low air permeability. The inventive inflatable fabrics are primarily for use in automotive restraint cushions that require low permeability characteristics (such as side curtain airbags). Traditionally, heavy, and thus expensive, coatings of compounds such as neoprene, silicones and the like, have been utilized to provide such required low permeability. The inventive fabric utilizes an inexpensive, very thin coating to provide such necessarily low permeability levels. Thus, the inventive coated inflatable airbag comprises a film laminated on at least a portion of the target fabric surface wherein the film possesses a tensile strength of at least 2,000 and an elongation at break of at least 180%. The film provides a low permeability airbag cushion exhibiting a leak-down time of at least 5 seconds as well as a very low packing volume (for more efficient use of storage space within a vehicle) for the target side curtain airbag.
Owner:MILLIKEN & CO
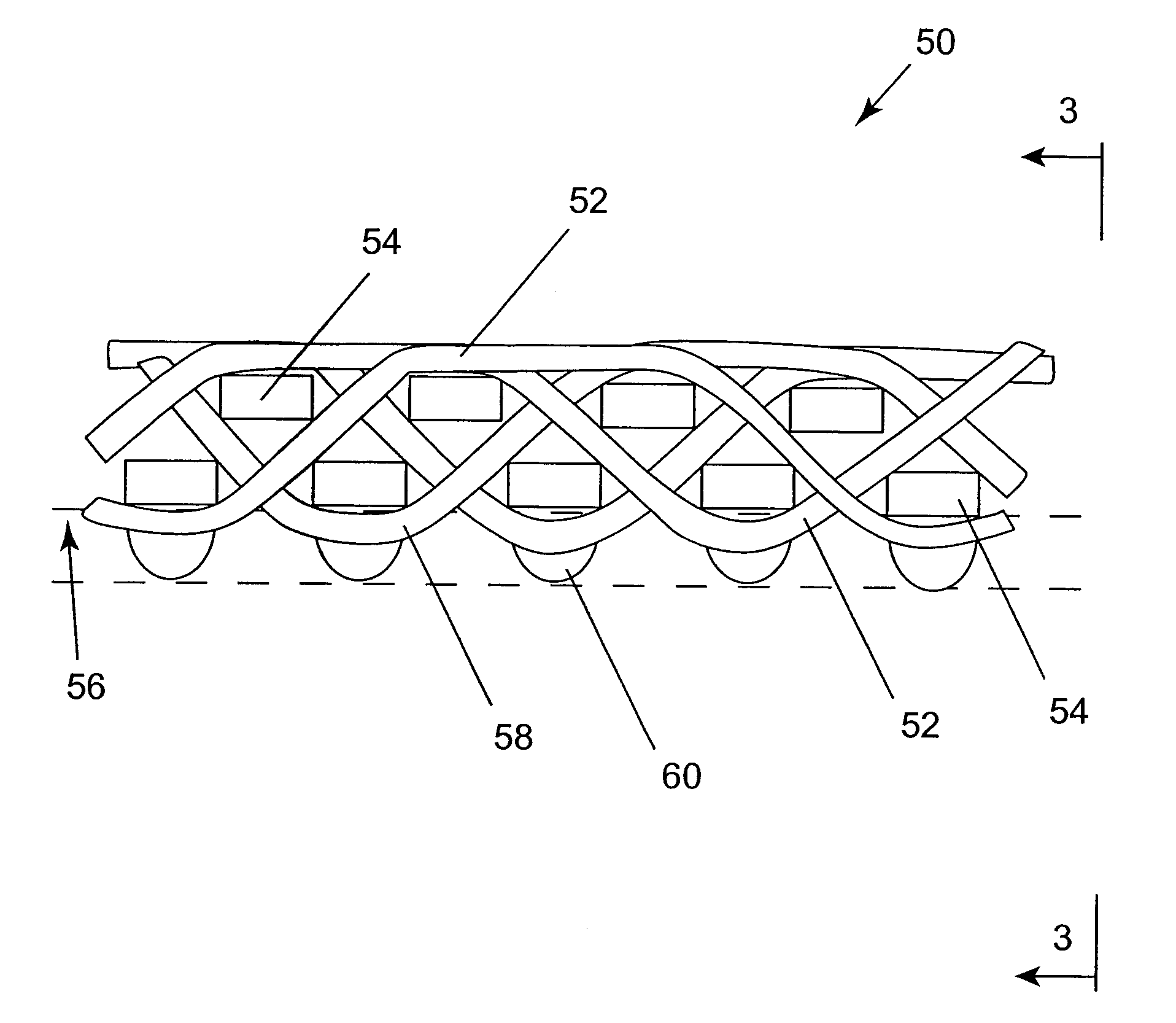
Self-curling sleeve
A substrate including a plurality of monofilaments, or a combination of monofilaments and multi-filament yarns oriented in perpendicular directions, has a tendency to curl around a central space. When all monofilaments are used, the monofilaments along one direction may have a larger diameter than the monofilaments along the other direction. The monofilaments are woven such that the larger diameter monofilaments form floats predominantly on one side of the substrate. For the monofilament-multifilament combination the monofilaments form floats predominantly on one side of the substrate. The substrate curls about an axis parallel to the monofilaments forming the floats. The side having the floats faces outwardly away from the central space. Preferably, the monofilaments are oriented in the warp direction along the substrate. The filaments may be woven in a herringbone twill weave, a double cloth herringbone twill weave or a satin weave to provide the floats.
Owner:FEDERAL MOGUL WORLD WIDE LLC
Composite papermaking fabric
A composite papermaking fabric having an upper support fabric including upper warp and weft yarns and a lower contact fabric including lower warp and weft yarns. The upper fabric is woven in a first weave pattern which forms a support surface and the lower fabric is woven in a broken twill weave pattern which forms the contact surface. The composite fabric includes paired binder yarns which weave in alternating sequences with the upper and lower fabrics binding them together. The broken twill weave pattern provides plural floats of cross-machine direction yarns passing outwardly of a plurality of adjacent lower warp yarns forming a plurality of adjacent cross-machine direction floats. Certain of the paired floats comprise a lower weft yarn and a binder yarn while others may comprise two lower weft yarns. The lower weft yarn floats are positioned to shield and protect the binder yarn floats along their entire length.
Owner:VOITH FABRICS
Woven fabric
InactiveUS20130260630A1Reduced aestheticsAvoid disconnectionMulti-ply fabricsUpholsteryYarnEngineering
A woven fabric having a high shrinkage yarn that has a predetermined shrinkage ratio and a low shrinkage yarn that has a relatively lower shrinkage ratio than the high shrinkage yarn, includes an inductive portion that is formed by the high shrinkage yarn, and allows displacement in a planar direction. At least a portion of the low shrinkage yarn is engaged with the inductive portion and bent in the planar direction.
Owner:TOYOTA BOSHOKU KK
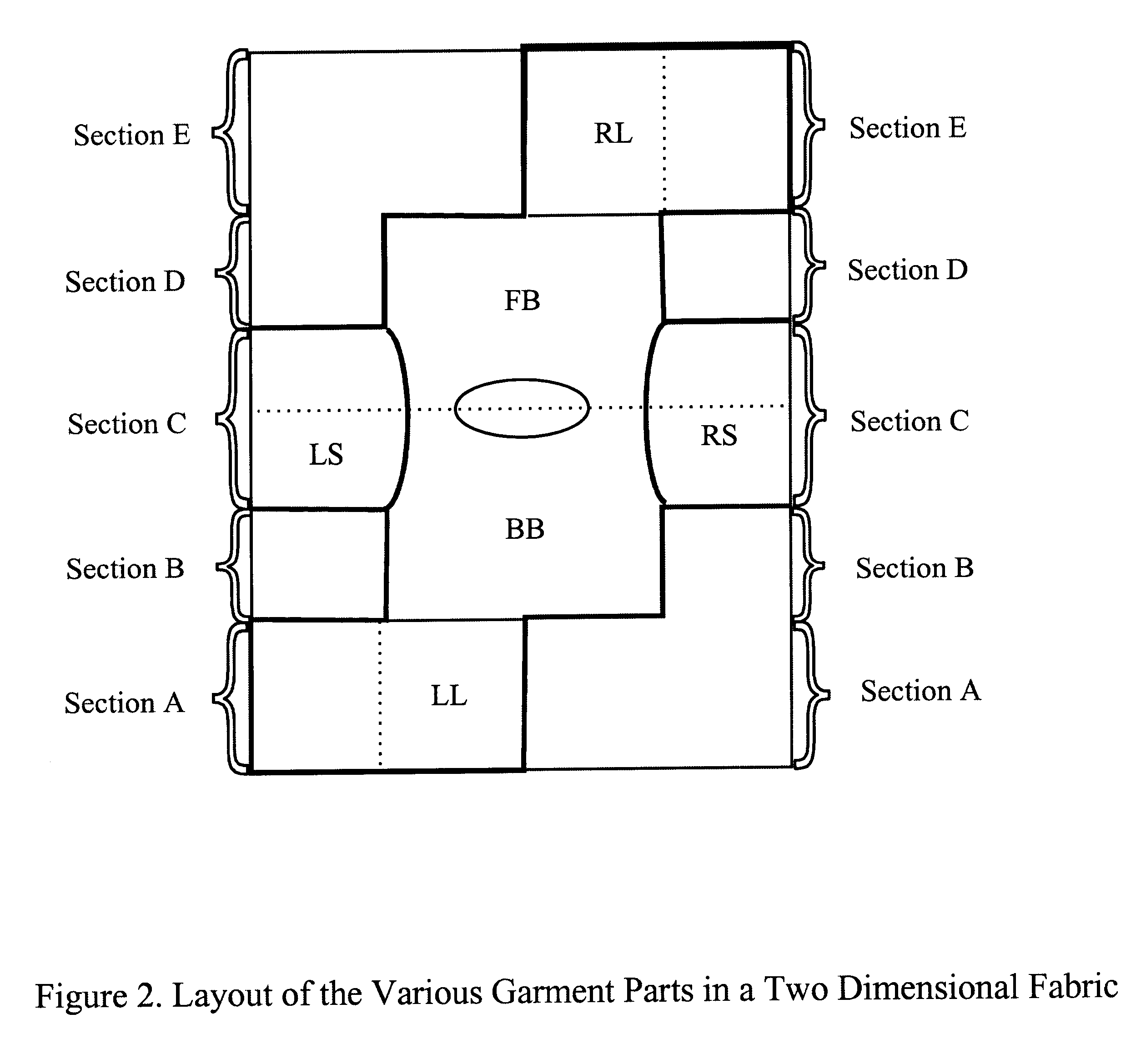
Full-fashioned garment in a fabric and optionally having intelligence capability
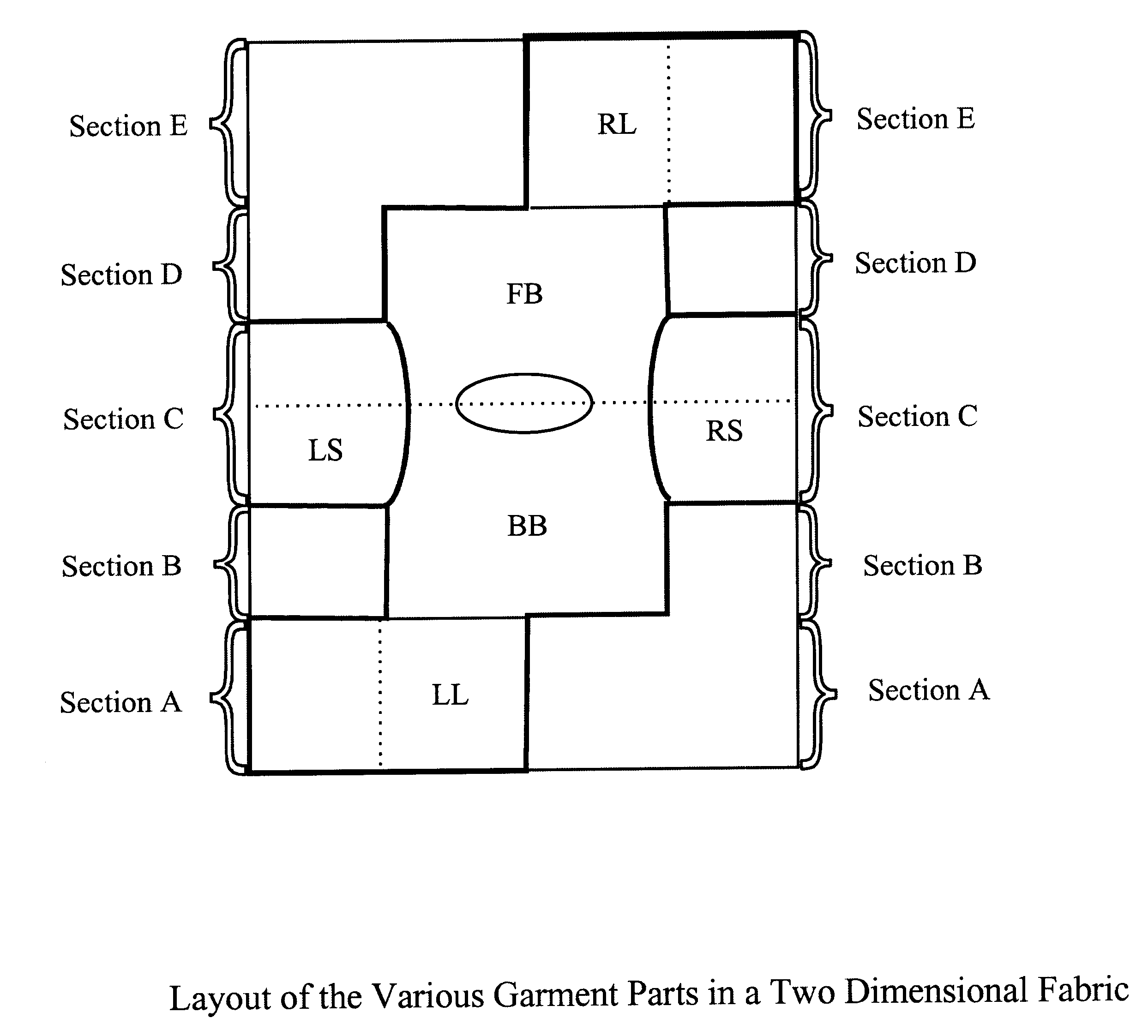
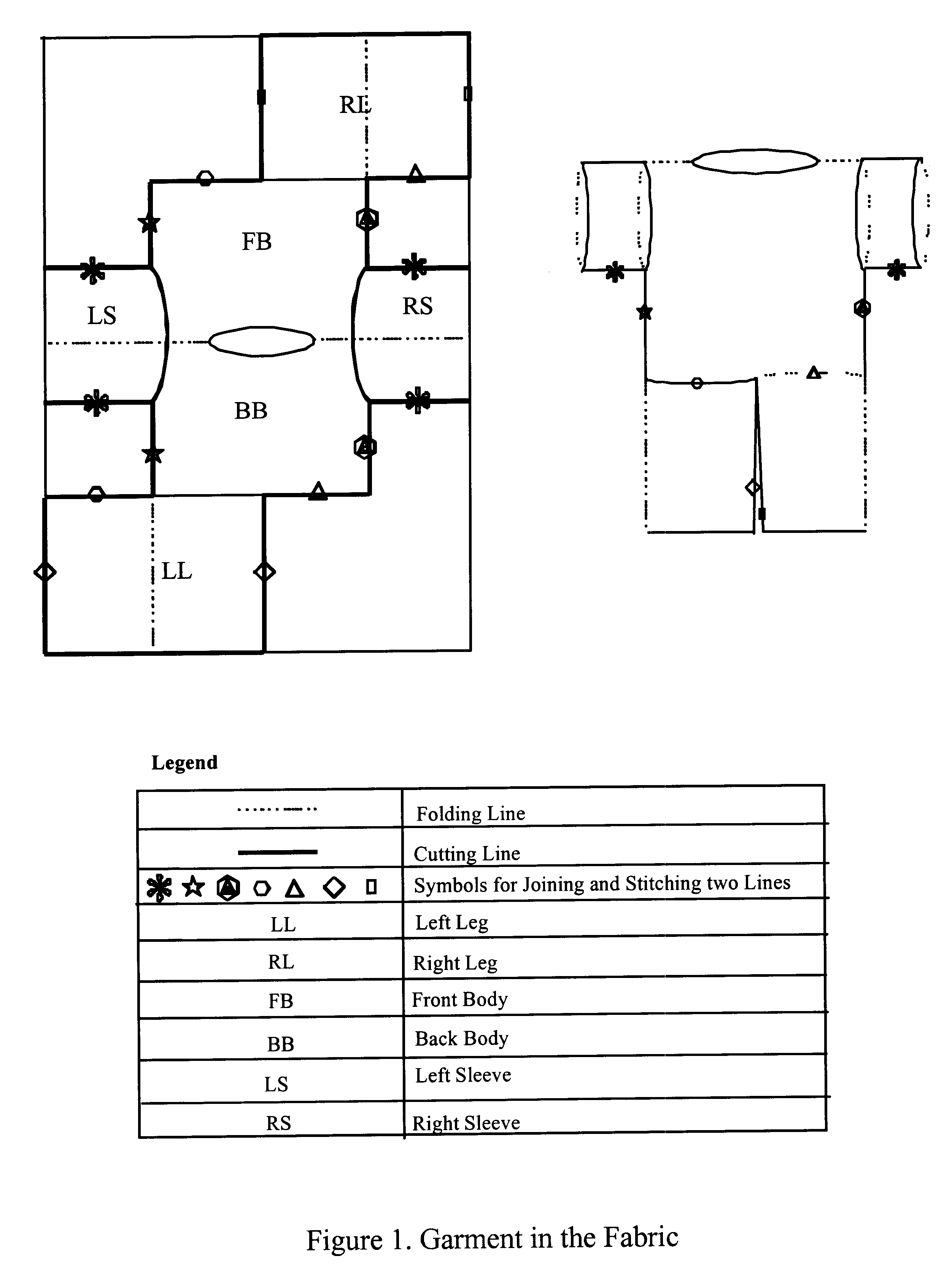
The present invention is directed to a process for the production of a single-piece woven garment which can be converted into a full-body garment, similar to an overall or a hospital gown, using a minimum number of seams and a minimum amount of cutting. The garment is made a two-dimensional fabric, with the various parts produced as a single piece. Additionally, the garment can include an integrated infrastructure component for collecting, processing, transmitting and receiving information, giving it intelligence capability.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com