Patents
Literature
6272 results about "Papermaking" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The art, science, and technology of papermaking addresses the methods, equipment, and materials used to make paper and cardboard, these being used widely for printing, writing, and packaging, among many other purposes and useful products. Today almost all paper is manufactured using industrial machinery, while handmade paper survives as a specialized craft and a medium for artistic expression.
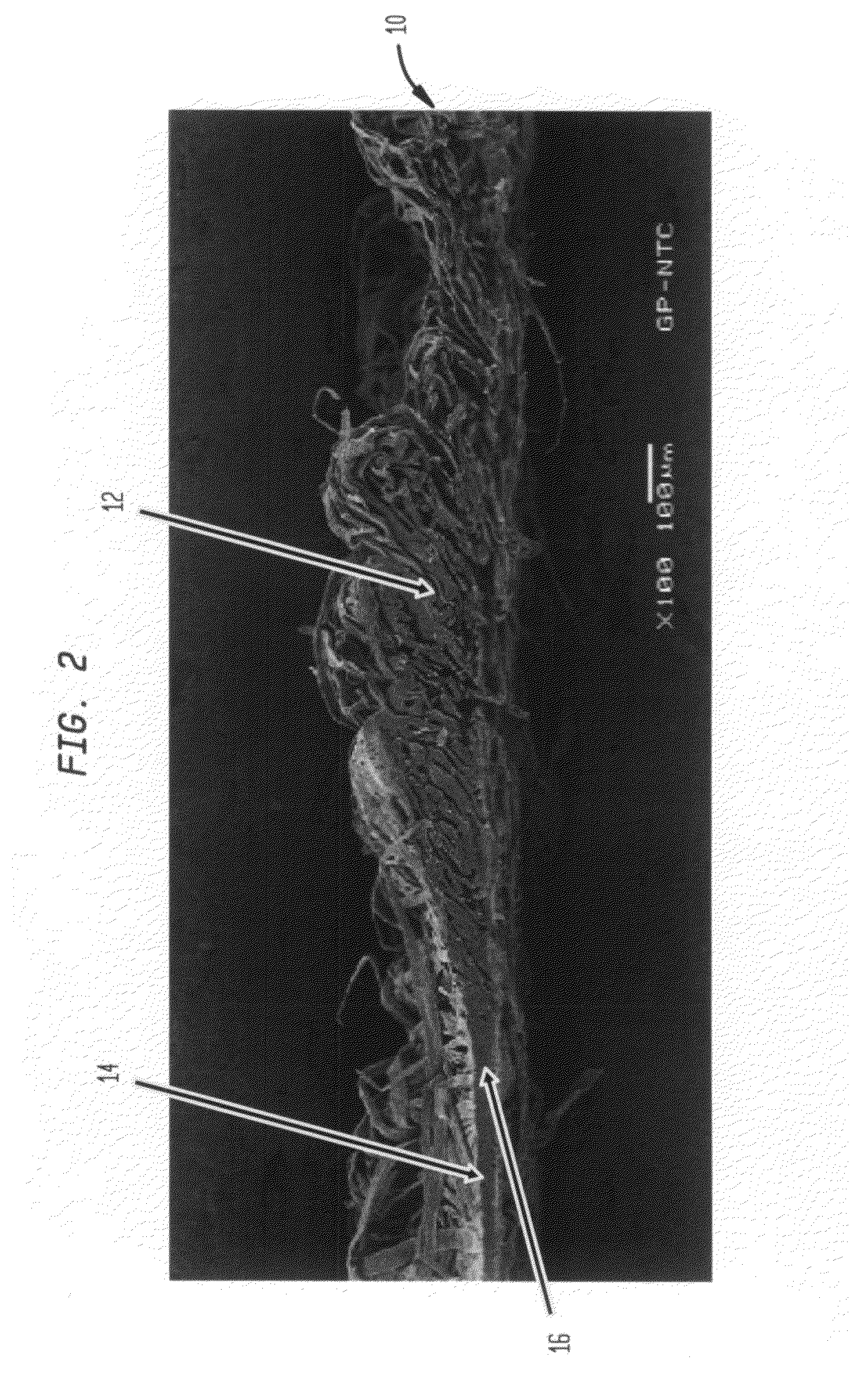
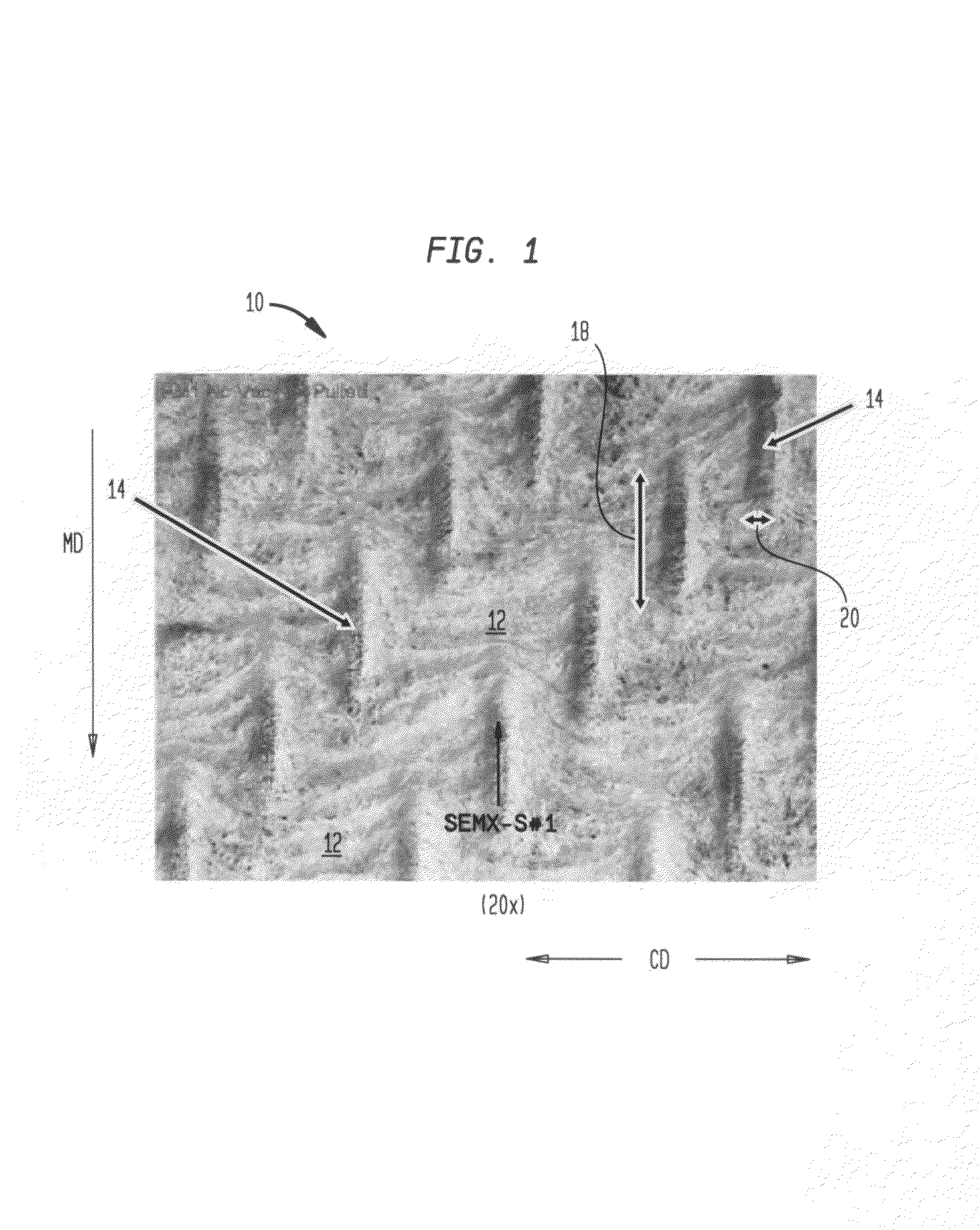
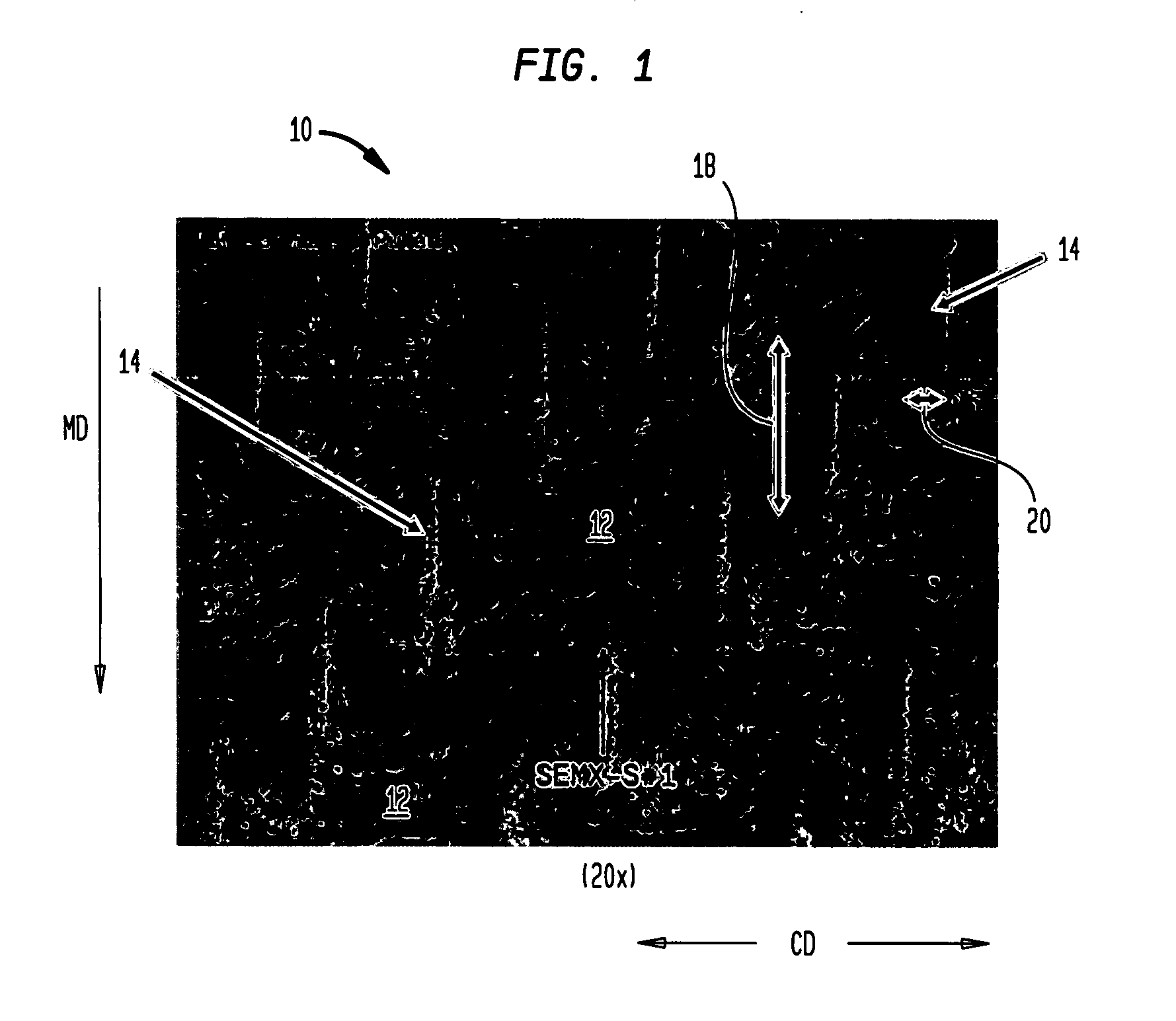
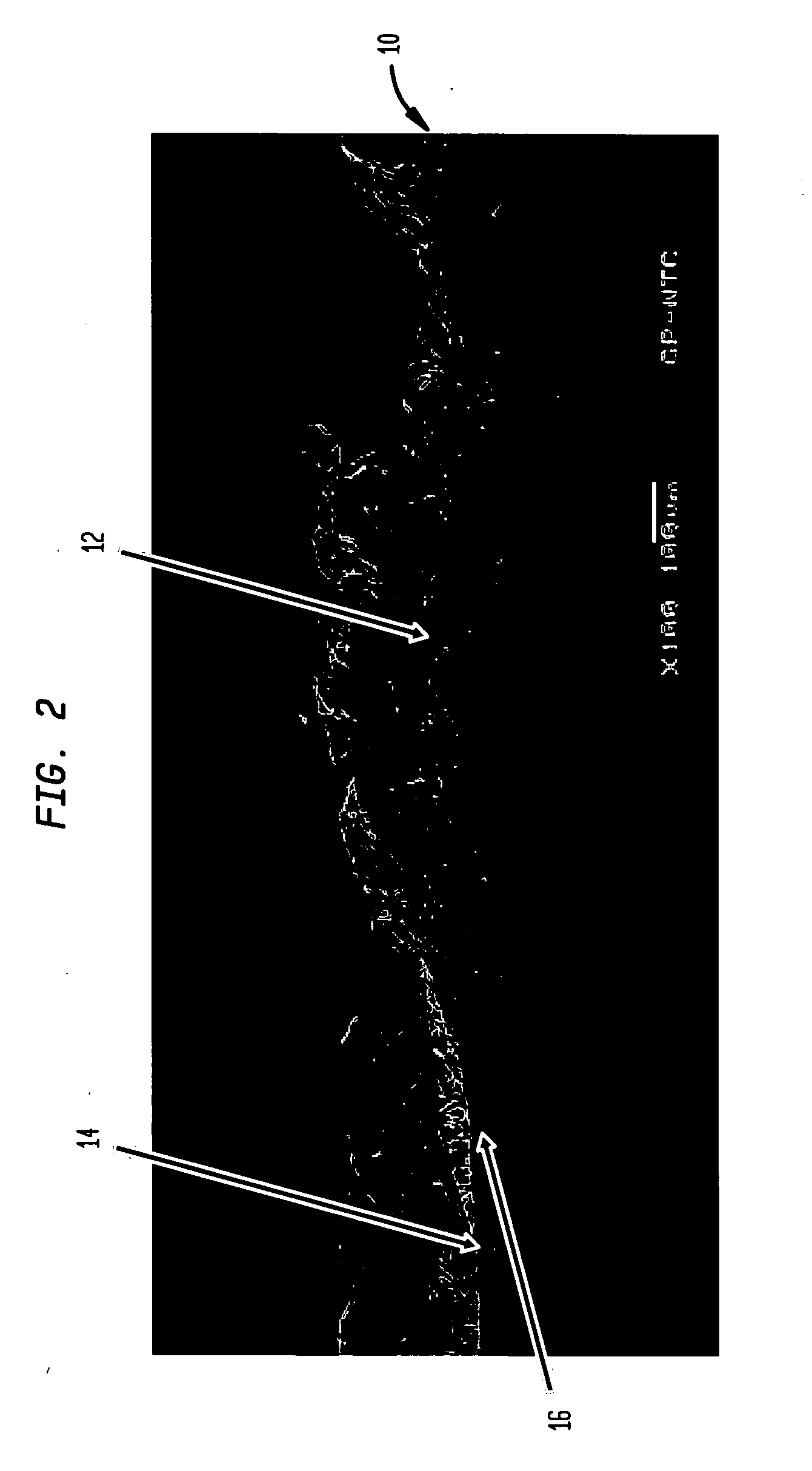
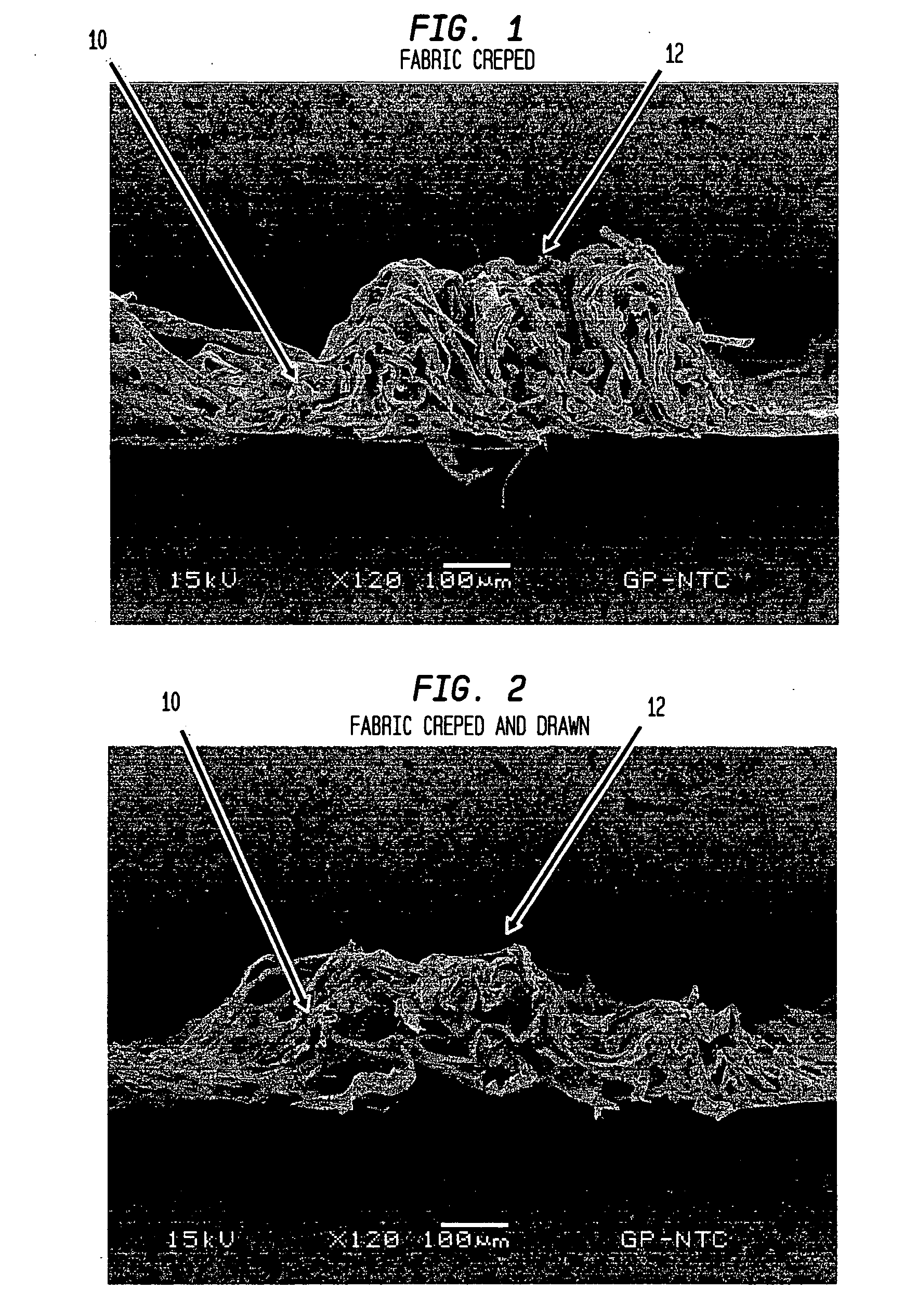
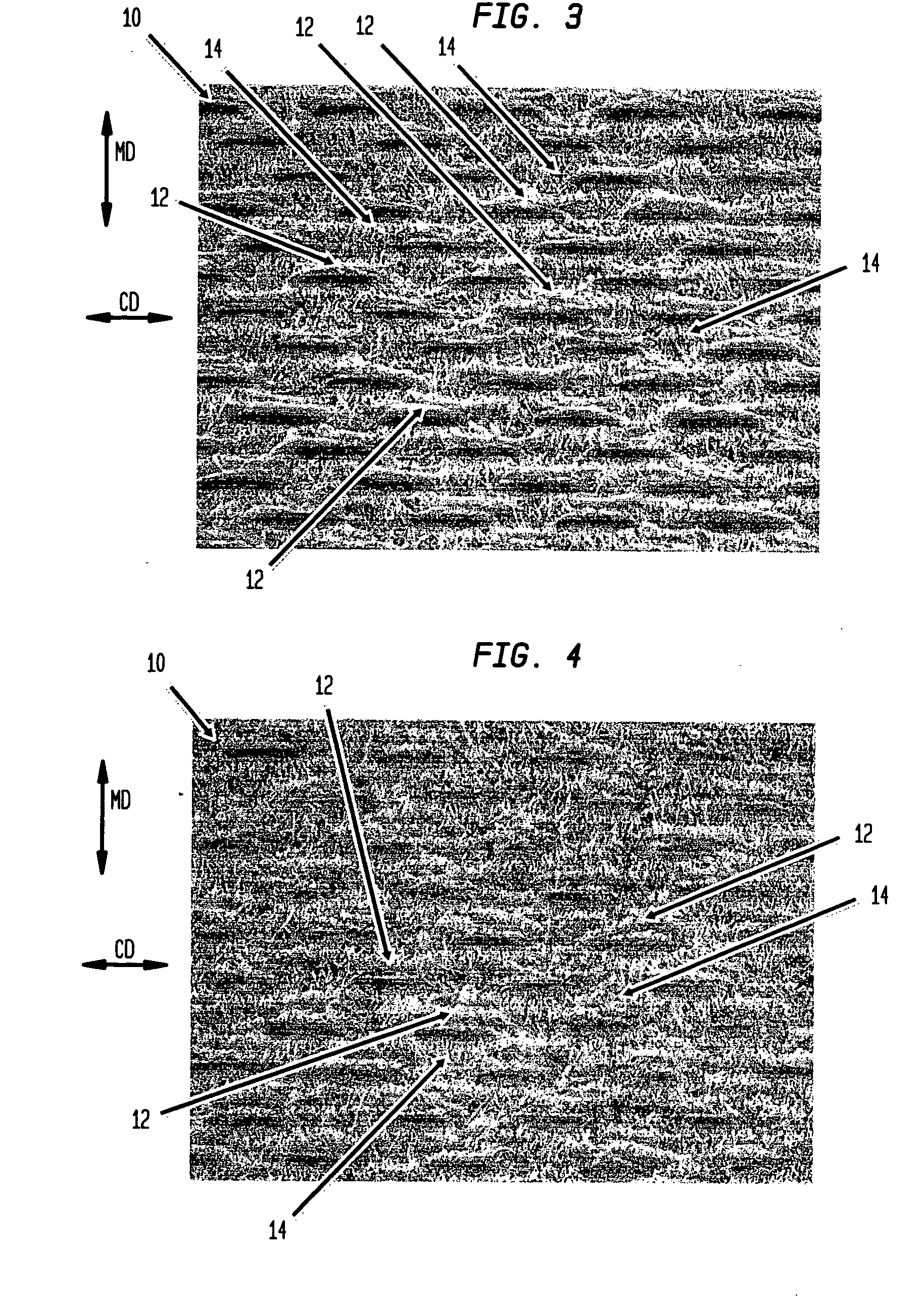
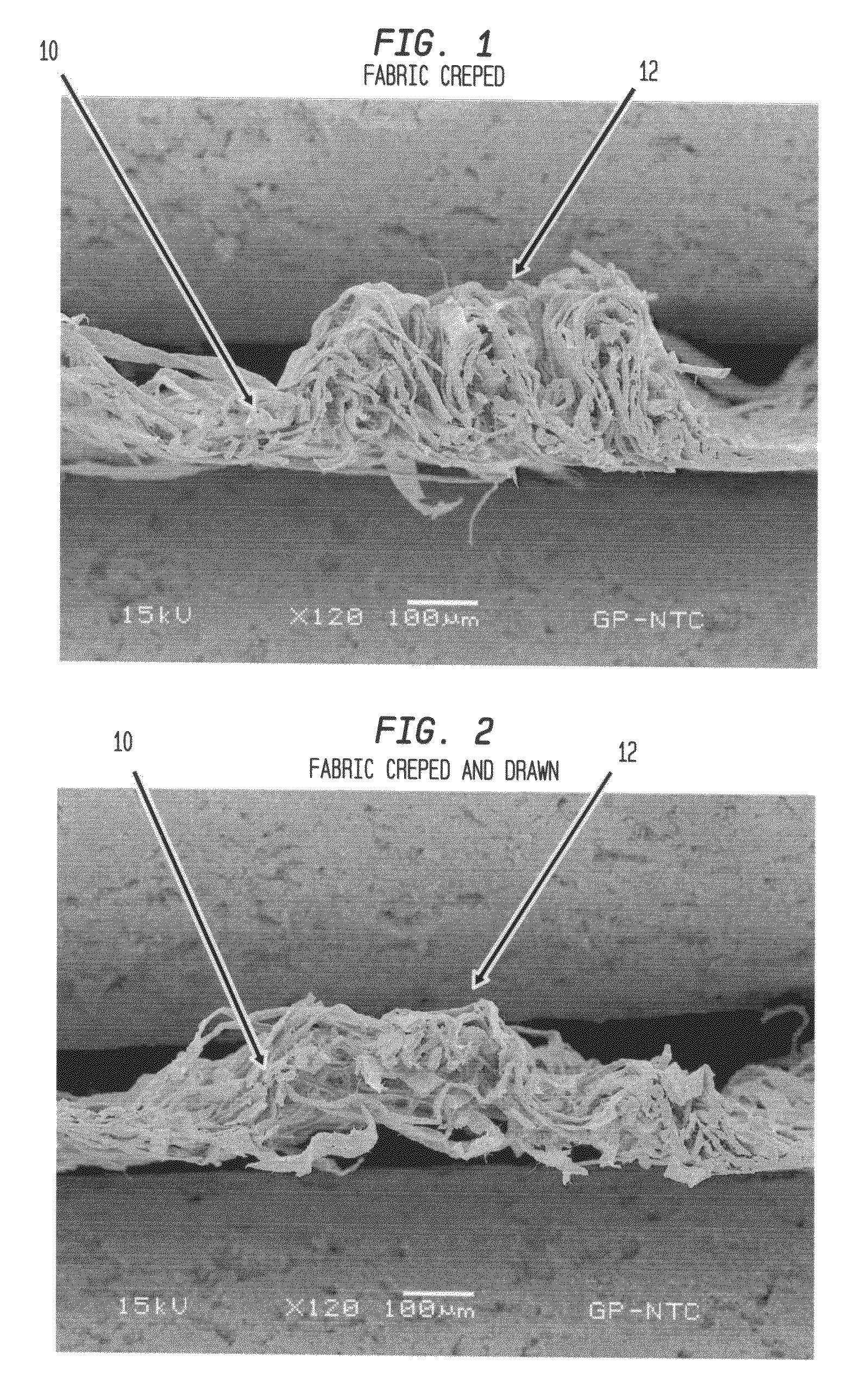
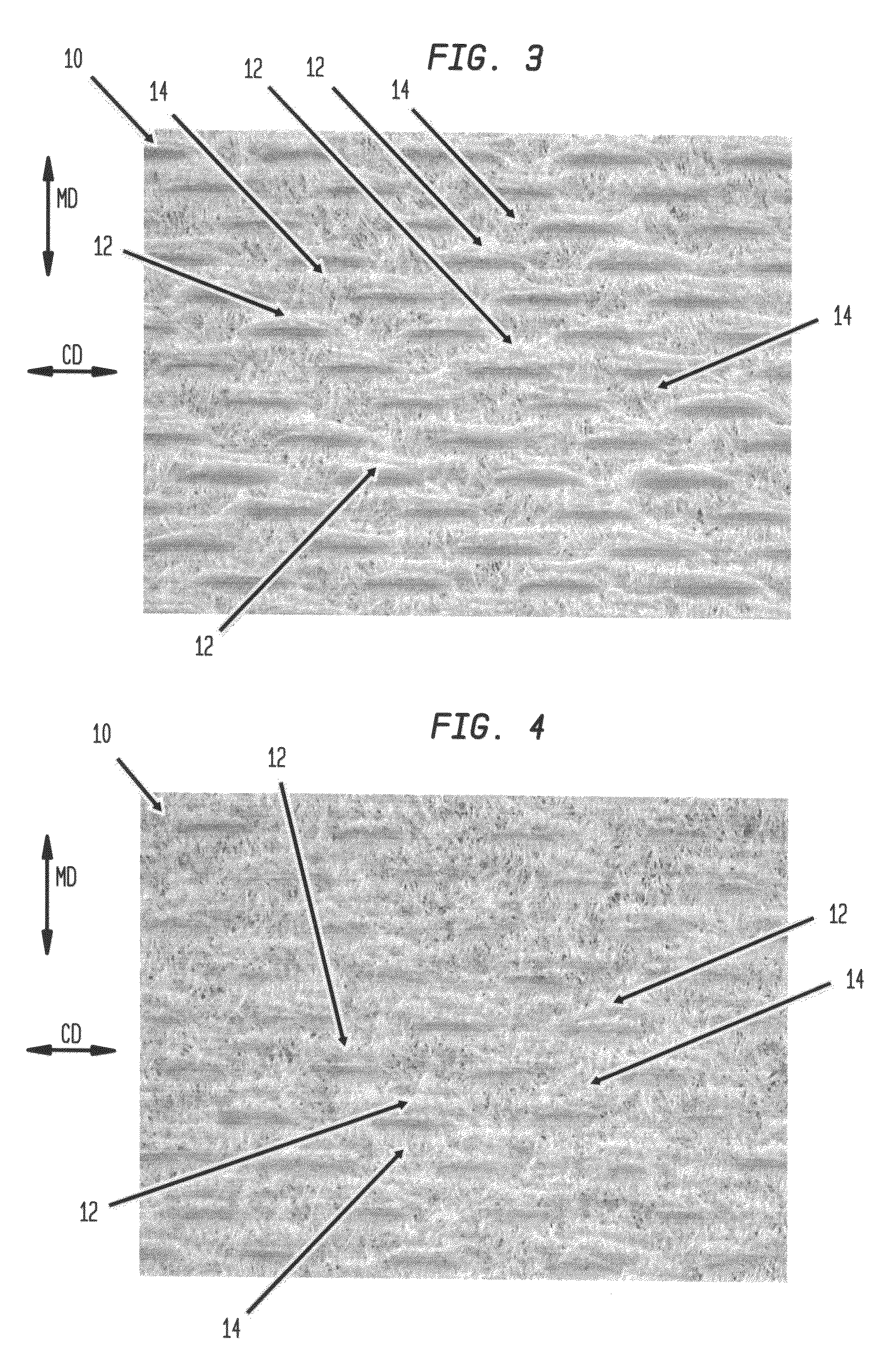
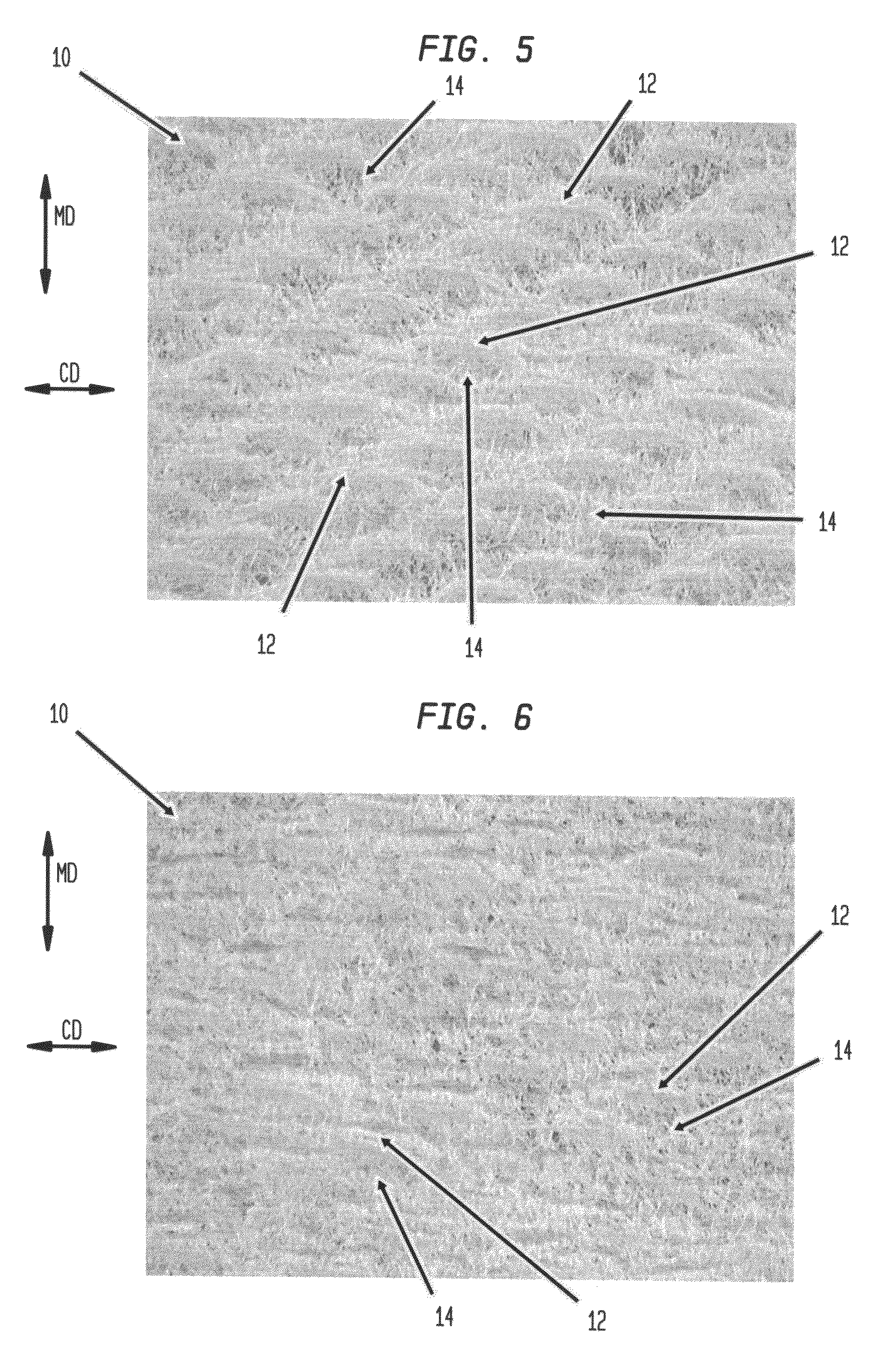
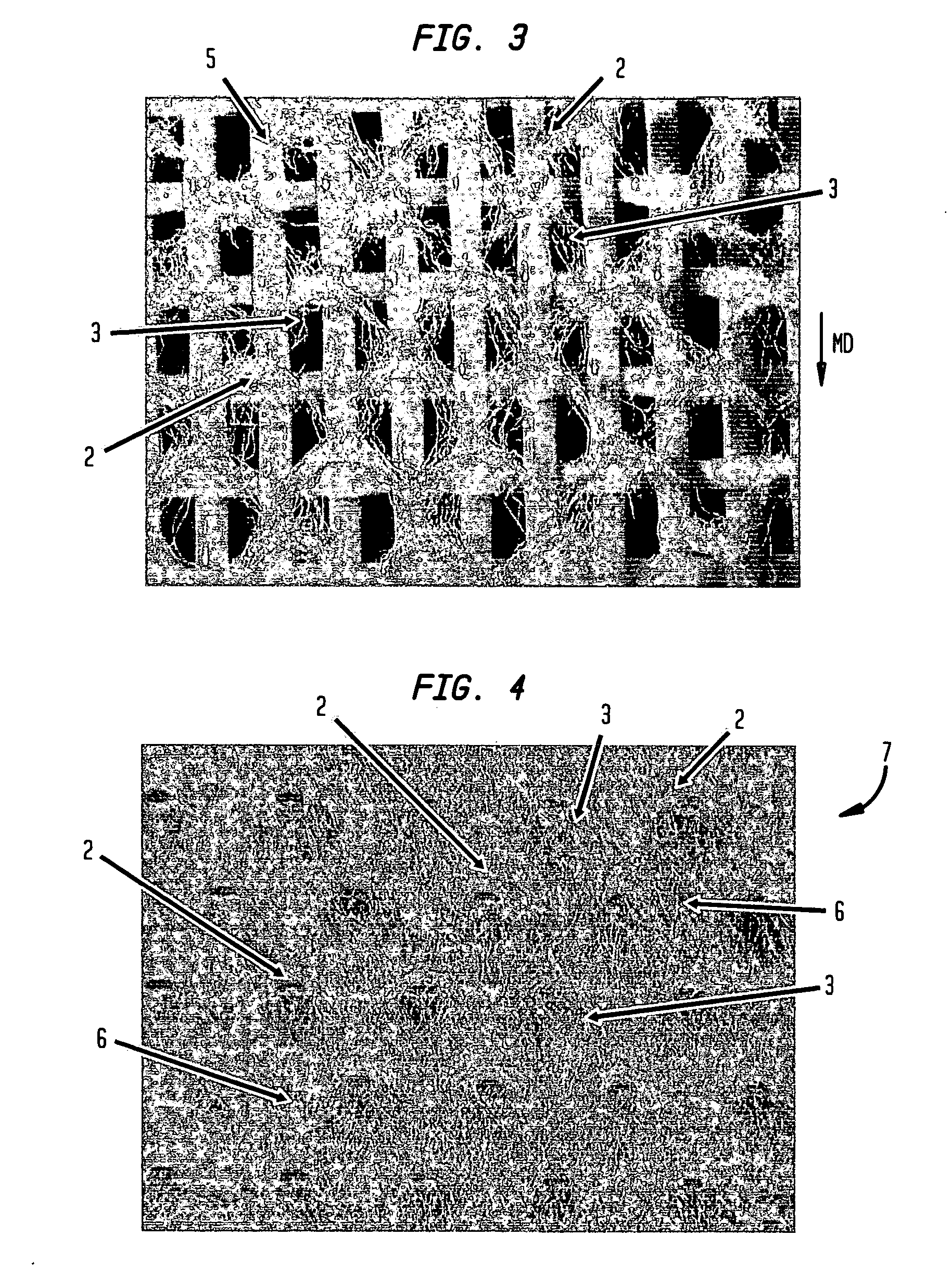
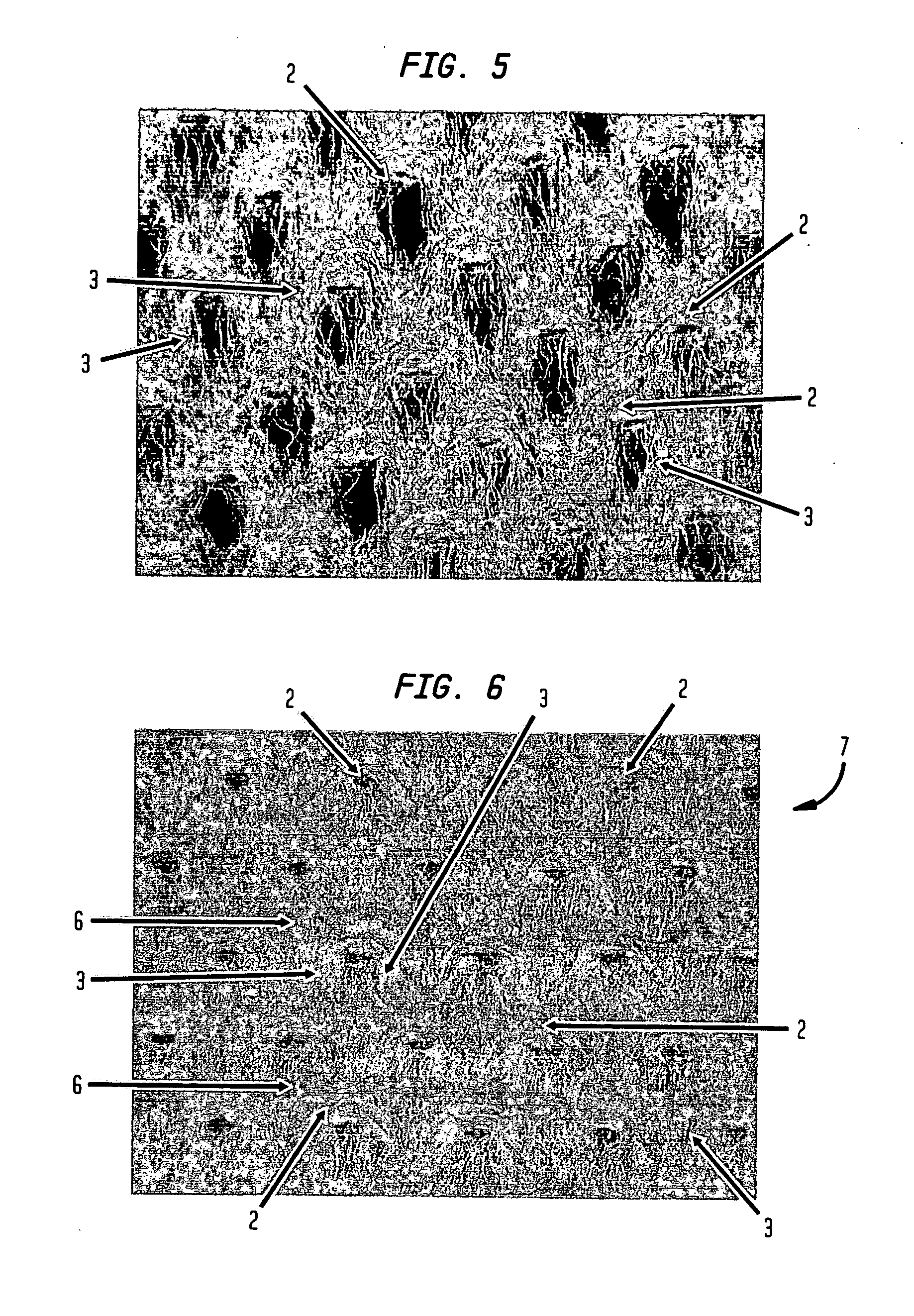
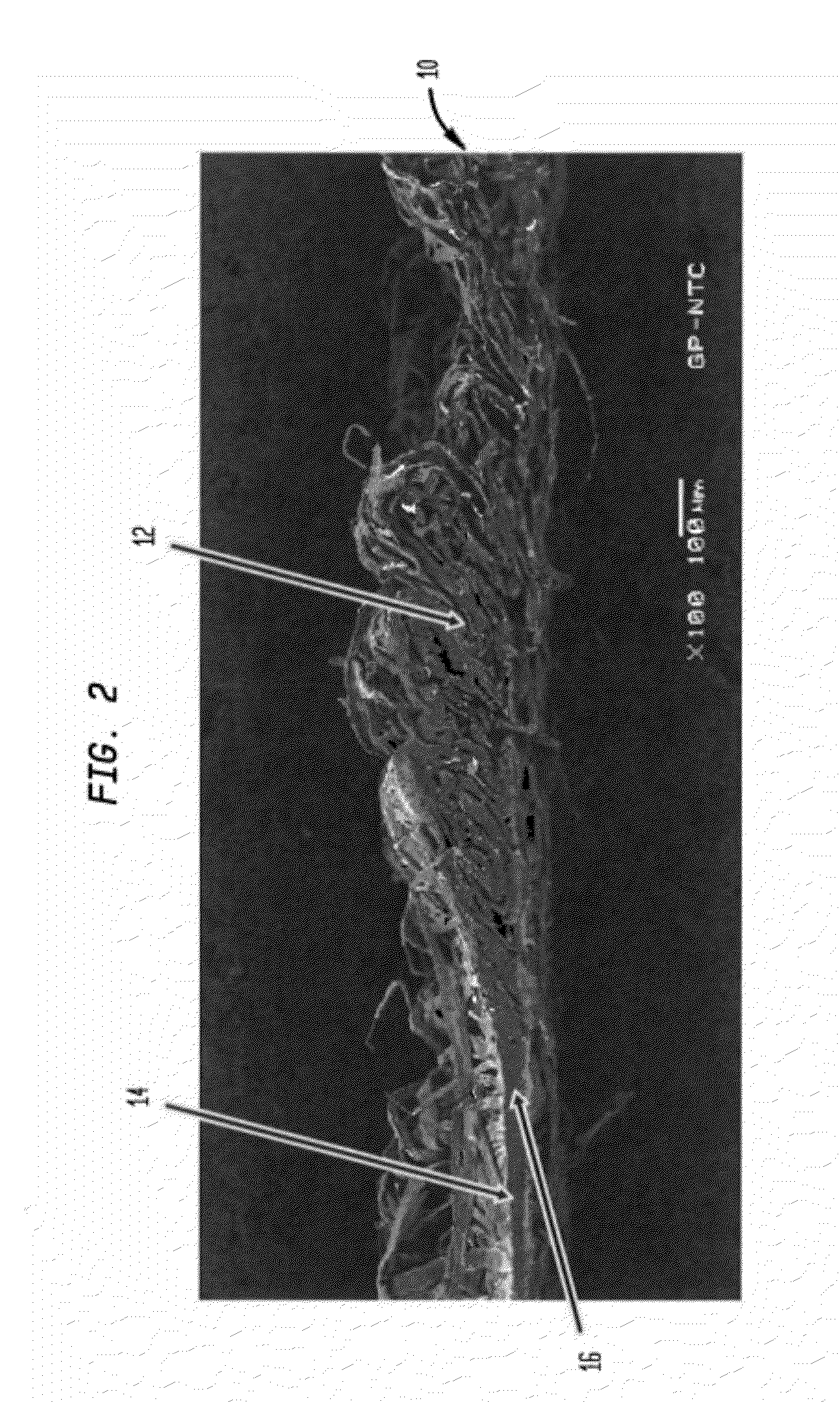
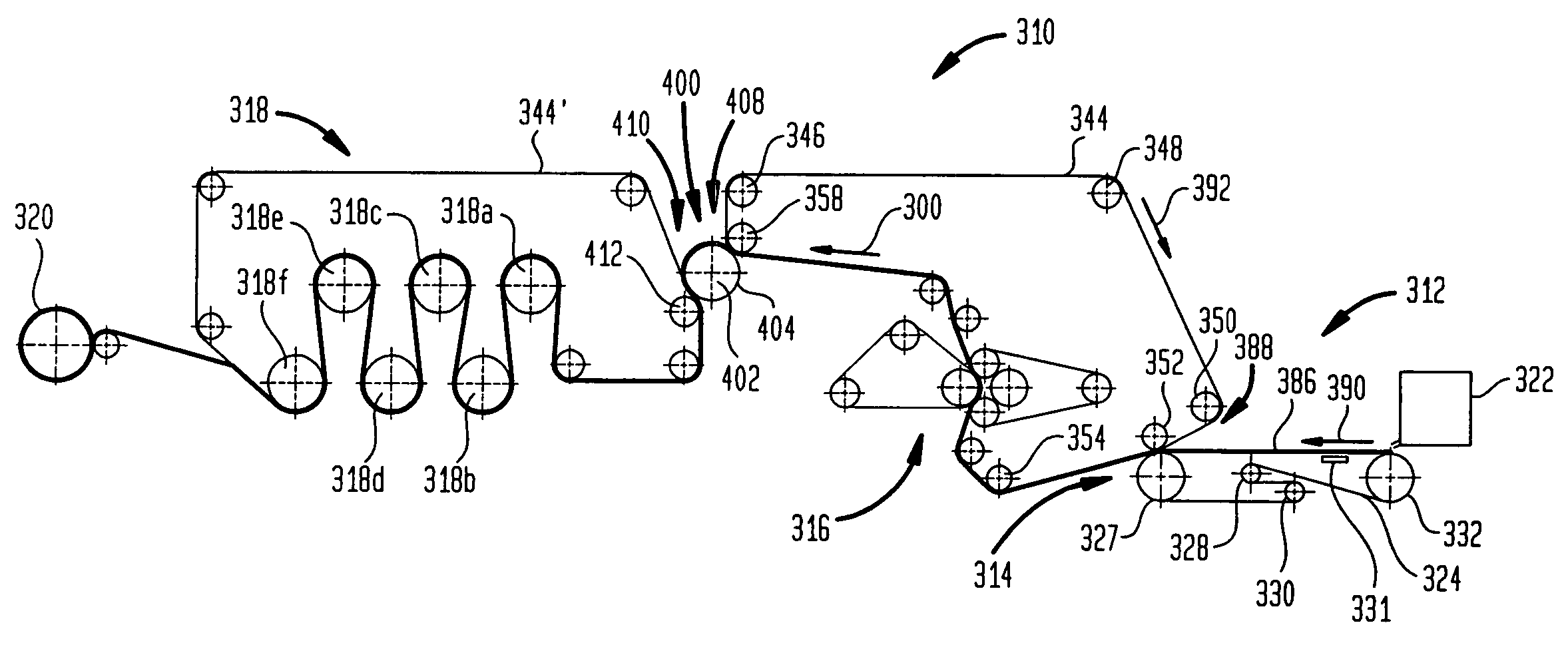
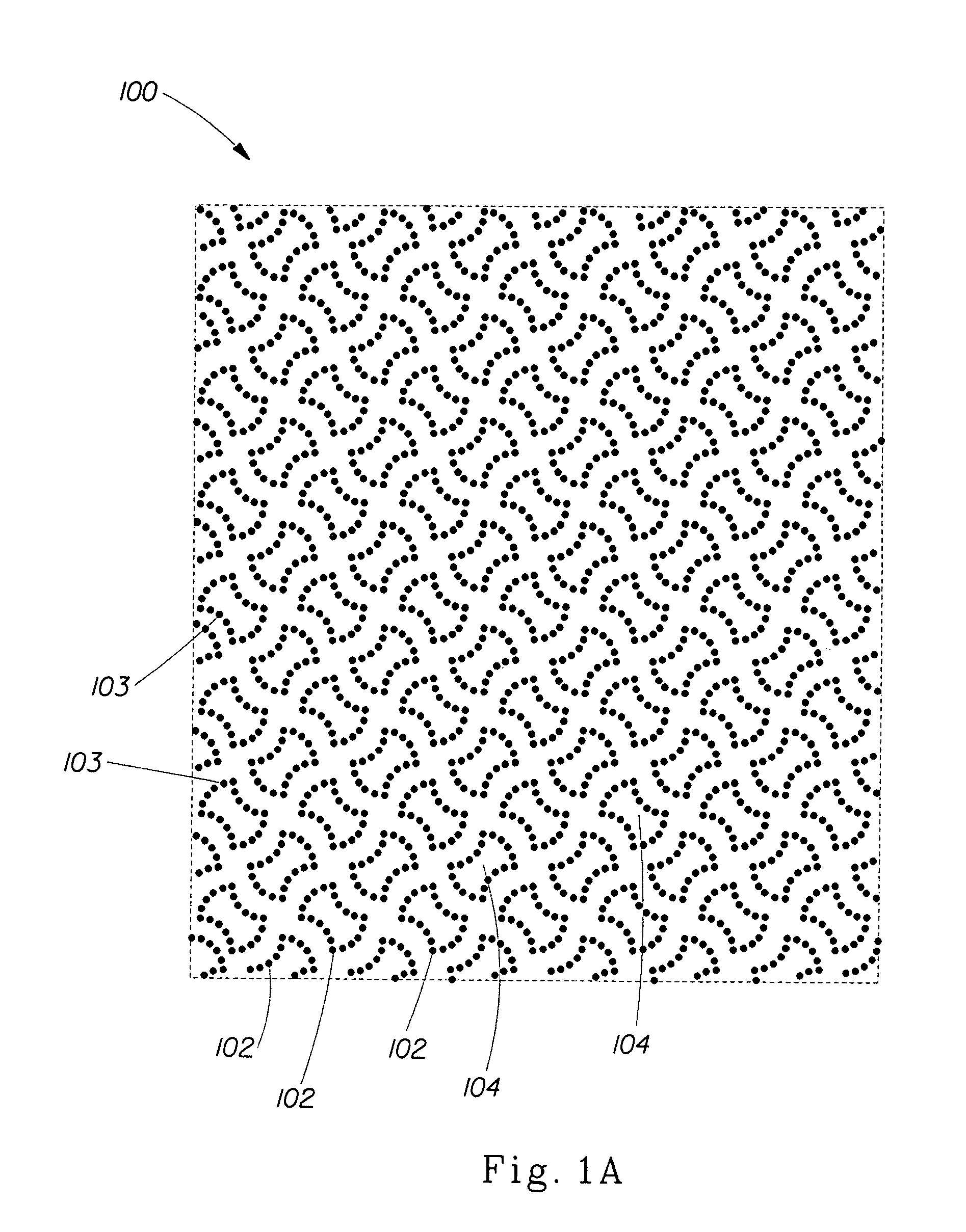
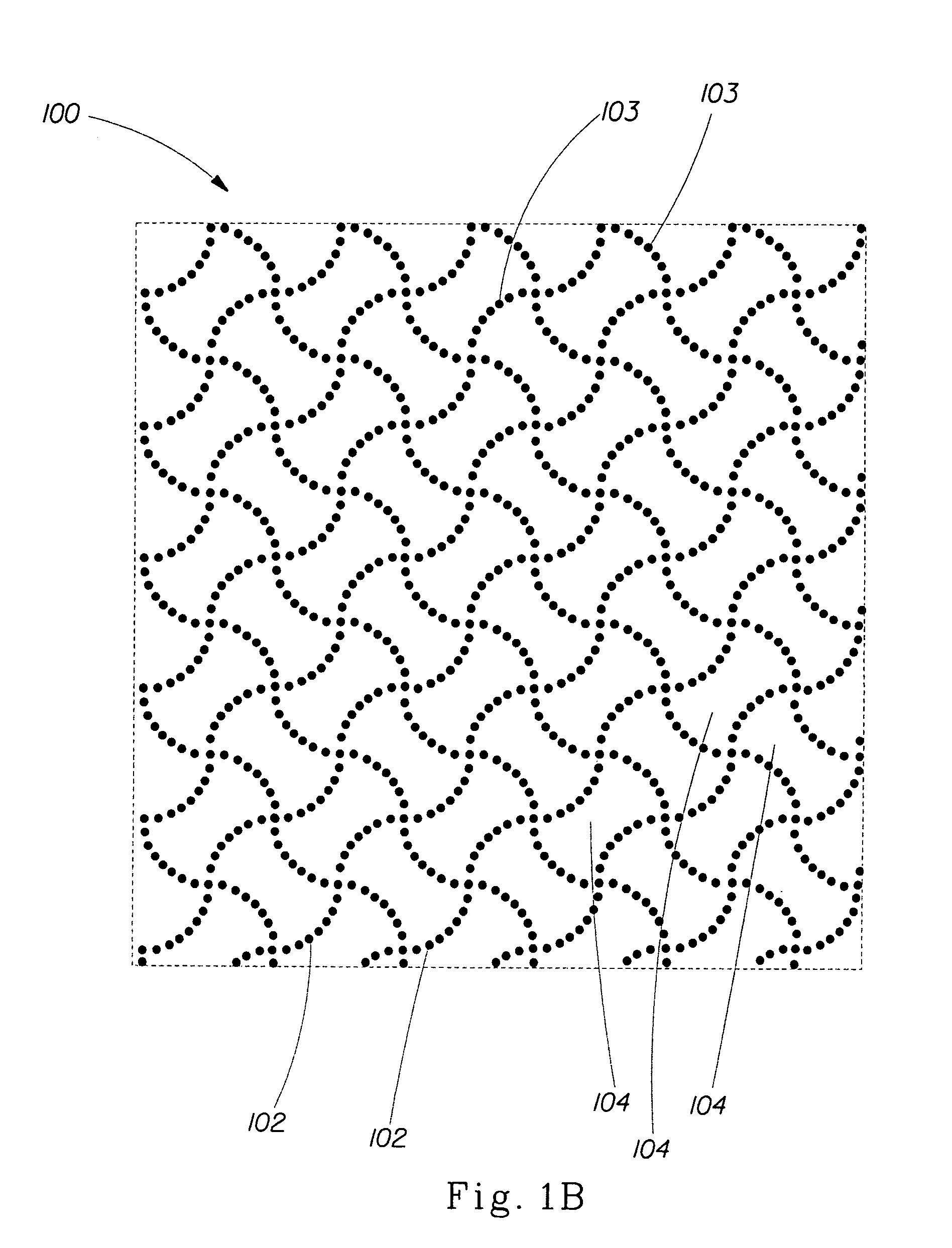
Fabric creped absorbent sheet with variable local basis weight
InactiveUS7494563B2Improve water absorptionSurprising softnessNatural cellulose pulp/paperMechanical working/deformationFiberPapermaking
An absorbent cellulosic sheet having variable local basis weight includes a papermaking-fiber reticulum provided with (i) a plurality of cross-machine direction (CD) extending, fiber-enriched pileated regions of relatively high local basis weight interconnected by (ii) a plurality of elongated densified regions of compressed papermaking fibers. The elongated densified regions have relatively low local basis weight and are generally oriented along the machine direction (MD) of the sheet and have an MD / CD aspect ratio of at least 1.5. The products are most preferably prepared by way of a compactive dewatering / wet crepe process.
Owner:GPCP IP HLDG LLC
Fabric creped absorbent sheet with variable local basis weight
InactiveUS20080029235A1Improve water absorptionSurprising softnessNatural cellulose pulp/paperMechanical working/deformationFiberPapermaking
An absorbent cellulosic sheet having variable local basis weight includes a papermaking-fiber reticulum provided with (i) a plurality of cross-machine direction (CD) extending, fiber-enriched pileated regions of relatively high local basis weight interconnected by (ii) a plurality of elongated densified regions of compressed papermaking fibers. The elongated densified regions have relatively low local basis weight and are generally oriented along the machine direction (MD) of the sheet and have an MD / CD aspect ratio of at least 1.5. The products are most preferably prepared by way of a compactive dewatering / wet crepe process.
Owner:GPCP IP HLDG LLC
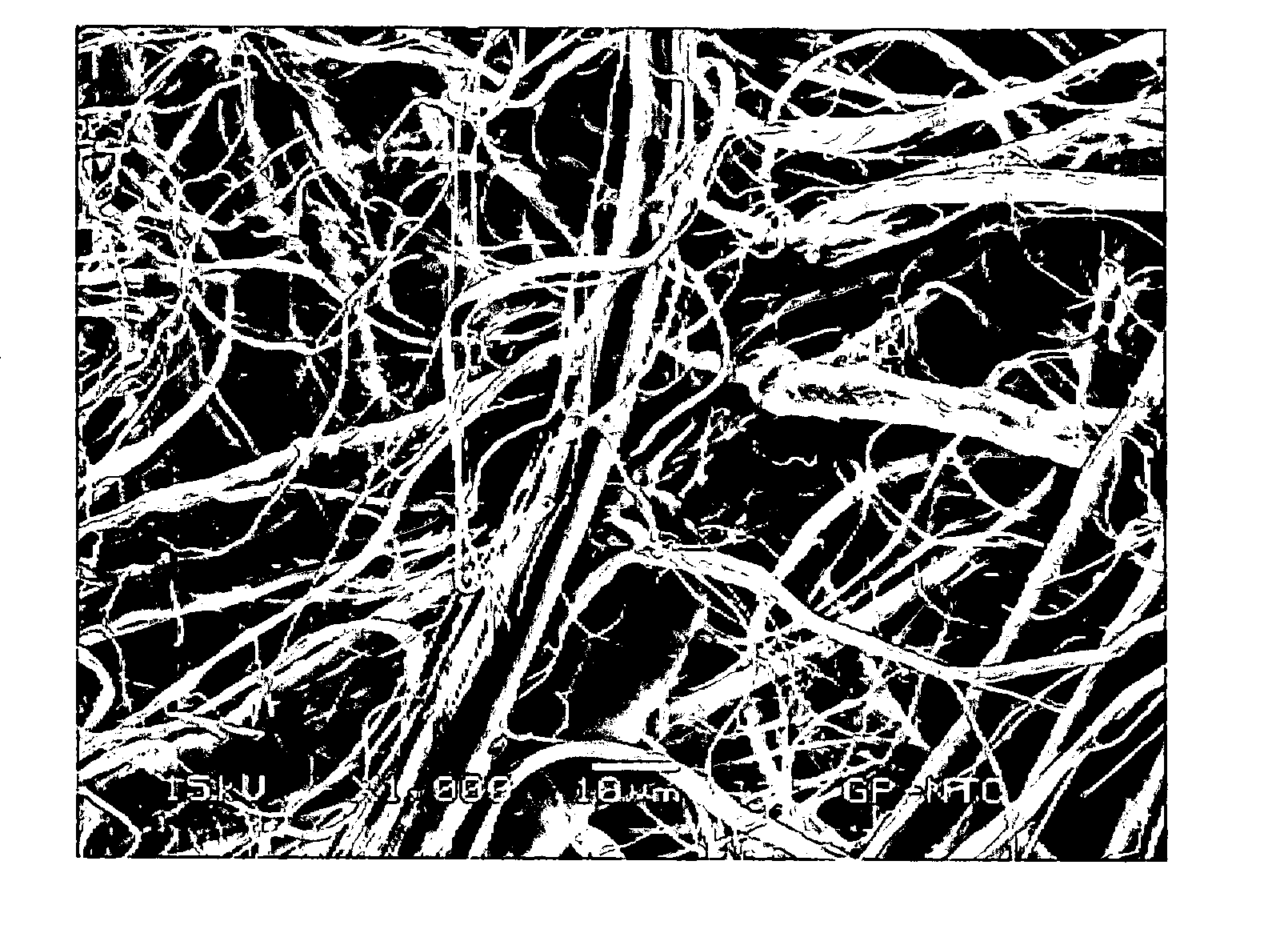
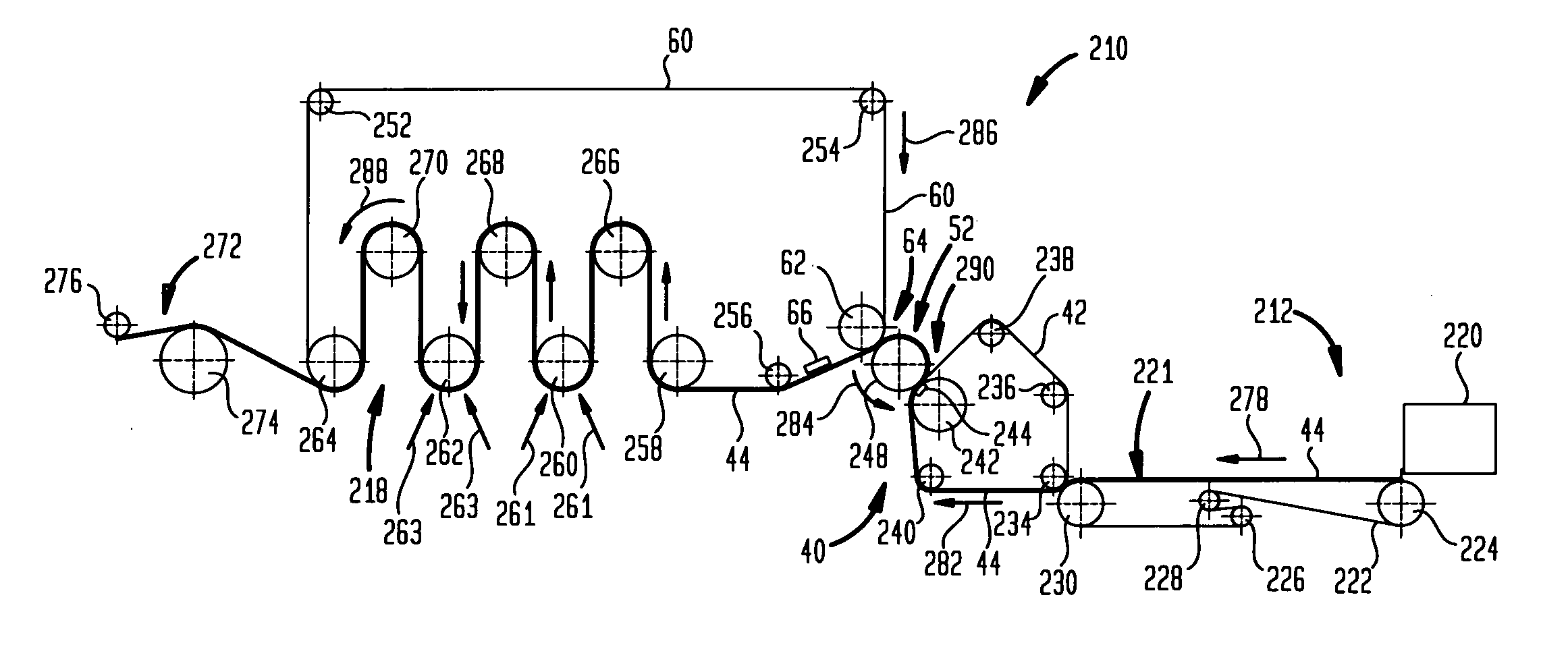
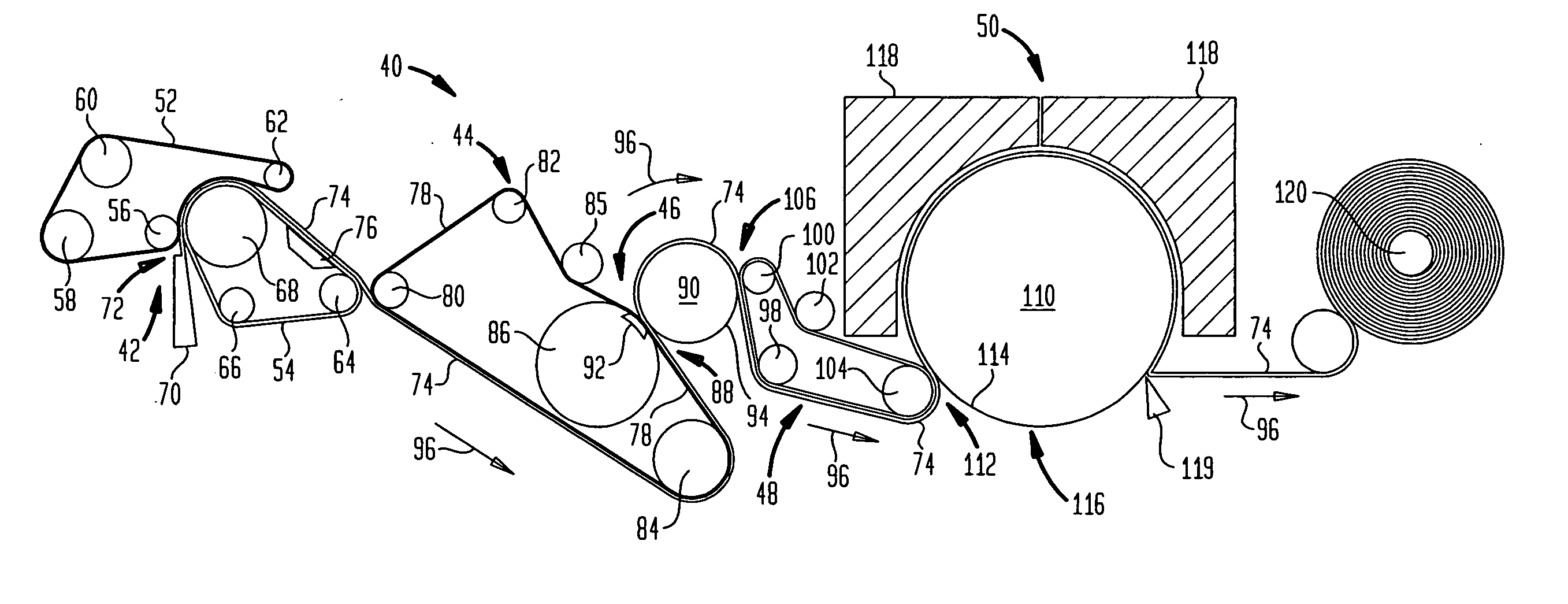
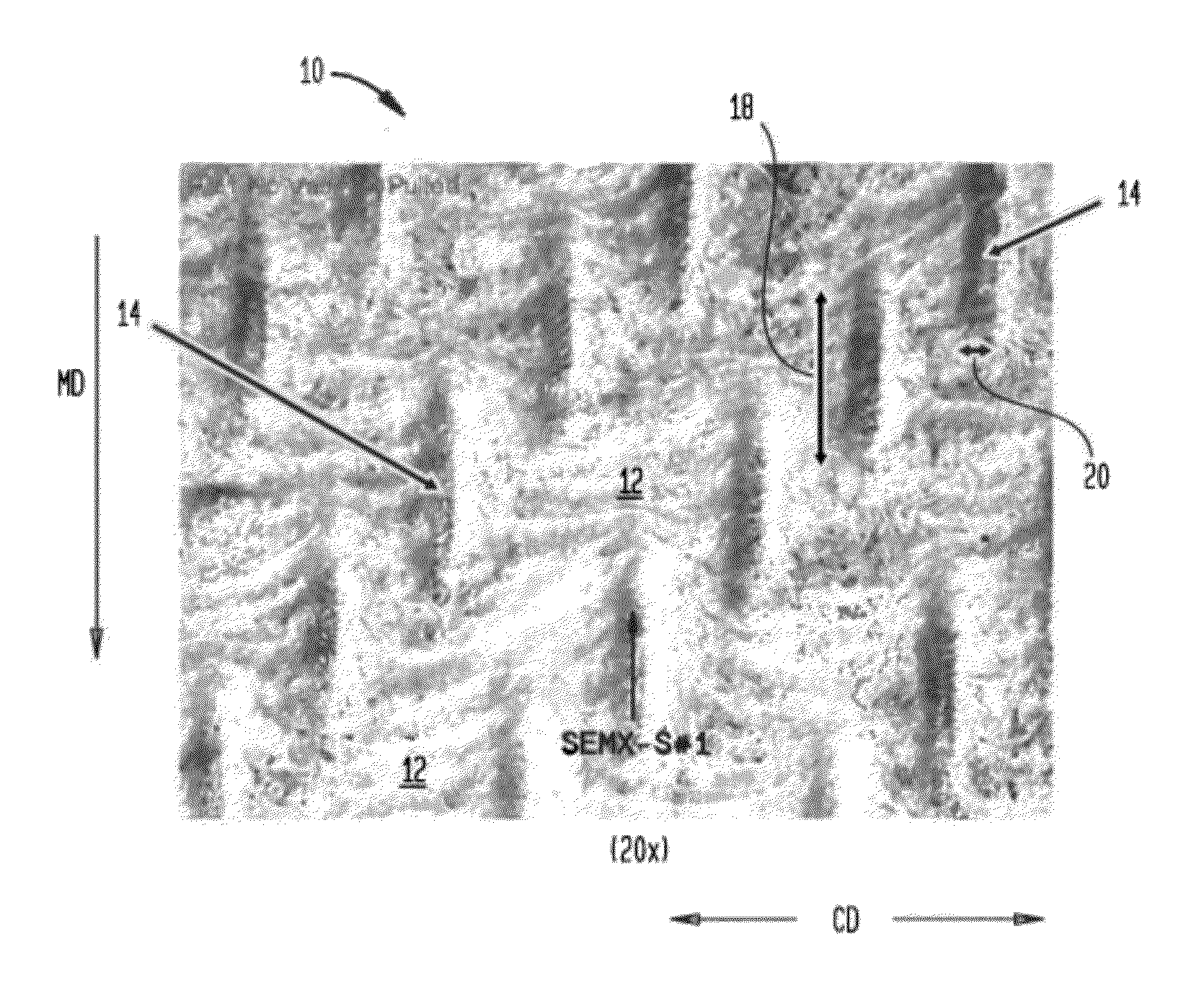
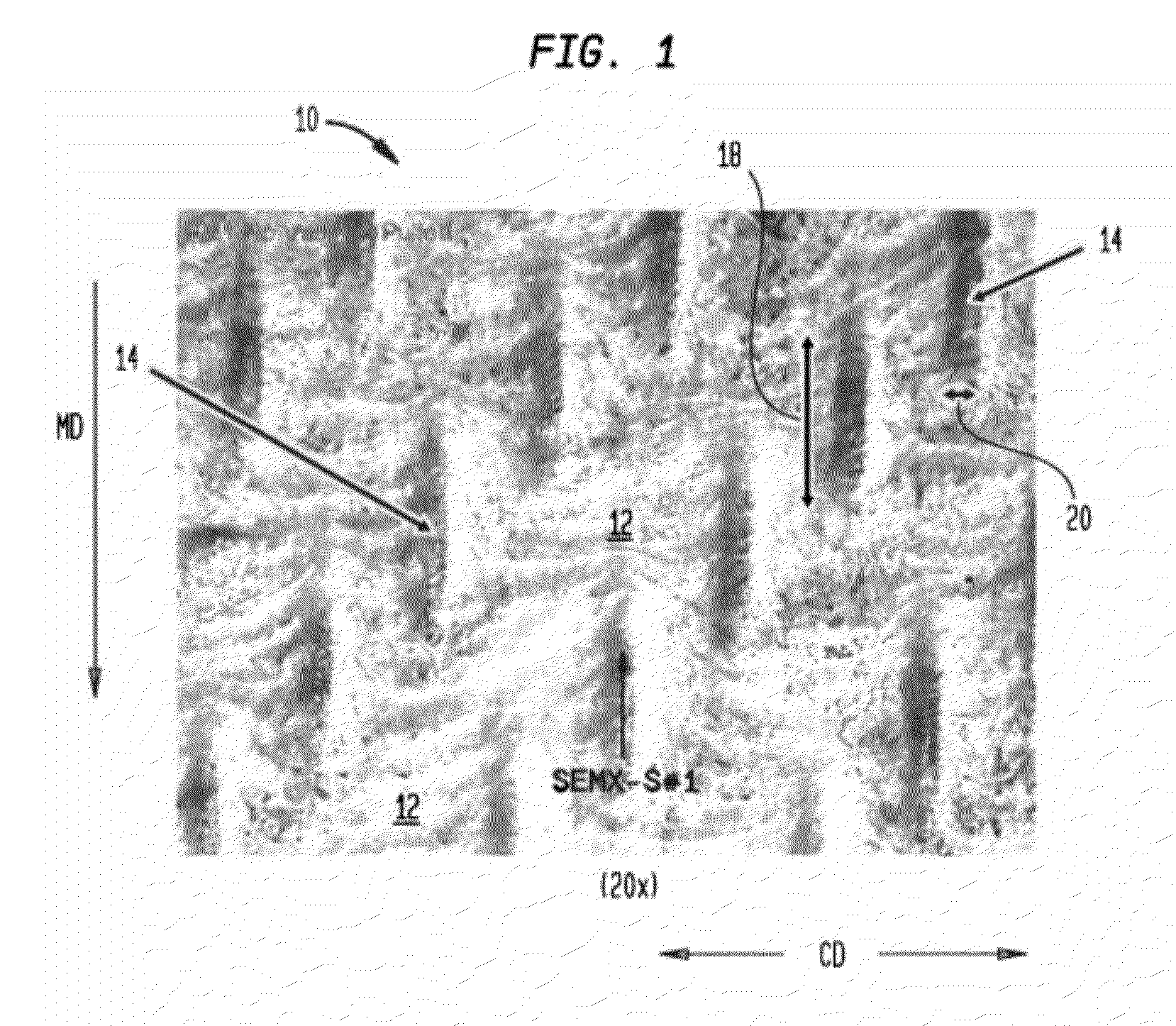
Fabric crepe/draw process for producing absorbent sheet
ActiveUS20050217814A1Increase in sizeDecrease sidednessMechanical working/deformationPaper coatingFiberPapermaking
A method of making a fabric-creped absorbent cellulosic sheet comprising: a) compactively dewatering a papermaking furnish to form a nascent web having an apparently random distribution of papermaking fiber; b) applying the dewatered web having the apparently random fiber distribution to a translating transfer surface moving at a first speed; c) fabric-creping the web from the transfer surface at a consistency of from about 30 to about 60 percent utilizing a patterned creping fabric, the creping step occurring under pressure in a fabric creping nip defined between the transfer surface and the creping fabric wherein the fabric is traveling at a second speed slower than the speed of said transfer surface, the fabric pattern, nip parameters, velocity delta and web consistency being selected such that the web is creped from the transfer surface and redistributed on the creping fabric to form a web with a drawable reticulum.
Owner:GPCP IP HLDG LLC
Fabric crepe/draw process for producing absorbent sheet
ActiveUS7789995B2Increase in sizeDecrease sidednessMechanical working/deformationPaper coatingCelluloseFiber
A method of making a fabric-creped absorbent cellulosic sheet comprising: a) compactively dewatering a papermaking furnish to form a nascent web having an apparently random distribution of papermaking fiber; b) applying the dewatered web having the apparently random fiber distribution to a translating transfer surface moving at a first speed; c) fabric-creping the web from the transfer surface at a consistency of from about 30 to about 60 percent utilizing a patterned creping fabric, the creping step occurring under pressure in a fabric creping nip defined between the transfer surface and the creping fabric wherein the fabric is traveling at a second speed slower than the speed of said transfer surface, the fabric pattern, nip parameters, velocity delta and web consistency being selected such that the web is creped from the transfer surface and redistributed on the creping fabric to form a web with a drawable reticulum.
Owner:GPCP IP HLDG LLC
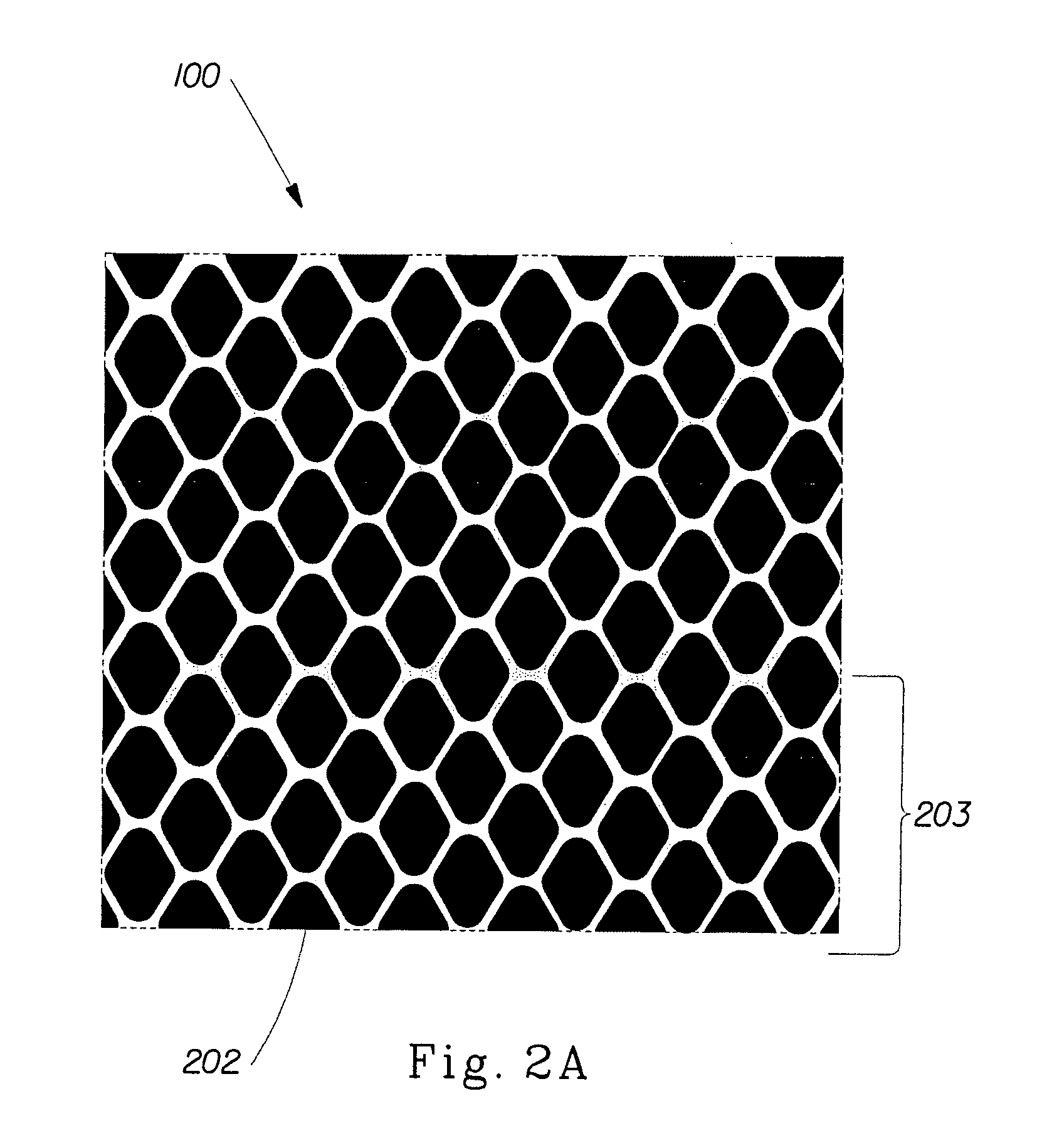
Embossed multi-ply fibrous structure product
A multi-ply fibrous structure product having two or more plies of fibrous structure where at least one of the plies has a plurality of domes formed during the papermaking process and there are from about 10 to about 1000 domes per square inch of the product. At least one of the plies of the multi-ply fibrous structure has a plurality of embossments thereon with a total embossment area of from about 3% to about 15%. The embossments may be arranged such that they define non-geometric foreground patterns of unembossed cells.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Absorbent sheet having regenerated cellulose microfiber network
ActiveUS20070224419A1High wet/dry tensile ratioImprove consistencyNon-fibrous pulp additionPaper after-treatmentPolymer sciencePapermaking
An absorbent paper sheet for tissue or towel includes from about 99 percent to about 70 percent by weight of cellulosic papermaking fiber and from about 1 percent to about 30 percent by weight fibrillated regenerated cellulose microfiber which was regenerated form a cellulosic dope utilizing a tertiary amine N-oxide solvent or an ionic liquid. Fibrillation of the microfiber is controlled such that it has a reduced coarseness and a reduced freeness as compared with unfibrillated regenerated cellulose microfiber from which it is made and provides at least one of the following attributes to the absorbent sheet: (a) the absorbent sheet exhibits an elevated SAT value and an elevated wet tensile value as compared with a like sheet prepared without fibrillated regenerated cellulose microfiber; (b) the absorbent sheet exhibits an elevated wet / dry CD tensile ratio as compared with a like sheet prepared without fibrillated regenerated cellulose microfiber; (c) the absorbent sheet exhibits a lower GM Break Modulus than a like sheet having like tensile values prepared without fibrillated regenerated cellulose microfiber; or (d) the absorbent sheet exhibits an elevated bulk as compared with a like sheet having like tensile values prepared without fibrillated regenerated cellulose microfiber. In some embodiments, the pulp is pre-treated with debonder to enhance the wet / dry CD tensile ratio of the sheet.
Owner:GPCP IP HLDG LLC
Method for reducing the polymer and bentonite requirement in papermaking
The present invention relates to a method for reducing the polymer and bentonite requirement in papermaking wherein medium and high molecular weight polymers are reacted with bentonite. Further, mechanical shearing of the furnish after polymer addition is not required.
Owner:BASF CORP
Continuous manufacture of superabsorbent/ion exchange sheet material
InactiveUS20020007166A1Increase in sizeNon-fibrous pulp additionWood working apparatusPapermakingIon exchange
A continuous sheet having a combination of acidic and basic water-absorbing resin particles that are essentially not neutralized and can be continuously manufactured on conventional papermaking apparatus, using a wet, dry, or wet-dry process to manufacture a water-absorbent sheet-like substrate containing 50%-100% by weight of the combination of acidic and basic water-absorbent particles. The acidic and basic essentially unneutralized resins can be contained in the sheet material articles of the present invention as separate acidic and basic resin particles, or as multicomponent particles containing both the acidic and basic resins. The sheet materials can be manufactured having new and unexpected structural integrity, with little or no shakeout or loss of superabsorbent particles during or after manufacture while exhibiting exceptional water absorption and retention properties. The sheet materials have an ability to absorb liquids quickly, demonstrate good fluid permeability and conductivity into and through the resin particles, and have a high gel strength such that the hydrogel formed from the SAP particles resists deformation under an applied stress or pressure, when used alone or in a mixture with other water-absorbing resins.
Owner:BASF AG
Absorbent sheet having regenerated cellulose microfiber network
An absorbent paper sheet for tissue or towel includes from about 99 percent to about 70 percent by weight of cellulosic papermaking fiber and from about 1 percent to about 30 percent by weight fibrillated regenerated cellulose microfiber which was regenerated form a cellulosic dope utilizing a tertiary amine N-oxide solvent or an ionic liquid. Fibrillation of the microfiber is controlled such that it has a reduced coarseness and a reduced freeness as compared with unfibrillated regenerated cellulose microfiber from which it is made and provides at least one of the following attributes to the absorbent sheet: (a) the absorbent sheet exhibits an elevated SAT value and an elevated wet tensile value as compared with a like sheet prepared without fibrillated regenerated cellulose microfiber; (b) the absorbent sheet exhibits an elevated wet / dry CD tensile ratio as compared with a like sheet prepared without fibrillated regenerated cellulose microfiber; (c) the absorbent sheet exhibits a lower GM Break Modulus than a like sheet having like tensile values prepared without fibrillated regenerated cellulose microfiber; or (d) the absorbent sheet exhibits an elevated bulk as compared with a like sheet having like tensile values prepared without fibrillated regenerated cellulose microfiber. In some embodiments, the pulp is pre-treated with debonder to enhance the wet / dry CD tensile ratio of the sheet.
Owner:GPCP IP HLDG LLC
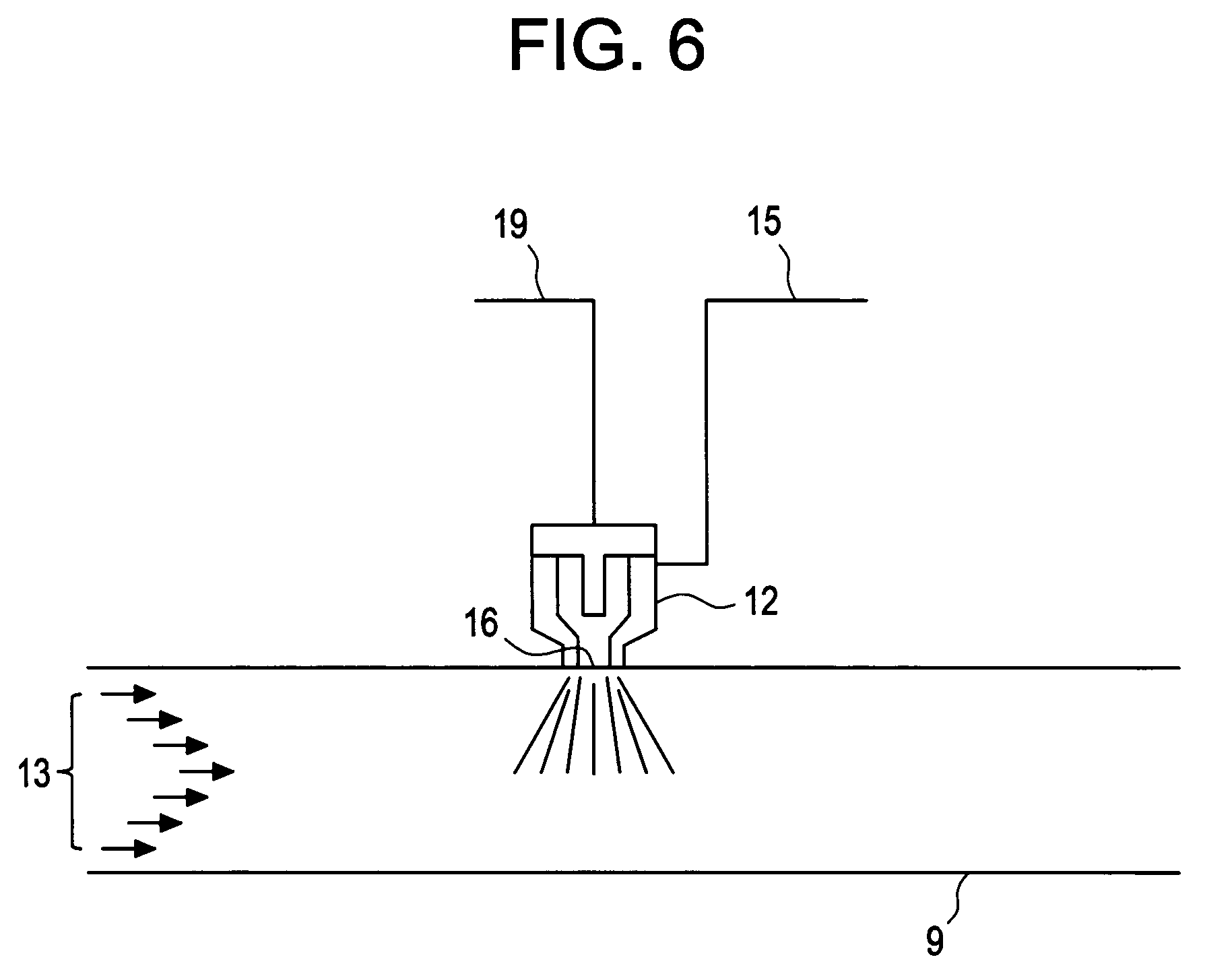
Method and arrangement for feeding chemicals into a process stream
An apparatus for feeding one or more chemicals into a process stream of a papermaking process is disclosed, as well as a method of utilizing the apparatus for feeding one or more chemicals into a process stream is disclosed.
Owner:ECOLAB USA INC
Process for making abrasion resistant paper and paper and paper products made by the process
InactiveUS20050155731A1Improve optical brightnessLow friction surfacePaper after-treatmentPaper coatingPapermakingPaper sheet
In this papermaking process, a first strength agent is added to a stock suspension containing pulp and optionally other additives prior to its being formed into a web at the wet end of a papermaking machine. The web is then formed and processed into paper. A second strength agent is then applied to the surface of the paper. The strength agents may be selected to have opposite charge.
Owner:NAT GYPSUM PROPERTIES
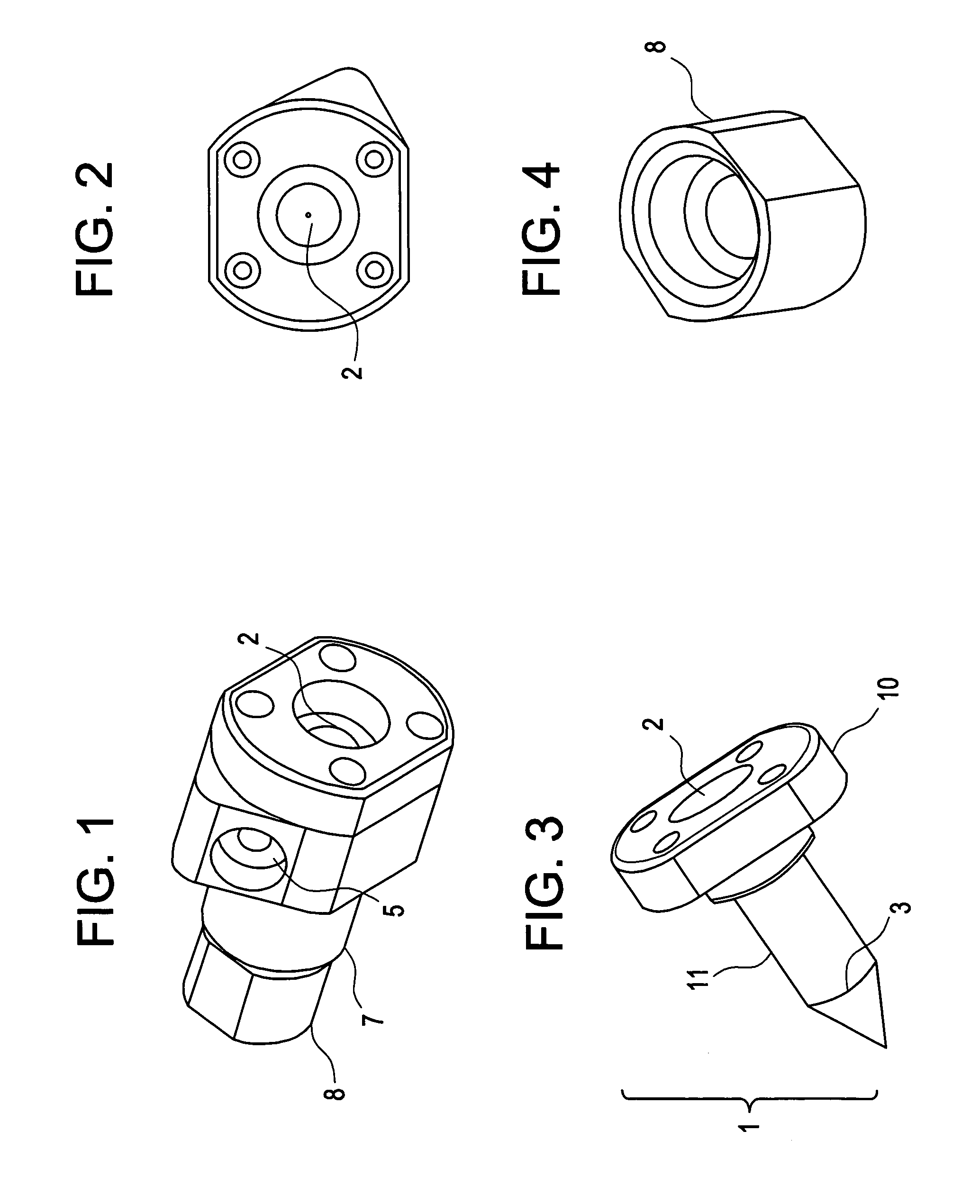
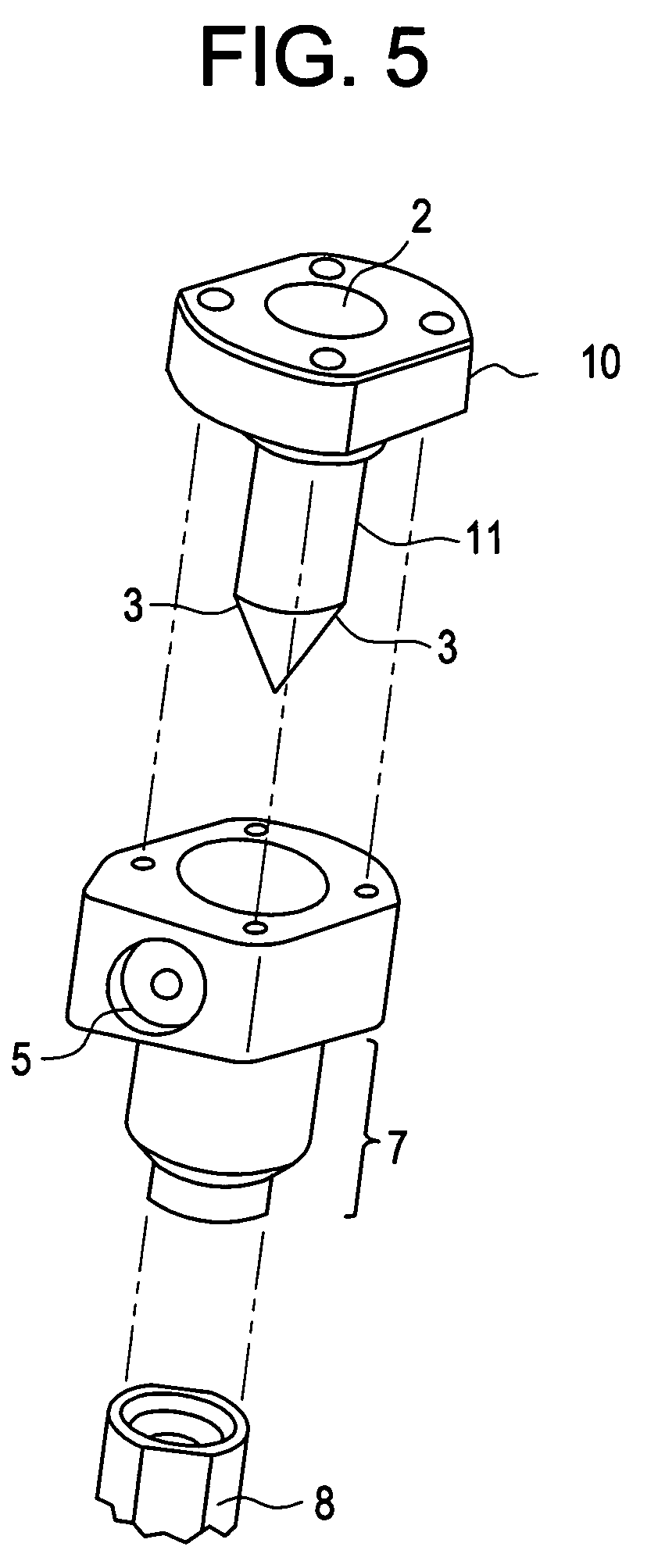
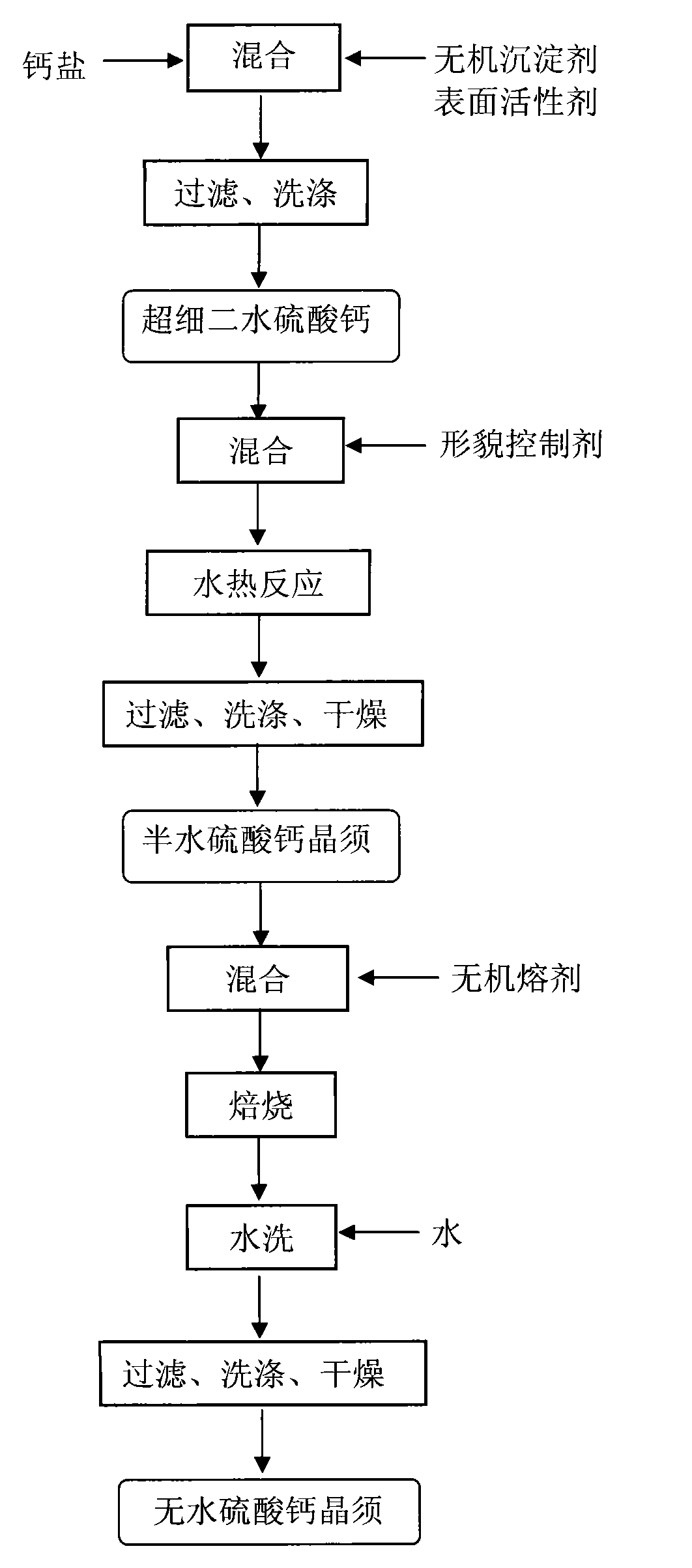
Preparation method of high length-diameter ratio anhydrous calcium sulfate whisker
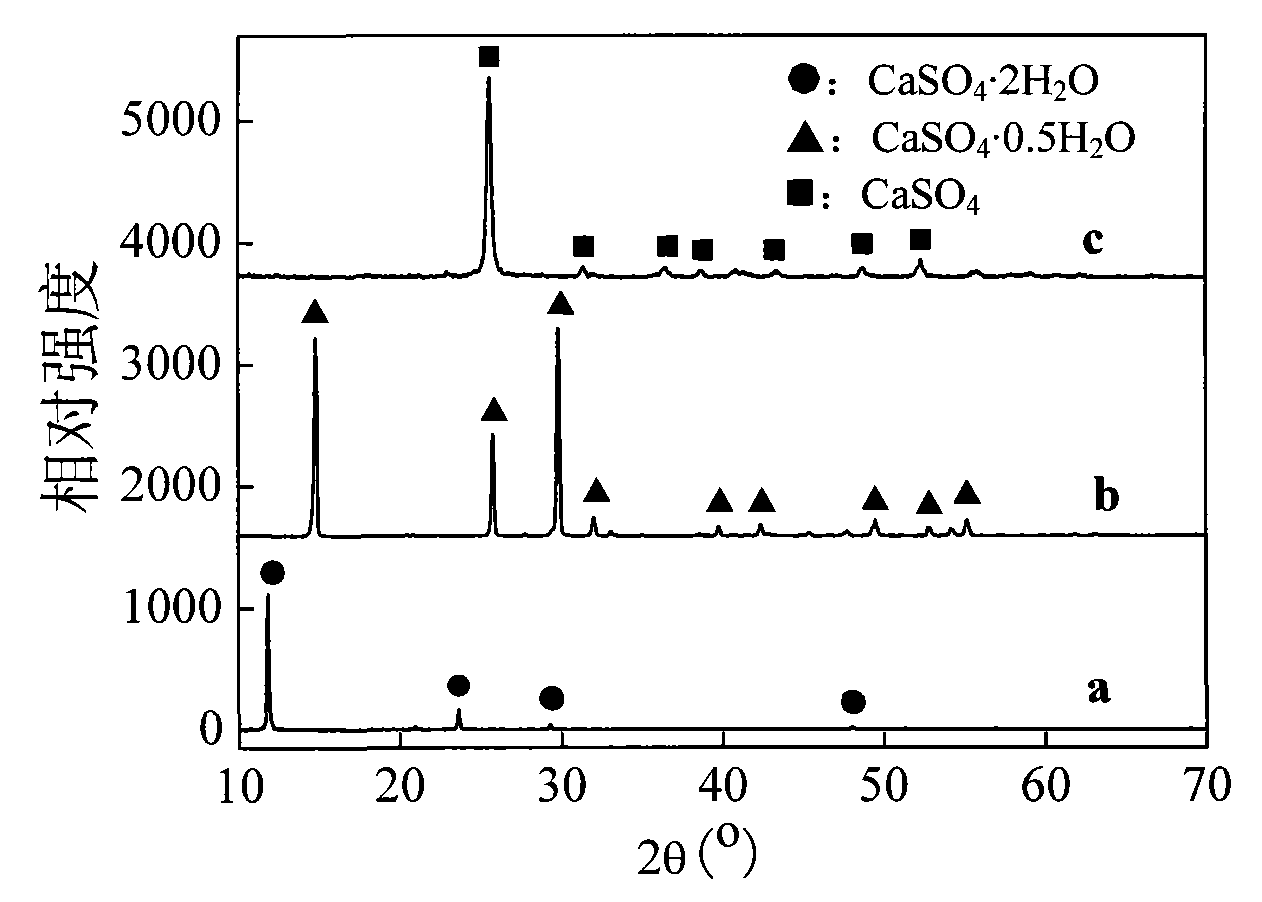
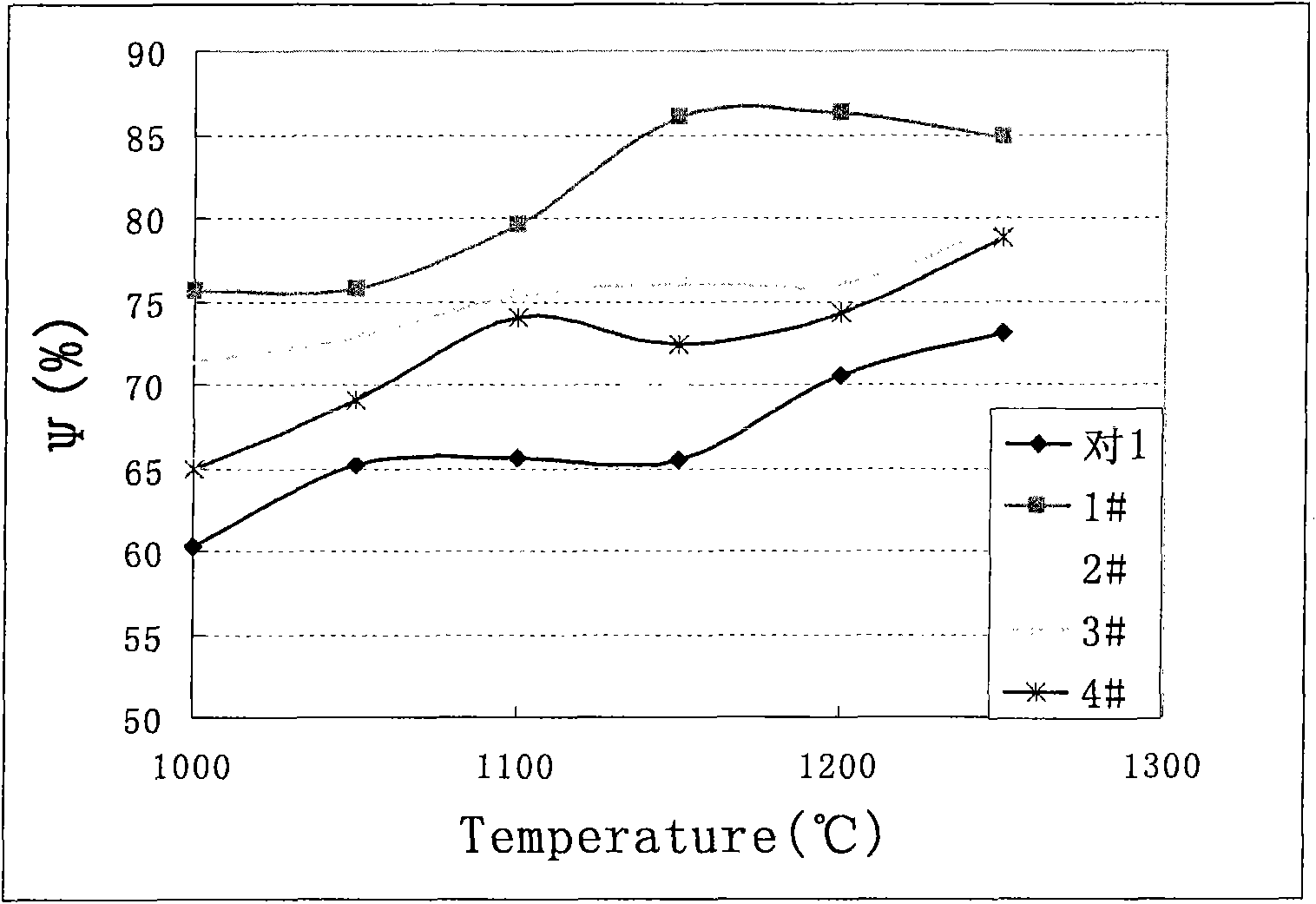
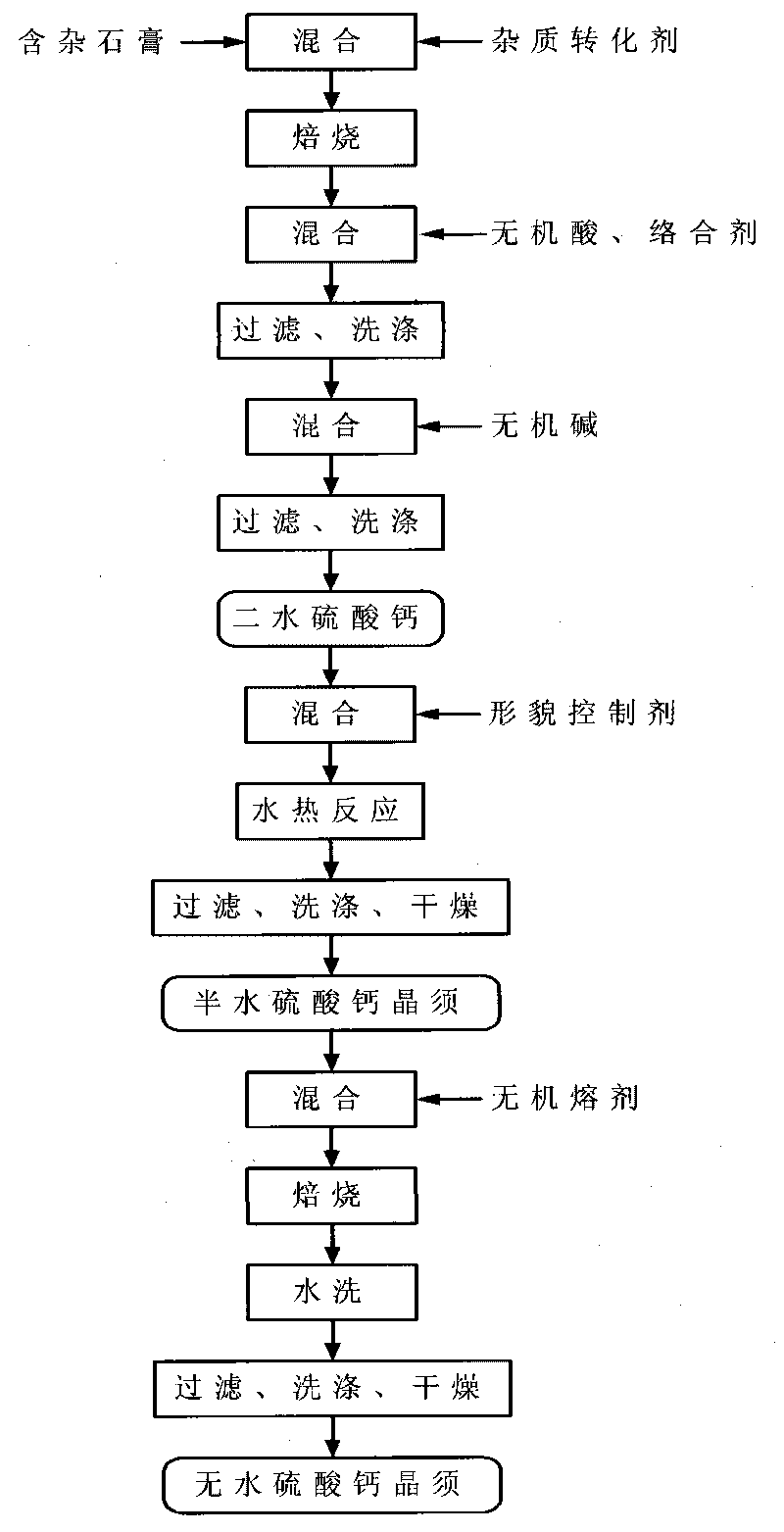
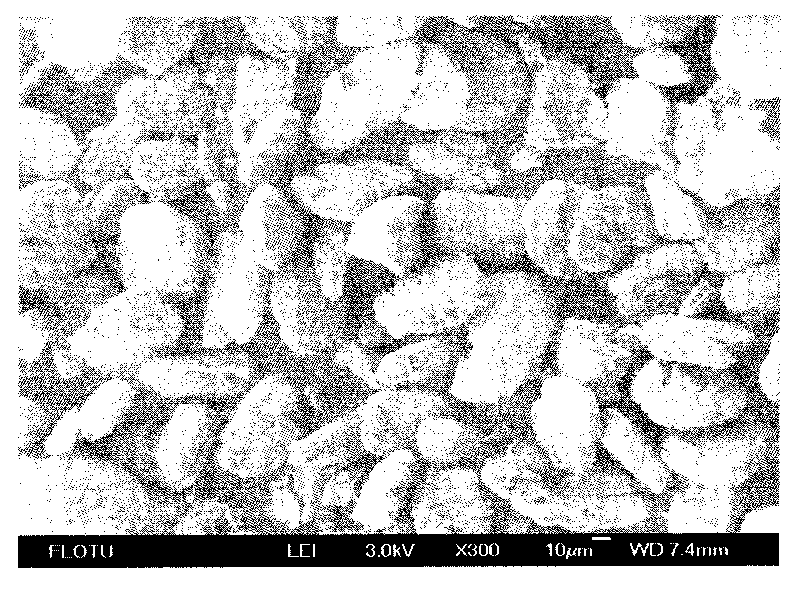
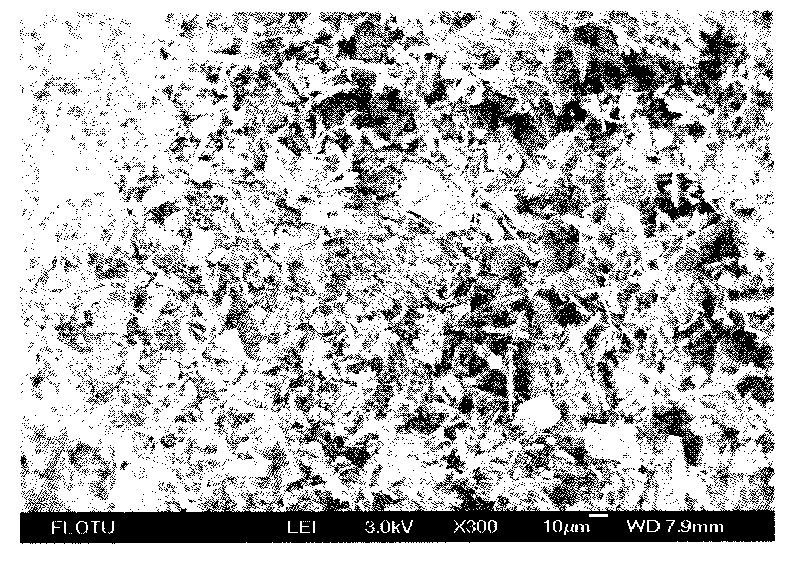
ActiveCN101671848AHigh crystallinityMorphological rulesPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsAnhydrous Calcium SulfatePapermaking
A preparation method of high length-diameter ratio anhydrous calcium sulfate whisker belongs to the technical field of inorganic chemical material preparation. The method takes inorganic calcium saltand inorganic precipitant as raw materials and surfactant as dispersant, and includes the following steps: first preparing superfine calcium sulphate dihydrate precursor with good dispersion at the temperature of 10-90 DEG C; then adding the precursor into water solution containing shape control agent to conduct hydrothermal reaction for 0.5-10h at the temperature of 100-250 DEG C, and obtaining calcium sulfate hemihydrate whisker; mixing the calcium sulfate hemihydrate whisker with inorganic solvent; and roasting the mixture for 0.5-6h at the temperature 200-800 DEG C to obtain anhydrous calcium sulfate whisker with the length of 20-2000mum, the diameter of 0.5-20mum, the length-diameter ratio of 40-1000 and the main content greater than 95wt% after washing and drying. The technology is simple, the cost is low and the added value of the product is high. The prepared calcium sulfate whisker has large length-diameter ratio and regular shape and can be used as reinforcing material to beapplied in industries such as plastics, rubber, ceramics, cement, papermaking and the like.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
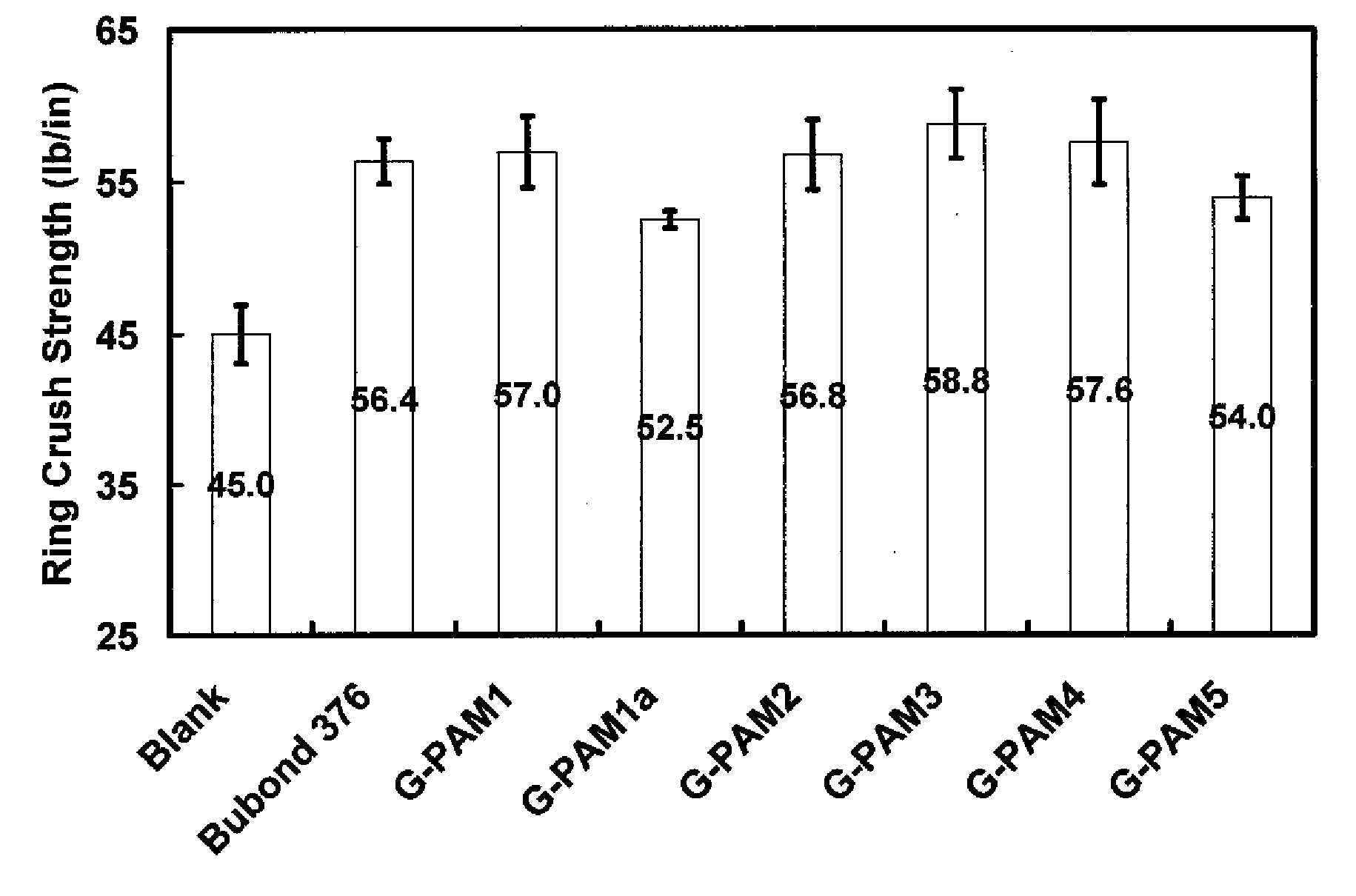
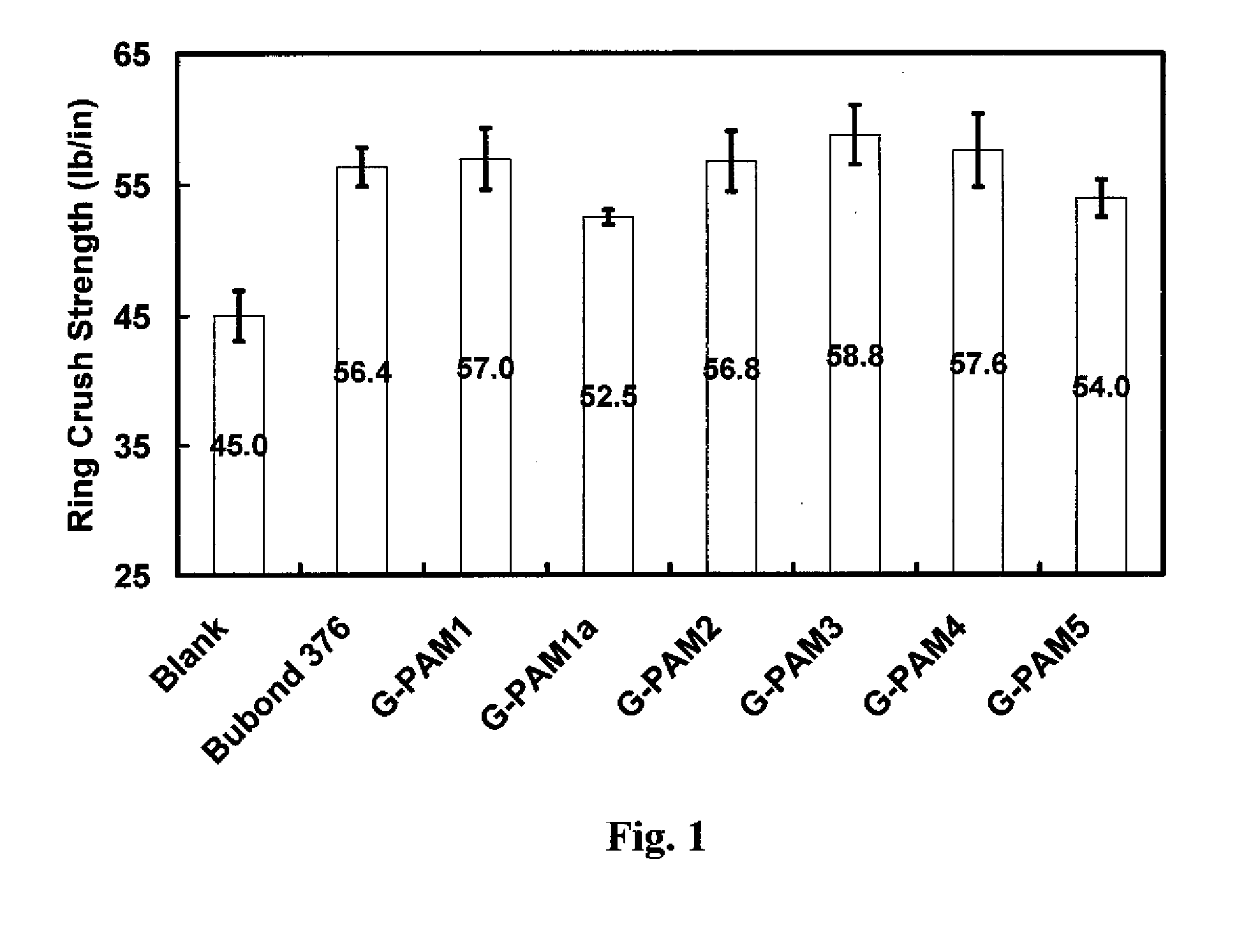
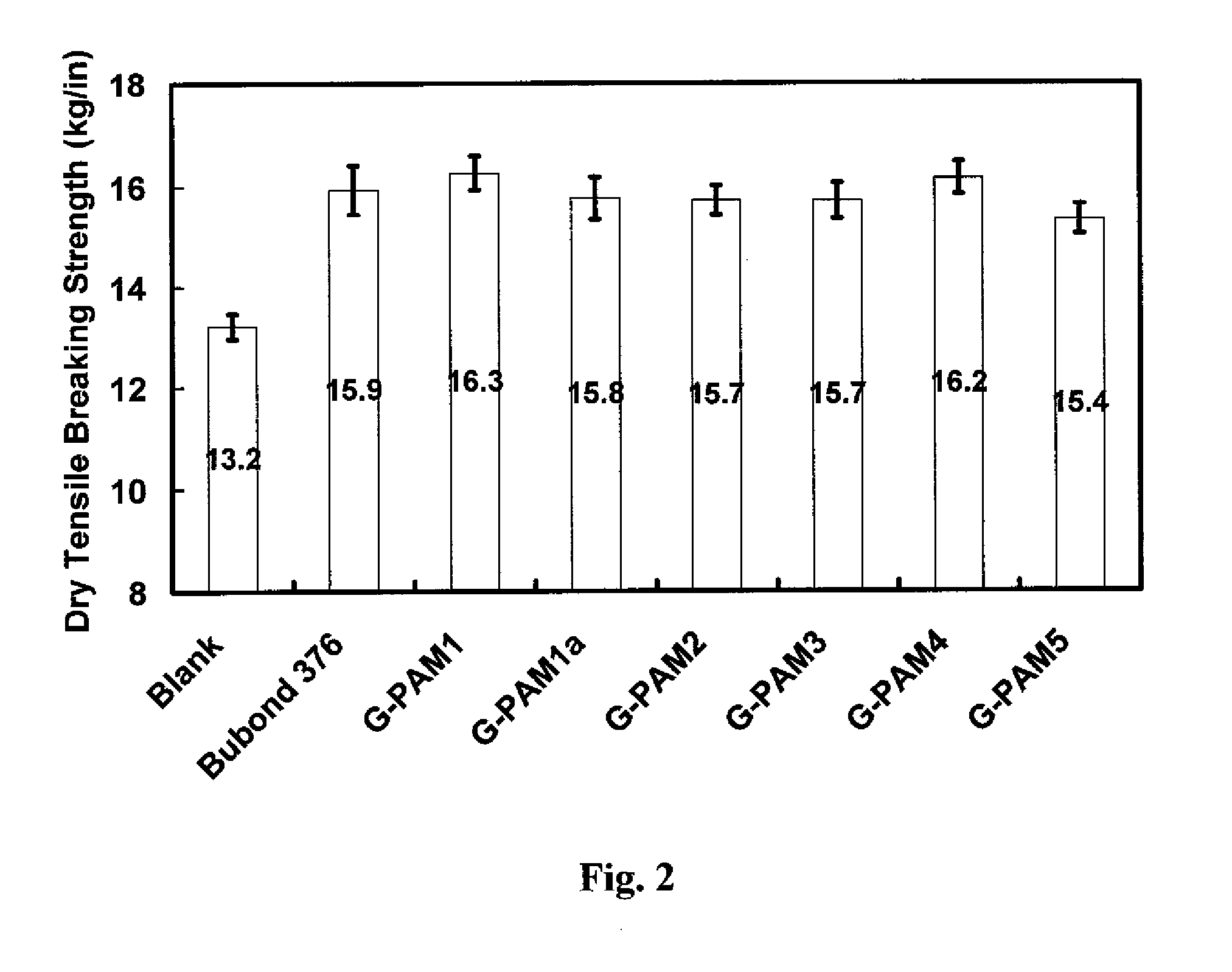
High Solids Glyoxalated Polyacrylamide
ActiveUS20080308242A1High solids glyoxalatedHigh strengthNatural cellulose pulp/paperSpecial paperPapermakingWet strength
Storage-stable glyoxalated polyacrylamide polymers and high solids aqueous compositions formulated with them are described. These glyoxalated polyacrylamide compositions can be used as additives for papermaking, providing paper with good dry and temporary wet strength, and increasing papermaking de-watering rates.
Owner:BUCKMAN LAB INT INC
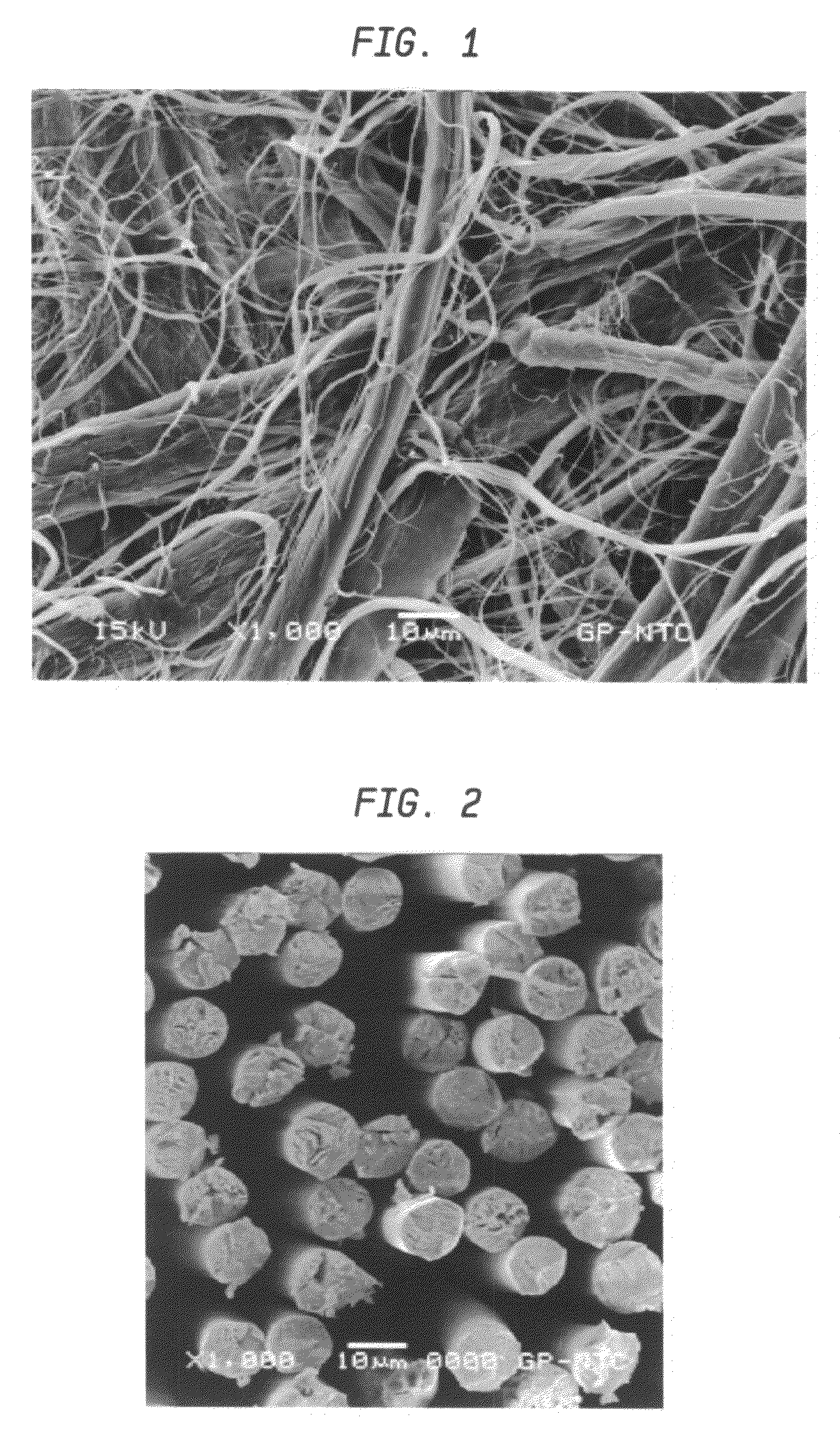
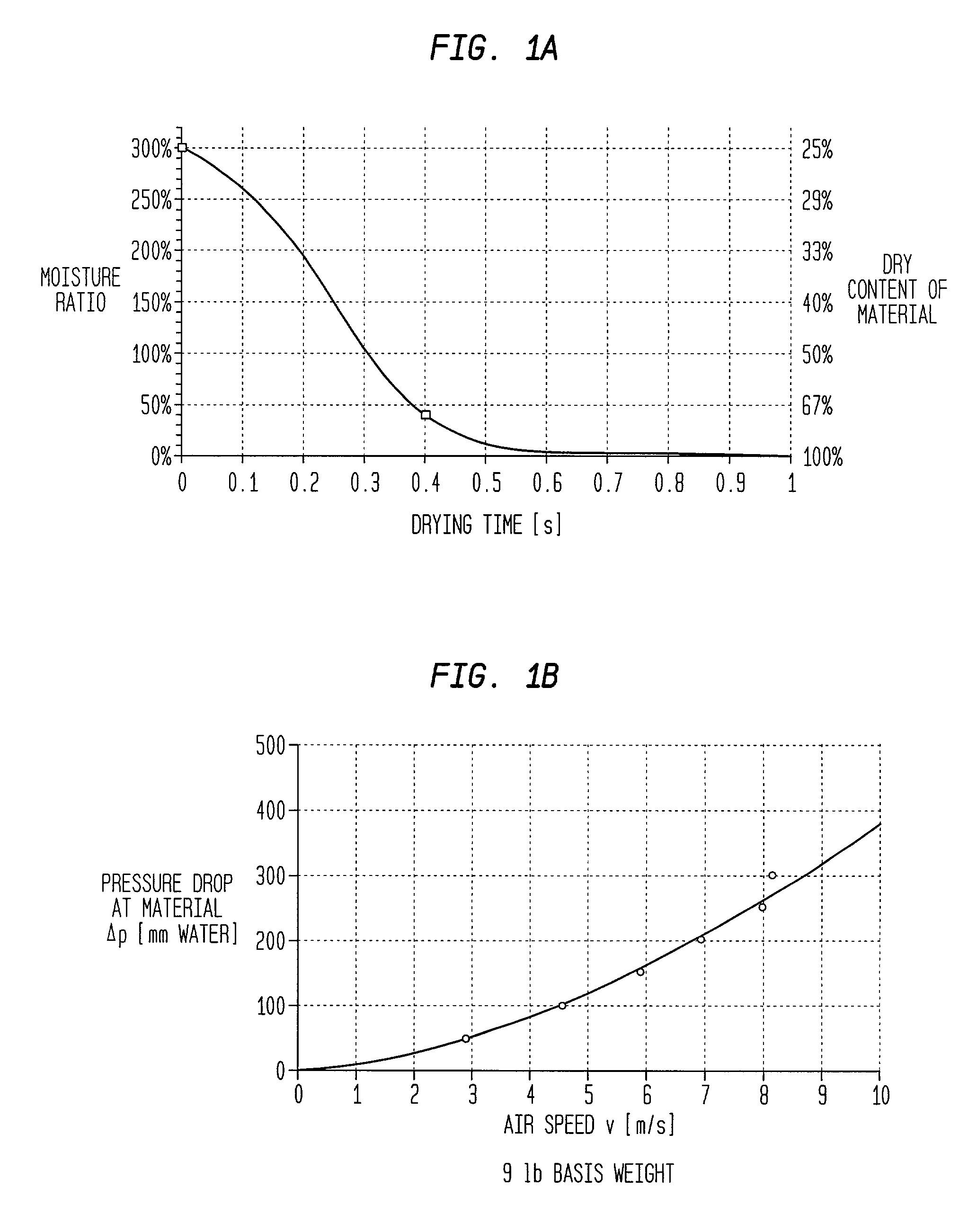
Impingement air dry process for making absorbent sheet
InactiveUS20020088577A1Easy to appreciateNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperPolymer sciencePapermaking
A process for making absorbent sheet includes: (a) depositing an aqueous furnish of cellulosic fiber on a forming fabric; (b) dewatering the wet web to a consistency of from about 15 to about 40 percent; (c) transferring the dewatered web from the forming fabric to another fabric traveling at a speed of from about 10 to about 80 percent slower than the forming fabric; (d) wet-shaping the web on an impression fabric whereby the web is macroscopically rearranged to conform to the surface of the impression fabric; and (e) impingement air drying the web. The process is particularly suitable for making high bulk products form difficult to process furnishes such as recycle furnishes and for making high basis weight products without compressive dewatering with a papermaking felt.
Owner:GPCP IP HLDG LLC
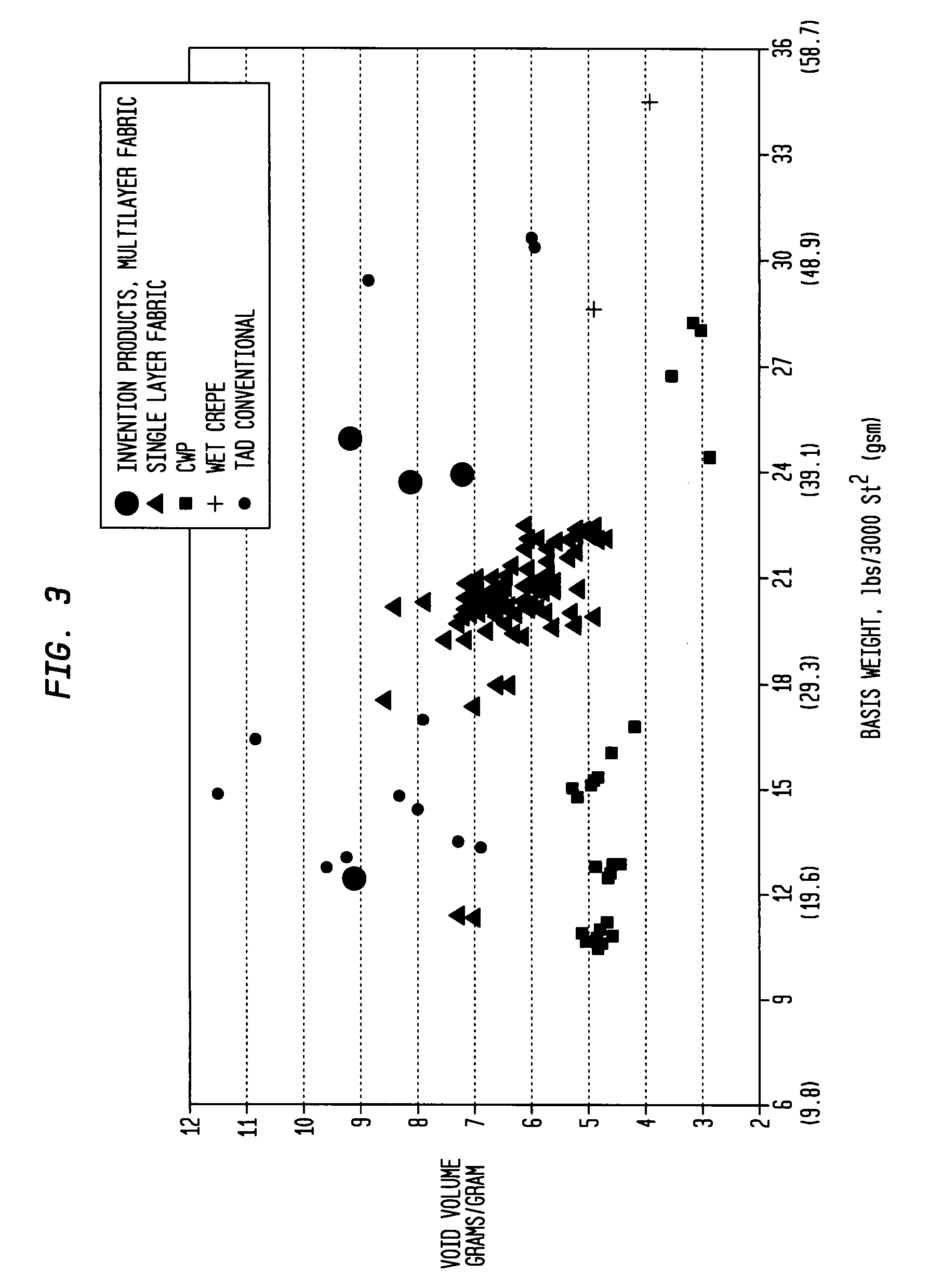
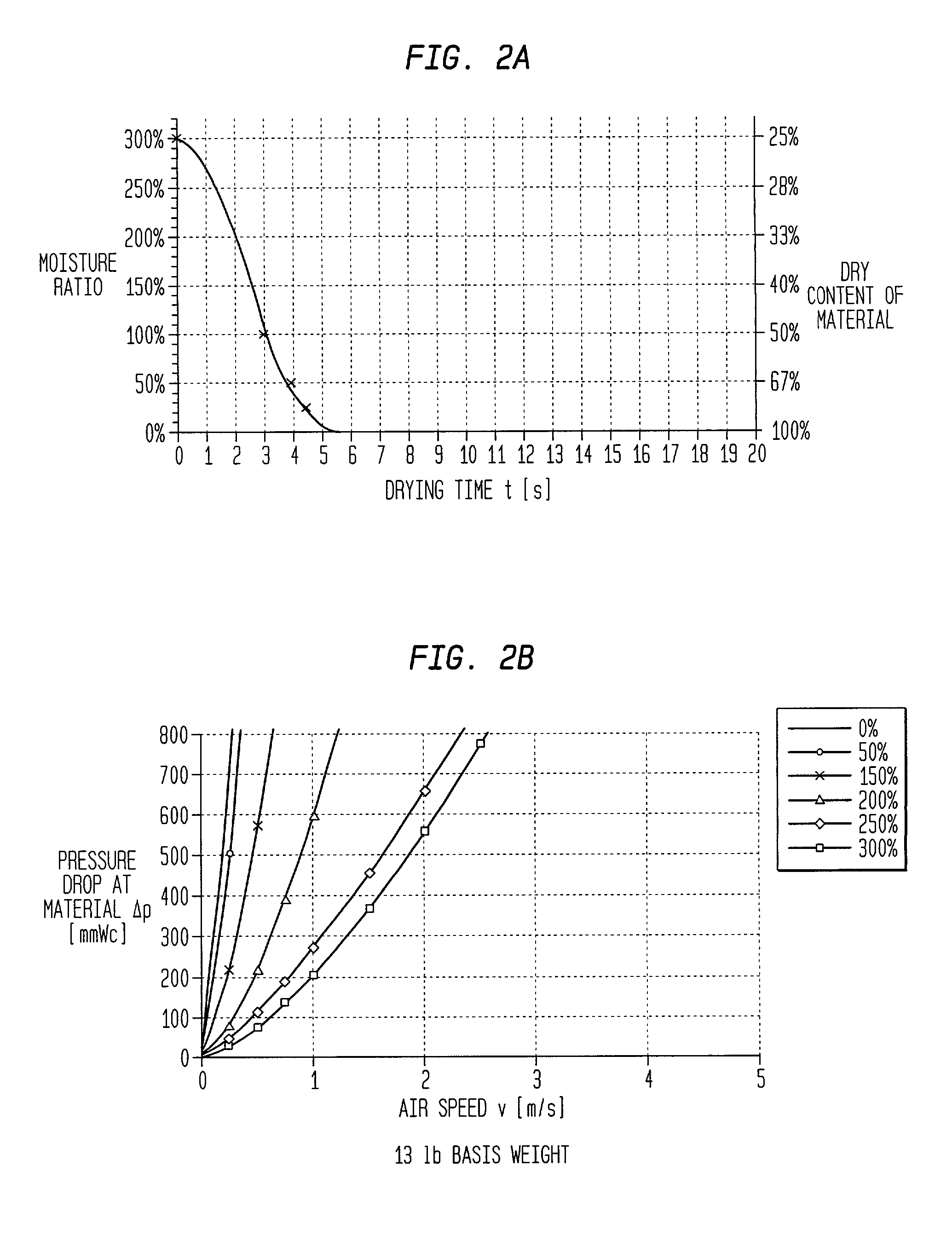
Low compaction, pneumatic dewatering process for producing absorbent sheet
ActiveUS20060000567A1High porosityLarge hydraulic diameterNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperFiberPapermaking
A low-compaction method of making an absorbent cellulosic web includes: forming a nascent web from a papermaking furnish; dewatering the nascent web to a consistency of from about 10 to about 30 percent on a foraminous forming support traveling at a first speed; rush-transferring the web at a consistency of from 10 to about 30 percent to an open texture fabric traveling at a second speed slower than the first speed of the forming support; further dewatering the web on the impression fabric to a consistency of from about 30 to about 60 percent by way of (i) combining the open texture fabric bearing said web with a fluid distribution membrane and an anti-rewet felt as the three pass through a nip into a pressure chamber defined in part by a plurality of nip rolls, the fluid distribution membrane bearing against the side of the open texture fabric away from the web, with the anti-rewet felt bearing against the web, and (ii) applying a pneumatic pressure gradient from the distributor membrane through the web thereby dewatering the web; and drying the web. Preferably the process includes the steps of selecting the papermaking furnish and controlling the process such that the dried web has a void volume fraction of at least 0.7, a hydraulic diameter in the range of from about 3 to about 20 microns and a Wet Springback Ratio of at least about 0.65. Optionally provided is a high solids fabric crepe in a pressure nip.
Owner:GPCP IP HLDG LLC
Method Of Making A Belt-Creped Absorbent Cellulosic Sheet
InactiveUS20120152475A1Improve efficiencyRaise the ratioNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperFiberPapermaking
Owner:GPCP IP HLDG LLC
Continuous manufacture of superabsorbent/ion exchange sheet material
A continuous sheet having a combination of acidic and basic water-absorbing resin particles that are essentially not neutralized and can be continuously manufactured on conventional papermaking apparatus, using a wet, dry, or wet-dry process to manufacture a water-absorbent sheet-like substrate containing 50%-100% by weight of the combination of acidic and basic water-absorbent particles. The acidic and basic essentially unneutralized resins can be contained in the sheet material articles of the present invention as separate acidic and basic resin particles, or as multicomponent particles containing both the acidic and basic resins. The sheet materials can be manufactured having new and unexpected structural integrity, with little or no shakeout or loss of superabsorbent particles during or after manufacture while exhibiting exceptional water absorption and retention properties.
Owner:BASF SE
Low compaction, pneumatic dewatering process for producing absorbent sheet
ActiveUS7416637B2Lower gradeReduce capital investmentNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperFiberPapermaking
A low-compaction method of making an absorbent cellulosic web includes: forming a nascent web from a papermaking furnish; dewatering the nascent web to a consistency of from about 10 to about 30 percent on a foraminous forming support traveling at a first speed; rush-transferring the web at a consistency of from 10 to about 30 percent to an open texture fabric traveling at a second speed slower than the first speed of the forming support; further dewatering the web on the impression fabric to a consistency of from about 30 to about 60 percent by way of (i) combining the open texture fabric bearing said web with a fluid distribution membrane and an anti-rewet felt as the three pass through a nip into a pressure chamber defined in part by a plurality of nip rolls, the fluid distribution membrane bearing against the side of the open texture fabric away from the web, with the anti-rewet felt bearing against the web, and (ii) applying a pneumatic pressure gradient from the distributor membrane through the web thereby dewatering the web; and drying the web. Preferably the process includes the steps of selecting the papermaking furnish and controlling the process such that the dried web has a void volume fraction of at least 0.7, a hydraulic diameter in the range of from about 3 to about 20 microns and a Wet Springback Ratio of at least about 0.65. Optionally provided is a high solids fabric crepe in a pressure nip.
Owner:GPCP IP HLDG LLC
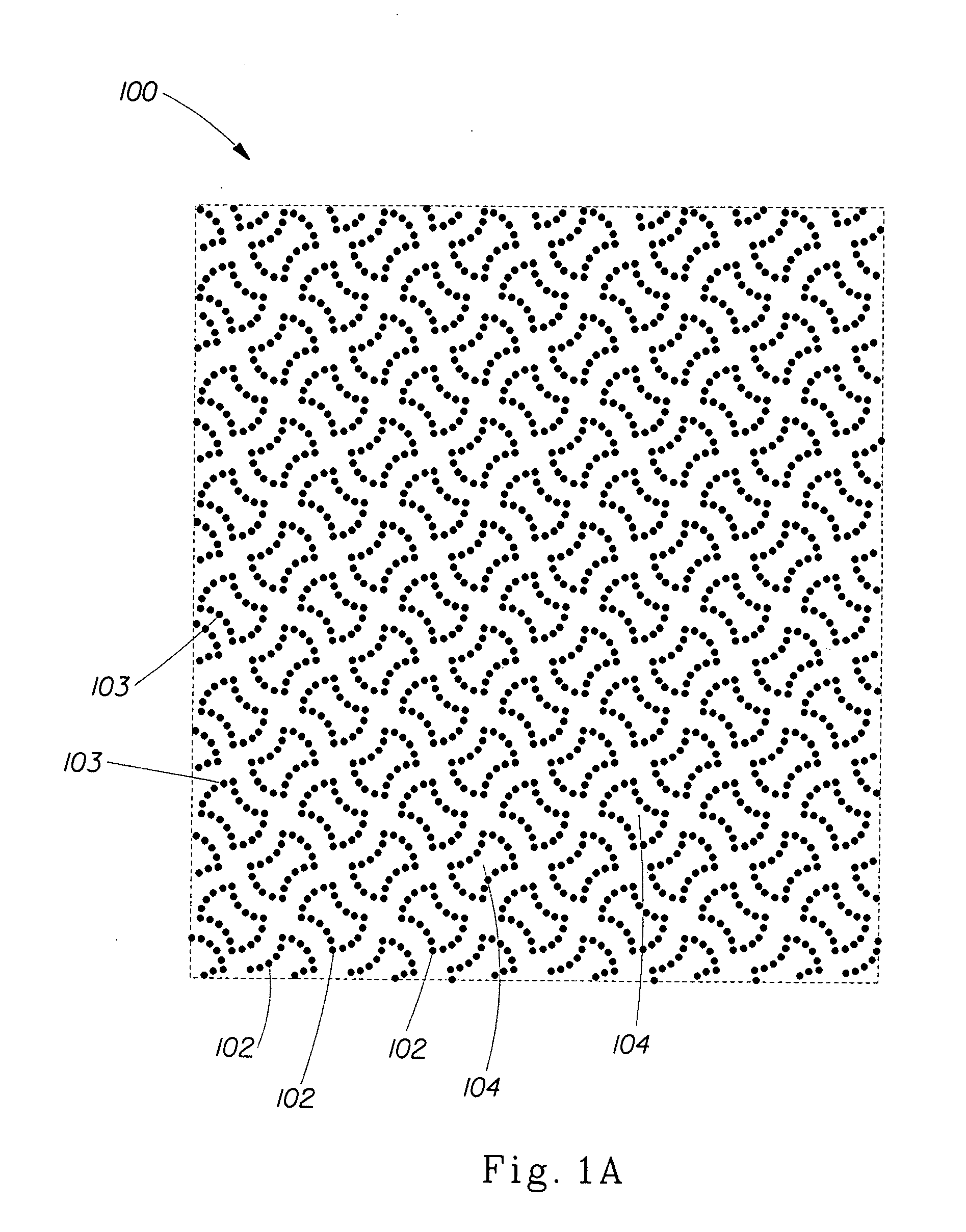
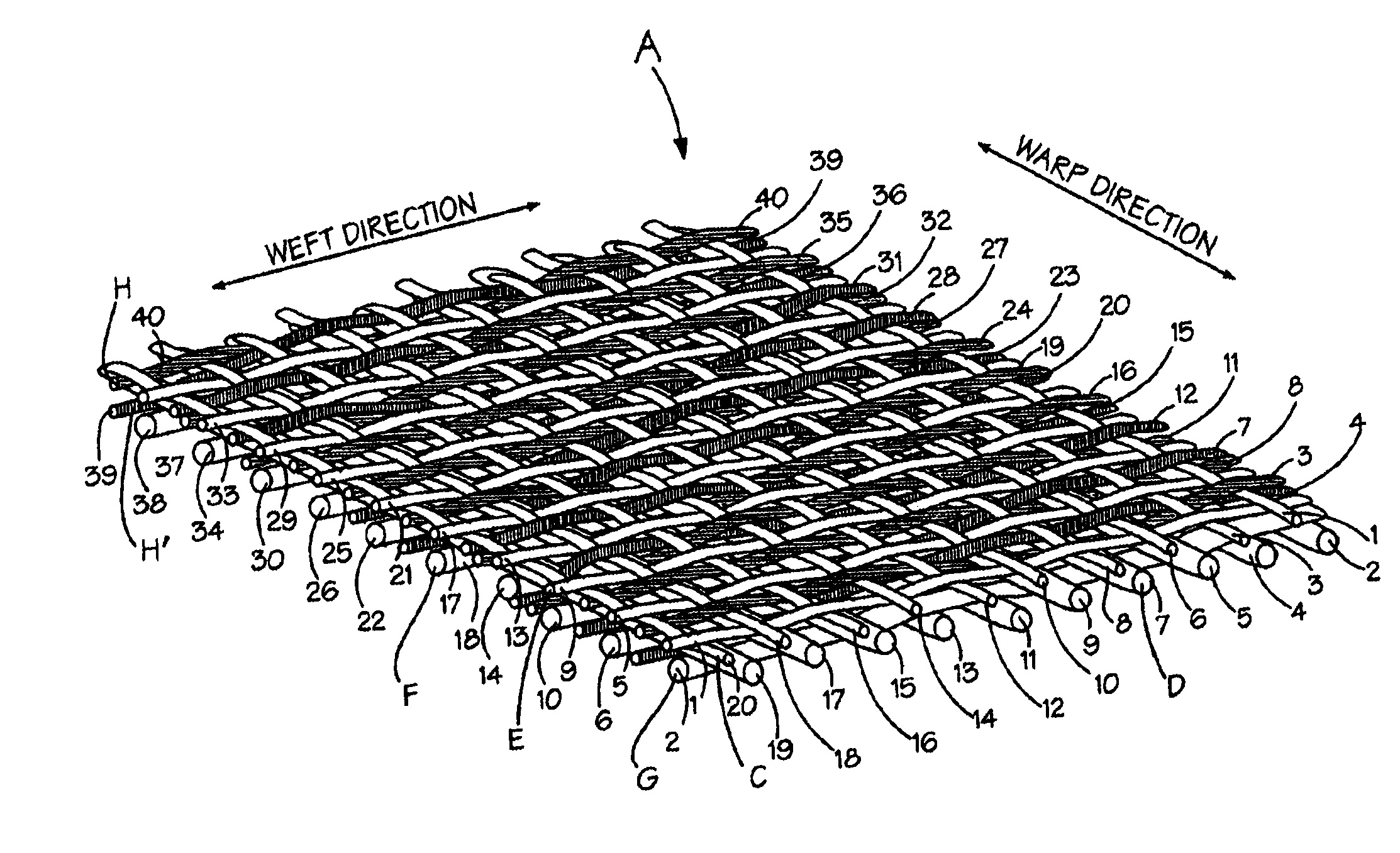
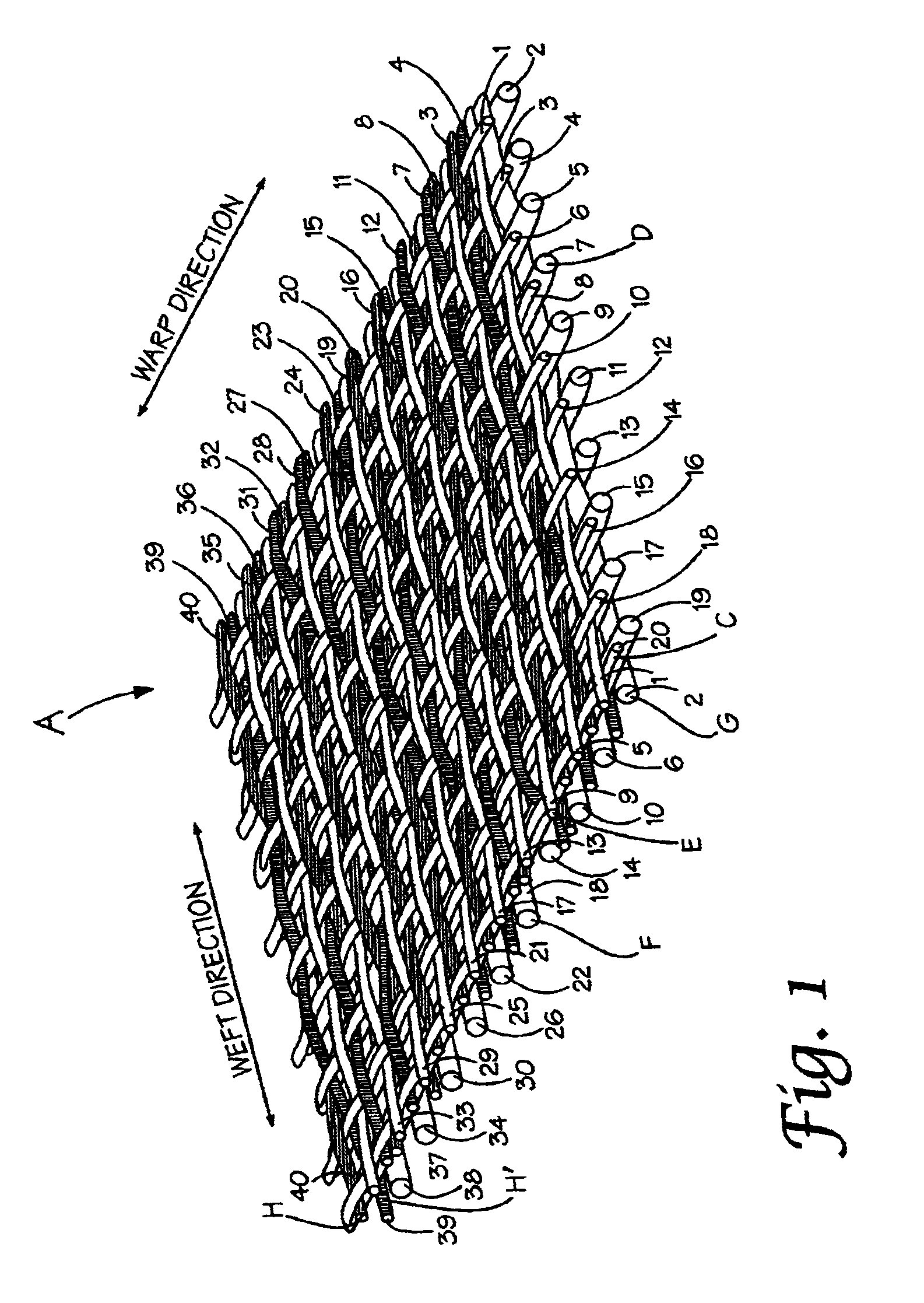
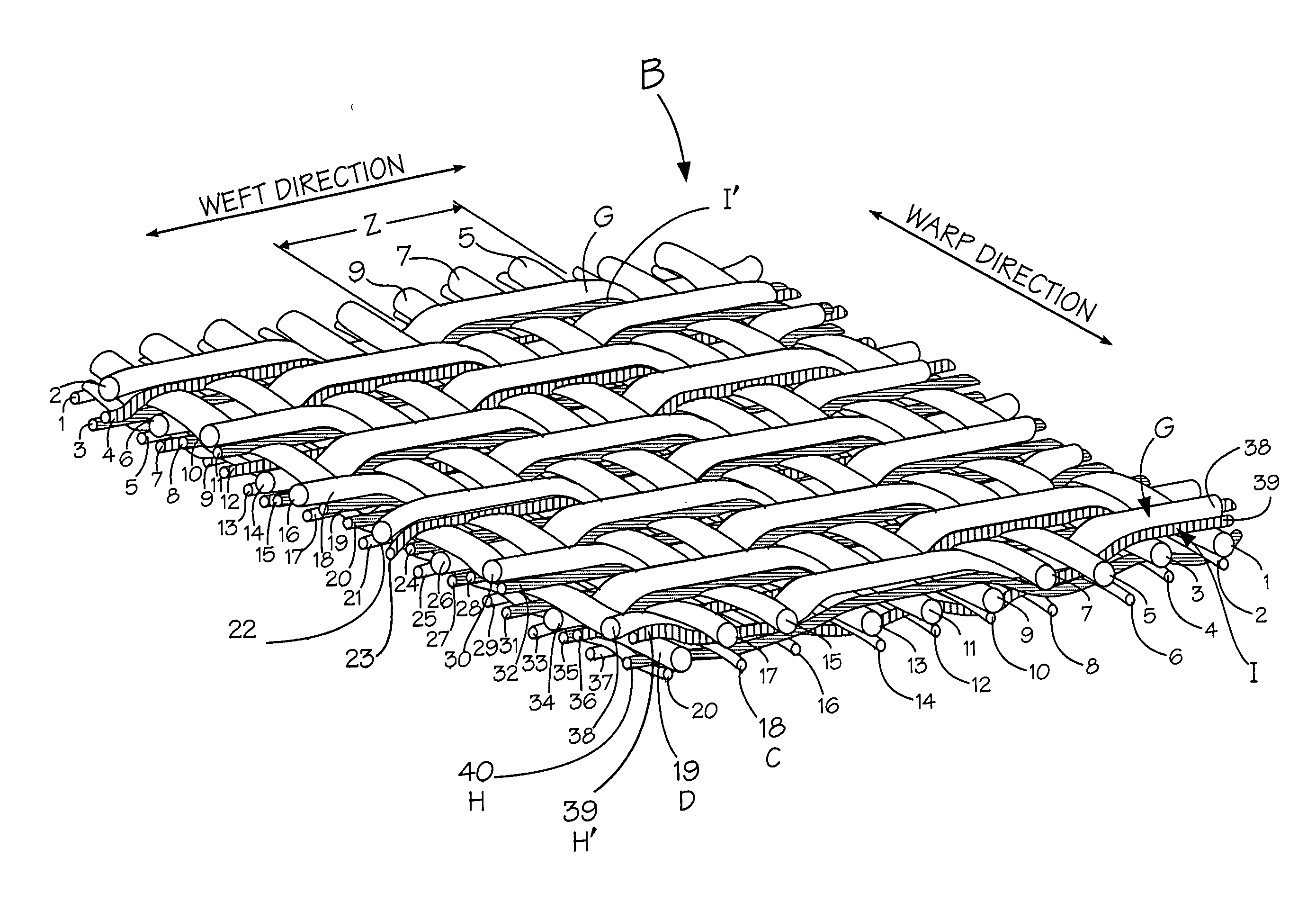
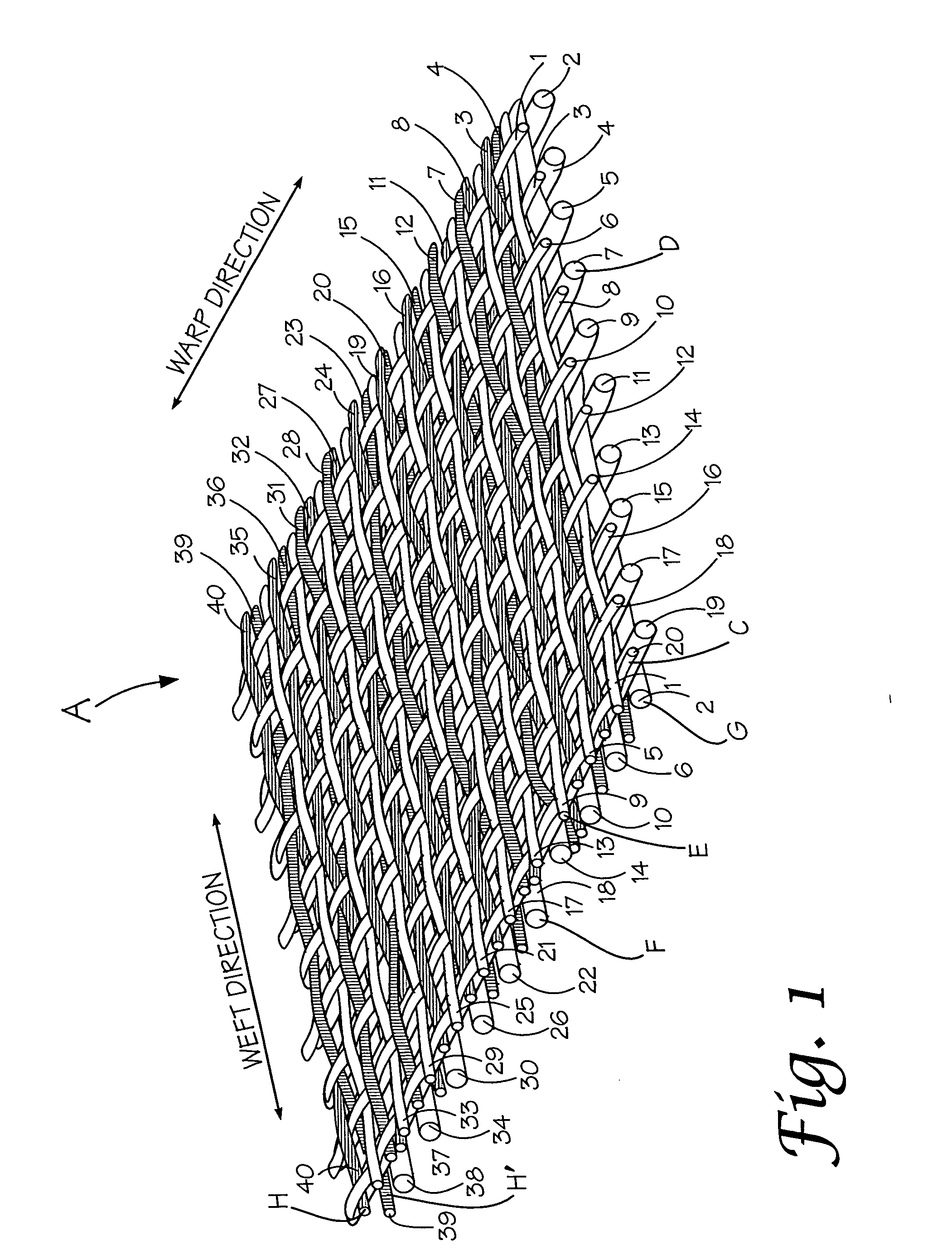
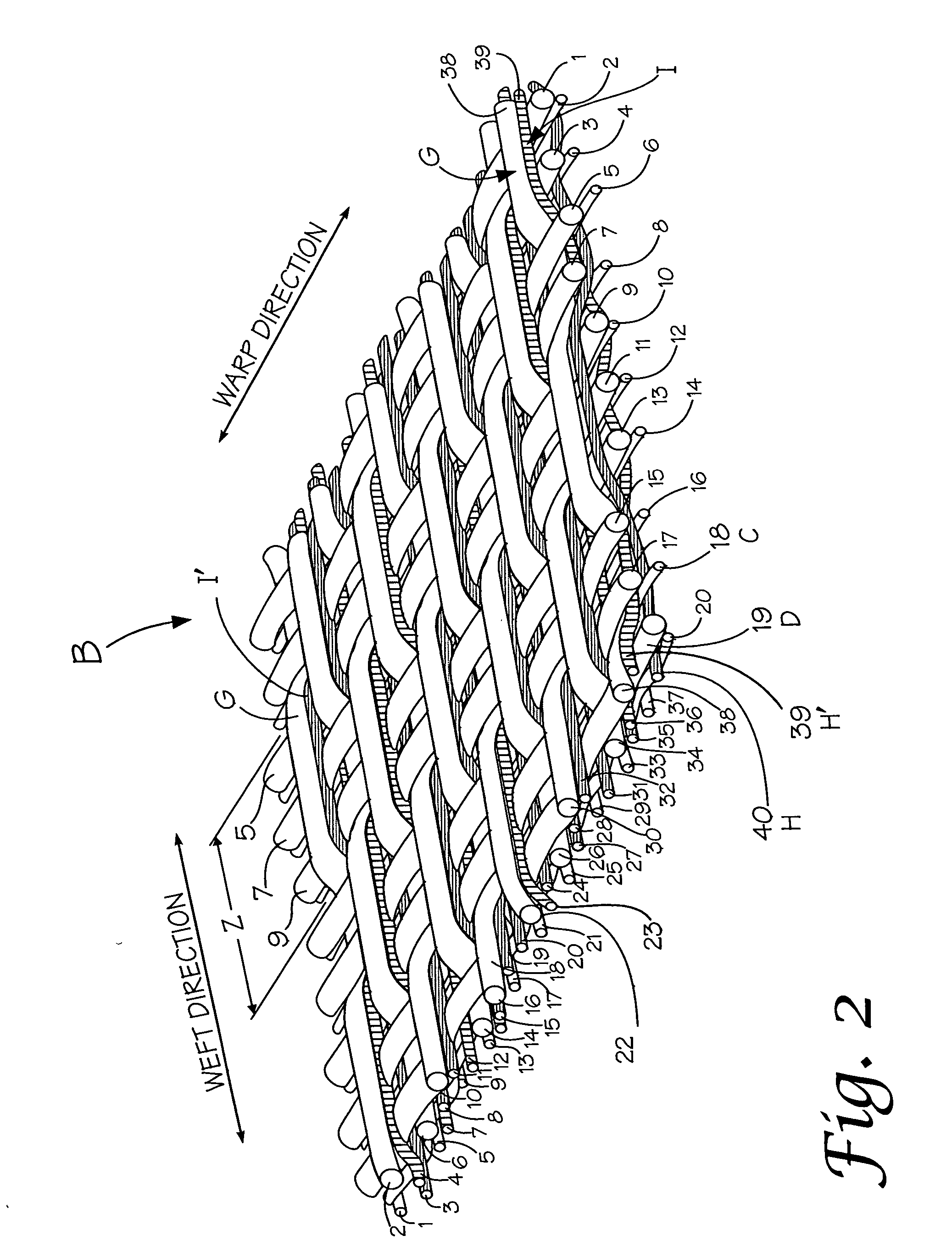
Composite papermaking fabric
A composite papermaking fabric having an upper support fabric including upper warp and weft yarns and a lower contact fabric including lower warp and weft yarns. The upper fabric is woven in a first weave pattern which forms a support surface and the lower fabric is woven in a broken twill weave pattern which forms the contact surface. The composite fabric includes paired binder yarns which weave in alternating sequences with the upper and lower fabrics binding them together. The broken twill weave pattern provides plural floats of cross-machine direction yarns passing outwardly of a plurality of adjacent lower warp yarns forming a plurality of adjacent cross-machine direction floats. Certain of the paired floats comprise a lower weft yarn and a binder yarn while others may comprise two lower weft yarns. The lower weft yarn floats are positioned to shield and protect the binder yarn floats along their entire length.
Owner:VOITH FABRICS
Swollen starch-latex compositions for use in papermaking
InactiveUS7074845B2High retention rateEasy to drainPigmenting treatmentNatural cellulose pulp/paperPaperboardPapermaking
A novel filler treatment comprising the preparation of swollen starch-latex compositions, prepared in the presence or absence of co-additives, and the addition of the said composition to a filler suspension, has been developed. Use of the treated filler during papermaking improves filler retention and produces filled papers where addition of the filler has only a minimal negative effect on strength properties. The swollen starch-latex compositions can be prepared in a batch or jet cooker, or by mixing with hot water under controlled conditions (i.e., temperature, pH, mixing, mixing time) in order to make the starch granules swell sufficiently to improve their properties as a filler additive but avoiding excess swelling leading to their rupture. The swollen starch-latex composition is then rapidly mixed with the filler slurry, preferably in a static mixer, and added to the papermaking furnish at a point prior to the headbox of the paper machine. The starch-latex composition can be used with wood-free or wood-containing furnishes. The treated filler is easily retained in the web during papermaking, improves drainage, and gives sheets having good formation. Sheets made with the treated fillers have higher bonding and tensile strengths than sheets produced using filler treated with either swollen starch alone or latex alone. Retention and drainage are further improved when conventional retention aid chemicals are added to the furnish containing the treated filler. The use of swollen starch-latex compositions could allow the papermaker to increase the filler content of the paper without sacrificing dry strength properties or increasing the amount, and hence the cost, of the retention aid added. The combination of swollen starch and latex could be used as furnish additives in the manufacture of both filled grades and grades that contain no filler such as sack papers and paperboard products.
Owner:FPINNOVATIONS INC
Highly dispersible hesperaloe tissue
ActiveUS20180142419A1Increased durabilityDry DurabilityPaper/cardboardTissue/absorbent paperPapermakingHardness
The invention provides tissue products comprising hesperaloe fibers and having satisfactory strength in-use and good dispersibility. To produce the instant tissue products the inventors have successfully moderated the changes in strength and stiffness typically associated with substituting conventional wood papermaking fibers, such as NSWK, with hesperaloe fibers. Not only have the inventors succeeded in moderating changes to strength and stiffness they have improved dispersibility. As such, the tissue products of the present invention have properties comparable to, or better than, those produced using conventional papermaking fibers, such as wood pulp fibers.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Embossed multi-ply fibrous structure product
A multi-ply fibrous structure product having two or more plies of fibrous structure where at least one of the plies has a plurality of domes formed during the papermaking process and there are from about 10 to about 1000 domes per square inch of the product. At least one of the plies of the multi-ply fibrous structure has a plurality of embossments thereon with a total embossment area of from about 3% to about 15%. The embossments may be arranged such that they define non-geometric foreground patterns of unembossed cells.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
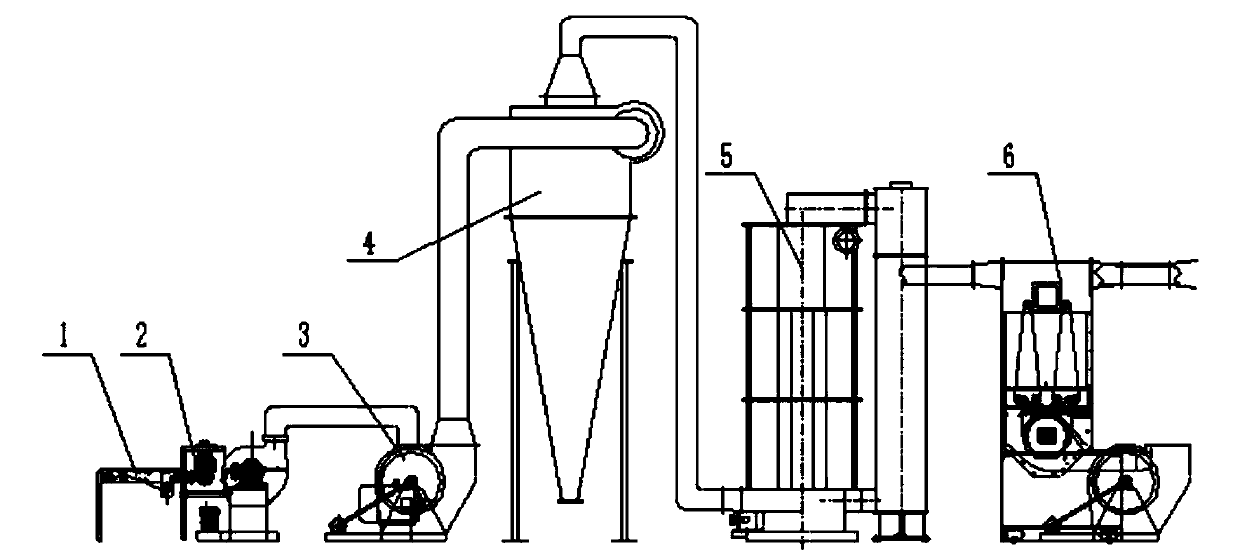
Bulk production line for reconstituted tobacco thin sheets by dry papermaking method
ActiveCN103431514AIncrease profitHigh degree of integration and automationTobacco preparationFiberProduction line
The invention discloses a bulk production line for reconstituted tobacco thin sheets by a dry papermaking method. The whole production line mainly comprises a raw material treatment part, a tobacco forming part and a thin sheet forming part, wherein material transportation is mainly executed through a carrying roller and a mesh belt, and is assisted through air flow of a fan; a conveying component of the whole production line is provided with a cleaning device, a tensioning device and a deviation correction device. According to the production line, wood pulp or tobaccos are smashed into fibers, then reconstituted tobaccos are produced through dry forming; finished products, namely the tobacco thin sheets, are produced through reconstituted tobacco treatment; the production requirements on the reconstituted tobacco thin sheet low sewage emission, low energy consumption and high quality are met.
Owner:SHANXI LIGONG MECHANICAL & ELECTRICAL TECH
Security paper and method and device for producing the same
ActiveUS20050224203A1Easy to produceHindering sheet formationNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperPapermakingPaper document
A security paper for producing security documents, such as bank notes, identity cards or the like, having at least one opening, whereby the opening is produced during papermaking and does not have a sharp limiting edge in the edge area.
Owner:GIESECKE & DEVRIENT CURRENCY TECHNOLOGY GMBH
Low viscosity bilayer disrupted softening composition for tissue paper
InactiveUS6855229B2Good flexibilityAcceptable strengthNatural cellulose pulp/paperSpecial paperCelluloseAmmonium compounds
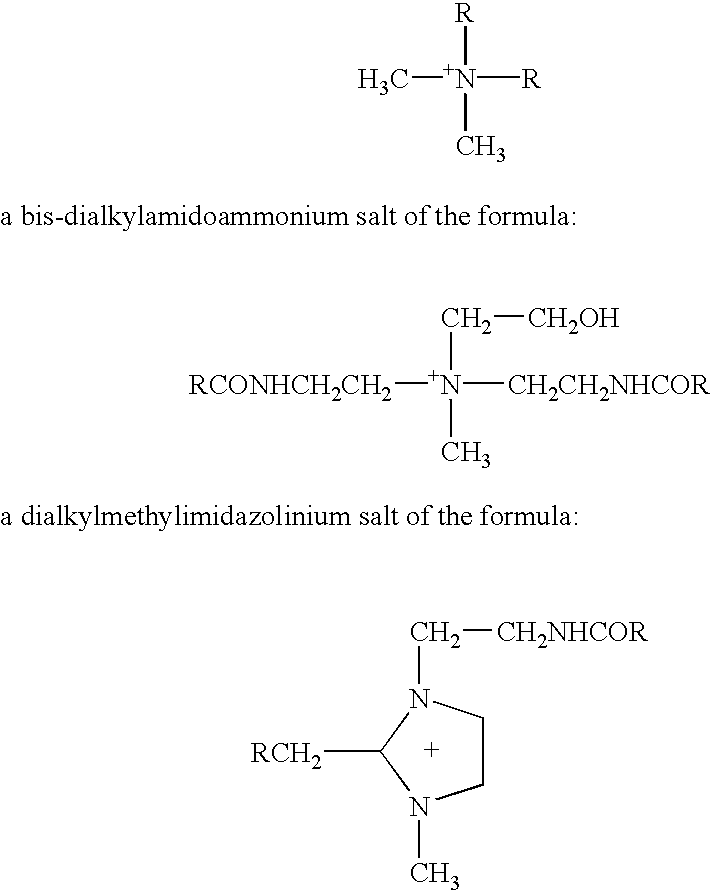
Disclosed is a composition for softening a wet laid cellulosic structure. A particularly preferred structure is an absorbent tissue. Further disclosed are tissue structures softened using the composition. The composition includes an effective amount of a softening active ingredient; a vehicle in which the softening active ingredient is dispersed; an electrolyte dissolved in the vehicle; and a bilayer disrupter. The electrolyte and the bilayer disrupter cooperate to cause the viscosity of the composition to be less than the viscosity of a dispersion of the softening active ingredient in the vehicle alone. Preferably, the softening active ingredient is a quaternary ammonium compound with the formula:(R1)4-m—N+—[(CH2)n—Y—R3]mX−the vehicle is water, the electrolyte is calcium chloride, and the bilayer disrupter is a nonionic surfactant. Also disclosed is a method of using the compound by adding it at a use concentration to the wet end of a papermaking process.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Diphase stainless steel and manufacturing method thereof
The invention discloses a diphase stainless steel, which comprises the following components in percentage by weight: less than or equal to 0.05 percent of C, 0.2 to 1.0 percent of Si, 0 to 2.0 percent of Mn, 22 to 27 percent of Cr, 0 to 2.0 percent of W, less than or equal to 0.1 percent of S, less than or equal to 0.03 percent of P, 0 to 0.003 percent of B, more than 0 and less than or equal to 0.2 percent rare earth of which the Ce content is more than 50 percent, and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities, wherein a casting blank of the diphase stainless steel comprises over 60 percent of isometric crystal. A method for manufacturing the diphase stainless steel comprises the following steps of: performing smelting, die casting or continuous casting to form the casting blank, wherein the thickness of a steel die is more than 30 mm during the die casting to ensure that the cooling velocity of the steel is more than 10 DEG C per minute, and in the process of the continuous casting, the degree of superheating of the casting is between 30 and 100 DEG C, and the casting speed is over 1.2 meters per minute; putting the casting blank into a heating furnace, heating the casting blank to the temperature of between 1,100 and 1,250 DEG C, performing heat preservation on the casting blank, and then forging or hot-rolling the casting blank to a required thickness; and annealing and pickling a steel plate or a plate coil after forging or hot-rolling, and controlling the annealing temperature to be between 1,000 and 1,100 DEG C. The diphase stainless steel has high corrosion resistance and high hot-working performance, and can be widely applied in the fields of petroleum, chemical industry, papermaking, marine engineering and the like in rigorous corrosion environments.
Owner:BAOSTEEL SPECIAL STEEL CO LTD +1
Method for preparing calcium sulfate crystal whiskers by using impurity-containing gypsum as raw material
InactiveCN101736403AHigh purityGood dispersionPolycrystalline material growthCalcium/strontium/barium sulfatesAnhydrous Calcium SulfateDihydrate Calcium Sulfate
The invention relates to a method for preparing calcium sulfate crystal whiskers (CaSO4) by using impurity-containing gypsum as a raw material. The method comprises the following steps of: removing main impurities in the raw material which is the low-priced impurity-containing gypsum resource in a mode of roasting, acid-complex leaching and alkaline leaching and simultaneously thinning crystal grains to obtain a superfine dihydrate calcium sulfate precursor which is high in purity and dispersibility; and preparing the anhydrous calcium sulfate crystal whiskers with a length of 20 to 2,000mu m, a diameter of 0.5 to 20 mu m, a length-diameter ratio of 40 to 1,000 and a weight percent content of over 95 percent in a mode of hydrothermal conversion-roasting of a fluxing agent. The method has the advantages of low-priced and easily bought raw materials, simple process, wide application range, and high added value. The calcium sulfate crystal whiskers prepared by the method have a big length-diameter ratio and regular shape, and can be used as reinforcing, heat insulating or flame retardant materials in industries of plastics, rubbers, coatings, papermaking, building materials and the like.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
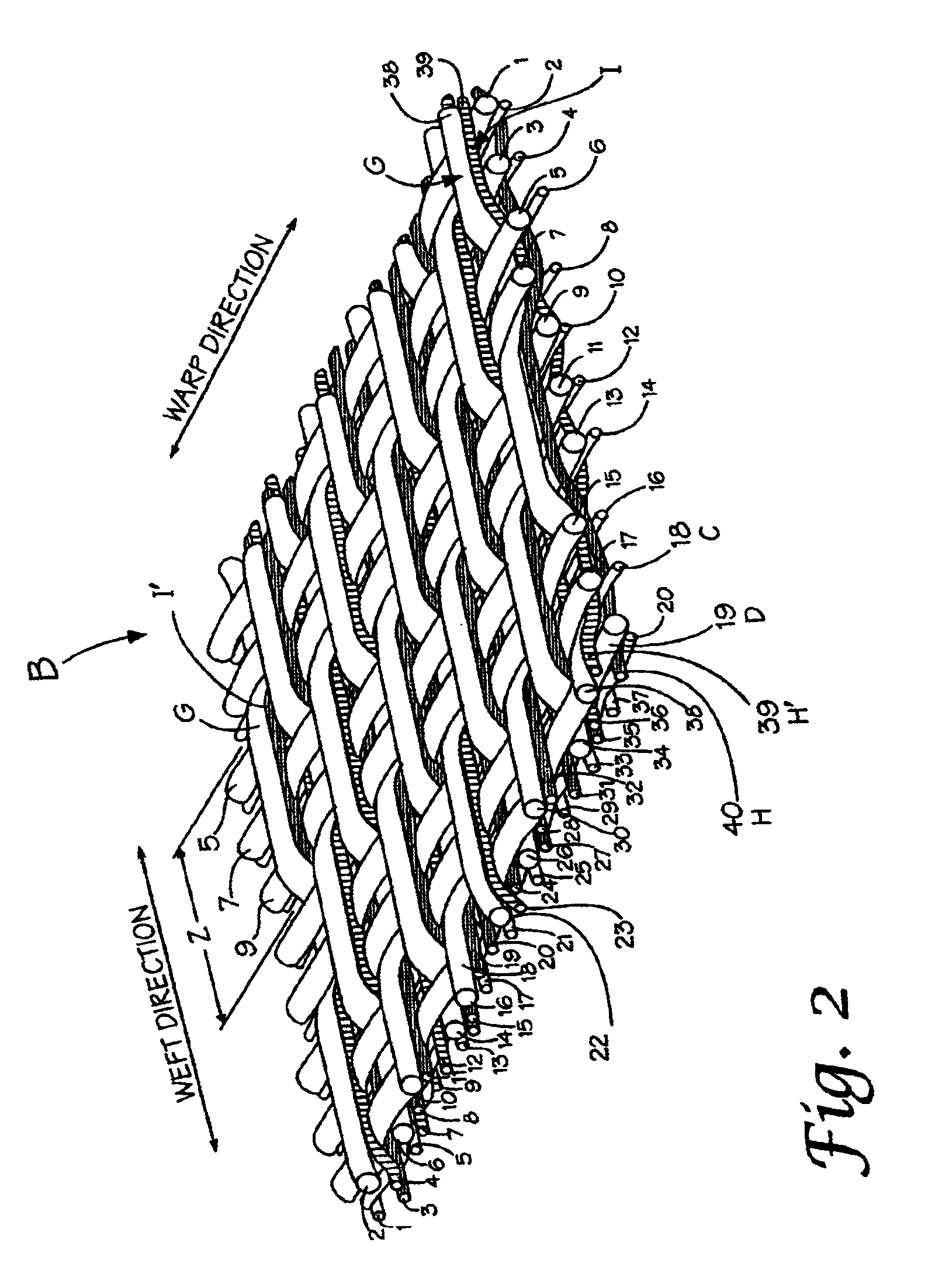
Composite papermaking fabric
A composite papermaking fabric having an upper support fabric including upper warp and weft yarns and a lower contact fabric including lower warp and weft yarns. The upper fabric is woven in a first weave pattern which forms a support surface and the lower fabric is woven in a broken twill weave pattern which forms the contact surface. The composite fabric includes paired binder yarns which weave in alternating sequences with the upper and lower fabrics binding them together. The broken twill weave pattern provides plural floats of cross-machine direction yarns passing outwardly of a plurality of adjacent lower warp yarns forming a plurality of adjacent cross-machine direction floats. Certain of the paired floats comprise a lower weft yarn and a binder yarn while others may comprise two lower weft yarns. The lower weft yarn floats are positioned to shield and protect the binder yarn floats along their entire length.
Owner:VOITH FABRICS
Compositions and processes for paper production
ActiveUS20080017337A1Avoid brightness lossIncrease brightnessNatural cellulose pulp/paperSpecial paperPaper productionPapermaking
Oxidative compositions and processes that preserve and enhance the brightness and improve color of pulp or paper when applied during different stages of the papermaking process are identified. The oxidative composition and method maintains and / or enhances brightness, prevents yellowing, and enhances the performance of paper products. Used in combination with optical brighteners and / or chelants the oxidative agents produce a synergistic effect not previously identified in the paper process.
Owner:ECOLAB USA INC
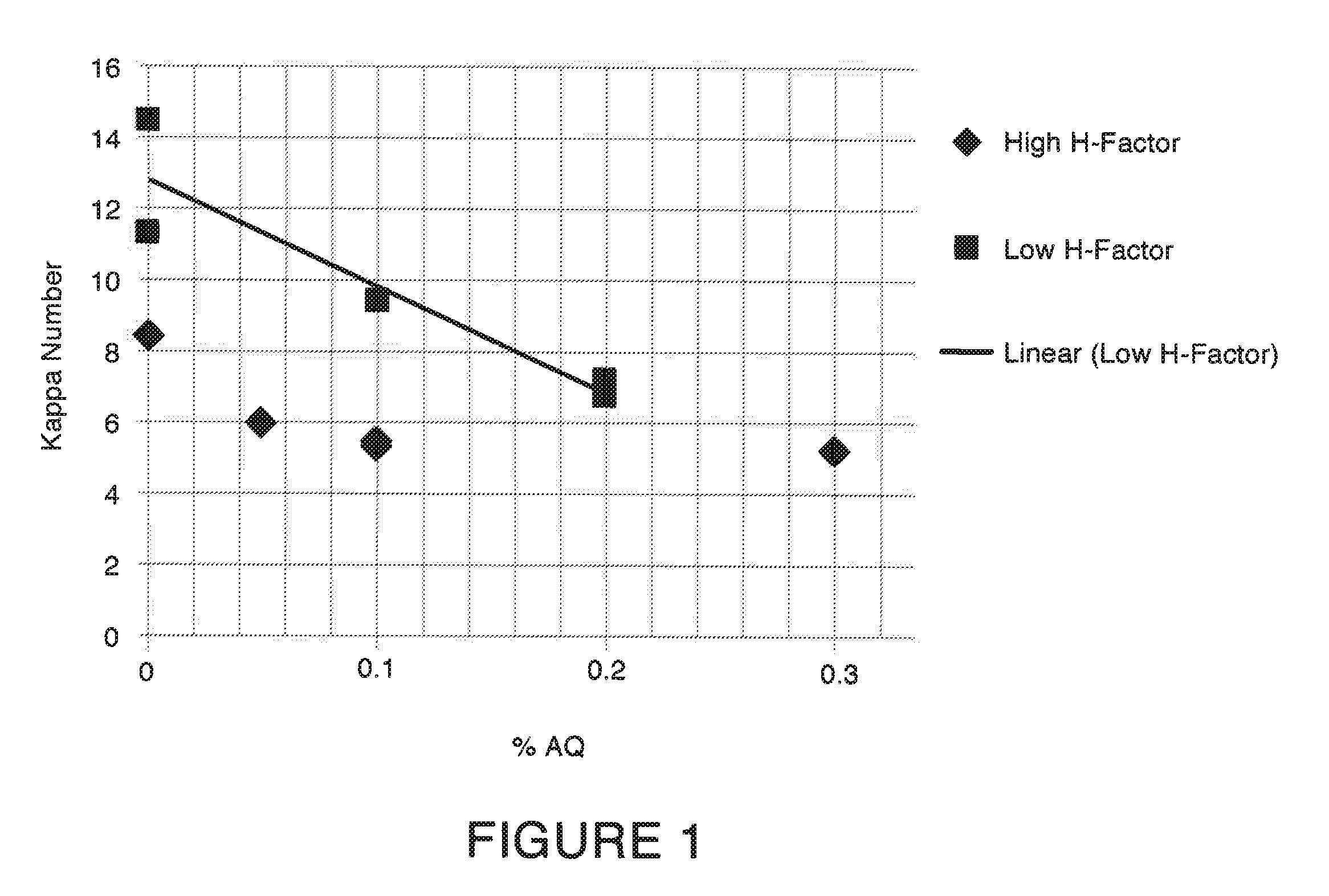
Pulping processes
A pulping process comprises using a high concentration of anthraquinone (AQ). The pulping process is capable of providing a pulp having low Kappa number with unexpectedly high strength. The pulping process can use wood or non-wood fibers (e.g., bagasse and corn stover) to provide pulp having good papermaking quality. The method for pulping a fiber comprising cooking a first mixture comprising the fibers, water, an alkali, and a delignification selectivity enhancing chemical for a cooking time and at a cooking condition sufficient to form a first pulp having a desired Kappa number of about 15 or less, and strength parameters that are sufficient for papermaking, where the starting material prior to cooking has a Kappa number of 60 or greater.
Owner:CARGILL INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com