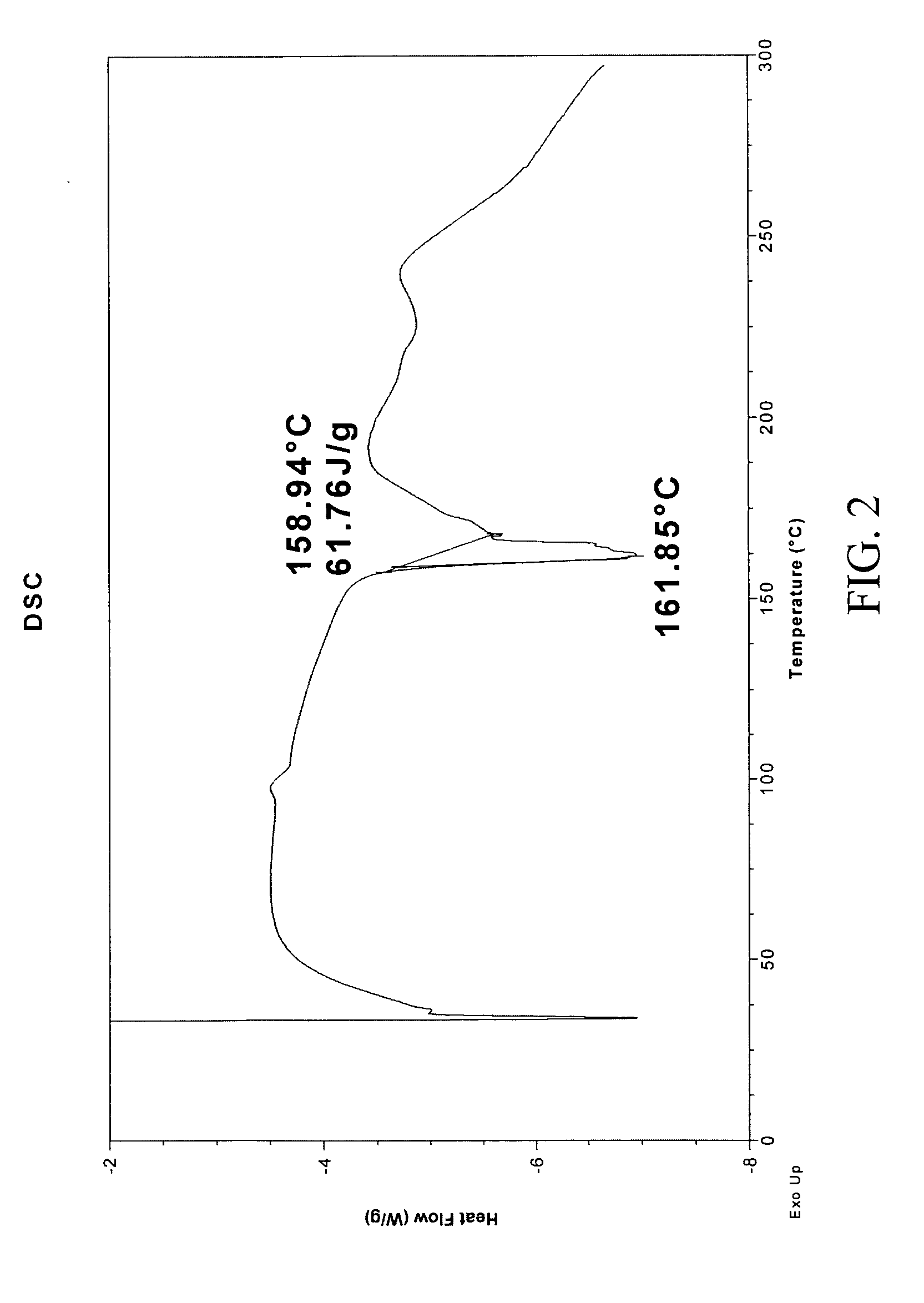
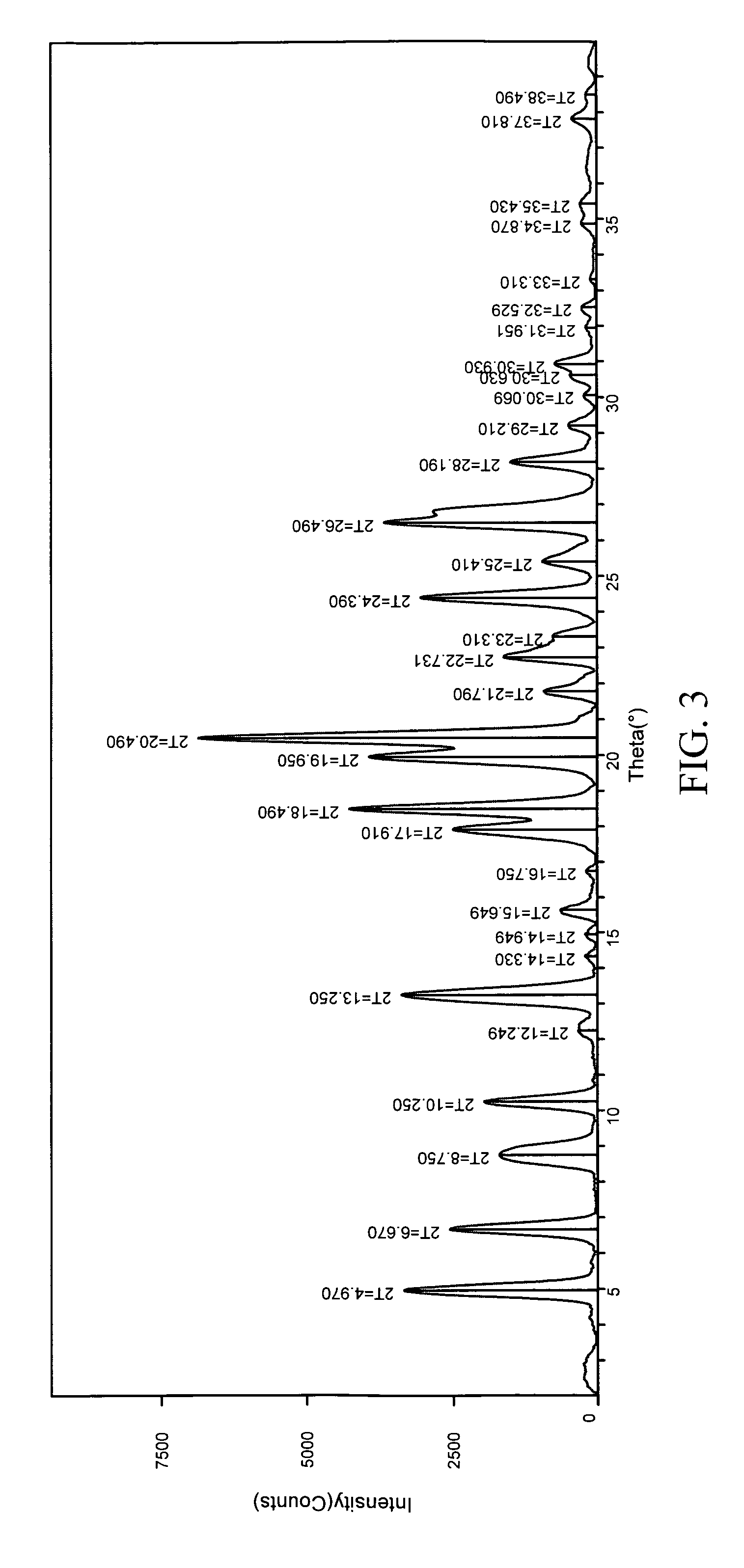
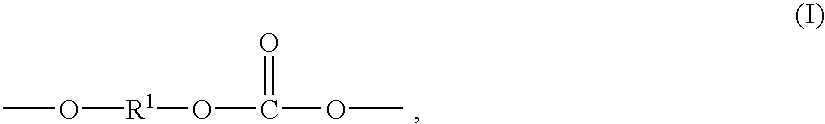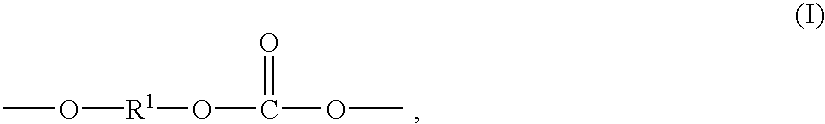Patents
Literature
4729 results about "Tertiary amine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Tertiary amine. noun. : an amine (as trimethylamine or nicotine) having three organic groups attached to the nitrogen in place of three hydrogen atoms.
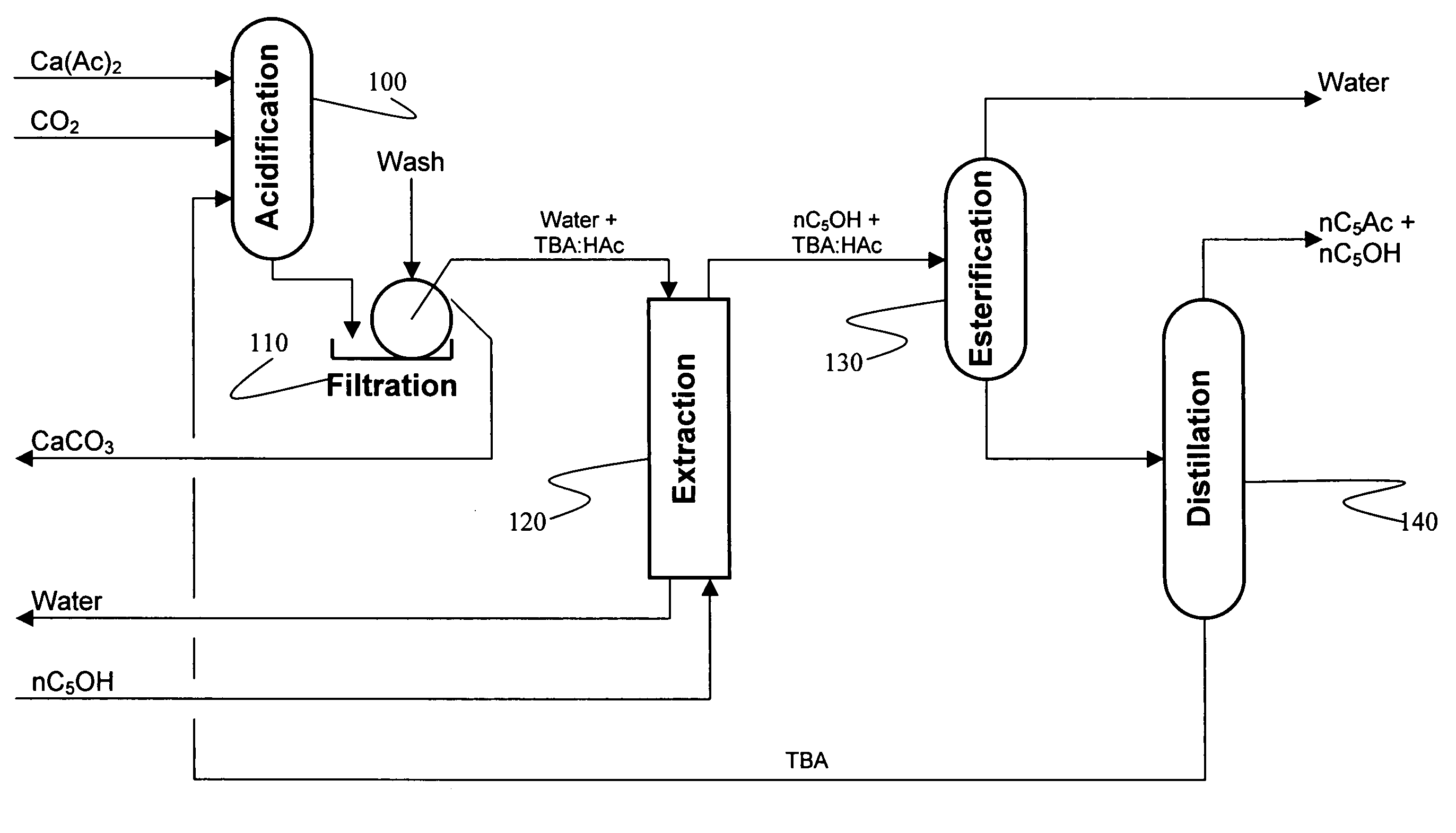
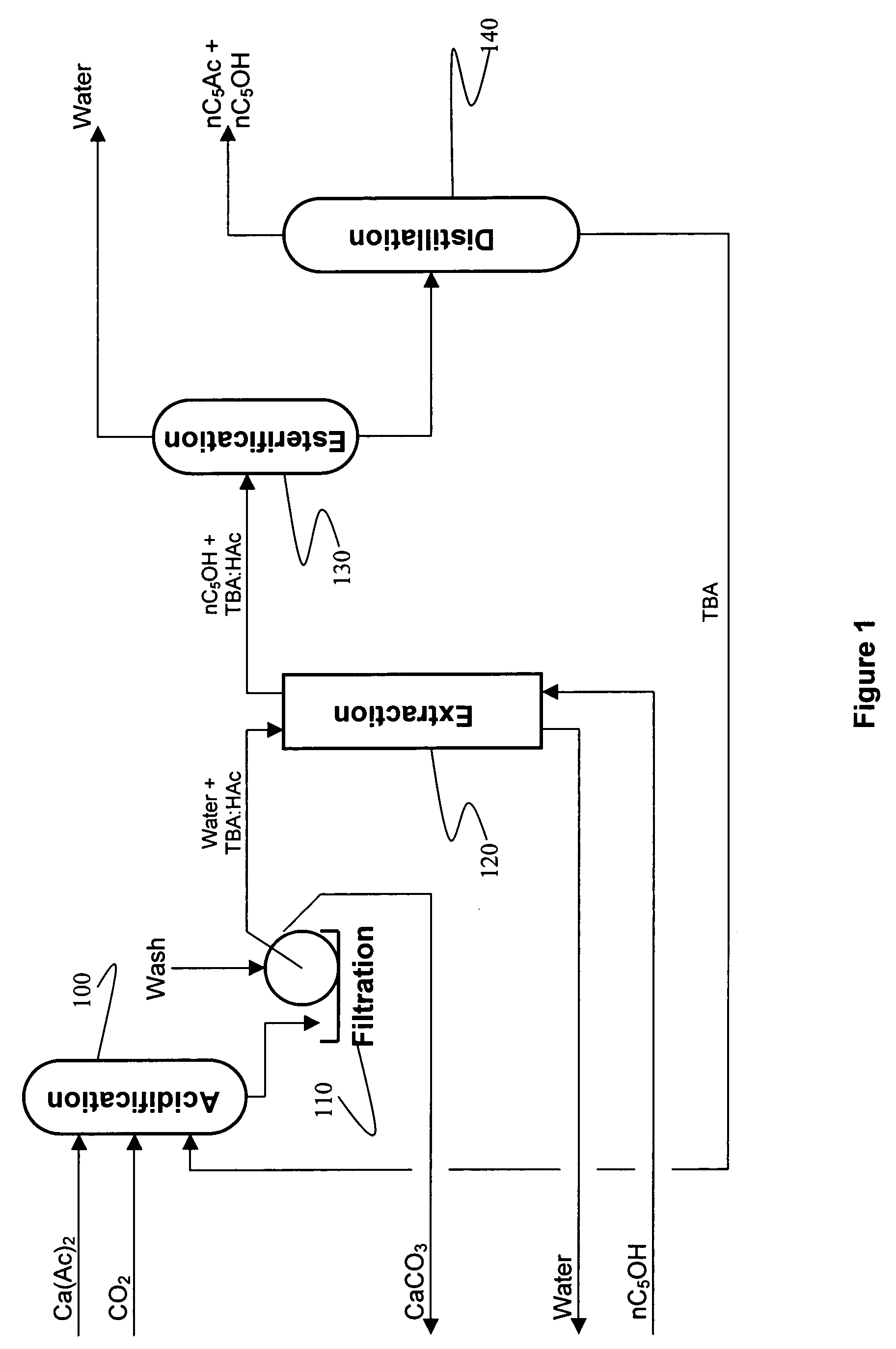
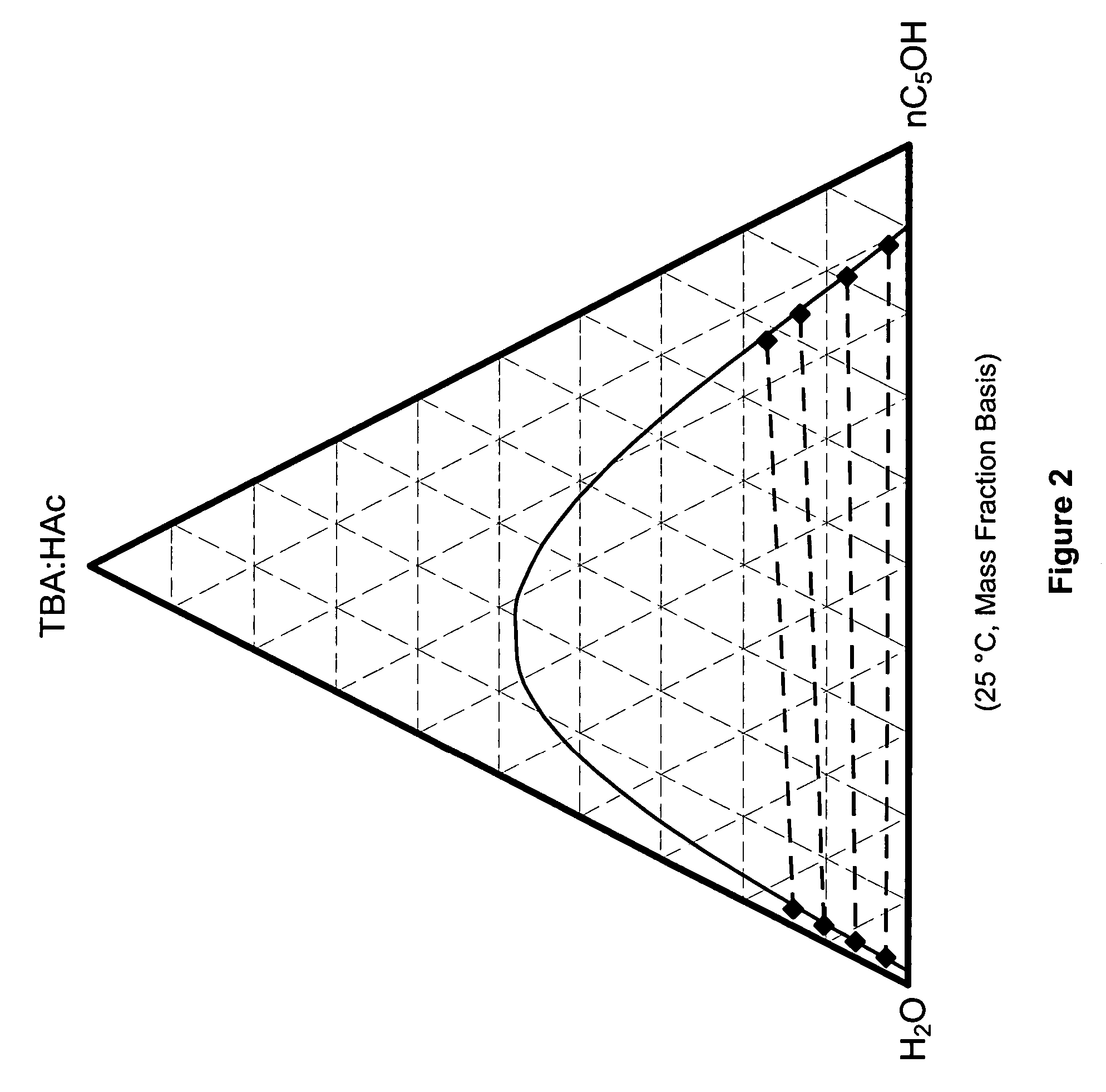
Recovery of organic acids
InactiveUS7601865B2Promote recoveryOvercome consumptionPreparation from carboxylic acid saltsOrganic compound preparationOrganic acidAlcohol
Owner:ZEACHEM
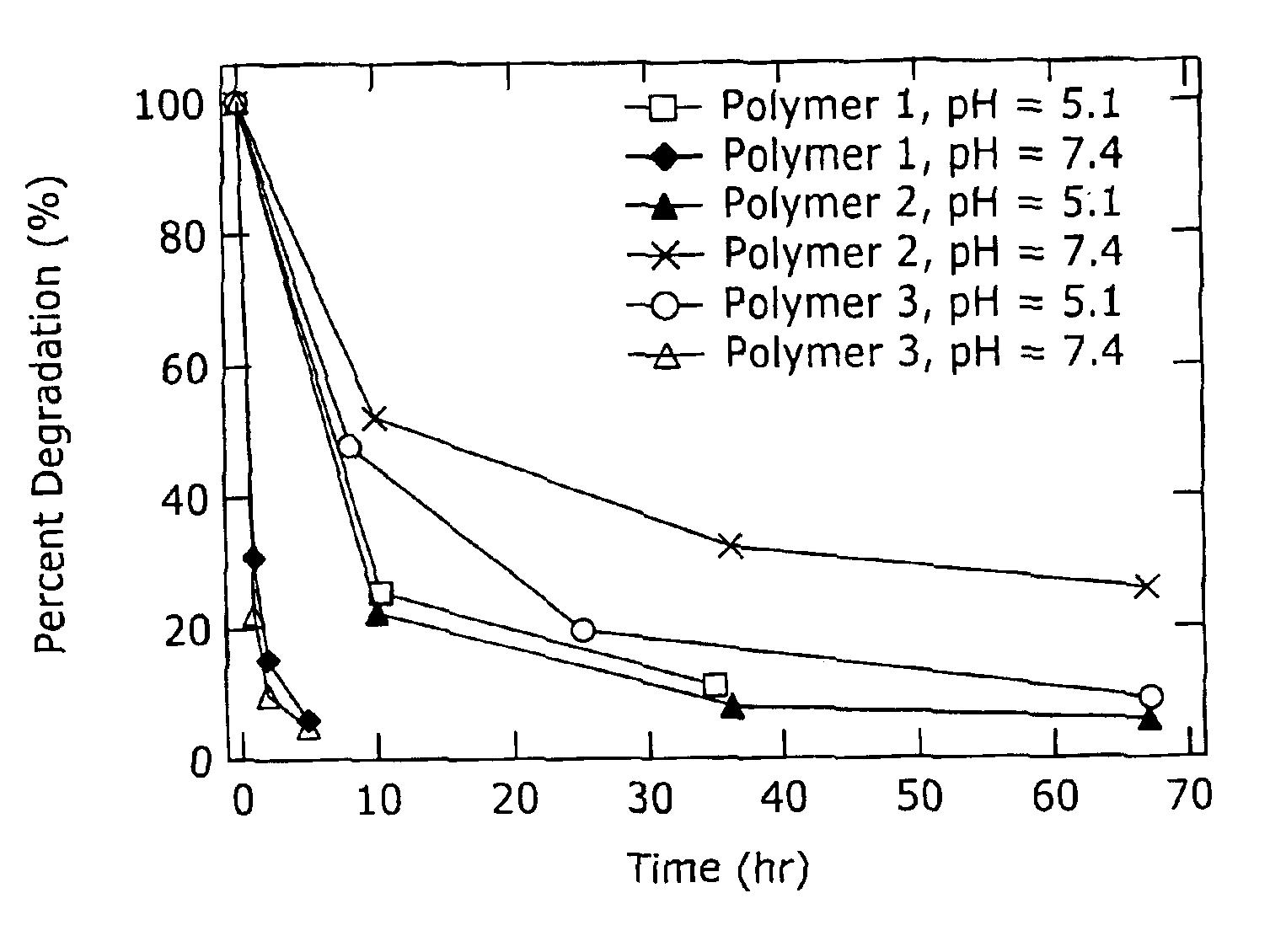
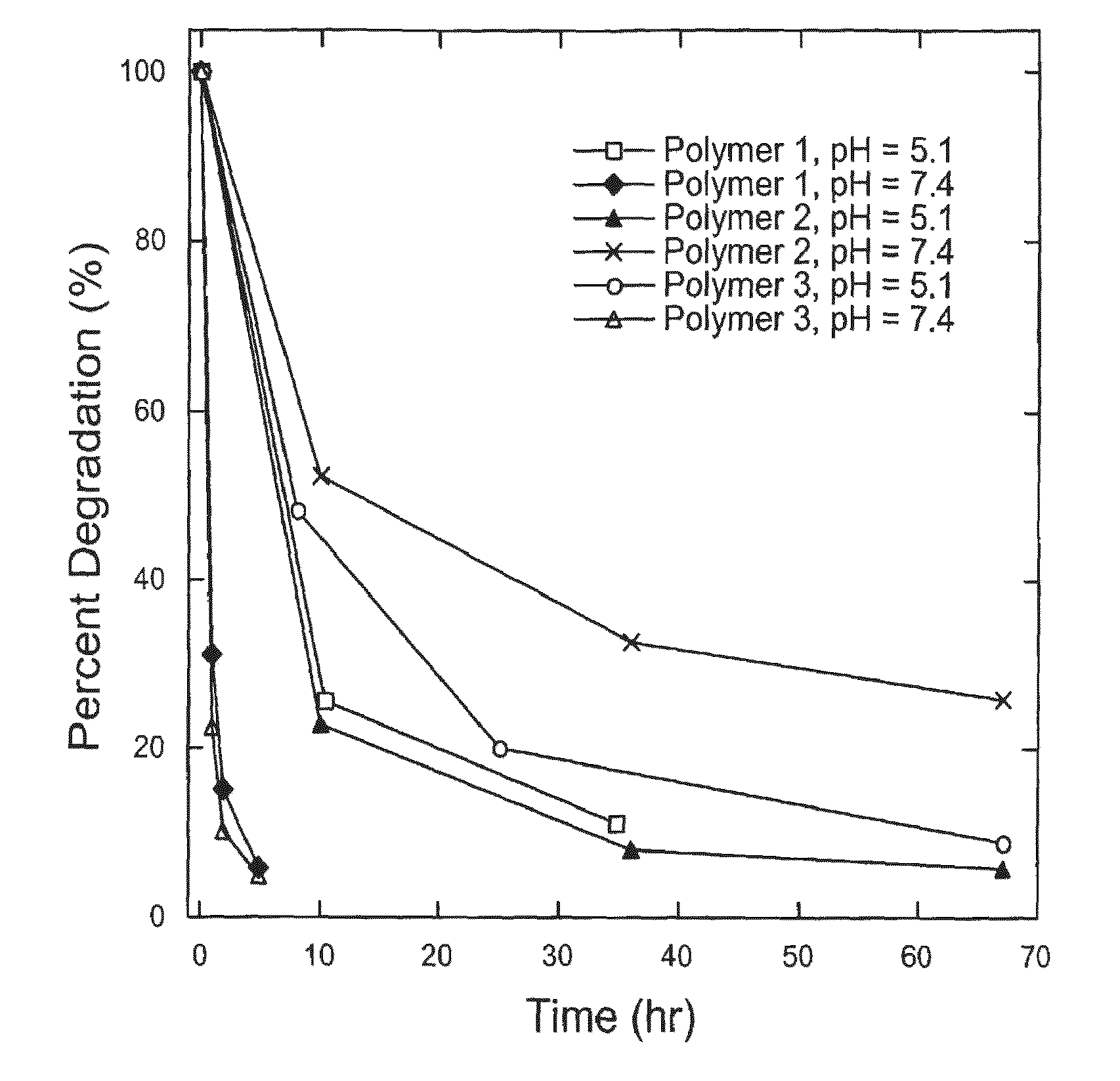
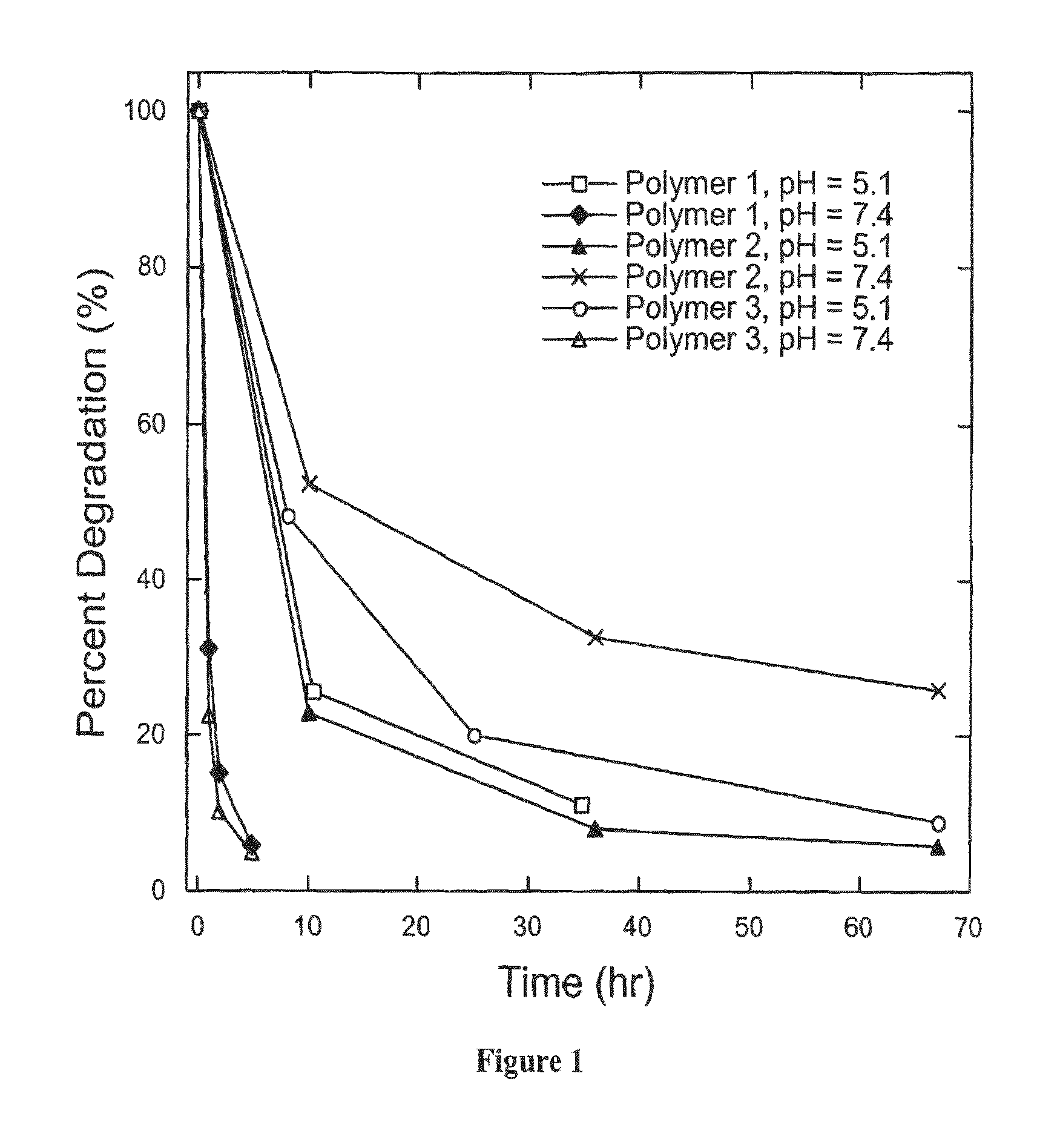
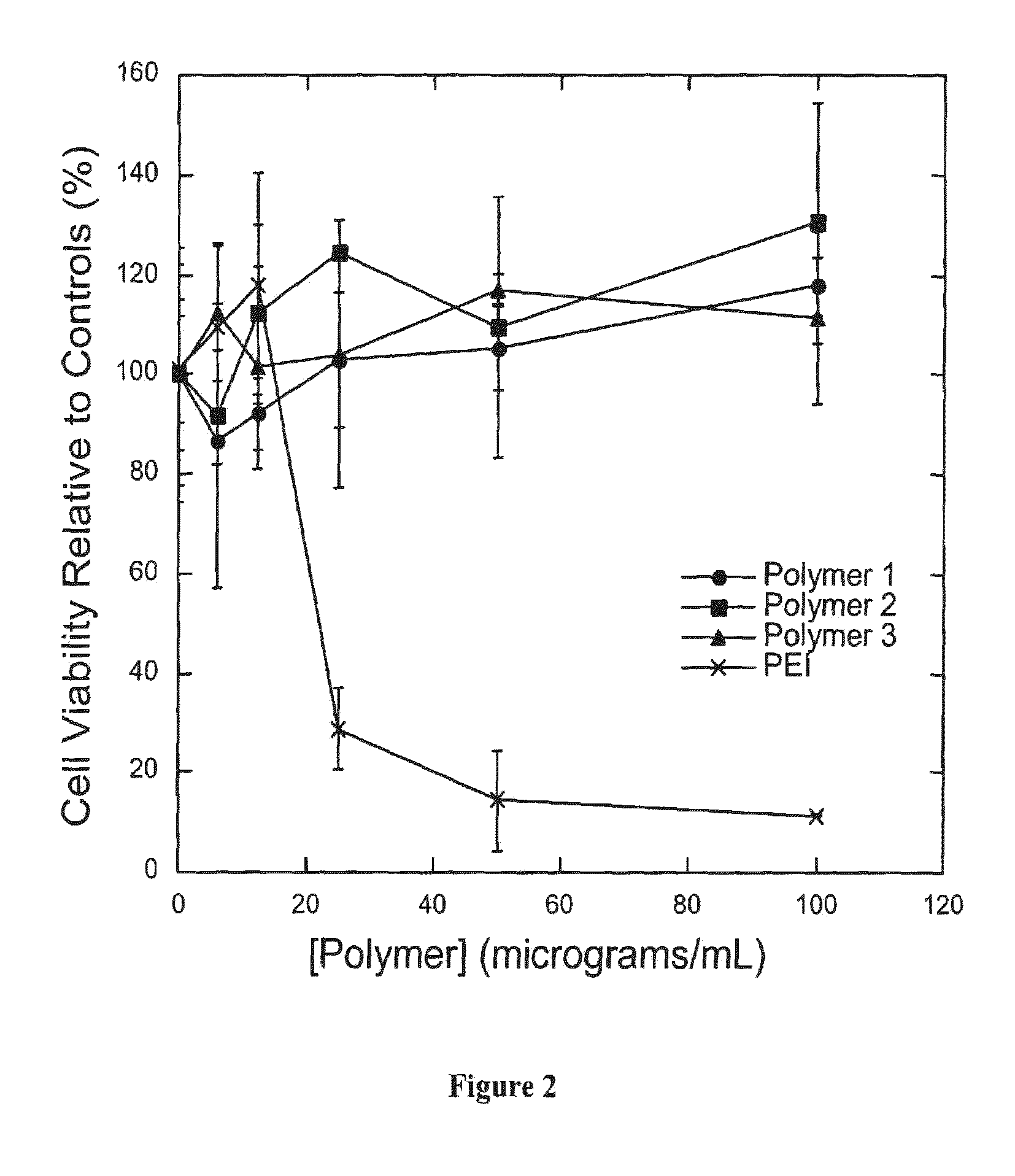
Biodegradable poly(β-amino esters) and uses thereof
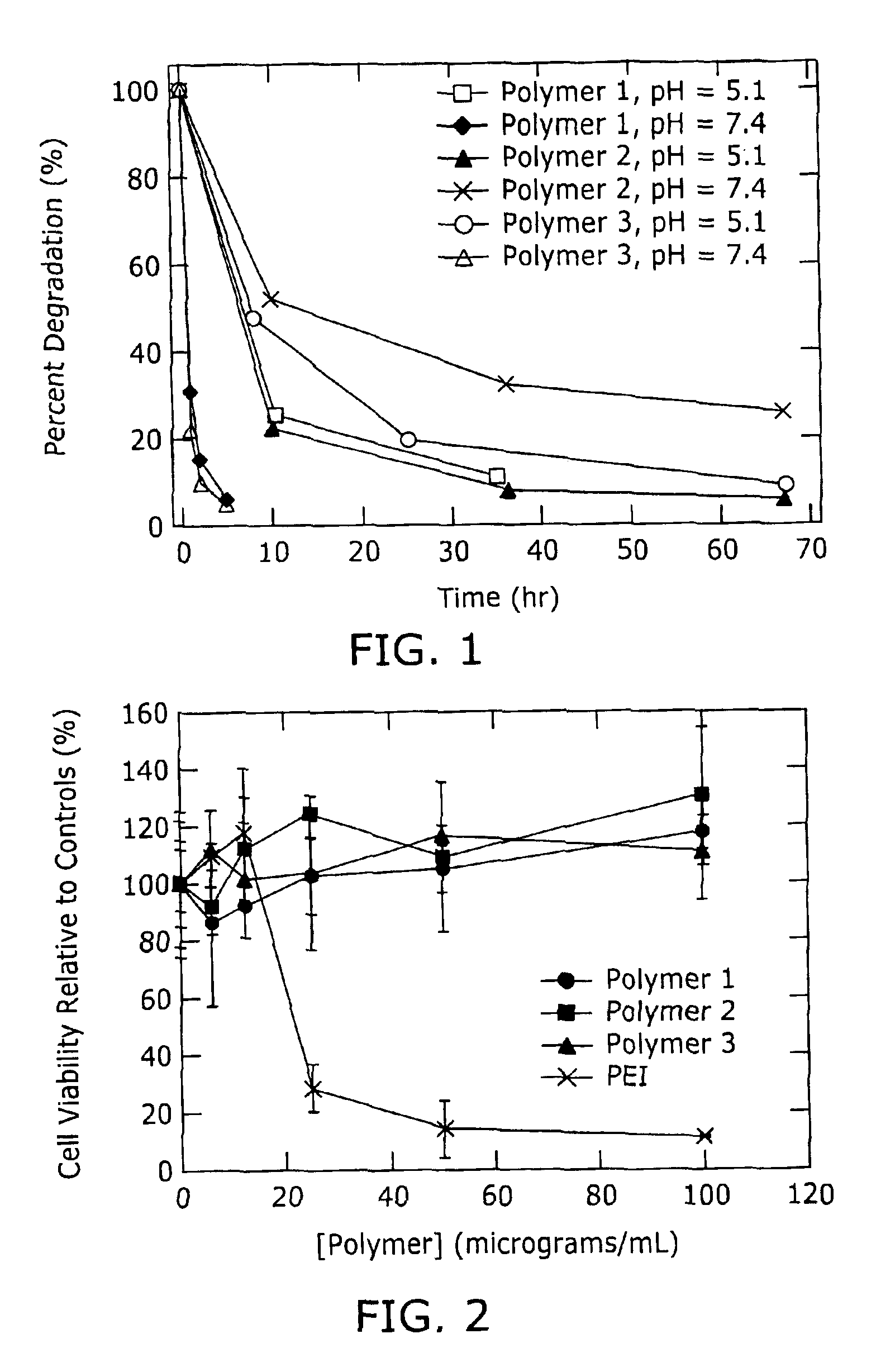
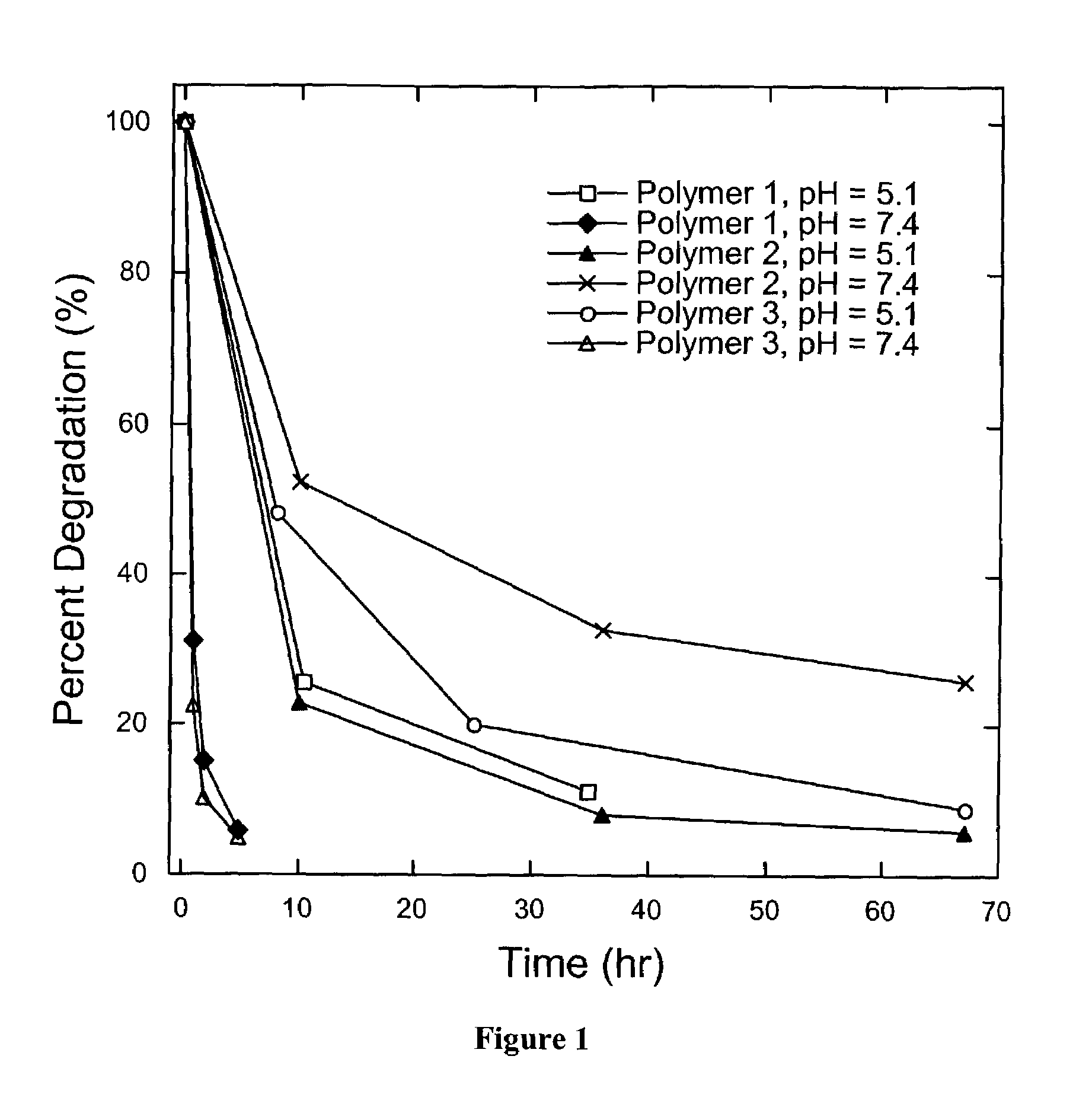
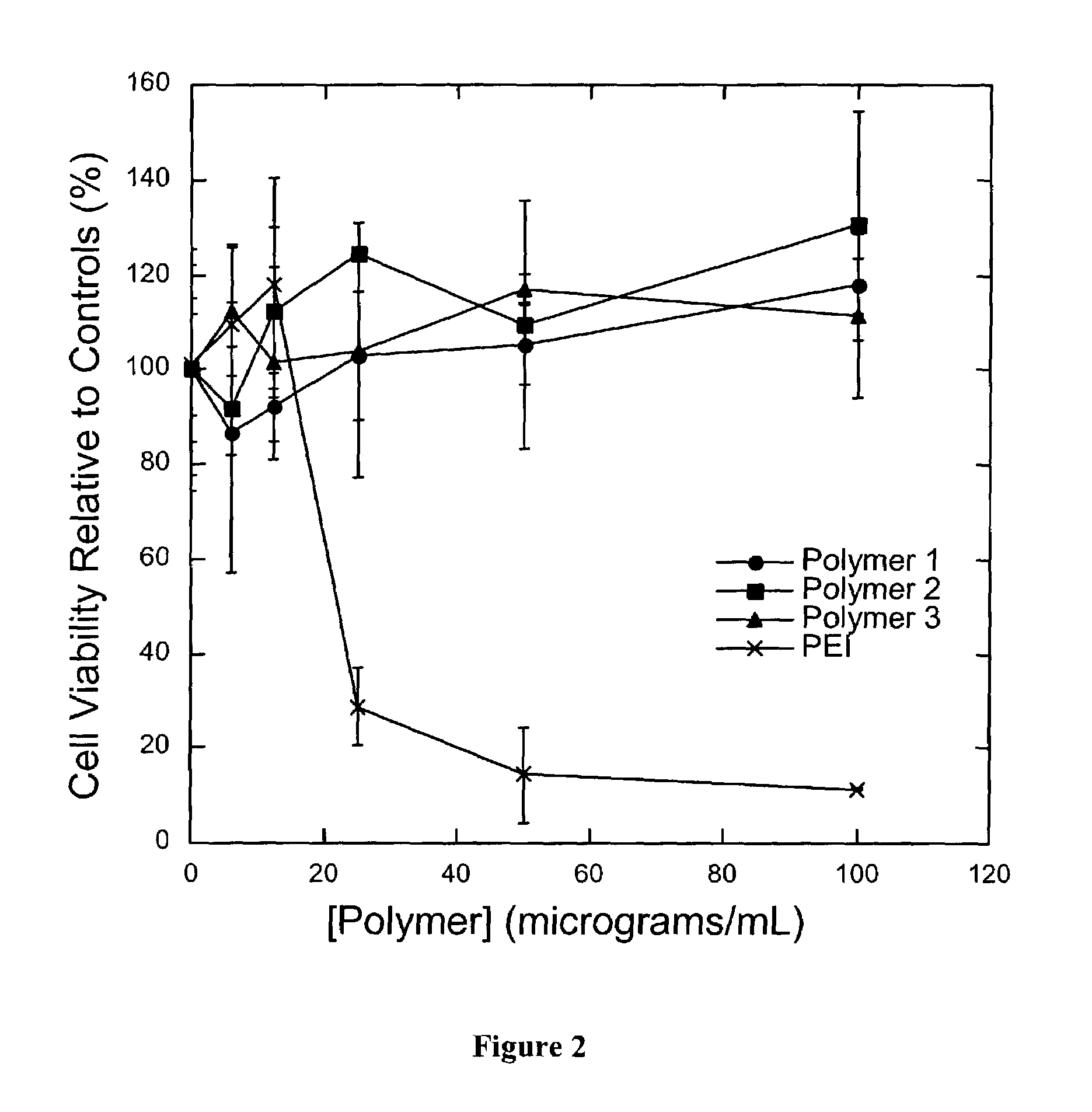
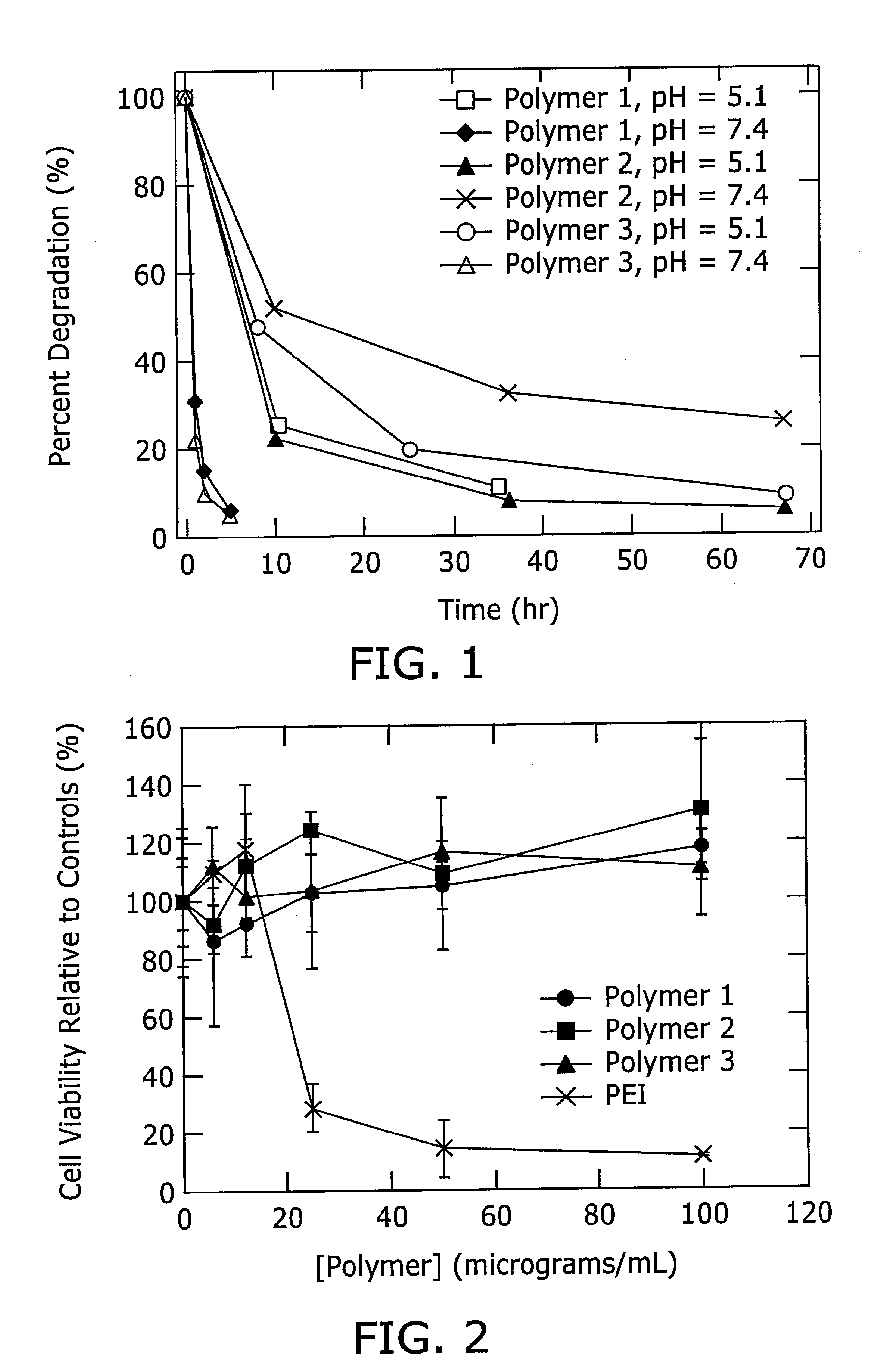
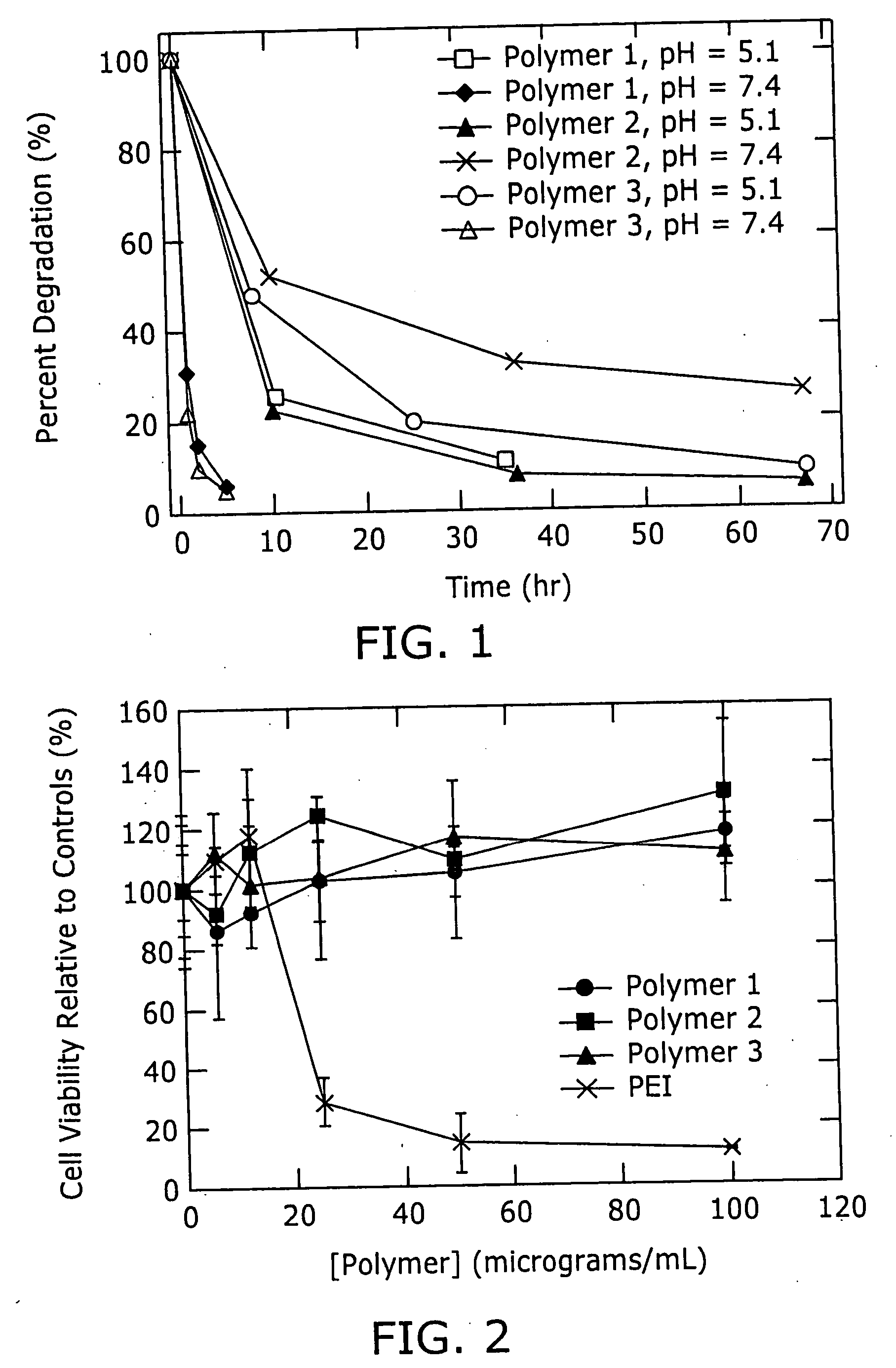
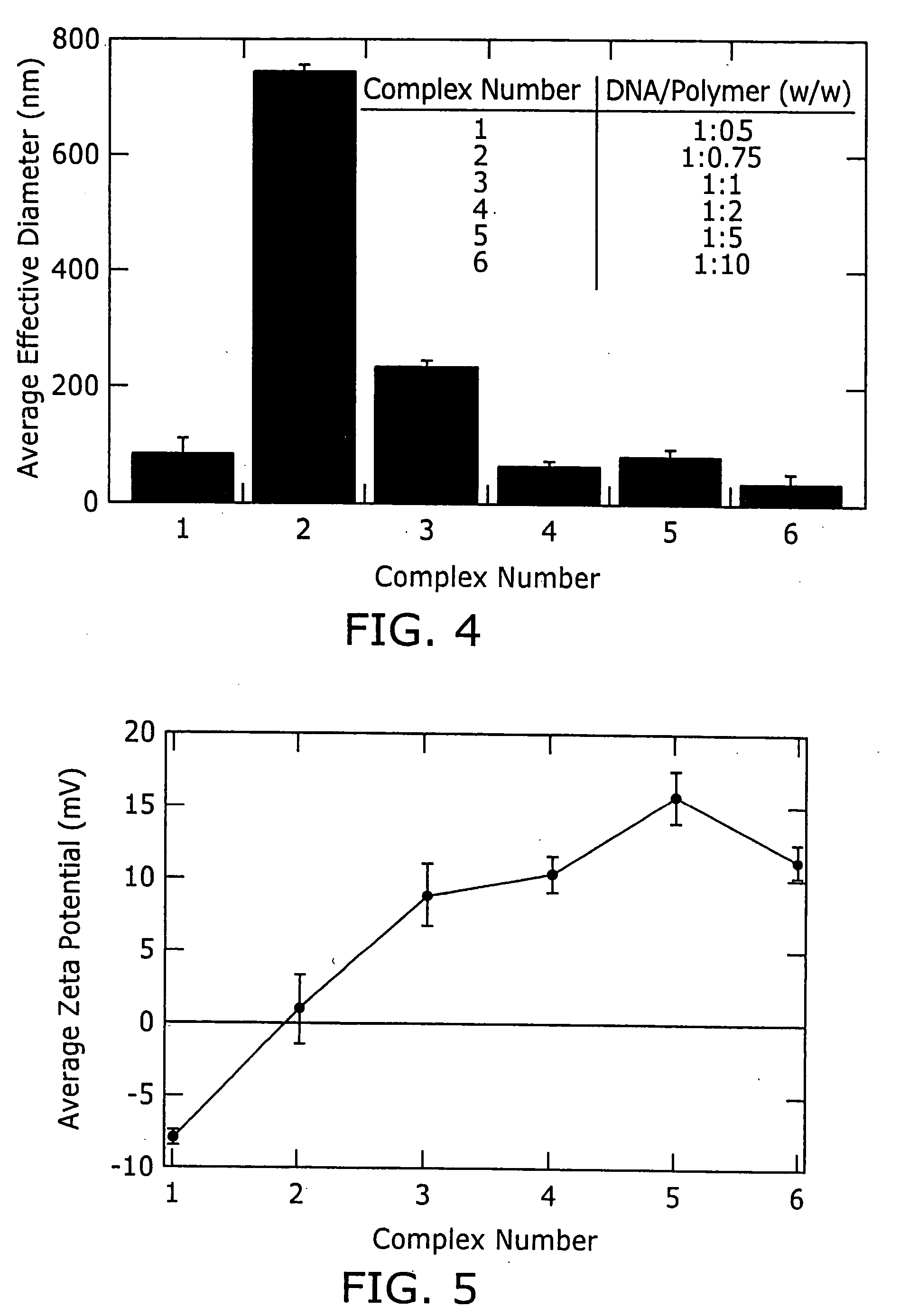
Poly(β-amino esters) prepared from the conjugate addition of bis(secondary amines) or primary amines to a bis(acrylate ester) are described. Methods of preparing these polymers from commercially available starting materials are also provided. These tertiary amine-containing polymers are preferably biodegradable and biocompatible and may be used in a variety of drug delivery systems. Given the poly(amine) nature of these polymers, they are particularly suited for the delivery of polynucleotides. Nanoparticles containing polymer / polynucleotide complexes have been prepared. The inventive polymers may also be used to encapsulate other agents to be delivered. They are particularly useful in delivering labile agents given their ability to buffer the pH of their surroundings.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Pharmaceutical co-crystal compositions
A pharmaceutical composition comprising a co-crystal of an API and a co-crystal former; wherein the API has at least one functional group selected from ether, thioether, alcohol, thiol, aldehyde, ketone, thioketone, nitrate ester, phosphate ester, thiophosphate ester, ester, thioester, sulfate ester, carboxylic acid, phosphonic acid, phosphinic acid, sulfonic acid, amide, primary amine, secondary amine, ammonia, tertiary amine, sp2 amine, thiocyanate, cyanamide, oxime, nitrile diazo, organohalide, nitro, s-heterocyclic ring, thiophene, n-heterocyclic ring, pyrrole, o-heterocyclic ring, furan, epoxide, peroxide, hydroxamic acid, imidazole, pyridine and the co-crystal former has at least one functional group selected from amine, amide, pyridine, imidazole, indole, pyrrolidine, carbonyl, carboxyl, hydroxyl, phenol, sulfone, sulfonyl, mercapto and methyl thio, such that the API and co-crystal former are capable of co-crystallizing from a solution phase under crystallization conditions.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON CONSUMER COPANIES +2
Method for recovery of CO2 from gas streams
InactiveUS7056482B2Reduce solubilityMinimizing its negative effectCarbon compoundsDispersed particle separationEnvironmental engineeringCarbon dioxide
A process for recovering CO2 from a feed gas stream comprises treating the feed gas stream with a regenerated absorbent comprising at least one tertiary amine absorbent having a pKa for the amino function of from about 6.5 to about 9 in the presence of an oxidation inhibitor to obtain a CO2 rich stream and subsequently treating the CO2 rich stream to obtain the regenerated absorbent and a CO2 rich product stream. The feed gas stream may also include SO2 and / or NOx.
Owner:CANSOLV TECH INC
Biodegradable poly(beta-amino esters) and uses thereof
InactiveUS7427394B2High molecular weightHigh transfection efficiencyAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsAmino estersNucleotide
Poly(β-amino esters) prepared from the conjugate addition of bis(secondary amines) or primary amines to a bis(acrylate ester) are described. Methods of preparing these polymers from commercially available starting materials are also provided. These tertiary amine-containing polymers are preferably biodegradable and biocompatible and may be used in a variety of drug delivery systems. Given the poly(amine) nature of these polymers, they are particularly suited for the delivery of polynucleotides. Nanoparticles containing polymer / polynucleotide complexes have been prepared. The inventive polymers may also be used to encapsulate other agents to be delivered. They are particularly useful in delivering labile agents given their ability to buffer the pH of their surroundings. A system for preparing and screening polymers in parallel using semi-automated robotic fluid delivery systems is also provided.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Absorbent sheet having regenerated cellulose microfiber network
ActiveUS20070224419A1High wet/dry tensile ratioImprove consistencyNon-fibrous pulp additionPaper after-treatmentPolymer sciencePapermaking
An absorbent paper sheet for tissue or towel includes from about 99 percent to about 70 percent by weight of cellulosic papermaking fiber and from about 1 percent to about 30 percent by weight fibrillated regenerated cellulose microfiber which was regenerated form a cellulosic dope utilizing a tertiary amine N-oxide solvent or an ionic liquid. Fibrillation of the microfiber is controlled such that it has a reduced coarseness and a reduced freeness as compared with unfibrillated regenerated cellulose microfiber from which it is made and provides at least one of the following attributes to the absorbent sheet: (a) the absorbent sheet exhibits an elevated SAT value and an elevated wet tensile value as compared with a like sheet prepared without fibrillated regenerated cellulose microfiber; (b) the absorbent sheet exhibits an elevated wet / dry CD tensile ratio as compared with a like sheet prepared without fibrillated regenerated cellulose microfiber; (c) the absorbent sheet exhibits a lower GM Break Modulus than a like sheet having like tensile values prepared without fibrillated regenerated cellulose microfiber; or (d) the absorbent sheet exhibits an elevated bulk as compared with a like sheet having like tensile values prepared without fibrillated regenerated cellulose microfiber. In some embodiments, the pulp is pre-treated with debonder to enhance the wet / dry CD tensile ratio of the sheet.
Owner:GPCP IP HLDG LLC
Carbon black composition and usage thereof
InactiveUS20130029183A1Good dispersionInhibition formationPigmenting treatmentMagnetic materials for record carriersCyclohexanoneOrganic solvent
An aspect of the present invention relates to a carbon black composition, which comprises carbon black; an organic tertiary amine selected from the group consisting of an aliphatic tertiary monoamine and an alicyclic tertiary amine; and at least one organic solvent selected from the group consisting of methyl ethyl ketone, cyclohexanone, isophorone, and ethanol.
Owner:SOITEC SA +1
Cross-linkable polyionic coatings for medical devices
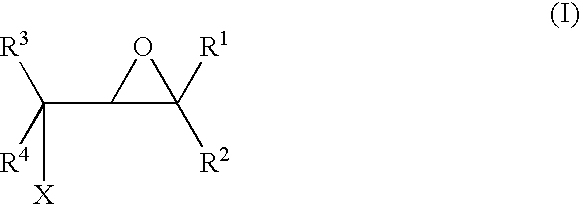
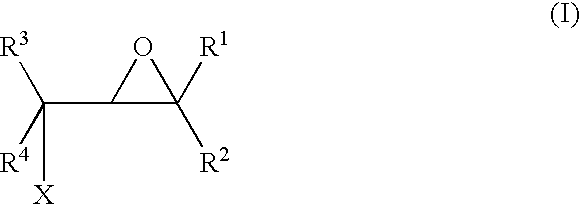
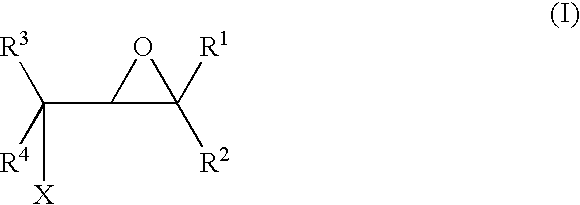
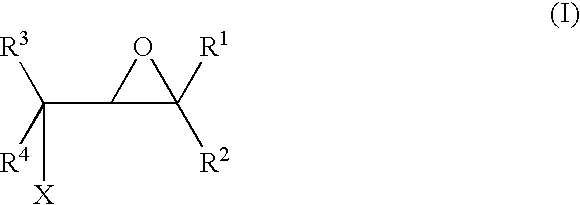
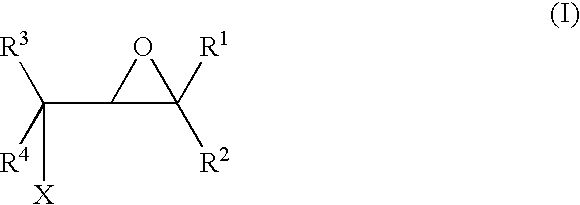
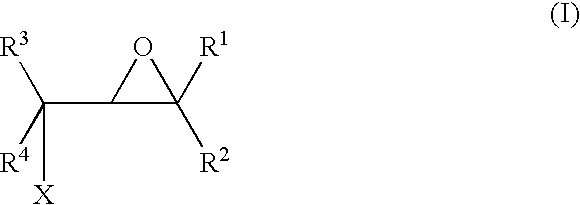
A method for making an article comprising a core material and a coating thereon, the method comprising the steps of:(a) providing the core material;(b) applying one or more layers of a crosslinkable polycationic material, wherein the polycationic material is a reaction product of:(i) an epoxide of formula (I)wherein X equals bromo, chloro, iodo, or cyano, and R1, R2, R3, R4, independently of one another, are selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, linear or branched C1-C6-alkyl, and linear or branched C1-C6-alkyl which is substituted with halogen, and(ii) a polymer having repeating units comprising one or more secondary or tertiary amine group(s);(c) applying one or more layers of a polyanionic material; and(d) cross-linking the layers of polyelectrolytes formed by steps (b) and (c).The articles obtainable by the method of the invention have desirable characteristics regarding adherence to the core material, durability, hydrophilicity, and wettability and are thus useful for the manufacture of medical articles such as ophthalmic devices.
Owner:ALCON INC
Pharmaceutical co-crystal compositions
InactiveUS20070026078A1Improve solubilityLow hygroscopicityBiocidePowder deliveryThioketoneHydroxamic acid
A pharmaceutical composition comprising a co-crystal of an API and a co-crystal former; wherein the API has at least one functional group selected from ether, thioether, alcohol, thiol, aldehyde, ketone, thioketone, nitrate ester, phosphate ester, thiophosphate ester, ester, thioester, sulfate ester, carboxylic acid, phosphonic acid, phosphinic acid, sulfonic acid, amide, primary amine, secondary amine, ammonia, tertiary amine, sp2 amine, thiocyanate, cyanamide, oxime, nitrile diazo, organohalide, nitro, s-heterocyclic ring, thiophene, n-heterocyclic ring, pyrrole, o-heterocyclic ring, furan, epoxide, peroxide, hydroxamic acid, imidazole, pyridine and the co-crystal former has at least one functional group selected from amine, amide, pyridine, imidazole, indole, pyrrolidine, carbonyl, carboxyl, hydroxyl, phenol, sulfone, sulfonyl, mercapto and methyl thio, such that the API and co-crystal former are capable of co-crystallizing from a solution phase under crystallization conditions.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON CONSUMER COPANIES +2
Cross-linkable polyionic coatings for medical devices
A method for making an article comprising a core material and a coating thereon, the method comprising the steps of:(a) providing the core material;(b) applying one or more layers of a crosslinkable polycationic material, wherein the polycationic material is a reaction product of:(i) an epoxide of formula (I)wherein X equals bromo, chloro, iodo, or cyano, and R1, R2, R3, R4, independently of one another, are selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, linear or branched C1-C6-alkyl, and linear or branched C1-C6-alkyl which is substituted with halogen, and(ii) a polymer having repeating units comprising one or more secondary or tertiary amine group(s);(c) applying one or more layers of a polyanionic material; and(d) cross-linking the layers of polyelectrolytes formed by steps (b) and (c).The articles obtainable by the method of the invention have desirable characteristics regarding adherence to the core material, durability, hydrophilicity, and wettability and are thus useful for the manufacture of medical articles such as ophthalmic devices.
Owner:ALCON INC
Biodegradable poly(beta-amino esters) and uses thereof
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Absorbent sheet having regenerated cellulose microfiber network
An absorbent paper sheet for tissue or towel includes from about 99 percent to about 70 percent by weight of cellulosic papermaking fiber and from about 1 percent to about 30 percent by weight fibrillated regenerated cellulose microfiber which was regenerated form a cellulosic dope utilizing a tertiary amine N-oxide solvent or an ionic liquid. Fibrillation of the microfiber is controlled such that it has a reduced coarseness and a reduced freeness as compared with unfibrillated regenerated cellulose microfiber from which it is made and provides at least one of the following attributes to the absorbent sheet: (a) the absorbent sheet exhibits an elevated SAT value and an elevated wet tensile value as compared with a like sheet prepared without fibrillated regenerated cellulose microfiber; (b) the absorbent sheet exhibits an elevated wet / dry CD tensile ratio as compared with a like sheet prepared without fibrillated regenerated cellulose microfiber; (c) the absorbent sheet exhibits a lower GM Break Modulus than a like sheet having like tensile values prepared without fibrillated regenerated cellulose microfiber; or (d) the absorbent sheet exhibits an elevated bulk as compared with a like sheet having like tensile values prepared without fibrillated regenerated cellulose microfiber. In some embodiments, the pulp is pre-treated with debonder to enhance the wet / dry CD tensile ratio of the sheet.
Owner:GPCP IP HLDG LLC
Radiation curable inkjet fluids and inks improved for photoyellowing
ActiveUS20100330296A1Intuitive effectEasy to observeLiquid surface applicatorsImpression capsVinyl etherTM compound
A radiation curable inkjet fluid includes a radiation curable composition including at least 25 wt % of a vinylether acrylate and at least 15 wt % of a polymerizable compound including at least three acrylate groups, each wt % being based upon the total weight of the radiation curable composition; and a photoinitiator including a tertiary amine group and 0 to 3 wt % of isopropylthioxanthone based upon the total weight of the radiation curable inkjet fluid. Also, an inkjet printing method using the radiation curable inkjet fluid.
Owner:AGFA NV
Biodegradable poly(beta-amino esters) and uses thereof
Poly(β-amino esters) prepared from the conjugate addition of bis(secondary amines) or primary amines to a bis(acrylate ester) are described. Methods of preparing these polymers from commercially available starting materials are also provided. These tertiary amine-containing polymers are preferably biodegradable and biocompatible and may be used in a variety of drug delivery systems. Given the poly(amine) nature of these polymers, they are particularly suited for the delivery of polynucleotides. Nanoparticles containing polymer / polynucleotide complexes have been prepared. The inventive polymers may also be used to encapsulate other agents to be delivered. They are particularly useful in delivering labile agents given their ability to buffer the pH of their surroundings.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
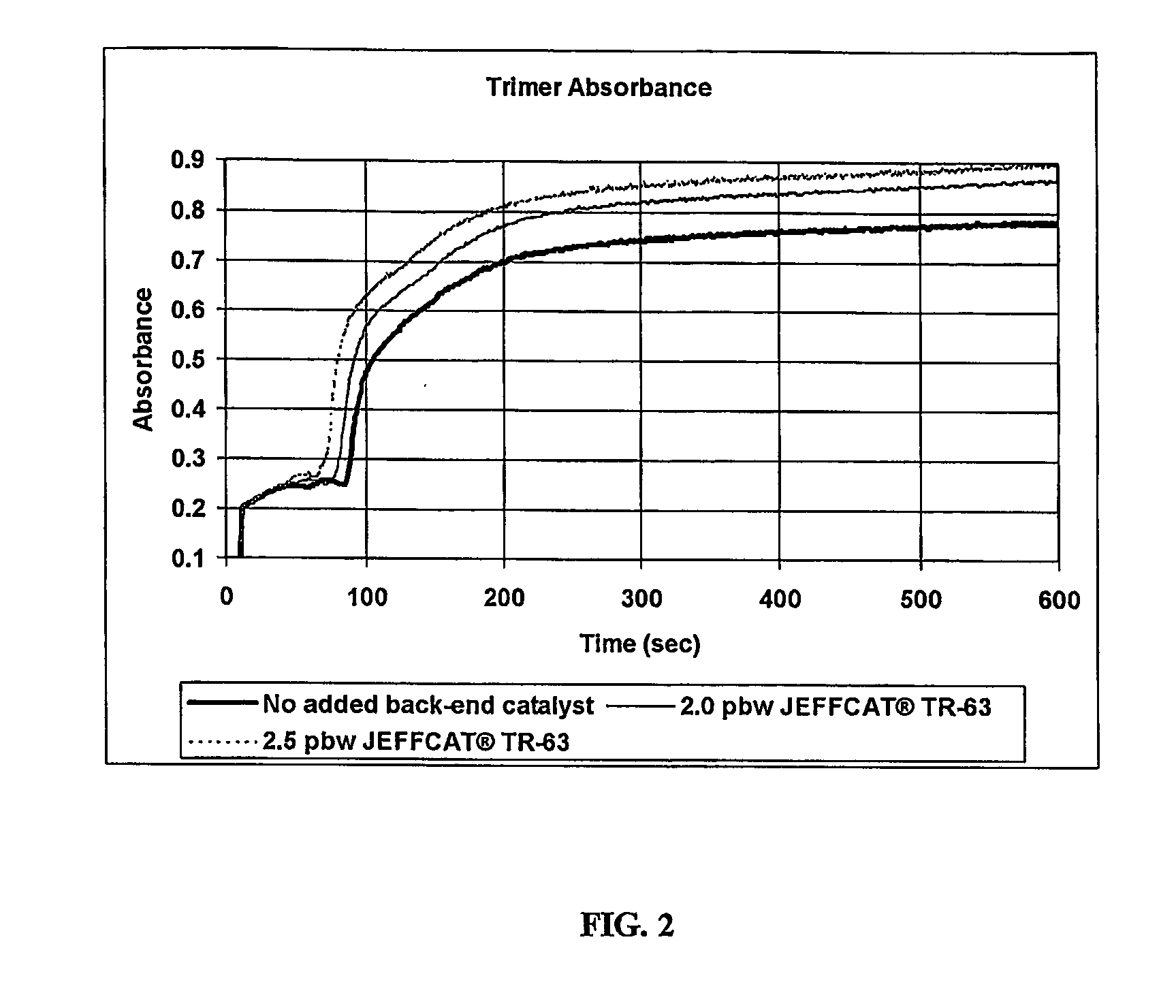
Low-Odor Catalyst for Isocyanate-Derived Foams and Elastomers
InactiveUS20070282026A1Other chemical processesOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsElastomerPolyisocyanurate
Provided herein are catalysts useful in providing foam products which are produced using an organic poly isocyanate as a starting material. A catalyst according to the present invention includes the tris-(hydroxyethyl)methyl ammonium cation, and optionally potassium cation, in combination with a variety of possible counter anions present to maintain charge balance and for compatibility. A catalyst according to the invention is preferably used in conjunction with one or more conventional tertiary amine catalysts in a foam producing process. The foams may be polyurethane foams, polyisocyanurate foams, flexible foams, or elastomeric foams.
Owner:HUNTSMAN PETROCHEMICAL LLC
Cellulose oxidation by nitrogen dioxide in a perfluorinated tertiary amine solvent
ActiveUS7645874B2Efficiently oxidizedReduce usageBiocideOrganic active ingredientsAqueous alcoholNitrogen dioxide
This invention relates to a process for preparing bioabsorbable oxidized cellulose comprising combining cellulose material, with nitrogen dioxide and a nonaqueous solvent chosen from the class of perfluorinated tertiary amines. This invention also relates to a method of oxidizing cellulose material comprising introducing a solvent into the vessel, circulating the solvent through the cellulose material, adding nitrogen dioxide to said vessel containing the solvent and cellulose in the required amounts, circulating the solution for 7 to 24 hours while controlling the reaction temperature, and isolating the oxidized material. Preferably, isolation of the oxidized product is followed by first washing the oxidized cellulose material with cold water, then washing the oxidized cellulose material with an aqueous alcohol solution several times, then washing the material with 100% alcohol several times, and finally drying the oxidized material.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
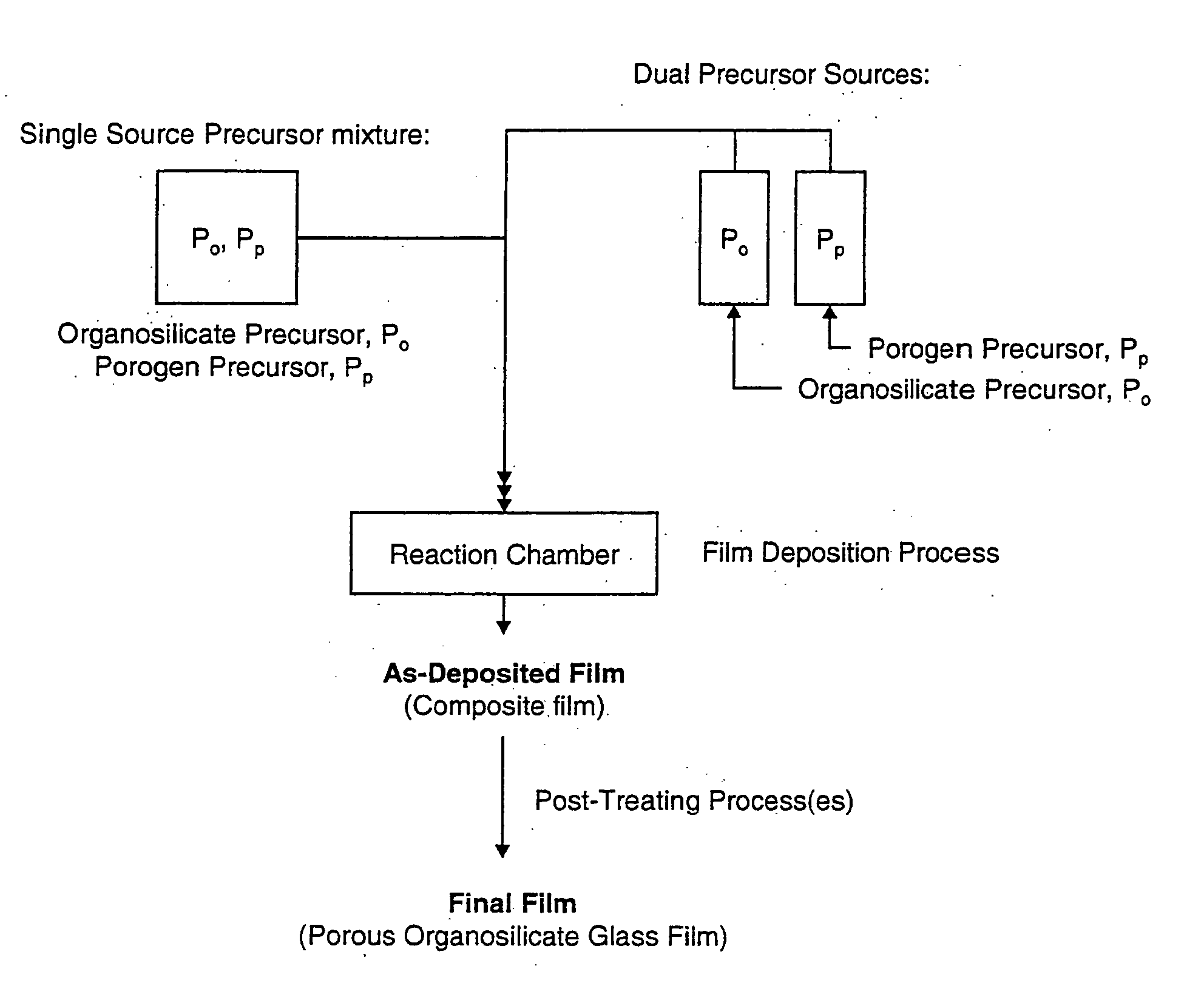
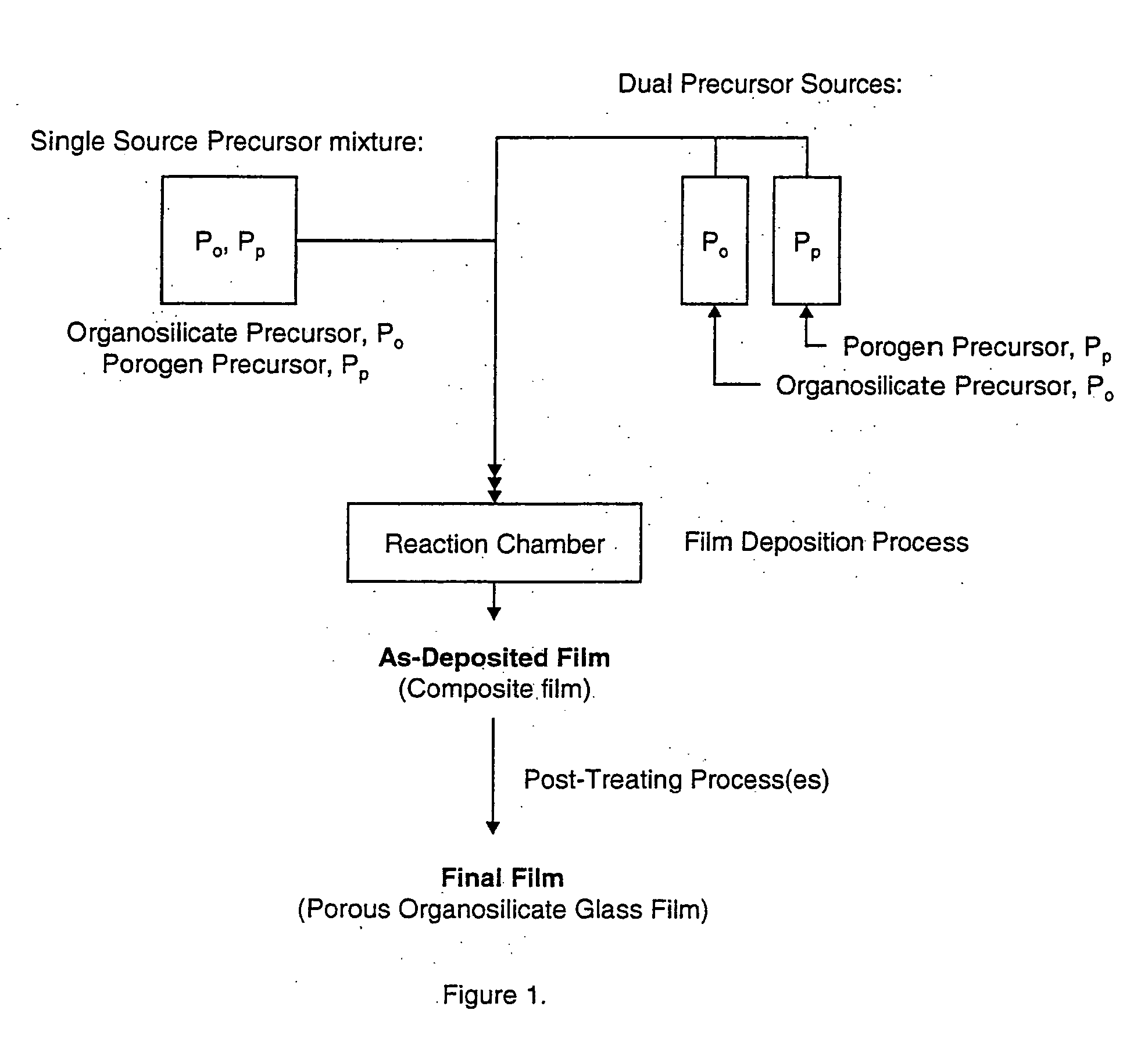
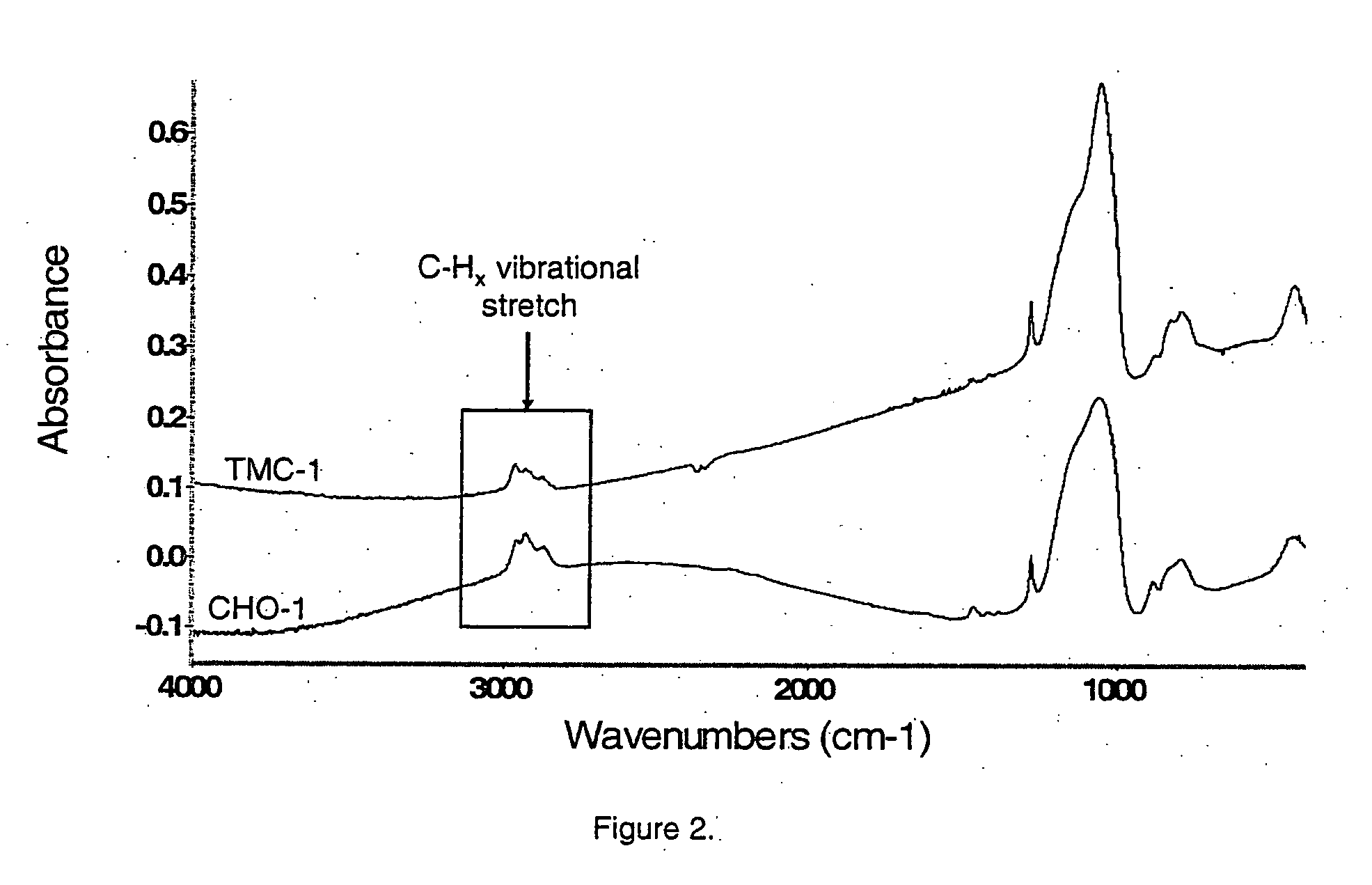
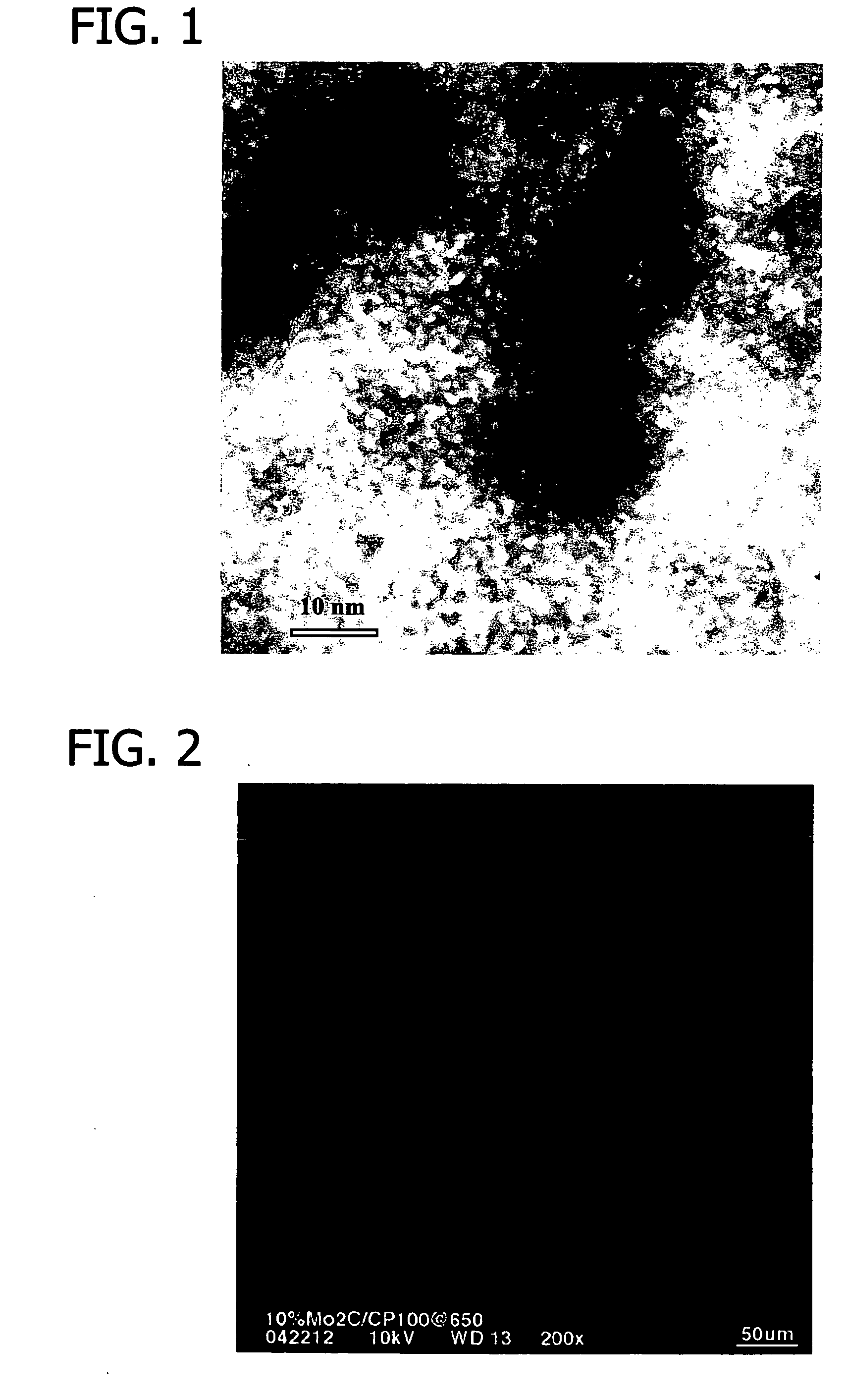
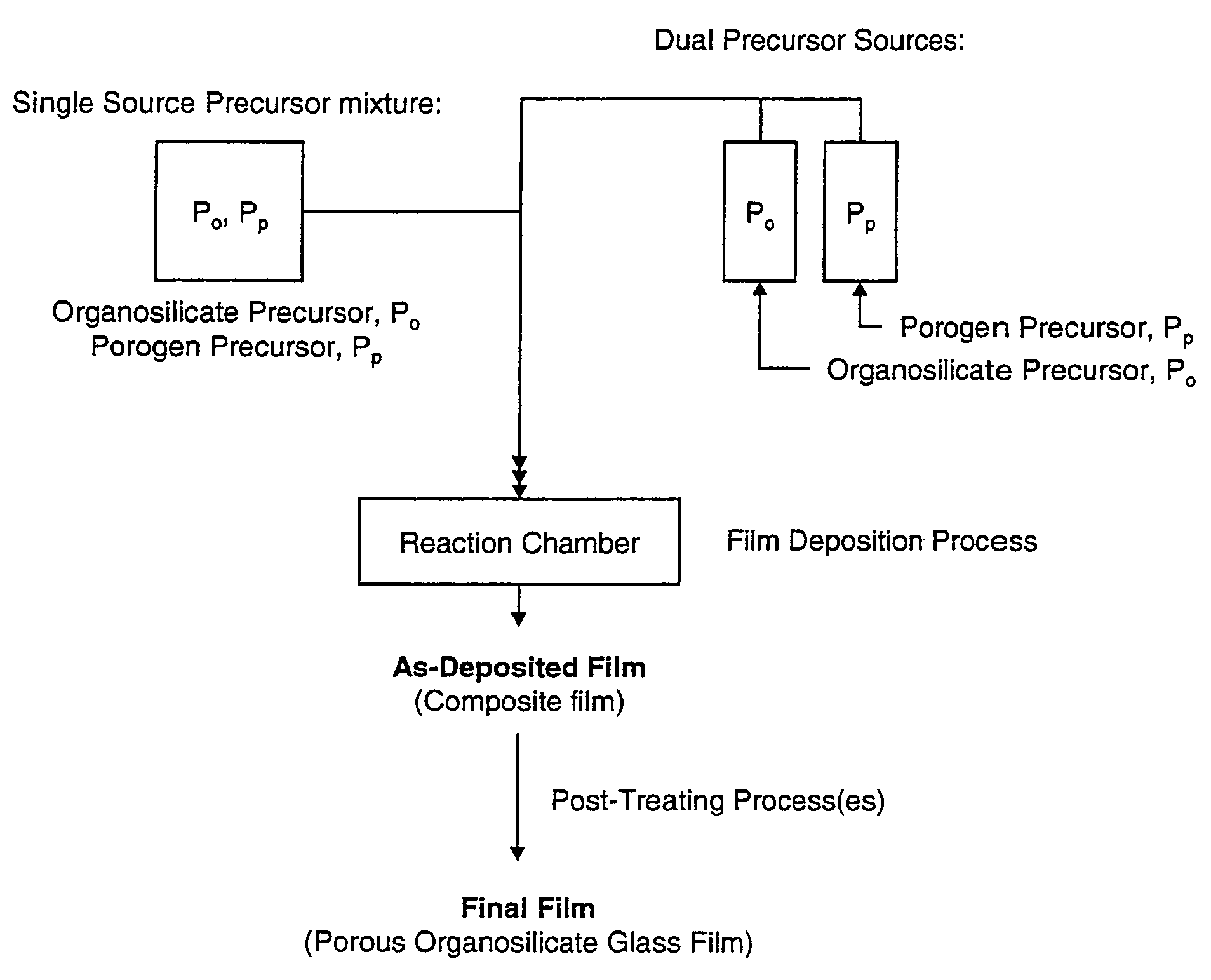
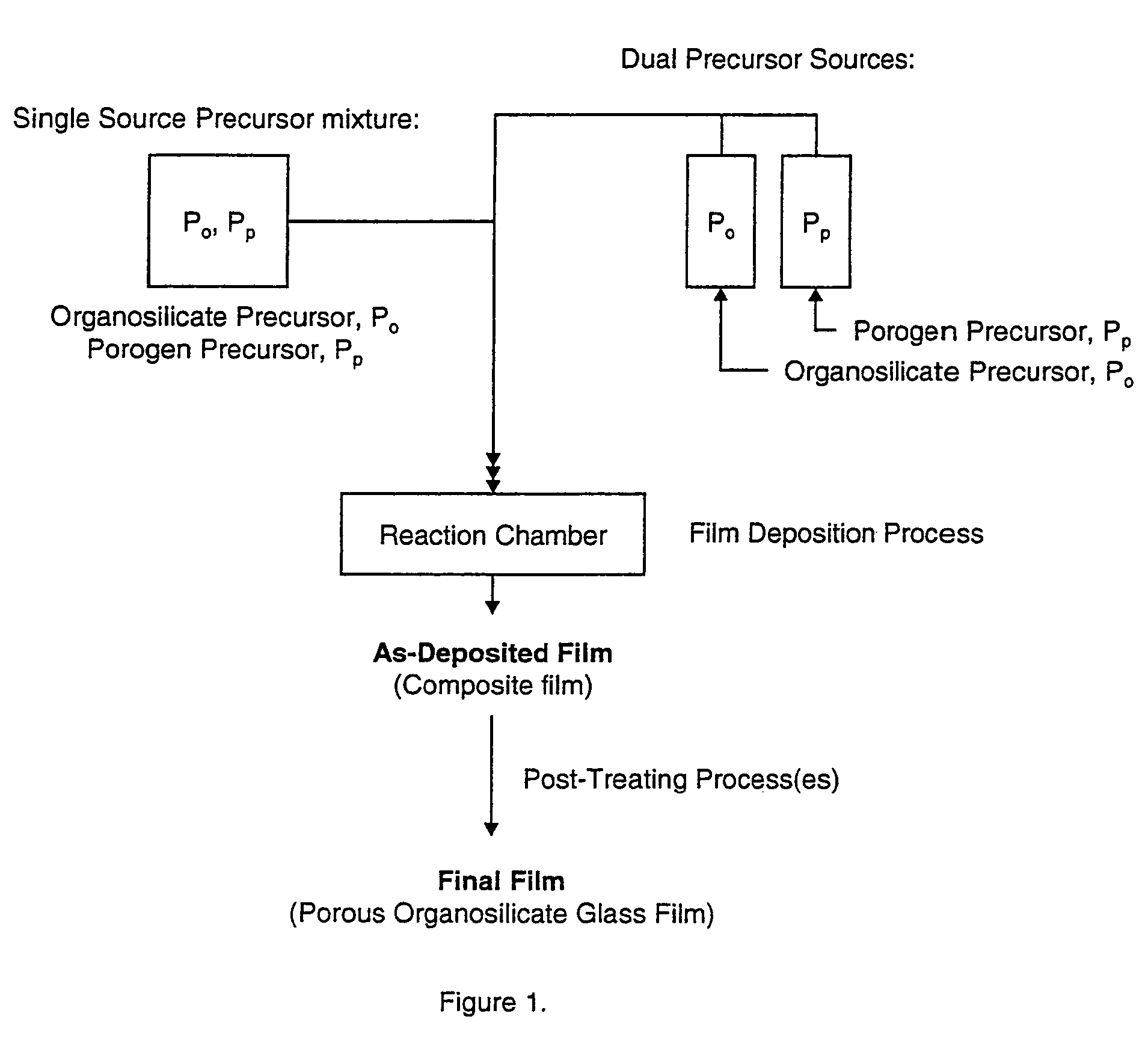
Porous low dielectric constant compositions and methods for making and using same
ActiveUS20060078676A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPretreated surfacesConstant compositionCarboxylic acid
A porous organosilicate glass (OSG) film: SivOwCxHyFz, where v+w+x+y+z=100%, v is 10 to 35 atomic %, w is 10 to 65 atomic %, x is 5 to 30 atomic %, y is 10 to 50 atomic % and z is 0 to 15 atomic %, has a silicate network with carbon bonds as methyl groups (Si—CH3) and contains pores with diameter less than 3 nm equivalent spherical diameter and dielectric constant less than 2.7. A preliminary film is deposited by a chemical vapor deposition method from organosilane and / or organosiloxane precursors, and independent pore-forming precursors. Porogen precursors form pores within the preliminary film and are subsequently removed to provide the porous film. Compositions, film forming kits, include organosilane and / or organosiloxane compounds containing at least one Si—H bond and porogen precursors of hydrocarbons containing alcohol, ether, carbonyl, carboxylic acid, ester, nitro, primary amine, secondary amine, and / or tertiary amine functionality or combinations.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
Biodegradable poly(β-amino esters) and uses thereof
InactiveUSRE43612E1High molecular weightHigh transfection efficiencyPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsAmino estersNanoparticle
Poly(β-amino esters) prepared from the conjugate addition of bis(secondary amines) or primary amines to a bis(acrylate ester) are described. Methods of preparing these polymers from commercially available starting materials are also provided. These tertiary amine-containing polymers are preferably biodegradable and biocompatible and may be used in a variety of drug delivery systems. Given the poly(amine) nature of these polymers, they are particularly suited for the delivery of polynucleotides. Nanoparticles containing polymer / polynucleotide complexes have been prepared. The inventive polymers may also be used to encapsulate other agents to be delivered. They are particularly useful in delivering labile agents given their ability to buffer the pH of their surroundings. A system for preparing and screening polymers in parallel using semi-automated robotic fluid delivery systems is also provided.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Oxidation catalyst and process
InactiveUS20050176990A1Amino preparation from aminesOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalytic oxidationNitrogen
This invention relates to the field of heterogeneous catalysis, and more particularly to catalysts including carbon supports having formed thereon compositions which comprise a transition metal in combination with nitrogen and / or carbon. The invention further relates to the fields of catalytic oxidation, including the preparation of secondary amines by the catalytic oxidation of tertiary amines.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Preparation method of high temperature resistant single-component solventless epoxy adhesive
InactiveCN101649174AConvenient sourceSimple preparation processEpoxy resin adhesivesSolventThermoplastic polyimide
The invention relates to a preparation method of high temperature resistant single-component solventless epoxy adhesive. The method comprises the following steps: adding aromatic binary primary amine and strongly polar non-proton organic solvent in a reaction tank, stirring at room temperature to dissolve, adding aromatic binary acid anhydride to perform refluxing and water-segregating reaction at 120-150 DEG C for 6-12h, cooling, adding the reaction solution in a stamp tank with precipitant to precipitate solid powder, namely white thermoplastic polyimide powder, adding white thermoplastic polyimide powder and tertiary amine compound or imidazole compound in epoxy resin to react for 1-2h, adding active diluent and latent curing agent to stir evenly and obtaining the product. The production process is easy and the cost is low so as to realize industrialized production; the tensile shear intensions of the epoxy adhesive at room temperature and 120 DEG C are respectively up to 28Mpa and26Mpa and the epoxy adhesive has broad application prospect in fields such as electronics and microelectronics, electrical motors, aviation and aerospace and the like.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Synthesis metal nanoparticle
A method for providing an anhydrous route for the synthesis of amine capped coinage-metal (copper, silver, and gold) nanoparticles (NPs) using the coinage-metal mesityl (mesityl=C6H2(CH3)3-2,4,6) derivatives. In this method, a solution of (Cu(C6H2(CH3)3)5, (Ag(C6H2(CH3)3)4, or (Au(C6H2(CH3)3)5 is dissolved in a coordinating solvent, such as a primary, secondary, or tertiary amine; primary, secondary, or tertiary phosphine, or alkyl thiol, to produce a mesityl precursor solution. This solution is subsequently injected into an organic solvent that is heated to a temperature greater than approximately 100° C. After washing with an organic solvent, such as an alcohol (including methanol, ethanol, propanol, and higher molecular-weight alcohols), oxide free coinage NP are prepared that could be extracted with a solvent, such as an aromatic solvent (including, for example, toluene, benzene, and pyridine) or an alkane (including, for example, pentane, hexane, and heptane). Characterization by UV-Vis spectroscopy and transmission electron microscopy showed that the NPs were approximately 9.2±2.3 nm in size for Cu°, (no surface oxide present), approximately 8.5±1.1 nm Ag° spheres, and approximately 8–80 nm for Au°.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
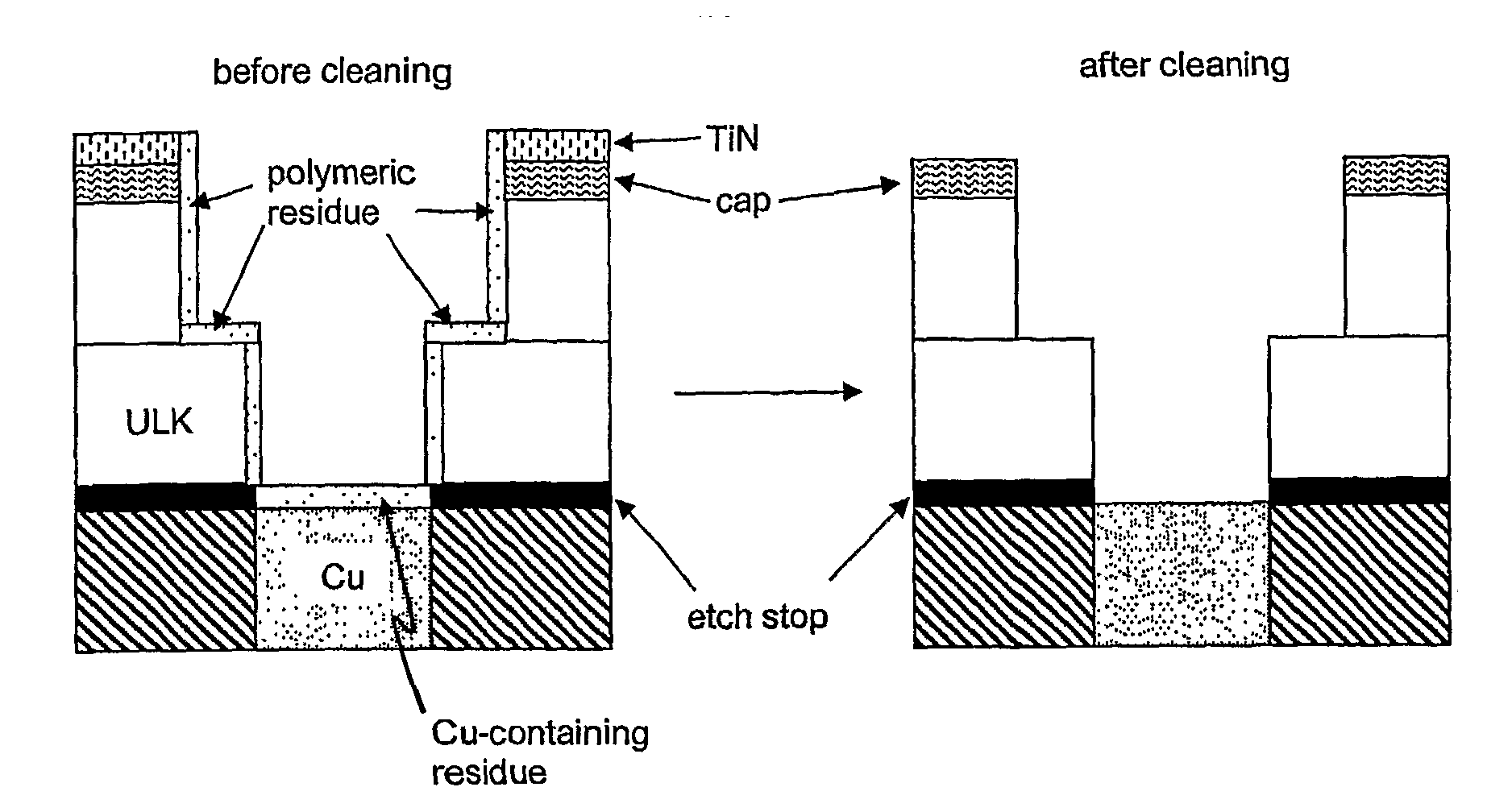
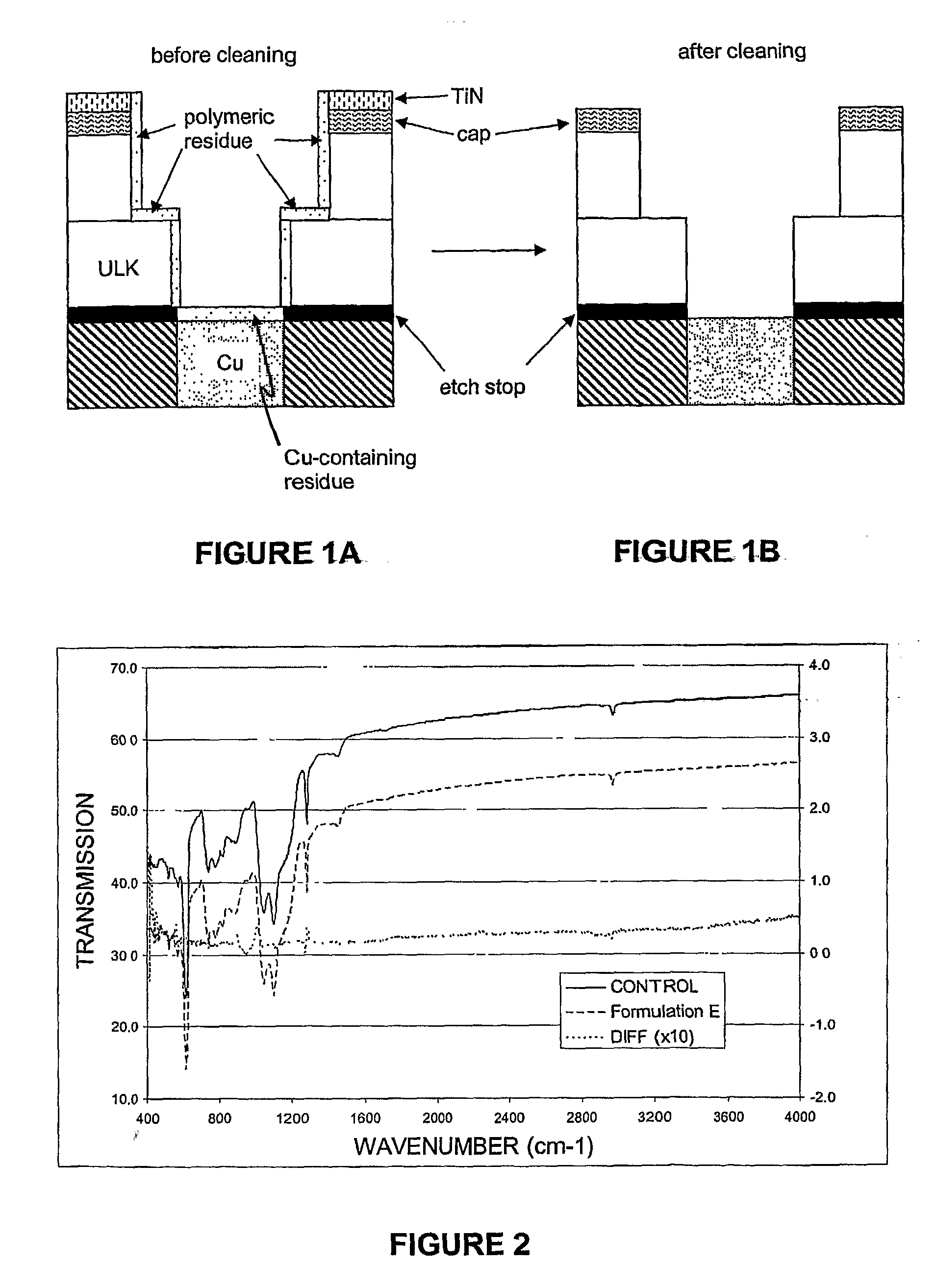
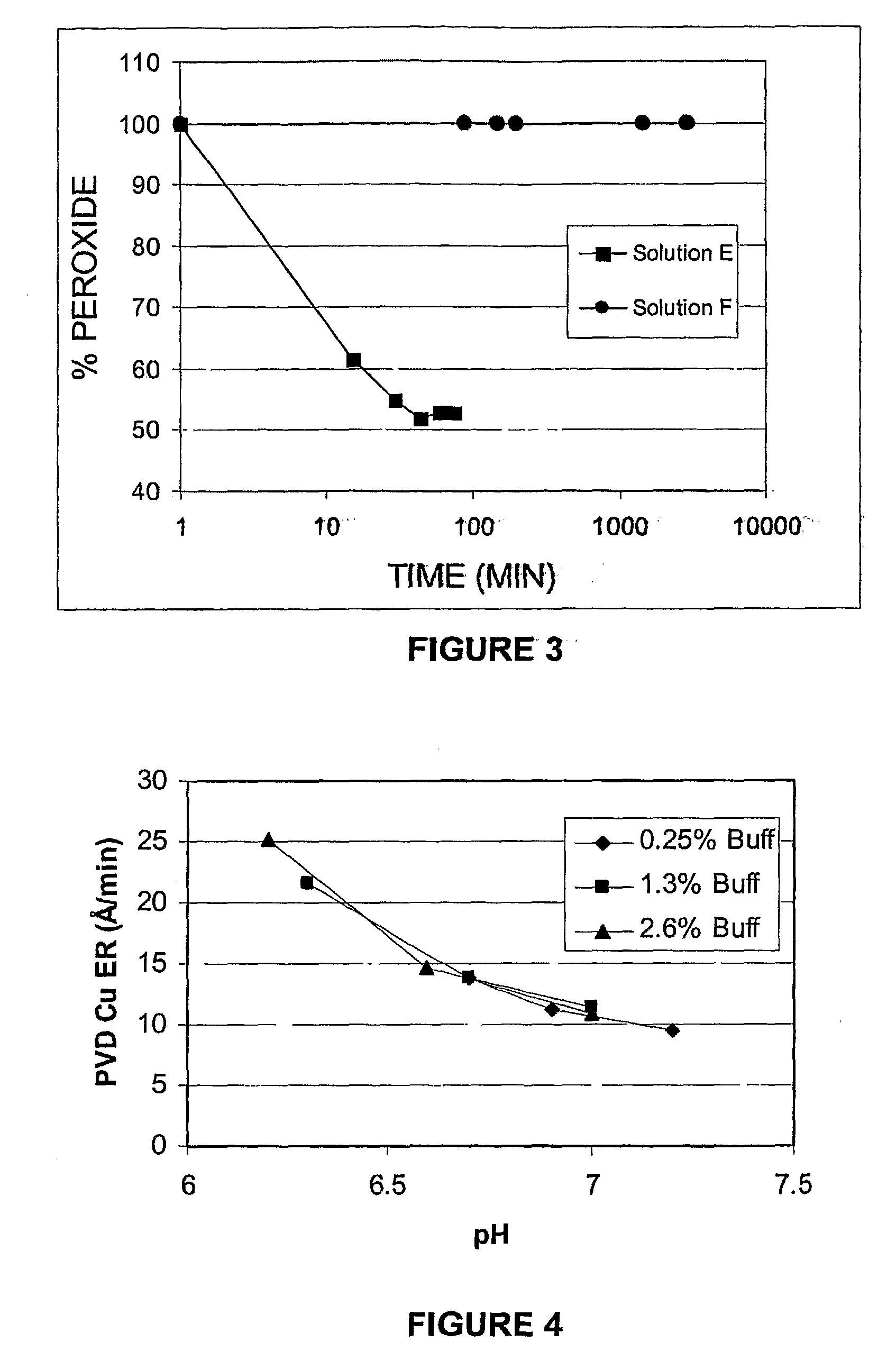
Oxidizing aqueous cleaner for the removal of post-etch residues
ActiveUS20090215658A1Organic detergent compounding agentsDetergent mixture composition preparationMetal interconnectOxygen
An oxidizing aqueous cleaning composition and process for cleaning post-plasma etch residue and / or hardmask material from a microelectronic device having said residue thereon. The oxidizing aqueous cleaning composition includes at least one oxidizing agent, at least one oxidizing agent stabilizer comprising an amine species selected from the group consisting of primary amines, secondary amines, tertiary amines and amine-N-oxides, optionally at least one co-solvent, optionally at least one metal-chelating agent, optionally at least one buffering species, and water. The composition achieves highly efficacious cleaning of the residue material from the microelectronic device while simultaneously not damaging the interlevel dielectric and metal interconnect material also present thereon.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
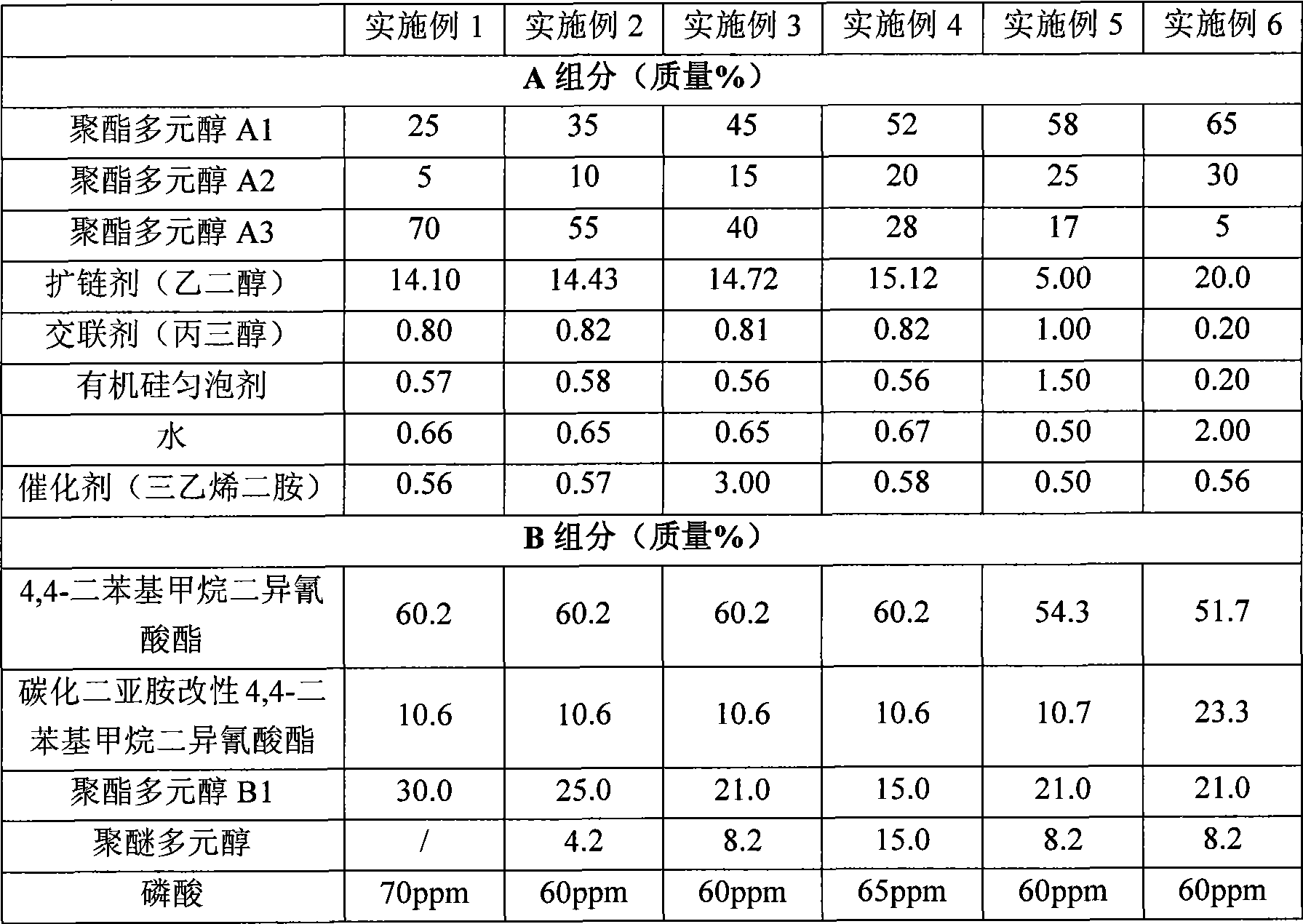
Low density high hardness polyurethane micropore elastomer and preparation thereof
The invention discloses a low-density high-hardness microporous polyurethane elastomer and a preparation method thereof; polyester polyol A1, polyester polyol A2, polyester polyol A3, Diol chain extender, crosslinking agent, tertiary amine or organic metal catalysts, organosilicone foam homogenizing agent and water foaming agent are placed in a reactor and then mixed for obtaining a component A; isocyanate, polyester polyol B1, polyether polyol, and side effect inhibitor are placed in the reactor and then reacted for preparing a component B; later, the two components are completely mixed and injected into a mold for being reacted and molded so as to obtain the microporous polyurethane elastomer. The microporous polyurethane elastomer which is produced by the method has the advantages of low density, high hardness, low product shrinkage rate and the like, and can be widely used in production of sole materials such as middle sole, large sole, and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HUAFON NEW MATERIALS CO LTD
Transition metal-containing catalysts and catalyst combinations including transition metal-containing catalysts and processes for their preparation and use as oxidation catalysts
ActiveUS20060229466A1Organic compound preparationGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsCatalytic oxidationNitrogen
This invention relates to the field of heterogeneous catalysis, and more particularly to catalysts including carbon supports having compositions which comprise one or more transition metals in combination with nitrogen and / or carbon formed on or over the surface of the carbon support. The present invention also relates to catalyst combinations comprising catalysts including carbon supports having compositions which comprise one or more transition metals in combination with nitrogen and / or carbon formed on or over the surface of a carbon support and a secondary catalyst or, co-catalyst, including a secondary transition metal. The invention further relates to the field of catalytic oxidation reactions, including the preparation of secondary amines by the catalytic oxidation of tertiary amines.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Cellulose oxidation by nitrogen dioxide in a perfluorinated tertiary amine solvent
ActiveUS20070054880A1Efficiently oxidizedReduce usageBiocideOrganic active ingredientsNitrogen dioxideAqueous alcohol
This invention relates to a process for preparing bioabsorbable oxidized cellulose comprising combining cellulose material, with nitrogen dioxide and a nonaqueous solvent chosen from the class of perfluorinated tertiary amines. This invention also relates to a method of oxidizing cellulose material comprising introducing a solvent into the vessel, circulating the solvent through the cellulose material, adding nitrogen dioxide to said vessel containing the solvent and cellulose in the required amounts, circulating the solution for 7 to 24 hours while controlling the reaction temperature, and isolating the oxidized material. Preferably, isolation of the oxidized product is followed by first washing the oxidized cellulose material with cold water, then washing the oxidized cellulose material with an aqueous alcohol solution several times, then washing the material with 100% alcohol several times, and finally drying the oxidized material.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Porous low dielectric constant compositions and methods for making and using same
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
Self-healing polyurethane resin containing disulfide bond and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to self-healing polyurethane resin containing disulfide bond and a preparation method thereof. The polyurethane resin comprises, by weight parts, 10-30 parts of polyether or polyester polyol, 3-20 parts of polyisocyanates, 1-10 parts of chain extender containing the disulfide bond, 0.001-1 part of organic tin or tertiary amine catalyst and 50-80 parts of organic solvent. The method for preparing the self-healing polyurethane resin containing the disulfide bond comprises the steps of weighing raw materials, stirring, heating and performing dehydration for the polyether or polyester polyol under vacuum conditions, lowering the temperature to 85 DEG C or below, adding the polyisocyanates and the organic tin or tertiary amine catalyst, reacting, lowering the temperature to 50 DEG C or below, adding the organic solvent and the chain extender containing the disulfide bond, reacting and performing vacuum defoamation to obtain the self-healing polyurethane resin. The self-healing polyurethane resin heals by itself under the heating or ultraviolet (UV) light conditions, the required conditions are mild, the healing speed is high, the effect is good, the preparation method is simple and easy to control, and raw materials are goods of commercialized production and are cheap and easy to obtain.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Method for preparation of copolyorganosiloxanecarbonates of high clarity
Owner:SHPP GLOBAL TECH BV
Biodegradable resin composition for molding and object molded or formed from the same
Owner:UNITIKA LTD
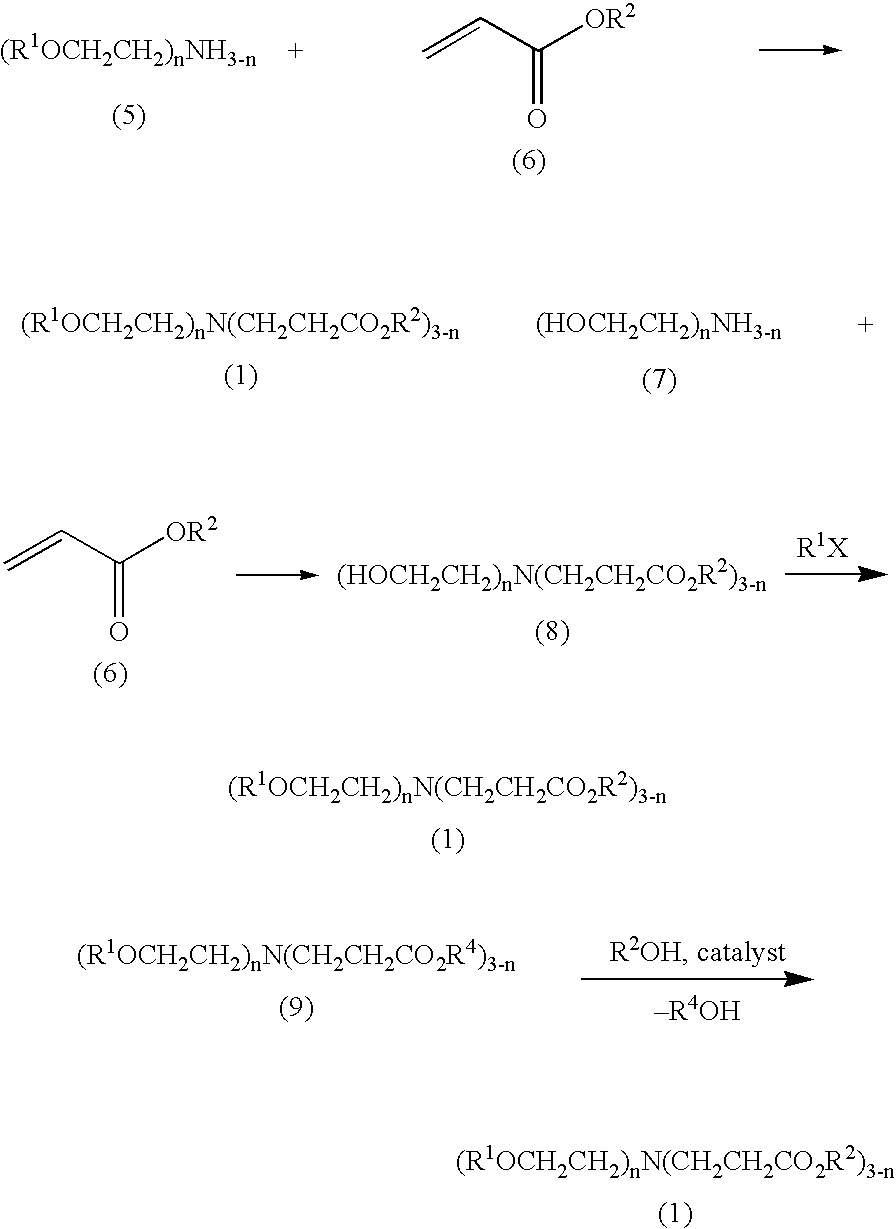
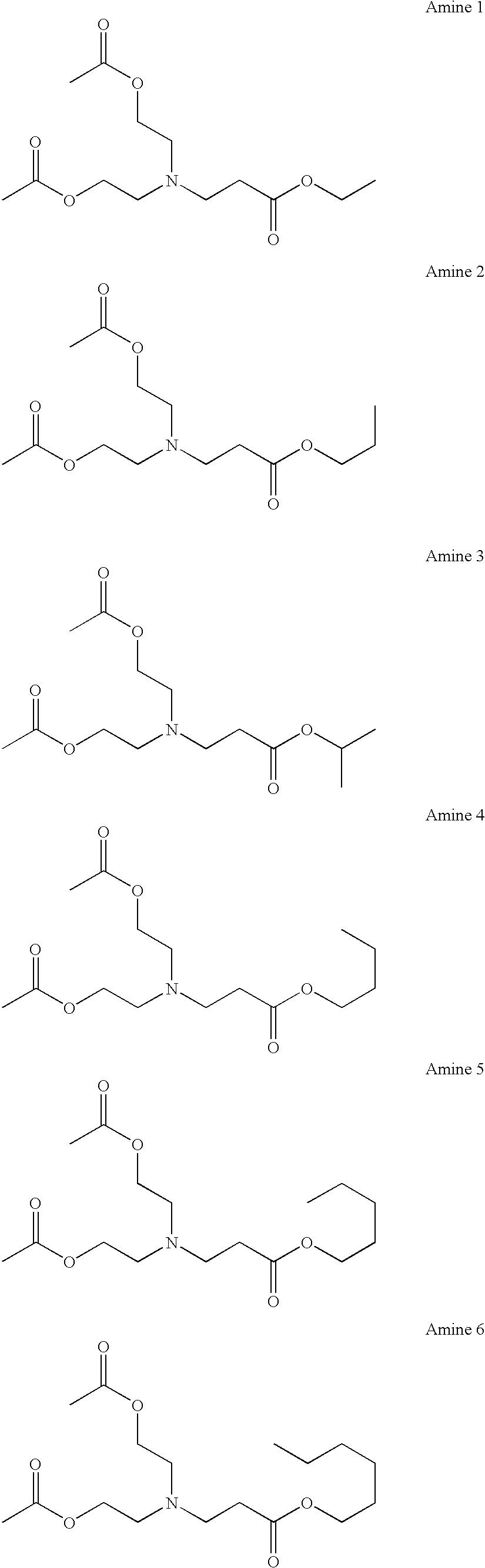
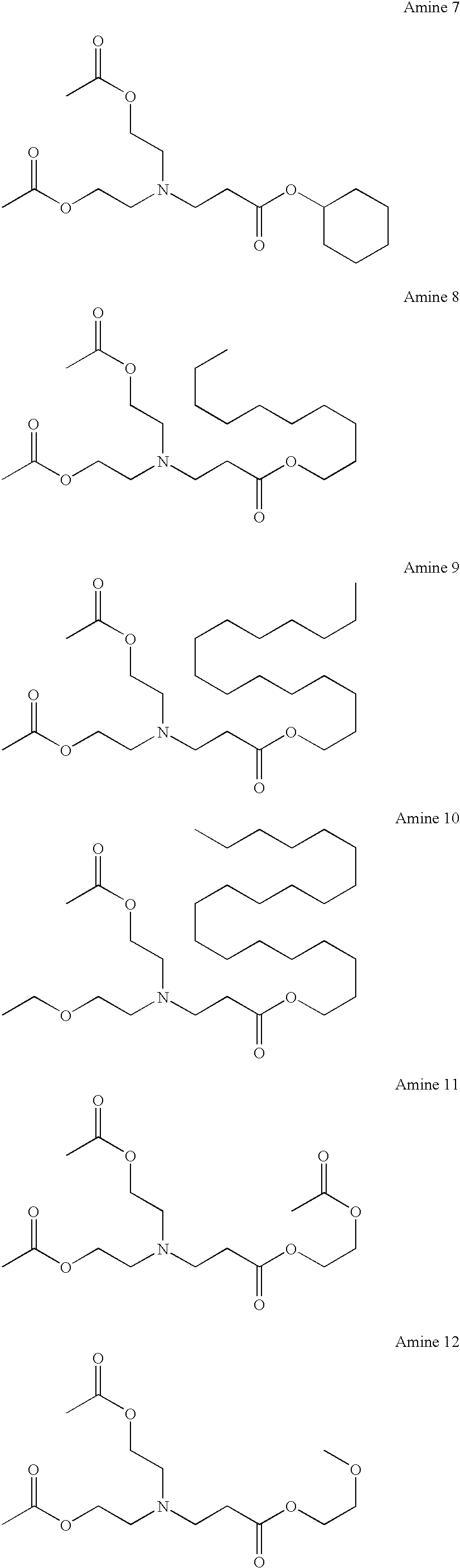
Tertiary amine compounds having an ester structure and processes for preparing same
InactiveUS7084303B2Preventing a film lossIncrease contrastOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationChemical amplificationPhotolithography
The present invention provides ester group-containing tertiary amine compounds of the formula (R1OCH2CH2)nN(CH2CH2CO2R2)3-n which, when used as additives in chemical amplification photolithography, can yield photoresists having a high resolution and an excellent focus margin. The present invention also provides a process comprising the step of subjecting a primary or secondary amine compound to Michael addition to an acrylic ester compound; a process comprising the steps of subjecting monoethanolamine or diethanolamine to Michael addition to an acrylic ester compound so as to form an ester group-containing amine compound and introducing a R1 group to the resultant ester group-containing amine compound; and a process comprising the step of effecting the ester exchange reaction of an ester group-containing tertiary amine with R2OH.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com