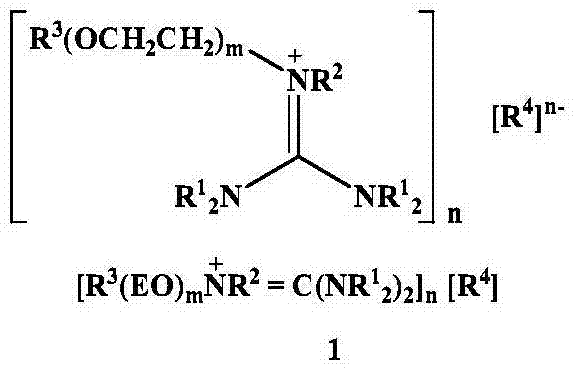
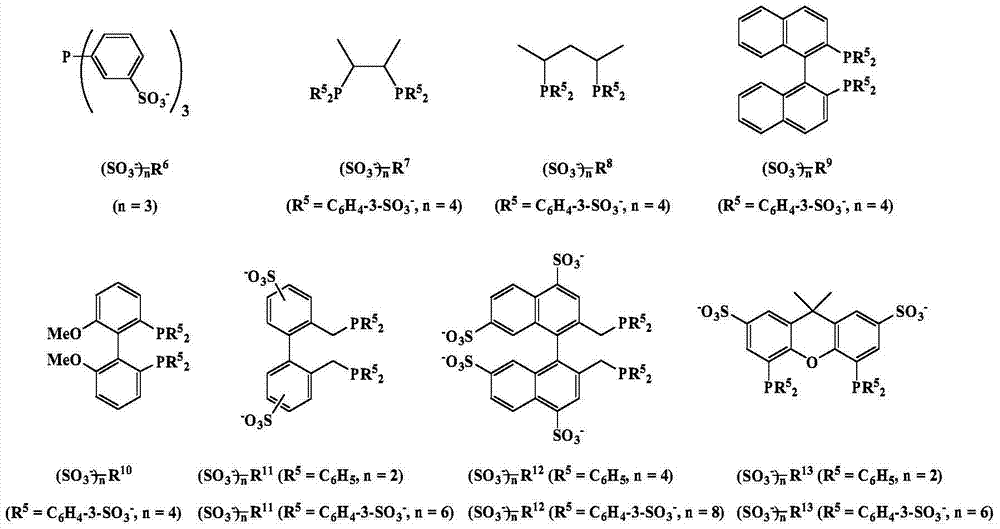
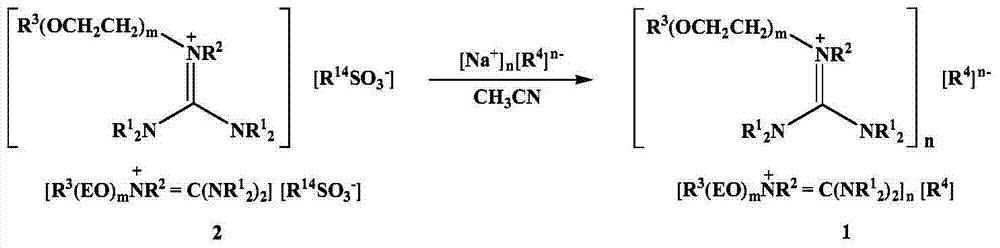
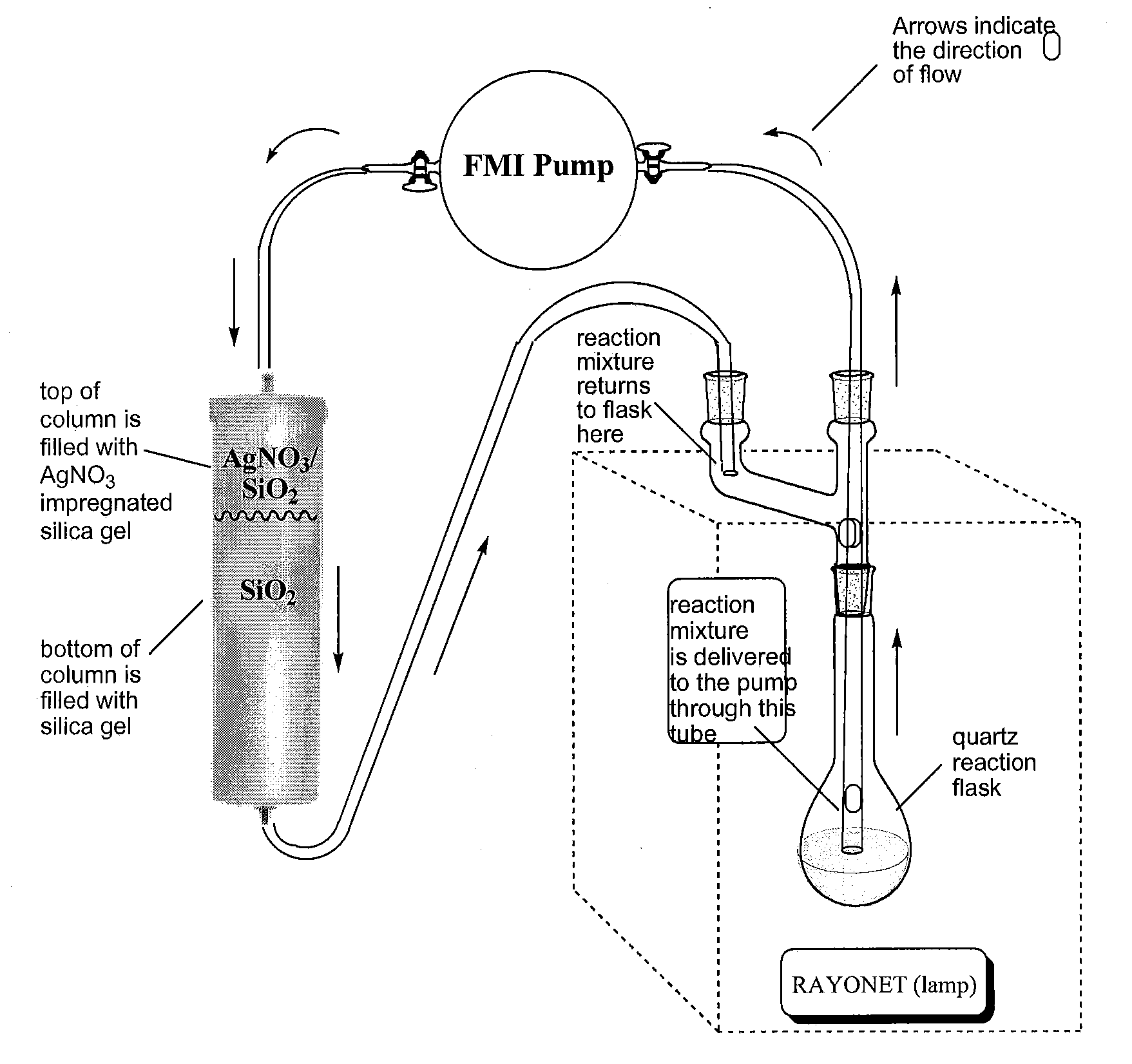
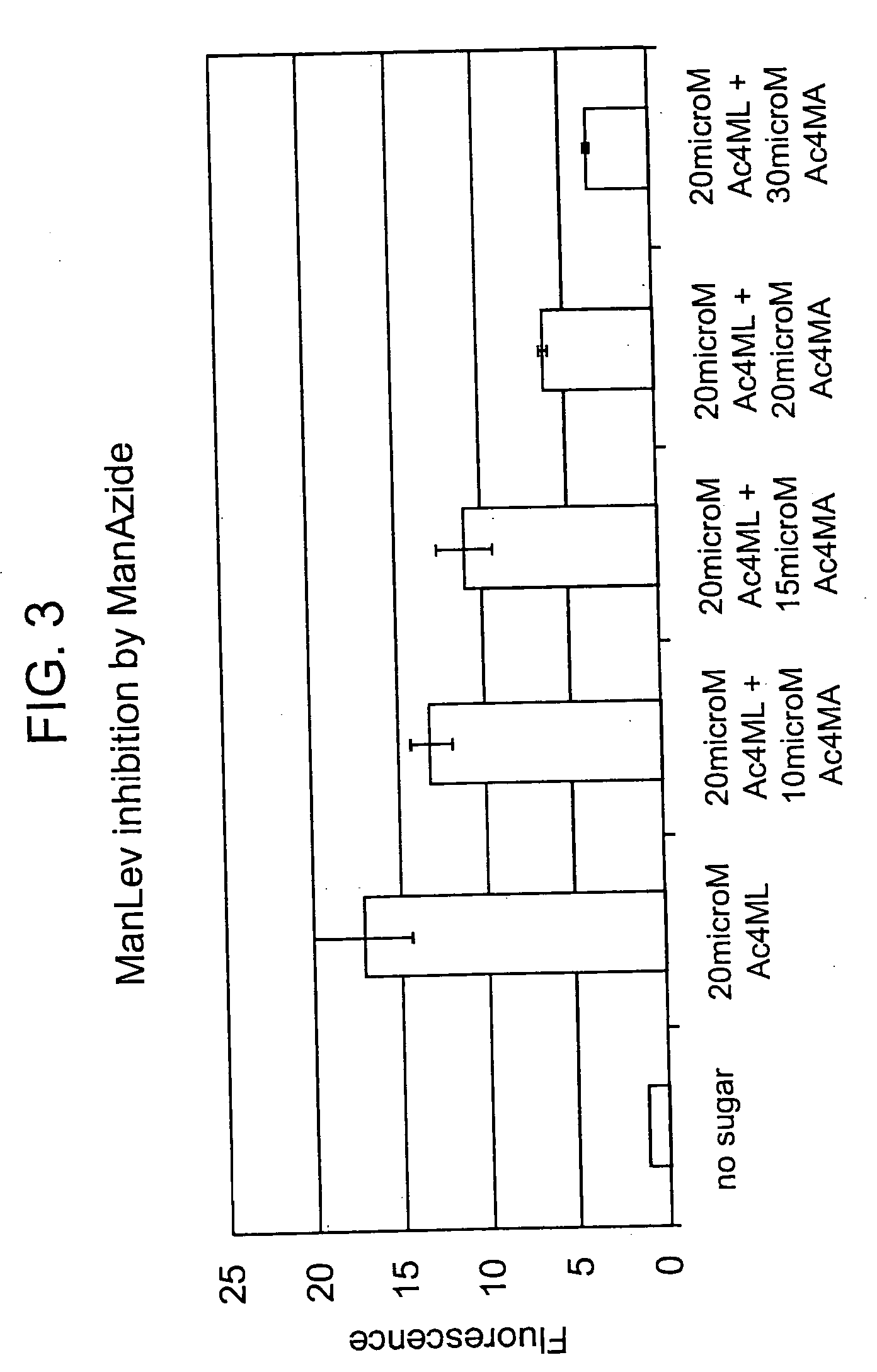
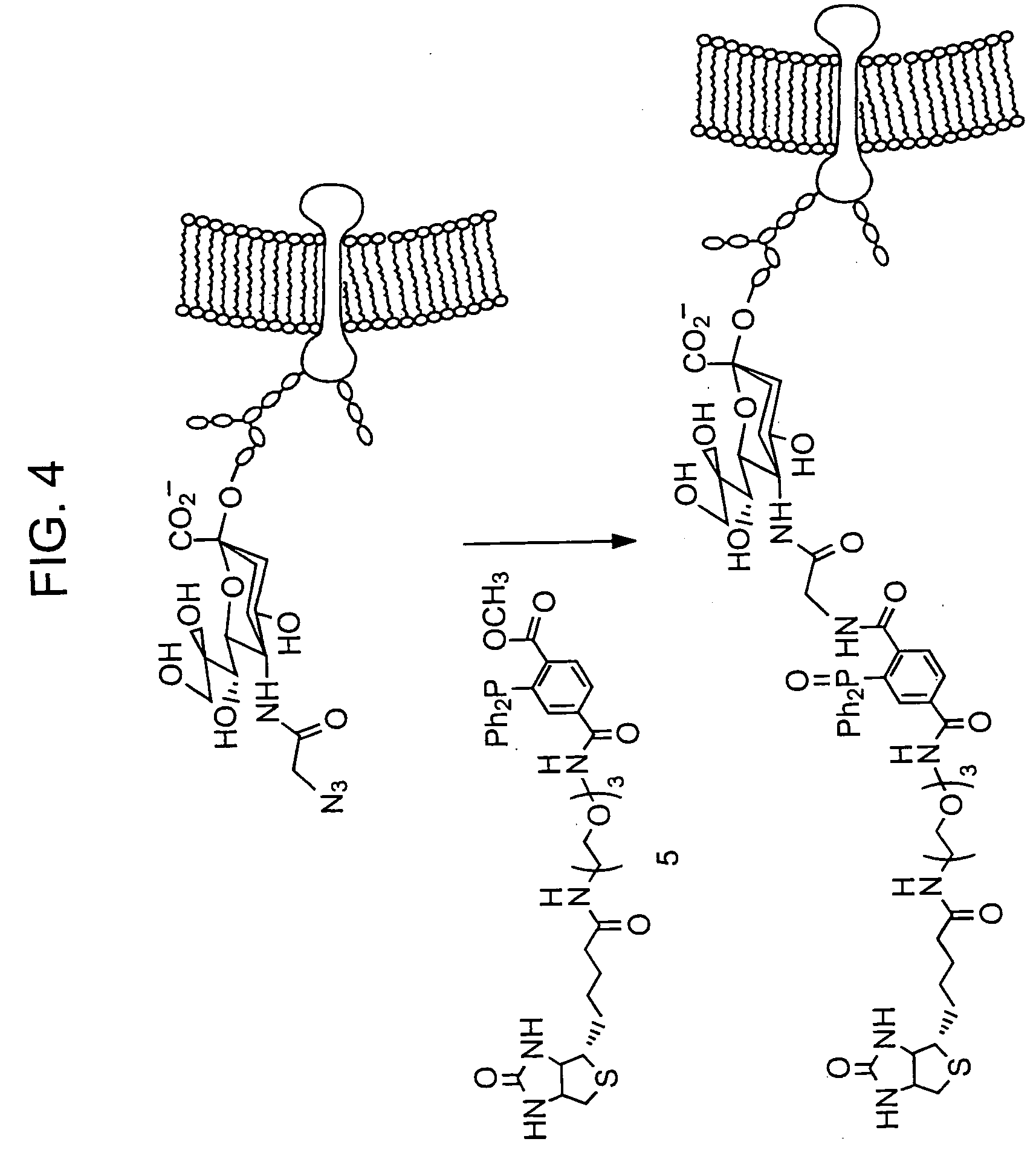
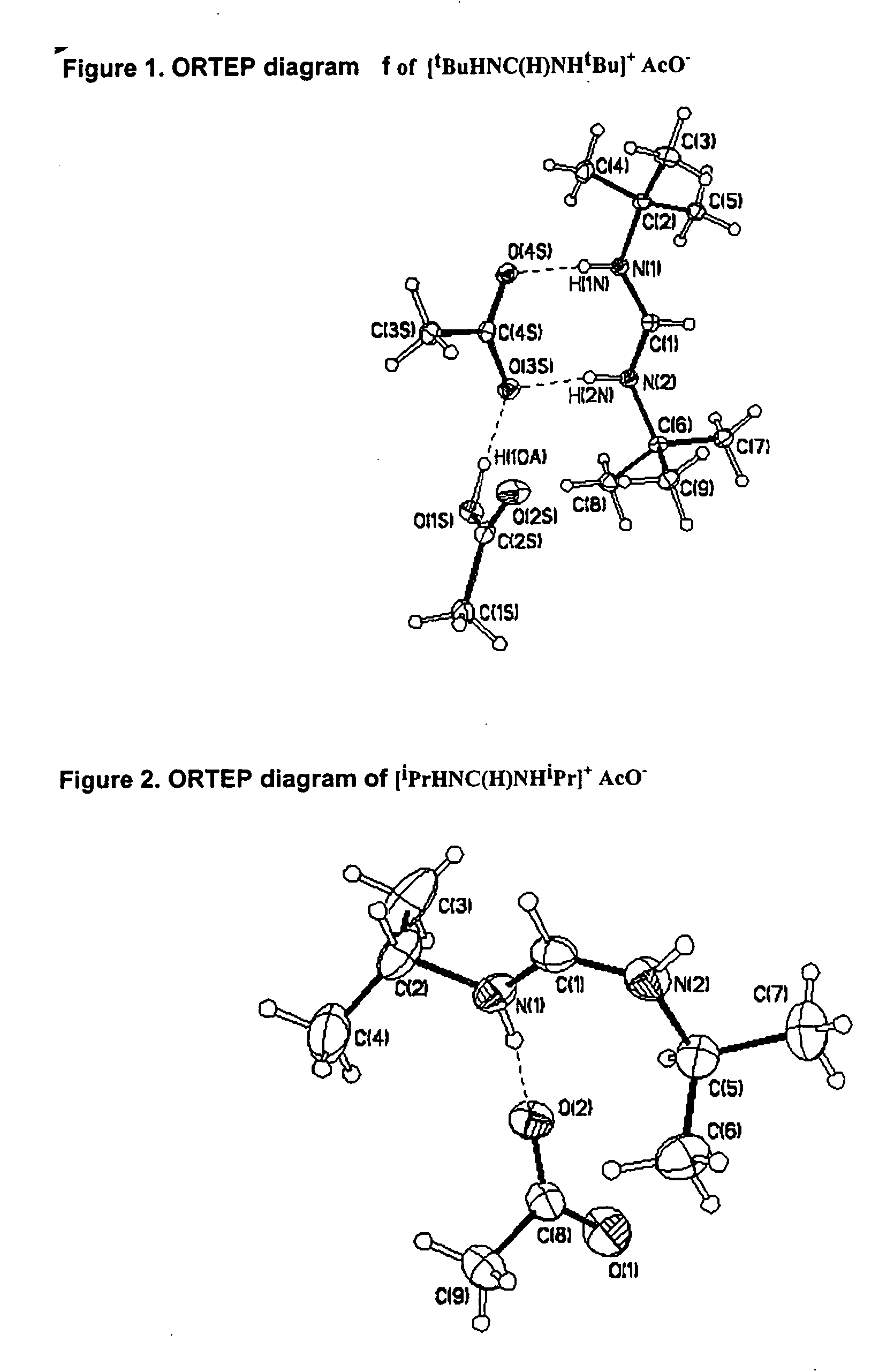
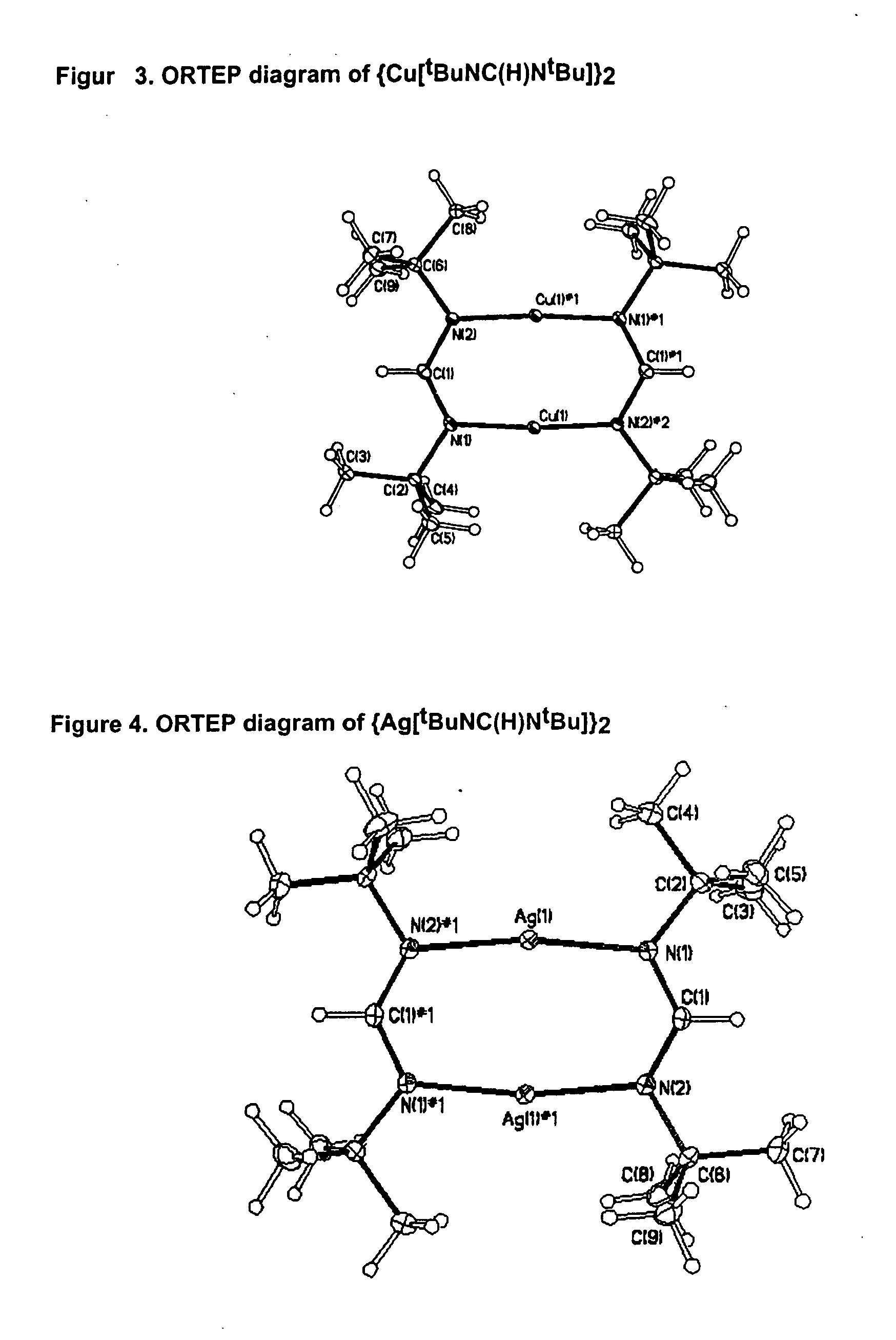
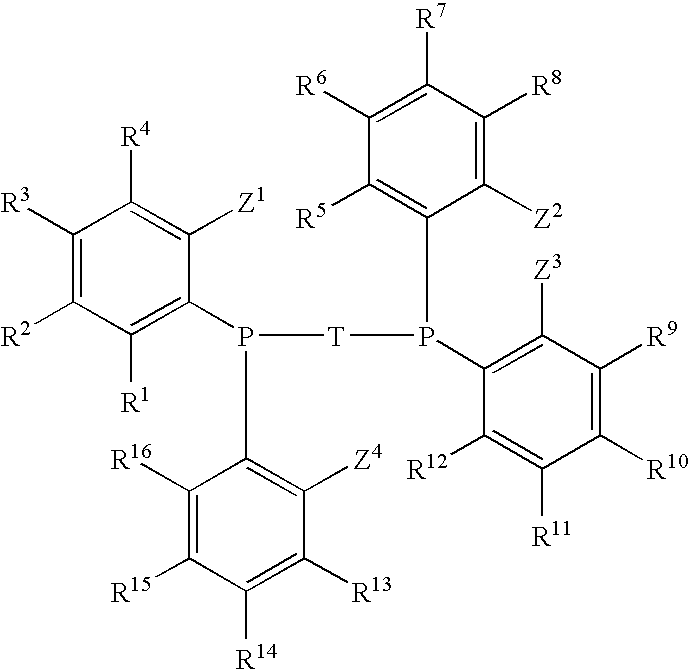
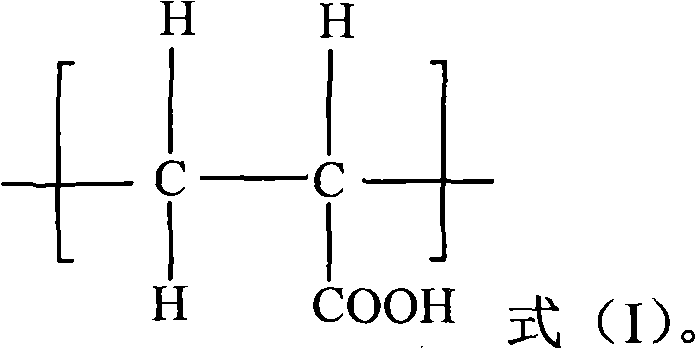
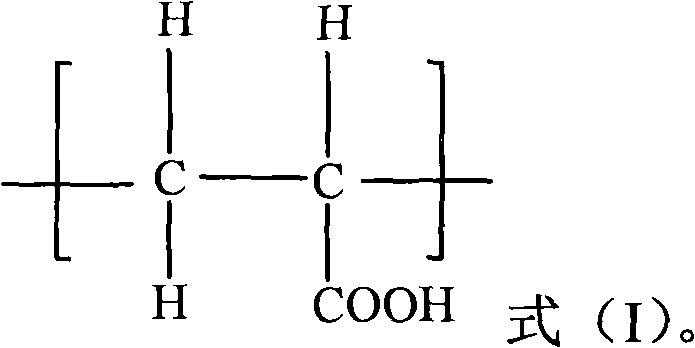
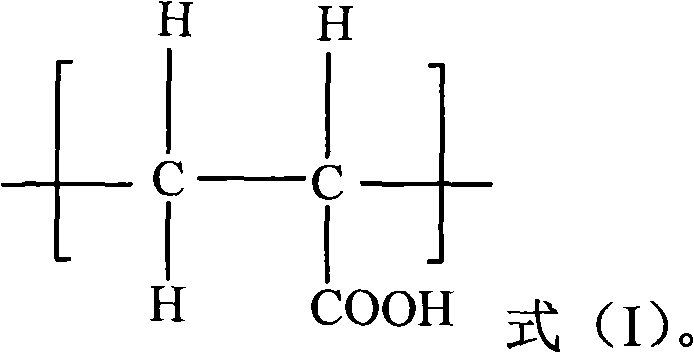
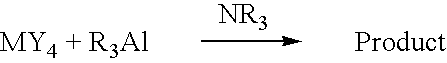Patents
Literature
3730 results about "Phosphine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Phosphine (IUPAC name: phosphane) is the compound with the chemical formula PH₃. It is a colorless, flammable, toxic gas and is classed as a pnictogen hydride. Pure phosphine is odorless, but technical grade samples have a highly unpleasant odor like garlic or rotting fish, due to the presence of substituted phosphine and diphosphane (P₂H₄). With traces of P₂H₄ present, PH₃ is spontaneously flammable in air (pyrophoric), burning with a luminous flame. Phosphines are also a group of organophosphorus compounds with the formula R₃P (R = organic derivative). Organophosphines are important in catalysts where they complex to various metal ions; complexes derived from a chiral phosphine can catalyze reactions to give chiral, enantioenriched products.
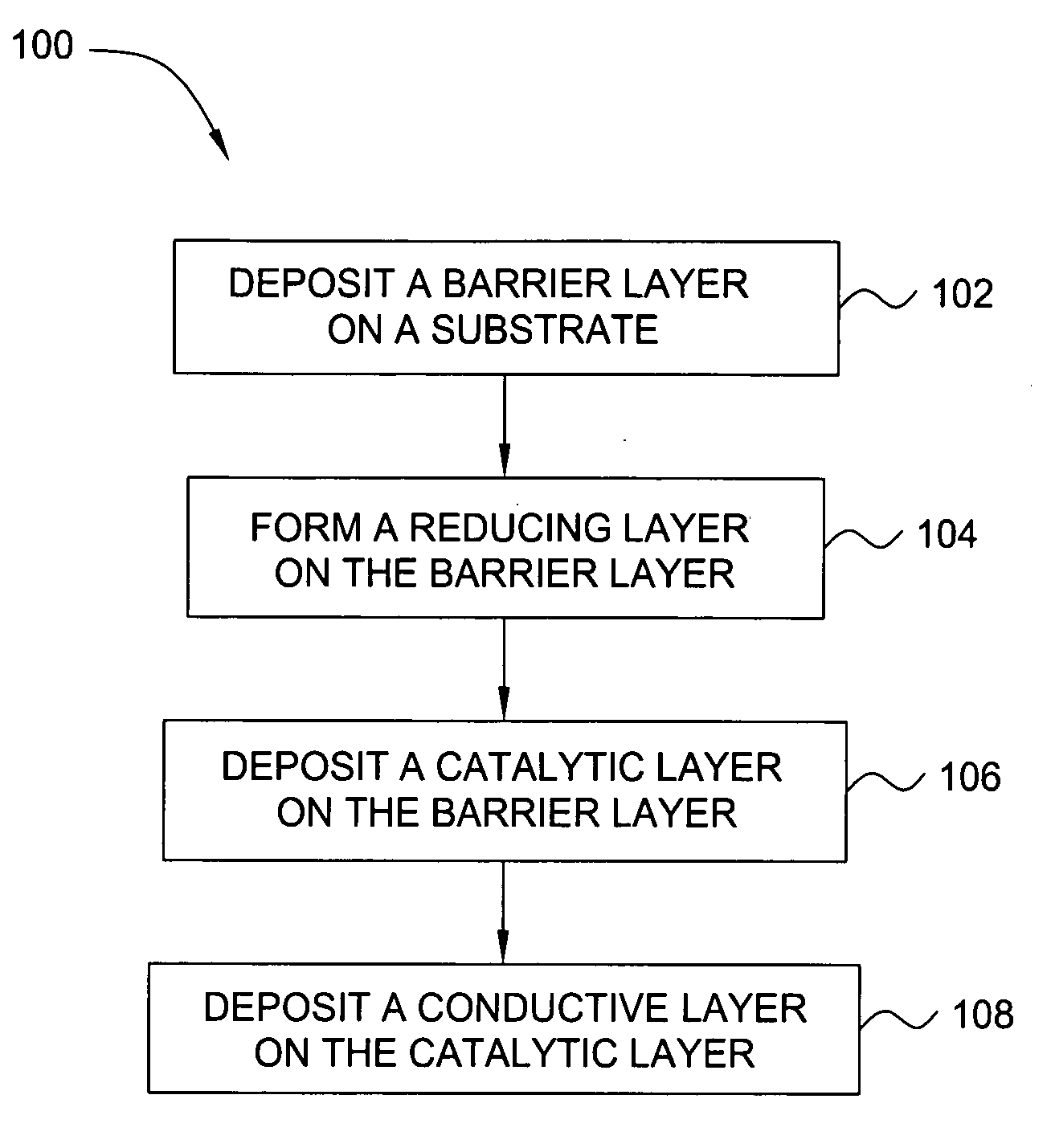
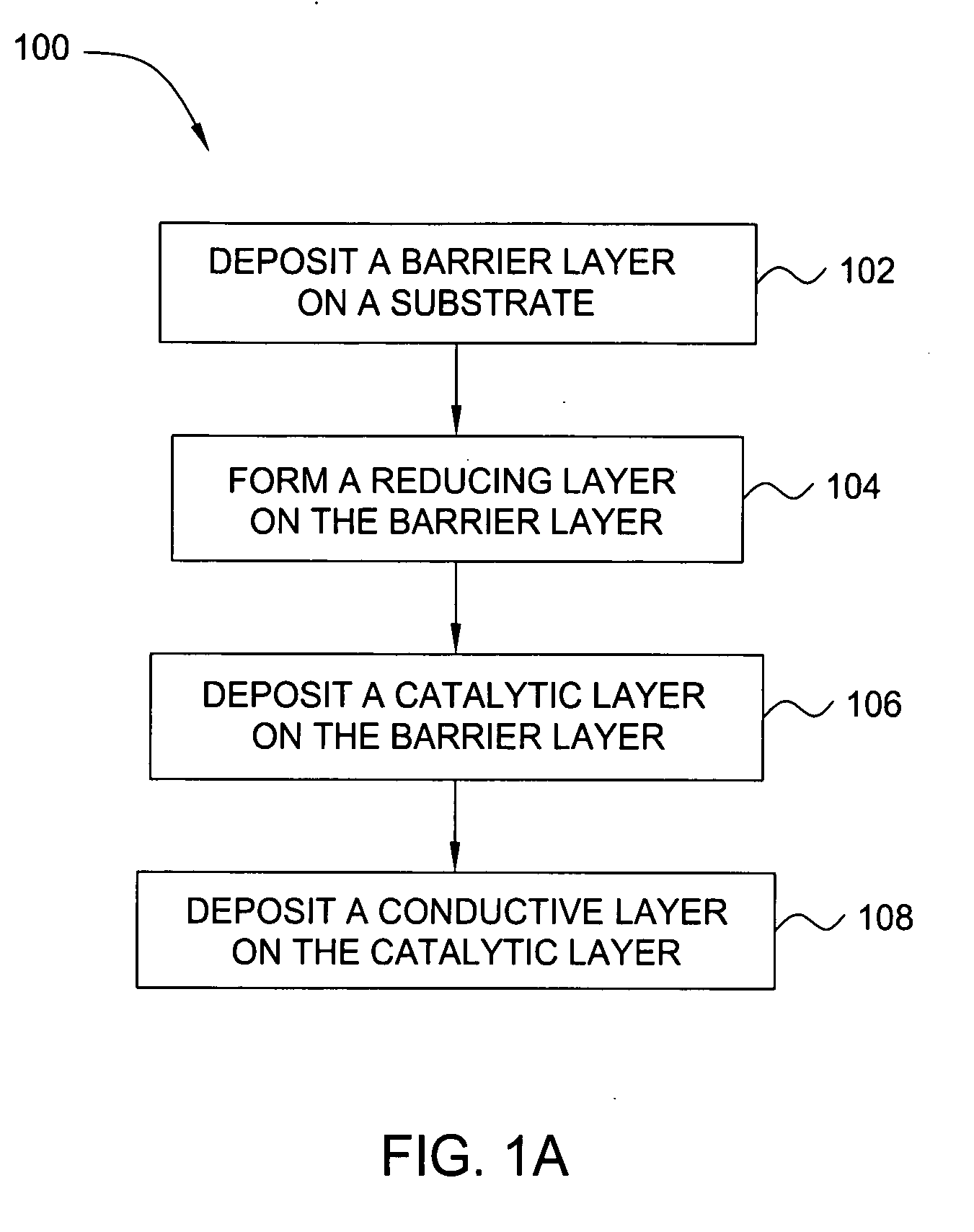
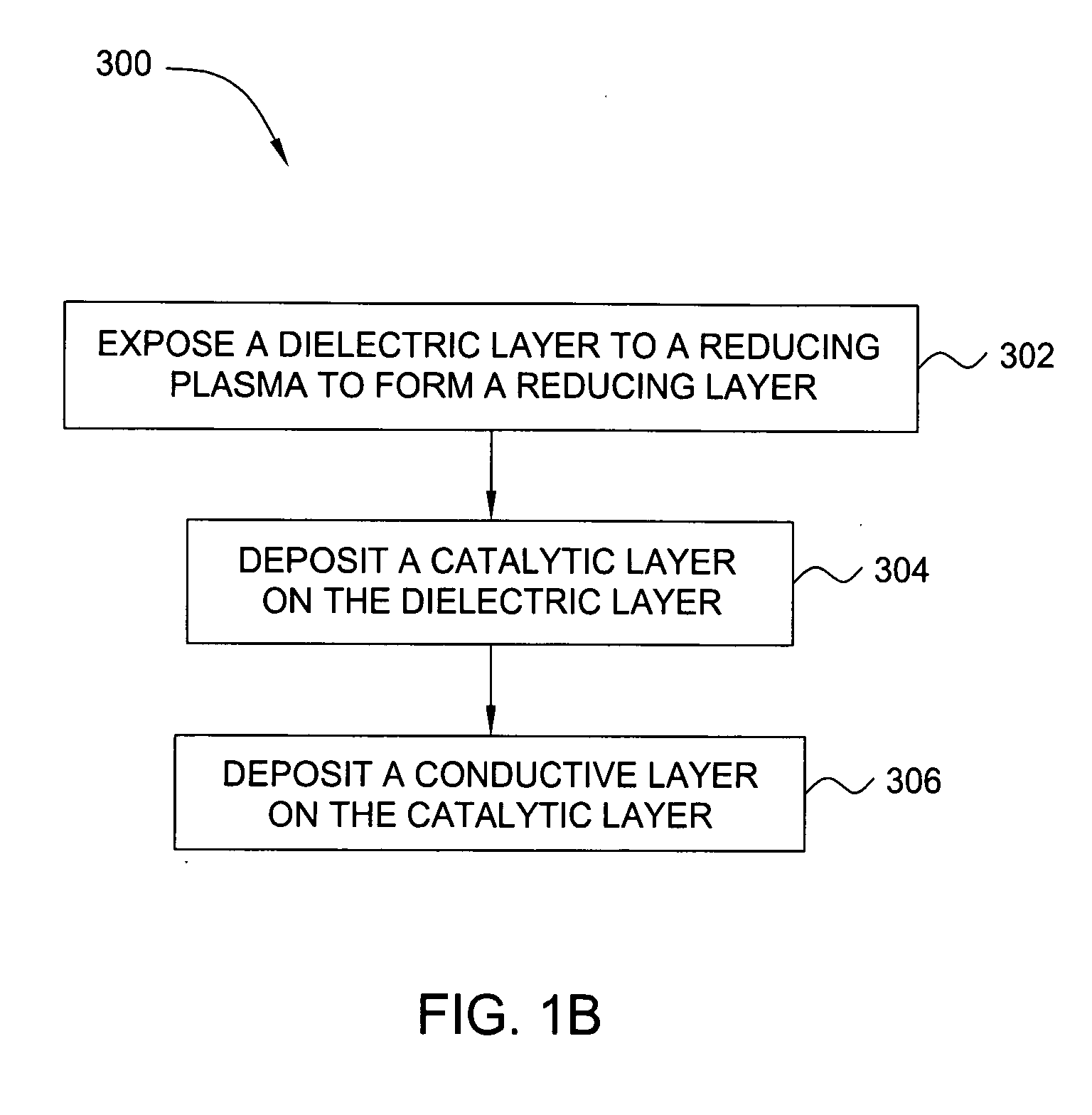
Deposition of an intermediate catalytic layer on a barrier layer for copper metallization
InactiveUS20060240187A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIridiumSilanes
In one embodiment, a method for depositing a conductive material on a substrate is provided which includes exposing a substrate containing a barrier layer to a volatile reducing precursor to form a reducing layer during a soak process, exposing the reducing layer to a catalytic-metal precursor to deposit a catalytic metal-containing layer on the barrier layer, and depositing a conductive layer (e.g., copper) on the catalytic metal-containing layer. The volatile reducing precursor may include phosphine, diborane, silane, a plasma thereof, or a combination thereof and be exposed to the substrate for a time period within a range from about 1 second to about 30 seconds during the soak process. The catalytic metal-containing layer may contain ruthenium, cobalt, rhodium, iridium, nickel, palladium, platinum, silver, or copper. In one example, the catalytic metal-containing layer is deposited by a vapor deposition process utilizing ruthenium tetroxide formed by an in situ process.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Halogen free syntheses of aminosilanes by catalytic dehydrogenative coupling
ActiveUS20150094470A1Silicon organic compoundsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsHydrogenGas phase
Compounds and method of preparation of Si—X and Ge—X compounds (X═N, P, As and Sb) via dehydrogenative coupling between the corresponding unsubstituted silanes and amines (including ammonia) or phosphines catalyzed by metallic catalysts is described. This new approach is based on the catalytic dehydrogenative coupling of a Si—H and a X—H moiety to form a Si—X containing compound and hydrogen gas (X═N, P, As and Sb). The process can be catalyzed by transition metal heterogenous catalysts such as Ru(0) on carbon, Pd(0) on MgO) as well as transition metal organometallic complexes that act as homogeneous catalysts. The —Si—X products produced by dehydrogenative coupling are inherently halogen free. Said compounds can be useful for the deposition of thin films by chemical vapor deposition or atomic layer deposition of Si-containing films.
Owner:LAIR LIQUIDE SA POUR LETUDE & LEXPLOITATION DES PROCEDES GEORGES CLAUDE
Cure catalyst, composition, electronic device and associated method
InactiveUS20060293172A1Molecular sieve catalystsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsSimple Organic CompoundsNitrogen
A cure catalyst is provided. The cure catalyst may include a Lewis acid and one or both of a nitrogen-containing molecule or a non-tertiary phosphine. The nitrogen-containing molecule may include a mono amine or a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound. A curable composition may include the cure catalyst. An electronic device may include the curable composition. Methods associated with the foregoing are provided also.
Owner:MOMENTIVE PERFORMANCE MATERIALS INC
Production of multimodal polythylene
A process for the preparation of polyethylene resins having a multimodal molecular weight distribution which comprises:(i) contacting ethylene monomer and a comonomer comprising an alpha-olefin having from 3 to 10 carbon atoms with a first catalyst system in a first reactor under first polymerisation conditions to produce a first polyethylene having a first molecular weight, an HLMI of not more than 0.5 g / 10 min and a first density of not more than 0.925 g / ml and the first catalyst system comprising (a) a metallocene catalyst comprising a bis tetrahydroindenyl compound of the general formula (IndH4)2R''MQ2 in which each Ind is the same or different and is indenyl or substituted indenyl, R'' is a bridge which comprises a C1-C20 alkylene radical, a dialkyl germanium or silicon or siloxane, or an alkyl phosphine or amine radical, which bridge is substituted or unsubstituted, M is a Group IVB transition metal or vanadium and each Q is hydrocarbyl having 1 to 20 carbon atoms or halogen; and (b) a cocatalyst which activates the catalyst component;(ii) providing a second polyethylene having a second lower molecular weight and second higher density than the first polyethylene, the second polyethylene having been produced using a catalyst other than the bis tetrahydroindenyl compound; and(iii) mixing together the first and second polyethylenes to form a polyethylene resin having a multimodal molecular weight distribution.
Owner:FINA RES SA
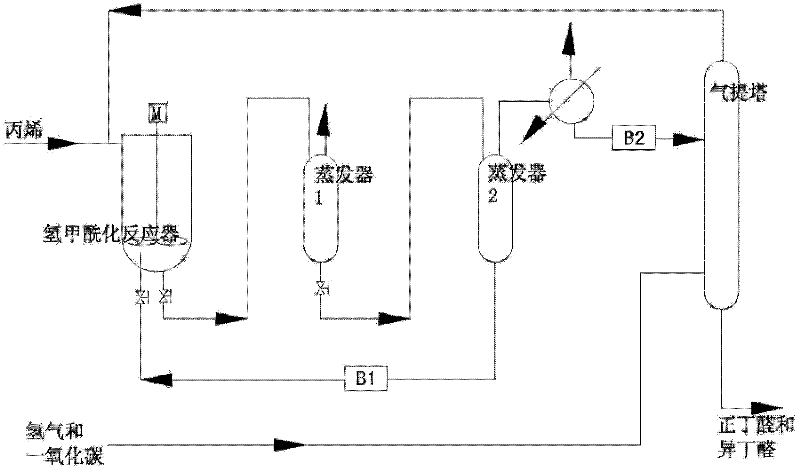
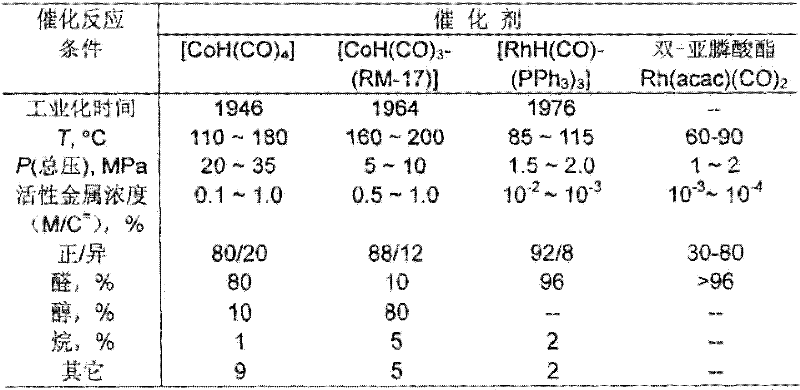
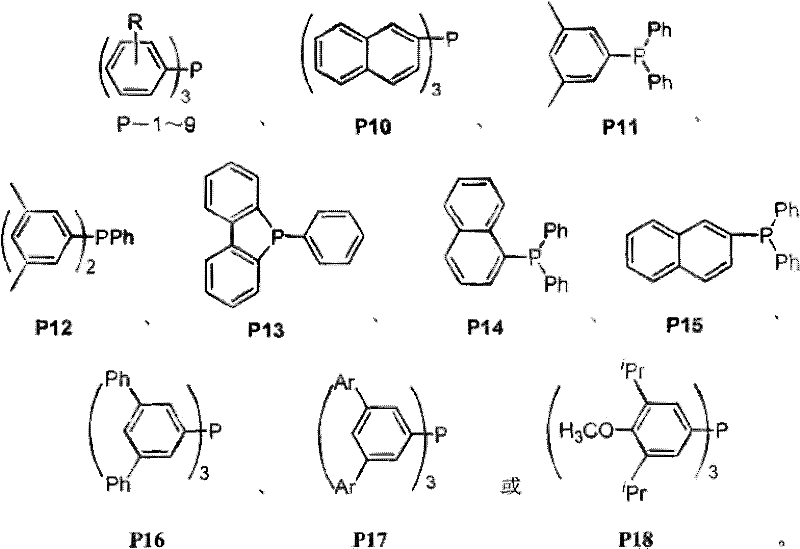
Catalyst system and catalyzing method of propylene hydrogenation and formylation
ActiveCN1986055AReduce dosageImprove stabilityOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsPreparation by carbon monoxide reactionFormylation reactionTriphenylphosphine
The present invention relates to catalyst system for propylene hydrogenation and formylation and process of catalytically synthesizing butyl aldehyde. The catalyst system is triaryl phosphine-Rh(I) catalyst system with proper additive, such as bisphosphite ester, in proper amount. Compared with similar available catalyst, the catalyst system has obviously higher catalytic acitivity, higher selectivity, higher stability and raised n-butyl aldehyde / isobutyl aldehyde ratio in the catalytically synthesized product.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Synthesis metal nanoparticle
A method for providing an anhydrous route for the synthesis of amine capped coinage-metal (copper, silver, and gold) nanoparticles (NPs) using the coinage-metal mesityl (mesityl=C6H2(CH3)3-2,4,6) derivatives. In this method, a solution of (Cu(C6H2(CH3)3)5, (Ag(C6H2(CH3)3)4, or (Au(C6H2(CH3)3)5 is dissolved in a coordinating solvent, such as a primary, secondary, or tertiary amine; primary, secondary, or tertiary phosphine, or alkyl thiol, to produce a mesityl precursor solution. This solution is subsequently injected into an organic solvent that is heated to a temperature greater than approximately 100° C. After washing with an organic solvent, such as an alcohol (including methanol, ethanol, propanol, and higher molecular-weight alcohols), oxide free coinage NP are prepared that could be extracted with a solvent, such as an aromatic solvent (including, for example, toluene, benzene, and pyridine) or an alkane (including, for example, pentane, hexane, and heptane). Characterization by UV-Vis spectroscopy and transmission electron microscopy showed that the NPs were approximately 9.2±2.3 nm in size for Cu°, (no surface oxide present), approximately 8.5±1.1 nm Ag° spheres, and approximately 8–80 nm for Au°.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Preparation method of first-class phosphorus functionalized ionic liquid and application of ionic liquid in hydroformylation
ActiveCN103483381AEasy to synthesizeThe synthetic method is matureOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsIon exchangeOrganic reaction
The invention relates to synthesis of first-class phosphorus functionalized polyether alkyl guanidinium ionic liquid, and an application of the first-class phosphorus functionalized polyether alkyl guanidinium ionic liquid in a homogeneous catalytic reaction. The functionalized ionic liquid of such class can be easily prepared by an ion exchange reaction between the polyether alkyl guanidinium ionic liquid and sulfonic acid type water soluble phosphine ligand. The designed phosphorus functionalized ionic liquid can be applied to organic reactions, including hydroformylation, hydroesterification, hydrocarboxylation and catalytic hydrogenation under the catalyzing of a transition metal; the dosage of the ionic liquid used in the catalytic reaction can be decreased; the activity of the catalytic reaction can be improved; a catalyst can be separated and cycled simply and conveniently.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Tetrazine-based bio-orthogonal coupling reagents and methods
ActiveUS20090023916A1Organic compound preparationCarboxylic compound preparationCell lysatesPhosphine
Coupling reactions, suitable for use in organic or aqueous media, are performed by contacting a 1,2,4,5-tetrazine with a dienophile. The dienophile may be covalently bonded to a protein, and the coupling reaction may be performed in biological media such as those containing cells or cell lysates. The reactions may be performed in the presence of primary amines, thiols, acetylenes, azides, phosphines, and products of Staudinger and / or Sharpless-Huisgen reactions Novel 3-substituted cyclopropene compounds and trans-cyclooctenes are exemplary dienophiles for these reactions.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF DELAWARE
Production of multimodal polyethylene
A process for the preparation of polyethylene resins having a multimodal molecular weight distribution which comprises:(i) contacting ethylene monomer and a comonomer comprising an alpha-olefin having from 3 to 10 carbon atoms with a first catalyst system in a first reactor under first polymerization conditions in a slurry process to produce a first polyethylene having a first molecular weight an HLMI of not more than 0.5 g / 10 min and a first density of not more than 0.925 g / ml and the first catalyst system comprising (a) a first metallocene catalyst of general formula R''(CpRm)(Cp'R'n)MQ2, wherein Cp is a cyclopentadienyl moiety, Cp' is a substituted or unsubstituted fluorenyl ring; each R is independently hydrogen or hydrocarbyl having 1 to 20 carbon atoms in which 0<=m<=4; each R' is independently hydrocarbyl having 1 to 20 carbon atoms in which 0<=n<=8, R'' is a bridge which comprises a C1-C20alkylene radical, a dialkyl germanium or silicon or siloxane, or an alkyl phosphine or amine radical, which bridge is substituted or unsubstituted, M is a Group IVB transition metal or vanadium and each Q is hydrocarbyl having 1 to 20 carbon atoms or halogen, the metallocene catalyst a centroid-M-centroid angle in the range 105° to 125°; and (b) a cocatalyst which activates the catalyst component;(ii) providing a second polyethylene having a second lower molecular weight and higher density than the first polyethylene; and(iii) mixing together the first and second polyethylenes to form a polyethylene resin having a multimodal molecular weight distribution.
Owner:FINA RES SA
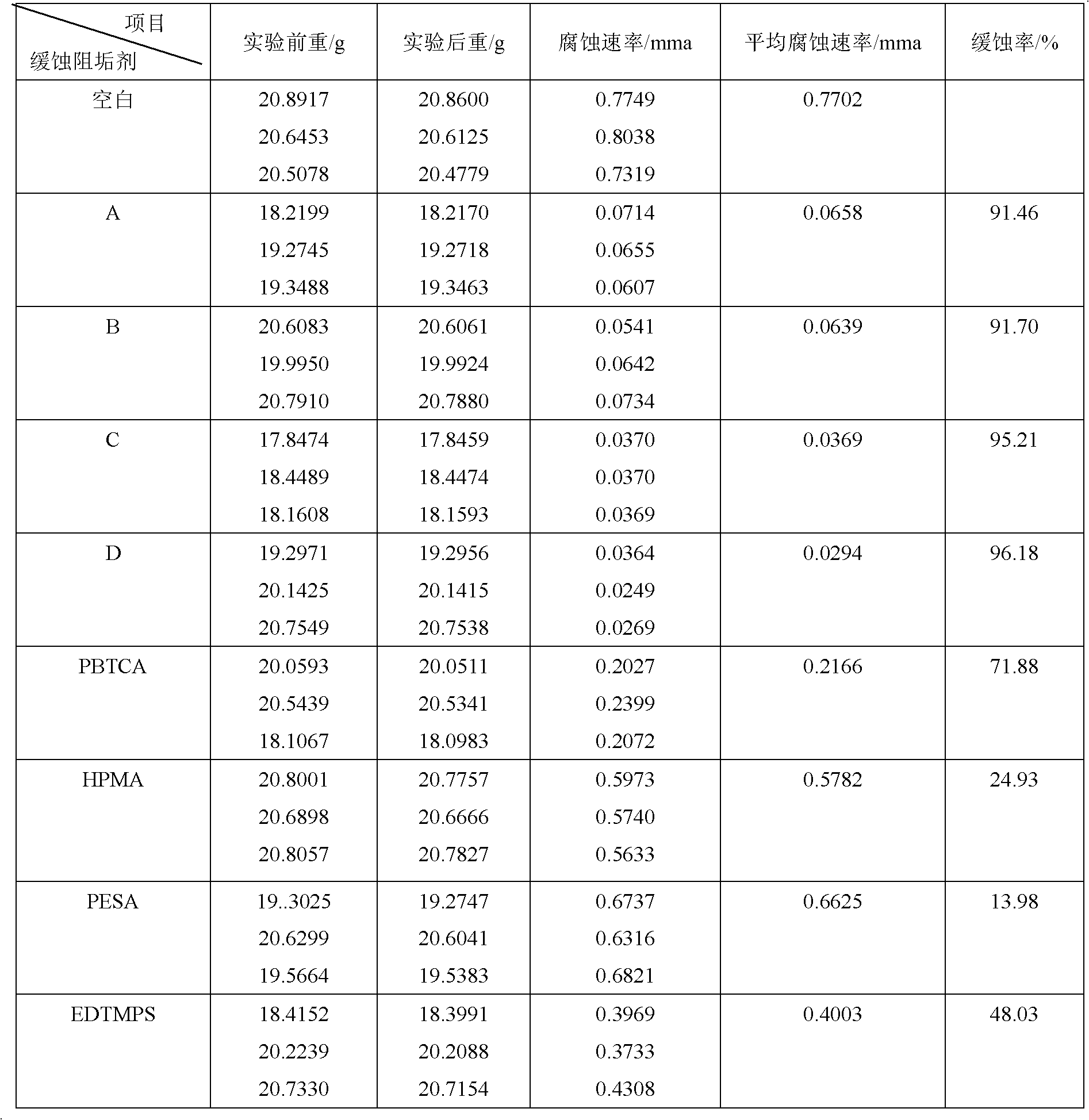
Corrosion and scale inhibitor for cooling water in petrochemical industry
ActiveCN102603086AStrong targetingLow phosphine contentScale removal and water softeningChemical industryPetrochemical
The invention belongs to the technical field of chemical industry, and relates to a cooling water corrosion inhibitor, in particular to an efficient composite corrosion and scale inhibitor which can remarkably reduce corrosion and scaling phenomena of the cooling water of a petrochemical system. The corrosion and scale inhibitor is prepared by evenly mixing organic phosphine carboxylic acid corrosion inhibitor, organic multi-element phosphine acid corrosion and scale inhibitor, polymer scale inhibitor, metal ion succimer, surface active agent, zinc salt, functionality additive and water. The corrosion and scale inhibitor prepared from the components has low phosphine content and excellent corrosion and scale inhibition performance, can prolong the service life of devices, improve the repeated utilization rate of cooling water and reduce the water resource consumption.
Owner:山东京博众诚清洁能源有限公司
Photo-curable conductive adhesive and method for making same
InactiveCN1699492ALow curing temperatureLow resistivityPolyureas/polyurethane adhesivesEster polymer adhesivesPolymer scienceSilver plate
Disclosed is a photo-curable conductive adhesive and method for preparation, which is prepared from light-sensitive high molecular polymer, reactive dilution monomer, conducting particles, light-summing heat initiating agent and anti-oxidant through mixing and grinding, wherein the light-sensitive high molecular polymer is epoxy acrylic resin or / and polyurethane-acrylate, the reactive dilution monomer is the single, double and multiple functional monomers of acrylic acid, the conducting particle is silver powder, copper powder or silver-plated copper powder, the light initiating agent is alpha-amine alkyl methyl ketone, benzoin (or substituted benzoin) ether or acyl phosphines, the heat initiating agent is azocompound or peralcohol, the antioxidant is hydroquinone, p-hydroxybenzene methyl ether, 2,6-ditertiary-butyl-4-methylphenol.
Owner:DALIAN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
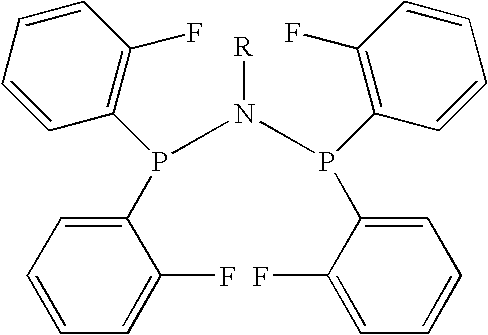
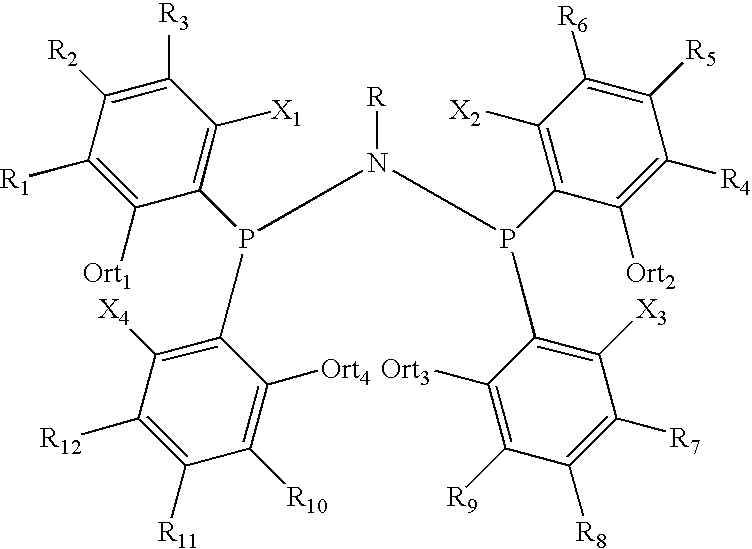
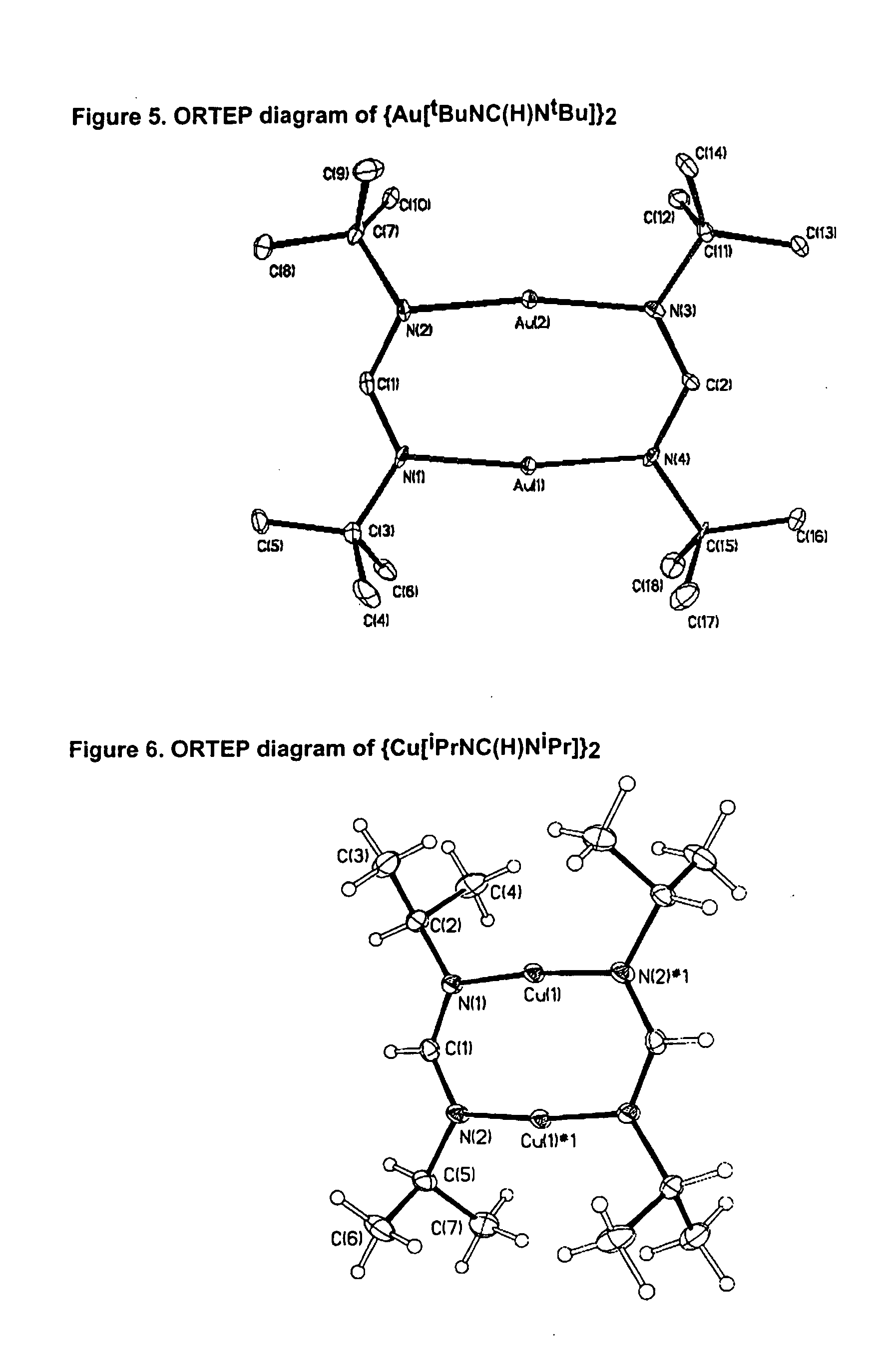
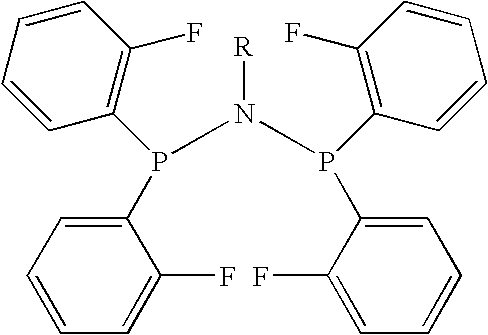
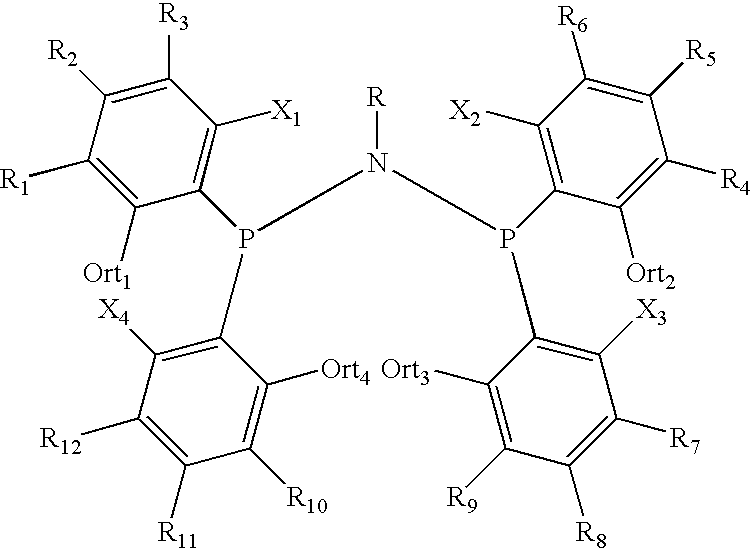
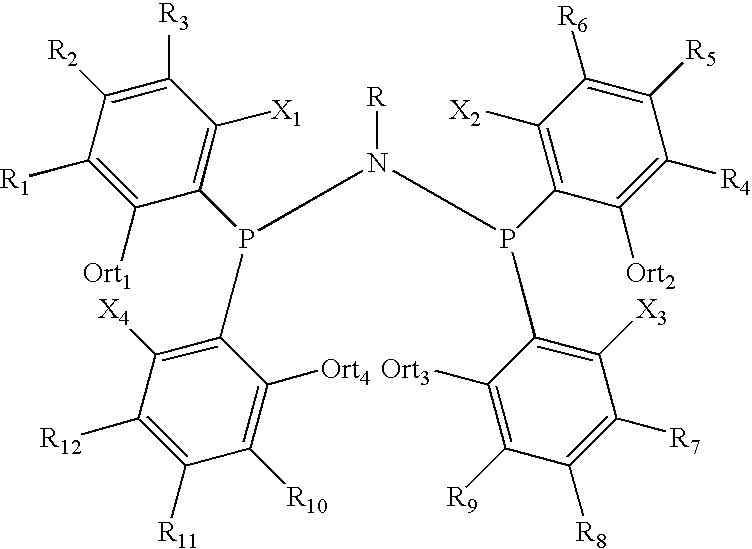
Amino phosphine
ActiveUS7994363B2Organic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalystsAluminoxaneOctene
A new P-N-P ligand in which each phosphorus atom is bonded to two ortho-fluorine substituted phenyl groups is useful in ethylene oligomerizations. In combination with i) a source of chromium and ii) an activator such as methalumoxane; the ligand of this invention may be used to prepare an oligomer product that contains a mixture of hexenes and octenes. The hexenes and octenes produced with this ligand contain very low levels of internal olefins when produced under preferred reaction conditions.
Owner:NOVA CHEM (INT) SA
Chemoselective ligation
InactiveUS20050148032A1Esterified saccharide compoundsSugar derivativesIn vivoChemoselective ligation
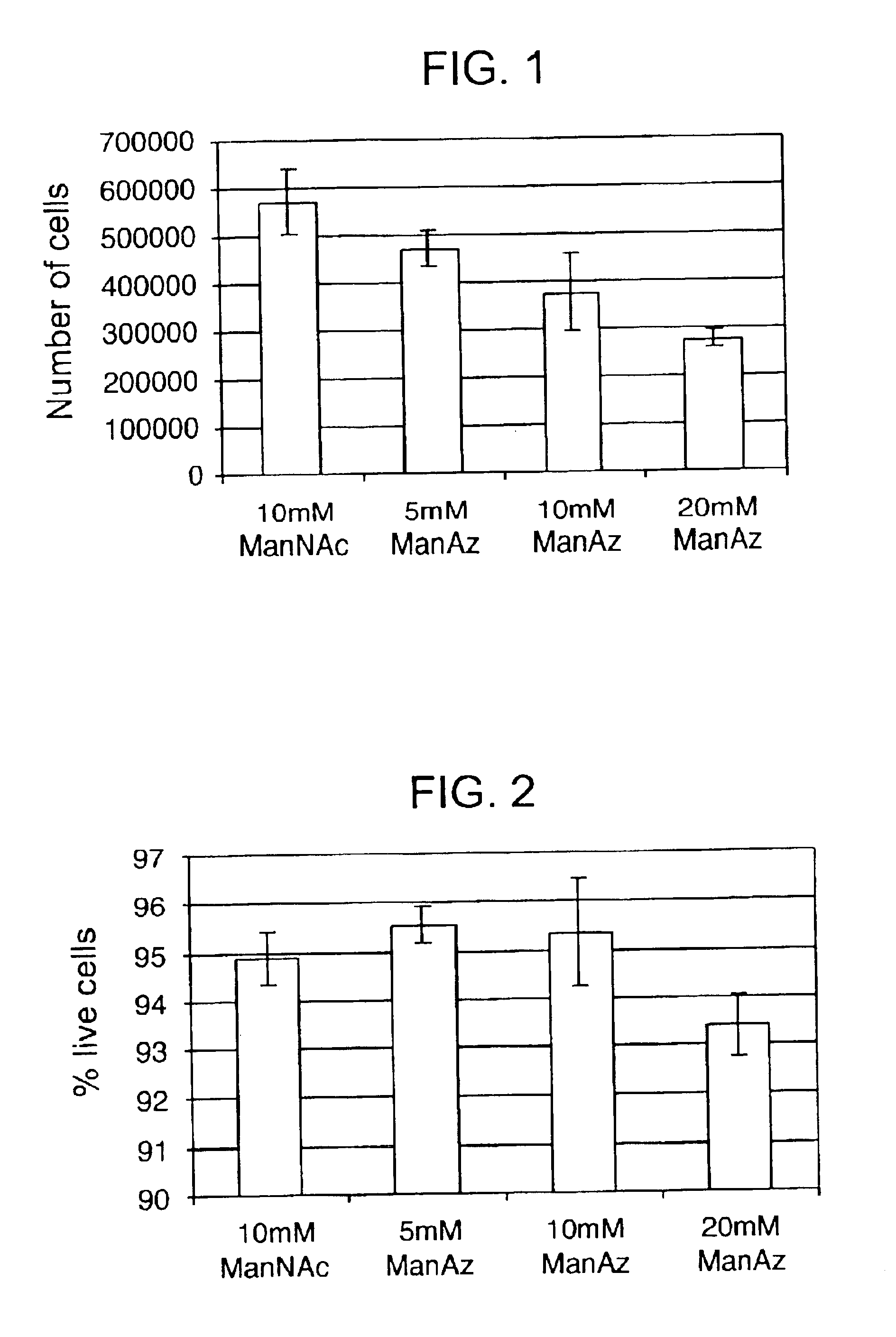
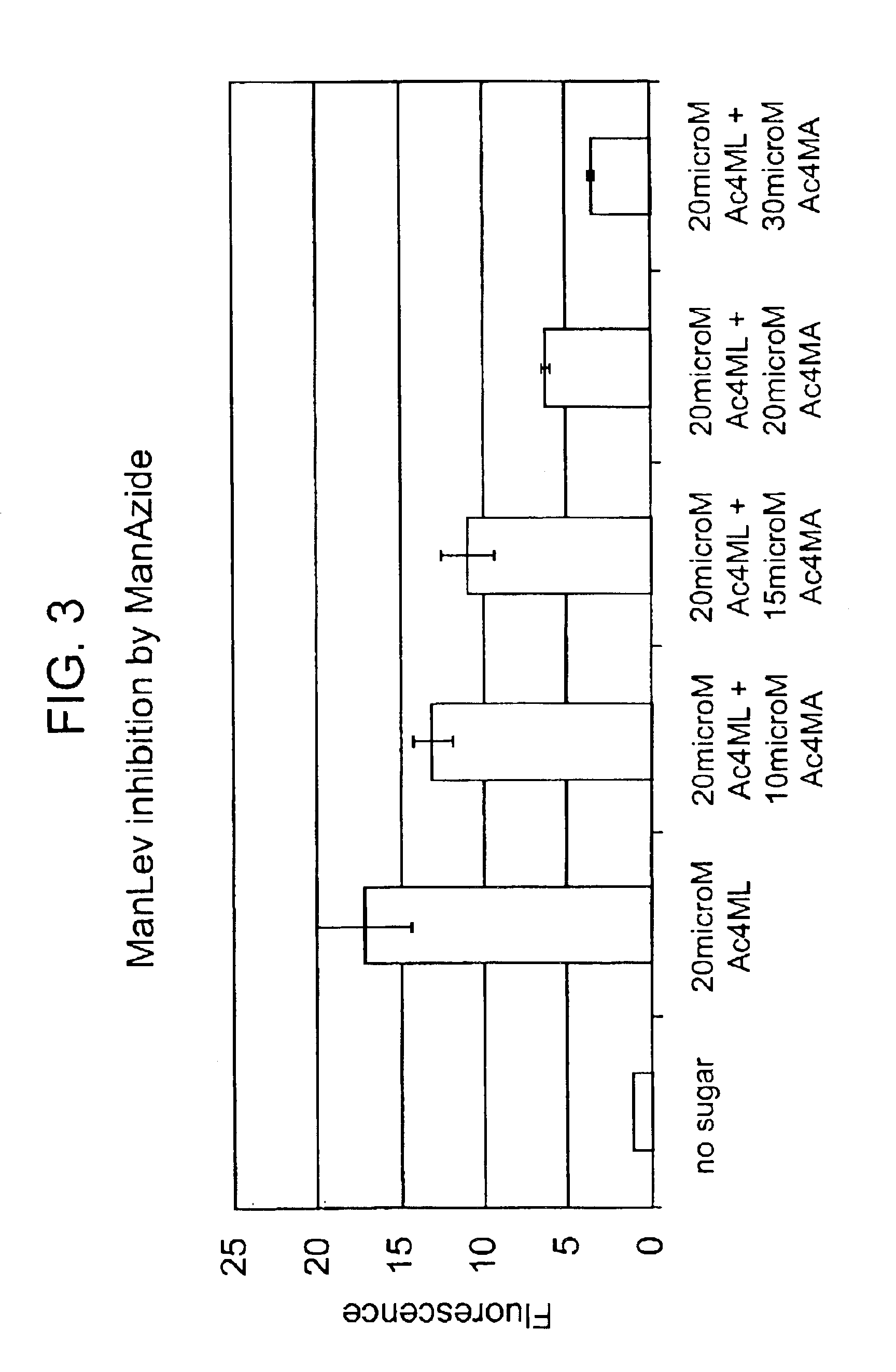
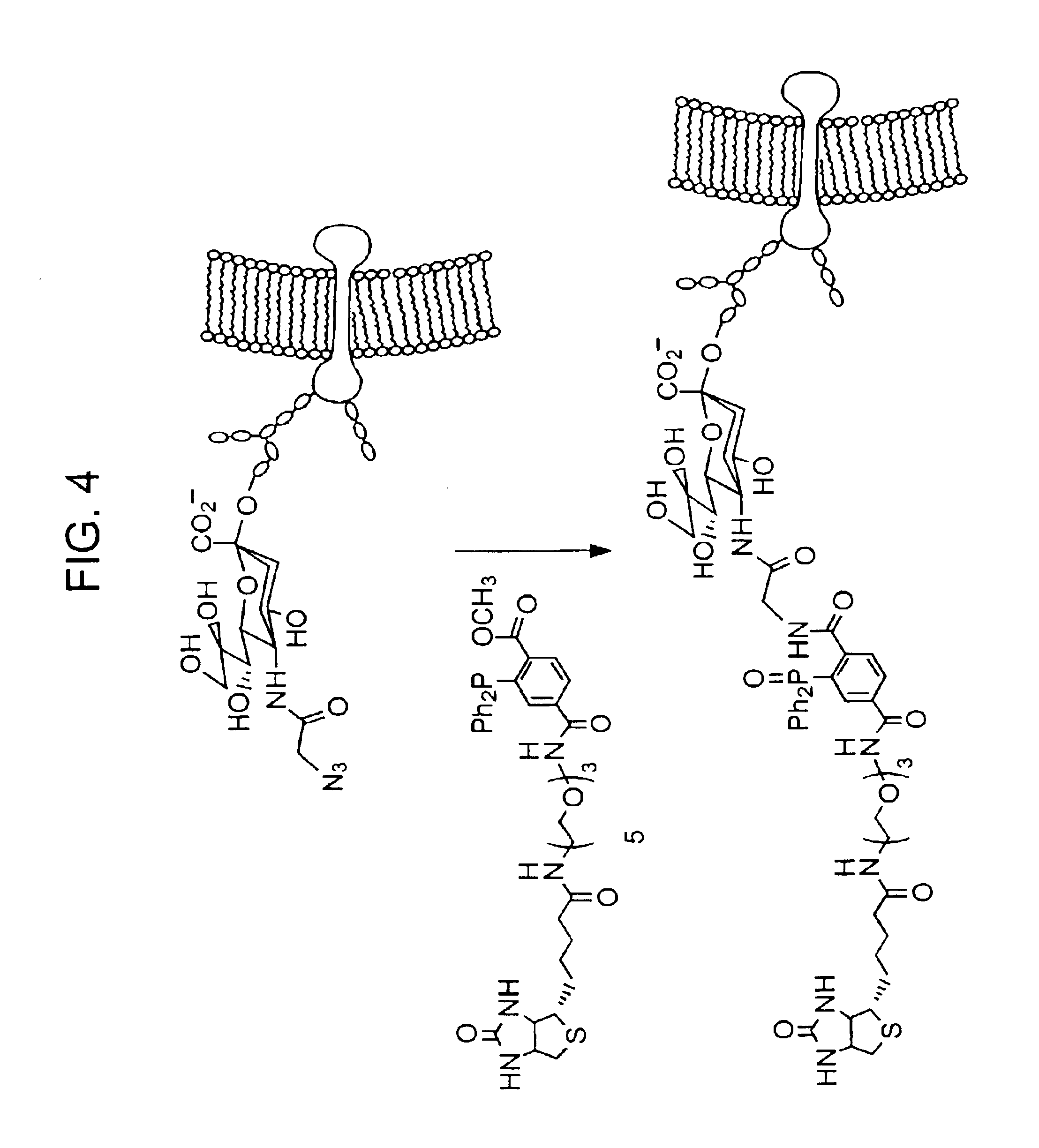
The present invention features a chemoselective ligation reaction that can be carried out under physiological conditions. In general, the invention involves condensation of a specifically engineered phosphine, which can provide for formation of an amide bond between the two reactive partners resulting in a final product comprising a phosphine moiety, or which can be engineered to comprise a cleavable linker so that a substituent of the phosphine is transferred to the azide, releasing an oxidized phosphine byproduct and producing a native amide bond in the final product. The selectivity of the reaction and its compatibility with aqueous environments provides for its application in vivo (e.g., on the cell surface or intracellularly) and in vitro (e.g., synthesis of peptides and other polymers, production of modified (e.g., labeled) amino acids).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Class of volatile compounds for the deposition of thin films of metals and metal compounds
The invention provides an organometallic complex, containing oxygen free organic ligands, for the deposition of a metal, preferably copper, silver or gold, and preferably by way of chemical vapor deposition. The organometallic complex having the formula [(Do)nMLx]k where M is a metal preferably selected from the group consisting of Cu, Ag and Au; Do is selected from the group comprising ethers, phosphines, olefins, sulfides, pyridines, carbonyl, hydroxyl, cyclopentadiene, benzene derivatives, allyls, alkyls, amines, polyamines, aniline derivatives, cyclooctadiene and combinations thereof; n is an integer having a value from 0 to 4; k is an integer having a value from 1 to 4; x is an integer having a value from 1 to 4; and L is an amidinate ligand of the formula R1—NC(R2)N—R3 where R1, R2 and R3 are selected from the group consisting of alkyls, allyls, aryls, heteroaryls, hydrogen, non-metals and metalloids; and where R1, R2 and R3 are different or the same.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
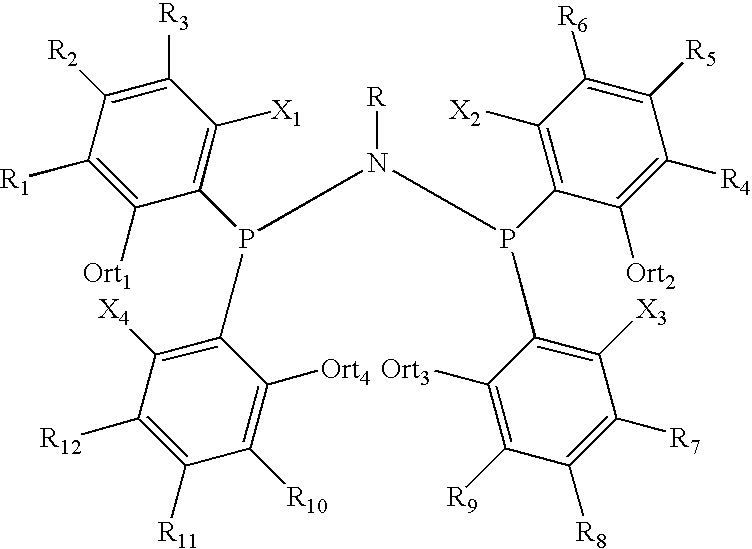
Amino phosphine
ActiveUS20080242811A1Sure easyOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalystsOligomerOctene
A new P—N—P ligand in which each phosphorus atom is bonded to two ortho-fluorine substituted phenyl groups is useful in ethylene oligomerizations. In combination with i) a source of chromium and ii) an activator such as methalumoxane; the ligand of this invention may be used to prepare an oligomer product that contains a mixture of hexenes and octenes. The hexenes and octenes produced with this ligand contain very low levels of internal olefins when produced under preferred reaction conditions.
Owner:NOVA CHEM (INT) SA
Chemoselective ligation
The present invention features a chemoselective ligation reaction that can be carried out under physiological conditions. In general, the invention involves condensation of a specifically engineered phosphine, which can provide for formation of an amide bond between the two reactive partners resulting in a final product comprising a phosphine moiety, or which can be engineered to comprise a cleavable linker so that a substituent of the phosphine is transferred to the azide, releasing an oxidized phosphine byproduct and producing a native amide bond in the final product. The selectivity of the reaction and its compatibility with aqueous environments provides for its application in vivo (e.g., on the cell surface or intracellularly) and in vitro (e.g., synthesis of peptides and other polymers, production of modified (e.g., labeled) amino acids).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for preparing annular phosphonate or annular phosphate flame retardant
InactiveCN101230274AThe preparation method is simple and environmentally friendlyEasy to operateFlame-proof filament manufactureGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsDimethyl methylphosphonateTriethylphosphite
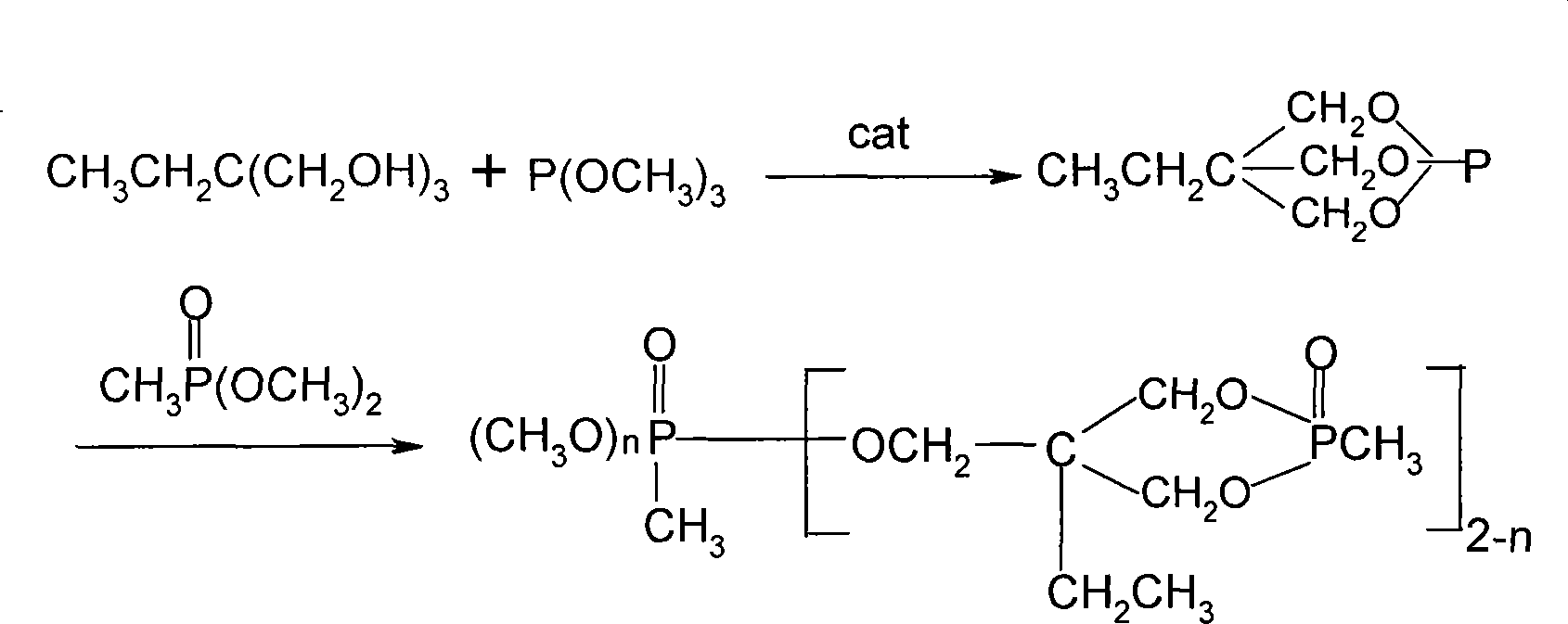
The invention provides a preparation method of annular phosphonate or annular organic phosphate flame retardant. The steps are that (1) trimethylolpropane and trimethyl phosphate or triethyl phosphate are taken as the material, and react to synthesize into midbody under the condition of catalyzer; (2) phosphonate or organic phosphate is added into the midbody and is heated, and then the product of annular phosphonate or annular organic phosphate flame retardant can be obtained. The phosphite ester is selected from trimethyl phosphate and triethyl phosphate. The phosphonate is selected from dimethyl-phosphine and diethyl ethyl phosphine. The organic phosphate is selected from trimethyl phosphate, triethyl phosphate, phosphate propyl, tributyl phosphate and tricresyl aromatic ester. The invention overcomes the shortcomings of the prior art, the new preparation method of annular phosphonate or annular organic phosphate flame retardant is environment-friendly, solution is not needed, and the operation is simple. The termination product has excellent color and luster, low acid value and excellent viscosity; and does not need additional decoloration.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY +1
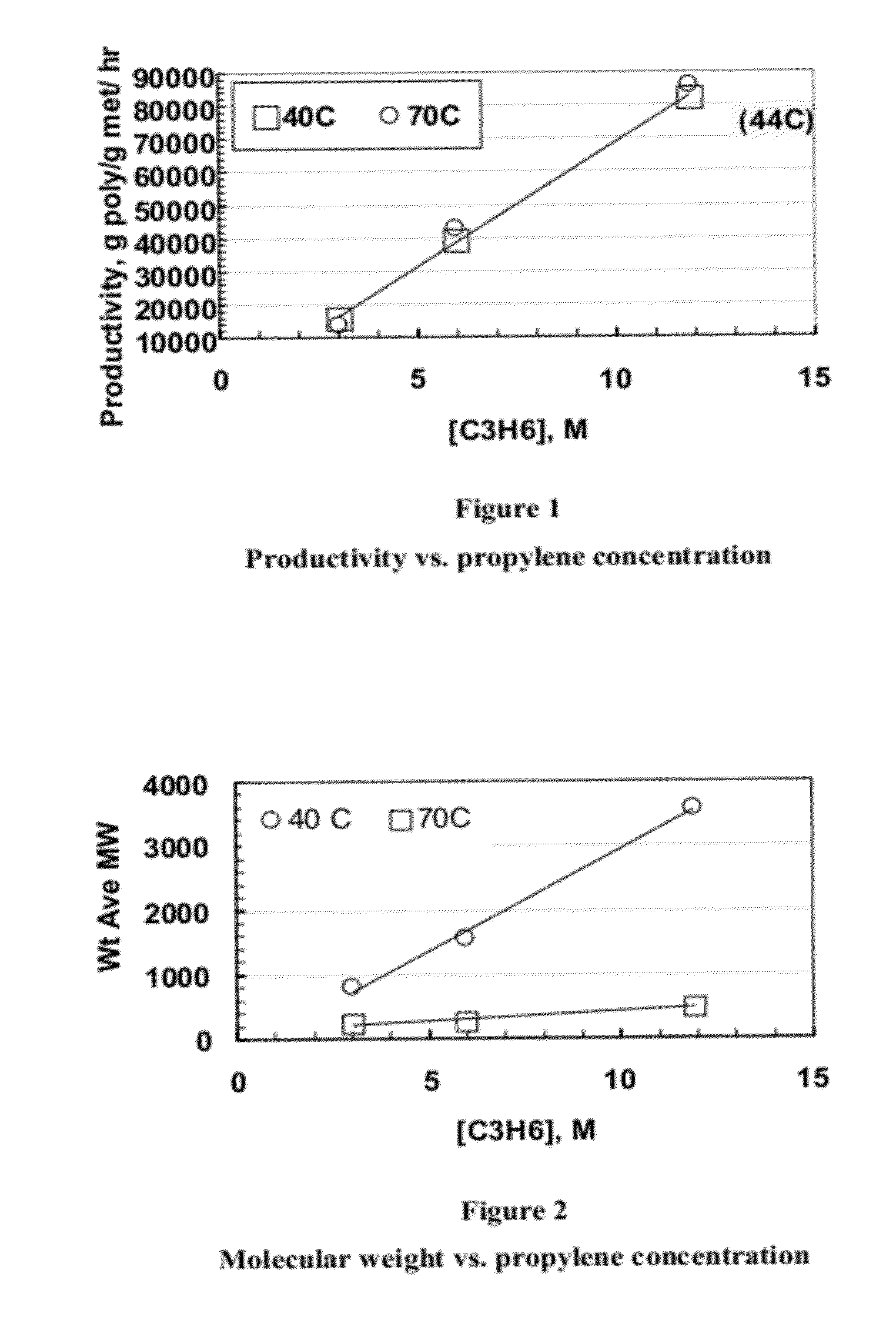
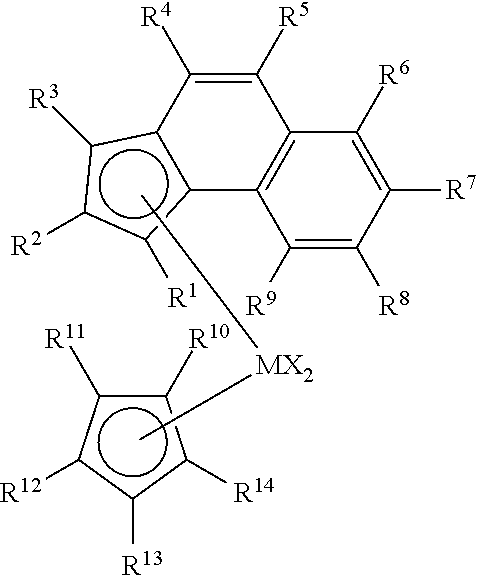
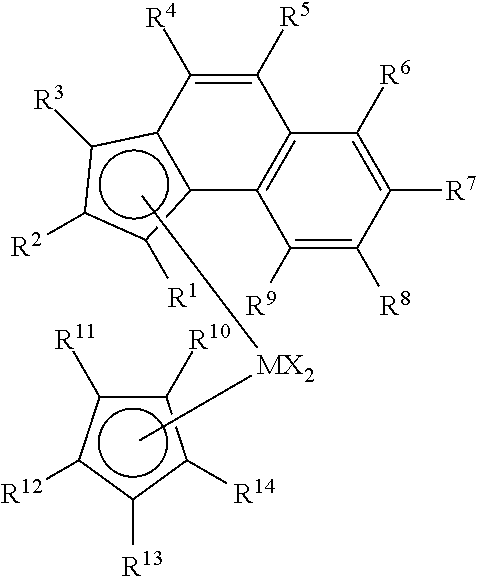
Enhanced catalyst performance for production of vinyl terminated propylene and ethylene/propylene macromers
ActiveUS8318998B2Hydrocarbon by isomerisationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsPolymer sciencePtru catalyst
This invention relates to a transition metal catalyst compound represented by the structure:whereinM is hafnium or zirconium;each X is, independently, selected from the group consisting of hydrocarbyl radicals having from 1 to 20 carbon atoms, hydrides, amides, alkoxides, sulfides, phosphides, halogens, dienes, amines, phosphines, ethers, or a combination thereof;each R1 and R3 are, independently, a C1 to C8 alkyl group; andeach R2, R4, R5, R6, R7, R8, R9, R10, R11, R12, R13, and R14 are, independently, hydrogen, or a substituted or unsubstituted hydrocarbyl group having from 1 to 8 carbon atoms, provided however that at least three of the R10-R14 groups are not hydrogen, compositions thereof and methods of use thereof to prepare polymers.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Composite corrosion-retarding antisludging agent for treating high-concentration multiple circulating water
InactiveCN101125715AGrowth inhibitionLimit metabolismScale removal and water softeningHigh concentrationCarboxylic acid
A compound inhibition antisludging agent is used for treating high-concentration circulation water, comprising a liquid part and a solid part. Based on that the total weight of the liquid part is deemed to be 100 percent, percentages of each component by weight are: organic phosphonic acid 5-40 percent, organic carboxylic acid 5-40 percent and water 20-90 percent; and based on that the total weight of the solid part is deemed to be 100 percent, percentages of each component by weight are: polymer with antisludging effect 5-35 percent, alkaline agent 45-80 percent, azoles 1-10 percent and zinc salt 1-10 percent. The concentrations of the liquid part and the solid part in the circulating water are that: the solid part: the dosage of the agent added into make-up water is 20-200mg / L; the liquid part: total phosphine kept in the circulating water system is 10-15mg / L. The invention has effects of inhibition, antisludging, sterilization and algae removal upon meeting the requirements of the state, can promote the concentration multiple of the circulating water system up to 7.5 or more and can be operated at normal temperature with good effect and without pre-membrane treatment.
Owner:上海潓溱环保科技股份有限公司
Organic silicon leaf fertilizer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101096326APromote early maturityPromote production increaseBiocideAnimal repellantsFruit treePlant growth
The invention discloses an organosilicon foliage fertilizer and making method, which is the leach of charred rice husk with water without polluting and side effect, wherein the foliage fertilizer is made of nitrogen, phosphine, potassium fertilizer, trace fertilizer, humic acid, plant growth modifier dissolved in the water with organosilicon fertilizer. The invention reaches effective utility due to kinds of nutritious element adsorbed by plant, which improves the crop production for forage crop, bean culture, vegetable and fruit tree.
Owner:黑龙江省苗必壮农业科技有限公司
D1369 d radiation curable secondary coating for optical fiber
A new radiation curable Secondary Coating for optical fibers is described and claimed wherein said composition comprises a Secondary Coating Oligomer Blend, which is mixed with a first diluent monomer; a second diluent monomer; optionally, a third diluent monomer; an antioxidant; a first photoinitiator; a second photoinitiator; and optionally a slip additive or a blend of slip additives; wherein said Secondary Coating Oligomer Blend comprises:α) an Omega Oligomer; andβ) an Upsilon Oligomer;wherein said Omega Oligomer is synthesized by the reaction ofα1) a hydroxyl-containing (meth)acrylate;α2) an isocyanate;α3) a polyether polyol; andα4) tripropylene glycol; in the presence ofα5) a polymerization inhibitor; andα6) a catalyst;to yield the Omega Oligomer;wherein said catalyst is selected from the group consisting of dibutyl tin dilaurate; metal carboxylates, including, but not limited to: organobismuth catalysts such as bismuth neodecanoate; zinc neodecanoate; zirconium neodecanoate; zinc 2-ethylhexanoate; sulfonic acids, including but not limited to dodecylbenzene sulfonic acid, methane sulfonic acid; amino or organo-base catalysts, including, but not limited to: 1,2-dimethylimidazole and diazabicyclooctane; triphenyl phosphine; alkoxides of zirconium and titanium, including, but not limited to Zirconium butoxide and Titanium butoxide; and Ionic liquid phosphonium salts; and tetradecyl(trihexyl)phosphonium chloride; andwherein said Upsilon Oligomer is an epoxy diacrylate.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Transition metal catalyst of polymerized ethene agent, prepartion method and application
ActiveCN1795988ALarge space for decorationEasy to implementOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsHydrocarbonsOligomerDimmer
The invention discloses a 2-(2-(diphenyl phosphine) phenyl) oxazoline nickel halogenide series complex. Said invention provides the structure formula of said complex and its preparation method. Said invention also provides catalyst composition containing said complex and its application in ethylene oligopolymerization. Said catalyst composition has higher ethylene oligopolymerization activity, and the obtained oligomer takes ethylene dimmer and trimer as main components.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP
Method of improving surface cure in digital flexographic printing plates
ActiveUS8808968B2Improve Surface CuringSimple working processPhotosensitive materialsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPolymer sciencePhosphite ester
Owner:MACDERMID PRINTING SOLUTIONS
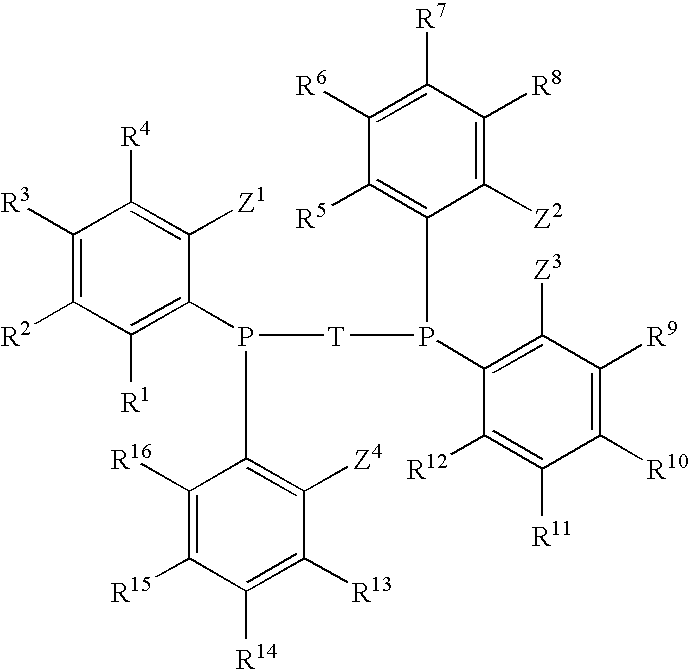
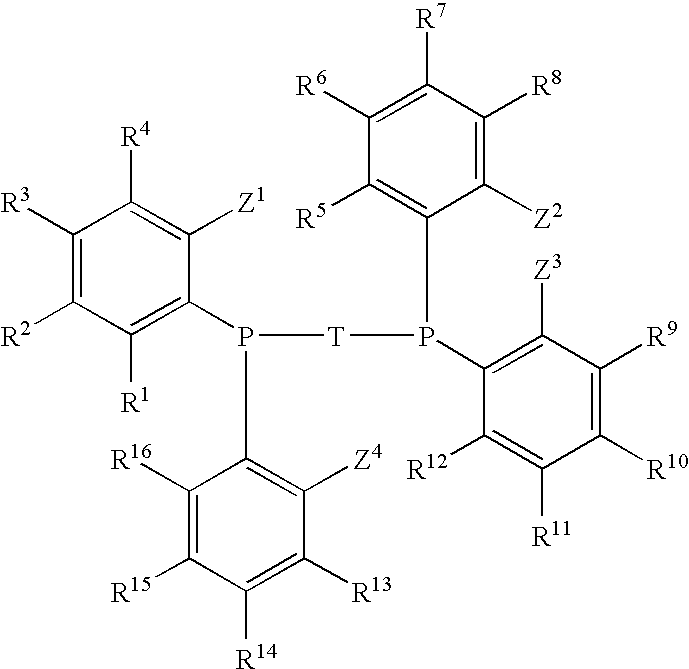
Phosphine Ligand-Metal Compositions, Complexes, and Catalysts For Ethylene Trimerizations
This invention relates to a method to selectively oligomerize olefins comprising contacting olefins with: 1) at least one diaryl-substituted diphosphine ligand; 2) a chromium metal precursor; and 3) optionally, one or more activators. In a particular embodiment, the method for selectively oligomerizing olefins includes trimerizing ethylene to selectively form 1-hexene.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
A kind of propylene hydroformylation catalytic system and method
InactiveCN102266796AReduce dosageImprove stabilityGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsFormylation reactionTriphenylphosphine
The invention relates to a propylene hydroformylation catalyst system and a method for catalyzing synthesis of butyraldehyde. In the present invention, in the propylene hydroformylation reaction system catalyzed by triarylphosphine-Rh(I), by using appropriate types and quantities of additives, such as bisphosphite, the performance of the Rh(I) / triarylphosphine catalyst can be significantly improved The activity and the positive-iso ratio of butyraldehyde in the product (molar ratio of n-butyraldehyde / isobutyraldehyde>20), and significantly prolong the service life of the bisphosphite ligand, and significantly reduce the amount of triarylphosphine. This type of catalyst system is characterized by higher activity and selectivity than third-generation Rh(I) / triphenylphosphine catalysts and better stability than fourth-generation Rh(I) / bisphosphite catalysts, so The novel catalyst system provided by the present invention can overcome the shortcomings of the third and fourth generation catalysts, reduce the cost of industrialized production of propylene hydroformylation, and provide a new catalyst technology for its industrial application.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Preparation of group IVA and group VIA compounds
Methods of preparing Group IVA and Group VIA organometallic compounds, particularly Group IVA organometallic compounds, are provided. Such manufacturing methods employ an amine and / or phosphine catalyst in a transalkylation step and may be performed in a batch, semi-continuous or continuous manner.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS ELECTRONICS MATERIALS LLC
Anti-Corrosion Conformal Coating for Metal Conductors Electrically Connecting an Electronic Component
InactiveUS20110189381A1Prolong lifeFinal product manufacturePretreated surfacesElectrical conductorPhosphine
An apparatus includes an electronic component mounted on a substrate and metal conductors electrically connecting the electronic component. A conformal coating overlies the metal conductors and comprises a polymer into which a phosphine compound is impregnated and / or covalently bonded. Accordingly, the conformal coating is able to protect the metal conductors from corrosion caused by sulfur components (e.g., elemental sulfur, hydrogen sulfide, and / or sulfur oxides) in the air. That is, the phosphine compound in the polymer reacts with any corrosion inducing sulfur component in the air and prevents the sulfur component from reacting with the underlying metal conductors. Preferably, the phosphine compound in the polymer does not react with other components in the air (e.g., carbon dioxide) which would otherwise deplete its availability for the target reaction. The phosphine compound may be rendered completely non-volatile by covalently bonding it directly into the polymer backbone.
Owner:IBM CORP
Corrosion-inhibition scale inhibitor composition and corrosion-inhibition scale inhibitor and application thereof
ActiveCN102786158AGood corrosion inhibition effectGood anti-scaling effectScale removal and water softeningPolyaspartic acidSuccinic acid
The invention provides a corrosion-inhibition scale inhibitor composition, a corrosion-inhibition scale inhibitor and an application thereof, wherein the corrosion-inhibition scale inhibitor composition comprises water-soluble oxidizable inorganic metal salts, water-soluble inorganic zinc salts, phosphine compounds and polymers; the weight ratio of the water-soluble oxidizable inorganic metal salts, the water-soluble inorganic zinc salts, the phosphine compounds and the polymers is 0.005-0.2:0.05-1:0.1-0.75:1; the polymer is selected from one or more than one of hydrolyzed polymaleic anhydride, polyaspartic acid, polyepoxy succinic acid, and polyacrylic acid polymers. The corrosion-inhibition scale inhibitor composition and the corrosion-inhibition scale inhibitor provided by the invention has both good corrosion inhibition and scale inhibition.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Alkaline ionic liquid as well as preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN102126968ACan be reusedExperimental effect is goodProductsOrganic compound preparationAlcoholDesorption
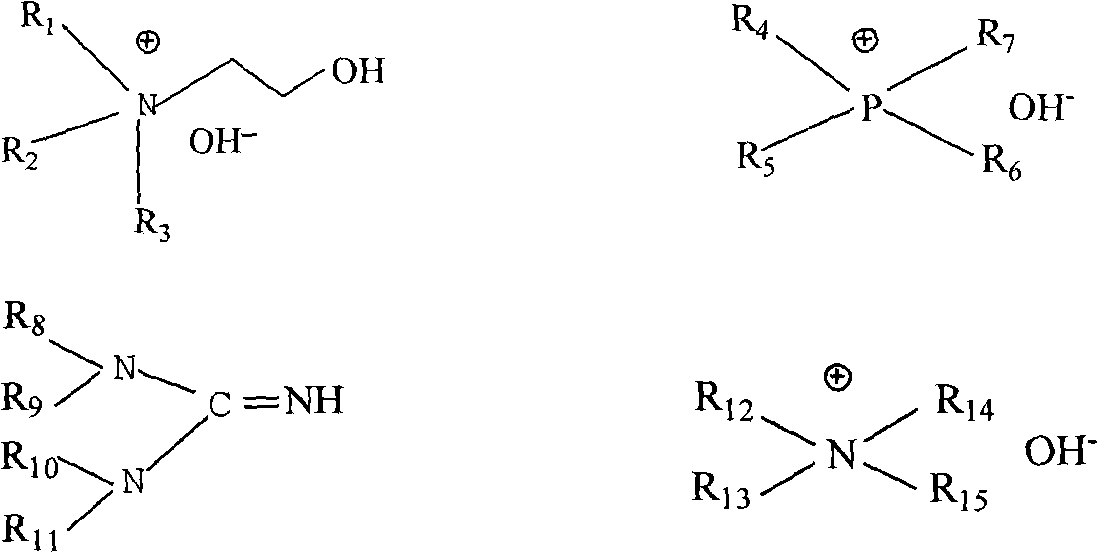
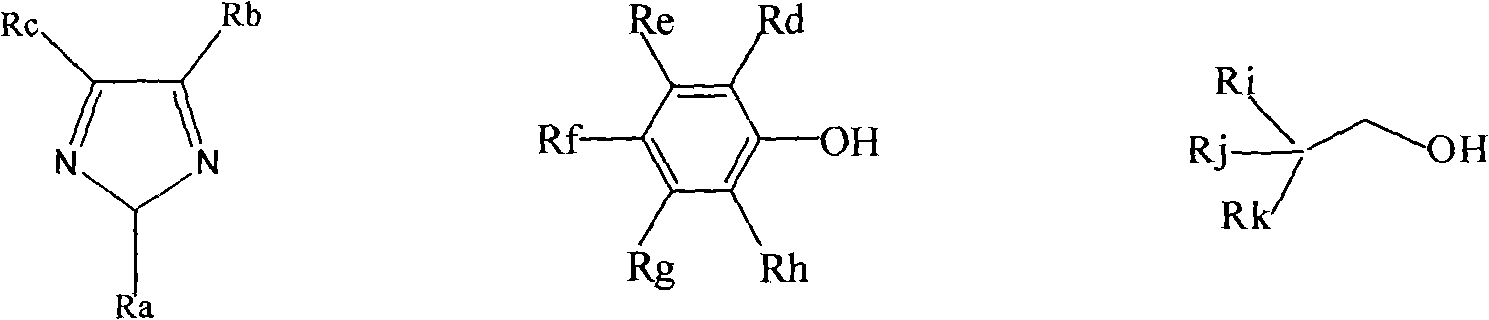
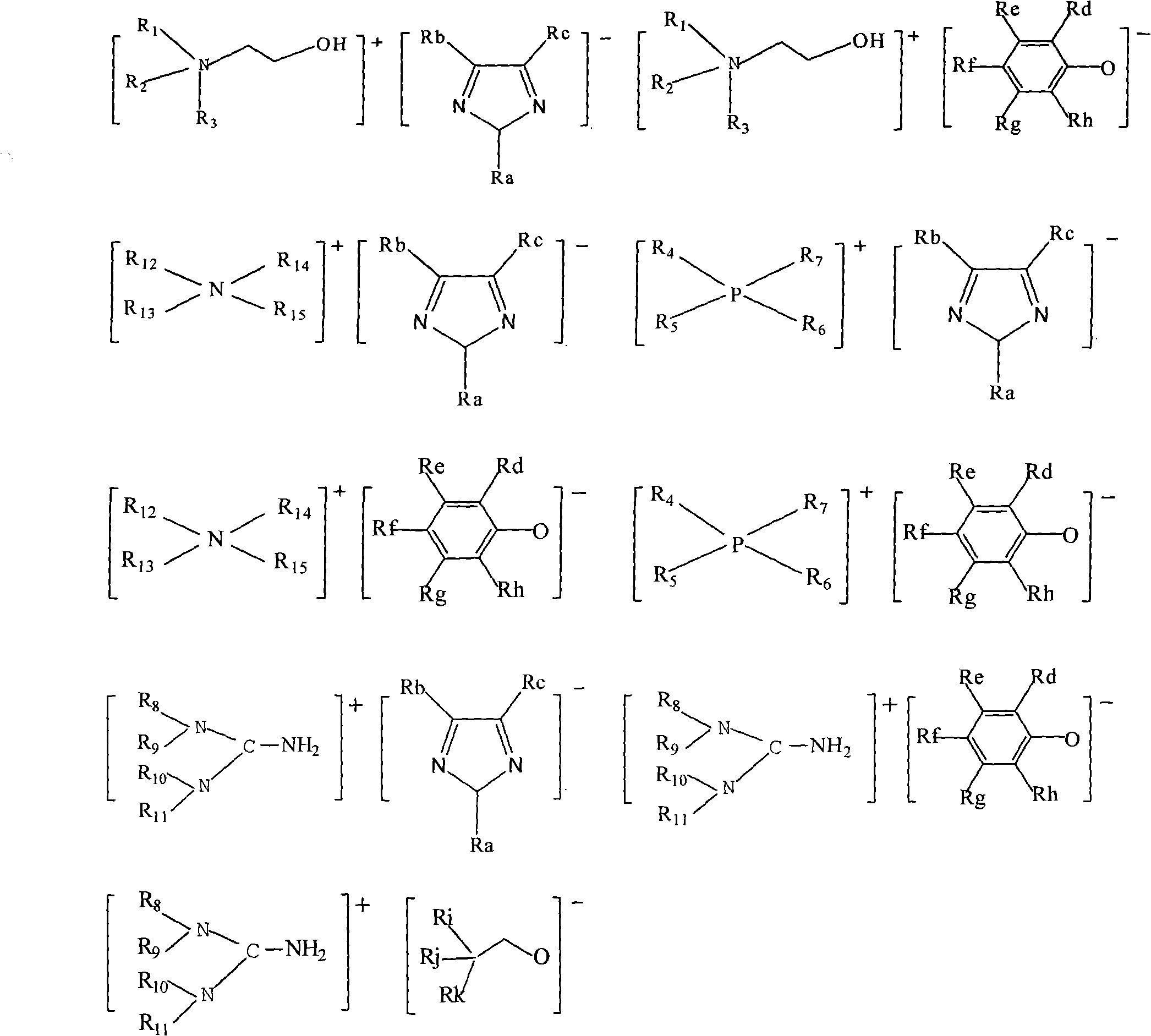
The invention relates to multiple kinds of alkaline ionic liquids as well as preparation methods and application thereof. The alkaline ionic liquid provided by the invention mainly comprises a cation X<+> and an anion Y<->, wherein the precursor of the cation X<+> is choline, phosphine, guanidine or amine; and the precursor of the anion Y<-> is imidazole, phenol or alcohol. The alkaline ionic liquid is prepared from the precursors of the cation and anion at room temperature in a certain ratio. The ionic liquid synthesized in the invention can be applied to the absorption of acidic gases such as carbon dioxide and sulfur dioxide, the absorption and desorption effects are good and the ionic liquid can be recycled.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
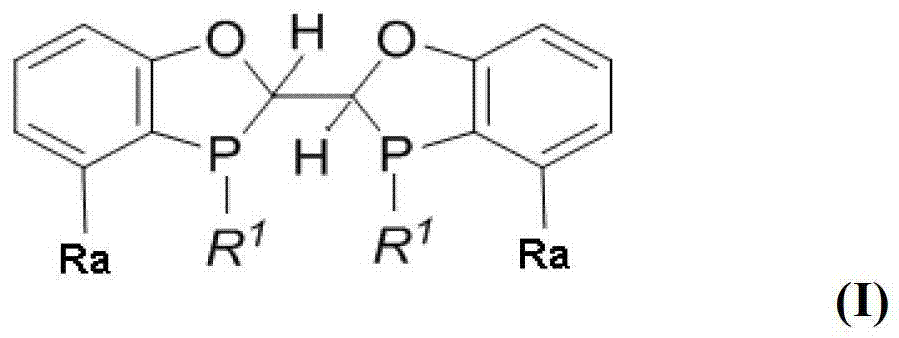
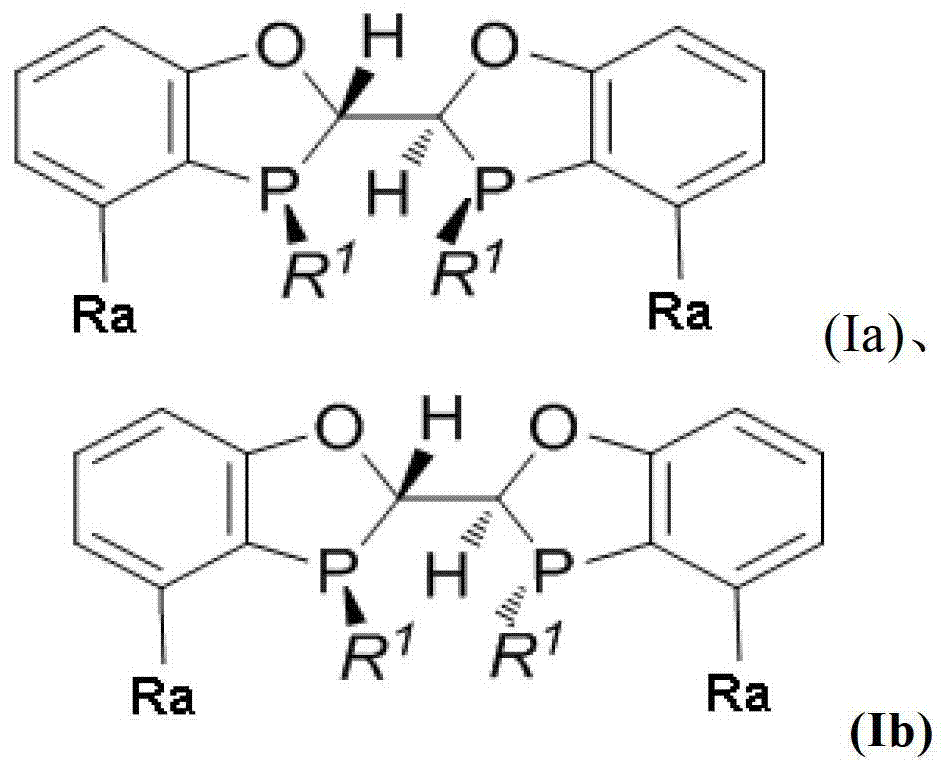
Chiral phosphine ligand and metal catalyst comprising same and application of chiral phosphine ligand and metal catalyst
ActiveCN103087105AEfficient synthesisEconomical and practicalOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsArylMetal catalyst
The invention discloses a chiral phosphine ligand or an enantiomer, a racemate or a diastereoisomer thereof and a transition metal catalyst comprising the chiral phosphine ligand, wherein the structure of the chiral phosphine ligand is shown as in formula I in the specification. The invention also discloses an application of the chiral phosphine ligand or the transition metal catalyst and a method for efficiently synthesizing chiral beta-aryl amide by using catalytic hydrogenation. The transition metal catalyst can be used for carrying out asymmetric catalytic hydrogenation reaction, thereby efficiently synthesizing the beta-aryl amide compound with a high optical purity.
Owner:宁波赜军医药科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com