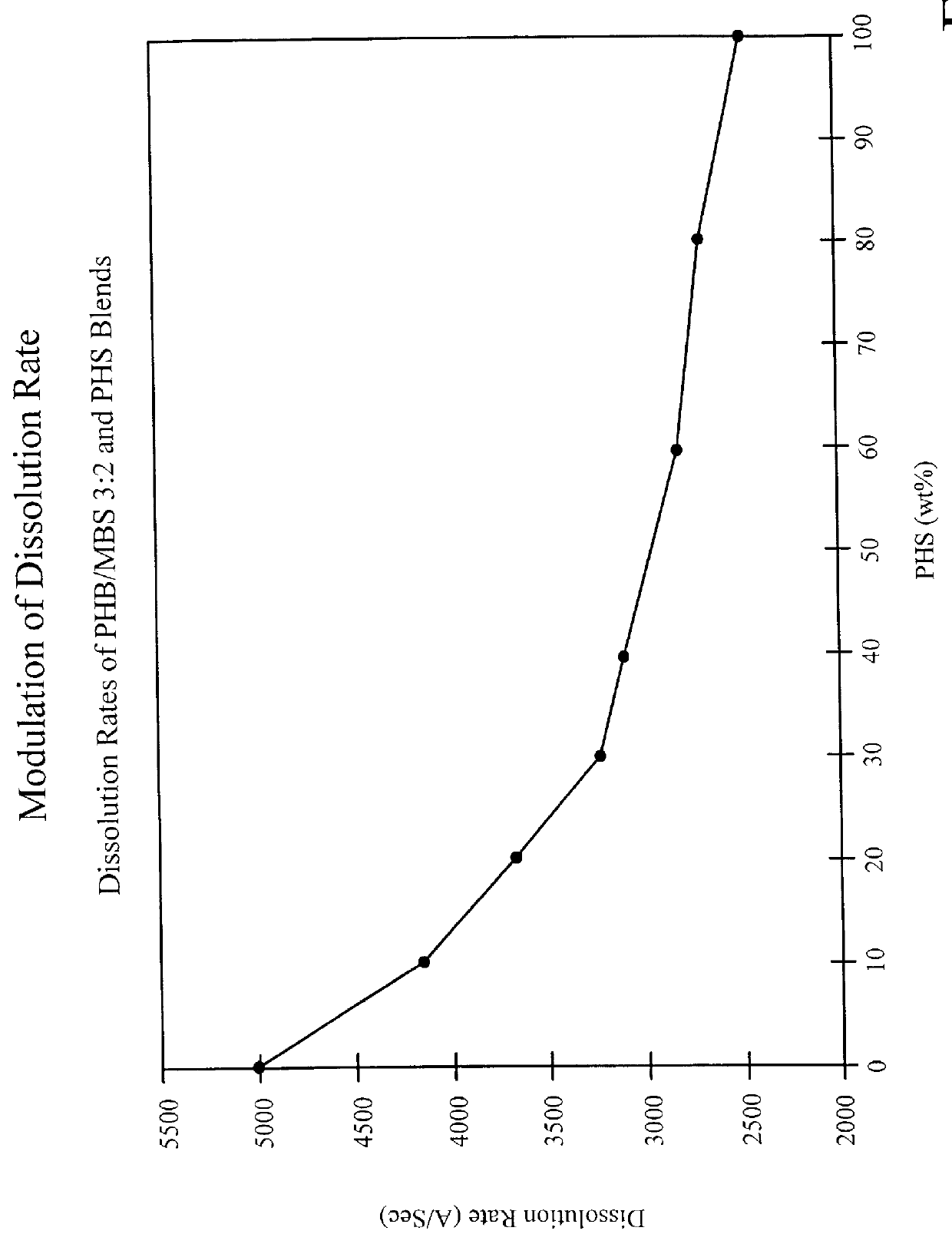
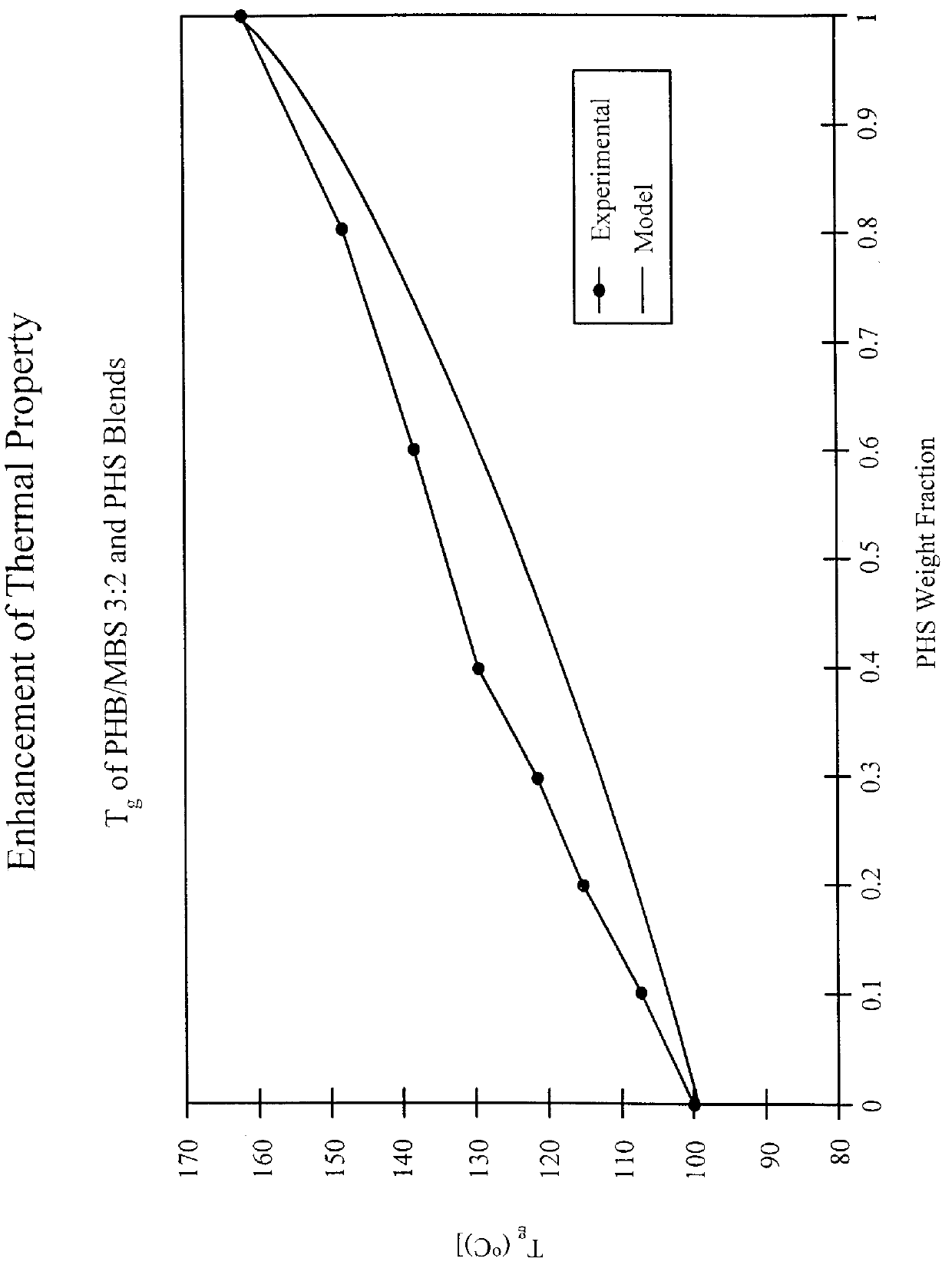
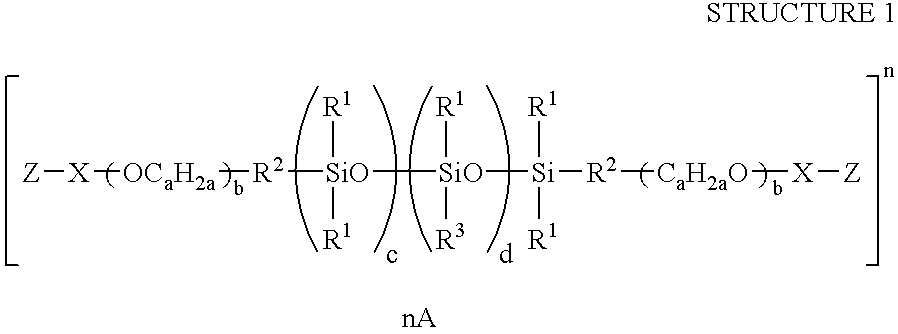
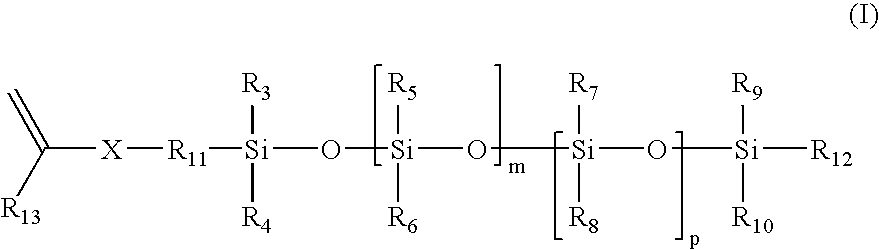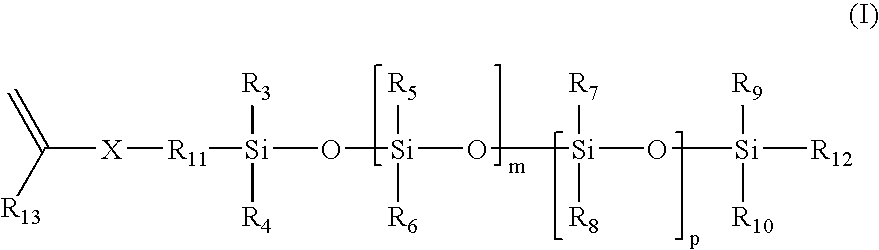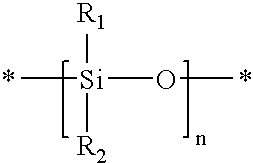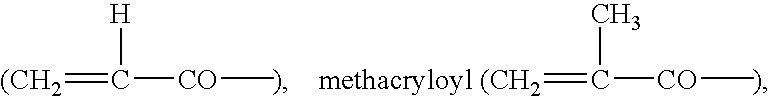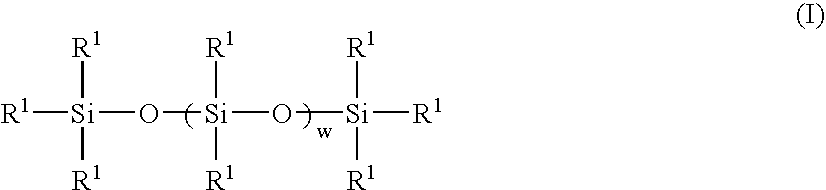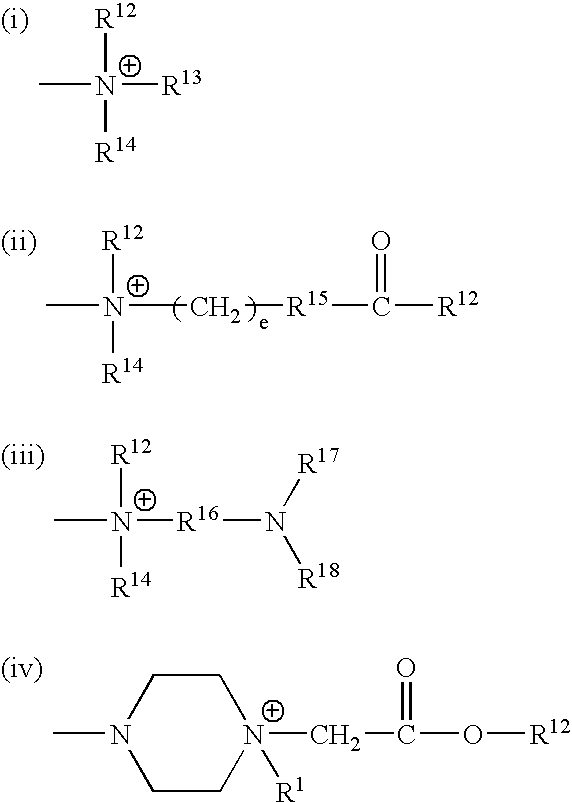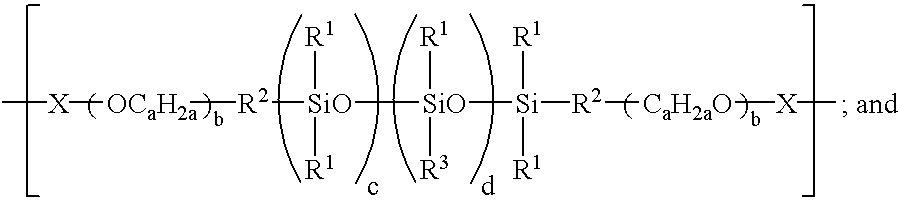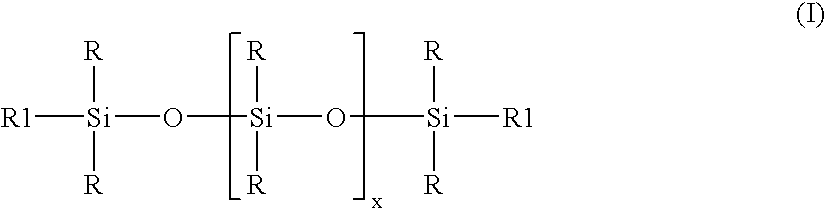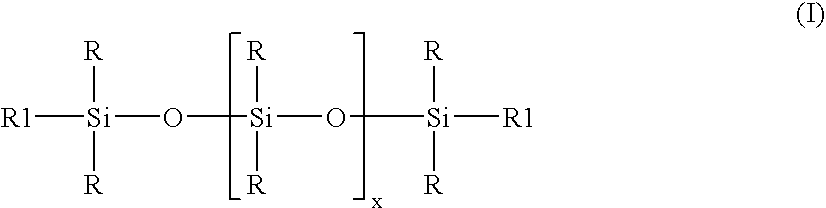Patents
Literature
20779 results about "Siloxane" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
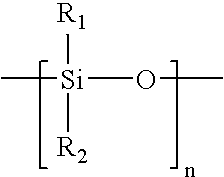
A siloxane is a functional group in organosilicon chemistry with the Si–O–Si linkage. The parent siloxanes include the oligomeric and polymeric hydrides with the formulae H(OSiH₂)ₙOH and (OSiH₂)ₙ. Siloxanes also include branched compounds, the defining feature of which is that each pair of silicon centres is separated by one oxygen atom. The siloxane functional group forms the backbone of silicones, the premier example of which is polydimethylsiloxane. The functional group R₃SiO- (where the three Rs may be different) is called siloxy. Siloxanes are manmade and have many commercial and industrial applications because of the compounds’ hydrophobicity, low thermal conductivity, and high flexibility.
Long wearable soft contact lens
The present invention relates to a soft contact lens, and provides a contact lens which shows small and stable contact angle to water at its surface in water as well as in air, little deposition in wearing, high oxygen permeability, no adhesion of lens to a cornea and superior extended-wearing characteristics. The present invention provides a hydrogel soft contact lens which has contact angle at a lens surface in a range of 10-50° by the captive bubble method in water and 30-90° by the sessile drop method in air, oxygen permeability of not less than 30 and water content of not less than 5%, and also a hydrogel soft contact lens consisting of a polymer comprising a hydrophilic siloxanyl monomer shown by a specified general formula.
Owner:COOPERVISION INT LTD
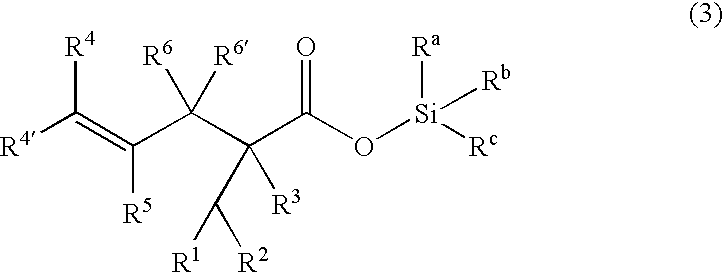
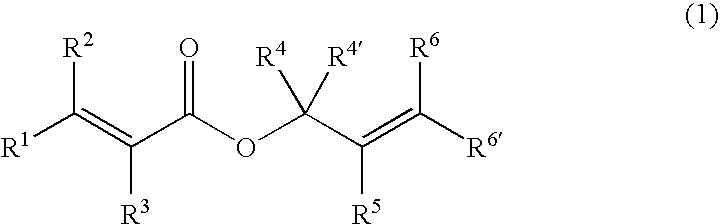
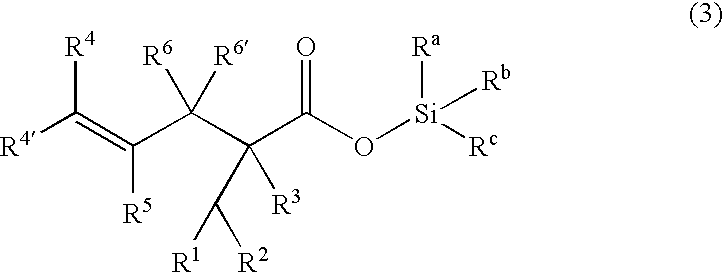
Processes of making gamma,delta-unsaturated carboxylic acid and silyl ester thereof, carboxyl group-containing organosilicon compound and process of making
ActiveUS7307178B2Few stepsHigh yieldSilicon organic compoundsPreparation from carboxylic acid esters/lactonesCarboxyl radicalPerylene derivatives
A γ,δ-unsaturated carboxylic acid silyl ester is prepared by reacting an α,β-unsaturated carboxylic acid ester with a hydrosilane or hydrosiloxane in the presence of tris(pentafluorophenyl)borane. γ,δ-Unsaturated carboxylic acid derivatives are readily prepared through fewer steps and in high yields.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM CO LTD
Method for forming dielectric film using siloxane-silazane mixture
ActiveUS8003174B2High densityHigh strengthPretreated surfacesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilazaneMetallurgy
Owner:ASM JAPAN
Processes of making gamma,delta-unsaturated carboxylic acid and silyl ester thereof, carboxyl group-containing organosilicon compound and process of making
ActiveUS20050070729A1High yieldFew stepsSilicon organic compoundsPreparation from carboxylic acid esters/lactonesCarboxyl radicalPerylene derivatives
A γ,δ-unsaturated carboxylic acid silyl ester is prepared by reacting an α,β-unsaturated carboxylic acid ester with a hydrosilane or hydrosiloxane in the presence of tris(pentafluorophenyl)borane. γ,δ-Unsaturated carboxylic acid derivatives are readily prepared through fewer steps and in high yields.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Home and personal care compositions comprising silicon-based lubricants
InactiveUS7465439B2Cosmetic preparationsOrganic detergent compounding agentsPersonal carePolymer science
A composition for personal, home, or laundry treatment comprising a polymer made up of one or more crosslinked rake or comb silicone copolymer segments. A process for making copolymers for use in such compositions involves hydrosilylation in the presence of a catalyst.
Owner:CONOPCO INC D B A UNILEVER
Organic electroluminescent materials and device made from such materials
Electroluminescent devices and materials including an electroluminescent organo-siloxane polymer. The main chain of the organo-siloxane polymer comprises an organic component that can be alkenyl, alkynyl, aralkyl, aryl, heteroaralkyl, and heteroaryl which can be substituted optionally with hydrogen, alkyl, aryl, heteroalkyl, heteroaralkyl, nitro, cyano, hydroxy, alkoxy, aryloxy, thio, alkylthio, arylthio, amino, halogen, dialkylamino, diarylamino, diaralkylamino, arylamino, alkylamino, arylalkylamino, carbonyloxy, carbonylalkoxy, carbonylalkyloxy, alkylcarbonyloxy, arylcarbonyloxy, alkoxylcarbonyloxy, sulfonyl, or sulfonyloxy. The organic component includes at least two covalent bonds coupling the organic component to the main chain of the organo-siloxane polymer. Such devices provide superior performance and mechanical stability compared with conventional organic electroluminescent materials and devices made from such materials.
Owner:ORGANIC DISPLAY TECH
Cosmetic composition and production thereof
InactiveUS20060018867A1Efficient use ofReduce the amount requiredCosmetic preparationsHair cosmeticsEpsilon-PolylysineEmulsion
It has been desired to develop a highly preservative and antibacterial cosmetic composition that can easily be applied to both emulsion and non-emulsion type cosmetics. It has also been desired to develop a method of improving a preservative and / or antibacterial effect(s) of a cosmetic composition comprising polyorganosiloxane-containing epsilon-polylysine and thereby reducing the amount of antibacterial preservative agent to be used. There is provided a cosmetic composition comprising one or a combination of two or more of polyorganosiloxane-containing epsilon-polylysine compounds obtained by reacting epsilon-polylysine with polyorganosiloxane or a physiologically acceptable salt thereof, and polyhydric alcohol.
Owner:CHISSO CORP
Wettable hydrogels comprising reactive, hydrophilic, polymeric internal wetting agents
The present invention relates to wettable silicone hydrogels comprising the reaction product of at least one siloxane containing component and at least one reactive, hydrophilic polymeric internal wetting agent. The present invention further relates to silicone hydrogel contact lenses comprising at least one oxygen permeable component, and an amount of reactive, hydrophilic polymeric internal wetting agent sufficient to impart wettability to said device.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON VISION CARE INC
Silsesquioxane polymers, method of synthesis, photoresist composition, and multilayer lithographic method
InactiveUS6087064AReduce usageAvoid pollutionPhotosensitive materialsRadiation applicationsResistPolymer science
Novel silsesquioxane polymers are formed by methods which avoid the use of BBr3. The novel silsesquioxane polymers are especially useful in negative photoresist compositions and photolithographic processes. Alternatively, improved silsesquioxane polymer-containing negative photoresist compositions are obtained by using a polymer component containing a blend of silsesquioxane polymer and non-silsesquioxane polymer. The photoresist compositions provide improved dissolution characteristics enabling the use of 0.26 N TMAH developer. The photoresist compositions also provide improved thermal characteristics enabling use of higher processing temperatures. The photoresist compositions are especially useful in a multilayer photolithographic processes and are capable of producing high resolution.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Prepolymers with dangling polysiloxane-containing polymer chains
The invention provide a new class of silicone-containing prepolymers containing dangling polysiloxane-containing polymer chains. This class of silicone-containing prepolymer is capable of being actinically crosslinked to form a silicone hydrogel material with a relatively high oxygen permeability, a reduced elastic modulus, and a relatively high ion permeability. The present invention is also related to silicone hydrogel contact lenses made from this class of silicone-containing prepolymers and to methods for making the silicone hydrogel contact lenses.
Owner:ALCON INC
Hydrophilic Polysiloxane Macromonomer, and Production and Use of the same
ActiveUS20090234089A1Improve compatibilityHigh oxygen permeabilitySilicon organic compoundsOptical articlesSide chainHydrophile
Problem to be Solved To provide an ophthalmic lens, which can be more safely worn, that is, to provide a material, which is transparent and has high oxygen permeability and a high hydrophilic property, and to provide a novel monomer to be a raw material thereof.Solution A hydrophilic polysiloxane macromonomer contains polyoxyethylene as a hydrophilic side chains in a polysiloxane main chain, wherein transparency, oxygen permeability, and hydrophilic properties of the material are controlled by regulating the length of the polysiloxane main chain, the length of the hydrophilic polyoxyethylene side chains, and the number of the side chains.
Owner:COOPERVISION INT LTD
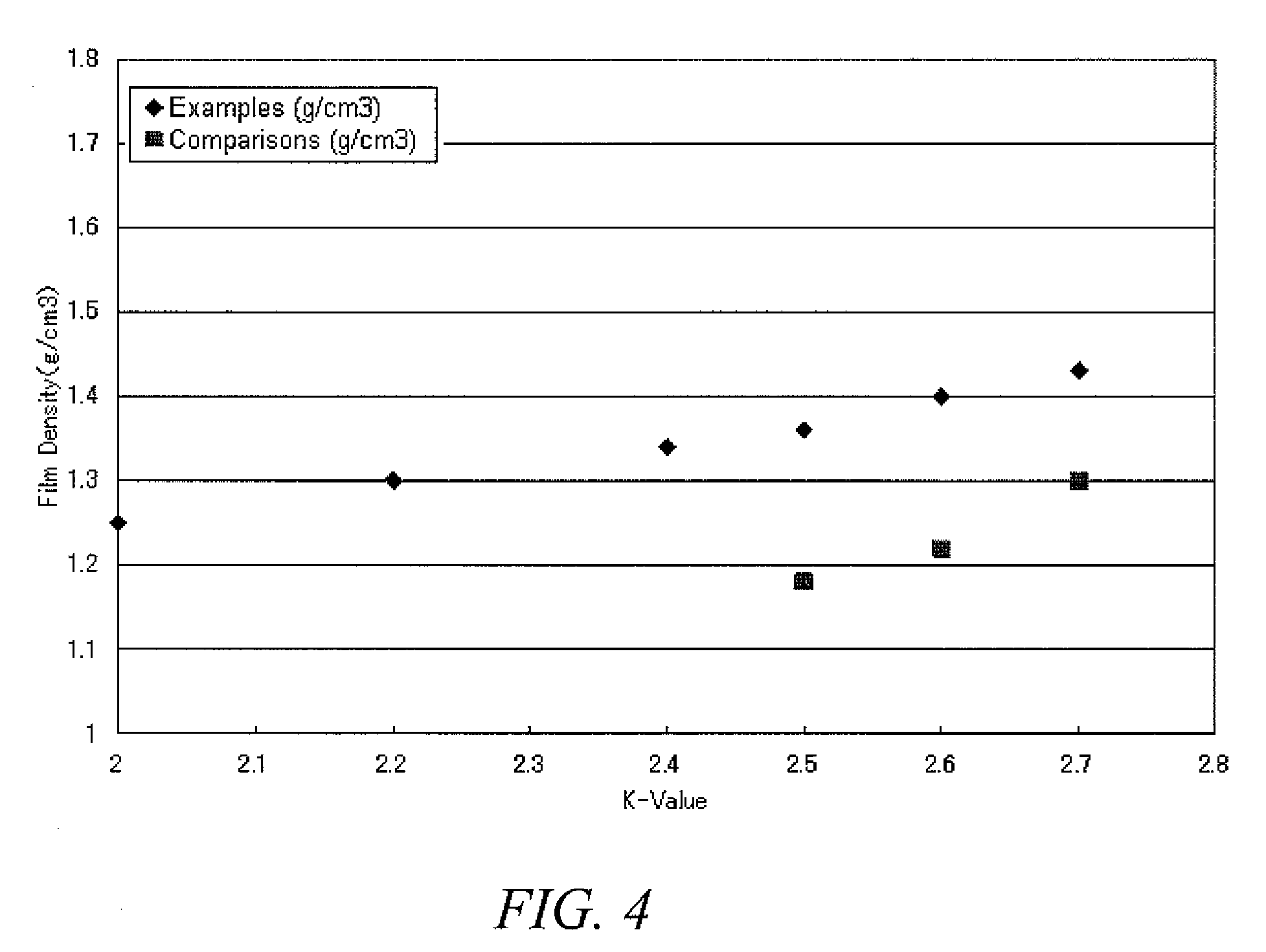
Low dielectric constant materials and method
InactiveUS6051321AImprove rotational flexibilityTightly boundSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSynthetic resin layered productsElectrical conductorCopper
Intermetal dielectric (IMD) and interlevel dielectric (ILD) that have dielectric constants (K) ranging from 2.0 to 2.6 are prepared from plasma or photon assisted CVD (PACVD) or transport polymerization (TP). The low K dielectric (LKD) materials are prepared from PACVD or TP of some selected siloxanes and F-containing aromatic compounds. The thin films combine barrier and adhesion layer functions with low dielectric constant functions, thus eliminating the necessity for separate adhesion and barrier layers, and layers of low dielectric constant. The LKD materials disclosed in this invention are particularly useful for <0.18 .mu.m ICs, or when copper is used as conductor in future ICs.
Owner:CANON USA
Silicone-containing prepolymers with dangling hydrophilic polymer chains
ActiveUS20080234457A1Reduce molecular weightHigh molecular weightOptical articlesProsthesisPolymer scienceHydrophilic polymers
The invention provide a new class of silicone-containing prepolymers containing dangling hydrophilic polymer chains. This class of silicone-containing prepolymer is capable of being actinically crosslinked to form a silicone hydrogel material with a hydrophilic surface without post curing surface treatment. The present invention is also related to silicone hydrogel contact lenses made from this class of silicone-containing prepolymers and to methods for making the silicone hydrogel contact lenses.
Owner:ALCON INC
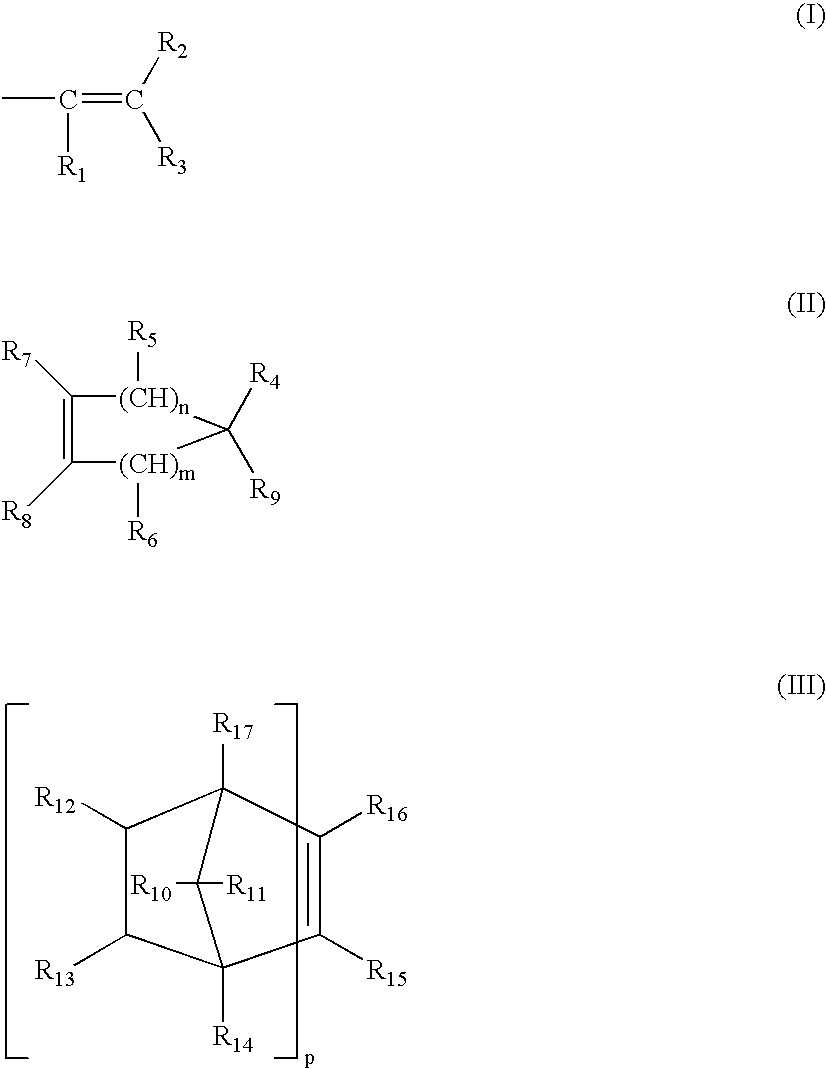
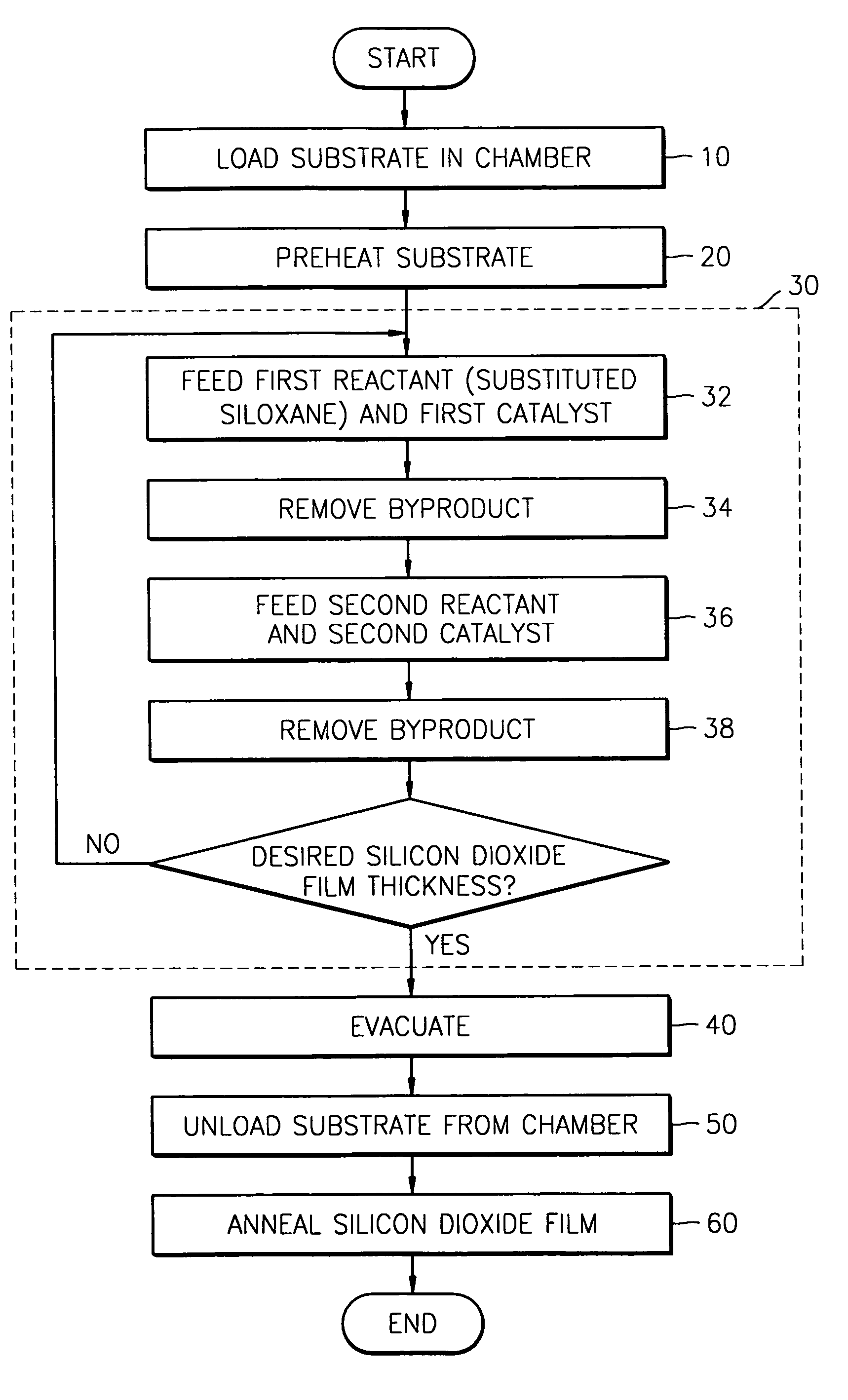
Method for forming silicon dioxide film using siloxane
InactiveUS7084076B2Improve film qualityReduce the presence of impuritiesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingHydrogenHalogen
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
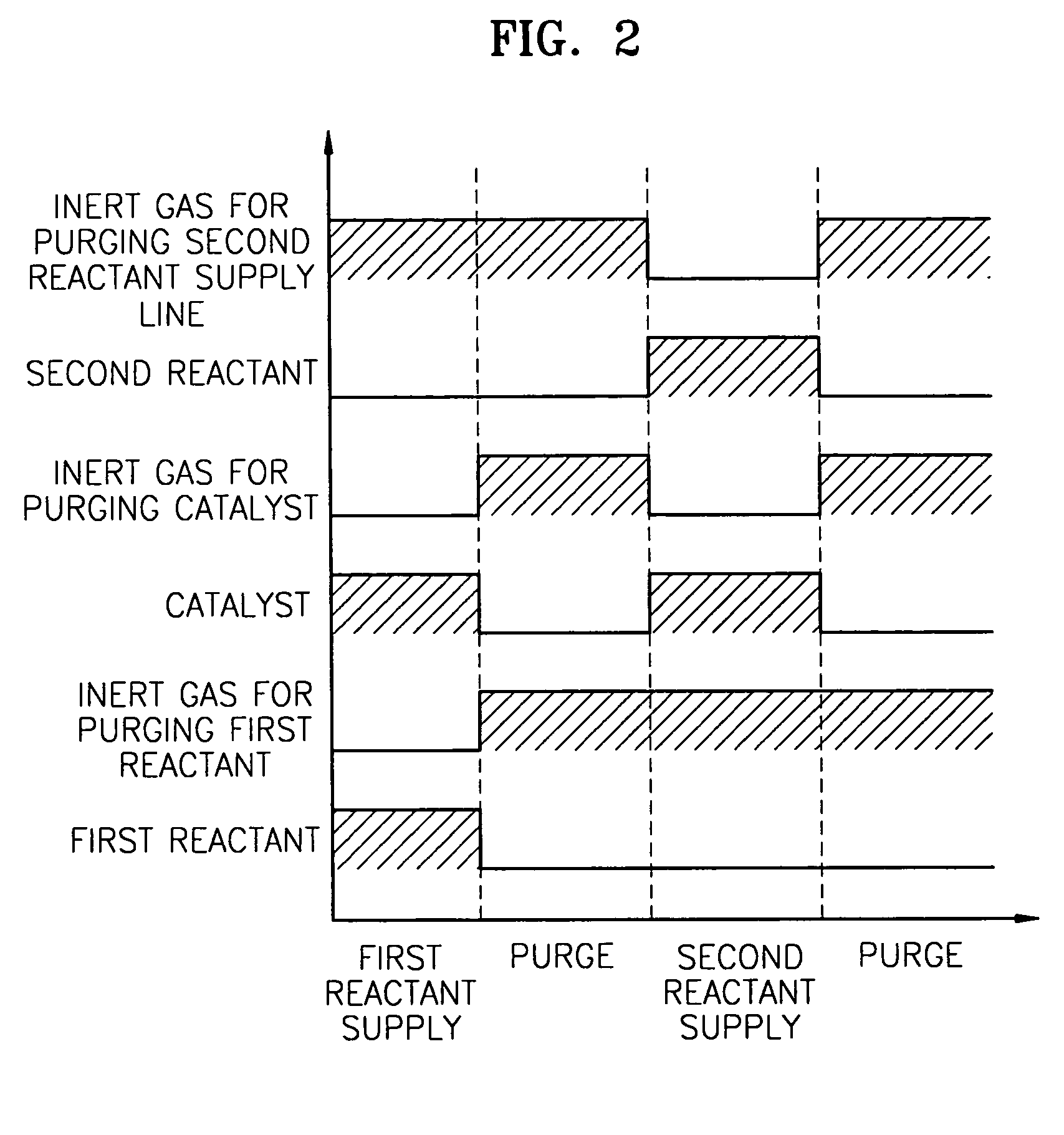
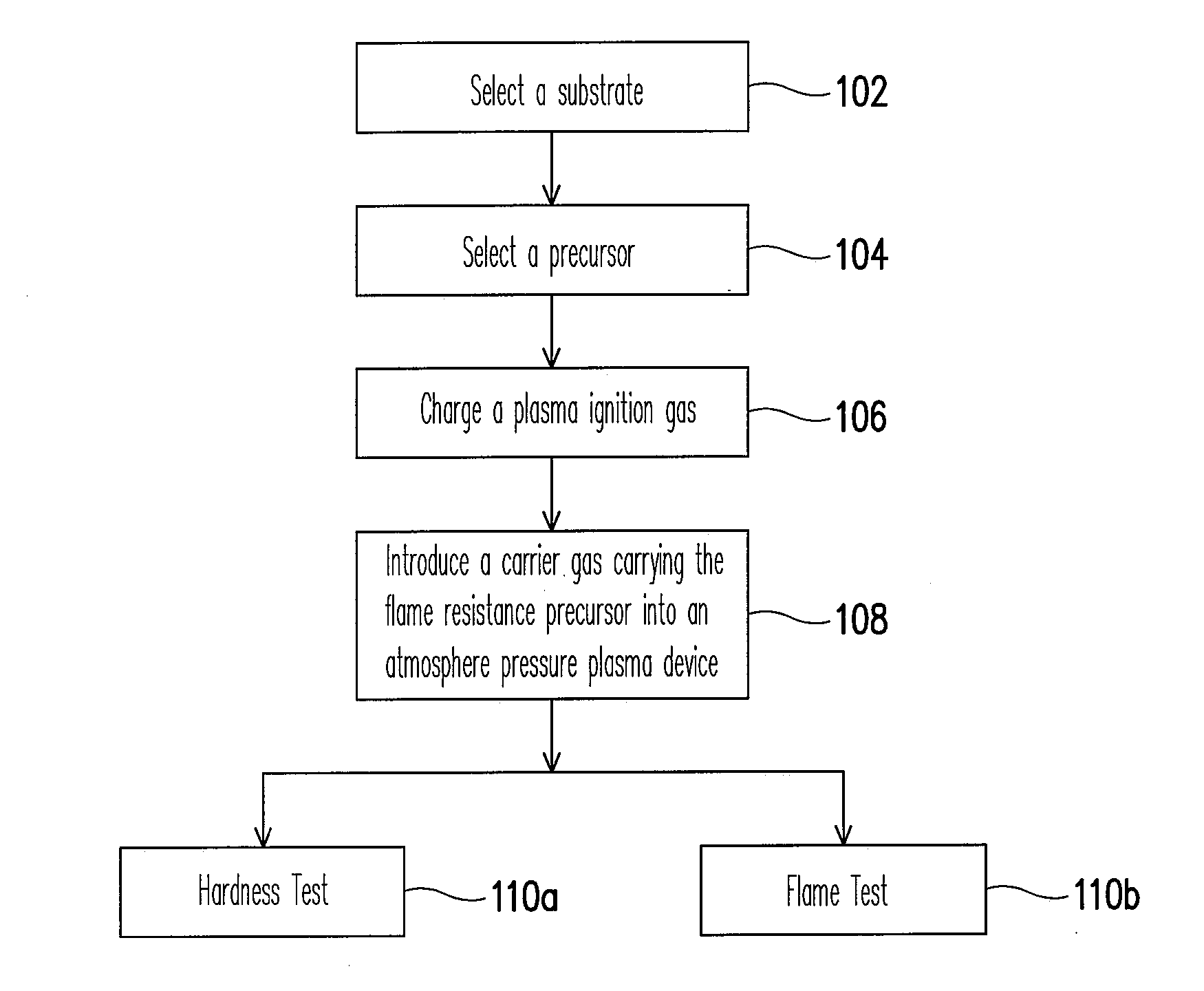
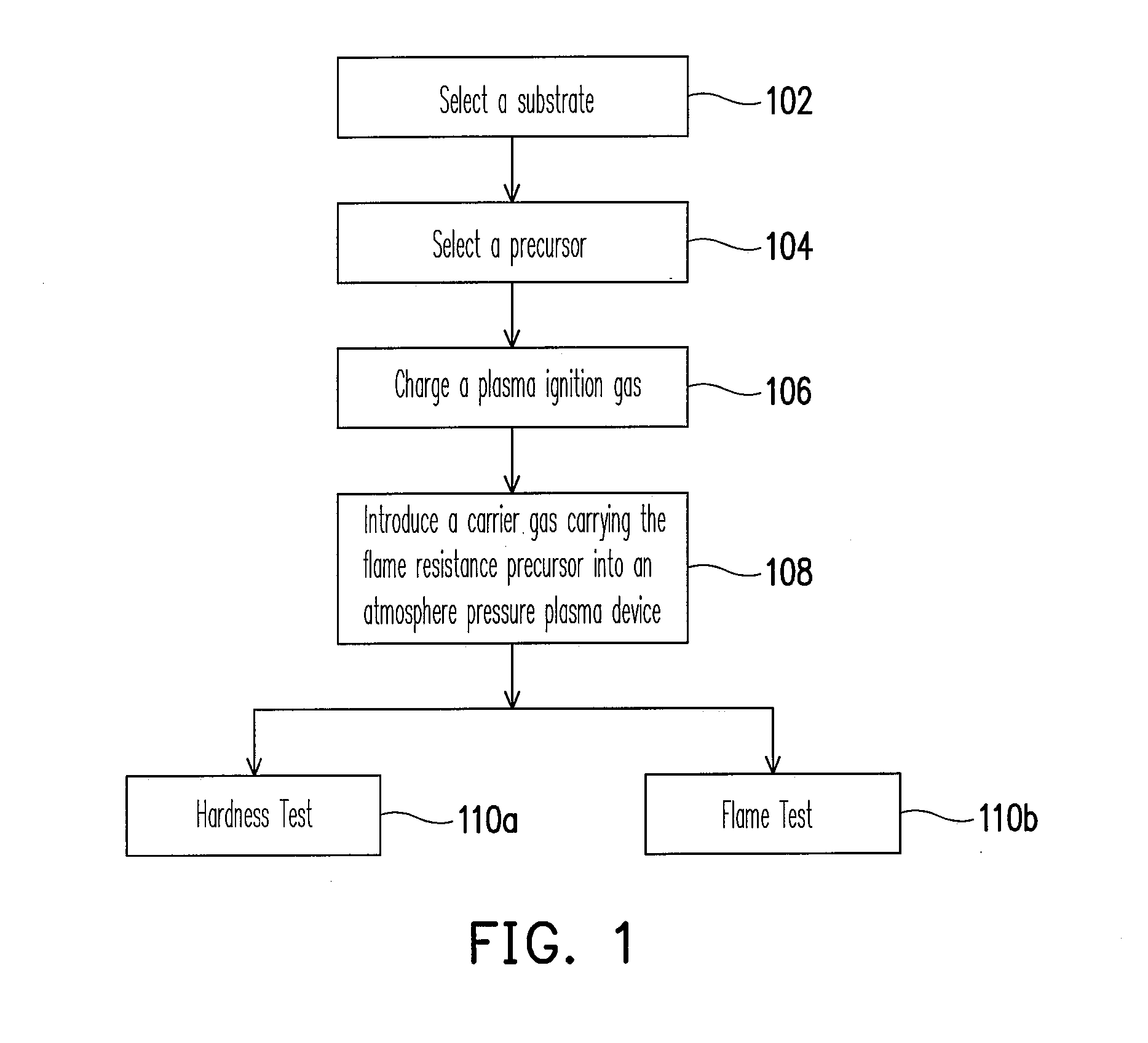
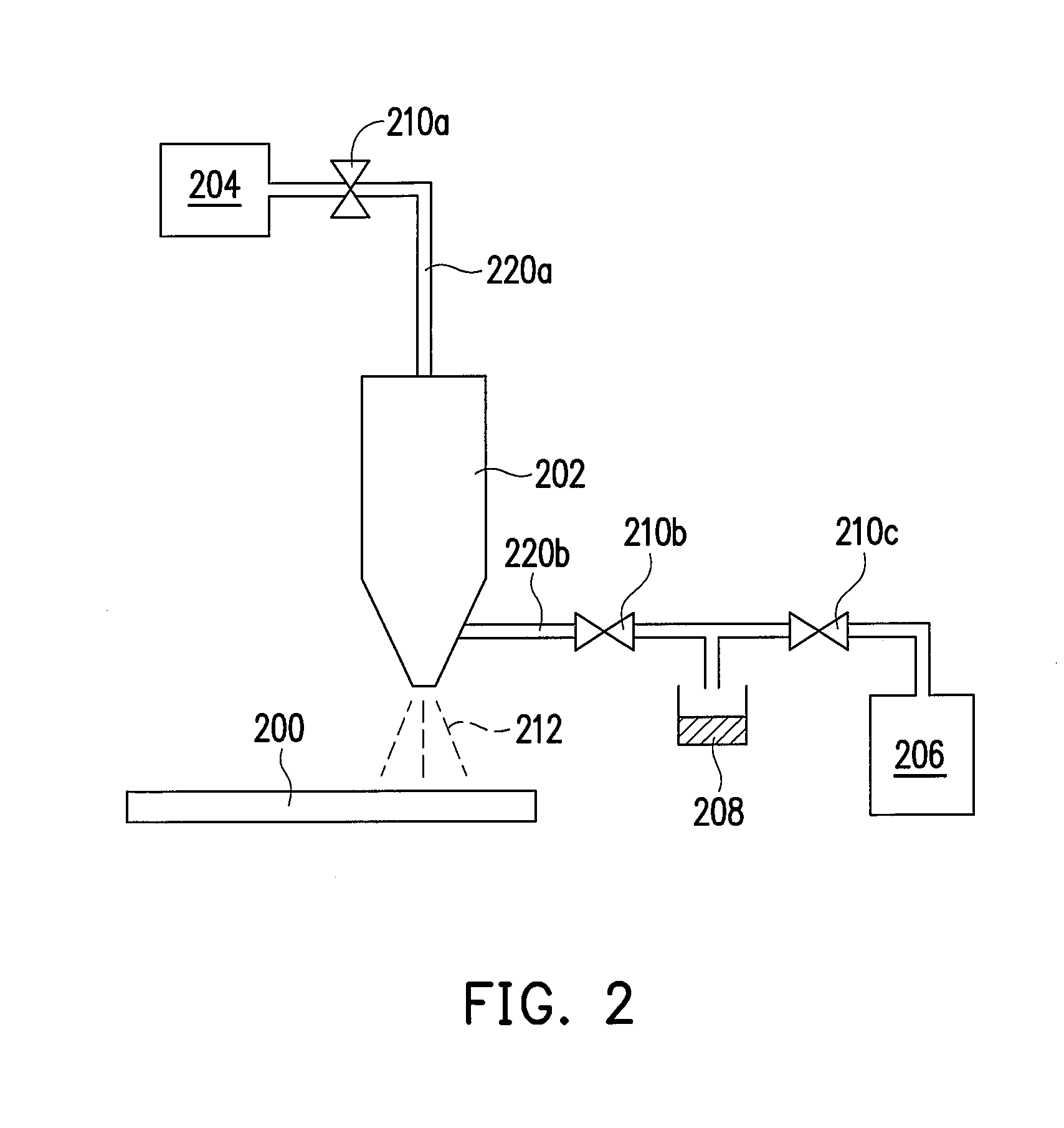
Method of improving surface flame resistnace of substrate
InactiveUS20080105276A1Improve flame retardant performanceSurface cleaningElectrostatic cleaningChemical vapor deposition coatingPlasma ignitionAtmosphere
A method of improving surface flame resistance of a substrate is provided. A substrate is provided. An atmosphere pressure plasma process is performed on the surface of the substrate to form an inorganic film layer on the surface of the substrate, wherein a process gas of the atmosphere plasma process includes a flame resistance precursor, a carrier gas, and a plasma ignition gas. Particularly, the flame resistance precursor is selected from a siloxane compound, an inorganic alkoxide compound and a combination thereof. The siloxane compound has a formula of Si(OCnH2(n+1))4, n=1˜5, and the inorganic alkoxide compound has a formula of A(OCmH2m+1)4, where A represents Sn, Ti, Zr, Ce and m=2.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Method for forming dielectric film using siloxane-silazane mixture
ActiveUS20090156017A1High densityHigh strengthPretreated surfacesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilazaneMetallurgy
A method of forming a dielectric film, includes: introducing a siloxane gas essentially constituted by Si, O, C, and H and a silazane gas essentially constituted by Si, N, H, and optionally C into a reaction chamber where a substrate is placed; depositing a siloxane-based film including Si—N bonds on the substrate by plasma reaction; and annealing the siloxane-based film on the substrate in an annealing chamber to remove Si—N bonds from the film.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
Dicarboxylic acid foamable vehicle and pharmaceutical compositions thereof
ActiveUS20080044444A1Convenient vehicle for topical deliveryGood treatment effectPowder deliveryBiocideDicarboxylic acidCarboxylic acid
The present invention teaches a foamable pharmaceutical carrier comprising a benefit agent, selected from the group consisting of a dicarboxylic acid and a dicarboxylic acid ester; a stabilizer selected from the group consisting of at least one surface-active agent; at least one polymeric agent and mixtures thereof; a solvent selected from the group consisting of water, a hydrophilic solvent, a hydrophobic solvent, a potent solvent, a polar solvent, a silicone, an emollient, and mixtures thereof, wherein the benefit agent, stabilizer and solvent are selected to provide a composition that is substantially resistant to aging and to phase separation and or can substantially stabilize other active ingredients. The invention further relates to a foamable composition further containing a liquefied hydrocarbon gas propellant.
Owner:VYNE THERAPEUTICS INC
Method for depositing a low k dielectric film (k<3.5) for hard mask application
InactiveUS20030113995A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesOptoelectronicsDielectric thin films
A method for depositing a silicon oxycarbide hard mask on a low k dielectric layer is provided. Substrates containing a silicon oxycarbide hard mask on a low k dielectric layer are also disclosed. The silicon oxycarbide hard mask may be formed by a processing gas comprising a siloxane.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Perfumed liquid laundry detergent compositions with functionalized silicone fabric care agents
InactiveUS20060003913A1Organic detergent compounding agentsNon-surface-active detergent compositionsLiquid laundry detergentNitrogen
The invention is directed to aqueous liquid laundry detergent compositions for cleaning and imparting fabric care benefits to fabrics laundered therewith and to methods for preparing such compositions. Such compositions comprise (A) at least one textile-cleaning surfactant; (B) droplets of miscible silicones comprising both a polarly-functionalized, preferably nitrogen-containing amino or ammonium functionalized, polysiloxane component and a nitrogen-free non-functionalized or non-polarly-functionalized polysiloxane component; and (C) a perfume component comprising fragrant aldehydes and / or ketones or a pro-perfume capable of providing such aldheyde and / or ketone perfume materials in situ. Incorporation of a polarly-functionalized polysiloxane fabric care agent into liquid laundry detergent compositions by miscibly combining it with a non-functionalized or non-polarly functionalized polysiloxane minimizes the undesirable interaction such polarly-functionalized silicone material might otherwise have with aldehyde and / or ketone perfume compounds.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
High water content silicone hydrogels
ActiveUS7934830B2Increase moisture contentSuitable oxygen permeability propertyLayered productsThin material handlingHydration reactionHydrophilic monomer
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
Fabric care and perfume compositions and systems comprising cationic silicones and methods employing same
InactiveUS6903061B2Superior fabric careGood lookingInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsCationic surface-active compoundsSiliconeChemistry
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Silanol-functionalized compounds for the preparation of polyurethane foams
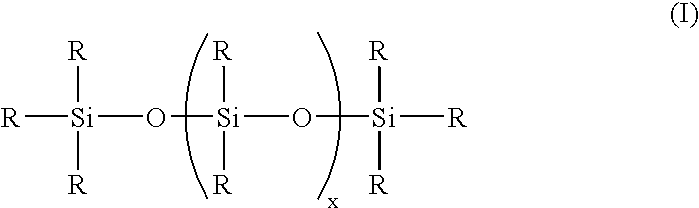
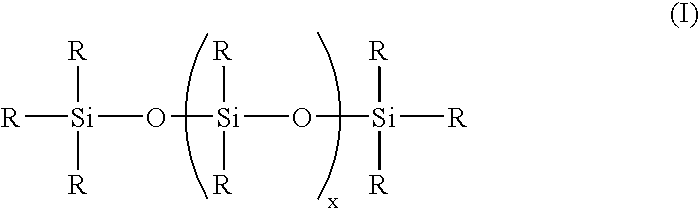
Methods for preparing polyurethane flexible foam are described, wherein an organic polyisocyanate is reacted with an active hydrogen-containing component such as an organic polyol, in the presence of a urethane catalyst, a blowing agent, optionally a cell opener, and a siloxane-based surfactant composition as a stabilizer for the foam. The siloxane-based surfactant composition comprises a silanol-functionalized organosiloxane having general formula (I), wherein: the R groups are independently a C1-C3 alkyl, phenyl, or —OSi(R)3; provided that at least one R group is a hydroxyl (—OH) bonded directly to any silicon atom and X is an integer from 0-200.
Owner:EVONIK OPERATIONS GMBH
Silicone hydrogels comprising n-vinyl amides and hydroxyalkyl (meth)acrylates or (meth)acrylamides
The present invention relates to a process comprising the steps of reacting a reactive mixture comprising at least one silicone-containing component, at least one hydrophilic component, and at least one diluent to form an ophthalmic device having an advancing contact angle of less than about 80°; and contacting the ophthalmic device with an aqueous extraction solution at an elevated extraction temperature, wherein said at least one diluent has a boiling point at least about 10° higher than said extraction temperature.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON VISION CARE INC
Polymerization of halogen-containing monomers using siloxane surfactant
Halogenated polymers are prepared by a process comprising polymerizing at least one halogen-containing monomer in an aqueous medium containing monomer, radical initiator, and siloxane surfactant. The medium may optionally contain one or more of an antifoulant, a buffering agent and a chain-transfer agent.
Owner:ARKEMA INC
Ionic silicone hydrogels
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON VISION CARE INC
Wettable hydrogels comprising reactive, hydrophilic, polymeric internal wetting agents
The present invention relates to wettable silicone hydrogels comprising the reaction product of at least one siloxane containing component and at least one reactive, hydrophilic polymeric internal wetting agent. The present invention further relates to silicone hydrogel contact lenses comprising at least one oxygen permeable component, and an amount of reactive, hydrophilic polymeric internal wetting agent sufficient to impart wettability to said device.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON VISION CARE INC
Amine organoborane complex initiated polymerizable compositions containing siloxane polymerizable components
InactiveUS6777512B1Easy to useBroaden applicationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsAminosilochromeOligomer
In one embodiment the invention is a polymerizable composition comprising a) an organoborane amine complex; b) one or more of monomers, oligomers or polymers having olefinic unsaturation which is capable of polymerization by free radical polymerization; c) one or more compounds, oligomers or prepolymers having a siloxane backbone and reactive moieties capable of polymerization; and d) a catalyst for the polymerization of the one or more compounds, oligomers or prepolymers having a siloxane backbone and reactive moieties capable of polymerization. This composition may further comprise a compound which causes the organoborane amine complex to disassociate. In a preferred embodiment, the two part composition further comprises a compound which is reactive with both the b) one or more of monomers, oligomers or polymers having olefinic unsaturation which is capable of polymerization by free radical polymerization; and the c) one or more compounds, oligomers or prepolymers having a siloxane backbone and reactive moieties capable of polymerization. This composition can be polymerized by contacting the two parts of the composition. In another embodiment the invention is an organoborane amine complex comprising an alkyl borane having ligands which are alkyl, cycloalkyl or both and an amino siloxane.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Manufacture of stable low particle size organopolysiloxane emuslion
ActiveUS20070276087A1Rapid emulsificationReduce polymerization timeMaterial nanotechnologyOther chemical processesPolymer scienceEmulsion
Stable high viscosity organopolysiloxane emulsions with particle sizes up to 150 nanometer may be made in a simple and cost-effective manner employing a standard homogenizer, and optional subsequent polymerization of the organopolysiloxan at controlled temperature. A combination of non-ionic emulsifier together with an at least one anionic emulsifier is employed, having an HLB value 12-15, while maintaining a temperature up to 50° C.
Owner:WACKER CHEM GMBH
Hydrophilic polysiloxane compositions
The instant invention provides a method for improving the miscibility of the lower molecular weight unsaturated siloxane-polyether copolymers with the alpha , omega -divinylpolysiloxanes without loss of storage stability, or delay of cure at the vulcanization temperature, or loss of permanent hydrophilicity or other desirable features of the cured polysiloxane. The compositions of the present invention comprise one or more alpha , omega -divinylpolysiloxanes, unsaturated polysiloxane-polyether copolymers having from 2 to 5 silicon atoms per molecule which are preferably trisiloxanes, and a compatibilizing additive. The permanently hydrophilic, rapidly wettable polysiloxane compositions yield static water contact angles <50 DEG dynamic advancing contact angles of less than about 100.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Ionic silicone hydrogels
The present invention relates to a process comprising the steps of reacting a reactive mixture comprising at least one silicone-containing component, at least one hydrophilic component, and at least one diluent to form an ophthalmic device having an advancing contact angle of less than about 80°; and contacting the ophthalmic device with an aqueous extraction solution at an elevated extraction temperature, wherein said at least one diluent has a boiling point at least about 10° higher than said extraction temperature.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON VISION CARE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com