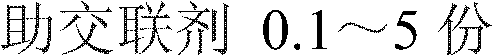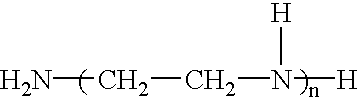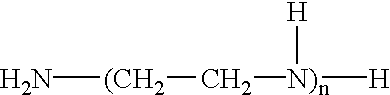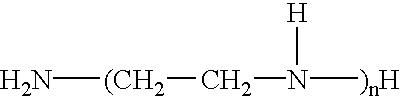Patents
Literature
2334 results about "Blowing agent" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
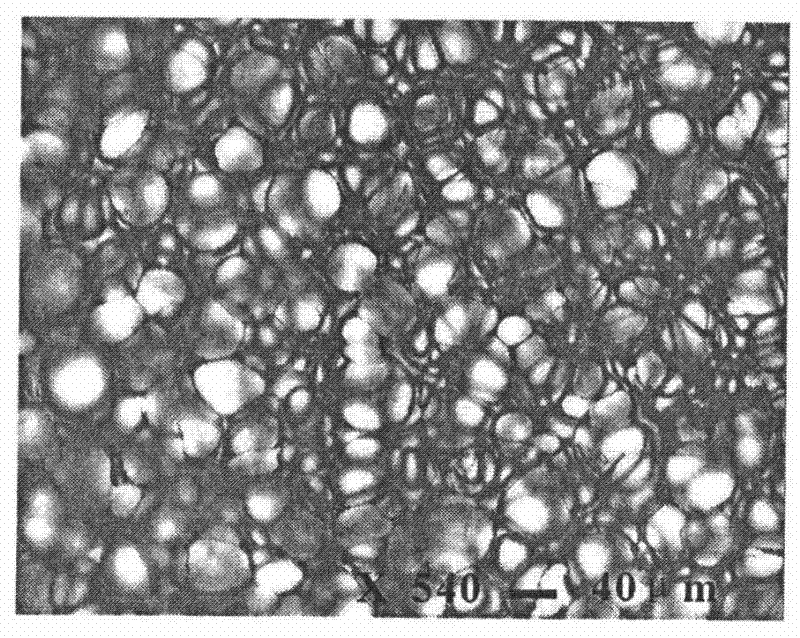
A blowing agent is a substance which is capable of producing a cellular structure via a foaming process in a variety of materials that undergo hardening or phase transition, such as polymers, plastics, and metals. They are typically applied when the blown material is in a liquid stage. The cellular structure in a matrix reduces density, increasing thermal and acoustic insulation, while increasing relative stiffness of the original polymer.
Pentafluoropropene-based compositions
ActiveUS6858571B2Reduce flammabilityMaximize effectivenessBiocideOrganic chemistry1,1-Difluoroethane1,3,3,3-Tetrafluoropropene
Provided are azeotrope-like compositions comprising pentafluoropropene (HFO-1225) and a fluid selected from the group consisting of 3,3,3-trifluoropropene (“HFO-1243zf”), 1,1-difluoroethane (“HFC-152a”), trans-1,3,3,3-tetrafluoropropene (“HFO-1234ze”), and combinations of two or more thereof. Also provided are uses thereof including as refrigerants, blowing agents, sprayable compositions, flame suppressant, and the like.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Silanol-functionalized compounds for the preparation of polyurethane foams
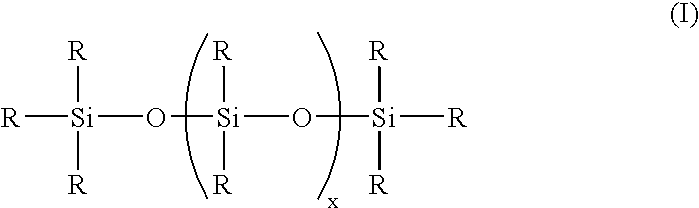
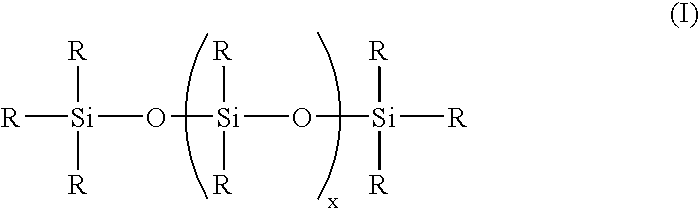
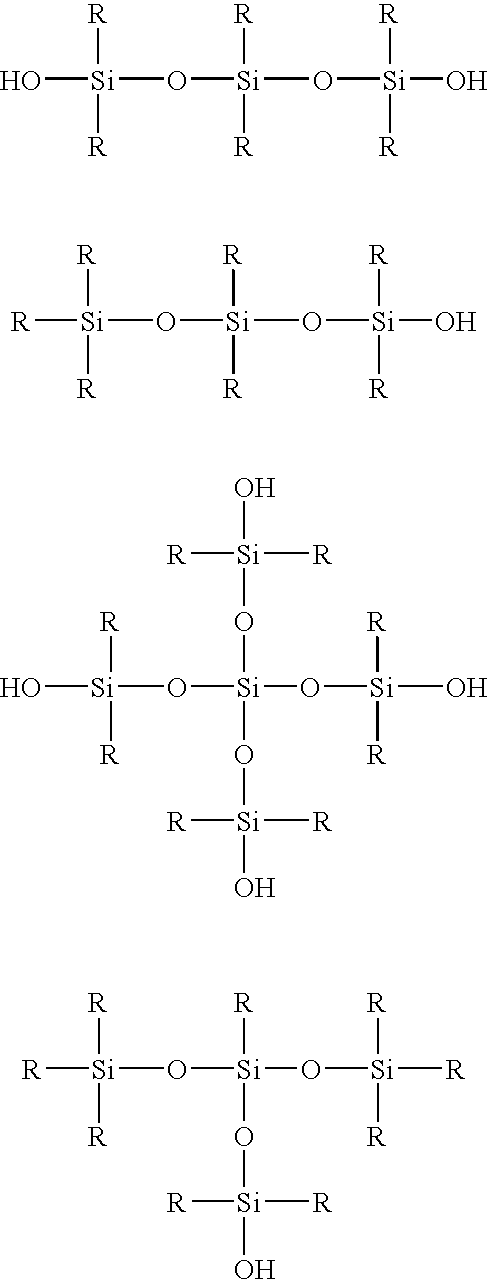
Methods for preparing polyurethane flexible foam are described, wherein an organic polyisocyanate is reacted with an active hydrogen-containing component such as an organic polyol, in the presence of a urethane catalyst, a blowing agent, optionally a cell opener, and a siloxane-based surfactant composition as a stabilizer for the foam. The siloxane-based surfactant composition comprises a silanol-functionalized organosiloxane having general formula (I), wherein: the R groups are independently a C1-C3 alkyl, phenyl, or —OSi(R)3; provided that at least one R group is a hydroxyl (—OH) bonded directly to any silicon atom and X is an integer from 0-200.
Owner:EVONIK OPERATIONS GMBH
Injection molding of polymeric material
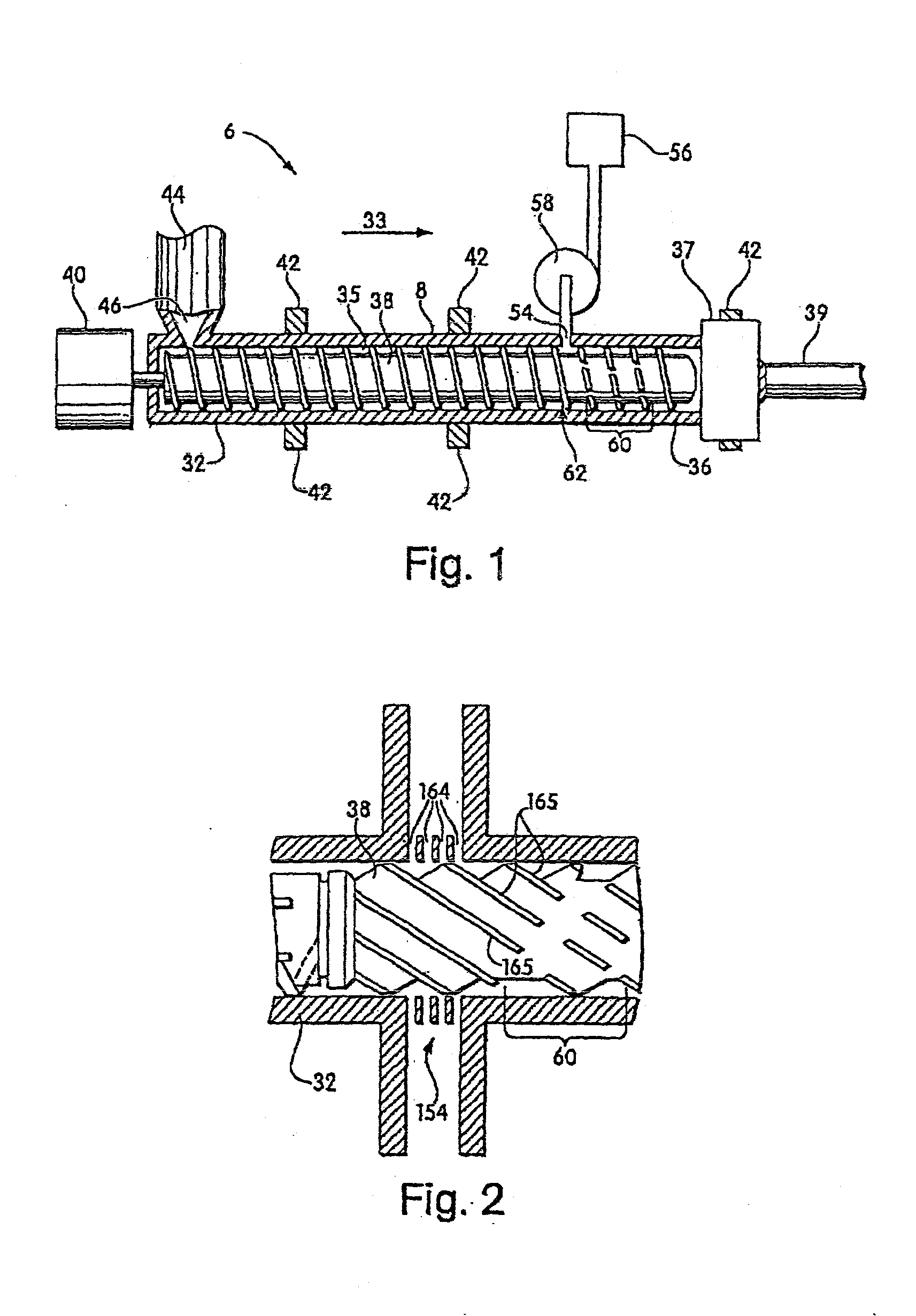
Injection molding systems and methods useful for making microcellular foamed materials are provided as well as microcellular articles. Pressure drop rate and shear rate are important features in some embodiments, and the invention provides systems for controlling these parameters in an injection molding system. Another aspect involves an injection molding system including a nucleator that is upstream of a pressurized mold. Another aspect involves an extrusion system with the reciprocating screw for forming a single phase solution of non-nucleated blowing agent and polymeric material. Another aspect involves very thin walled microcellular material and very thin walled polymeric material. Another aspect provides a method for producing high weight reductions in very thin-walled parts with surfaces that have no noticeable differences from non-foamed parts.
Owner:TREXEL
High-resilience chemical crosslinked polyethylene foam material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a high-resilience chemical crosslinked polyethylene foam material and a preparation method thereof. The material mainly comprises the following components by weight: 50-100 parts of polyethylene resin, 0.1-50 parts of elastomer, 5-50 parts of foaming agent, 0.1-5 parts of cross-linking agent, 0.1-10 parts of foaming assistant, and 0.1-5 parts of cross-linking assistant; the components are internally mixed, pelletized, mixed, extruded, and formed into non-cross-linking extruded master slices, and then the master slices are cross-linked and foamed by heating. According to the invention, the elastomer is mixed into PE (poly ethylene) resin to form the foam material, so the resilience of the product is high; meanwhile, the product further has high elongation at break and tensile strength, excellent toughness, and stable chemical and physical properties, so that the product can be widely used in the fields of packaging, sports and protection, transportation and the like.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Structural hot melt material and methods
InactiveUS6887914B2Reduce and eliminate stepAvoid corrosionAdhesive processesNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesEpoxyHot melt
The present invention relates to a material, method, and application for reinforcement of structural members, especially joints such as a hem flange joint of an automobile. The method and material of the present invention comprises of combining, in parts by weight: less than about twenty percent (<20%) ethylene copolymer, less than about forty percent (<40%) epoxy, less than about thirty percent (<45%) epoxy-based resin, less than about two percent (<2%) blowing agent and from about one percent (1%) to about five percent (5%) curing agent (and optionally add any of the following components: less than about two percent (<2%) curing agent accelerator, from about twenty-five percent (25%) to fifty-five percent (55%) filler, and less than about one percent (<1%) of coloring agent). The application of the present invention comprises of: (1) providing a structural member having two substrates forming a space to be joined; (2) placing the material of the present invention in proximity of the space to be joined; (3) exposing the material to a heat source causing it to flow, fill, and cure in the defined area or space to be joined.
Owner:ZEPHYROS INC
Two component thermosettable compositions useful for producing structural reinforcing adhesives
InactiveUS6451876B1Uniform cell structureExcessive heat dissipationEpoxy resin adhesivesEpoxyPartial system
A two part system for producing structural reinforcing adhesives is provided wherein one component containing epoxy resin is combined with a second component containing a specified curative system. An aliphatic polyamine, an amidoamine, an alcohol and an adduct of a polyamine and an epoxide are present in the curative system. When a thermally activated blowing agent is utilized, the resulting foam is remarkably uniform in cell structure and has improved strength and modulus. Hollow inorganic microspheres are employed to reduce the density of the thermoset produced from the two part system.
Owner:HENKEL KGAA
Wood-Plastic Composites Using Recycled Carpet Waste and Systems and Methods of Manufacturing
InactiveUS20080128933A1Reduce material costsPlastic recyclingBuilding constructionsFoaming agentVolumetric Mass Density
An extruded composite utilized as a building material includes a base polymer, unseparated processed recycled carpet waste, and a filler material, which may be a wood filler or other natural fiber. The recycled carpet waste may be used to decrease the amount of both base polymer and wood filler to achieve an equivalent product at lower cost. The extruded composite may also utilize chemical foaming agents to reduce density. Both foamed and non-foamed composites may be capstocked.
Owner:MATERIAL INNOVATIONS LLC
Toughened adhesive material
An adhesive material and articles incorporating the same is disclosed. The adhesive material includes at least three of epoxy resin; impact modifier; flexibilizer, blowing agent; curing agent; and filler. The adhesive material is preferably used for structural adhesion but may be used for sealing, baffling or reinforcing an article of manufacture such as an automotive vehicle.
Owner:ZEPHYROS INC
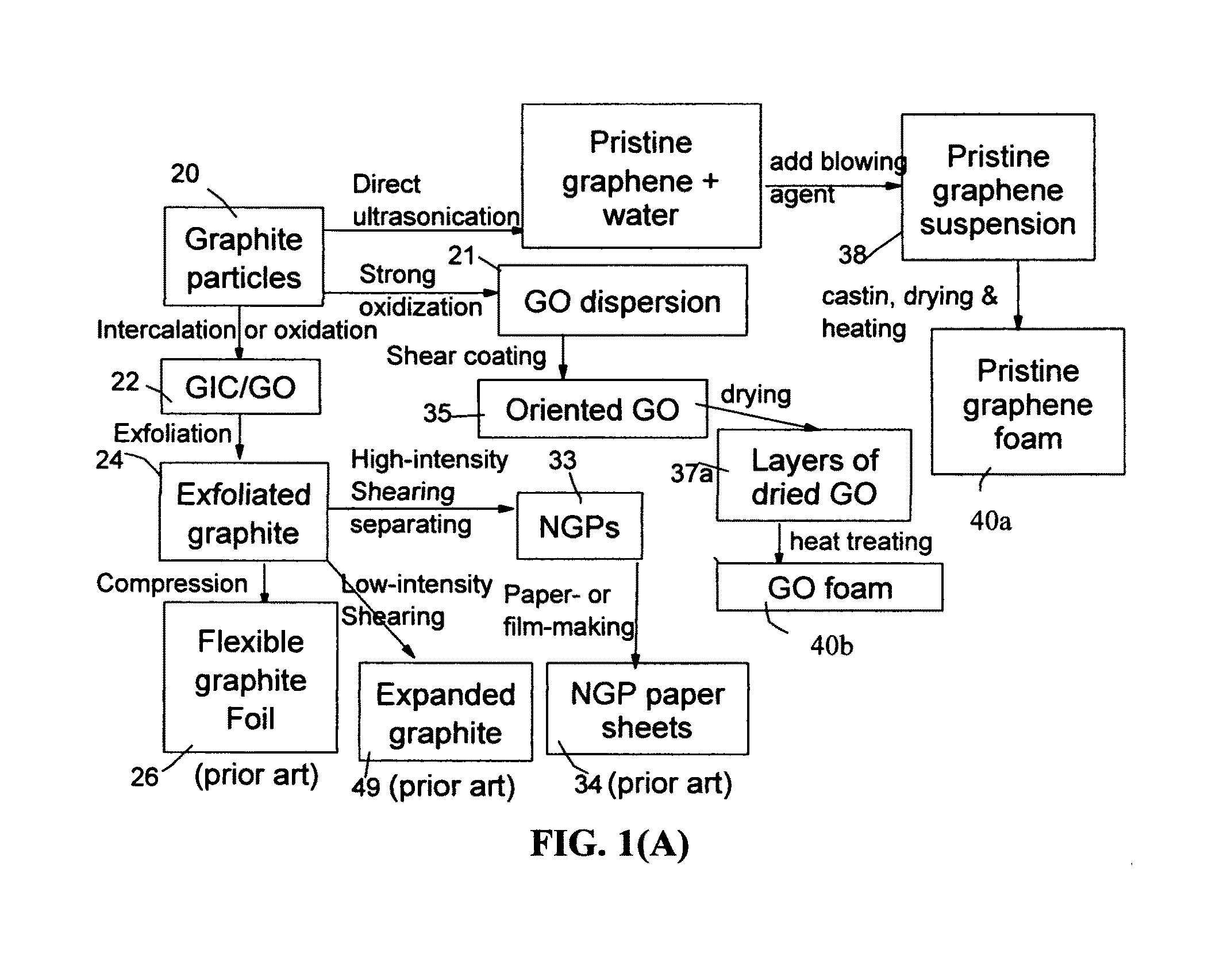
Process for producing graphene foam supercapacitor electrode
ActiveUS9437372B1Effective orientation-inducing stressEasy to mergeCarbon compoundsHybrid capacitor electrodesLiquid mediumMass loading
A process for producing a supercapacitor electrode, comprising: (a) preparing a graphene dispersion containing an optional blowing agent; (b) depositing the dispersion onto a supporting substrate to form a wet layer; (c) removing the liquid medium from the wet layer to form a dried layer of graphene material; (d) heat treating the dried layer at a temperature from 80° C. to 3,200° C. to induce volatile gas molecules from the non-carbon elements or to activate the blowing agent for producing a layer of solid graphene foam having a physical density from 0.01 to 1.7 g / cm3 and a specific surface area from 50 to 3,300 m2 / g; and (e) impregnating the foam with an electrolyte to form a layer of pre-impregnated graphene foam, which is compressed to form the electrode. This process leads to a supercapacitor having a large electrode thickness, high active mass loading, high tap density, and exceptional energy density.
Owner:NANOTEK INSTR GRP LLC
Process for preparing thermoplastic vulcanizates
This invention includes a process for forming a thermoplastic vulcanizate comprising: (a) admixing a C-H insertion curing agent with at least one elastomeric phase polymer to form a first admixture; (b) admixing at least one non-elastomeric polyolefin with the first admixture to form a second admixture; and (c) heating the second admixture to a temperature at least the decomposition temperature of the curing agent to crosslink the elastomeric phase while mixing the admixture to an extent sufficient to result in the formation of a thermoplastic material, hereinafter referred to as a thermoplastic vulcanizate, and optionally including an additional step (d) of shaping the resulting thermoplastic vulcanizate, especially by heating and foaming or molding the TPV. The C-H insertion curing agent is preferably selected from alkyl and aryl azides (R-N3), acyl azides (R-C(O)N3), azidoformates (R-O-C(O)-N3), sulfonyl azides (R-SO2-N3), phosphoryl azides ((RO)2-(PO)-N3), phosphinic azides (R2-P(O)-N3) and silyl azides (R3-Si-N3), with poly(sulfonyl azide) most preferred. Additionally, the invention includes a thermoplastic vulcanizate comprising a blend of: (1) an elastomeric phase crosslinked using a C-H insertion curing agent dispersed in; (2) at least one non-elastomeric thermoplastic polyolefin. The invention also includes a foamable composition comprising (1) an elastomeric phase crosslinked using a C-H insertion curing agent dispersed in; (2) at least one non-elastomeric thermoplastic polyolefin; and (3) from about 0.1 to about 25 percent by weight based on the combined weight of components (1) and (2) of at least one foaming agent as well as a fabricated part, cable jacket, cable insulation, or foam comprising the thermoplastic vulcanizate or the invention or resulting from the process of the invention.
Owner:THE DOW CHEM CO
Gold ball having a foamed layer created by infrared radiation
InactiveUS20070155542A1Avoid excessive densityDomestic articlesSolid ballsGold ballCompound (substance)
This invention is directed to a golf ball having a foamed layer and the method for creating the foamed layer by the heating of blowing agents with infrared radiation. Either physical blowing agents can be de-volatized, or chemical blowing agents (both organic and inorganic) may be decomposed wherein the blowing agents are generated within the layer. The resultant layer is less dense than the core layer beneath it.
Owner:ACUSHNET CO
Hydrofluoroolefin compositions
The present invention relates to compositions containing hydrofluoroolefins and to the uses thereof as heat transfer fluids, blowing agents, solvents and aerosols. More particularly, the invention relates to compositions having: 5 to 65% by weight, preferably from 5 to 15% by weight, of 2,3,3,3-tetrafluoropropene, 5 to 70% by weight, preferably 40 to 60% by weight, of HFC-134a and 25 to 42% by weight of HFC-32.
Owner:ARKEMA FRANCE SA
Filled polymer composite and synthetic building material compositions
ActiveUS20050163969A1Improve mechanical propertiesLow costSolid waste managementLayered productsPolyesterFiber
The invention relates to composite compositions having a matrix of polymer networks and dispersed phases of particulate or fibrous materials. The polymer matrix contains a polyurethane network formed by the reaction of a poly- or di-isocyanate and one or more saturated polyether or polyester polyols, and an optional polyisocyanurate network formed by the reaction of optionally added water and isocyanate. The matrix is filled with a particulate phase, which can be selected from one or more of a variety of components, such as fly ash particles, axially oriented fibers, fabrics, chopped random fibers, mineral fibers, ground waste glass, granite dust, or other solid waste materials. The addition of water can also serve to provide a blowing agent to the reaction mixture, resulting in a foamed structure, if such is desired.
Owner:BORAL IP HLDG
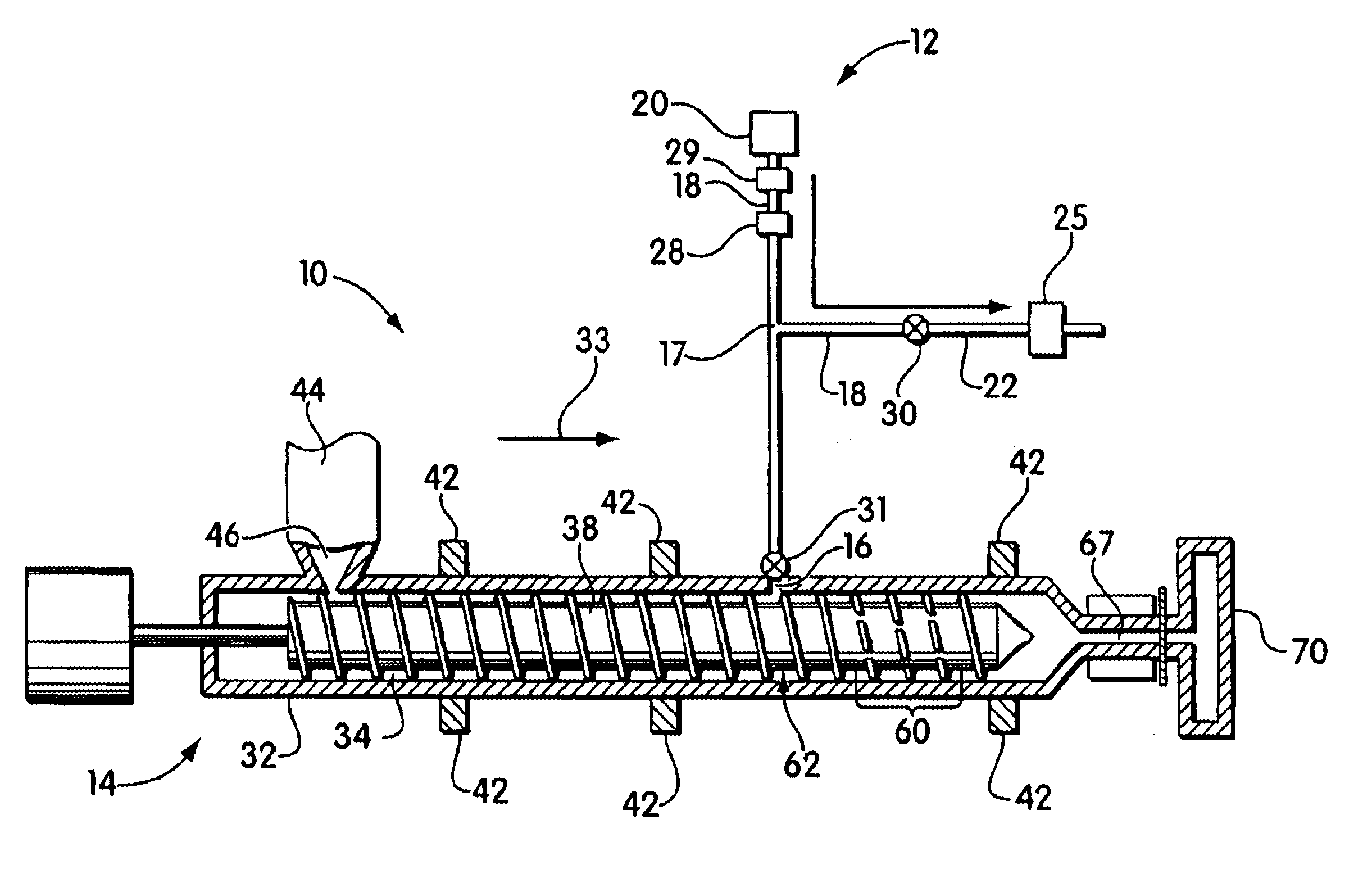
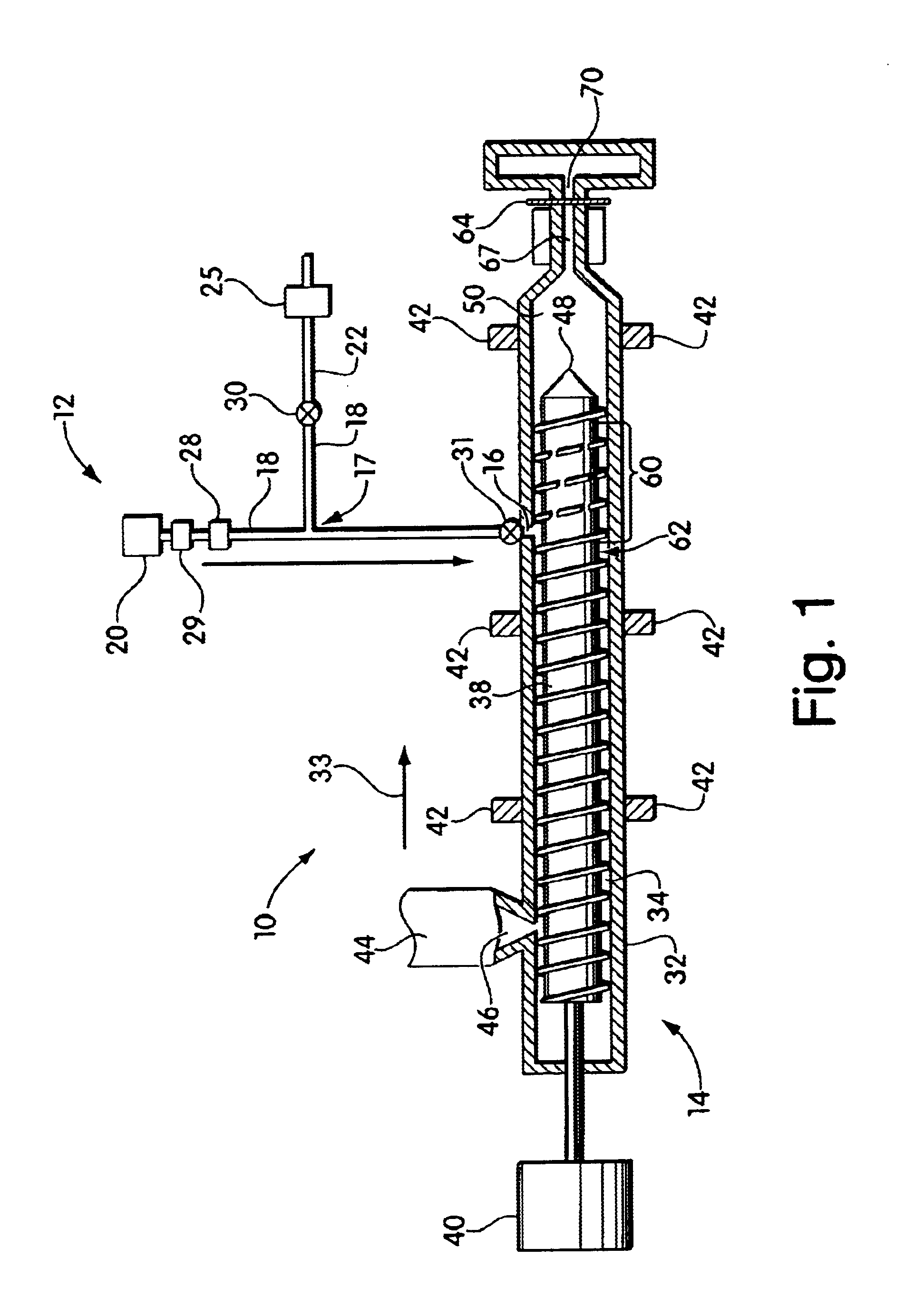
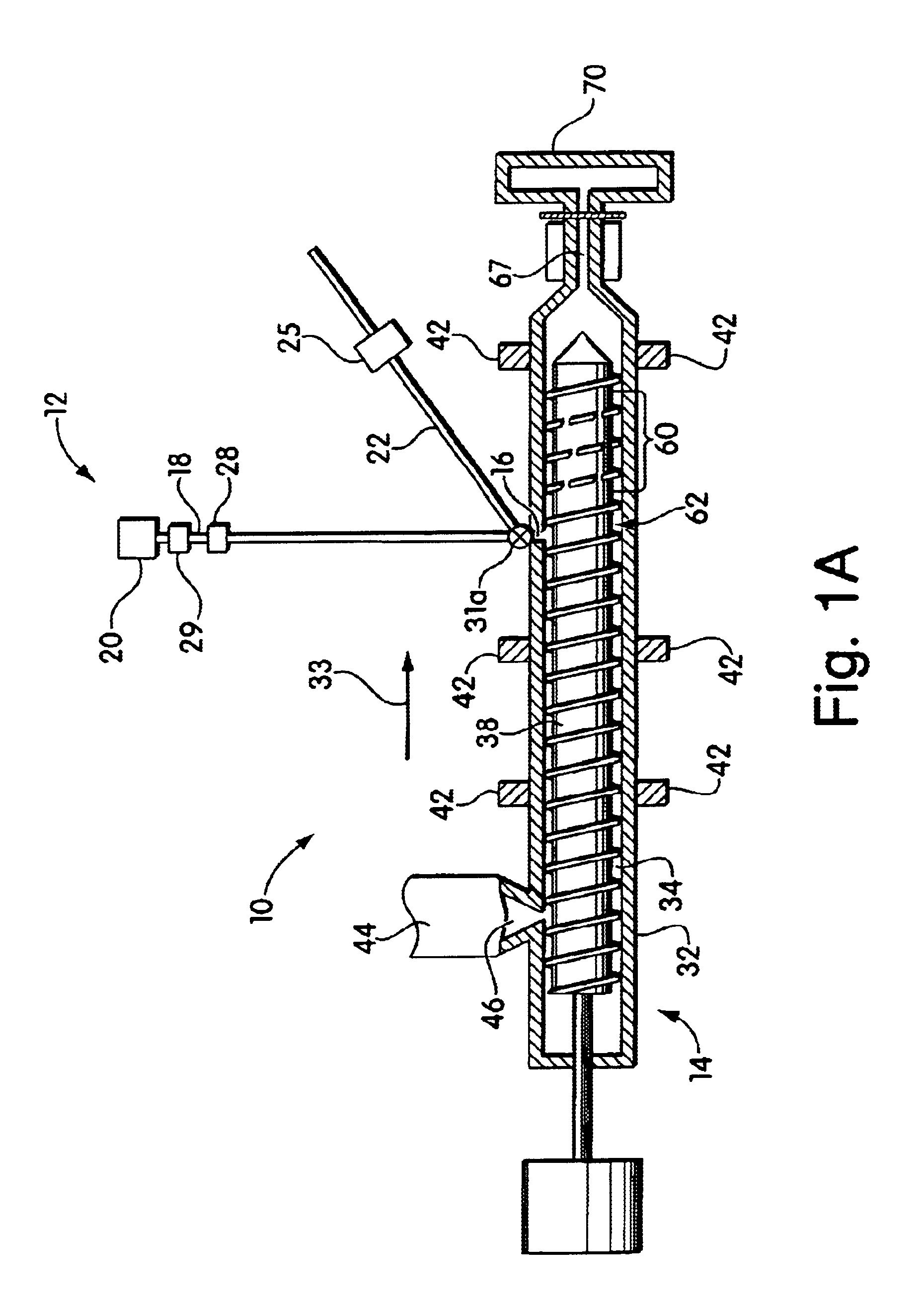
Blowing agent delivery system
InactiveUS6926507B2Easy to controlPrevents output inconsistencyAuxillary shaping apparatusFood shapingBlow moldingInjection molding machine
The invention provides a blowing agent delivery system for introducing a blowing agent into a polymeric foam processing system. The delivery system is designed to discontinuously introduce blowing agent from a continuous source into polymeric material within an extruder. The system, thus, may improve control over blowing agent delivery in discontinuous polymer processing systems such as injection molding or blow molding. In some embodiments, the blowing agent delivery system selectively directs blowing agent flow from the source to the extruder barrel, or through a bypassing passageway. In this manner, blowing agent may be continuously supplied by the source but discontinuously injected into the extruder barrel. During use, the delivery system may cause blowing agent to flow through the bypassing passageway, for example, when the screw stops plasticating polymeric material.
Owner:TREXEL
Hydrofluoroolefin compositions
The present invention relates to compositions containing hydrofluoroolefins and to the uses thereof as heat transfer fluids, blowing agents, solvents and aerosols. More particularly, the invention relates to compositions having: 2 to 55% by weight, of 2,3,3,3-tetrafluoropropene, 2 to 55% by weight of HFC-152a and 30 to 55% by weight of HFC-32.
Owner:ARKEMA FRANCE SA
Process for the manufacturing of an improved core for decorative laminates and a decorative laminate obtained by the process
InactiveUS6841023B2Improve brittlenessImprove the overall coefficientOrganic chemistryLamination ancillary operationsPolyesterFiber
A process for the manufacturing of a core forming a carrying structure for decorative laminates. The core comprises particles of cured, and optionally foamed, rigid, polyurethane, polyisocyanurate and / or phenolic resin. The particles are bonded to each other in a pressing procedure with a bonding agent comprising an adhesive such as a polymerizing monomer.i) The particles are achieved by grinding cured, and optionally foamed, rigid, polyurethane, polyisocyanurate and / or phenolic resin so that it passes through a 2 mm screen, preferably a 1 mm screen,ii) 100 parts per weight of particles is mixed with 1-100 parts per weight of fiber, the fiber additive having an average length in the range 1-15 mm.iii) The particle-fiber mixture is allowed to absorb a selected amount of water, the amount of water being in the range 1-15% by weight, The water is either added at any stage before the adding of bonding agent, and / or being used as a solvent in the bonding agent, and that,iv) 85 parts per weight of the particle mixture is mixed with 2-15 parts per weight of a bonding agent, the bonding agent selected from the group consisting of,a) A mixture of polyols, such as polyester or polyether, crude methylene diphenyl diisocyanate and possibly a small amount of blowing agent in a ratio forming a polymeric resin with a density in the range 600-1400 kg / m3.b) A formaldehyde based resin such as phenol-formaldehyde resin, urea-formaldehyde resin, melamine-urea-formaldehyde resin, melamine-urea-phenol-formaldehyde resin or phenol-resorcinol-formaldehyde resin, orc) Polyvinyl acetate resin.v)The mixture is applied between the belts of the continuos belt press or the press plates of a static press, optionally with at least one intermediate carrier web, the belts or press plates allowing a mainly uniform and specified material thickness to form. A slightly porous and preconditioned core with a selected water content in the range 0.8-12% is hereby achieved. The invention also relates to a decorative laminate achieved through the process.
Owner:PERGO
Hydrofluoroolefin compositions
The present invention relates to compositions containing hydrofluoroolefins and to the uses thereof as heat transfer fluids, blowing agents, solvents and aerosols. More particularly, the invention relates to compositions having: 10 to 55% by weight, of 2,3,3,3-tetrafluoropropene, 5 to 50% by weight of HFC-152a and 30 to 55% by weight of HFC-32.
Owner:ARKEMA FRANCE SA
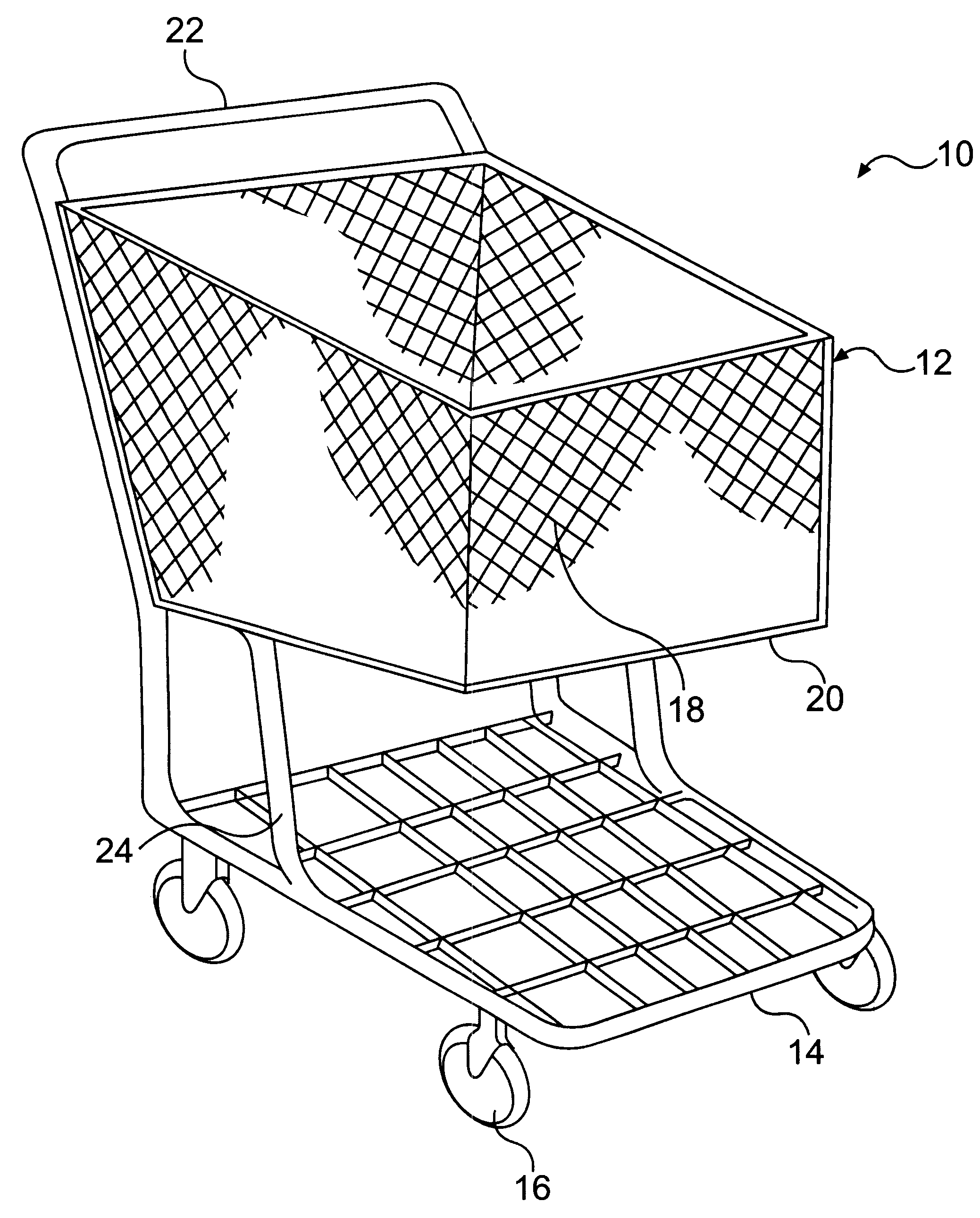
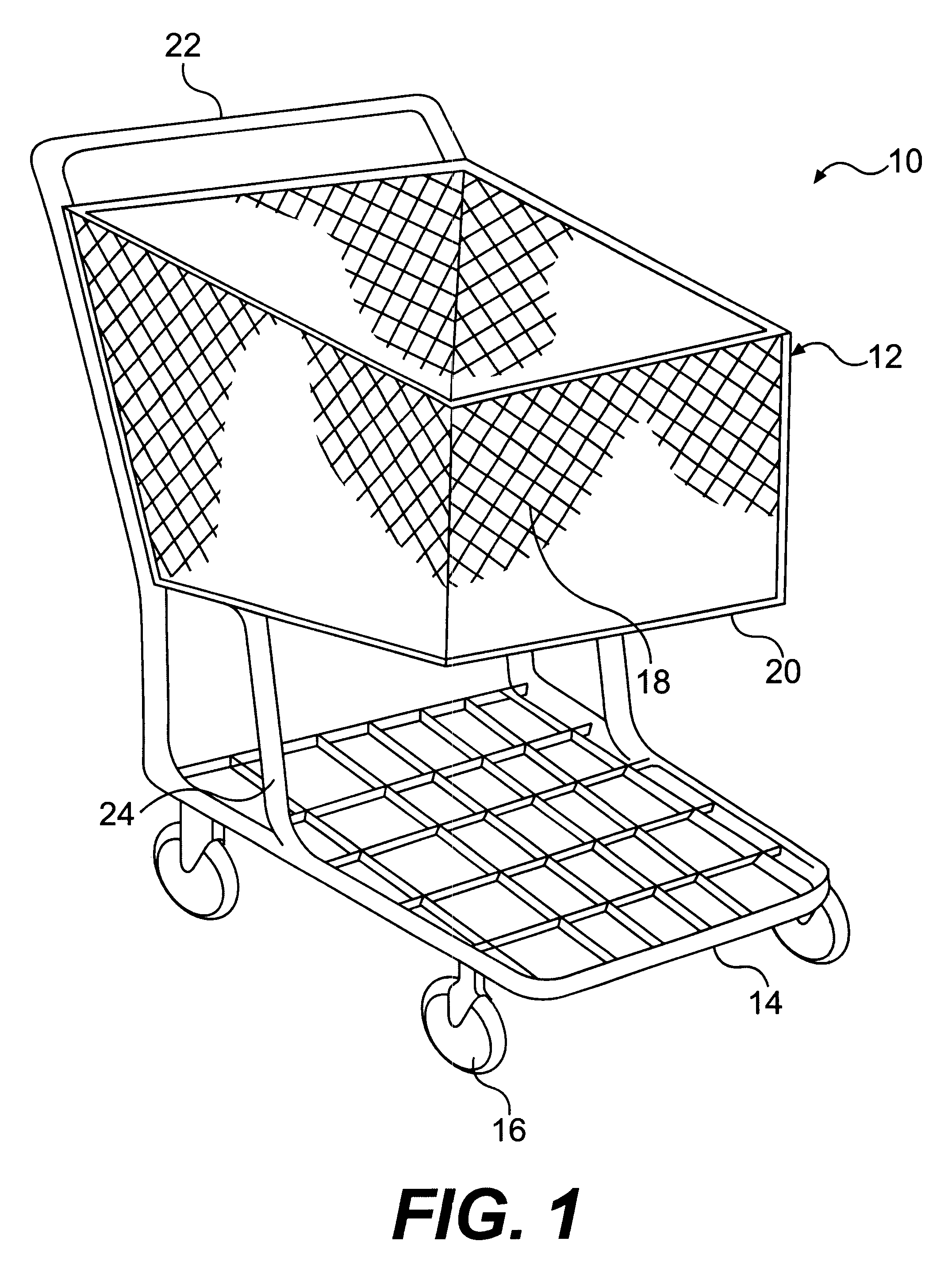
Method of molding a cart using molding processes
Owner:REHRIG INT INC +1
Two-component on-site foam system and its use for foaming openings for the purpose of fire protection
InactiveUS20020020827A1High foaming rateIncreased fire resistance enduranceOther chemical processesGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsPolyesterVolumetric Mass Density
A two-component on-site foam system for producing an intumescing fire protection foam is described with a density of less than 200 kg / m3 and an increased fire resistance endurance, with a polyol component (A), which contains at least one polyol, one catalyst for the reaction between the polyol and the polyisocyanate, water or a blowing agent based on a compressed or liquefied gas as foam-forming agent and at least one intumescing material based on an acid-forming agent, a carbon-supplying compound and a gas-forming agent, and a polyisocyanate component (B), which contains at least one polyisocyanate, wherein the polyol component (A) contains at least one polyester polyol, at least one aminopolyol, at least one halogen-containing polyol, at least one acidforming agent, expanding graphite and at least one ash crust stabilizer, the quantitative ratios of the polyols to the polyisocyanate or polyisocyanates being matched so that, when the polyol component (A) is mixed with the polyisocyanate component (B) as specified, the molar ratio of isocyanate groups of the polyisocyanate to the hydroxyl groups of the polyol (NCO: OH ratio) is larger than 1: 1, as well as to the use of this system for filling openings, cable and pipe leadthroughs in walls, floors and / or ceilings of buildings with foam for the purpose of fire protection.
Owner:HILTI AG
Hydrofluoroolefin compositions
The present invention relates to compositions containing hydrofluoroolefins and to the uses thereof as heat transfer fluids, blowing agents, solvents and aerosols. More particularly, the invention relates to compositions having from 5 to 65% by weight, preferably from 5 to 15% by weight, of 2,3,3,3-tetrafluoropropene, 5 to 70% by weight, preferably 40 to 60% by weight, of HFC-134a and 25 to 42% by weight of HFC-32.
Owner:ARKEMA FRANCE SA
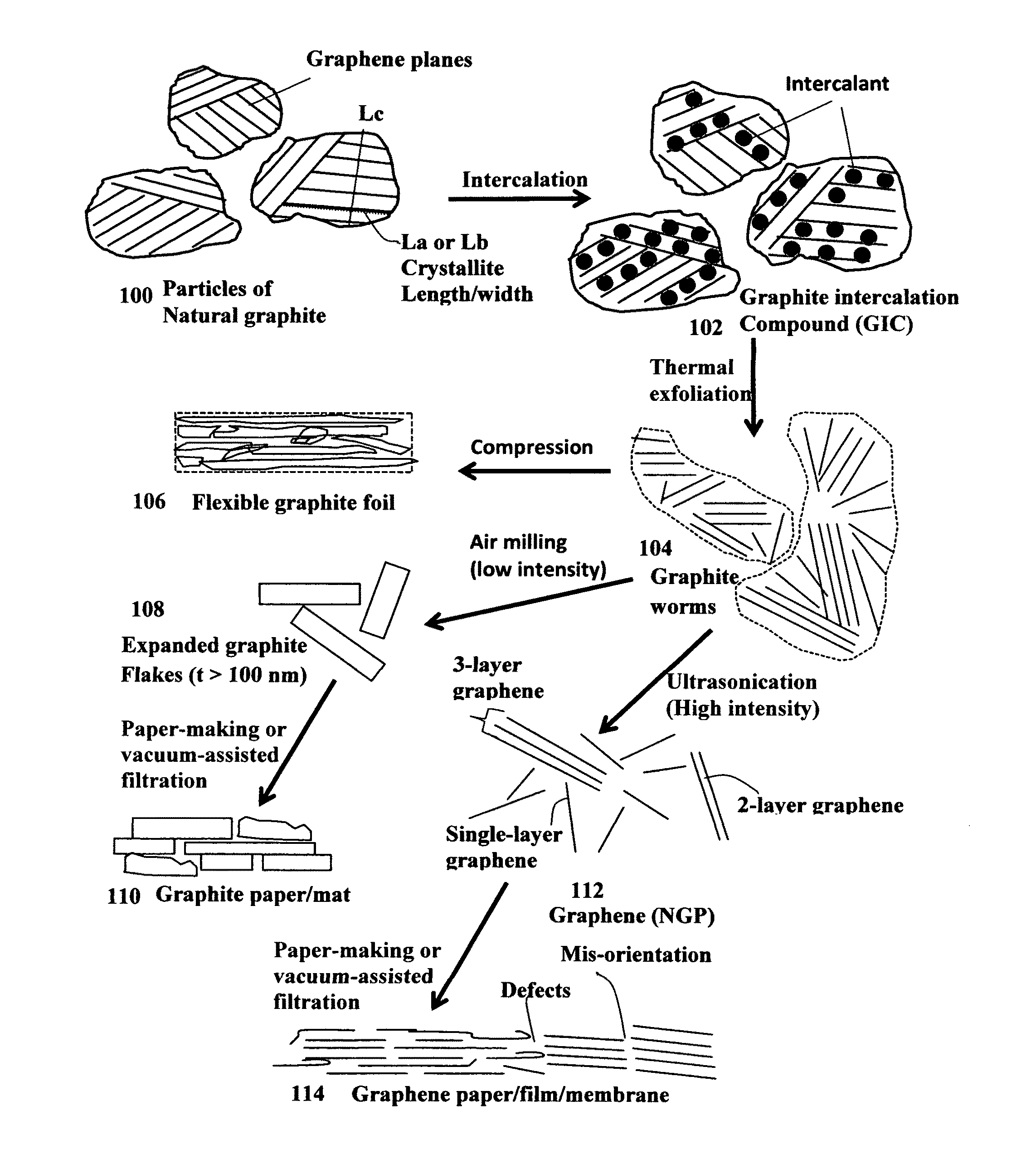
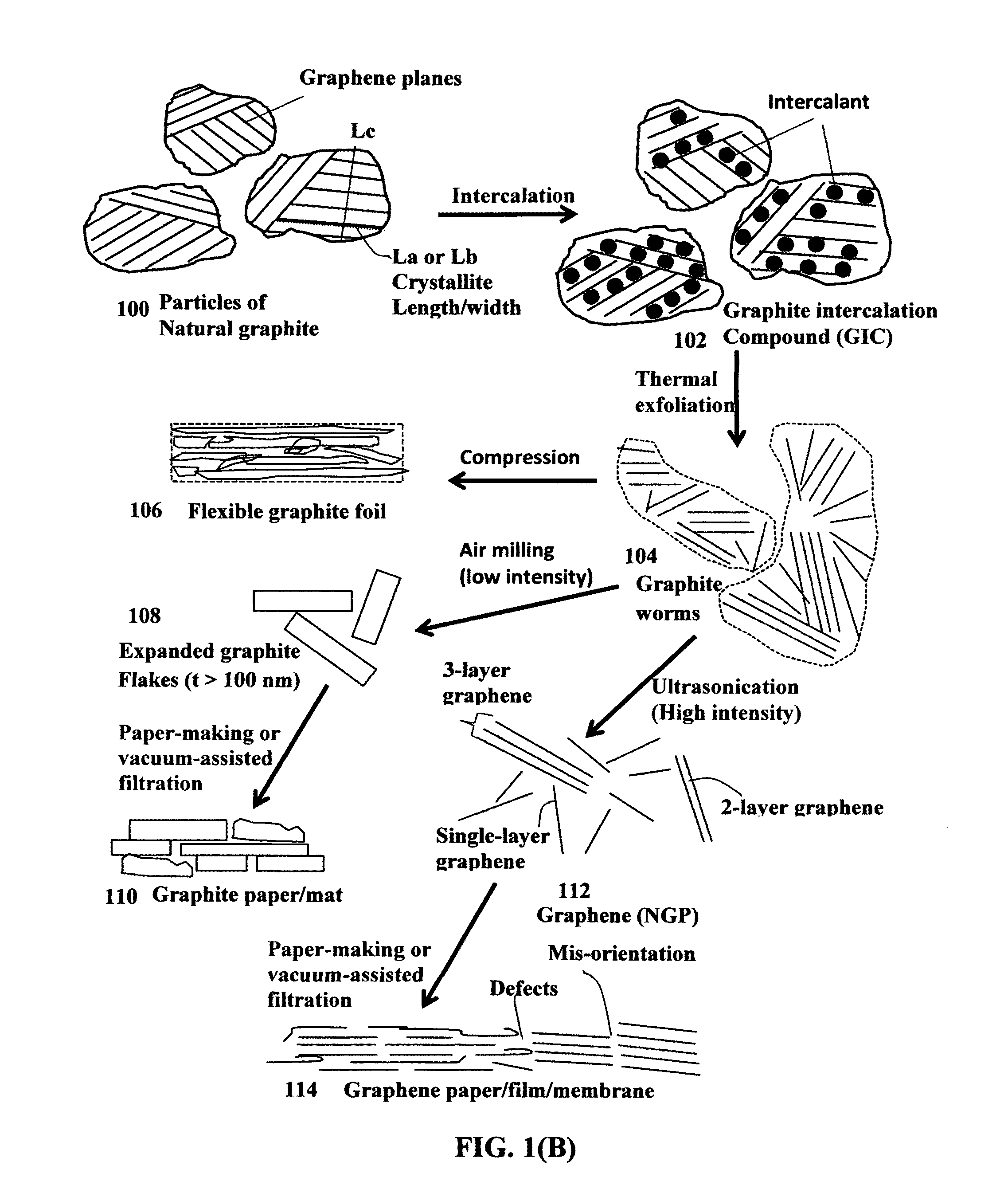
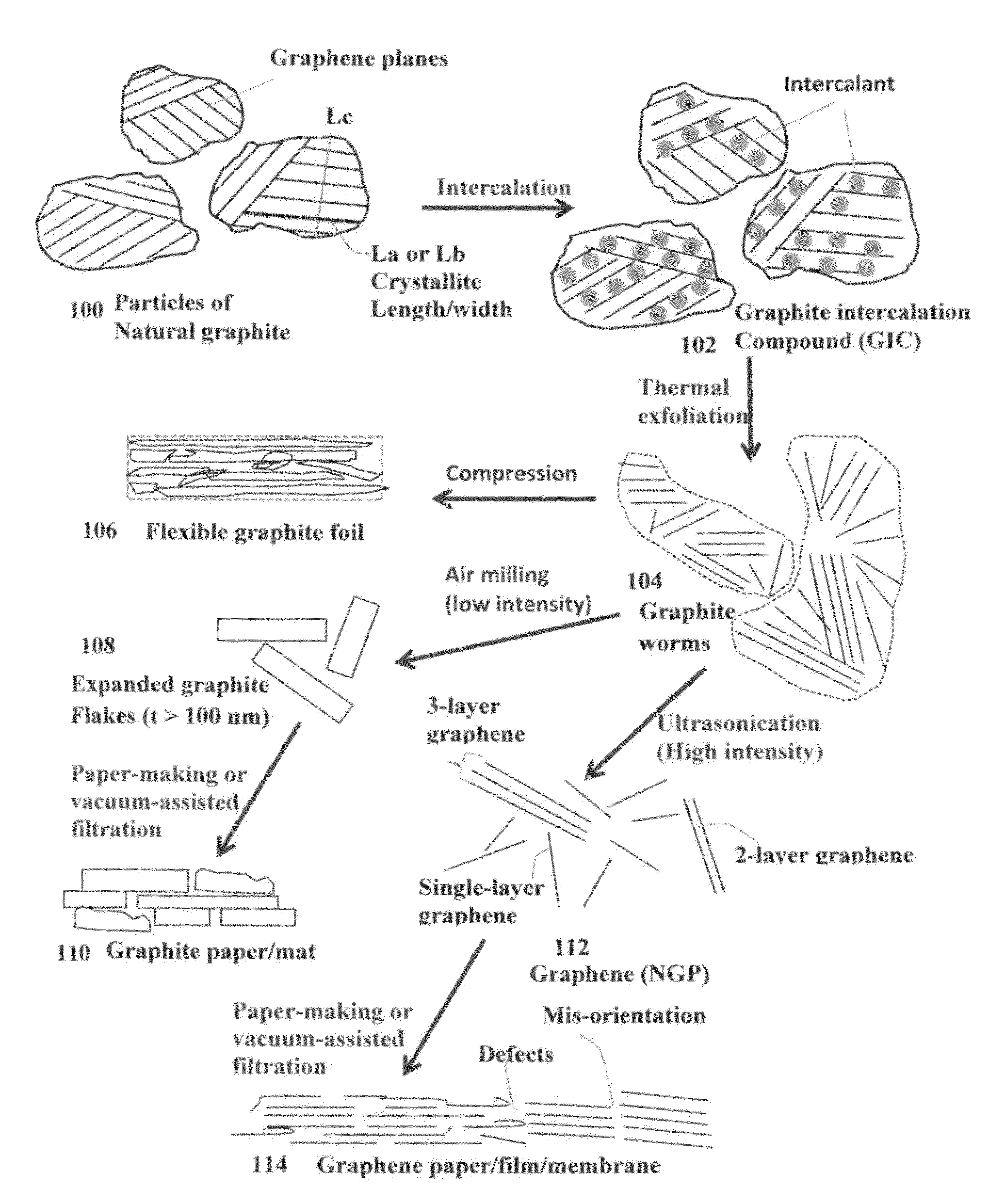
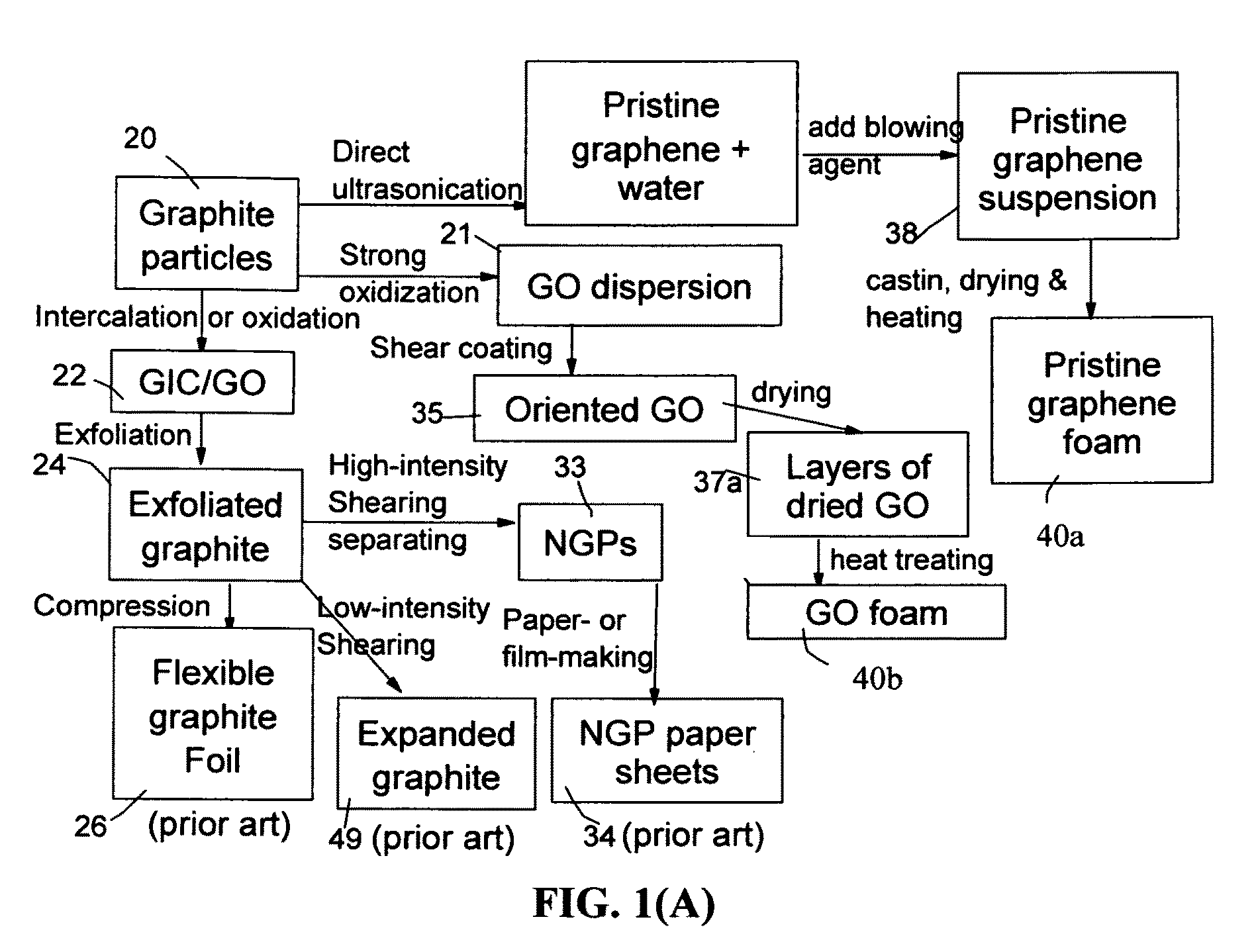
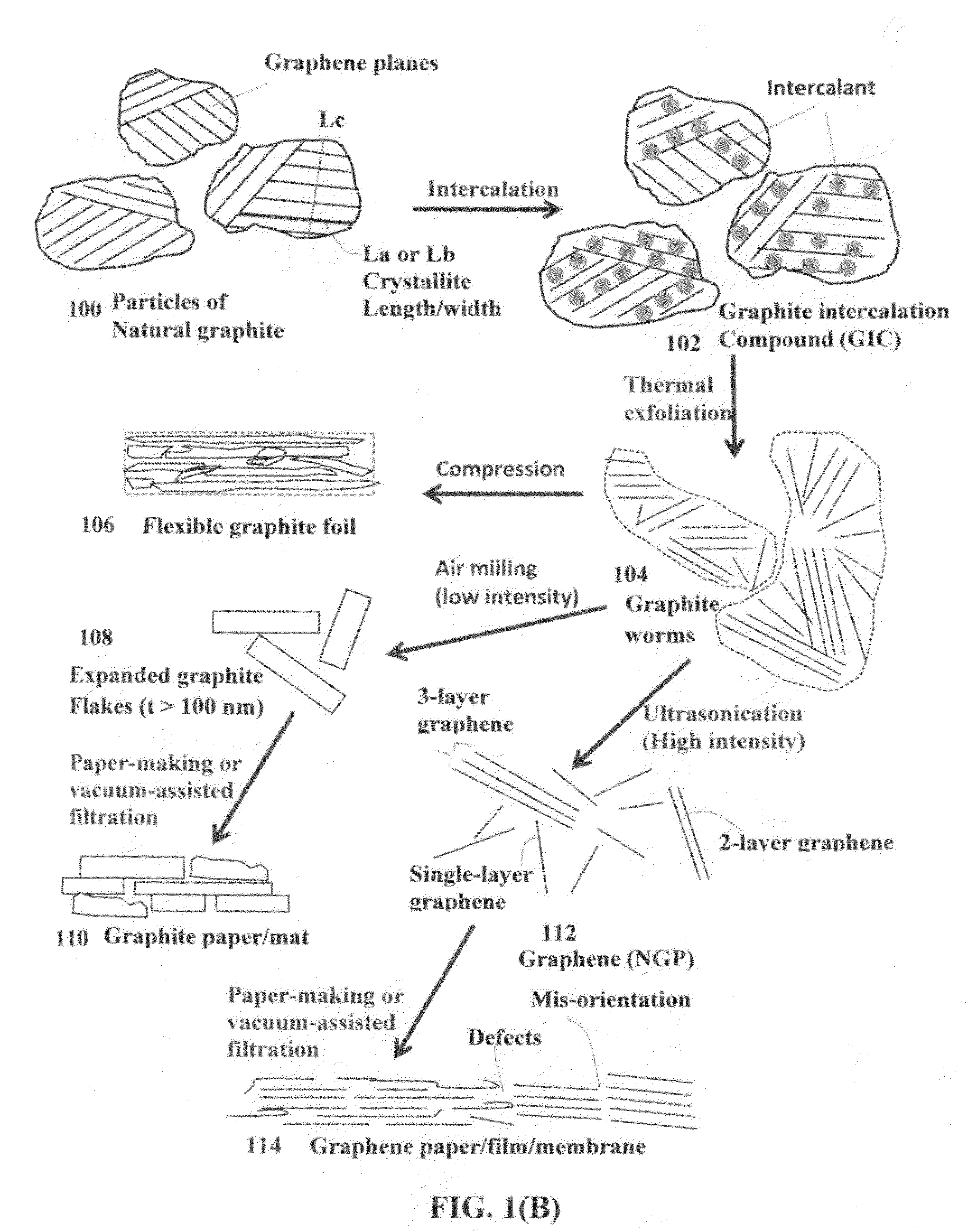
Highly conductive graphene foams and process for producing same
ActiveUS20160019995A1Effective orientation-inducing stressIncrease flexibilityNon-insulated conductorsGraphitePolymer scienceLiquid medium
A process for producing a solid graphene foam composed of multiple pores and pore walls The process comprises: (a) preparing a graphene dispersion having a graphene material dispersed in a liquid medium, which contains an optional blowing agent; (b) dispensing and depositing the graphene dispersion onto a supporting substrate to form a wet layer of graphene material having a preferred orientation; (c) partially or completely removing the liquid medium from the wet layer of graphene material to form a dried layer of graphene material having a content of non-carbon elements no less than 5% by weight (including blowing agent weight); and (d) heat treating the layer of graphene material at a first heat treatment temperature from 80° C. to 3,200° C. at a desired heating rate sufficient to induce volatile gas molecules from the non-carbon elements or to activate the blowing agent for producing the graphene foam having a density from 0.01 to 1.7 g / cm3 or a specific surface area from 50 to 3,000 m2 / g.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
Nontoxic, odorless and recoverable environmentally-friendly polyurethane foaming material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102229709ANo chemical reactions involvedHuge energy savingCoatingsEnvironmental resistanceHuman health
The invention discloses a nontoxic, odorless and recoverable environmentally-friendly polyurethane foaming material and a preparation method thereof. The foaming material is characterized in that a raw material of polyurethane is adopted and is directly subjected to a physical gas foaming in the presence of a physical gas foaming agent to prepare the foaming material. The foaming material has a foaming density of 0.08-0.80 g / cm<3>, a foaming ratio of 1.5-15 times, a average pore diameter of 10-100 [mu]m, uniform distribution of cells, wherein diameter deviations of 95% of the cells do not exceed 10% of the average pore diameter. In addition, the foaming material has no surface structure and can be the foaming material with any shape. The foaming material has an adjustable softness and hardness and excellent performance, and can be widely applicable for the fields of packaging, human protector, shoe product, automobile inner garnish, amortization cushion, building energy conservation, acoustic insulating material and the like. According to the present invention, the following problems that: harmful gas is discharged during the production process of the polyurethane foaming material, and monomer residues are harmful to human health and cause environmental pollution, are thoroughly solved from the source, such that a practicable development approach is provided for green environmental protection, energy saving and emission reduction of the foaming material.
Owner:浙江博发新材料股份有限公司
Process for manufacturing a floor covering having a foamed backing formed from recycled polymeric material
The present invention provides a cushioned floor covering having a backing material formed from waste polymeric material and a blowing agent wherein the blowing agent may be activated either before or after the backing material is adhered to the floor covering. The waste polymeric material includes from about 0 to 40 percent aliphatic polyamide material and is granulated, densified and extruded at a temperature that does not exceed the temperature at which the blowing agent would be activated.
Owner:TANDUS FLOORING INC
Foam core imaging element with gradient density core
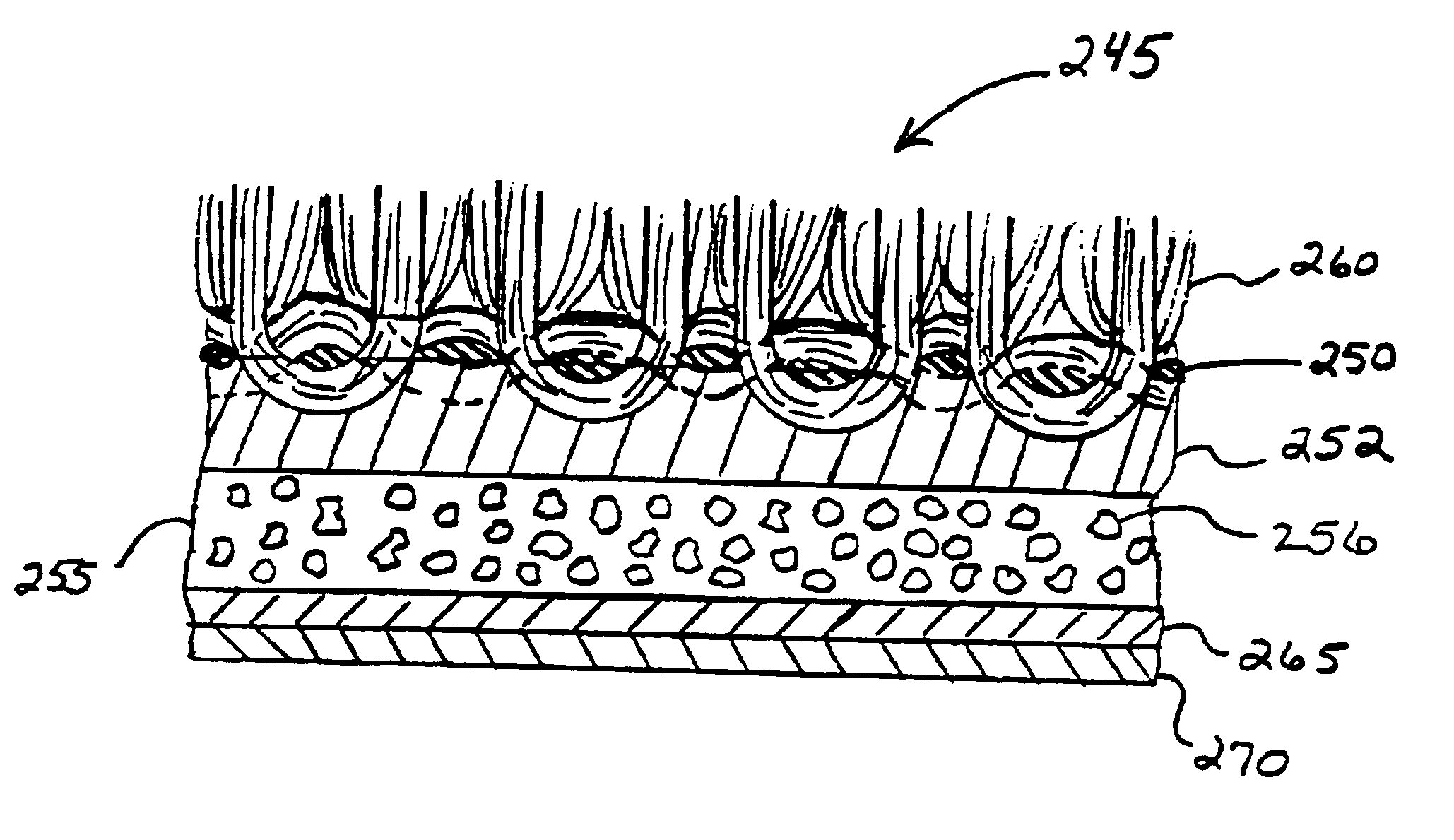
InactiveUS20050181196A1Easy to optimizeIncrease stiffnessNatural cellulose pulp/paperDecorative surface effectsVolumetric Mass DensityBlowing agent
The invention relates to a base comprising a closed cell foam core sheet having a closed cell foam layer with a density gradient between the center of the core and the surfaces of the core. The invention also relates to a method of making such a base by adding a first concentration of a first blowing agent to a first polymer to form a first mixture, adding a second concentration of a second blowing agent to a second polymer to form a second mixture, and extruding the mixtures to form the closed cell foam core sheet. The invention also relates to a method of making such a closed cell foam core sheet base comprising the steps of adding a blowing agent to a polymer to form a mixture, melting the mixture, extruding the mixture from a die, and rapidly quenching the mixture against a high heat transfer surface.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Thermoplastic elastomeric foam materials and methods of forming the same
InactiveUS20040038018A1Low water absorptionImprove water absorptionLayered productsThin material handlingThermoplastic elastomerMelt temperature
Foams with low water absorption are provided, along with thermoplastic elastomeric foam materials and methods of forming the same. In some embodiments, the TPE foams have a low water absorption. Microcellular foams are included. Processing conditions (e.g., blowing agent type and content, die geometry, exit melt temperature, among others) may be controlled to produce foams having desirable characteristics, such as low water absorption.
Owner:MUCELL EXTRUSION
Biodegradable foams with improved dimensional stability
InactiveUS20120225961A1Good dimensional stabilityLow densityOther chemical processesTransportation and packagingHydrofluoroetherLow density
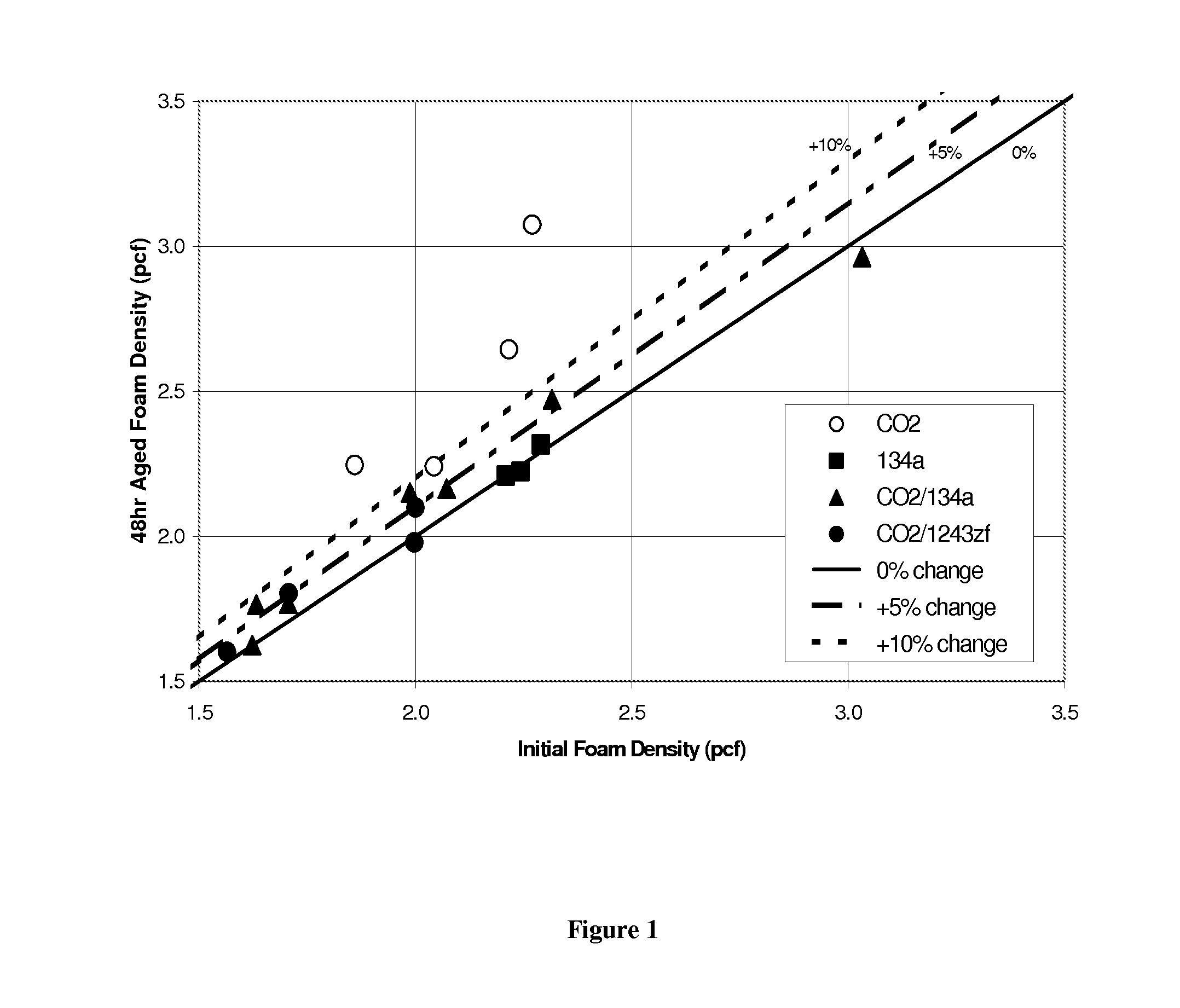
The invention provides a blowing agent composition and method of making the same comprising mixing carbon dioxide and a co-blowing agent or a blowing agent selected from the group consisting of hydrofluorocarbons, hydrochlorofluorocarbons, hydrofluoroethers, hydrofluoroolefms, hydrochlorofluoroolefms, hydrobromofluoroolefms, hydrofluoroketones, hydrochloroolefins, fluoroiodocarbons, alkyl esters, water, and mixtures thereof. Also provided is a method of making a low density foam using the blowing agent composition, and a biodegradable or biorenewable foam formed from a foamable biodegradable or biorenewable resin composition and the blowing agent composition.
Owner:ARKEMA INC
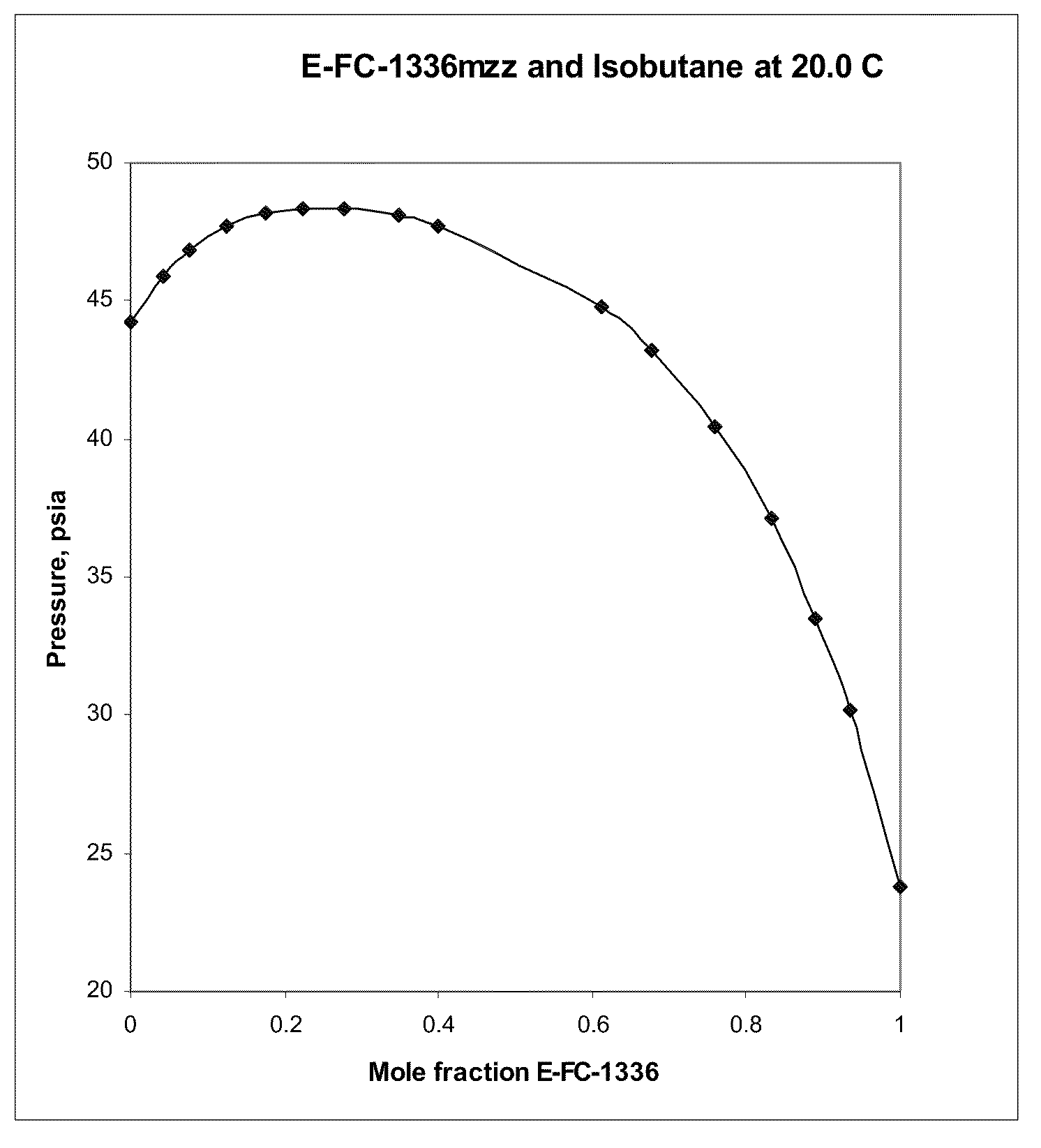
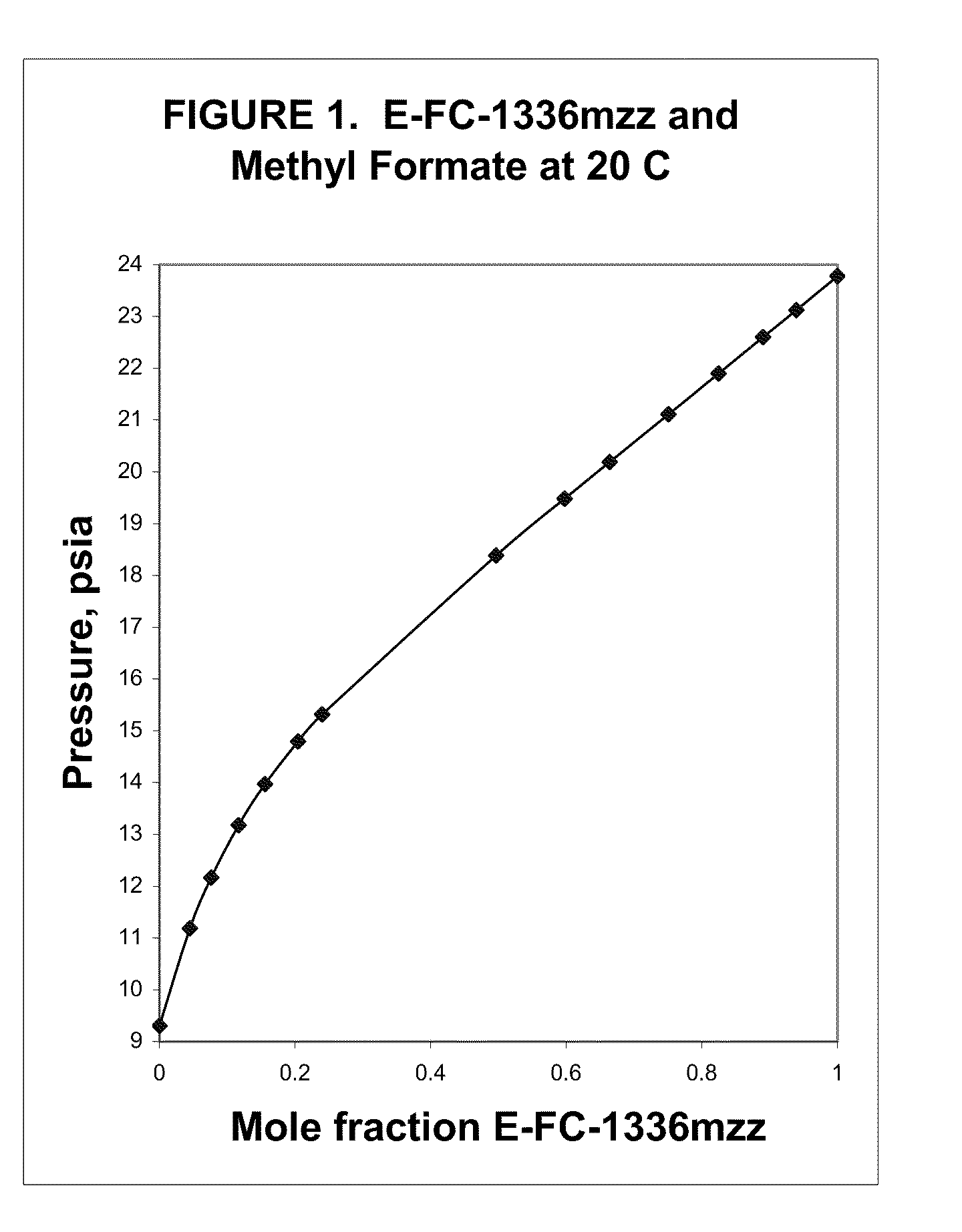
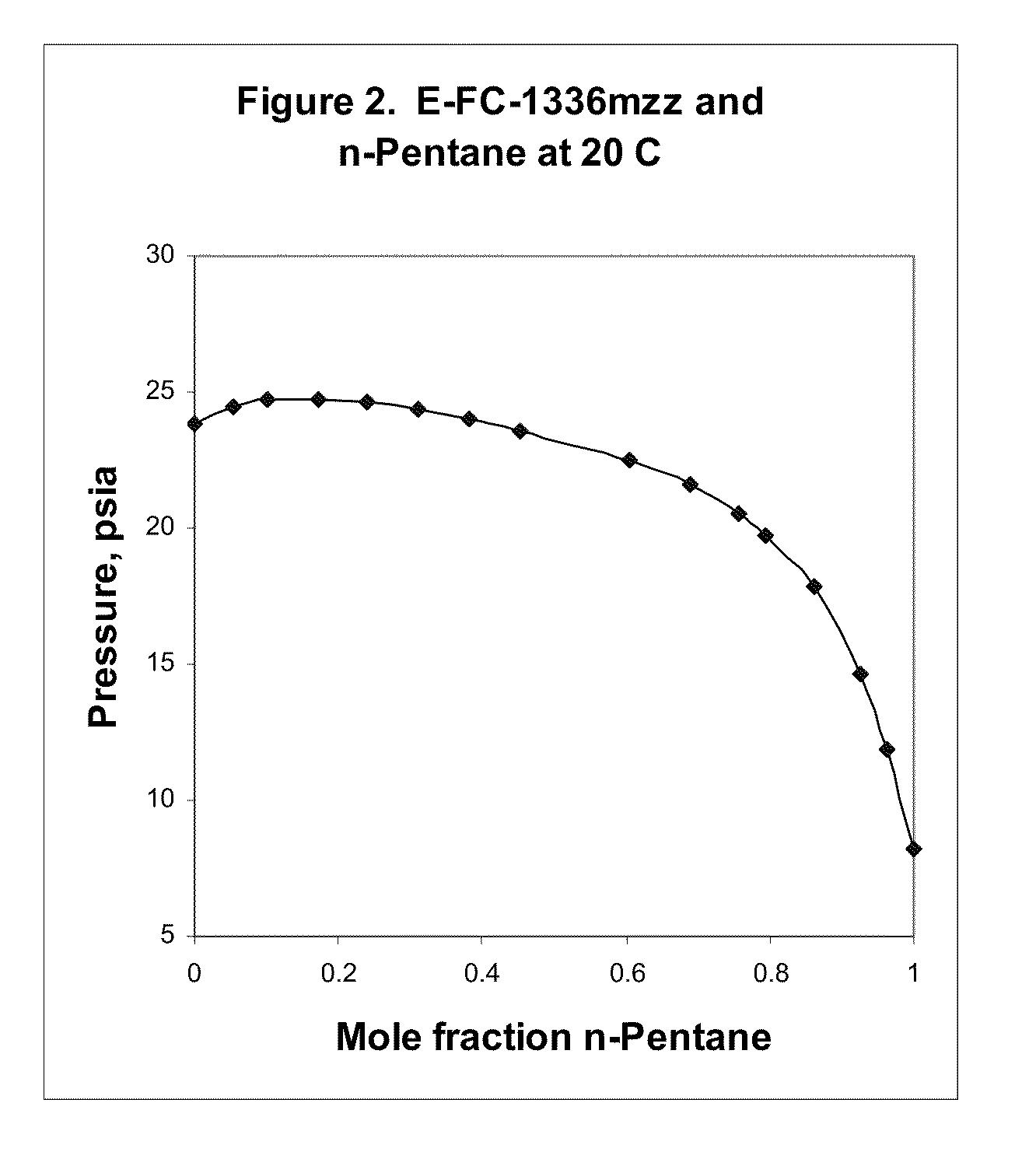
Azeotropic and azeotrope-like compositions of e-1,1,1,4,4,4-hexafluoro-2-butene
Azeotropic or azeotrope-like compositions are disclosed. The azeotropic or azeotrope-like compositions are mixtures of E-1,1,1,4,4,4-hexafluoro-2-butene with methyl formate, n-pentane, 2-methylbutane trans-1,2-dichloroethylene, 1,1,1,3,3-pentafluoropropane, n-butane or isobutane. Also disclosed is a process of preparing a thermoplastic or thermoset foam by using such azeotropic or azeotrope-like compositions as blowing agents. Also disclosed is a process of producing refrigeration by using such azeotropic or azeotrope-like compositions. Also disclosed is a process of using such azeotropic or azeotrope-like compositions as solvents. Also disclosed is a process of producing an aerosol product by using such azeotropic or azeotrope-like compositions. Also disclosed is a process of using such azeotropic or azeotrope-like compositions as heat transfer media. Also disclosed is a process of extinguishing or suppressing a fire by using such azeotropic or azeotrope-like compositions. Also disclosed is a process of using such azeotropic or azeotrope-like compositions as dielectrics.
Owner:THE CHEMOURS CO FC LLC
Preparation method for rigid polyurethane foam
The present invention relates to a preparation method for low-density polyurethane foam excelling in the flame retardance and the dimensional stability, wherein rigid polyurethane foam having the average value for the ratio of lengthwise direction diameter / cross direction diameter of cells being 1.0 to 1.4 and the density of 20 to 40 kg / m<3 >is prepared by combining, as blowing agent, carbon dioxide generated in the reaction between water and polyisocyanate and carbon dioxide under supercritical state, subcritical state or liquid state, and by adding said water and said carbon dioxide under liquid state into said polyol component prior to mixing the polyisocyanate component and the polyol component, and to rigid polyurethane foam obtained by said method.
Owner:ACHILLES CORP
Formula of soles of PU-simulated foaming sneakers through injection and manufacturing method
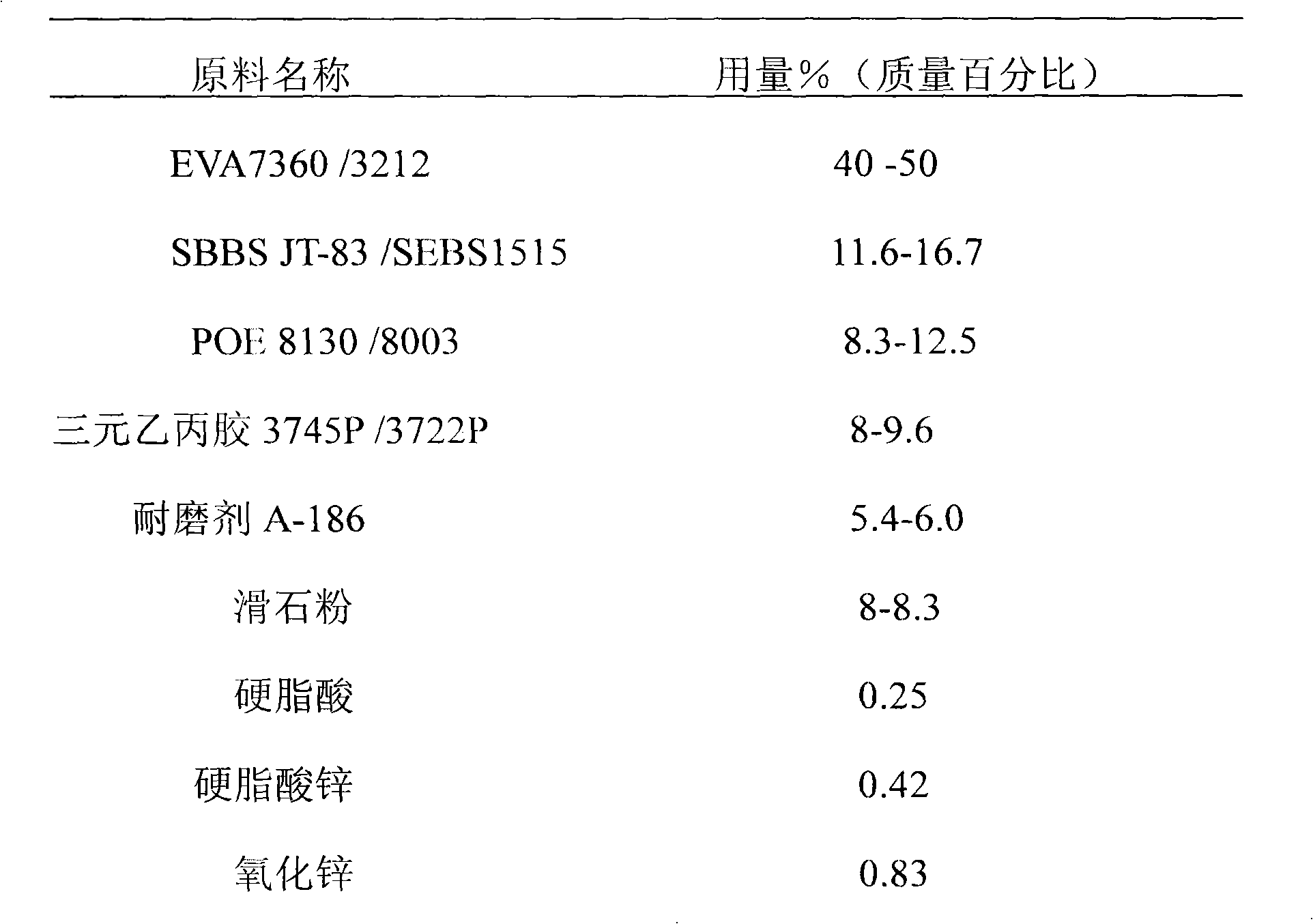
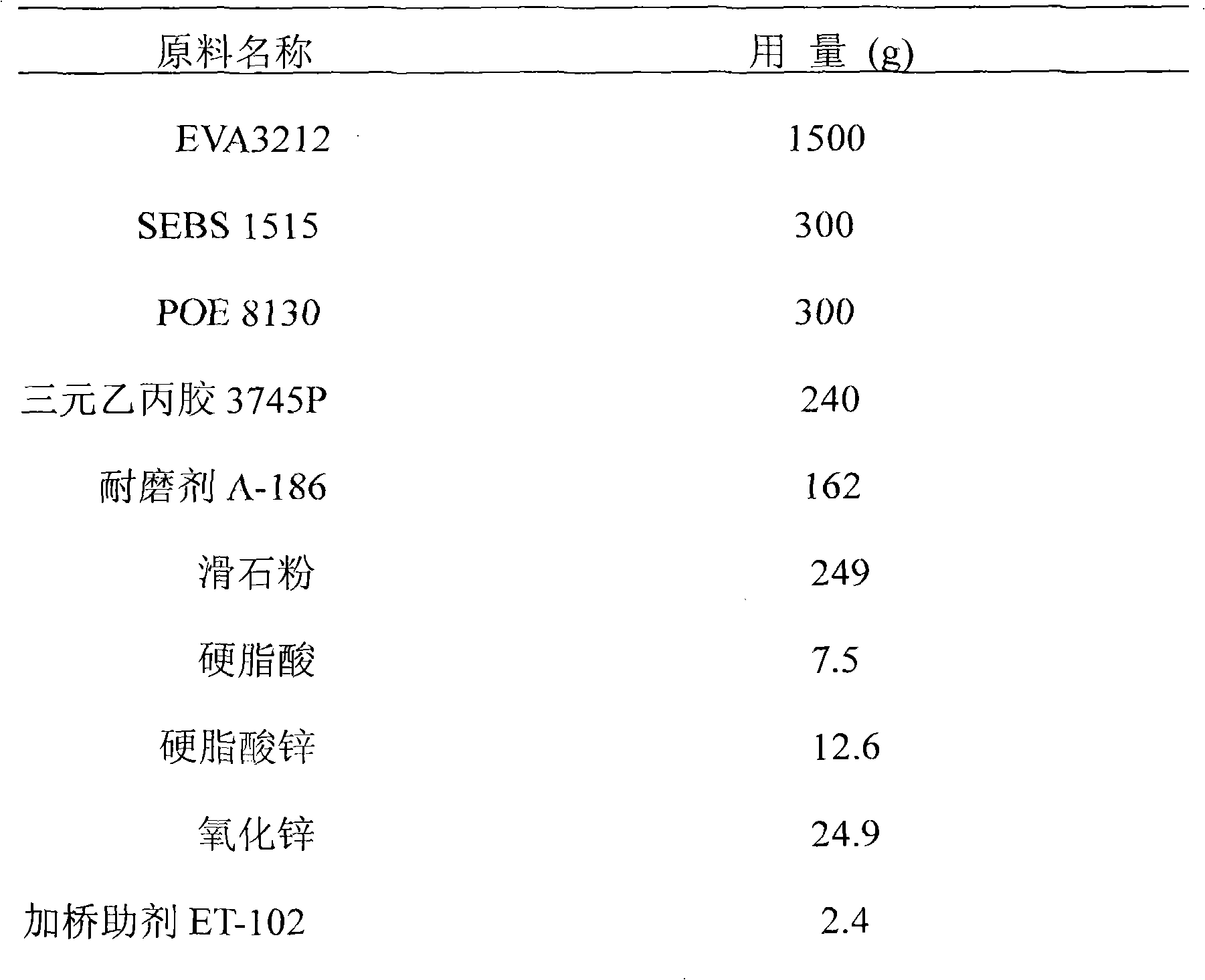
The invention relates to a formula of soles of PU-simulated foaming sneakers through injection, which comprises the following raw materials in percentage by mass: 40 percent of 21 percent ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer (EVA 7360), 16.7 percent of styrene butadiene copolymer SBBSJT-83, 12.5 percent of ethylene octylene copolymer POE8130, 8.3 percent of ethylene-propylene-diene copolymer 3745P, 65.9 percent of wear-resisting agent A-18, 8.3 percent of talcpowder, 0.25 percent of stearic acid, 0.42 percent of zinc stearate, 0.9 percent of zinc oxide, 0.08 percent of bridging auxiliary agent ET-102, 0.75 percent of bridging agent DCP, 1.7 percent of high-temperature foaming agent AC-6000H, 2.5 percent of titanium white powder R-103 and 1.7 percent of master batch. The preparation method comprises the steps of banburying, mixing, granulation, injection molding, physical property tests and the like. Thus, in the research and development and application, the PU-simulated foaming soles not only have the physical and chemical properties of no crease marks, high elasticity, low compression and wear resistance of PU soles, and but also have the advantages of low production cost, light specific gravity, good limited-slip properties, no hydrolysis and long service life.
Owner:泰亚投资集团有限公司
Nano foamed concrete, reinforced insulation wallboard and preparation method of reinforced insulation wallboard
ActiveCN103359997AAvoid interferenceAvoid pollutionBuilding componentsFoam concreteAdditive ingredient
The invention belongs to the field of building materials and construction technologies and relates to nano foamed concrete, a reinforced insulation wallboard and a preparation method of the reinforced insulation wallboard. The nano foamed concrete disclosed by the invention is prepared from the following ingredients in parts by weight: 100 parts of cement, 0.1-5 parts of desulfurized oil coke ash residue, 0.012 part of waterproofing agent, 10-30 parts of fly ash, 0.1-6 parts of superplasticizer, 50-200 parts of water, 1-20 parts of foamer and 0.01-5 parts of nano wave absorbing agent. Thus, when a wallboard product, prepared by embedding steel wire meshes in the nano foamed concrete disclosed by the invention, is applied nearby airports, docks, navigation marks, television stations and receiving stations or applied to concrete-based retaining walls of electromagnetic wave interference preventing scientific research departments, precise instrument plants and information leakage prevention high-grade buildings of national confidential units and the like, the most basic physical, mechanical, heat preservation and heat insulation properties are guaranteed on one hand, and the wallboard product has the capabilities of lowering noise and insulating sound on the other hand.
Owner:QINGDAO TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com