Patents
Literature
2446 results about "Butene" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Butene, also known as butylene, is a series of alkenes with the general formula C₄H₈. The word butene may refer to any of the individual compounds, or to a mixture of them. They are colourless gases that are present in crude oil as a minor constituent in quantities that are too small for viable extraction. Butene is therefore obtained by catalytic cracking of long-chain hydrocarbons left during refining of crude oil. Cracking produces a mixture of products, and the butene is extracted from this by fractional distillation.
Preparation of olefins
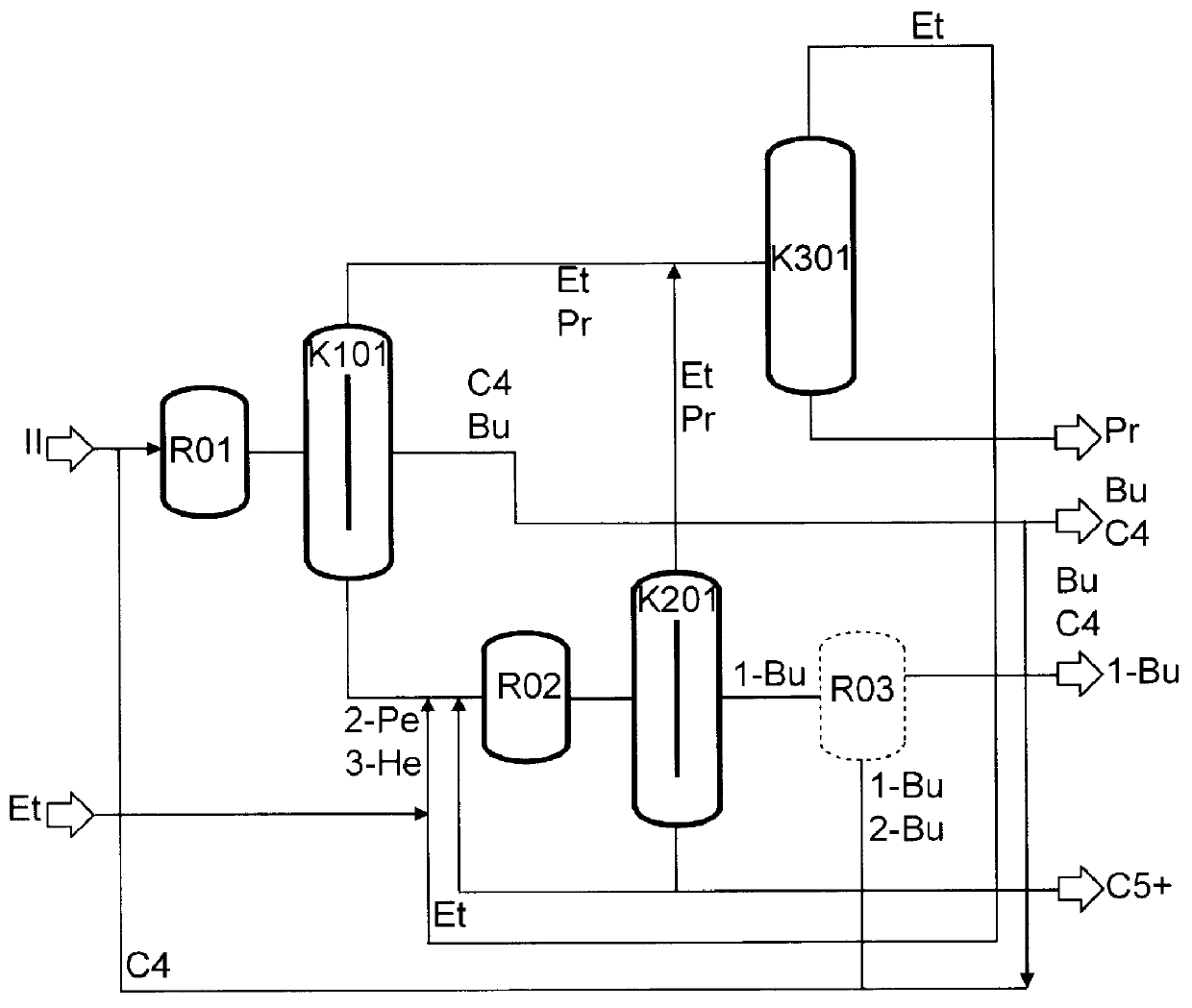
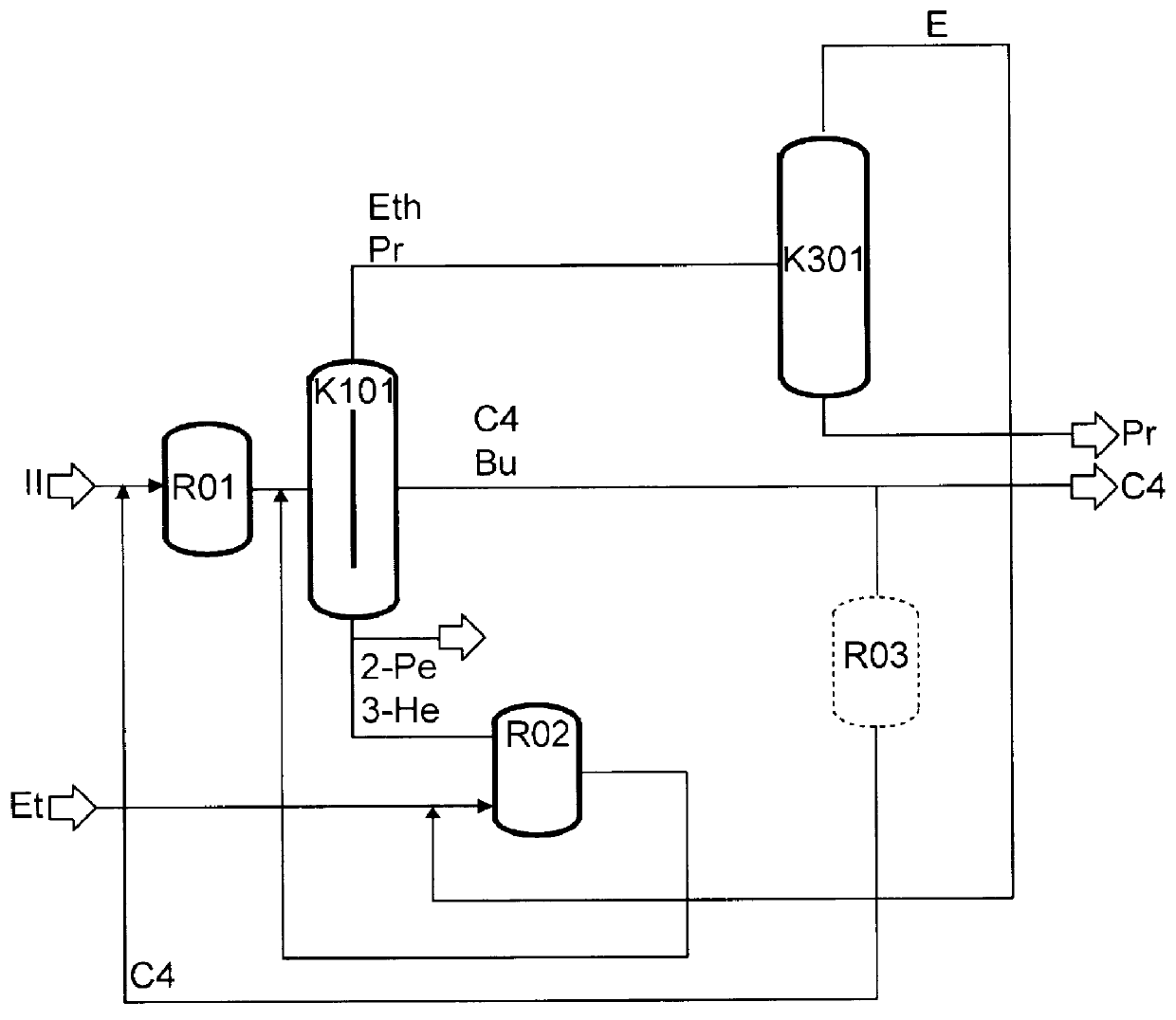
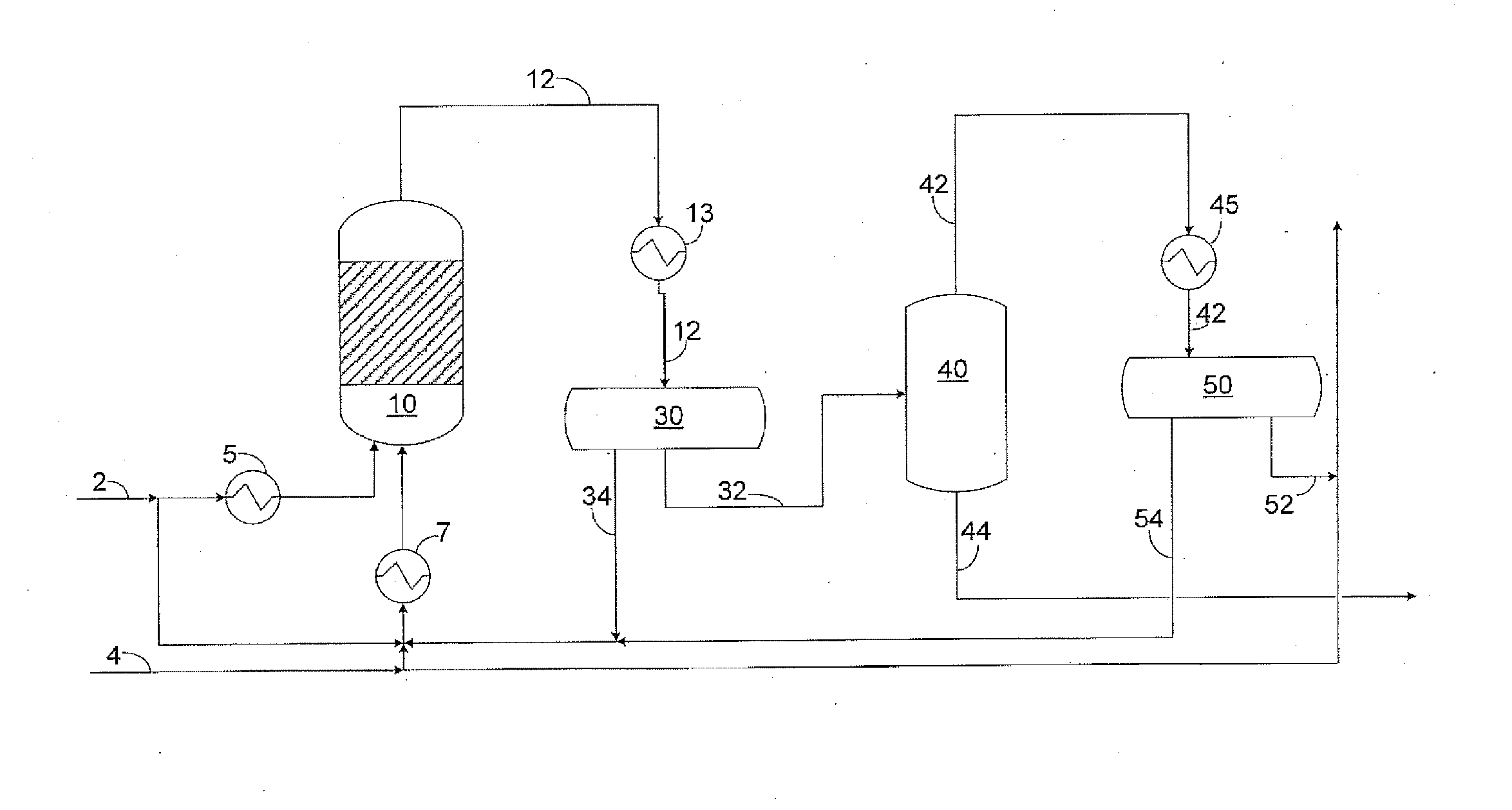
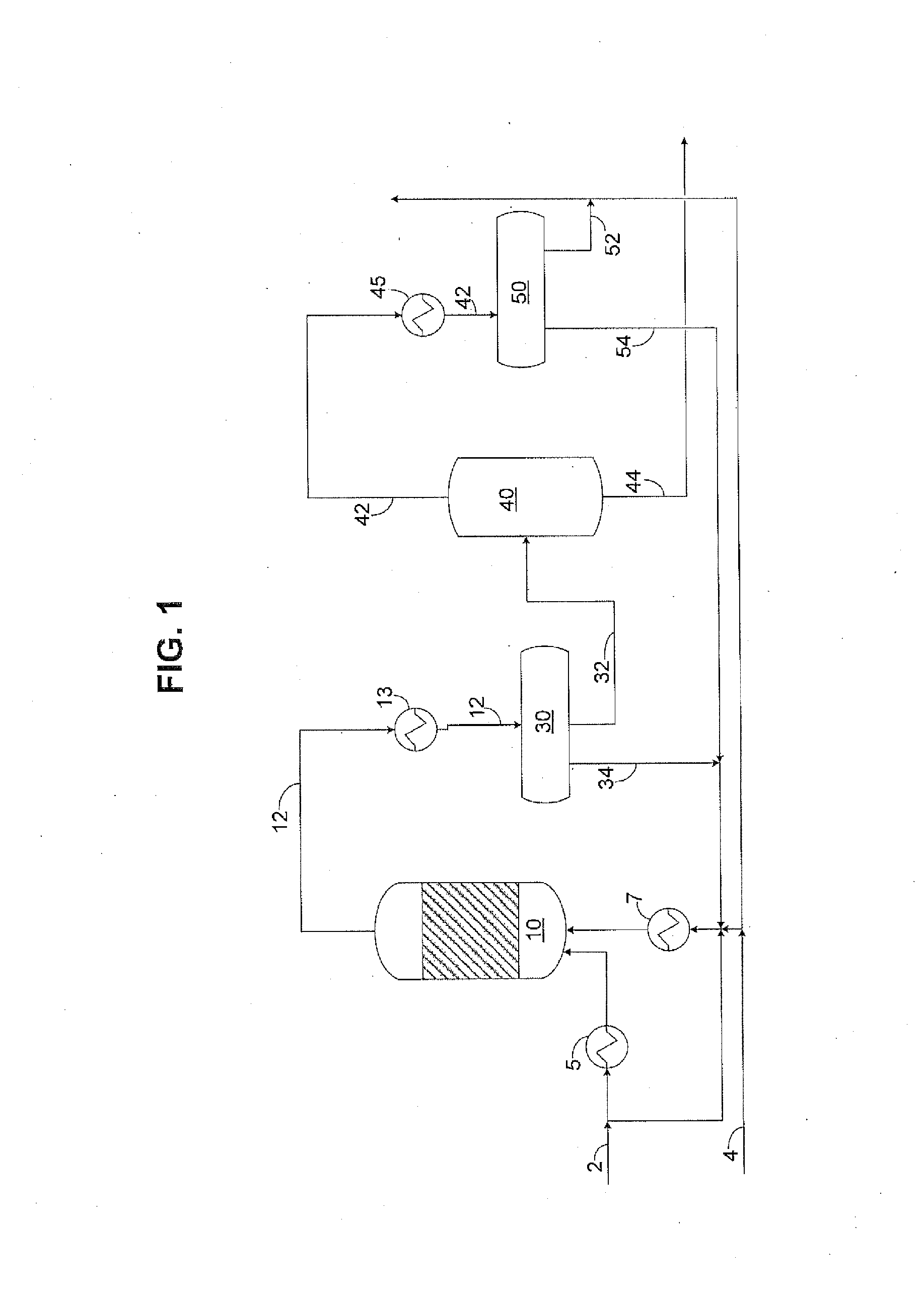
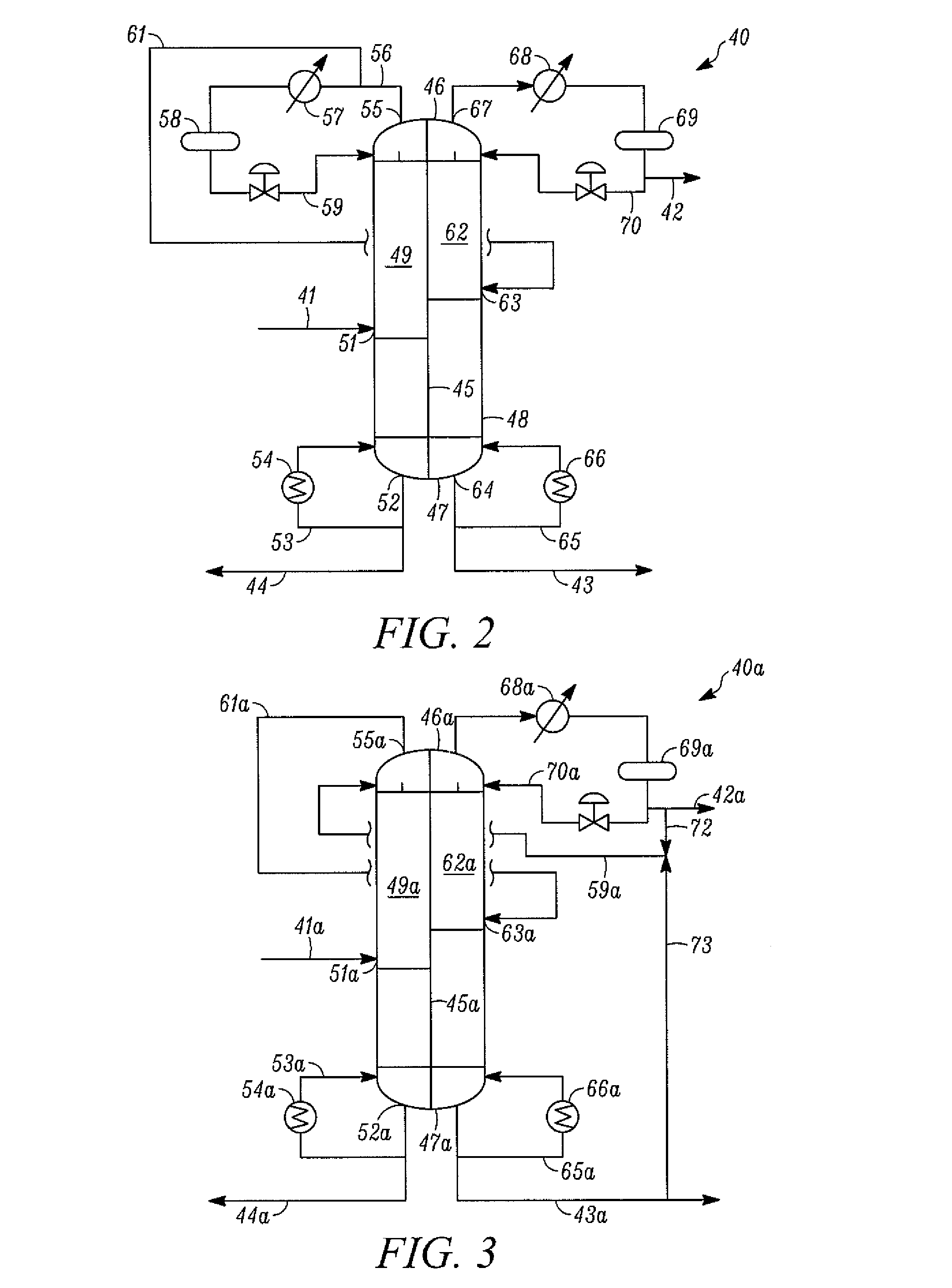
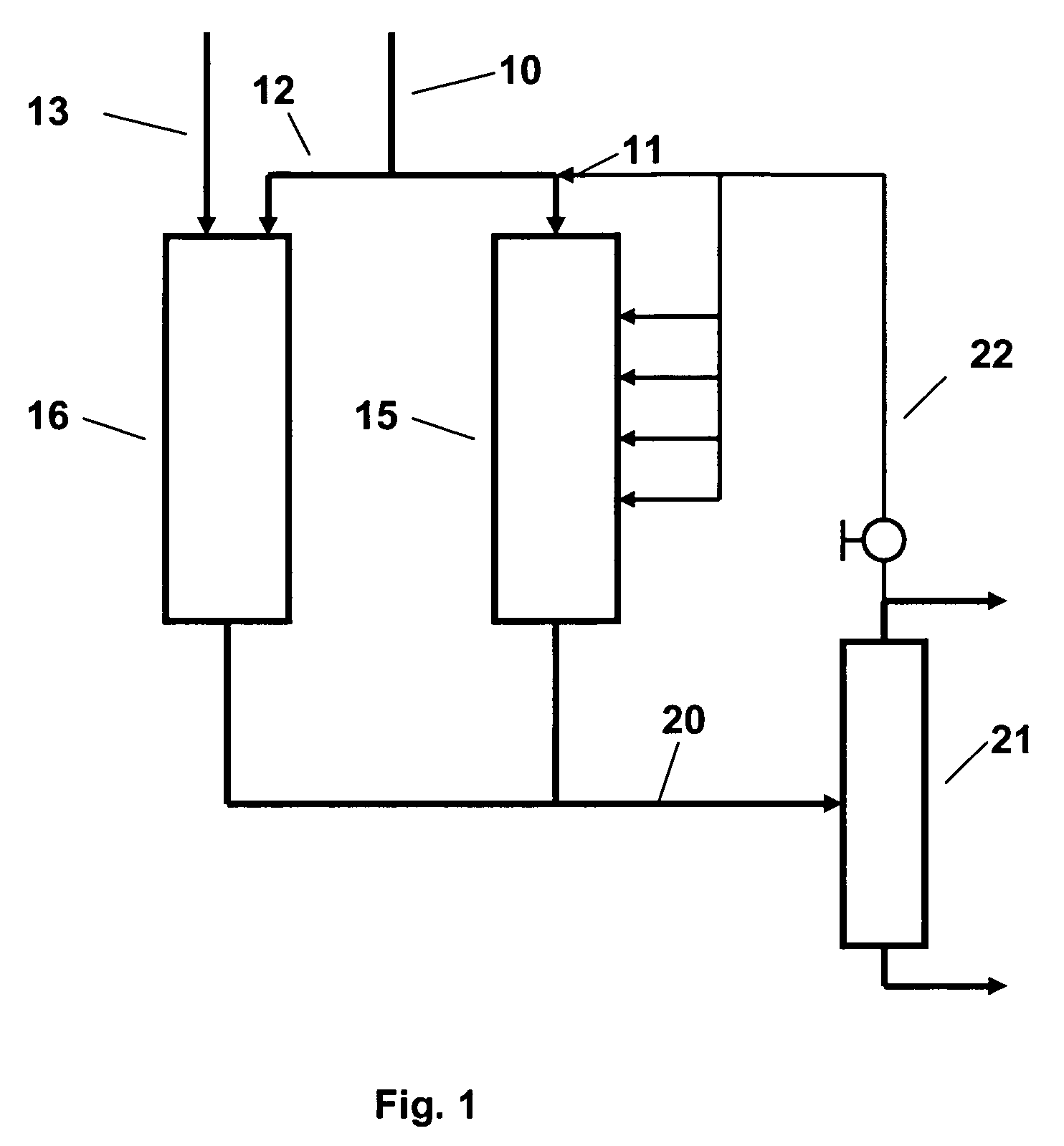
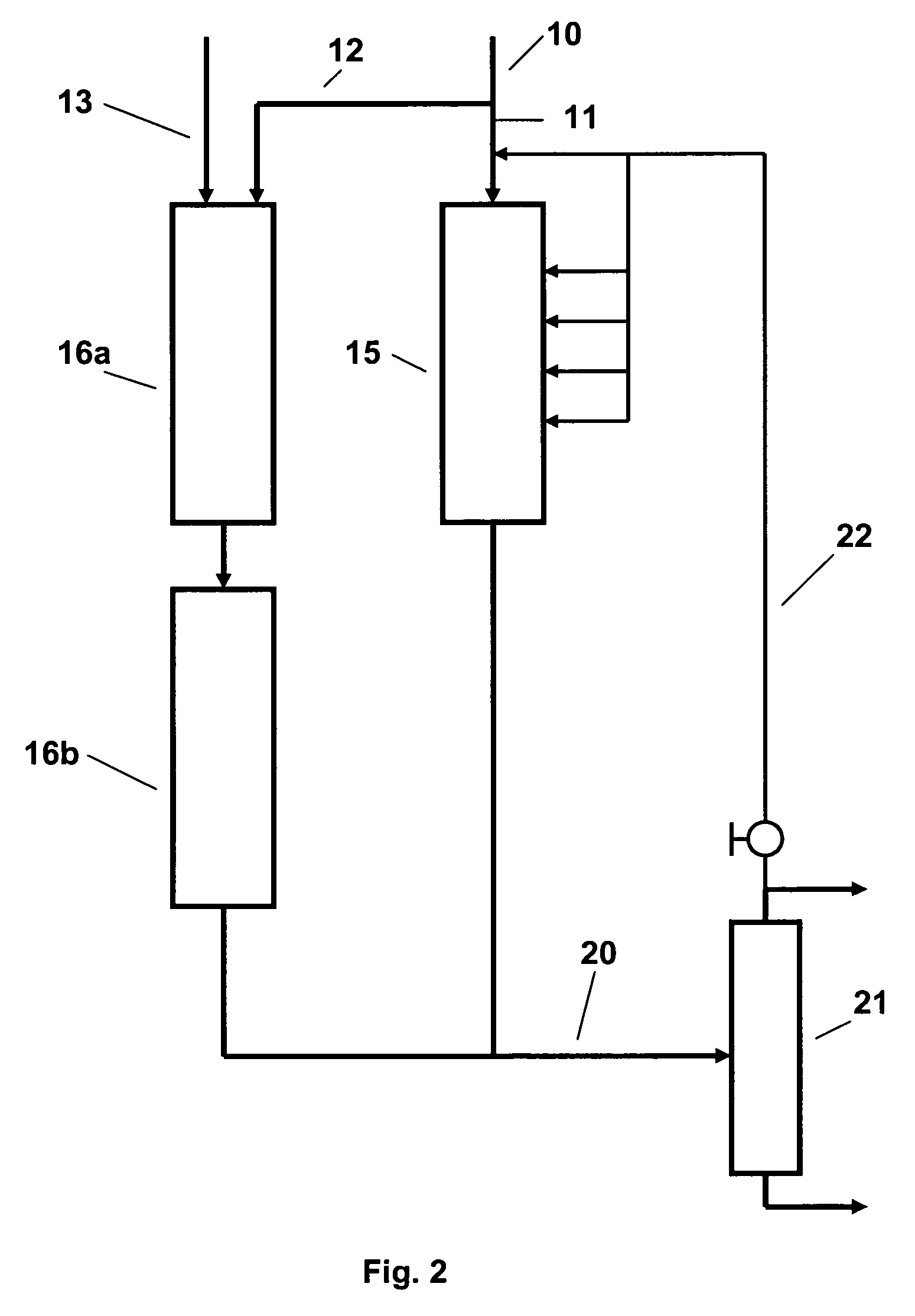
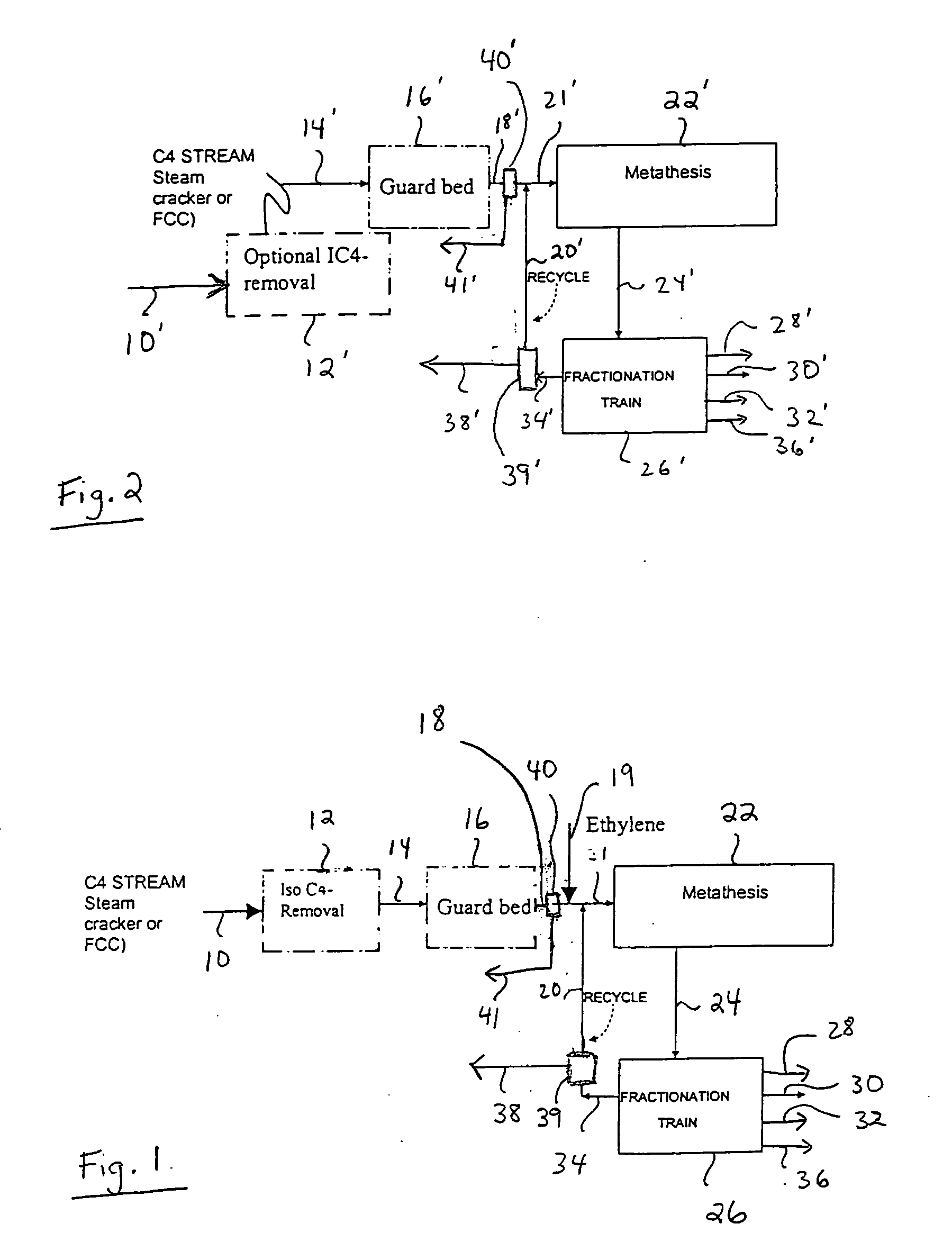
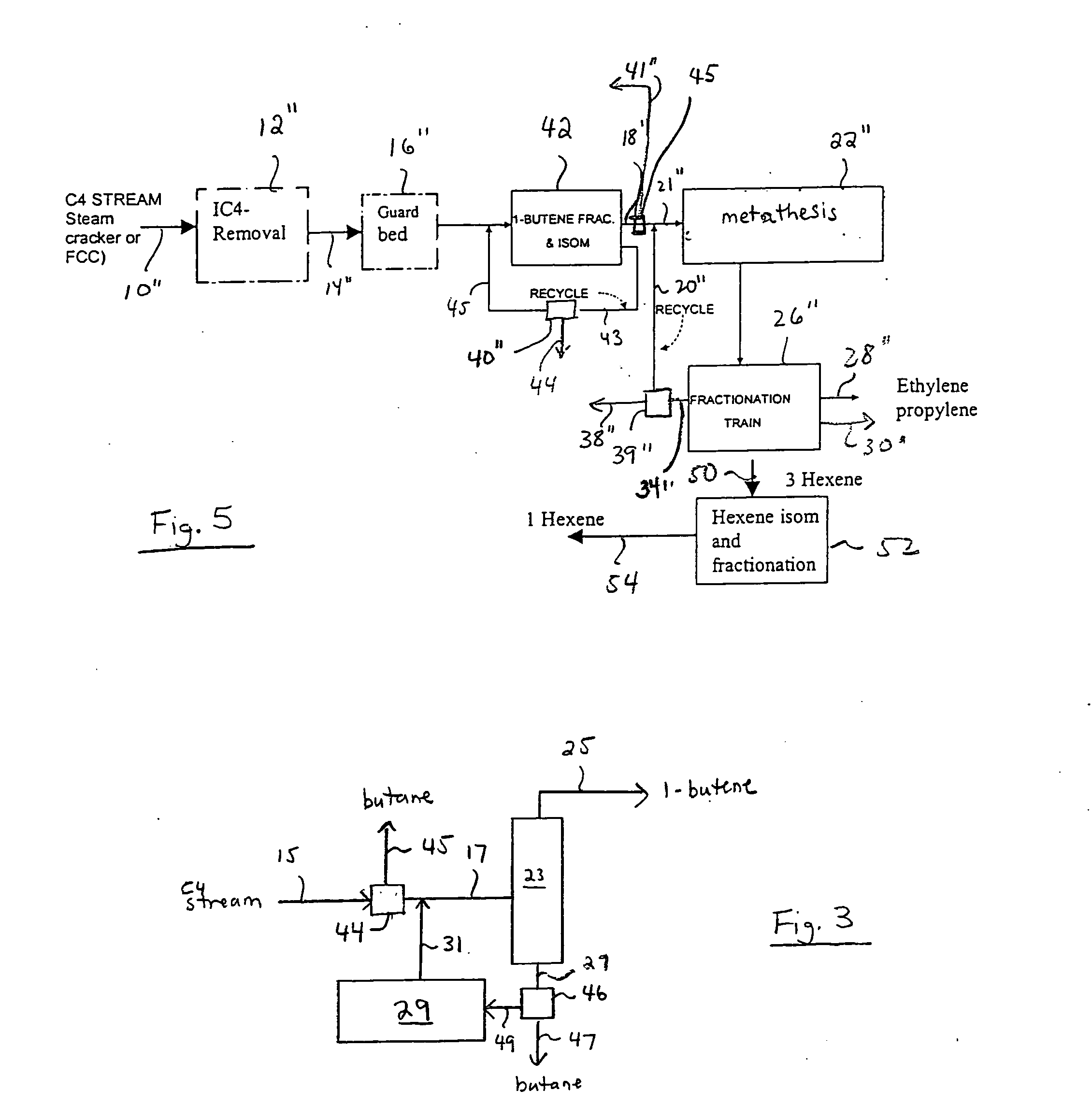
The preparation of olefins from steam cracker or refinery C4 streams is carried out by selective hydrogenation of butadienes and acetylenic impurities in the steam cracker or refinery C4 stream, with simultaneous or subsequent, at least partial isomerization of 1-butene to 2-butene, followed by removal of i-butene from the C4 stream by reaction with an alcohol to form an ether, followed by removal of oxygen-containing impurities from the C4 stream using adsorber materials, followed by two-stage metathesis of the butenes in the C4 stream by conversion of 1-butene and 2-butene present in the C4 stream into propene and 2-pentene and subsequent reaction of the 2-pentene with ethene in the presence of a metathesis catalyst to form propene and 1-butene. Optionally, butadiene may be removed from the C4 stream by extractive distillation in a preliminary step.
Owner:BASF AG
Ionomer/rubber/polyolefin blend and uses thereof
A thermoplastic ionomer blend or alloy exhibiting advantageous properties upon molding or extrusion and / or thermoforming, consisting essentially of the following components:A. about 15 to 85 parts by weight of a thermoplastic copolymer containing about 91 to 80 weight percent of alpha-olefin units and about 9 to 20 weight percent of alpha, beta-ethylenically unsaturated carboxylic acid units said carboxylic acid units being about 20 to 90 percent neutralized with metal ions, preferably zinc,B. about 10 to 80 parts by weight of a rubber, preferably a thermoplastic elastomer selected from the group consisting of (a) crosslinked ethylene-propylene-diene copolymers and equivalent polyolefin copolymers such as ethylene-butene, hexene, or octene, (b) acrylonitrile-butadiene copolymers, (c) styrene-butadiene copolymers, and (d) styrene acrylonitrile graft-crosslinked butadiene rubbers, andC. about 5 to 40 parts by weight of a thermoplastic polymer selected from the group consisting of polyethylene and polypropylene copolymers and homopolymers, the total number of parts being 100,and molded or extruded and / or thermoformed products produced from the same.
Owner:LYONDELLBASELL ADVANCED POLYMERS INC
Zinc ferrite catalysts, method of preparing thereof and method of preparing 1,3-butadiene using thereof
ActiveCN101674883ASimple structureEasy to synthesizeHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsCatalystsButeneDehydrogenation
Owner:SK INNOVATION CO LTD +1
Olefin isomerization process
InactiveUS6875901B2High catalytic activityHydrocarbon by isomerisationPhysical/chemical process catalystsButeneIsomerization
An olefin isomerization process employs a basic metal oxide catalyst, such as magnesium oxide, which retains at least about 85 percent of its initial activity for at least about 168 hours of on-stream time. The catalyst is preferably a high purity magnesium oxide. The olefin isomerization process and catalyst described herein are advantageously used for the production of a terminal olefin such as 1-butene from an internal olefin such as 2-butene.
Owner:ABB LUMMUS GLOBAL INC
Process for Preparing Butadiene by Oxidative Dehydrogenation of N-Butenes with Monitoring of the Peroxide Content During Work-Up of the Product
InactiveUS20140200381A1Analysis using chemical indicatorsHydrocarbon by hydrogenationWater vaporDesorption
The invention relates to a process for preparing butadiene from n-butenes, which comprises the following steps:A) provision of a feed gas stream a comprising n-butenes;B) introduction of the feed gas stream a comprising n-butenes and an oxygen-comprising gas into at least one dehydrogenation zone and oxidative dehydrogenation of n-butenes to butadiene, giving a product gas stream b comprising butadiene, unreacted n-butenes, water vapor, oxygen, low-boiling hydrocarbons, possibly carbon oxides and possibly inert gases;C) cooling and compression of the product gas stream b in at least one cooling stage and at least one compression stage, with the product gas stream b being brought into contact with a circulated coolant to give at least one condensate stream c1 comprising water and a gas stream c2 comprising butadiene, n-butenes, water vapor, oxygen, low-boiling hydrocarbons, possibly carbon oxides and possibly inert gases;D) separation of incondensable and low-boiling gas constituents comprising oxygen, low-boiling hydrocarbons, possibly carbon oxides and possibly inert gases as gas stream d2 from the gas stream c2 by absorption of the C4-hydrocarbons comprising butadiene and n-butenes in a circulated absorption medium, giving an absorption medium stream loaded with C4-hydrocarbons and the gas stream d2, and subsequent desorption of the C4-hydrocarbons from the loaded absorption medium stream to give a C4 product gas stream d1;E) separation of the C4 product stream d1 by extractive distillation using a solvent which is selective for butadiene into a stream e1 comprising butadiene and the selective solvent and a stream e2 comprising n-butenes;F) distillation of the stream e1 comprising butadiene and the selective solvent to give a stream f1 consisting essentially of the selective solvent and a stream f2 comprising butadiene;where samples are taken from the circulated coolant in step C) and / or the circulated absorption medium in step D) and the peroxide content of the samples taken is determined by means of iodometry, differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) or microcalorimetry.
Owner:BASF AG
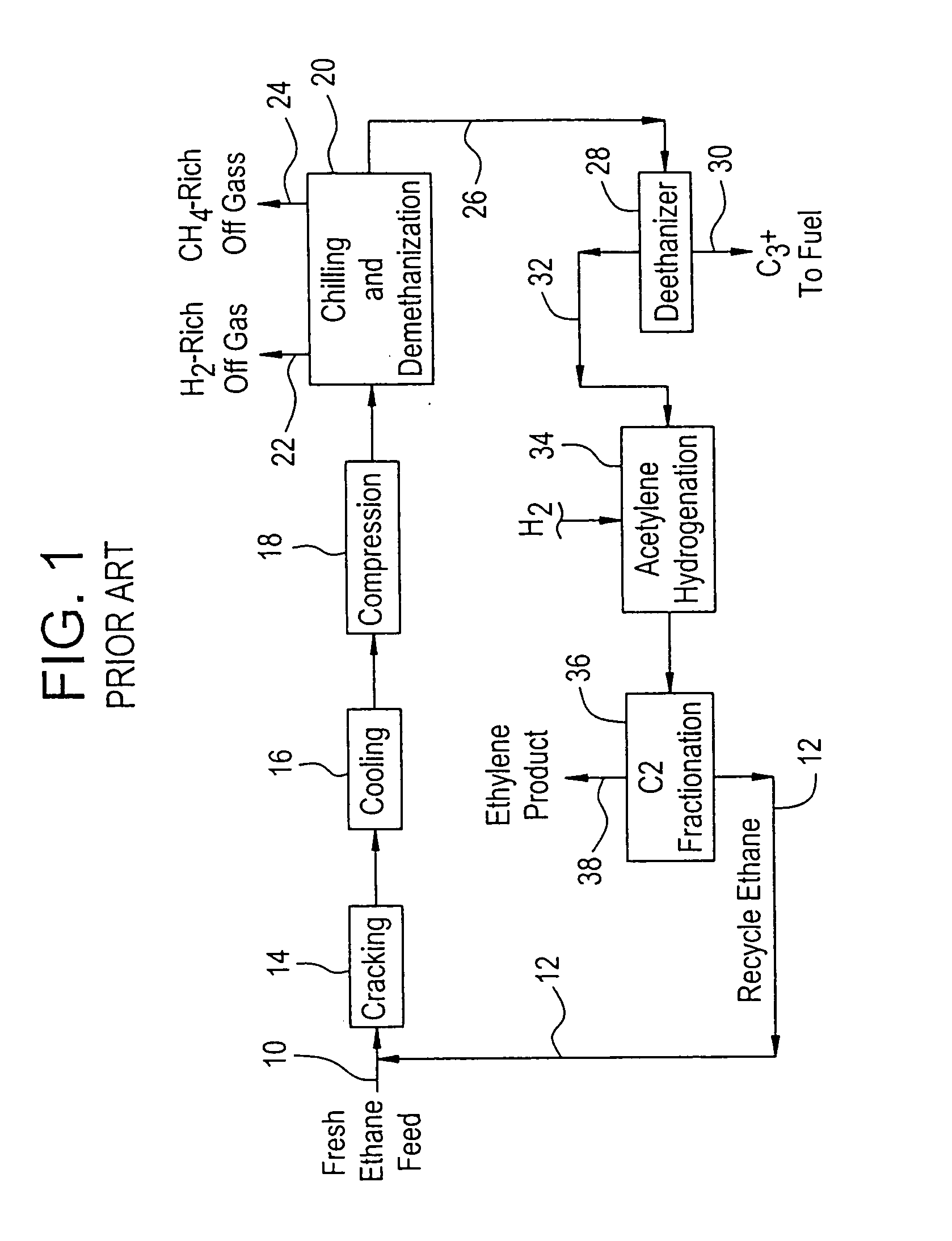
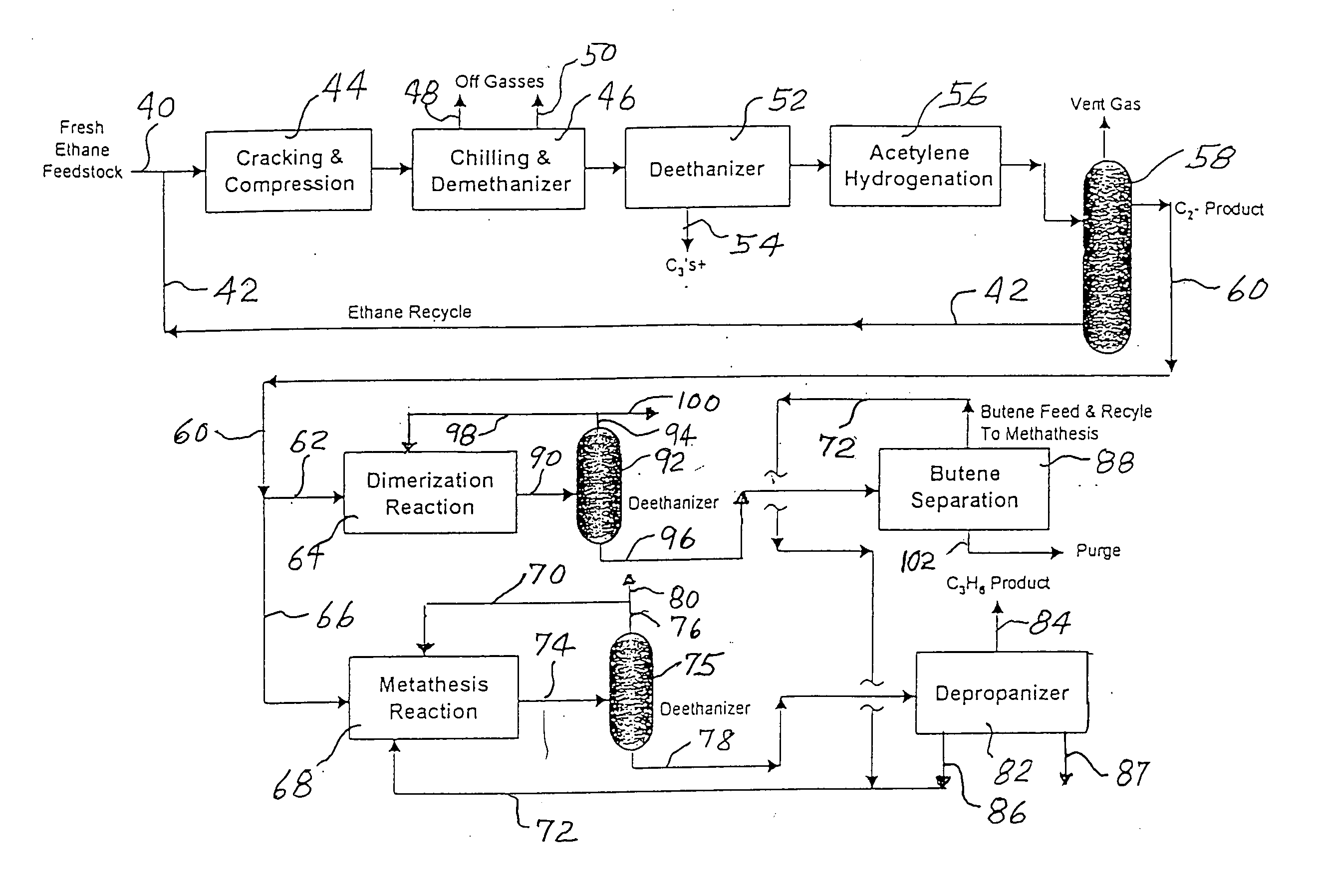
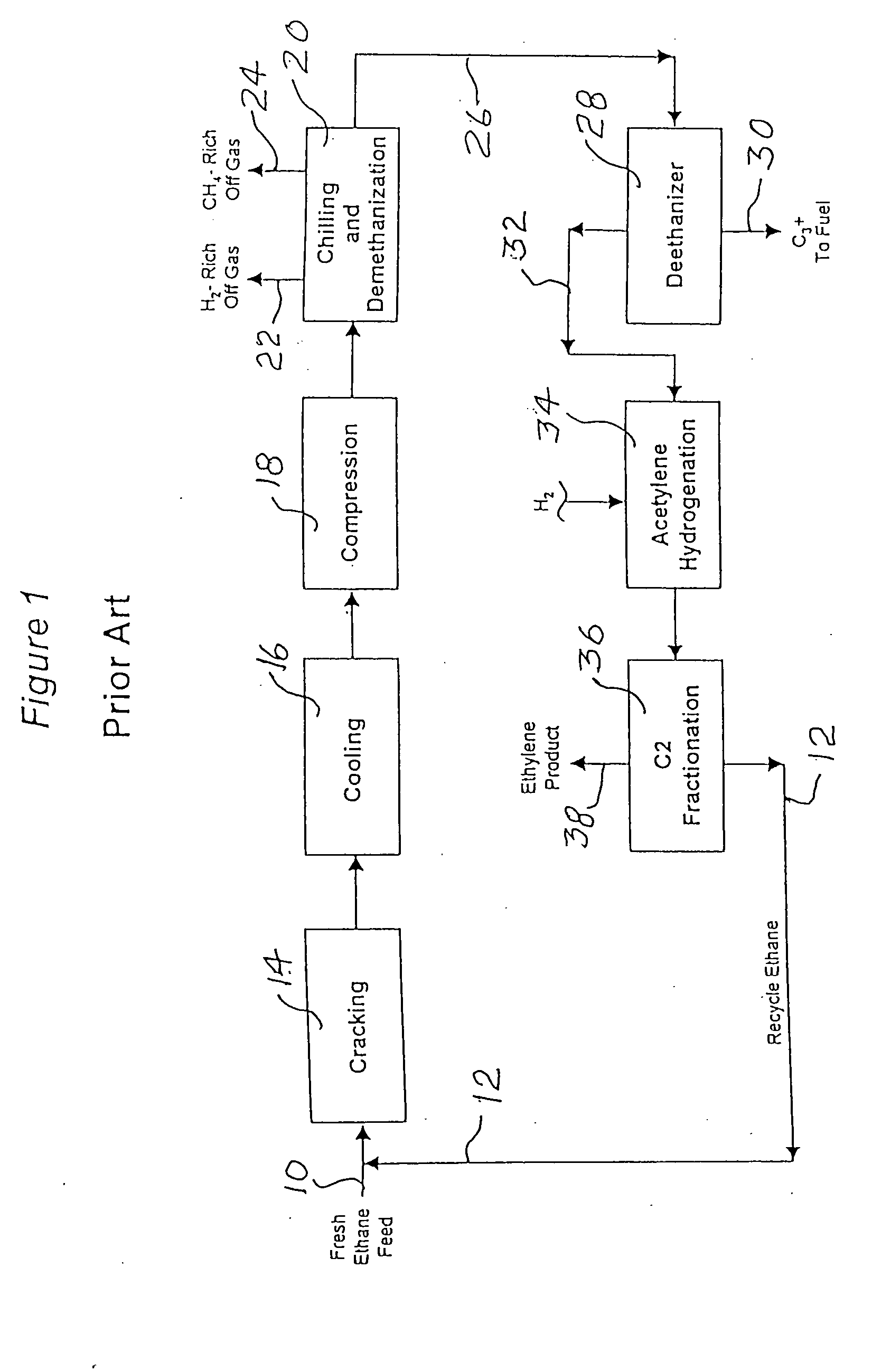
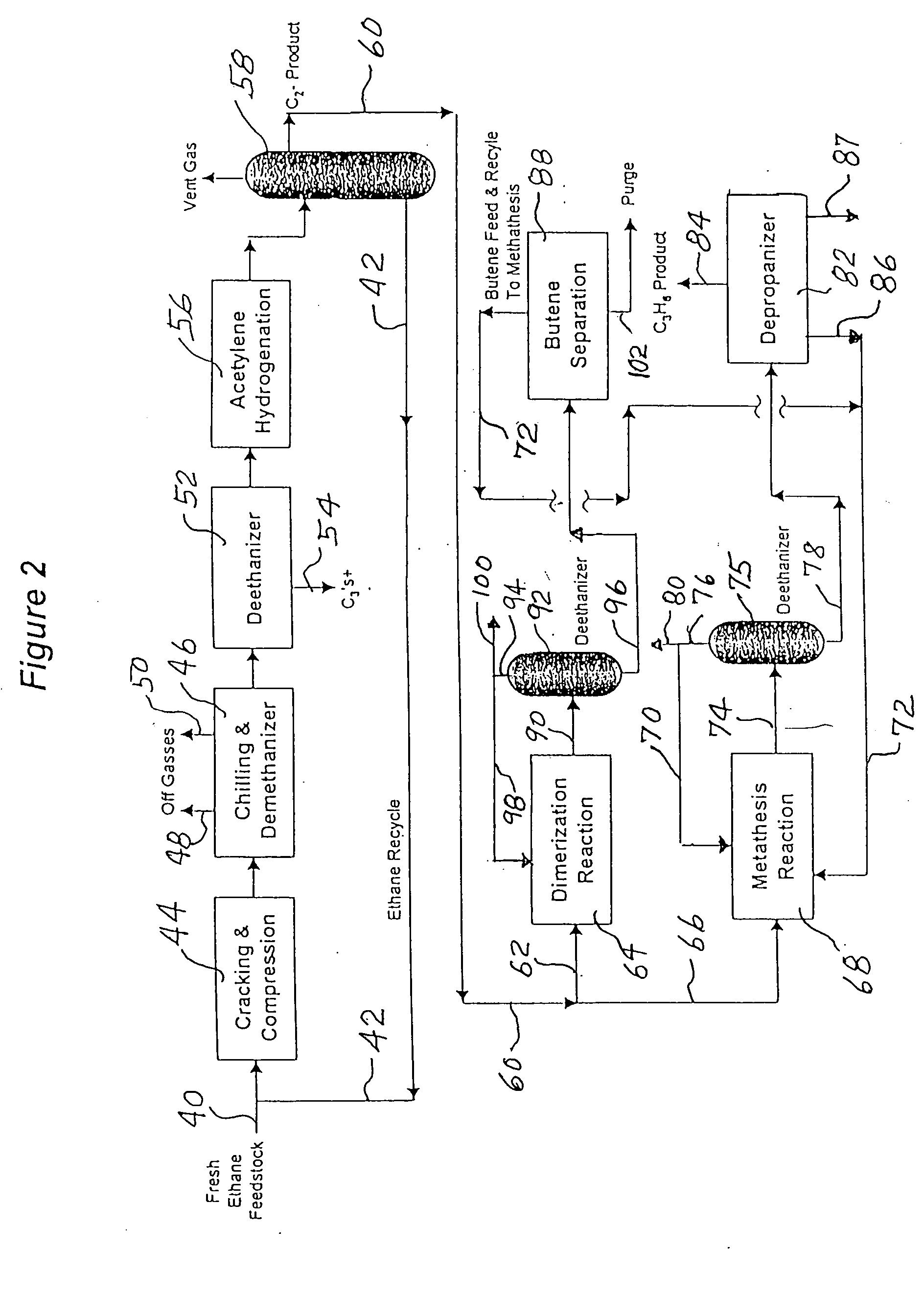
Production of propylene from steam cracking of hydrocarbons, particularly ethane
ActiveUS7223895B2Thermal non-catalytic crackingHydrocarbons from unsaturated hydrocarbon additionButenePolymer science
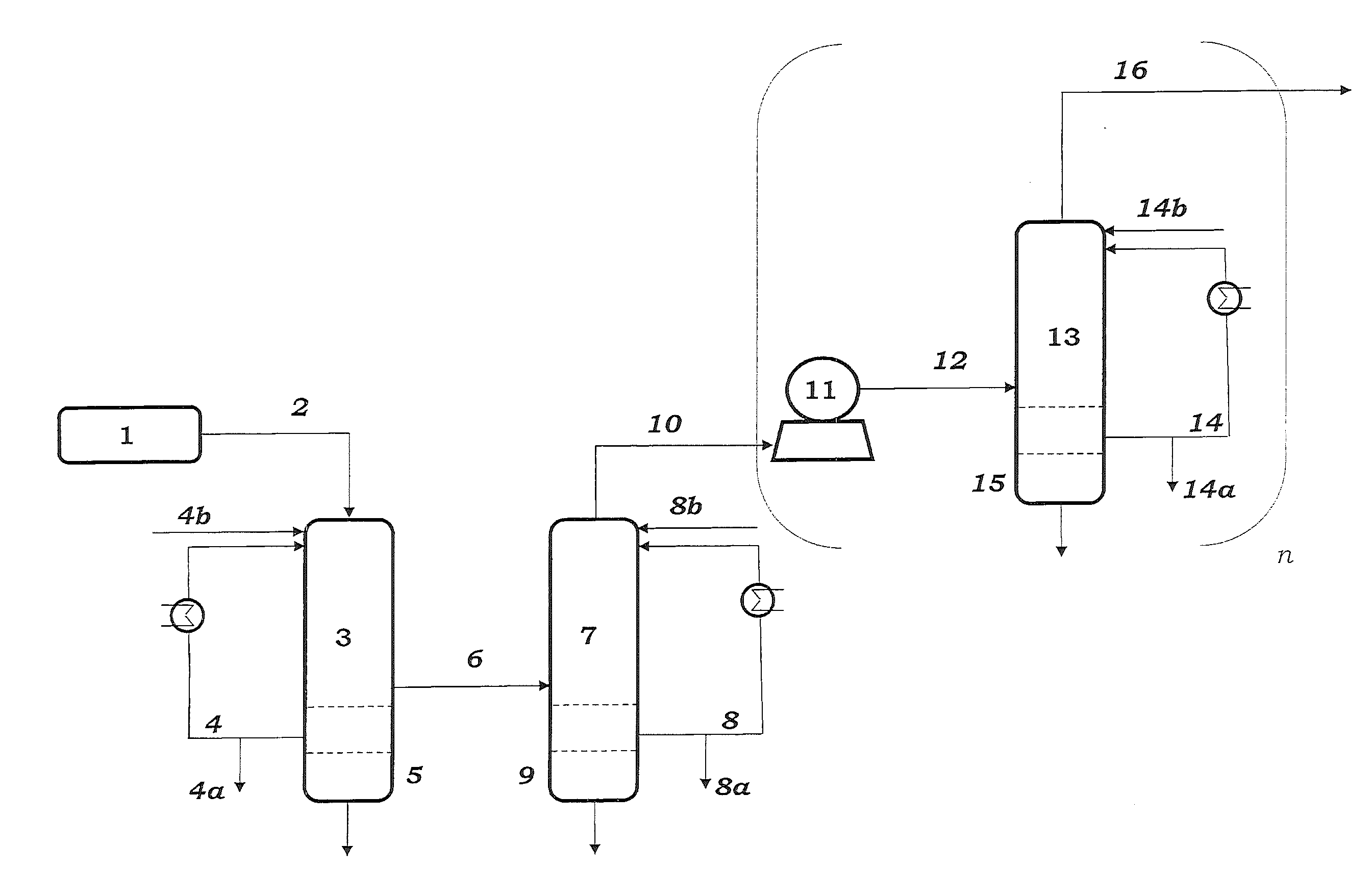
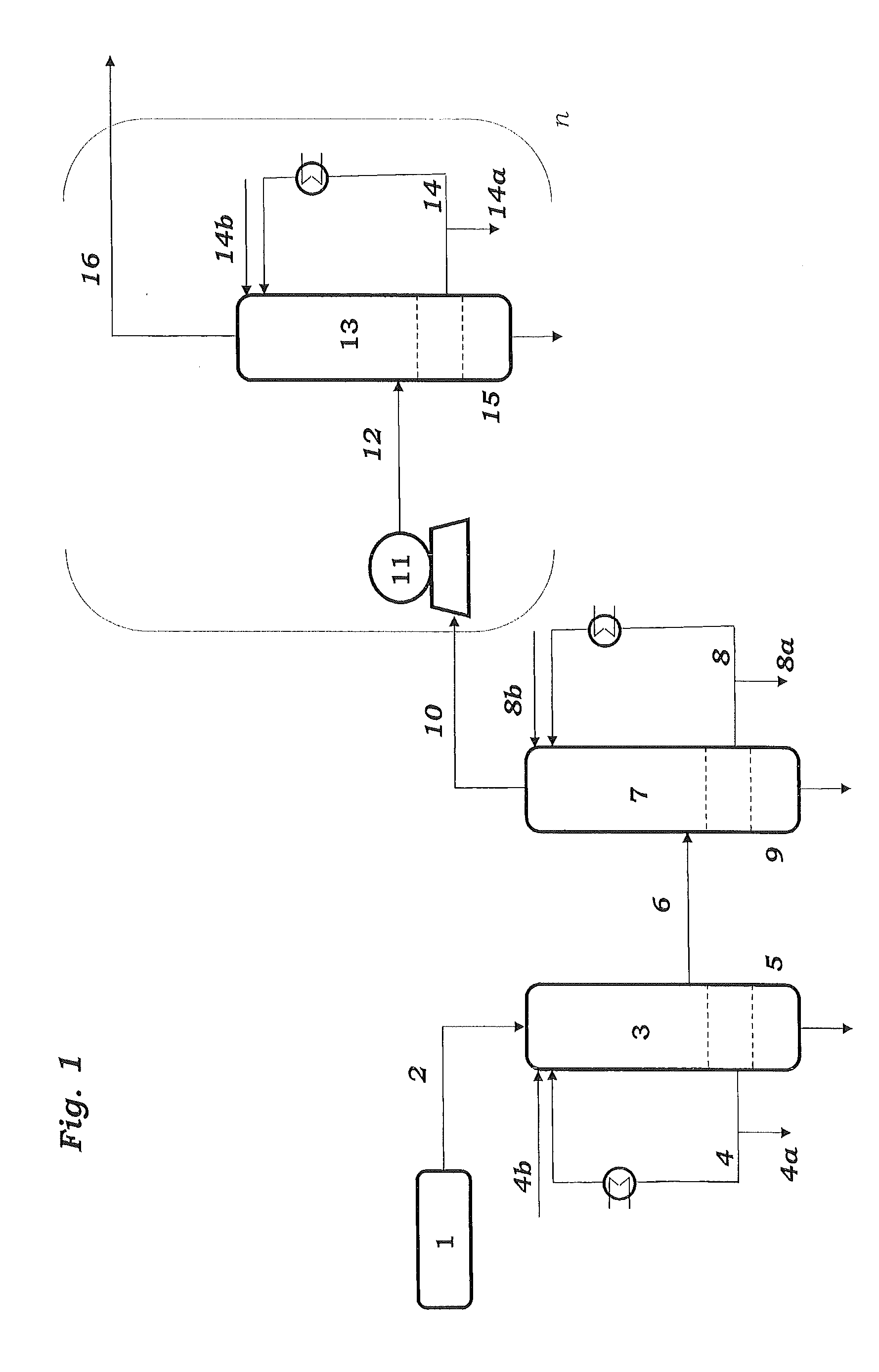
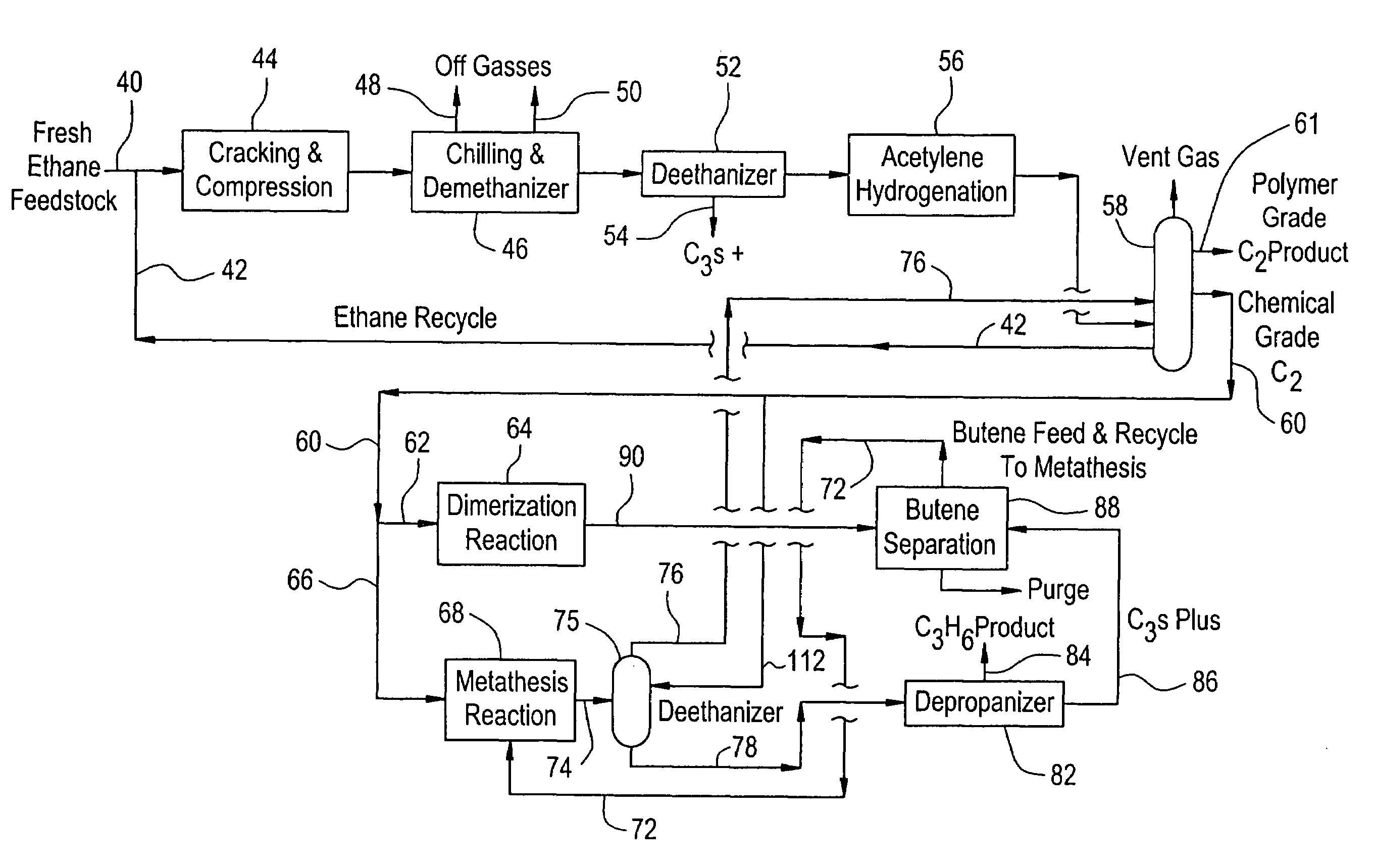
An ethane or other hydrocarbon feedstock is steam cracked to produce an ethylene stream which is processed in an ethylene plant recovery section to separate an ethane recycle and a polymer grade or chemical grade ethylene product stream. A portion of the ethylene product stream may then be reacted by dimerization to produce a butene stream. These formed butenes and / or butenes recovered from other sources and another portion of the ethylene product stream are reacted by metathesis to produce a propylene stream which is deethanized and separated from heavier hydrocarbons to produce the propylene product. The butene product stream may also be deethanized and is separated from heavier hydrocarbons. The overhead from the metathesis section deethanizer may be recycled to the ethylene plant recovery section. The reflux for the metathesis section deethanizer may be generated from the overhead or may be a portion of the ethylene product stream.
Owner:ABB LUMMUS GLOBAL INC
Method for contemporaneously dimerizing and hydrating a feed having butene
ActiveUS20130104449A1Increased research octane numberImprove responseLiquid hydrocarbon mixtures productionCatalystsButeneOligomer
Methods for producing alcohols and oligomers contemporaneously from a hydrocarbon feed containing mixed butenes using an acid based catalyst are provided. Additionally, methods for producing fuel compositions having alcohols and oligomers prepared from mixed olefins are also provided as embodiments of the present invention. In certain embodiments, the catalyst can include a dual phase catalyst system that includes a water soluble acid catalyst and a solid acid catalyst.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
A kind of polybutene alloy material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a polybutene alloy material and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of polyolefin material, specifically relates to a polybutene alloy material and a preparation method thereof. The polybutene alloy material provided by the present invention comprises, by mass, 50-99% of poly-1-butene, 1-40% of polypropylene and 0-10% of a butane-propylene copolymer. Thepreparation method is characterized by: adopting a TiCl4 / MgCl2 supported titanium catalyst for synthesis of the polybutene alloy material through a two-phase polymerization method. The polybutene alloy material provided by the present invention has a core-shell structure, and has advantages of the combination of the excellent impact resistance of the poly-1-butene, the heat resistance and creep property of the poly-1-butene, the low shrinkage rate of the poly-1-butene, the high modulus of the polypropylene, the high surface hardness of the polypropylene, the rapid shaping of the polypropylene, and the like, such that the polybutene alloy material can replace the partial use of the poly-1-butene and the polypropylene. In addition, the polybutene alloy material can be applicable for preparation of the pipe and the pipe fitting, toughening modification of the polypropylene, or the polybutene alloy material can be used as the general polyolefin material.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Bulk depositing synthesis process of isotactic polybutylene-1
The invention discloses a bulk precipitation synthesis method of high isotactic polybutene-1, which belongs to high molecular polymer technology. It uses butene-1 as monomer and reaction medium, under the condition of reaction temperature of 0-70 ℃, adopts supported titanium catalyst to catalyze butene-1, and synthesizes powdery polybutene-1 polymerization by bulk precipitation polymerization The unpolymerized monomers are removed and re-polymerized by flash evaporation to obtain a powdery granular product of high isotactic polybutene-1. It can adopt organometallic aluminum AlR 3 As a cocatalyst, an external electron donor compound can be added to the catalyst system, and hydrogen can also be added as a molecular mass regulator. The polymerization process is carried out in a polymerization tank with ribbon stirring. It has simple process, high efficiency and low cost. The prepared high stereoregular polybutene-1 polymer with an isotactic content of more than 98% has a crystallinity of more than 60% and a melting point of 127.5°C, which is completely close to similar foreign products. Can be widely promoted and applied.
Owner:SHANDONG ORIENT HONGYE CHEM +1
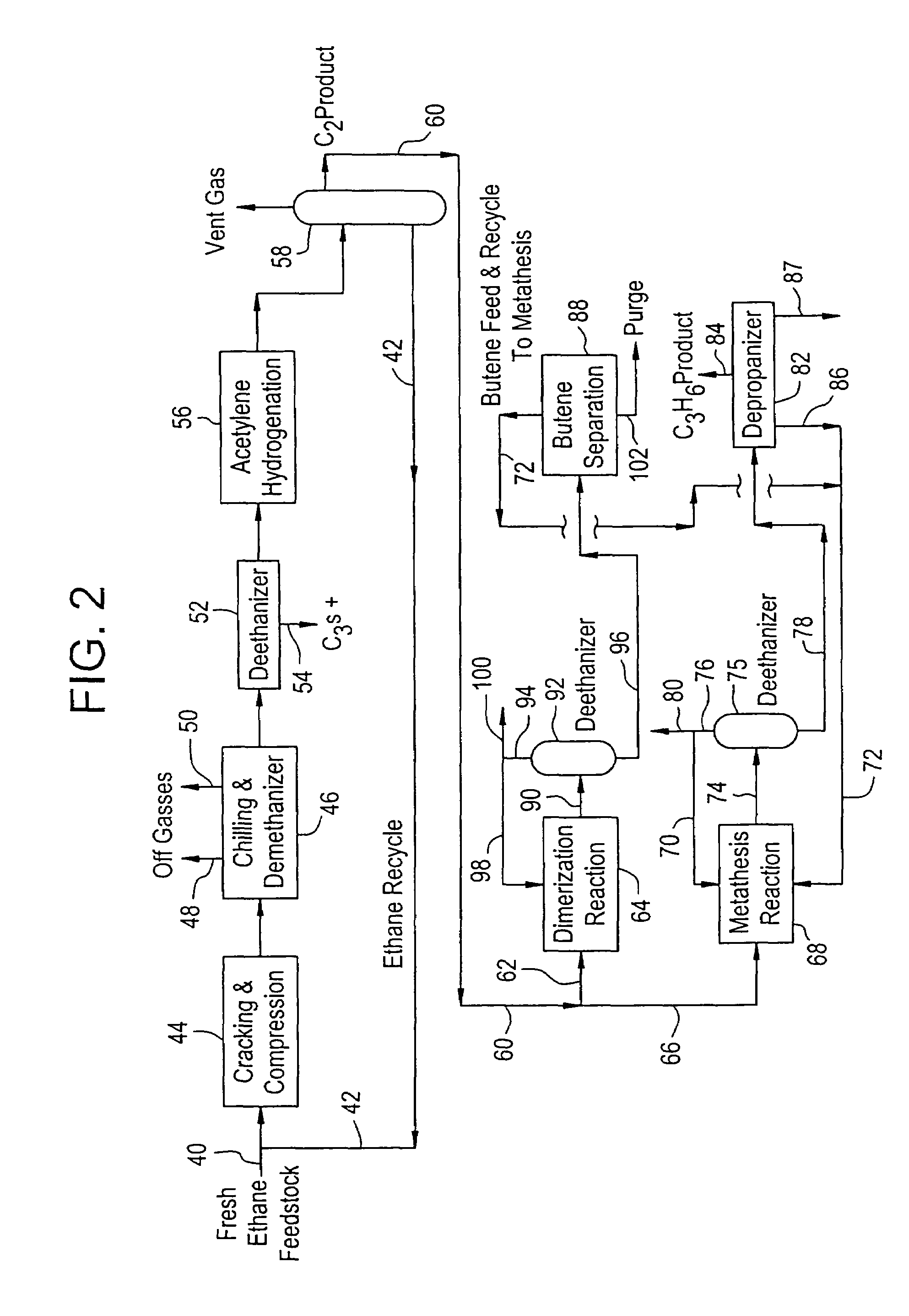
Production of propylene from steam cracking of hydrocarbons, particularly ethane
ActiveUS20050107650A1Improved and economical methodThermal non-catalytic crackingHydrocarbons from unsaturated hydrocarbon additionButenePolymer science
An ethane or other hydrocarbon feedstock is steam cracked to produce an ethylene stream which is processed in an ethylene plant recovery section to separate an ethane recycle and a polymer grade or chemical grade ethylene product stream. A portion of the ethylene product stream may then be reacted by dimerization to produce a butene stream. These formed butenes and / or butenes recovered from other sources and another portion of the ethylene product stream are reacted by metathesis to produce a propylene stream which is deethanized and separated from heavier hydrocarbons to produce the propylene product. The butene product stream may also be deethanized and is separated from heavier hydrocarbons. The overhead from the metathesis section deethanizer may be recycled to the ethylene plant recovery section. The reflux for the metathesis section deethanizer may be generated from the overhead or may be a portion of the ethylene product stream.
Owner:ABB LUMMUS GLOBAL INC
Tie-layer adhesive compositions for styrene polymers and articles
Tie-layer adhesives for styrene polymer resins are provided. The adhesive compositions suitable for use in multi-layer film and sheet constructions are blends comprising ethylene-butene-1 LLDPE resins, styrene-isoprene-styrene triblock copolymers, graft-modified polyethylene and, optionally, ethylene-propylene elastomers.
Owner:EQUSR CHEM LP
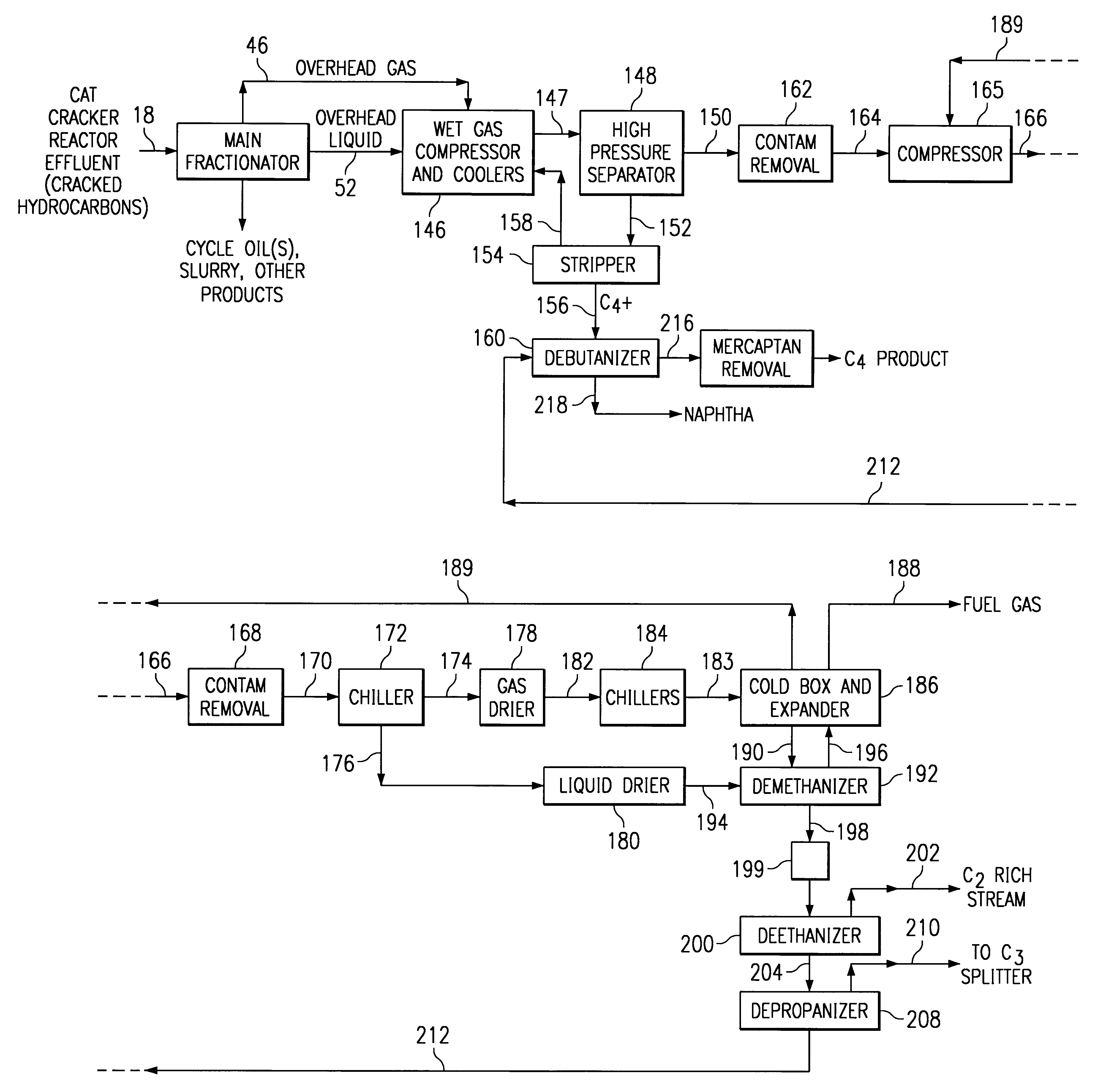
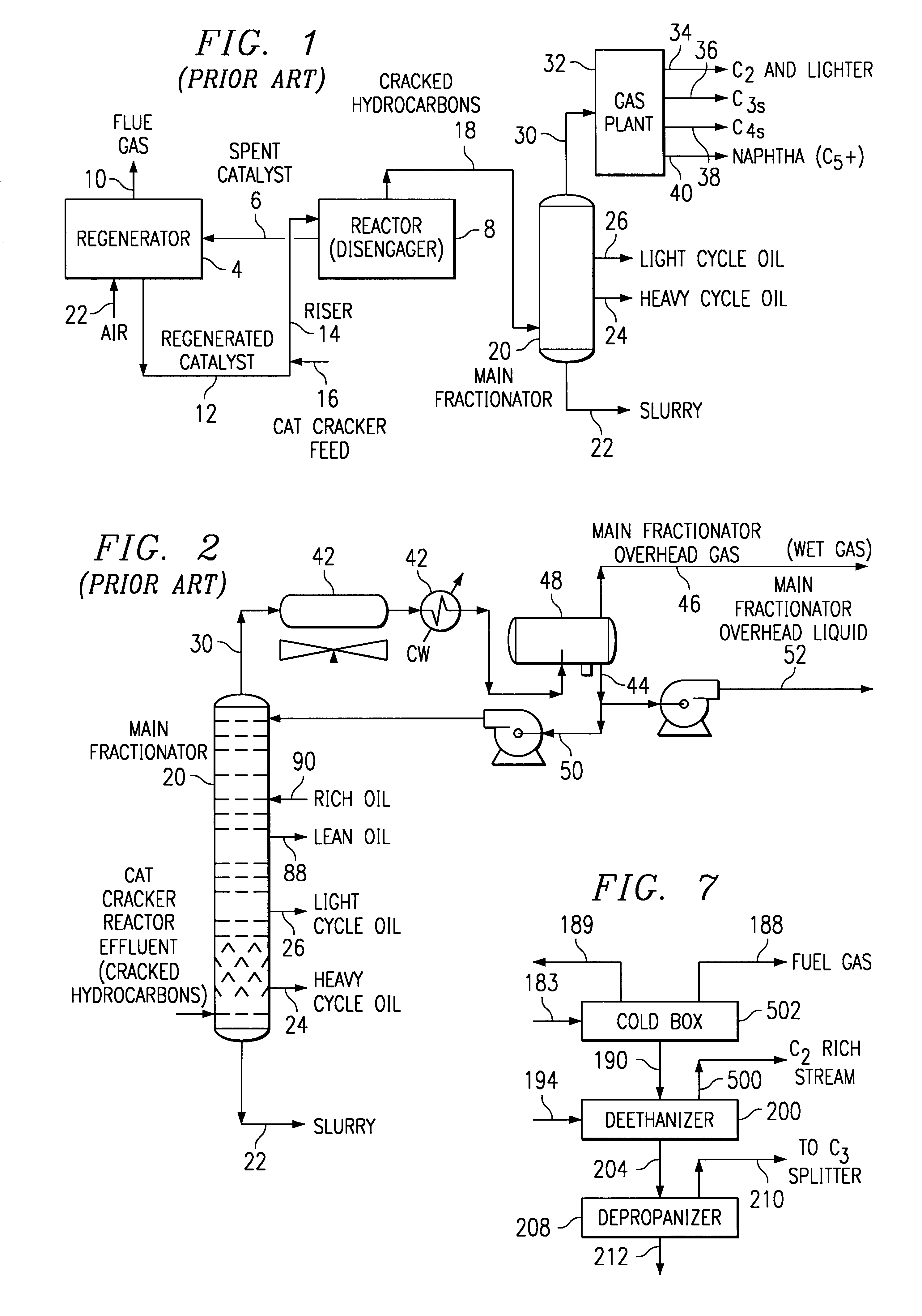
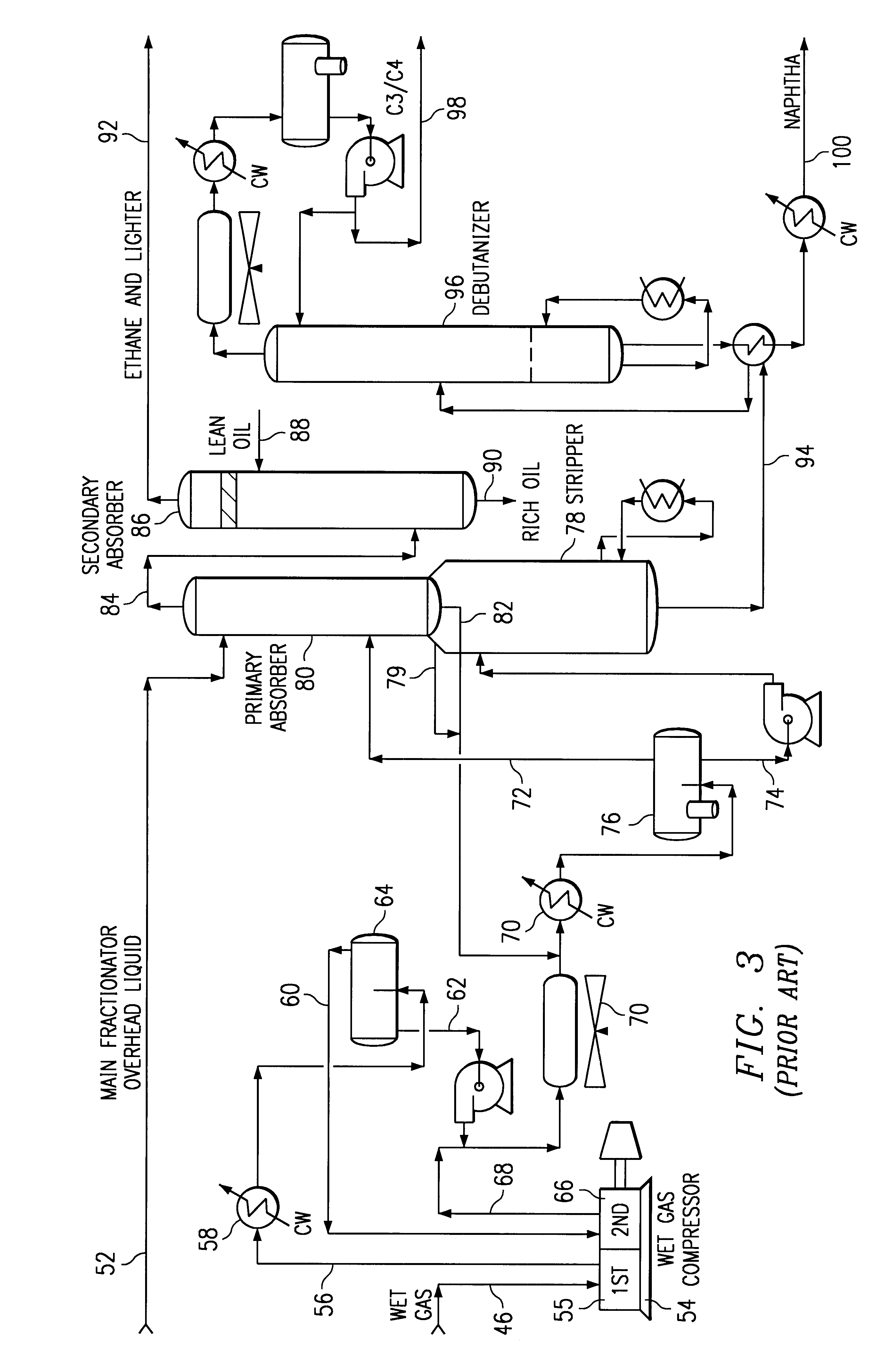
Cat cracker gas plant process for increased olefins recovery
The invention relates to a new process for more efficient separation and recovery of light olefins such as ethylene and propylene from a fluid catalytic cracking unit. The new process invention for recovering olefins from a mixture of cracked hydrocarbons from a fluid catalytic cracker comprises the steps of: (a) providing a mixture of cracked hydrocarbons including methane, ethylene, ethane, propylene, propane, butylene, butane and heavier hydrocarbons such as naphtha produced in a fluid catalytic cracker; (b) separating said mixture into (i) a first stream comprising substantially all of said ethane, ethylene, and methane and a major portion of said propane and propylene and (ii) a second stream comprising a portion of said butylene and butane, and a major portion of said heavier hydrocarbons; and (c) processing said first stream to recover the ethylene and propylene therefrom, and the details of such process described herein.
Owner:STONE & WEBSTER PROCESS TECH
Apparatus and Methods for Separating Butene-1 from a Mixed C4 Feed
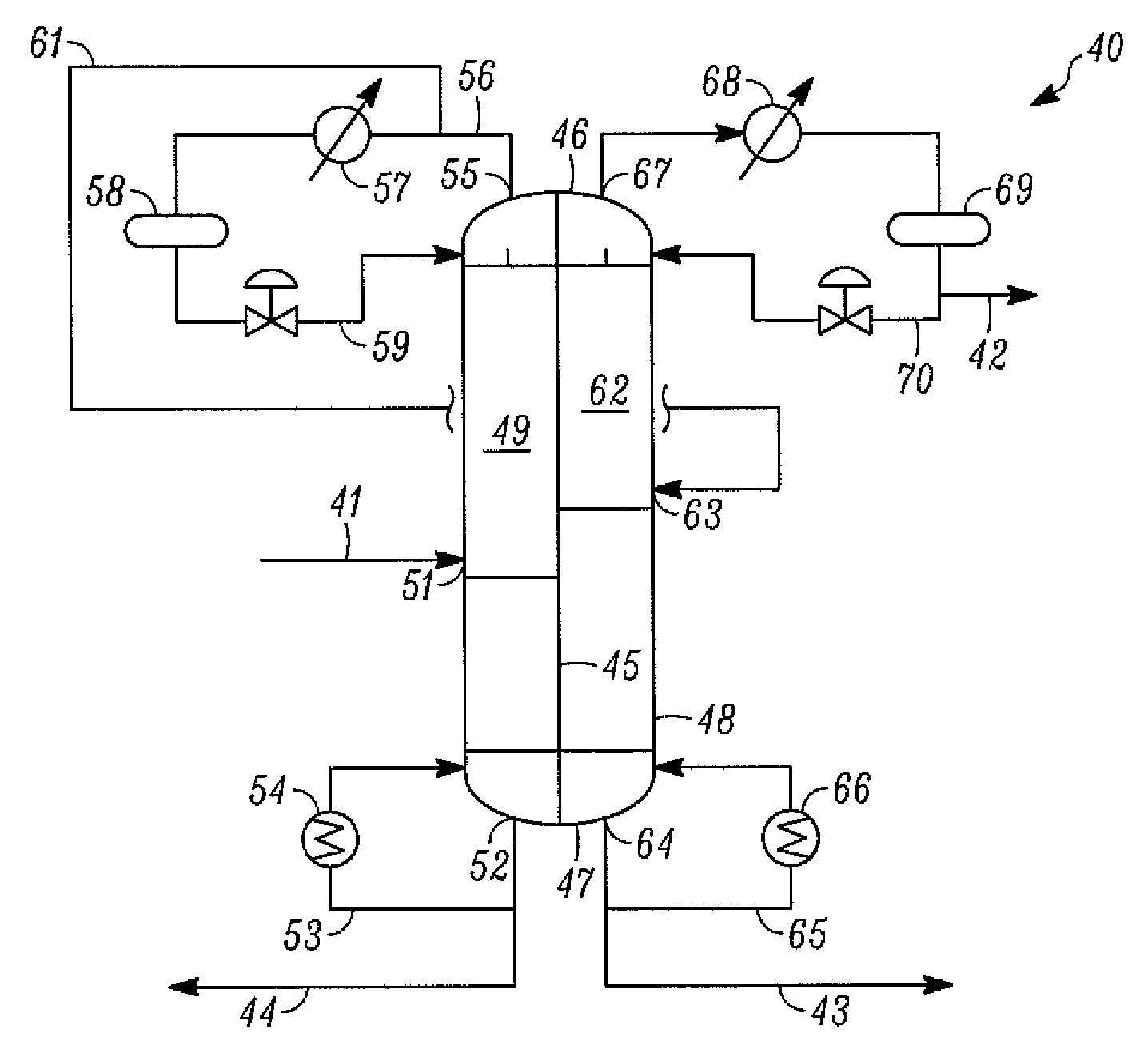
ActiveUS20080161618A1Reduce constructionLow costSolvent extractionDistillation in boilers/stillsButeneFractionating column
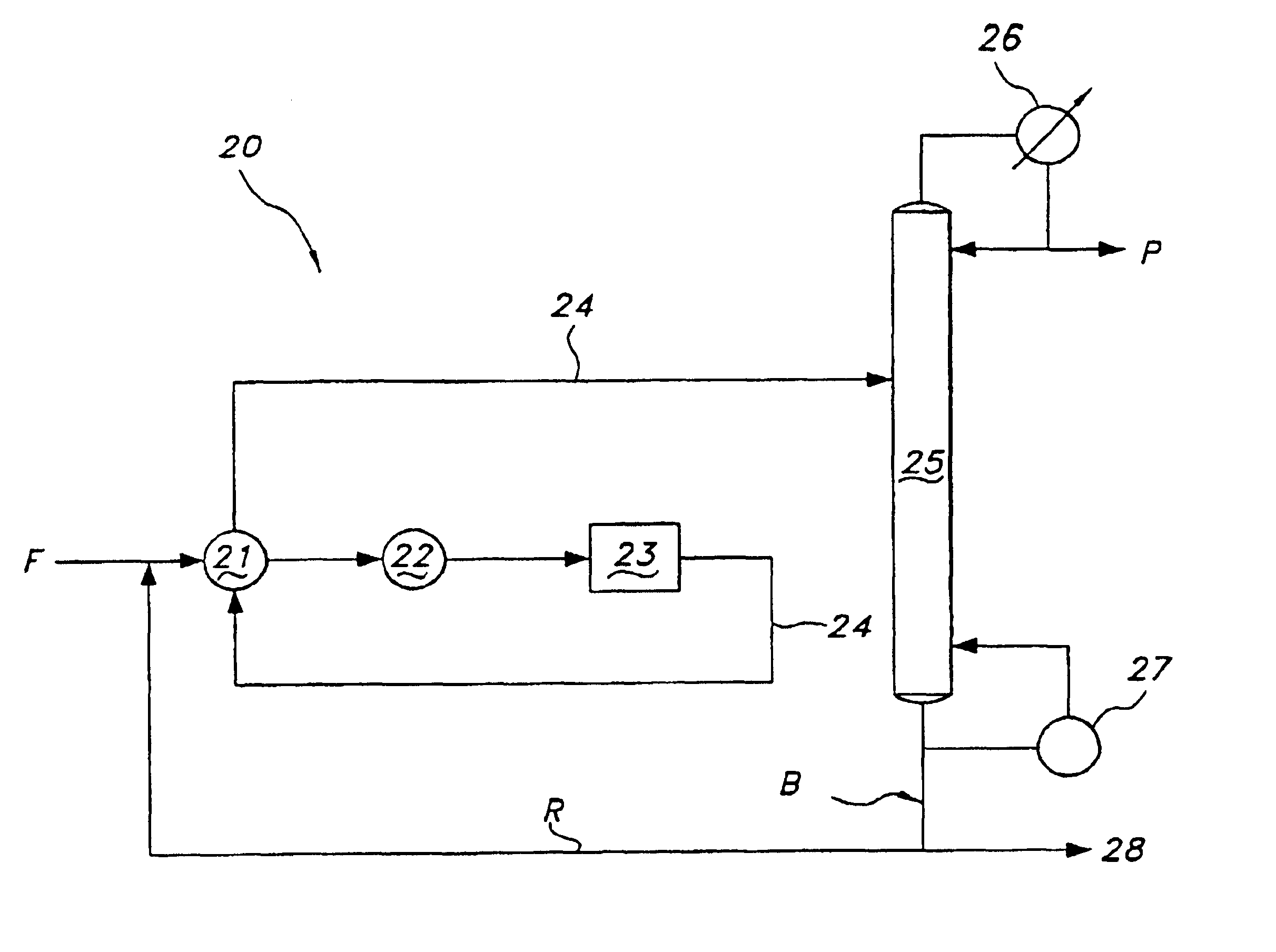
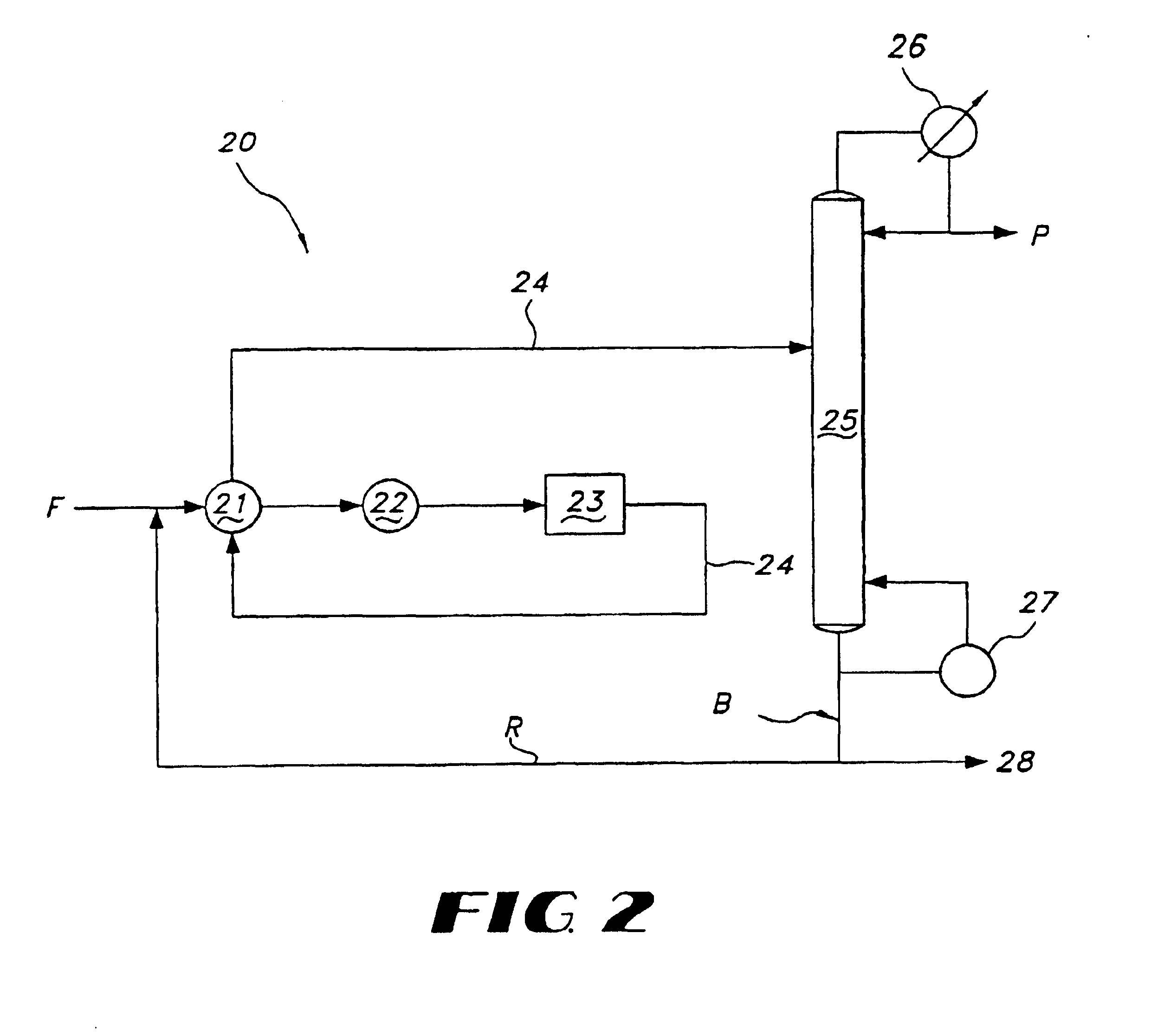
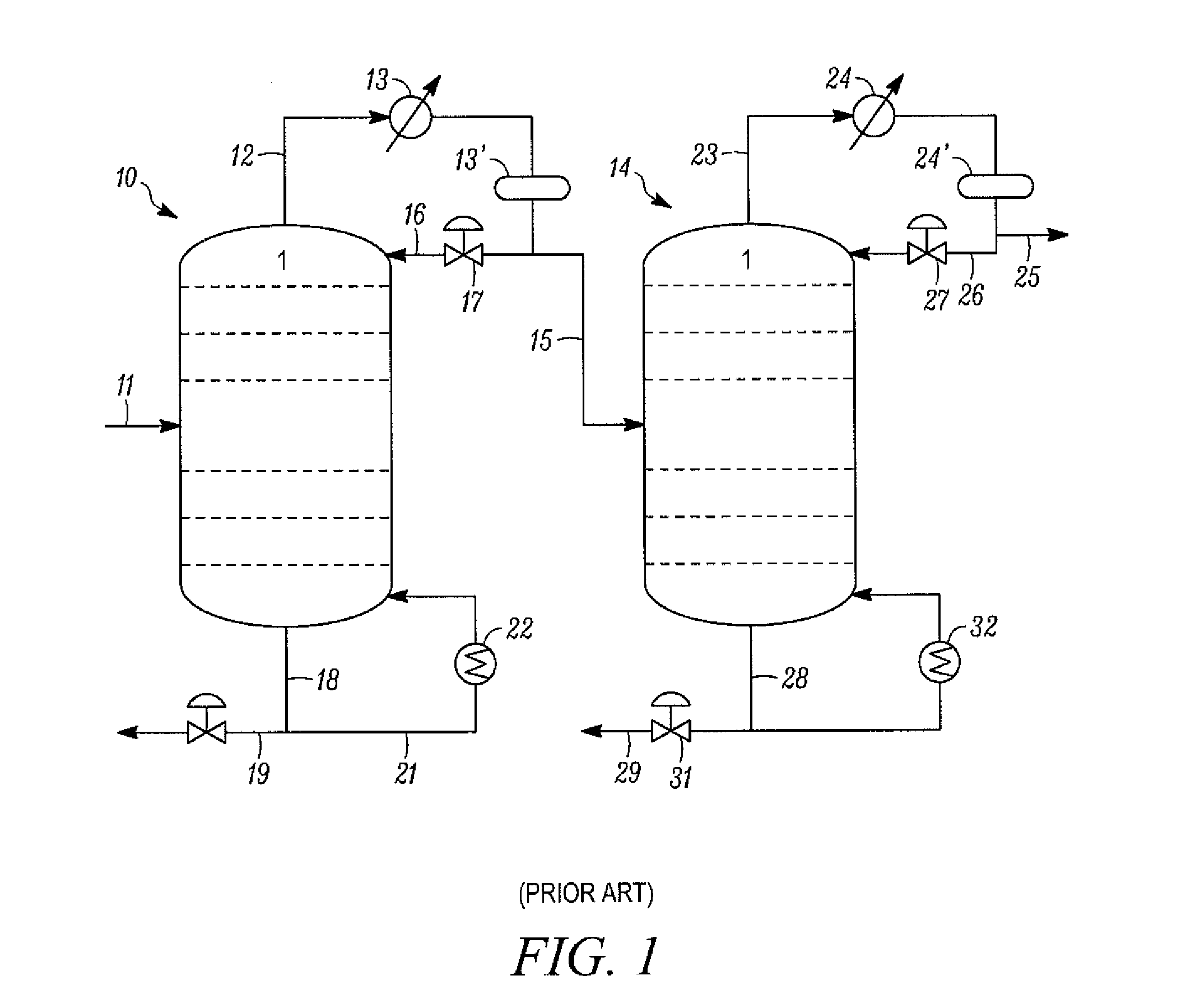
A process is disclosed for recovering 1-butene from a feed steam comprising n-butane, isobutane and butene isomers using a single, divided wall distillation column. The disclosed process includes introducing the feed steam into an inlet of a first side of a distillation column, wherein the distillation column comprises a top, a bottom and a center dividing wall extending between the bottom and the top of the column and dividing the column into the first side and a second side. The process includes taking off an isobutane stream from the top of the second side of column, taking off a 1-butene stream as a bottoms stream from the second side of the column, and taking off a combination 2-butene and n-butane stream as a bottom stream from the first side of column.
Owner:UOP LLC
Catalyst composition and olefin polymerization using same
InactiveUS6911506B2High purityOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsHydrocarbons from unsaturated hydrocarbon additionButeneOligomer
Novel metal complexes, particularly chromium complexes, which contain at least one tridentate ligand are disclosed and prepared. Olefins, particularly ethylene, can be reacted to form butene and / or other homo- or co-oligomers and / or polymers with high α-olefin concentrations by contacting a metal catalyst which contains a transition metal, particularly chromium, complexes having per metal atom at least one tridentate ligand with N, O, or N and O coordinating sites.
Owner:CHEVRON PHILLIPS CHEMICAL CO LP
Method of Producing Propylene Containing Biomass-Origin Carbon
InactiveUS20080312485A1Quality improvementSwitch-over frequencyMolecular sieve catalystsBiofuelsButeneDecomposition
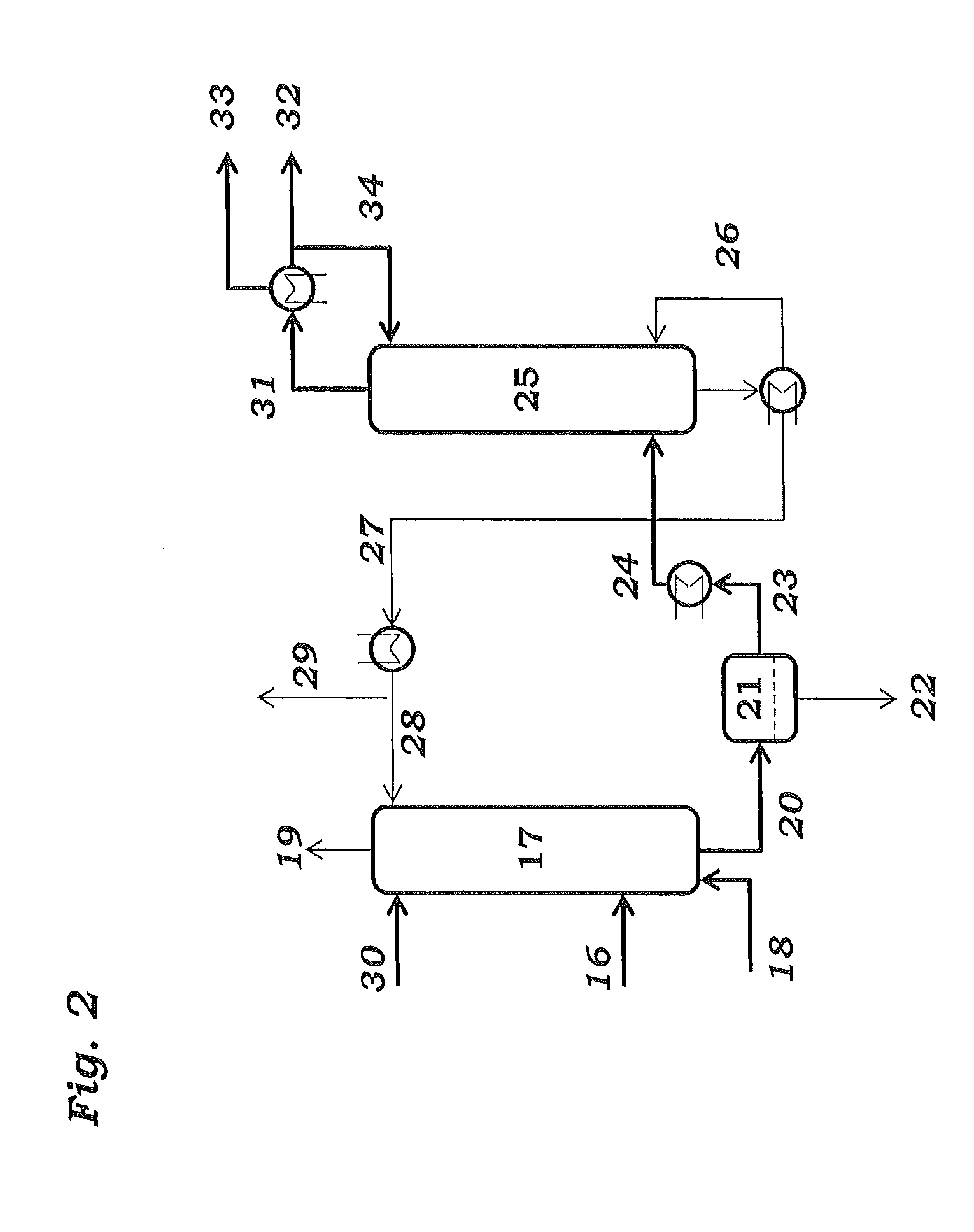
Ethanol obtained from ordinary biomass resources contains many impurities other than water and these impurities themselves or their decomposition products contaminate ethylene when the ethylene is produced by a dehydration reaction, whereby the activity of metathesis catalyst is adversely affected. A method for producing propylene of the present invention is characterized in that the ethanol obtained from biomass is converted to ethylene by a dehydration reaction, the ethylene is separated from the generated water, the separated ethylene is purified by adsorption in an adsorption tower filled with an adsorbent, and then a metathesis reaction is carried out along with a raw material containing n-butene. With the present invention, propylene having biomass-derived carbon and reduced-environmental burden can be efficiently produced without lowering the catalysis activity.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
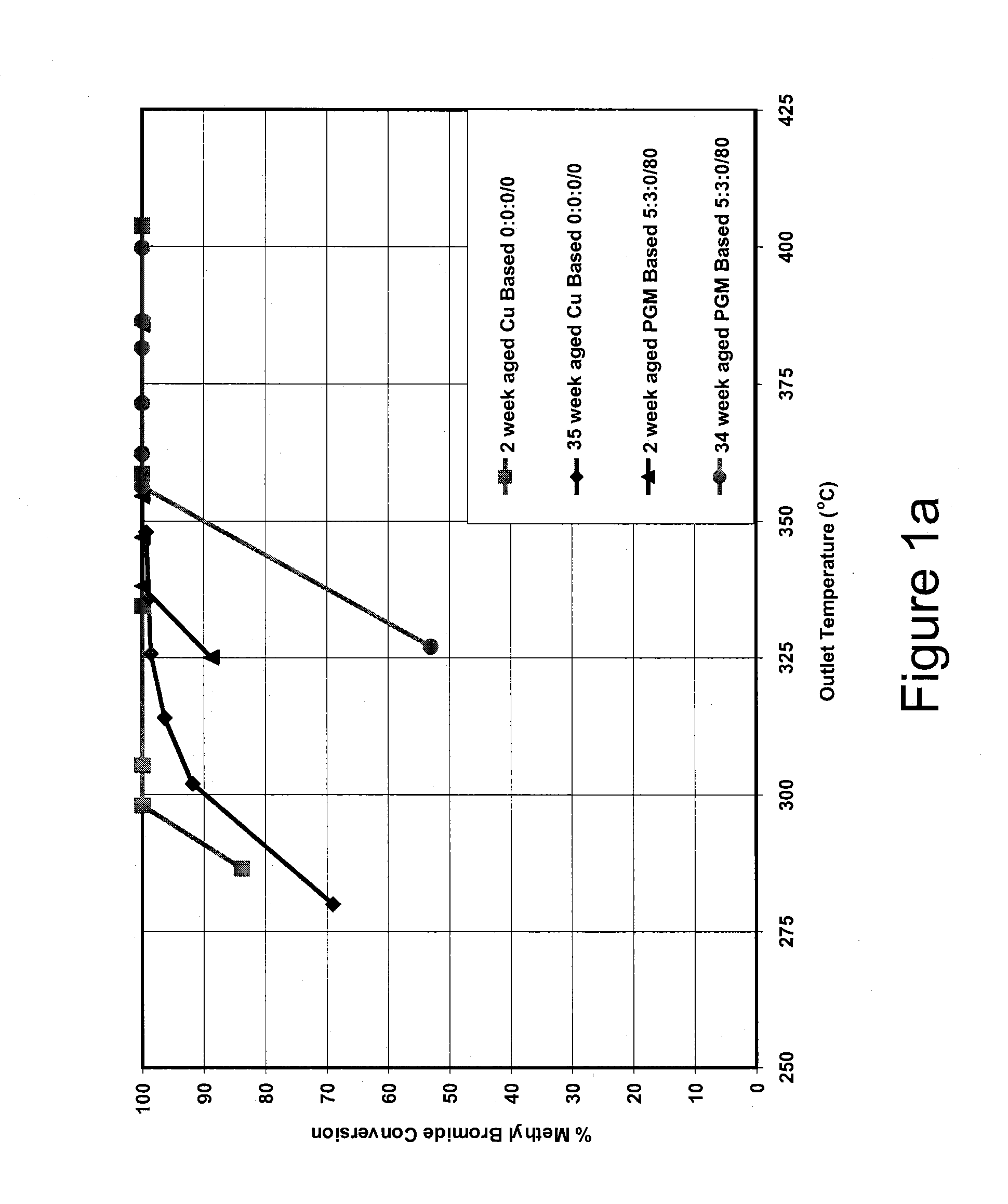
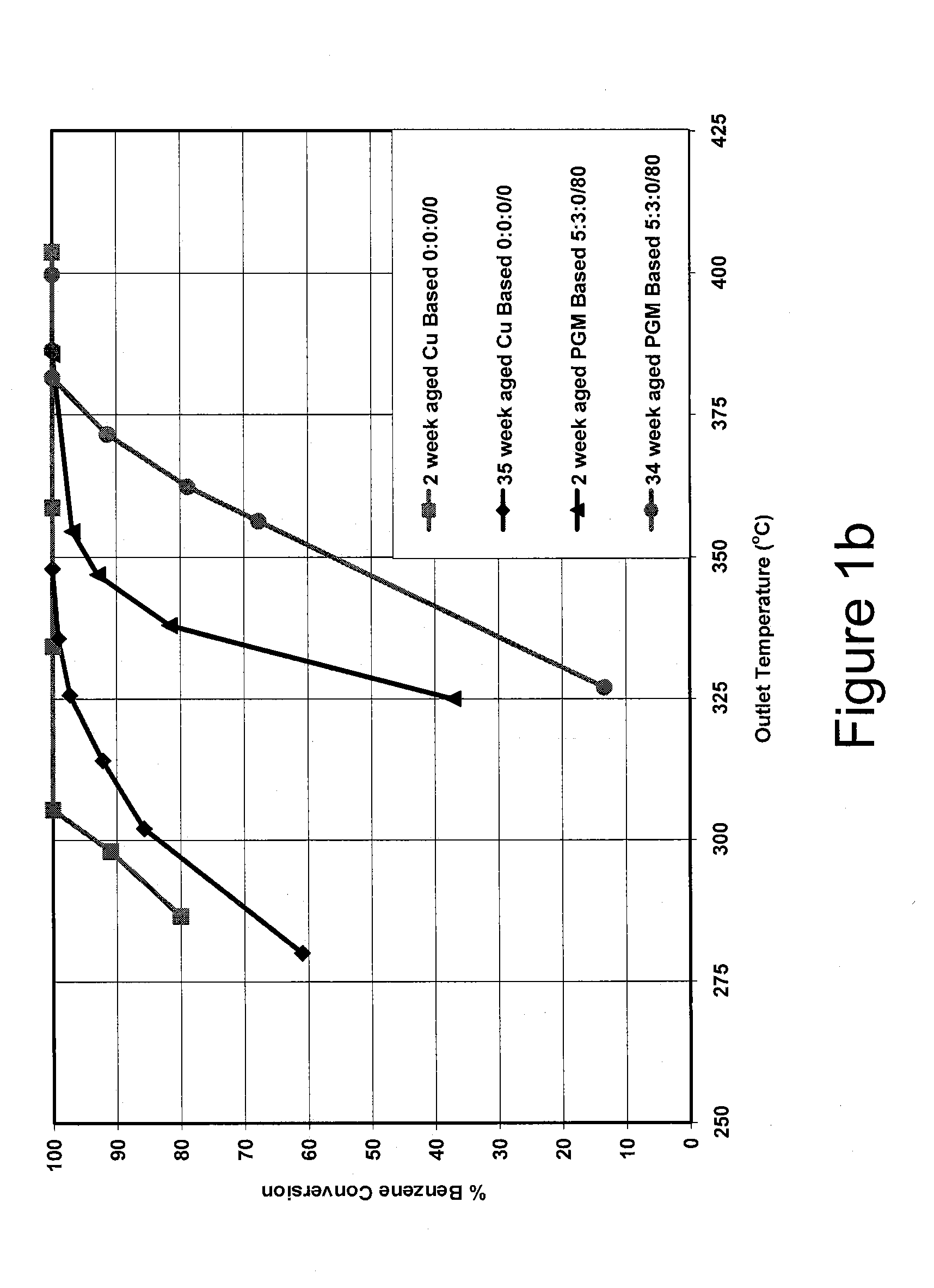
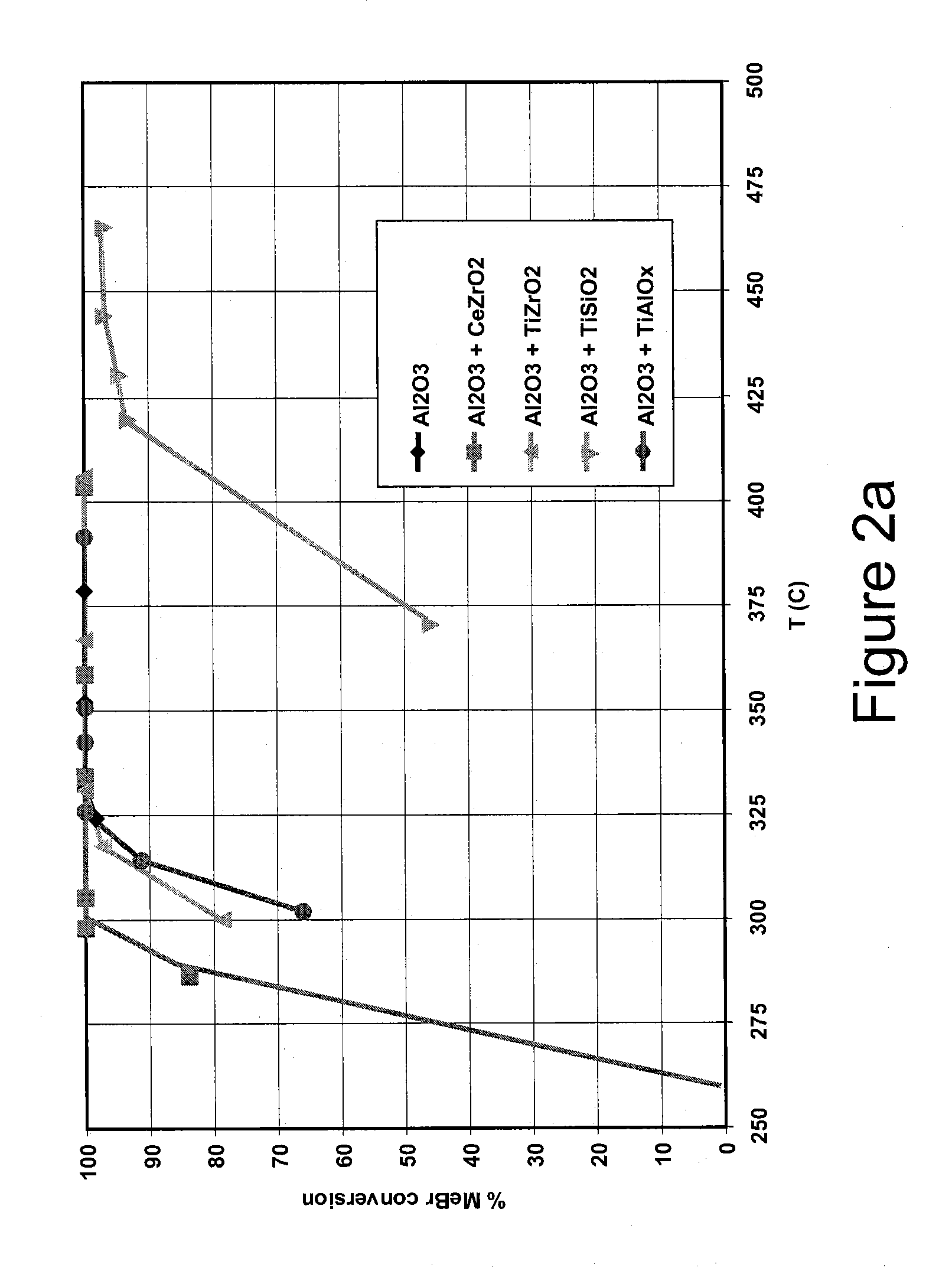
Base metal catalysts for the oxidation of carbon monoxide and volatile organic compounds
A method for oxidizing carbon monoxide (CO) and volatile organic compounds (VOCS) comprises contacting a gas containing water vapor and said CO and VOCs with a catalyst composition comprising at least one base metal promoter and at least one base metal catalyst supported on an oxide support material comprising one or more of alumina, silica, zirconia, ceria, and titania, wherein the VOCs comprise one or more of methyl acetate, methane, methyl bromide, benzene, methanol, methyl ethyl ketone, butane, and butene.
Owner:JOHNSON MATTHEY PLC
A selective hydrogenation process for C4 stream with high butadiene content
ActiveCN102285859AReasonable useHydrocarbon by hydrogenationHydrocarbon purification/separationHigh concentrationButene
The invention relates to a selective hydrogenation process for a C4 material flow with high concentration of butadiene. The selective hydrogenation process comprises the following steps of: enabling the C4 material flow with the high concentration of butadiene to pass through one or more fixed bed hydrogenation reactors (I) with circulation pipelines, carrying out a selective hydrogenation reaction on the C4 mixture with high concentration of butadiene under the action of a catalyst to remove the butadiene and alkyne and generate butylene, enabling the reactor to pass through a terminal reactor (II) without the circulation pipeline, and further removing the residual butadiene and alkyne from the C4 material flow with the low concentration of butadiene. By utilizing the selective hydrogenation process and the catalyst provided by the invention, the controlled concentration range of the butadiene and the C4 alkyne of the C4 material flow is 5-80wt%, the concentrations of the butadiene and the alkyne of the hydrogenated C4 material flow can be respectively reduced to below 10ppm, the selectivity of the 1-butene generation by the butadiene can be more than 50%, and the butadiene can be taken as the raw material of preparing the 1-butene. According to the selective hydrogenation process disclosed by the invention, the C4 material flow is reasonably utilized.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Gasoline production by olefin polymerization with aromatics alkylation
InactiveUS20060194995A1Improve overall utilizationBoost octaneHydrocarbons from unsaturated hydrocarbon additionLiquid carbonaceous fuelsGas phaseAlkylation
A process for the production of high octane number gasoline from light refinery olefins, typically from the catalytic cracking unit, and benzene-containing aromatic streams such as reformate. A portion of the light olefins including ethylene and propylene is polymerized to form a gasoline boiling range product and another portion is used to alkylate the light aromatic stream. The alkylation step may be carried out in successive stages with an initial low temperature stage using a catalyst comprising an MWW zeolite followed by a higher temperature stage using a catalyst comprising an intermediate pore size zeolite such as ZSM-5. Using this staged approach, the alkylation may be carried out in the vapor phase. Alternatively, the alkylation may be carried out in the liquid phase using the heavier olefins (propylene, butene) dissolved into the aromatic stream by selective countercurrent extraction; a separate alkylation step using the ethylene not taken up in the extraction is carried out at a higher temperature.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Adhesives
This invention relates to an adhesive including (a) a copolymer including butene, at least 40 mol % propylene, and from 0 to 30 mol % of a termonomer selected from ethylene and C5 to C20 linear, branched or cyclic alpha olefins, wherein the copolymer has (i) a weight average molecular weight of 100,000 or less; (ii) a number average molecular weight of 20,000 or less; (iii) an Mw / Mn of 5 or more; and (iv) a viscosity of 8000 mPa.sec or less at 190° C.; and (b) a hydrocarbon resin, and / or (c) a polypropylene having at least 30% crystallinity having a viscosity of 1500 mPa.s or less at 190° C., or a tactic polypropylene having a viscosity of 1500 mPa.s or less at 190° C., provided that if the tactic polypropylene is not present, then the hydrocarbon resin is a cyclopentadiene-based hydrocarbon resin. This invention also relates to blends of the copolymer described above and isotactic polypropylene without hydrocarbon resin.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
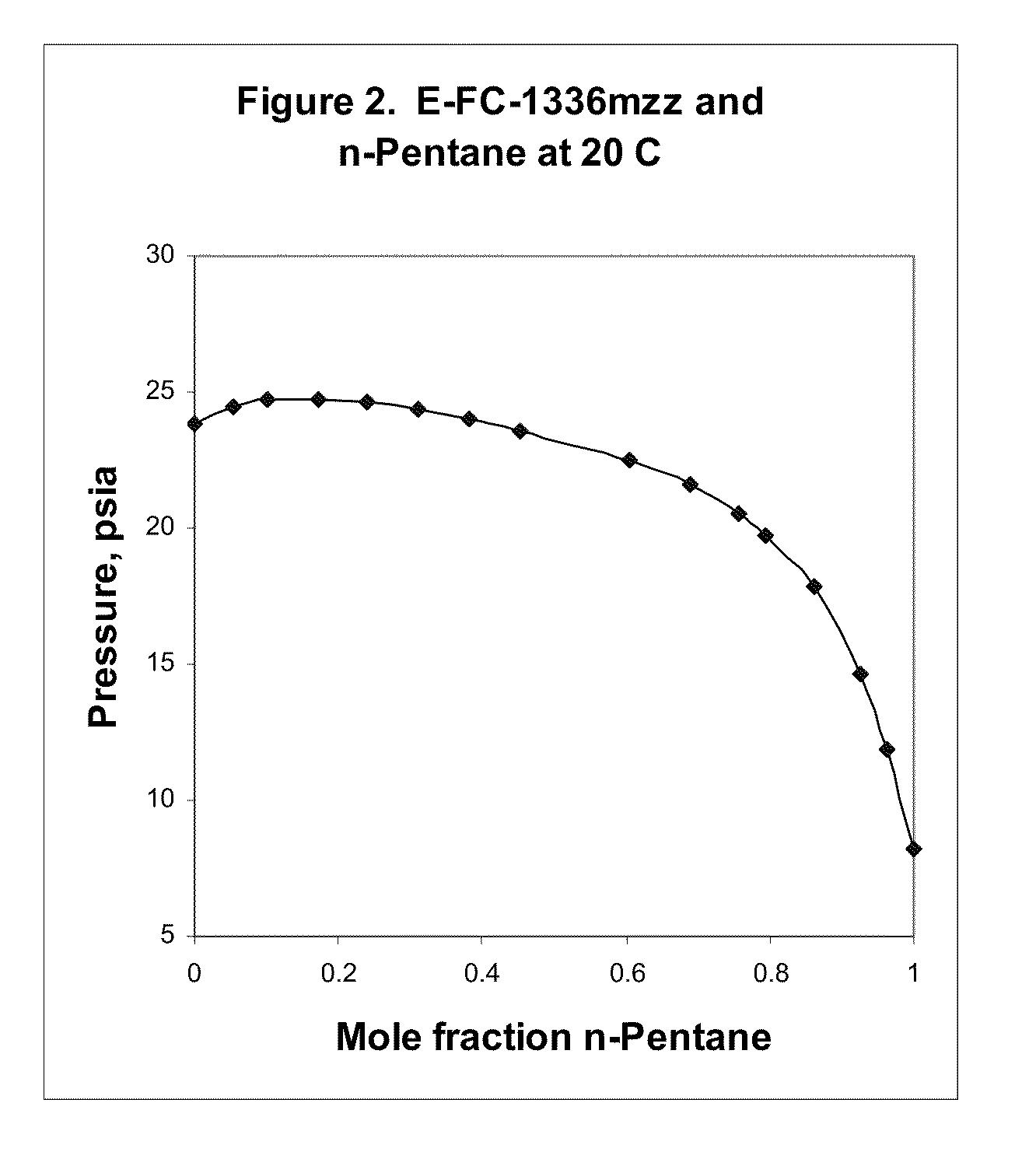
Azeotropic and azeotrope-like compositions of e-1,1,1,4,4,4-hexafluoro-2-butene
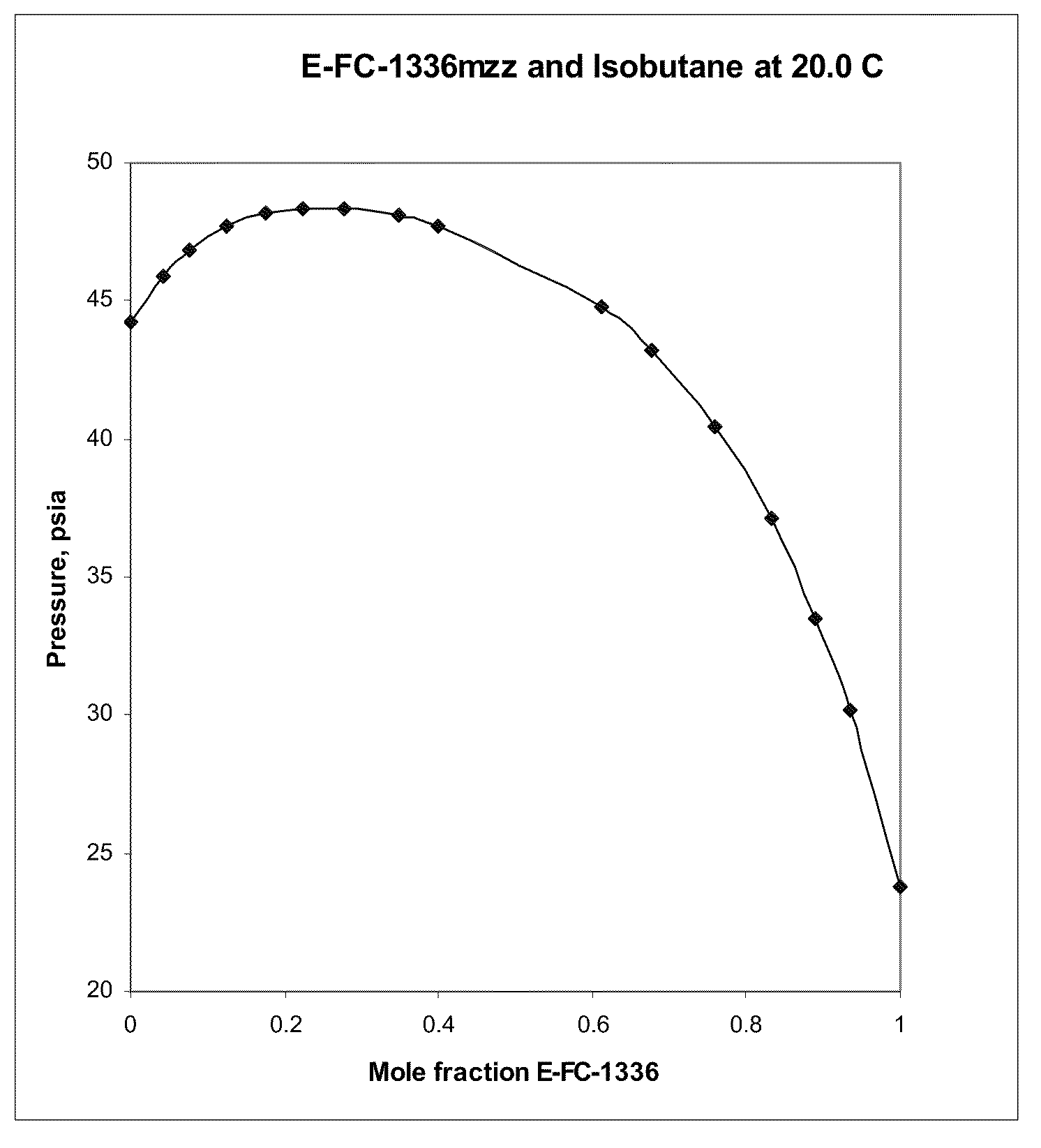
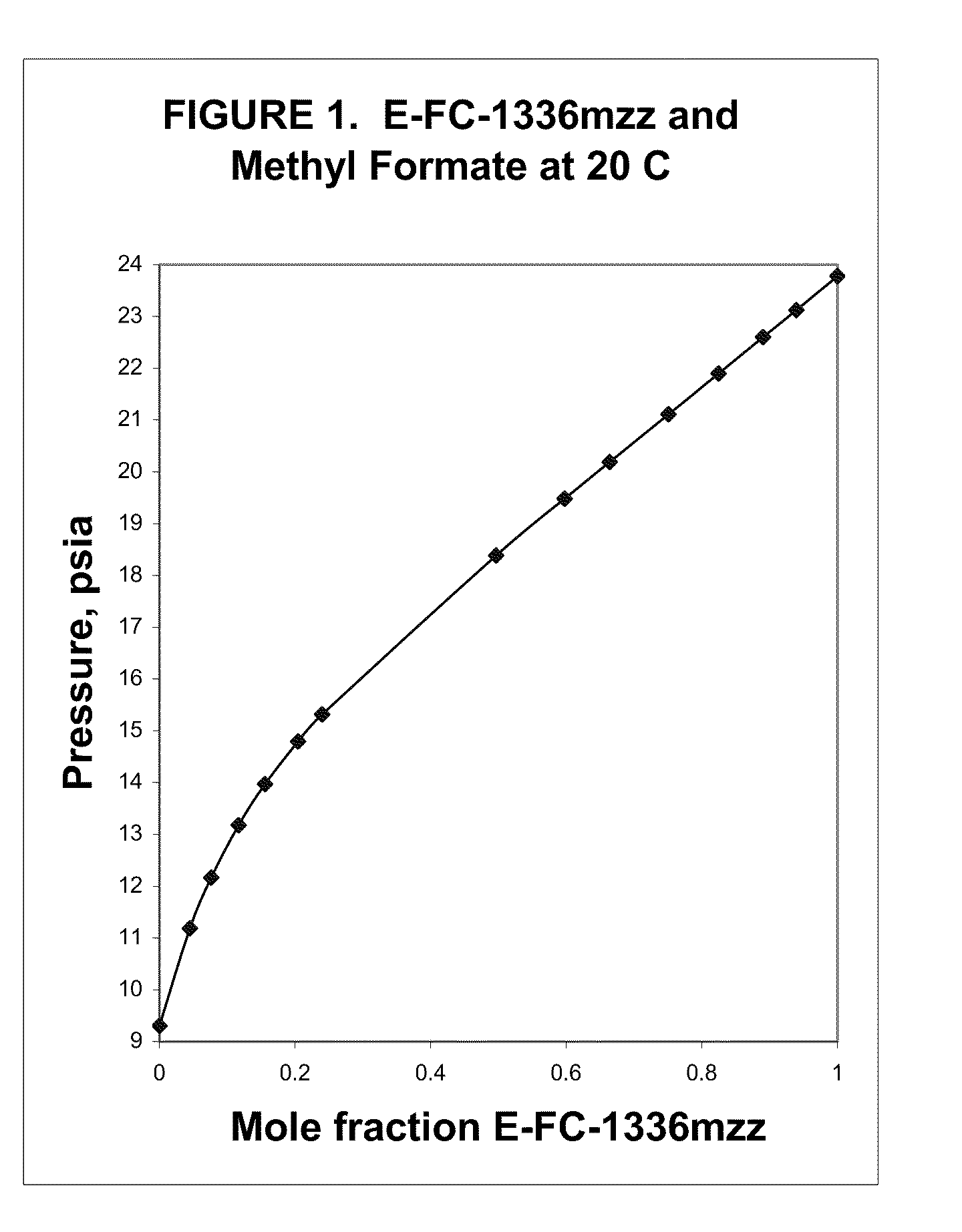
Azeotropic or azeotrope-like compositions are disclosed. The azeotropic or azeotrope-like compositions are mixtures of E-1,1,1,4,4,4-hexafluoro-2-butene with methyl formate, n-pentane, 2-methylbutane trans-1,2-dichloroethylene, 1,1,1,3,3-pentafluoropropane, n-butane or isobutane. Also disclosed is a process of preparing a thermoplastic or thermoset foam by using such azeotropic or azeotrope-like compositions as blowing agents. Also disclosed is a process of producing refrigeration by using such azeotropic or azeotrope-like compositions. Also disclosed is a process of using such azeotropic or azeotrope-like compositions as solvents. Also disclosed is a process of producing an aerosol product by using such azeotropic or azeotrope-like compositions. Also disclosed is a process of using such azeotropic or azeotrope-like compositions as heat transfer media. Also disclosed is a process of extinguishing or suppressing a fire by using such azeotropic or azeotrope-like compositions. Also disclosed is a process of using such azeotropic or azeotrope-like compositions as dielectrics.
Owner:THE CHEMOURS CO FC LLC
Radiation cross-linked low-smoke halogen-free red phosphorus-free flame retardant material and its application
ActiveCN102766293AImprove flame retardant performanceAvoid it happening againInsulated cablesCable/conductor manufactureCross-linkAluminium hydroxide
The invention discloses a radiation cross-linked low-smoke halogen-free red phosphorus-free flame retardant material, which comprises the following components of: by weight, 10-80 parts of ethene-vinyl acetate copolymer, 5-30 parts of ethylene-octene copolymer and / or ethene-butene copolymer and / or terpolymer EP rubber, 0-100 parts of polyethylene, 1-20 parts of a polymer compatilizer, 0.5-10 parts of organosilicon polymer, 1-10 parts of a composite anti-oxidant, 0-200 parts of aluminium hydroxide and / or magnesium hydroxide and / or modified aluminium hydroxide and / or modified magnesium hydroxide, 0.1-100 parts of high molecular weight ammonium polyphosphate and / or 0.1-50 parts of a phosphate ester fire retardant and / or 0.1-50 parts of MCA. The material provided by the invention reaches American UL224VW-1 standard when applied in thermal shrinkable tubes, reaches American UL1581VW-1 standard when applied in electric wires and cables, contains no halogen or red phosphorus, and is environmentally friendly.
Owner:SHENZHEN WOER HEAT SHRINKABLE MATERIAL
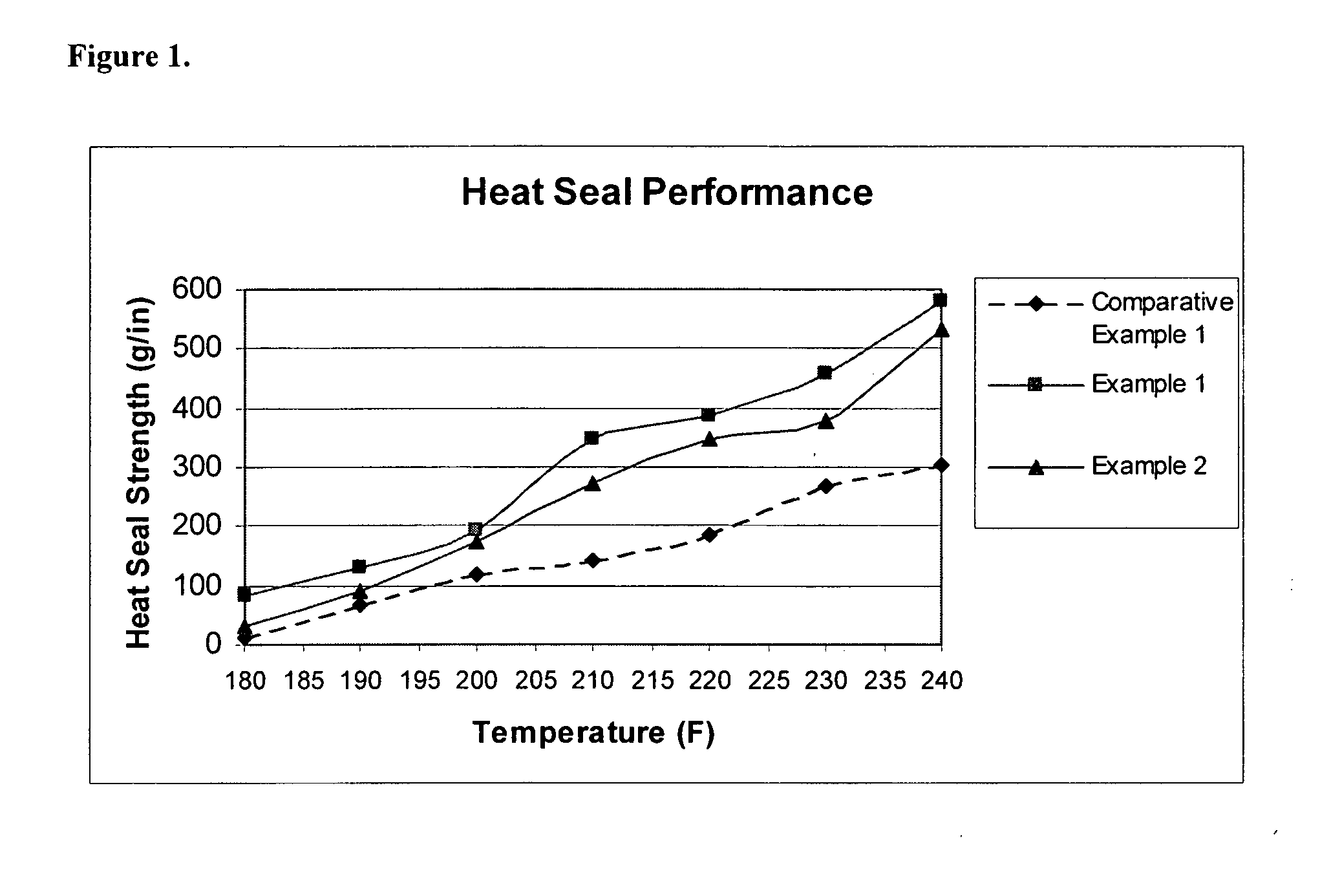
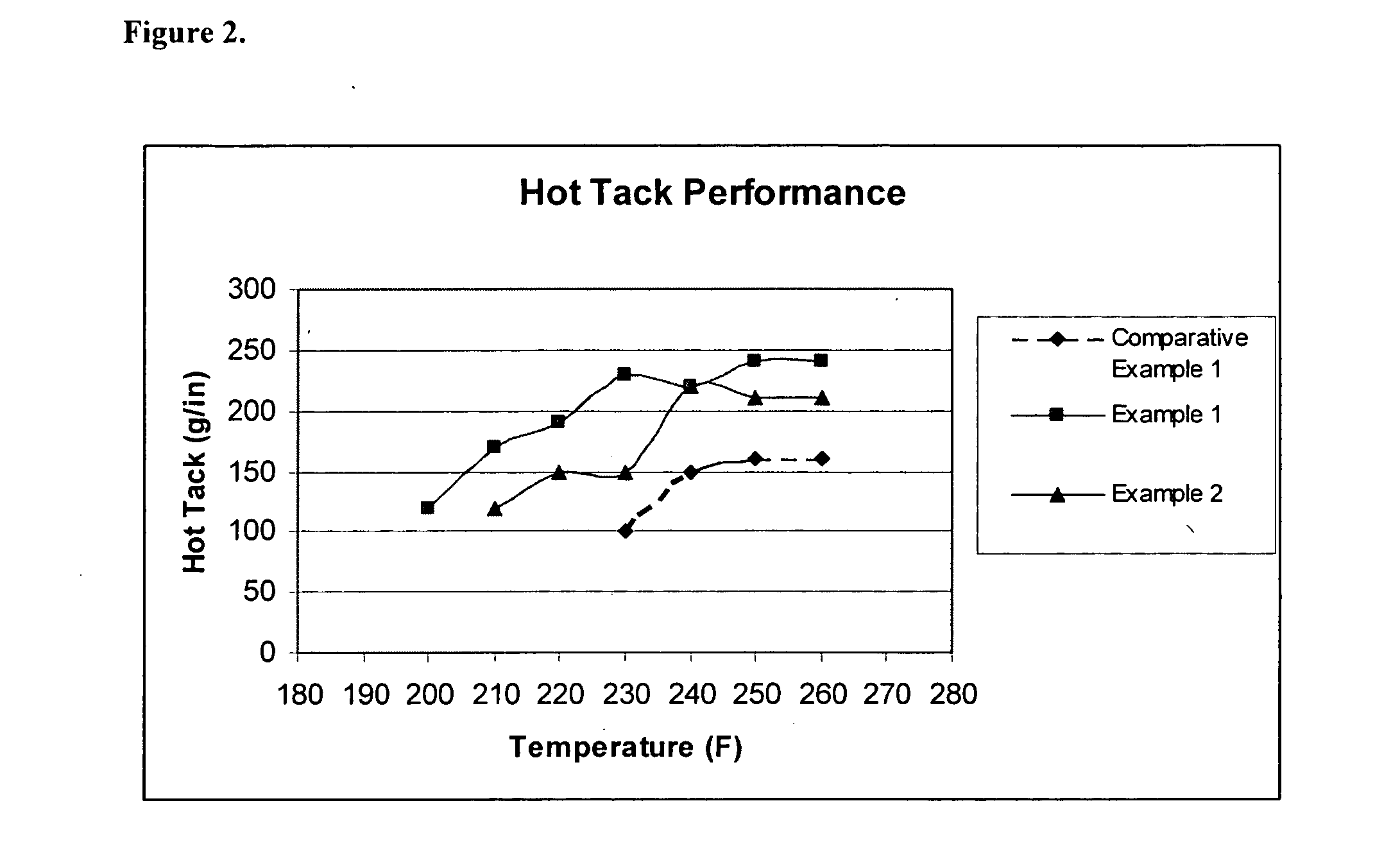
Heat sealable biaxially oriented polypropylene film
InactiveUS20050142367A1Low sealing temperatureSeal contaminationSynthetic resin layered productsDomestic containersButenePolyolefin
A polyolefin multilayer film comprising (a) a polyolefinic core layer and (b) at least one skin layer adjacent to the care layer comprising about 30%-90% by weight of a propylene-ethylene-butene terpolymer and about 10%-70% by weight of a metallocene catalyzed polyethylene or a metallocene catalyzed ethylene copolymer is disclosed. Preferably, a propylene-ethylene-butene terpolymer-containing component and a metallocene catalyzed polyethylene-containing component or a metallocene catalyzed ethylene copolymer-containing component are in distinct separate phases in an incompatible blend of the propylene-ethylene-butene terpolymer-containing component and the metallocene catalyzed polyethylene-containing component or the metallocene catalyzed ethylene copolymer-containing component.
Owner:TORAY PLASTICS AMERICA
Carbon Fiber Strand for Reinforcing Thermoplastic Resins and Method of Producing the Same
InactiveUS20090062426A1Superior in adhesivityHigh mechanical strengthCarbon fibresPretreated surfacesFiberButene
There are disclosed a carbon fiber strand for reinforcement of thermoplastic resin, wherein a sizing agent containing a resin composition obtained by mixing a component [A], i.e. an acid-modified polyolefin copolymer having a weight-average molecular weight of 15,000 to 150,000, which has, as the main chain, an ethylene-propylene copolymer, a propylene-butene copolymer or an ethylene-propylene-butene copolymer and in which the main chain has been modified with 0.1 to 20% by mass of an unsaturated carboxylic acid, and a component [B], i.e. an acid-modified polypropylene having a weight-average molecular weight of 3,000 to 150,000, which has, as the main chain, a polypropylene and in which the main chain has been modified with 0.1 to 20% by mass of an unsaturated carboxylic acid, at a mass ratio of 1:20 to 10:5, is adhered to 100 parts by mass of a carbon fiber in an amount of 0.1 to 8.0 parts by mass; a method for producing the above strand; and a carbon fiber-reinforced thermoplastic resin containing the above strand.
Owner:TEIJIN TECHNO PRODUCTS LTD
Metallized films
InactiveUS6033786AImprove propertiesImprove adhesionSynthetic resin layered productsGlass/slag layered productsButeneMetal coating
A biaxially oriented, heat-set, multilayer film includes a core layer, a bonding layer having a surface adhered to the core layer and a flame treated surface opposite the surface adhered to the core layer. A metal coating for providing oxygen and moisture barrier properties deposited on the flame treated surface and a protective plastic film adhered to said metal coating. The core layer and bonding layer either are free of void-creating additives or include only a quantity of such additives that does not create a matte surface adversely affecting the barrier properties of the metal coating. The bonding layer comprising a mixture including 40 to 100% by weight of propylene / butene-1 copolymer containing up to about 14% by weight of butene-1 (PBC), 0 to 60% of an isotactic polypropylene (PP) and 0 to 50% of a copolymer of ethylene and propylene wherein propylene is the predominant component by weight (EPC).
Owner:APPLIED EXTRUSION TECH
Process for Producing Propylene and Aromatics from Butenes by Metathesis and Aromatization
InactiveUS20110263917A1Molecular sieve catalystDistillation purification/separationIsomerizationOctene
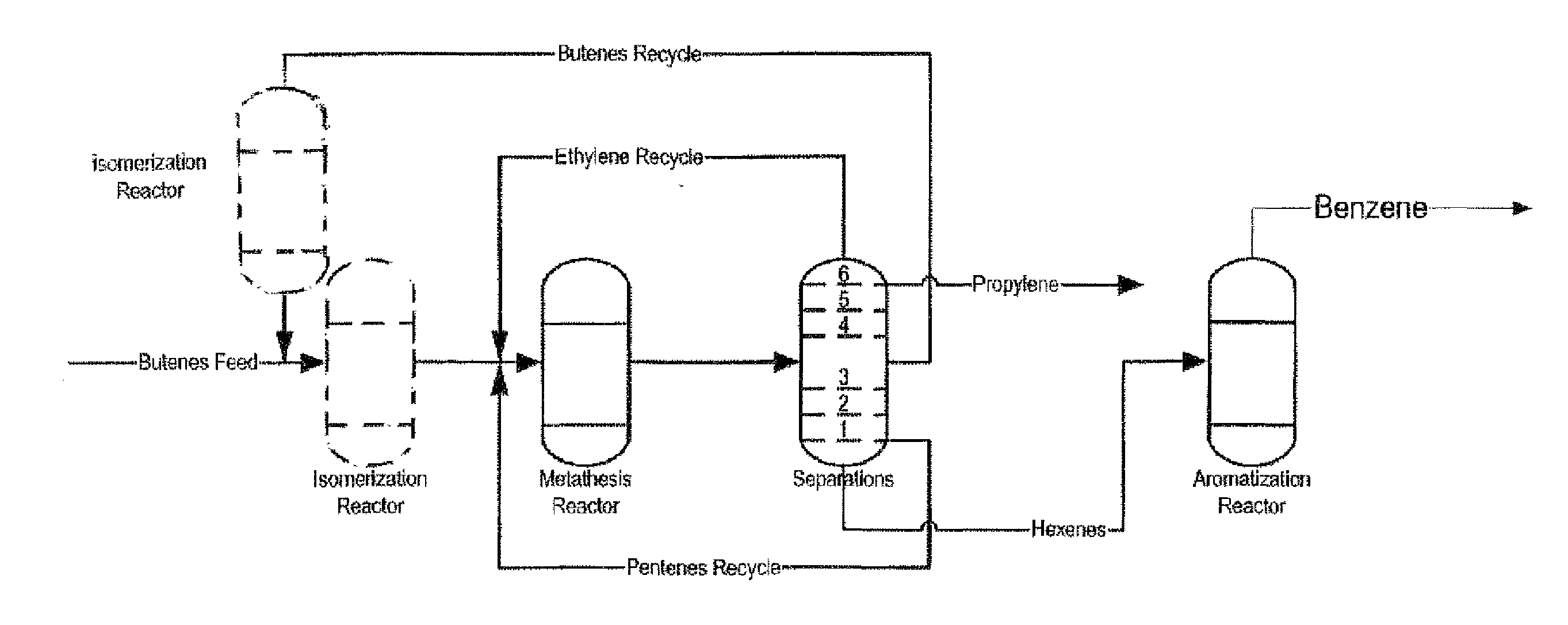
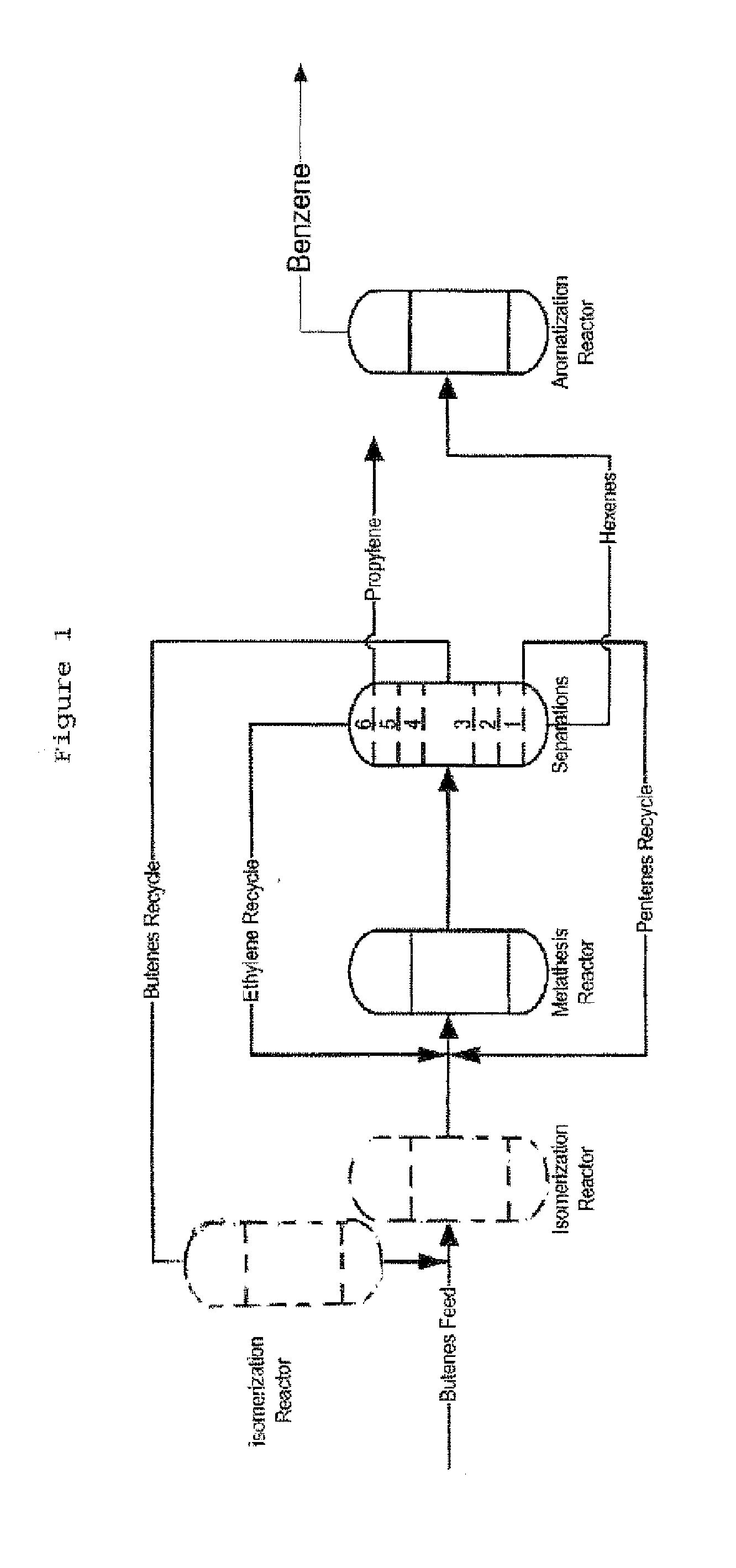
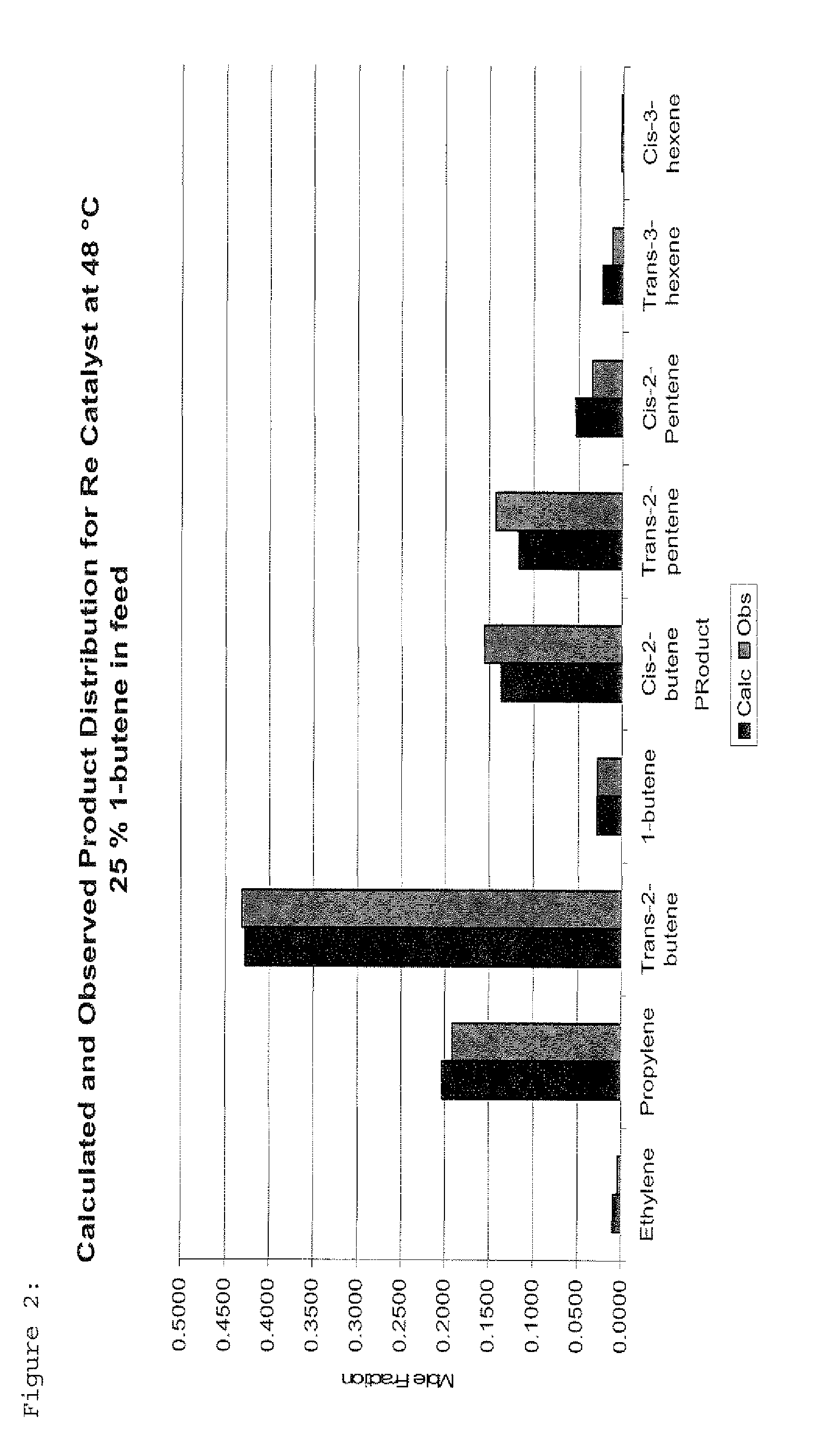
The invention is for a process for producing propylene and hexene (along with ethylene, pentenes, product butenes, heptenes and octenes) by metathesis from butenes (iso-, 1- and cis and trans 2-) and pentenes and then aromatizing the hexenes (along with higher olefins, such as heptenes and octenes) to benzene (along with toluene, xylenes, ethylbenzene and styrene). Since the desired products of the metathesis reaction are propylene and hexene, the feed to the metathesis reaction has a molar ratio for 1-butene:2-butene which favors production of propylene and 3-hexene with the concentration of hexenes and higher olefins in the metathesis product being up to 30 mole %. An isomerization reactor may be used to obtain the desired molar ratio of 1-butene:2-butene for the feed composition into the metathesis reactor. After the metathesis reaction, of hexene and higher olefins are separated for aromatization to benzene and other aromatics.
Owner:SAUDI BASIC IND CORP SA
Processing olefin copolymers
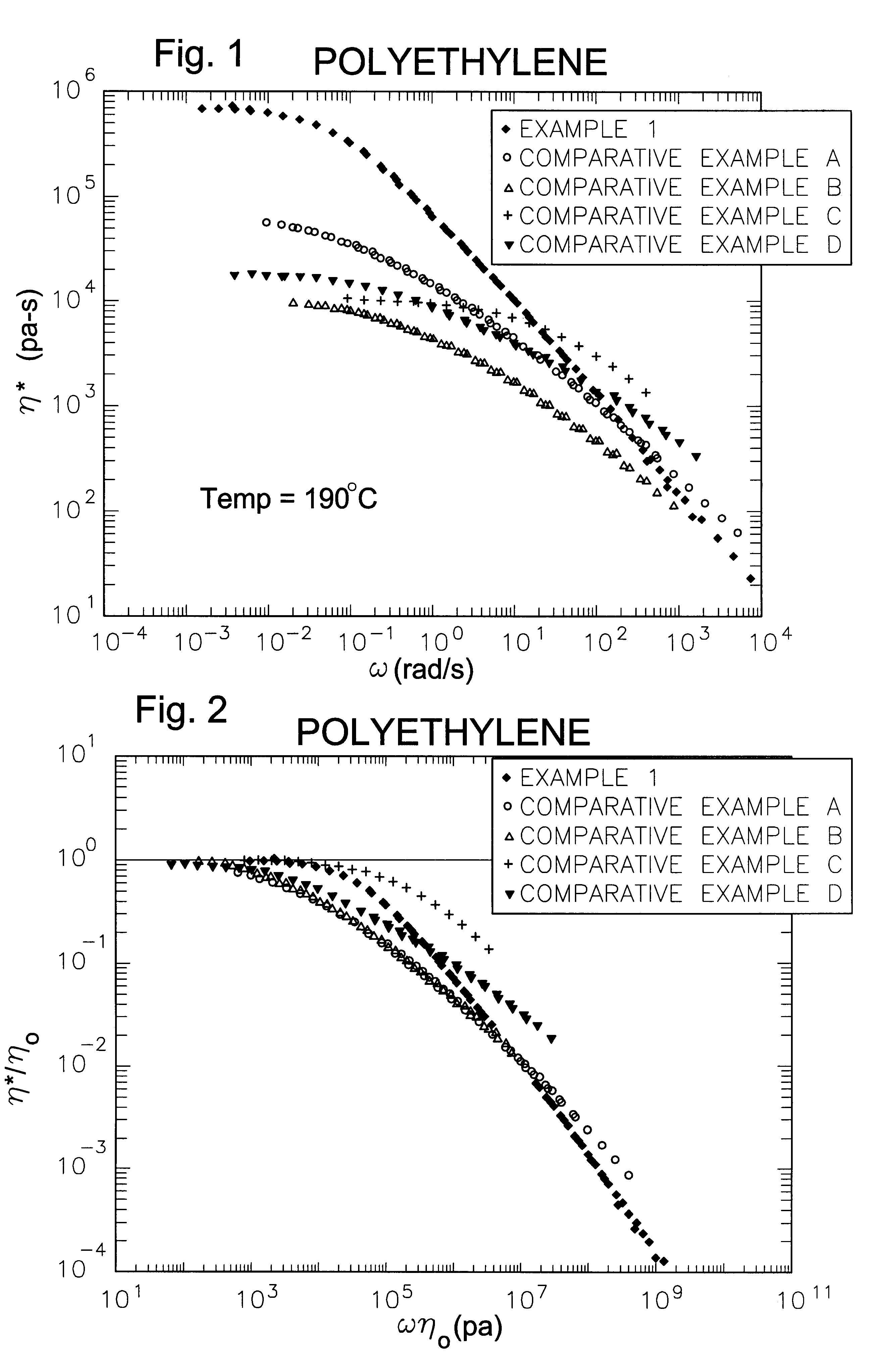
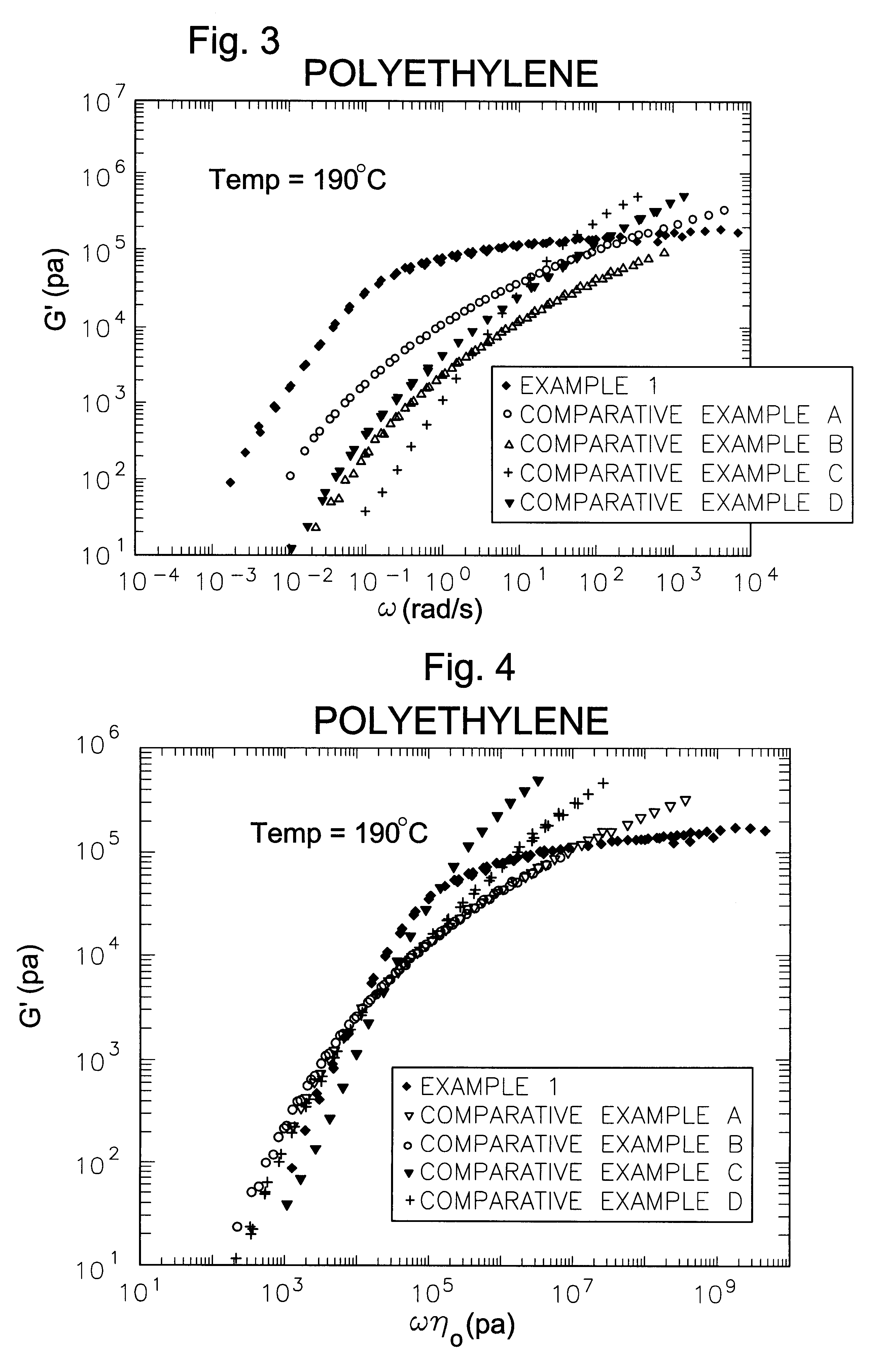
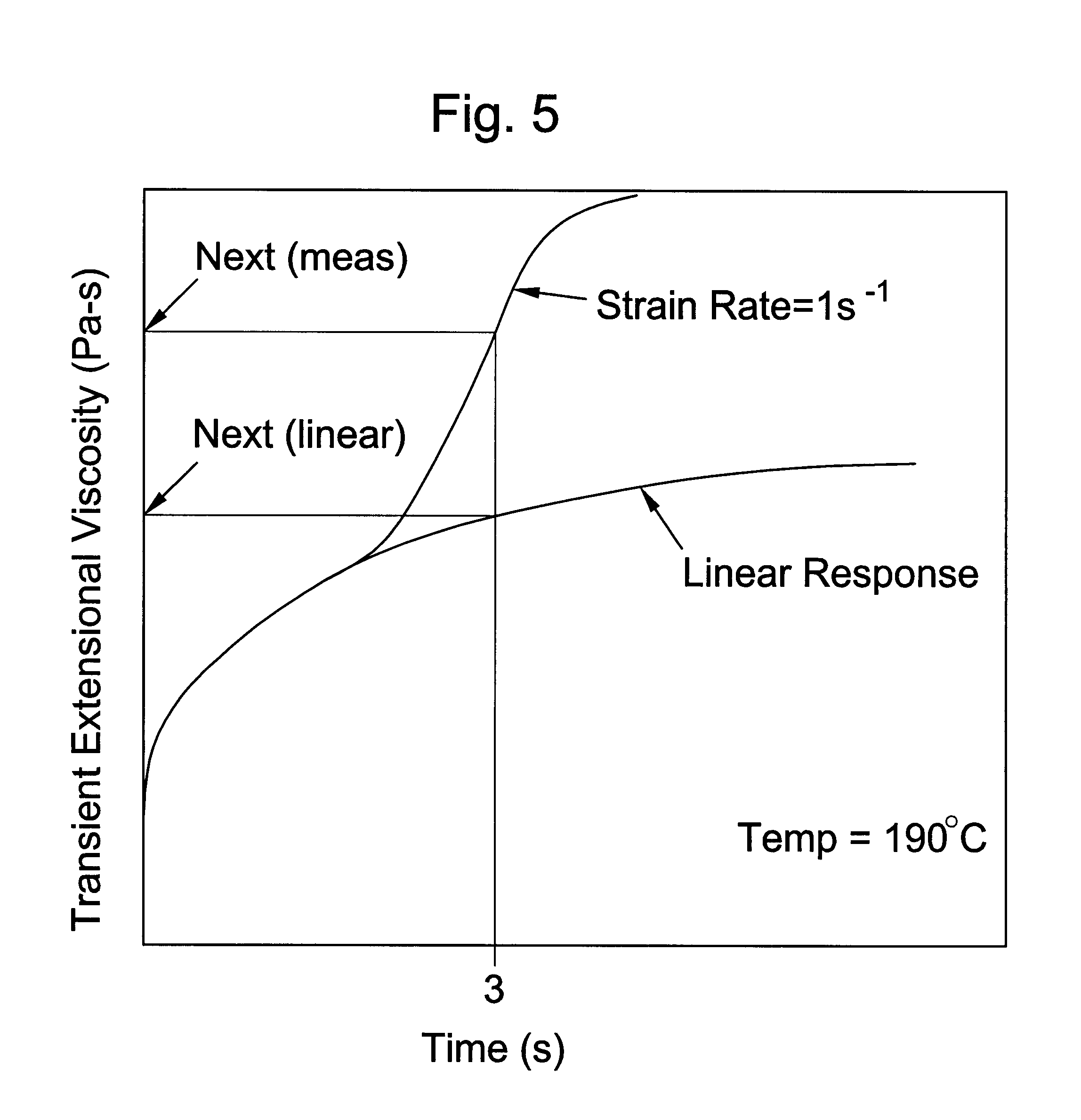
The invention is directed to essentially saturated hydrocarbon polymer composition comprising essentially saturated hydrocarbon polymers having A) a backbone chain, B) a plurality of essentially hydrocarbyl sidechains connected to A), said sidechains each having a number-average molecular weight of from 2500 Daltons to 125,000 Daltons and a MWD by SEC of 1.0-3.5; and having A) a Newtonian limiting viscosity (eta0) at 190° C. at least 50% greater than that of a linear olefinic polymer of the same chemical composition and weight average molecular weight, preferably at least twice as great as that of said linear polymer, B) a ratio of the rubbery plateau modulus at 190° C. to that of a linear polymer of the same chemical composition less than 0.5, preferably <0.3, C) a ratio of the Newtonian limiting viscosity (eta0) to the absolute value of the complex viscosity in oscillatory shear (eta*)at 100 rad / sec at 190° C. of at least 5, and D) a ratio of the extensional viscosity measured at a strain rate of 1 sec-1, 190° C., and time=3 sec (i.e., a strain of 3) to that predicted by linear viscoelasticity at the same temperature and time of 2 or greater. Ethylene-butene prepared by anionic polymerization and hydrogenation illustrate and ethylene-hexene copolymers prepared by coordination polymerization illustrate the invention. The invention polymers exhibit improved processing characteristics in that the shear thinning behavior closely approaches that of ideal polymers and exhibit improved strain thickening.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Gas-barrier heat-seal composite films and vacuum insulation panels comprising the same
ActiveUS20120148785A1High gas barrierImprove adhesionSynthetic resin layered productsRecord information storageLow-density polyethyleneLinear low-density polyethylene
A gas-barrier heat-seal composite film is provided. The gas-barrier heat-seal composite film includes a heat-seal layer including very low density polyethylene (VLDPE), low density polyethylene (LDPE), linear low density polyethylene (LLDPE), high density polyethylene (HDPE), metallocene polyethylene (mPE), metallocene linear low density polyethylene (mLLDPE), ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) copolymer, ethylene-propylene (EP) copolymer or ethylene-propylene-butene (EPB) terpolymer, and a gas-barrier layer formed on the heat-seal layer, wherein the gas-barrier layer includes a plurality of composite layers, each including a polymer substrate and a single layer or multiple layers of metal or oxide thereof which is formed on one side or both sides of the polymer substrate, and the polymer substrate includes uniaxial-stretched or biaxial-stretched polyethylene terephthalate (PET), polybutylene terephthalate (PBT), polyimide (PI), ethylene / vinyl alcohol (EVOH) copolymer or a combination thereof. The invention also provides a vacuum insulation panel including the composite film.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Linear alpha-olefin dimers possessing substantial linearity
InactiveUS7223893B2Less leachingQuality improvementHydrocarbons from unsaturated hydrocarbon additionCatalystsAlcoholPlasticizer
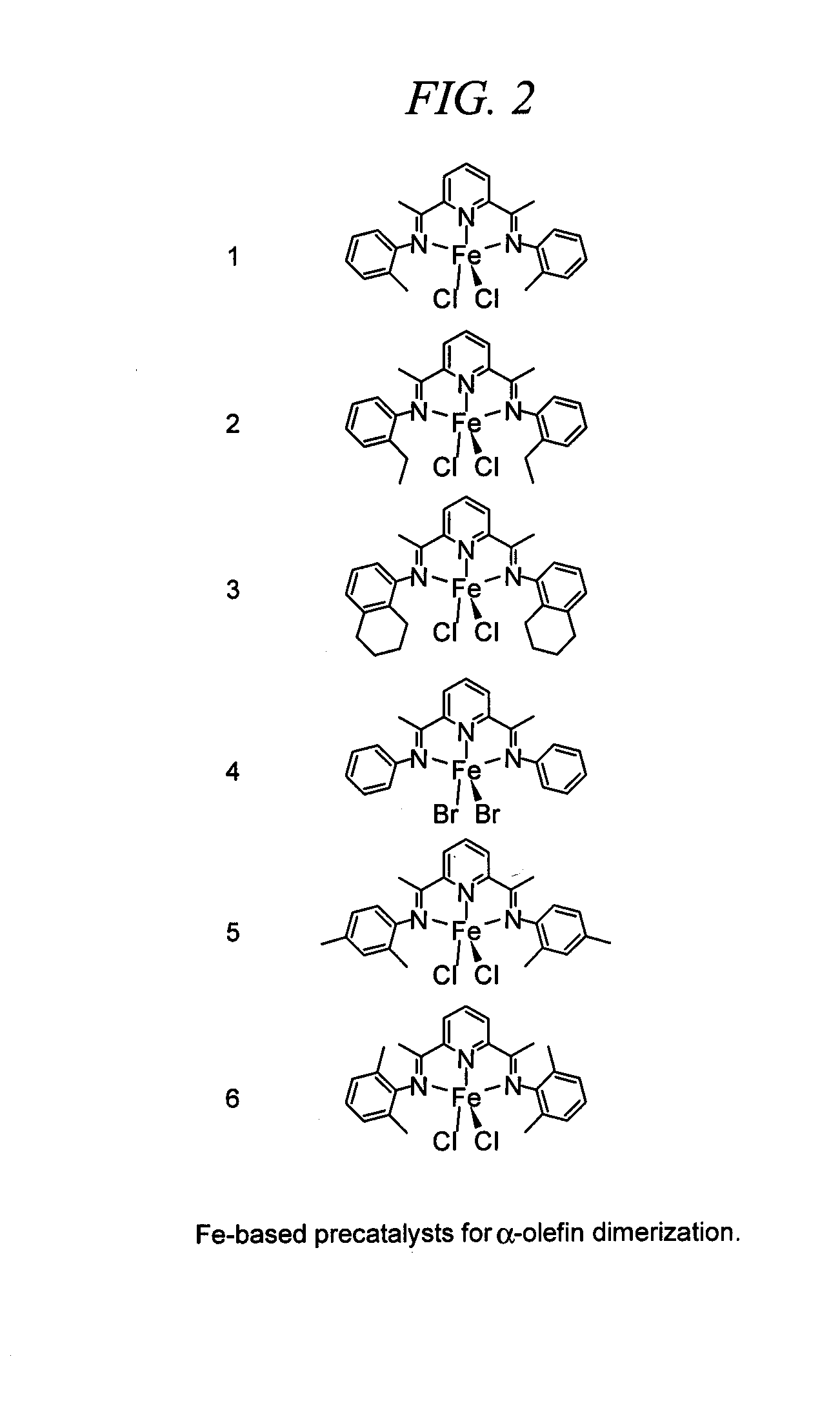
Linear 1-butene dimers and other linear alpha-olefin dimers are manufactured in high yield and with high selectivity by coupling of alpha-olefins. The coupling is accomplished by contacting alpha olefins with an iron-based catalyst activated with an aluminum-based co-catalyst. The catalyst is structured to preclude formation of multiple dimer products, and the byproducts of the olefin coupling consist almost exclusively of methyl branched olefin dimers. The dimers have potentially diverse use in areas stretching form pharmaceuticals to plastics. Linear 1-butene dimers may be particularly useful in the production of plasticizer alcohols which may in turn be used to manufacture high quality plastics with reduced leaching.
Owner:CHEVRON PHILLIPS CHEMICAL CO LP
Butane removal in C4 upgrading processes
InactiveUS20060047176A1High efficiency and low costHydrocarbon by isomerisationChemical industryButeneAlkane
Disclosed herein is a process for producing a selected butene, comprising obtaining a C4 feed stream comprising C4 paraffins and C4 olefins, splitting the C4 feed stream to form a first stream comprising a first butene and a second stream comprising a second butene, isomerizing at least a part of the second stream to convert a portion of the second butene to the first butene, and recycling at least some of the isomerized part of the second steam to the splitting step, wherein a portion of at least one of the C4 feed stream and the second stream is passed through a facilitated transport membrane to remove butanes, forming at least one purge stream comprising butanes. A process for the conversion of C4 olefins, comprising obtaining a C4 feed stream comprising C4 paraffins and C4 olefins, including 1-butene and 2-butene, and reacting the C4 feed stream in a metathesis reactor to form a second stream is also disclosed. The second stream is fractionated to form one or more product streams and a recycle stream primarily containing C4 olefins and C4 paraffins. The recycle stream and / or the C4 feed stream is passed through a facilitated transport membrane to remove butanes, forming at least one purge stream.
Owner:ABB LUMMUS GLOBAL INC
Method for preparing isobutylene by comprehensively using mixed C4
InactiveCN102070391AHigh purityIncrease added valueHydrocarbon by isomerisationChemical industryButeneHigh concentration
The invention provides a method for preparing isobutylene by comprehensively using mixed C4 and mainly solves the problems of low overall utilization efficiency and low additional value of the mixed C4 byproduct of a refinery or a steam cracking device. An aim is fulfilled by adopting a technical scheme which comprises the following steps of: (1) selectively hydrogenating to remove butadiene in the mixed C4; (2) isomerizing butylenes-1 in the mixed C4 obtained in the first step into butylenes-2 by using catalytic distillation technology, and simultaneously dividing the mixed C4 into two strands of materials, namely the first material comprising isobutylene and iso-butane, and the second material comprising n-butane and butylenes-2; (3) separating the first material through an etherifying device to obtain high-purity isobutylene and high-concentration iso-butane; (4) dehydrogenating the iso-butane to obtain the high-purity isobutylene; and (5) isomerizing the butylenes-2 of the second material into the isobutylene by using isomerizing technology, and simultaneously separating to obtain higher-purity n-butane. The method can be applied to the industrial field of producing the high-purity isobutylene.
Owner:王伟跃
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com