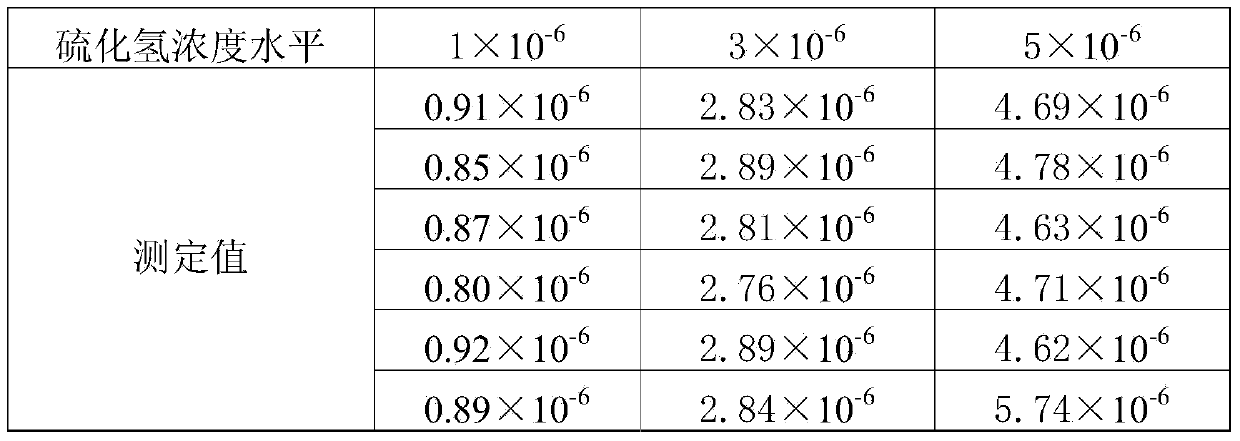
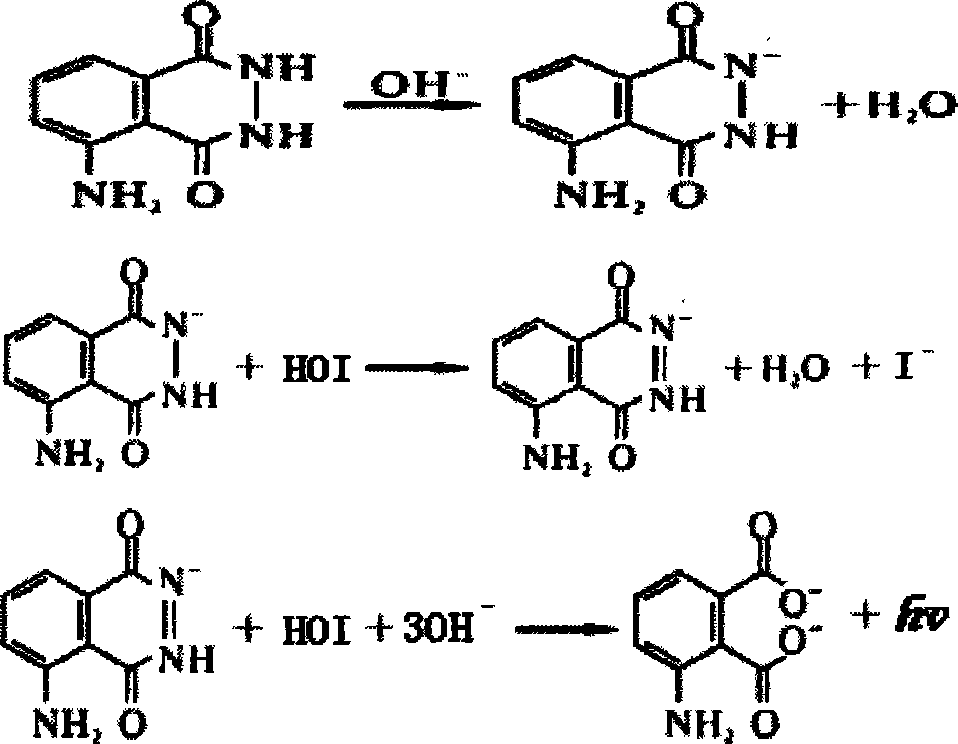
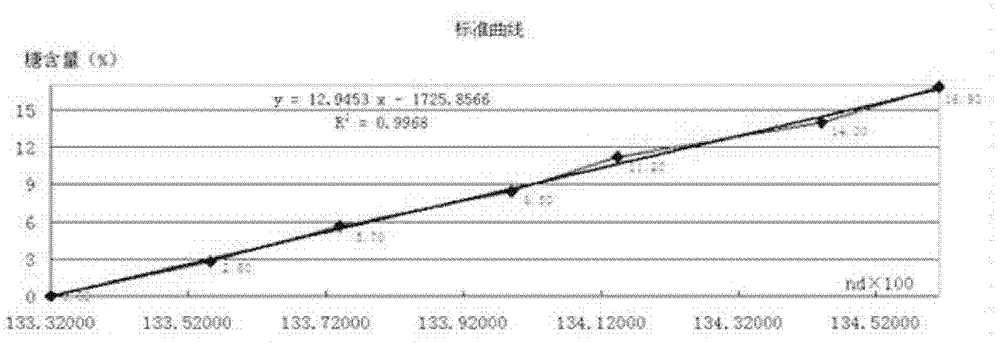
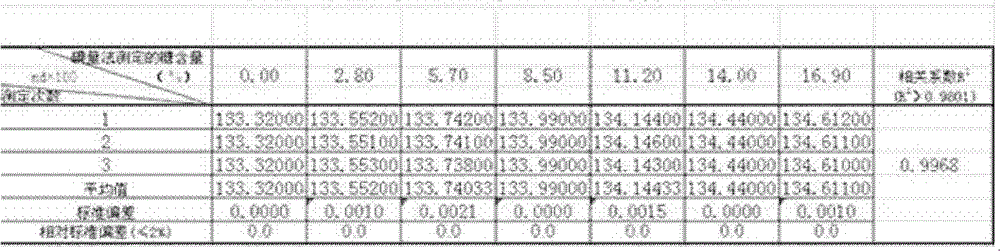
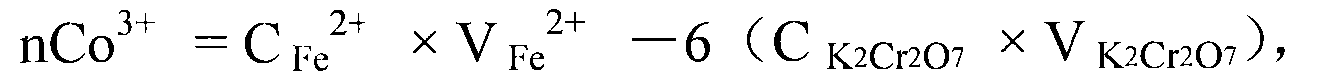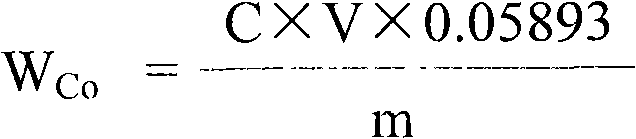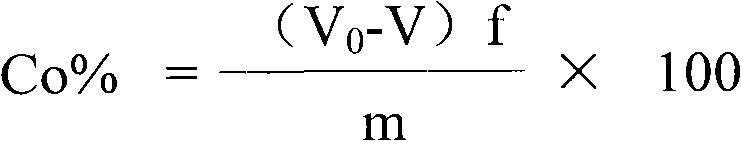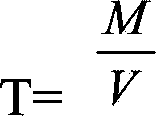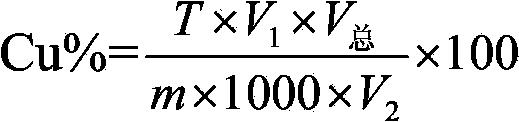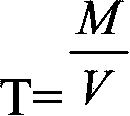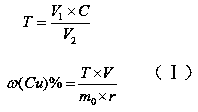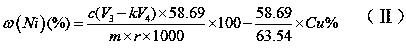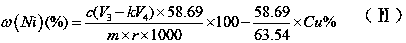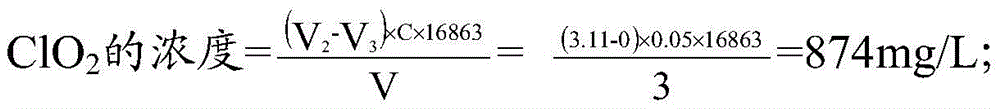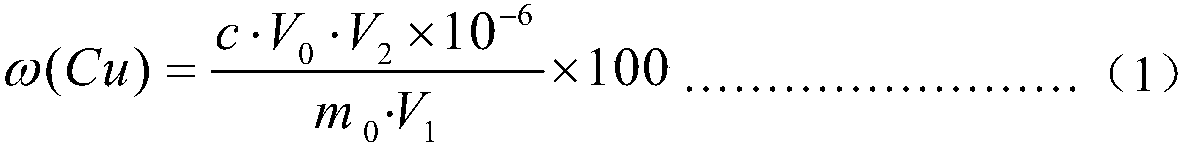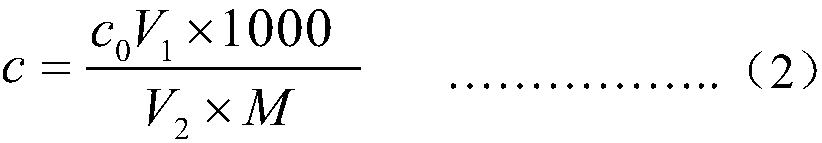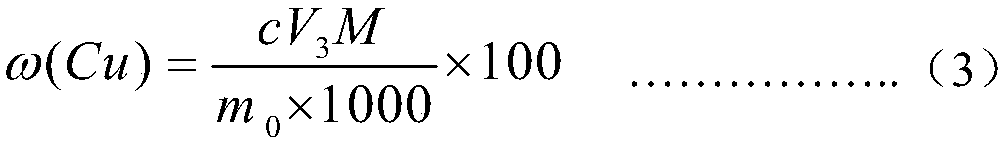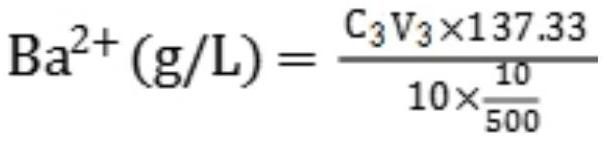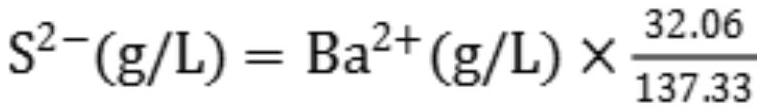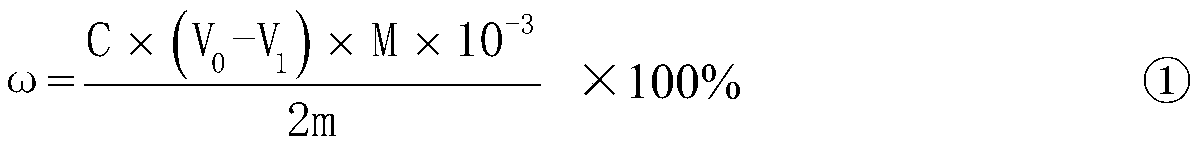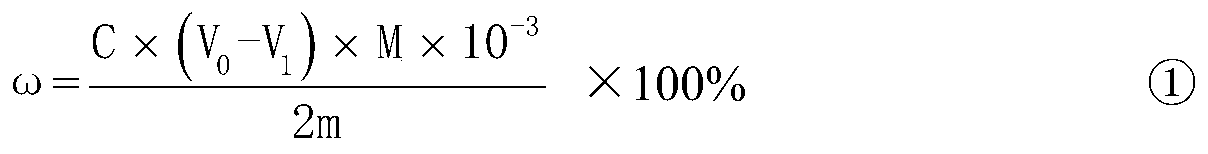Patents
Literature
44 results about "Iodometry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
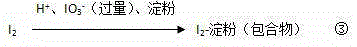
Iodometry, known as iodometric titration, is a method of volumetric chemical analysis, a redox titration where the appearance or disappearance of elementary iodine indicates the end point. Note that iodometry involves indirect titration of iodine liberated by reaction with the analyte, whereas iodimetry involves direct titration using iodine as the titrant. Iodometric titration is used to find cl2 conc.
Measuring method of divalent cobalt content in lithium cobalt oxide
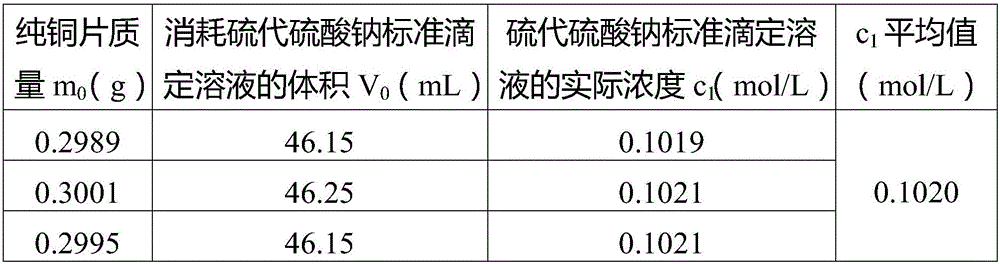
InactiveCN101685067AEasy to judgeImprove electrochemical performanceMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorAcetic acidAmmonium ferrous sulfate
The invention belongs to a measuring method of divalent cobalt content in lithium cobalt oxide in the metallic ion quantitative detection field; the measuring method is characterized in that: total cobalt content and trivalent cobalt ion content in the lithium cobalt oxide are respectively measured, and then the total cobalt content subtracts the trivalent cobalt ion content for obtaining the divalent cobalt content in lithium cobalt oxide; wherein, the measuring method of the total cobalt content in the lithium cobalt oxide adopts ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA) chelatometrie volumetric method, an iodometry method or a potassium ferricyanide oxidimetry method, and the measuring method of the trivalent cobalt ion content in the lithium cobalt oxide adopts an ammonium ferrous sulfate oxidimetry method. The measuring method in the invention makes up the disadvantage that the prior art has no measuring method of divalent cobalt content in lithium cobalt oxide and provides a measuring method of divalent cobalt content in lithium cobalt oxide in the metallic, wherein the method has simple operation, easy judgment of a finishing point and accurate measuring result, thereby providing powerful reference for judging the purity of the lithium cobalt oxide products and ensuring the lithium cobalt oxide products to have good electro-chemical performance.
Owner:SHENZHEN BAK BATTERY CO LTD
Method for determining sulfur content in iron ore by combustion iodometry
ActiveCN102818876AThe measurement results are stable, accurate and reliableIncrease air velocityChemical analysis using combustionIronstoneAir pump
The invention relates to a method for determining the sulfur content in iron ore by a combustion iodometry and belongs to the material test or analysis technology. According to the method, an iron ore test sample is placed in a porcelain boat and is put into a 1200-1300 DEG C tubular furnace to be heated for 1.52 minutes, a miniature air pump is started, exhausted air is introduced into the tubular furnace for sufficient burning, the burnt mixed gas is introduced into starch absorption liquid, the blue color of the starch absorption liquid starts to fade away, then, potassium iodate standard solution is immediately used for dripping into the starch absorption liquid, the blue color is recovered, when the color fading of the starch absorption liquid is slow, the dripping speed of the otassium iodate standard solution is decelerated until the color of the starch absorption liquid is same as the original blue color and is not changed, the miniature air pump is closed, the porcelain boat is taken out, the milliliter number of the dripped otassium iodate standard solution is read, and the sulfur content is calculated according to a formula S percent=T(V-V0) / W*100percent. The method has the advantages that the determined result of the sulfur content of the ore test sample is accurate and stable, the measurement process is safe, and no potential safety hazard exists.
Owner:WUHU XINXING DUCTILE IRON PIPES
Method for measuring copper content in tin-silver-copper solder through iodometry
InactiveCN103776820AAccurate measurementReduce distractionsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorPreparing sample for investigationPotassium thiocyanateDissolution
Provided is a method for measuring copper content in tin-silver-copper solder through iodometry. The method comprises the following steps: a copper standard solution is prepared and the titer of the copper standard solution is measured. A sample to be measured is weighed and added into an Erlenmeyer flask. Concentrated sulfuric acid is added and the mixture is heated for dissolution. The above solution is cooled to the room temperature, perchloric acid is added, after the sample is dissolved fully, heating is carried out until white smoke is generated, concentrated hydrochloric acid is dropwise added into the above solution in batches to remove the tin element in the solution, and the solution is subjected to concentration. The Erlenmeyer flask is taken down and cooled to the room temperature, deionized water is added, the constant volume is 100mL and the above solution is shaken up. Then an ammonium hydroxide solution is added and copper ammonia complex ions are formed. Then ammonium bifluoride is added into the solution and stirred until the blue color disappears. The above solution is cooled to the room temperature by utilization of running water. The solution is placed for half a minute, then potassium iodide is added, and immediately the solution is subjected to titration by a sodium hyposulfite standard solution until a shallow yellow color appears. Then a potassium thiocyanate solution and a starch solution are added, and the solution is subjected to titration by the sodium hyposulfite standard solution until a blue color disappears. The volume of the consumed sodium hyposulfite solution is recorded, and the content of copper in the sample is calculated.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF NONFERROUS METALS & RARE EARTH
Iodometry process of measuring gold content in high accuracy and precision
ActiveCN101046453AImprove accuracyGood reproducibilityMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorPreparing sample for investigationWater bathsGold content
The present invention relates to gold content measuring method, and is especially iodometry process of measuring gold content in high accuracy. The iodometry process include the following steps: 1. preparing standard gold solution through weighing gold in 0.1000g, setting in a 50 ml beaker, adding aqua regia in 10 ml, heating to dissolve, adding 5 drops of 200g / l concentration potassium chloride solution, evaporating to dry in a water bath, adding 2 ml of hydrochloric acid, evaporating to dry, repeating for three times, adding 10 ml hydrochloric acid and 3-5 drops of hydrogen peroxide to dissolve, and adding water to 100 ml to form solution of gold content of 1 mg / ml; and 2. preparing standard work solution of gold content 0.1 mg / ml with the standard gold solution. The present invention is suitable for gold content detection of different kinds of gold content material.
Owner:青海西部矿业科技有限公司 +1
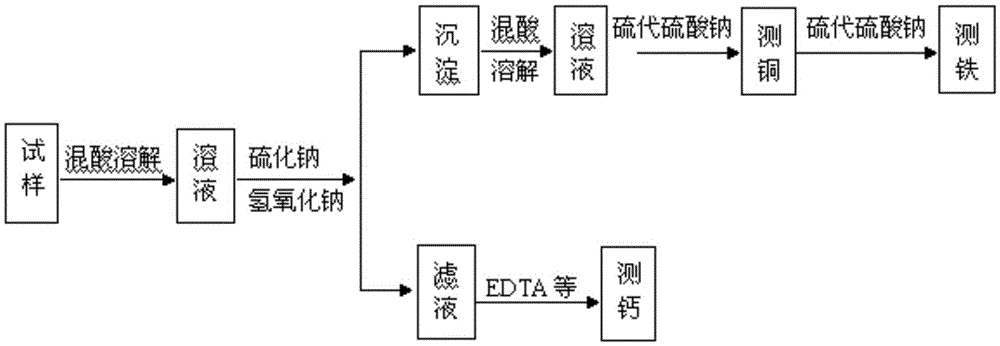
Method for detecting copper, iron and calcium in flash converting furnace slag
InactiveCN105467068AThe detection method is simpleEasy to operateChemical analysis using titrationEthylenediamineSlag
The invention provides a method for detecting copper, iron and calcium in flash converting furnace slag. The method comprises the following steps: (A) dissolving a flash converting furnace slag test sample with acid to obtain a first solution containing copper ions, iron ions and calcium ions, performing reaction on the first solution, sodium sulfide and sodium hydroxide, and filtering to obtain precipitates and filtrate; (B) dissolving the obtained precipitates with acid to obtain a second solution containing bivalent copper ions and iron ions, masking iron with ammonium bifluoride in the second solution, detecting copper by adopting an iodometry method to obtain the copper content, releasing iron in the solution subjected to copper detection with aluminium trichloride, and detecting iron by adopting the iodometry method to obtain the iron content; (C) titrating the filtrate obtained in the step (A) with edetic acid, thus obtaining the calcium content. The procedures of the detection method provided by the invention are simple, one-step sample weighing is realized, and the contents of three key elements, copper, iron and calcium, in the flash converting furnace slag can be quickly, accurately and continuously measured.
Owner:YANGGU XIANGGUANG COPPER
Method for measuring copper content in copper, nickel and manganese brazing filler metal
InactiveCN104568943ASolve solubilitySolve difficult problems such as cumbersome experimental stepsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorElement analysisManganese
The invention belongs to the elemental analytic technology of copper, nickel and manganese brazing filler metal and relates to a method for measuring copper content in copper, nickel and manganese brazing filler metal. By treating the copper, nickel and manganese brazing filler metal by adopting 5-10mL of nitric acid, 5-10mL of hydrochloric acid and 0-10 drops of hydrofluoric acid, the method solves the problems that in the prior art, a sample dissolving reagent is great in dosage, samples are incompletely dissolved, experimental procedures are relatively tedious and the like. Copper in the copper, nickel and manganese brazing filler metal is measured by adopting a classical chemical method-sodium thiosulfate iodometry. As the copper, nickel and manganese brazing filler metal is free of standard substances matched with major elements, interference of coexistence elements on measuring the copper content is determined through a coexistence element interference test. The coexistence elements nickel and manganese do not affect measurement of the copper content but the coexistence element cobalt affects the judgment of a titration end point due to the inherent color of the element so as to affect the accuracy of the titration result. By integrating the conditions, the accuracy of analytic measurement is improved by selecting a nickel and copper alloy standard substances without cobalt element or with cobalt being less than or equal to 0.05%.
Owner:AVIC BEIJING INST OF AERONAUTICAL MATERIALS
Method for measuring contents of nickel and copper serving as main elements in nickel-copper alloy
InactiveCN108982749AEasy to operateImprove accuracyChemical analysis using titrationMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorManganeseDissolution
The invention discloses a method for measuring contents of nickel and copper serving as main elements in a nickel-copper alloy. The method comprises the steps: (1) dissolving a sample by using nitricacid and hydrochloric acid to prepare a sample solution; (2) taking the sample solution, and measuring the content of copper in the sample by using a sodium thiosulfate iodometry; and (3) regulating the sample solution to form a slightly acidic solution, then, masking iron, aluminum and titanium by using a fluoride, masking manganese by using sodium hexametaphosphate, adding excessive EDTA, titrating excessive EDTA by using a copper standard titration solution by taking PAN as an indicator; and carrying out calculation according to the consumption of the copper standard titration solution to obtain the contents of nickel and copper in the sample, and deducting the content of copper to obtain the content of nickel in the sample. By using the method, the operation process of sample dissolution is simple, the main element detection works detected by using two chemical titration methods can be simultaneously finished by dissolving the sample once, and the distribution condition of nickel and copper serving as the main elements of the nickel-copper alloy can be more truly reflected; in addition, the precision and accuracy of analysis and measurement are improved, and the method is highin measurement speed and simple and convenient to operate.
Owner:HEBEI IRON AND STEEL
Method for preparing enzyme electrode and rapidly detecting peroxide value of vegetable oil
InactiveCN102435650AHigh sensitivityHigh precisionMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansVegetable oilHorse radish peroxidase
The invention belongs to the field of food detection, and particularly relates to a method for preparing an enzyme electrode and rapidly detecting the peroxide value of vegetable oil. The method comprises the steps of: selecting a glassy carbon electrode for use; firstly preparing a Nafion-methylene blue membrane electrode, then adopting a bovine serum albumin-glutaraldehyde crosslinking method to fix horse radish peroxidase (HRP), and obtaining a final HRP electrode; and then using the HRP electrode to rapidly detect the peroxide value of the vegetable oil. The method is high in sensitivity, good in selectivity, high in accuracy, short in response time, less in interference and superior to the traditional iodometry, thus being a simple, rapid, convenient and easy method for measuring the peroxide value and having the potential of realizing automatic on-site measurement.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Rapid analysis method of copper in leachate
InactiveCN103175829AReduce pollutionShorten analysis and measurement timeMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorPreparing sample for investigationRoom temperatureStrong acids
The invention relates to a rapid analysis method of copper in a leachate. The method comprises the following steps: transferring 3-10mL of a leachate to be measured to a triangular flask, adding an oxidant, heating for evaporating to a small volume, cooling to room temperature, and adopting iodometry to determine the concentration of copper ions in the obtained solution, wherein the oxidant preferably selects hydrogen peroxide having a concentration of 30wt%, and the addition amount of the oxidant is 0.5-3.0mL. The addition of a certain amount of hydrogen peroxide to process the leachate in the invention allows a small amount of a strong acid to be used, so the analytic determination time is shortened, and the pollution to the environment is reduced. The method has the advantages of simplicity, rapidness, and easy control and grasping of the operation process, so the method is very suitable for analyzing and determining the flow sample of the leachate, and the obtained result has a good accuracy and a good precision.
Owner:GENERAL RESEARCH INSTITUTE FOR NONFERROUS METALS BEIJNG
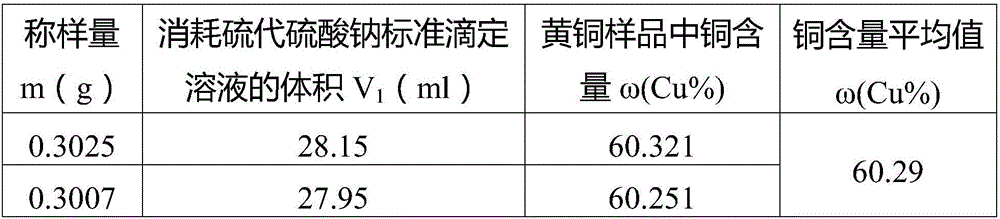
Method for detecting copper content in brass through iodometry
InactiveCN106770266AImprove accuracyShorten detection timeChemical analysis using titrationMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorPotassium thiocyanatePotassium iodine
The invention discloses a method for detecting copper content in brass through iodometry. The method for detecting the content of copper in brass through iodometry comprises the following steps: 1, weighing a brass sample of a certain mass, adding a nitric acid solution so that the brass sample is completely dissolved, and diluting with deionized water so as to obtain a diluted solution; 2, dripping ammonia water into the diluted solution, dripping until a blue copper hydroxide precipitate appears, and adding glacial acetic acid so as to obtain a brass sample solution; 3, adding a potassium iodide solution into the brass sample solution in the step 2, immediately titrating with a sodium thiosulfate standard titration solution until the solution is light yellow, adding a starch solution, continuously titrating until the solution is light blue, adding a potassium thiocyanate solution, and titrating until the light blue color disappears; and 4, calculating the copper content in the brass sample. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the content of copper in the brass is detected through the iodometry, the detection time can be reduced, the detection period is greatly shortened, and the method is applicable to batch and rapid detection in the enterprise production process.
Owner:武汉泛洲中越合金有限公司
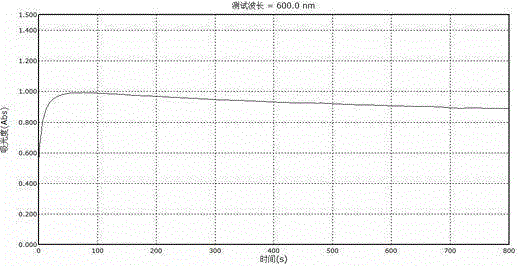
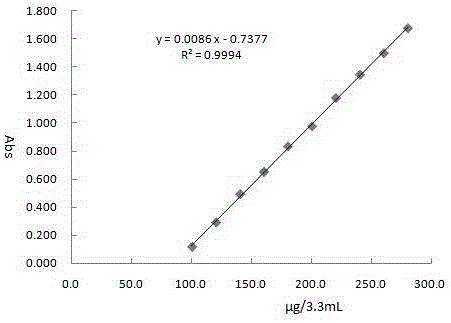
Indirect iodometry dynamics spectrophotometry for measuring vitamin C
InactiveCN105067538AReduce usageImprove linearityPreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsVitamin CPharmaceutical Substances
The invention belongs to the field of analytical chemistry, and particularly discloses indirect iodometry dynamics spectrophotometry for measuring vitamin C. The spectrophotometry specifically comprises steps as follows: at the room temperature, using a cuvette of 1 cm as a reaction container, adding 0.50-1.40 mL of a 200 mu g / mL vitamin C standard solution and 1.60-2.50 mL of a 0.5% starch solution to enable the volume of the mixed solution to be 3.00 mL, adding 0.20 mL of a 0.200 mg / mL potassium iodate solution and 0.10 mL of a 0.15 mol / L of sulfuric acid solution, evenly shaking the mixture, quickly placing the mixture into a reagent blank for a photometer, performing dynamics spectrophotometry scanning at the wavelength of 600 nm to measure the peak absorbance within a short time, wherein the peak absorbance has a good linear relation with the concentration of the vitamin C. The spectrophotometry has the advantages that the spectrophotometry is convenient, accurate, micro and quick, used drugs are low in cost, easy to obtain, non-toxic, pollution-free and environment-friendly and the like, and is used for measuring the vitamin C in biological samples, drug samples and the like.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV +1
Method and standard for testing quality of medical artemisia pigweed
InactiveCN1387041AQuality improvementImprove accuracyChemical analysis using titrationColor/spectral properties measurementsVisual observationAtomic absorption spectroscopy
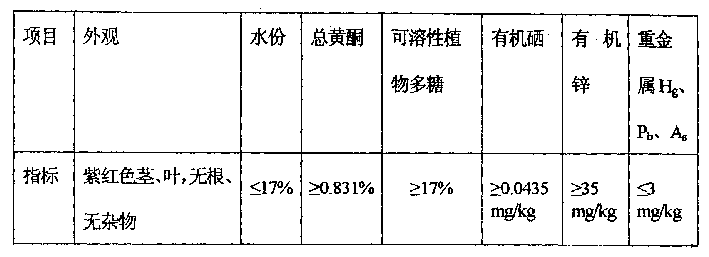
A quality standard for medical artemisia pig weed is disclosed. Its verifying method includes examining appearance by visual observation, measuring water content by fast driver, testing general flavone by ultraviolet spectrophotometry, measuring soluble plant polyose by acid hydrolyzing for 10 min and iodometry, and testing organoselenium, organozinc and heavy metals (Hg, Pb and As) by atomic absorption spectrametry. Its advantage is high correctness.
Owner:王群 +1
One-step method for detecting concentration of chlorine and chlorinated hydrogen in pollution source waste gas
The invention discloses a one-step method for detecting the concentration of chlorine and chlorinated hydrogen in pollution source waste gas, which has the following steps of: connecting in series two absorption bottles respectively filled with 50 ml of alkali absorption solution with concentration of 0.1-0.2 mol / L for sampling; after collecting the samples, mixing sample solutions in the two bottles, and adding the alkali absorption solution with concentration of 0.1-0.2 mol / L until the total sample solution volume reaches 125 ml; moving 25 ml of solution from the total sample solution to an iodine flask for detecting the concentration of chlorine by using iodometry, and then moving 25 ml of solution sample solution for detecting the concentration of total chlorinated hydrogen in the sample solution by using silver nitrate volumetric method; and finally, calculating the actual concentration of chlorinated hydrogen by using a corrector formula. The method can be used for simultaneously analyzing chlorine and chlorinated hydrogen by one share of absorption solution, and eliminate the positive interference of chlorine to chlorinated hydrogen, thereby accurately determining the concentration of chlorine and chlorinated hydrogen in pollution source waste gas.
Owner:BAIYIN NONFERROUS GROUP
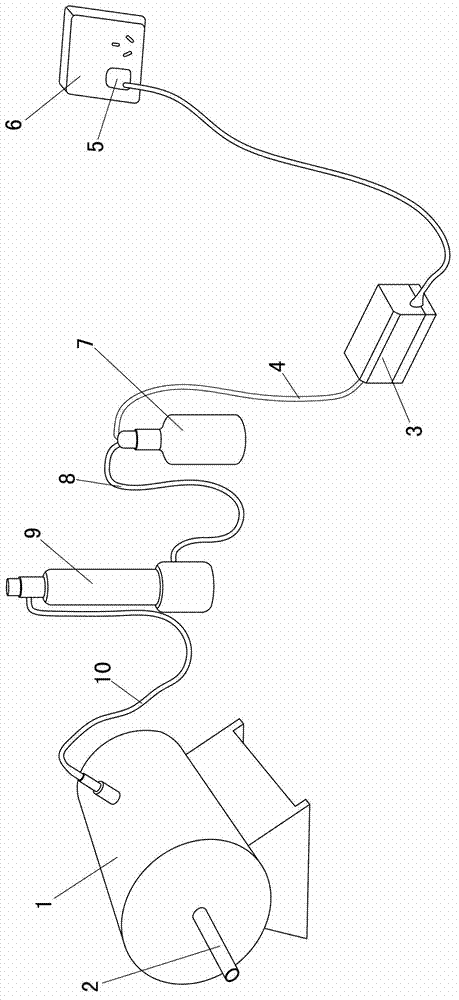
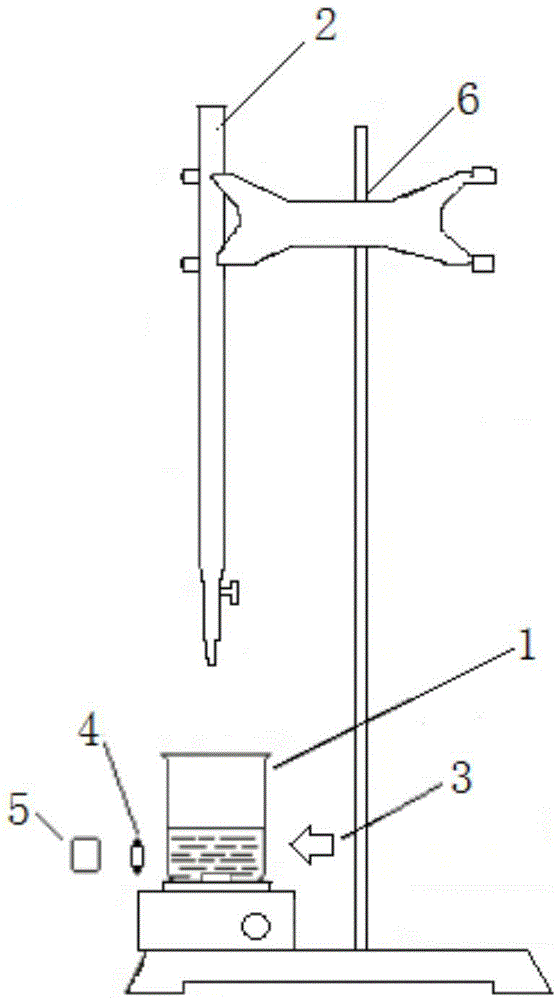
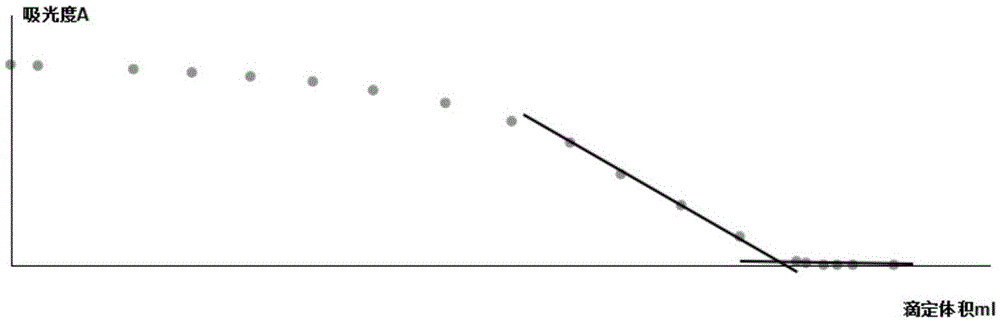
Reaction endpoint judgment device and five-step iodometry
ActiveCN105606761AHigh sensitivityHigh precisionChemical analysis using titrationMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorHigh concentrationData processing system
The invention discloses a reaction endpoint judgment device. The device comprises a reaction container, a burette arranged above the reaction container, a monochromatic light source arranged on one side of the outside of the reaction container and a photoelectric receiver located on the other side of the reaction container and opposite to the monochromatic light source, wherein the photoelectric receiver is connected with a data processing system. The invention further discloses five-step iodometry without the step of starch adding. The device and the method effectively solve the problems that color change of a reaction endpoint is influenced and errors are caused to judgment of the titration endpoint due to the fact that a starch indictor is likely to have a reaction with high-concentration iodine in advance in step 2 and step 4 in traditional five-step iodometry and starch forms colloid and wraps the iodine, the device is simple in structure, the method is simple and convenient to operate, and the sensitivity and the accuracy are high.
Owner:SHENZHEN SINSCHE TECH
Detection method of hydrogen sulfide
InactiveCN103558334AAppropriate carrier gas flow rateRight timeChemical analysis using titrationPreparing sample for investigationNitrogenPre treatment
The invention relates to a detection method of hydrogen sulfide. The hydrogen sulfide in crude oil is detected through using a nitrogen air stripping method, the crude oil is pretreated by adopting warming and stirring, the temperature is set to be 30-90 DEG C; condensed crude oil is obtained at the temperature of 30-40 DEG C during warming and pretreating, and thickened oil is obtained at the temperature of 70-75 DEG C during the warming and the pretreating. The flow velocity of the nitrogen is controlled to be 0.1L / min for 5min, and to be 0.05L / min for 10min. According to the detection method, a method in which the hydrogen sulfide in the crude oil is stripped by using nitrogen, the hydrogen sulfide in the nitrogen is detected by using iodometry, and the detected content of the hydrogen sulfide in the nitrogen is converted to the content of the hydrogen sulfide in the crude oil; the proper crude oil temperature, the proper carrier gas flow rate and stripping time are selected, and the precision is high.
Owner:大连大公检验检测有限公司
Method for measuring copper content in high-lead-gold concentrates
InactiveCN108303389AImprove accuracyImprove stabilityChemical analysis using titrationPreparing sample for investigationIonHydrochloric acid
The invention relates to a method for measuring the copper content in high-lead-gold concentrates, and belongs to a method for measuring the copper content in ores. According to the method, a nitric acid-potassium chlorate saturated solution is used for dissolving a test specimen; sulfuric acid is used for precipitating lead ions; after the filtering, filter liquid is distilled until sulfuric acidsmoke thoroughly disappears; materials with the copper content being less than 2 percent are leached by hydrochloric acid; AAS determination is performed; the materials with the copper content beinggreater than 2 percent are leached by distilled water; the iodometry titration determination is performed. The copper content determination range in the lead concretes is 0.050 to 25.00 percent; the determination accuracy is improved; the copper measurement stability of the high-lead gold concentrates is improved; the measurement range is expanded; good application performance is realized.
Owner:CHANGCHUN GOLD RES INST
Method for determining content of dimethyl sulfoxide in sample in purification process
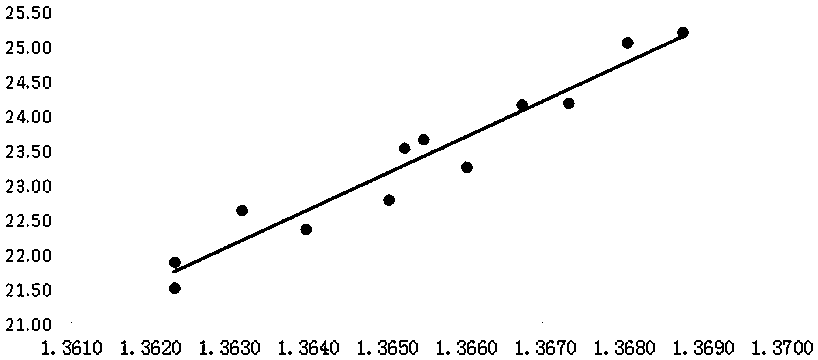
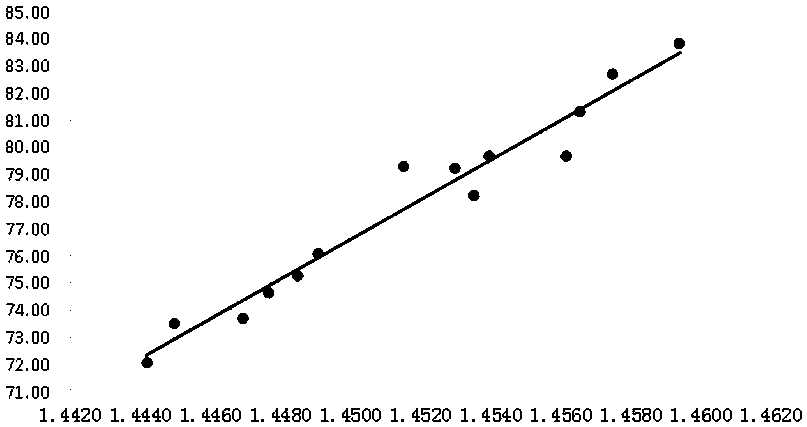
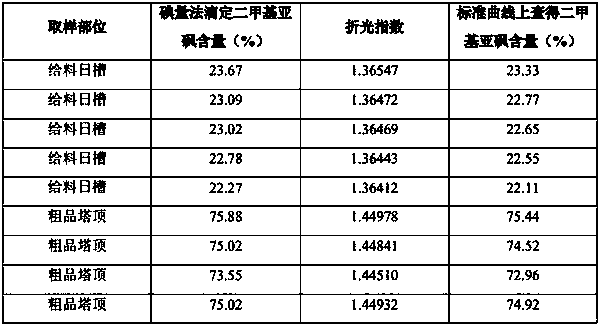
PendingCN111551425AMeet monitoring requirementsShorten detection timePreparing sample for investigationPhase-affecting property measurementsPhysical chemistryRefractive index
The invention discloses a method for determining the content of dimethyl sulfoxide in a sample in a purification process, belongs to the technical field of carbon fiber solvent recovery, and solves the technical problem of dimethyl sulfoxide content detection in a sample in a purification process. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, performing sampling and respectively titrating thecontent of dimethyl sulfoxide in a sample solution by adopting an iodometry to obtain a sample solution with known dimethyl sulfoxide content; secondly, preparing dimethyl sulfoxide solutions with different contents by adopting a sample solution with known dimethyl sulfoxide contents, measuring the refractive indexes of the prepared dimethyl sulfoxide solutions with different contents by utilizing a refractive index instrument, and drawing a curve corresponding to the refractive indexes and the dimethyl sulfoxide contents; thirdly, placing the to-be-detected sample on the refractive index instrument, and reading the refractive index of the to-be-detected sample; finally, enabling the read refractive index of the sample to be detected to correspond to the standard curve, and finding the dimethyl sulfoxide content of the sample to be detected. The detection time is shortened, production can be rapidly guided, and the detection cost is saved.
Owner:山西钢科碳材料有限公司 +1
Method for determining content of organic peroxide
PendingCN111189953AThere is no problem of decompositionImprove accuracyComponent separationNonanoic acidHplc method
The invention relates to the field of organic peroxide analysis. The invention discloses a method for determining the content of an organic peroxide. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly drawing an organic peroxide standard curve by using a reversed-phase C18 chromatographic column through HPLC method, then acquiring the content of the organic peroxide in a to-be-detected sample under the same condition according to the standard curve, wherein the organic peroxide is selected from at least one of tert-butyl peroxy-2-ethylhexanoate, tert-butyl peroxyisononanoate, tert-butyl peroxypivalate and di-tert-butyl peroxide. The method for determining the content of the organic peroxide has the advantages of time saving, labor saving, high accuracy and good repeatability, can overcome errors during iodometry determination, and can avoid the problem that the organic peroxide is easy to decompose at a high temperature and cannot be accurately determined during gas chromatographic analysis.
Owner:CHINA SHENHUA COAL TO LIQUID & CHEM CO LTD +1
Chemiluminescence system and method for measuring dissolved oxygen
InactiveCN101368911AHigh sensitivityModerate response speedChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceLuminous intensityFree iodine
Owner:ZHENGZHOU XIANJIE TECH
Analysis method for determining copper in tin-silver-copper solder through iodometry
InactiveCN104749170AEliminate distractionsReduce distractionsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorPreparing sample for investigationPotassium rhodanidePotassium iodine
The invention discloses an analysis method for determining copper in a tin-silver-copper solder through iodometry. The method comprises the steps of weighing a unit of a sample and putting into a 250 ml conical flask, adding a proper amount of concentrated sulfuric acid, heating, dissolving the sample, taking down the conical flask, cooling to room temperature, adding a proper amount of perchloric acid, heating till a perchloric acid white smoke is emitted after the sample is completely dissolved, dropwise adding hydrochloric acid for a plurality of times to remove tin, concentrating the solution to a small volume, taking down the flask, cooling to the room temperature, and shaking uniformly. Adding a proper amount of ammonium hydroxide solution into the sample to form a solution which is complex copper ammine ion blue, adding a proper amount of ammonium bifluoride, shaking till the blue disappears, cooling the flask to the room temperature with a cold water flow, standing for 30 seconds, adding a proper amount of potassium iodide, titrating with a sodium thiosulfate standard solution immediately to light yellow, adding a proper amount of potassium rhodanide and a starch solution, titrating continuously with the sodium thiosulfate standard solution till the blue disappears, and recording the milliliter quantity.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF NONFERROUS METALS & RARE EARTH
Test method for determination of total sugar content in chlortetracycline fermentation broth by refractometer
ActiveCN102297847AEasy to operateReduce labor intensityPhase-affecting property measurementsOriginal dataSugar
The invention relates to a method for measuring the total sugar content of a chlortetracycline fermentation broth with a refractometer, and the method is characterized by accurate measuring result and low cost. The method comprises the steps of: (1) collecting original data: measuring the sugar content data of a standard sample by iodimetry, with the sugar content of the sample at a gradient concentration of 0-17%; (2) inputting the data measured in step (1) into the refractometer; (3) dropping the sample with sugar content of 0-17% for measuring directly in a determination analysis pool so as to conduct measuring. The method of the invention has the advantages of accurate measuring result and fast detection speed. Meanwhile, after one time of standard data input, no input and detection through iodometry are needed once again during sugar content detection of the sample at a later stage, so that a lot of reagents can be saved. The method of iodometry is complicated for operation, while the adoption of a refractometer is simple in operation. The employment of a refractometer for detection reduces the labor intensity of technicists and improves the working efficiency.
Owner:PUCHENG CHIA TAI BIOCHEM
Method for rapidly analyzing and detecting impurity sodium sulfide in barium sulfide solution
PendingCN113237994ADiscoloration sharpEasy to observeMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorChemical analysis using titrationBarium solutionBarium sulfide
The invention provides a method for rapidly analyzing and detecting impurity sodium sulfide in a barium sulfide solution, and relates to the field of production of precipitated barium sulfate. The method mainly comprises the following steps: (1) measuring the total content of sulfur in a solution by iodometry; (2) measuring the content of barium in the solution by using an Mg-EDTA replacement method; (3) calculating the content of sulfur in barium sulfide according to the content of barium; and (4) calculating the content of sulfur in sodium sulfide by subtracting the content of sulfur in barium sulfide from the total content of sulfur so as to obtain the content of impurity sodium sulfide. The method fills the gap of a method for analyzing and detecting the impurity sodium sulfide in the barium sulfide solution, has the advantages of acute color change at the titration end point, easiness in observation, simplicity, convenience, rapidness, economy, practicability and the like, and has an important guiding effect on reaching the end point of the combination reaction in the production of precipitated barium sulfate.
Owner:南风化工(运城)集团有限公司
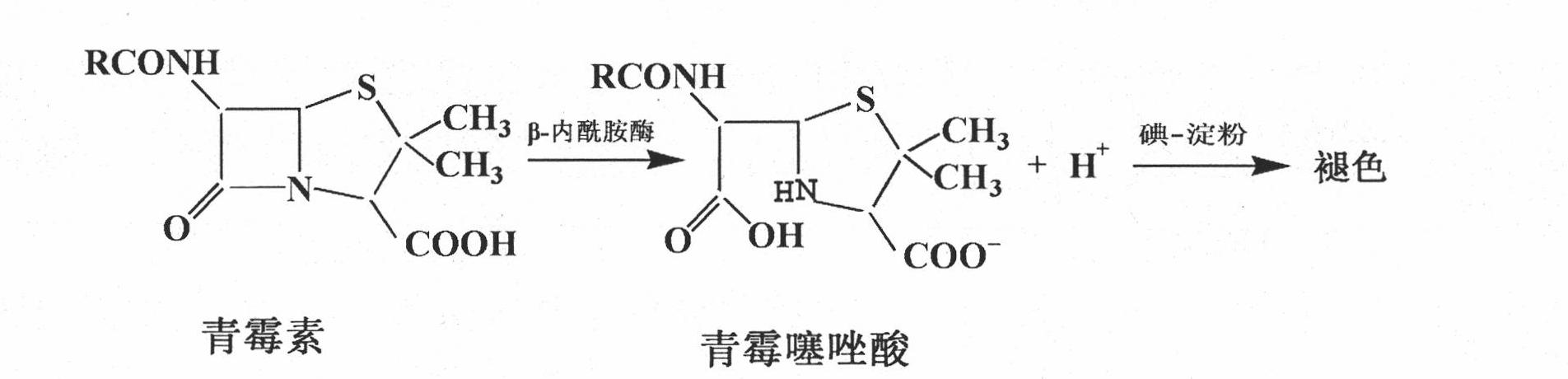
Detection of beta-lactamase in milk and milk products by iodometry
InactiveCN102042980AReal-time detectionOnline testMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorFree iodineDecomposition
The invention relates to a method for rapidly detecting beta-lactamase in milk and milk products. The fundamental principle is that: the beta-lactamase can decompose penicillin, and a decomposition product penicilloic acid competes with starch for free iodine to damage a composite formed by the iodine and the starch to further change blue solution into colorless solution; and the penicillin and an iodine-starch color reagent are added into the treated milk and the treated milk products, blank control is performed, and qualitative and semi-quantitative analysis is performed on the beta-lactamase according to the change of the color of the solution. In the invention, the novel method for detecting the beta-lactamase in the milk and the milk products is established in terms of the concentration of the penicillin, a pH value of buffer solution, the concentration and proportion of the color reagent, actual sample purification conditions, reaction temperature, centrifugation conditions and the like. In the method, the lowest qualitative and semi-quantitative detection limit is 1.5 U / mL. The technology is popularized, and a detection kit is researched and developed to realize real-time online detection, thereby bringing good social and economic benefits.
Owner:BEIJING WUZI UNIVERSITY
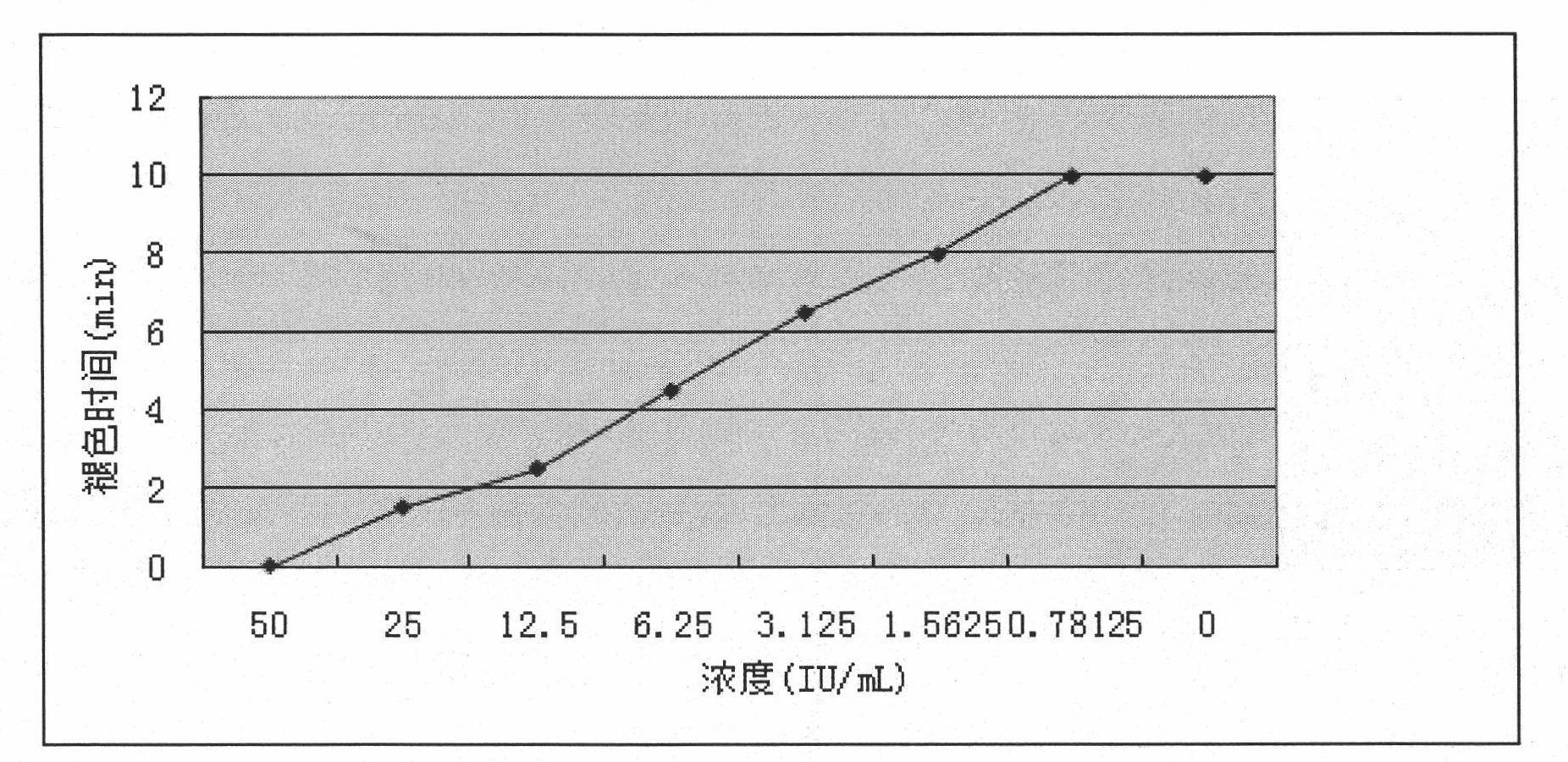
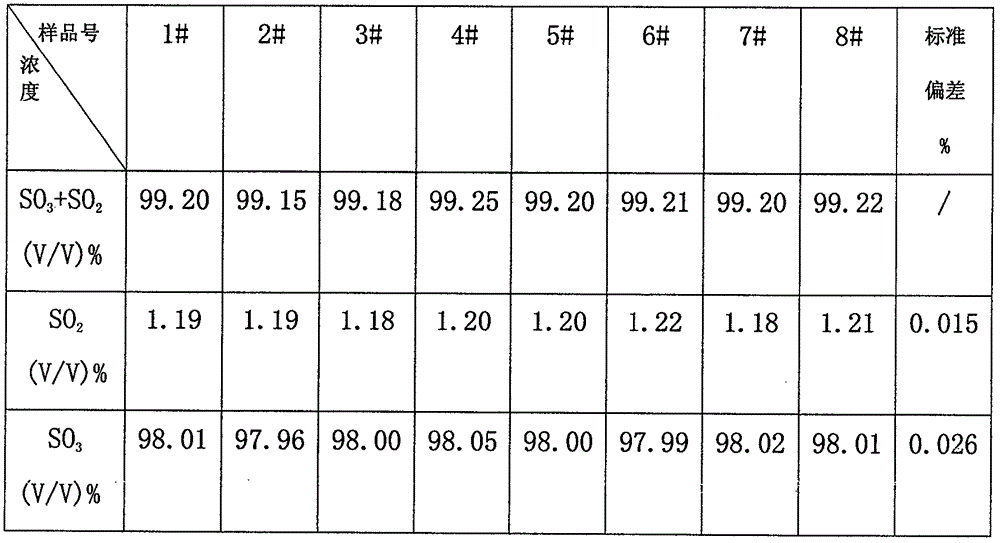
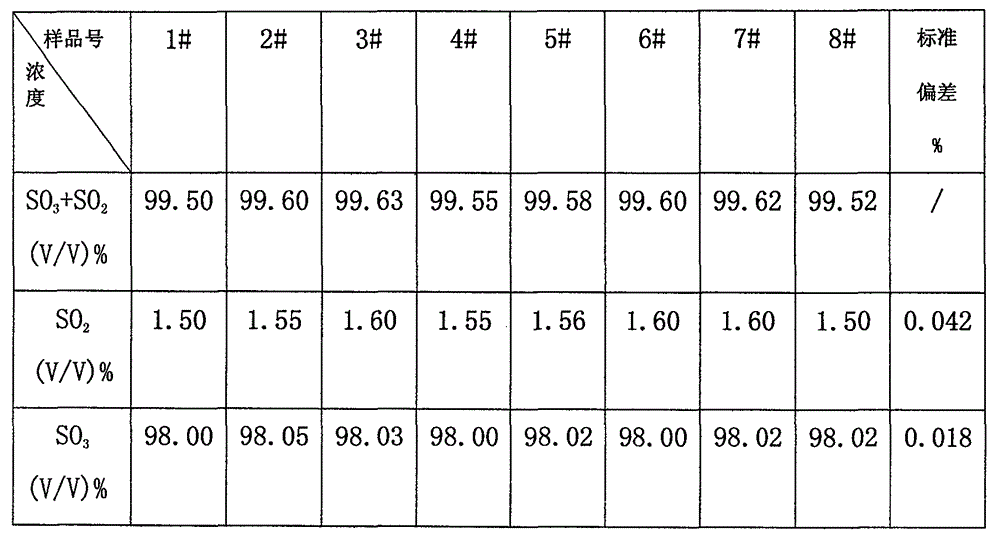
Joint detection method for high-purity SO3 gas and impurity SO2 gas therein
InactiveCN105891406APrevent liquefactionGood measurement precisionChemical analysis using titrationPhysical chemistryProduct gas
The invention relates to a joint detection method for high-purity SO3 gas and impurity SO2 gas therein. The joint detection method comprises the following steps of: using an absorbing device for sampling at constant volume, and then using an aqueous alkali for absorbing, thereby acquiring a total volume percentage concentration of the high-purity SO3 gas and impurity SO2 gas therein; treating the absorption liquid; adopting a direct iodometry for measuring the volume percentage concentration of SO2 gas; subtracting the volume percentage concentration of SO2 gas from the total volume percentage concentration of the high-purity SO3 gas and impurity SO2 gas therein, thereby acquiring the concentration of high-purity gas. According to the method provided by the invention, the measuring precision of high-purity SO3 gas is high and the measuring standard deviation is not more than 0.1%. The method provided by the invention can be used for detecting the high-purity SO3 gas and is especially fit for the detection for the high-purity SO3 gas containing few SO2 gas and inert gas.
Owner:CHONGQING AOGEMEI GAS CO LTD
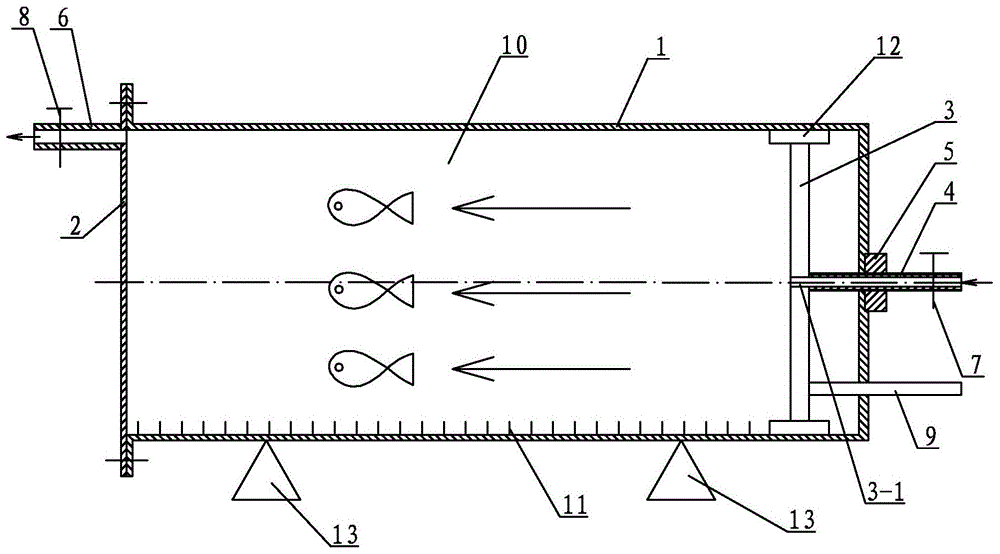
A fish oxygen consumption rate and suffocation point measuring device
InactiveCN103975881BReduce measurement errorReduce cost of measurementClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaRespiration chamberInlet valve
The invention provides an oxygen consumption rate and choke point measuring device of fishes, and relates to a device for measuring oxygen consumption rate and choke point of the fishes. The invention aims to solve the problems that a special device for measuring the choke point of the fishes is lacked, and the existing oxygen consumption rate and choke point of the fishes cannot be measured in the same device by an iodometry method. A respiratory chamber of the device is of a cylinder structure; a cover plate is arranged at an opening end of the respiratory chamber; a water outlet pipe is arranged on the cover plate; a water outlet valve is formed on the water outlet pipe; an axis, vertical to the cylinder, of a pushing plate is arranged in the respiratory chamber; screw threads are formed at the external surface of a water inlet pipe; one end of the water inlet pipe is fixedly connected with the pushing plate, and the other end of the water inlet pipe is in threaded connection with a nut after penetrating through a closed end of the respiratory chamber; the nuts are in embedded connection with the external wall of the respiratory chamber; a water inlet communicated with the water inlet pipe is formed in the pushing plate; a water inlet valve is formed on the water inlet pipe; one end of a round bar is fixedly connected with the pushing plate, and the other end of the round bar penetrates through the closed end of the respiratory chamber. The device is used for measuring the oxygen consumption rate and choke point of the fishes.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG RIVER FISHERY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF FISHERIES SCI
Method for measuring total sugar content of chlortetracycline fermentation broth with refractometer
ActiveCN102297847BEasy to operateReduce labor intensityPhase-affecting property measurementsOriginal dataSugar
The invention relates to a method for measuring the total sugar content of a chlortetracycline fermentation broth with a refractometer, and the method is characterized by accurate measuring result and low cost. The method comprises the steps of: (1) collecting original data: measuring the sugar content data of a standard sample by iodimetry, with the sugar content of the sample at a gradient concentration of 0-17%; (2) inputting the data measured in step (1) into the refractometer; (3) dropping the sample with sugar content of 0-17% for measuring directly in a determination analysis pool so as to conduct measuring. The method of the invention has the advantages of accurate measuring result and fast detection speed. Meanwhile, after one time of standard data input, no input and detection through iodometry are needed once again during sugar content detection of the sample at a later stage, so that a lot of reagents can be saved. The method of iodometry is complicated for operation, while the adoption of a refractometer is simple in operation. The employment of a refractometer for detection reduces the labor intensity of technicists and improves the working efficiency.
Owner:PUCHENG CHIA TAI BIOCHEM
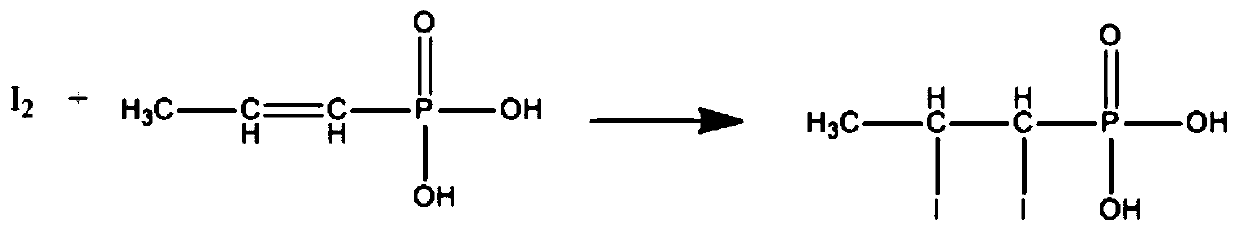
Industrial-grade cis-propenyl phosphoric acid analysis method
InactiveCN110487955AEasy to prepareEasy to operateChemical analysis using titrationPhosphoric acidDouble bond
The invention discloses an industrial-grade cis-propenyl phosphoric acid analysis method, which belongs to the technical field of chemical analysis and detection. Specifically, the content of cis-propenyl phosphoric acid is determined by measuring unsaturated double bonds in industrial cis-propenyl phosphoric acid through iodometry. The method is simple and convenient in experimental operation, common and easily available in experimental instruments and reaction reagents, strong in convenience and practicability and low in cost, can be used for similar reaction analysis, and has certain significance for quality monitoring in the research and development pharmaceutical process.
Owner:WUHAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
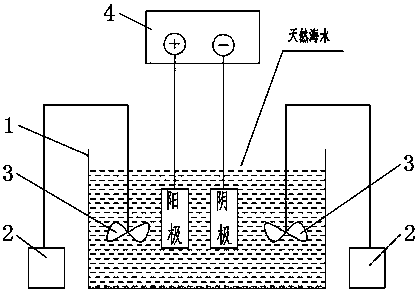
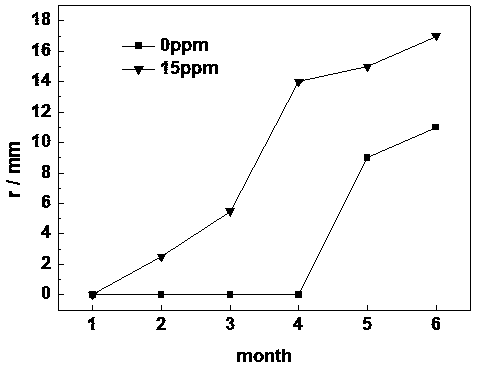
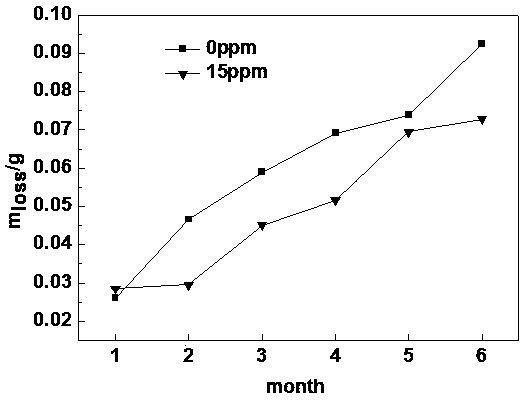
Method for testing performance of coatings of ballast tank and piping system thereof in electrolytic ballast water environment
InactiveCN108344681AShorten the development cycleImprove detection efficiencyWeather/light/corrosion resistancePreparing sample for investigationTest performanceElectrolysis
The invention provides a method for testing the performance of coatings of a ballast tank and a piping system thereof in an electrolytic ballast water environment. Electrolytic seawater is prepared through a seawater electrolysis device; after being prepared, the electrolytic seawater is saved airtightly in a dark place; the electrolytic seawater is mixed with natural seawater according to different proportions, the concentration of the electrolytic seawater is titrated through iodometry, and electrolytic seawater with different chlorine residue concentrations is prepared; a soaking experimentand a PSPC ballast tank simulation experiment are carried out in the electrolytic seawater with the different chlorine residue concentrations. The requirements for testing the performance changes ofship protection coatings, especially the protection coatings of the ship ballast tank and the piping system thereof in the electrolytic seawater in a laboratory can be met, therefore, the paint research and development period is shortened, the detection efficiency is improved, and great practical significance is achieved.
Owner:725TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING INDAL CORP
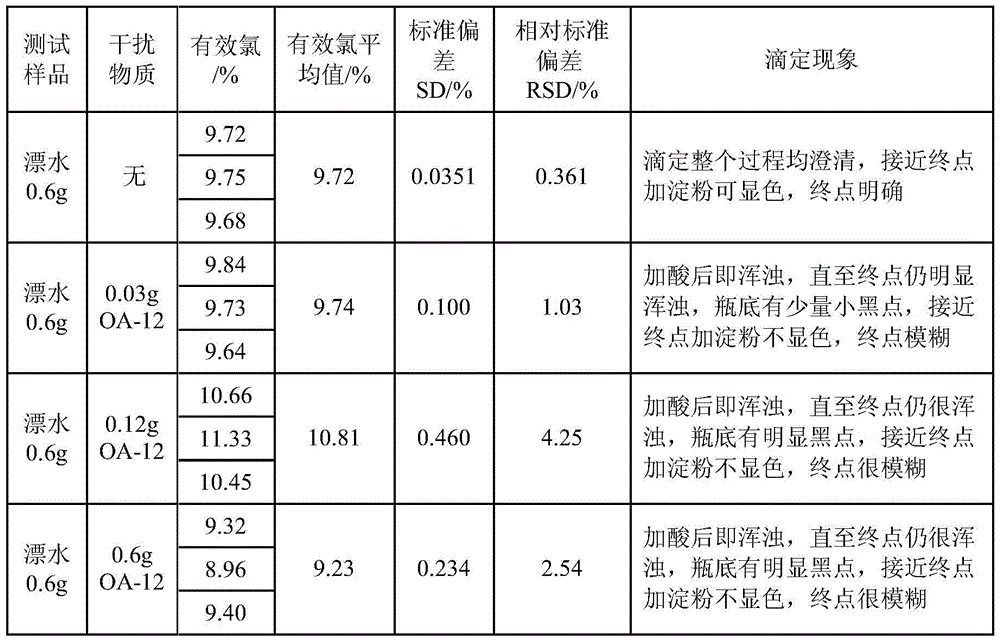
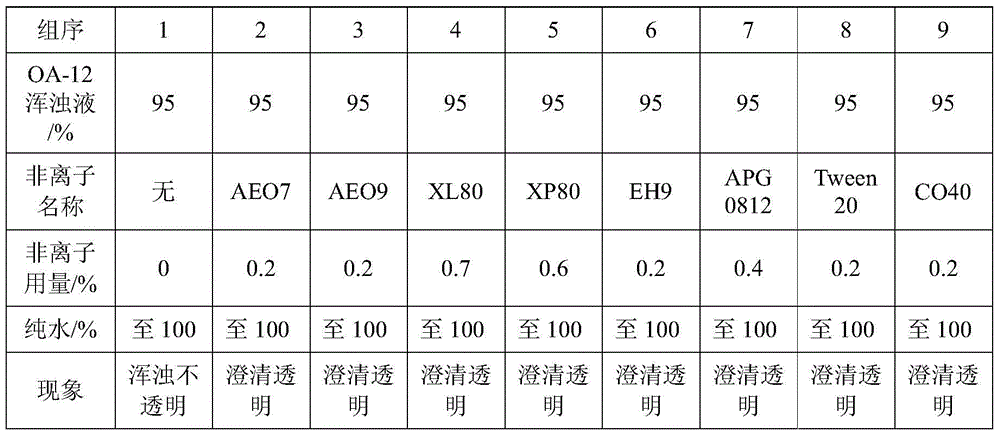
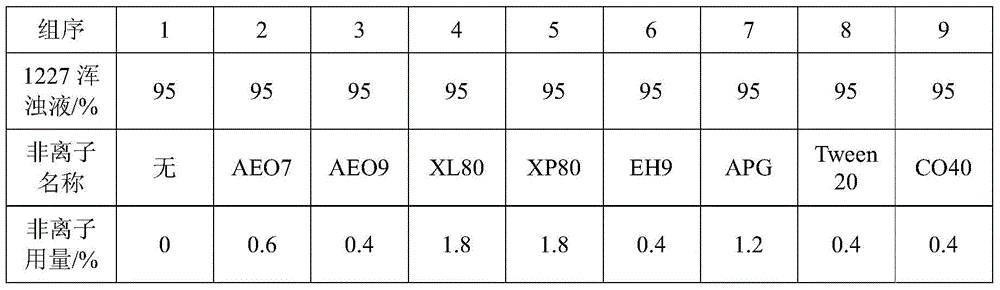
A method for improving the accuracy of iodometric measurement of samples containing interfering substances
ActiveCN105259300BOvercome the problem of inaccurate measurementReduce dosageChemical analysis using titrationIodineColor changes
The invention discloses a method for improving iodometry measurement accuracy of samples containing interfering substances. According to the method, a proper amount of nonionic surfactant is added on the basis of a conventional iodometry, and the problems that certain samples containing the interfering substances become turbid in the titration testing process and even accurate measurement is difficult due to iodine precipitation are successfully solved. By means of the method, a titration reaction is quick and sufficient, a titration end point is clear and transparent, the end point is accurately judged through color changes of iodine even if starch can not normally display colors, and a test result is good in precision and accuracy. Reagents used in the method are all conventional, safe, free of harm, easy to operate and suitable for being popularized in detection organizations and research institutions.
Owner:广州超威生物科技有限公司
Determination method for free sulfite in cyanide-free gold plating solution
PendingCN114137150AMeet the testing requirementsAccurate measurementChemical analysis using titrationCyanideSulfite
The invention provides a method for measuring free sulfite in a cyanide-free gold plating solution, which comprises the following steps: detecting the total sulfite concentration by iodometry, then measuring the gold concentration in a sample to be measured by an analytical instrument, and calculating the concentration of the free sulfite according to a formula. The determination method is simple, rapid, low in cost, feasible in technology, reasonable in economy and wide in application prospect.
Owner:CHENGDU HIWAFER SEMICON CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com